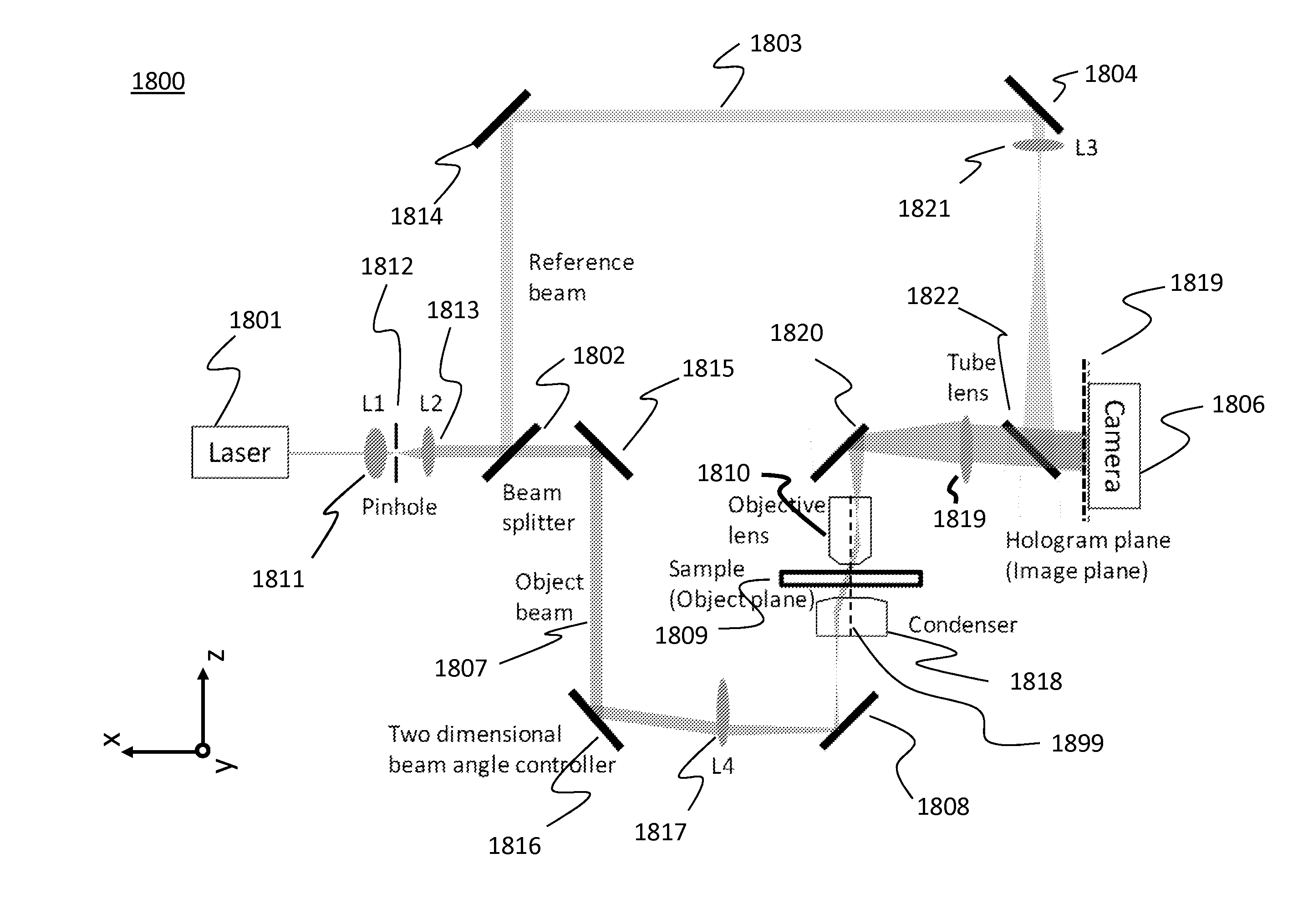
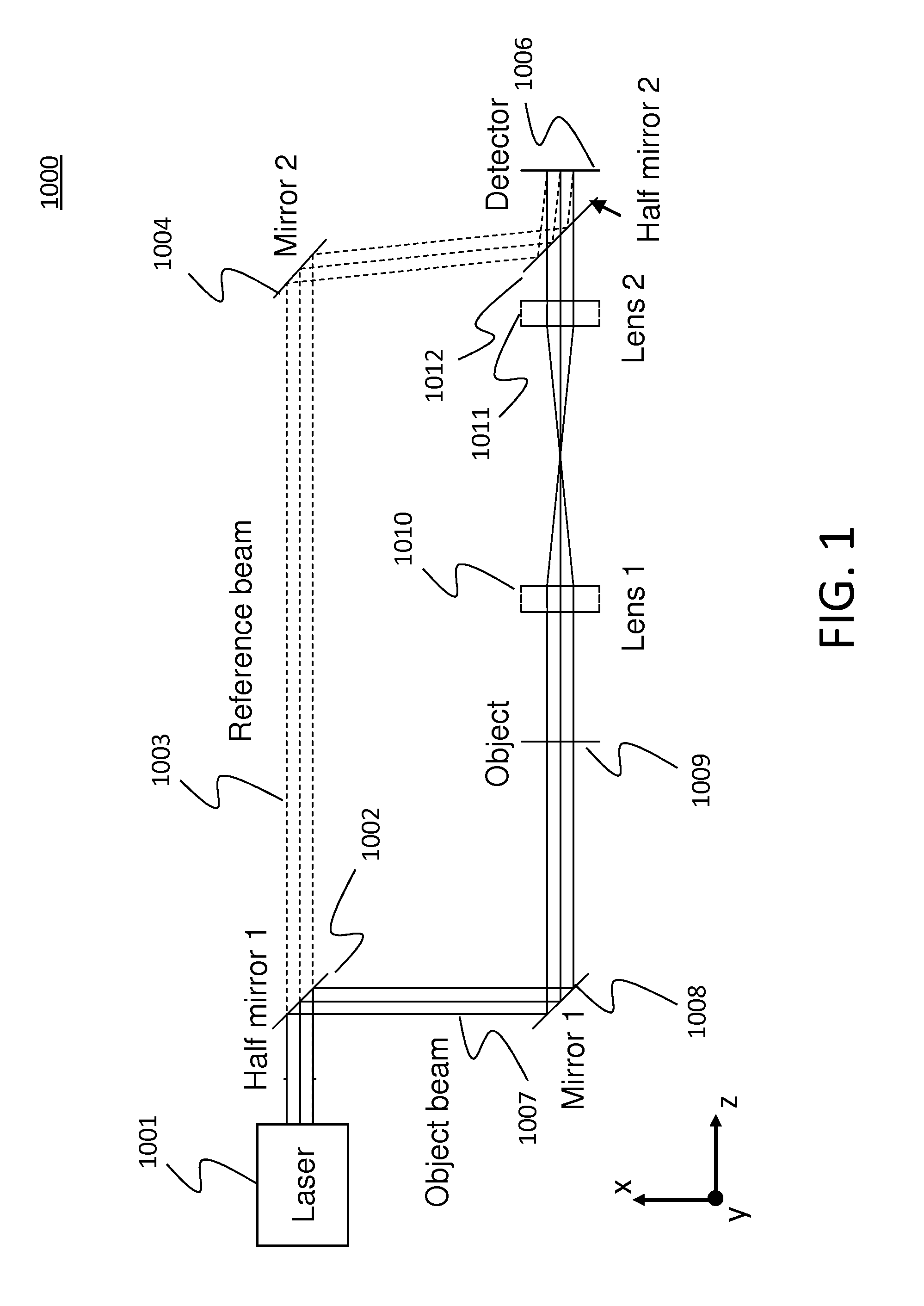
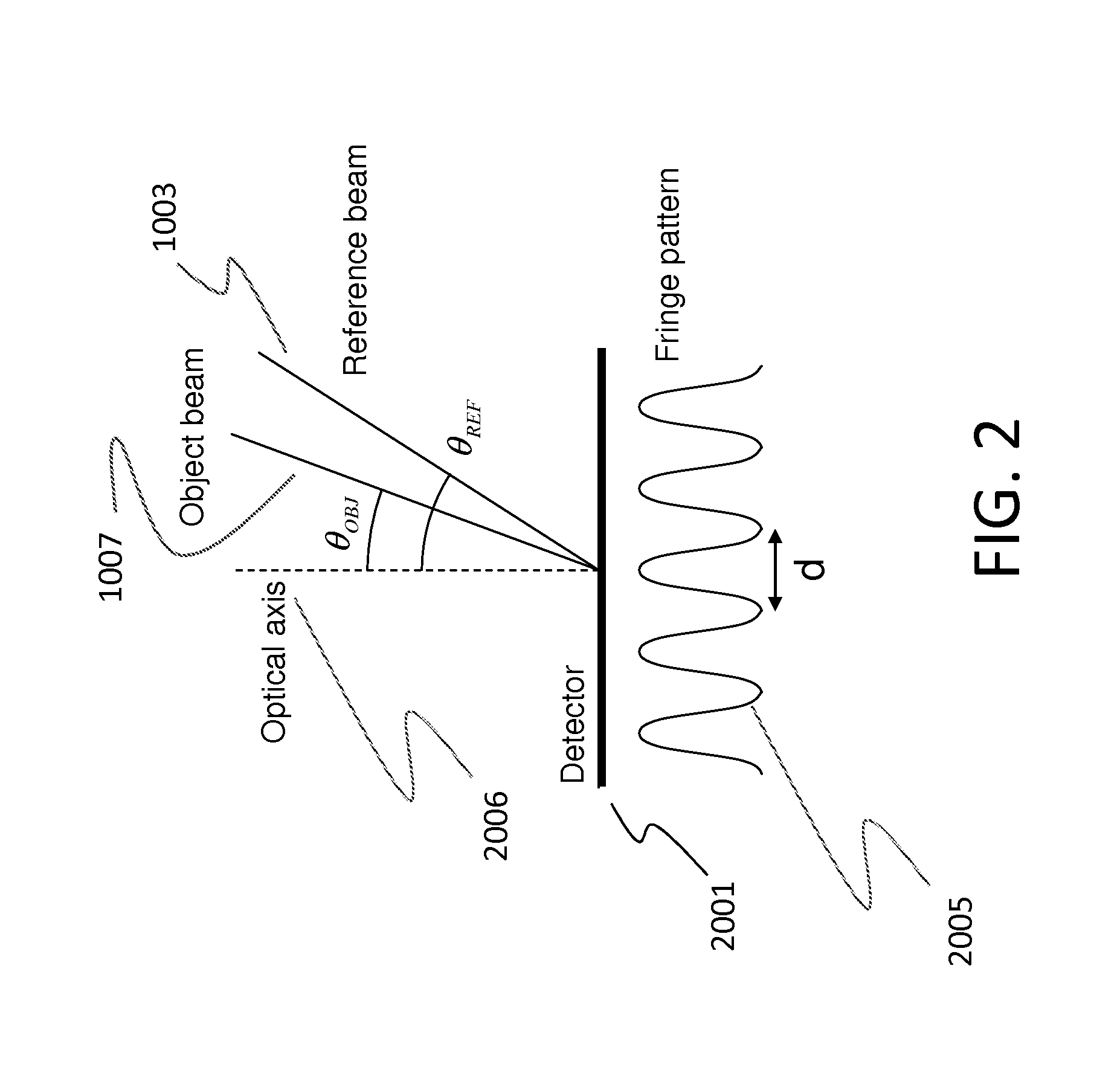
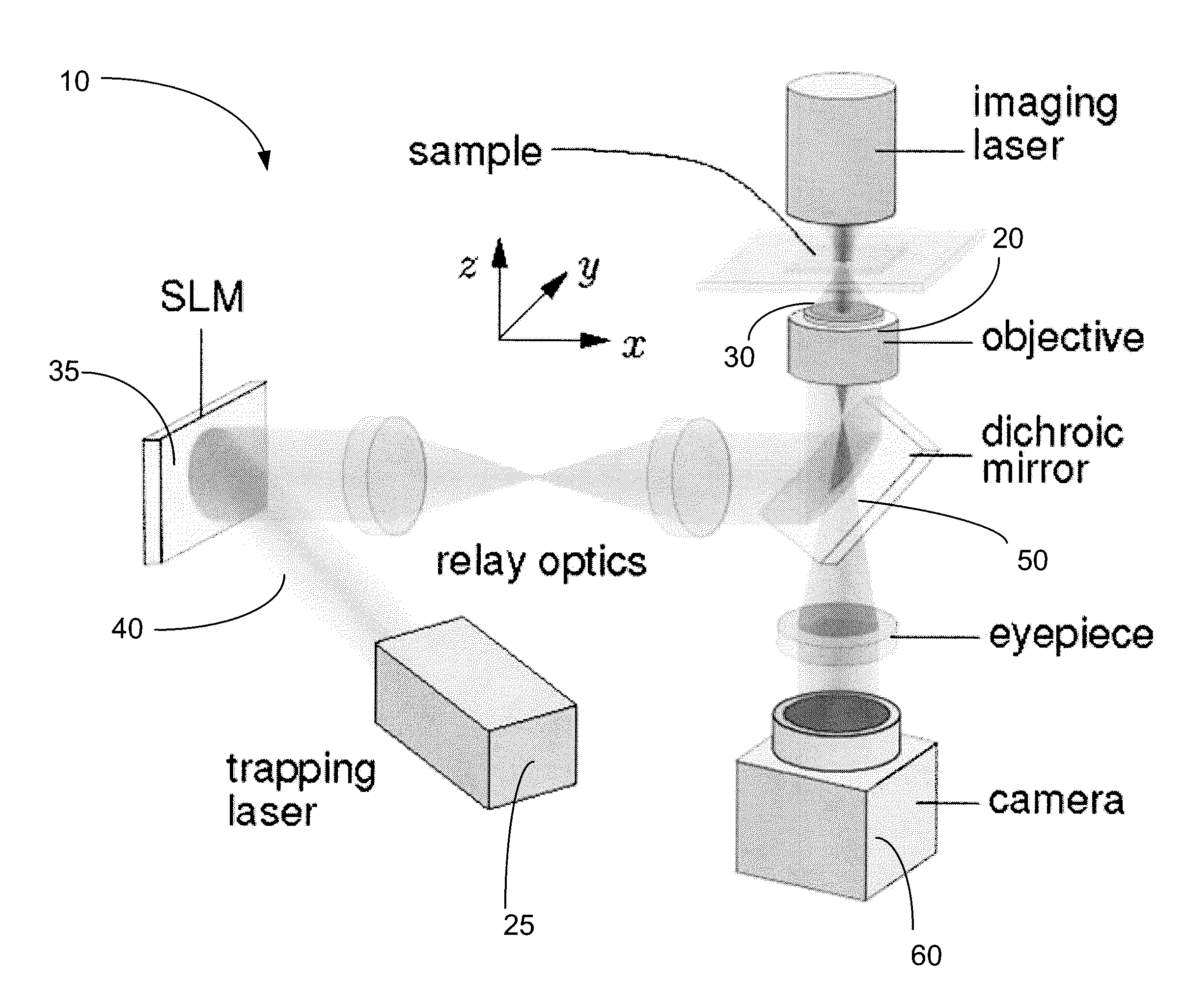
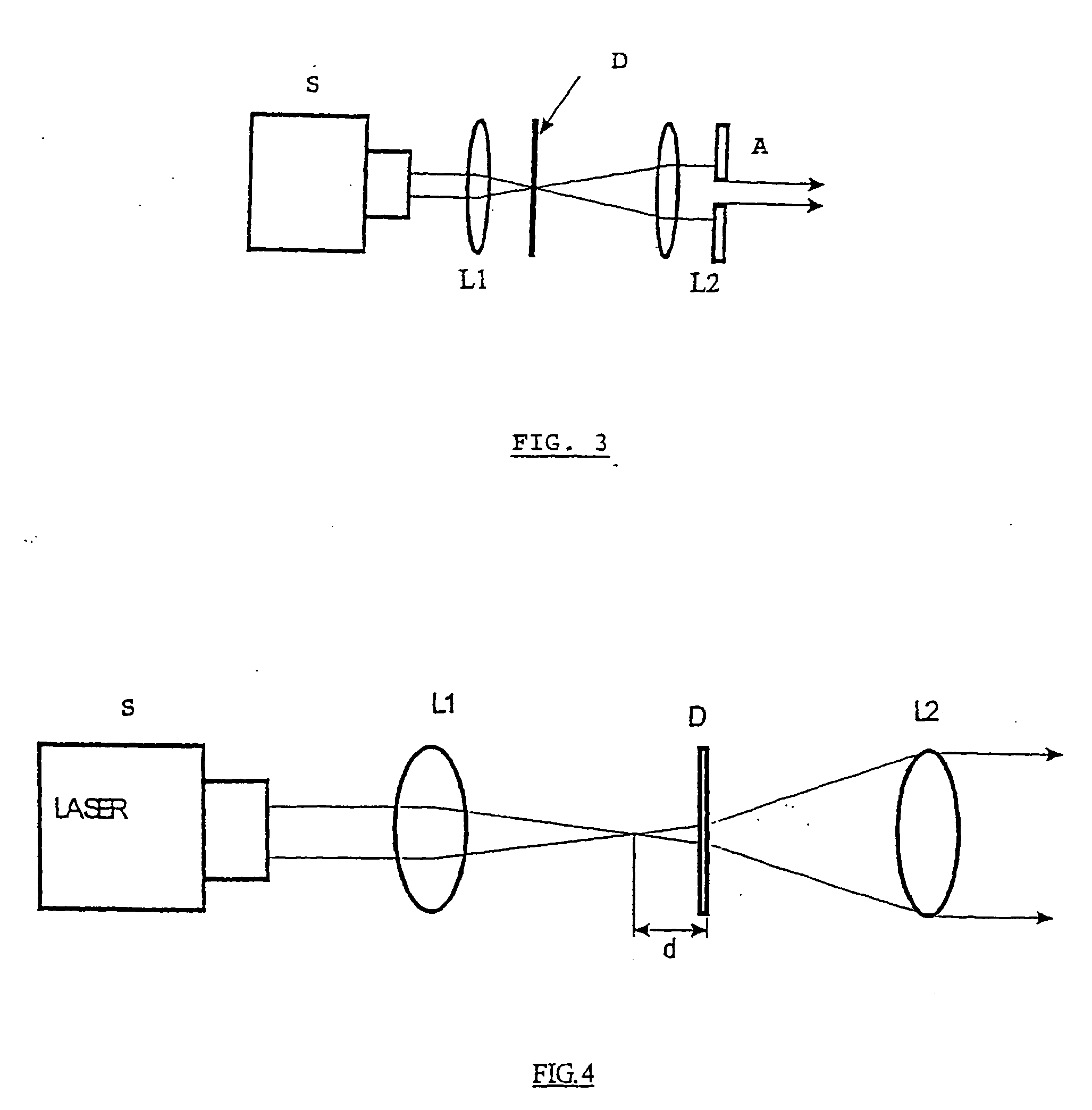
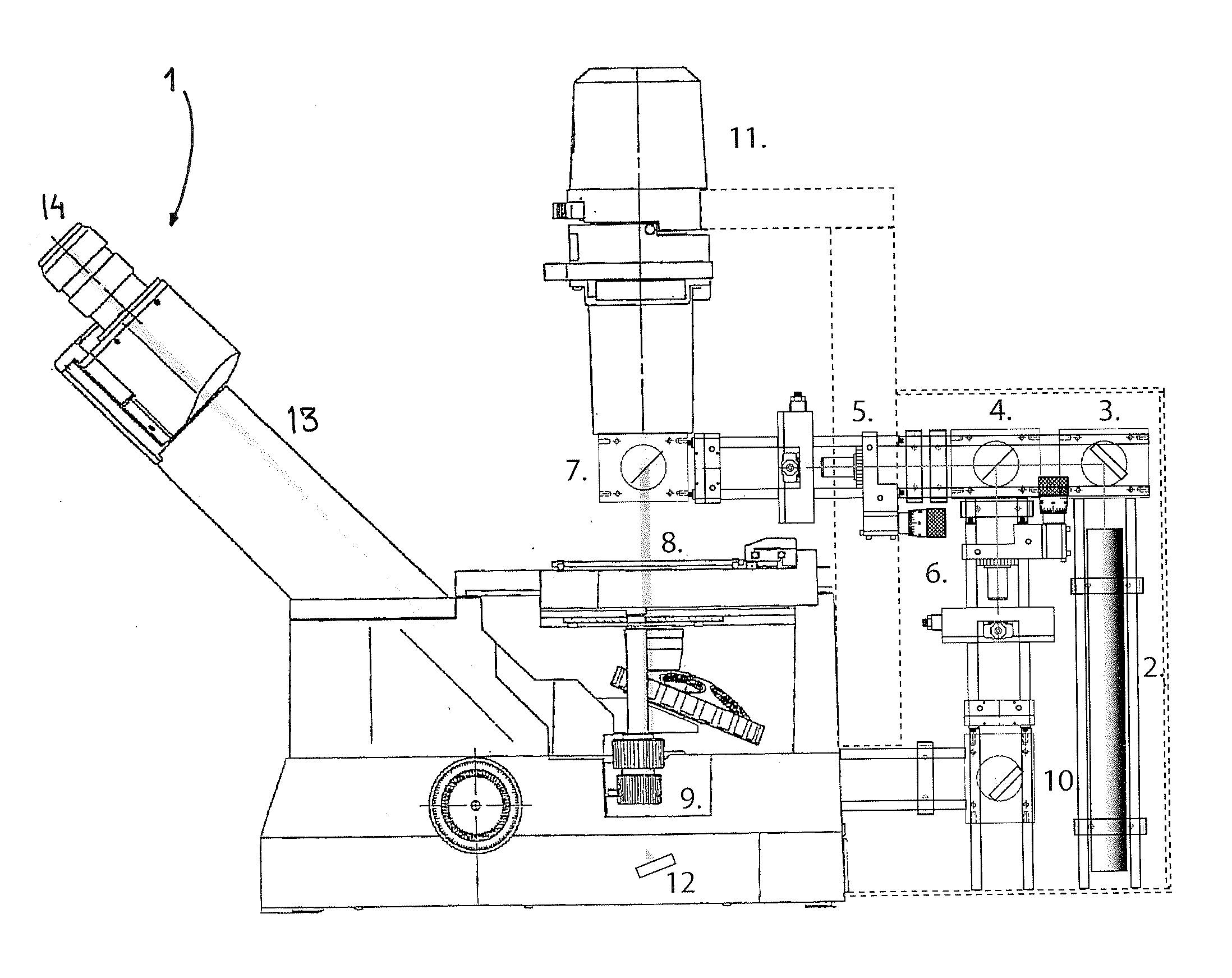
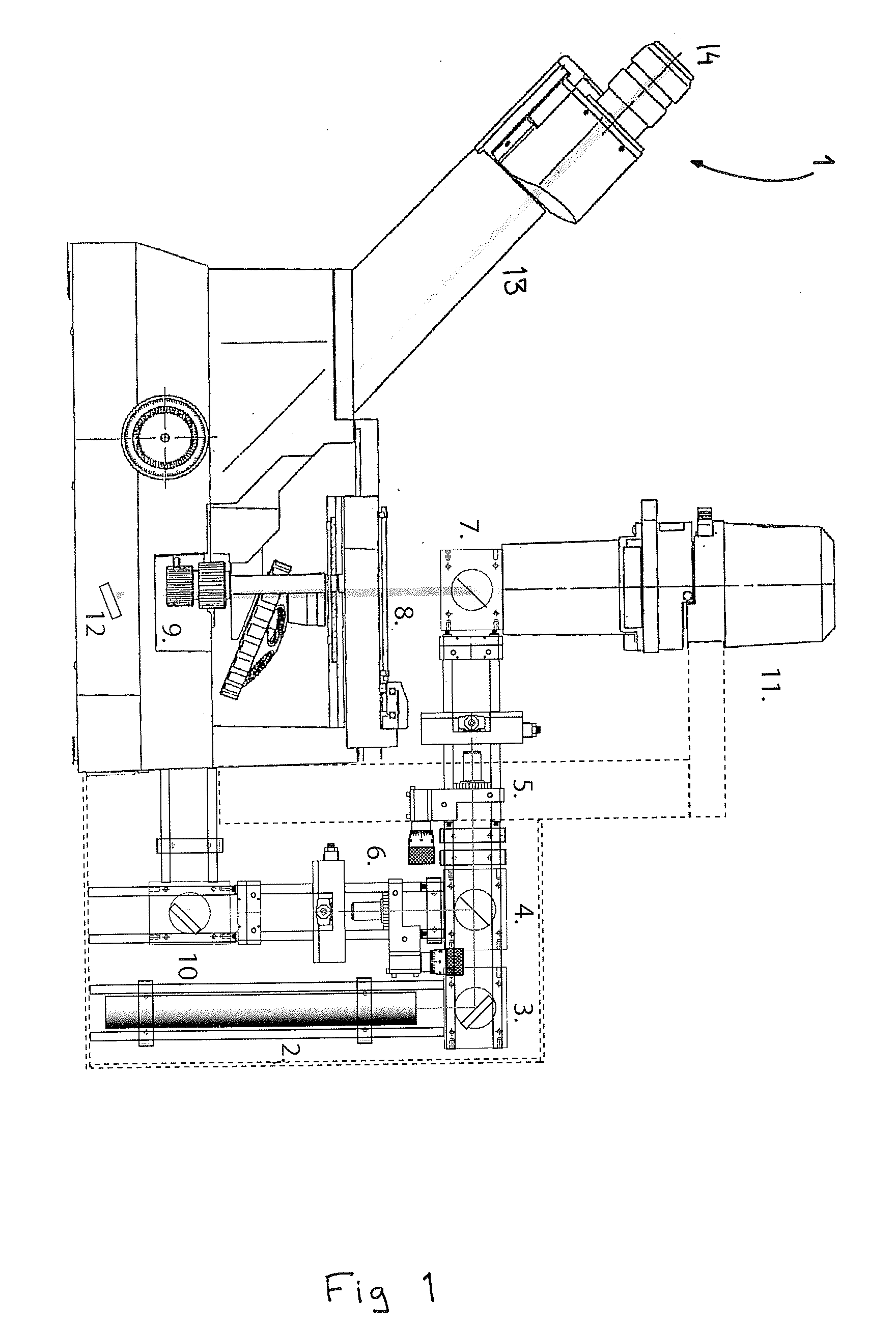
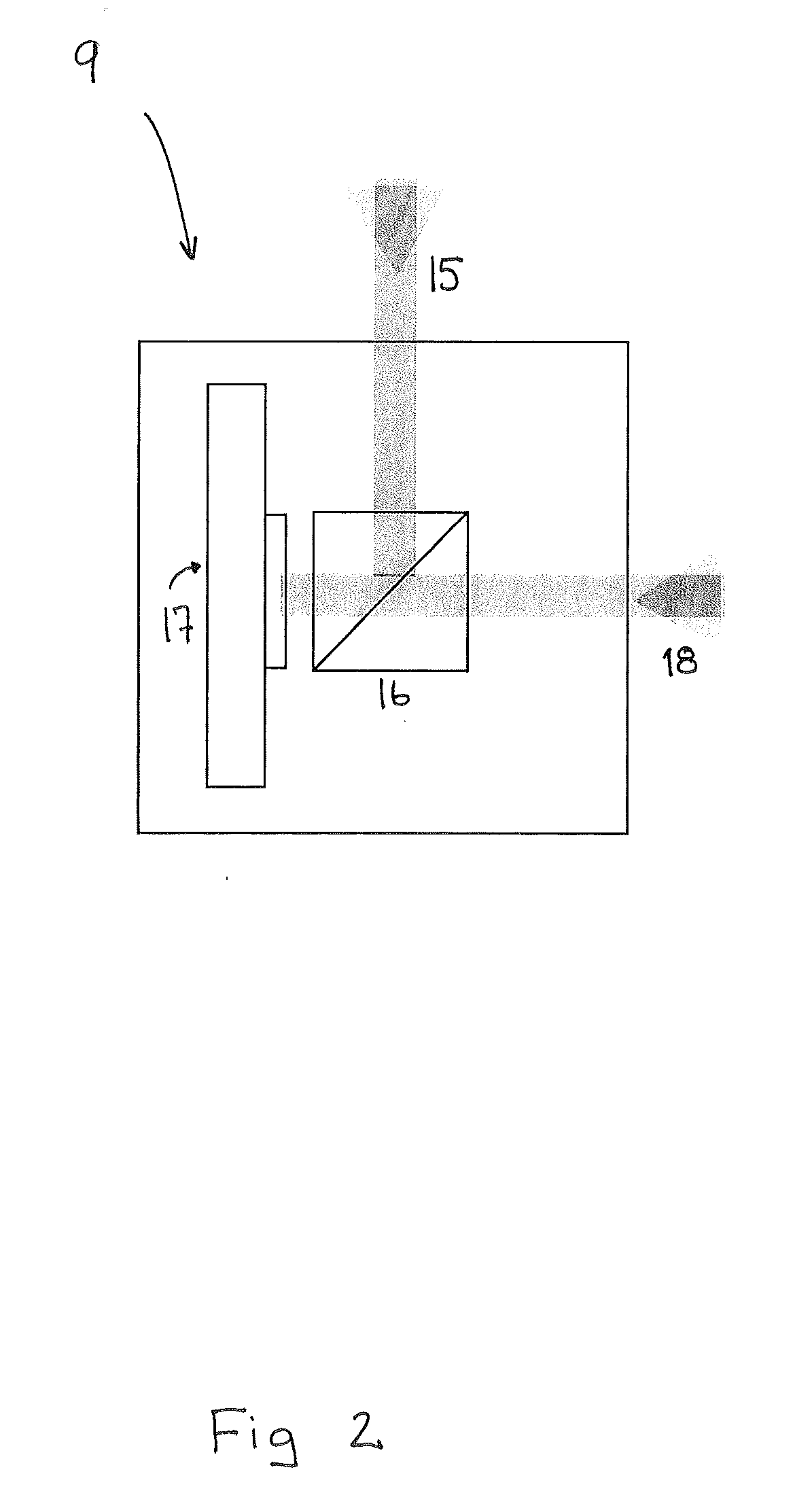
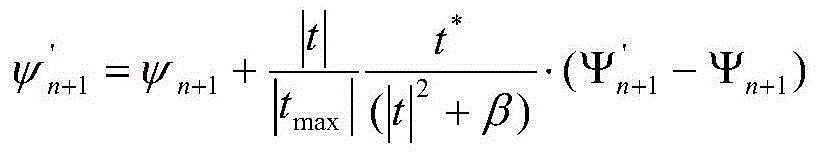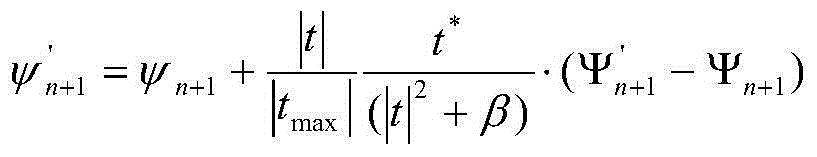Patents
Literature
155 results about "Digital holographic microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
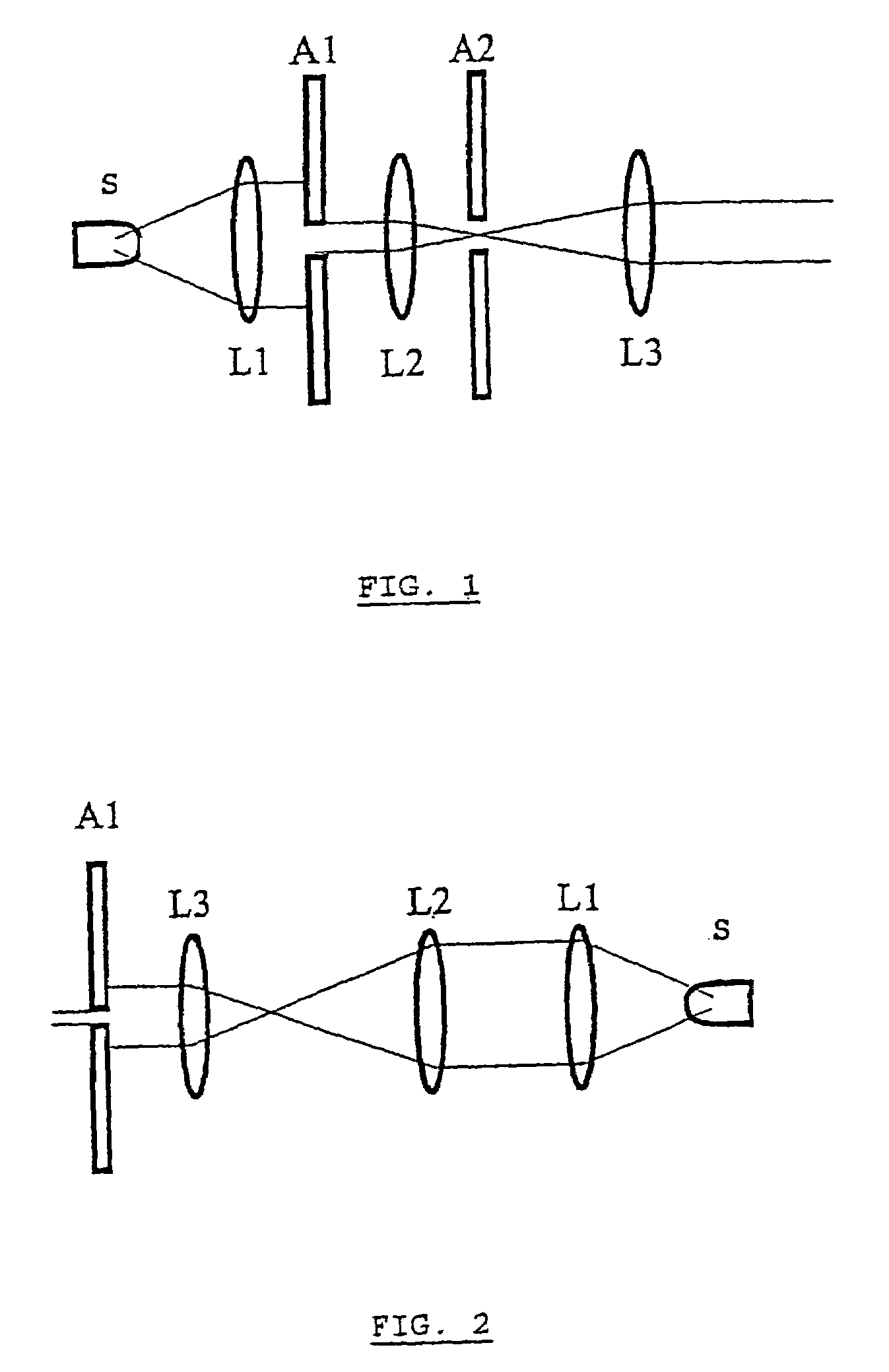
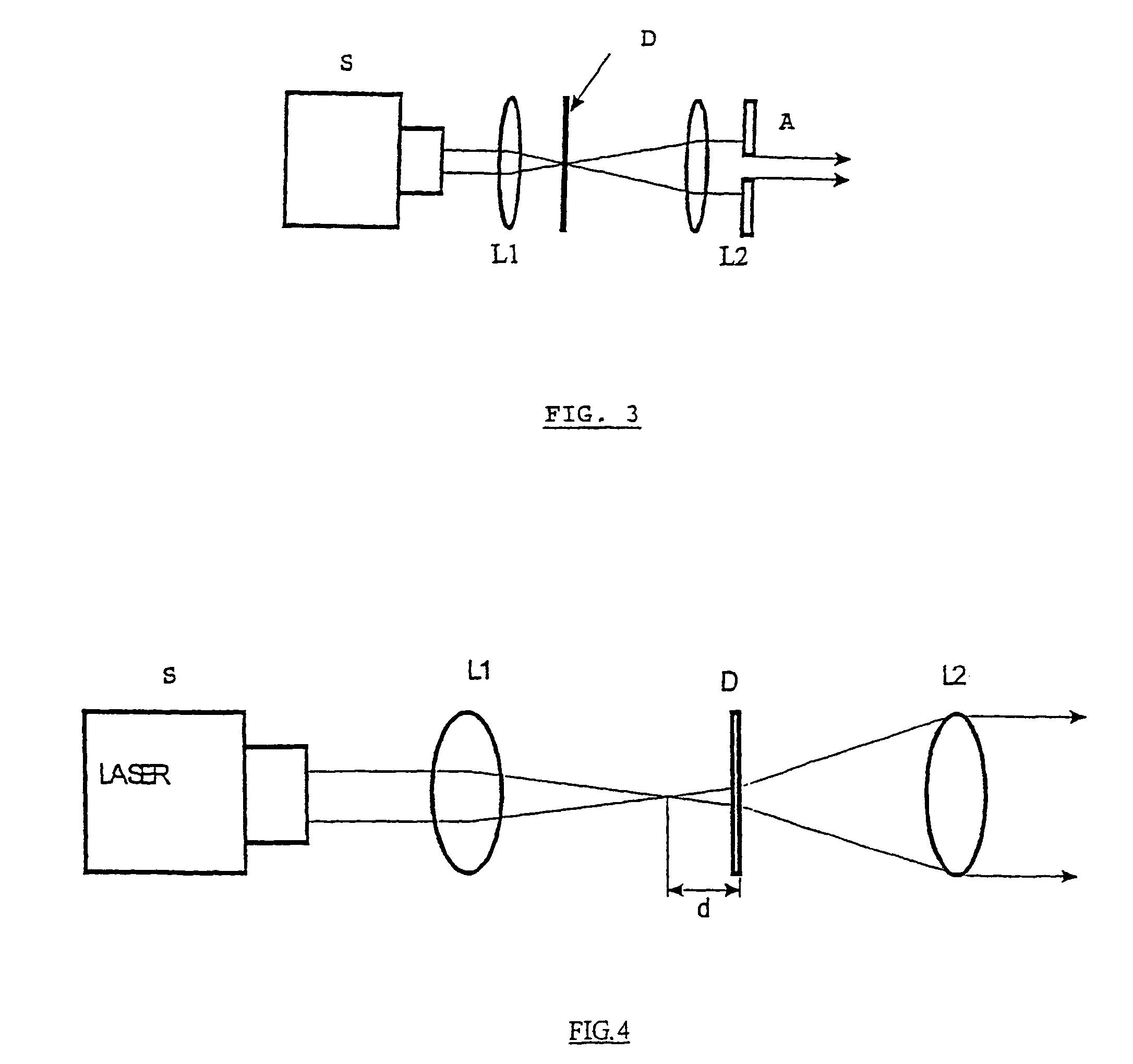
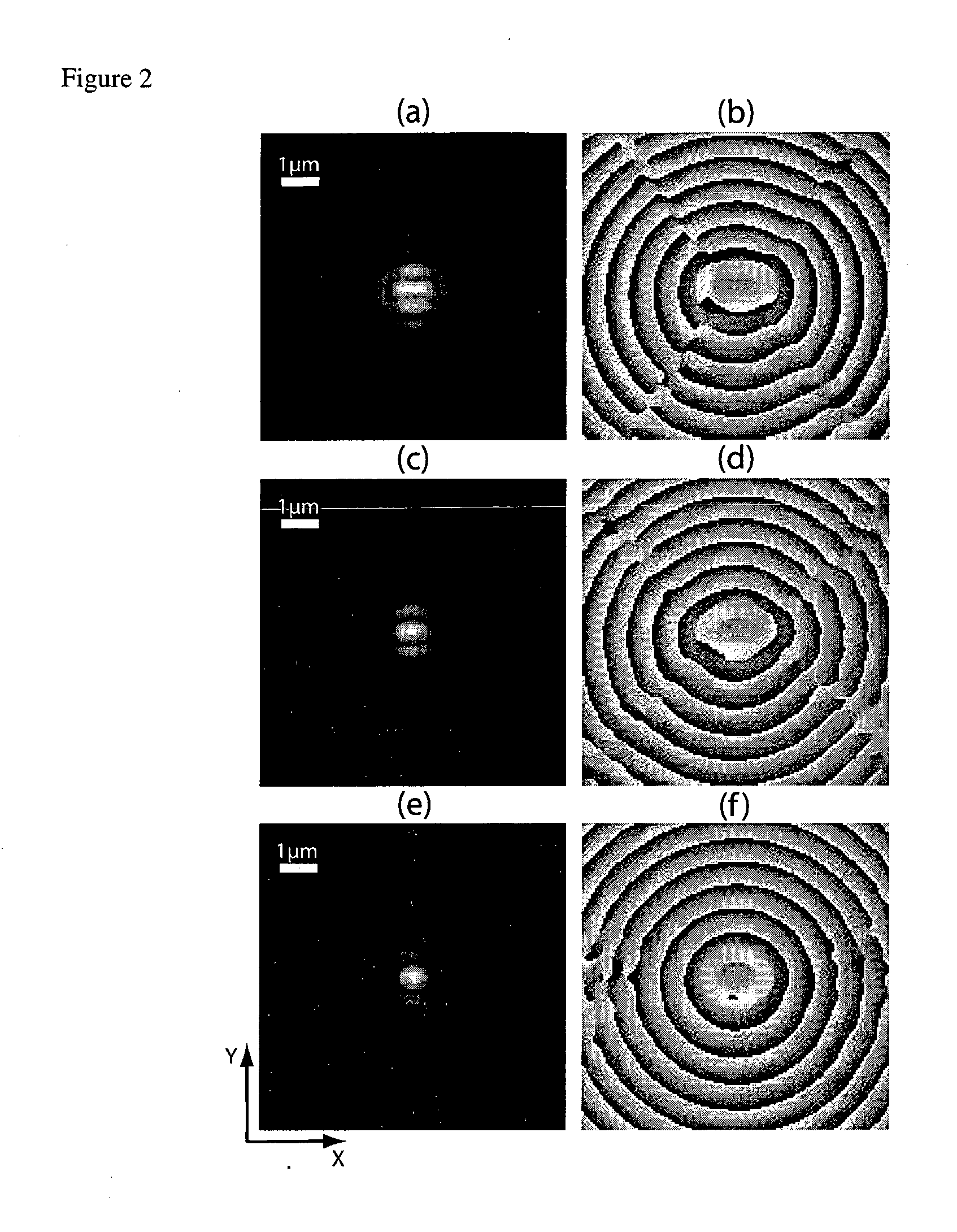
Digital holographic microscopy (DHM) is digital holography applied to microscopy. Digital holographic microscopy distinguishes itself from other microscopy methods by not recording the projected image of the object. Instead, the light wave front information originating from the object is digitally recorded as a hologram, from which a computer calculates the object image by using a numerical reconstruction algorithm. The image forming lens in traditional microscopy is thus replaced by a computer algorithm. Other closely related microscopy methods to digital holographic microscopy are interferometric microscopy, optical coherence tomography and diffraction phase microscopy. Common to all methods is the use of a reference wave front to obtain amplitude (intensity) and phase information. The information is recorded on a digital image sensor or by a photodetector from which an image of the object is created (reconstructed) by a computer. In traditional microscopy, which do not use a reference wave front, only intensity information is recorded and essential information about the object is lost.
Wave front sensing method and apparatus
ActiveUS7649160B2Reduce fieldHigh resolutionImage enhancementOptical measurementsWavefront sensorMetrology
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Wave Front Sensing Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20080265130A1Improve performanceHigh imaging performanceImage enhancementPhotometry using reference valueWavefront sensorMetrology
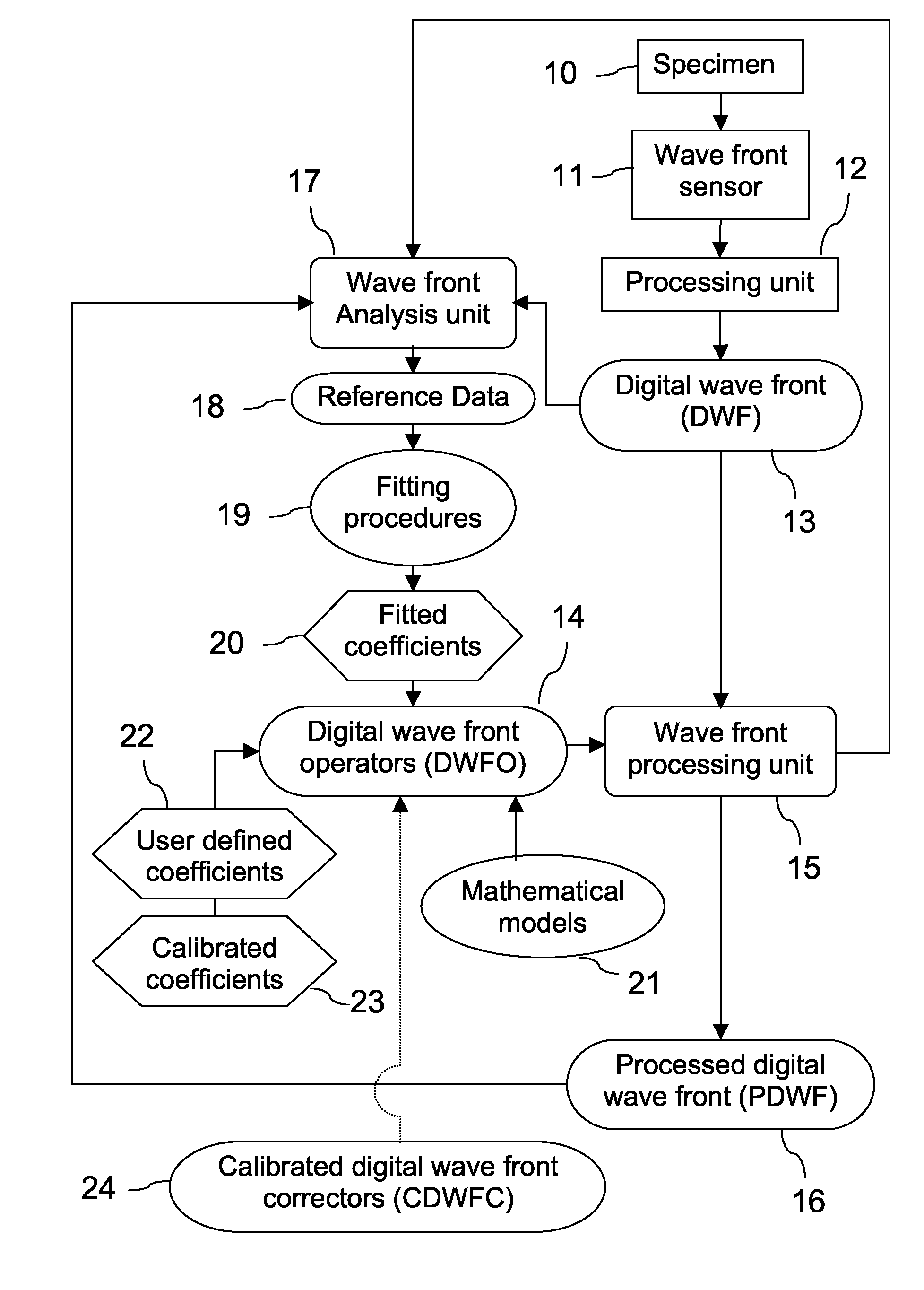
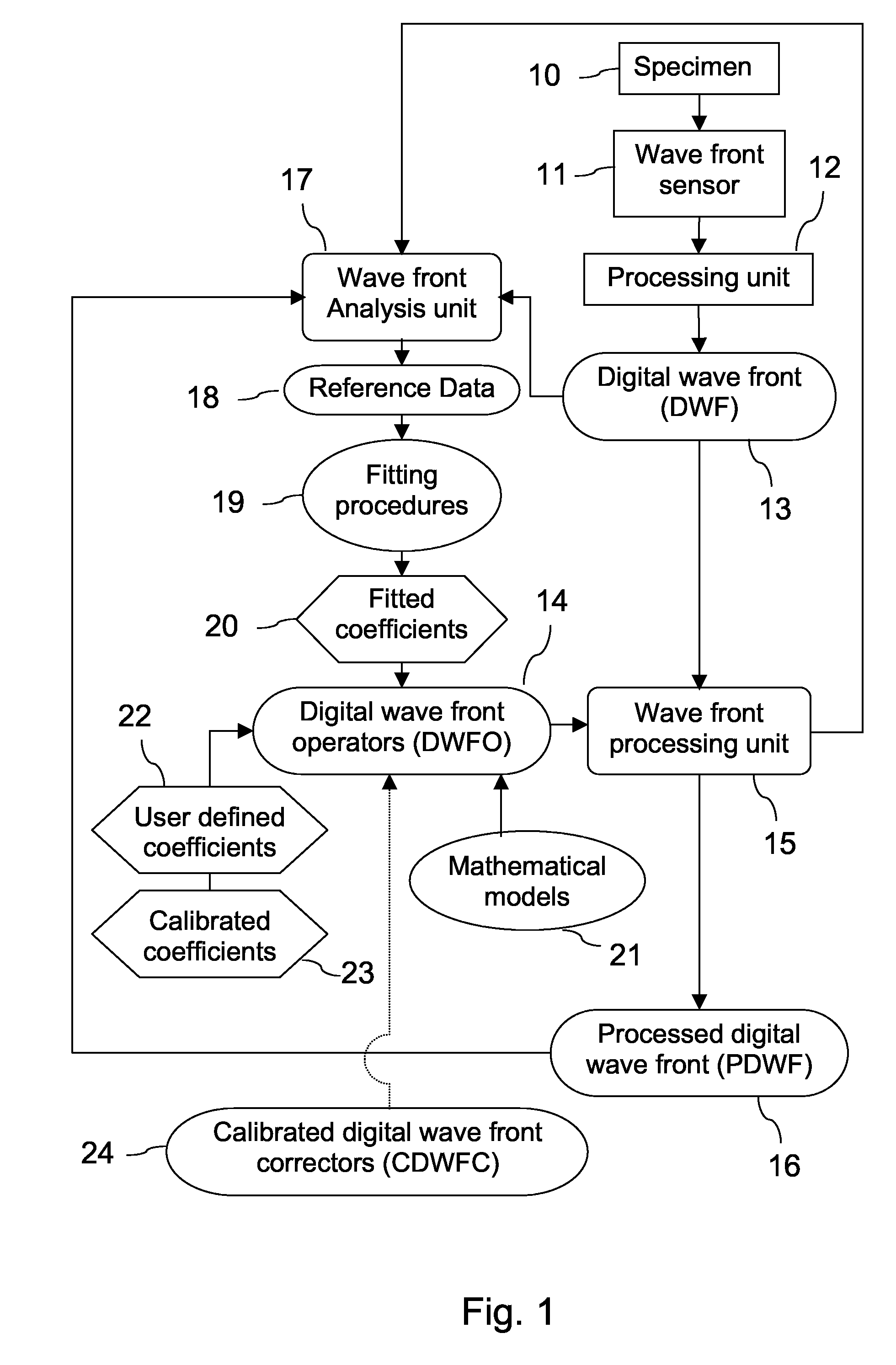
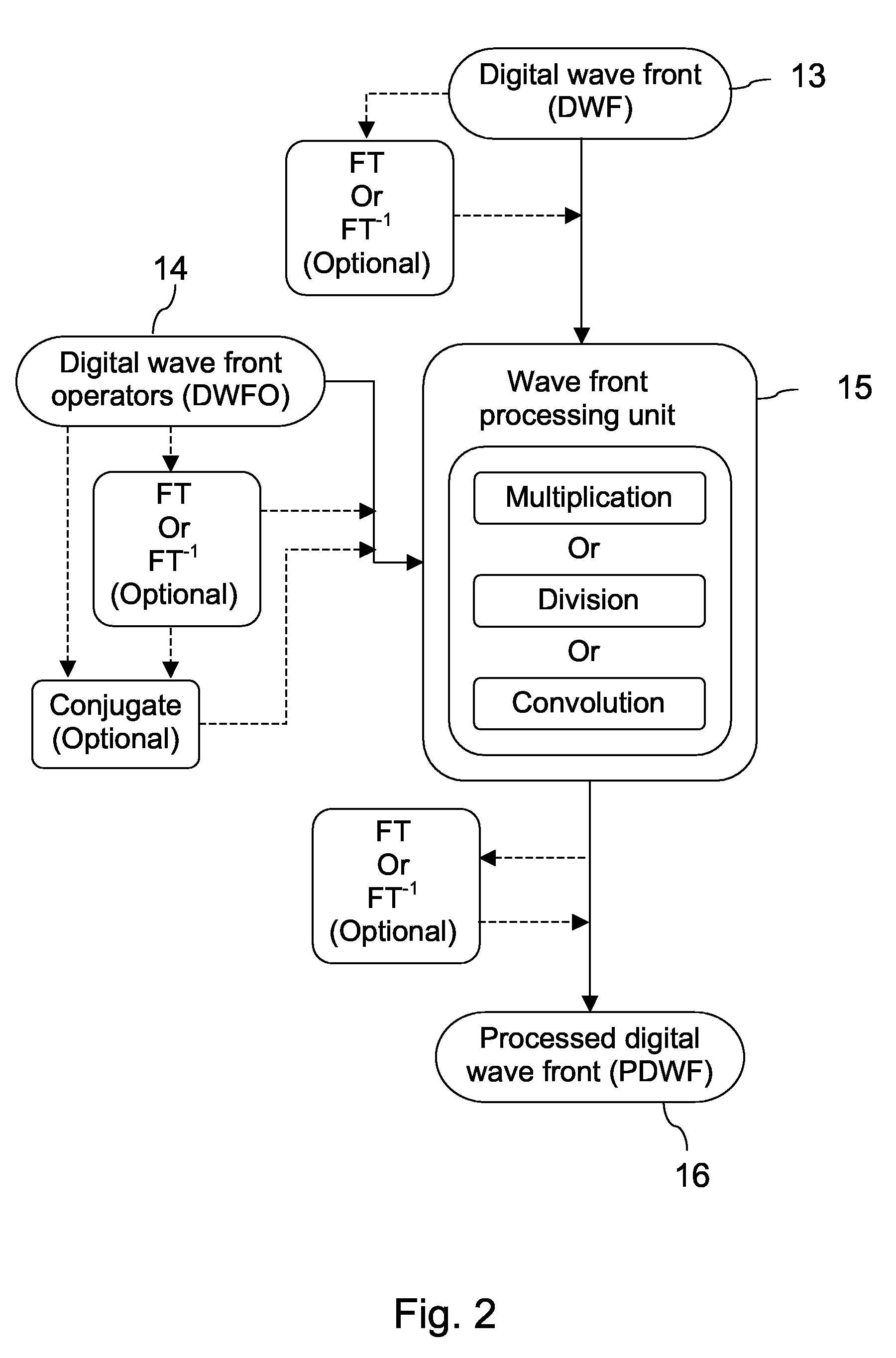
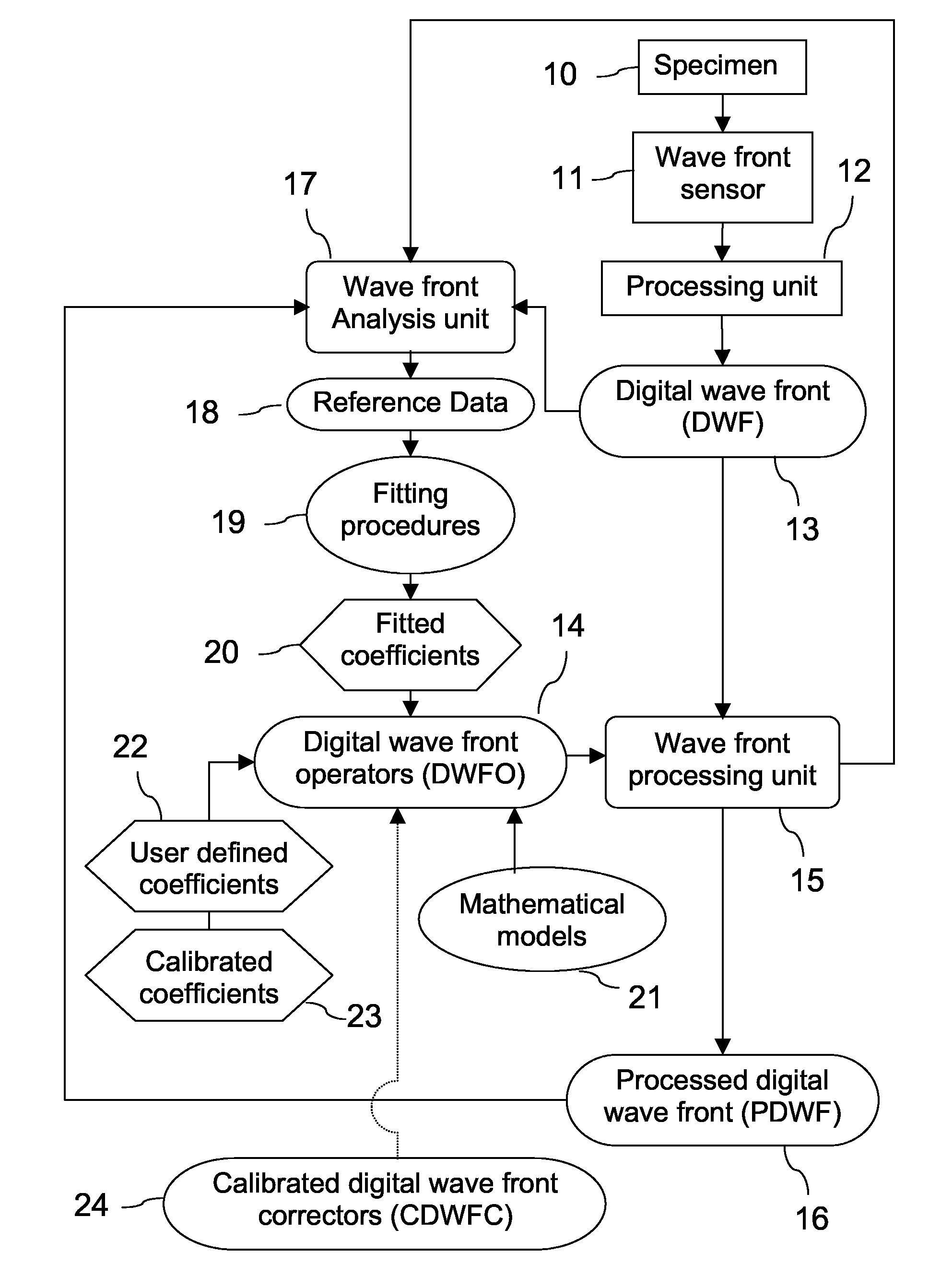
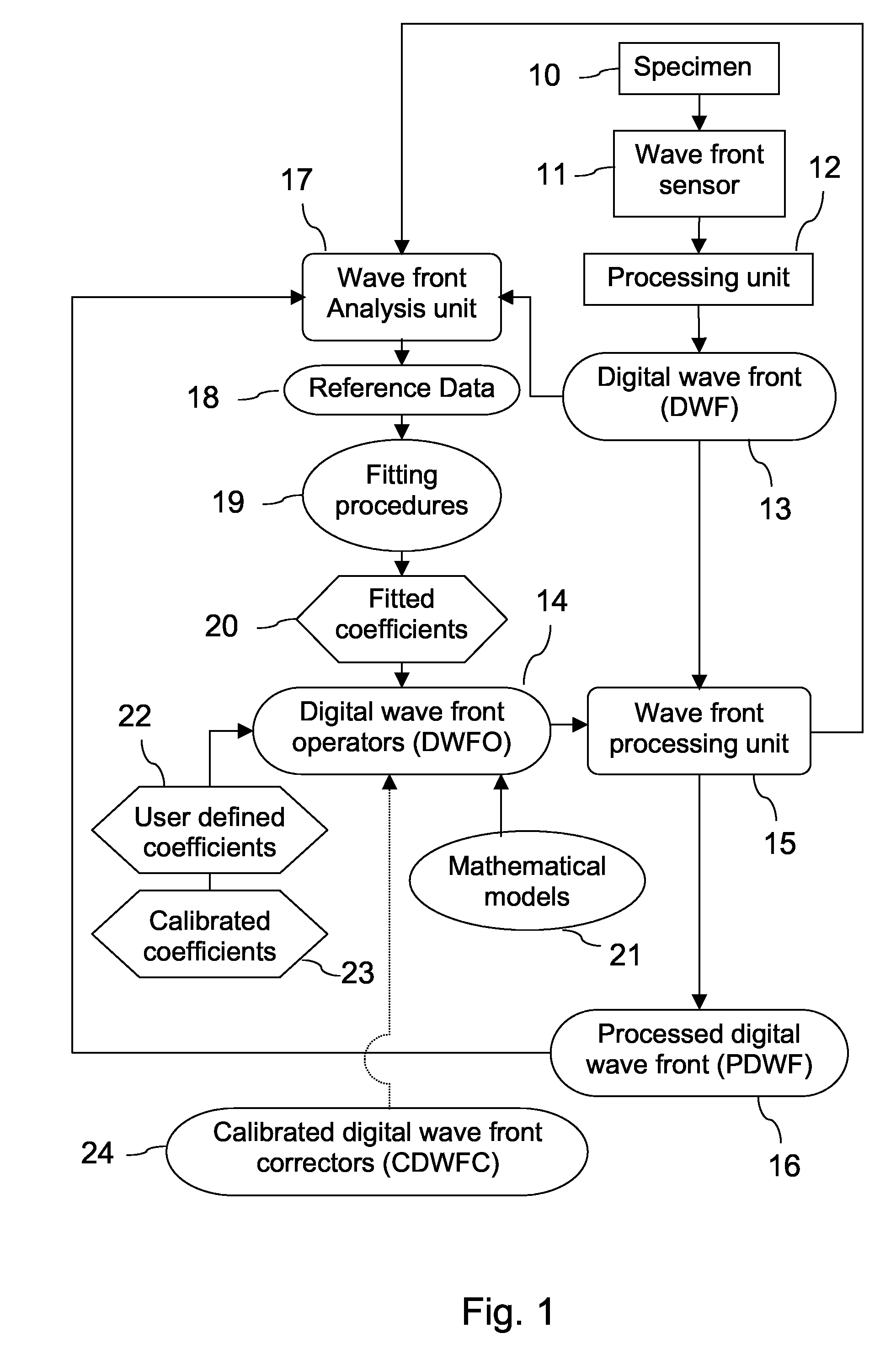
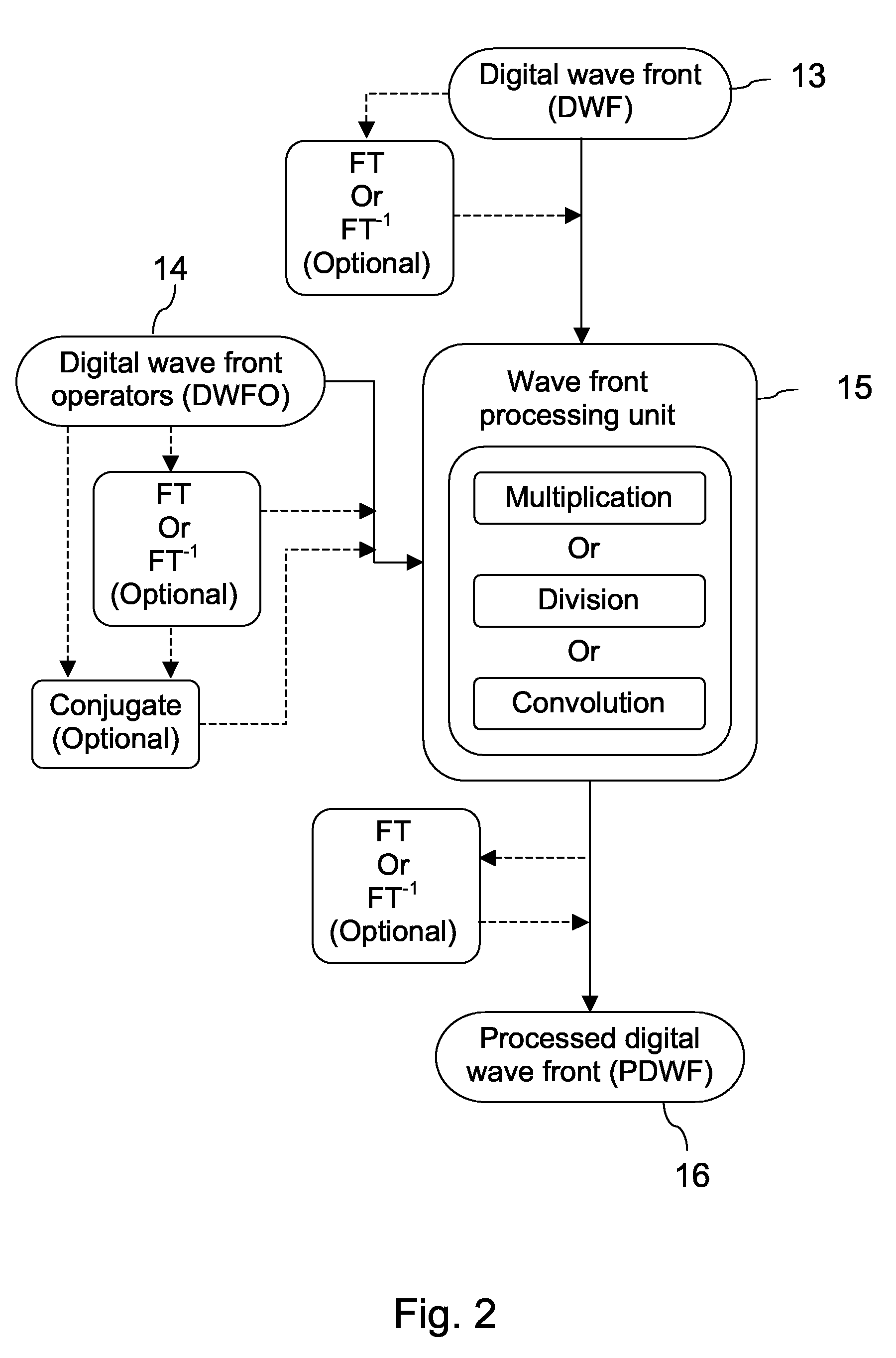
A new way of mixing instrumental and digital means is described for the general field of wave front sensing. The present invention describes the use, the definition and the utility of digital operators, called digital wave front operators (DWFO) or digital lenses (DL), specifically designed for the digital processing of wave fronts defined in amplitude and phase. DWFO are of particular interest for correcting undesired wave front deformations induced by instrumental defects or experimental errors. DWFO may be defined using a mathematical model, e.g. a polynomial function, which involves coefficients. The present invention describes automated and semi-automated procedures for calibrating or adjusting the values of these coefficients. These procedures are based on the fitting of mathematical models on reference data extracted from specific regions of a wave front called reference areas, which are characterized by the fact that specimen contributions are a priori known in reference areas. For example, reference areas can be defined in regions where flat surfaces of a specimen produce a constant phase function. The present invention describes also how DWFO can be defined by extracting reference data along one-dimensional (1D) profiles. DWFO can also be defined in order to obtain a flattened representation of non-flat area of a specimen. Several DWFO or DL can be combined, possibly in addition with procedures for calculating numerically the propagation of wave fronts. A DWFO may also be defined experimentally, e.g. by calibration procedures using reference specimens. A method for generating a DWFO by filtering in the Fourier plane is also described. All wave front sensing techniques may benefit from the present invention. The case of a wave front sensor based on digital holography, e.g. a digital holographic microscope (DHM), is described in more details. The use of DWFO improves the performance, in particular speed and precision, and the ease of use of instruments for wave front sensing. The use of DWFO results in instrumental simplifications, costs reductions, and enlarged the field of applications. The present invention defines a new technique for imaging and metrology with a large field of applications in material and life sciences, for research and industrial applications.
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Digital holographic microscope for 3D imaging and process using it
InactiveUS20080018966A1Reduce spatial coherenceReduce coherent noiseHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopes3d imageDigital holographic microscopy
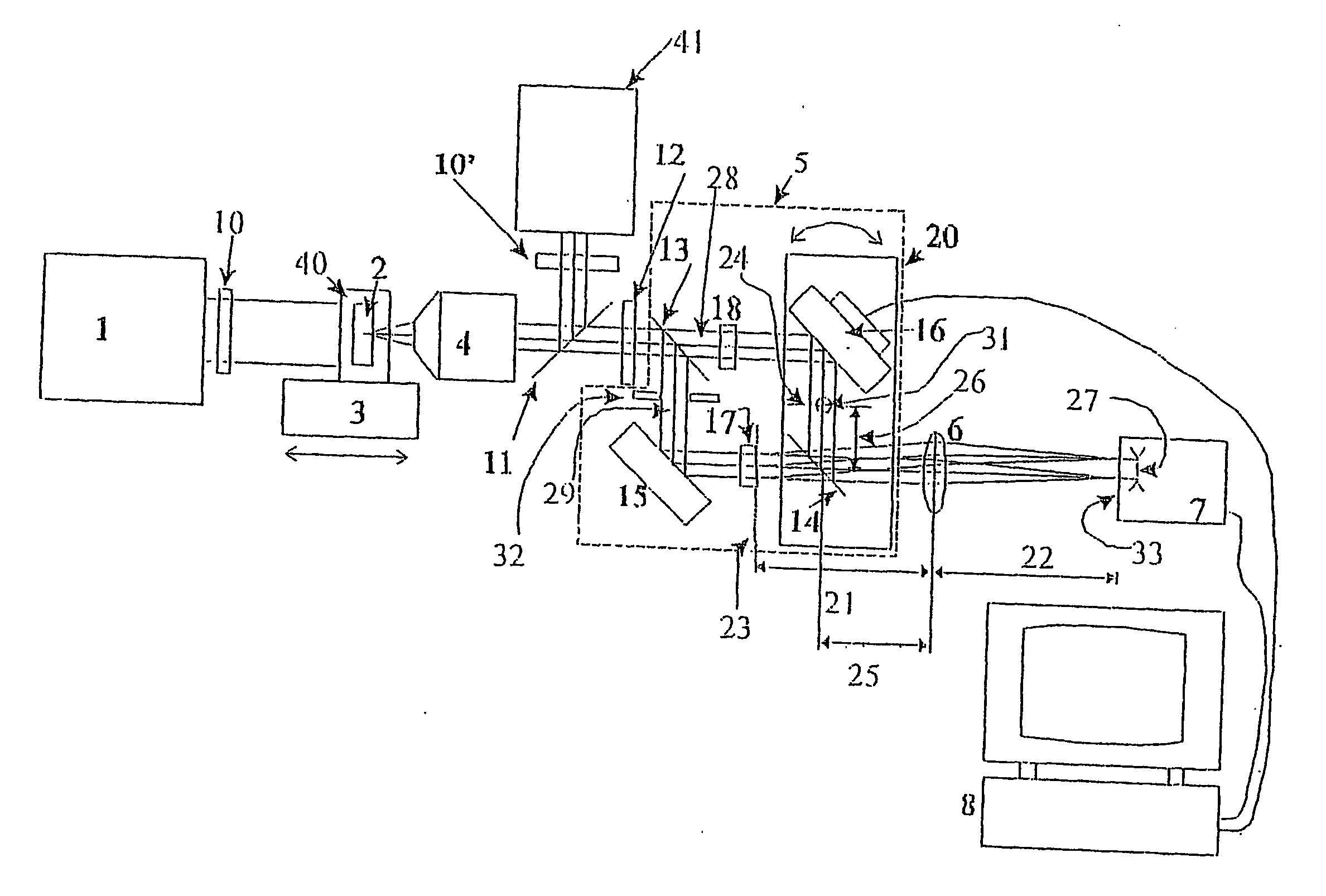
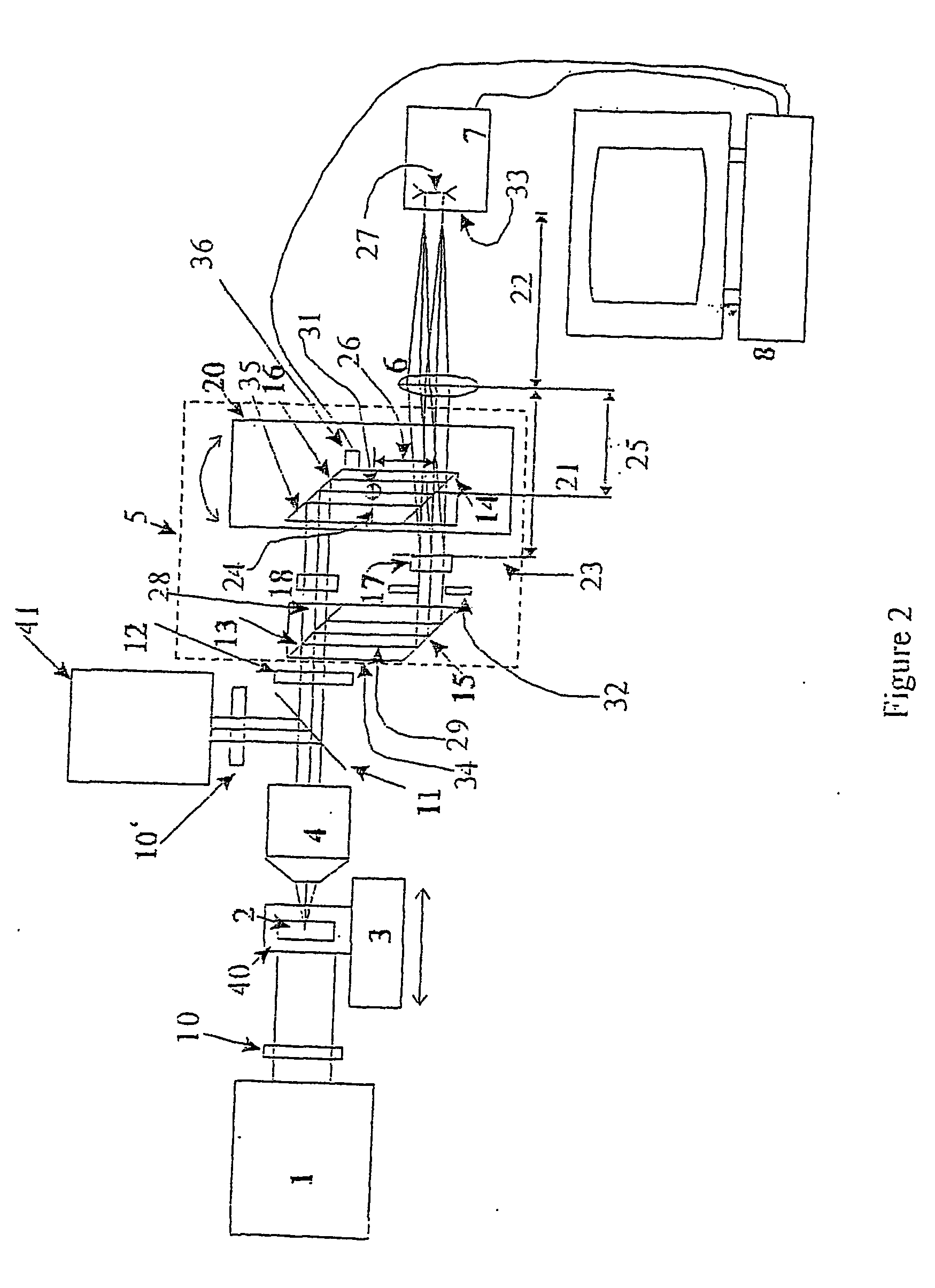
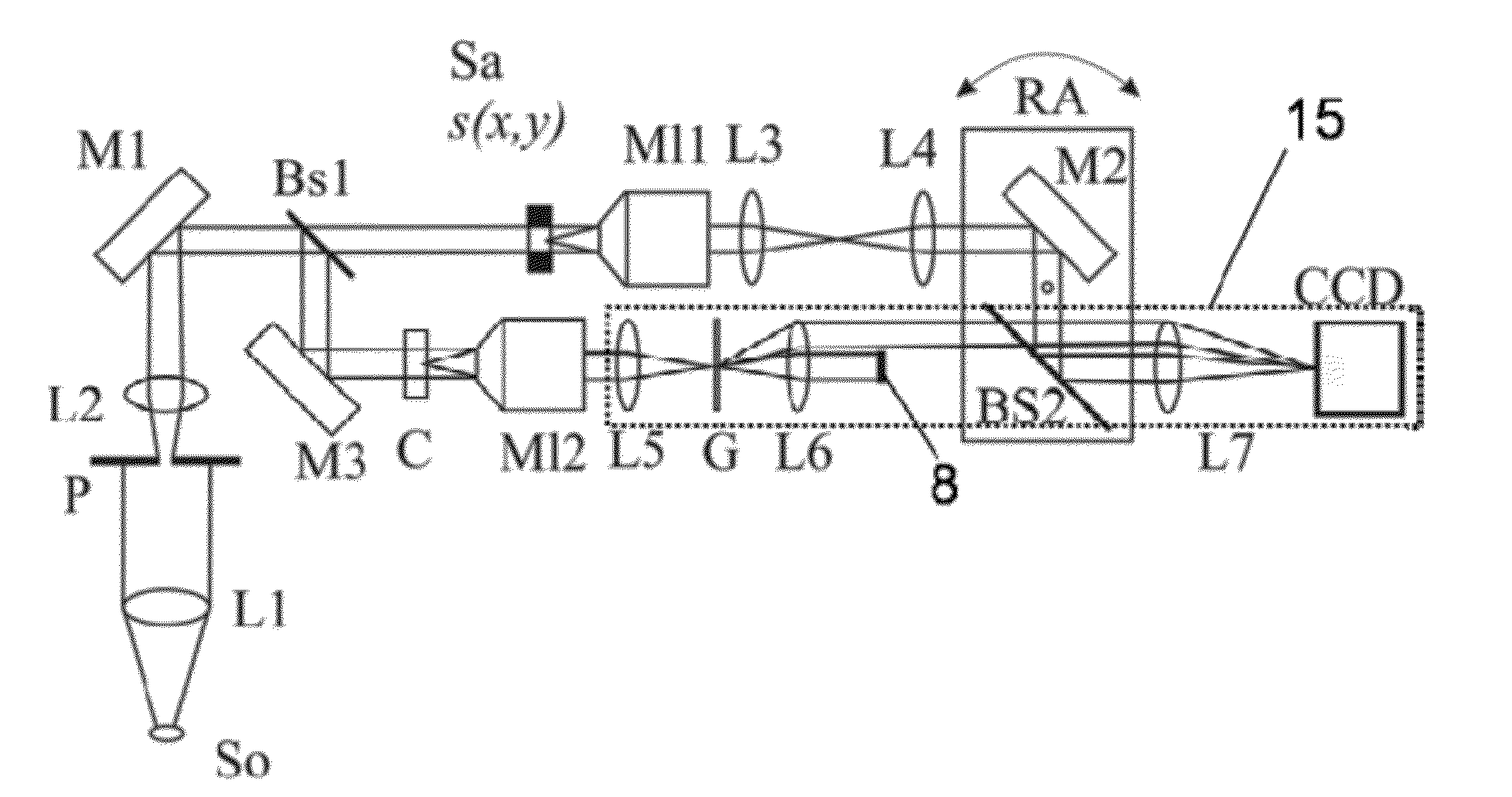
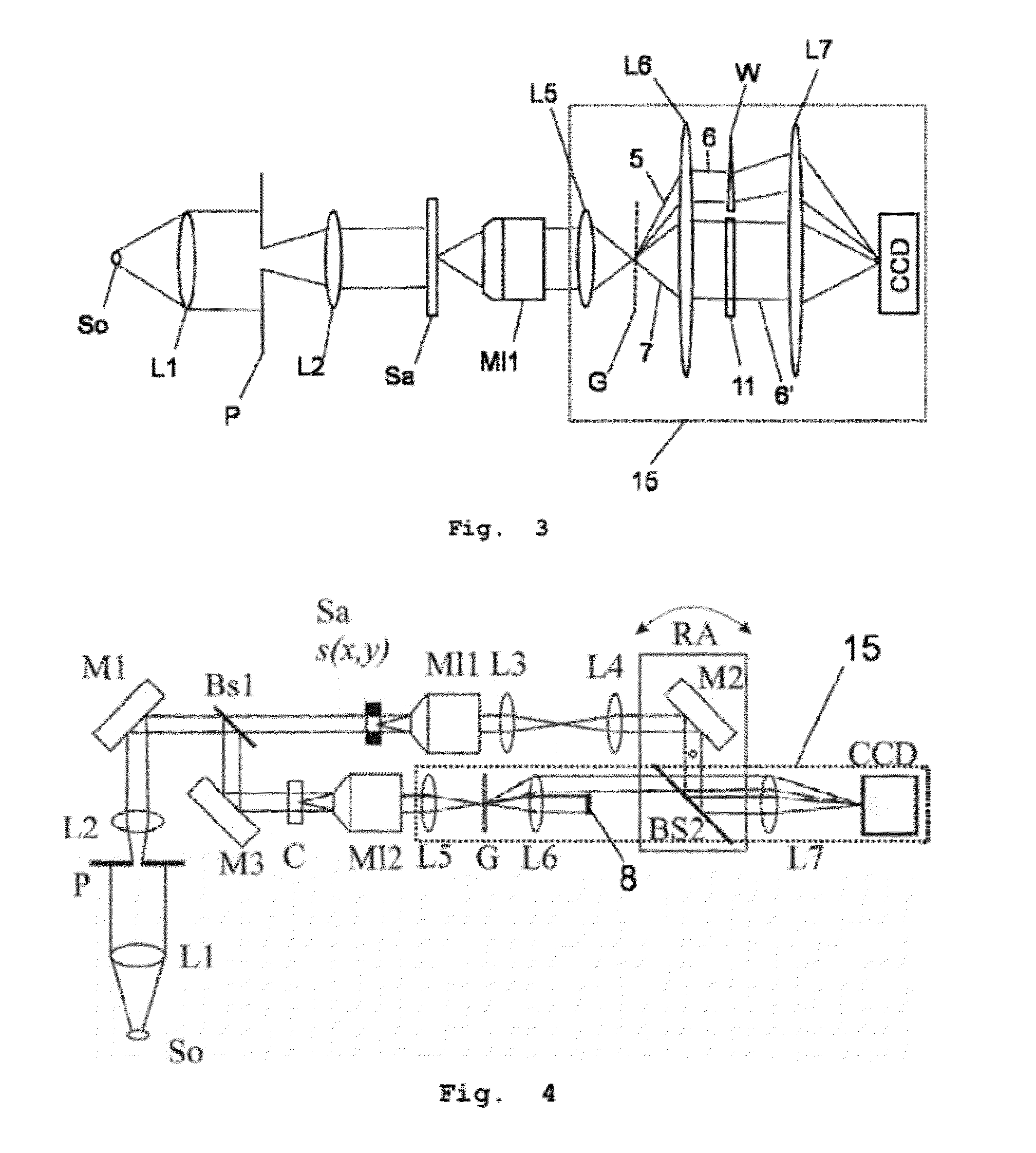
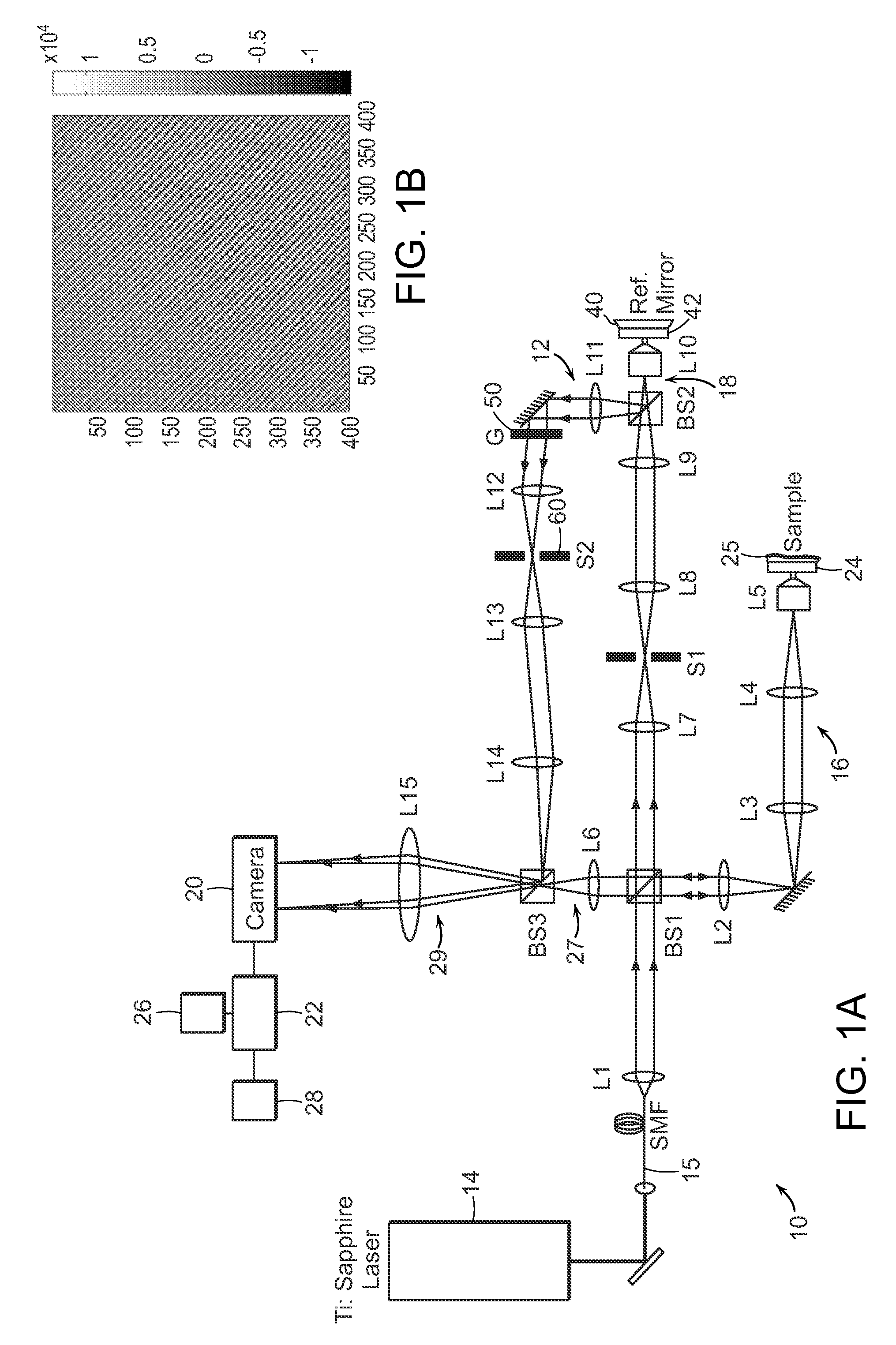
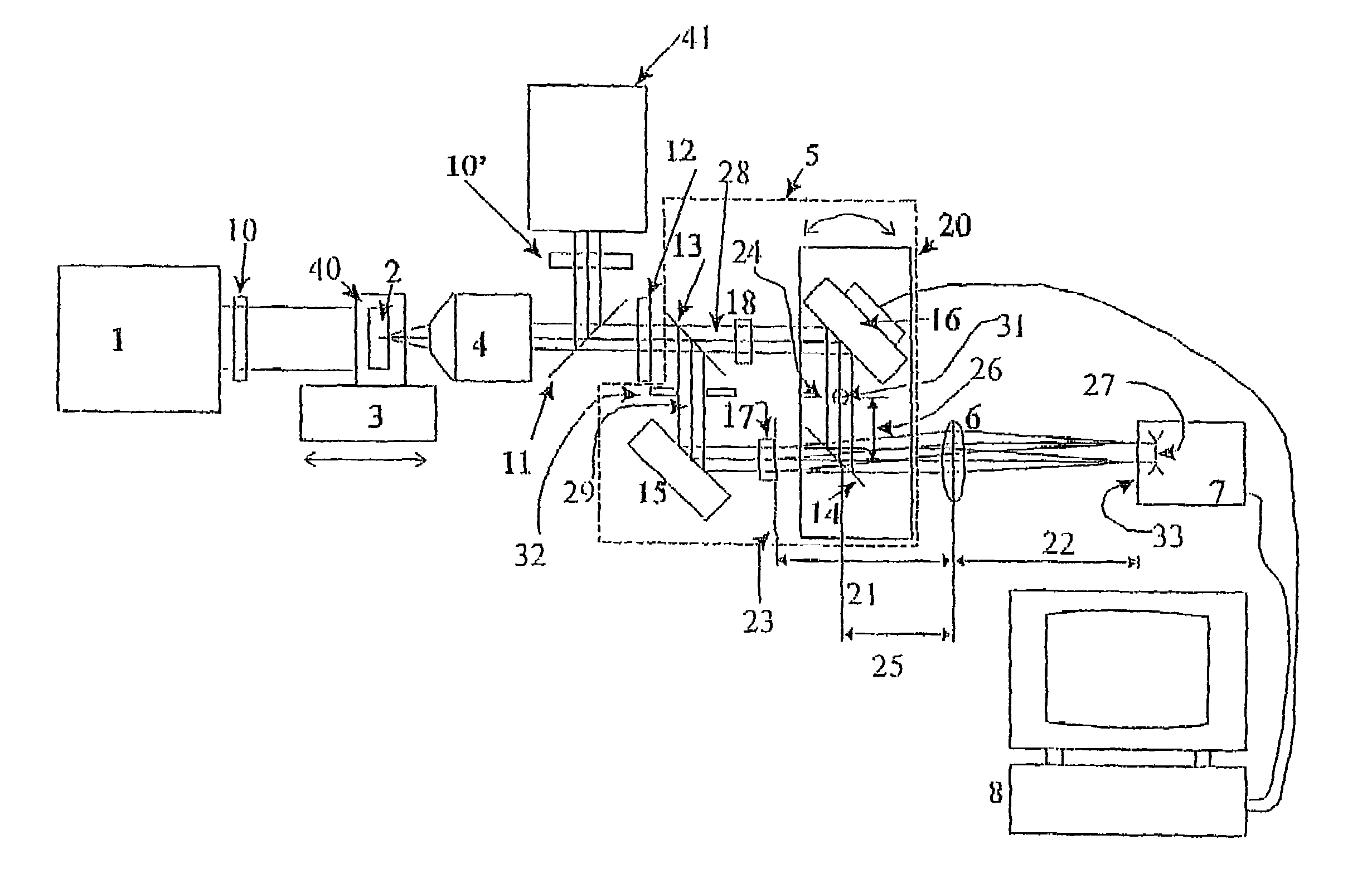
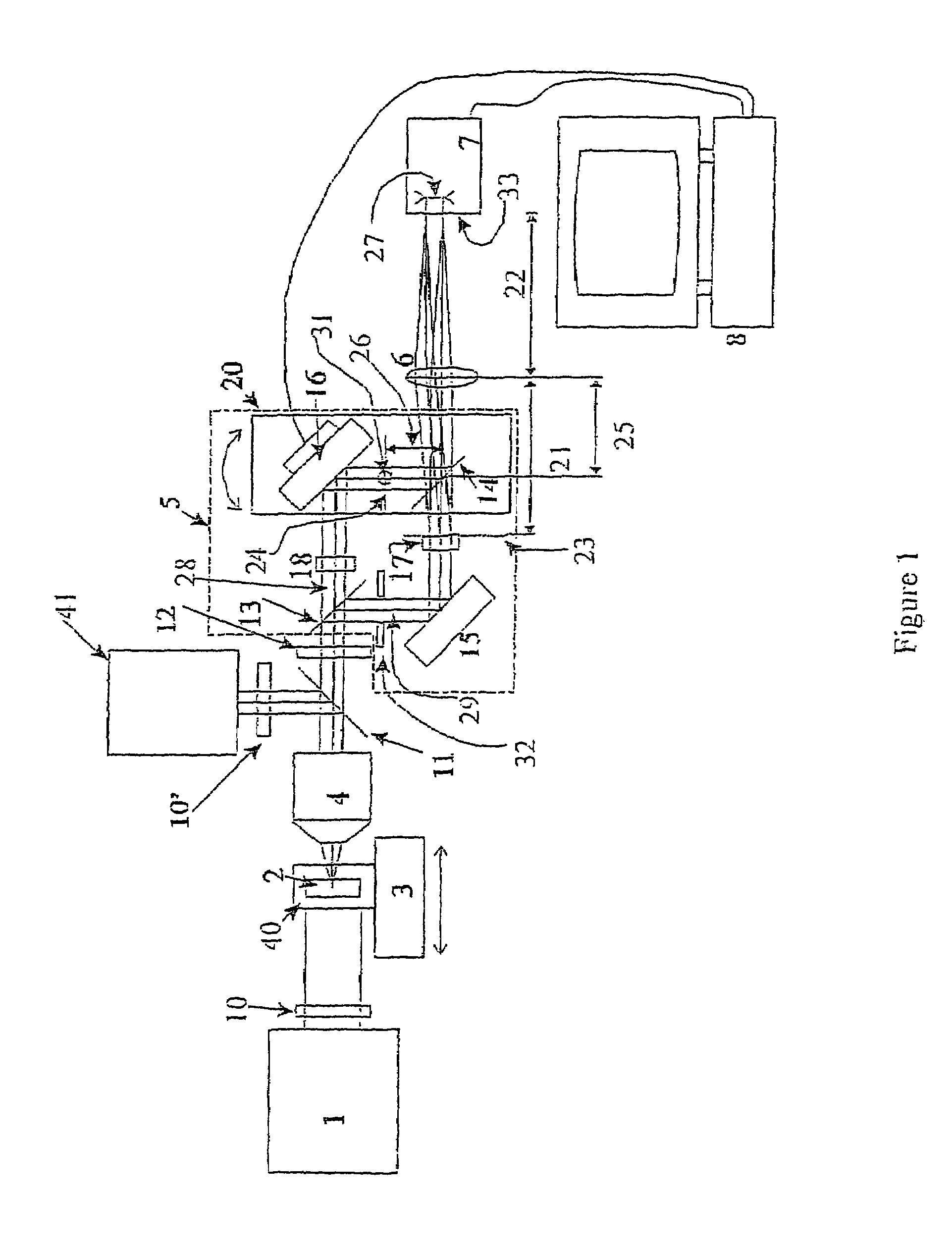
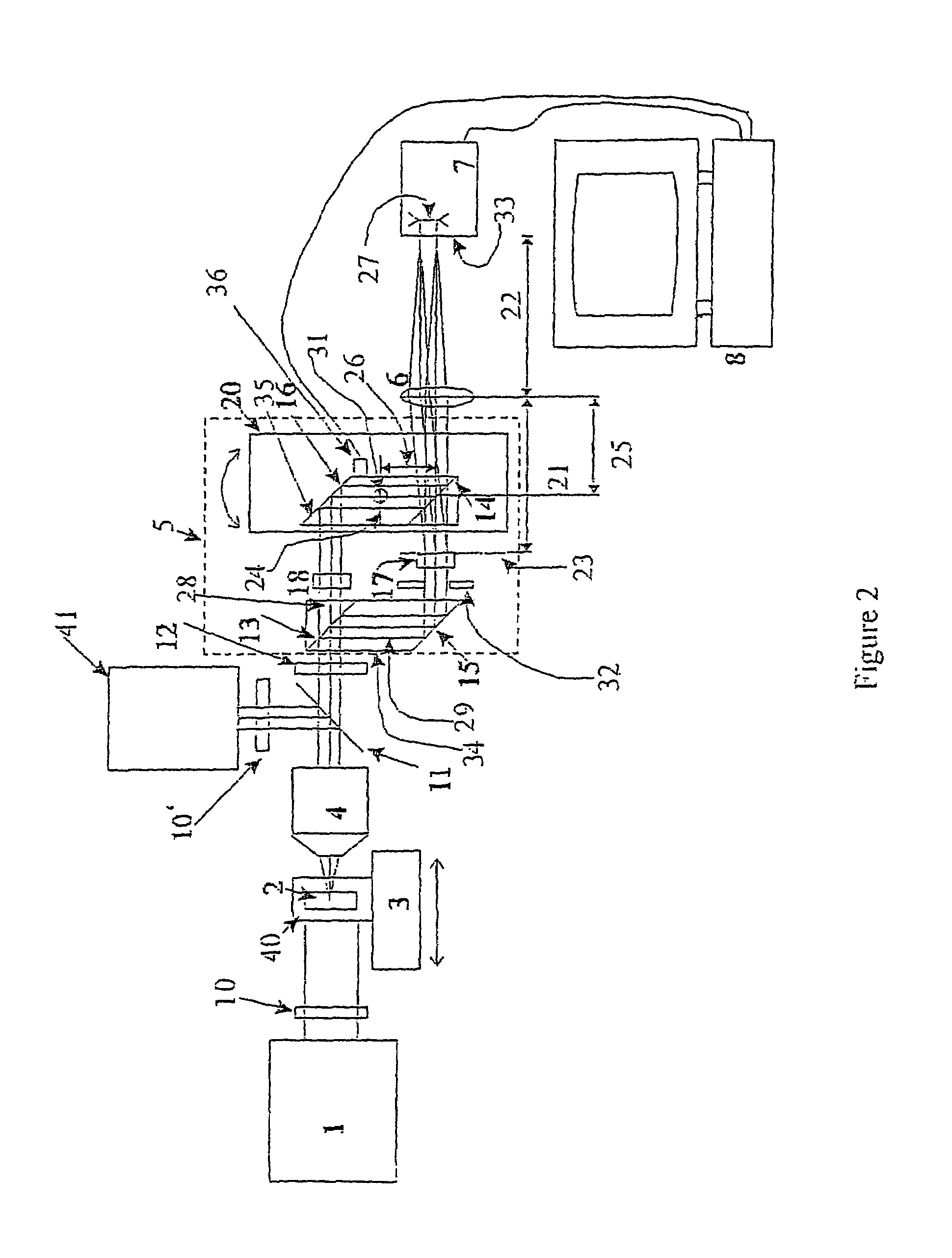
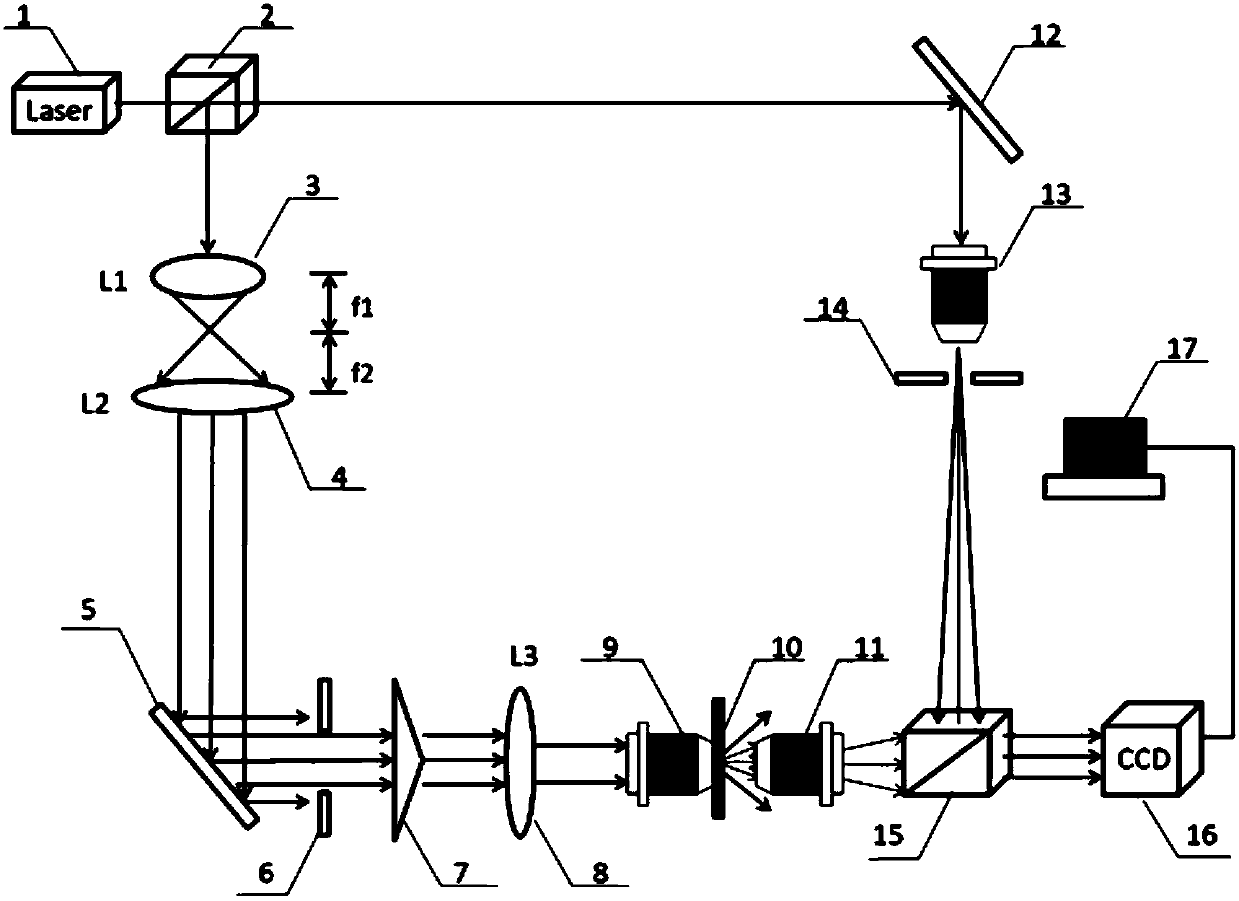
The present invention is related to a compact microscope able to work in digital holography for obtaining high quality 3D images of samples, including fluorescent samples and relatively thick samples such as biological samples, said microscope comprising illumination means (1,41) at least partially spatially coherent for illuminating a sample (2) to be studied and a differential interferometer (5) for generating interfering beams from said sample (2) on the sensor (33) of an electronic imaging device (7), said interferometer (5) comprising namely tilting means (17) for tilting by a defined angle one the interfering beams (28 or 29) relatively to the other, said tilting resulting into a defined shift (27) of said interfering beam on the sensor of the electronic imaging device (7), said shift (27) being smaller than spatial coherence width of each beam, said microscope being able to be quasi totally preadjusted independently from the samples so that minimum additional adjustments are required for obtaining reliable 3D images of samples.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Method and device for obtaining a sample with three-dimensional microscopy
InactiveUS7009700B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFluorescenceDigital holographic microscopy
A method and device for obtaining a sample with three-dimensional microscopy, in particular a thick biological sample and the fluorescence field emitted by the sample. One embodiment includes obtaining interferometric signals of a specimen, obtaining fluorescence signals emanating from the specimen, recording these signals, and processing these signals so as to reconstruct three-dimensional images of the specimen and of the field of fluorescence emitted by the specimen at a given time. Another embodiment includes a digital holography microscope, a fluorescence excitation source illuminating a specimen, where the microscope and the fluorescence excitation source cooperate to obtain interferometric signals of the specimen and obtain fluorescence signals emanating from the specimen, means for recording the interferometric signals and fluorescence signals, and means for processing the interferometric signals and the fluorescence signals so as to reconstruct three-dimensional images of the specimen and of the field of fluorescence emitted by the specimen at a given time.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Off-axis interferometer
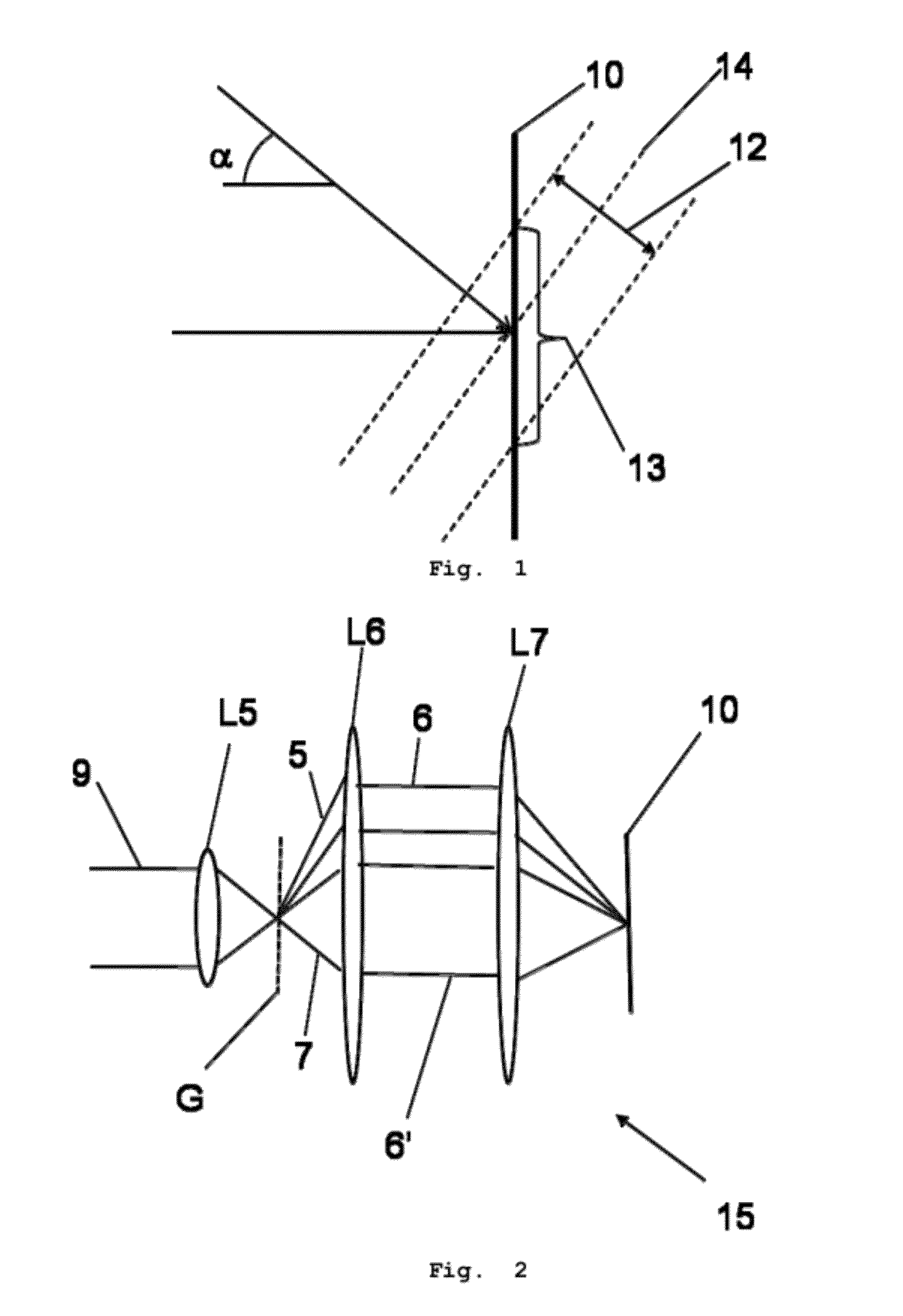
ActiveUS20120200901A1Avoid spreadingHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopesGratingDiffraction order
An Interferometer for off-axis digital holographic microscopy includes a recording plane, and a grating located in a plane optically conjugated with the recording plane. The grating defining a first and a second optical path, the optical path corresponding to different diffraction order.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
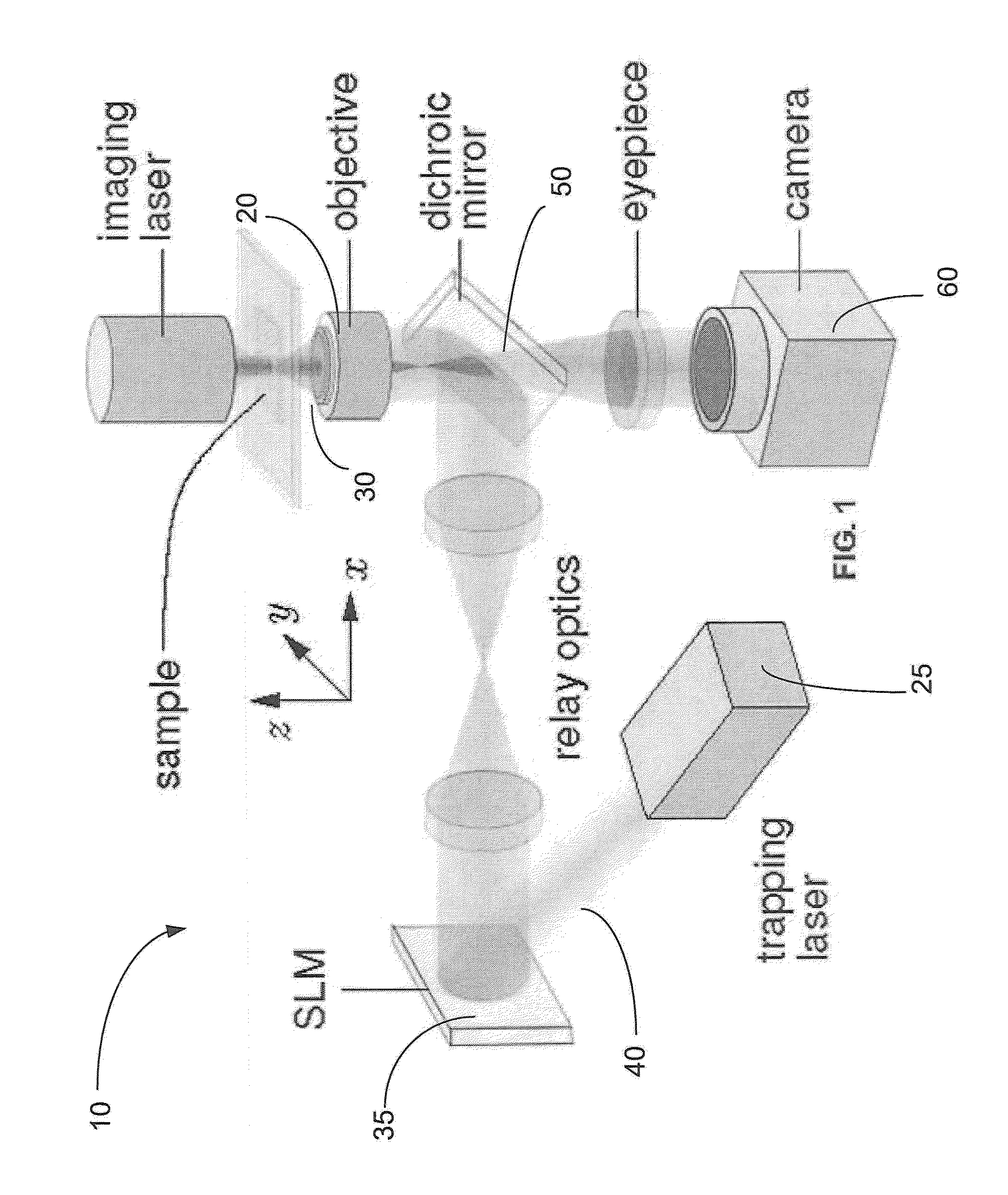
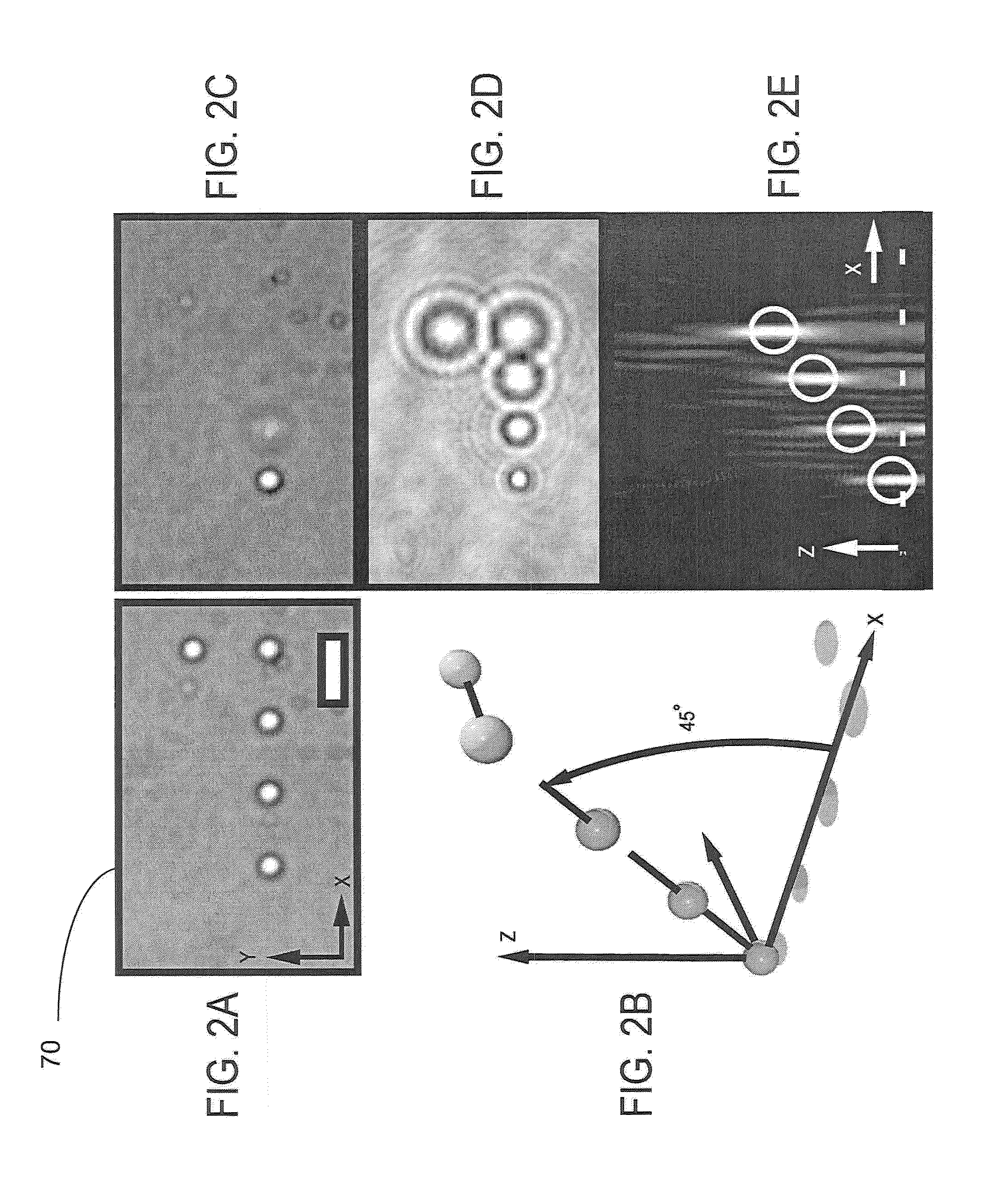
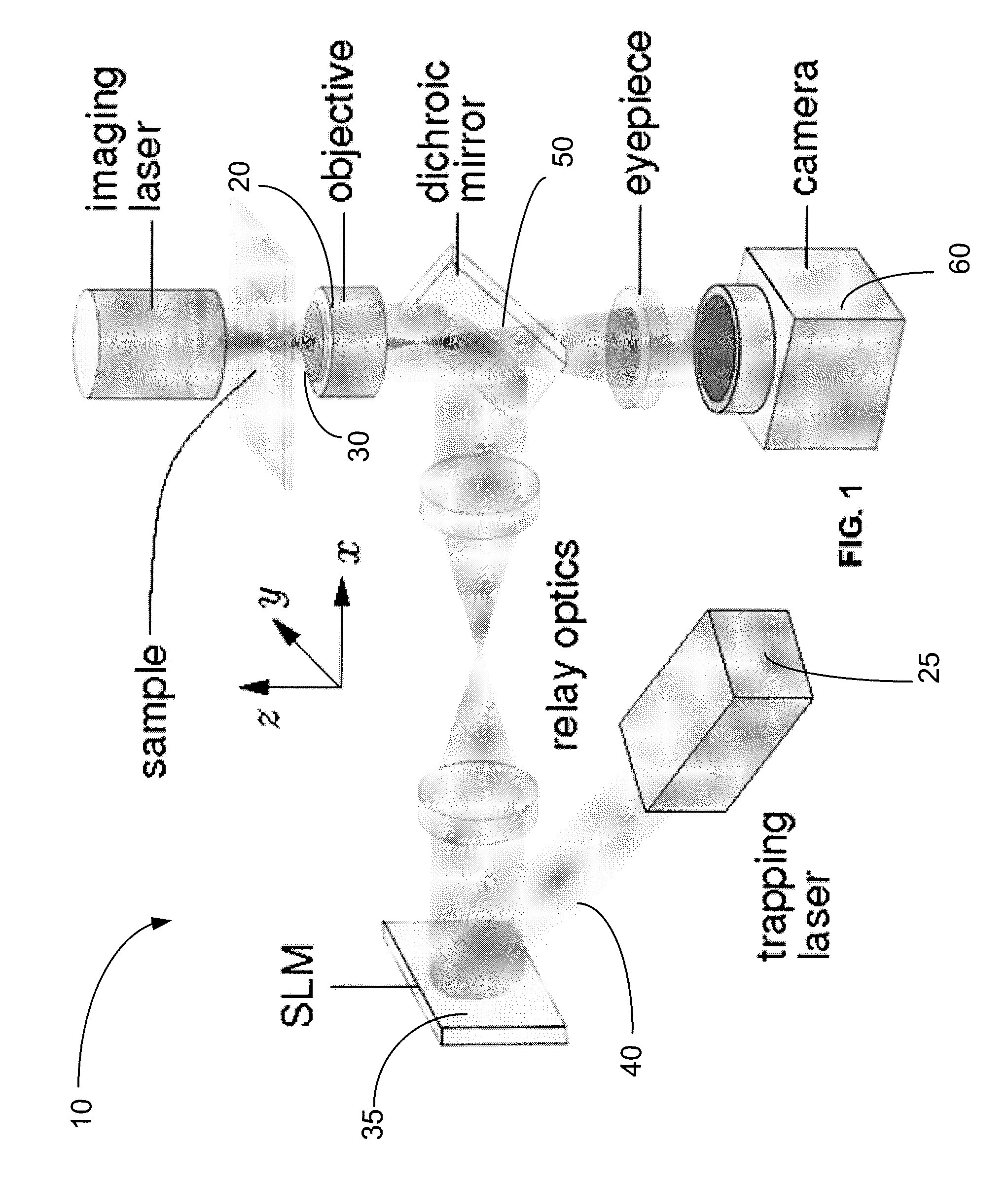
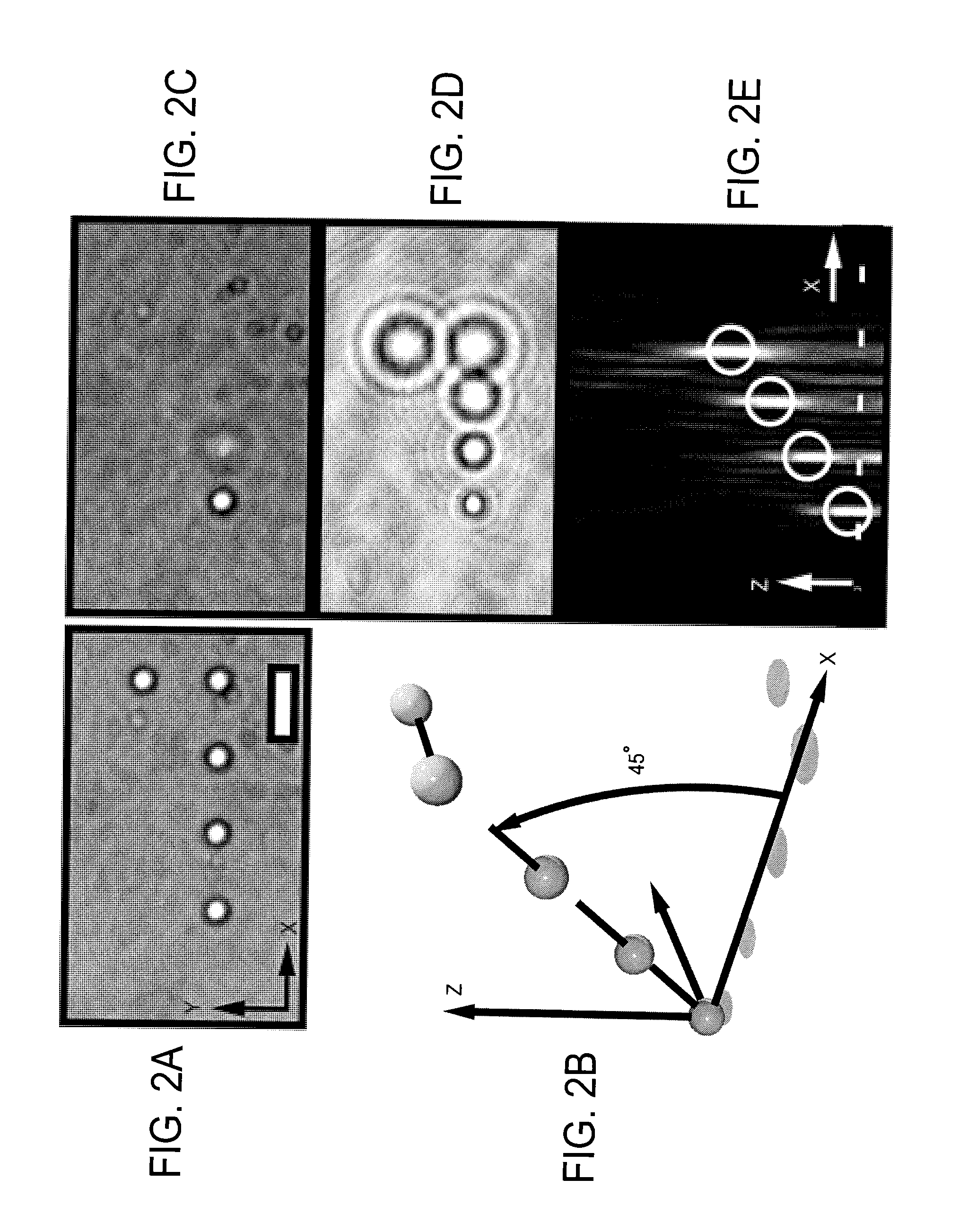
Holographic microscopy of holographically trapped three-dimensional structures
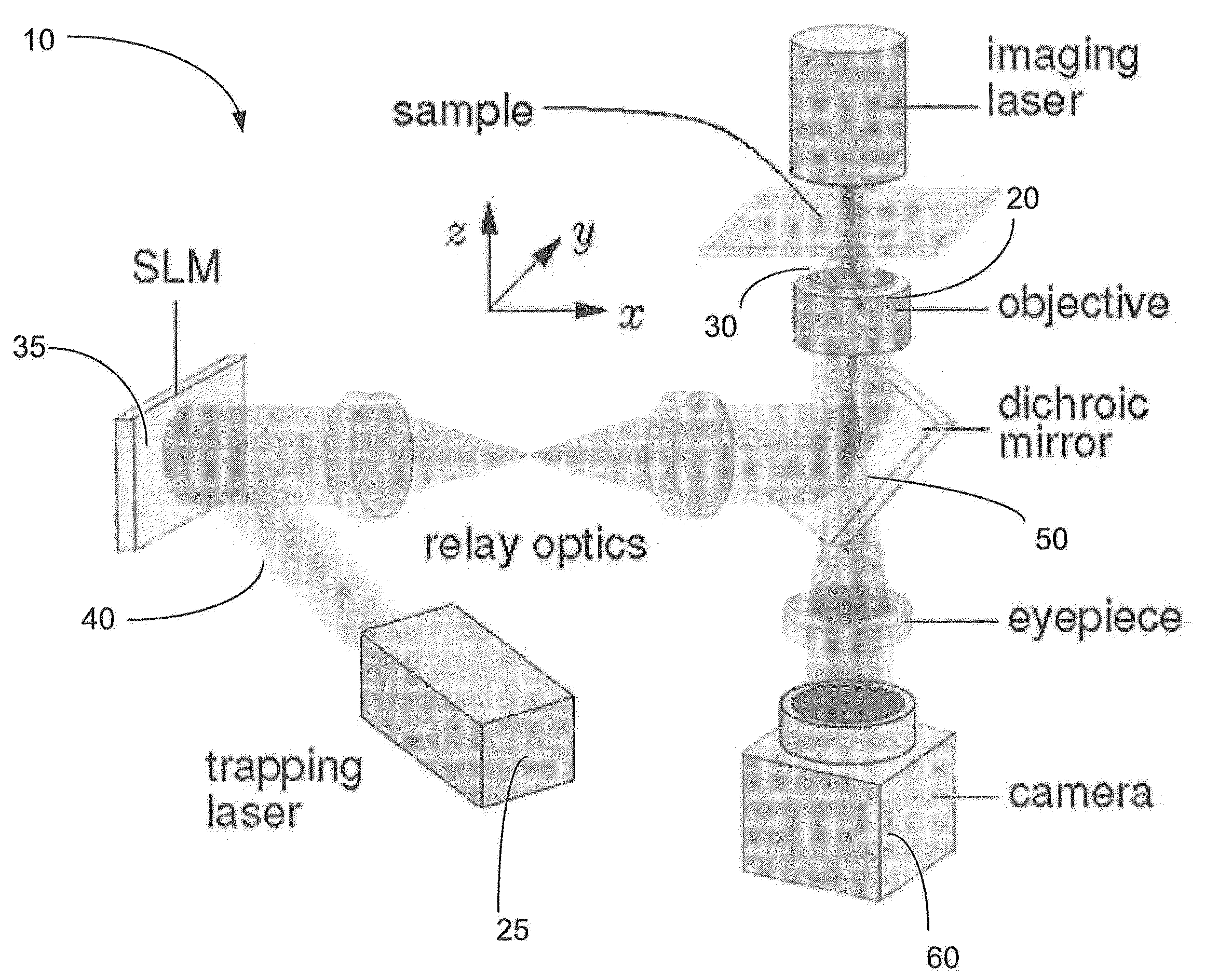
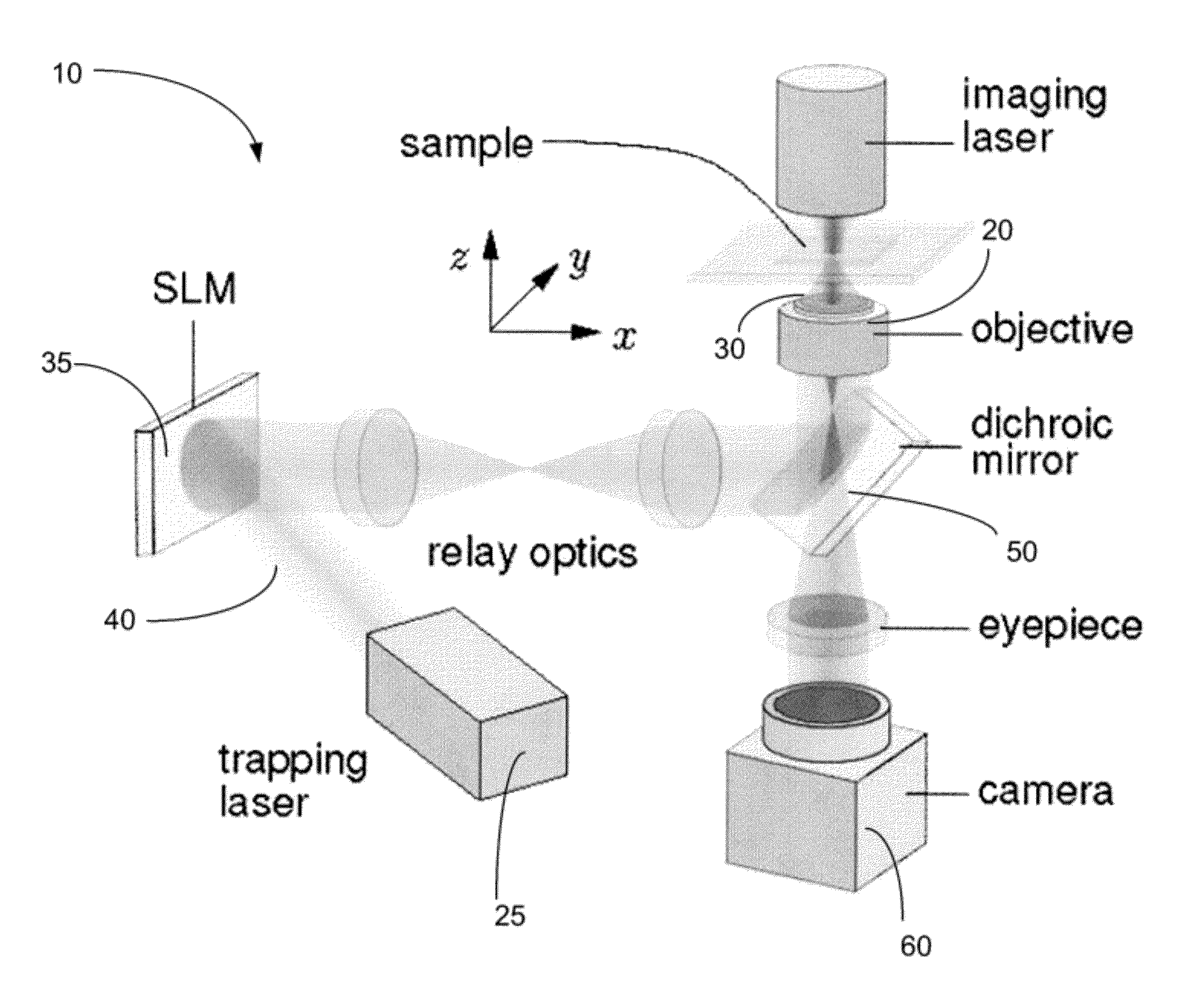
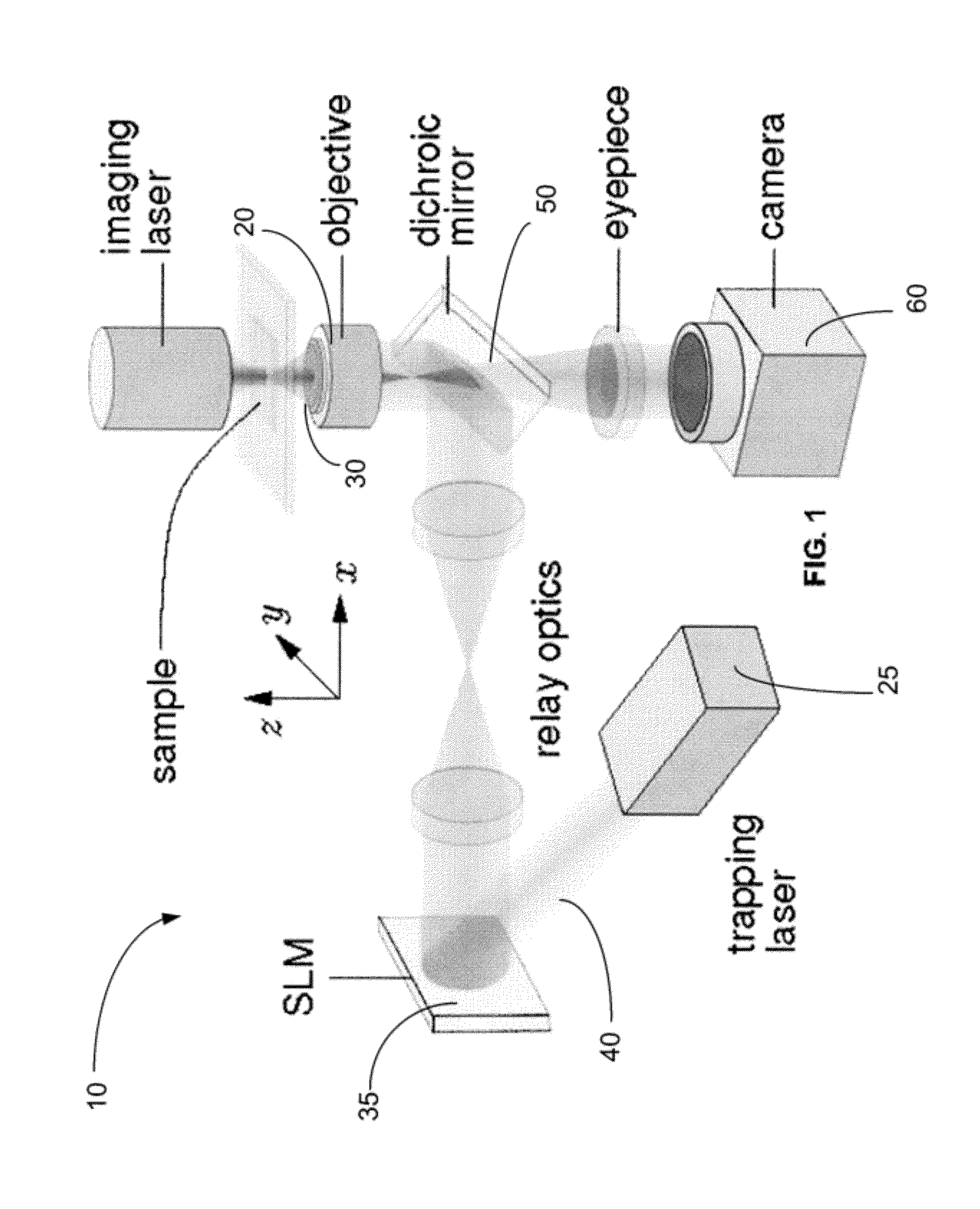
A method and system for performing three-dimensional holographic microscopy of an optically trapped structure. The method and system use an inverted optical microscope, a laser source which generates a trapping laser beam wherein the laser beam is focused by an objective lens into a plurality of optical traps. The method and system also use a collimated laser at an imaging wavelength to illuminate the structure created by the optical traps. Imaging light scattered by the optically tapped structure forms holograms that are imaged by a video camera and analyzed by optical formalisms to determine light field to reconstruct 3-D images for analysis and evaluation.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Complex index refraction tomography with sub lambda/6-resolution
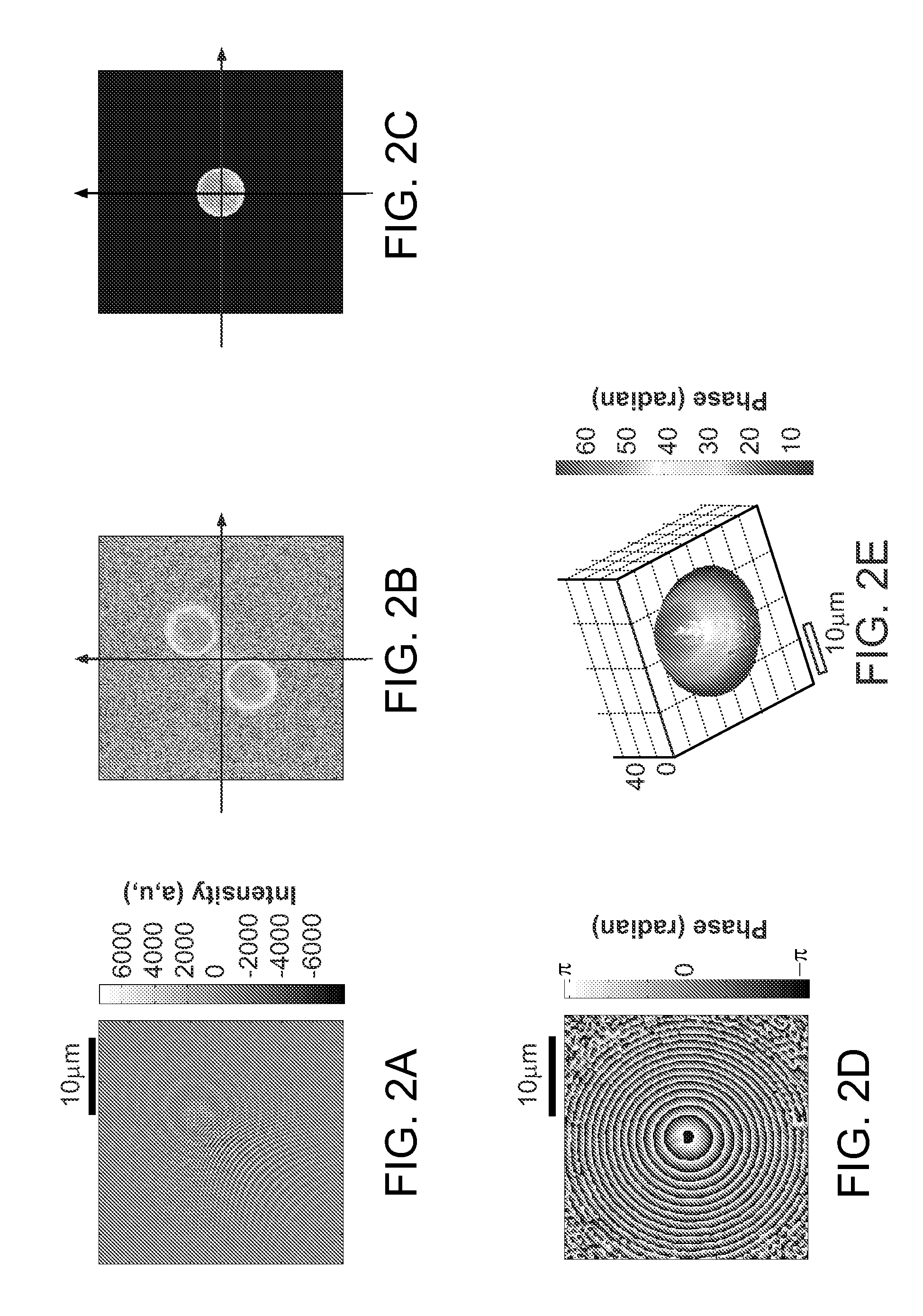
The present invention discloses a method to improve the image resolution of a microscope. This improvement is based on the mathematical processing of the complex field computed from the measurements with a microscope of the wave emitted or scattered by the specimen. This wave is, in a preferred embodiment, electromagnetic or optical for an optical microscope, but can be also of different kind like acoustical or matter waves. The disclosed invention makes use of the quantitative phase microscopy techniques known in the sate of the art or to be invented. In a preferred embodiment, the complex field provided by Digital Holographic Microscopy (DHM), but any kind of microscopy derived from quantitative phase microscopy: modified DIC, Shack-Hartmann wavefront analyzer or any analyzer derived from a similar principle, such as multi-level lateral shearing interferometers or common-path interferometers, or devices that convert stacks of intensity images (transport if intensity techniques: TIT) into quantitative phase image can be used, provided that they deliver a comprehensive measure of the complex scattered wavefield. The hereby-disclosed method delivers superresolution microscopic images of the specimen, i.e. images with a resolution beyond the Rayleigh limit of the microscope. It is shown that the limit of resolution with coherent illumination can be improved by a factor of 6 at least. It is taught that the gain in resolution arises from the mathematical digital processing of the phase as well as of the amplitude of the complex field scattered by the observed specimen. In a first embodiment, the invention teaches how the experimental observation of systematically occurring phase singularities in phase imaging of sub-Rayleigh distanced objects can be exploited to relate the locus of the phase singularities to the sub-Rayleigh distance of point sources, not resolved in usual diffraction limited microscopy. In a second, preferred embodiment, the disclosed method teaches how the image resolution is improved by complex deconvolution. Accessing the object's scattered complex field—containing the information coded in the phase—and deconvolving it with the reconstructed complex transfer function (CTF) is at the basis of the disclosed method. In a third, preferred embodiment, it is taught how the concept of “Synthetic Coherent Transfer Function” (SCTF), based on Debye scalar or Vector model includes experimental parameters of MO and how the experimental Amplitude Point Spread Functions (APSF) are used for the SCTF determination. It is also taught how to derive APSF from the measurement of the complex field scattered by a nanohole in a metallic film. In a fourth embodiment, the invention teaches how the limit of resolution can be extended to a limit of λ / 6 or smaller based angular scanning. In a fifth embodiment, the invention teaches how the presented method can generalized to a tomographic approach that ultimately results in super-resolved 3D refractive index reconstruction.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Total internal reflection holographic microscope
ActiveUS7812959B1Fast imagingEasy accessUsing optical meansOptical elementsTotal internal reflectionPhase shifted
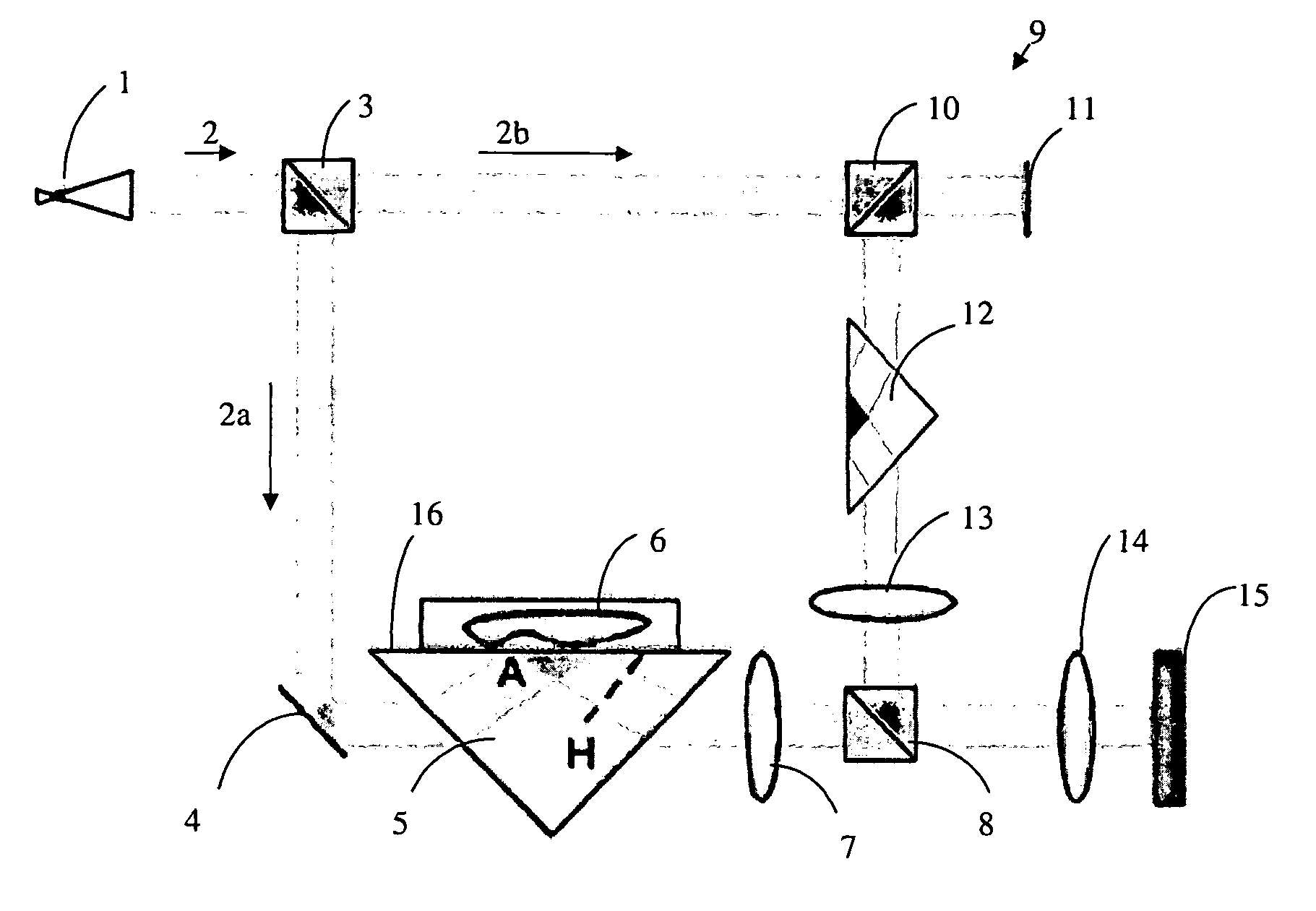
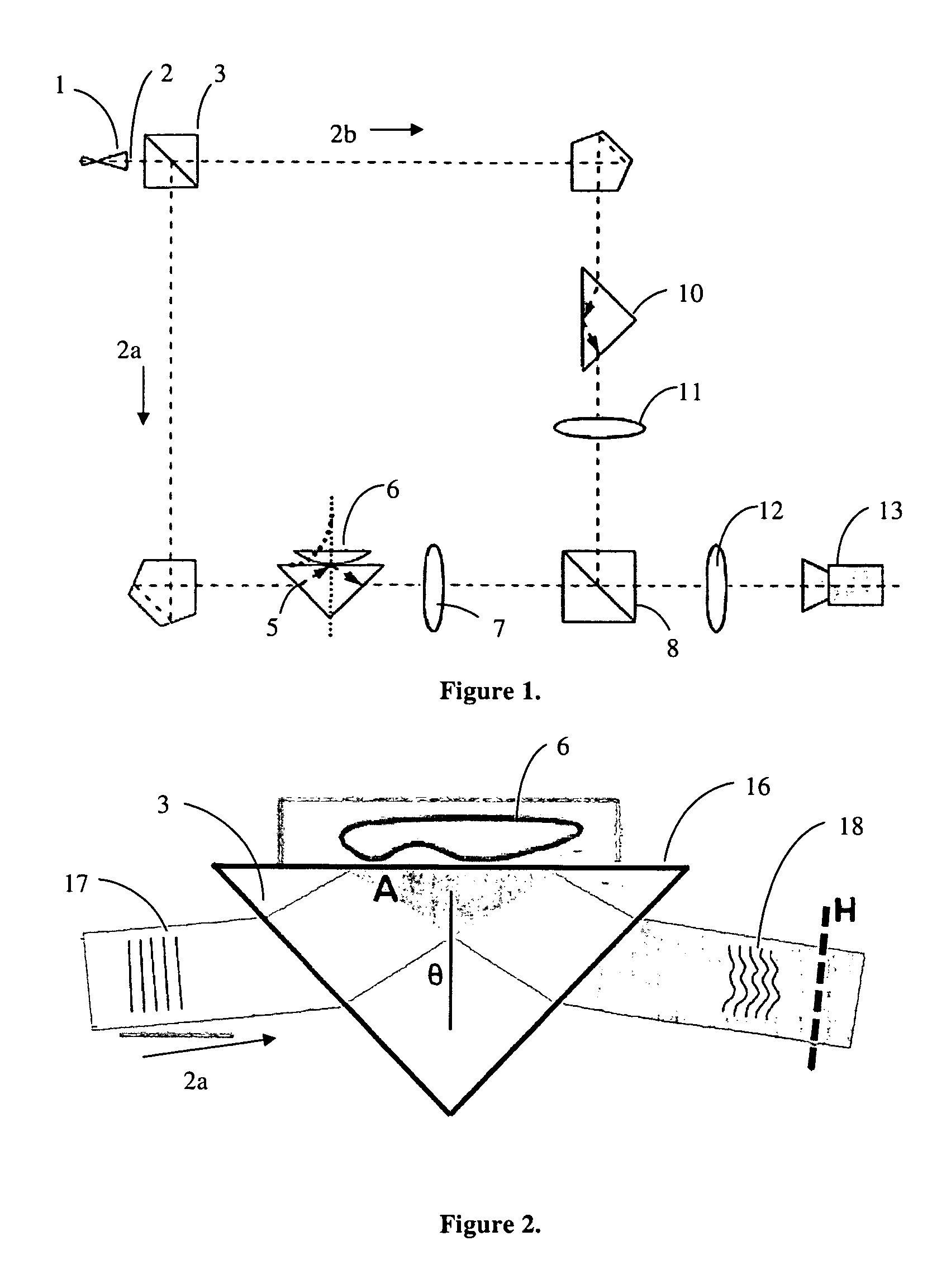
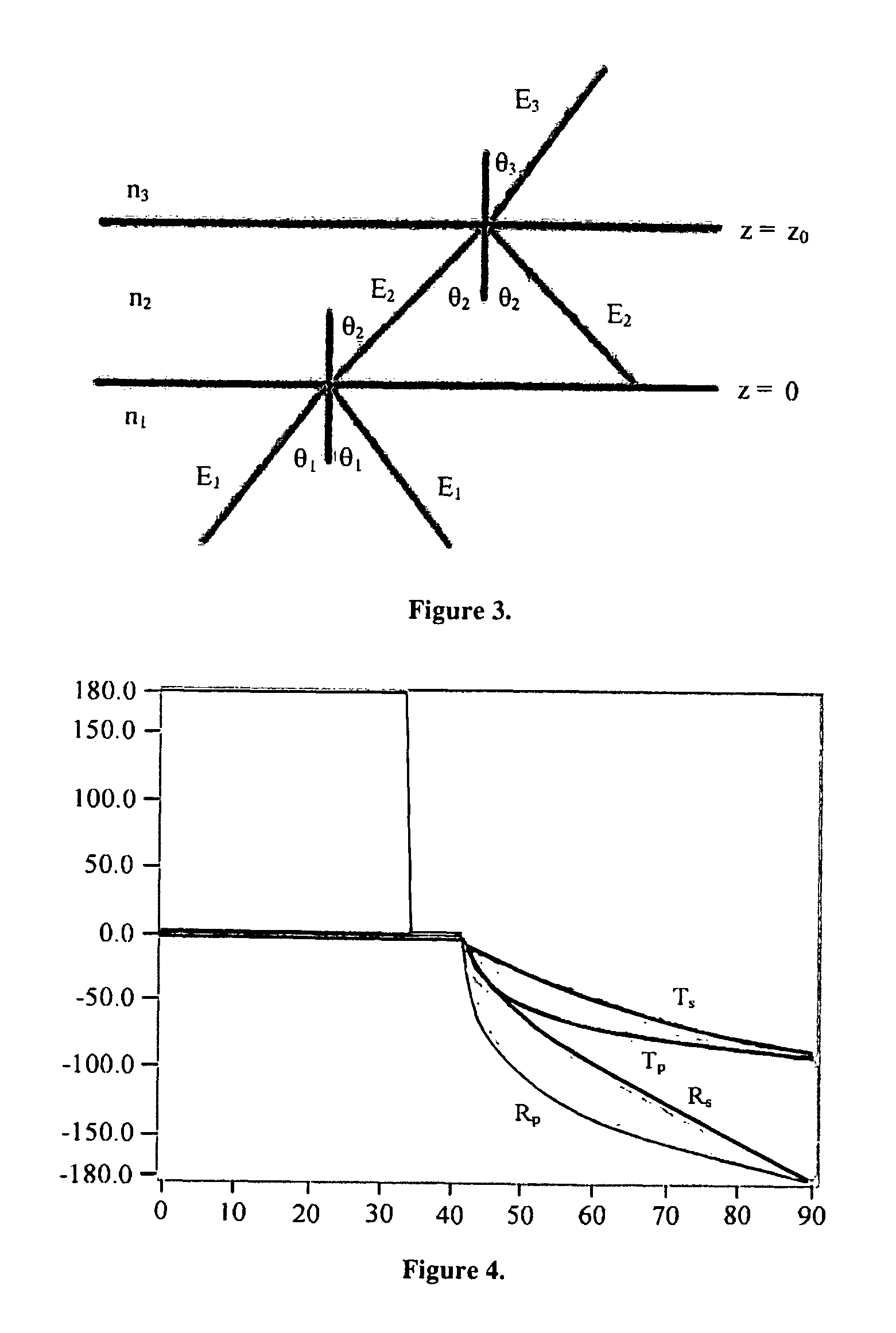
The present invention provides for a digital holographic microscope using a holographic interferometer and incorporating a TIR sample mount and microscopic imaging optics. The microscope uses phase shifting from frustrated internal reflection within a prism to measure nanometric distances. The invention also provides for a numerical reconstruction algorithm of an inclined surface of the object / prism.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Holographic microscopy of holographically trapped three-dimensional nanorod structures
ActiveUS8331019B2Television system detailsColor television detailsTrappingDigital holographic microscopy
A method and system for performing three-dimensional holographic microscopy of an optically trapped one dimensional structure. The method and system use an inverted optical microscope, a laser source which generates a trapping laser beam wherein the laser beam is focused by an objective lens into a plurality of optical traps. The method and system also use a collimated laser at an imaging wavelength to illuminate the structure created by the optical traps. Imaging light scattered by the optically tapped structure forms normalized intensity holograms that are imaged by a video camera and analyzed by optical formalisms to determine light field to reconstruct 3-D images for analysis and evaluation.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Single-shot full-field reflection phase microscopy
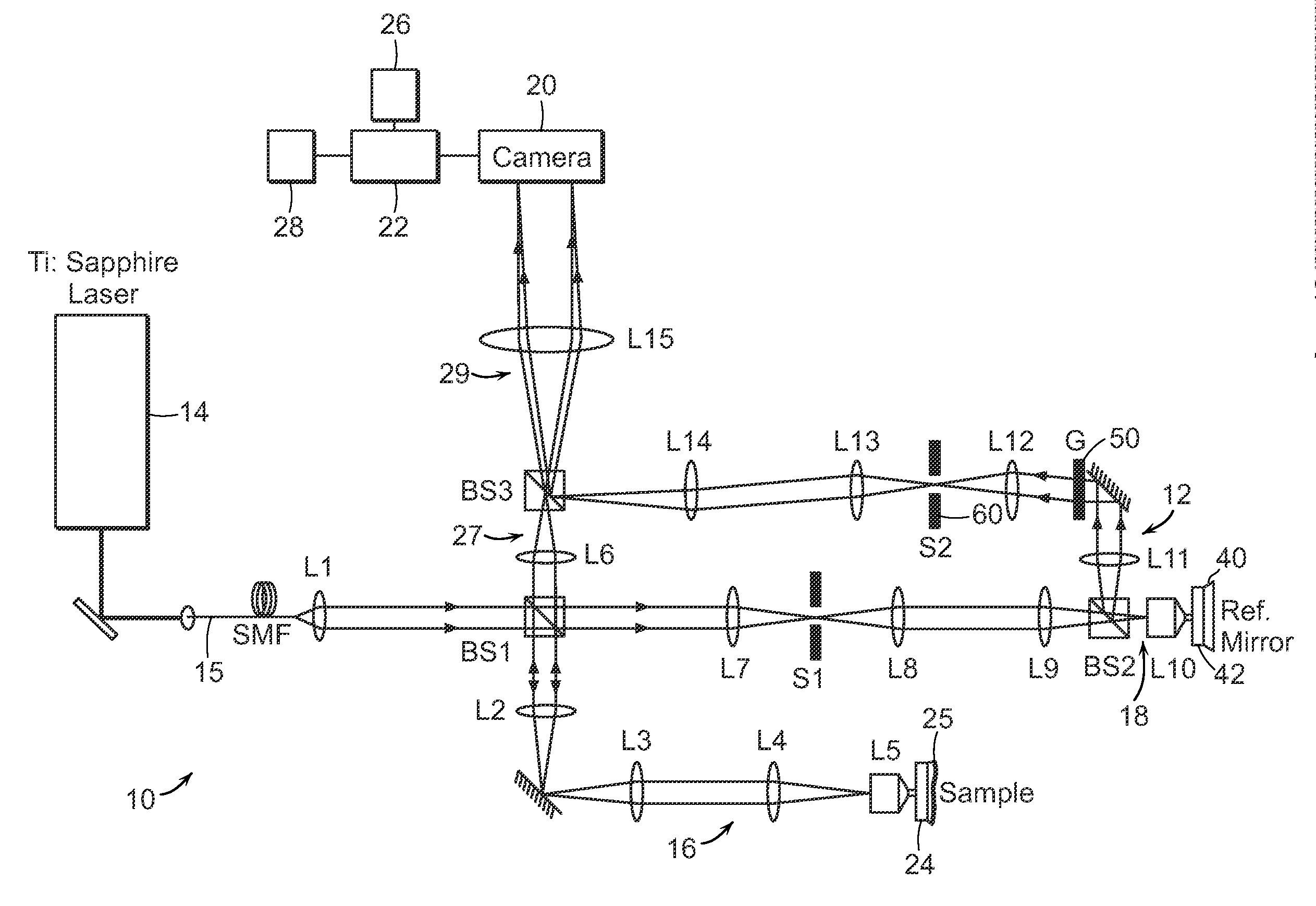
ActiveUS20120307035A1Advantage in measurement sensitivityProvide imagePhase-affecting property measurementsHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesPath lengthDigital holographic microscopy
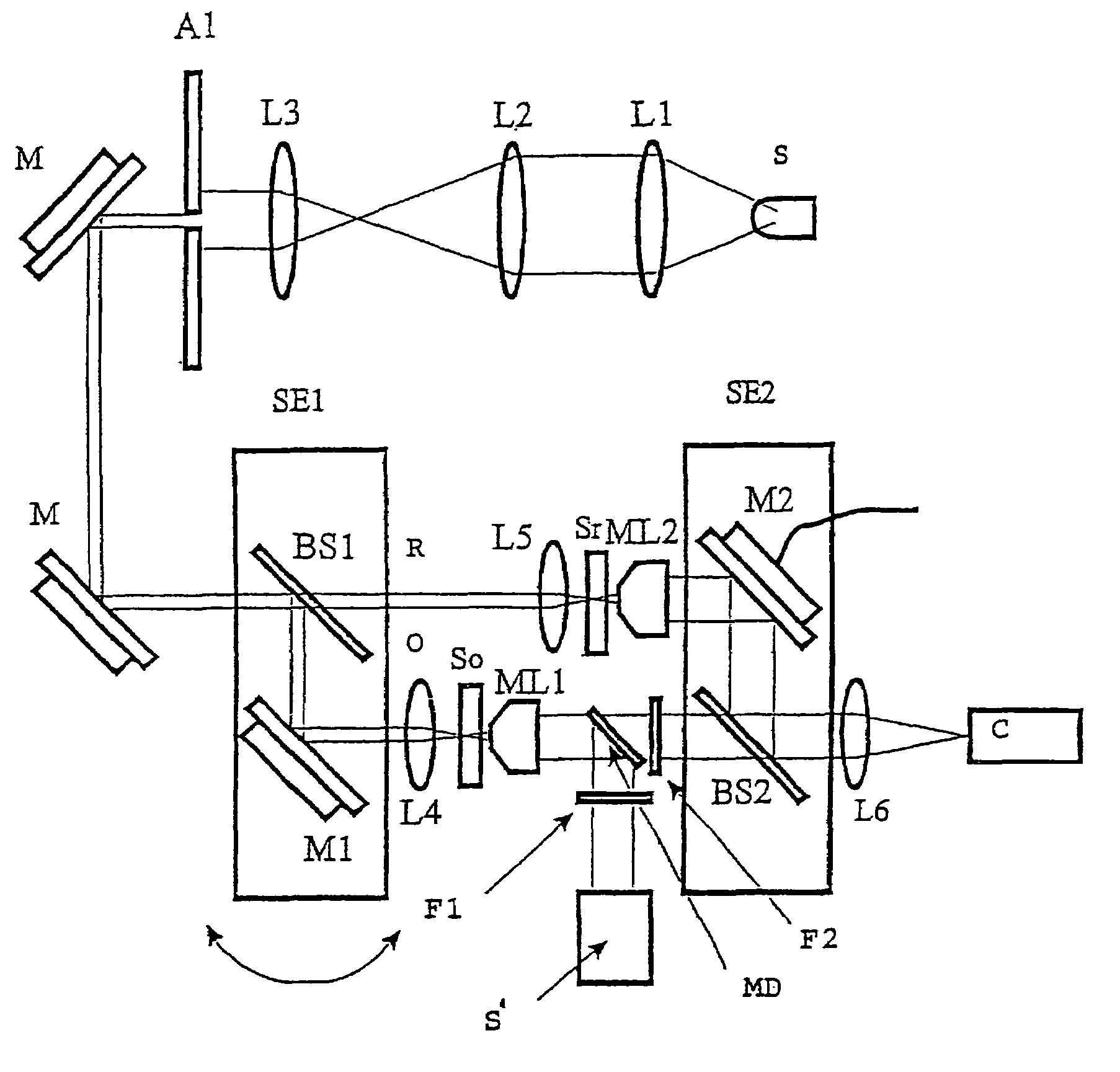
The present invention relates to a full-field reflection phase microscope. In a preferred embodiment, the invention can combine low-coherence interferometry and off-axis digital holographic microscopy (DHM). The reflection-based DHM provides highly sensitive and a single-shot imaging of cellular dynamics while the use of low coherence source provides a depth-selective measurement. A preferred embodiment of the system uses a diffraction grating in the reference arm to generate an interference image of uniform contrast over the entire field-of-view albeit low-coherence light source. With improved path-length sensitivity, the present invention is suitable for full-field measurement of membrane dynamics in live cells with sub-nanometer-scale sensitivity.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK +1
Digital holographic microscope for 3D imaging and process using it
InactiveUS7362449B2Reduce spatial coherenceHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopesFluorescence3d image
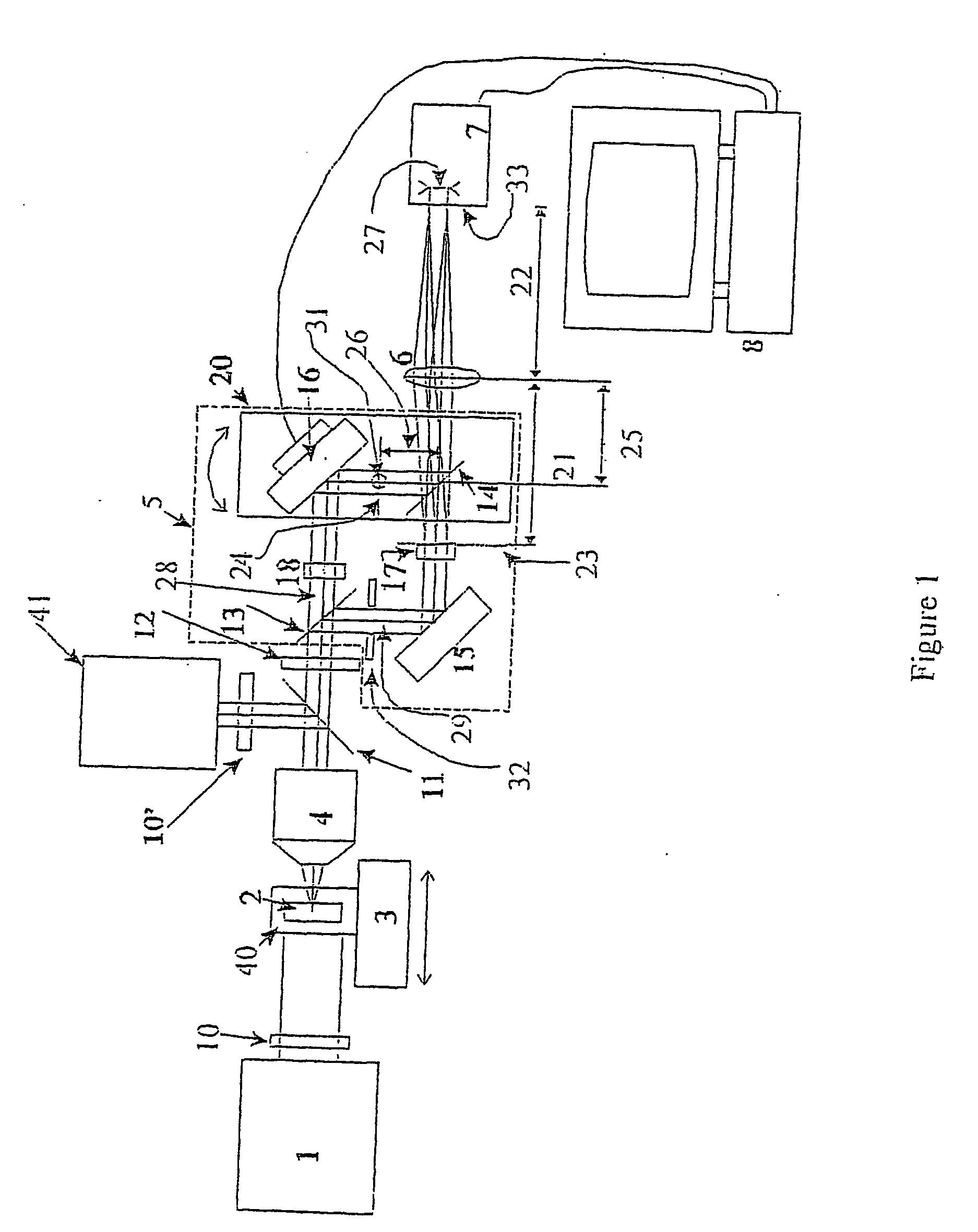
The present invention is related to a compact microscope able to work in digital holography for obtaining high quality 3D images of samples, including fluorescent samples and relatively thick samples such as biological samples, said microscope comprising illumination means (1,41) at least partially spatially coherent for illuminating a sample (2) to be studied and a differential interferometer (5) for generating interfering beams from said sample (2) on the sensor (33) of an electronic imaging device(7), said interferometer (5) comprising namely tilting means (17) for tilting by a defined angle one the interfering beams (28 or 29) relatively to the other, said tilting resulting into a defined shift (27) of said interfering beam on the sensor of the electronic imaging device (7), said shift (27) being smaller than spatial coherence width of each beam, said microscope being able to be quasi totally preadjusted independently from the samples so that minimum additional adjustments are required for obtaining reliable 3D images of samples.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Physical parameter common-channel phase-shift digital holographic microscopic device based on diffraction grating
ActiveCN102147233AVibration insensitiveImprove stabilityUsing optical meansDigital holographic microscopyBeam splitting
The invention relates to a physical parameter common-channel phase-shift digital holographic microscopic device based on a diffraction grating, which comprises a lighting unit, a microscopic unit, an interference generating unit and an imaging unit, wherein the lighting unit and the microscopic unit are respectively arranged at two sides of a sample; the lighting unit comprises a laser and a light intensity controller arranged in front of the laser; the microscopic unit comprises a second telescope unit which consists of a microobjective and a third lens; the sample is placed on the front focal plane of the second telescope unit; the interference generating unit comprises a beam splitting unit, a filtering unit, a beam combining unit and a contrast control unit sequentially arranged in the light path direction; and the imaging unit comprises a CCD (charge coupled device) camera which is arranged on the rear focal plane of a seventh lens. The digital holographic microscopic device has the advantages of good stability and no sensitivity to ambient vibration.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Interferometric method and digital holographic microscope
ActiveUS20130286403A1Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansDigital holographic microscopyLight beam
An interferometric method for detecting information about a sample includes emitting a laser beam; splitting the laser beam into a reference beam and an object beam; transmitting the object beam through the sample in an incident angle; combining the reference beam with the object beam passed through the sample to form an interference pattern; detecting the interference pattern, and non-linearly scanning the object beam in order to detect a plurality of interference patterns.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Holographic microscopy of holographically trapped three-dimensional nanorod structures
ActiveUS20100253762A1Better track informationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsForm analysisDigital holographic microscopy
A method and system for performing three-dimensional holographic microscopy of an optically trapped one dimensional structure. The method and system use an inverted optical microscope, a laser source which generates a trapping laser beam wherein the laser beam is focused by an objective lens into a plurality of optical traps. The method and system also use a collimated laser at an imaging wavelength to illuminate the structure created by the optical traps. Imaging light scattered by the optically tapped structure forms normalized intensity holograms that are imaged by a video camera and analyzed by optical formalisms to determine light field to reconstruct 3-D images for analysis and evaluation.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
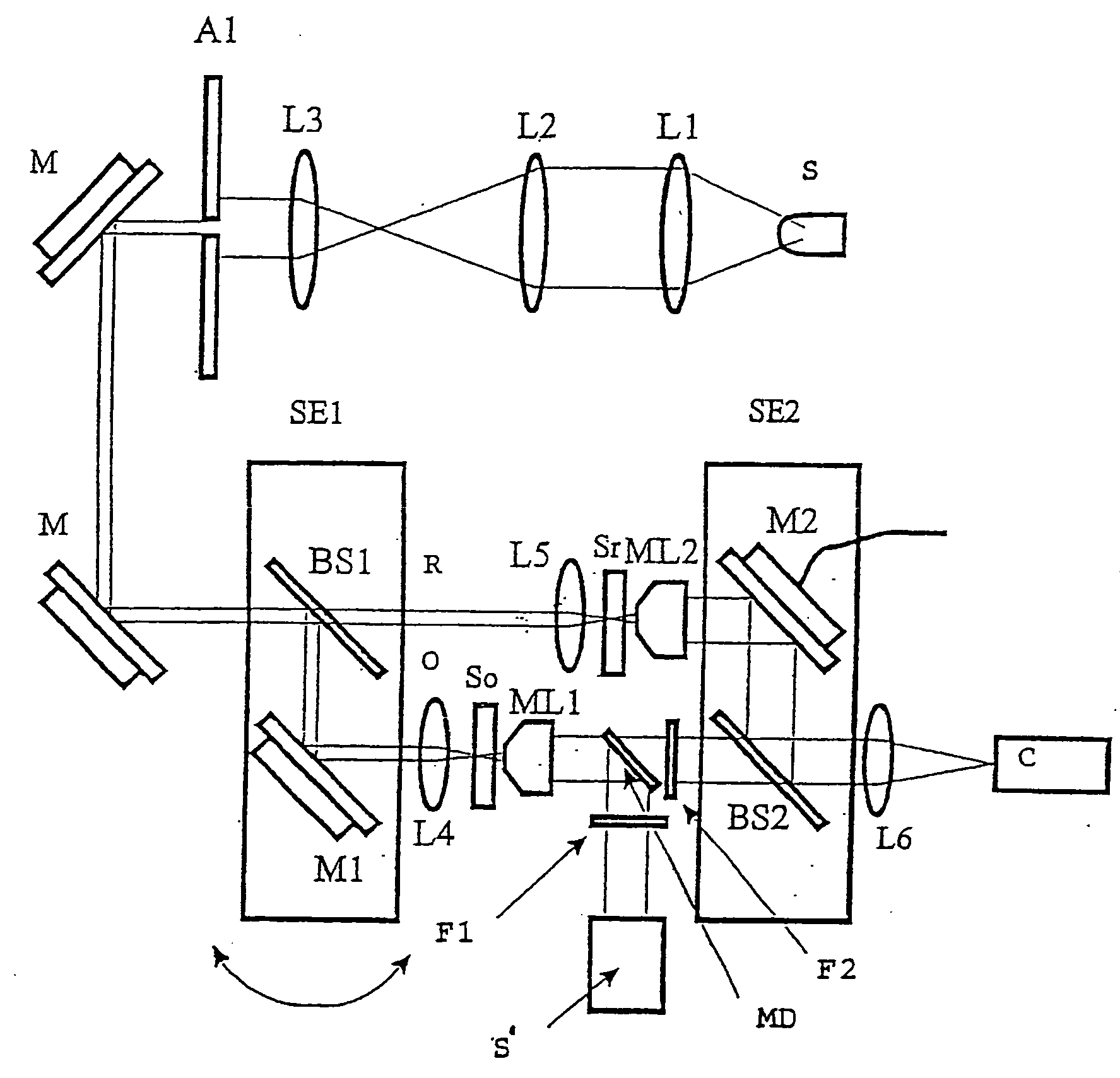
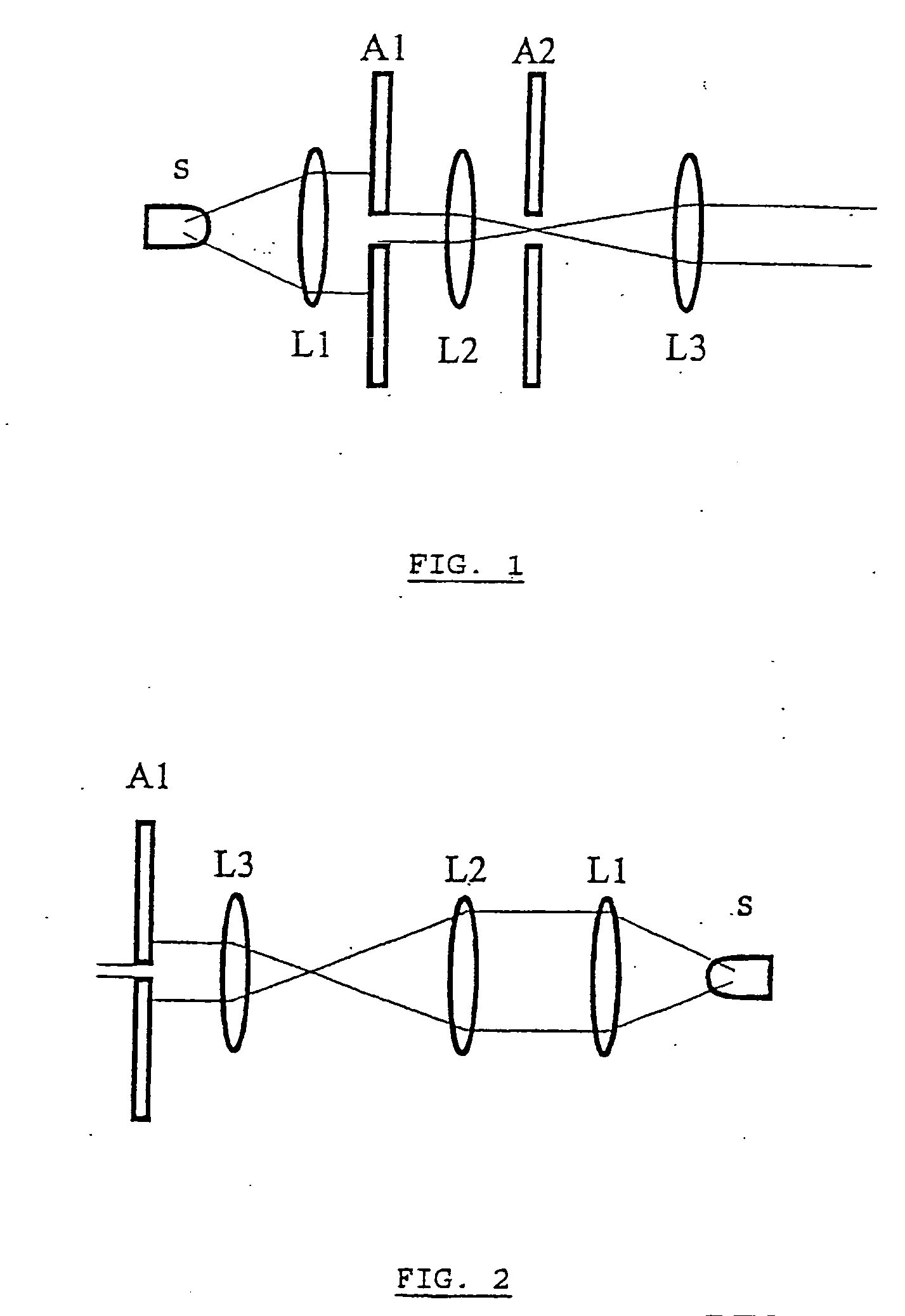
Digital holographic microscope
InactiveUS20060132799A1Minimum delayCompetitive costHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsFluorescenceDigital holographic microscopy
A method and device for obtaining a sample with three-dimensional microscopy, in particular a thick biological sample and the fluorescence field emitted by the sample. One embodiment includes obtaining interferometric signals of a specimen, obtaining fluorescence signals emanating from the specimen, recording these signals, and processing these signals so as to reconstruct three-dimensional images of the specimen and of the field of fluorescence emitted by the specimen at a given time. Another embodiment includes a digital holography microscope, a fluorescence excitation source illuminating a specimen, where the microscope and the fluorescence excitation source cooperate to obtain interferometric signals of the specimen and obtain fluorescence signals emanating from the specimen, means for recording the interferometric signals and fluorescence signals, and means for processing the interferometric signals and the fluorescence signals so as to reconstruct three-dimensional images of the specimen and of the field of fluorescence emitted by the specimen at a given time.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Method and apparatus for analysis of a sample of cells
ActiveUS20100060897A1Simplify and complement analyzingHolographic object characteristicsMicroscopesNon destructiveCMOS
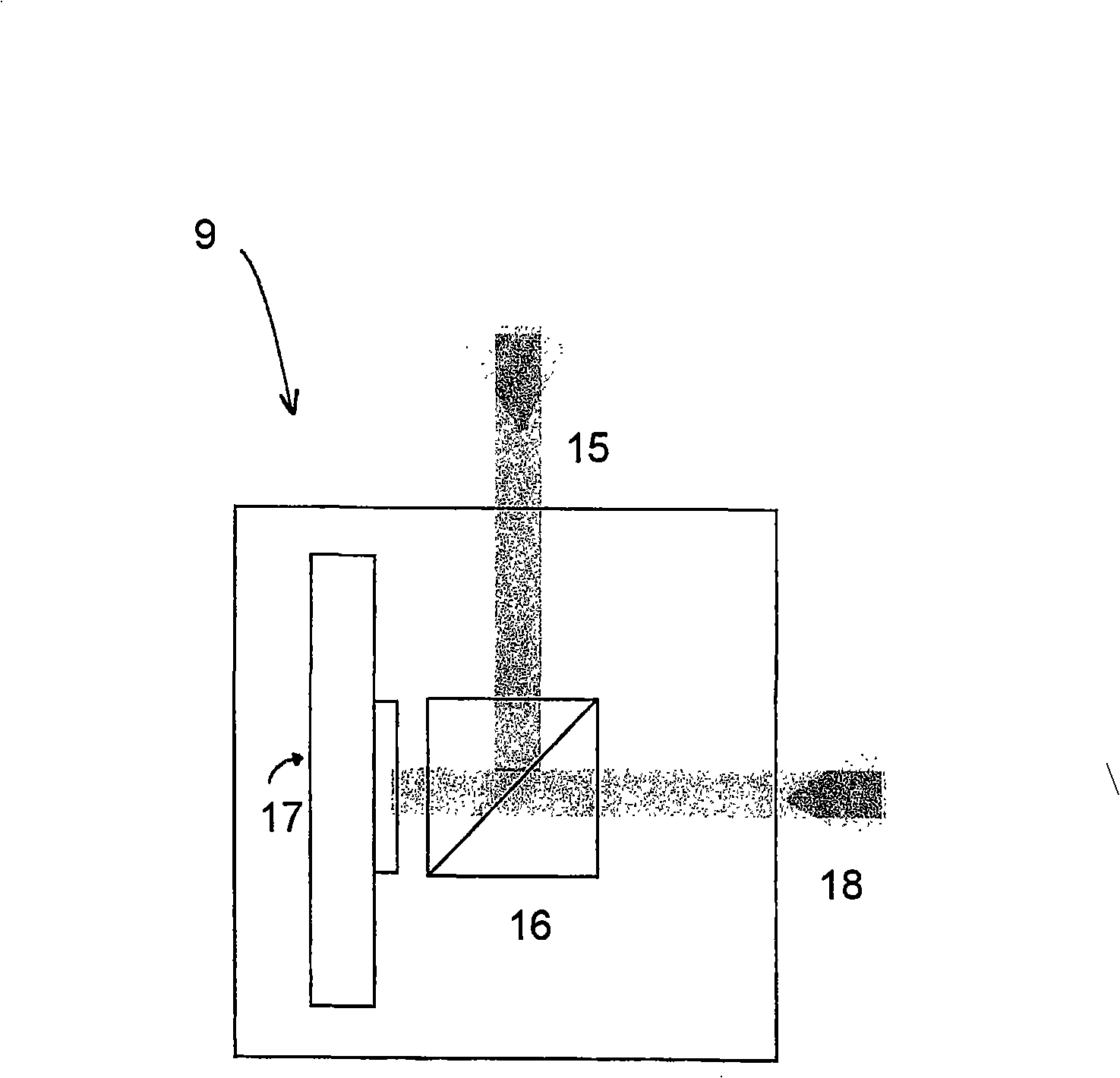
A non-destructive method and device for analyzing a sample comprising transparent living and / or dead cells, by 5 means of a digital holographic microscope, where the sample (8) is exposed to light from a laser (2). The light that travels through the cells in the sample will experience a difference in the optical path length compared to the surrounding media and the wave front that emerges from the 10 cells will thus be phase shifted. This distortion can be detected in the digital hologram, which is reconstructed from the interference pattern detected by a digital sensor (17), such as a CCD or a CMOS, as phase differences or phase shifts and thereby creating a digital hologram. The 15 phase shift of each element of the hologram is then used for analyzing the characteristics of the cells in the sample.
Owner:PHASE HOLOGRAPHIC IMAGING PHI
Inverted digital holographic microscope
InactiveCN102122063AHighly integratedReduce volumeMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansBeam splitterDigital holographic microscopy
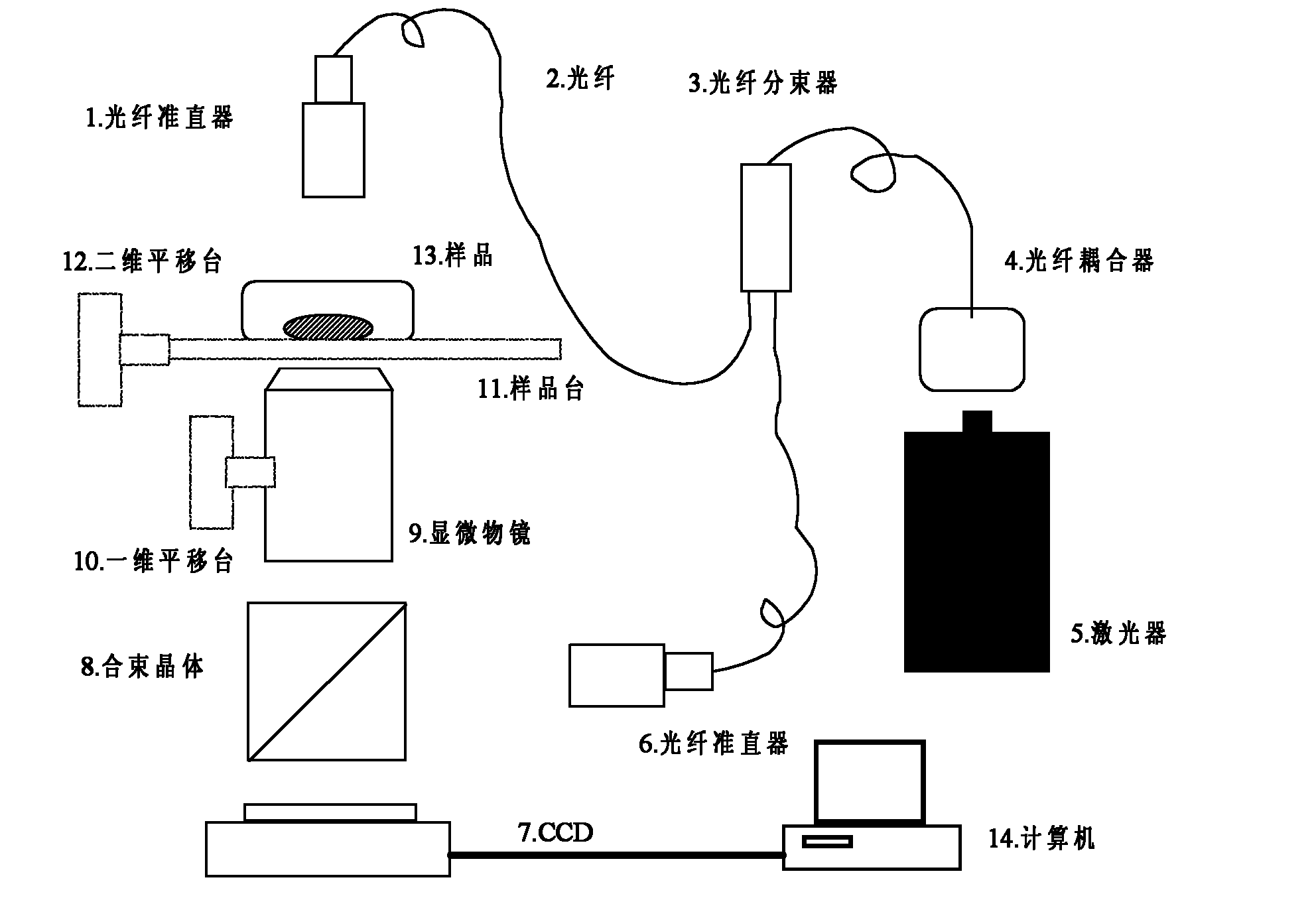
The invention discloses an inverted digital holographic microscope, which belongs to the digital holographic technical field, and can be used for three-dimensional real-time appearance measurement and biological cell imaging. In the inverted digital holographic microscope, an optical fiber coupler 4 is arranged in front of a laser 5 and connected with an optical fiber beam splitter 3 through an optical fiber; the optical fiber beam splitter 3 is connected with two paths of optical fibers respectively connected with an optical fiber collimator 1 and an optical fiber collimator 6, a sample stage 11 for placing a sample 13 is arranged under the optical fiber collimator 1, and the sample stage 11 is connected with a two-dimensional translation stage 12; a micro objective mounted on a one-dimensional translation stage 10 is located under the sample stage 11, and the micro objective 9 and the optical fiber collimator 6 are aligned with two mutually vertical sides of a beam combination crystal 8; and a CCD (charge-coupled device) camera 7 is located under the beam combination crystal 8. The inverted digital holographic microscope can be used for observing the living cell which is located at the bottom of a culture dish and grows along a wall of the culture dish with a high resolution ratio for long time, and is highly integrated and small in volume; moreover, with the optical fiber connection, the laser can be freely mounted on other parts of the system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for analysis of a sample of cells
ActiveCN101346673AQuantitative settingsQuantitative and even automatic settingsHolographic object characteristicsMicroscopesPhase differenceDigital holographic microscopy
A non-destructive method and device for analyzing a sample comprising transparent living and / or dead cells, by means of a digital holographic microscope, where the sample (8) is exposed to light from a laser (2). The light that travels through the cells in the sample will experience a difference in the optical path length compared to the surrounding media and the wave front that emerges from the cells will thus be phase shifted. This distortion can be detected in the digital hologram, which is reconstructed from the interference pattern detected by a digital sensor, such as a CCD or a CMOS, as phase differences or phase shifts and thereby creating a digital hologram. The phase shift of each element of the hologram is then used for analyzing the characteristics of the cells in the sample.
Owner:PHASE HOLOGRAPHIC IMAGING PHI
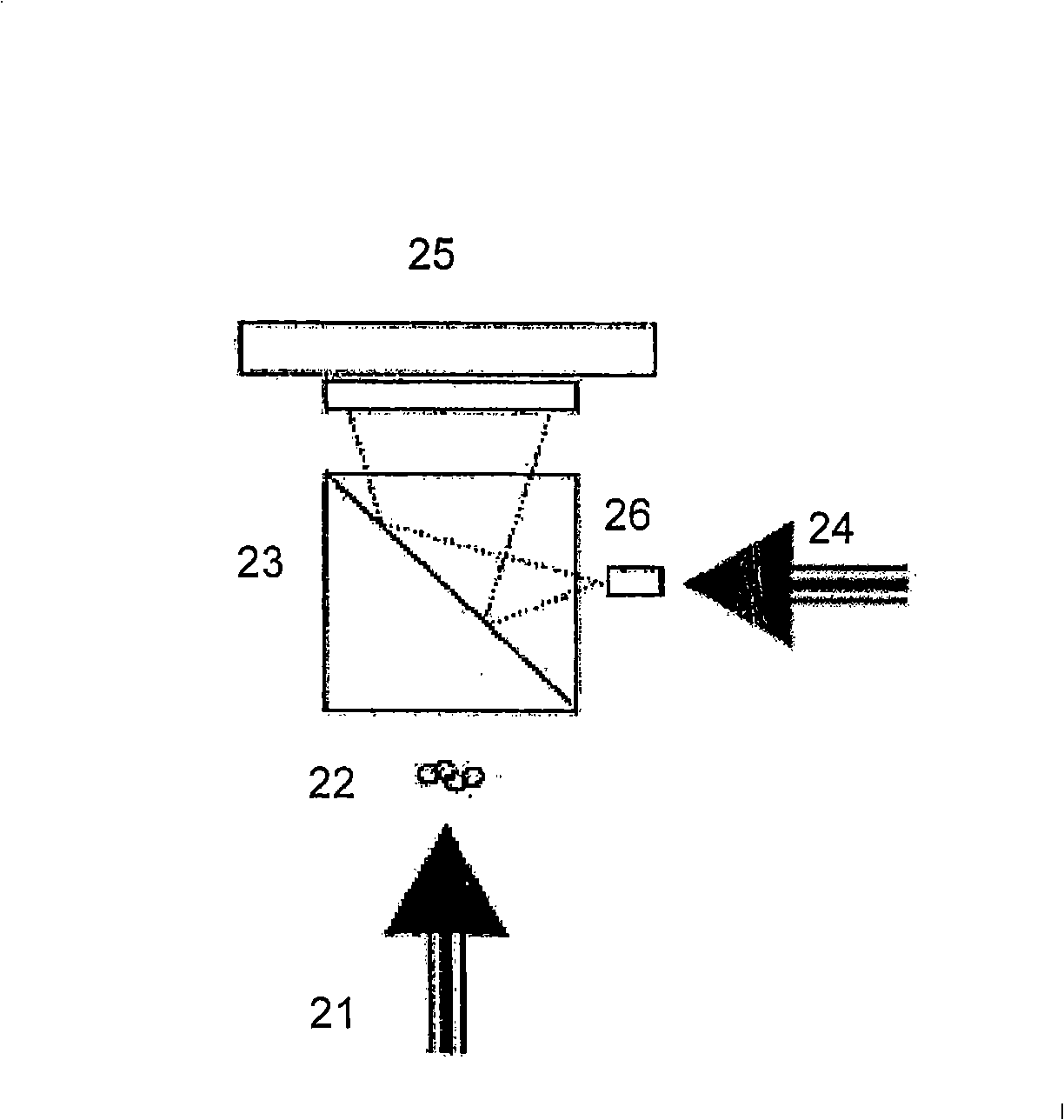
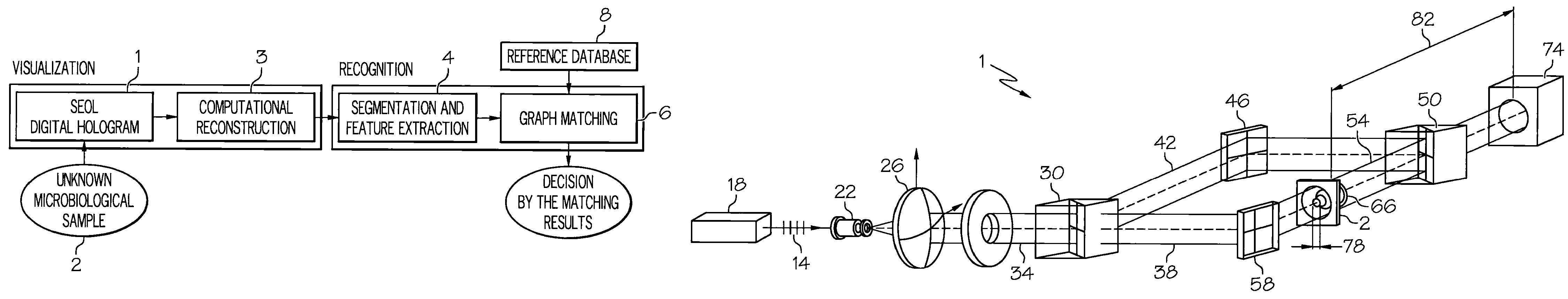
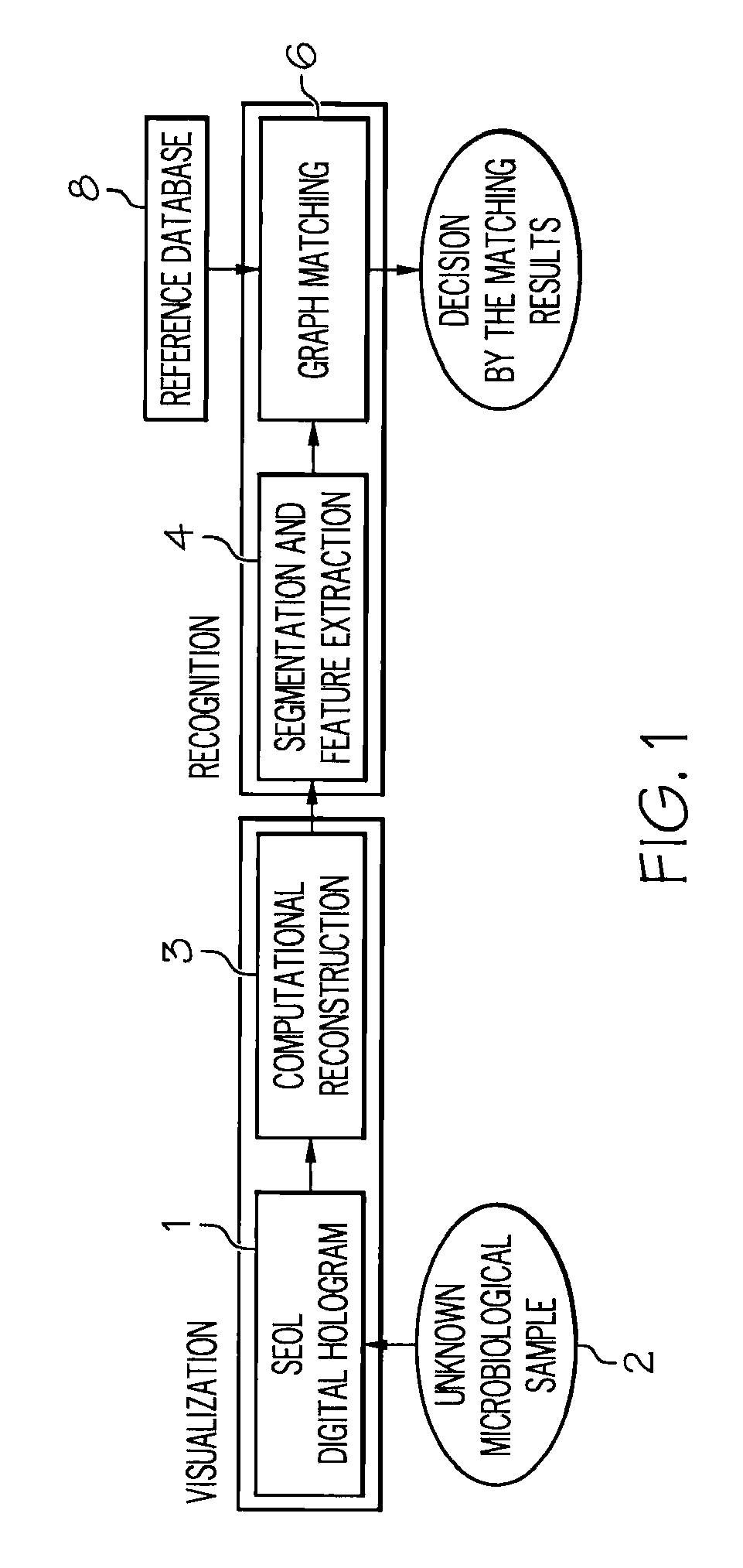
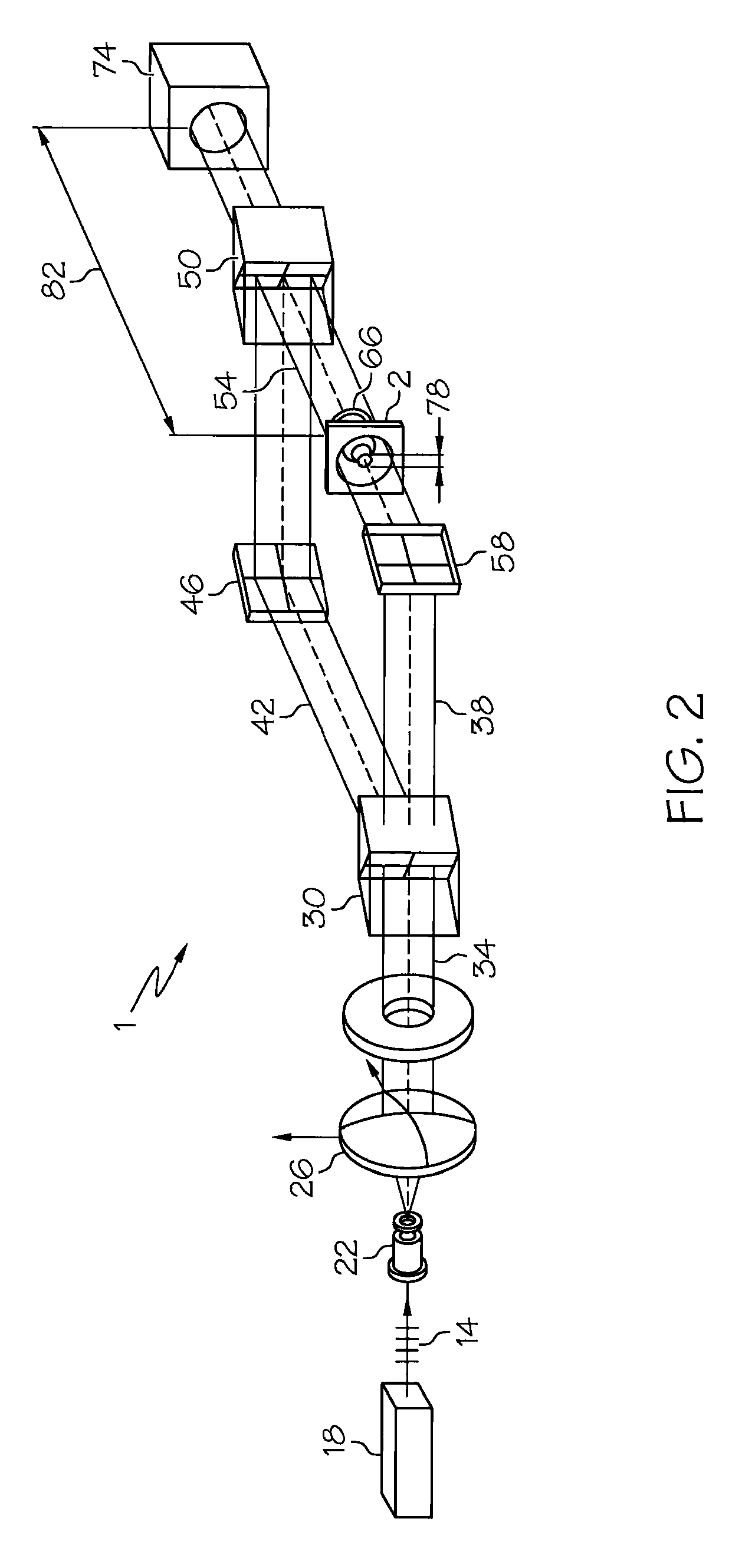
Method and apparatus for recognition of microorganisms using holographic microscopy
ActiveUS7616320B2Material analysis by optical meansHolographic object characteristicsDigital holographic microscopyDetector array
Disclosed herein is a method that relates to identifying a microorganism. The method comprising, diffracting laser light through a microorganism, combining a reference beam with the diffracted light on a single axis, and recording the combined light holographically as a three-dimensional image with a single exposure on a detector array. The method further comprising, reconstructing the holographic image and matching the reconstructed image with reference images of known microorganisms. Further disclosed herein is an apparatus for identifying a microorganism. The apparatus comprising, an interferometer to record an image of an unknown microorganism using single-exposure on-line (SEOL) digital holography, a means for reconstructing the recorded image, and a means for matching the reconstructed image with images of known microorganism.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Systems and Methods of Dual-Plane Digital Holographic Microscopy
ActiveUS20130070251A1Holographic optical componentsHolographic object characteristicsDigital holographic microscopyFourier transform on finite groups
An embodiment of the disclosed DHM system includes a light source configured to emit coherent optical waves, a first optical Fourier element configured to Fourier transform the optical waves from the object area, wherein the Fourier transform occurs at a Fourier plane and the optical waves from the object area includes directly transmitted waves and diffracted waves, a phase modulator at the Fourier plane configured to introduce a phase delay between the directly transmitted waves and the diffracted waves, a second optical Fourier element configured to receive the directly transmitted waves and the diffracted waves from the phase modulator and to inversely Fourier transform the directly transmitted waves and the diffracted waves to provide interfered optical waves, and at least one imaging device configured to record the interfered optical waves at two image planes to generate a first interferogram and a second interferogram.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Digital holographic micro-measuring device
InactiveCN1971253AAdjustable wavelengthImprove dynamic performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopic imageShape change
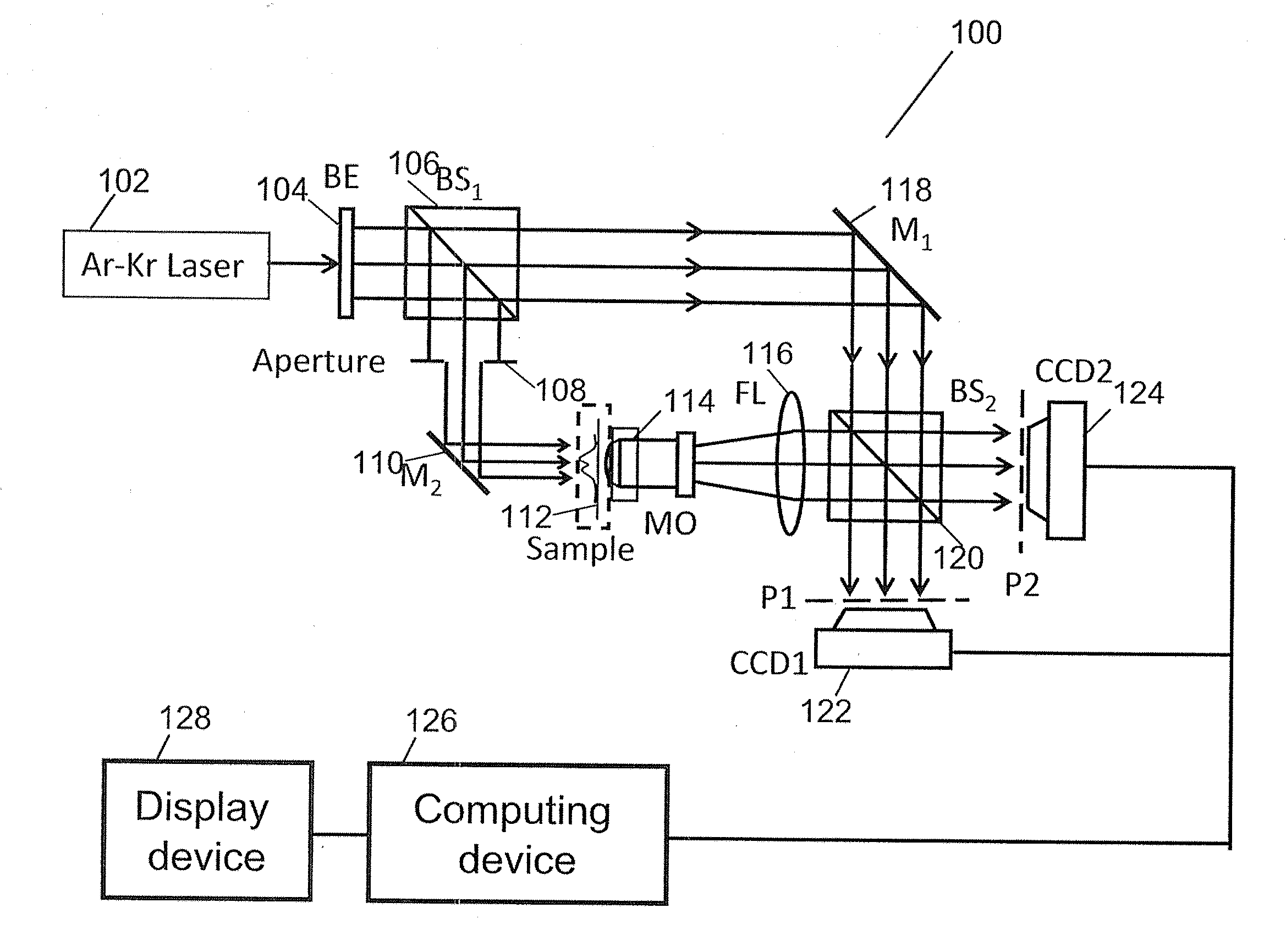
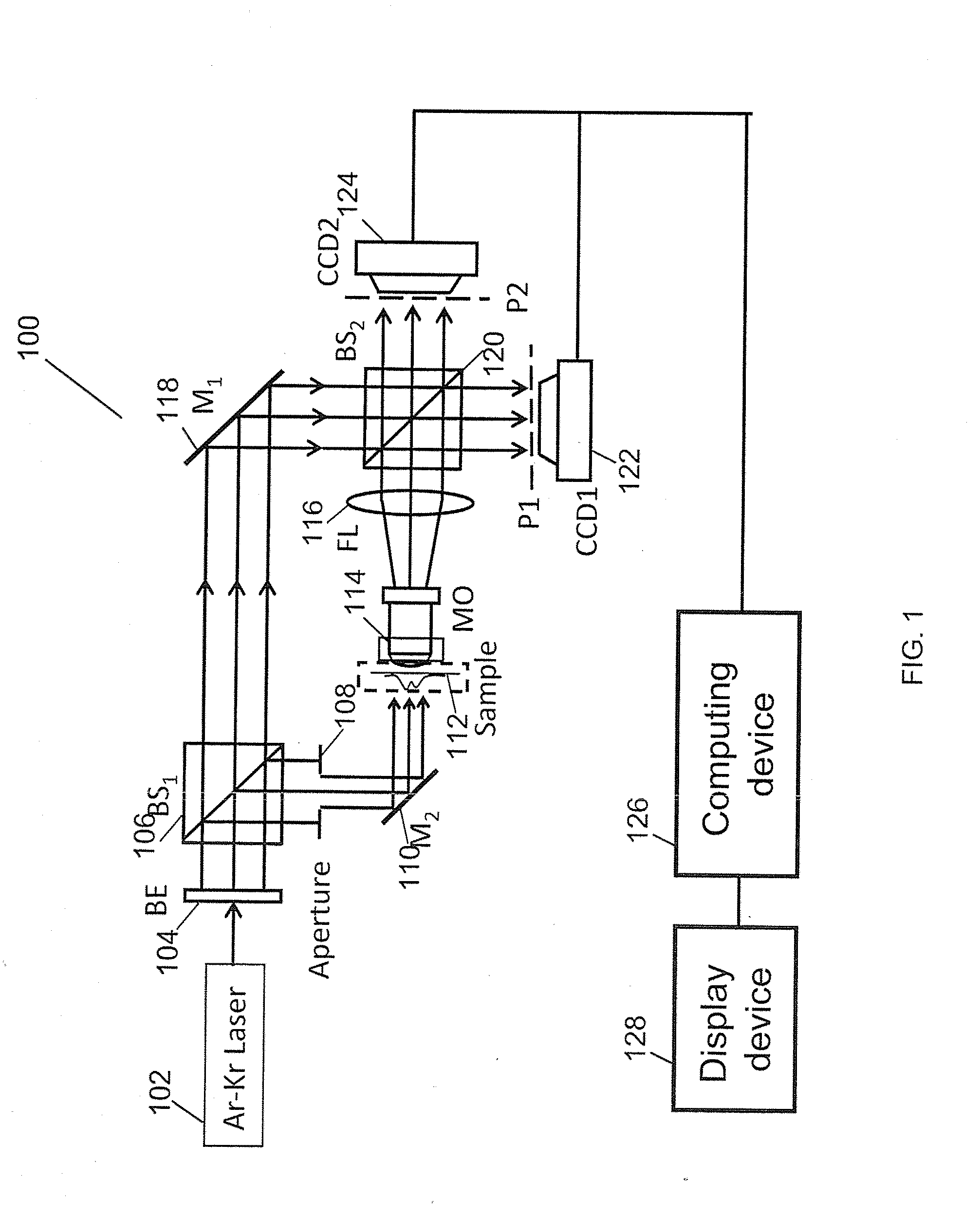
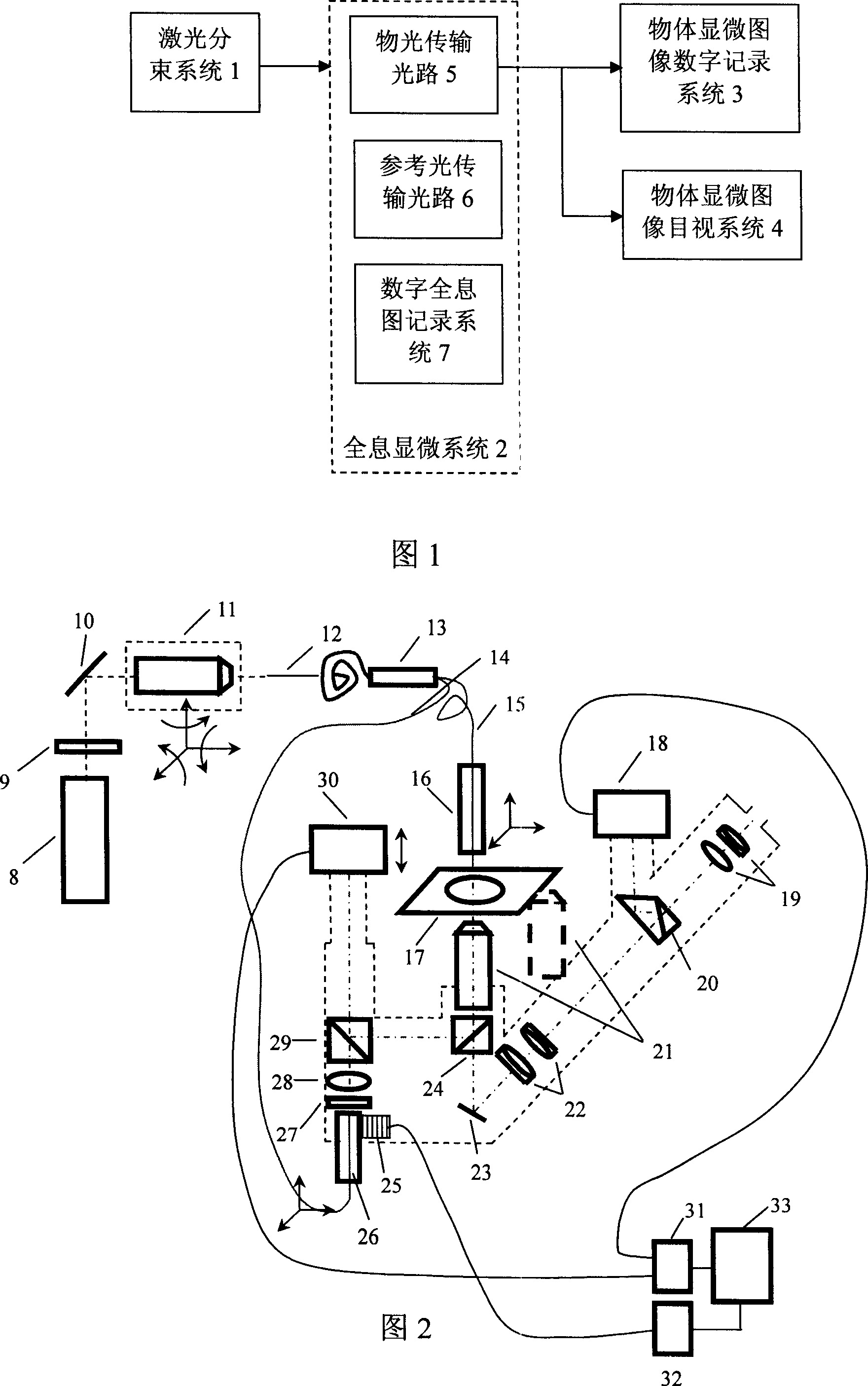
The invention relates to a digital holographic microscopy measuring device. It includes a laser beam splitting system which is connected with a digital microscopic image register system via a holographic microscopy system, said digital holographic microscopy system comprises object light transmission path, reference light transmission path and digital holographic image register system , the output of holographic microscopy system is connected with a object microscopic image visual system. The invention can realize the configuration measurement and the deformation detection of transparent microscopic object, and monitor the shape change of transparent microscopic object, the visual and digital recording of the microscopic image are also realized. The device can realize the non-contacting gauge of transparent substance fine texture which is based on the digital holographic microscopy; the dynamic property is well, substance to be measured don't need preparation of fluorescence and section.
Owner:江苏斯特郎电梯有限公司
Method and system for detecting and/or classifying cancerous cells in a cell sample
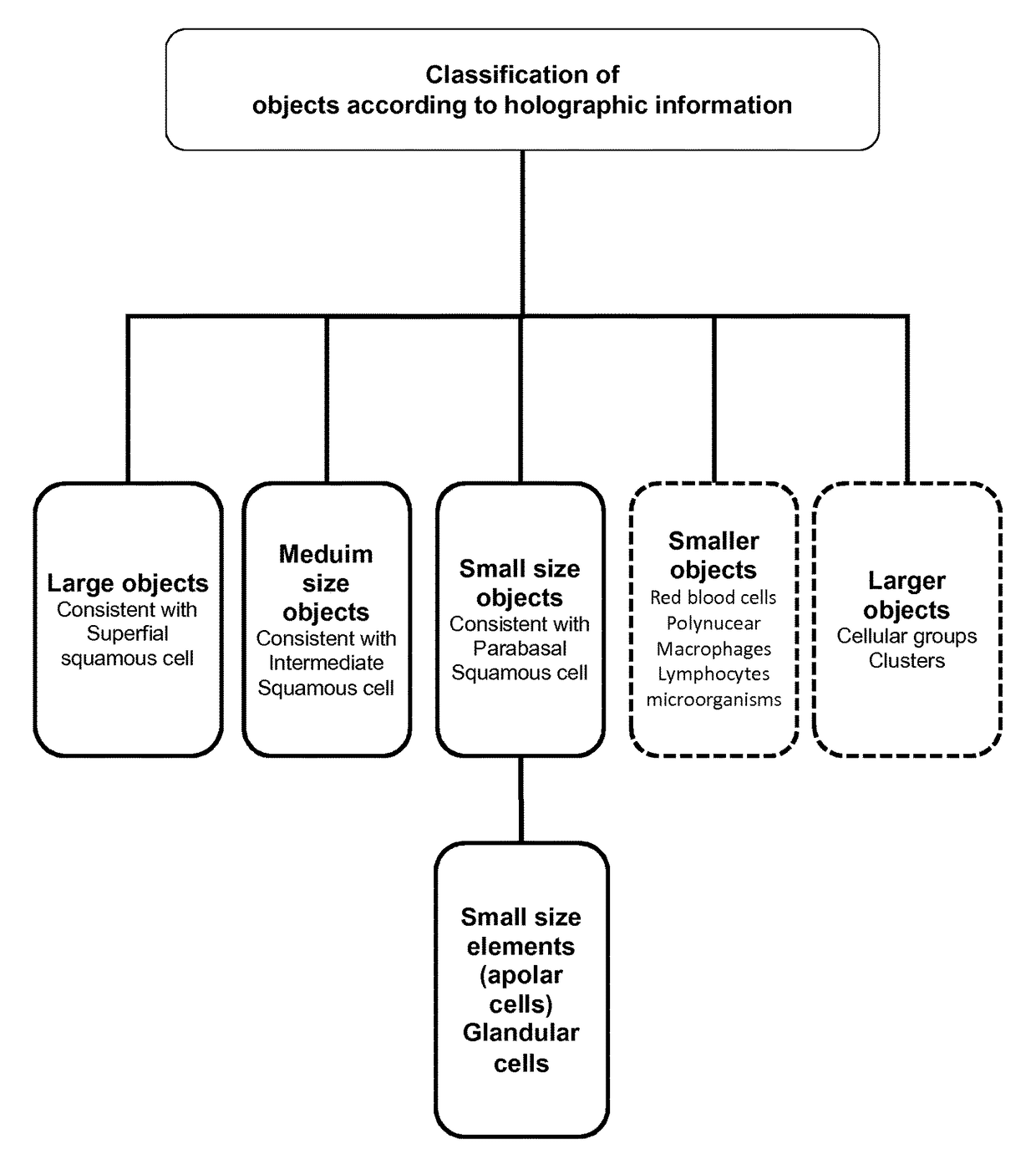
ActiveUS9684281B2Increased riskFast and inexpensivePhase-affecting property measurementsStill image data indexingCancer cellDigital holographic microscopy
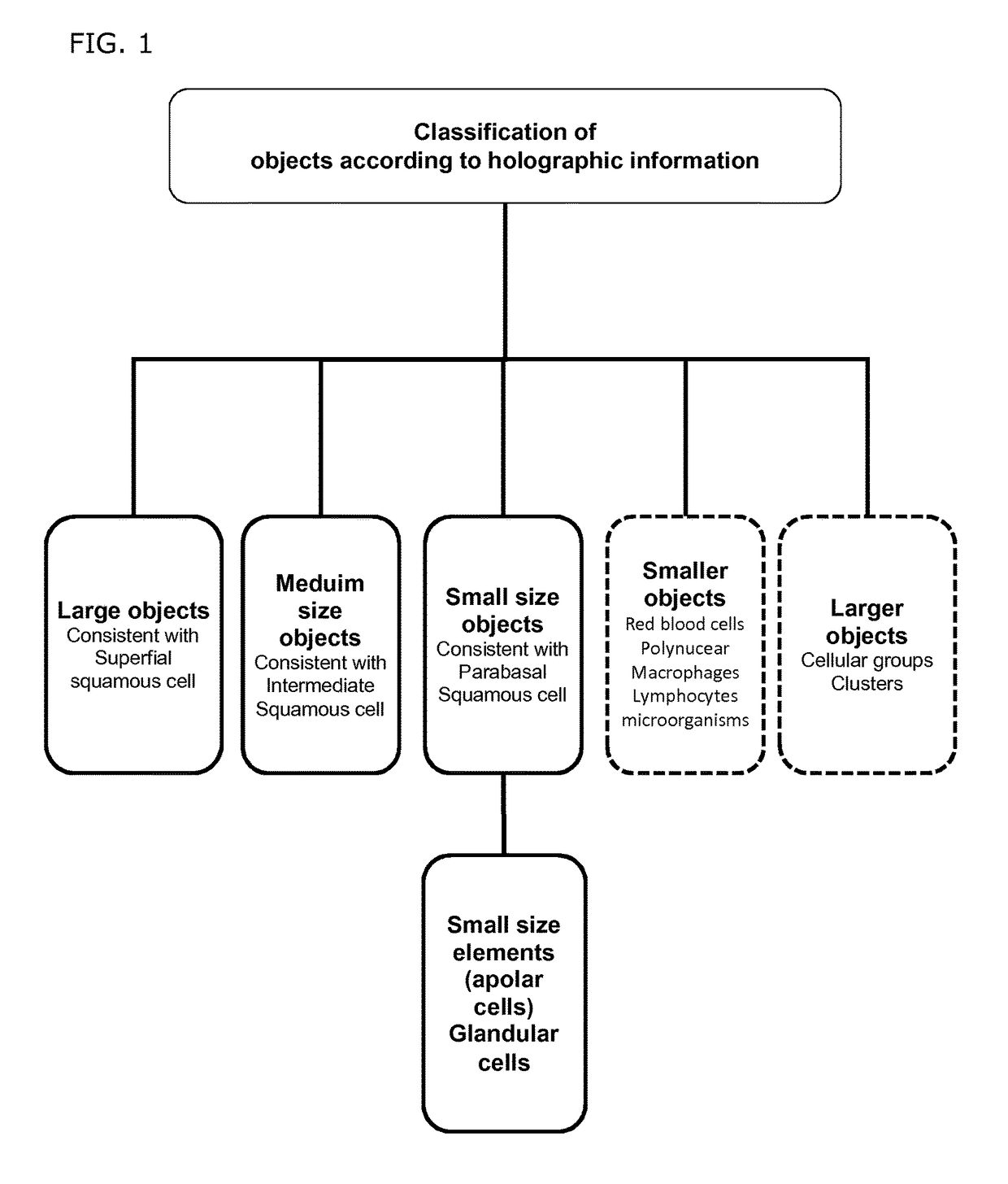
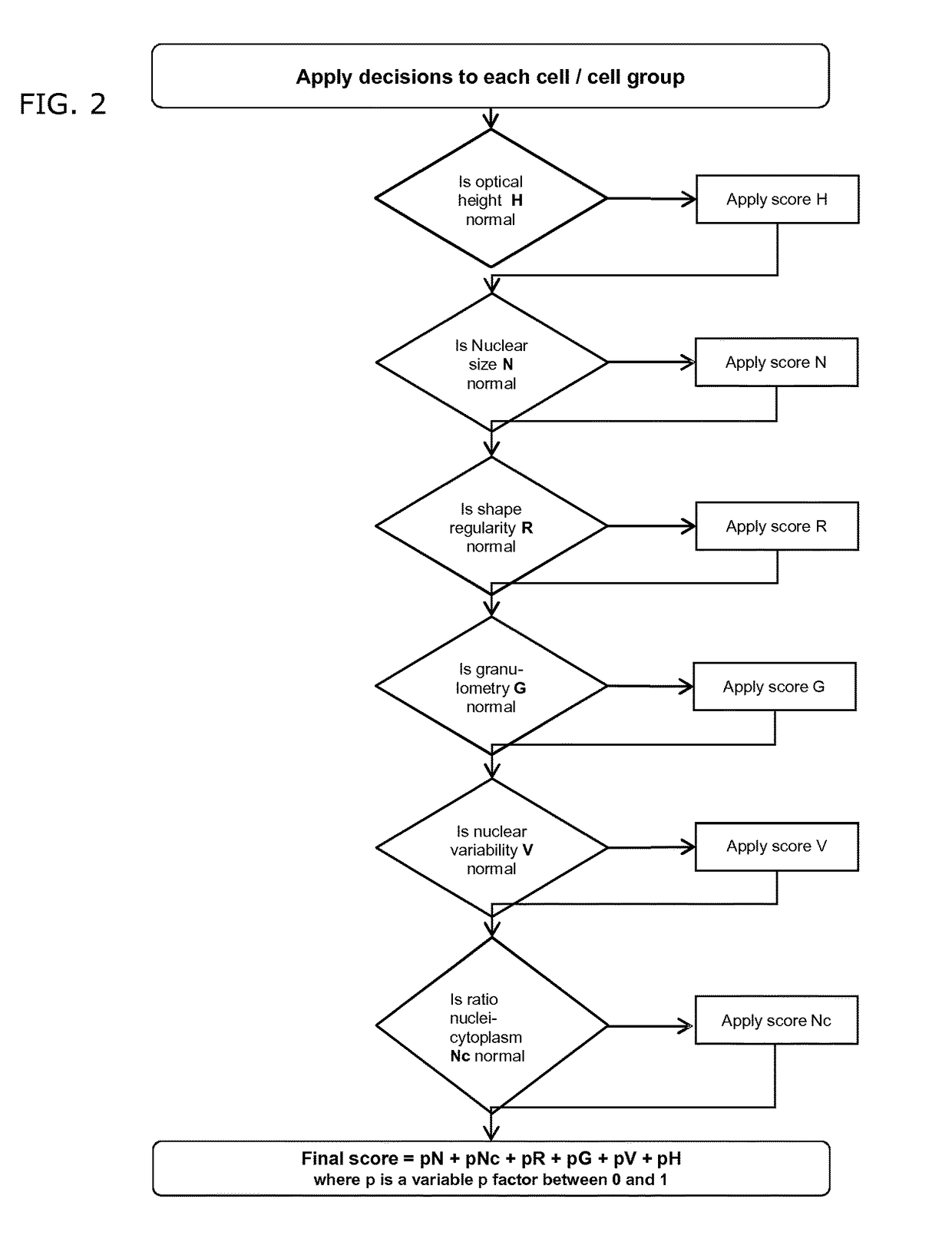
The current invention concerns a method for detecting cancerous cells and / or classifying cells in a cell sample comprising the following steps: providing a cell sample; obtaining holographic information from said cell sample by digital holographic microscopy (DHM); deriving at least one cellular parameter from said holographic information, and; classifying said cells of cells sample; characterized in that said classification occurs by appointing a Scoring Factor to said cells of cell sample, based on said cellular parameters. In a second aspect, a system for the detection of cancerous cells and / or classification of cells in a cell sample is provided, employing the method as disclosed in the invention. In a final aspect, a method for updating and / or improving a database comprising thresholds linked to holographic information and the database related thereof is equally disclosed.
Owner:OVIZIO IMAGING SYST NV SA
Off-axis interferometer
ActiveCN102576209AHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopesDiffraction orderGrating
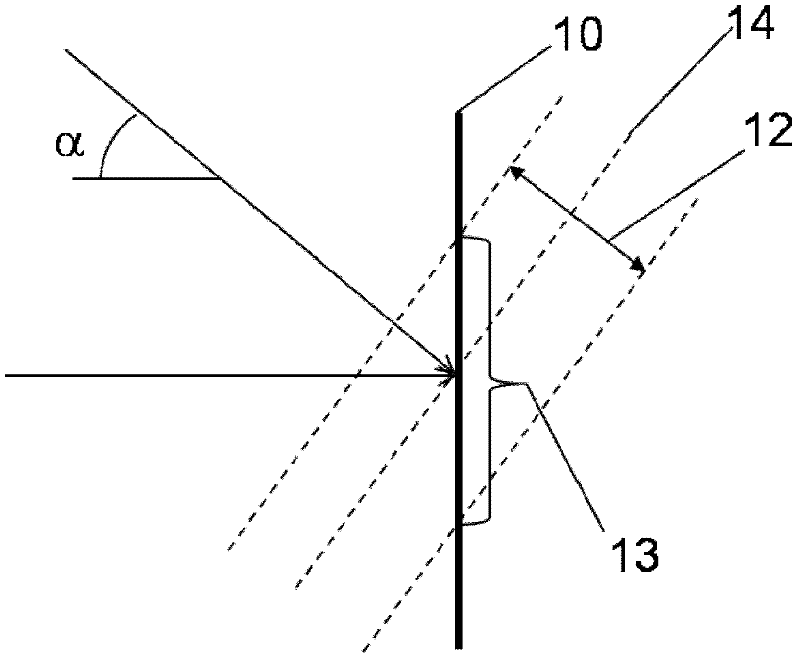
The present invention is related to an Interferometer for off-axis digital holographic microscopy (15) comprising: -a recording plane (10); -a grating (G) located in a plane optically conjugated with said recording plane (10), said grating (G) defining a first and a second optical path, said optical path corresponding to different diffraction order.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Reflection-type off-axis digital holographic microscopy measurement device
InactiveCN106292238AReduce usageOvercome the problems of complex structure, not compact and difficult instrumentationUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceImaging processing
The invention discloses a reflection-type off-axis digital holographic microscopy measurement device, which comprises a light source unit, an object light adjusting unit, a reference light adjusting unit and an image processing unit. The reference light adjusting unit comprises an optical path adjustment reflector group and an optical path guidance reflector group. The optical path adjustment reflector group comprises a first reflector and a second reflector, the positions of which are relatively fixed. The first reflector is used for reflecting the reference light R to the second reflector; the second reflector is used for reflecting the input reference light R to the optical path guidance reflector group; the optical path of the reference light R can be adjusted by moving the optical path adjustment reflector group wholly; the optical path guidance reflector group can guide the reference light R, the optical path of which is adjusted, to be input to the image processing unit to have interference with reflected light O'; and the image processing unit is used for processing interference fringes to obtain a sample three-dimensional image. The device can improve the quality of the holographic image.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
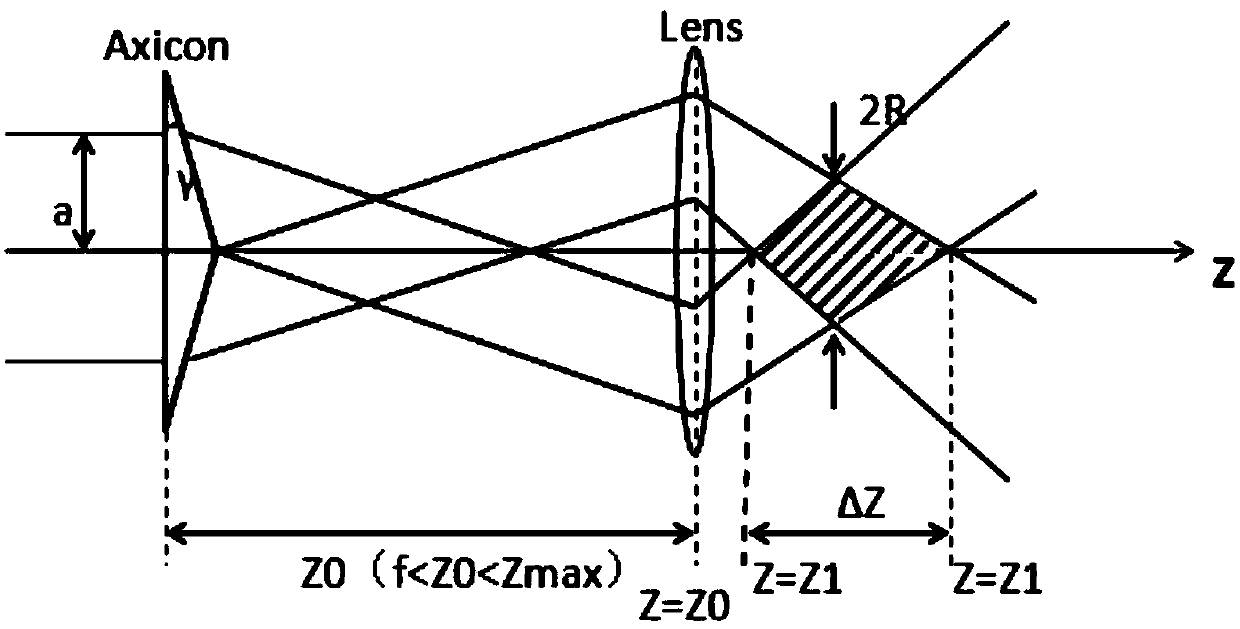
High-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging device and high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging method
ActiveCN104808469AHigh resolutionFast convergenceInstrumentsTarget surfaceDigital holographic microscopy
The invention discloses a high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging device and a high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging method. Based on a normal holographic device, the high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging device is improved by adding a distribution-known random phase plate between a small-hole diaphragm and an imaging device, so that more object light information can be scattered on a target surface of the imaging device after a sample to be tested is added. The high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging method includes the steps of collecting a group of holographic data, processing the holographic data by a filtering method to obtain distribution of object diffraction spots on the target surface of the imaging device, processing the diffraction spots by an improved iterative restoration algorithm similar to coherent diffractive imaging, and finally restoring a restructured image with the resolution rate much higher than that of a normal holographic image. The high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging device and the high-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging method have the advantage that a solution for current low-resolution digital holographic microscopy imaging is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vortex light lighting-based dark field digital holographic microscopy device and method
InactiveCN104567659AObserve and study convenienceIncrease contrastUsing optical meansMicro imagingSpatial light modulator
The invention provides a vortex light lighting-based dark field digital holographic microscopy device and a vortex light lighting-based dark field digital holographic microscopy method. The device comprises a laser, a beam splitting prism I, a beam splitting prism II, a plane reflecting mirror, a microscope objective spatial filter, a microscope objective I, a Fourier lens, a diaphragm, a beam splitting prism III, a spatial light modulator, a dark field microscope objective, a small ball sample, a microscope objective II, a beam splitting prism IV and an photoelectric coupling device. The method comprises three steps: first, lighting an object by utilizing an annular light cone formed by vortex light after the vortex light enters the dark field microscope objective; then, recording interference fringes of scattered light of the object and reference light into a computer through the photoelectric coupling device by a digital holographic technology; finally, reconstructing the image of the object by utilizing a digital reconstructing technology. Compared with the traditional bright field digital holographic microscopy imaging method, the device and the method have the advantages of high resolution, high contrast and the like, and are applicable to the field of researching the characteristics of a vortex light beam, observing a small phase object and the like in a laboratory.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A Synthetic Aperture Digital Holographic 3D Microscopic Observation Device with Smooth Reflective Surface
The invention discloses a three-dimensional micro-observation apparatus for a smooth reflective surface and the apparatus is based on synthetic aperture in digital holography. The apparatus comprises a light source, light splitting unit, space filters, plano-convex lenses, a planar mirror, a depolarization beam splitter prism, a beam adjuster, a rotating stage and a complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) camera. A light path of the apparatus is characterized in that: a laser emitted by the light source is incident to the light splitting unit; after a light splitting processing is carried out by the light splitting unit, illuminating light and reference light are output; two beams of light respectively pass through the space filters and the plano-convex lenses in order so as to be processed by beam expansion and shaping; the illuminating light passes through the planar mirror and outputs parallel light that penetrates the depolarization beam splitter prism and is incident inclinedly to a surface of an observed object on the rotating stage; and then reflected light of the object surface is again incident to the depolarization beam splitter prism; an angle and a position of the reference light are adjusted by the beam adjuster and the reference light is also incident to the depolarization beam splitter prism; and light composition processing is carried out on the incidentreference light and an object light by the depolarization beam splitter prism so as to obtain a combined light beam; and an interference hologram formed by the combined light beam is captured by a photosensitive surface of the CMOS camera. During the obtaining process, the rotating stage is rotated and an incident angle of the illuminating light is adjusted many times, so that an object surface hologram that contains different frequency components is obtained; and then fusion is carried out, thereby realizing a three-dimensional micro-observation based on the synthetic aperture in digital holography.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
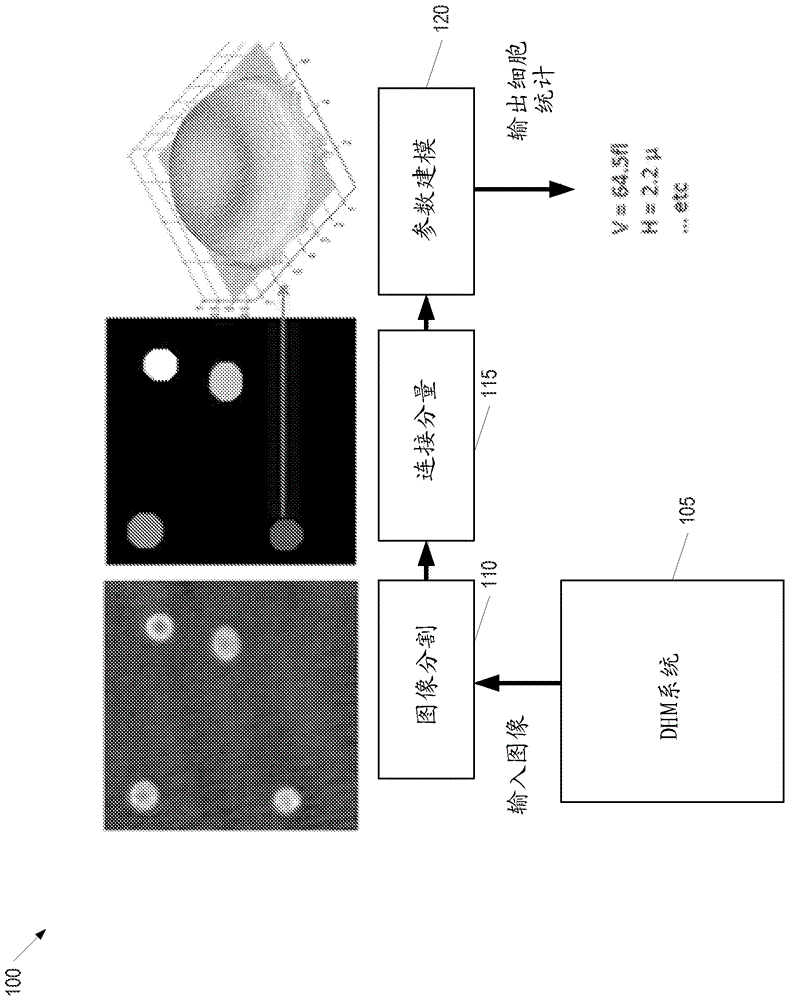
Analyzing digital holographic microscopy data for hematology applications
A method for analyzing digital holographic microscopy (DHM) data for hematology applications includes receiving a plurality of DHM images acquired using a digital holographic microscopy system. One or more connected components are identified in each of the plurality of DHM images and one or more training white blood cell images are generated from the one or more connected components. A classifier is trained to identify a plurality of white blood cell types using the one or more training white blood cell images. The classifier may be applied to a new white blood cell image to determine a plurality of probability values, each respective probability value corresponding to one of the plurality of white blood cell types. The new white blood cell image and the plurality of probability values may then be presented in a graphical user interface.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Digital holographic microscopy device based on local hollow beam illumination and working method thereof
InactiveCN107907983ABreak through the limit resolutionHigh resolutionMicroscopesHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesOptical reflectionDigital holographic microscopy
The invention, which belongs to the field of digital holographic microscopy (DHM), relates to a digital holographic microscopy device based on local hollow beam illumination and a working method thereof. The digital holographic microscopy device is composed of a laser device, an optical beam splitter I, an optical beam splitter II, an optical reflector I, an optical reflector II, a dark field condenser, a microscope objective I, a microscope objective II, a spatial filter, a first lens L1, a second lens L2, a third lens L3, a computer, and other components. The digital holographic microscopy device is implemented as follows: after incidence of a generated local hollow light beam to the dark field condenser, an annular light cone illumination experiment sample is formed; with the digital holography, interference fringes of diffracted light and reference light of the sample are recorded to the computer by an optocoupler device; and then on the basis of a reconstructive technique, a three-dimensional image of an object is reproduced. Compared with the traditional digital holographic microscopy, the digital holographic microscopy device provided by the invention has the higher resolution and contrast ratio and is suitable for microcosmic fields such as observation of living cells and solvent particles in biomedical detection.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
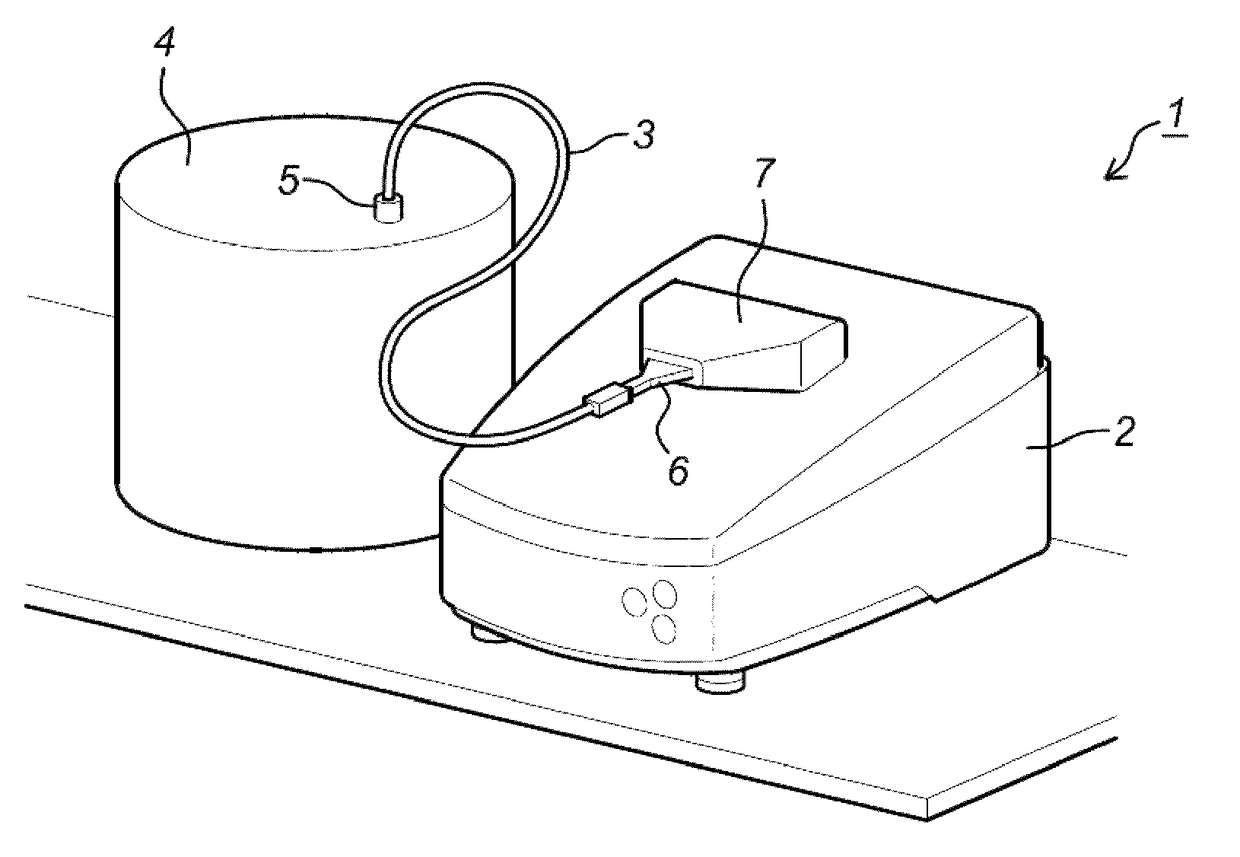
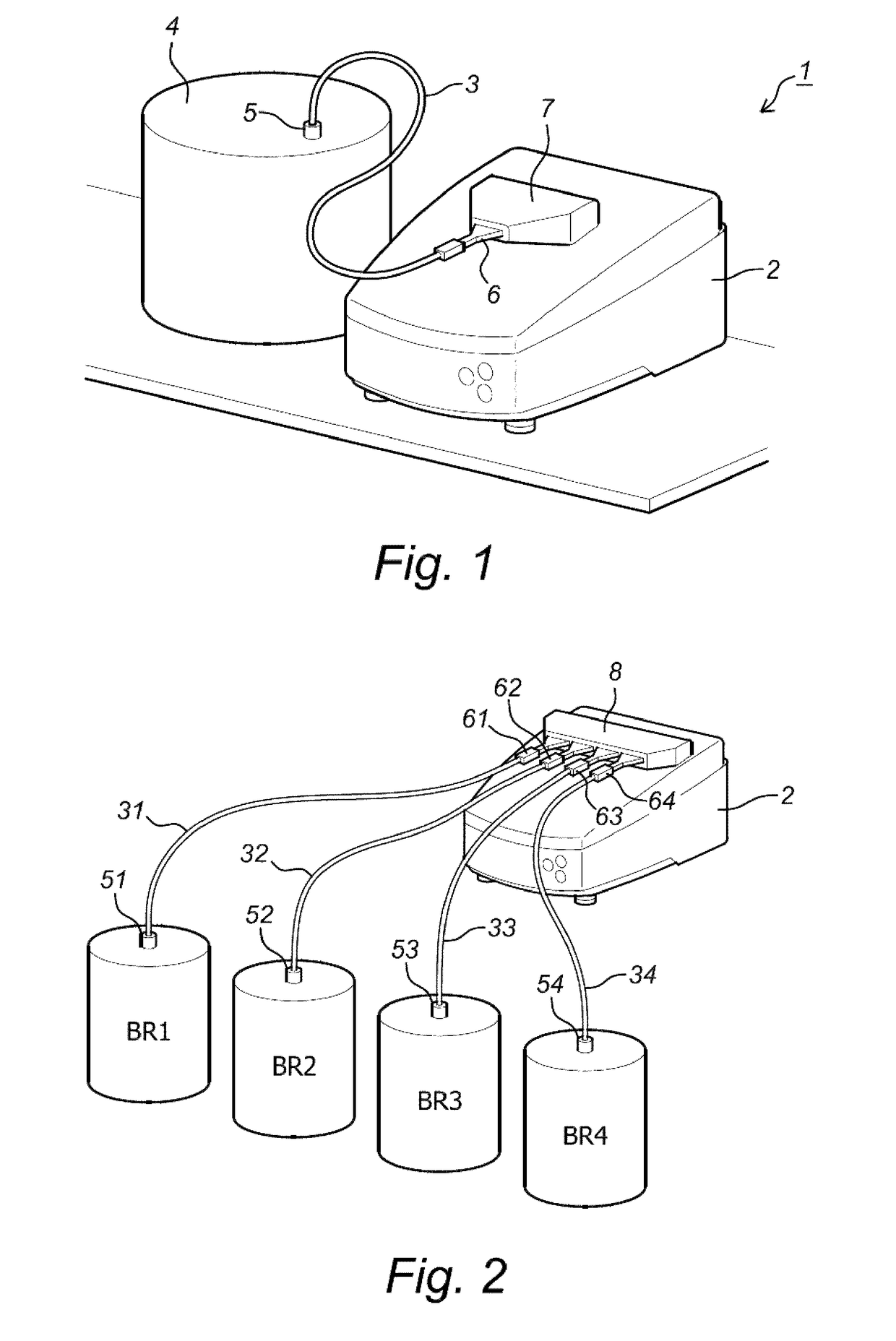
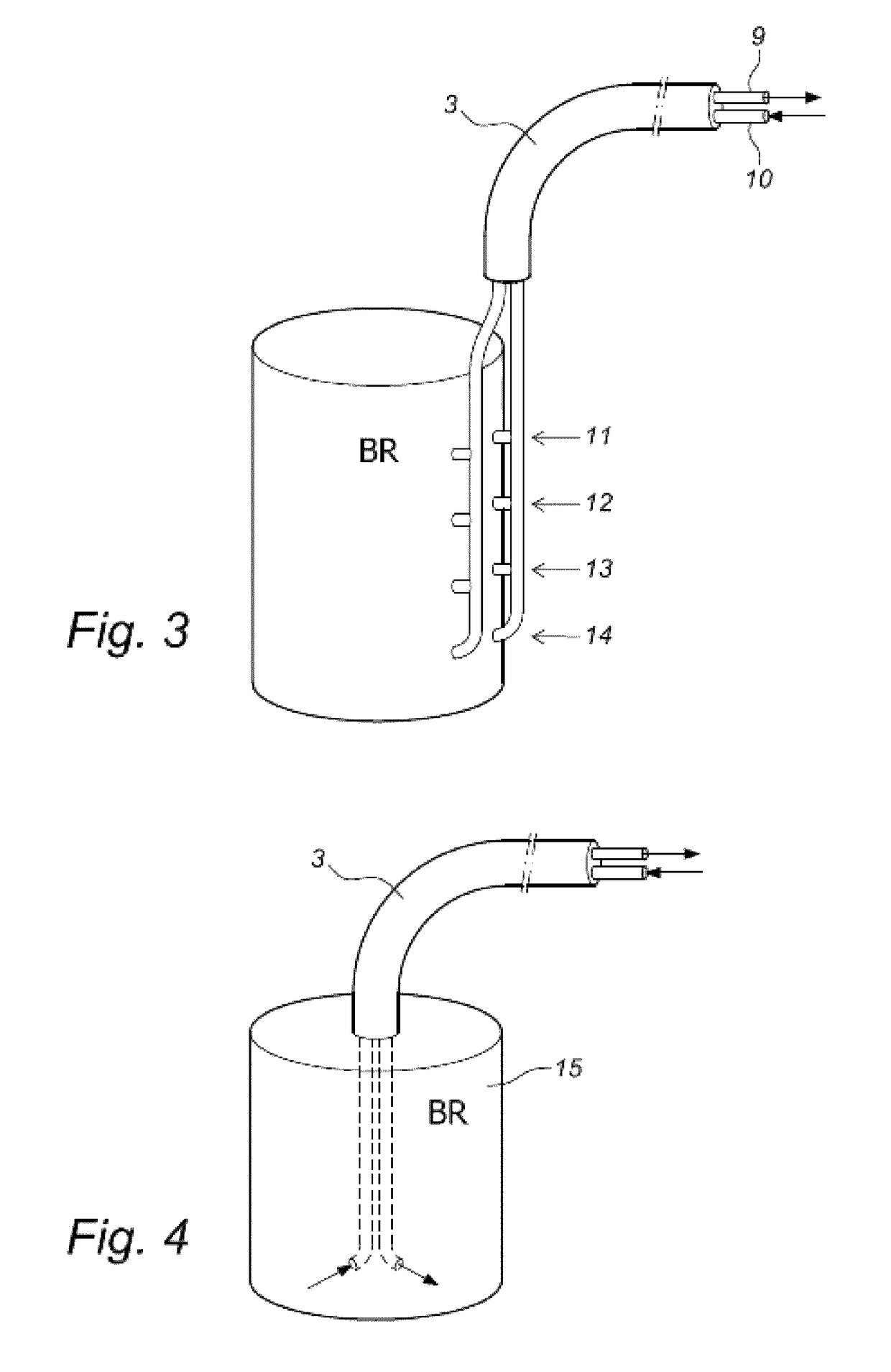
Digital holographic microscope with fluid systems
ActiveUS9904248B2Good adhesionPrevent liquid leakageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDigital holographic microscopyBiomedical engineering
The current invention concerns a fluid microscope system for analyzing and / or monitoring the contents of one or more fluid-based reactors or canalizations such as bio-reactors, micro-reactors, brewing reactors, water supply systems or sewer systems comprising a digital holographic microscope (DHM) capable of obtaining phase information of a fluid sample and comprising illumination means and one or more fluidic systems connected to said reactors and to said DHM, capable of guiding fluid from said reactors to said DHM, whereby at least one fluidic system comprises one or more tubes which may come in direct contact with fluid from said reactor, characterized in that at least one tube comprises a part which is at least partially transparent for the illumination means of said DHM for obtaining holographic information of said fluid sample. The current invention also concerns a tube and a fluidic system for such a fluid microscope.
Owner:OVIZIO IMAGING SYST NV SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com