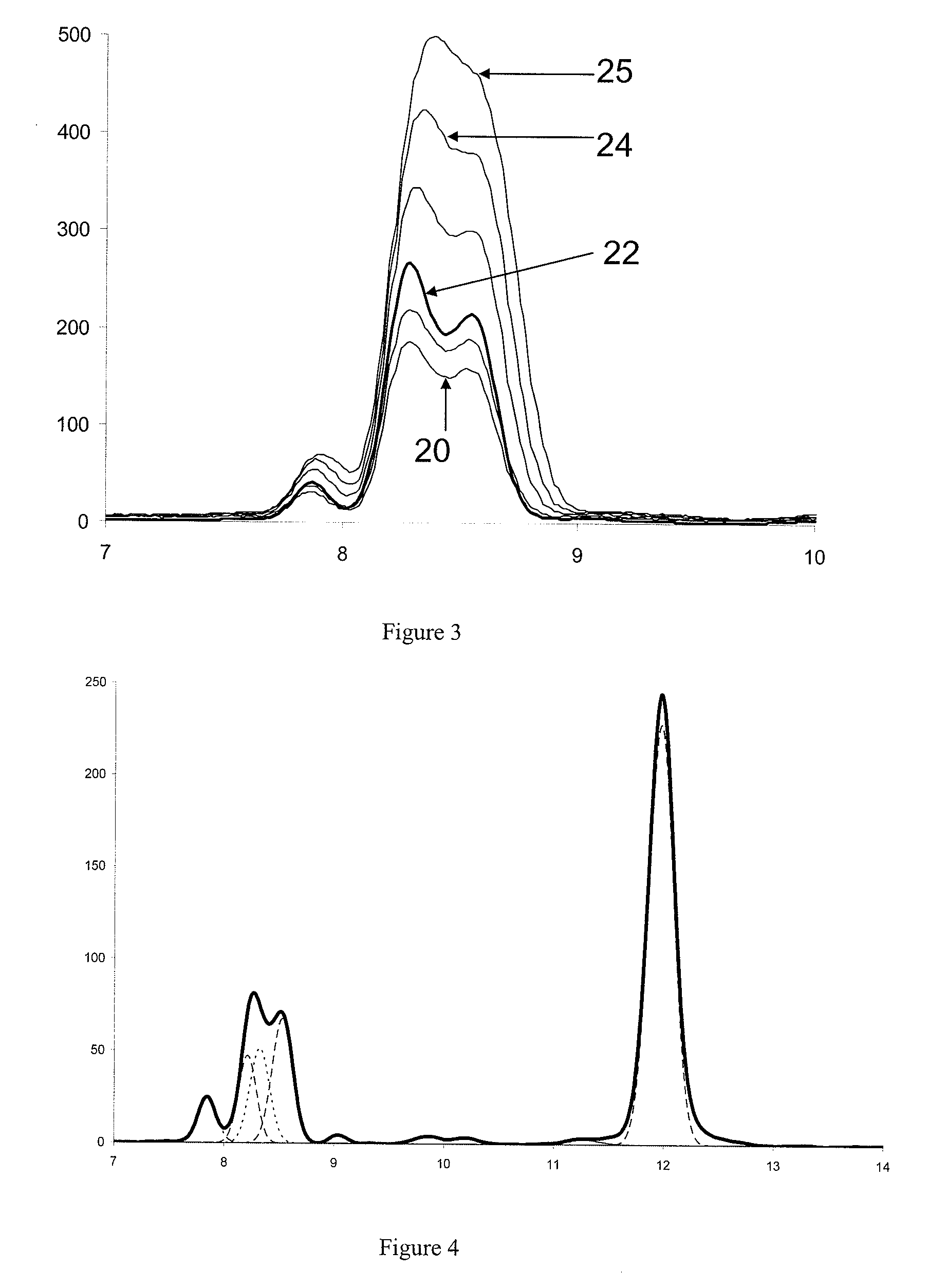
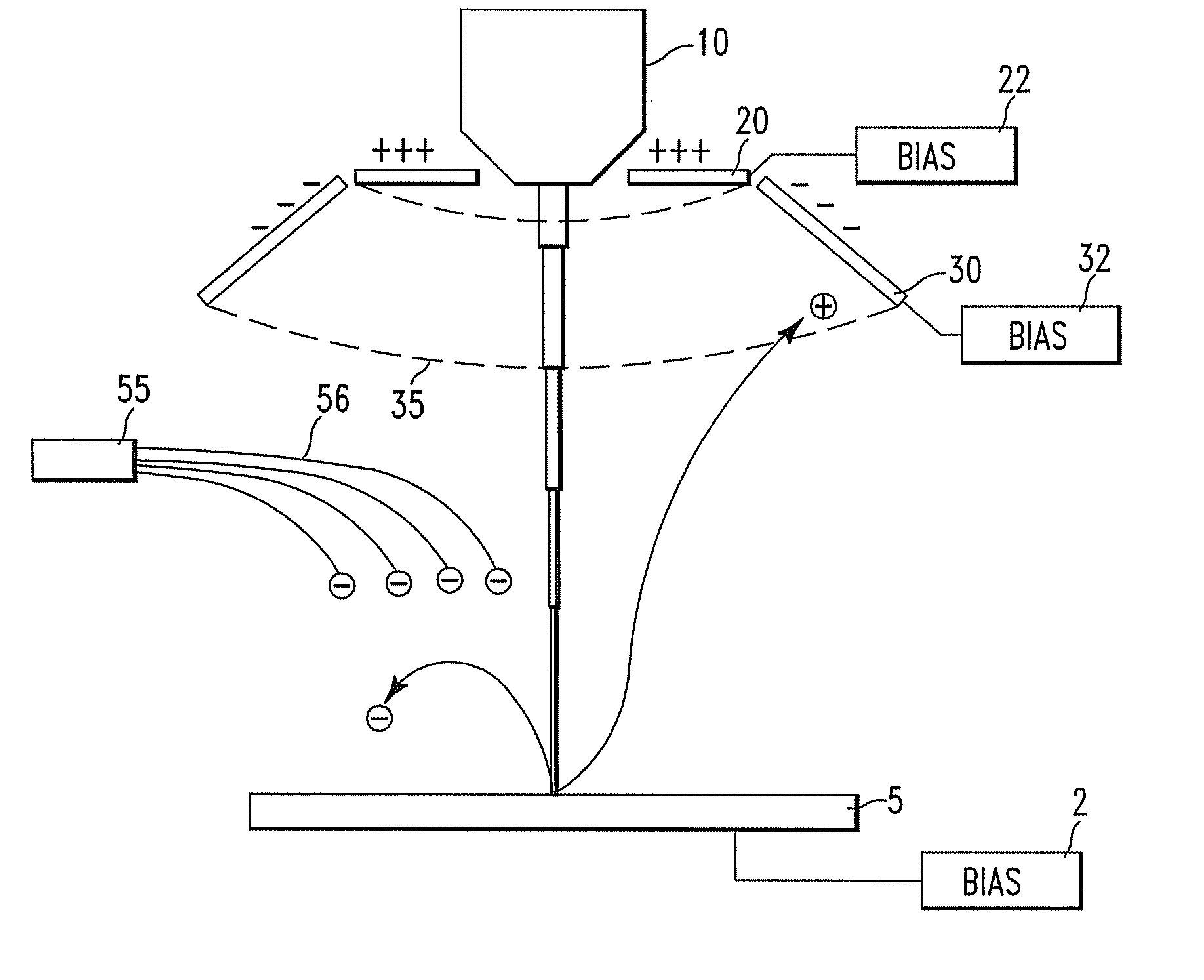
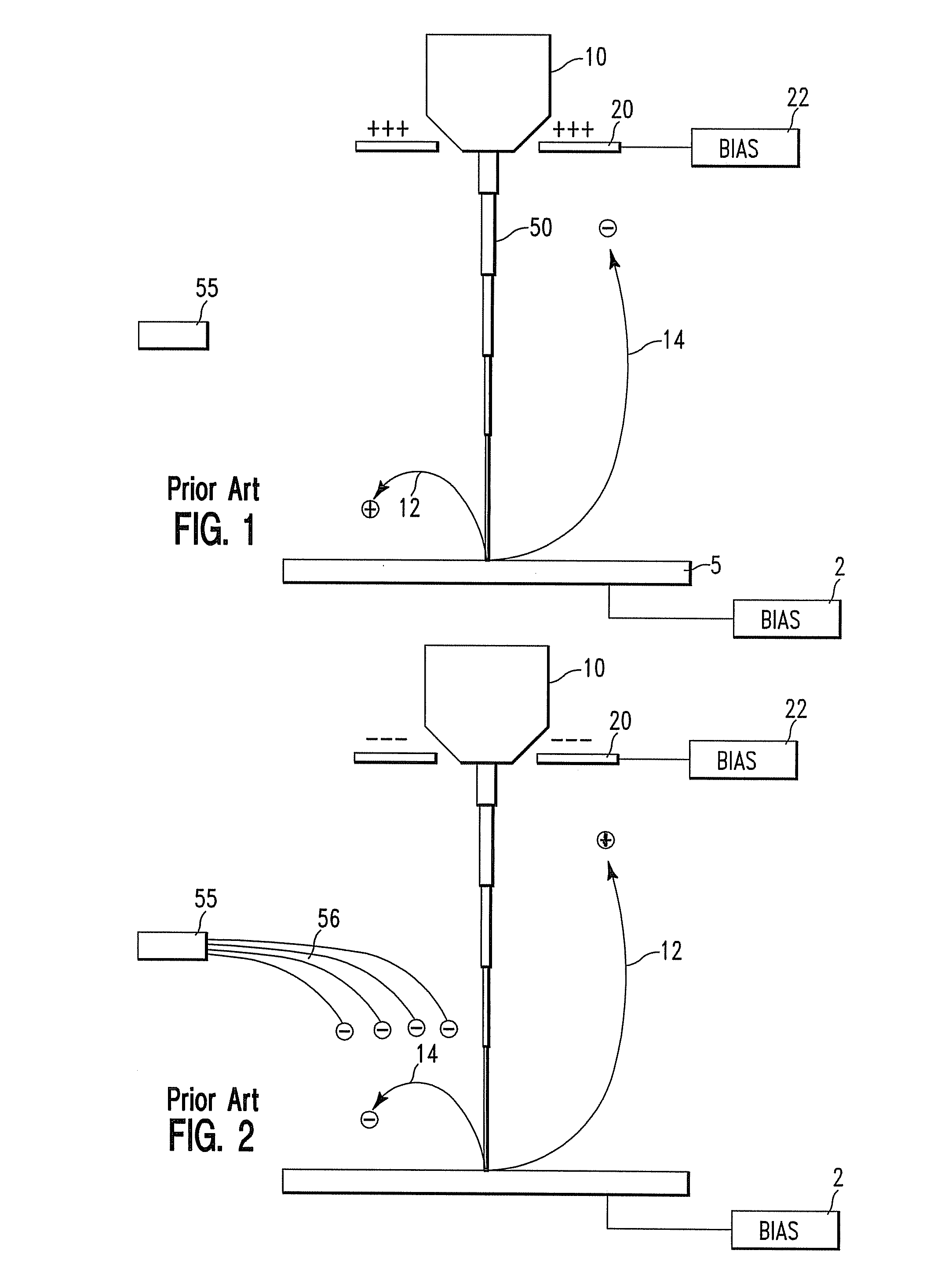
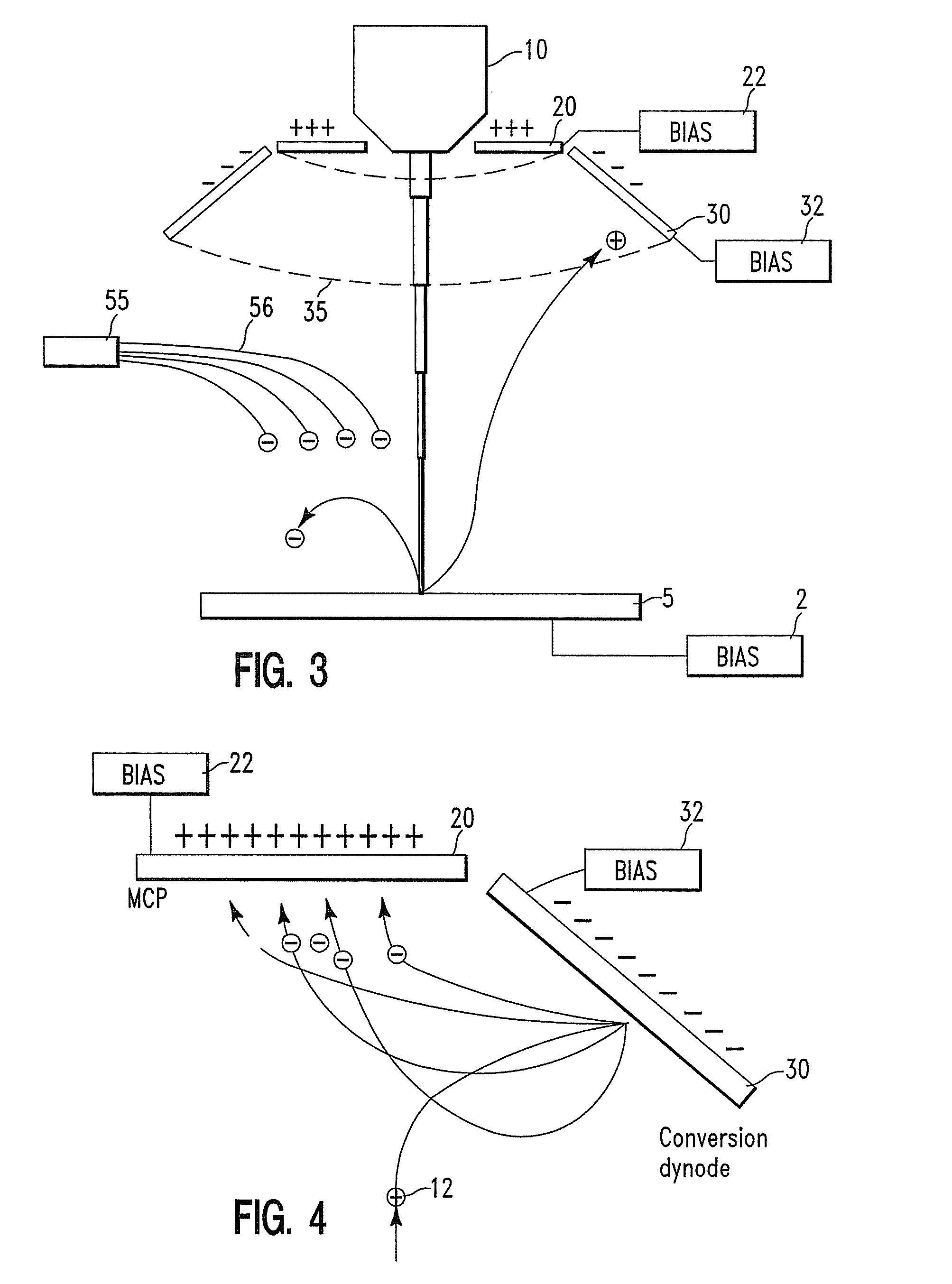
Patents
Literature
622 results about "Ion current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
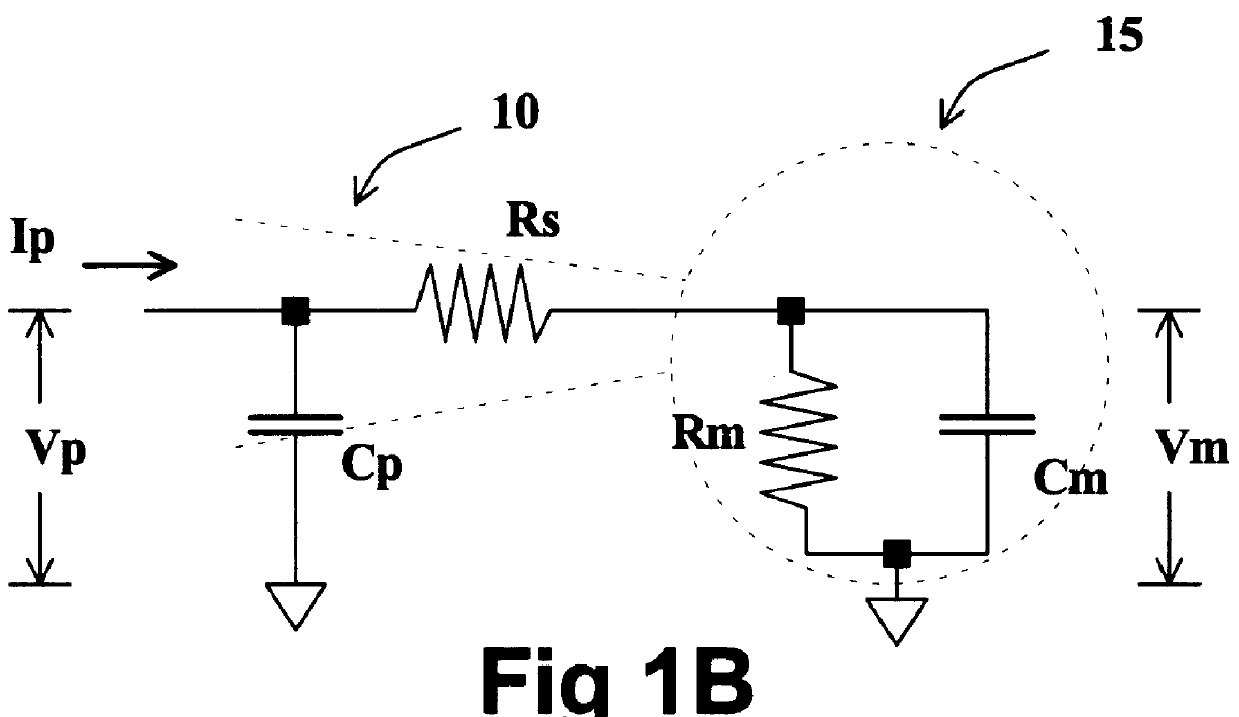
An ion current is the influx and/or efflux of ions through an ion channel.
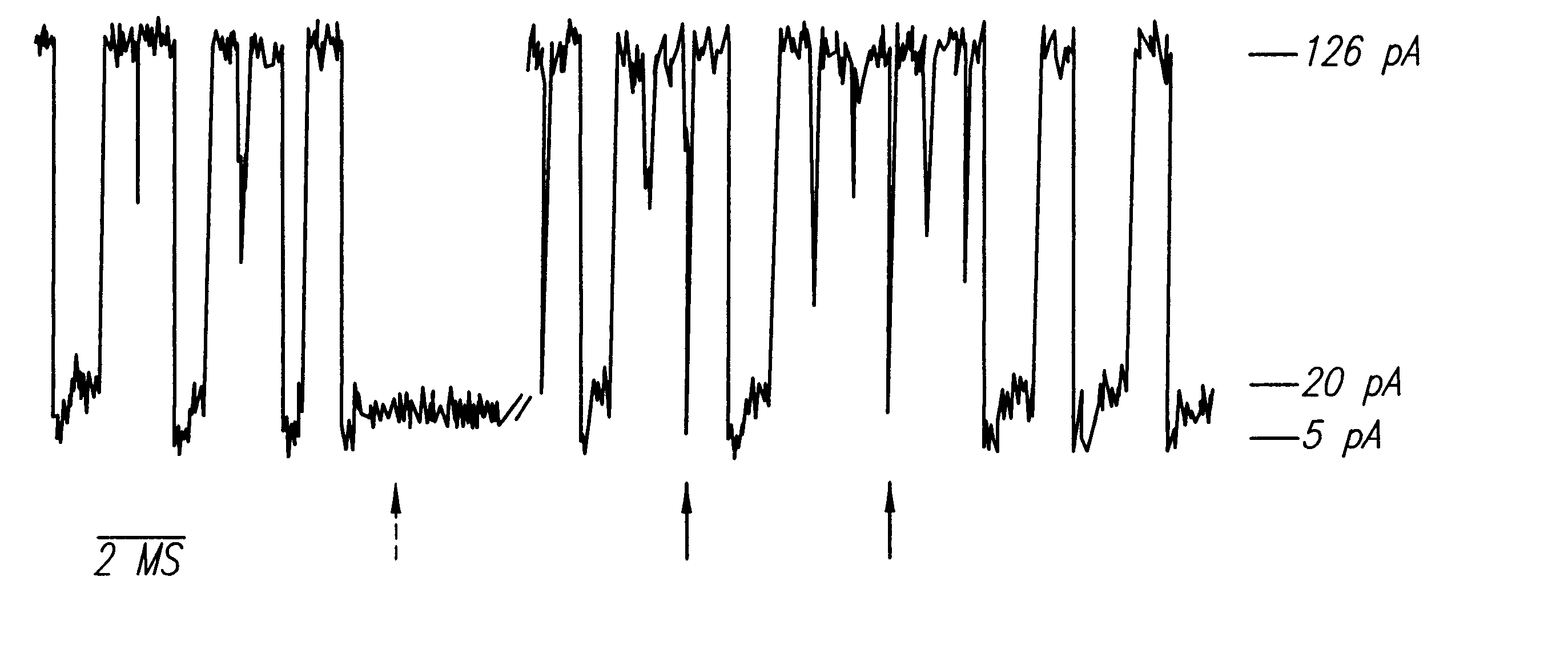
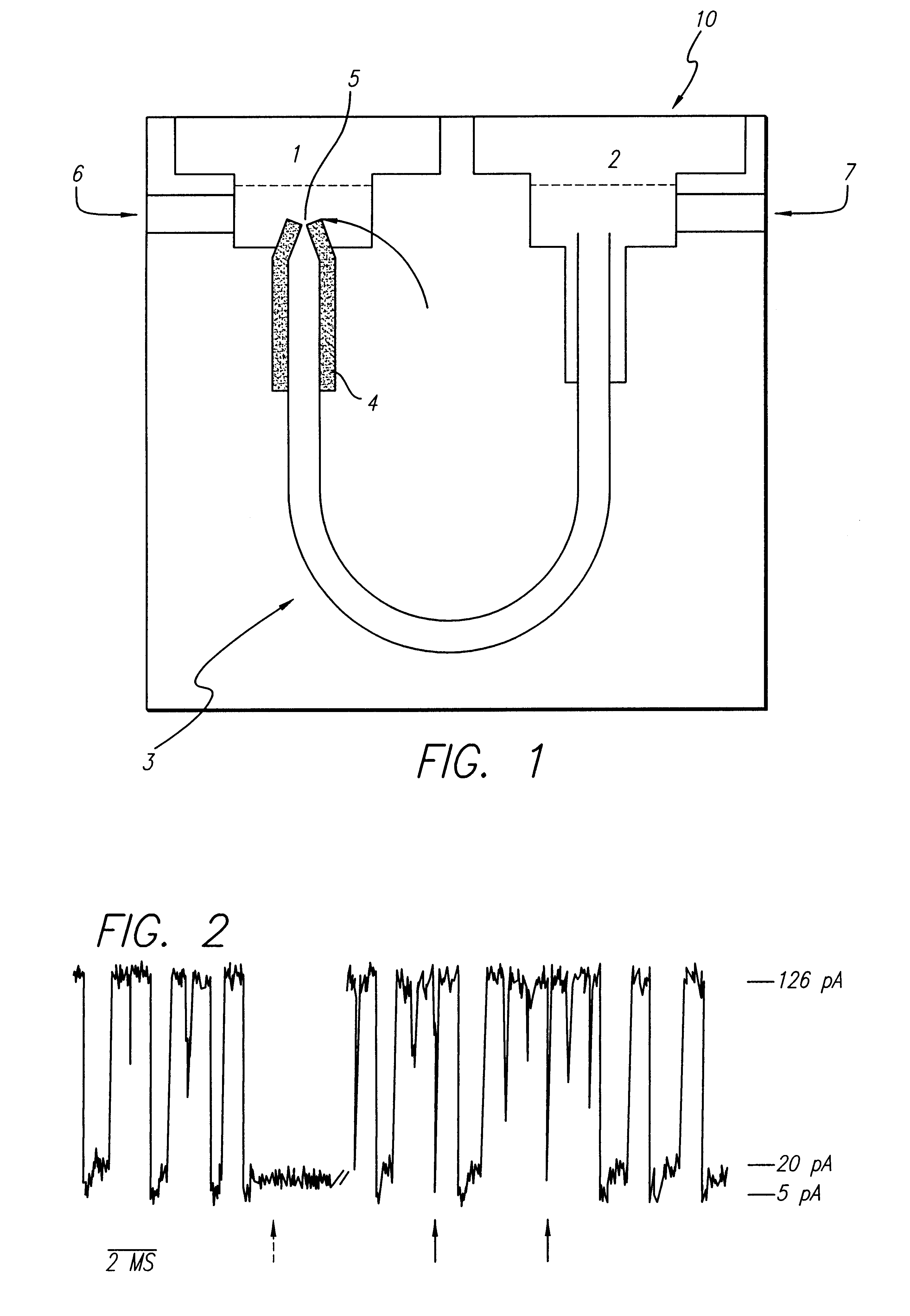
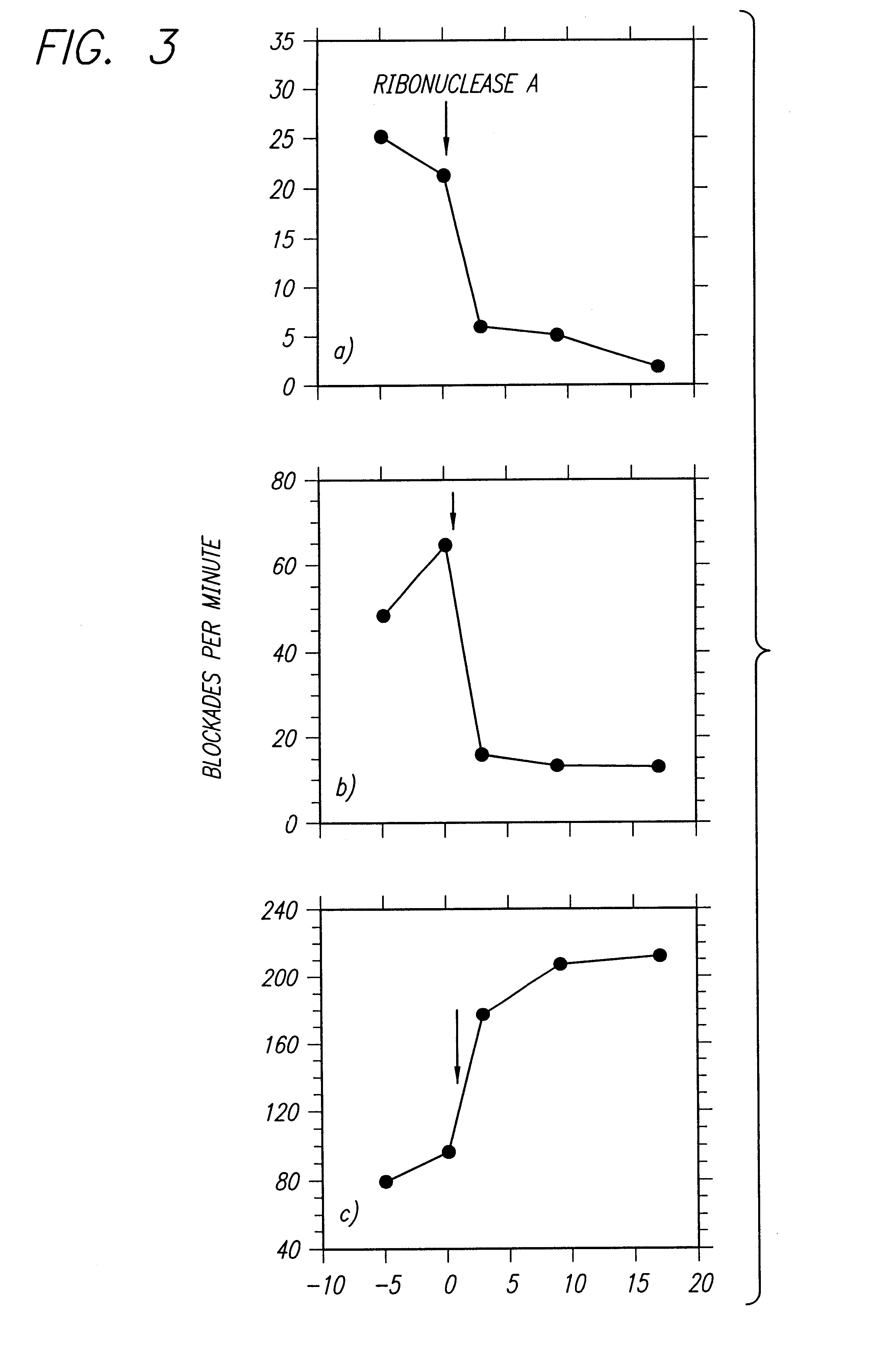
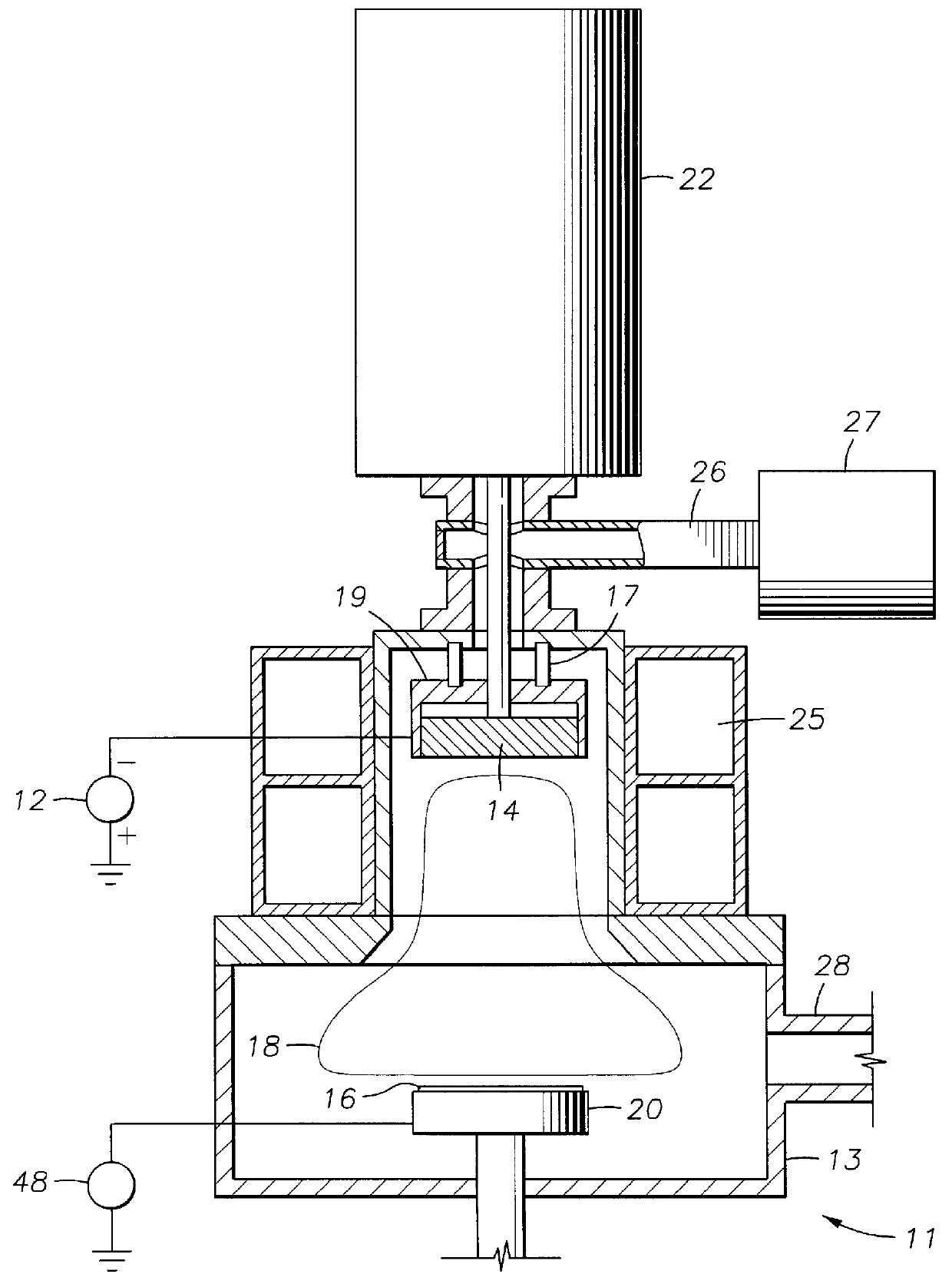
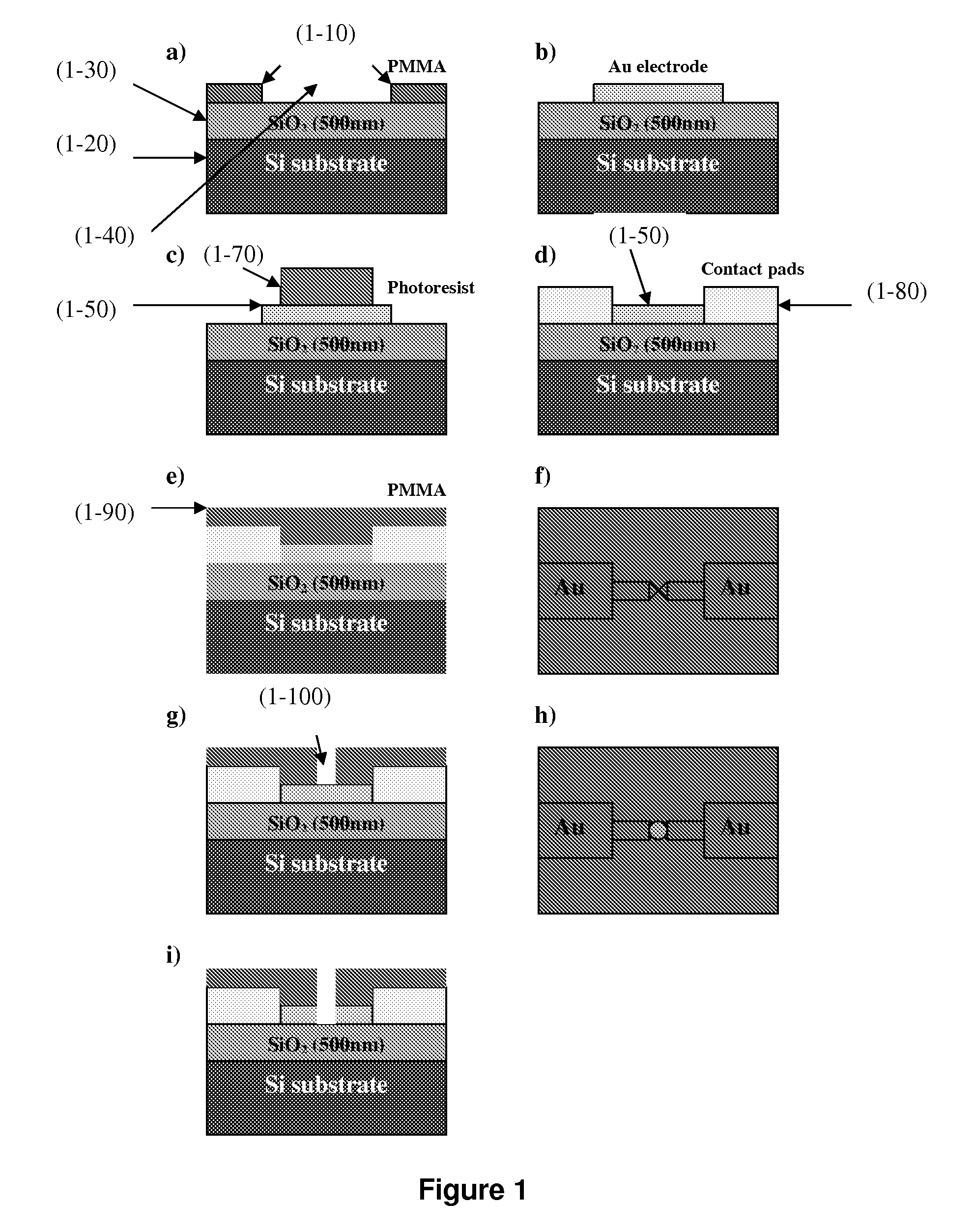
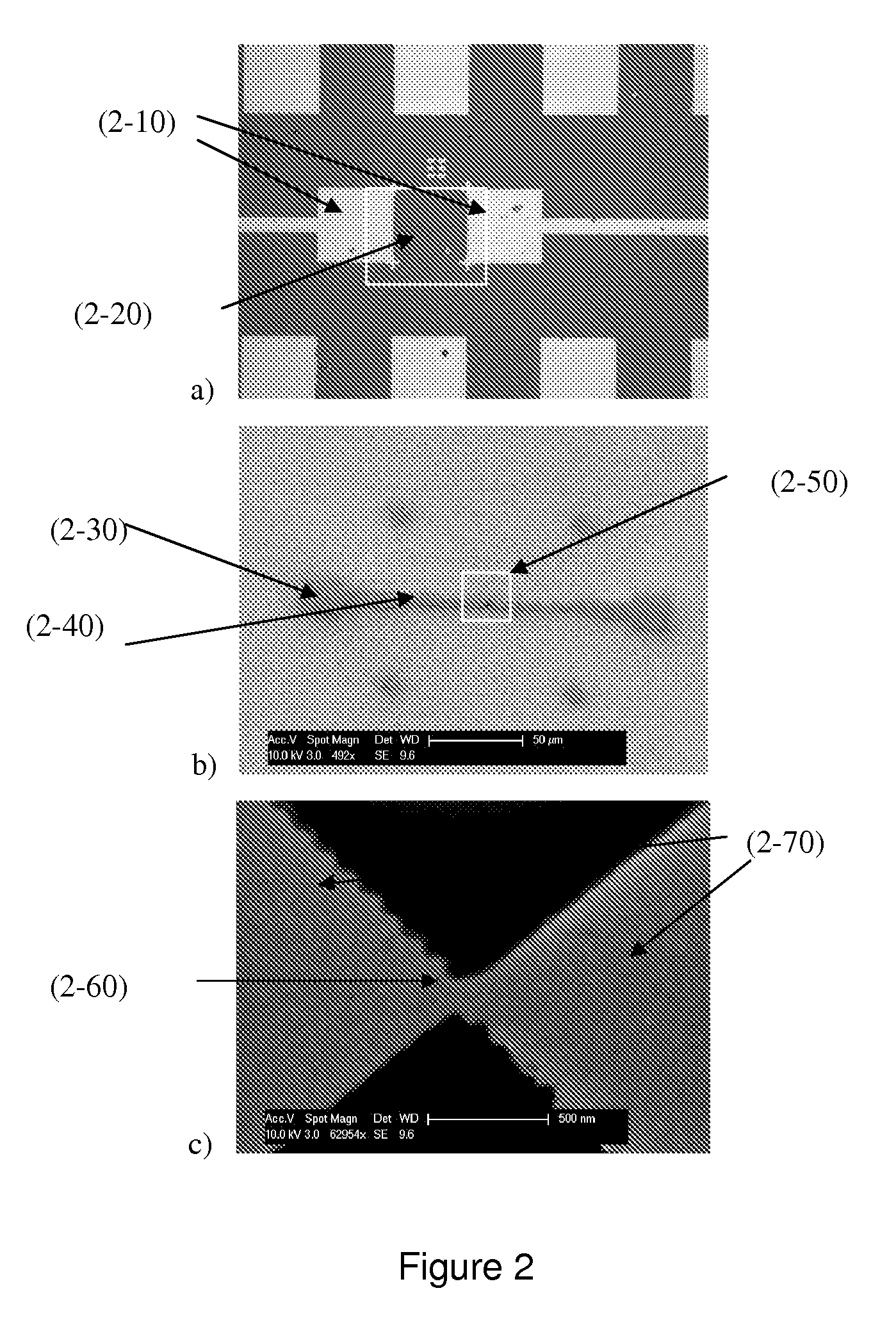
Miniature support for thin films containing single channels or nanopores and methods for using same
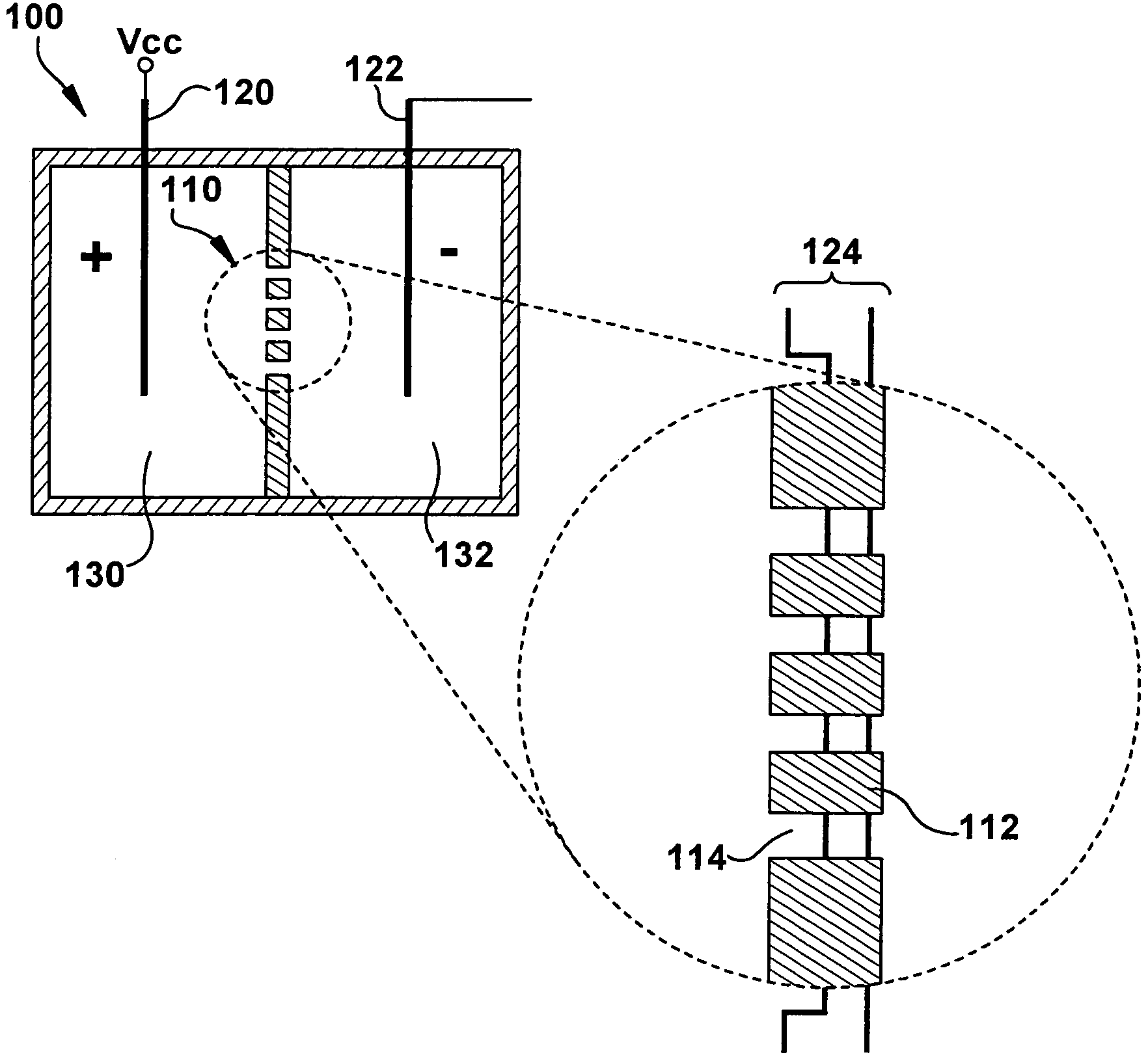
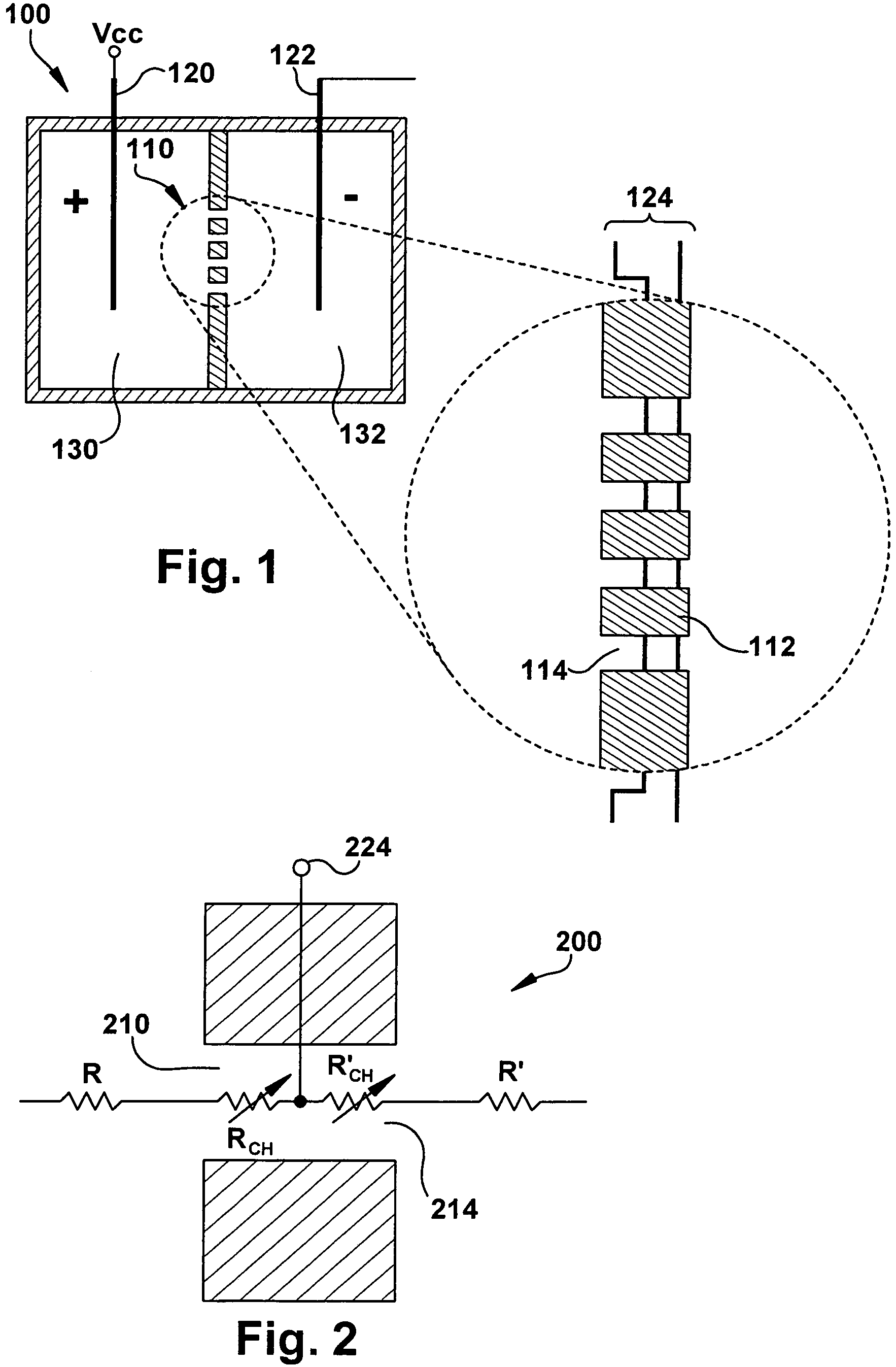
Single-channel thin film devices and methods for using the same are provided. The subject devices comprise cis and trans chambers connected by an electrical communication means. At the cis end of the electrical communication means is a horizontal conical aperture sealed with a thin film that includes a single nanopore or channel. The devices further include a means for applying an electric field between the cis and trans chambers. The subject devices find use in applications in which the ionic current through a nanopore or channel is monitored where such applications include the characterization of naturally occurring ion channels, the characterization of polymeric compounds, and the like.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Use of pulsed-DC wafer bias for filling vias/trenches with metal in HDP physical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6051114AControl depositionPrevent openingCellsElectric discharge tubesCapacitanceIon current
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for preferential PVD conductor fill in an integrated circuit structure. The present invention utilizes a high density plasma for sputter deposition of a conductive layer on a patterned substrate, and a pulsed DC power source capacitively coupled to the substrate to generate an ion current at the surface of the substrate. The ion current prevents sticking of the deposited material to the field areas of the patterned substrate, or etches deposited material from the field areas to eliminate crowning or cusping problems associated with deposition of a conductive material in a trench, hole or via formed on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
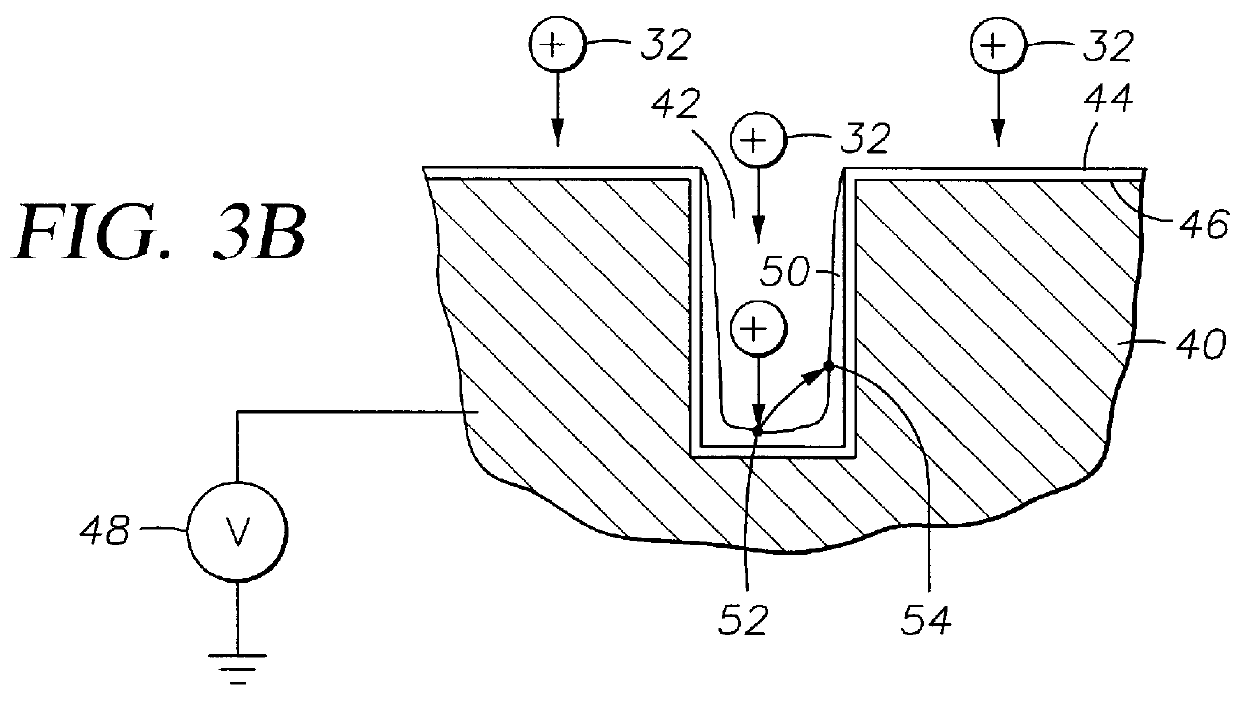
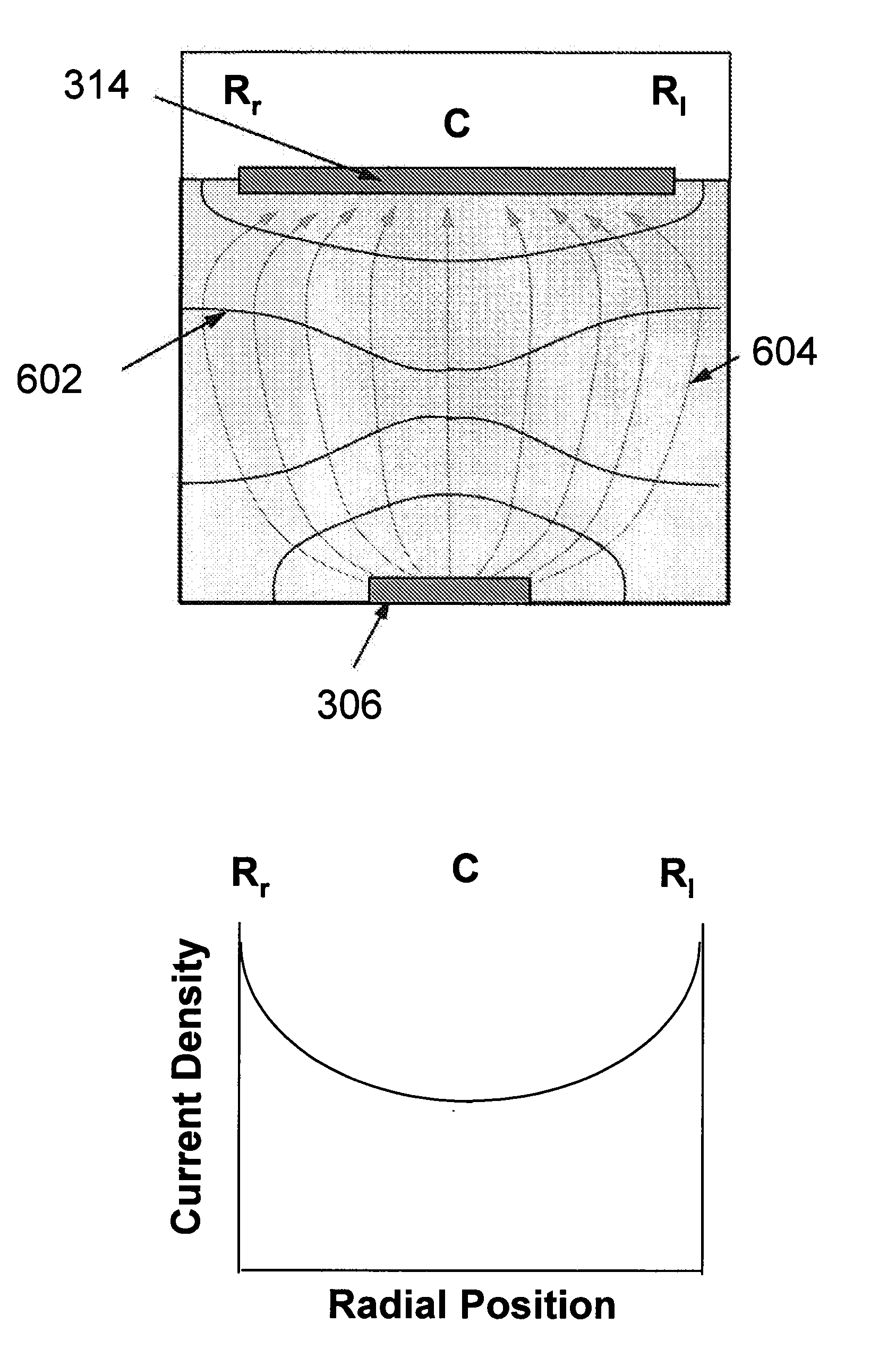
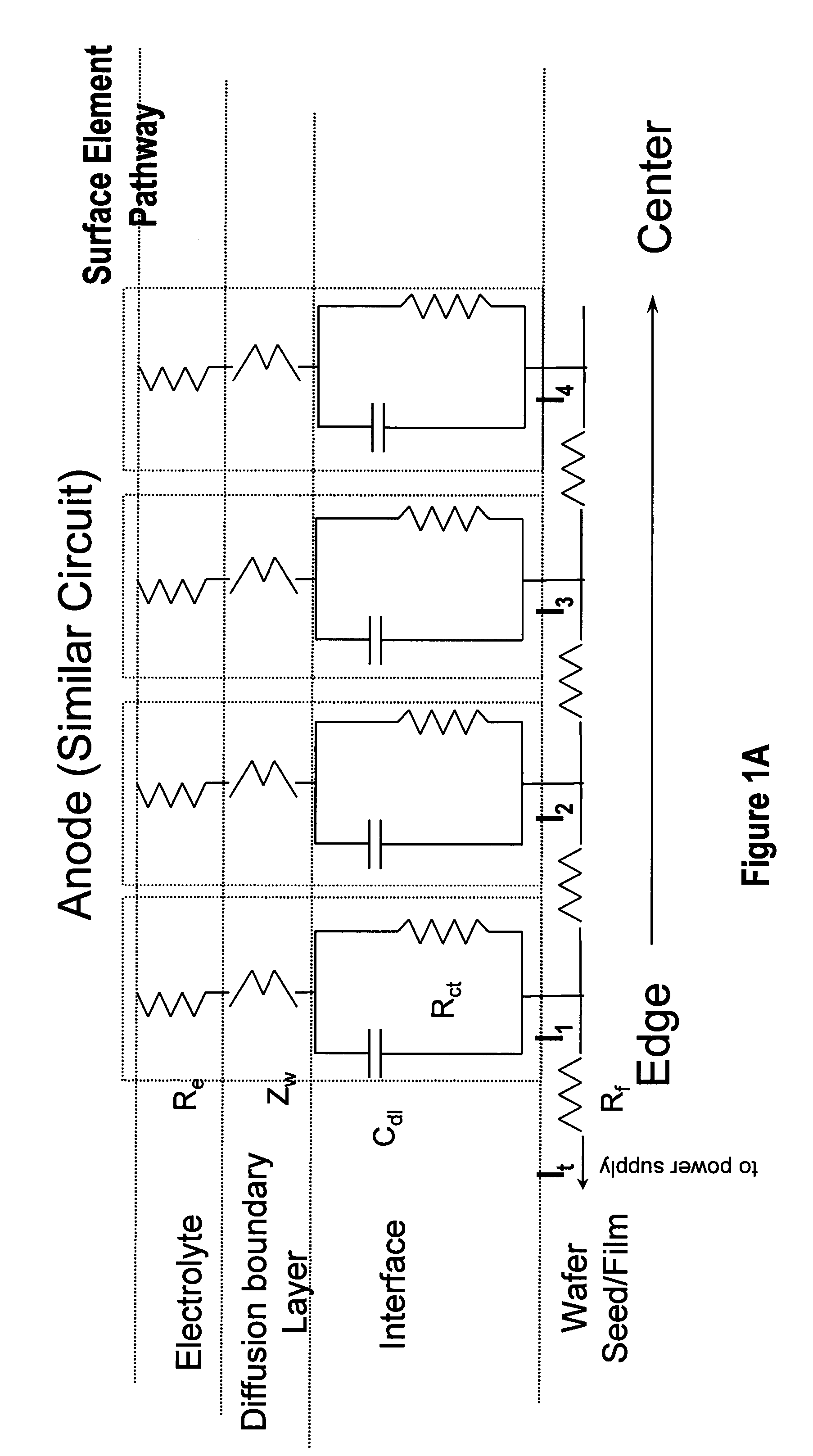
Method and apparatus for electroplating
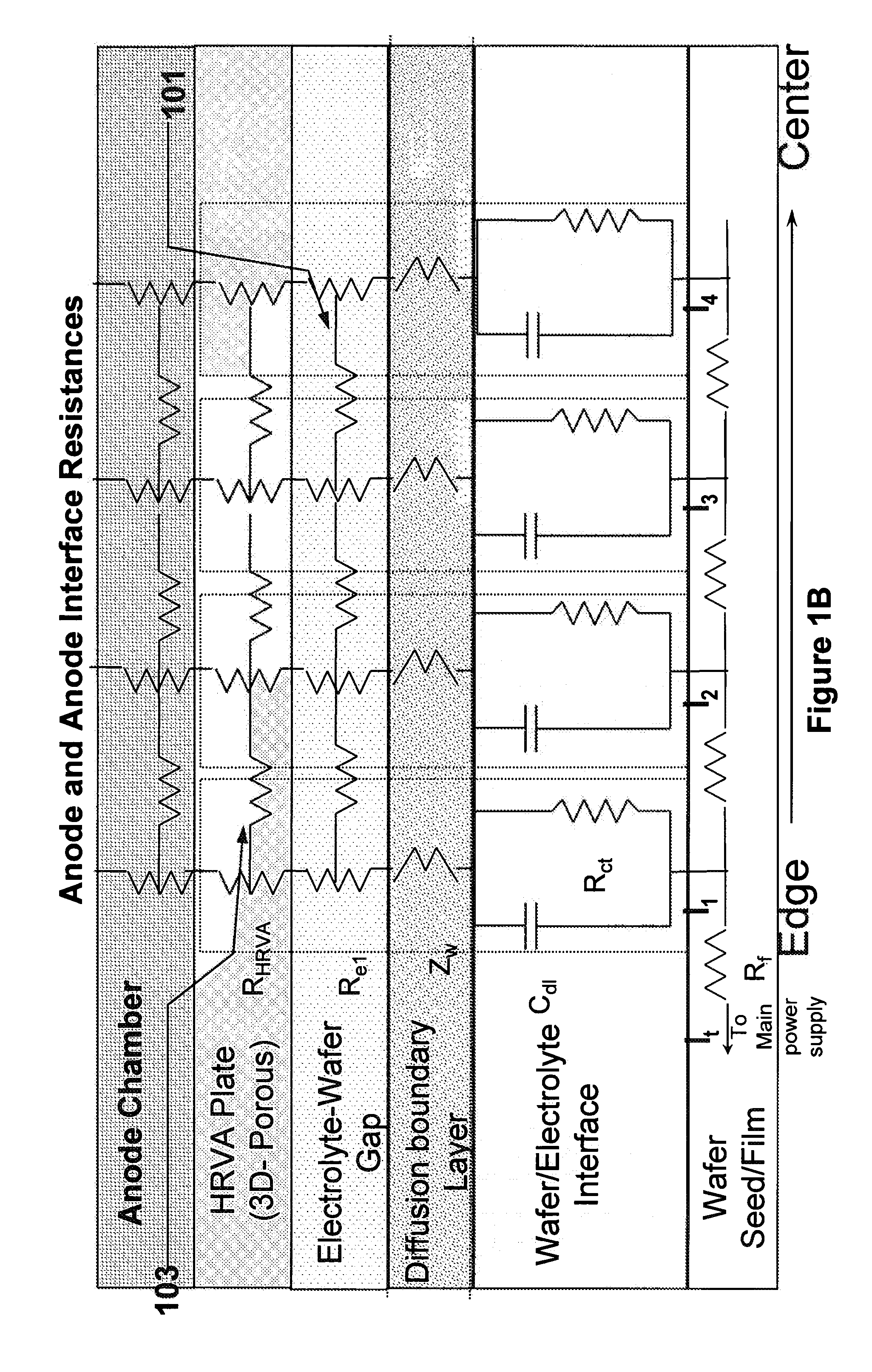
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer and an auxiliary cathode located between the anode and the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface. The auxiliary cathode is configured to shape the current distribution from the anode. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Coulter counter having a plurality of channels
InactiveUS7397232B2Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansIndividual particle analysisIon currentComputer science
The present invention generally relates to a method for rapidly counting micron and / or submicron particles by passing such particles through any of a plurality of orifices simultaneously with an ion current and measuring the signal generated thereby. The present invention also generally relates to a device for practicing the method of the present invention. Some embodiments can include methods and / or devices for distinguishing between and counting particles in mixtures. Still other embodiments can include methods and / or devices for identifying and / or counting bioparticles and / or bioactive particles such as pollen.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Method and apparatus for sensing a time varying current passing through an ion channel
ActiveUS7622934B2High sensitivityLess dependentCapacitance measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementCapacitanceIon current
A capacitive sensing system is used to measure a time-varying ion current through a channel, such as an ion channel or protein pore. Such a capacitive system does not suffer problems of electrode corrosion and, when used with methods to control a build up of ion concentration, allows the use of measurement volumes around the channel with dimensions on a scale of nanometers.
Owner:ELECTRONICS BIOSCI
Inductively-coupled plasma etch apparatus and feedback control method thereof
InactiveUS20060226786A1Lengthy and laborious R & DImprove quality stabilityElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsIon currentEngineering
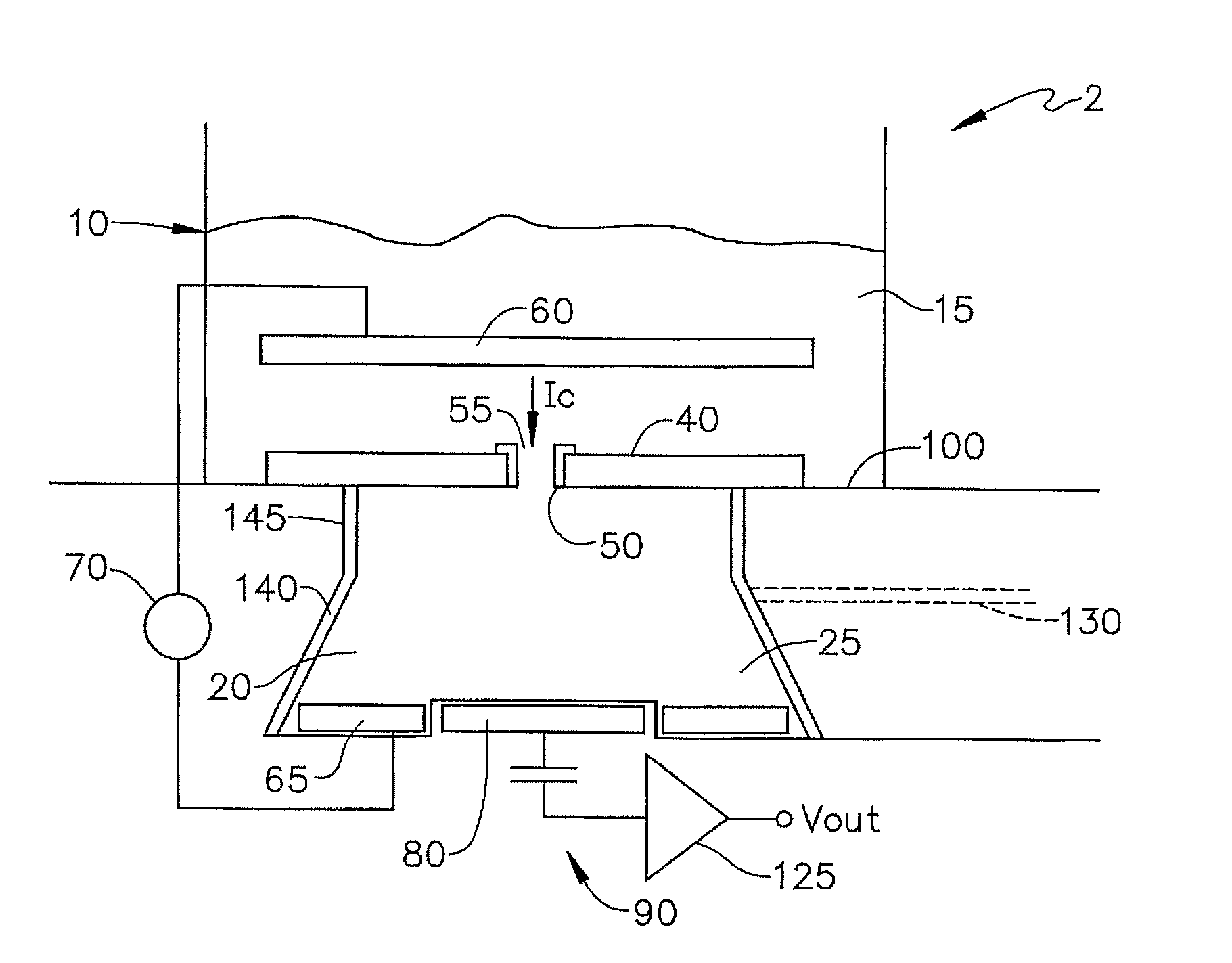
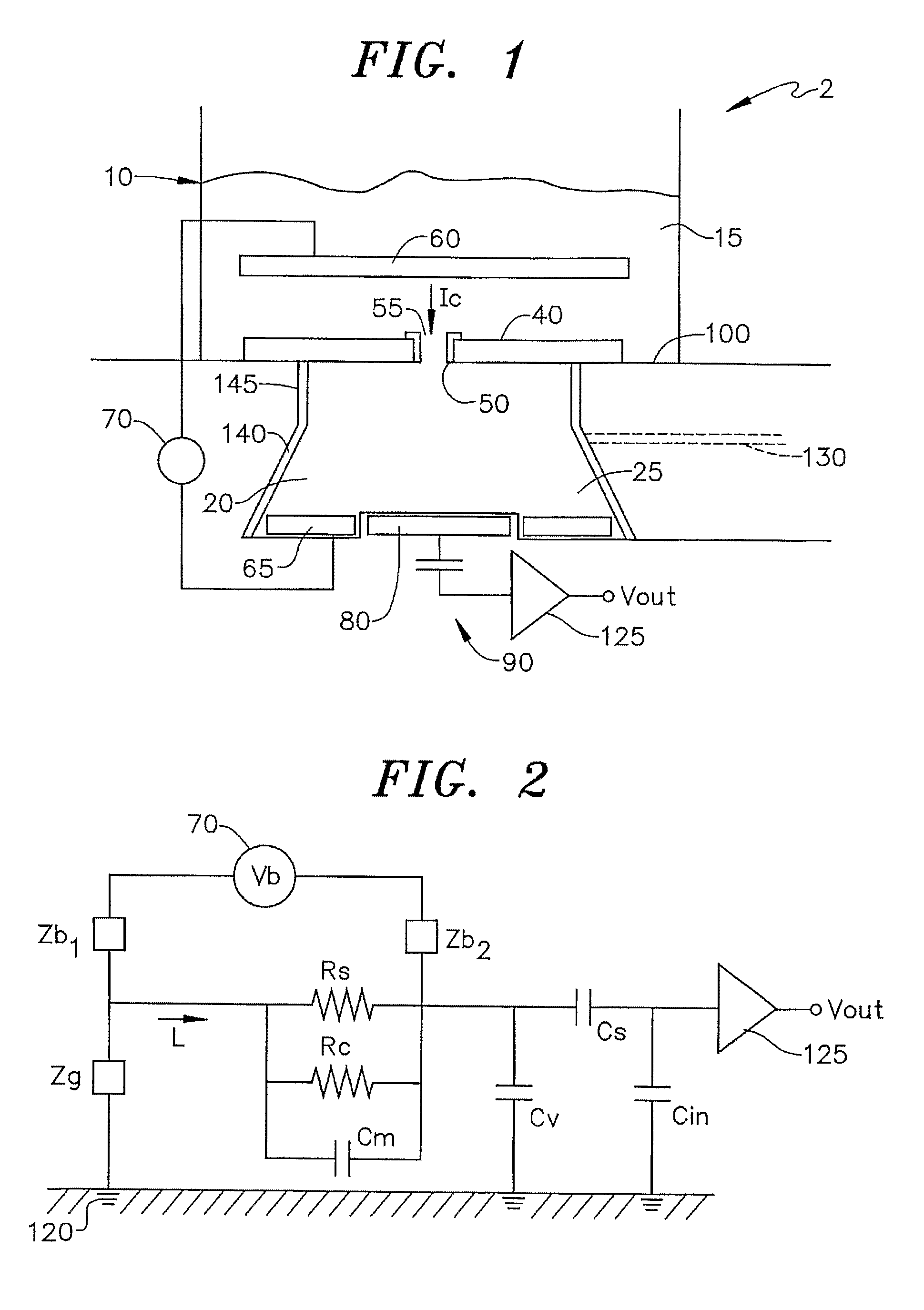
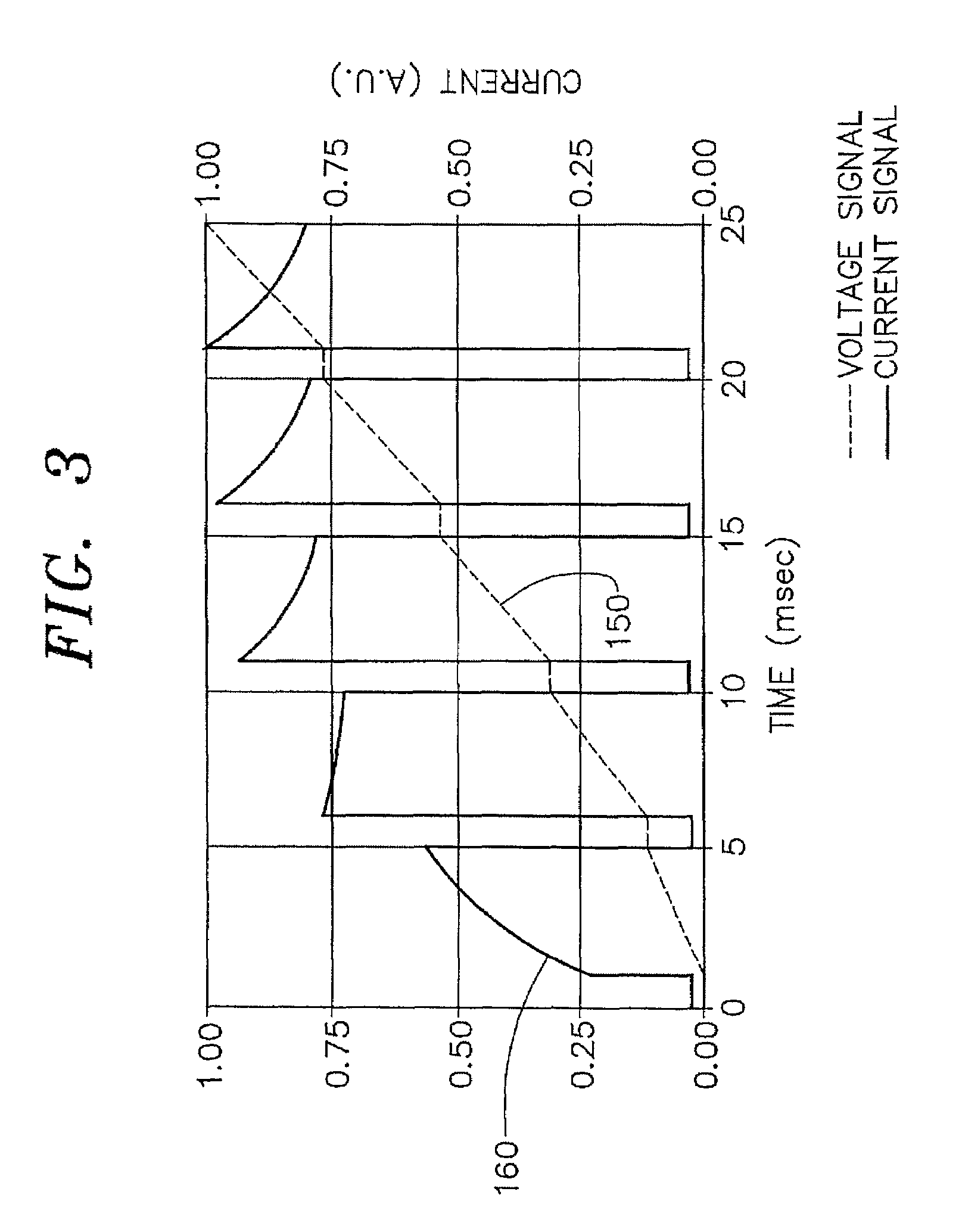
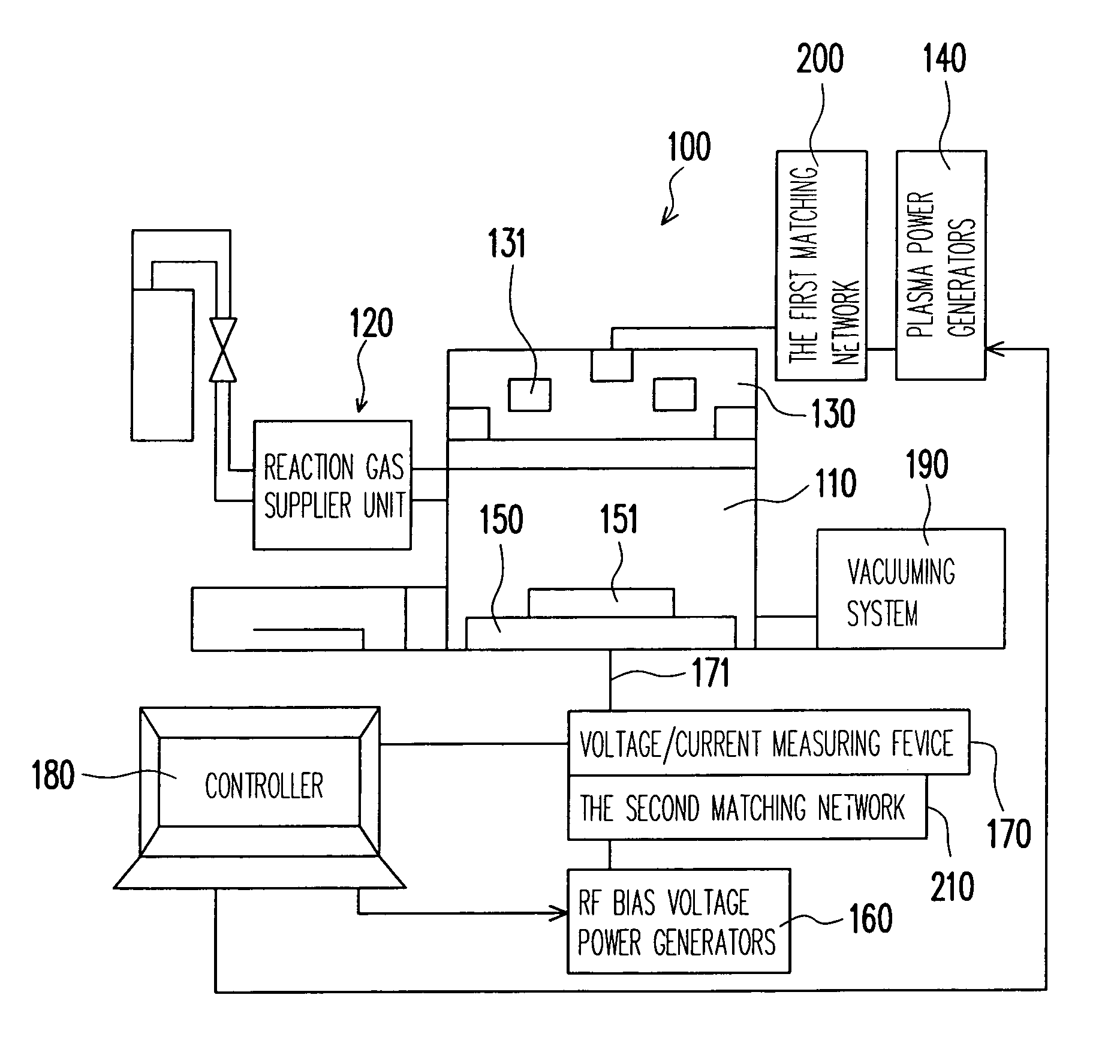
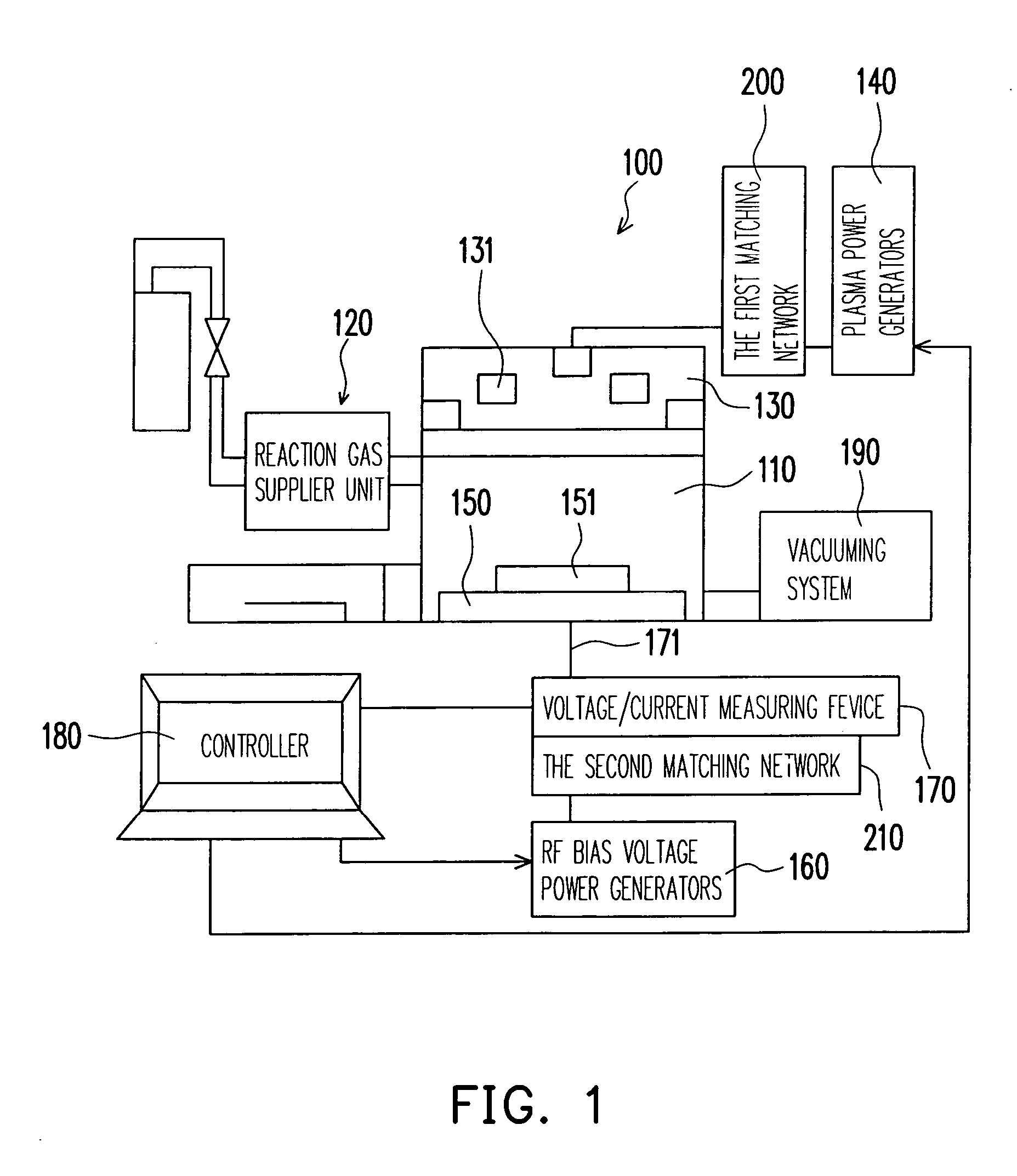
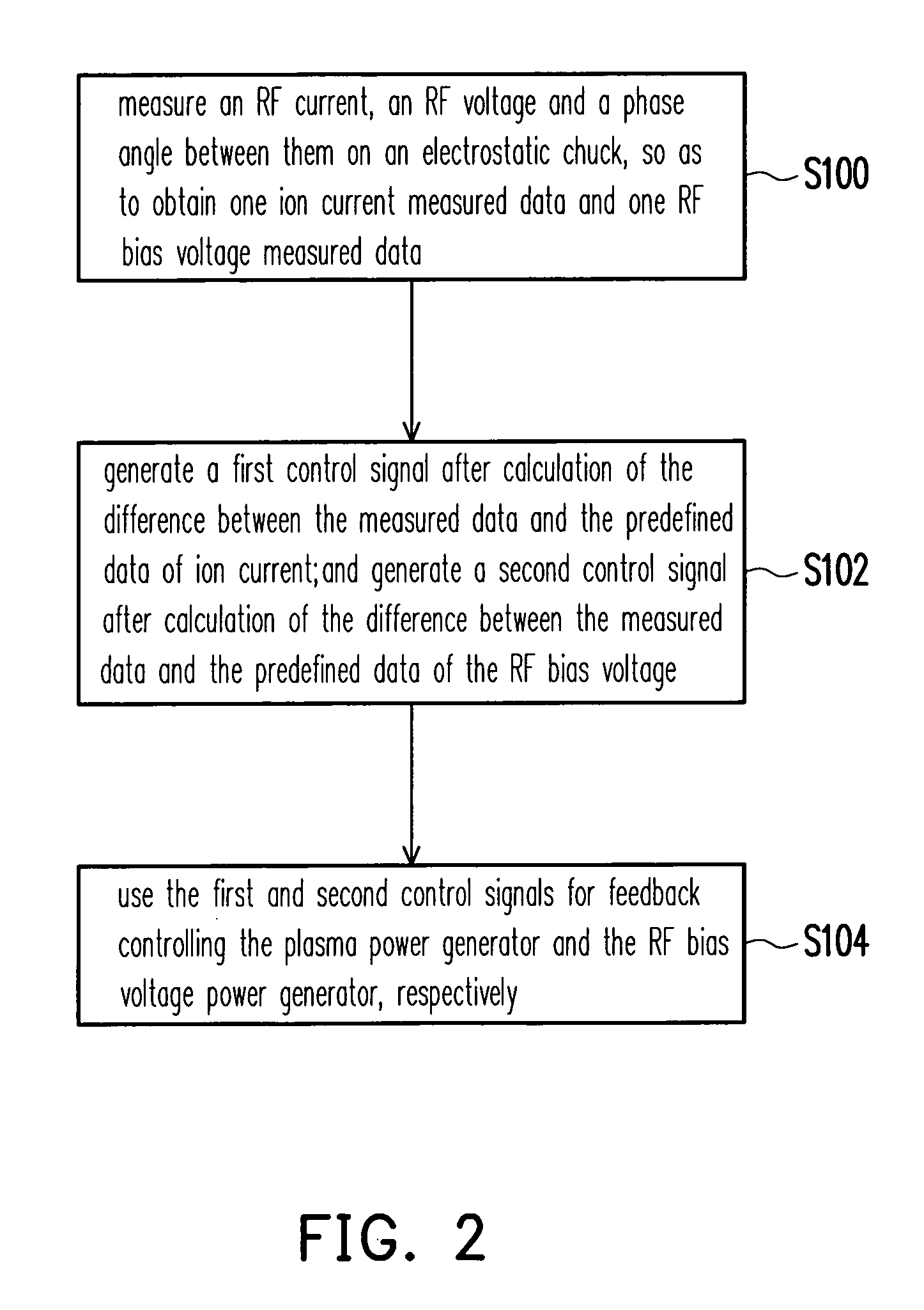
An inductively-coupled plasma etch apparatus and a feedback control method thereof are provided. A voltage / current measuring device is connected to an electrostatic chuck of the plasma etching apparatus, so as to measure the RF current, voltage and the phase angle between them on the electrostatic chuck. The ion current and the RF bias voltage are obtained by calculation of the RF current, voltage and the phase angle. Finally, using the obtained ion current and the RF bias voltage to feedback control the RF power generator in order to achieve the desired plasma status.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
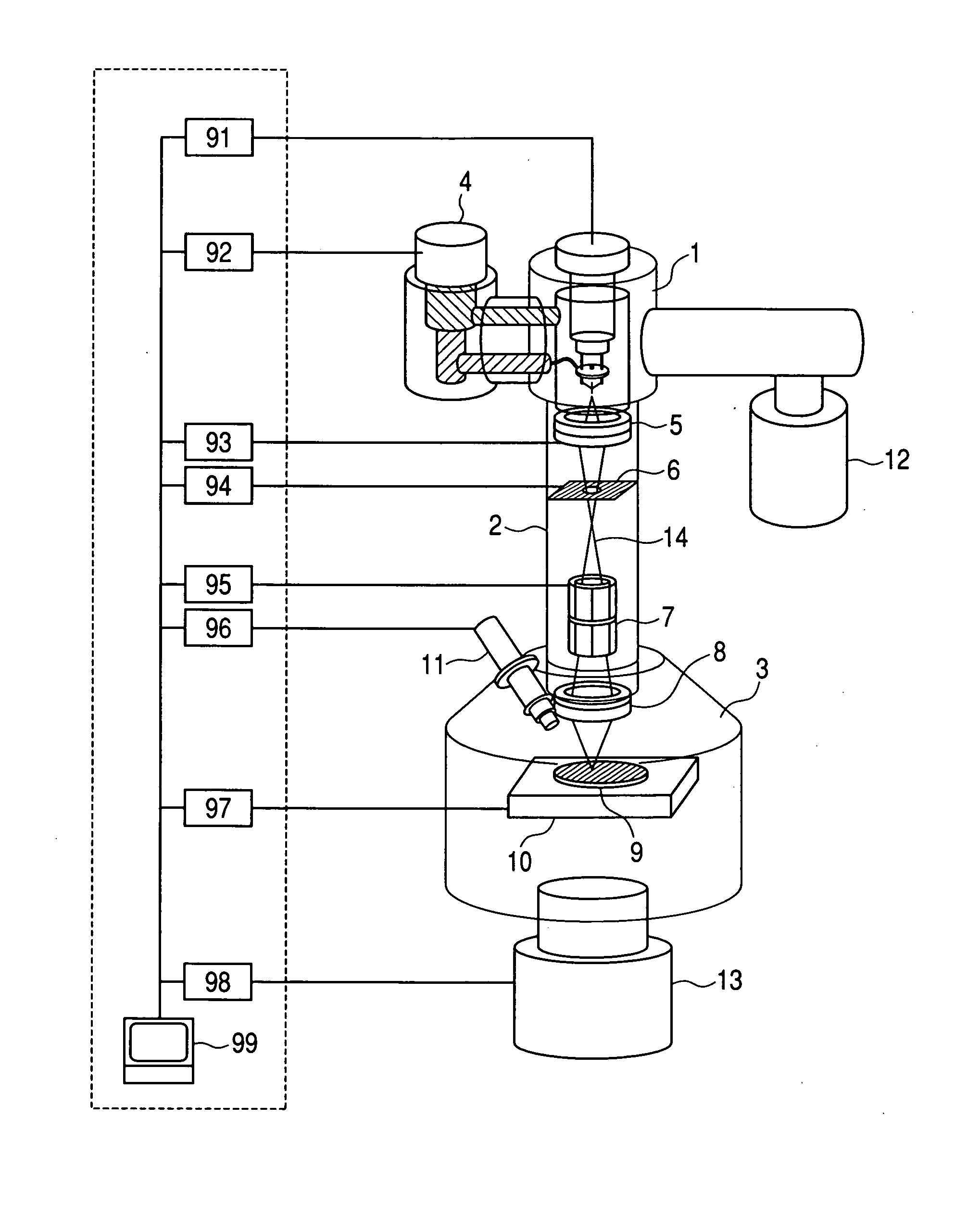
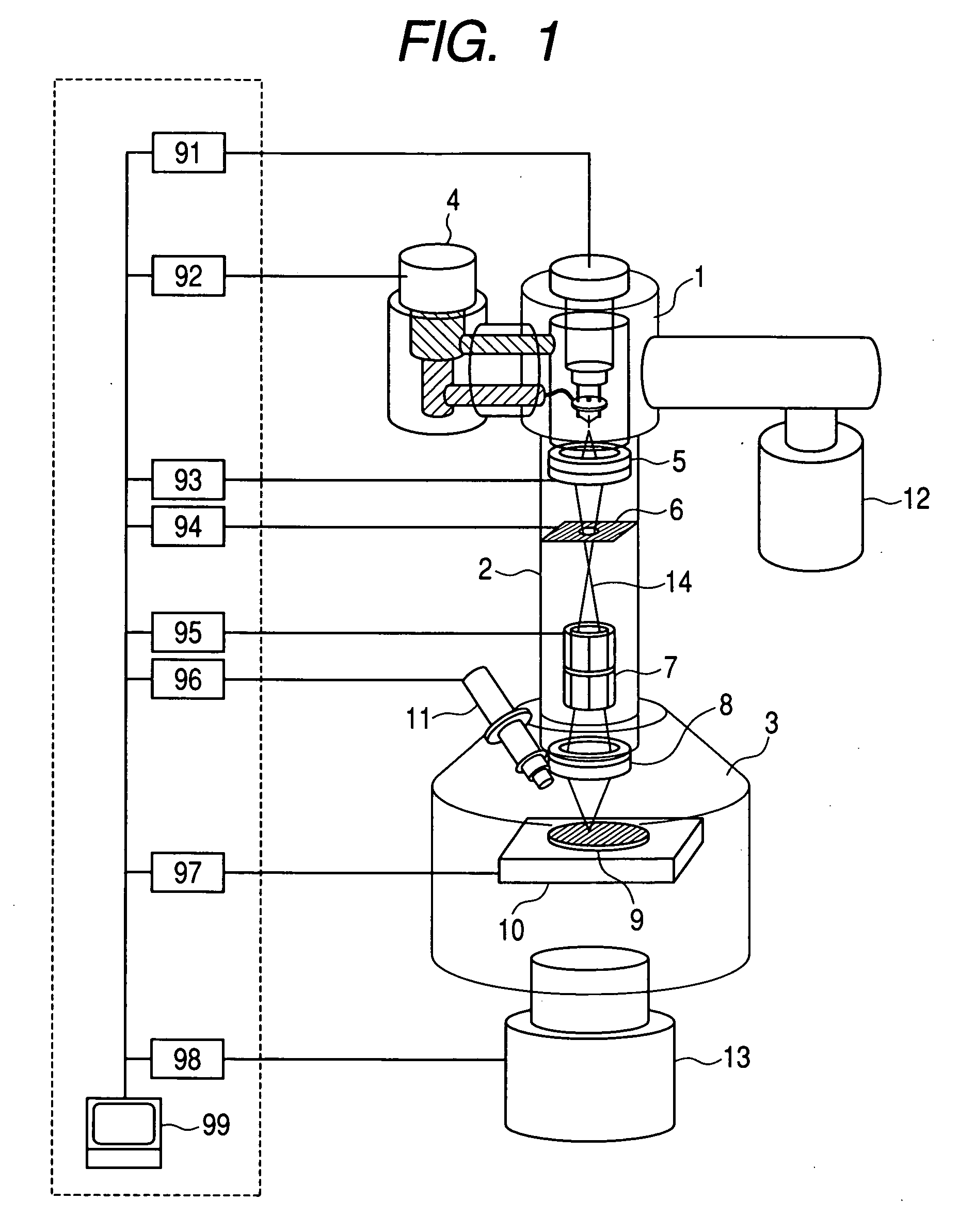
Methods and apparatus for self-optimization of electrospray ionization devices
InactiveUS20050072915A1Efficient interfaceSamples introduction/extractionIsotope separationMass spectrometricSpectrometer
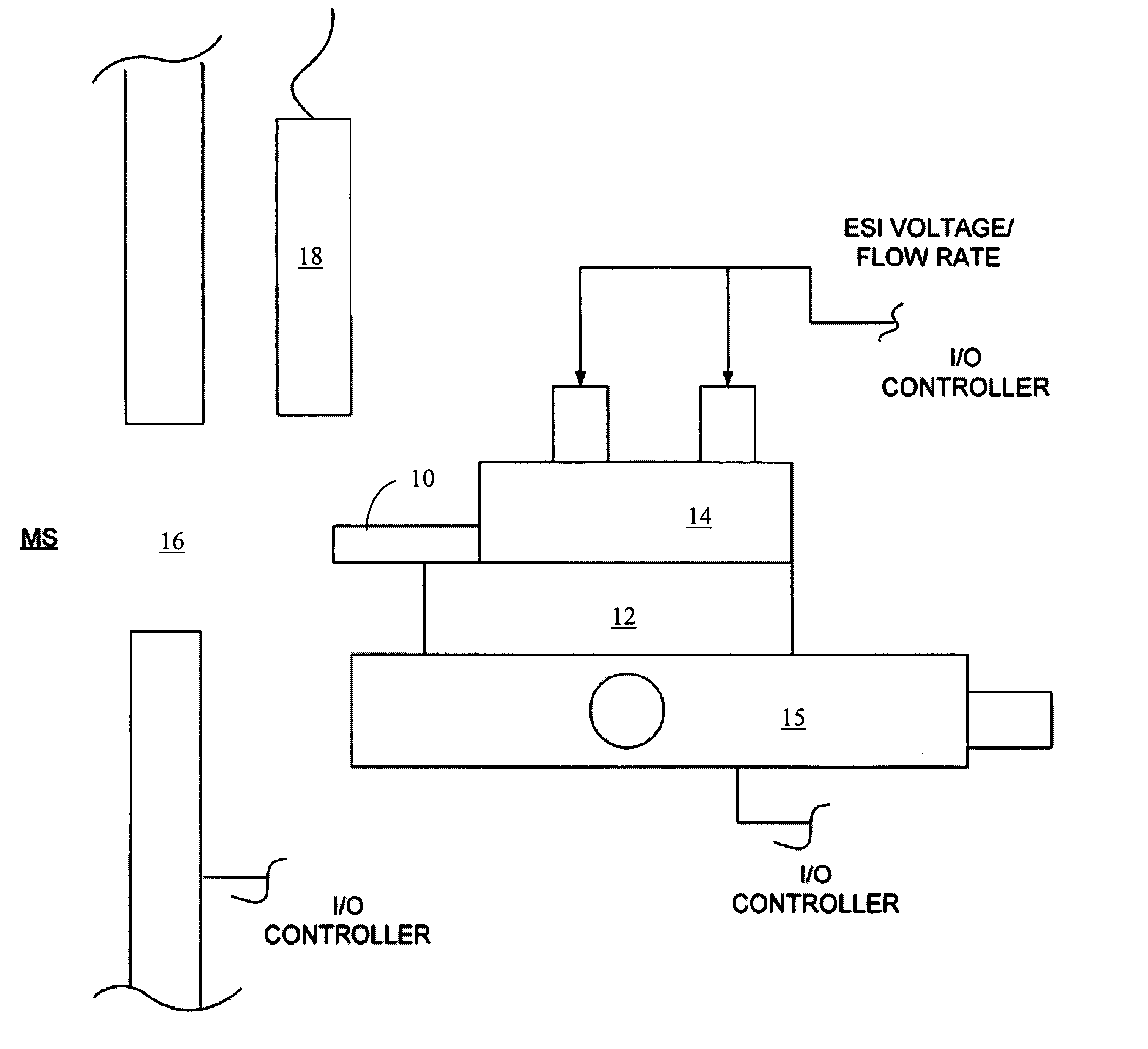
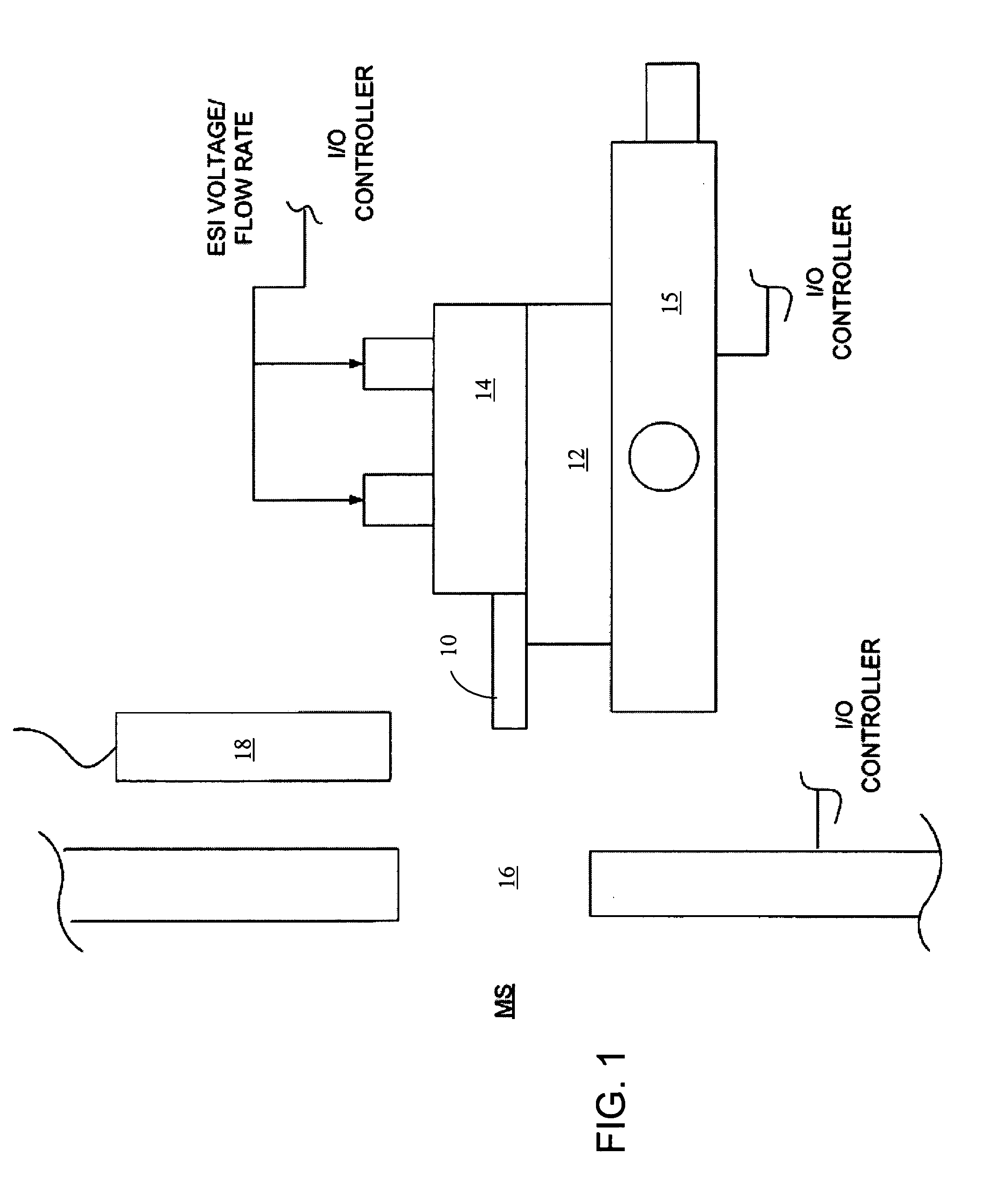
An automated electrospray ionization (ESI) device and related methods to optimize electrospray interface conditions for mass spectrometric analysis. The optimization process can be performed with calibration or optimization solutions that produce expected ESI parameters such as an ESI signal or an ion current. The ESI device may include an input / output (I / O) controller that is coupled to an electrospray assembly including an XYZ stage for positioning an electrospray emitter relative to a mass spectrometer orifice. The I / O controller may be connected to a power supply for applying an adjustable electrospray ionization voltage, and an adjustable flow regulator that alters the flow of solution by modifying applied voltage and / or pressure. A central processing unit instructs the I / O controller to control selectively the electrospray assembly based on the resultant signals from the mass spectrometer or the ion currents within the mass spectrometer in accordance with a predetermined optimization algorithm. The resulting ESI signal or ion currents are monitored and provide feedback to the I / O controller which can automatically instruct selected system components to make adjustments as needed to attain optimal settings that produce expected ESI signals or ion currents in the mass spectrometer for selected solutions.
Owner:NORVIEL VERN
Gas field ion source, charged particle microscope, and apparatus
ActiveUS20090173888A1Reduce mechanical vibrationHigh conductanceThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIon currentIon beam
A gas field ion source that can simultaneously increase a conductance during rough vacuuming and reduce an extraction electrode aperture diameter from the viewpoint of the increase of ion current. The gas field ion source has a mechanism to change a conductance in vacuuming a gas molecule ionization chamber. That is, the conductance in vacuuming a gas molecule ionization chamber is changed in accordance with whether or not an ion beam is extracted from the gas molecule ionization chamber. By forming lids as parts of the members constituting the mechanism to change the conductance with a bimetal alloy, the conductance can be changed in accordance with the temperature of the gas molecule ionization chamber, for example the conductance is changed to a relatively small conductance at a relatively low temperature and to a relatively large conductance at a relatively high temperature.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
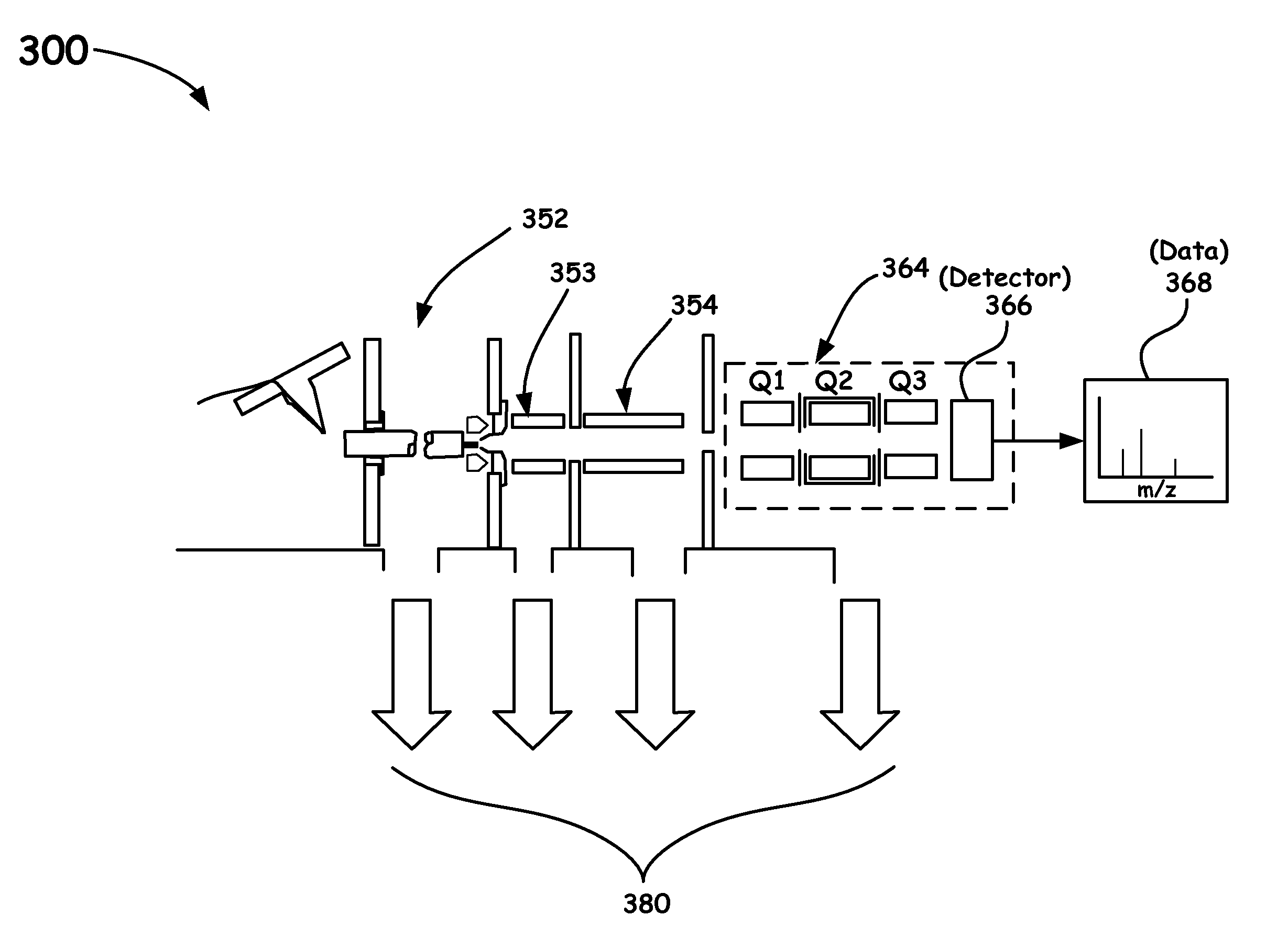
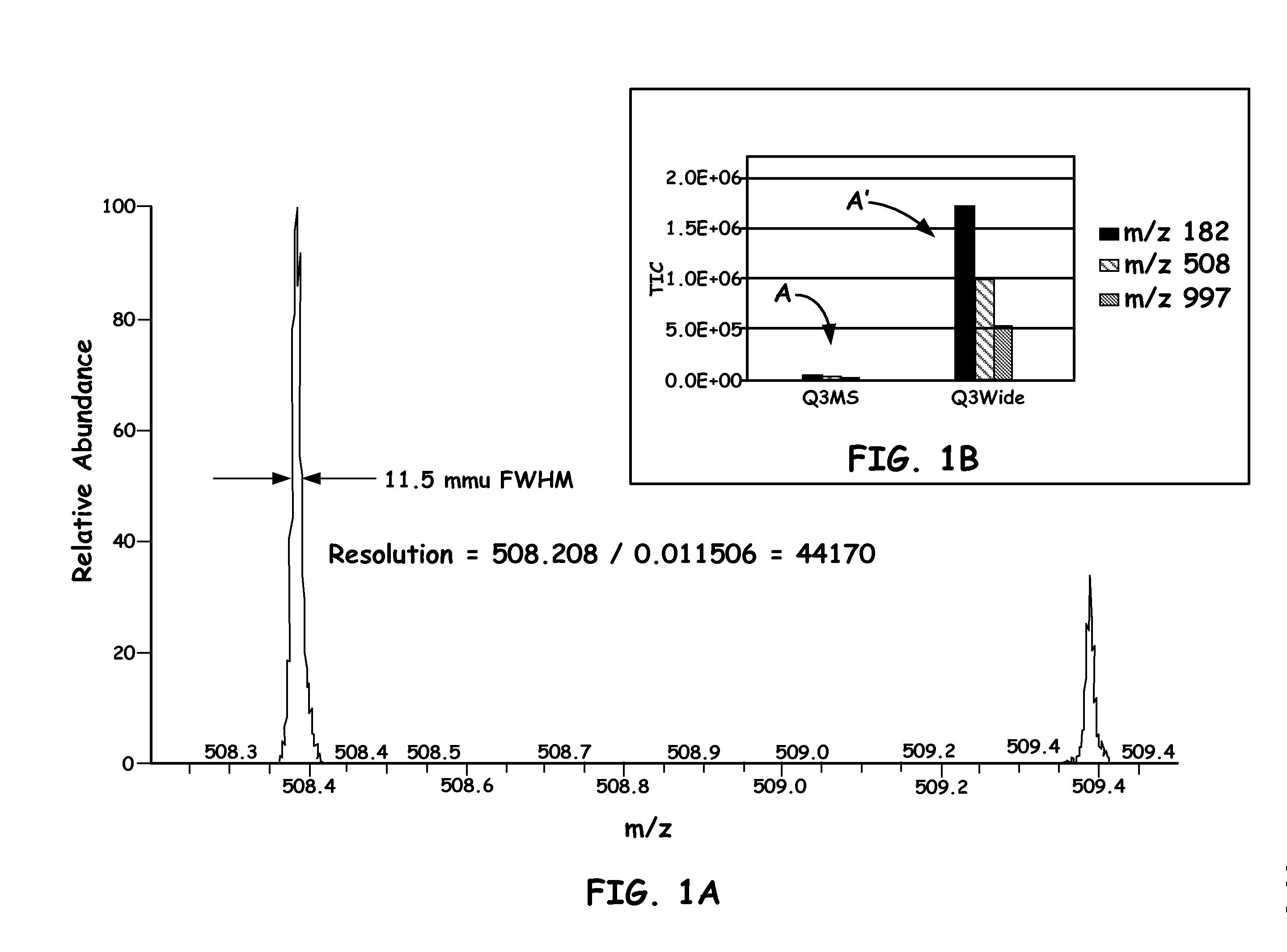
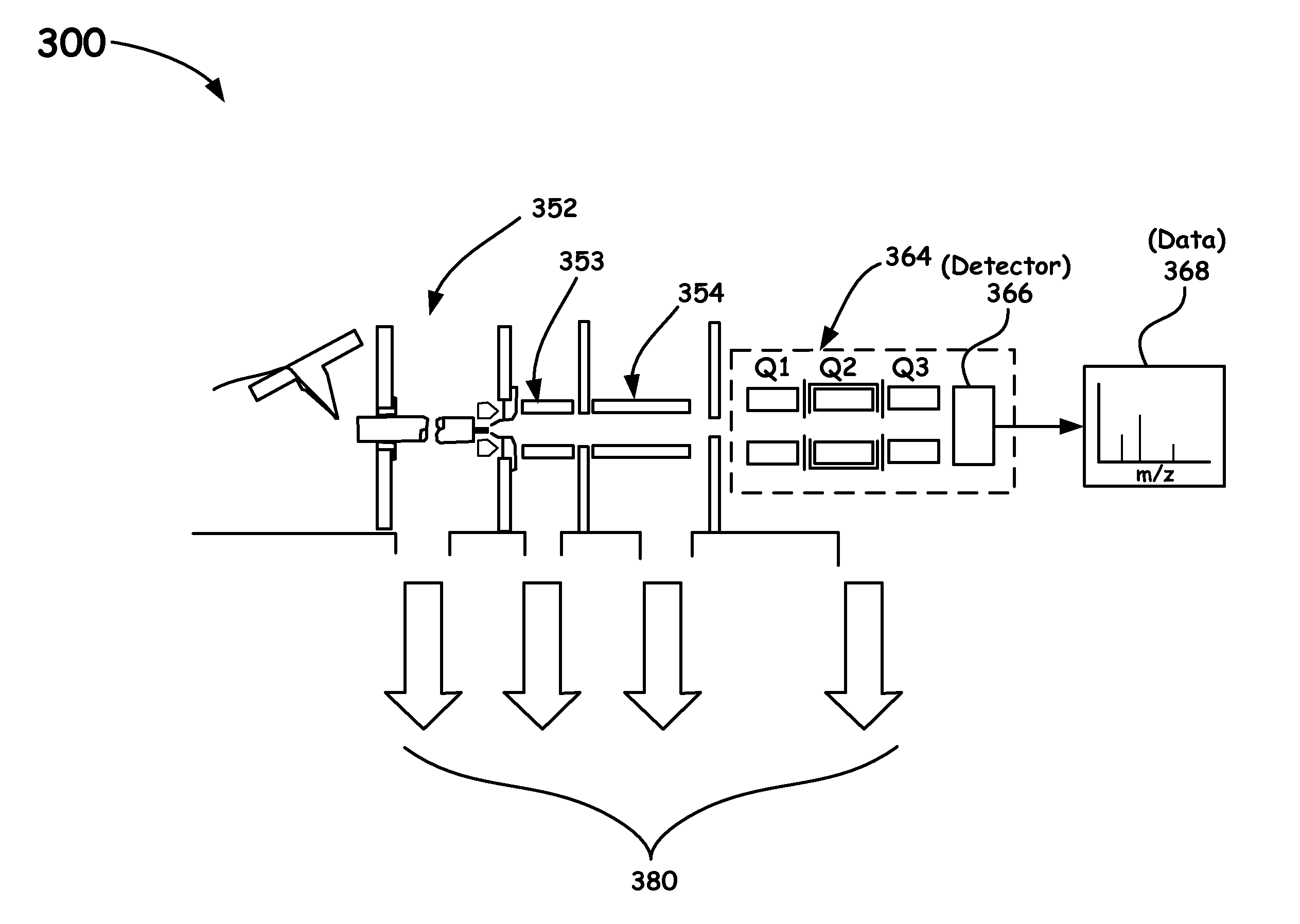
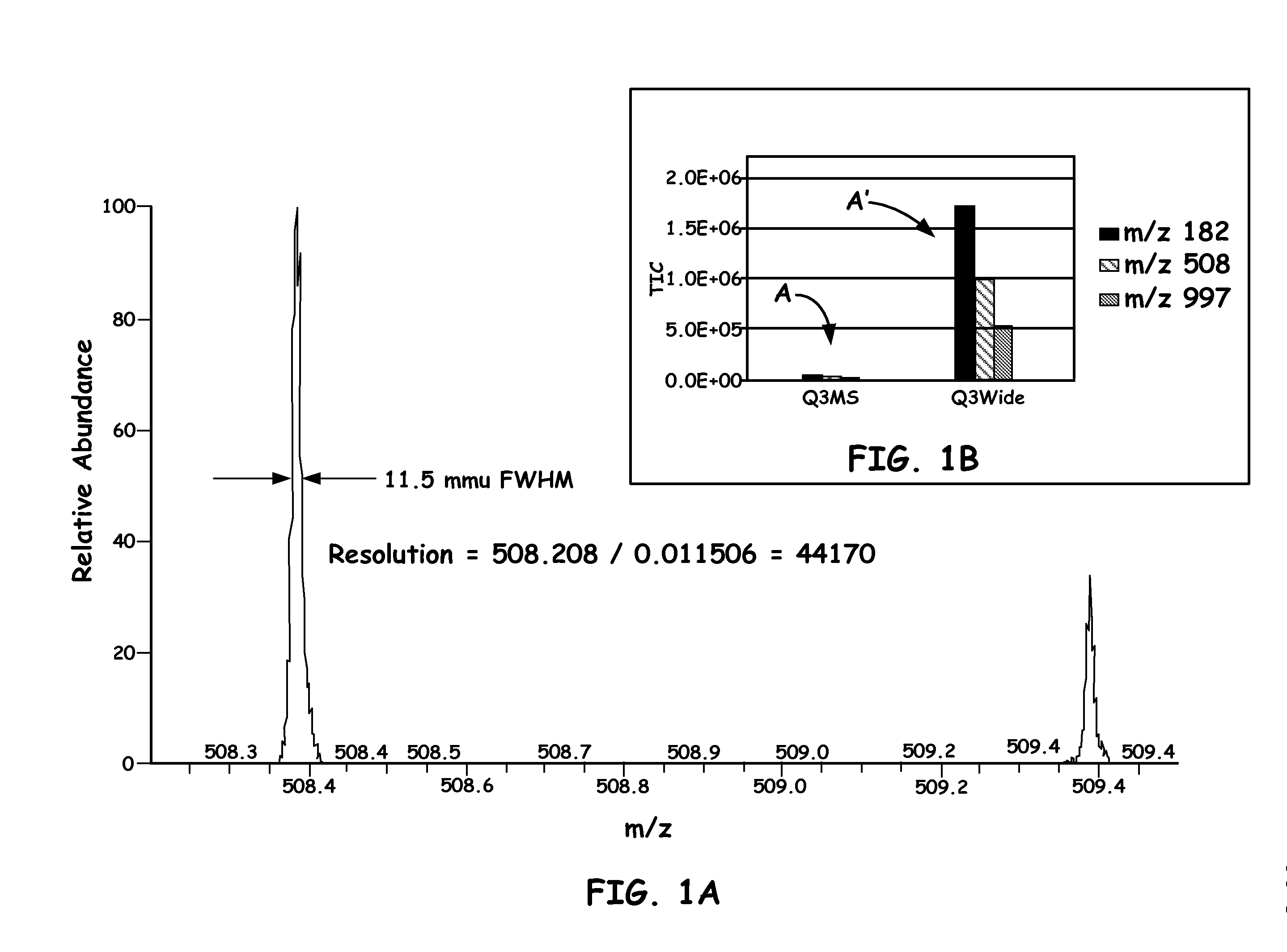
Quadrupole mass spectrometer with enhanced sensitivity and mass resolving power
ActiveUS8389929B2Low costImprove robustnessStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsMass analyzerQuadrupole
A novel method and mass spectrometer apparatus is introduced to spatially and temporally resolve images of one or more ion exit patterns of a multipole instrument. In particular, the methods and structures of the present invention measures the ion current as a function of time and spatial displacement in the beam cross-section of a quadrupole mass filter via an arrayed detector. The linearity of the detected quadrupole ion current in combination with it reproducible spatial-temporal structure enables the deconvolution of the contributions of signals from individual ion species in complex mixtures where both sensitivity and mass resolving power are essential.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
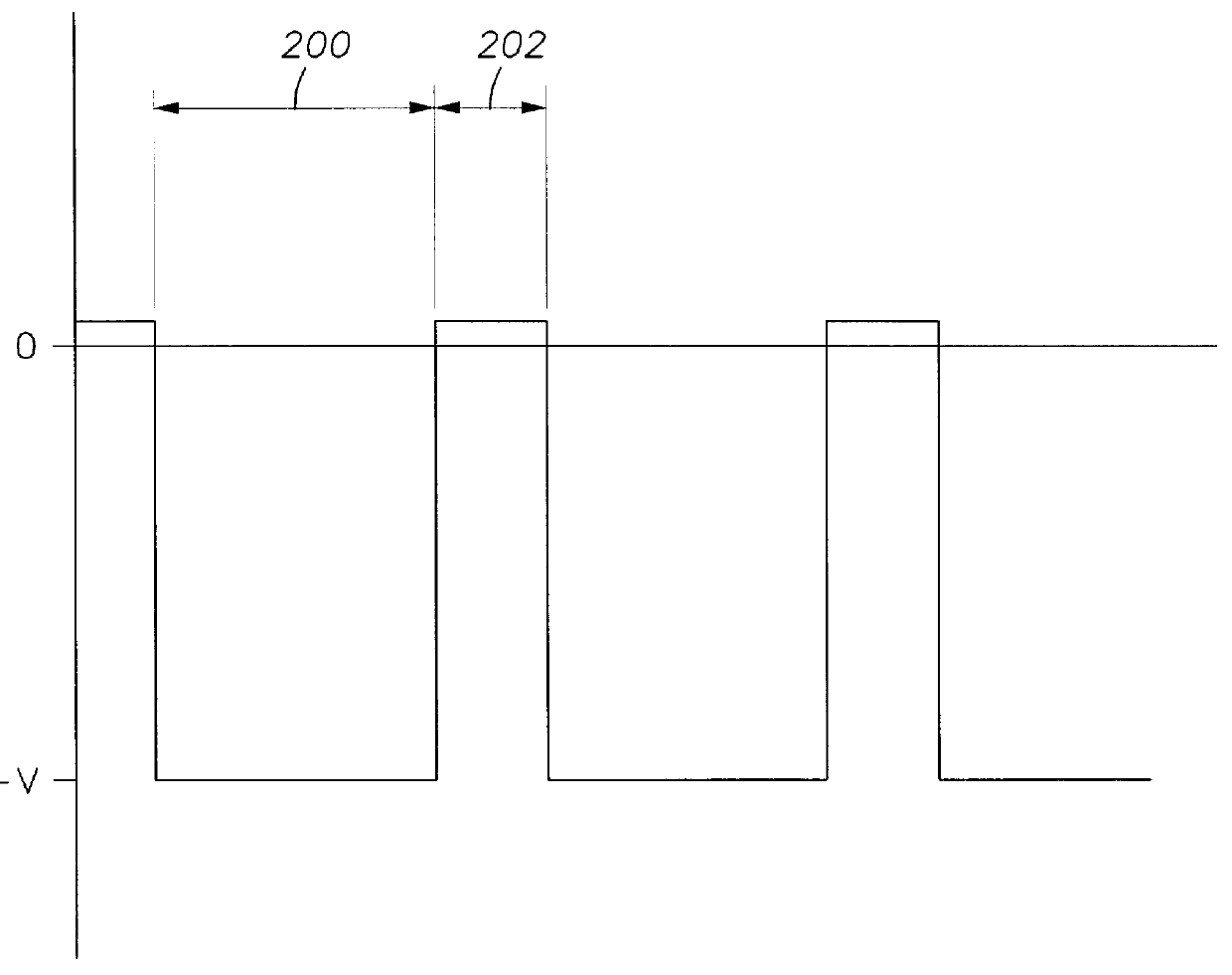
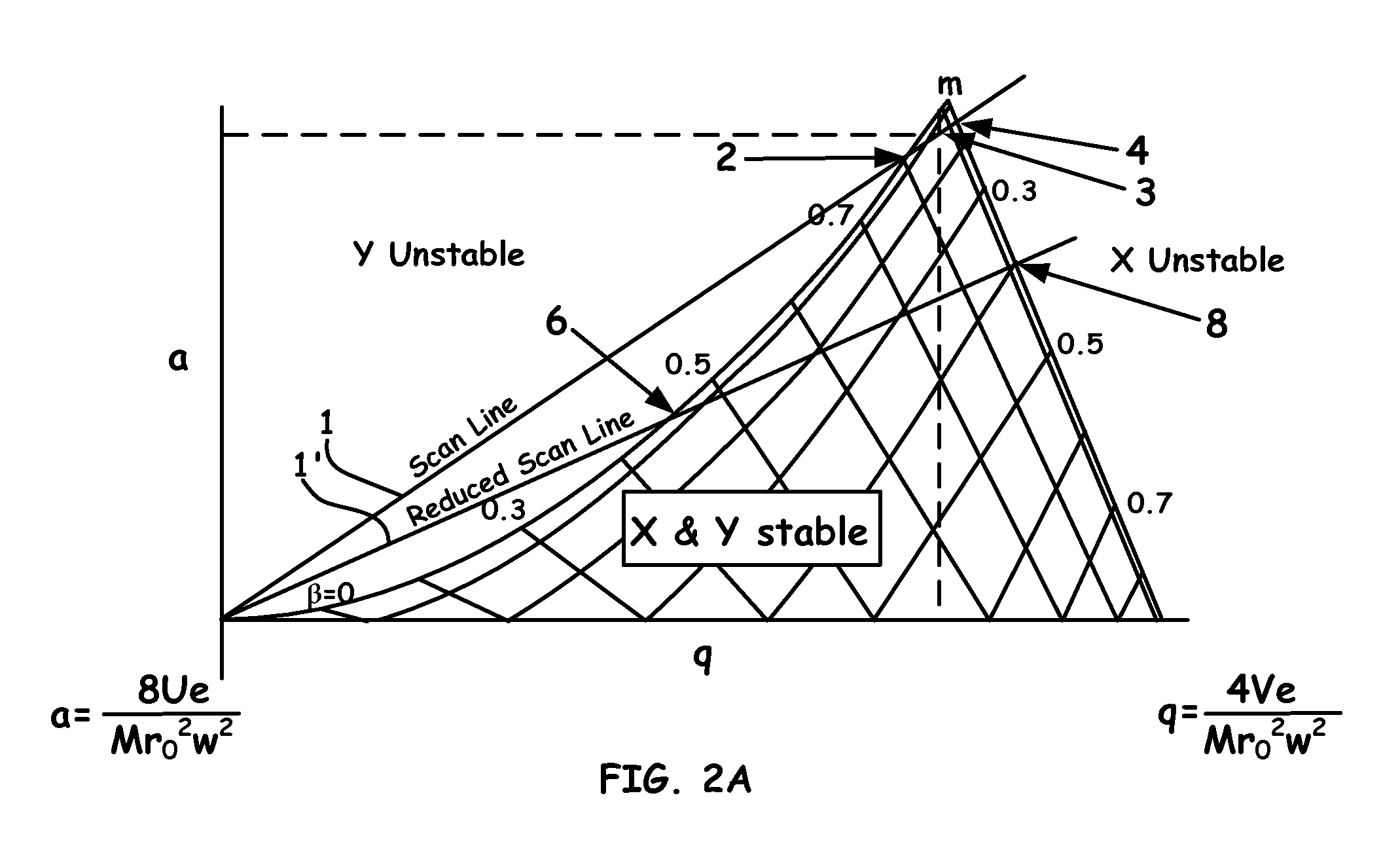
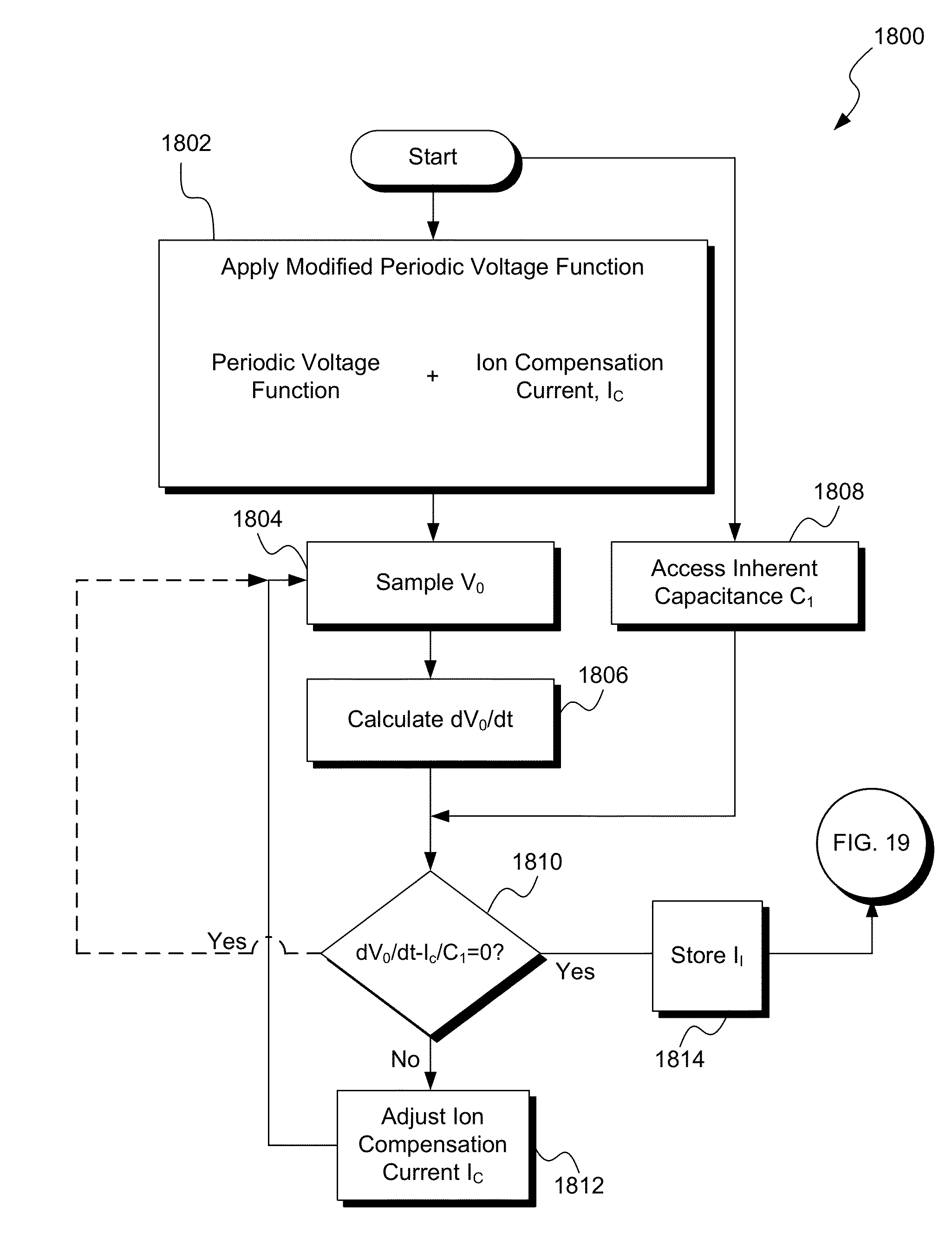
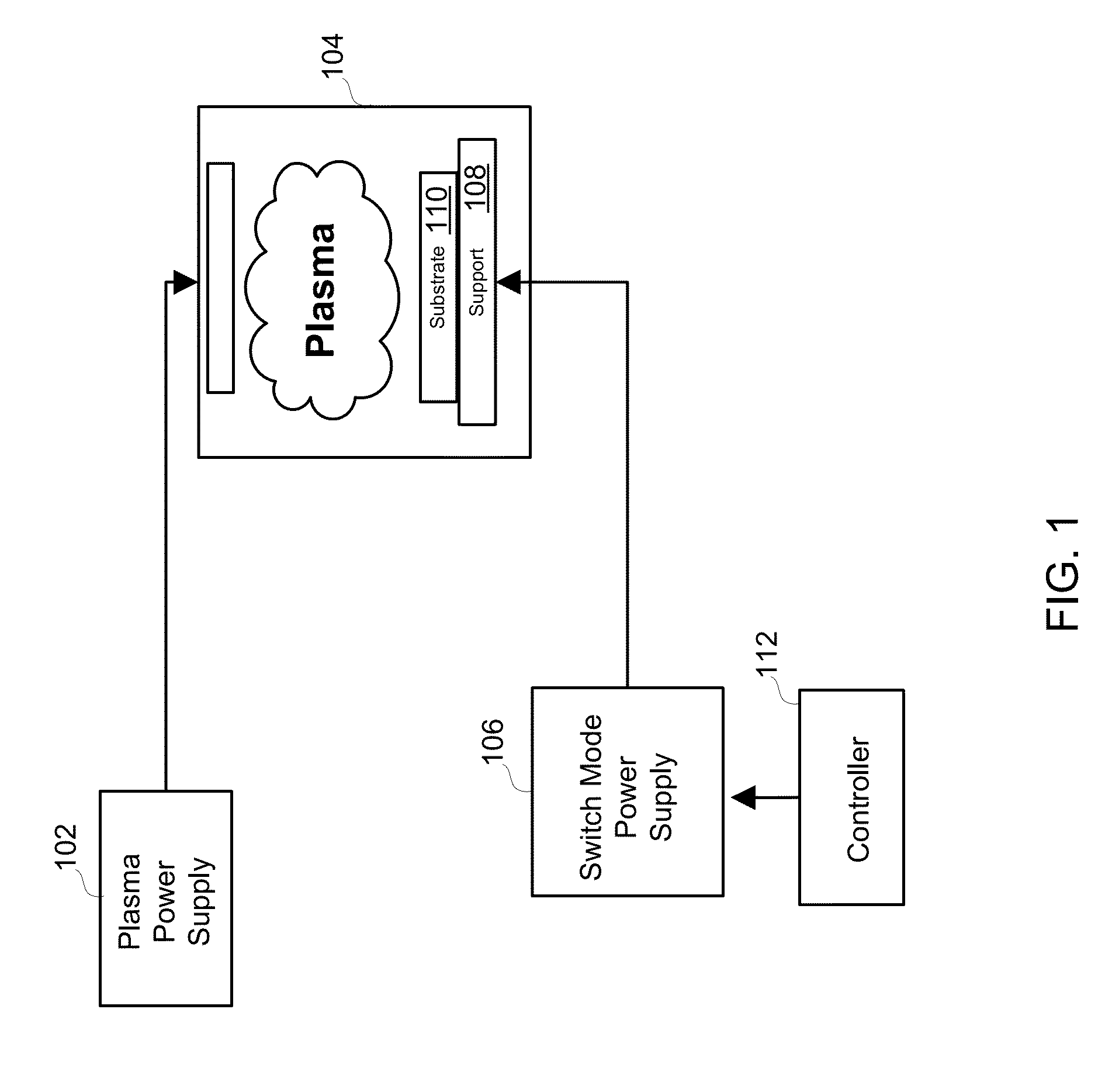
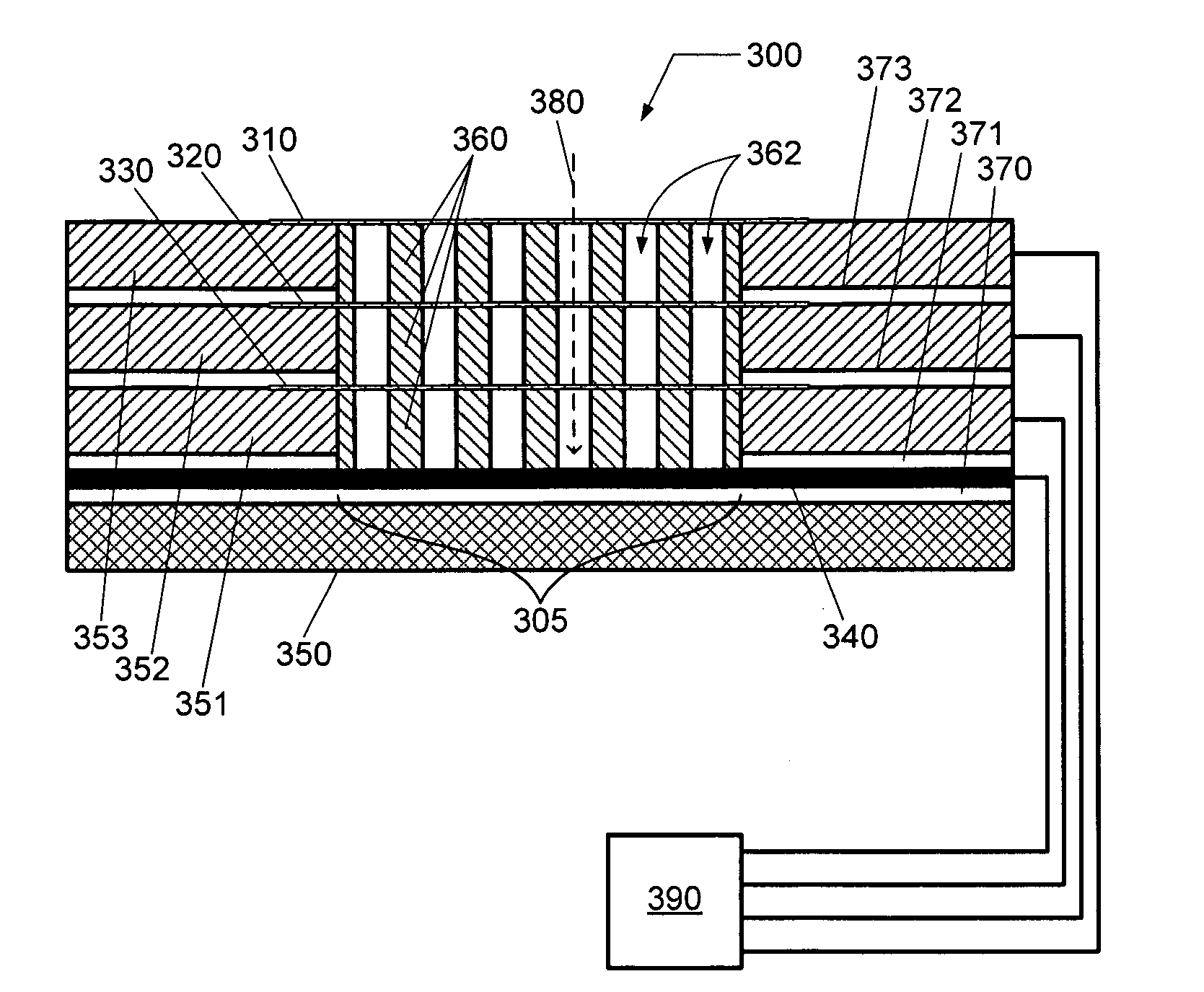
Wide dynamic range ion energy bias control; fast ion energy switching; ion energy control and a pulsed bias supply; and a virtual front panel
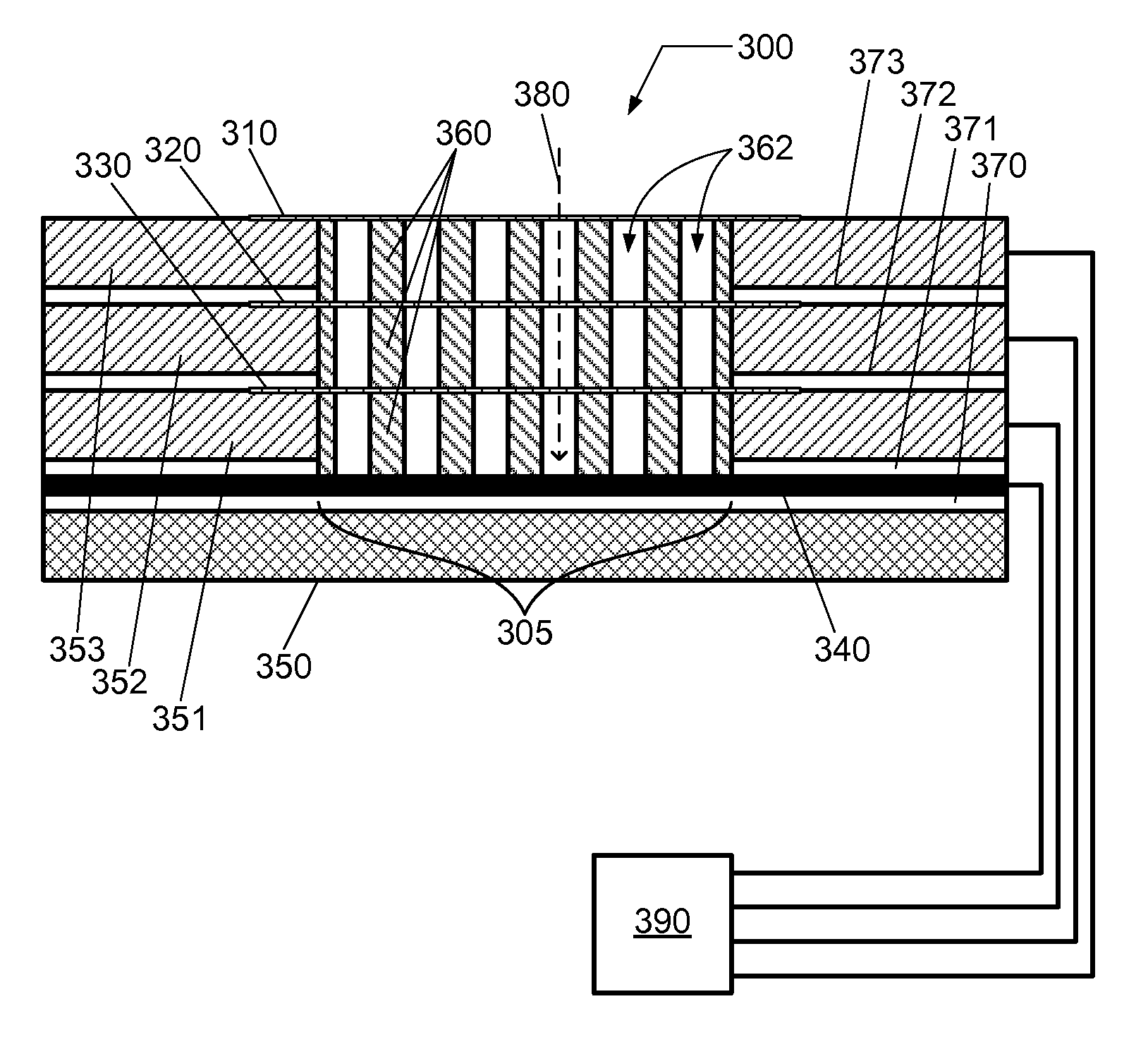
This disclosure describes systems, methods, and apparatus for operating a plasma processing chamber. In particular, a periodic voltage function combined with an ion current compensation can be provided as a bias to a substrate support as a modified periodic voltage function. This in turn effects a DC bias on the surface of the substrate that controls an ion energy of ions incident on a surface of the substrate. A peak-to-peak voltage of the periodic voltage function can control the ion energy, while the ion current compensation can control a width of an ion energy distribution function of the ions. Measuring the modified periodic voltage function can provide a means to calculate an ion current in the plasma and a sheath capacitance of the plasma sheath. The ion energy distribution function can be tailored and multiple ion energy peaks can be generated, both via control of the modified periodic voltage function.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
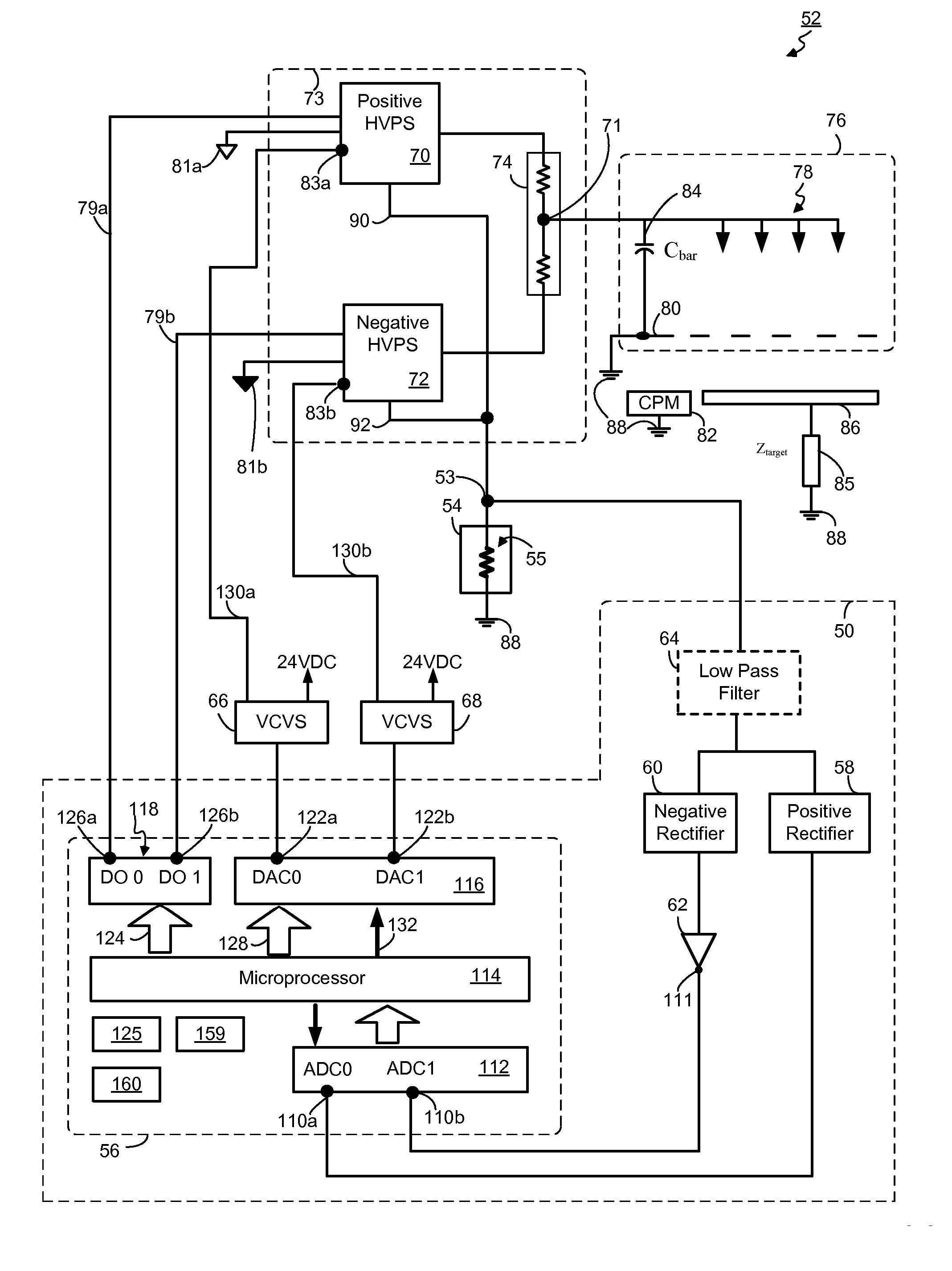
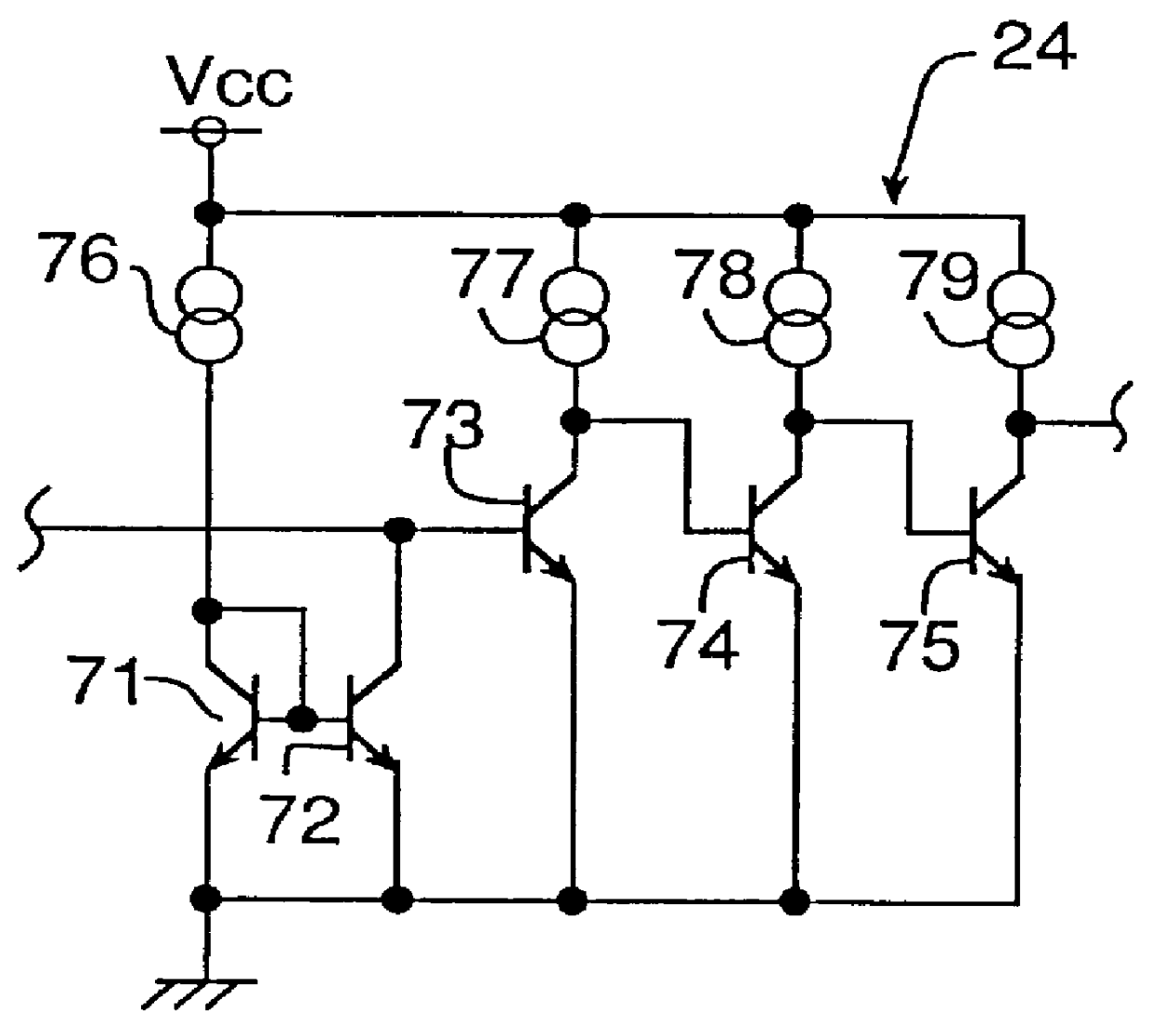
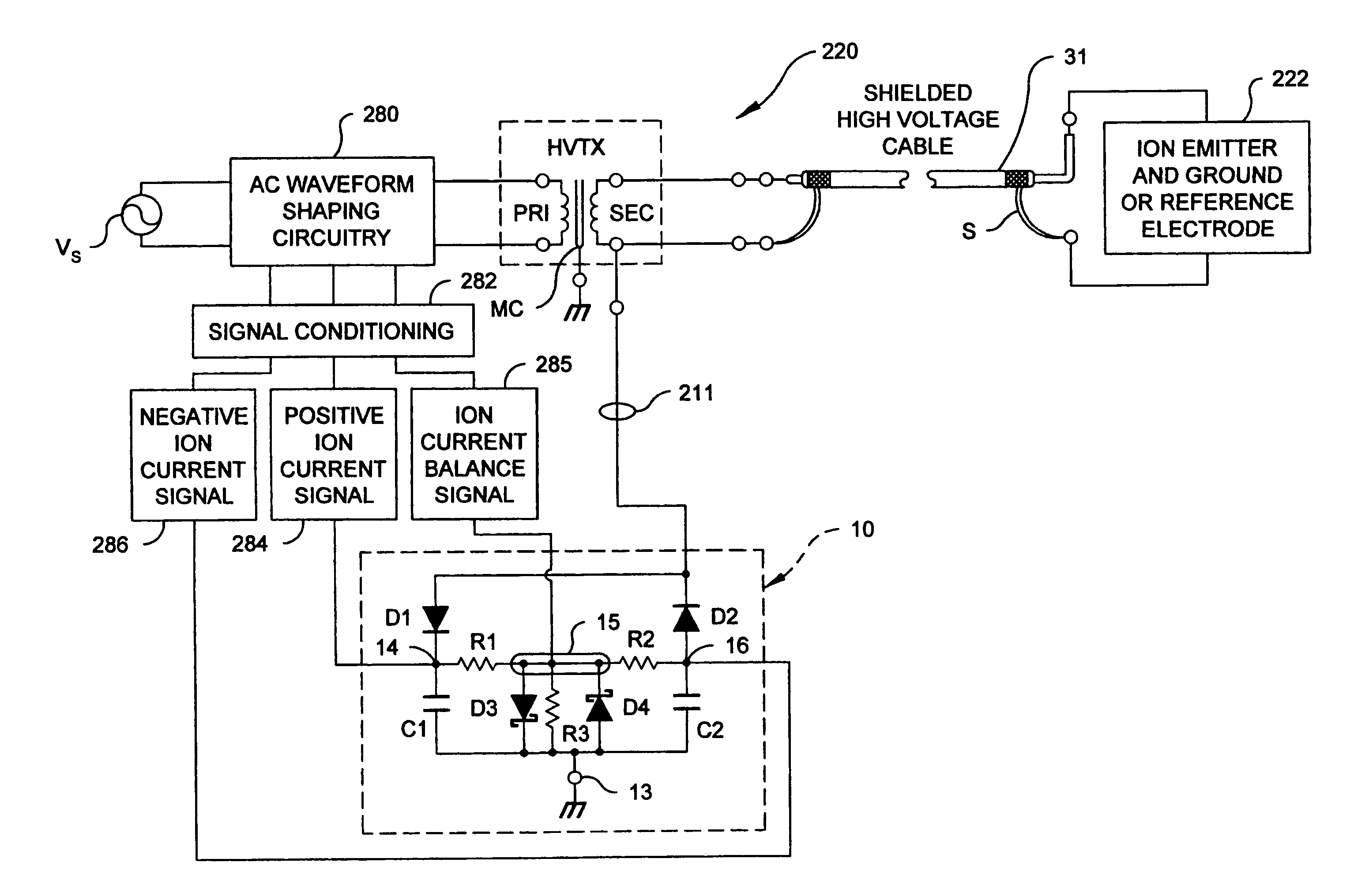
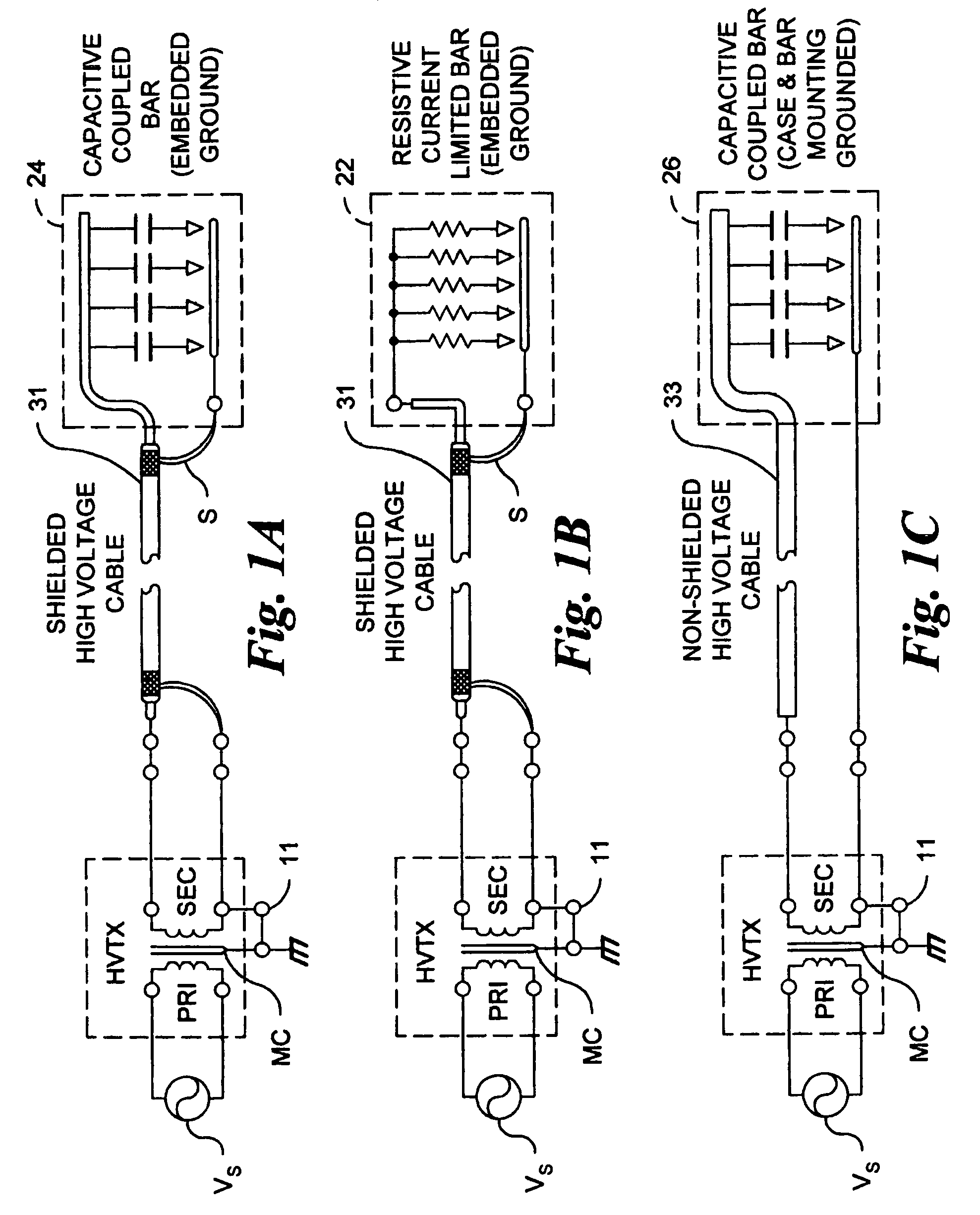
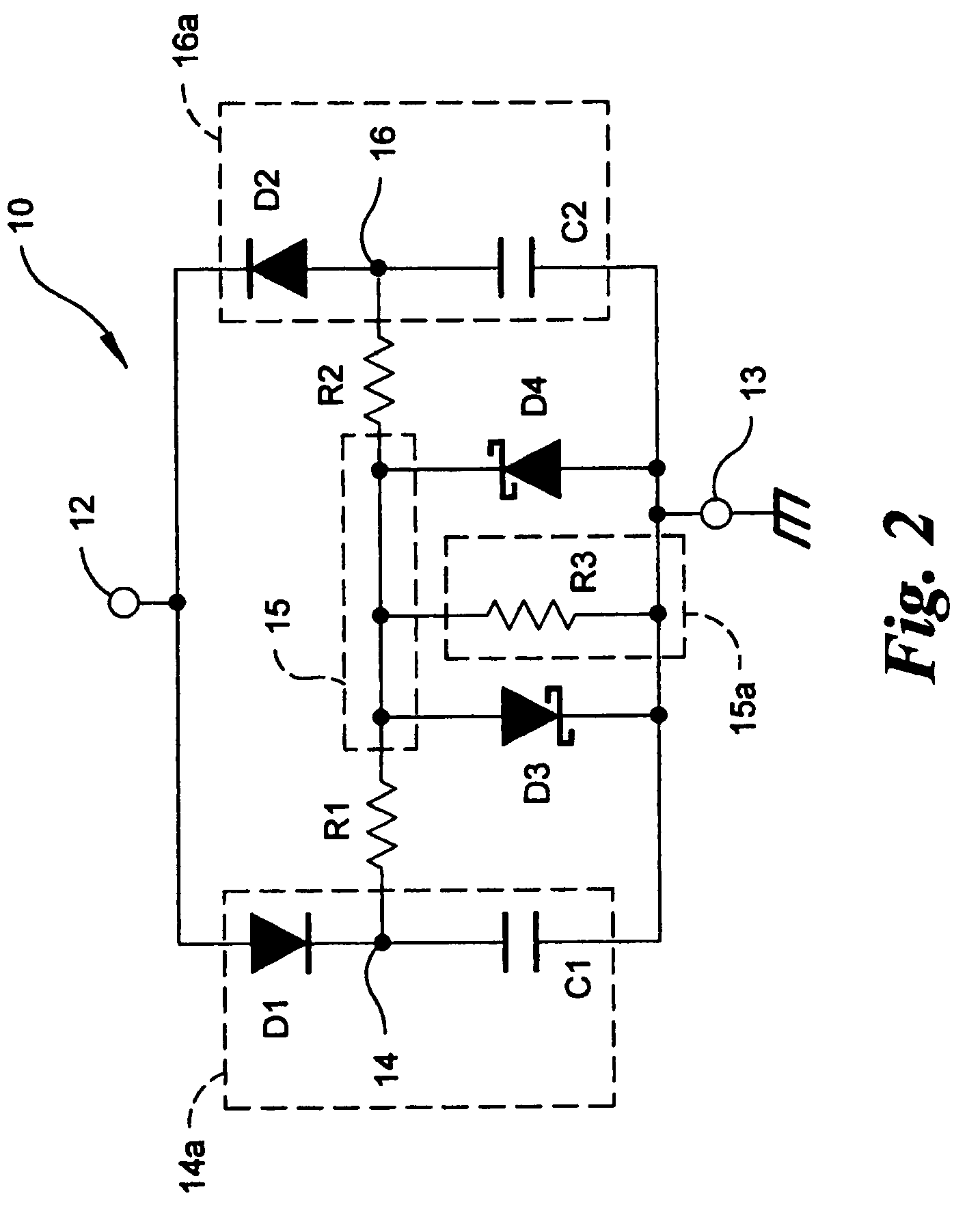
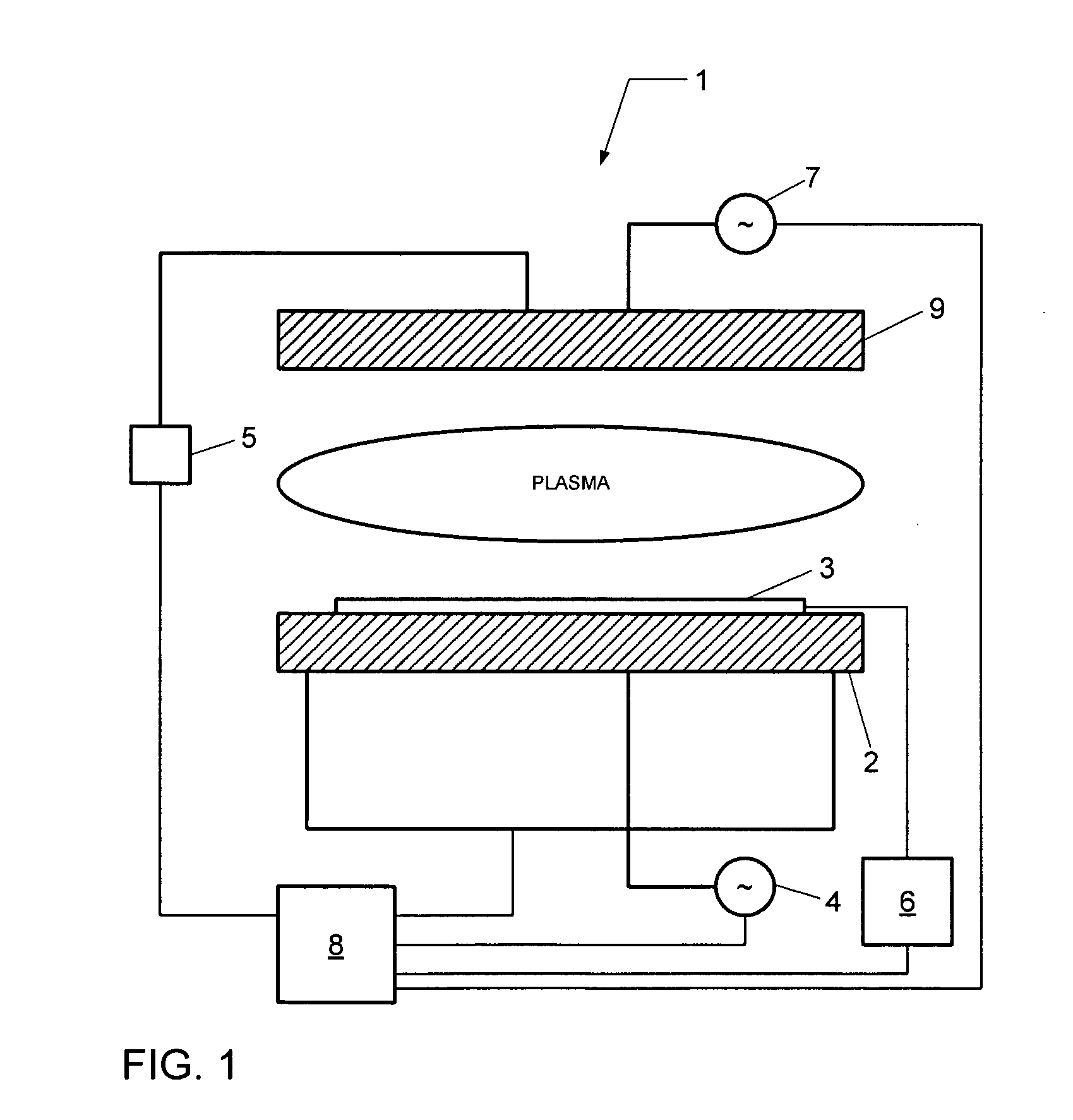
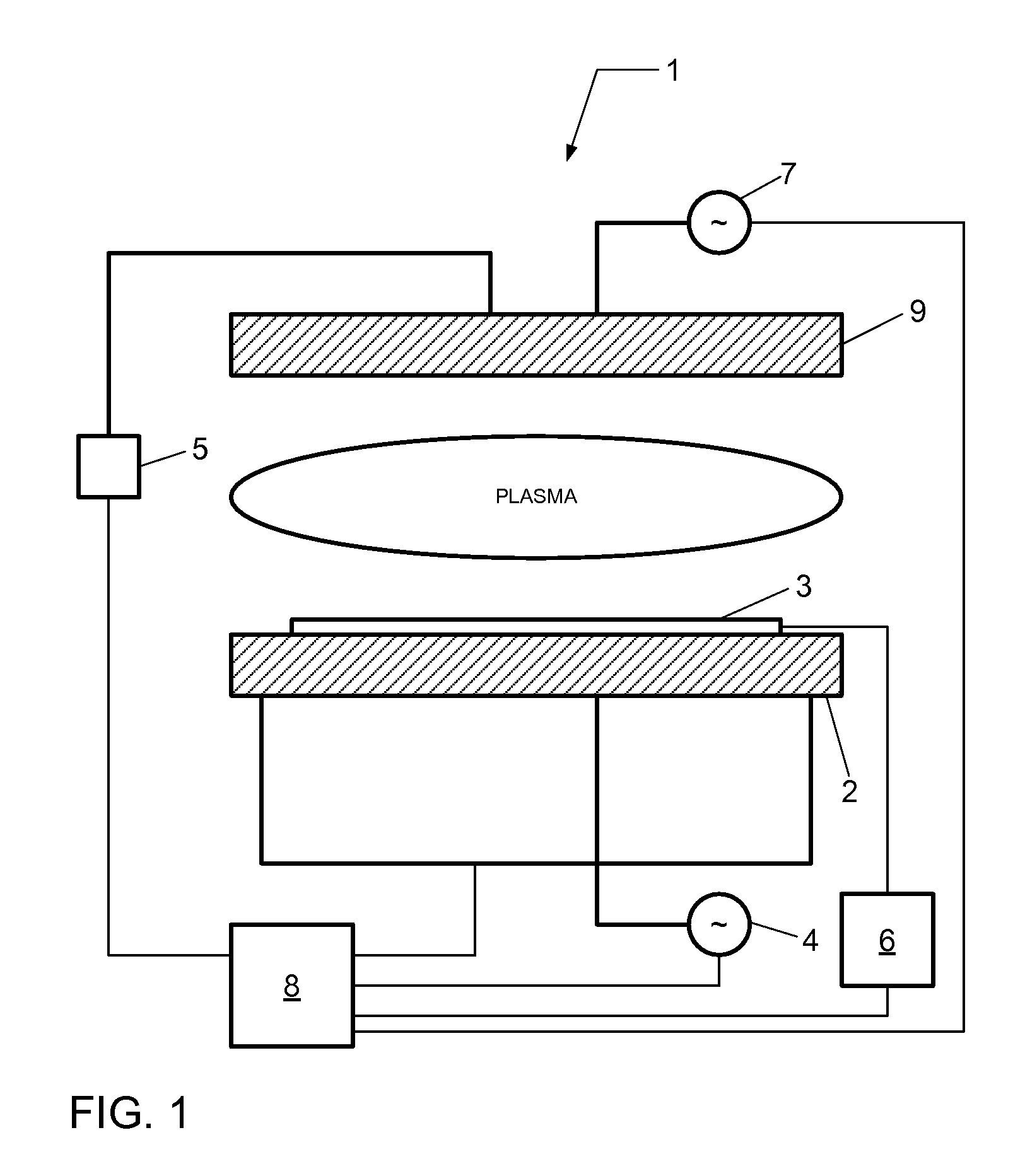
Control system for static neutralizer
The present invention pertains to various embodiments for managing ion current balance by independently controlling positive ion current and negative ion current generated during static neutralization. In another embodiment, E-Field compensation may be provided. These embodiments disclose both method and apparatus implementations.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
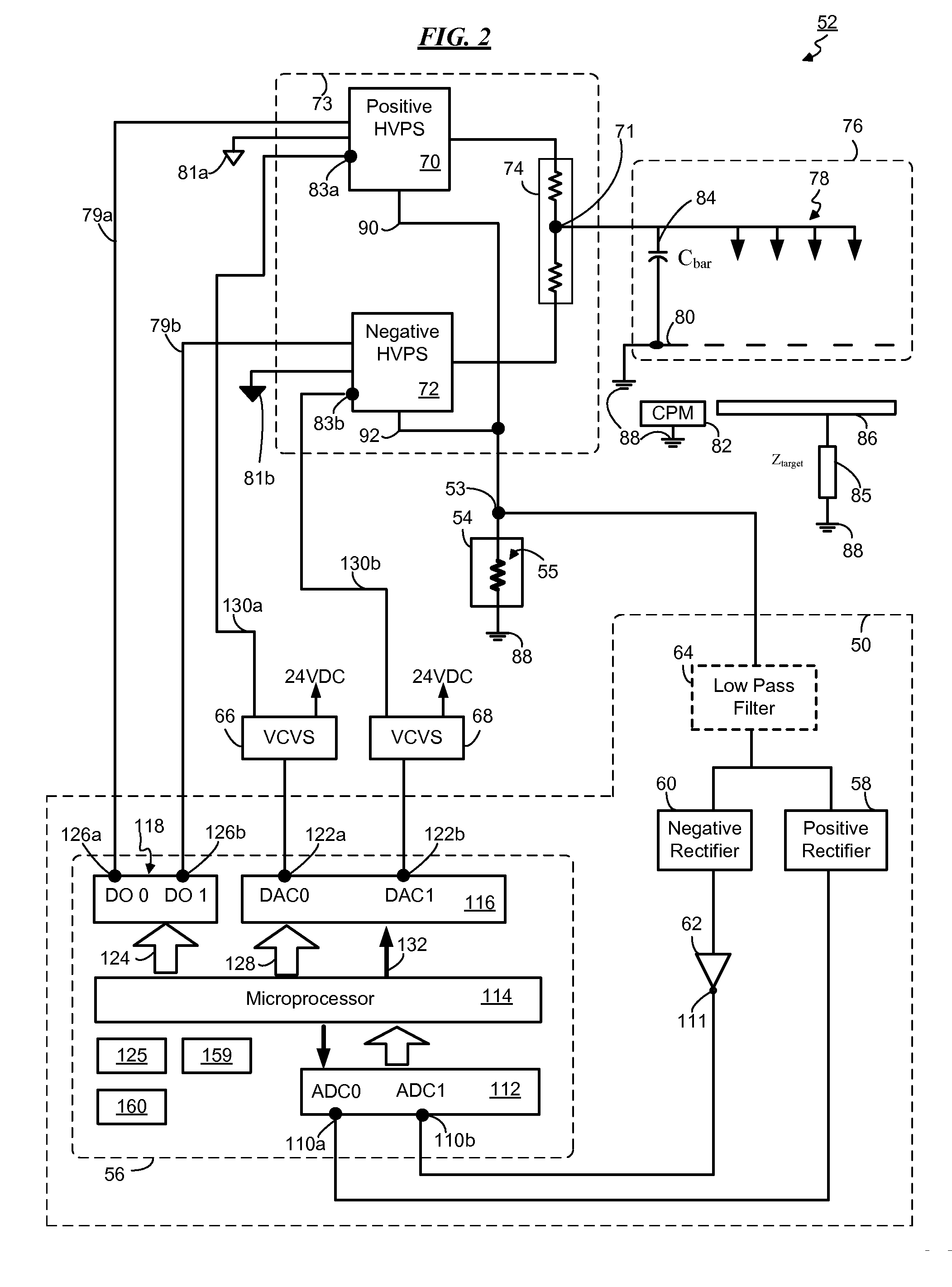
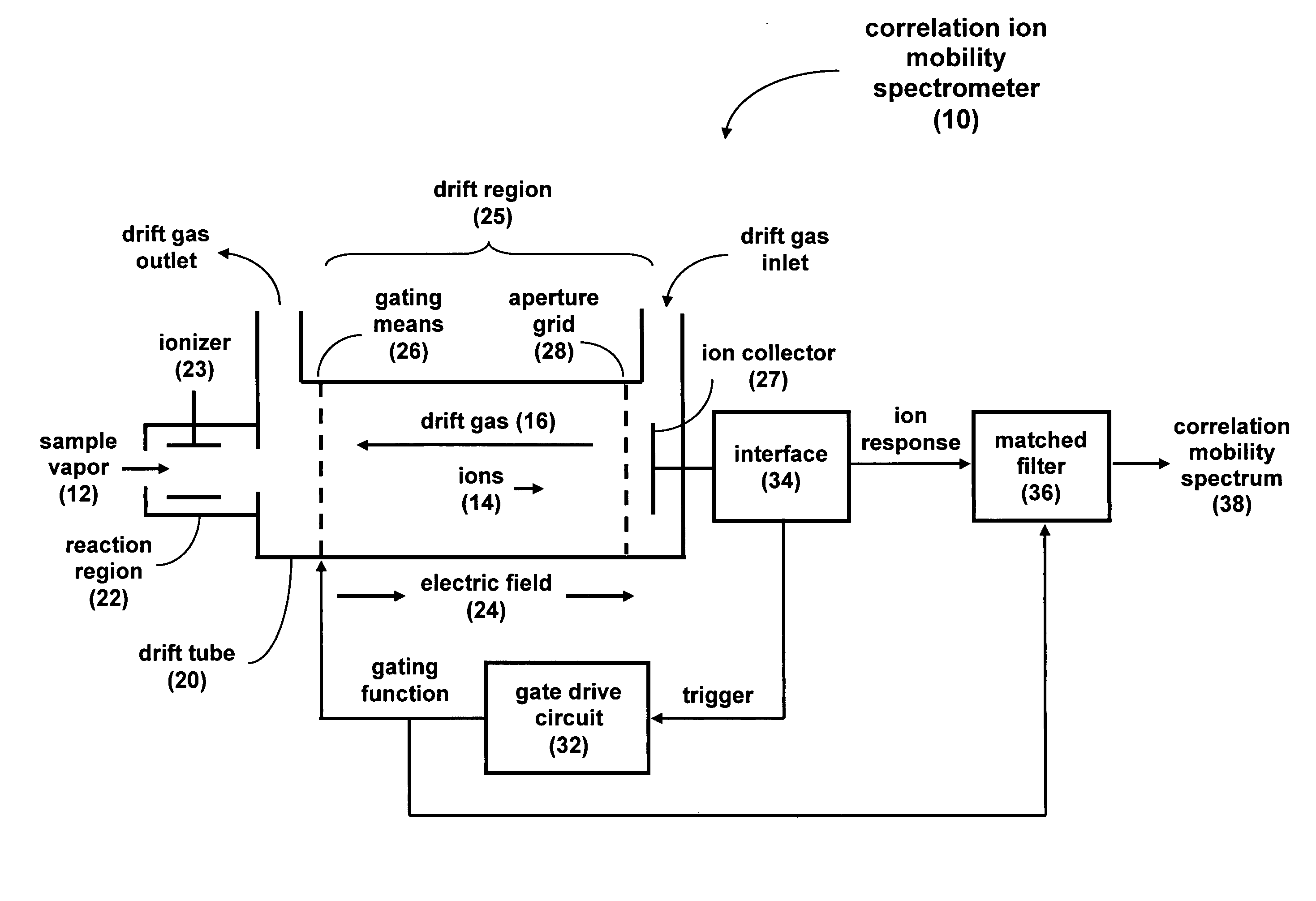
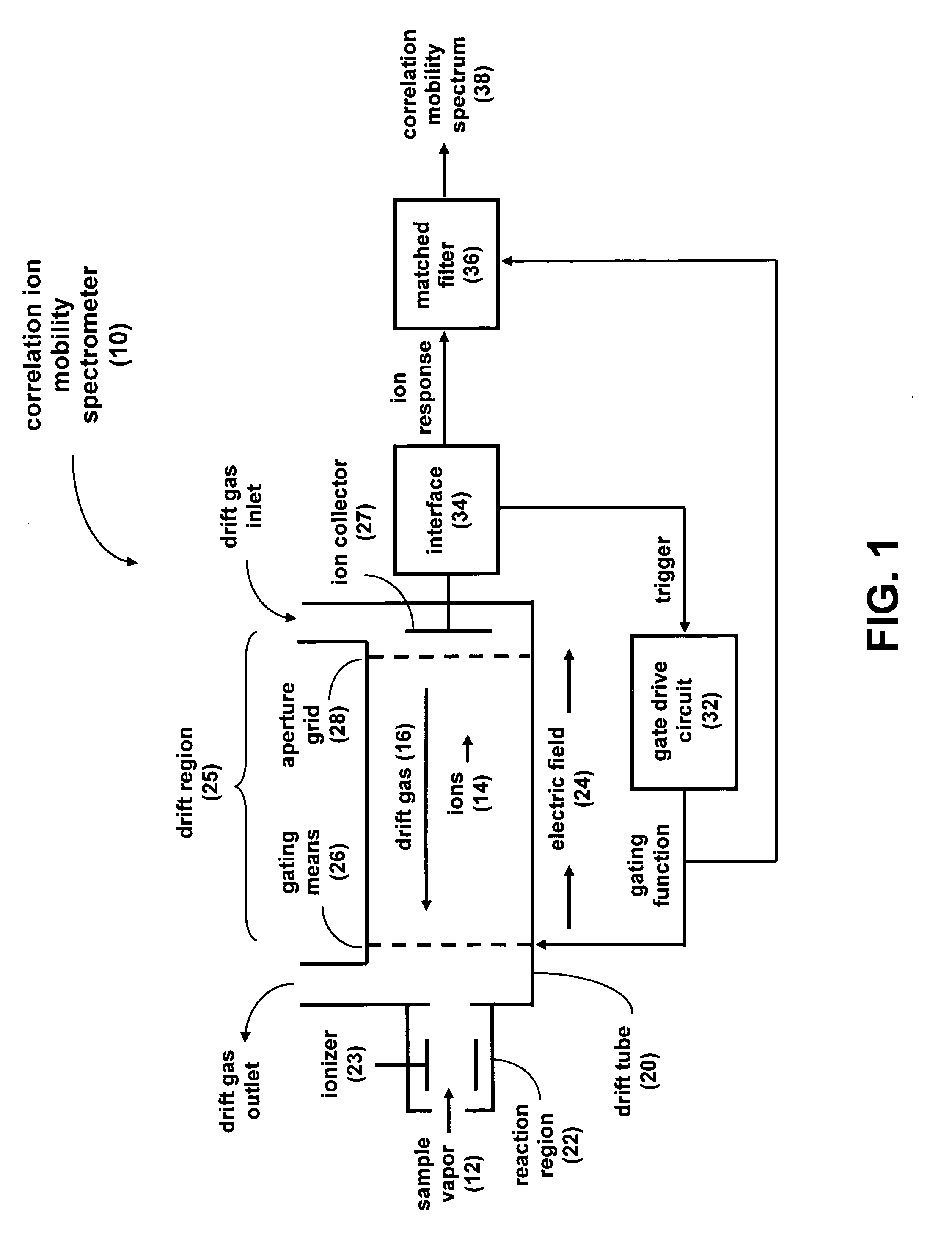
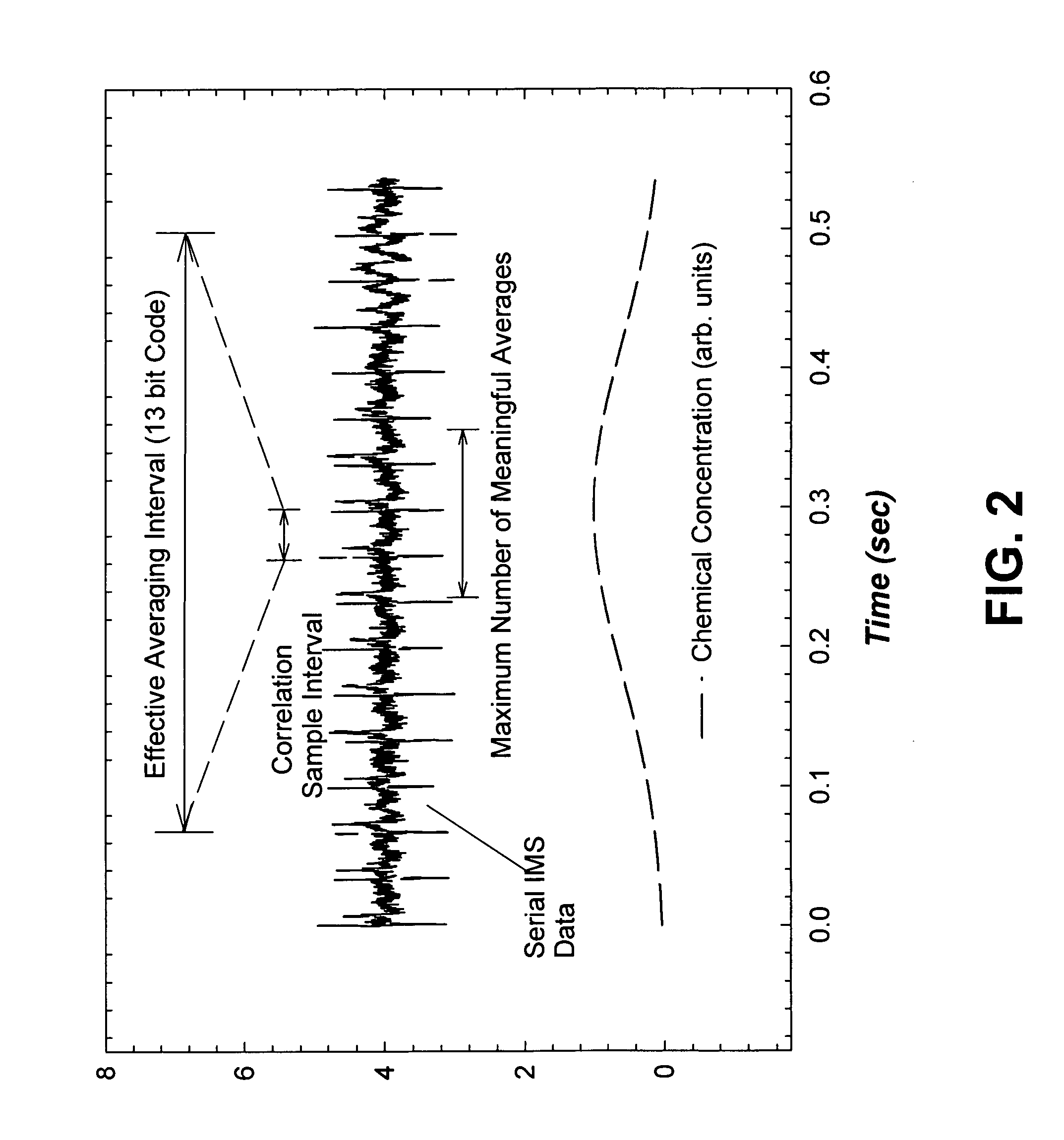
Correlation ion mobility spectroscopy
ActiveUS7417222B1Time-of-flight spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsIon currentImage resolution
Correlation ion mobility spectrometry (CIMS) uses gating modulation and correlation signal processing to improve IMS instrument performance. Closely spaced ion peaks can be resolved by adding discriminating codes to the gate and matched filtering for the received ion current signal, thereby improving sensitivity and resolution of an ion mobility spectrometer. CIMS can be used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio even for transient chemical samples. CIMS is especially advantageous for small geometry IMS drift tubes that can otherwise have poor resolution due to their small size.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Biological membrane voltage estimator
InactiveUS6163719ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrical resistance and conductanceExcitable cell
A method and apparatus for estimating the membrane voltage of a cell that is independent of cell conductance. This estimated voltage is used to implement stable, complete (100%) series resistance compensation for a single electrode voltage clamp amplifier, enabling the recording of rapid ionic currents in single, excitable cells.
Owner:ALEMBIC INSTR
Insulated nanogap devices and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS8304273B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementIon currentElectrode pair
The present invention provides a method to eliminate undesired parallel conductive paths of nanogap devices for aqueous sensing. The method involves the electrical insulation of an electrode pair, except for the nanogap region wherein electrical response is measured. The magnitude of undesired ionic current in a measurement is reduced by two orders of magnitude. The process to accomplish the present invention is self-aligned and avoids fabrication complexity. The invention has a great potential in nanogap device applications.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer With Enhanced Sensitivity And Mass Resolving Power
ActiveUS20110215235A1Low costImprove robustnessStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsMass analyzerQuadrupole
A novel method and mass spectrometer apparatus is introduced to spatially and temporally resolve images of one or more ion exit patterns of a multipole instrument. In particular, the methods and structures of the present invention measures the ion current as a function of time and spatial displacement in the beam cross-section of a quadrupole mass filter via an arrayed detector. The linearity of the detected quadrupole ion current in combination with it reproducible spatial-temporal structure enables the deconvolution of the contributions of signals from individual ion species in complex mixtures where both sensitivity and mass resolving power are essential.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Large area plasma source
An all permanent magnet Electron Cyclotron Resonance, large diameter (e.g., 40 cm) plasma source suitable for ion / plasma processing or electric propulsion, is capable of producing uniform ion current densities at its exit plane at very low power (e.g., below 200 W), and is electrodeless to avoid sputtering or contamination issues. Microwave input power is efficiently coupled with an ionizing gas without using a dielectric microwave window and without developing a throat plasma by providing a ferromagnetic cylindrical chamber wall with a conical end narrowing to an axial entrance hole for microwaves supplied on-axis from an open-ended waveguide. Permanent magnet rings are attached inside the wall with alternating polarities against the wall. An entrance magnet ring surrounding the entrance hole has a ferromagnetic pole piece that extends into the chamber from the entrance hole to a continuing second face that extends radially across an inner pole of the entrance magnet ring.
Owner:UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT ADMINISTRATOR OF NASA
Two-grid ion energy analyzer and methods of manufacturing and operating
An ion energy analyzer is described for use in diagnosing the ion energy distribution (IED) of ions incident on a radio frequency (RF) biased substrate immersed in plasma. The ion energy analyzer comprises an entrance grid exposed to the plasma, an electron rejection grid disposed proximate to the entrance grid, and an ion current collector disposed proximate to the electron rejection grid. The ion current collector is coupled to an ion selection voltage source configured to positively bias the ion current collector by an ion selection voltage, and the electron rejection grid is coupled to an electron rejection voltage source configured to negatively bias the electron rejection grid by an electron rejection voltage. Furthermore, an ion current meter is coupled to the ion current collector to measure the ion current.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Dosimetry using optical emission spectroscopy/residual gas analyzer in conjuntion with ion current
ActiveUS20080075834A1Liquid surface applicatorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDosimetry radiationOptical emission spectrometry
The present invention generally provides methods and apparatus for controlling ion dosage in real time during plasma processes. In one embodiment, ion dosages may be controlled using in-situ measurement of the plasma from a mass distribution sensor combined with in-situ measurement from an RF probe.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
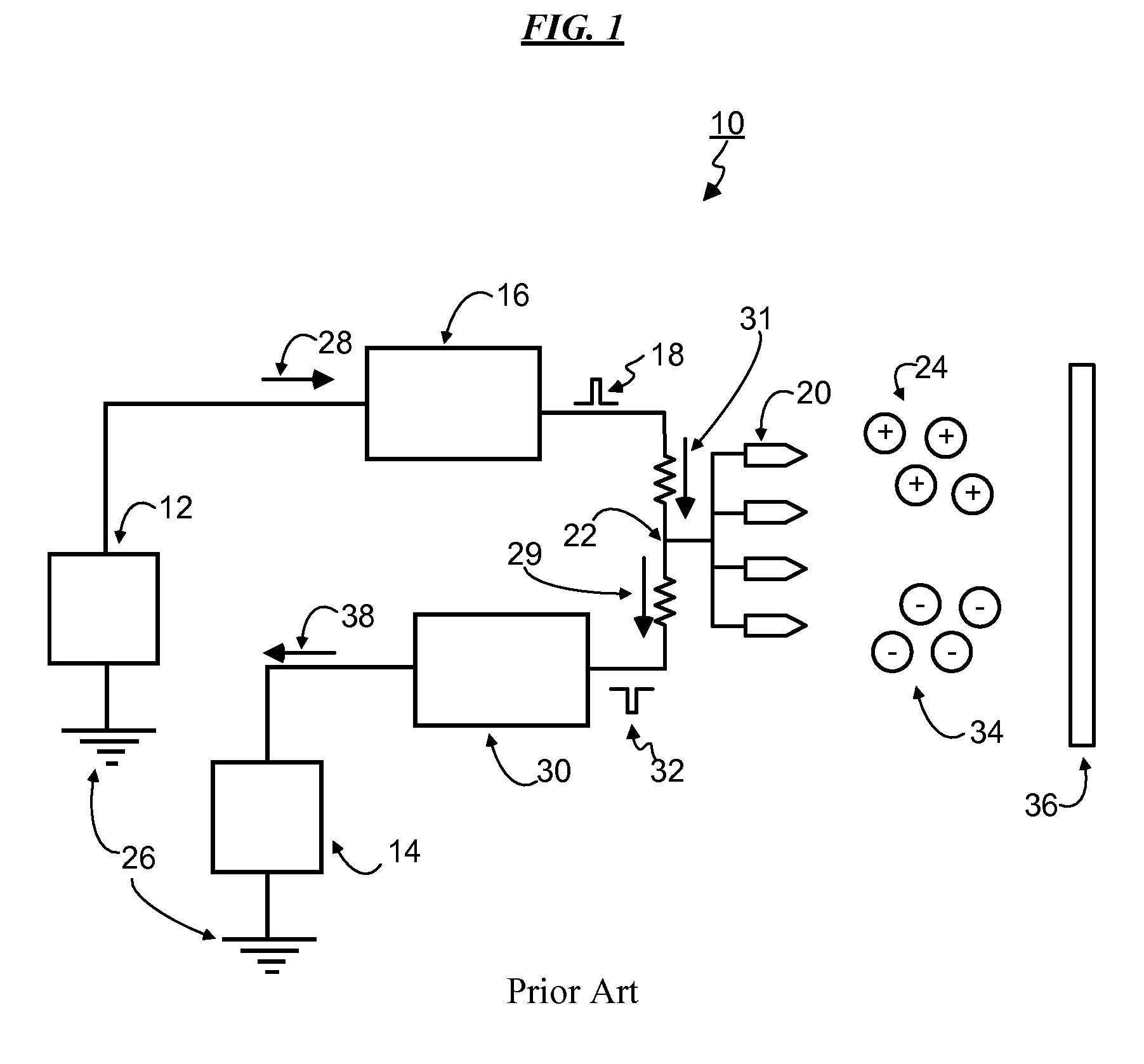
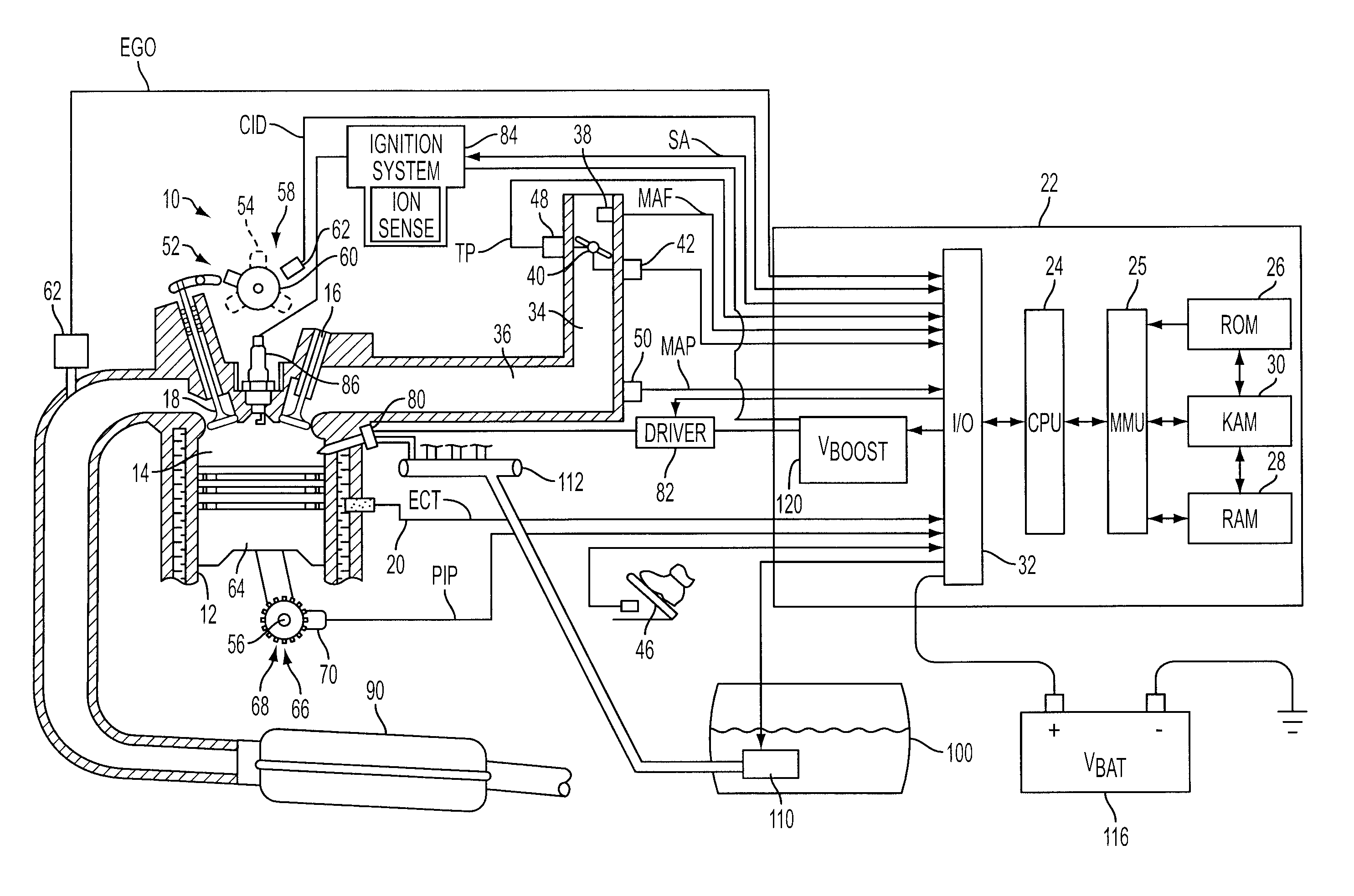
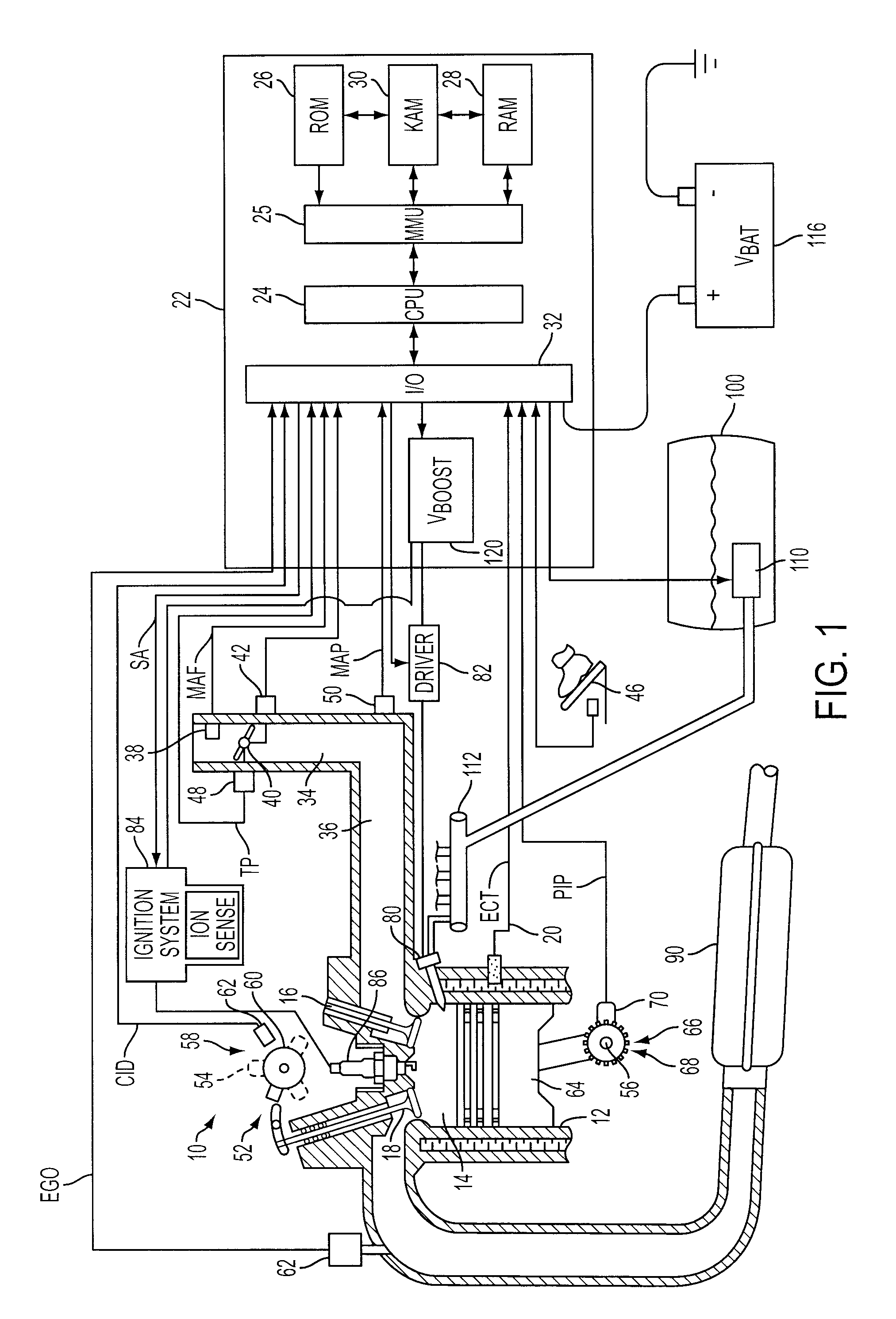
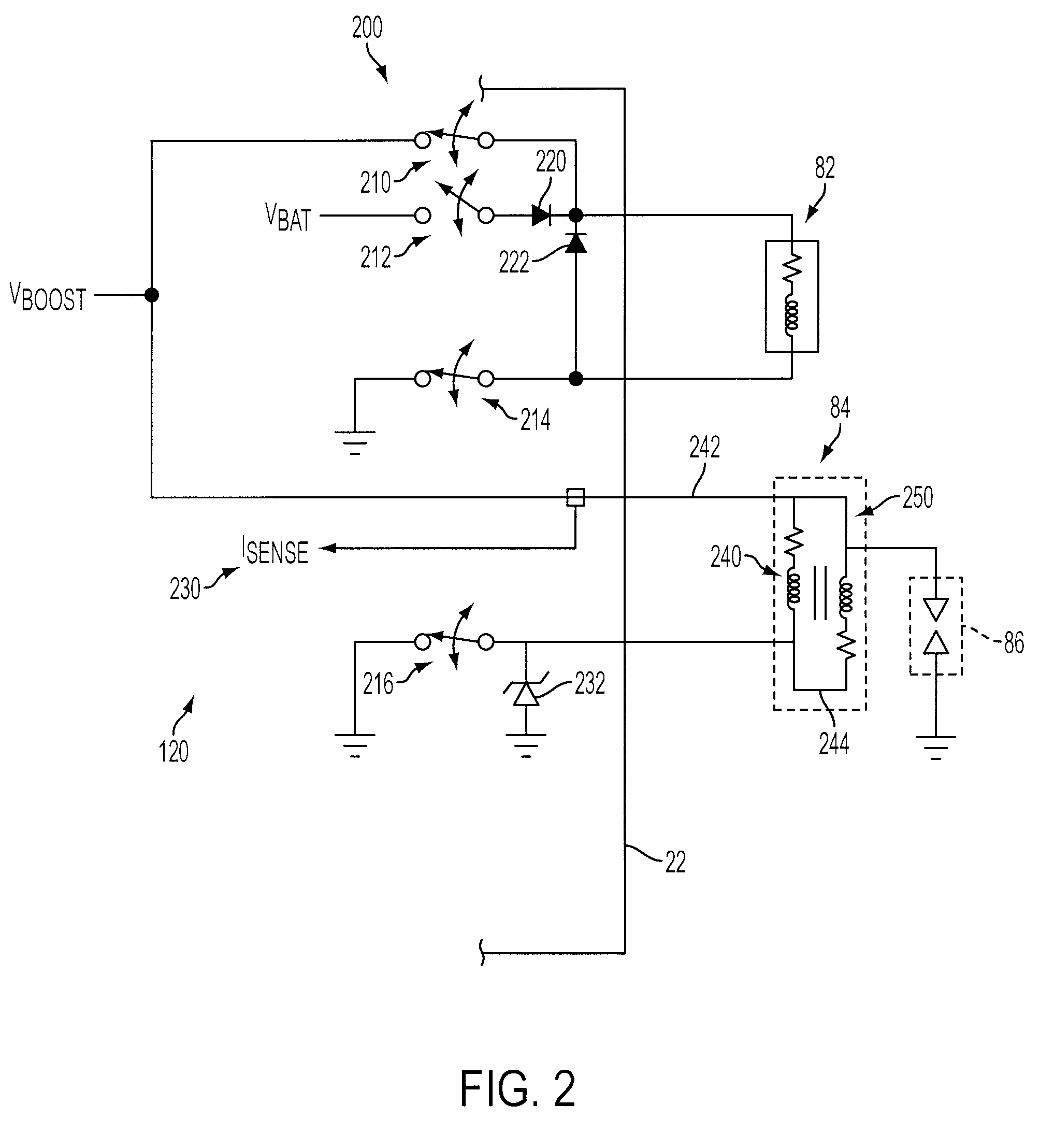
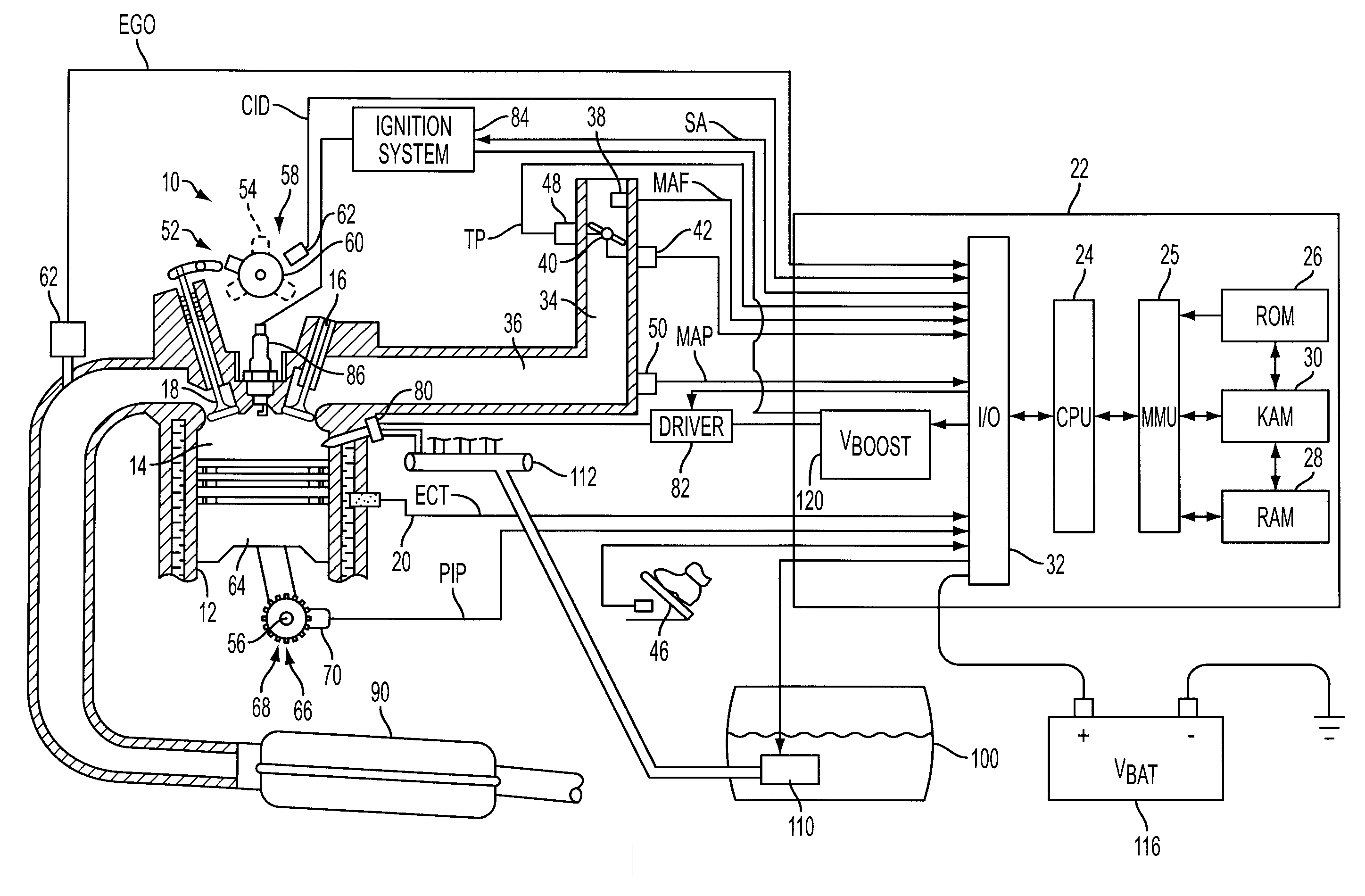
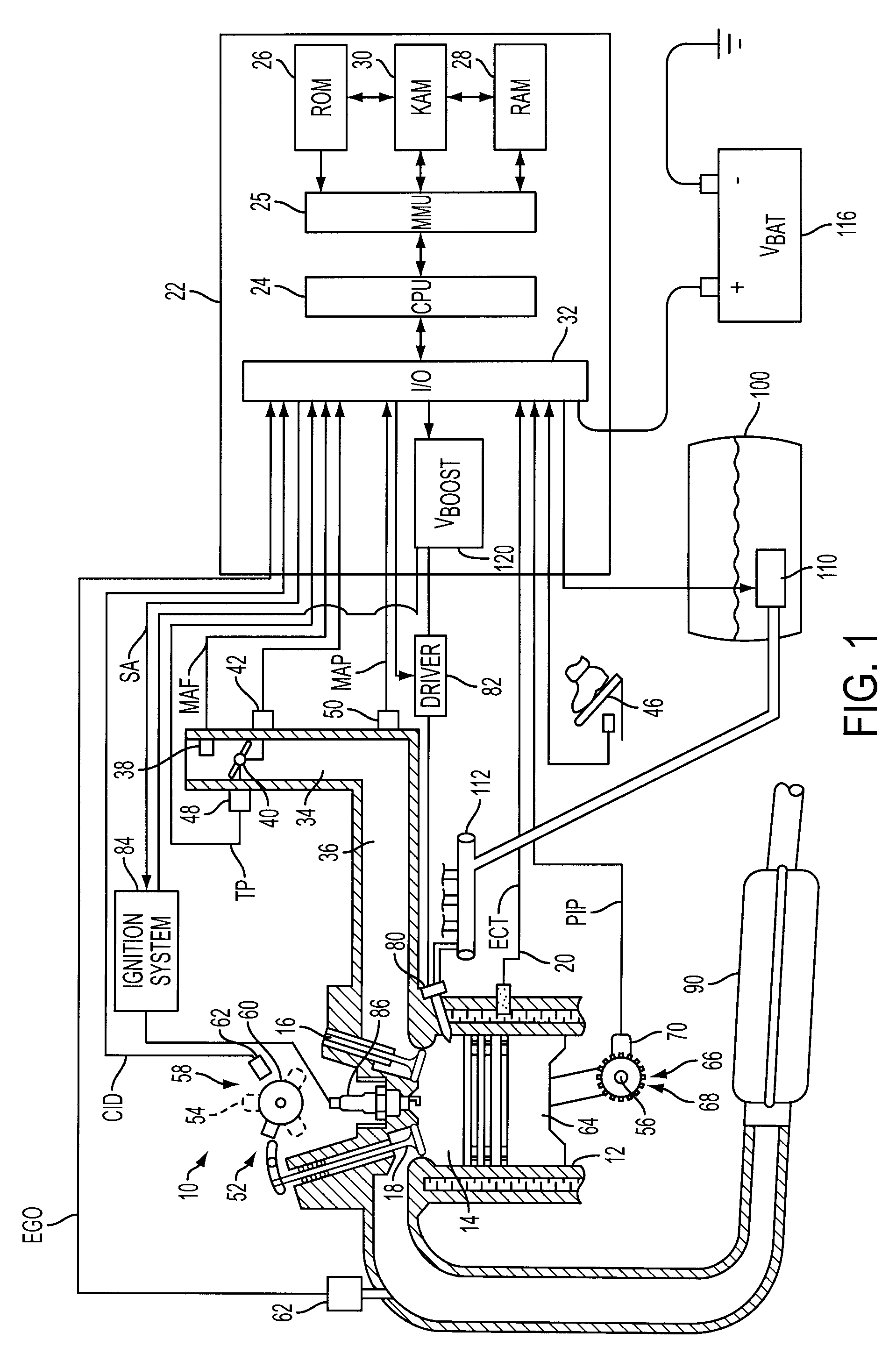
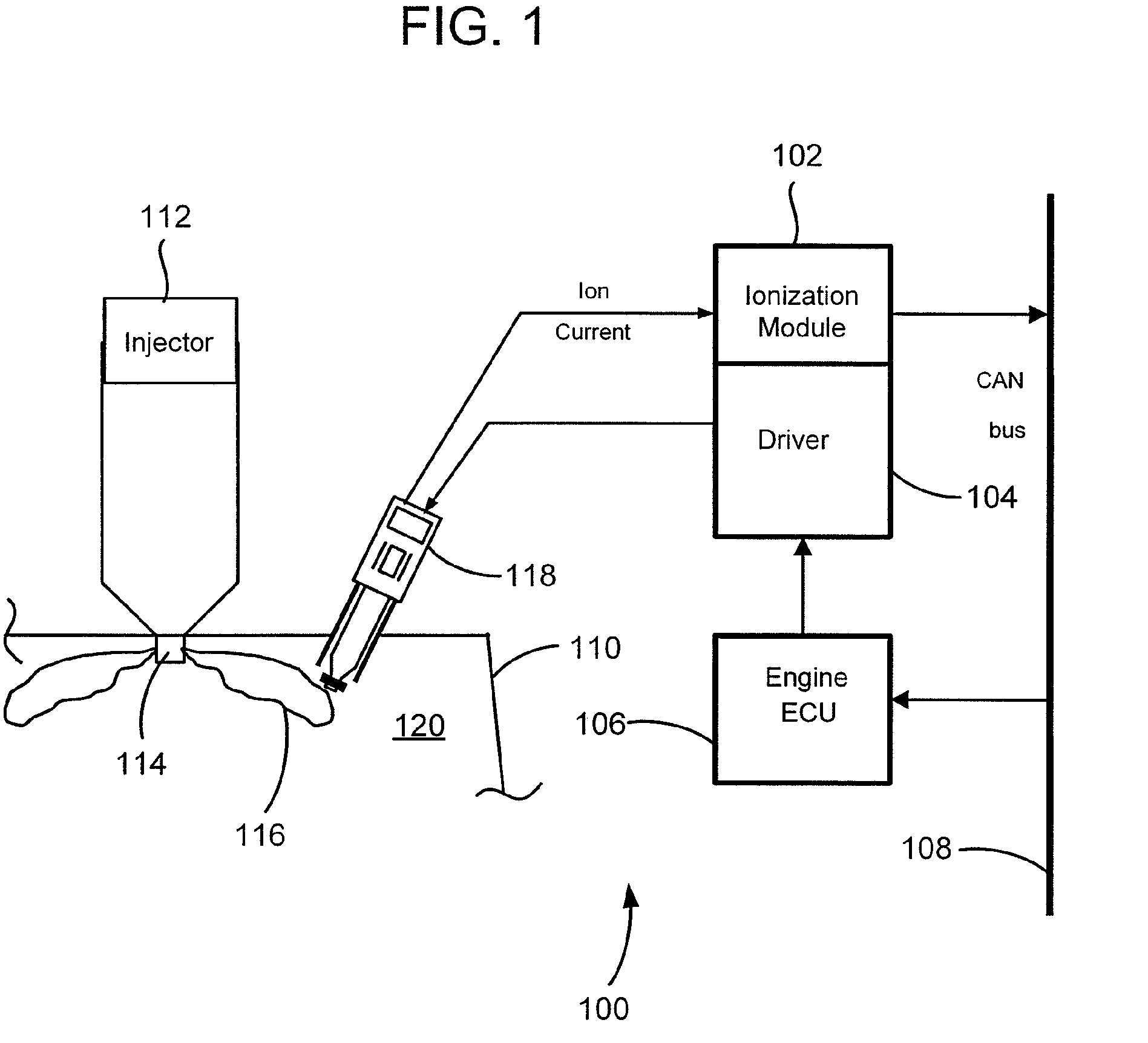
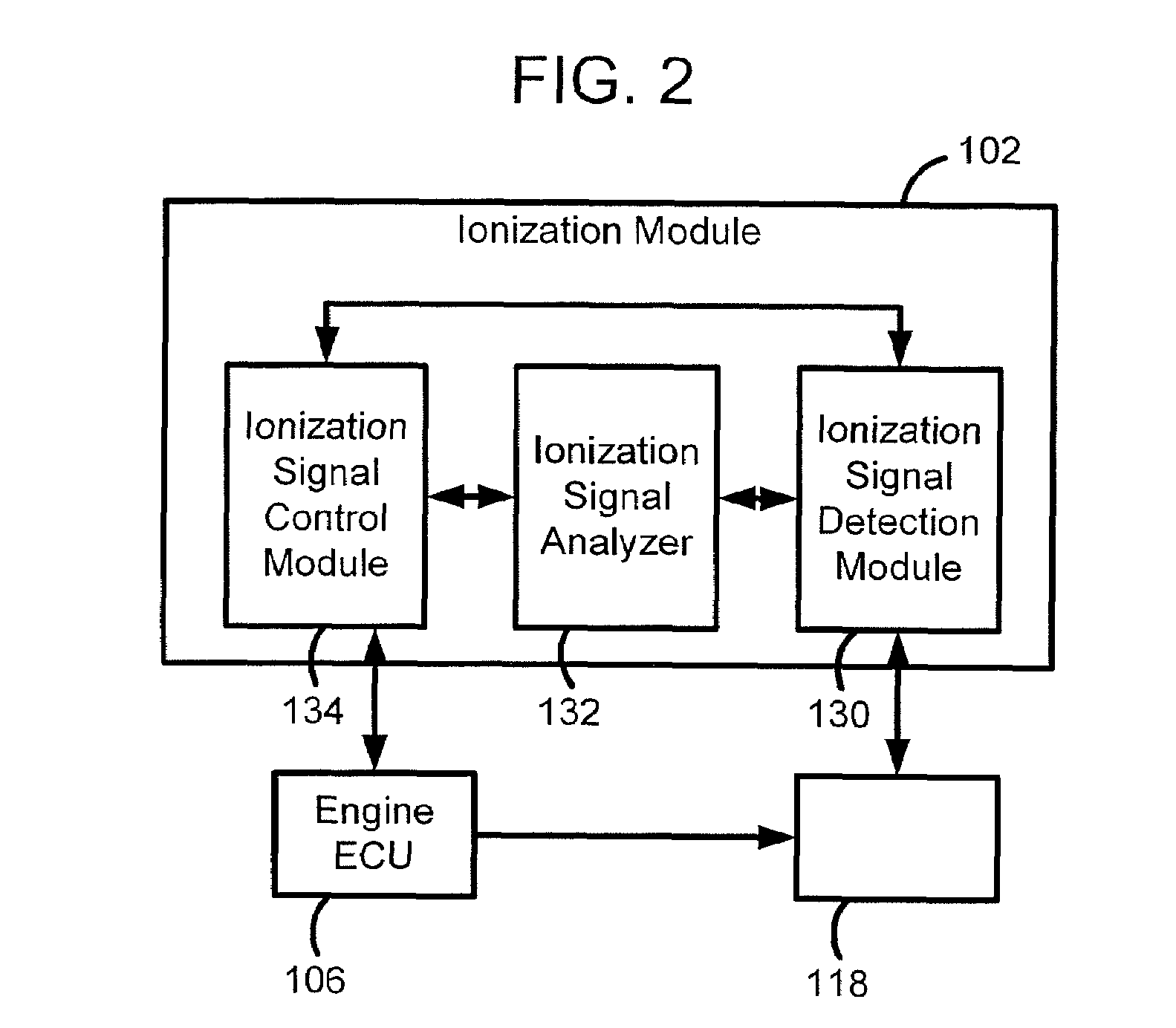
Ion current detection device for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6011397AInternal-combustion engine testingElectric ignition installationBandpass filteringIon current
An ion current detection device of an internal combustion engine includes a detection voltage generation device which applies a voltage to an ignition plug to generate an ion current in a cylinder of the engine. A current to voltage conversion circuit detects and converts the generated ion current to a voltage signal. A bandpass filter extracts an ac component within a specified frequency range from the voltage signal produced by the current to voltage conversion circuit. An ion current threshold detection portion produces an ion current detection signal when the detected ion current exceeds a predetermined threshold current. A filter characteristic control circuit controls the characteristic of the bandpass filter to suppress the sensitivity of the filter for a predetermined period of time right after the ion current detection signal is detected and, after the predetermined period of time, increase the sensitivity of the filter for detection of the ac signal with the specific frequency.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Alternating current monitor for an ionizer power supply
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
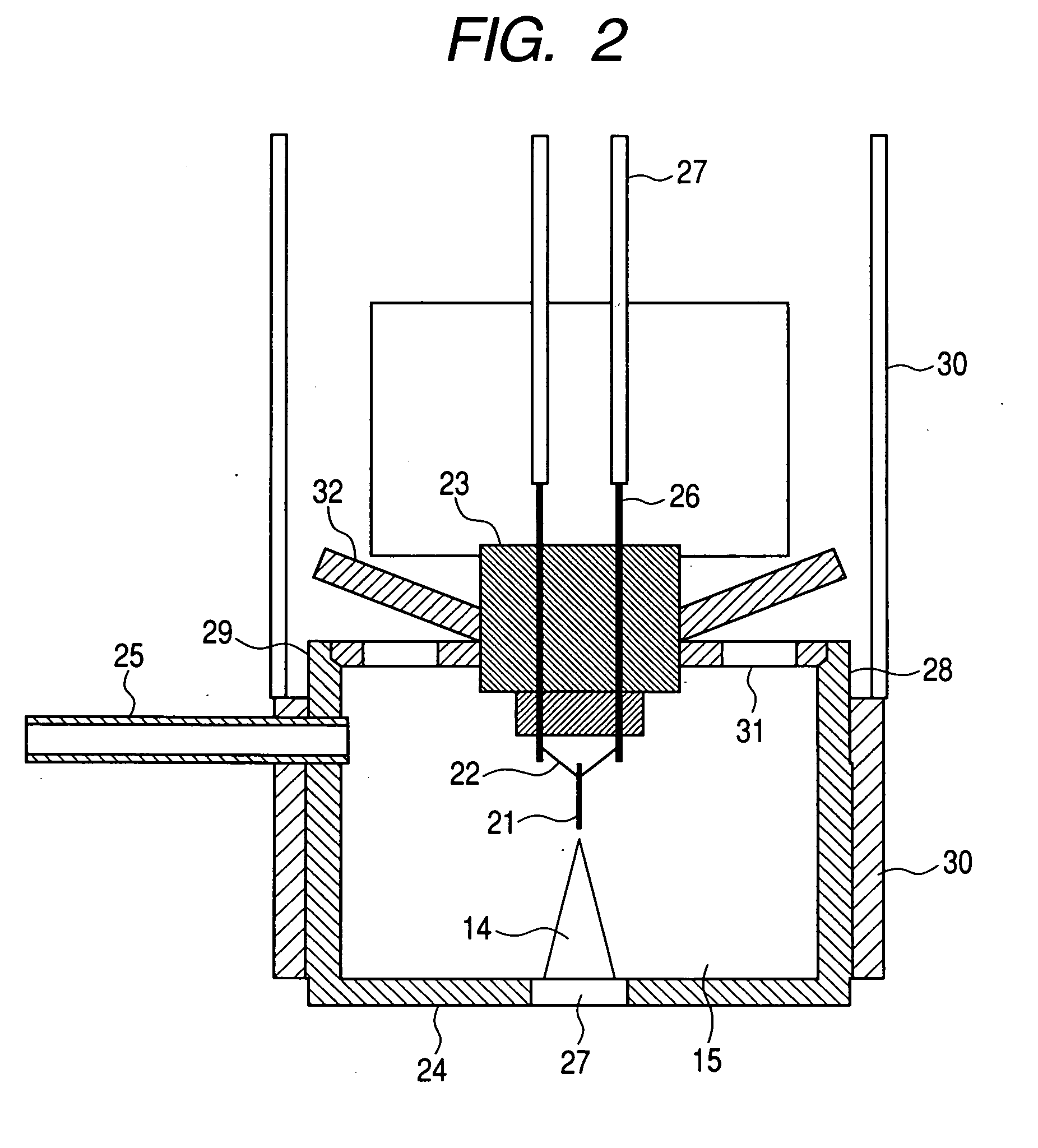
Near-field plume mass-spectroscopic diagnostic E*B probe based on Faraday cup
InactiveCN104730066AGuaranteed OrthogonalityGuaranteed collimationAnalysis by thermal excitationMass spectrometryDrift tube
The invention discloses a near-field plume mass-spectroscopic diagnostic E*B probe based on the Faraday cup and belongs to the technical field of plasma mass-spectroscopic diagnosis. The probe mainly applied to measuring near-field plumes of an ion thruster and of a Hall thruster comprises a central frame, ferrite permanent magnets, a flat electrode plate, an electrode plate holder, a collimator tube, a drift tube, a Faraday cup, six carbon steel shells and an anti-sputtering heat-insulating layer. According to the connectional relation, the central frame is used as a core part, the ferrite permanent magnets are distributed on upper and lower surfaces of the central frame, the electrode plate is fixed in the central frame, and an orthogonal electromagnetic field area is formed. The six carbon steel shells are used for packaging, and the front ends of the shells are coated with an anti-sputtering heat-insulating layer. The collimator tube of stainless steel and the drift tube are fitly fixed to the centers of two ends of the central frame through shaft holes. Ions different in valence are screened by adjusting voltage among the electrode plates, univalent and bivalent ion currents are acquired with the Faraday cup of aluminum, and the ratio of near-field plum bivalent ions is acquired by analytical computing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Ignition Energy Management With Ion Current Feedback To Correct Spark Plug Fouling
ActiveUS20100057324A1Reduce and eliminate plug foulingPrevent wrong actionAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlPower flowIon current
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Measurement of ion mobility spectra
ActiveUS20090236514A1High mobility resolutionHigh detection sensitivityTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionLow noiseModulation function
The invention relates to measuring the mobility spectra of ions with ion mobility spectrometers (IMS). The invention provides an analog modulation of the ion current of an IMS ion source with a continuous modulation function, the instantaneous frequency of which temporally varies across a large frequency range, and a generation of the mobility spectrum from the measured ion current by a correlation analysis with the modulation pattern. The modulation can, for example, be produced by the gating grid, which is usually present. The analog modulation removes many of the difficulties which occur with square-wave modulation and leads to a surprisingly stable evaluation which is relatively insensitive to noisy signals and produces a high mobility resolution at very low noise.
Owner:BRUKER OPTICS GMBH & CO KG
Ion detector for ion beam applications
ActiveUS7119333B2Increase volumeThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIon currentIon beam
Detection of weak ion currents scattered from a sample by an ion beam is improved by the use of a multiplier system in which a conversion electrode converts incident ions to a number of secondary electrons multiplied by a multiplication factor, the secondary electrons being attracted to an electron detector by an appropriate bias. In one version, the detector is a two stage system, in which the secondary electrons strike a scintillator that emits photons that are detected in a photon detector such as a photomultiplier or a CCD.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Two-grid ion energy analyzer and methods of manufacturing and operating
ActiveUS20090242791A1Thermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsIon currentTwo grid
An ion energy analyzer is described for use in diagnosing the ion energy distribution (IED) of ions incident on a radio frequency (RF) biased substrate immersed in plasma. The ion energy analyzer comprises an entrance grid exposed to the plasma, an electron rejection grid disposed proximate to the entrance grid, and an ion current collector disposed proximate to the electron rejection grid. The ion current collector is coupled to an ion selection voltage source configured to positively bias the ion current collector by an ion selection voltage, and the electron rejection grid is coupled to an electron rejection voltage source configured to negatively bias the electron rejection grid by an electron rejection voltage. Furthermore, an ion current meter is coupled to the ion current collector to measure the ion current.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
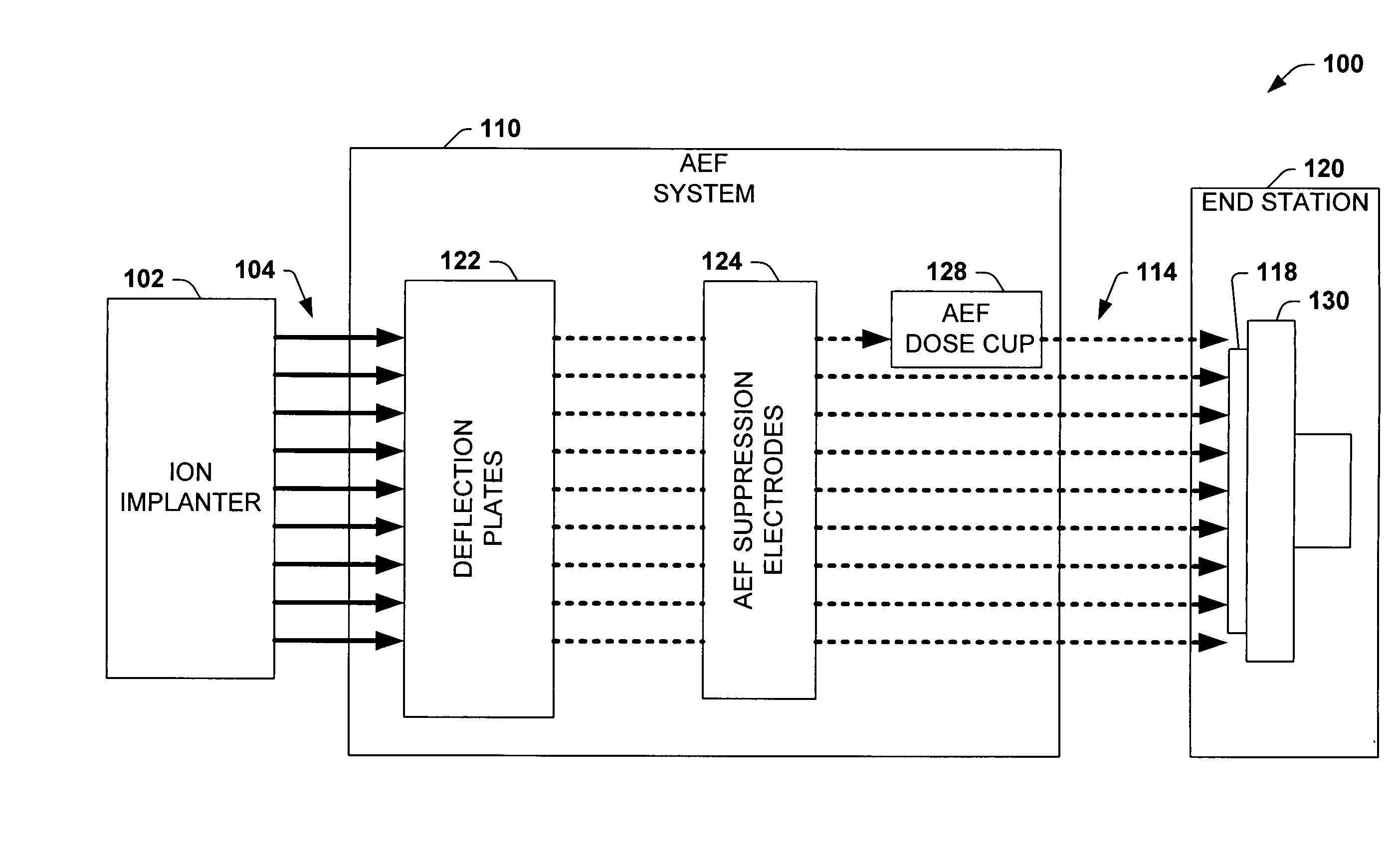
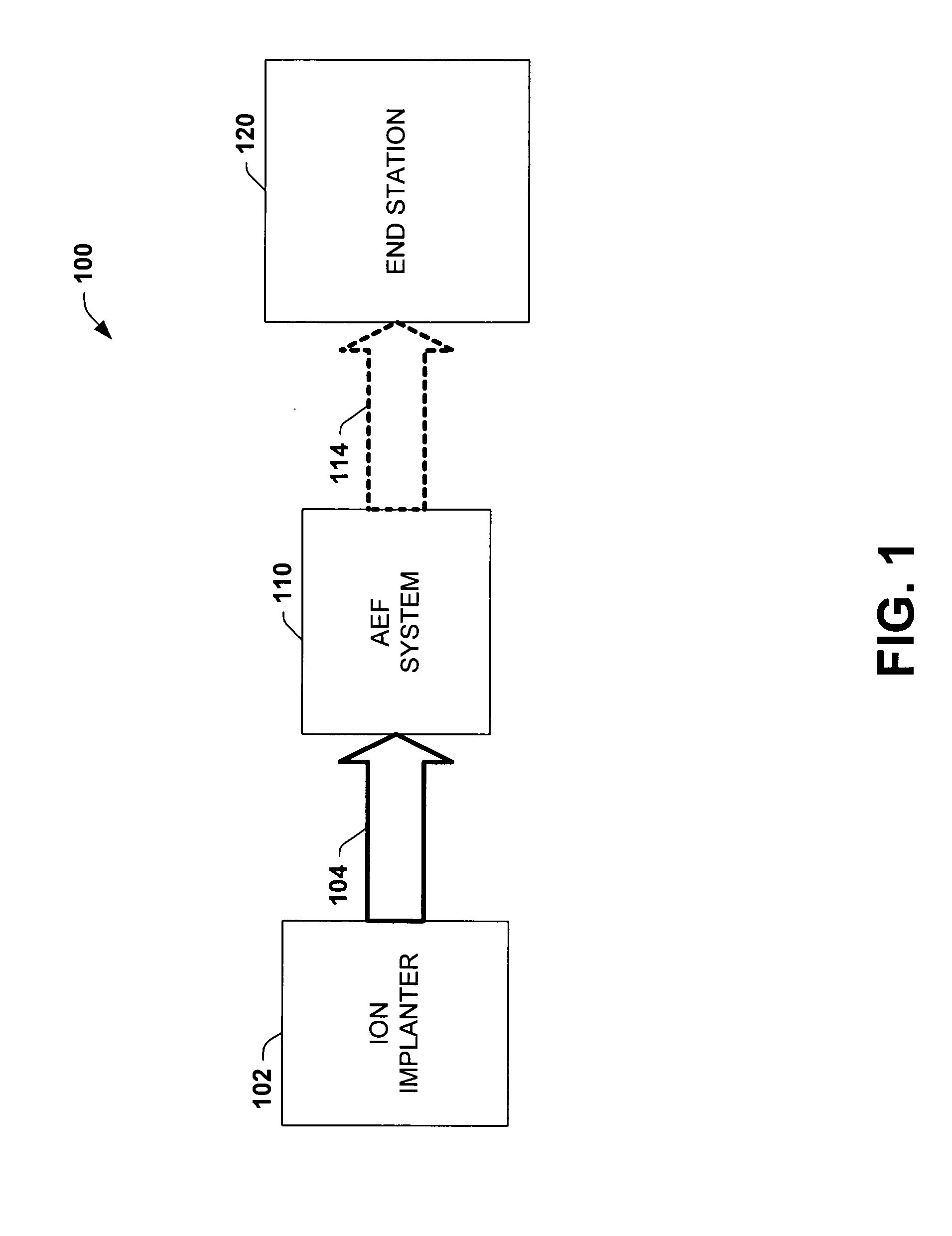
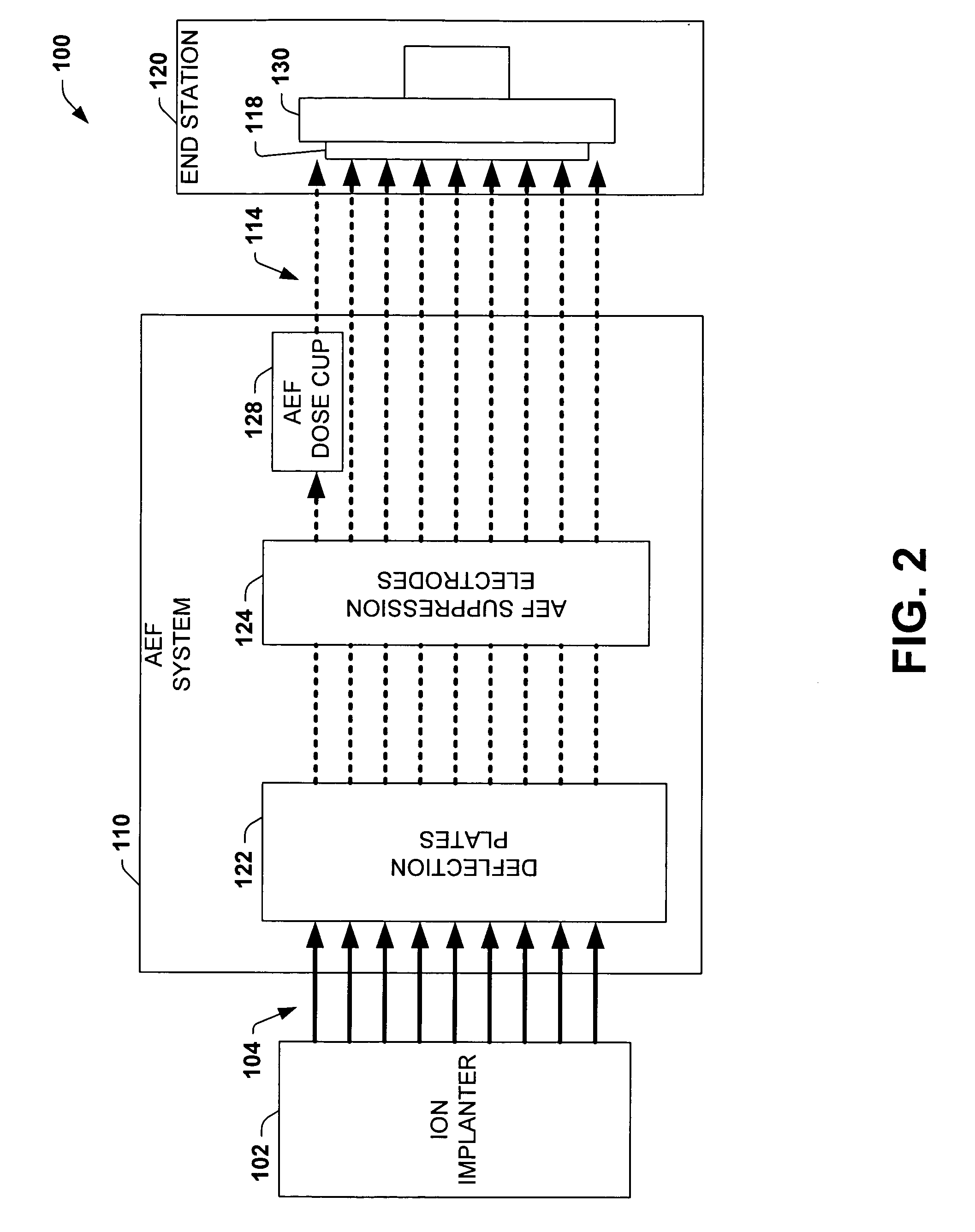
Dose cup located near bend in final energy filter of serial implanter for closed loop dose control
ActiveUS20050269526A1Reduce pressureEliminate the effects ofElectric discharge tubesRadiation therapyIon currentDosimetry radiation
An ion implantation system having a dose cup located near a final energy bend of a scanned or ribbon-like ion beam of a serial ion implanter for providing an accurate ion current measurement associated with the dose of a workpiece or wafer. The system comprises an ion implanter having an ion beam source for producing a ribbon-like ion beam. The system further comprises an AEF system configured to filter an energy of the ribbon-like ion beam by bending the beam at a final energy bend. The AEF system further comprises an AEF dose cup associated with the AEF system and configured to measure ion beam current, the cup located substantially immediately following the final energy bend. An end station downstream of the AEF system is defined by a chamber wherein a workpiece is secured in place for movement relative to the ribbon-like ion beam for implantation of ions therein. The AEF dose cup is beneficially located up stream of the end station near the final energy bend mitigating pressure variations due to outgassing from implantation operations at the workpiece. Thus, the system provides accurate ion current measurement before such gases can produce substantial quantities of neutral particles in the ion beam, generally without the need for pressure compensation. Such dosimetry measurements may also be used to affect scan velocity to ensure uniform closed loop dose control in the presence of beam current changes from the ion source and outgassing from the workpiece.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
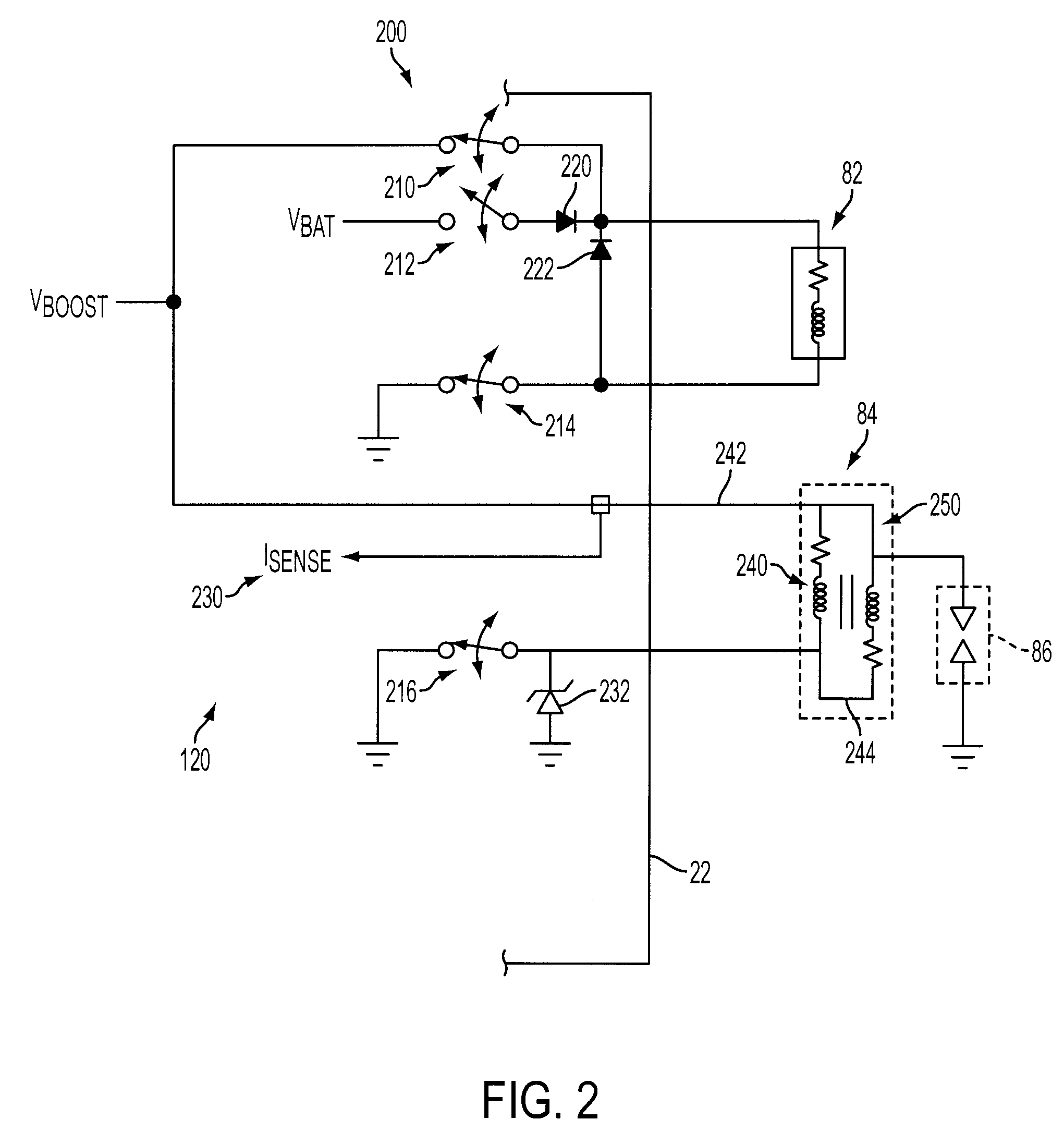
Internal Combustion Engine Having Common Power Source For Ion Current Sensing and Fuel Injectors
InactiveUS20090101114A1Facilitates ignition timingShort charging timeElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsIonization currentIon current
A system and method for controlling operation of a multiple cylinder internal combustion engine having fuel injectors and an ionization current sensor include a high-voltage power supply connectable to, and supplying substantially the same nominal boosted voltage relative to nominal battery voltage to, the fuel injectors and ionization sensor during at least a portion of the engine operation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
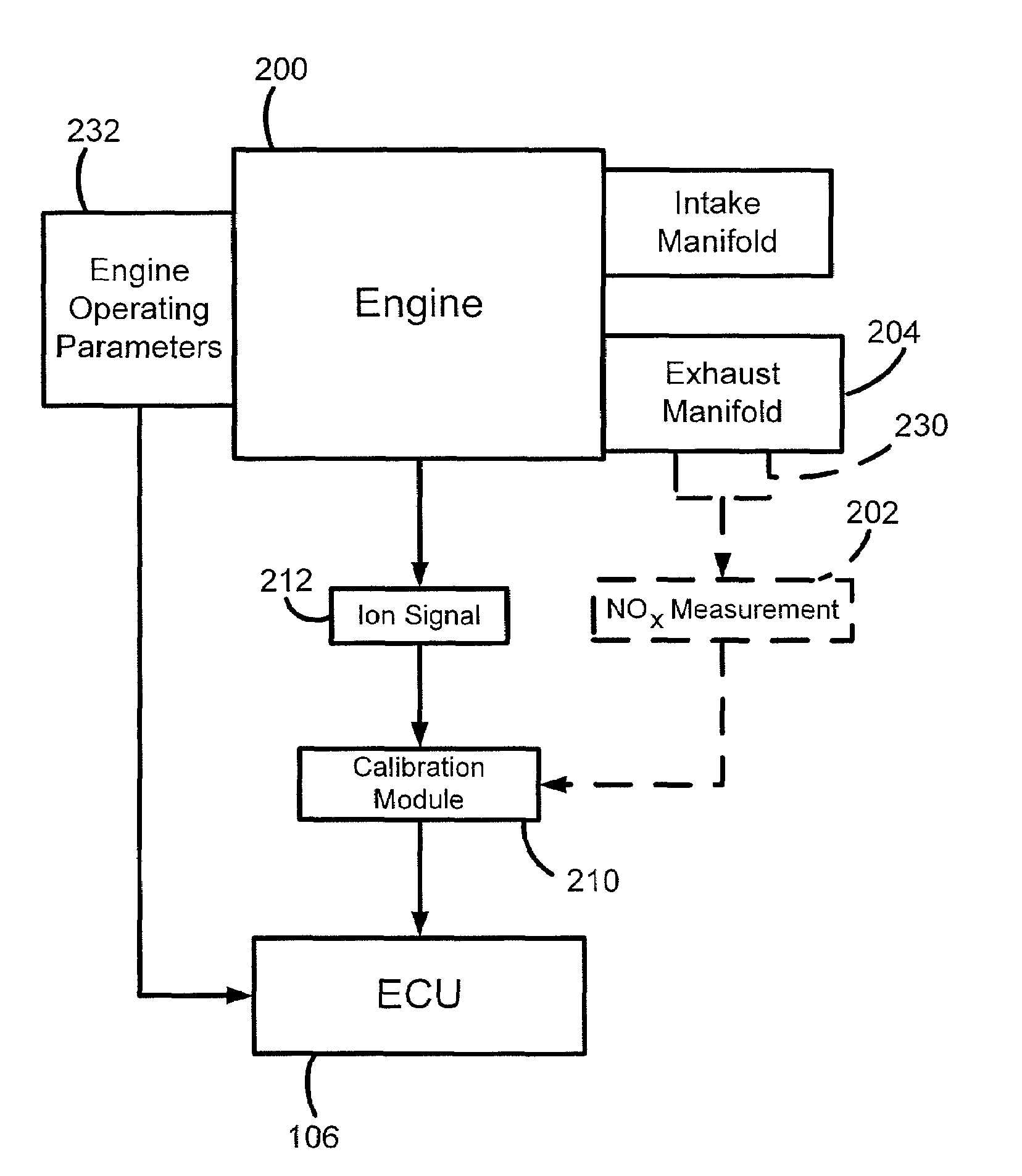
Using ion current for in-cylinder NOx detection in diesel engines and their control
ActiveUS7603226B2Electrical controlDigital data processing detailsSignal processing circuitsAlternative fuels
Presented is a technique that utilizes ion current to determine the concentration of nitrogen oxides (NOx) produced in the combustion chamber(s) of diesel engines, on a cycle by cycle basis during the combustion of conventional petroleum-based fuels, other alternate fuels, and renewable fuels. The technique uses an ion current measuring circuitry, a calibration circuit and a signal processing circuit connected to the engine control unit (ECU). The ion current sensing circuitry is positioned in the chamber(s) of the engine, to measure the ion current produced during the combustion process. The calibration circuit utilizes NOx values measured in the exhaust port or manifold of the engine to calibrate the ion current signal. The calibrated ion current signal is fed into a processor that is connected to the ECU to adjust various operating parameters to improve the trade-off between NOx and other emissions, fuel economy, and power output.
Owner:HENEIN NAEIM A
Ion energy analyzer and methods of manufacturing and operating
An ion energy analyzer is described for use in diagnosing the ion energy distribution (IED) of ions incident on a radio frequency (RF) biased substrate immersed in plasma. The ion energy analyzer comprises an entrance grid exposed to the plasma, an ion selection grid disposed proximate to the entrance grid, an electron rejection grid disposed proximate to the ion selection grid, and an ion current collector disposed proximate to the electron rejection grid. The ion selection grid is coupled to an ion selection voltage source configured to positively bias the ion selection grid by an ion selection voltage, and the electron rejection grid is coupled to an electron rejection voltage source configured to negatively bias the electron rejection grid by an electron rejection voltage. Furthermore, an ion current meter is coupled to the ion current collector to measure the ion current.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
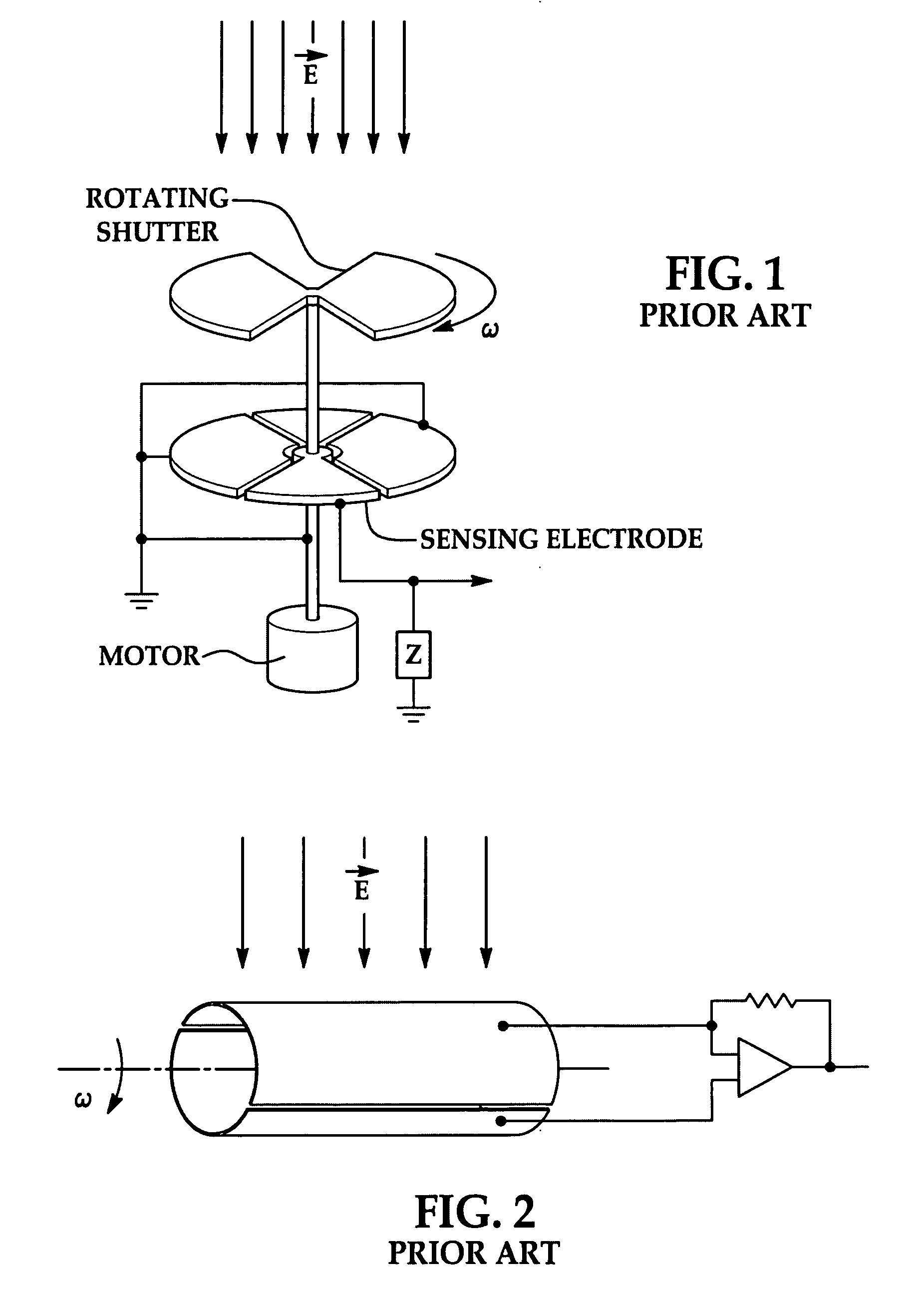
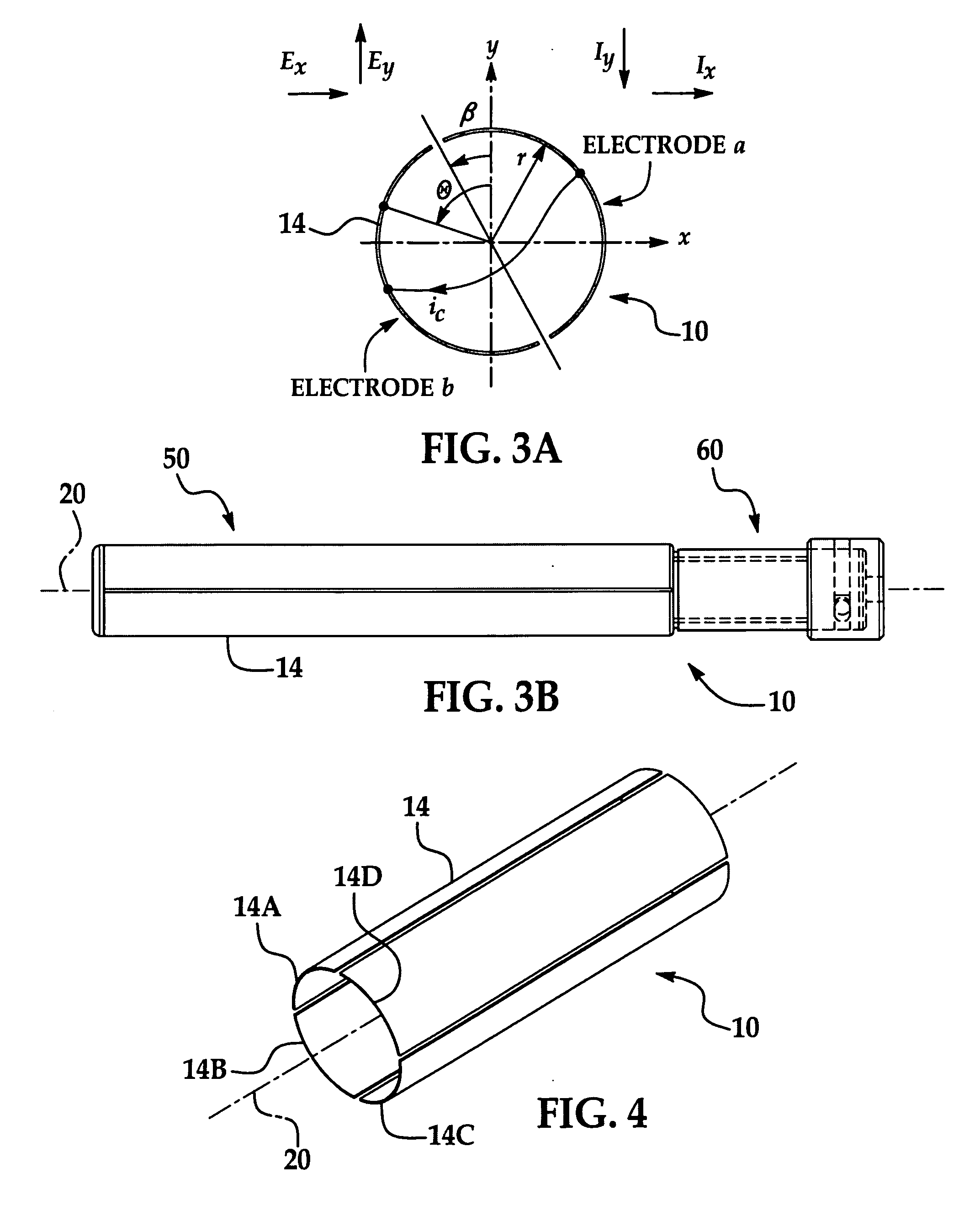
Rotating electric-field sensor
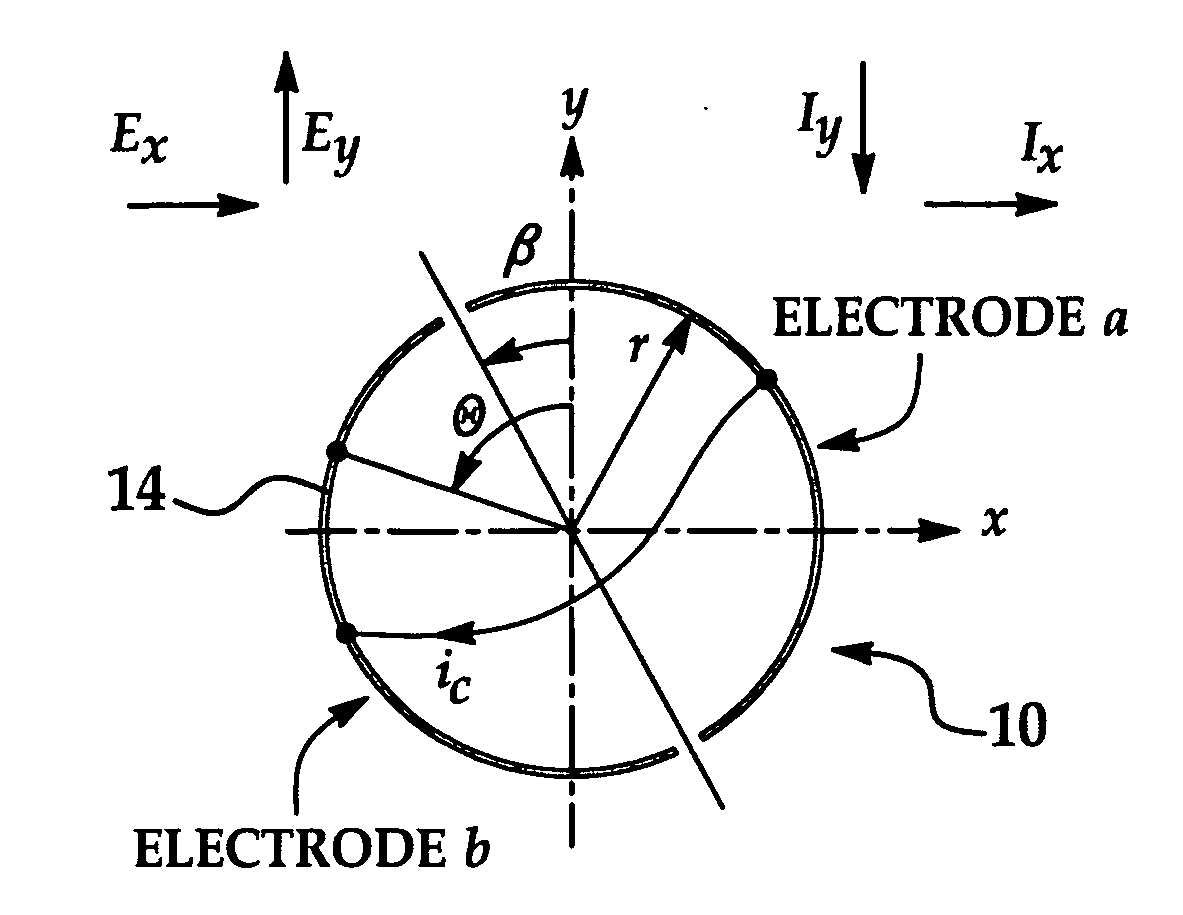
ActiveUS20110062968A1Cancellation effectInductance measurementsElectronic commutatorsDigital signal processingElectric field sensor
A compact instrument package consisting of a rotating sensor and supporting signal-processing electronics is capable of measuring two-dimensional electric-field vectors, ranging from DC to an arbitrary upper AC frequency not limited by the rotation rate, with highly improved accuracy and sensitivity when compared with previous art. In addition, contrary to previous art, the sensor can measure the electric field gradient at its location. This is achieved by the use of a combination of quadrature modulation and phase-sensitive quadrature demodulation digital signal processing in a generic rotating electric-field sensor. Ground isolated versions of the instrument can be used singly or in arrays when precise measurements of the electric fields are necessary. Either grounded or isolated versions of the instrument can operate continuously without the need for internal batteries, making it extremely attractive for a wide-range of industrial and space applications. Operational modes have been developed to distinguish the effects of ion currents and charged particles impacting the sensor from the local ambient electric field. Moreover, particular versions of the instrument can be operated in corrosive environments and conducting fluids.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com