Patents
Literature
1610 results about "Dispersion compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
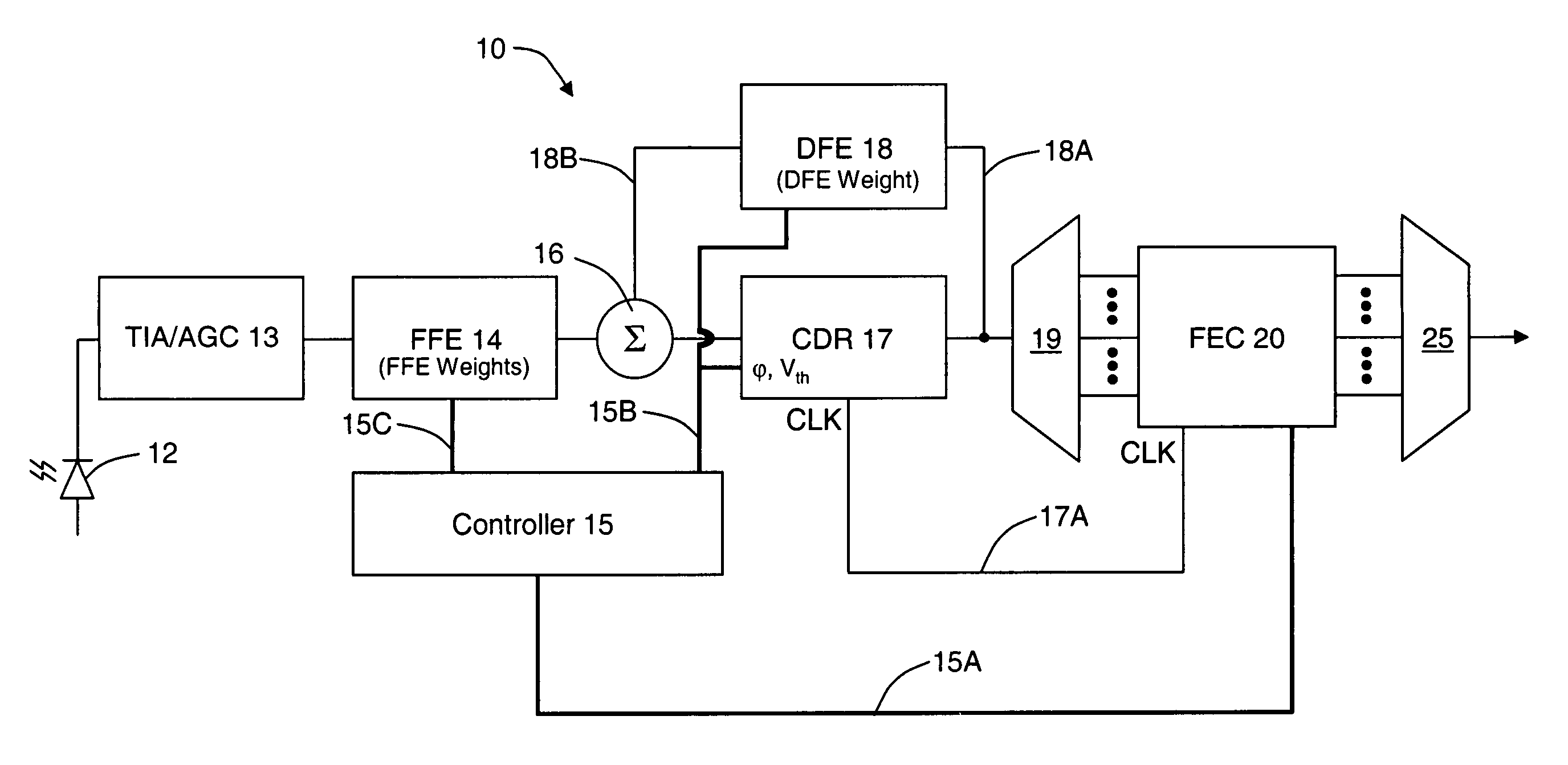
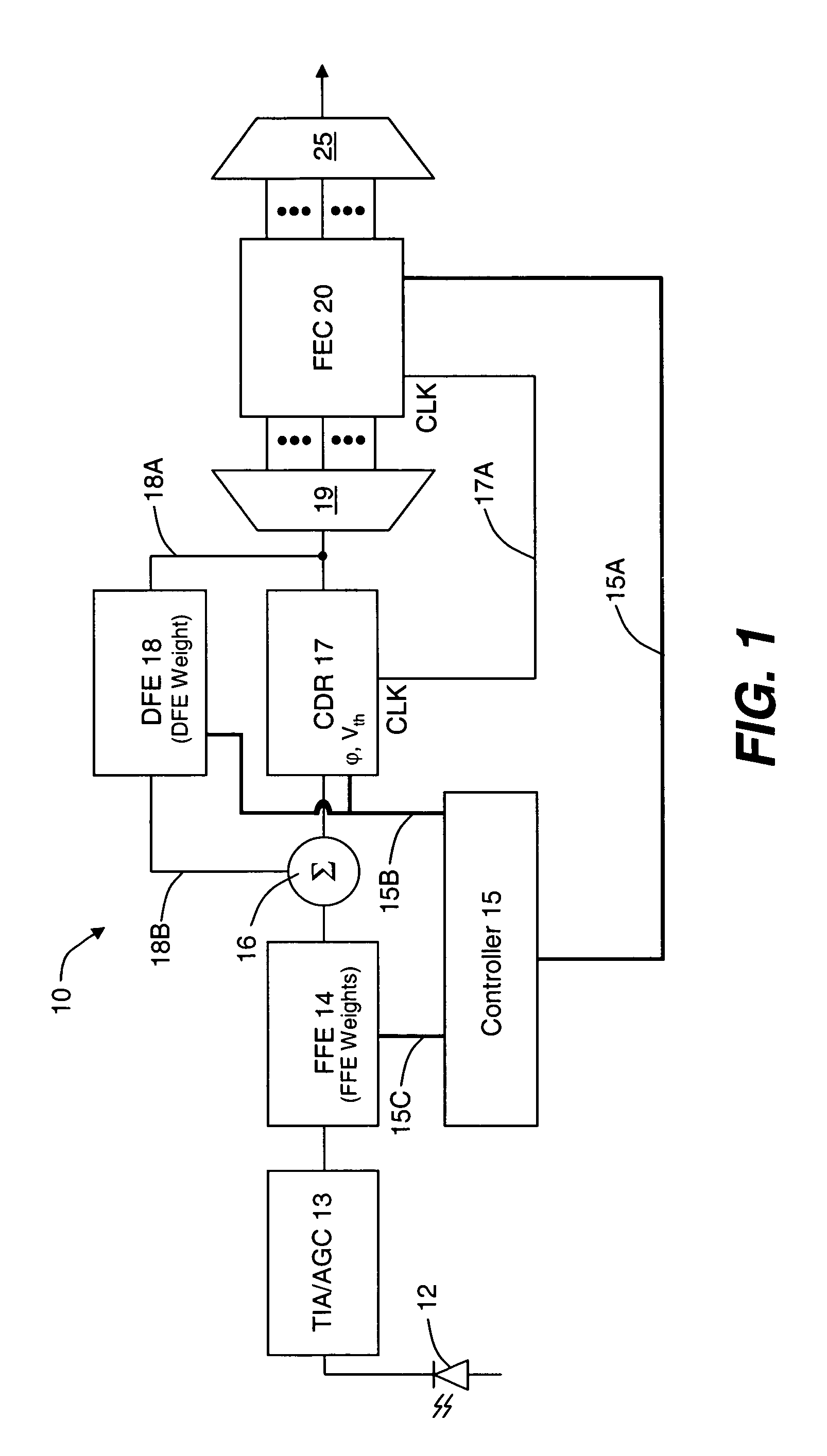
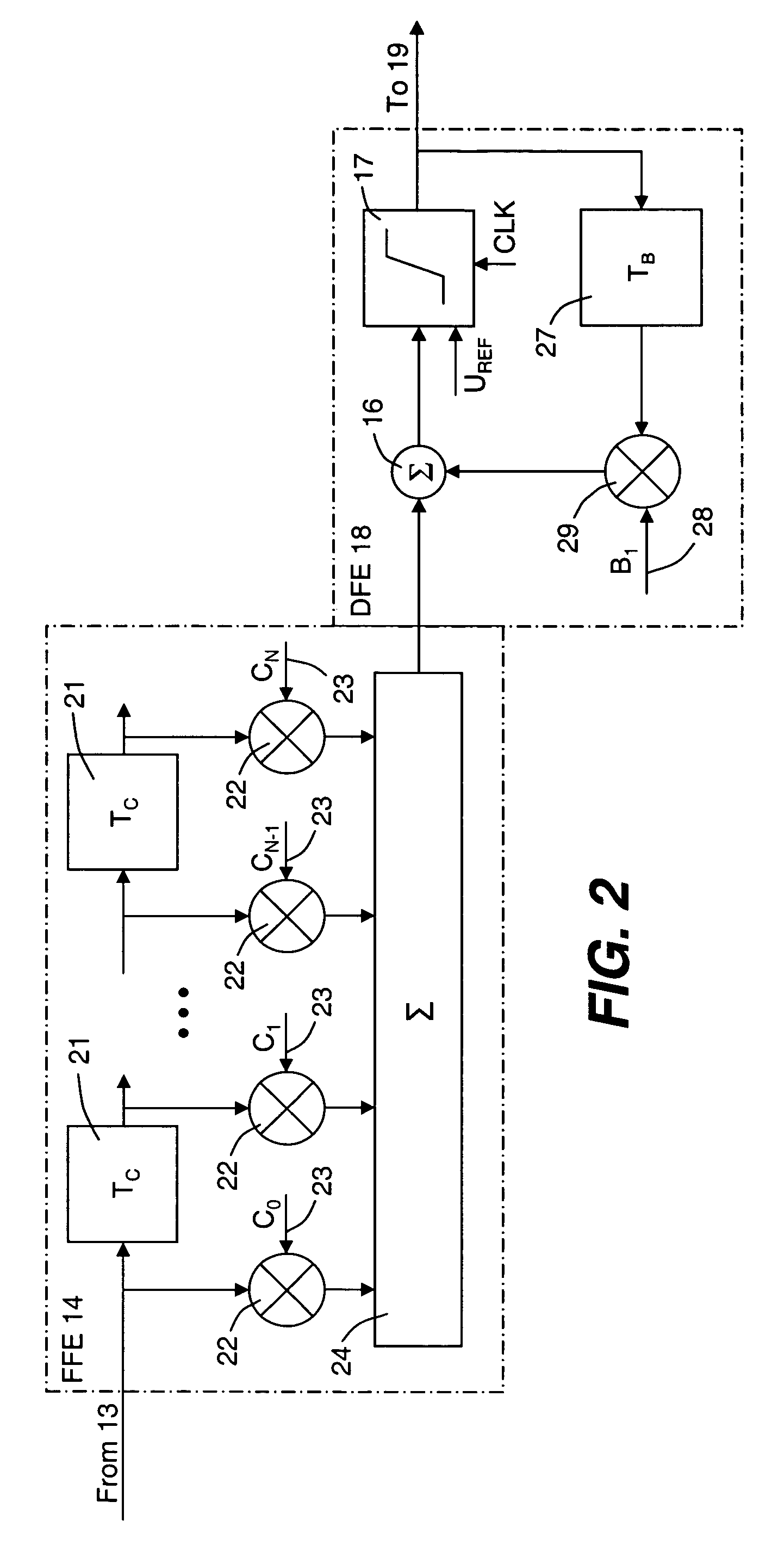
Dispersion compensation or dispersion management is the process of designing the fibers and compensating elements in the transmission path to control the total dispersion of a system to a small number.
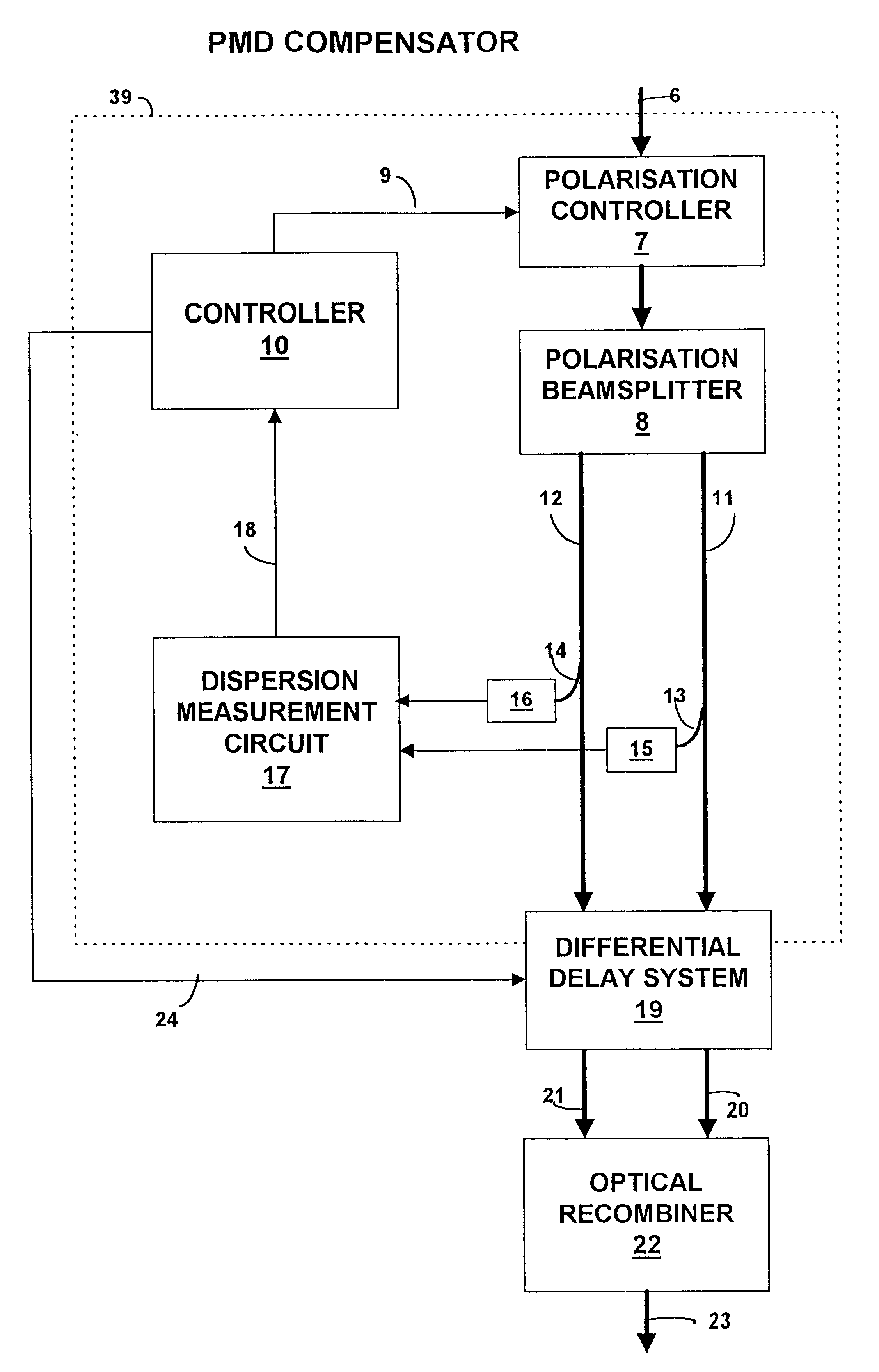
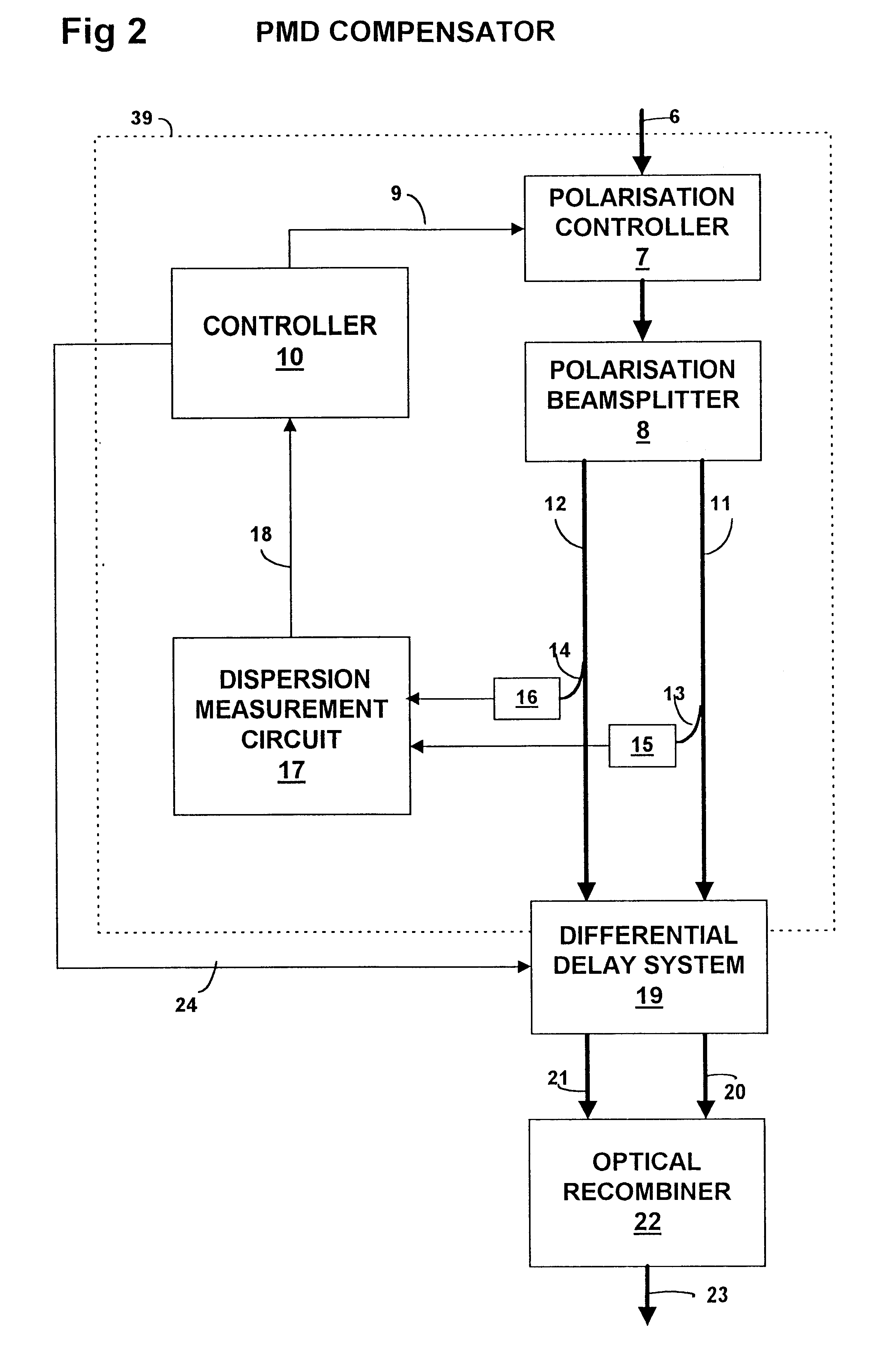
Polarization mode dispersion compensation
InactiveUS6271952B1Producing strainTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsGratingCommunications system
Polarization mode dispersion in an optical signal transmitted through a waveguide of a communications system is compensated by separating the dispersed signal into components corresponding to principal polarization states. The components are delayed by respective delays differing by a delay increment which is controlled to correspond to the dispersion delay and the delayed components are recombined to provide a dispersion compensated optical output signal. Each of the delays is provided by an chirped Bragg reflector forming part of a delay line, the Bragg reflectors comprising optical fibres with chirped intracore index gratings. Transducers or temperature controllers acting on one of the fibres allows dimensional control of the grating periodicity such that the position of Bragg reflection is variable. Wavelength division multiplexed optical signals are compensated using sampled gratings which allow a common Bragg reflection position for each wavelength.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
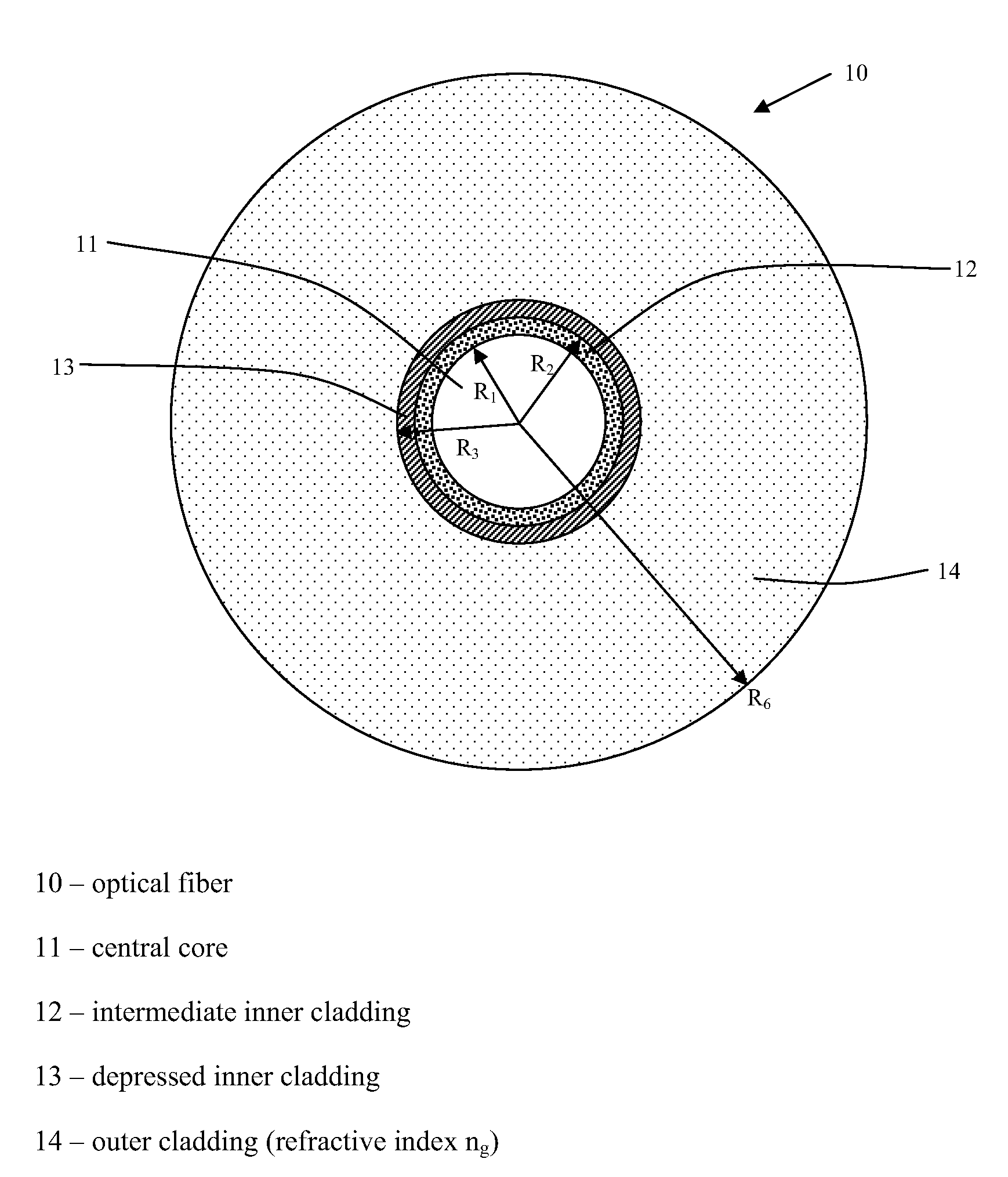
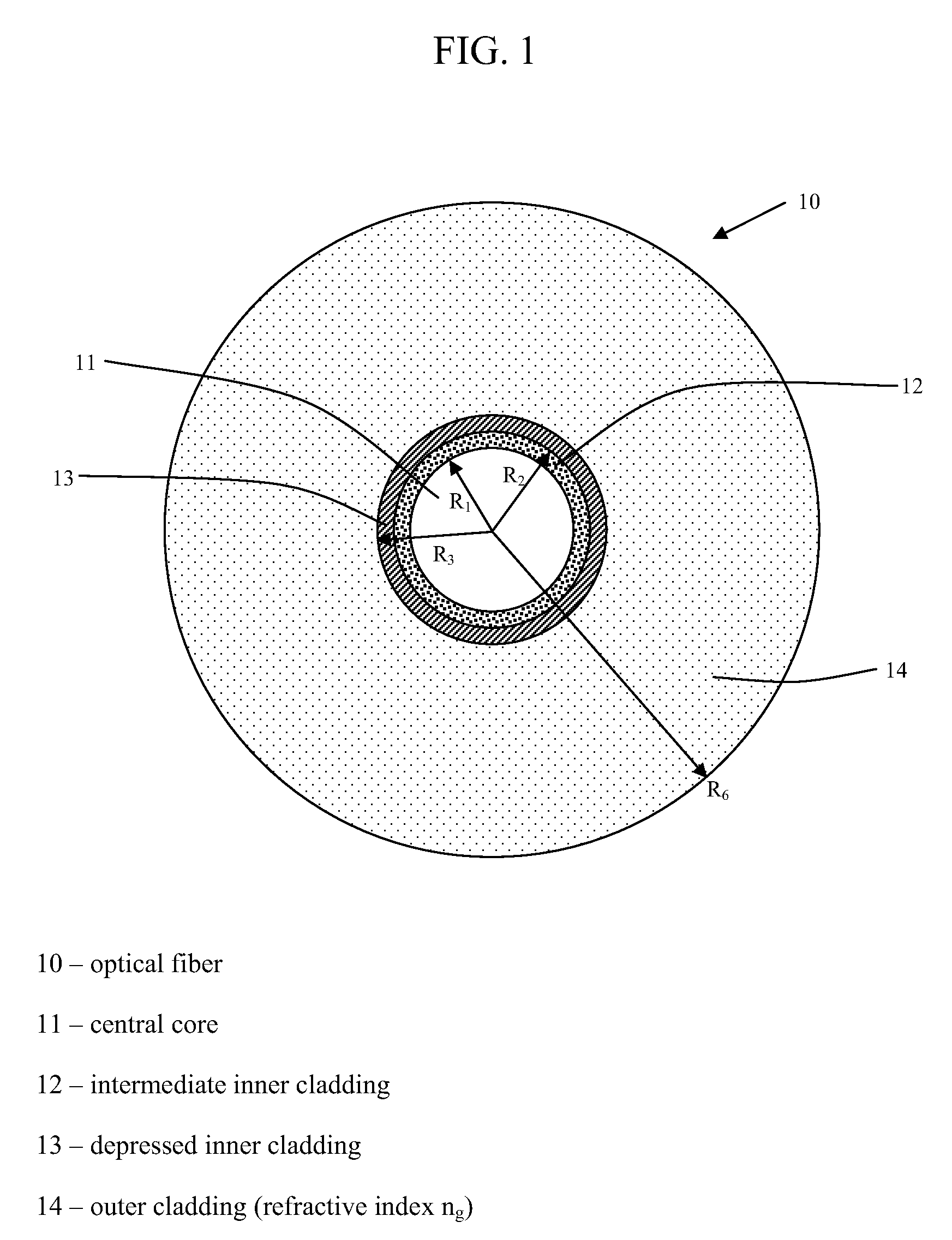
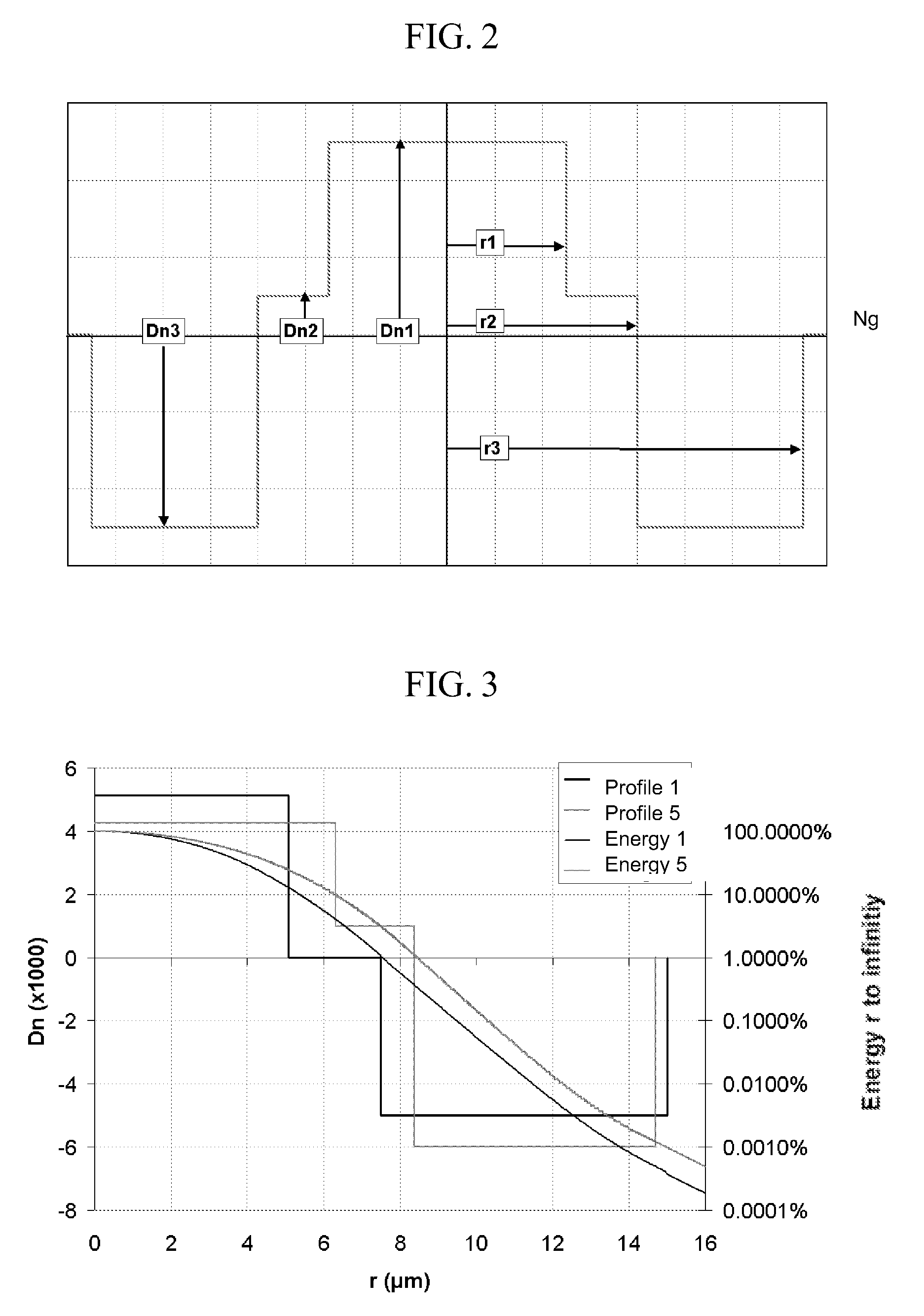
Chromatic dispersion compensating fiber
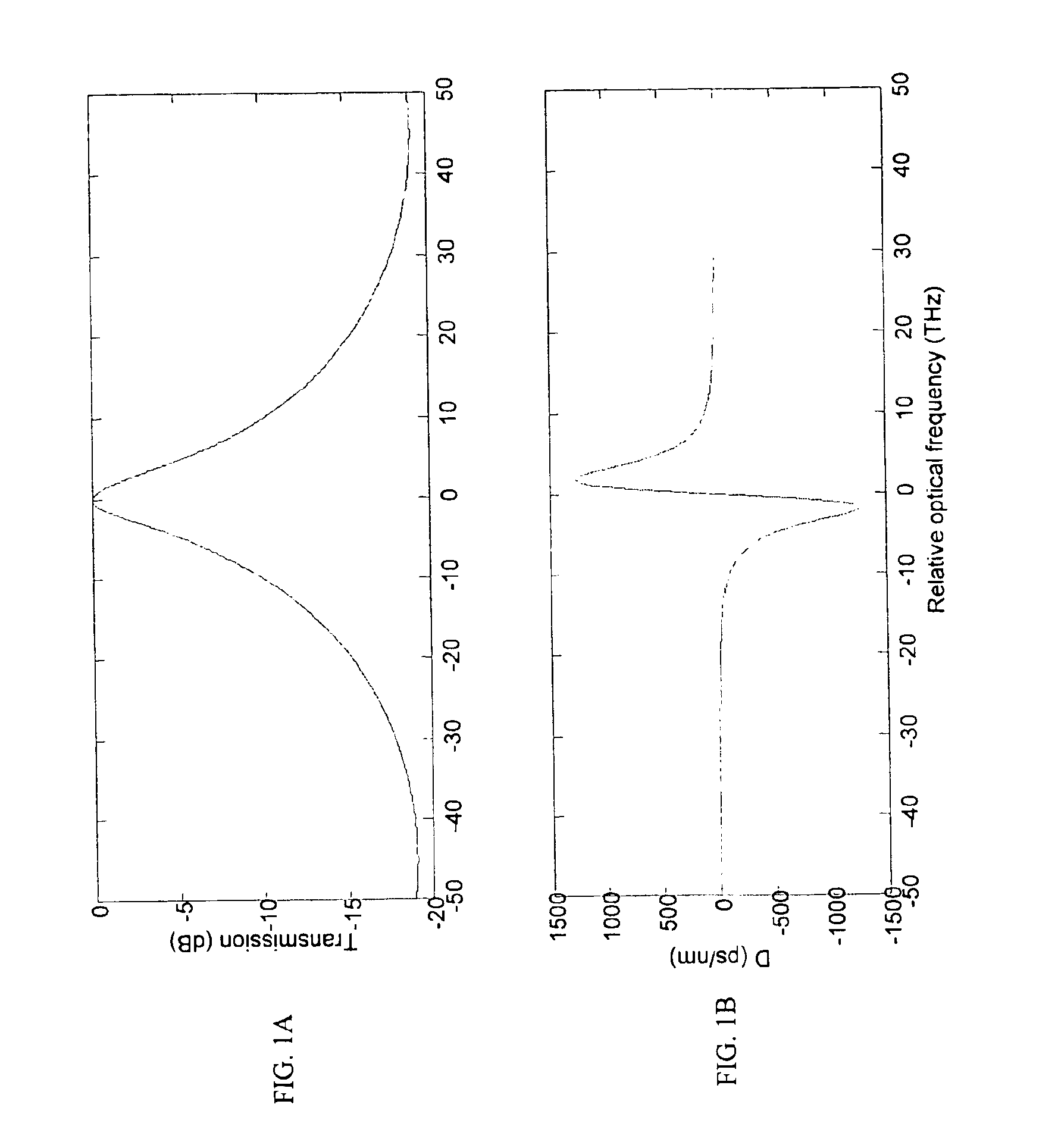
ActiveUS7356234B2Improved FOM valueLimited bending and micro-bending lossesOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideOptical ModuleRefractive index
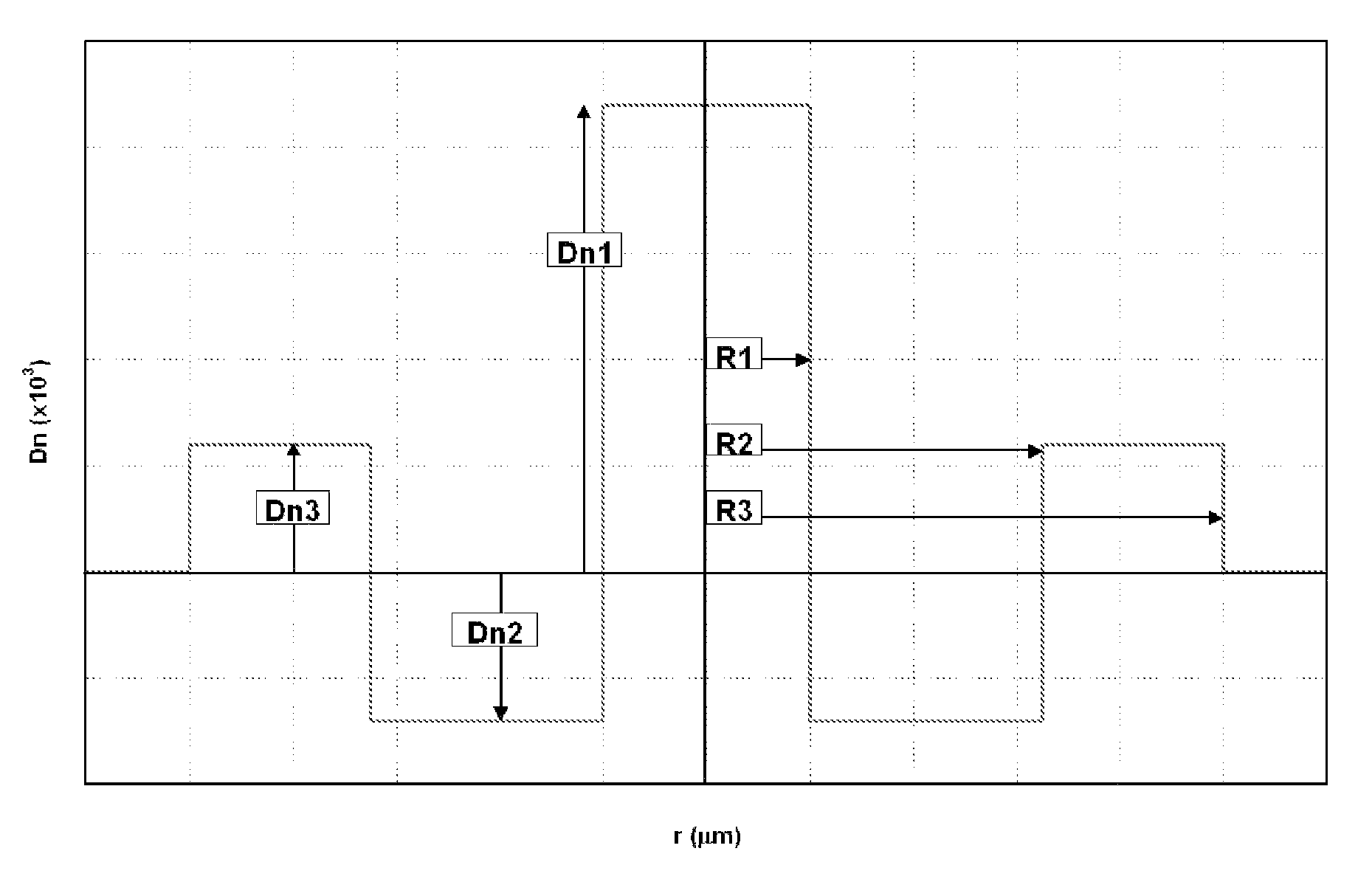
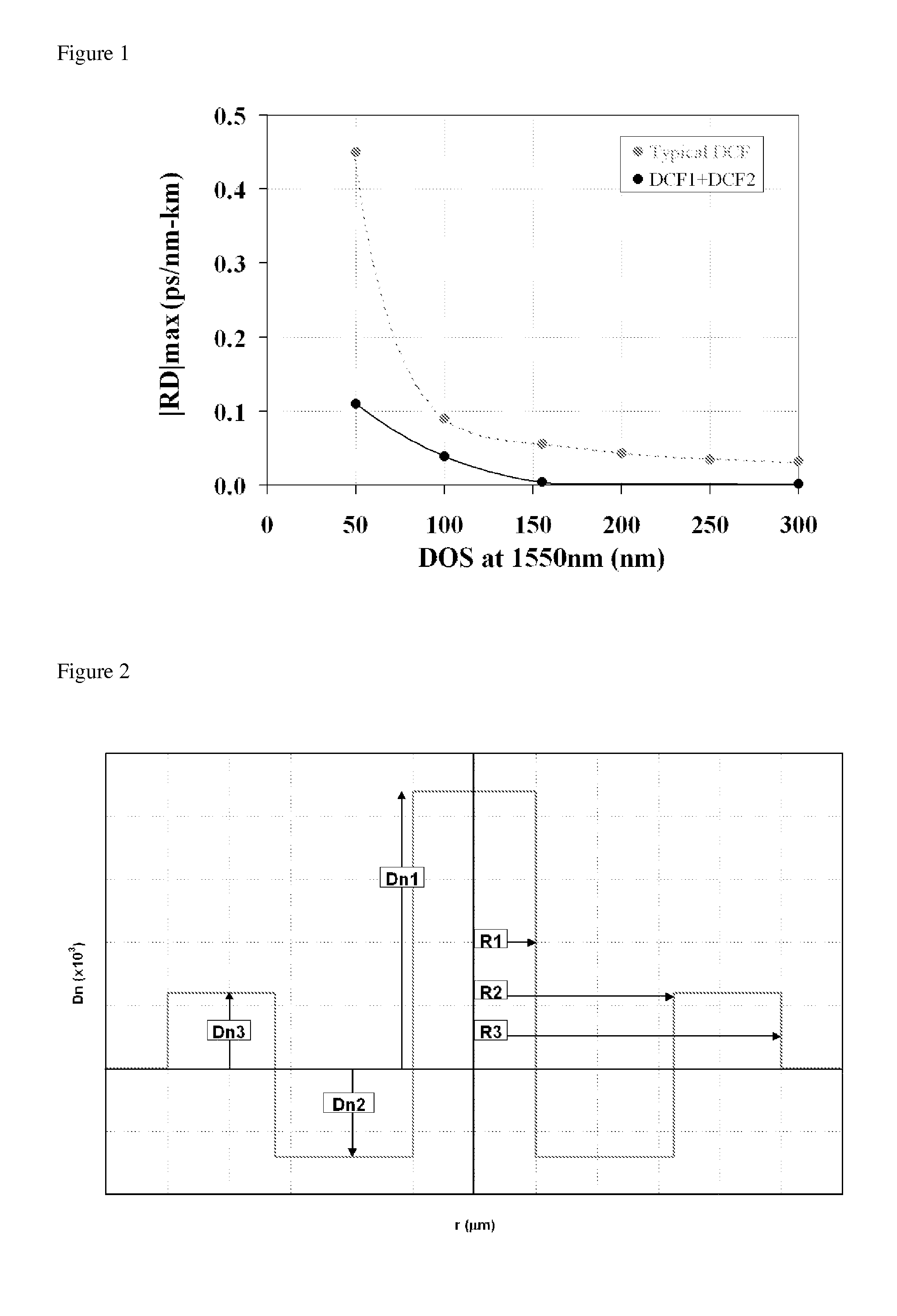
Disclosed is a chromatic dispersion compensating optical fiber comprising a central core, an intermediate cladding having a width (r2−r1) of 2.0 microns or greater, and a depressed inner cladding having a refractive index difference Dn3 with the external optical cladding of −3.0×10−3 or lower. At a wavelength of 1550 nm, the optical fiber exhibits a positive chromatic dispersion of 21 ps / (nm·km) or higher and a ratio of mode radius to intermediate cladding radius of (W02 / r2) of 0.7 or less. The present optical fiber has a good figure of merit value and limited bending and microbending losses. The optical fiber can be rolled up in a housing of reduced size in a chromatic dispersion compensating optical module having limited insertion losses and reduced polarization mode dispersion.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
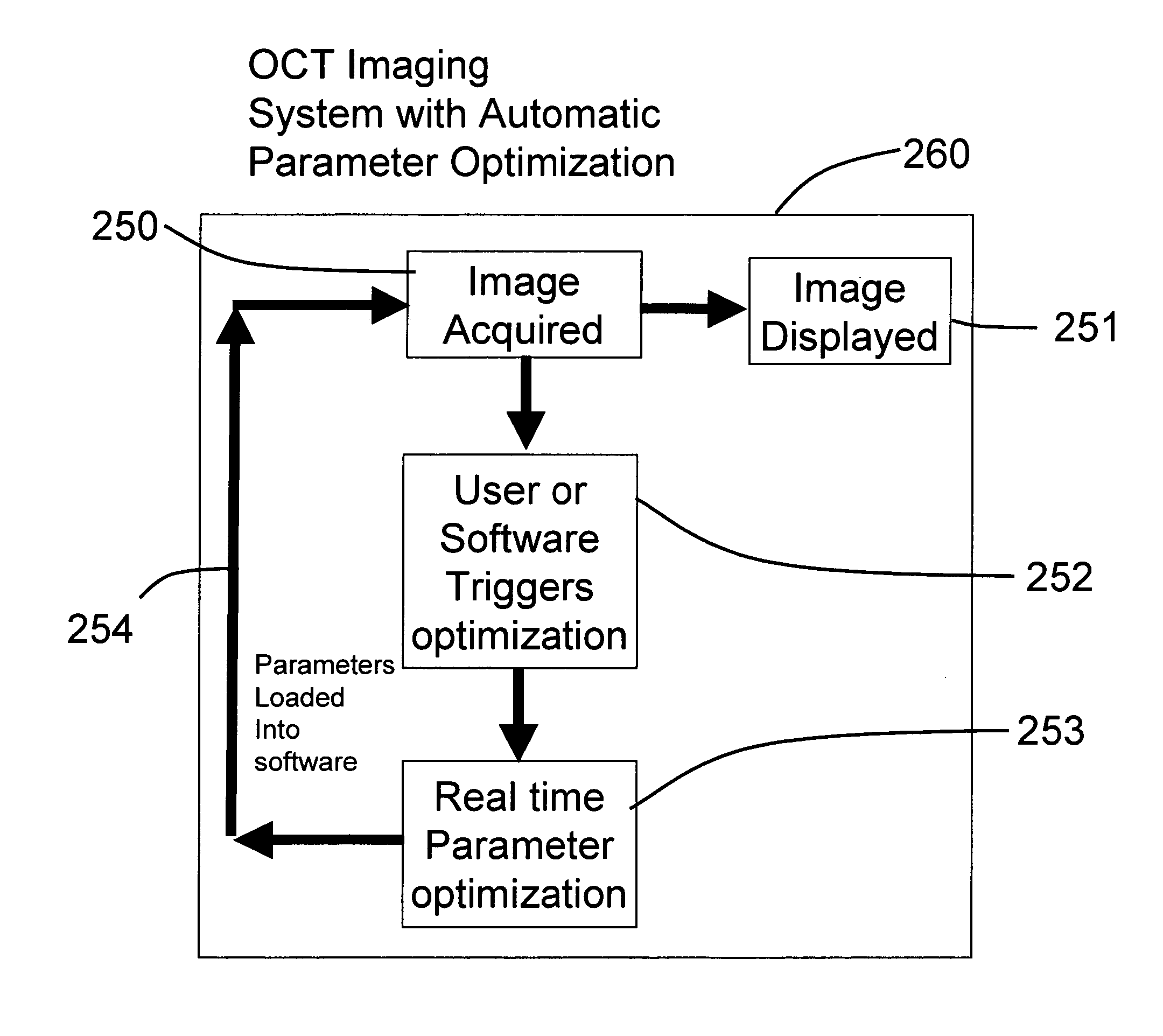
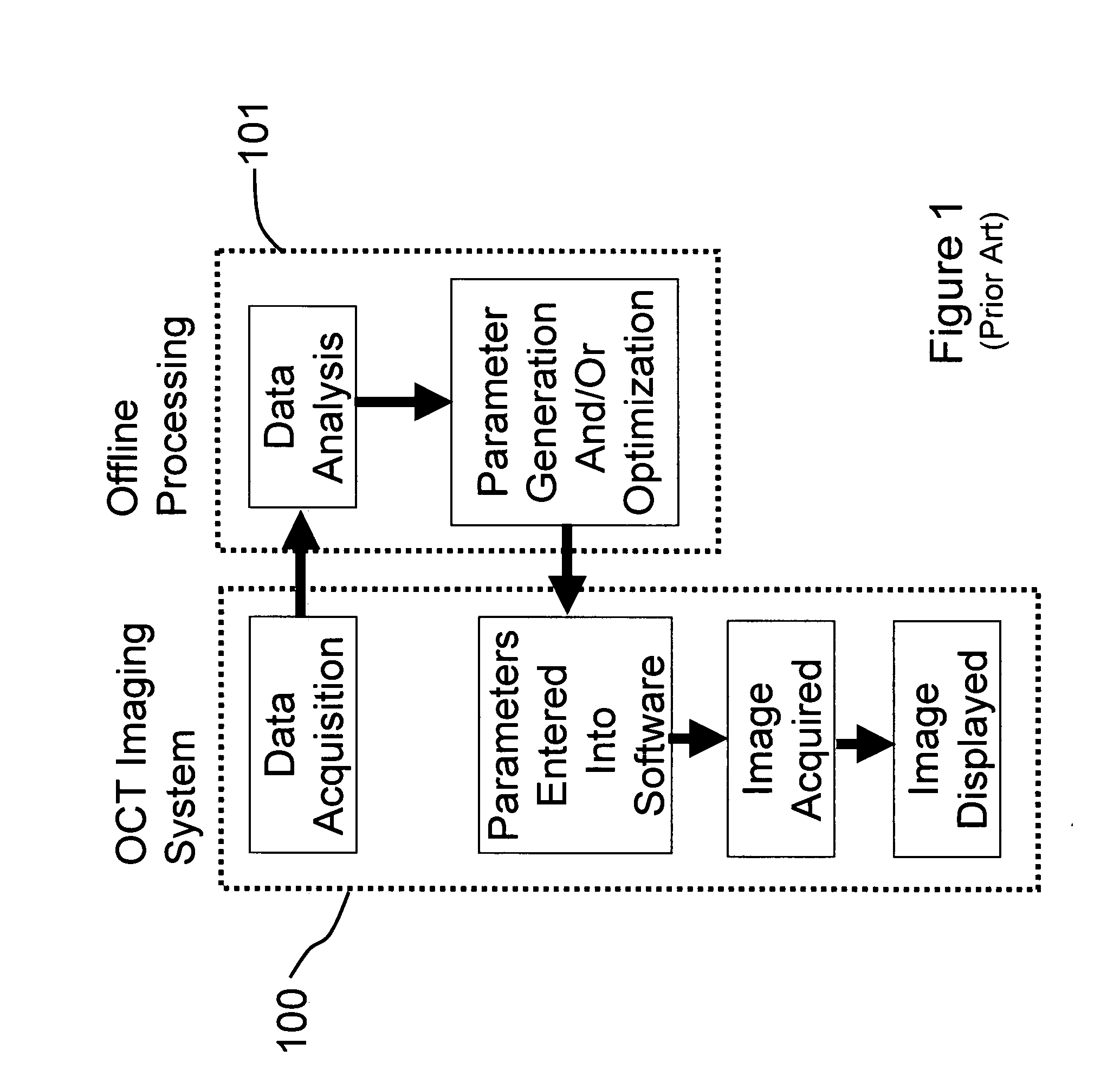
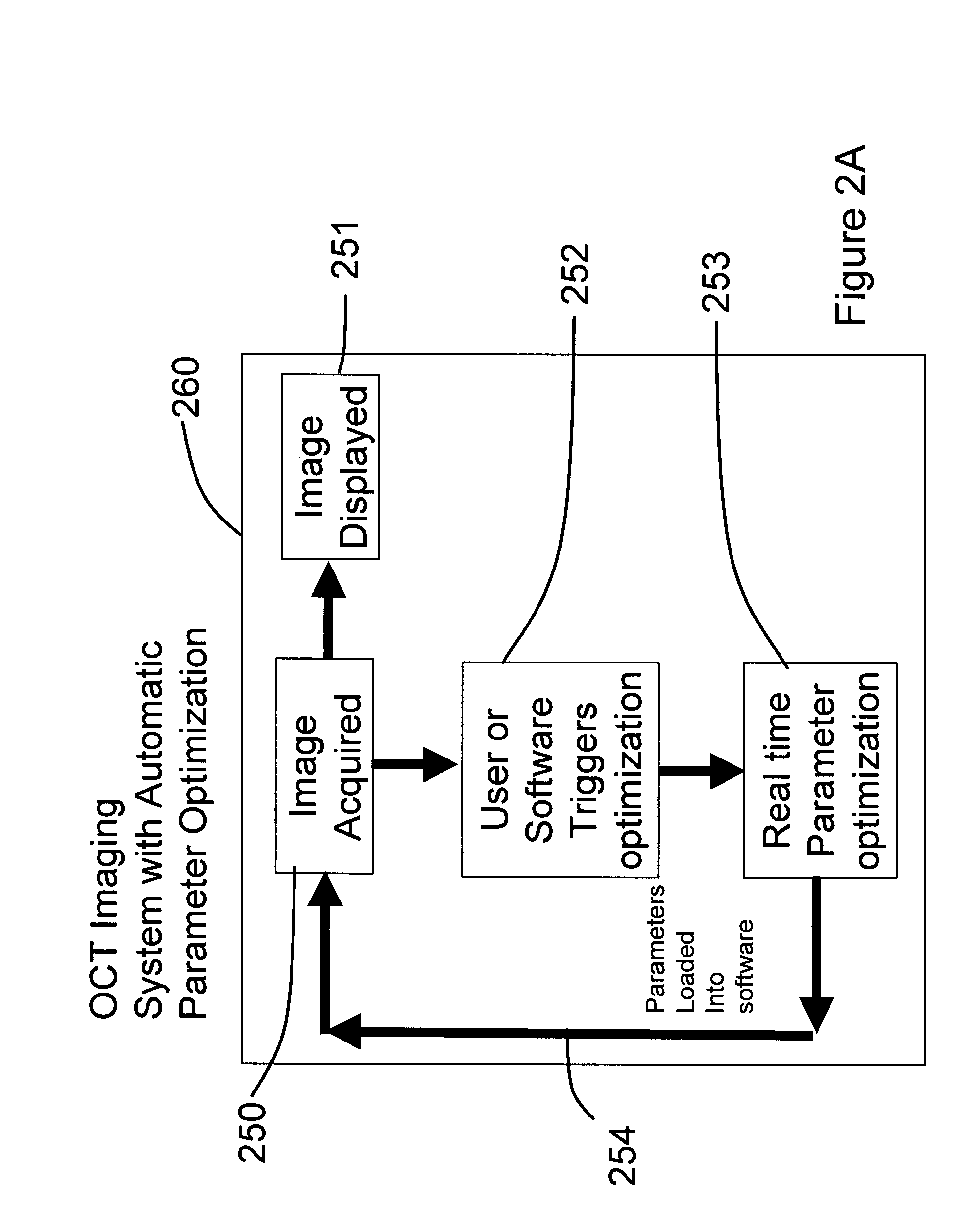
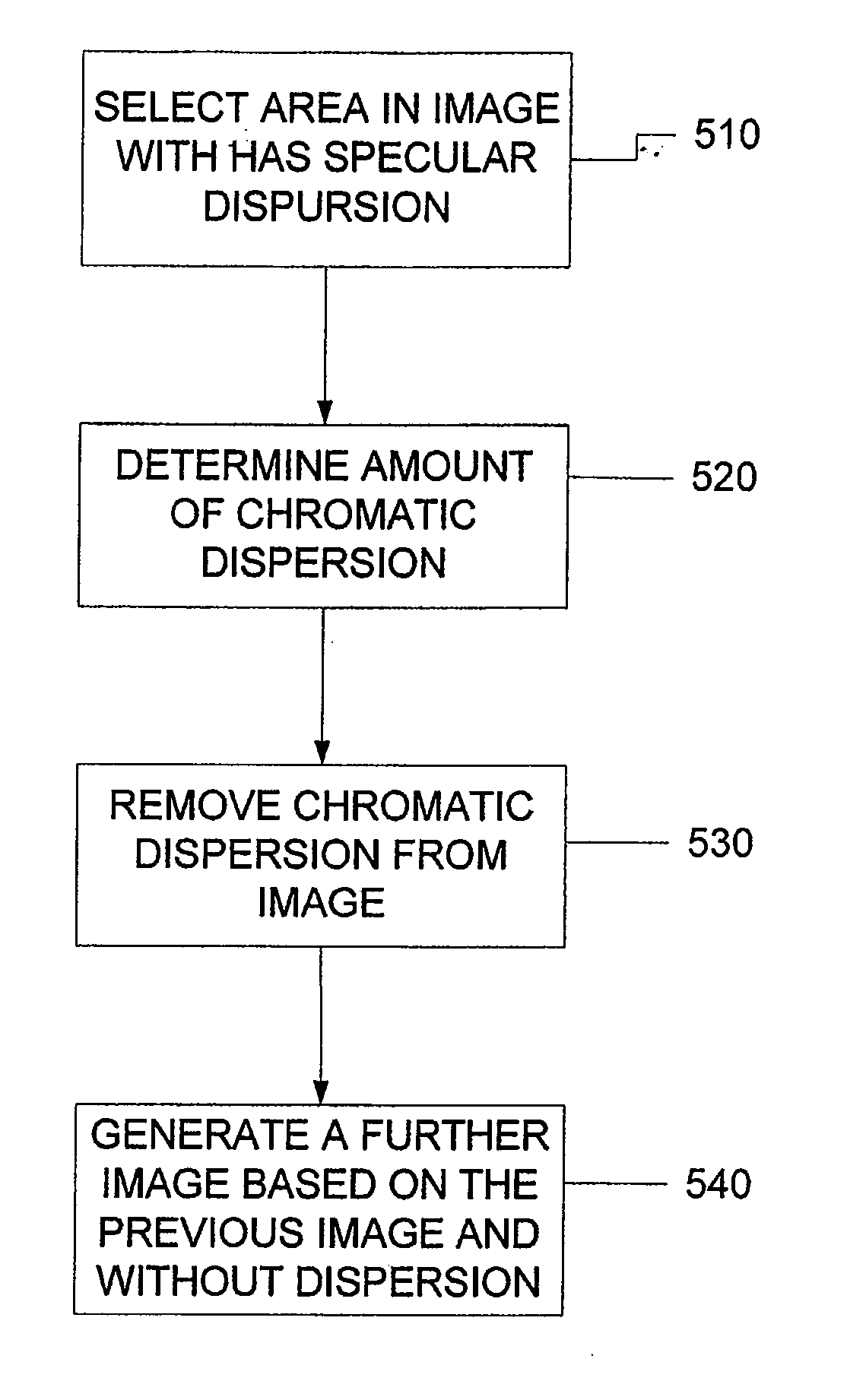
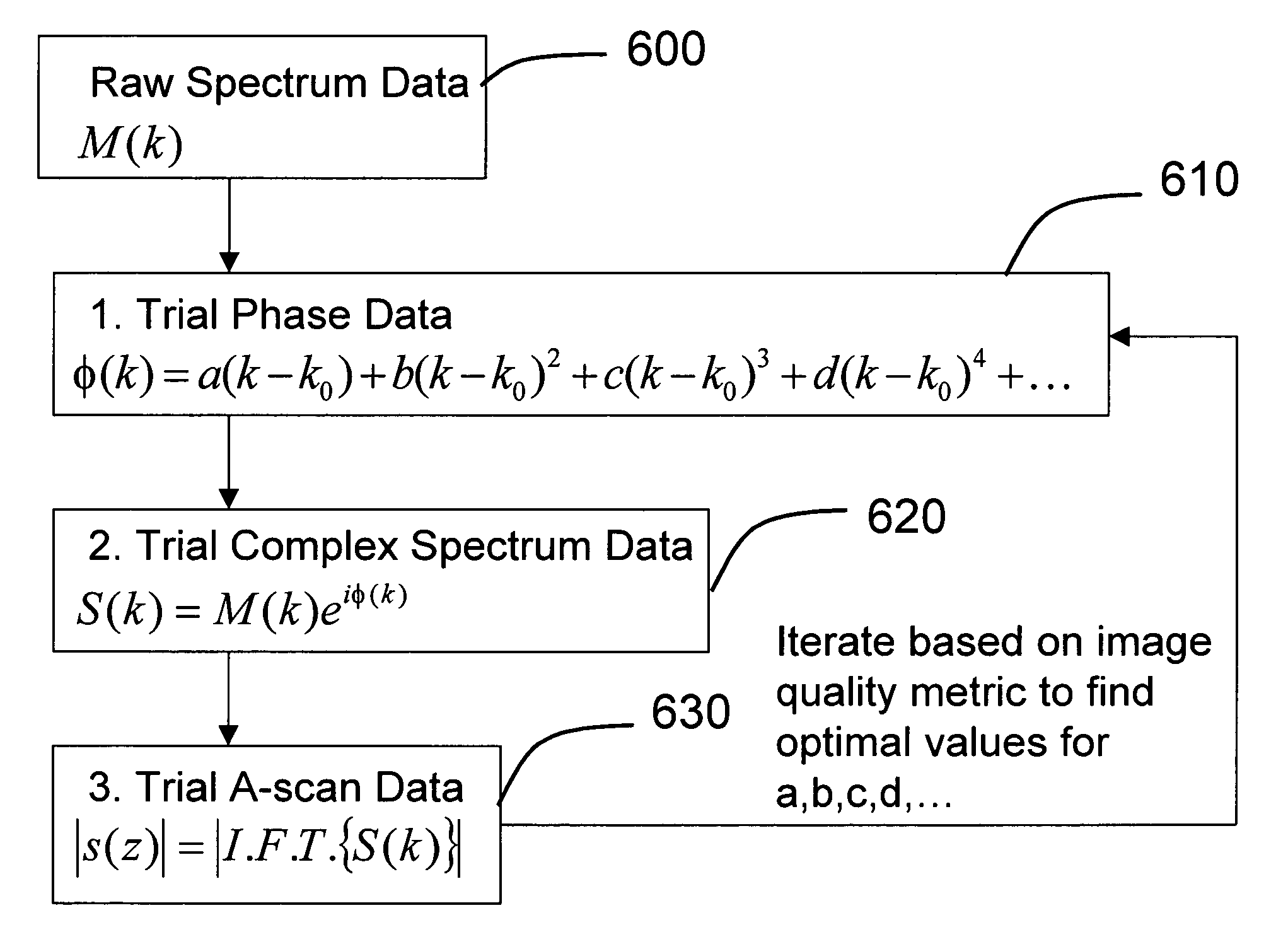
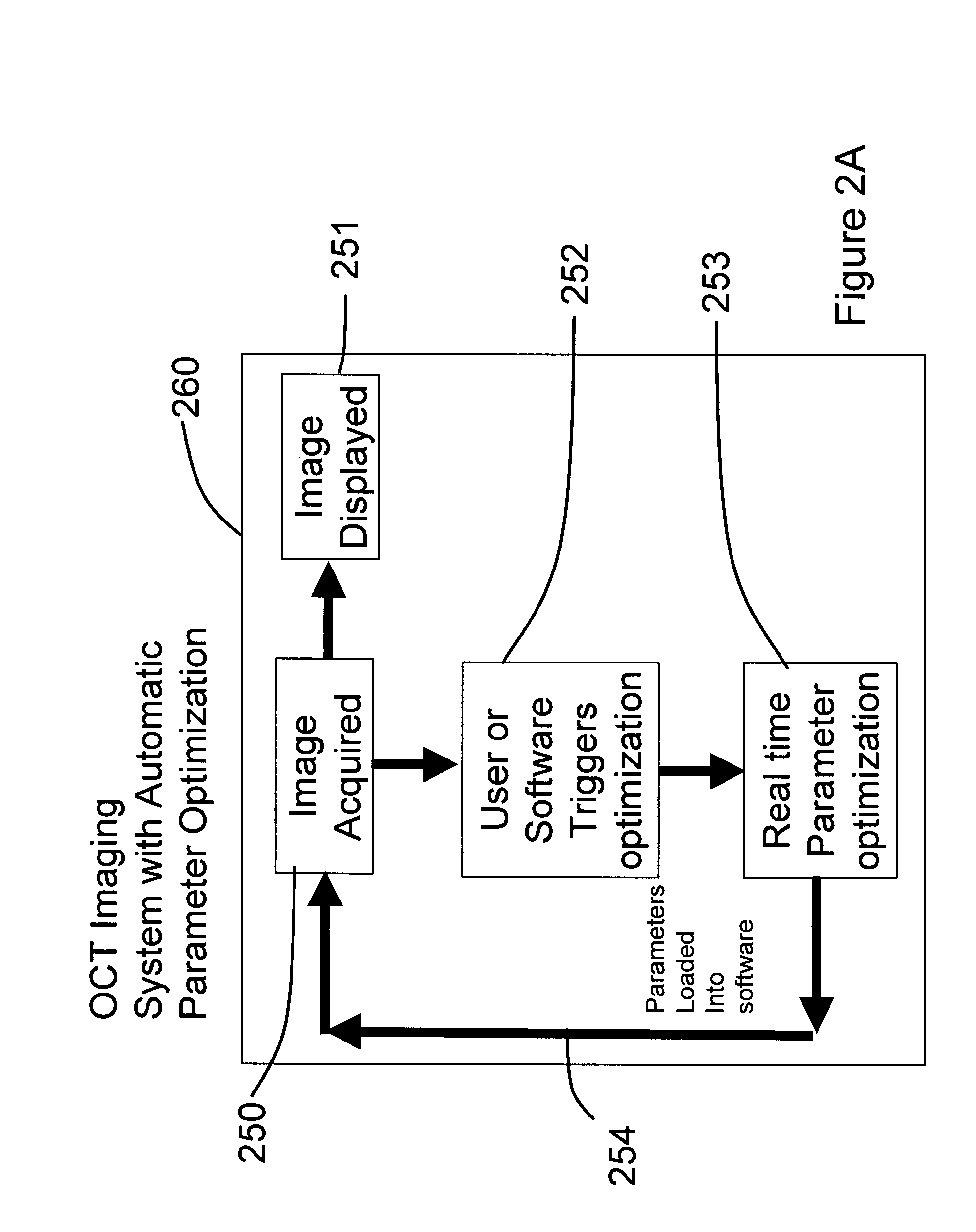
Methods, systems and computer program products for optical coherence tomography (OCT) using automatic dispersion compensation
ActiveUS20070258094A1Extended processing timeRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryComputer scienceDispersion compensation
Methods, systems and computer program products for generating parameters for software dispersion compensation in optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems are provided. Raw spectral interferogram data is acquired for a given lateral position on a sample and a given reference reflection. A trial spectral phase corresponding to each wavenumber sample of the acquired spectral interferogram data is postulated. The acquired raw spectral data and the postulated trial spectral phase data are assembled into trial complex spectrum data. Trial A-scan data is computed by performing an inverse Fourier transform on the trial complex spectrum data and determining the magnitude of a result.
Owner:BIOPTIGEN
Chromatic dispersion compensating fiber
InactiveUS7483613B2Reduce the valueOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWavelength-division multiplex systemsSpectral bandsEngineering
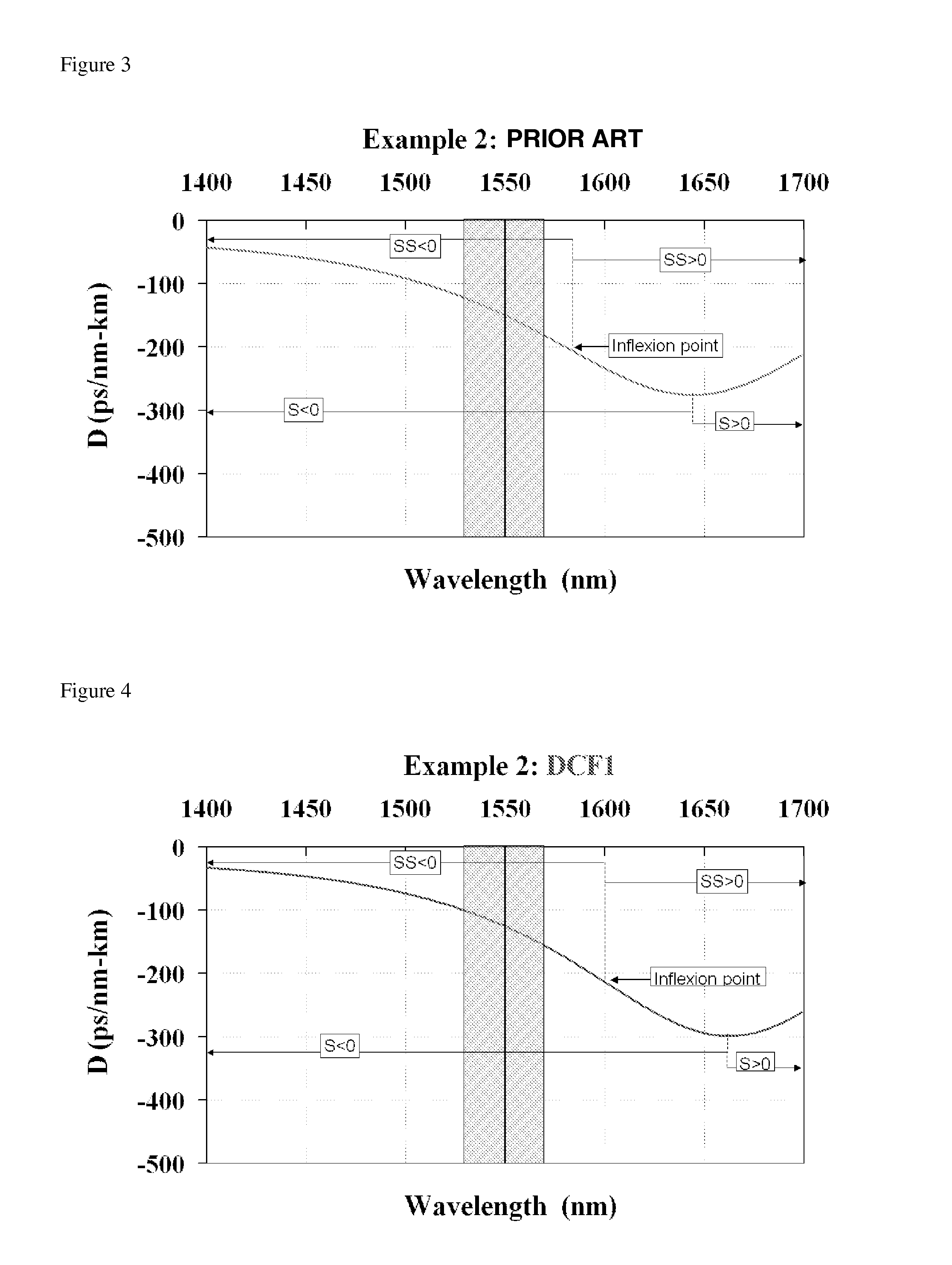
Disclosed are an improved system and a related method for compensating the chromatic dispersion of a given length of a transmission fiber over a given spectral band by employing at least two chromatic dispersion compensating fibers that, with respect to the slope of the slope of the chromatic dispersion (SSi), have values of opposite signs.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
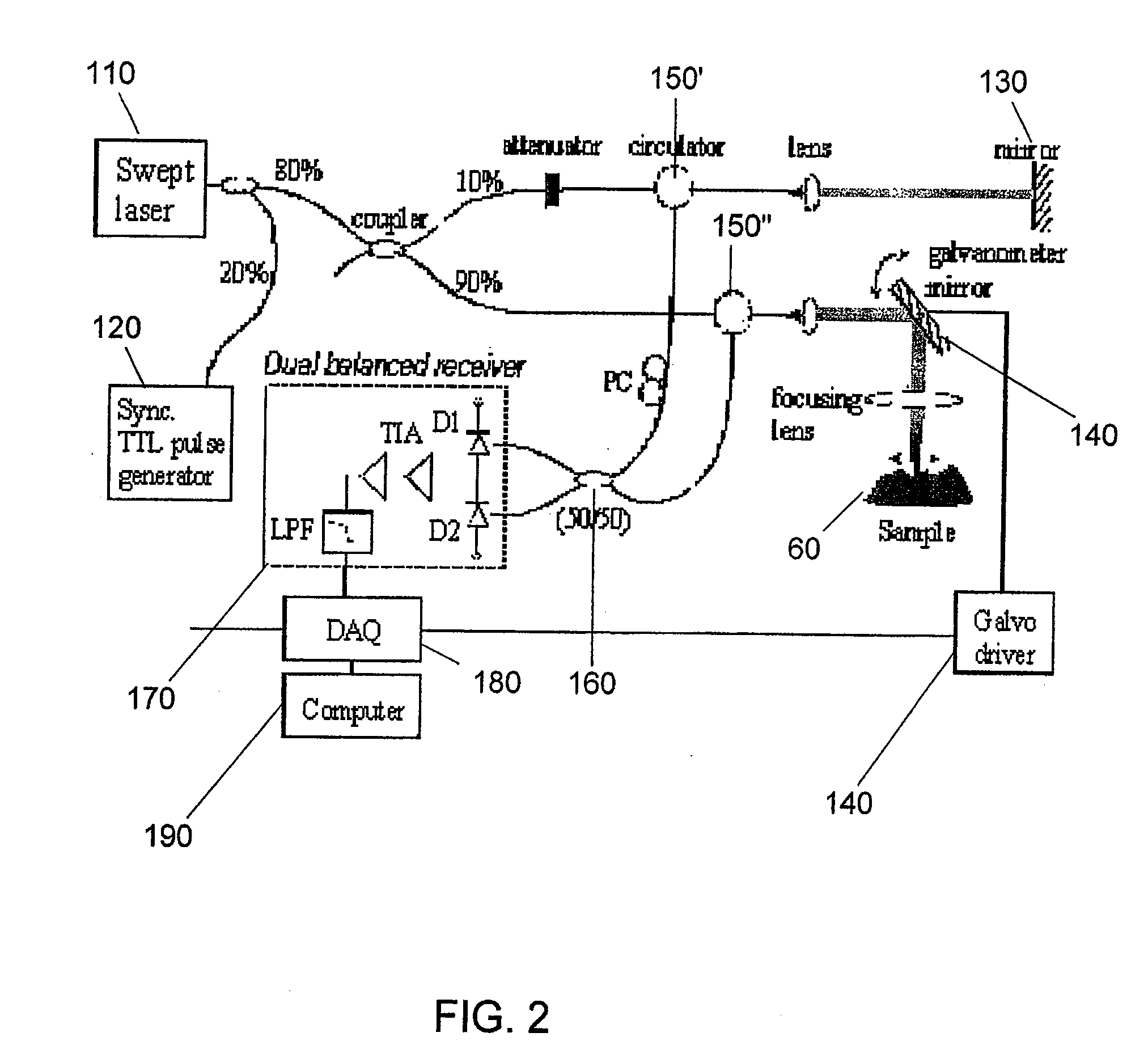
Process, System And Software Arrangement For A Chromatic Dispersion Compensation Using Reflective Layers In Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Imaging
ActiveUS20090196477A1Compensation for dispersionEasy to implementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumReflective layer
A system, process and software arrangement are provided to compensate for a dispersion in at least one portion of an image. In particular, information associated with the portion of the image is obtained. The portion of the image can be associated with an interference signal that includes a first electromagnetic radiation received from a sample and a second electromagnetic radiation received from a reference. The dispersion in the at least one portion of the image can be compensated by controlling a phase of at least one spectral component of the interference signal.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
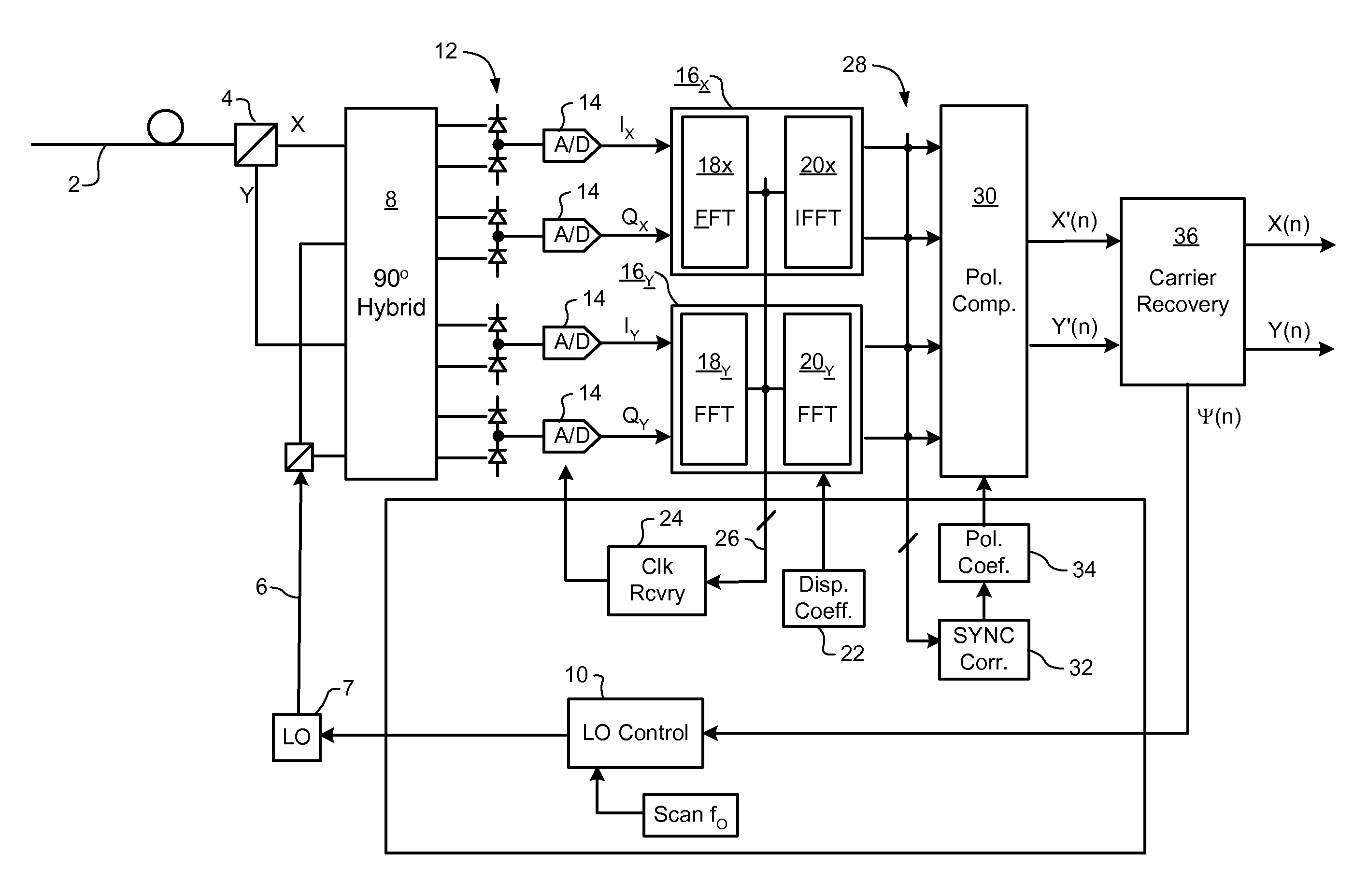
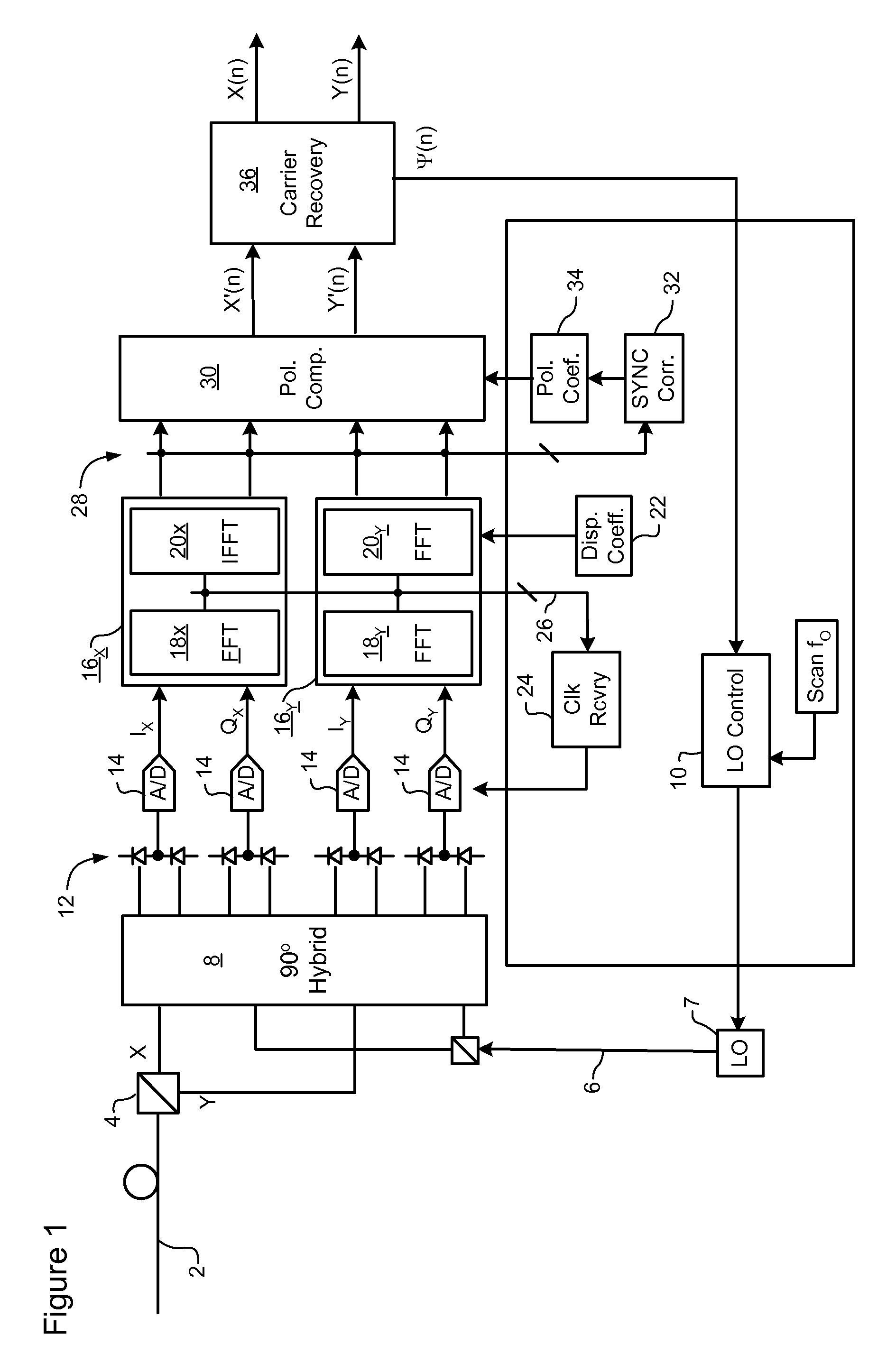
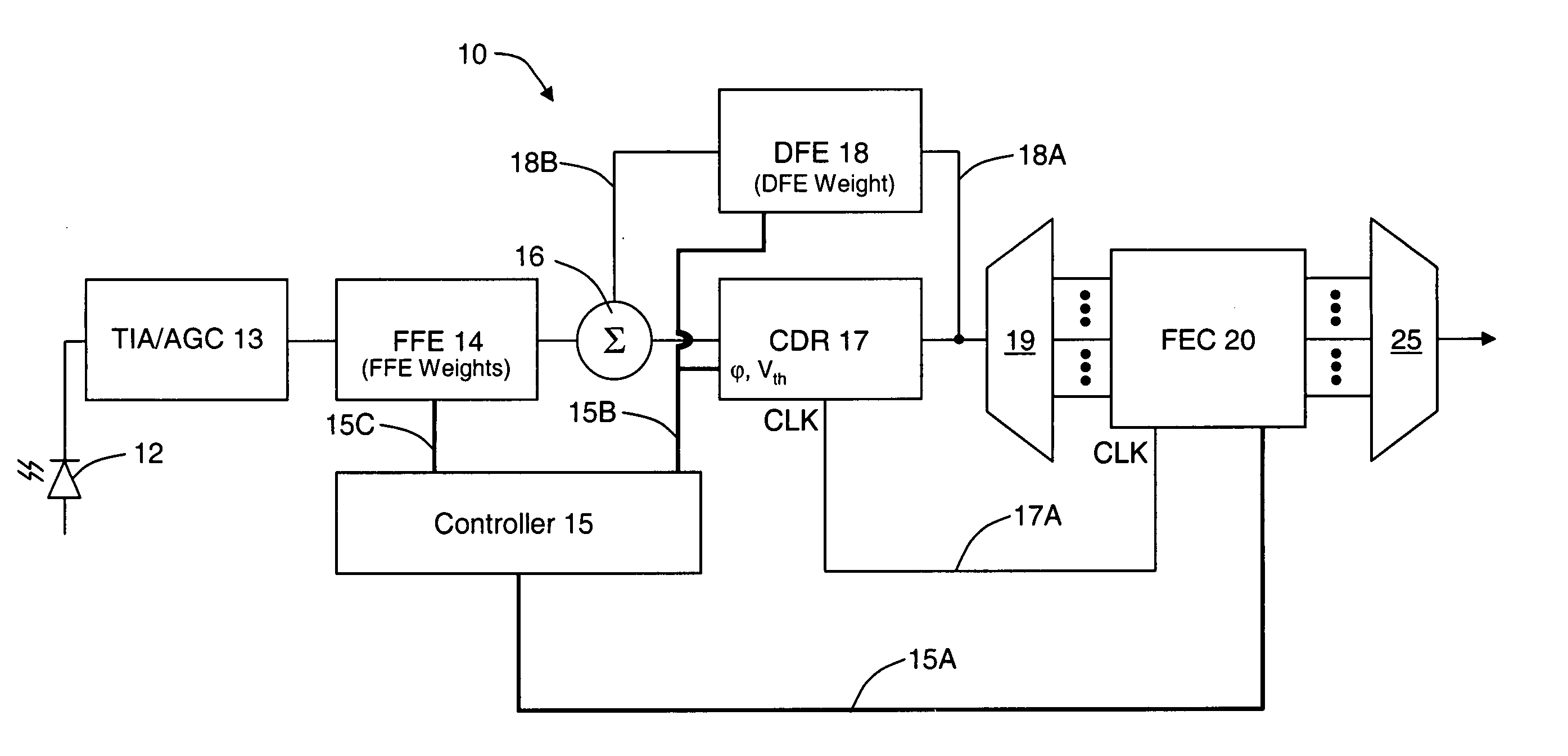
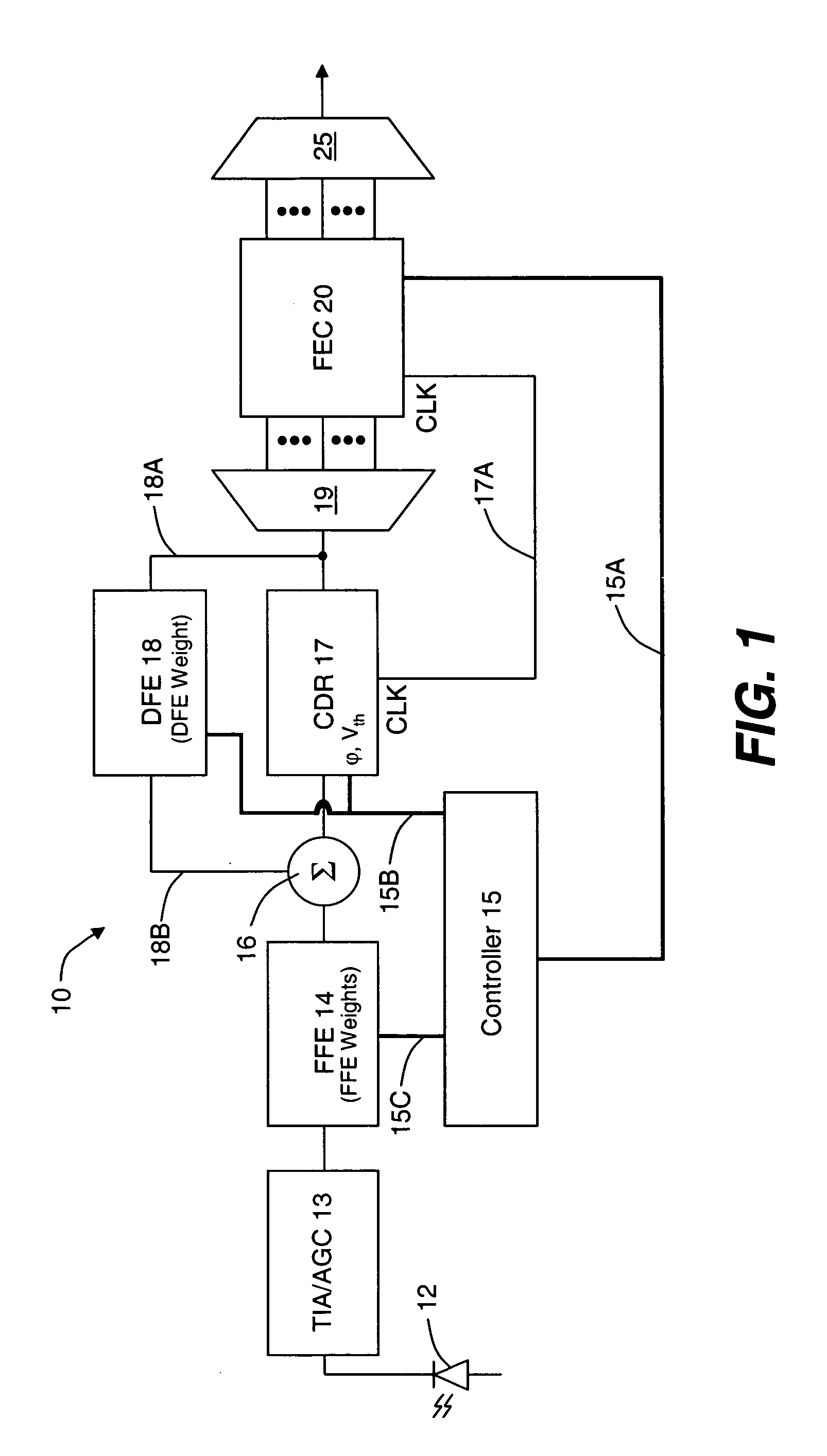
Signal acquisition in a coherent optical receiver
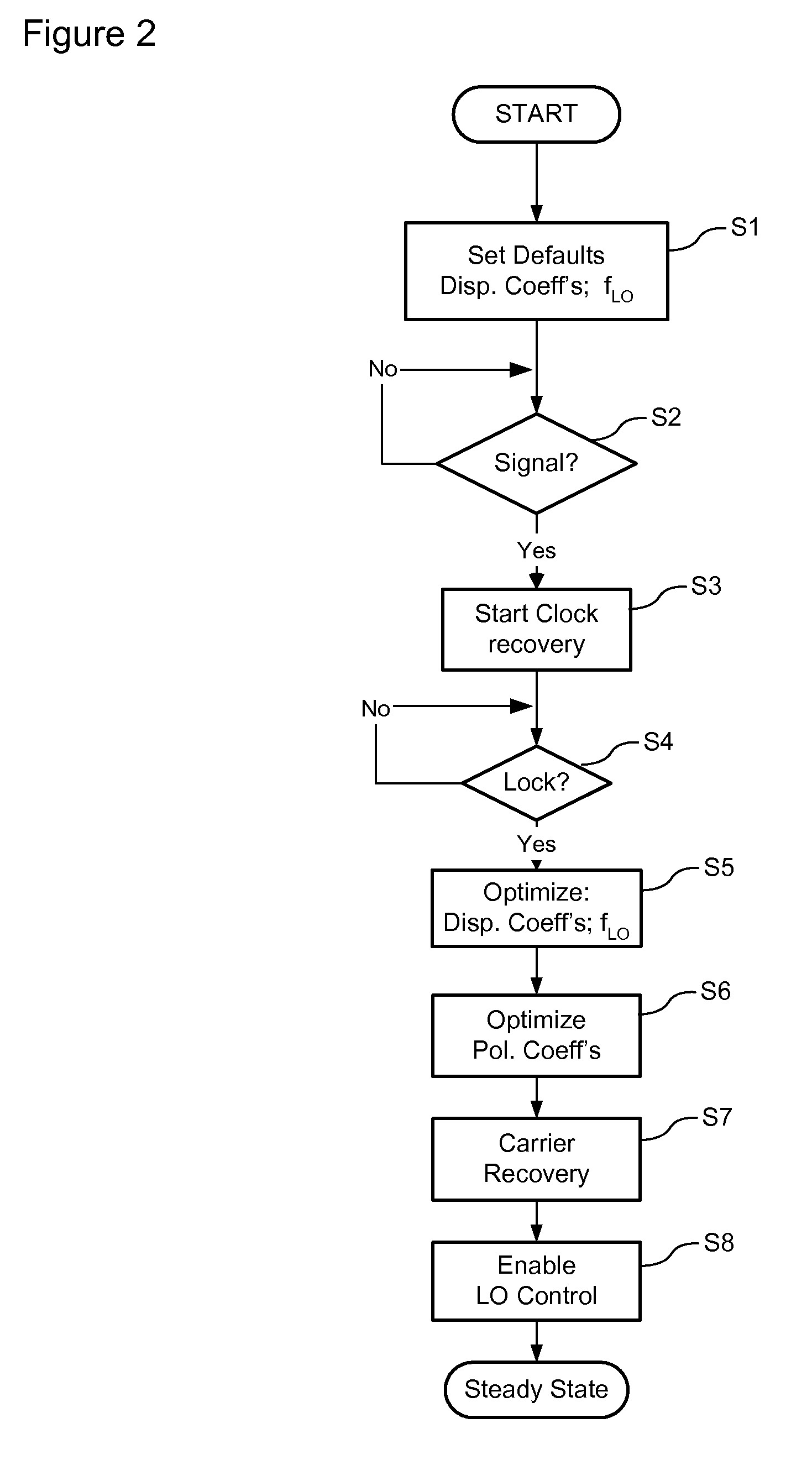
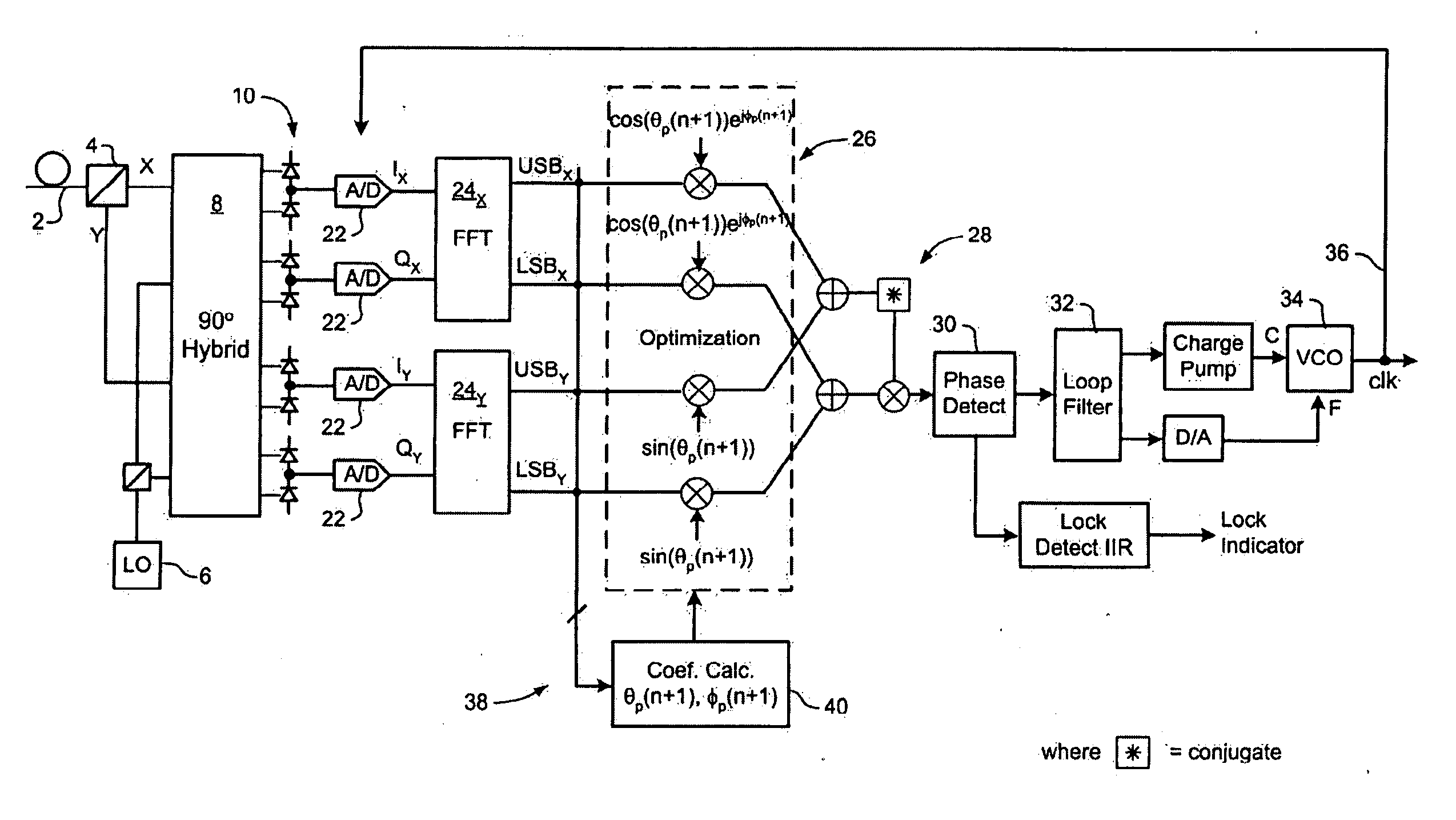
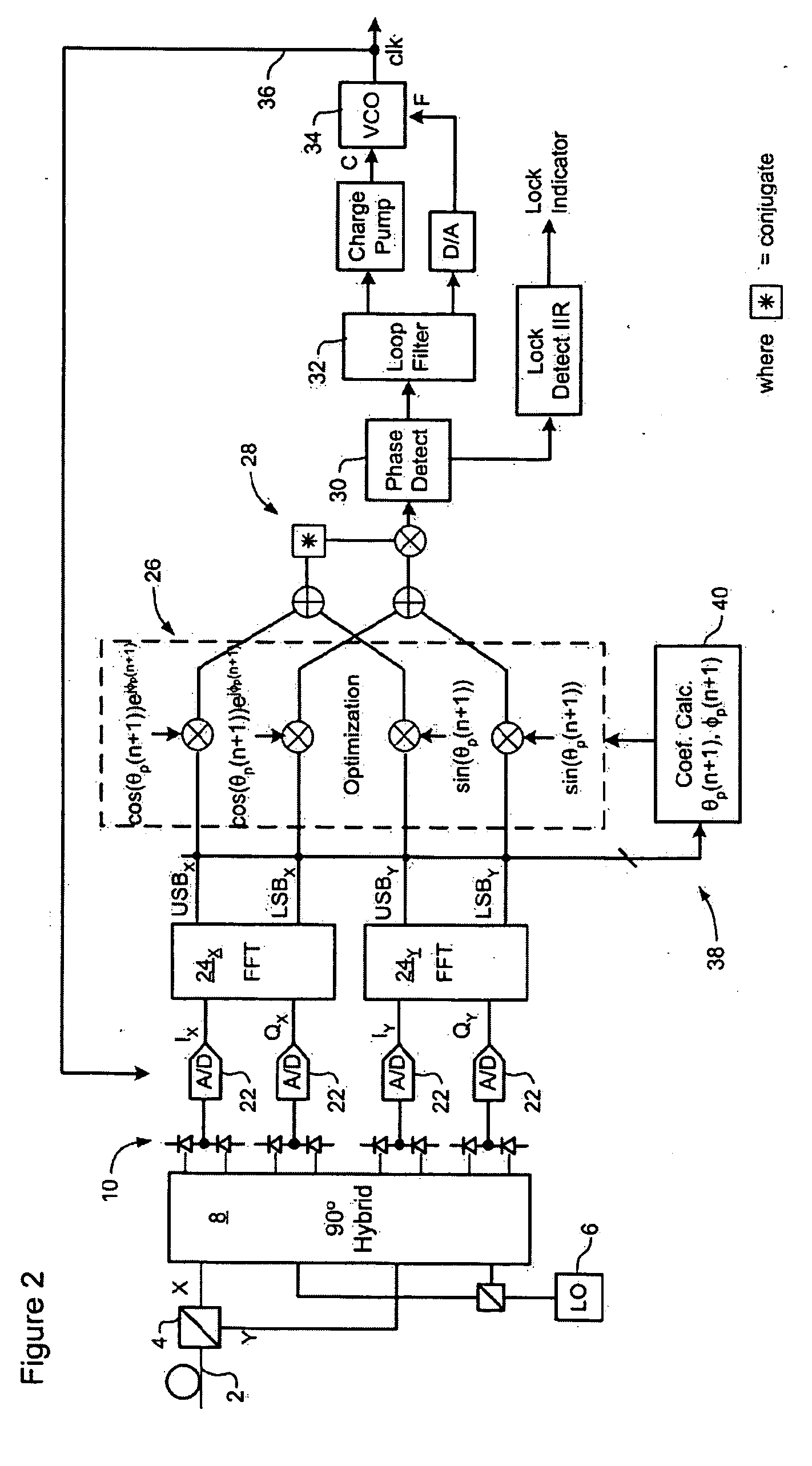
ActiveUS7636525B1Reliably acquire signalSteady-state operationReceiver initialisationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansClock recoveryEngineering
A method and system for initializing a coherent optical receiver. Upon detection of an optical signal, a multi-bit digital sample stream of the optical signal is digitally processed to initialize each one of a plurality of adaptive control blocks of the coherent optical receiver. The adaptive control blocks include at least a dispersion compensation block and a clock recovery block. The dispersion compensation block is initialized before initializing the clock recovery block.
Owner:CIENA
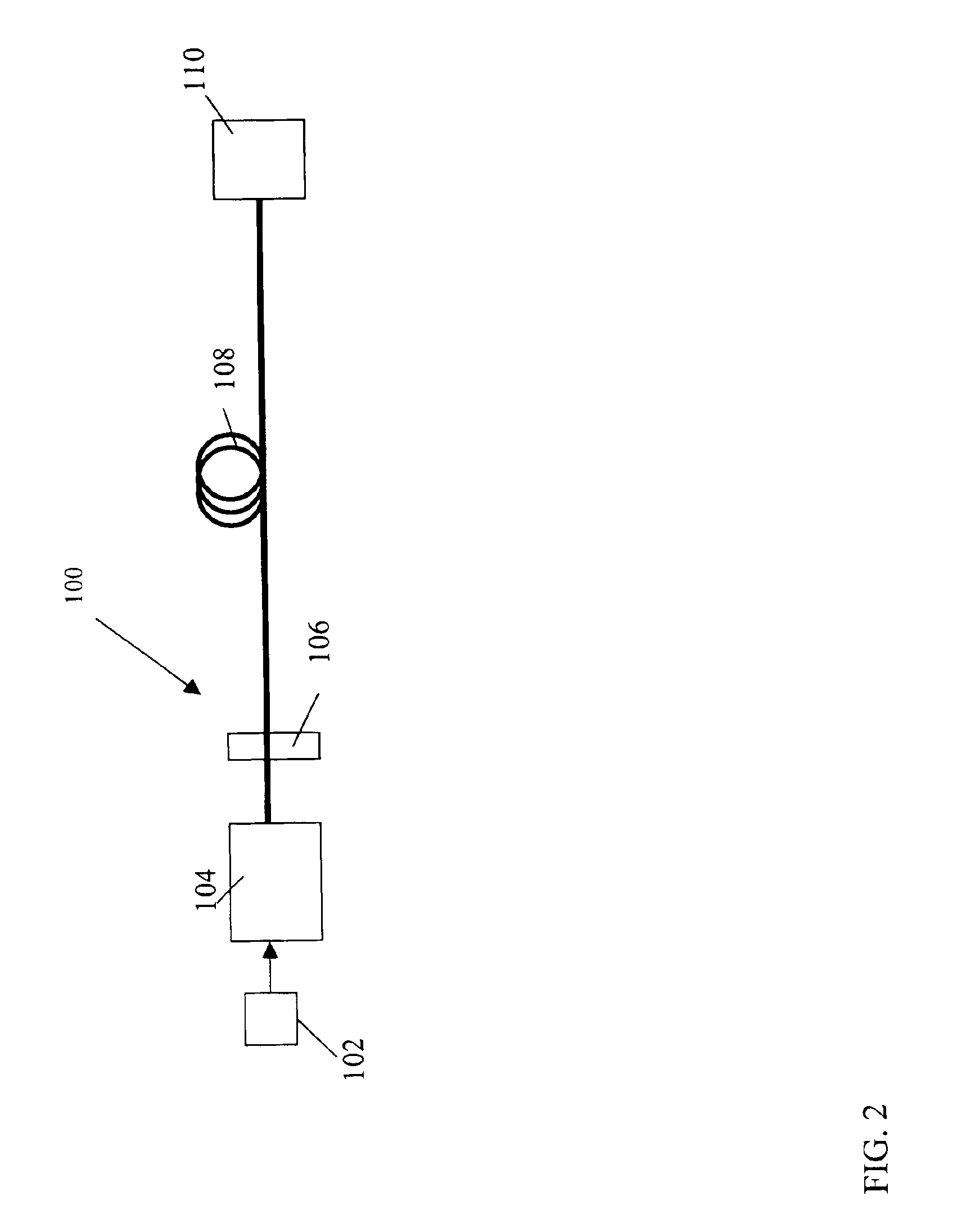
Power source for a dispersion compensation fiber optic system
InactiveUS6963685B2Minimize signalingIncrease bitrateCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency modulationDispersion compensation
Owner:OPTICAL HORIZONS CORP +1
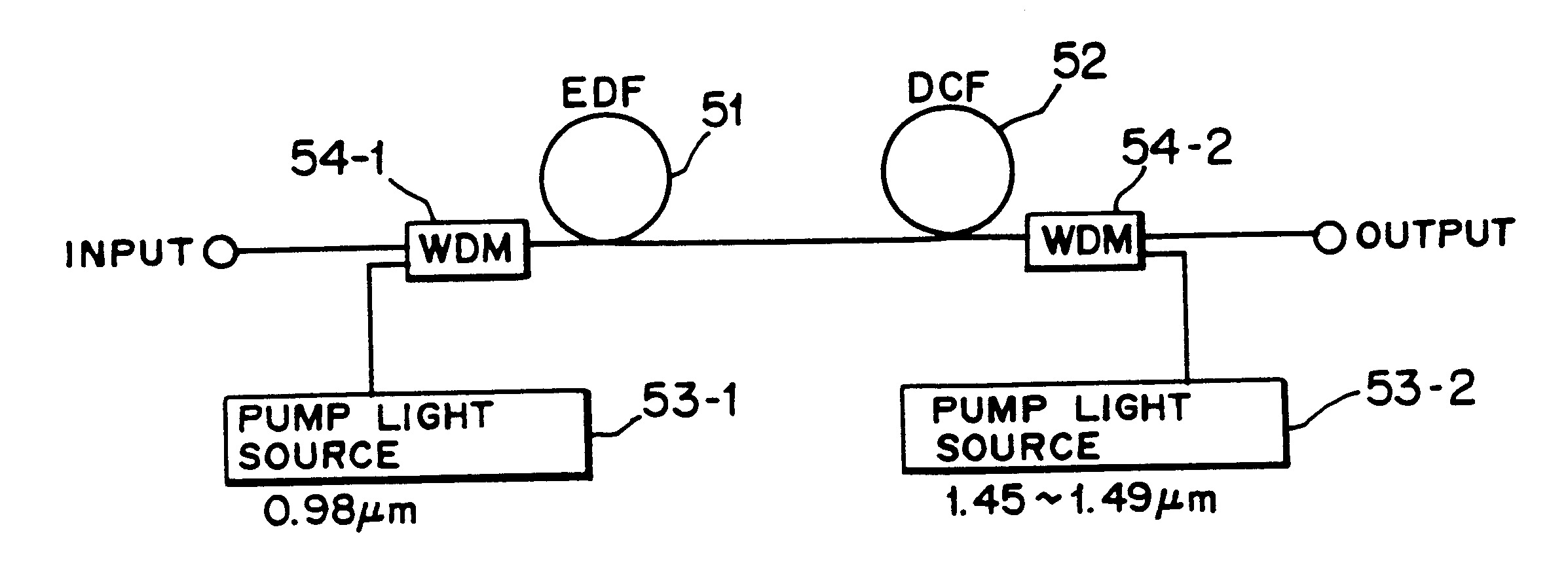
Optical fiber amplifier and dispersion compensating fiber module for optical fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6342965B1Guaranteed uptimeImprove conversion efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical fiber amplifiersRare earth
The invention provides an optical fiber amplifier which assures stable operation of a pump light source and efficiently makes use of residual pump power to achieve improvement in conversion efficiency. The optical fiber amplifier includes a rare earth doped fiber. Pump light from a pump light source is introduced into one end of the rare earth doped fiber by way of a first optical coupler, and residual pump light originating from the pump light and arriving at the other end of the rare earth doped fiber is applied to the other rare earth doped fiber amplifier or the loss compensation of a dispersion compensating fiber by Raman amplification.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Apparatus and method of compensating for compact digital domain chromatic dispersion
InactiveUS20090238578A1Reduce in quantitySave computing resourcesDistortion/dispersion eliminationFinite impulse responseDigital signal processing
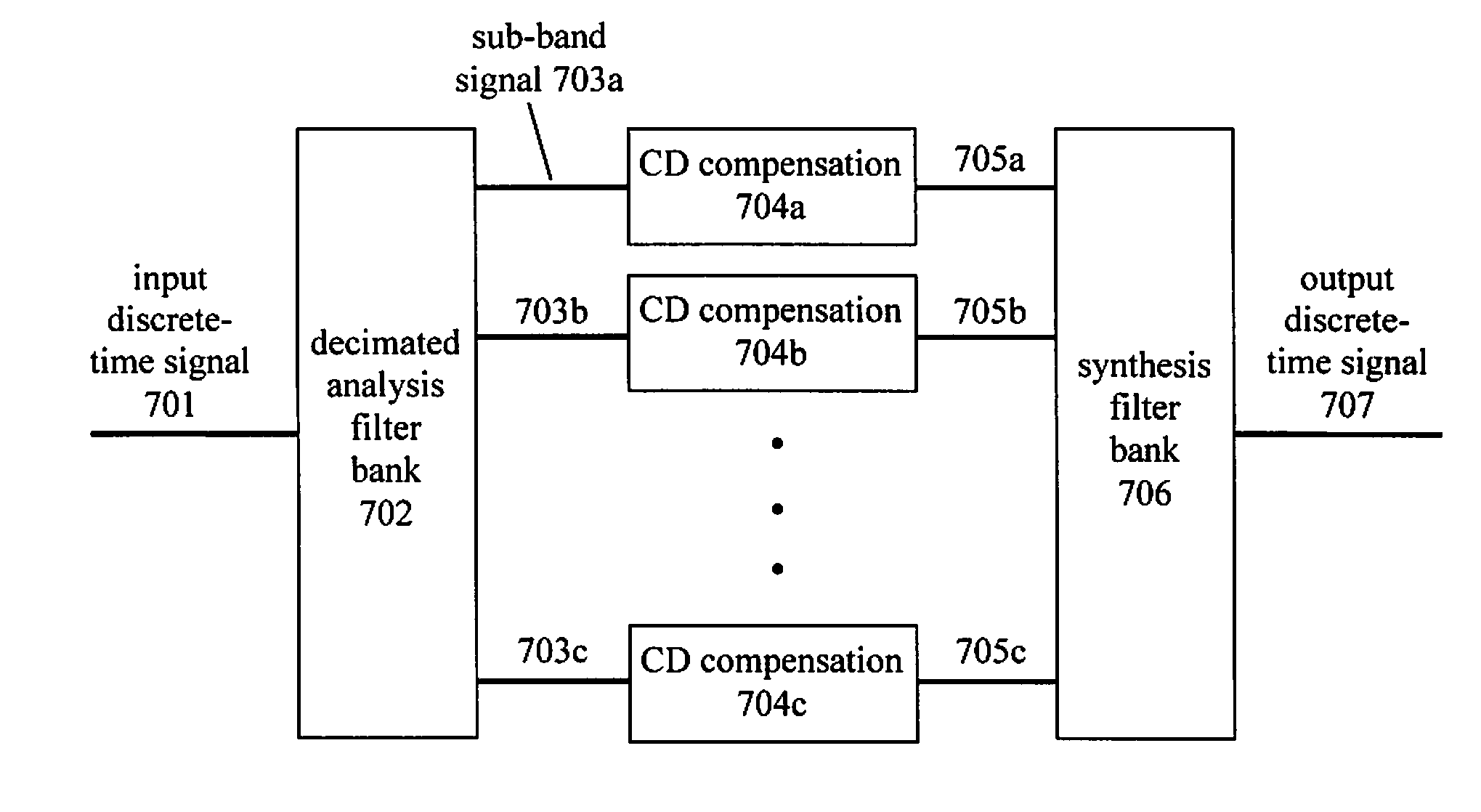
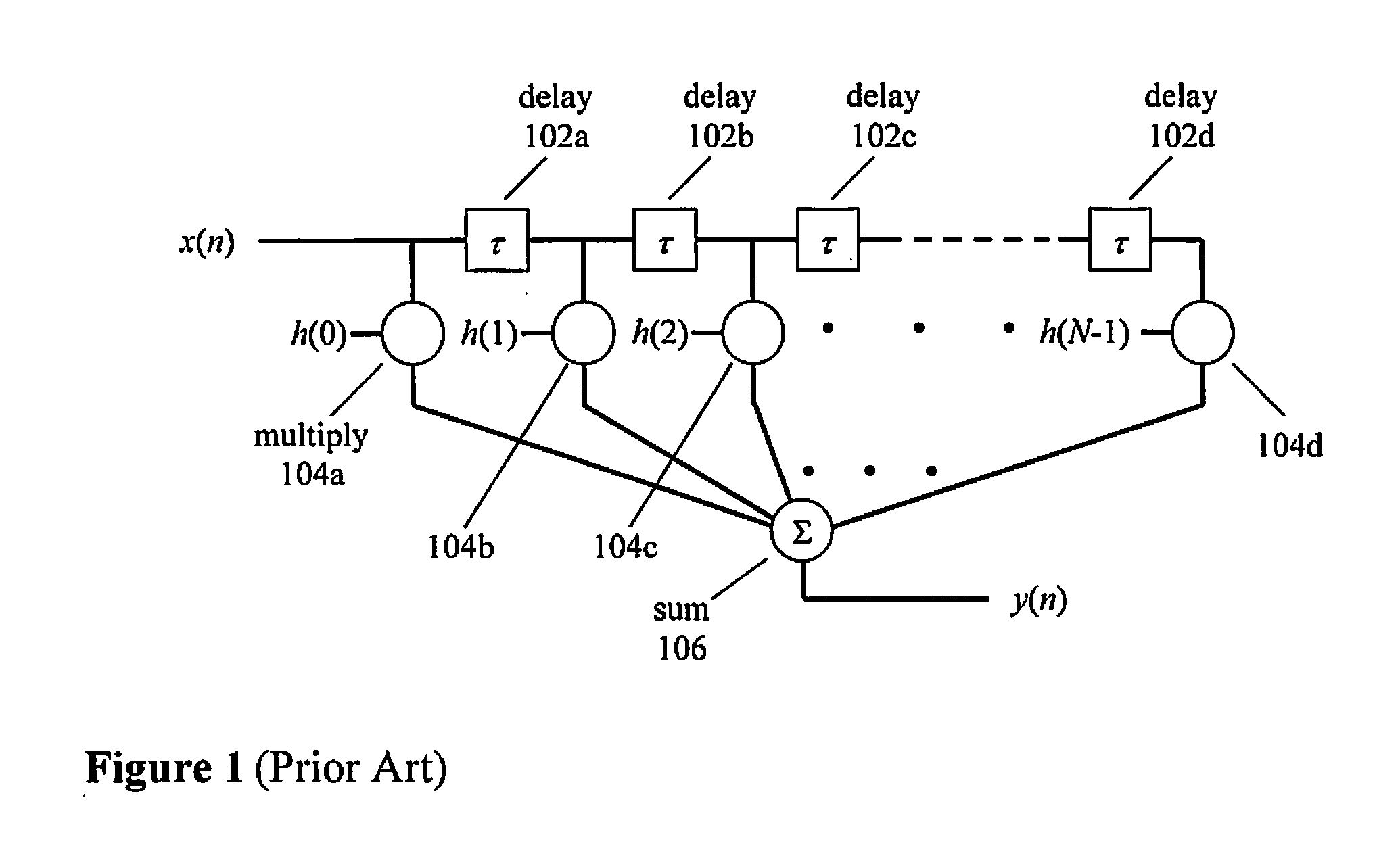
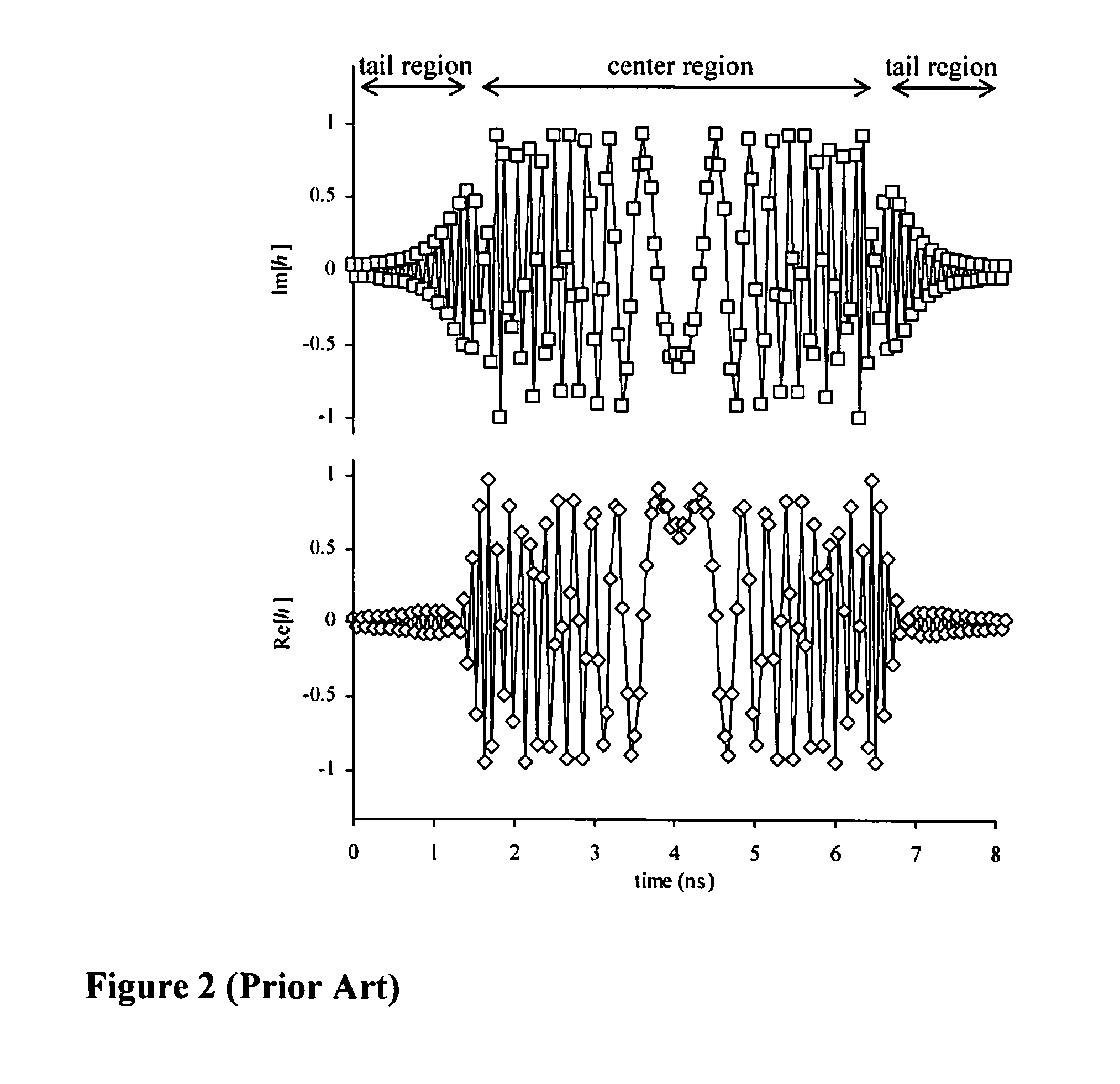
A method and apparatus of compensating for compact digital domain chromatic dispersion. The distortion of an optical signal due to chromatic dispersion is compensated by a digital signal processing in the electrical domain, either prior to the optical transmitter or following the receiver. The circular coefficient approximation and sub-band processing reduce the amount of computations to execute a given level of chromatic dispersion compensation compared to a direct finite impulse response filter implementation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Wavelength selective optical couplers
InactiveUS6289699B1Eliminate undesired leakageEasy to separateGlass making apparatusMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGratingOptical communication
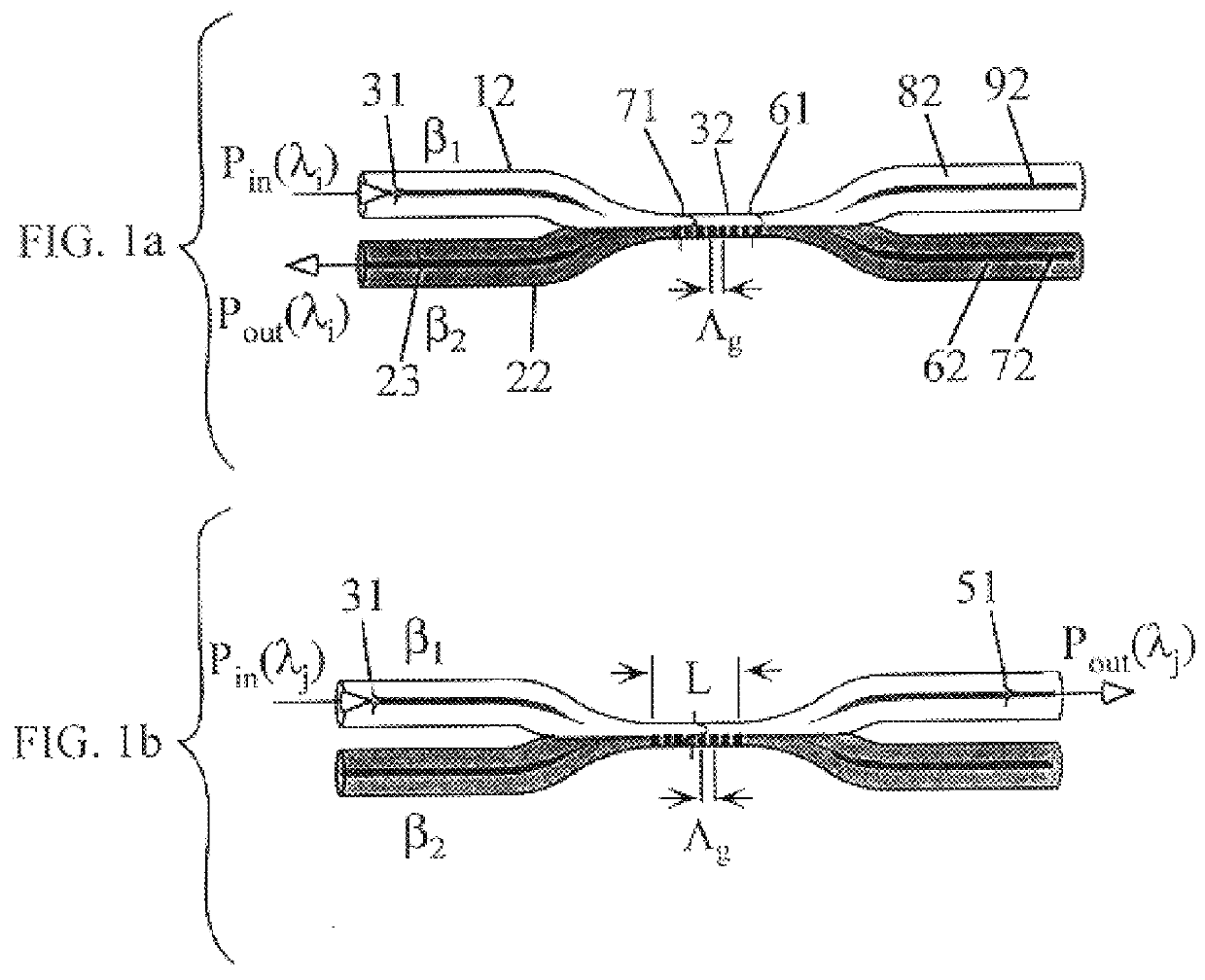
A wavelength selective optical fiber coupler having various applications in the field of optical communications is disclosed. The coupler is composed of dissimilar waveguides in close proximity. A light induced, permanent index of refraction grating is recorded in the coupler waist The grating filters and transfers energy within a particular range of wavelengths from a first waveguide to a second waveguide. Transversely asymmetric gratings provide an efficient means of energy transfer. The coupler can be used to combine or multiplex a plurality of lasers operating at slightly different wavelengths into a single fiber. Other embodiments such as a dispersion compensator and gain flattening filter are disclosed.
Owner:ARROYO OPTICS
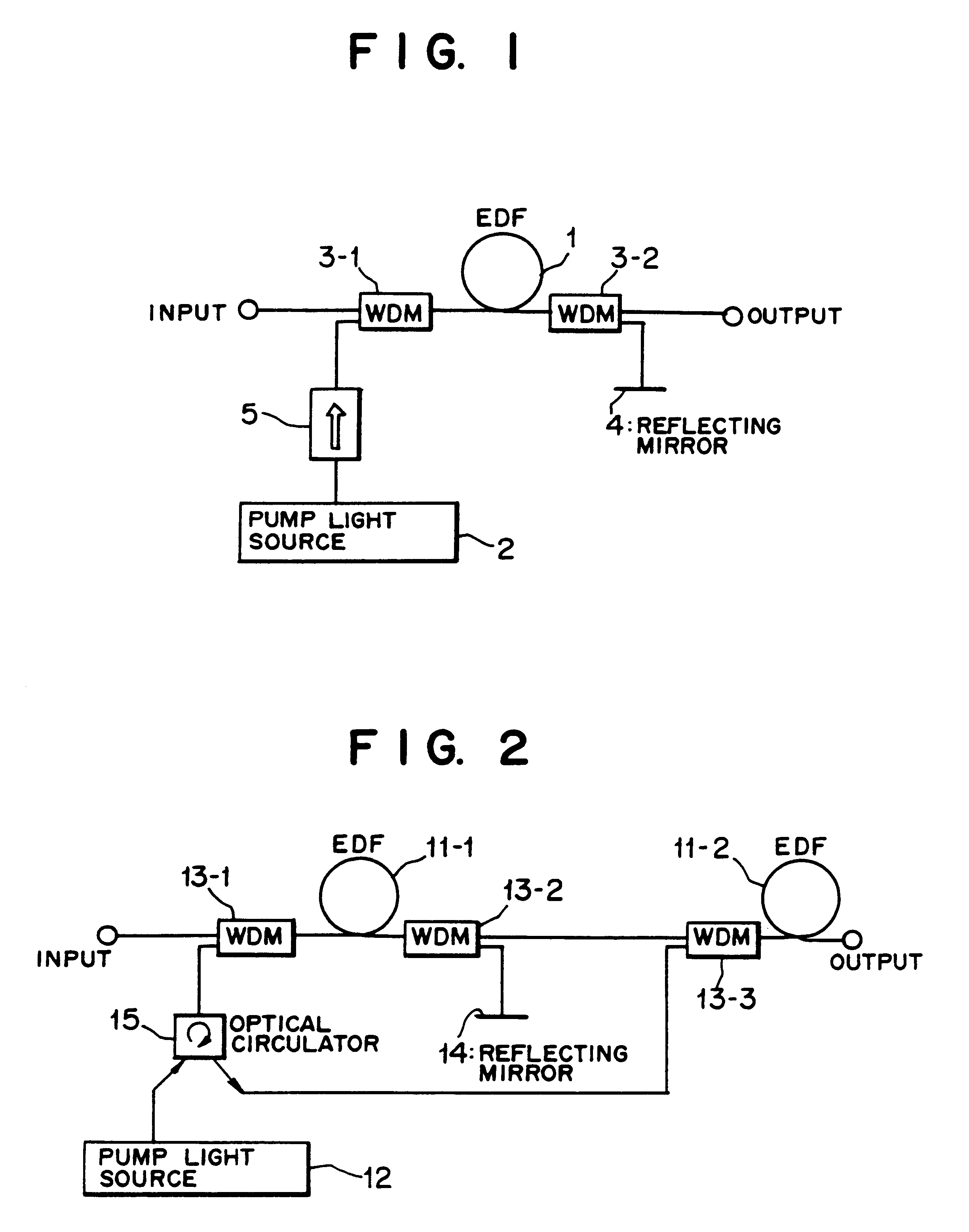
Optical communication system incorporating automatic dispersion compensation modules
InactiveUS6370300B1Improve system performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingData integrity
In accordance with the invention, an optical communication system is provided with one or more automatic dispersion compensation modules. Each module has an adjustable dispersion element, a data integrity monitor and a feedback network whereby the monitor adjusts the dispersion element to optimize system performance. In a preferred embodiment the dispersion compensating modules comprise chirped fiber Bragg gratings in which the chirp is induced in the grating by passing a current along distributed thin film heaters deposited along the length of the fiber. The magnitude of the applied current determines the dispersion of the grating. A data integrity monitor is configured to sense the integrity of transmitted data and to provide electrical feedback for controlling the current applied to the grating.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Clock recovery from an optical signal with polarization impairments
ActiveUS20060285855A1Pulse automatic controlPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemClock recovery
A method of recovering a clock signal from an optical signal received through an optical communications system. A digital sample stream is processed to generate a dispersion compensated signal. The dispersion compensated signal is then tapped to obtain upper side band and lower side, band signals of each received polarization of the optical signal. The upper side band sand lower side band signals are then processed to compensate polarization dependent impairments and the clock recovered from the resulting optimized.
Owner:CIENA
Low conversion rate digital dispersion compensation
ActiveUS20090201796A1Eliminate the effects ofIncrease speedModulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexPhase distortionLow-pass filter
A method of suppressing effects of aliasing in a system for digitally processing a high speed signal having a symbol rate of 1 / T. The high speed signal is sampled at a fractional multiple (N) of the symbol rate, wherein 1<N<2, to generate a corresponding sample stream, and filtered using a low-pass filter characteristic having a cut-off frequency corresponding to 1 / 2T. Phase distortions due to the filtering are compensated by digitally processing the sample stream.
Owner:CIENA
Optical waveguide with non-uniform sidewall gratings
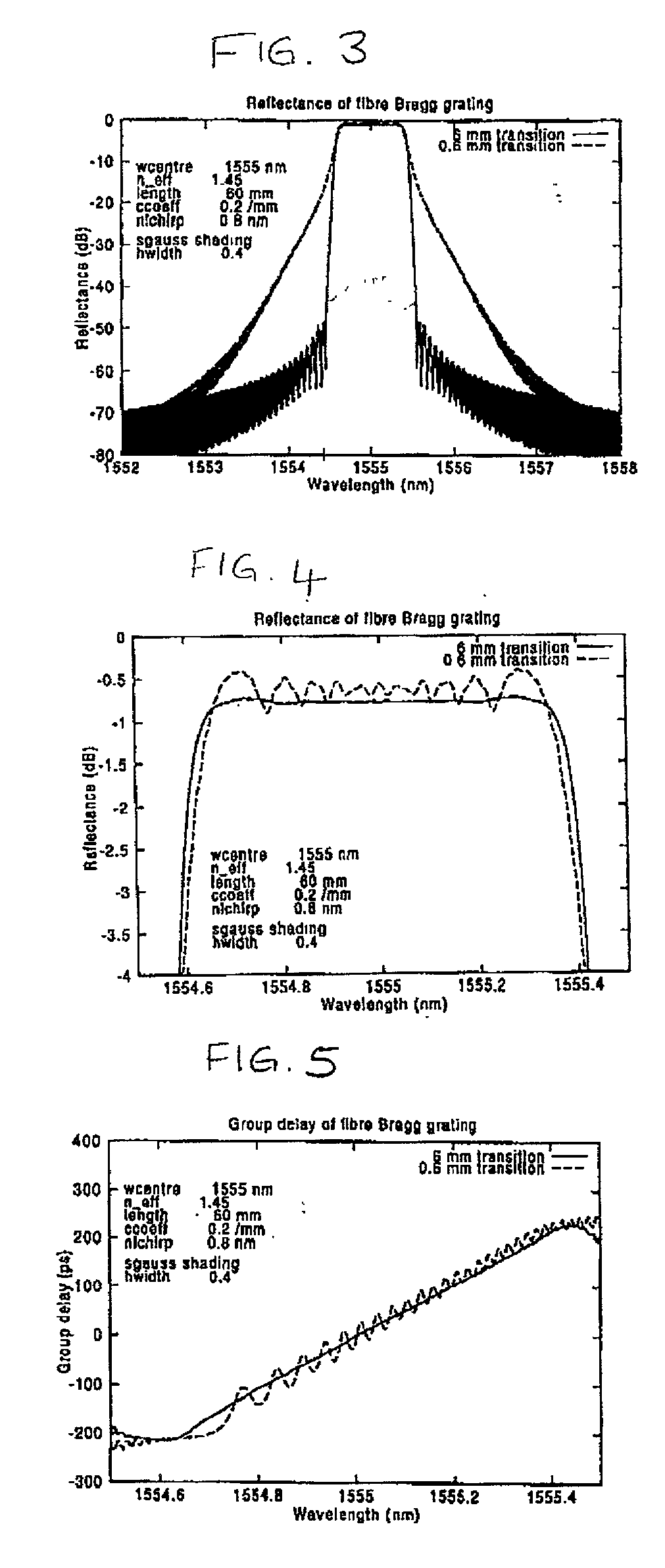
A diffraction grating of non-uniform strength is introduced into an optical waveguide by modulating its width. The waveguide may be fabricated using one of several planar processing techniques. Varying the size, position, and / or thickness of the grating teeth provides the desired variation of grating strength. Certain functional variations of grating strength suppress side-lobe levels in the grating reflection and transmission spectra. This process, termed apodization, is necessary for precise wavelength filtering and dispersion compensation. If desired, different periodicity gratings can be introduced in each side of the waveguide, multiple periodicities can be superimposed, the grating can be angled with respect to the waveguide, and the grating period and phase can be varied.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Communication through multiplexed one-dimensional optical signals
ActiveUS20130136449A1Effectively cancellingImprove signal qualityPolarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultiplexingCarrier signal
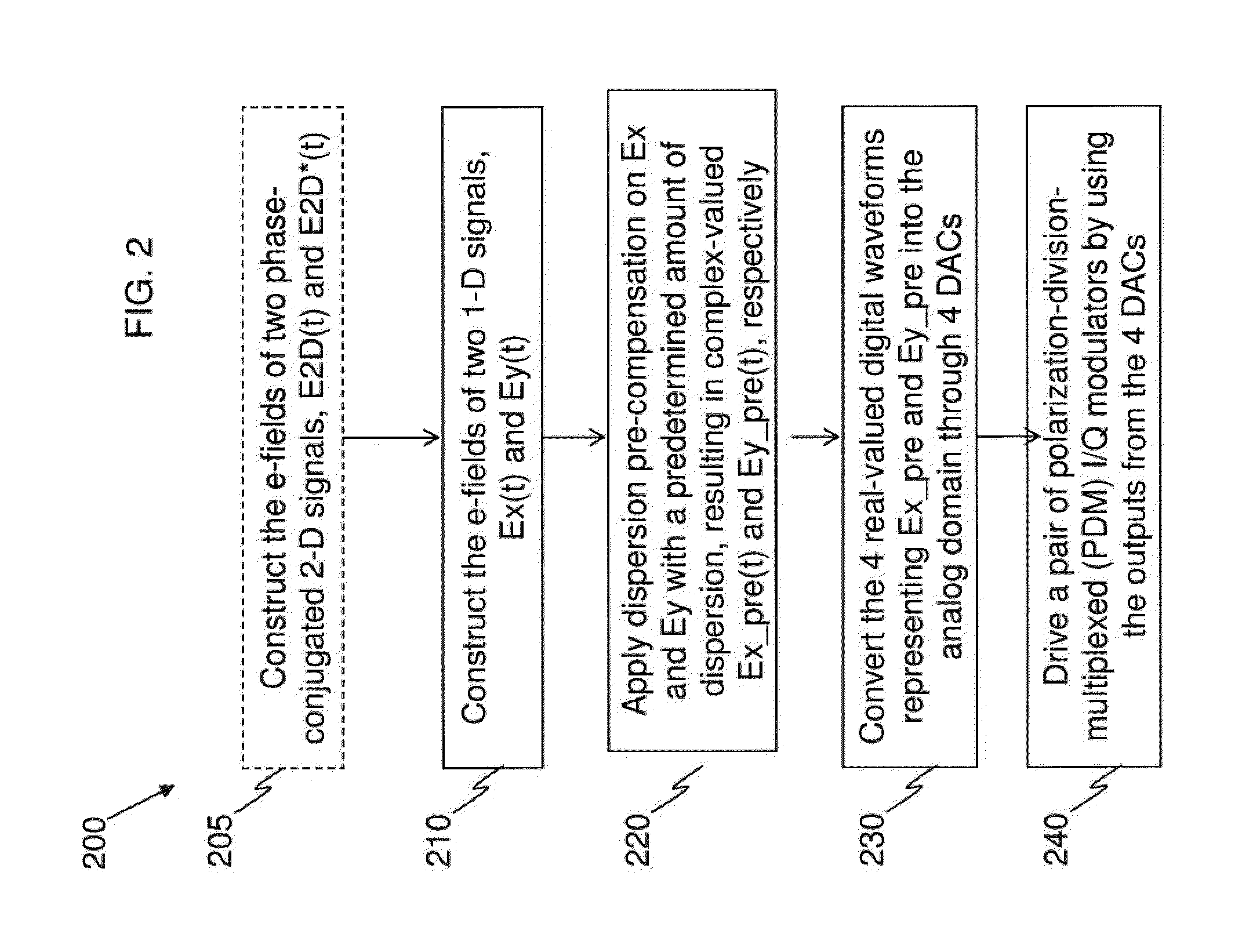
An example apparatus comprises an optical transmitter which includes a first processor and at least two optical modulators. The first processor is configured to generate a first electronic representation for each of at least two optical signals for carrying payload data modulated according to a one-dimensional (1-D) modulation format, and to induce on respective ones of the first electronic representations an amount of dispersion that depends on a power-weighted accumulated dispersion (ADPW) of a transmission link through which the at least two optical signals are to be transmitted thereby generating complex-valued electronic representations of pre-dispersion-compensated optical signals. Each of the at least two optical modulators modulate a respective analog version corresponding to a respective one of the complex-valued electronic representations onto a polarization of an optical carrier.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
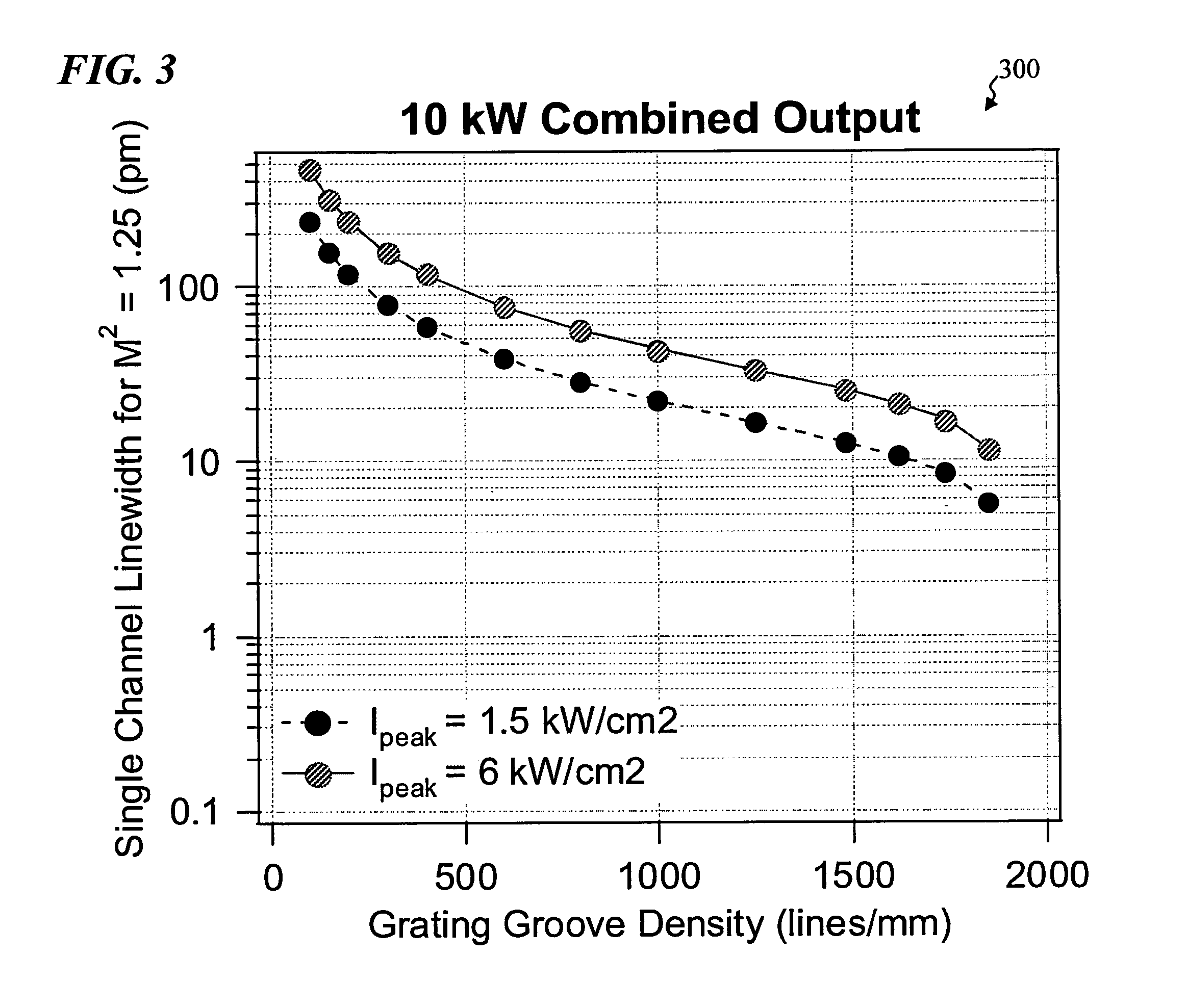
Spectral-beam combining for high-power fiber-ring-laser systems
ActiveUS8526110B1Reduce energy absorptionReduce and prevent chromatic dispersionLaser detailsOptical elementsDielectricGrating
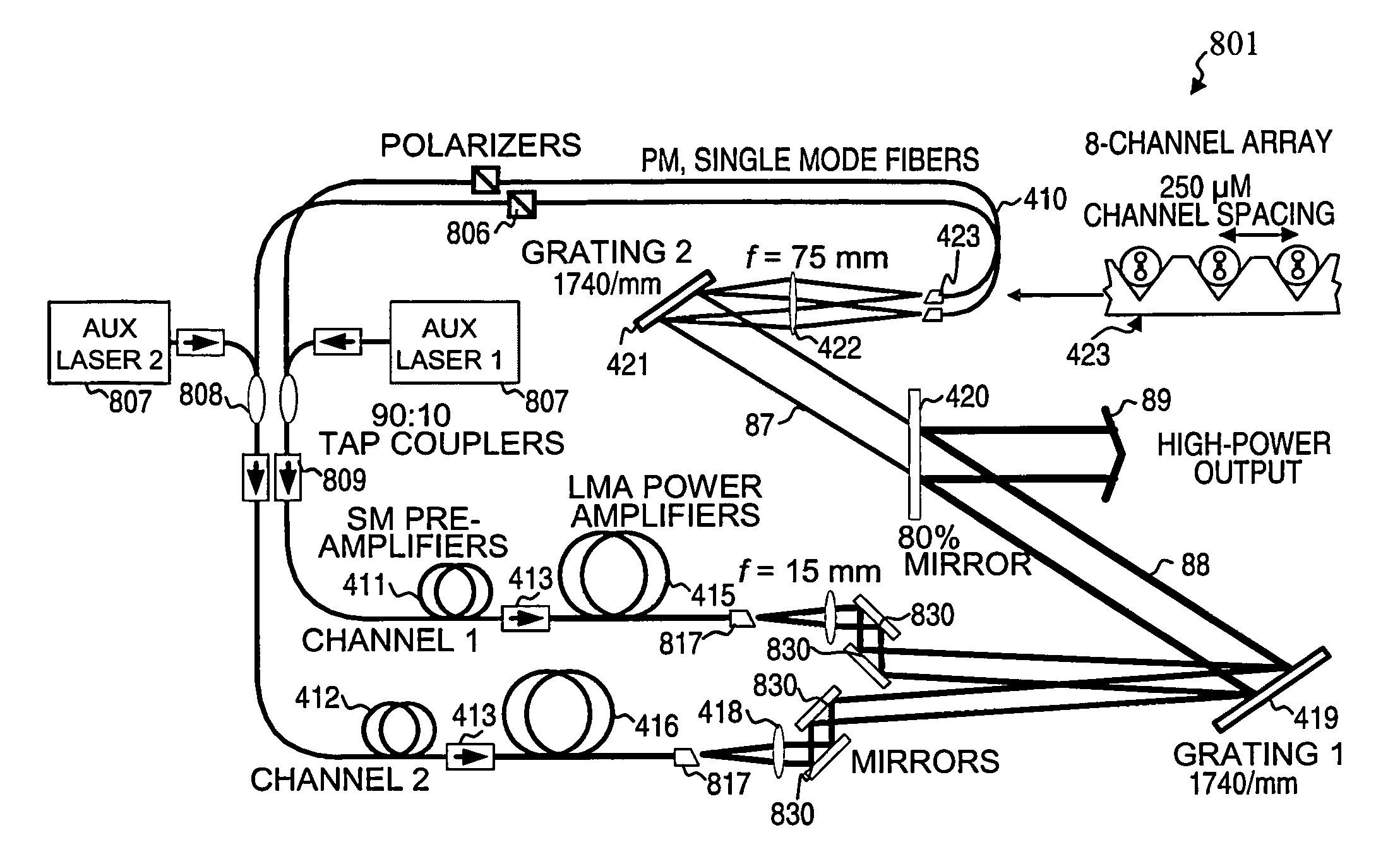
A ring-laser system that includes a plurality of ring-laser gain elements and a spectral-beam-combining output stage configured to combine a plurality of beams coming from the gain elements into an output beam and that includes chromatic-dispersion compensation. In some embodiments, the output stage includes a plurality of highly reflective dielectric-coated focussing elements. In some embodiments, the output stage includes a plurality of high-efficiency dielectric-coated grating elements. In some embodiments, the output stage includes a mostly reflective but partially transmissive output mirror and a highly reflective beam-reversing mirror configured to reflect a majority of a backward-traveling signal beam such that it becomes forward traveling. In some embodiments, each gain element further includes a photonic-crystal-rod power amplifier. Some embodiments have an amplitude modulator configured to pulse the plurality of beams, and a timing controller configured to synchronize the pulses of the plurality of beams. Some embodiments further include a non-linear wavelength-conversion device.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Pattern-dependent error counts for use in correcting operational parameters in an optical receiver
ActiveUS7574146B2Accurate methodReduce manufacturing costMultiple-port networksError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorWeight coefficientSemiconductor chip
An optical transmission network includes an optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC) chip, utilized in an optical transmitter and has a plurality of monolithic modulated sources integrated for multiple signal channels on the same semiconductor chip is provided with channel equalization at the optical receiver side of the network that permits one or more such integrated modulated sources in the TxPIC chip to be out of specification thereby increasing the chip yield and reducing manufacturing costs in the deployment of such TxPIC chips. FEC error counts at the FEC decoder on the optical receiver side of the network includes counters that accumulate a plurality of bit pattern-dependent error counts based on different N-bit patterns in the received data bit stream. The accumulated counts of different N-bit patterns are utilized to provide for corrections to threshold and phase relative to the bit eye pattern as well as provided for weight coefficients for the optical receiver equalization system. The deployment of this type of equalization in a digital OEO REGEN network substantially reduces, if not eliminates, the need for dispersion compensating fiber (DCF) or EDFAs in an optical link of the network and enhances the optical receiver tolerance to chromatic dispersion (CD) so that an increase in chip yield is realized for TxPIC chips not operating with acceptable operational parameters, particularly with a desired frequency chirp parameter relative to at least one of the TxPIC modulated sources.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
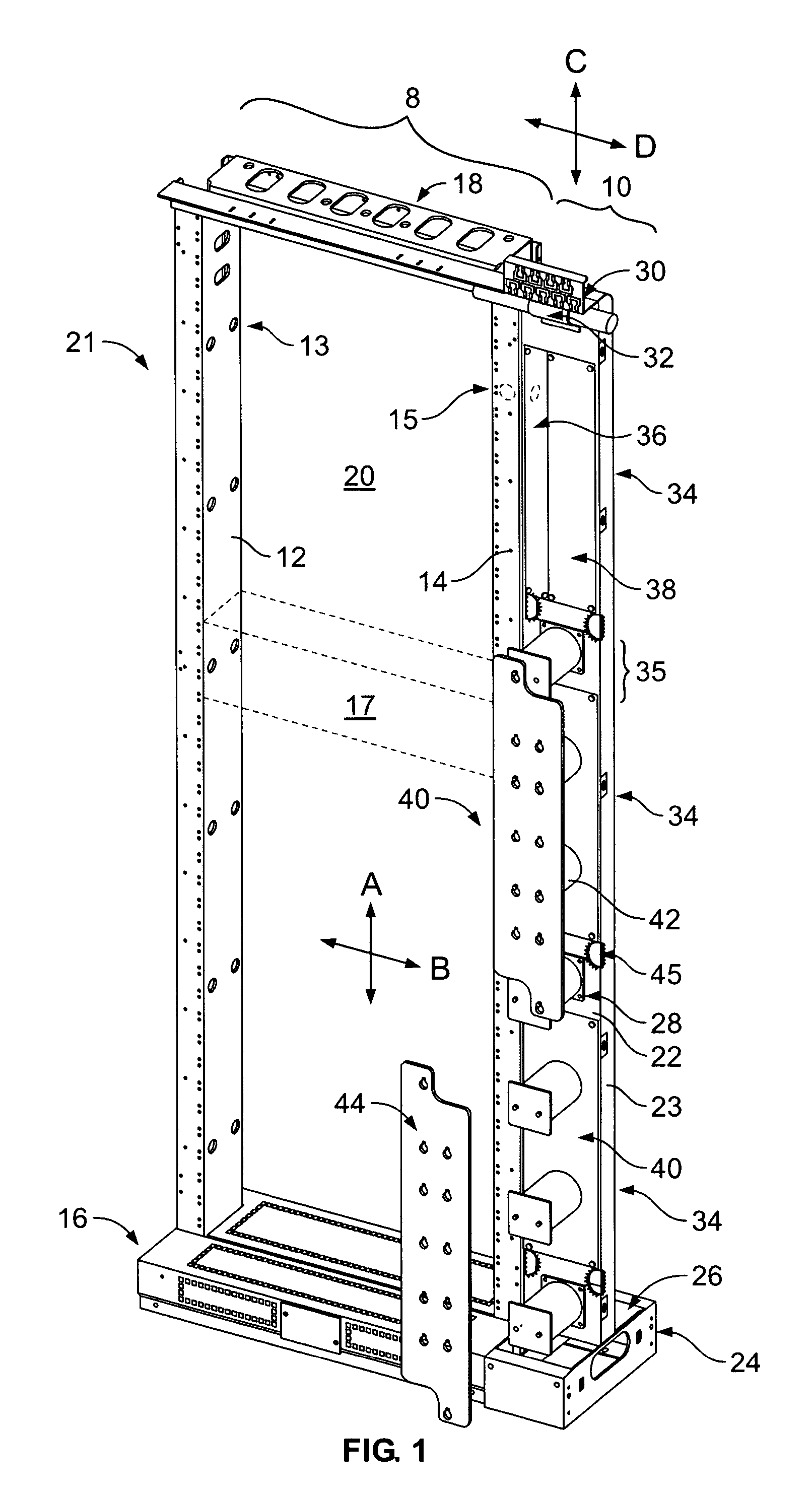
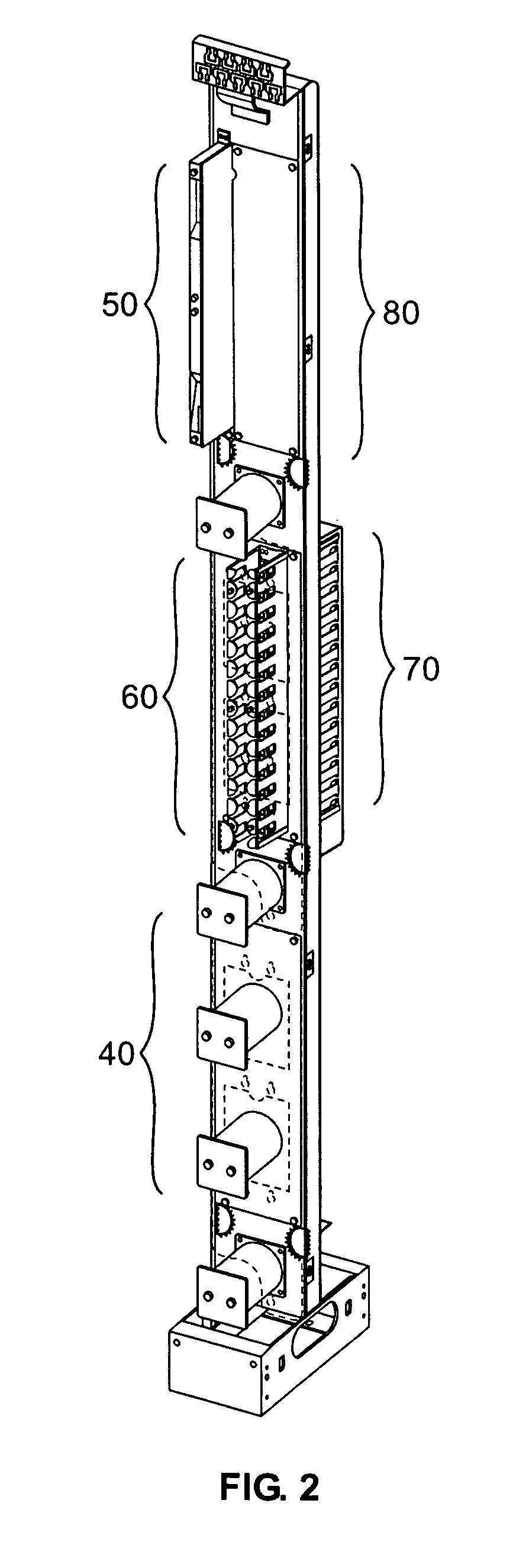
Equipment bay cable management system
InactiveUS7437048B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesPatch panelDispersion compensation
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Pattern-dependent error counts for use in correcting operational parameters in an optical receiver
ActiveUS20060008279A1Accurate methodReduce manufacturing costMultiple-port networksError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorWeight coefficientSemiconductor chip
An optical transmission network includes an optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC) chip, utilized in an optical transmitter and has a plurality of monolithic modulated sources integrated for multiple signal channels on the same semiconductor chip is provided with channel equalization at the optical receiver side of the network that permits one or more such integrated modulated sources in the TxPIC chip to be out of specification thereby increasing the chip yield and reducing manufacturing costs in the deployment of such TxPIC chips. FEC error counts at the FEC decoder on the optical receiver side of the network includes counters that accumulate a plurality of bit pattern-dependent error counts based on different N-bit patterns in the received data bit stream. The accumulated counts of different N-bit patterns are utilized to provide for corrections to threshold and phase relative to the bit eye pattern as well as provided for weight coefficients for the optical receiver equalization system. The deployment of this type of equalization in a digital OEO REGEN network substantially reduces, if not eliminates, the need for dispersion compensating fiber (DCF) or EDFAs in an optical link of the network and enhances the optical receiver tolerance to chromatic dispersion (CD) so that an increase in chip yield is realized for TxPIC chips not operating with acceptable operational parameters, particularly with a desired frequency chirp parameter relative to at least one of the TxPIC modulated sources.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
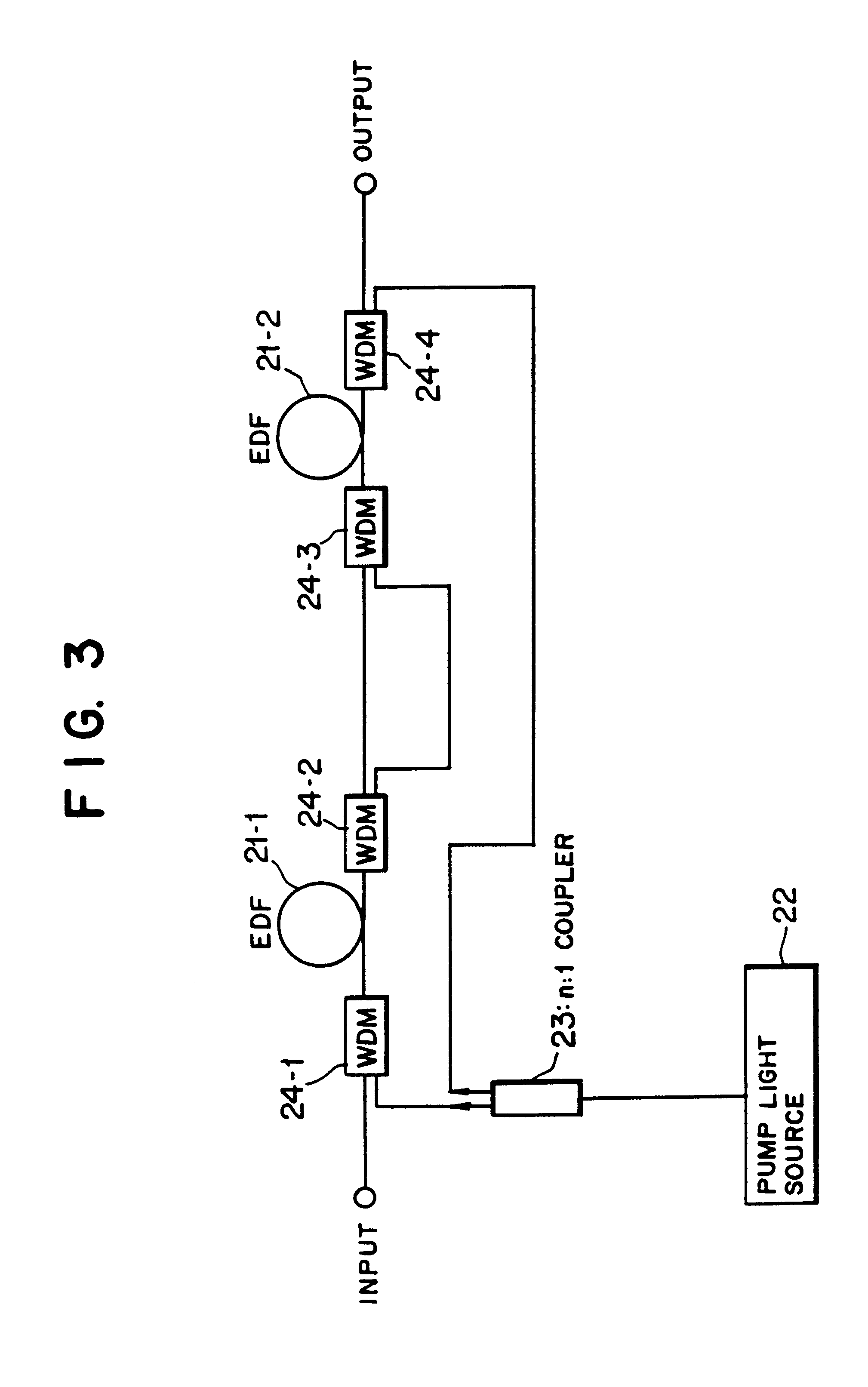
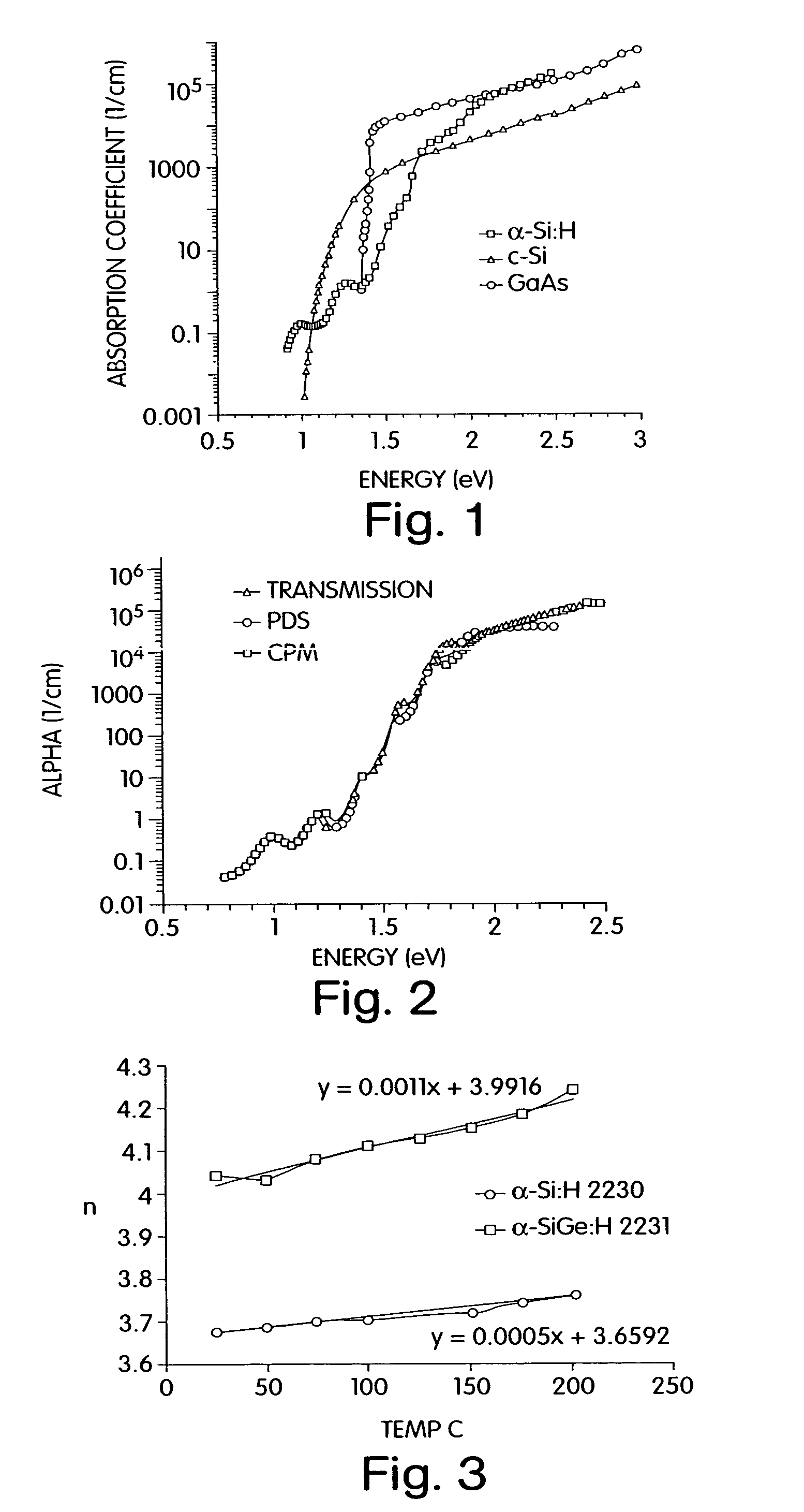
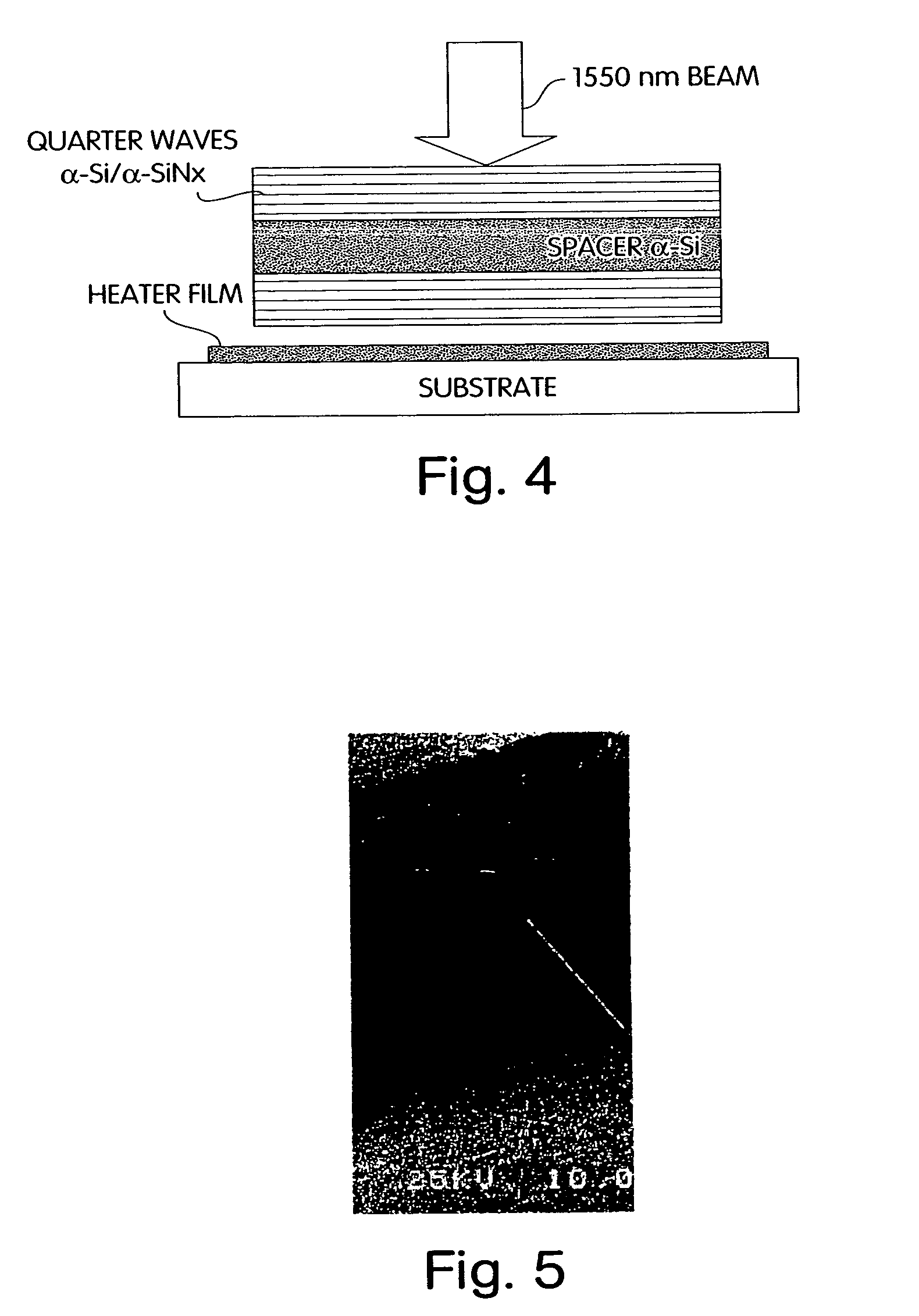
Tunable dispersion compensator
An optical dispersion compensator including: a spacer element having a top surface and a bottom surface; a thin film, multi-layer mirror formed on the top surface of the spacer element, the thin film mirror having a thermally tunable reflectivity; a highly reflective mirror element formed on the bottom surface of the spacer element; and a heater element for controlling a temperature of the thermally tunable thin film mirror.
Owner:AEGIS SEMICON
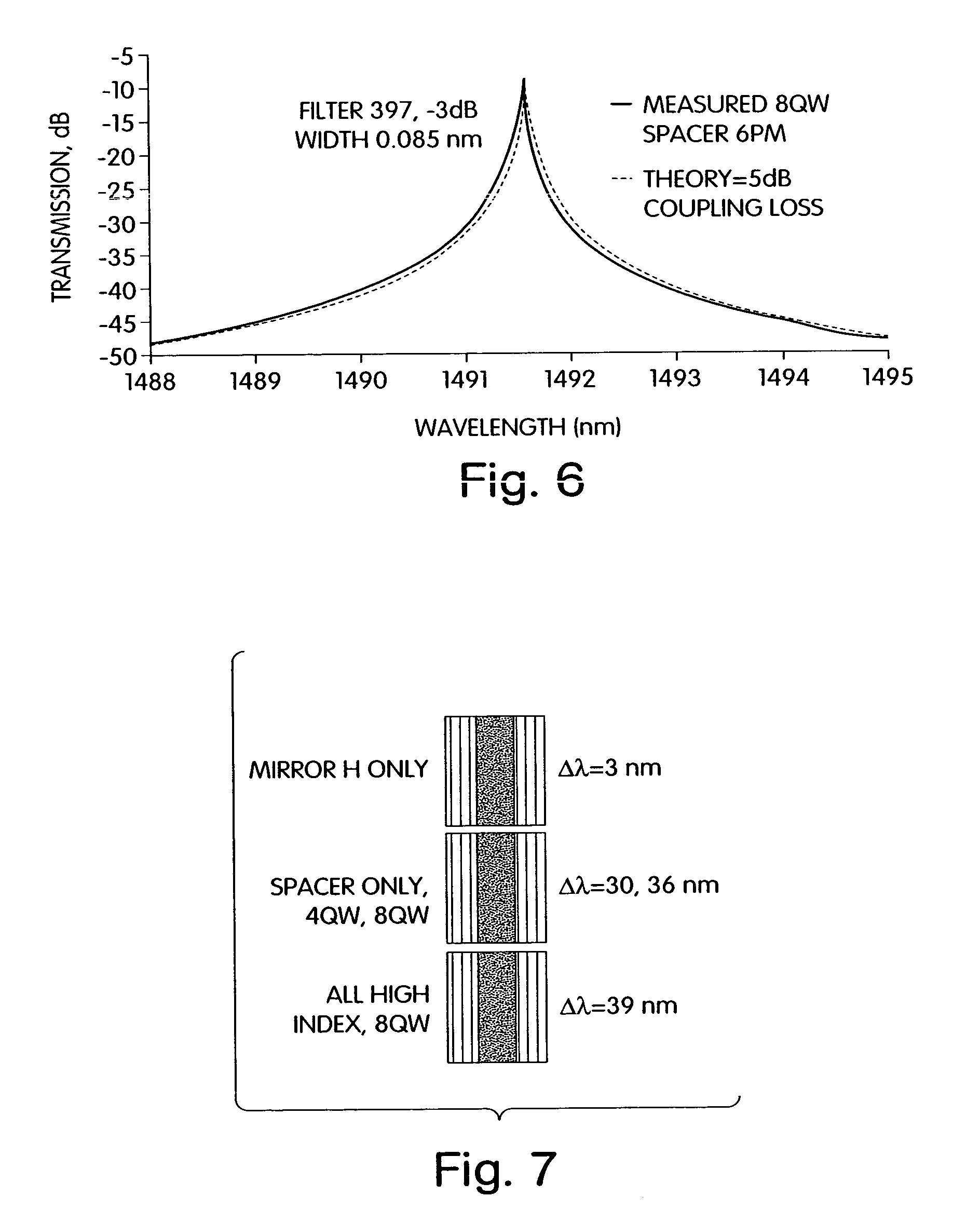
Index tunable thin film interference coatings
According to various embodiments and aspects of the present invention, there is provided a dynamically tunable thin film interference coating including one or more layers with thermo-optically tunable refractive index. Tunable layers within thin film interference coatings enable a new family of thin film active devices for the filtering, control, modulation of light. Active thin film structures can be used directly or integrated into a variety of photonic subsystems to make tunable lasers, tunable add-drop filters for fiber optic telecommunications, tunable polarizers, tunable dispersion compensation filters, and many other devices.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
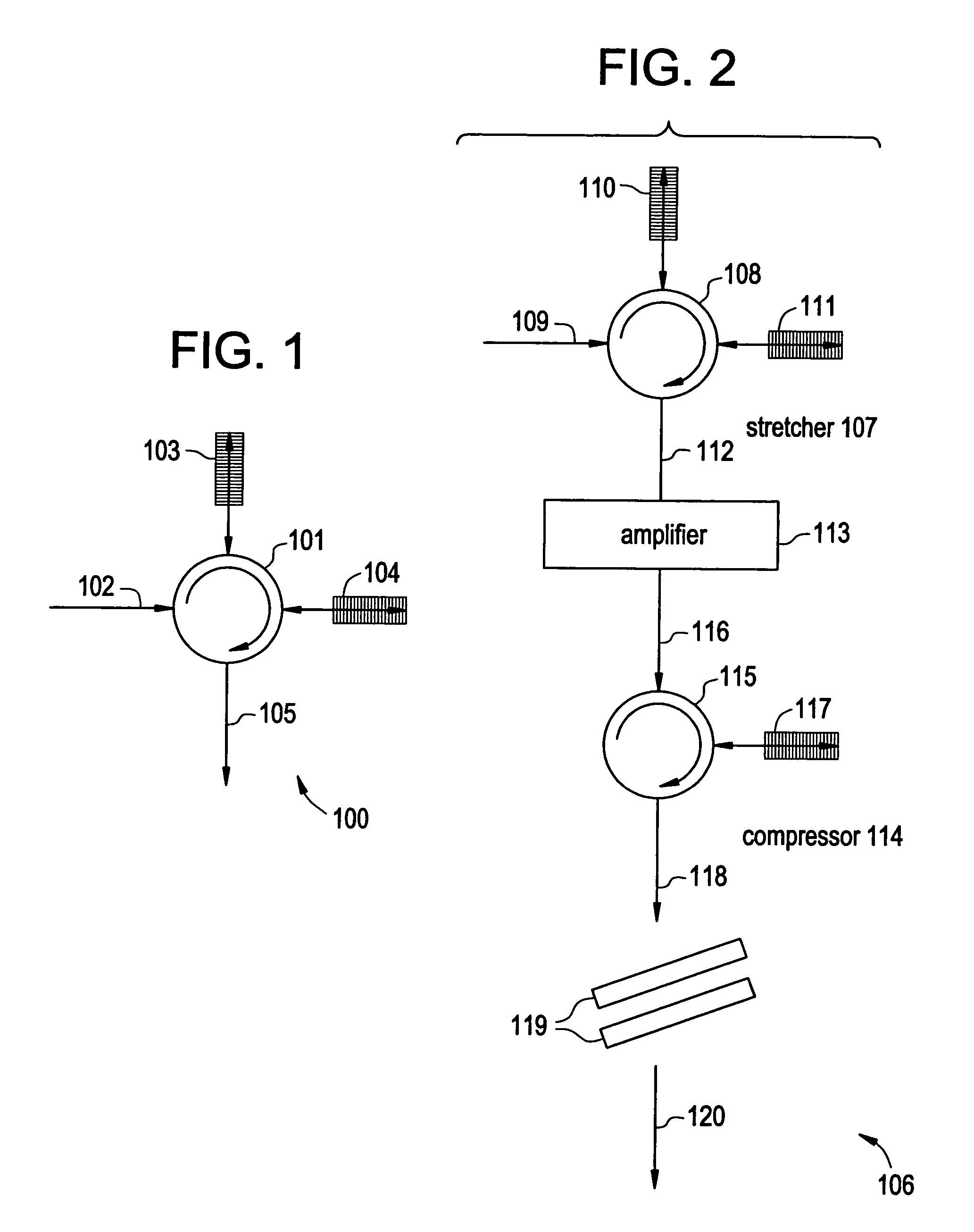
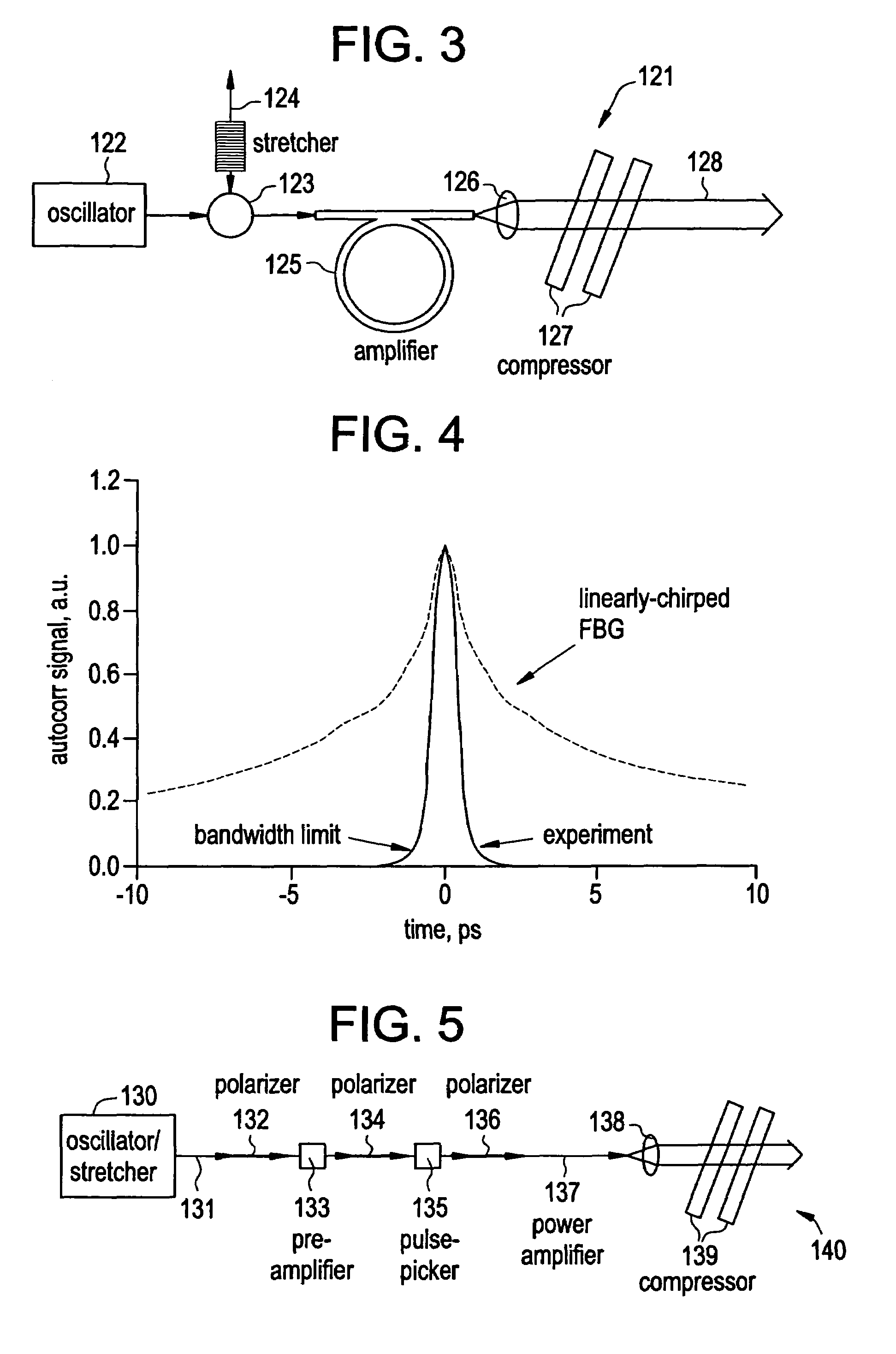
In-line, high energy fiber chirped pulse amplification system
InactiveUS7257302B2Accurately dispersion matchedBig ratioOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLaser arrangementsGratingHigh energy
By writing non-linear chirp into fiber Bragg gratings, greater control over dispersion compensation in CPA systems is obtained, such that, for example, the dispersion profile of the fiber Bragg grating and a bulk compressor may be matched. An iterative method of writing the fiber grating can reduce the group delay ripple to very low levels; and adaptive control of the fiber grating dispersion profile can further reduce these levels, while in addition offering greater acceptable yield in the manufacture of such gratings. Fiber Bragg gratings may be designed so as to provide customized pulse shapes optimized for various end uses, such as micromachining, for example, and may also be used to counteract gain-narrowing in a downstream amplifier.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
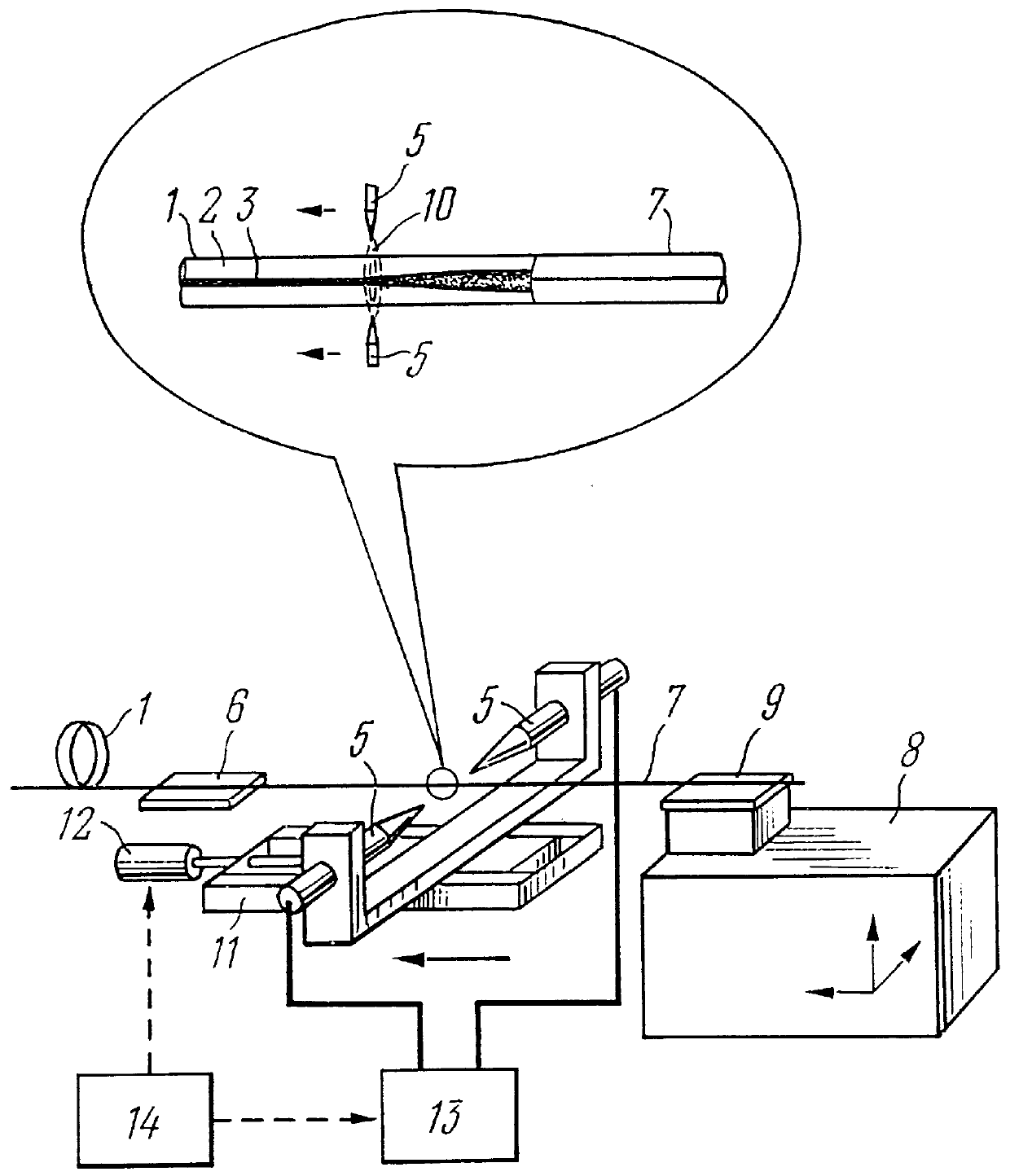
Mode field diameter conversion fiber, method for locally changing a refractive index of optical waveguides and method for fabricating optical waveguide preforms
InactiveUS6125225AAvoid mechanical stressGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingGratingRefractive index
PCT No. PCT / RU97 / 00278 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 9, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 9, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 3, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 28643 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 2, 1998The invention relates to fiber optics and can be employed in fiber radiation collimators, optical waveguide couplers, spectral filters, optical isolators, long-period gratings, dispersion compensators, cascade mode field diameter conversion fibers on simulated Raman effect, physical value sensors, radiation suppression units for predetermined wavelengths, and for smoothing the gain spectrum in erbium fiber amplifiers. The invention facilitates fabrication of optical waveguides and apparatuses based on them. To produce preforms for optical waveguides (1) by a plasma chemical vapor deposition method, molecular gaseous agents, fed to a substrate tube (24), are mixed so that less than five atoms of oxygen fall on every atom of silicon and more than one atom of nitrogen falls on every 1000 atoms of oxygen. The refractive index is locally changed by heating a length of an optical waveguide (1). This causes a local thermal diffusion of elements contained in a core (3) into a cladding (2), or vice versa. The length of the optical waveguide (1) is heated by current of an electric arc (10) or by radiation (16) of an infrared laser (15). The core (3) is doped with nitrogen at concentration from 0.01 at. % to 5 at. %. In the mode field diameter conversion fiber, a diameter of the core (3) changes along the length of the optical waveguide (1), increasing towards its end (4).
Owner:VOLOKONNO OPTICHESKAYA TEKHNIKA KAPITAL +2
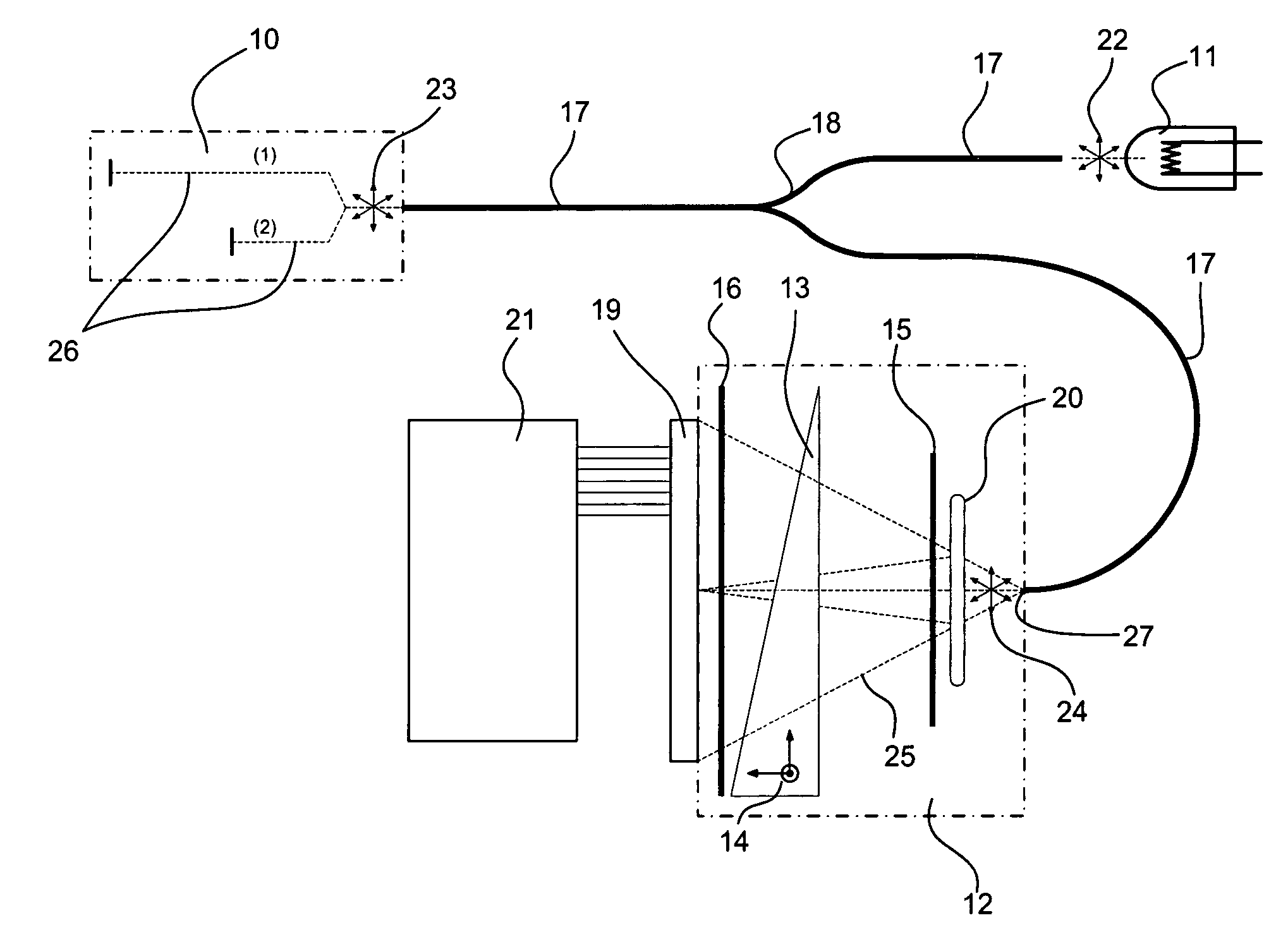
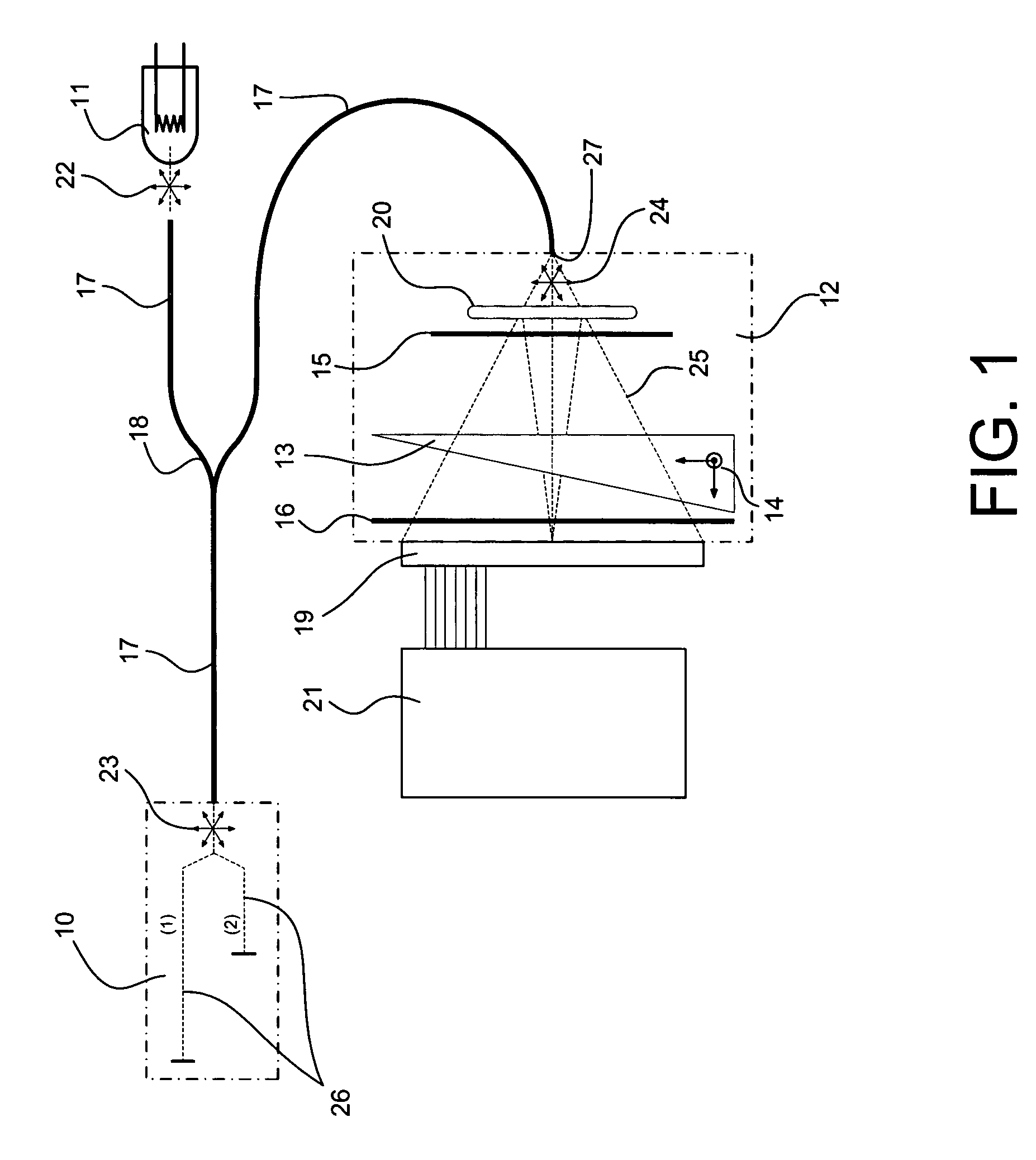
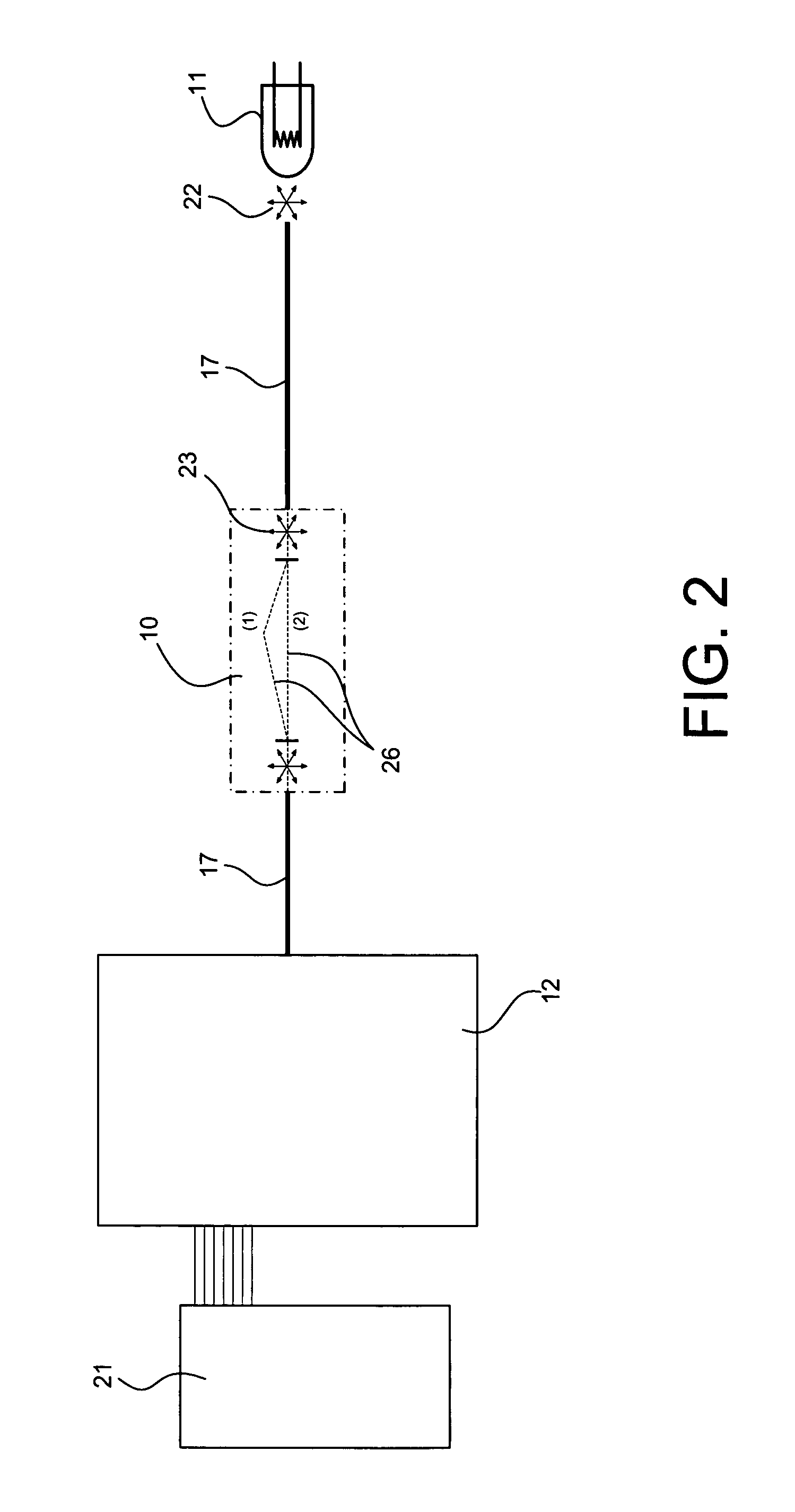
Low-coherence interferometry optical sensor using a single wedge polarization readout interferometer
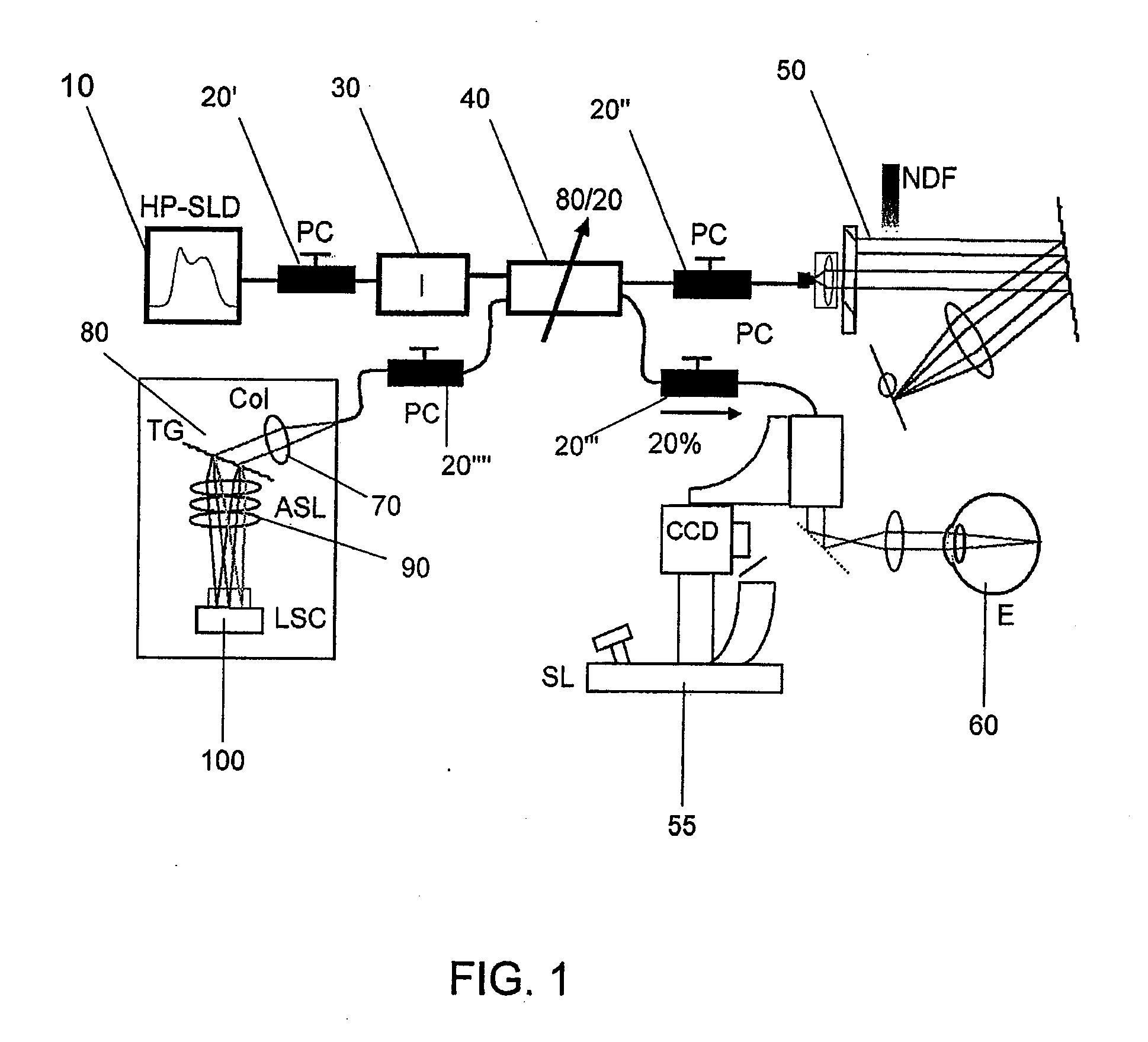
ActiveUS7259862B2Simple and robustOptical measurementsInterferometersLighting systemDispersion compensation
The invention provides a method and a system for measuring a physical quantity by means of a tandem interferometer optical sensor system based on low-coherence interferometry. The system comprises a light system, a sensing interferometer and a polarization readout interferometer. The invention provides a polarization interferometer comprising a single birefringent wedge. The invention also provides for a dispersion-compensated optical sensor system. The invention also provides an interferometer sensitive to temperature that comprises a trajectory in a LiB3O5 crystal with an x-cut orientation.
Owner:OPSENS
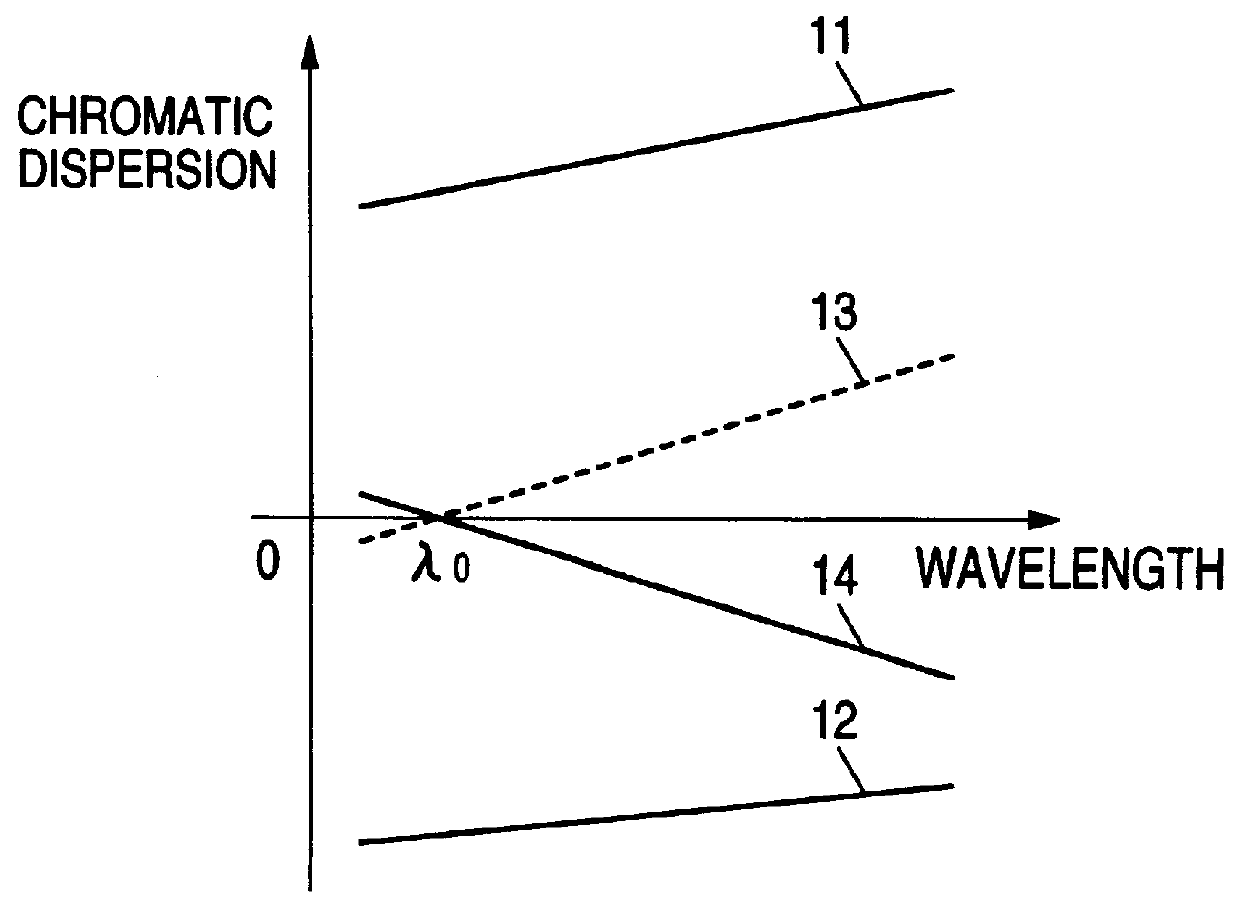
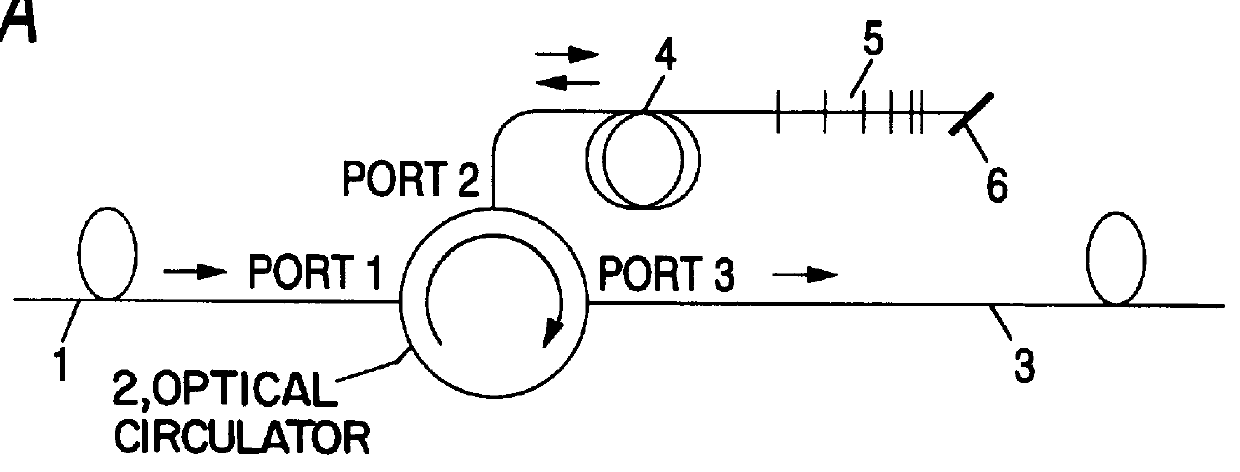
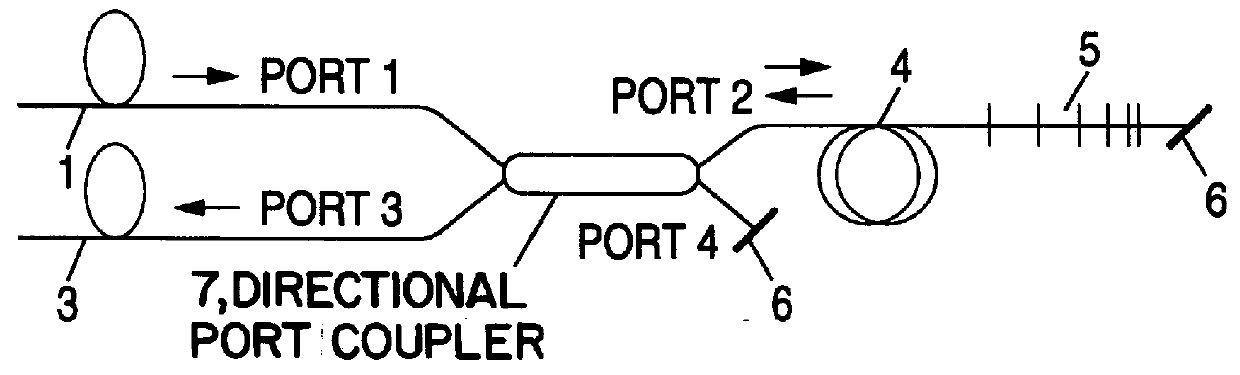
Chromatic dispersion compensator and chromatic dispersion compensating optical communication system
InactiveUS6055081AShorten the lengthReduced insertion lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationCommunications systemGrating
In a chromatic dispersion compensator, an optical signal directing unit such as an optical circulator or a directional coupler having a first, second, third and fourth ports. The optical signal directing unit directs an optical signal inputted from one of the ports to another port of the ports. A reflection-type compensator including a dispersion compensating fiber, a reflecting portion and changing unit for changing a polarization direction of a reciprocating signal light, in which the dispersion compensating fiber is connected to the reflecting portion via the changing unit. An input transmission path which is connected to the first port; and an output transmission path which is connected to the fourth port so that the signal light is outputted from the fourth port. The reflection-type compensating unit is connected to one of the second and third ports, and the chirped grating is connected to the other port.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical amplifier
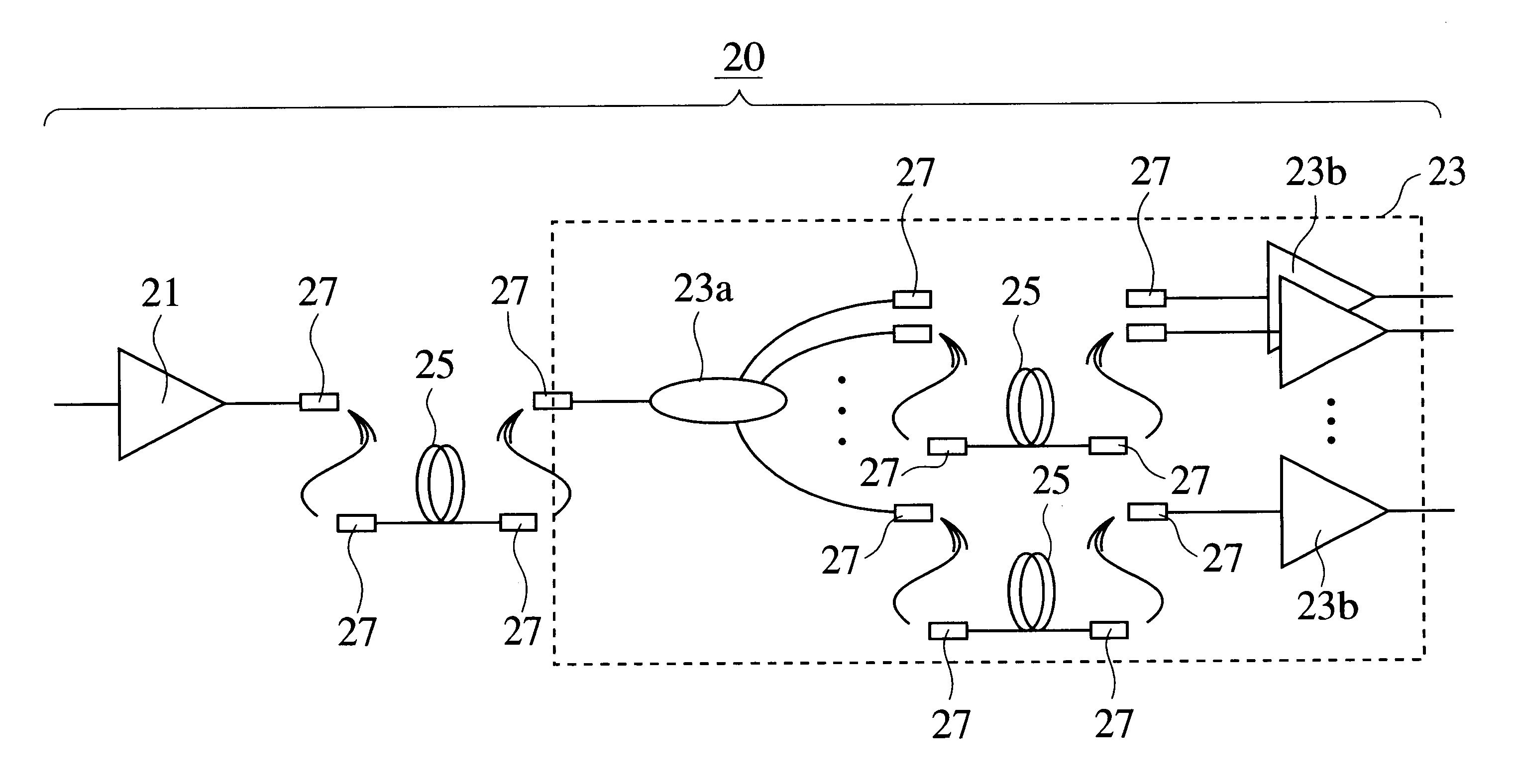
InactiveUS6236500B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrangementsAudio power amplifierLength wave
There is provided an optical amplifier for reducing the optical output power difference and / or obtaining high output power across a wide wavelength band. The optical amplifier comprises a plurality of optical amplifier units connected in two or more stages. At least one of the optical amplifier units comprises a first optical component of a single input and N outputs that has an optical-demultiplexing function, and P units of optical amplification means for the individual amplification of light that is output from P (where 1<=P<=N) output terminals selected from the N (integer) output terminals of the first optical component. Second optical components are provided to the input side of the first optical component or between the output side of the first optical component and the input side of the optical amplification means. The second optical components are optical components having chromatic dispersion compensation functions, optical components having functions designed to compensate for wavelength dependency output power difference, or optical components demonstrating other required effects. The optical components are DCFs, FBGs, SMFs, optical filters, attenuators, or the like. The second optical components are provided nonselectively or selectively.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Methods, systems and computer program products for optical coherence tomography (OCT) using automatic dispersion compensation
Methods, systems and computer program products for generating parameters for software dispersion compensation in optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems are provided. Raw spectral interferogram data is acquired for a given lateral position on a sample and a given reference reflection. A trial spectral phase corresponding to each wavenumber sample of the acquired spectral interferogram data is postulated. The acquired raw spectral data and the postulated trial spectral phase data are assembled into trial complex spectrum data. Trial A-scan data is computed by performing an inverse Fourier transform on the trial complex spectrum data and determining the magnitude of a result.
Owner:BIOPTIGEN
Tunable dispersion compensator
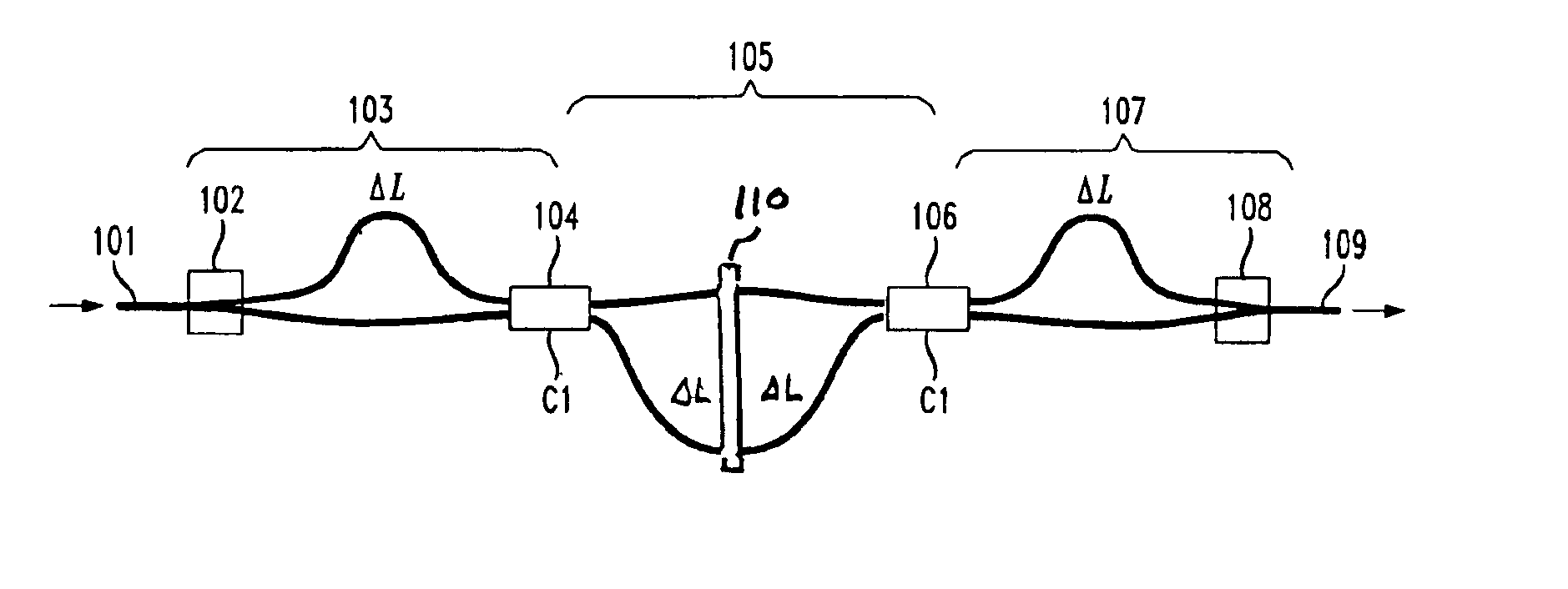
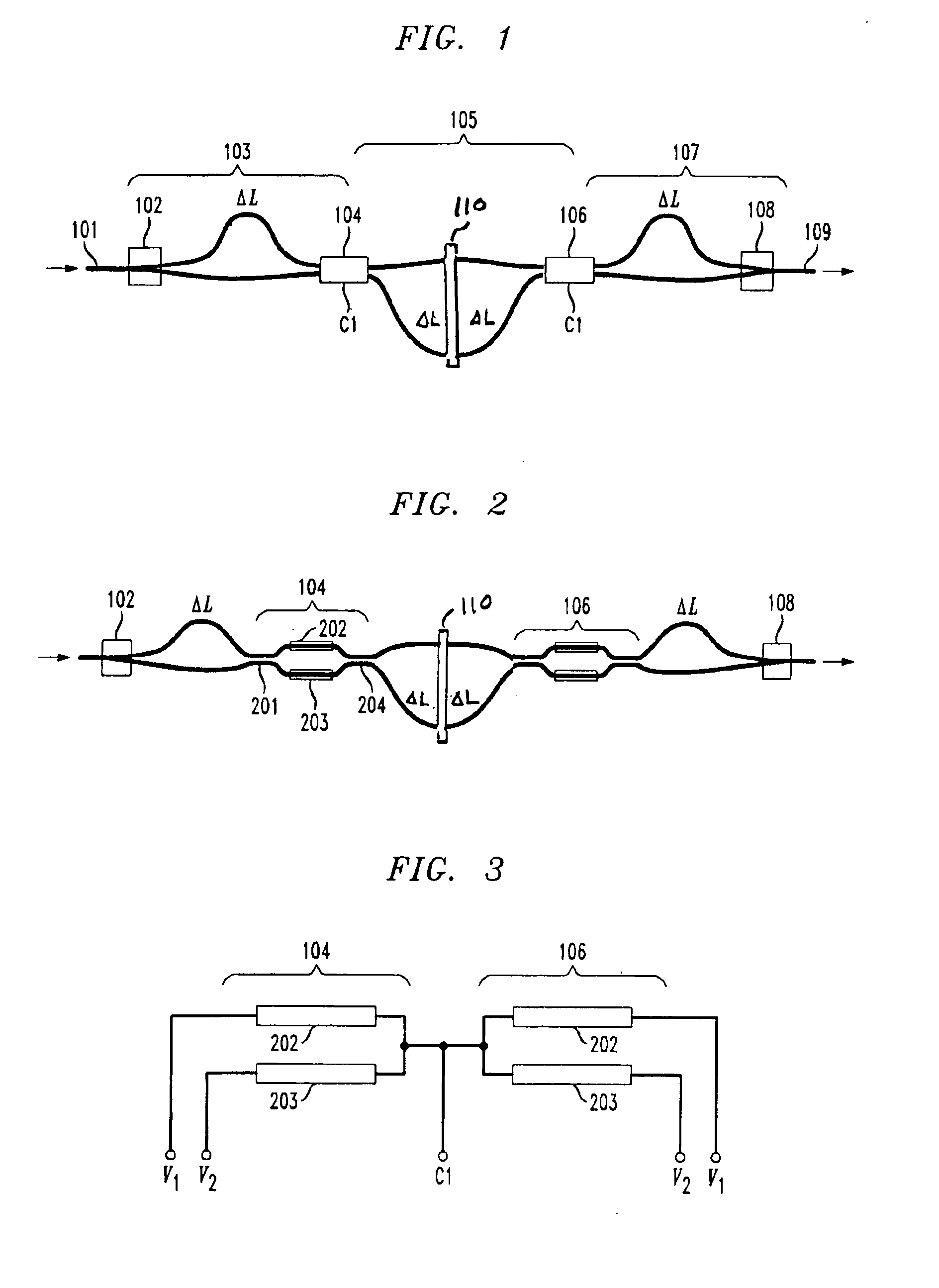
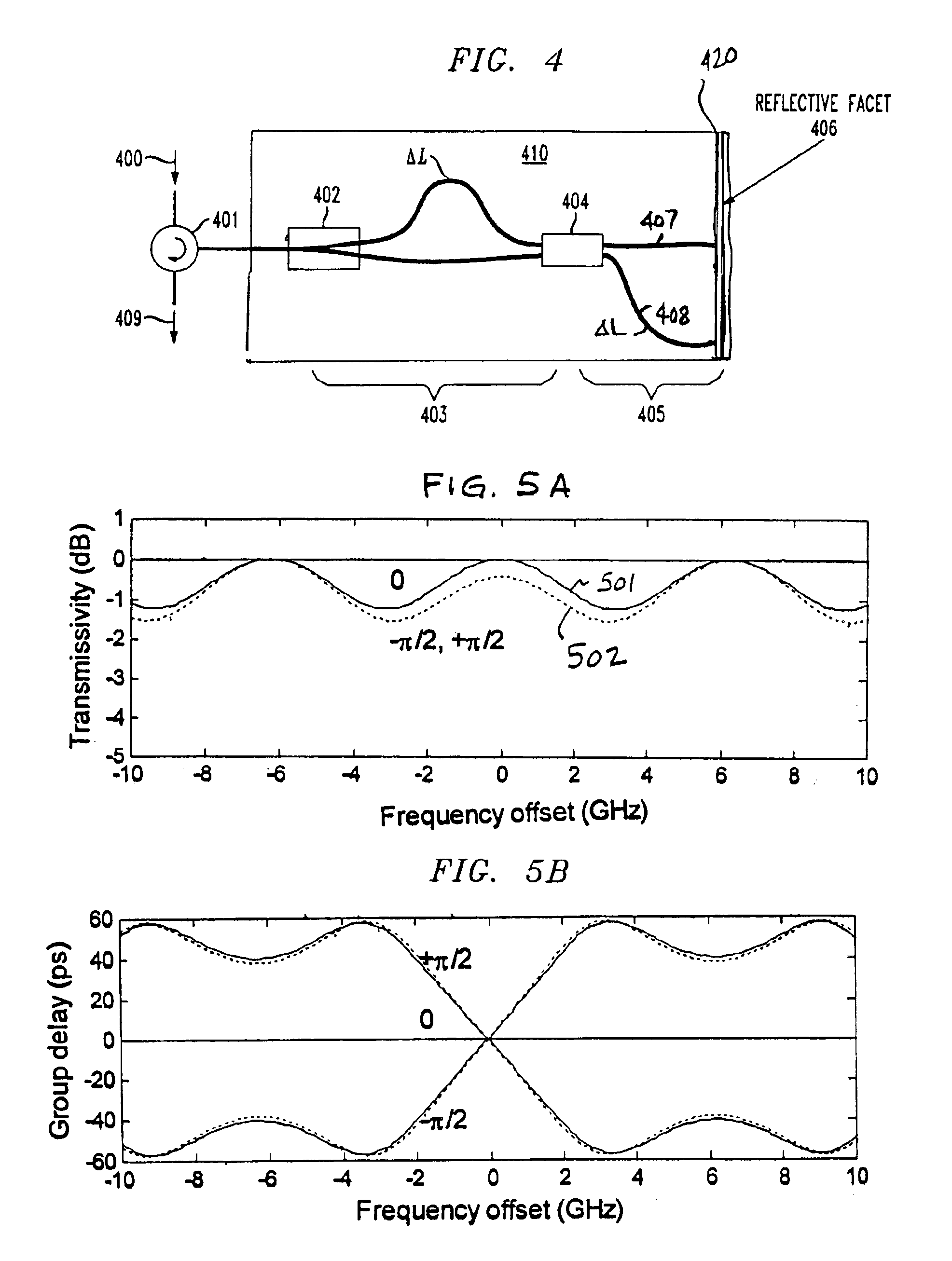
InactiveUS6961492B2Low powerSimple to fabricateCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionPath lengthThree stage
A method and apparatus for implementing a colorless polarization independent Mach-Zehnder-interferometer (MZI)-based tunable dispersion compensator (TDC) that has only three MZI stages (two in a reflective MZI-TDC) and two adjustable couplers which are responsive to one control voltage, making it compact, low power, and simple to fabricate, test, and operate. Polarization independence is obtained by using a half-wave plate positioned across the midpoints of the two path lengths of middle stage MZI of the three stage MZI-TDC and by using a quarter-wave plate in front of a reflective facet of the reflective MZI-TDC. A cascaded MZI-TDC arrangement with also only a single control is formed by cascading two MZI-TDC arrangements and driving all adjustable couplers with the same control signal.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
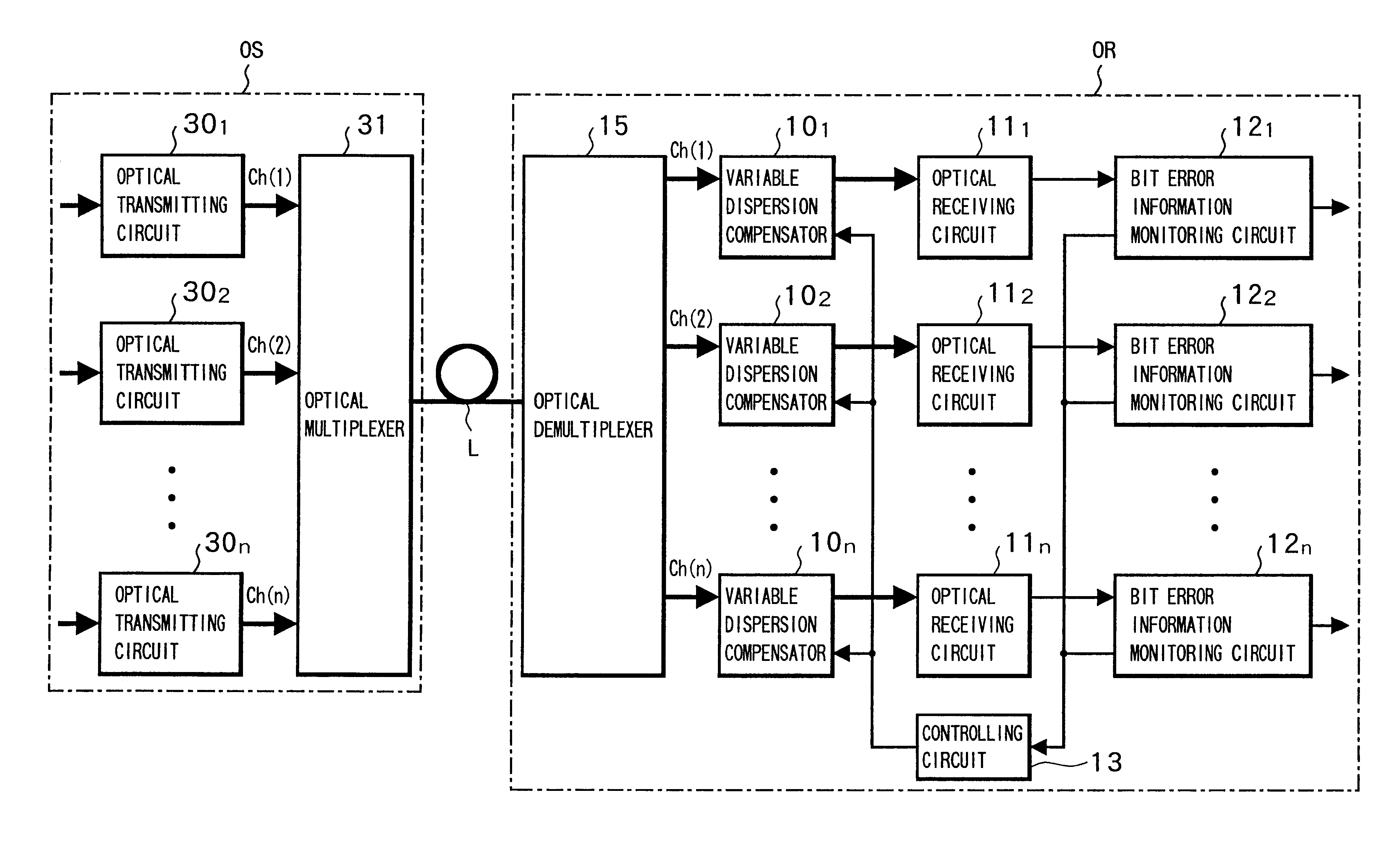
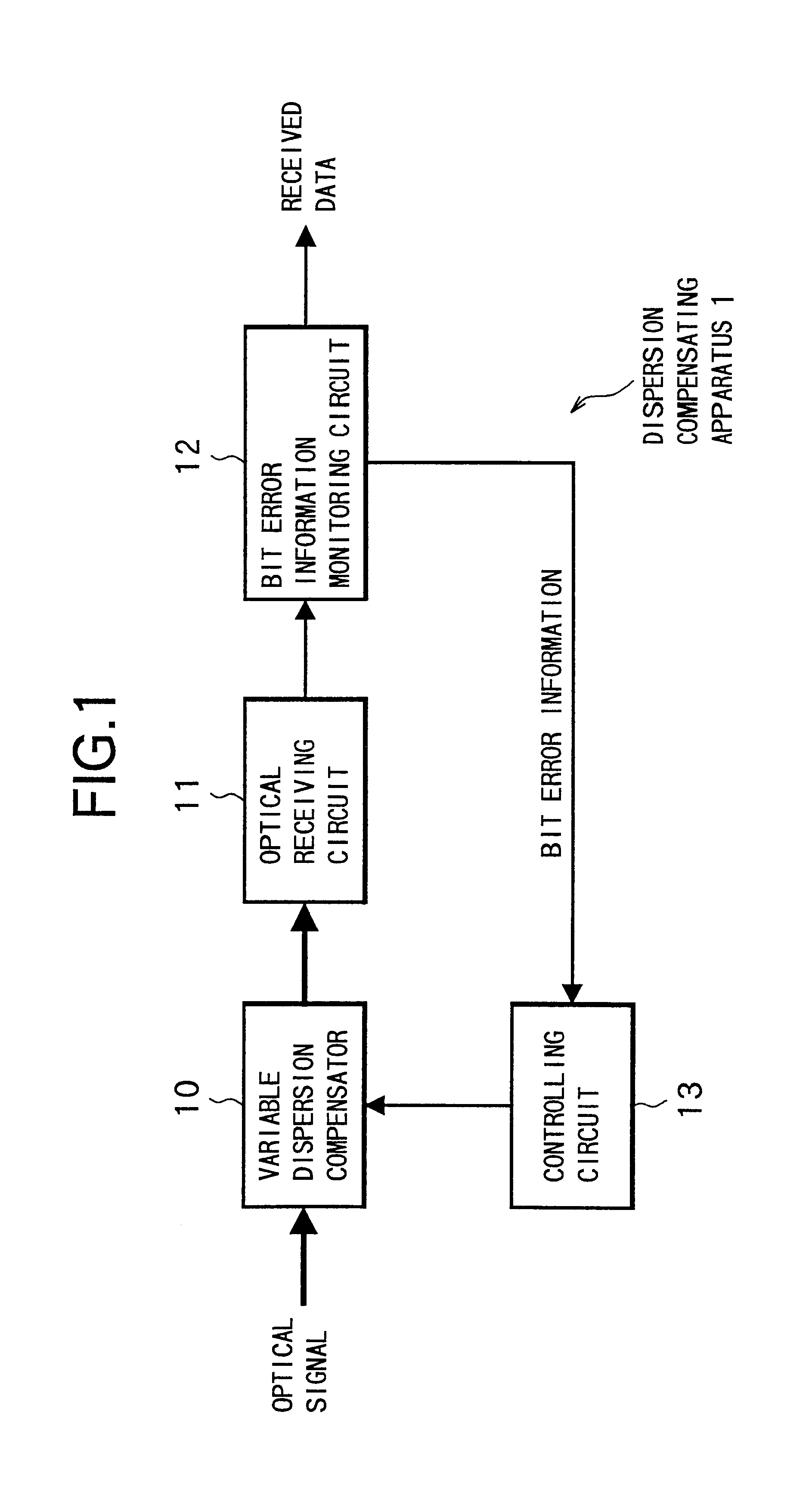
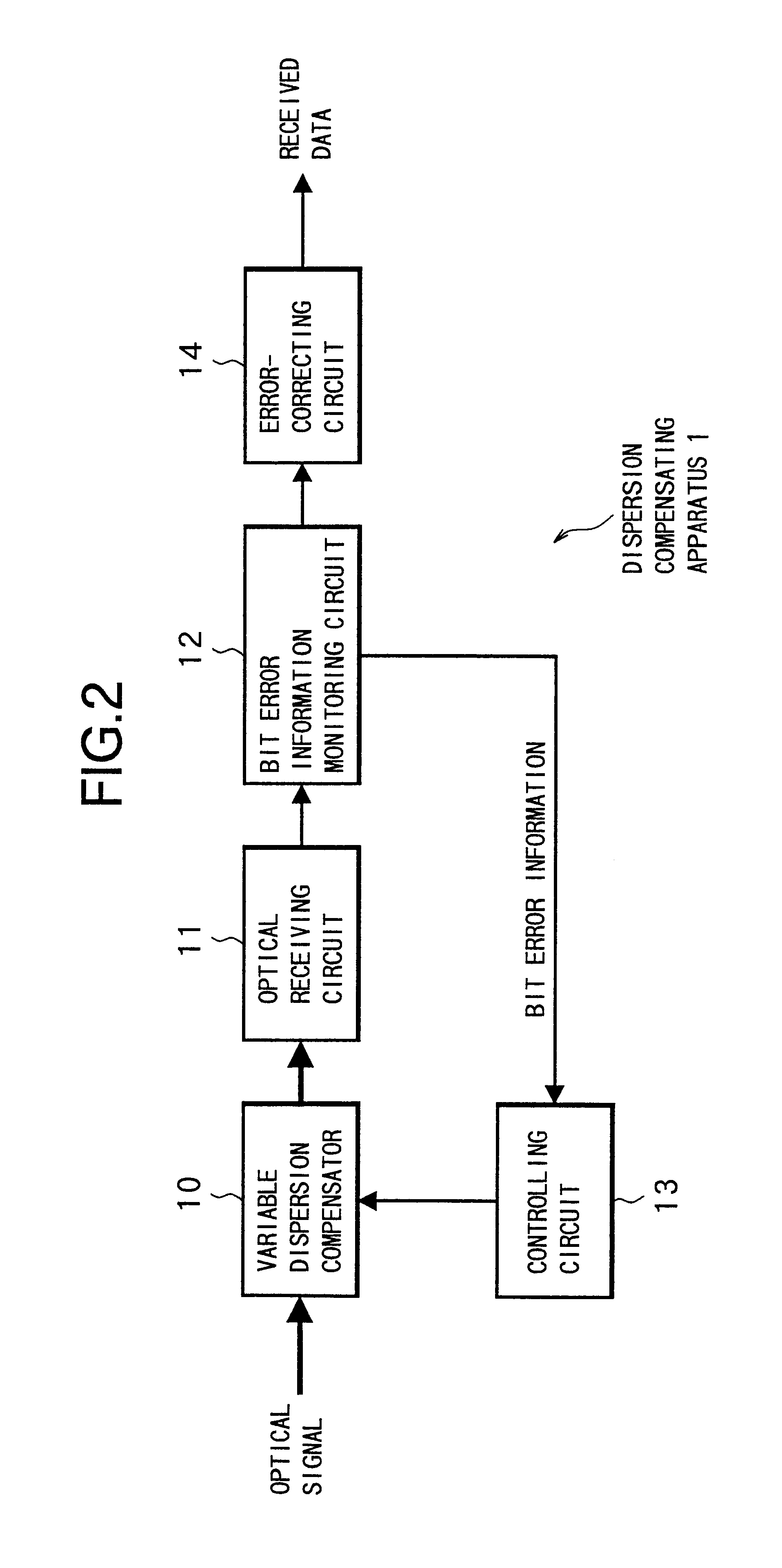
Dispersion compensating method, dispersion compensating apparatus and optical transmission system
InactiveUS6871024B2Small sizeLow costWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationEngineeringLength wave
The present invention aims at realizing a dispersion compensating method capable of readily conducting automatic compensation of waveform degradation caused by dispersion characteristics of an optical transmission path, and at providing a dispersion compensating apparatus and an optical transmission system, of a smaller size at a reduced cost. To this end, the dispersion compensating apparatus of the present invention comprises: a variable dispersion compensator for compensating for the dispersion of optical signal input via an optical transmission path; a bit error information monitoring circuit for generating bit error information of a received signal output from the variable dispersion compensator via an optical receiving circuit; and a controlling circuit for optimally controlling a wavelength dispersion value of the variable dispersion compensator based on the bit error information from the bit error information monitoring circuit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
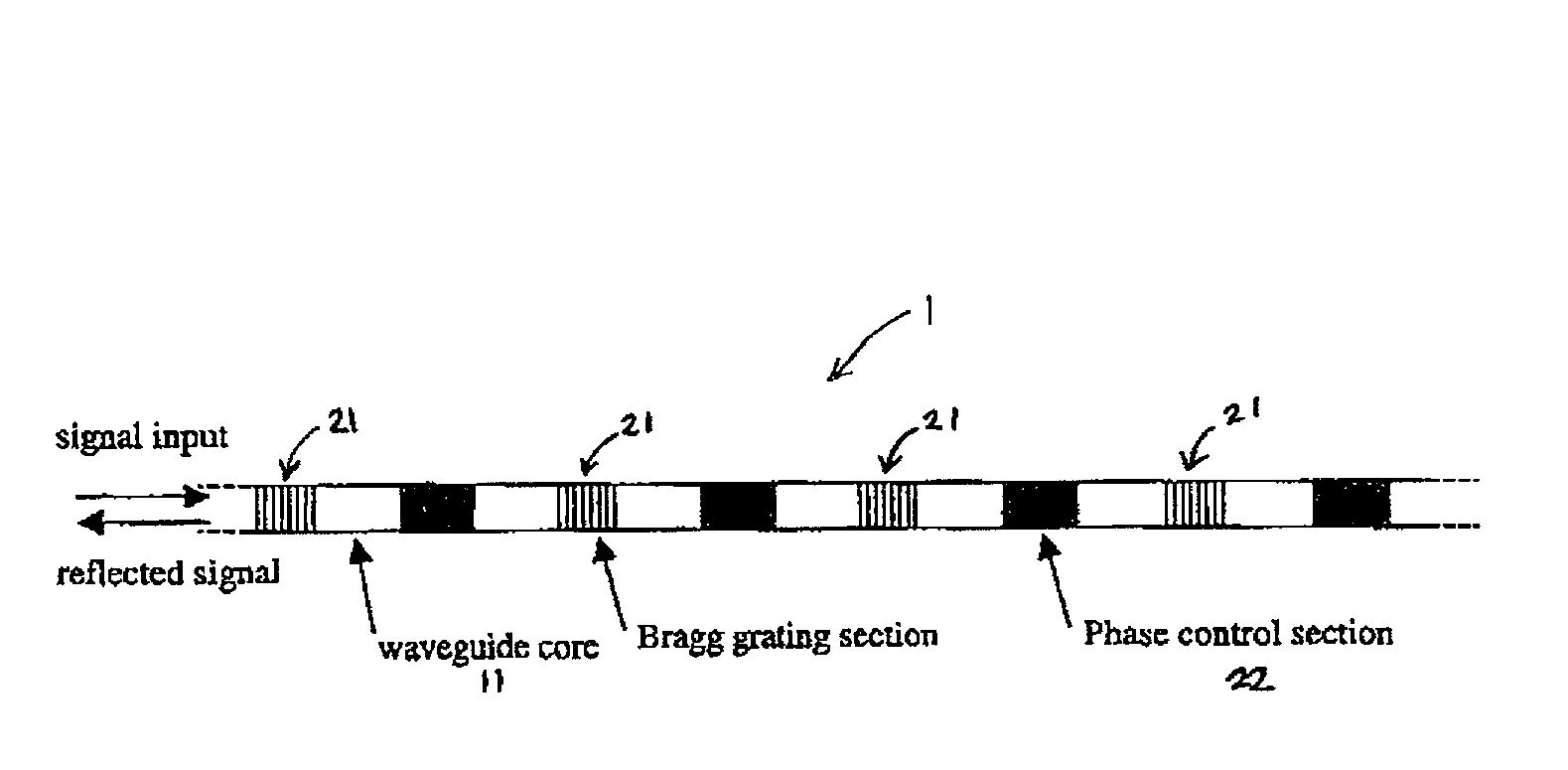
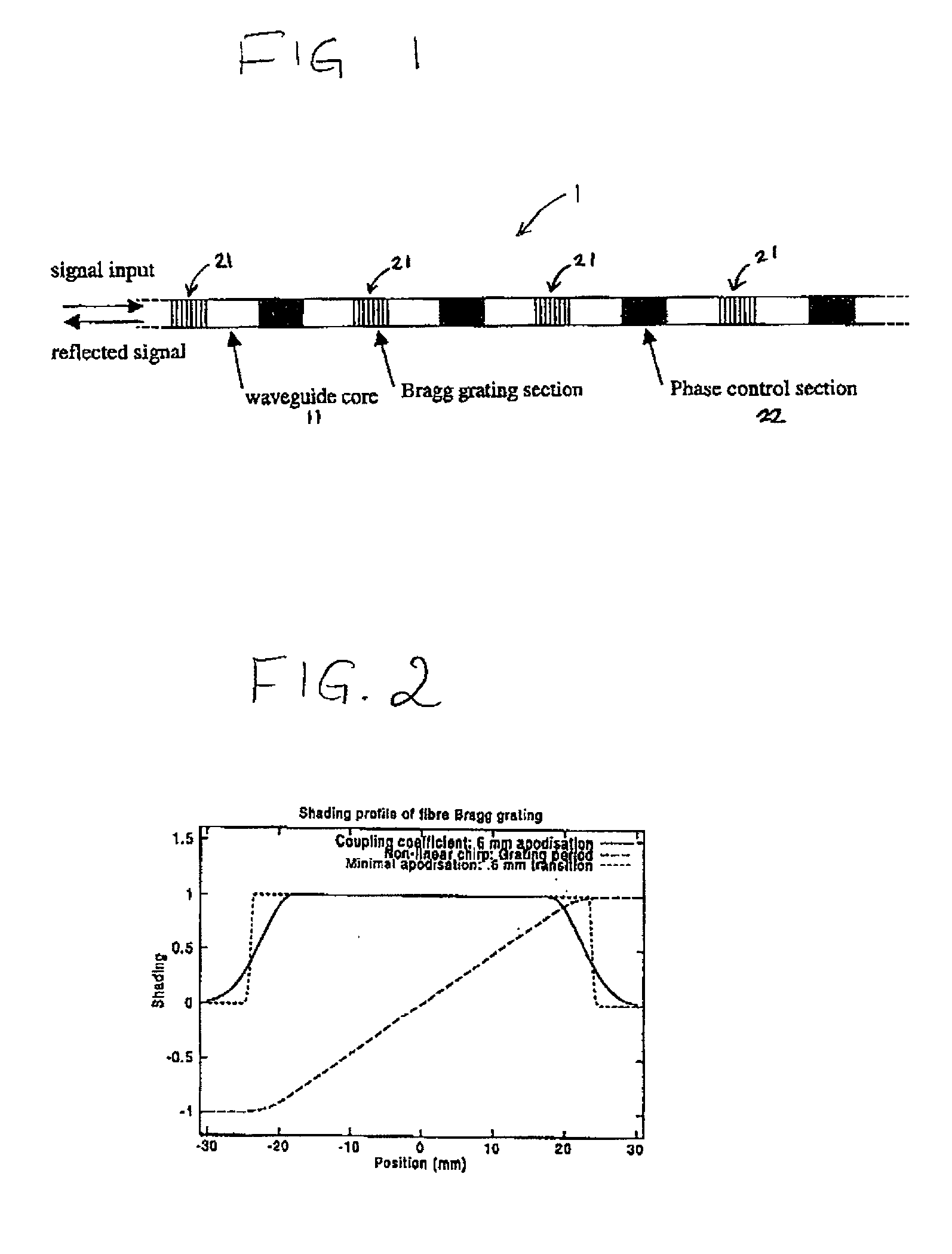
Compensation apparatus and method utilising sampled bragg gratings
Dispersion compensation devices are described which comprise waveguides including sampled Bragg gratings which exhibit comb-like reflectance characteristics. The profile of effective refractive index along the length of the grating is controlled to adjust the position of the teeth and / or to control the dispersion exhibited by the device (i.e. to control the chirp of the grating). The devices can thus be used to provide dispersion compensation to any one of a number of wavelength channels in a WDM system. In preferred arrangements, the effective refractive index distribution is set by a applying a temperature distribution along the length of the grating, or by setting an applied electric field.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com