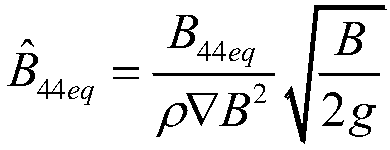Patents
Literature
1160 results about "Incident wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
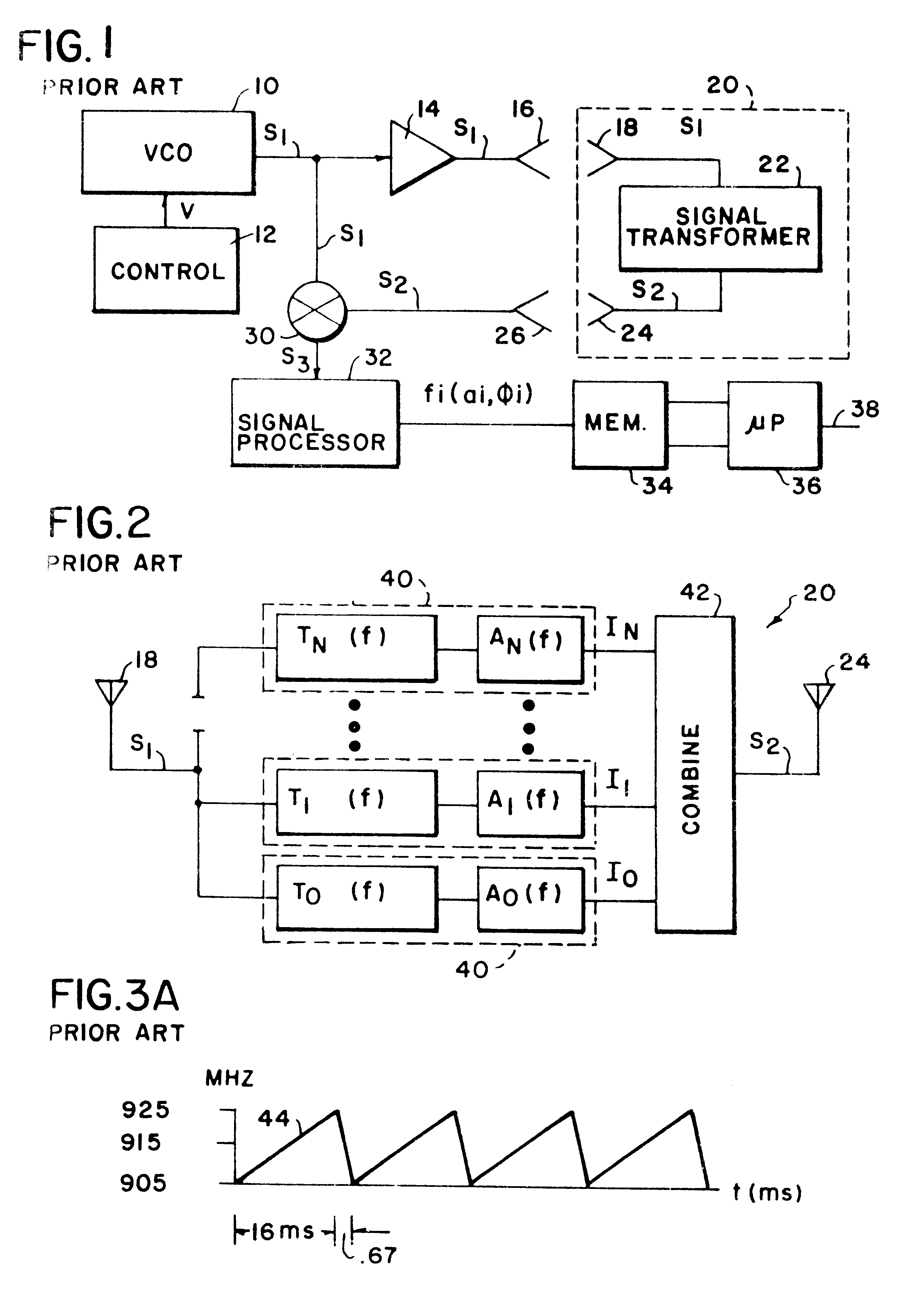
Incident Wave. An incident wave is a current or voltage wave that travels through a transmission line from the generating source towards the load.
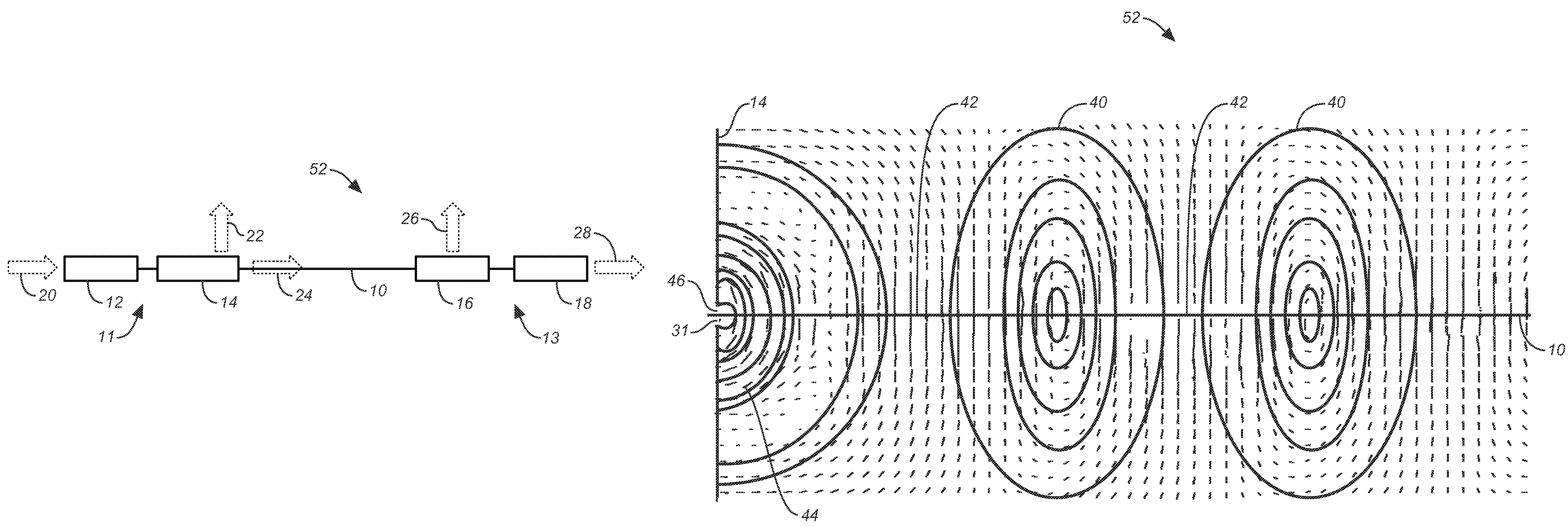
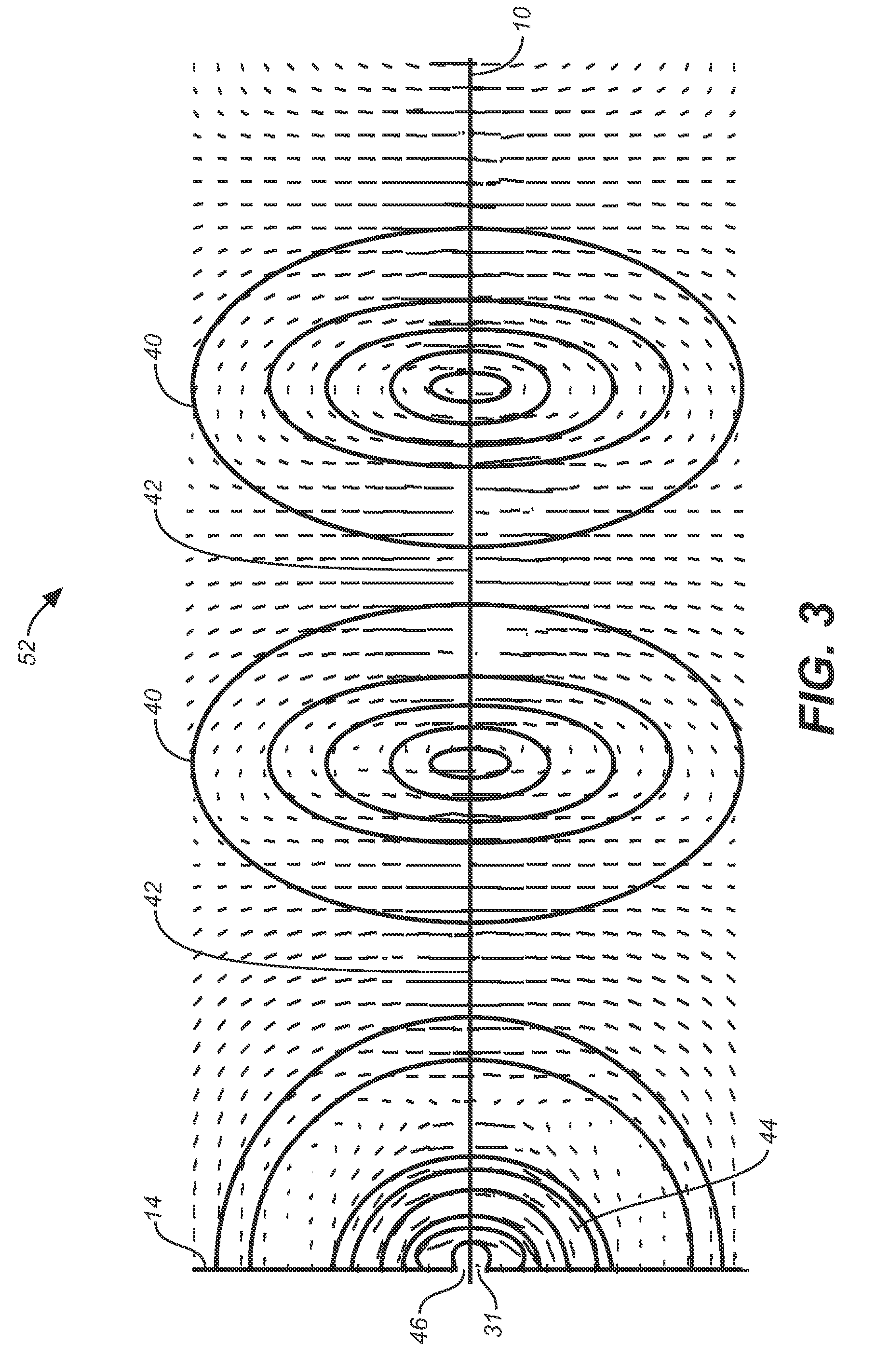
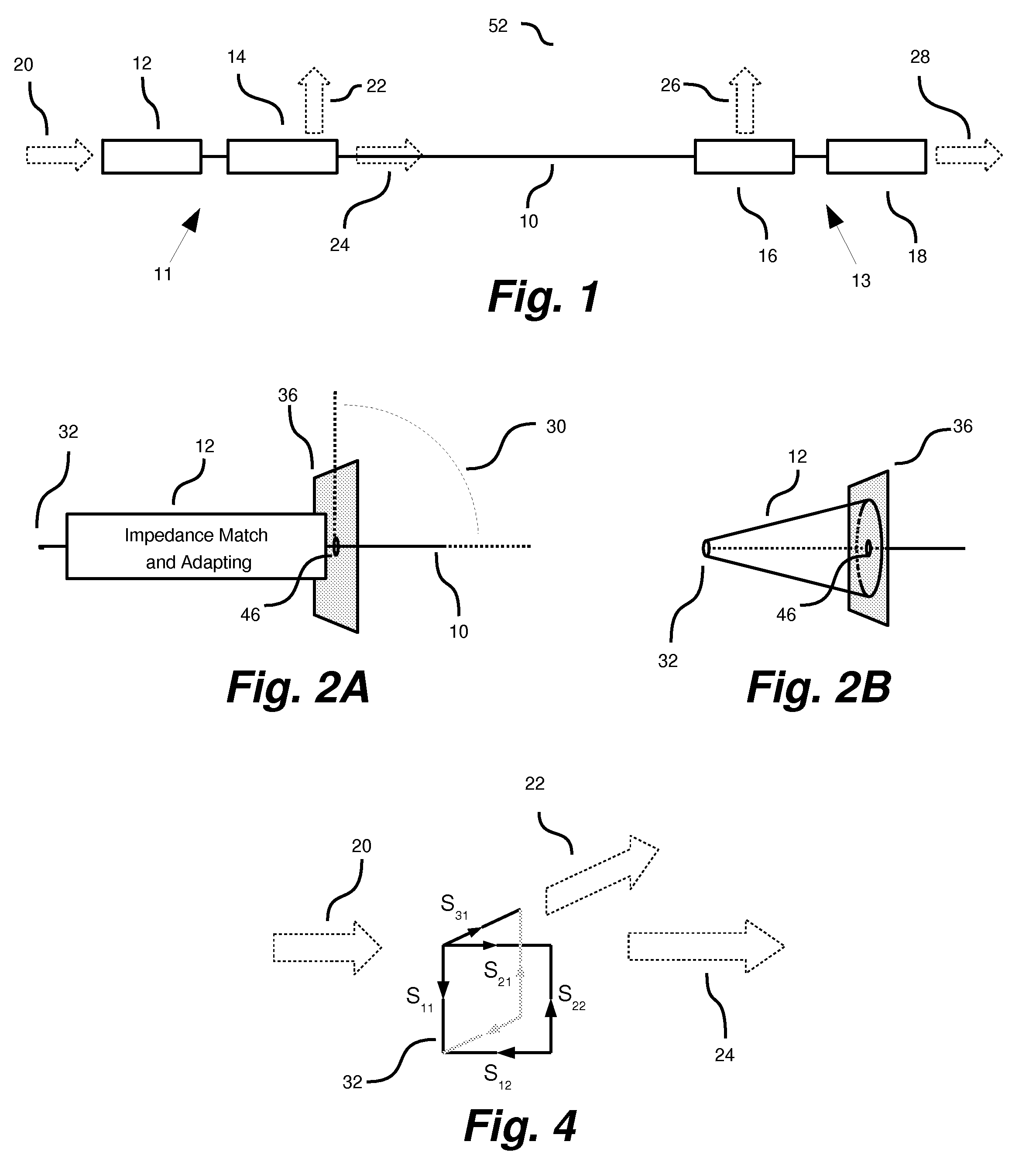
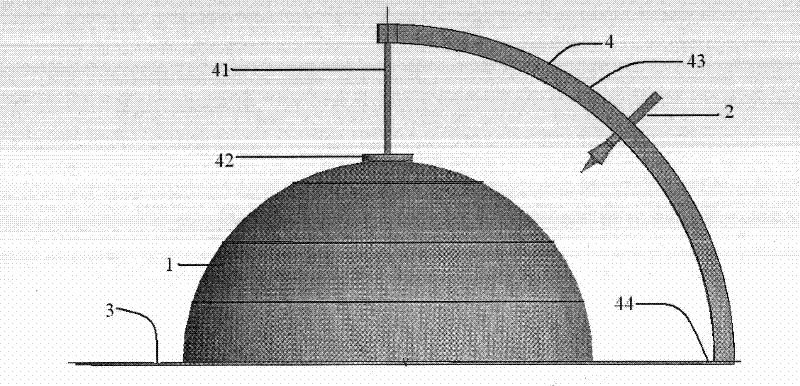
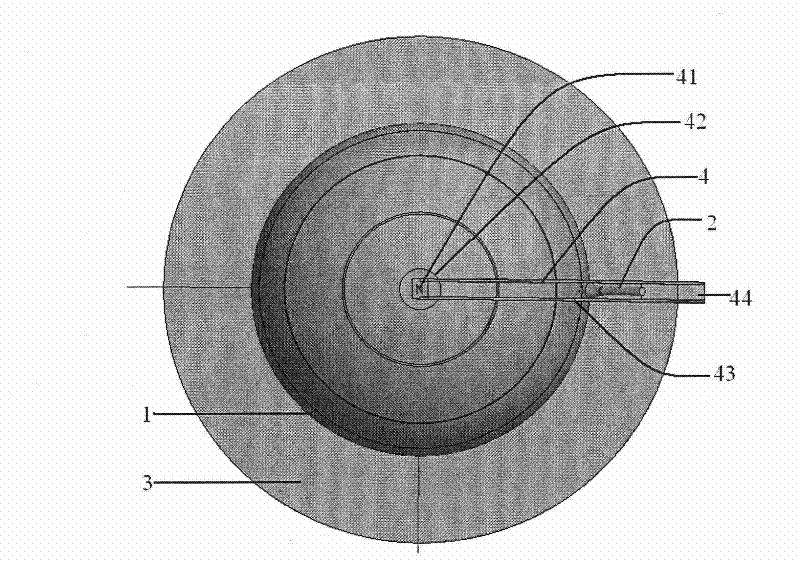
Surface wave transmission system over a single conductor having E-fields terminating along the conductor
ActiveUS7567154B2Reduce energy costsEnable economicMultiple-port networksWaveguidesElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
A low attenuation surface wave transmission line system for launching surface waves on a bare and unconditioned conductor, such as are found in abundance in the power transmission lines of the existing power grids. The conductors within the power grid typically lack dielectric and special conditioning. Accordingly, the present invention includes a first launcher, preferably including a mode converter and an adapter, for receiving an incident wave of electromagnetic energy and propagating a surface wave longitudinally on the power lines. The system includes at least one other launcher, and more likely a number of other launchers, spaced apart from one another along the constellation of transmission lines. The system and associated electric fields along any given conductor are radially and longitudinally symmetrical.
Owner:CORRIDOR SYST INC
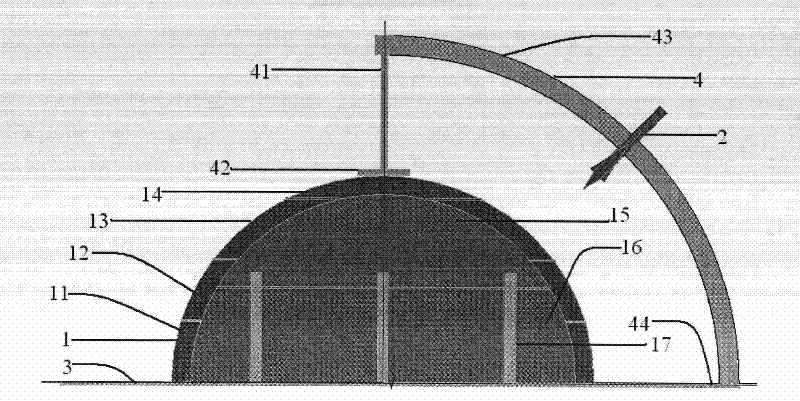
System and apparatus for transmitting a surface wave over a single conductor
ActiveUS20080211727A1Reduce radiationSmall sizeWaveguide hornsMultiple-port networksElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
A low attenuation surface wave transmission line system for launching surface waves on a bare and unconditioned conductor, such as are found in abundance in the power transmission lines of the existing power grids. The conductors within the power grid typically lack dielectric and special conditioning. Accordingly, the present invention includes a first launcher, preferably including a mode converter and an adapter, for receiving an incident wave of electromagnetic energy and propagating a surface wave longitudinally on the power lines. The system includes at least one other launcher, and more likely a number of other launchers, spaced apart from one another along the constellation of transmission lines. The system and associated electric fields along any given conductor are radially and longitudinally symmetrical.
Owner:CORRIDOR SYST INC
Low cost millimeter wave imager
InactiveUS7583074B1Low costUseful sensitivity levelMeasurement using dc-ac conversionMeasurement using ac-dc conversionLow noiseTunnel diode
Low cost millimeter wave imagers using two-dimensional focal plane arrays based on backward tunneling diode (BTD) detectors. Two-dimensional focal arrays of BTD detectors are used as focal plane arrays in imagers. High responsivity of BTD detectors near zero bias results in low noise detectors that alleviate the need for expensive and heat generating low noise amplifiers or Dicke switches in the imager. BTD detectors are installed on a printed circuit board using flip chip packaging technology and horn antennas direct the waves toward the flip chip including the BTD detectors. The assembly of the horn antennas, flip chips, printed circuit board substrate, and interconnects together work as an imaging sensor. Corrugated surfaces of the components prevent re-radiation of the incident waves.
Owner:HRL LAB
High efficiency optical diffraction device
ActiveUS7454103B2Diffraction efficiencyWide choiceMechanical apparatusDiffraction gratingsOptical diffractionDevice form
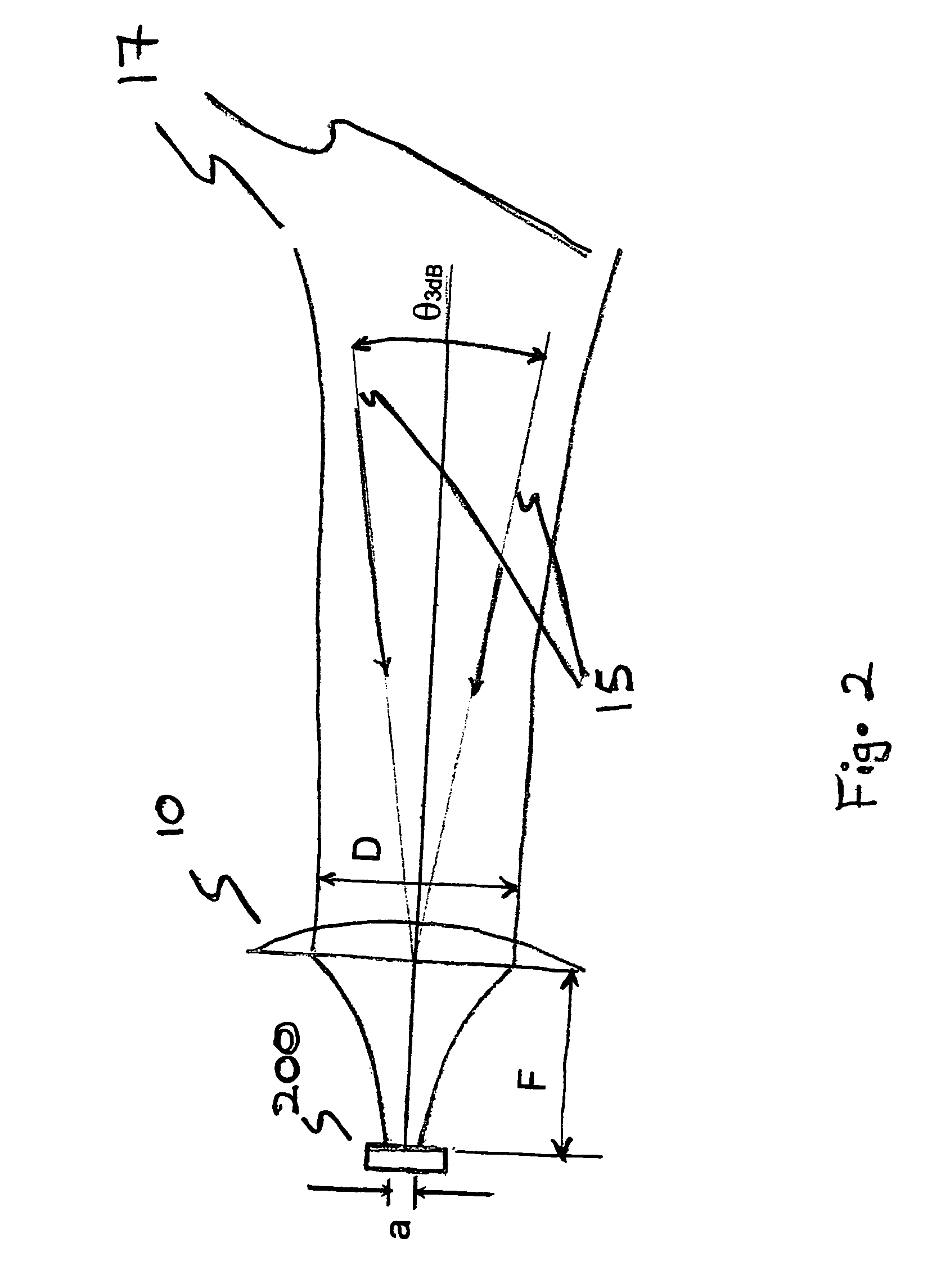
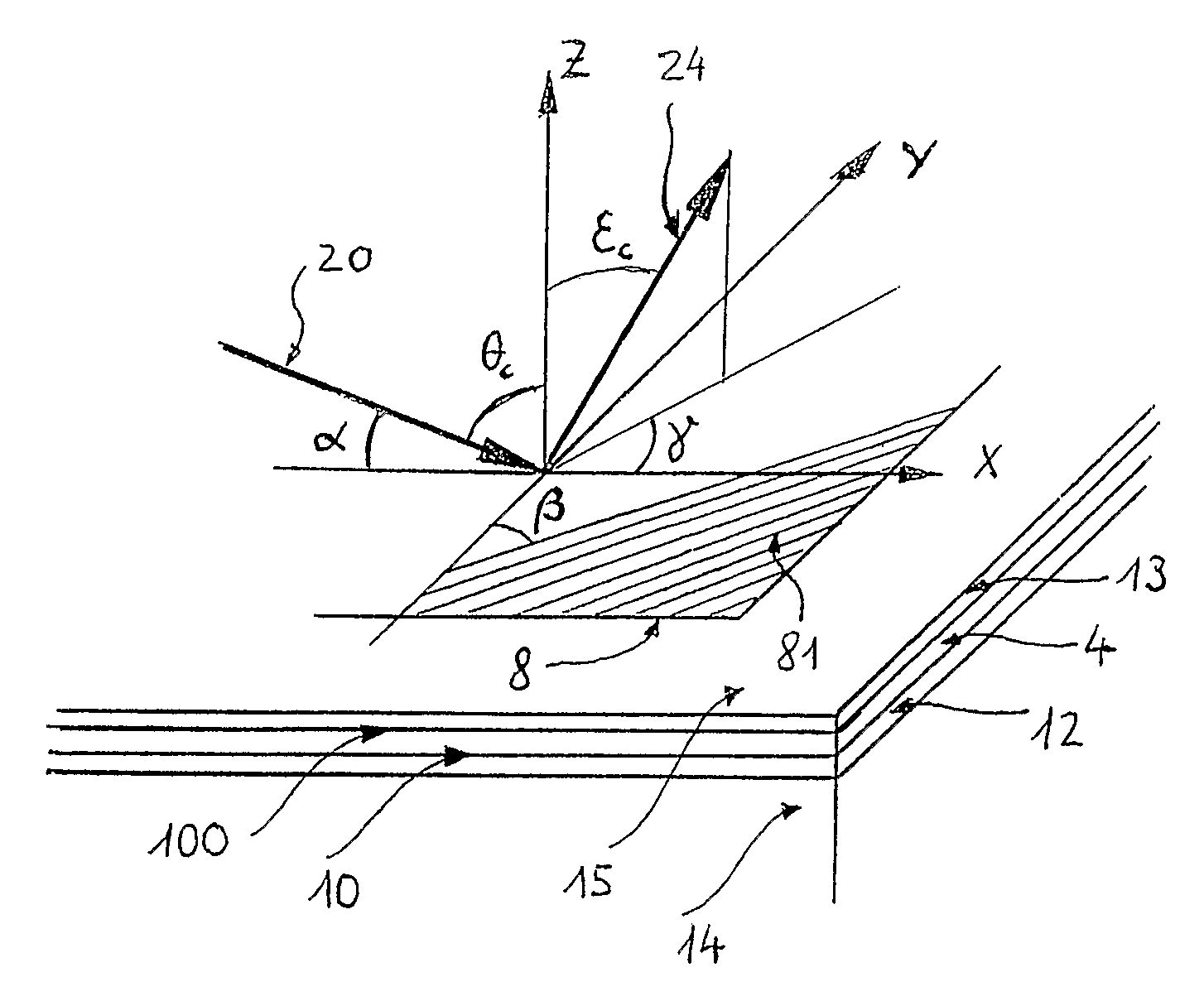
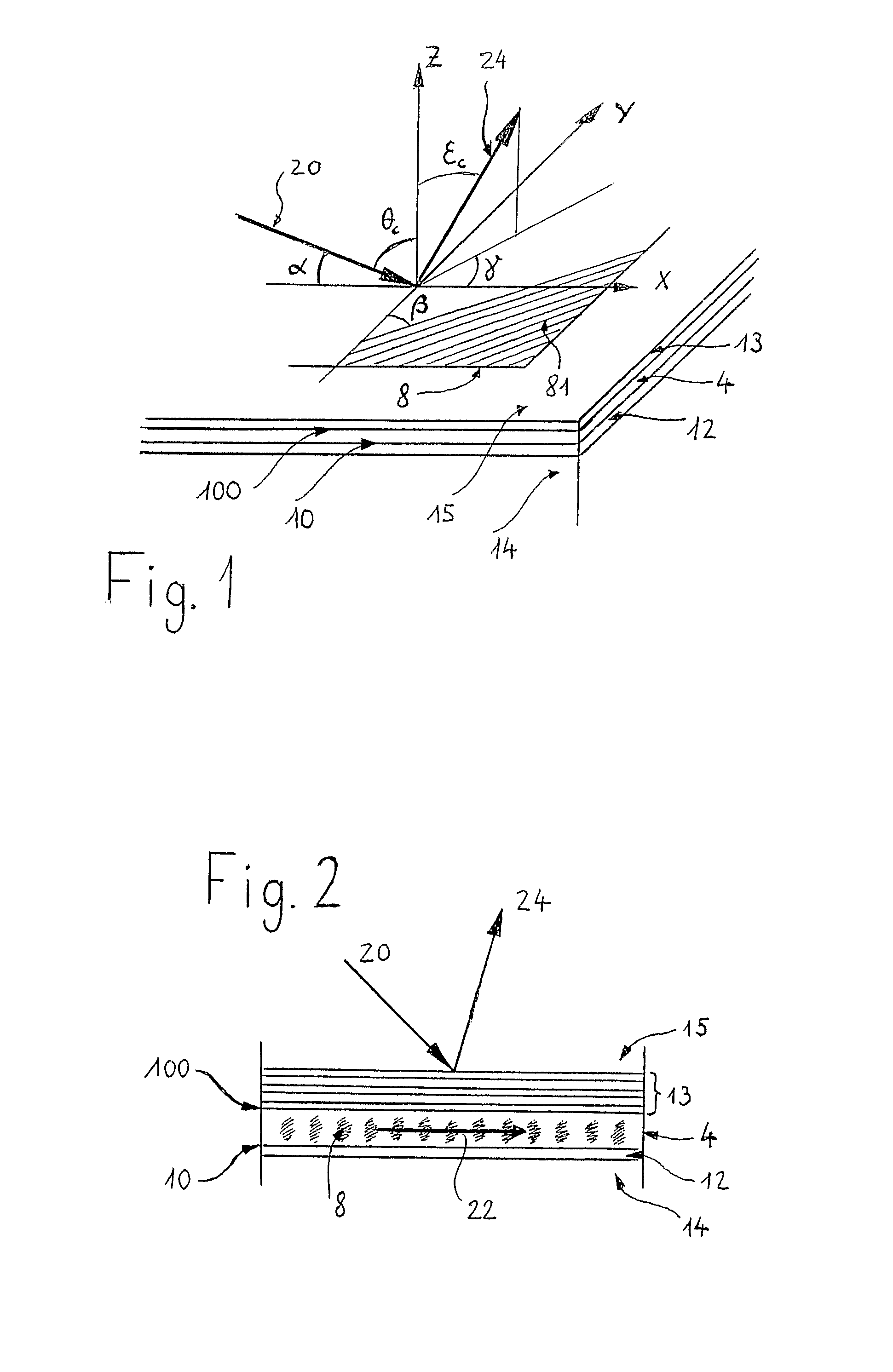
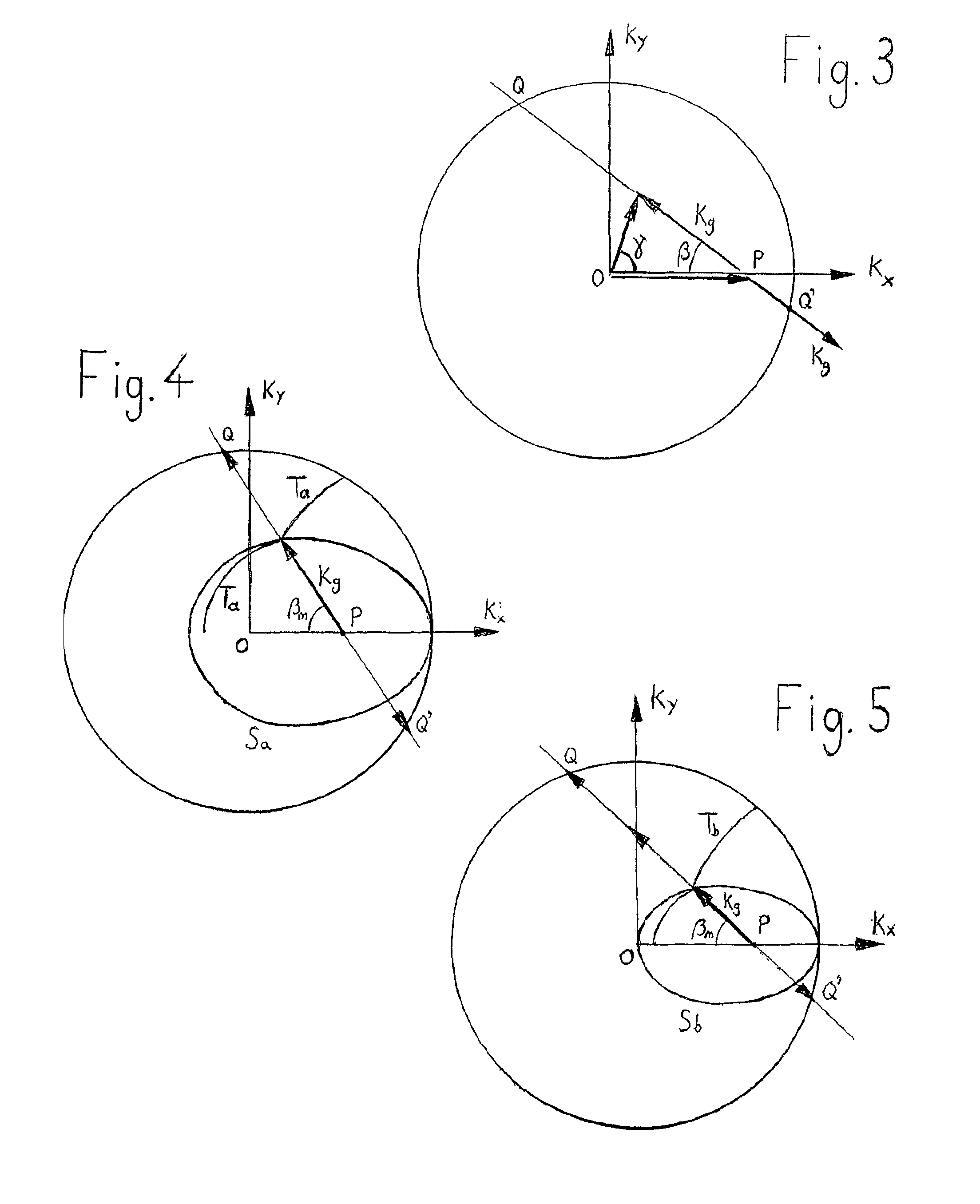
Lightwave diffraction device formed of a dielectric layer (4), a mirror (12) arranged at the lower face (10) of said layer, a semi-reflective structure (13) arranged at the upper face (100) of said layer, and a diffractive structure (8) arranged in said layer or on its faces. The height (H) of the layer is chosen so as to substantially satisfy the resonance condition for at least one leaky mode propagating in said layer for at least one given incident wave having a determined wavelengthλ and a determined incidence angle θc. Next, the diffractive structure is arranged so that there is no propagating positive diffracted order, and so that all negative orders other than the −1st propagating order have zero or a relatively small diffraction efficiency, the reflected −1st order propagating in a direction non-parallel to the incident wave. This diffraction device allows a high diffraction efficiency of up to 100% for the −1st order.
Owner:PARRIAUX OLIVIER M
Apparatus and method for imaging objects with wavefields
InactiveUS20060293597A1Improve ultrasound reflectivity spatial resolutionReduce the valueTexturing/coloringOrgan movement/changes detectionData setWave field
A transmission wave field imaging method, comprising the transmission of an incident wave field into an object, the incident wave field propagating into the object and, at least, partially scattering. Also includes the measuring of a wave field transmitted, at least in part, through an object to obtain a measured wave field, the measured wave field based, in part, on the incident wave field and the object. Additionally, the processing of the measured wave field utilizing a parabolic approximation reconstruction algorithm to generate an image data set representing at least one image of the object.
Owner:TECHNISCAN
Apparatus and method for imaging objects with wavefields
InactiveUS20060287596A1Maximize functionalityOrgan movement/changes detectionTexturing/coloringData setWave field
A transmission wave field imaging method, comprising the transmission of an incident wave field into an object, the incident wave field propagating into the object and, at least, partially scattering. Also includes the measuring of a wave field transmitted, at least in part, through an object to obtain a measured wave field, the measured wave field based, in part, on the incident wave field and the object. Additionally, the processing of the measured wave field utilizing a parabolic approximation reconstruction algorithm to generate an image data set representing at least one image of the object.
Owner:TECHNISCAN
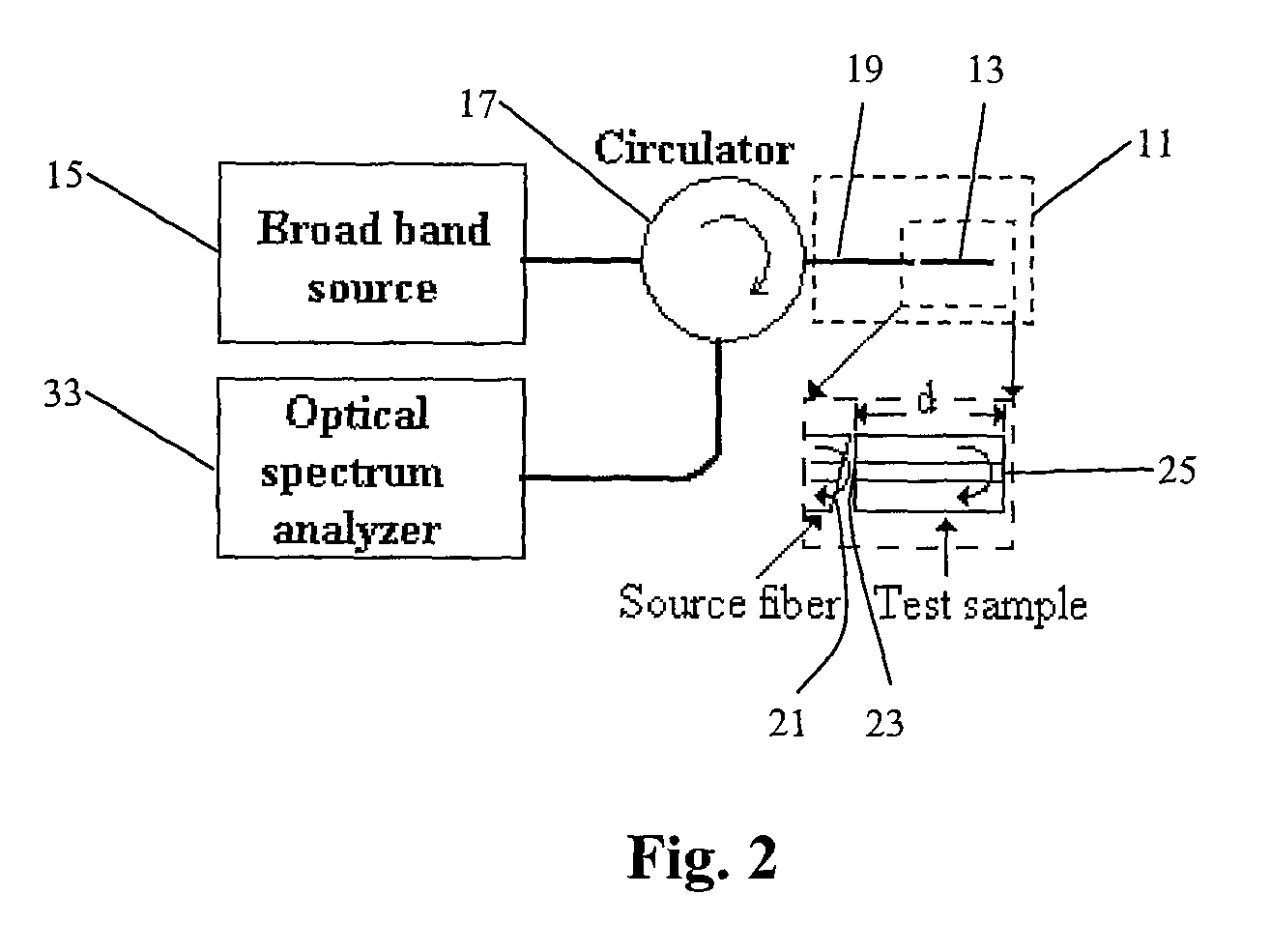
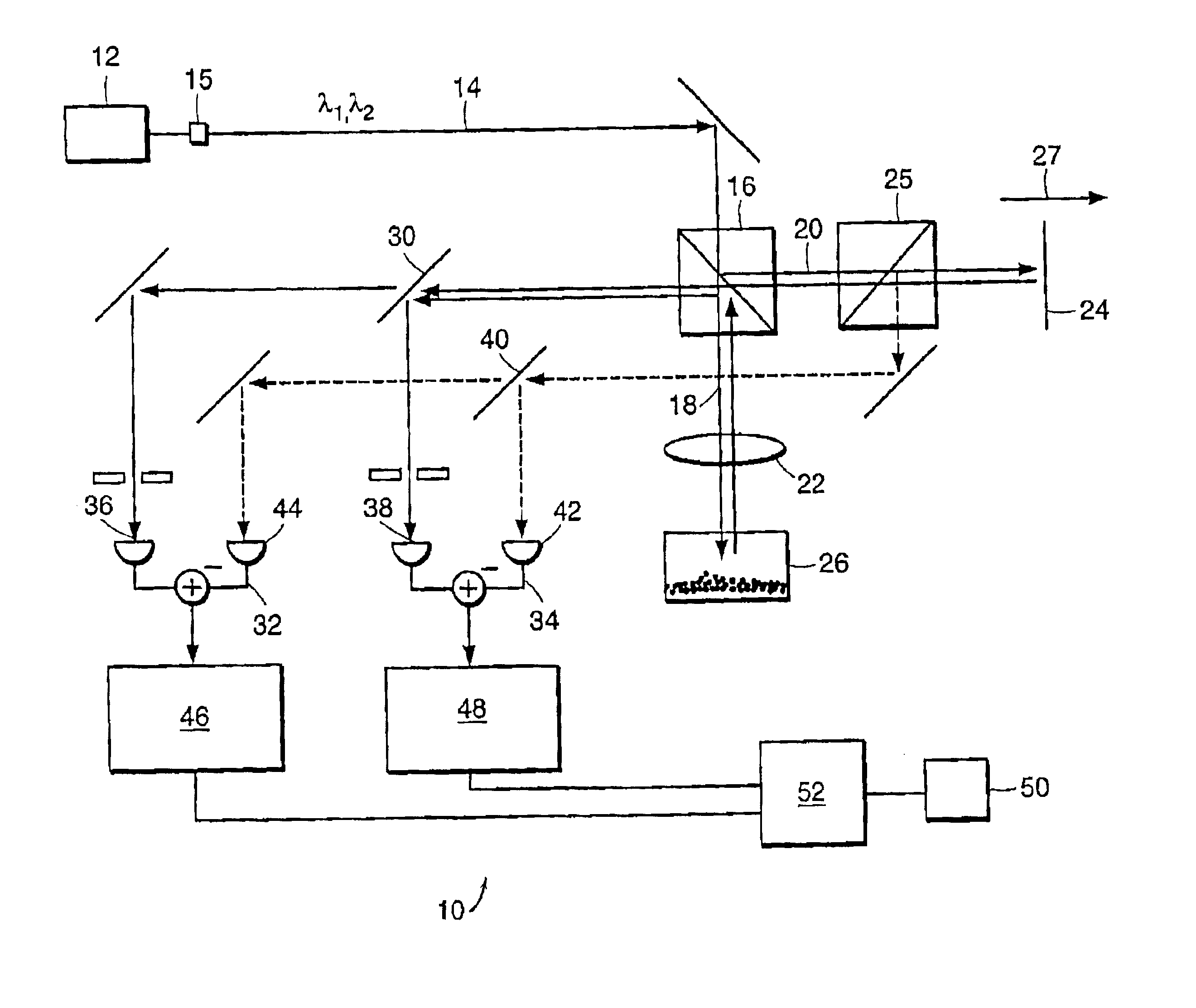
System and method to determine chromatic dispersion in short lengths of waveguides using a common path interferometer
InactiveUS7787127B2Material analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansReflected wavesIncident wave
The present invention relates to a system and method to determine chromatic dispersion in short lengths of waveguides using a two wave interference pattern and a common path interferometer. Specifically the invention comprises a radiation source operable to emit radiation connected to a means for separating incident and reflected waves; the means for separating incident and reflected waves possessing an output arm adjacent to a first end of the waveguide; and the means for separating incident and reflected waves further connected to an optical detector operable to record an interference pattern generated by a reflected test emission from the radiation source. The interference pattern consists of two waves: one reflected from a first facet of a waveguide and the second reflected from a second facet of the same waveguide.
Owner:GALLE MICHAEL +2
Ultrasound coating for enhancing visualization of medical device in ultrasound images
InactiveUS20050074406A1Improve visualizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryContrast mediumIncident wave
The invention enhances ultrasonic visualization of a medical device by coating the surface of the medical device with a contrast agent preferably comprising microbubbles. The contrast agent responds to incident ultrasound waves to generate vibrations at a harmonic frequency (i.e., a harmonic of the frequency of the incident wave), non-harmonic vibrations or a combination of harmonic and non-harmonic vibrations. In one embodiment, the microbubbles are coated on the medical device using an intermediate adhesion layer that adheres to the surface of the device. In a second embodiment, the microbubbles are incorporated in the adhesion layer.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Apparatus and method for imaging objects with wavefields
InactiveUS20070282200A1Vibration measurement in fluidMaterial analysis using microwave meansData setWave field
A transmission wave field imaging method, comprising the transmission of an incident wave field into an object, the incident wave field propagating into the object and, at least, partially scattering. Also includes the measuring of a wave field transmitted, at least in part, through an object to obtain a measured wave field, the measured wave field based, in part, on the incident wave field and the object. Additionally, the processing of the measured wave field utilizing a recursive reconstruction algorithm to generate an image data set representing at least one image of the object.
Owner:QT ULTRASOUND +1
Apparatus and method for imaging objects with wavefields
A transmission wave field imaging method, comprising the transmission of an incident wave field into an object, the incident wave field propagating into the object and, at least, partially scattering. Also includes the measuring of a wave field transmitted, at least in part, through an object to obtain a measured wave field, the measured wave field based, in part, on the incident wave field and the object. Additionally, the processing of the measured wave field utilizing a parabolic approximation reconstruction algorithm to generate an image data set representing at least one image of the object.
Owner:TECHNISCAN
Device for the plasma treatment of gases
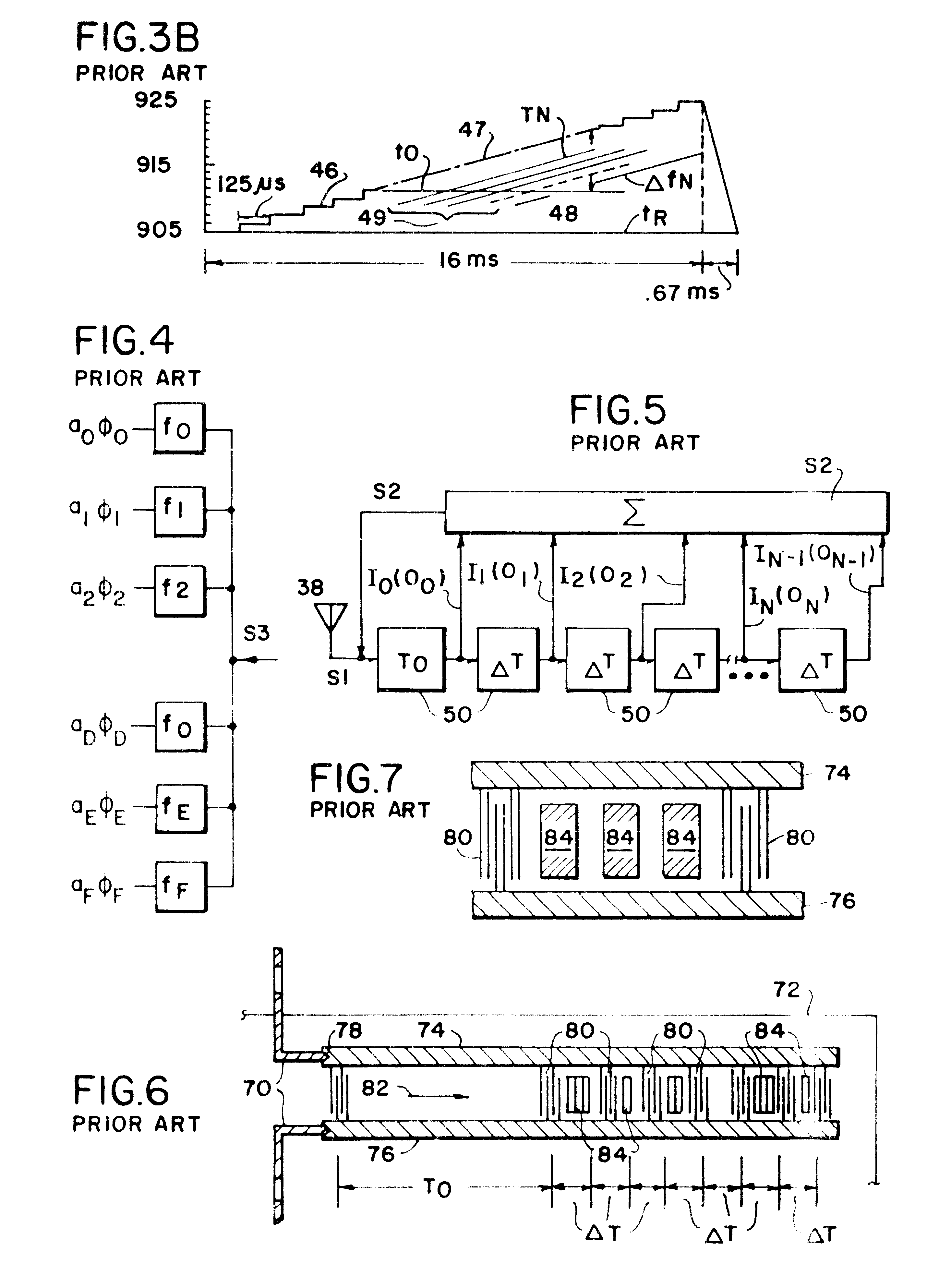
Provided is a device for the microwave-sustained plasma treatment of gases, which comprises a hollow structure forming a waveguide intended to be connected to a microwave generator, and means for making the gas to be treated flow through the said structure in a region in which the amplitude of the electric field associated with the incident wave is high. The means for making the gas flow comprise a plasma torch for producing a plasma in the gas. The torch comprises an injector made of an electrically conducting material mounted on a first large face of the said structure and extending so as to project through an orifice made in a second large face opposite the said first large face. A gap for passage of the incident waves lies around the injector.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Apparatus and method for imaging objects with wavefields
InactiveUS7841982B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setWave field
A transmission wave field imaging method, comprising the transmission of an incident wave field into an object, the incident wave field propagating into the object and, at least, partially scattering. Also includes the measuring of a wave field transmitted, at least in part, through an object to obtain a measured wave field, the measured wave field based, in part, on the incident wave field and the object. Additionally, the processing of the measured wave field utilizing a parabolic approximation reconstruction algorithm to generate an image data set representing at least one image of the object.
Owner:TECHNISCAN
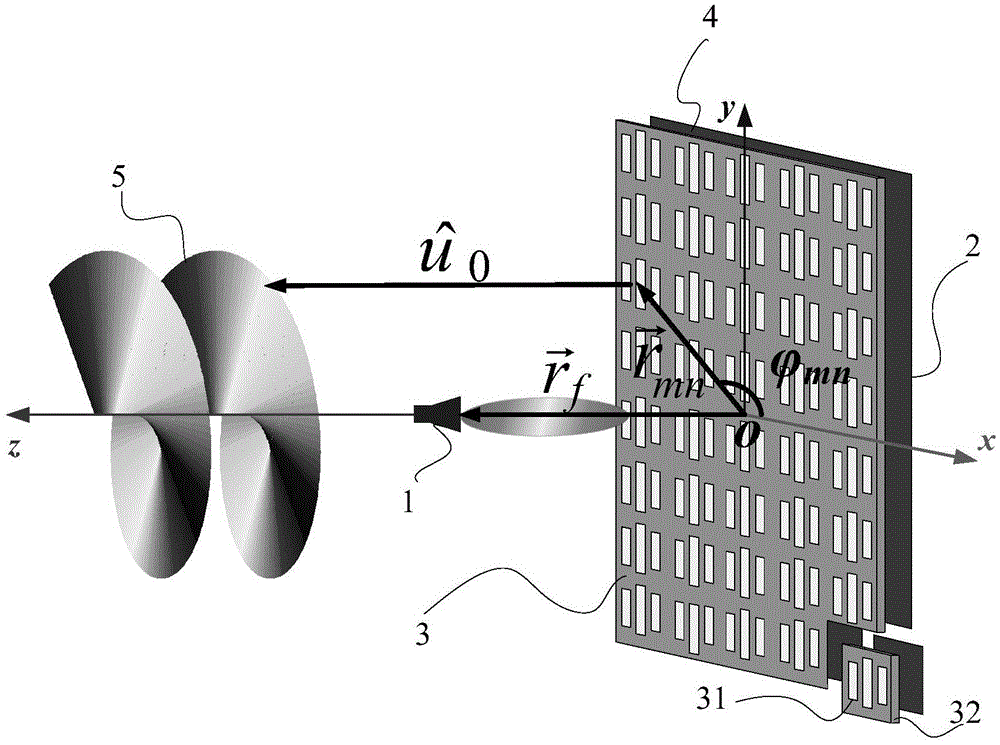
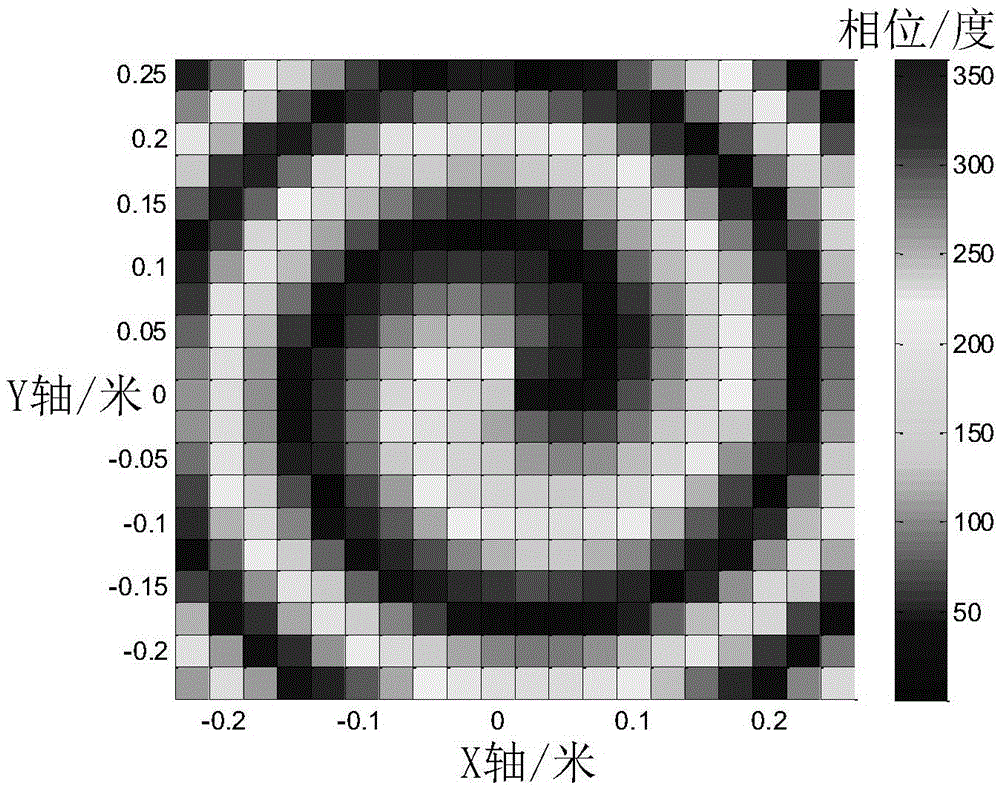
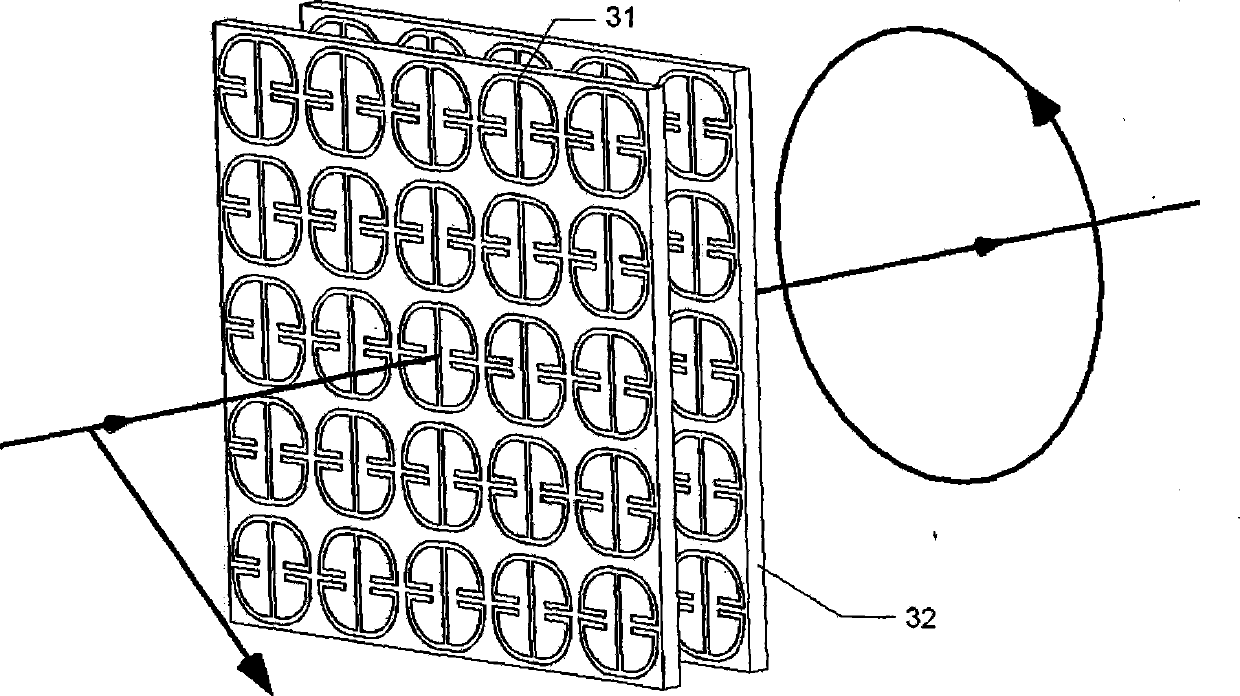
Orbital angular momentum vortex wave beam generation apparatus and method
The invention discloses an orbital angular momentum vortex wave beam generation apparatus and method. According to the technical scheme, an electromagnetic super-surface structure (3) is formed by M lines and N columns of electromagnetic super-surface reflection units (31) and dielectric substrates (32); a phase-shifting network (4) is formed by the electromagnetic super-surface structure (3) and a metal back plate (2); the metal back plate (2) is positioned on the back surface of the electromagnetic super-surface structure (3), and the metal back plate is also used as an earth plate; a feed source (1) is put in the central axial position of the electromagnetic super-surface structure (3); incident wave from the feed source (1) irradiates on the electromagnetic super-surface structure; and after the incident wave obtains compensated phase position from the electromagnetic super-surface structure, the incident wave is reflected by the phase-shifting network (4) to generate the orbital angular momentum vortex wave beam(5) with an intrinsic mode 1. According to the orbital angular momentum vortex wave beam generation apparatus and method, the problems of complex technical structure, high cost, beam divergence and low efficiency in the prior art are solved; and the apparatus and method can be used for information transmitting and receiving in the communication technology, and the communication capacity can be increased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
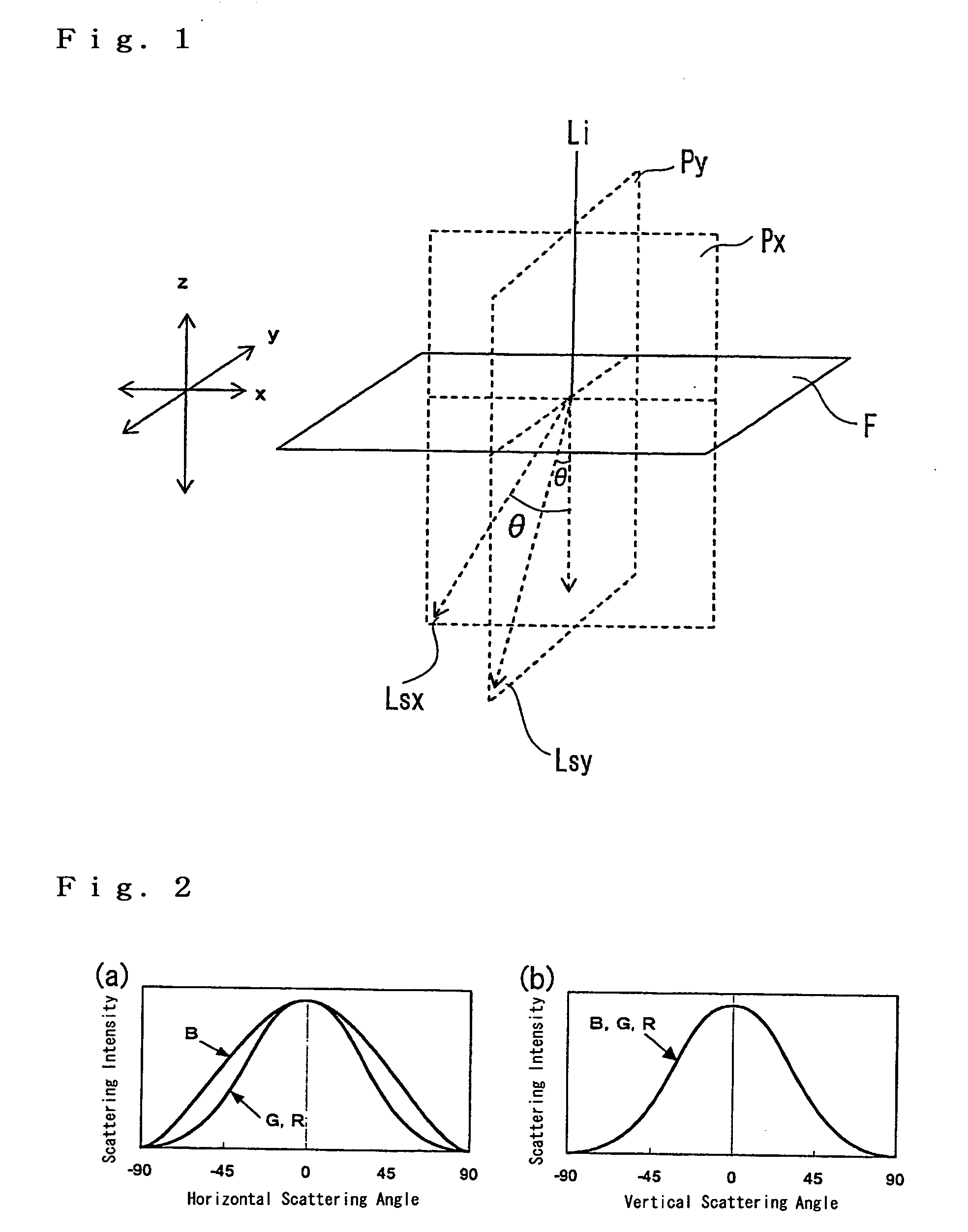
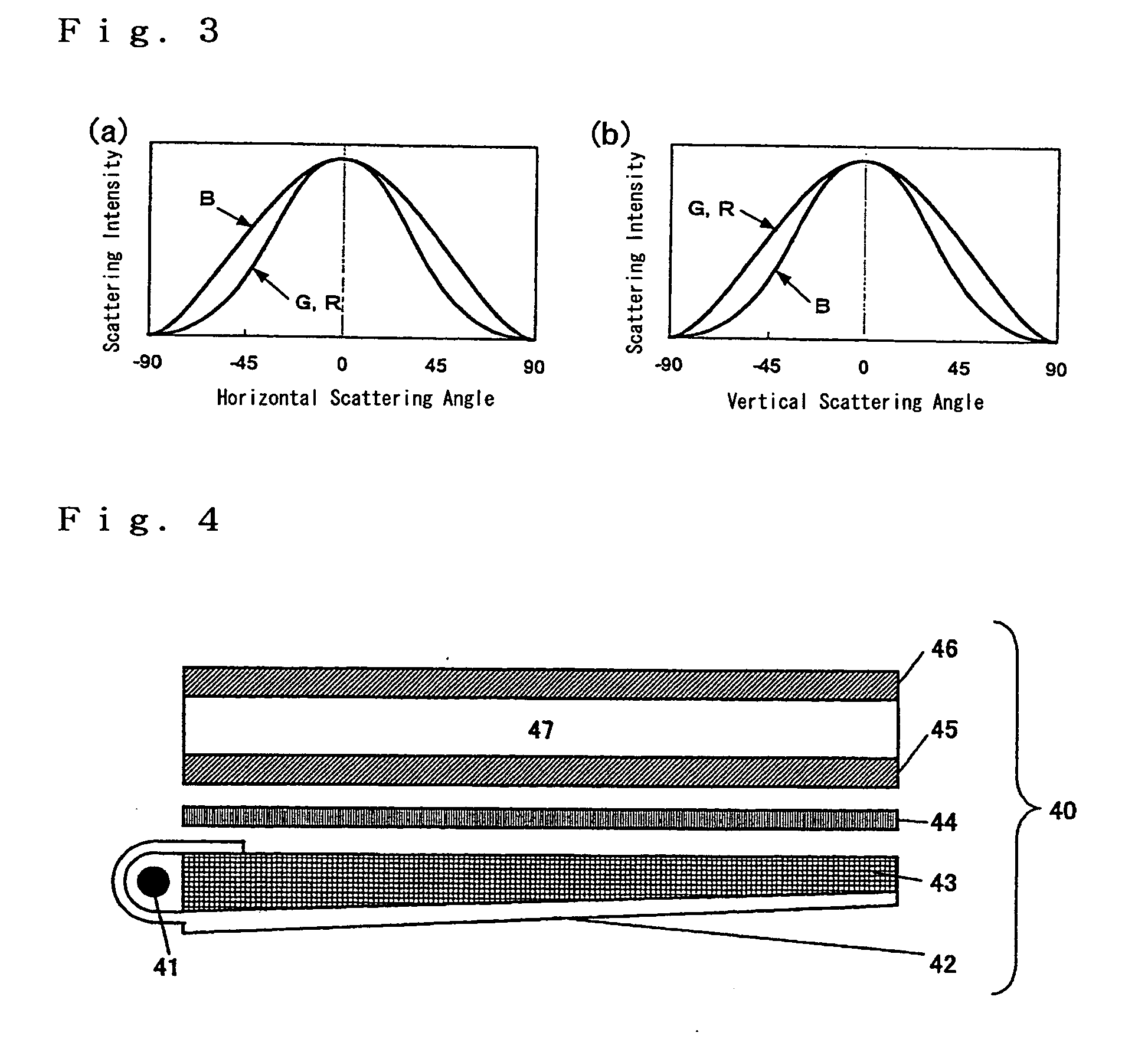
Anisotropic spectral scattering films, polarizers and liquid crystal displays
ActiveUS20050001957A1Improving color-viewing angle characteristicExcellent color compensation functionMechanical apparatusDiffusing elementsDisplay devicePolarizer
A novel anisotropic spectral scattering film is disclosed. The scattered light intensity Fx(λ, θ) at azimuthal angle θ and incident wavelength λ in an arbitrary scattering plane with respect to a surface of the film, and the scattered light intensity Fy(λ,θ) at azimuthal angle θ and incident wavelength λ in a scattering plane orthogonal to said scattering plane satisfy the following equations (1) and (2): Fx(λ, θ) / Fx(545, θ)≧1.2 (1) {Fx(λ, θ) / Fx(545, θ)−Fy(λ, θ) / Fy(545, θ)}≧0.1 (2) provided that λ is 435 or 610 nm and θ is an arbitrary angle selected from 30-70°.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Polarization conversion method and polarization converter based on artificial electromagnetic material
InactiveCN101431171AFlexible designReduce reflectionWaveguide type devicesRectangular coordinatesRelative phase
The invention relates to a polarization conversion method based on artificial electromagnetic materials. Electromagnetic waves are controlled to be spread in the artificial electromagnetic materials which constitute a polarization converter by designing the structure of the artificial electromagnetic materials, thereby leading the relation of the transmission coefficients of an electric field in the different directions to achieve the conversion from one incident wave polarization state to another emergent wave polarization state in a plane which is perpendicular to the wave spread direction, the relation of the transmission coefficients needs to be met is as follows: if the spread direction of the electromagnetic waves is defined as an X axis of a three-dimensional rectangular coordinate, the electric field E is decomposed to two electric field components of Ey and Ez which are mutually perpendicular, E is equal to yEy plus zEz, the transmission coefficients of T<y> and T<z> of the electric field in the two directions which pass the materials that constitute the polarization converter meet the following conditions: 1) for the situation of converting the incident waves with any polarization state to the emergent waves with the linear polarization, the absolute value of T<y>\the absolute value of T<z> is equal to p multiplied by the absolute value of Ez\the absolute value of Ey; ang(T<y>) minus ang(T<z>) is equal to plus or minus n pai minus (ang(Ey) minus ang(Ez)); wherein, n is equal to 0, 1, 2,..., p is the tangent value of an included angle theta between the linear polarization direction of the emergent waves and a z axis, p is not less than 0 and not more than 1, ang(T<y>) and ang(T<z>) represent the relative phases of T<y> and T<z>, ang(Ey) and ang(Ez) represent the relative phases of Ey and Ez. The polarization conversion method has the advantages of low cost, low energy consumption, high efficiency and compact structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
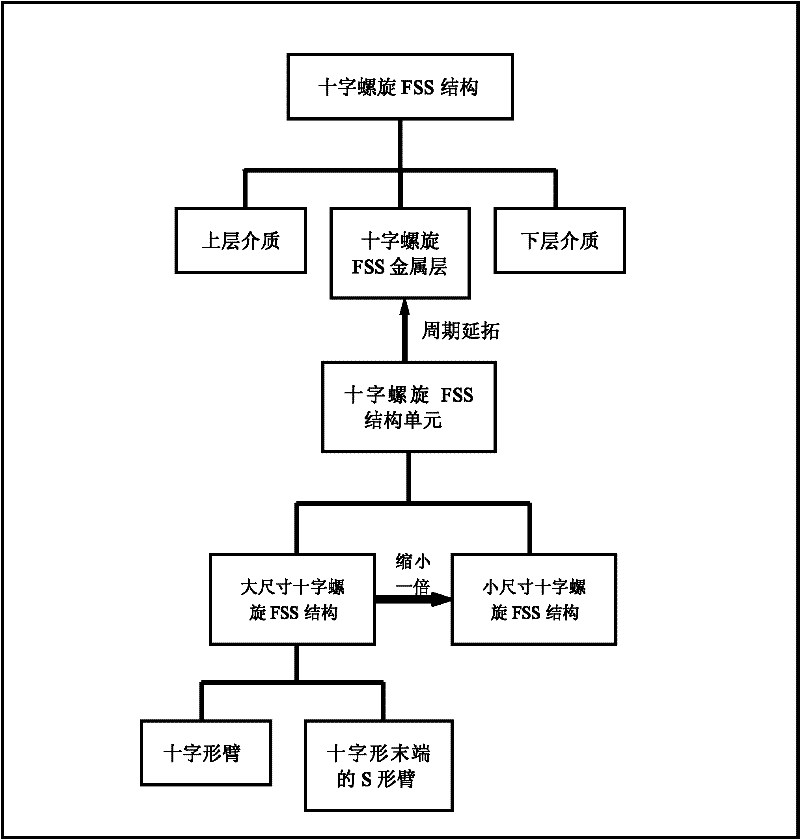
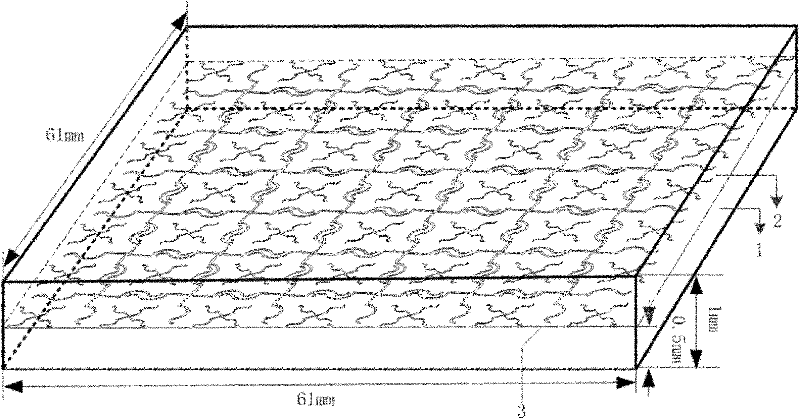
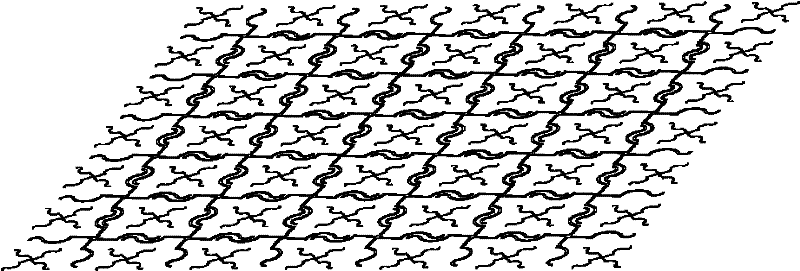
Cross spiral frequency selective surface (FSS) structure with dual band characteristics and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a cross spiral frequency selective surface (FSS) structure with dual band characteristics and a construction method thereof. The structure consists of an upper dielectric layer, a lower dielectric layer and an intermediate cross spiral FSS structure layer. The construction method comprises the following six steps of: 1, establishing structure units of the cross spiral FSS structure layer with the thickness of zero by using computer simulation technology (CST) software; 2, periodically extending the structure units towards directions X and Y to obtain the integrated 6*6 cross spiral FSS structure layer; 3, establishing the dielectric layers of the cross spiral FSS structure, and embedding the cross spiral FSS structure layer into a dielectric substrate by using the CST software; 4, capturing the cross spiral FSS structure unit from the CST software for incident wave transmittance analysis, regulating parameters of the structure unit, changing the resonance frequency of a stop band, and replacing an original structure by using the regulated structure unit; 5, setting the parameters such as boundaries and the like of the constructed cross spiral FSS structure, and testing the bandwidth stability and frequency selectivity of the structure; and 6, machining and manufacturing the cross spiral FSS structure by adopting a double-sided copper-clad plate according to an optimal size determined by the step 4.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Small and omni-directional biconical antenna for wireless communications
InactiveUS6943747B2Small sizeBroaden applicationWaveguide hornsSlot antennasShortest distanceIncident wave
A biconical antenna for wireless communications includes a conical upper conductive body and a conical lower conductive body having a common apex, which is used as a power feed point, wherein a space between the conical upper and lower conductive bodies is filled with a dielectric material such that a shortest distance connecting the conical upper and lower conductive bodies along a surface of the dielectric material is a curve at which an incident angle of an incident wave incident on the surface of the dielectric material through the dielectric material from the common apex is a Brewster angle over the entire surface of the dielectric material.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
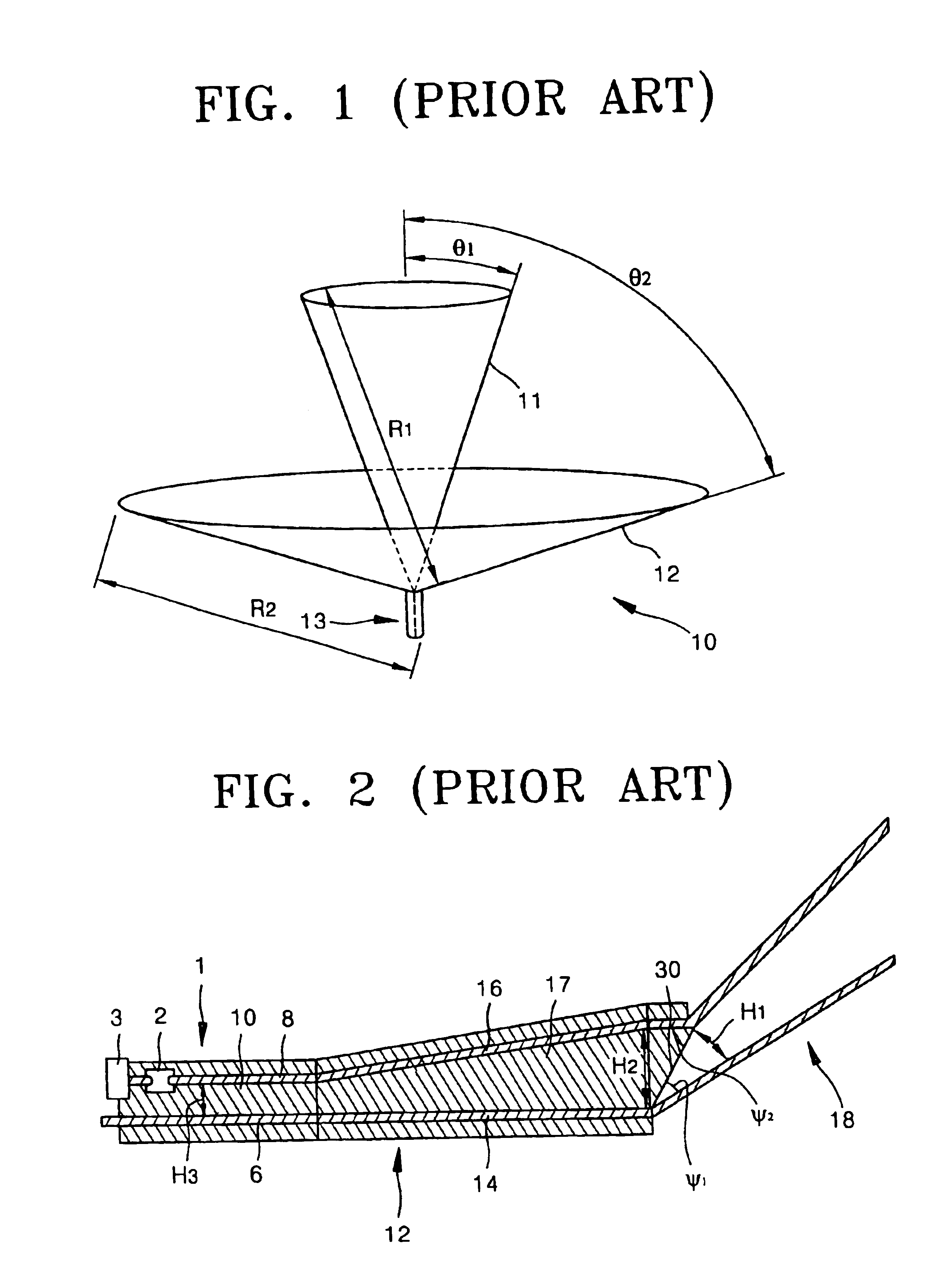
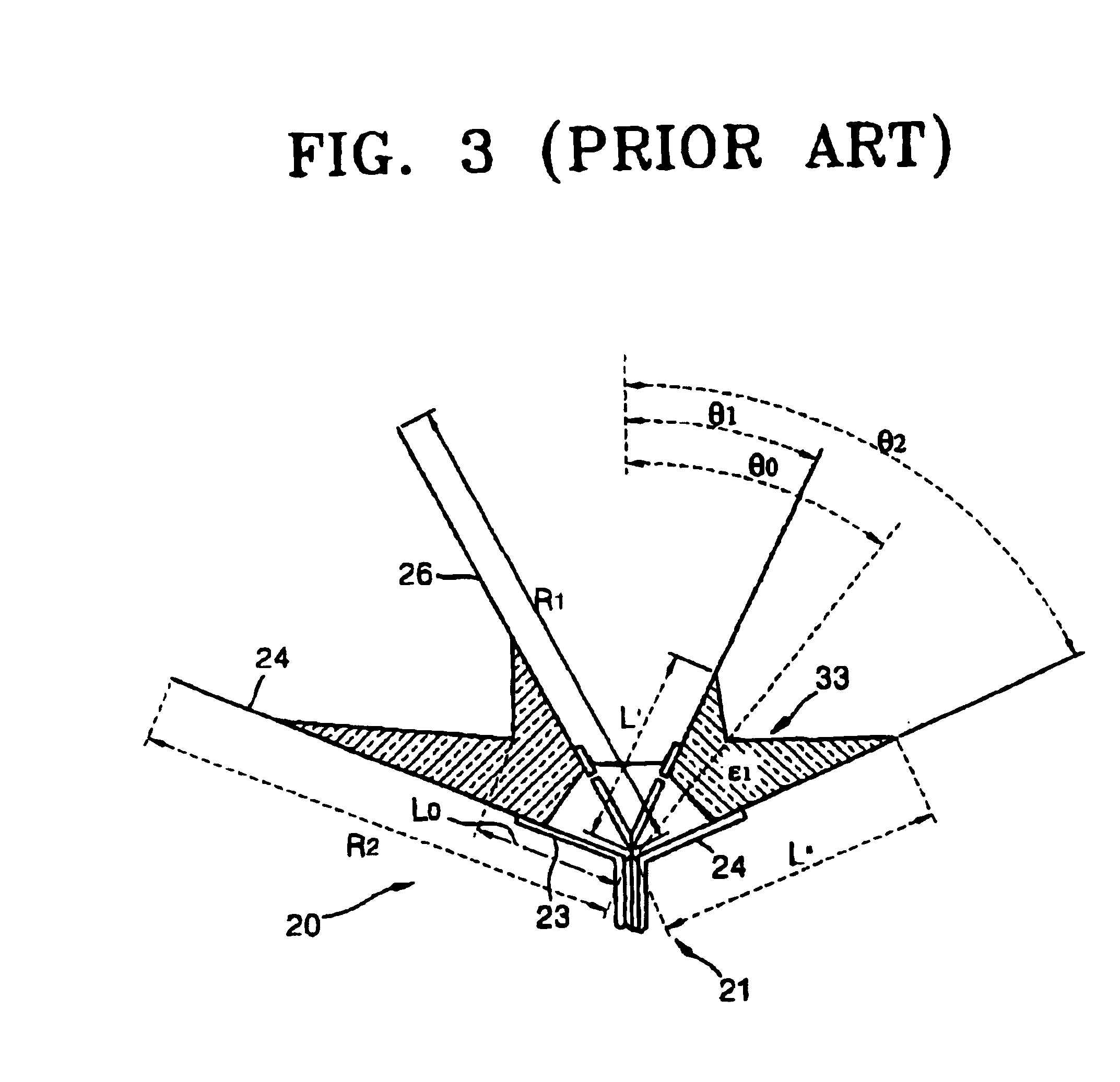
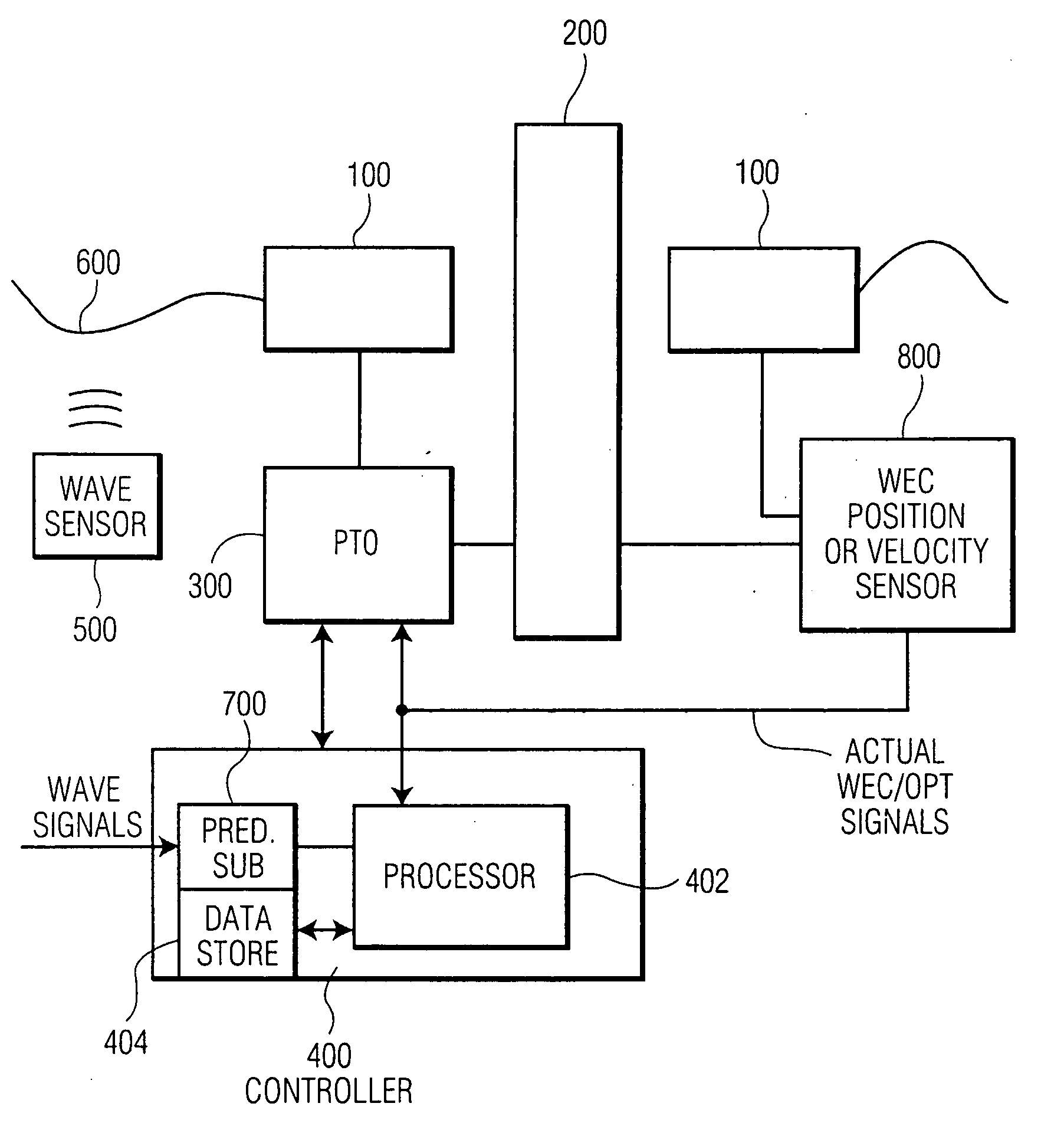
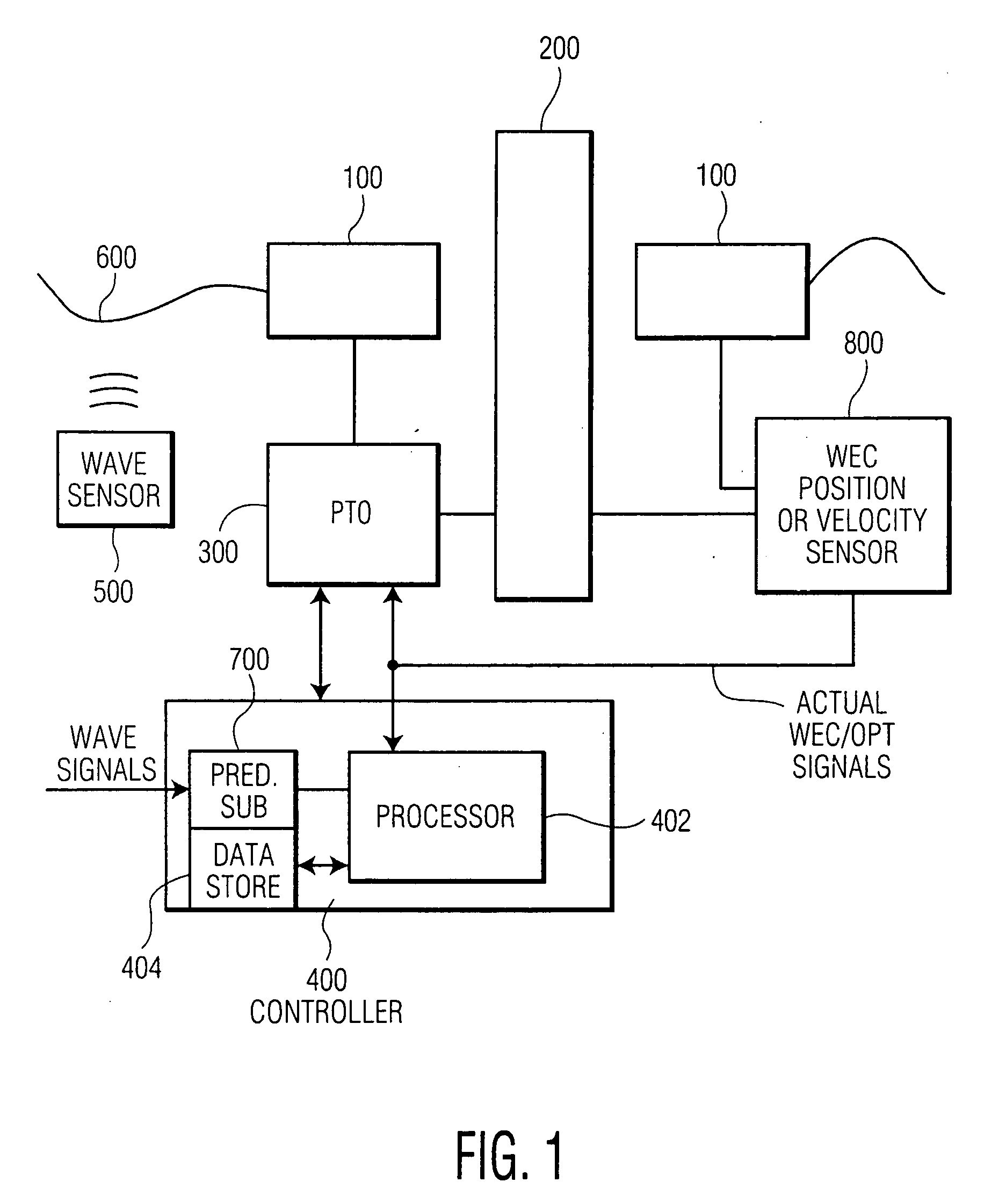
Advanced wave energy converter control
ActiveUS20100148504A1Simple control systemLess errorOptimise machine performanceEngine fuctionsRelative motionEngineering
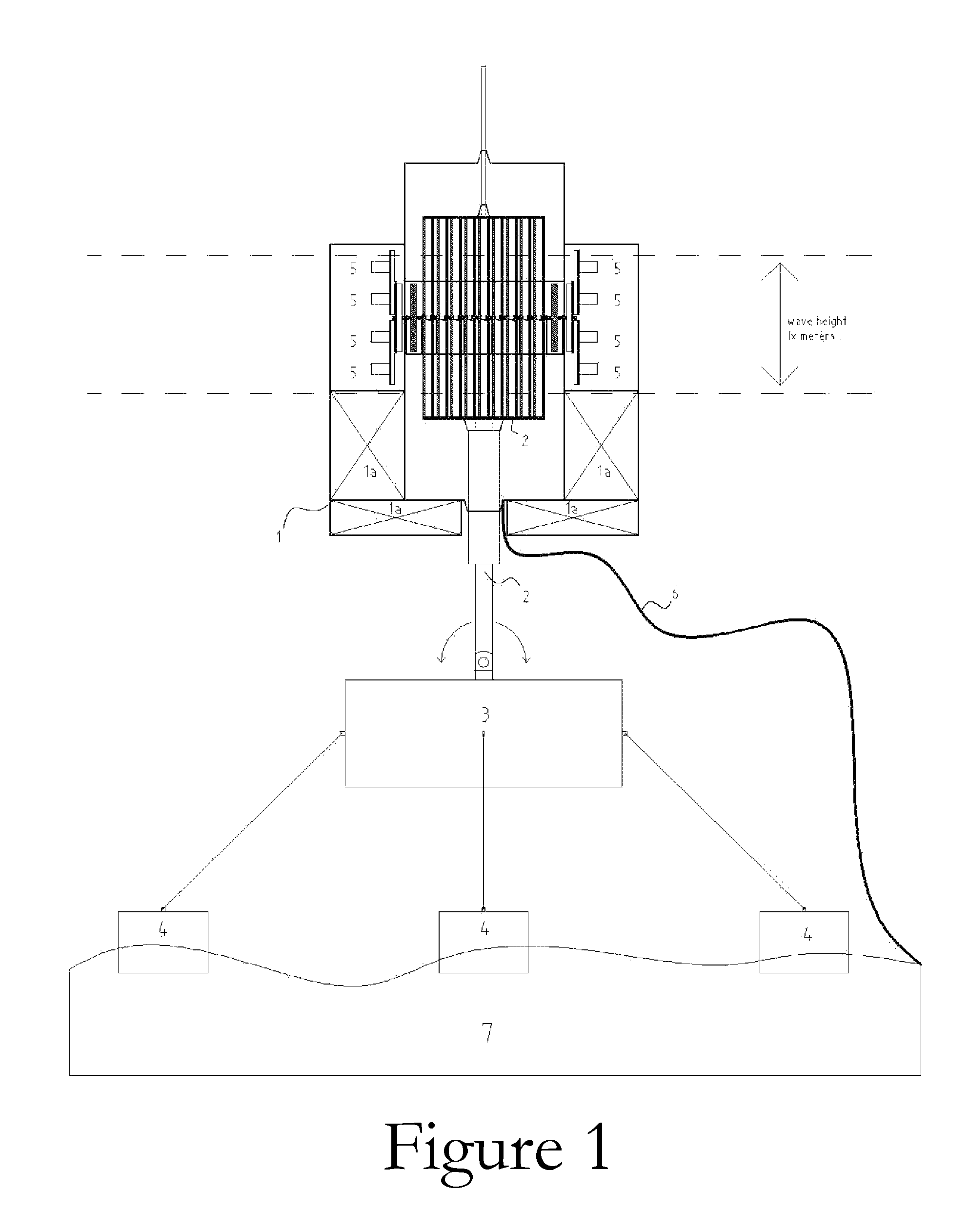
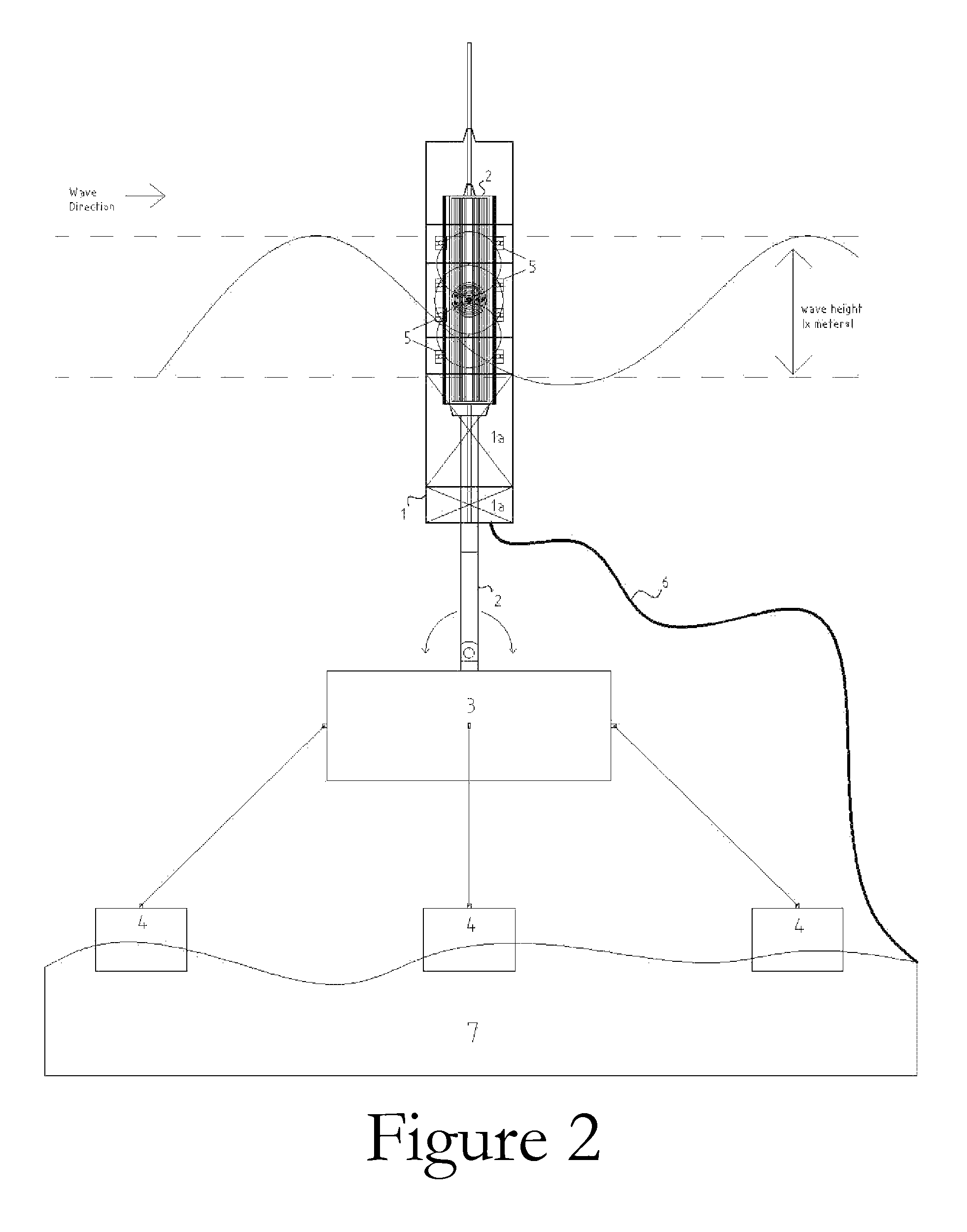
A wave energy converter (WEC) system includes first and second bodies which can move relative to each other in response to waves and a power-take-off (PTO) device coupled between the two bodies to convert their relative motion into energy. A sensor is used to sense selected characteristics of an incoming wave and produce signals which are applied to a control computer for predicting the impact of the incoming waves on the WEC. Simultaneously, signals indicative of the actual conditions (e.g. the velocity) of the WEC are also supplied to the control computer which is programmed to process the predicted and actual information in order to generate appropriate signals (forces) to the components of the WEC such that the average wave power captured by the PTO is maximized.
Owner:OCEAN POWER TECHNOLOGIES
Liquid crystal optics phased-array antenna implementation method
The invention discloses a liquid crystal optics phased-array antenna implementation method. A liquid crystal optics phased-array antenna comprises a common electrode and a grating electrode, the common electrode is designed into a high impedance liquid crystal optical wedge electrode, and two electrodes are arranged at the two ends of the high impedance liquid crystal optical wedge electrode for respectively loading voltage with different voltage values to generate one slope phase distribution, which is equivalent to a liquid crystal prism with an adjustable slope gradient, so continuous deflection control can be performed over an incident wave beam, and meanwhile, the quantitative voltage is loaded onto the grating electrode, so that stepping deflection control over the incident wave beam can be realized.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Electrically large highly-efficient luneberg lens antenna with the smallest layering number
InactiveCN102176545AAvoid deterioration of radiation characteristicsReduce manufacturing difficultyAntennasPlastic materialsIncident wave
The invention discloses an electrically large highly-efficient luneberg lens antenna with the smallest layering number, which is applied to wideband high-capacity satellite communication. The basic structure of the antenna comprises a semispherical luneberg lens antenna, a highly-efficient Ku / Ka feed source, a metal baffle board and dual quarter annular guide rails, wherein the semispherical luneberg lens antenna adopts polytetrafluoroethylene as an outer layer, adopts polyethylene as an inner core, and is fixed on the surface of the metal baffle board; the feed source can slide along the dual annular guide rails, and simultaneously can radially regulate a focal length, so that incident wave beams of the feed source in the different frequency ranges of Ku and Ka can cover the lens antenna to different extents, and can be aligned with a satellite for tracking and uplink or downlink communication. Based on the basic structure, industrial plastic material sorts, a board number and board connecting ways are rationally changed to form other specific embodiments.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Methods and systems using field-based light scattering spectroscopy
InactiveUS6847456B2High degreeDiagnostics using lightPhase-affecting property measurementsWavefrontIncident wave
The present invention relates to systems and methods of field-based light scattering spectroscopy. These systems and methods provide for the diagnosis of tissue by measuring the size and distribution of cellular characteristics. Field based measurements provide phase information resulting from the interaction of scatterers within the material and the incident wavefront. These measurements can be used to provide three dimensional images of tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Wave energy harnessing device
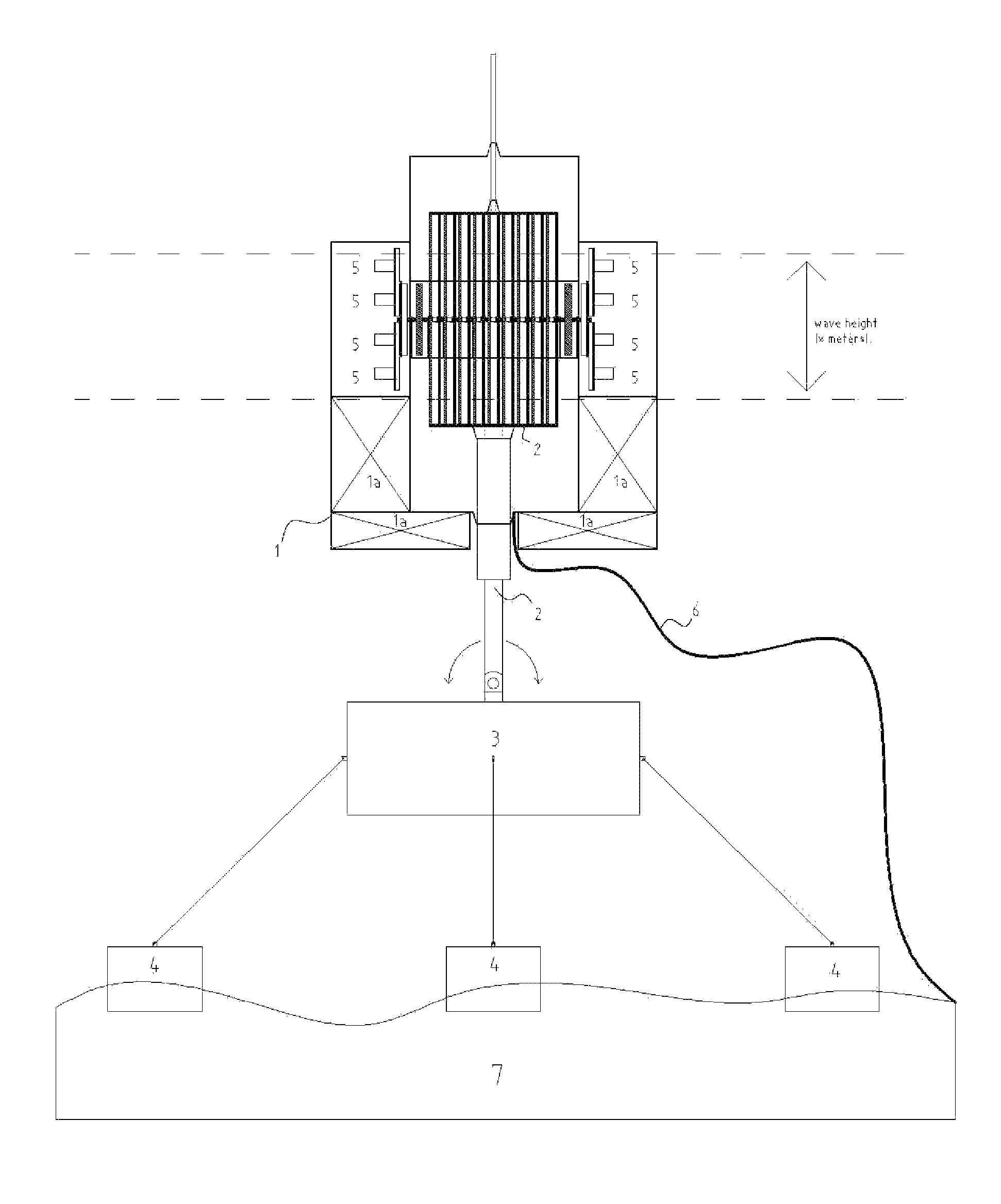
ActiveUS8093736B2Increasing combined wave energy extraction efficiencyReducing kinematic and dynamic loadMachines/enginesEngine componentsWave shoalingResponse Frequency
A hydrokinetic device having a water surface float tethered to a submerged buoyant housing is provided with mechanisms for optimizing the amount of wave energy extracted from the waves by the device. Based on wave conditions, the optimization functionalities include controlling the depth of the housing to produce wave shoaling or storm avoidance, as well as to perform continuous phase control and load control for the purpose of matching the response frequency of the device to the frequency of the incident waves.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Device for the non-invasive measurement of blood glucose concentration by millimeter waves and method thereof
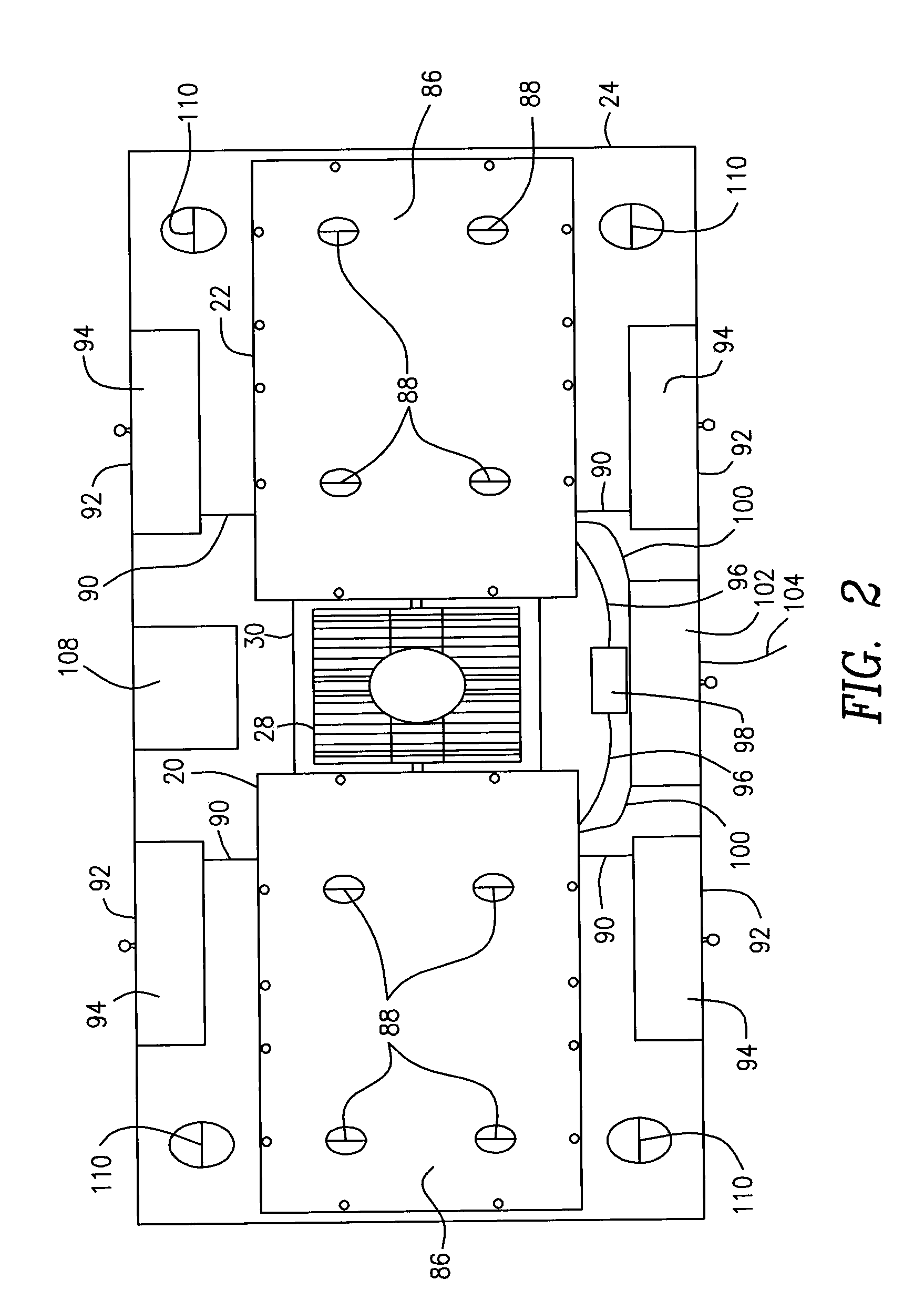
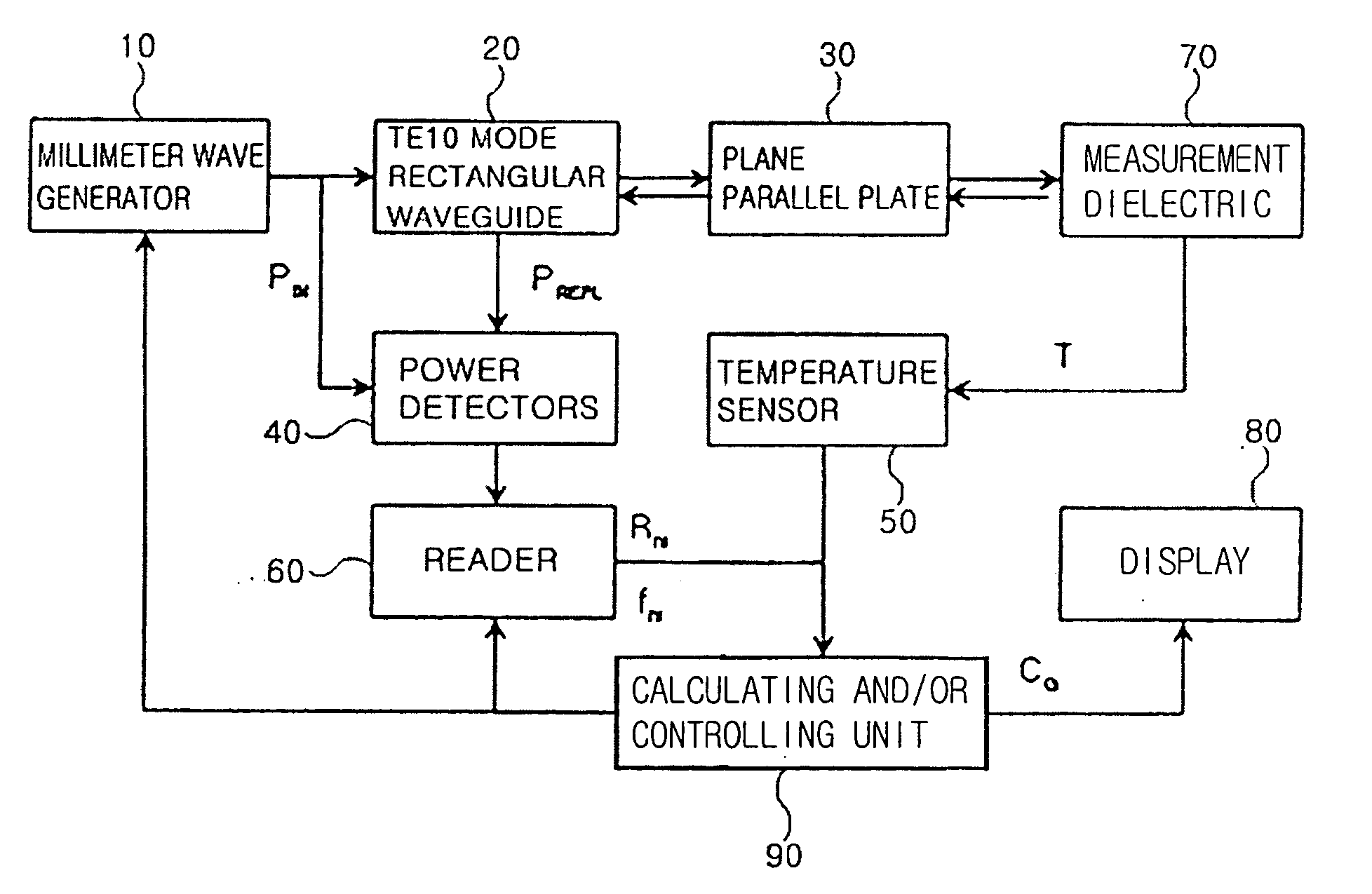
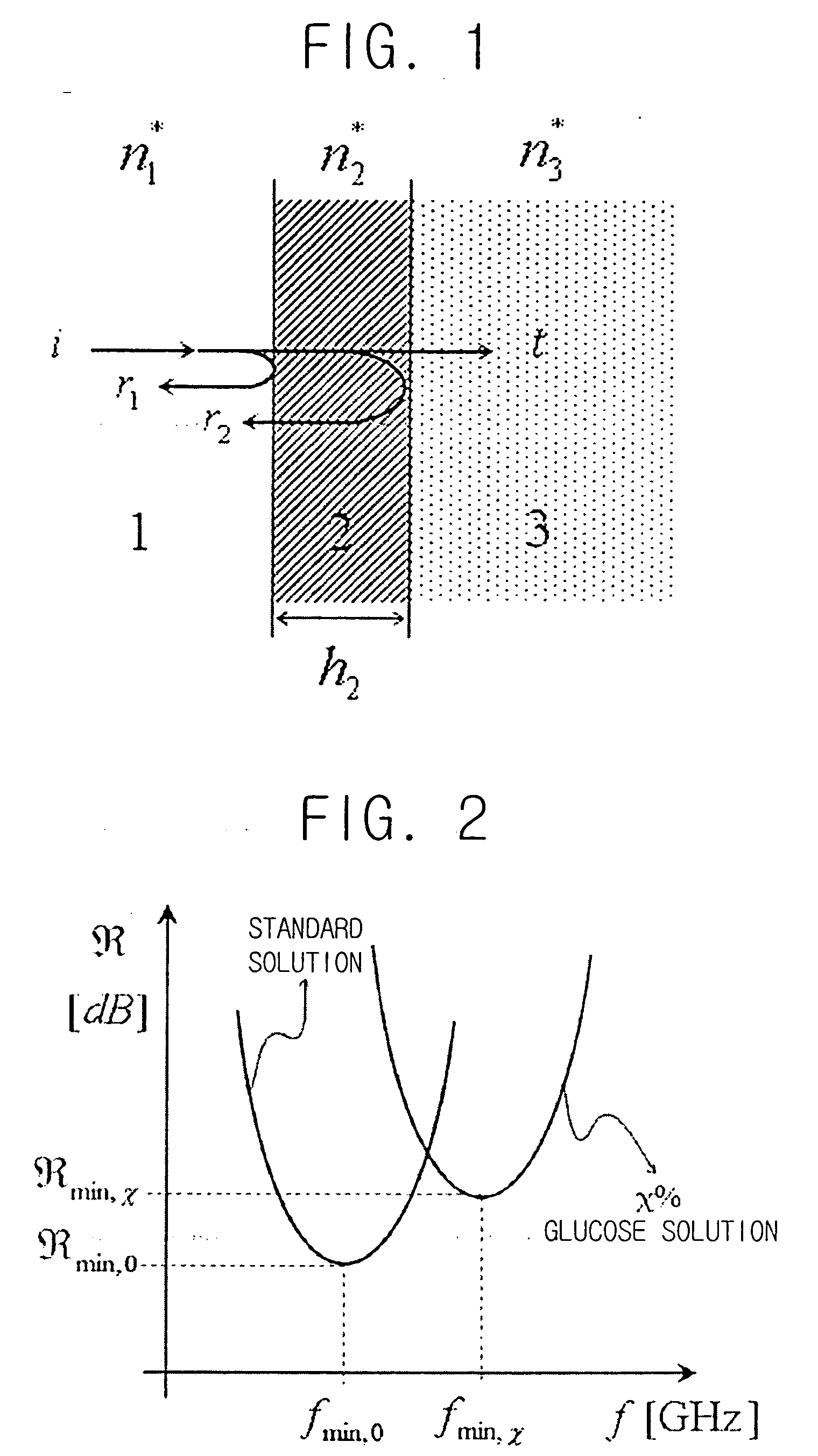
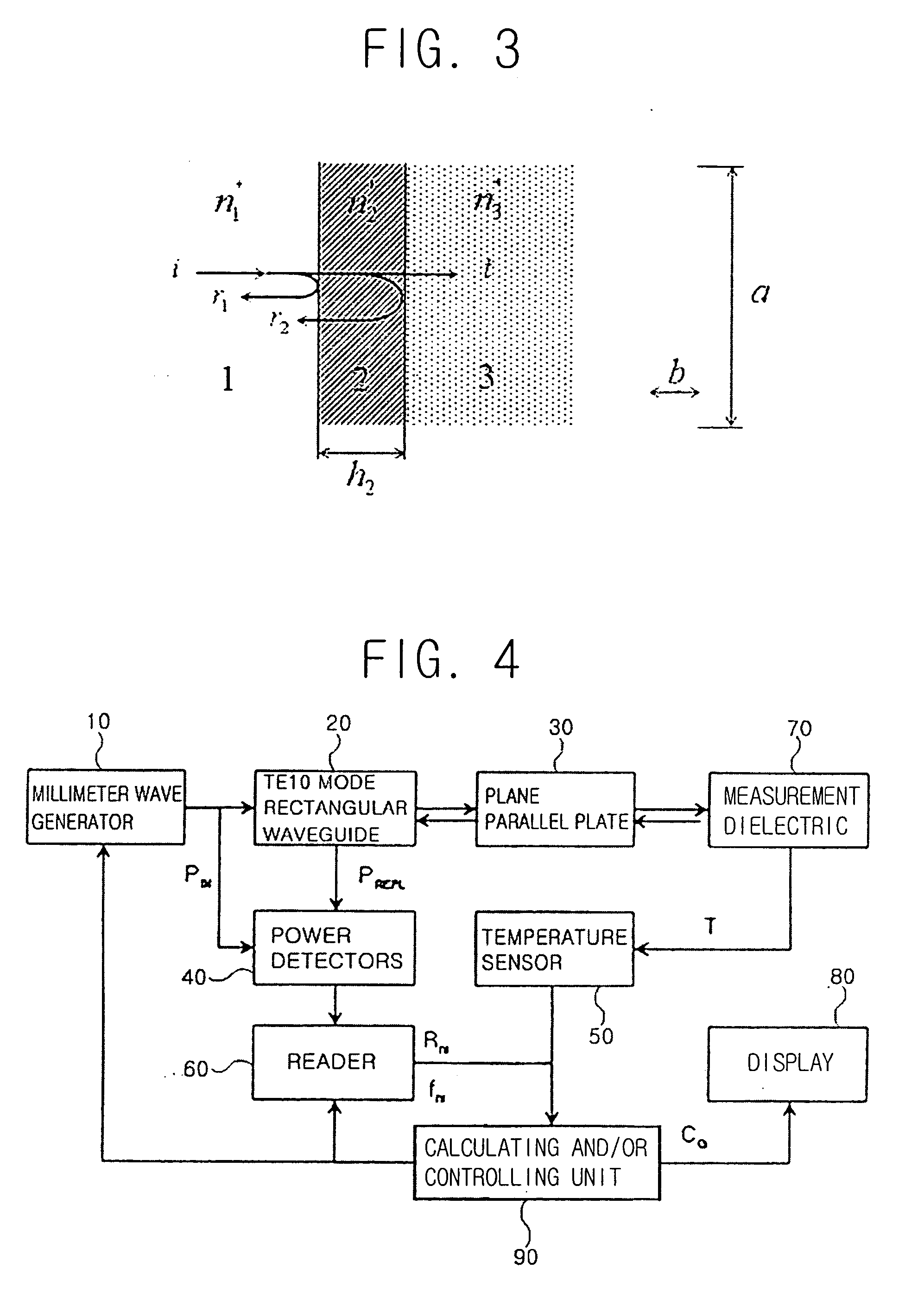
ActiveUS20060025664A1Reduction factorSensorsBlood characterising devicesParallel plateReflected waves
A device and method for the non-invasive measurement of blood glucose concentrations by millimeter waves. The device includes a millimeter wave generator; a TE10 mode rectangular waveguide transmitting a millimeter wave generated by the millimeter wave generator; and a plane parallel plate chosen to yield a minimal point of the power reflection coefficient of the millimeter wave incident to and reflected from the dielectric object under test via the TE10 mode rectangular waveguide and the plane parallel plate. The device also includes power detectors detecting the powers of the incident wave generated by the millimeter wave generator and the reflected wave from the dielectric object via the plane parallel plate; a temperature sensor measuring a temperature of the dielectric object; and a reader reading the minimum power reflection coefficient and a corresponding frequency from the incident and reflected wave detected by the power detectors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
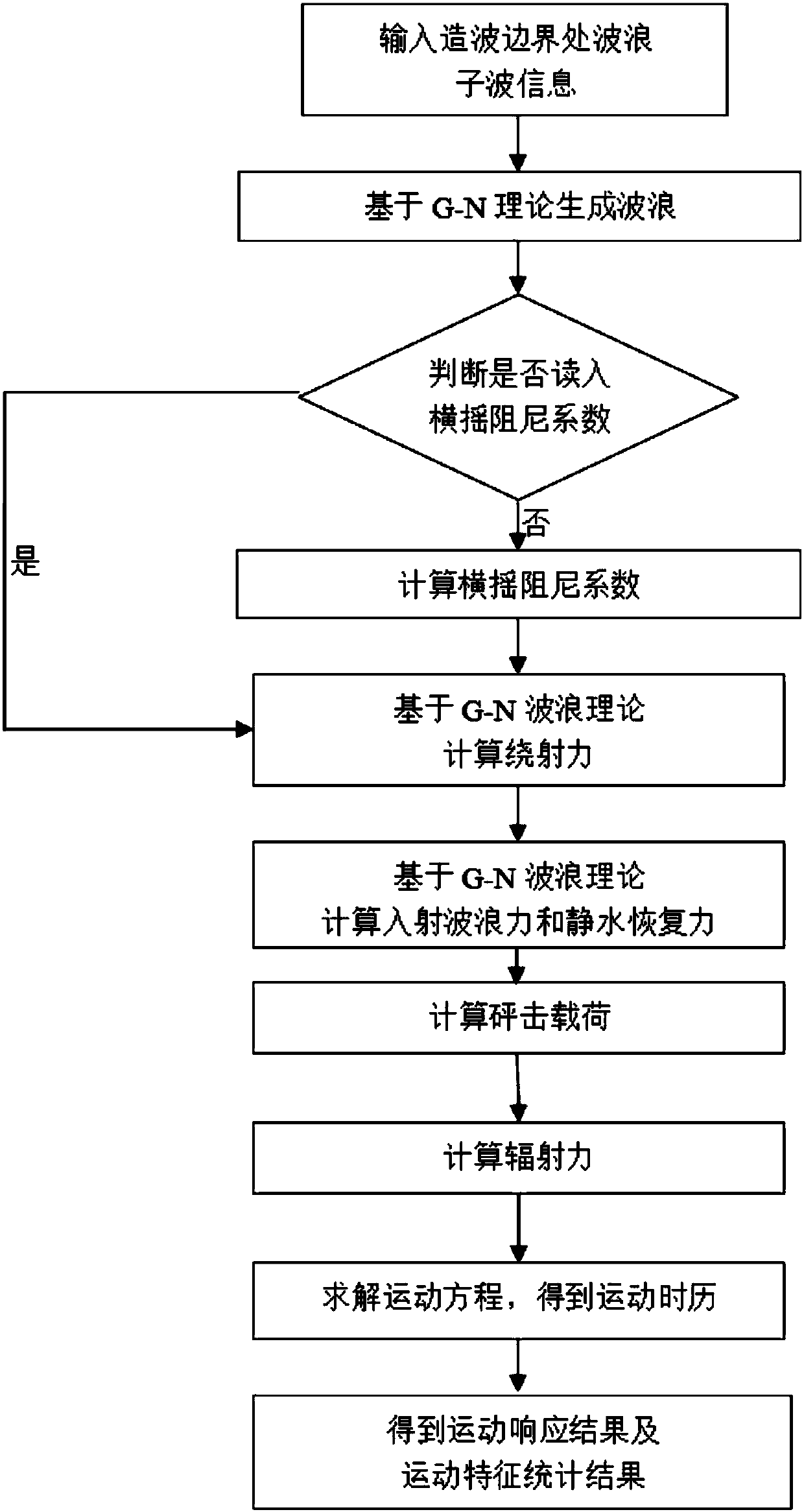
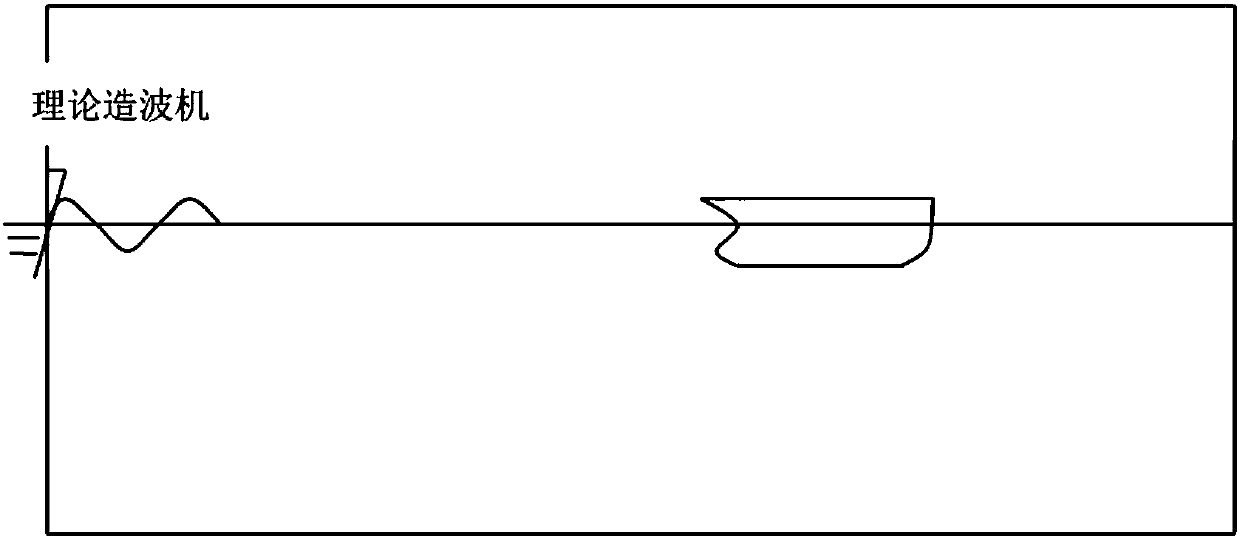
G-N wave model-based forecast method for large-amplitude motion of ship in severe sea condition
The invention discloses a G-N wave model-based forecast method for a large-amplitude motion of a ship in a severe sea condition, and belongs to the technical field of ship motion forecast. Through nonlinear simulation of the motion of the ship in waves, a nonlinear effect of an incident wave force and a hydrostatic restoring force of a ship body is considered, and an incident wave pressure on thewet surface of the ship body is calculated. A fluid pressure is solved based on a G-N wave theory, so that the incident wave force and a hydrostatic pressure are obtained; a radiation force and a diffraction force are solved by adopting an impulse response function method, wherein the wave surface of the diffraction force is obtained by a G-N wave model; and consistency correction can be performedin calculation. The large-amplitude motion of the ship is forecast by adopting a weak nonlinear motion equation based on coupling of three freedom degrees including heaving, pitching and rolling; RAOis calculated for analyzing motion characteristics of the ship; a simulated motion response time history significant valve, a motion extremum value and oscillation statistics are analyzed by utilizing a wave-by-wave analysis theory; and the motion of the ship body can be forecast more accurately.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Surface acoustic wave transponder configuration
InactiveUS6208062B1Efficient receptionGuaranteed normal transmissionImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerIncident wave
An acoustic wave identification transponder device, having a substrate, an electroacoustic transducer generating an acoustic wave in said substrate and a set of encoding elements disposed in a path of the acoustic wave for modifying the acoustic wave, having elements which reflect portions of the acoustic wave having a component orthogonal to the incident wave. The reflectors may be, for example, trackchangers or reflective arrays compressors (RAC). The wave may be phase-amplitude modulated for increased efficiency expressed in bits per tap. Such phase amplitude modulation is preferably imposed by partial beam width phase delay elements disposed within an acoustic beam path.
Owner:X CYTE
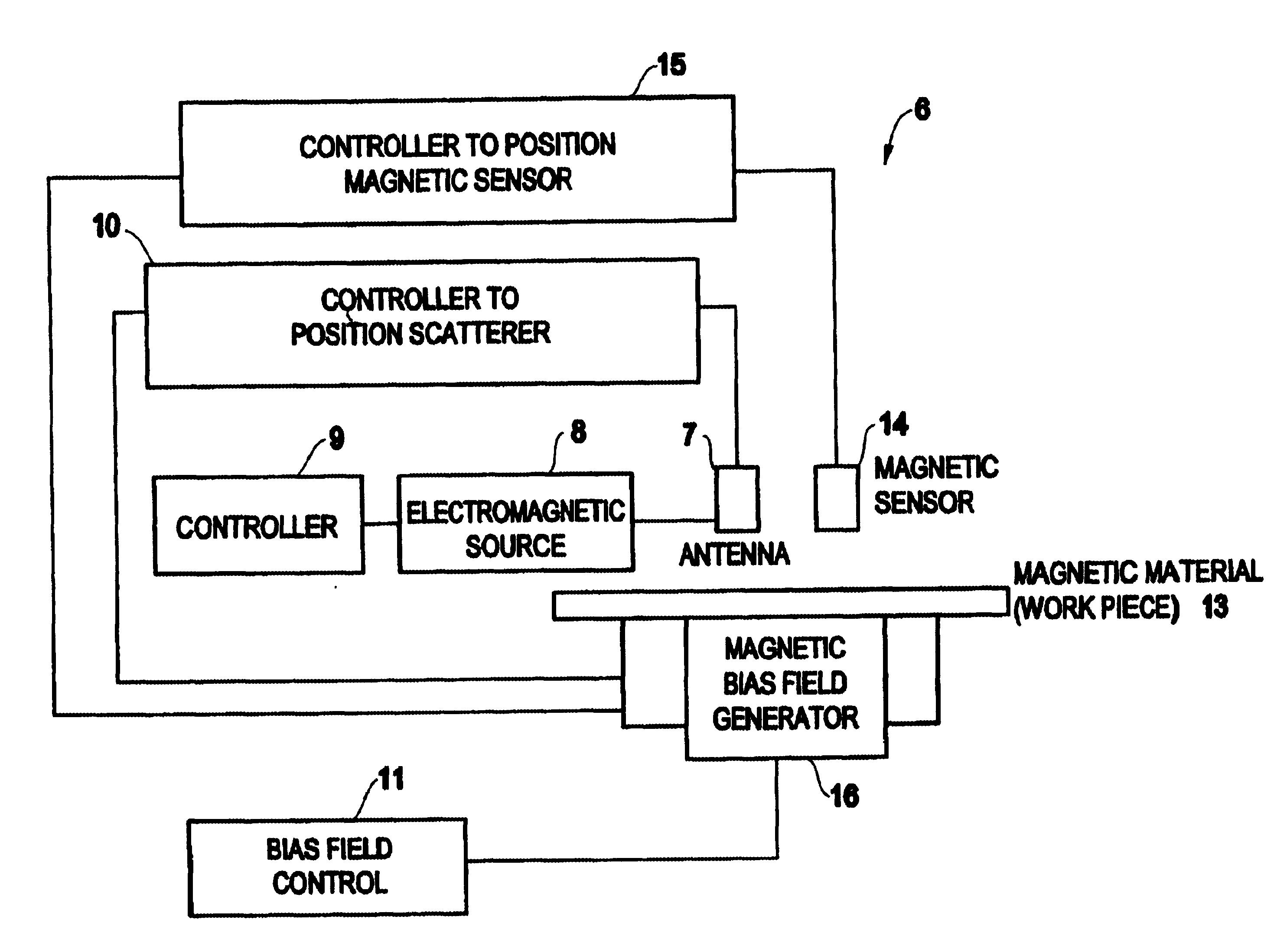
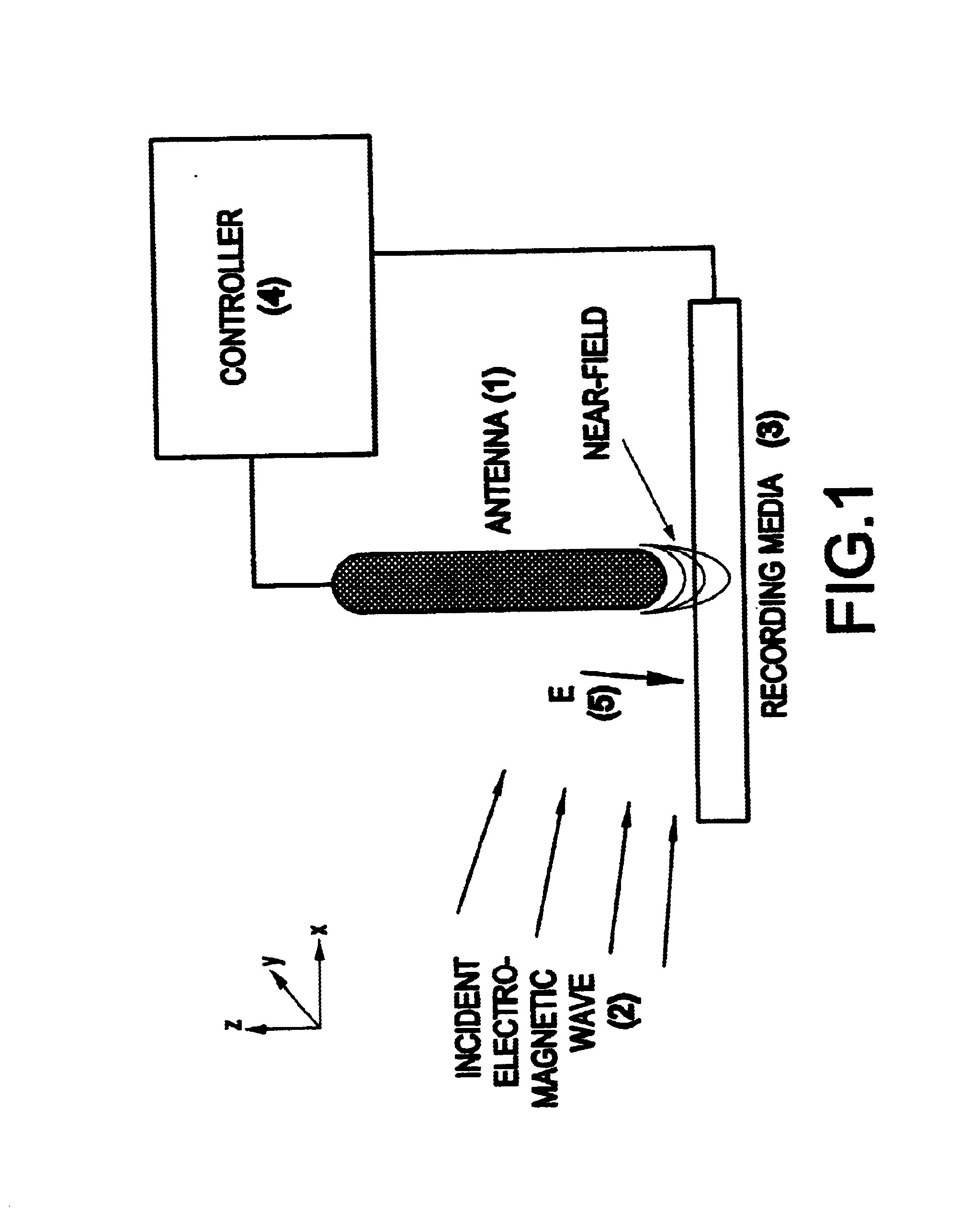
Assembly and method suitable for thermo-magnetic writing/reading of data
An assembly for writing / reading high-density data on a recording media as a series of tags comprising a magnetic information bit pattern. The assembly includes an antenna positionable near the media; a source of electromagnetic radiation for producing an incident wave at least a portion of which can be coupled to the antenna; and, a means for coordinating a mutual positioning of the source of the electromagnetic radiation and the antenna, so that the antenna can generate a highly localized electromagnetic field in the vicinity of the media for inducing localized heating of the media. The assembly is capable of writing / erasing said high-density data by using an information signal for modulating the localized field generated in the vicinity of the media; the assembly is capable of reading by coordinating the mutual positioning of the antenna and the media.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
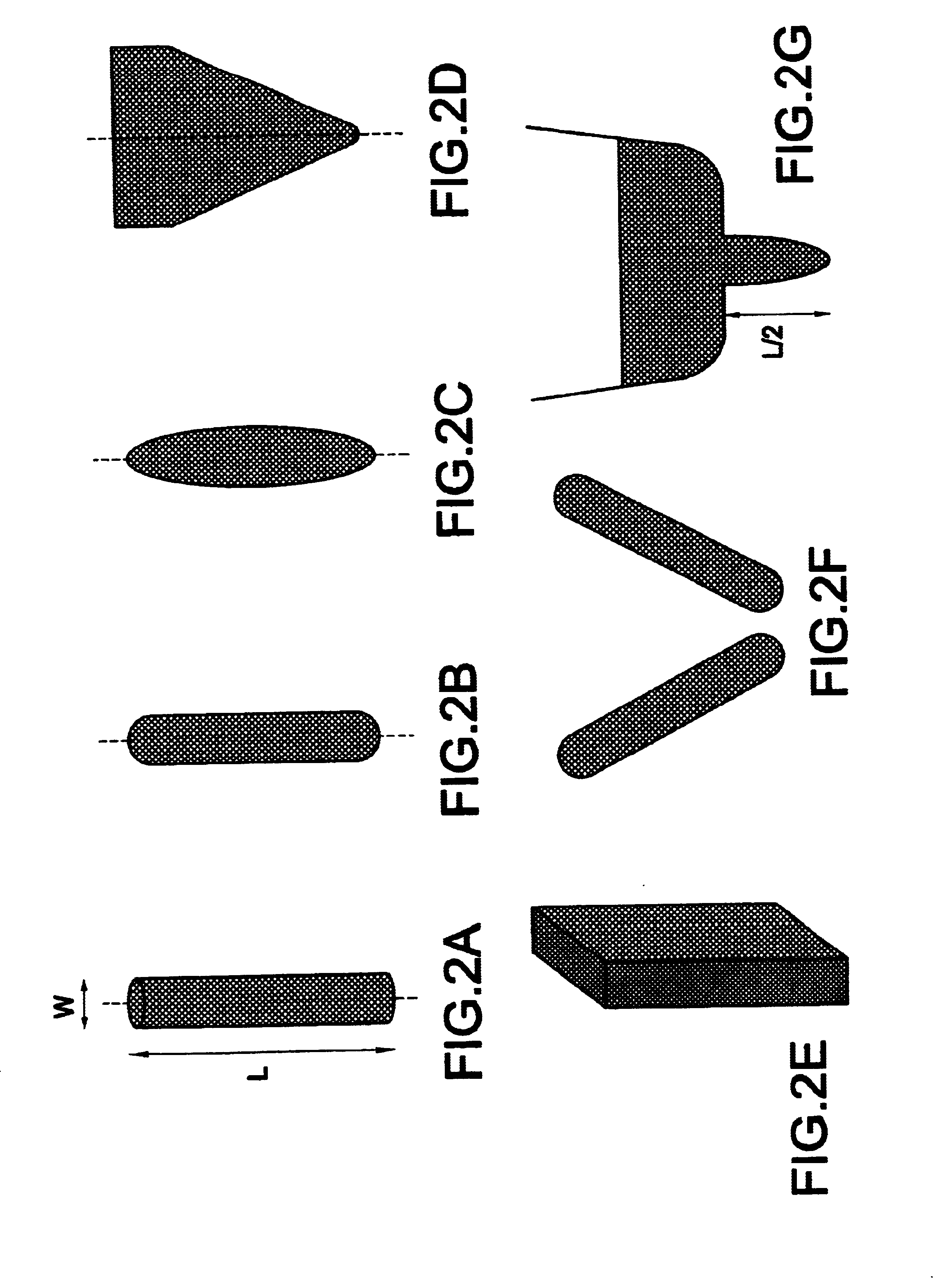
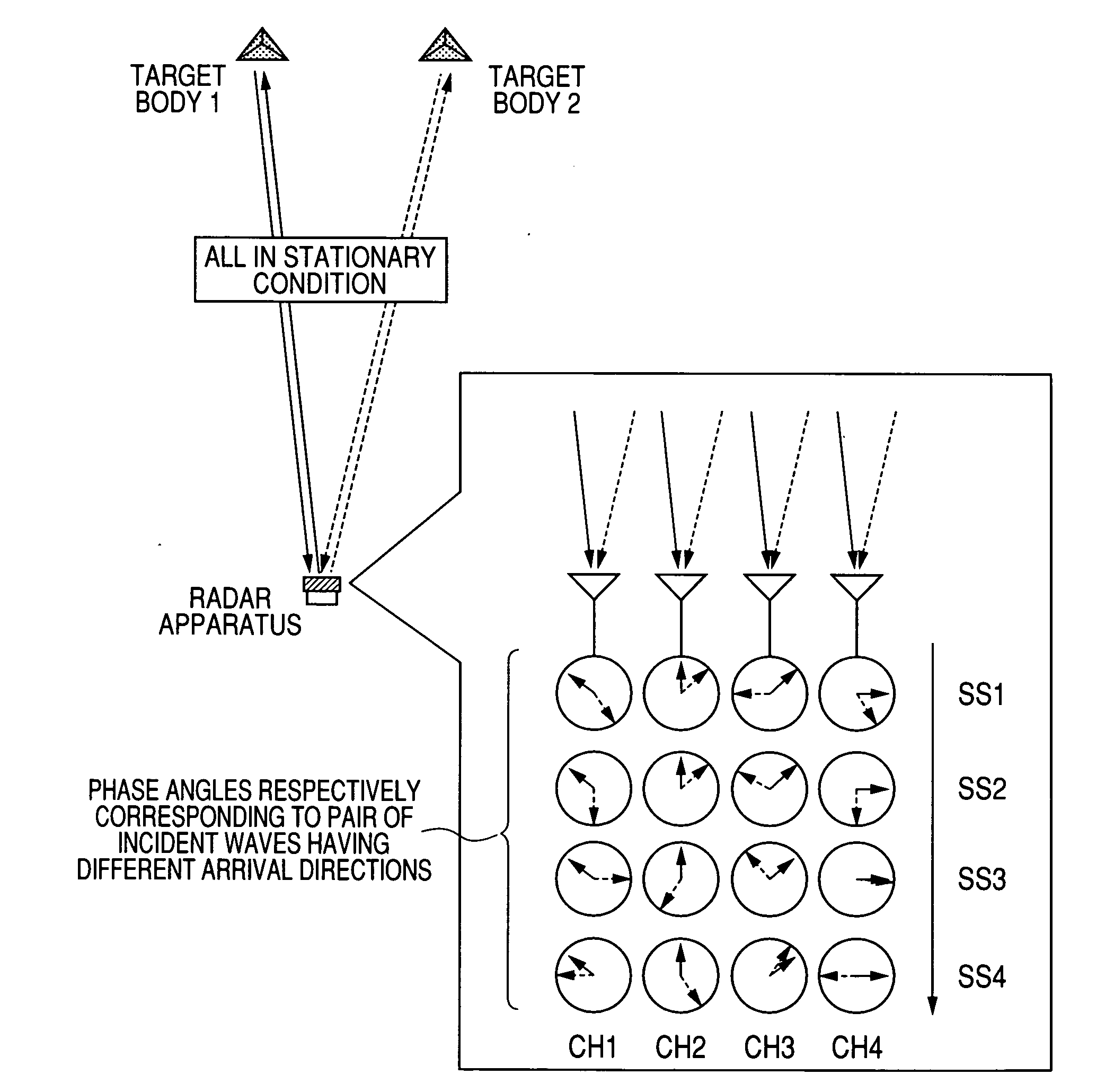
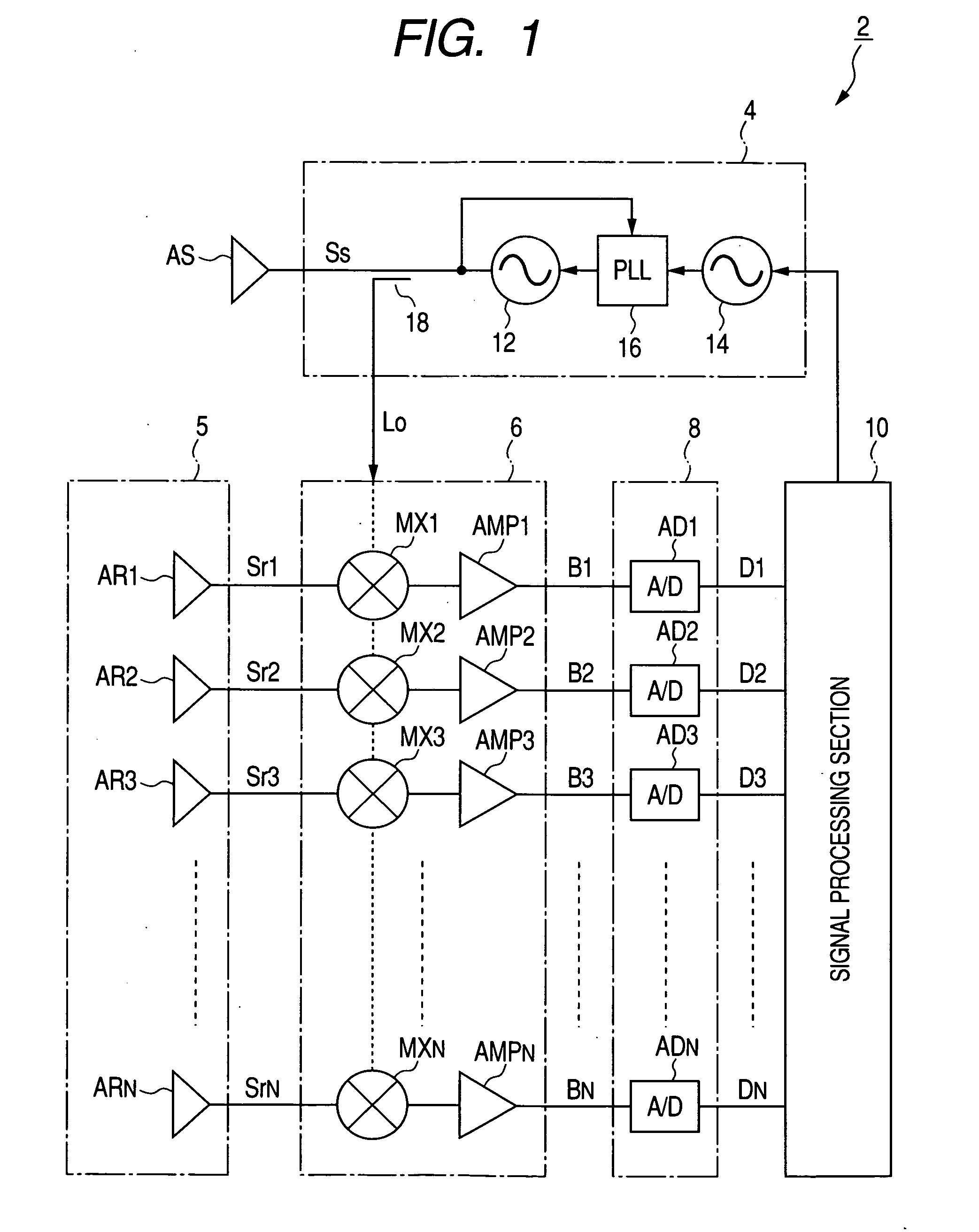
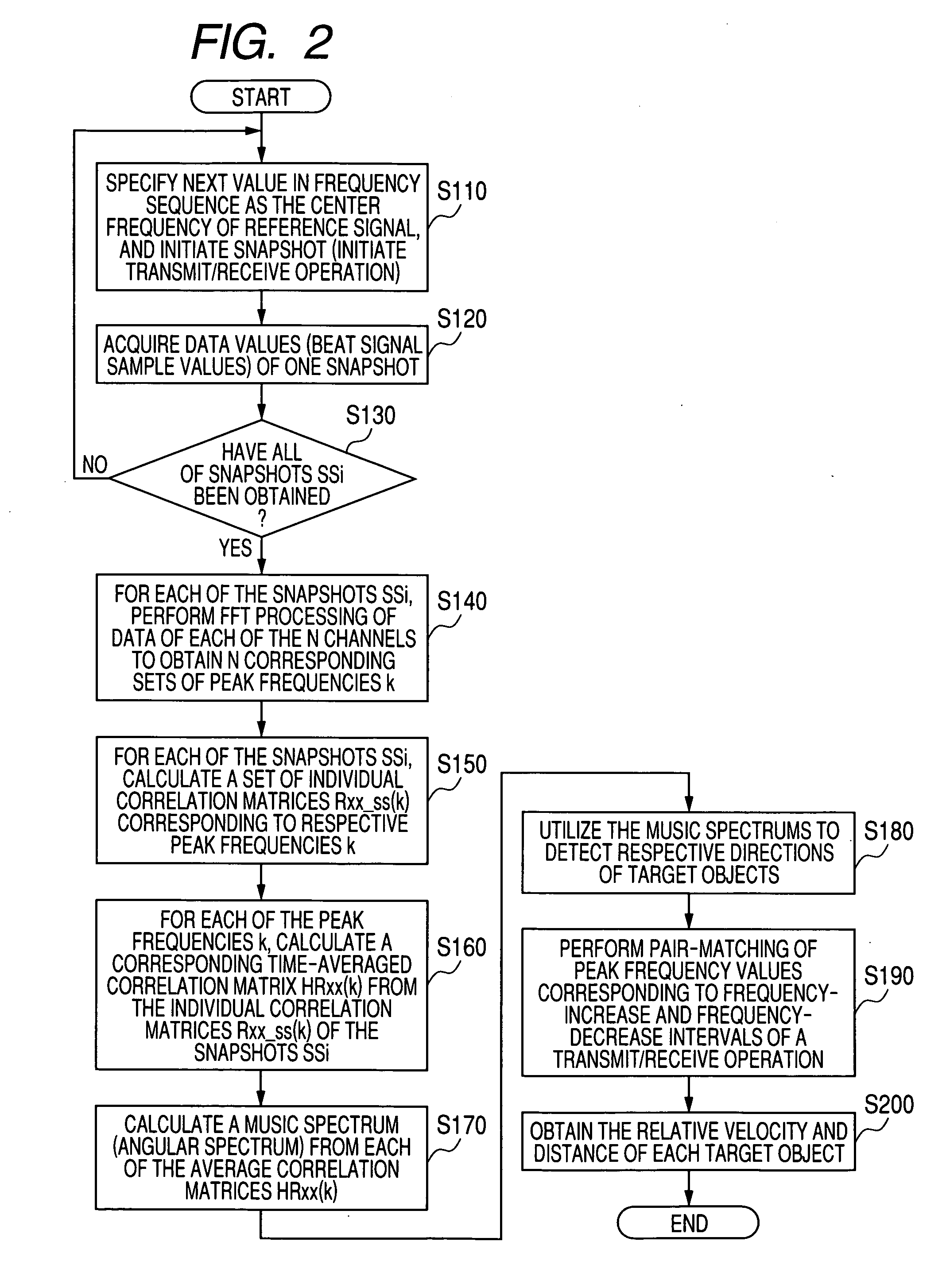
Target object detection apparatus for acquiring information concerning target objects based on correlation matrix derived from signal values corresponding to reflected electromagnetic waves
ActiveUS20090309784A1Improve accuracyHigh degreeMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionObject basedRadar
A target object detection apparatus periodically executes a transmit / receive operation to transmit radar waves and obtain received signals from resultant incident reflected waves from respective target objects. An individual correlation matrix of received signal values is derived for each one of a fixed plurality of successive transmit / receive operations, with the transmission frequency being changed at successive operations. Individual correlation matrices derived from respective transmit / receive operations are time-averaged to obtain an average correlation matrix for use in obtaining target object information such as direction or velocity, with effects of correlation between respective incident waves being suppressed.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method for attenuating rayleigh wave scattered noise in earthquake data-handling
The invention provides a method for attenuating Rayleigh wave scattering noise during the seismic data processing, the method only carries out the scattering noise attenuation processing of a frequency band which mainly contains a scattering wave field and does not affect the characteristics of the original wave fields of other frequency bands, so the method is the noise removing method with the relative fidelity. The method comprehensively utilizes the linear wave field transform, the wavelet transform and the Alpha-trimmed filtering technology to extract the Rayleigh wave scattering incident wave field and calculate the wavelet, then the best estimation of the scattering wave field is realized through the inversion technology of the scattering wave field, and the estimated scattering noise is further subtracted from the original wave fields, thereby effectively improving the signal-to-noise ratio of seismic information.
Owner:徐基祥
Wave-power system and method for generating energy at constant rotational speed at variable significant wave heights and periods
InactiveUS7525214B2Continuous tuningPositive displacement enginesEngine fuctionsFreewheelEnergy absorption
A wave energy conversion system or device is provided which includes a hull that serves as a float, moving up and down with incoming waves. The power take-off system contained within the hull comprises a longitudinal main rotary shaft upon which a series different diameter sets of dual same-diameter pinions interact with the main rotary shaft through their corresponding freewheels. This interaction only allows the main rotary shaft to rotate in only one direction. A fork-like rod system member that is either fixed directly to a base on the seabed or to a supporting underwater taut moored floating platform. This fork-like rod system member has an alternate rod in permanent contact with each pinion (two rods per each set of dual same-diameter pinions). The device also is capable of self-adjusting its mechanical properties and orientation to take into account the predominant wave frequency and direction over a period of time in a practical way to provide continuous, or multiple level, tuning of the system and is self-orienting for maximum and minimum energy absorption depending on sea conditions.
Owner:NOVA OCEANIC ENERGY SYST
Metamaterial-based terahertz adjustable polarized wave insensitive electromagnetically-induced transparency device
InactiveCN108390156AAvoid replacementSame electromagnetically induced transparencyAntennasAdhesiveWave detection
The invention discloses a metamaterial-based terahertz adjustable polarized wave insensitive electromagnetically-induced transparency device, and belongs to the fields of electromagnetic wave detection and sensor. The electromagnetically-induced transparency device comprises multiple basic units periodically arranged in the same direction; each basic unit comprises an upper layer graphene layer and a lower layer dielectric layer, and the dielectric layer is fixed on a substrate device; graphene is cut to form graphene square rings with openings in the adjacent edges; after the graphene layer is completely cut in one time, the middle part of the substrate device is hollow out; and finally, electroplating of a layer of conductive adhesive is carried out. The electromagnetically-induced transparency device has the same electromagnetically-induced transparency phenomenon on line polarized light in the x and y directions; when the polarized mode of incident wave is changed, device replacement is not needed; and in addition, an adjustable electromagnetically-induced transparency phenomenon can be realized by regulating the externally applied voltage without changing the device structure,thereby achieving important guidance significance and reference value on the development of an adjustable terahertz functional device.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com