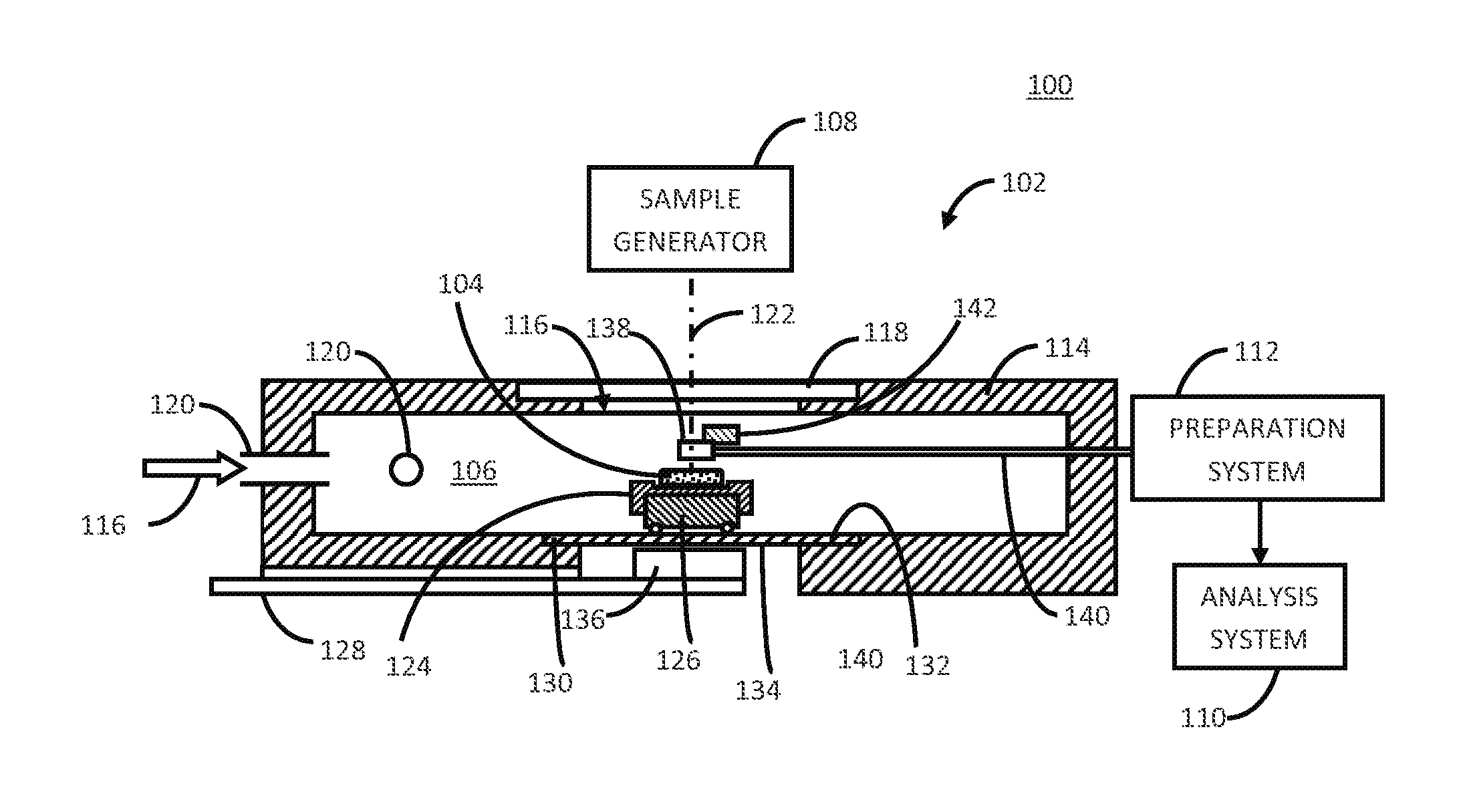
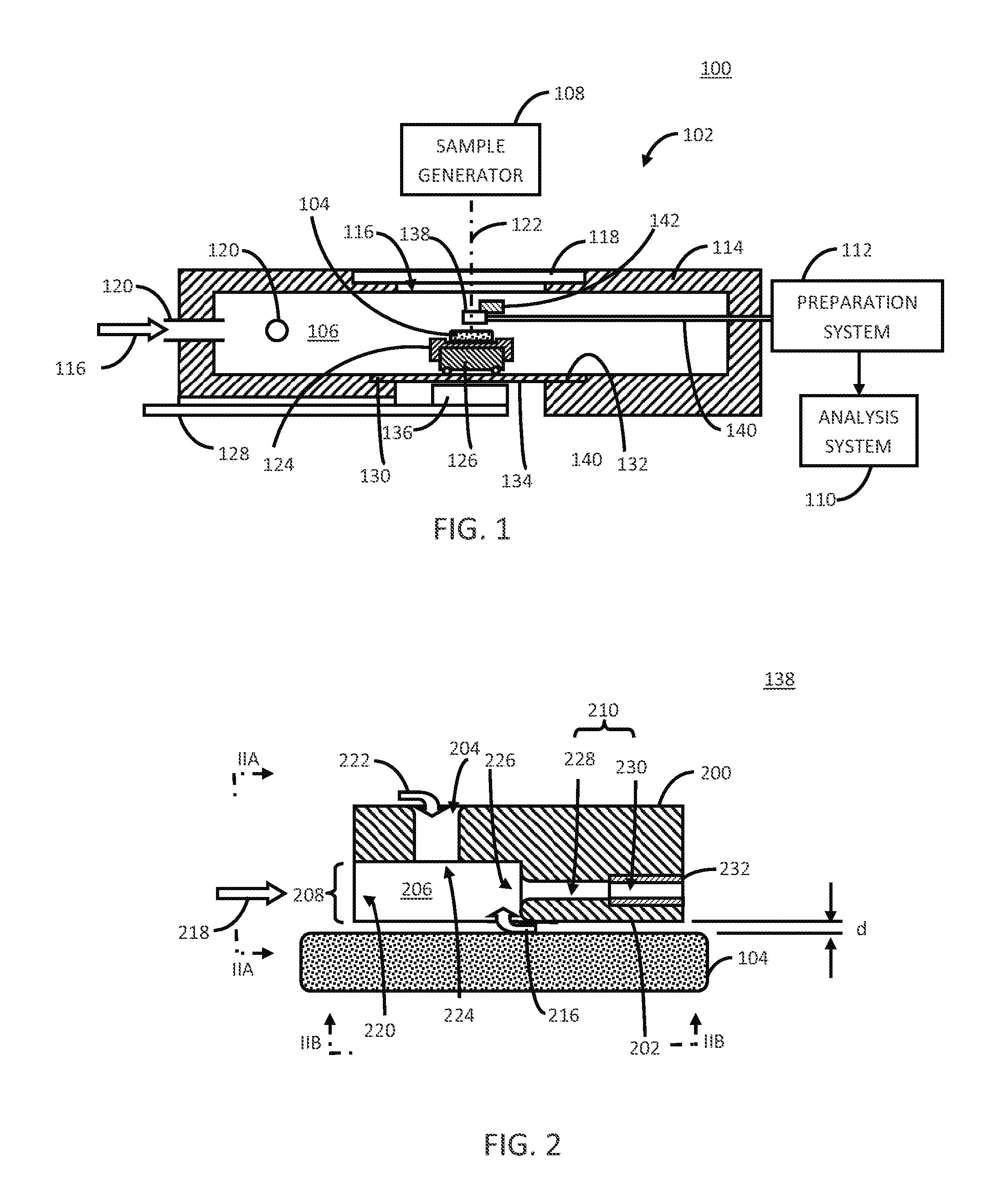
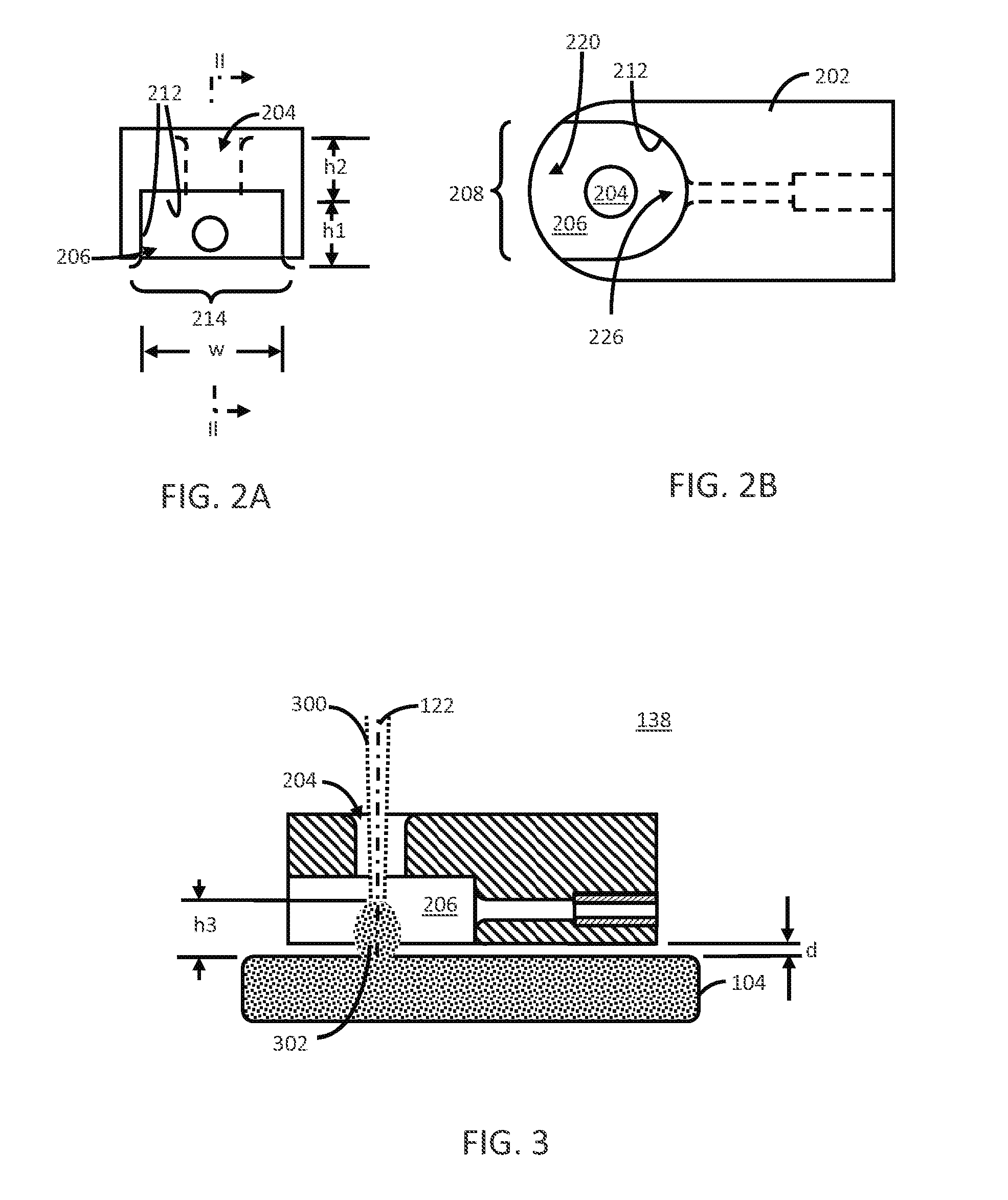
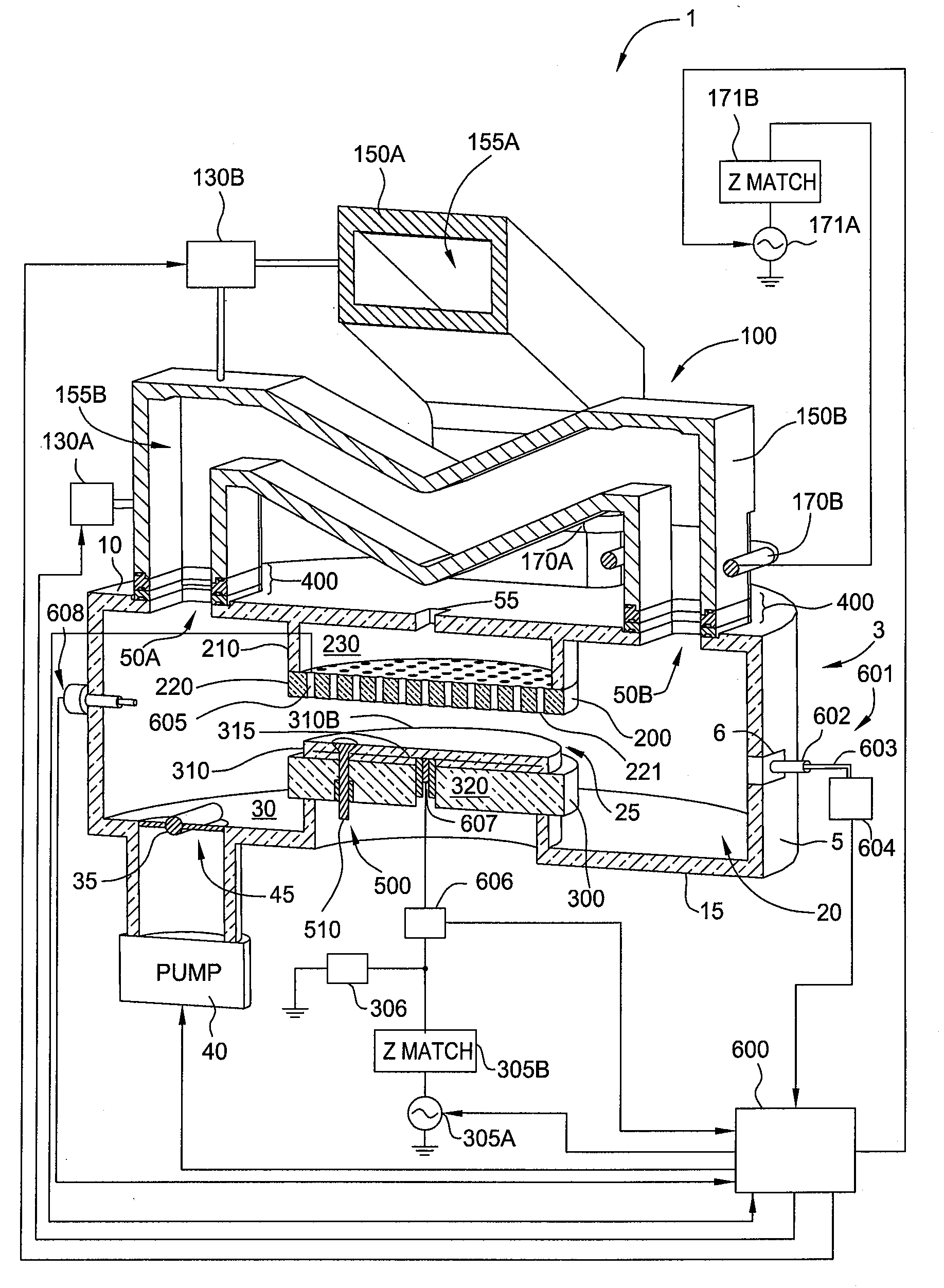
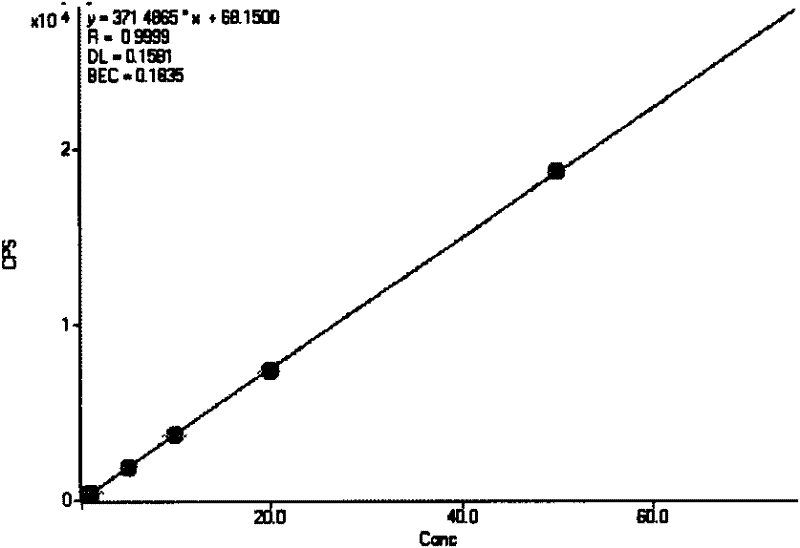
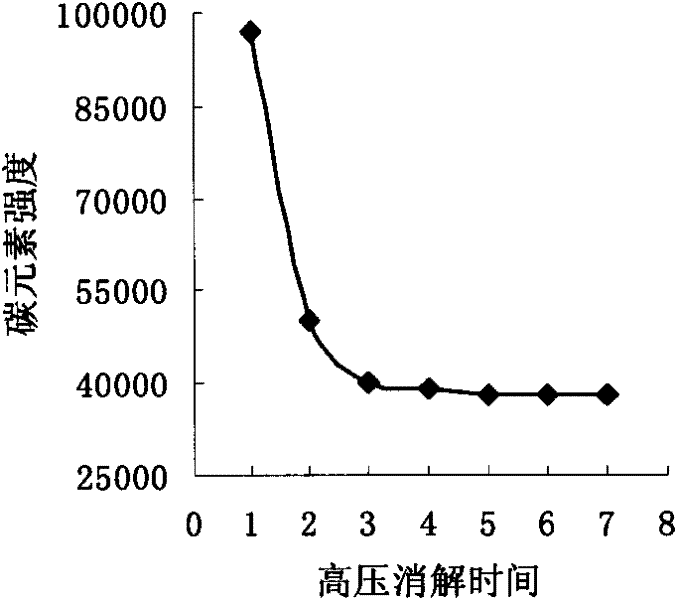
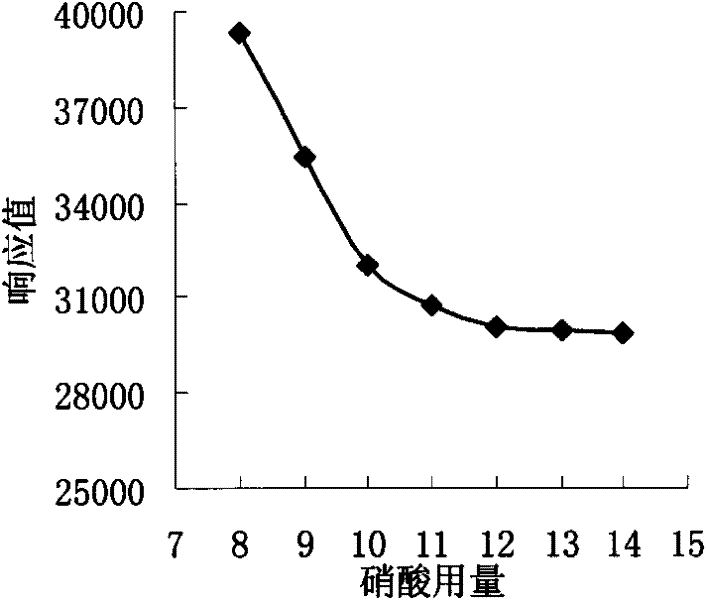
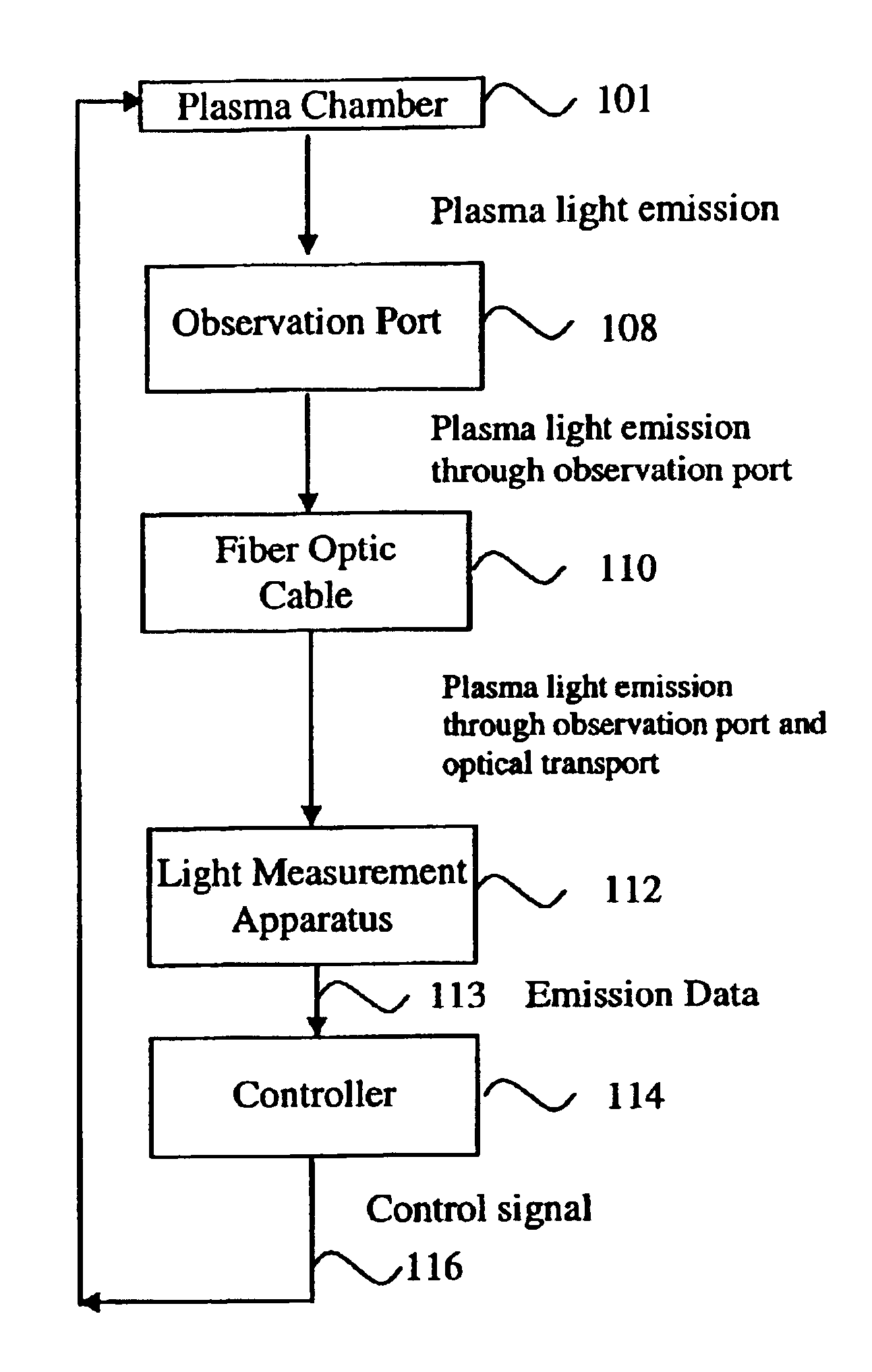
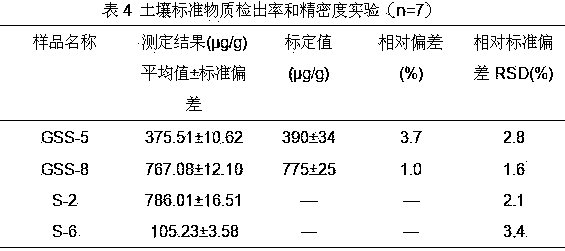
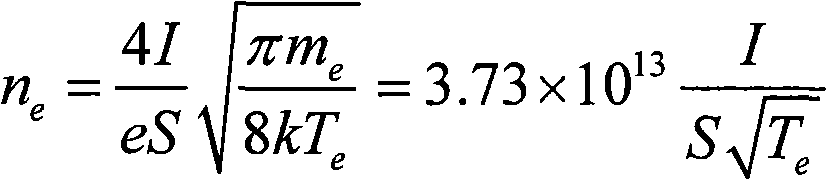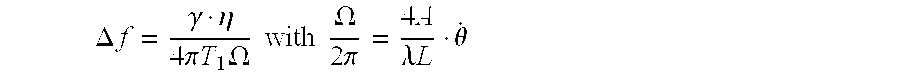Patents
Literature
133 results about "Optical emission spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
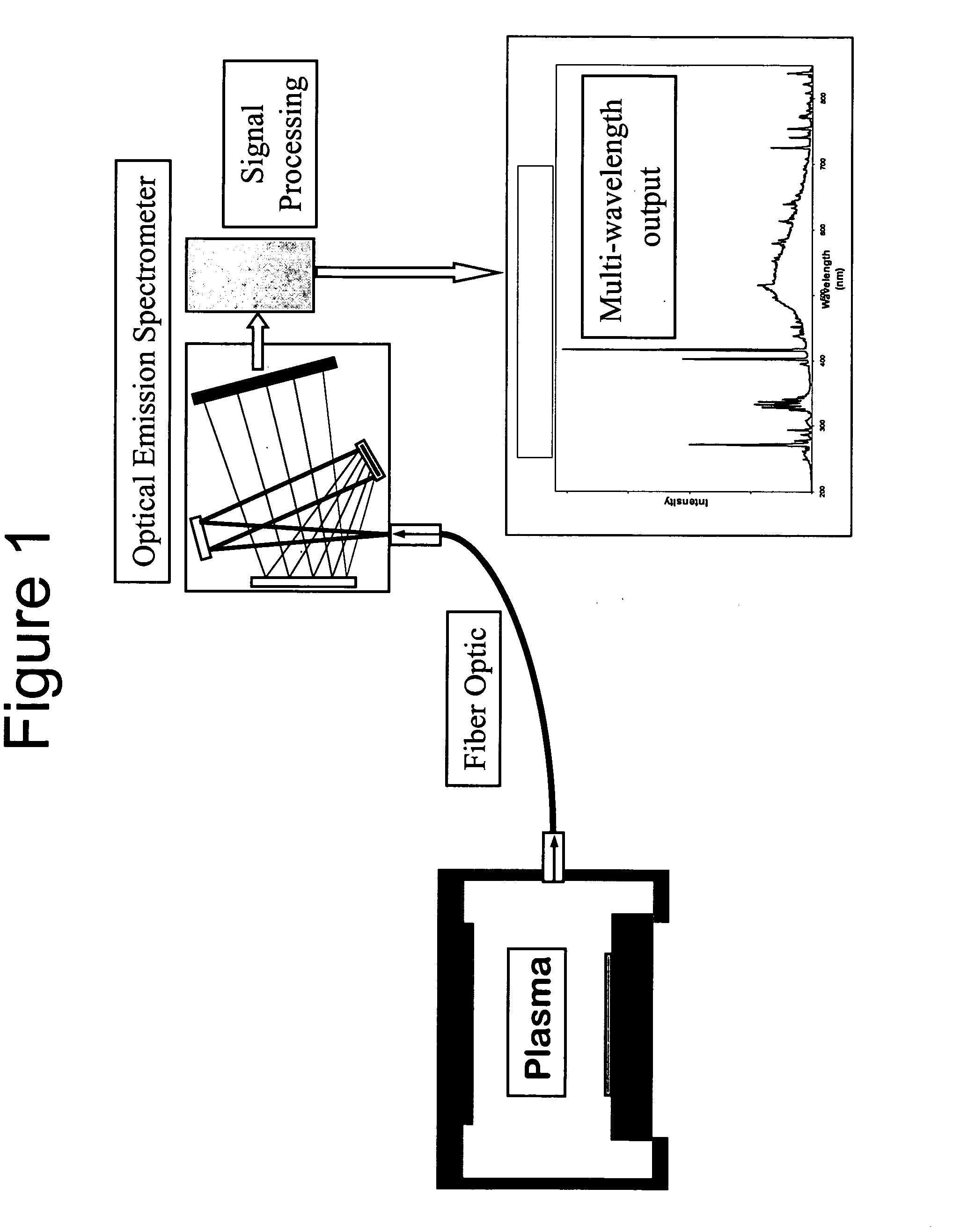
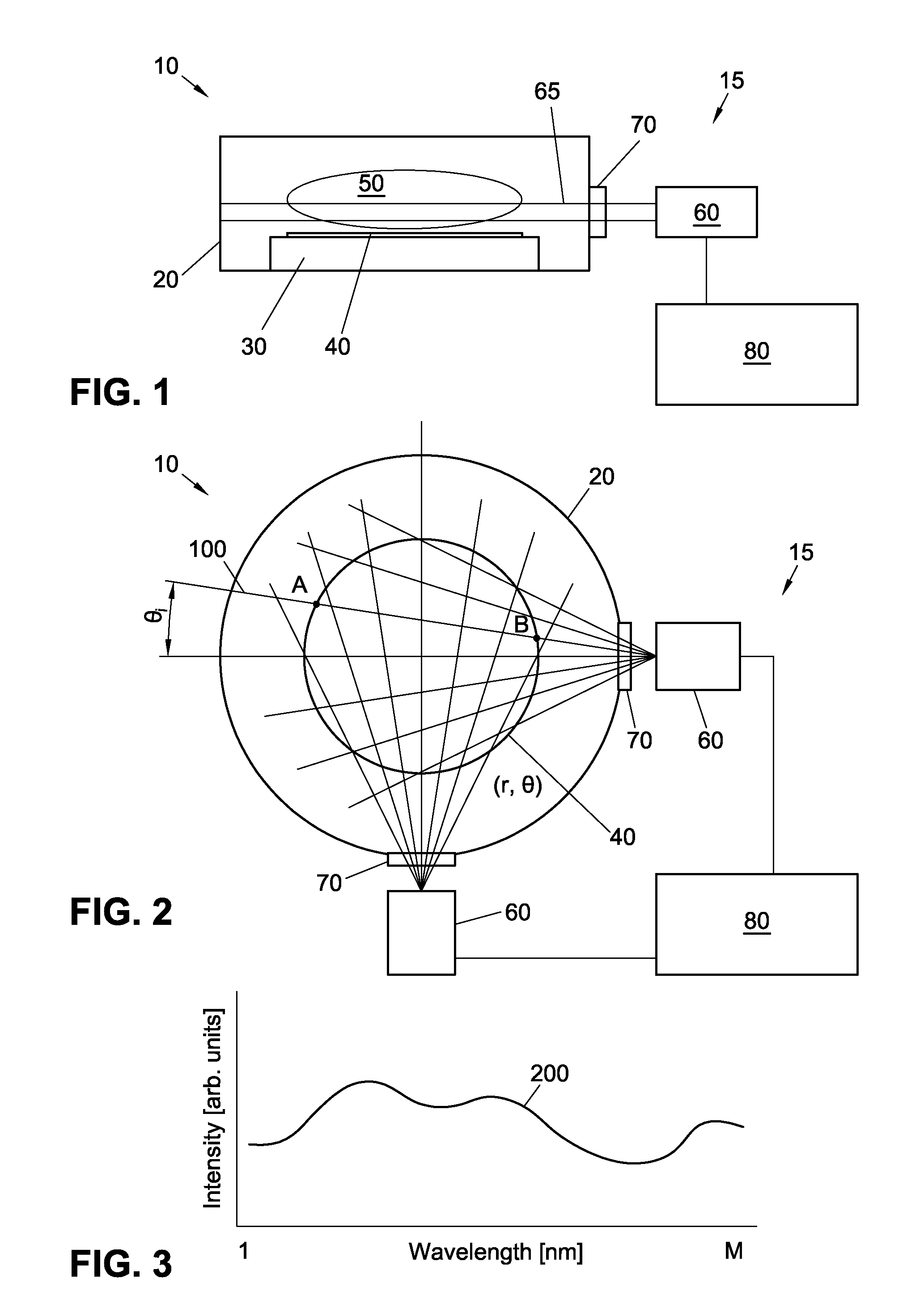
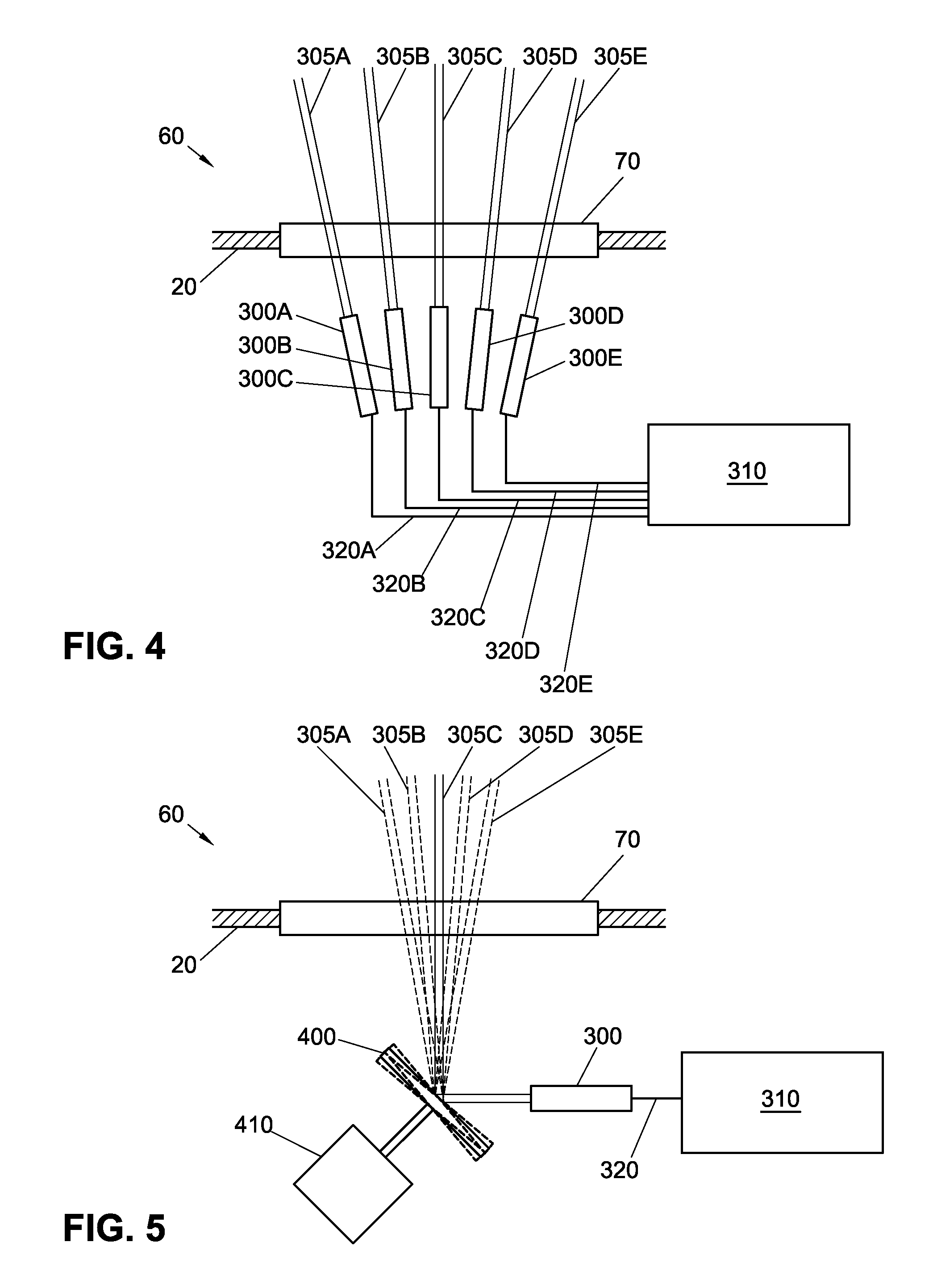
Optical emission spectrometry involves applying electrical energy in the form of spark generated between an electrode and a metal sample, whereby the vaporized atoms are brought to a high energy state within a so-called “discharge plasma”.
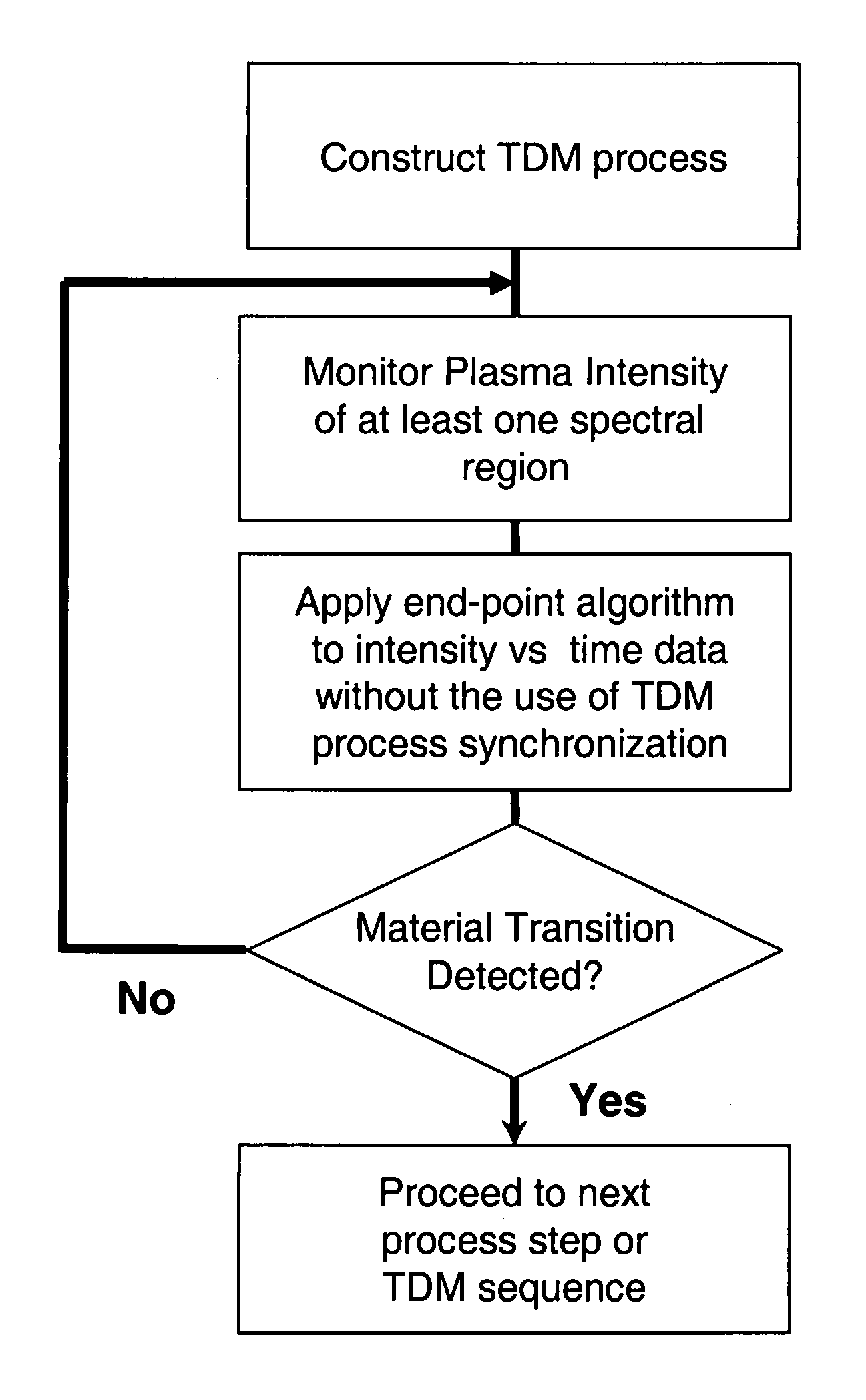
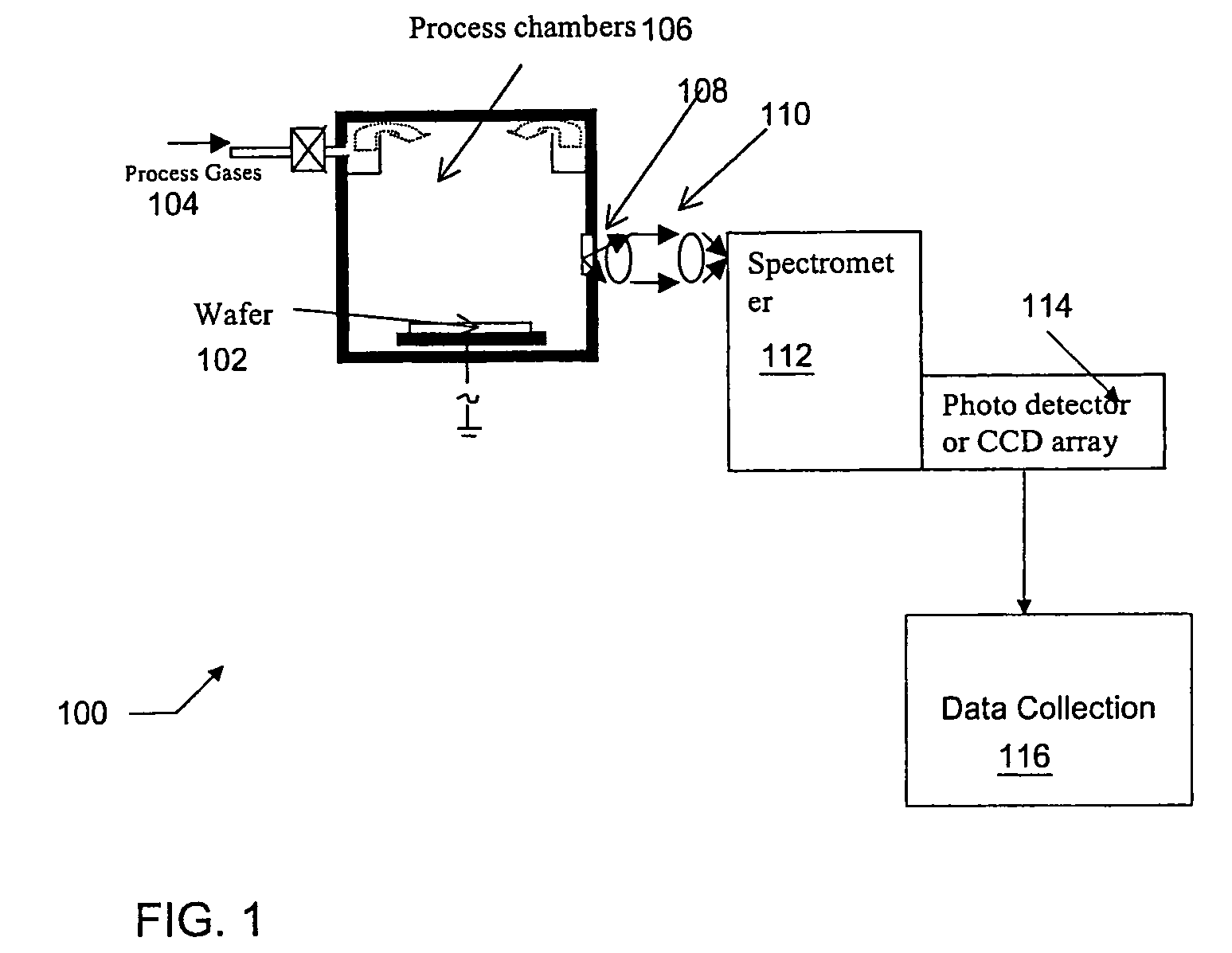
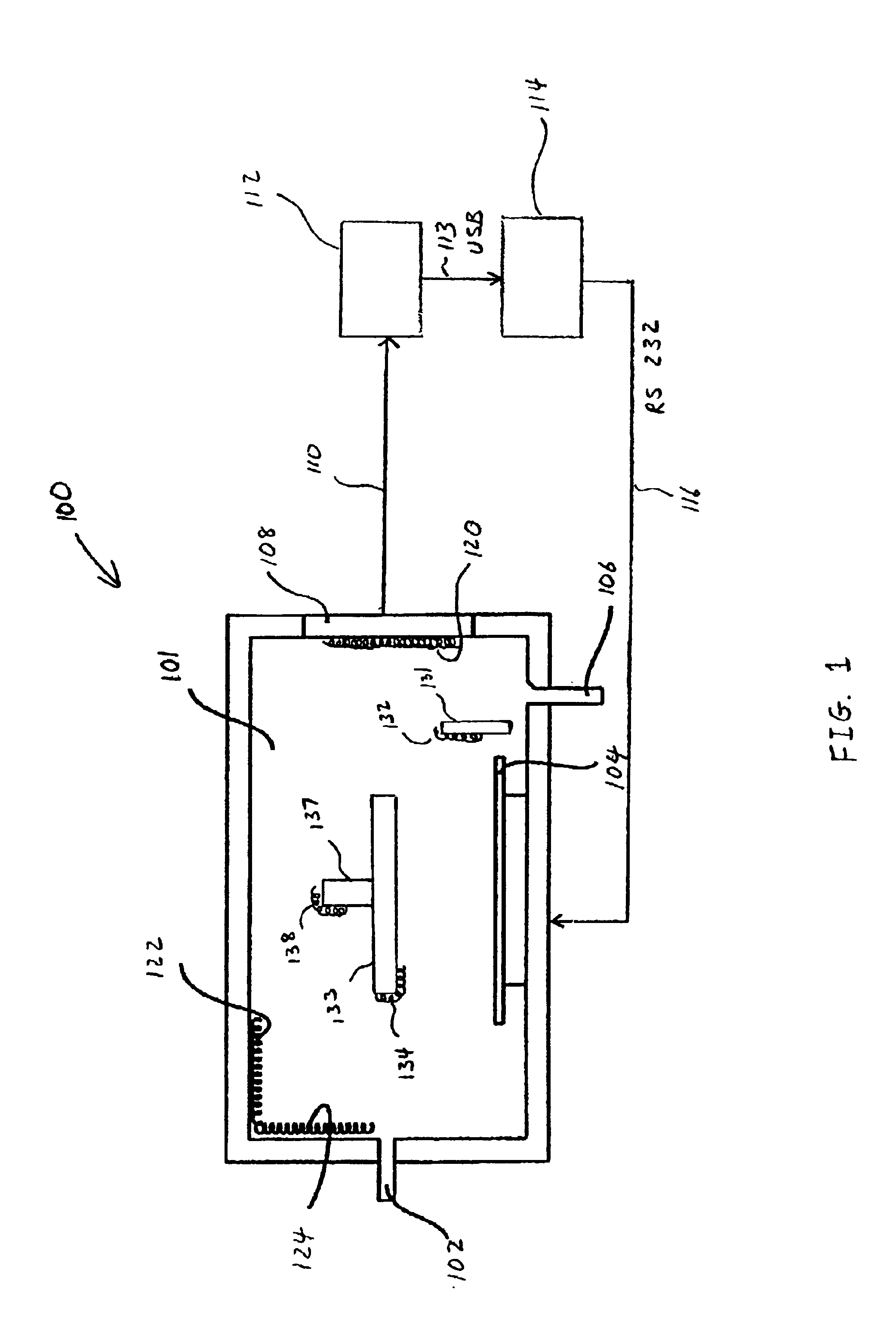
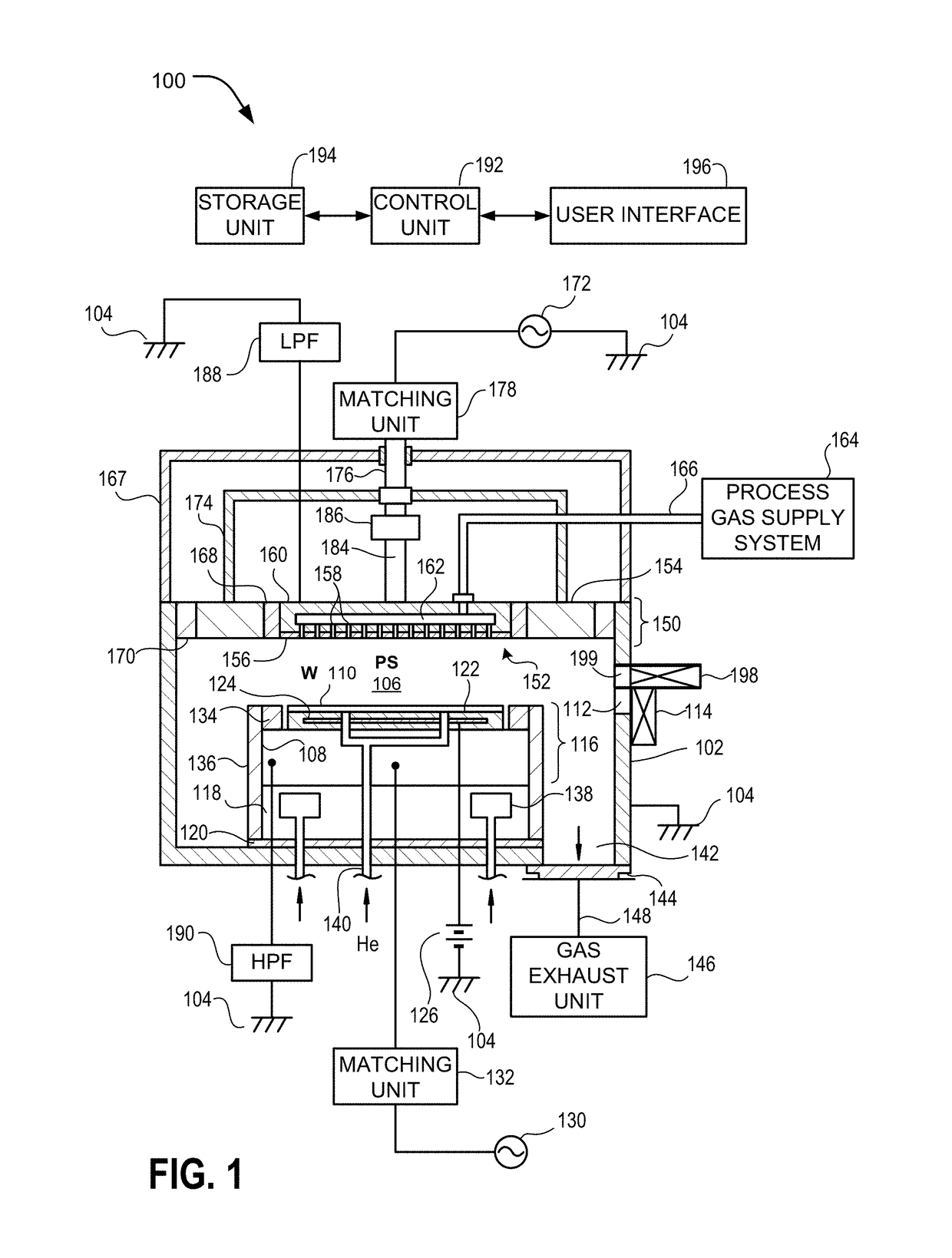
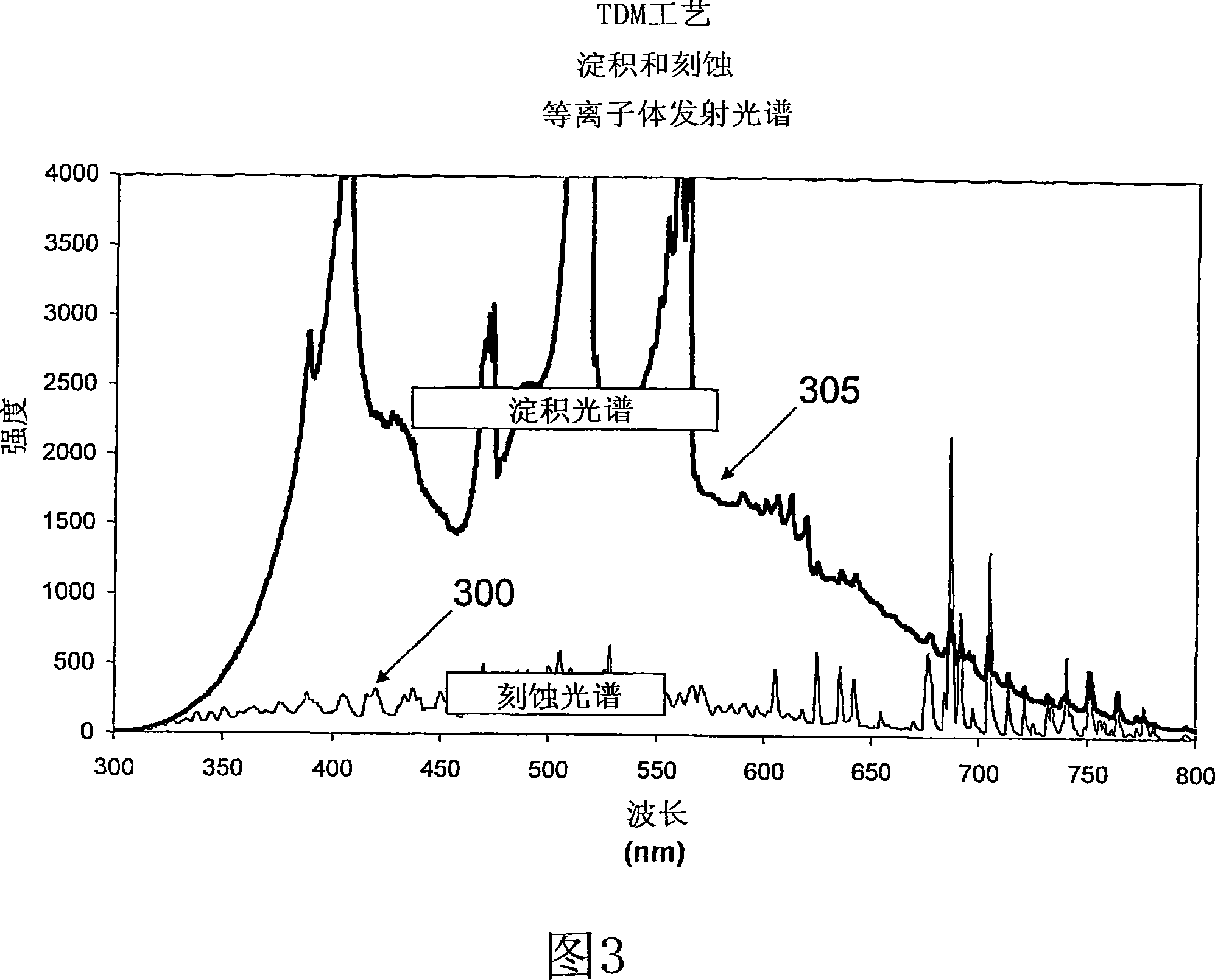
Envelope follower end point detection in time division multiplexed processes
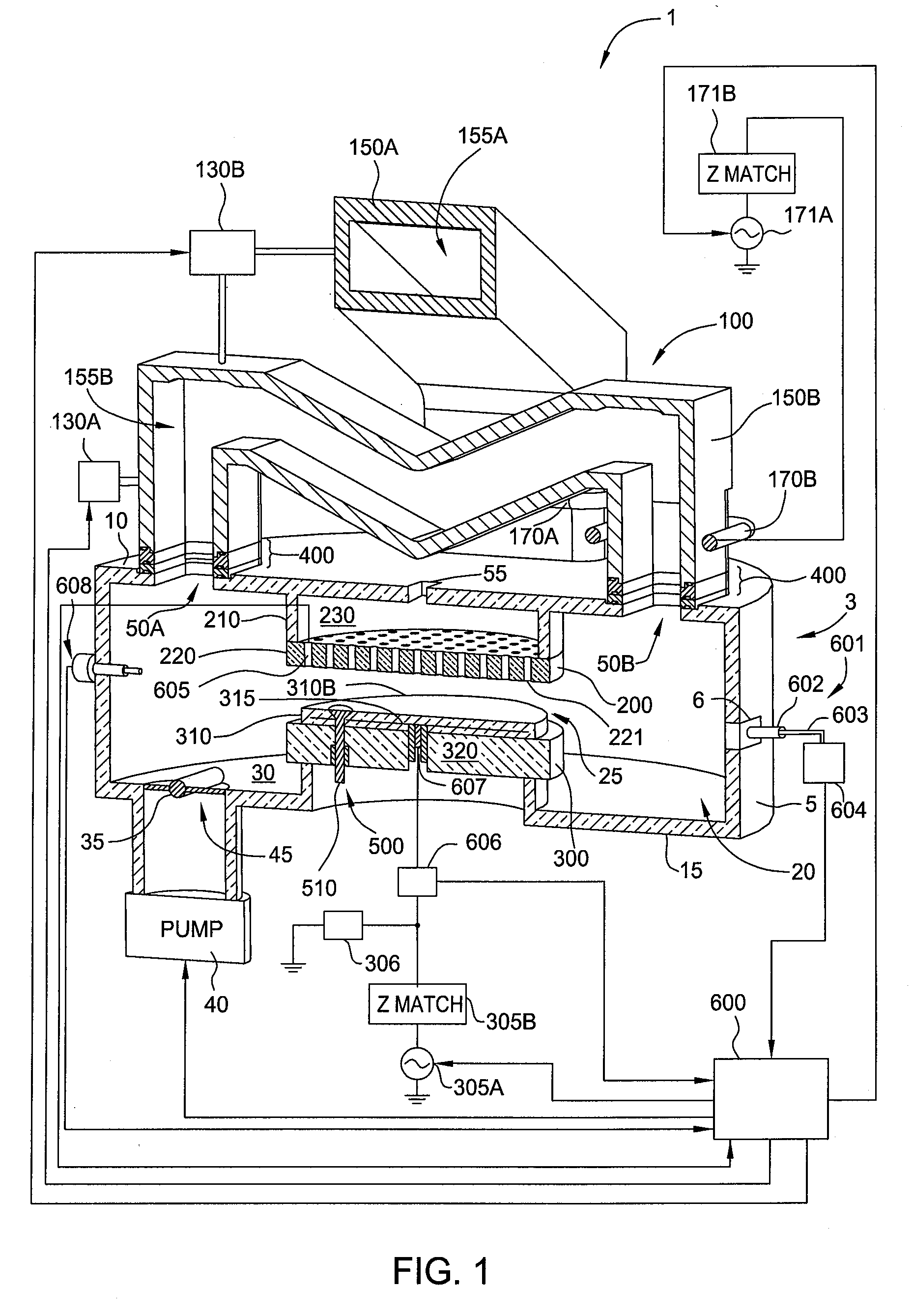
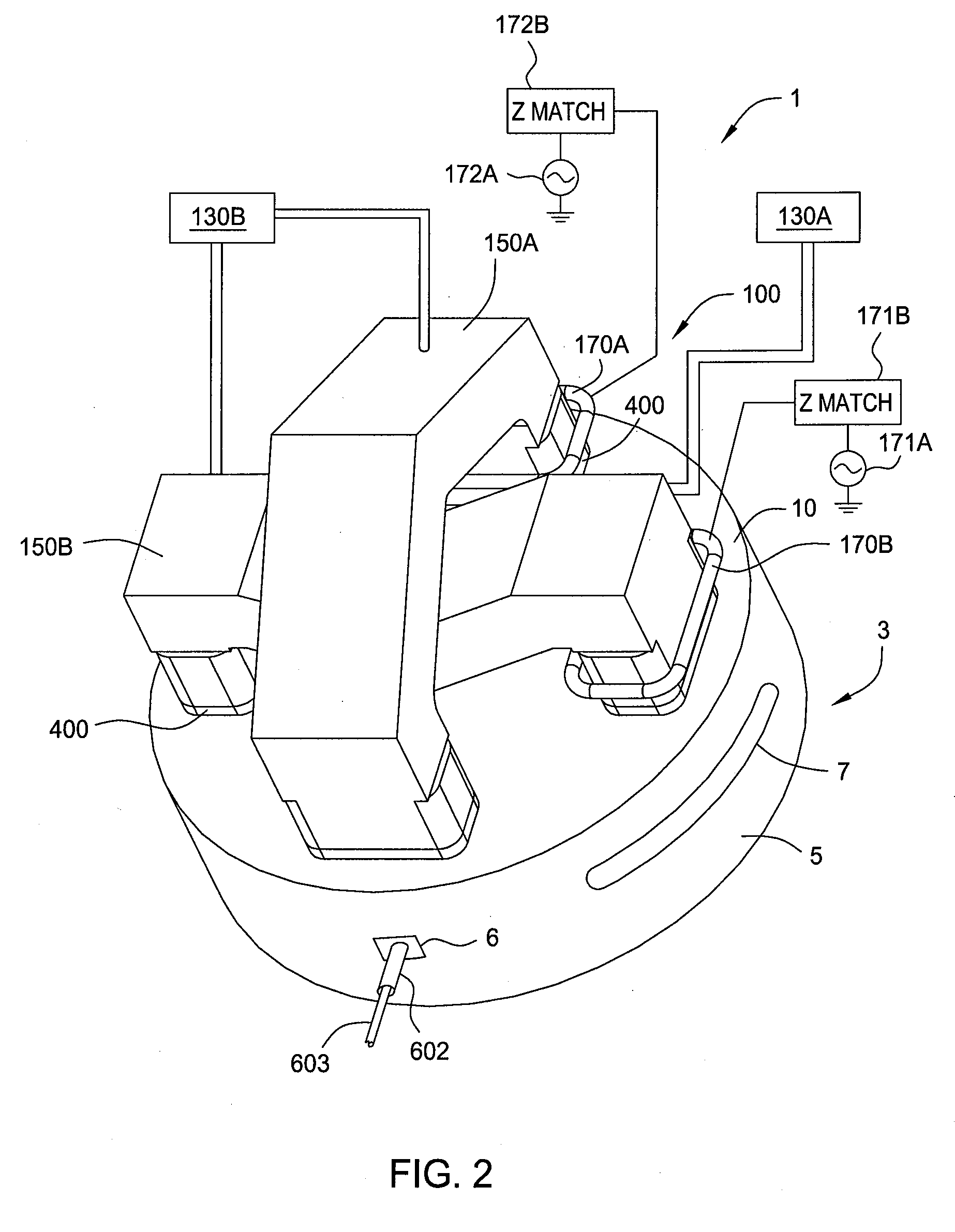
ActiveUS7101805B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesOptical emission spectrometryPlasma chamber
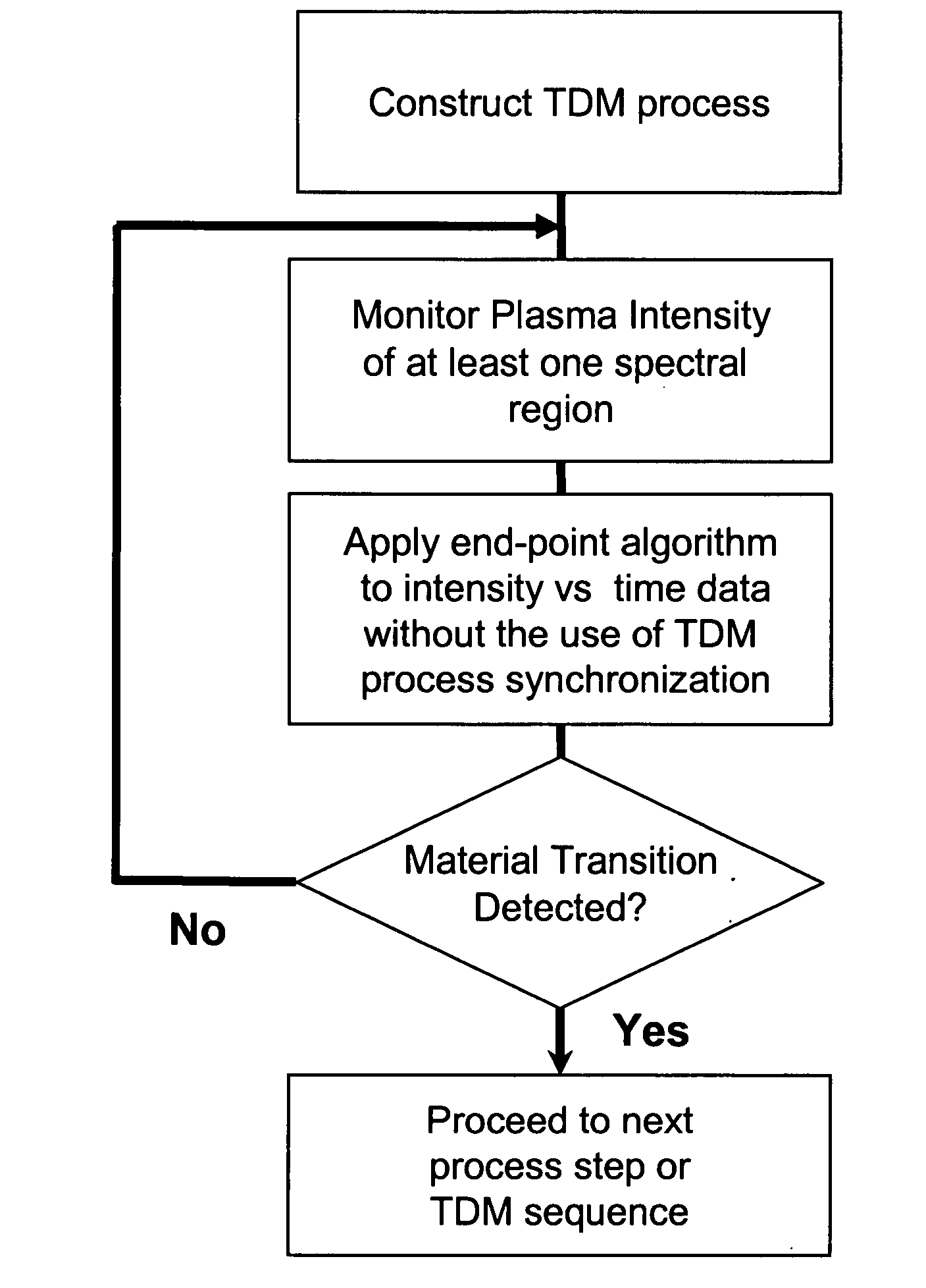
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for establishing endpoint during an alternating cyclical etch process or time division multiplexed process. A substrate is placed within a plasma chamber and subjected to an alternating cyclical process having an etching step and a deposition step. A variation in plasma emission intensity is monitored using known optical emission spectrometry techniques. An amplitude information is extracted from a complex waveform of the plasma emission intensity using an envelope follower algorithm. The alternating cyclical process is discontinued when endpoint is reached at a time that is based on the monitoring step.
Owner:PLASMA THERM
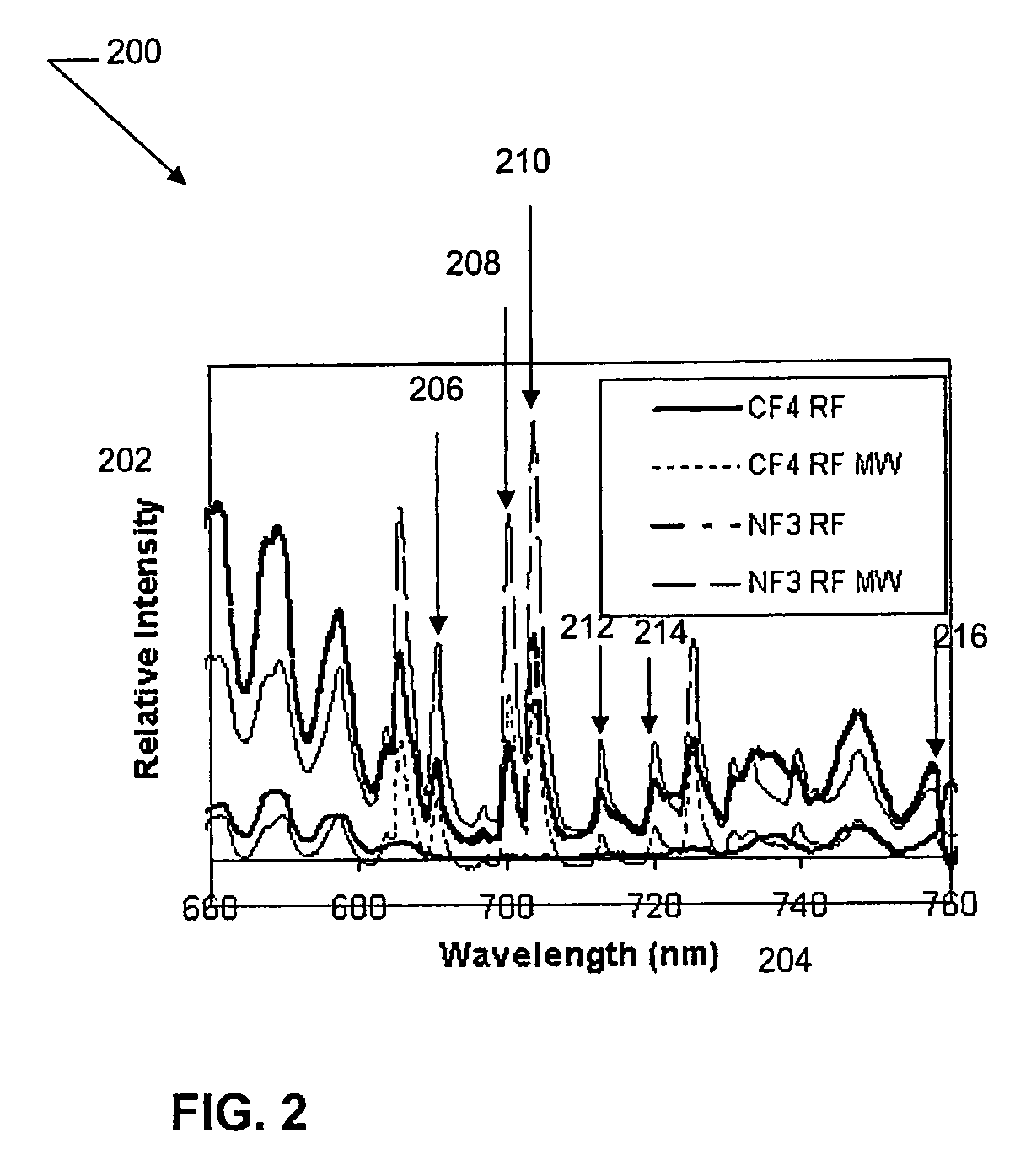
Method of reducing process plasma damage using optical spectroscopy
InactiveUS6972840B1Avoid plasma processing damageSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesSpectroscopyEngineering
Optical emission spectra from a test wafer during a plasma process are measured using a spectrometer. The plasma charging voltage retained by (detected by) the test wafer is measured after the process step is completed. The emission spectra are correlated with the plasma charging voltage to identify the species contributing to the plasma charging voltage. The optical emission spectra are monitored in real time to optimize the plasma process to prevent plasma charging damage. The optical emission spectra are also monitored to control the plasma process drift.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
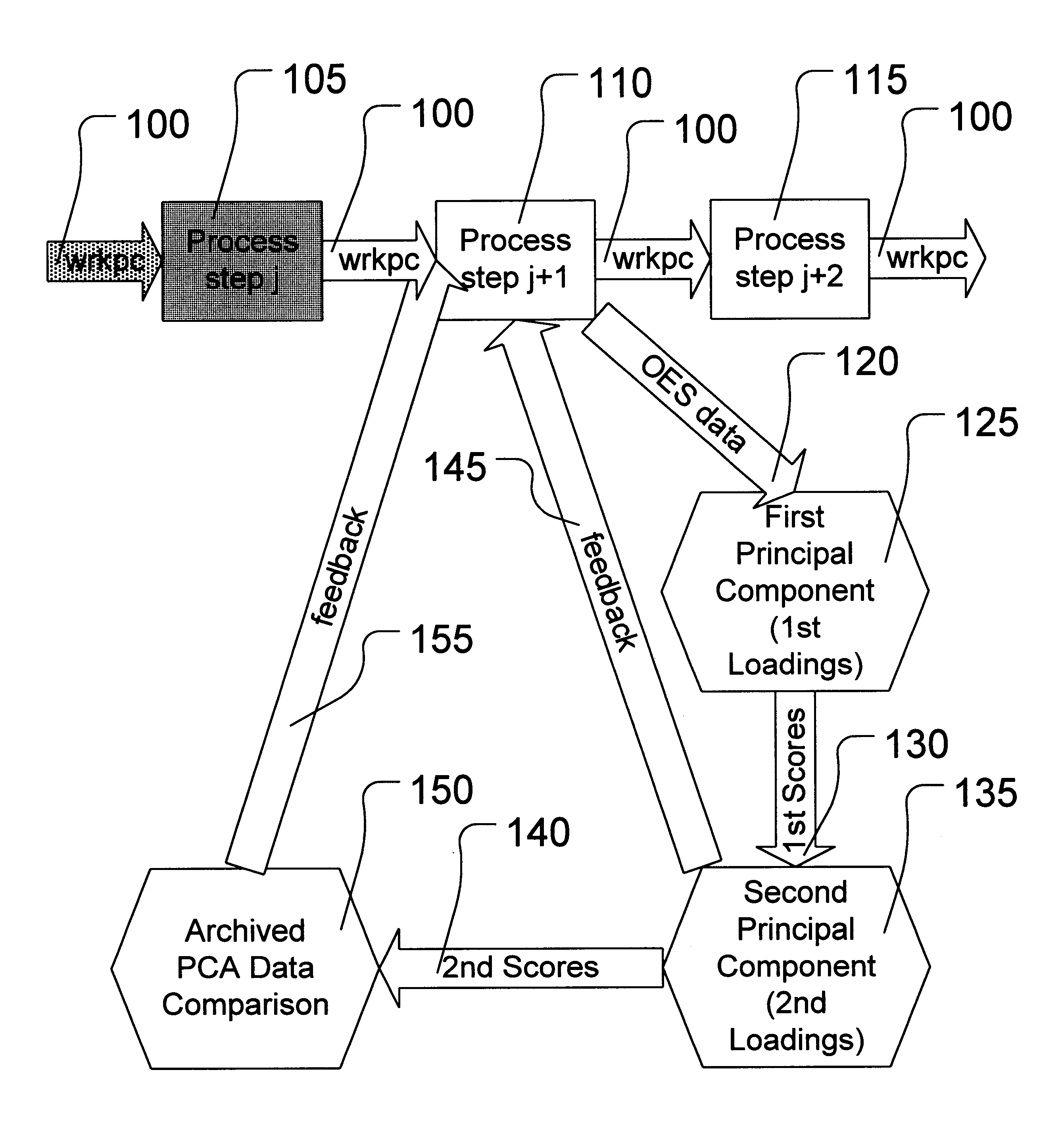
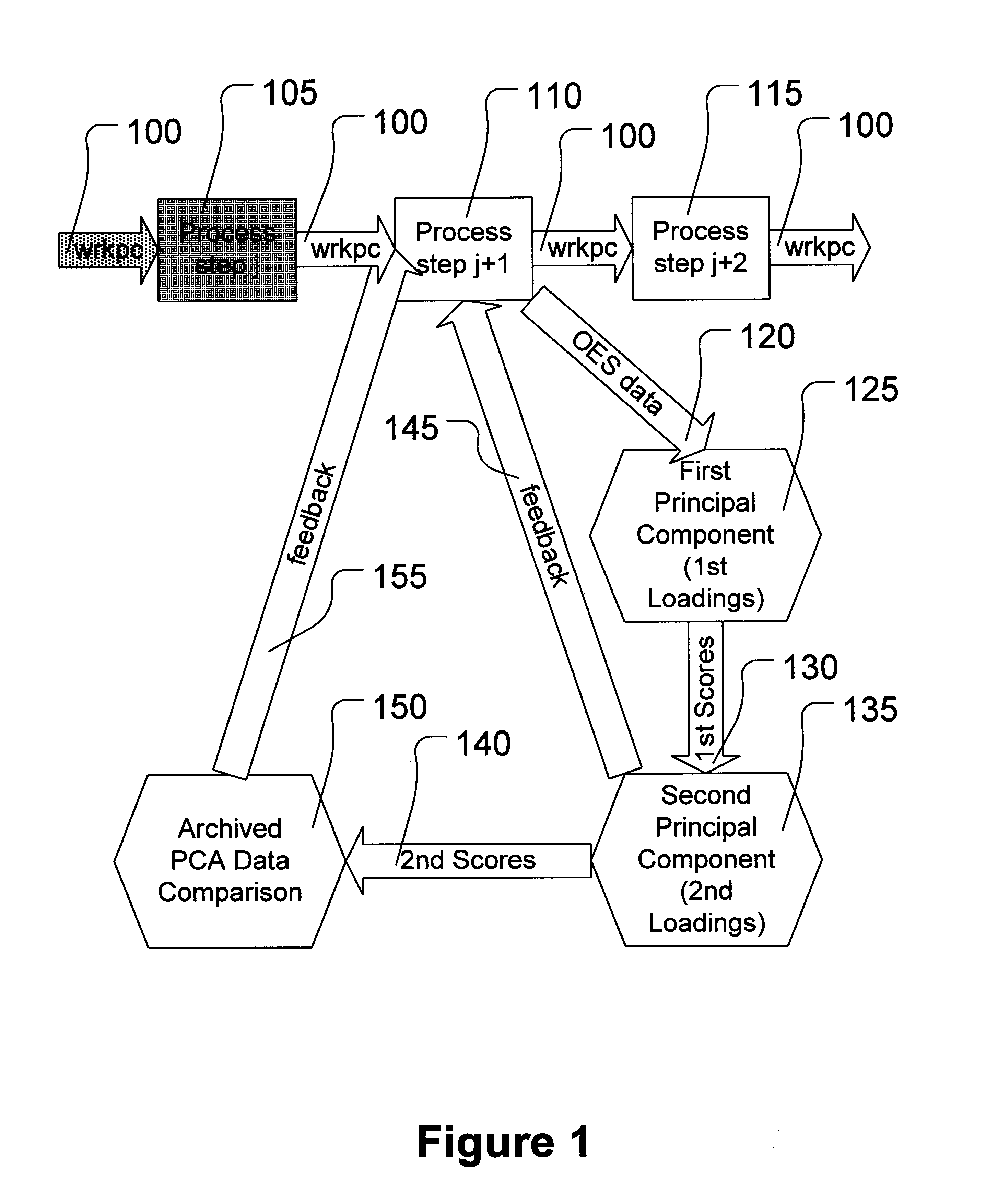
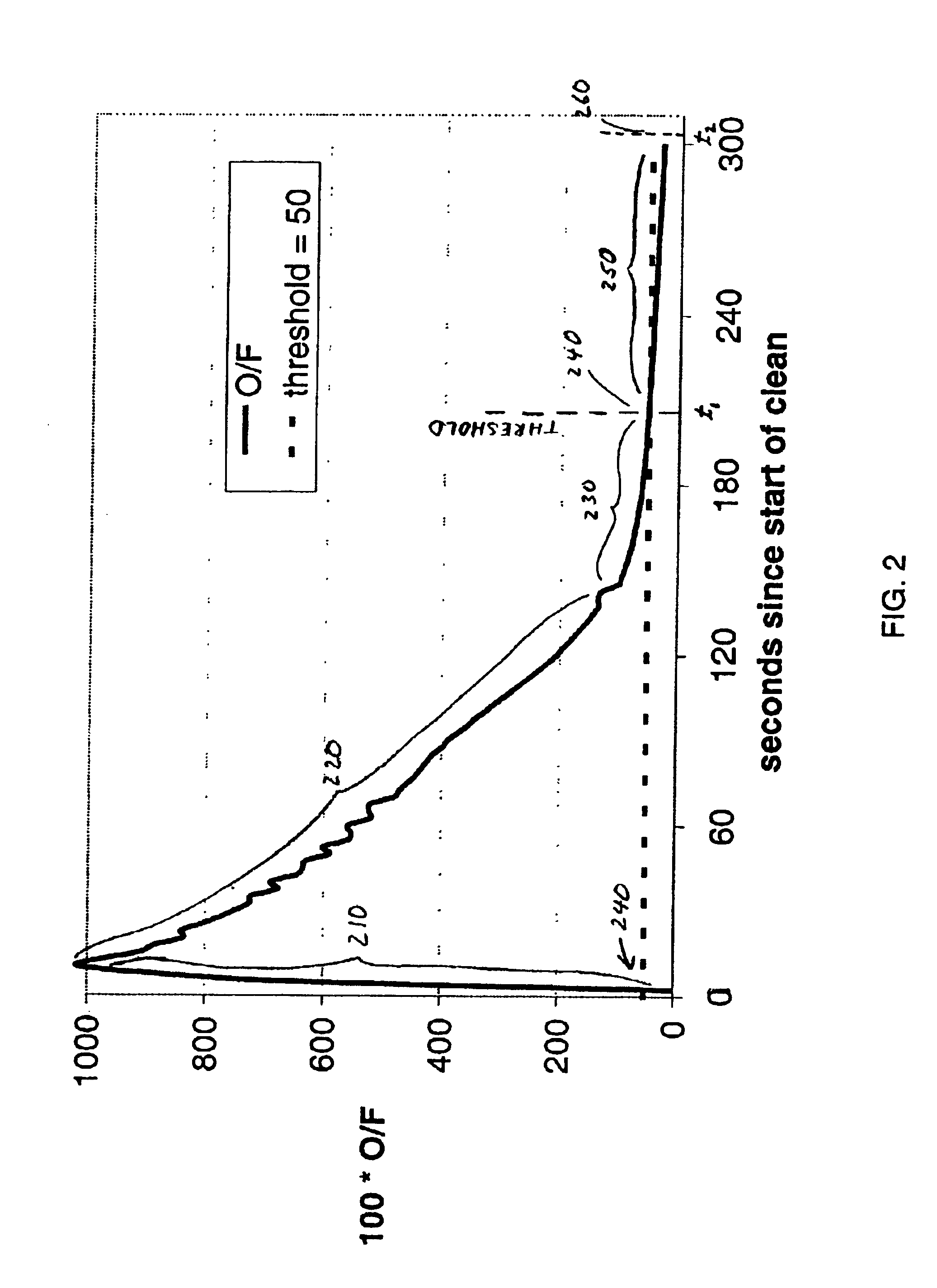
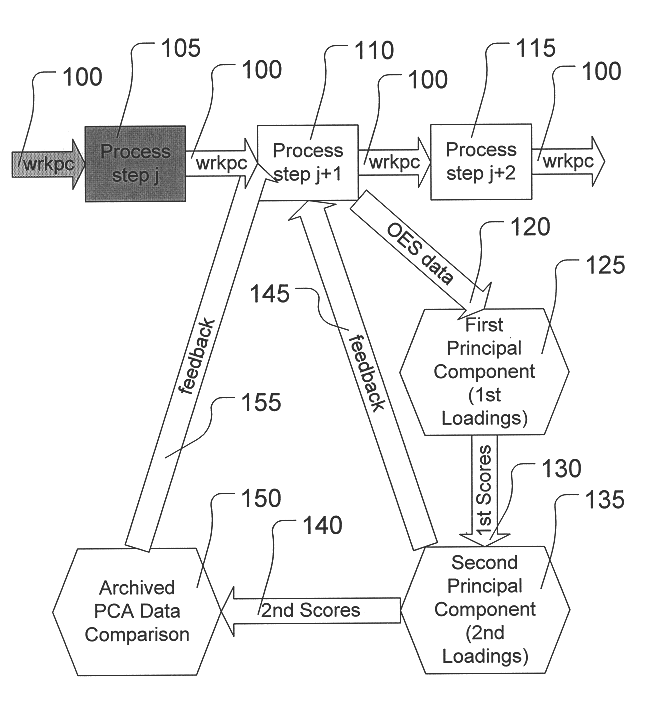
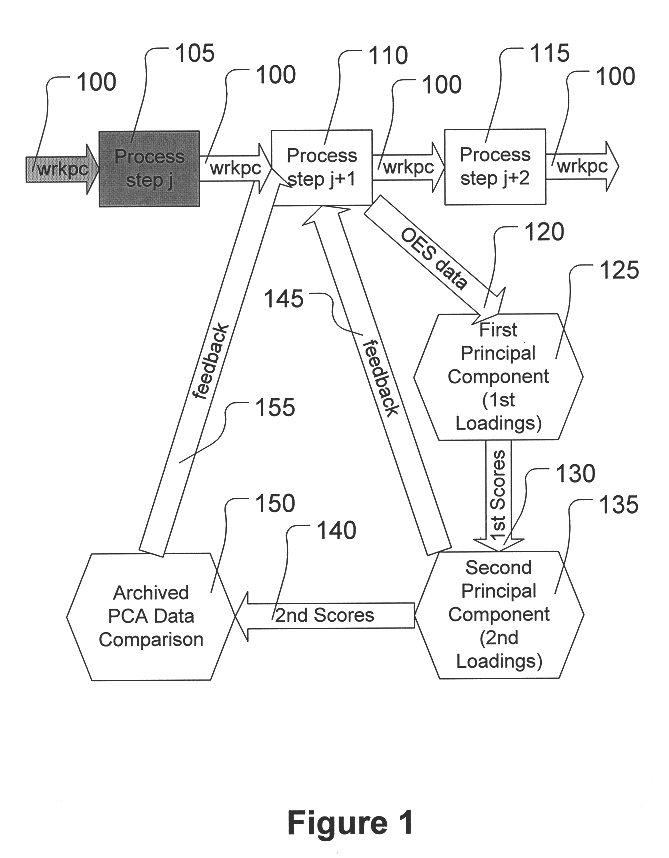
Determining endpoint in etching processes using principal components analysis of optical emission spectra with thresholding
InactiveUS6238937B1Programme controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPrincipal component analysisOptical emission spectrometry
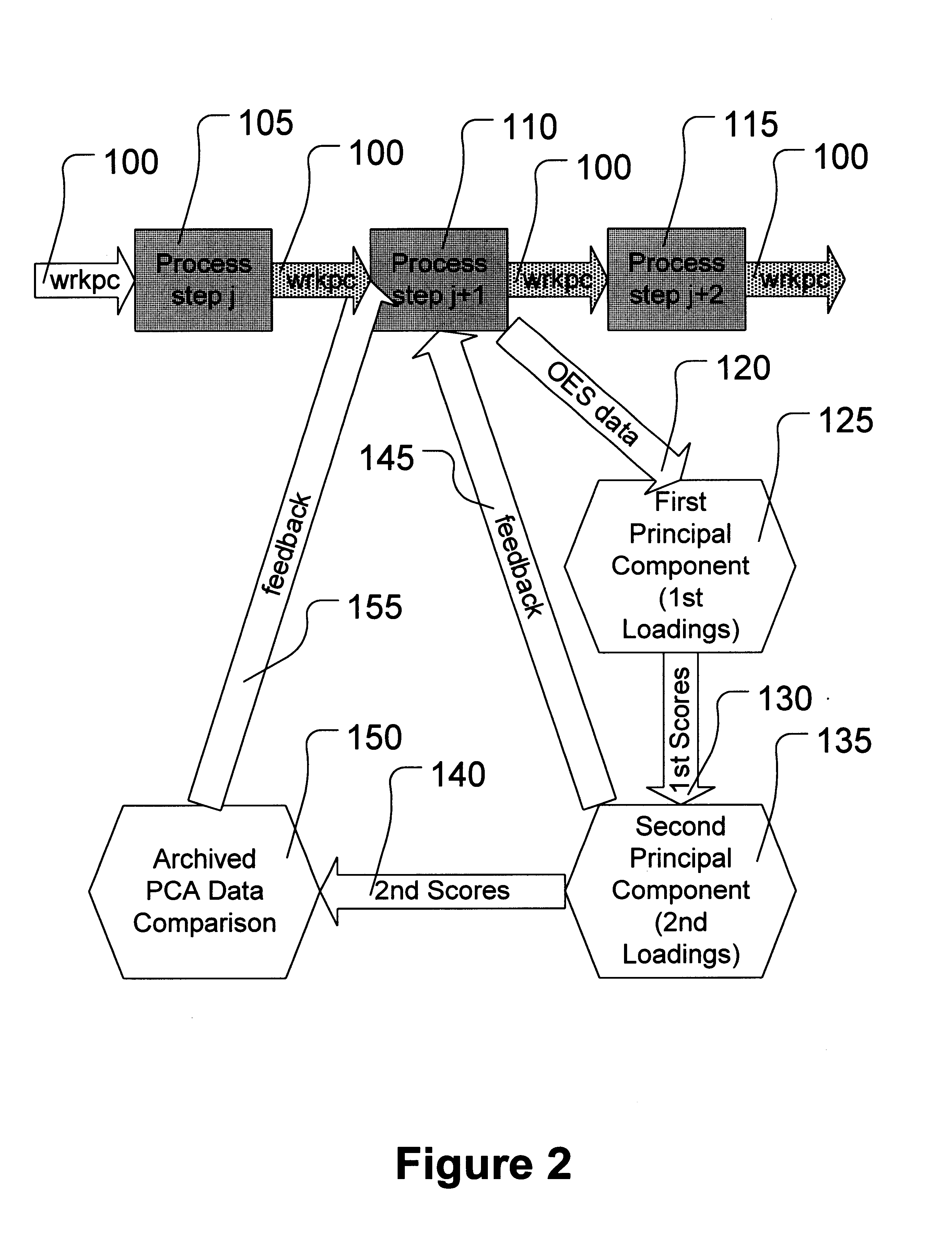
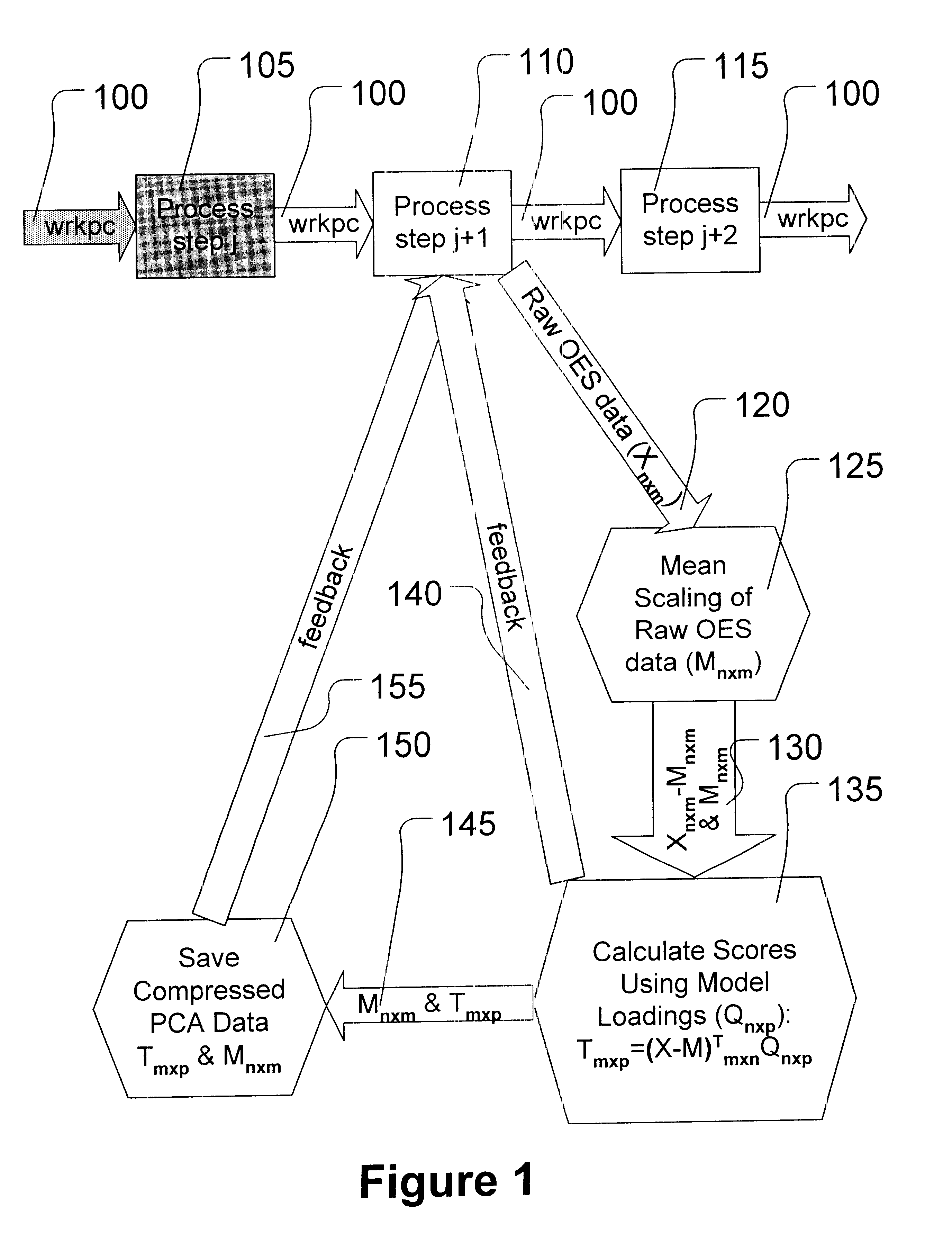
A method is provided for determining an etch endpoint. The method includes collecting intensity data representative of optical emission spectral wavelengths during a plasma etch process. The method further includes analyzing at least a portion of the collected intensity data into at most first and second Principal Components with respective Loadings and corresponding Scores. The method also includes determining the etch endpoint using the respective Loadings and corresponding Scores of the second Principal Component as an indicator for the etch endpoint using thresholding applied to the respective Loadings of the second Principal Component.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of determining etch endpoint using principal components analysis of optical emission spectra
InactiveUS6582618B1Programme controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPrincipal component analysisOptical emission spectrometry
A method is provided for determining an etch endpoint. The method includes collecting intensity data representative of optical emission spectral wavelengths during a plasma etch process. The method further includes calculating Scores from at least a portion of the collected intensity data using at most first, second, third and fourth Principal Components derived from a model. The method also includes determining the etch endpoint using Scores corresponding to at least one of the first, second, third and fourth Principal Components as an indicator for the etch endpoint.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Laser sampling methods for reducing thermal effects
InactiveUS20140268134A1Reduce thermal effectsEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryTarget surfaceOptical emission spectrometry
A method for reducing thermal effects in laser ablation optical emission spectrometry includes creating discrete ablation spots along an analysis line on a target surface. At least one of the following is also carried out. First, the ablation spots are positioned so that a pair of successive ablation spots are spaced apart from one another along the analysis line and are separated from one another by another ablation spot. Second, when the analysis line comprises generally parallel, adjacent analysis line segments, the ablation spots are positioned so that (A) a pair of successive ablation spots are on different analysis line segments, and (B) the successive ablation spots are positioned to be at different longitudinal positions along the analysis line segments when the different analysis line segments are adjacent to one another. As a result, a linear scan of isolated ablation spots can be generated.
Owner:ELEMENTAL SCI LASERS LLC
Dosimetry using optical emission spectroscopy/residual gas analyzer in conjuntion with ion current
ActiveUS20080075834A1Liquid surface applicatorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDosimetry radiationOptical emission spectrometry
The present invention generally provides methods and apparatus for controlling ion dosage in real time during plasma processes. In one embodiment, ion dosages may be controlled using in-situ measurement of the plasma from a mass distribution sensor combined with in-situ measurement from an RF probe.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
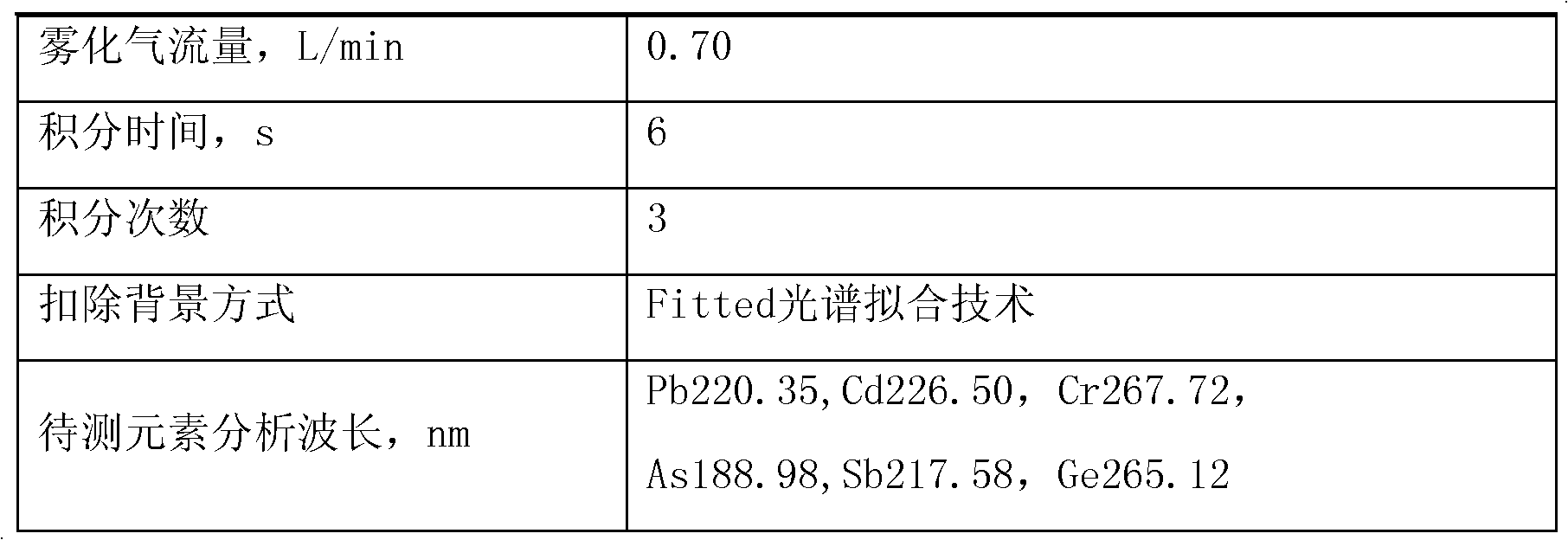
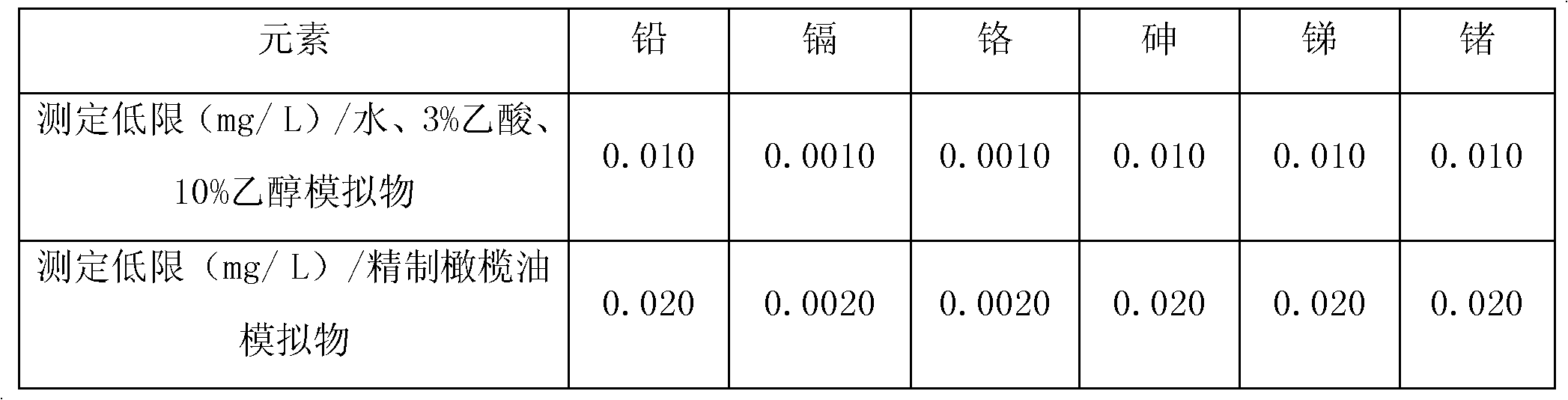
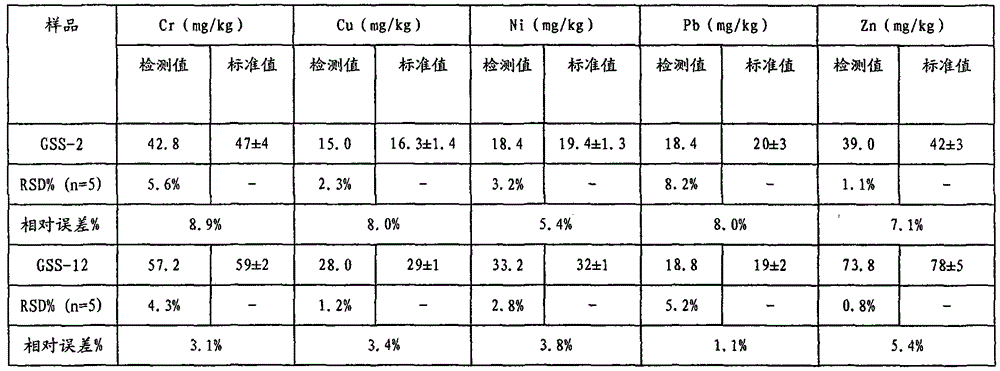
Detection method for simultaneously measuring migrated masses of lead, cadmium, chromium, arsenic, antimony and germanium in plastic packaging container for foods by ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry) method
InactiveCN102023155AEfficient determinationEasy to measurePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical emission spectrometryRadio frequency
The invention relates to a detection method of harmful element migrated masses in a plastic packaging container for foods, in particular to a detection method for simultaneously measuring migrated masses of lead, cadmium, chromium, arsenic, antimony and germanium in a plastic packaging container for foods by an ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry) method. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out a migration test; 2, carrying out a blank test; and 3, carrying out measurement by an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer. The ways of RF (radio frequency) power amplification (for a 3% acetic acid simulacrum test solution), ethanol removal (for a 10% ethanol simulacrum test solution) and microwave digestion (for a delicate olive oil test solution) are used to efficiently, simply and quickly measure the migrated masses of various harmful elements in four simulacrums in the plastic packaging container for the foods simultaneously.
Owner:THE INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT ZHEJIANG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
High pressure digestion ICP-MS method for determining rare earth element content in crude oil
ActiveCN102253108AGood digestion effectReduce distractionsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRare-earth elementInternal standard
A high pressure digestion ICP-MS (inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry) method for determining rare earth element contents in crude oil belongs to a chemical detection method for detecting 16 rare earth elements in crude oil, such as Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, and Lu, etc. In a sample high pressure digestion process, an ICP-OES (inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry) method is first used to determine a wave spectrum intensity at 193.027nm of a carbonaceous element in a digestion solution, in order to determine a digestion degree; so that problems of apparatus loss and pollution caused by incomplete digestion and large result deviation caused by high matrix interference in a high pressure digestion method are solved. In an ICP-MS apparatus determination of the sample digestion solution, an on-line adding of internal standard solution and a collision reaction cell technology are employed to eliminate interferences and optimize apparatus working conditions. The method has a detection limit reaching 0.01[mu]g / kg-0.7[mu]g / kg and a recovery rate between 80.4%-105.2%, has advantages of low detection limit, rapidness and accuracy, etc., and can satisfy detection requirements of rare earth elements in crude oil.
Owner:邬蓓蕾
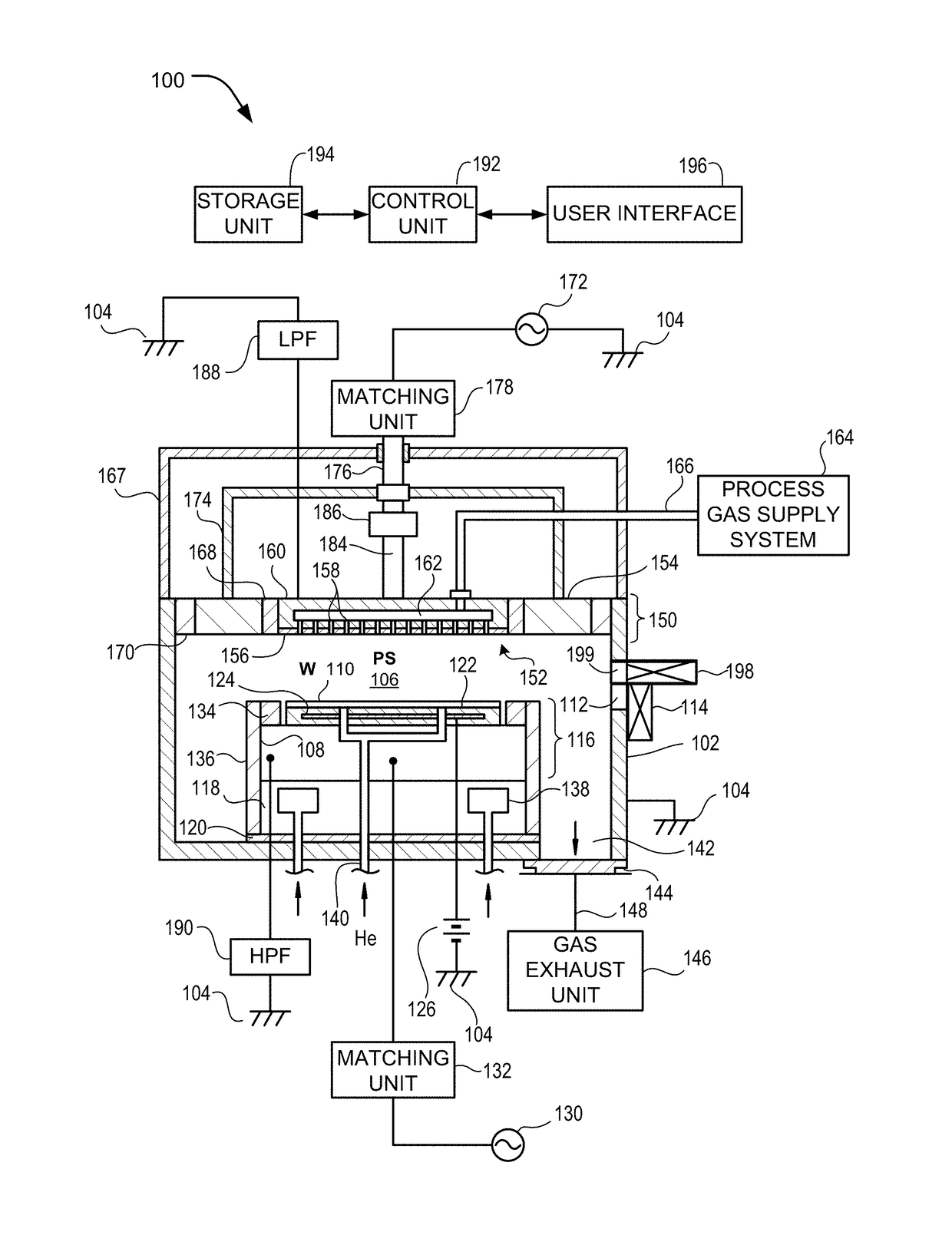
Endpoint detection for high density plasma (HDP) processes
InactiveUS6919279B1Optimal plasma etching and cleaningAvoids over-cleaning/etching and under-cleaning/etchingElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpectral emissionHigh density
A method and system are provided for endpoint detection of plasma chamber cleaning or plasma etch processes. Optical emission spectroscopy is utilized to determine a spectral emission ratio of two or more light emitting reaction components at wavelengths in close proximity. When a spectral emission ratio or derivative thereof or mathematical function thereof falls below a selected threshold value, the plasma process may be terminated within a calculated time from the threshold value prior to an endpoint value cutoff. Advantageously, the system and methods of the present invention provide real-time, in-situ monitoring of plasma clean or etch processes to optimize the process and avoid under-cleaning or over-cleaning.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS +1
Determining endpoint in etching processes using principal components analysis of optical emission spectra
InactiveUS6419846B1Programme controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPrincipal component analysisOptical emission spectrometry
A method is provided for determining an etch endpoint. The method includes collecting intensity data representative of optical emission spectral wavelengths during a plasma etch process. The method further includes analyzing at least a portion of the collected intensity data into at most first and second Principal Components with respective Loadings and corresponding Scores. The method also includes determining the etch endpoint using the respective Loadings and corresponding Scores of the second Principal Component as an indicator for the etch endpoint using Principal Components Analysis applied to archived optical emission spectral data.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
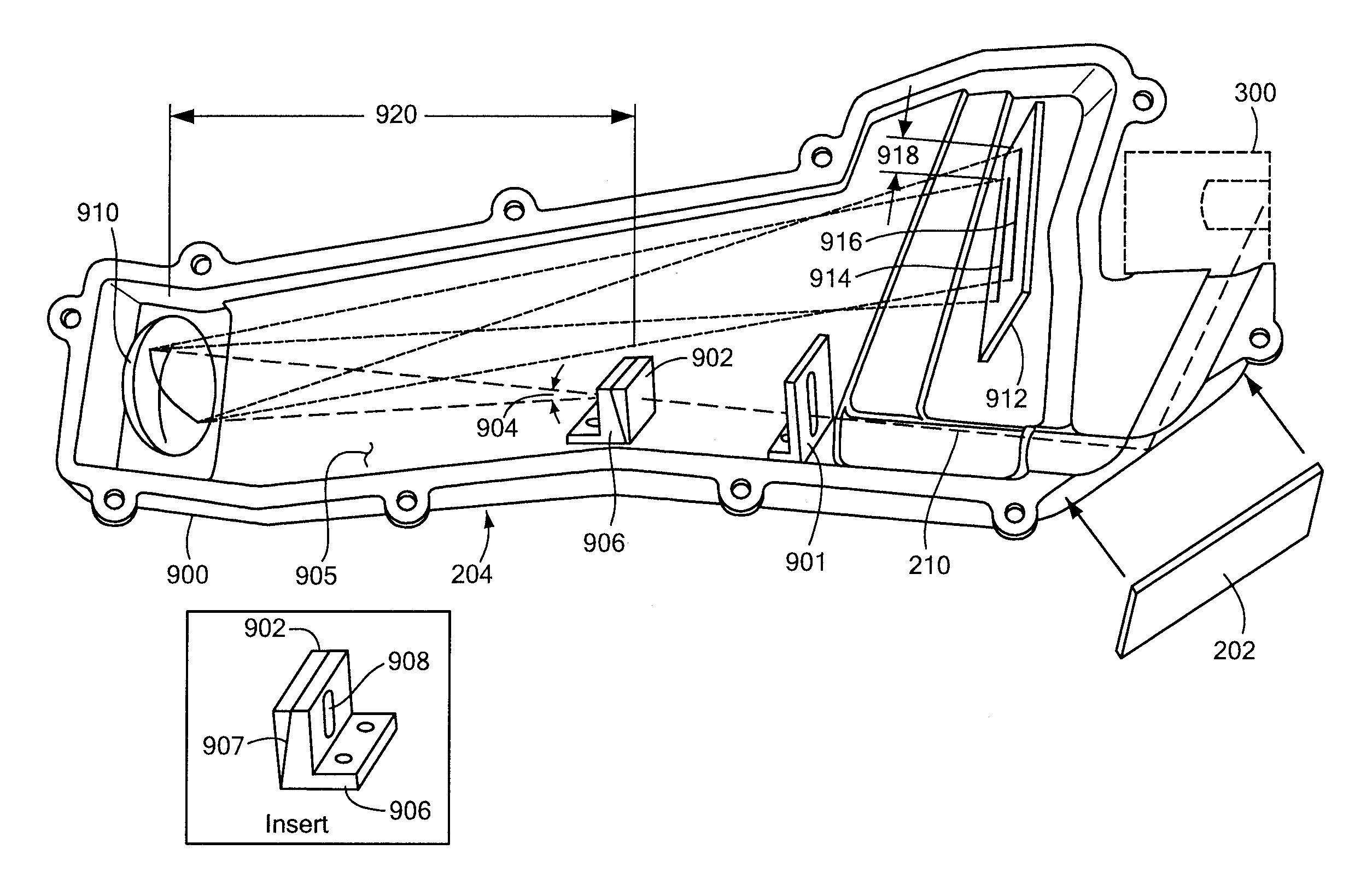
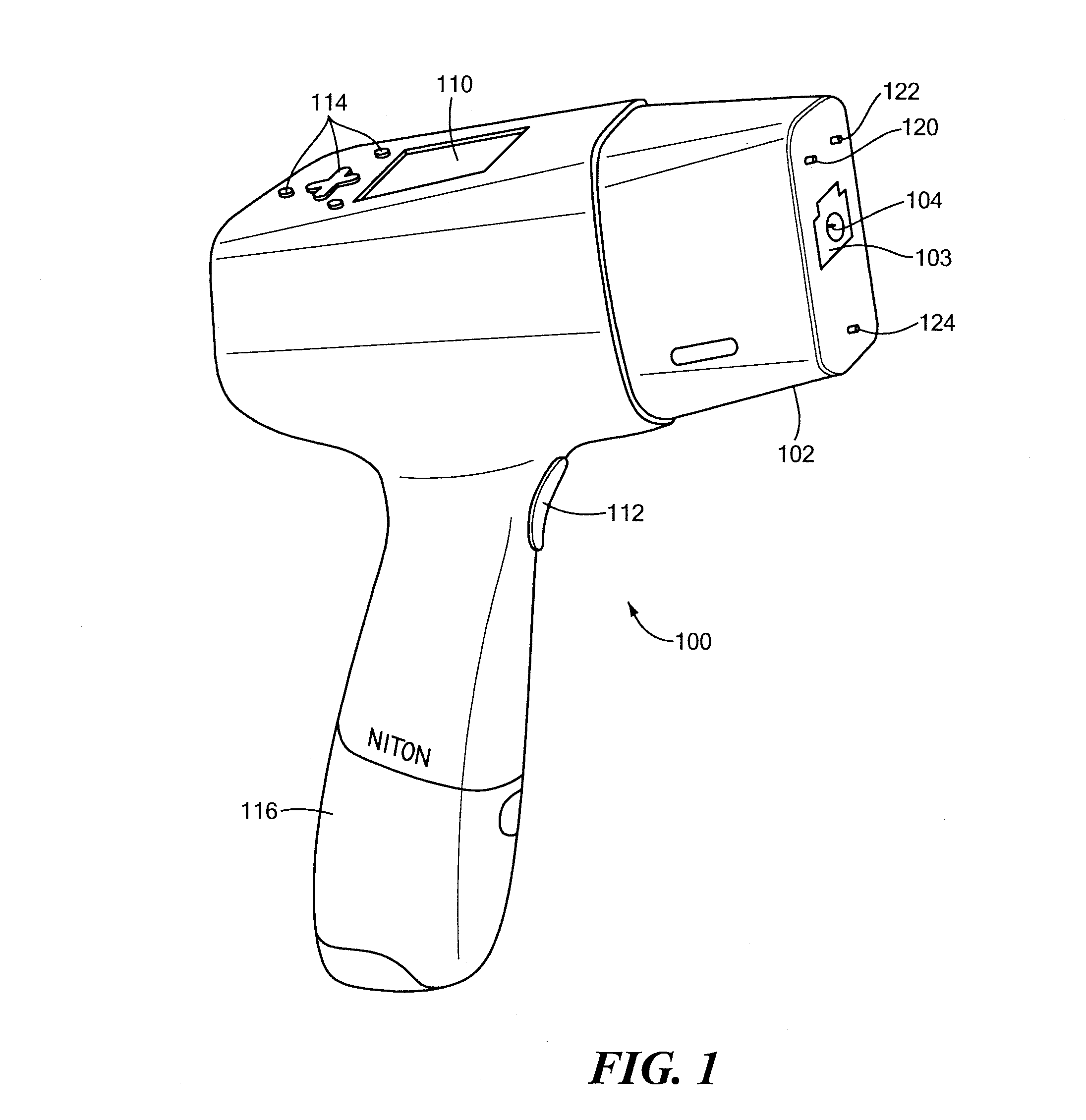
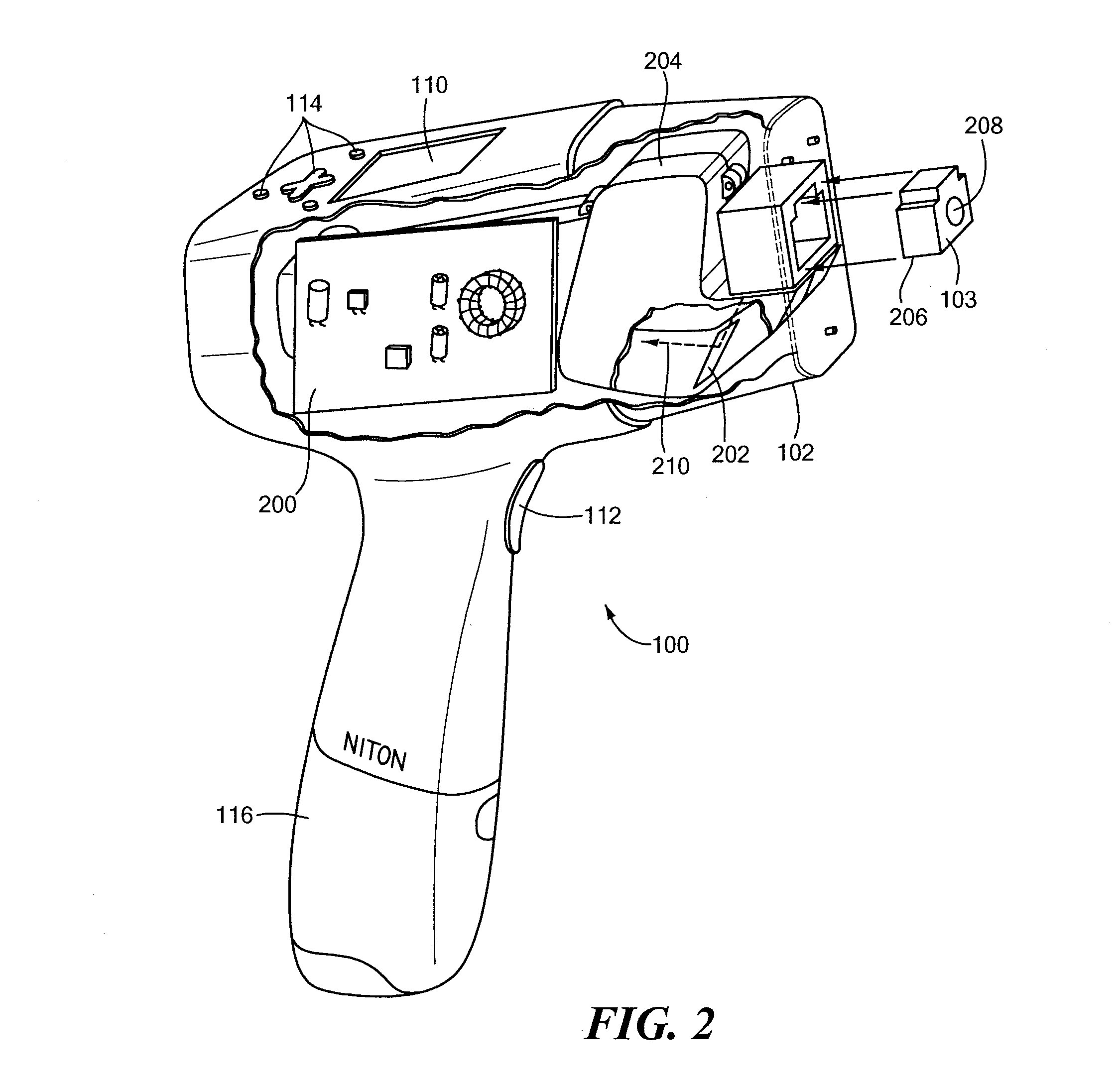
Hand-held, self-contained optical emission spectroscopy (OES) analyzer
A hand-held, self-contained, battery-powered test instrument for analyzing composition of a sample includes an exciter for exciting at least a portion of the sample, a compact cross-dispersed spectrometer for receiving an optical signal from the excited portion of the sample and a processor for processing spectral data about the optical signal from the spectrometer. The exciter may include a spark generator and a counter electrode, a laser or other device for generating the optical signal from the sample portion. The spectrometer has a wavelength range broad enough to enable the test instrument to detect and determine relative quantities of carbon, phosphorous, sulfur, manganese, silicon, iron and other elements necessary to identify common alloys. The spectrometer includes a structural member made of a light-weight material having a small coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). The spectrometer is dimensionally stable over a range of expected ambient temperatures, without controlling the temperature of the spectrometer.
Owner:THERMO SCI PORTABLE ANALYTICAL INSTR INC
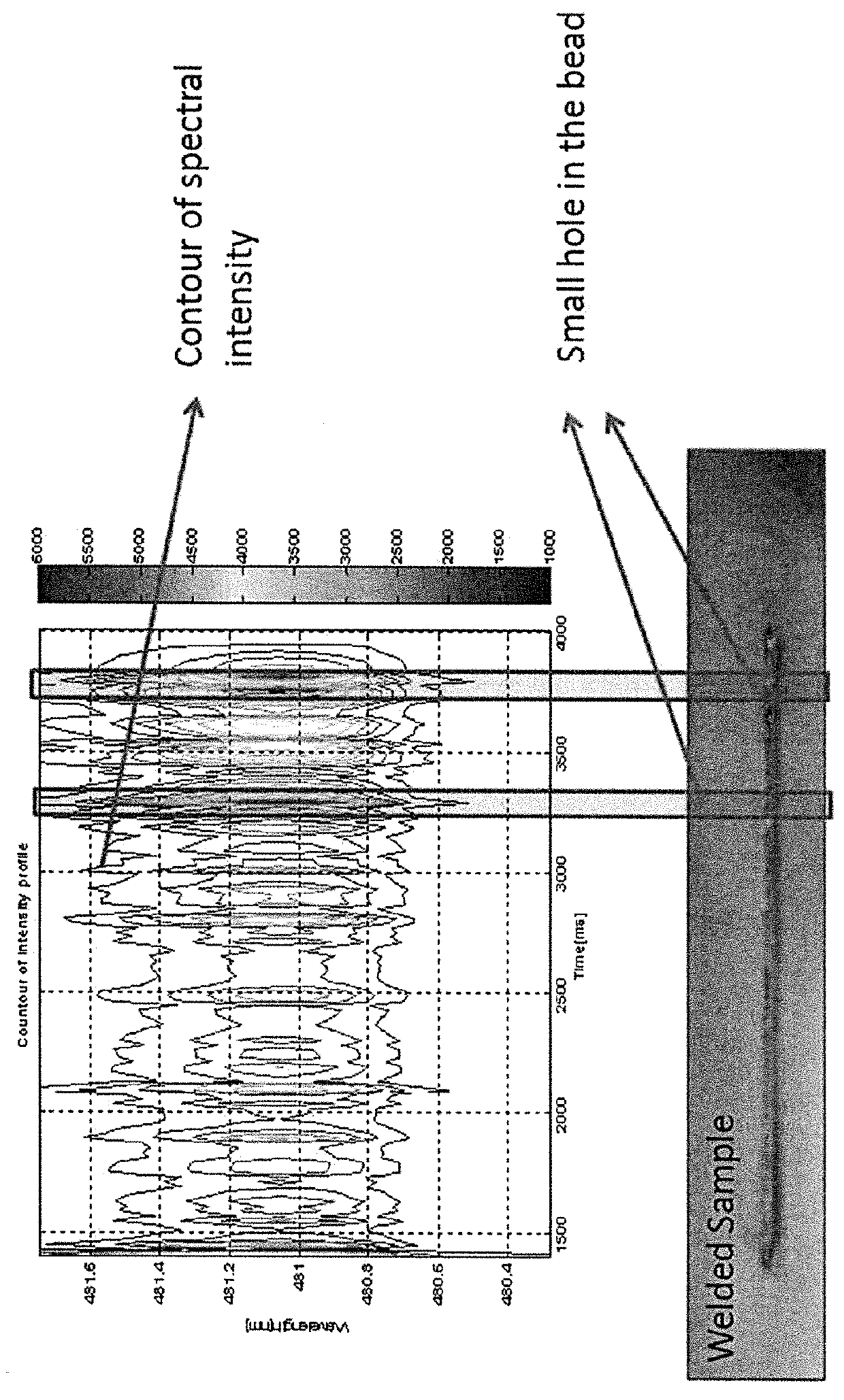
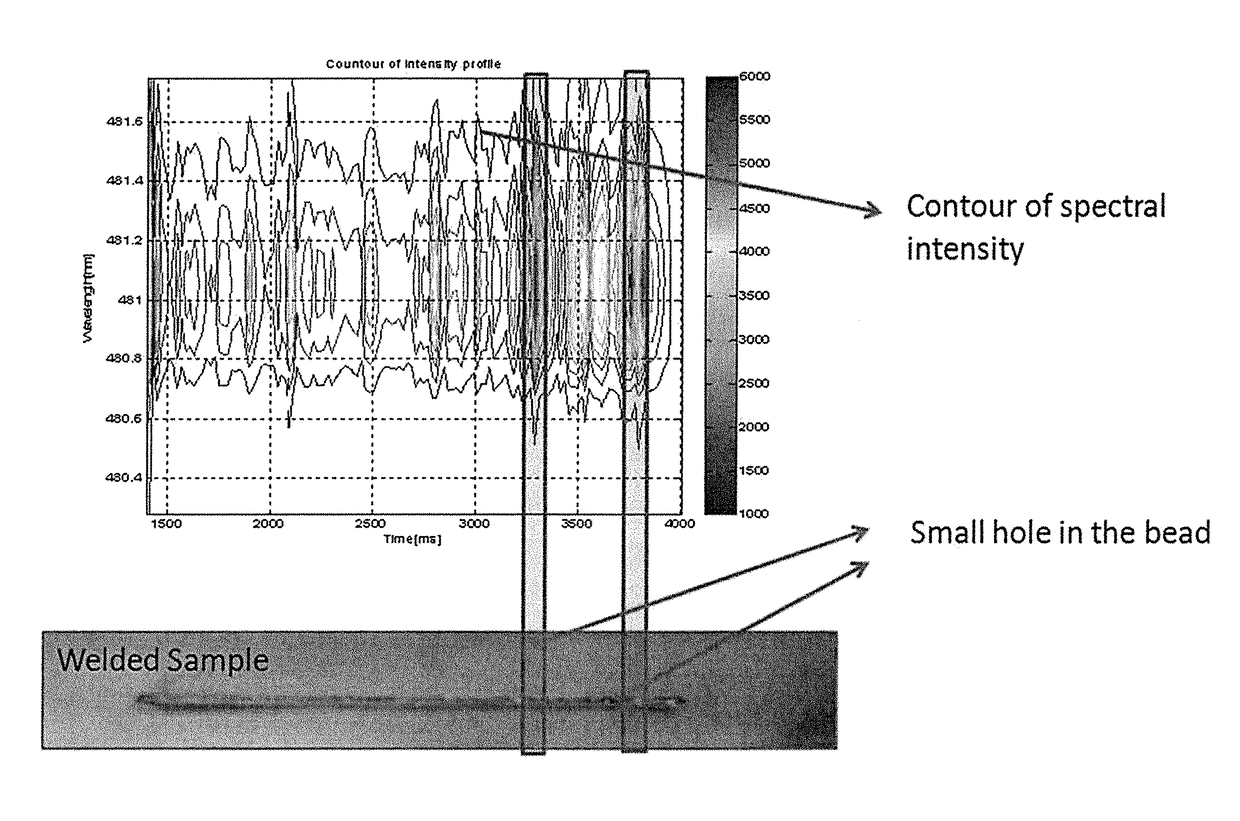
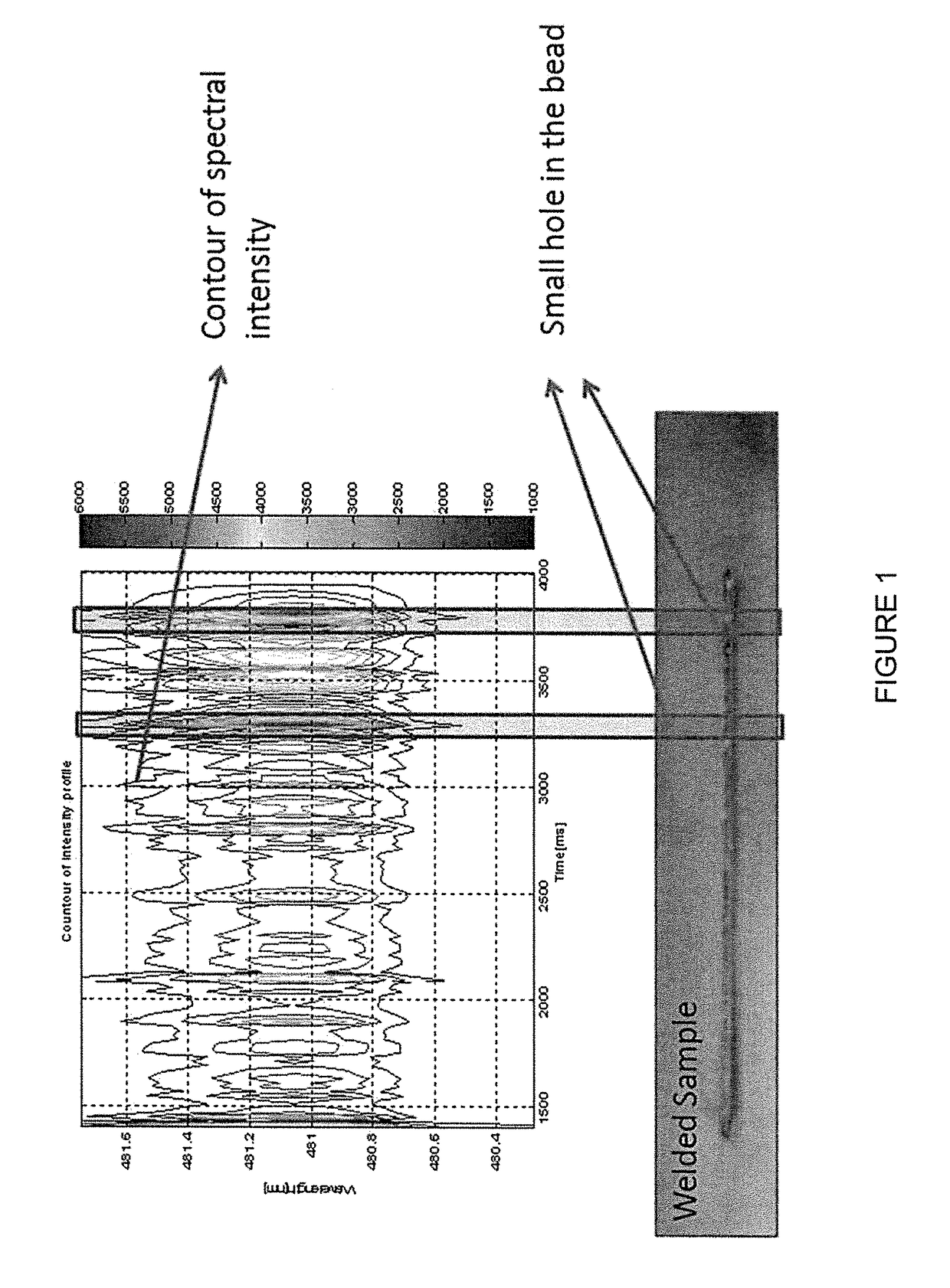
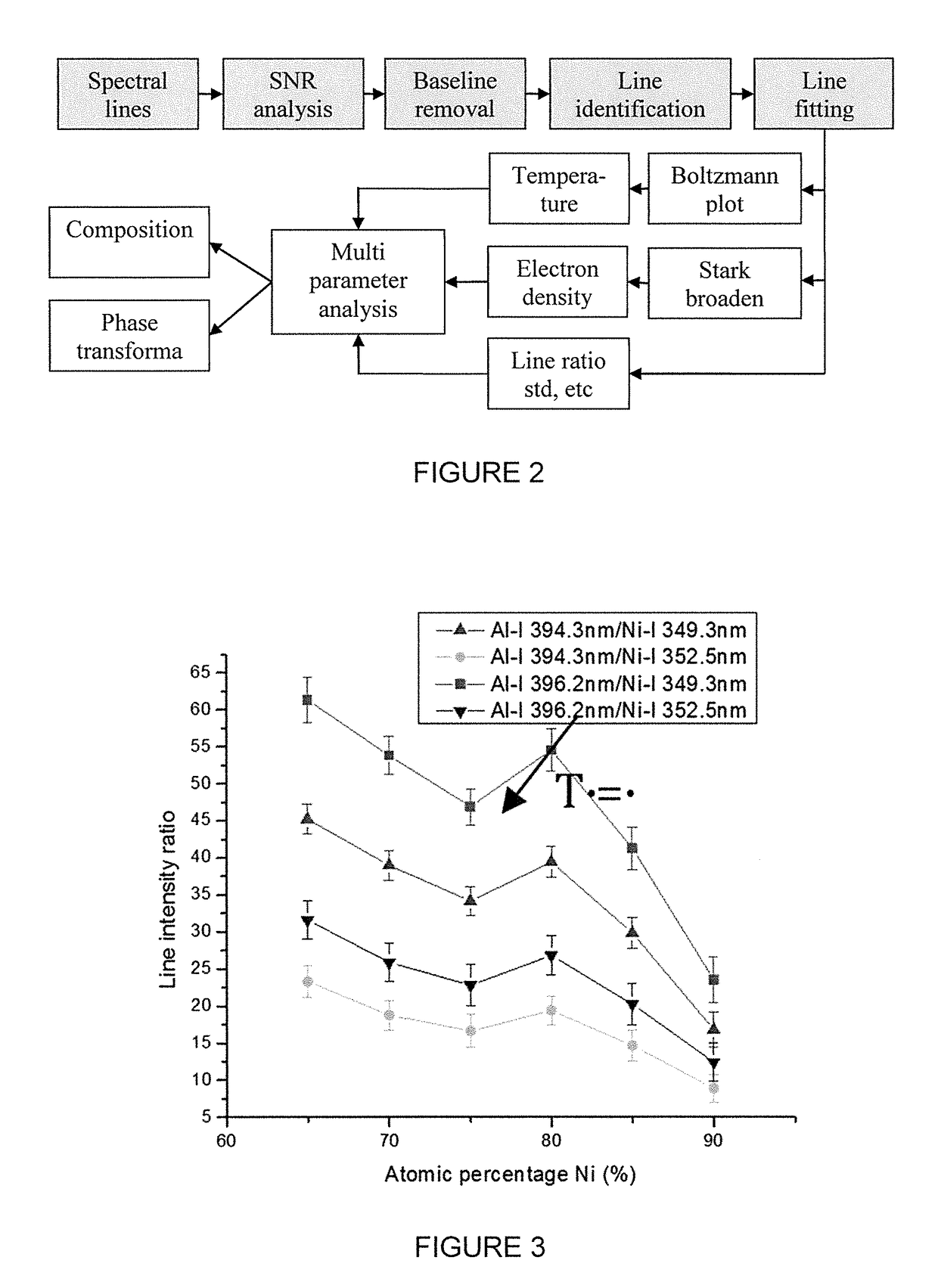
Smart additive manufacturing system (SAMS)
ActiveUS20160052086A1Additive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusEngineeringOptical emission spectrometry
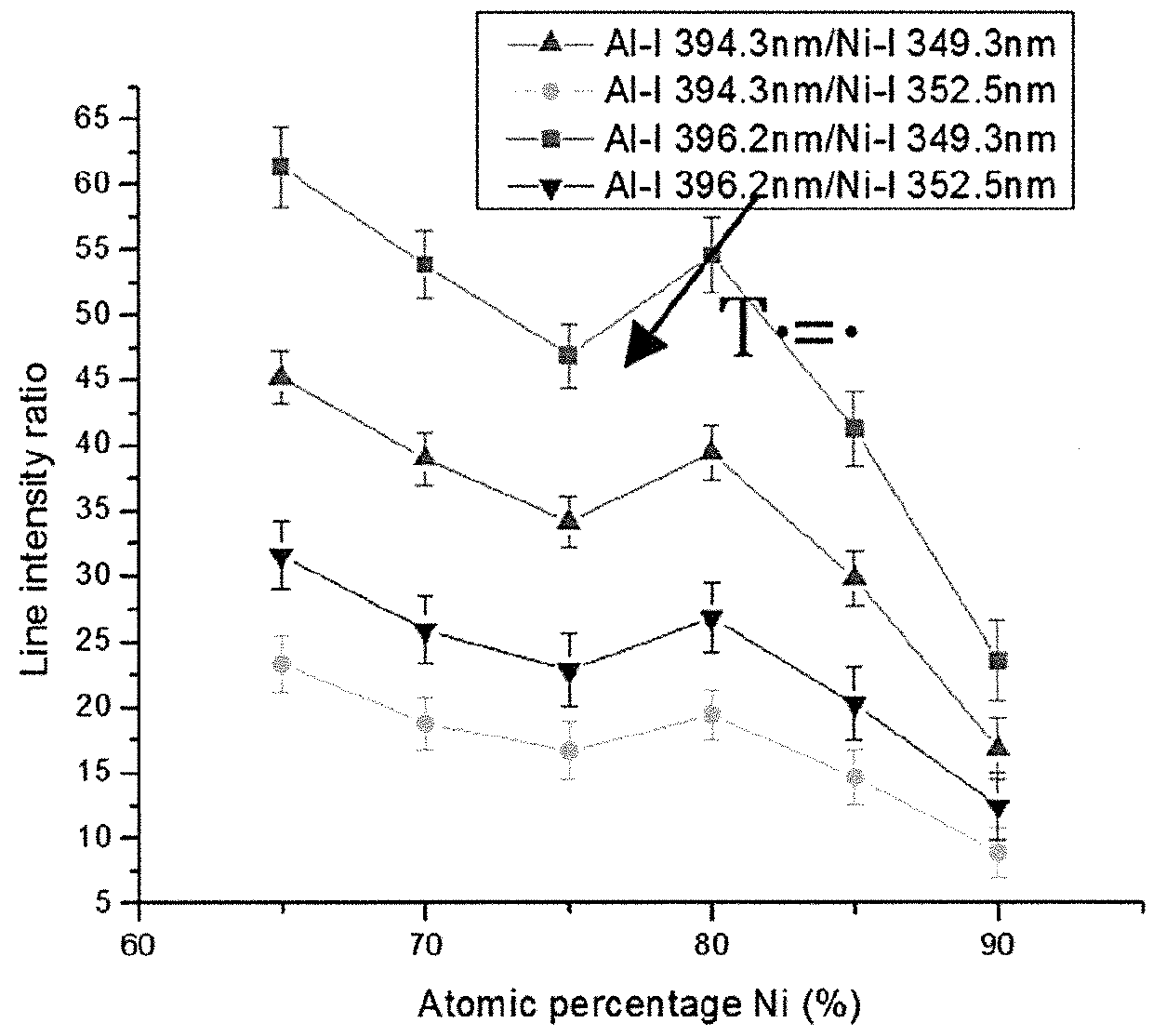
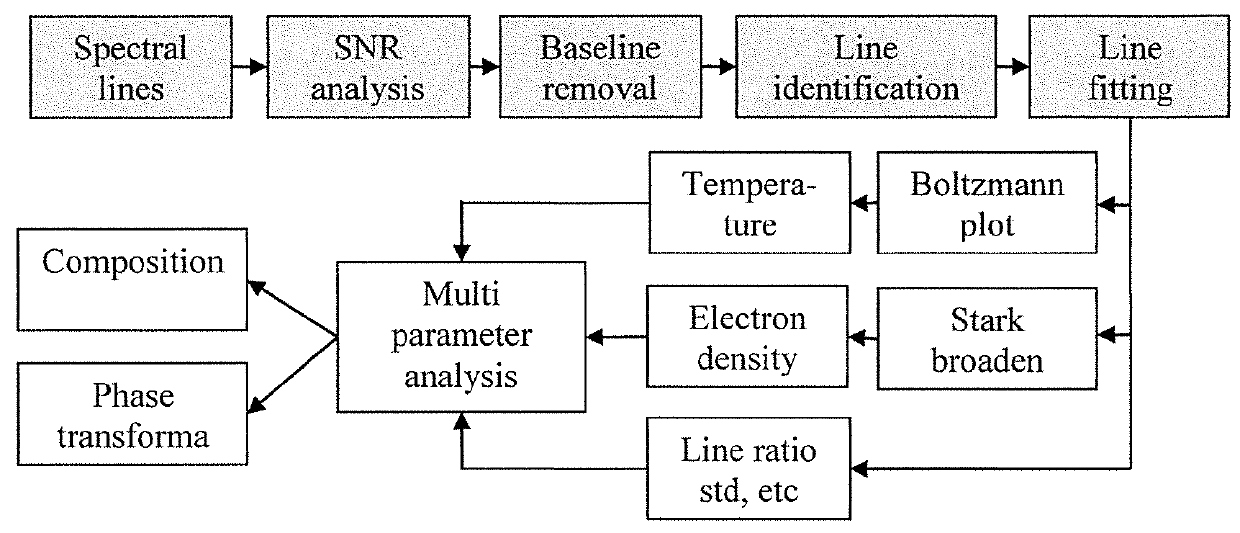
An additive manufacturing process is monitored, in situ, using optical emission spectroscopy to analyze the composition, phase transformation or manufacturing defects. The system or method may include an analysis of contours of the plasma line intensity, or pre-processing of the plasma spectral line including signal-to-noise ratio analysis, baseline removal, line identification, line de-convolution and fitting. Improvements may additionally involve consideration of plasma parameters such as plasma spectral line intensity, line ratio, plasma temperature and electron density using high-resolution optical emission spectroscopy in both visible and ultraviolet regions. Parameters of the plasma may be determined using an intensity ratio of the ions or atoms emission lines, a FWHM of the line profile for electron density estimation, or a Boltzmann plot for plasma temperature estimation. One or more techniques may be used to monitor when there is a lack of deposition.
Owner:MAZUMDER JYOTI +1
Selection of wavelengths for end point in a time division multiplexed process
InactiveUS20060006139A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesOptical emission spectrometryTime-division multiplexing
The present invention provides a method for establishing endpoint during an alternating cyclical etch process or time division multiplexed process. A substrate is placed within a plasma chamber and subjected to an alternating cyclical process having an etching step and a deposition step. A variation in plasma emission intensity is monitored using known optical emission spectrometry techniques. A first wavelength region is selected based on a plasma emission from an etch by product and a second wavelength region is selected based on a plasma emission from a plasma background. A ratio of the first wavelength region to the second wavelength region is computed and used to adjust the monitoring of an attribute of a signal generated from the time division multiplex process. The alternating cyclical process is discontinued when endpoint is reached at a time that is based on the monitoring step.
Owner:PLASMA THERM
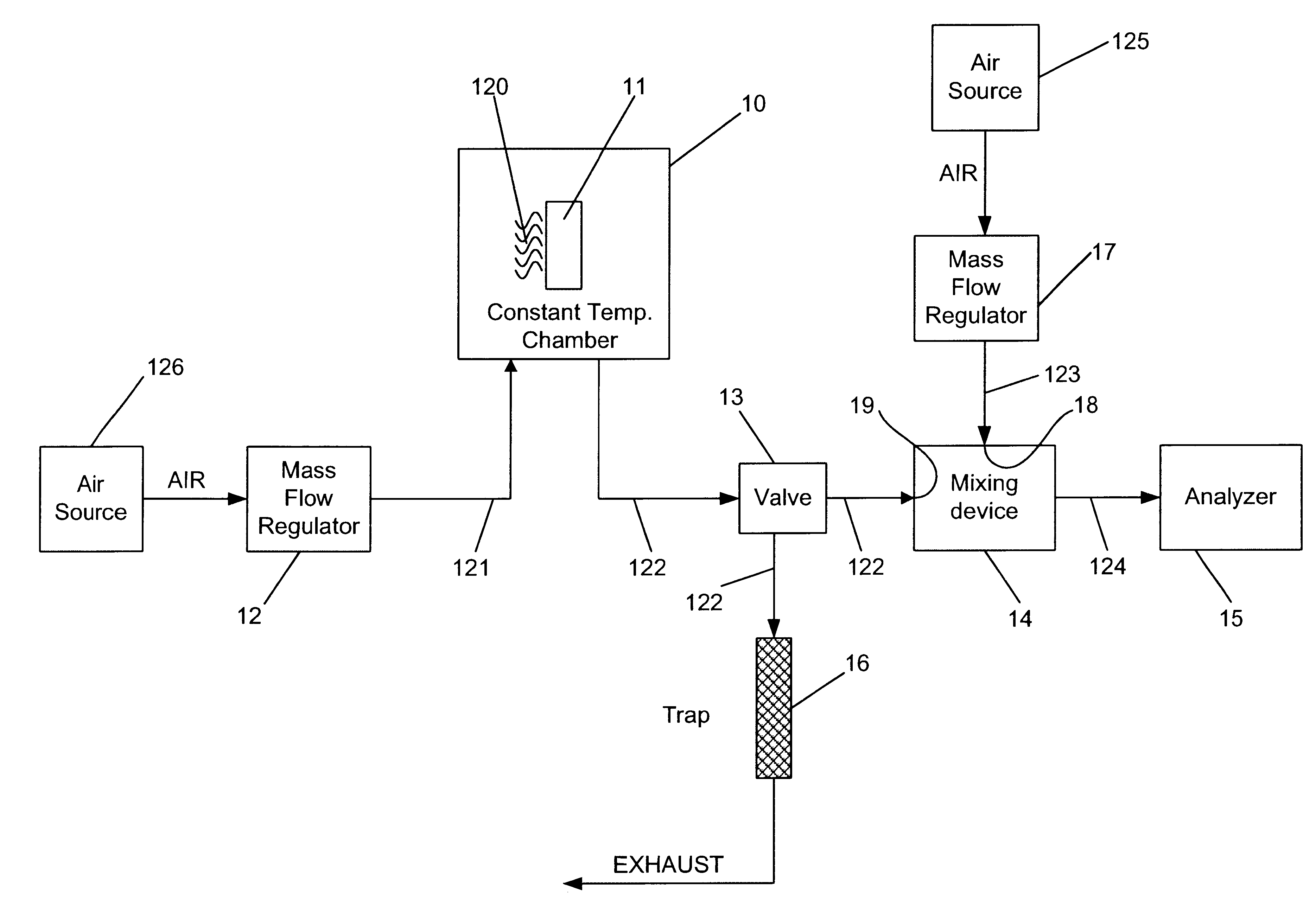
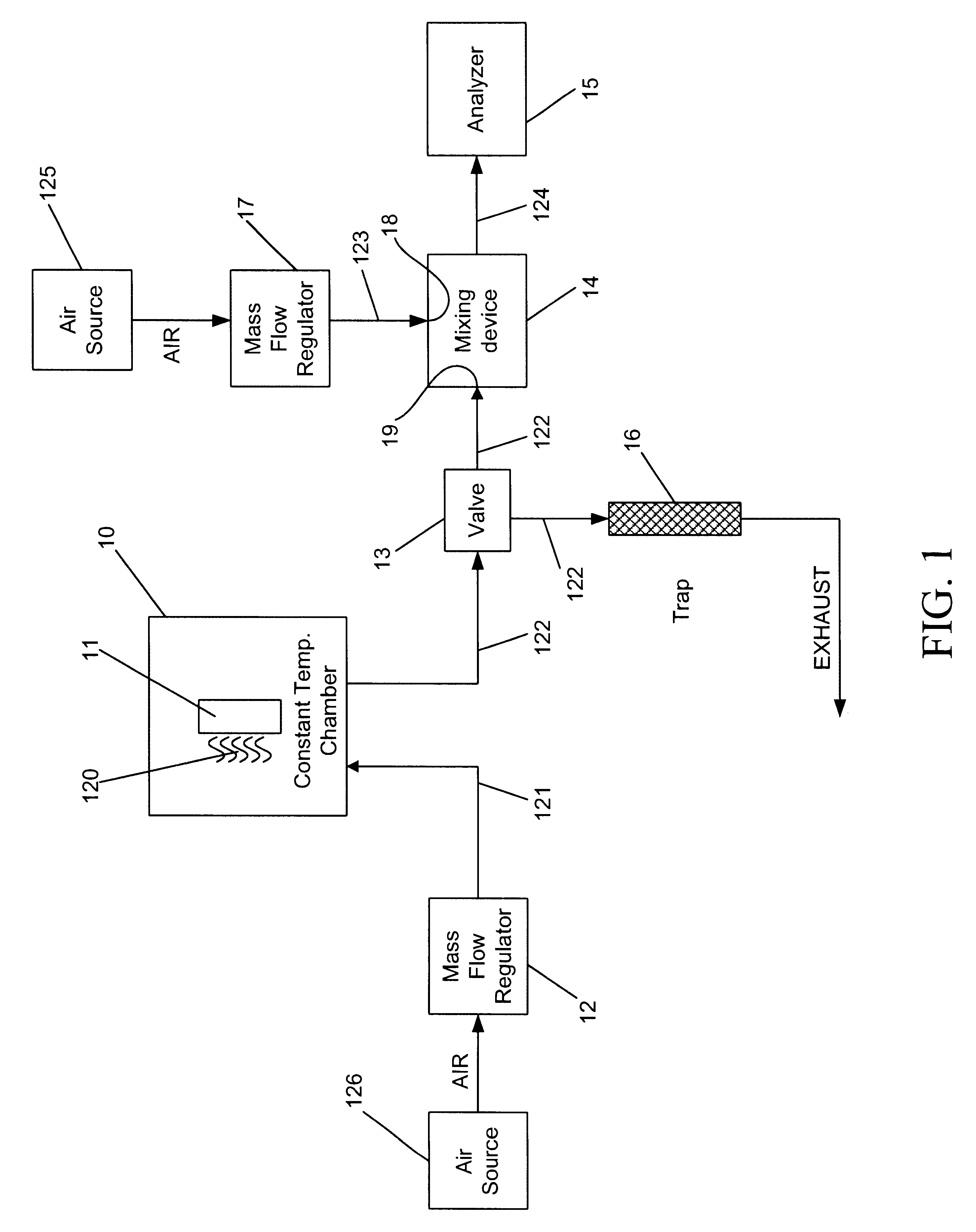
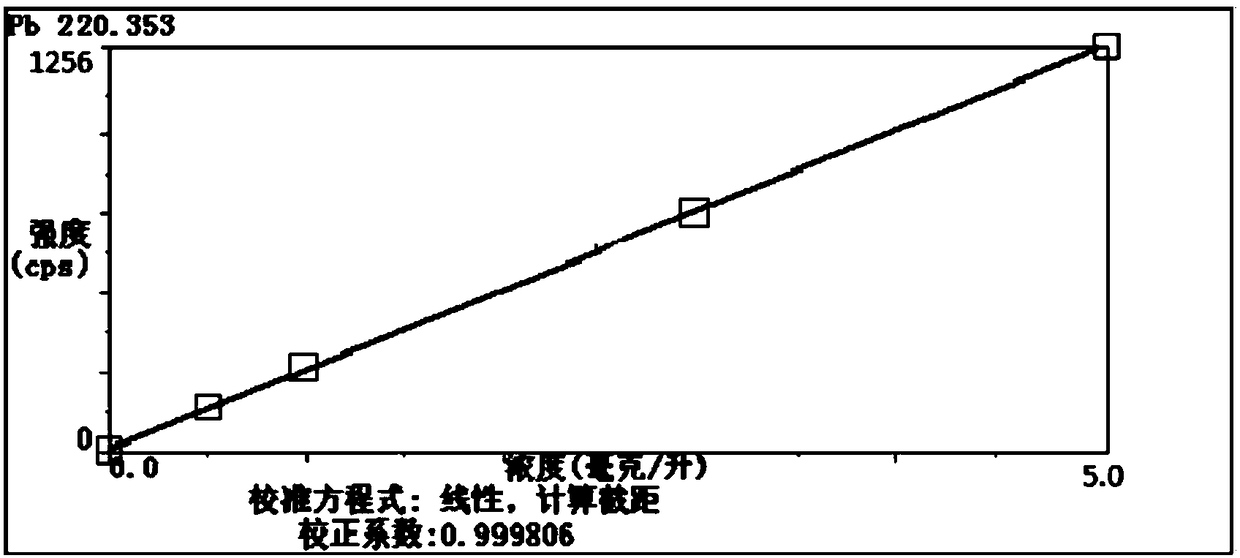
Calibration scheme for continuous monitoring of mercury emissions from stationary sources by plasma emission spectrometry
InactiveUS6690462B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLinear relationshipOptical emission spectrometry
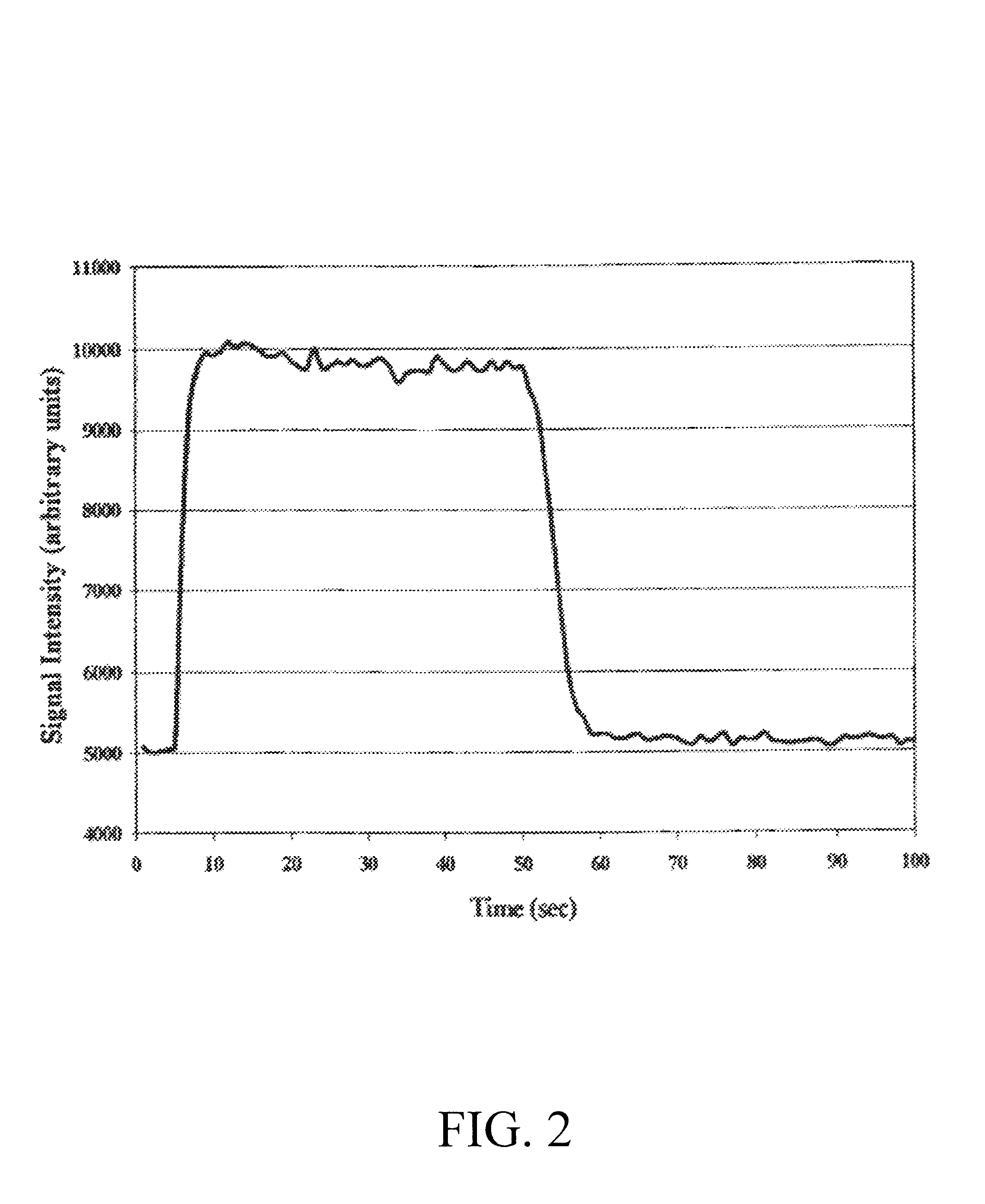
The disclosed invention relates to a calibration method, system and apparatus for a multimetals continuous emissions monitor system (hereinafter "multimetals CEMS"). More specifically, this invention relates to a calibration scheme for continuous monitoring of mercury emissions from stationary sources by plasma emission spectrometry. A source of mercury vapor, preferably a mercury permeation tube, entrains mercury vapor into a constant flow of carrier air. The carrier air mixes with a constant flow of diluent air in an aerosol mixer. The mixer is operably coupled to the analyzer. A gaseous mixture having a calibration mercury concentration flows from the mixer into the analyzer at a constant rate. A graph having coordinates of analyzer signal intensity and mercury concentration is used to plot the calibration scheme. A first signal intensity generated by the analyzer in response to the calibration mercury concentration is used for the first plot on the graph. A second signal intensity generated by the analyzer in response to a blank having zero mercury concentration is used as the second plot on the graph. A linear relationship between the analyzer signal intensity and the mercury concentration on the graph is established from the first plot and the second plot. The slope intercept and slope are used to create a mathematical relationship between the analyzer signal intensity and the mercury concentration. This enables the analyzer to be calibrated by inserting a known mercury concentration into the analyzer and adjusting the signal intensity to conform to the signal intensity calculated from the graph or mathematical relationship.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
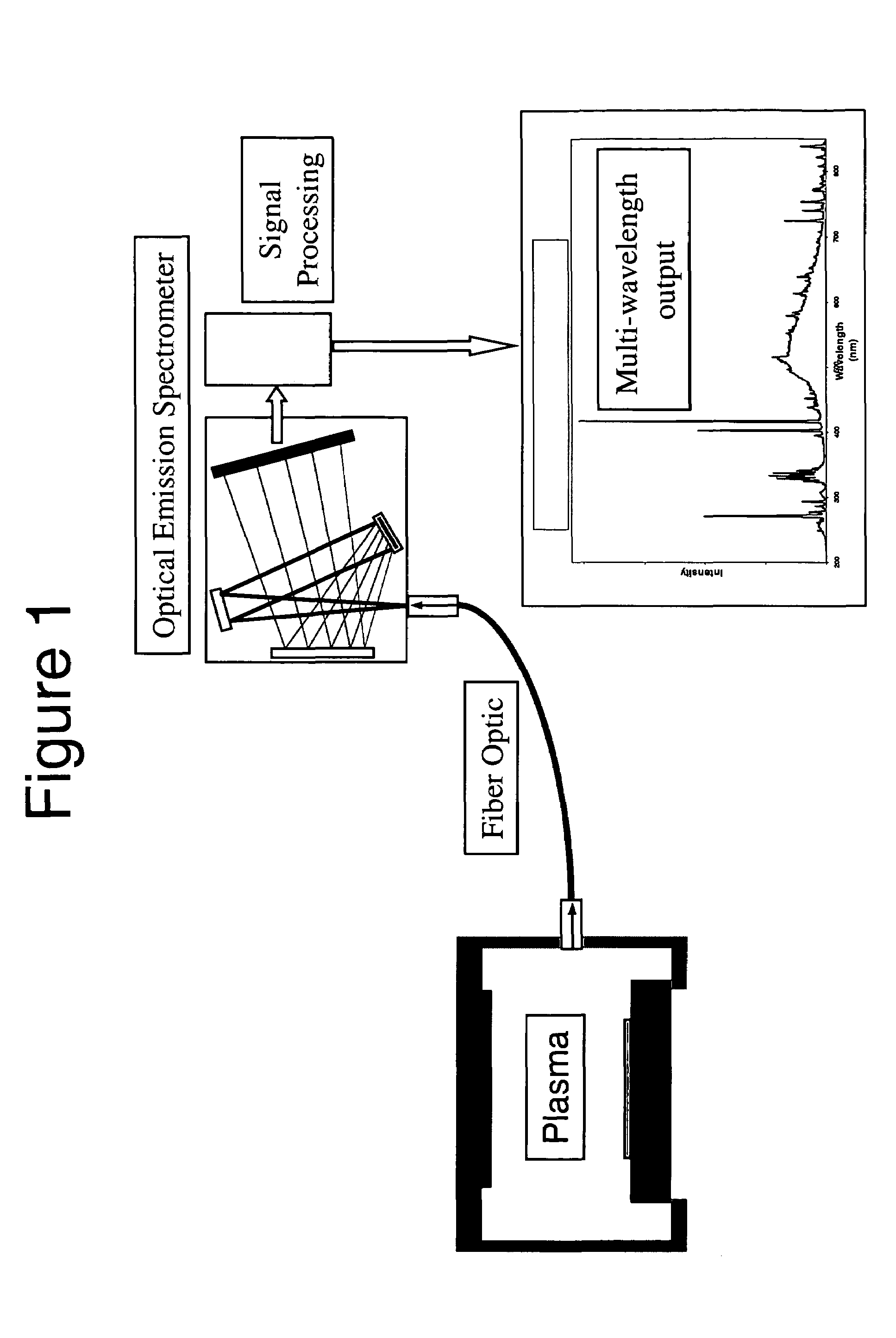
Optical Emission Spectroscopy Process Monitoring and Material Characterization
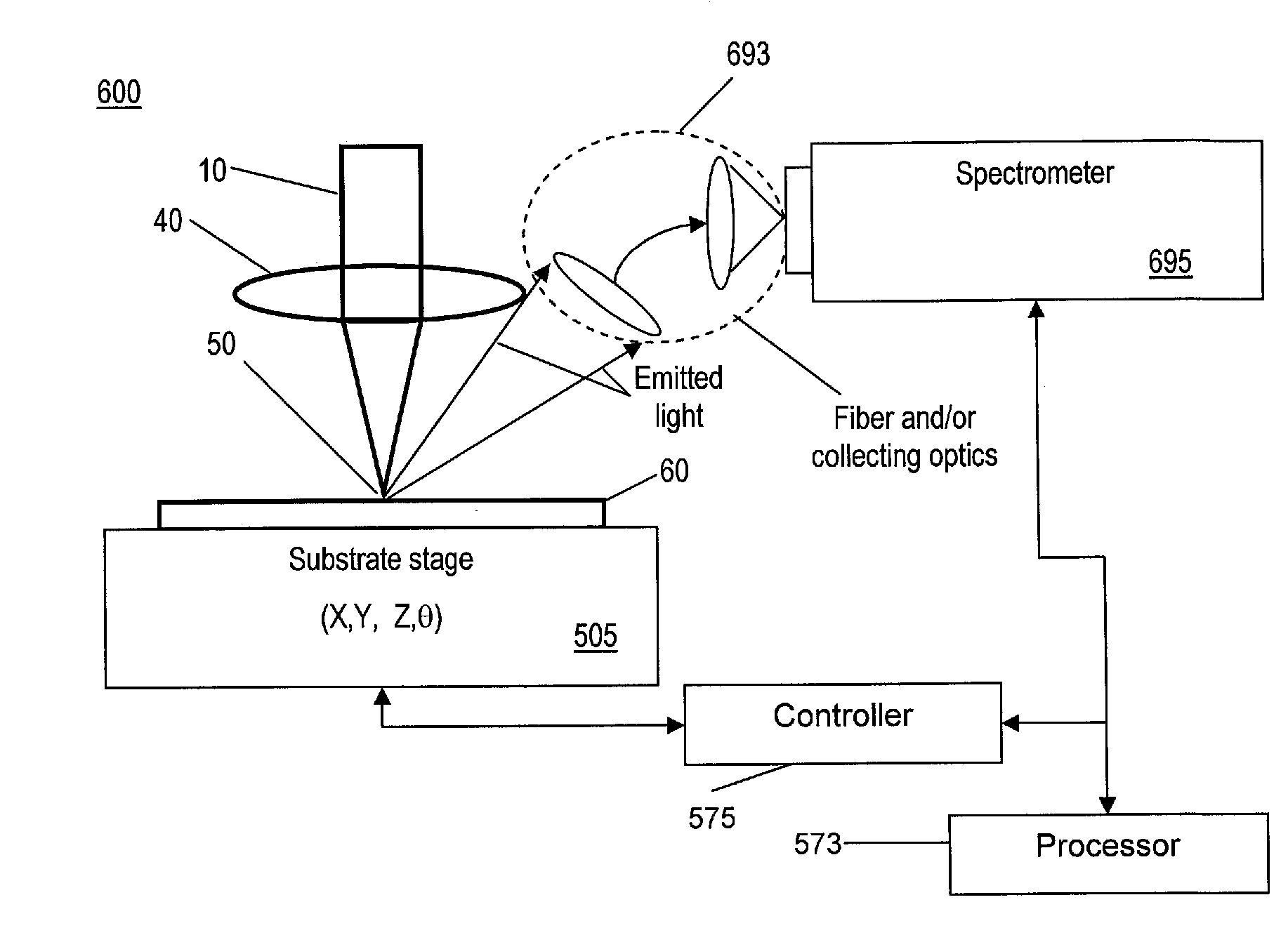
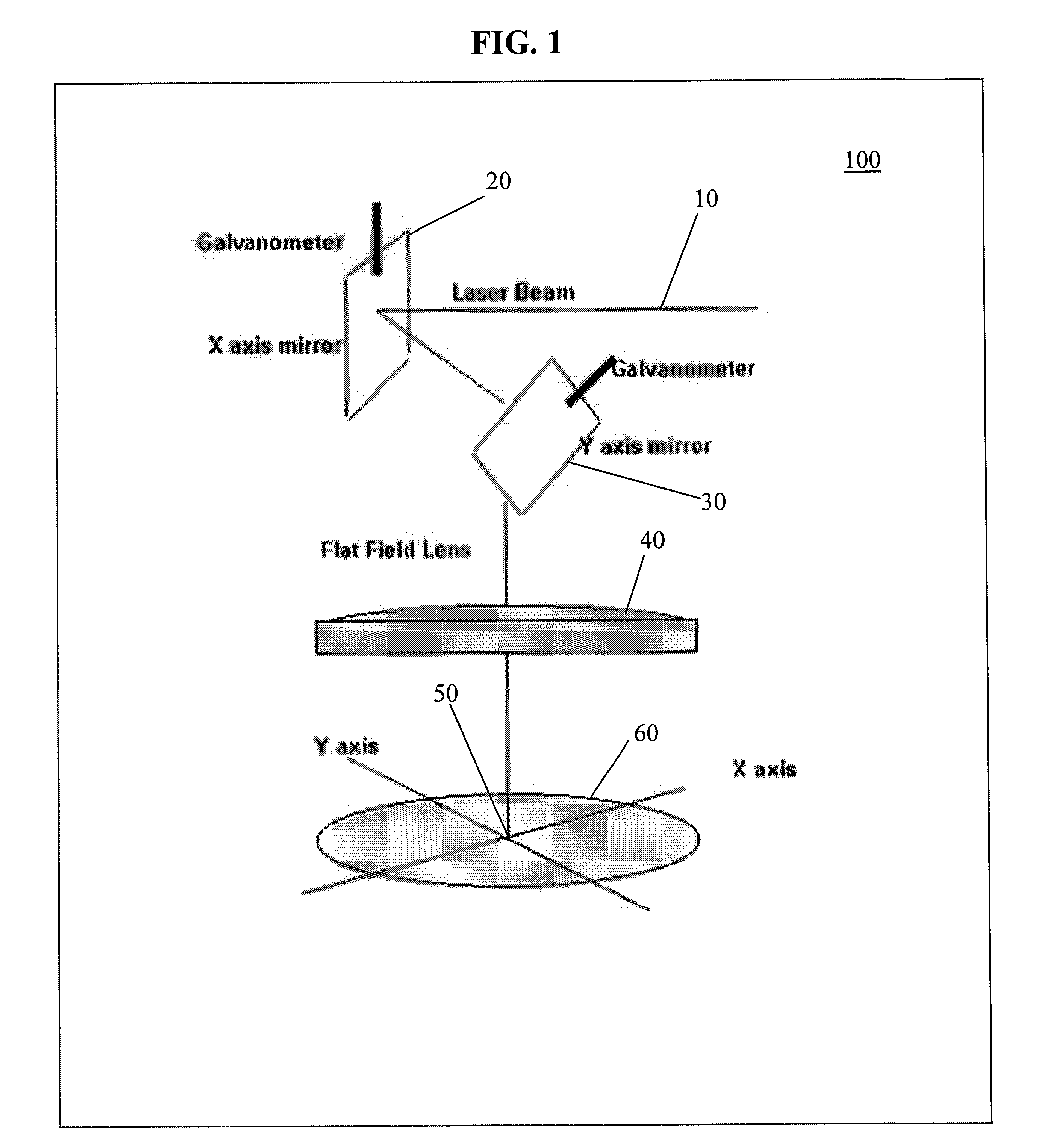
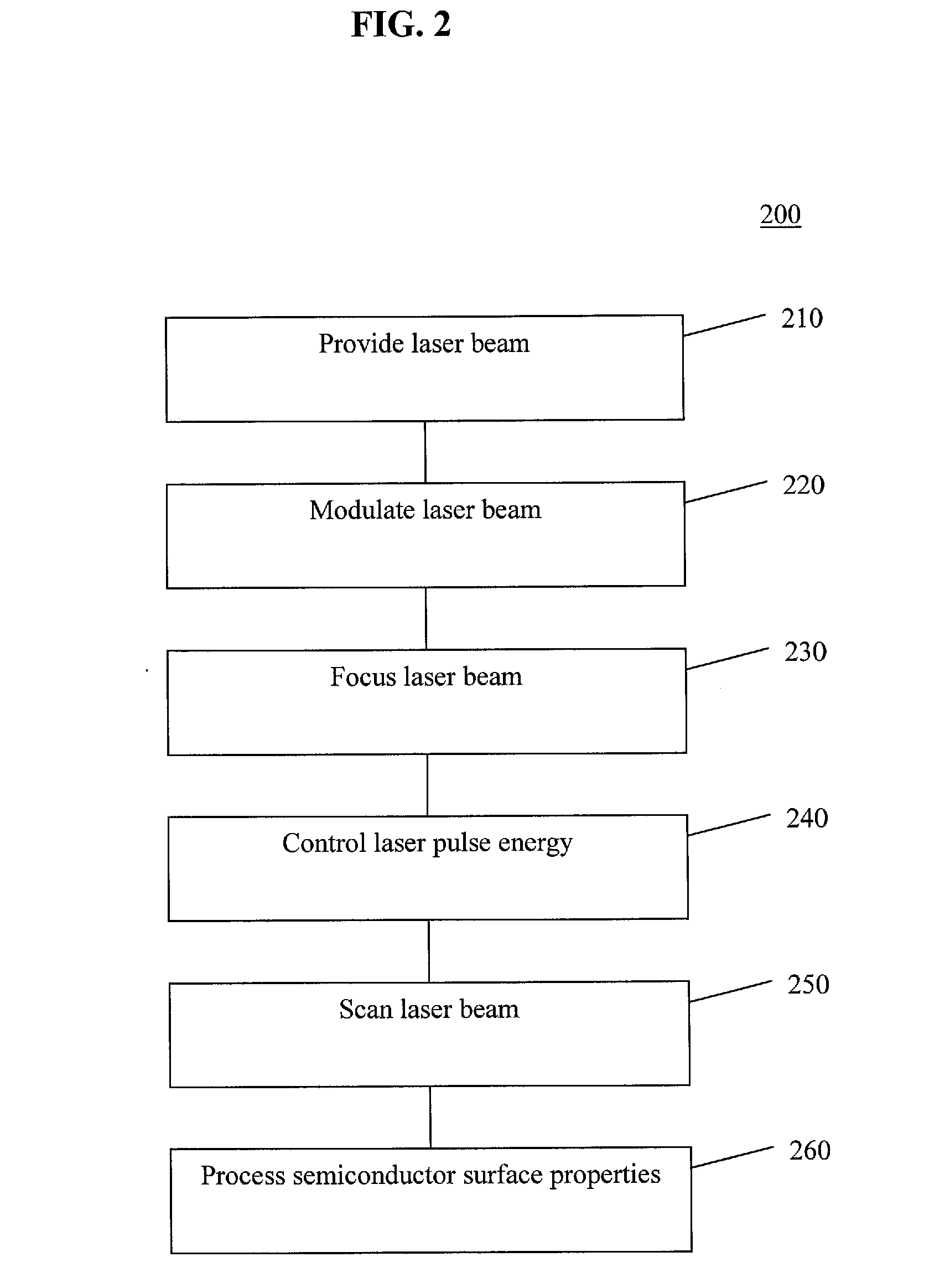
Methods and systems for control and monitoring processing of semiconductor materials with a focused laser beam. Laser light may be focused on a sample to excite optical emission at the sample surface during processing, which may include laser processing. Optical emission spectra produced may be analyzed for various properties effectively during the process. For example, process effects such as chemical composition analysis, species concentration, depth profiling, homogeneity characterization and mapping, purity, and reactivity may be monitored by optical spectral analysis. The wavelength may be selected to be appropriate for the process effect chosen.
Owner:WAFERMASTERS
Controlling dry etch process characteristics using waferless dry clean optical emission spectroscopy
InactiveUS20170287791A1Slow changeMinimize deposition build-upSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesOptical emission spectrometryEngineering
Described herein are architectures, platforms and methods for acquiring optical emission spectra from an optical emission spectroscopy system by flowing a dry cleaning gas into a plasma processing chamber of the plasma processing system and igniting a plasma in the plasma processing chamber to initiate the waferless dry cleaning process.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Digestion method of detection of heavy metals in soil
InactiveCN104931330AReduce dosagePromote digestionPreparing sample for investigationEarth material testingHydrofluoric acidOptical emission spectrometry
The invention discloses a digestion method of detection of heavy metals in soil. The digestion method is characterized by comprising the following steps: only adding a small amount of nitric acid and a small amount of hydrofluoric acid into a sample; after leaving the mixture to stand overnight, digesting on a graphite digestion device at a certain temperature to completely digest the soil sample; detecting with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry or inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. The digestion method is accurate and reliable, and meets the detection demands.
Owner:DALIAN PONY TESTING TECH CO LTD
Method for measuring plasma electron density by fiber spectrum synergizing discharge current
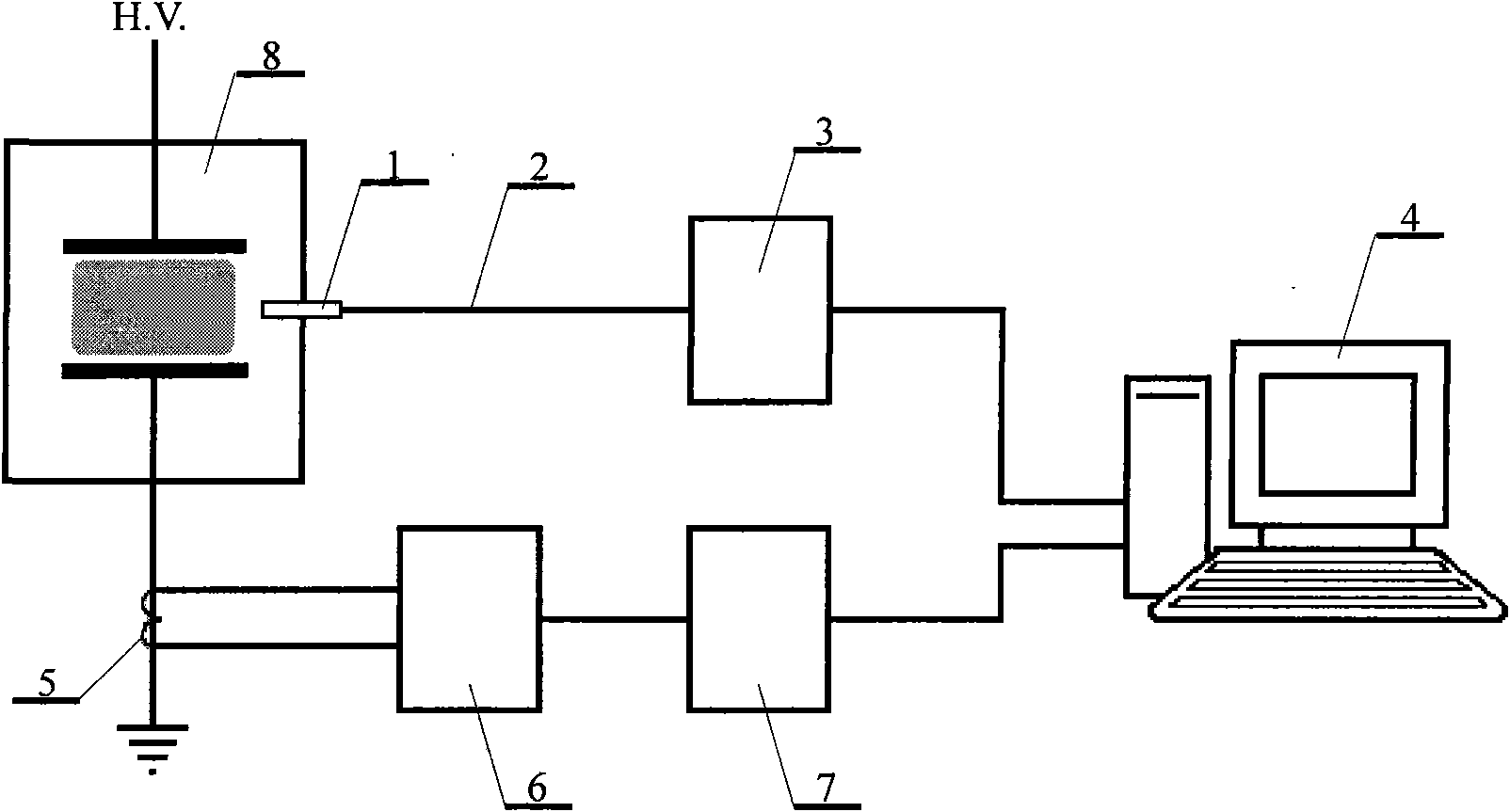
InactiveCN101566501AIncrease flexibilityReduce biasRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical radiationPlasma electron
The invention relates to a method for measuring plasma electron density by fiber spectrum synergizing discharge current, and belongs to the technical field of discharge plasma diagnosis. The method is technically characterized by comprising the following steps: using a micro fiber spectrum measuring path and a discharge current measuring circuit at the same time to acquire real-time parameters of optical radiation spectrum of discharge plasma and discharge current, comprehensively analyzing the parameters through a computer data processing system, and calculating the electron density of the plasma. The micro fiber spectrum measuring path consists of a fiber probe, a conducting fiber and a micro fiber spectrometer, which are connected in turn; the discharge current measuring circuit consists of a current sensor, a current signal amplifier and a data acquisition device, which are connected in turn; and the computer data processing system calculates the electron density of the discharge plasma by using the acquired data according to the gas molecule motion theory. The method has the advantage that the application range of the discharge plasma electron density diagnosed by optical emission spectrometry is expanded to an imbalance state from a local thermal balance state.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
In-situ process diagnostics of in-film aluminum during plasma deposition
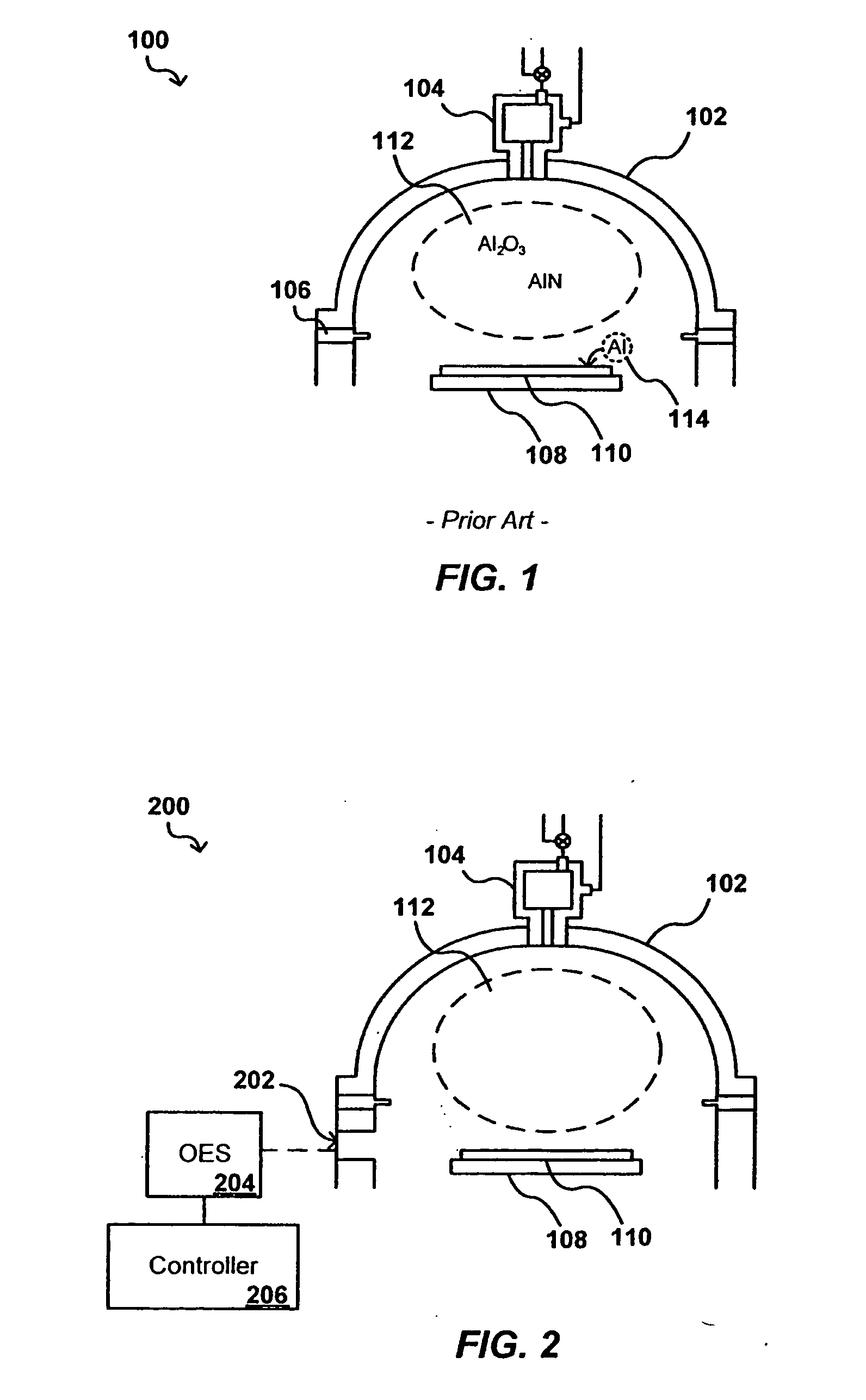
InactiveUS20080029484A1Less expensiveReduce the amount requiredElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsOptical Emission SpectrometerPlasma deposition
The concentration of various contaminants in a plasma can be monitored during processing of a substrate such as a silicon wafer, in order to prevent an unacceptable amount of contamination from being deposited on the substrate. The radiation emitted from the plasma through a window in the processing chamber during processing can be detected and measured by a tool such as an optical emission spectrograph (OES) and the relative intensity of peaks in the spectrum corresponding to various contaminants can be analyzed in order to determine contaminant concentration. In one embodiment, the concentration of aluminum in a plasma is monitored during a plasma chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process in order to ensure that the amount of aluminum in the produced device is lower than a maximum threshold amount.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
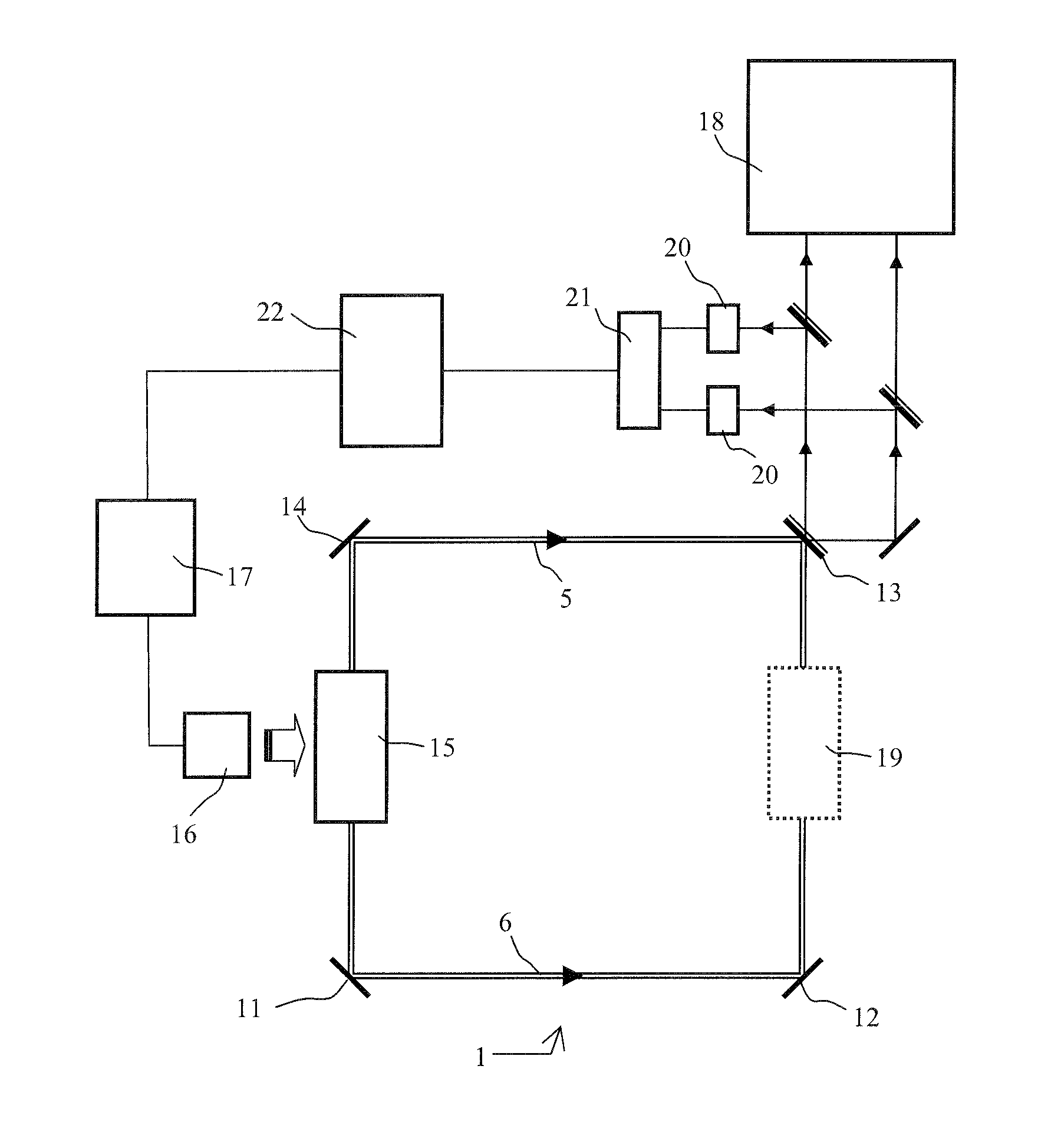
Elementary analysis device by optical emission spectrometry on laser produced plasma
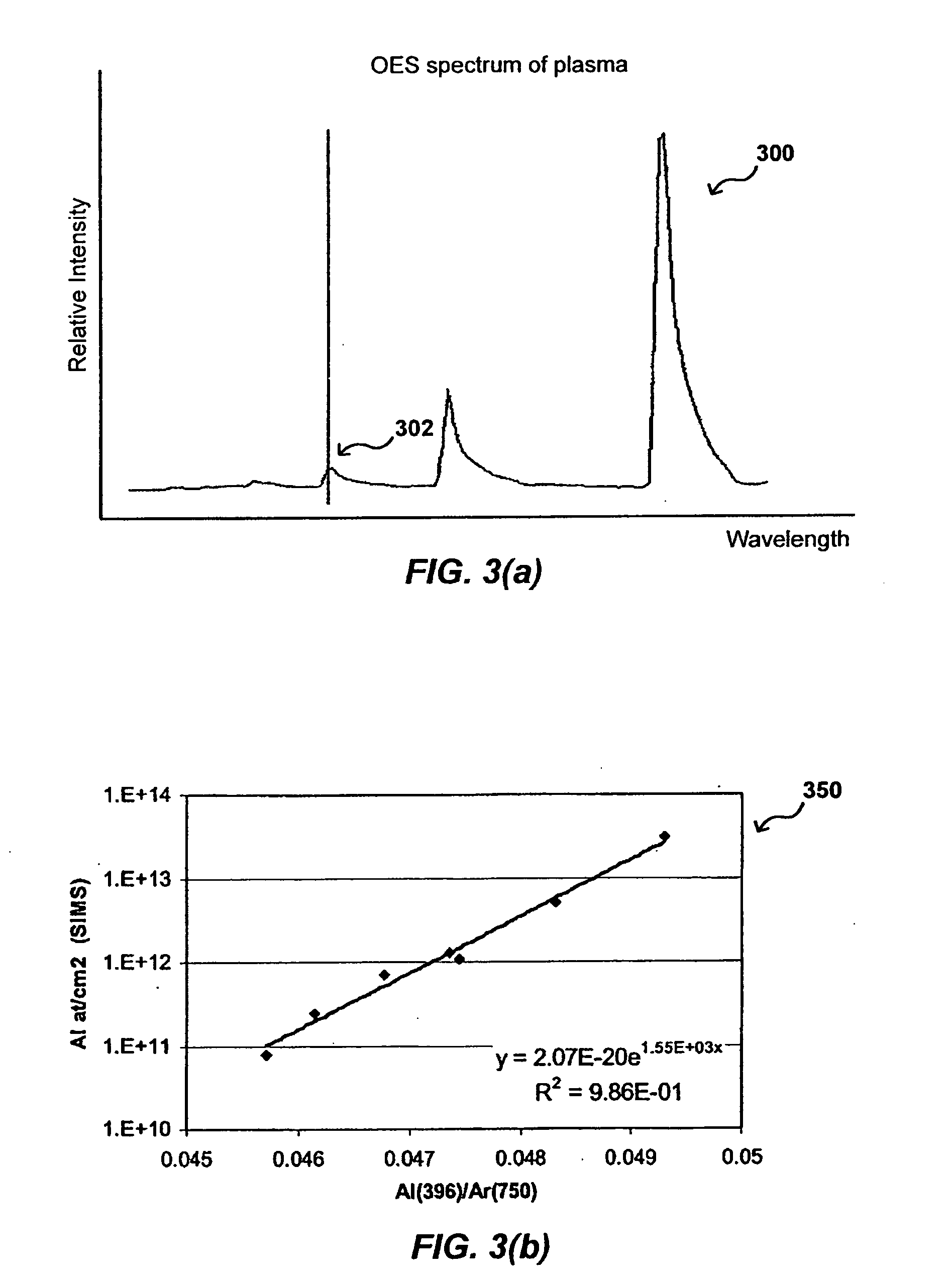
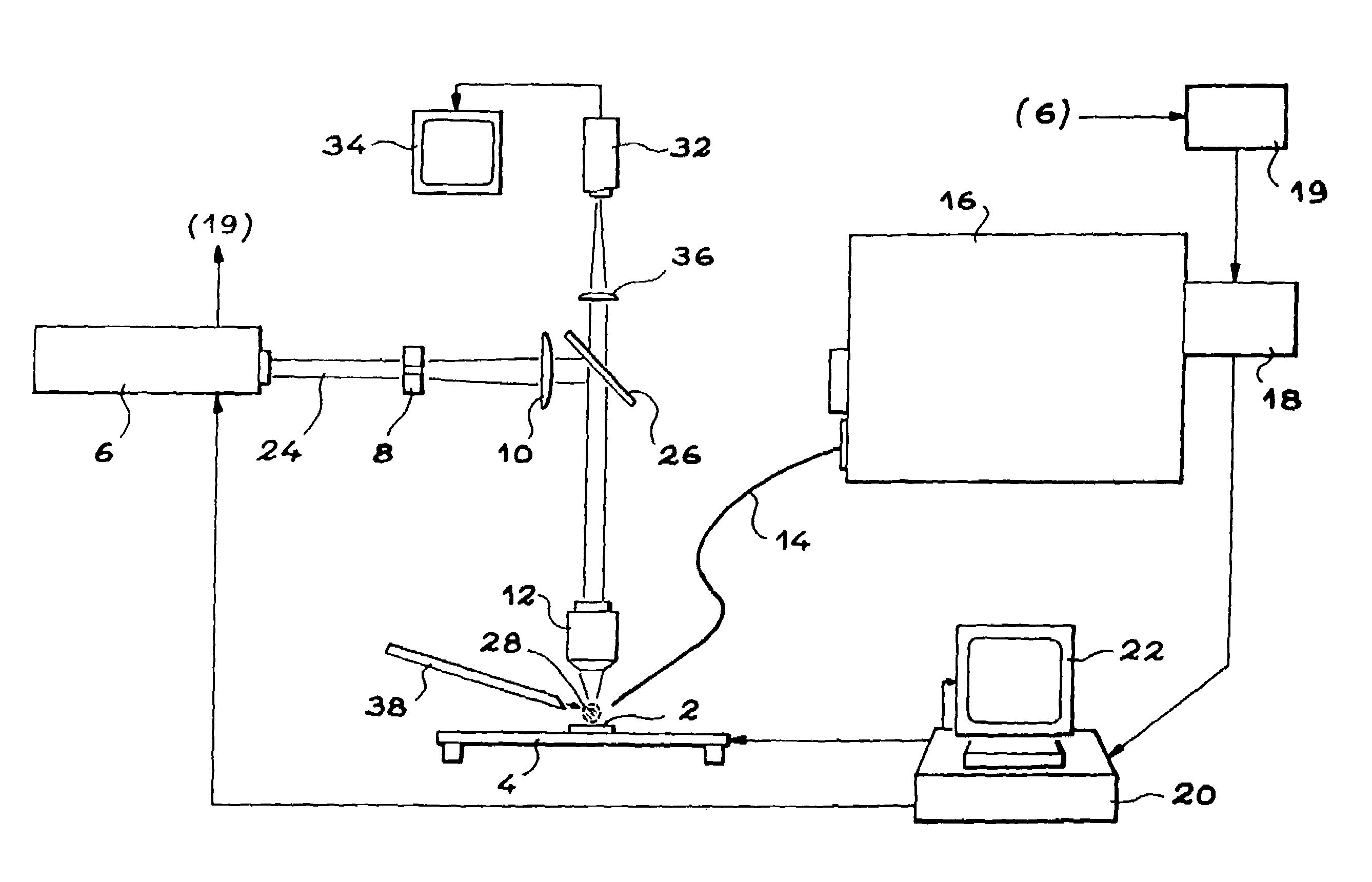
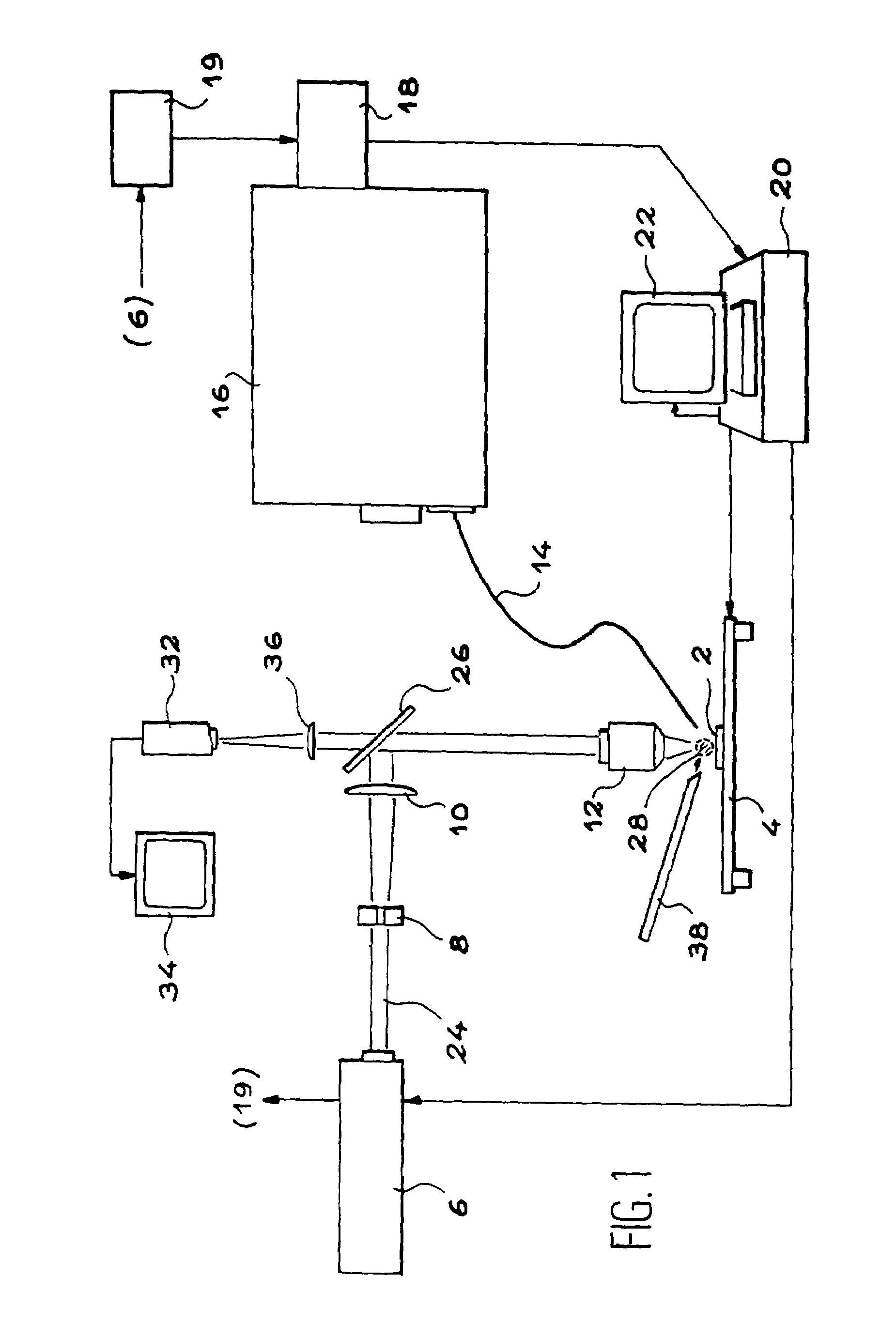
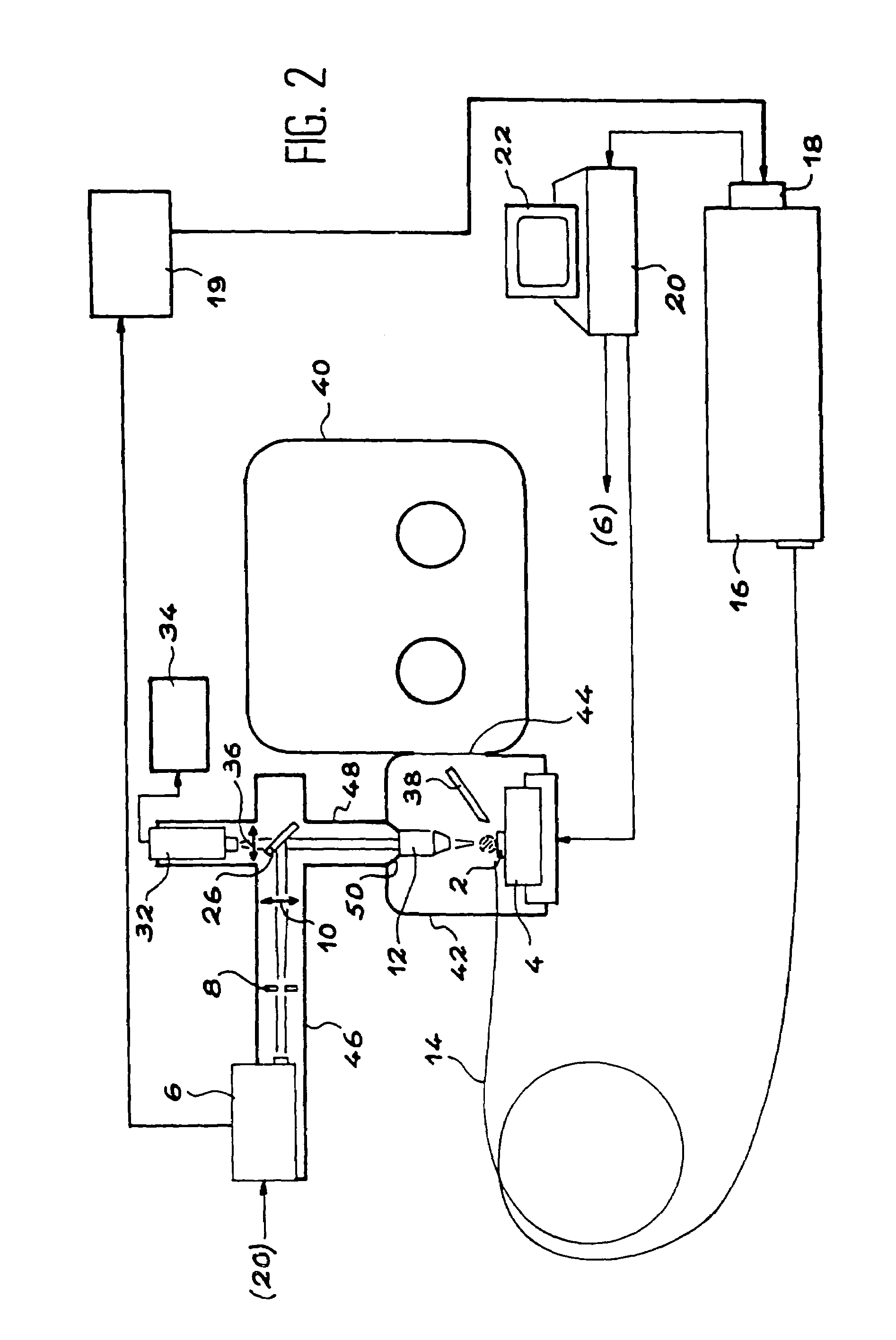
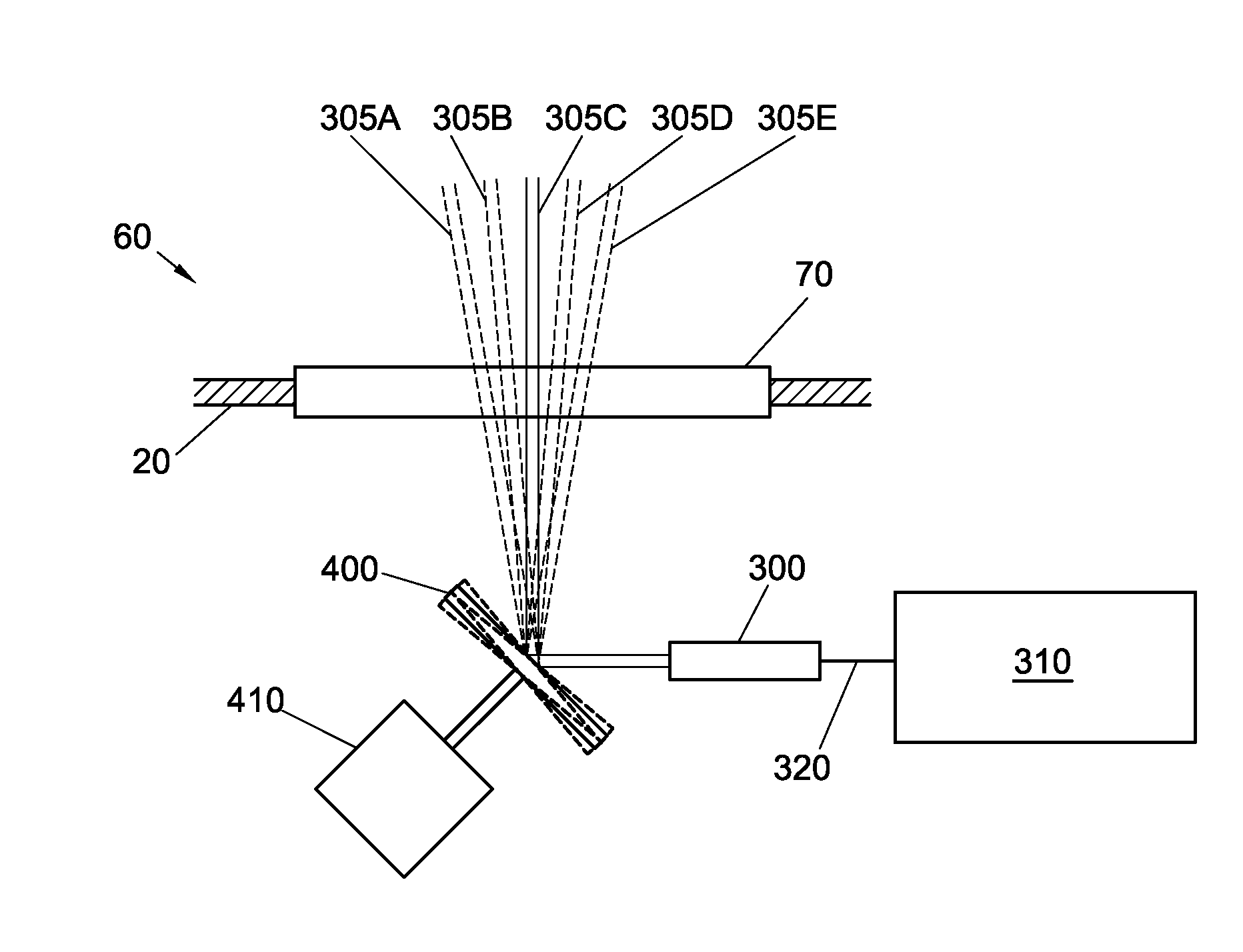
InactiveUS7106439B2Minimize degradationImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical emission spectrometryLaser source
This device comprises a pulsed laser source (6), means (8, 10, 12) for focusing light from this source onto an object to be analysed (2) to produce plasma on the surface of the object, means (16, 18) of analyzing a plasma radiation spectrum, means (20) of determining the elementary composition of the object from this analysis, and possibly means (4) for displacing the object. The invention is particularly applicable to test radioactive materials.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method for analysis of a molten material, device and immersion sensor
InactiveUS20060250614A1Easy to analyzeReduce economic costsEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySlagOptical emission spectrometry
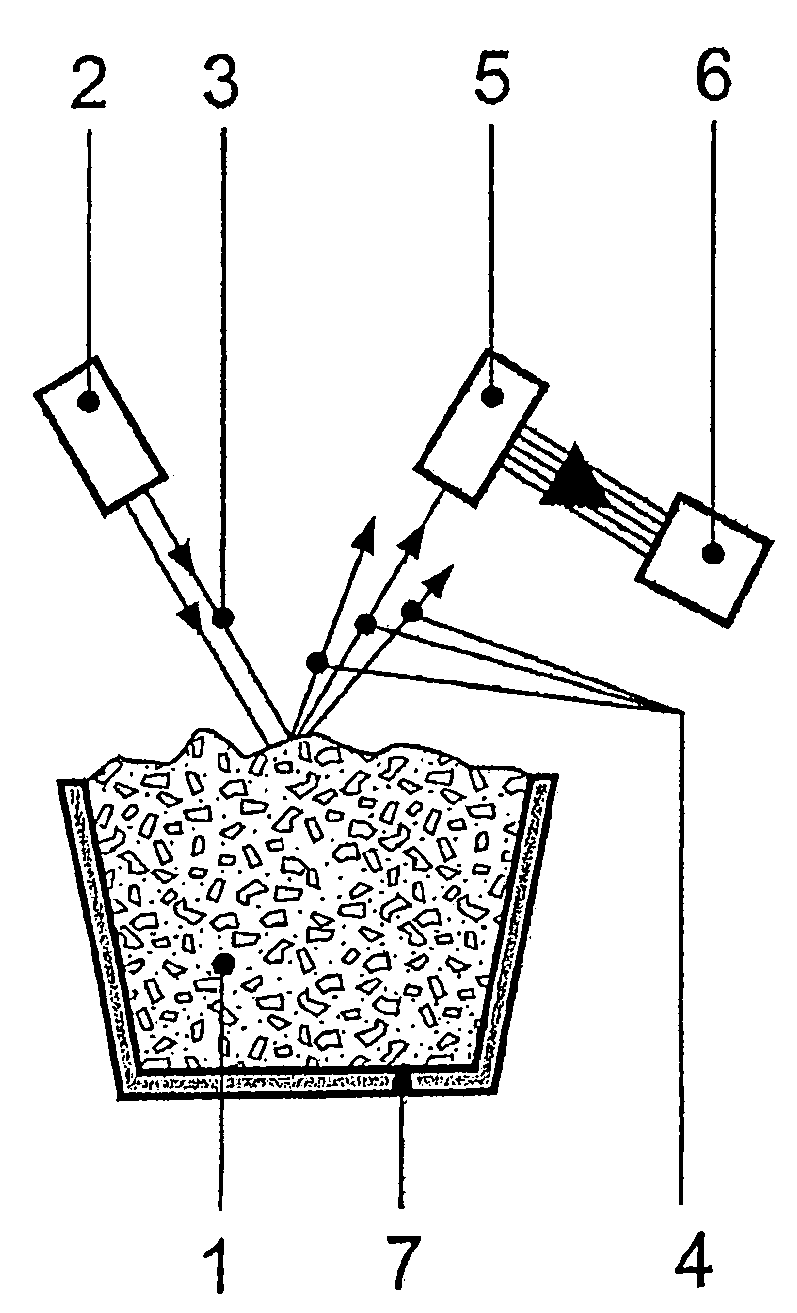
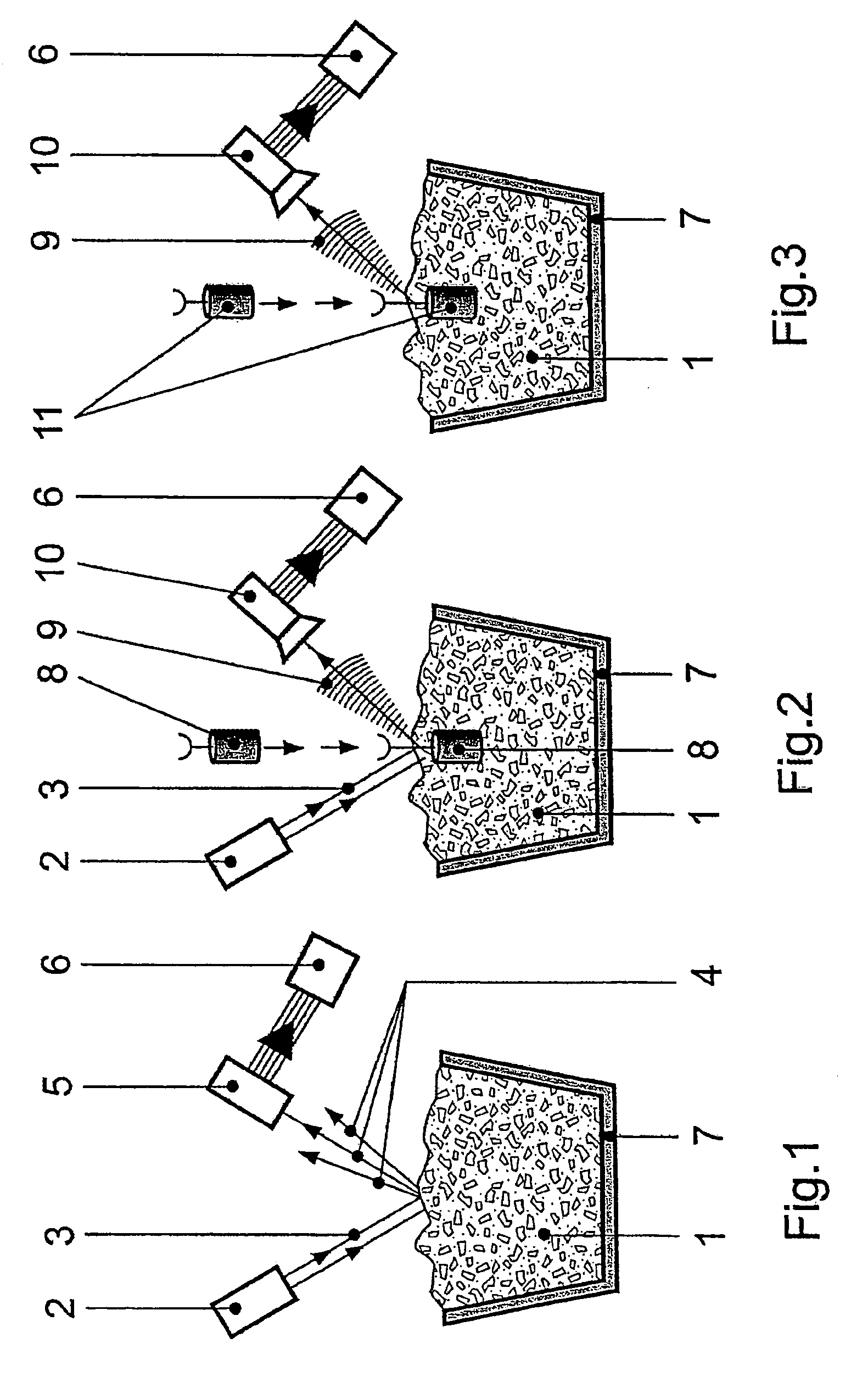
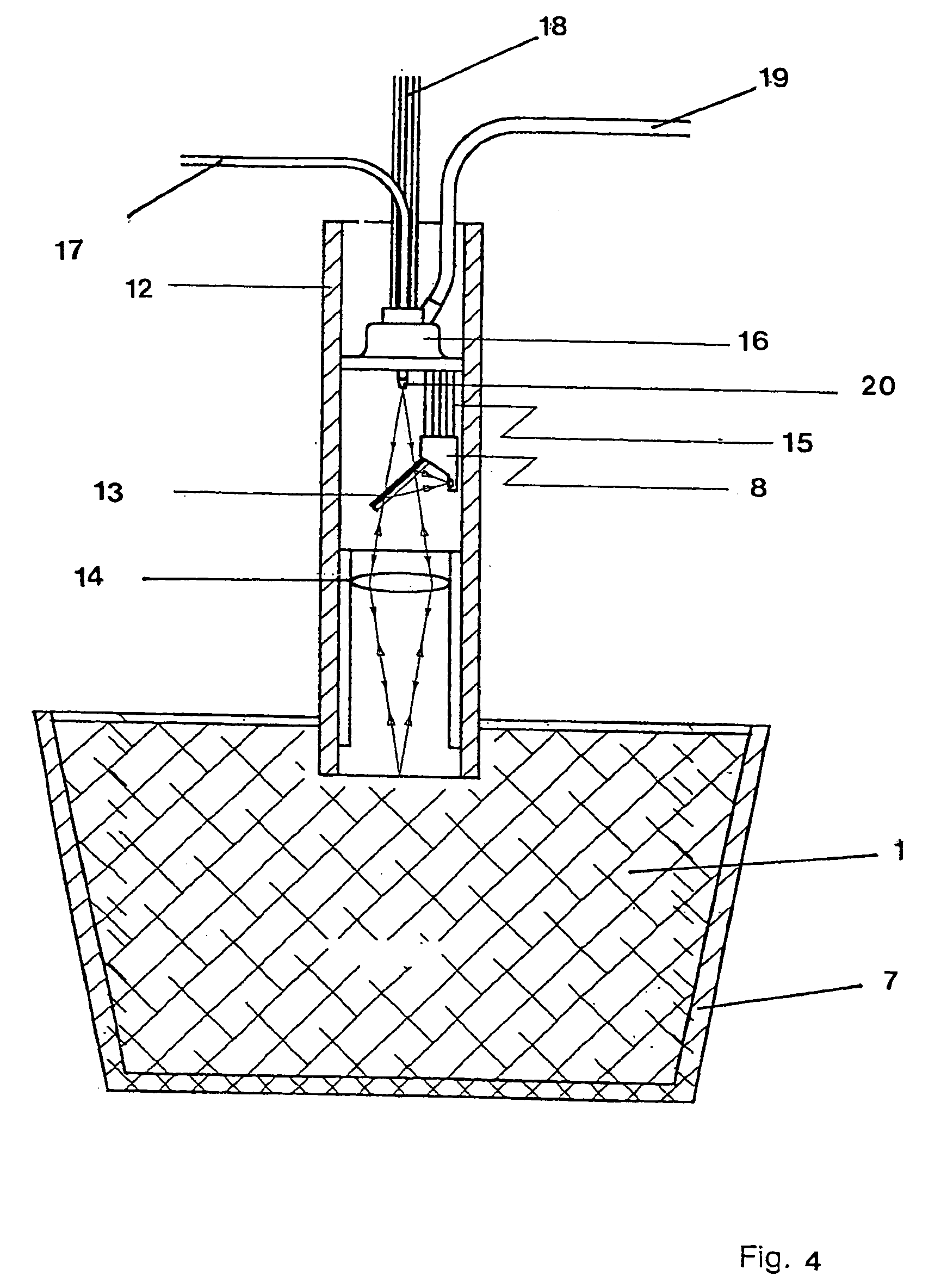
A method and device are provided for analysis of a molten material using optical emission spectrometry. The molten material may be, for example, a molten metal, such as casting iron or steel, or slag, glass, or lava. A sensitive element is used having at least one emission spectrometer and at least one excitation device to effect the excitation of the molten material and to enable the partial or complete generation of a radiation to be analyzed by a spectrometer present in the sensitive element. The sensitive element is brought into contact with the molten material and transmits information, which contains analysis elements supplied by the spectrometer. An immersion sensor is also provided for carrying at least part of the device for performing the analysis method.
Owner:HERALUS ELECTRO NITE INT NV
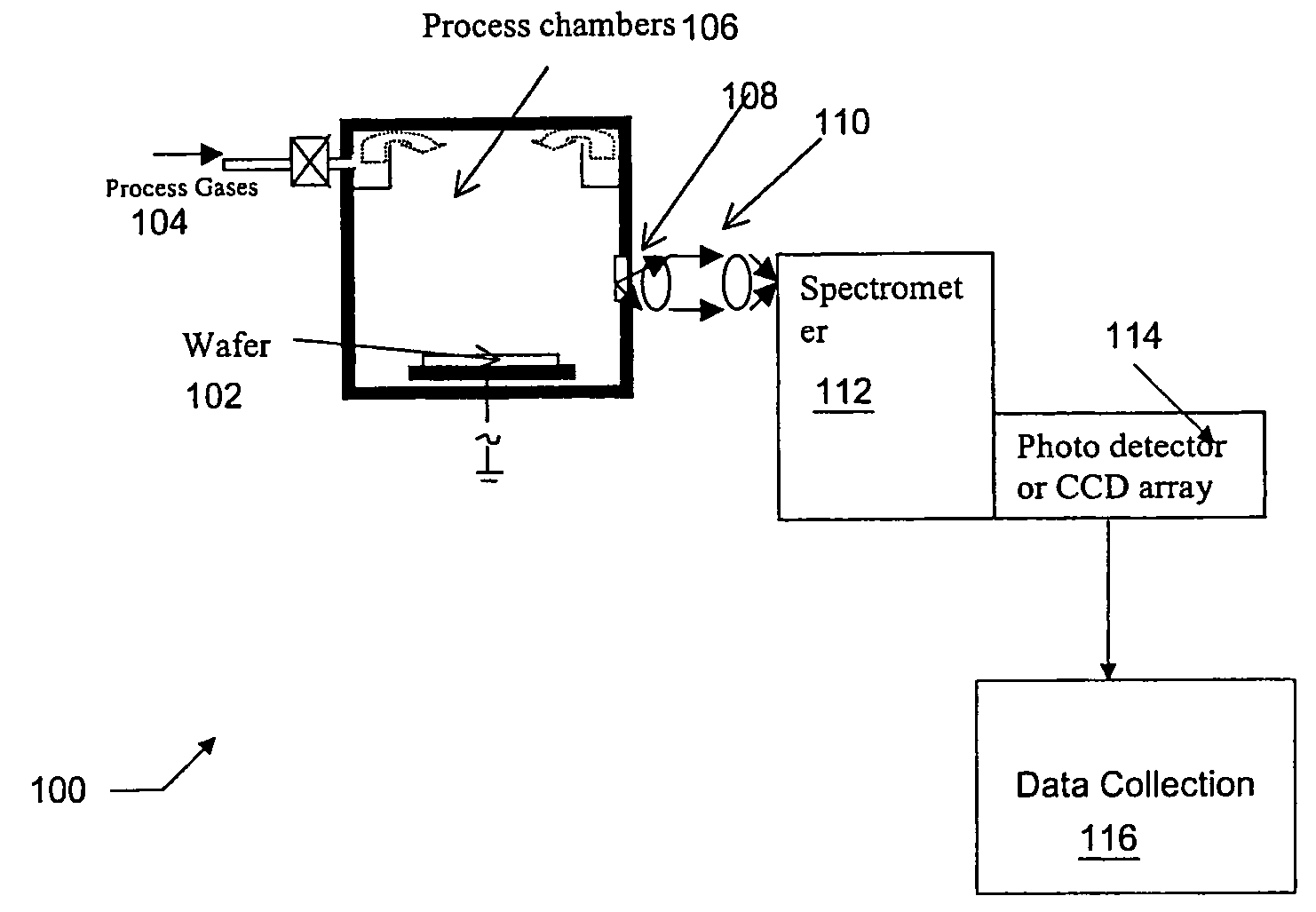
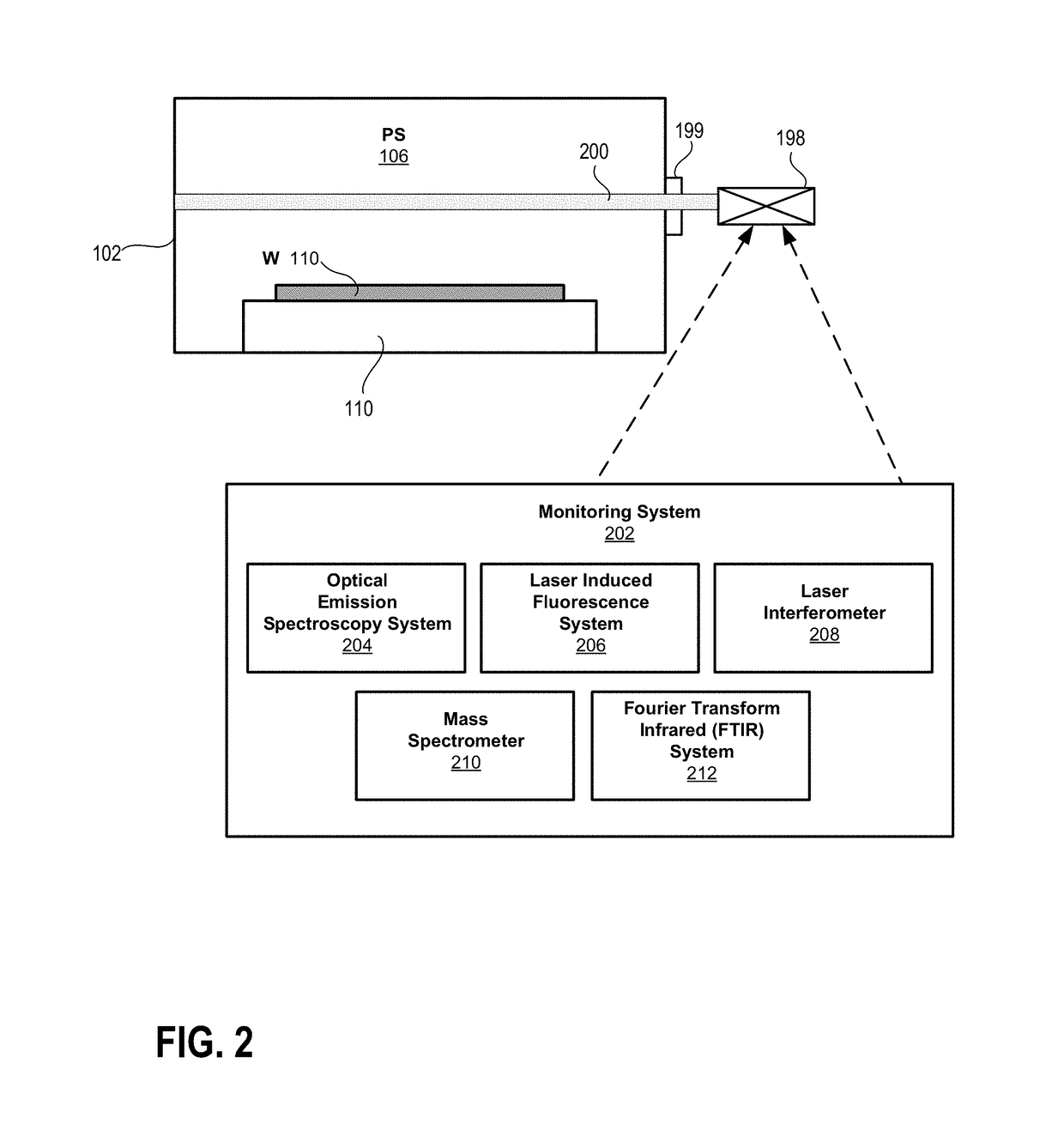
Spatially resolved optical emission spectroscopy (OES) in plasma processing
ActiveUS20150124250A1Emission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryProcess developmentOptical emission spectrometry
Disclosed is a method, computer method, system, and apparatus for measuring two-dimensional distributions of optical emissions from a plasma in a semiconductor plasma processing chamber. The acquired two-dimensional distributions of plasma optical emissions can be used to infer the two-dimensional distributions of concentrations of certain chemical species of interest that are present in the plasma, and thus provide a useful tool for process development and also for new and improved processing tool development. The disclosed technique is computationally simple and inexpensive, and involves the use of an expansion of the assumed optical intensity distribution into a sum of basis functions that allow for circumferential variation of optical intensity. An example of suitable basis functions are Zernike polynomials.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for testing total phosphorus in soil and sediments by virtue of microwave digestion ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry)
InactiveCN104198415AEasy and fast handlingEasy and fast determinationWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCorrelation coefficientRelative standard deviation
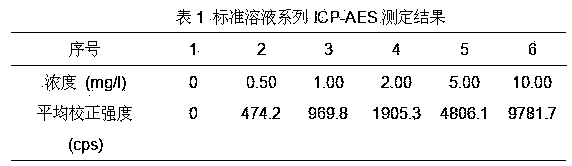
The invention provides a method for testing total phosphorus in soil and sediments by virtue of a microwave digestion ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry). According to the method, the recovery rate is 97.5%-106.2%, the relative standard deviation is 1.6%-3.4%, the detection limit is 5.74mg / kg (when the weighing dosage of a sample is 0.2500g and the volume of a digestion solution is set as 50ml); the correlation coefficient of a working curve is more than 0.9999 at 0-10.00mg / L, and the linearity is good; the method has no obvious difference from a national standard method on the testing result, and moreover the sample processing and testing processes are simple, convenient and rapid, so that the method has a preferable practical value.
Owner:浙江中一检测研究院股份有限公司
Selection of wavelenghts for end point in a time division multiplexed process
InactiveCN101248507ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesOptical emission spectrometryLength wave
The present invention provides a method for establishing endpoint during an alternating cyclical etch process or time division multiplexed process. A substrate is placed within a plasma chamber and subjected to an alternating cyclical process having an etching step and a deposition step. A variation in plasma emission intensity is monitored using known optical emission spectrometry techniques. A first wavelength region is selected based on a plasma emission from an etch by product and a second wavelength region is selected based on a plasma emission from a plasma background. A ratio of the first wavelength region to the second wavelength region is computed and used to adjust the monitoring of an attribute of a signal generated from the time division multiplex process. The alternating cyclical process is discontinued when endpoint is reached at a time that is based on the monitoring step.
Owner:UNAXIS USA
Method for determining impurity elements in high-purity aluminum through microwave digestion-inductive coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer
InactiveCN108375568ALow detection limitAccurate measurementPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical Emission SpectrometerMethod test
The invention provides a method for determining impurity elements in high-purity aluminum through a microwave digestion-inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer and belongs to the technical field of analysis and test. The invention provides an analysis method for determining 20 impurity elements including Ag, Ba, Bi, Cd, Co, Cu, Ga, Fe, In, Li, Mg, Mn, Mo, Pb, Sb, Ti, V, Sr, Zn and Zr in the high-purity aluminum through a microwave digester and an inductive coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) by adopting a standard curve method. A sample is dissolved into a sealed high-pressure microwave digestion tank by utilizing a proper amount acid, so as to avoid external factor pollution better. Optimal working parameters of an instrument are determined through a single-factor experiment. A standard curve-method test sample is selected so that matrix interference is reduced. The method is a simple, rapid and accurate modern detection technology capable of determining 20elements in one step.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Smart additive manufacturing system (SAMS)
ActiveUS9981341B2Additive manufacturing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesOptical emission spectrometryEngineering
An additive manufacturing process is monitored, in situ, using optical emission spectroscopy to analyze the composition, phase transformation or manufacturing defects. The system or method may include an analysis of contours of the plasma line intensity, or pre-processing of the plasma spectral line including signal-to-noise ratio analysis, baseline removal, line identification, line de-convolution and fitting. Improvements may additionally involve consideration of plasma parameters such as plasma spectral line intensity, line ratio, plasma temperature and electron density using high-resolution optical emission spectroscopy in both visible and ultraviolet regions. Parameters of the plasma may be determined using an intensity ratio of the ions or atoms emission lines, a FWHM of the line profile for electron density estimation, or a Boltzmann plot for plasma temperature estimation. One or more techniques may be used to monitor when there is a lack of deposition.
Owner:MAZUMDER JYOTI +1
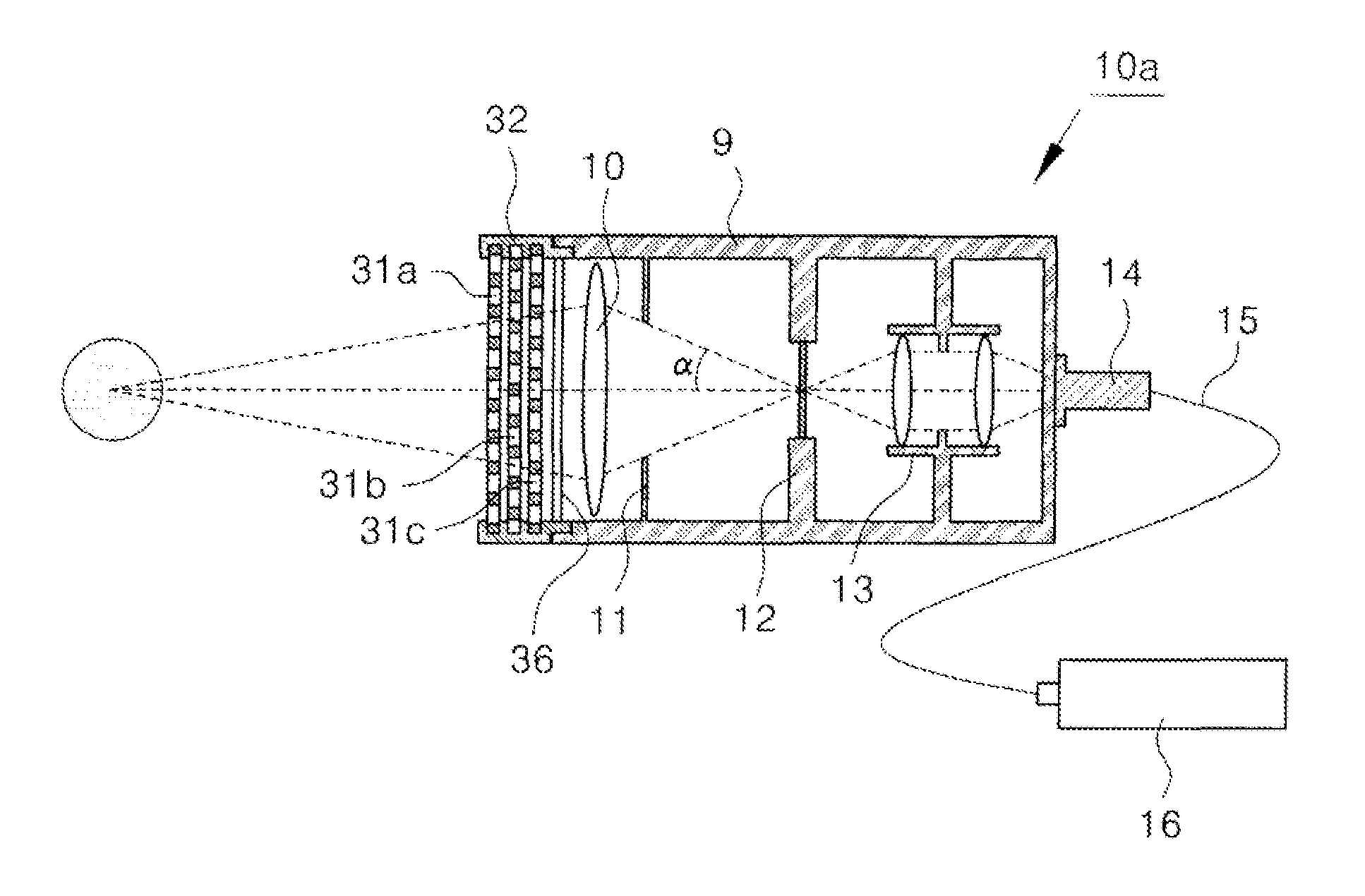
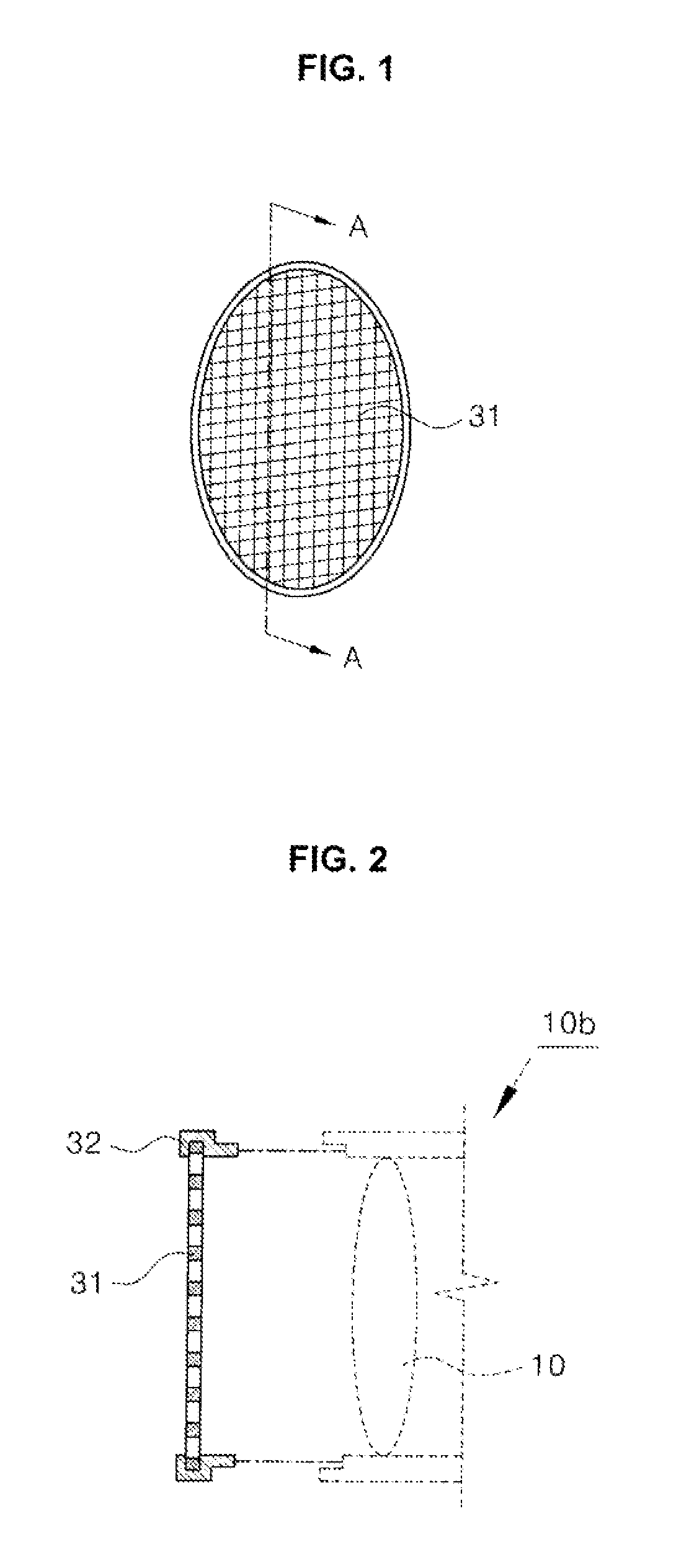
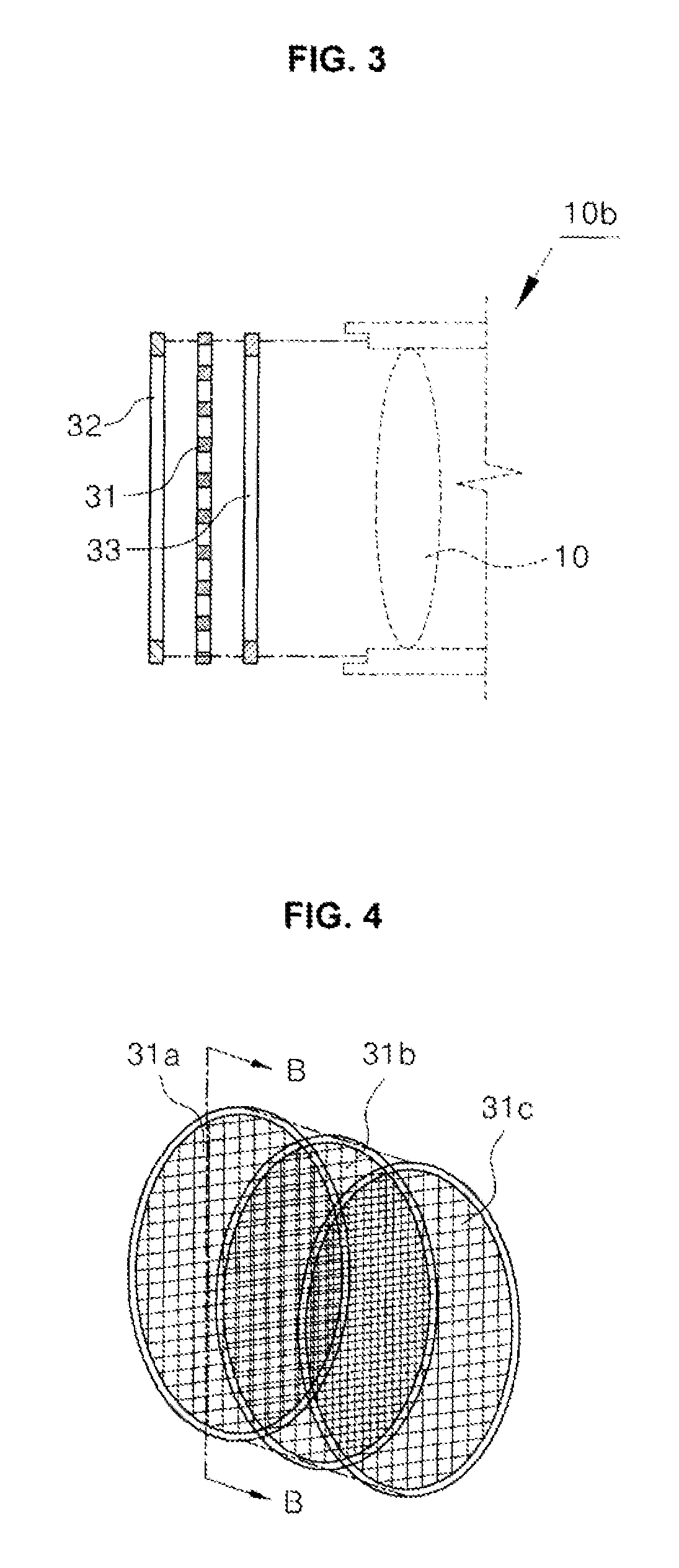
Device for preventing intensity reduction of optical signal, optical emission spectrometer, optical instrument, and mass spectrometer including the same
ActiveUS9025143B2Avoid intensitySolve the real problemEmission spectroscopyShielding materialsOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical emission spectrometry
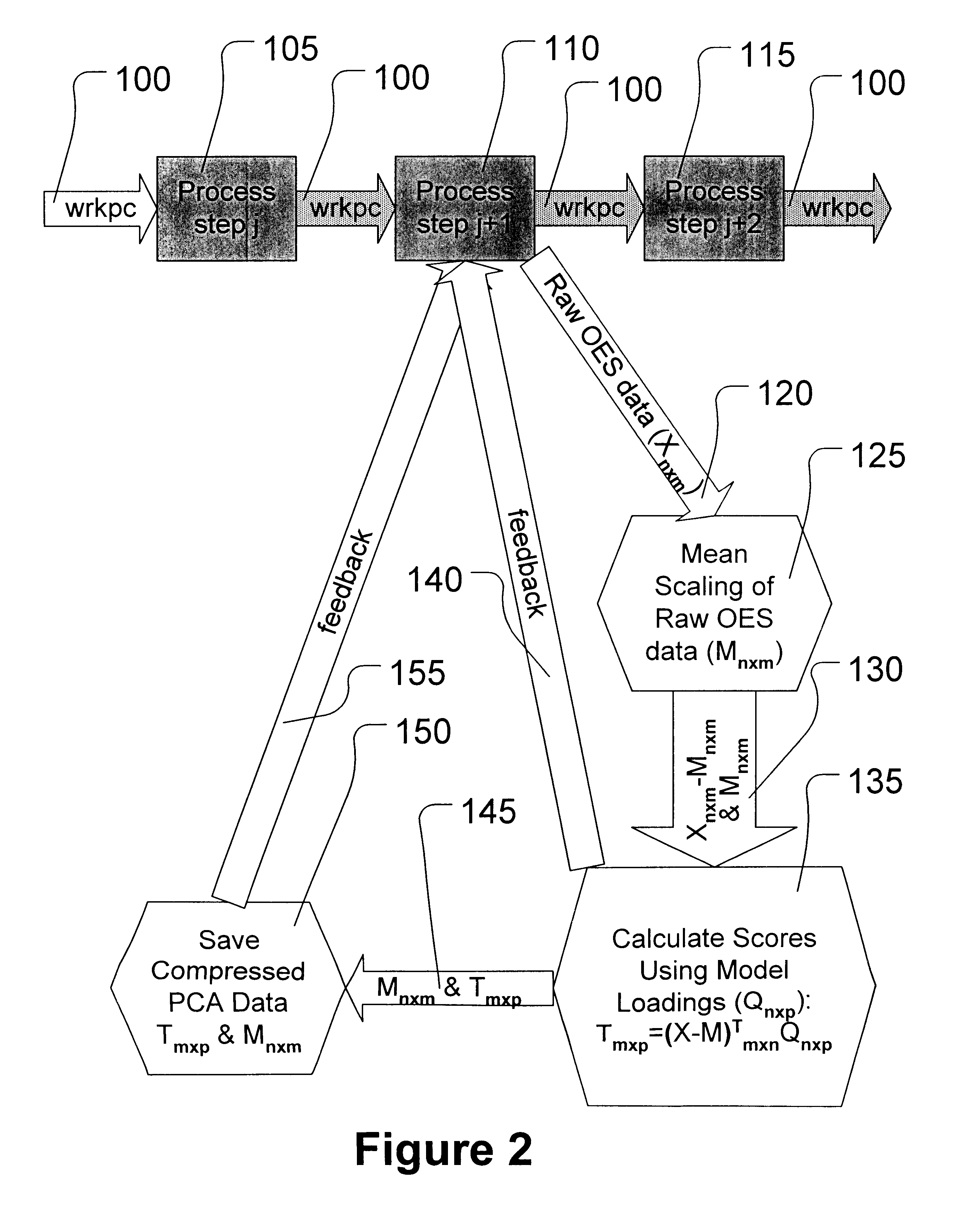
A device for a device for preventing the intensity reduction of an optical signal, an optical emission spectrometer, an optical instrument, and a mass spectrometer including the same are provided. The device for preventing the intensity reduction includes a shielding filter which has a mesh structure capable of blocking RF electromagnetic waves radiated from a plasma field for a wafer processing, is installed in the front of an optical window of an optical emission spectrometer for measuring the plasma field from an emission spectrum image of the plasma field, and collects charging particles passing through the mesh.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Measuring method for content of aluminium in water by utilizing ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry)
The invention discloses a measuring method for the content of metal aluminium in water. The method can be used for measuring the content of the metal aluminium in the water by adopting an ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry) method. The measuring method comprises the following steps of: firstly dissolving an aqueous-solution sample containing the aluminium, and carrying out secondary heating for digestion by adding a certain amount of sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide solution and hydrochloric acid solution to so as to effectively dissolve the metal aluminium; then measuring the content of the aluminium by adopting an ICP-AES spectrometer. By adoption of the method for detection, the matrix interference is small, and the need for production can be met.
Owner:四川国测检测技术有限公司
Method for measuring content of metal element cadmium Cd by ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry) method
The invention relates to a method for measuring metal element cadmium Cd in slag, which is used for measuring the content of trace metal cadmium by an ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry). The method comprises the following steps of: fetching 0.05-0.1g of slag sample; putting the sample into a high-temperature high-pressure digestion tank, and adding a proper amount of potassium permanganate, nitric acid and hydrochloric acid for digestion; putting the high-pressure digestion tank with sample liquid into a blast drying oven, and performing high-temperature digestion in an environment at 200-220 DEG C to obtain a digestion sample; and measuring the content of metal element cadmium Cd in an analysis solution according to certain instrument working parameters by use of the ICP-AES. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of sufficient digestion of measured samples, short measurement time and simple technology, and can meet the needs for production and life.
Owner:广东量源检测技术有限公司
Solid State Gyrolaser with Controlled Optical Pumping
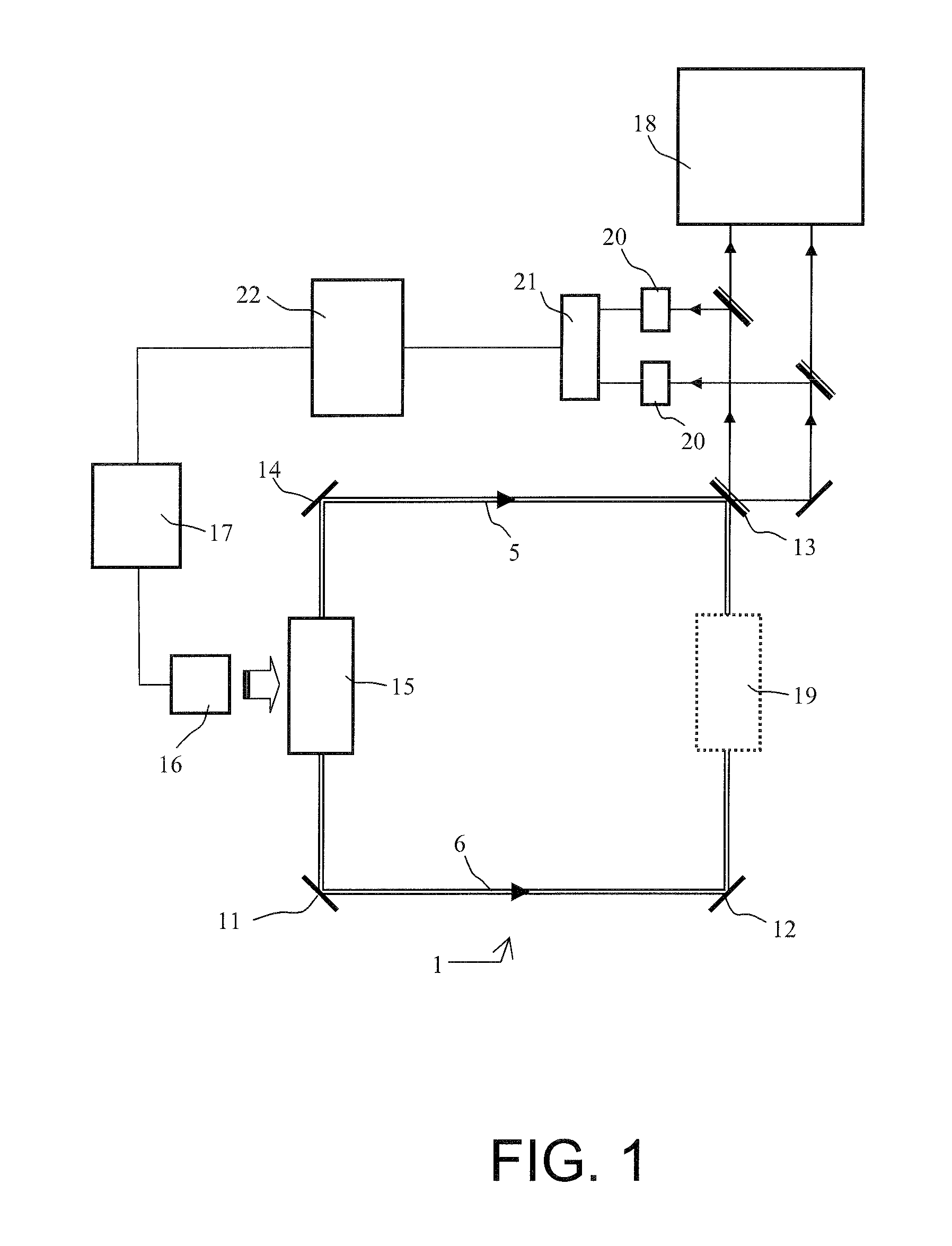
InactiveUS20100123901A1Sagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeSpectral bands
The general field of the invention is that of gyrolasers comprising at least one ring-shaped optical cavity comprising at least three mirrors, a solid state amplifying medium pumped by a laser diode whose optical emission power is determined by a current supply source, the cavity and the amplifying medium being such that two so-called contra-rotating optical modes propagate in opposite directions to each other within the said optical cavity, the gyrolaser being a class B gyrolaser, the gyrolaser also comprising means of measuring the difference in optical frequency existing between the two optical modes. The gyrolaser comprises means of measuring the total optical power circulating in the optical cavity and first means of control of the current delivered by the supply source in such a way as to maintain the total optical power substantially constant in a narrow spectral band centred on the relaxation frequency of the laser.
Owner:THALES SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com