Method for detecting impurity element in tungsten carbide
A technology of impurity elements and detection methods, applied in the field of detection, can solve the problems of long analysis period, low detection results, narrow detection range, etc., and achieve the effects of eliminating tungsten spectral interference, simple sample processing, and simple operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1 (No. 1 sample)
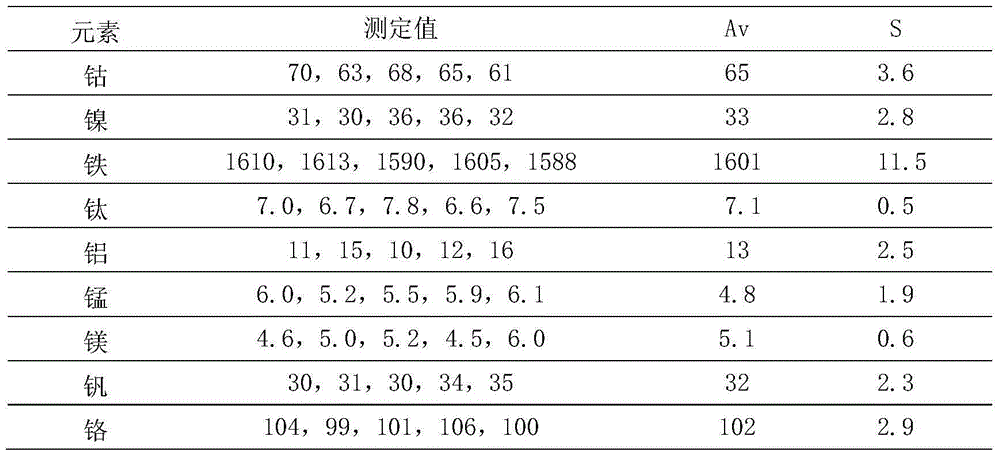
[0037] Detect the amount of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid of cobalt, nickel, iron, titanium, aluminum, manganese, magnesium, vanadium, chromium, copper, molybdenum in single crystal cast tungsten carbide and the detection wavelength of the elements to be measured.
[0038] 1. Reagents
[0039] Nitric acid (excellent grade)
[0040] Hydrofluoric acid (excellent grade)
[0041] PTFE digestion tube (50mL)
[0042] Polyvinyl chloride volumetric flask (100mL)
[0043] PTFE reagent bottle (100mL)
[0044] High-purity argon (≥99.99%): After being purified by an argon purifier, the purity reaches ≥99.999%.
[0045] High-purity tungsten powder (≥99.99%)
[0046] Single element standard storage solution: national standard solution, cobalt, nickel, iron, titanium, aluminum, manganese, magnesium, vanadium, chromium, copper, molybdenum, the concentration is 1000μg / mL.
[0047] Standard solution 1: (medium: acidic) Use an automatic pipette gun t...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2 (No. 2 sample)
[0068] Detect the amount of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid of cobalt, nickel, iron, titanium, aluminum, manganese, magnesium, vanadium, chromium, copper, molybdenum in tungsten carbide and the detection wavelength of the analyte.
[0069] 1. Test reagent
[0070] With embodiment 1.
[0071] 2. Instruments and equipment
[0072] With embodiment 1.
[0073] Step 1 Prepare standard working curve
[0074] Weigh four parts of 0.0940g high-purity tungsten powder matrix in parallel, place them in four 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene digestion tubes, rinse the tube wall with 1mL water, add 1.0mL hydrofluoric acid, 2.0mL nitric acid, and cover the digestion tube cap , digested in a 160°C electrothermal digestion apparatus for 15min. Dissolve the sample completely, take it off and cool slightly, and transfer the test solution into a 100mL polyvinyl chloride volumetric flask, and all the other operations are the same as in Example 1.
[0075] St...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Embodiment 3 (No. 3 sample)
[0086] Detect the amount of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid of cobalt, nickel, iron, titanium, aluminum, manganese, magnesium, vanadium, chromium, copper, molybdenum in tungsten carbide and the detection wavelength of the analyte.
[0087] 1. Test reagent
[0088] With embodiment 1.
[0089] 2. Instruments and equipment
[0090] With embodiment 1.
[0091] Step 1 Prepare standard working curve
[0092] Weigh four parts of 0.4700g high-purity tungsten powder matrix in parallel, place them in four 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene digestion tubes, rinse the tube wall with 3mL water, add 3.0mL hydrofluoric acid, 5.0mL nitric acid, and cover the digestion tube cap , digested in a 200°C electrothermal digestion apparatus for 20min. Dissolve the sample completely, take it off and cool slightly, and transfer the test solution into a 100mL polyvinyl chloride volumetric flask, and all the other operations are the same as in Example 1.
[0093] St...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com