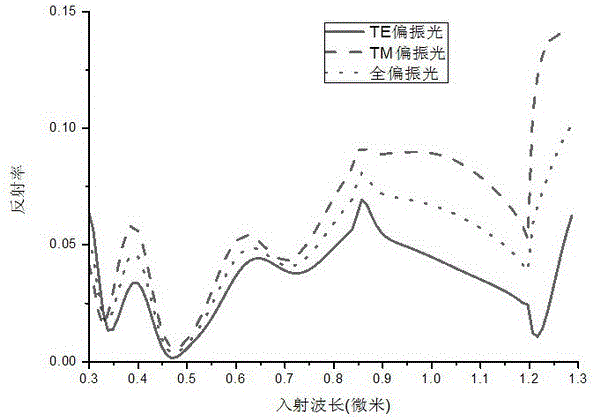
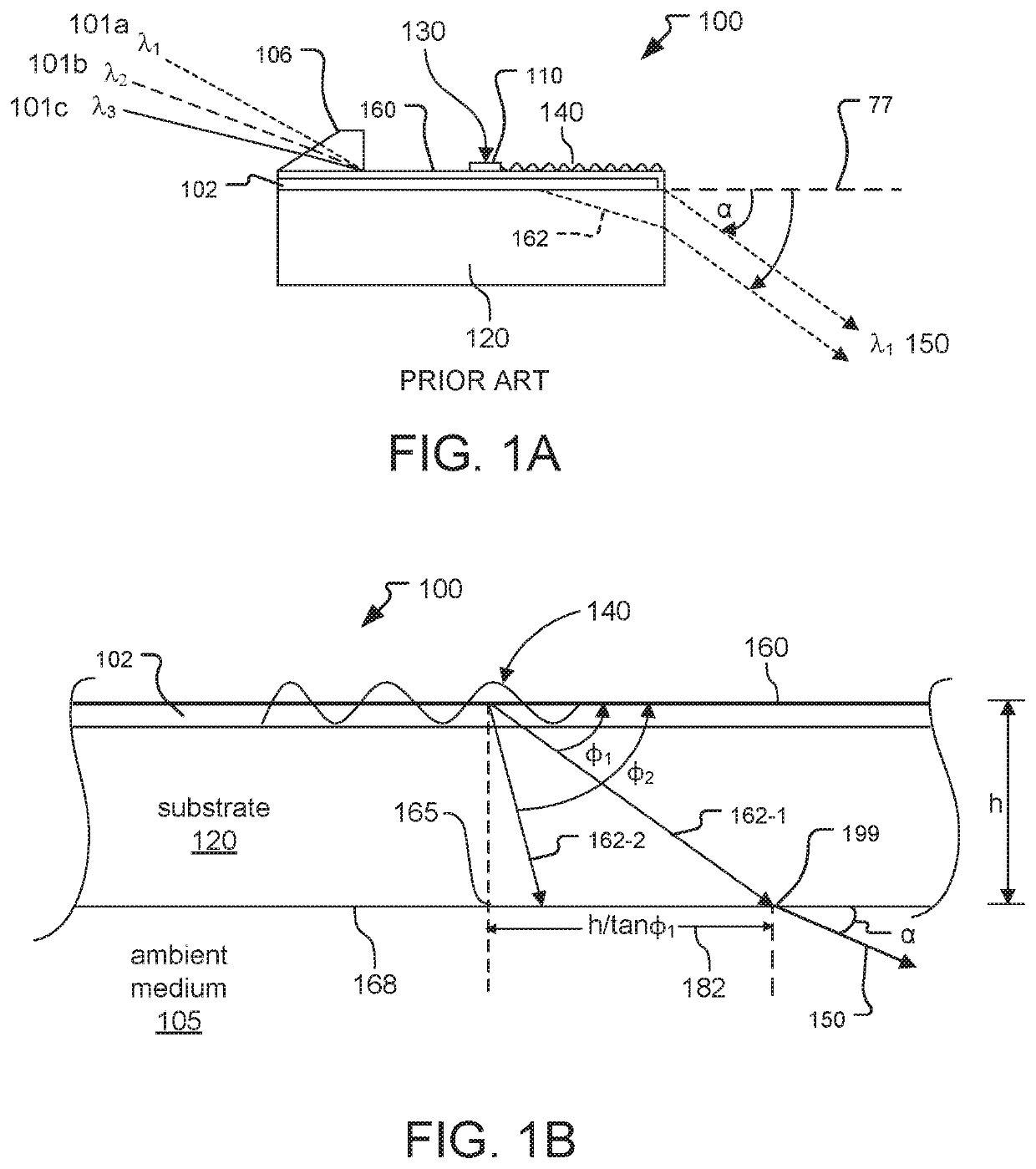
Patents
Literature
68 results about "Leaky mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
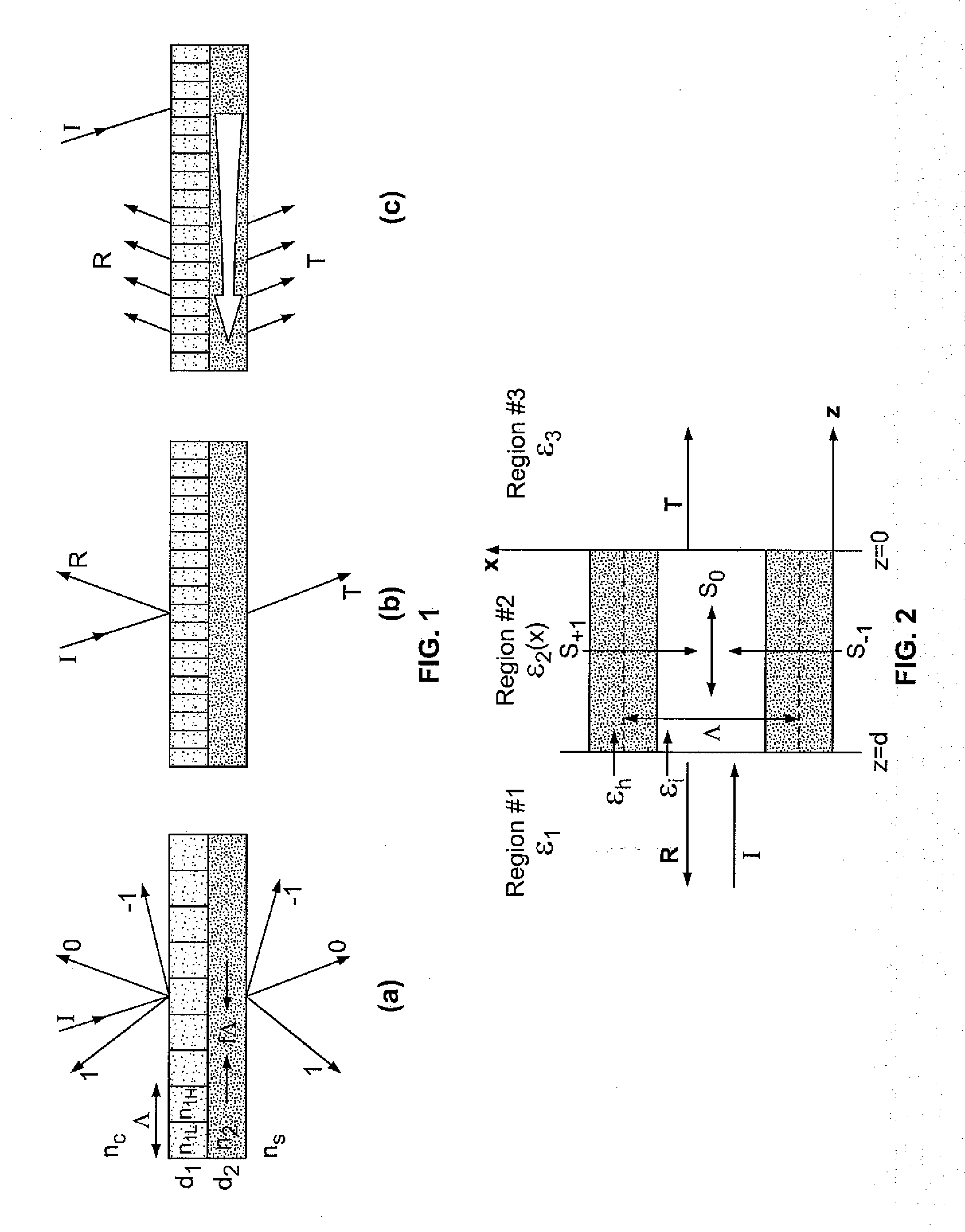
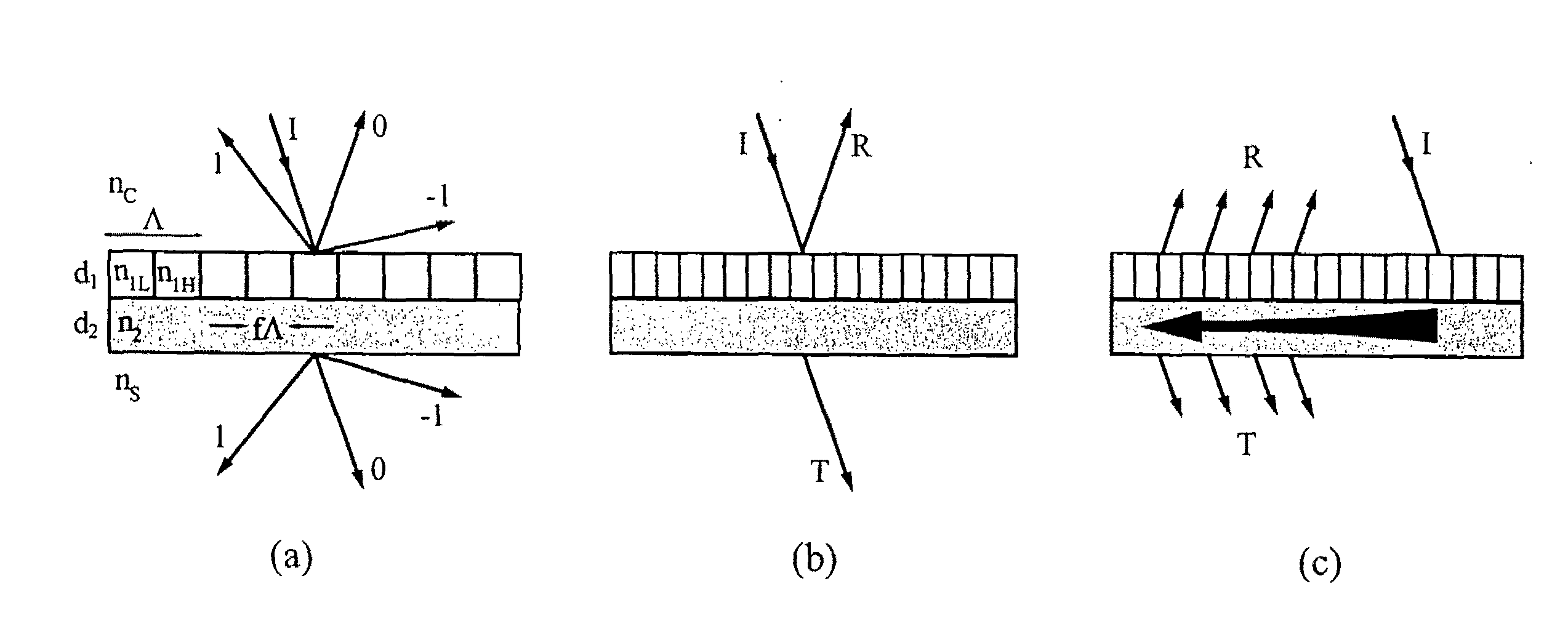
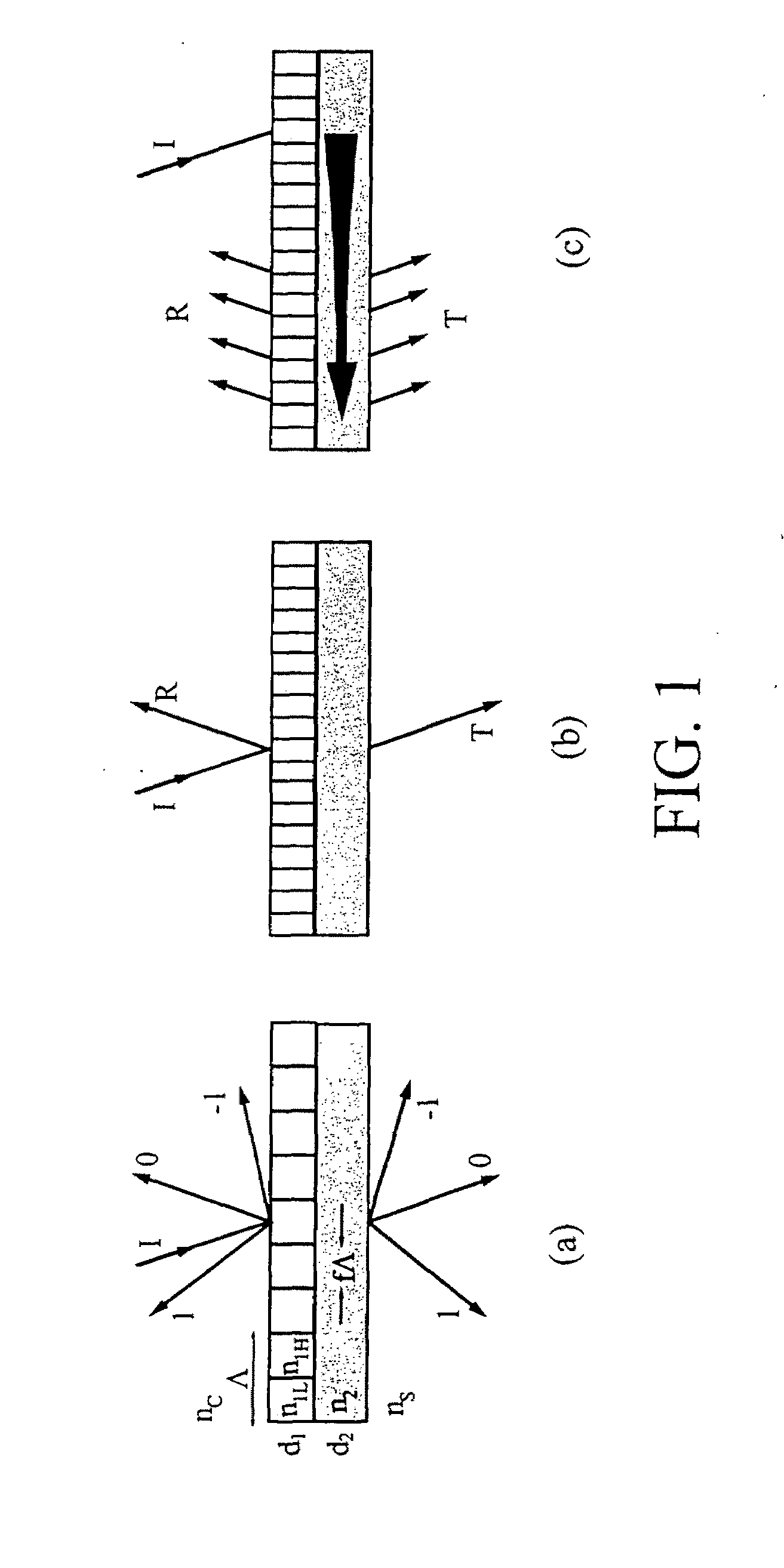
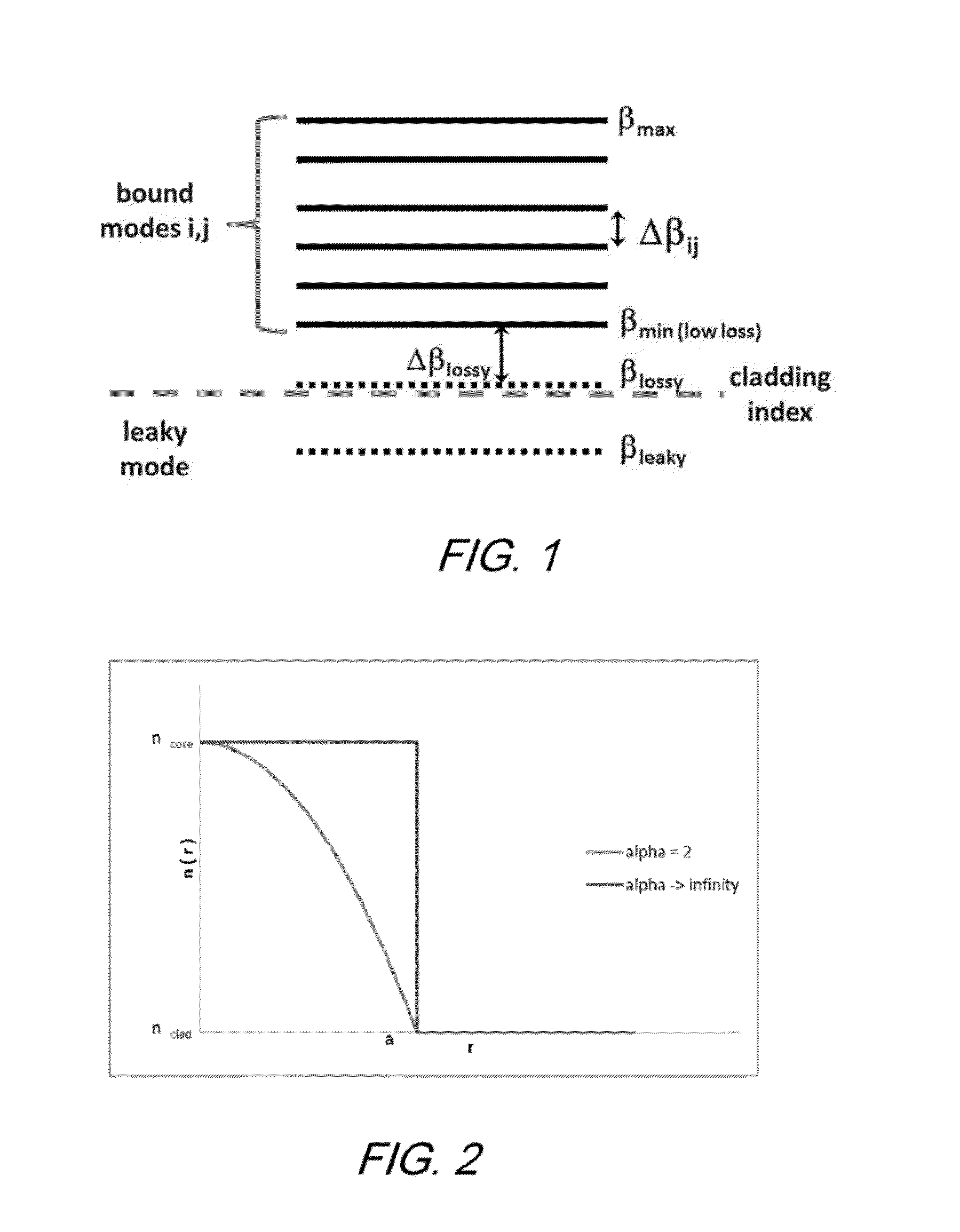
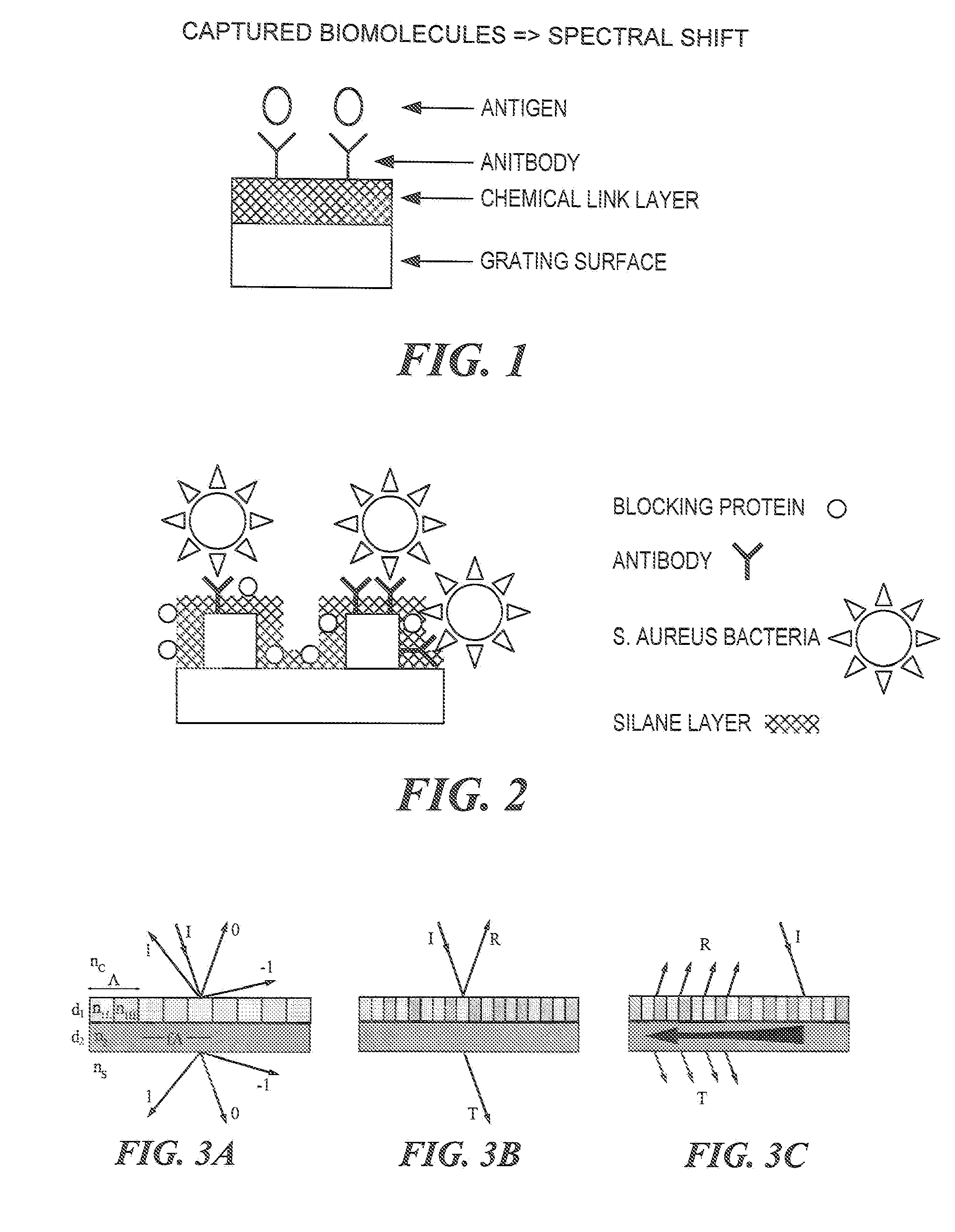
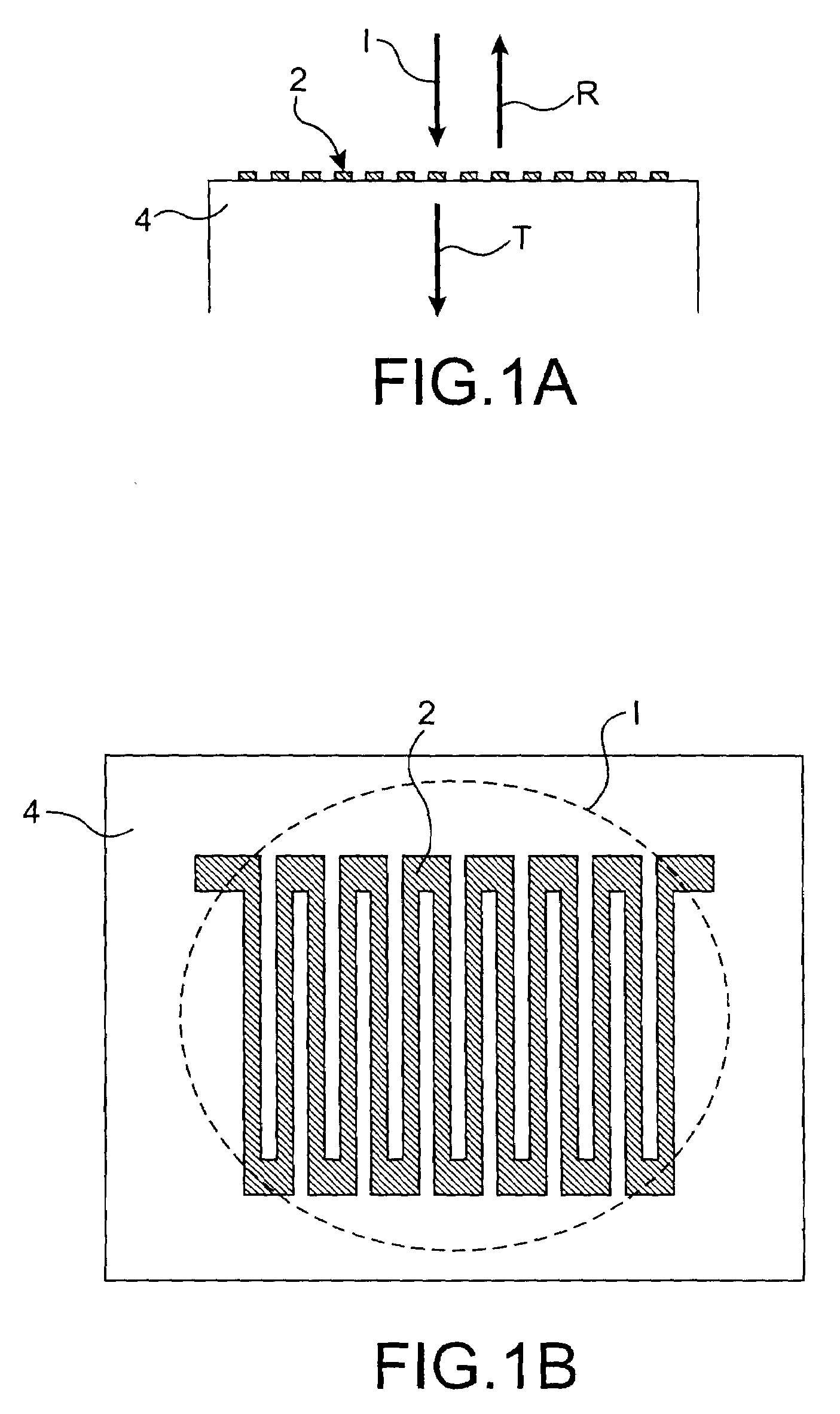
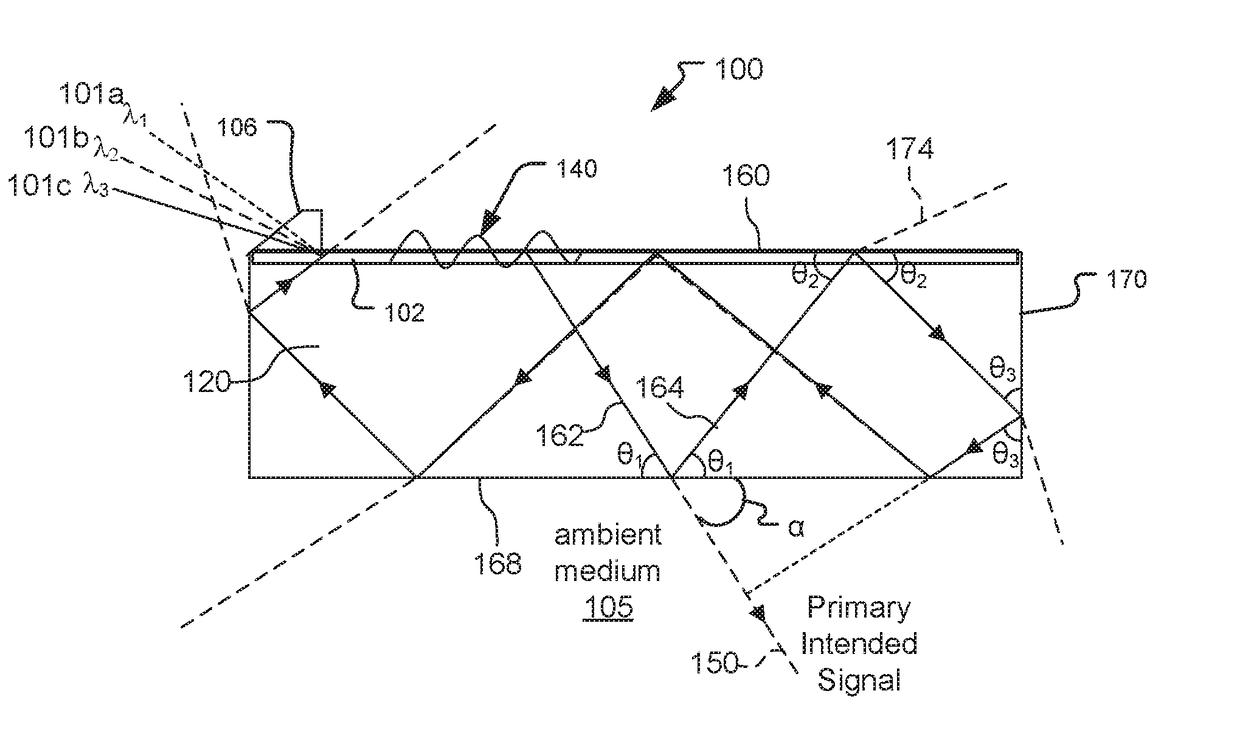
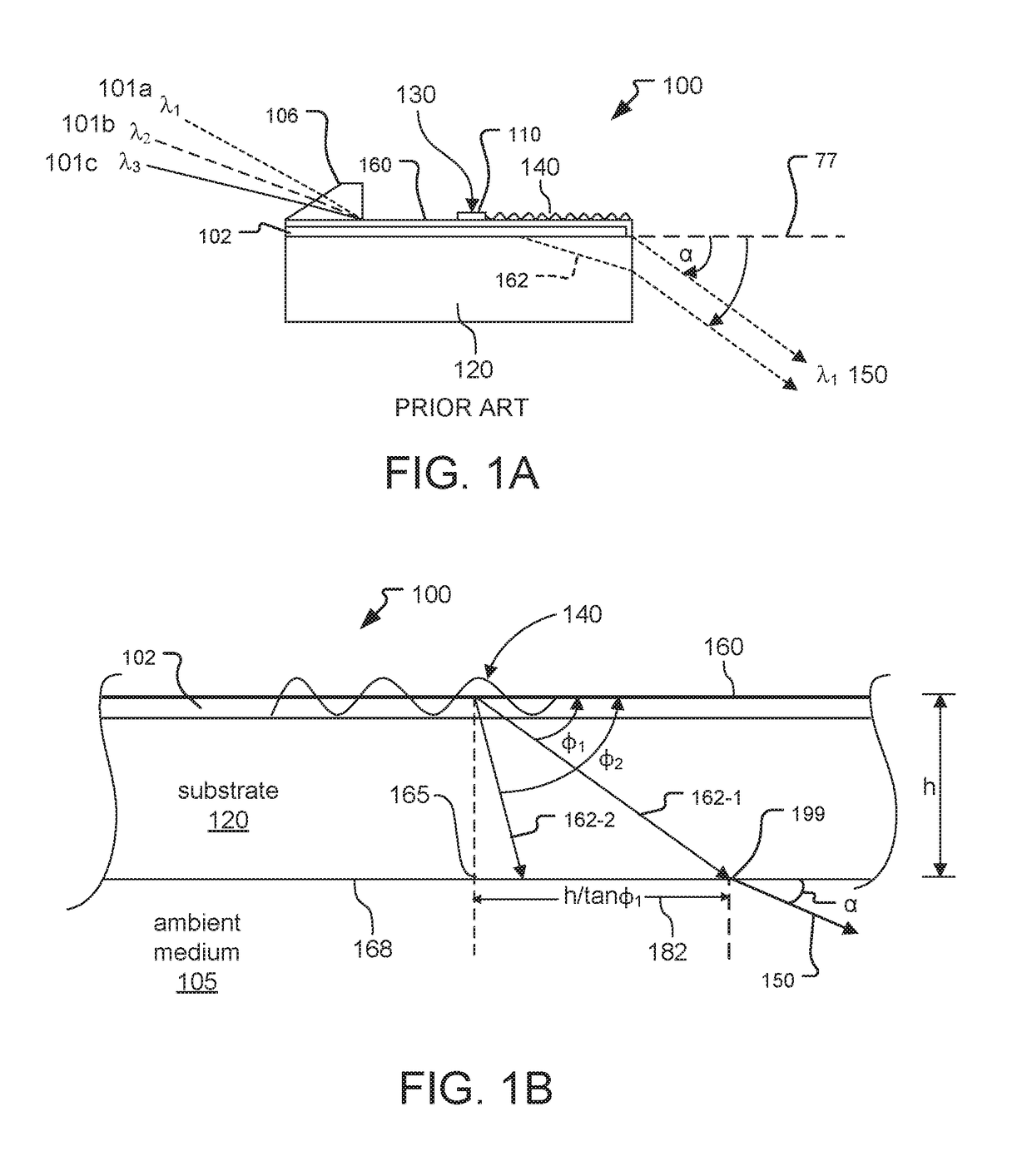
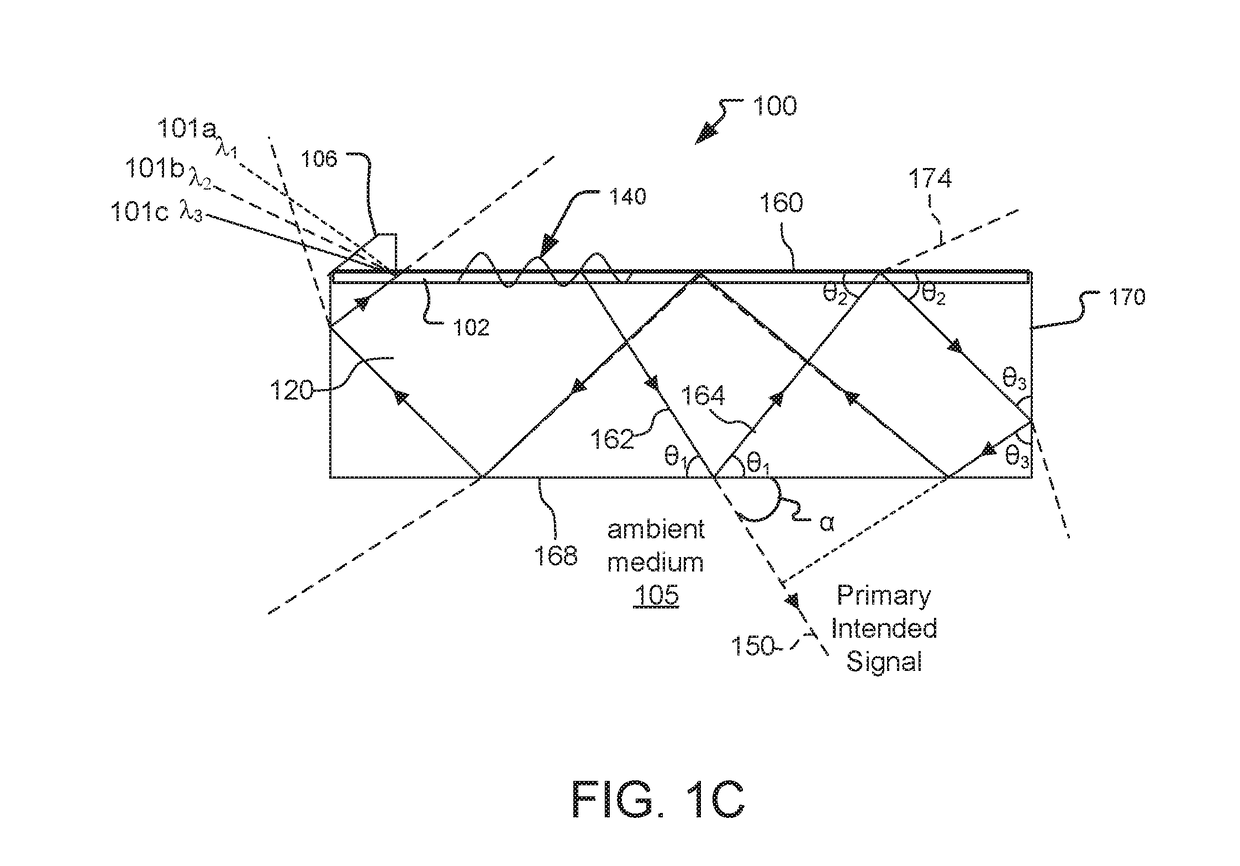
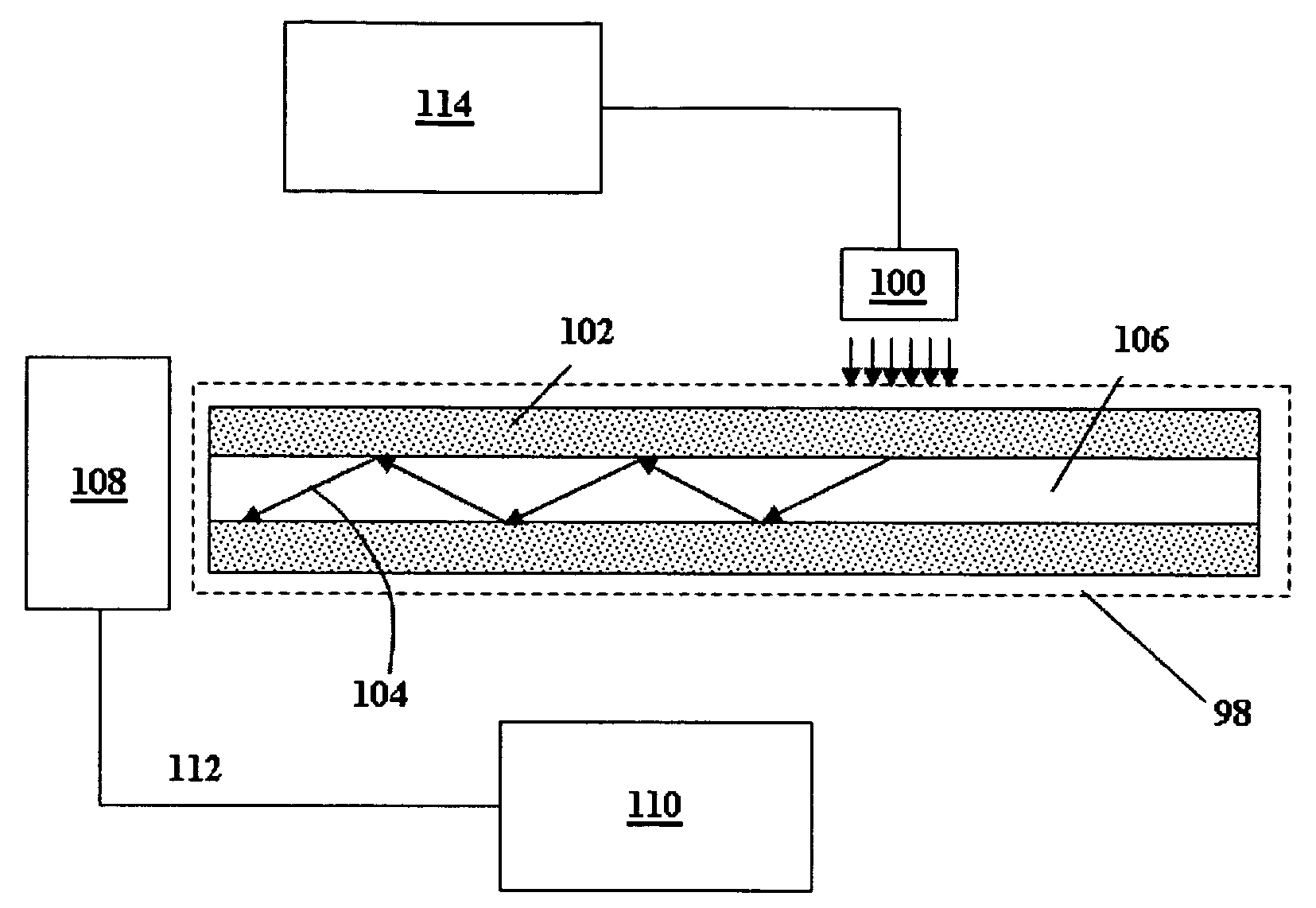
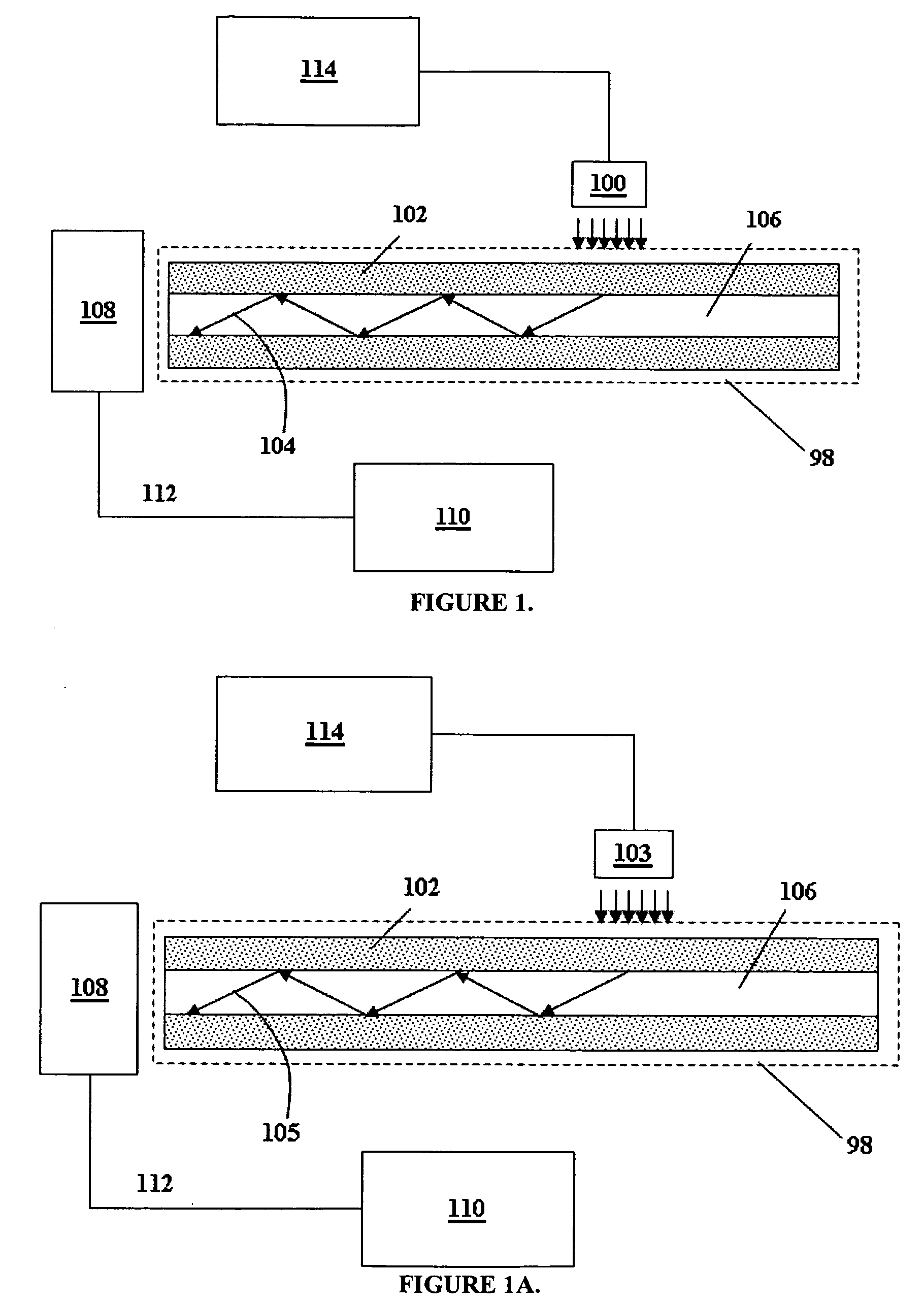
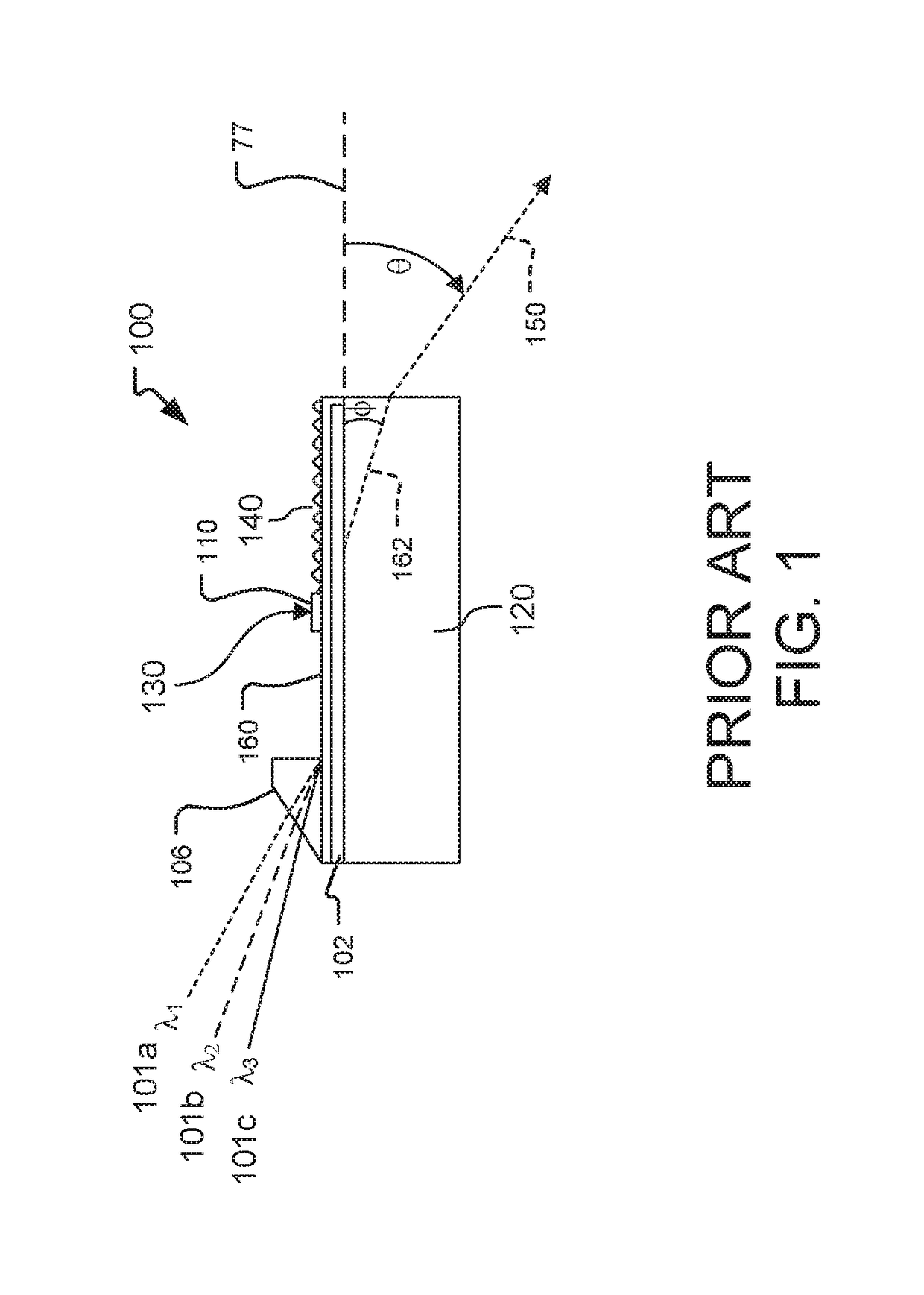
A leaky mode or tunneling mode in an optical fiber or other waveguide is a mode having an electric field that decays monotonically for a finite distance in the transverse direction but becomes oscillatory everywhere beyond that finite distance. Such a mode gradually "leaks" out of the waveguide as it travels down it, producing attenuation even if the waveguide is perfect in every respect. In order for a leaky mode to be definable as a mode, the relative amplitude of the oscillatory part (the leakage rate) must be sufficiently small that the mode substantially maintains its shape as it decays.
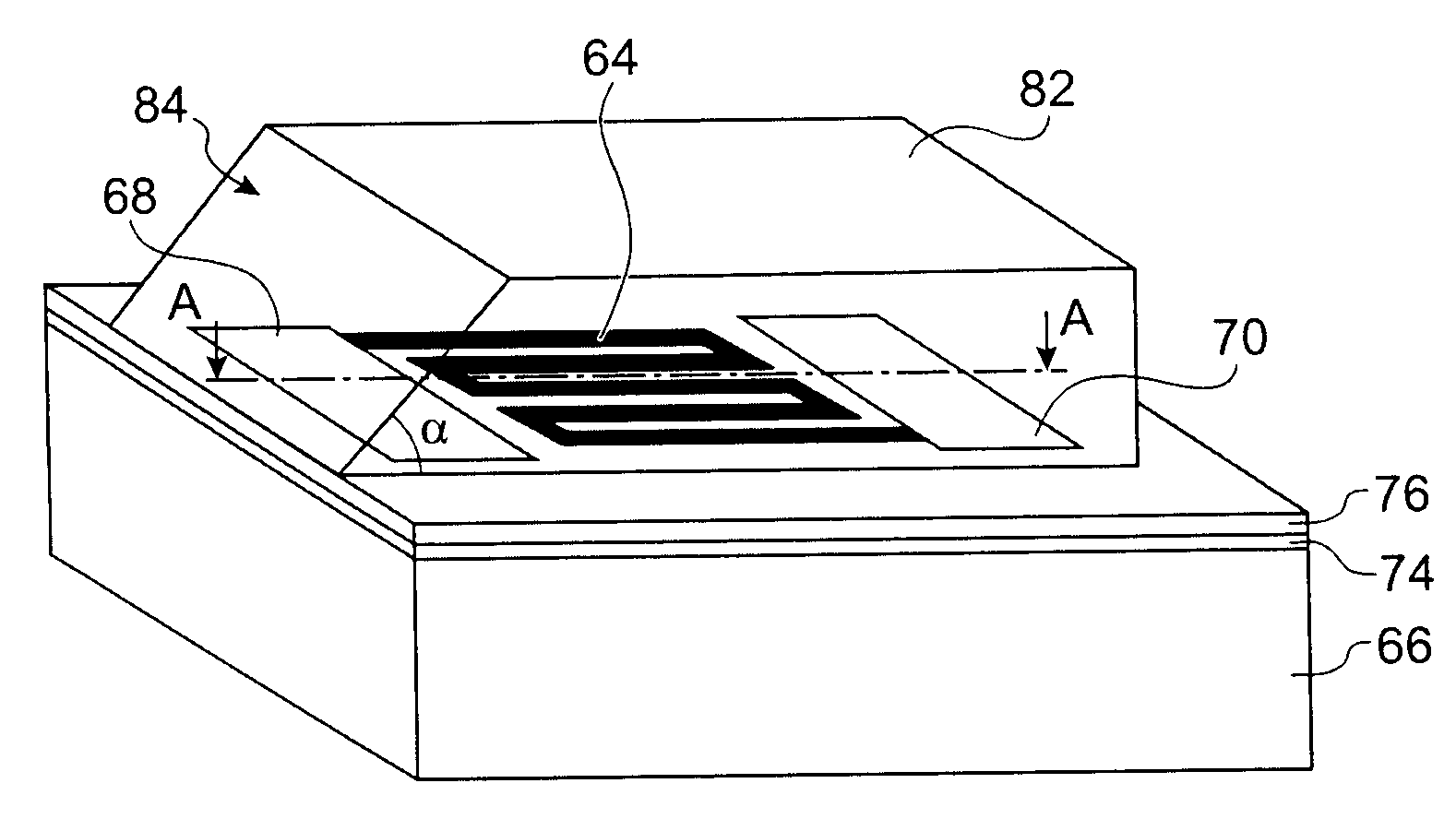
High efficiency optical diffraction device
ActiveUS7454103B2Diffraction efficiencyWide choiceMechanical apparatusDiffraction gratingsOptical diffractionDevice form
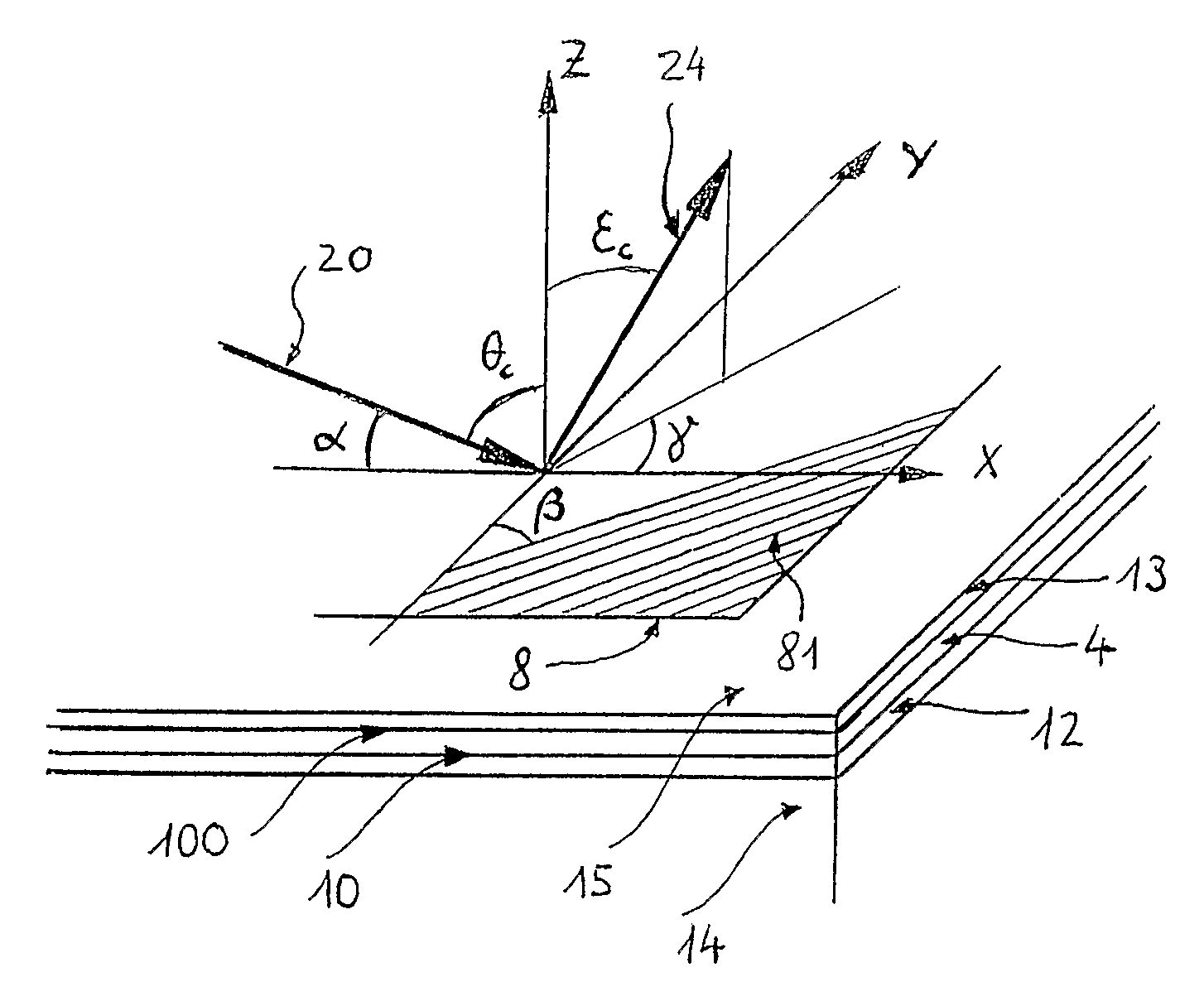
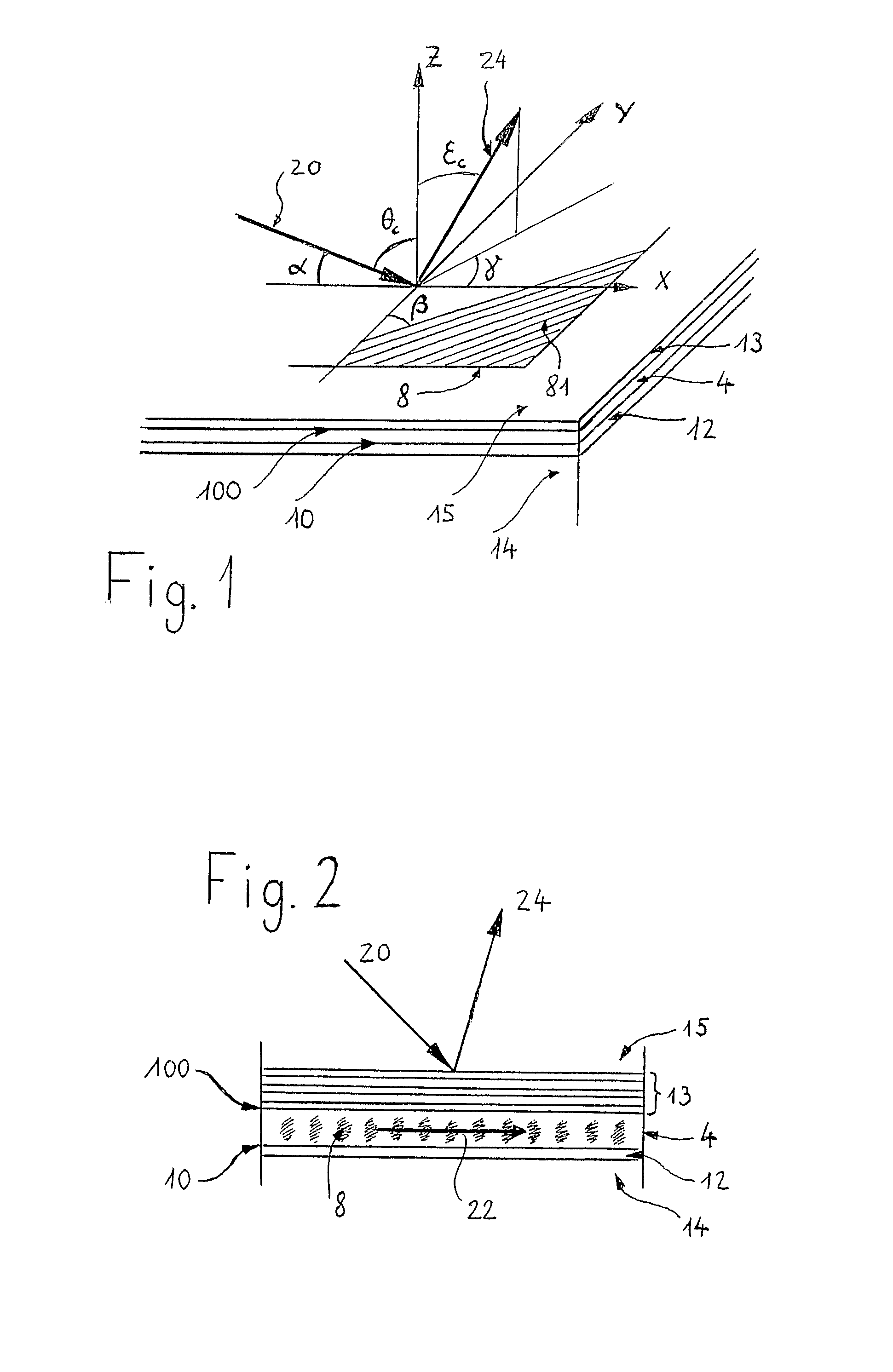
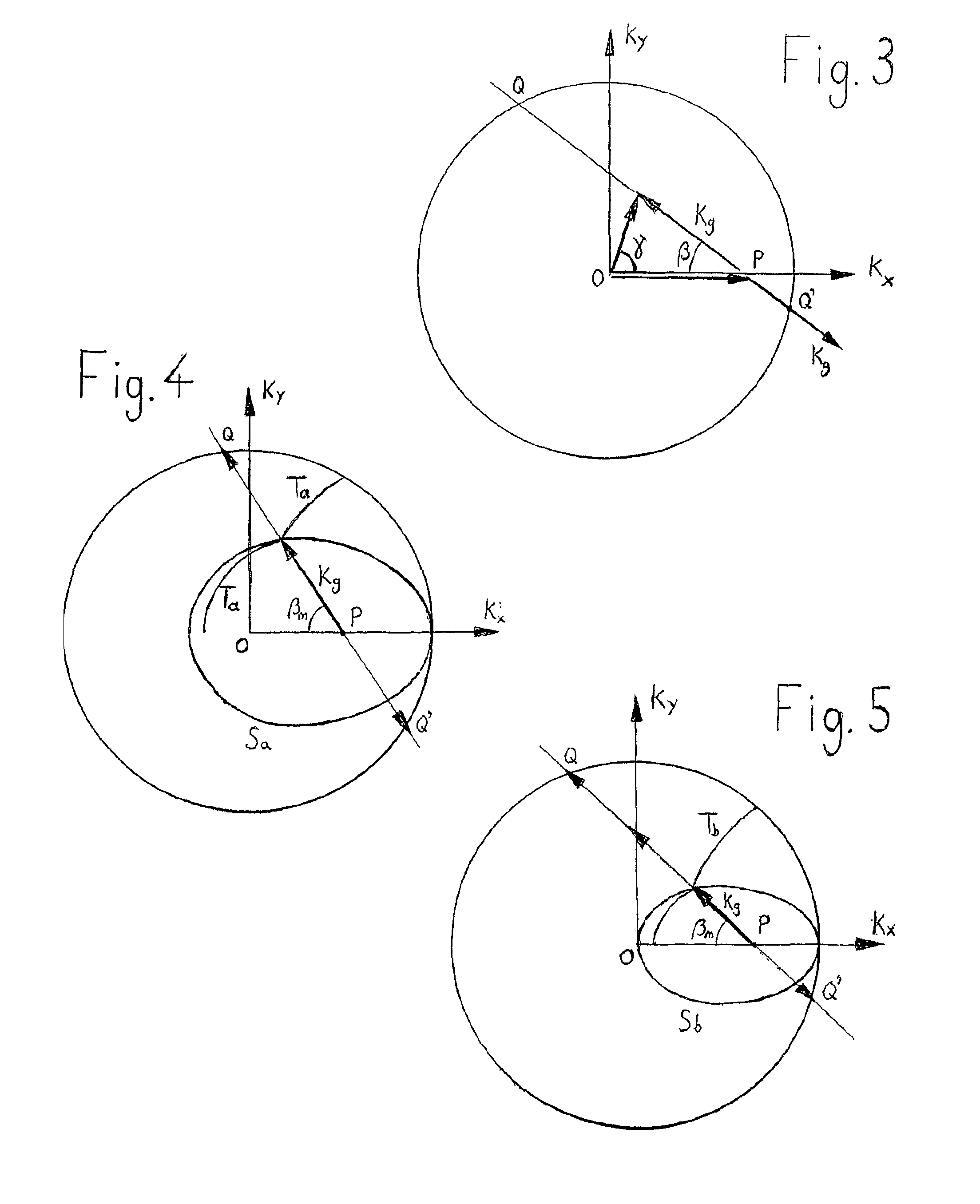
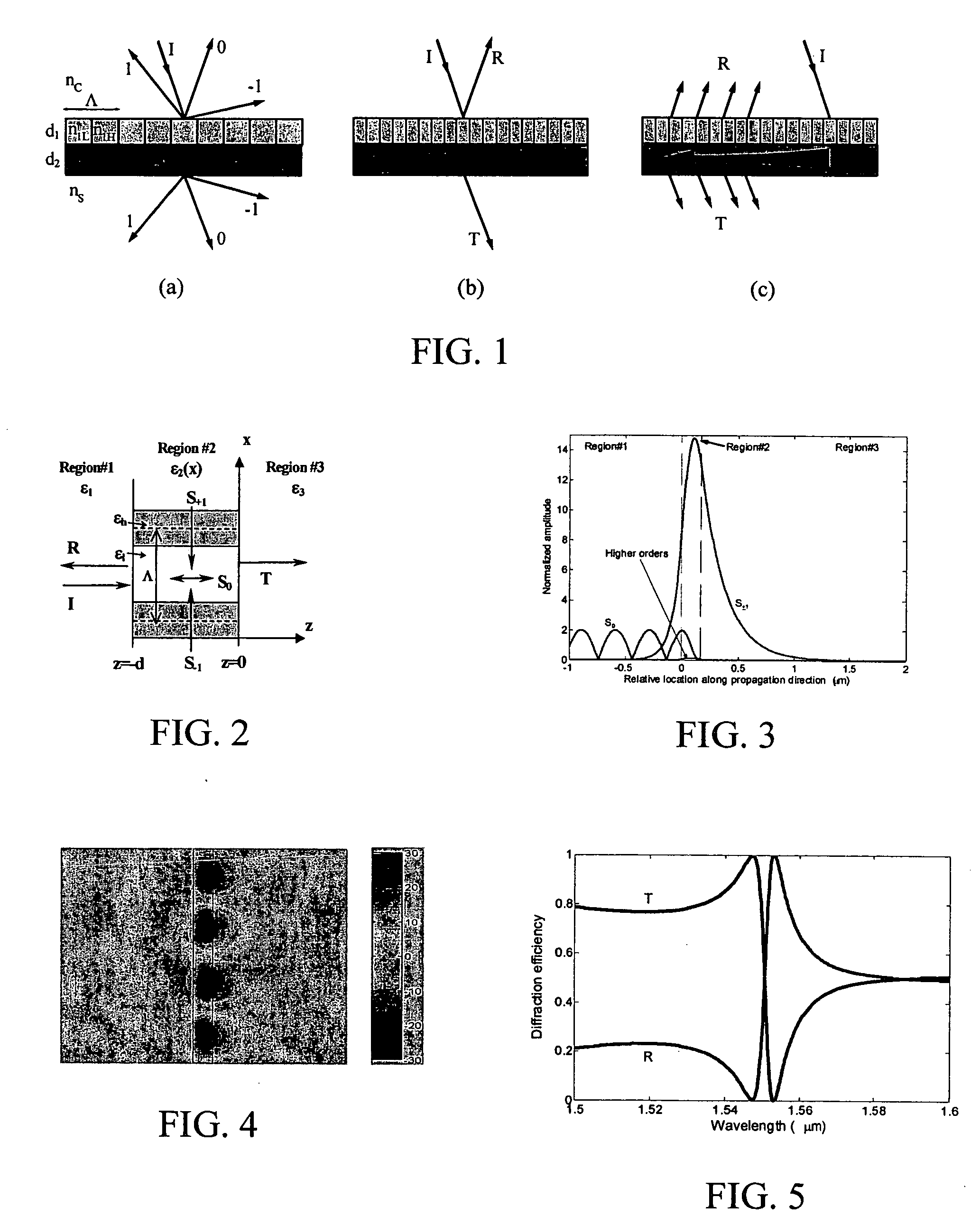
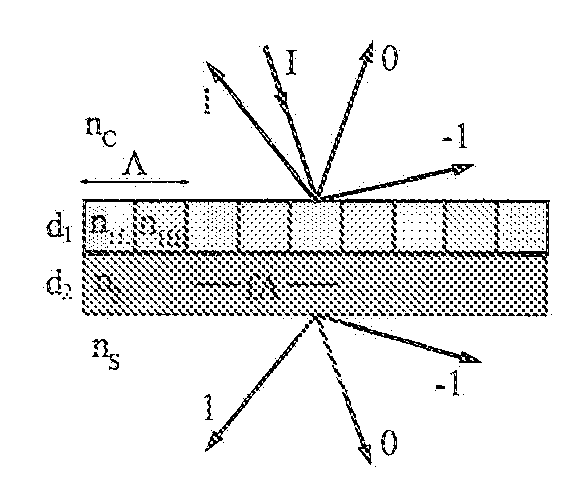
Lightwave diffraction device formed of a dielectric layer (4), a mirror (12) arranged at the lower face (10) of said layer, a semi-reflective structure (13) arranged at the upper face (100) of said layer, and a diffractive structure (8) arranged in said layer or on its faces. The height (H) of the layer is chosen so as to substantially satisfy the resonance condition for at least one leaky mode propagating in said layer for at least one given incident wave having a determined wavelengthλ and a determined incidence angle θc. Next, the diffractive structure is arranged so that there is no propagating positive diffracted order, and so that all negative orders other than the −1st propagating order have zero or a relatively small diffraction efficiency, the reflected −1st order propagating in a direction non-parallel to the incident wave. This diffraction device allows a high diffraction efficiency of up to 100% for the −1st order.
Owner:PARRIAUX OLIVIER M
Tunable resonant leaky-mode N/MEMS elements and uses in optical devices
ActiveUS20090067774A1Increase varietyImprove utilizationLaser detailsNanoopticsDielectricUnit operation
Mechanically tunable electromagnetic and photonic devices featuring enhanced spectral tunability with minimal mechanical movement are provided. These nano / micro-electromechanically (N / MEMS) tunable elements, including filters and pixels, rely on leaky-mode resonance effects in subwavelength photonic lattices that constitute periodic wavelengths. Such elements can operate in reflection (bandstop) or transmission (bandpass) modes, and can be arranged in one-dimensional or two-dimensional arrays, or operated as single units, and their spectral regions are controlled by the element design. Input electromagnetic radiation illuminates the element and is then filtered, modulated, analyzed or tuned by the element. Mechanical motion alters the structural symmetry, and therefore, the tuning properties, of the nanostructured subwavelength resonance elements. Further, incorporating metals and dielectrics to generate coexisting plasmonic and leaky-mode resonance effects adds to the versatility of the potential applications.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Resonant Leaky-Mode Photonic Elements and Methods for Spectral and Polarization Control
ActiveUS20100092124A1Increase varietyImprove performanceCoupling light guidesSpecial surfacesDiffraction orderFtir spectra
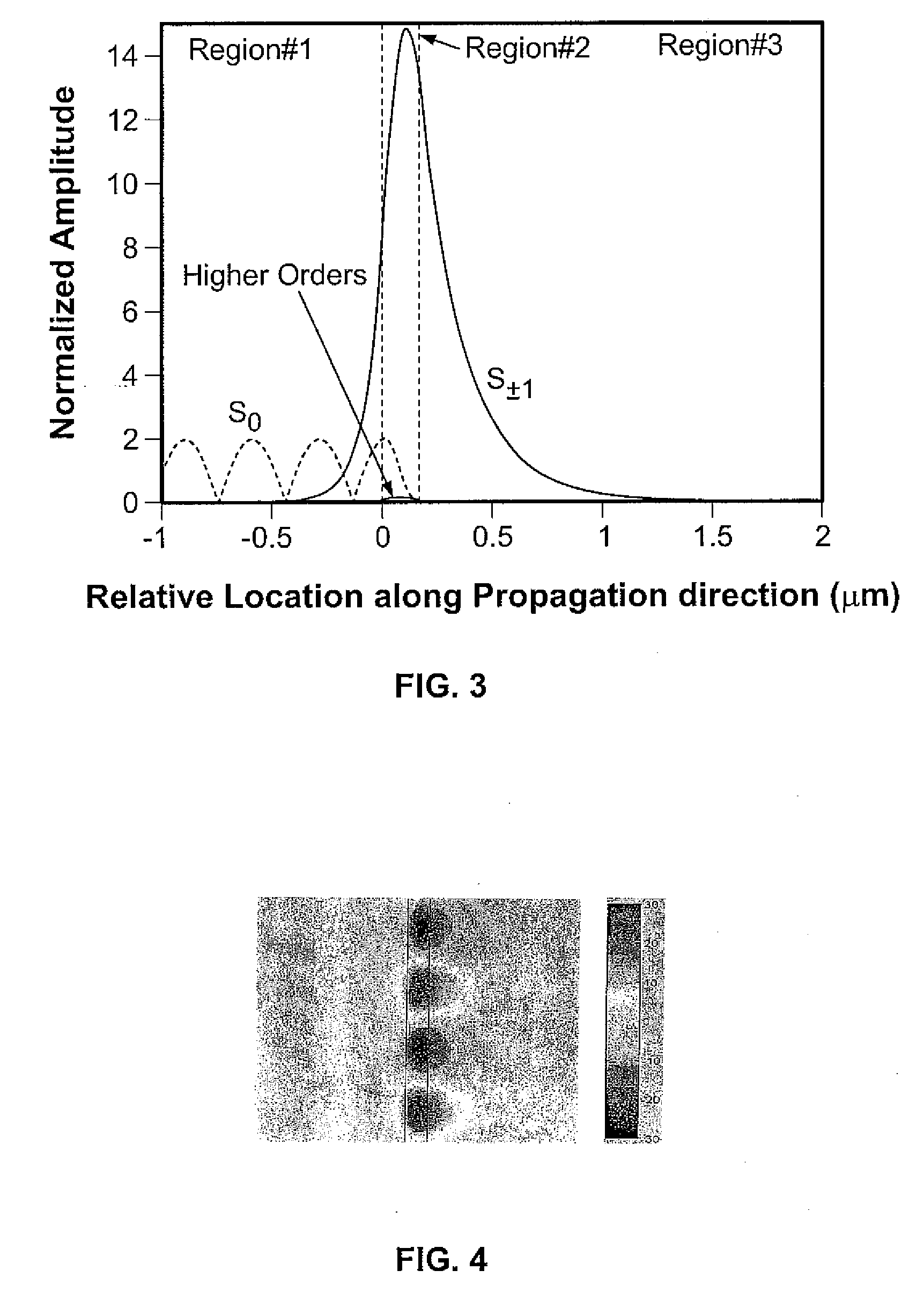
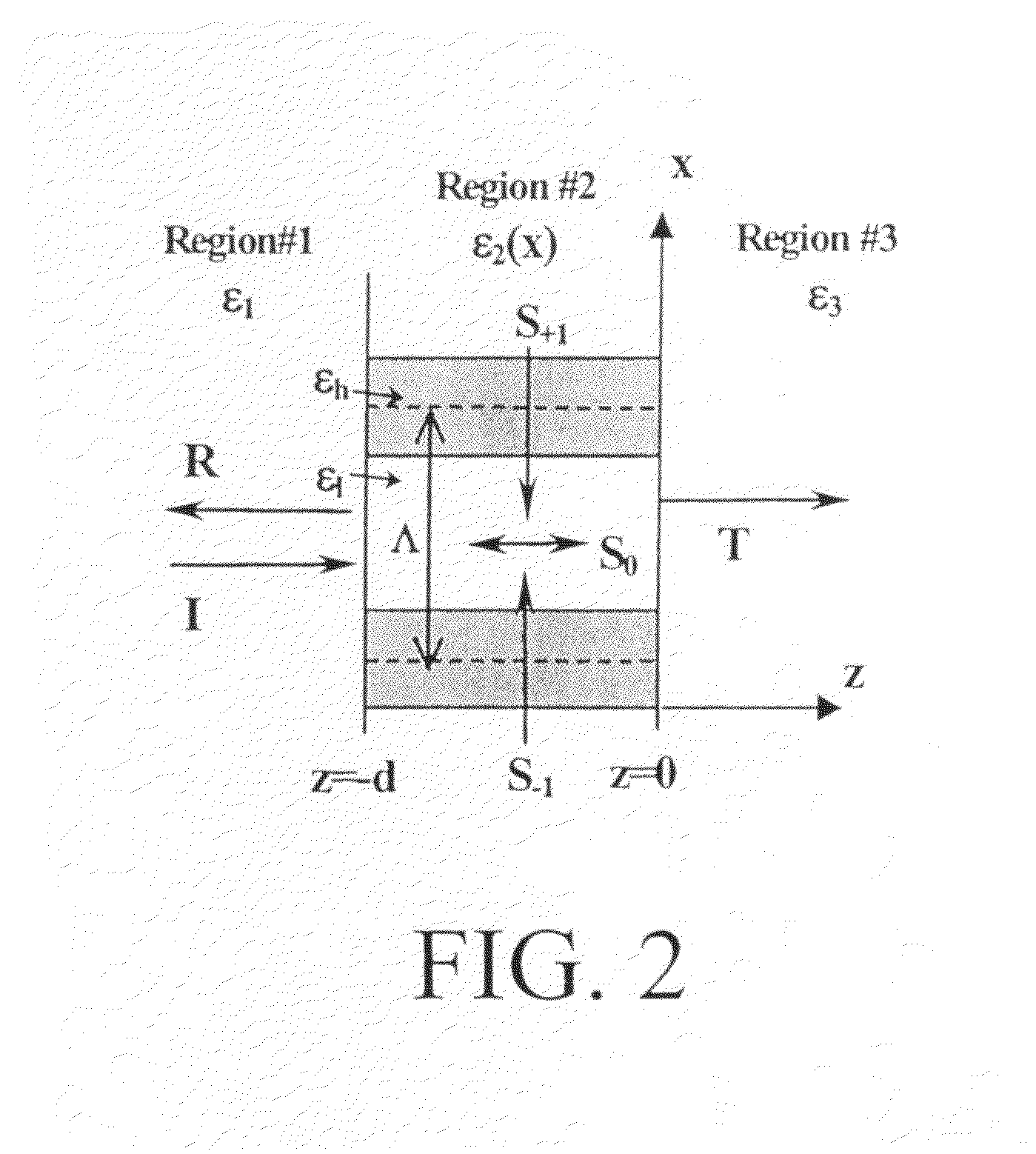
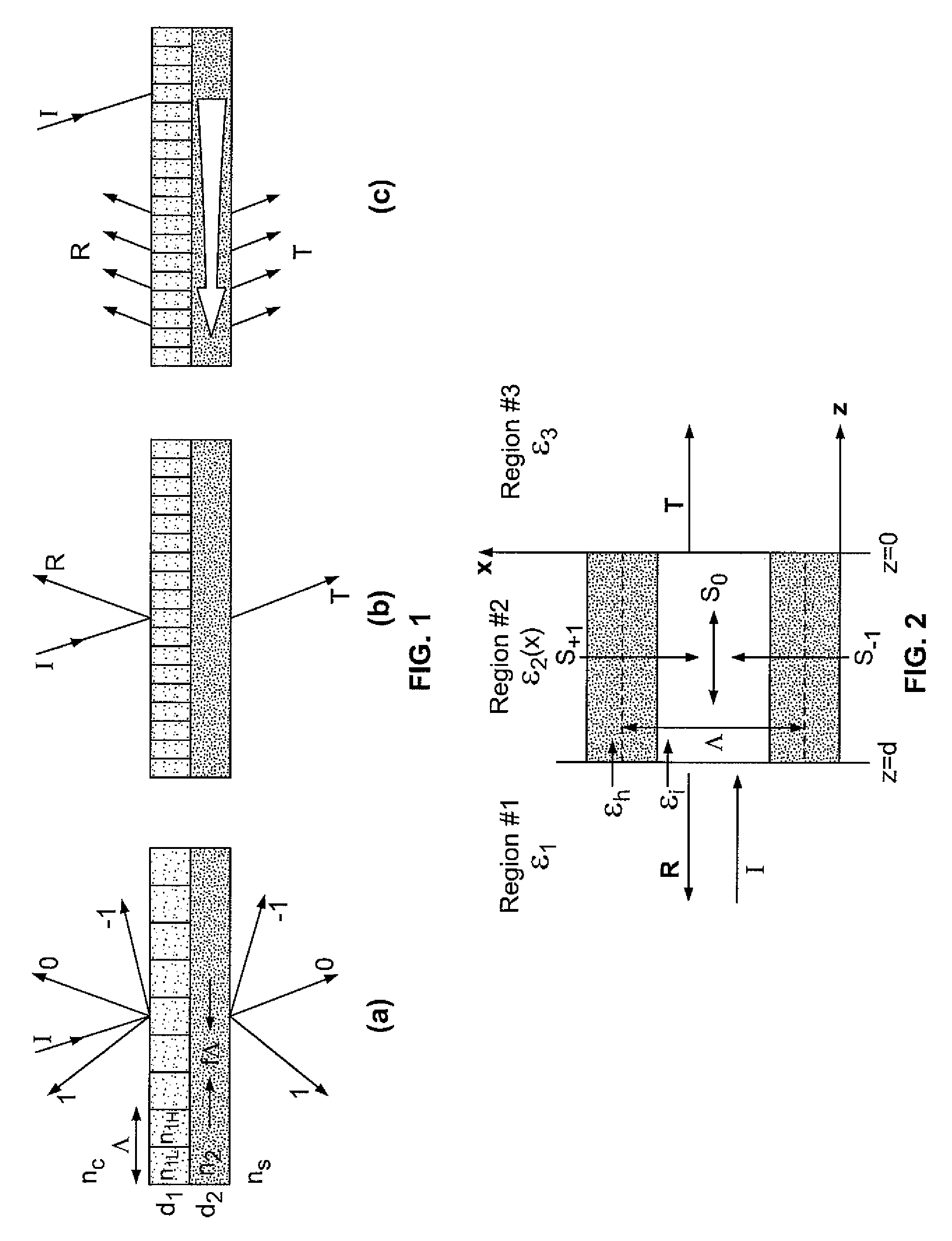
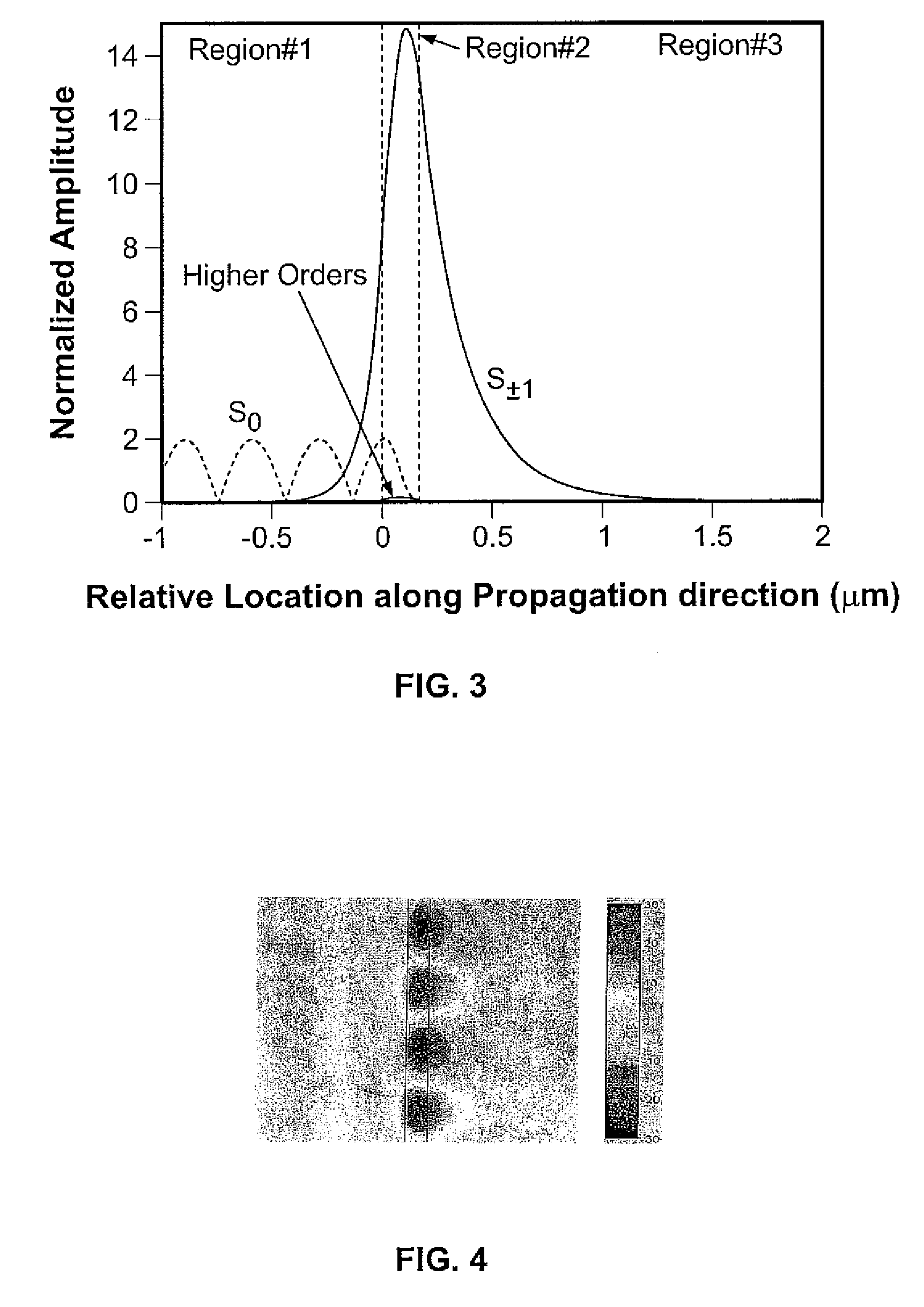
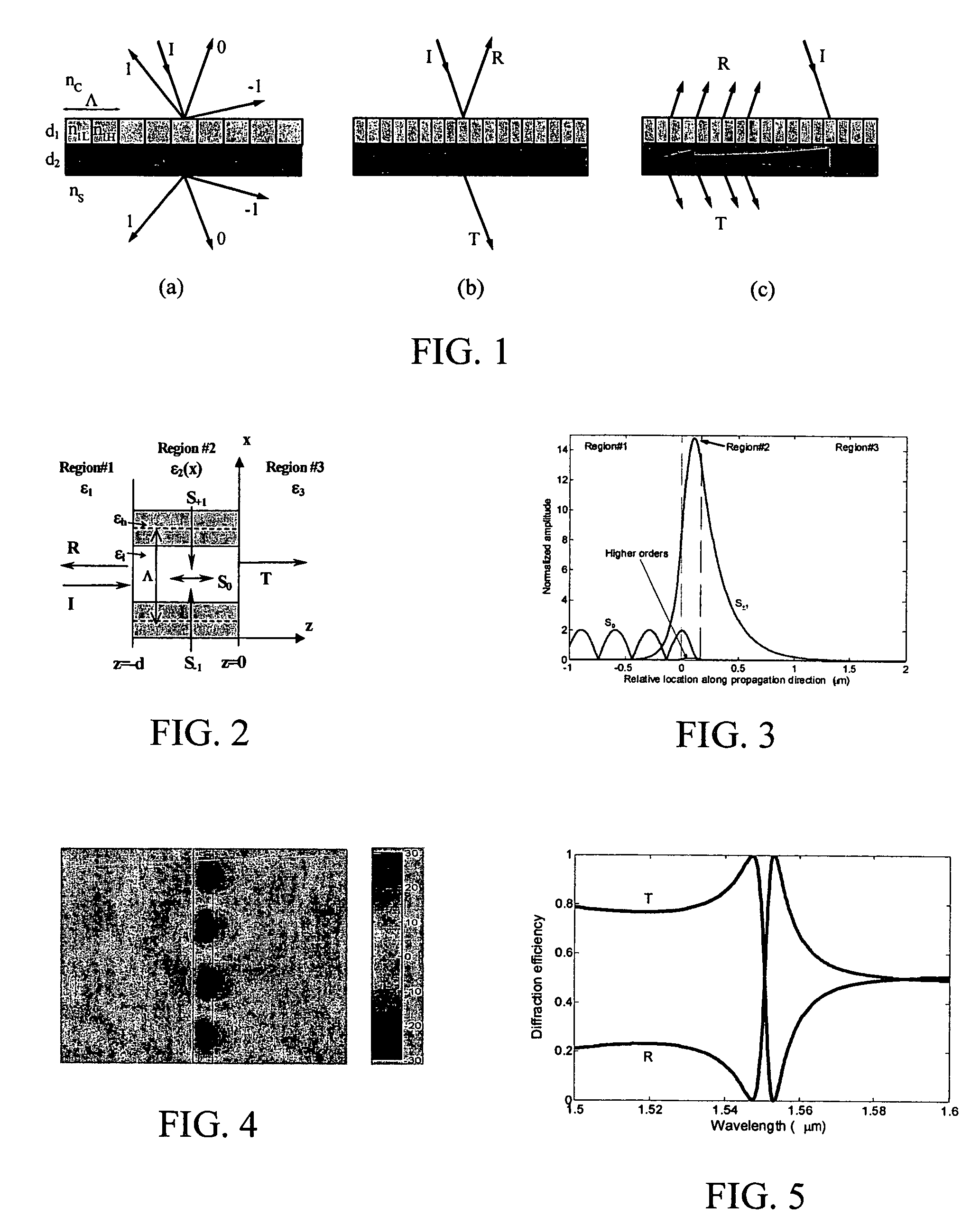
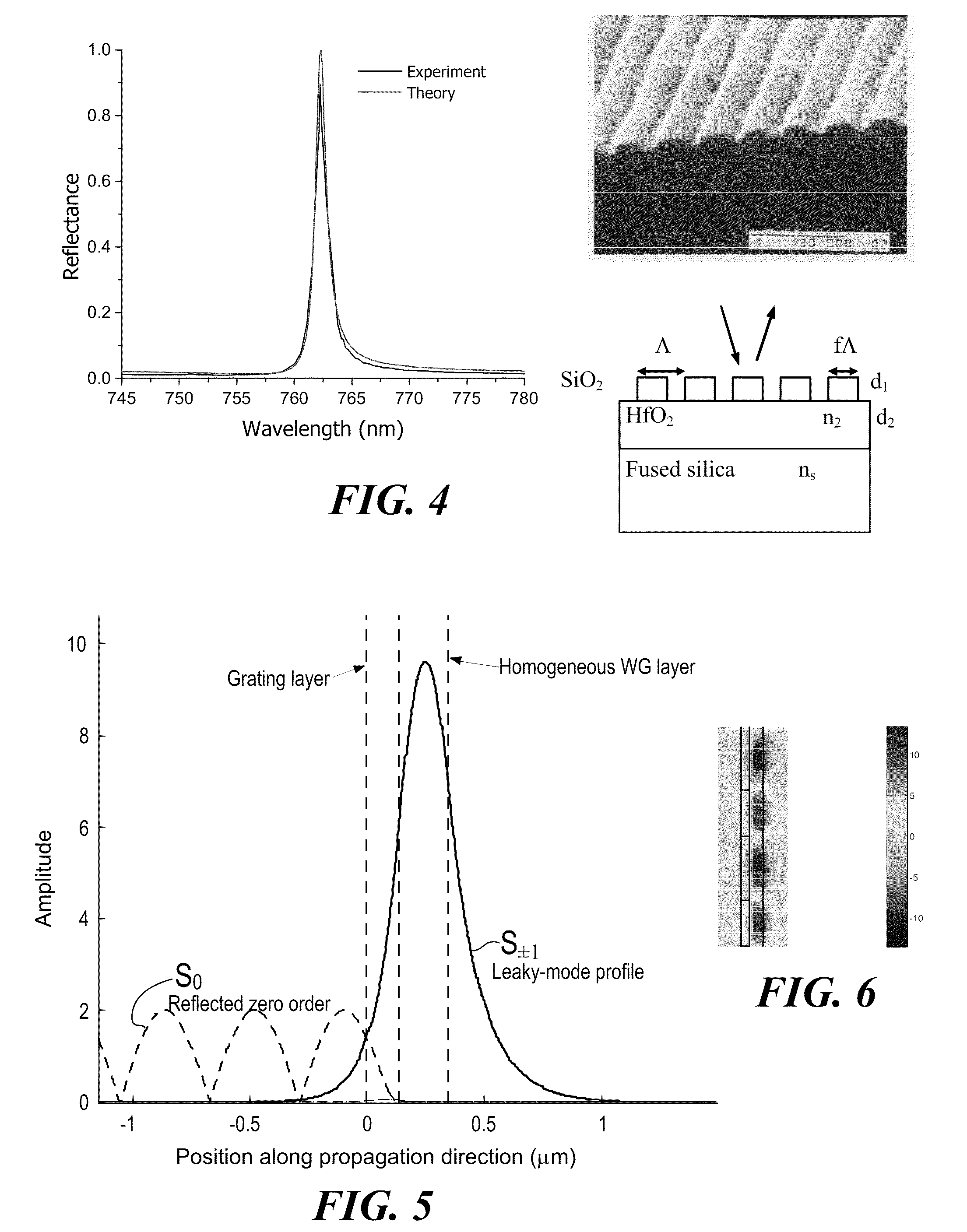
Optical devices with versatile spectral attributes are provided that are implemented with one or more modulated and homogeneous layers to realize leaky-mode resonance operation and corresponding versatile spectral-band design. The first and / or higher multiple evanescent diffraction orders are applied to excite one or more leaky modes. The one- or two-dimensional periodic structure, fashioned by proper distribution of materials within each period, can have a resulting symmetric or asymmetric profile to permit a broadened variety of resonant leaky-mode devices to be realized. Thus, the attributes of the optical device permit, among other things, adjacent, distinct resonance frequencies or wavelengths to be produced, convenient shaping of the reflection and transmission spectra for such optical device to be accomplished, and the wavelength resonance locations to be precisely controlled so as to affect the extent to which the leaky modes interact with each other. Further, the profile asymmetry allows for the precise spectral spacing of interactive leaky modes so as to provide greater flexibility in optical device design.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Tunable resonant leaky-mode N/MEMS elements and uses in optical devices
ActiveUS8938141B2Increase varietyEnhancing utility significanceLaser detailsNanoopticsDielectricElectricity
Mechanically tunable electromagnetic and photonic devices featuring enhanced spectral tunability with minimal mechanical movement are provided. These nano / micro-electromechanically (N / MEMS) tunable elements, including filters and pixels, rely on leaky-mode resonance effects in subwavelength photonic lattices that constitute periodic wavelengths. Such elements can operate in reflection (bandstop) or transmission (bandpass) modes, and can be arranged in one-dimensional or two-dimensional arrays, or operated as single units, and their spectral regions are controlled by the element design. Input electromagnetic radiation illuminates the element and is then filtered, modulated, analyzed or tuned by the element. Mechanical motion alters the structural symmetry, and therefore, the tuning properties, of the nanostructured subwavelength resonance elements. Further, incorporating metals and dielectrics to generate coexisting plasmonic and leaky-mode resonance effects adds to the versatility of the potential applications.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Resonant leaky-mode optical devices and associated methods
ActiveUS20060024013A1Increase varietyImprove utilizationSemiconductor lasersOptical waveguide light guideSpectral bandsDiffraction order
Optical devices with versatile spectral attributes are provided that are implemented with one or more modulated and homogeneous layers to realize leaky-mode resonance operation and corresponding versatile spectral-band design. The first and / or higher multiple evanescent diffraction orders are applied to excite one or more leaky modes. The one- or two-dimensional periodic structure, fashioned by proper distribution of materials within each period, can have a resulting symmetric or asymmetric profile to permit a broadened variety of resonant leaky-mode devices to be realized. Thus, the attributes of the optical device permit, among other things, adjacent, distinct resonance frequencies or wavelengths to be produced, convenient shaping of the reflection and transmission spectra for such optical device to be accomplished, and the wavelength resonance locations to be precisely controlled so as to affect the extent to which the leaky modes interact with each other. Further, the profile asymmetry allows for the precise spectral spacing of interactive leaky modes so as to provide greater flexibility in optical device design.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
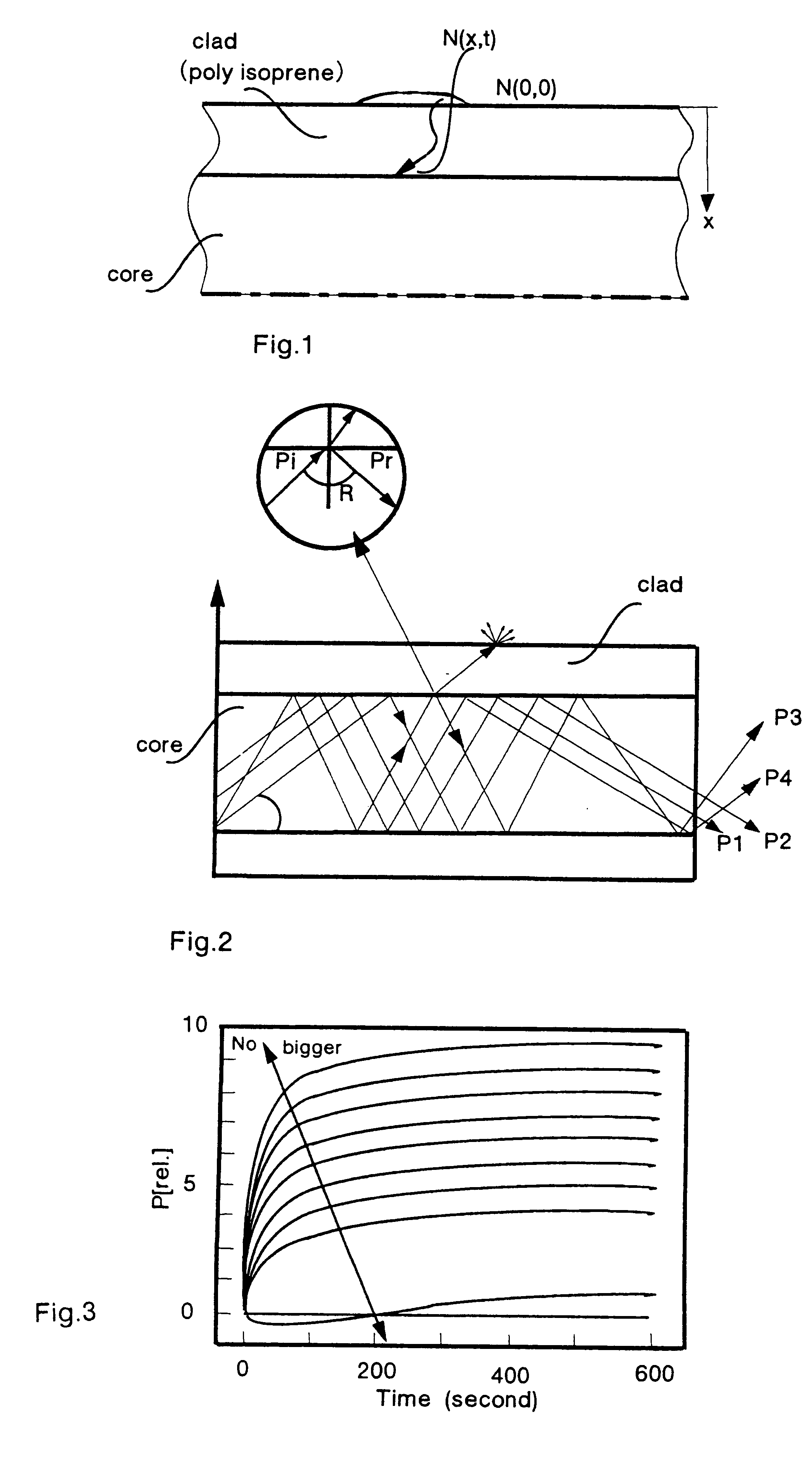
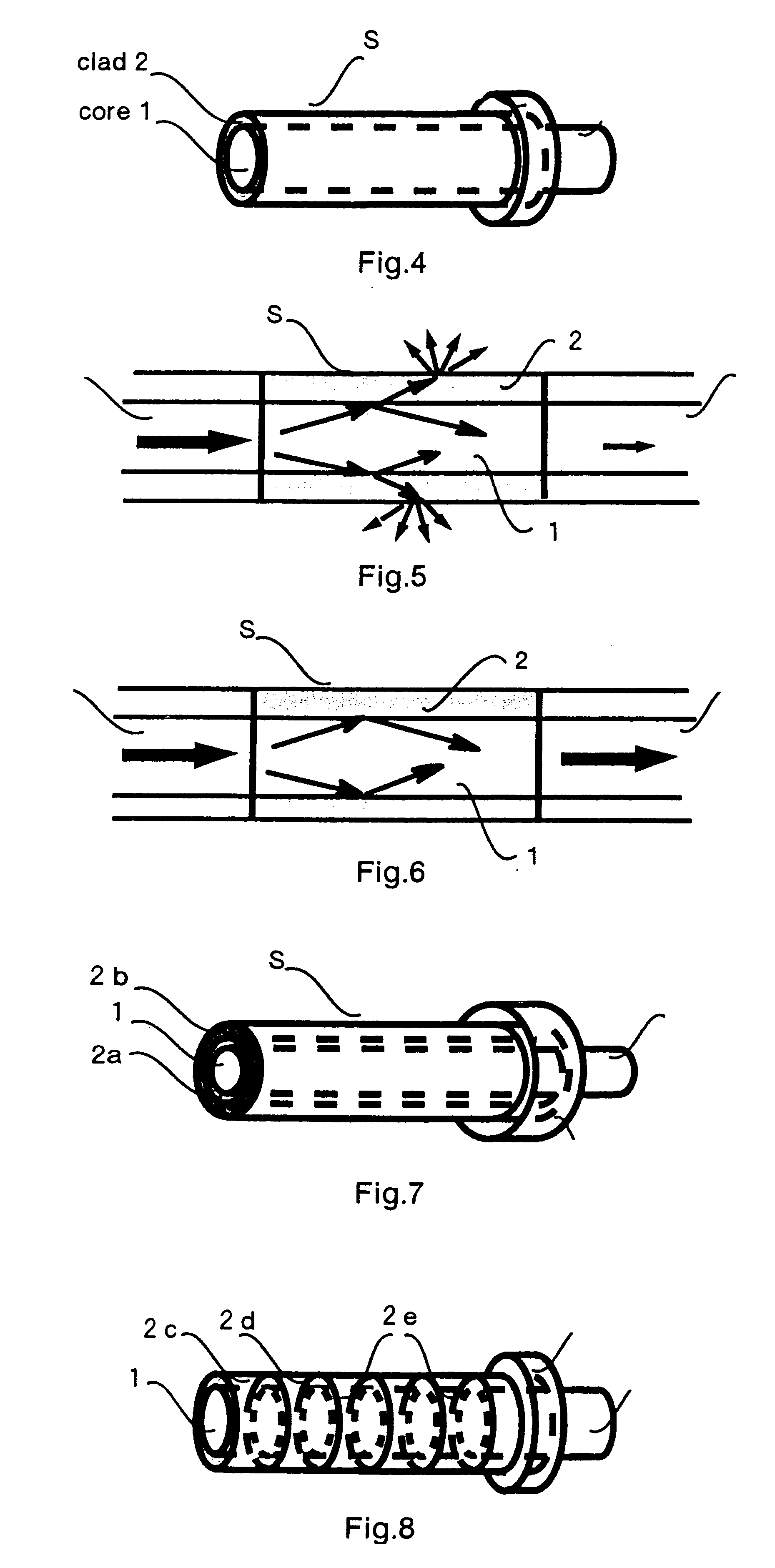
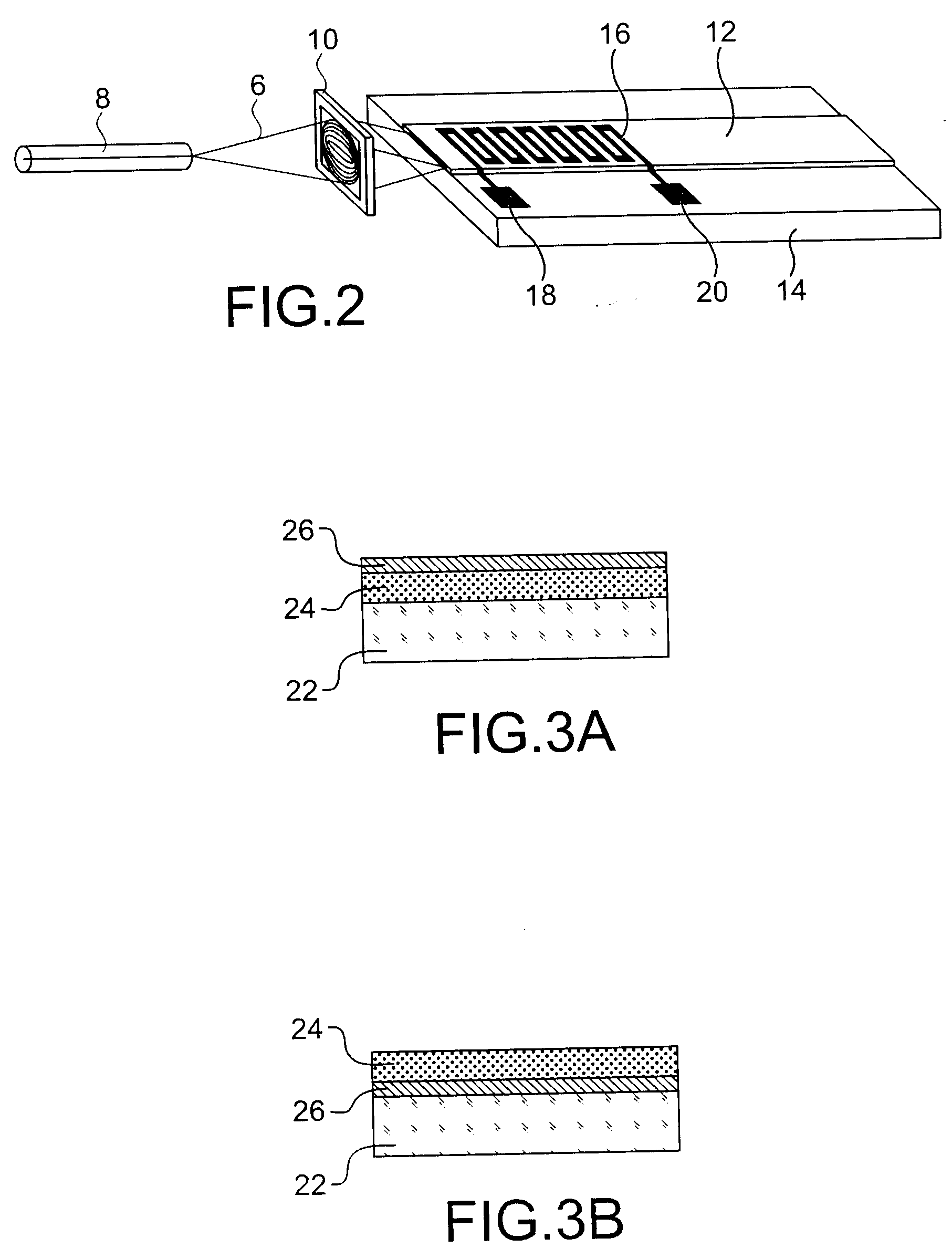
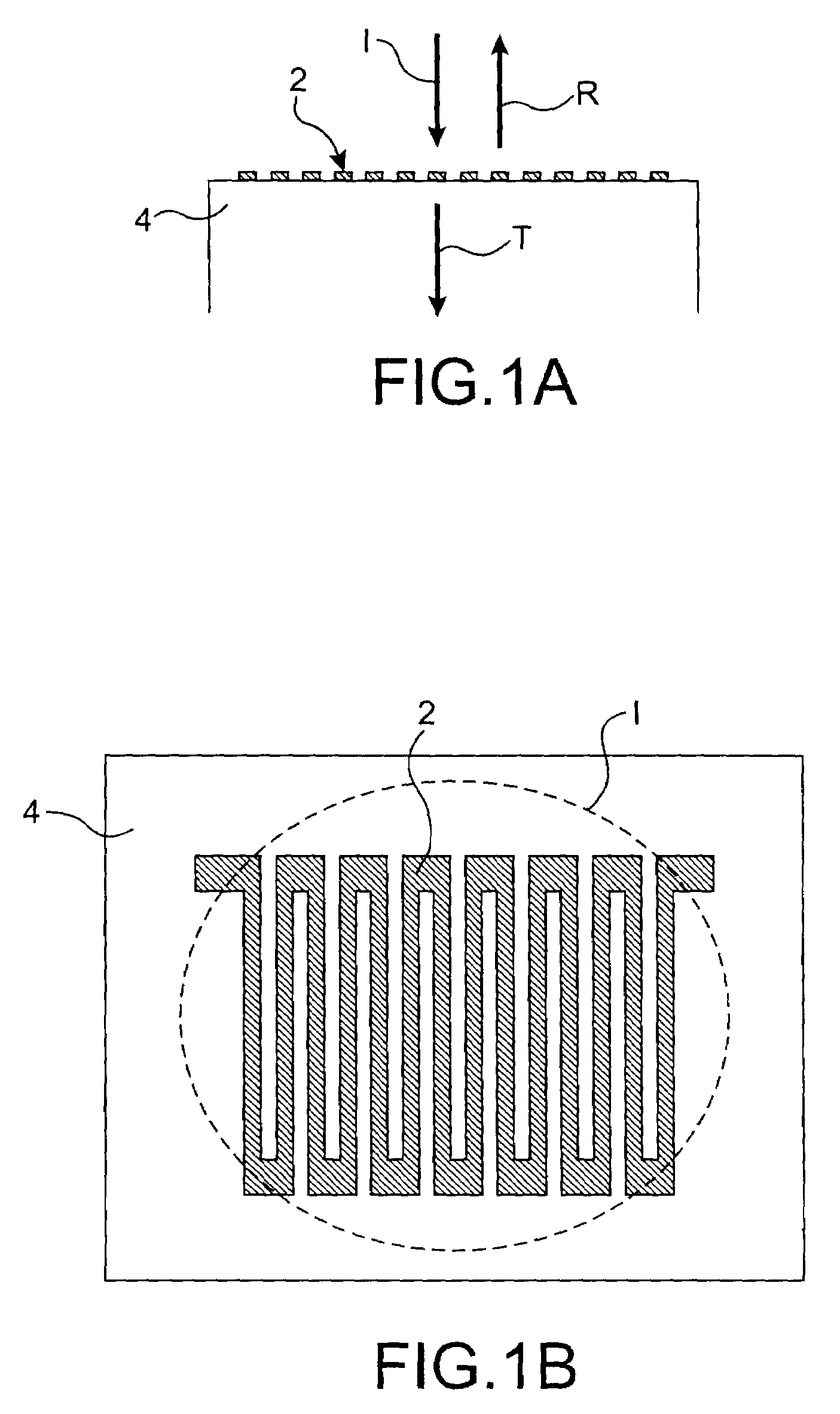
Optical sensor and sensing method
InactiveUS6278106B1High sensitivityLower refractive indexRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorRefractive indexLeaky mode
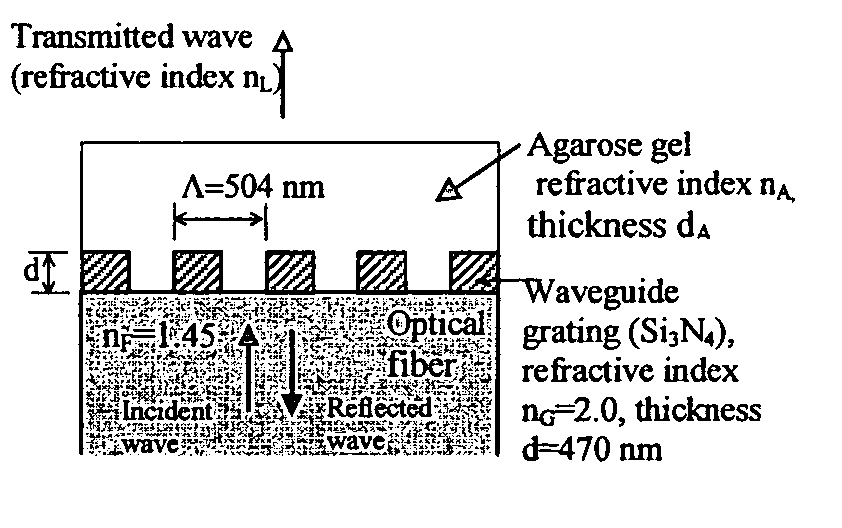
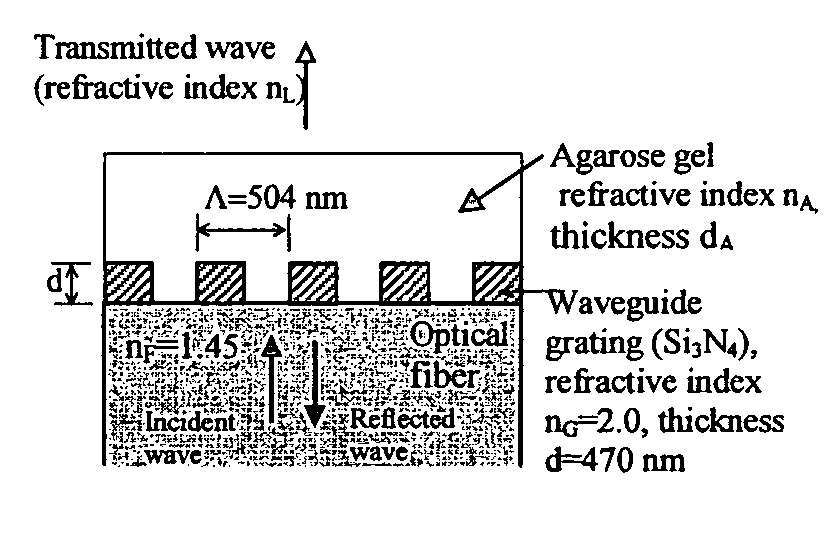
The optical sensor of the present invention detects both the existence and concentration of substances by changing from light leakage mode to wave guide mode when the sensor is exposed to the substances to be detected. The changes in the mode results in a large change in optical output. This change is measured and the substance is identified and / or measured with high sensitivity.The change in light leakage mode to wave guide mode of the sensor is possible by having a clad material around the core material, with the clad material decreasing in the index of refraction when exposed to the substance to be detected. When the index of refraction of the clad becomes less than that of the core material, the sensor changes from the light leakage mode and operates in the wave guide mode. Changes in light intensity output from the sensor is measured over time, and correlated to the substance to be detected.
Owner:MUTO SHINZO
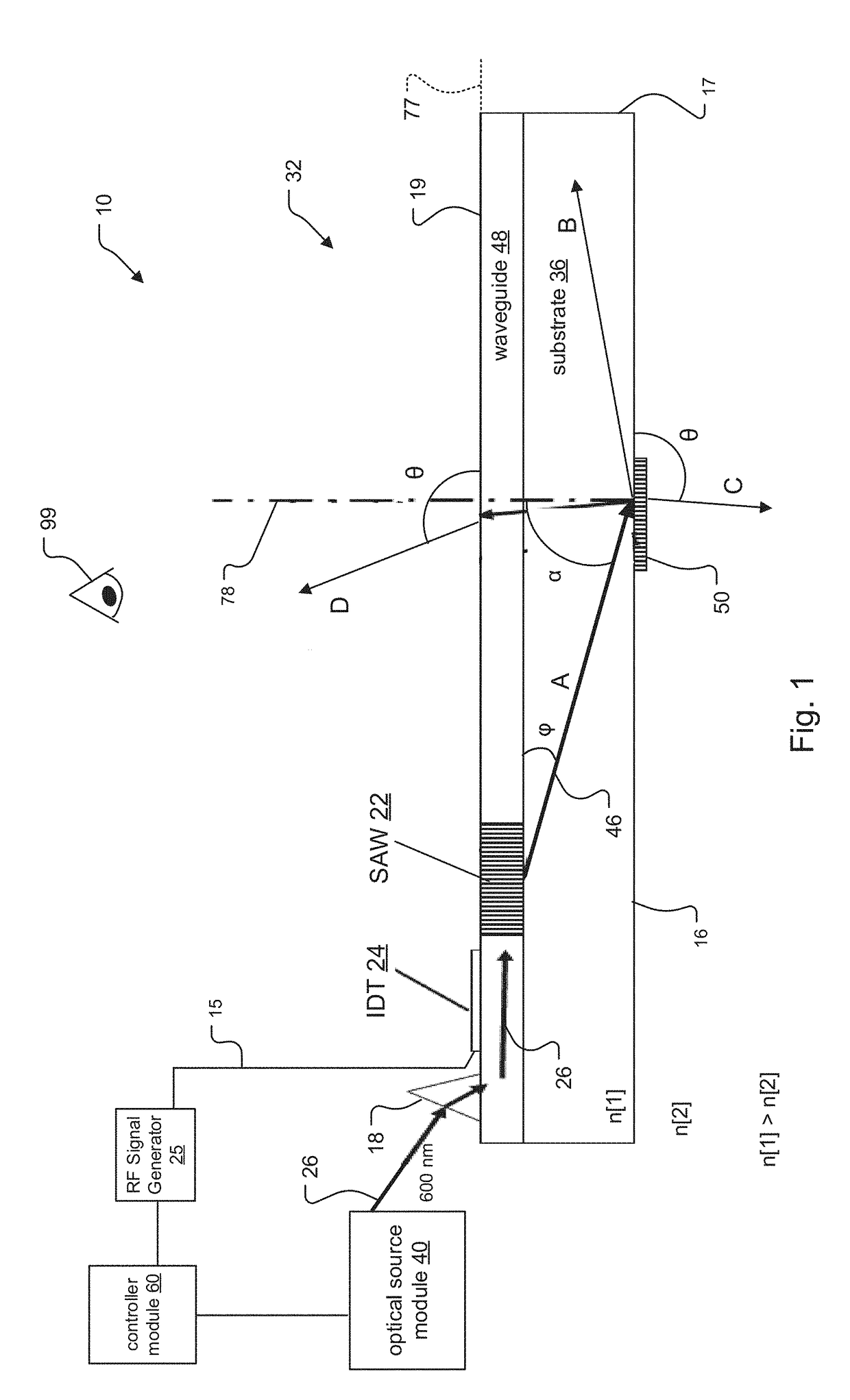
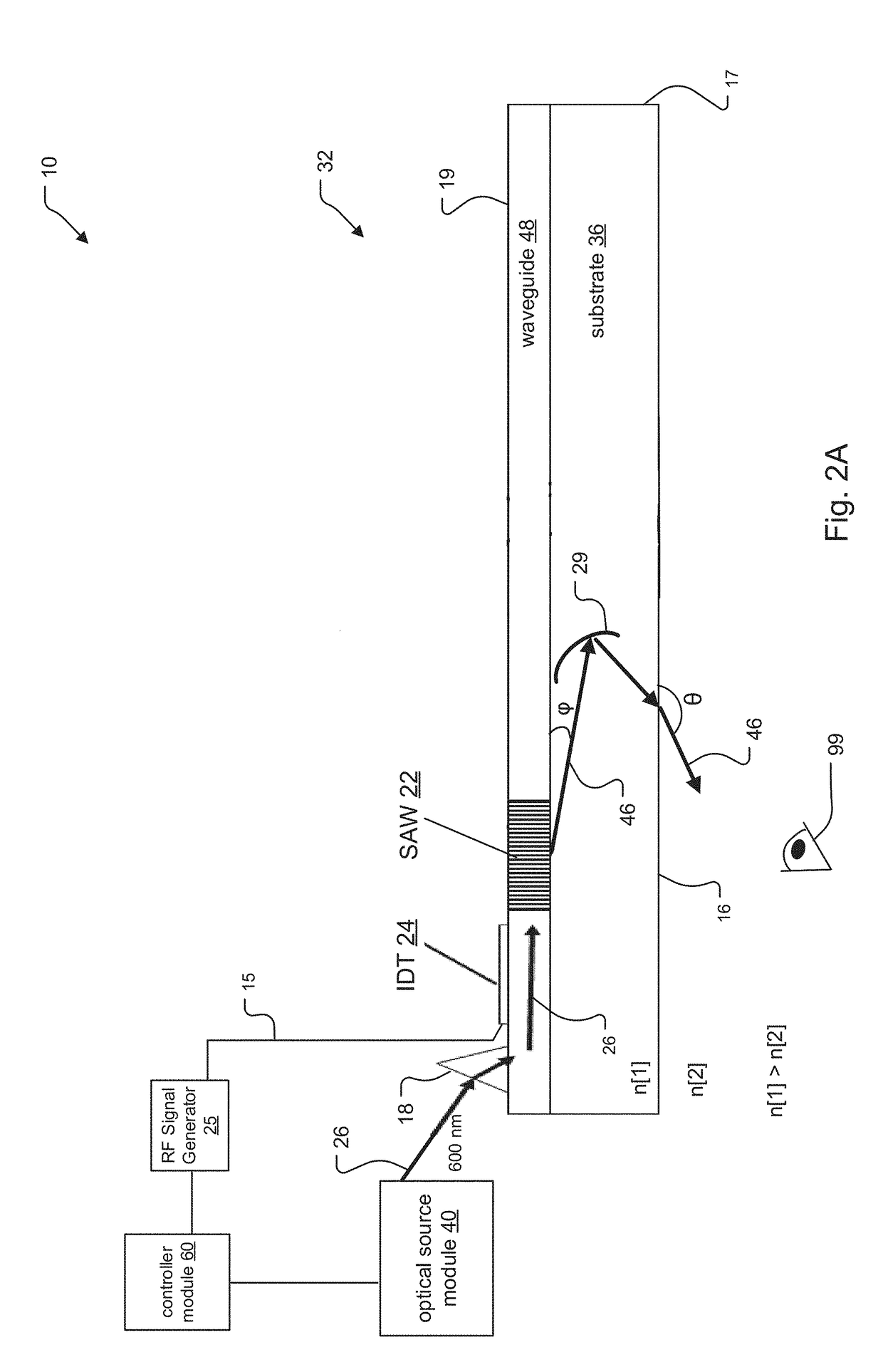
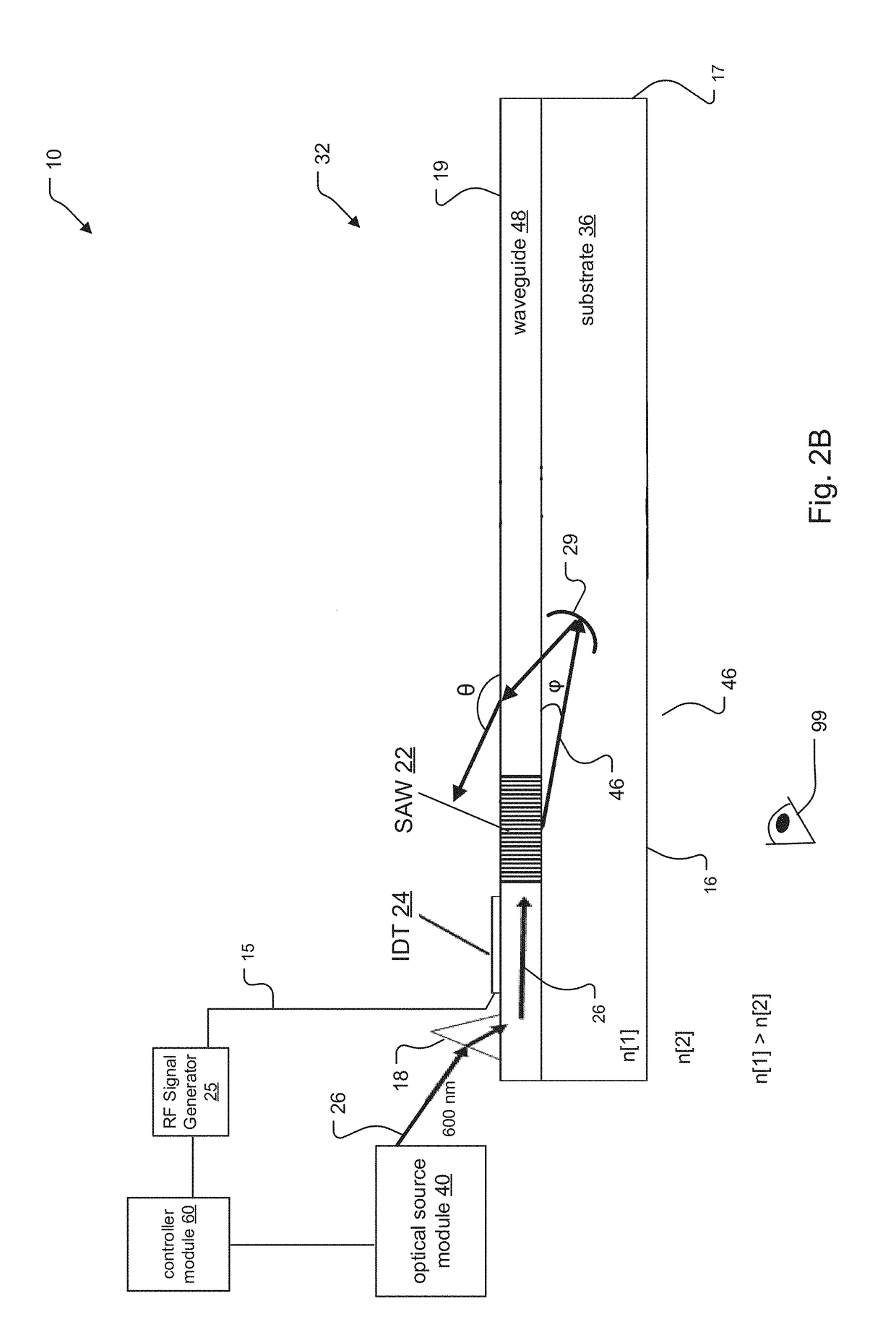
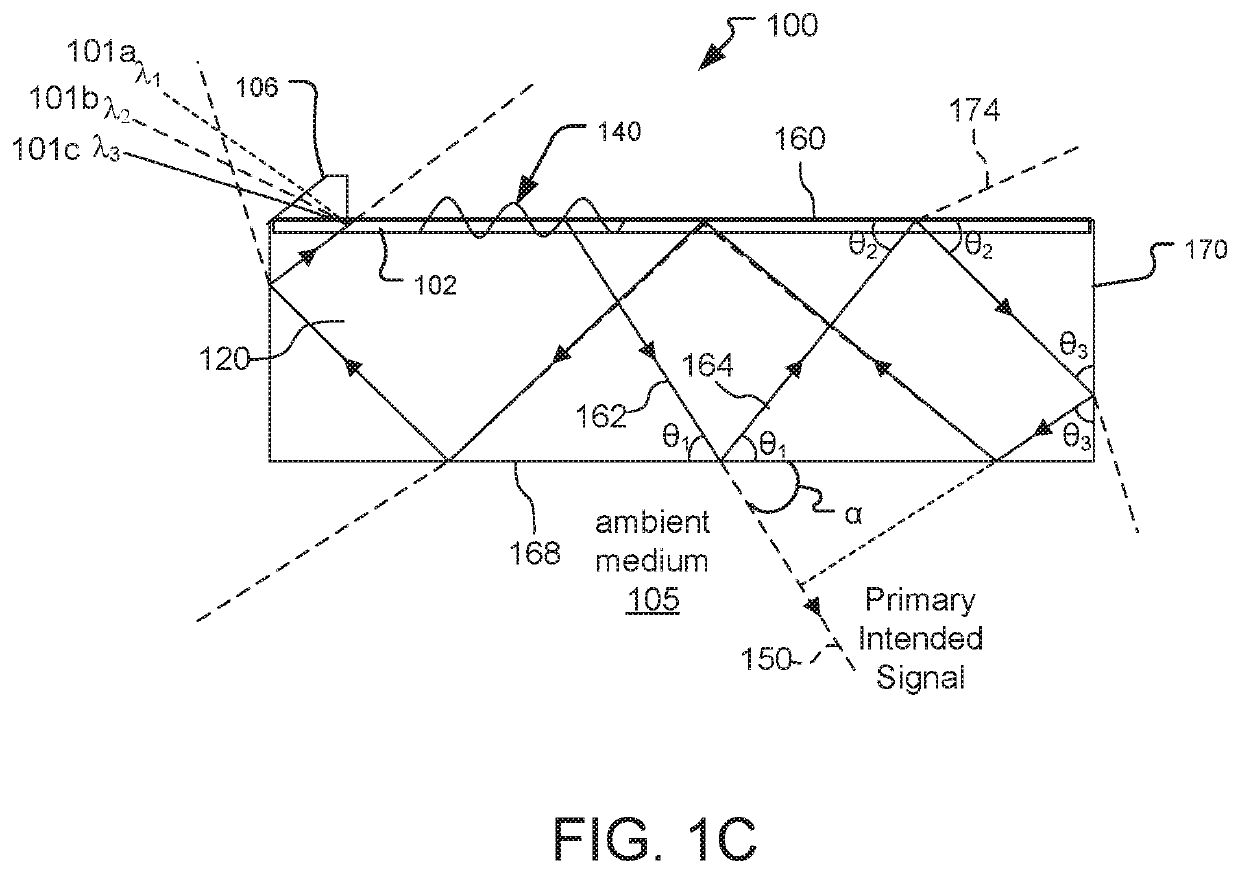
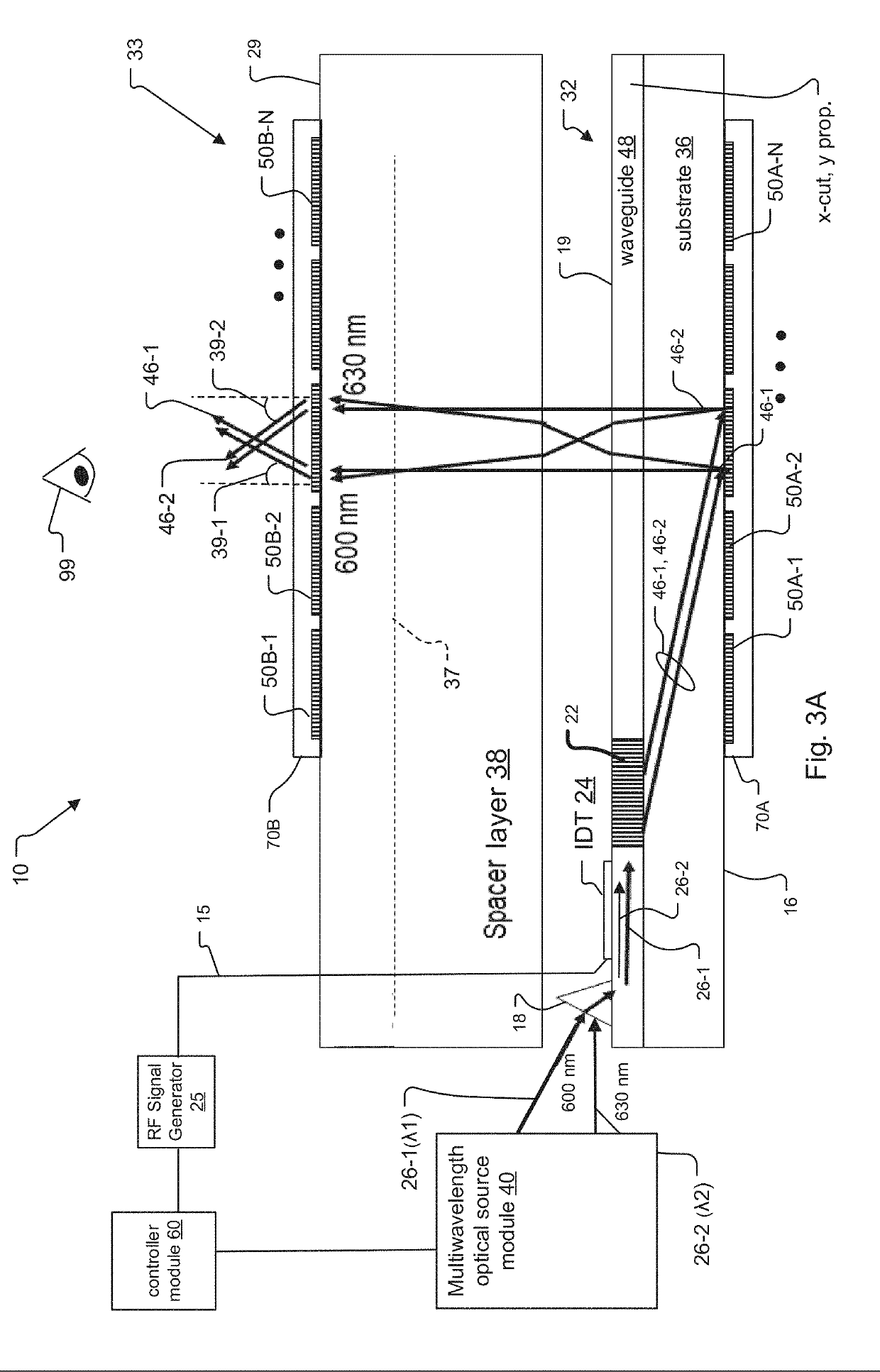
Saw Modulator Having Optical Power Component for Extended Angular Redirection of Light
A light field generator system including a leaky-mode SAW modulator is disclosed. The modulator incorporates at least one optical power component, such as a concave mirror or volume grating having a non-zero diopter rating. In some embodiments, the system incorporates the at least one optical power component by embedding the optical power component within a substrate of the SAW modulator and / or by placing the optical power component upon a surface of the SAW modulator.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
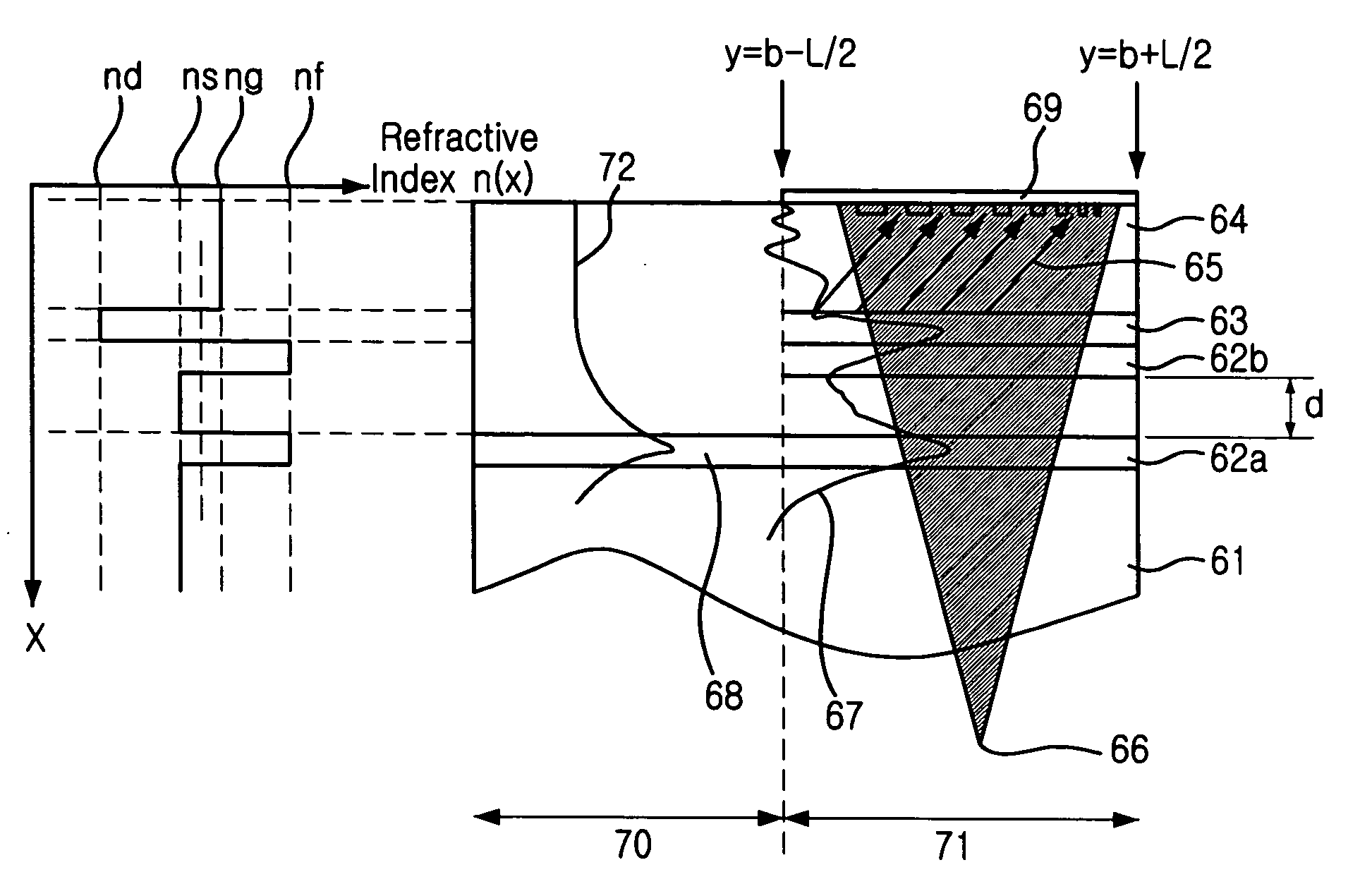
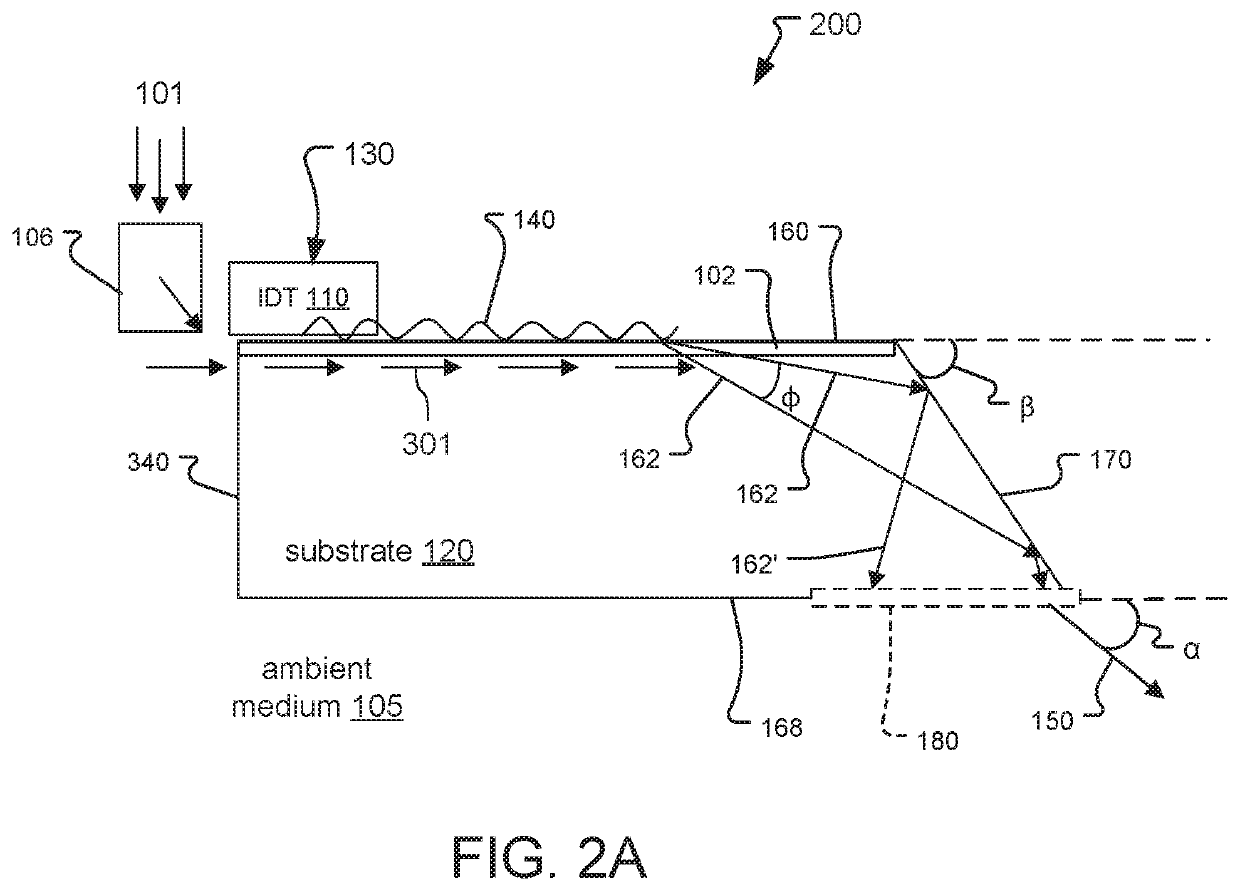
Highly efficient focusing waveguide grating coupler using leaky mode
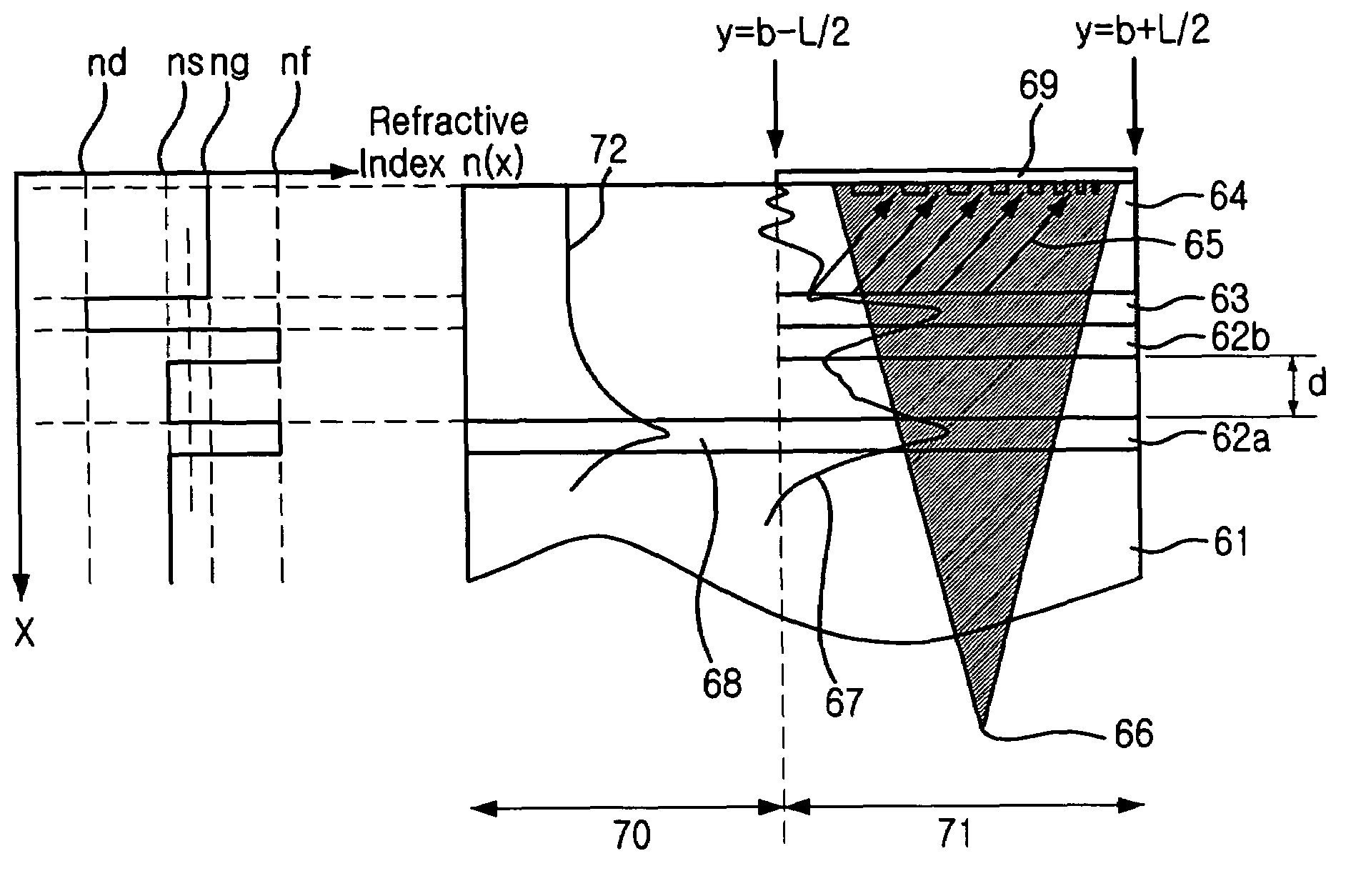
InactiveUS20050008294A1Coupling efficiency is highReduce dependenceCoupling light guidesFresnel lensManufacturing technology
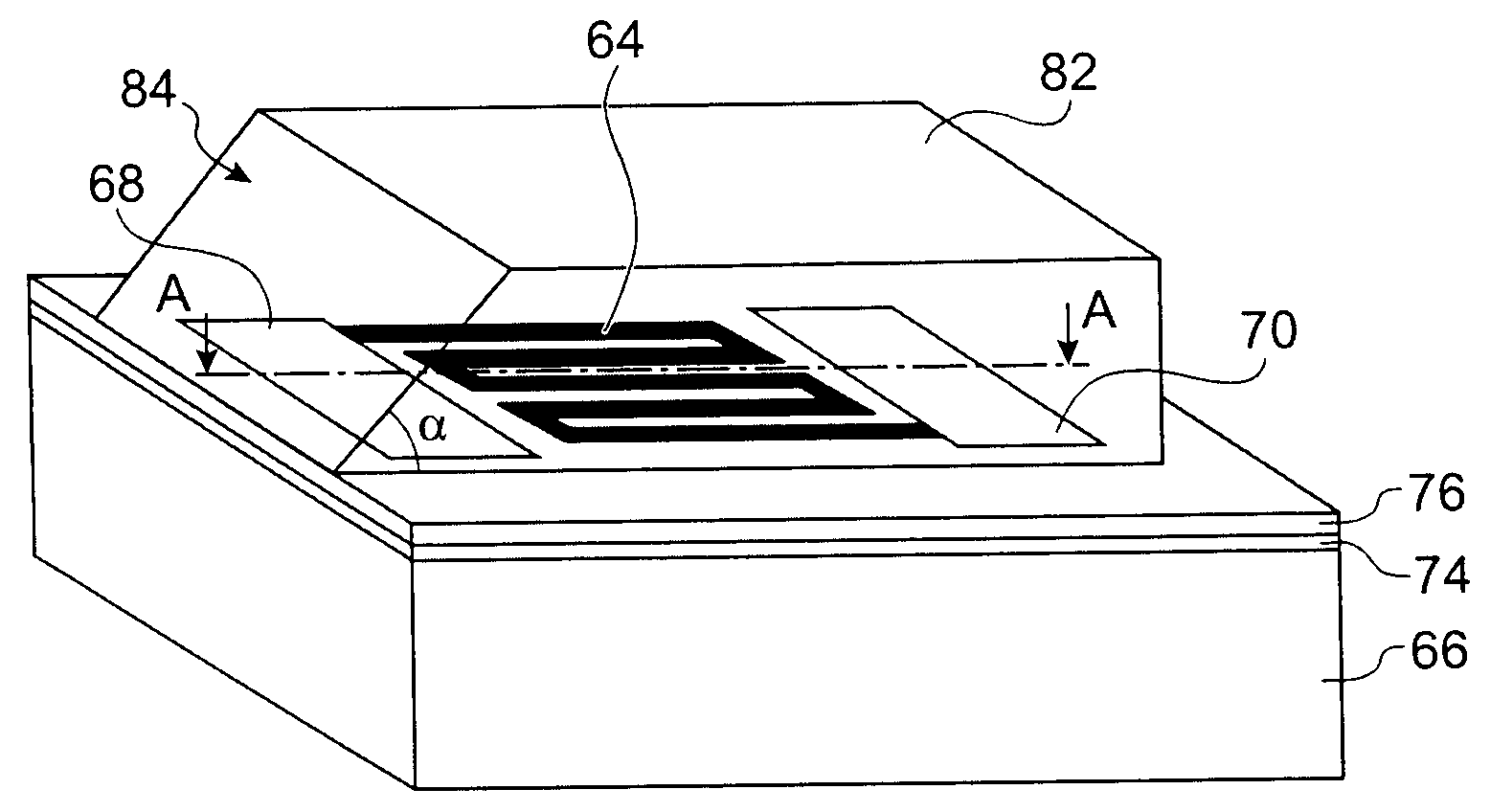
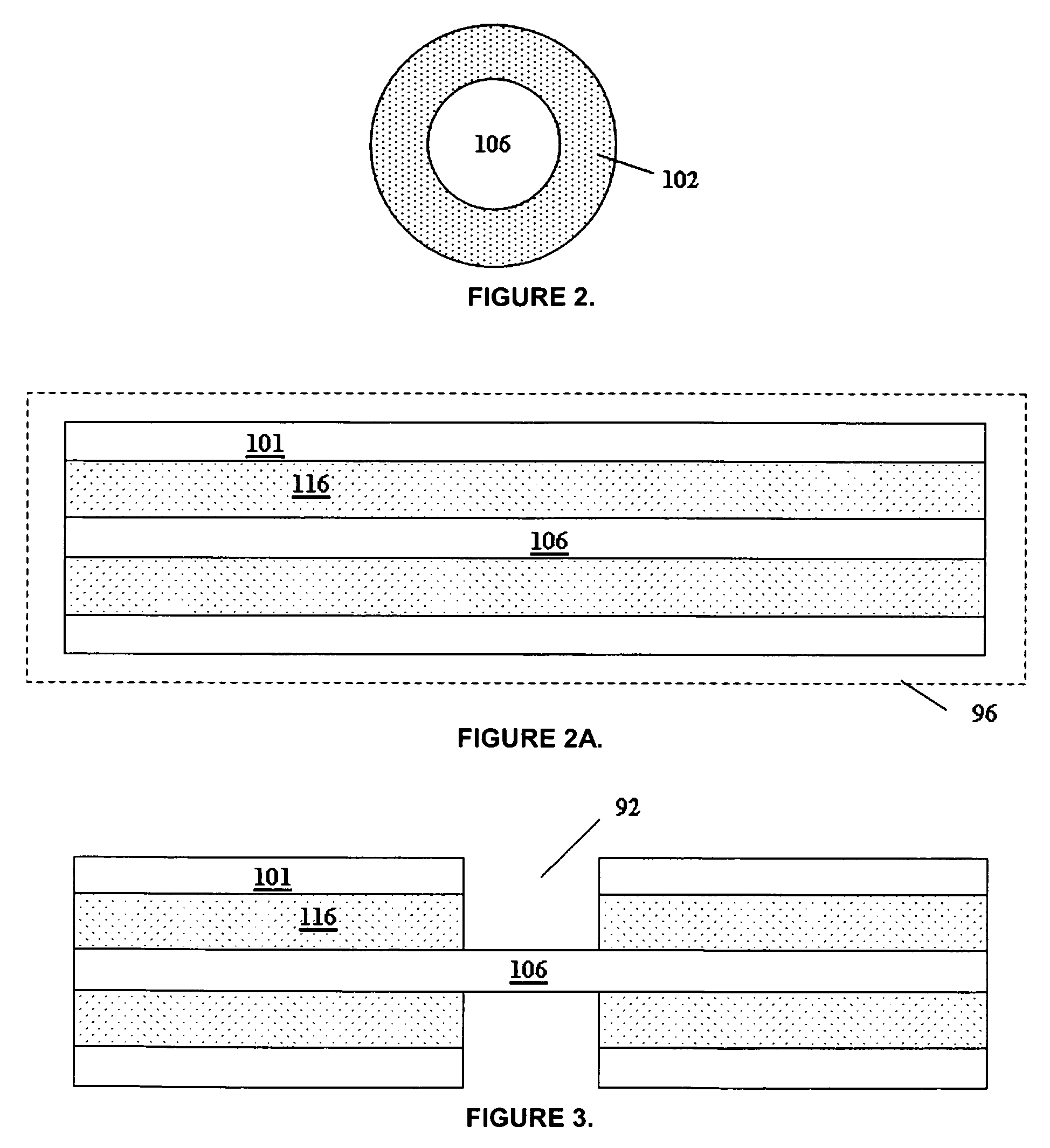
Provided is a focusing waveguide grating coupler using a leaky mode which can form single output beam while relieving the dependency on manufacturing processes. The focusing waveguide grating coupler of the present research includes: a substrate having a first refraction index n1; a first core layer having a second refraction index n2, the first core layer being formed on the substrate; a second core layer having a third refraction index n3, the second core layer being formed on the first core layer apart from the first core layer with a space d in between; a first cladding layer having a fourth refraction index n4, the first cladding layer being formed on the second core layer; a second cladding layer having a fifth refraction index n5, the second cladding layer being formed on the first cladding layer and inserted between the first core layer and the second core layer; and a Fresnel lens positioned on the second cladding layer, wherein the refractive indexes satisfy conditions of n5>(n2, n3)>n1 and n5>n4; and light inputted through the first and second core layers to the Fresnel lens as radiated leaky beam by a leaky mode formed according to the conditions, and the leaky beam forms an optical focus by performing single directional coupling.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
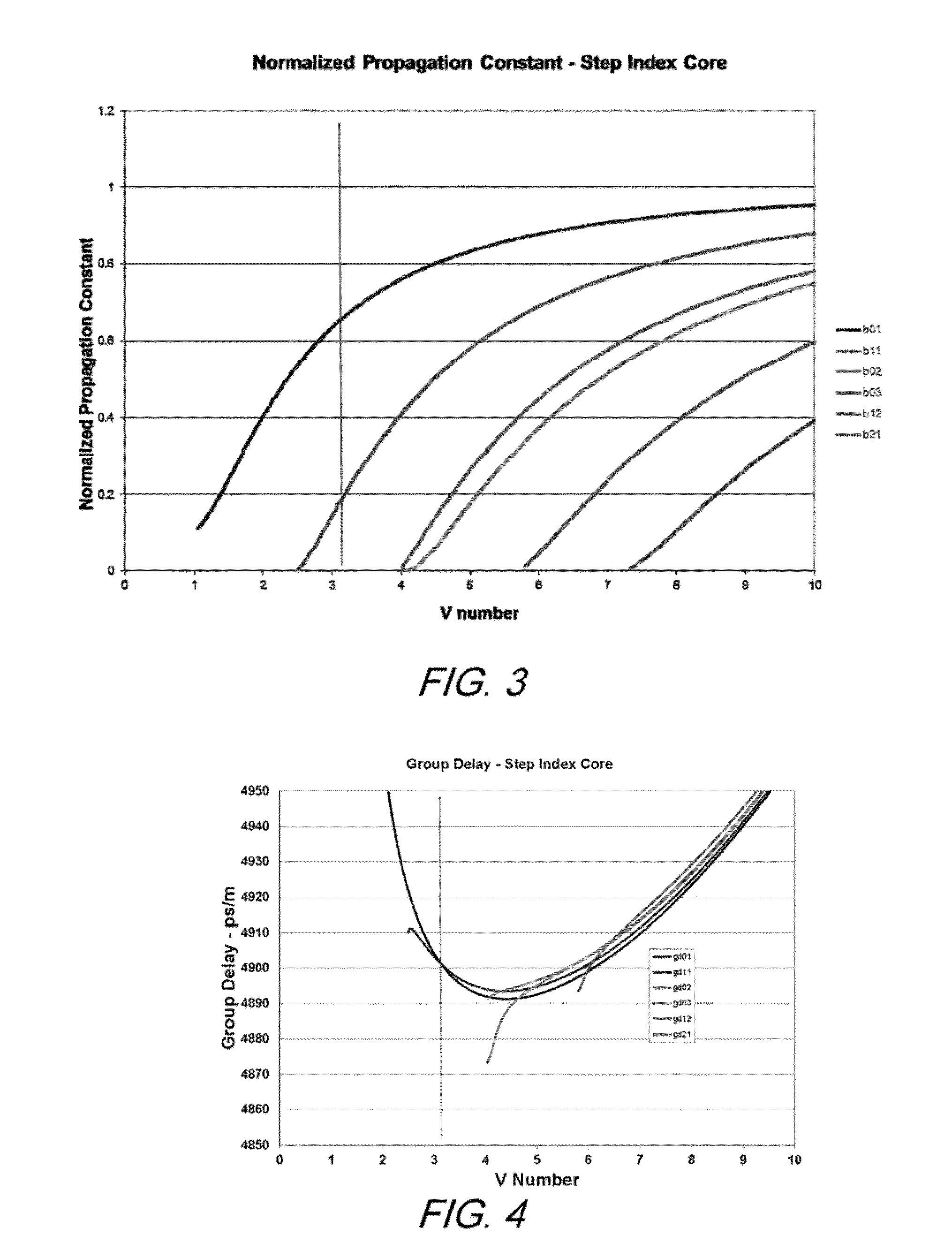
Step-Index Few-Mode Fiber Designs For Spatial Multiplexing
ActiveUS20140093205A1Avoid couplingLower levelCoupling light guidesMulticore optical fibreFew mode fiberCoupling
A few-mode optical fiber comprises a core surrounded by a cladding, having a step index profile that is structured to support propagation of a plurality of desired signal-carrying modes, while suppressing undesired modes. The core and cladding are configured such that the undesired modes have respective effective indices that are close to, or less than, the cladding index such that the undesired modes are leaky modes. The index spacing between the desired mode having the lowest effective index and the leaky mode with the highest effective index is sufficiently large so as to substantially prevent coupling therebetween.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
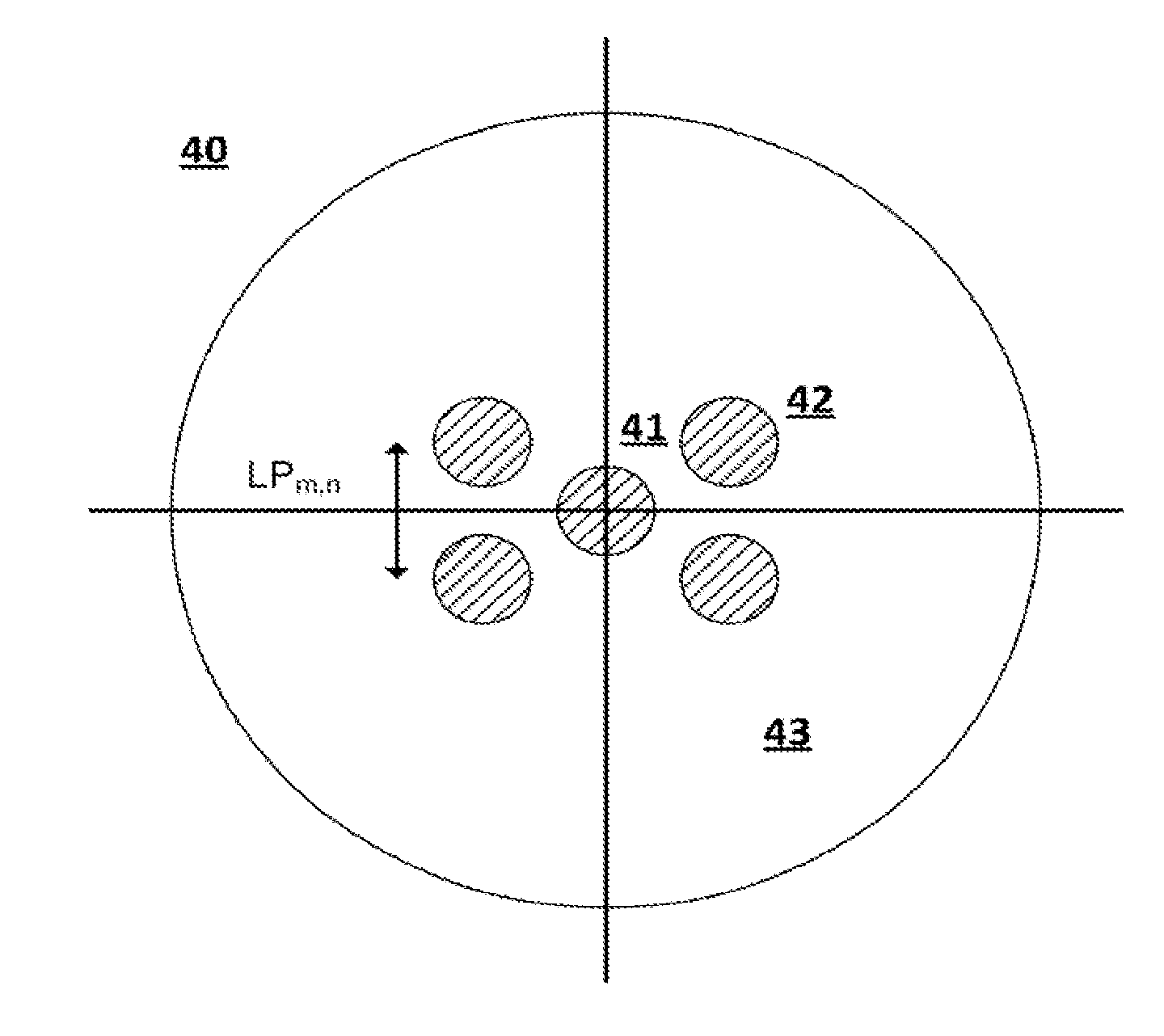
Multiple LP-mode fiber designs for mode-division multiplexing
ActiveUS20150168643A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFew mode fiberCoupling
A few-mode fiber is described, having a graded-index core and a surrounding cladding comprising a ledge between the core and the trench, a down-doped trench abutting the ledge, and an undoped cladding region abutting the trench. The fiber's refractive index profile is configured to support 9 or more LP modes for transmission of a spatially-multiplexed optical signal. Undesired modes have respective effective indices that are close to, or less than, the cladding index so as to result in leakage of the undesired modes into the outer cladding. The index spacing between the desired mode having the lowest effective index and the leaky mode with the highest effective index is sufficiently large so as to substantially prevent coupling therebetween.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Guided-mode resonance sensors employing angular, spectral, modal, and polarization diversity for high-precision sensing in compact formats
InactiveUS20080062418A1Quality improvementHigh precisionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPolarization diversityLeaky mode
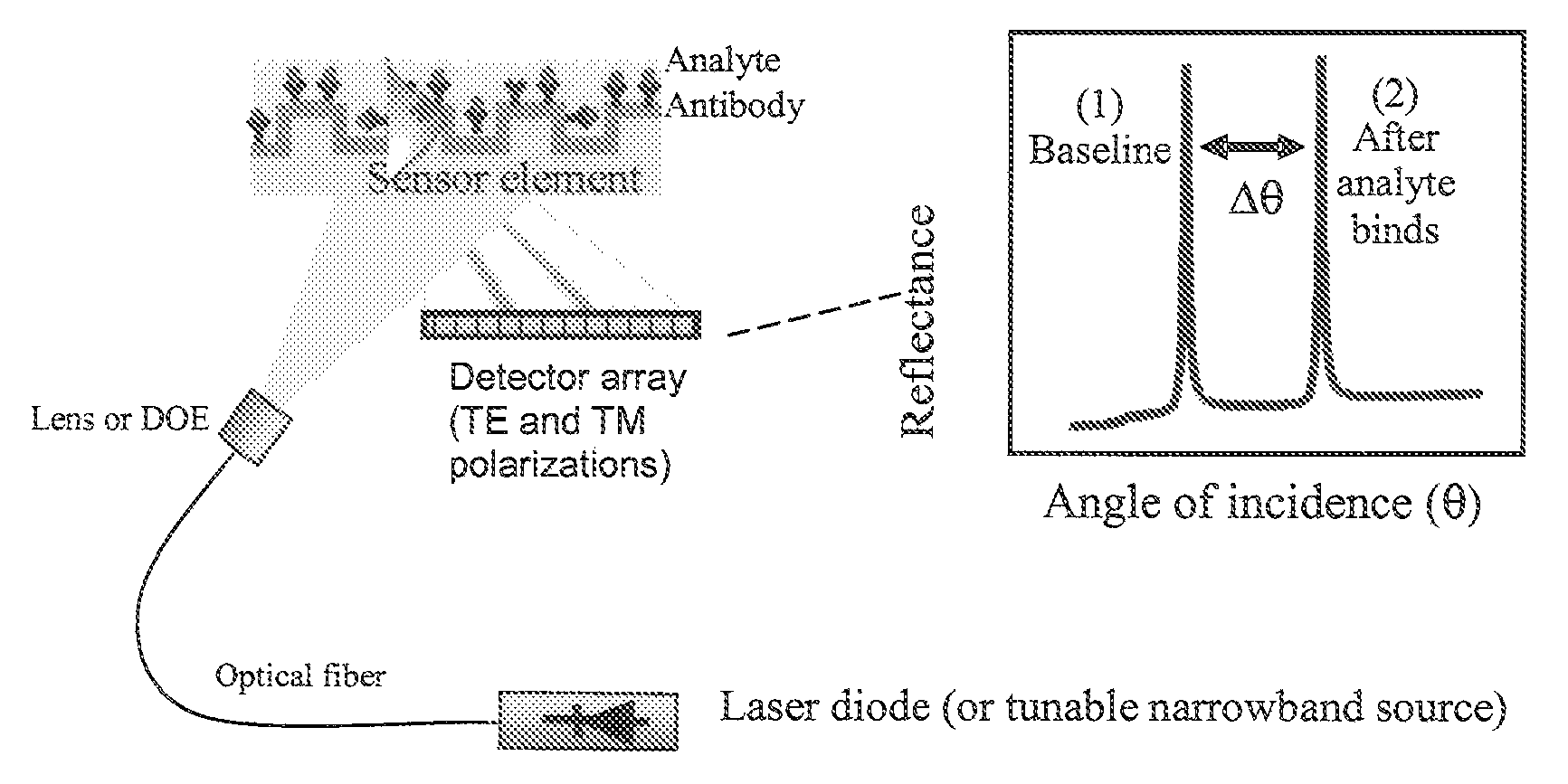
A guided mode resonance (GMR) sensor assembly and system are provided. The GMR sensor includes a waveguide structure configured for operation at or near one or more leaky modes, a receiver for input light from a source of light onto the waveguide structure to cause one or more leaky TE and TM resonant modes and a detector for changes in one or more of the phase, waveshape and / or magnitude of each of a TE resonance and a TM resonance to permit distinguishing between first and second physical states of said waveguide structure or its immediate environment.
Owner:MAGNUSSON ROBERT +1
Reversible, low cost, distributed optical fiber sensor with high spatial resolution
ActiveUS7473906B2Improve spatial resolutionIntenseMaterial analysis by optical meansLuminescent dosimetersHigh spatial resolutionImage resolution
A spectroscopic based optical fiber sensor includes a sensitive optical fiber, a probing light source, a power supply, a detector means, a signal processing means, and a display means. The sensitive optical fiber is optically affected by the presence of at least one measurand. The probing light source, adjacent to the sensitive fiber, transversely illuminates the fiber from the outside. The probing light is modified by the sensitive fiber, coupled into the optical fiber core, either as bound modes or leaky modes, as a light signal and guided to a detector means located at the terminus of the optical fiber. The detector means correlates the intensity of the light signal with an electric signal and transmits the electric signal to the signal processing means, wherein the electric signal is correlated to the quantity being measured. The correlated quantity being transmitted and displayed on the display means.
Owner:EGALON CLAUDIO OLIVEIRA
Resonant leaky-mode optical devices and associated methods
ActiveUS7689086B2Increase varietyEnhancing utility significanceSemiconductor lasersOptical waveguide light guideDiffraction orderSpectral bands
Optical devices with versatile spectral attributes are provided that are implemented with one or more modulated and homogeneous layers to realize leaky-mode resonance operation and corresponding versatile spectral-band design. The first and / or higher multiple evanescent diffraction orders are applied to excite one or more leaky modes. The one- or two-dimensional periodic structure, fashioned by proper distribution of materials within each period, can have a resulting symmetric or asymmetric profile to permit a broadened variety of resonant leaky-mode devices to be realized. Thus, the attributes of the optical device permit, among other things, adjacent, distinct resonance frequencies or wavelengths to be produced, convenient shaping of the reflection and transmission spectra for such optical device to be accomplished, and the wavelength resonance locations to be precisely controlled so as to affect the extent to which the leaky modes interact with each other. Further, the profile asymmetry allows for the precise spectral spacing at interactive leaky modes so as to provide greater flexibility in optical device design.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Guided-mode resonance sensors employing angular, spectral, modal, and polarization diversity for high-precision sensing in compact formats
InactiveUS8111401B2Quality improvementHigh precisionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPolarization diversityLeaky mode
A guided mode resonance (GMR) sensor assembly and system are provided. The GMR sensor includes a waveguide structure configured for operation at or near one or more leaky modes, a receiver for input light from a source of light onto the waveguide structure to cause one or more leaky TE and TM resonant modes and a detector for changes in one or more of the phase, waveshape and / or magnitude of each of a TE resonance and a TM resonance to permit distinguishing between first and second physical states of said waveguide structure or its immediate environment.
Owner:MAGNUSSON ROBERT +1
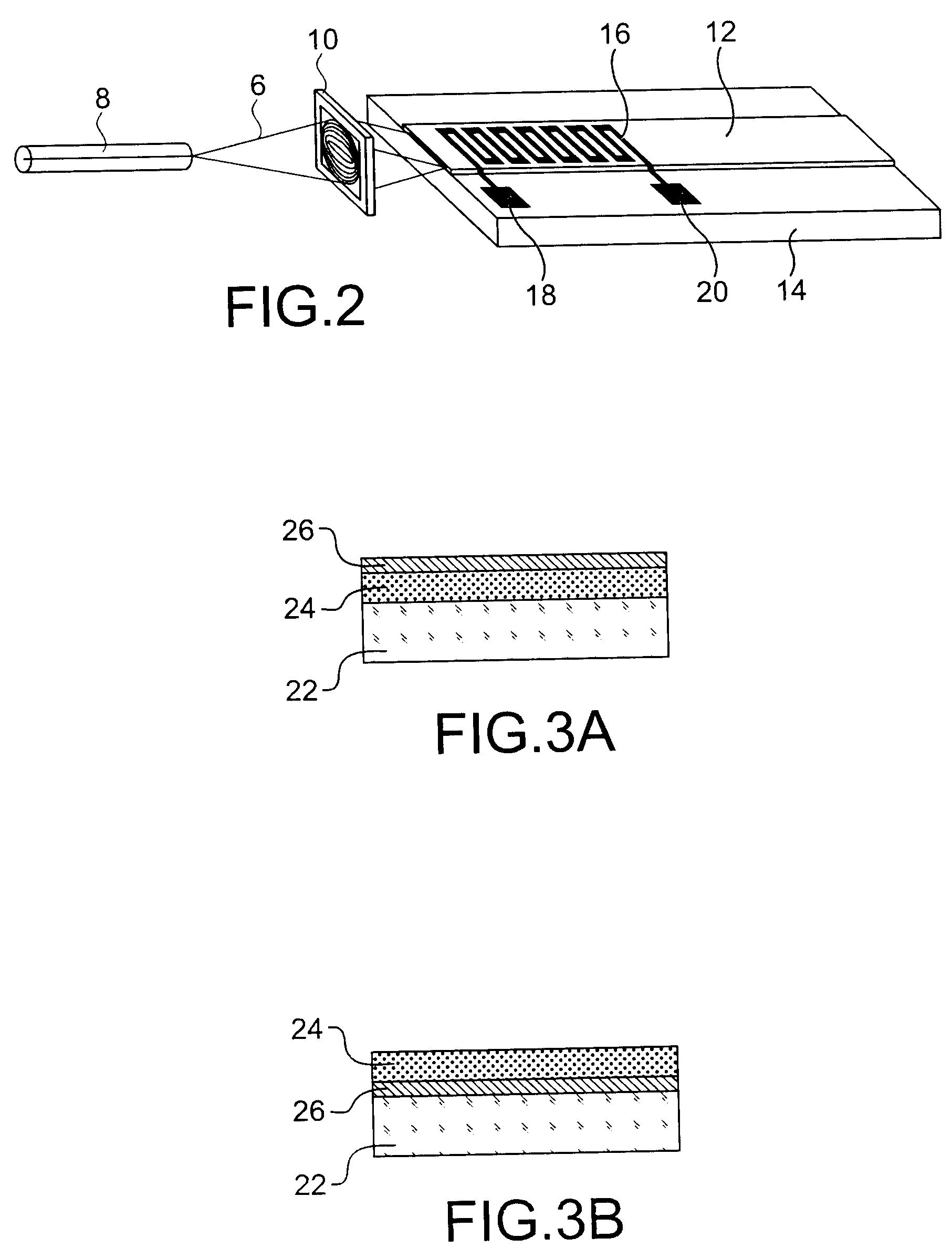
High time-resolution ultrasensitive optical sensor using a planar waveguide leakage mode, and methods for making same
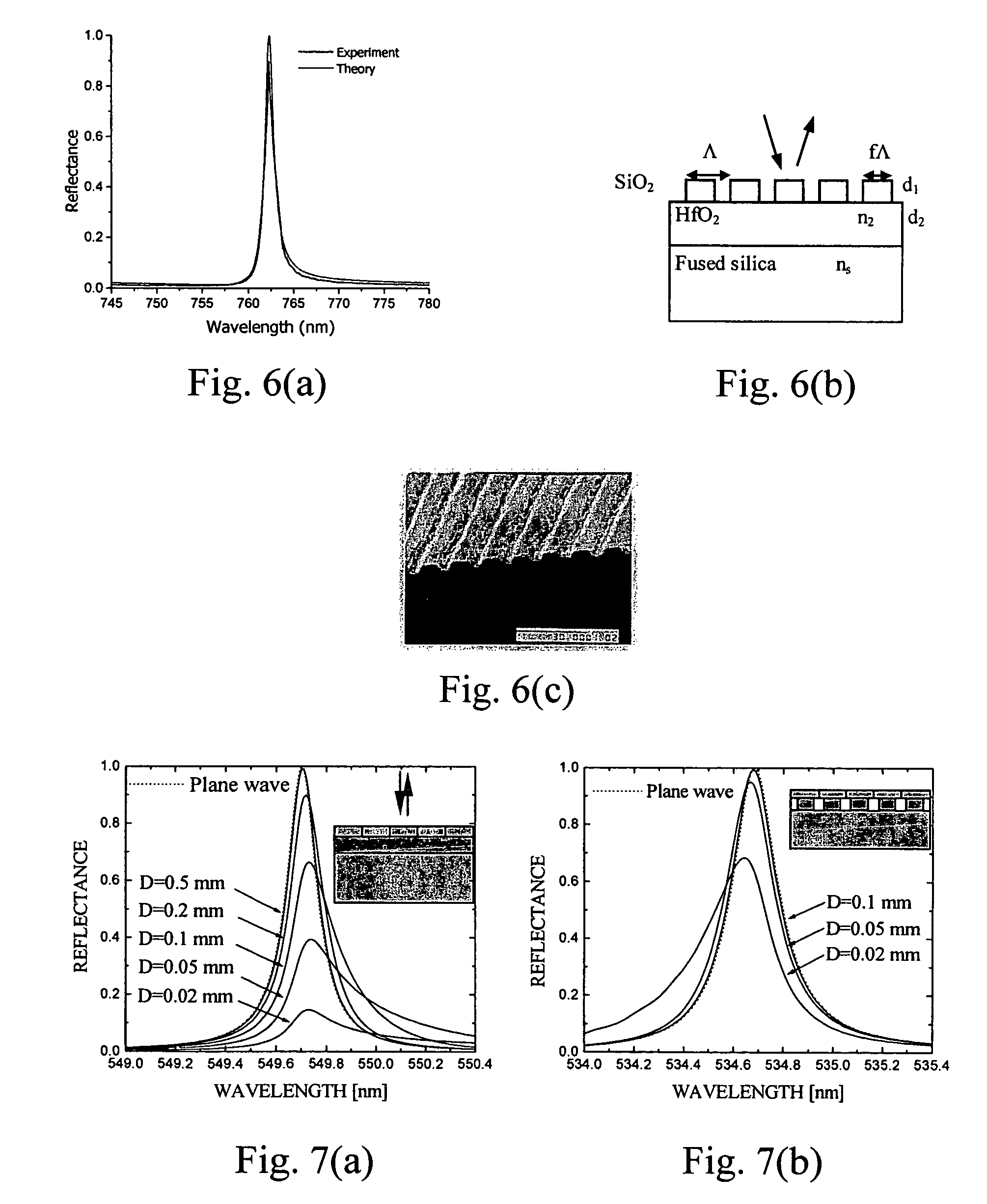
A high time-resolution ultrasensitive optical detector, using a planar waveguide leakage mode, and methods for making the detector. The detector includes a stacking with a dielectric substrate, a detection element, first and second dielectric layers, and a dielectric superstrate configured to send photon(s) into the light guide formed by the first layer. The thicknesses of the layers is chosen to enable a resonant coupling between the photon(s) and a leakage mode of the guide, the stacking having an absorption resonance linked to the leakage mode for a given polarization of the photon(s).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
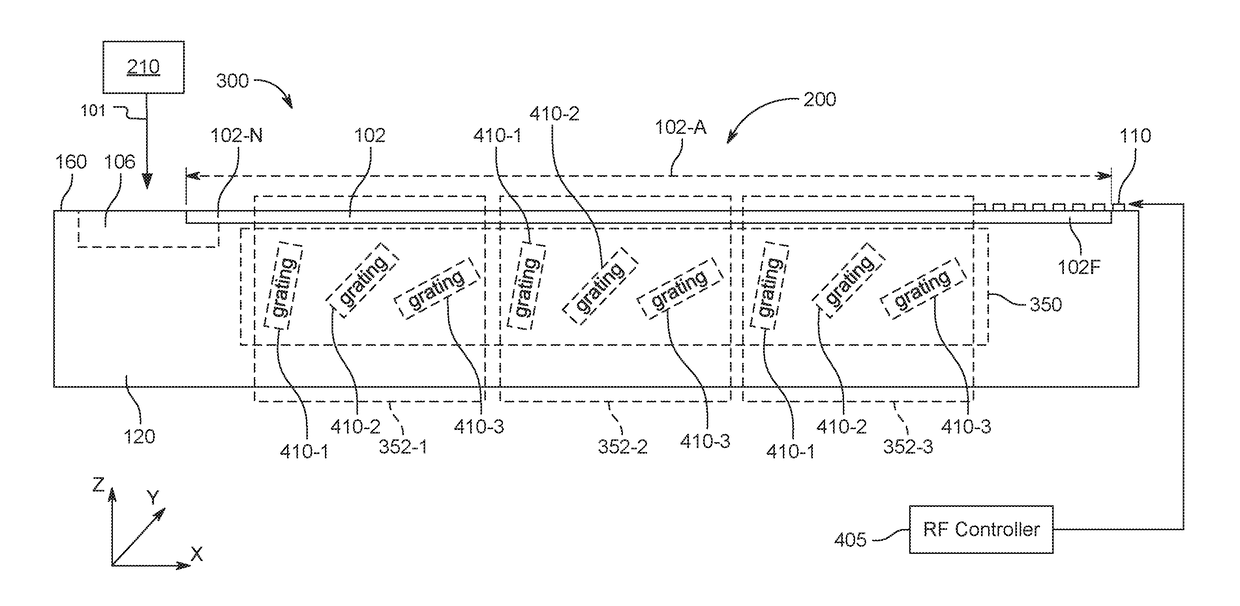
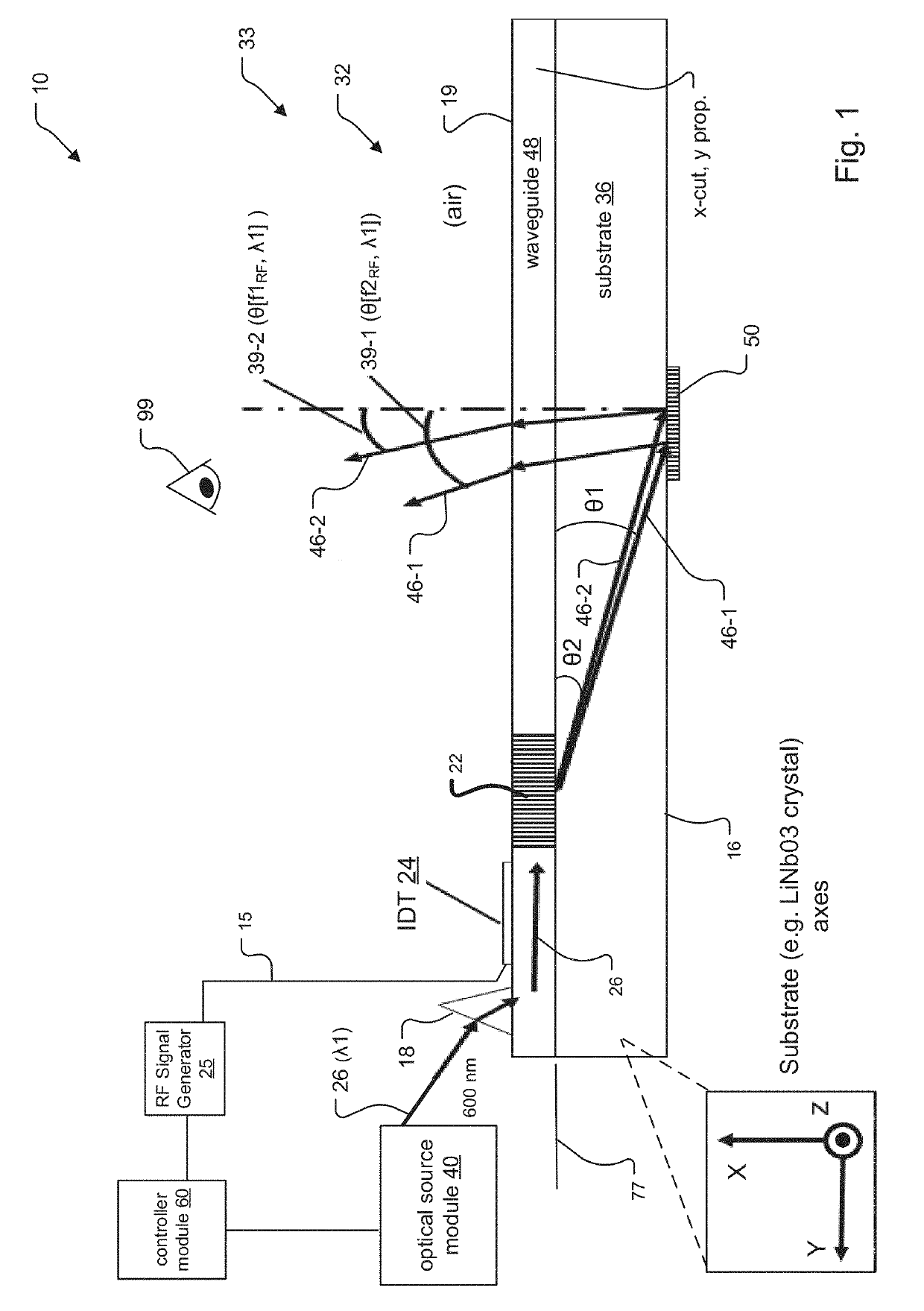
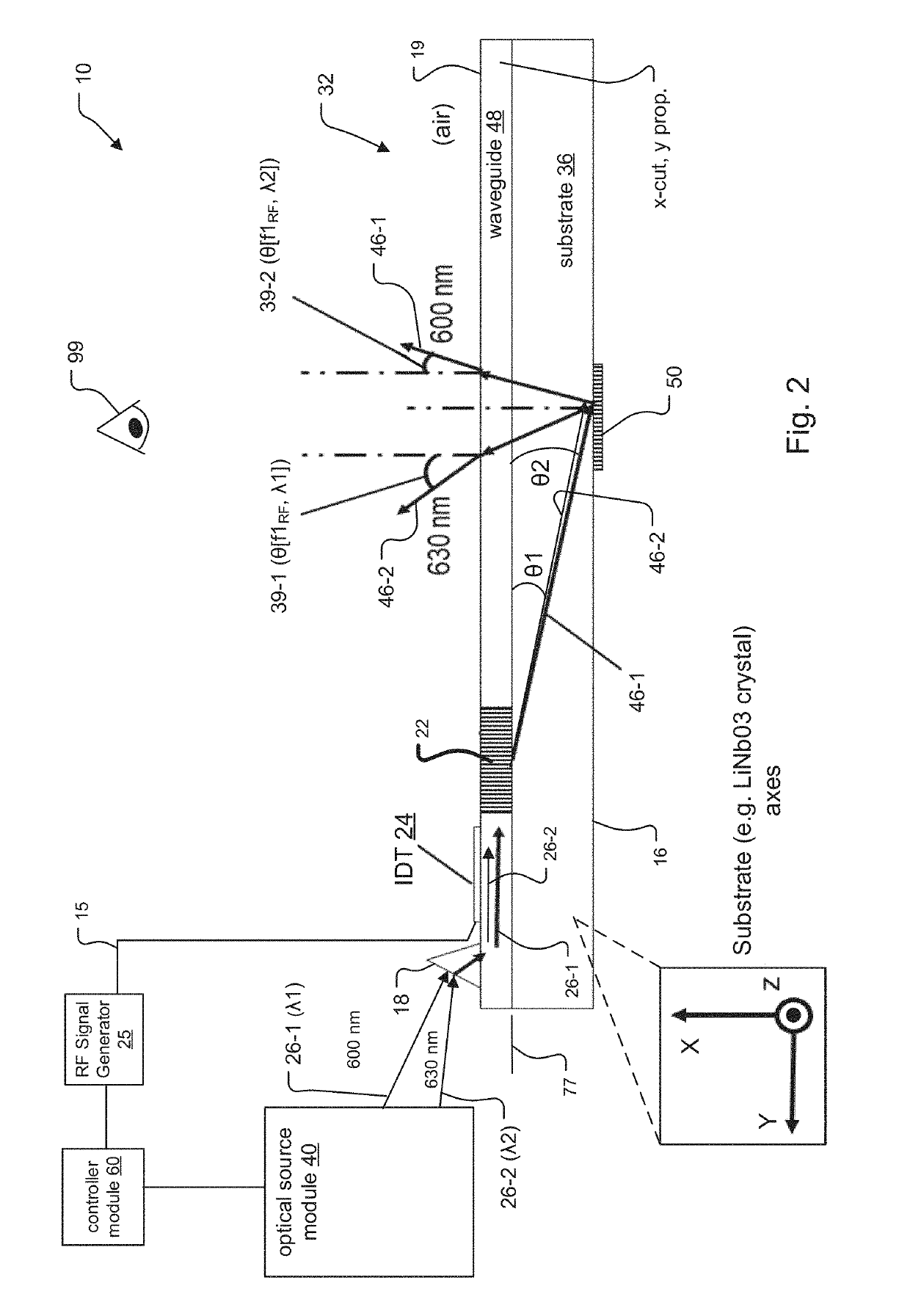
SAW Modulators and Light Steering Methods
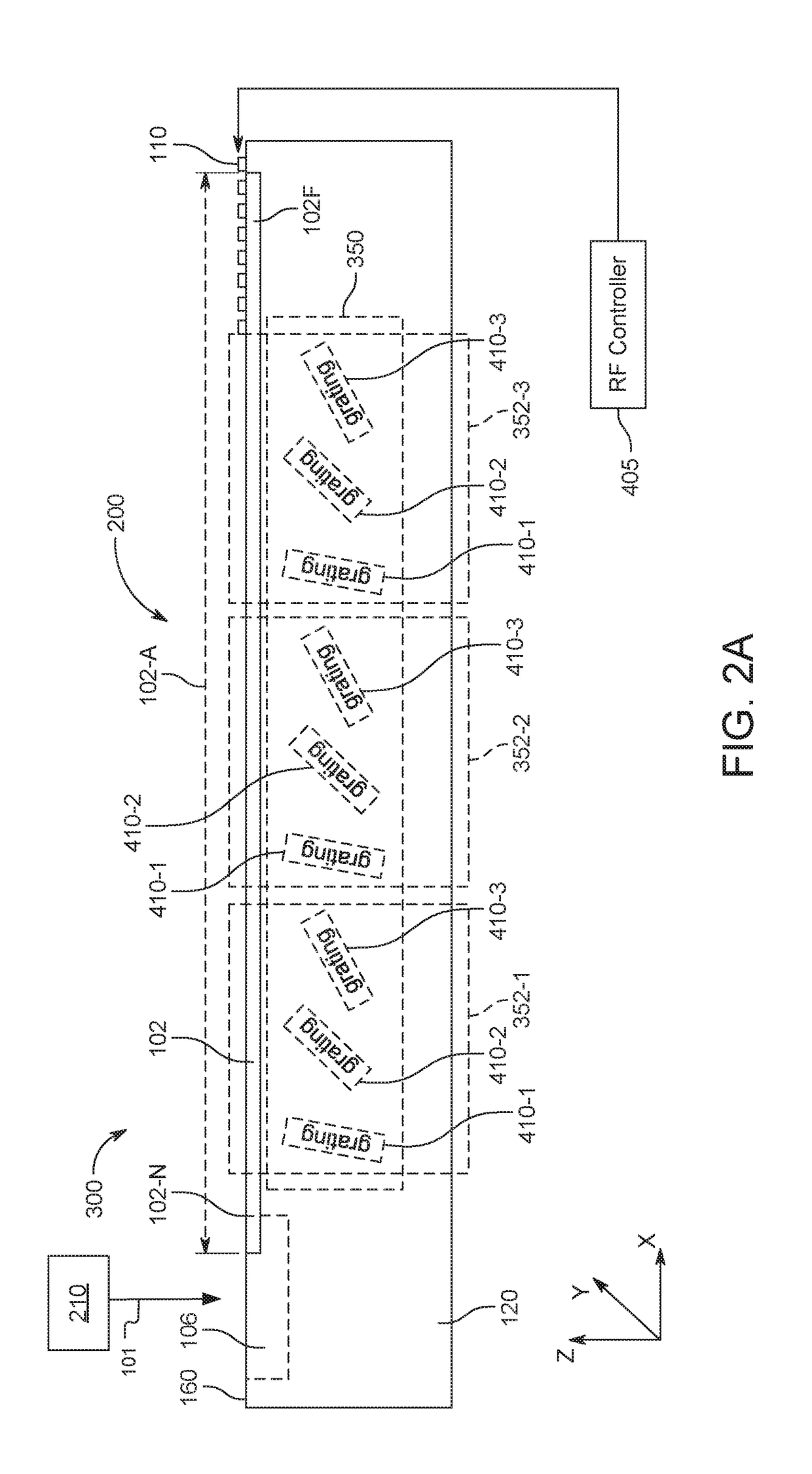
An electro-holographic light field generator device is disclosed. The light field generator device has an optical substrate with a waveguide face and an exit face. One or more surface acoustic wave (SAW) optical modulator devices are included within each light field generator device. The SAW devices each include a light input, a waveguide, and a SAW transducer, all configured for guided mode confinement of input light within the waveguide. A leaky mode deflection of a portion of the waveguided light, or diffractive light, impinges upon the exit face. Multiple output optics at the exit face are configured for developing from each of the output optics a radiated exit light from the diffracted light for at least one of the waveguides. An RF controller is configured to control the SAW devices to develop the radiated exit light as a three-dimensional output light field with horizontal parallax and compatible with observer vertical motion.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Improved Reversible, low cost, distributed optical fiber sensor with high spatial resolution
ActiveUS20080272311A1Increase heightHigh strengthLuminescent dosimetersPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsHigh spatial resolutionImage resolution
A spectroscopic based optical fiber sensor includes a sensitive optical fiber, a probing light source, a power supply, a detector means, a signal processing means, and a display means. The sensitive optical fiber is optically affected by the presence of at least one measurand. The probing light source, adjacent to the sensitive fiber, transversely illuminates the fiber from the outside. The probing light is modified by the sensitive fiber, coupled into the optical fiber core, either as bound modes or leaky modes, as a light signal and guided to a detector means located at the terminus of the optical fiber. The detector means correlates the intensity of the light signal with an electric signal and transmits the electric signal to the signal processing means, wherein the electric signal is correlated to the quantity being measured. The correlated quantity being transmitted and displayed on the display means.
Owner:EGALON CLAUDIO OLIVEIRA
Multimode optical fiber
ActiveCN102854563AOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringLeaky mode
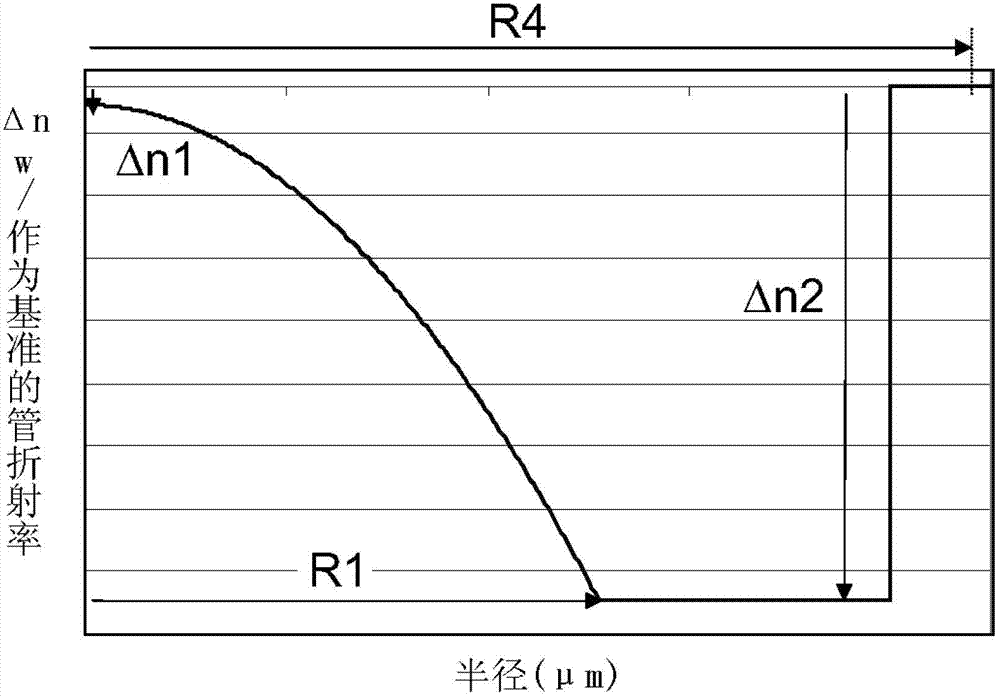
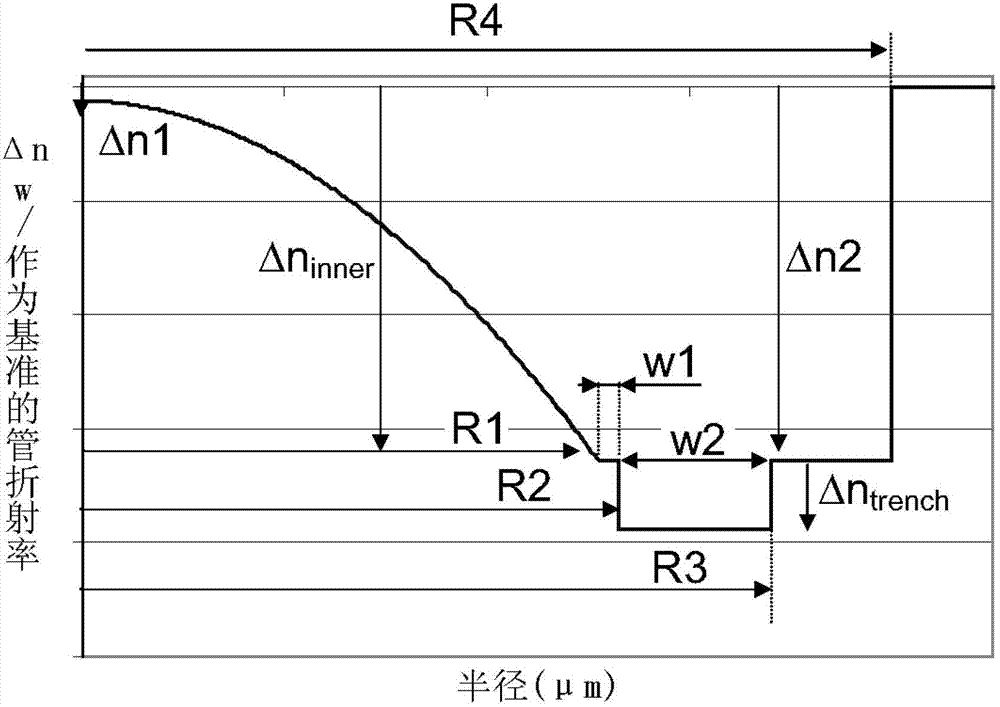
It is proposed a multimode optical fiber including a central core, an inner depressed cladding, a depressed trench, an outer depressed cladding, and an outer cladding. The central core has an alpha-index profile. The depressed claddings limit the impact of leaky modes on optical-fiber performance characteristics (e.g., bandwidth, core size, and / or numerical aperture).
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Process for inversing soft ground horizontal wave velocity by leaky mode waves
InactiveCN101285381AOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to directly measure formation shear wave velocityBorehole/well accessoriesWave shapeLeaky mode
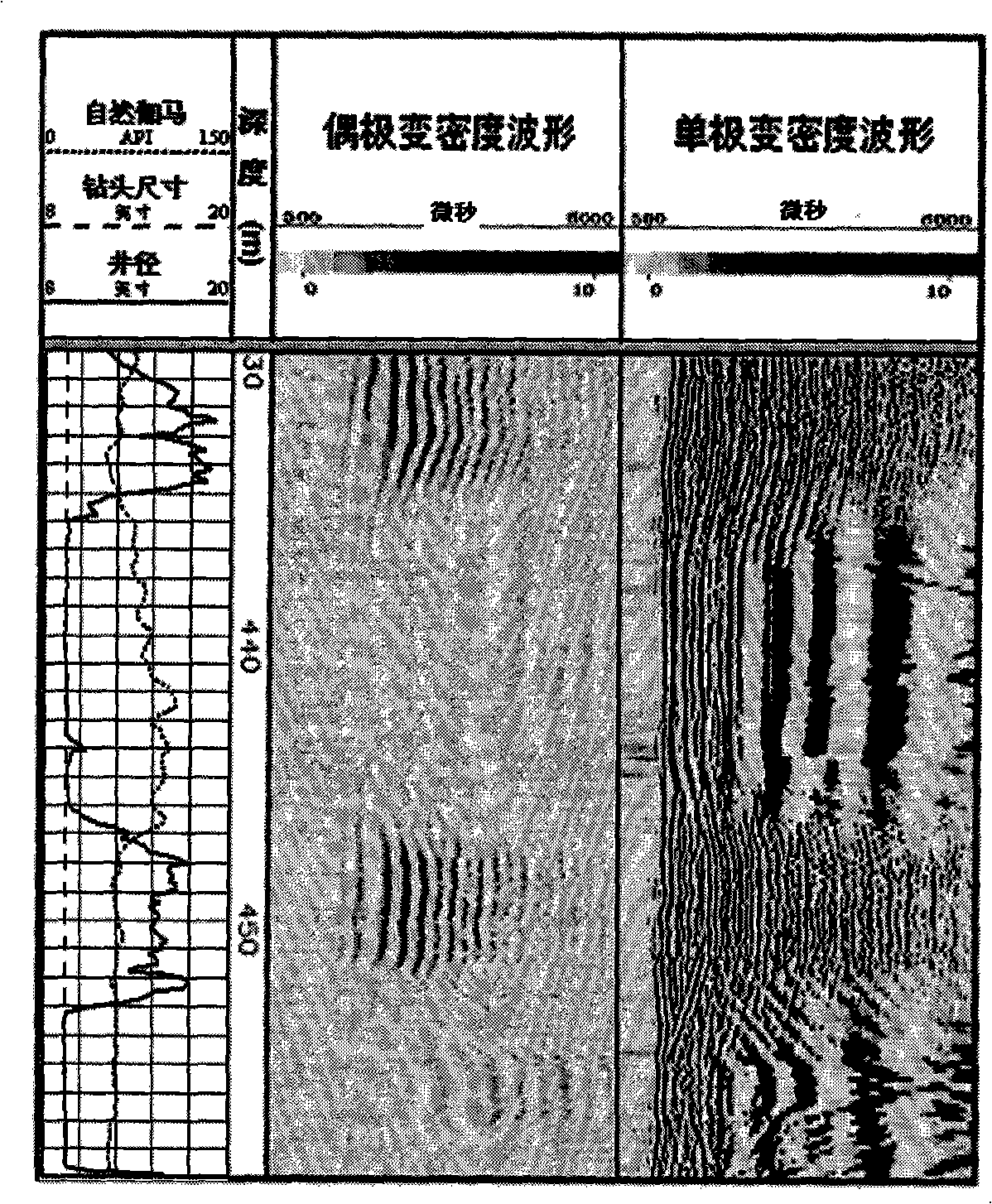
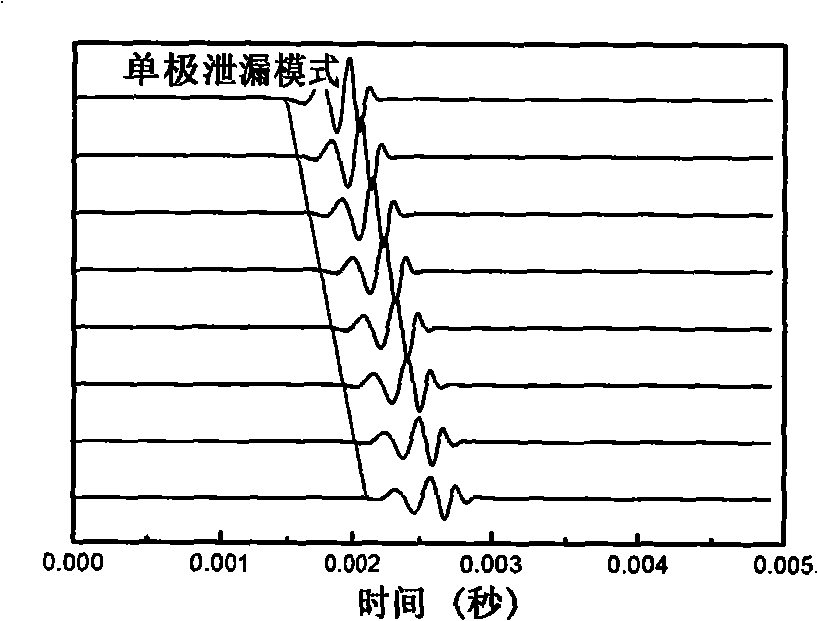
The invention provides a method for inversion of speed of soft formation transverse waves by leaky mode waves, belonging to a logging technology applying physical geophysical sound waves. The specific steps are as follows: inputting wave shape of monopole or dipole leaky mode waves of a soft formation well section with serious diameter extension and conventional well measurement data of corresponding well section formation; extracting a phase velocity dispersion curve of the leaky mode waves from array wave shape and determining the main energy frequency range of the leaky mode waves; at various speeds of formation transverse waves, calculating variance between the leaky mode waves speed calculated by theoretical arithmetic and the leaky mode waves phase velocity extracted from field array wave shape; determining the corresponding formation transverse wave speed in a state in which the variance is zero so as to carry out successive well section processing and output an inversion transverse speed result map. The invention solves the problem of the prior multipole subarray acoustic logging apparatus that the formation transverse wave speed can not be directly measured in the soft formation well sections with ultra-large well diameters, loose superficial layers or serious diameter extension. The method expands the application fields of the borehole acoustic logging technology in oil exploration process and oil development process, and improves the application value of the borehole acoustic logging technology.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
Semiconductor micro-resonator for monitoring an optical device
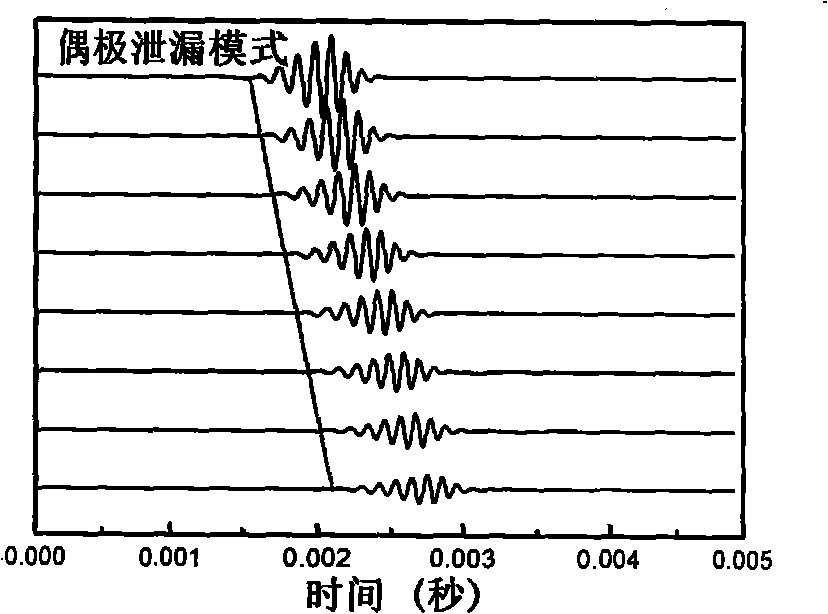
An optical device includes an optical waveguide through which light propagates and a micro-resonator structure including an optical sensor. The micro-resonator is configured to resonate at a wavelength of light that may be transmitted through the optical waveguide. When light at that wavelength is transmitted through the optical waveguide, it resonates in the resonator and is detected by the optical sensor to produce an electrical signal. The optical resonator may be a micro-cylinder, disc or ring resonator and may be coupled to the waveguide via evanescent coupling or leaky-mode coupling. Multiple resonators may be implemented proximate to the waveguide to allow multiple wavelengths to be detected. When the waveguide is coupled to a tunable laser, signals provided by the optical sensor may be used to tune the wavelength of the laser.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
High time-resolution ultrasensitive optical sensor using a planar waveguide leakage mode, and methods for making same
InactiveUS7718964B2Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDielectric substrateOptoelectronics
A high time-resolution ultrasensitive optical detector, using a planar waveguide leakage mode, and methods for making the detector. The detector includes a stacking with a dielectric substrate, a detection element, first and second dielectric layers, and a dielectric superstrate configured to send photon(s) into the light guide formed by the first layer. The thicknesses of the layers is chosen to enable a resonant coupling between the photon(s) and a leakage mode of the guide, the stacking having an absorption resonance linked to the leakage mode for a given polarization of the photon(s).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Light field generator devices with series output couplers
ActiveUS20180284466A1Increase angular fanLight providedImpedence networksHolographic optical componentsGratingCoupling
Electro-holographic light field generator devices comprising surface acoustic wave (SAW) optical modulators are disclosed that employ multiple output couplers. These output couplers might be distributed along waveguides of the SAW modulators, within output coupling regions. Each of these output couplers can be configured for directing an incident leaky mode light at different output angles. In some cases, it may be desirable to employ the output couplers to function as different sub-pixels, to provide light to different viewing directions. The output couplers may be mirrors, volume gratings, chirped gratings, reflection gratings, two dimensional gratings, and / or transmission gratings. The output couplers may be angled so that the coupling output fans for each optical modulator are offset from the waveguide for that optical modulator.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Highly efficient focusing waveguide grating coupler using leaky mode
InactiveUS6999660B2Coupling efficiency is highReduce dependenceCoupling light guidesFresnel lensManufacturing technology
Provided is a focusing waveguide grating coupler using a leaky mode which can form single output beam while relieving the dependency on manufacturing processes. The focusing waveguide grating coupler of the present research includes: a substrate having a first refraction index n1; a first core layer having a second refraction index n2, the first core layer being formed on the substrate; a second core layer having a third refraction index n3, the second core layer being formed on the first core layer apart from the first core layer with a space d in between; a first cladding layer having a fourth refraction index n4, the first cladding layer being formed on the second core layer; a second cladding layer having a fifth refraction index n5, the second cladding layer being formed on the first cladding layer and inserted between the first core layer and the second core layer; and a Fresnel lens positioned on the second cladding layer, wherein the refractive indexes satisfy conditions of n5>(n2, n3)>n1 and n5>n4; and light inputted through the first and second core layers to the Fresnel lens as radiated leaky beam by a leaky mode formed according to the conditions, and the leaky beam forms an optical focus by performing single directional coupling.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Chip-Scale Slow-Light Buffers Fashioned with Leaky-Mode Resonant Elements and Methods of Using Leaky-Mode Resonant Elements for Delaying Light
A method for delaying transmitted light. The method may include illuminating a leaky-mode resonant element with light pulses of short duration and sequences of such pulses. The leaky-mode resonant element may include a spatially modulated periodic layer and may be configured so that at least some of the light is transmitted in a delayed manner.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Broadband micro nano two-dimensional multitooth grating trap filter
InactiveCN105866868AFlexible regulationImprove performanceNanotechnologyDiffraction gratingsMicro nanoGrating
The invention discloses a broadband micro nano two-dimensional multitooth grating trap filter, for the purpose of improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of a silicon solar film battery. The structure is as follows: gratings periodically changing along two directions are arranged at the upper surface of a silicon active layer, each of the gratings in the two directions has two teeth, and the teeth are non-uniformly distributed in the two directions of the gratings. According to the invention, through adjusting structural dimensions of the micro nano two-dimensional multitooth gratings and positions of the grating teeth, by use of a leaky-mode resonance effect, the device has the advantages of high transmission efficiency, large bandwidth and wide angle spectrum for transverse electric wave (TE wave) and transverse magnetic wave (TM wave) incident light.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
SAW modulators and light steering methods
ActiveUS10795235B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksTransducerEngineering
An electro-holographic light field generator device is disclosed. The light field generator device has an optical substrate with a waveguide face and an exit face. One or more surface acoustic wave (SAW) optical modulator devices are included within each light field generator device. The SAW devices each include a light input, a waveguide, and a SAW transducer, all configured for guided mode confinement of input light within the waveguide. A leaky mode deflection of a portion of the waveguided light, or diffractive light, impinges upon the exit face. Multiple output optics at the exit face are configured for developing from each of the output optics a radiated exit light from the diffracted light for at least one of the waveguides. An RF controller is configured to control the SAW devices to develop the radiated exit light as a three-dimensional output light field with horizontal parallax and compatible with observer vertical motion.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
System and Method for Diffractive Steering of Electromagnetic Radiation
ActiveUS20190094652A1Improve angular dynamic rangeIncrease the angleCoupling light guidesPhase-modulated carrier systemsGratingDisplay device
A light steeling system and method for diffractive steering of electromagnetic radiation such as visible light is disclosed. Embodiments of the light steering system include leaky-mode SAW modulators as light modulator devices. The SAW modulators preferably include reflective diffractive gratings. The gratings are mounted to / patterned upon an exit face that opposes an exit surface of the SAW modulator, in one example. Steering of light signals emitted from the SAW modulators in these systems can be accomplished by varying wavelength of light signals introduced to the SAW modulators, and / or by varying frequency of RF drive signals applied to the SAW modulators. In addition, light field generators that incorporate SAW modulators of the proposed light steering system within displays of the light field generators are also disclosed.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Few mode optical fiber links for space division multiplexing having trenched fibers with high leak losses for leaky modes and low bend losses
ActiveUS10007055B2Reduce group velocity mismatchExcellent indicatorsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLeaky modeOptical link
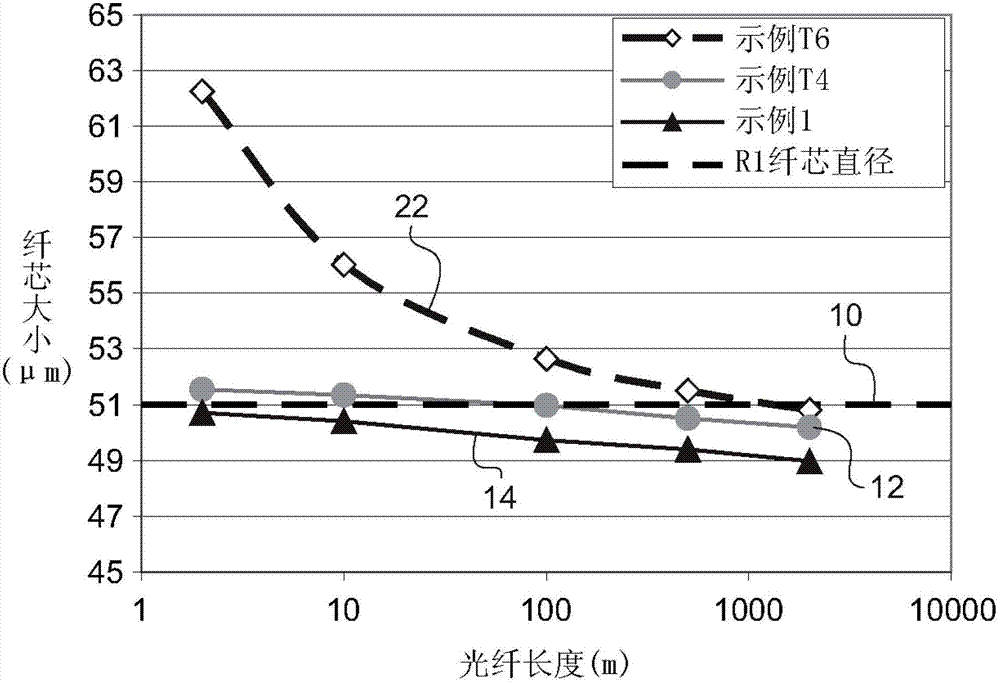
The invention relates to an optical link comprising N optical fibers, with N≥2. Each optical fiber comprises an optical core and an optical cladding surrounding the optical core, the optical core having a single αi graded-index profile with αi≥1, and the optical core having a radius R1i, where i E [1; N] is an index designating said optical fiber. Said optical cladding comprises a region of depressed refractive index ntrenchi, called a trench, surrounding the optical core. According to embodiments of the invention, for all optical fibers in said link, said optical core radius R1i and said length Li are chosen such that R1i≥13.5 μm and so as to satisfy a criterion C of quality. Thus, the invention provides a few-mode optical fiber link, which allow guiding an increased number of LP modes as compared to prior art FMF links, while reaching low Differential Mode Group Delay.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
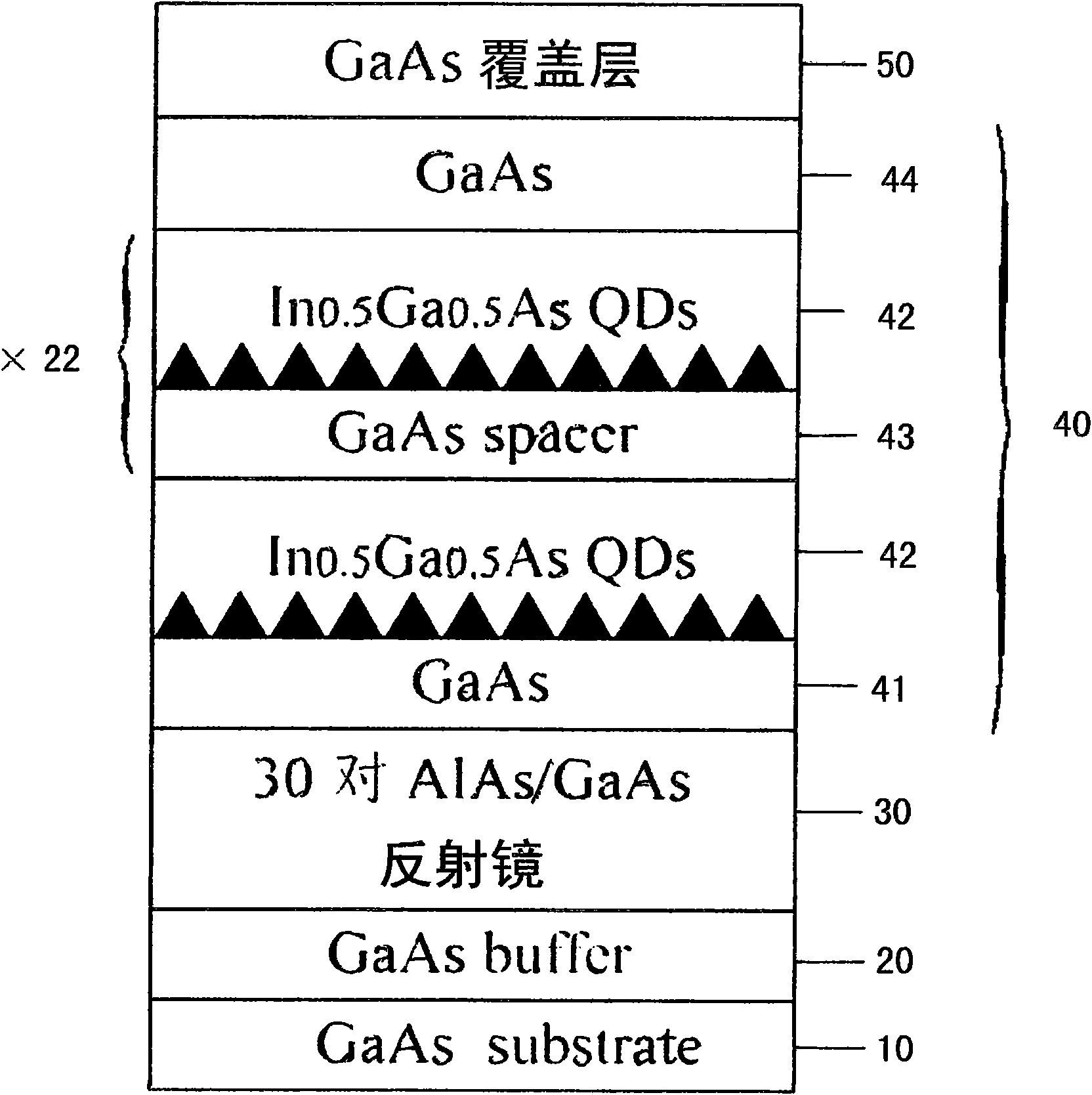
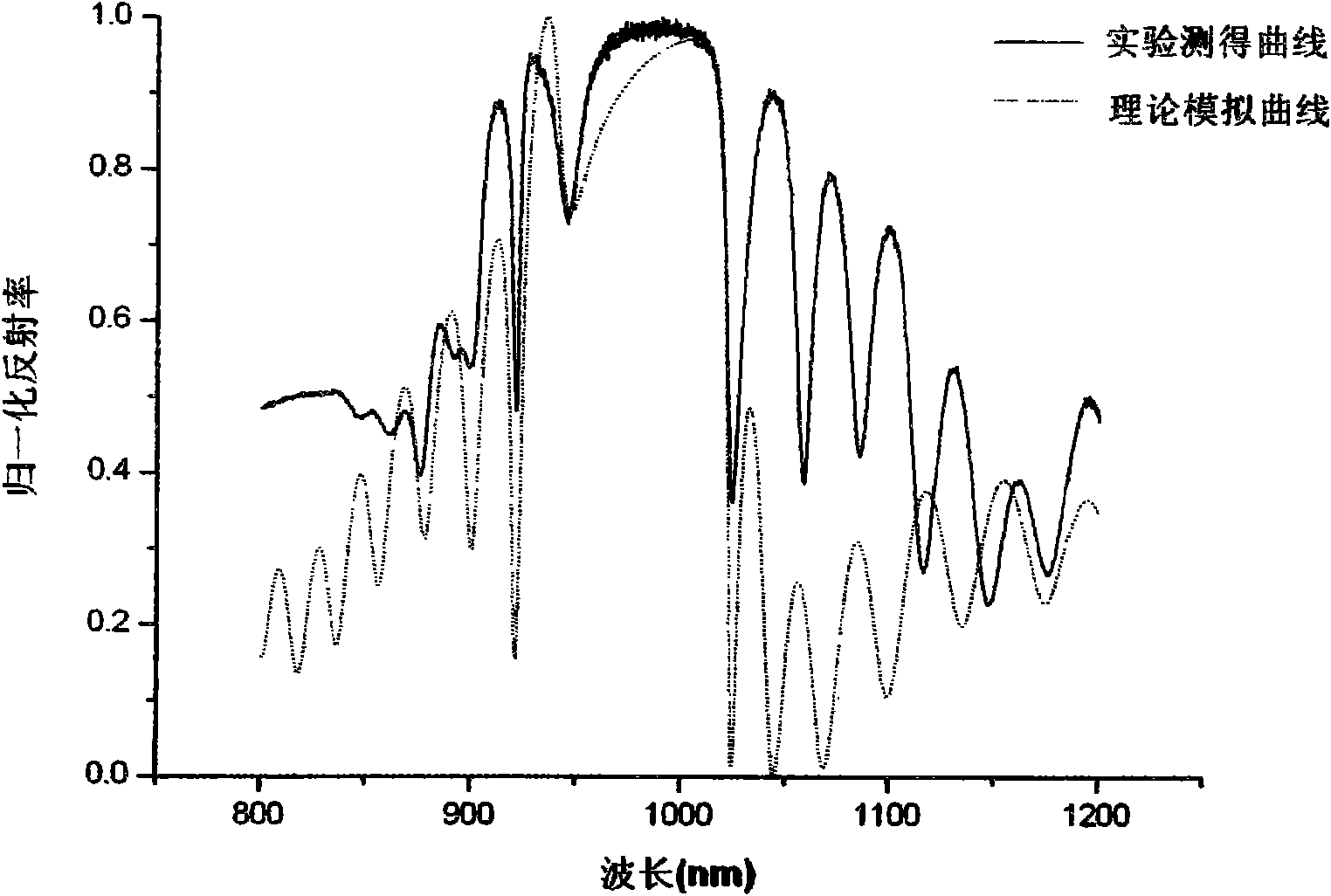
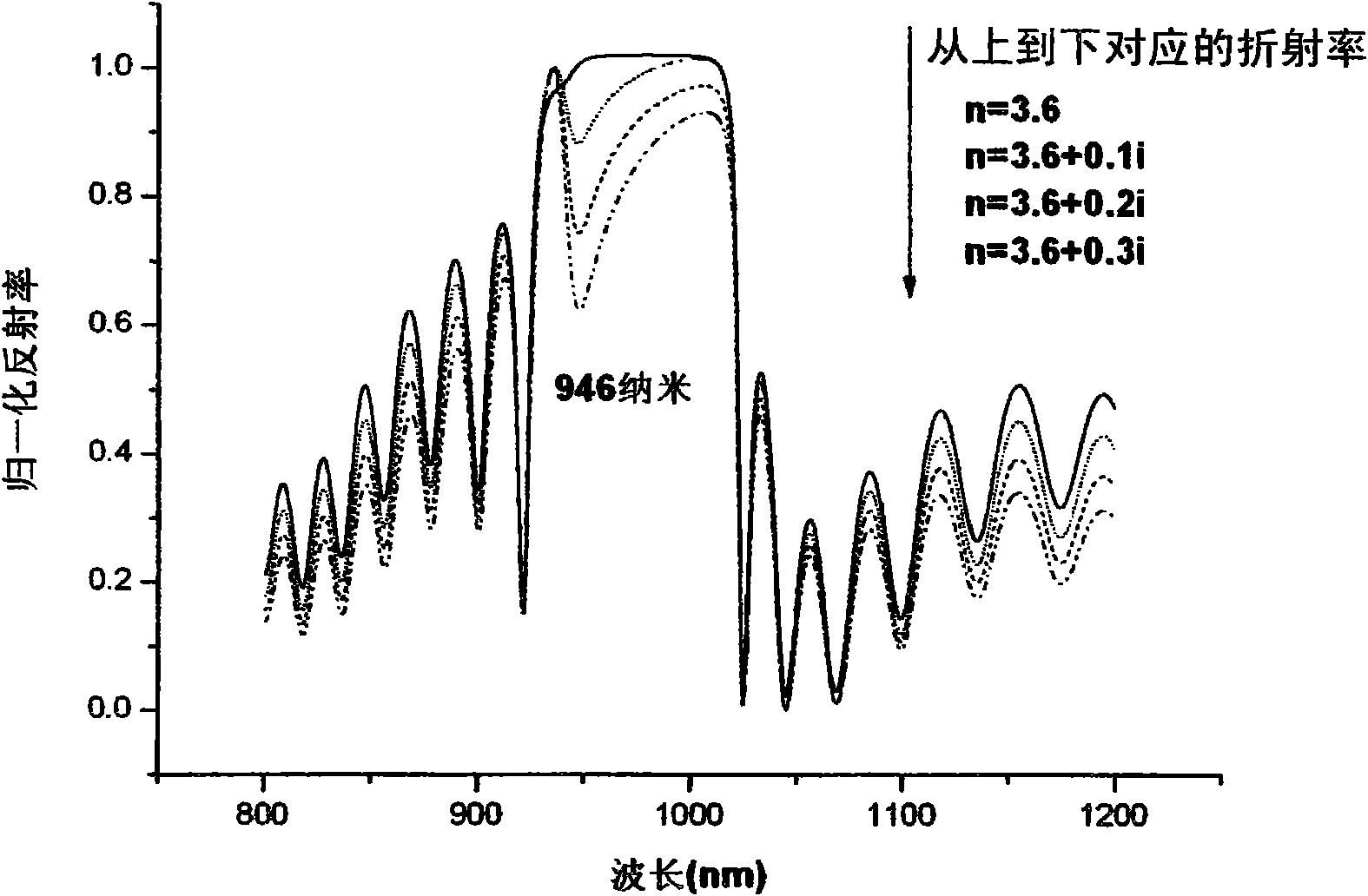
Method for judging effective cavity mode of resonant cavity enhanced photodetector without upper reflector
InactiveCN101915657AScattering properties measurementsTesting optical propertiesResonant cavityTransmission matrix
The invention discloses a method for judging an effective cavity mode of a resonant cavity enhanced photodetector without an upper reflector, which comprises the following steps: designing a structure of the resonant cavity enhanced photodetector without the upper reflector to form a detector sample; growing the designed detector sample, measuring the reflection spectrum of the sample by a spectrometer and marking the leaky modes of a high-reflectivity belt area in the reflection spectrum; editing a simulation program according to the principle of an optical transmission matrix and simulating to obtain a theoretically simulated reflection spectrum which is completely consistent with the designed resonant cavity enhanced photodetector without the upper reflector in terms of structure and layer thickness; adjusting the thickness of each layer of the reflector and the cavity in the simulation program so that the simulated reflection spectrum is always consistent with the reflection spectrum measured by test; then changing the absorption coefficient of an absorption layer in the simulation program and observing the change of each leaky mode in the simulated reflection spectrum, wherein the leaky mode deriving from the resonant cavity mode, namely the cavity mode, does not changes at the same time, so as to judge whether the leaky modes in the reflection spectrum of the resonant cavity enhanced photodetector without the upper reflector are from active area absorption or from the cavity mode.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
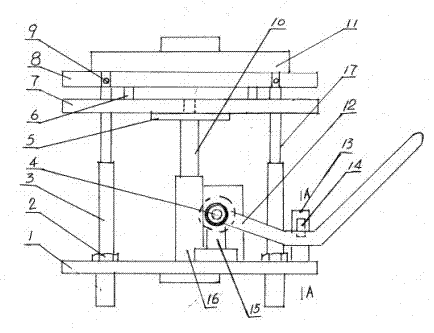
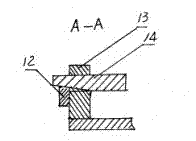
Multi-purpose box dividing modeling leaky-mode machine
The invention discloses a multi-purpose box dividing modeling leaky-mode machine which comprises a machine base (1), a column, a lifting mechanism, a sand box (11), a section plate (7) and a mould frame plate (8). The machine is characterized in that four column guide shafts (3) are arranged on the base, one ends of the column guide shafts are fixedly connected with the base through nuts (2), the other ends of the column guide shafts are sleeved with a carbon steel column (17), the upper end of the carbon steel column penetrates through a column hole arranged on the section plate to be fixedly connected with the mould frame plate (8) through a locking bolt (9), the lower end of the column is fixedly connected with the base, the lifting mechanism is fixedly connected onto the middle of the base, a universal coordinate location hole is arranged on the section plate, a model lining plate is arranged between the mould frame plate and the section plate, a plurality of balance adjusting blocks (6) are arranged at the bottom of the model lining plate, a pin seat (13) is fixedly connected with the outer lateral portion of the base provided with the handle side, and a location pin hole is arranged on the pin seat to be connected with an adjusting location pin (14) in insertion mode. The machine is high in production efficiency, accurate in product geometrical size, simple in structure and good in generality.
Owner:NANCHONG HAOHUA AUTO PARTS MFG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com