Patents
Literature
379 results about "Nanohole" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
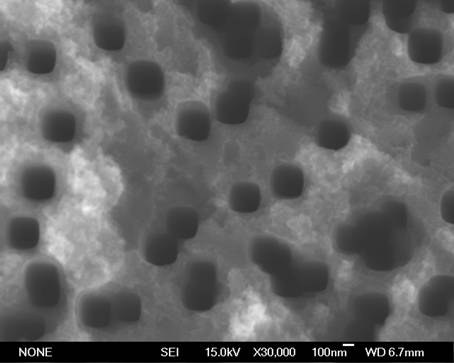
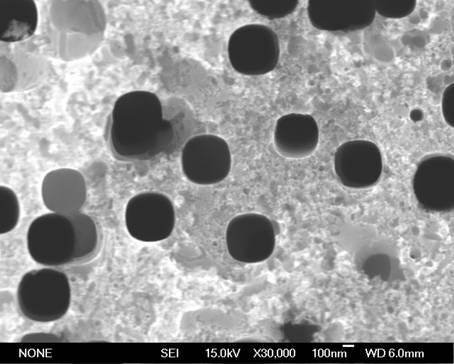
Nanoholes are a class of nanostructured material consisting of nanoscale voids in a surface of a material. Not to be confused with nanofoam or nanoporous materials which support a network of voids permeating throughout the material (often in a disordered state), nanohole materials feature a regular hole pattern extending through a single surface. These can be thought of as the inverse of a nanopillar or nanowire structure.
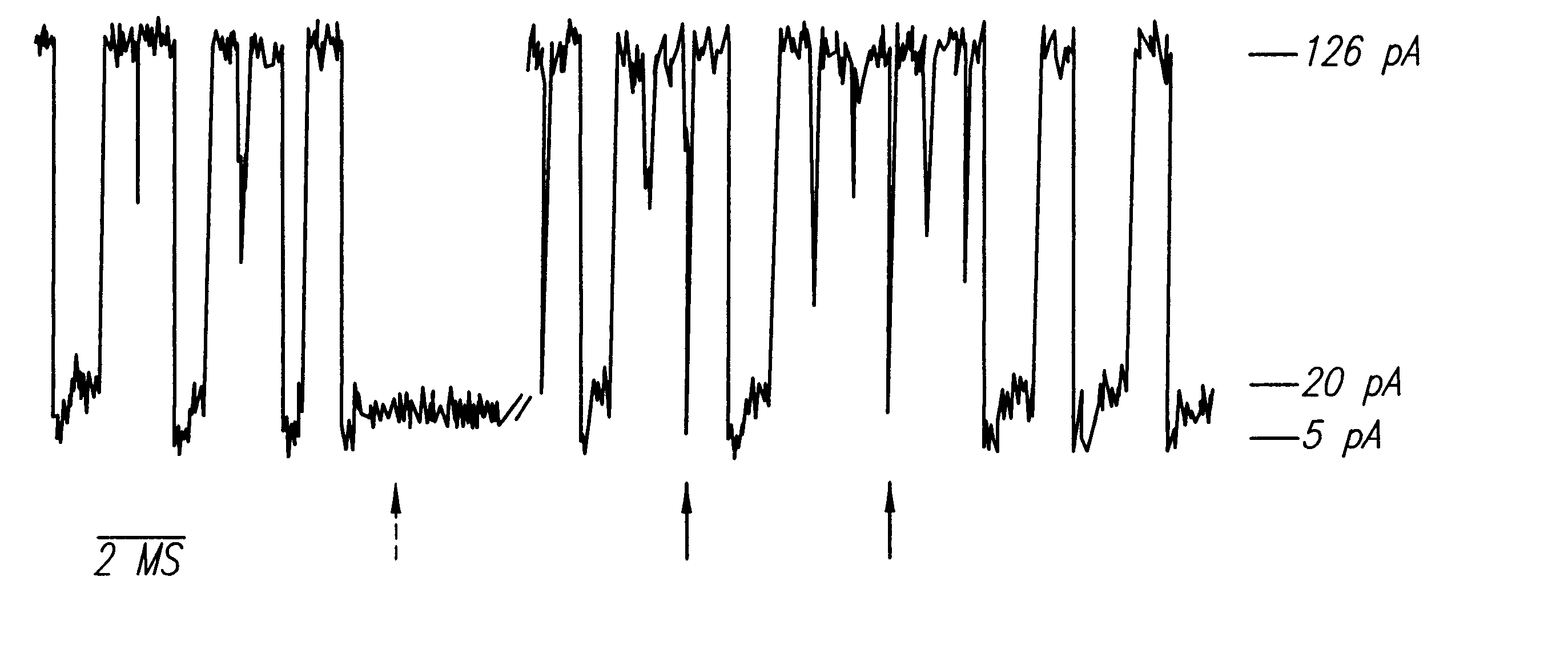
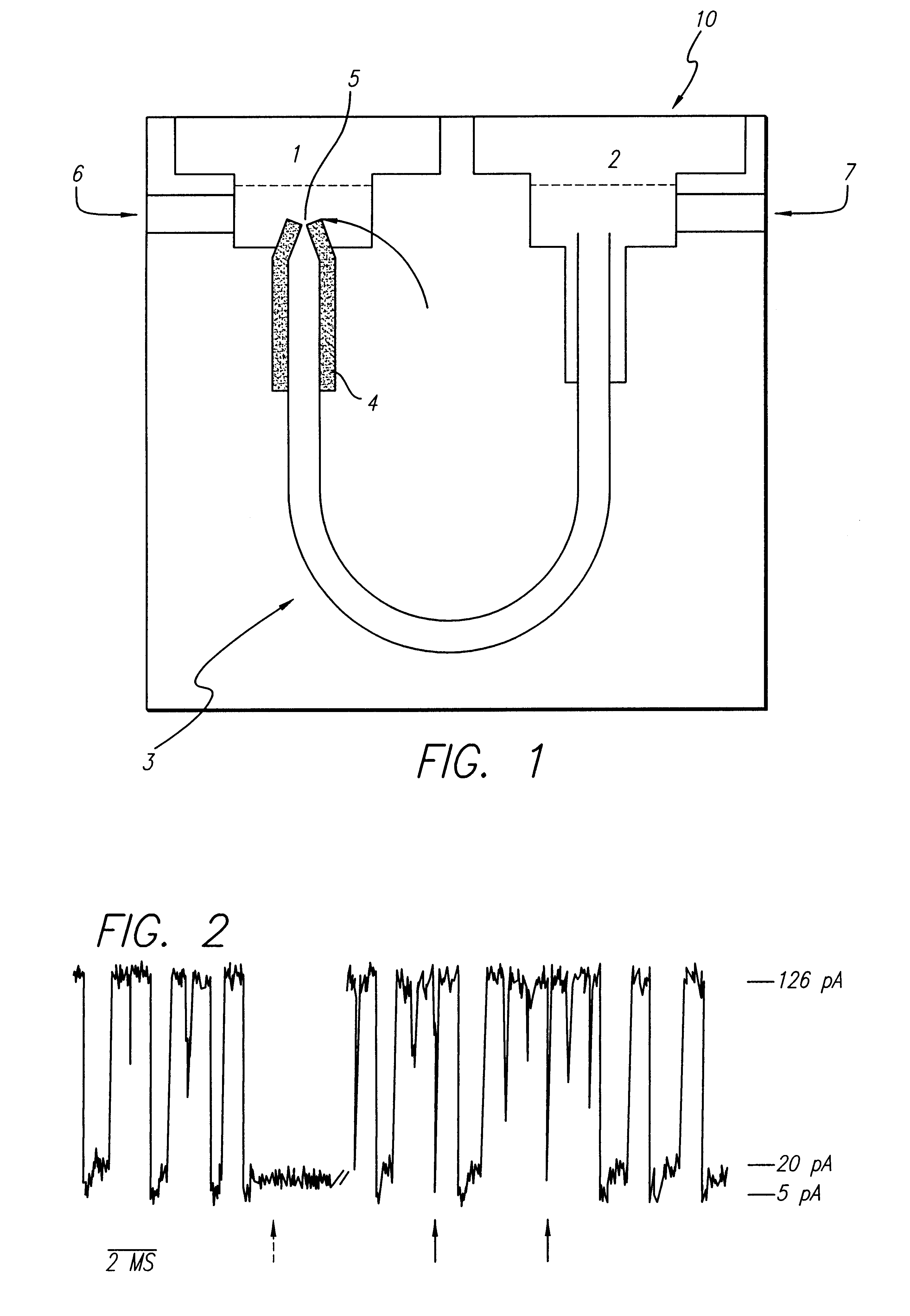
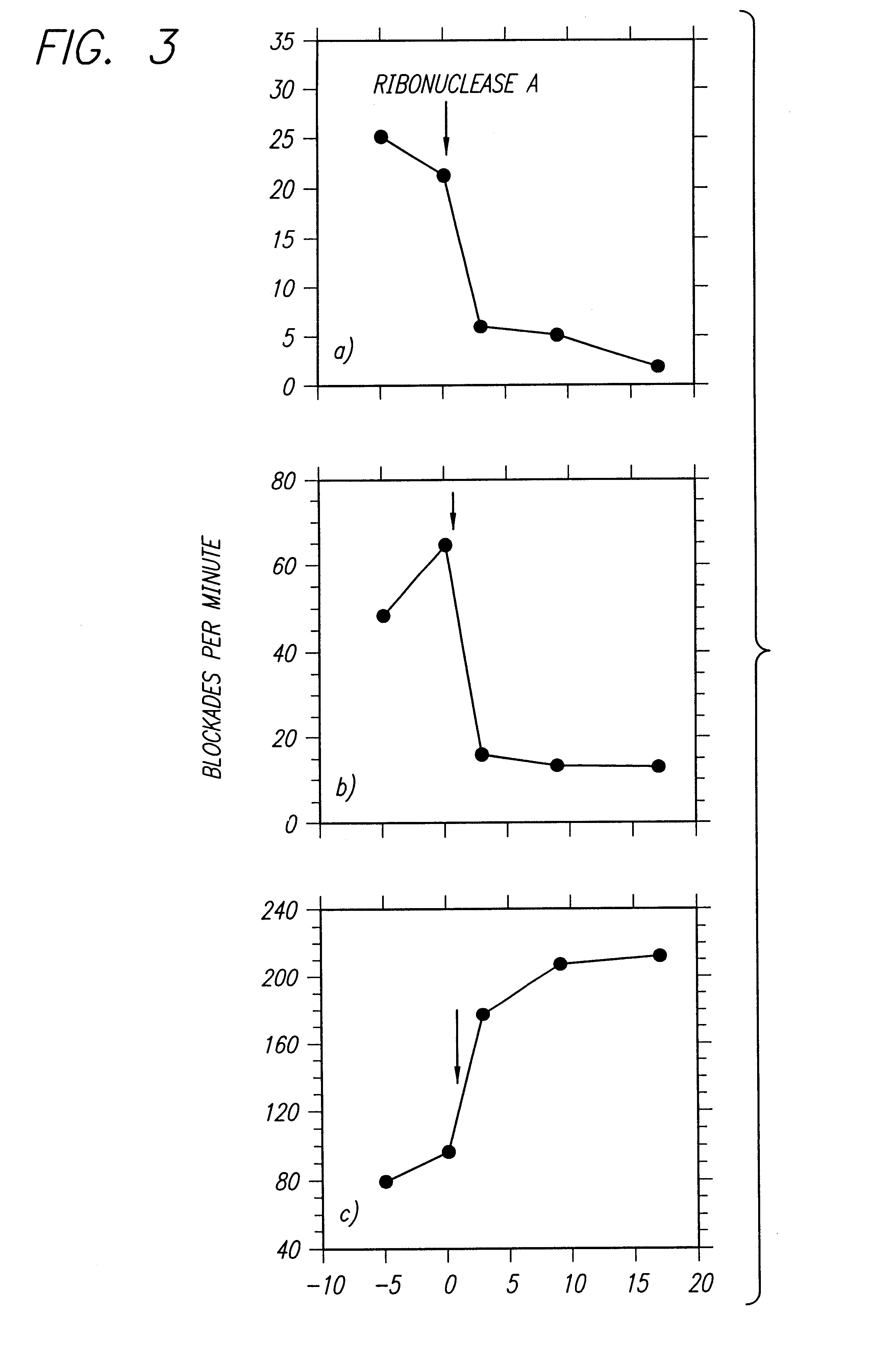
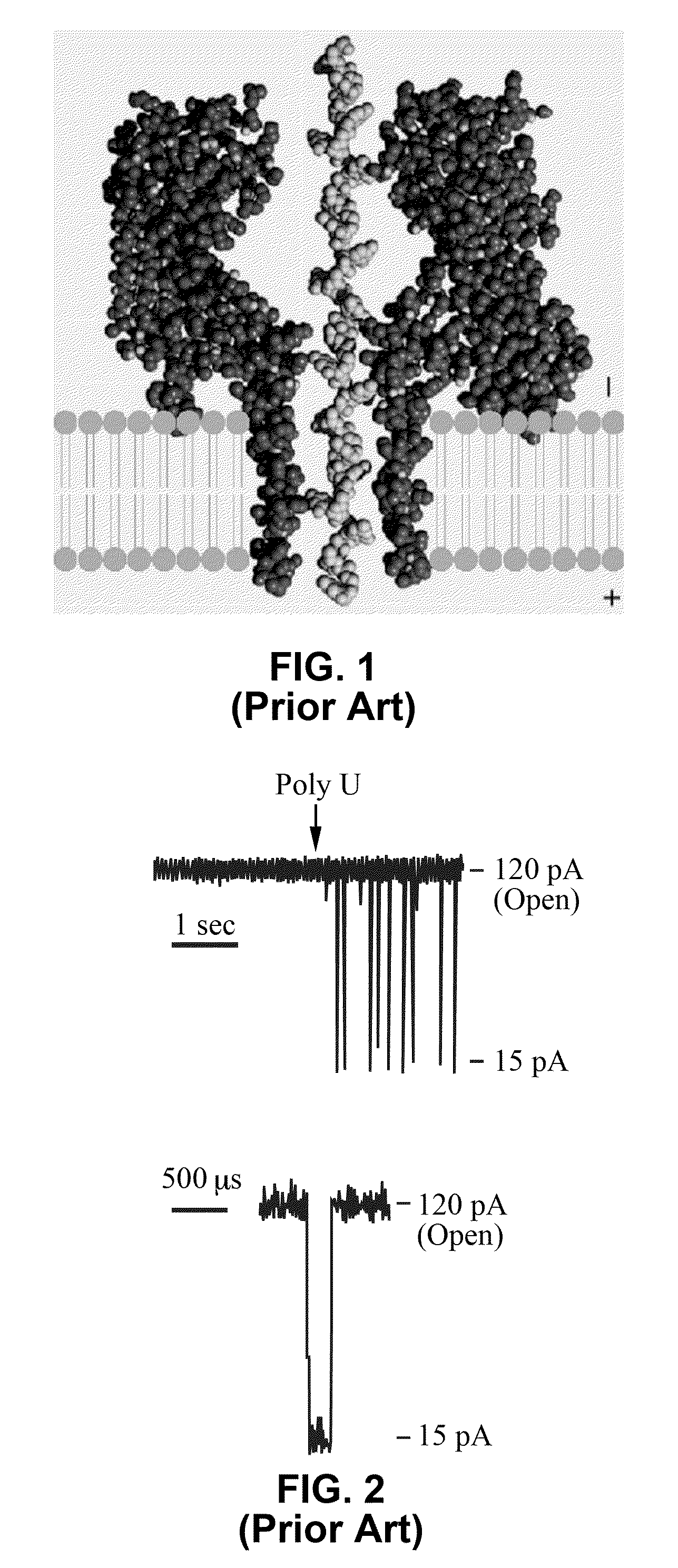
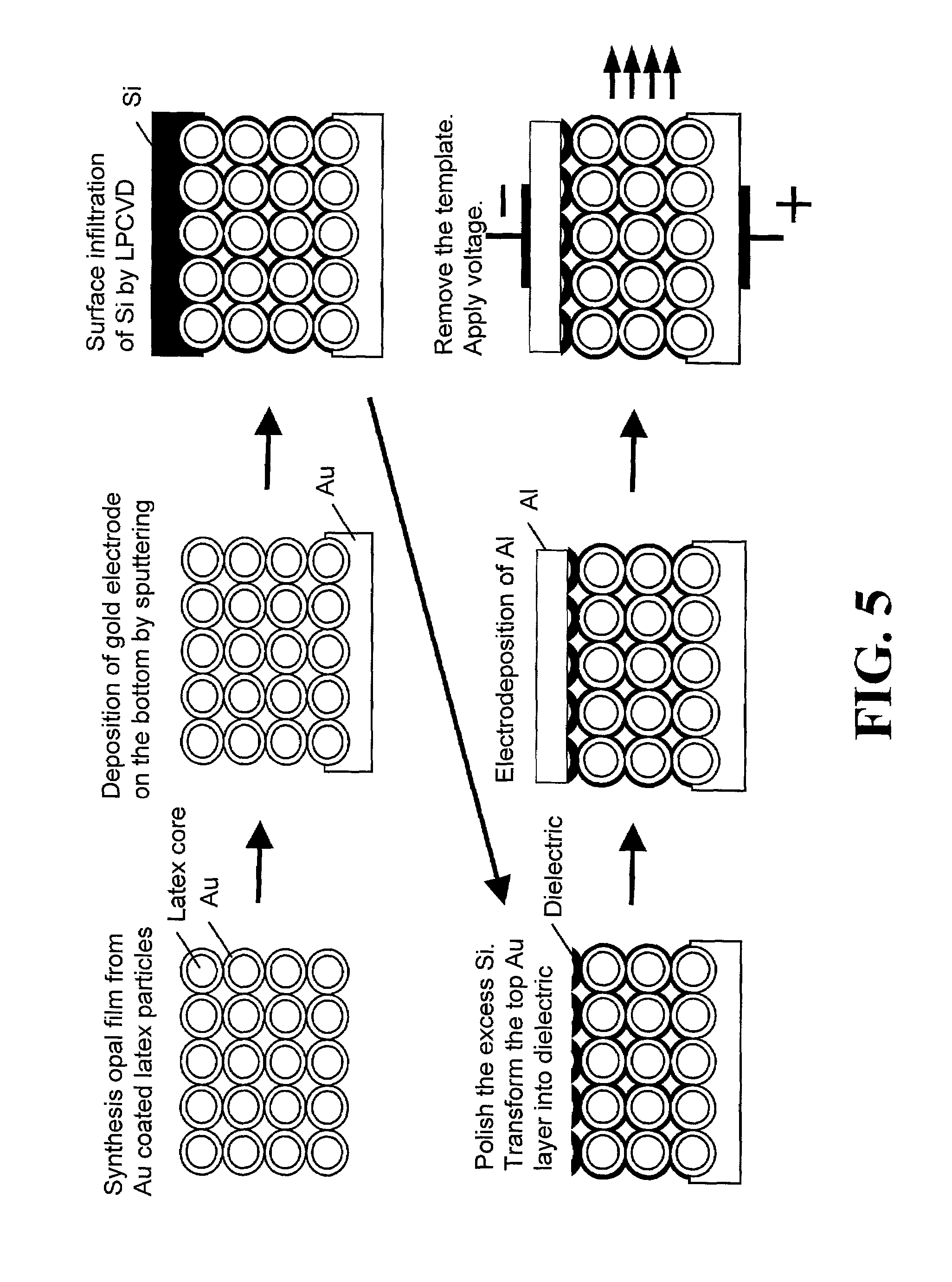
Miniature support for thin films containing single channels or nanopores and methods for using same
Single-channel thin film devices and methods for using the same are provided. The subject devices comprise cis and trans chambers connected by an electrical communication means. At the cis end of the electrical communication means is a horizontal conical aperture sealed with a thin film that includes a single nanopore or channel. The devices further include a means for applying an electric field between the cis and trans chambers. The subject devices find use in applications in which the ionic current through a nanopore or channel is monitored where such applications include the characterization of naturally occurring ion channels, the characterization of polymeric compounds, and the like.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Nanostructure, electron emitting device, carbon nanotube device, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6838297B2Good shape uniformityReliably producedNanostructure manufactureNanomagnetismNanoholeCarbon nanotube
Owner:CANON KK
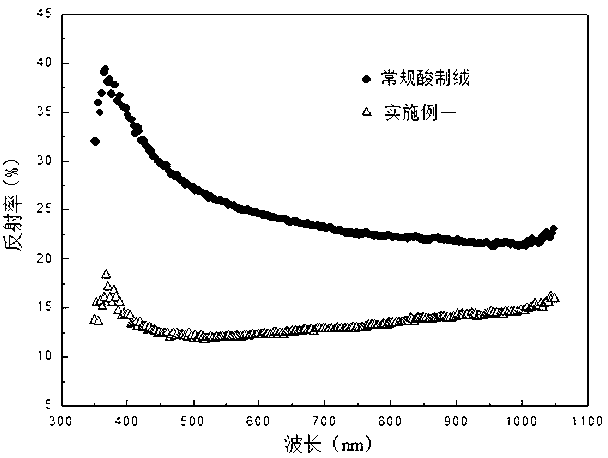
Textured structure of crystalline silicon solar cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103219428AImprove conversion efficiencySimple manufacturing methodPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesMicrometerSpins
The invention discloses a preparation method of a textured structure of a crystalline silicon solar cell. The method includes the steps of (1) cleaning and texture preparation, (2) soaking a silicon wafer in a solution containing metal ions to enable the surface of the silicon wafer to be coated with a layer of metal nanometer particles, (3) corroding the surface of the silicon wafer to form a nanometer-grade texture, (4) cleaning to remove the metal particles, (5) carrying out microstructure amendment etching in second chemical corrosive liquid, and (6) cleaning and spin-drying. As is proved by a test, the size of the textured structure is between 100nm-500nm; the textured structure is of a nanopore shape with a large hole diameter and a small depth, or a nanometer pyramid with edge angles, or of a nanometer pit shape structure with an edge angle nanometer cone body or with an edge angle; and compared with a nanometer-micrometer composite textured structure disclosed in CN102610692A, the textured structure enables conversion efficiency of a cell piece to be improved by about 0.2%-0.5%, and an unexpected effect is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Fluidic nanotubes and devices
InactiveUS20110168968A1Decrease size weight costImprove accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthPower flowElectrophoresis
Fluidic nanotube devices are described in which a hydrophilic, non-carbon nanotube, has its ends fluidly coupled to reservoirs. Source and drain contacts are connected to opposing ends of the nanotube, or within each reservoir near the opening of the nanotube. The passage of molecular species can be sensed by measuring current flow (source-drain, ionic, or combination). The tube interior can be functionalized by joining binding molecules so that different molecular species can be sensed by detecting current changes. The nanotube may be a semiconductor, wherein a tubular transistor is formed. A gate electrode can be attached between source and drain to control current flow and ionic flow. By way of example an electrophoretic array embodiment is described, integrating MEMs switches. A variety of applications are described, such as: nanopores, nanocapillary devices, nanoelectrophoretic, DNA sequence detectors, immunosensors, thermoelectric devices, photonic devices, nanoscale fluidic bioseparators, imaging devices, and so forth.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
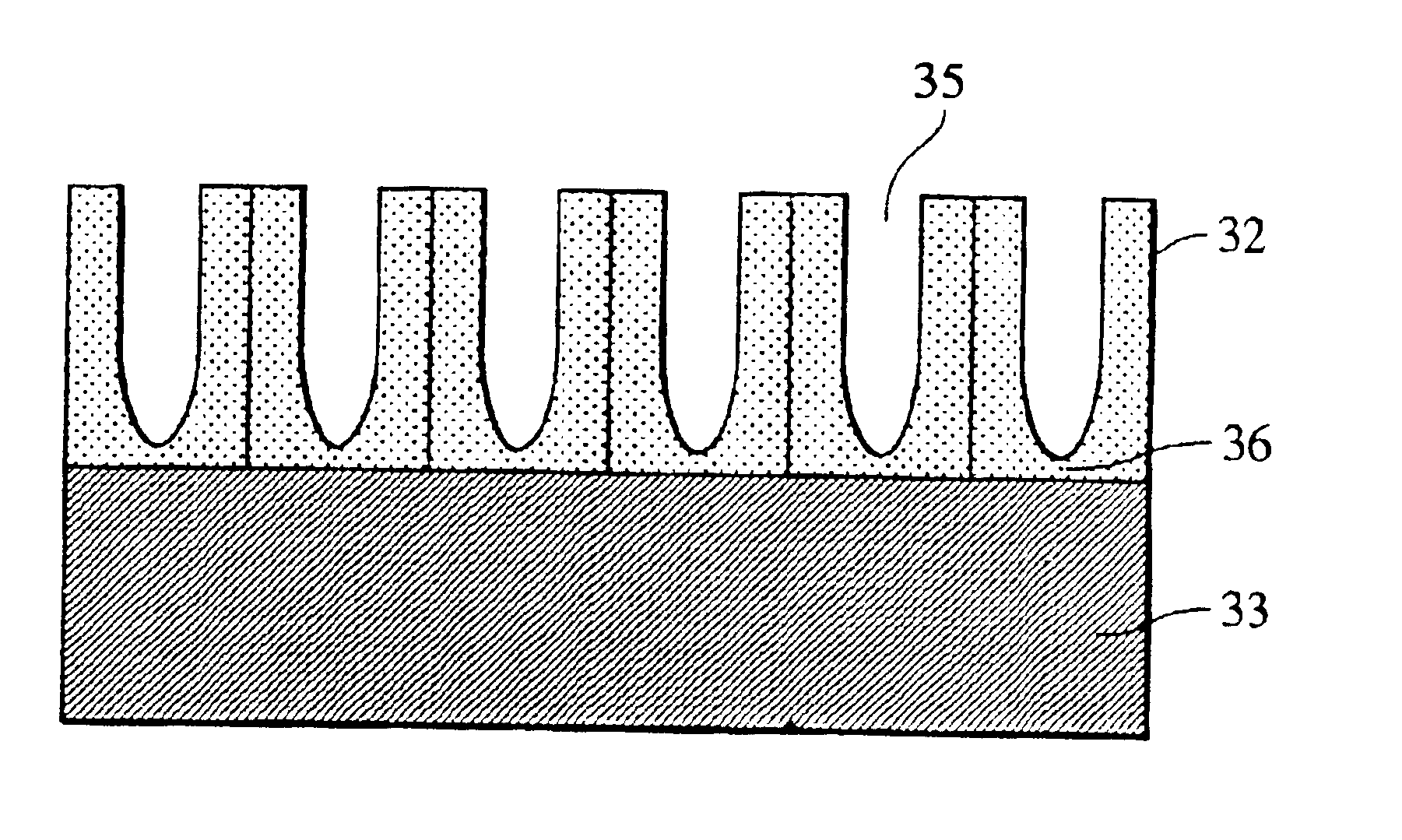
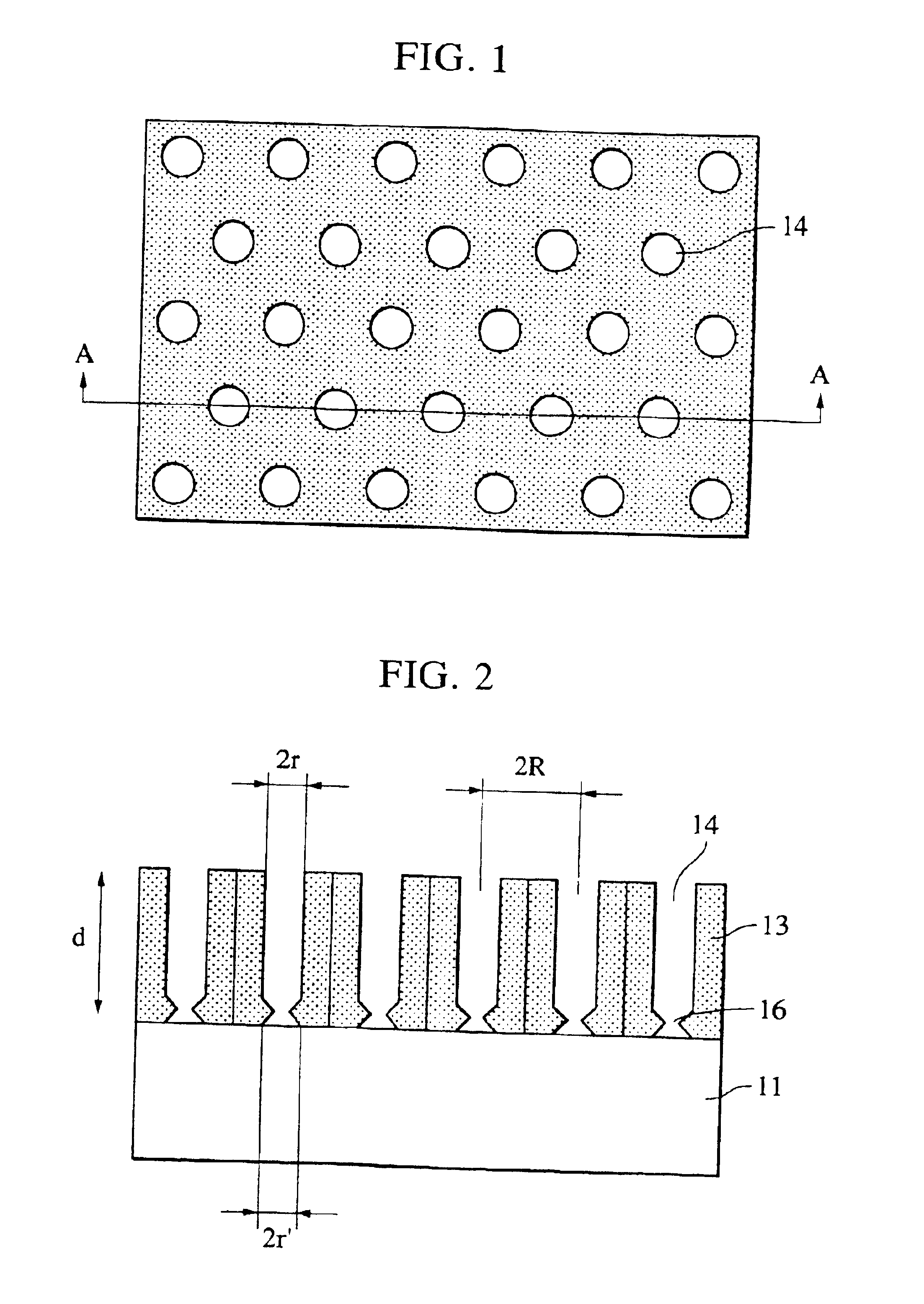
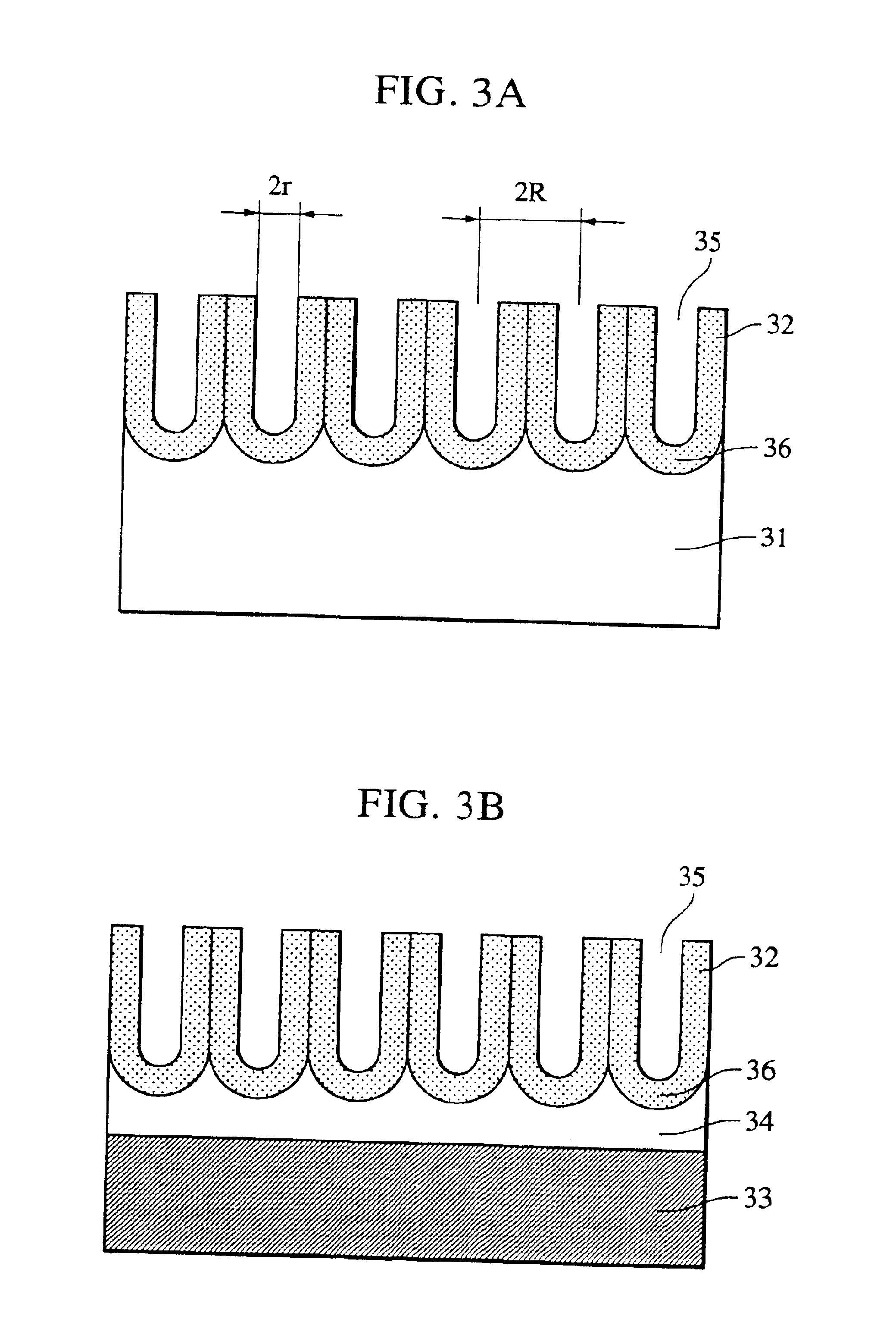
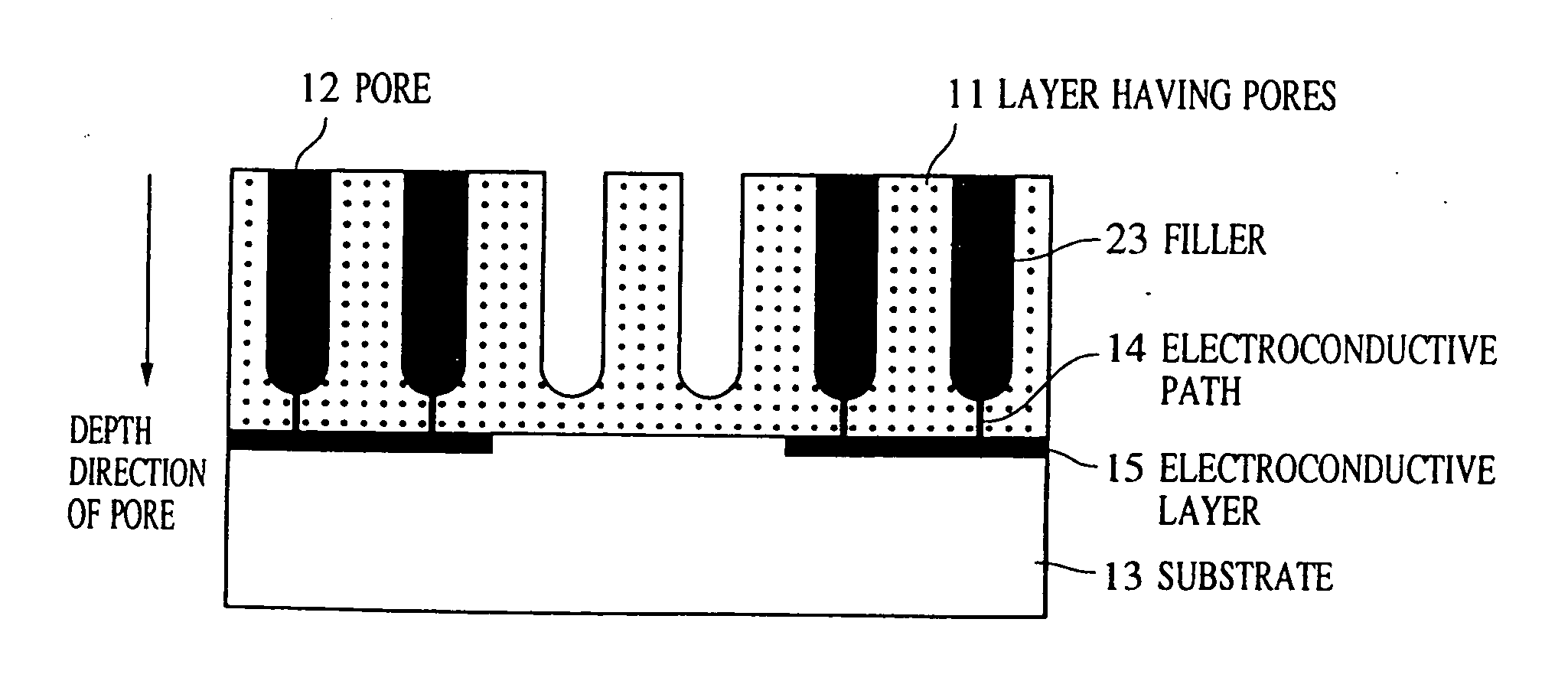
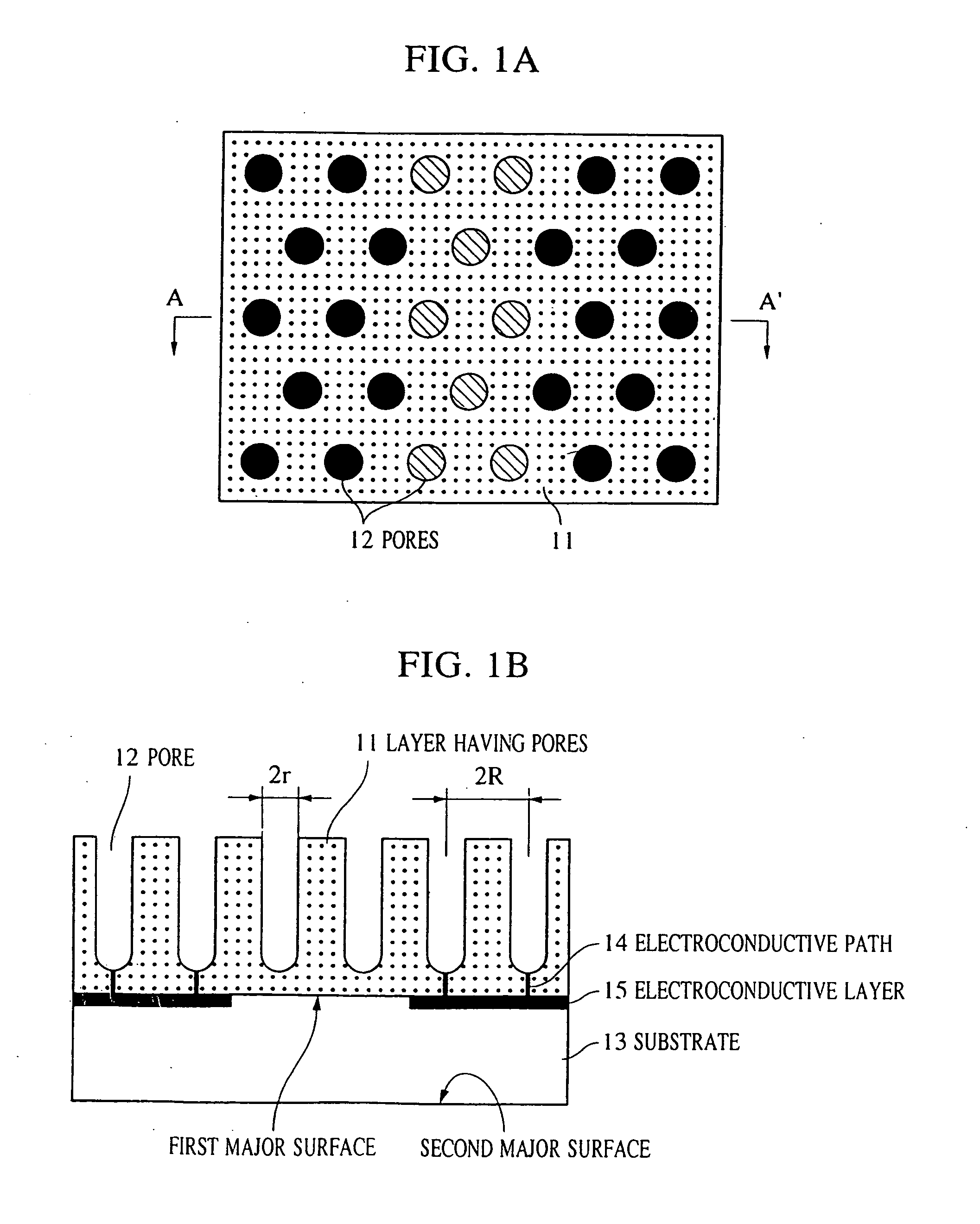
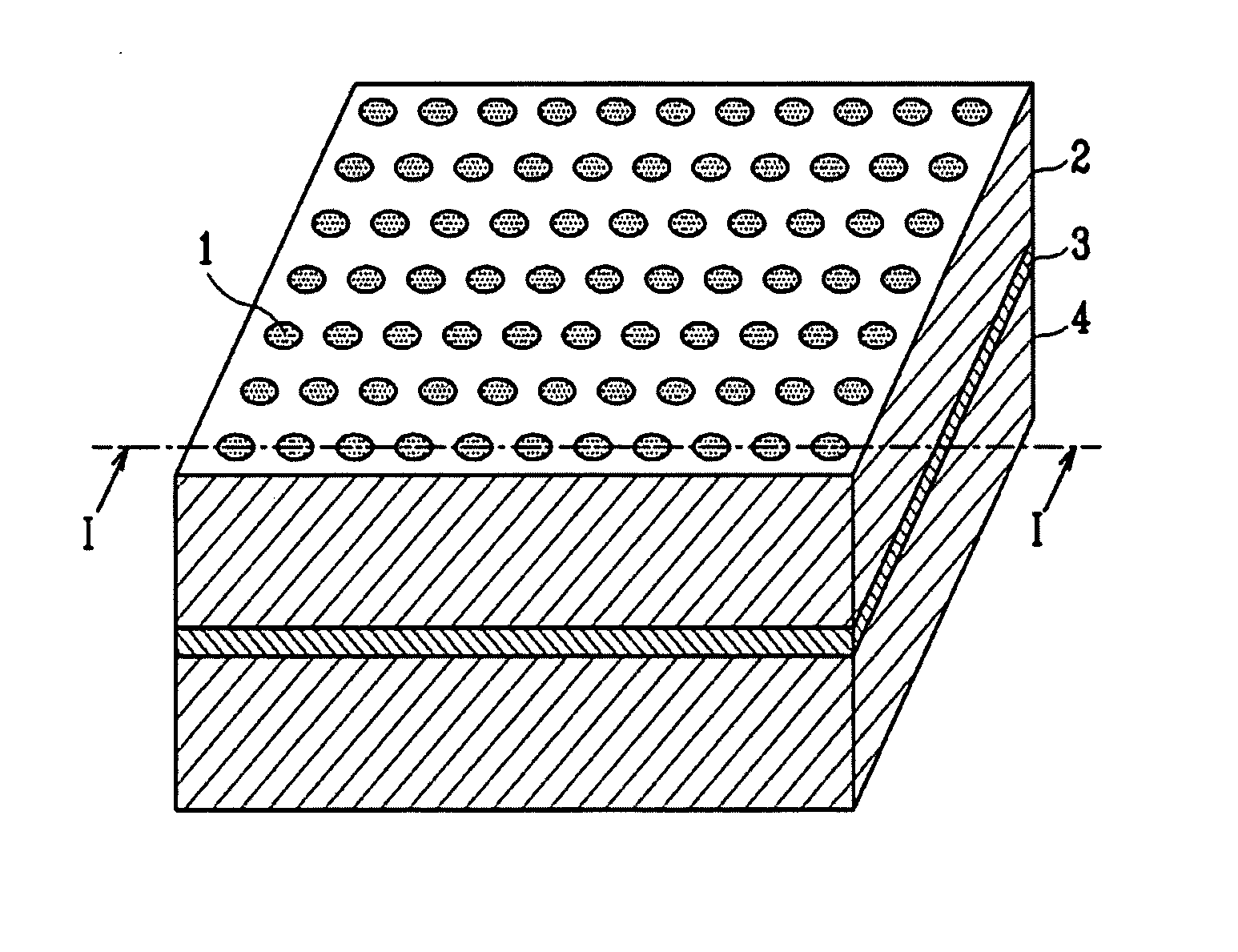
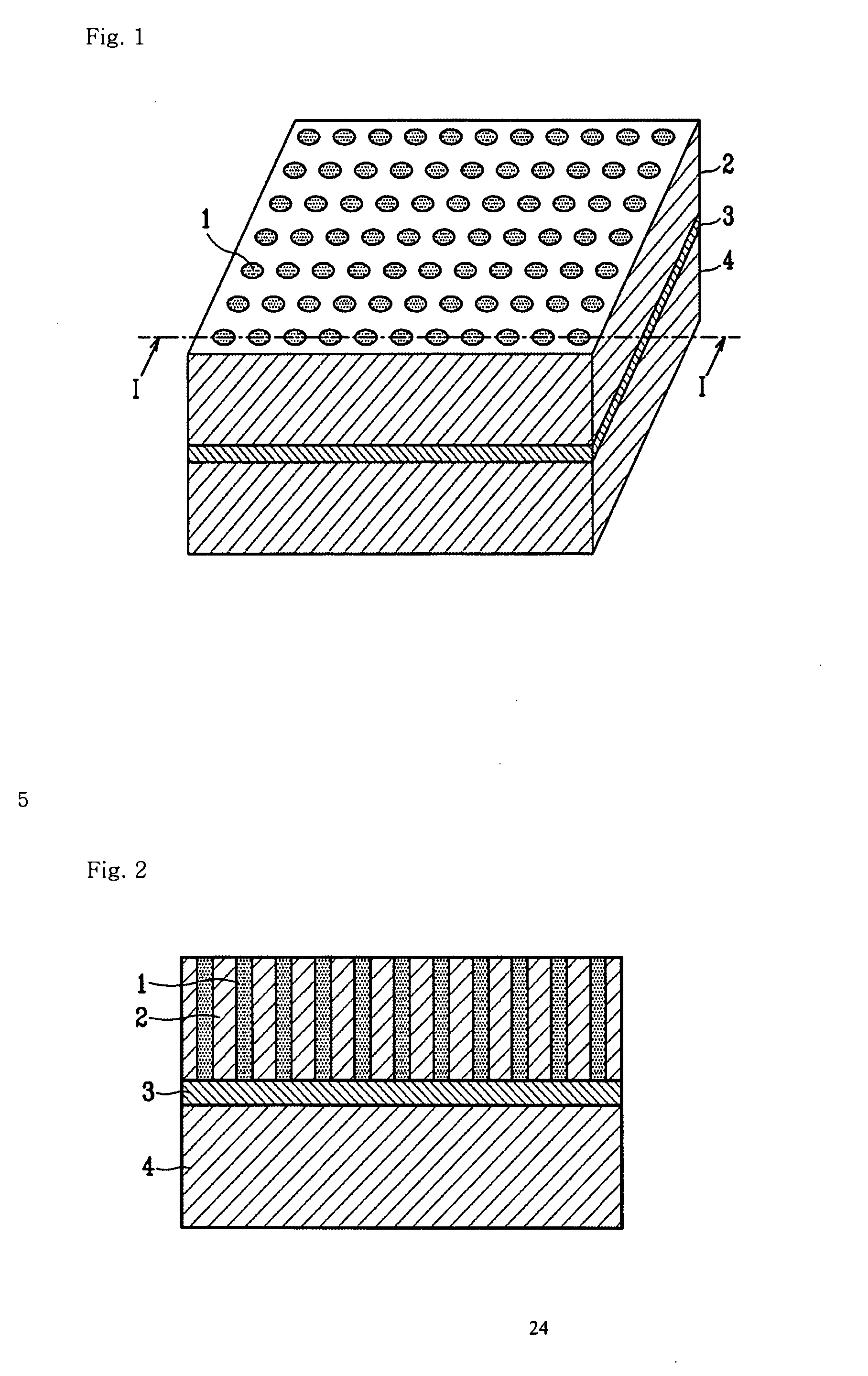
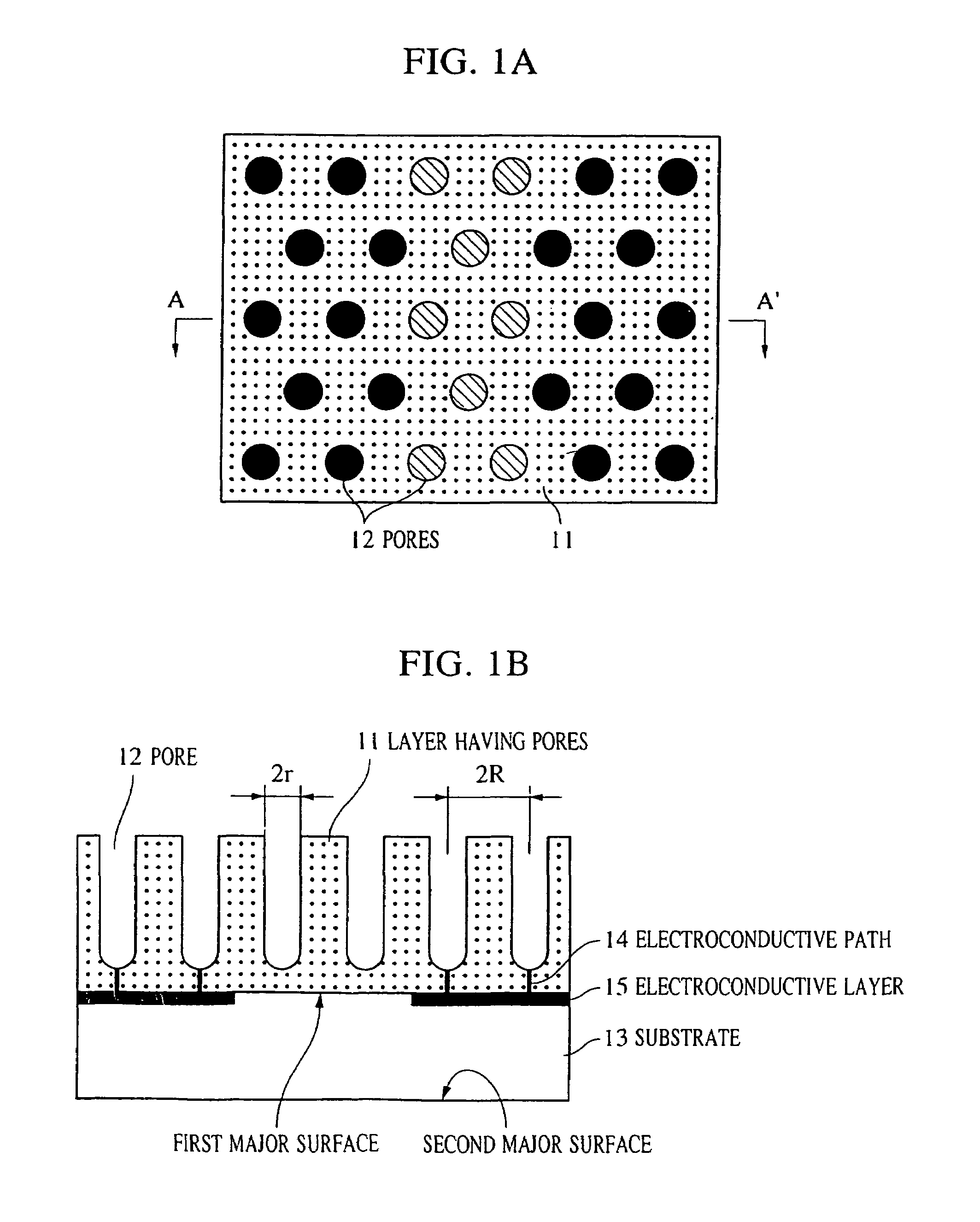
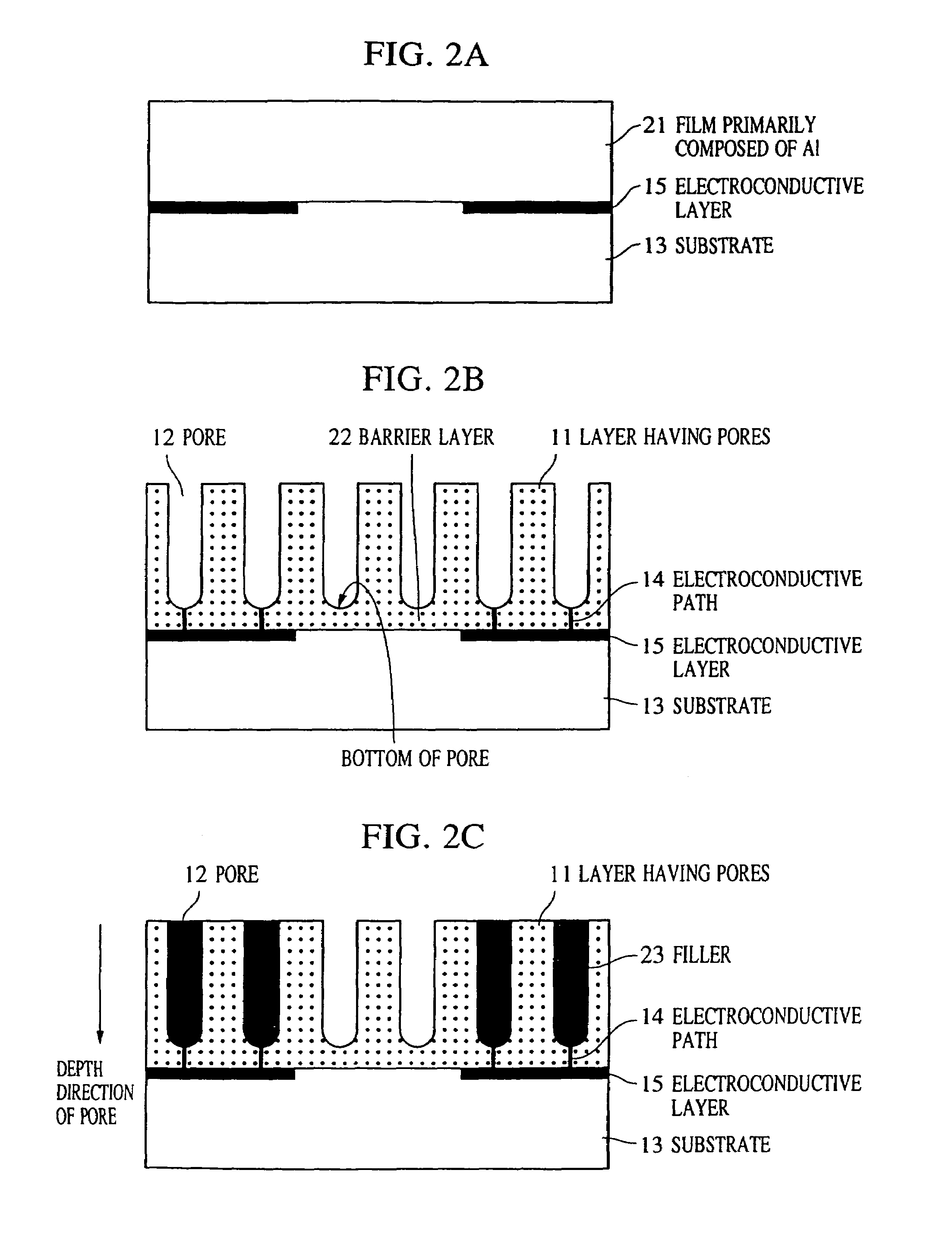
Structure having pores, device using the same, and manufacturing methods therefor
InactiveUS20060138394A1Novel and effective minute structureNovel structureVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFixed microstructural devicesNanoholeNanometre
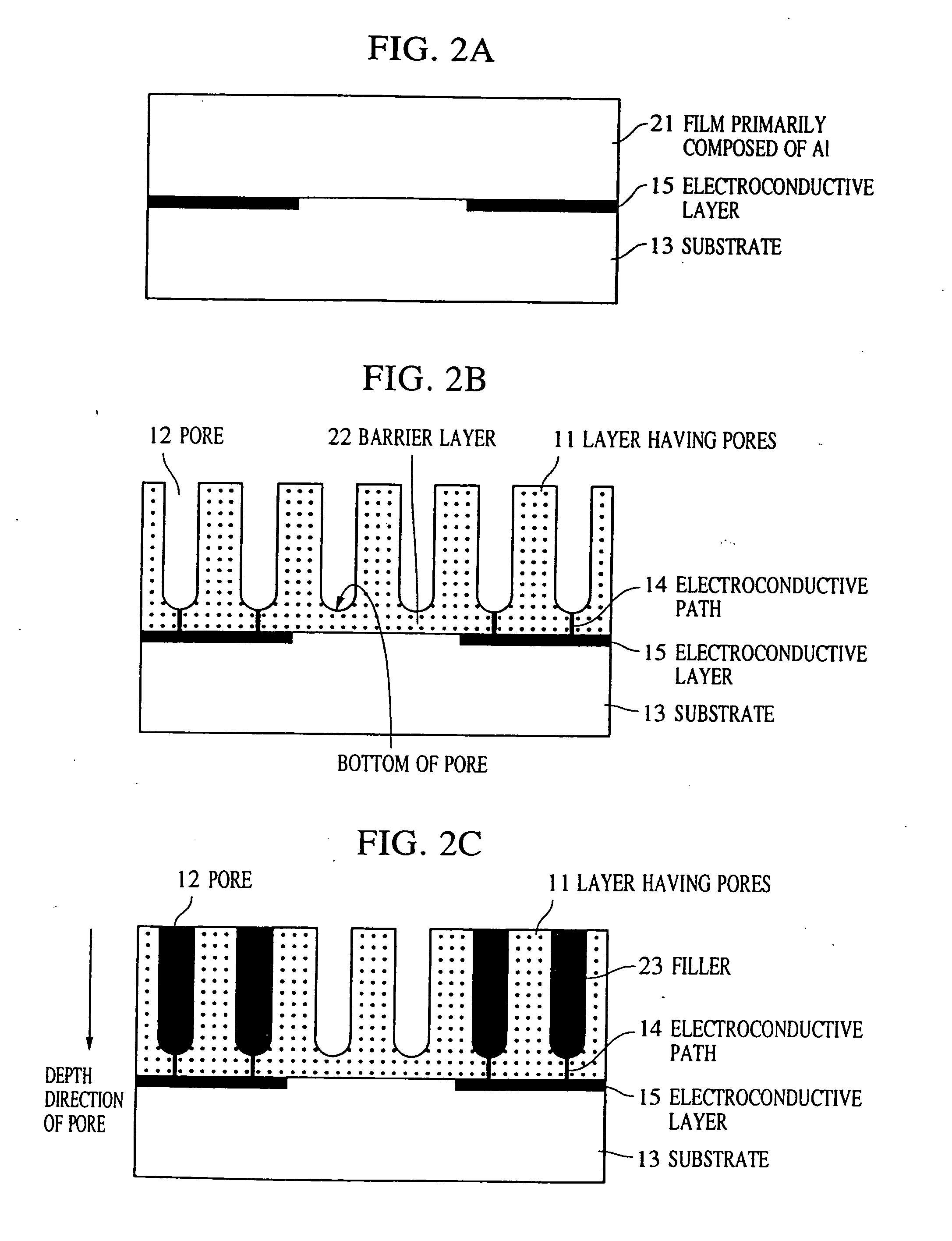
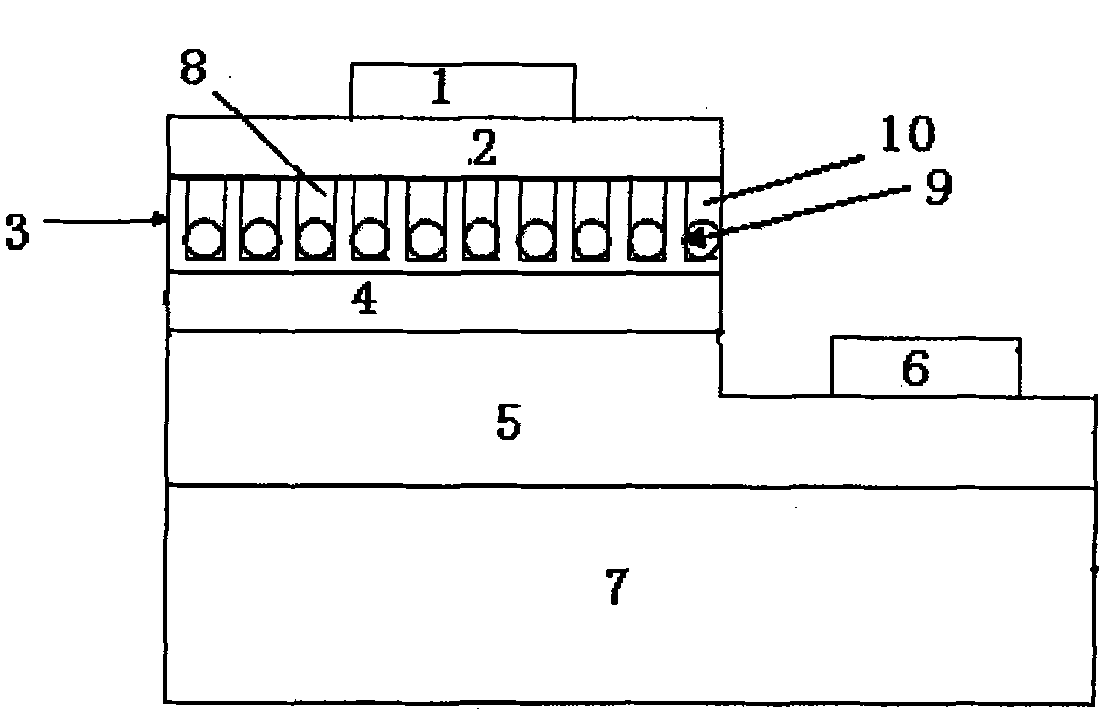
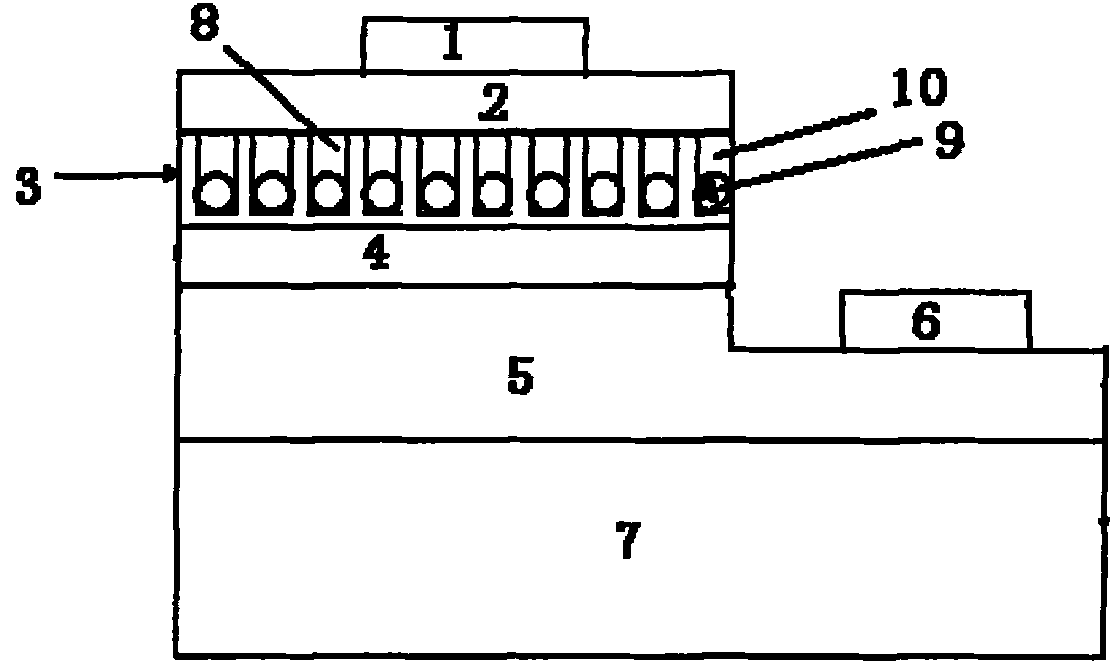
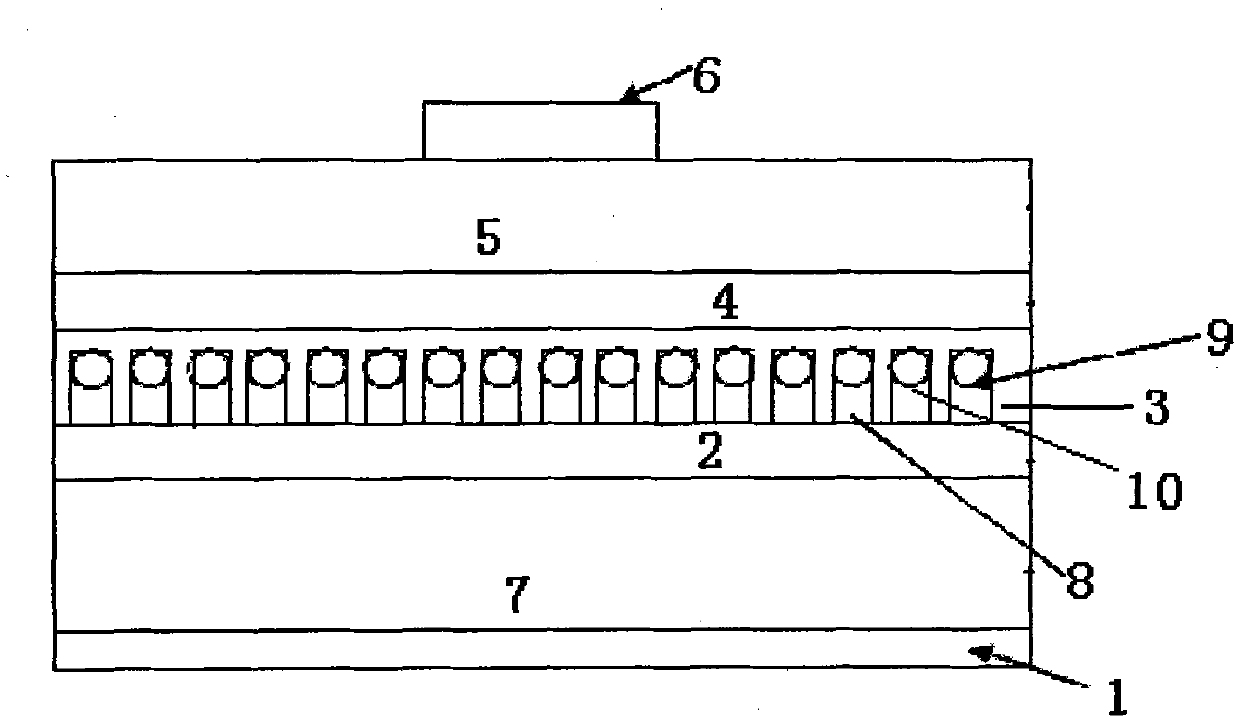
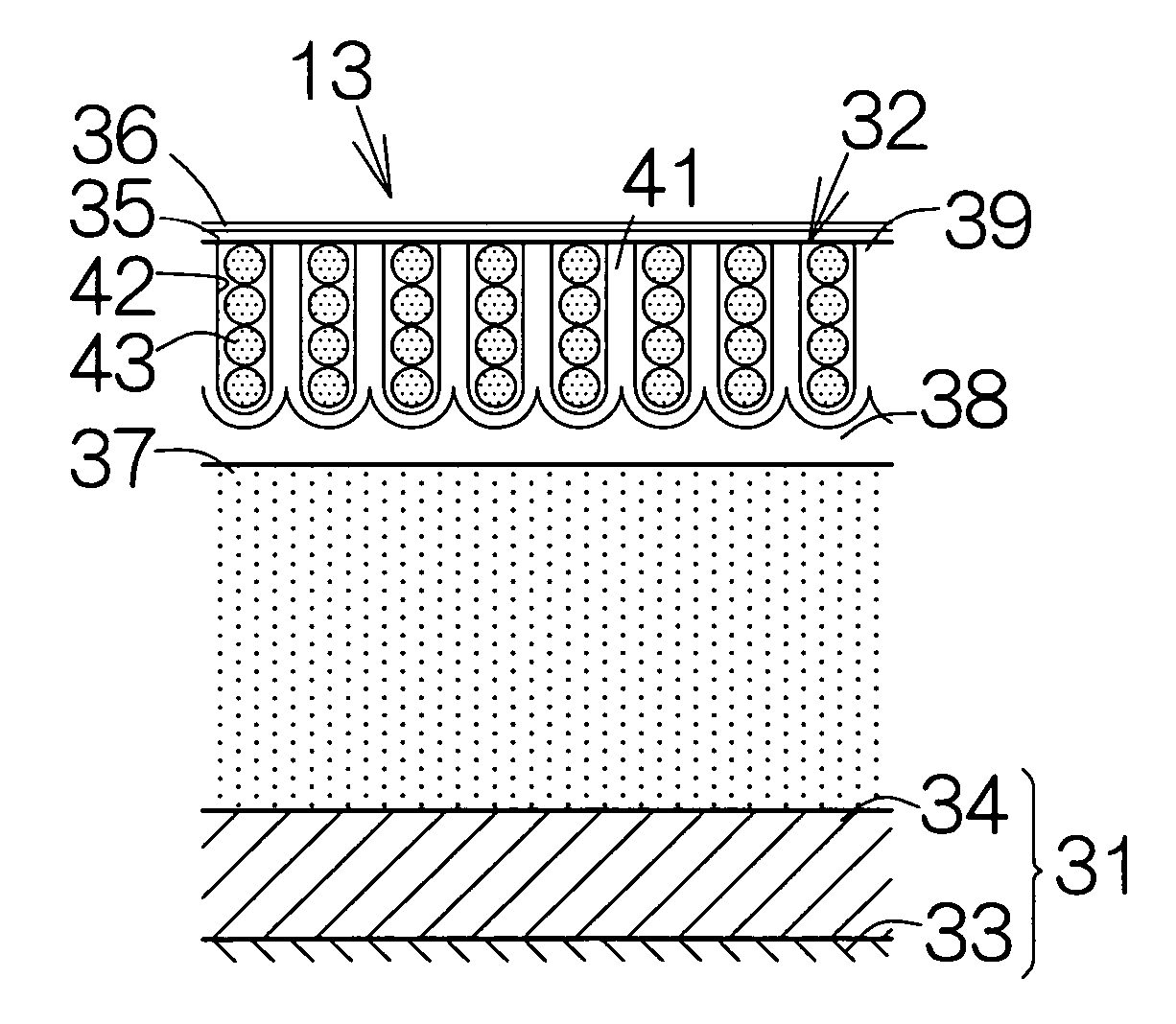
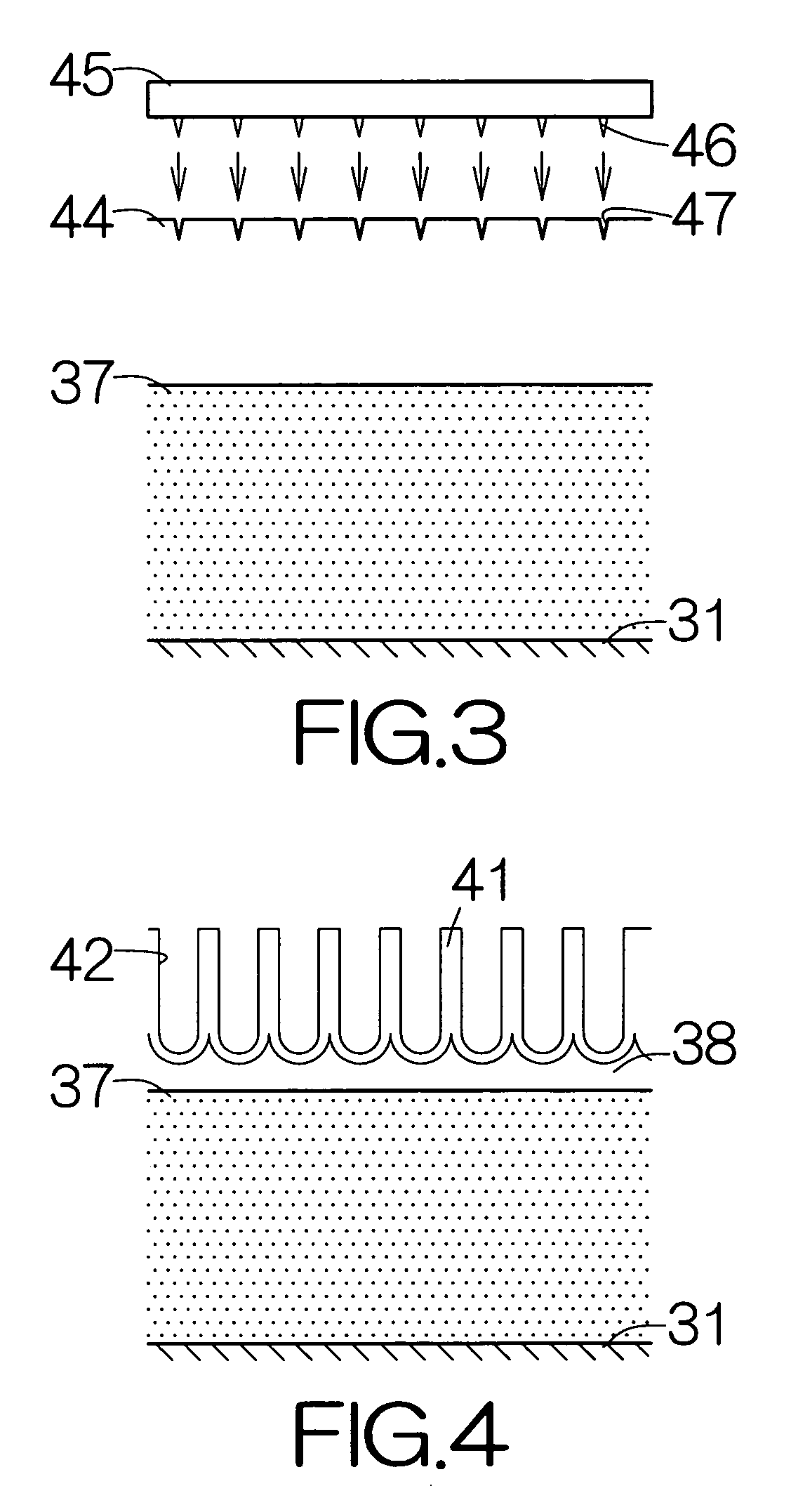
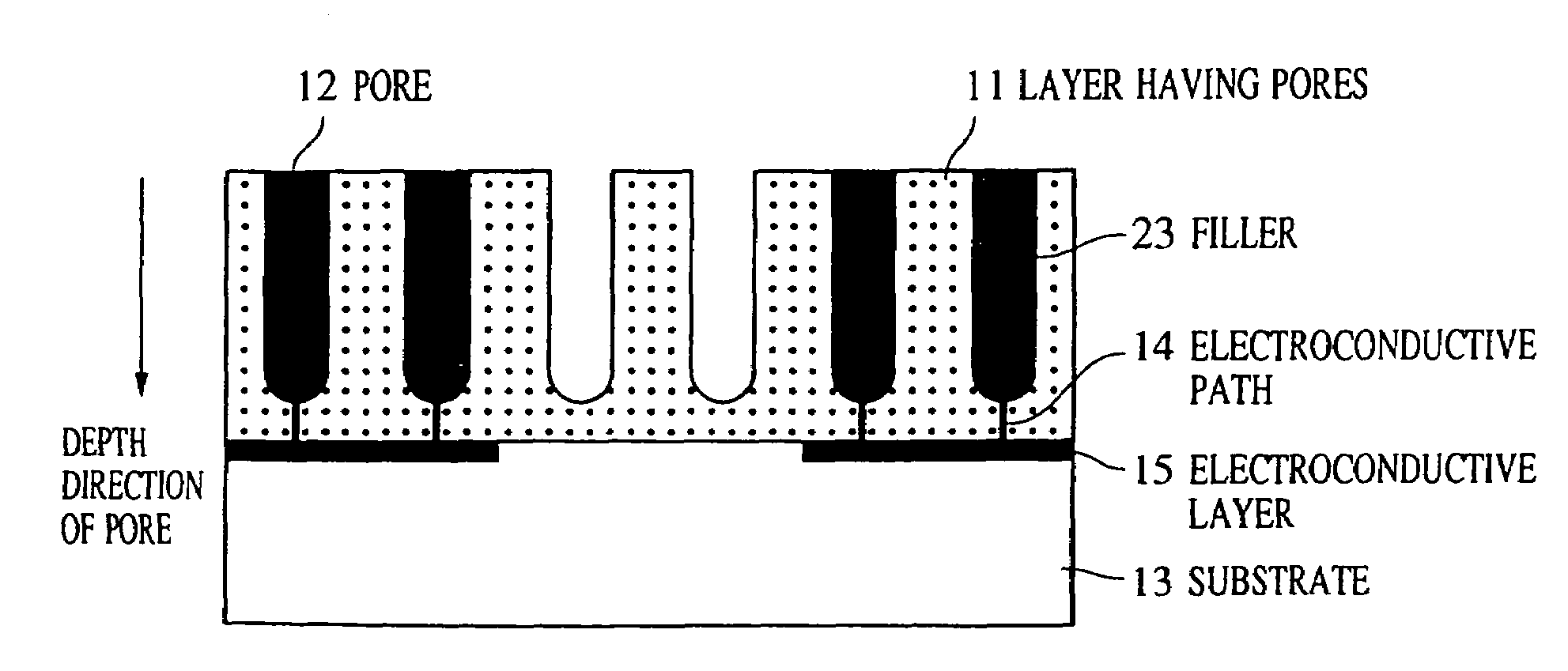
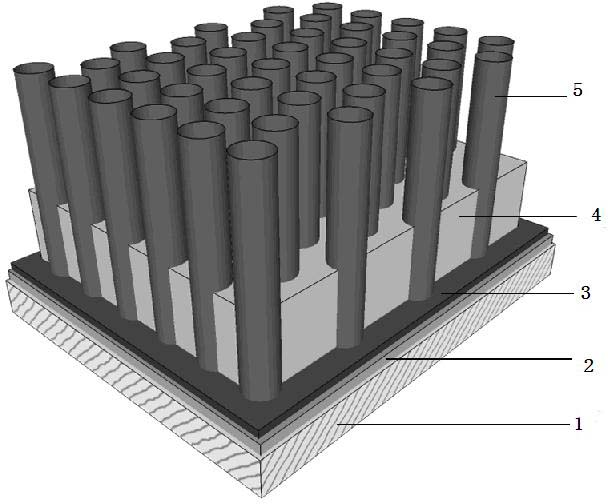
A minute structure is provided in which electroconductive paths are only formed in nanoholes, and a material is filled in the nanoholes, which are disposed in a specific area, by using the electroconductive paths. The minute structure comprising pores comprises a) a substrate, b) a plurality of electroconductive layers formed on a surface of the substrate, c) a layer primarily composed of aluminum oxide covering the plurality of electroconductive layers and a surface of the substrate where no electroconductive layer is formed, and d) a plurality of pores formed in the layer primarily composed of aluminum oxide, in which the pores are disposed above the electroconductive layers and the surface of the substrate where no electroconductive layers is formed, with a part of the layer primarily composed of aluminum oxide provided under the bottoms of the pores, and in which the layer primarily composed of aluminum oxide provided between the electroconductive layer and the bottoms of the pores disposed above the electroconductive layer comprises a material forming the electroconductive layer.
Owner:CANON KK
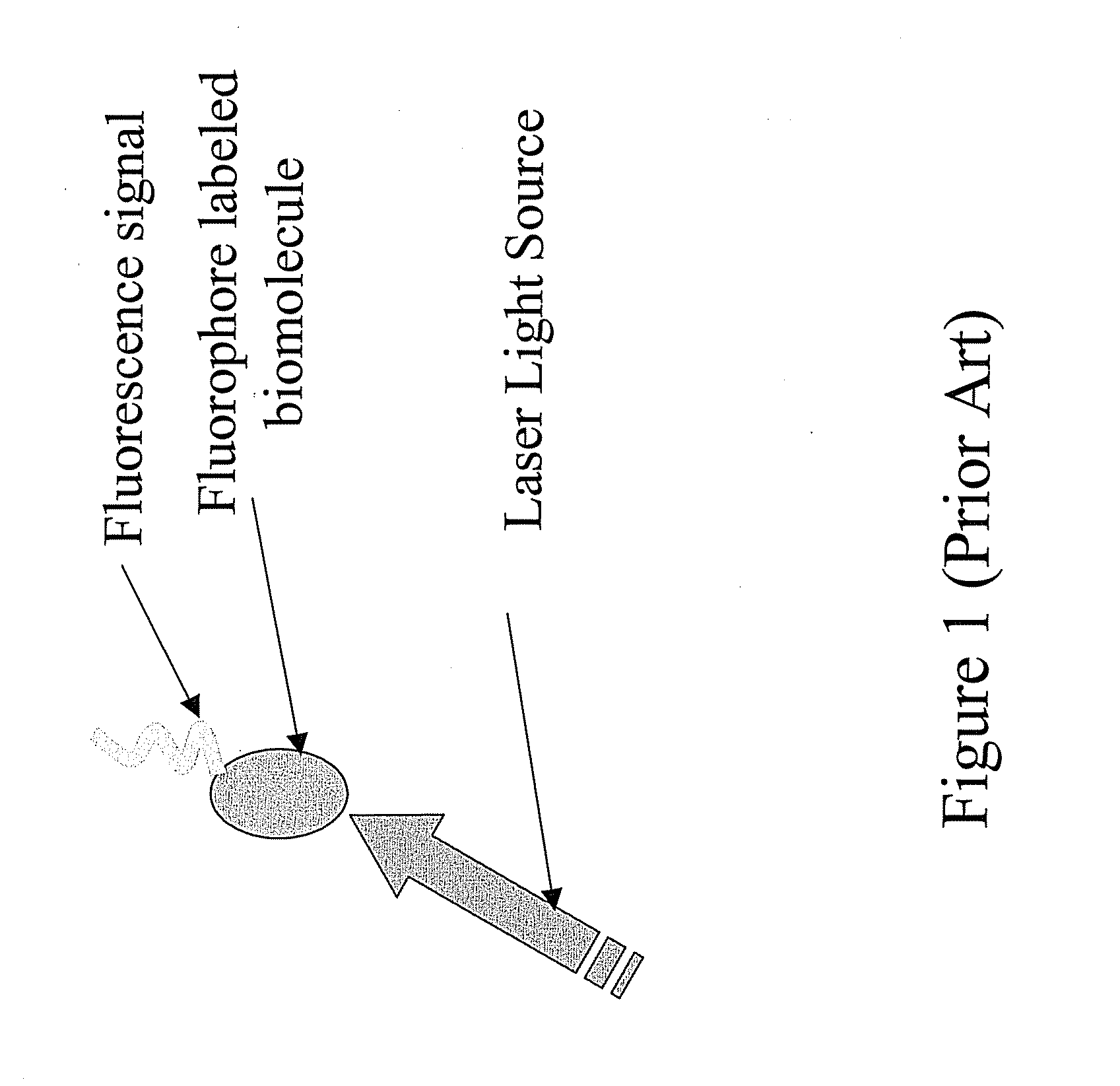
Apparatus for single-molecule detection
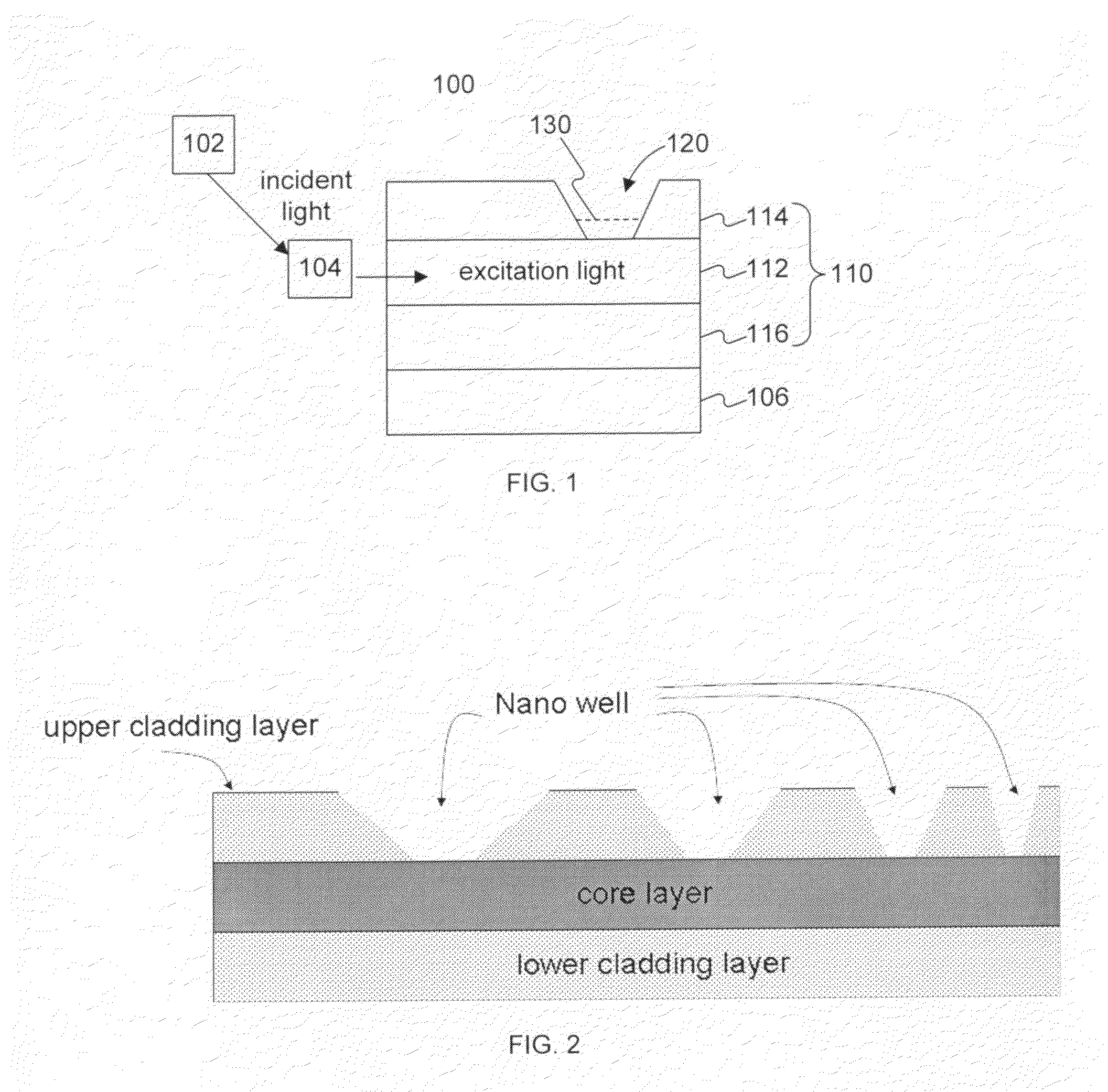
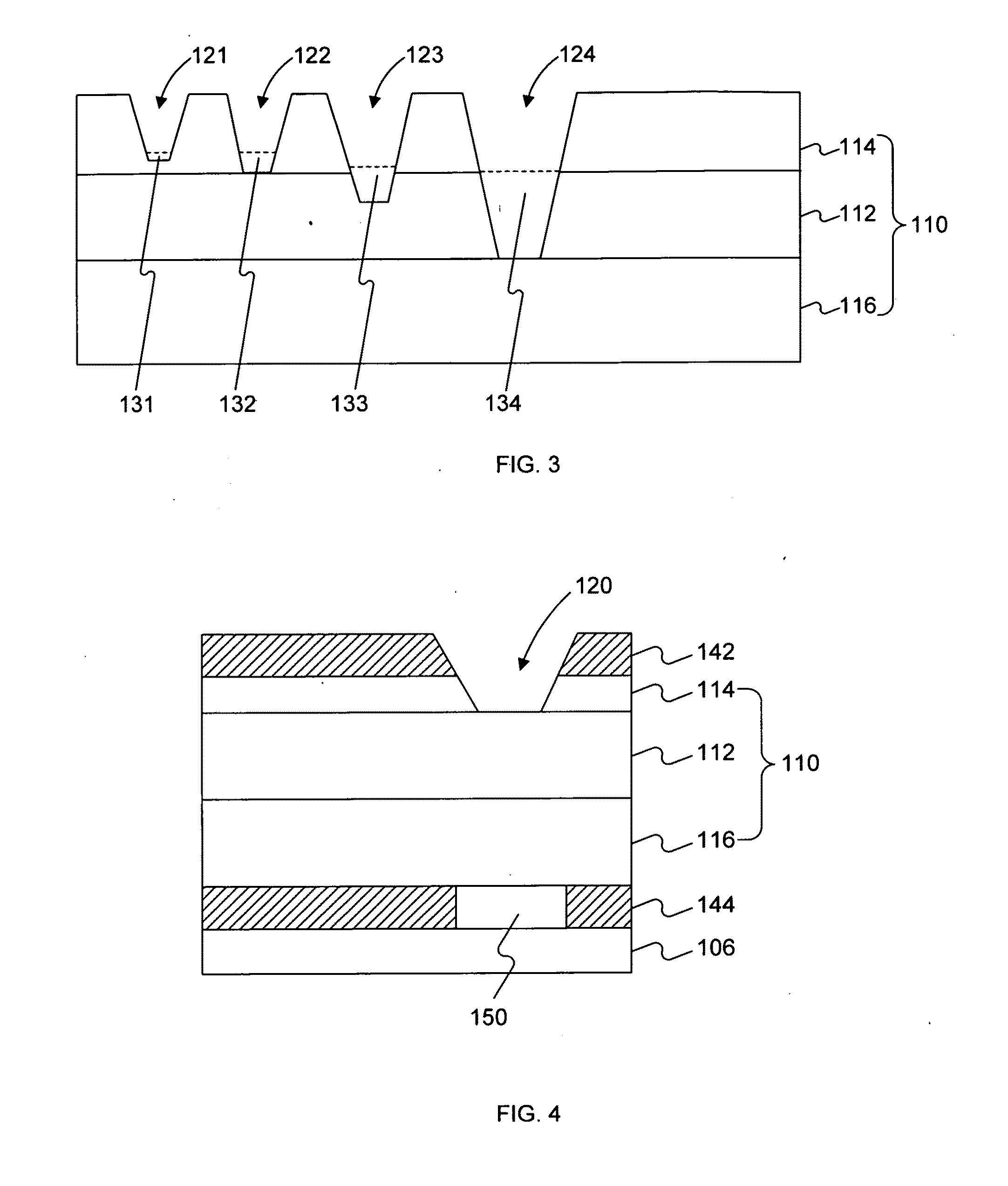
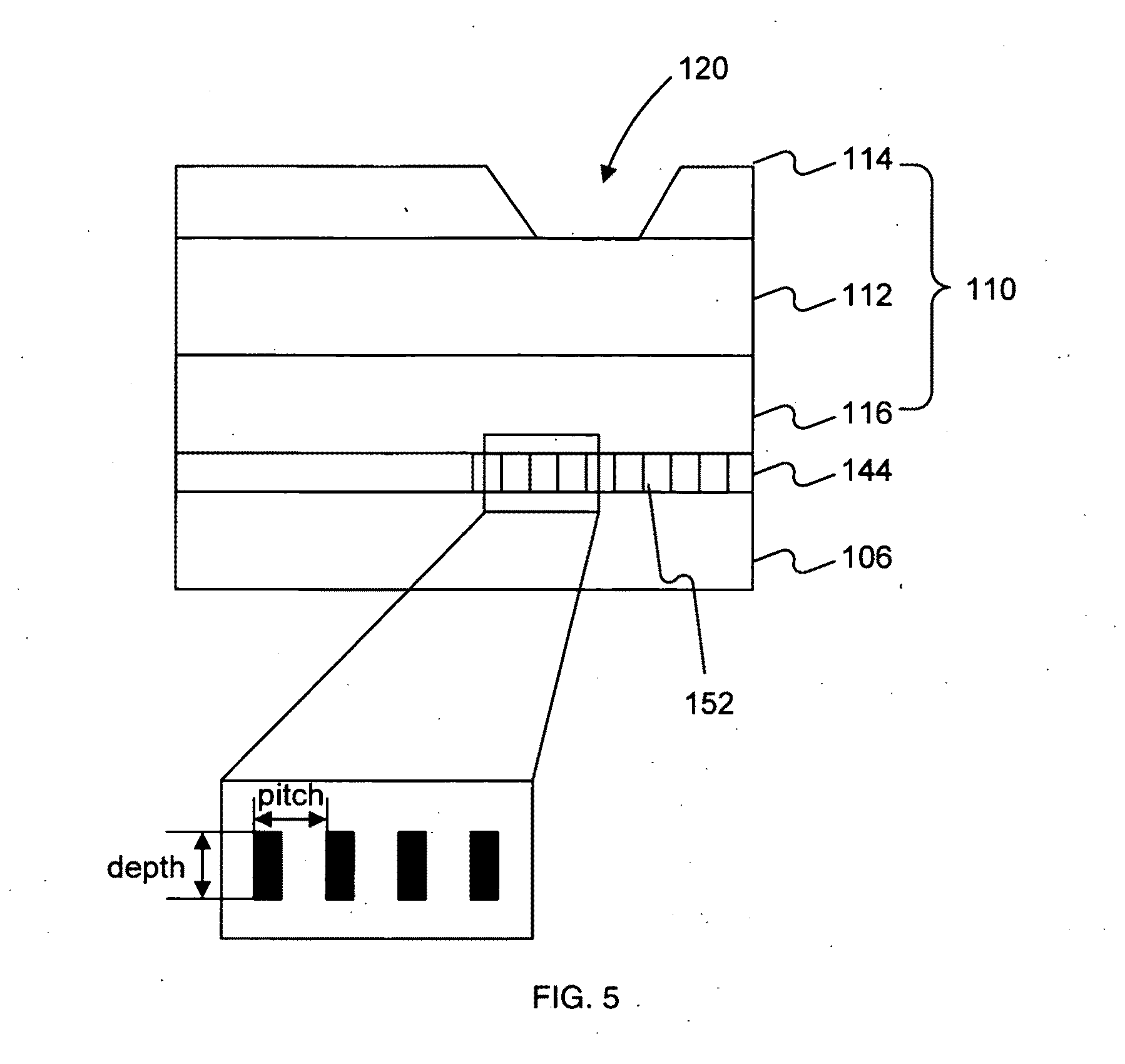
An apparatus for detecting an object capable of emitting light. The apparatus comprises a light source and a waveguide. The waveguide comprises a core layer and a first cladding layer. At least one nanowell is formed in at least the first cladding layer. The apparatus further comprises a light detector. The light detector can detect a light emitted from a single molecule object contained in the at least one nanowell.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for preparing electrode system, electrode system prepared therefrom, and electric device comprising the same
ActiveUS20050117194A1Improve response speedRaise transfer toHybrid capacitor electrodesFinal product manufactureElectron holeSupercapacitor
Provided are a method for preparing an electrode system, an electrode system prepared therefrom, and an electric device including the same. The method includes the steps of forming a porous template having nanopores on a first electrode, wherein a diameter of the nanopores is between 5 to nm 500 nm; and forming a rod-type / tube-type second electrode inside the nanopores which are connected to the first electrode, the electrode system prepared therefrom, and an electric device including the same. With the large surface area, the electrode system of the present research improves efficiency and performance of various electric devices. The contrast and respond speed of the electrochromic device can be increased, and the number of electron-hole pairs of a solar cell is increased. The loss of electron-hole pairs is minimized, and charge storage of the supercapacitor and charge respond speed is heightened.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Nanopore with resonant tunneling electrodes
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Magnetic recording medium including aluminum layer having holes and production method thereof
InactiveUS6858319B2Magnetic materials for record carriersMagnetic layer production by platingNanoholeOptoelectronics
To provide a magnetic recording medium with good record and reproduction characteristics. In the magnetic recording medium having an anodic oxidized alumina nanohole film filled with a magnetic substance, the anodic oxidized alumina nanohole film 13 is formed on a substrate 16 with at least one base electrode layer 15 sandwiched therebetween, the base electrode layer 15 is a film that has fcc structure and whose (111) face is oriented in the direction perpendicularly to a substrate, and the fillers 14 in the alumina nanoholes 10 have hcp structure and include hard magnetic substance whose principal component is Co and whose c-axis is perpendicular to the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Complex index refraction tomography with sub lambda/6-resolution
The present invention discloses a method to improve the image resolution of a microscope. This improvement is based on the mathematical processing of the complex field computed from the measurements with a microscope of the wave emitted or scattered by the specimen. This wave is, in a preferred embodiment, electromagnetic or optical for an optical microscope, but can be also of different kind like acoustical or matter waves. The disclosed invention makes use of the quantitative phase microscopy techniques known in the sate of the art or to be invented. In a preferred embodiment, the complex field provided by Digital Holographic Microscopy (DHM), but any kind of microscopy derived from quantitative phase microscopy: modified DIC, Shack-Hartmann wavefront analyzer or any analyzer derived from a similar principle, such as multi-level lateral shearing interferometers or common-path interferometers, or devices that convert stacks of intensity images (transport if intensity techniques: TIT) into quantitative phase image can be used, provided that they deliver a comprehensive measure of the complex scattered wavefield. The hereby-disclosed method delivers superresolution microscopic images of the specimen, i.e. images with a resolution beyond the Rayleigh limit of the microscope. It is shown that the limit of resolution with coherent illumination can be improved by a factor of 6 at least. It is taught that the gain in resolution arises from the mathematical digital processing of the phase as well as of the amplitude of the complex field scattered by the observed specimen. In a first embodiment, the invention teaches how the experimental observation of systematically occurring phase singularities in phase imaging of sub-Rayleigh distanced objects can be exploited to relate the locus of the phase singularities to the sub-Rayleigh distance of point sources, not resolved in usual diffraction limited microscopy. In a second, preferred embodiment, the disclosed method teaches how the image resolution is improved by complex deconvolution. Accessing the object's scattered complex field—containing the information coded in the phase—and deconvolving it with the reconstructed complex transfer function (CTF) is at the basis of the disclosed method. In a third, preferred embodiment, it is taught how the concept of “Synthetic Coherent Transfer Function” (SCTF), based on Debye scalar or Vector model includes experimental parameters of MO and how the experimental Amplitude Point Spread Functions (APSF) are used for the SCTF determination. It is also taught how to derive APSF from the measurement of the complex field scattered by a nanohole in a metallic film. In a fourth embodiment, the invention teaches how the limit of resolution can be extended to a limit of λ / 6 or smaller based angular scanning. In a fifth embodiment, the invention teaches how the presented method can generalized to a tomographic approach that ultimately results in super-resolved 3D refractive index reconstruction.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Structure of P-type GaN layer of GaN-based light-emitting diode chip
The invention provides a structure of a P-type GaN layer of a GaN-based light-emitting diode (LED) chip, wherein the P-type GaN layer is provided with pores, the distance from the bottoms of pores to the quantum-well active area of the LED chip is 10-100nm, metal particles are filled in the pores, and transparent dielectric films are filled at the pore openings to block the metal particles. The P-type GaN layer of the invention is provided with nano-pores, each pore is provided with a metal particle; the metal particle-active layer dielectric heterostructure is transplanted at the nanoscale to form the dielectric heterostructure coupled by the nanometer metal particles and the quantum-well active area; and the coupling of the surface plasmon polariton (SPP) and excitons increases the luminous efficiency of the GaN-based LED.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method of flaky nanoholes carbon and carbon nanotube composite
InactiveCN105776181AShorten the diffusion distanceImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyChemical compositionNanohole
A preparation method of a flaky nanoholes carbon and carbon nanotube composite belongs to the technical field of new materials. The flaky nanoholes carbon and carbon nanotube composite is obtained based on intercalation growth of a metal-organic framework compound in two-dimensional nanoholes of a lamellar inorganic template, confinement carbonization and template removal by acid corrosion. The method is simple and reliable, the large-scale production of two-dimensional nanoholes carbon flake material and one-dimensional carbon nanotube composite is easy to implement. The obtained nanoholes carbon flake and carbon nanotube composite has highly controllable chemical composition and pore structure height and has a promising application prospect in the catalysis field, the energy storage and conversion field and other fields.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Optical Sensor with Enhanced Sensitivity
ActiveUS20130323858A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioComponent separationRaman scatteringAnalyteNanohole
The invention is a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor to determine the presence and quantity of biological or chemical entities in an analyte. The sensor comprises a metal periodic structure deposited as a thin layer of a noble metal, comprising a one dimensional array of nanoslits or a two dimensional array of nanoholes on a transparent dielectric substrate, a nm-thick layer of transparent dielectric protection layer on top of the metal periodic structure and a functionalization layer, which acts as a binding layer to biological or biochemical entities in an analyte that is in contact with the functionaliztion layer.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Composite material, structure and polycrystalline structure film and method of making particles
InactiveUS20050196606A1Reliable and uniform filling of magnetic materialCrystal grain size may decreaseLayered productsPatterned record carriersNanoparticleNanohole
A substrate defines minute holes or nanoholes over its surface in a composite material. Particles or nanoparticles are filled within the minute holes. The composite material enables a reliable disposition of the particles within the minute holes. The position of the minute holes can reliably be controlled. This serves to establish regularly ordered particles based on the regularly ordered minute holes. This composite material is applicable to a magnetic recording medium.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Structure having pores, device using the same, and manufacturing methods therefor
InactiveUS7319069B2Novel structureFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsNanoholeMaterials science
A minute structure is provided in which electroconductive paths are only formed in nanoholes, and a material is filled in the nanoholes, which are disposed in a specific area, by using the electroconductive paths. The minute structure comprising pores comprises a) a substrate, b) a plurality of electroconductive layers formed on a surface of the substrate, c) a layer primarily composed of aluminum oxide covering the plurality of electroconductive layers and a surface of the substrate where no electroconductive layer is formed, and d) a plurality of pores formed in the layer primarily composed of aluminum oxide, in which the pores are disposed above the electroconductive layers and the surface of the substrate where no electroconductive layers is formed, with a part of the layer primarily composed of aluminum oxide provided under the bottoms of the pores, and in which the layer primarily composed of aluminum oxide provided between the electroconductive layer and the bottoms of the pores disposed above the electroconductive layer comprises a material forming the electroconductive layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Light emitting photonic crystals
The invention relates to processes for the synthesis of 2-D and 3-D periodic porous silicon structures and composites with improved properties having the advantages of porous silicon and photonic bandgap materials. Photonic crystals comprise a two dimensionally periodic or three dimensionally periodic microporous structural matrix of interconnecting, crystallographically oriented, monodispersed members having voids between adjacent members, and said members additionally having randomly nanoporous surface porosity. The silicon nanofoam material shows enhanced and spectrally controlled / tunable photoluminescence and electroluminesce and finds use as transparent electrodes, high-lumonosity light emitting diodes (LEDs), wavelength division multiplexors, high-active-area catalyst supports, photonic bandgap lasers, silicon-based UV detectors, displays, gas sensors, and the like.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for forming silicon oxide and metal nanopattern's, and Magnetic recording medium for information storage using the same
ActiveUS20150228298A1Well formedEasy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsNanodotNanohole
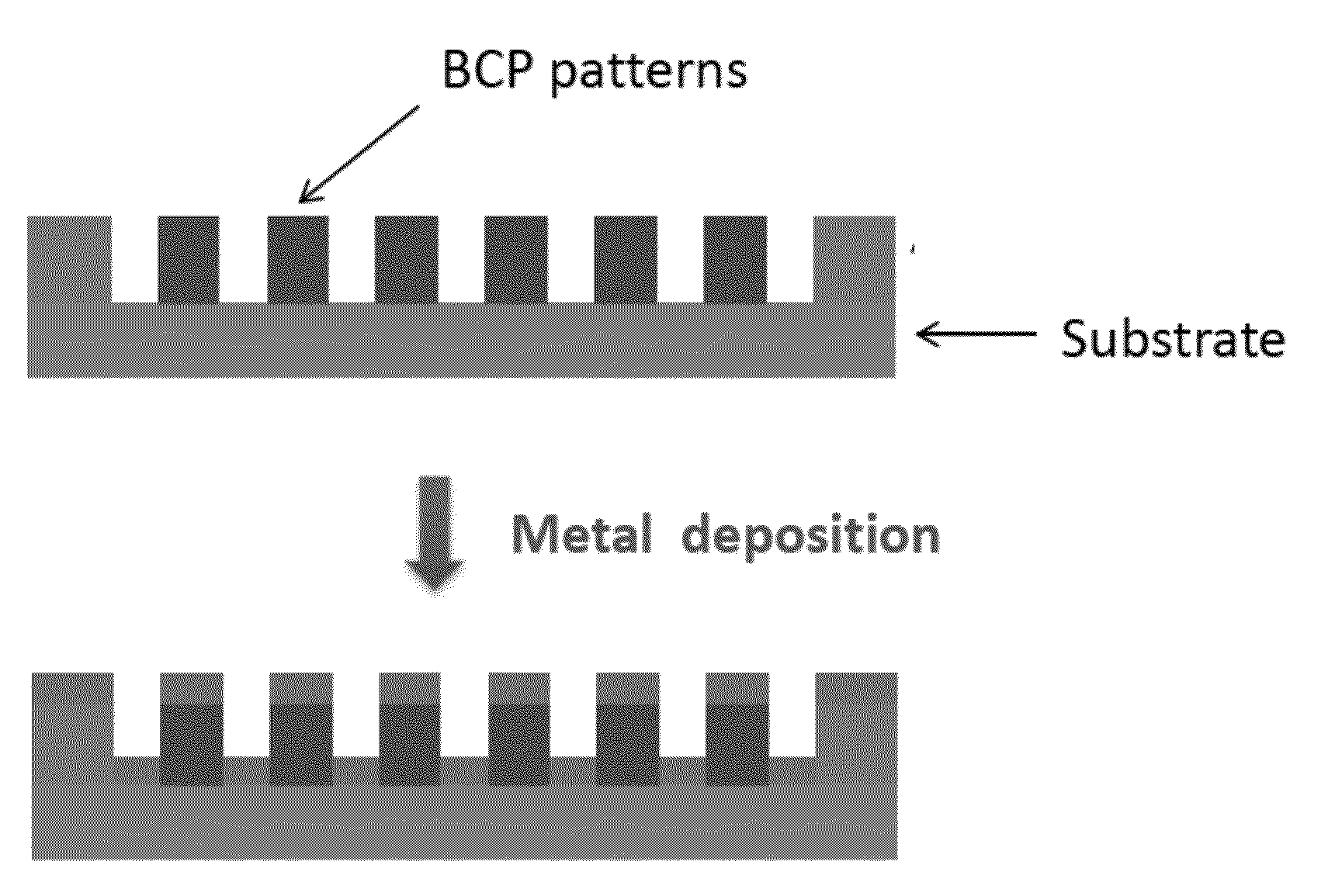
The present invention relates to a method for forming a silicon oxide nanopattern, in which the method can be used to easily form a nanodot or nanohole-type nanopattern, and a metal nanopattern formed by using the same can be properly applied to a next-generation magnetic recording medium for storage information, etc., a method for forming a metal nanopattern, and a magnetic recording medium for information storage using the same.The method for forming a silicon oxide nanopattern includes the steps of forming a block copolymer thin film including specific hard segments and soft segments containing a (meth)acrylate-based repeating unit on silicon oxide of a substrate; conducting orientation of the thin film; selectively removing the soft segments from the block copolymer thin film; and conducting reactive ion etching of silicon oxide using the block copolymer thin film from which the soft segments are removed, as a mask to form a silicon oxide nanodot or nanohole pattern.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
Method and device for preparing ordered porous alumina template
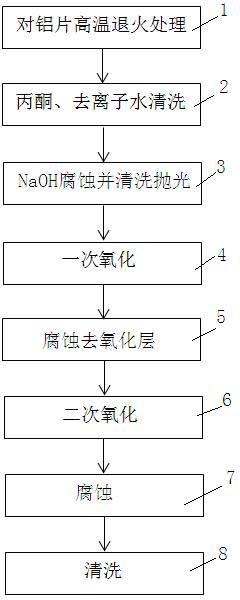
The invention relates to a method and a device for preparing an ordered porous alumina template, thereby being capable of realizing large-scale preparation of the ordered porous alumina templates with low cost. The method comprises the steps of: 1) removing stains and an oxide film on an aluminum sheet and polishing; and 2) using the aluminum sheet as an anode, adopting a base metal as a cathode and adopting the secondary anode oxidation method for preparing the nano-ordered porous alumina template. The cathodes and the anodes are multiple and are respectively connected in parallel by adopting guide wires, thereby controlling the anode oxidation of the aluminum sheets. The device is a cuboid groove structure, a plurality of pairs of small holes are formed on two sides and used for containing the cathodes and the anodes which are connected with a power supply, and electrolyte is contained in the groove. An magnetic stirrer and other stirring equipment can be adopted for carrying out stirring on the electrolyte during the anode oxidation process. The method and the device can realize the low-cost, large-scale and rapid preparation of a nano-pore path array with high order degree and adjustable pore size.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Homogeneous multiple band gap devices
InactiveUS20130099205A1Easy to makeImprove efficiencyNanoopticsPhotovoltaic energy generationSchottky barrierNanohole
An electrical device comprising (A) a substrate having a surface and (B) a nanohole superlattice superimposed on a portion of the surface is provided. The nanohole superlattice comprises a plurality of sheets having an array of holes defined therein. The array of holes is characterized by a band gap or band gap range. The plurality of sheets forms a first edge and a second edge. A first lead comprising a first electrically conductive material forms a first junction with the first edge. A second lead comprising a second electrically conductive material forms a second junction with the second edge. The first junction is a Schottky barrier with respect to a carrier. In some instances a metal protective coating covers all or a portion of a surface of the first lead. In some instances, the first lead comprises titanium, the second lead comprises palladium, and the metal protective coating comprises gold.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Transplantable ultrathin nano-porous gold film and method for preparing the same
The preparation method for transplantable ultrathin nano porous gold film comprises: preparing Au-Cu alloy with vacuum evaporation method, thermal annealing, and removing alloy with acidic solution. This product can be used in catalysis, bio-sense, porous electrode and other fields as well as nano grating and non-linear optics fields for special optical and high light transmission features
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Nanostructures for dislocation blocking in group ii-vi semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20100140735A1Reduce defect densityIncreased durabilityPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsNanohole
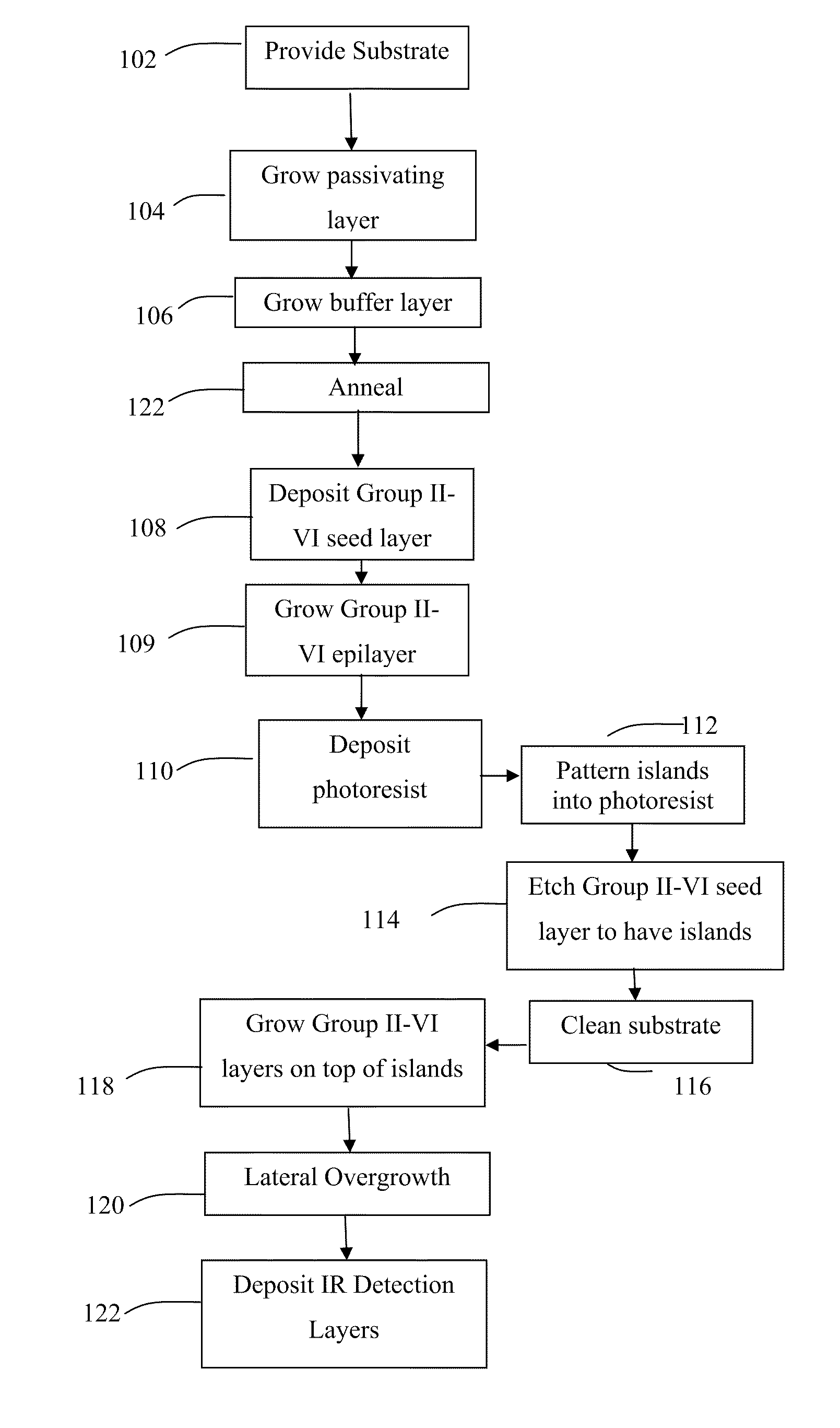
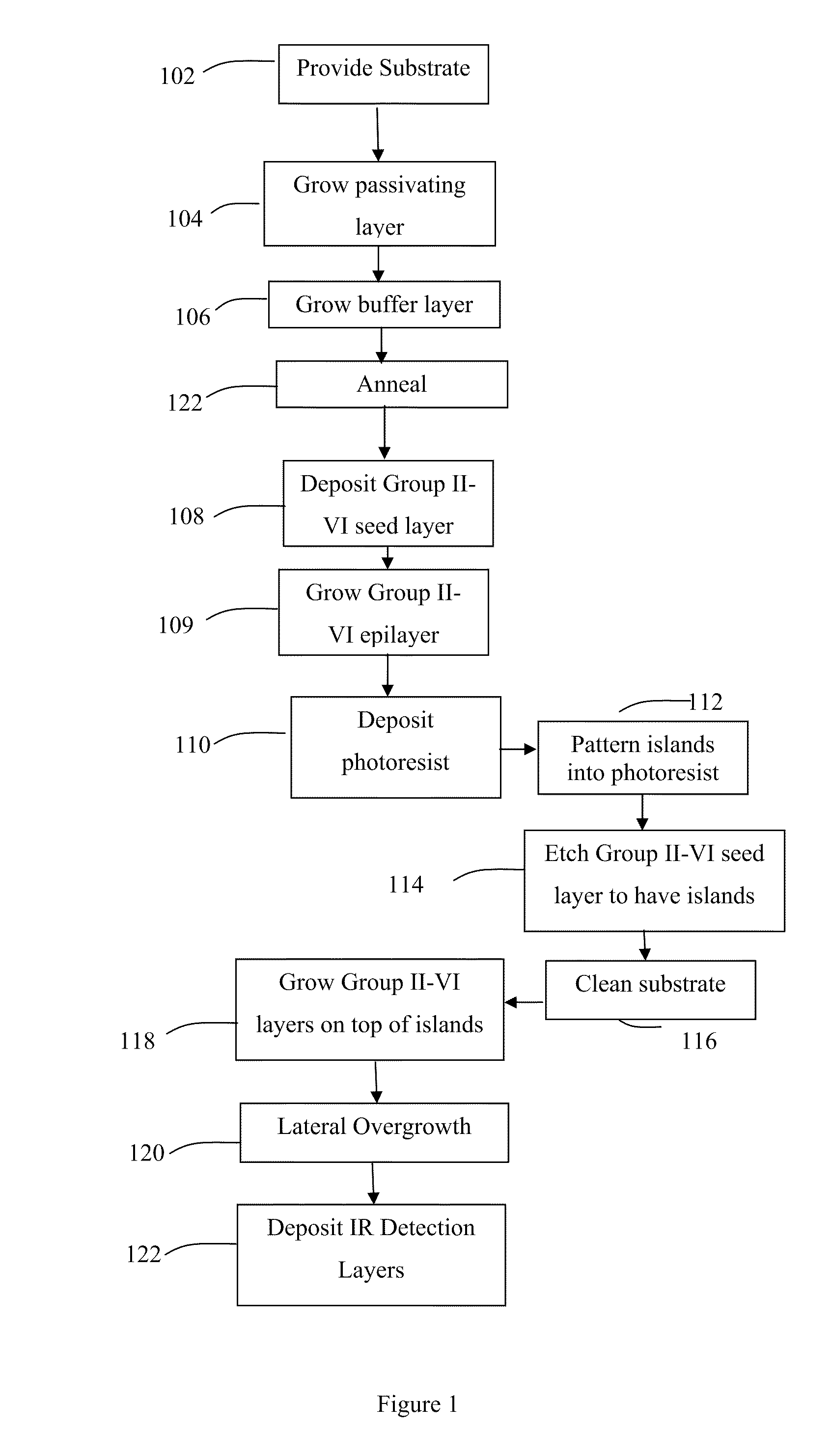
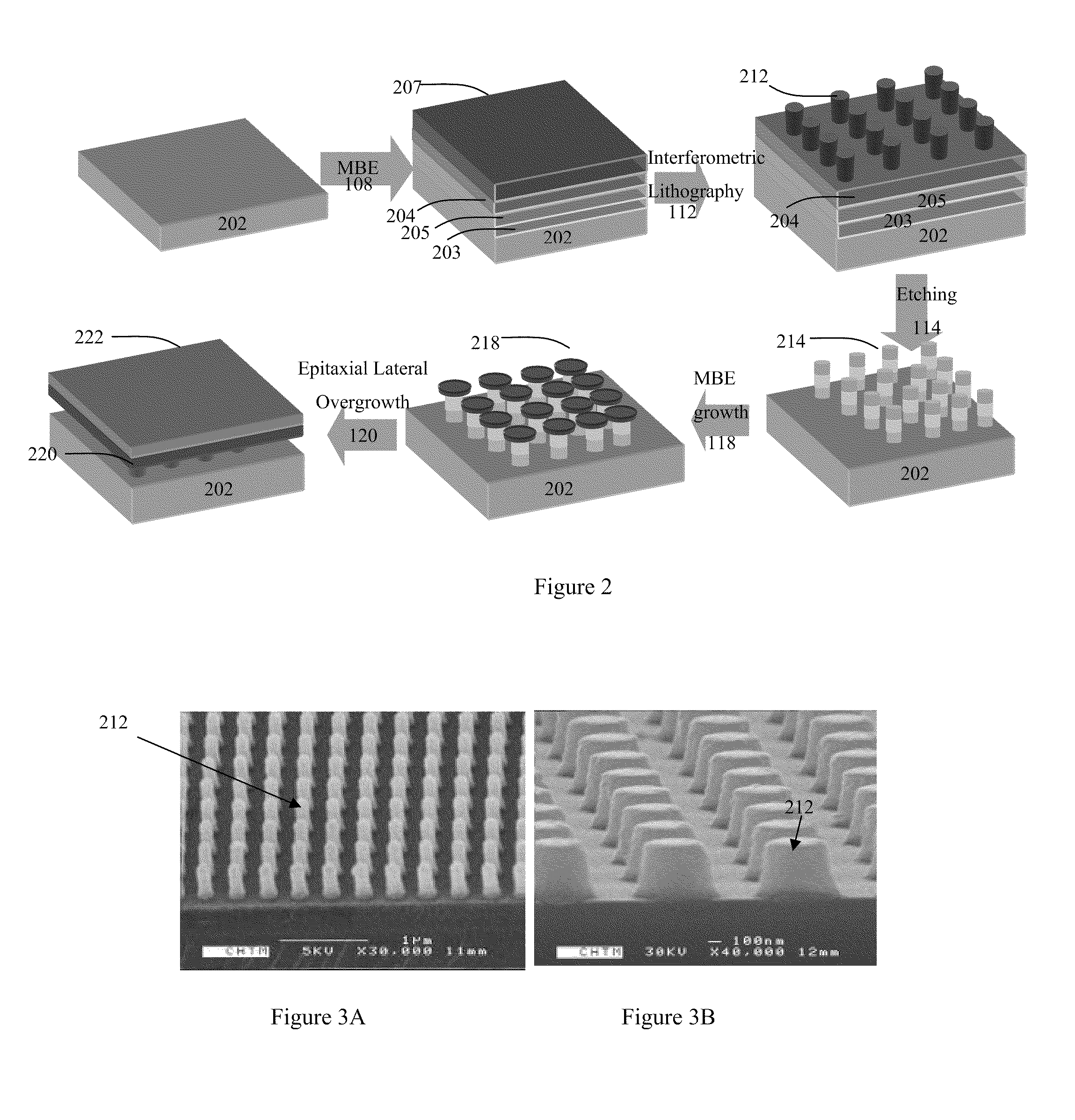
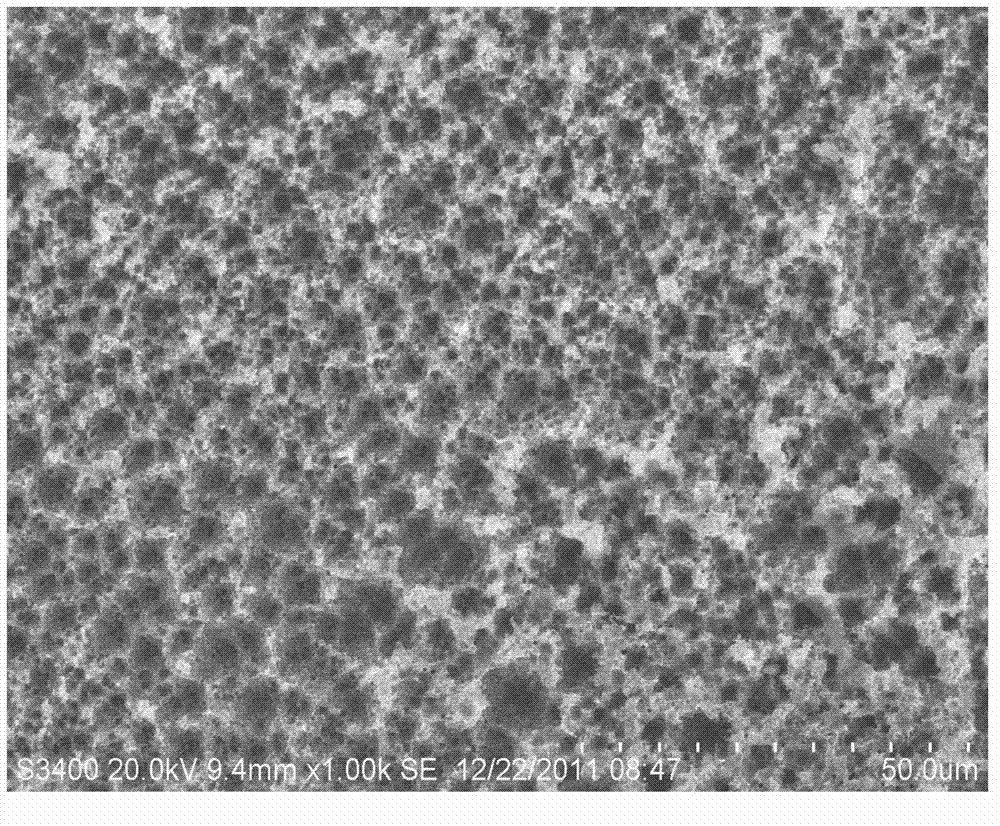
A compound semiconductor workpiece with reduced defects and greater strength that uses Group II-VI semiconductor nanoislands on a substrate. Additional layers of Group II-VI semiconductor are grown on the nanoislands using MBE until the newly formed layers coalesce to form a uniform layer of a desired thickness. In an alternate embodiment, nanoholes are patterned into a silicon nitride layer to expose an elemental silicon surface of a substrate. Group II-VI semiconductor material is grown in the holes until the layers fill the holes and coalesce to form a uniform layer of a desired thickness. Suitable materials for the substrate include silicon and silicon on insulator materials and cadmium telluride may be used as the Group II-VI semiconductor.
Owner:EPIR TECH INC
Method for preparing black silicon by metallic copper ion auxiliary etching
InactiveCN102768951AEasy to cleanAvoid residueSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingNanohole
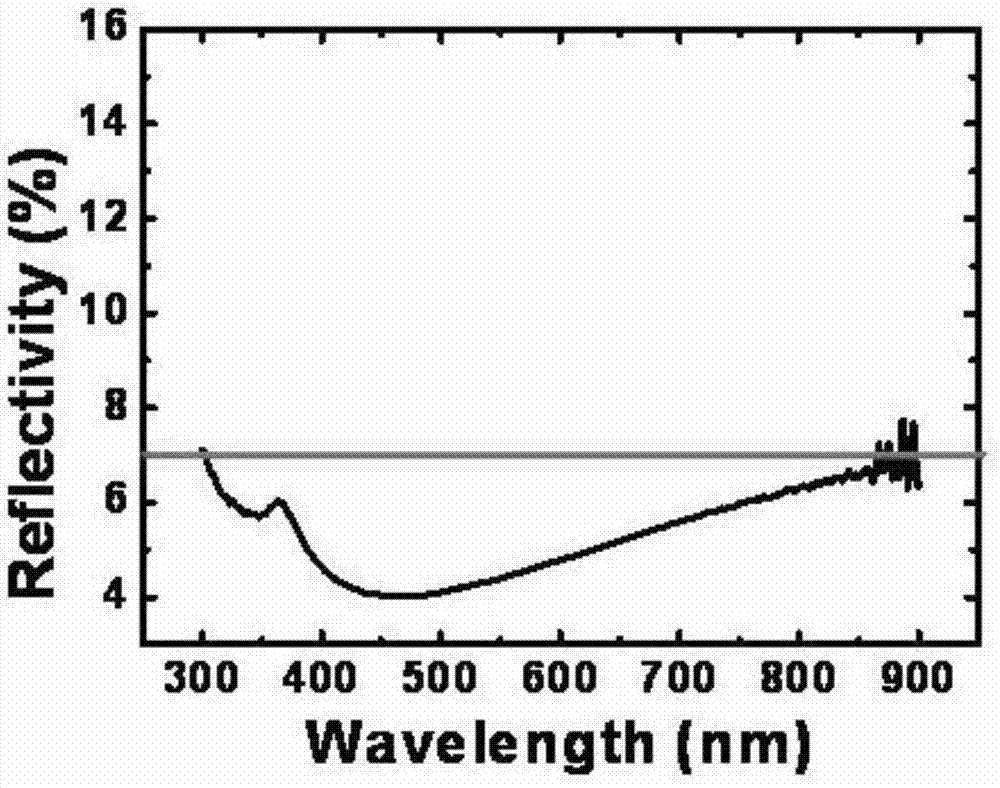
The invention discloses a method for preparing black silicon by using metallic copper ion auxiliary etching, comprising the following steps of (1) preparing an etchant solution which is a mixed solution composed of hydrofluoric acid, hydrogen peroxide and cupric nitrate; (2) placing a monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon wafer into the etchant solution which contains metallic copper ions, and controlling the temperature of the etchant solution and the reaction time; and (3) taking out the reacted silicon wafer, washing the silicon wafer with an oxidative acid liquor to remove metallic residues, washing, with ionized water, and drying the silicon wafer so as to obtain a black silicon material. Monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon surfaces are etched in a texturing manner by the catalytic action of the metal copper ions, and the black silicon material with uniform nano-pores at the surface is prepared, so that the reflectivity of monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon materials in a light absorption waveband is obviously reduced, and conversion efficiency of silicon-based solar cells is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for making anodized aluminum template and method for making field emission cathode array material using the template
ActiveCN102262989AArrangement rulesImprove uniformityAnodisationCold cathode manufactureNanoholeCarbonization
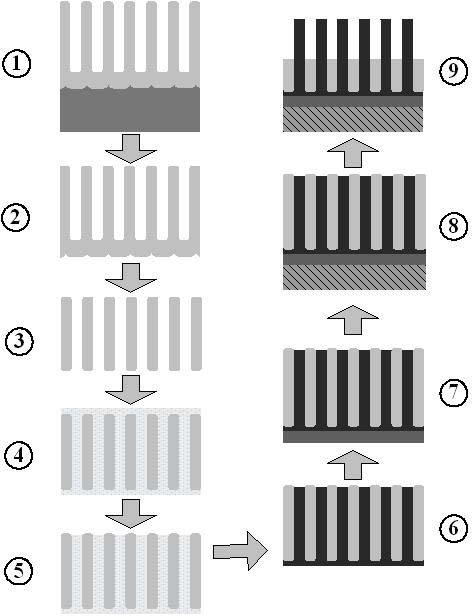
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing an anodic aluminum oxide template and a method for manufacturing a field emission cathode array material by using the aluminum oxide template. The anodic aluminum oxide template with a regular appearance and a clean surface is manufactured by adopting a series of surface protection measures; and a field emission vertical nanowire or nanotube array cathode material is manufactured by pouring organic substances, metal organic solution or sol into a nano hole of the aluminum oxide template by a water method, a heat method and the like through processes such as gelation, high temperature carbonization, aluminum oxide template removal and the like. The field emission cathode material manufactured by the method has regular appearance and low starting voltage during field emission performance test; furthermore, the method process is simpler; and manufacturing of large-area field emission materials can be realized easily.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Nanowires and Method for the Production there of
InactiveUS20110174069A1Process stabilityProcess economyMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesNanowireTemplate based
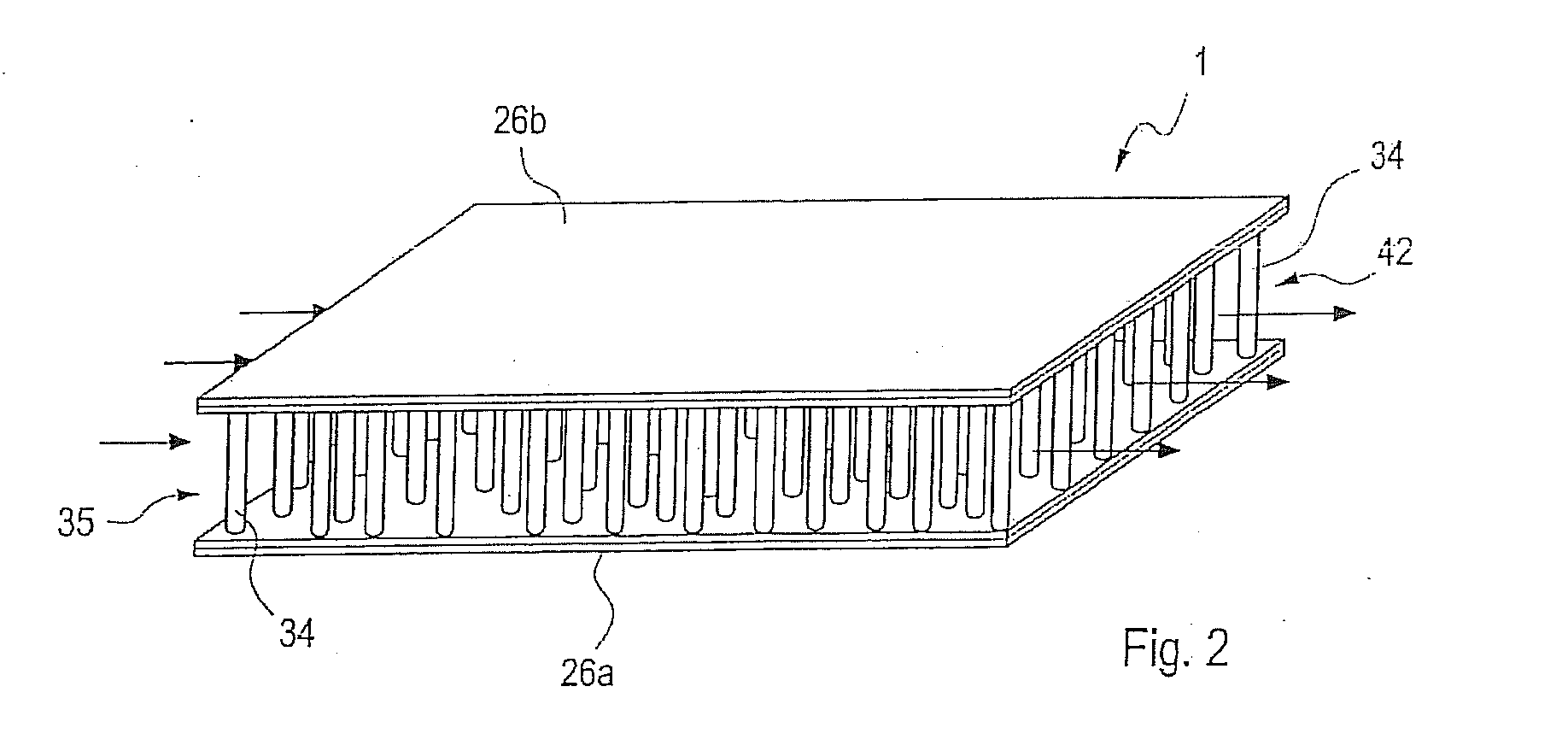
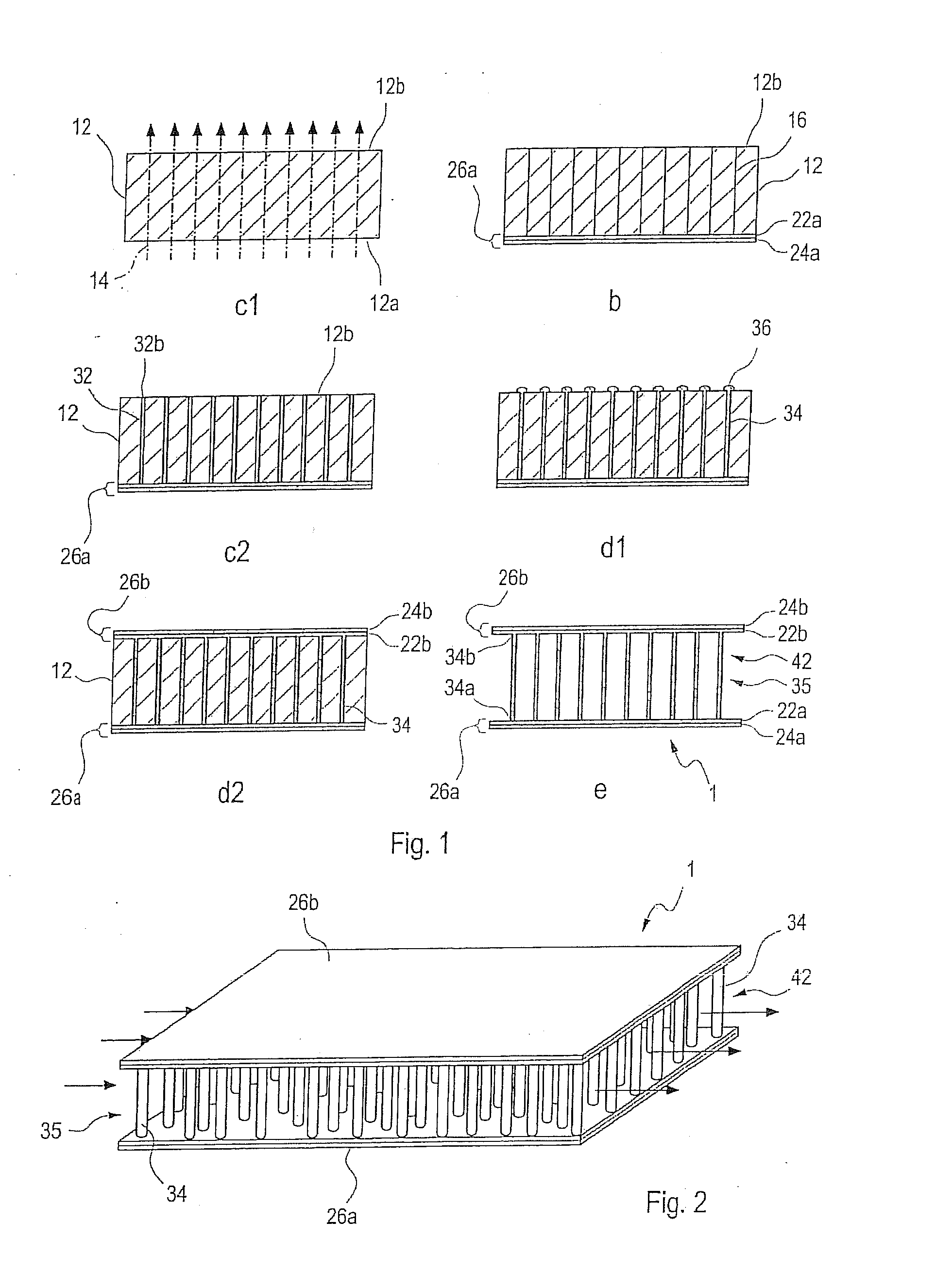
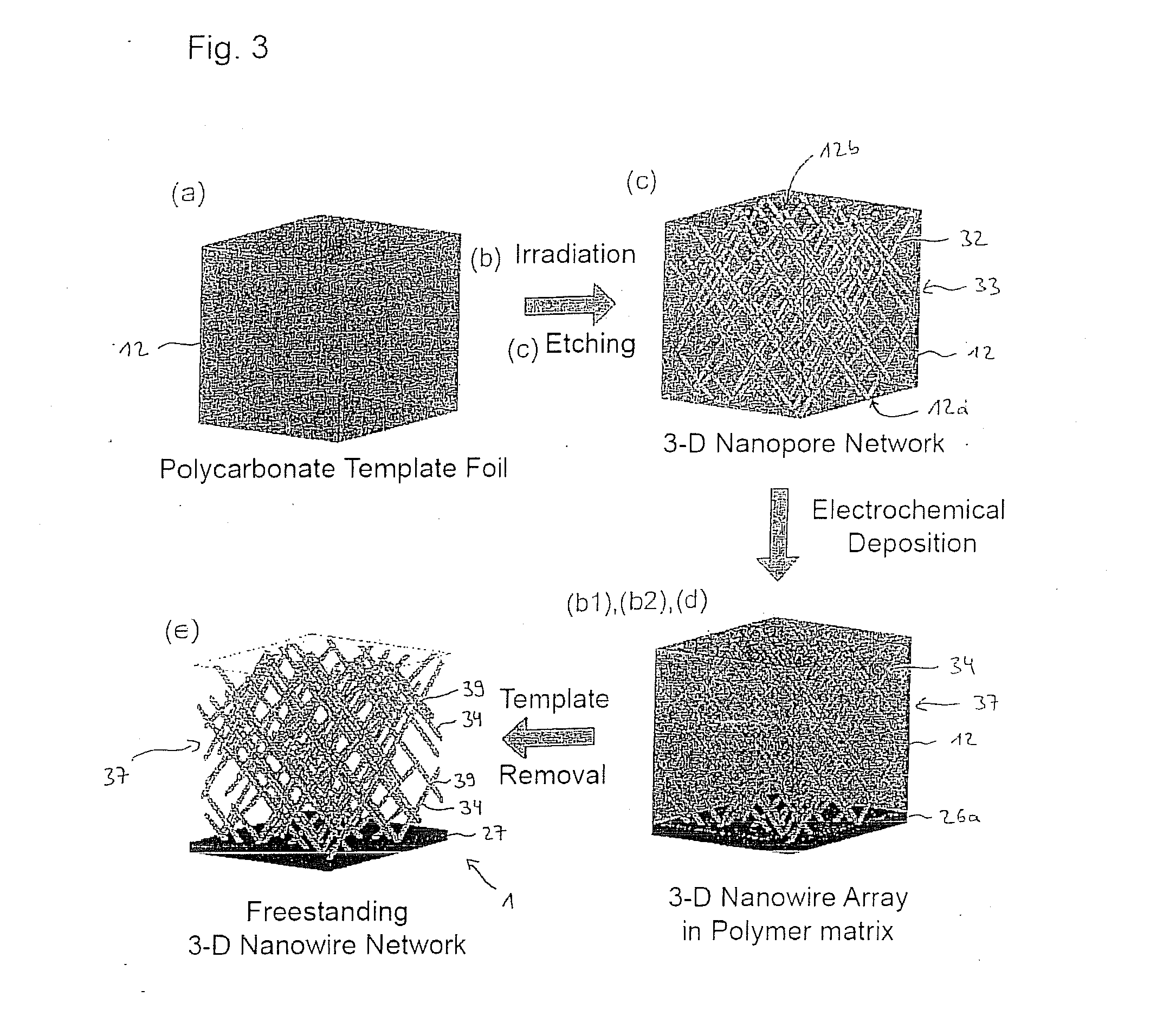
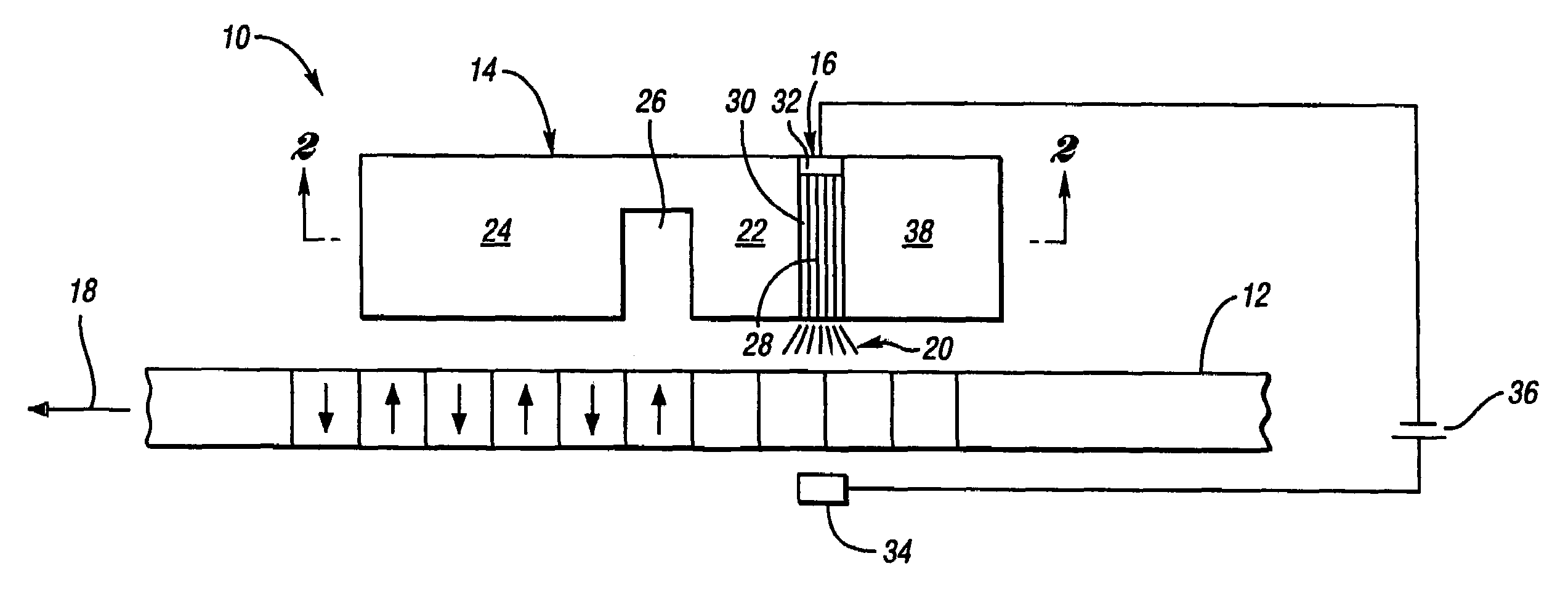
The invention concerns the production of segmented nanowires and components having said segmented nanowires.For the production of the nanowire structural element, a template based process is used preferably, wherein the electrochemical deposition of the nanowires in nanopores is carried out. In this manner, numerous nanowires are created in the template foil.For the electrochemical deposition of the nanowires, a reversed pulse procedure with an alternating sequence consisting of cathodic deposition pulses and anodic counter-pulses is carried out. By this means, segmented nanowires can be produced.
Owner:GSI HELMHOLTZZENT FUR SCHWERIONENFORSCHUNG
Magnetic recorder having carbon nanotubes embedded in anodic alumina for emitting electron beams to perform heat-assisted magnetic recording
A heat-assisted magnetic recorder for magnetically recording information onto a recording medium having a given recording coercive field includes an electron beam generator and a magnetic recording head. The electron beam generator directs an electron beam onto the recording medium in order to locally heat a portion of the recording medium such that the heated recording medium portion has a recording coercive field lower than the given recording coercive field. The magnetic recording head generates a magnetic recording field having an intensity greater than the recording coercive field of the heated recording medium portion in order to magnetically record information onto the heated recording medium portion. The electron beam generator includes a plurality of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) embedded in nanoholes of an anodic alumina template for generating the electron beam. A heat-assisted magnetic recording method is associated with the heat-assisted magnetic recorder.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
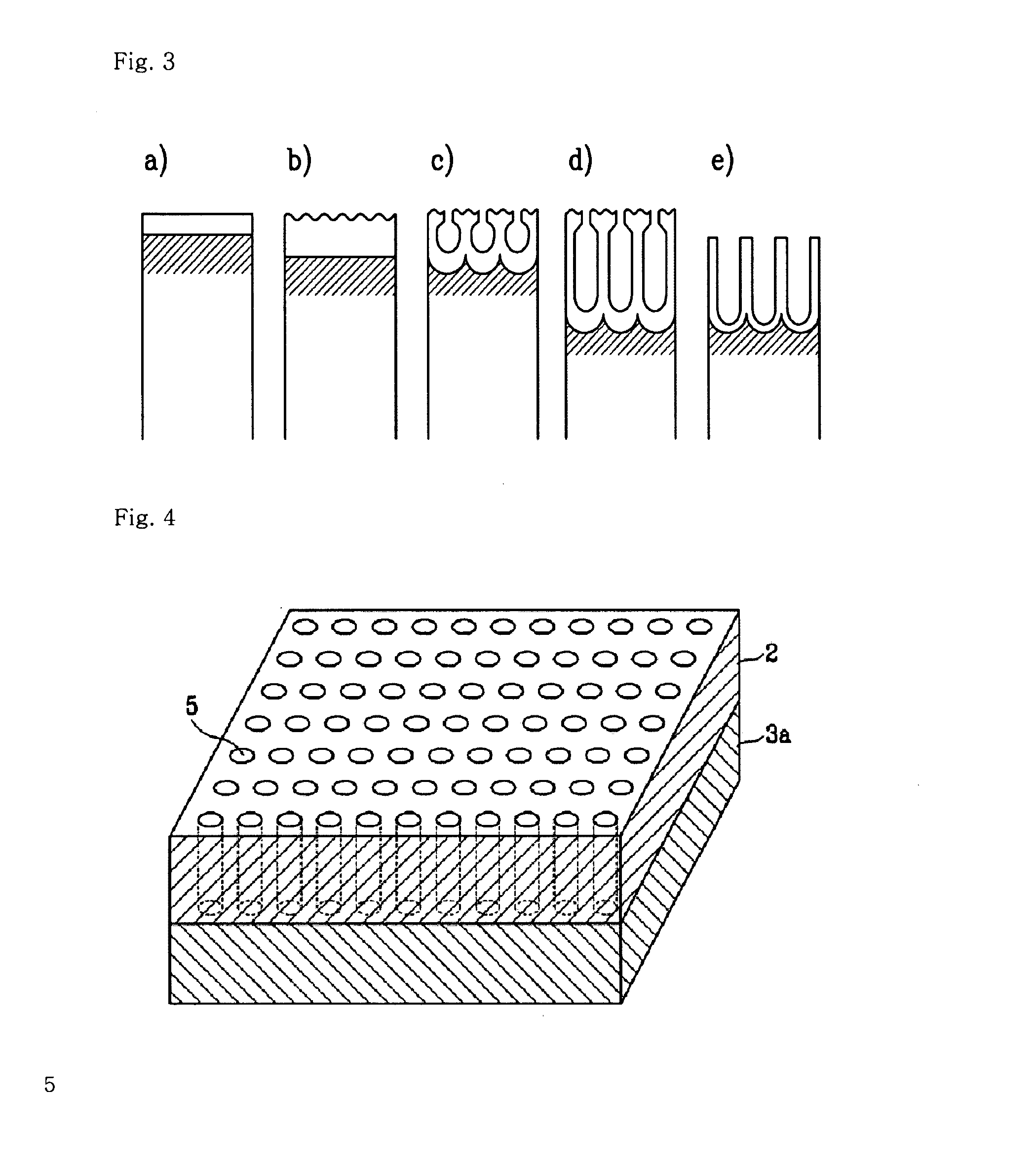
Zero-order diffractive filter
InactiveUS20080225391A1Minimize optical scatteringHigh indexNanoopticsDiffraction gratingsPorous layerRefractive index
A Zero-order diffractive filter comprising a first layer (1) with a periodic diffractive microstructure, forming a waveguide, and at least one adjacent second layer (2, 4, 5), wherein said first layer (1) has a refractive index that is higher than the refractive index of said second layer (2, 4, 5) by at least 0.2. At least one of said second layers (2, 4, 5) is a porous layer comprising nanopores. The period Λ of the diffractive microstructure is between 100 nm and 3000 nm.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
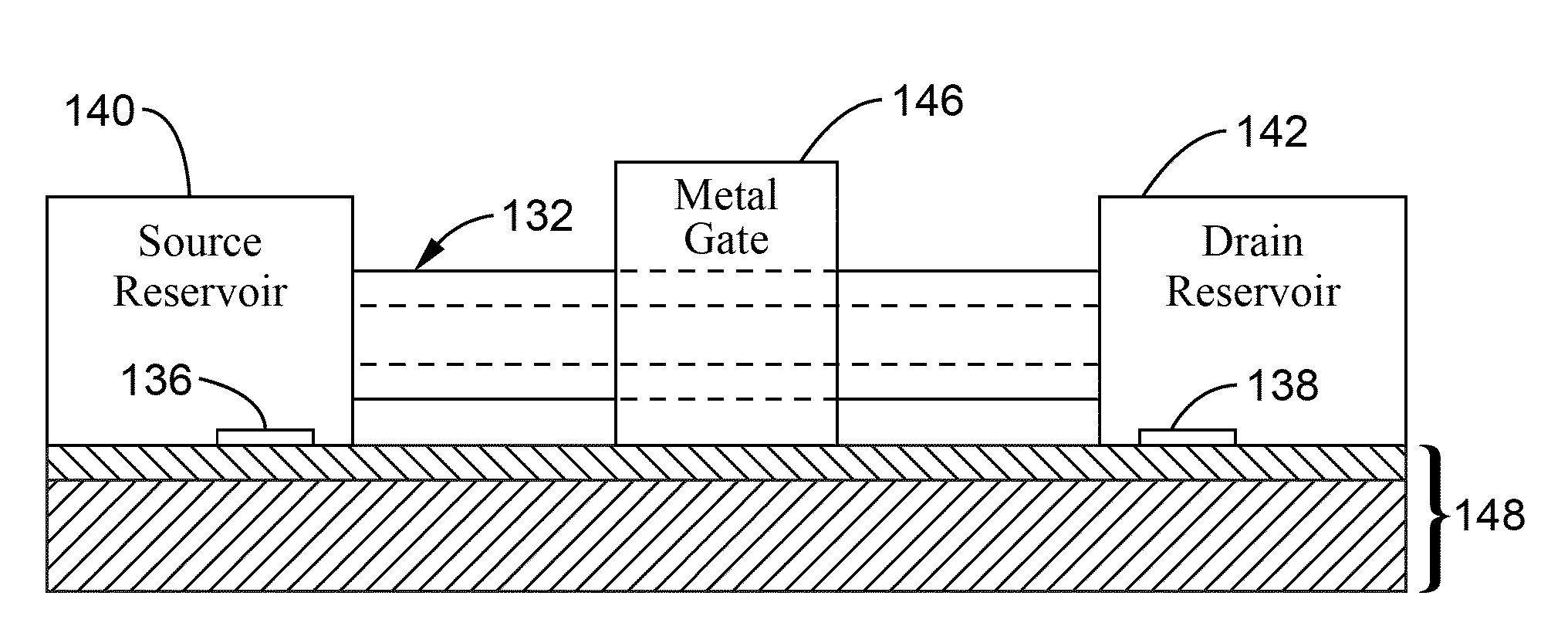
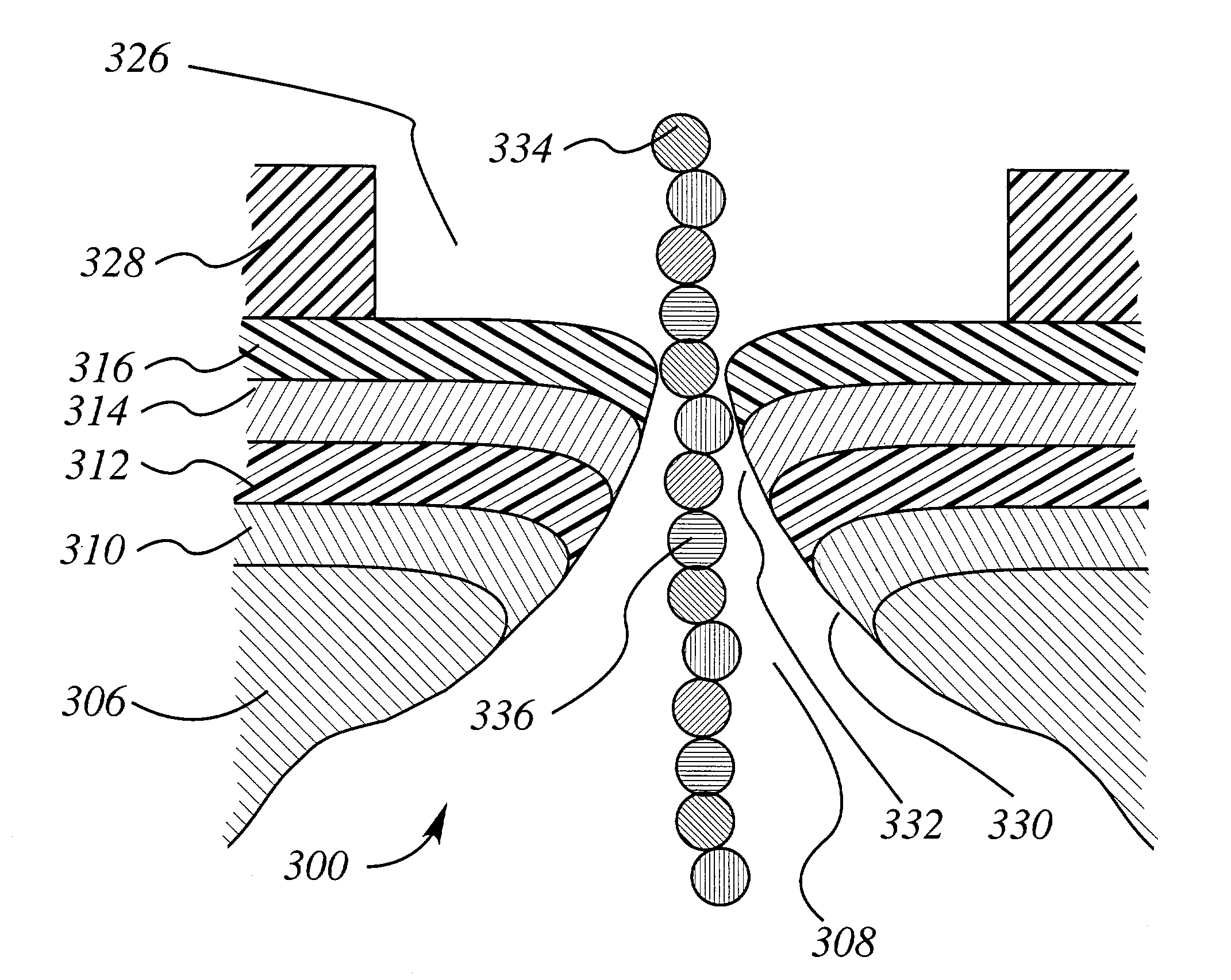
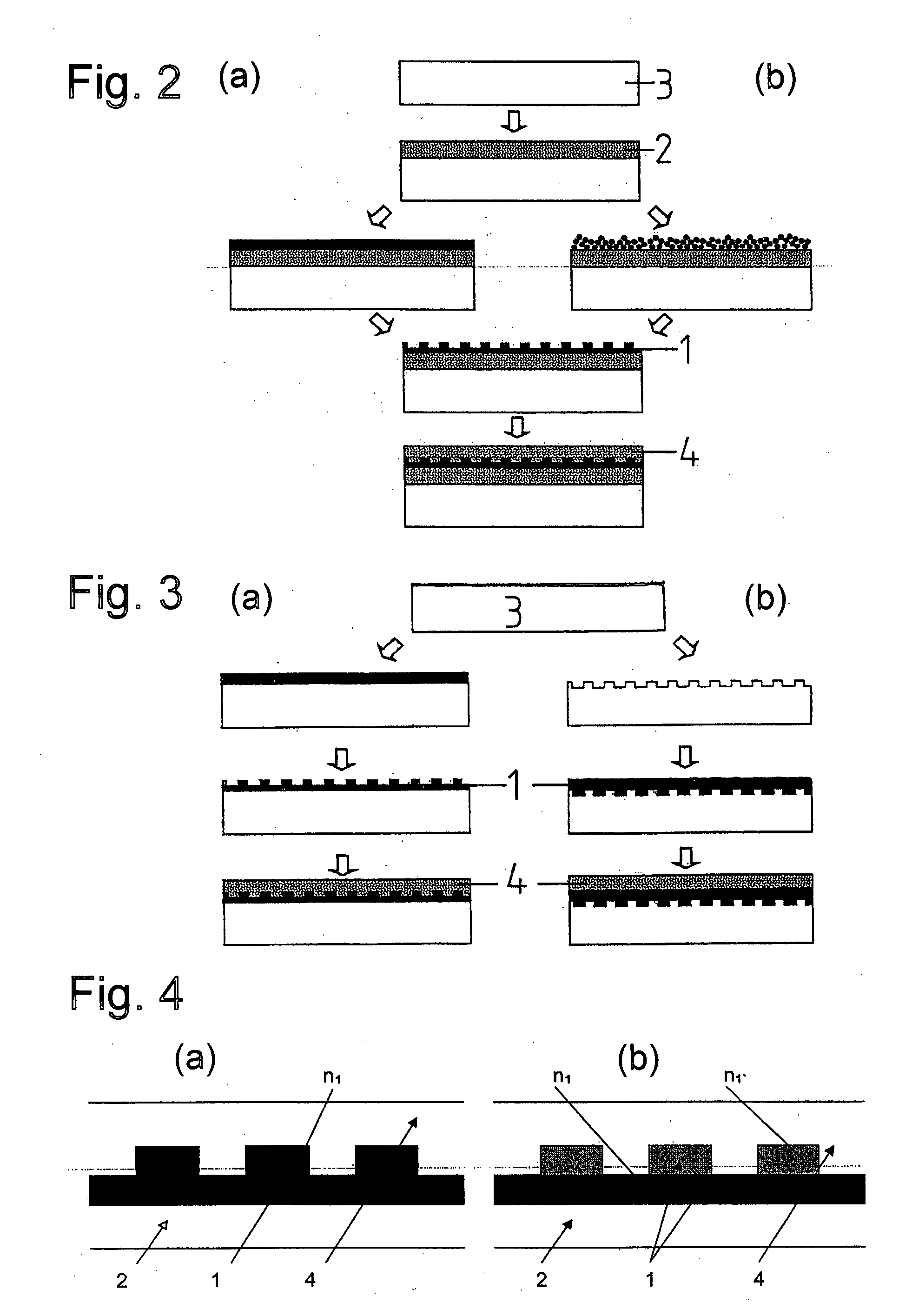
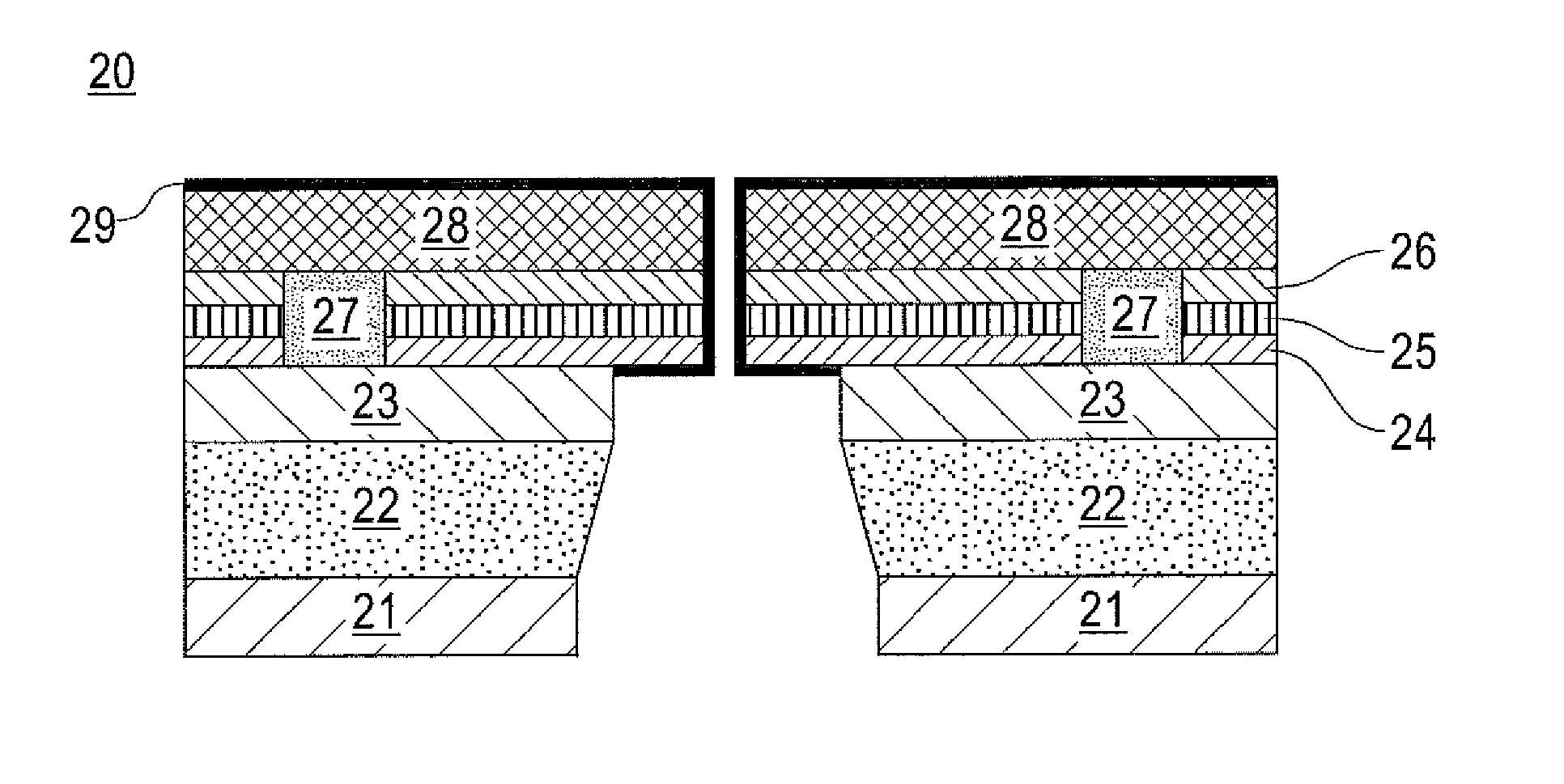
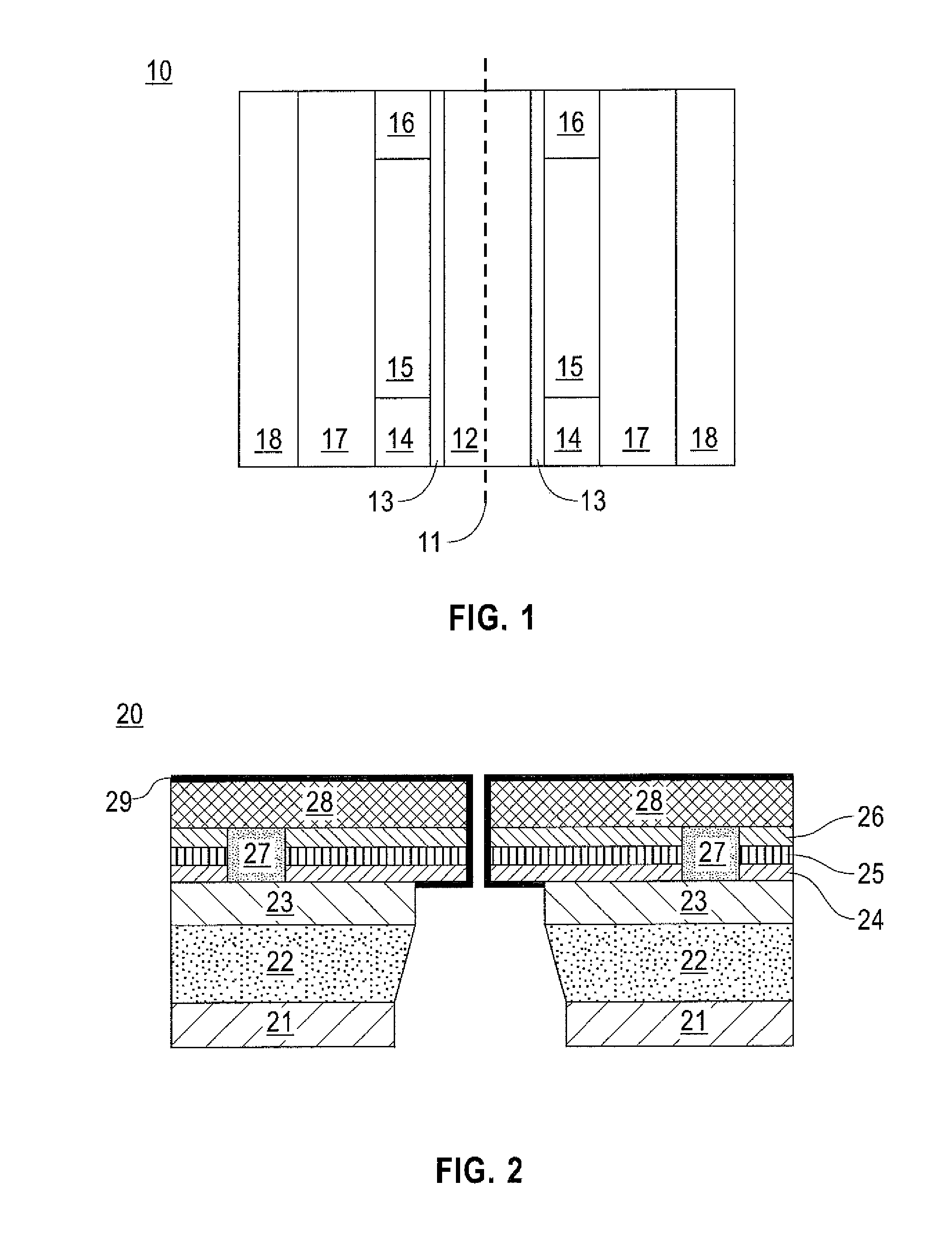
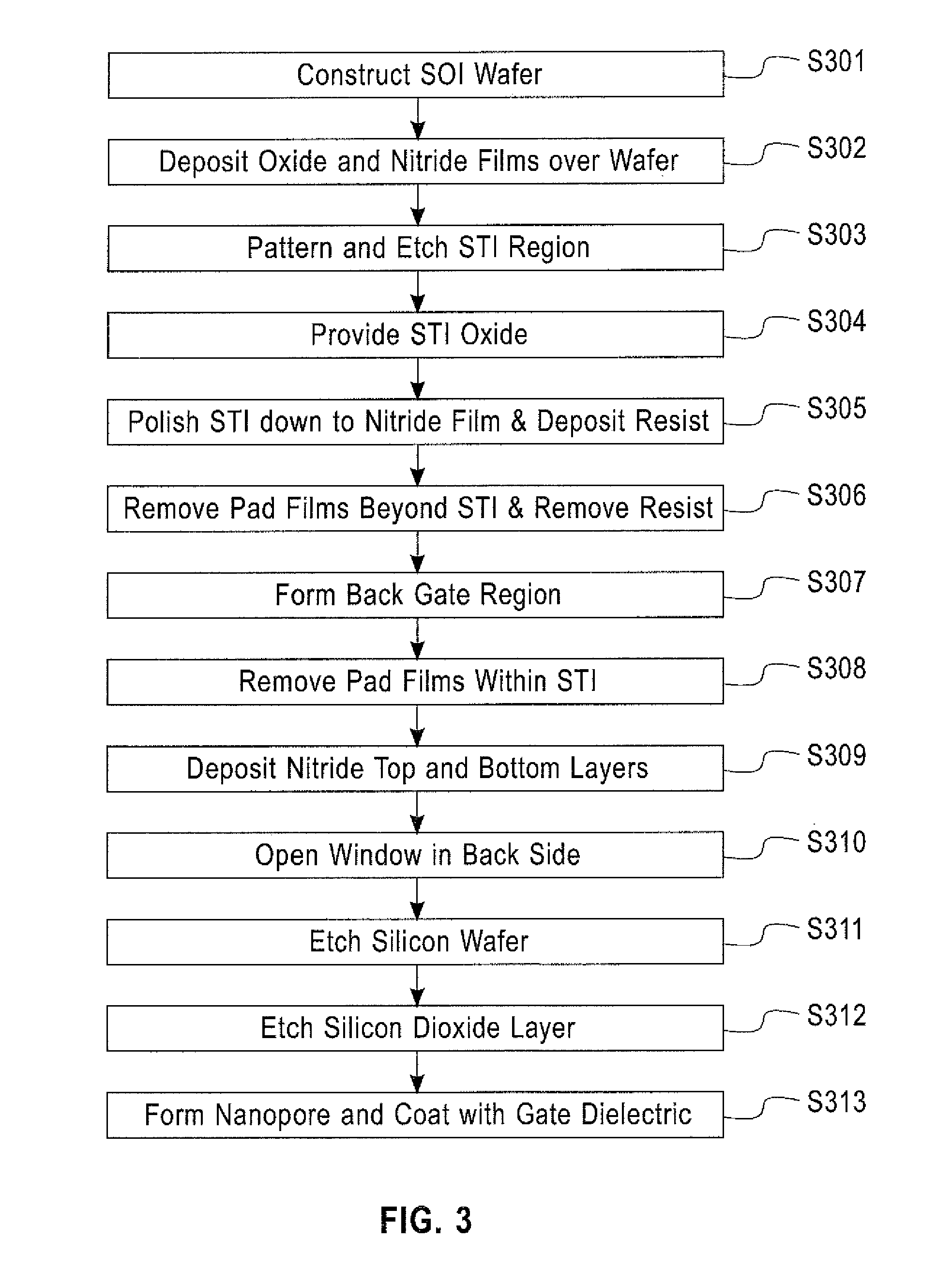
Thin body FET nanopore sensor for sensing and screening biomolecules
InactiveUS20150014752A1Improve sensor sensitivityHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
A thin body field effect transistor (FET) nanopore sensor includes a silicon on insulator (SOI) structure having an annular shape and comprising a source, a drain and a thin body channel interposed therebetween. A nanopore is formed in a central opening of the SOI structure. A gate dielectric is disposed on the SOI structure insulating the SOI structure from a liquid gate within the nanopore. A back gate is formed around the SOI structure. A shallow trench isolation (STI) layer is formed between the SOI structure and the back gate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
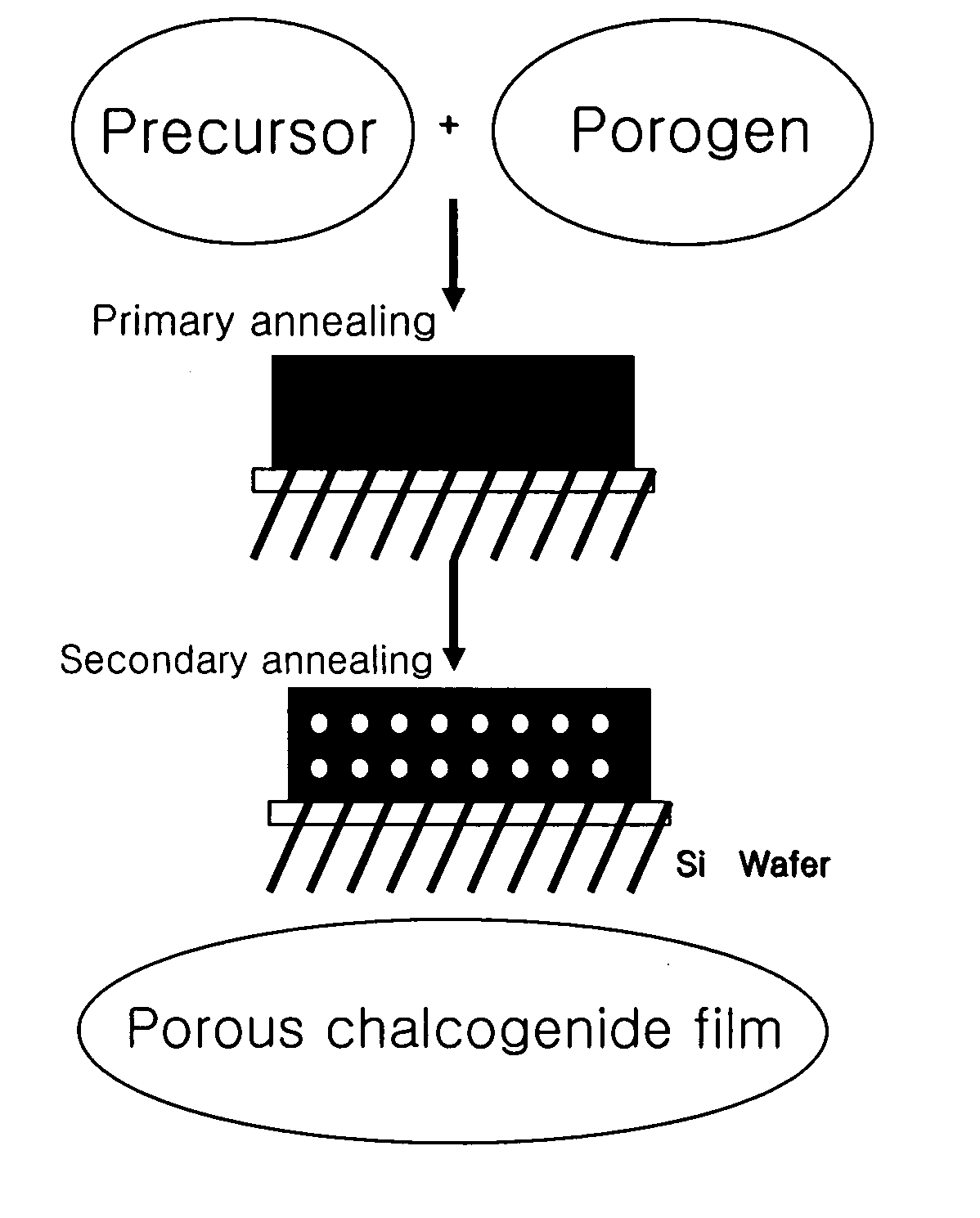
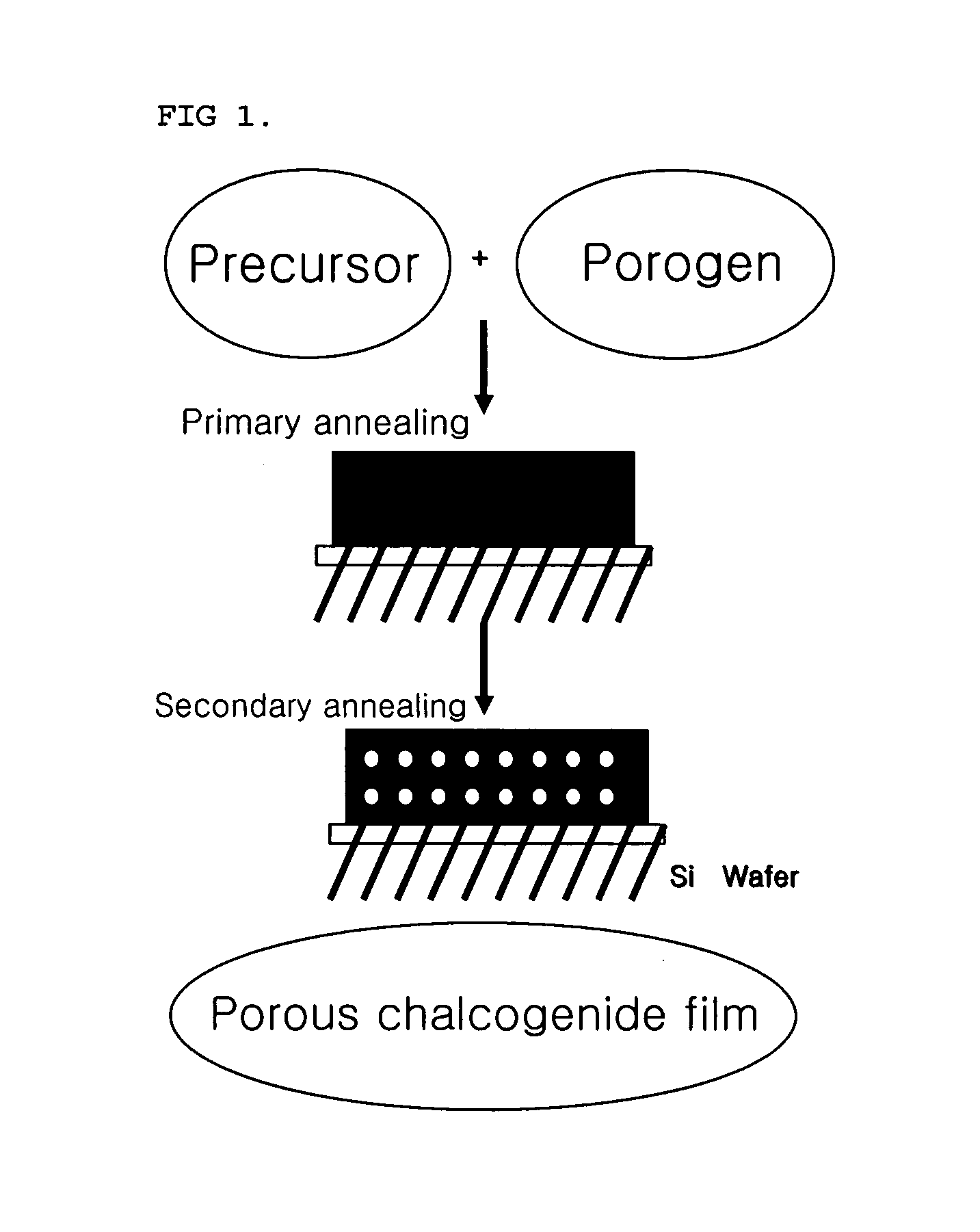
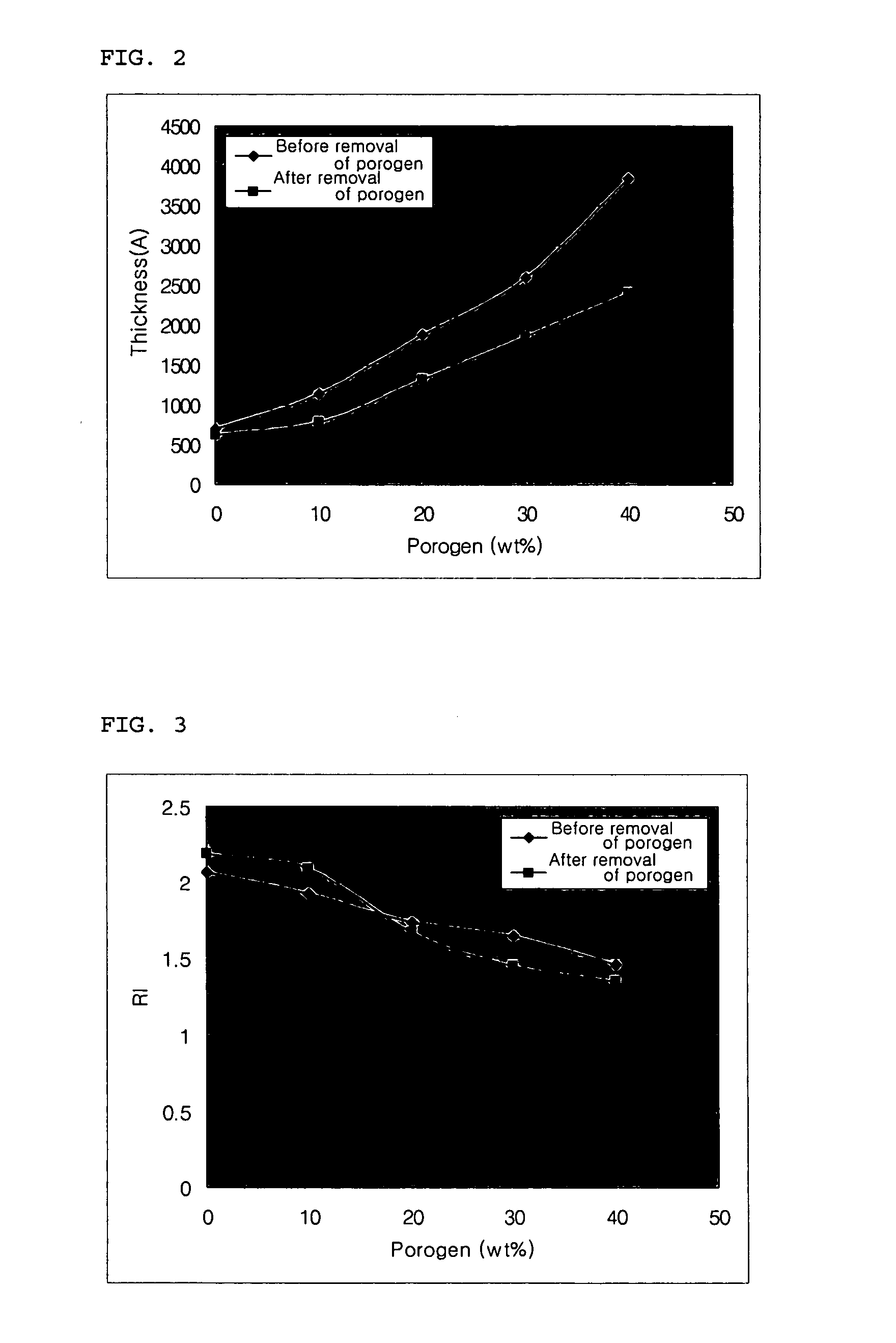
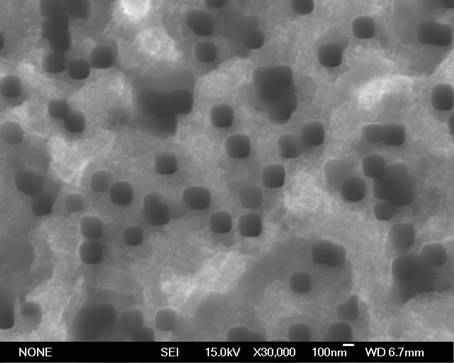
Porous chalcogenide thin film, method for preparing the same and electronic device using the same
InactiveUS20070090346A1High crystallinityImprove electrical performanceGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCadmium sulfidesSulfurCrystallinity
A porous chalcogenide thin film having a microporous structure, a method for preparing the chalcogenide thin film and an electronic device employing the chalcogenide thin film, are provided. The porous chalcogenide thin film has superior crystallinity and can be applied as a semiconductor layer having superior electrical properties to the fabrication of devices by inserting functional metal or semiconductor nanoparticles into nanopores of the thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING CO LTD
Square silicon nanometer hole and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102157621APromote absorptionImprove efficiencyFinal product manufactureNanotechnologyNanoholeMembrane technology
The invention discloses a preparation method of a square silicon nanometer hole, wherein a square silicon nanometer hole structure is prepared by adopting a method combining metal catalysis corrosion with a silicon wet etching technology. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) depositing a metal film of 5-200 nanometers on the surface of a silicon slice; (2) carrying out heat treatment on the silicon slice with the deposited silicon slice to obtain metal nanoparticles with specific shapes; and (3) corroding the annealed silicon slice to form the square silicon nanometer hole. The invention does not need a mask technology and has the advantages of wet corrosion, such as low cost, easiness and convenience for operation and short using time and the advantages of dry corrosion, such as good corrosion uniformity and repeatability; and addition, the square silicon nanometer hole structure has wide application prospect on solar cells, integrated circuits, and the like.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Dynamic plasmonics-enabled signal enhancement, a device comprising the same, and a method using the same
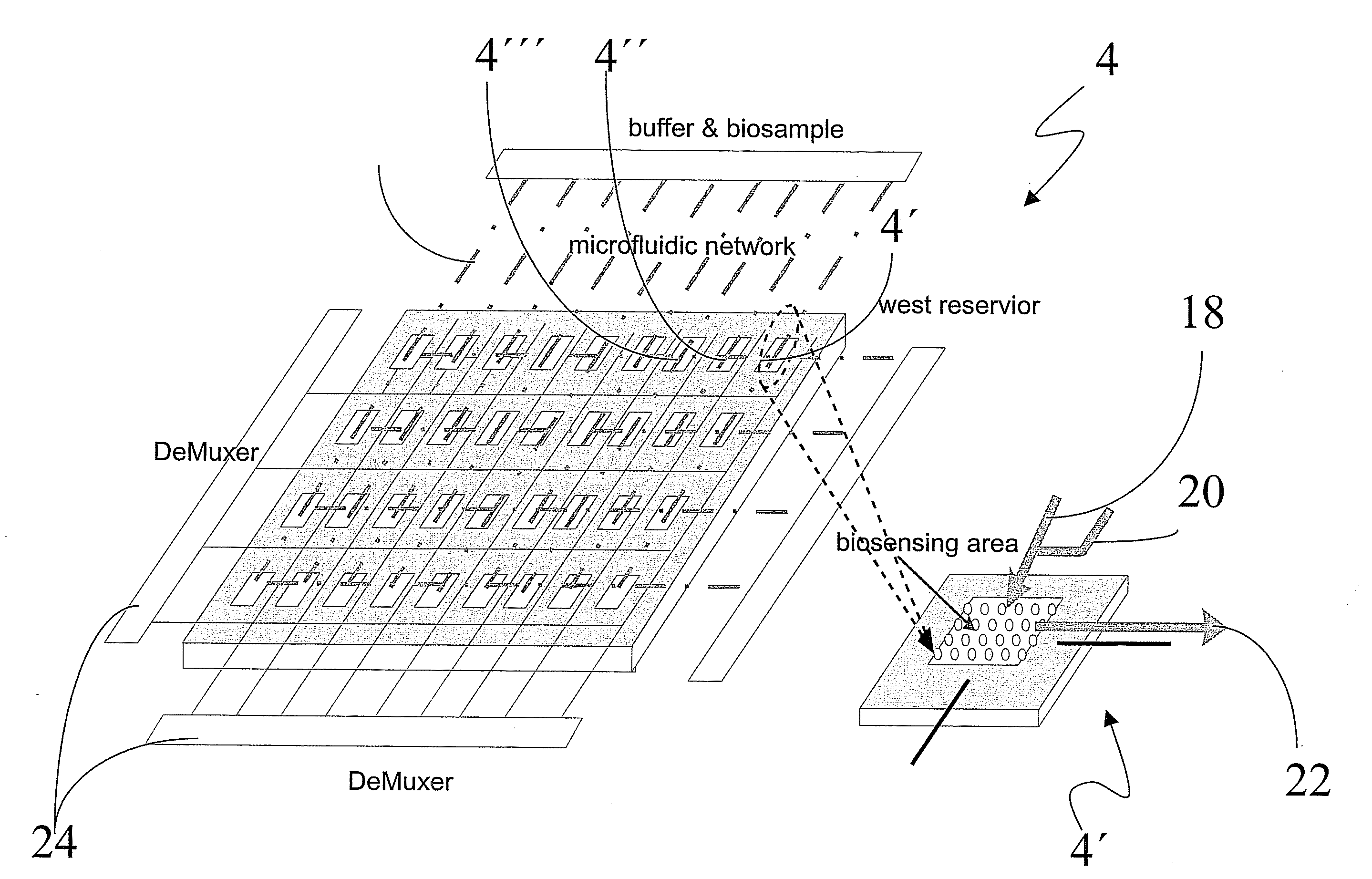
Disclosed herein is a plasmonics platform comprising a substrate; a plurality of periodically spaced nanoholes and / or nanoparticles disposed upon the substrate; wherein the average first order of periodicity between the nanoholes and / or the nanoparticles is about 5 to about 1,000 nm; and a microelectromechanical and / or a nanoelectromechanical system in operative communication with the substrate so as to vary the average first order of periodicity between the nanoholes and / or the nanoparticles.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com