Multimode optical fiber
A multi-mode optical fiber and core technology, applied in clad optical fiber, multi-layer core/clad optical fiber, optics, etc., can solve the problems of small diameter, increased manufacturing cost, width deposition, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
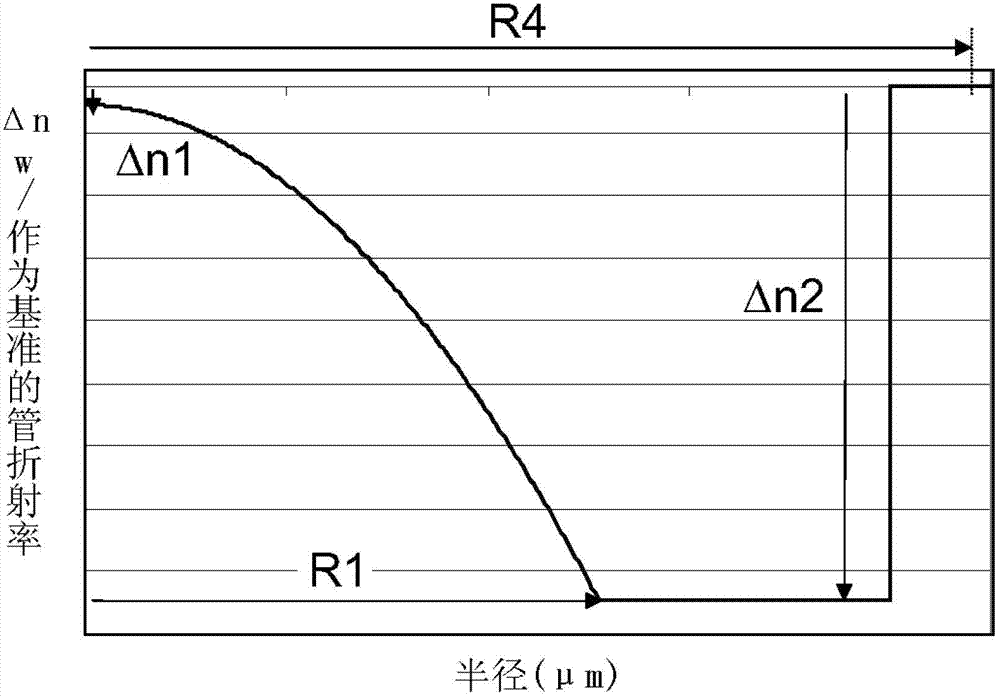
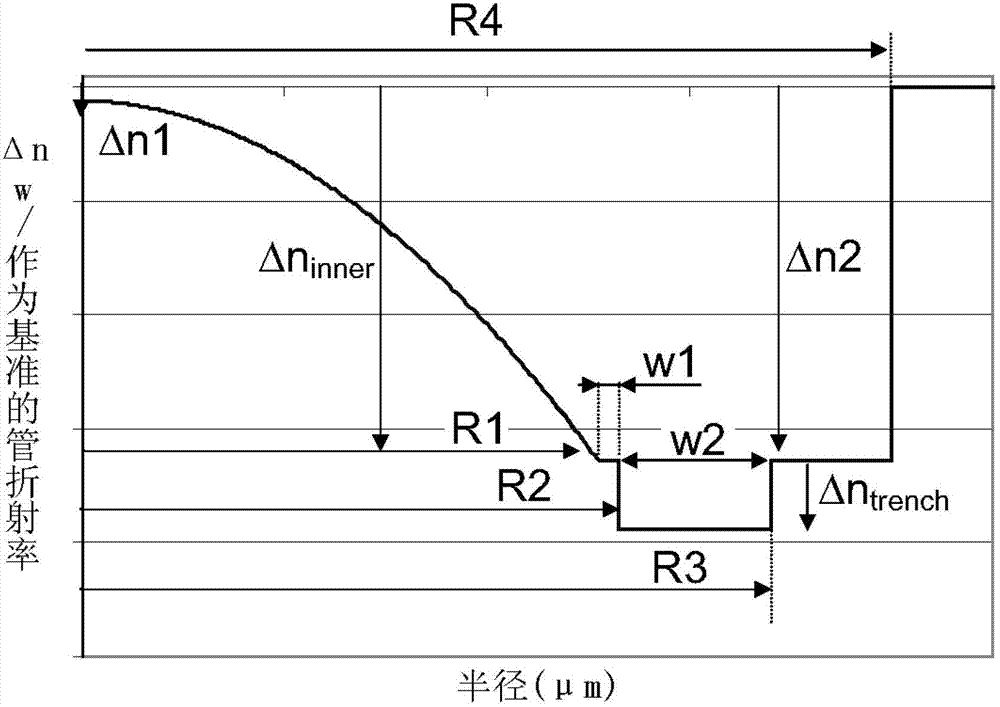
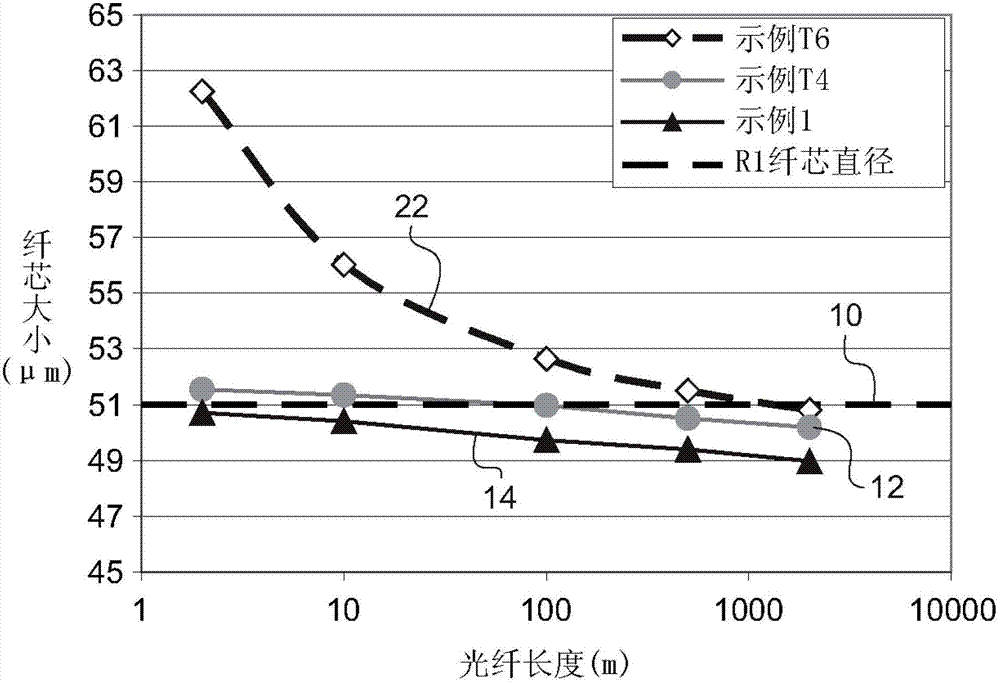
[0053] The present invention relates to concave graded-index multimode optical fibers comprising a depressed cladding that limits the contribution of leaky modes to other fiber characteristics (e.g., bandwidth, core size, and / or numerical aperture) influences.
[0054] There is increasing interest in the use of optical fibers in nuclear power plants and other radiation-rich environments such as particle acceleration laboratories and satellites. For example, optical fibers can be used in optical data communication links, distributed sensors, plasma diagnostics, and instrumentation systems. In these applications, optical fibers typically transmit signals through noisy electromagnetic environments, high gamma ray doses and / or dose rates, and high neutron fluxes.
[0055] Signals transmitted via optical fibers typically suffer from accumulated optical loss (ie, attenuation) over the distance traveled. These transmission losses increase substantially when the fiber is exposed to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com