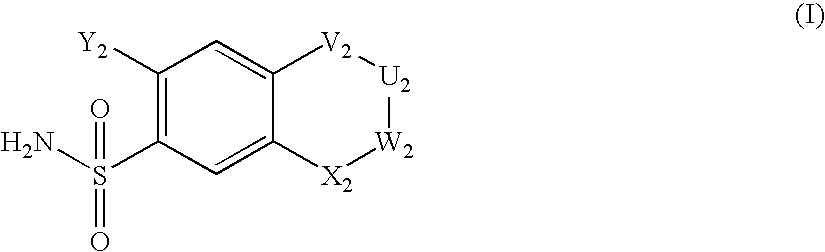Patents
Literature
1954 results about "Oxidative stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal redox state of cells can cause toxic effects through the production of peroxides and free radicals that damage all components of the cell, including proteins, lipids, and DNA. Oxidative stress from oxidative metabolism causes base damage, as well as strand breaks in DNA. Base damage is mostly indirect and caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated, e.g. O₂⁻ (superoxide radical), OH (hydroxyl radical) and H₂O₂ (hydrogen peroxide). Further, some reactive oxidative species act as cellular messengers in redox signaling. Thus, oxidative stress can cause disruptions in normal mechanisms of cellular signaling.
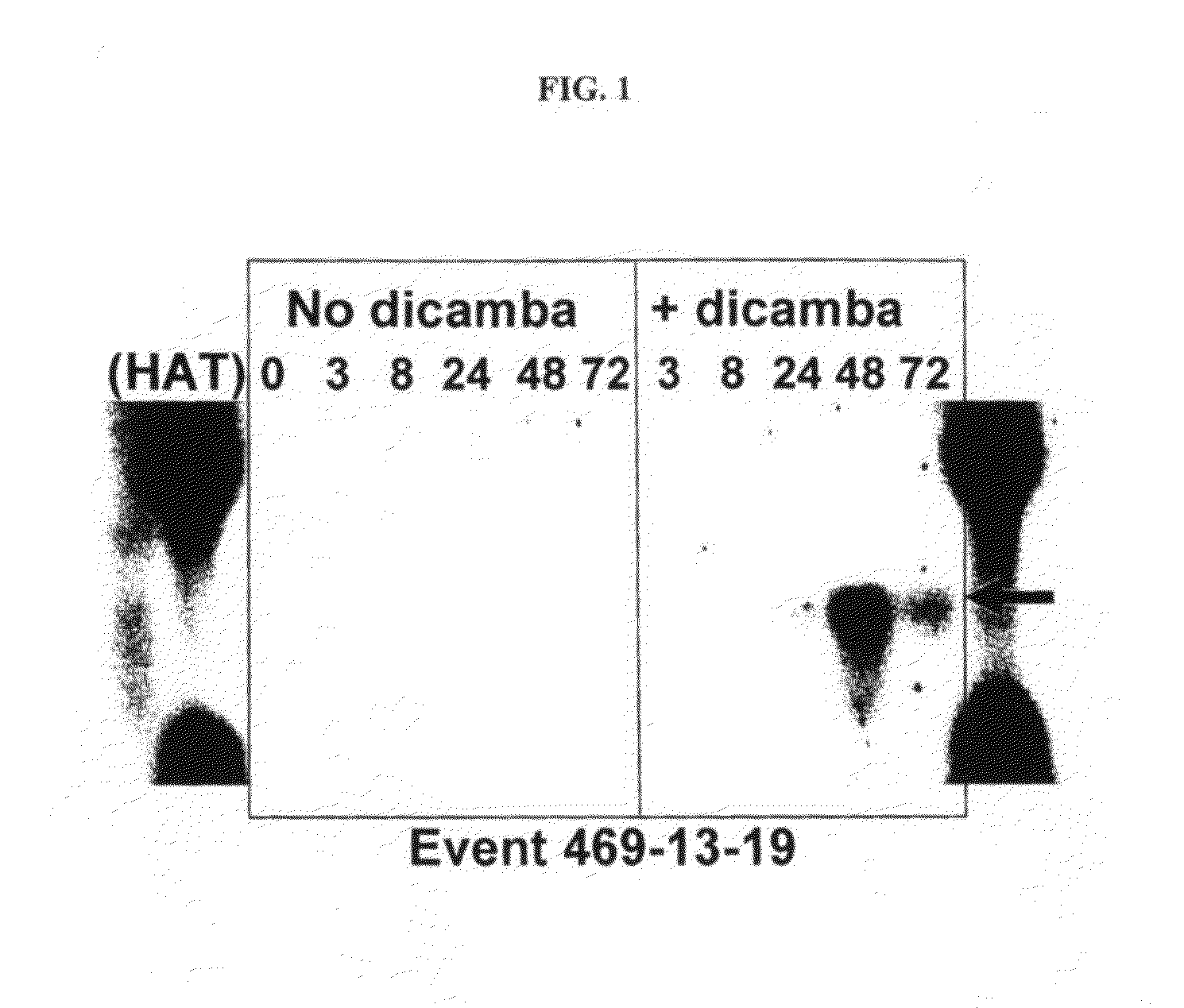
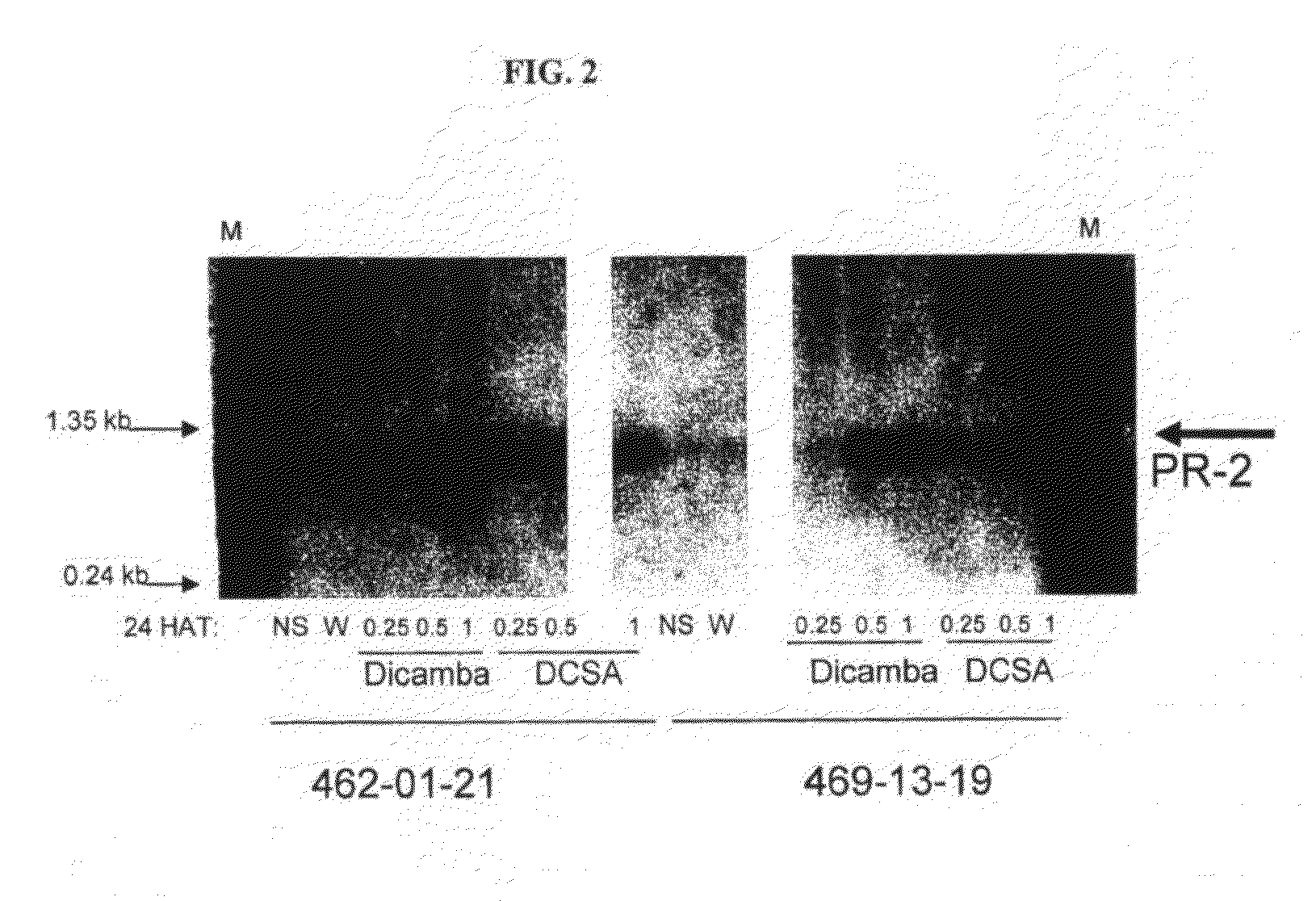
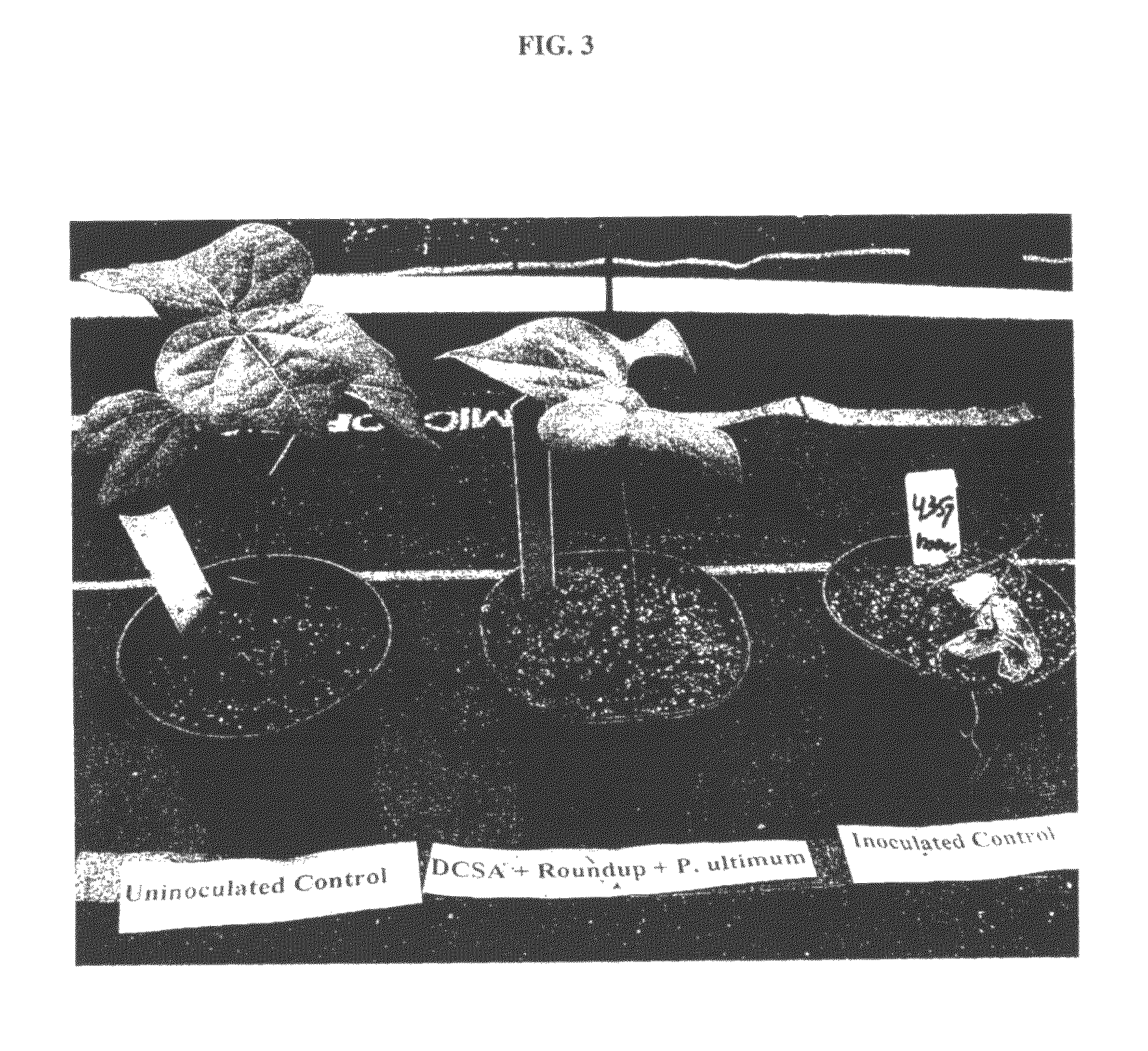
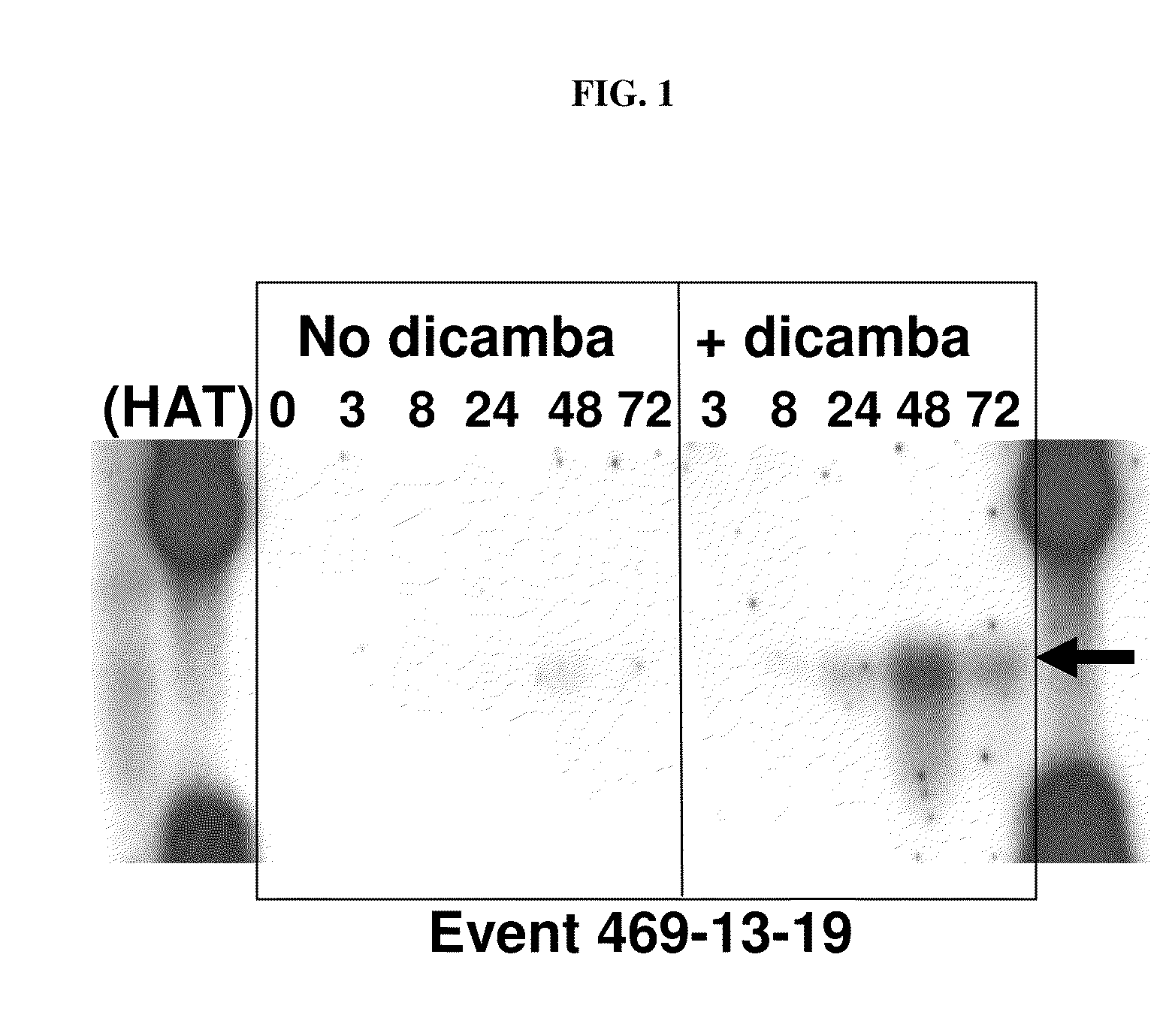
Methods and compositions for improving plant health
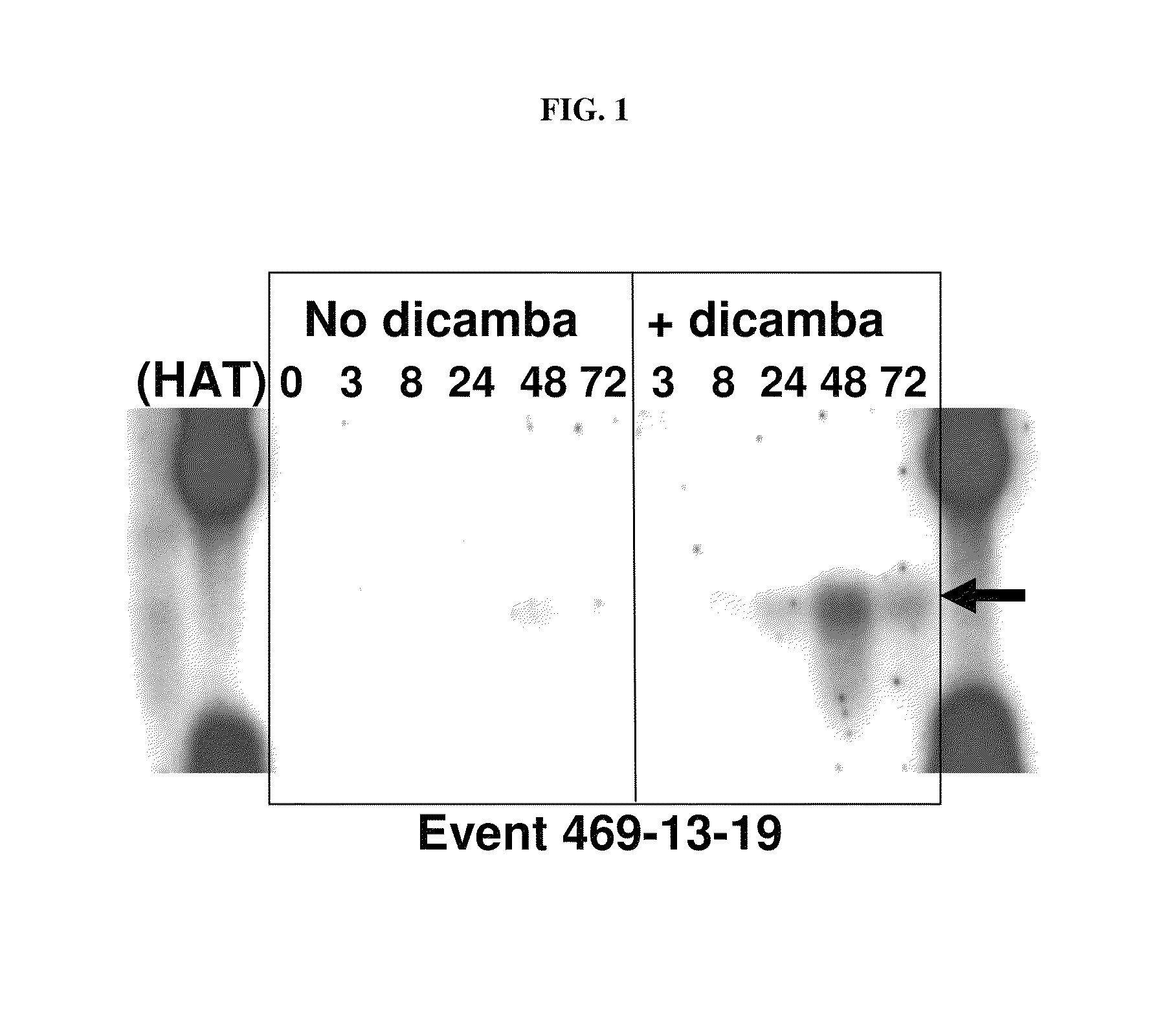
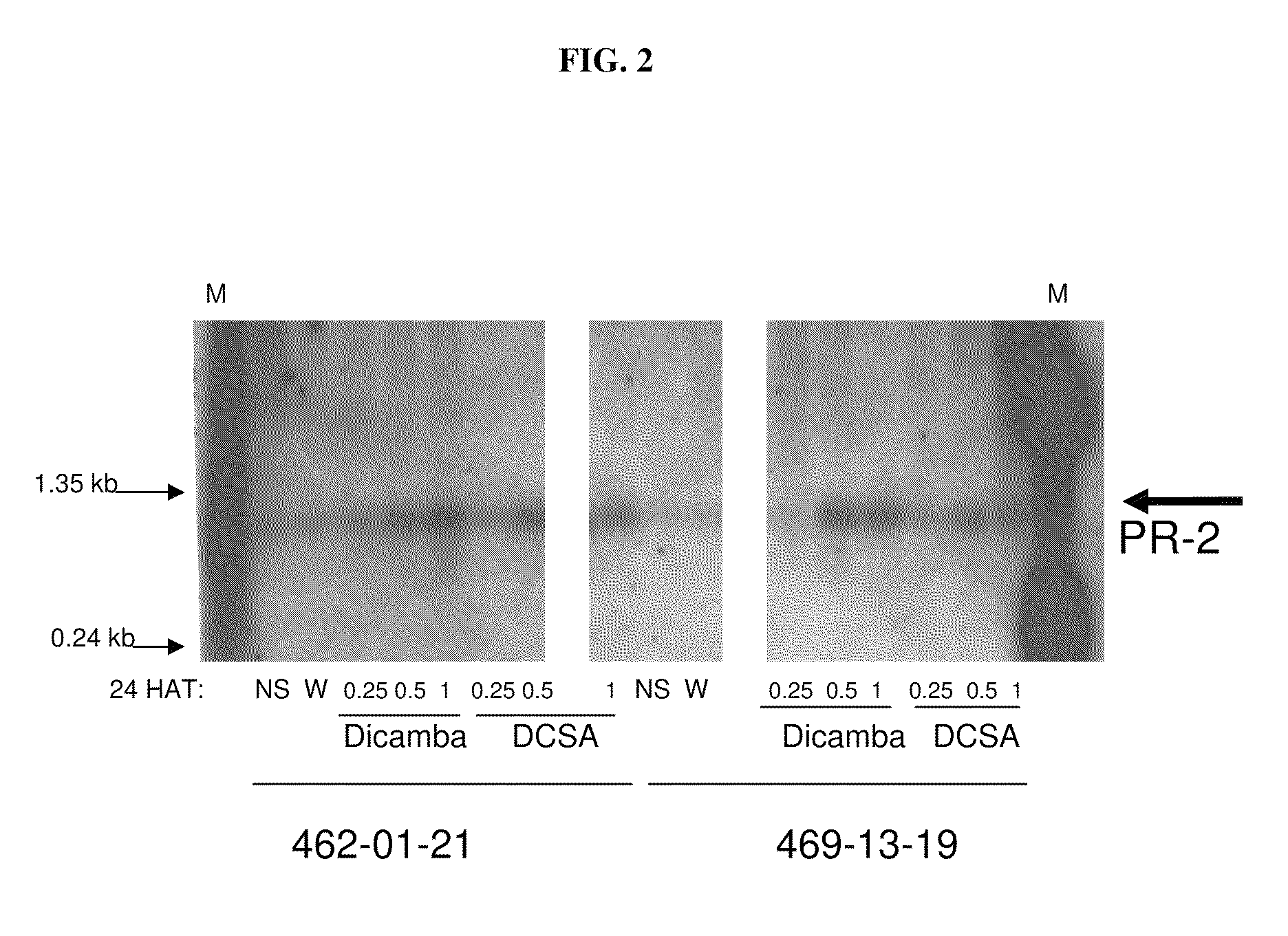
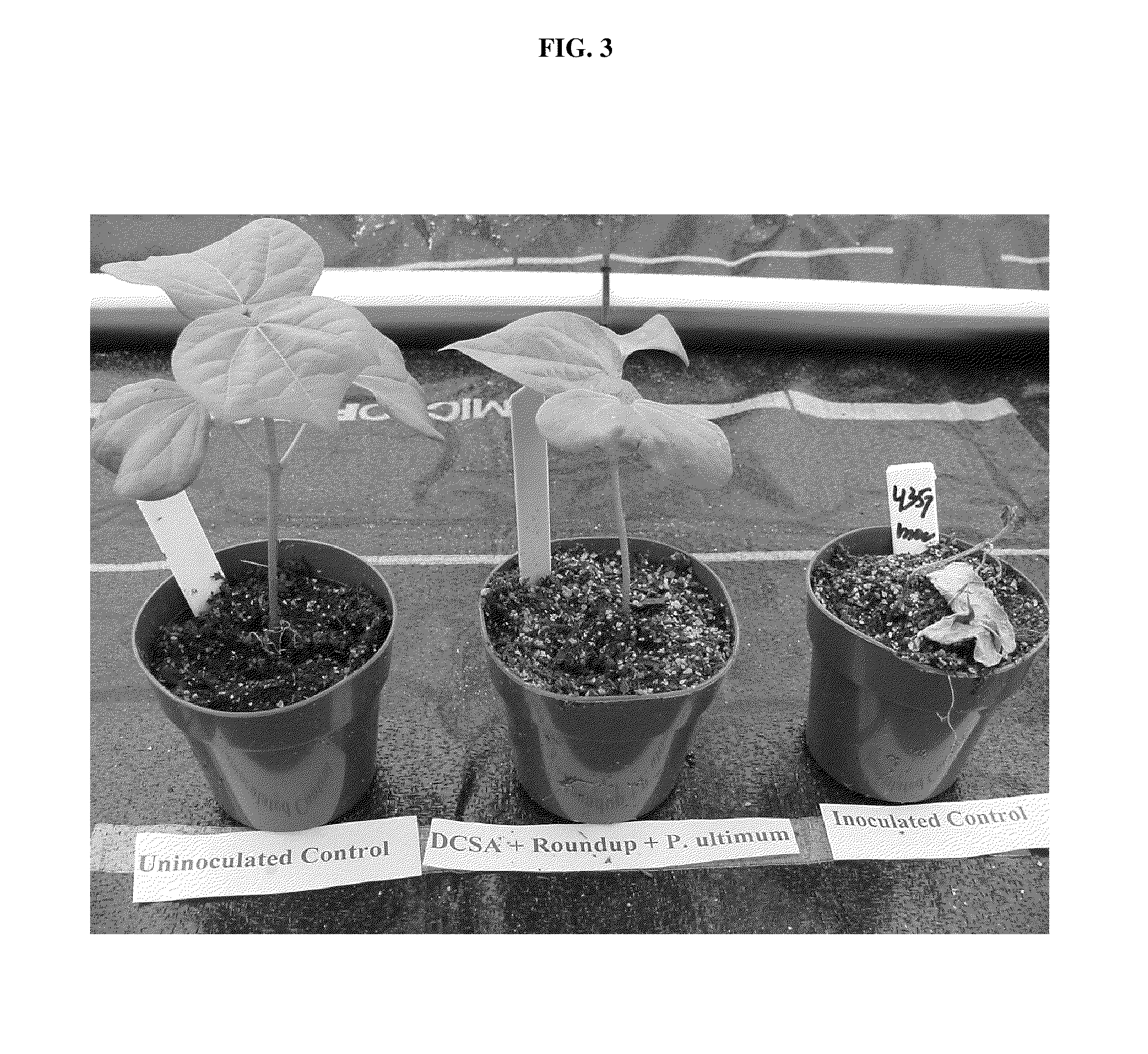
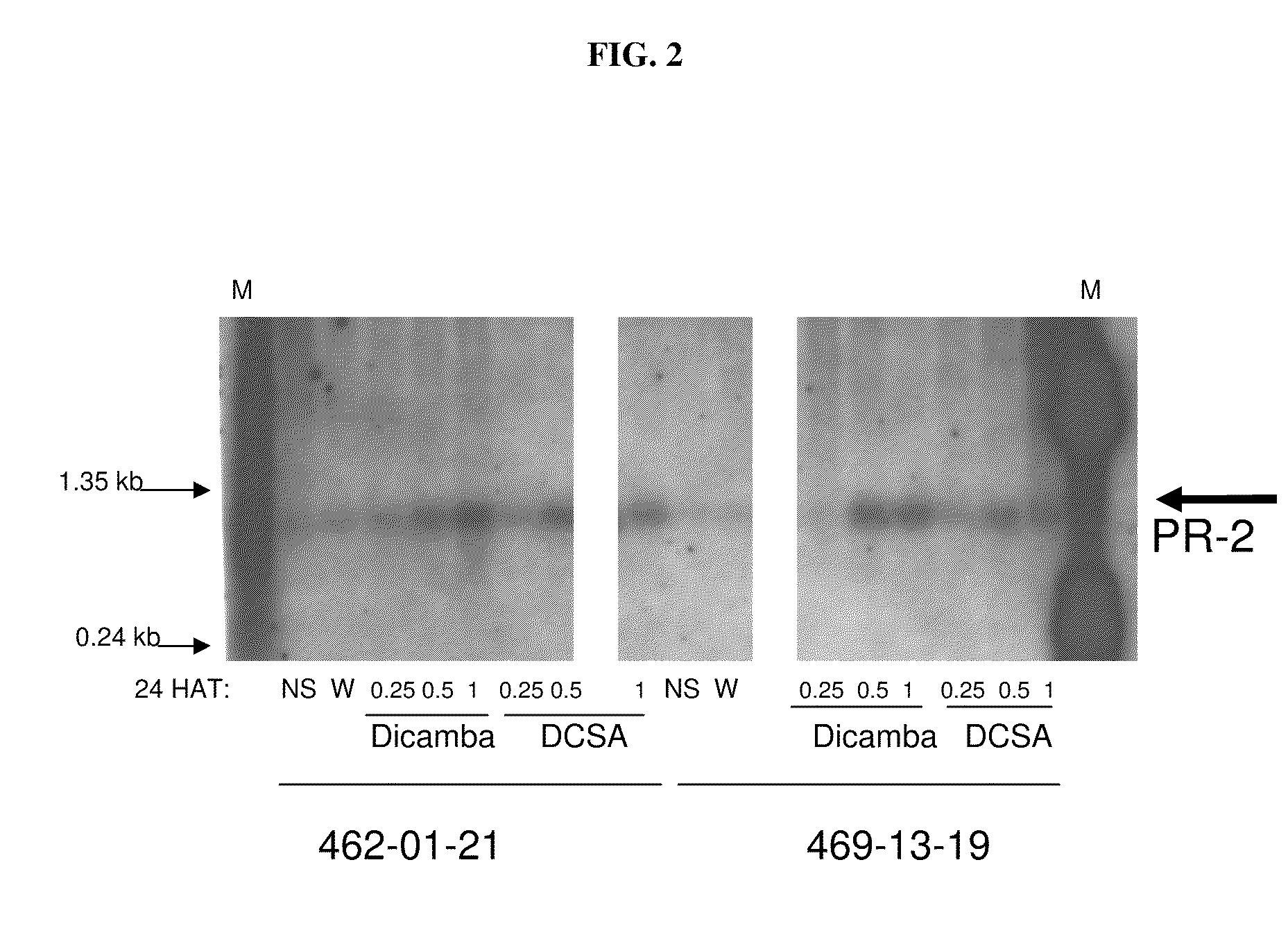
The present invention provides methods and compositions for improving plant health. In particular, application of dicamba or another substrate of DMO, or metabolites thereof including DCSA, to a plant confers tolerance to, or defense against, abiotic or biotic stresses such as oxidative stress including herbicide application, and plant disease, and enhances crop yield. Such application may be in combination with the application of another herbicide such as glyphosate.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods and compositions for improving plant health
ActiveUS8754011B2Good for healthTolerance to oxidative stressBiocideOrganic chemistryMetaboliteGlyphosate
The present invention provides methods and compositions for improving plant health. In particular, application of dicamba or another substrate of DMO, or metabolites thereof including DCSA, to a plant confers tolerance to, or defense against, abiotic or biotic stresses such as oxidative stress including herbicide application, and plant disease, and enhances crop yield. Such application may be in combination with the application of another herbicide such as glyphosate.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods and compositions for improving plant health
ActiveUS20090105077A1Improve efficiencyGood for healthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMetaboliteGlyphosate
The present invention provides methods and compositions for improving plant health. In particular, application of dicamba or another substrate of DMO, or metabolites thereof including DCSA, to a plant confers tolerance to, or defense against, abiotic or biotic stresses such as oxidative stress including herbicide application, and plant disease, and enhances crop yield. Such application may be in combination with the application of another herbicide such as glyphosate.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Metabolic capacity enhancing compositions and methods for use in a mammal
InactiveUS20060024385A1Increase vitalityImproved and increased energy processing of given caloric foods)BiocideOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationMammal
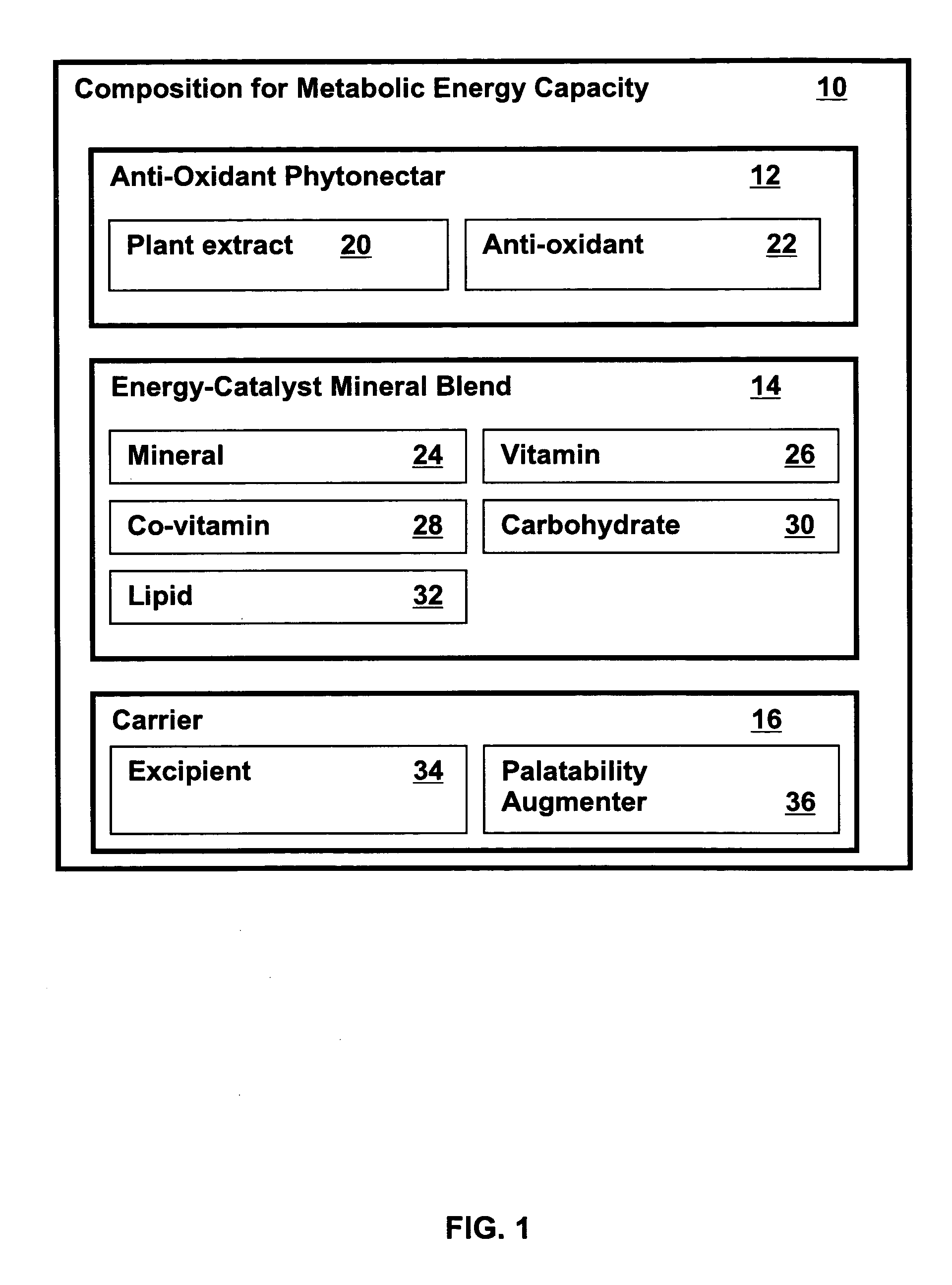
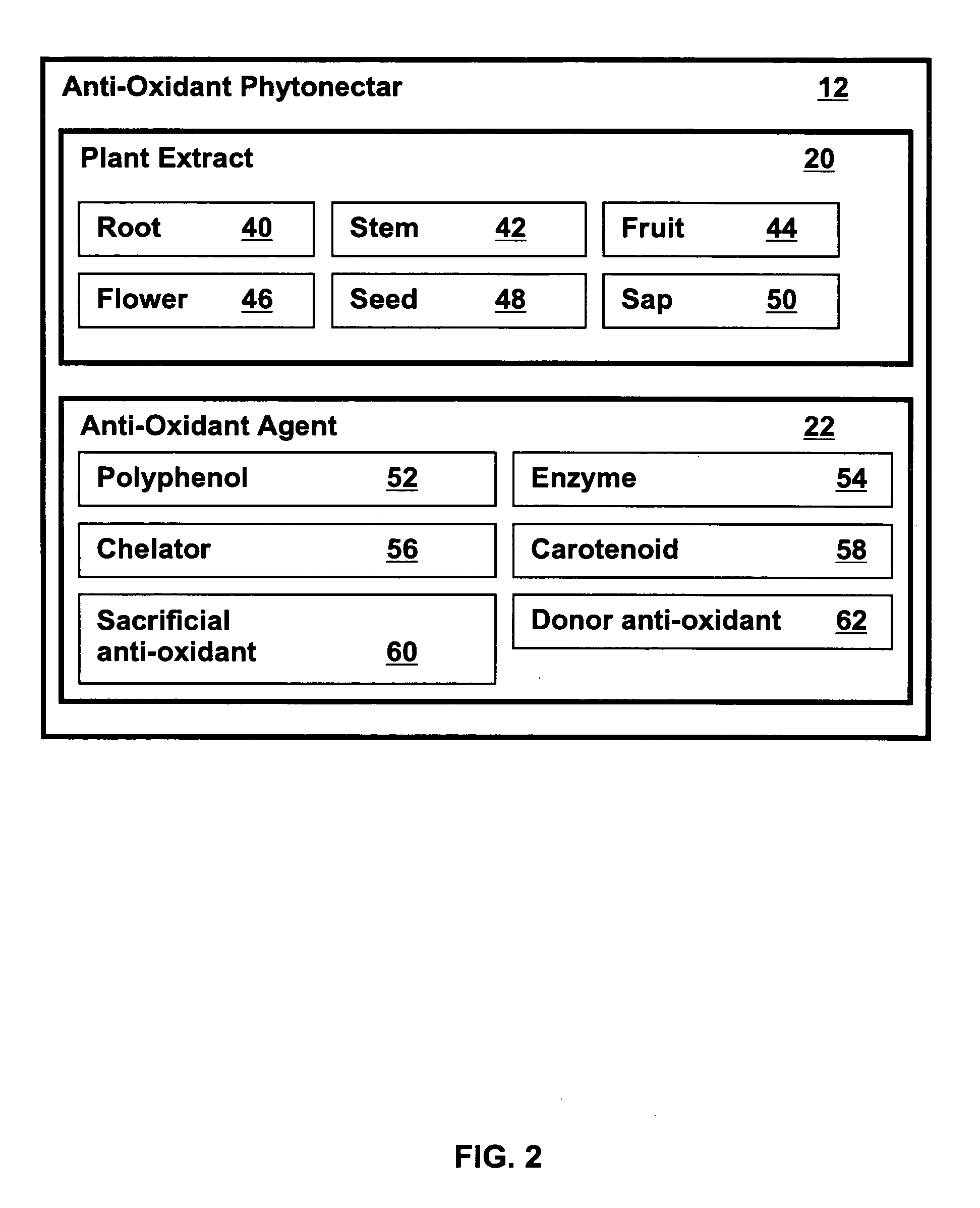
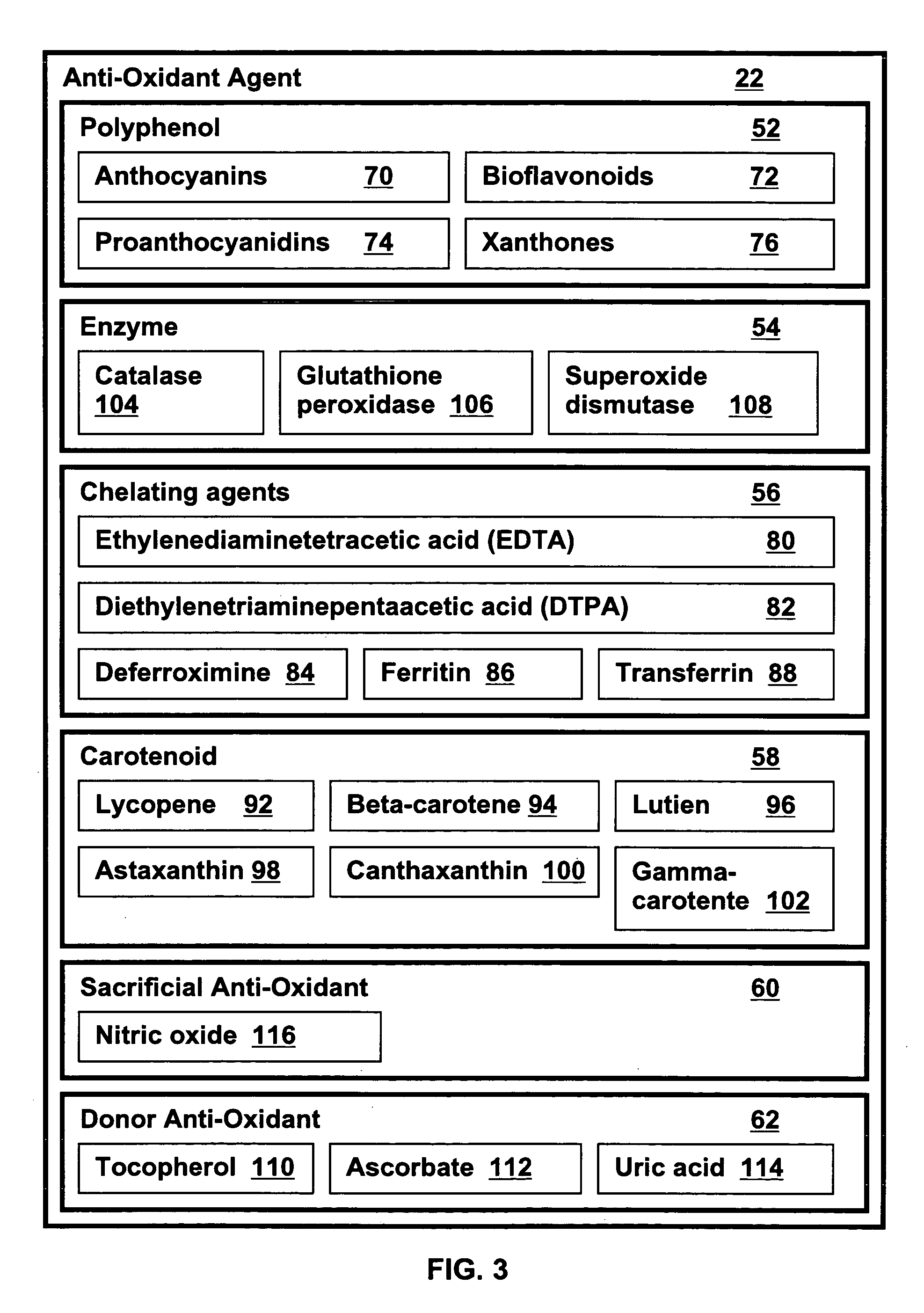
Metabolic energy capacity enhancing compositions and methods for reducing oxidative stress and improving vitality in a mammal are disclosed. A composition for increasing metabolic energy capacity may be in a palatable liquid formulation or a solid dosage form and typically includes an anti-oxidant containing phytonectar and an energy catalyst. An anti-oxidant may include a polyphenol, anthrocyanin, bioflavonoid, proanthocyanidin, and a xanthone. An energy catalyst may include a mineral, vitamin, co-vitamin, carbohydrate and a lipid. In a presently preferred embodiment a composition includes phytonectar extracts from grape, aloe vera, apple, morinda citrifolia, scullcap, blueberry, prune, cranberry, elderberry, bilberry, and gentain and a mineral blend containing calcium, magnesium, manganese, zinc, chromium, selenium, iron, copper, molybdenum, vanadium, potassium, iodine, and cobalt. A method for increasing metabolic energy capacity in a mammal may include consuming a chemical component having the ability to undergo oxidation, producing free radicals and administering a composition having an anti-oxidant containing phytonectar and an energy catalyst.
Owner:PEDERSEN MARK A
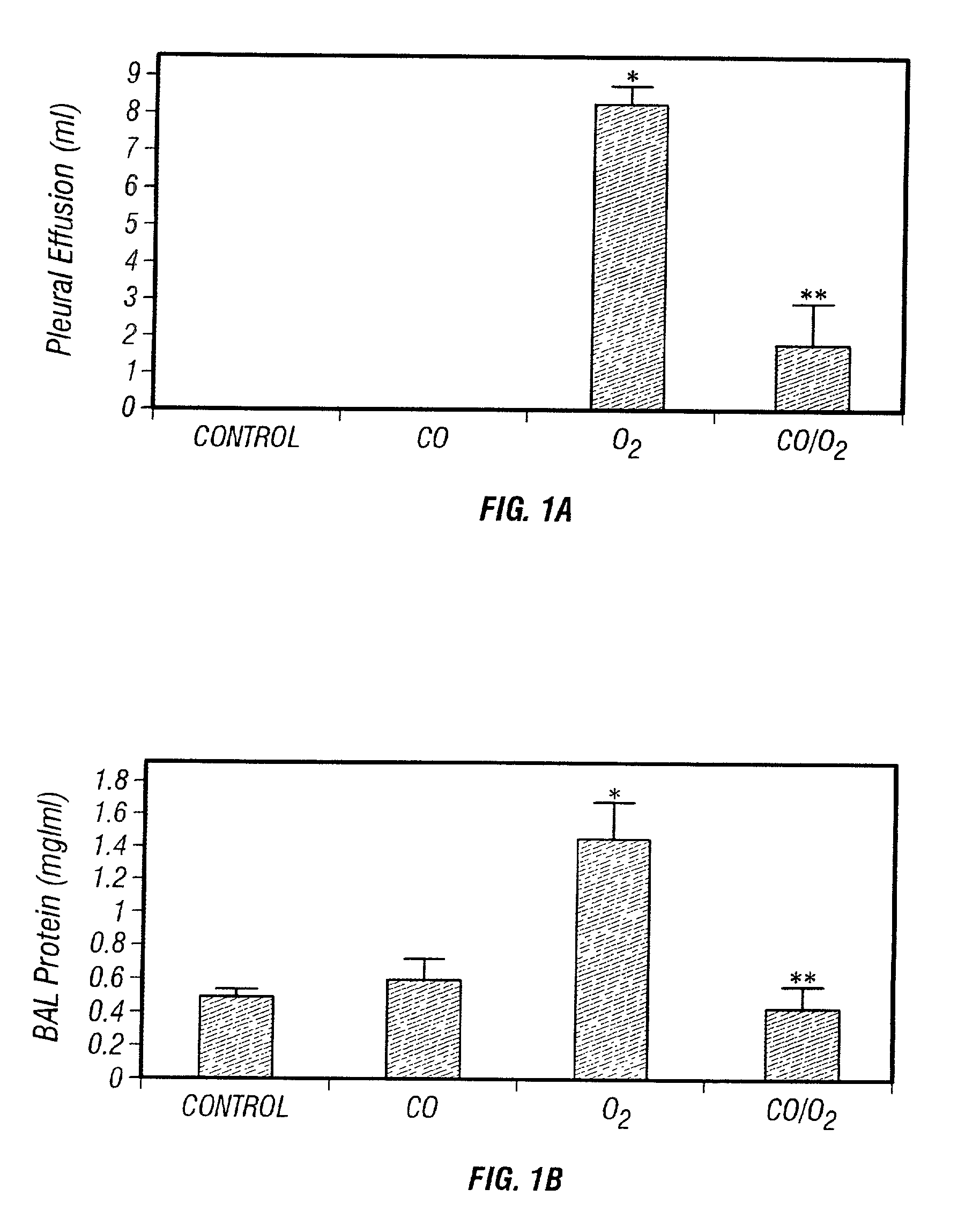
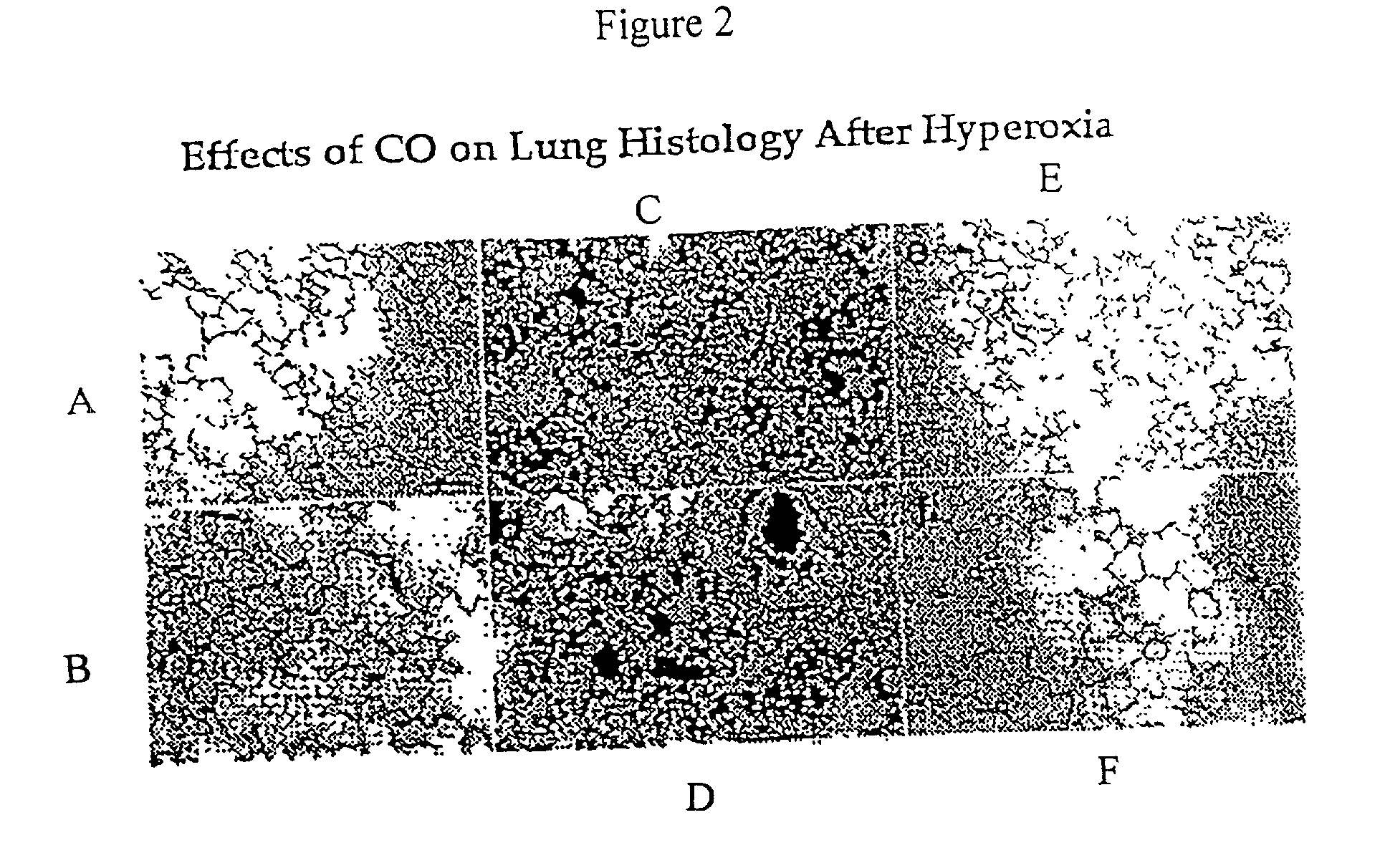
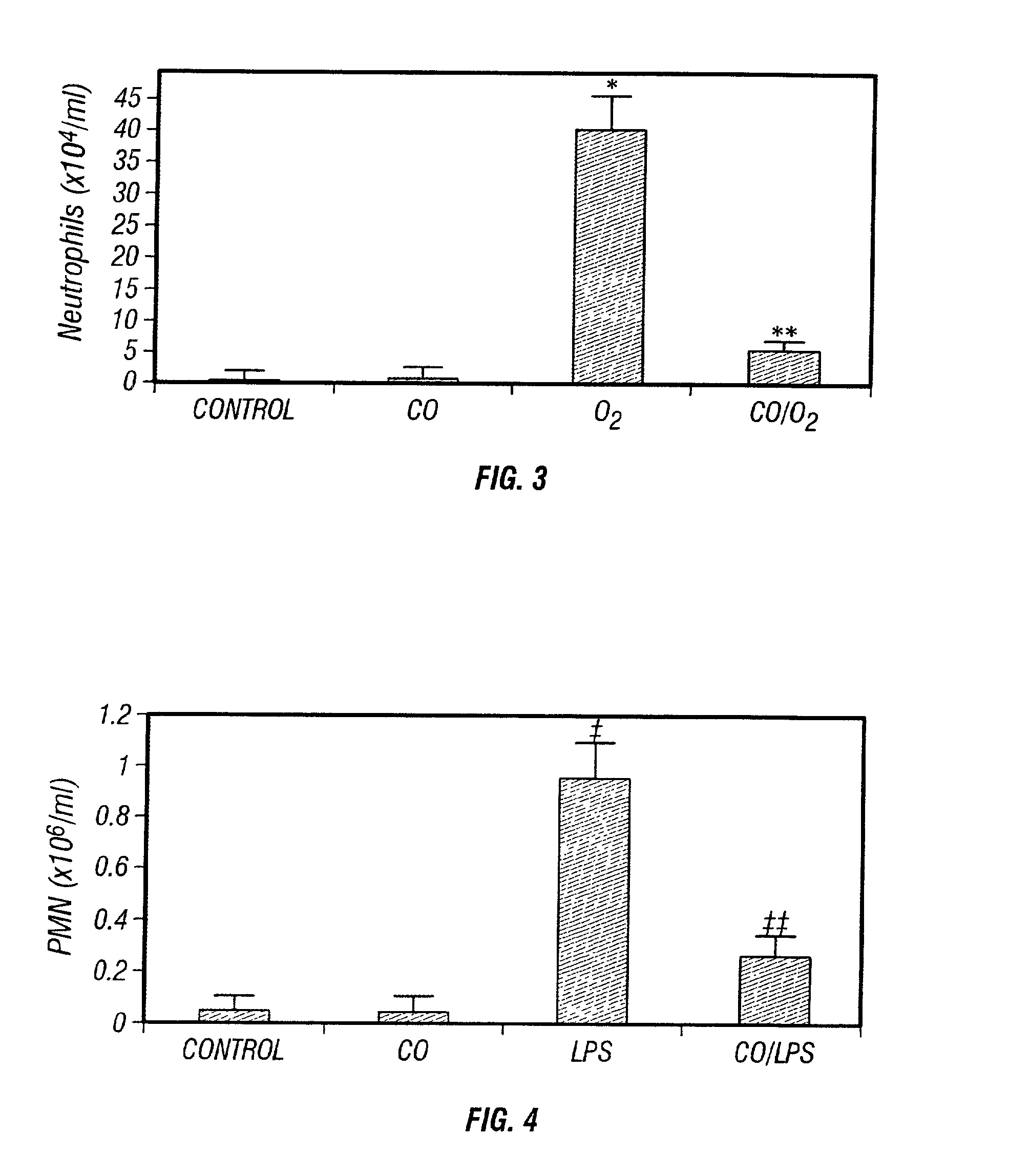
Carbon monoxide as a biomarker and therapeutic agent
InactiveUS20020155166A1Reduce concentrationBiocideInorganic active ingredientsInterstitial lung diseaseRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULT
The present invention relates to the use of carbon monoxide (CO) as a biomarker and therapeutic agent of heart, lung, liver, spleen, brain, skin and kidney diseases and other conditions and disease states including, for example, asthma, emphysema, bronchitis, adult respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, cystic fibrosis, pneumonia, interstitial lung diseases, idiopathic pulmonary diseases, other lung diseases including primary pulmonary hypertension, secondary pulmonary hypertension, cancers, including lung, larynx and throat cancer, arthritis, wound healing, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, peripheral vascular disease and pulmonary vascular thrombotic diseases such as pulmonary embolism. CO may be used to provide anti-inflammatory relief in patients suffering from oxidative stress and other conditions especially including sepsis and septic shock. In addition, carbon monoxide may be used as a biomarker or therapeutic agent for reducing respiratory distress in lung transplant patients and to reduce or inhibit oxidative stress and inflammation in transplant patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Treatment of inflammatory conditions
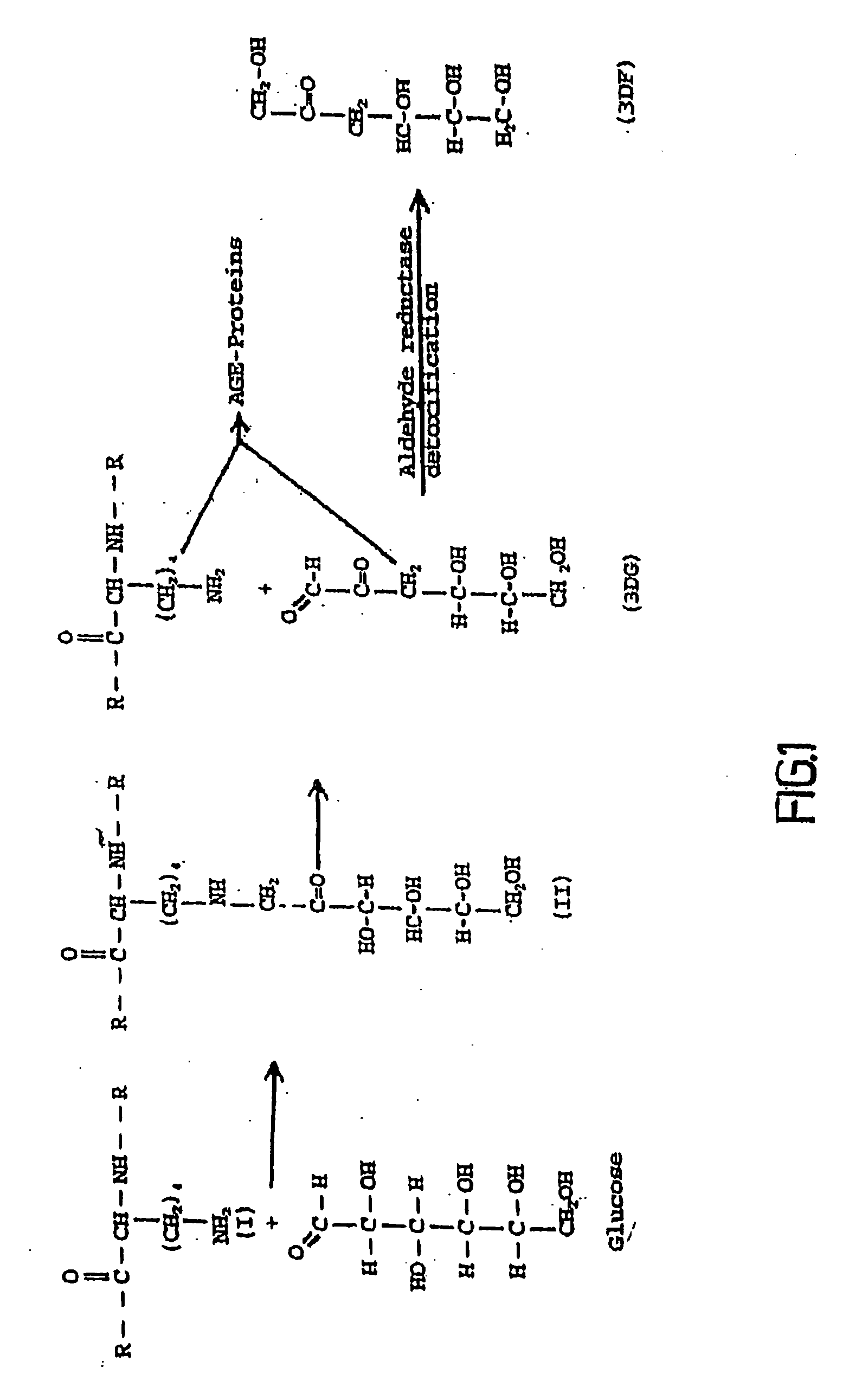
InactiveUS20070021357A1Reduction and elimination and inhibition of functionTreat painBiocideSenses disorderOxidative stressSugar
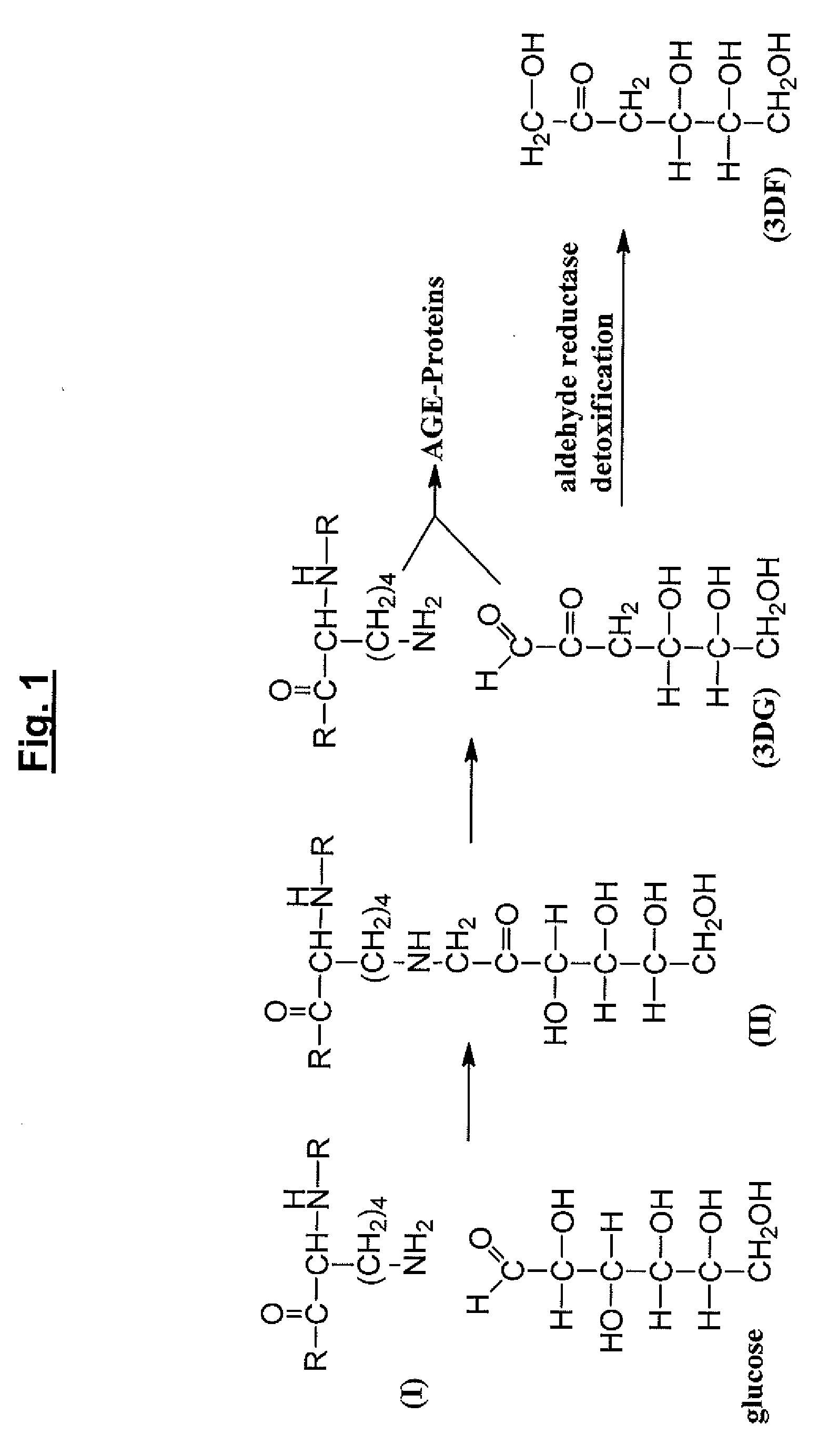
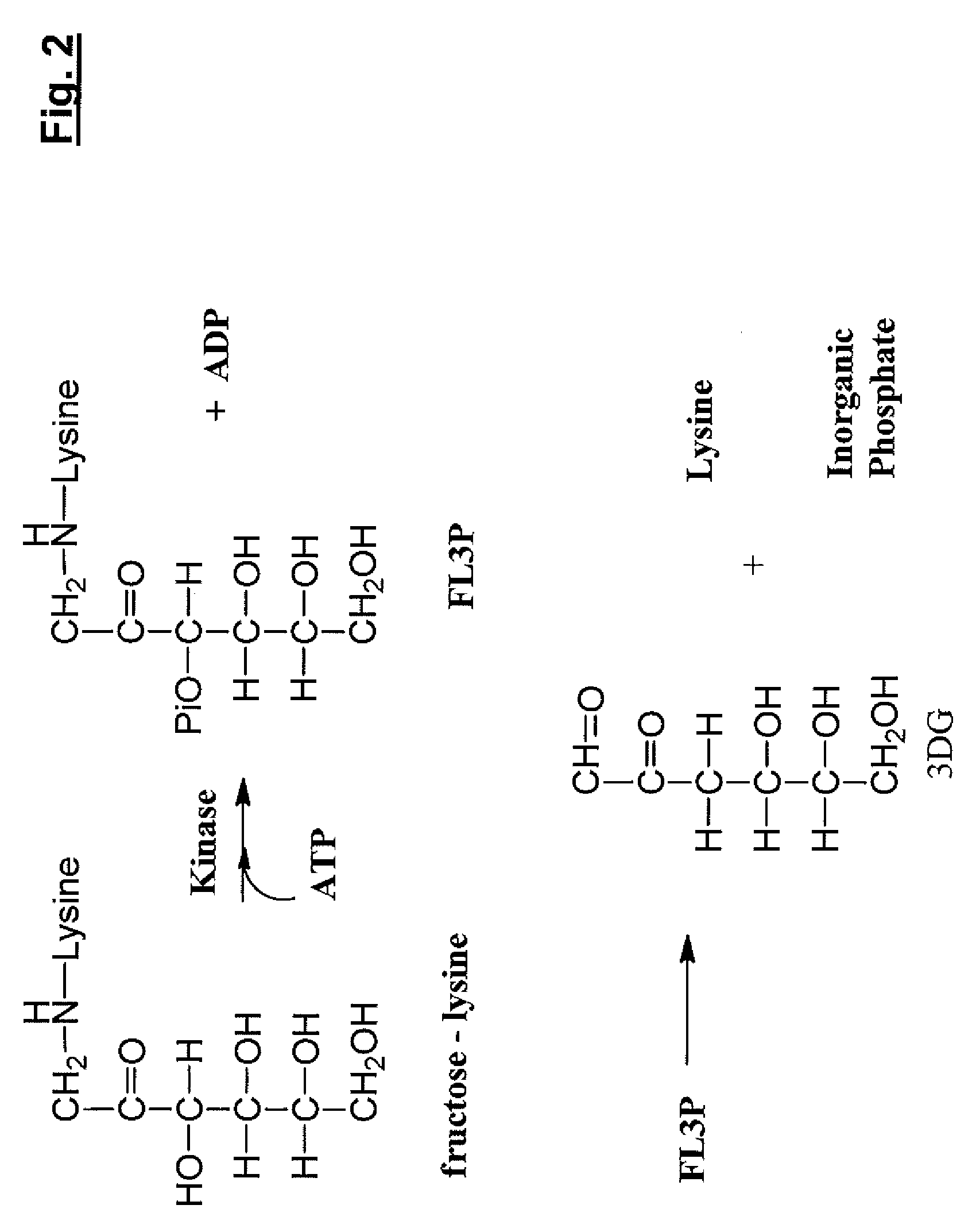
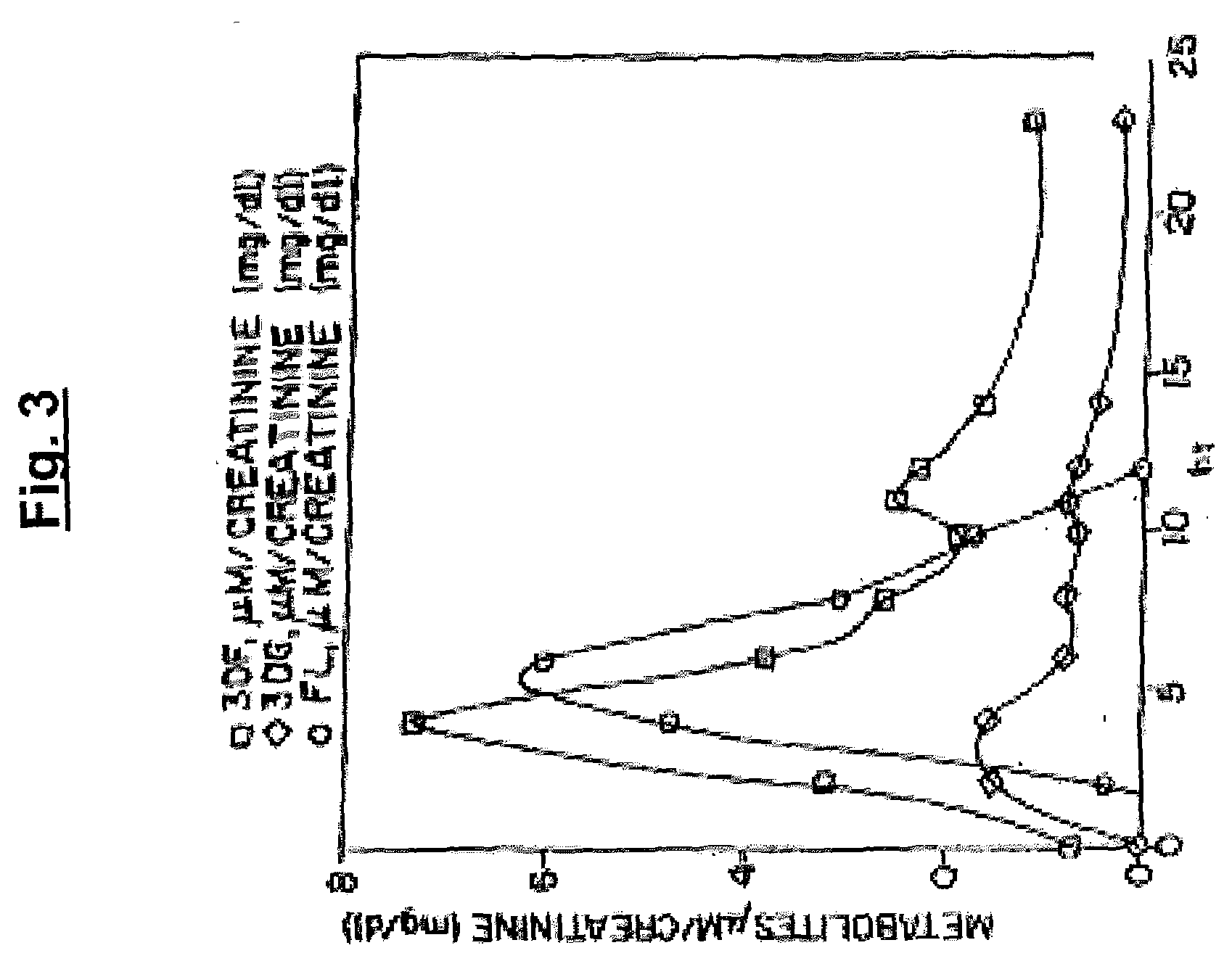
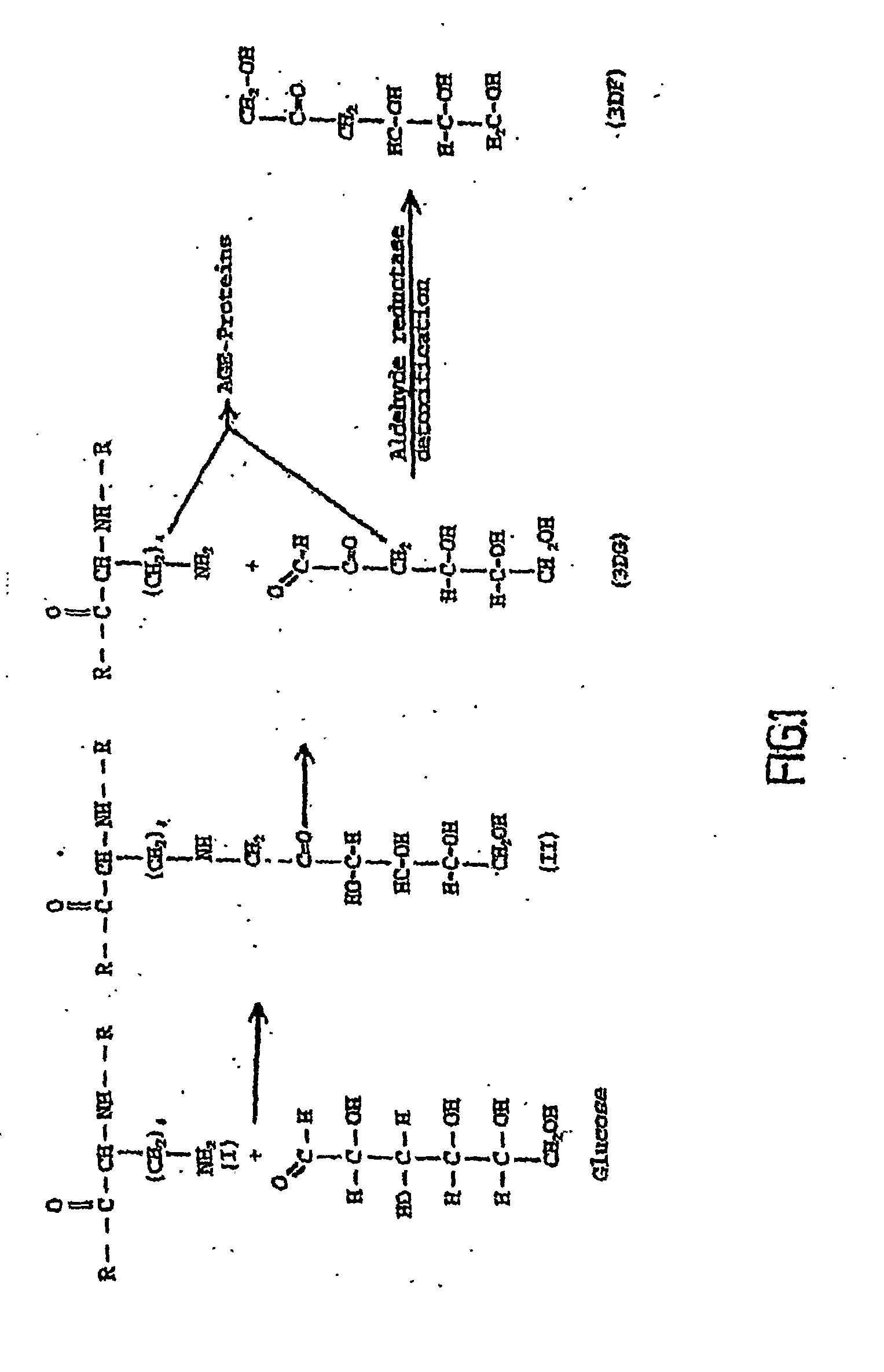
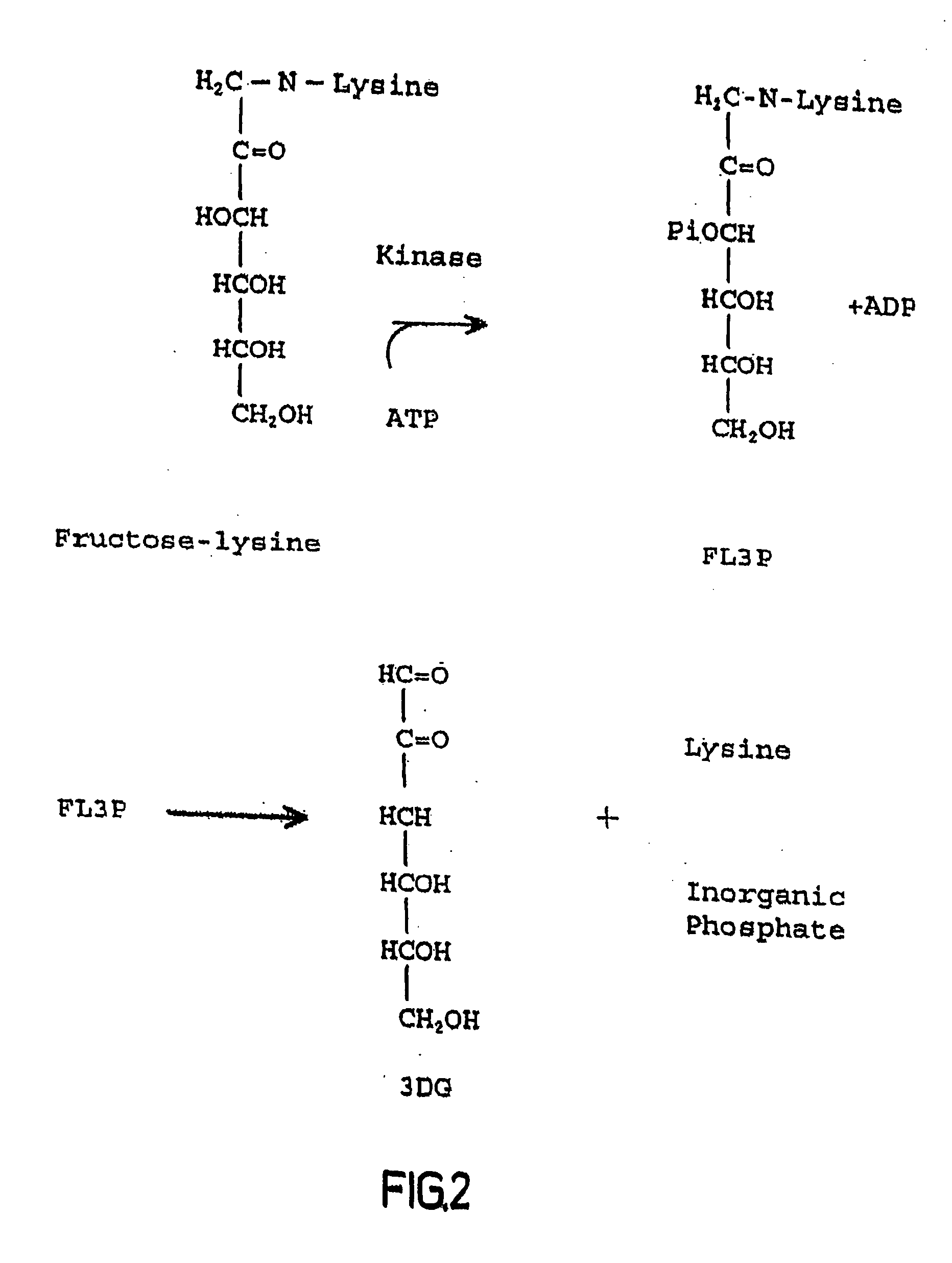
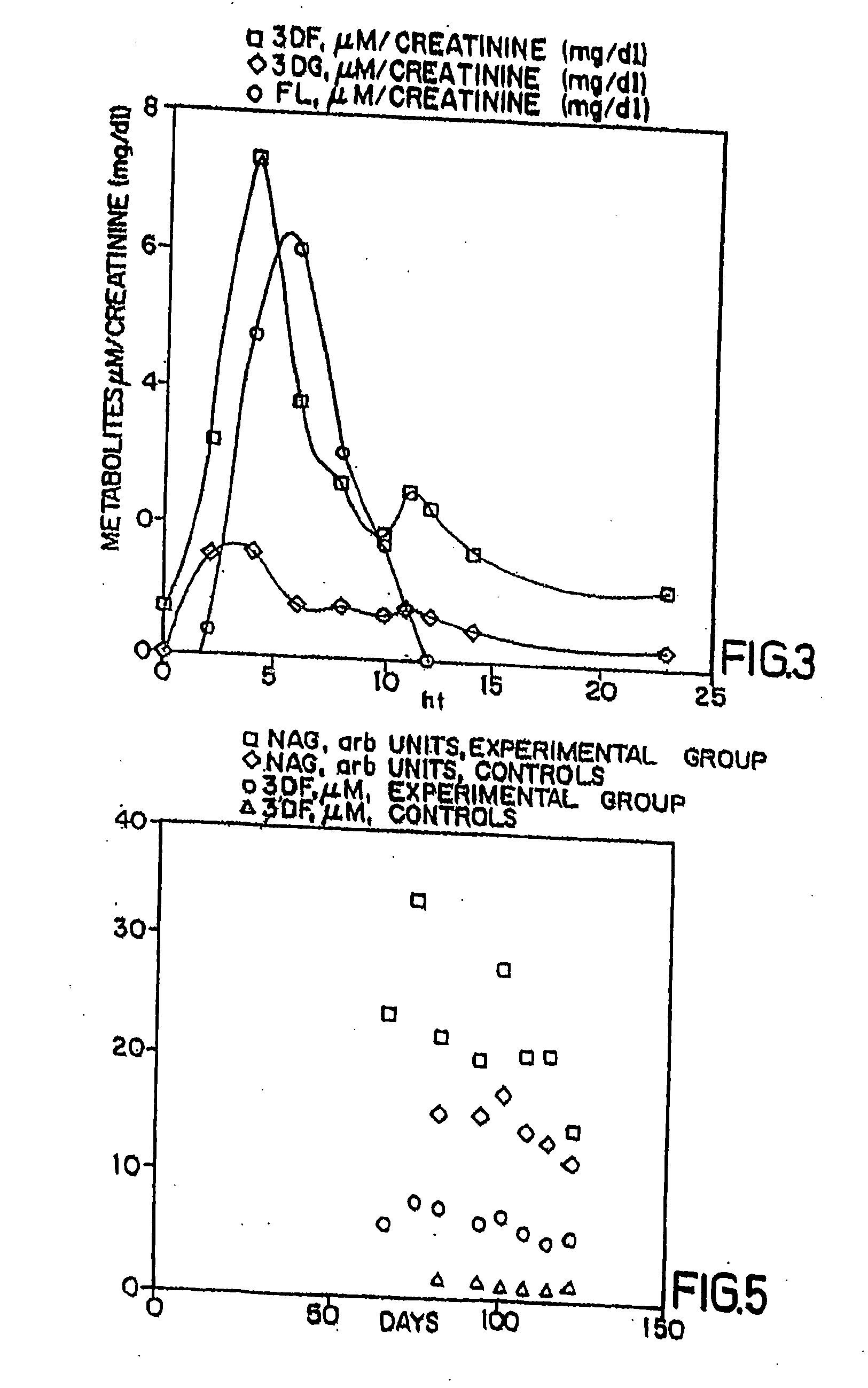
The invention relates to methods of inhibiting production and function of 3-deoxyglucosone and other alpha-dicarbonyl sugars in skin thereby treating or prevention various diseases, disorders or conditions. Additionally, the invention relates to treatment of various diseases, disorders or conditions associated with or mediated by oxidative stress since 3DG induces ROS and AGEs, which are associated with the inflammatory response caused by oxidative stress.
Owner:DYNAMIS THERAPEUTICS
Methods of delivering therapeutics to the brain
Intranasal iontophoretic administration of therapeutics such as Reduced Water (RW) or lubeluzole as a means of treating diseases of the CNS involving oxidative stress.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
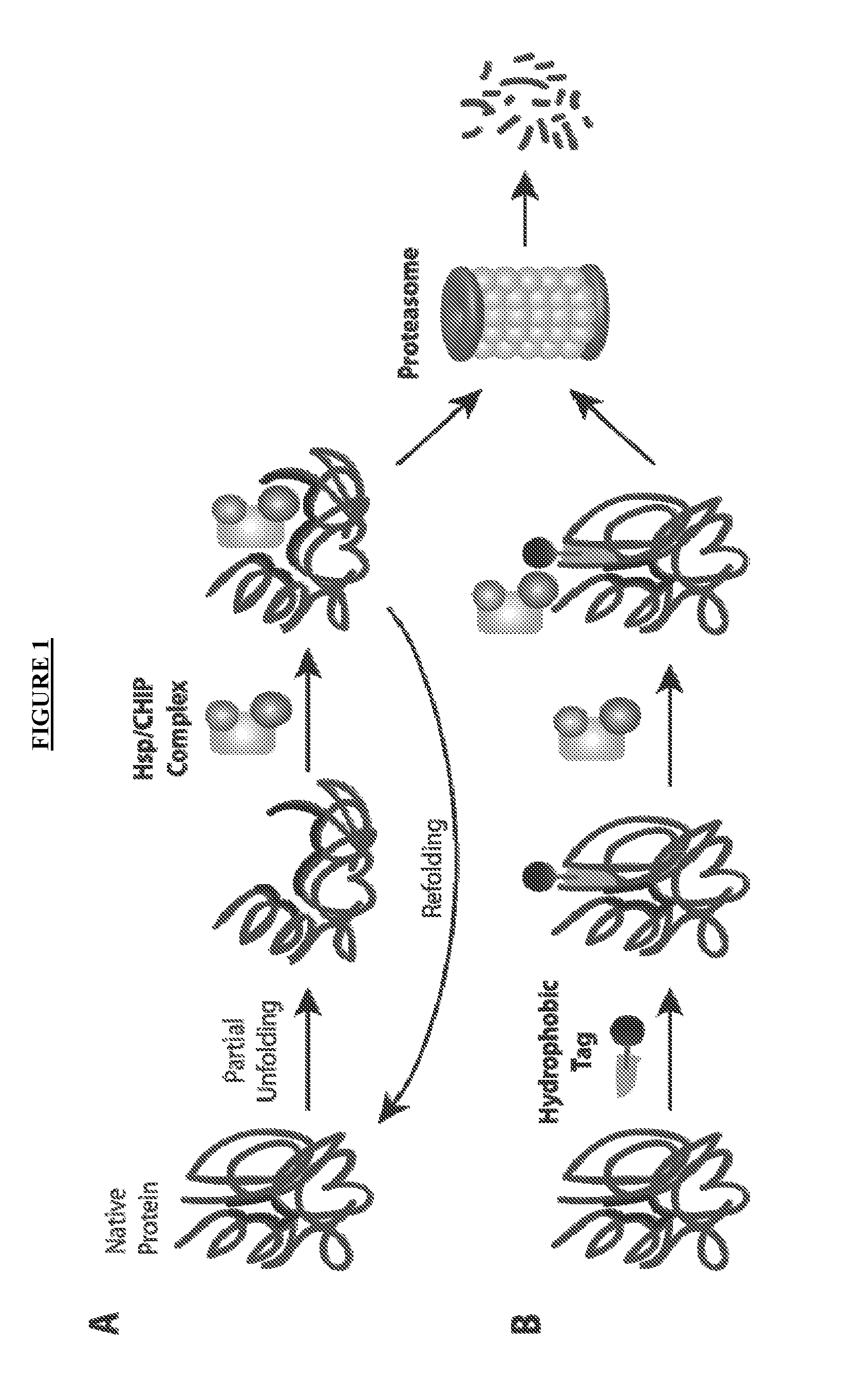
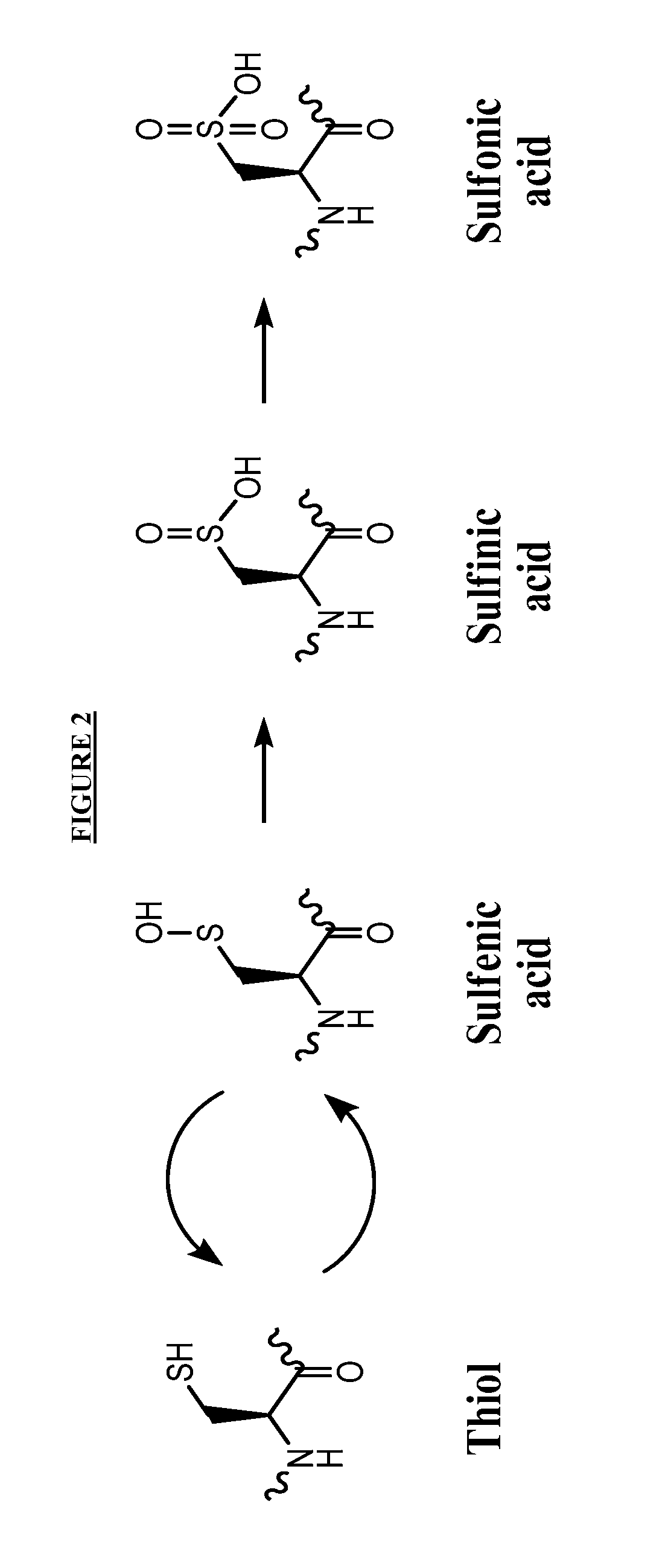
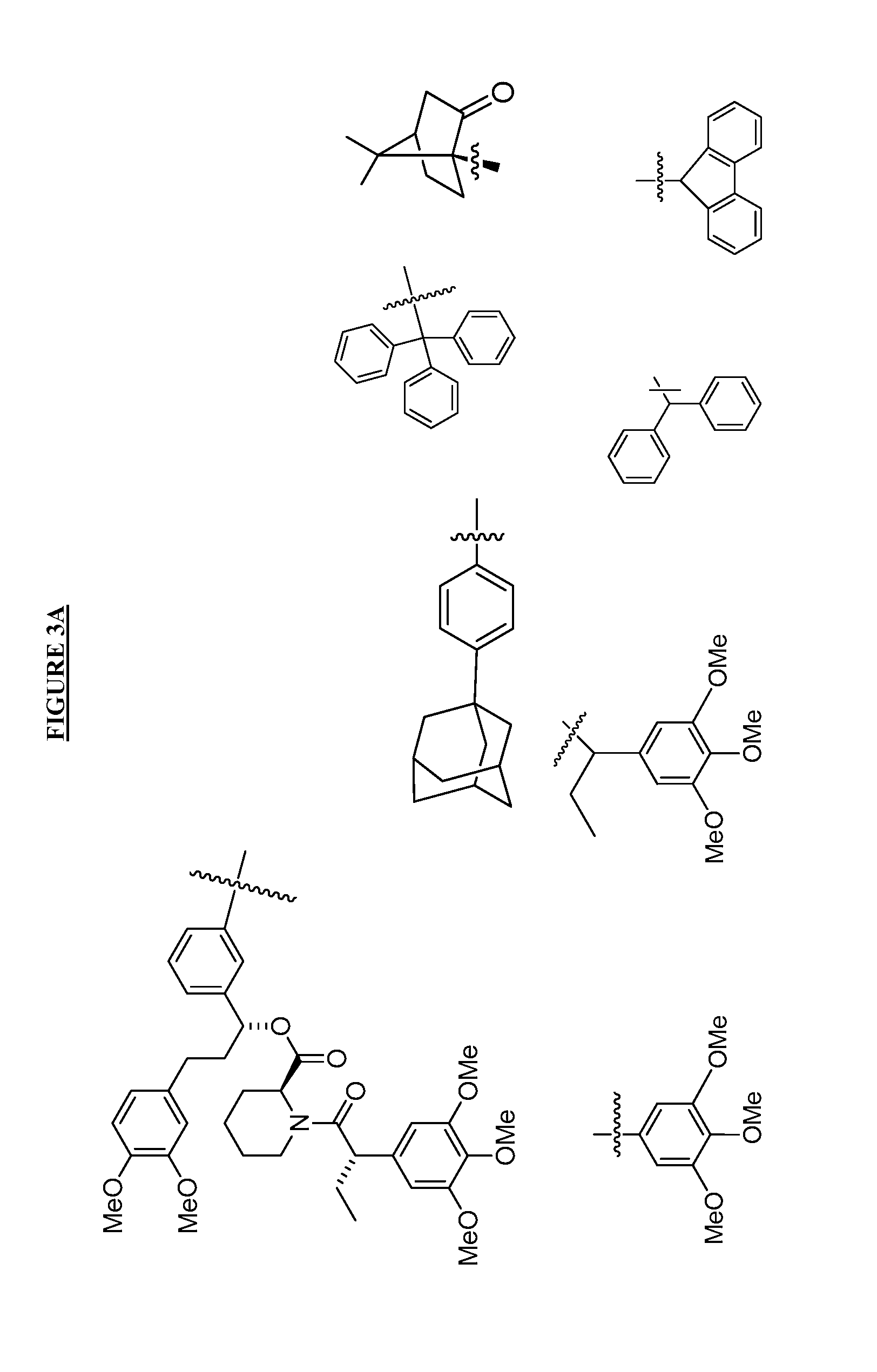
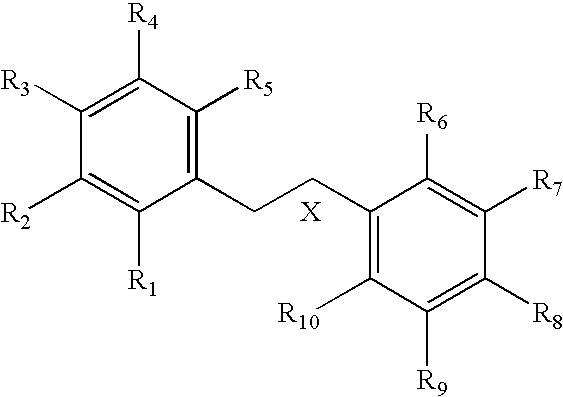
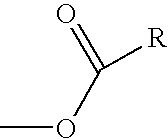
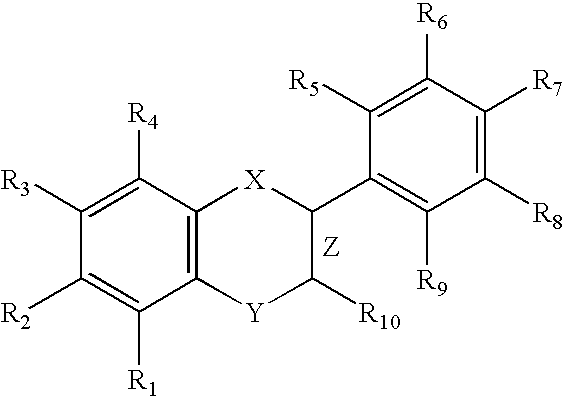
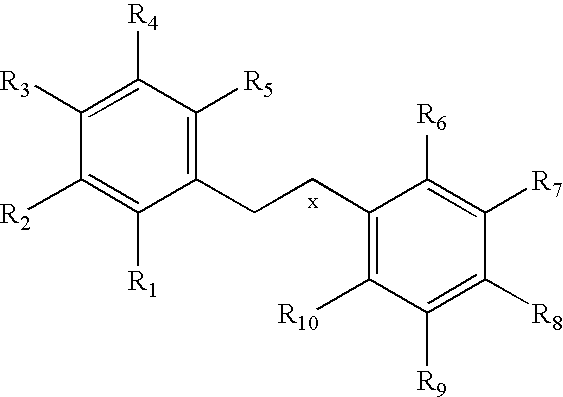
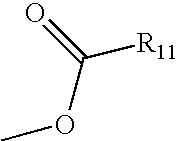
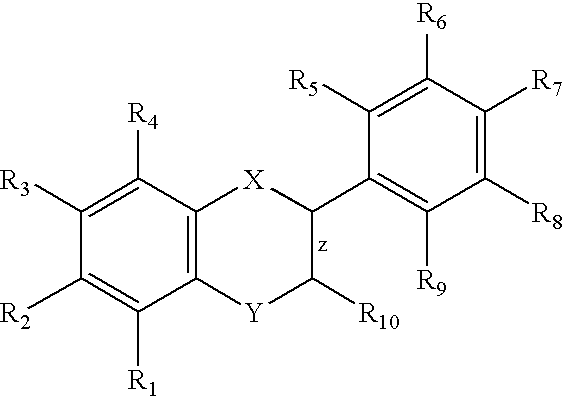
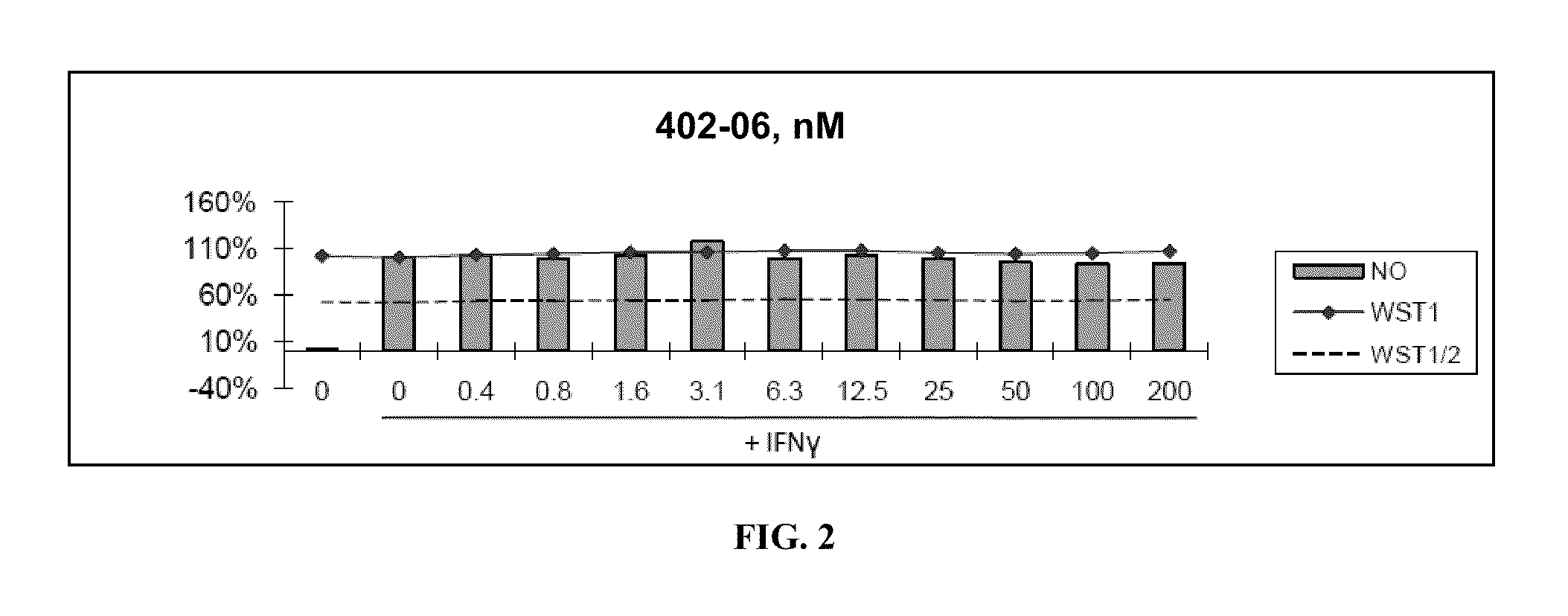
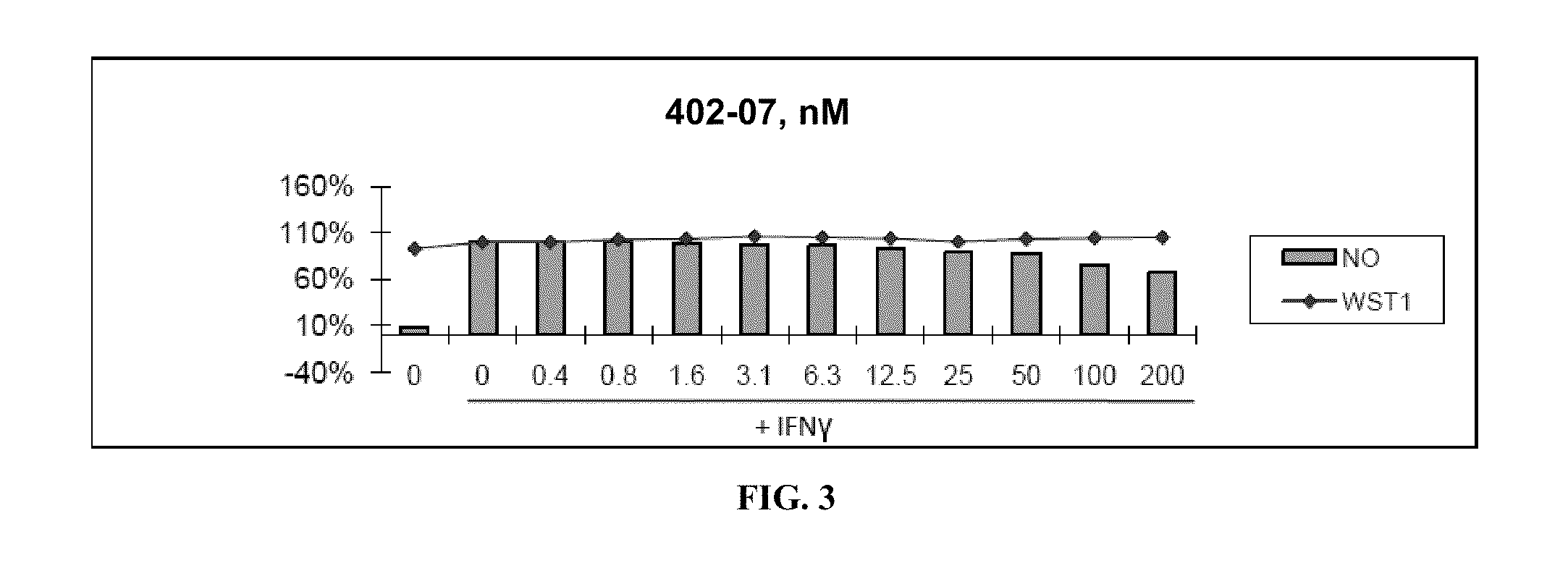
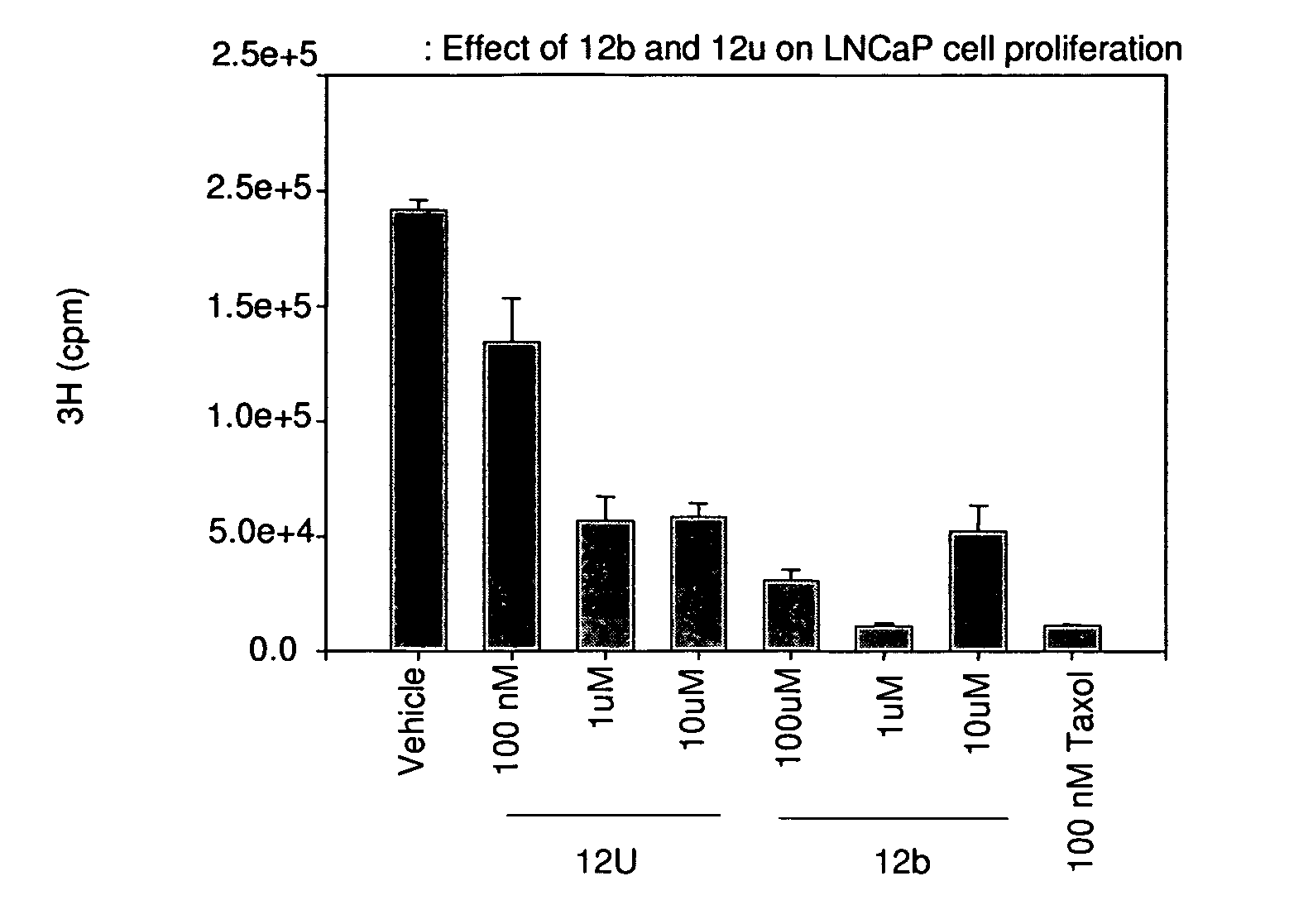
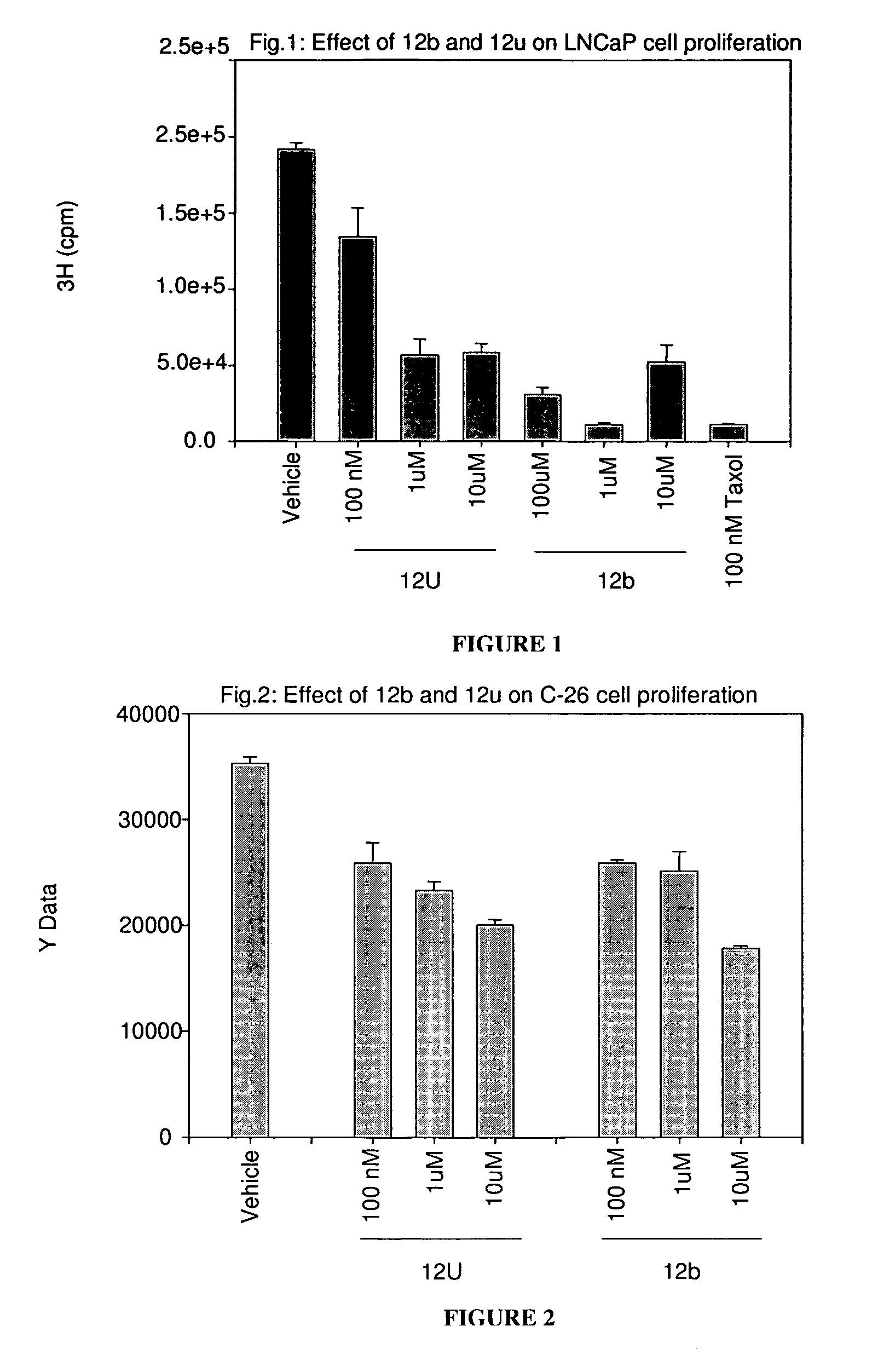
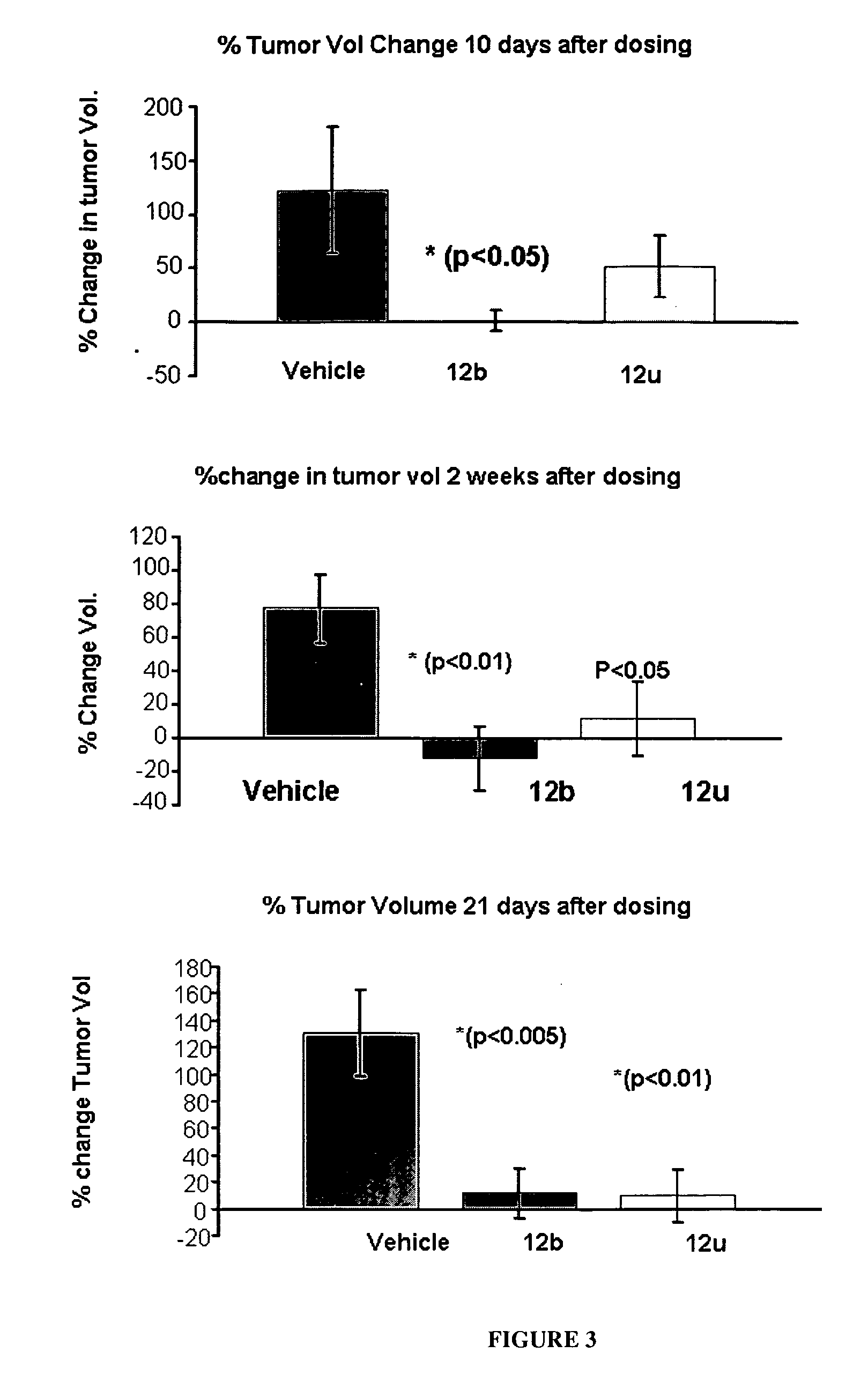
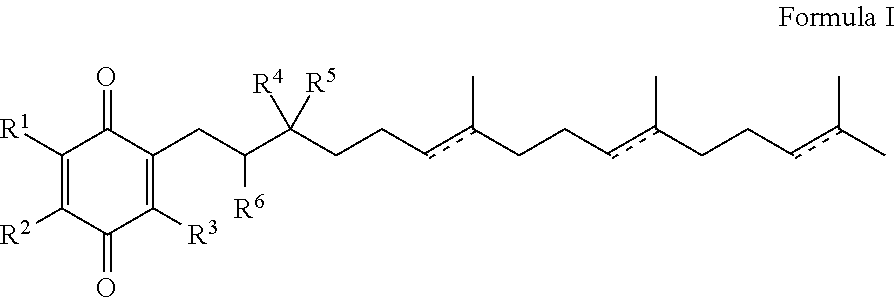
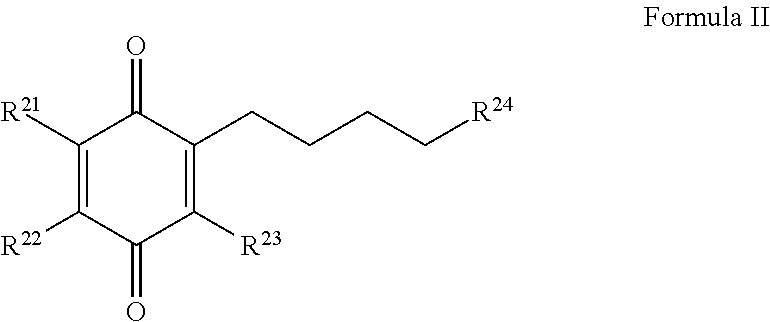
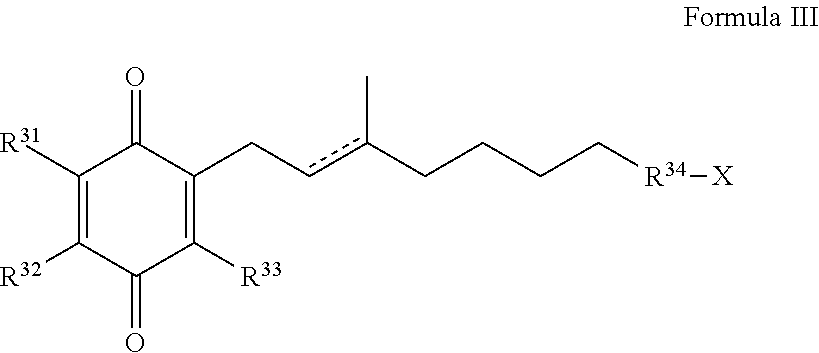
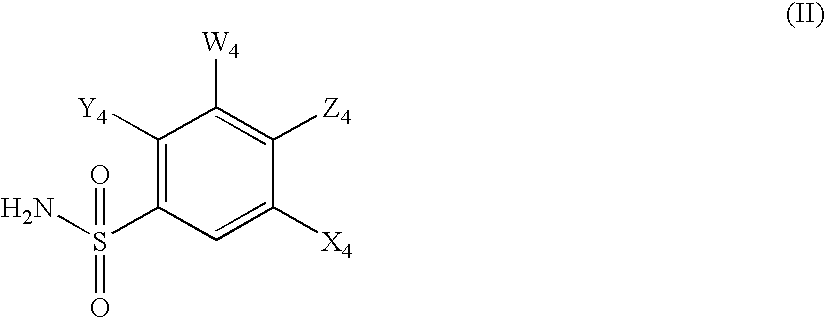
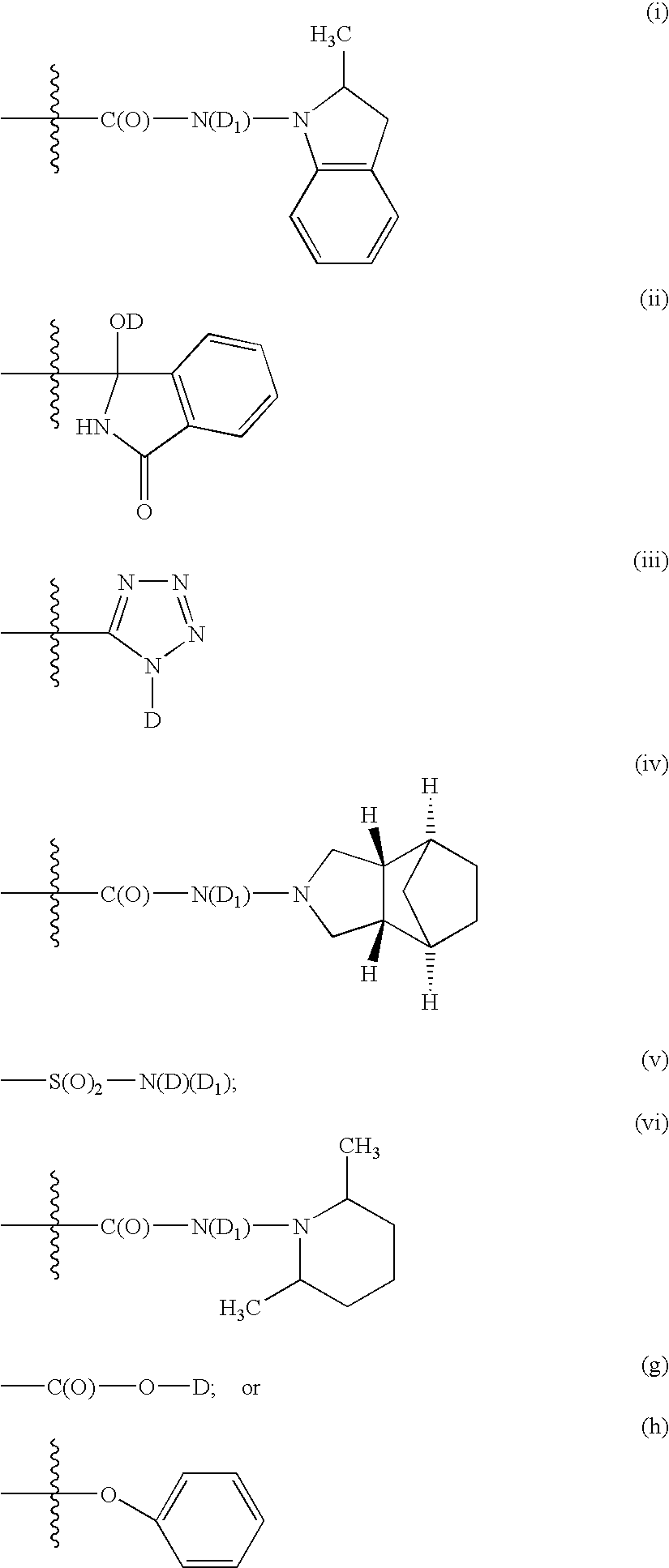
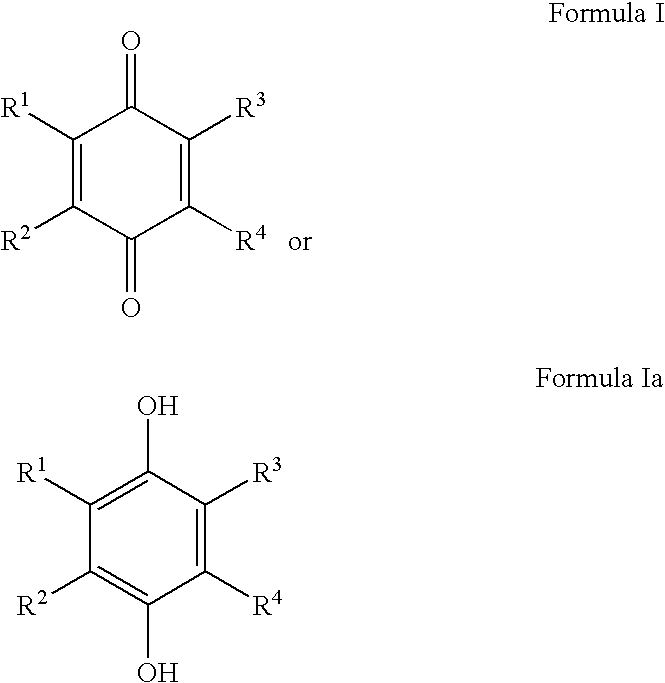
HYDROGENATED PYRIDO[4,3-b]INDOLES FOR THE TREATMENT OF OXIDATIVE STRESS
InactiveUS20100029706A1Modulate level of energyLower Level RequirementsBiocideDrug compositionsDiseaseDiabetes mellitus
Methods of treating or suppressing oxidative stress diseases including mitochondrial diseases, impaired energy processing disorders, and diseases of aging such as diabetes and cancer with hydrogenated pyrido[4,3-b]indoles such as dimebolin, are disclosed.
Owner:EDISON PHARMA
Nitric oxide donating derivatives for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders
InactiveUS20050080024A1Increases extentIncreases pathological severityBiocideSugar derivativesVascular diseaseEndothelial dysfunction
Compounds comprising nitric oxide derivatives of stilbenes, polyphenols and flavonoids and methods of their use are provided for treating patients suffering from any of hypercholesterolemia, vascular oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction.
Owner:RESVERLOGIX
Skin care compositions
InactiveUS20060286046A1Prevention and amelioration and treatment of pathological conditionAvoid skin diseasesBiocideCosmetic preparationsSun damageOxidative stress
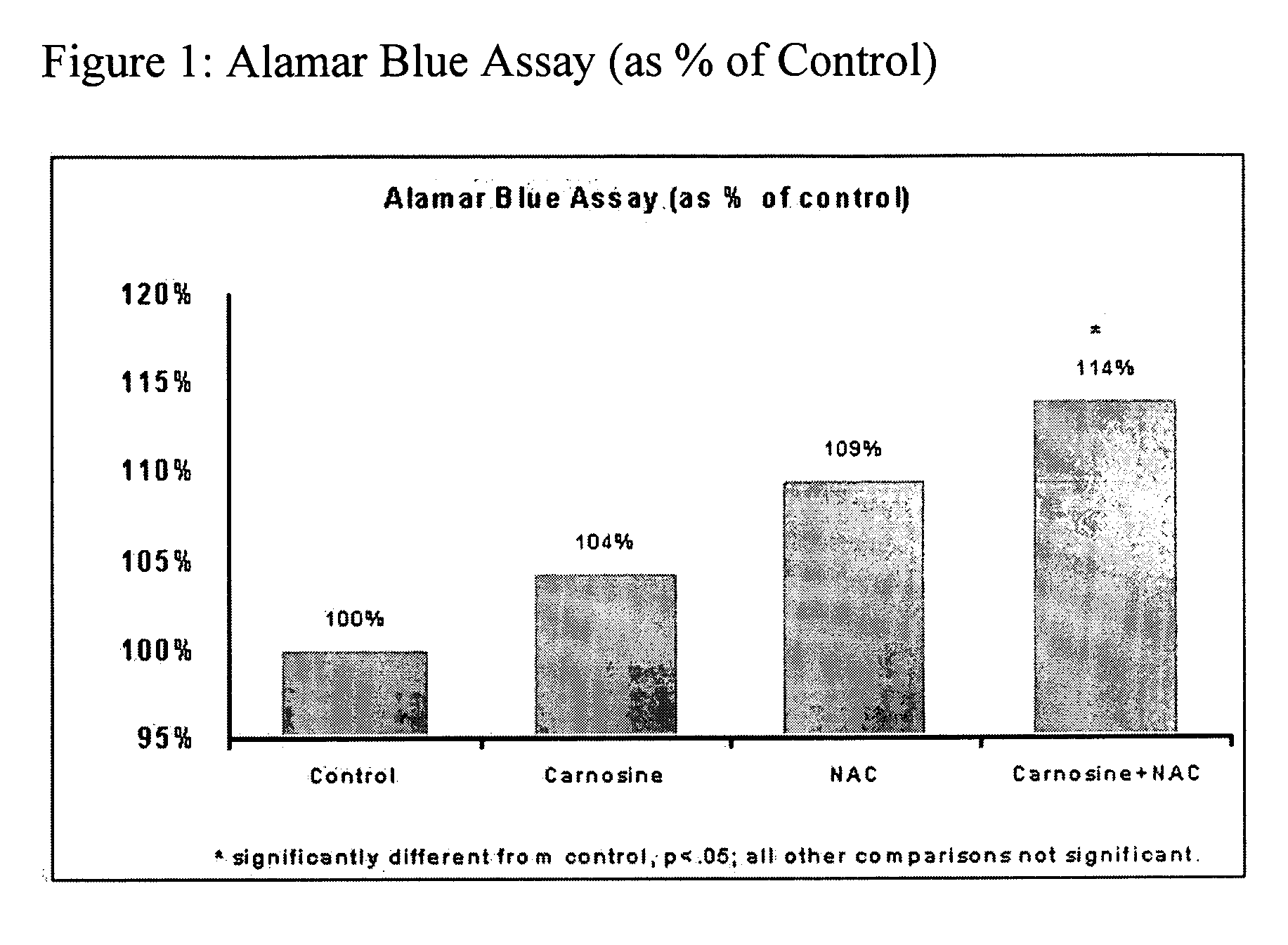
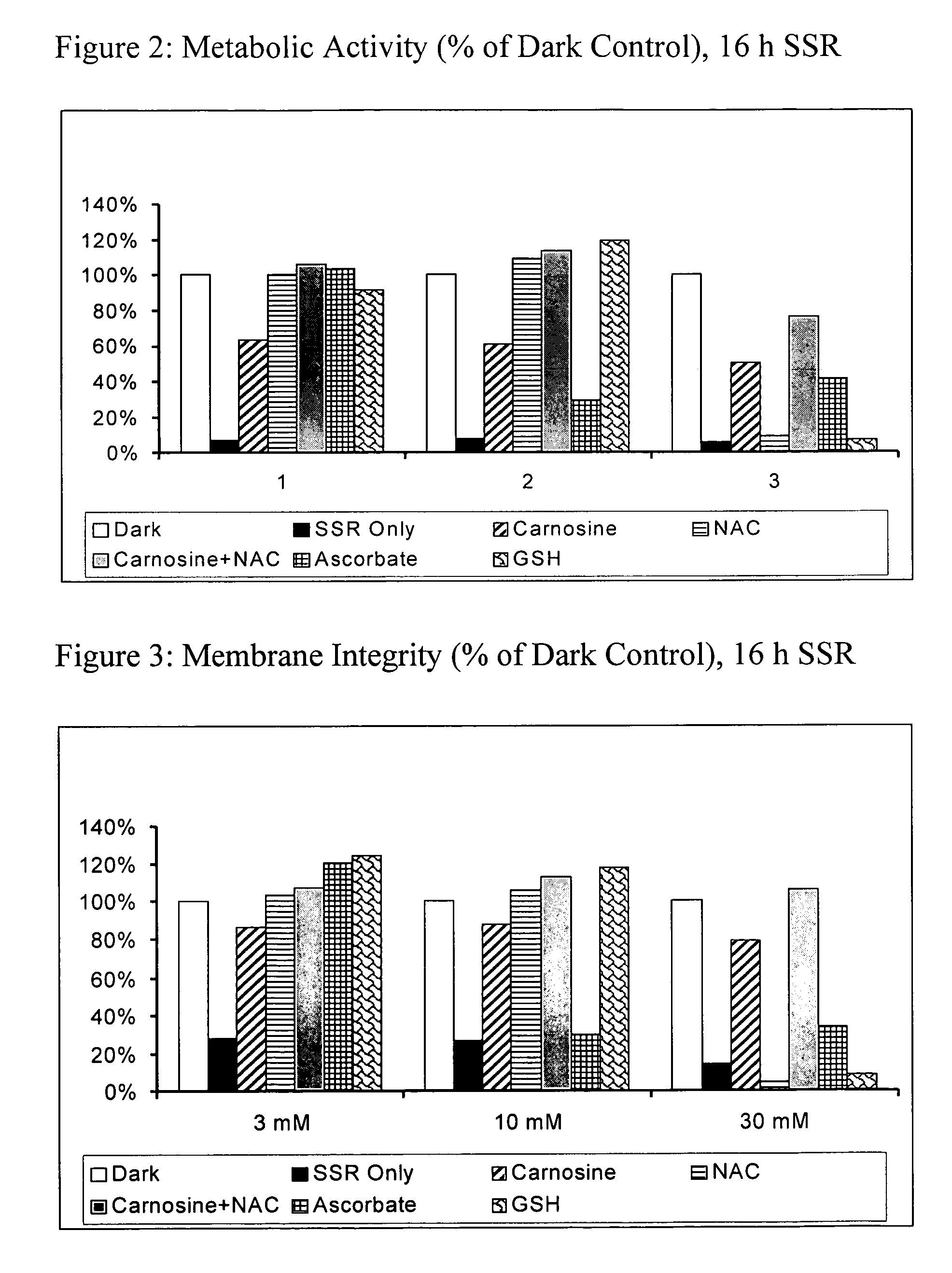
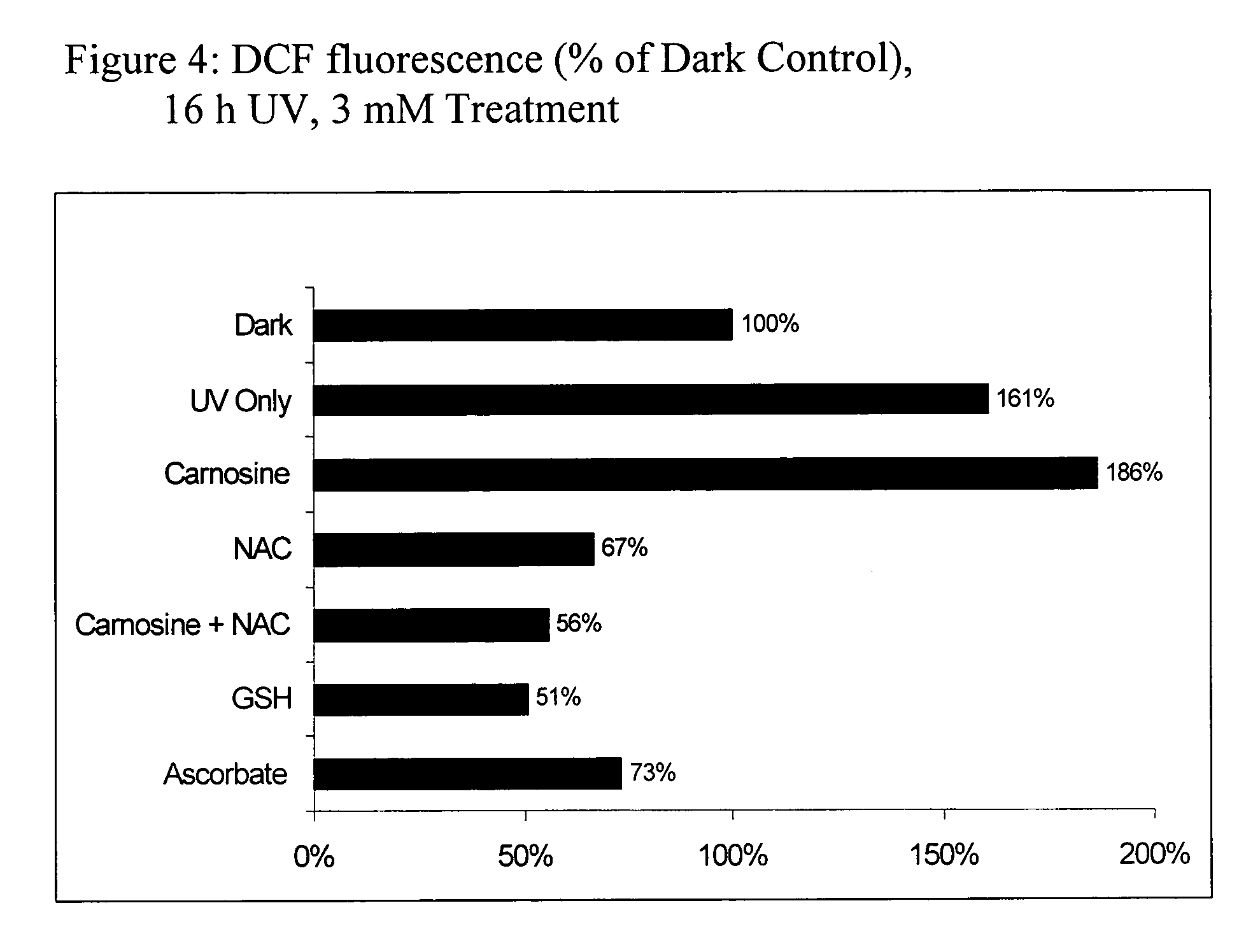
A skin care composition is provided which preferably comprises a mixture of N-acetylcysteine and L-carnosine in combination with a cosmetic, dermatological or pharmaceutically acceptable carrier therefor. The composition may optionally be provided as a sunscreen formulation, and provides a method for the prevention, amelioration or treatment of pathological conditions of the skin, including, but not limited to, intrinsic or chronological aging, or aging due to sun damage (photoaging), and which conditions are caused by, or exacerbated by, oxidative stress, carbonyl stress, or a combination of both.
Owner:HABER C ANDREW
Nitric oxide donating derivatives of stilbenes, polyphenols and flavonoids for the treatment of cardiovascular disorders
InactiveUS20050080021A1Increase transcription factor bindingRegulate expressionBiocideSugar derivativesNitric oxidePolyphenol
Compounds and methods are provided for treating patients suffering from any of hypercholesterolemia, vascular oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction.
Owner:RESVERLOGIX
Resorcinol compounds for dermatological use
Provided herein are methods and compositions comprising resorcinol derivatives for the use of treating, regulating or preventing a skin condition characterized by oxidative stress or a degenerative process. Methods of preventing, lightening or reducing the appearance of visible discontinuities of the skin resulting from skin pigmentation, skin aging, or other disorders are also disclosed.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Nanoparticles for Protection of Cells from Oxidative Stress
InactiveUS20100172994A1Increase the number ofImprove survivabilityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideMetal oxide nanoparticlesMedicine
The present invention concerns metal oxide semiconductor nanoparticles with free radical scavenging activity, compositions comprising such nanoparticles, methods for their use, and methods for their production. In one aspect, the invention concerns a method for enhancing the survival or viability of transplanted cells, comprising administering an effective amount of metal oxide semiconductor nanoparticles to a target anatomical site of a subject before, during, or after administration of transplant cells to the subject. Preferably, the metal oxide nanoparticle is a cerium oxide (ceria) nanoparticle.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: novel derivatives of oleanolic acid
InactiveUS20120238767A1Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionNervous disorderSteroidsDiseaseOxidative stress
Disclosed herein are novel oleanolic acid derivatives. Methods of preparing these compounds are also disclosed. The oleanolic acid derivatives of this invention may be used for the treatment and prevention of many diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, inflammation, and pathologies involving oxidative stress.
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
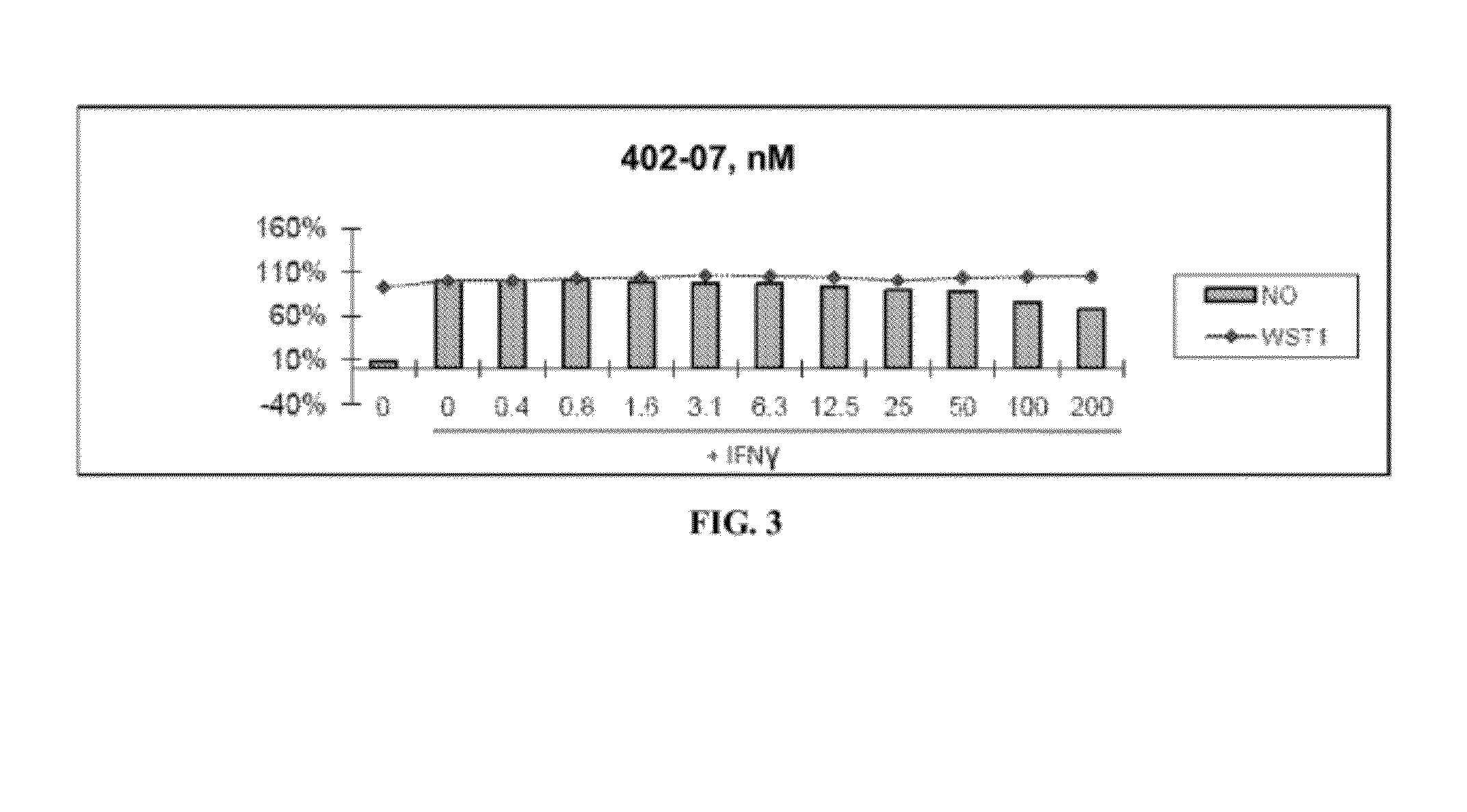
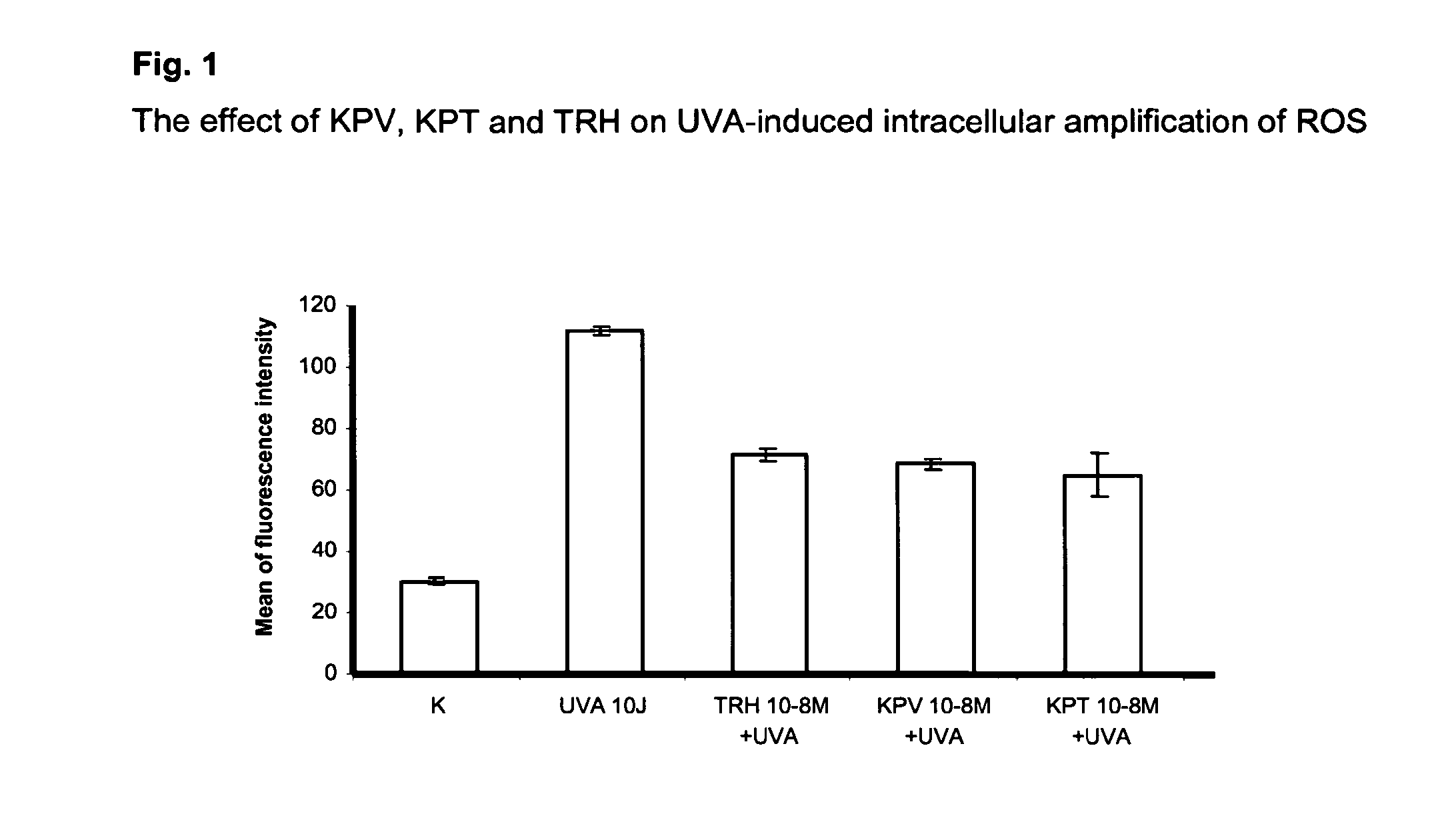
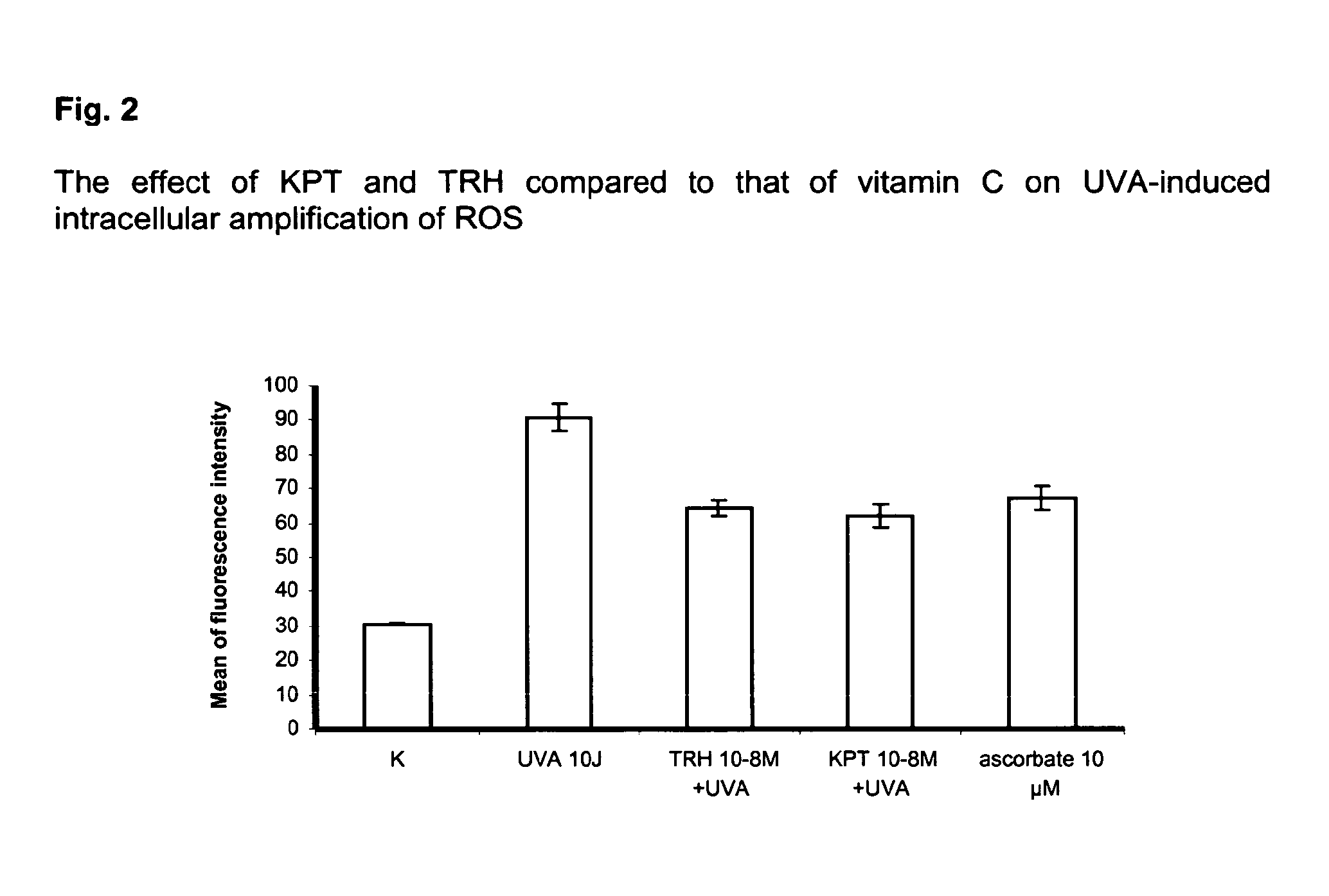
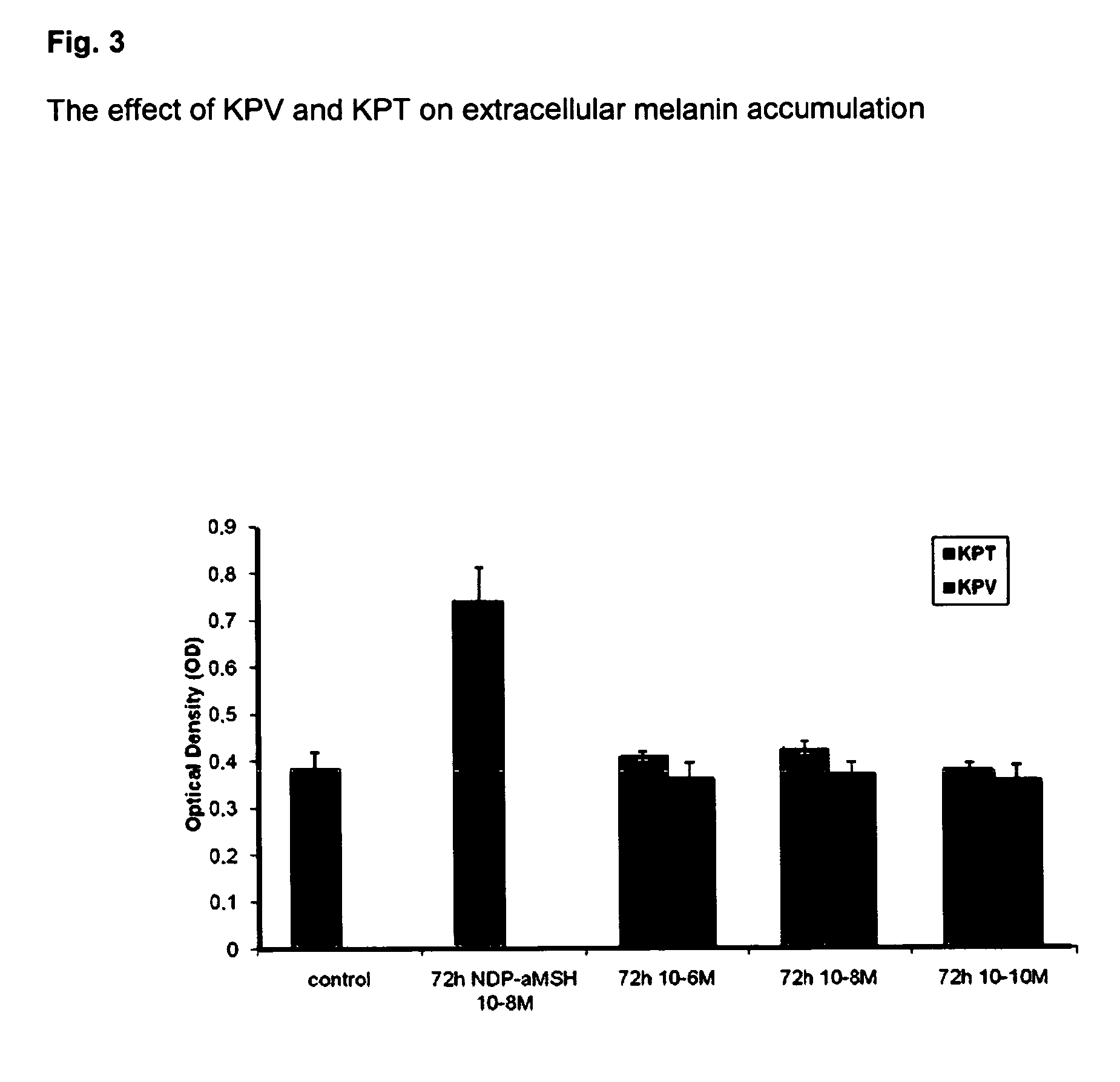
Compositions for reducing oxidative stress and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100286056A1Reduce oxidative stressGood dispersionCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsDiseaseMedicine
The present invention relates to the use of one or more tripeptides selected from the group consisting of NLys-Pro-ValC, NLys-Pro-ThrC and NpGLu-His-ProC for the reduction of oxidative stress. The above tripeptides are particularly useful for the treatment of a disease or damage caused by oxidative stress; such as vitiligo, scleroderma, necrosis, or erythema; furthermore, a disease or damage of the hair, like premature hair loss or premature formation of grey hair. Furthermore the invention relates the cosmetic use of the above tripeptides, in particular against skin aging. Further the invention relates cosmetic compositions containing at least one of said tripeptides.
Owner:UNIVSKLINIKUM MUNSTER
Neuroprotectin D1 protects against cellular apoptosis, stroke damage, alzheimer's disease and retinal diseases
InactiveUS20050075398A1Increase secretionReduce secretionBiocideSenses disorderRisk strokeRetinal pigment epithelial cell
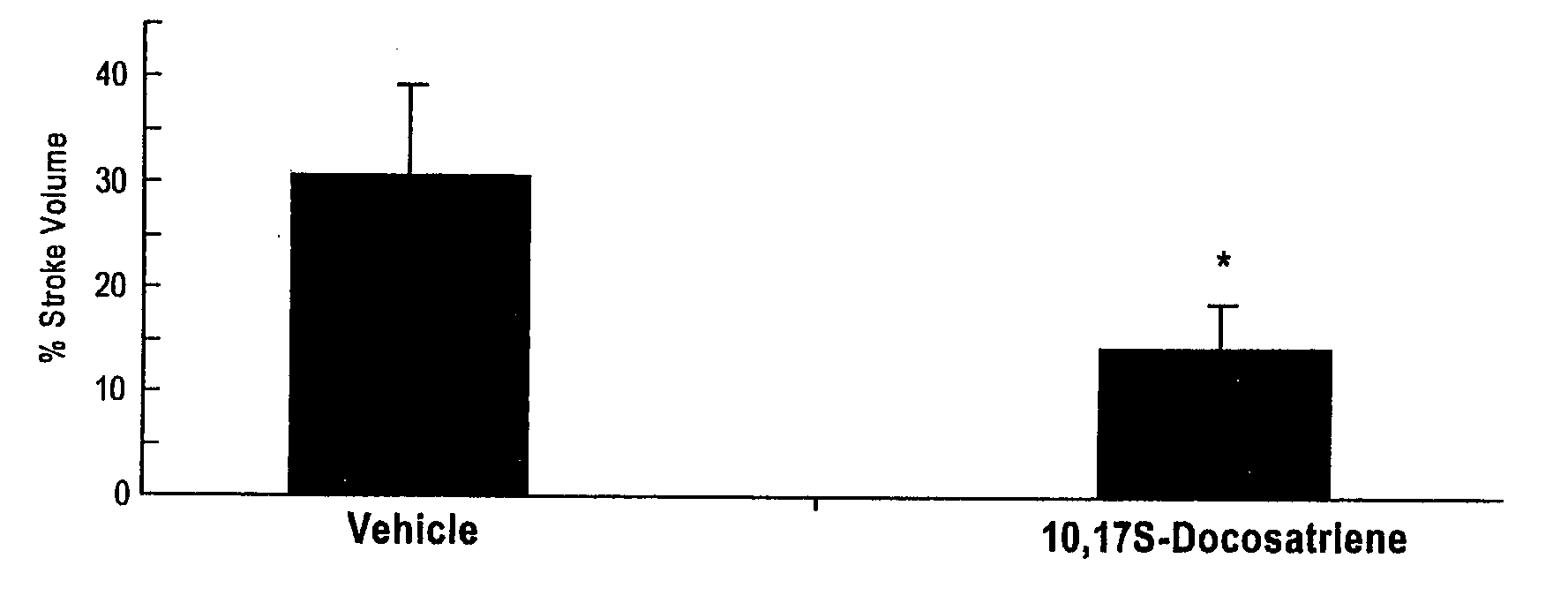
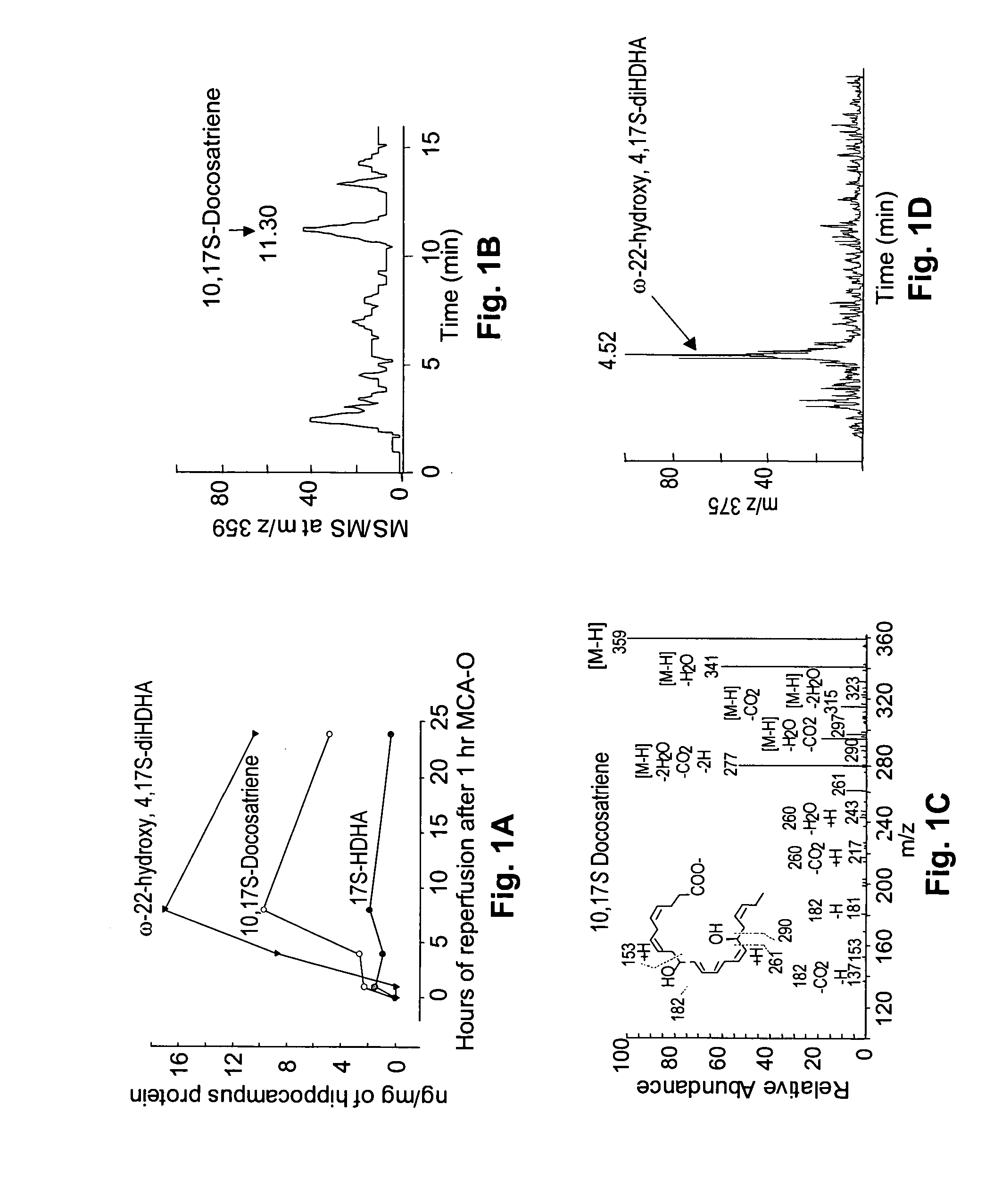
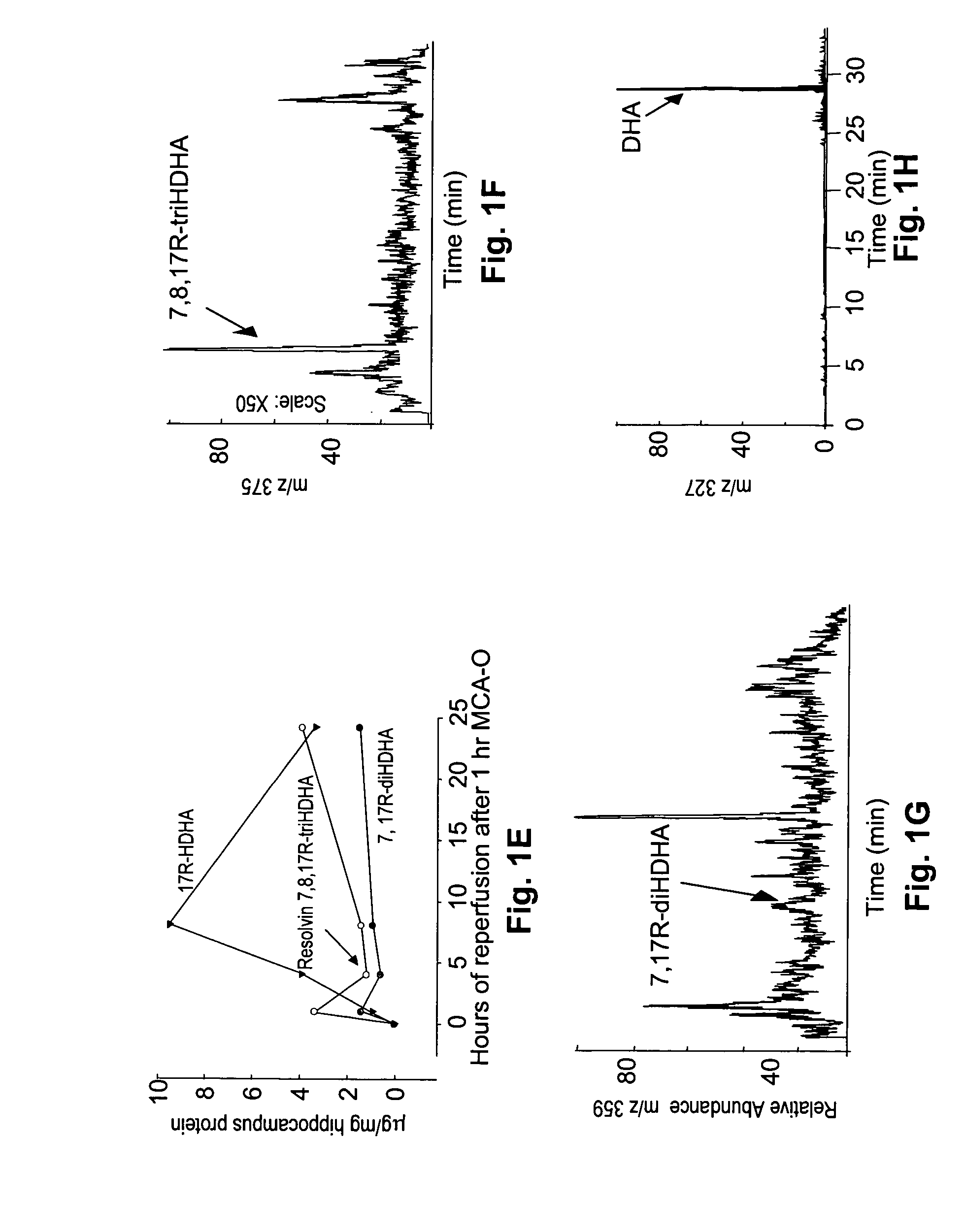
A unique DHA product, 10, 17S-docosatriene (“Neuroprotectin D1” or “NPD1”), was found to provide surprisingly effective neuroprotection when administered right after an experimental stroke. Moreover, both nerve cells and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells were found to synthesize 10,17S-docosatriene (NPD1) from DHA. NPD1 also potently counteracted H2O2 / TNFα oxidative stress-mediated cell apoptotic damage. Under the same oxidative-stress conditions, NPD1 up-regulated the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, and decreased expression of the pro-apoptotic proteins, Bad and Bax. Moreover, in RPE cells NPD1 inhibited oxidative stress-induced caspase-3 activation, IL-1β-stimulated human COX-2 promoter expression, and apoptosis due to N-retinylidene-N-retinylethanolamine (A2E). Overall, NPD1 protected both nerve and retinal pigment epithelial cells from cellular apoptosis and damage due to oxidative stress. NPD1 concentration in the brain of Alzheimer's patients was found to be significantly decreased from that of controls. In cultured human brain cells, NPD1 synthesis was up-regulated by neuroprotective soluble β amyloid, and NPD1 was found to inhibit secretion of toxic β amyloid peptides.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Antioxidant inflammation modulators: novel derivatives of oleanolic acid
ActiveUS8071632B2Suppresses demyelinationSuppresses transectionBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseMedicine
Owner:REATA PHARMA INC
Nuclear receptor binding agents
InactiveUS20090030036A1Treating and ameliorating and preventing generationPromotes and enhances activityBiocideSenses disorderProstate cancerRisk stroke
The present invention relates to a novel class of nuclear receptor binding agents (NRBAs). The NRBAs are applicable for use in the prevention and / or treatment of a variety of diseases and conditions including prevention and treatment of cancers such as prostate and breast cancer, osteoporosis, hormone-related diseases, inflammatory diseases, oxidative stress related disorders such as Parkinson's and stroke, neurological disorders, ophthalamic disorders, cardiovascular disease, and obesity.
Owner:GTX INCORPORATED
Treatment of oxidative stress disorders including contrast nephropathy, radiation damage and disruptions in the function of red cells
InactiveUS20110269776A1Promote resultsEfficient administrationBiocideKetone active ingredientsElectron flowOxygen
Methods of treating or suppressing oxidative stress diseases and symptoms related to oxidative stress affecting normal electron flow in the cells or caused by reactive oxygen species with redox-active therapeutics. Use of redox-active therapeutics for the reduction, suppression or treatment of oxidative stress induced by chemical agents such as contrast agents and other nephrotoxic agents, by radiation exposure, and by disruptions in the transport of oxygen to tissues, is disclosed.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
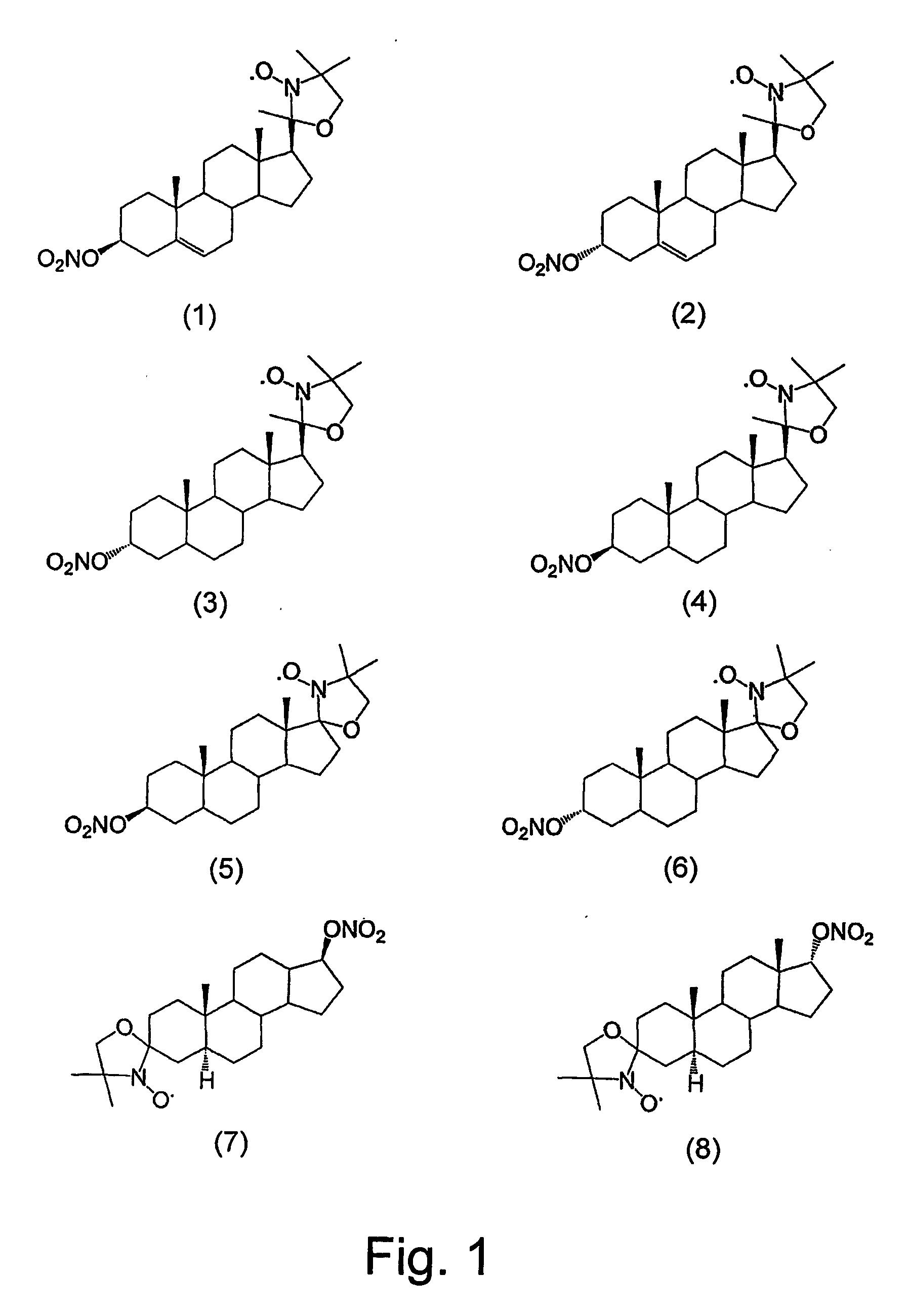
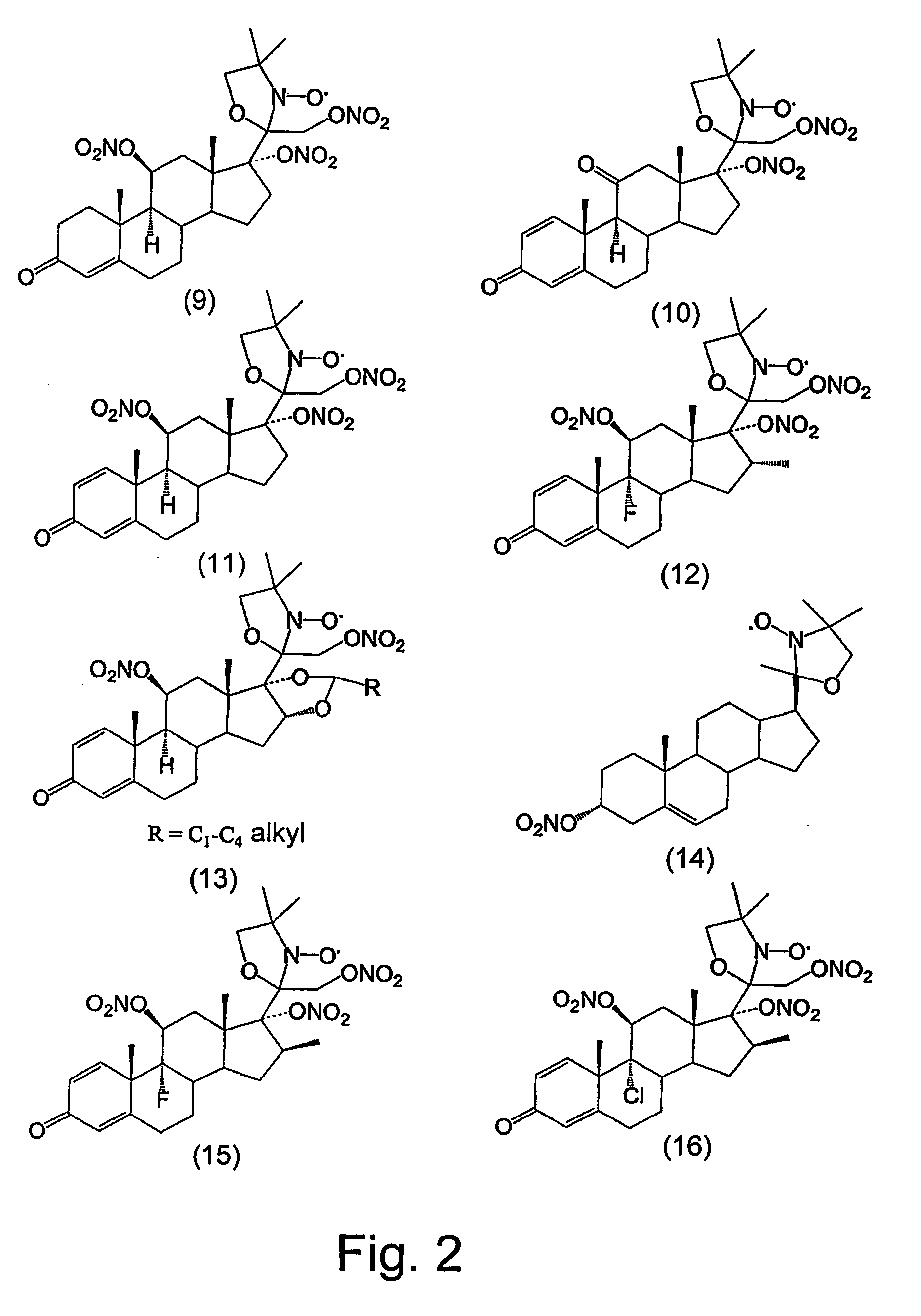
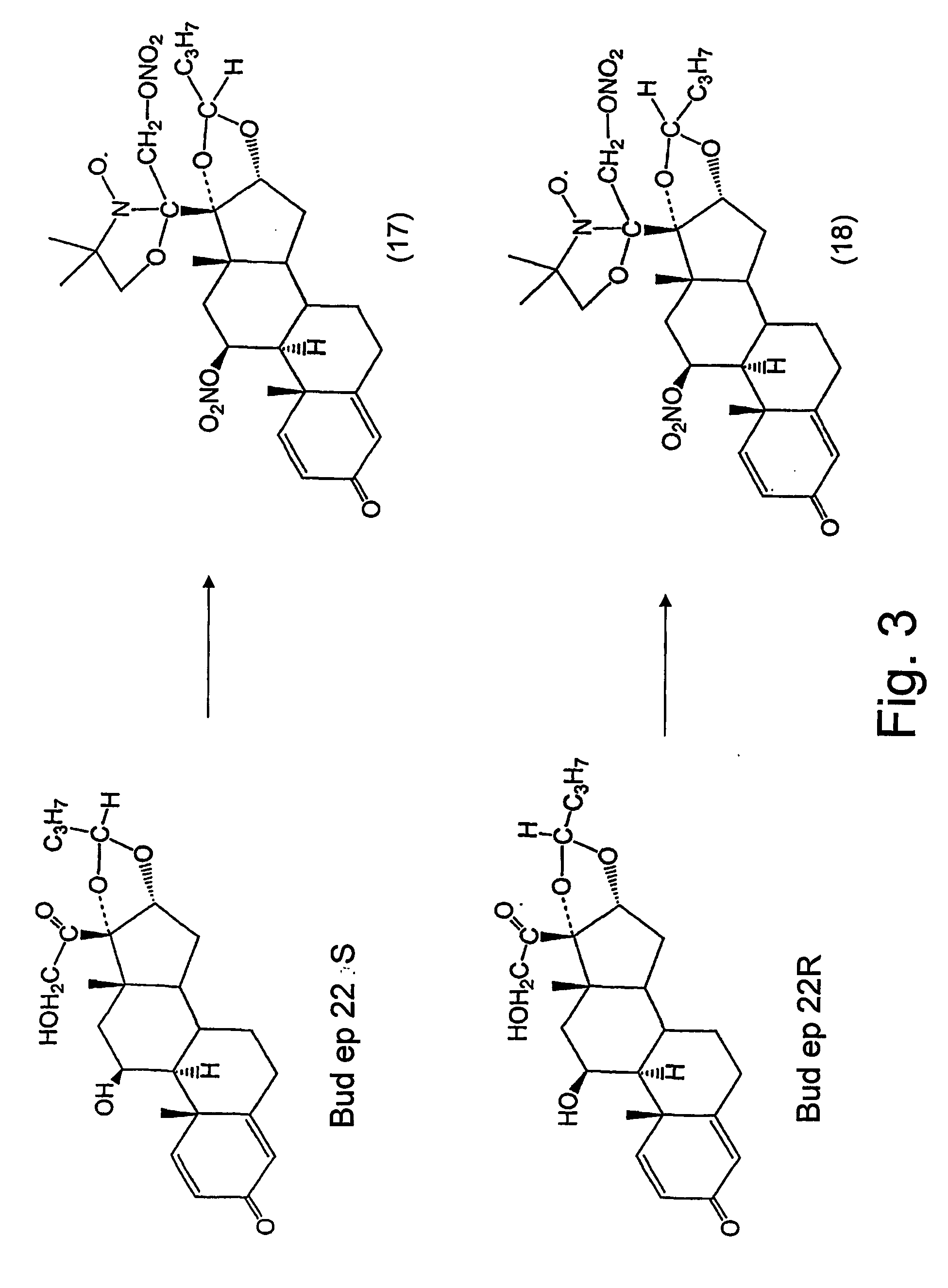
Steroid compounds comprising superoxide dismutase mimic groups and nitric oxide donor groups, and their use in the preparation of medicaments
The present invention relates to multifunctional steroid compounds combining a steroid component with SOD mimic component and optionally also with NO donor component, and to their use in treating and preventing disorders associated with oxidative stress and free radical injury, or disorders in which treatment with steroids is indicated, whereas such combination increases the efficacy of treatment and reduces side effects associated with steroid treatment. The invention further relates to methods and devices for administering the compounds.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Treatment of Inflammatory Conditions
InactiveUS20110112188A1Reduction and elimination and inhibition of functionTreat painBiocideSenses disorderOxidative stressSugar
The invention relates to methods of inhibiting production and function of 3-deoxyglucosone and other alpha-dicarbonyl sugars in skin thereby treating or prevention various diseases, disorders or conditions. Additionally, the invention relates to treatment of various diseases, disorders or conditions associated with or mediated by oxidative stress since 3DG induces ROS and AGEs, which are associated with the inflammatory response caused by oxidative stress.
Owner:DYNAMIS THERAPEUTICS
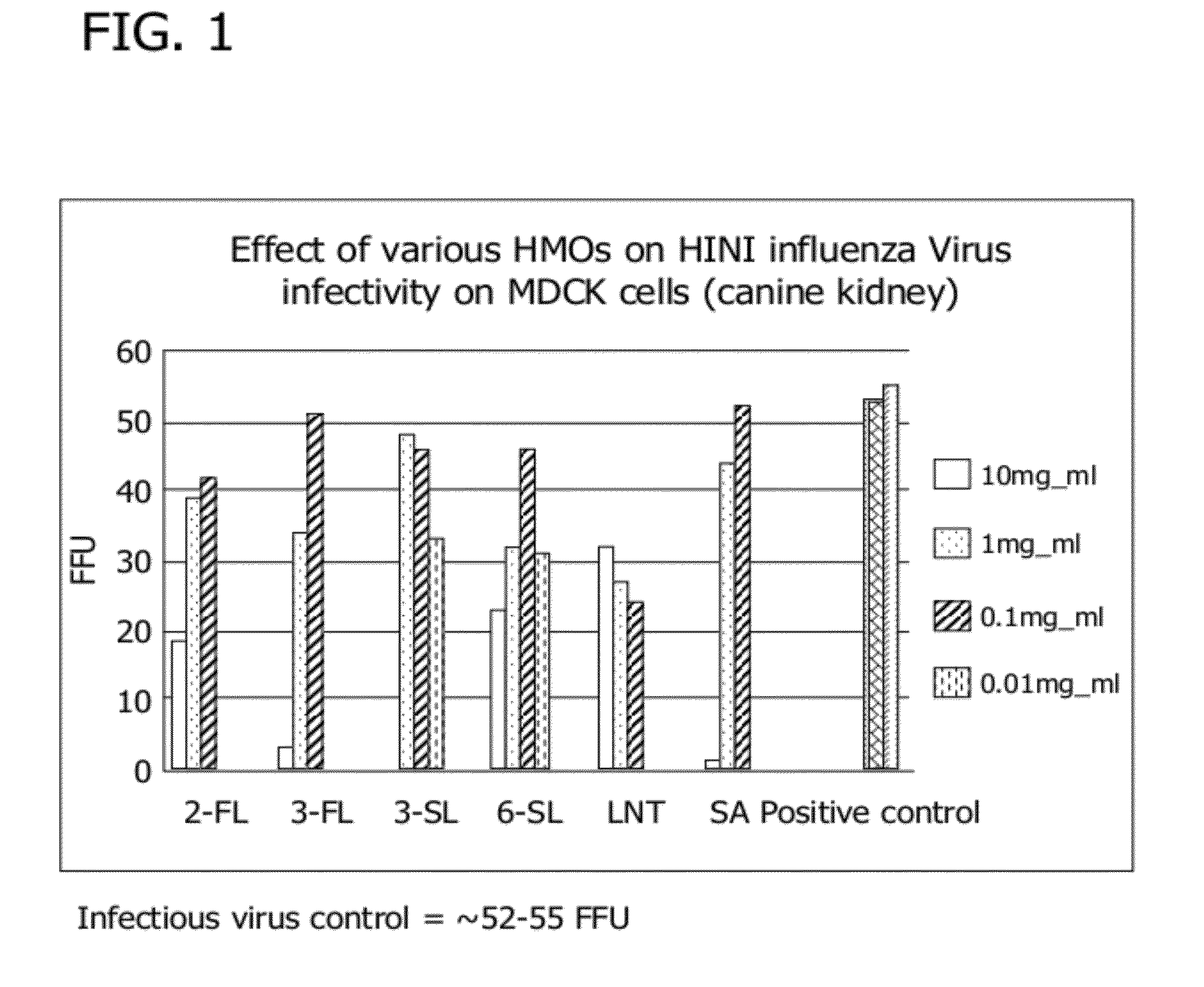
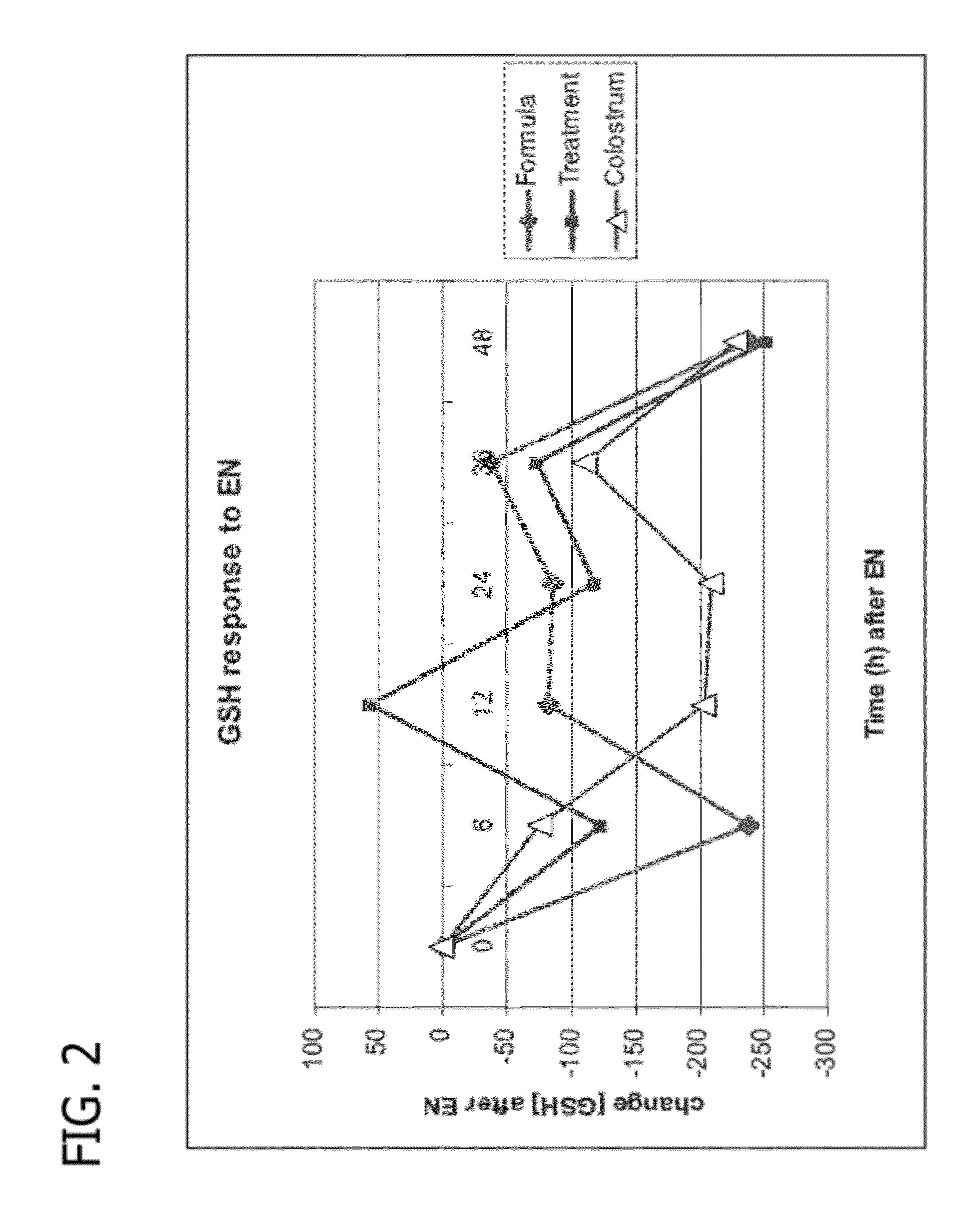
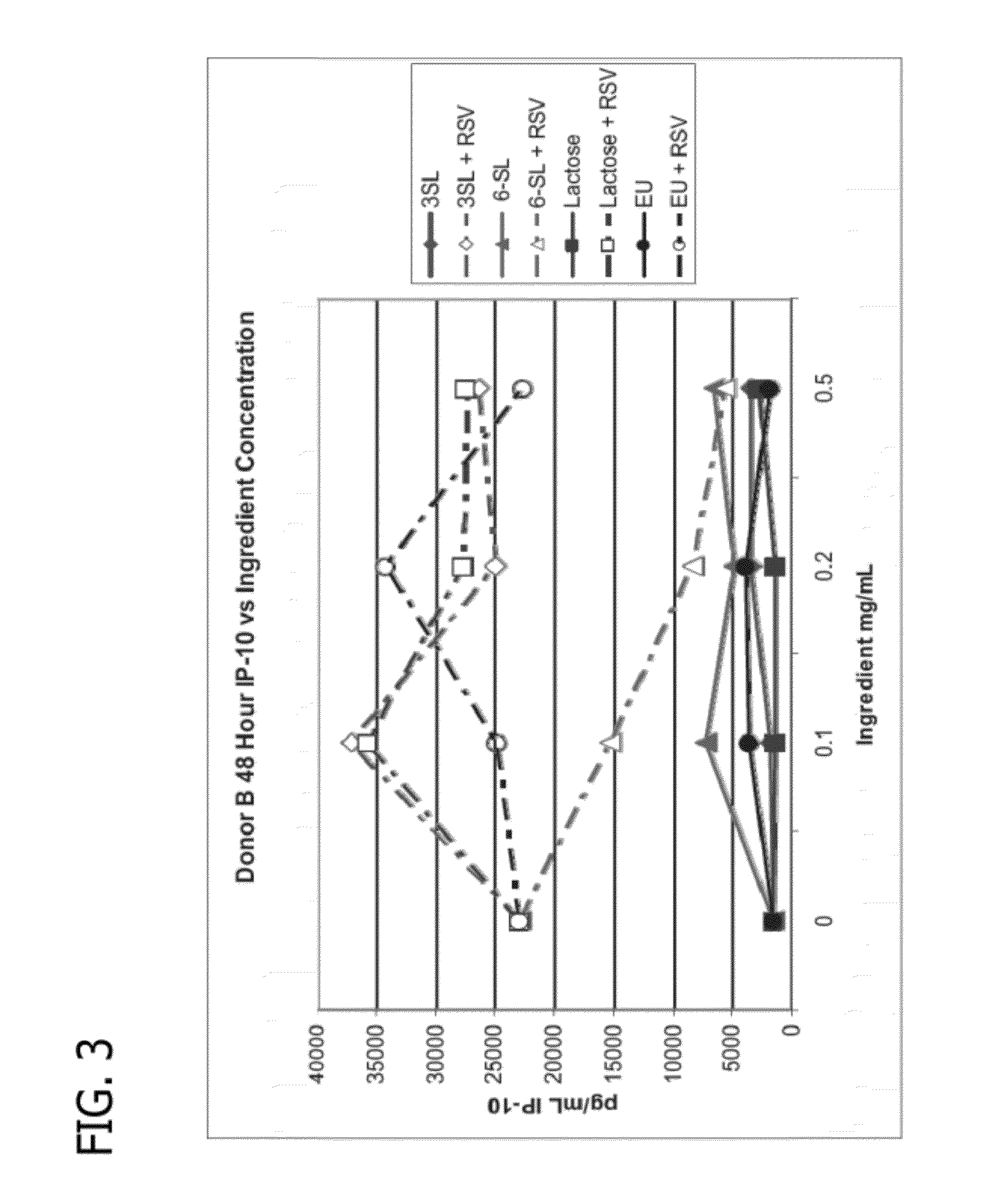
Methods for reducing the incidence of oxidative stress using human milk oligosaccharides, vitamin c and Anti-inflammatory agents
ActiveUS20120172307A1Avoid developmentReduce oxidative stressBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseVitamin C
Disclosed are methods of reducing the incidence of oxidative stress in infants, toddlers, and children using nutritional compositions including human milk oligosaccharides. The nutritional compositions including the human milk oligosaccharides are effective at reducing inflammation and the incidence of inflammatory diseases.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
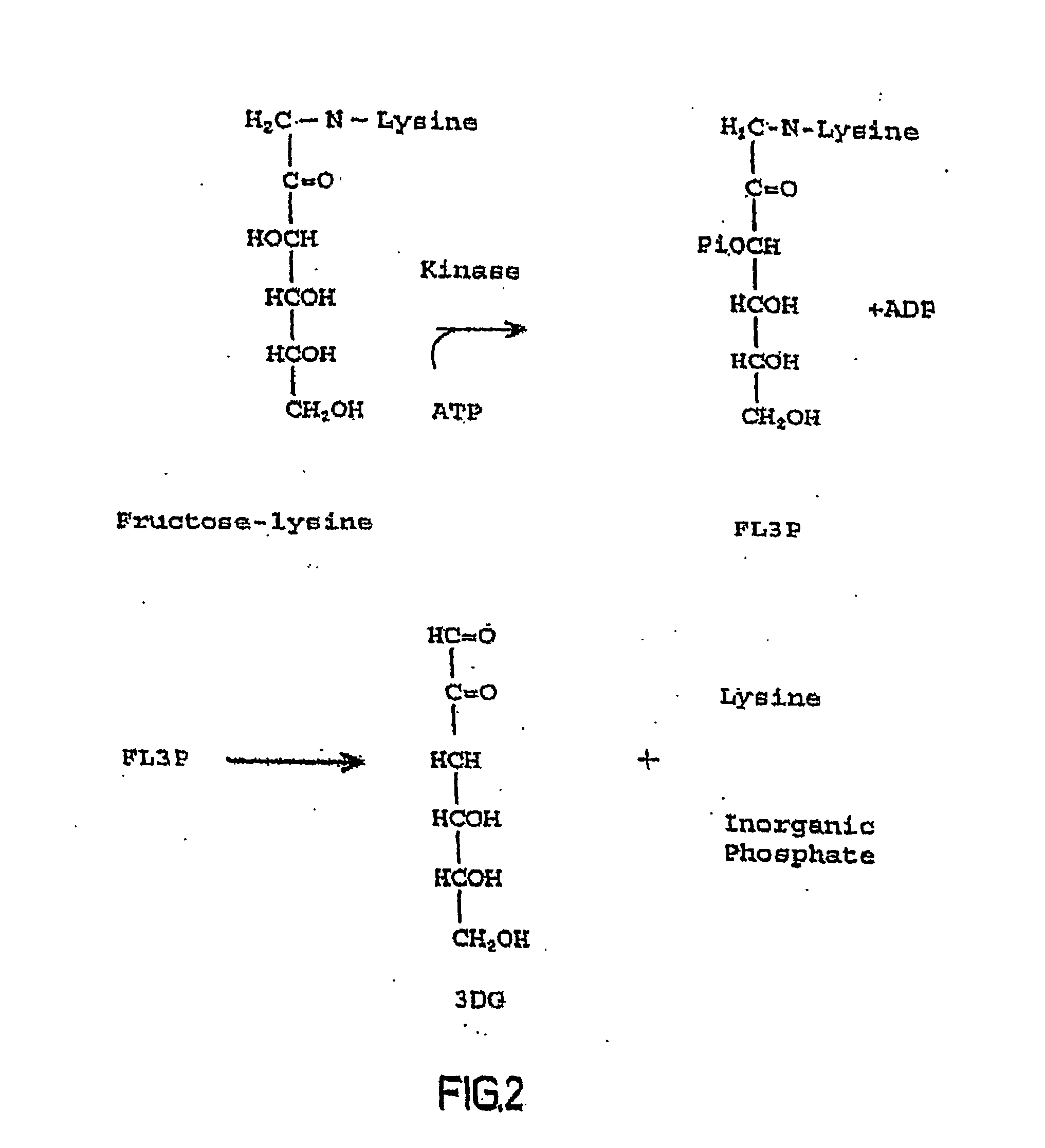
Compositions and Methods Related to Fructosamine-3-Kinase Inhibitors
The invention relates to compounds and methods for inhibiting production and function of 3-deoxyglucosone and other alpha-dicarbonyl sugars in skin, by way of fructosamine-3-kinase inhibition, thereby treating or prevention various diseases, disorders or conditions. Additionally, the invention relates to treatment of various diseases, disorders or conditions associated with or mediated by oxidative stress since 3DG induces ROS and AGEs, which are associated with the inflammatory response caused by oxidative stress.
Owner:DYNAMIS THERAPEUTICS
Nitrosated and nitrosylated diuretic compounds, compositions and methods of use
The invention describes novel nitrosated and / or nitrosylated diuretic compounds or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, and novel compositions comprising at least one nitrosated and / or nitrosylated diuretic compound, and, optionally, at least one nitric oxide donor and / or at least one therapeutic agent. The invention also provides novel compositions and kits comprising at least one diuretic compound of the invention, that is optionally nitrosated and / or nitrosylated, and, optionally, at least one nitric oxide donor compound and / or at least one therapeutic agent. The invention also provides methods for (a) treating conditions resulting from excessive water and / or electrolyte retention; (b) treating cardiovascular diseases; (c) treating renovascular diseases; (d) treating diabetes; (e) treating diseases resulting from oxidative stress; (f) treating endothelial dysfunctions; (g) treating diseases caused by endothelial dysfunctions; (h) treating cirrhosis; (j) treating pre-eclampsia; (k) treating osteoporosis; and (l) treating nephropathy.
Owner:NICOX SA
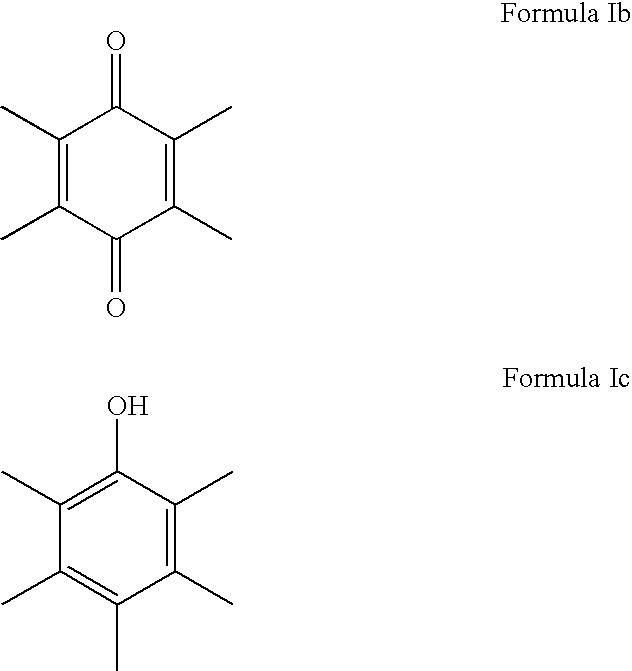
Dermatological compositions with Anti-aging and skin even-toning properties
InactiveUS20100010100A1Good lookingReduce appearance problemsCosmetic preparationsBiocideOxidative stressSkin color
The present invention relates to methods and compositions comprising benzoquinones such as Duroquinone, for the use of treating, regulating or preventing a skin condition characterized by oxidative stress or a degenerative process. Methods of preventing, lightening or reducing the appearance of visible and / or tactile discontinuities of the skin resulting from skin pigmentation or skin aging are also disclosed.
Owner:EDISON PHARMA
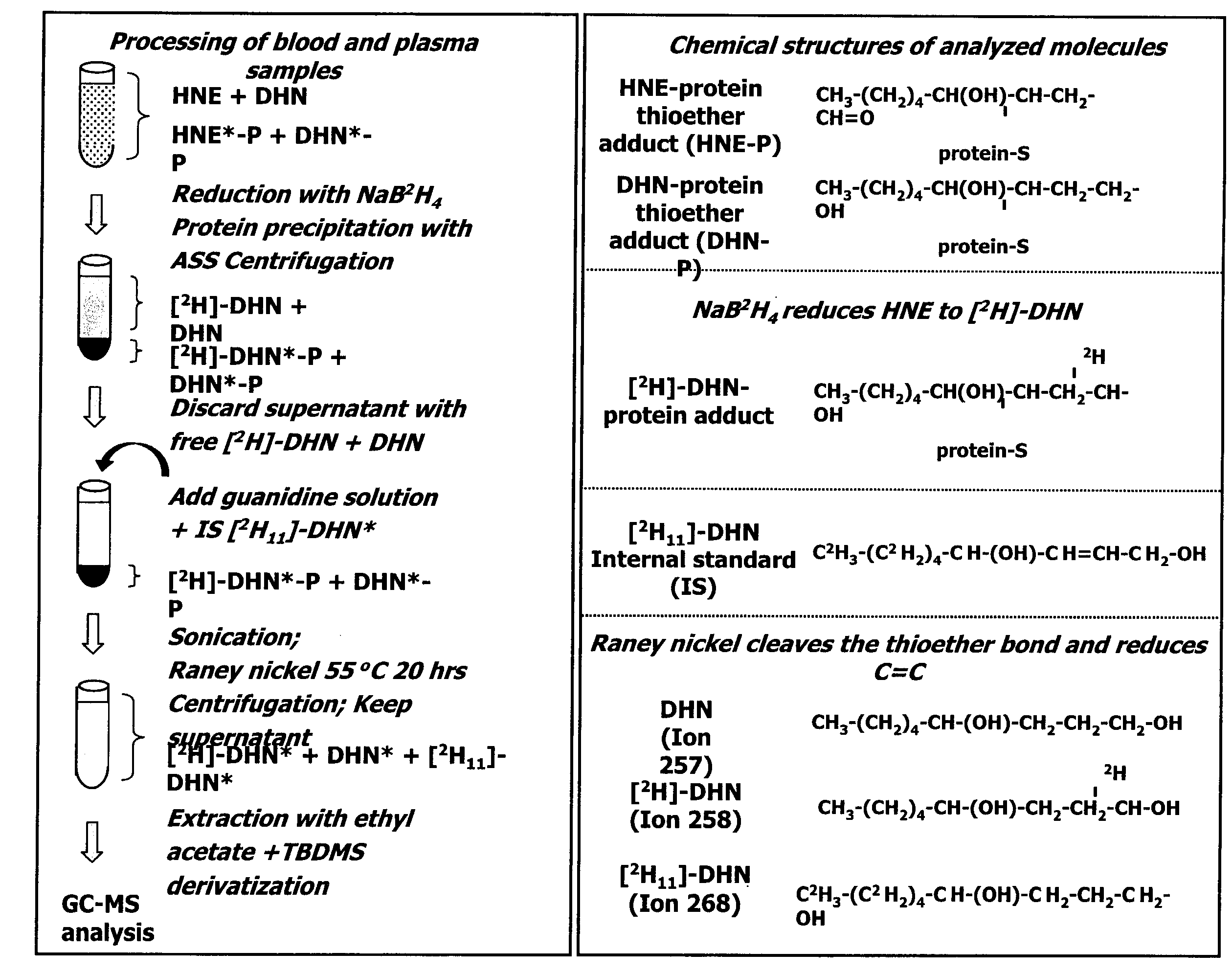
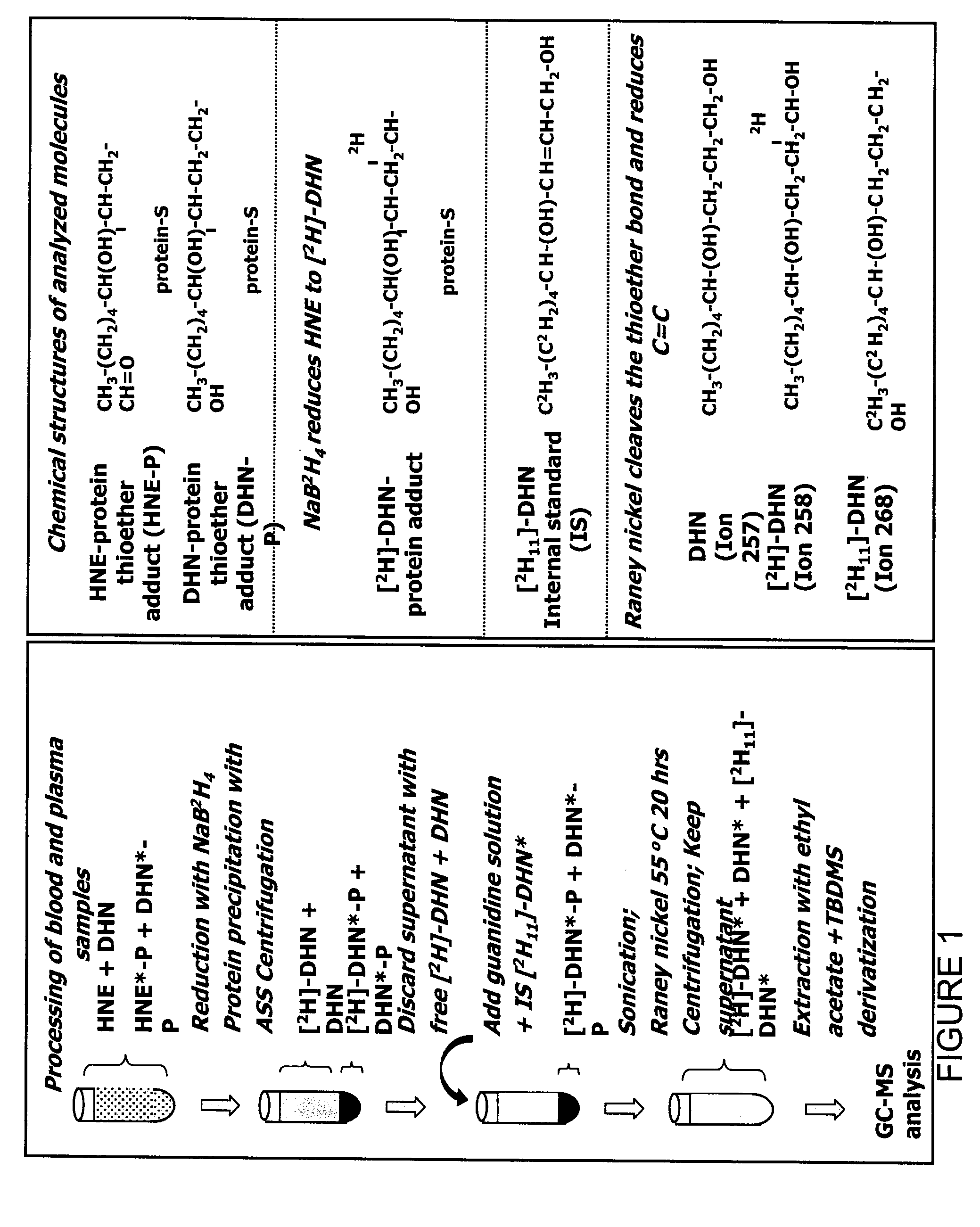
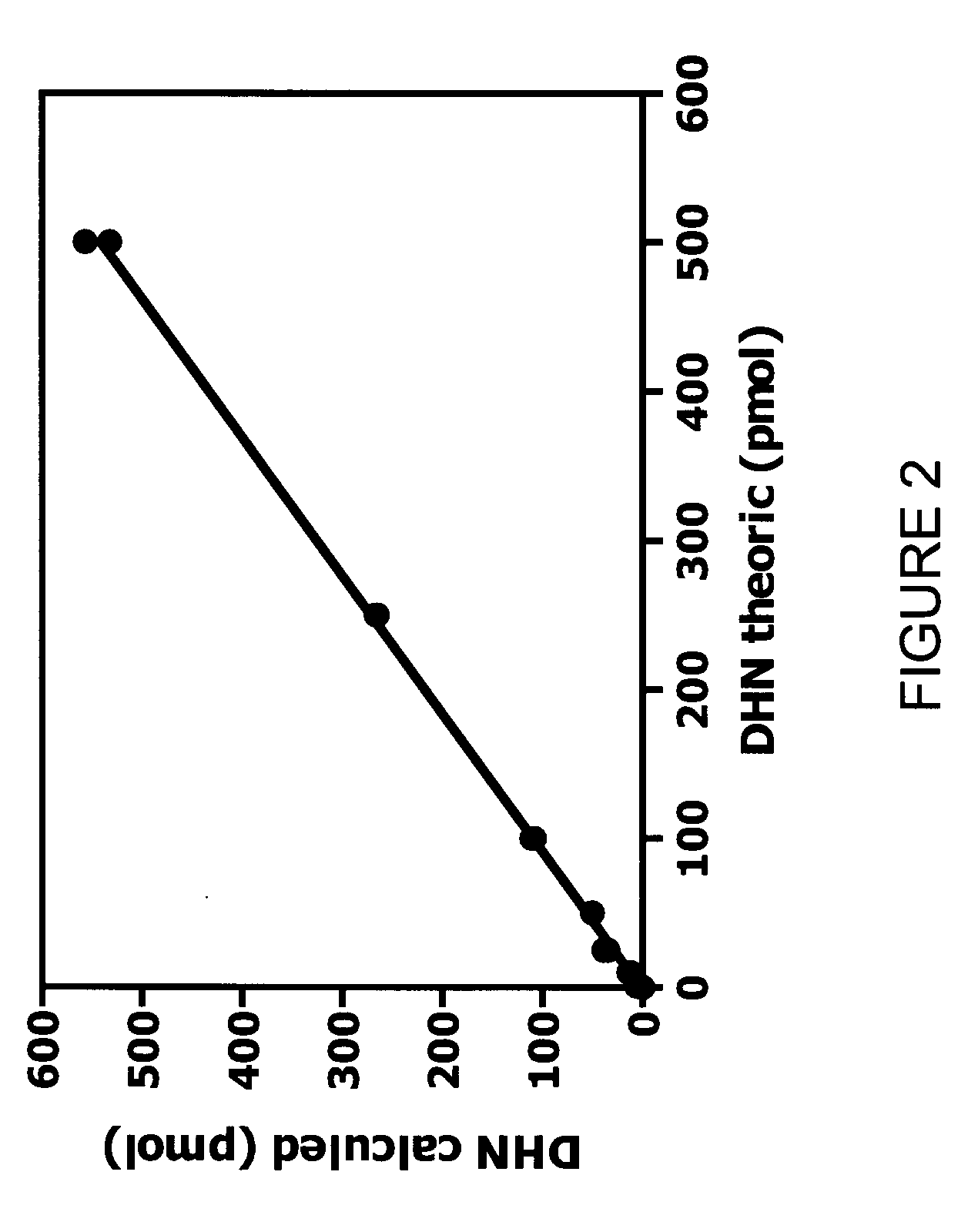
Method for detecting a biomarker of oxidative stress in a biological sample
InactiveUS20090111121A1Easy to implementEffectively and simply performPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsMedicineOxidative stress
A method for characterizing oxidative stress. The method includes dosing a ratio of HNE-to-DHN-protein in blood; comparing the ratio of HNE-to-DHN-protein in blood to a predetermined interval of ratio values associated with a predetermined level of oxidative stress; and classifying the oxidative stress as having reached the predetermined level if the ratio of HNE-to-DHN-protein in blood is within the predetermined interval of ratio values.
Owner:INST DE CARDIOLOGIE DE MONTREAL
Systems and methods for cell preservation
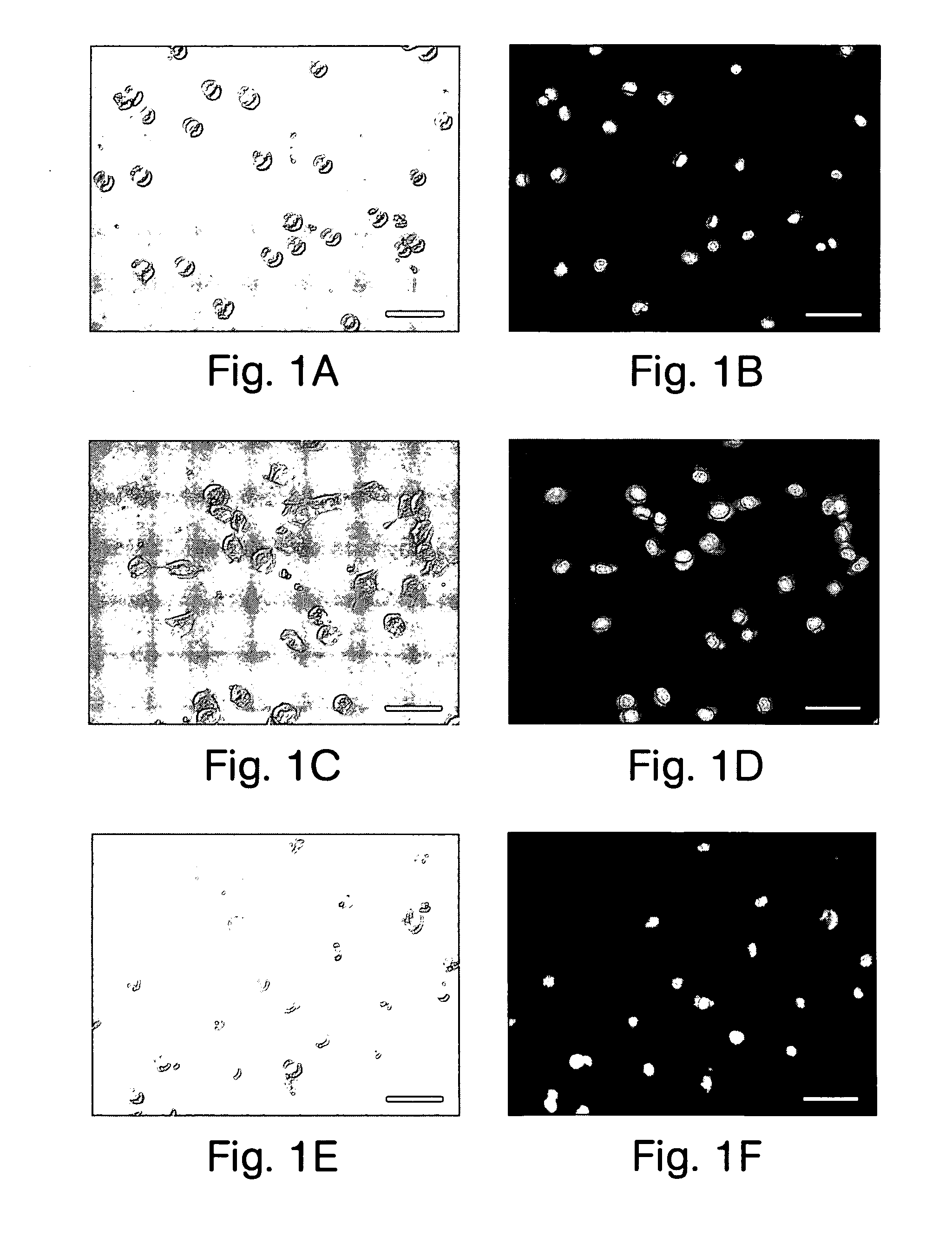
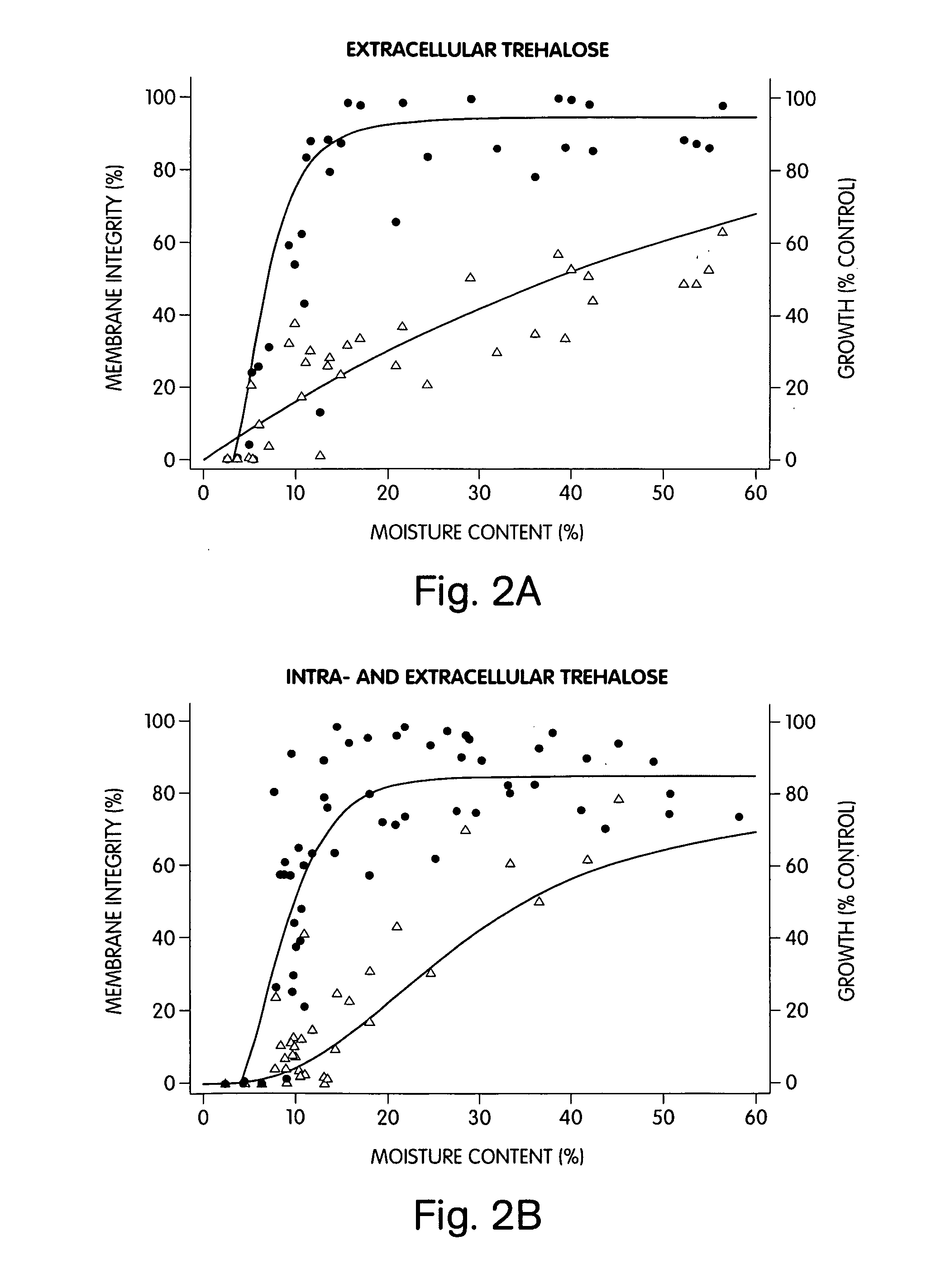
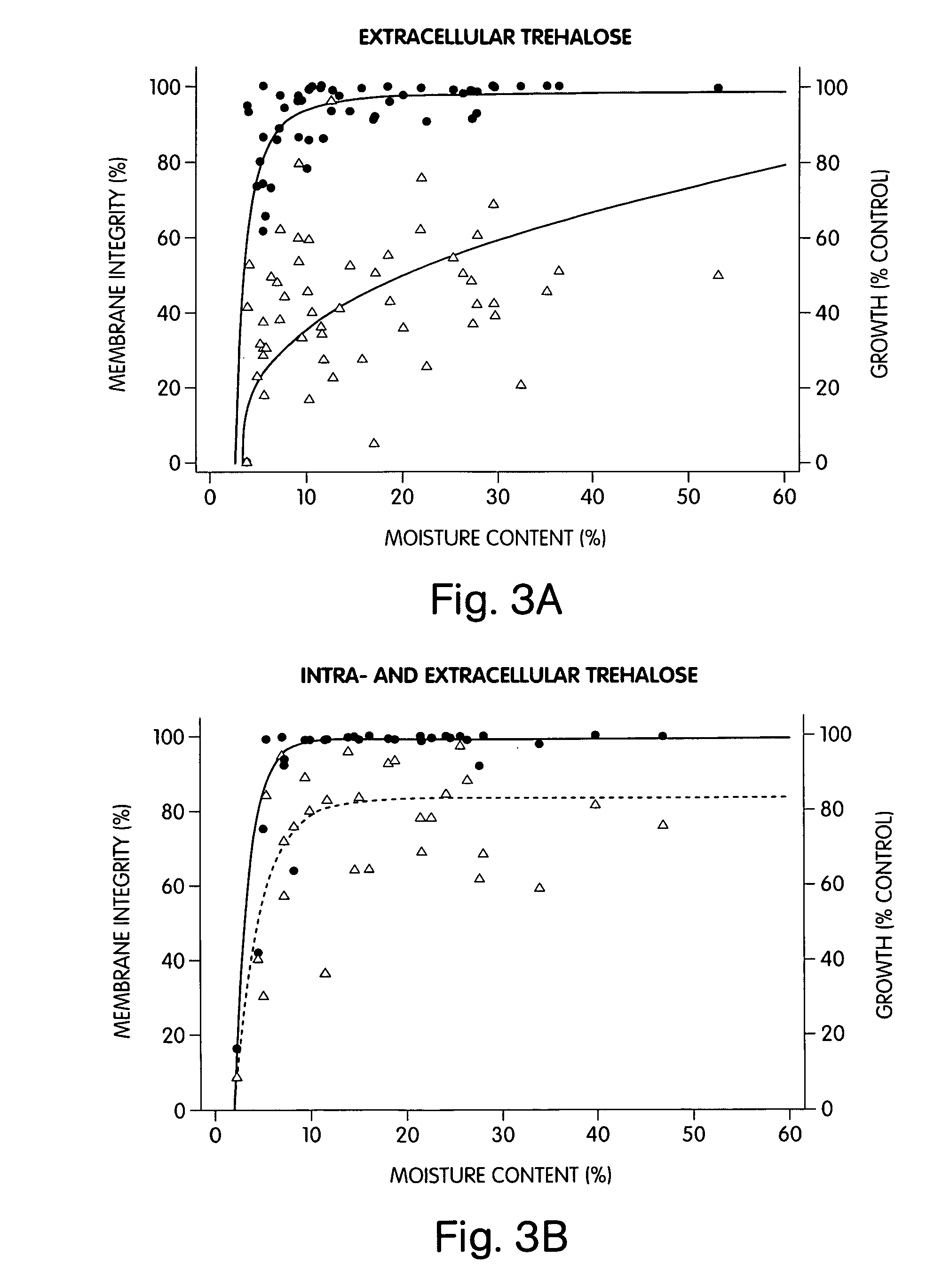
The present invention generally relates to devices and methods for the preservation of cells using drying, freezing, and other related techniques. In one set of embodiments, the invention allows for the preservation of cells in a dried state. In another set of embodiments, the invention allows for the preservation of cells within a glass or other non-viscous, non-frozen media. In some embodiments, the invention allows for the preservation of cells at temperatures below the freezing point of water, and in some cases at cryogenic temperatures, without inducing ice formation. The cells, in certain embodiments, may be preserved in the presence of intracellular and / or extracellular carbohydrates (which may be the same or different), for example, trehalose and sucrose. Carbohydrates may be transported intracellularly by any suitable technique, for example, using microinjection, or through non-microinjected methods such as through pore-forming proteins, electroporation, heat shock, etc. In certain instances, the glass transition temperature of the cells may be raised, e.g., by transporting a carbohydrate intracellularly. In some cases, the cells may be dried and / or stored, for example, in a substantially moisture-saturated environment or a desiccating environment. The cells may also be stored in a vacuum or a partial vacuum. The cells may be protected from oxygen, moisture, and / or light during storage. In certain cases, an inhibitor, such as a cell death inhibitor, a protease inhibitor, an apoptosis inhibitor, and / or an oxidative stress inhibitor may be used during preservation of the cells. The cells may be stored for any length of time, then recovered to a viable state, e.g., through rehydration, for further use.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
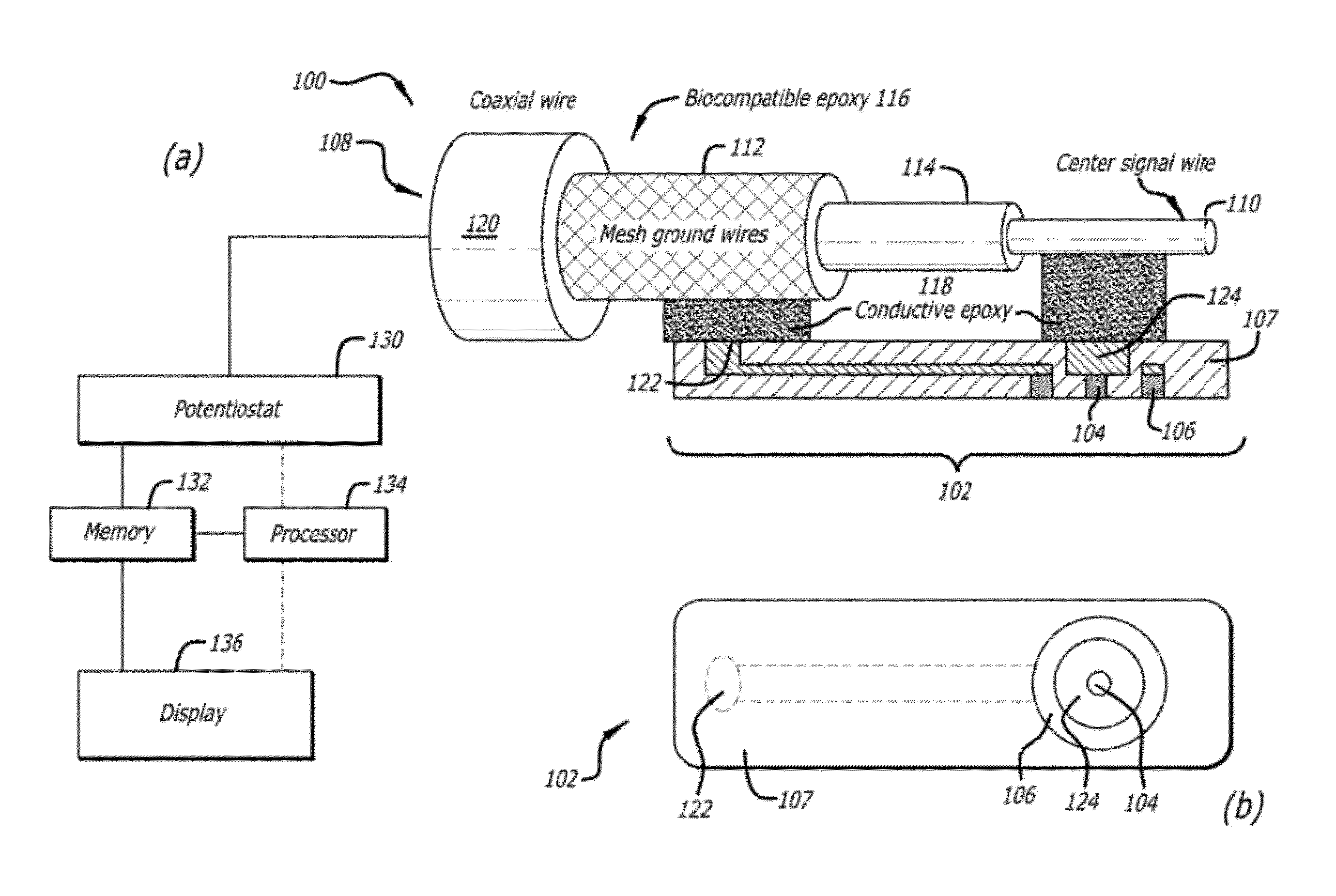
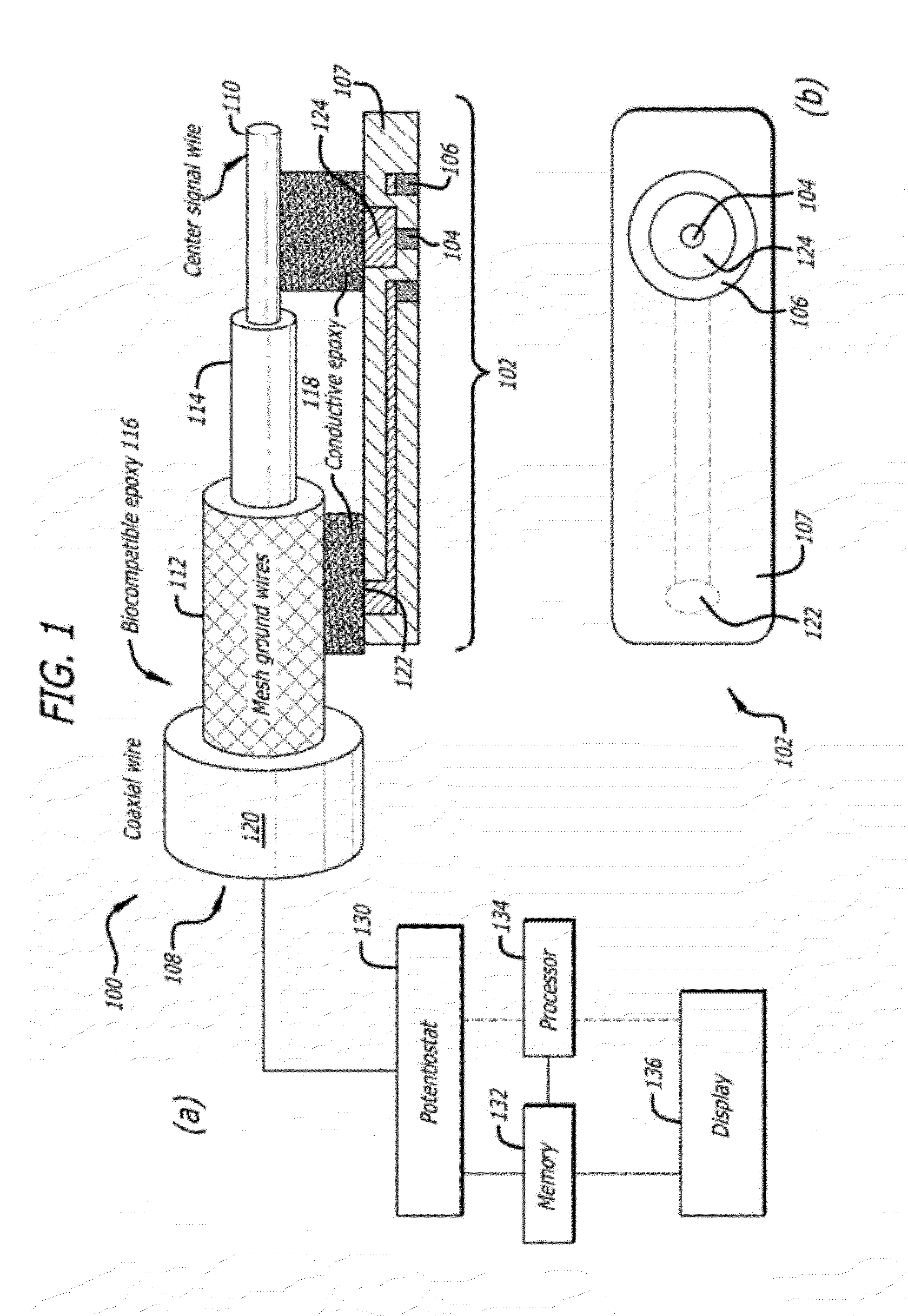
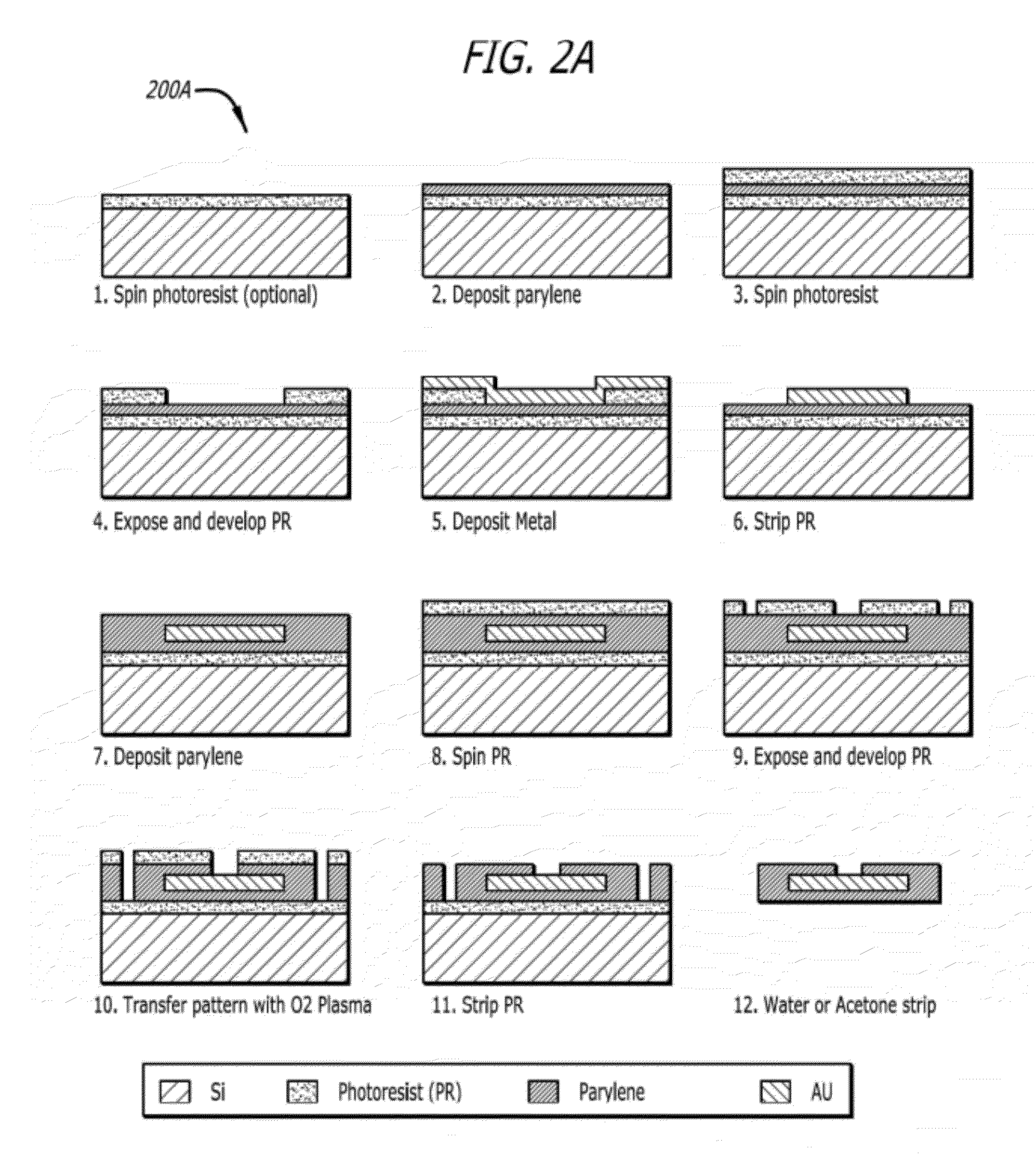
Concentric bipolar electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to assess vascular oxidative stress
InactiveUS20120061257A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsManufacturing technologySpectroscopy
Concentric bipolar electrode sensors and assemblies provide for and / or facilitate detection and diagnosis of the non-obstructive and pro-inflammatory atherosclerotic lesions in human arteries during catheterization using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Fabrication techniques for concentric bipolar electrode sensors are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
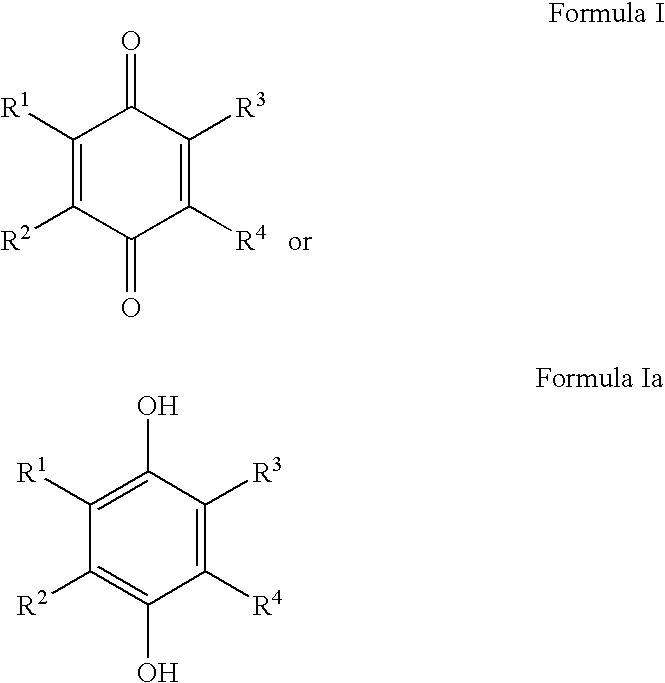
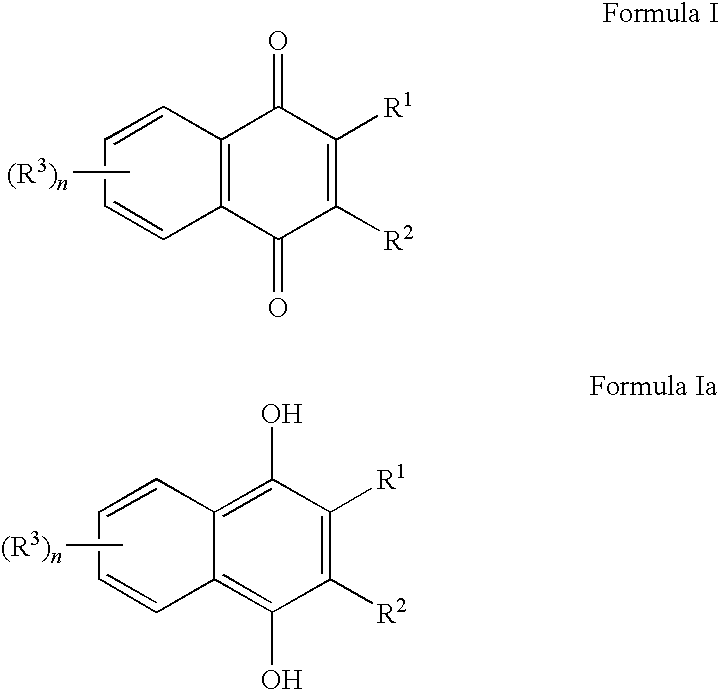
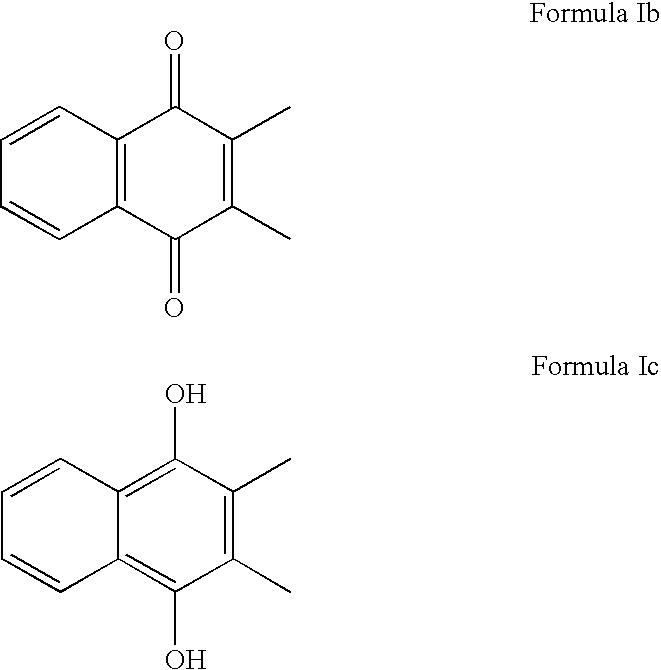
Naphthoquinone compositions with Anti-aging, Anti-inflammatory and skin even-toning properties
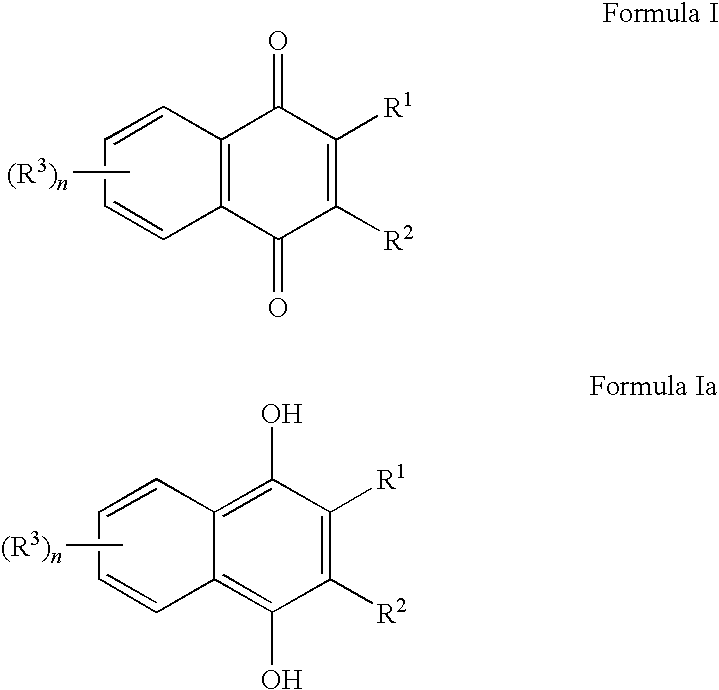
InactiveUS20100029784A1Reduce and treat and prevent signEffective protectionCosmetic preparationsBiocideOxidative stressNaphthoquinone
The present invention relates to methods and compositions comprising naphthoquinones such as 2,3-dimethylnaphthalene-1,4-dione, for the use of treating, regulating or preventing a skin condition characterized by oxidative stress or a degenerative process. Methods of preventing, lightening or reducing the appearance of visible and / or tactile discontinuities of the skin resulting from skin pigmentation or skin aging are also disclosed.
Owner:AMPERE LIFE SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![HYDROGENATED PYRIDO[4,3-b]INDOLES FOR THE TREATMENT OF OXIDATIVE STRESS HYDROGENATED PYRIDO[4,3-b]INDOLES FOR THE TREATMENT OF OXIDATIVE STRESS](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/39066d90-fef6-412e-9a19-f91ca924d615/US20100029706A1-20100204-C00001.png)
![HYDROGENATED PYRIDO[4,3-b]INDOLES FOR THE TREATMENT OF OXIDATIVE STRESS HYDROGENATED PYRIDO[4,3-b]INDOLES FOR THE TREATMENT OF OXIDATIVE STRESS](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/39066d90-fef6-412e-9a19-f91ca924d615/US20100029706A1-20100204-C00002.png)
![HYDROGENATED PYRIDO[4,3-b]INDOLES FOR THE TREATMENT OF OXIDATIVE STRESS HYDROGENATED PYRIDO[4,3-b]INDOLES FOR THE TREATMENT OF OXIDATIVE STRESS](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/39066d90-fef6-412e-9a19-f91ca924d615/US20100029706A1-20100204-C00003.png)