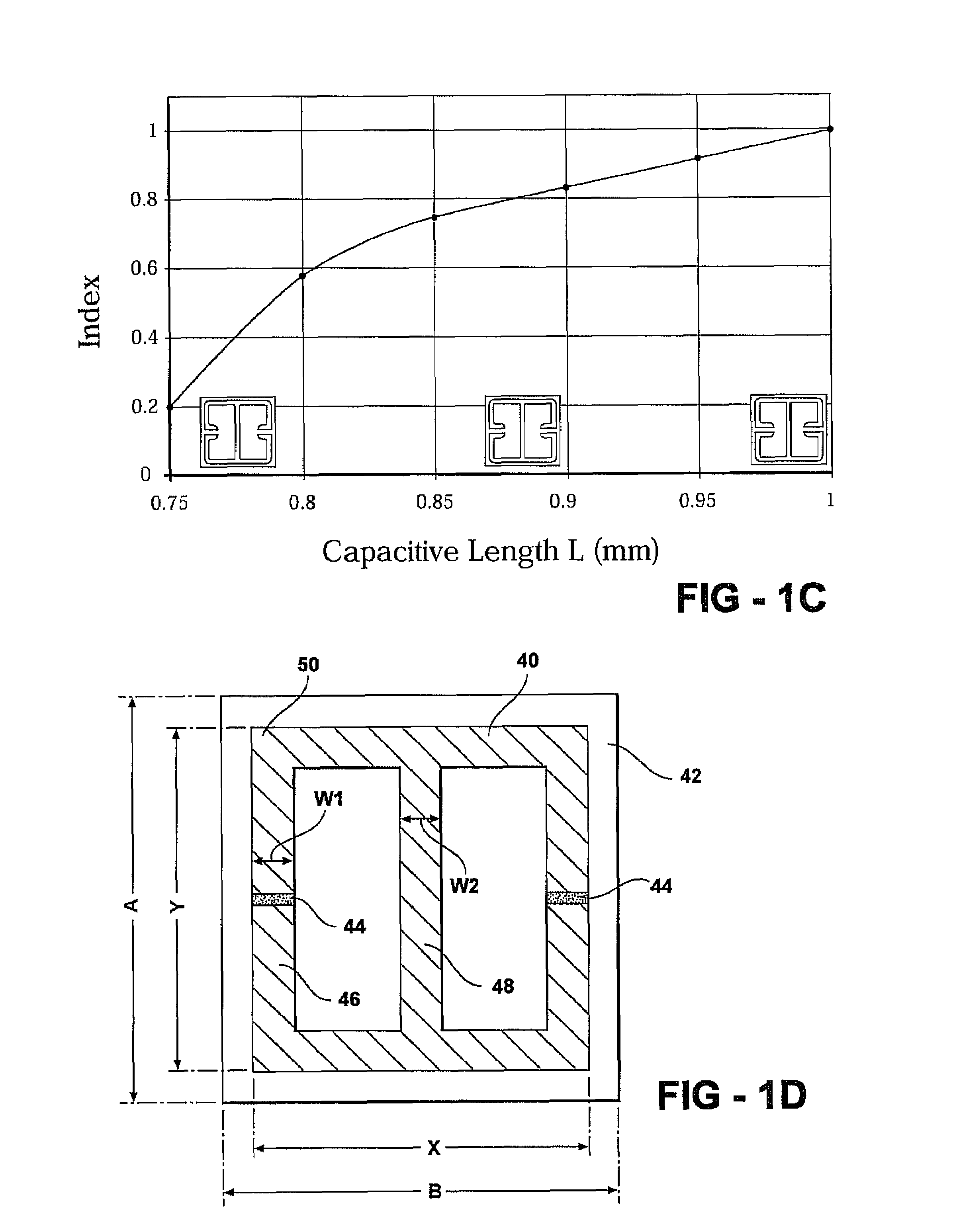
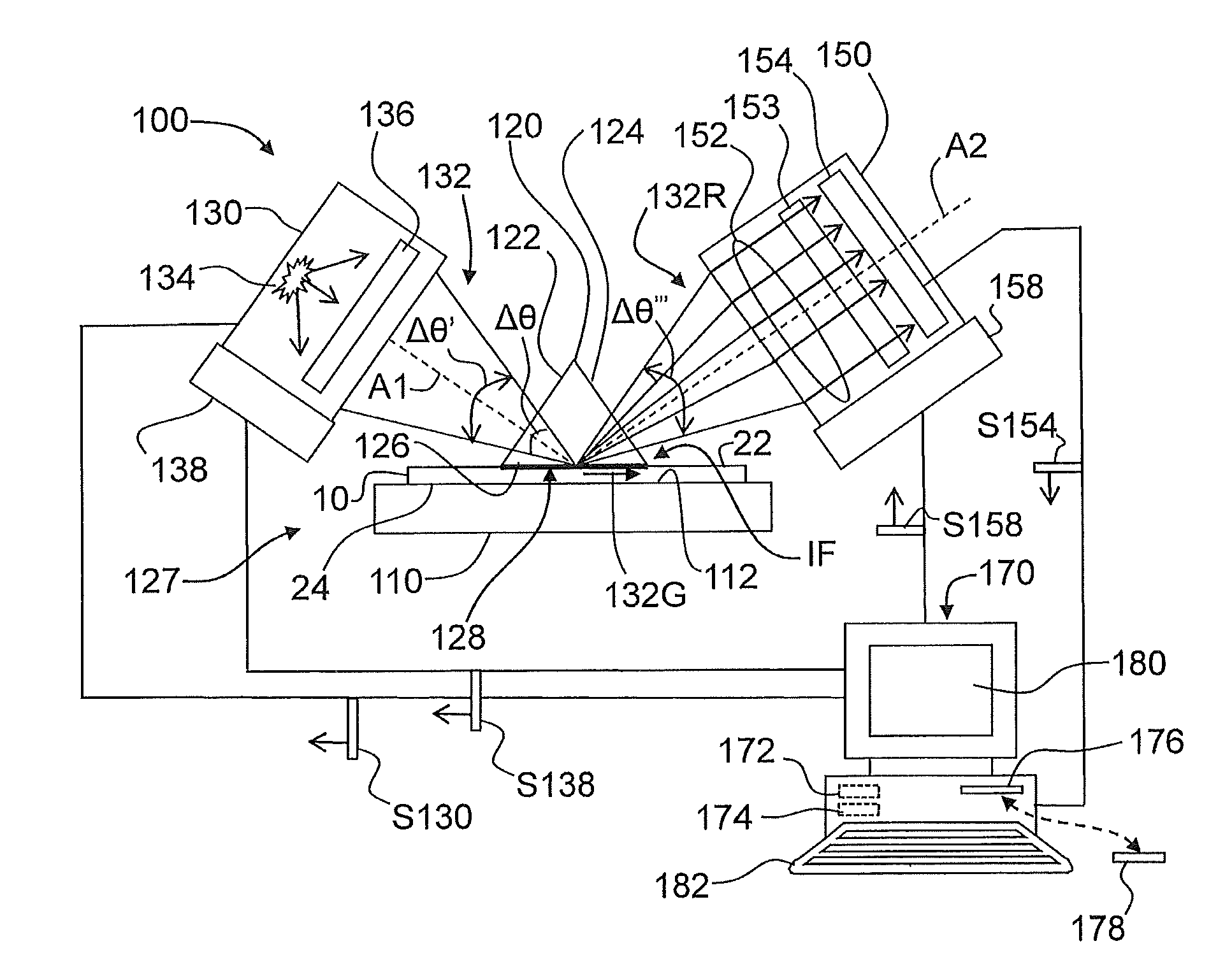
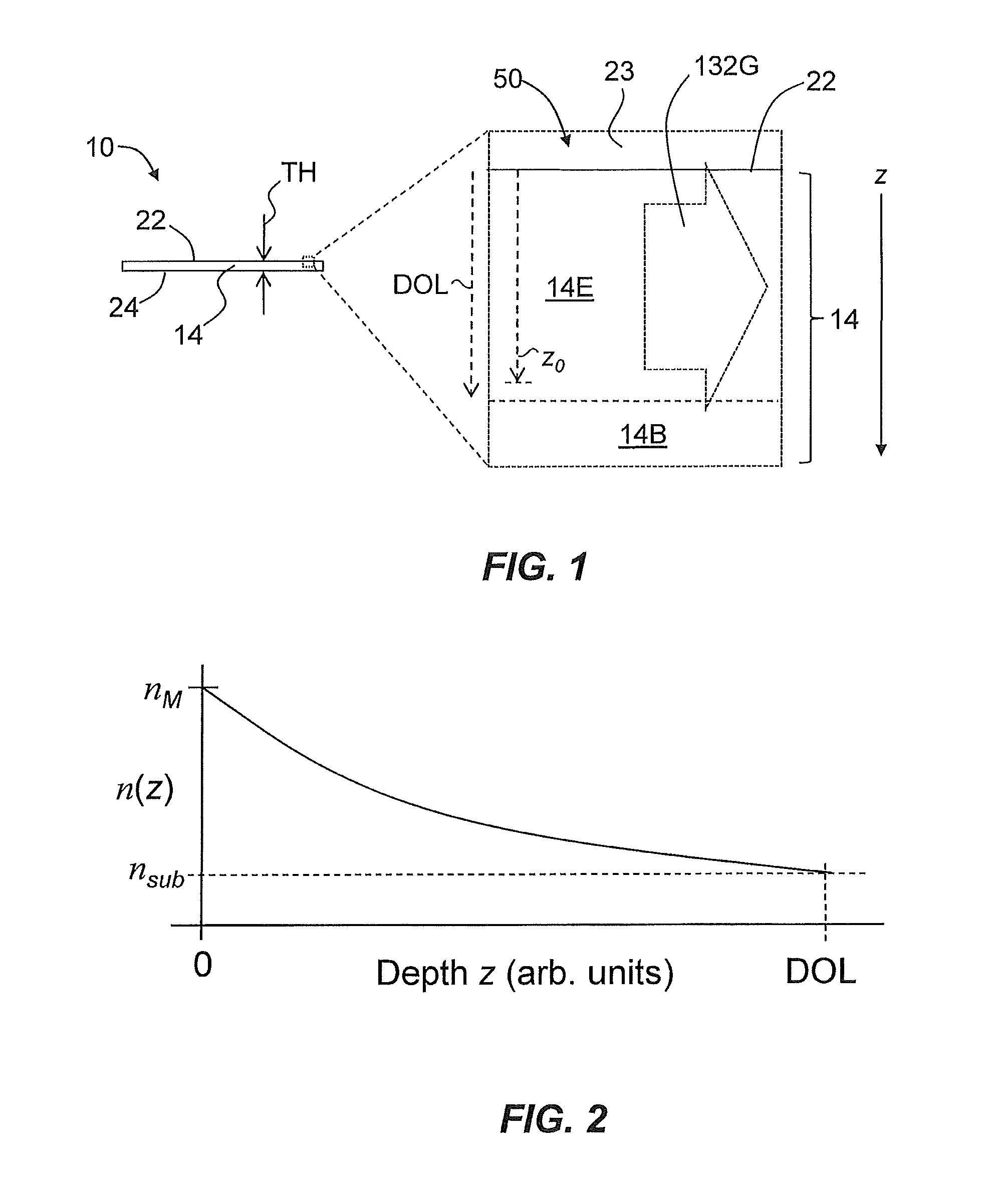
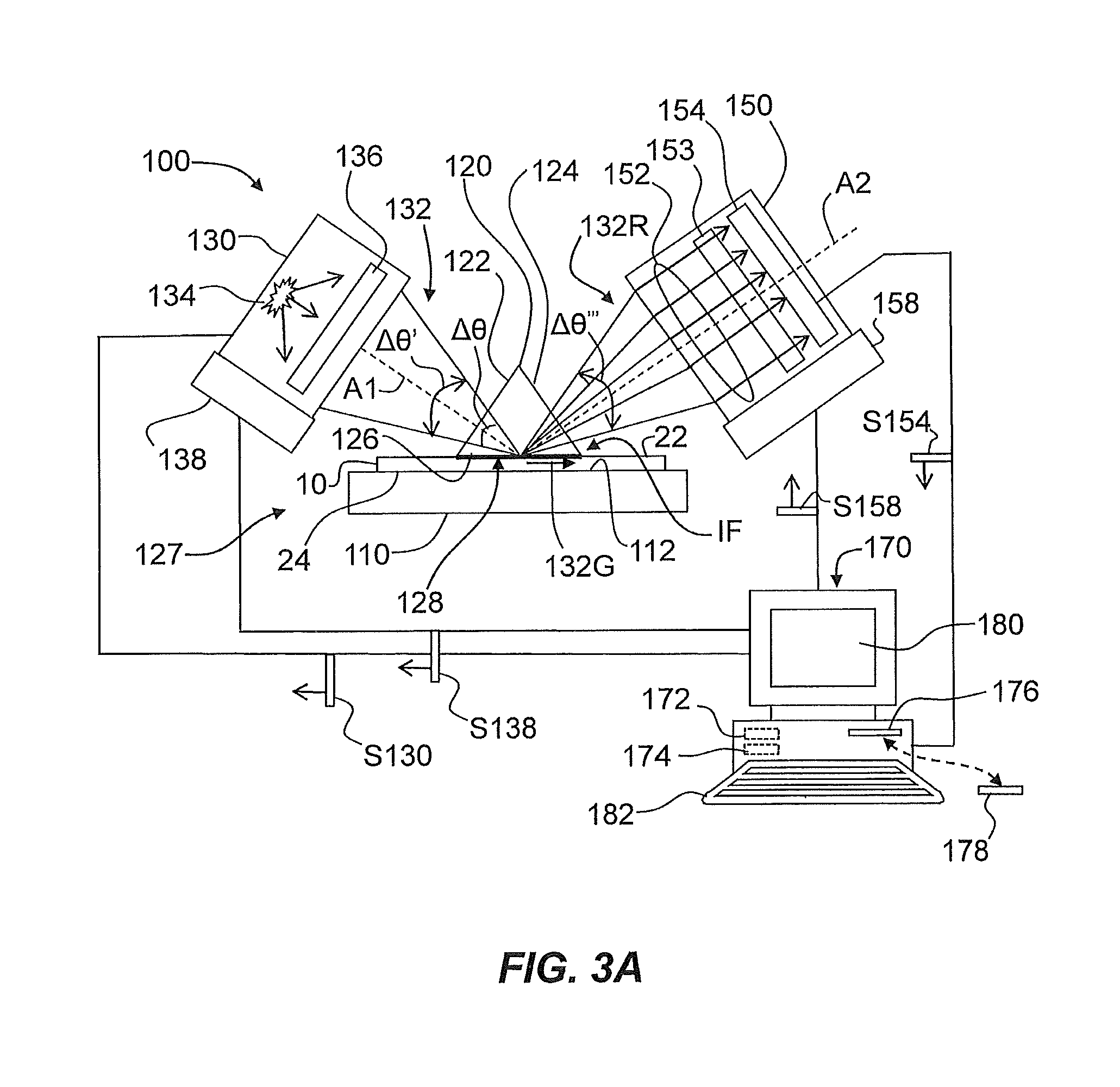
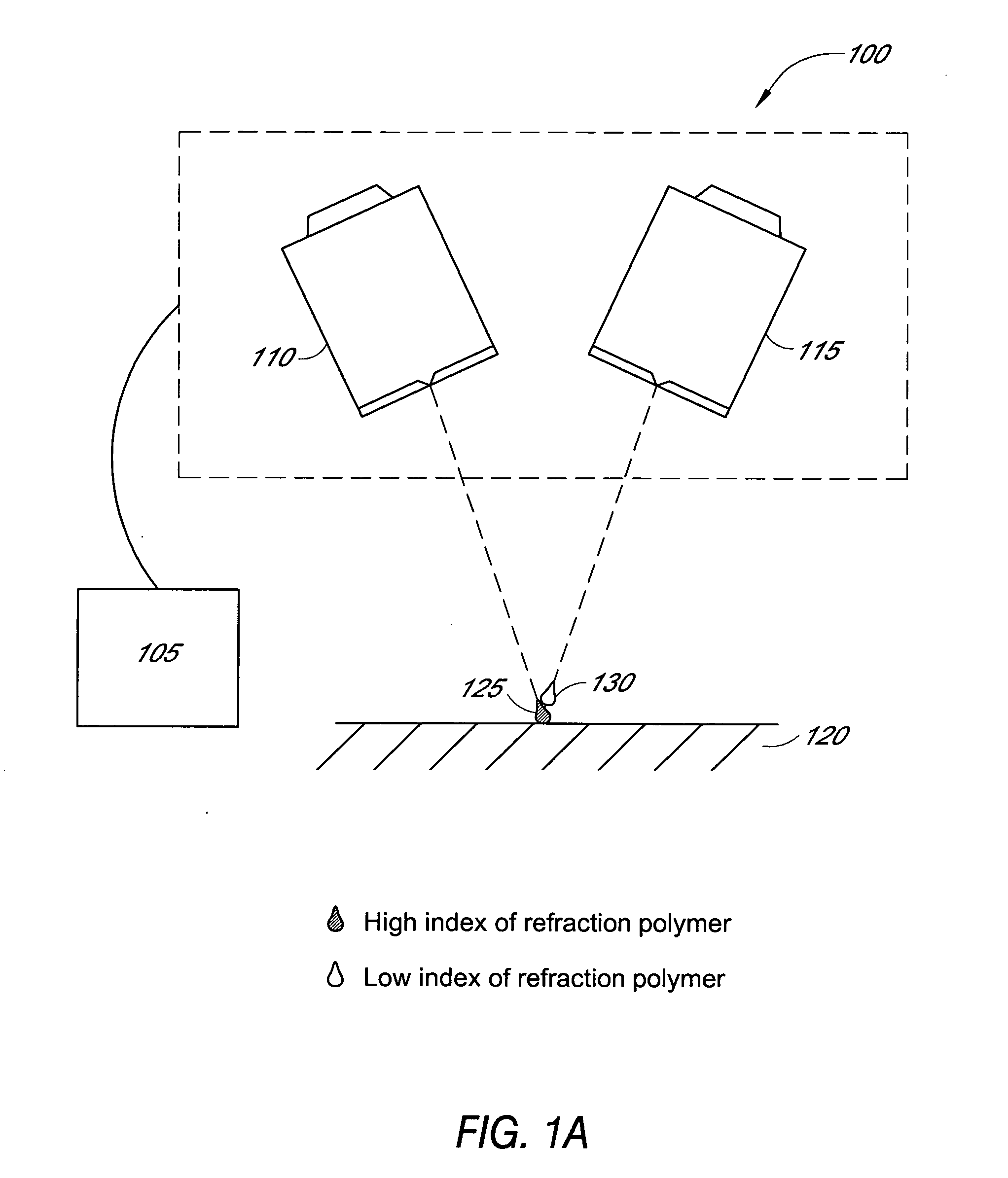
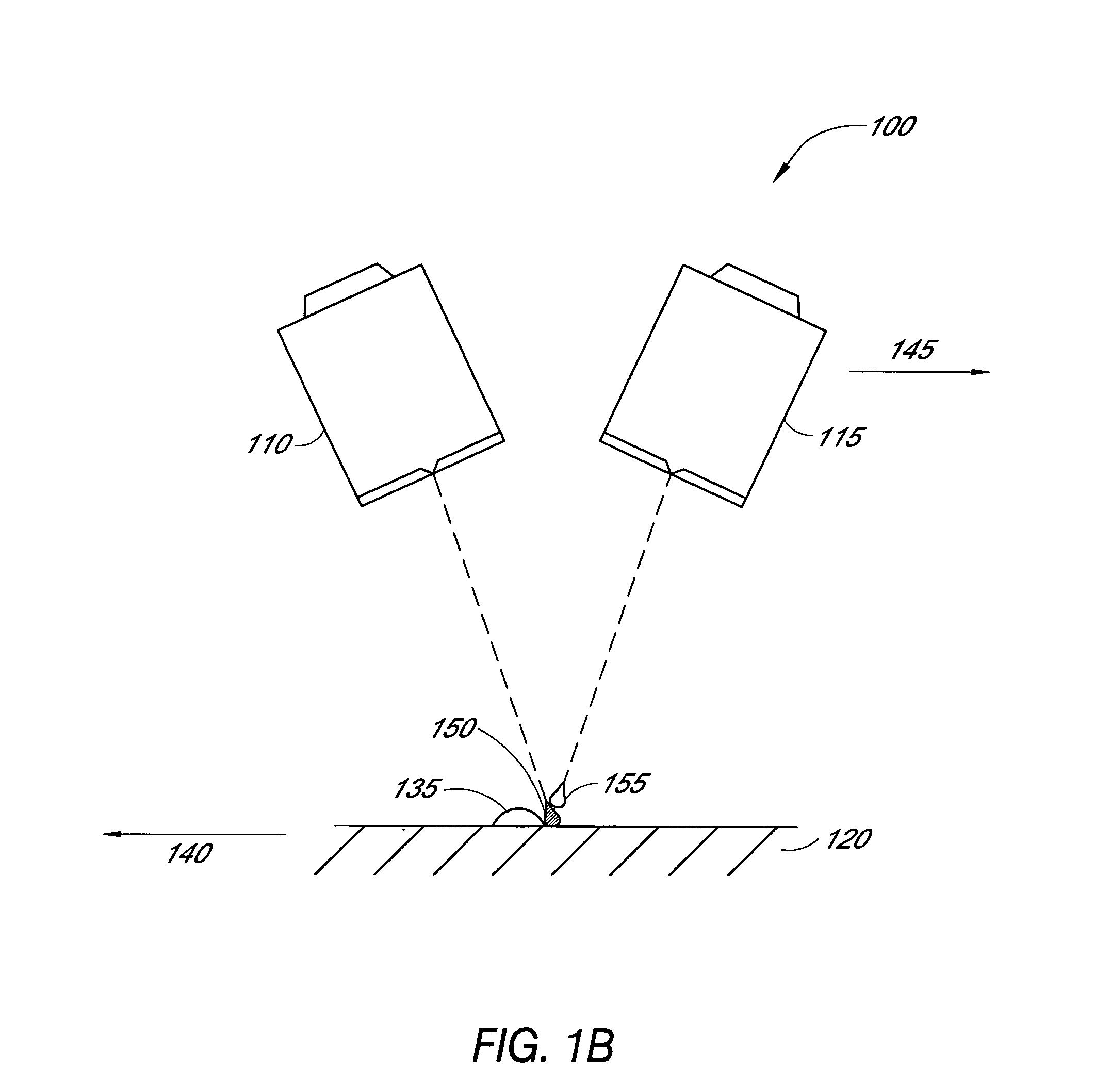
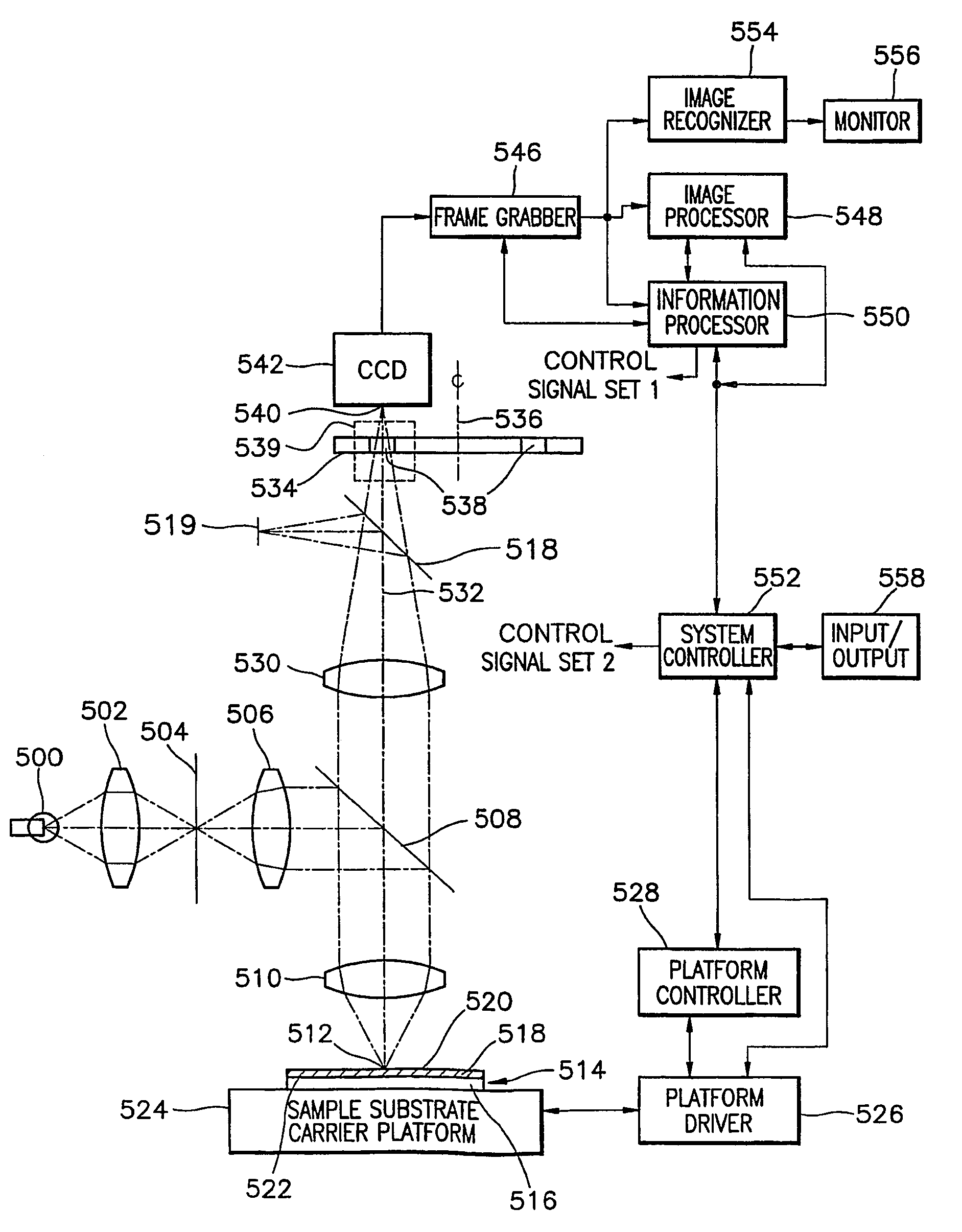
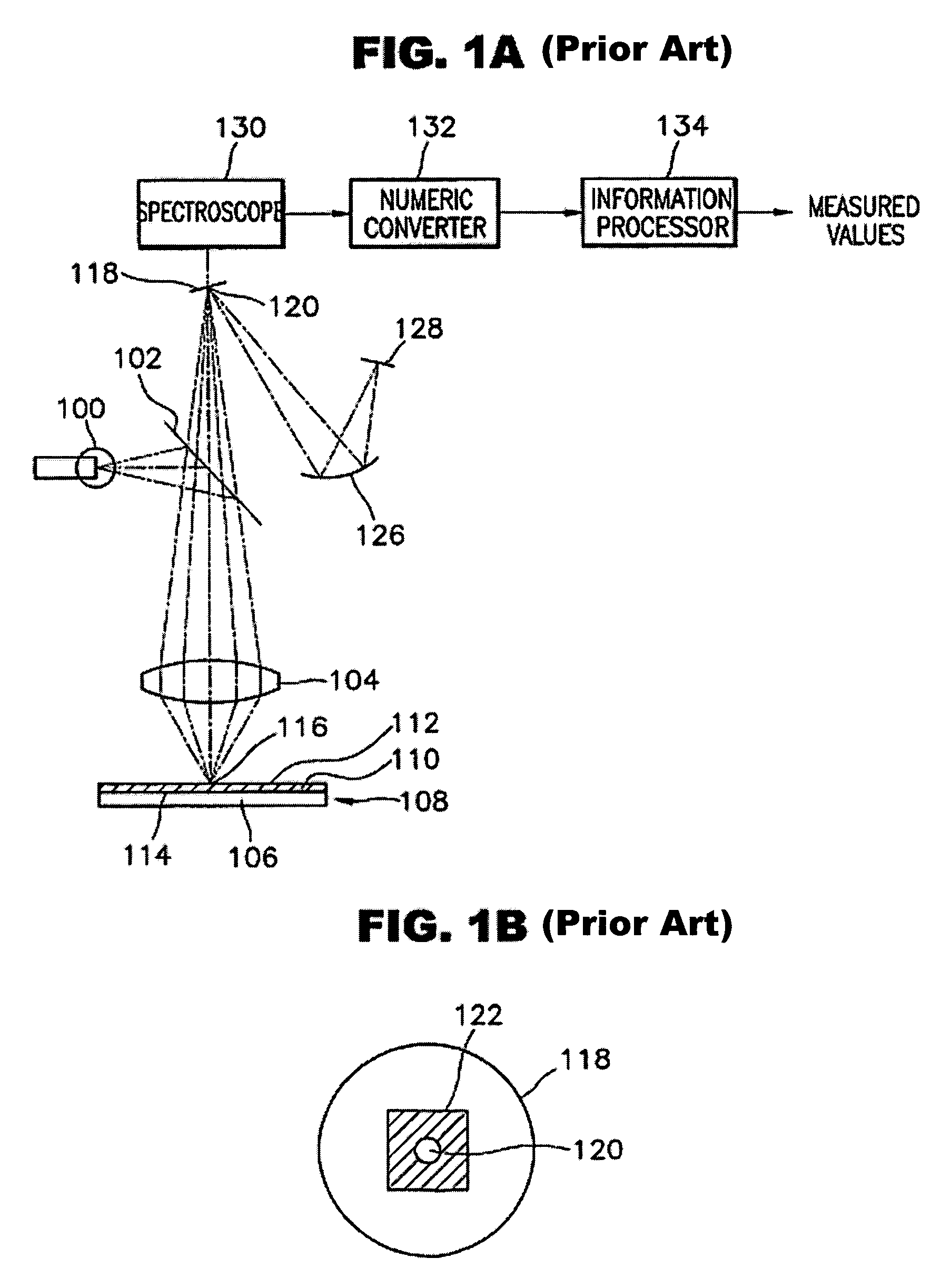
Patents
Literature
1552 results about "Refractive index profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
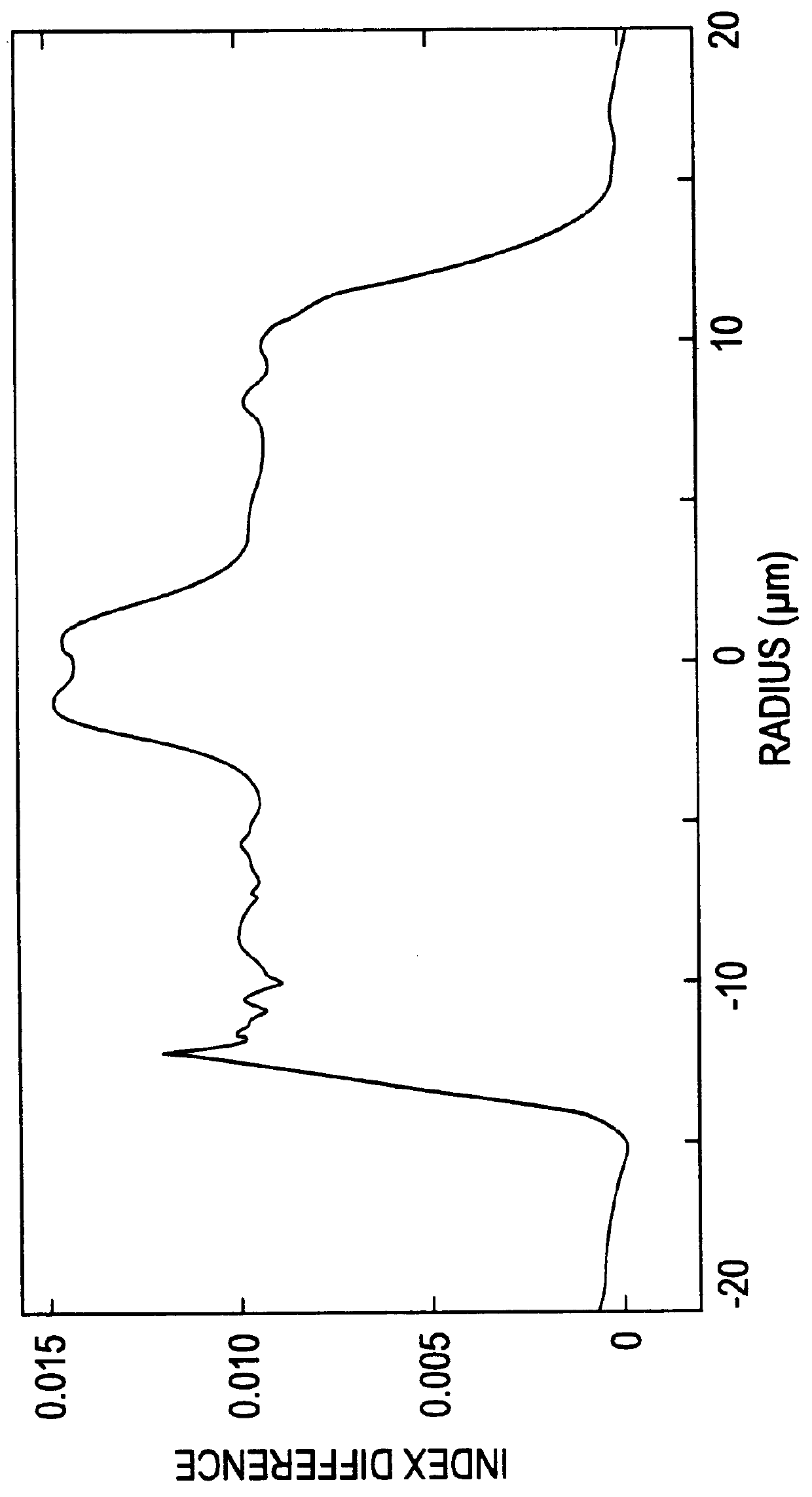
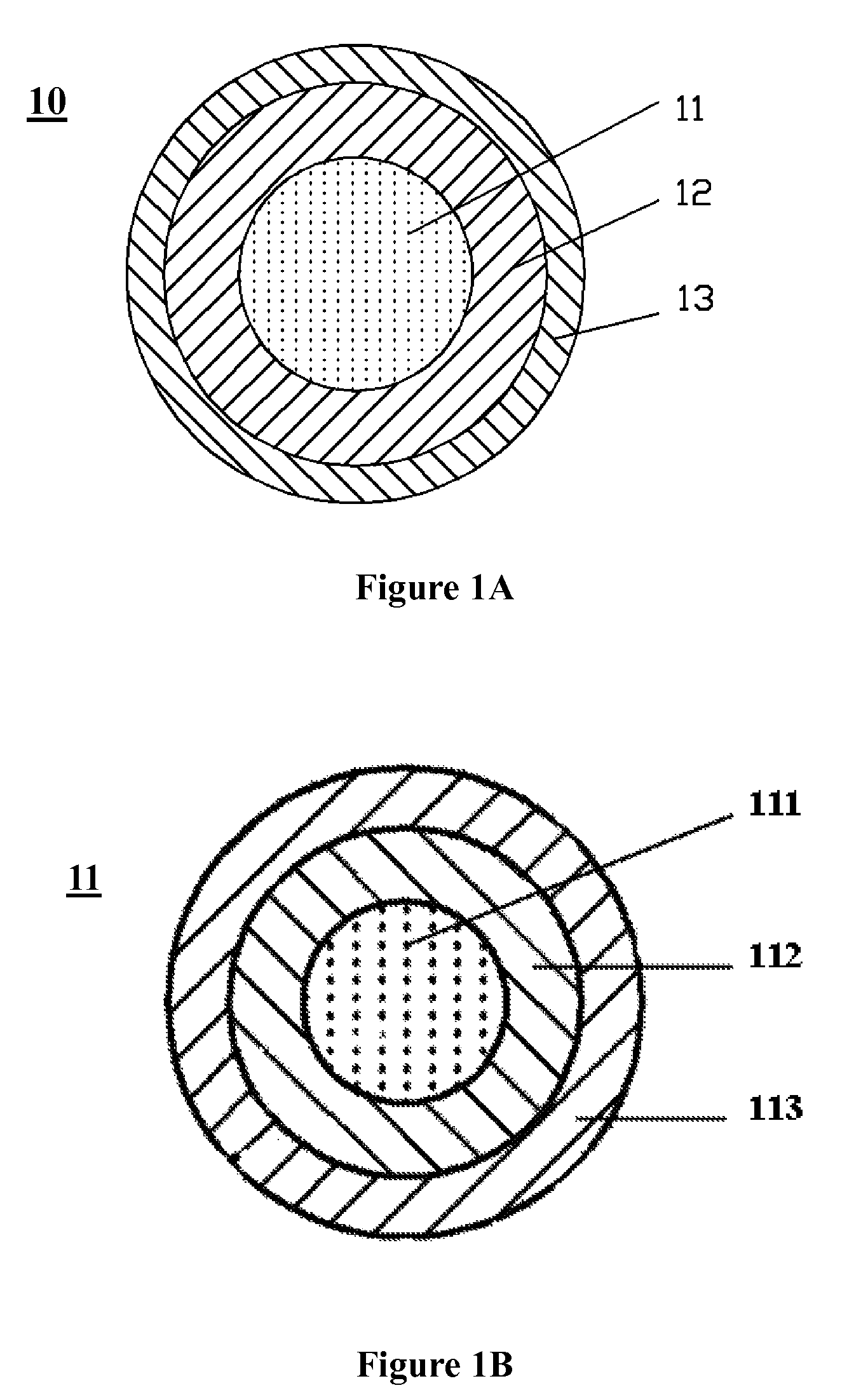
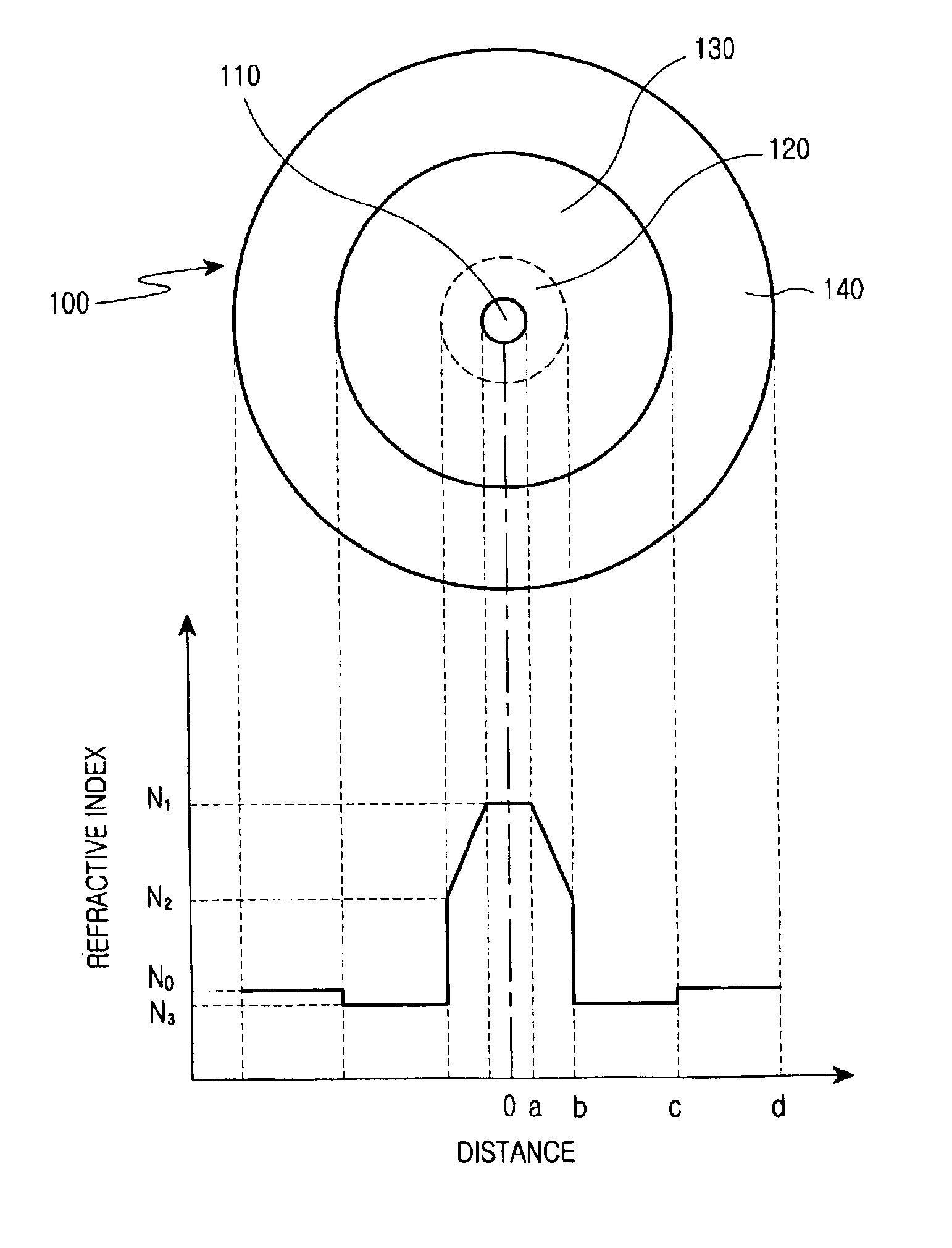
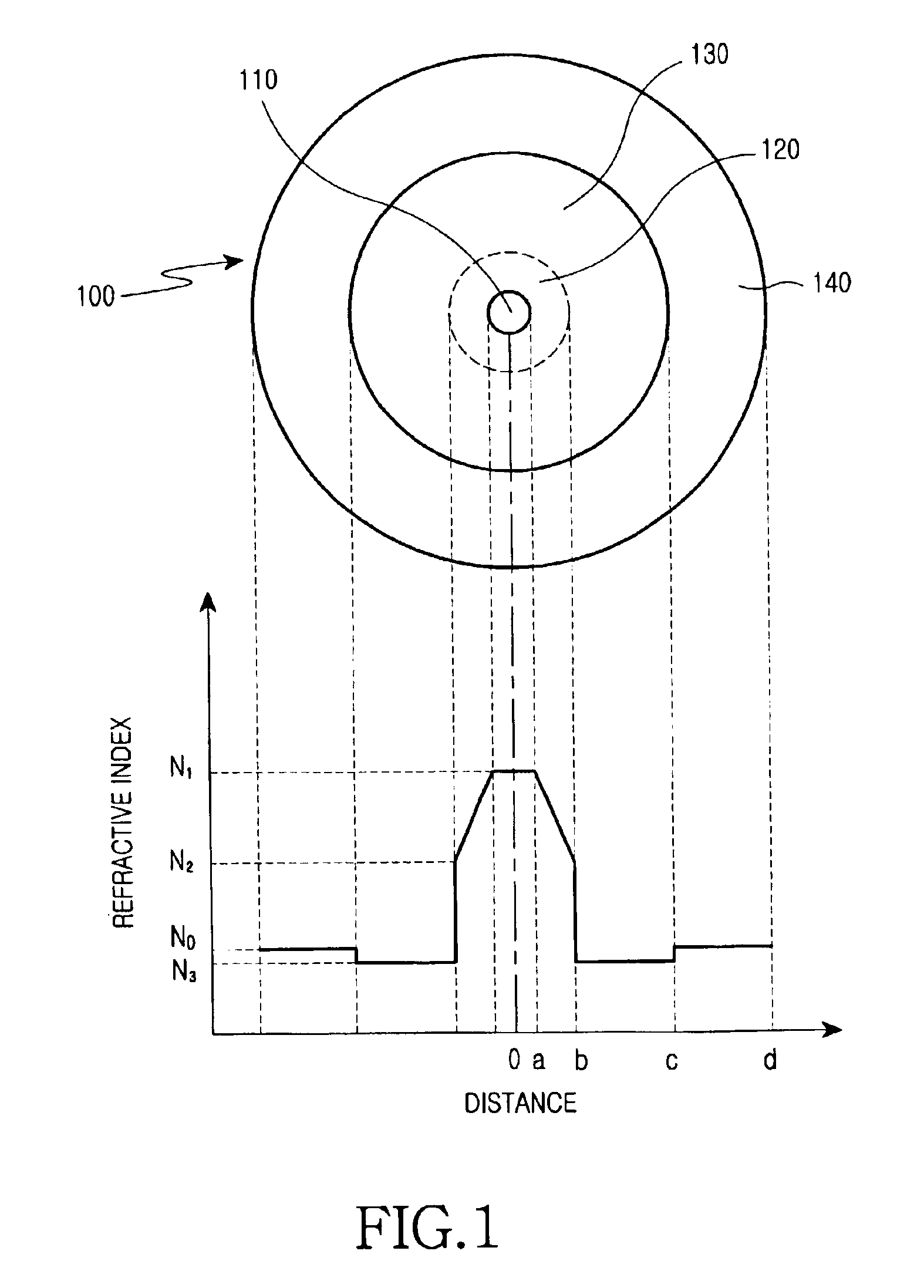
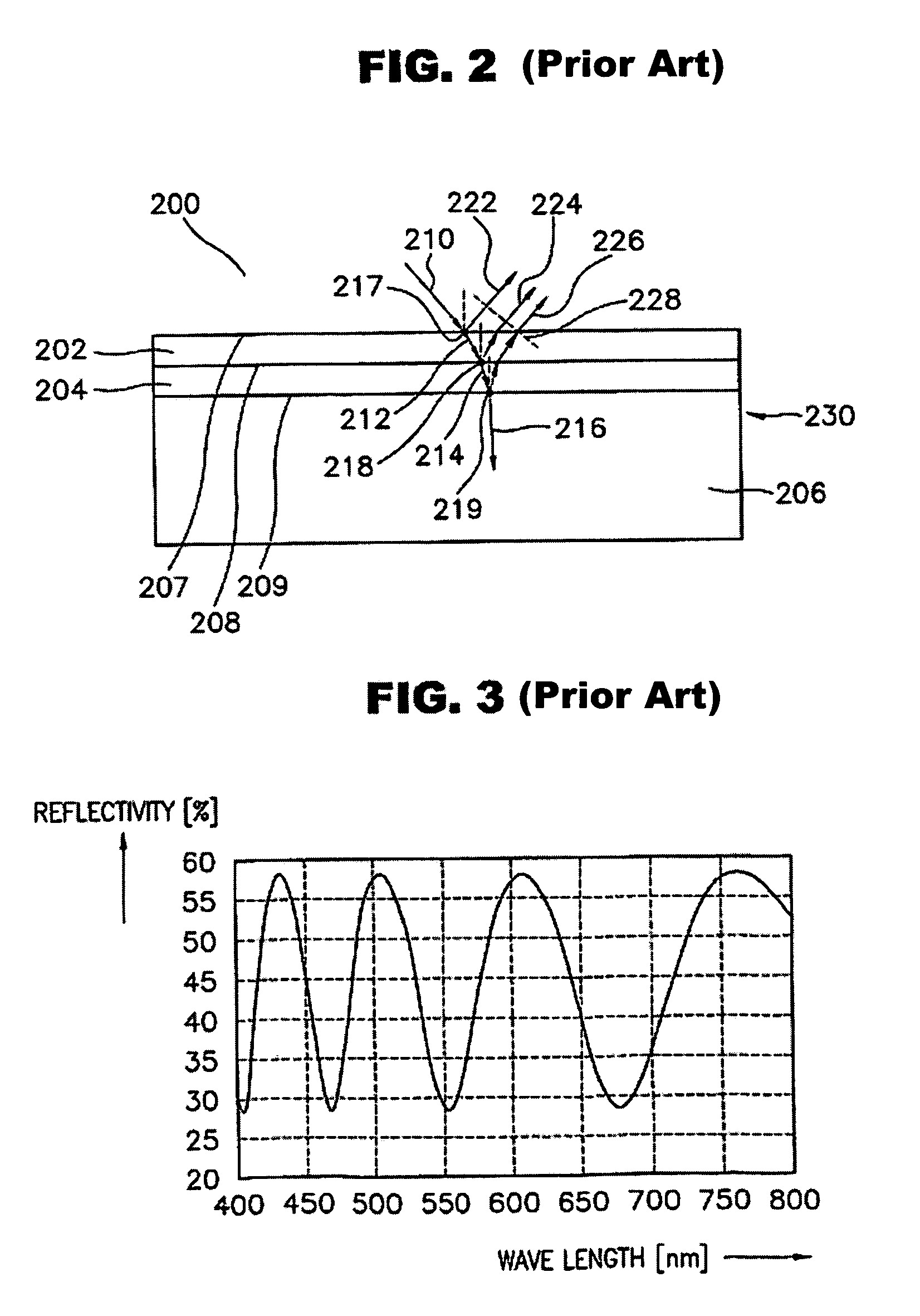
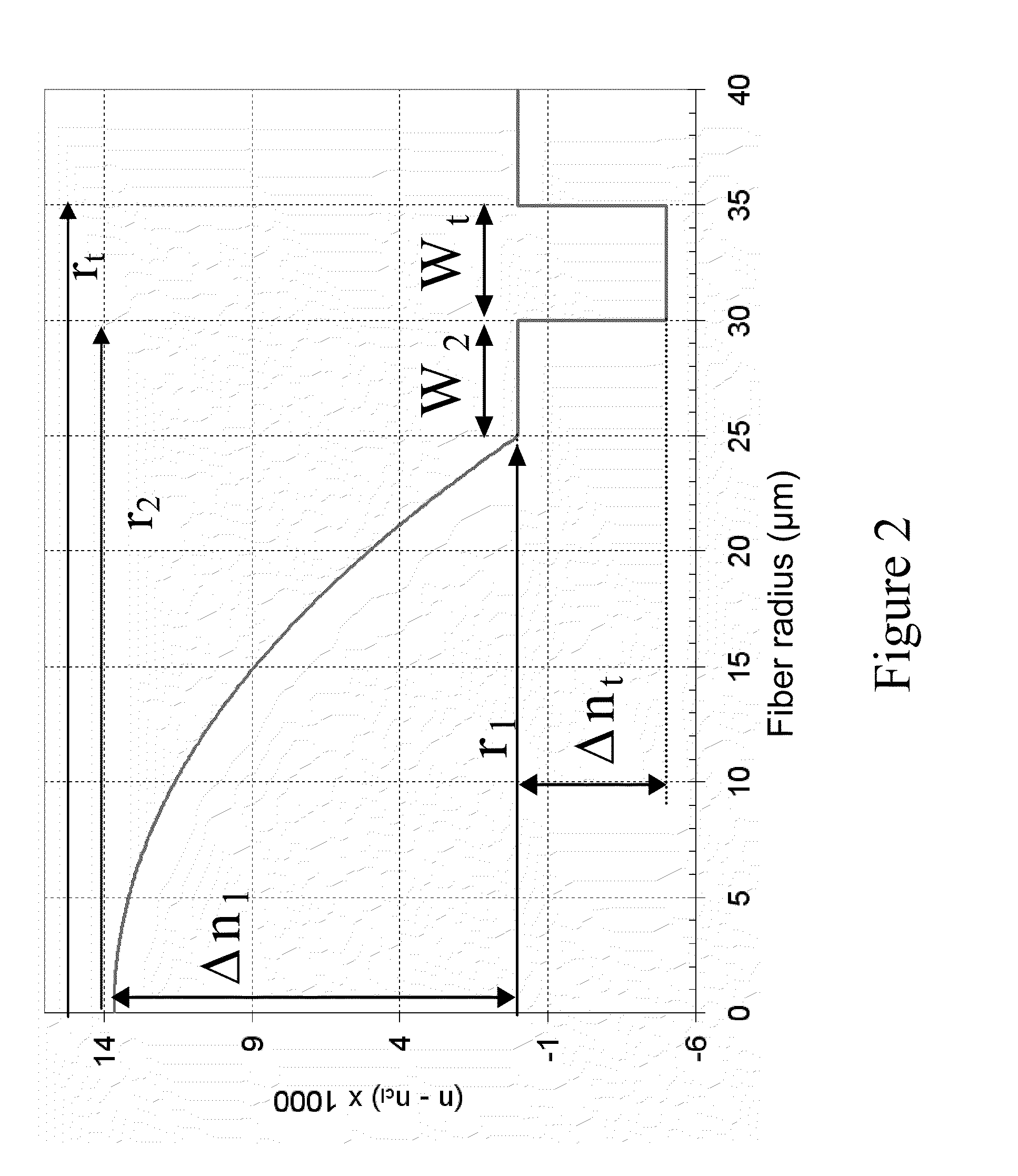
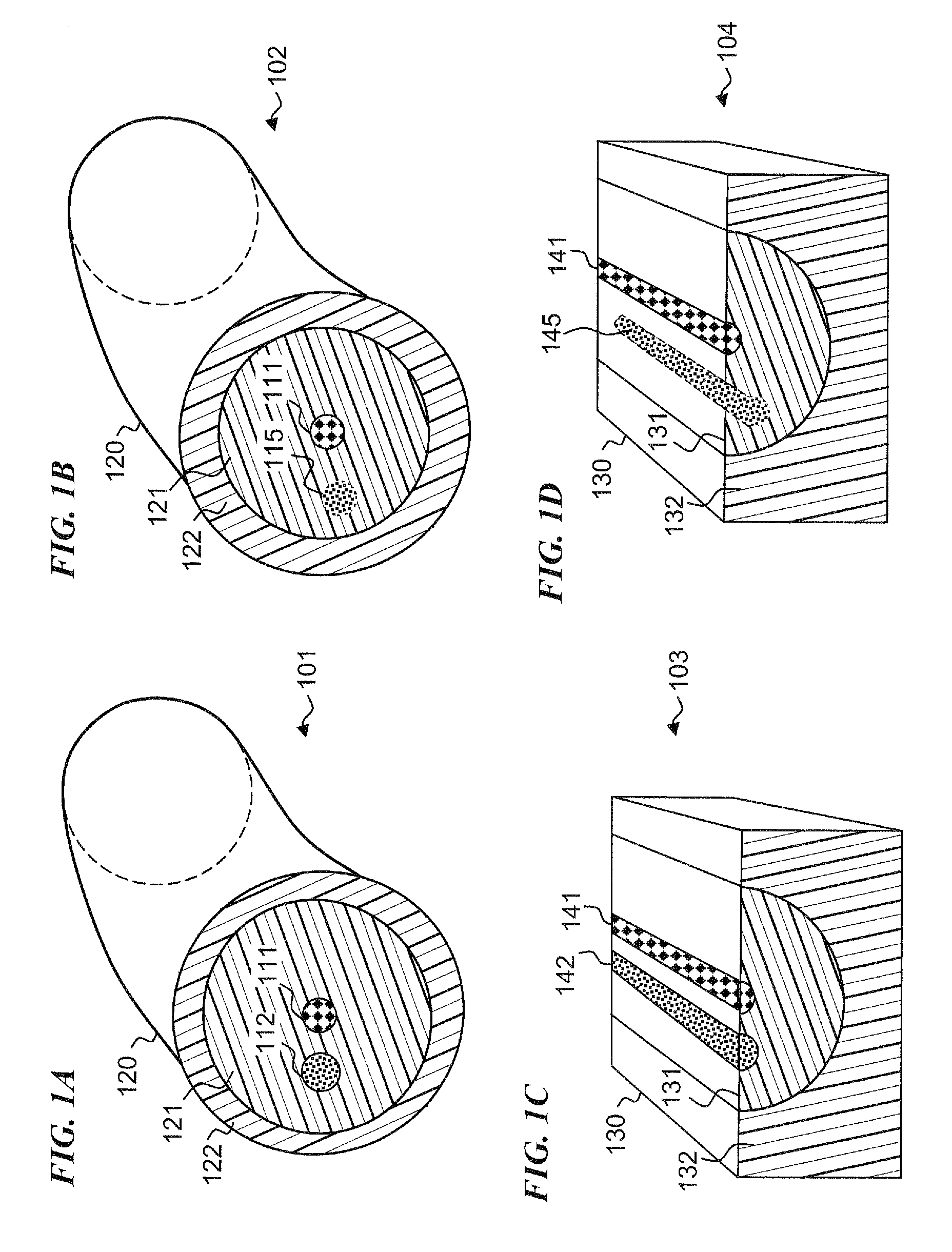
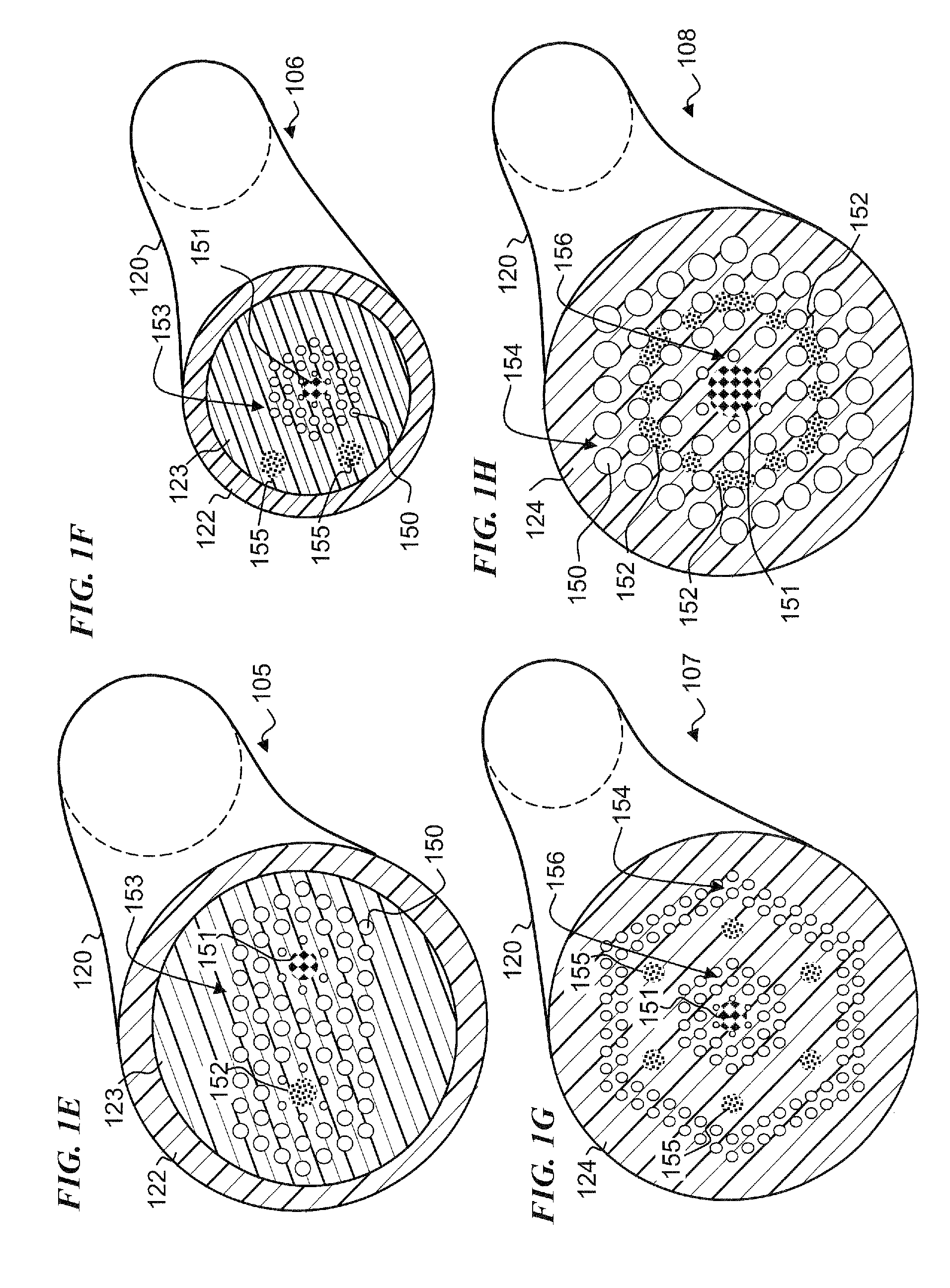
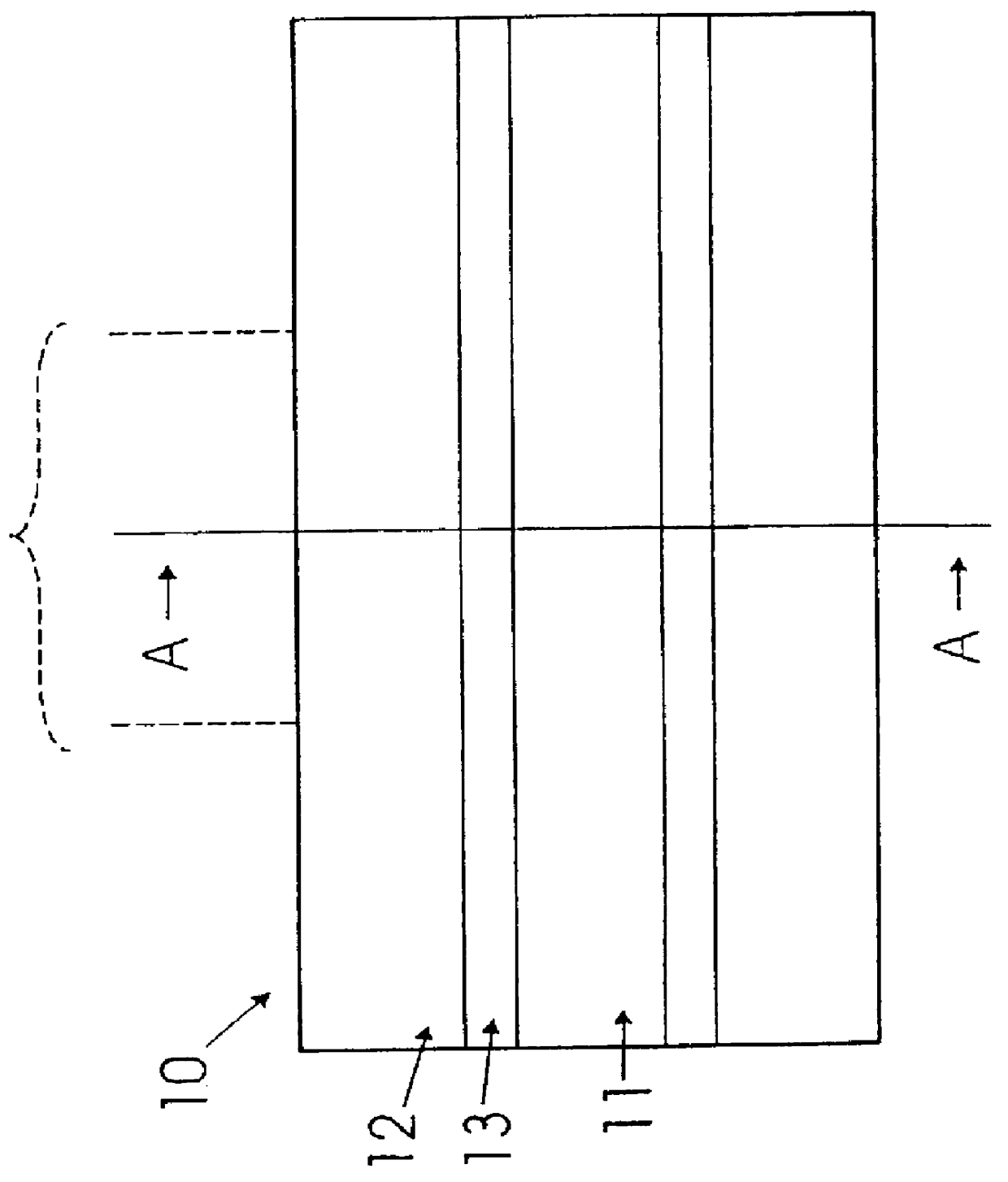
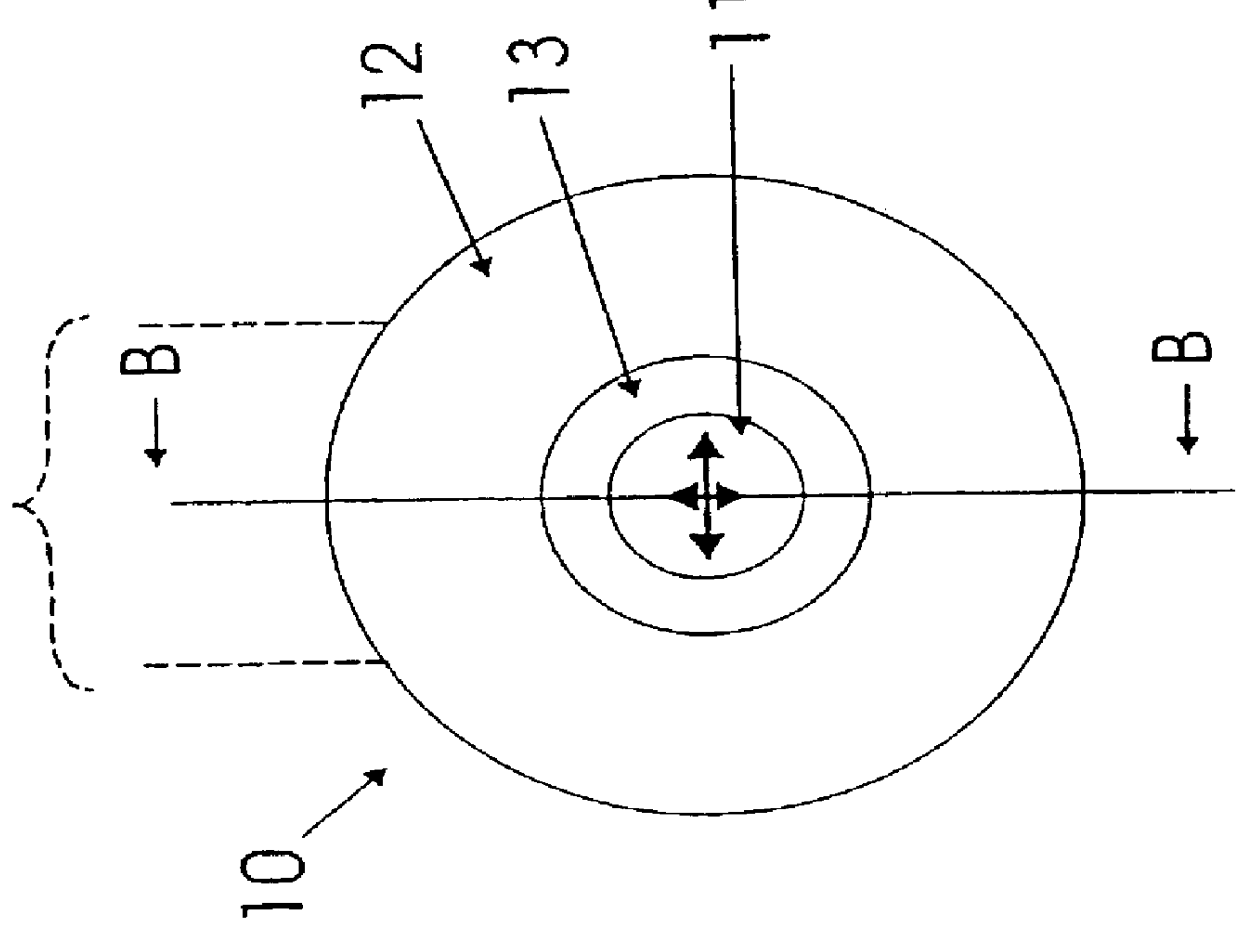
A refractive index profile is the distribution of refractive indices of materials within an optical fiber. Some optical fiber has a step-index profile, in which the core has one uniformly-distributed index and the cladding has a lower uniformly-distributed index. Other optical fiber has a graded-index profile, in which the refractive index varies gradually as a function of radial distance from the fiber center. Graded-index profiles include power-law index profiles and parabolic index profiles.
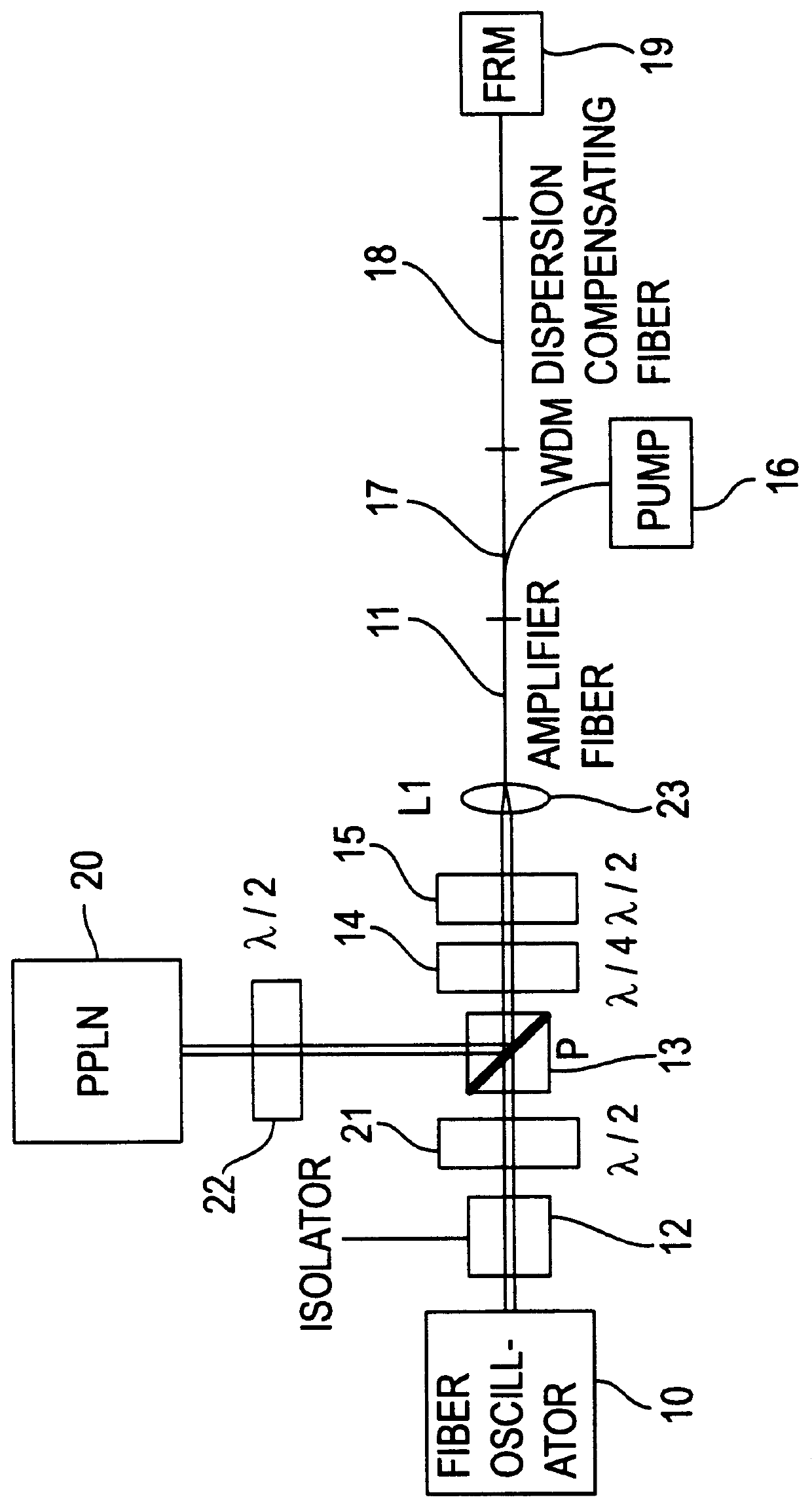
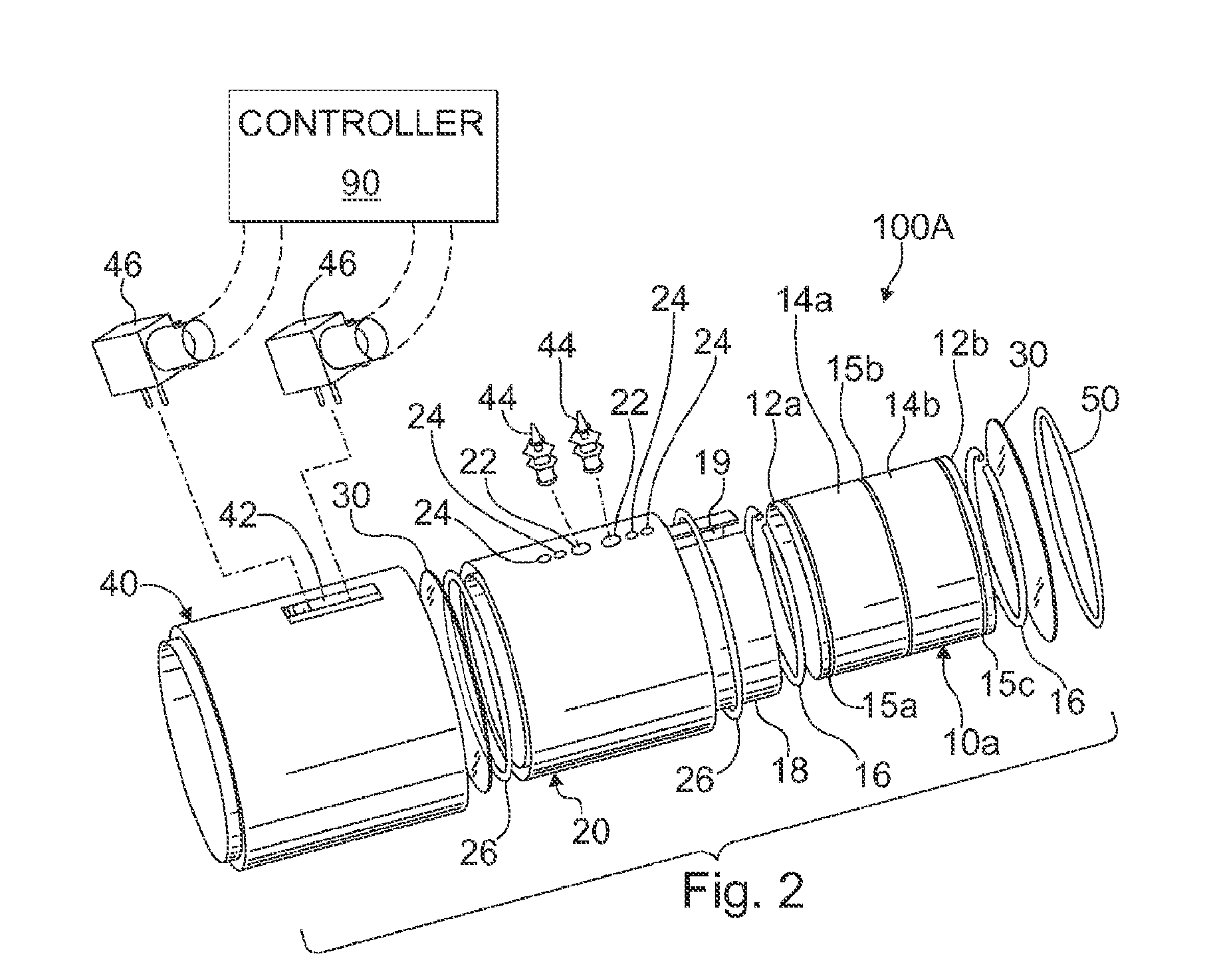
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Metamaterial gradient index lens
Examples of the present invention include a gradient index element formed from a material such as a metamaterial, the material having an index profile and an index gradient profile, where the index profile includes at least one discontinuity and the index gradient profile is substantially continuous.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Metamaterial gradient index lens
Examples of the present invention include a gradient index element formed from a material such as a metamaterial, the material having an index profile and an index gradient profile, where the index profile includes at least one discontinuity and the index gradient profile is substantially continuous.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Systems and methods for measuring the stress profile of ion-exchanged glass
ActiveUS9140543B1Force measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansOptical coefficientMaterials science
Systems and methods for measuring the stress profile of ion-exchanged glass are disclosed, based on the TM and TE guided mode spectra of the optical waveguide formed in the ion-exchanged glass. The method includes digitally defining from the TM and TE guided mode spectra positions of intensity extrema, and calculating respective TM and TE effective refractive indices from these positions. The method also includes calculating TM and TE refractive index profiles nTM(z) and nTE(z) using either an inverse WKB calculation or a fitting process that employs assumed functions for nTM(z) and nTE(z). The method also includes calculating the stress profile S(z)=[nTM(z)−nTE(z)] / SOC, where SOC is a stress optic coefficient for the glass substrate. Systems for performing the method are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Bend insensitive single mode fiber
ActiveUS8750664B2Manufacturing toleranceReduce manufacturing costGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fiberAccess network
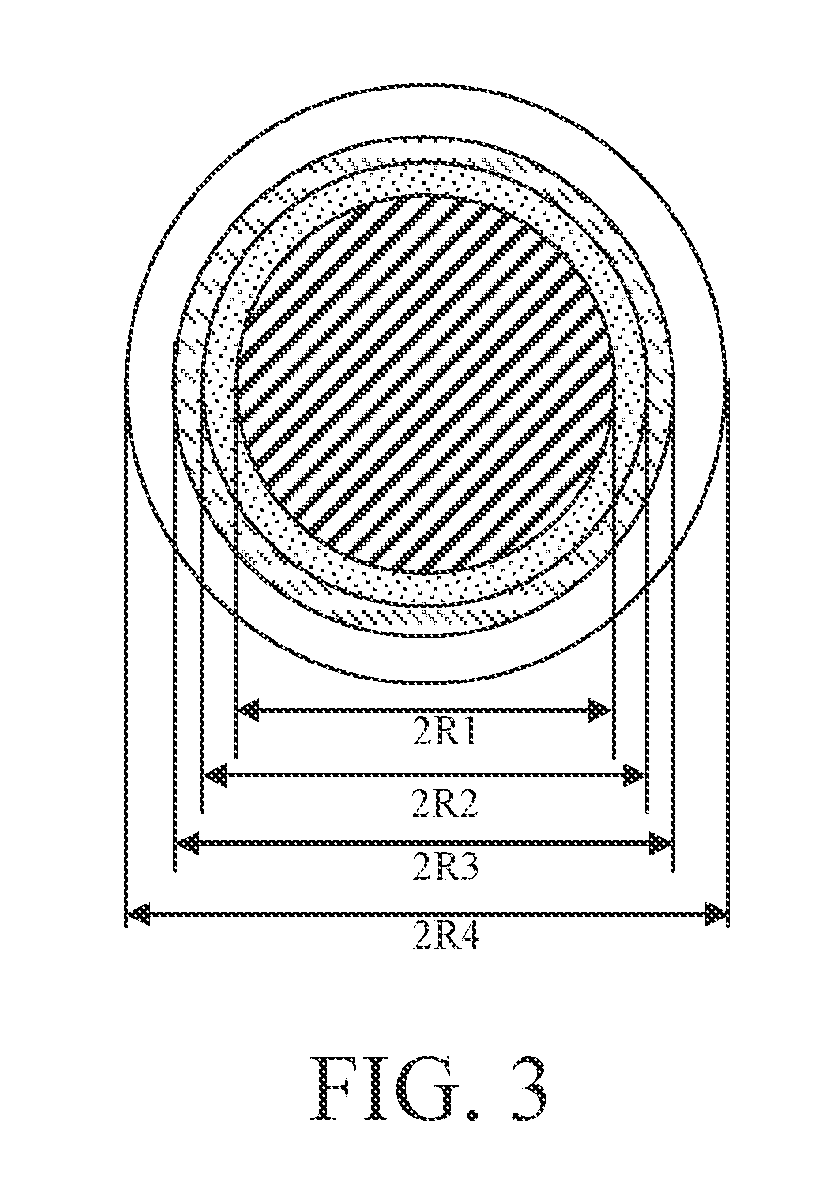
This invention discloses a bend insensitive single mode fiber, which is composed by a bare glass fiber with a round cross section and two resin protective layers with circular cross sections surrounding the outer of the bare glass fiber. It is characterized in that the bare glass fiber is composed by a core layer with a round cross section and two claddings with circular cross sections. The refractive index of the core layer is higher than the index of the two claddings and the refractive index difference between the core layer and the first cladding is larger than the difference between the first and second claddings. The second cladding is made of pure SiO2. The refractive index profile of the core layer follows a power function, and the refractive index profile of the two claddings follow a ladder-type distribution. The loss of the invented fiber is insensitive to the bending of the fiber, which meets the requirements of ITU.T G.657.A and G.657.B standards, respectively. It is applicable to the Fiber To The Home (FTTH) and other local area network and the access network systems.
Owner:FUTONG GROUP CO LTD
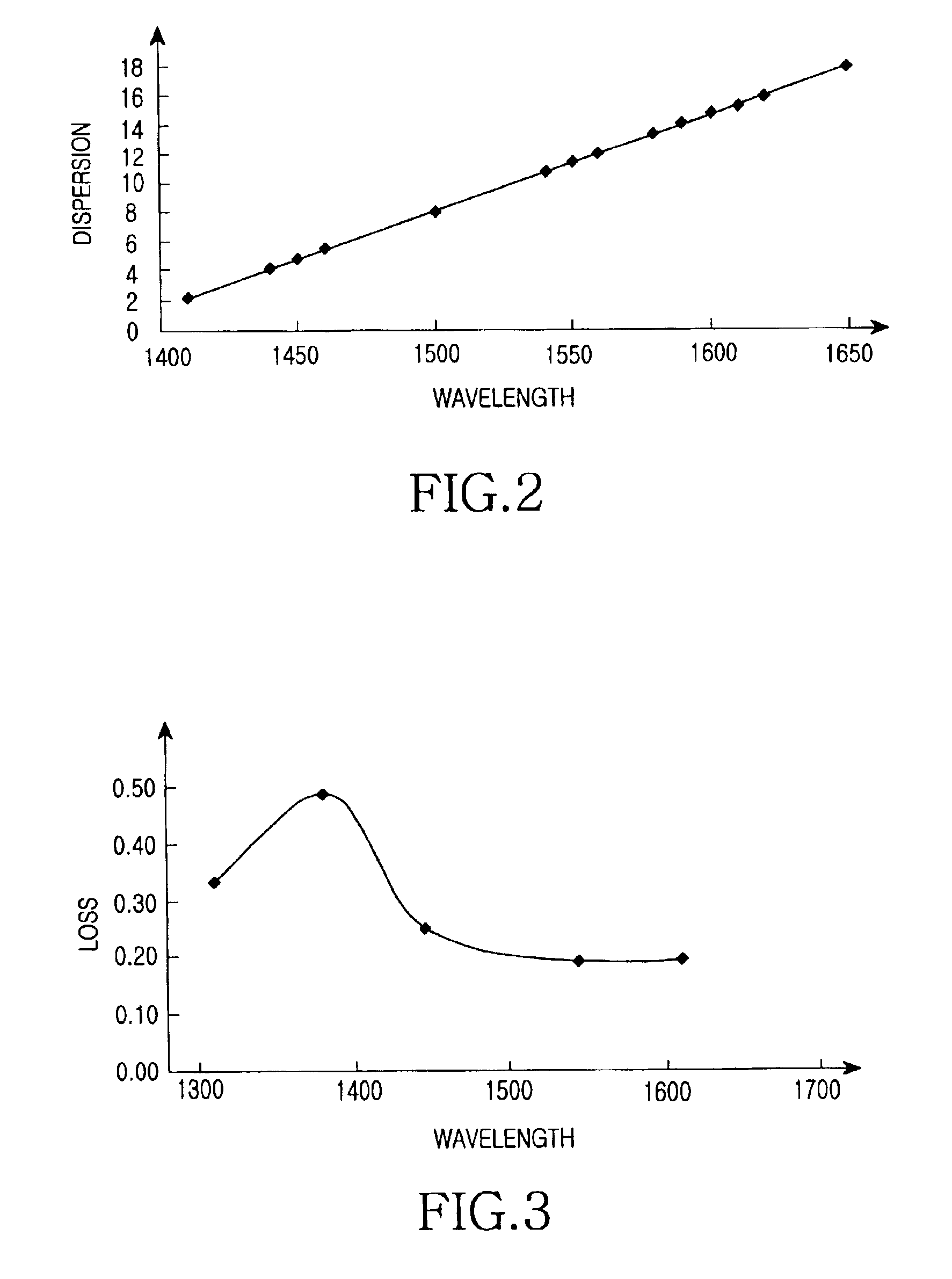
Dispersion-controlled optical fiber
ActiveUS6999667B2Low loss characteristicIncrease the areaOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive index profile
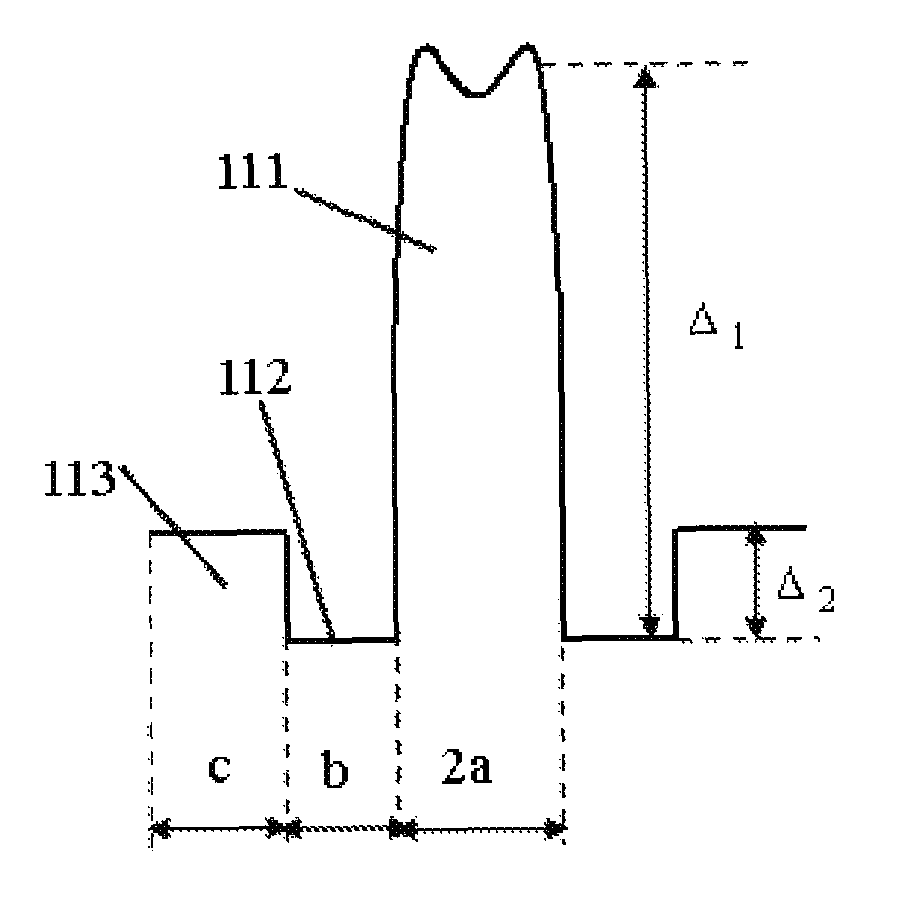
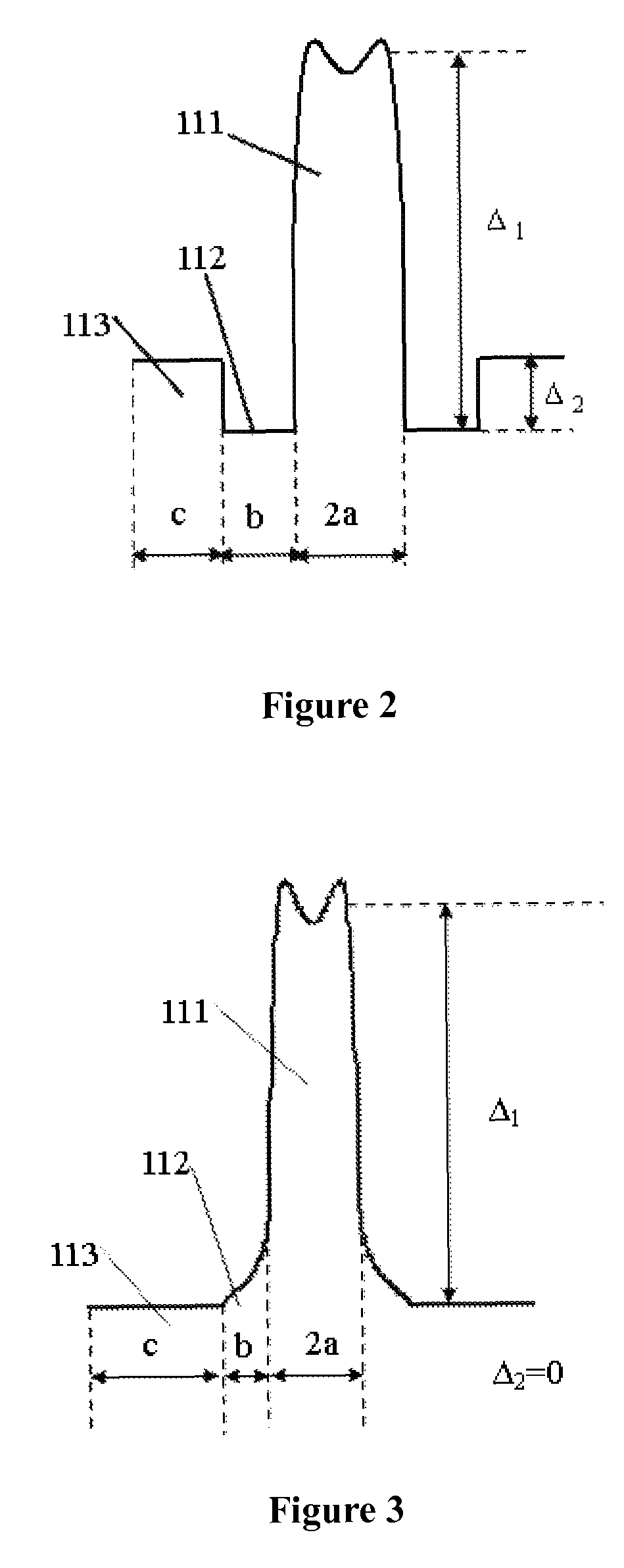
Disclosed is an optical fiber comprising a center core which forms a passageway for transmitting optical signals and has a refractive index N1, and a cladding which encloses the center core and has a refractive index N0. The optical fiber further comprises an upper core, which has a distribution of refractive indices increased starting from a refractive index N2 (>N0) at its outer circumference to the refractive index N1 at its internal circumference, and a minutely depressed refractive index region, which is interposed between said upper core and cladding and has a refractive index N3. The refractive index N3 is lower than the refractive index N0.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
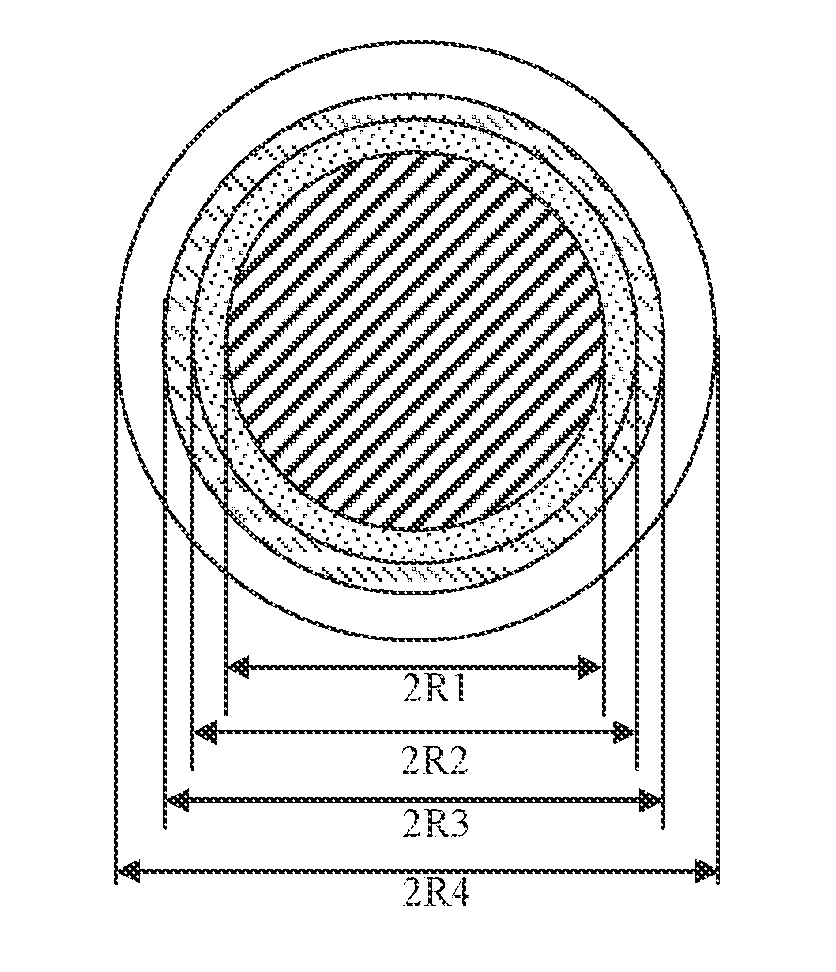
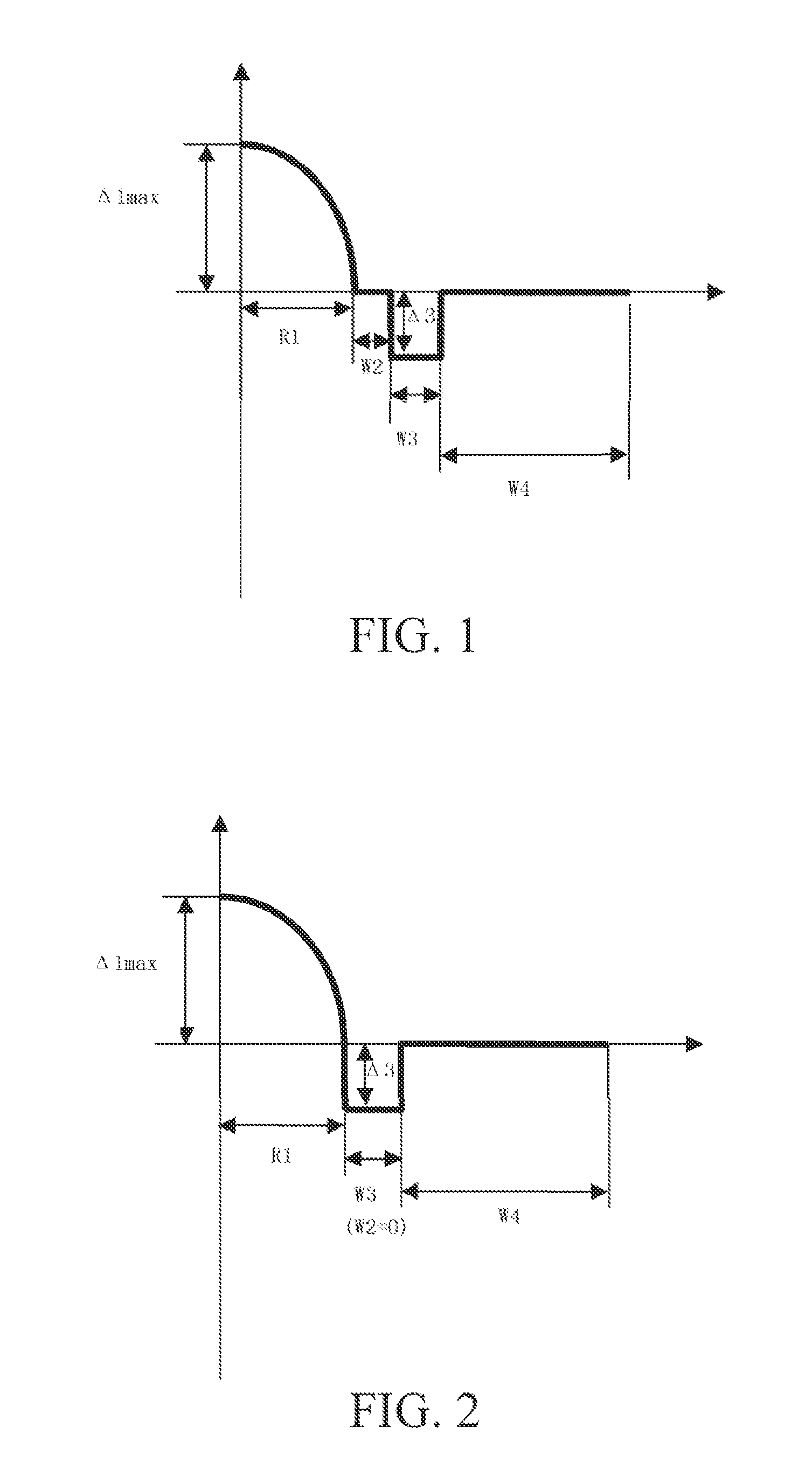
Bending-resistant large core diameter high numerical aperture multimode fiber
ActiveUS20130279868A1Convenient lightingReduce configuration costsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideHigh numerical apertureRelative refractive index
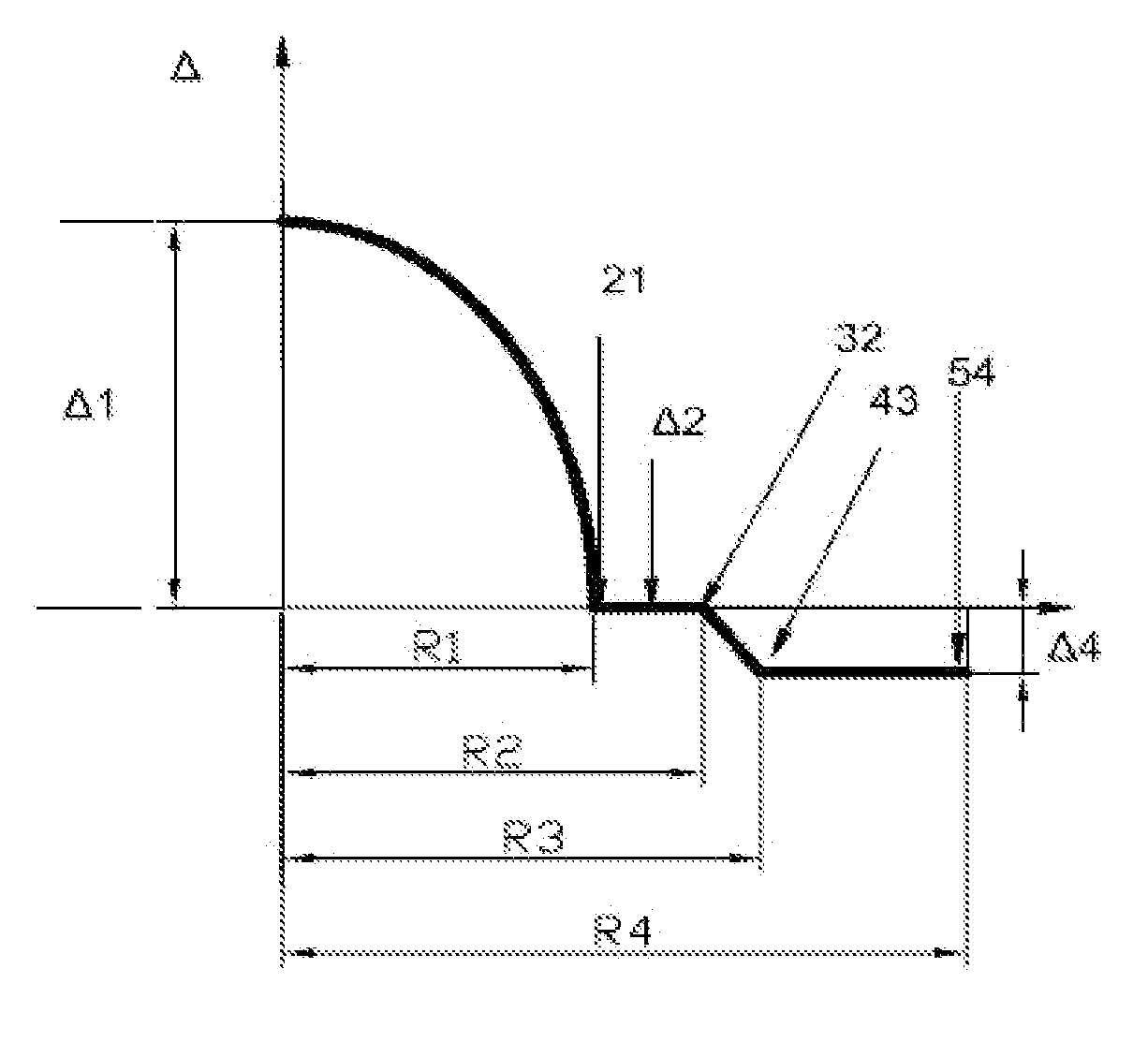
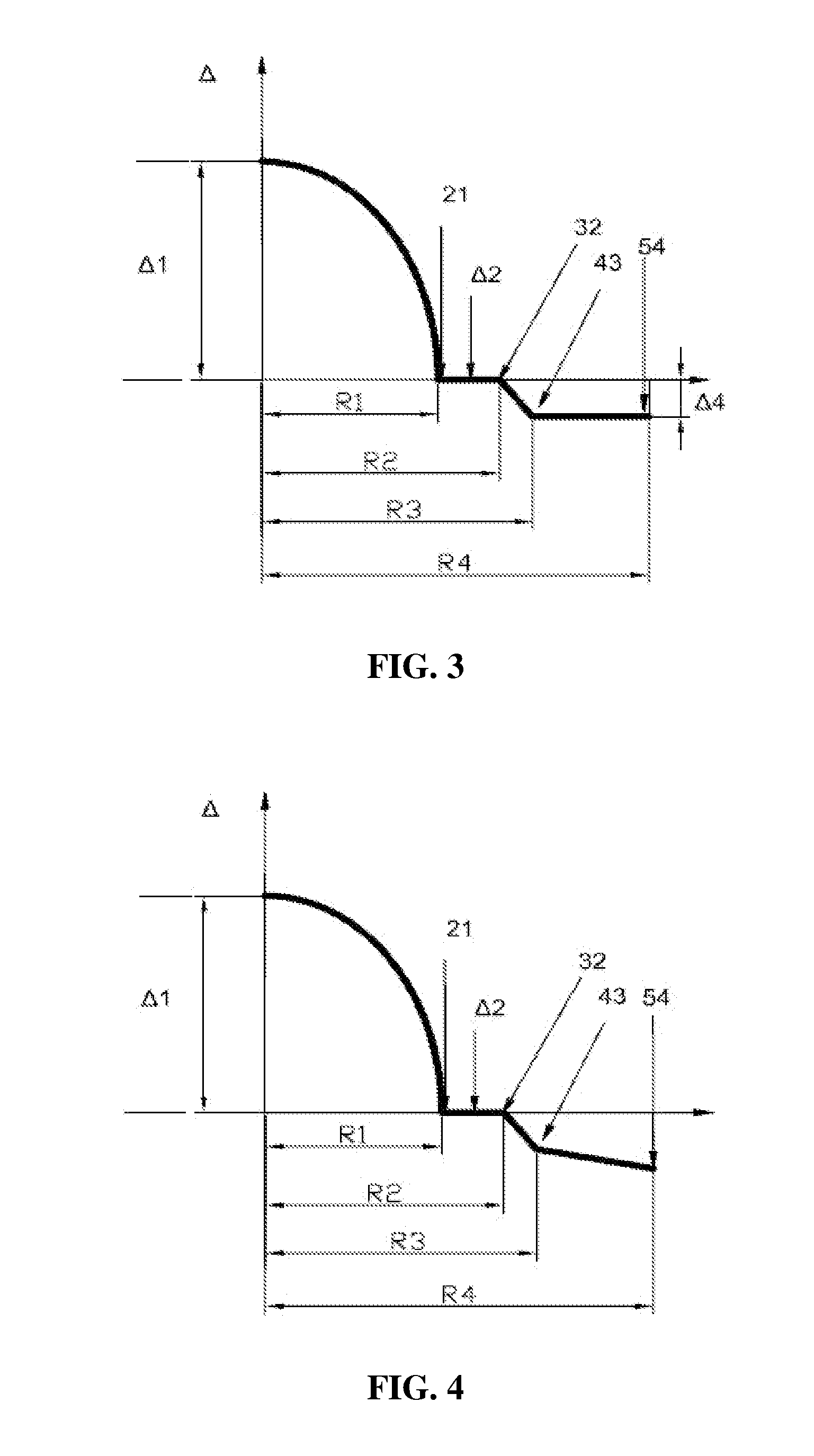
A bending-resistant large core diameter high numerical aperture multimode fiber includes a core and a cladding surrounding the core. The core has a radius R1 in a range of 28 to 50 microns, a refractive index profile of a parabola shape with α being in a range of 1.9 to 2.2, and a maximum relative refractive index difference Δ1% max being in a range of 1.9% to 2.5%. The cladding includes an inner cladding and / or a trench cladding, and an outer cladding disposed from the inner to the outer in sequence. The radius R2 of the inner cladding is in a range of 28 to 55 microns, and the relative refractive index difference Δ2% is −0.1% to 0.1%. The radius R3 of the trench cladding is in a range of 28 to 60 microns, and the relative refractive index difference Δ3% is in a range of −0.15% to −0.8%.
Owner:EVERPRO TECH COMPANY
Polarization-maintaining optical fiber, method of manufacturing polarization-maintaining optical-fiber connecting portion, and polarization-maintaining optical-fiber connecting portion
InactiveUS7809223B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with polarisationShortest distancePolarization-maintaining optical fiber
A polarization-maintaining optical fiber includes a core region and a cladding region formed around the core region. The cladding region has a refractive index lower than a refractive index of the core region. A refractive index profile of the core region is either one of a step shaped or a concave shaped. The cladding region includes two holes formed in such a manner that a shortest distance from the core region is virtually zero at locations in opposite to each other across the core region.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Multi-core fiber
ActiveUS7418178B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingBundled fibre light guideQuartzNumerical aperture
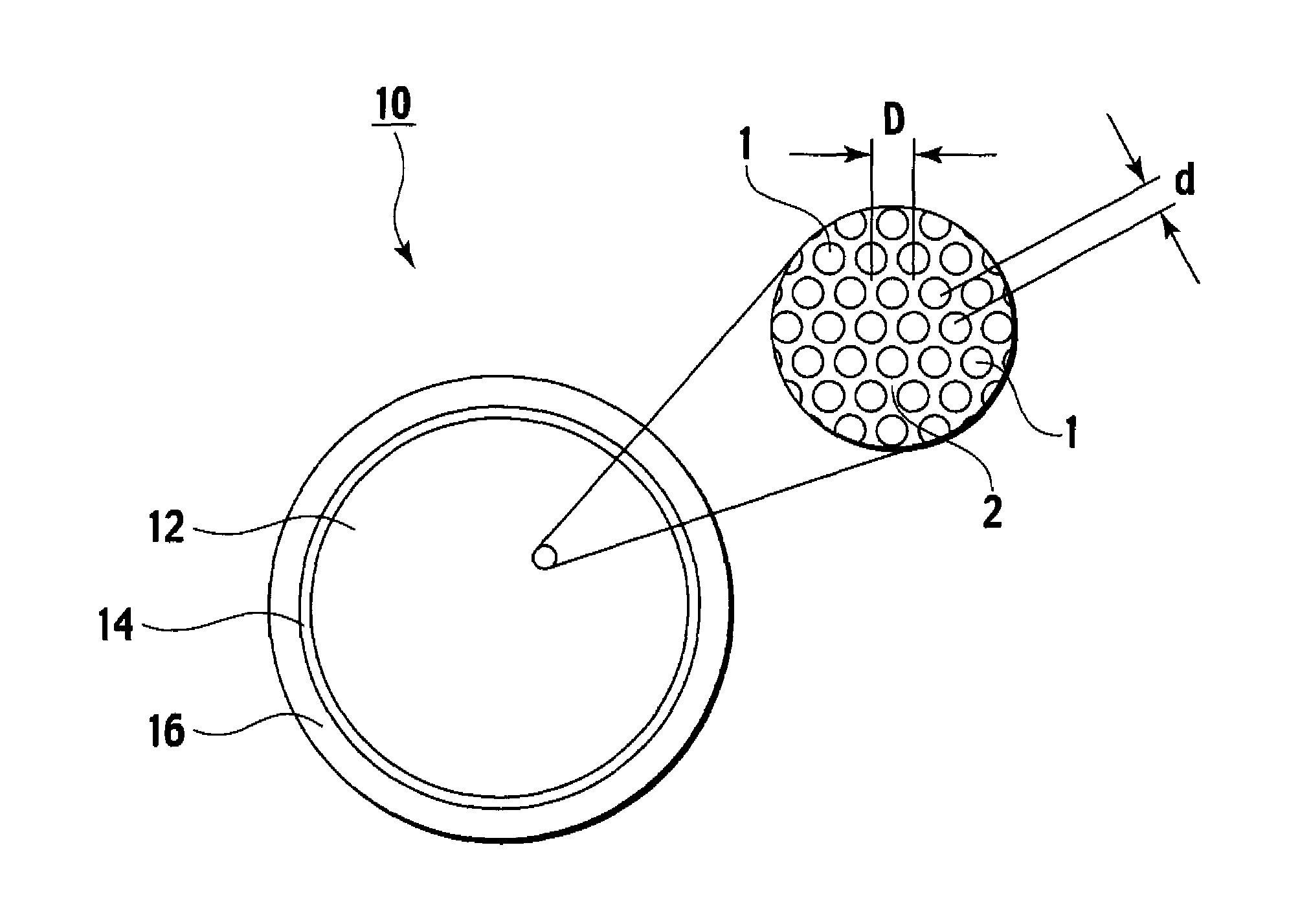
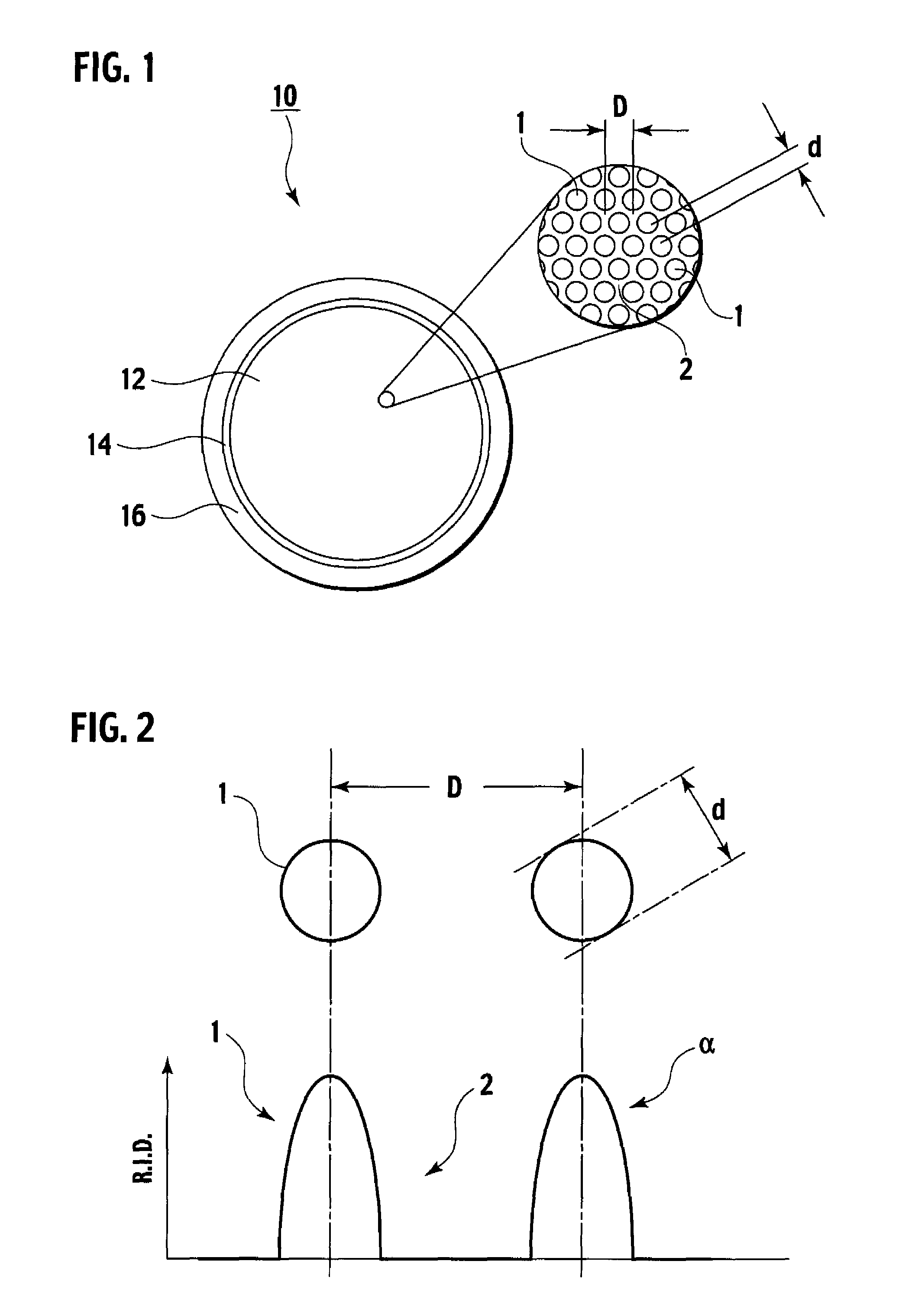
A multi-core optical fiber apparatus is disclosed. The multi-core optical fiber apparatus includes a cladding comprising quartz and a plurality of cores embedded in the cladding. Each of the cores has a diameter (D) ranging from 1.3 μm to 2.0 μm, a numerical aperture (NA) from 0.35 to 0.45 and a refractive index profile factor (α) from 2.0 to 4.0. A center of each of the cores has a germanium content of 20 wt % to 30 wt %. An interval between adjacent cores is 3.0 μm or more.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Broad band cylindrical lens antenna based on artificial electromagnetic materials
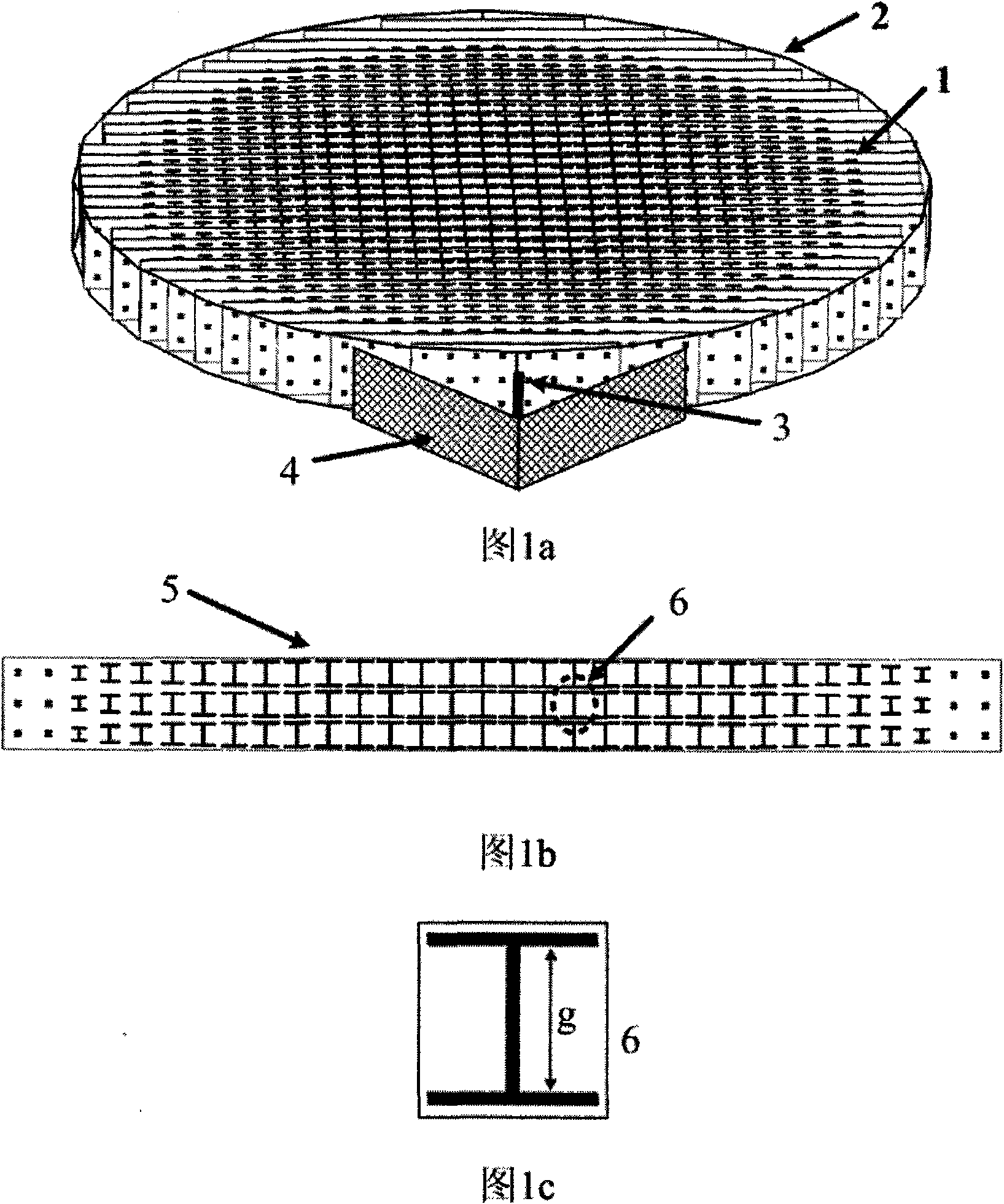
Broad band cylindrical lens antenna based on novel artificial electromagnetic materials is formed by arranging a series of novel artificial electromagnetic materials in definite regulation, composing equivalent artificial medium with gradient refractive index. The novel lens antenna includes a cylindrical lens 2 based on novel artificial electromagnetic material 1, feed source 3 used as excitation, reflector 4 for repressing backward radiation. Specific structure 5 of one printed circuit board in the novel artificial electromagnetic material 1 is a series of 'I' shaped units 6 printed on medium substrate arranged according to specific regulation. Regulating size of the 'I' shaped structure to obtain the lens needed refractive index distribution. Selecting suitable and ideal reflector 4 and disposing it back of the feed source 3 for reducing backward radiation generated by the feed source, so as to improve gain and directivity of the antenna. The invention is provided with advantages of high gain, broadband, high directivity, easy manufacture, low cost, light weight and convenient integration.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Transverse closed-loop resonator
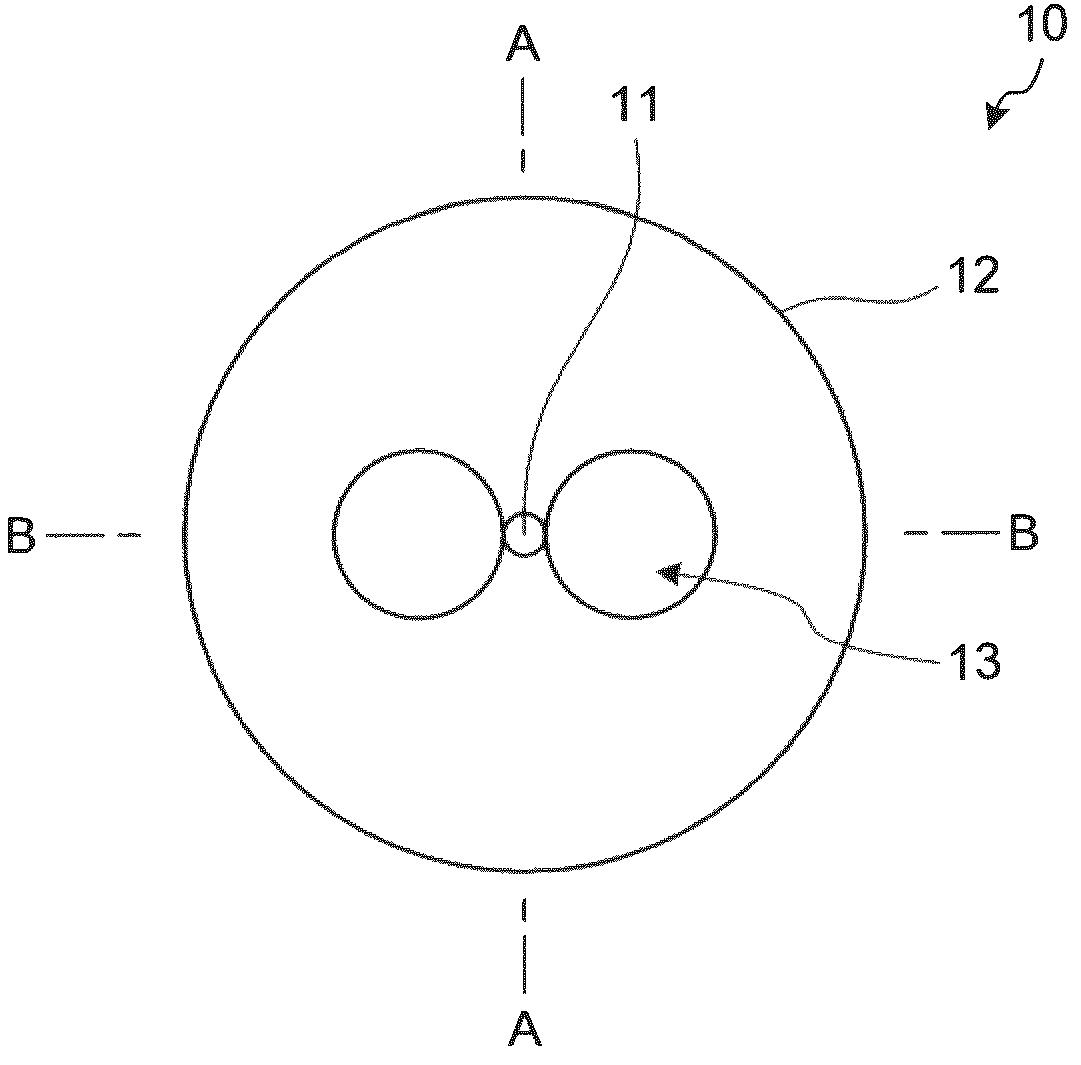
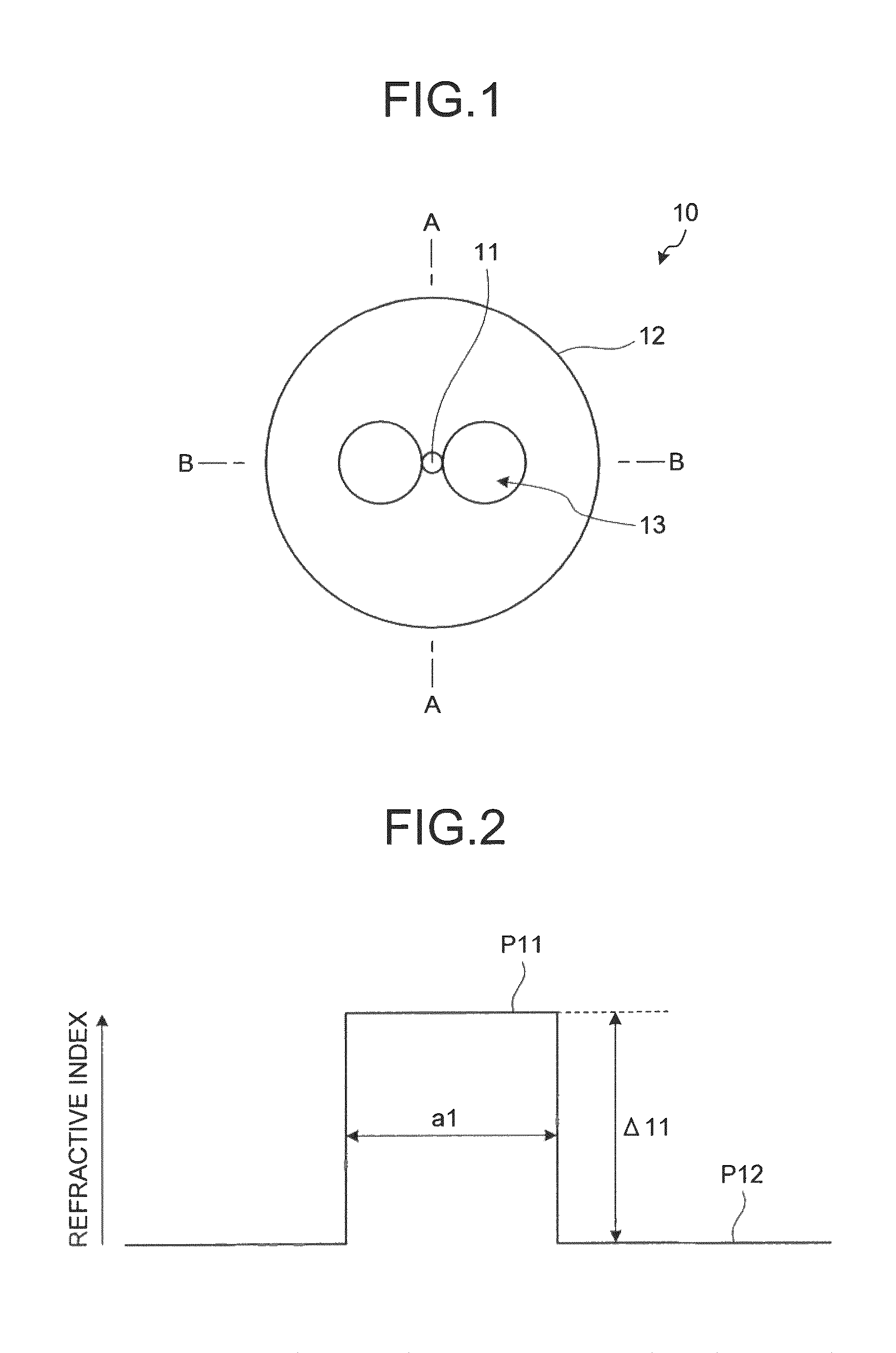
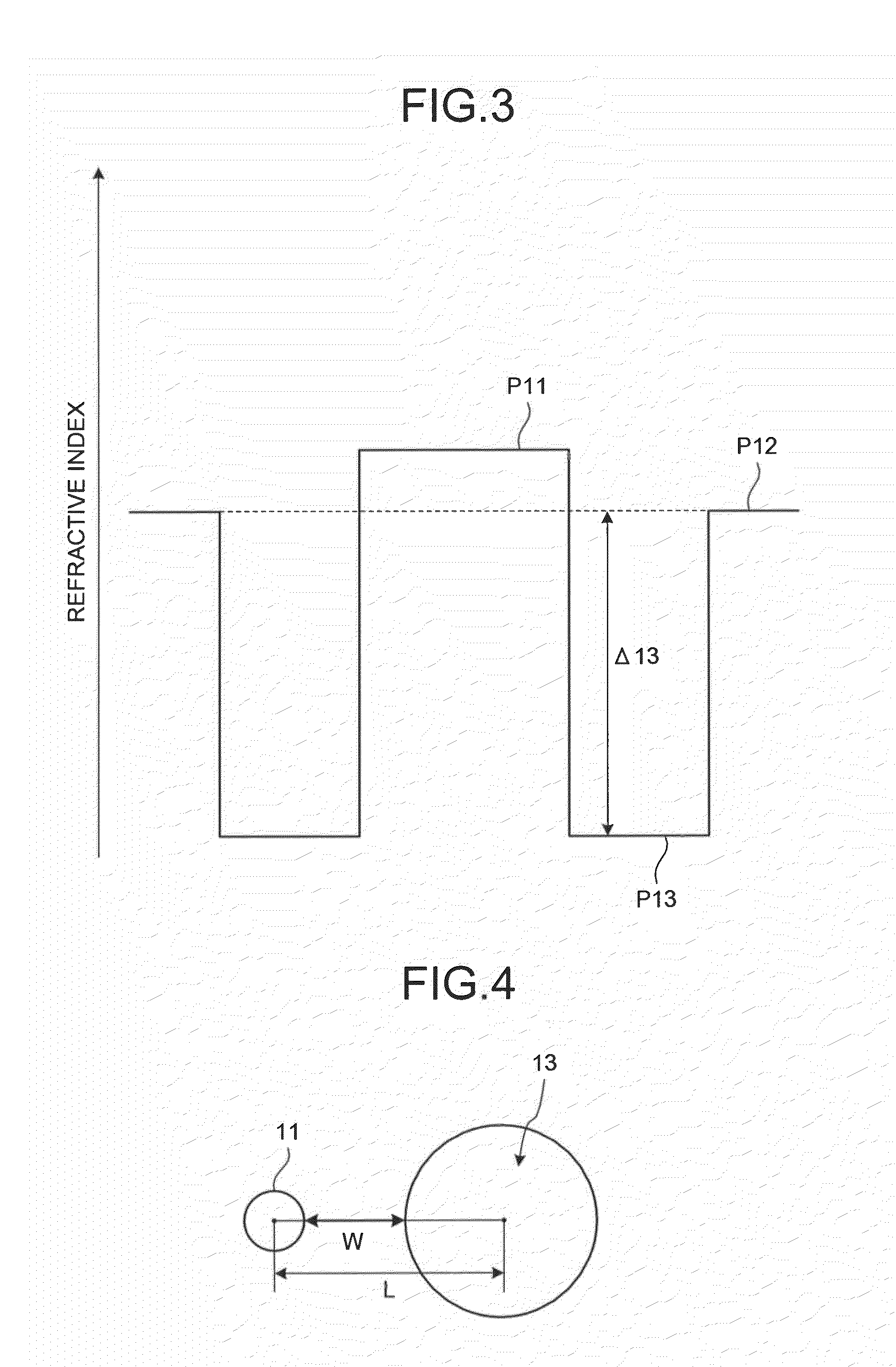
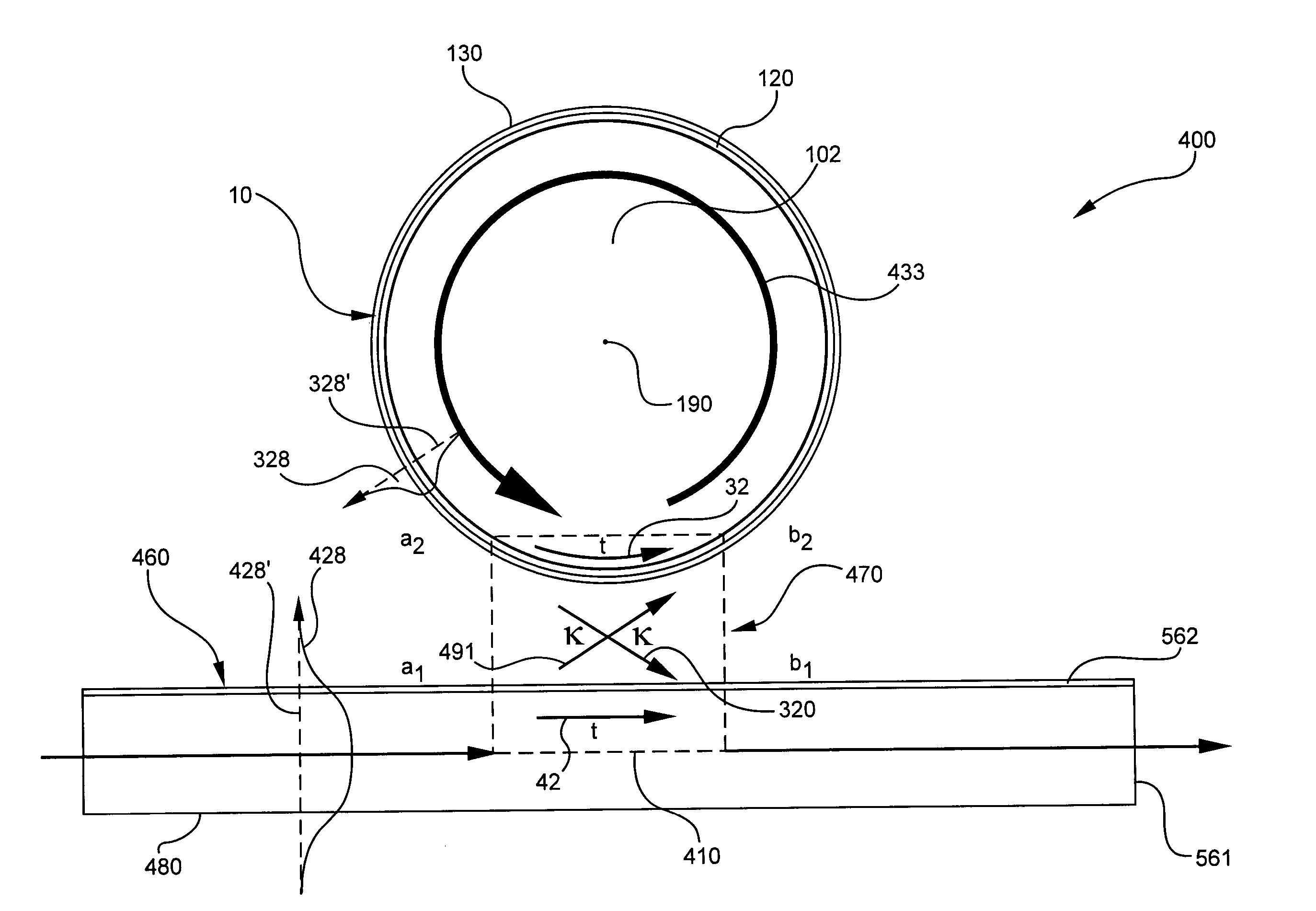
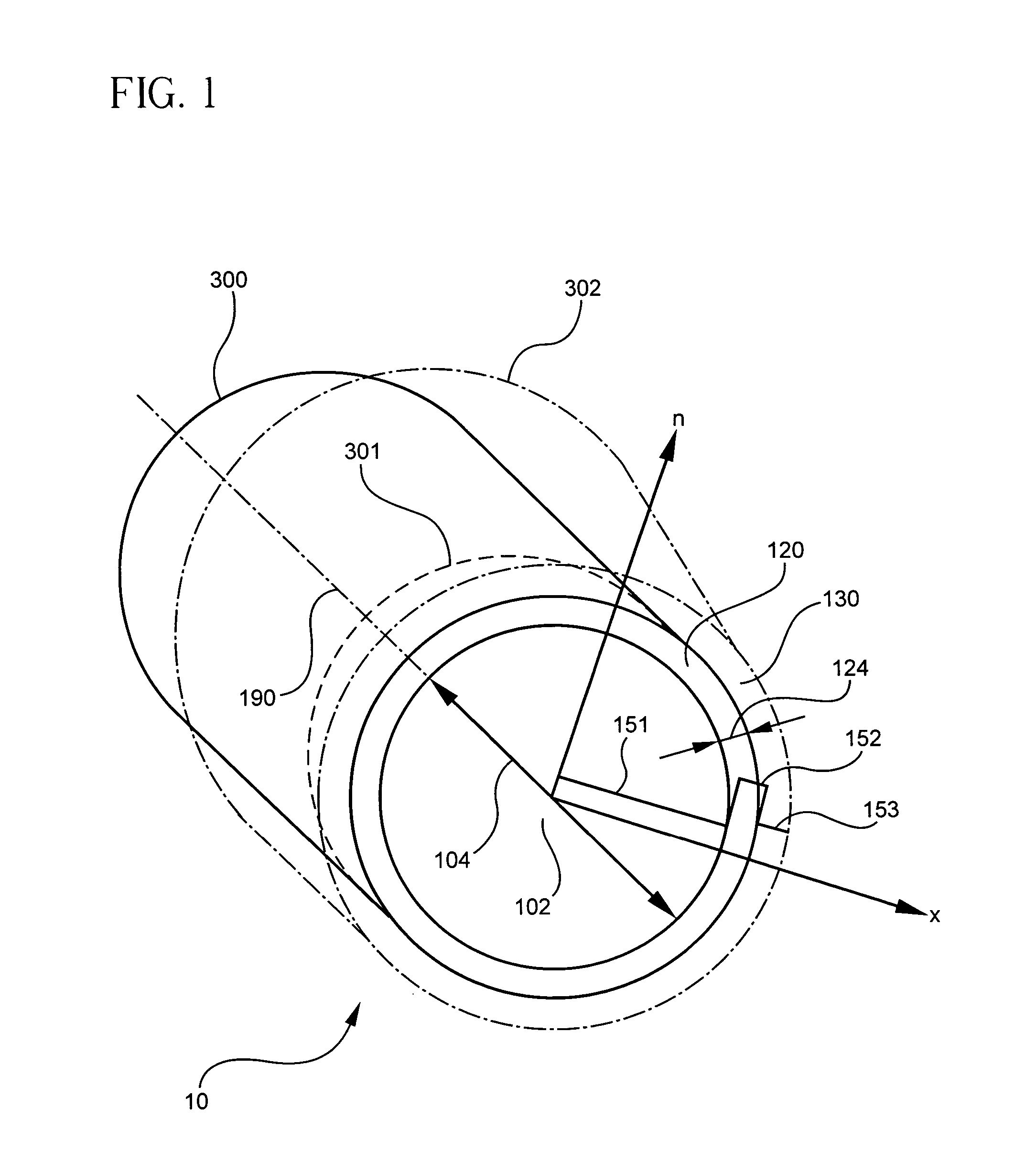
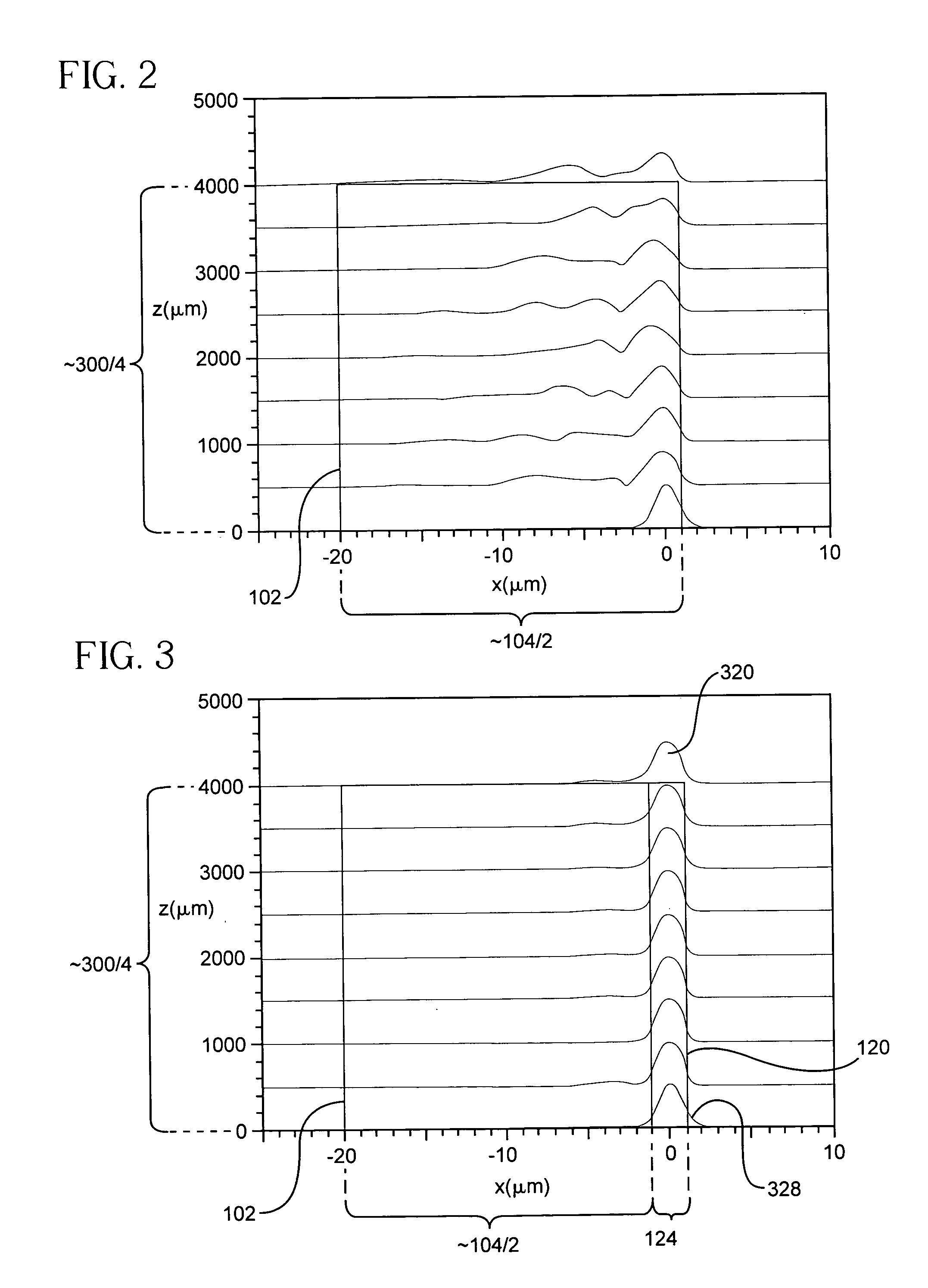
A transverse closed-loop fiber resonator (10) includes an inner cladding (102) having a surface (300) peripherally forming a closed-loop shape for confining light to the surface (300). The inner cladding has a first diameter thickness (104) and a first index of refraction profile in a cross-sectional portion of the transverse closed-loop fiber resonator (10). A ringed-core (120) corresponding to the closed-loop shape is disposed on the corresponding surface of the inner cladding (102). The ringed-core (120) has a second thickness (124) of material thinner than the first diameter thickness (104), and a second index of refraction profile greater than the first index of the inner cladding by an index delta in the cross-sectional portion of the transverse closed-loop fiber resonator such that the ringed-core can guide light within the ringed-core traversely around the closed-loop shape.
Owner:CORNING INC
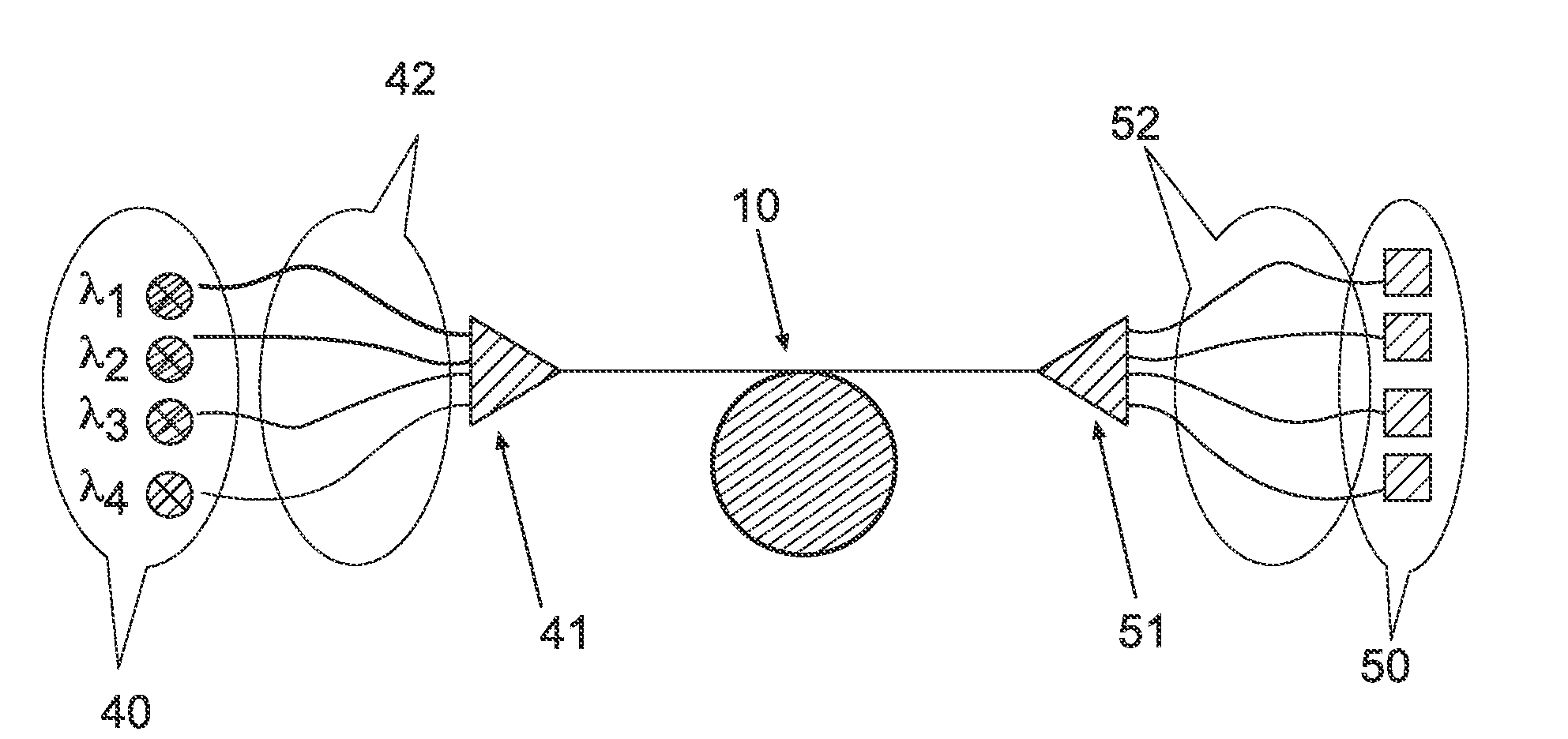
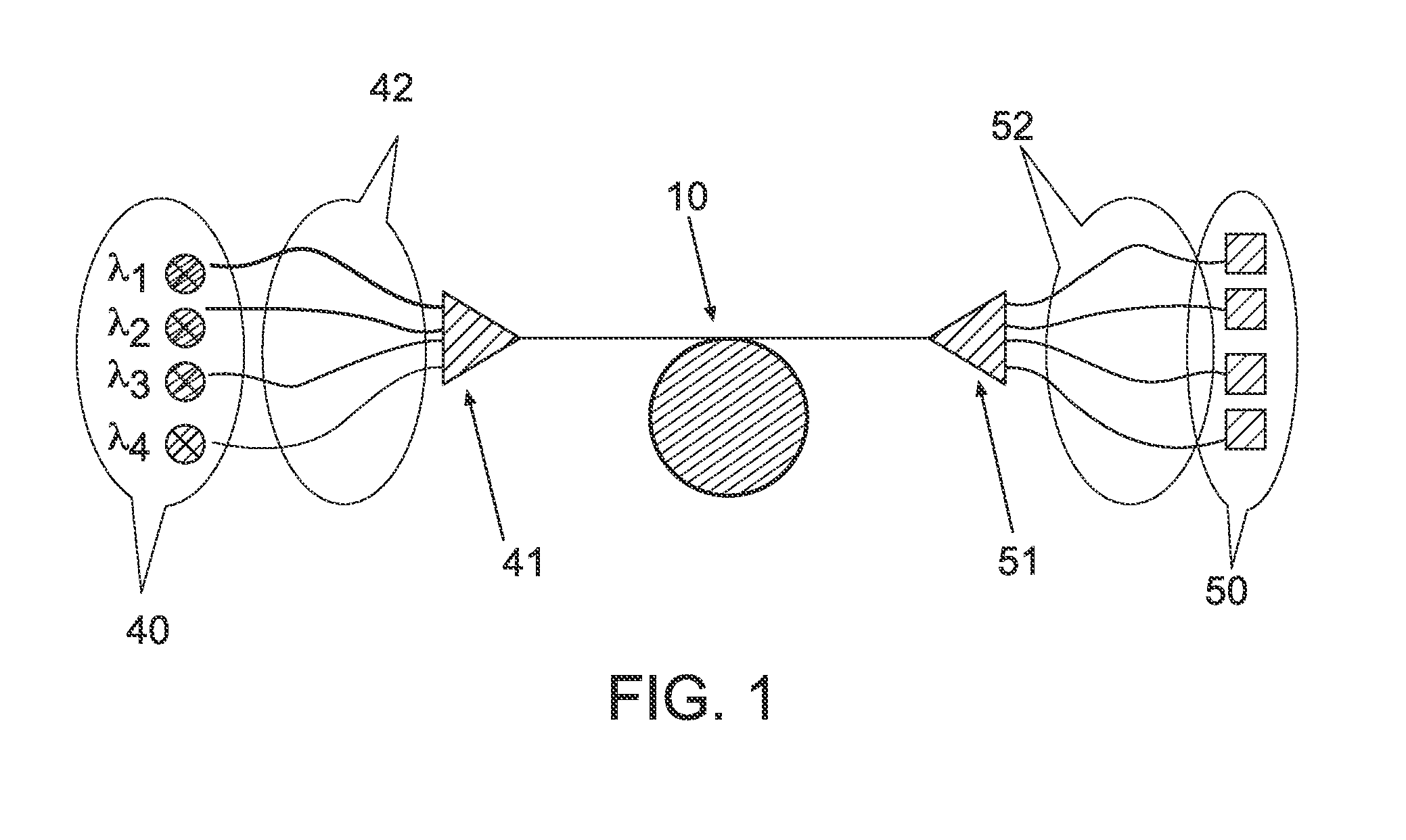
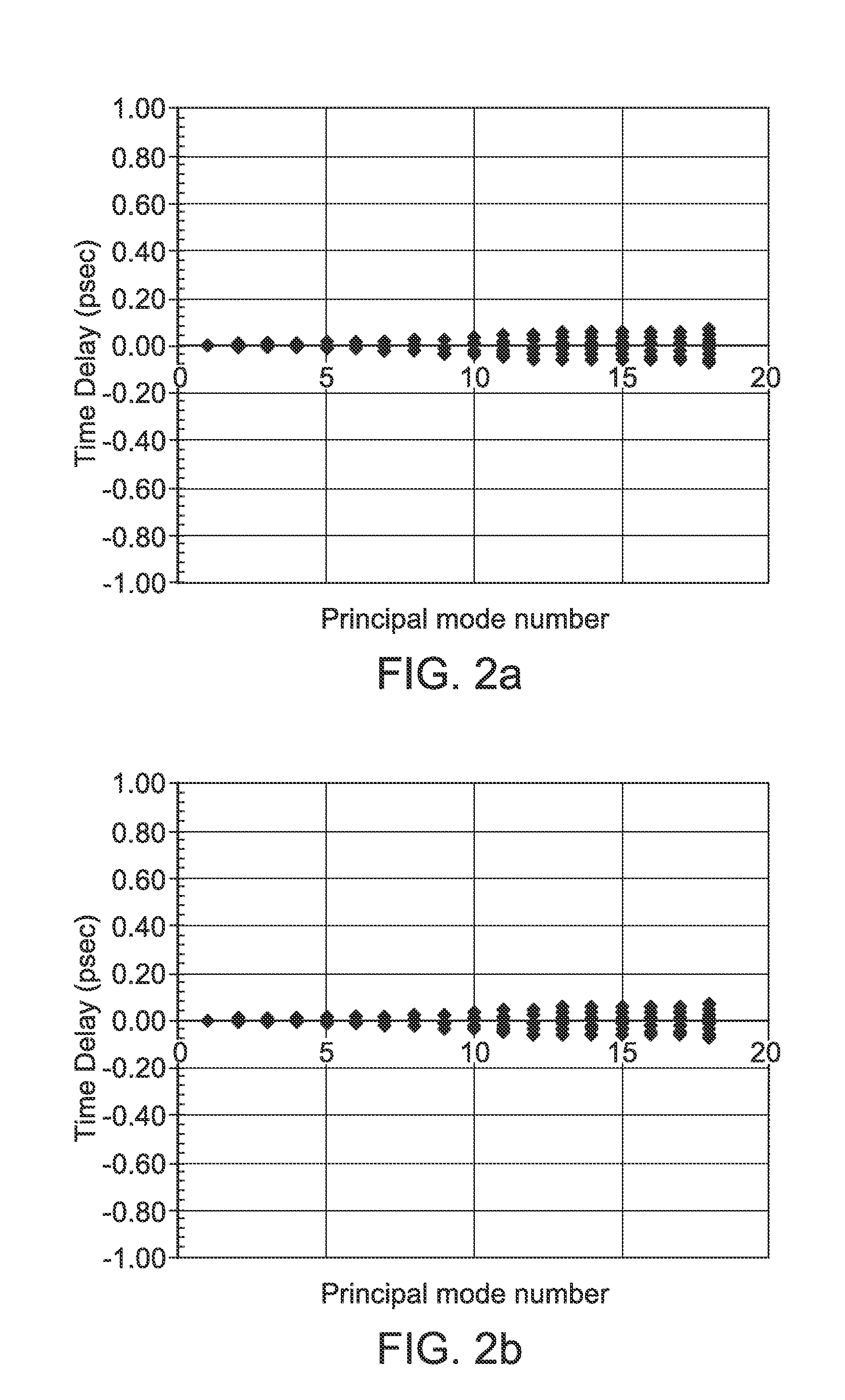
Wavelength Multiplexed Optical System with Multimode Optical Fibers
ActiveUS20100021170A1Minimize modal dispersionReduced Modal DispersionWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionModal dispersionLength wave
The present wavelength multiplexed optical system includes a multimode optical fiber that transmits wavelength multiplexed optical signals and a plurality of multimode modal dispersion compensation optical fibers. Each modal dispersion compensation optical fiber can transmit one of the multiplex wavelengths, and each modal dispersion compensation optical fiber has an optimized index profile such that the modal dispersion for the transmitted wavelength is approximately inversely equal to the modal dispersion induced in the multimode optical fiber. The wavelength multiplexed optical system facilitates an increased bitrate without reducing bandwidth.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
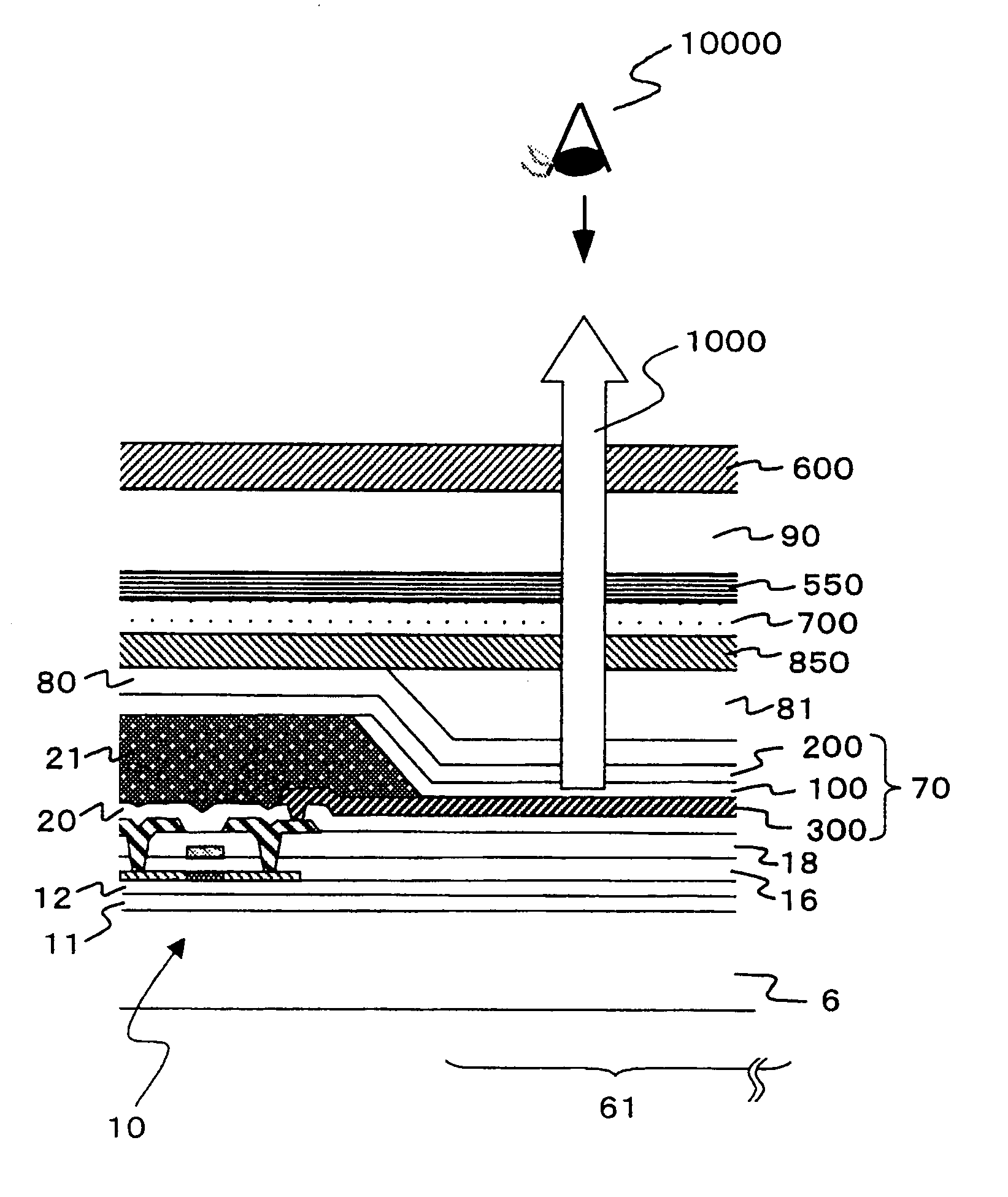
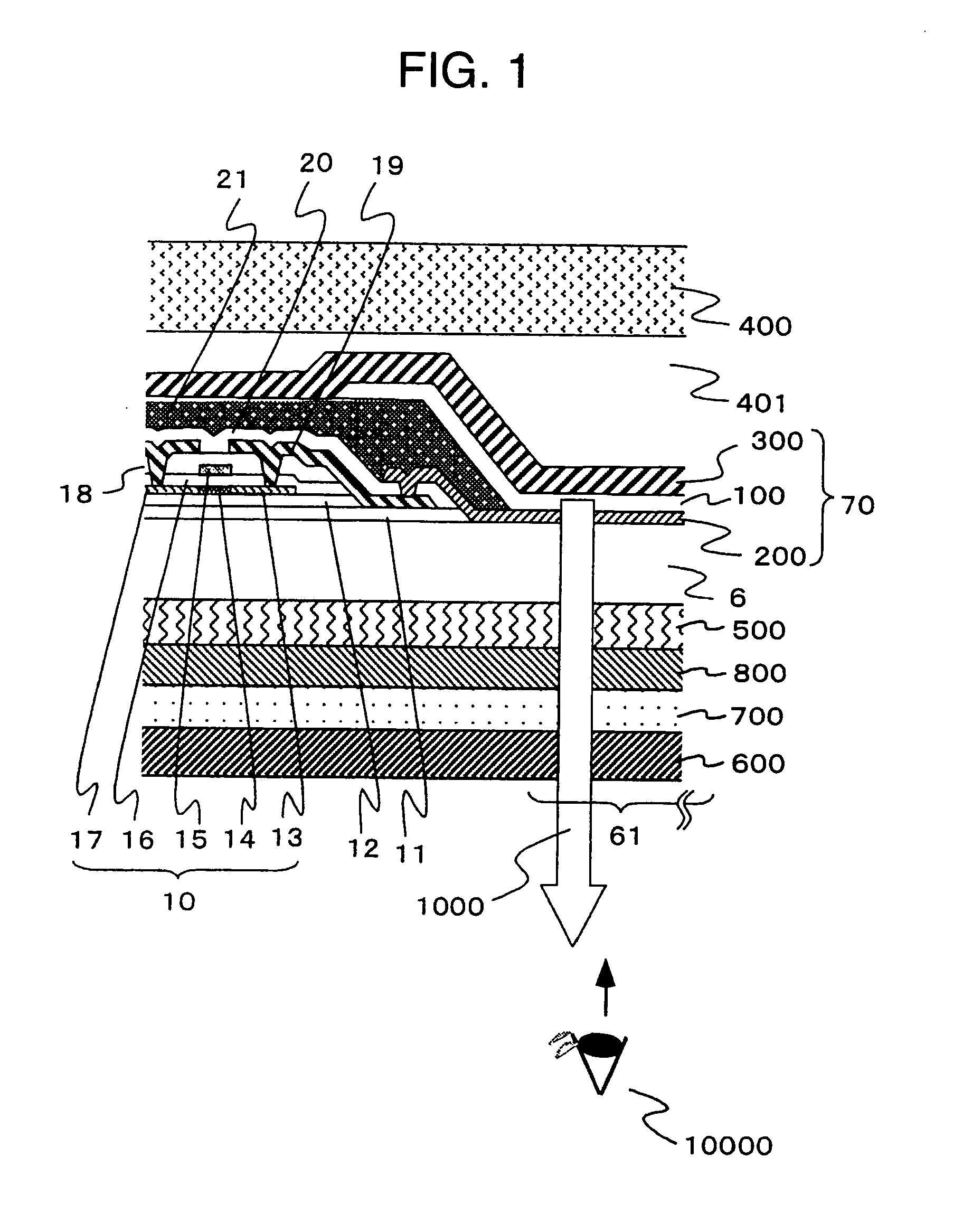
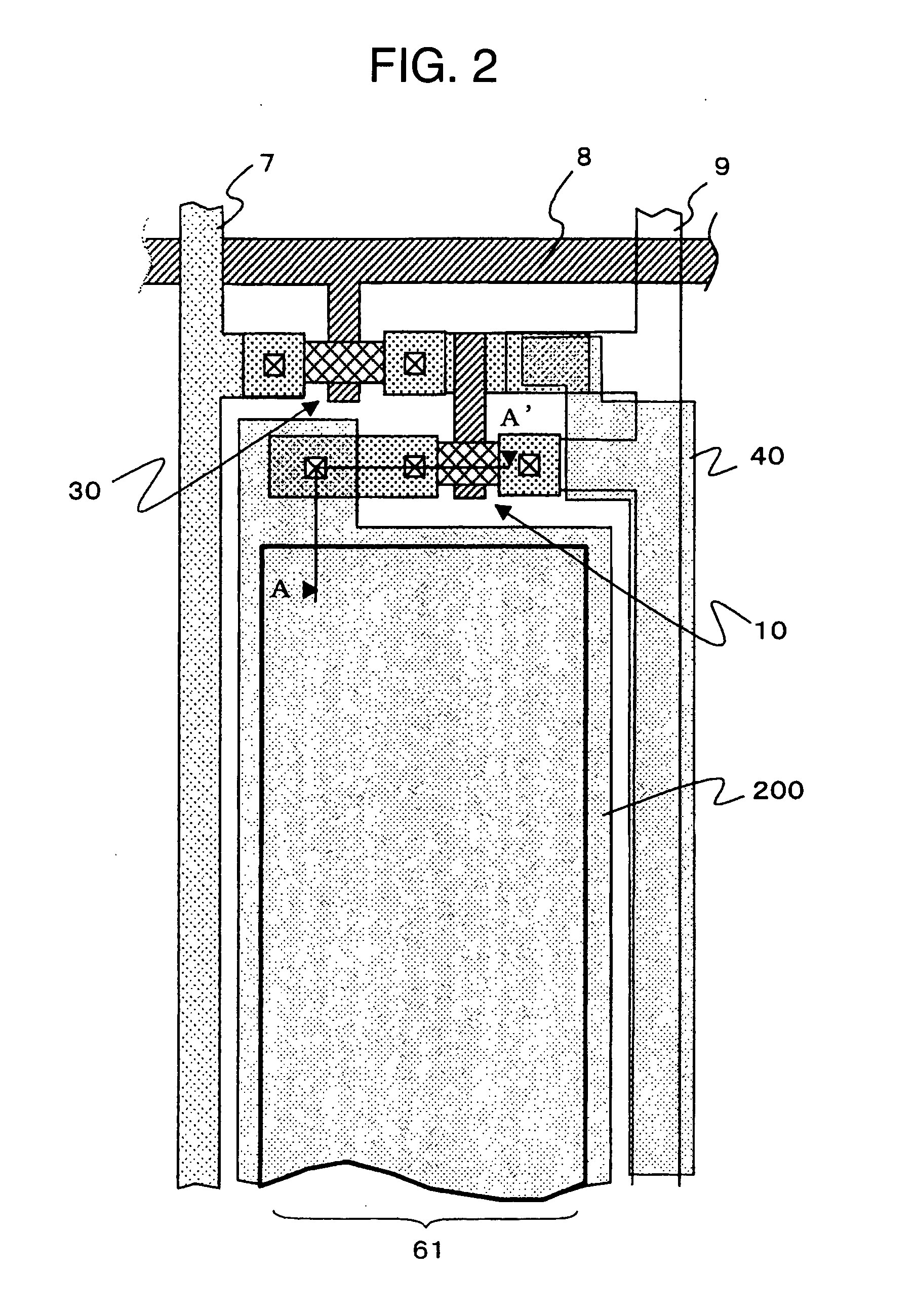
Light emitting display
ActiveUS20050035353A1Increase contrastEfficient processElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesIn planeDisplay device
The present invention provides light emitting displays which produce a bright image by efficiently emitting light radiated from a light-emitting thin-film layer to the viewer side, and also produces a high-quality image of high contrast ratio and changing in color to a limited extent over a wide viewing angle range even in a bright atmosphere. The light emitting displays are provided with a plurality of light-emitting devices 70, each device 70 having a light-emitting thin-film layer 100 and a light reflective surface 300 in this order on the back side, and a circularly polarized light reflective layer 500 which separates incident light into two types of circularly polarized components, one being reflected and the other transmitted by the reflective layer, an optical compensation layer 800, a quarter-wave plate 700 and a polarizer 600 on the front side, wherein the optical compensation layer 800 is composed of a transparent body working as an optical indicatrix having little refractive index distribution in the in-plane direction and having a refractive index in the thickness direction different from that in the in-plane direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
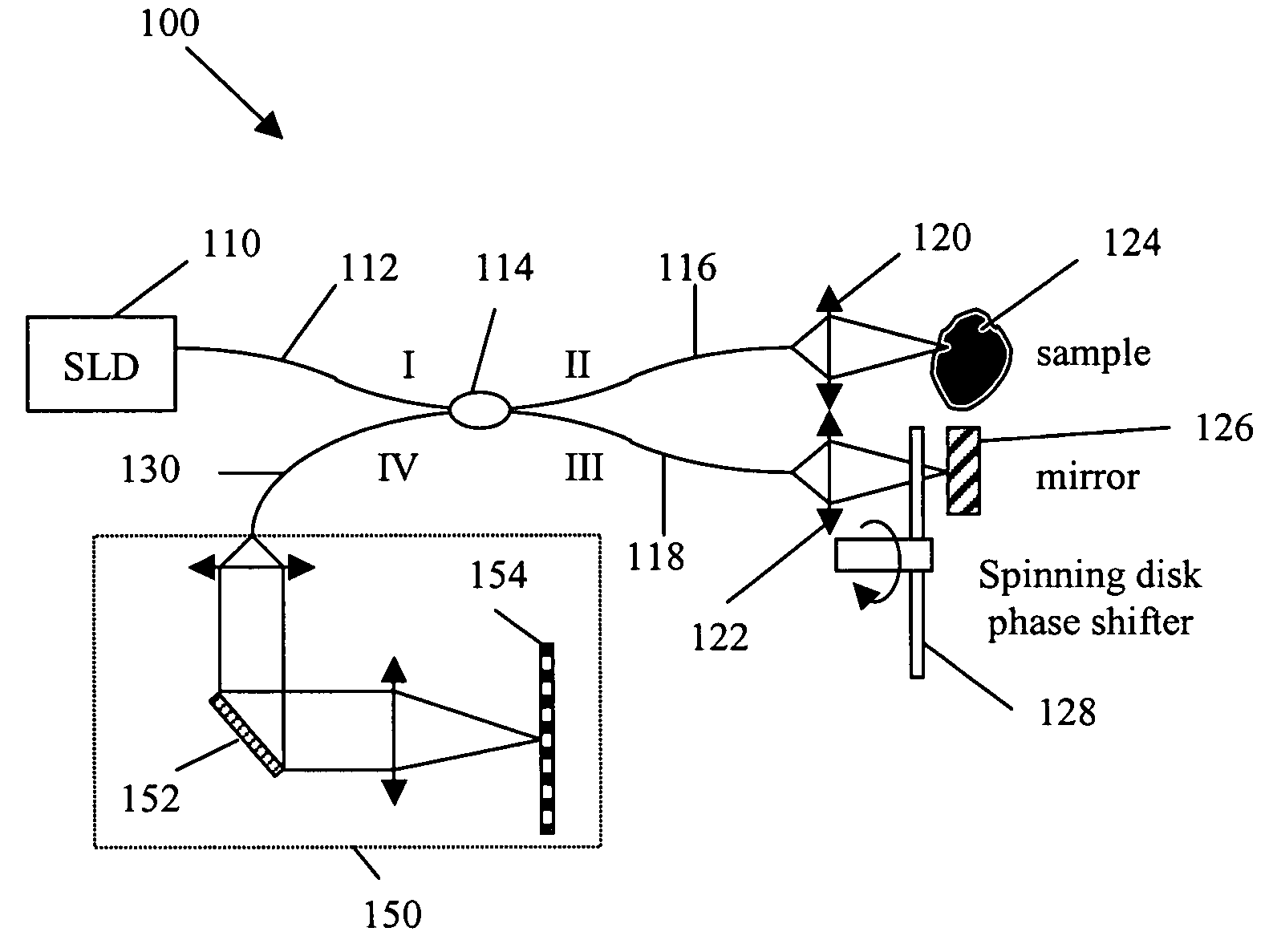
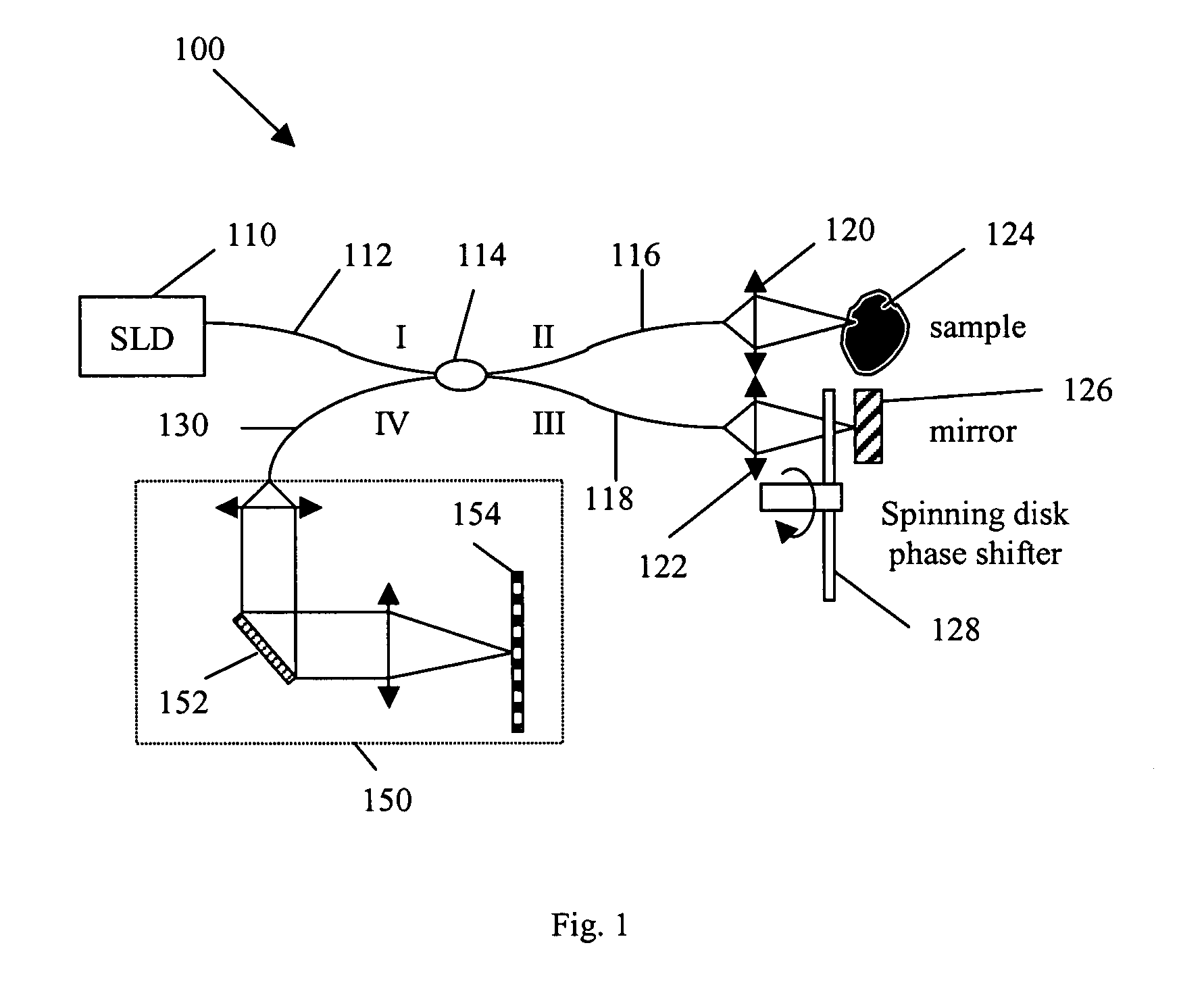
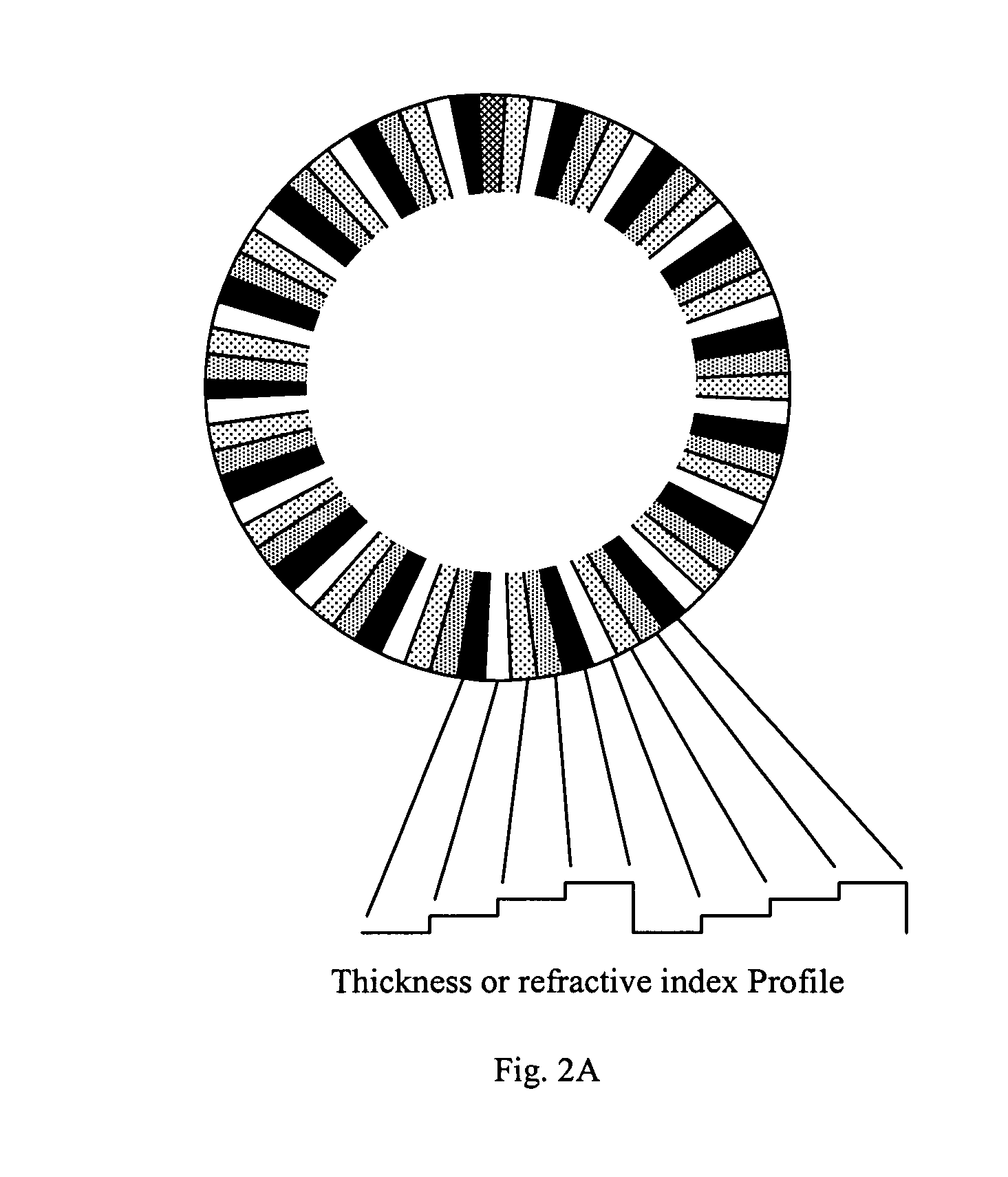
Patterned spinning disk based optical phase shifter for spectral domain optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS7433046B2Low costSolve the slow scanning speedInterferometersEye diagnosticsPhase shiftedPhase retardation
A low cost patterned spinning disk is disclosed for achieving relatively rapid discrete optical phase shifts for an optical beam. The invention is particularly useful in a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system. The disk contains stepped patterns of different heights and / or refractive index distribution such that as it spins, an optical beam passing through or being reflected by the disk will experience different discrete optical phase delays. The disk can be operated as a phase shifter or it can be operated in synchronization with an intensity modulating chopper disk or a direct intensity modulation of the light source. The disk can also contain intensity modulating patterns such that both phase shifting and intensity modulation can be achieved at the same time. Various possible methods are also disclosed for the fabrication of the disk.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction lens and system
A tunable acoustic gradient index of refraction (TAG) lens and system are provided that permit, in one aspect, dynamic selection of the lens output, including dynamic focusing and imaging. The system may include a TAG lens and at least one of a source and a detector of electromagnetic radiation. A controller may be provided in electrical communication with the lens and at least one of the source and detector and may be configured to provide a driving signal to control the index of refraction and to provide a synchronizing signal to time at least one of the source and the detector relative to the driving signal. Thus, the controller is able to specify that the source irradiates the lens (or detector detects the lens output) when a desired refractive index distribution is present within the lens, e.g. when a desired lens output is present.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
System and method for providing a compact, flat, microwave lens with wide angular field of regard and wideband operation
PendingUS20180183152A1High instantaneous bandwidthLow overall depthAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDesign optimisation/simulationInterference (communication)Engineering
A system designs a thin and relatively flat microwave focusing lens that can produce multiple simultaneous beams, using readily-available isotropic dielectric materials, and having a gradient-index (GRIN) profile. The design optimizes the lens to achieve beam scanning and / or multiple beams over a wide field of regard (FOR) with broad bandwidth and a very short focal length compared with conventional lenses. The lens can be used individually or as an element in a more complex antenna having multiple lenses in various orientations that are independently switched, selected and / or excited simultaneously as elements in a phased array. The antenna terminal incorporates such lens into an array of lenses along with one or more feeds to produce single or multiple beams covering a broad field of regard for such applications as satellite communications on-the-move, cellular, broadband point-point or point-multipoint and other terrestrial or satellite communications systems. The lens and array design support multiple simultaneous independently steerable beams as well as null placement for interference cancellation.
Owner:ALL SPACE NETWORKS LTD
Low bending loss multimode fiber transmission system
ActiveUS20090092365A1Low bend-lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringEffective refractive index
A bend-loss tolerant multimode fiber transmission system is provided. The system includes: a transmission fiber having a core and a cladding, and a mode-launching system for selectively exciting only a useful portion of the transmission modes, that portion corresponding to high effective refractive indices relative to a refractive index of the cladding the useful portion corresponding to a substantial number of modes. The mode-launching system may include a lead-in fiber, coupled to the transmission fiber, supporting a number of lead-in modes substantially corresponding to the number of transmission modes in the useful portion. The transmission fiber may have a refractive index profile, within a region of its core that is aligned with the lead-in fiber core, which has a shape that matches a refractive index profile shape in the lead-in fiber core. The transmission fiber core may have a graded refractive index profile that is parabolic or nearly parabolic or truncated.
Owner:LUMENTUM D O O OPTICNA VLAKNA
Optical elements and methods for making thereof
InactiveUS20050046957A1Unique optical propertyControl over optical propertySpectales/gogglesOptical articlesPolymer scienceOptical property
Optical elements are made using micro-jet printing methods to precisely control the type, position and amount of polymer deposited onto a substrate. In preferred embodiments, the proportions of two or more different polymer compositions are varied over the course of the deposition process to deposit adjoining polymer pixels in the form of a film on the substrate surface. The optical properties of each adjoining polymer pixel can be selected to provide a predetermined optical property, including a specific value of index of refraction. Preferably, the film has a radially non-monotonic refractive index profile and / or an angularly non-monotonic refractive index profile.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE +1
Apparatus for measuring characteristics of thin film by means of two-dimensional detector and method of measuring the same
InactiveUS7286242B2Simple structurePhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansNon destructiveTwo dimensional detector
The present invention relates to a non-contact, non-destructive measuring apparatus that measures thickness profile and refractive index distribution of a single or multiple layers of thin films by means of the principle of reflectometry. According to the present invention, by employing more than one narrow band-pass optical filters and a two-dimensional array of CCD sensors, and by finding an optimal solution for the nonlinear functional relationship between the thickness of said thin film or thin films and the corresponding refractive indexes by using an iterative numerical computation method, said apparatus simultaneously measures local area-wise thickness profile and refractive index distribution among others of said a single layer or multiple layers of thin films on a substrate.
Owner:HB SOLUTION CO LTD
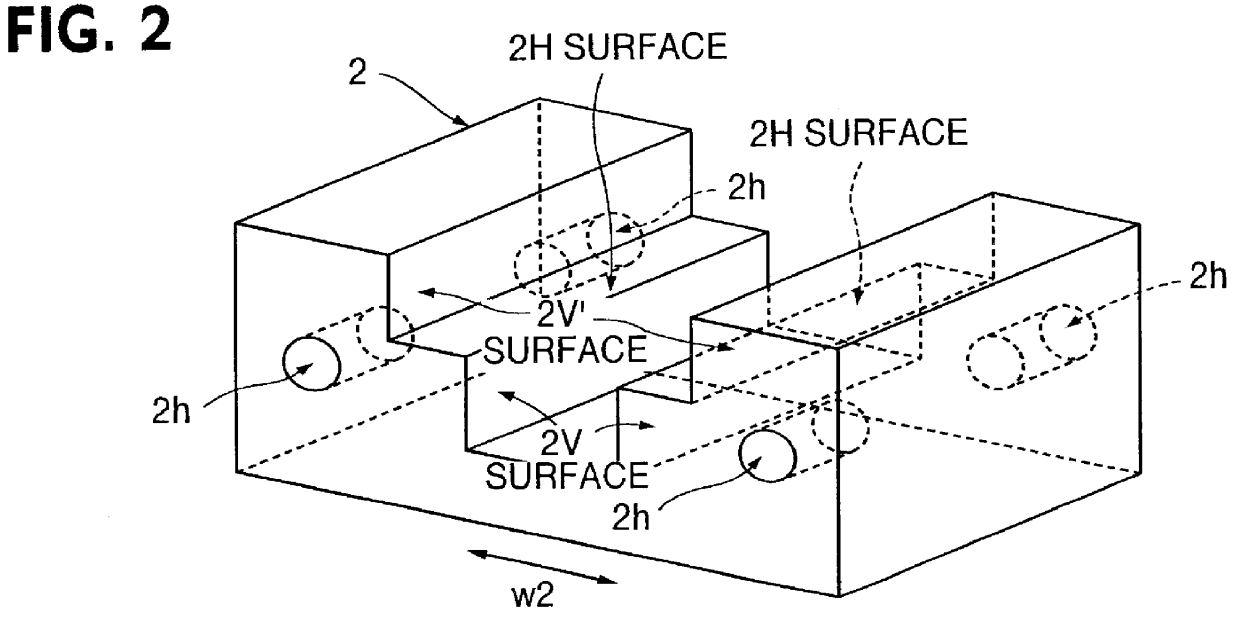
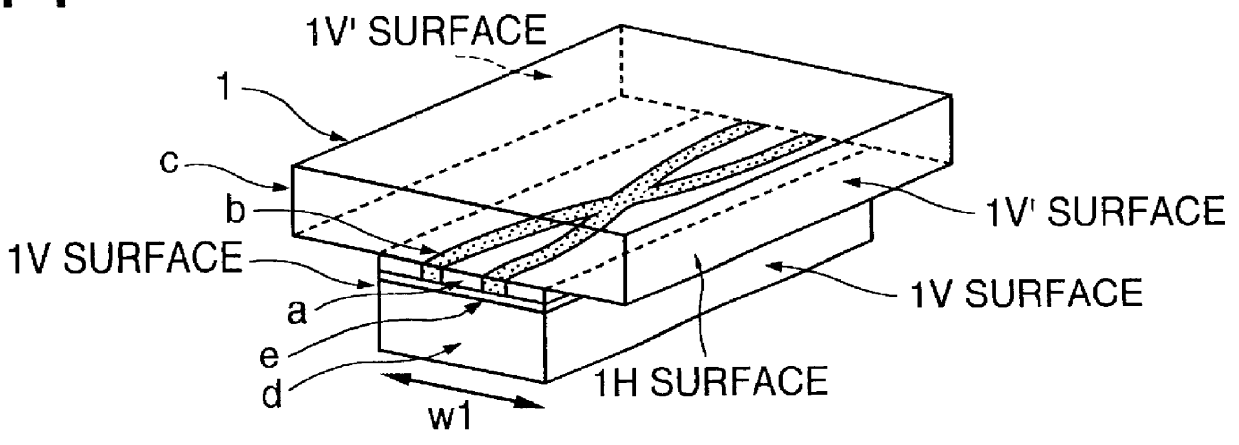
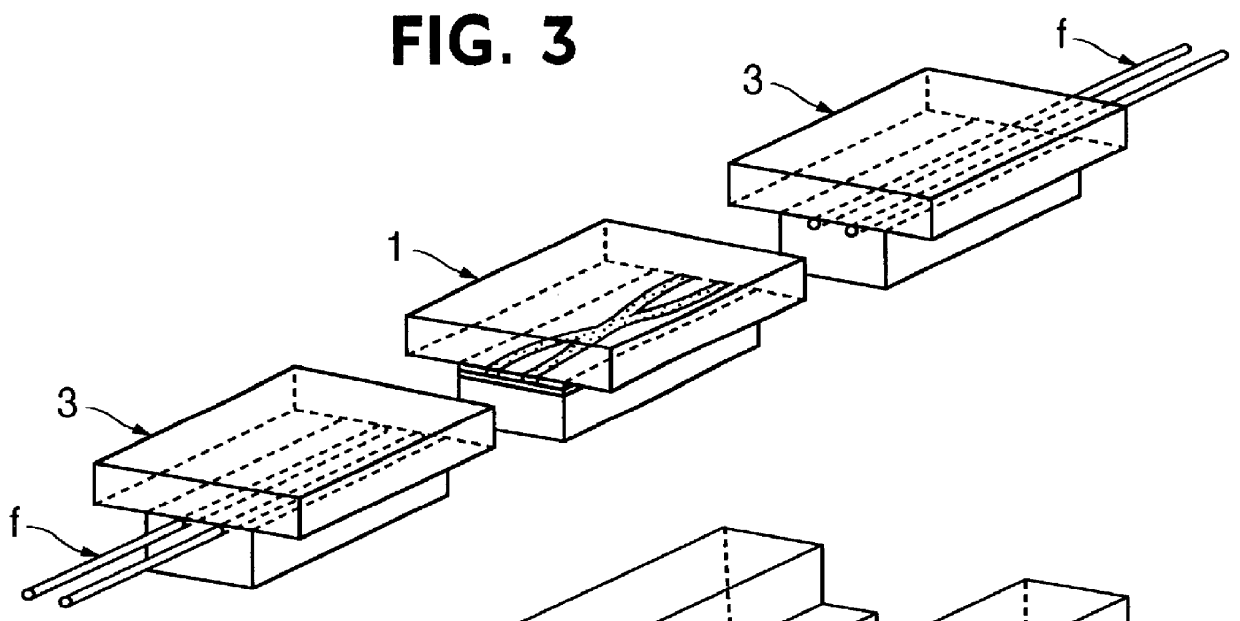
Optical waveguide device for connections without optical axis adjustment
An optical device which can be fabricated without any axial alignment by optical measurement and can therefore be produced at a remarkably decreased cost, and which is composed of an optical waveguide part (1) obtained by perpendicularly cutting an optically-transparent polymer film having a glass substrate attached thereto and having a refractive index distribution formed, in a predetermined position measured from the position of the refractive index distribution as a reference, and a holder part (2) for holding the optical waveguide part (1) in a predetermined position, the holder part (2) having a horizontal guide surface (2H) and a vertical guide surface (2V), the optical waveguide part (1) having a glass substrate surface or a polymer film surface coherently attached to the horizontal guide surface (2H) of the holder part (2), and the optical waveguide part (1) having a perpendicularly cut surface coherently attached to the vertical guide surface (2V) of the holder part (2).
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Multi-mode bending-resistant fiber and production method thereof
ActiveUS20110044596A1High mechanical reliabilityEasy to useOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical articlesMedicineRelative refractive index
A multimode fiber including a core and a cladding. The core has a radius (R1) of 24-26 μm, the refractive index profile thereof is a parabola, and the maximum relative refractive index difference (Δ1) is 0.9-1.1%. The cladding surrounds the core and includes from inside to outside an inner cladding, a middle cladding, and an outer cladding; a radius (R2) of the inner cladding is 1.04-1.6 times that of the core, and a relative refractive index difference (Δ2) thereof is −0.01-0.01%; the middle cladding is a graded refractive index cladding whose radius (R3) is 1.06-1.8 times that of the core, and a relative refractive index difference thereof is decreased from Δ2 to Δ4; and a radius (R4) of the outer cladding is 2.38-2.63 times that of the core, and a relative refractive index difference (Δ4) thereof is between −0.20 and −0.40%. The invention reduces the additional bending loss of the fiber, improves the bending resistance and mechanical properties, basically eliminates the internal stress, and ensures the service life even working for a long term under the condition of low radius. The method for producing the fiber is simple, effective, and suitable for mass production.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
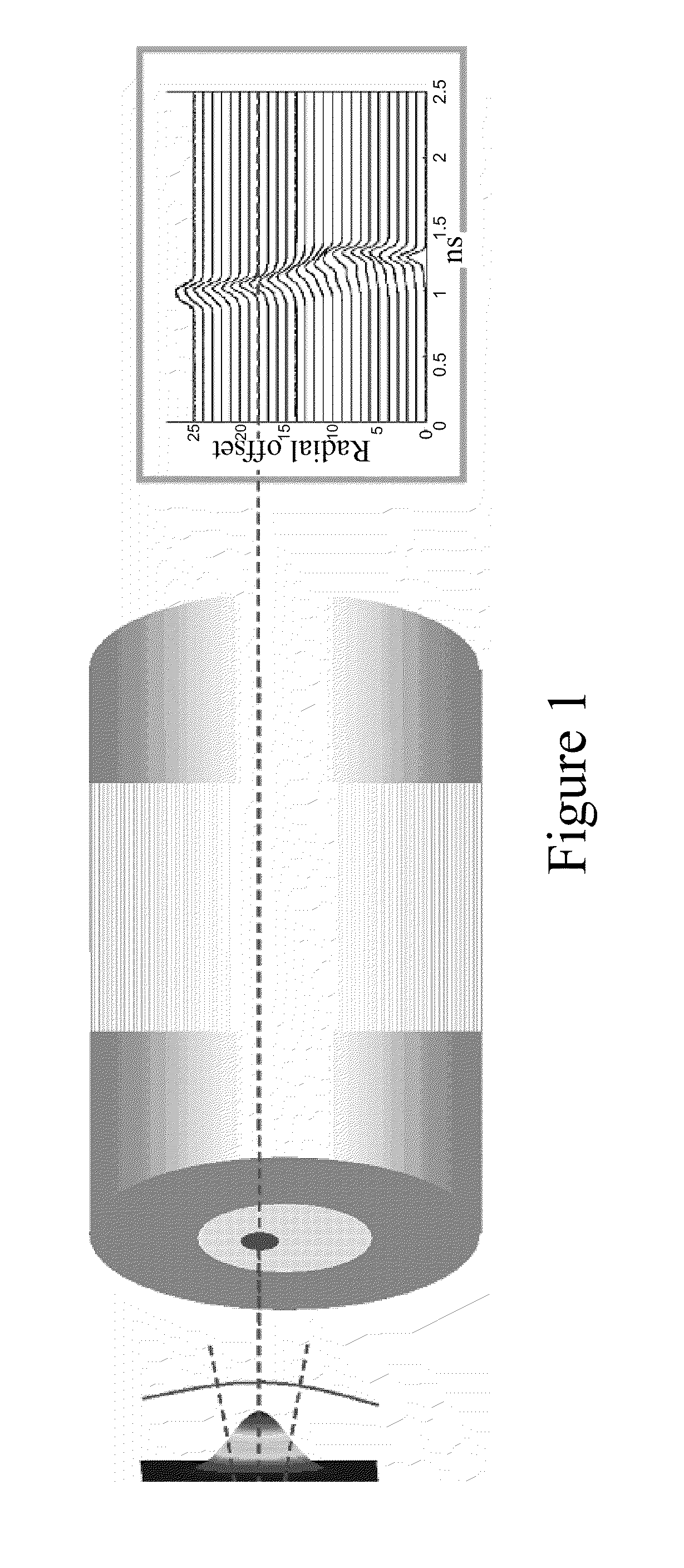
Micro-structured fiber profiles for mitigation of bend-loss and/or mode distortion in LMA fiber amplifiers, including dual-core embodiments
ActiveUS7924500B1Improved amplification characteristicReduce numerical apertureOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFibre transmissionMicro structureDual core
An apparatus and method for compensating for mode-profile distortions caused by bending optical fibers having large mode areas. In various embodiments, the invention micro-structures the index of refraction in the core and surrounding areas of the inner cladding from the inner bend radius to the outer bend radius in a manner that compensates for the index changes that are otherwise induced in the index profile by the geometry and / or stresses to the fiber caused by the bending.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
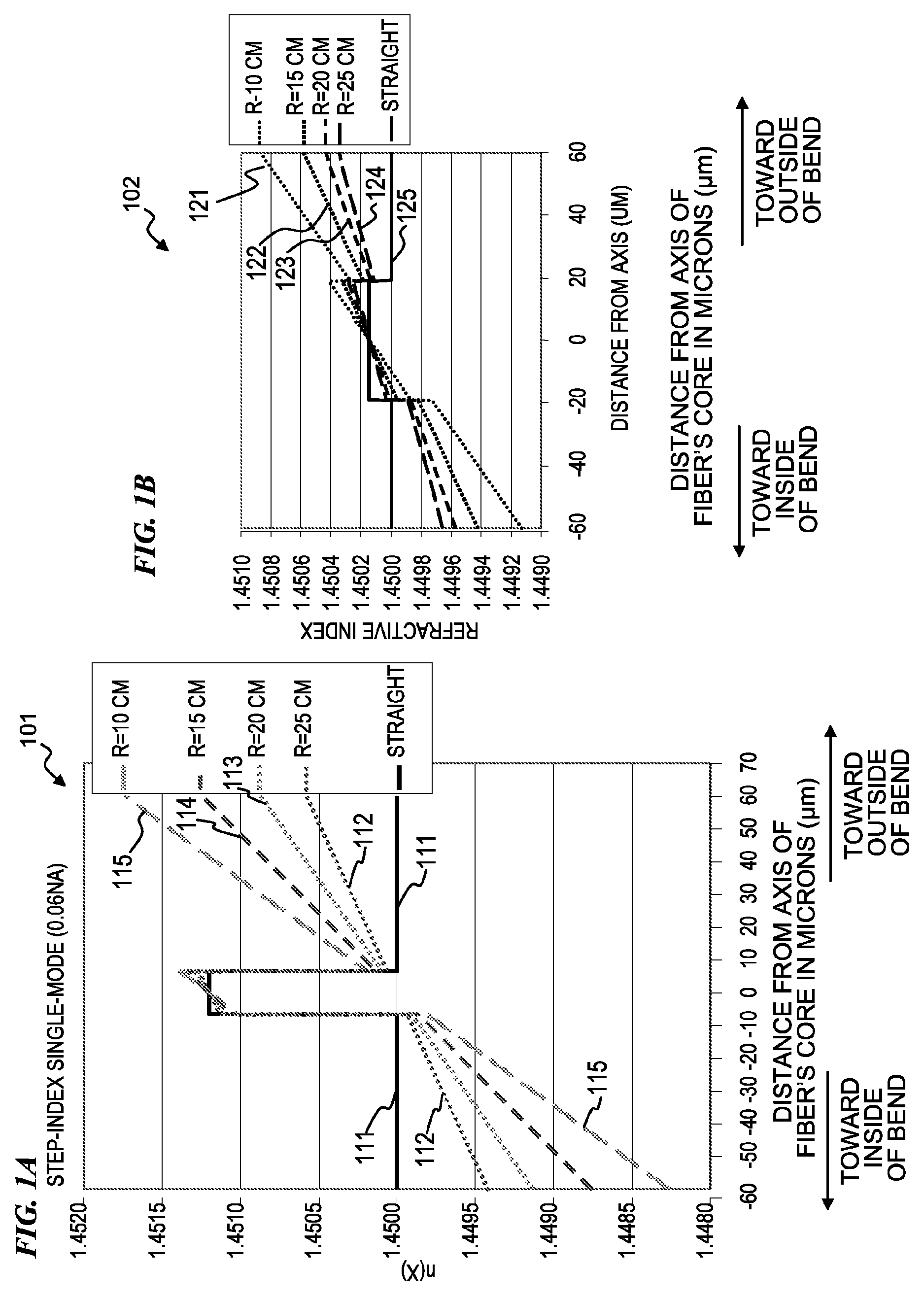
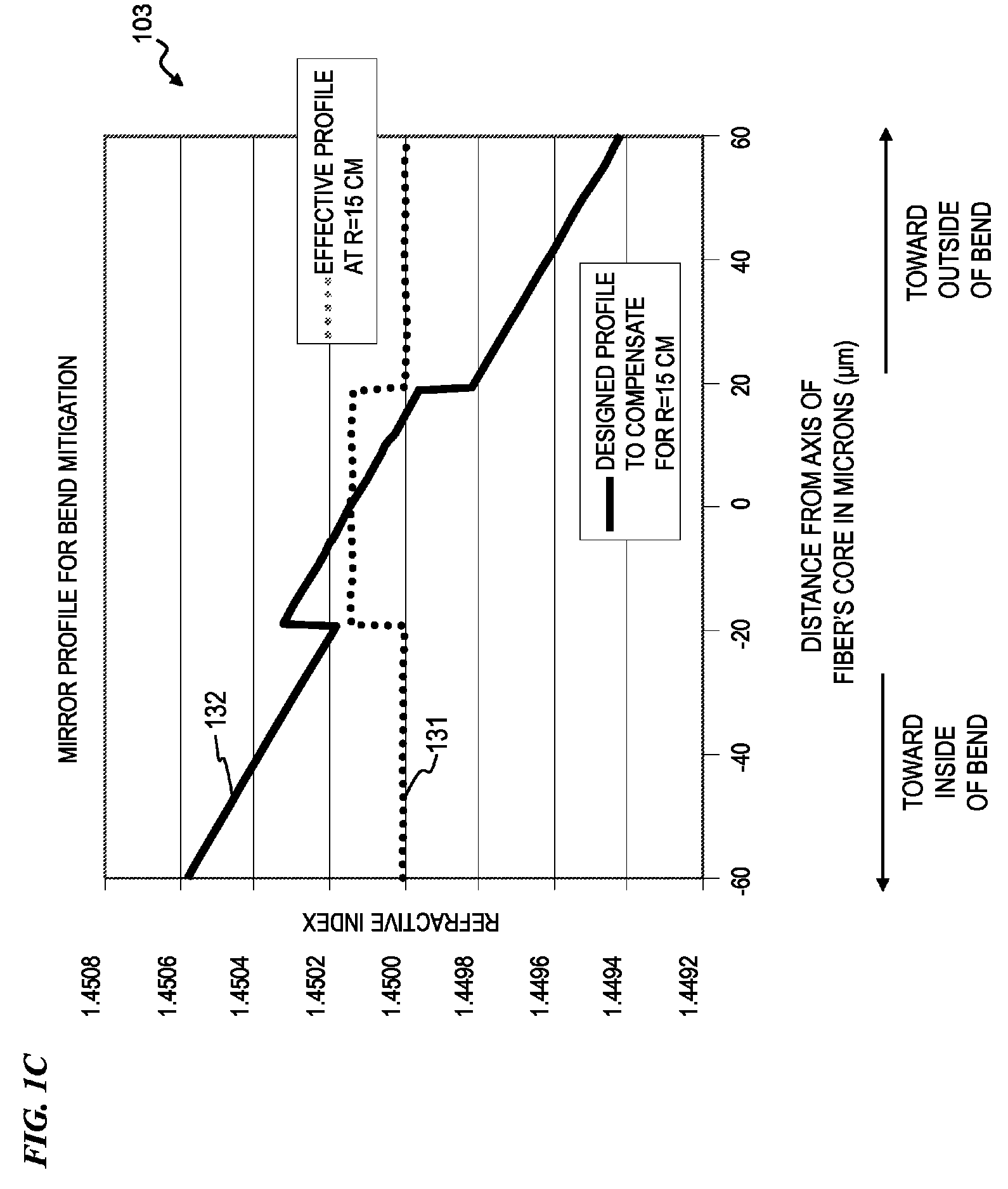
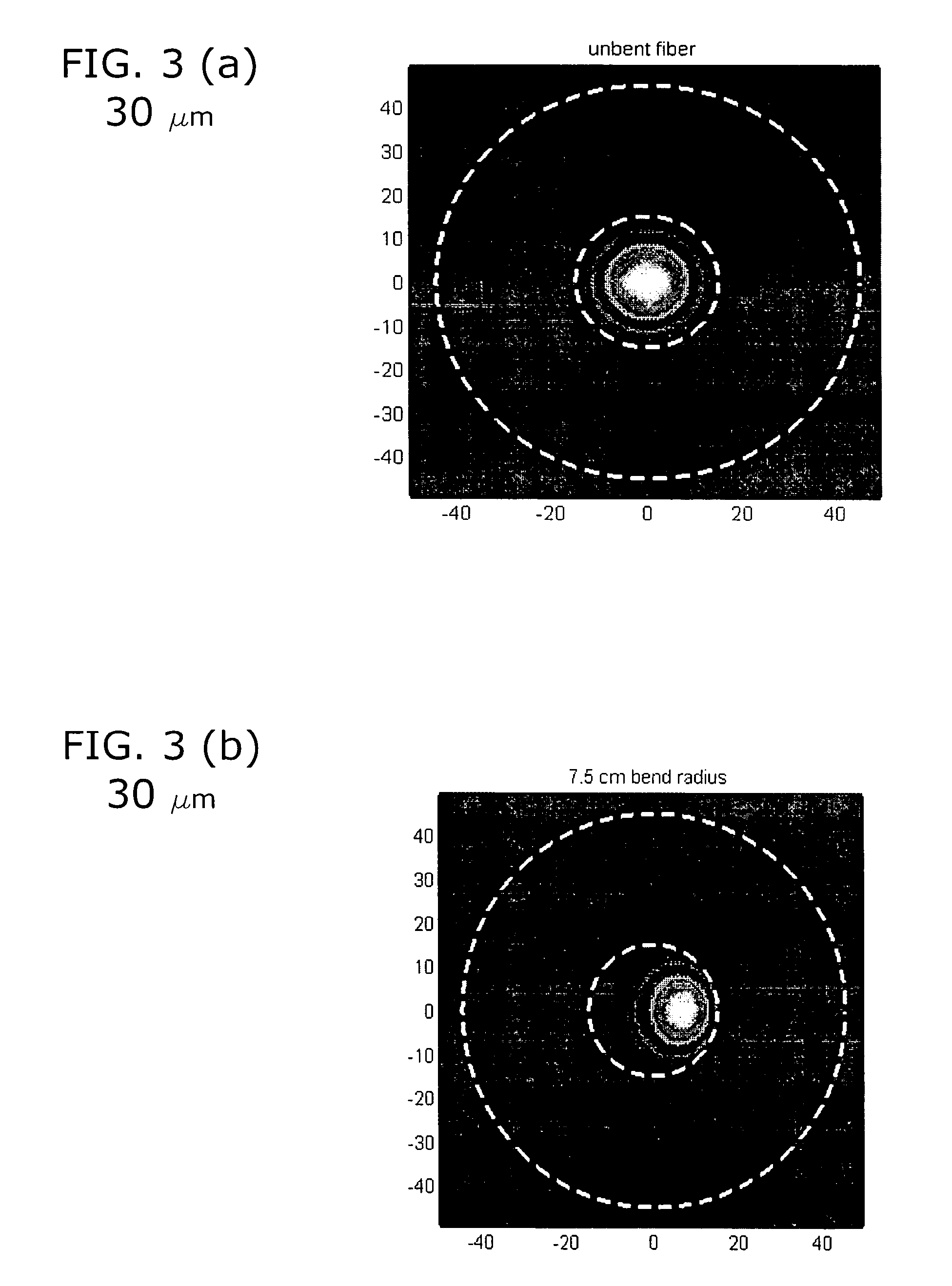
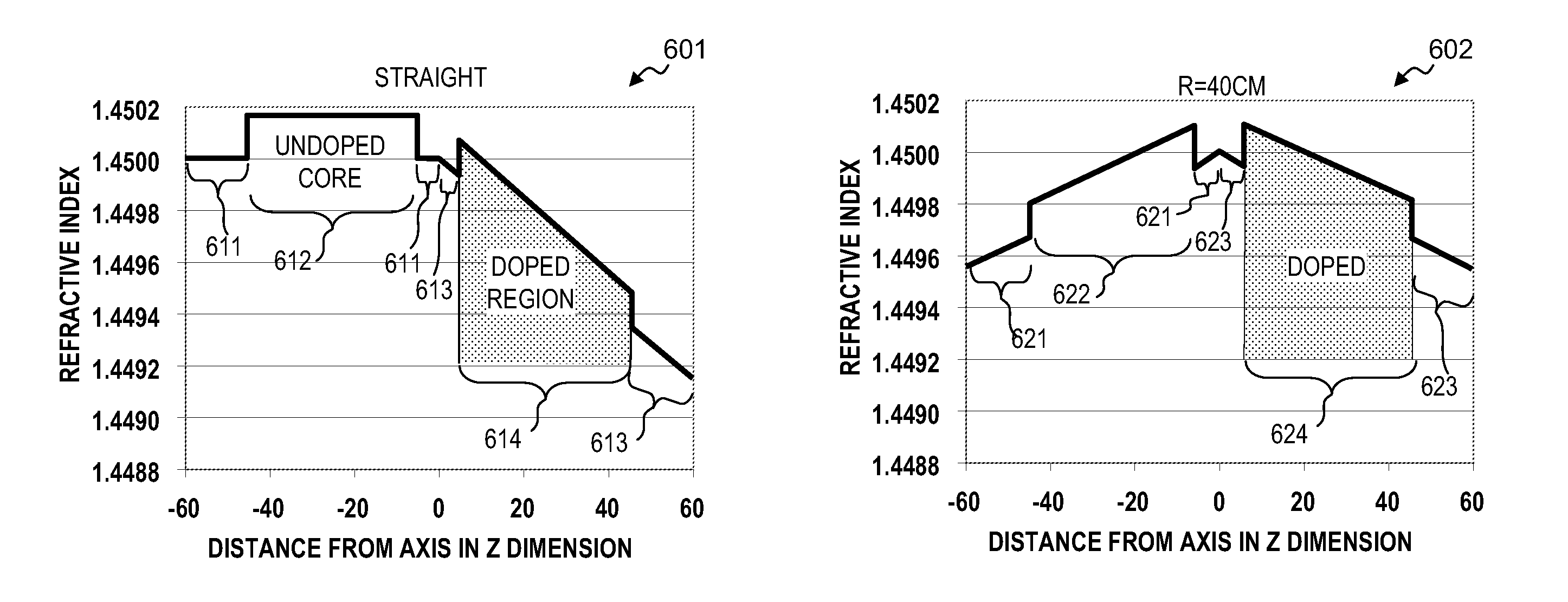
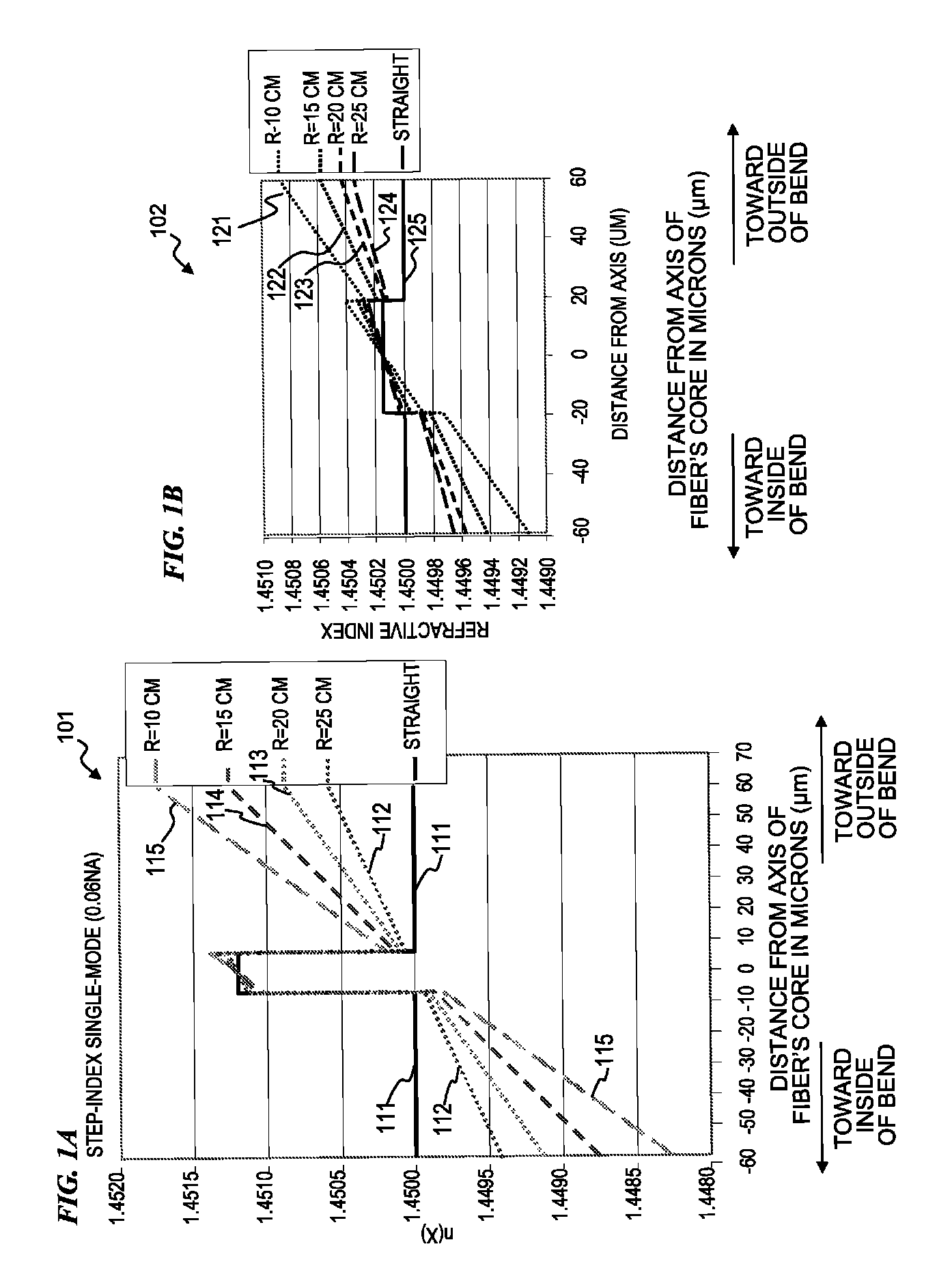
Optical fiber with specialized index profile to compensate for bend-induced distortions
InactiveUS20070147751A1Minimize impactLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingPhotonic bandgapEngineering
An optical fiber that exhibits reduced mode distortions as the fiber is bent is formed by properly defining its refractive index profile during fabrication. The as-fabricated profile is defined as a “pre-distorted” profile that takes into account the gradient introduced by bending the fiber. A parabolic index profile is one exemplary bend-resistant profile that exhibits a quadratic form. A raised-cone index is another profile that may be used as the “as-fabricated” profile. In any properly configured form, factors such as bend loss and mode distortion are significantly reduced, since the profile undergoes a shift of essentially constant gradient as a bend is introduced. The resultant effective area of the inventive fiber is substantially improved over state-of-the-art fiber that is subjected to bending during installation. The as-fabricated profile may be incorporated into various types of fibers (birefringent, photonic bandgap, etc.), and is particularly well-suited for use in a fiber amplifier arrangement.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Apparatus and method for compensating for and using mode-profile distortions caused by bending optical fibers
An apparatus and method for compensating for mode-profile distortions caused by bending optical fibers having large mode areas. In various embodiments, the invention micro-structures the index of refraction in the core and surrounding areas of the inner cladding from the inner bend radius to the outer bend radius in a manner that compensates for the index changes that are otherwise induced in the index profile by the geometry and / or stresses to the fiber caused by the bending. Some embodiments of an apparatus and method include a fiber having a plurality of substantially parallel cores, the fiber including a straight section and a curved section; guiding signal light primarily in a second core in the straight section; guiding the signal light from the second core into a first core between the straight section and the curved section; and guiding the signal light primarily in the first core in the curved section.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
High-Bandwidth Multimode Optical Fiber with Reduced Cladding Effect
ActiveUS20110123161A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingHigh bandwidthHigh data rate
The present invention embraces an optical fiber that includes a central core having an alpha refractive index profile with respect to an outer cladding. The optical fiber also includes an inner cladding, a depressed trench, and an outer cladding. The optical fiber achieves reduced bending losses and a high bandwidth with a reduced cladding effect for high-data-rate applications.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Retardation film and method of producing the same, and optical film, liquid crystal panel, and liquid crystal display apparatus all using the retardation film
InactiveUS20060062934A1High mechanical strengthSmall coefficientLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingLiquid-crystal displayPolycarbonate
A retardation film which hardly causes shift or unevenness in retardation values and which has a refractive index profile of nx>nz>ny (that is, 0<Rth[590] / Re[590]<1) is provided. A retardation film according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises a stretched polymer film containing a styrene-based resin and a polycarbonate-based resin, which satisfies the following expressions (1) and (2): 100 nm≦Re[590]≦350 nm (1) 0.2≦Rth[590] / Re[590]≦0.8 (2)
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
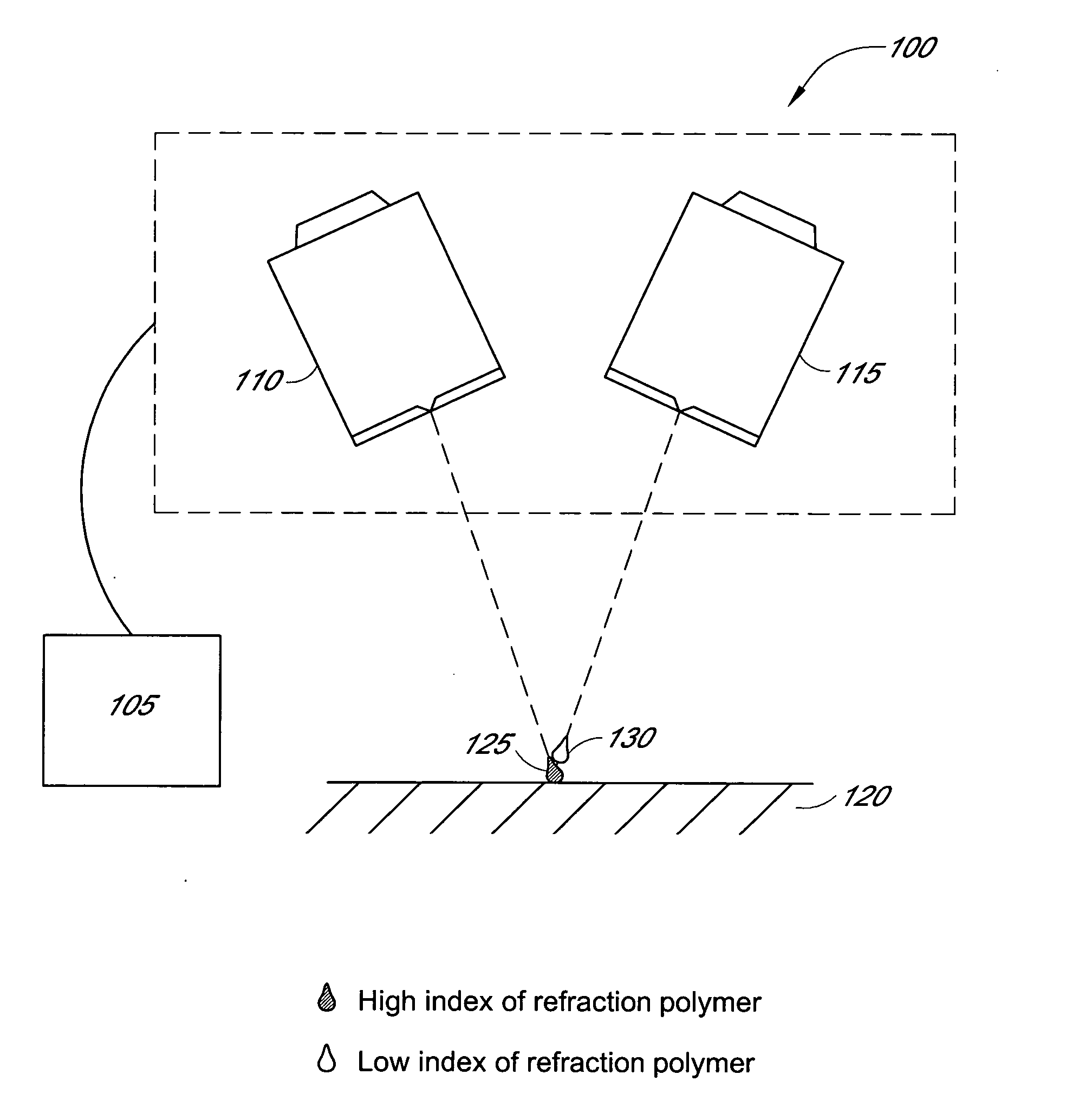
Method of producing large polymer optical blanks with predictable axil refractive index profile
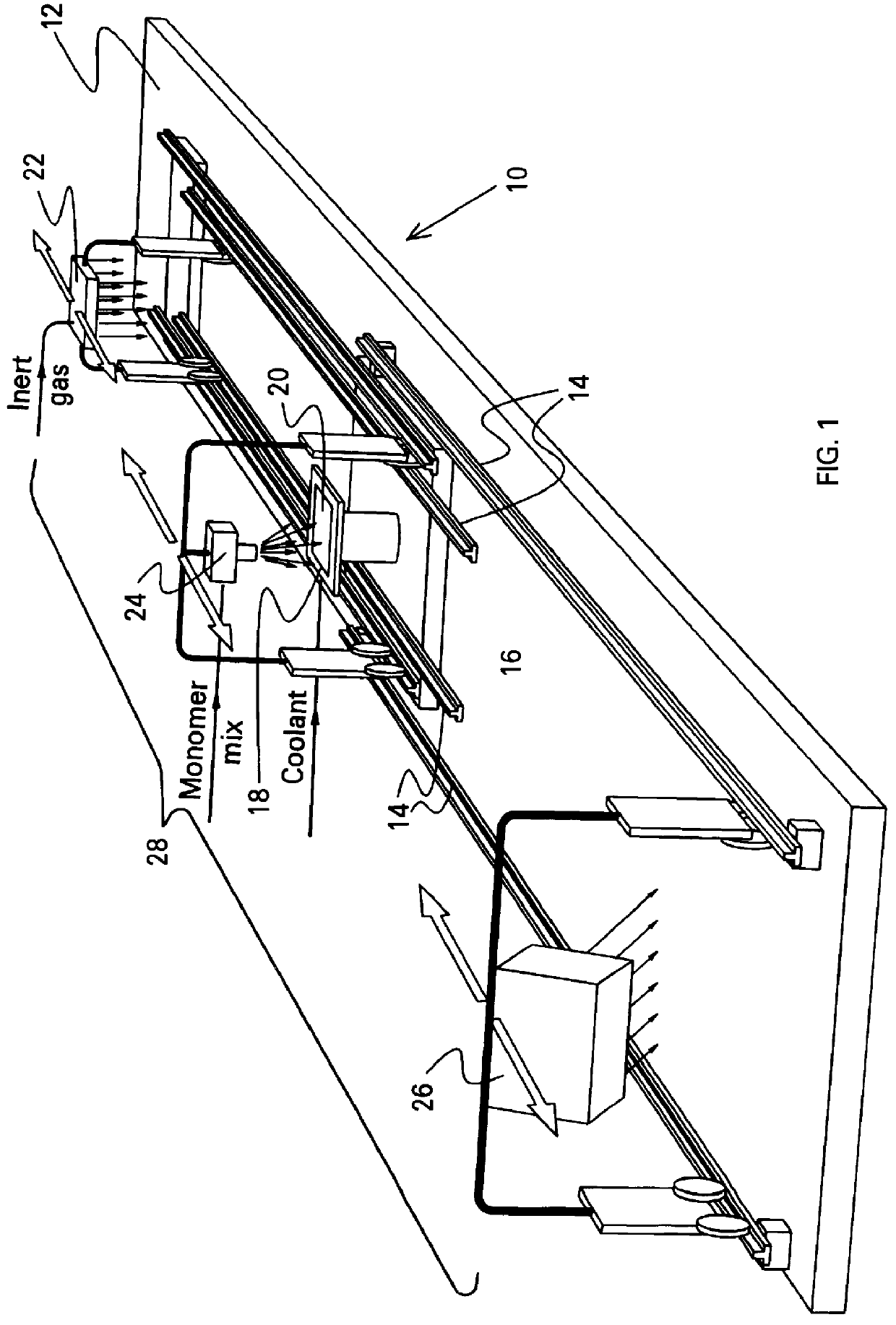
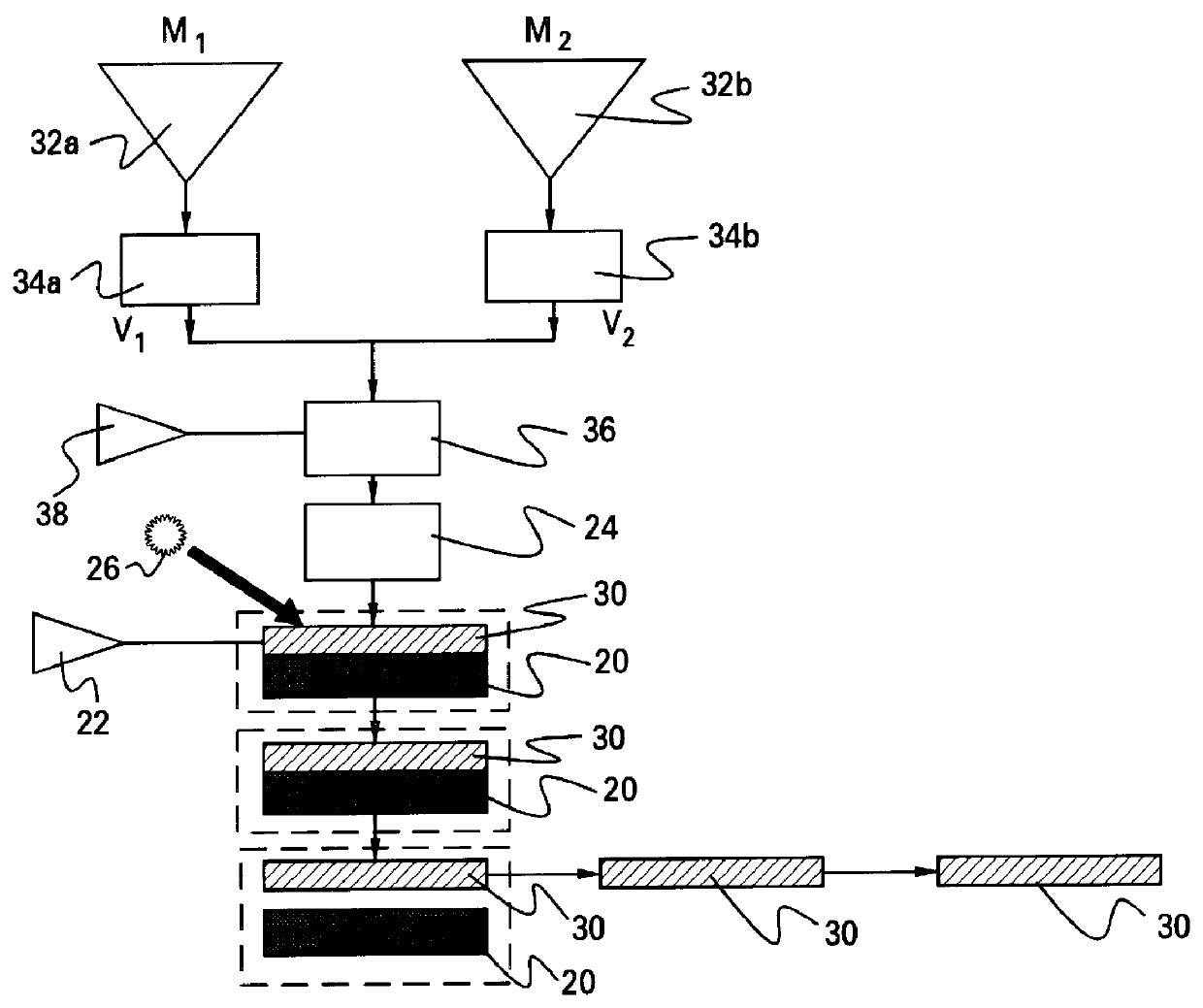
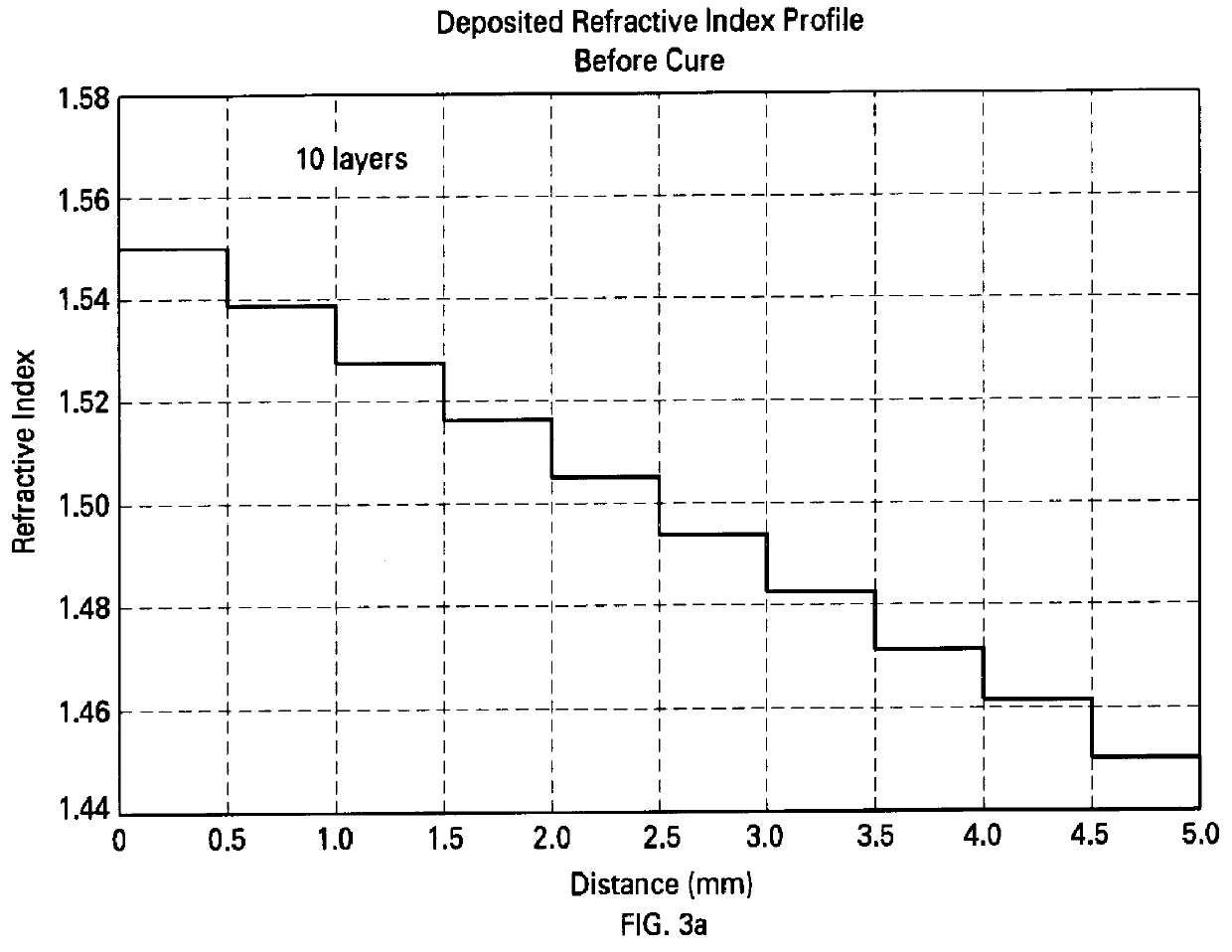
An apparatus and process are provided for depositing a polymeric element having a gradient in index of refraction that traverses the element from one surface to an opposite surface (axially graded refractive index). Two (or more) monomers are mixed in varying proportions and spray-deposited onto a substrate to form a layer. Each layer is then exposed to light to form a polymeric layer, and another layer deposited. Where the light is UV radiation and a light-sensitive catalyst that is also sensitive to the ambient atmosphere is used, then an inert gas dispenser, which provides an inert gas over the monomer layer, may be employed in conjunction with the UV radiation. Several layers are thus spray-deposited and exposed to light, each layer comprising a different mix of the two monomers, thereby providing each layer with a different index of refraction. After the prescribed number of layers has been deposited, the polymeric element is heat-treated to cause fusion of the layers and diffusion of components, thereby smoothing out the gradient profile. The apparatus and process of the invention are also useful in producing structural gradients in polymeric elements.
Owner:LIGHTPATH TECH INC
Apparatus and method for a high-gain double-clad amplifier
ActiveUS7526167B1Suppress instabilityEffectiveLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberLength wave
An optical apparatus design and method for suppressing cladding-mode gain in fiber- and other waveguide-amplification devices. In some embodiments, a signal-wavelength-absorbing core or region is included within the pump cladding or the pump waveguide, in order to absorb signal-wavelength radiation that occurs in the regions where only pump-wavelength radiation is wanted. This absorbing region prevents cladding-mode gain, thus preserving more pump-wavelength excitation for amplifying the desired signal radiation. In other embodiments, the refractive-index profile of the fiber or other waveguide is adjusted to reduce the numeric aperture and thus reduce the angle of light that will remain in the cladding. Since amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) occurs at all angles, a lower-NA fiber will leak a higher proportion of ASE (since a relatively lower portion of the ASE radiation is within the smaller angle that is retained within a low-NA fiber), while pump light, which was introduced into the fiber within the lower-NA angle will remain in the cladding.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Polarisation asymmetric active optical waveguide, method of its production, and its uses
InactiveUS6151429AIncrease photosensitivityHigh refractive indexOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical resonator shape and constructionDopantWaveguide lasers
A method of producing an active optical waveguide having asymmetric polarization, said method comprising the steps of (a) providing an active optical waveguide (10) comprising: (i) a transverse refractive index profile (21) comprising a guiding region (11), an intermediate region (13), and a non-guiding region (12); (ii) a transverse photorefractive dopant profile (31) comprising a constant or graded photorefractive dopant concentration within at least one of the guiding, non-guiding and intermediate regions, except that the photorefractive dopant is not located solely in the guiding region; and (iii) exhibiting in said guiding region, intermediate region, or both, light guiding modes having different polarizations; and (b) exposing at least a part (10a, 10b) of the active optical waveguide to an effective transverse illumination of light (20) reacting with the photorefractive dopant and modifying said transverse refractive index profile; said part of the active optical waveguide being exposed to a fluence selectively suppressing the propagation of the light guiding modes having different polarizations so that the propagation of one mode is less suppressed than the propagation of the other mode(s). Such an active optical waveguide, single polarization mode optical waveguide lasers and multi-wavelength single polarization mode optical waveguide lasers comprising such an active optical waveguide, methods of their production, and their uses in telecommunications, in spectroscopy, in sensors and in absolute calibrated laser light sources.
Owner:KOHERAS +1
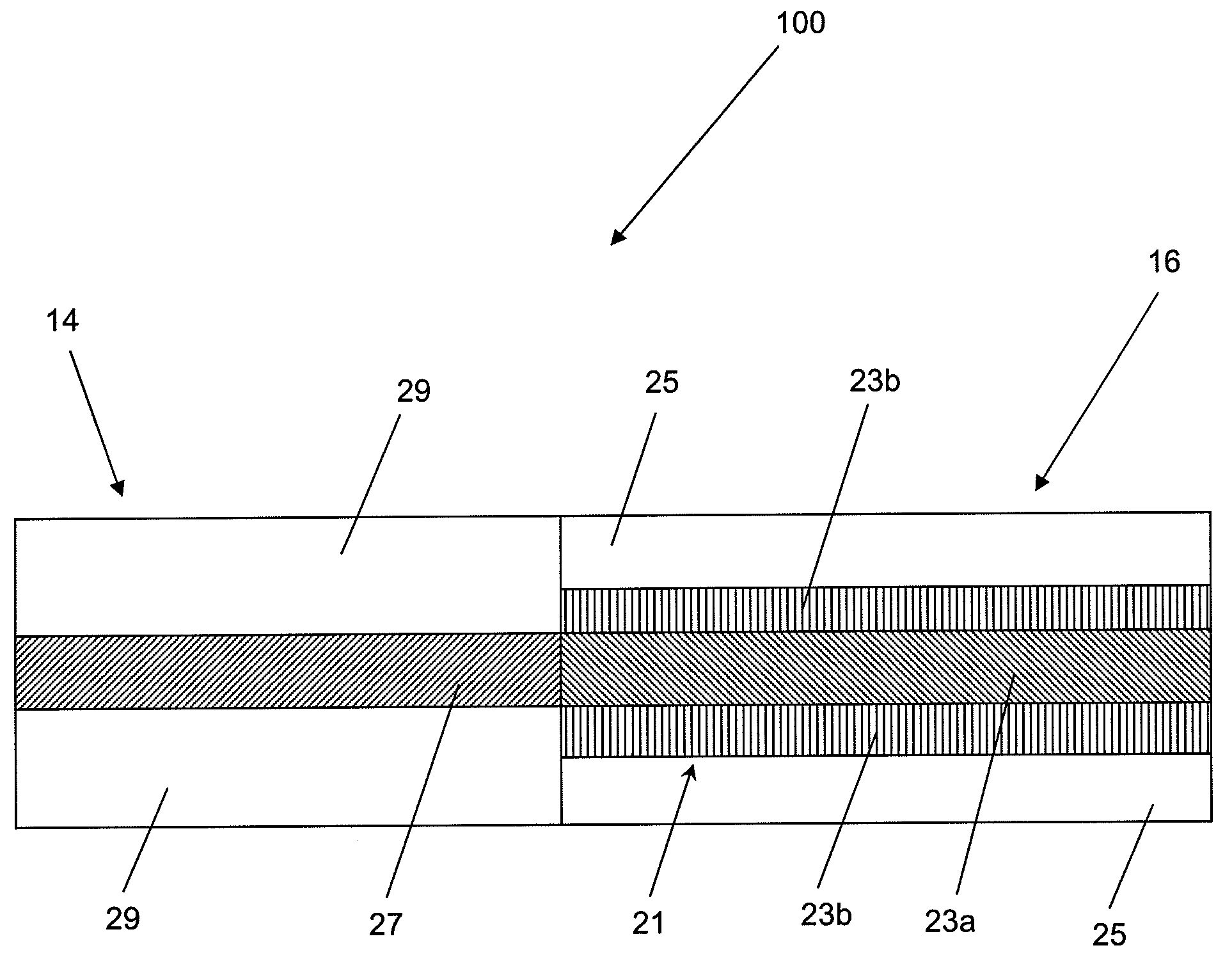
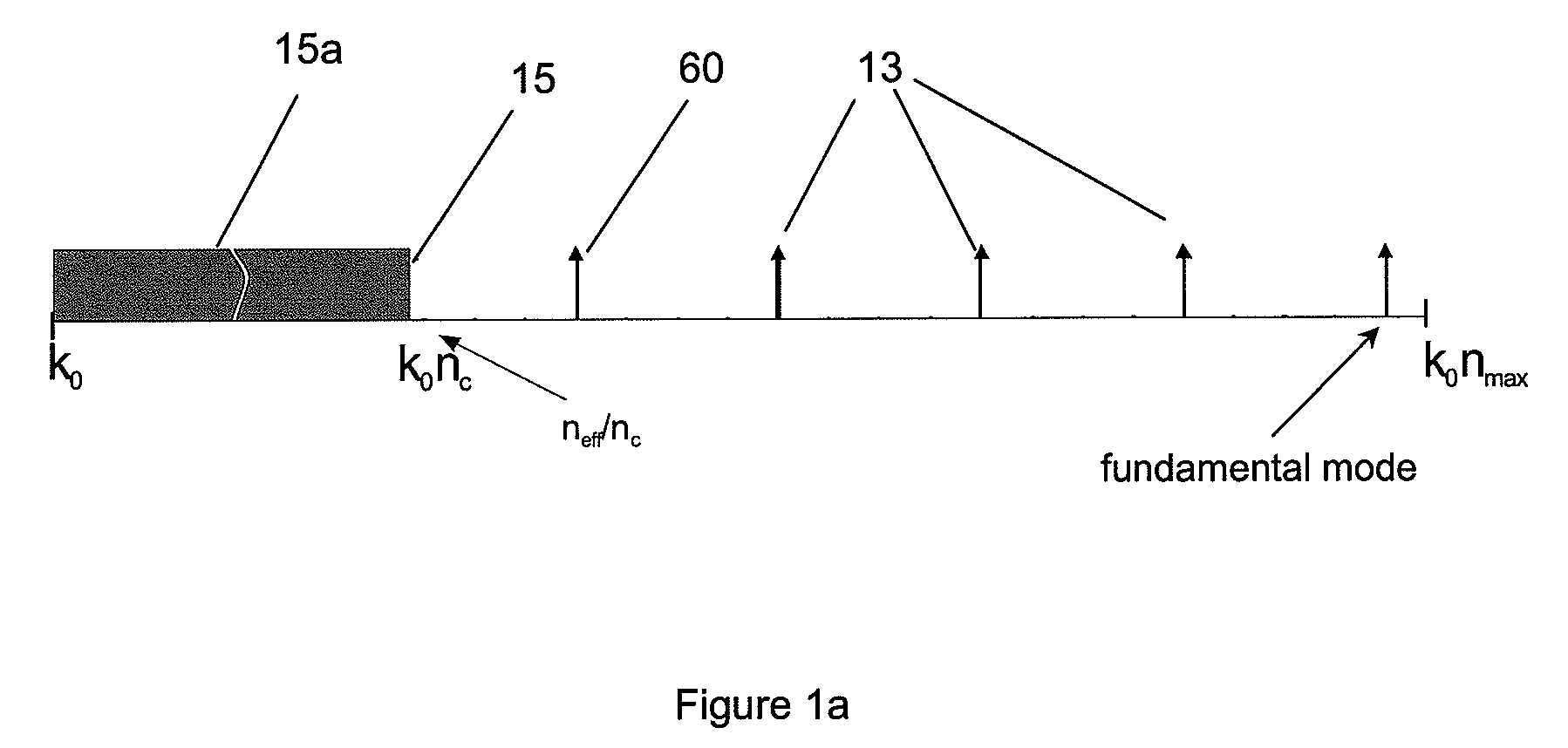
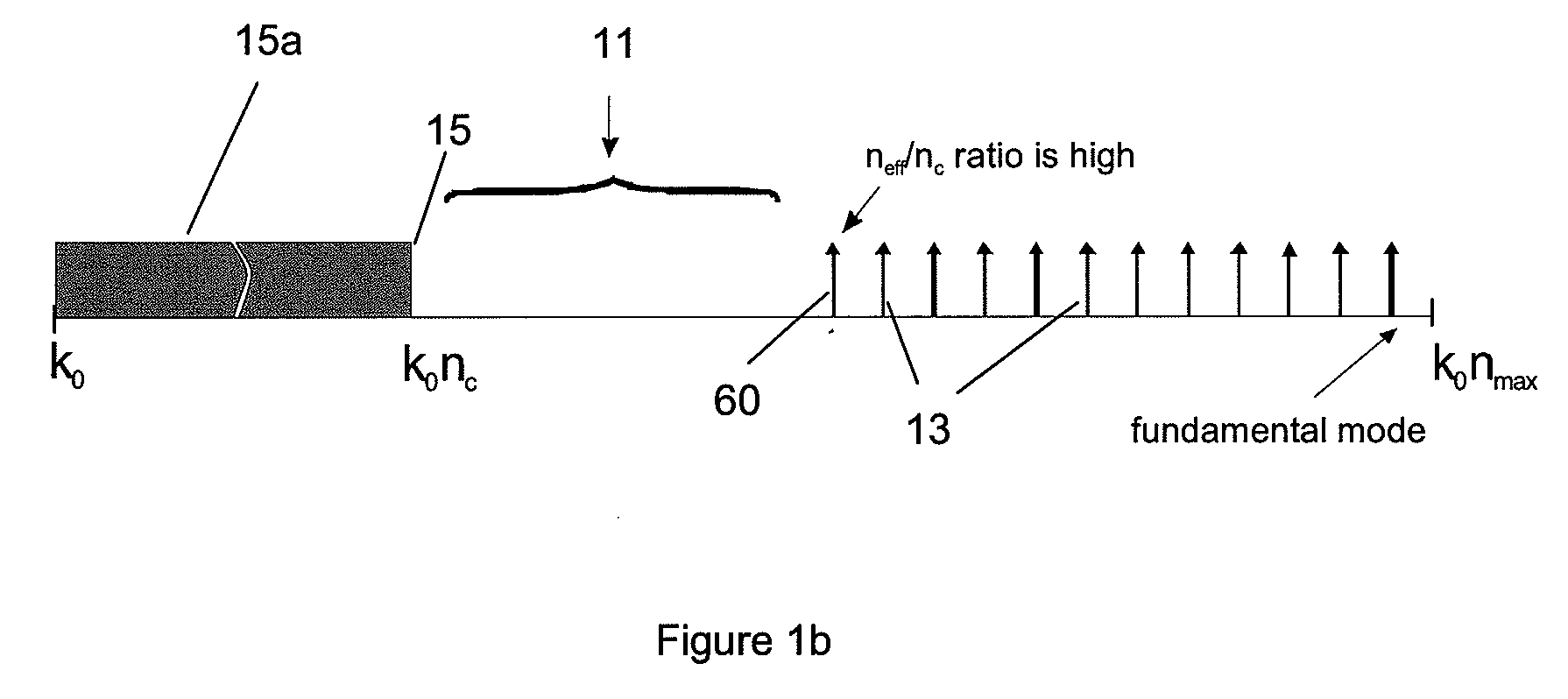
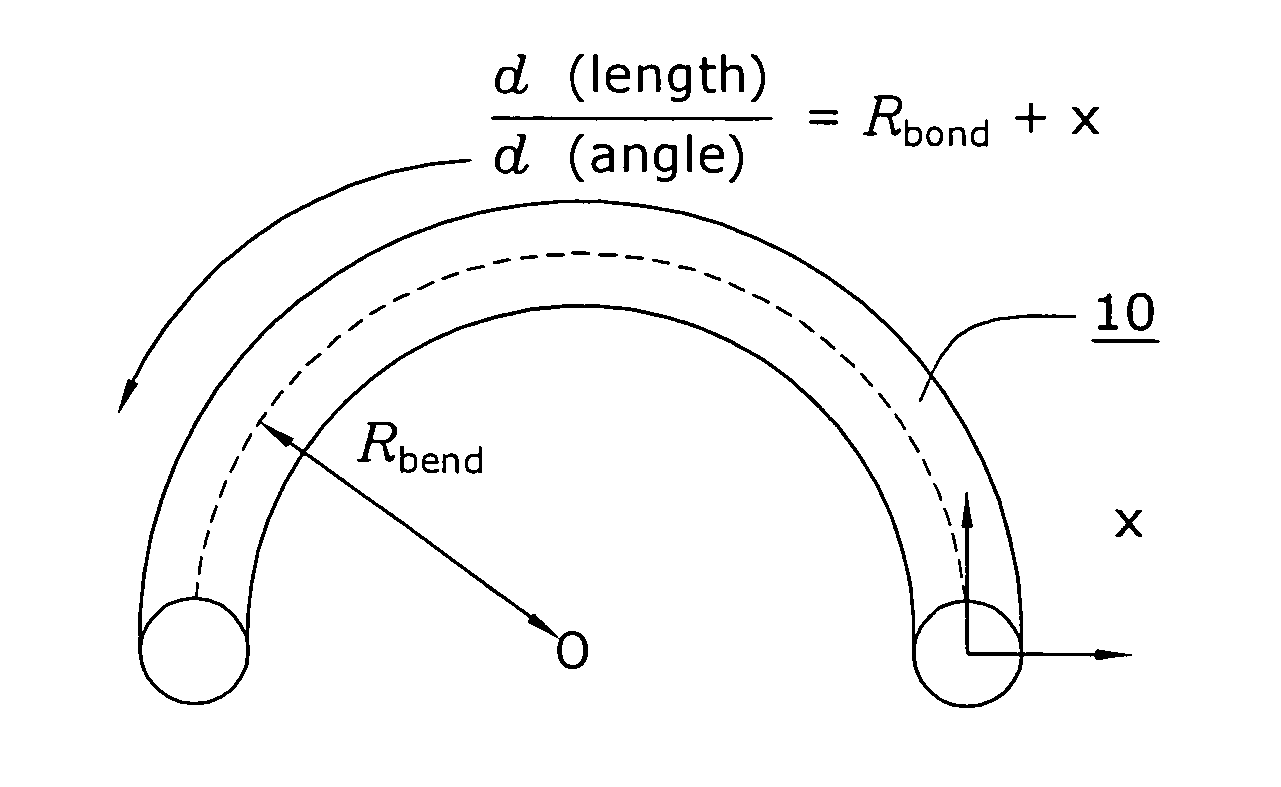
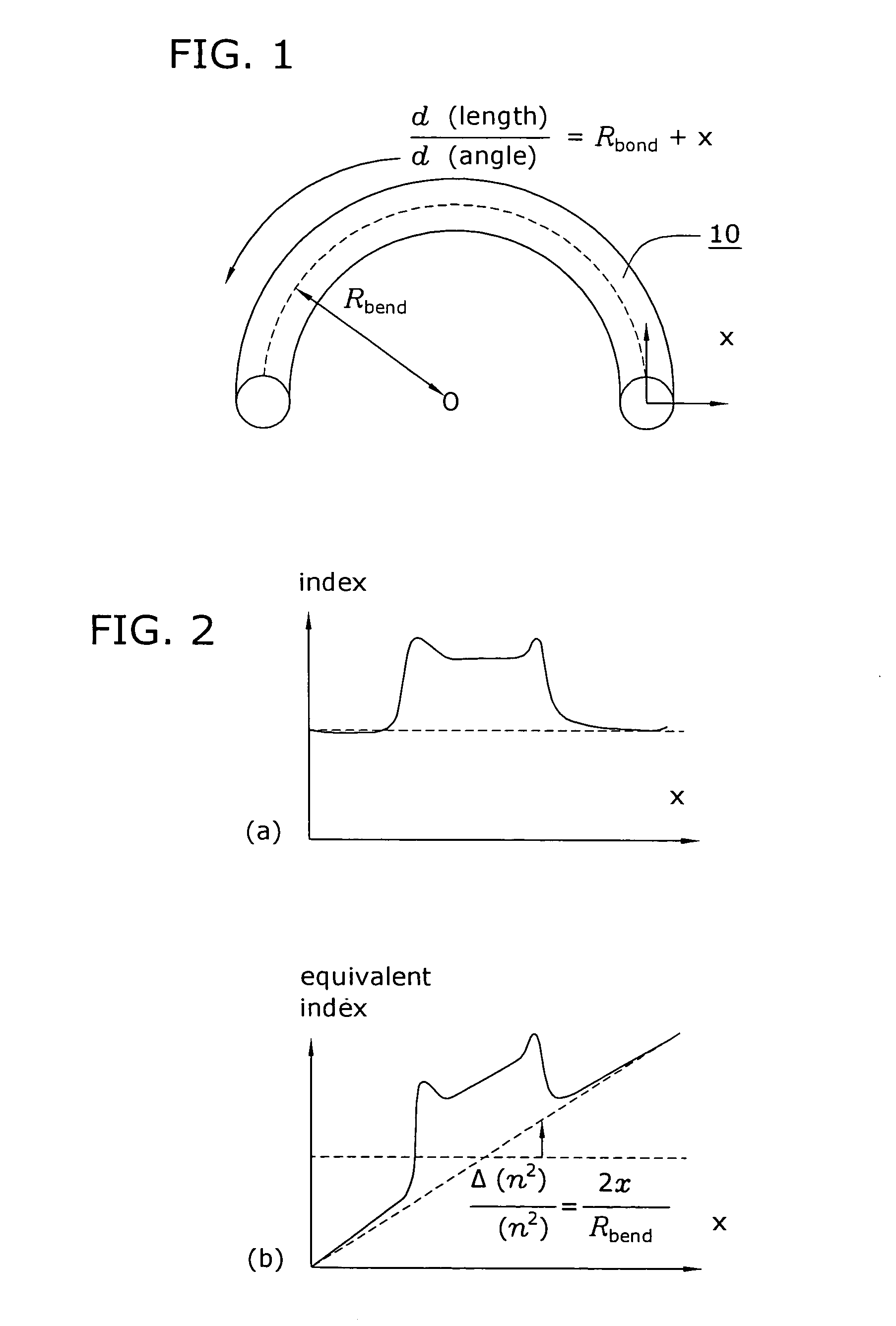
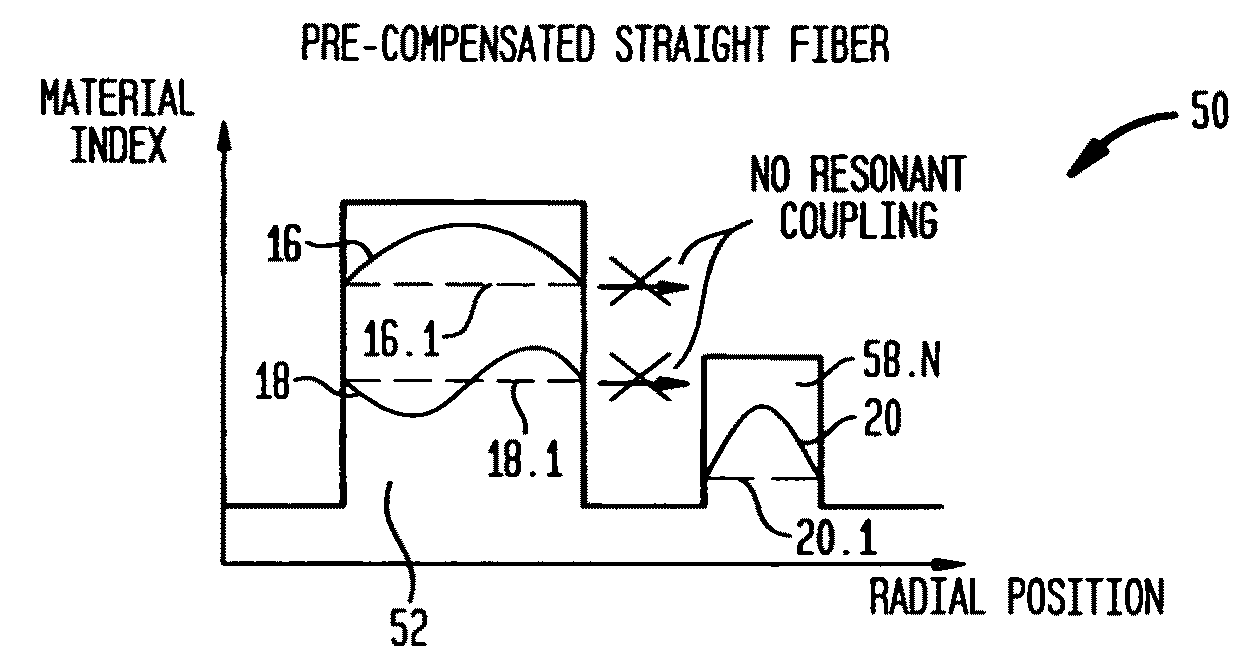
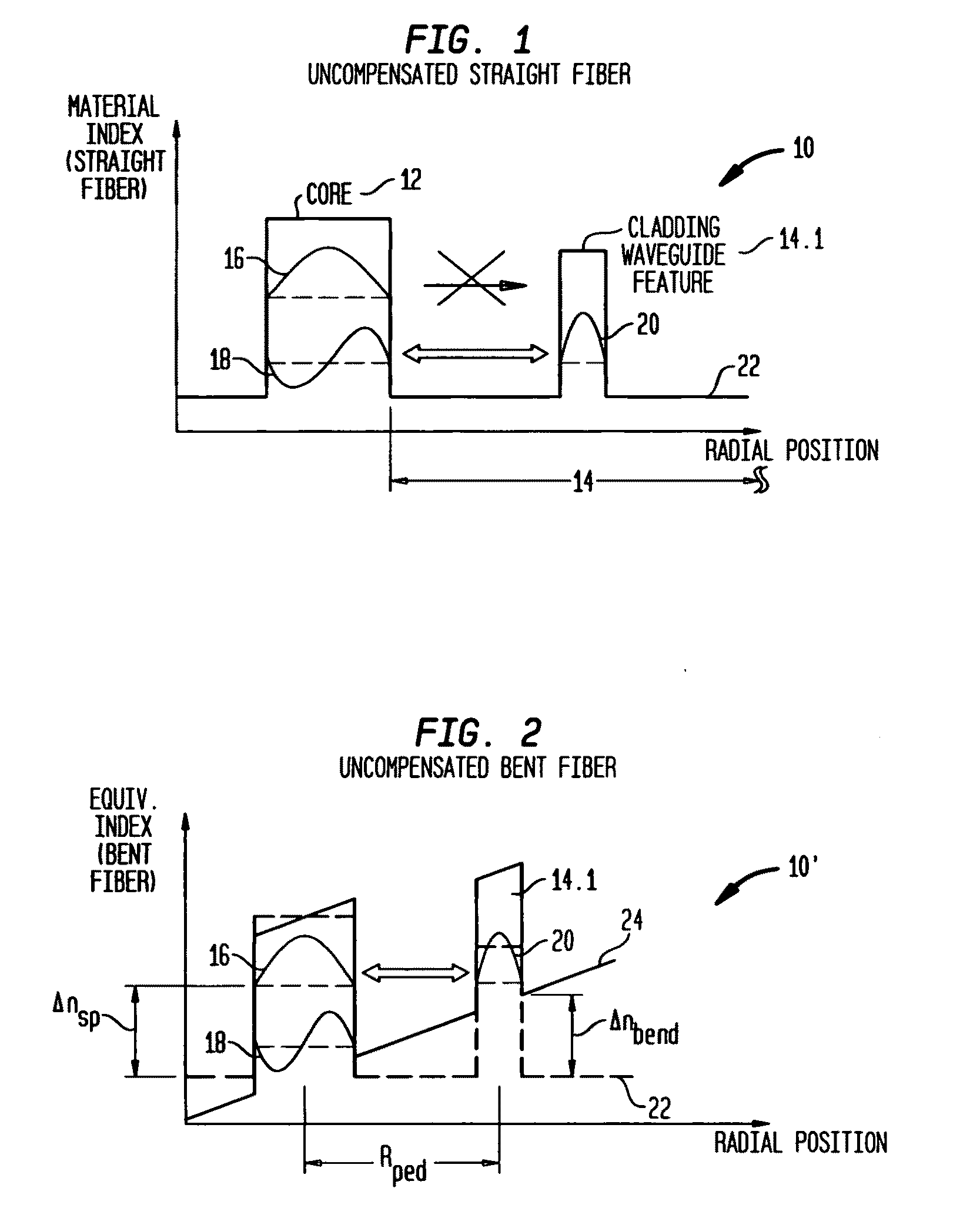
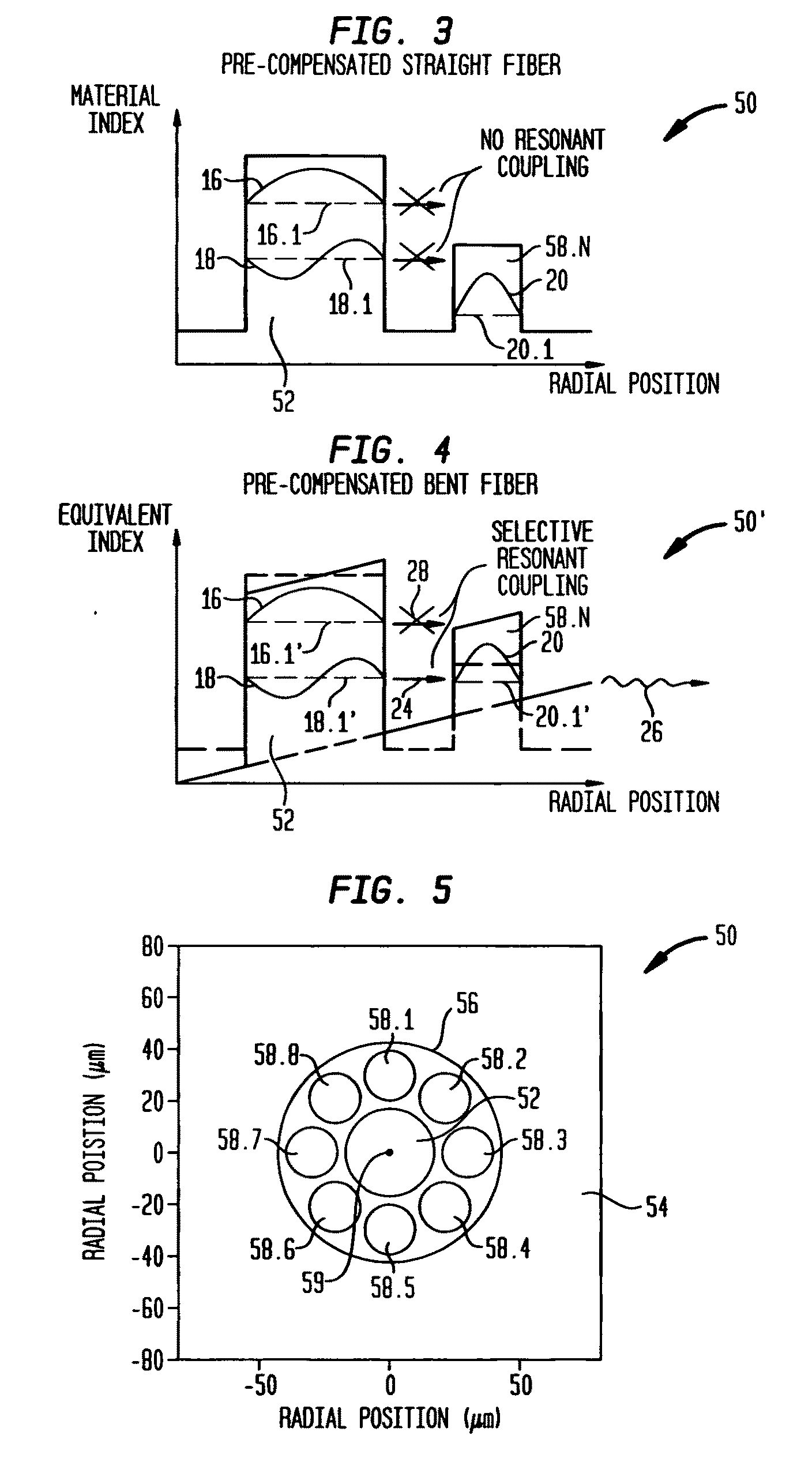
Suppression of higher-order modes by resonant coupling in bend-compensated optical fibers
ActiveUS20090034059A1High fundamental mode lossLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberCoupling
The effect of bending is anticipated in an optical fiber design, so that resonant coupling remains an effective strategy for suppressing HOMs. The index profile of the fiber and its bend radius are configured so that there is selective resonant coupling of at least one HOM, but not the fundamental mode, in the bent segment of the fiber. In an illustrative embodiment, the bend radius (or predetermined range of bend radii) of an optical fiber is known a priori. The core and cladding regions are configured to support (guide) the propagation of signal light in a fundamental transverse mode and at least one higher-order transverse mode in the core region. The cladding region includes an outer cladding region and an annular trench region. The trench region includes at least one axially extending, raised-index pedestal (waveguide) region having a refractive index higher than that of the outer cladding region. Within at least the bent segment the at least one pedestal region is configured (i) to support the propagation of at least one transverse mode and (ii) to resonantly couple at least one of the higher-order transverse modes (HOMs) of the core region to at least one transverse mode (e.g., the fundamental mode) of the pedestal region when the fiber is bent to a radius within the predetermined range of radii. In effect, the pedestal regions are configured so that the fiber is pre-compensated for the effect of bending; that is, an uncompensated bent fiber segment suffers high fundamental mode loss due to resonant coupling, whereas the pre-compensated bent fiber segment selectively couples any unwanted HOM from the core region into the pedestal region. In a preferred embodiment, the optical fiber is a LMA fiber incorporated in an optical fiber amplifier or laser package.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com