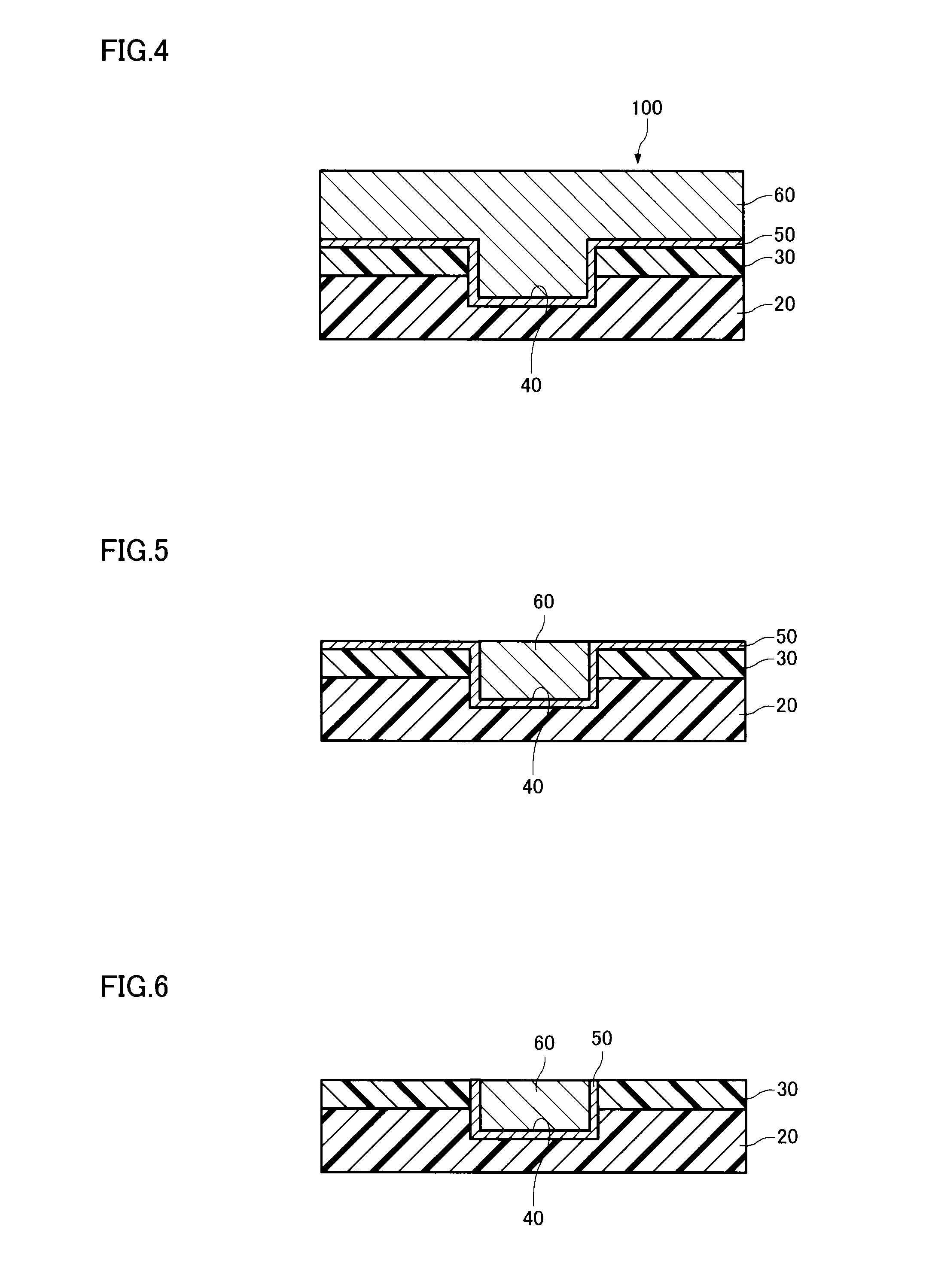
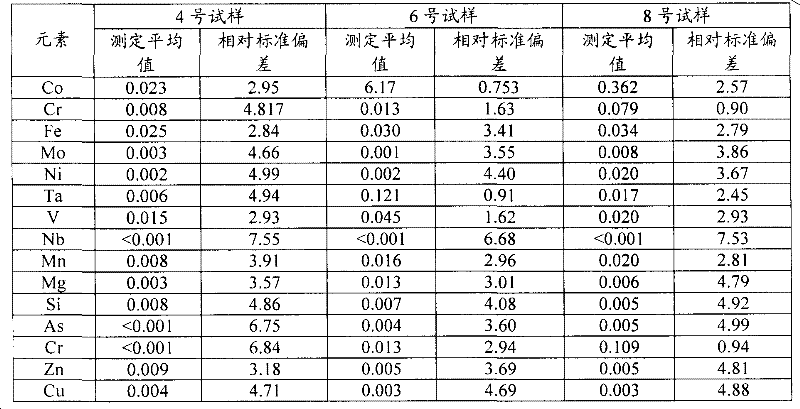
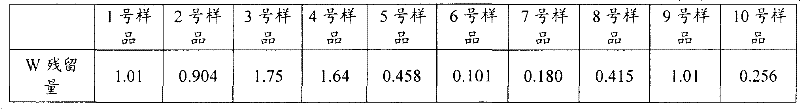
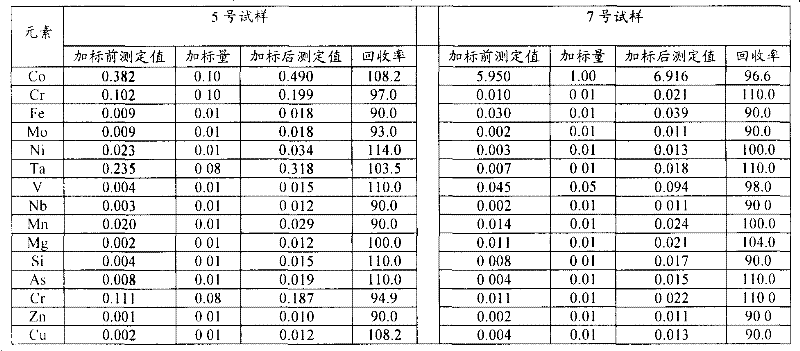
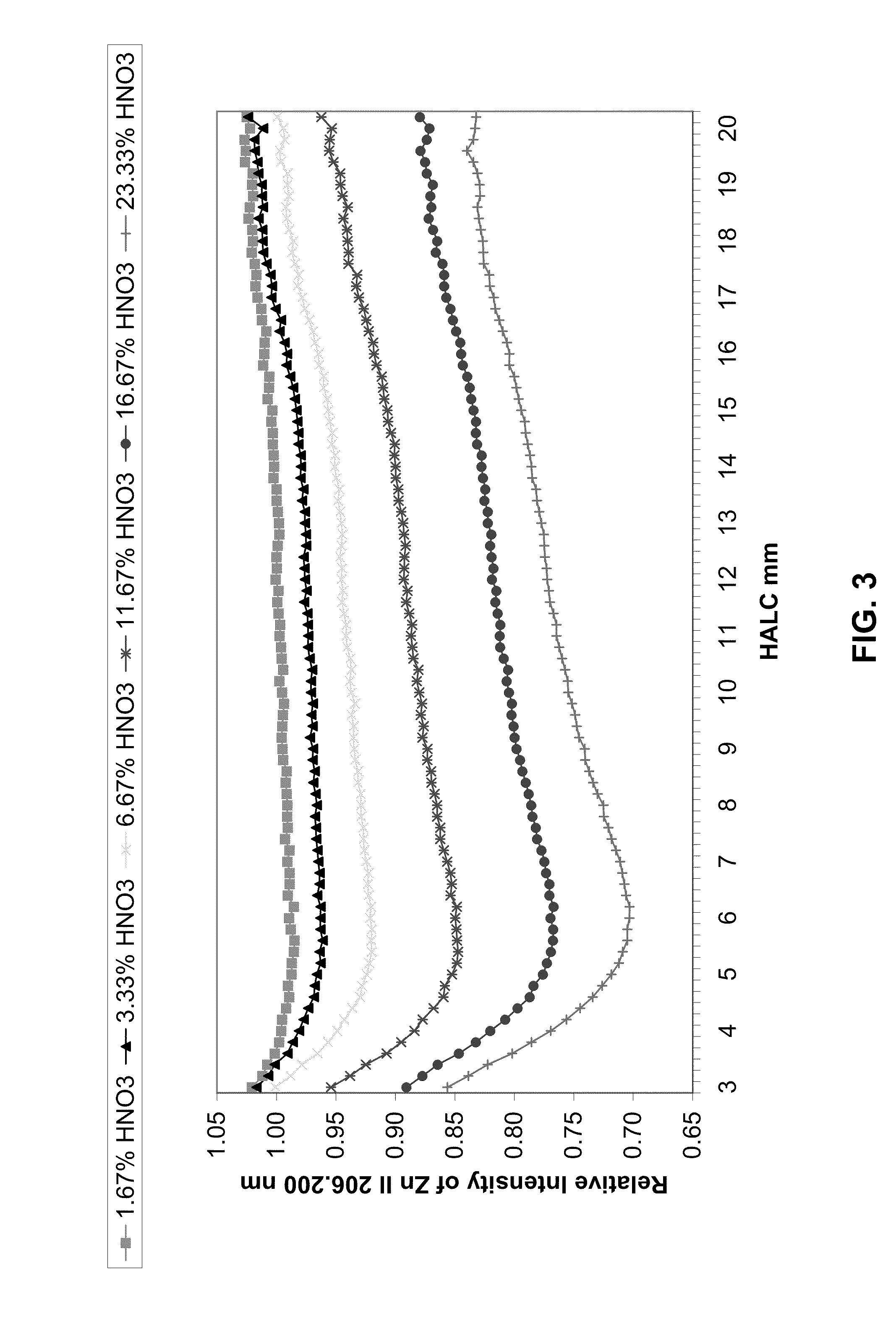
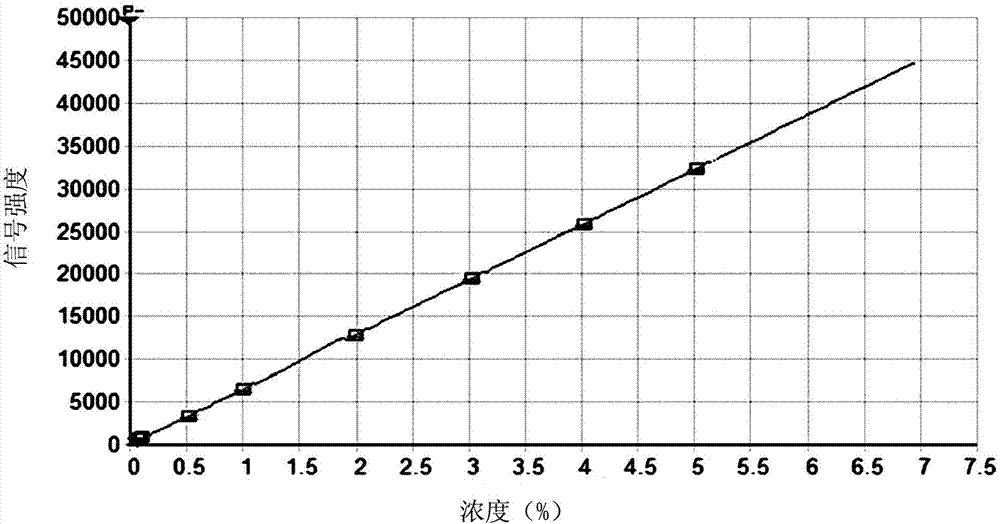
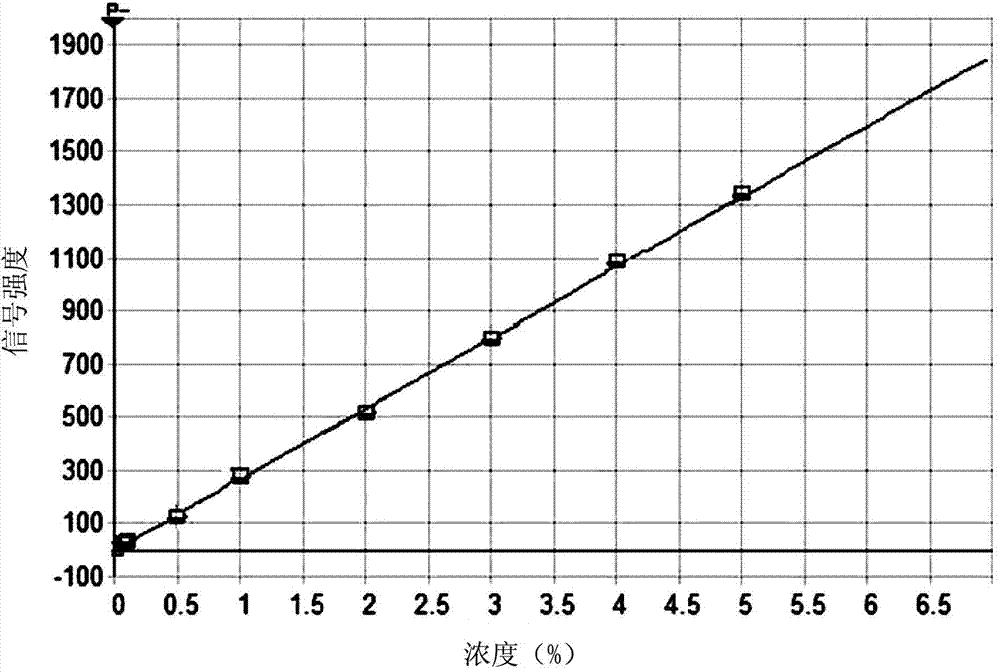
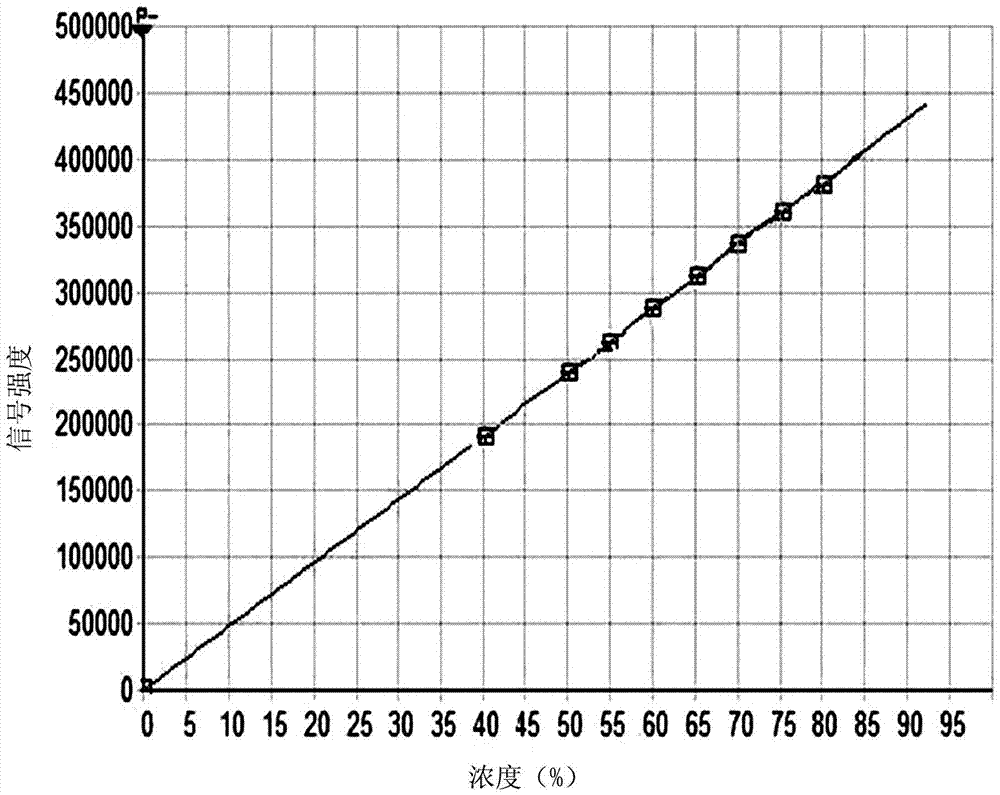
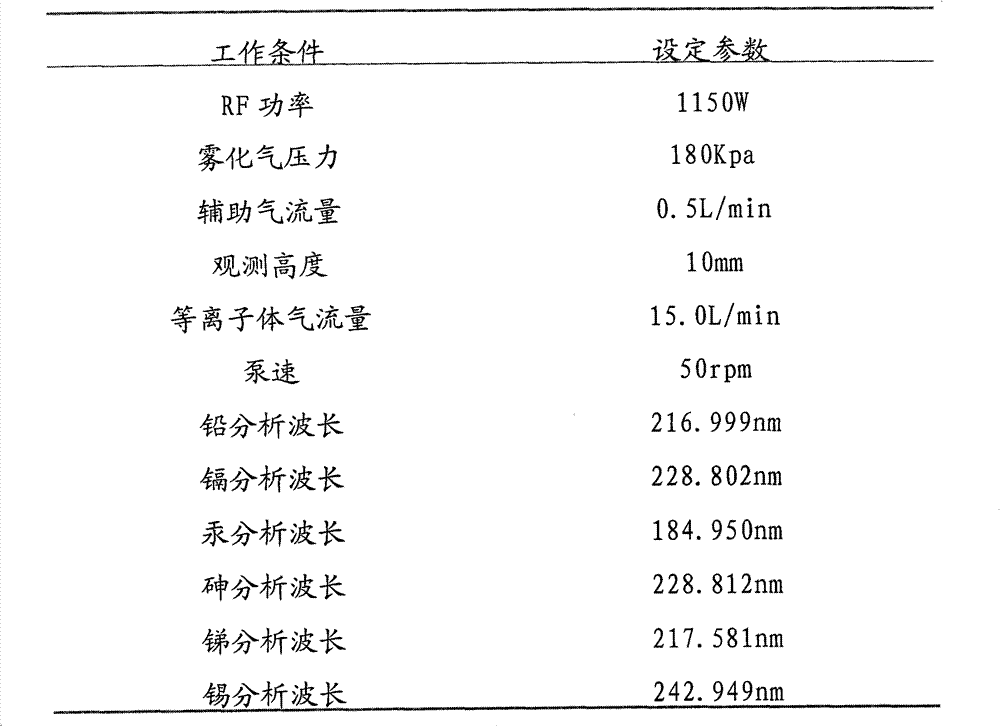
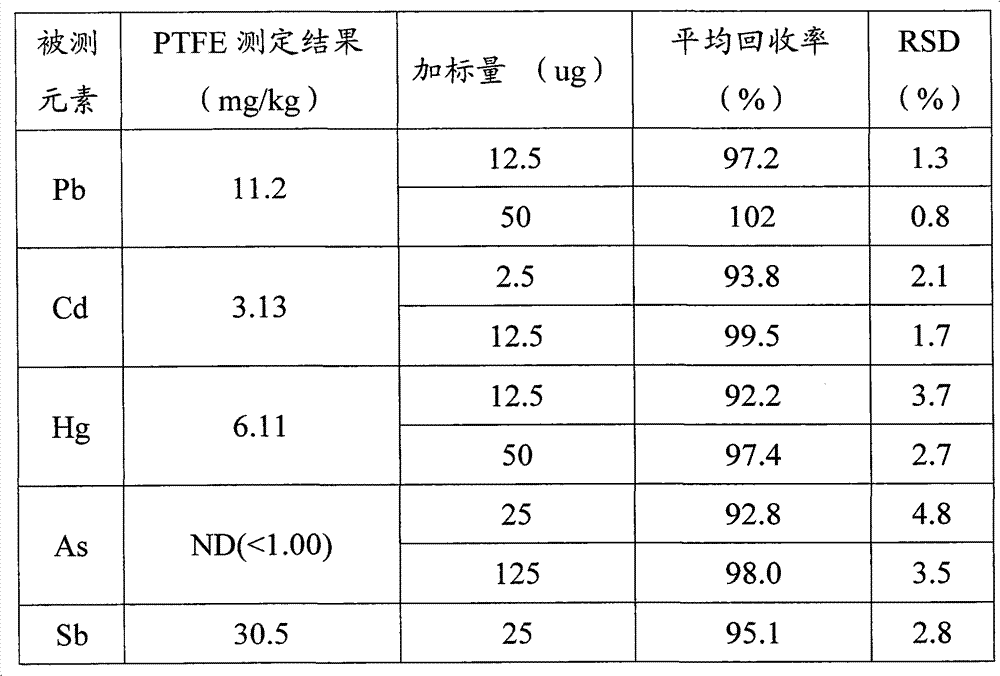
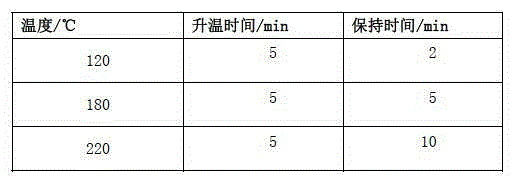
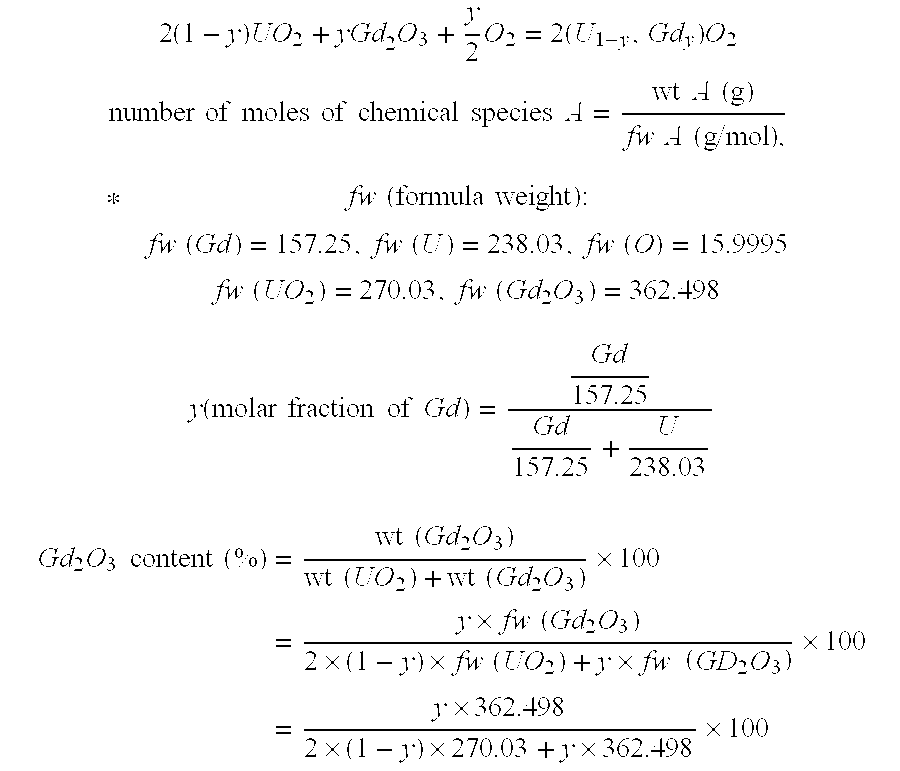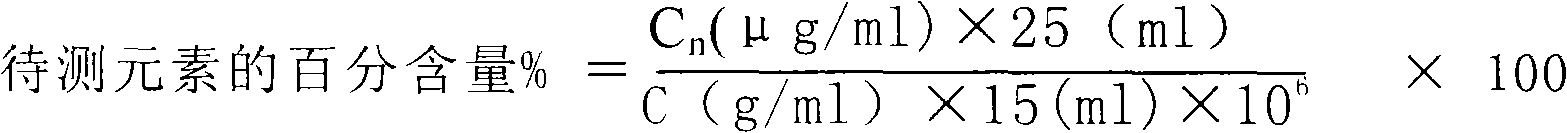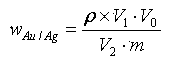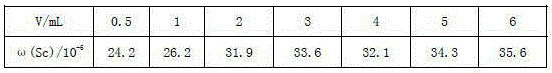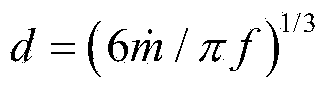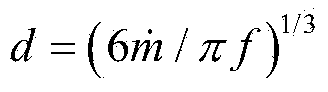Patents
Literature
282 results about "Atomic emission spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
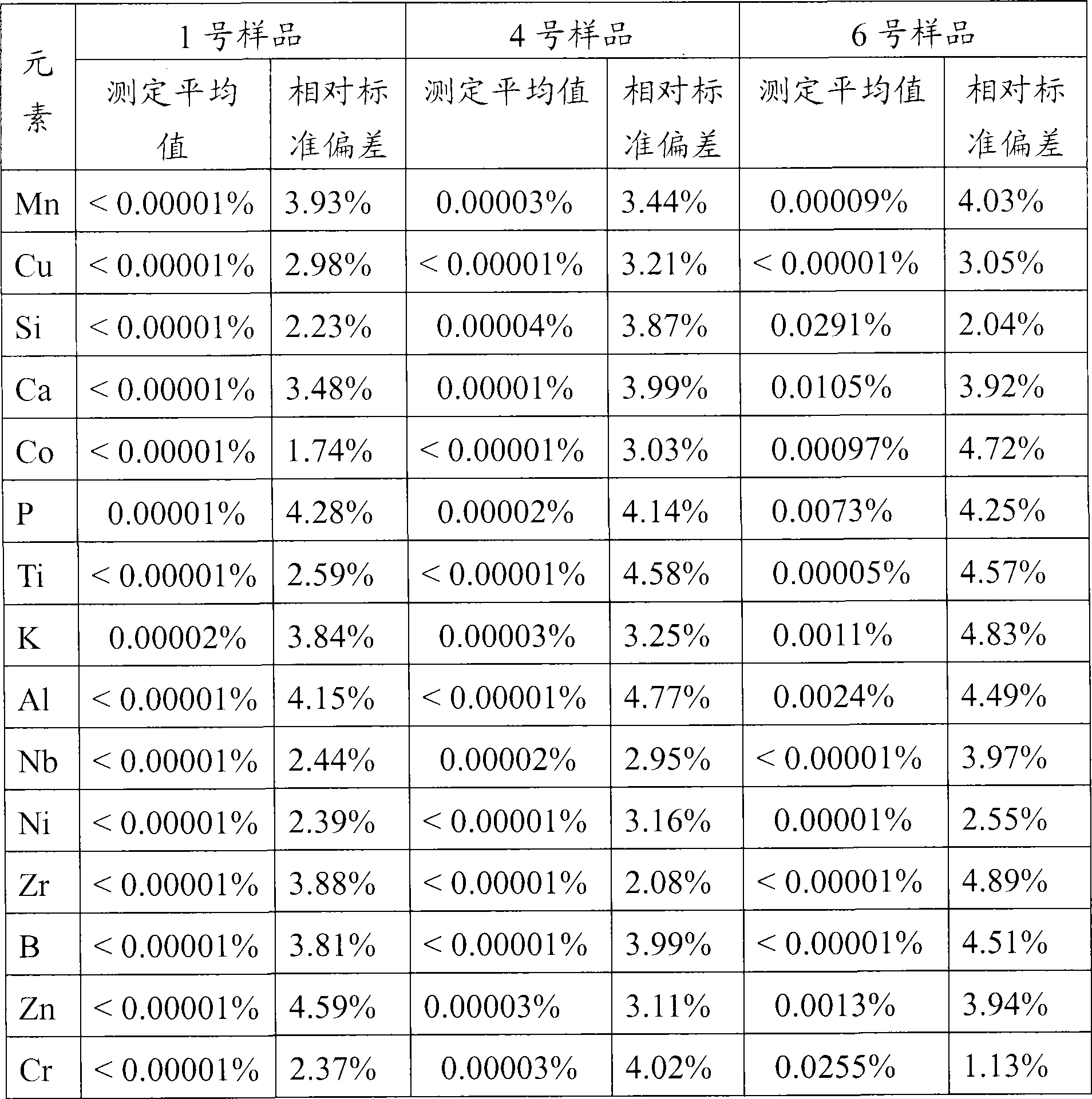
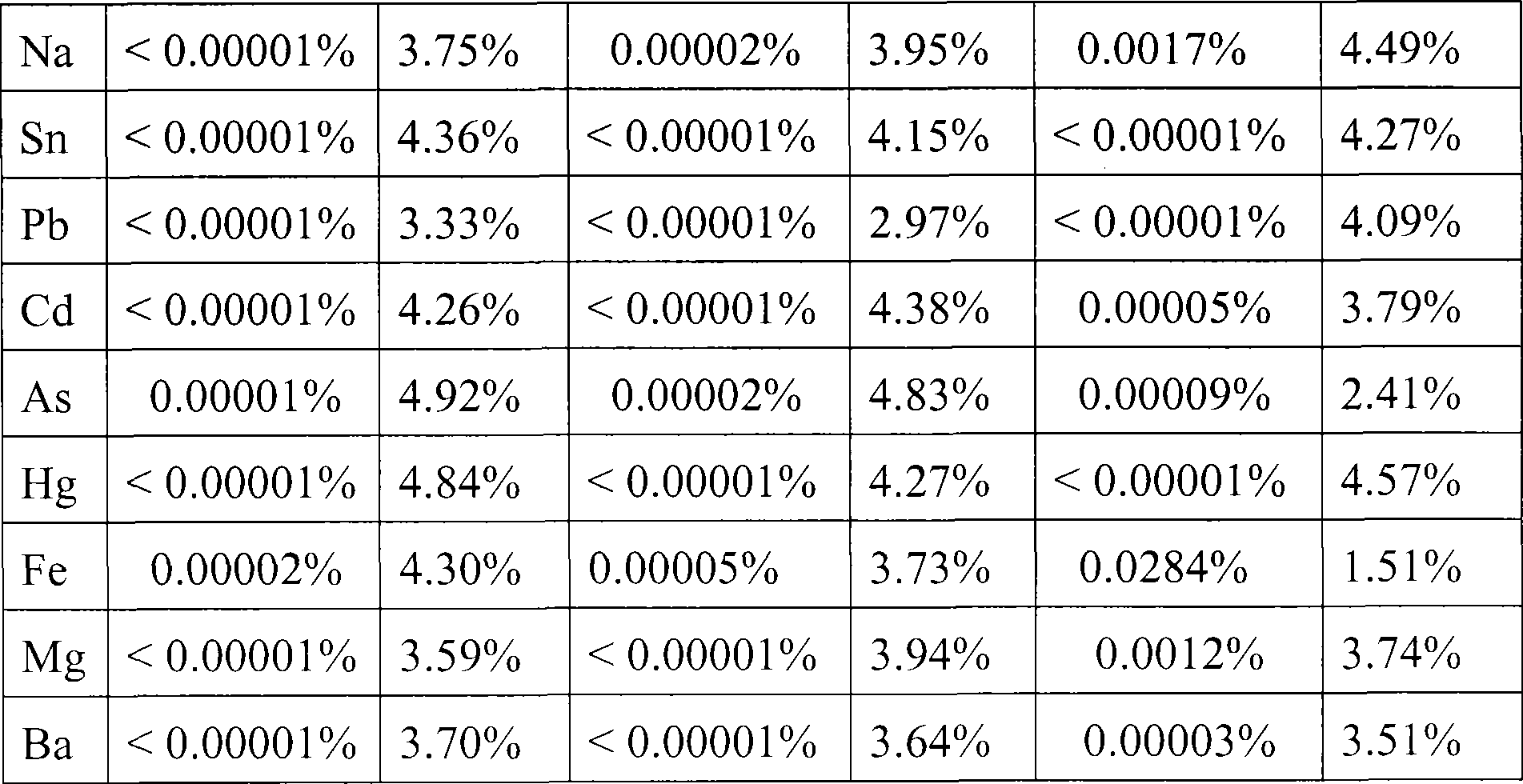
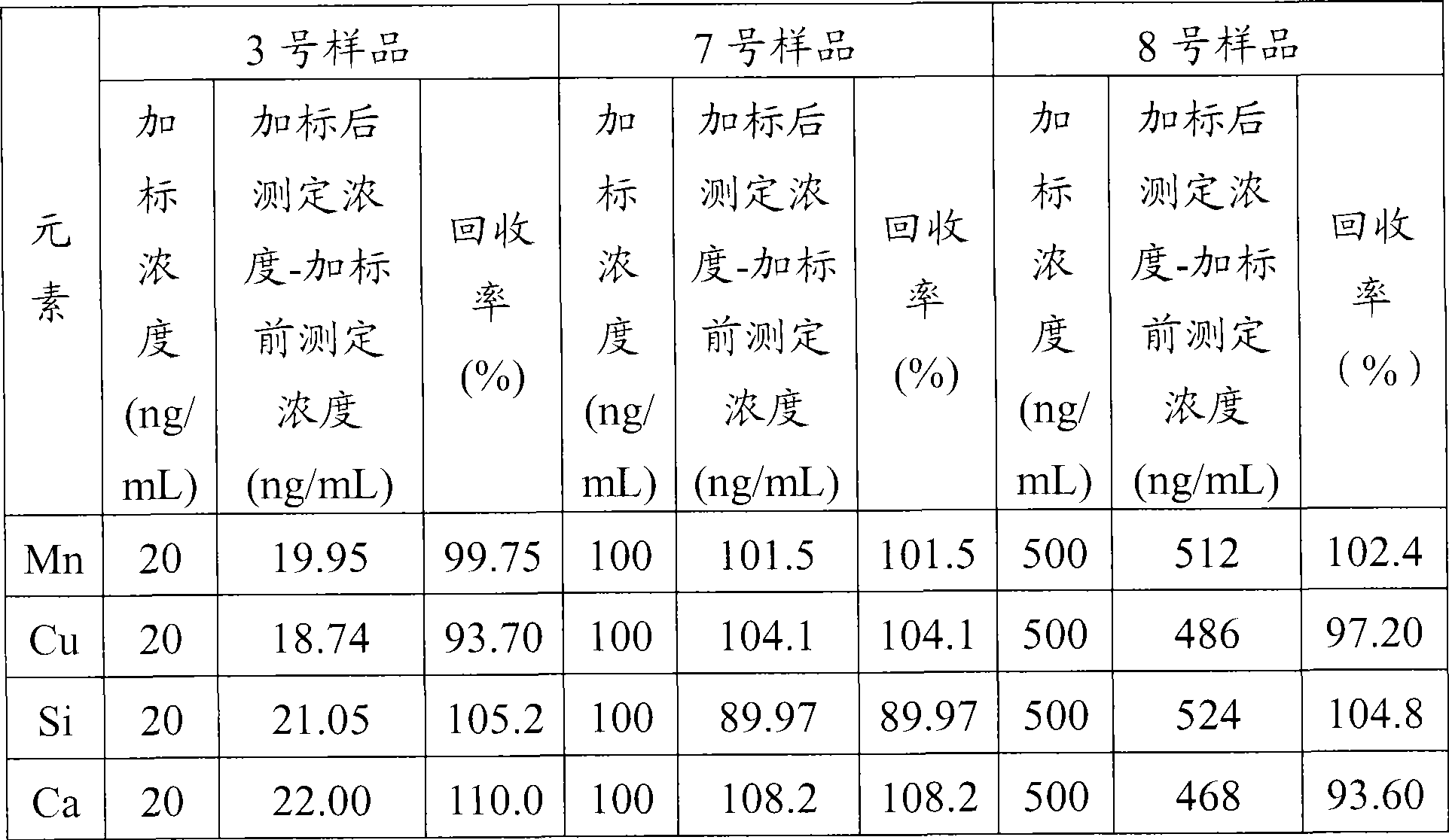
An atomic emission spectrophotometer consists of an atomic generator of the element to be determined (such as flame, plasma, arc etc), a monochromator and a detector. If a flame is used for generating the vapor, water is the usual solvent for preparing the test and reference solutions.
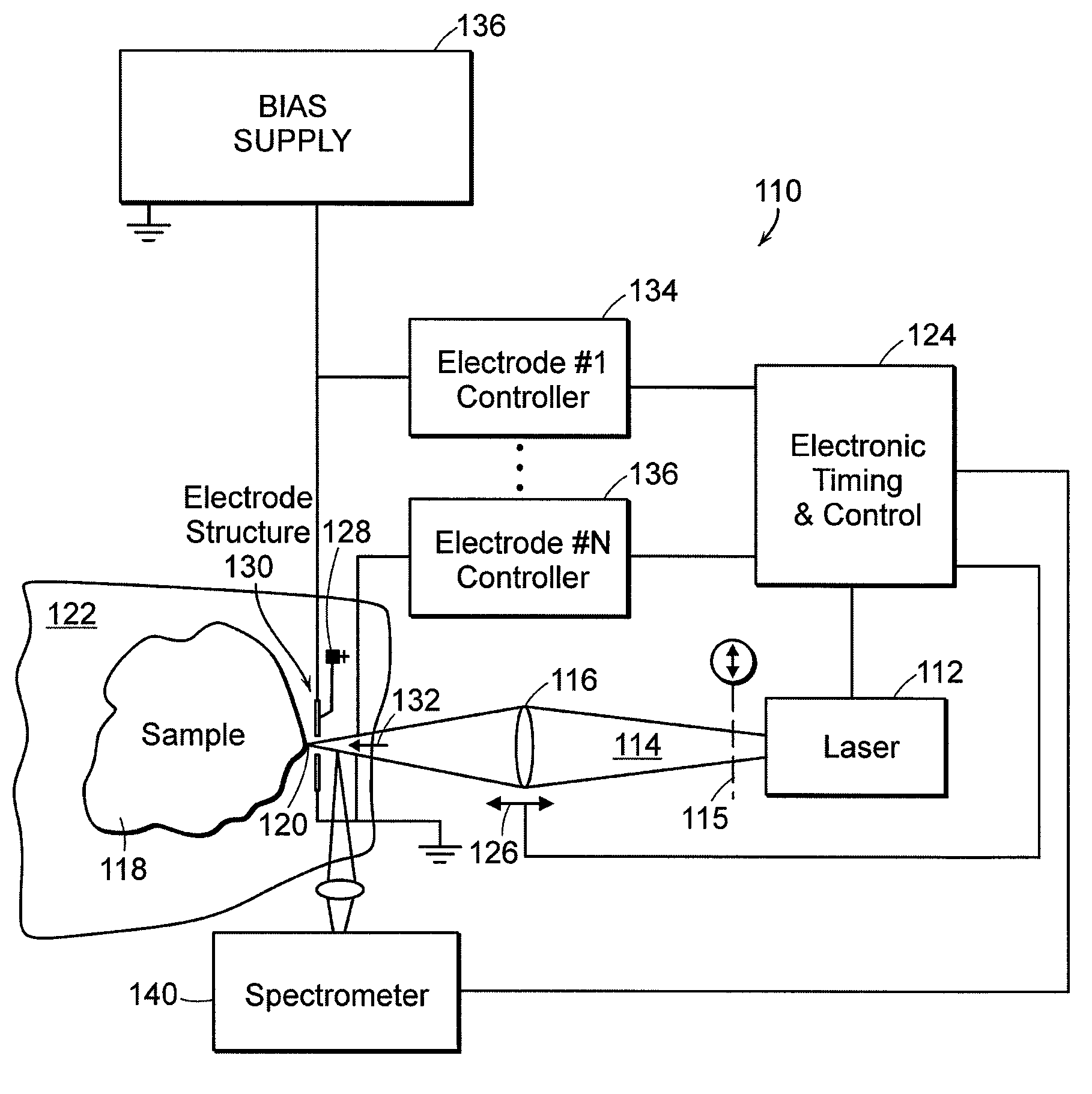
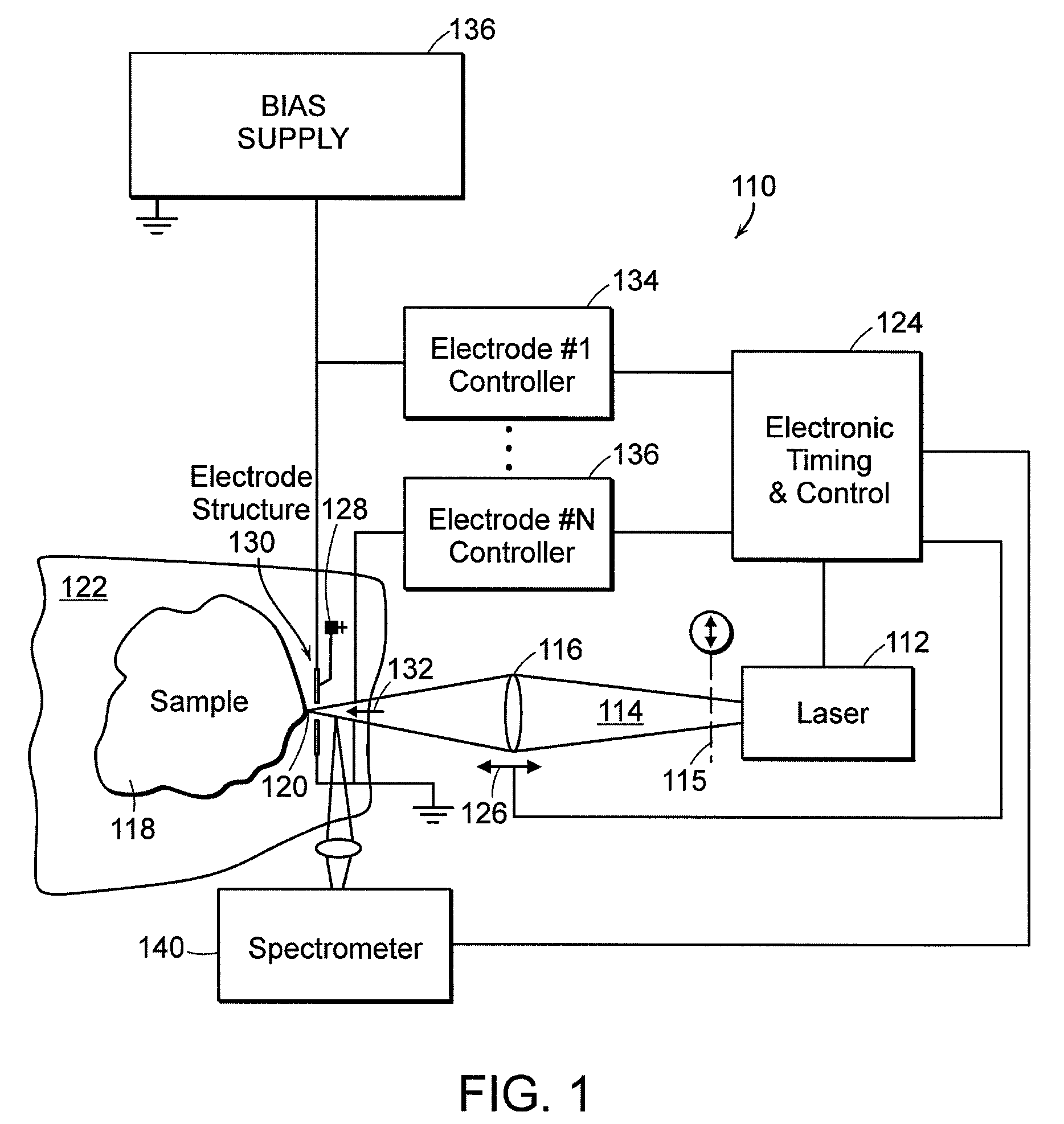
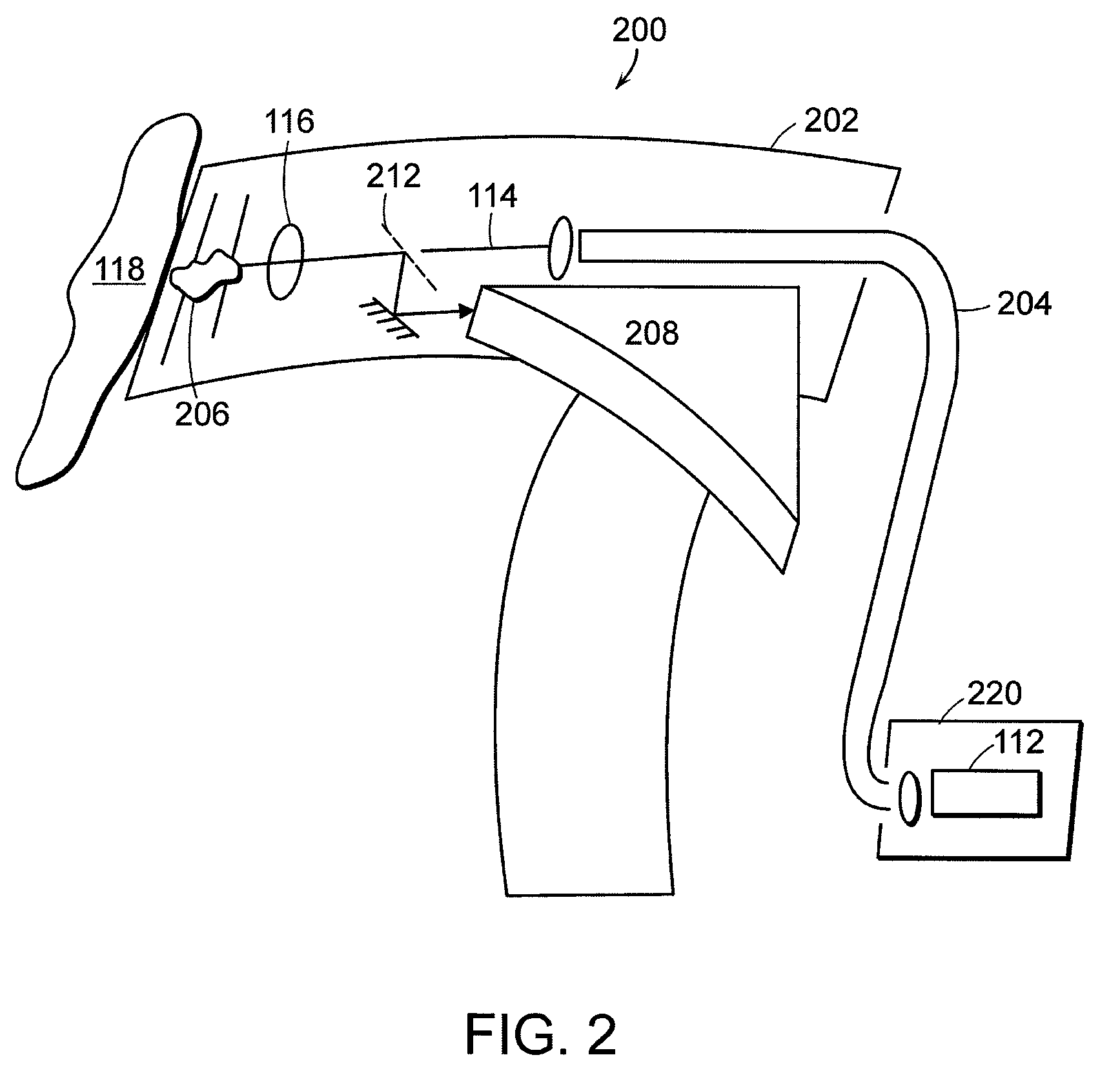
Laser-triggered plasma apparatus for atomic emission spectroscopy
Multiple energy sources, such as a laser and electrical current, are employed, in close coordination, spatially and temporally, to clean a sample, vaporize its material and excite vapor atoms for the purpose of atomic emission spectroscopy. These methods permit better monitoring and control of the individual processes in real time, lead to higher consistency and higher quality optical emission spectra, and enhance the measurements of non-conducting solids, liquids and gases. Additionally, a portable instrument is provided with both laser source and spectrometer optically coupled to a hand-holdable unit.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
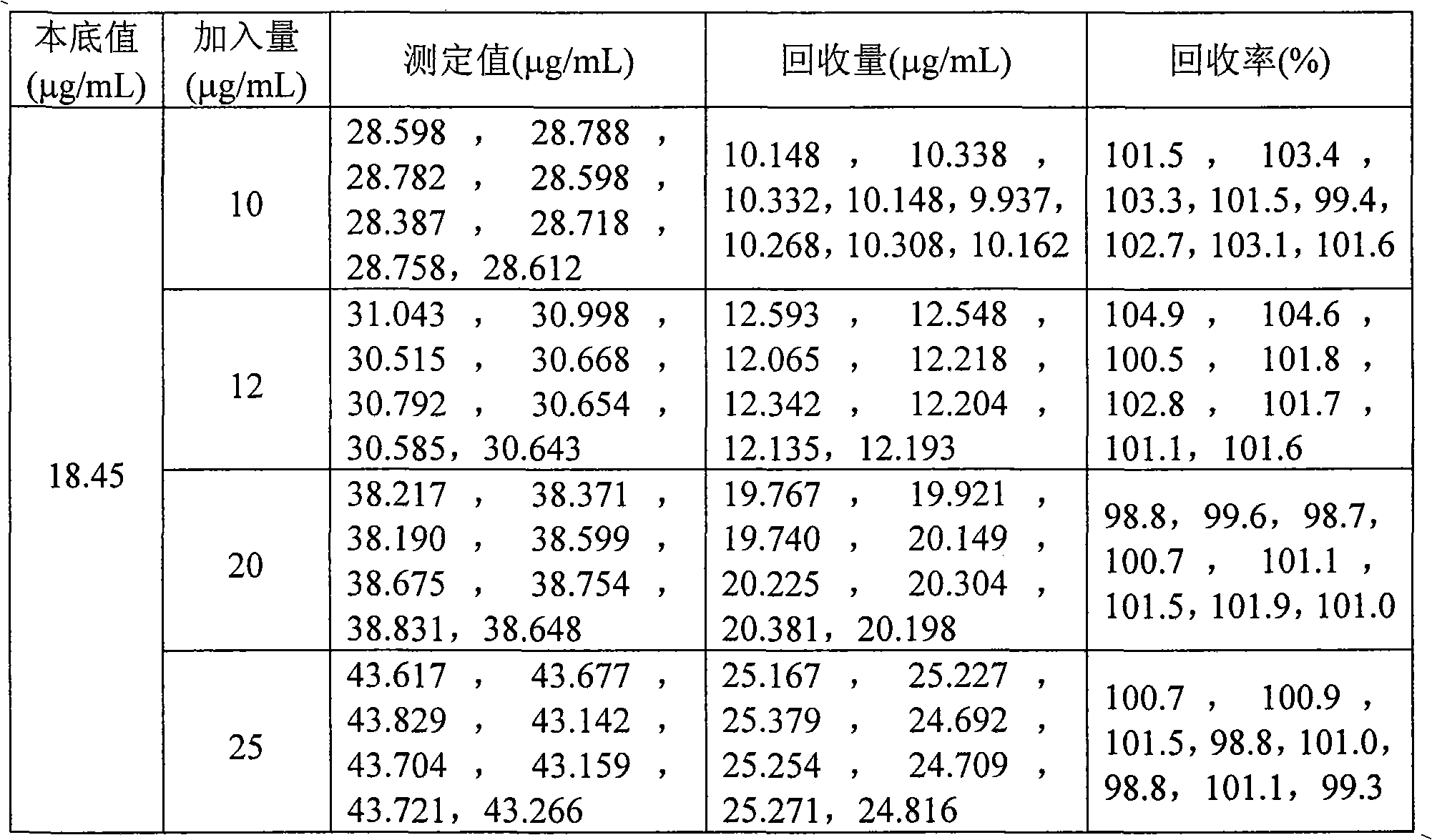
Digestion method and detection method for iron ore
InactiveCN101839828AAvoid influenceImprove detection accuracyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsDigestionHigh pressure
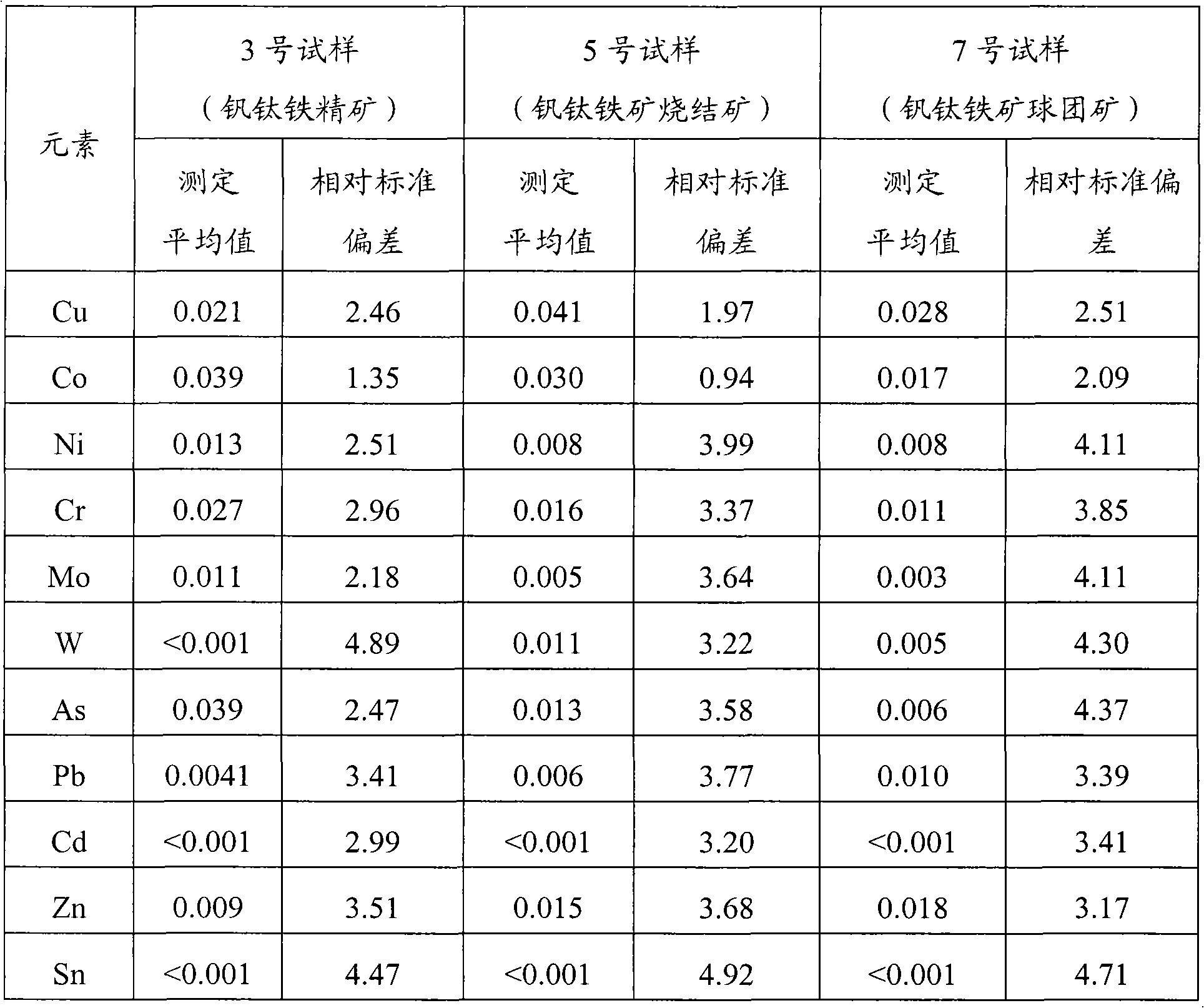
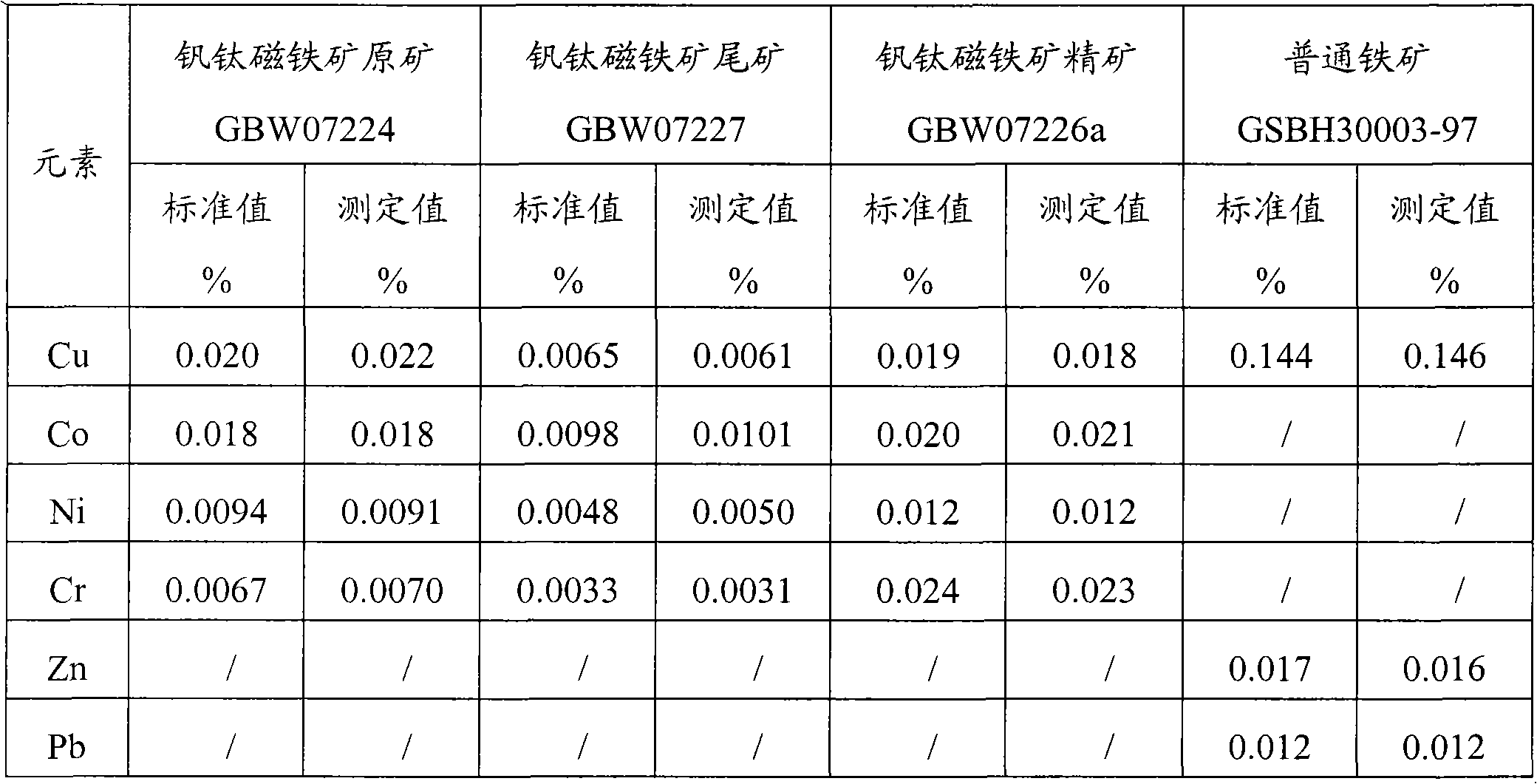
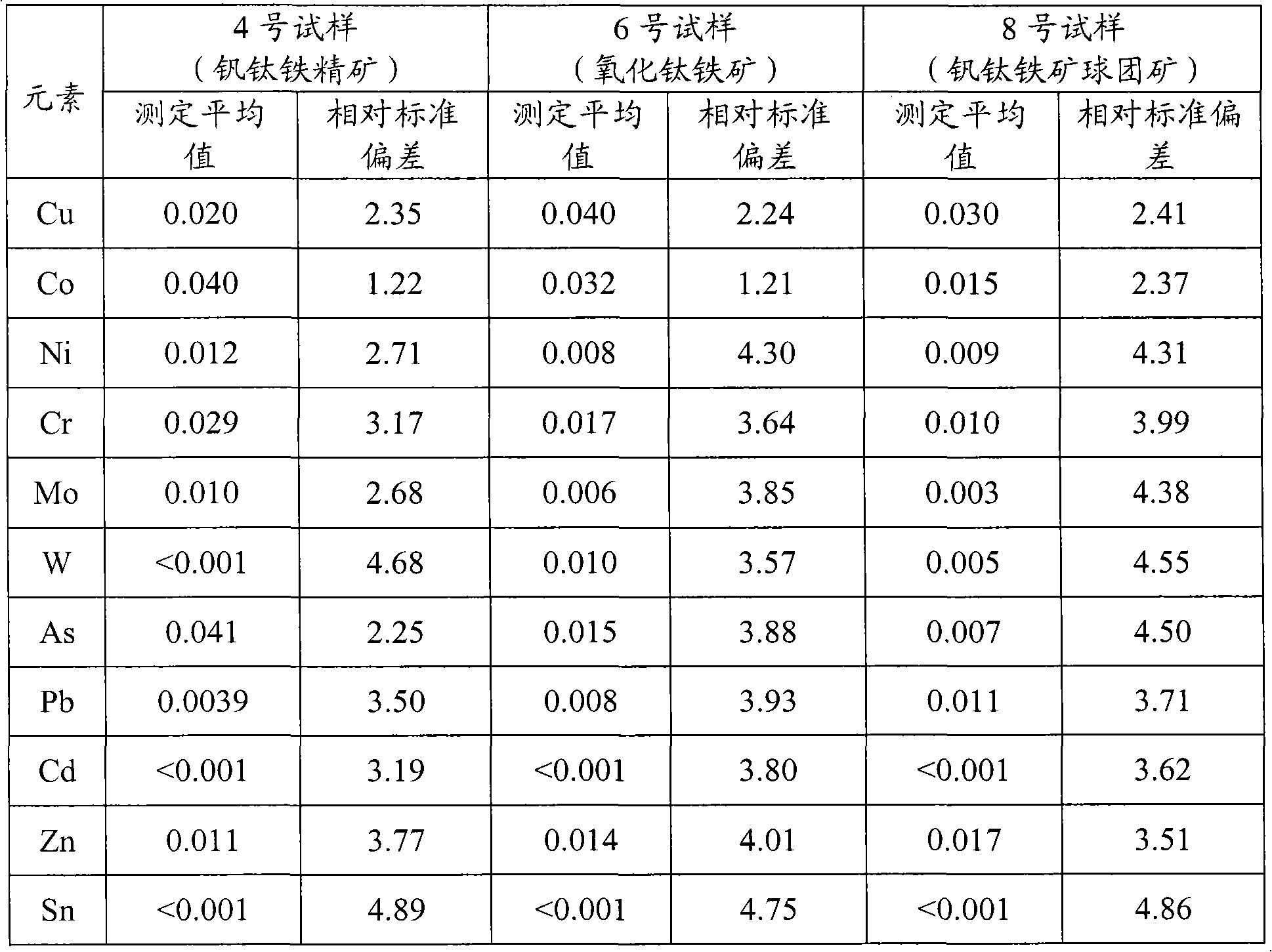
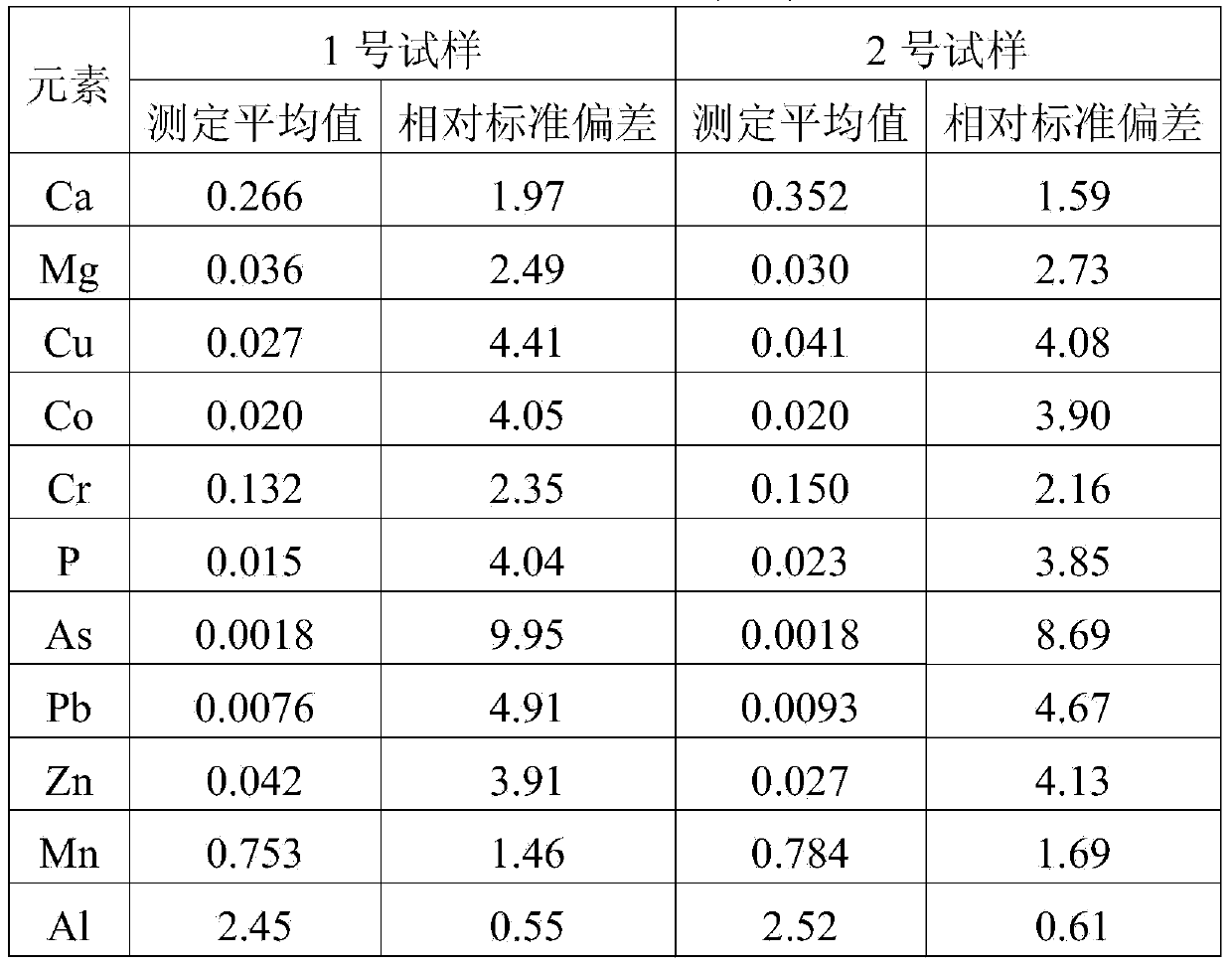
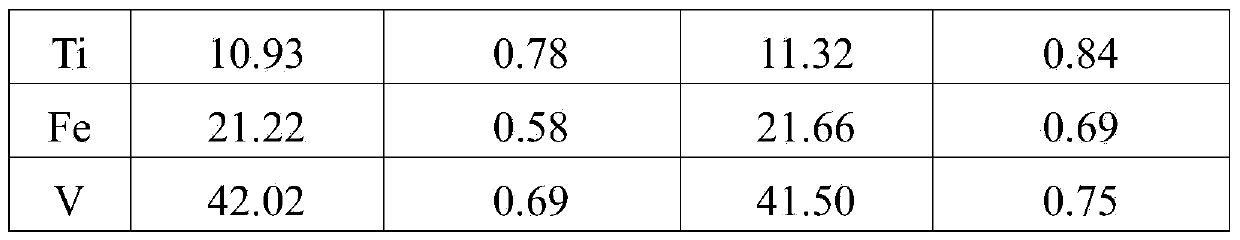
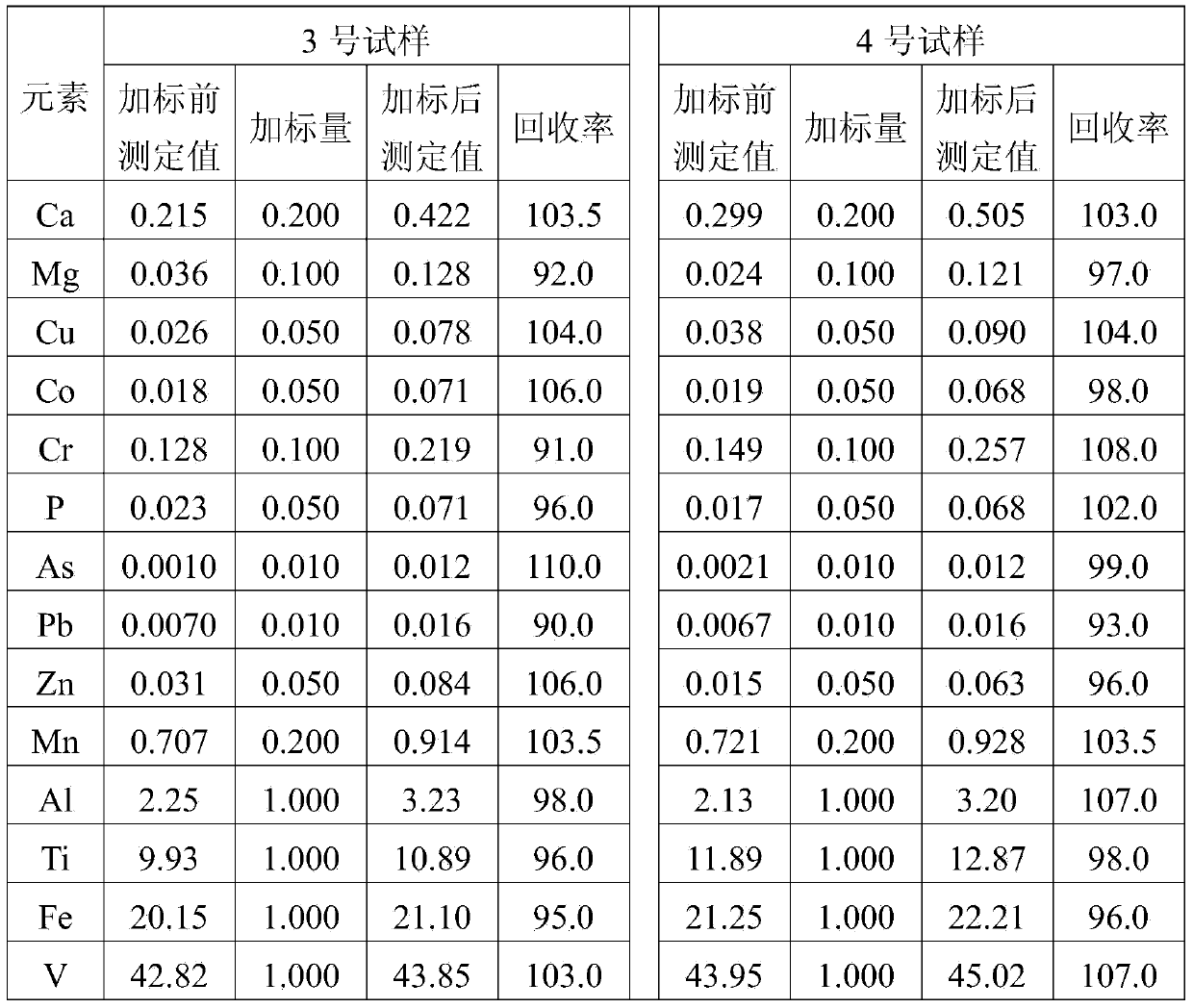
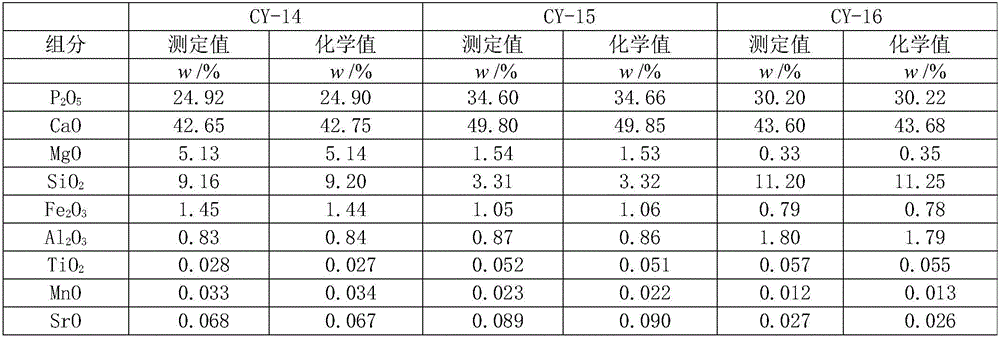
The invention provides a digestion method and a detection method for iron ore. The digestion method comprises the following steps: adding an iron ore sample in which hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid (or sulfuric acid) are mixed, then carrying out high-pressure closed microwave digestion to obtain a suspension; and heating the suspension in an unclosed system to secure the second digestion with residual nitric acid (or residual sulfuric acid) and added perchloric acid and hydrogen peroxide, thereby obtaining a solution which is digested fully. The detection method comprises the following steps: preparing a solution with the digested solution, and detecting the prepared solution by inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry, thereby obtaining content of each element of the iron ore sample. The invention has the advantages of high efficiency, high accuracy, and simple and fast process. Especially, the invention realizes accurate detection of key element content in iron ore, such as As, Pb, Zn, W, Sn, Ca, Mg, Cu, Co, Ni, Cr and Mo which affect product quality of iron and steel smelting and vanadium / titanium extraction.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +2
Aqueous dispersion for chemical mechanical polishing and chemical mechanical polishing method
InactiveUS20110053462A1Reduce polishing rateHigh polishing rateOther chemical processesDecorative surface effectsIon contentIon chromatography
A chemical mechanical polishing aqueous dispersion including (A) silica particles, and (B1) an organic acid, the sodium content, the potassium content, and the ammonium ion content of the silica particles (A) determined by ICP atomic emission spectrometry, ICP mass spectrometry, or ammonium ion quantitative analysis using ion chromatography having a relationship in which the sodium content is 5 to 500 ppm and at least one of the potassium content and the ammonium ion content is 100 to 20,000 ppm.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
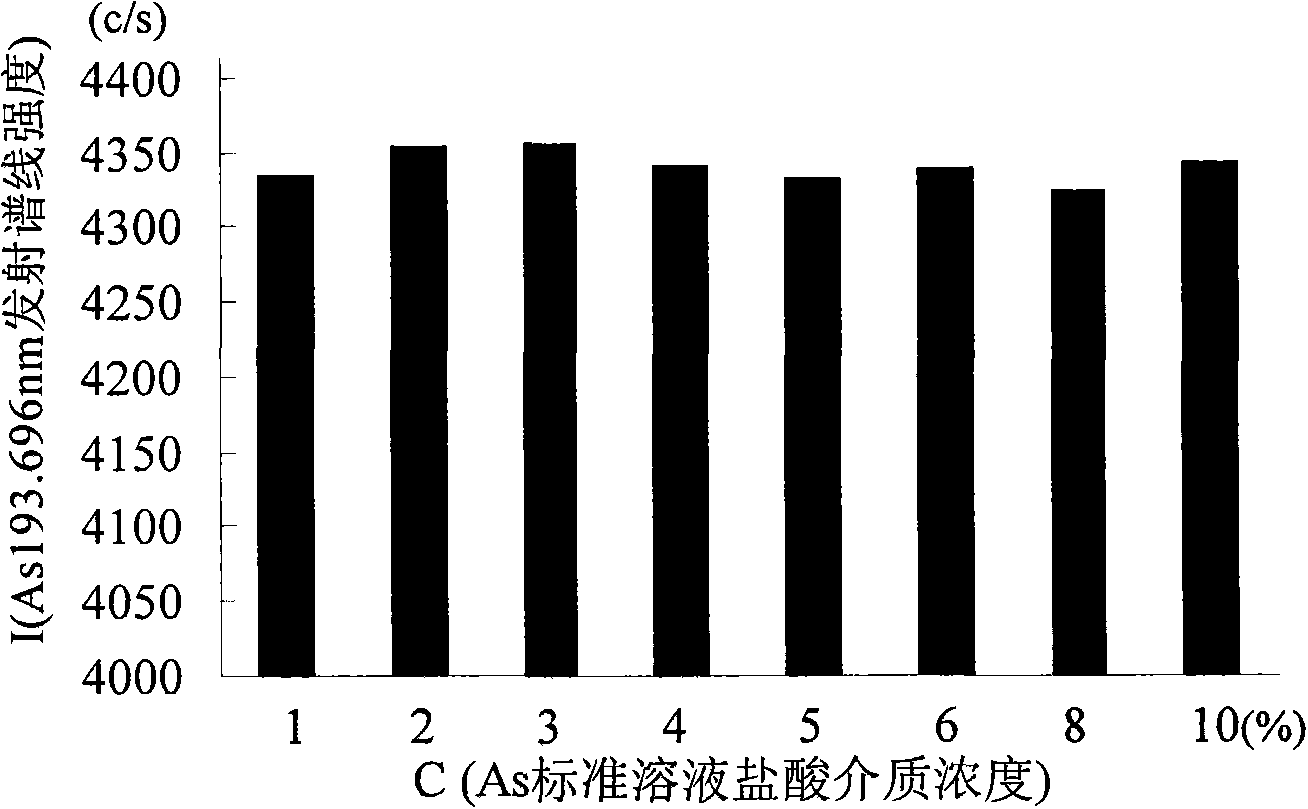
Stibium, barium, arsenic, zinc, strontium, zirconium rapid measuring method for TFT substrate glass
InactiveCN101344485AFit closelyImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by electrical excitationLinearityInductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy
The invention discloses a method that is used for quickly measuring the content of stibium, barium, arsenic, zinc, strontium and zirconium in a TFT substrate glass, realizes measurement on the basis of the inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, comprises the steps of experimental condition preparation, sample processing, working curve plotting, interfering and eliminating, and building of the linear relation condition, the detection limit condition and the accuracy condition of the method, wherein, the experimental condition preparation comprises instrument selection, acidity selection and analyzing spectral line selection; the sample processing comprises test sample processing, blank test fluid processing and the measurement, the working curve plotting comprises configuration of a solution in the standard series and the plotting of the working curve; the interfering and eliminating comprises chemical, physical and spectral interfering, background removing and building of the related coefficient between each measured element and the linear relation between the working curves; the blank sample is continuously measured for 10 times, the detection limit of the method is obtained according to a formula, the sample of the same TFT substrate glass is repeatedly measured for 10 times, the precision experiment is implemented, and finally the labeled recovery experiment of the sample is implemented.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Method of digesting, settling and separating tungsten-based samples and detection method for tungsten-based samples
ActiveCN102230861APreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectrophotometryInductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy
The invention discloses a method of digesting, settling and separating tungsten-based samples and a detection method for tungsten-based samples. The method of digesting, settling and separating tungsten-based samples comprises the following steps: putting a tungsten-based sample in a container, adding water and nitric acid into the container, keeping the container airtight, carrying out microwavedigestion and settlement-separation on the sample under gradient temperatures, and restarting microwave for rinsing and deposition after the temperature of the solution decreases and is close to the boiling point of water so as to obtain a sample solution for detection and precipitates of tungstic acid. The detection method for tungsten-based samples in the invention is to analyze the digested sample solution with at least one analytical method selected from the group consisting of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, flame atomic absorption spectrometry, graphite oven atomic absorption spectrometry and spectrophotometry so as to obtain the content of elements in the tungsten-based sample.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL +1
Method for clearing and detecting vanadic oxide
InactiveCN101532929AAvoid volatile lossAvoid pollutionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMulti methodPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for clearing and detecting vanadic oxide which includes steps as follows: taking vanadic oxide to a container, adding nitric acid to the container, processing pre-action under the normal temperature, then closing the container, processing microwave clearing. The detecting method includes steps as follows: using one or many methods of an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, a flame atomic absorption spectrometry and a graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for analyzing the cleared vanadic oxide, accordingly, obtaining elementary content of vanadic oxide sample.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +3
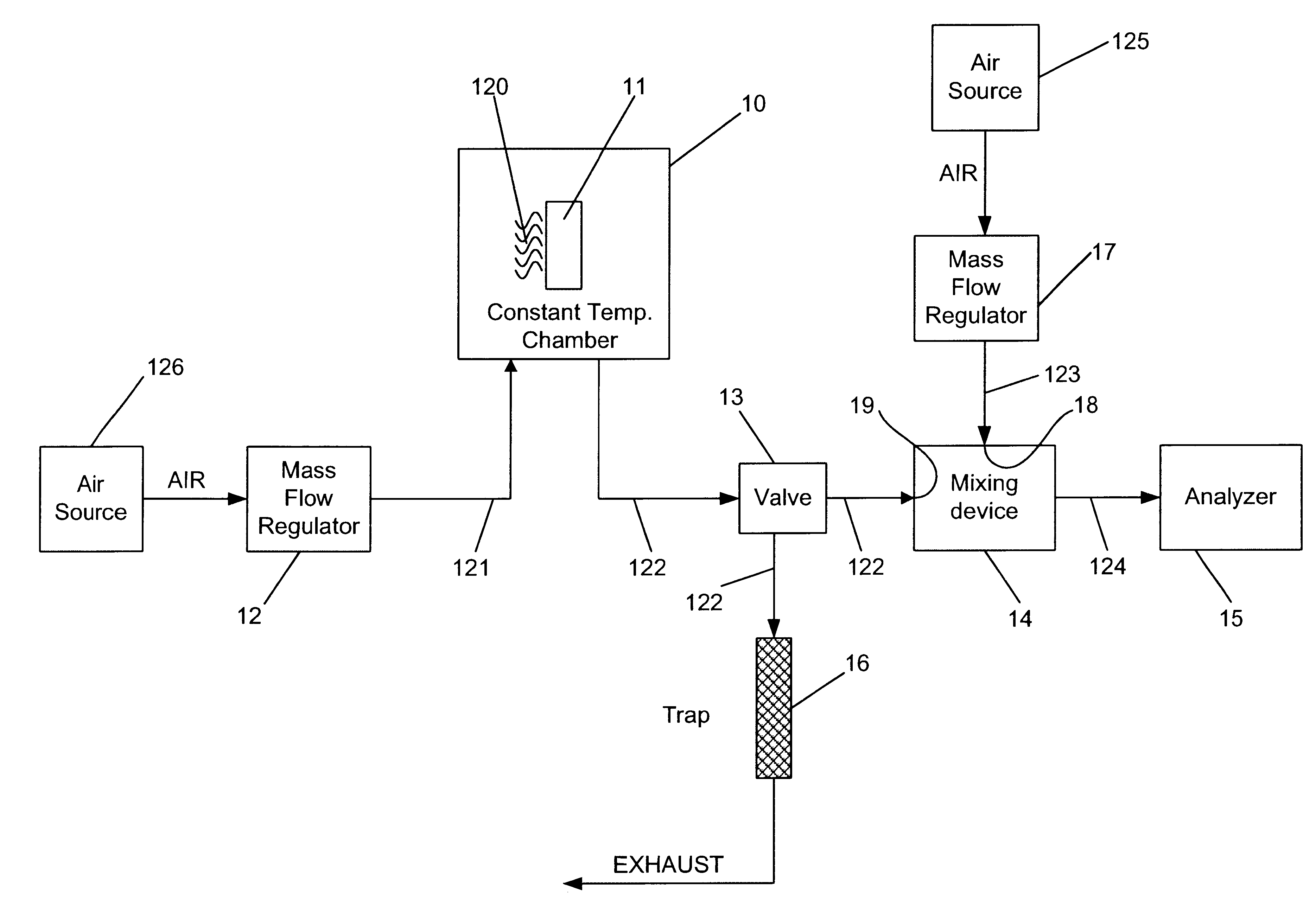
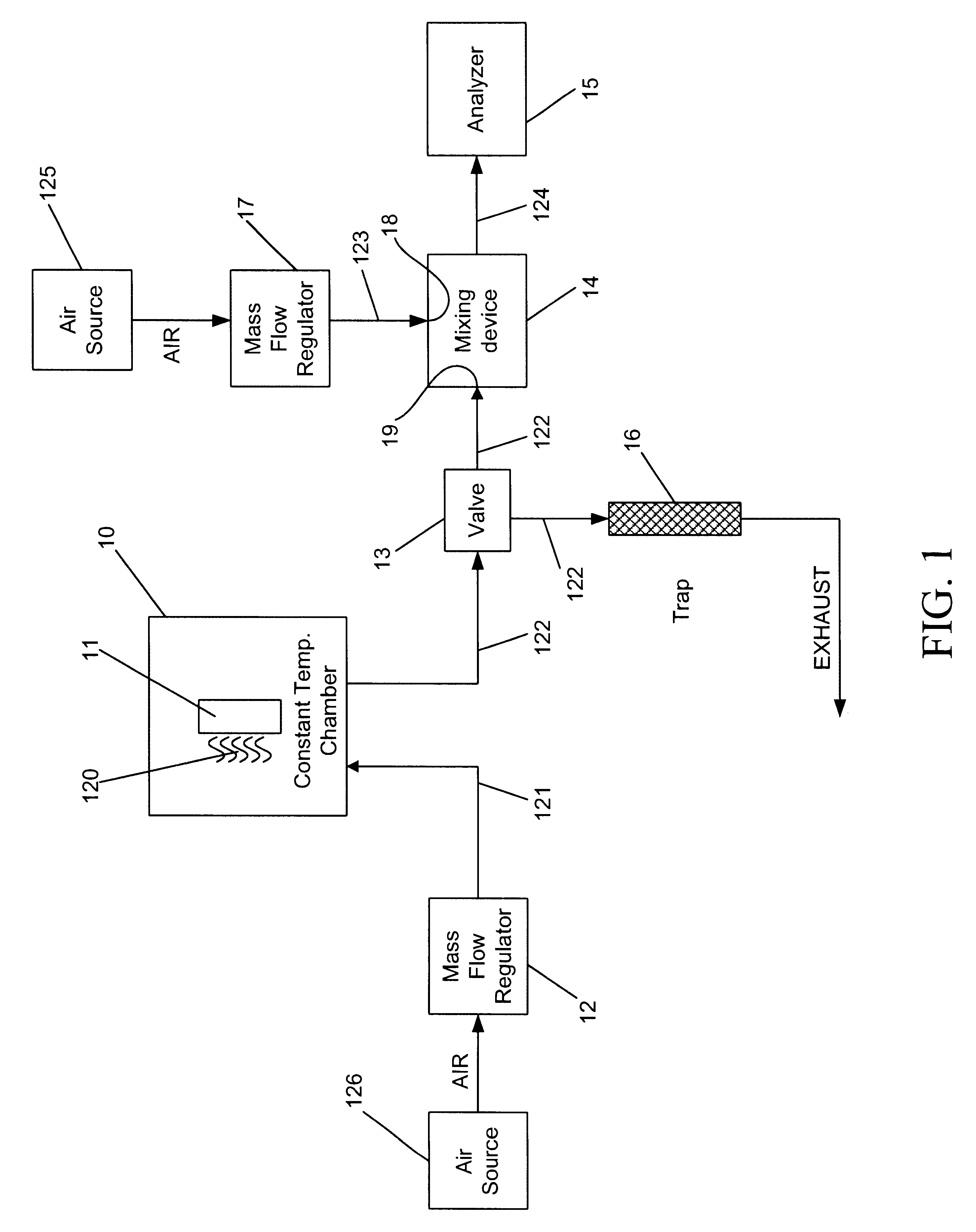
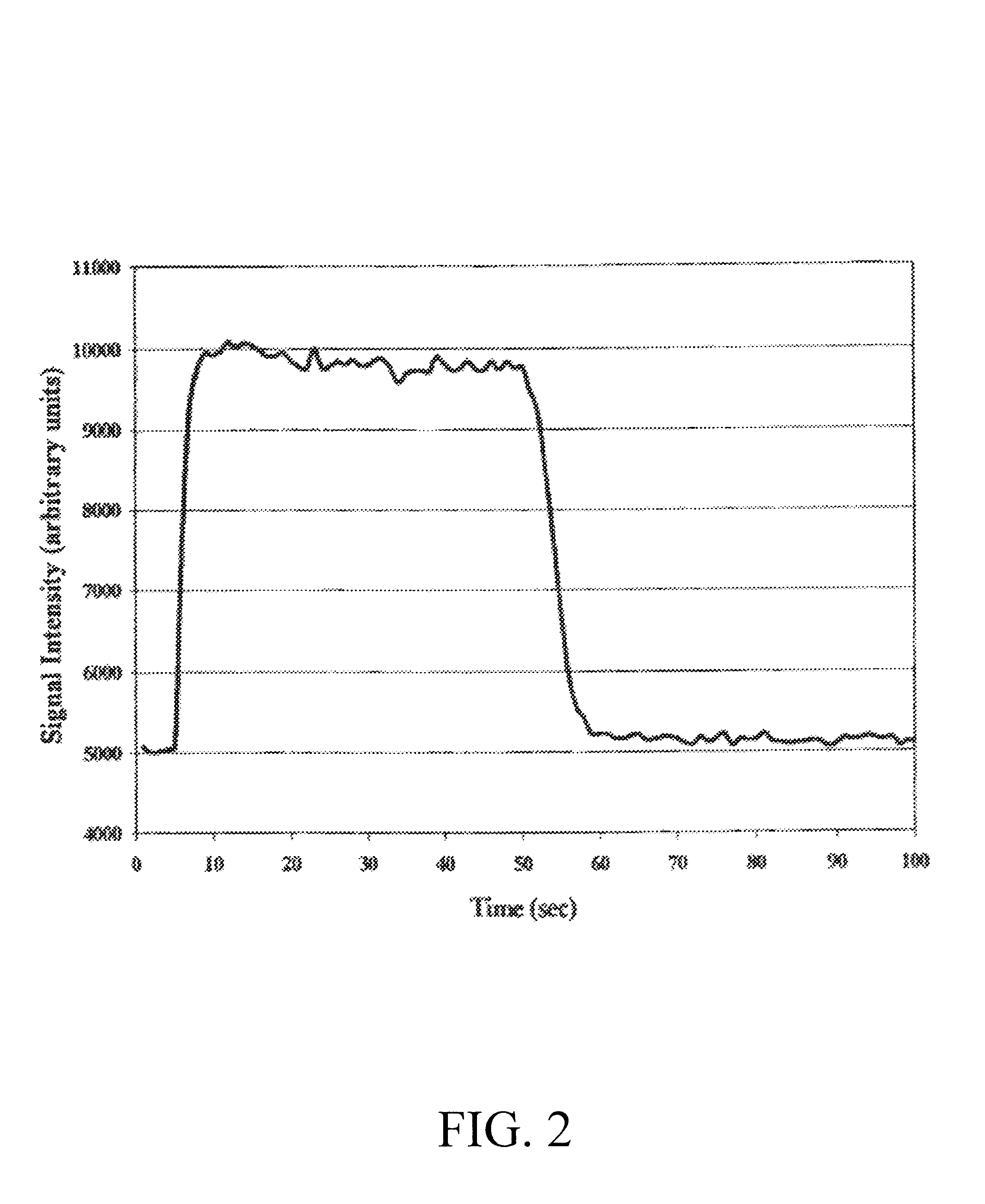
Calibration scheme for continuous monitoring of mercury emissions from stationary sources by plasma emission spectrometry
InactiveUS6690462B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLinear relationshipOptical emission spectrometry
The disclosed invention relates to a calibration method, system and apparatus for a multimetals continuous emissions monitor system (hereinafter "multimetals CEMS"). More specifically, this invention relates to a calibration scheme for continuous monitoring of mercury emissions from stationary sources by plasma emission spectrometry. A source of mercury vapor, preferably a mercury permeation tube, entrains mercury vapor into a constant flow of carrier air. The carrier air mixes with a constant flow of diluent air in an aerosol mixer. The mixer is operably coupled to the analyzer. A gaseous mixture having a calibration mercury concentration flows from the mixer into the analyzer at a constant rate. A graph having coordinates of analyzer signal intensity and mercury concentration is used to plot the calibration scheme. A first signal intensity generated by the analyzer in response to the calibration mercury concentration is used for the first plot on the graph. A second signal intensity generated by the analyzer in response to a blank having zero mercury concentration is used as the second plot on the graph. A linear relationship between the analyzer signal intensity and the mercury concentration on the graph is established from the first plot and the second plot. The slope intercept and slope are used to create a mathematical relationship between the analyzer signal intensity and the mercury concentration. This enables the analyzer to be calibrated by inserting a known mercury concentration into the analyzer and adjusting the signal intensity to conform to the signal intensity calculated from the graph or mathematical relationship.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
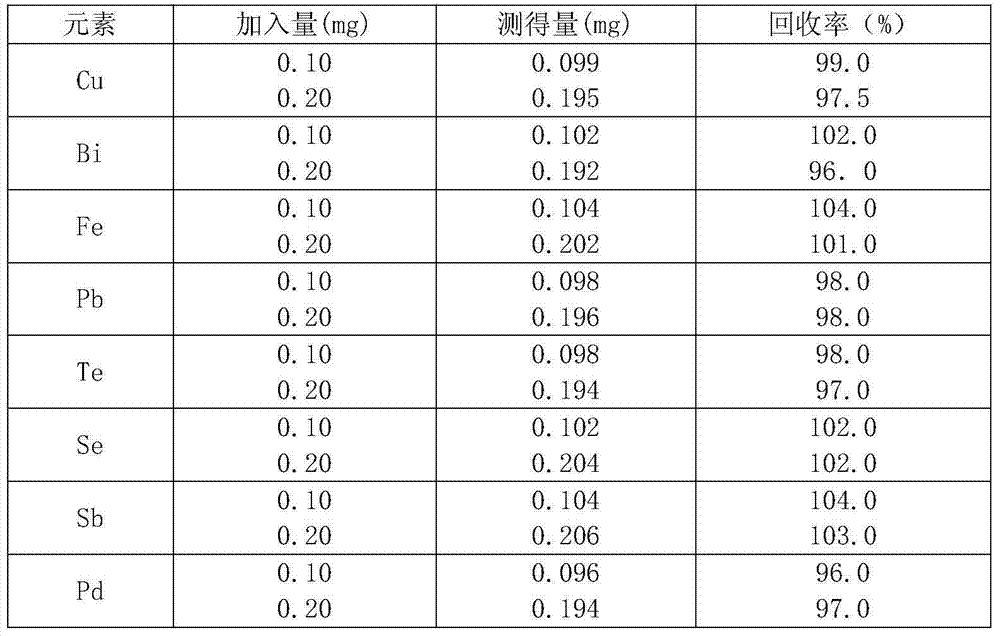
Method for synchronously detecting copper, bismuth, iron, lead, tellurium, selenium, antimony and palladium in electrolytic silver through ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry)
InactiveCN104237209AMeet the needs of rapid analysisReduce weightPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationSpectrographTe element
The invention relates to a method for synchronously detecting copper, bismuth, iron, lead, tellurium, selenium, antimony and palladium in electrolytic silver through ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry). The method is characterized in that the method for synchronously detecting copper, bismuth, iron, lead, tellurium, selenium, antimony and palladium in electrolytic silver by the ICP-AES is adopted. The method comprises the following main steps: sampling 5.0000g of electrolytic silver; decomposing the sample with proper amount of superior pure nitric acid; precipitating through proper amount of hydrochloric acid to obtain silver; filtering to obtain analytic solution to be detected; detecting the contents of eight impurity elements in the analytic solution to be detected by an ICP-AES spectrograph under a certain instrument working parameter conditions. Compared with the national standard GB / T11067 Silver Chemical Analysis Method, the method has the advantages that the detecting matrix is small in interference, weight impurity elements of copper, bismuth, iron, lead, tellurium, selenium, antimony and palladium can be quickly and synchronously detected, the detecting needs a short time, and thus the demand on quick analyzing of the electrolytic silver can be met.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
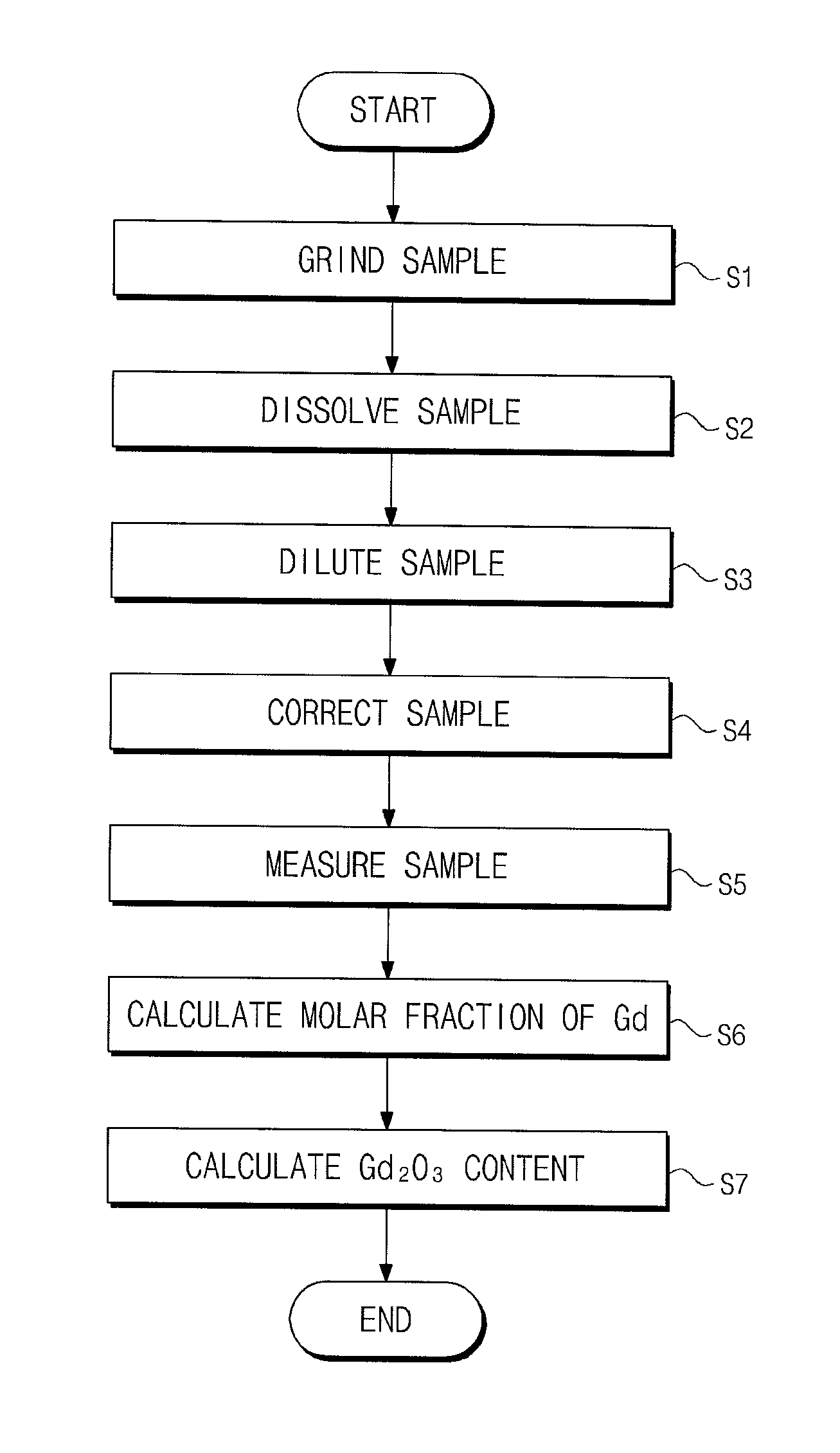
Method of measuring gadolinia content using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry
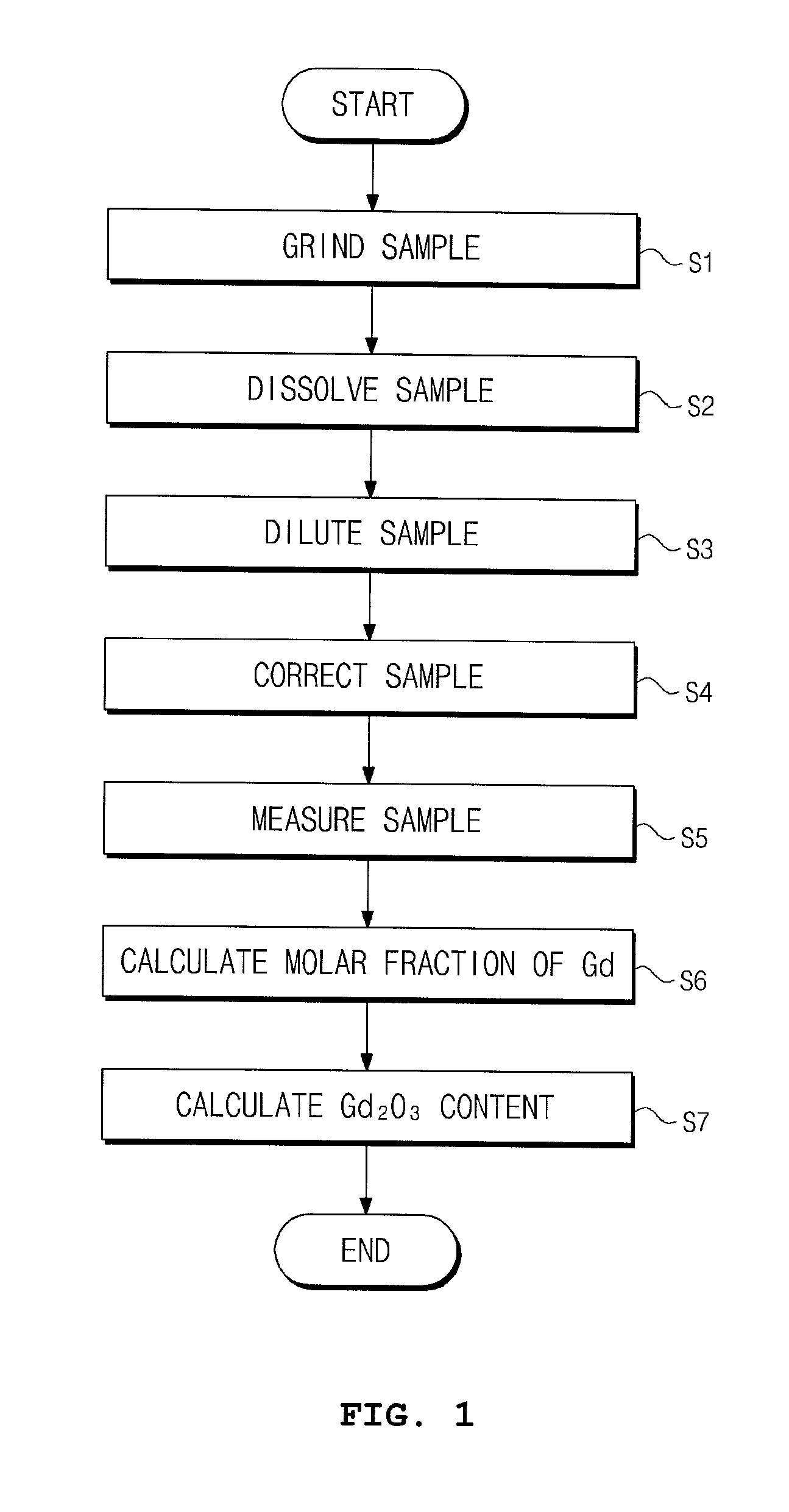
A method of measuring a gadolinia content using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry is provided. The method can include grinding sintered gadolinium using a percussion mortar to obtain a ground sample; warming the ground sample and then dissolving it with an acid solution to obtain dissolved gadolinia; diluting the dissolved gadolinia with distilled water to obtain a diluted gadolinia solution; measuring mass of each of a uranium element and a gadolinium element in the diluted gadolinia solution by a unit of ppm using the inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry; and calculating a molar fraction of gadolinium from the diluted gadolinia solution and then calculating the gadolinia content using the molar fraction of gadolinium.
Owner:KEPCO NUCLEAR FUEL CO LTD
Method for detecting impurity element in tungsten carbide
ActiveCN105823772ASuitable for accurate determinationSuitable for determinationPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationManganeseCobalt
The invention provides a method for detecting impurity elements in tungsten carbide, and concretely relates to the method for rapidly detecting tungsten carbide as well as cobalt, nickel, iron, titanium, aluminum, manganese, magnesium, vanadium, chromium, copper, and molybdenum in casting of tungsten carbide by using an inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. A sample is digested in an electrothermal digestion instrument by employing hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid, under condition that a tungsten matrix is not separated, the high purity tungsten matrix is used for preparing a standard work curve, spectrum interference of the tungsten matrix to a to-be-measured element is solved, optimum wavelength of each element is selected, background correction is carried out, and tungsten carbide as well as cobalt, nickel, iron, titanium, aluminum, manganese, magnesium, vanadium, chromium, copper, and molybdenum in casting of tungsten carbide are rapidly detected by using the inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. The detection method has the advantages of simple operation, short detection period, simple sample processing, and wide detection scope, and is suitable for batch production analysis.
Owner:ZIGONG CEMENTED CARBIDE CORP
Method for analyzing arsenic content in glass refining agent
InactiveCN101620186AAvoid volatile lossSimplify the analysis processAnalysis by thermal excitationOperabilityDigestion
The invention discloses a method for analyzing arsenic content in a glass refining agent, which comprises the following steps: processing samples by a potassium permanganate preoxidation-hydrofluoric acid wet digestion method to obtain a sample digestion solution; measuring the content of arsenic in the digestion solution by an inductance coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry. By using potassium permanganate as a pre-oxidizing agent to carry out routine wet acid digestion on glass refining agent samples, the method can effectively avoid volatilizable loss of low-valent arsenic components in the preliminary processing of the samples, therefore, a routine inductance coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometer can be used to directly measure the content of the effective content-arsenic in the glass refining agent without allocating a hydride generator or an atomic fluorescence spectrometer. The method has the advantages of high operability, high analysis speed, high accuracy and favorable sensitivity and repetitiveness.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for detecting and correcting inaccurate results in inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry
A method for detecting and correcting inaccurate results in inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). ICP-AES analysis is performed across a plurality of selected locations in the plasma on an unknown sample, collecting the light intensity at one or more selected wavelengths of one or more sought-for analytes, creating a first dataset. The first dataset is then calibrated with a calibration dataset creating a calibrated first dataset curve. If the calibrated first dataset curve has a variability along the location within the plasma for a selected wavelength, errors are present. Plasma-related errors are then corrected by diluting the unknown sample and performing the same ICP-AES analysis on the diluted unknown sample creating a calibrated second dataset curve (accounting for the dilution) for the one or more sought-for analytes. The cross-over point of the calibrated dataset curves yields the corrected value (free from plasma related errors) for each sought-for analyte.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Combined method for measuring content of impurity elements and matrix element niobium in niobium-iron alloy
ActiveCN103926236AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityAnalysis by thermal excitationNiobiumCombined method
The invention provides a combined method for measuring the content of impurity elements and a matrix element niobium in a niobium-iron alloy. The method comprises the following steps: digesting a sample at room temperature by concentrated hydrofluoric acid, concentrated nitric acid and concentrated hydrogen peroxide, thereby forming a to-be-measured solution; and respectively preparing series standard solutions comprising impurity elements and a niobium element, detecting the standard solutions by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, drawing an impurity element calibration curve and a niobium element calibration curve, measuring the to-be-measured solution by the inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, and combining the measurement result with the calibration curves to obtain the content of the impurity elements and the niobium element in the niobium-iron alloy sample. The method has the advantages that the content of the impurity elements such as silicon, tantalum, tungsten, titanium, aluminum, copper, phosphorus, manganese, lead, tin and vanadium and the content of the matrix element niobium in the niobium-iron alloy can be simultaneously measured; the method is high in accuracy and reliability and has the characteristics of convenience in operation, rapidness, environment friendliness, low cost and the like.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for measuring impurity in high pure gold by plasma atomic emission spectrometer
ActiveCN101349646AAccurate measurementEliminate distractionsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by electrical excitationAnalytical controlImpurity
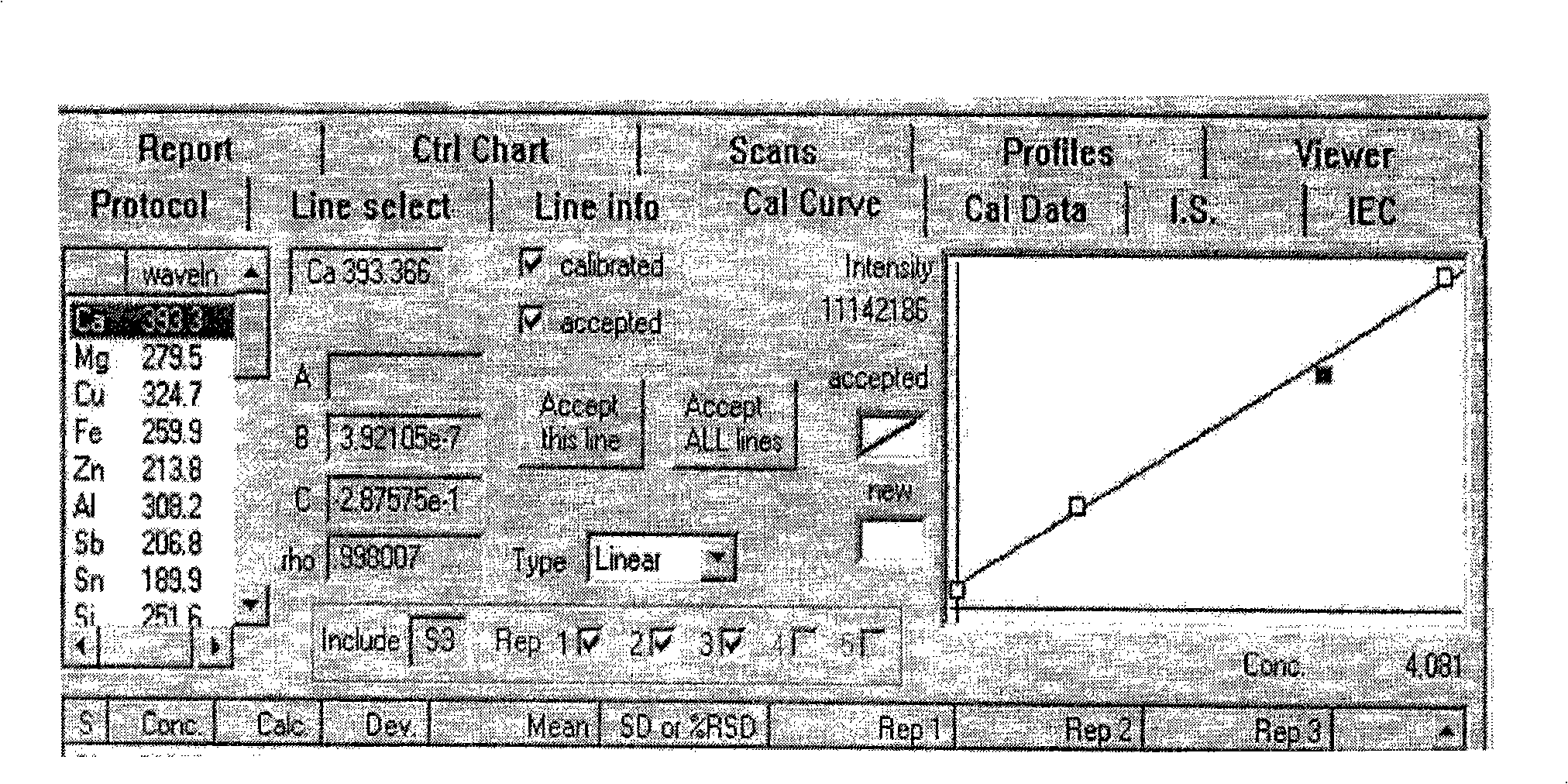
The invention relates to a method for using a plasma atomic emission spectrometer to measure impurities in high-purity gold, which comprises the following steps: weighing one unit of sample in a bunsen beaker, adding aqua regia to dissolve, replenishing hydrochloric acid deionized water to do constant volume to a scale after dissolving, respectively getting sample solution in more than two colorimetric tubes, solution in each tube is 15ml, adding gold standard solution which is mixed by elements according to a multiple relation in turn, doing constant volume by deionized water, starting the plasma atomic emission spectrometer, starting a circulating water pump, opening analytic control software, entering a 'standard addition method' control procedure, choosing a spectral line for measuring in a spectral line base, setting the concentration value of curved lines, scanning a whole band, sucking sample solution in each colorimetric tube in an instrument in turn according to the sequence that the concentration is from low to high, clicking a feeler switch to get an initial curve point of the point after sucking in each time, assuring curved lines, and leading the linear coefficient to be more than 0.99, outputting the concentration value result of each determined element, and calculating the result of the percentage content of each determined element according to the calculating formula.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NONFERROUS METALS & RARE EARTH
Method for rapidly measuring gold and silver in crude copper
InactiveCN103728289APreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationWorking environmentAnalysis method
The invention discloses a method for rapidly measuring gold and silver in crude copper and relates to a precious metal testing analysis method, in particular to a method for rapidly measuring precious metals of gold and silver in the crude copper. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps in the measuring process: (1) dissolving a crude copper sample by acid to separate out copper to obtain filter residues; (2) then dissolving the filter residues by mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid; (3) carrying out analytic determination of gold and silver by adopting an ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry). The method for rapidly measuring gold and silver in the crude copper, disclosed by the invention, is an analysis method of dissolving and separating a copper matrix by sulfuric acid, then directly dissolving the obtained filter residues by the mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid and measuring gold and silver in the crude copper on the ICP-AES; the method does not adopt the fire assay enrichment and ash blowing operation, improves the working environment of workers and shortens the analysis process.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Digestion method and detection method for vanadium-nitrogen-titanium-iron mixed alloy conductor
ActiveCN103808558APromotes fast digestionStable storagePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationAlloyDigestion
The invention provides a digestion method and a detection method for a vanadium-nitrogen-titanium-iron mixed alloy cored wire. The digestion method comprises the following steps: putting a cored wire into a container, adding a concentrated nitric acid and a concentrated hydrochloric acid to the container; carrying out first time of pre-reaction under an open state; adding a concentrated sulfuric acid and carrying out second time of pre-treatment under the open state; carrying out digestion and complexation reaction by microwave in a closed state, so as to obtain a solution. The detection method comprises the following steps: cooling the solution, diluting and fixing volume to obtain a sample solution; determining the content of elementary compositions in one or more sample solutions by using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, flame atomic absorption spectrometry, titration, spectrophotometry and an electrochemical process. The digestion method and the detection method have the advantages of being safe to operate, simple and rapid, efficient and complete, fewer in man-made factors, and easy to accurately control and repeatedly reappear, and technical indexes such as the accuracy, the precision and the like of an analysis result are improved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for measuring content of heavy metal in polymer
InactiveCN102928400AReduce dosageEasy to implementAnalysis by thermal excitationCadmium CationAntimony
The invention relates to a method for measuring the content of a heavy metal in a polymer, and in particular relates to a method for synchronously testing the contents of lead, cadmium, mercury, arsenic, antimony, tin, copper and zinc in the polymer by processing the polymer using oxygen bomb combustion, concentrating absorption liquid, carrying out acid digestion and subsequently using a plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) method. The method for measuring the content of the heavy metal in a polymer material comprises the following steps of: firstly, combusting oxygen bomb, secondly, carrying out acid digestion, and thirdly, testing by using an inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry instrument. The polymer is sufficiently combusted under a rich oxygen condition by using an oxygen combustion method, the combustion product is absorbed by water, and the absorption liquid is concentrated and subjected to acid digestion; and with the adoption of the method, the treatment to the polymer is efficient, simple, convenient and rapid.
Owner:谱尼测试集团深圳有限公司
Method for determining content of manganese, phosphorus, arsenic, potassium, sodium and copper in direct reduced iron
InactiveCN102252883AImprove accuracyEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationPotassiumManganese
The invention provides a method for determining the content of manganese, phosphorus, arsenic, potassium, sodium and copper in direct reduced iron. The method comprises the following steps: using the conventional inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry to determine spectral line strength of test sample liquid and getting the corresponding content values of the manganese, the phosphorus, the arsenic, the potassium, the sodium and the copper from standard working curves of the manganese, the phosphorus, the arsenic, the potassium, the sodium and the copper according to the spectral line strength, and the method is characterized by sequentially adding mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid and perchloric acid into a test sample for dissolving, adding dilute hydrochloric acid for dissolving salts and filtering the dissolved liquid so as to prepare the test sample liquid. Not only is the operation convenient, but also the determined content of the manganese, the phosphorus, the arsenic, the potassium, the sodium and the copper is high in accuracy and the determination result further has good stability, reproducibility and accuracy. Tests prove that the method in the invention is reliable and practical and can meet the daily need of determining the content of the manganese, the phosphorus, the arsenic, the potassium, the sodium and the copper in the direct reduced iron.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
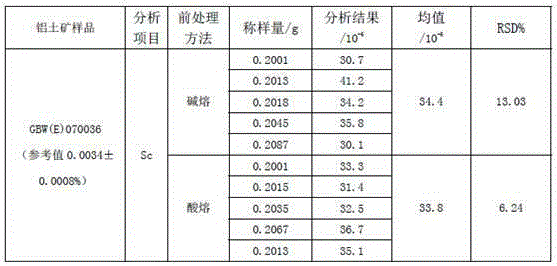
Method for determination of scandium in bauxite by microwave digestion inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry
InactiveCN105223050AReduce dosageReduce consumptionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by material excitationO-Phosphoric AcidScandium
The invention provides a method for determination of scandium in bauxite by microwave digestion inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Specifically, a sample is digested through hydrofluoric acid, nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide and phosphoric acid under the action of microwave, ultrapure water is added to a constant volume, an inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer is employed to determine Sc so as to realize accurate determination of the trace element Sc in the bauxite sample. The method provided by the invention reduces tedious operation process, employs microwave to digest the sample and direct instrument determination, and has no need for acid removal. Compared with the traditional sample processing method, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation steps, little reagent consumption, and rapid analysis speed. At the same time, the method employs microwave digestion to decompose the sample, and can greatly lower the reagent dosage, reduce the reagent blank and matrix interference, and improve the sensitivity and accuracy of analysis elements.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Determination method for calcium, cobalt, chromium and iron in tungsten carbide
InactiveCN103257136AAnalytical methods are accurate and reliableMeet the requirements of scientific research and productionAnalysis by thermal excitationMaterial resourcesDissolution
The invention provides a determination method for calcium, cobalt, chromium and iron in tungsten carbide. The method employs inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry for determination of the content of calcium, cobalt, chromium and iron in tungsten carbide, and analytical ranges are as follows: Ca 0.005 to 2%, Co 1 to 15%, Cr 1 to 15% and Fe 0.005 to 10%. According to the invention, a tungsten carbide sample can be effectively dissolved, so the problem of difficult dissolution of the sample is overcome and a sample dissolution speed is accelerated; an optimal analytical line is found through interference experiments and spectrum analysis, interference among spectral lines is eliminated, accurate and reliable determination of the content of calcium, cobalt, chromium and iron in tungsten carbide is realized, and requirements of scientific research and production are met; and the method has the advantages of rapid measurement, easy and convenient operation and conservation of considerable manpower and material resources.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
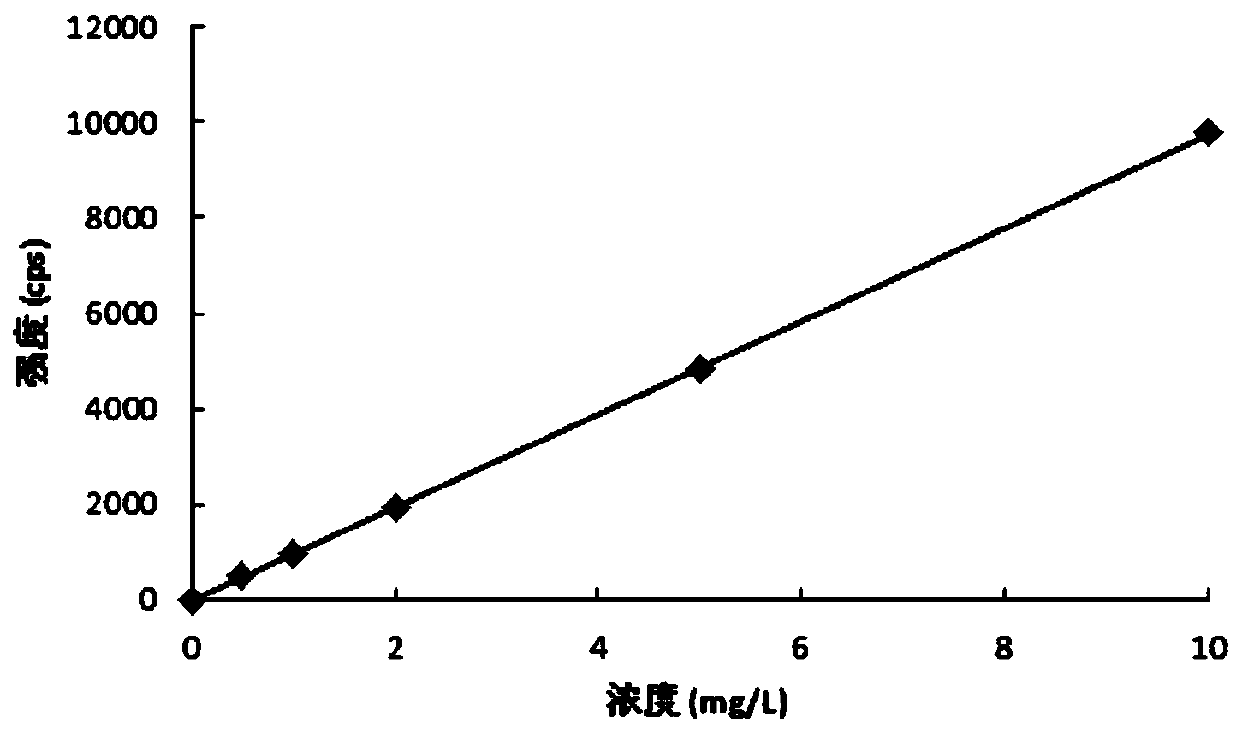
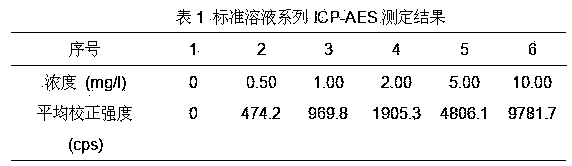
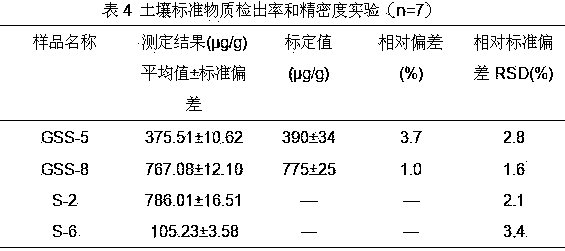
Method for testing total phosphorus in soil and sediments by virtue of microwave digestion ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry)
InactiveCN104198415AEasy and fast handlingEasy and fast determinationWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCorrelation coefficientRelative standard deviation
The invention provides a method for testing total phosphorus in soil and sediments by virtue of a microwave digestion ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry). According to the method, the recovery rate is 97.5%-106.2%, the relative standard deviation is 1.6%-3.4%, the detection limit is 5.74mg / kg (when the weighing dosage of a sample is 0.2500g and the volume of a digestion solution is set as 50ml); the correlation coefficient of a working curve is more than 0.9999 at 0-10.00mg / L, and the linearity is good; the method has no obvious difference from a national standard method on the testing result, and moreover the sample processing and testing processes are simple, convenient and rapid, so that the method has a preferable practical value.
Owner:浙江中一检测研究院股份有限公司
Preparation method of fusion reactor cladding neutrons and tritium breeding agent beryllium acid lithium pellets
InactiveCN103854706ASolve self-sustaining problemsImprove utilization efficiencyNuclear energy generationThermonuclear fusion reactorLithium hydroxideLithium titanate
The invention discloses a preparation method of fusion reactor cladding neutrons and tritium breeding agent beryllium acid lithium pellets. The preparation method of the fusion reactor cladding neutrons and tritium breeding agent beryllium acid lithium pellets comprises the following steps: preparing a beryllium acid lithium material, representing, preparing beryllium acid lithium pellets with the diameter of 1mm, detecting performances, preparing lithium hydroxide and beryllium oxide raw materials at room temperature, putting into a container according to the proportion of 1 of Li / Bi molecule mole ratio, rotating and stirring for about 20 hours, mixing fully and uniformly, putting dried gel in a sintering furnace, warming to 1073K under an air environment, forging for 5 hours, and carrying out solid phase reaction fully; taking a beryllium acid lithium sample, grinding fully into particles, analyzing the formation of components by adopting XDR (external data representation; analyzing the Li / Bi mole ratio by adopting ICP-AES (inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry). According to the invention, the problem that when lithium silicate or lithium titanate pellets are originally adopted as breeding agents, a plurality of layers of beryllium zone breeding neutrons are required to be arranged in a cladding is overcome, so that the utilization efficiency of breeding agents in a limited space of the cladding is improved extremely, and the fusion reactor tritium self-sustaining difficulty can be solved effectively.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军军官学院
Inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry for determining elements in nuclear-grade zirconium alloy
InactiveCN104568916ASimplify detection stepsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationNuclear gradeRelative standard deviation
The invention discloses an inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry for determining elements in a nuclear-grade zirconium alloy. The inductive coupling plasma atomic emission spectrometry is used for determining 4 types of macroelements and 13 types of trace elements in the nuclear-grade zirconium alloy. The macroelements including tin, niobium, iron and chromium, and the trace elements including aluminum, cobalt, copper, molybdenum, magnesium, manganese, nickel, lead, silicon, tantalum, titanium, vanadium and tungsten in the nuclear-grade zirconium alloy are successfully determined by carrying out base body match on high-purity sponge zirconium and main alloy elements and selecting a suitable spectral line as an analysis line of detected elements. The determination of tin, iron, chromium and nickel in a 360b zirconium alloy in NIST is carried out and determination results are the same as standard values of a standard substance certificate. The nuclear-grade zirconium alloy is subjected to a marking recovery test; and a result shows that the recovery rates of niobium, cobalt, copper, molybdenum, magnesium, manganese, silicon, titanium, vanadium and tungsten are 92%-108% except that the recovery rate of tantalum is low and the recovery rates of aluminum and lead are high. According to the method, the determination result is stable; and the relative standard deviations (RSD) of the determination results of 3 days are lower than 6% and can meet the requirements of Westinghouse certification standards (RSD is less than 10%).
Owner:QINGDAO TIANHENG MACHINERY
Method for determining tungsten content in ferroniobium
InactiveCN104062284AQuick analysisAccurate analysisPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationO-Phosphoric AcidAcid dissolution
The invention discloses a method for determining tungsten content in ferroniobium. The method comprises steps of pre-treating, preparing a standard solution and determining. The method comprises the specific steps of adding hydrofluoric acid into a sample to be tested; dropwise adding concentrated nitric acid and adding concentrated phosphoric acid and sulfuric acid; dissolving the test sample and making up to the volume; and uniformly shaking for later detection; drawing a tungsten spectral line intensity-mass fraction working curve on a plasma atomic emission spectrometer by a prepared tungsten standard solution; and analyzing the sample to be tested by using the curve to obtain the tungsten content in the ferroniobium. According to the method, a plasma atomic emission spectrometry is used for determining the tungsten content in the ferroniobium to make up the technical blank of a detection project; reagents and time are saved and the labor cost is also saved; the tungsten content in the ferroniobium can be rapidly and accurately analyzed; the checking requirements of products of iron and steel enterprises in a ferroniobium utilization process are met. The method is convenient and rapid to operate, the analyzing cost is low; a determination result has good stability, repeatability and accuracy; the determination requirements on the tungsten content in the daily ferroniobium can be met.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
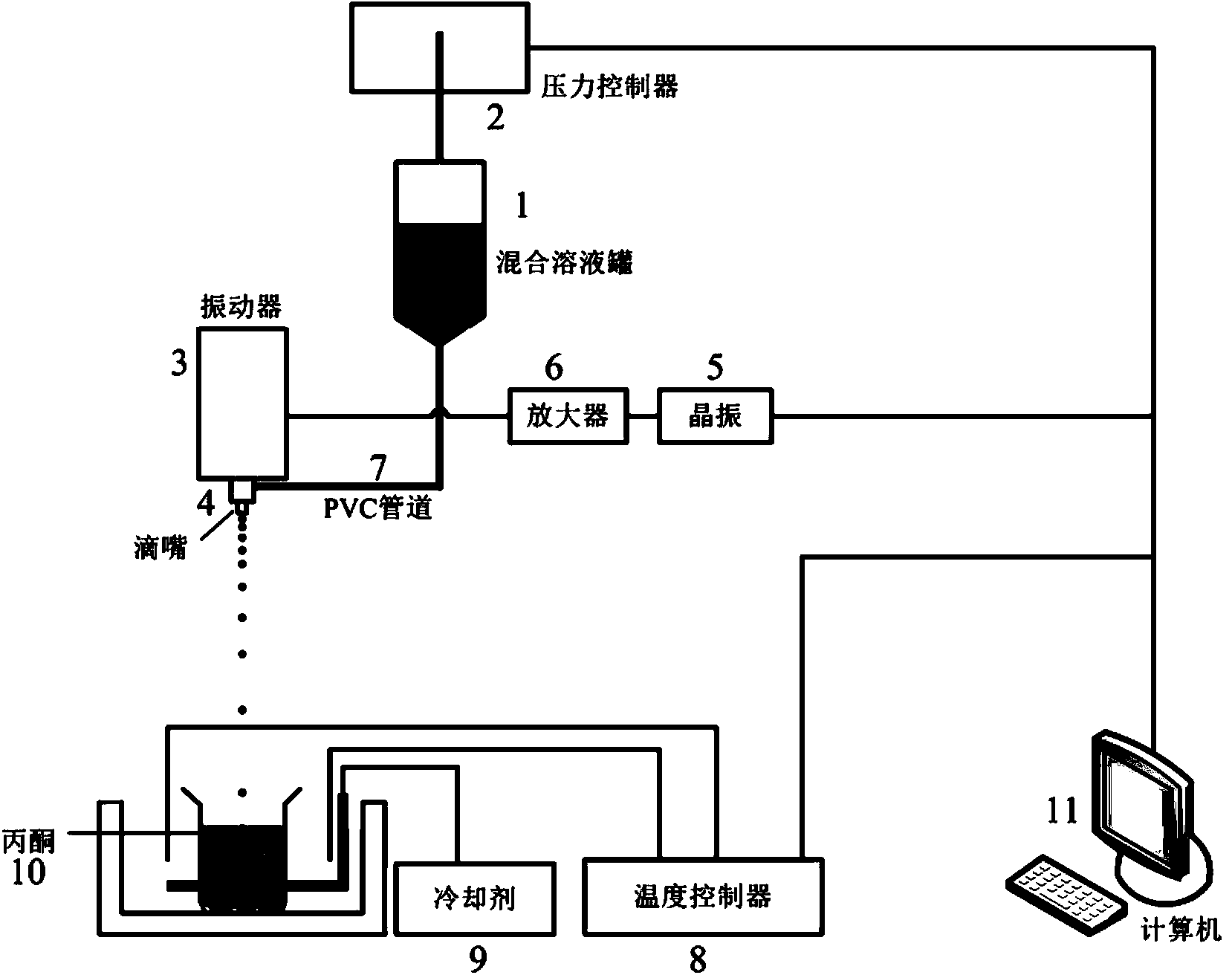
Microwave plasma atomic emission spectrometry directly analyzing solid sample and system thereof
ActiveCN107664633AEasy to carryFast testAnalysis by thermal excitationCollection systemData analysis system
The invention discloses a microwave plasma atomic emission spectrometry and system allowing solid sampling. The method comprises the following steps of (1) using a standard solid sample with element content known as a reference substance directly or tableting the standard solid sample to obtain the reference substance; (2) using a to-be-tested solid sample as a reference substance directly or tableting the to-be-tested solid sample to obtain a test article; and (3) detecting the reference substance and the test article by the microwave plasma spectrometer, selecting an element characteristic spectrum according to a detection result of the reference substance, drawing a standard curve, and calculating according to a position and / or strength of each spectrum in the test article so as to obtain the type and / or content of each element in the test article. The invention further discloses a microwave plasma atomic emission spectrometer that comprises a microwave plasma system, an air transmission system, a sample bearing system, a signal collection system and a data analysis system. The test method is easy to operate, has high analysis speed, uses no chemical reagents, and is environment-friendly.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Measuring method for content of aluminium in water by utilizing ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry)
The invention discloses a measuring method for the content of metal aluminium in water. The method can be used for measuring the content of the metal aluminium in the water by adopting an ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry) method. The measuring method comprises the following steps of: firstly dissolving an aqueous-solution sample containing the aluminium, and carrying out secondary heating for digestion by adding a certain amount of sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide solution and hydrochloric acid solution to so as to effectively dissolve the metal aluminium; then measuring the content of the aluminium by adopting an ICP-AES spectrometer. By adoption of the method for detection, the matrix interference is small, and the need for production can be met.
Owner:四川国测检测技术有限公司
Method for measuring content of metal element cadmium Cd by ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry) method
The invention relates to a method for measuring metal element cadmium Cd in slag, which is used for measuring the content of trace metal cadmium by an ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry). The method comprises the following steps of: fetching 0.05-0.1g of slag sample; putting the sample into a high-temperature high-pressure digestion tank, and adding a proper amount of potassium permanganate, nitric acid and hydrochloric acid for digestion; putting the high-pressure digestion tank with sample liquid into a blast drying oven, and performing high-temperature digestion in an environment at 200-220 DEG C to obtain a digestion sample; and measuring the content of metal element cadmium Cd in an analysis solution according to certain instrument working parameters by use of the ICP-AES. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of sufficient digestion of measured samples, short measurement time and simple technology, and can meet the needs for production and life.
Owner:广东量源检测技术有限公司
Method for measuring content of plumbum element in soil with ICP method
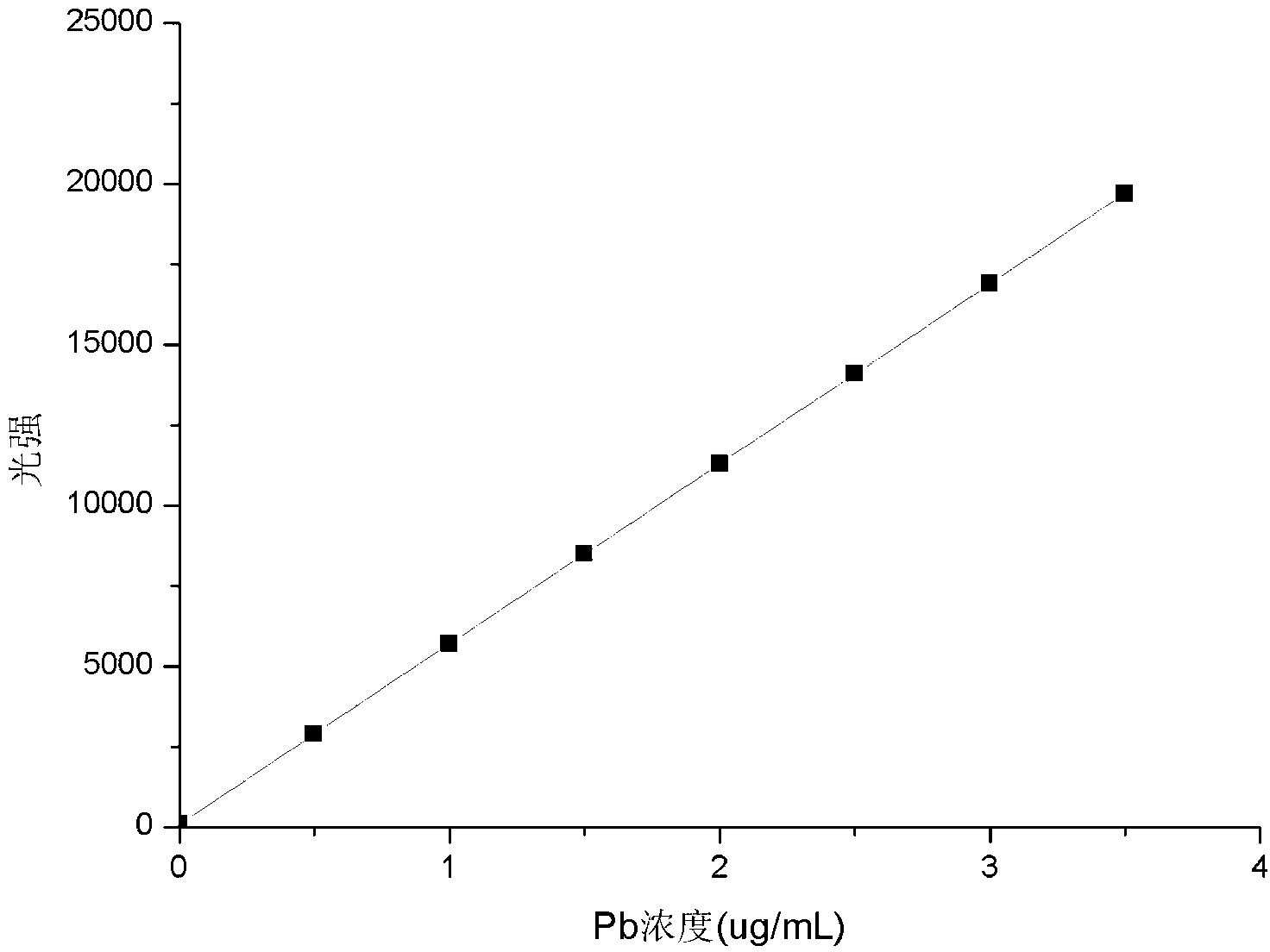
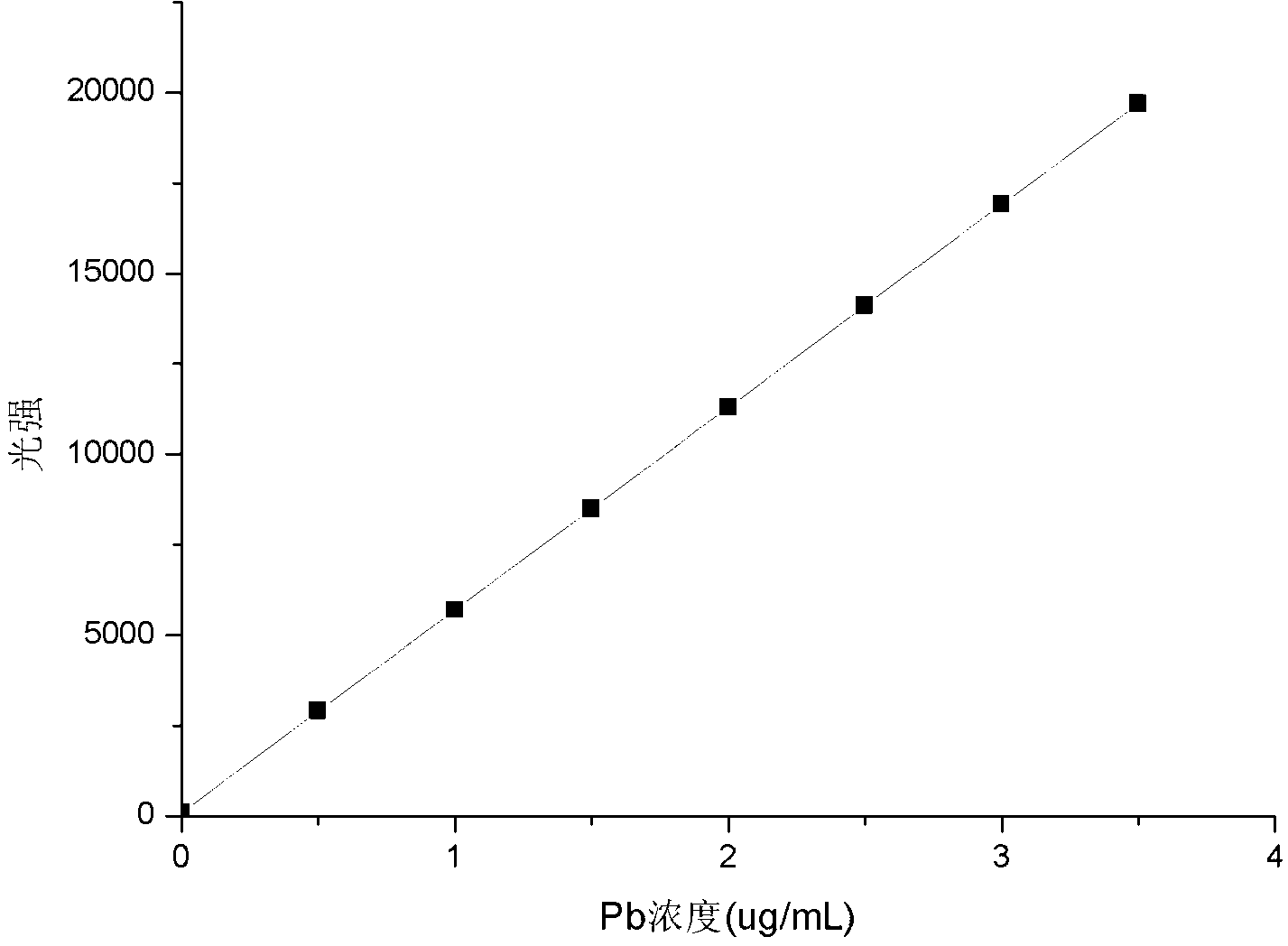
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of a plumbum element in soil with an ICP (inductively coupled plasma) method. An ICP-AES (atomic emission spectrometry) method is used for measuring the content of plumbum in a soil sample. The method comprises the steps as follows: a certain amount of a hydrofluoric acid solution is added to a lead-bearing sample in the soil, then high-concentration nitric acid and high-concentration sulfuric acid are added, and then microwave digestion is performed; and high-temperature digestion is performed in a focus digestion tank, then an ICP-AES spectrograph is used for measuring the content of plumbum, and during measurement, experiment parameters are chosen reasonably according to requirements of an experiment, so that the content of plumbum in the soil sample can be measured more conveniently, rapidly and accurately. The detection limit of the method is 0.15 mu g / mL, and requirements of production and living can be met.
Owner:HANGZHOU PROCESS DETECTION TECH CO LTD
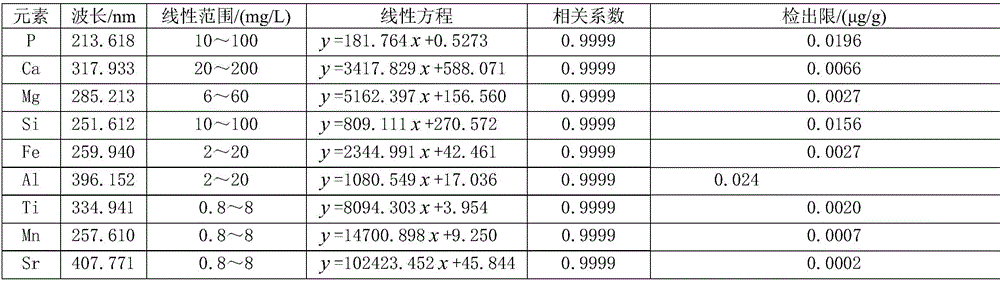
Method for simultaneously determining content of phosphorus, magnesium, iron, aluminum, silicon, calcium, titanium, manganese and strontium in phosphorite by adopting ICP-AES
InactiveCN106290318ANo distractionNo apparent interferencePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationLithium metaborateLithium bromide
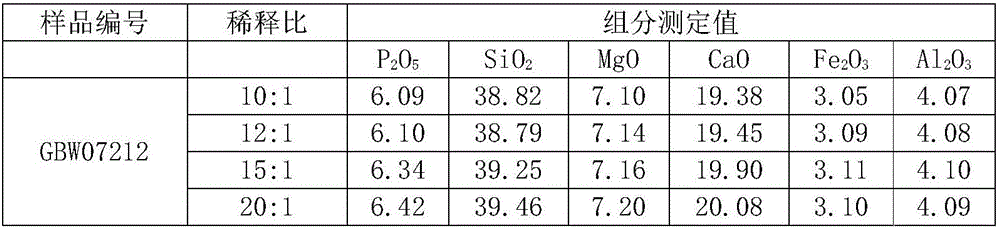
The invention relates to the technical field of analysis test, and in particular relates to a method for simultaneously determining content of phosphorus, magnesium, iron, aluminum, silicon, calcium, titanium, manganese and strontium in phosphorite by adopting inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). Specifically, lithium metaborate is a non-oxidant solvent with a high melt point, has high decomposition capacity for a majority of test samples, and can effectively decompose rocks and minerals difficult to dissolve. The method comprises the following steps: placing a phosphorite test sample into a platinum crucible, adding the lithium metaborate solvent and a lithium bromide releasing agent, melting and decomposing the phosphorite sample by using a high-frequency sample melting machine, pouring in a polytetrafluoroethylene beaker with 10 percent nitric acid at a high temperature by virtue of a magnetic stirrer, after the primary sample melting acidification sizing, performing matrix matching by adopting a national grade-I phosphorite, establishing a standard curve by adopting a Yttrium internal standard method, and determining the content of phosphorus pentoxide, magnesium oxide, iron oxide, aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, calcium oxide, titanium oxide, manganese oxide and strontium oxide in the phosphorite by adopting the ICP-AES. The method has the advantages of rapidness, convenience and accuracy, and is particularly suitable for batch determining the phosphorite samples.
Owner:YUNNAN PHOSPHATE CHEM GROUP CORP
Aqueous dispersion for chemical mechanical polishing and chemical mechanical polishing method
InactiveUS8506359B2Raise the pHGood dispersionOther chemical processesDecorative surface effectsIon contentIon chromatography
A chemical mechanical polishing aqueous dispersion including (A) silica particles, and (B1) an organic acid, the sodium content, the potassium content, and the ammonium ion content of the silica particles (A) determined by ICP atomic emission spectrometry, ICP mass spectrometry, or ammonium ion quantitative analysis using ion chromatography having a relationship in which the sodium content is 5 to 500 ppm and at least one of the potassium content and the ammonium ion content is 100 to 20,000 ppm.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com