Patents
Literature
627 results about "Electronic imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
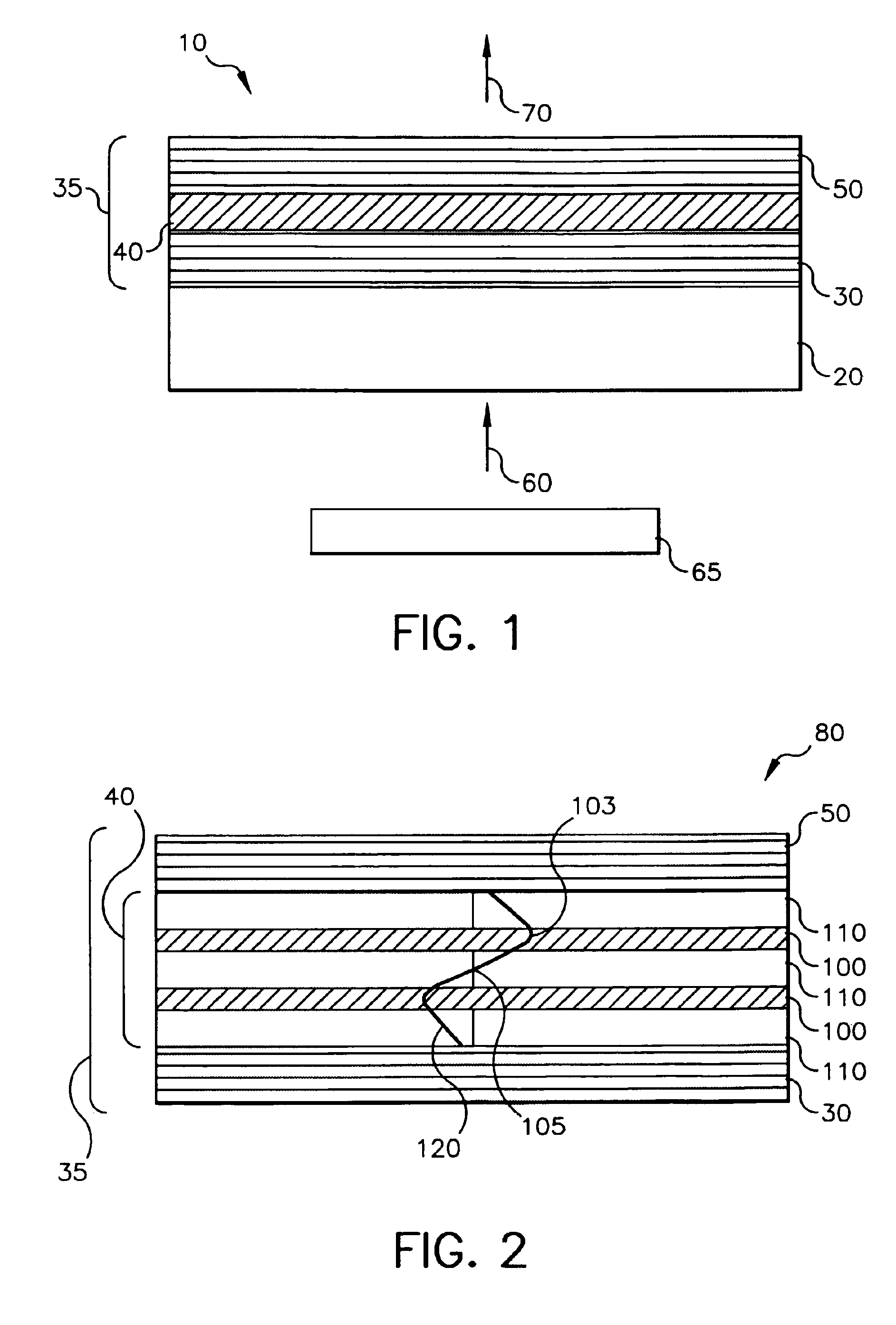
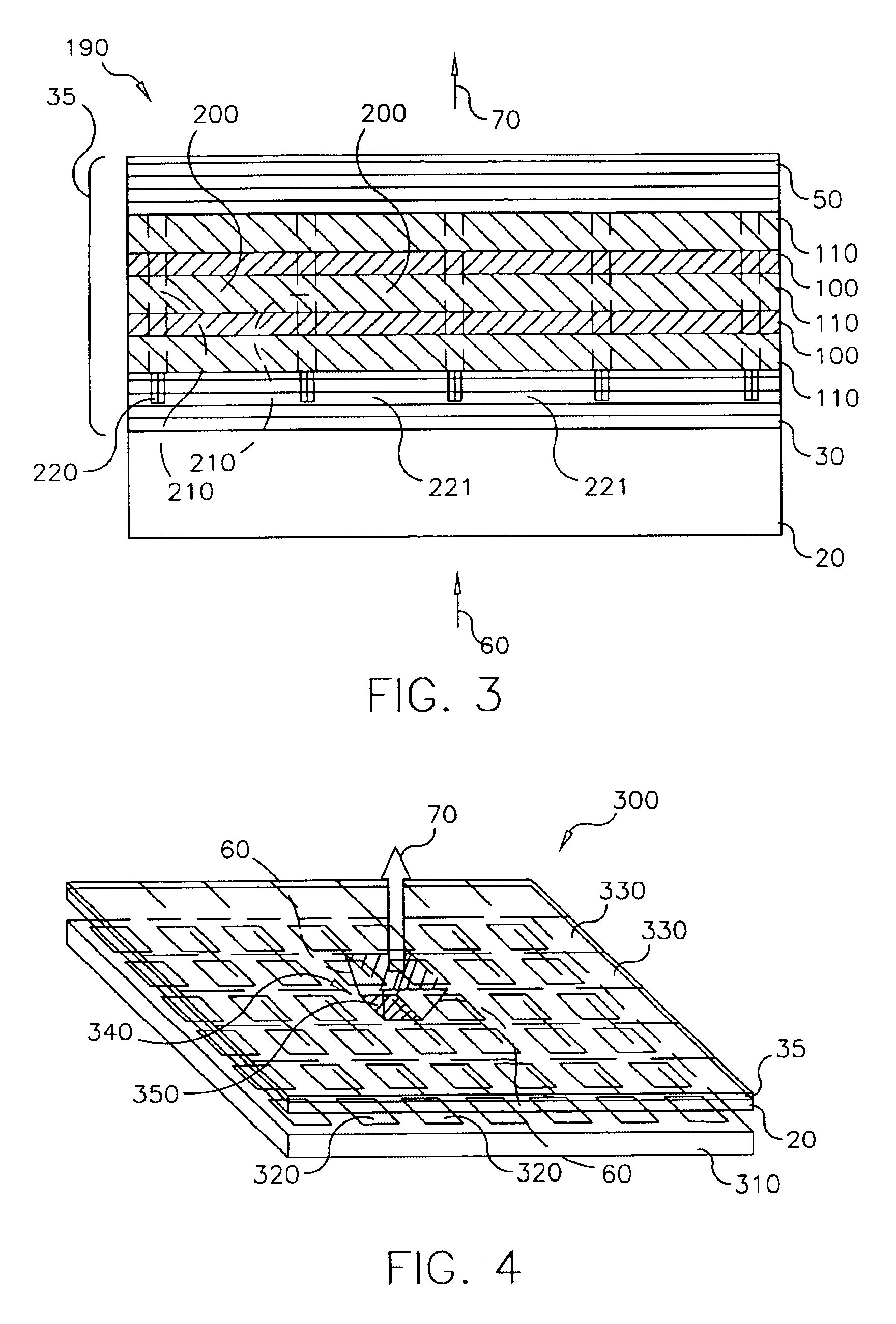
Apparatus and method for reducing imaging errors in imaging systems having an extended depth of field
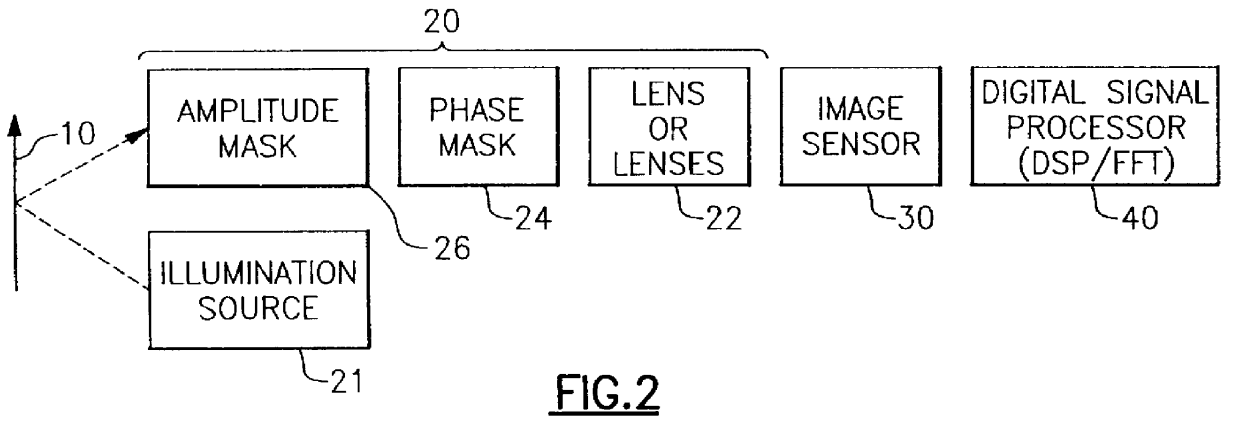
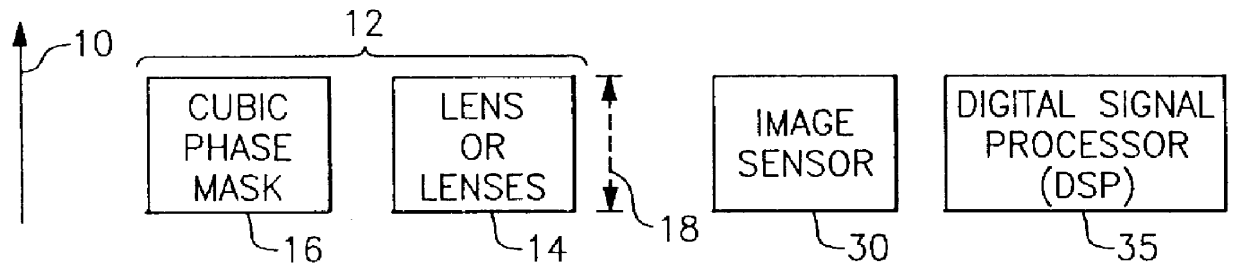
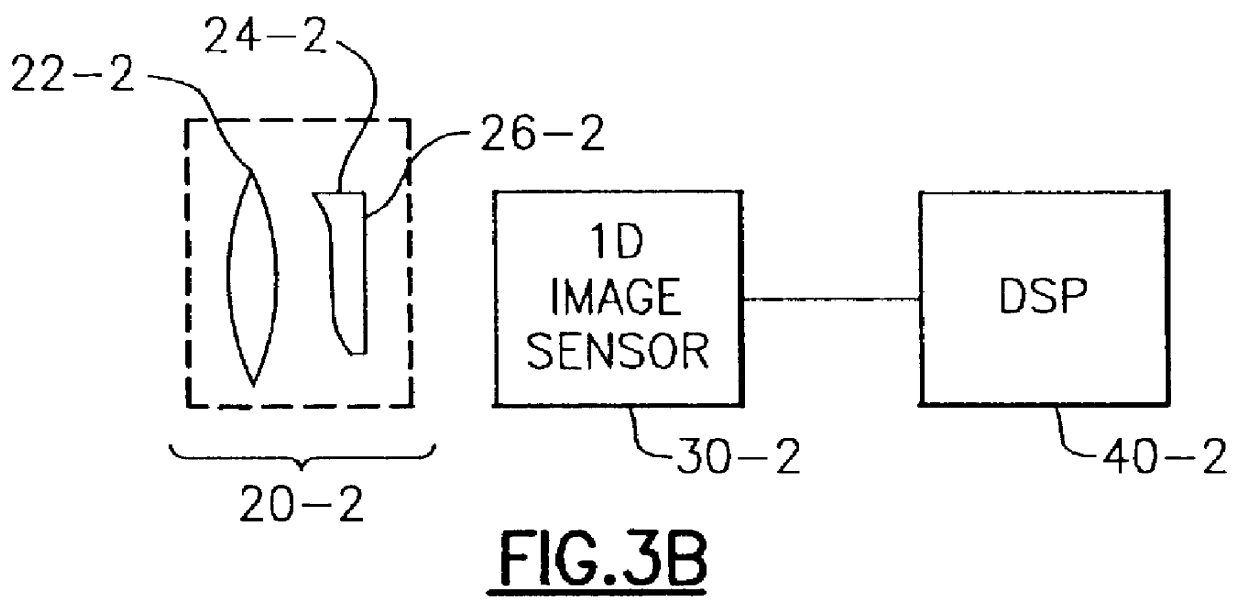
An improved opto-electronic imaging system which is adapted for use with incoherently illuminated objects, and which produces final images having a reduced imaging error content. The imaging system includes an optical assembly for forming an intermediate image of the object to be imaged, an image sensor for receiving the intermediate image and producing an intermediate image signal, and processing means for processing the intermediate image signal to produce a final image signal having a reduced imaging error content. A reduction in imaging error content is achieved, in part, by including in the optical assembly a phase mask for causing the OTF of the optical assembly to be relatively invariant over a range of working distances, and an amplitude mask having a transmittance that decreases continuously as a function of distance from the center thereof. The reduction in imaging error content is also achieved, in part, by including in the processing means an improved generalized recovery function that varies in accordance with at least the non-ideal calculated IOTF of the optical assembly under a condition of approximately optimum focus.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
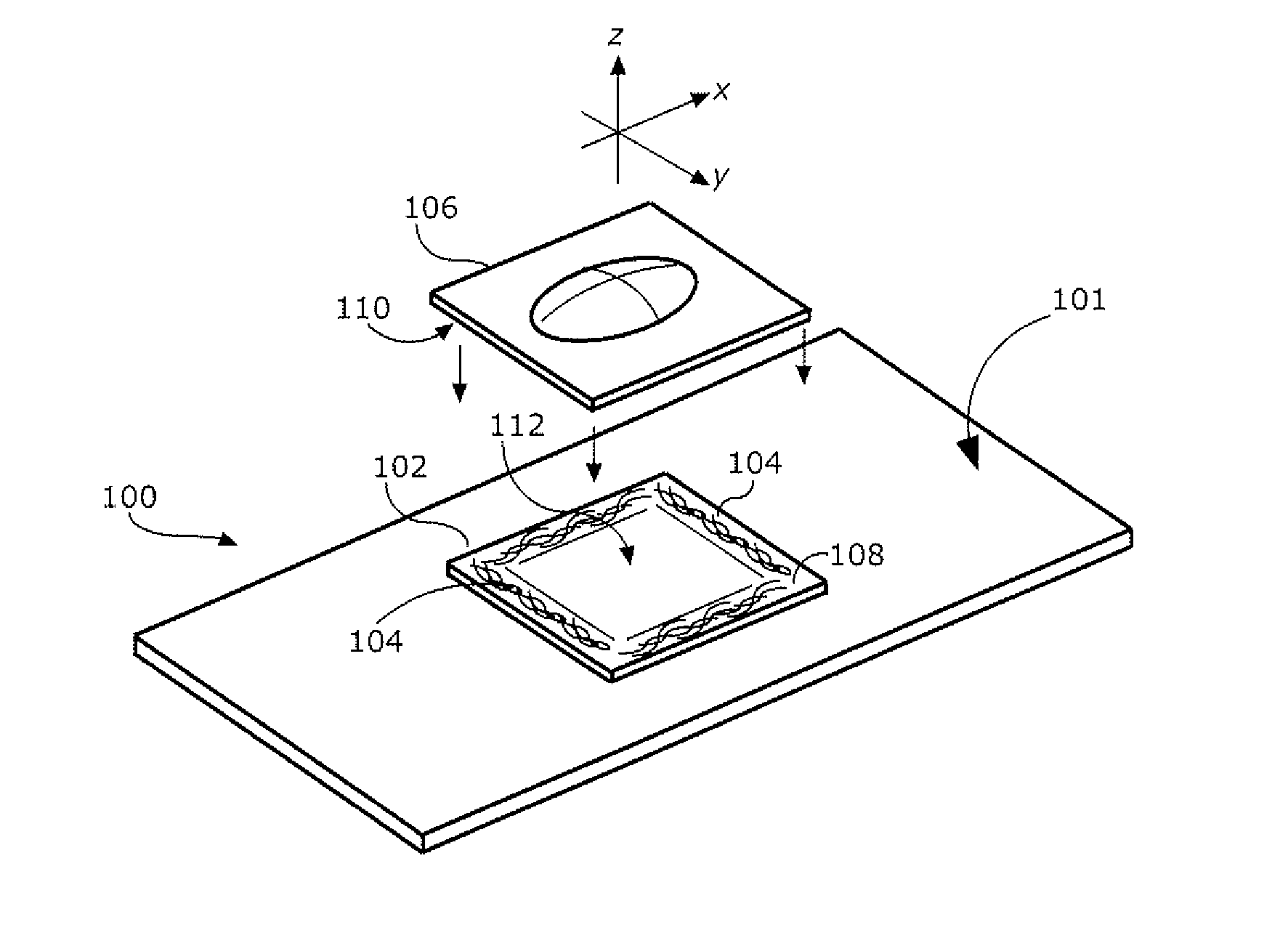
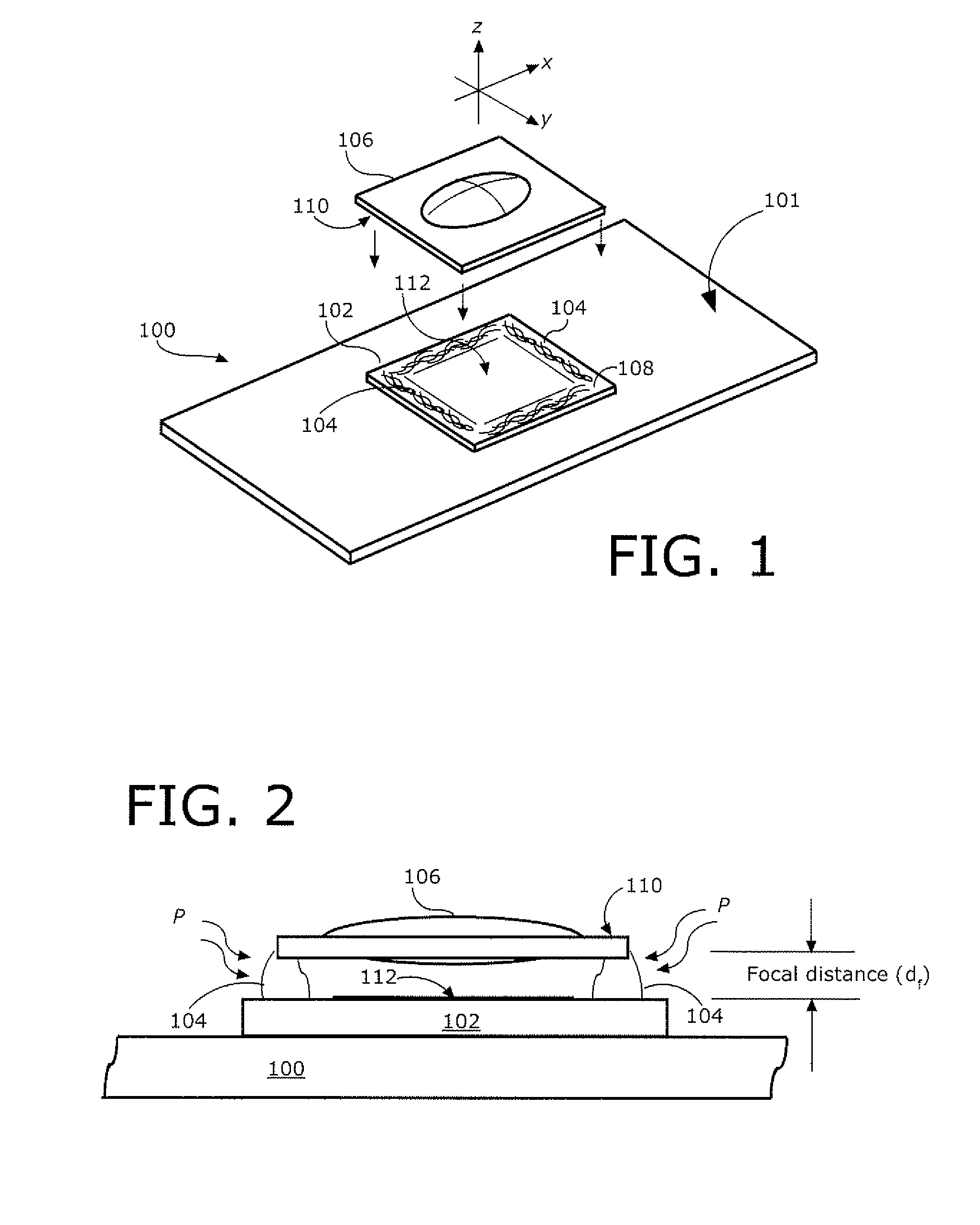
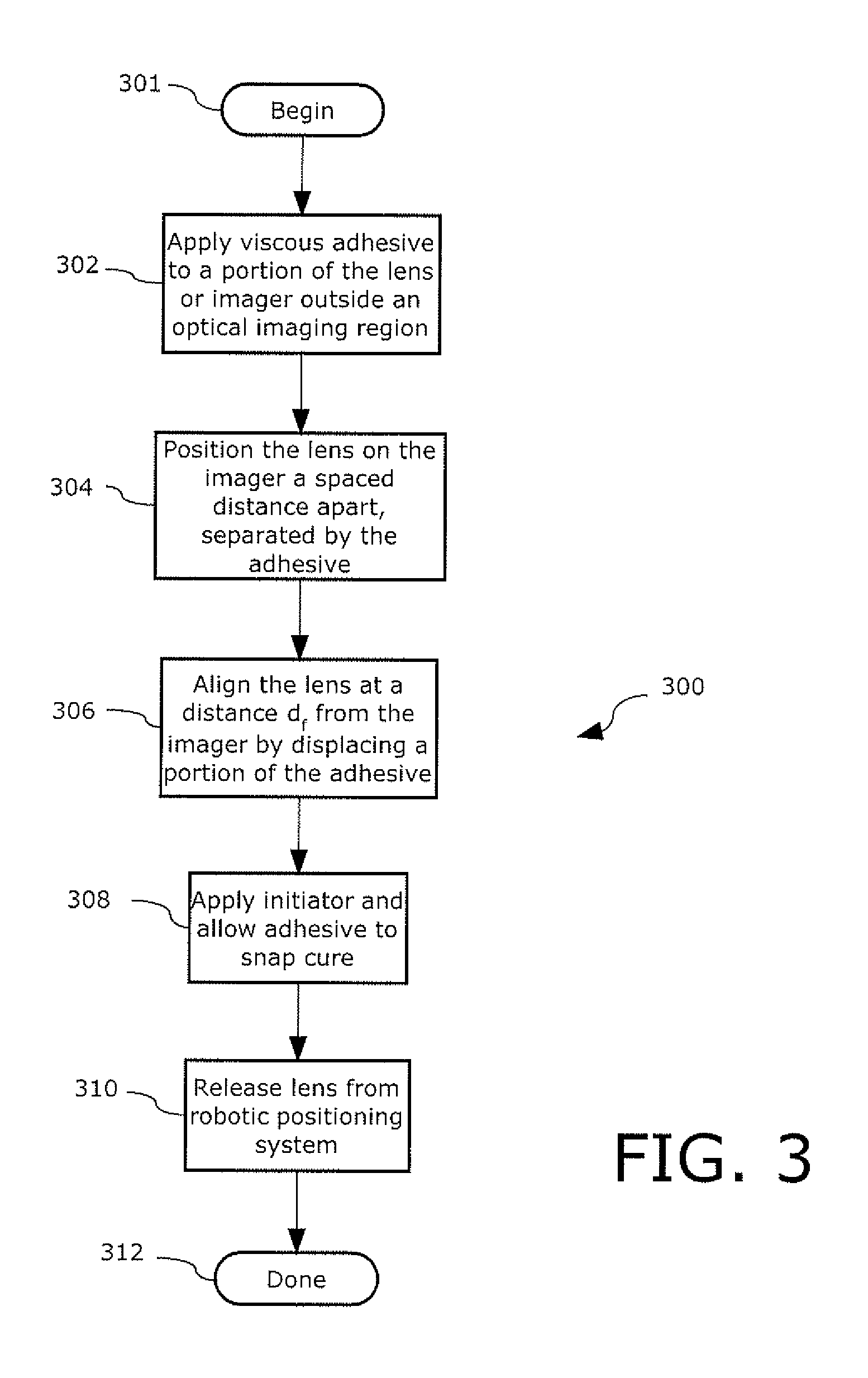
Positioning wafer lenses on electronic imagers
ActiveUS20100103308A1Cost reductionLow production costTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesOptical pathEngineering
A low cost manufacturing method (300) and assembly (100) for positioning a lens (106) relative to an electronic imager (102). A viscous adhesive (104) is applied to the lens (106) or the electronic imager (102) outside of the optical path. The lens (106) is disposed on the electronic imager (102) exclusively with the adhesive (104) disposed between them.
Owner:JABIL CIRCIUT
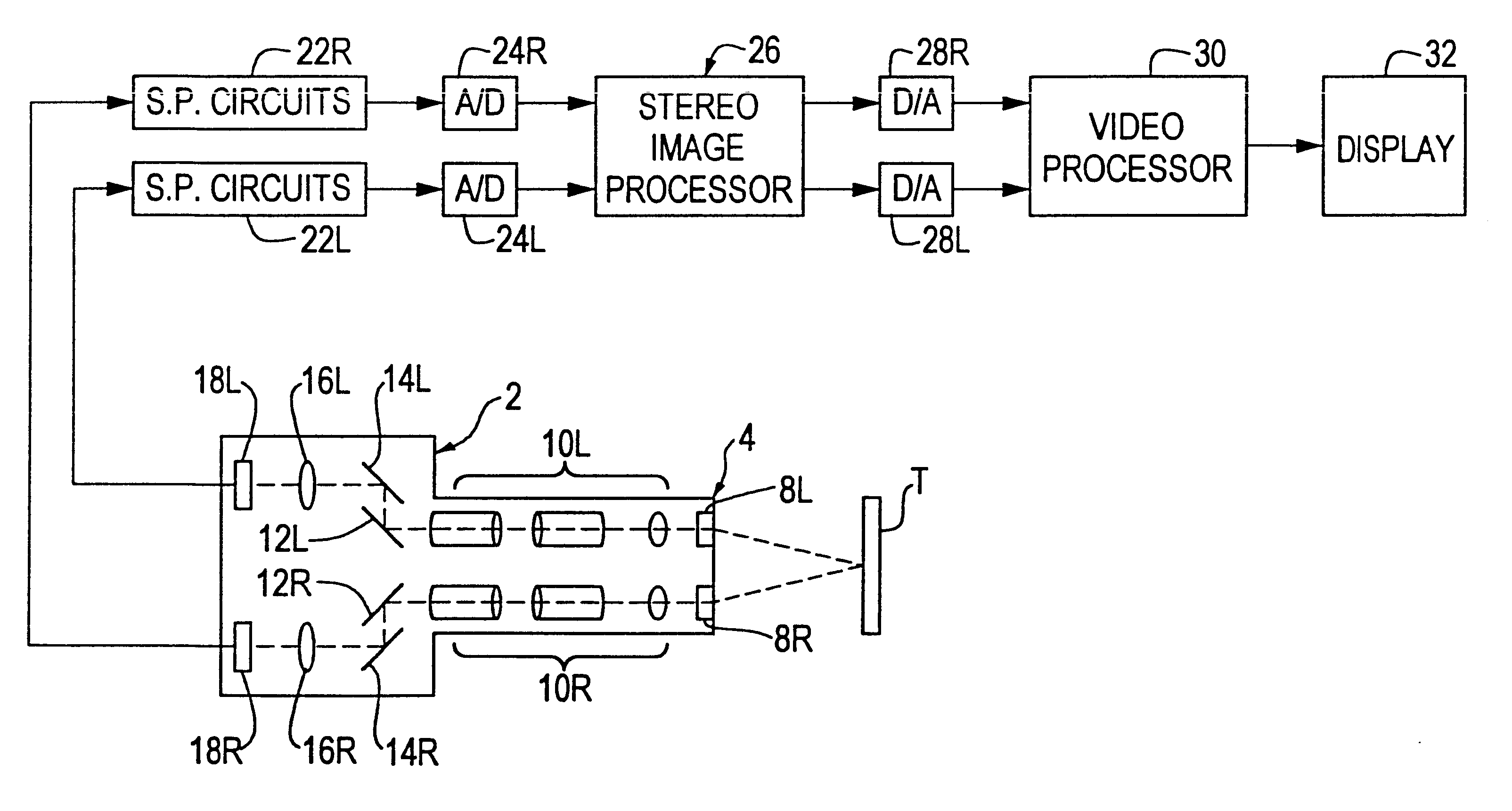
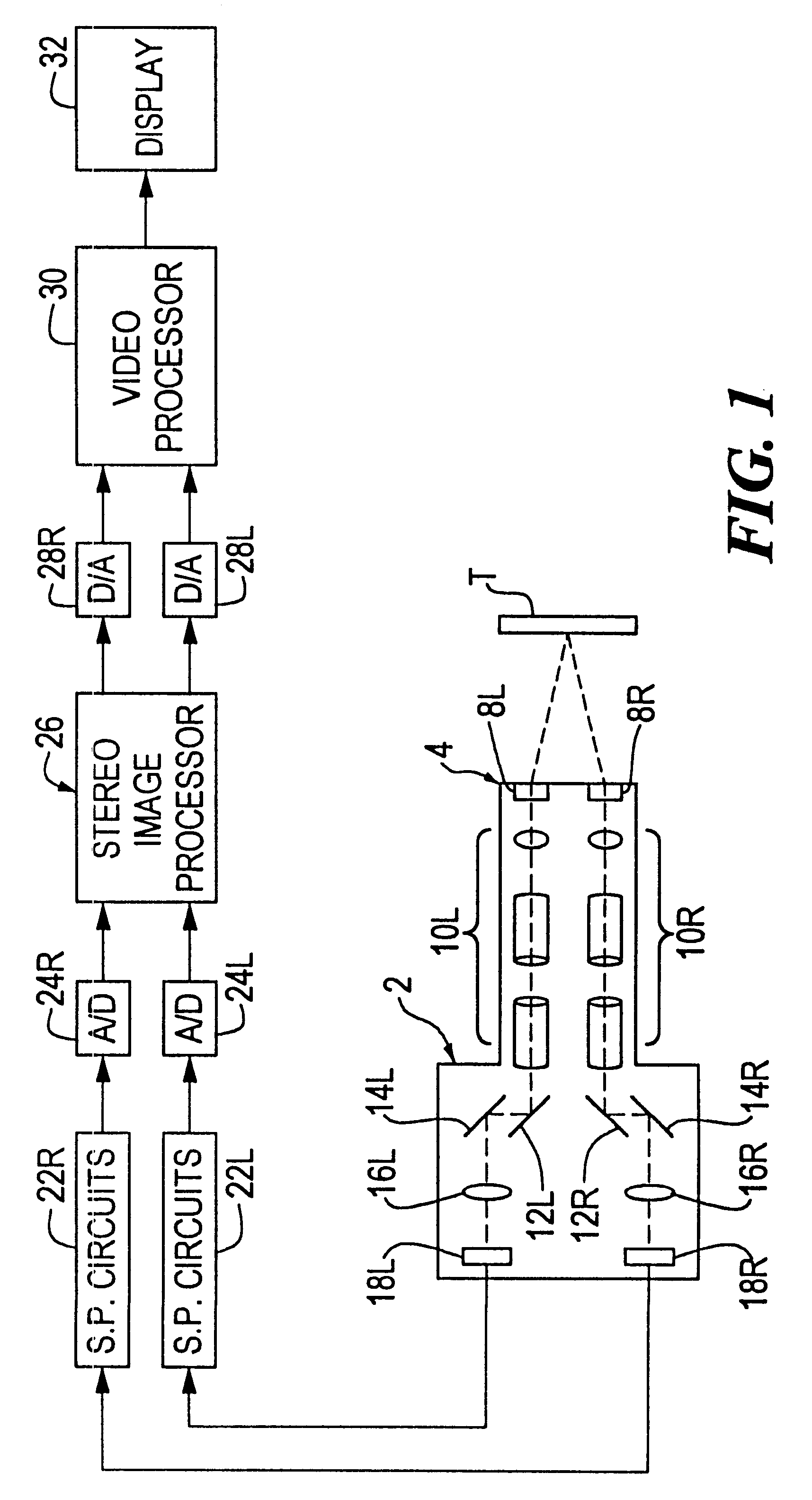
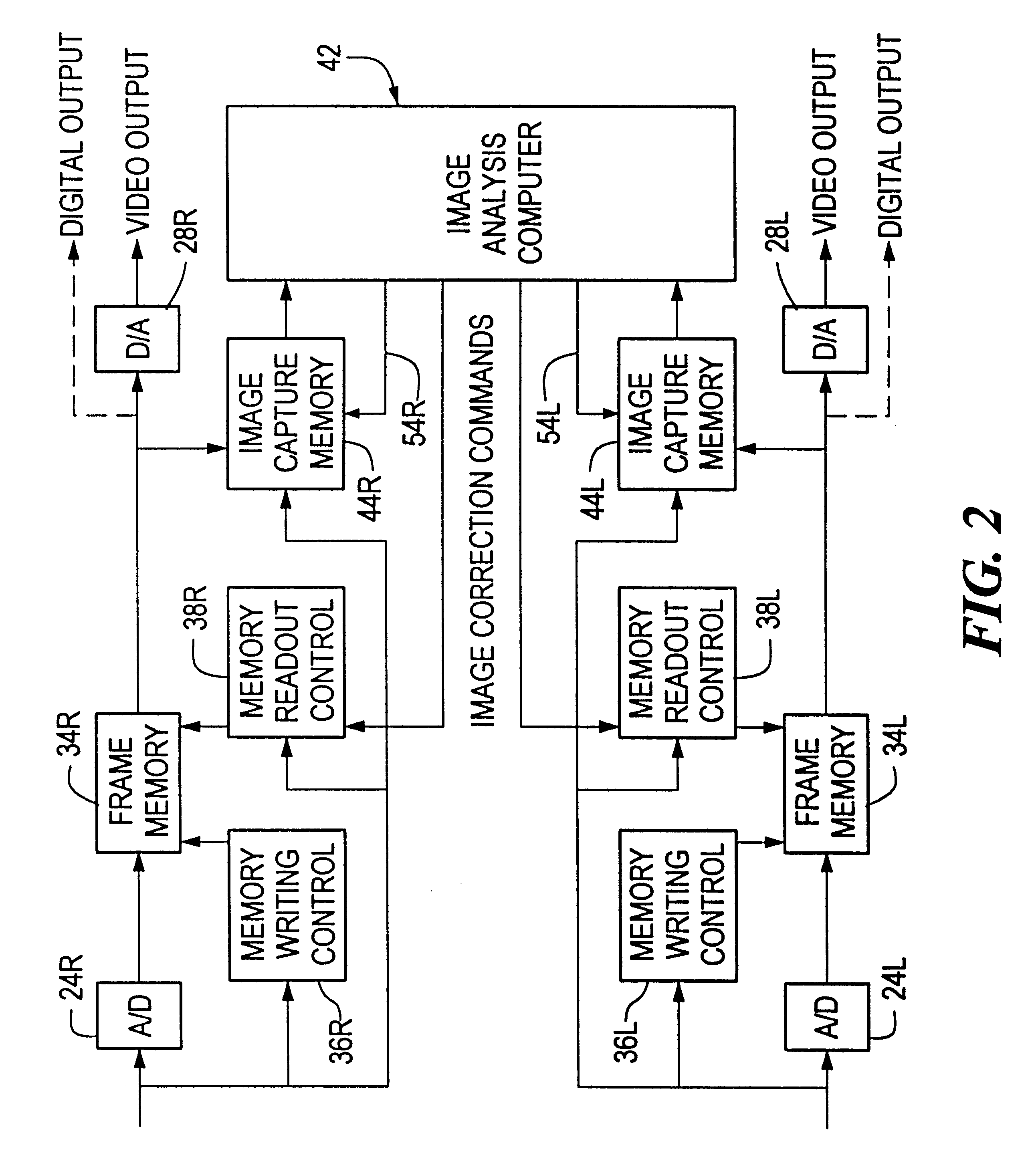
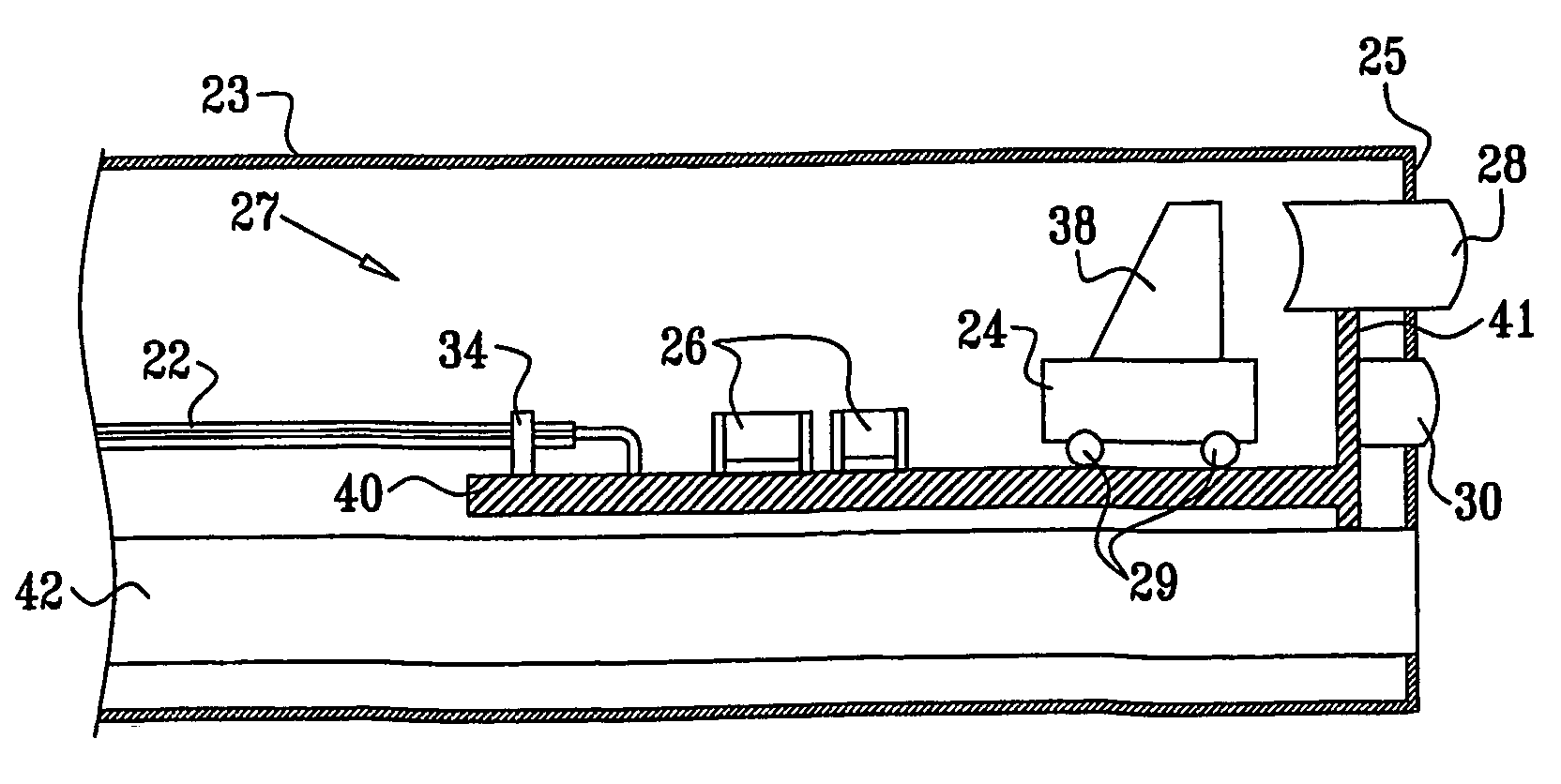
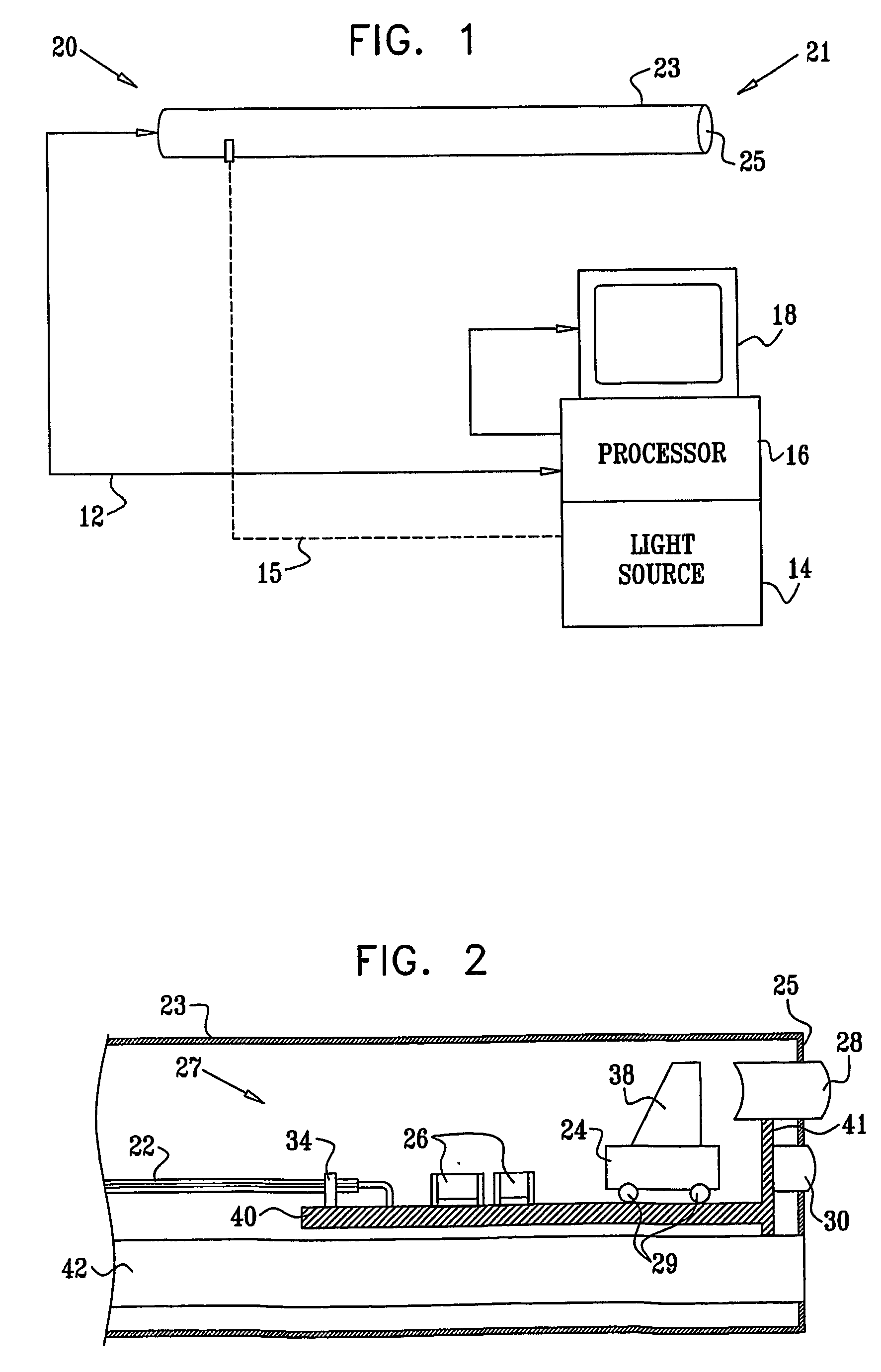
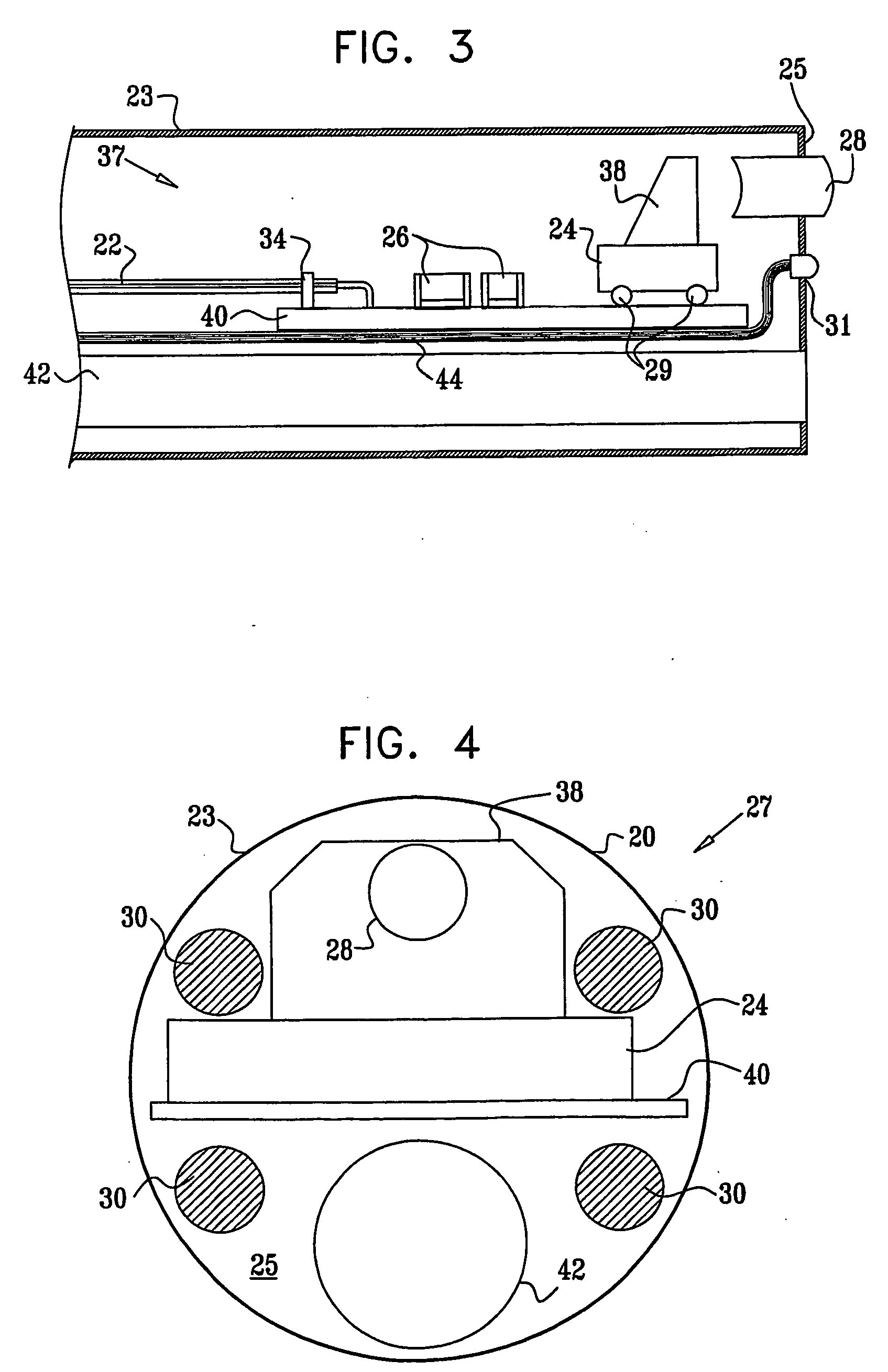
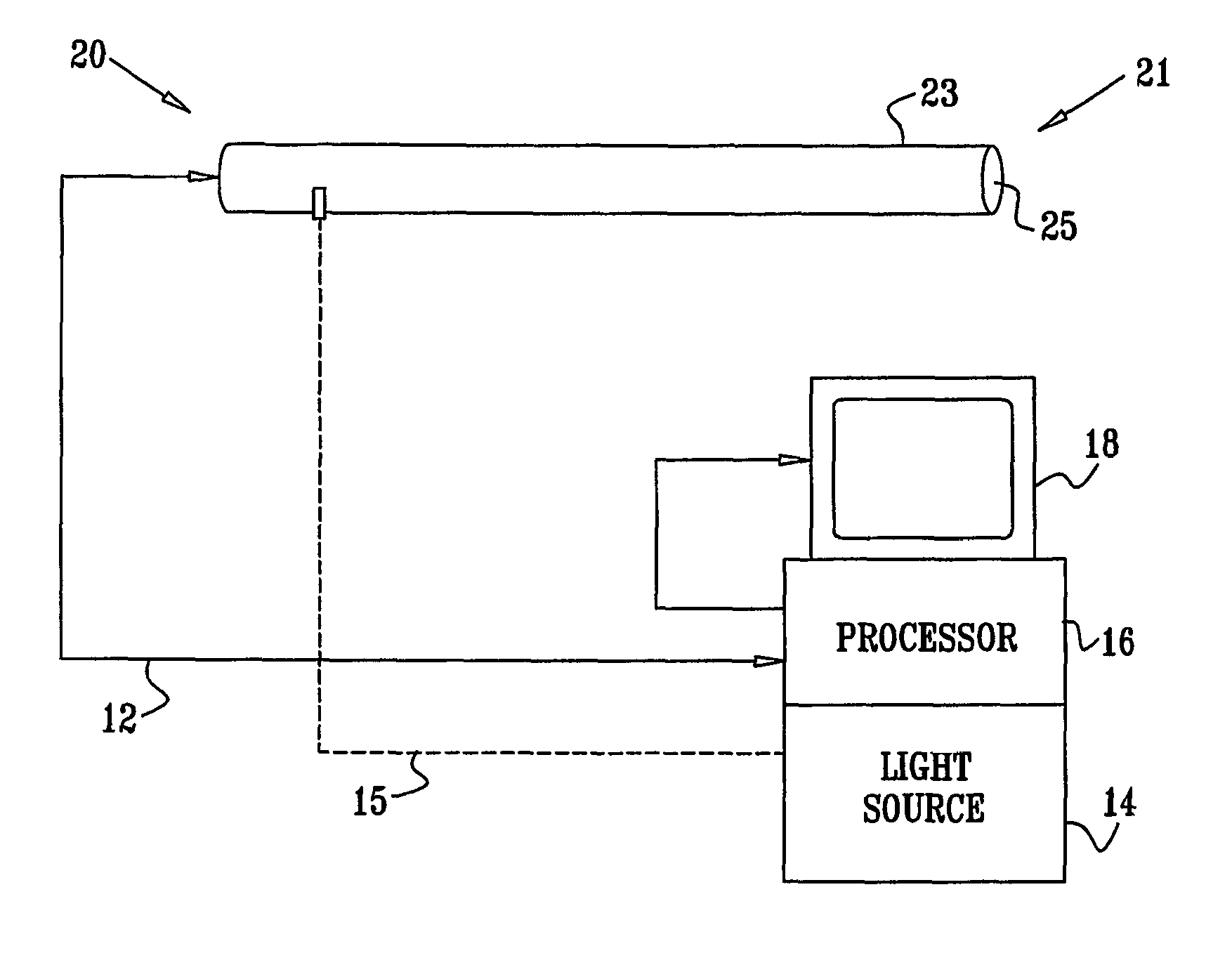
Method and apparatus for aligning stereo images
A method and apparatus are provided for correcting for optical misalignment of the dual (left and right) images produced by a stereo electronic endoscope, or of the corresponding dual images produced by coupling electronic imaging devices to each of two monocular teaching ports of a stereo optical endoscope. The stereo image alignment technique comprises electronically capturing the video image data of the dual images, and subsequently processing that data electronically to correct for optical alignment errors. The method involves digitizing the electronic data and digitally performing the equivalent of vertical image shift, and / or image size change, and / or image rotation as required to correct for any visual image misalignment.
Owner:VISTA MEDICAL TECH +1
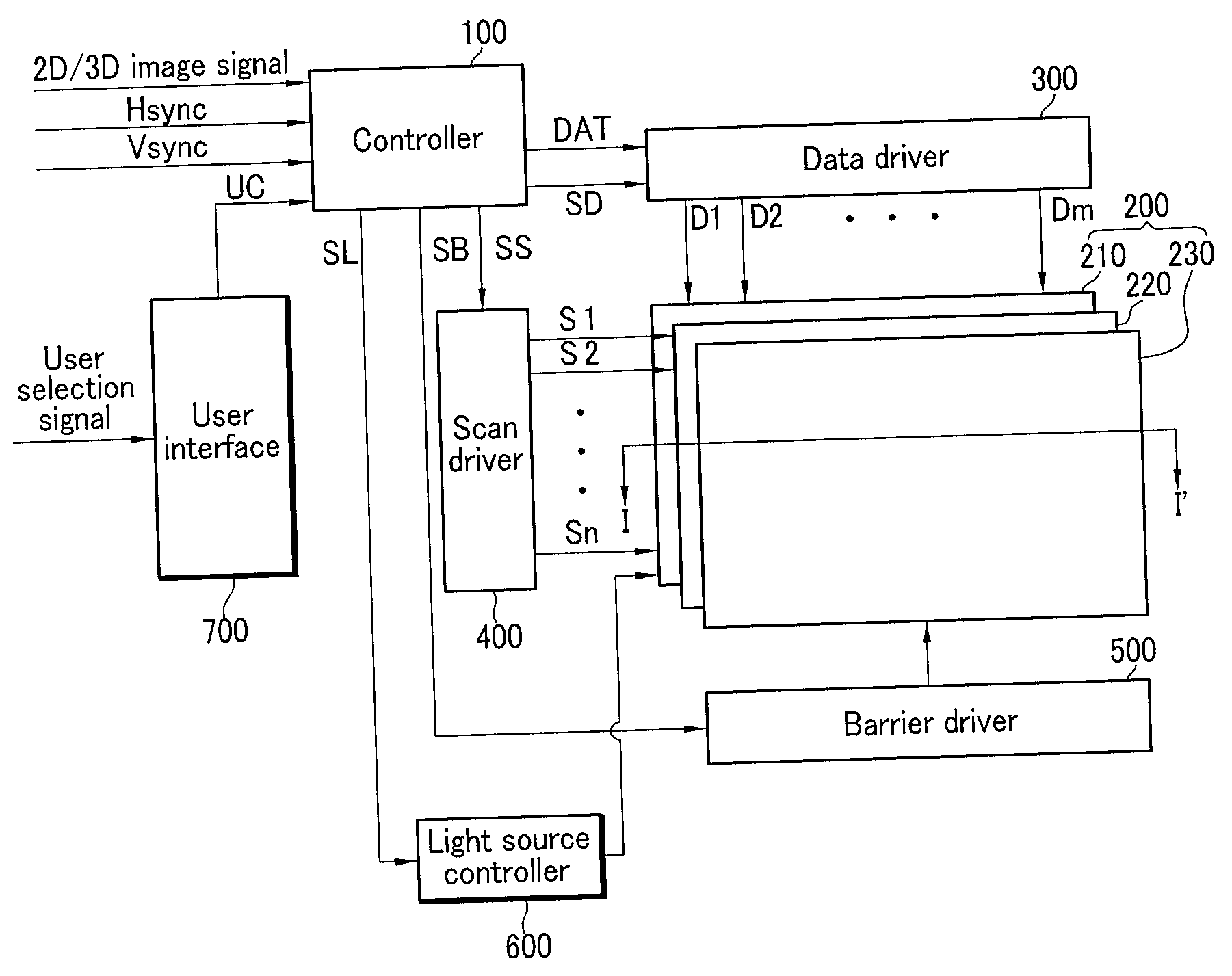
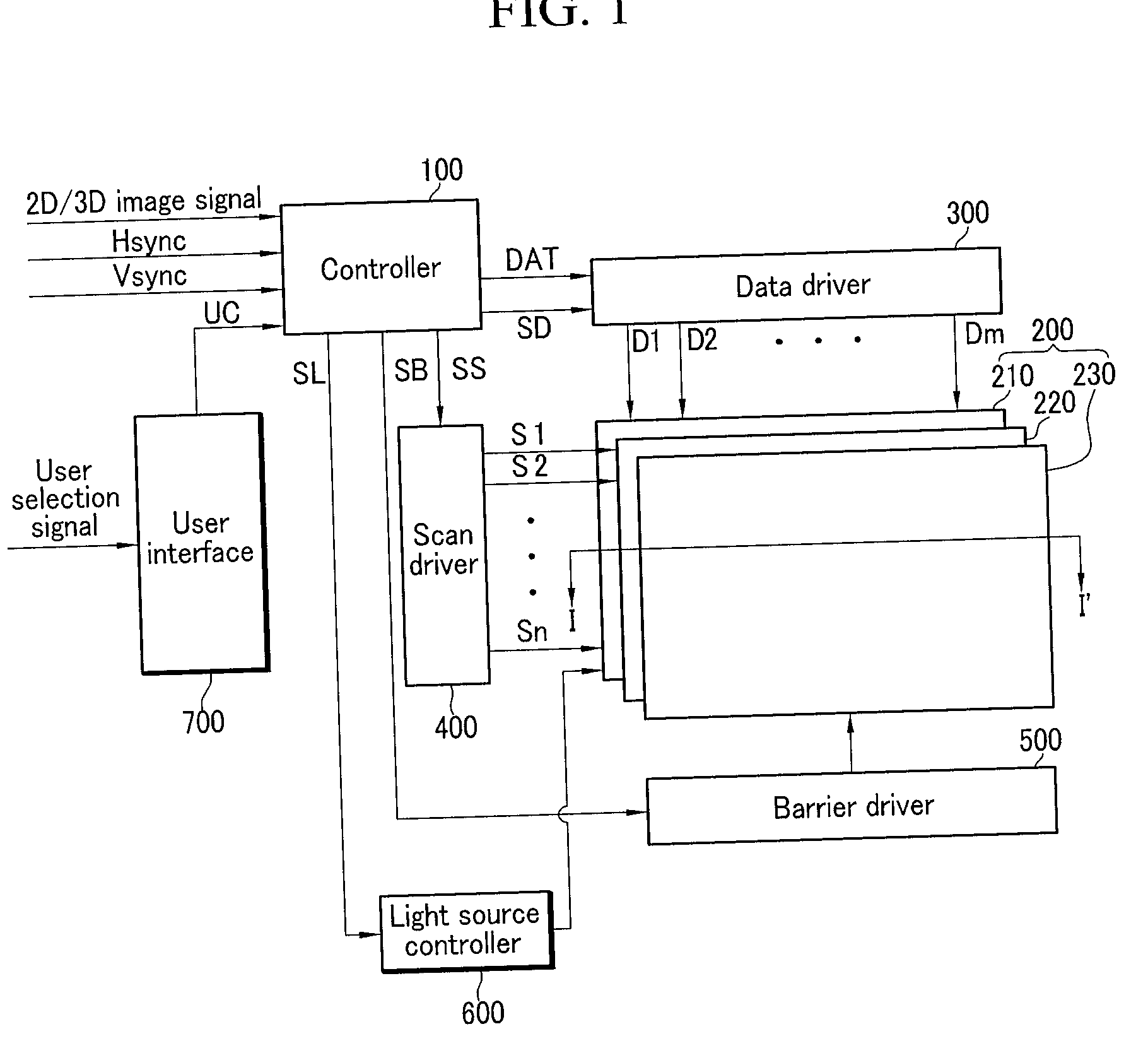
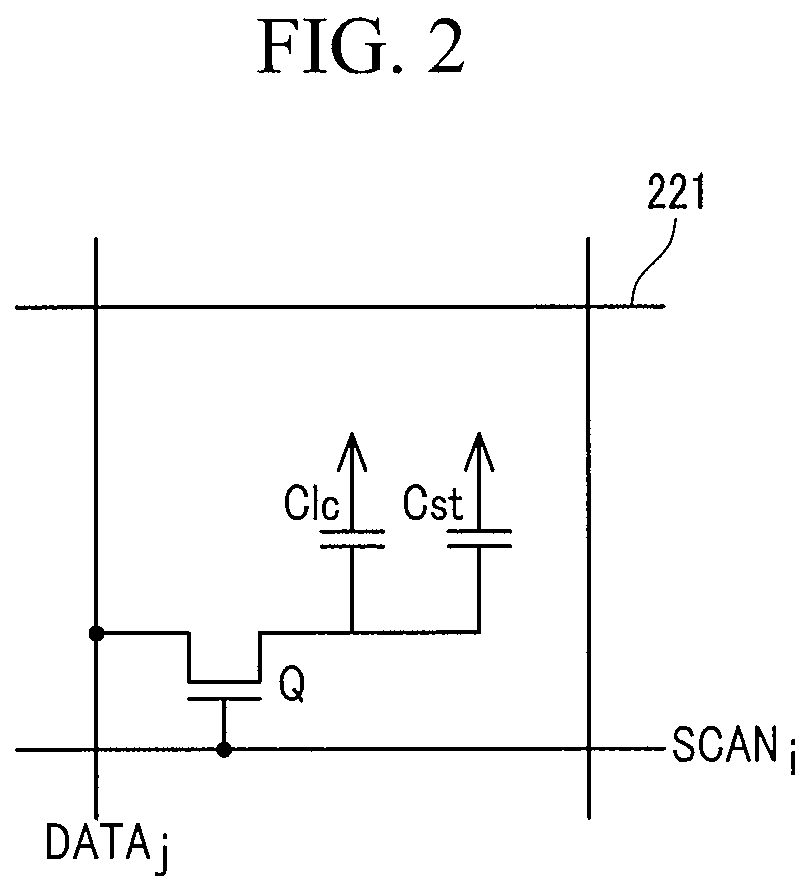
2d/3d image display device, electronic imaging display device, and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20070242068A1Reducing and preventing image quality deteriorationReducing and preventing image qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsData display3d image
A 2-dimensional (2D) / 3-dimensional (3D) image display device generates 2D or 3D image data according to an input image signal and displays them on a display unit. The display unit includes a display panel for displaying an image in response to the 2D or 3D image data and an optical element layer operative during first and second driving modes in accordance with the 3D and 2D image data. A controller converts the optical element layer to be in the first driving mode in a first period before a 3D image signal is displayed when the input image signal changes from a 2D image signal to the 3D image signal, and converts the optical element layer to be in the second driving mode in a second period after the 2D image signal is displayed when the input image signal changes from the 3D image signal to the 2D image signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Multipurpose navigation keys for an electronic imaging device
InactiveUS20050283729A1Save spaceReduce errorsRecording carrier detailsRecord information storageMarine navigationElectronic imaging
A method and apparatus for a portable electronic imaging device, comprising a display screen for displaying objects including any combination of digital still images, video clips, menu items, and icons; and a navigation controller comprising navigation keys for allowing a user to navigate between the displayed objects, wherein the user may select a currently displayed object without moving a finger from a navigation key last pressed, thereby implementing navigation and select functions on a single controller.
Owner:SCENERA TECH
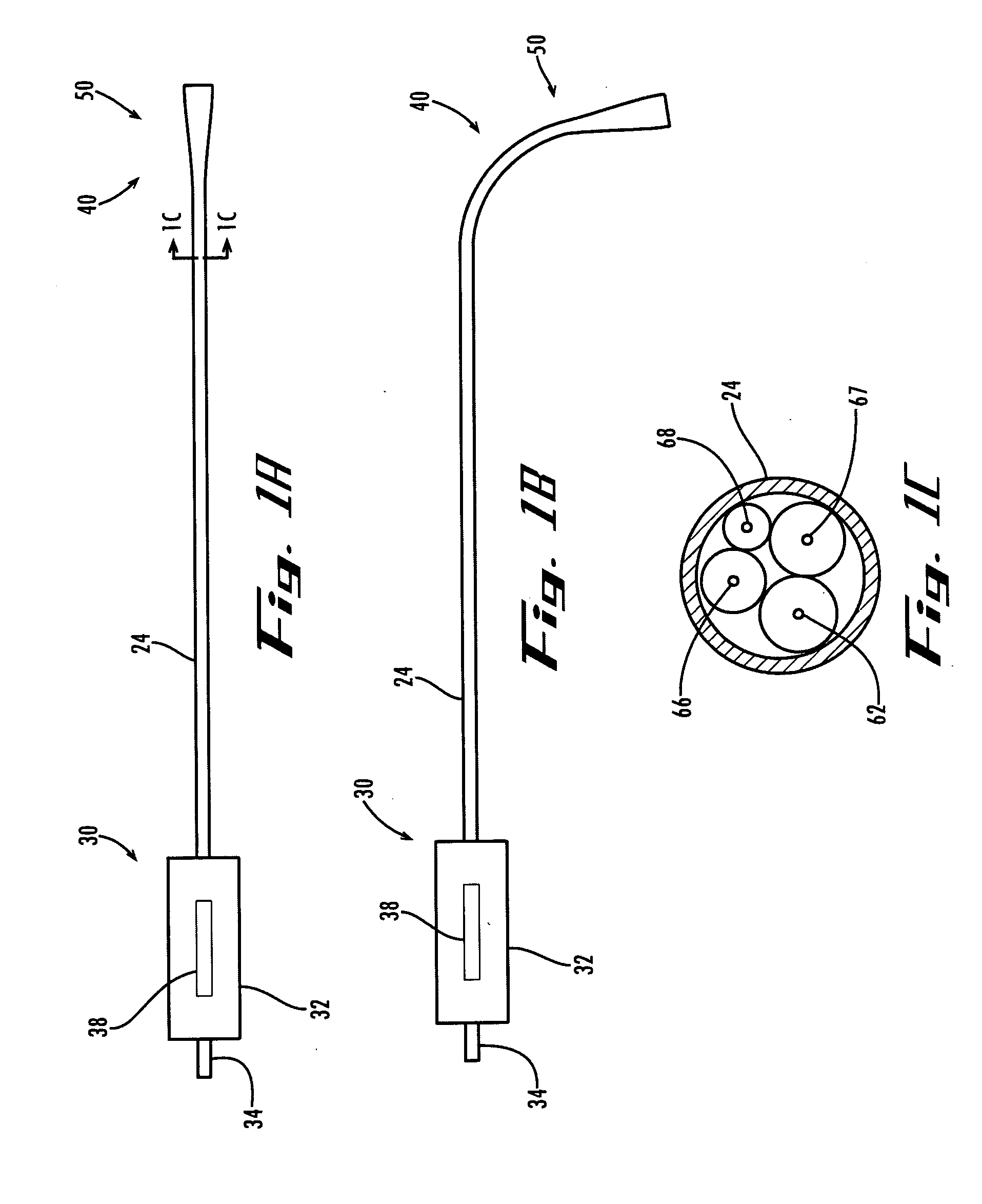
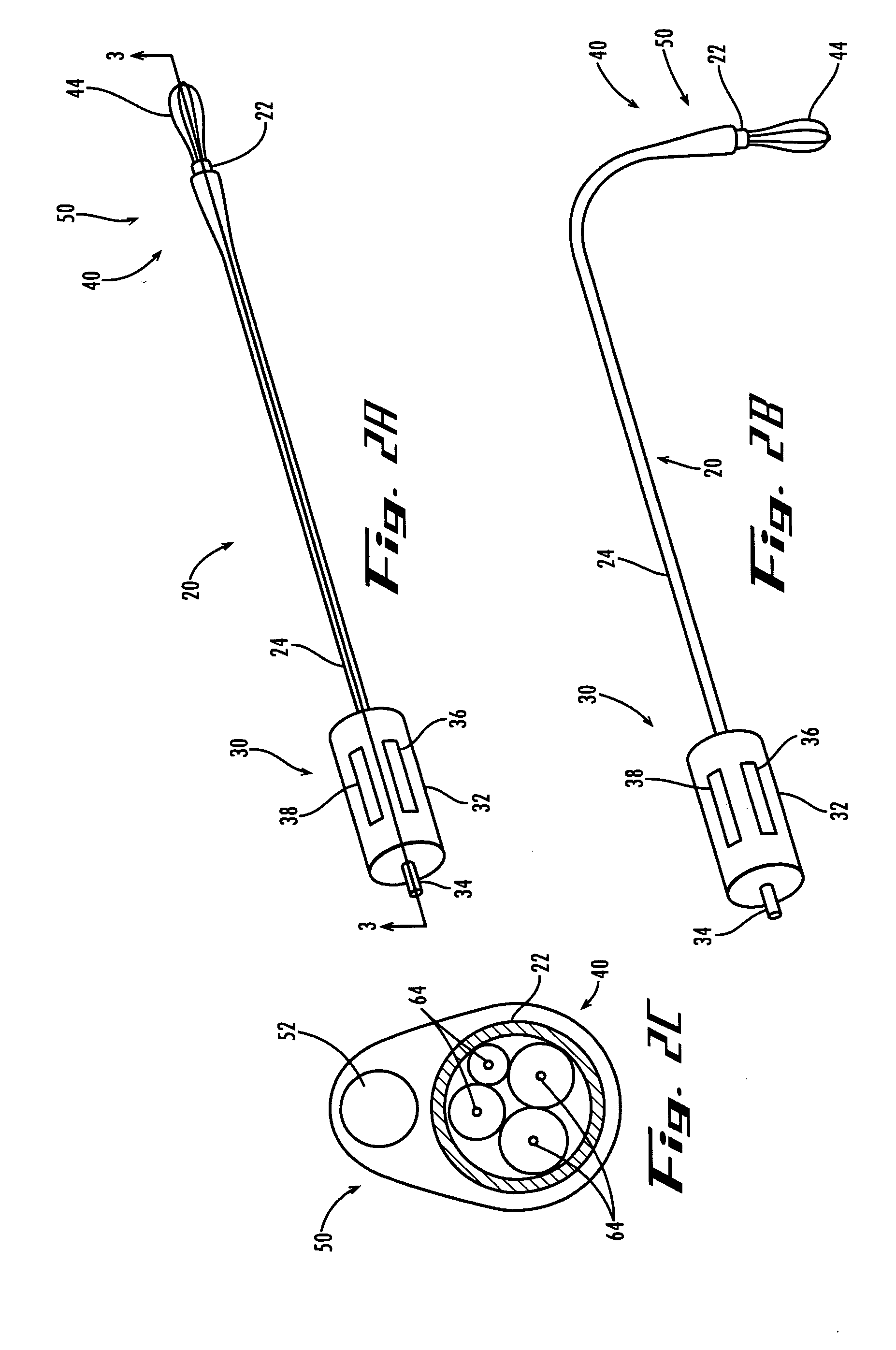
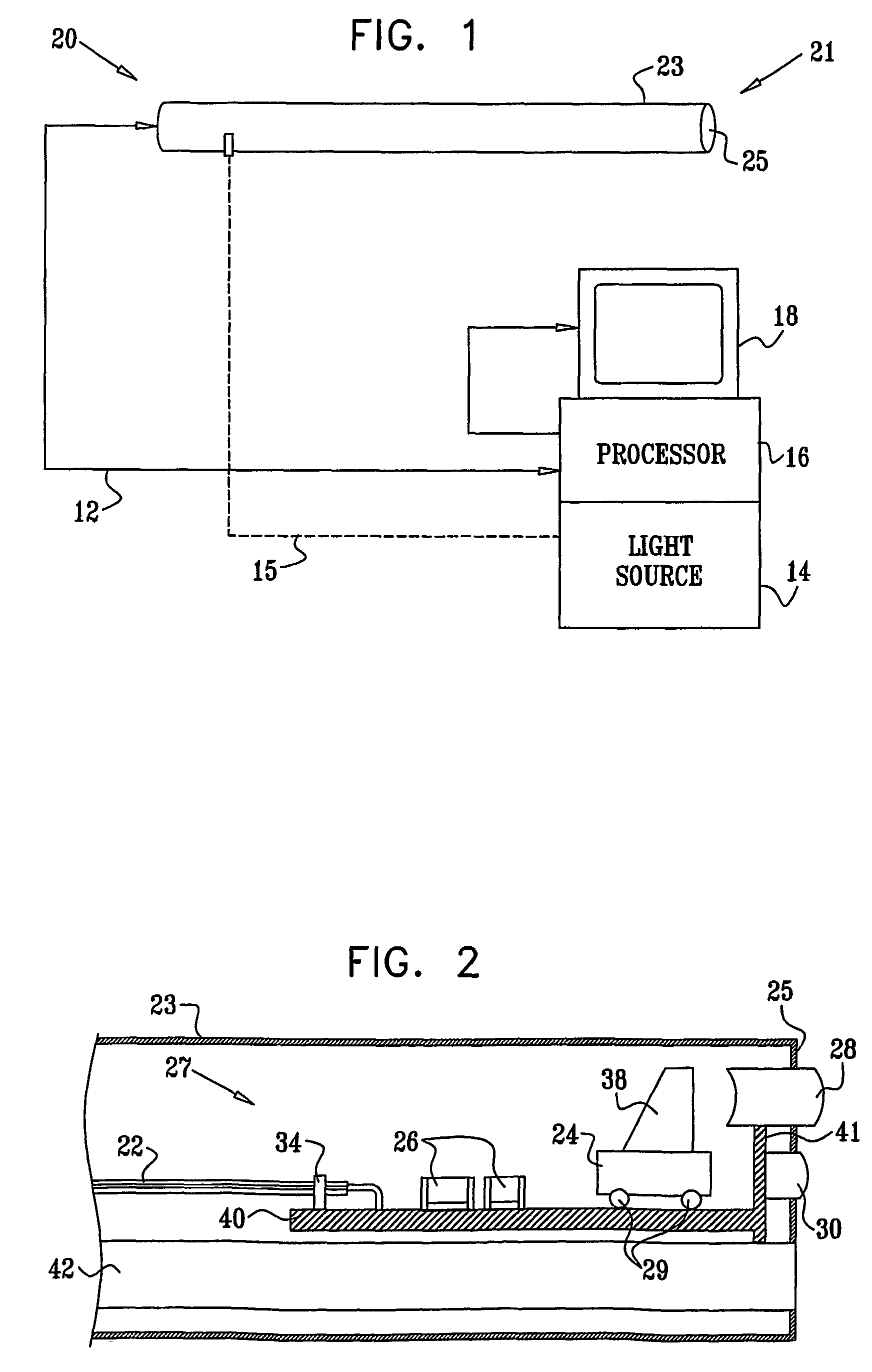
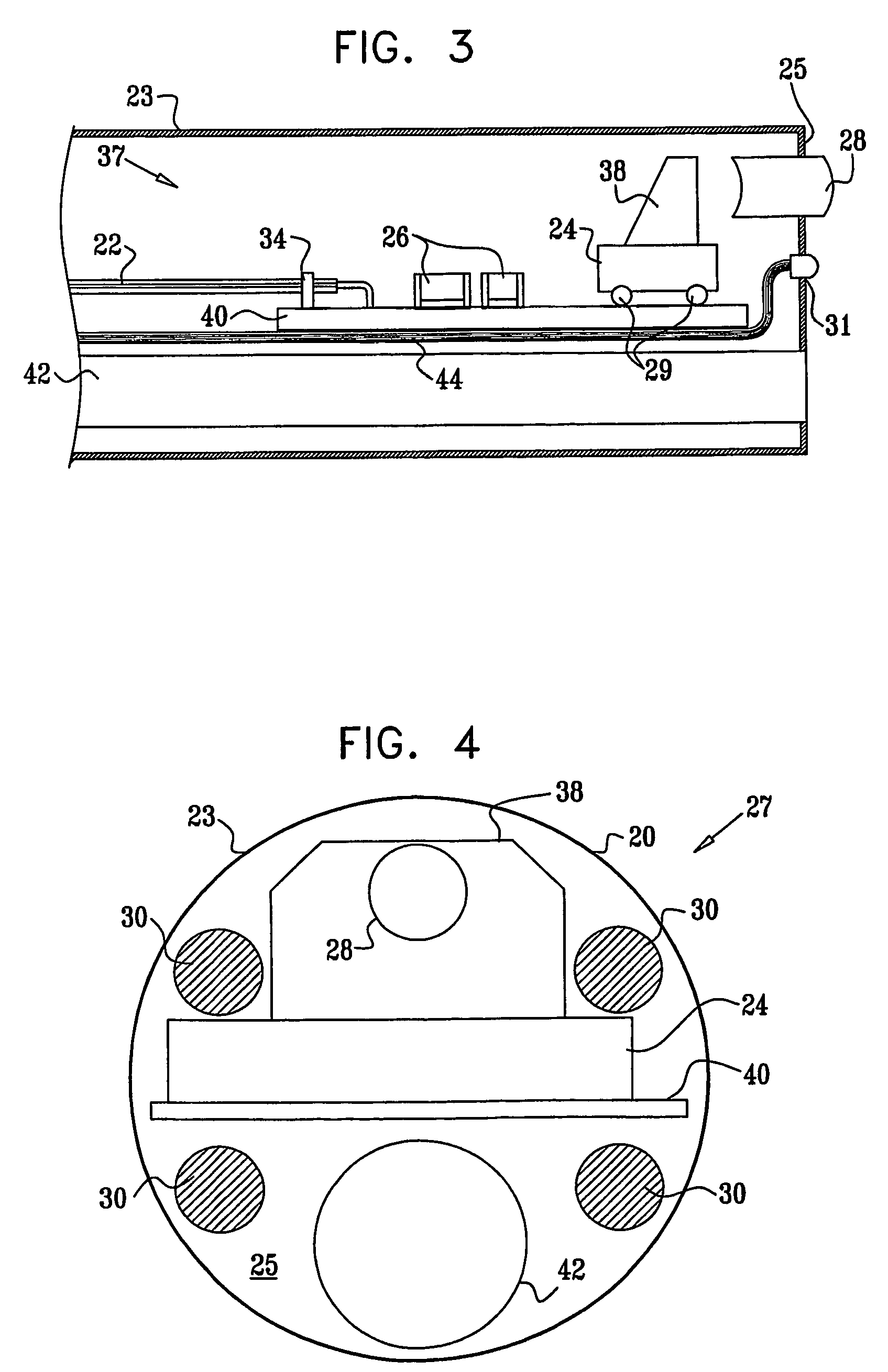
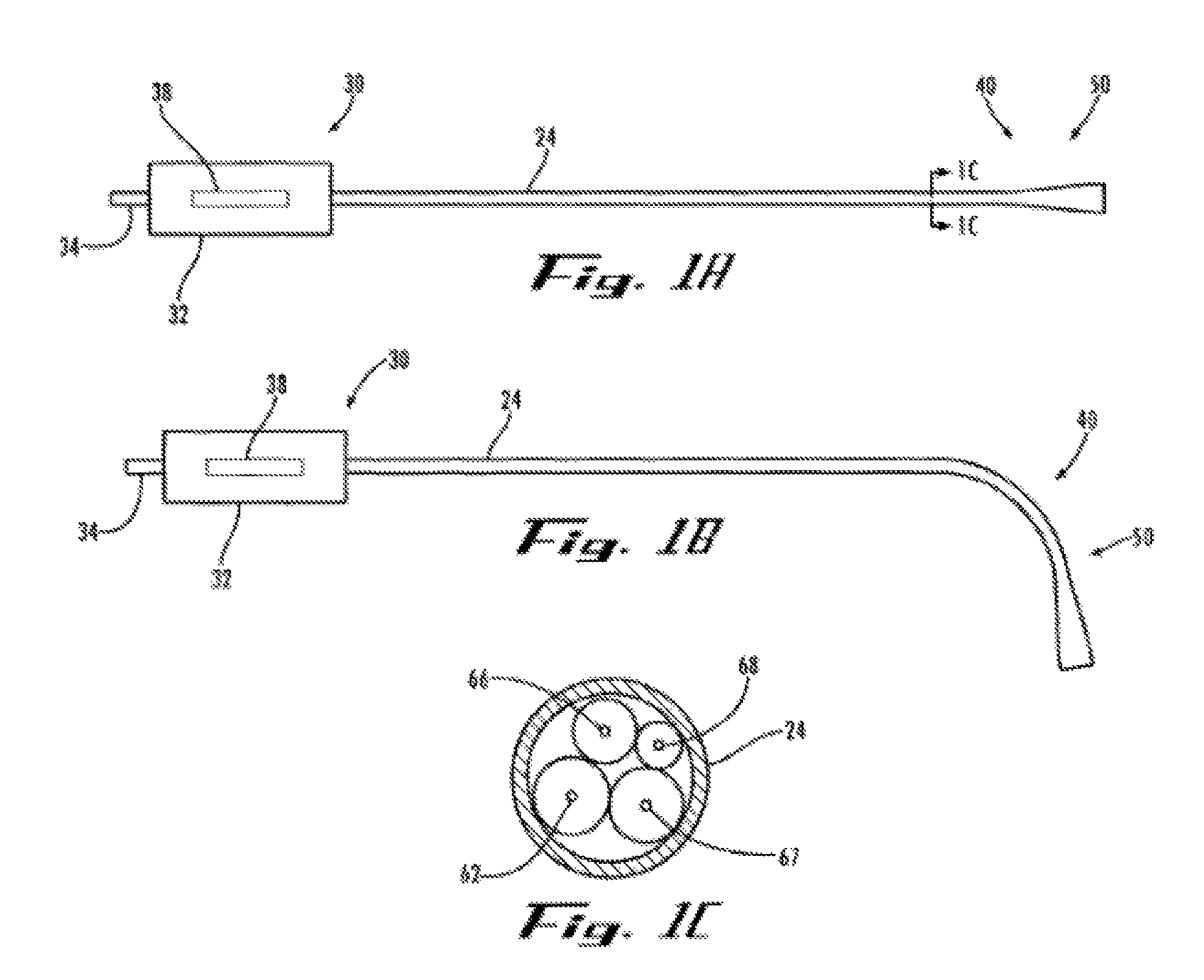
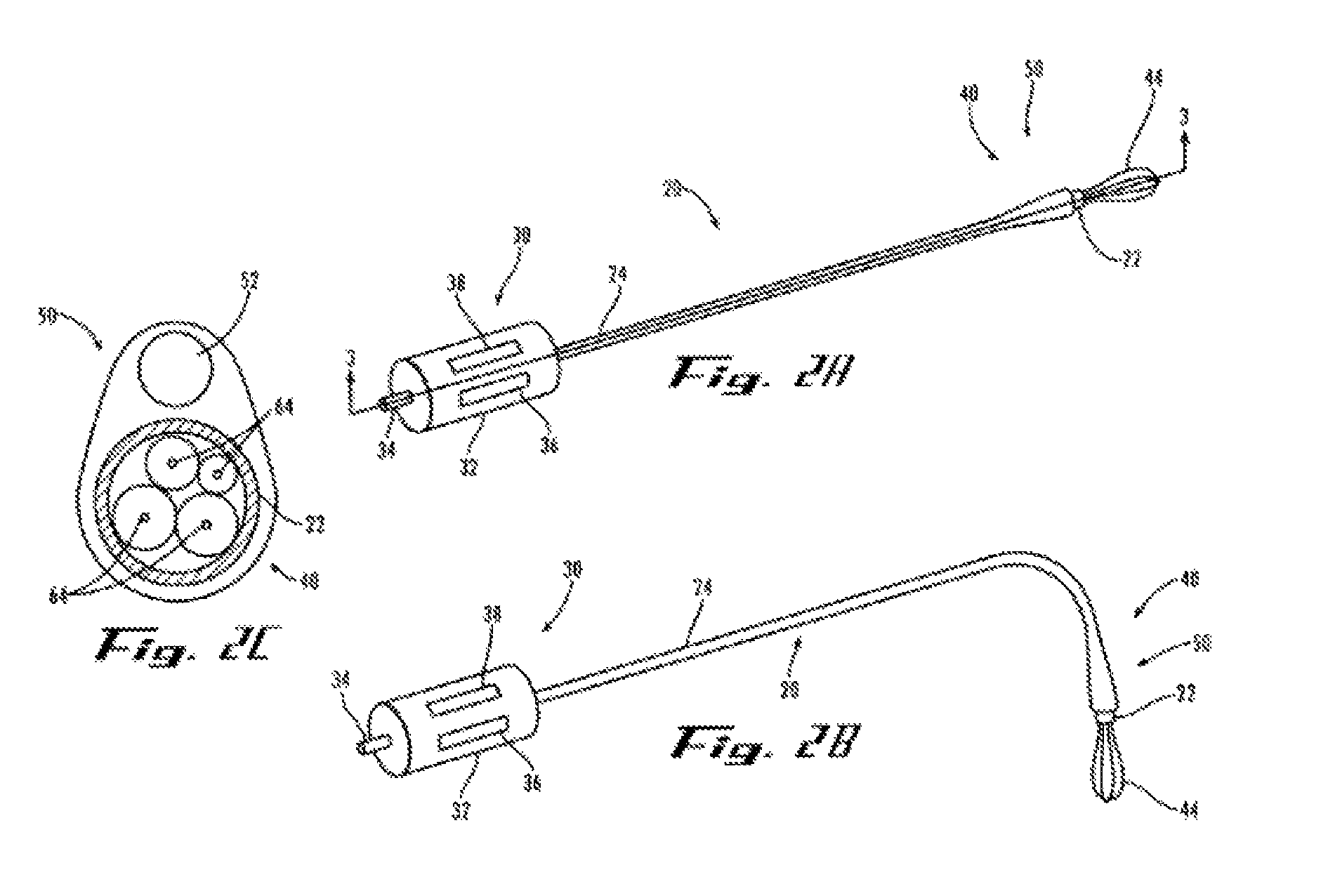
Endoscopic instrument having reduced diameter flexible shaft
A medical instrument comprising a flexible, filamentous shaft slideably disposed in a sheath, the instrument including an electronic imaging system comprising an image sensor carried on a distal end portion of the instrument. The shaft may be used as a guidewire for a complementary guided device, or it may be used to carry a functional element for performing a procedure at a target site in a patient's body. In other embodiments, the present invention contemplates a flexible sheath, preferably having a simple tubular construction, with an electronic imaging system at its distal end. The sheath is adapted to slideably receive a shaft, preferably a filamentous shaft, that closely fits the sheath. The shaft carries functional element at its distal end. The instruments according to the present invention may include one or more filaments along their length for deflecting an insertable portion of the instrument.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Electronic image sensor
InactiveUS20060164533A1Avoid complicationsAccurate exposureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFrame rate
An electronic imaging sensor. The sensor includes an array of photo-sensing pixel elements for producing image frames. Each pixel element defines a photo-sensing region and includes a charge collecting element for collecting electrical charges produced in the photo-sensing region, and a charge storage element for the storage of the collected charges. The sensor also includes charge sensing elements for sensing the collected charges, and charge-to-signal conversion elements. The sensor also includes timing elements for controlling the pixel circuits to produce image frames at a predetermined normal frame rate based on a master clock signal (such as 12 MHz or 10 MHz). This predetermined normal frame rate which may be a video rate (such as about 30 frames per second or 25 frames per second) establishes a normal maximum per frame exposure time. The sensor includes circuits (based on prior art techniques) for adjusting the per frame exposure time (normally based on ambient light levels) and novel frame rate adjusting features for reducing the frame rate below the predetermined normal frame rate, without changing the master clock signal, to permit per frame exposure times above the normal maximum exposure time. This permits good exposures even in very low light levels. (There is an obvious compromise of lowering of the frame rate in conditions of very low light levels, but in most cases this is preferable to inadequate exposure.) These adjustments can be automatic or manual.
Owner:E PHOCOS
Disposable Stereoscopic Endoscope System
A disposable simultaneous stereo endoscope system is disclosed. The disposable endoscope does not include image relay. Instead, two electronic imaging sensors and solid illumination lighting are arranged inside the endoscope. A demultiplexing beam splitter is used for splitting the two imaging light beams to the two imaging devices. A wedged multi-facet illumination window is used to create an illumination field that is larger than the field of view of the imaging optics. An electrically conductive heat sink is engaged for dissipating the heat generated by the solid light source and also for shielding end side of the endoscope. The disposable endoscope is shielded from electromagnetic interferences. A repeater unit is used to electrically connect the disposable endoscope with a remote receiver and to increase the data transfer rate. An electrical isolation means is provided between the endoscope and an image processing and power conditioning unit to protect the endoscope against electric shock.
Owner:SU WEI +1
Miniature camera head
ActiveUS20050267328A1Small sizeReduce the overall diameterTelevision system detailsSurgeryOptical radiationOptical axis
An electronic imaging device (27) includes an optical objective (28) for collecting optical radiation from an object, the objective having an optical axis, and an image sensor (24), including a matrix of optical detectors arranged in a plane that is substantially non-perpendicular to the optical axis, the image sensor having a lateral dimension in the plane. A turning mirror (38) has an optical surface that is positioned so as to reflect the radiation collected by the objective in order to form a focused image in the plane of the image sensor, while a maximum distance from the optical surface to the plane of the image sensor is substantially less than the lateral dimension of the image sensor.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Image enhancement by sub-pixel imaging
InactiveUS7323681B1Increase effective resolutionEfficient solutionImage enhancementBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsImage resolutionElectron
Methods and apparatus for improving the resolution of an electronic imaging device having an array of pixels. Sub-pixel dimension movements between an object and the array of pixels are made, and an image is formed at each position. Resulting shifted images are combined to yield an effective resolution corresponding to an array having smaller pixels. Such methods and apparatus allow optical systems with existing pixel devices to form effective images of smaller feature sizes.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Electronic side view display system
InactiveUS20110181728A1Improve fuel economyImprove securityColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsActive matrixOLED
An apparatus provides an electronic replacement for driver and passenger side view minor systems. Specifically, a set of unique features provide enhanced fuel economy, safety and convenience. The invention relies upon electronic imaging cameras and electronic active matrix displays (e.g. LCD, OLED, etc.) for reproducing the image, with the addition of reality enhancing features.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Optical filter, method of manufacturing optical filter, optical system, and imaging apparatus
An imaging apparatus comprises an optical system including a plurality of optical elements having finite refractive power and an electronic imaging device disposed at an image side of the optical system. At least one of the plurality of optical elements is made of resin, and an infrared-cut coating is applied to at least one face of the optical element that is made of resin.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Image enhancement by sub-pixel imaging
InactiveUS7199357B1Increase effective resolutionEfficient solutionBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsImage resolutionElectron
Methods and apparatus for improving the resolution of an electronic imaging device having an array of pixels. Sub-pixel dimension movements between an object and the array of pixels are made, and an image is formed at each position. Resulting shifted images are combined to yield an effective resolution corresponding to an array having smaller pixels. Such methods and apparatus allow optical systems with existing pixel devices to form effective images of smaller feature sizes.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Electronic imaging system using organic laser array illuminating an area light valve
InactiveUS6950454B2Good image uniformityFlare can be reducedProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionColor imageData stream
An electronic imaging system for providing a viewable color image from an image data stream, including: a plurality of different colored laser light sources arranged in an at least one array with each such colored laser light source including a vertical cavity design; at least one area light valve for receiving the laser light and producing the viewable color image from the image data stream; and a projection lens for projecting the viewable color image onto a target plane.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
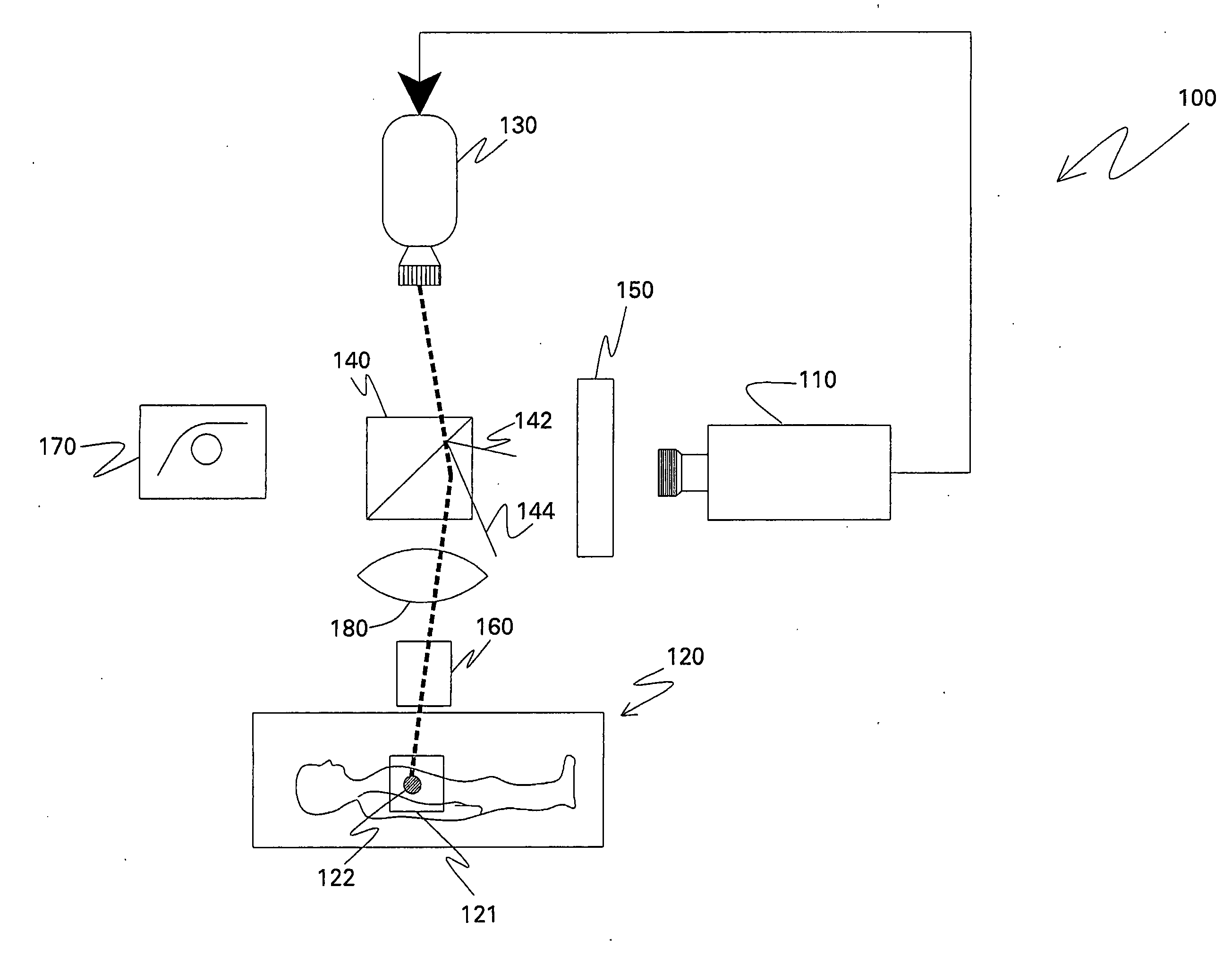
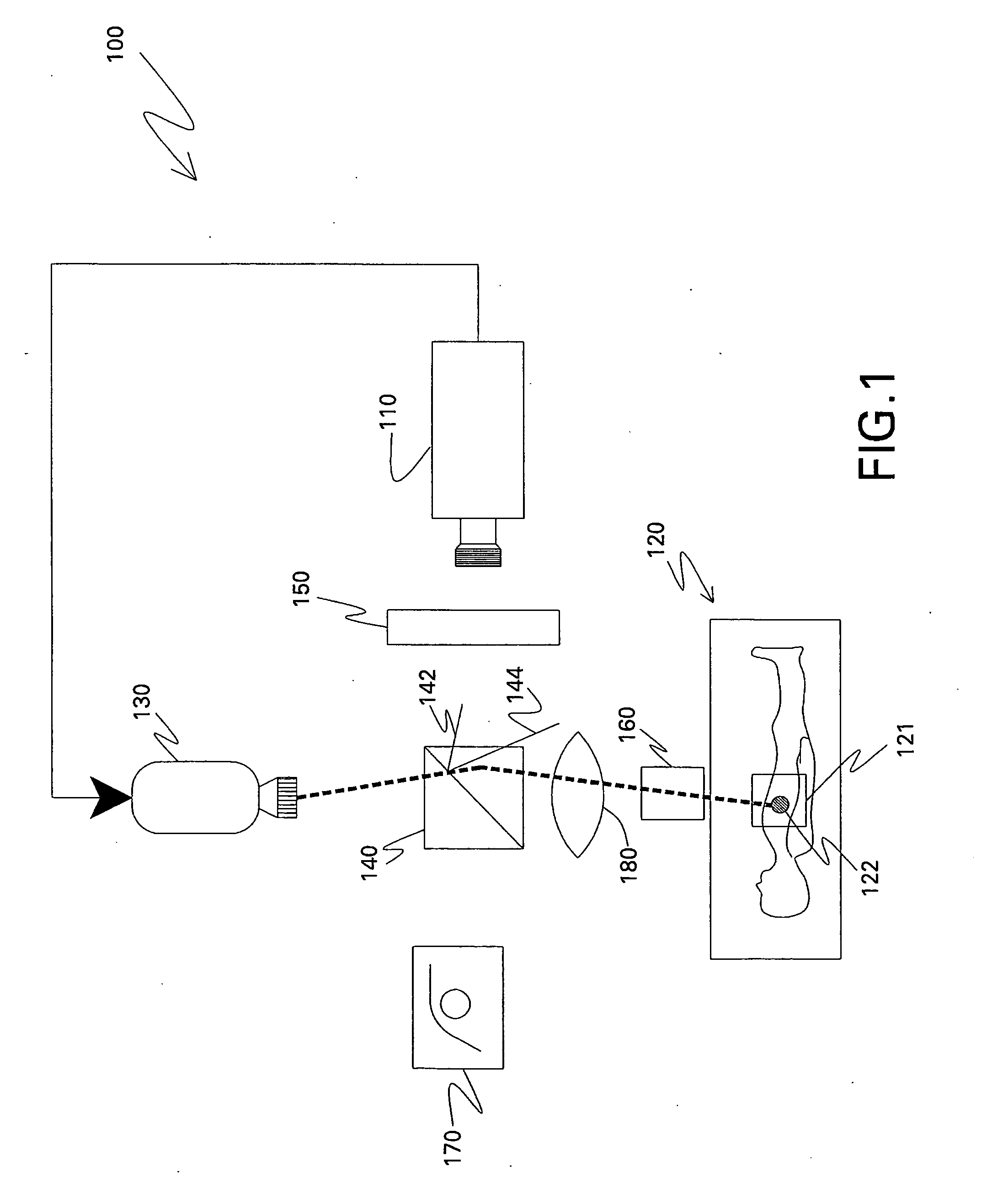
Optical imaging systems and methods
Optical imaging systems and methods are disclosed. The optical imaging system includes an electronic imaging device configured to capture an image of a site and a projector. An optical imaging system includes a projector configured to project a visible representation of the captured image onto the site during surgery. Another optical imaging system includes an optical element capable of aligning an optical axis of the electronic imaging device and the projector on a same optical axis. Also disclosed are methods for displaying an image on to a site. A method includes capturing a fluorescent image of a surgical site; and projecting a visible representation of the captured image onto the surgical site during surgery. Another method includes projecting a visible representation of a captured image of a site onto the site along a same optical axis along which the image is captured.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
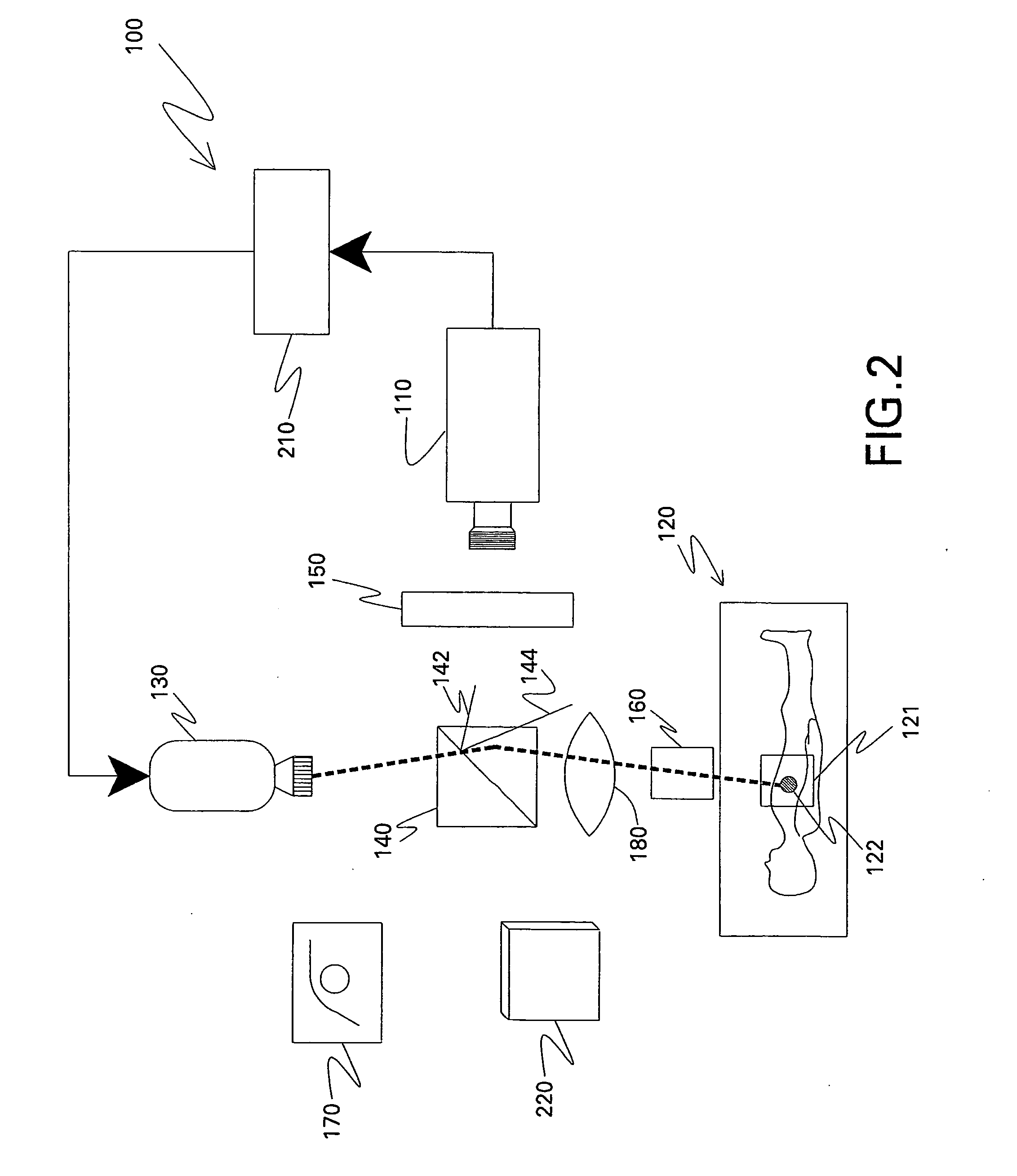
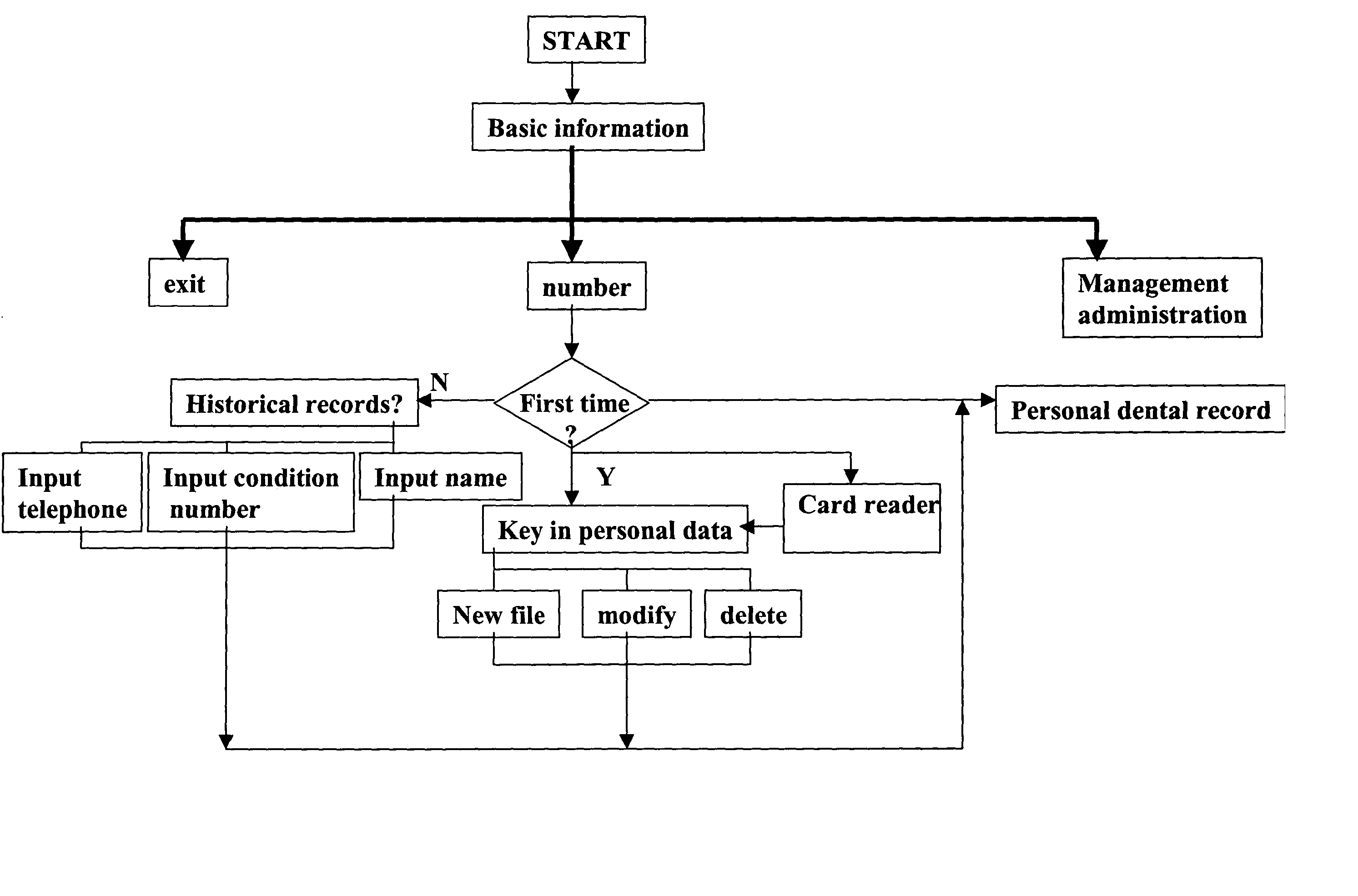
Electronic imaging dental record management system
InactiveUS20050043970A1Quickly and easily and analyzeQuickly and easily viewCharacter and pattern recognitionOffice automationDental recordTherapy planning
A computerized electronic dental record management system that allows dentists to quickly and easily view and analyze patient's dental conditions and clearly explain and show their diagnosis to the patients. The dentist uses a flexible thin camera to take photographs or images of the teeth. These images are stored in a patient's electronic dental record. At any time, the dentist can use these images to analyze or diagnose the patient's condition and formulate a treatment plan. The dentist can also use these images to clearly show and explain the patient's condition and proposed treatment plan to the patient. Additionally, using a hand-held monitor, the patient can also view the images in real time as the dentist is inspecting the patient's teeth.
Owner:HSIEH KENT
Electronic imaging system
InactiveUS20050178950A1Improve efficiencyGood power savingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An electronic imaging system having an image sensor array that includes photodetectors arranged in rows and a rolling shutter for initiating charge integration by row and reading out pixel signals by row after a lapse of a predetermined integration time is equipped with a lighting unit having an LED array including rows of LED elements for producing flashes in different directions, respectively, and a circuitry for exciting and extinguishing the LED rows, one at a time. The LED rows are allocated to a plurality of sections into which the image sensor array is divided, one row to each section. The circuitry initiates excitation of each LED row allocated to a given section of the array at the beginning of charge integration of a first row of the given section and extinguishes the LED row at termination of charge integration of a last row of the given section.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Digital holographic microscope for 3D imaging and process using it
InactiveUS20080018966A1Reduce spatial coherenceReduce coherent noiseHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopes3d imageDigital holographic microscopy
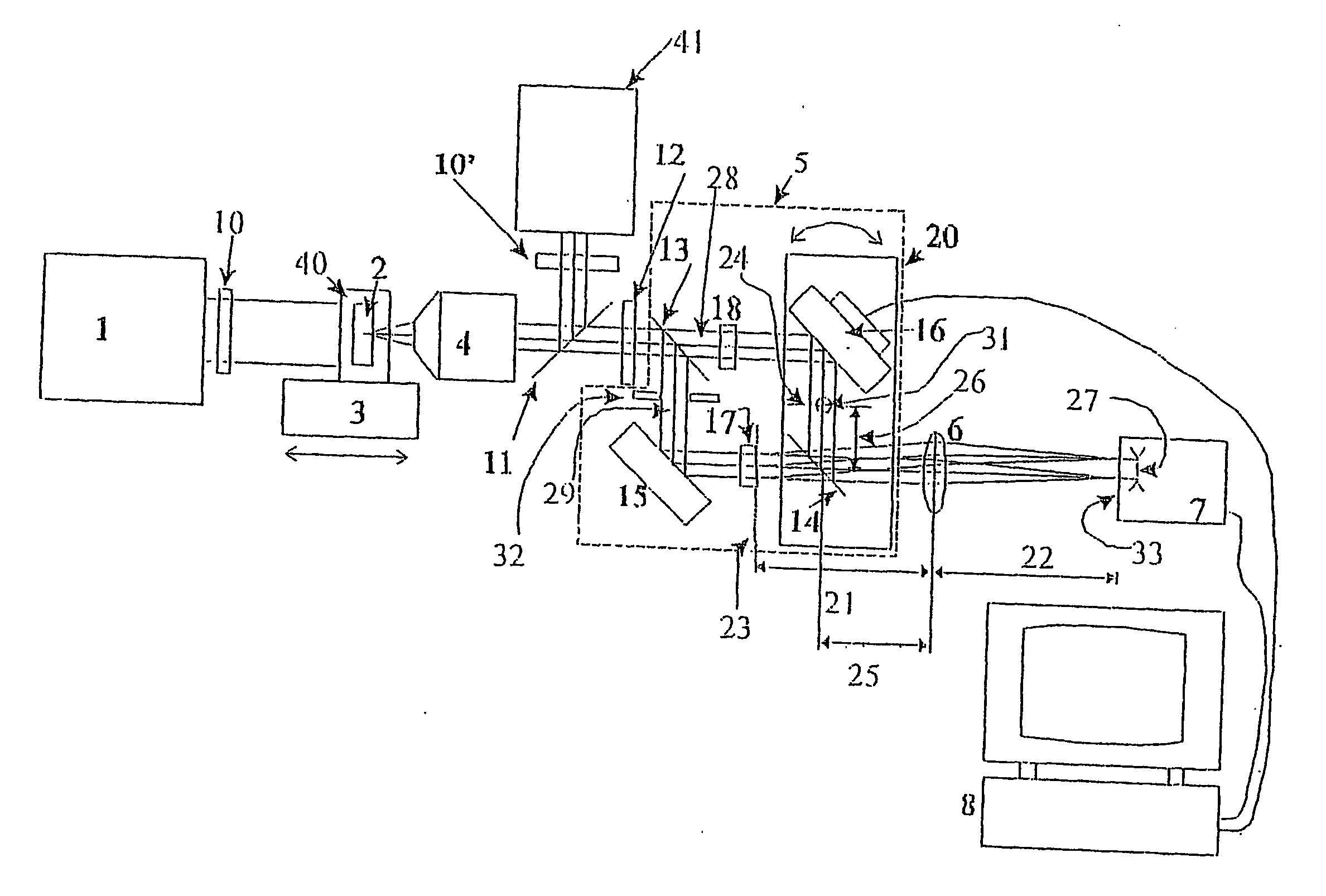
The present invention is related to a compact microscope able to work in digital holography for obtaining high quality 3D images of samples, including fluorescent samples and relatively thick samples such as biological samples, said microscope comprising illumination means (1,41) at least partially spatially coherent for illuminating a sample (2) to be studied and a differential interferometer (5) for generating interfering beams from said sample (2) on the sensor (33) of an electronic imaging device (7), said interferometer (5) comprising namely tilting means (17) for tilting by a defined angle one the interfering beams (28 or 29) relatively to the other, said tilting resulting into a defined shift (27) of said interfering beam on the sensor of the electronic imaging device (7), said shift (27) being smaller than spatial coherence width of each beam, said microscope being able to be quasi totally preadjusted independently from the samples so that minimum additional adjustments are required for obtaining reliable 3D images of samples.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Electronic imaging device with photosensor arrays
InactiveUS20070187574A1Television system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhysicsElectronic imaging
An electronic imaging device is provided that includes a plurality of sensor elements, such as multiple photosensor arrays, wherein some of the sensor elements have a different numerical aperture value than the others, and wherein the sensor elements can be arranged such that their electrical signals can be combined to produce a composite electrical signal.
Owner:GE INSPECTION TECH
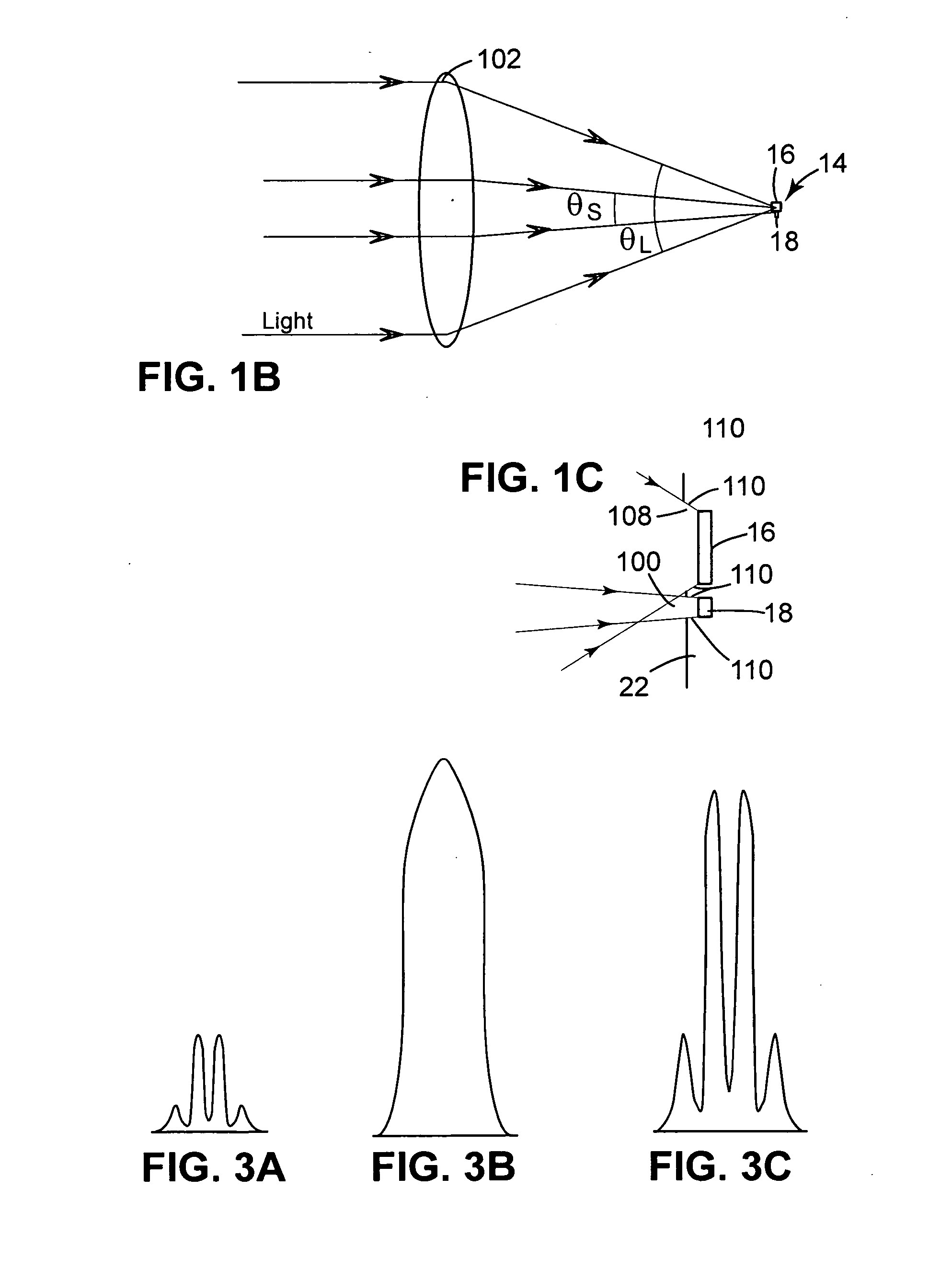
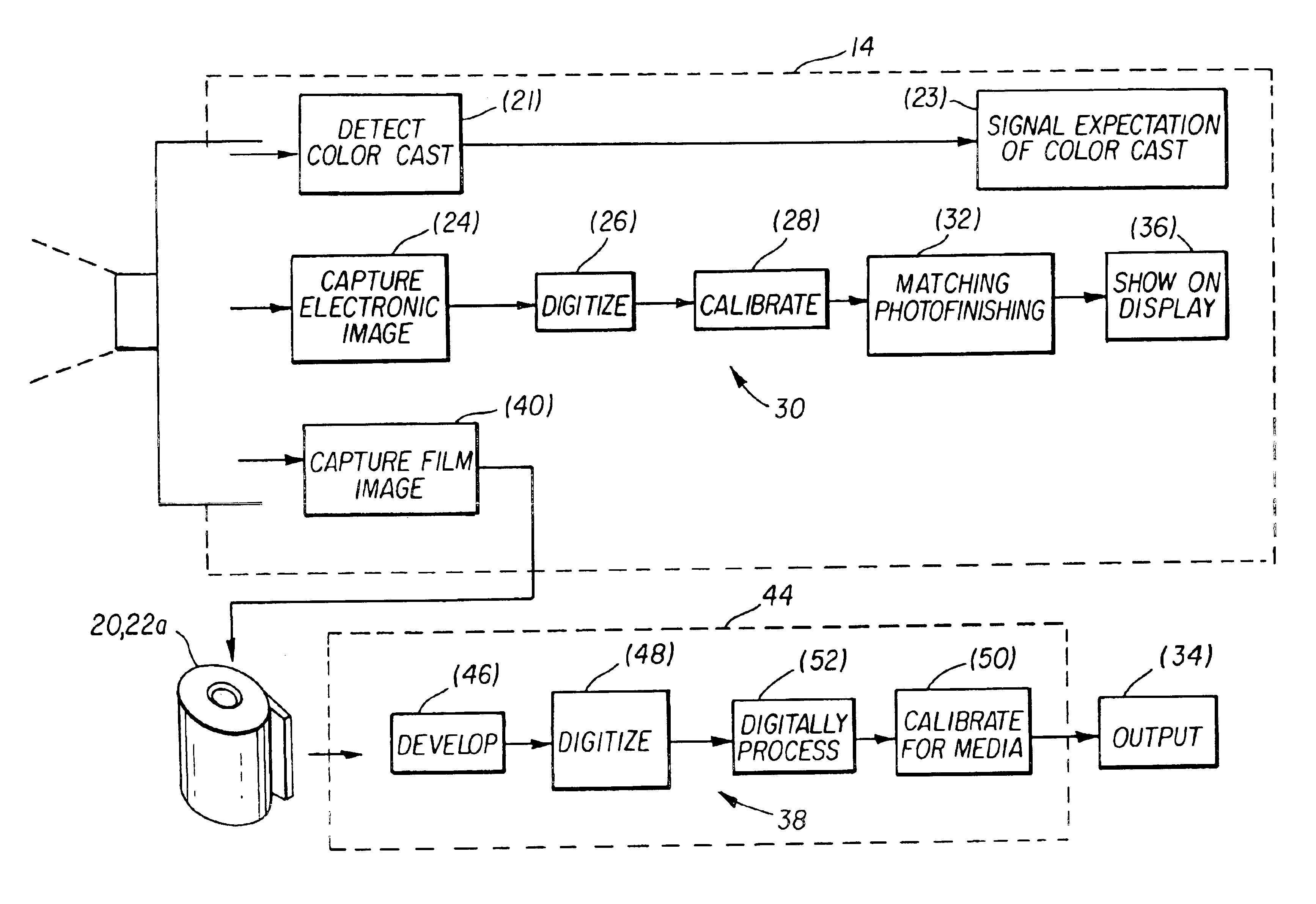
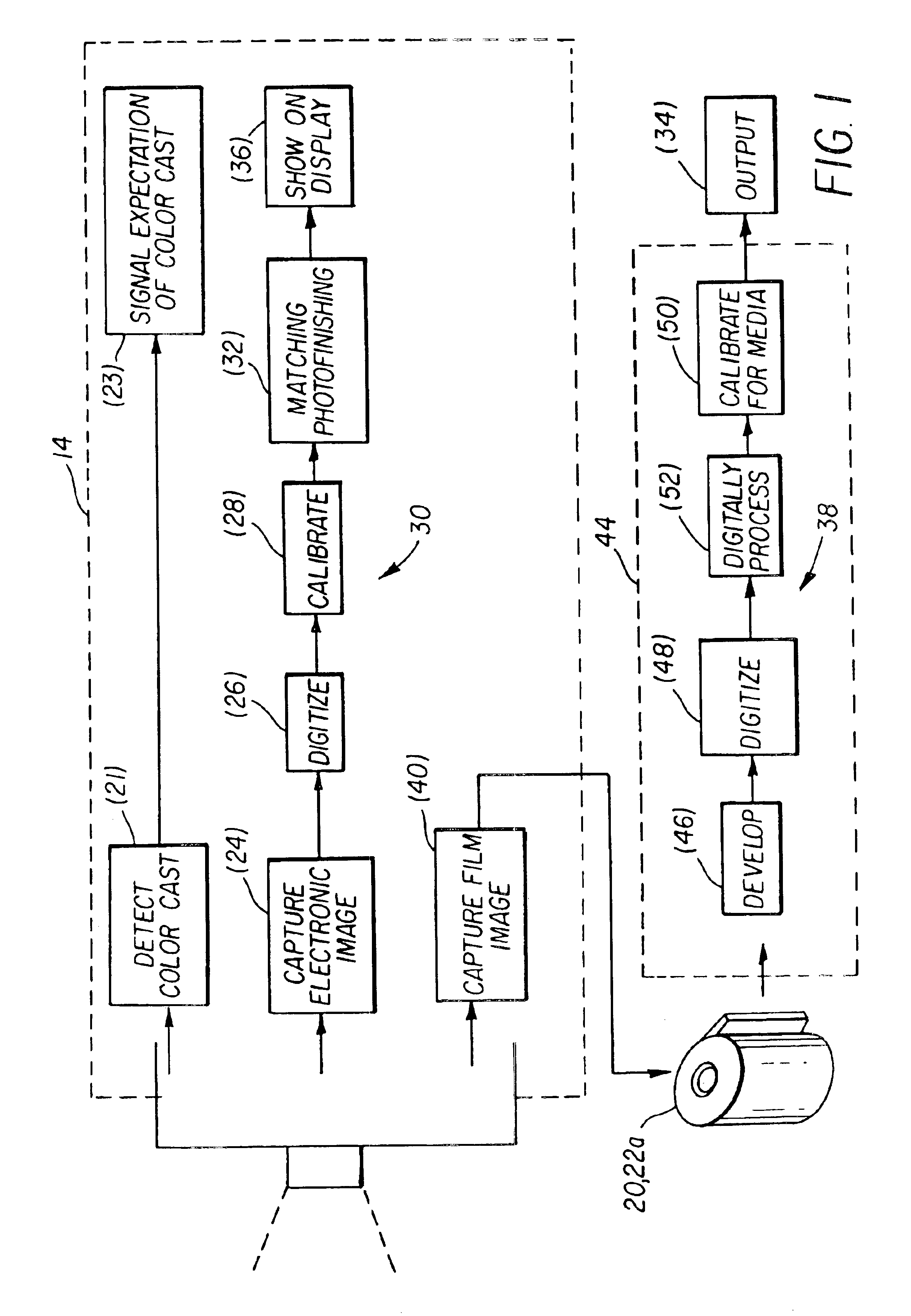
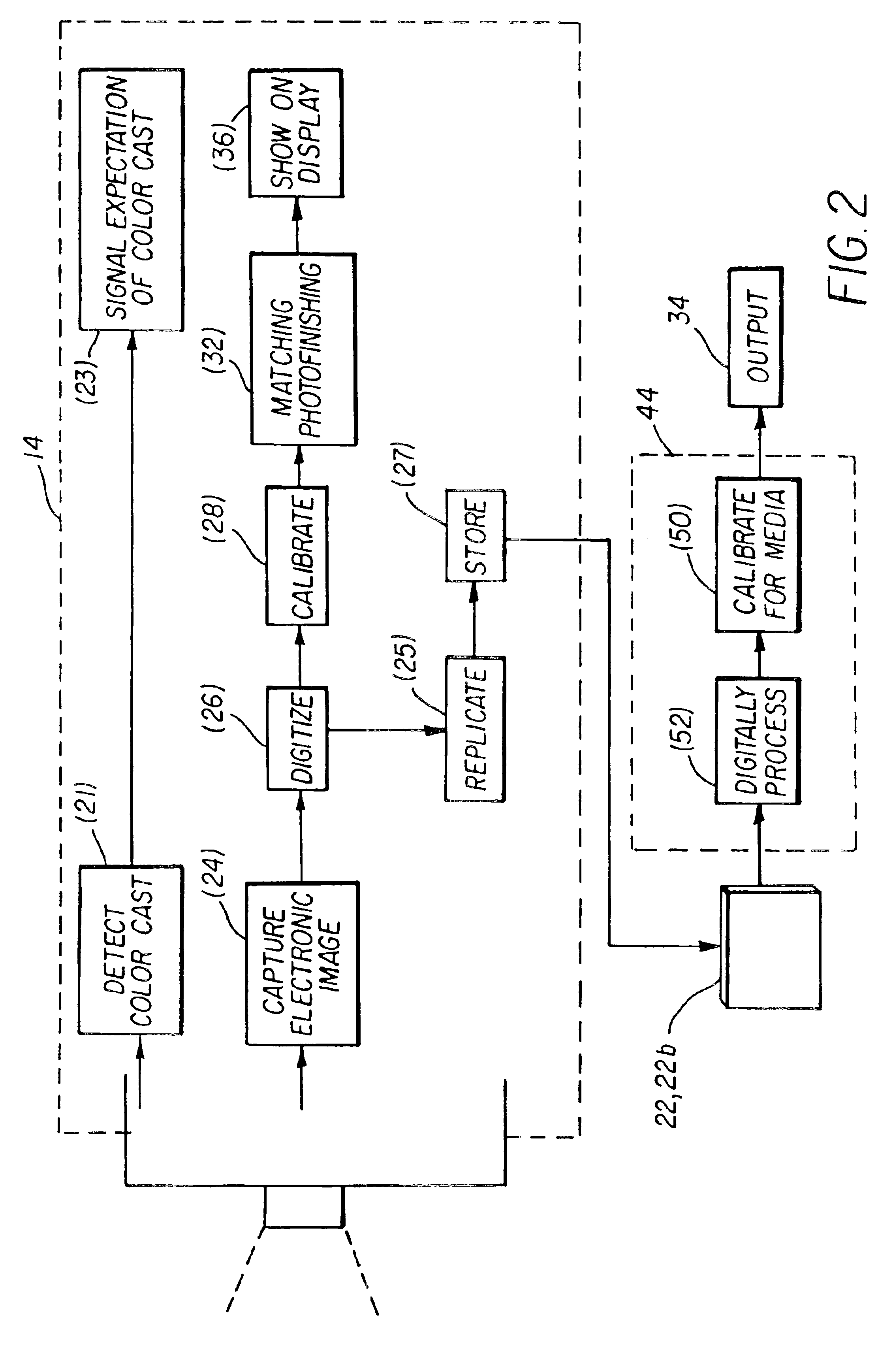
Camera having user interface with verification display and color cast indicator
InactiveUS6870567B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer graphics (images)Electronic imager
A camera and method are usable for capturing images of scenes illuminated by ambient light. The camera has a body and an electronic imager disposed in the body. The electronic imager captures an ambient light image as a multicolored electronic image. A color detector is disposed in the body. The color detector measures the ambient light to provide a color value. A user interface disposed on the outside of said body, shows the electronic image and an indication of the color value. The indication is independent of the color balance of the electronic image.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Miniature camera head
ActiveUS8194121B2Reduce the overall diameterReduce the overall heightTelevision system detailsSurgeryOptical radiationOptical axis
An electronic imaging device (27) includes an optical objective (28) for collecting optical radiation from an object, the objective having an optical axis, and an image sensor (24), including a matrix of optical detectors arranged in a plane that is substantially non-perpendicular to the optical axis, the image sensor having a lateral dimension in the plane. A turning mirror (38) has an optical surface that is positioned so as to reflect the radiation collected by the objective in order to form a focused image in the plane of the image sensor, while a maximum distance from the optical surface to the plane of the image sensor is substantially less than the lateral dimension of the image sensor.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
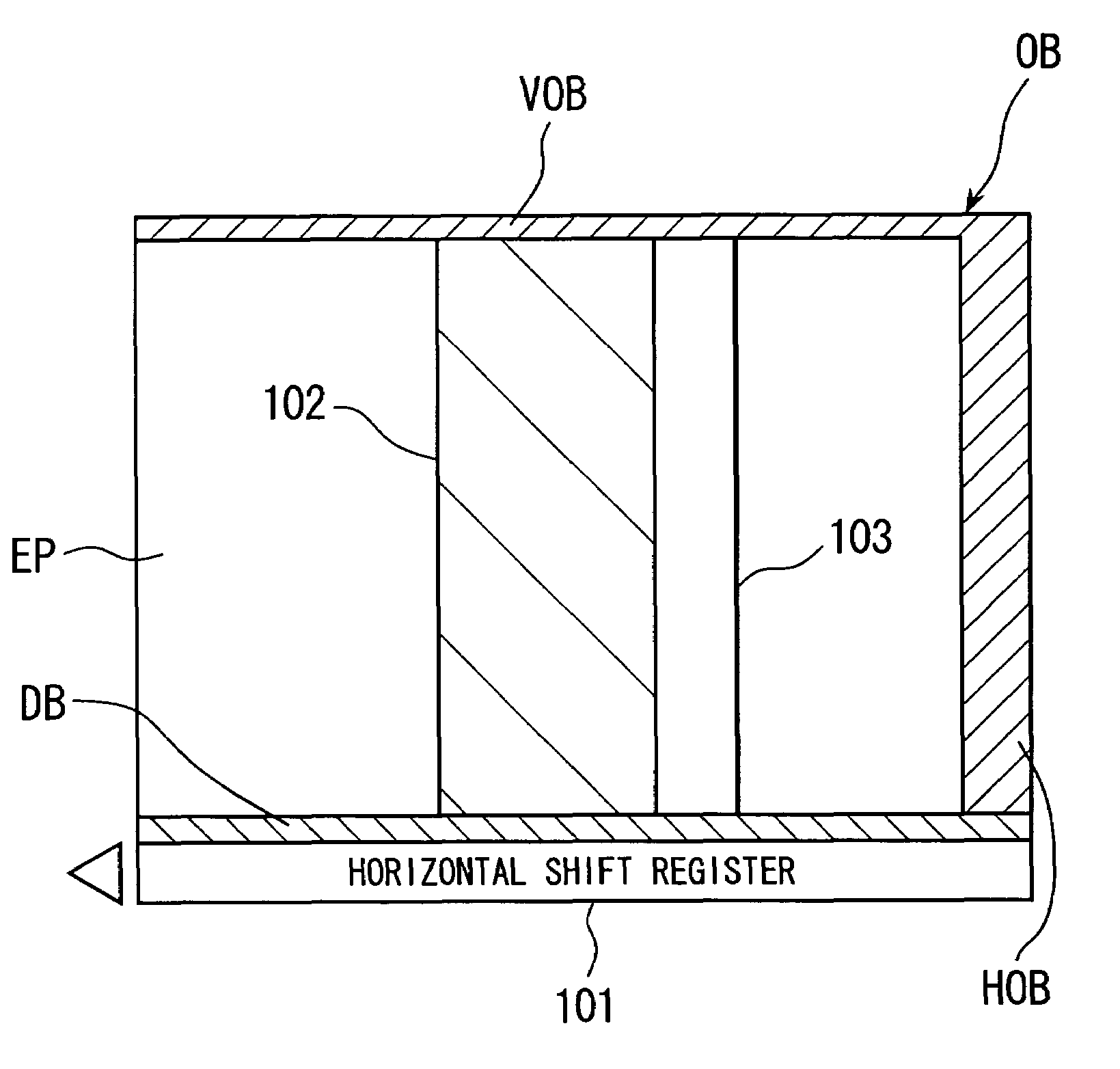
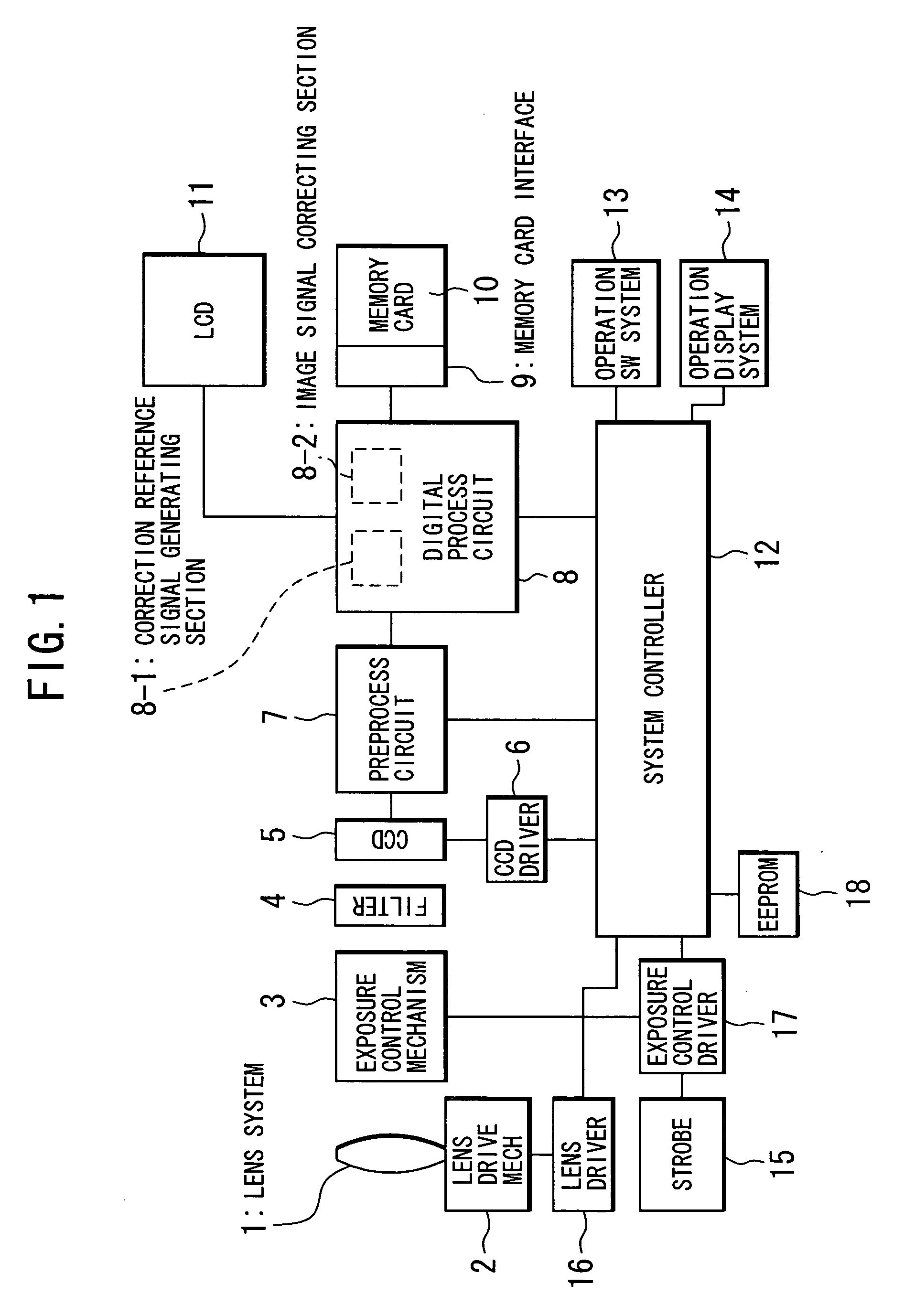
Electronic imaging apparatus operable in two modes with a different optical black correction procedure being effected in each mode
InactiveUS6970193B1Eliminate the effects ofImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsSignal correctionImage signal
An image pickup apparatus including: CCD image pickup device; a correction reference signal generating section for generating a correction reference signal for correcting effective image signals of the image pickup device from output signals of a vertical optical black pixel portion of the image pickup device; an image signal correcting section for subtracting the correction reference signal from an effective image signal; and CCD driver having a plurality of drive modes for driving the image pickup device to read pixel charges as output signals; wherein, when generating the reference signal, said correction reference signal generating section performs different types of reference signal generation processing corresponding to the plurality of drive modes of the CCD driver.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
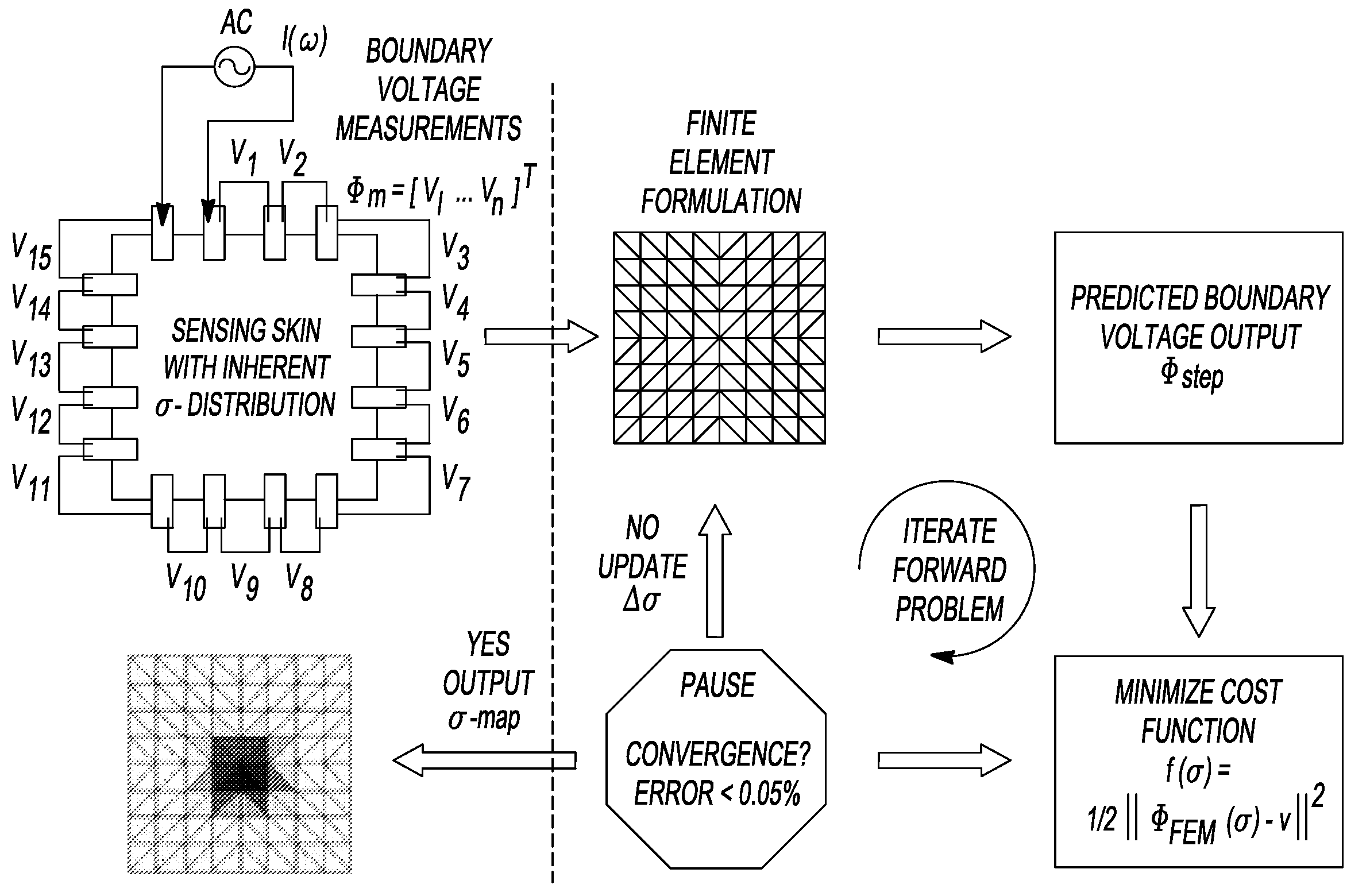
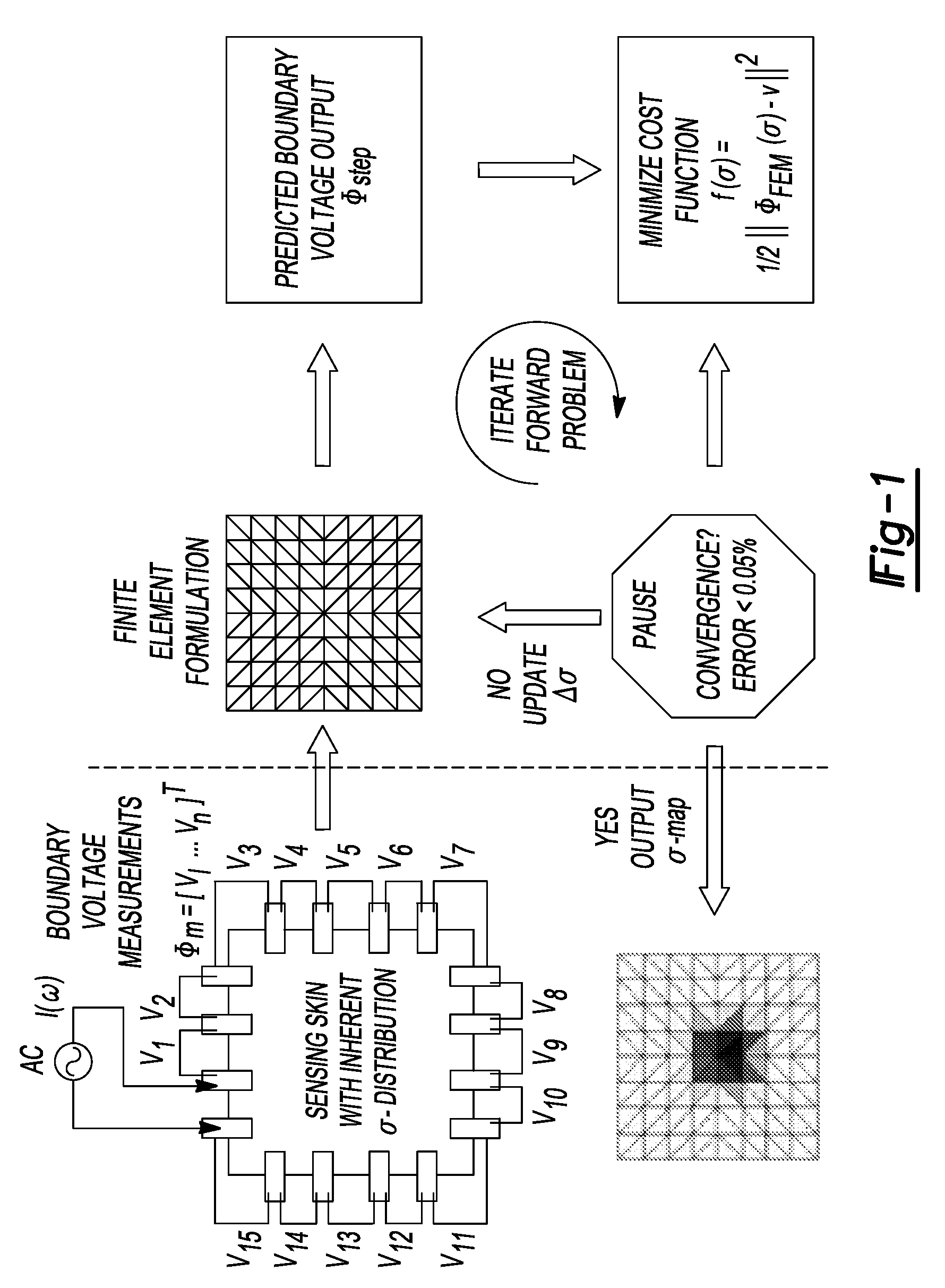
Electrical impedance tomography of nanoengineered thin films
ActiveUS20090121727A1Accurate detection of damageConvenient and accurateResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial impedancePotential measurementBoundary potential
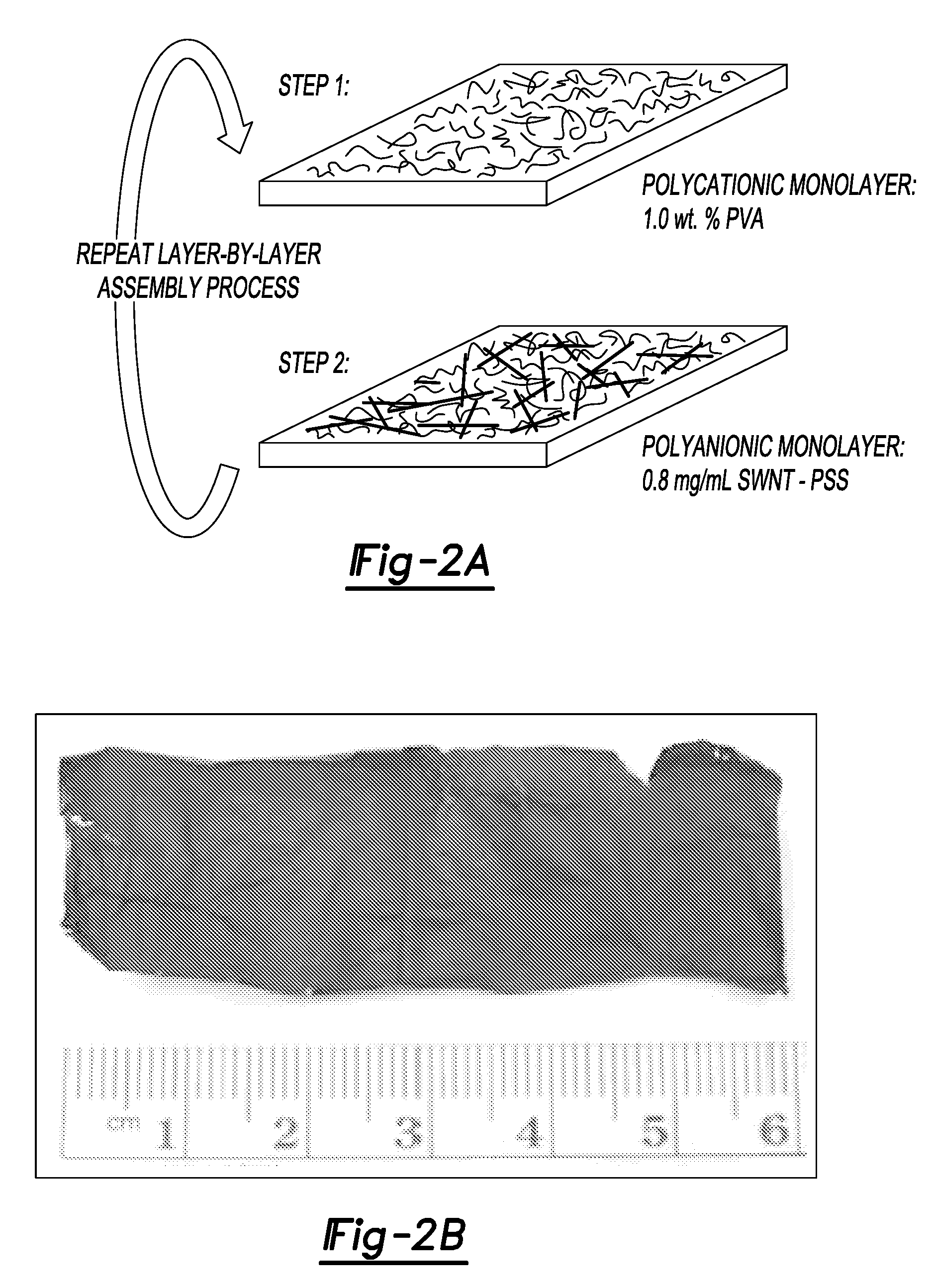
The present teachings relate to the application of electrical impedance tomography (EIT) to demonstrate the multifunctionality of carbon nanocomposite thin films under various types of environmental stimuli. Carbon nanotube (CNT) thin films are fabricated by a layer-by-layer (LbL) technique or other techniques and mounted with electrodes along their boundaries. The response of the thin films to various stimuli determined by relying on electric current excitation and corresponding boundary potential measurements. The spatial conductivity variations are reconstructed based on a mathematical model for the EIT technique. Here, the ability of the EIT method to provide two-dimensional mapping of the conductivity of CNT thin films is validated by (1) electrically imaging intentional structural defects in the thin films and (2) mapping the film's response to various pH environments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method of automatically detecting and tracking successive frames in a region of interesting by an electronic imaging device
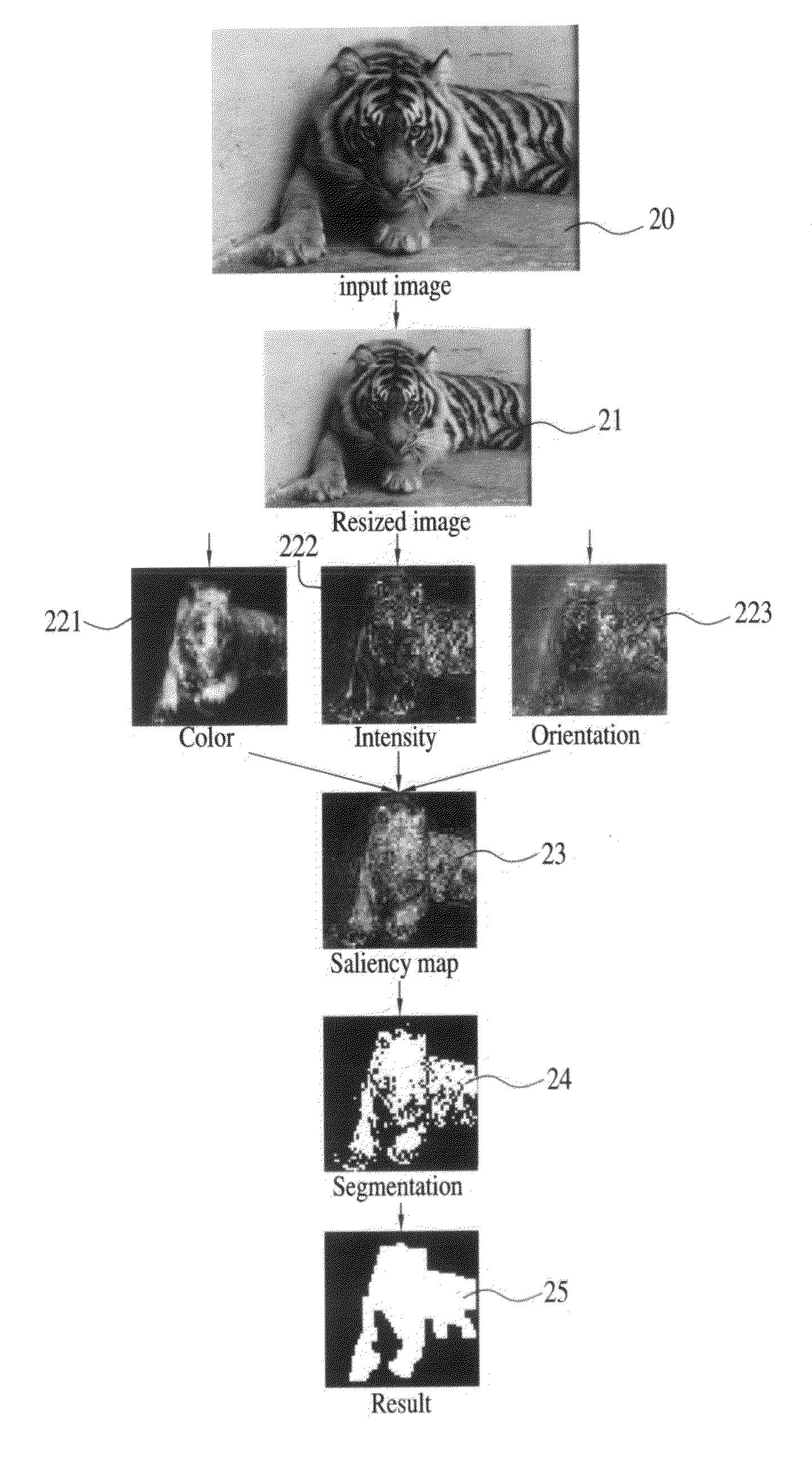
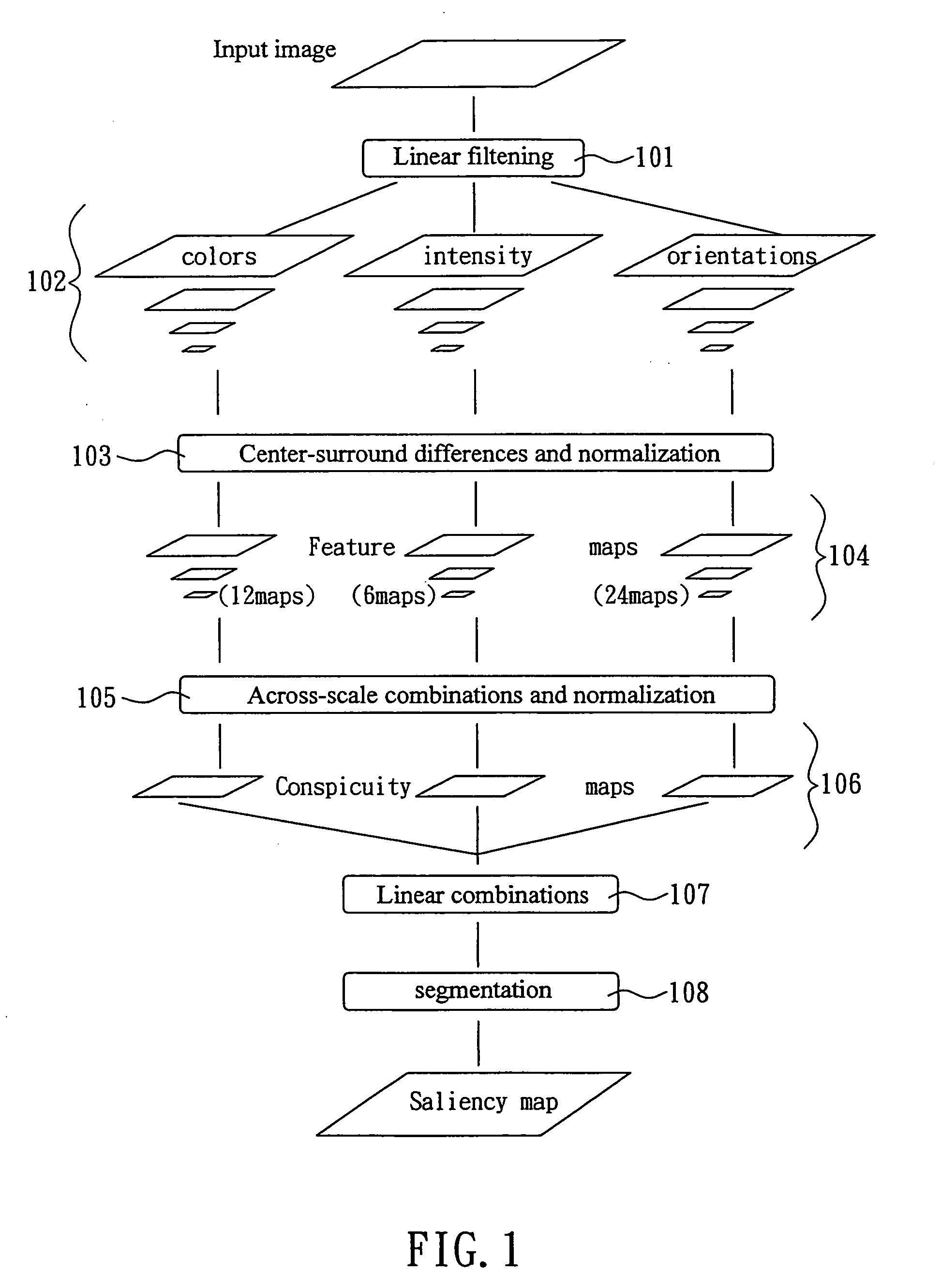
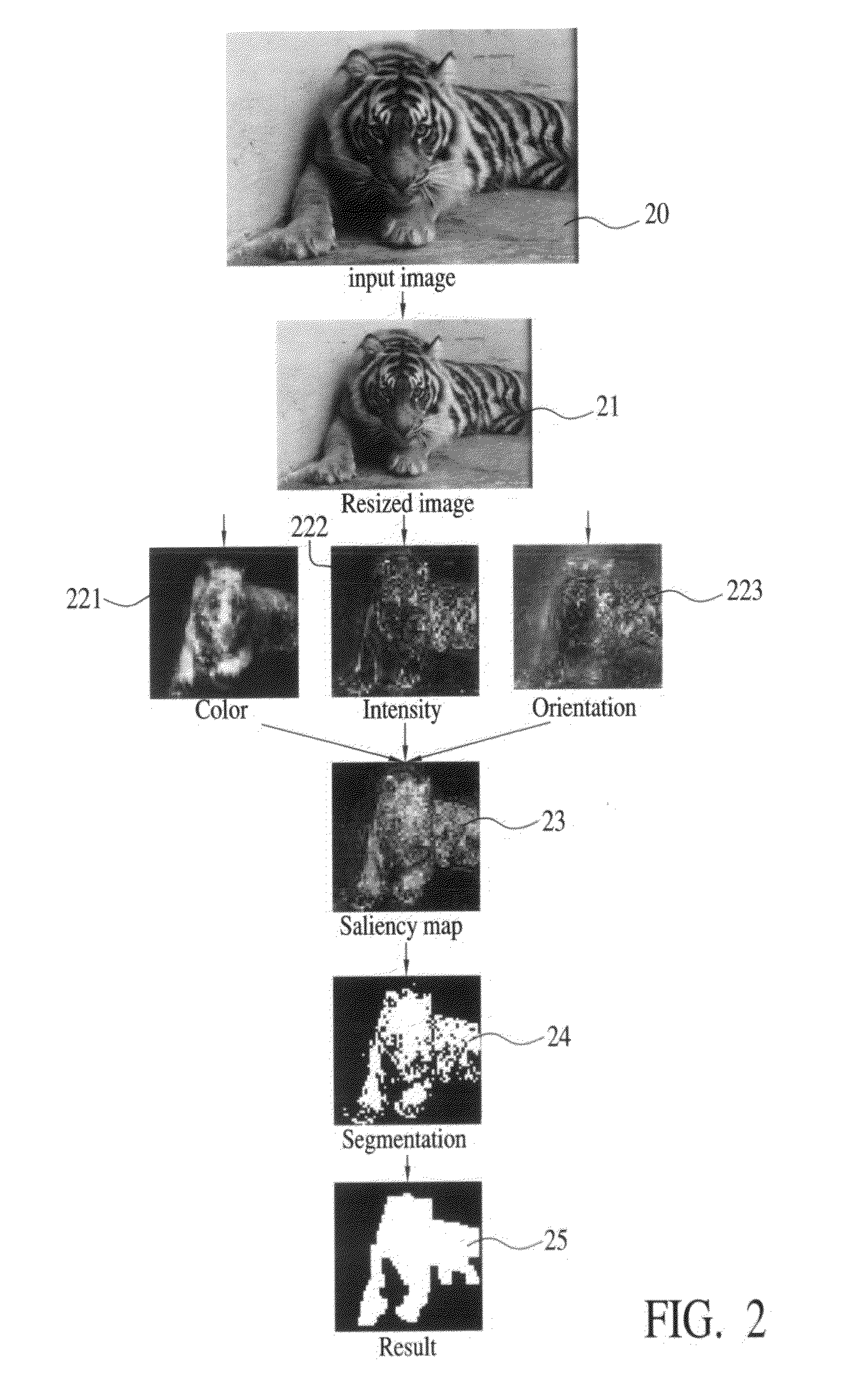
ActiveUS20090304231A1Improvement of capability of identifyingImprove computing speedCharacter and pattern recognitionSaliency mapPattern perception
A method of automatically detecting and tracking successive frames in a region of interesting by an electronic imaging device includes: decomposing a frame into intensity, color and direction features according to human perceptions; filtering an input image by a Gaussian pyramid to obtain levels of pyramid representations by down sampling; calculating the features of pyramid representations; using a linear center-surround operator similar to a biological perception to expedite the calculation of a mean value of the peripheral region; using the difference of each feature between a small central region and the peripheral region as a measured value; overlaying the pyramid feature maps to obtain a conspicuity map and unify the conspicuity maps of the three features; obtaining a saliency map of the frames by linear combination; and using the saliency map for a segmentation to mark an interesting region of a frame in the large region of the conspicuity maps.
Owner:ARCSOFT
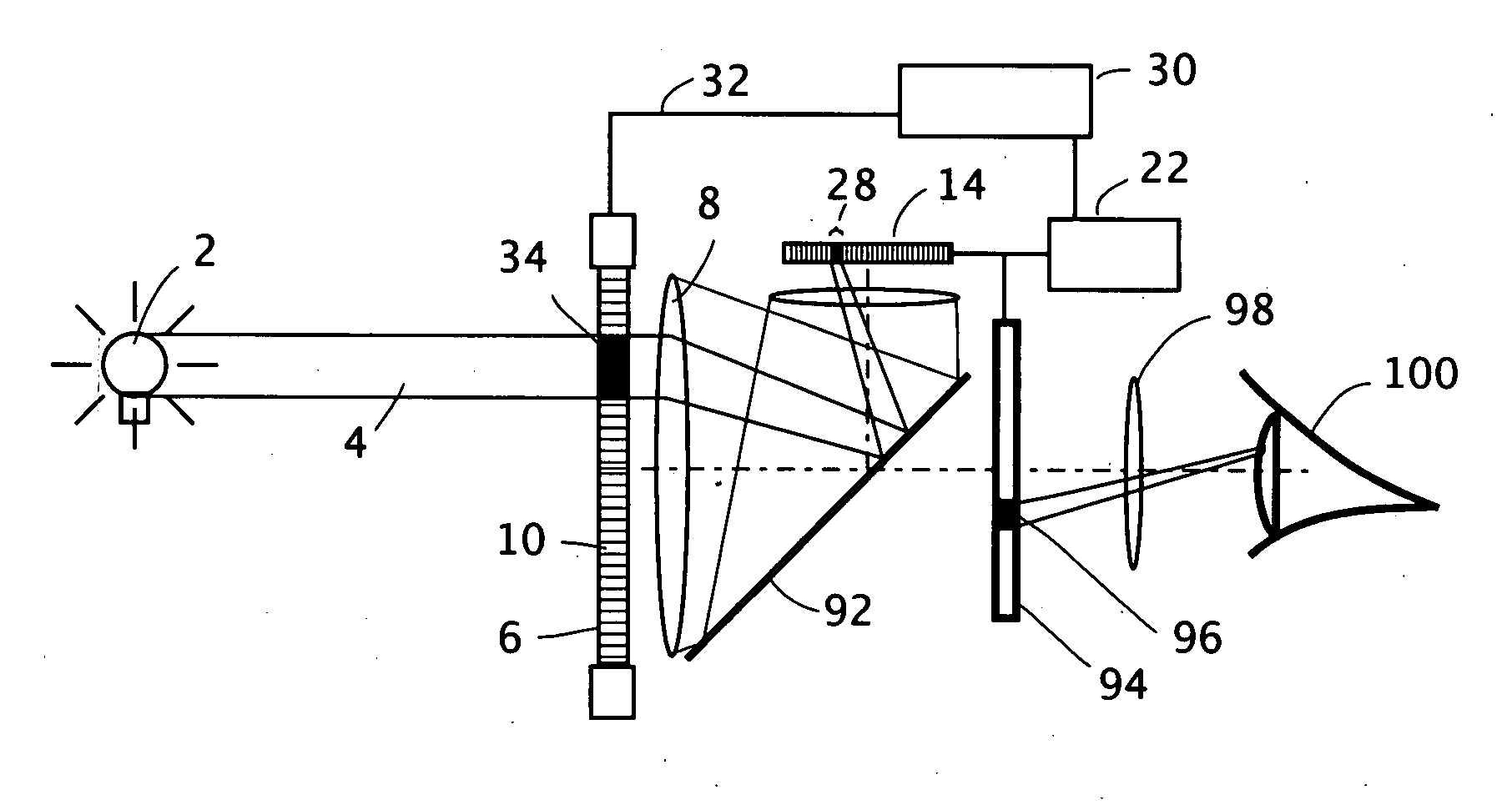
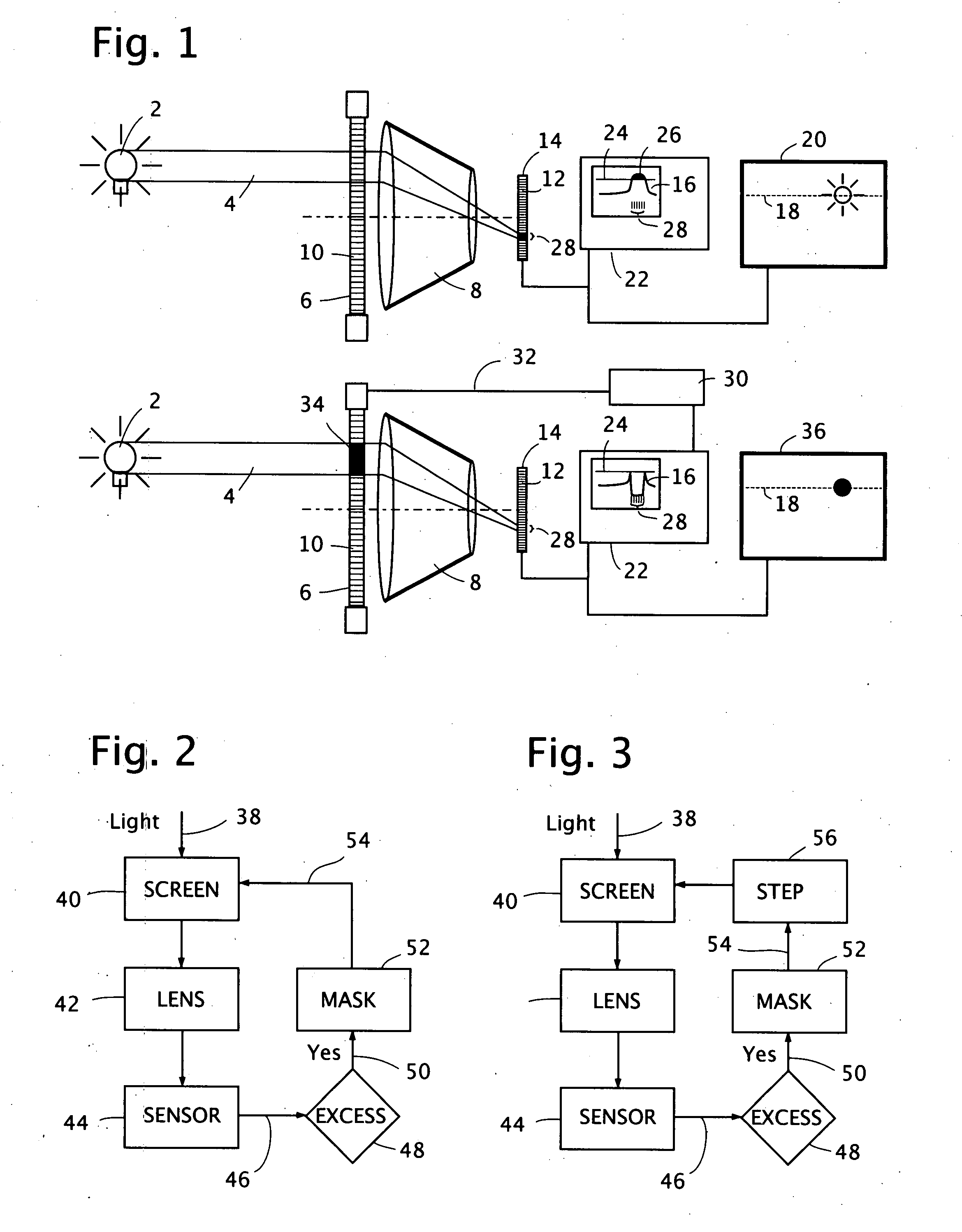
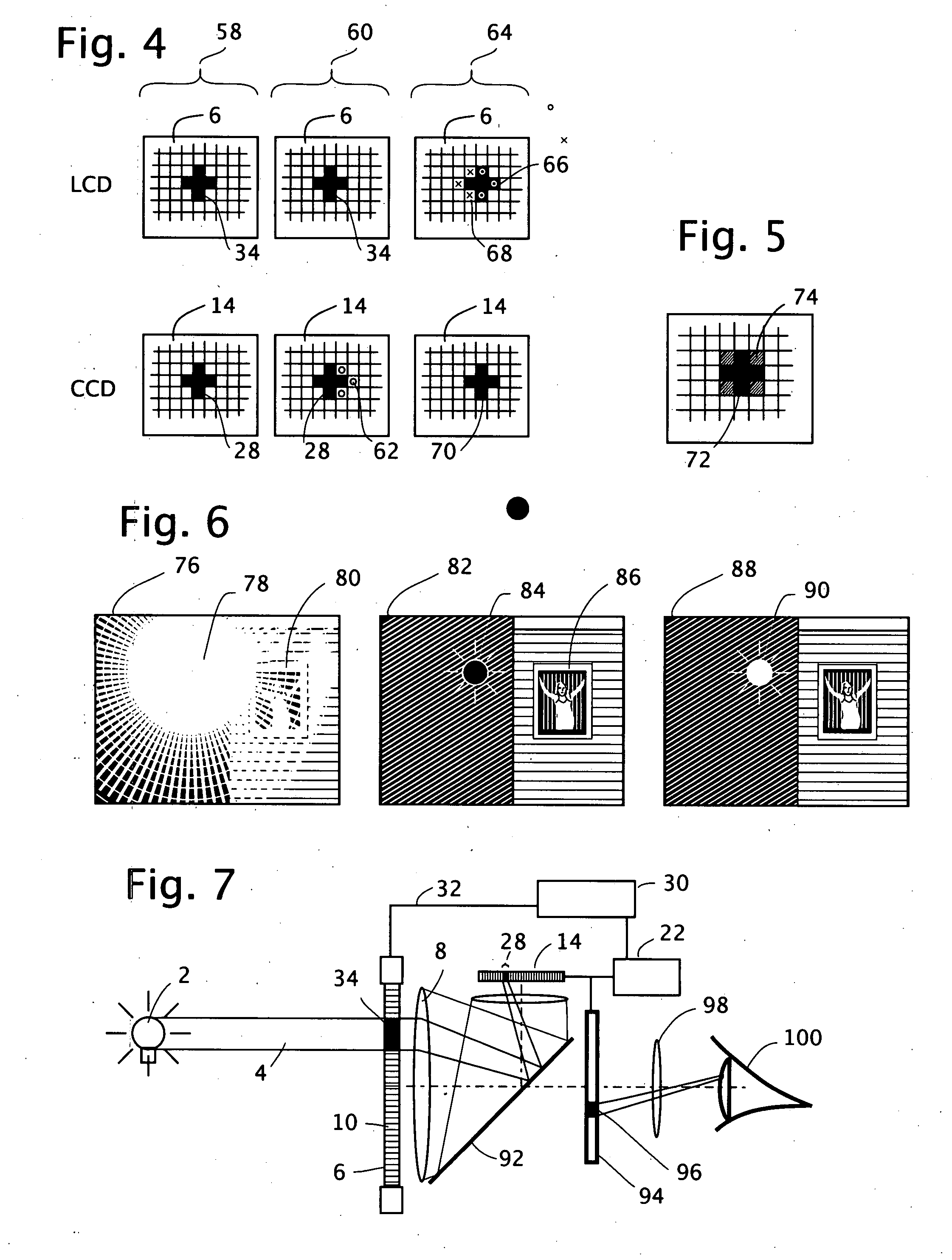
Active mask for electronic imaging system
InactiveUS20080007645A1Reduce and eliminate effect of glareOptimization of detailsTelevision system detailsPhotometry using reference valueElectronElectronic imaging
An active pixel masking system for automatic glare suppression uses a variably transmissive screen such as an LCD in front of a lens. A measurement by an image sensor of oversaturated pixels from one or more extremely bright lights is used to generate corresponding opaque pixels in the variably transmissive screen, thereby preventing the excess light from entering the lens, and thereby clarifying the appearance of any objects near to the bright light. A continuous reading of a motion picture image is used to move the location and area of the opaque pixels in response to the motion and area of the light.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
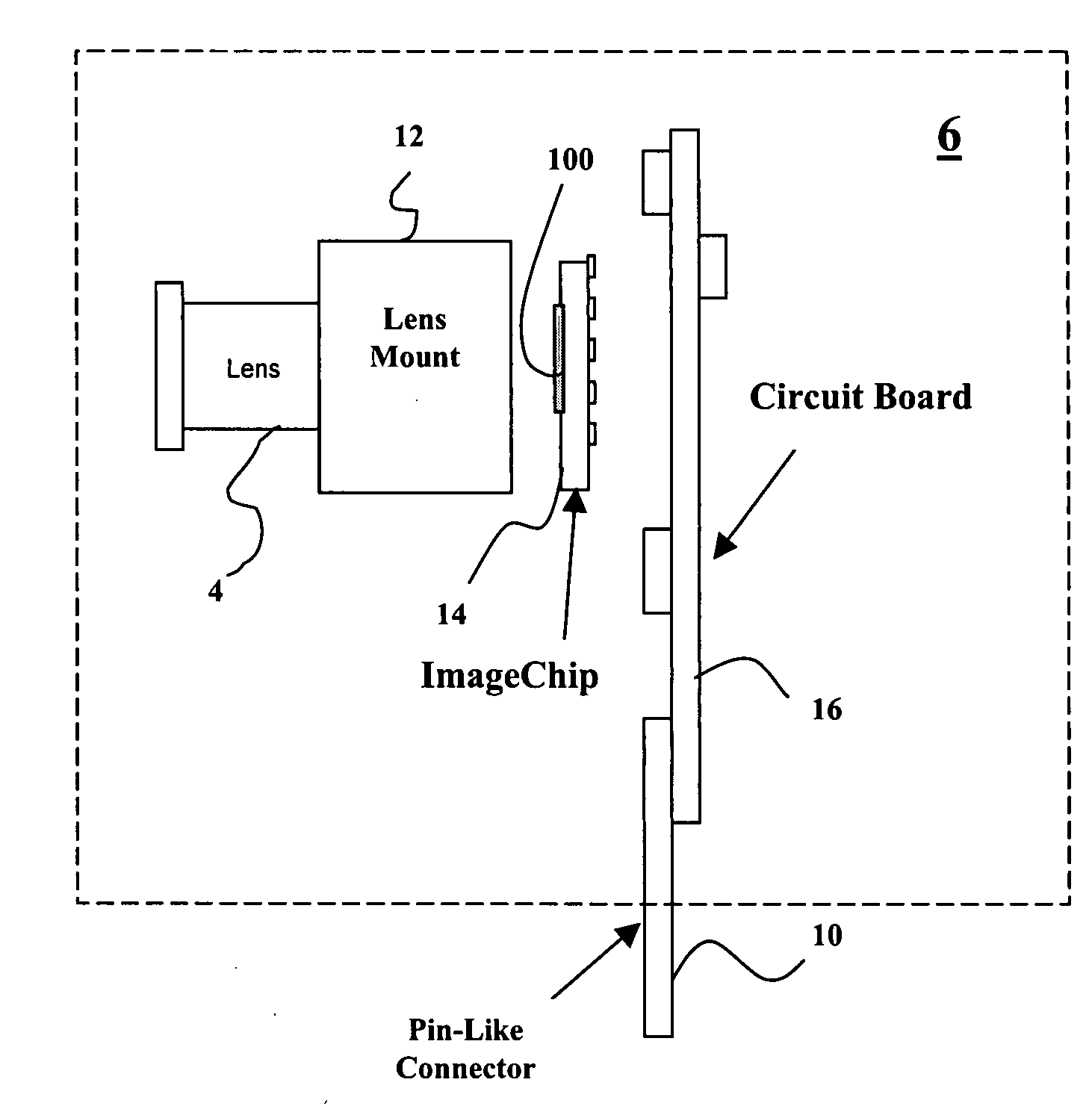
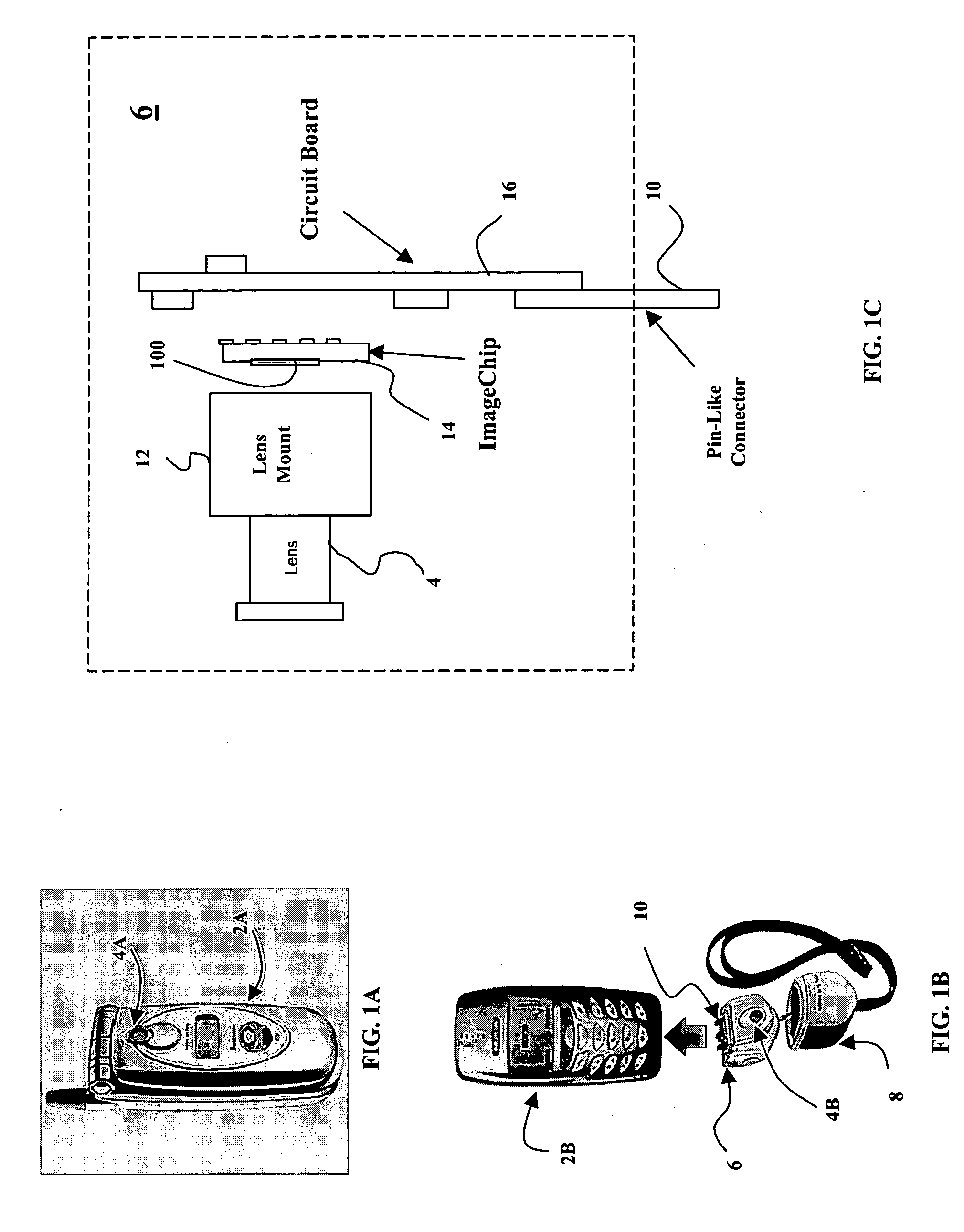
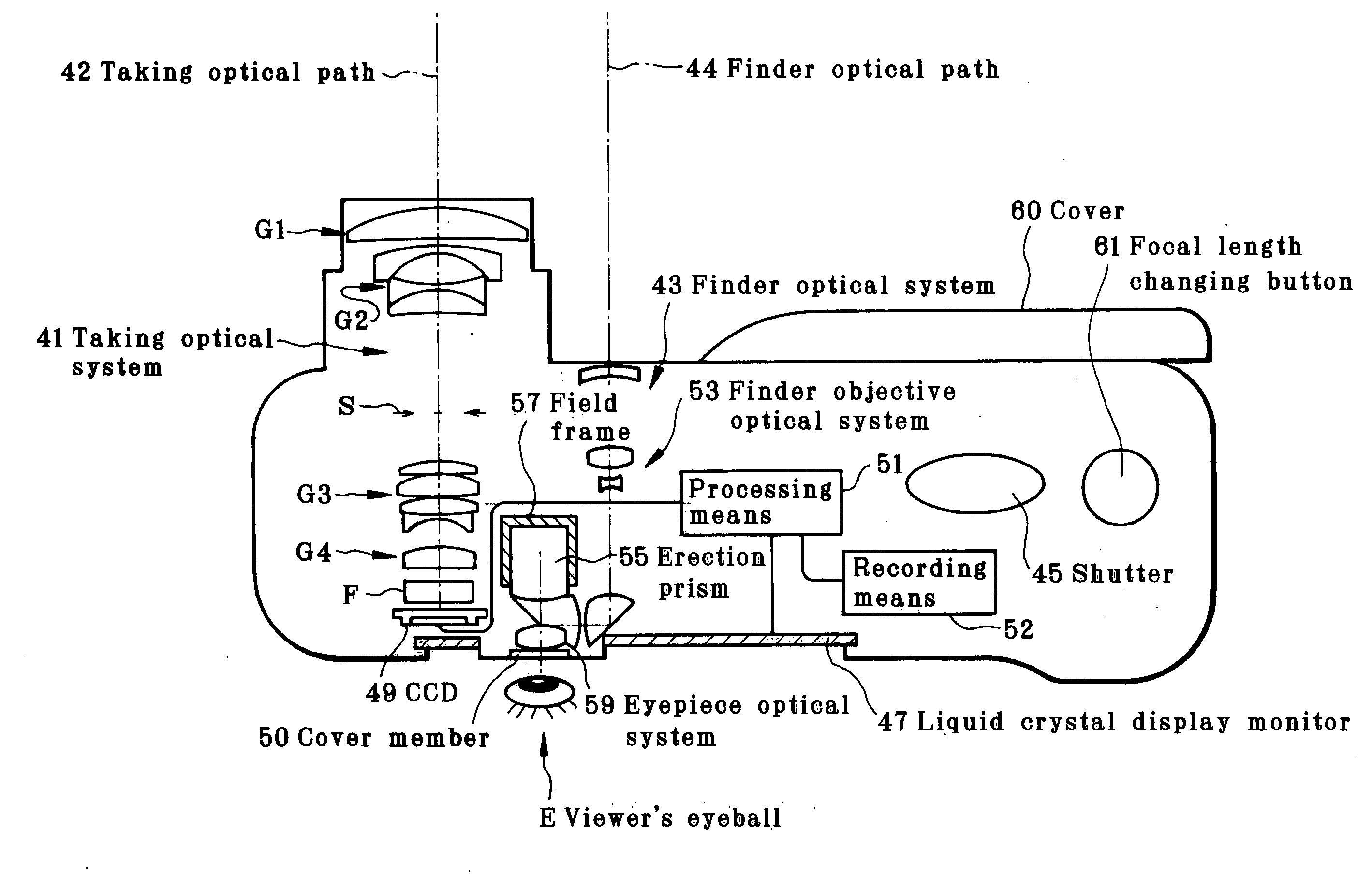
Taking apparatus
InactiveUS20070177047A1Implementation processSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight sensingMedicine
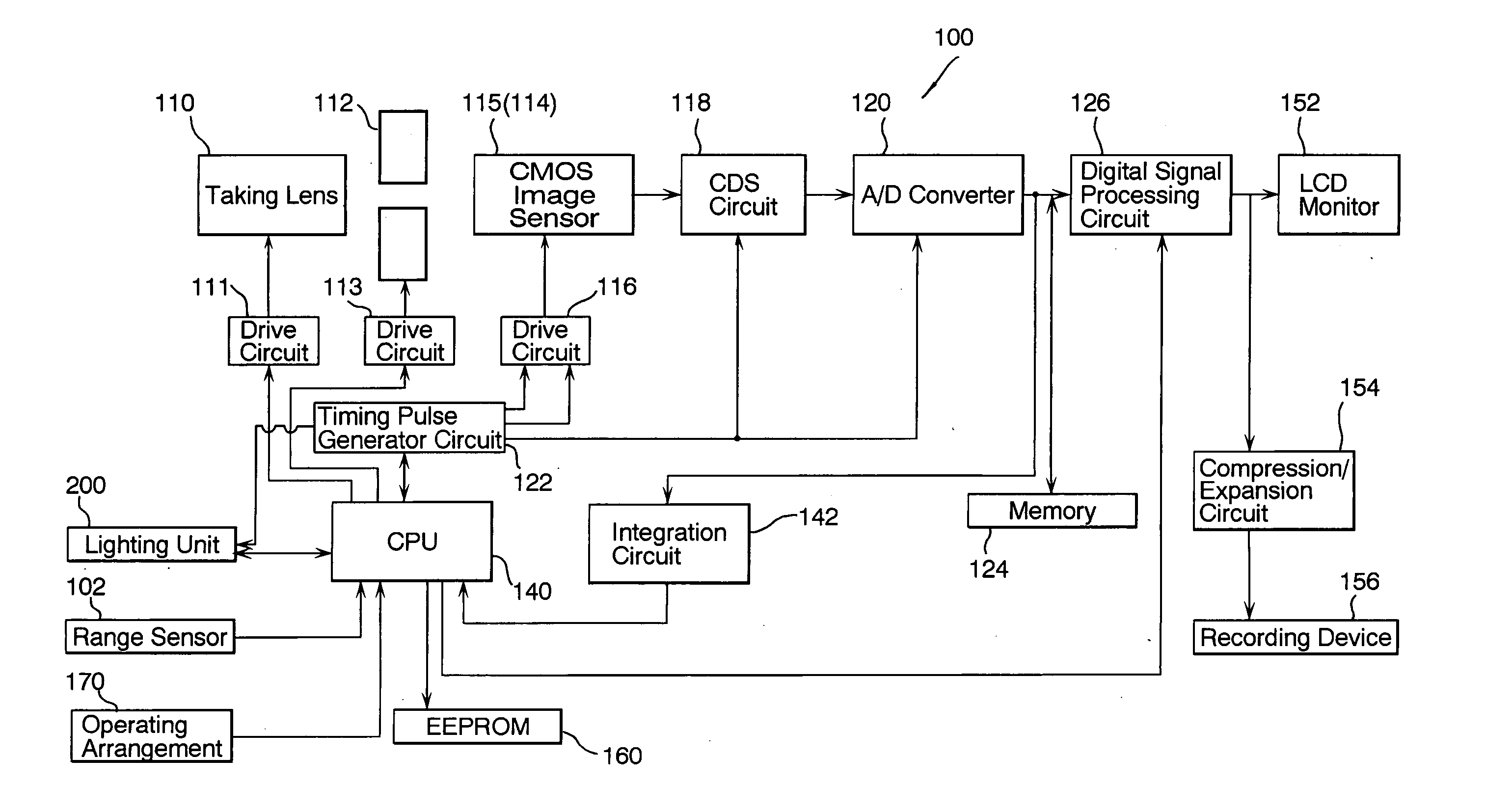
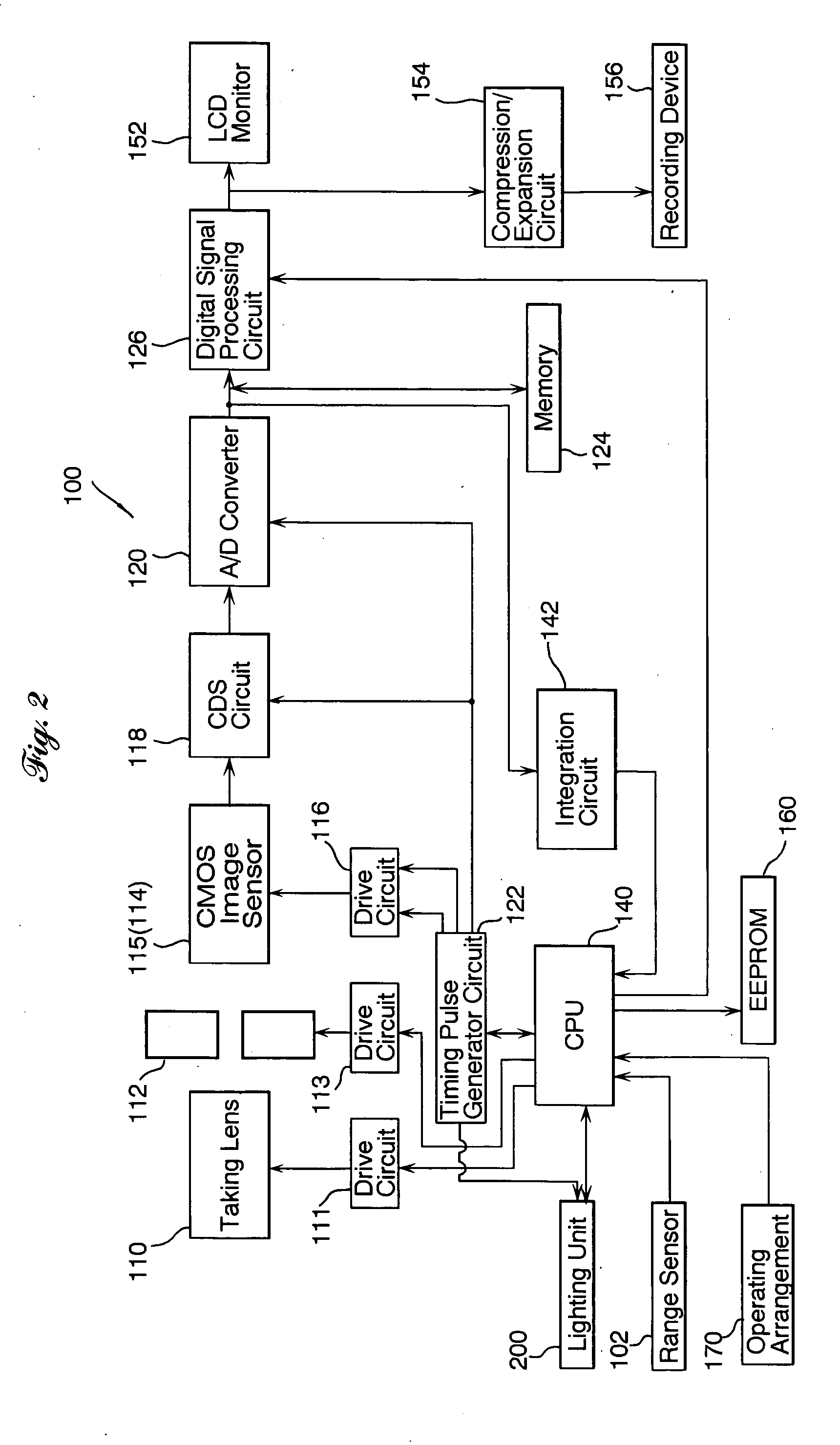
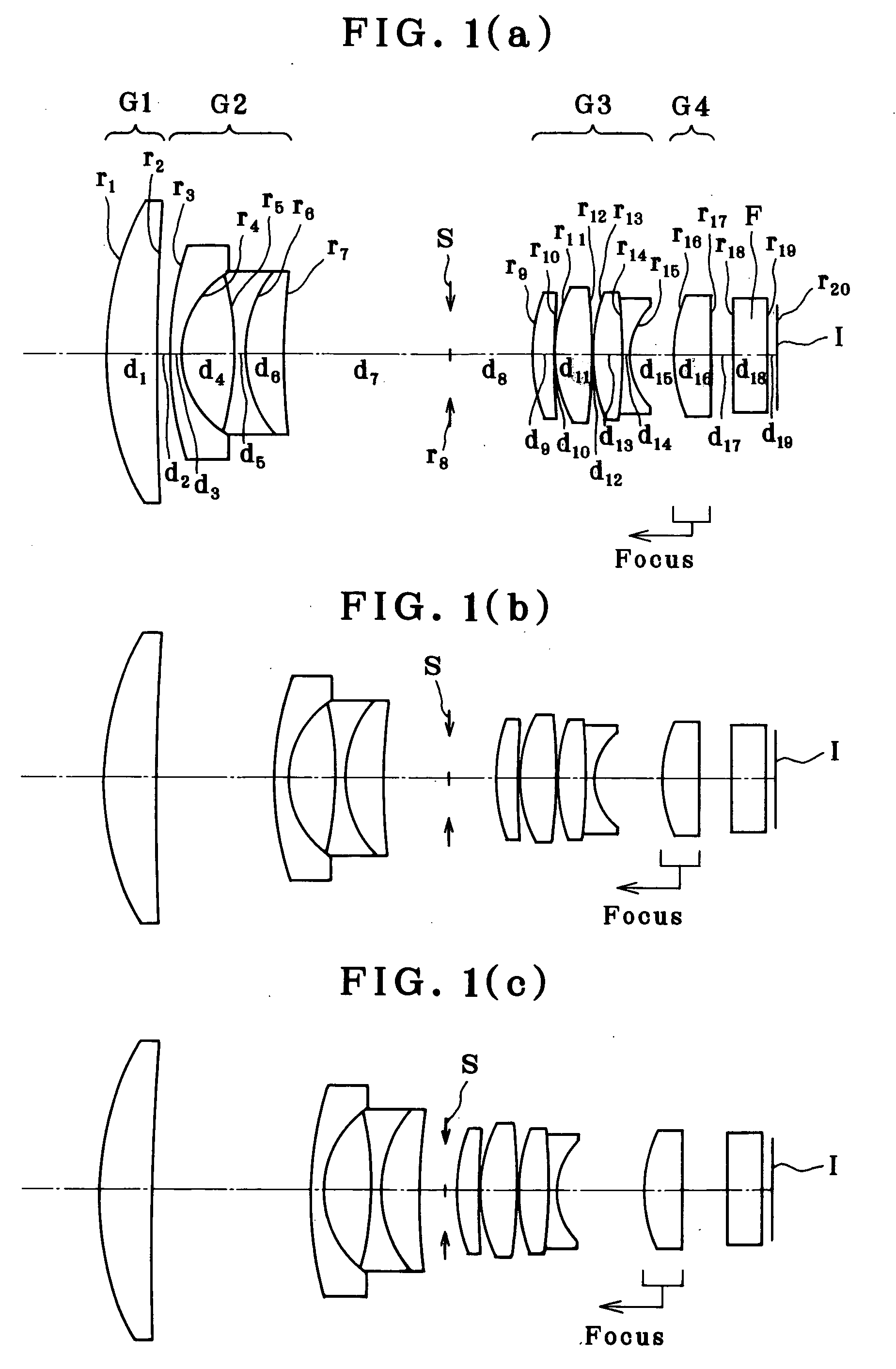
The present invention concerns an imaging apparatus which works for size reductions, power savings, the efficient attainment of the quantity of light sensed, and prevention of contrast decreases due to a diffraction phenomenon, is well fit for the taking and appreciation of common still pictures, and comprises a taking lens and electronic imaging device combination that takes full advantage of the characteristics of an imaging device. The imaging apparatus comprises a taking optical system, and an electronic imaging device which is located on an image side of said taking optical system, includes an imaging plane I with a plurality of two-dimensionally arranged light sensors, and is adapted to convert an image formed through said imaging optical system into electrical signals. In at least one taking state, the apparatus satisfies at the same time condition (1) about relations of the area of the entrance pupil to the focal length of the taking optical system, condition (2) about the number of effective pixels of the imaging plane, condition (3) about the effective area of the imaging plane, and condition (4) about the division of the effective area of the imaging plane by the number of effective pixels.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
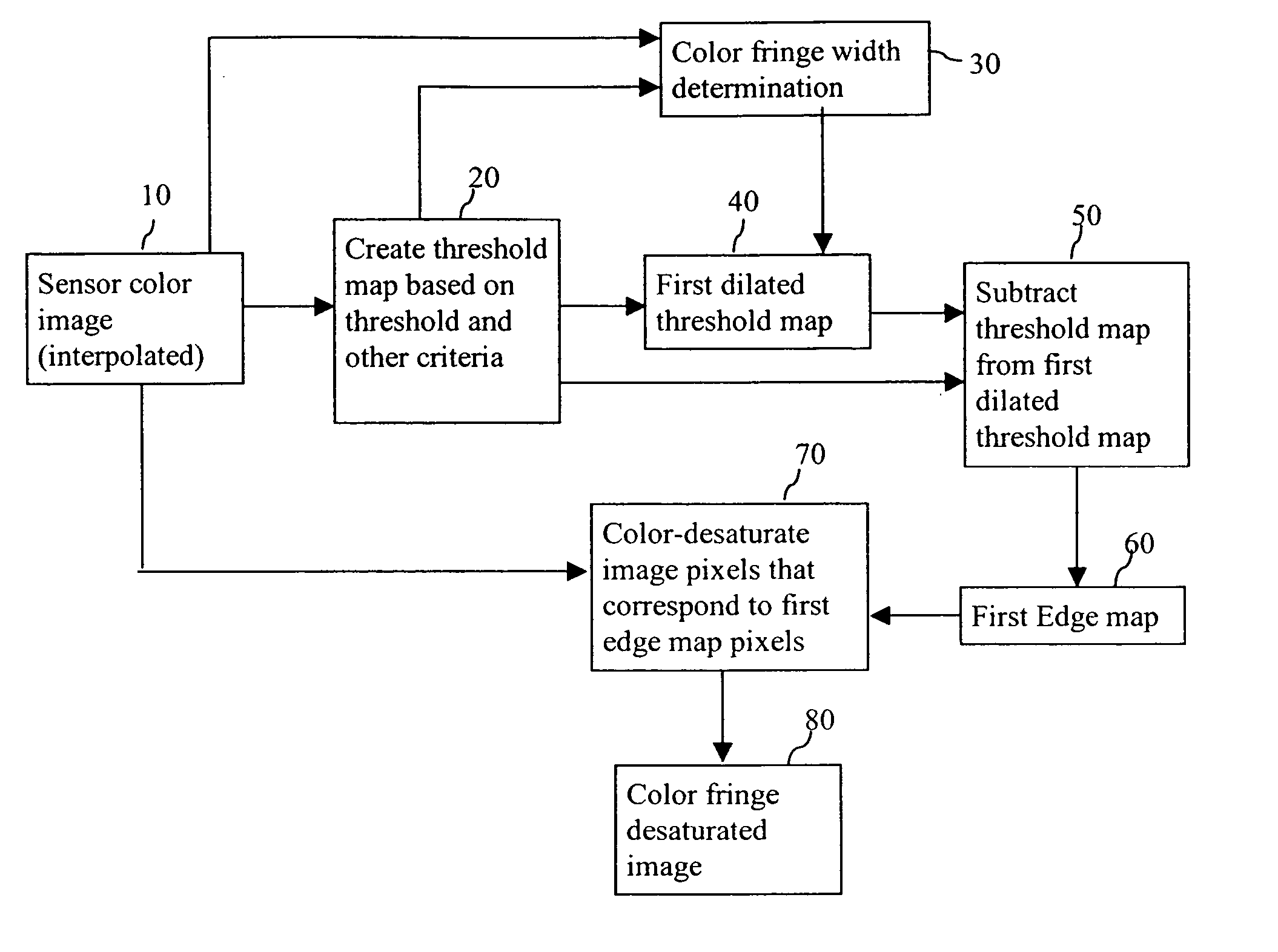
Color fringe desaturation for electronic imagers
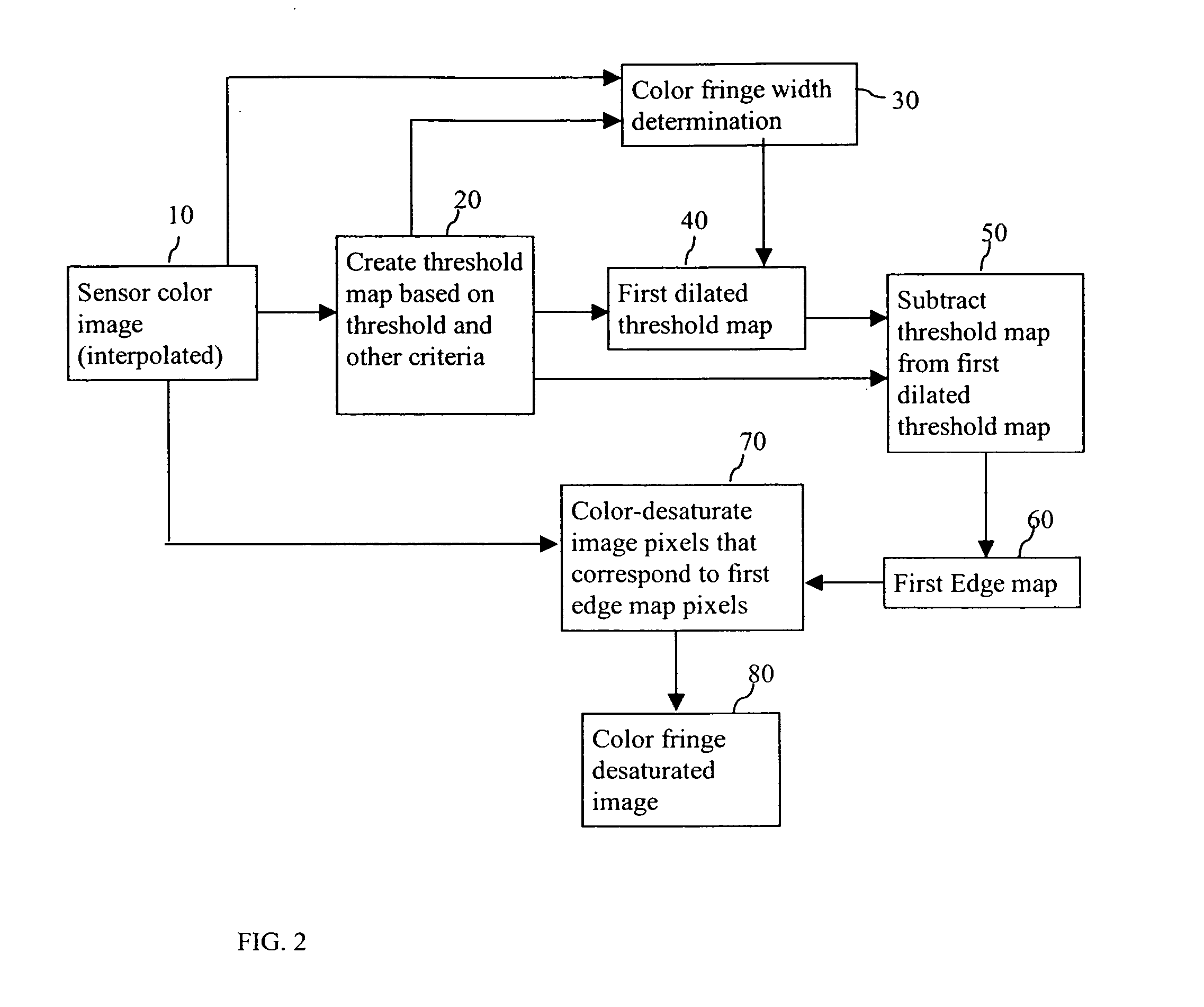
A method for correcting colored fringe artifacts in a region of an image around saturated pixels captured by an electronic imager associated with a color filter array, includes providing a threshold map of the image based on thresholding one or more color channels with a common or separate threshold value for each color channel; providing a first edge map by dilating the threshold map as a function of the color fringe width, producing a first dilated threshold map and subtracting the threshold map from the first dilated threshold map; and color-desaturating image pixels that correspond to the first edge map.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method And Apparatus For Imaging Of Scenes Having Large Intensity Variance
InactiveUS20080136953A1Reduce sensitivityReduce radiation intensityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsVoltage referenceElectronic component
The present invention is an electronic imaging device and method of expanding its dynamic range. The invention comprises modifying the imaging device by providing a comparator and reset trigger circuit located at or near the site of each of the pixels. The comparator triggers a reset mechanism when the voltage in the charged pixel reaches a reference voltage. During the global exposure time each individual pixel can be self-reset several times, depending on the intensity of the radiation incident upon it. At the end of the global exposure time, each pixel contains only the “residual value” of voltage that remains from the last individual self-reset to the end of the global integration time. An algorithm is implemented, which estimates and determines the number of resets undergone by each pixel during the global exposure time. From this number of resets the algorithm is able to reconstruct the true image. As opposed to prior art methods that make use of pixel reset the device of the invention does not contain electronic components for counting and remembering the number of times that each of the pixels was reset.
Owner:BARNEA DANIEL I +1
Electronic imaging system
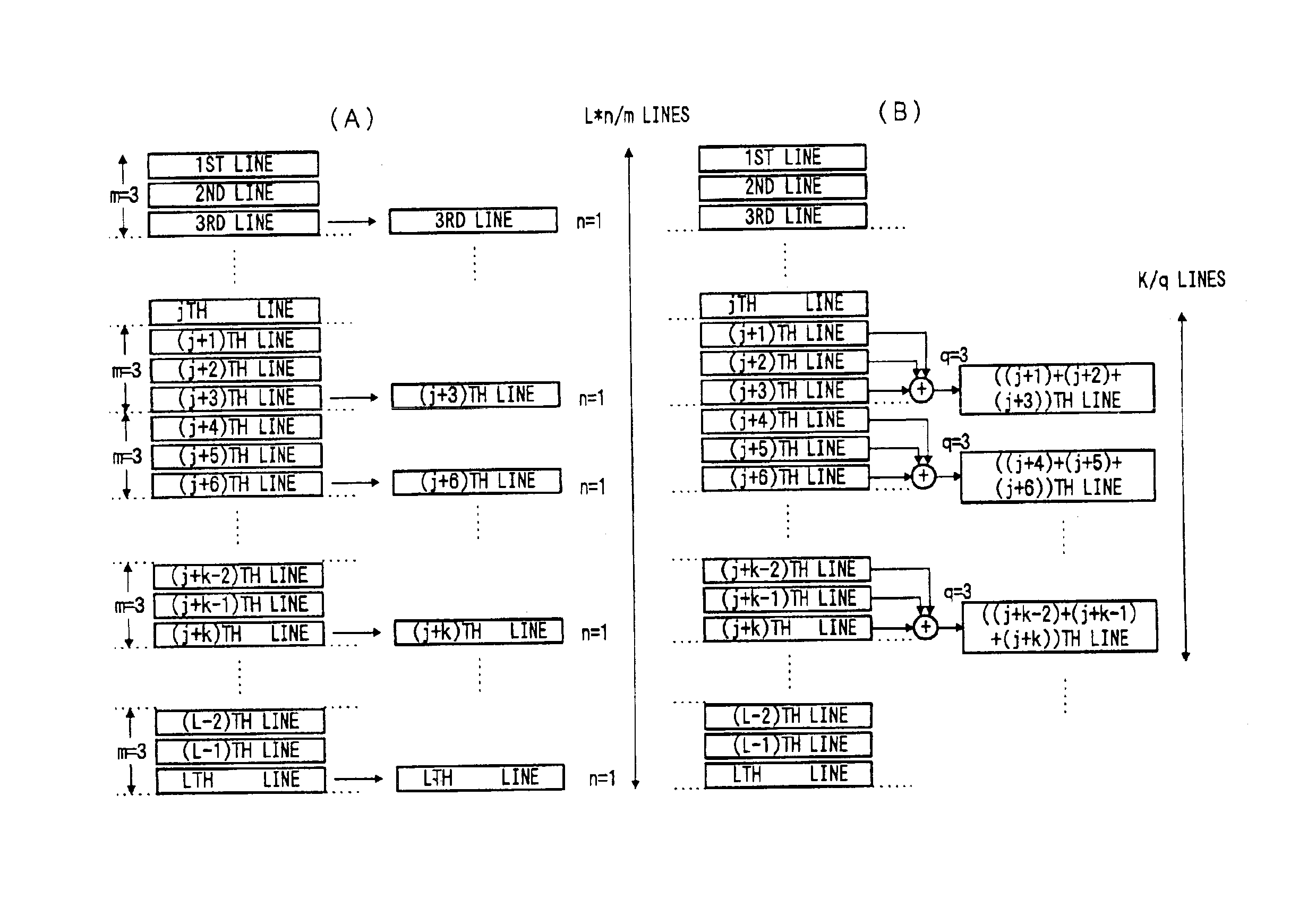
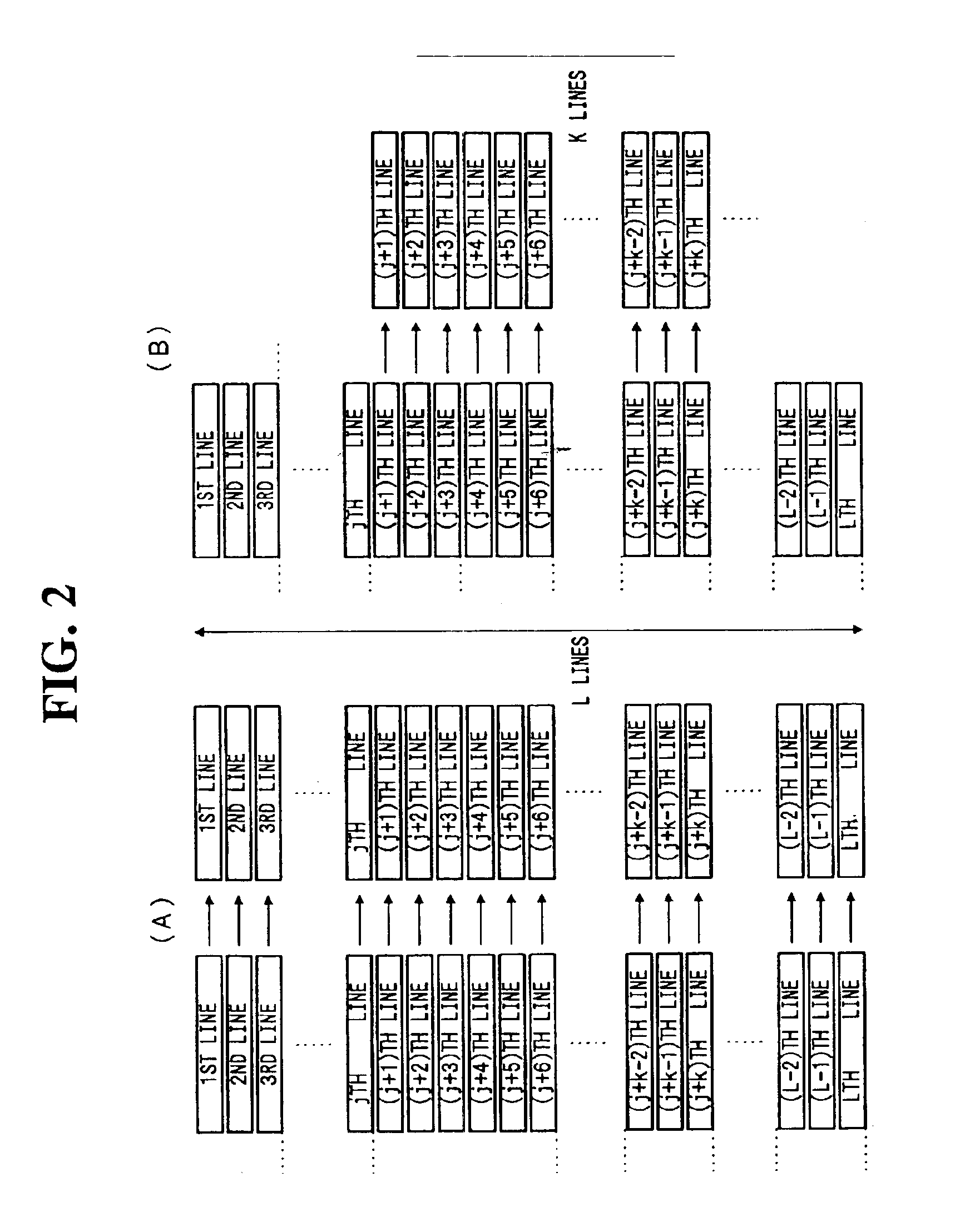
InactiveUS6882366B1High rate outputHigh outputTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHigh frame ratePixel density
An electronic imaging system includes a CCD image sensor arrangement having a two dimensional array of pixels. The pixel array converts light incident thereon to an electric signal. The pixels are arranged in a plurality of horizontal rows or lines, the lines being arranged vertically. A control arrangement selectively controls operational modes of the system. One mode provides for sequential scan reading out of pixel signals for entire lines of the CCD for still picture recording. Another mode provides for reading out pixel signals concerning k (k is a positive integer) vertically continuous lines of the CCD for still picture recording or dynamic image processing. Thus it is possible to provide a high pixel density solid-state image sensor output at a high frame rate without use of any high drive frequency.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Endoscopic instrument having reduced diameter flexible shaft
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com