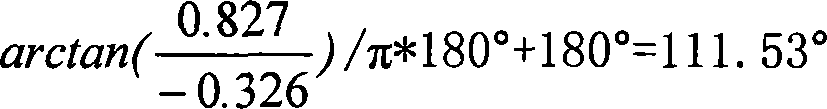Patents
Literature
1608 results about "Iterative method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computational mathematics, an iterative method is a mathematical procedure that uses an initial guess to generate a sequence of improving approximate solutions for a class of problems, in which the n-th approximation is derived from the previous ones. A specific implementation of an iterative method, including the termination criteria, is an algorithm of the iterative method. An iterative method is called convergent if the corresponding sequence converges for given initial approximations.
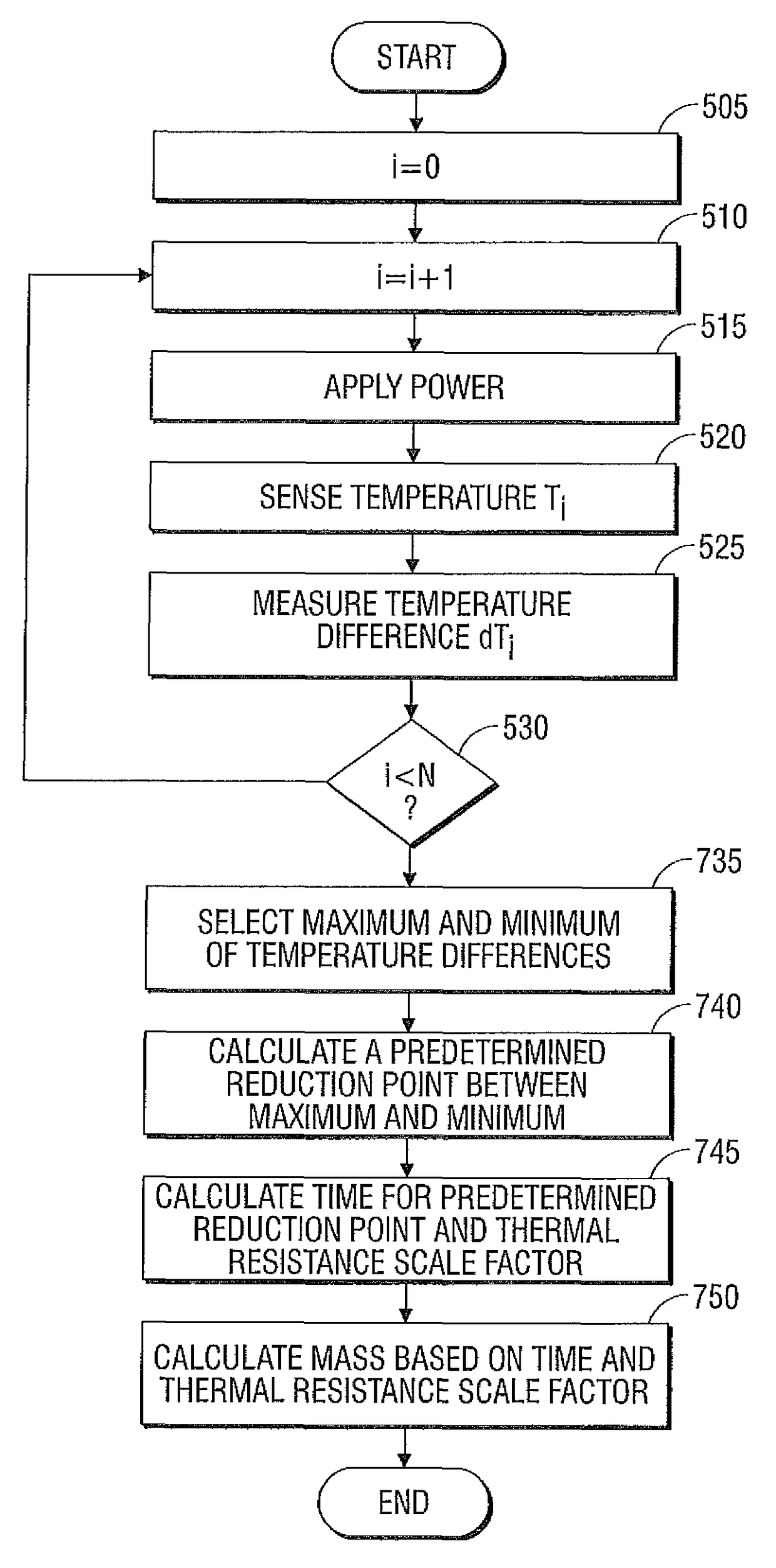
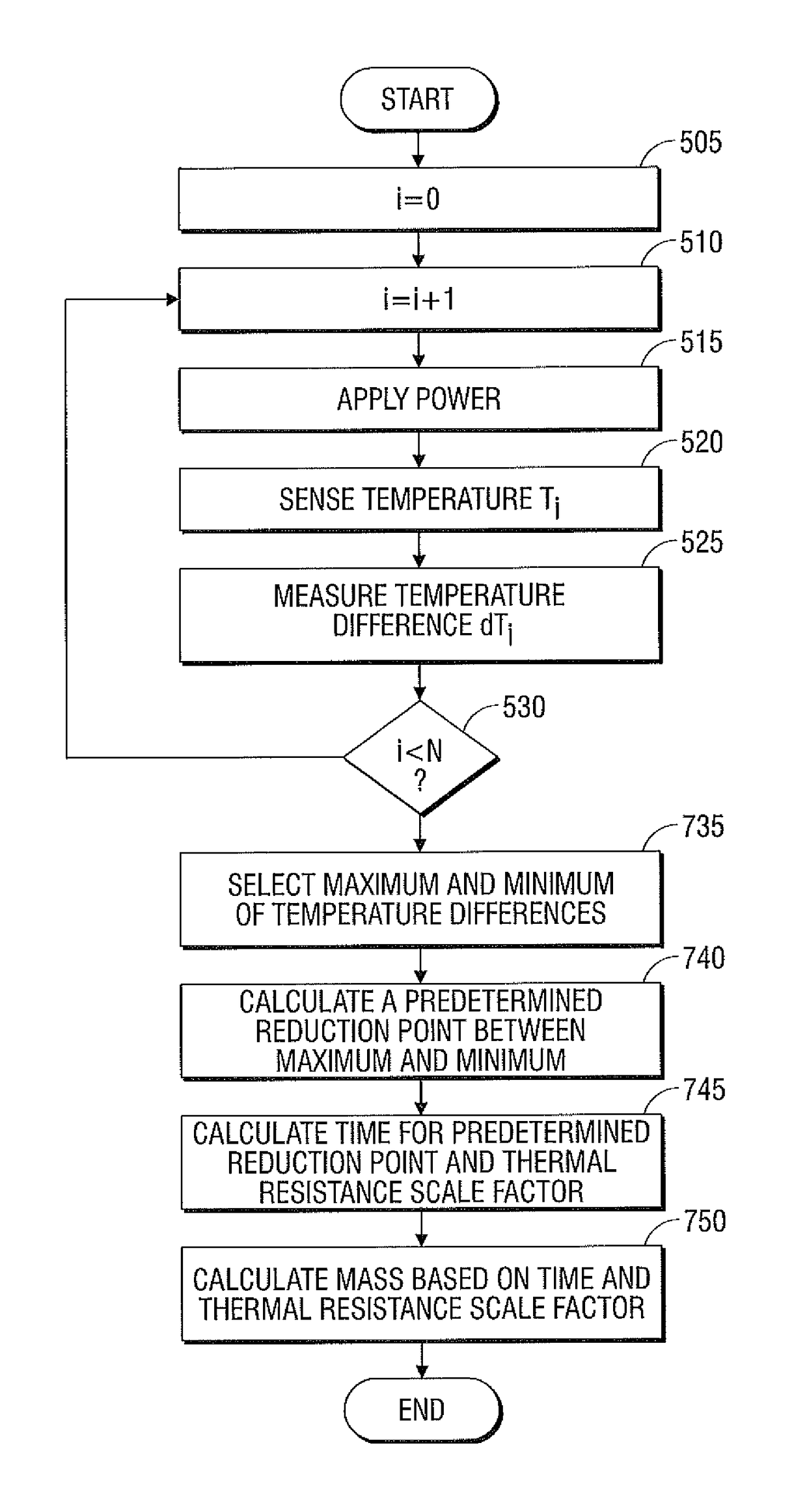
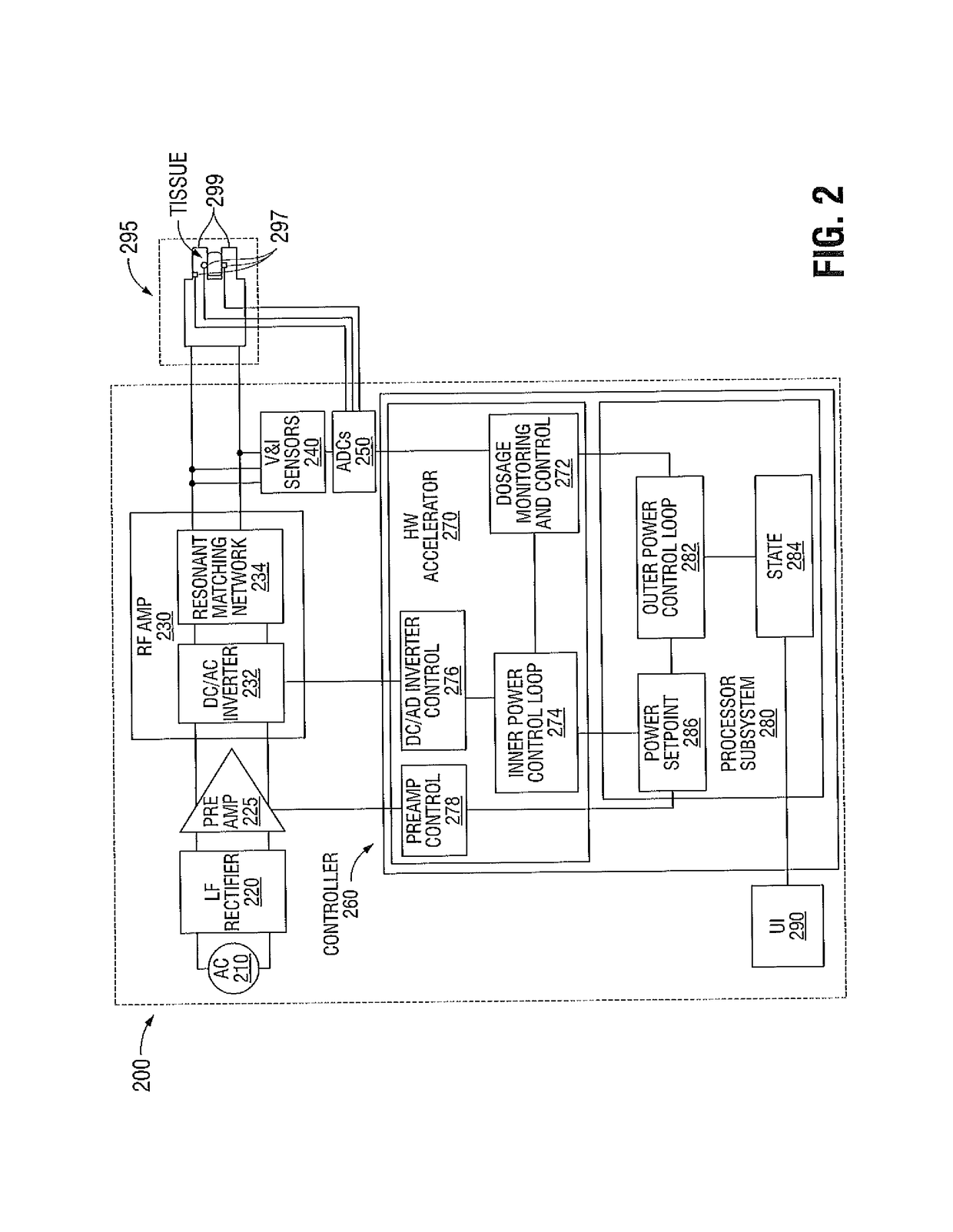
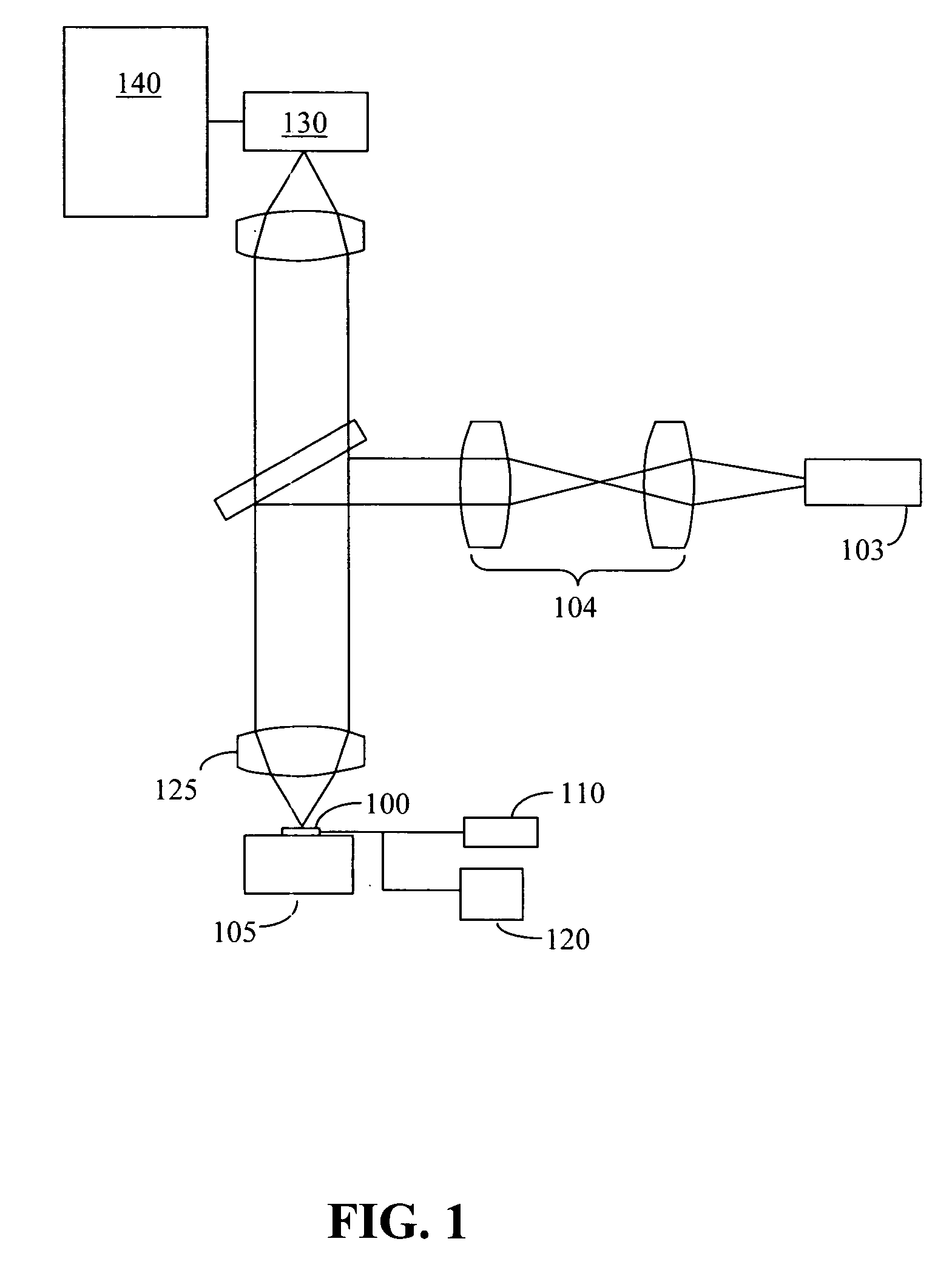
Systems and methods for estimating tissue parameters using surgical devices
Systems and methods for estimating tissue parameters, including mass of tissue to be treated and a thermal resistance scale factor between the tissue and an electrode of an energy delivery device, are disclosed. The method includes sensing tissue temperatures, estimating a mass of the tissue and a thermal resistance scale factor between the tissue and an electrode, and controlling an electrosurgical generator based on the estimated mass and the estimated thermal resistance scale factor. The method may be performed iteratively and non-iteratively. The iterative method may employ a gradient descent algorithm that iteratively adds a derivative step to the estimates of the mass and thermal resistance scale factor until a condition is met. The non-iterative method includes selecting maximum and minimum temperature differences and estimating the mass and the thermal resistance scale factor based on a predetermined reduction point from the maximum temperature difference to the minimum temperature difference.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
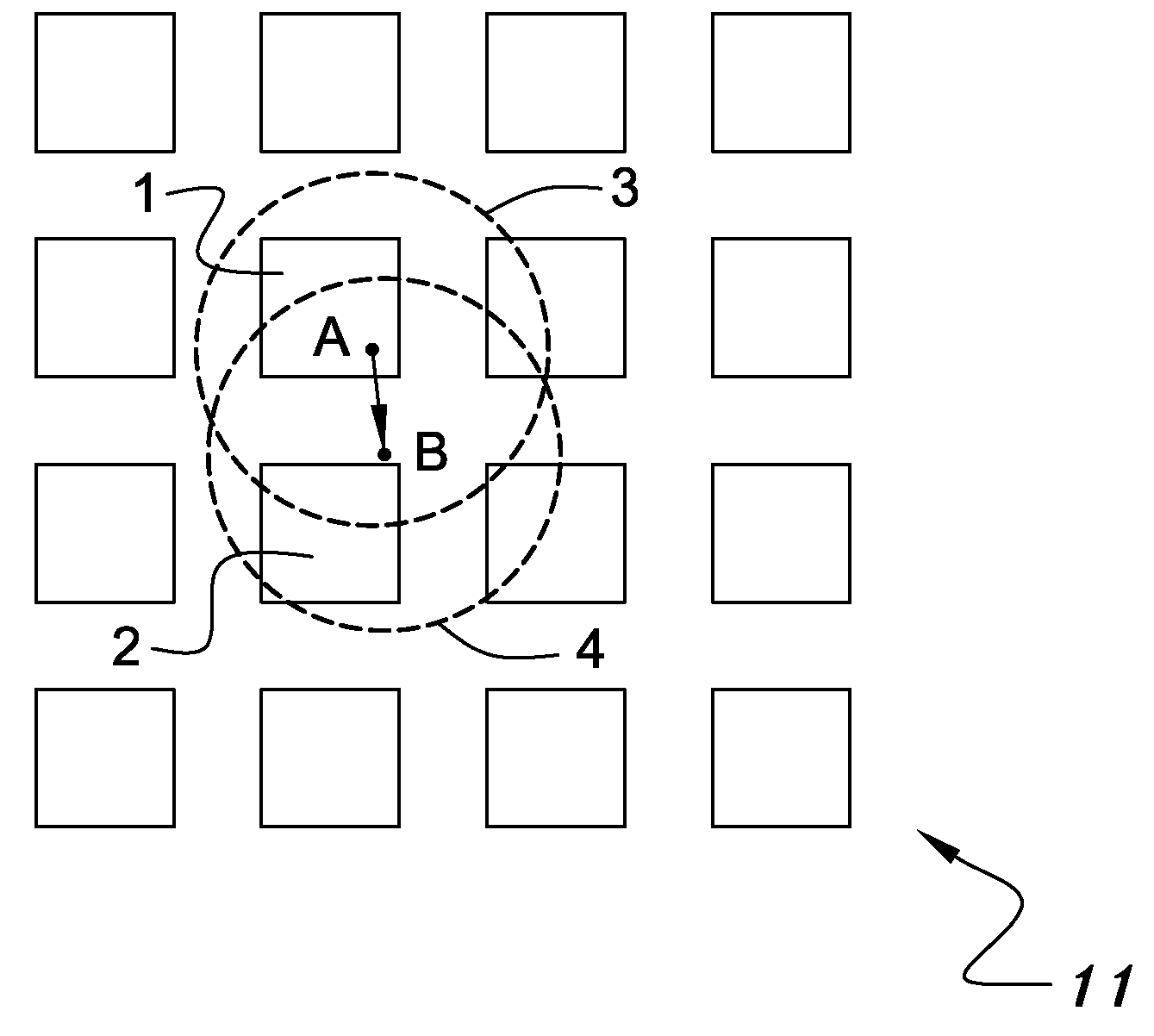
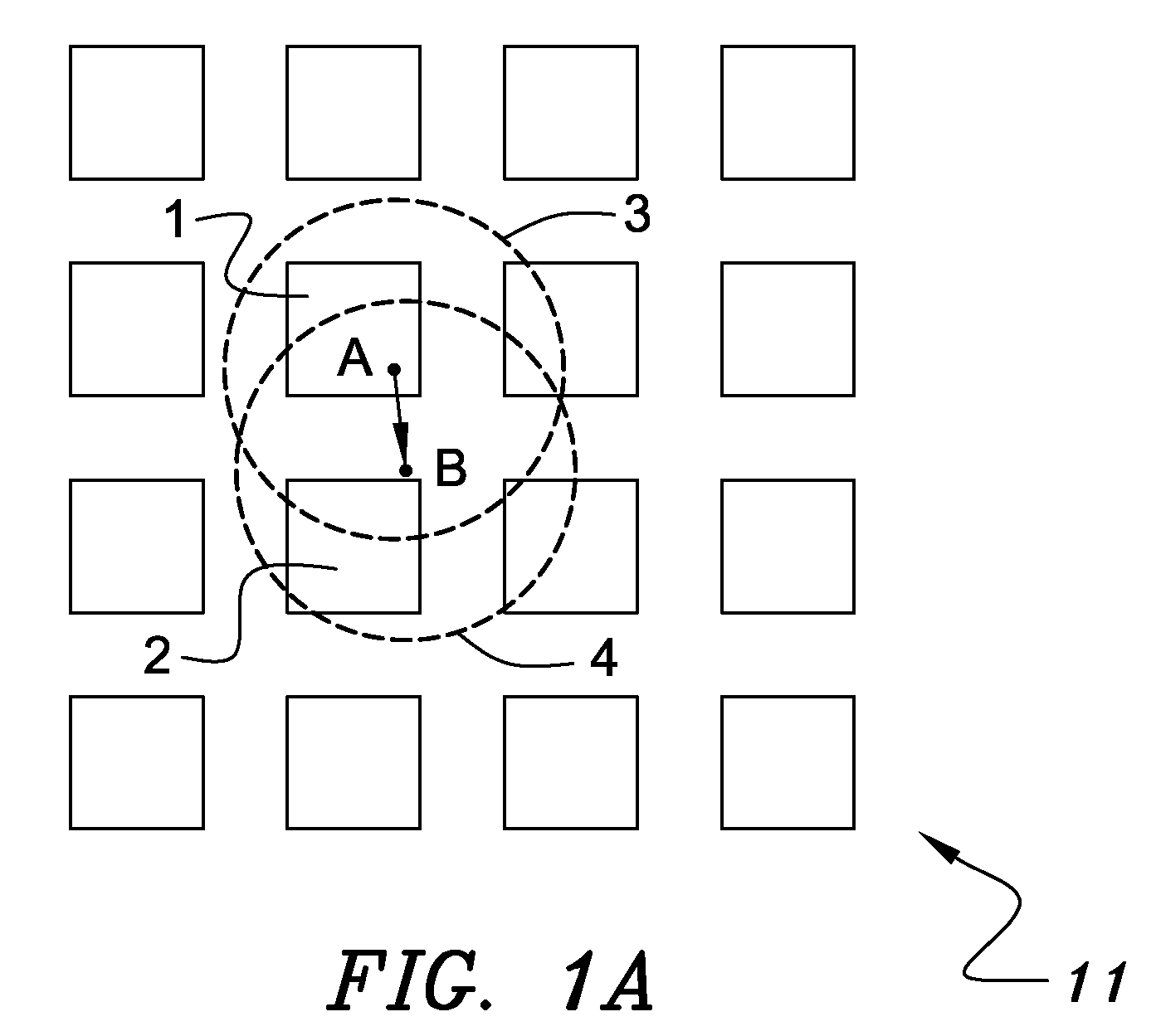
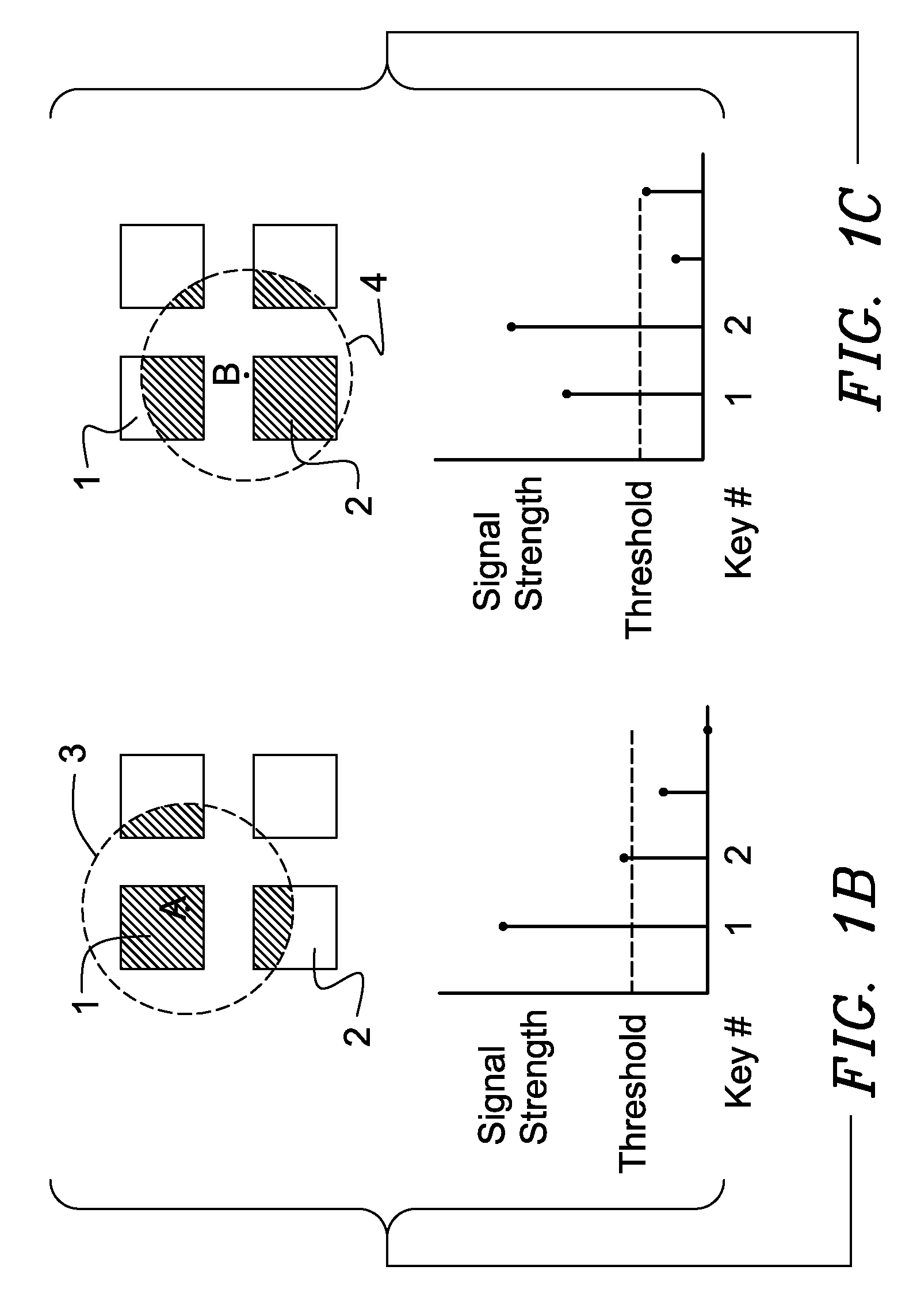
Keyboard with reduced keying ambiguity
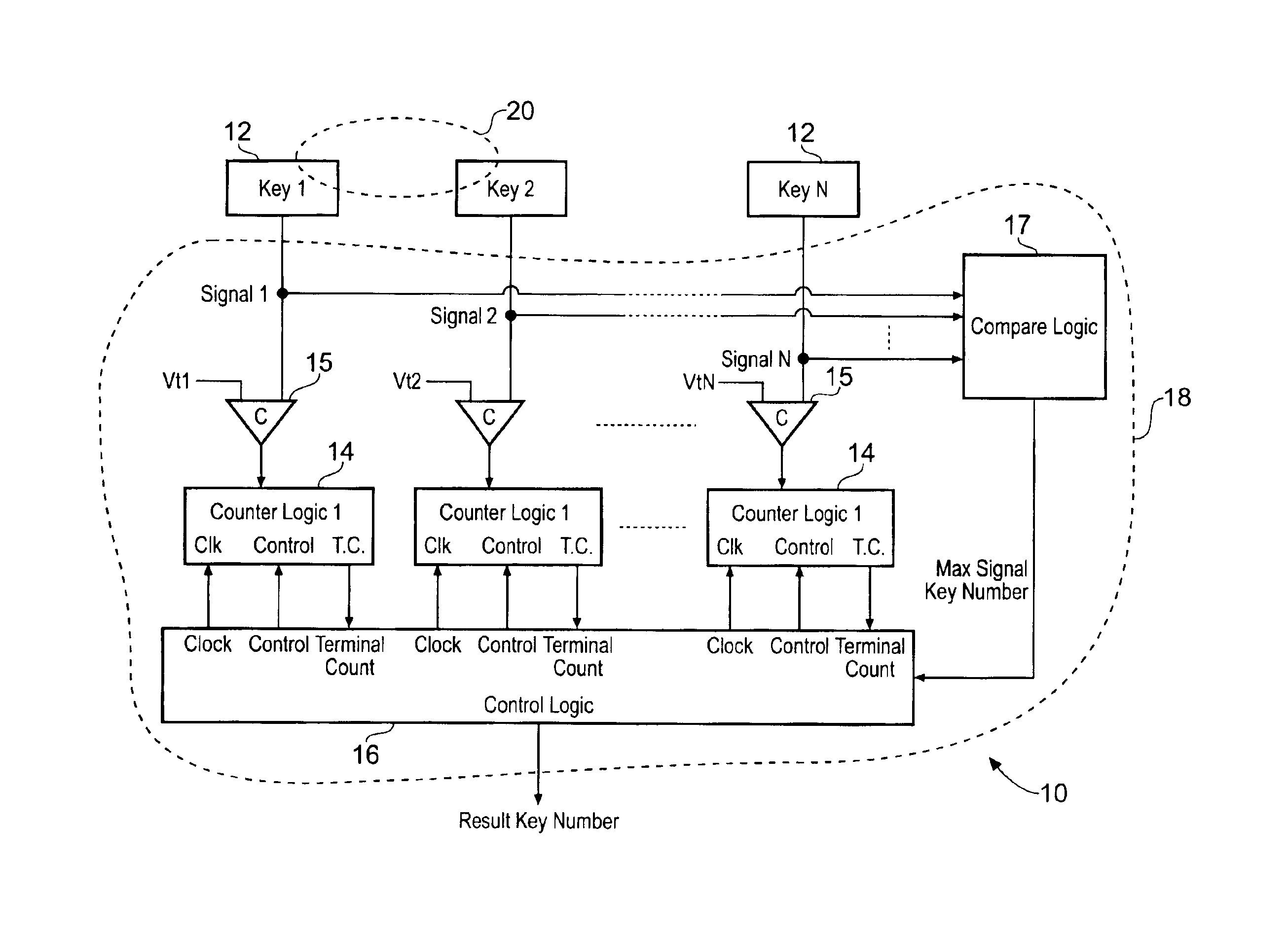
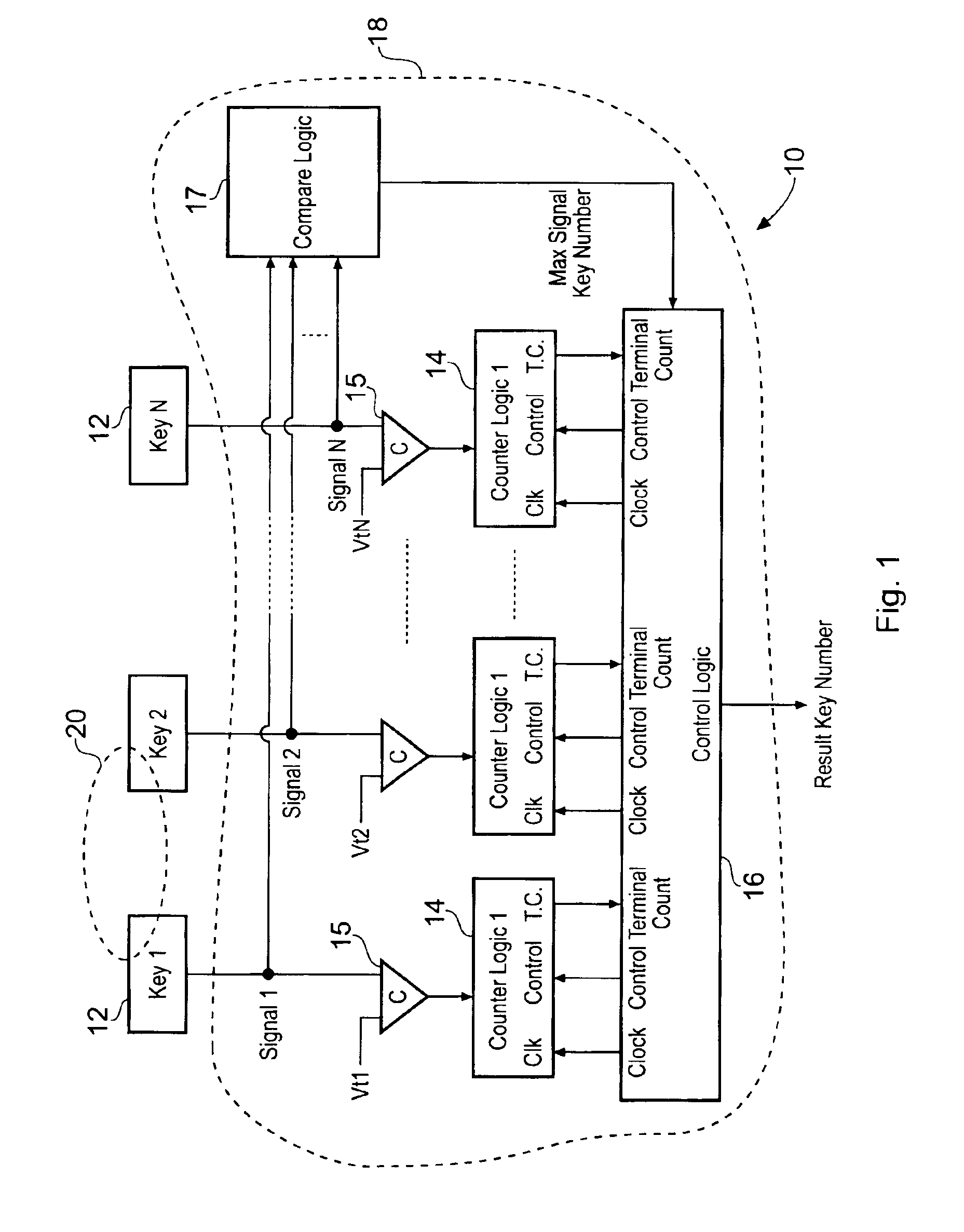
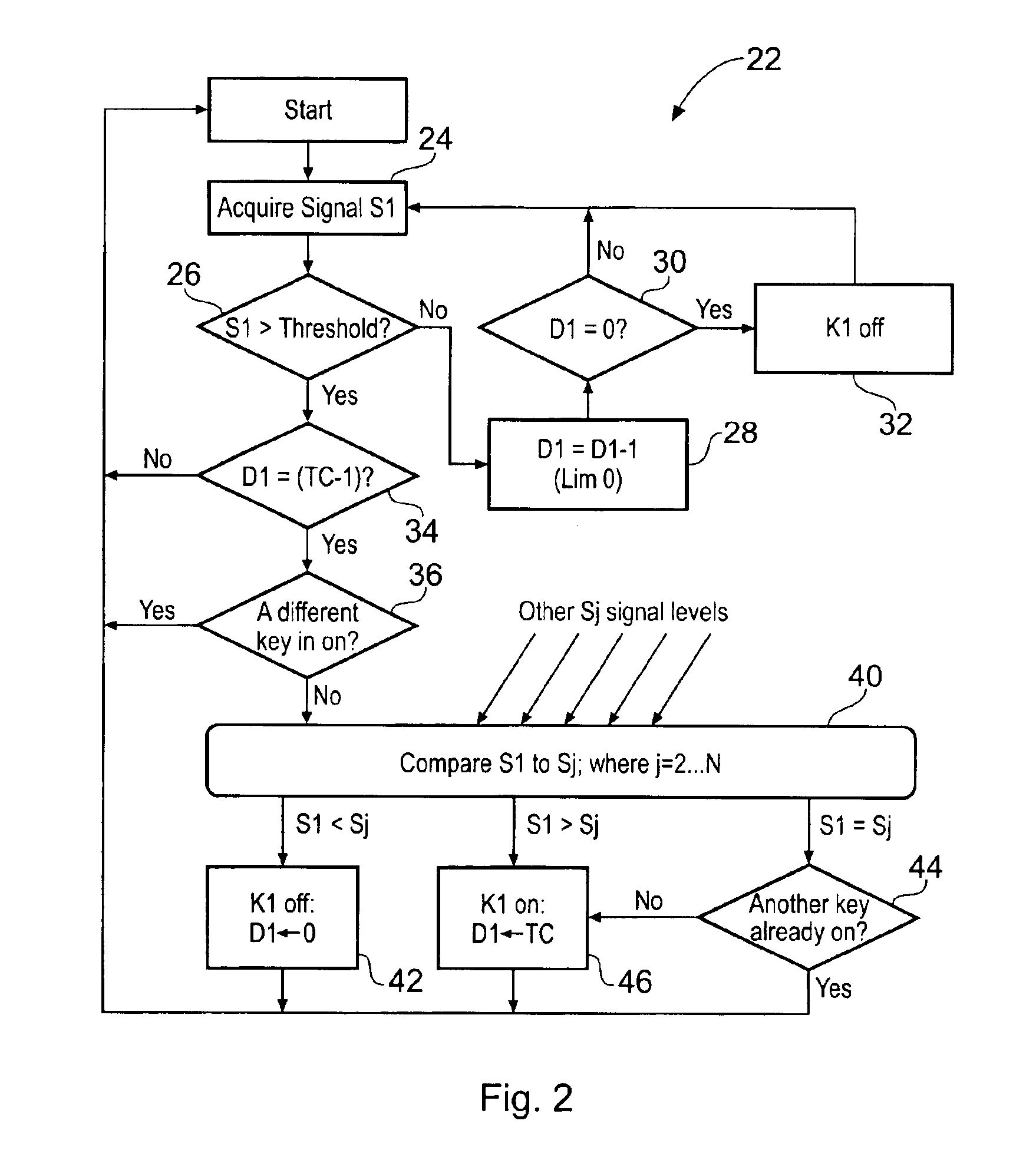
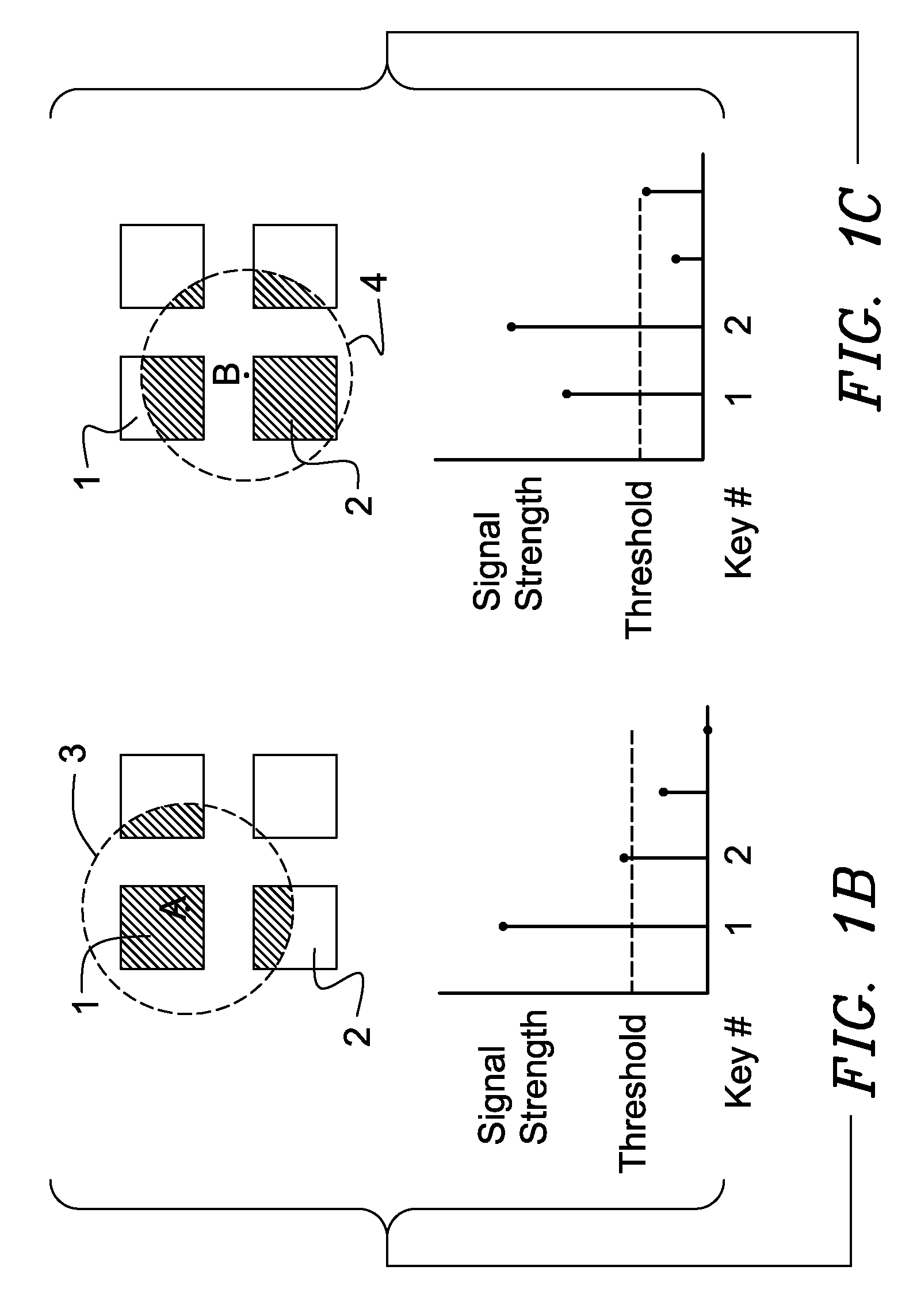
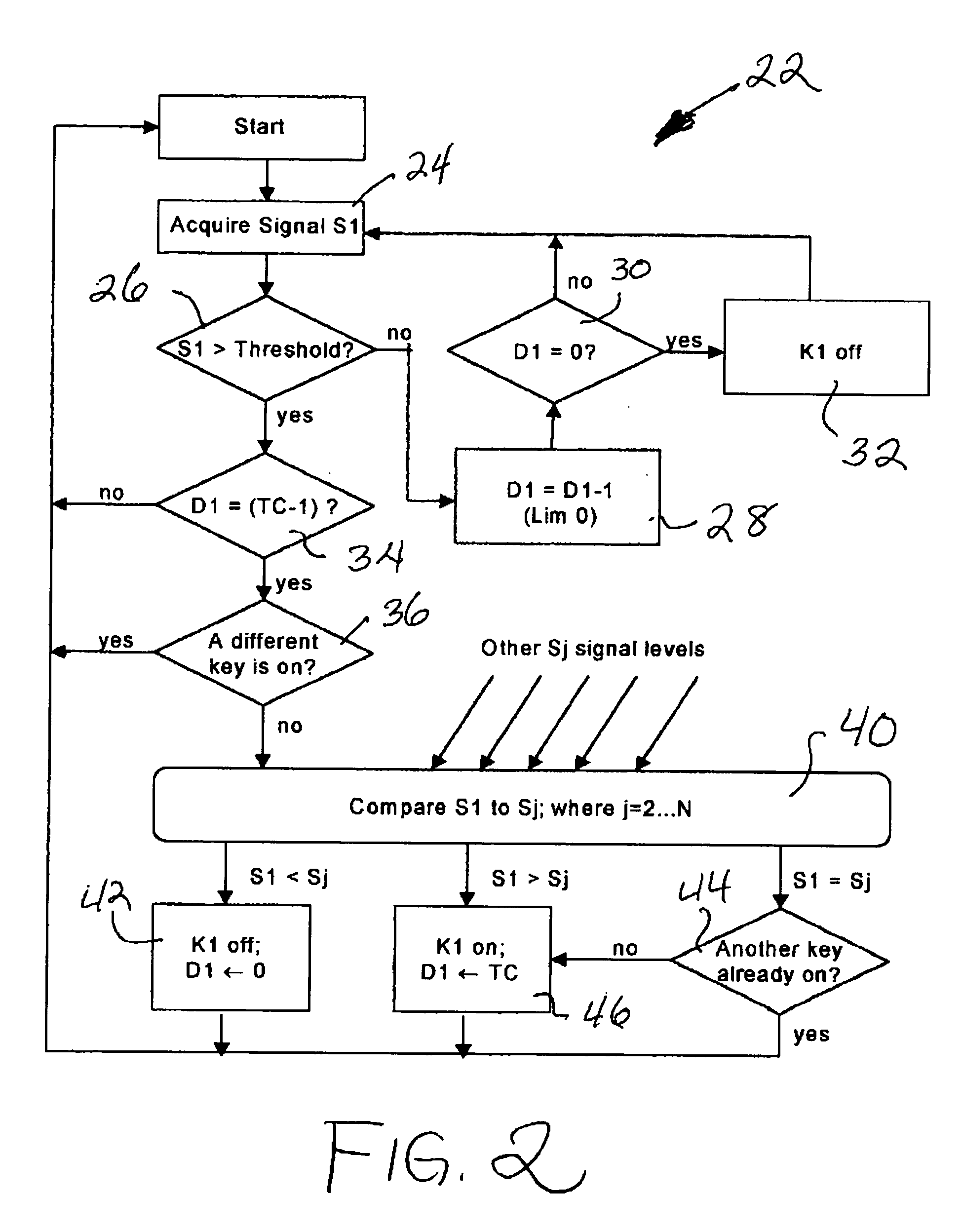
When an array of proximity sensors is used as a keyboard, it can provide an ambiguous output if a user's finger overlaps several keys or if liquid is spilled on the keyboard. This ambiguity is reduced by an iterative method that repeatedly measures a detected signal strength associated with each key, compares all the measured signal strengths to find a maximum, determines that the key having the maximum signal strength is the unique user-selected key and then suppresses or ignores signals from all other keys as long as the signal from the selected key remains above some nominal threshold value.
Owner:NEODRON LTD
Capacitive Keyboard with Non-Locking Reduced Keying Ambiguity
ActiveUS20060192690A1Reduce ambiguitySignal strength valueElectronic switchingDevice coding detailsEngineeringIterative method
Keyboards, keypads and other data entry devices can suffer from a keying ambiguity problem. In a small keyboard, for example, a user's finger is likely to overlap from a desired key to onto adjacent ones. An iterative method of removing keying ambiguity from a keyboard comprising an array of capacitive keys involves measuring a signal strength associated with each key in the array, comparing the measured signal strengths to find a maximum, determining that the key having the maximum signal strength is the unique user-selected key, and maintaining that selection until either the initially selected key's signal strength drops below some threshold level or a second key's signal strength exceeds the first key's signal strength.
Owner:NEODRON LTD
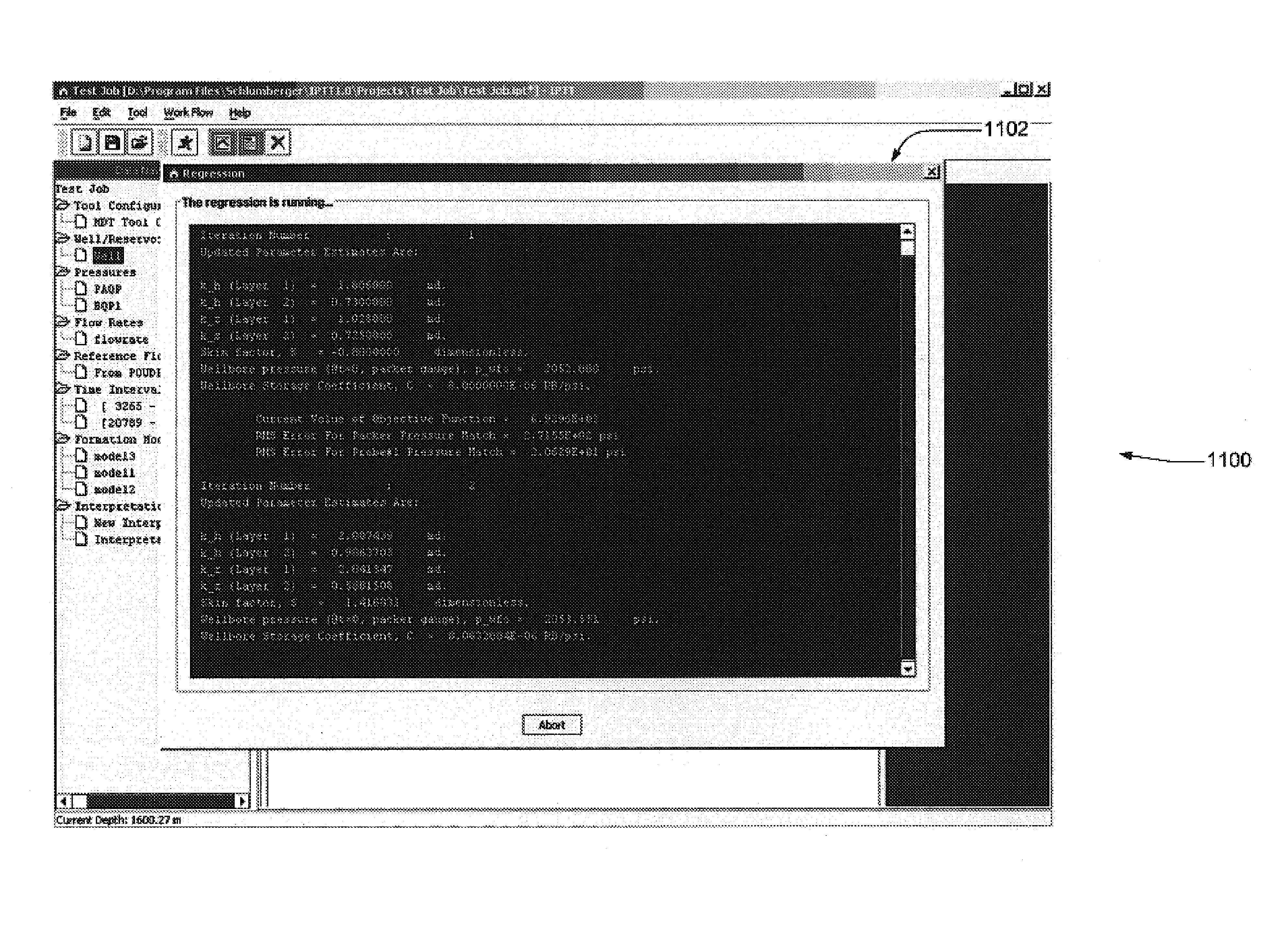
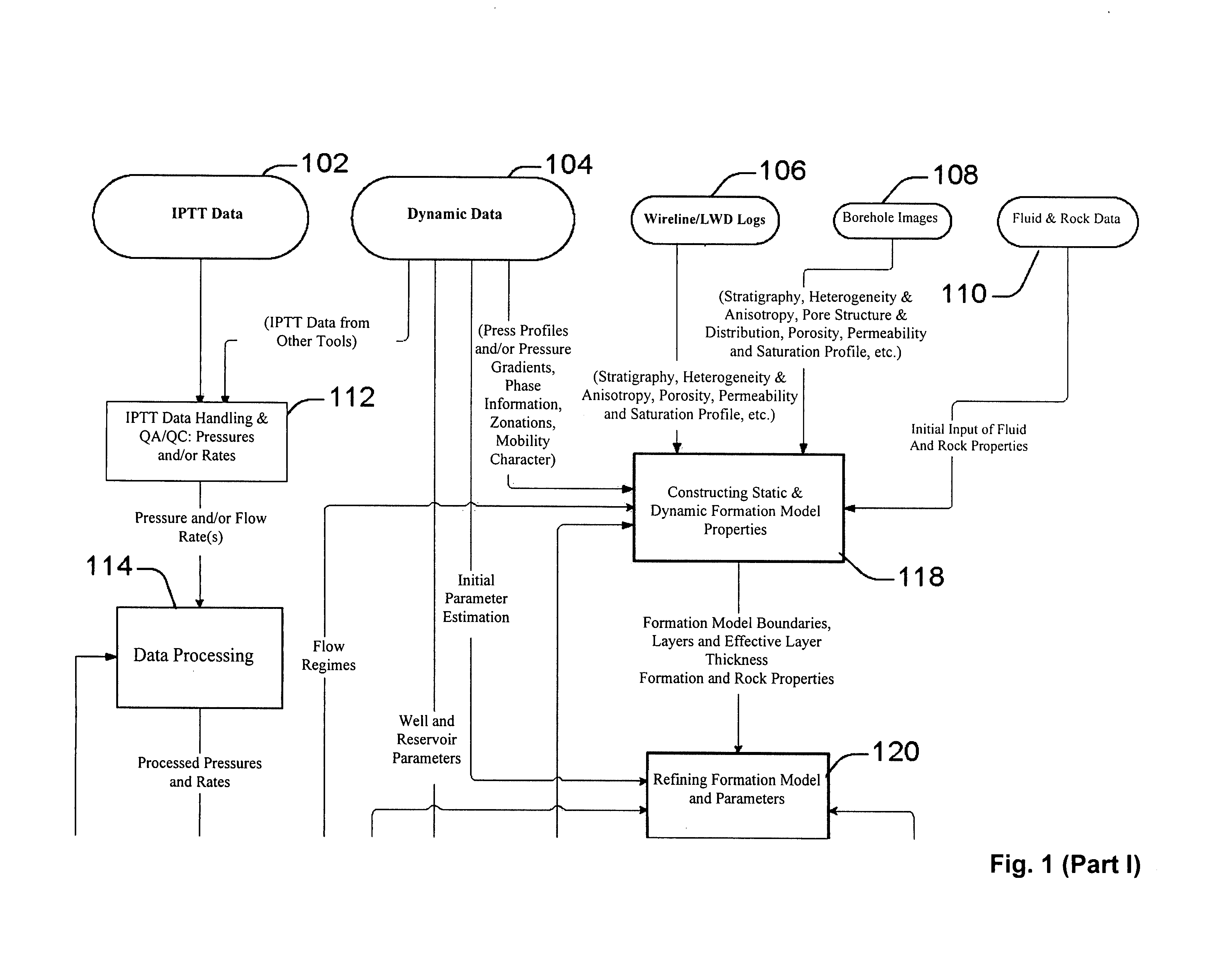
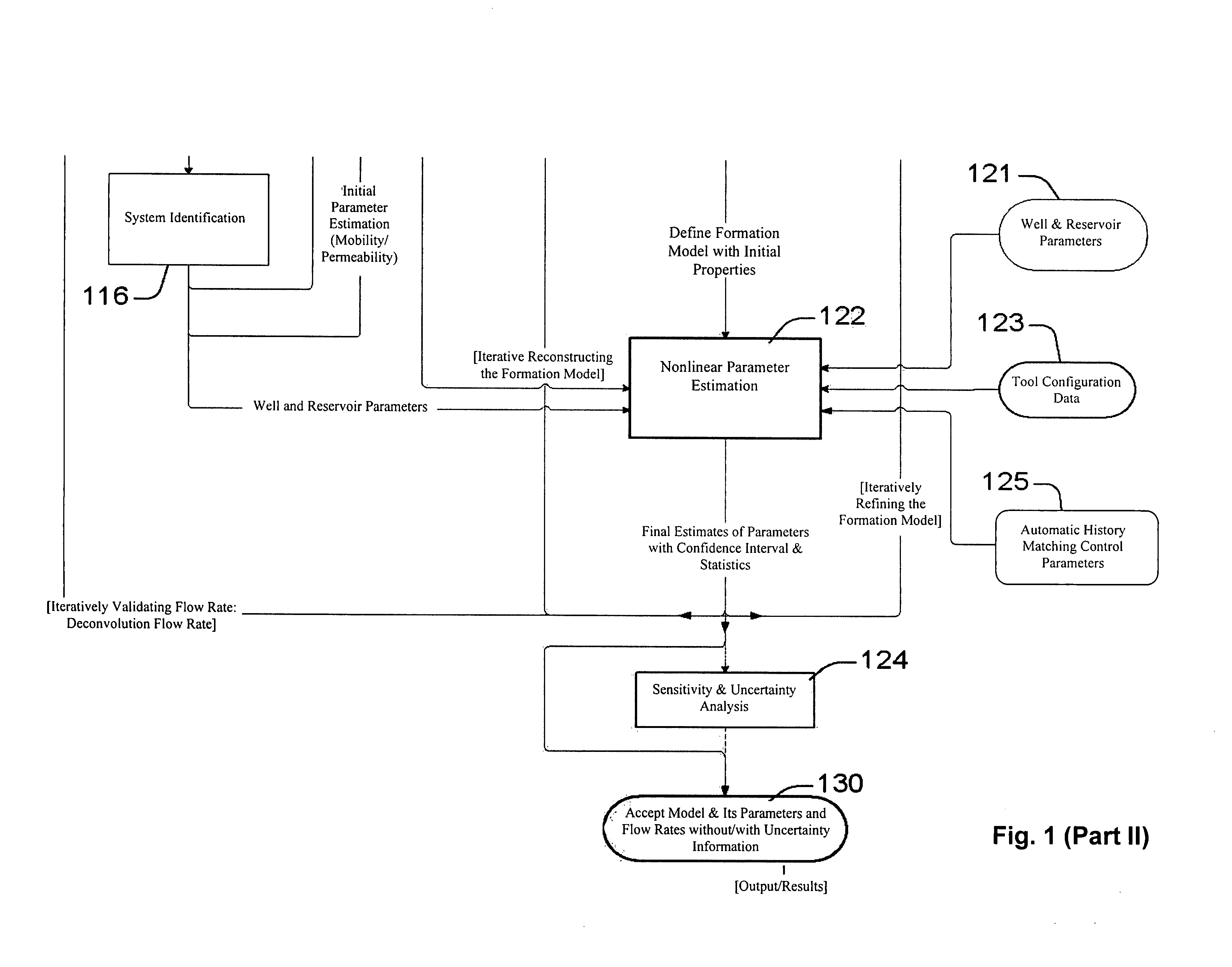
System and methods of characterizing a hydrocarbon reservoir
ActiveUS20060241867A1Facilitating in performing data processing operationEasy to operateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisCompressibilityWork flow
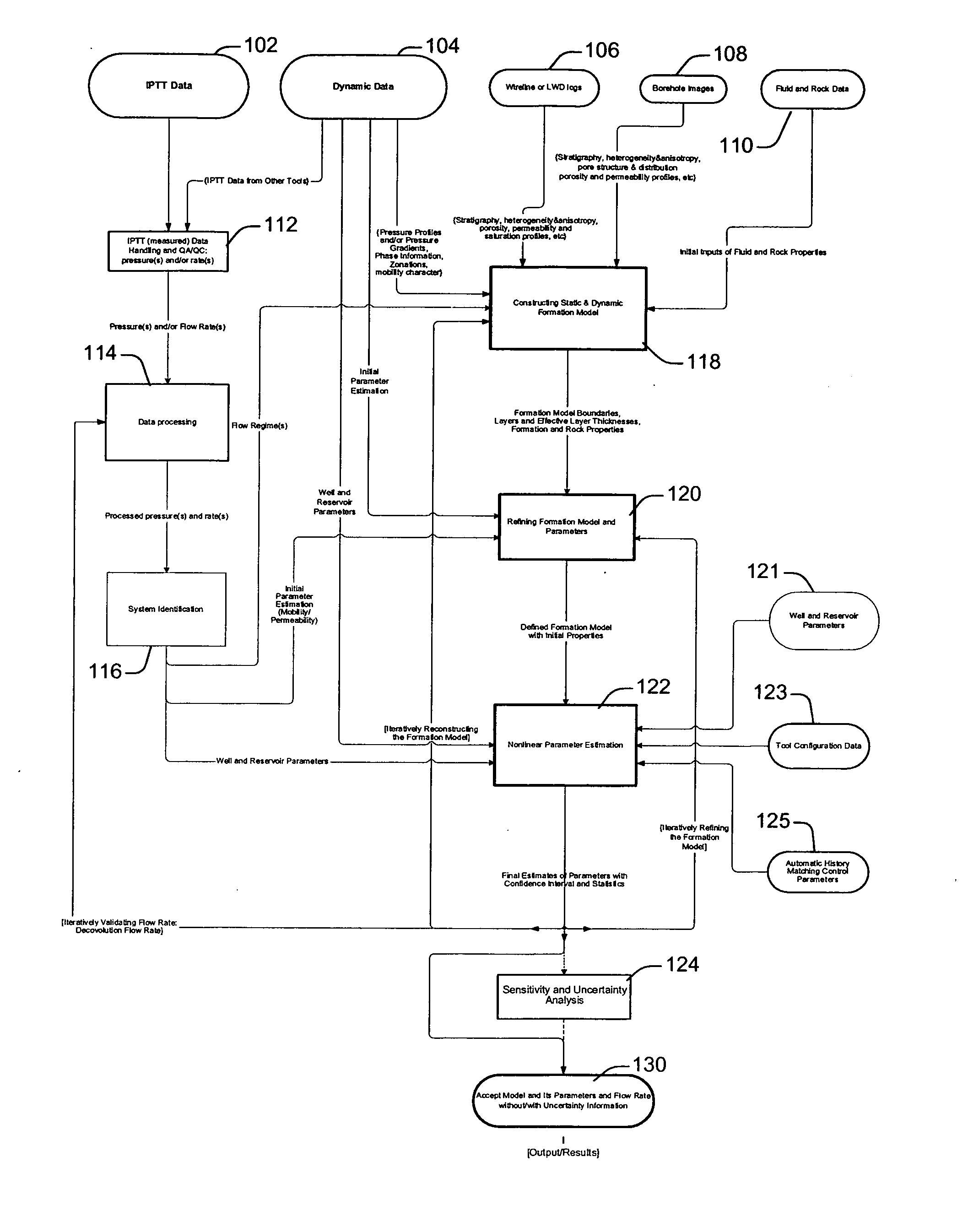
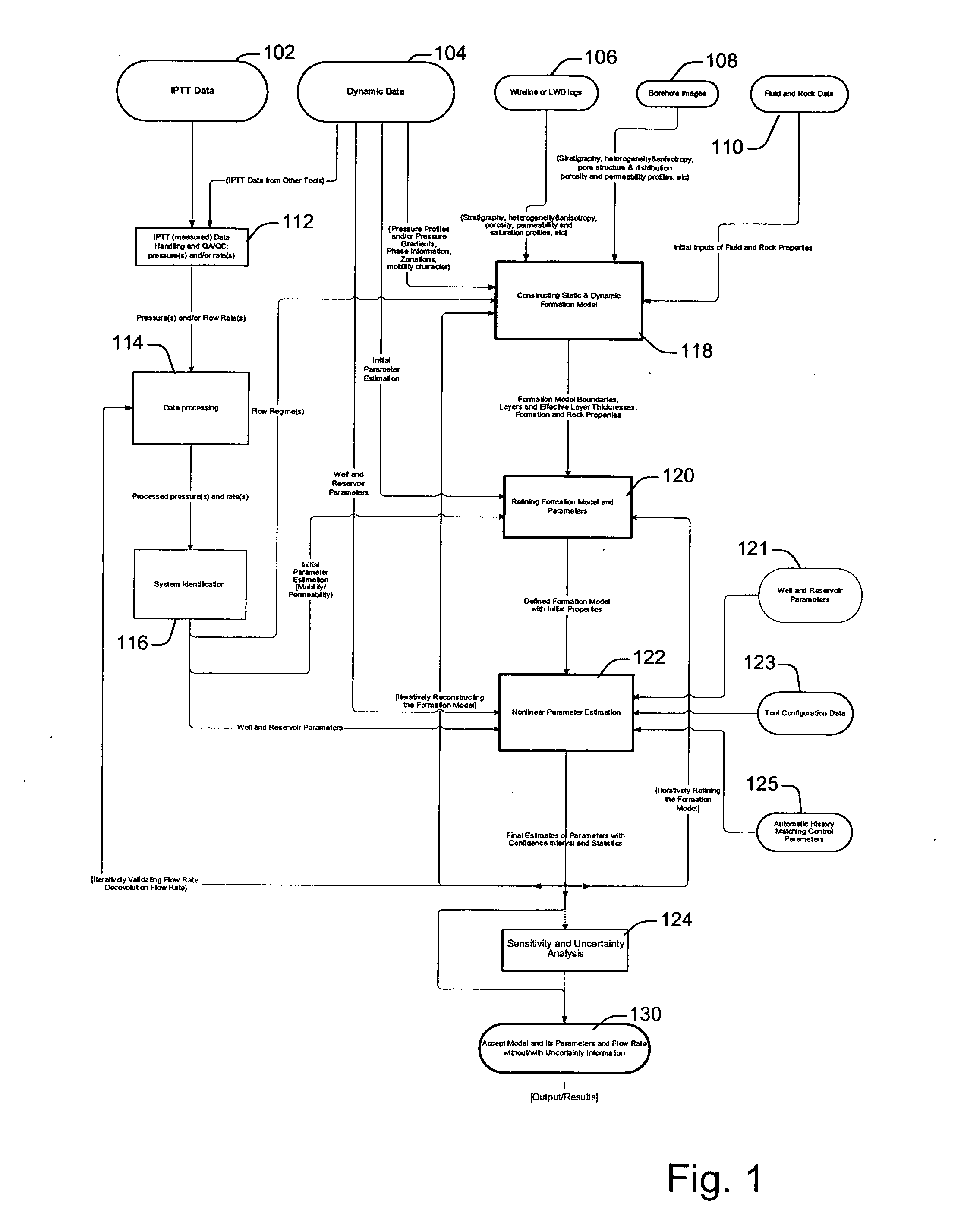
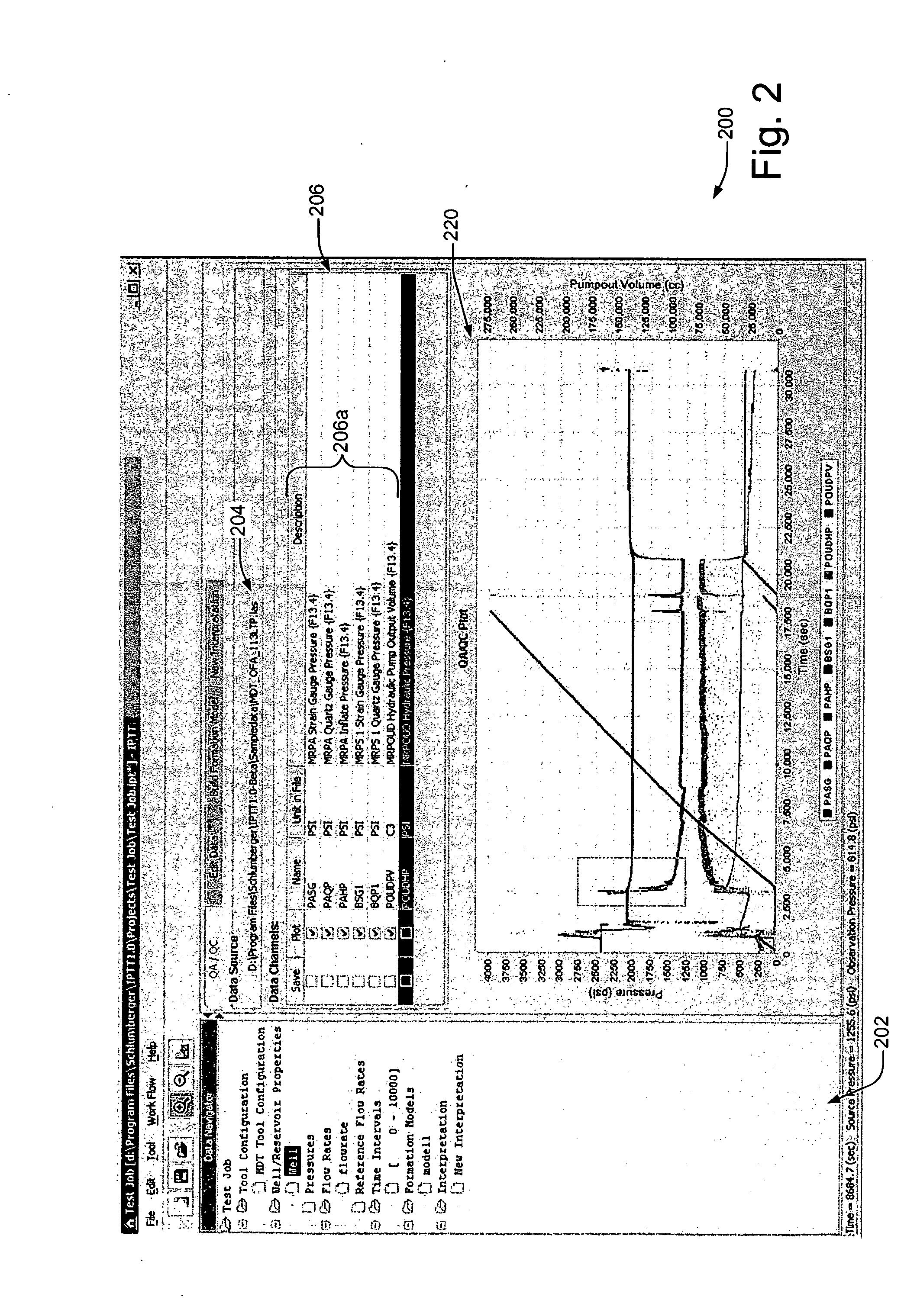
A technique is described for interpretation of IPTT tests. In one implementation, the technique may be configured or designed to standardize the complete interpretation procedure of IPTT in a heterogeneous reservoir, using if available, modern wireline logs (such as, for example, nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging), dynamic data from wireline formation testers and / or any other relevant information (such as, for example, geological description, core data and local knowledge) as constraints on the interpretation. Additionally, an iterative method may be used to define formation layering. An advanced regression technology may also be used to obtain optimized horizontal and vertical permeabilities of reservoir layers. Further a graphical user interface (GUI) based IPTT workflow technique of the present invention provides an integrated user-friendly interpretation platform for analyzing formation testing pressures and flow rate measurements in order to estimate the values and associated uncertainties of local characteristics of a hydrocarbon reservoir such as, for example, local permeability, local reservoir pressure, local compressibility, etc.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Systems and methods for estimating tissue parameters using surgical devices
Systems and methods for estimating tissue parameters, including mass of tissue to be treated and a thermal resistance scale factor between the tissue and an electrode of an energy delivery device, are disclosed. The method includes sensing tissue temperatures, estimating a mass of the tissue and a thermal resistance scale factor between the tissue and an electrode, and controlling an electrosurgical generator based on the estimated mass and the estimated thermal resistance scale factor. The method may be performed iteratively and non-iteratively. The iterative method may employ a gradient descent algorithm that iteratively adds a derivative step to the estimates of the mass and thermal resistance scale factor until a condition is met. The non-iterative method includes selecting maximum and minimum temperature differences and estimating the mass and the thermal resistance scale factor based on a predetermined reduction point from the maximum temperature difference to the minimum temperature difference.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
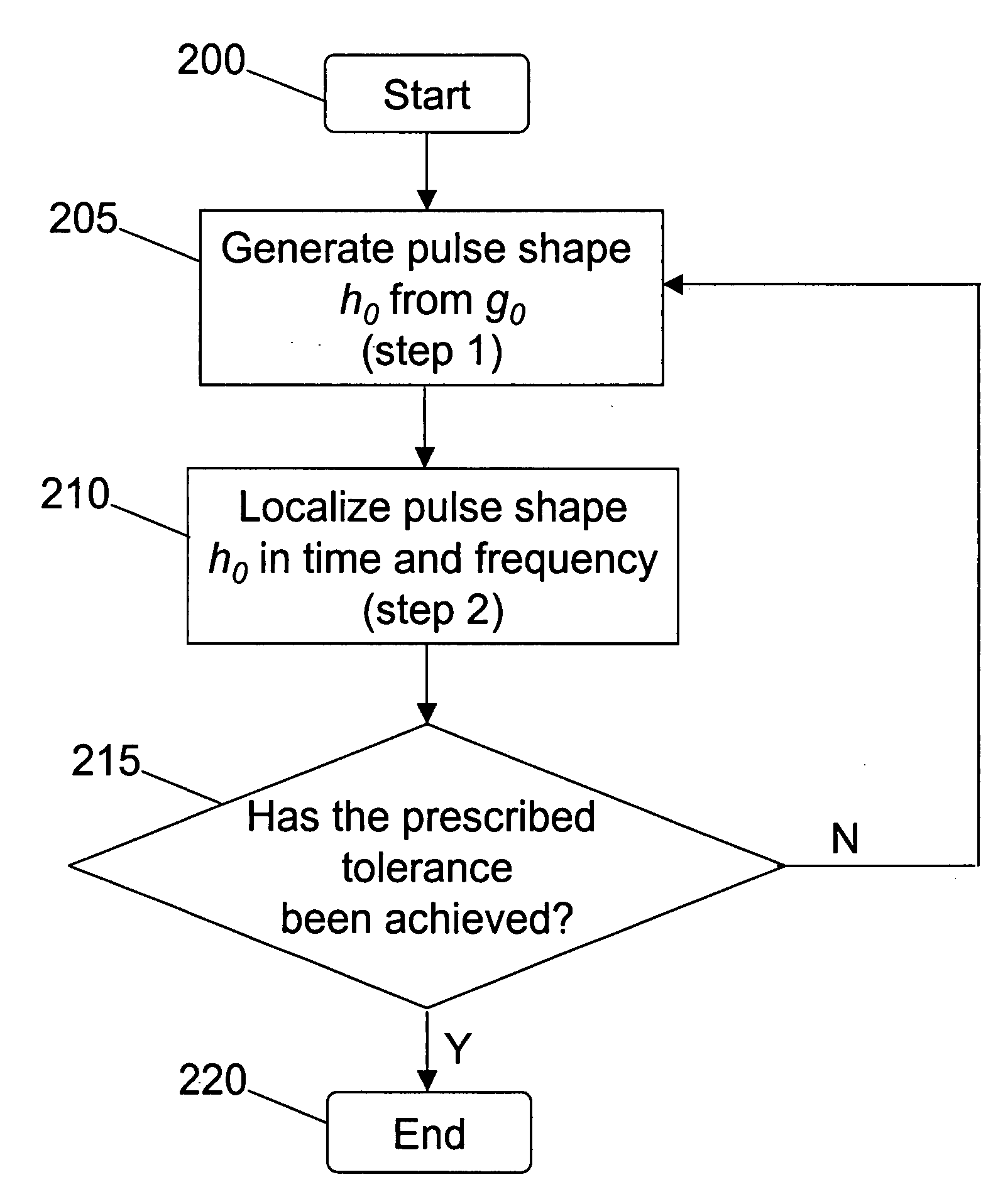
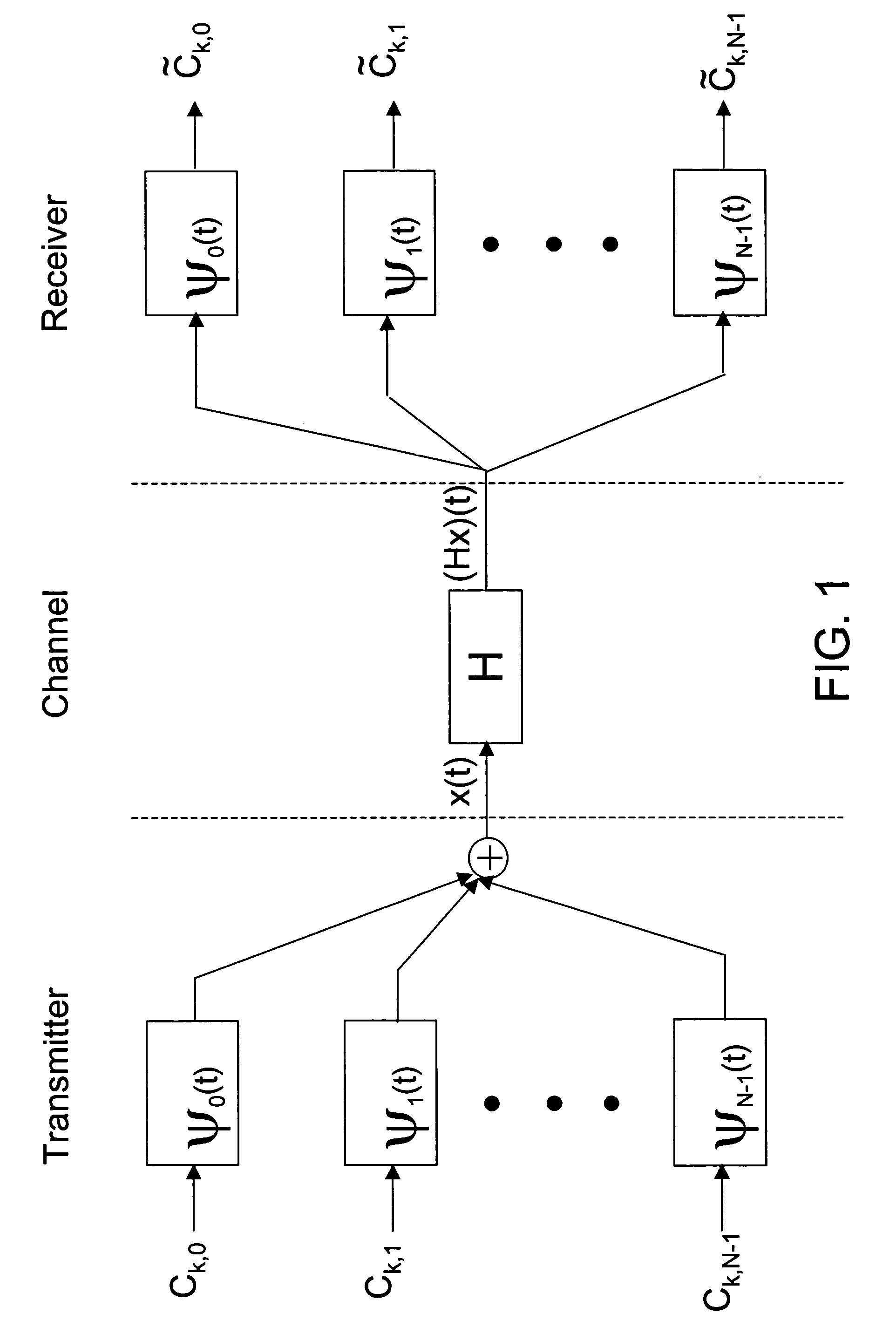
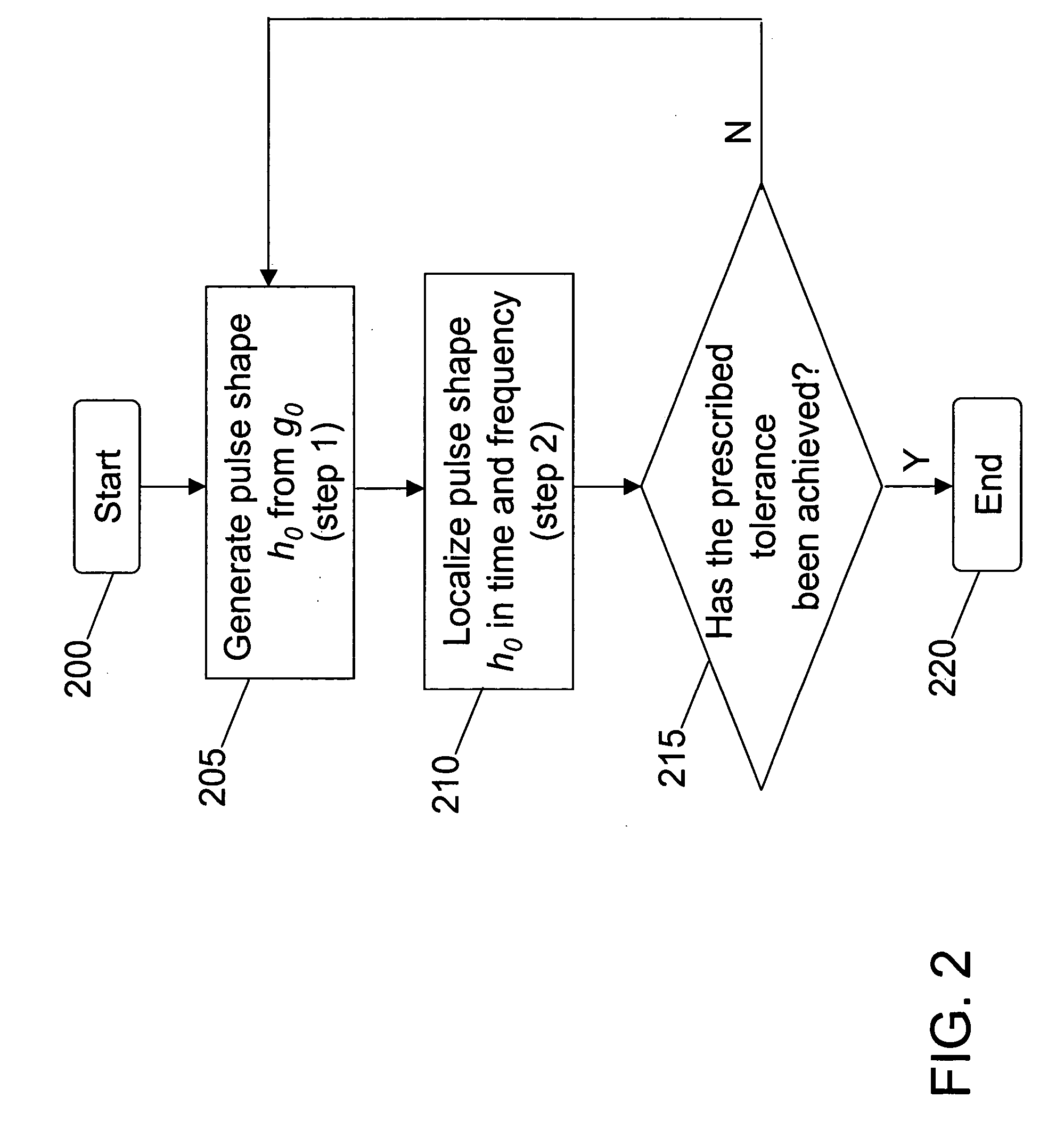
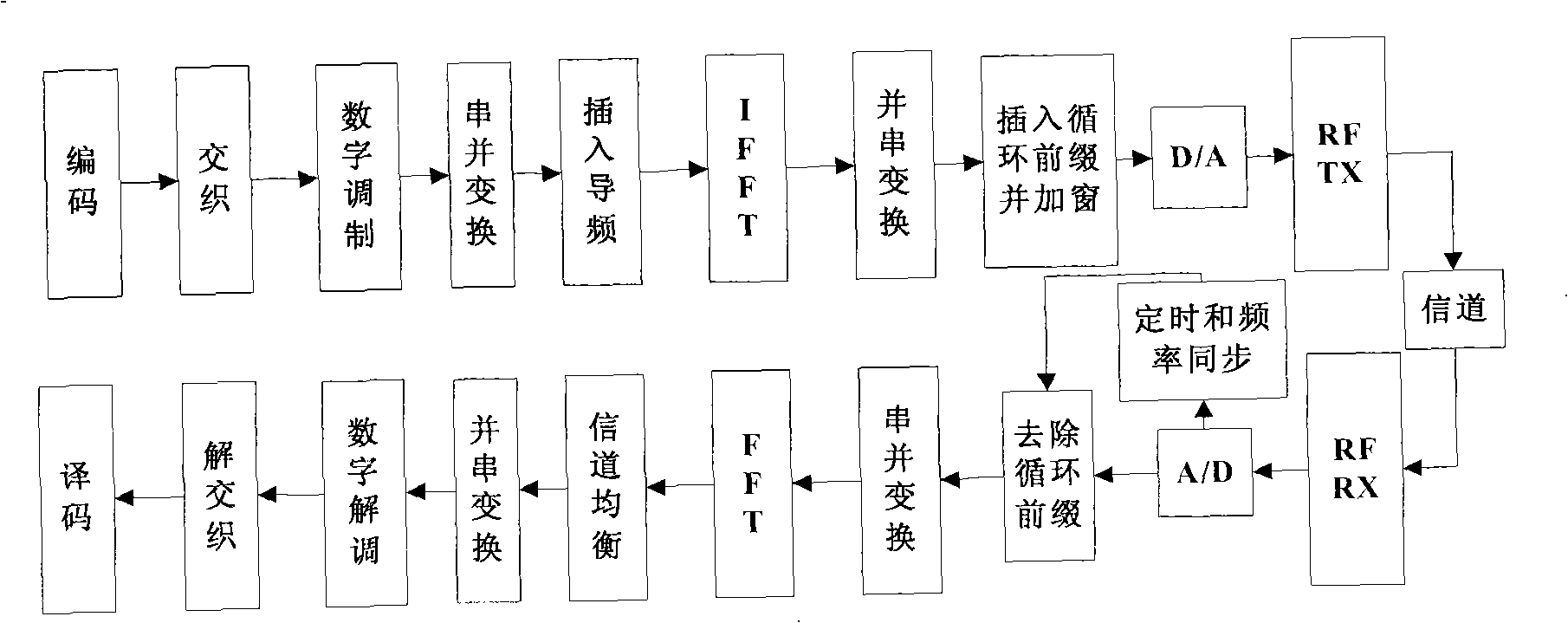
Method for pulse shape design for OFDM
InactiveUS20060039270A1Maximizing bit-error performanceIncrease data rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationFrequency spectrumWireless transmission
A computationally efficient pulse shaping method for OFDM that produces mutually orthogonal transmission pulses having fast spectral decay is provided. The pulse shaping method comprises an iterative method for designing OFDM transmission pulses that satisfy prescribed time-frequency localization conditions. The iterative method may be implemented in a computationally efficient way and can be used to adapt the transmission pulses to time-varying channel conditions in real-time, thereby maximizing the bit-error performance of an OFDM system while maintaining high data rates in wireless transmission.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Filter structure for iterative signal processing
InactiveUS20080317150A1Reduce disadvantagesEasy to useError preventionTime-division multiplexMulti user interferenceIterative method
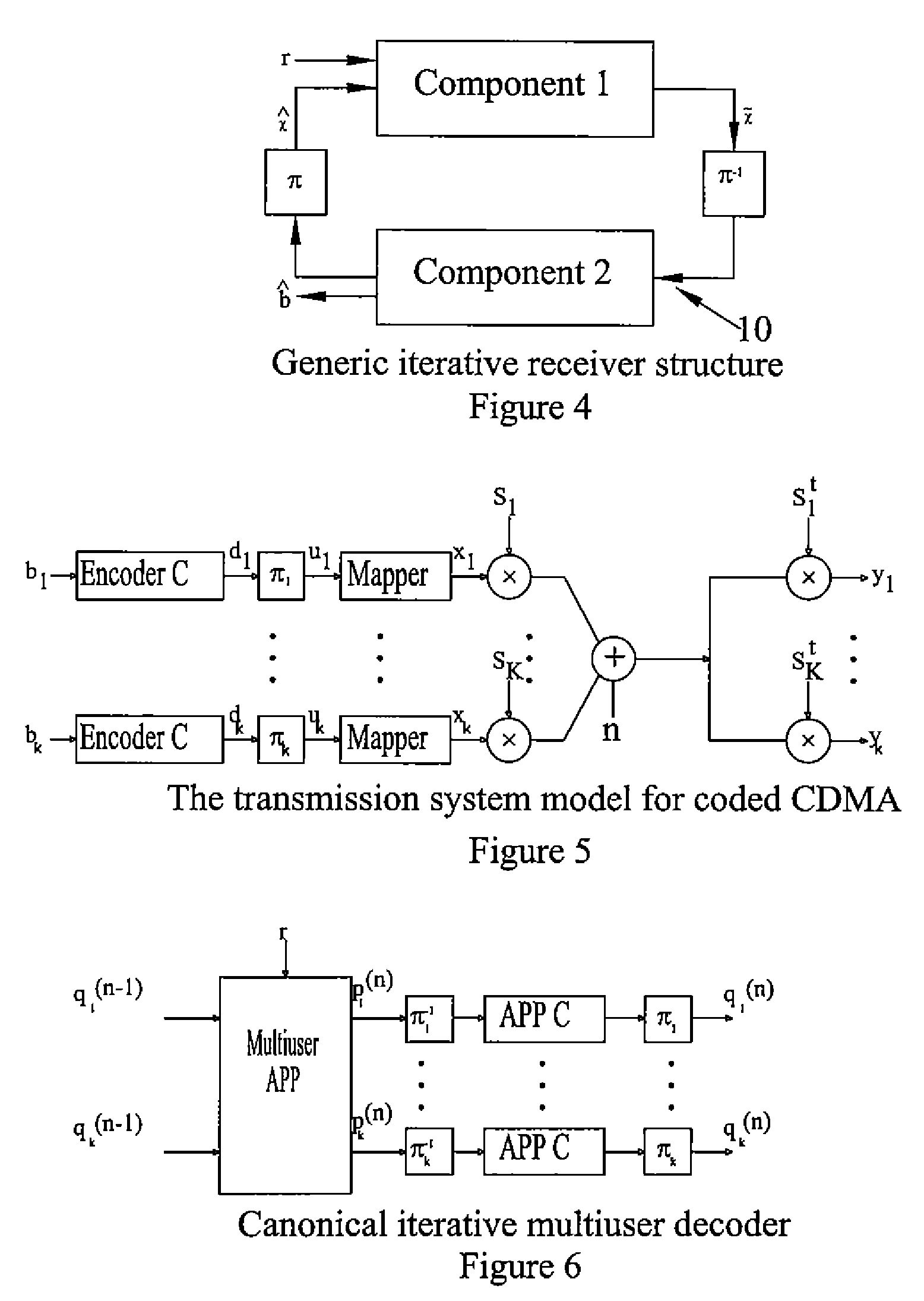
The present invention relates to improved multiple access communications. In one form, the invention relates to an improved signal processing method and apparatus for an iterative method of determining the reception of a signal in a multi user packet based wireless OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) communication system. In other forms the present invention provides recursive filtering for joint iterative decoding in a variety of systems and functions such as linear multiple access channel decoders, iterative equalisation, iterative joint channel estimation and detection / decoding, iterative space-time processing, iterative multi user interference cancellation and iterative demodulation. In one particular form the present invention provides an iterative decoding circuit for a wireless multiuser communications receiver comprising a first signal processing means for receiving at least one received signal, said first signal processing means comprising at least two linear iterative filters such that the first linear iterative filter provides an estimate of a selected received signal to an estimated signal output and a second linear iterative filter provides estimates of at least one other received signal, delayed by one iteration cycle, to an input of said first linear iterative filter, a second signal processing means for receiving the estimated signal output of the first linear iterative filter and providing a further received signal estimate to the input of the first signal processing means in a succeeding iteration cycle of the decoding circuit.
Owner:COHDA WIRELESS
Multi-pass interference reduction in a GSM communication system
ActiveUS20050084045A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionFinite impulse responseCommunications system
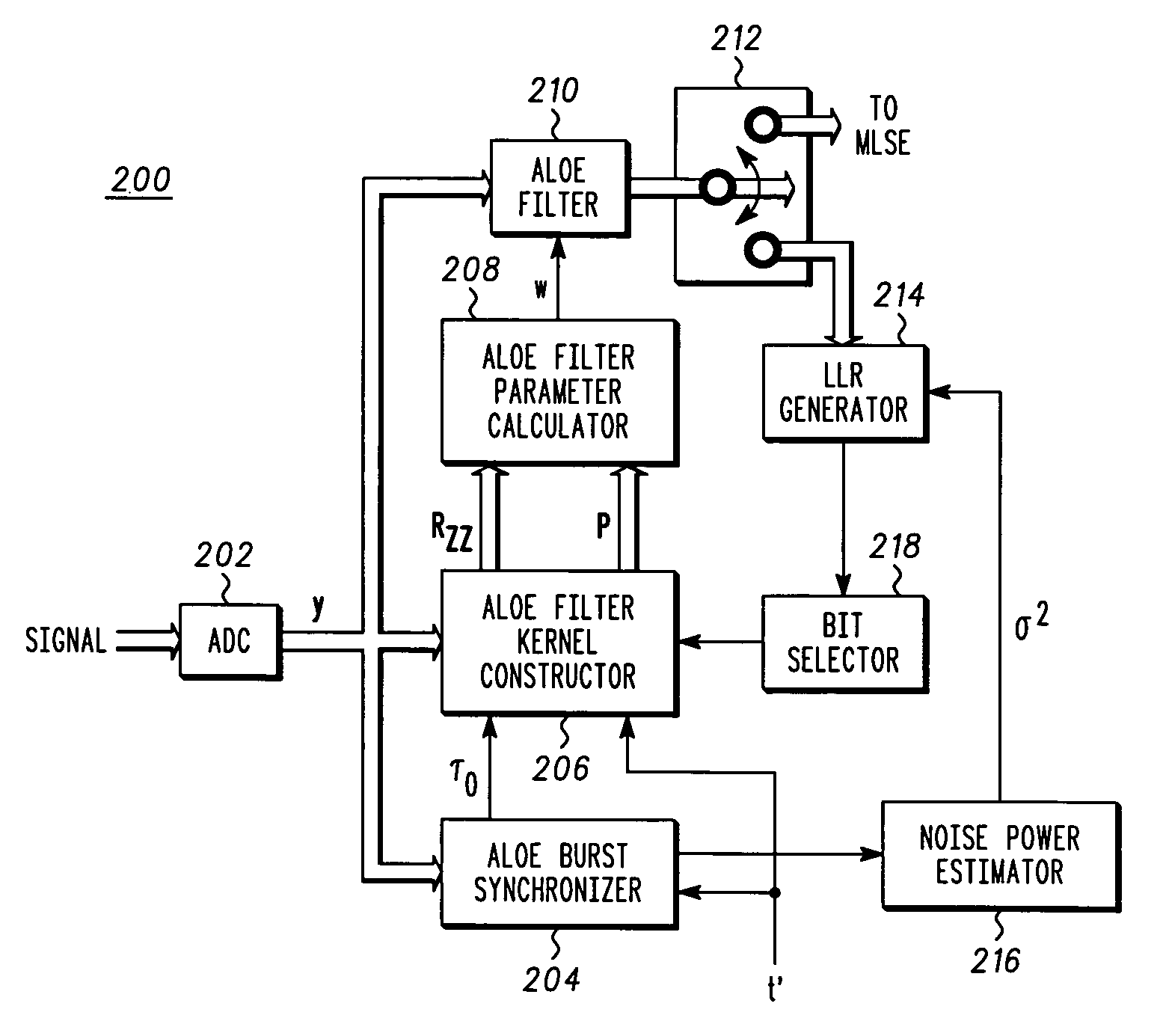
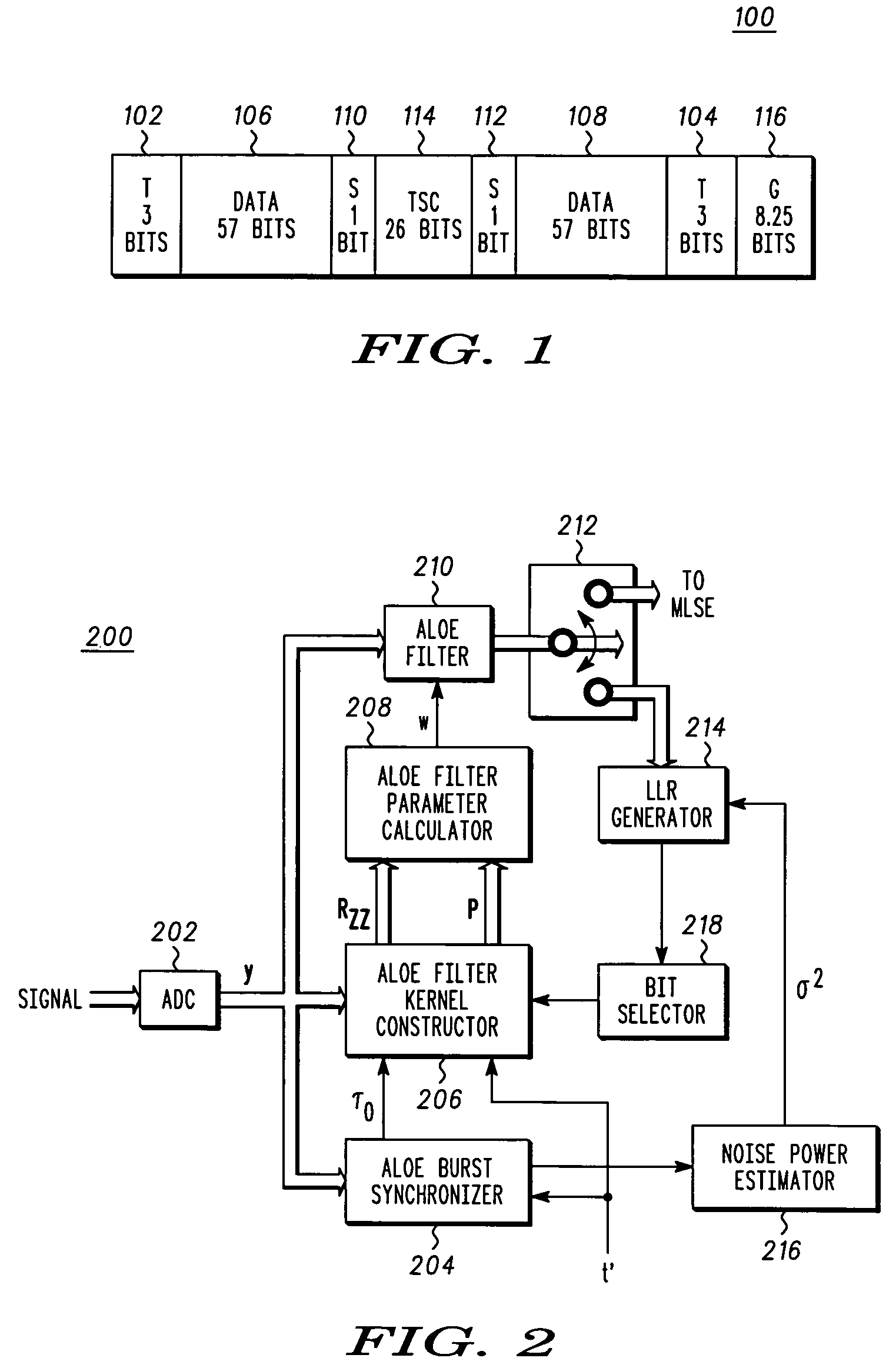
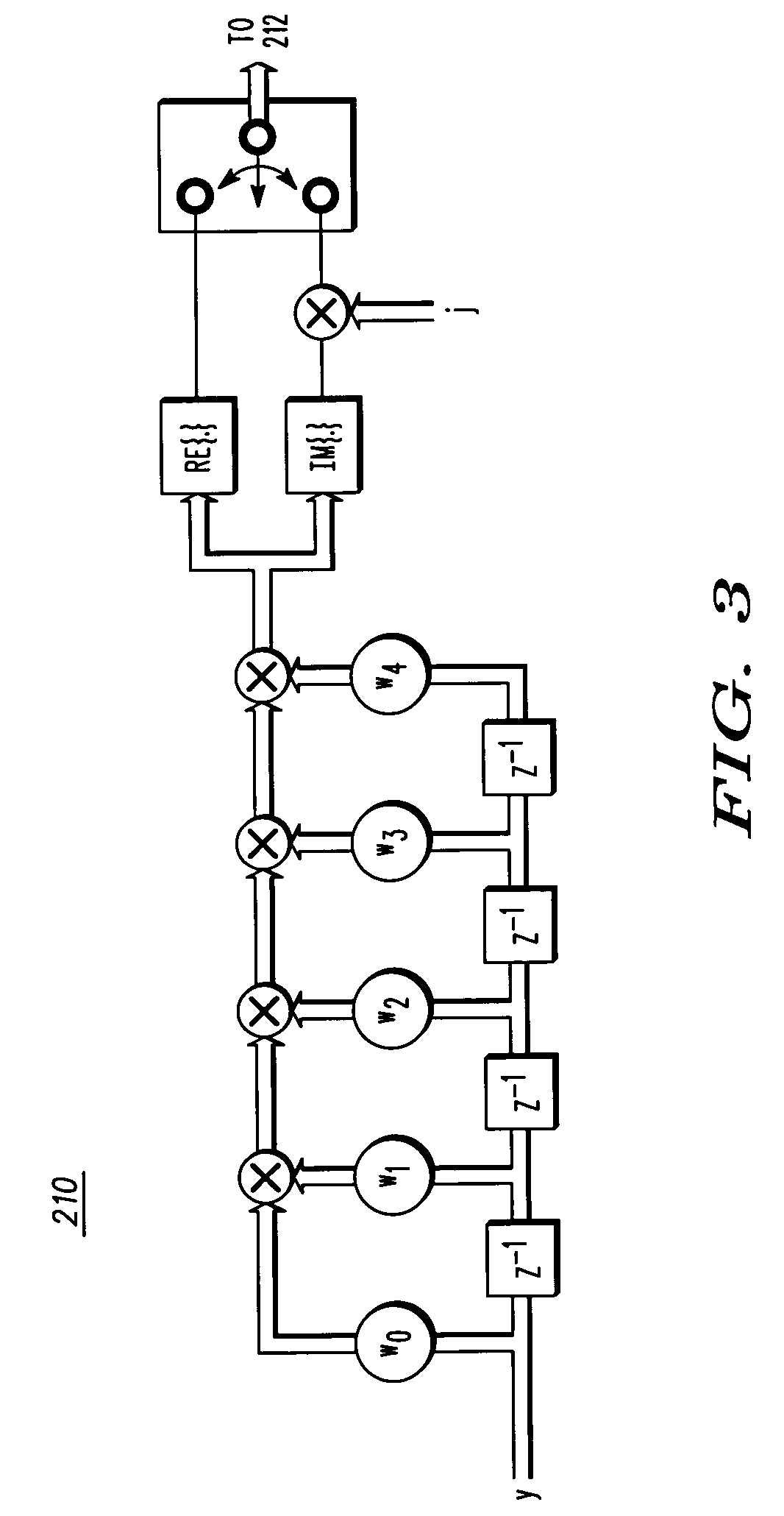
An iterative method (400) and apparatus (200) for a receiver for reducing interference in a desired signal in a GSM communication system uses a finite-impulse-response filter combined with alternate quadrature component output selection for alternate linear equalization are disclosed The method includes inputting a burst of data of a received waveform including interference, training an alternate linear output filter with a midamble of known quadrature phase, providing an estimate of the desired signal by operating on the received waveform with the finite-impulse-response filter, generating log likelihood ratio estimates for a plurality of bits in the burst of data, selecting bits from the burst of data base upon a predetermined condition, and re-training the alternate linear output filter to provide a second improved estimate of the desired signal.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
System and methods of characterizing a hydrocarbon reservoir
ActiveUS7277796B2Facilitating in performing data processing operationEasy to operateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisCompressibilityIterative method
A technique is described for interpretation of IPTT tests. In one implementation, the technique may be configured or designed to standardize the complete interpretation procedure of IPTT in a heterogeneous reservoir, using if available, modern wireline logs (such as, for example, nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging), dynamic data from wireline formation testers and / or any other relevant information (such as, for example, geological description, core data and local knowledge) as constraints on the interpretation. Additionally, an iterative method may be used to define formation layering. An advanced regression technology may also be used to obtain optimized horizontal and vertical permeabilities of reservoir layers. Further a graphical user interface (GUI) based IPTT workflow technique of the present invention provides an integrated user-friendly interpretation platform for analyzing formation testing pressures and flow rate measurements in order to estimate the values and associated uncertainties of local characteristics of a hydrocarbon reservoir such as, for example, local permeability, local reservoir pressure, local compressibility, etc.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
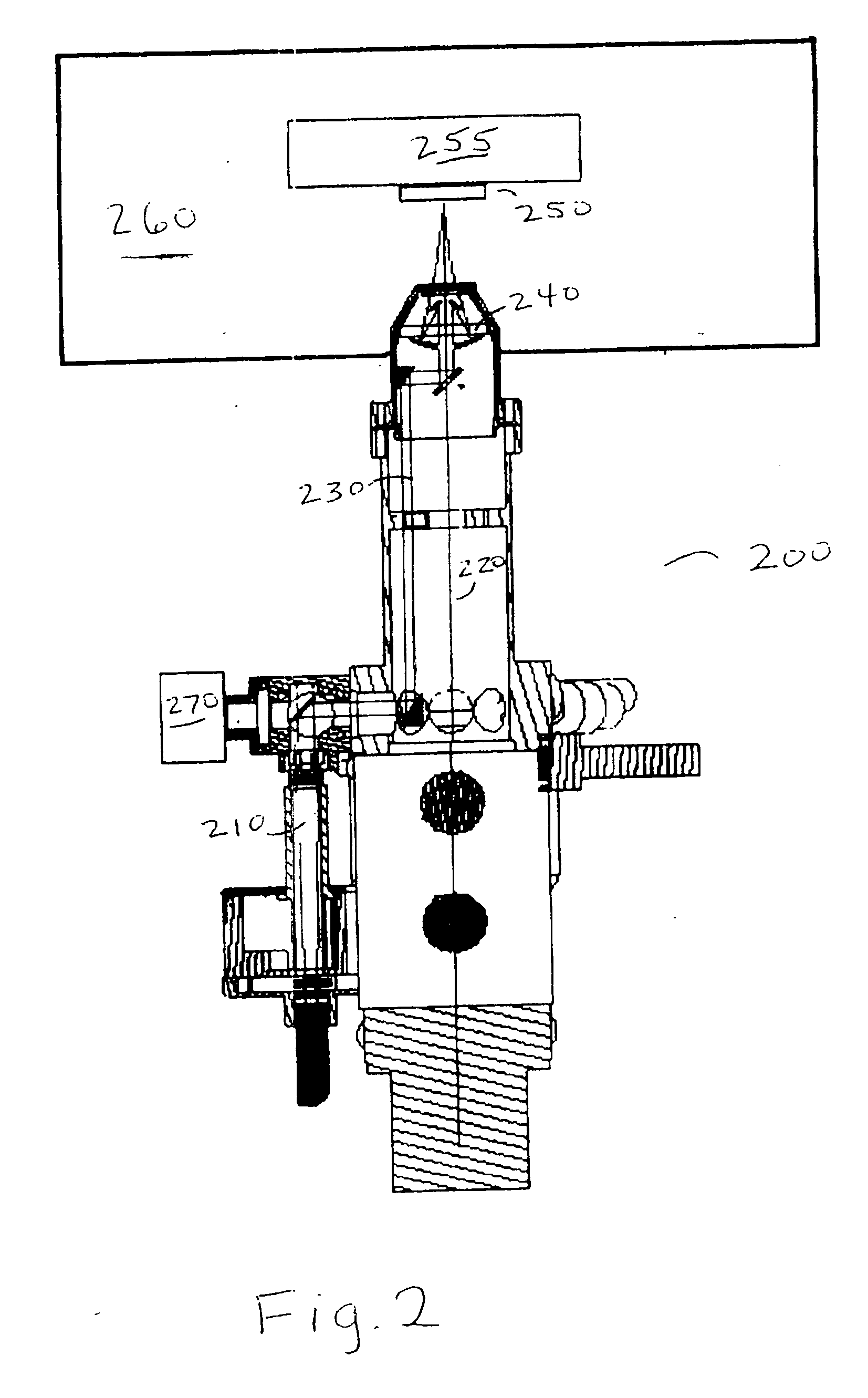
Integration of photon emission microscope and focused ion beam
InactiveUS20060012385A1Vacuum gauge using ionisation effectsFault location by increasing destruction at faultPhoton emissionIon beam
An integrated FIB / PEM apparatus and method for performing failure analysis on integrated circuits. In-situ failure analysis is enabled by integrating Photon Emission Microscopy into a Focused Ion Beam system, thereby improving throughput and efficiency of Failure Analysis. An iterative method is described for identifying and localizing fault sites on the circuit.
Owner:DCG SYST
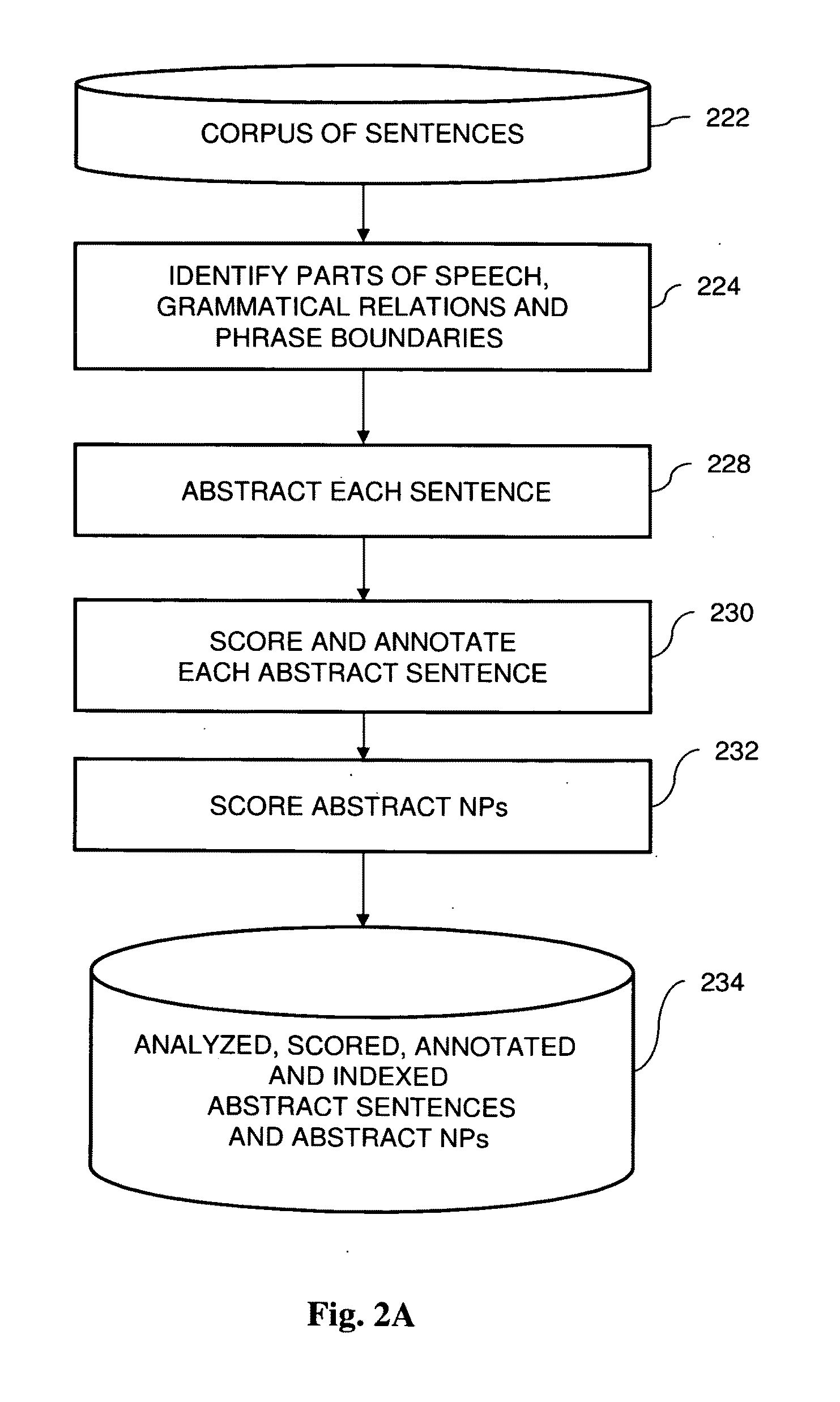
Method for text improvement via linguistic abstractions
InactiveUS20100332217A1Quality improvementReduce in quantitySemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsIterative methodHuman language
This invention provides hierarchical, gradual and iterative methods, systems, and software for improving and correcting natural language text. The methods comprise the steps of applying natural language processing (NLP) algorithms to a corpus of sentences so as to abstract each sentence; applying scoring and linguistic annotation to each abstract sentence; applying NLP algorithms to abstract input sentences; applying search algorithms to match an abstract input sentence to at least one abstract corpus sentence; and applying NLP algorithms to adapt said matched abstract corpus sentence to the input sentence.
Owner:WINTNER SHALOM +3
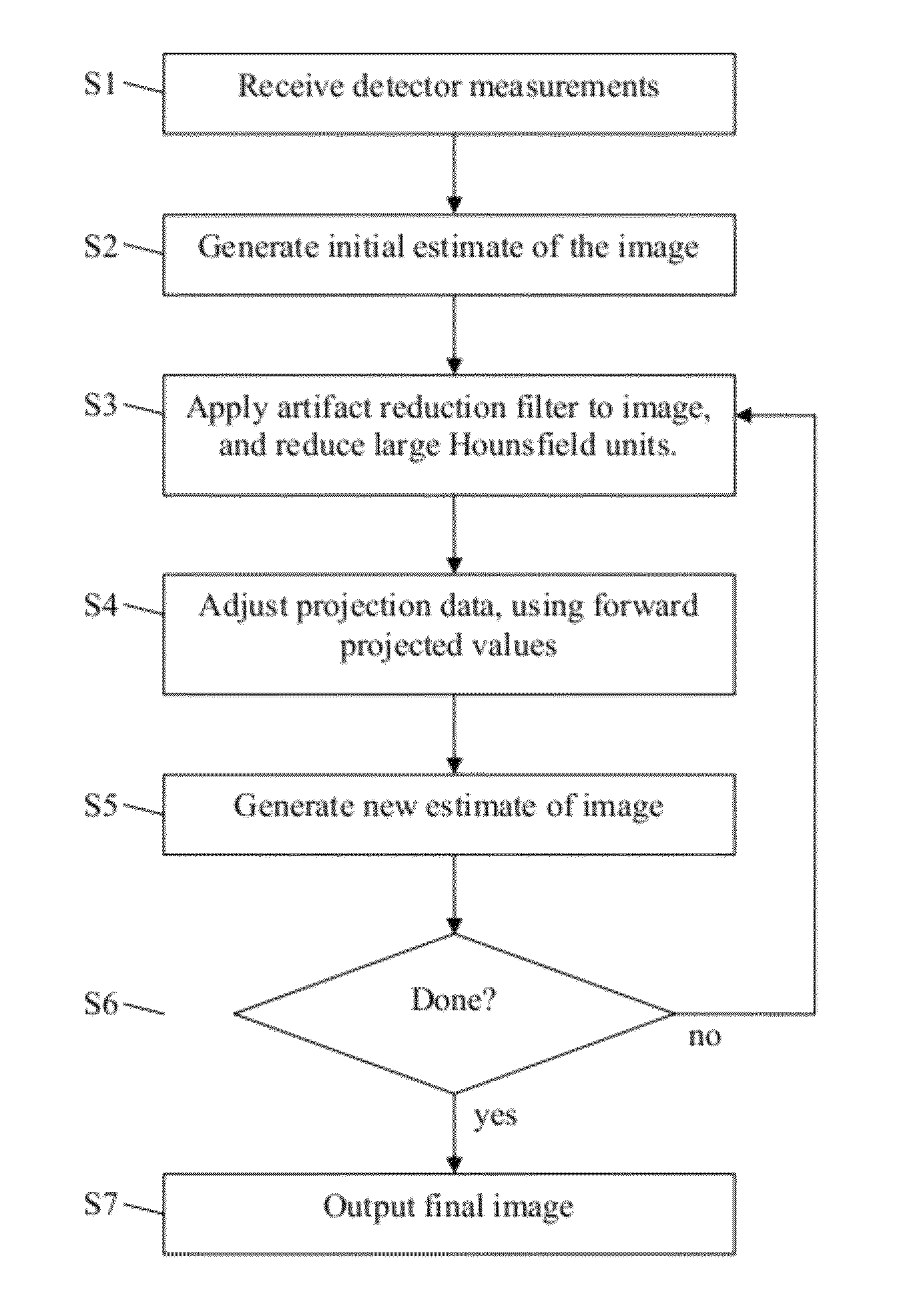
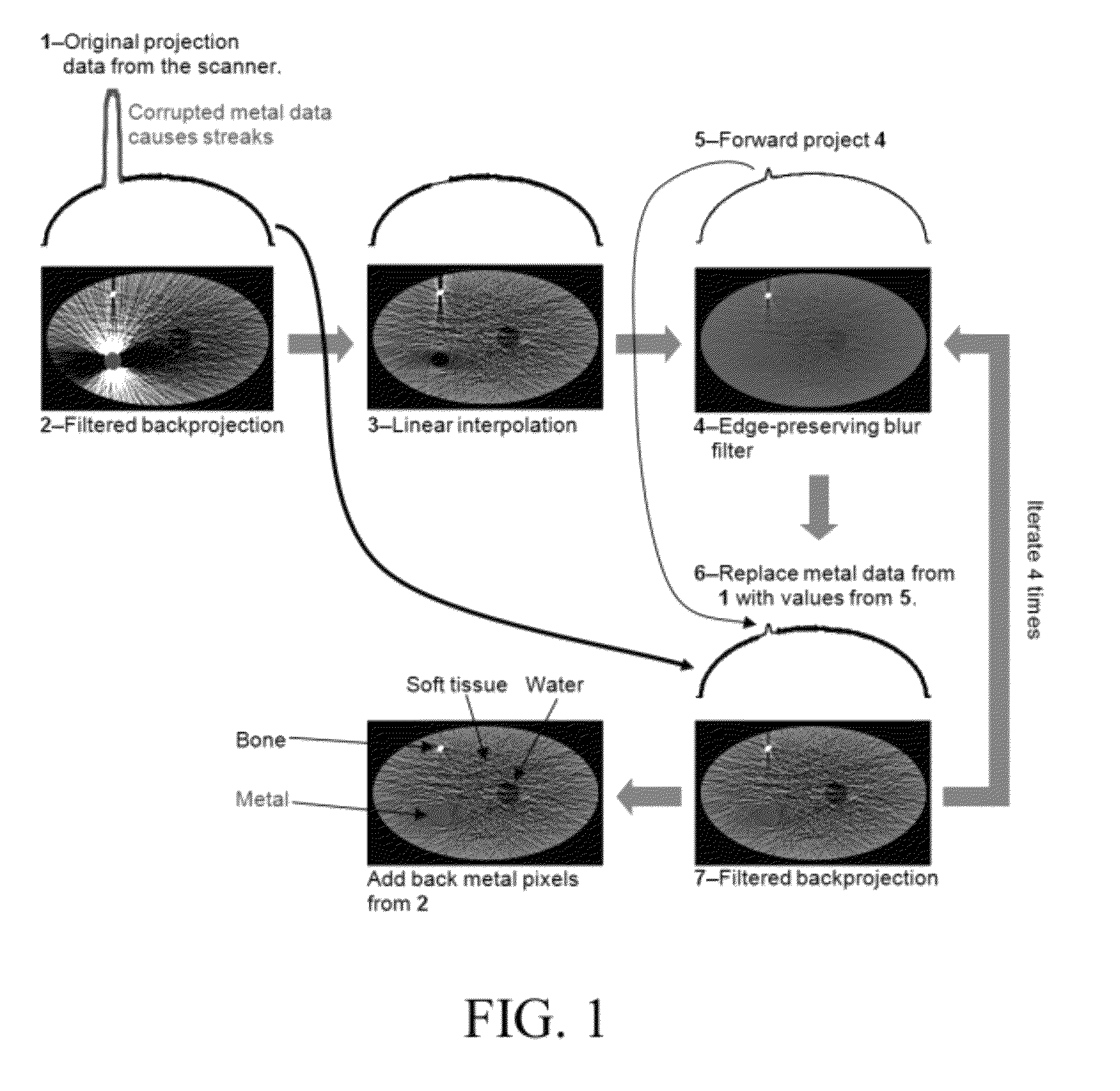
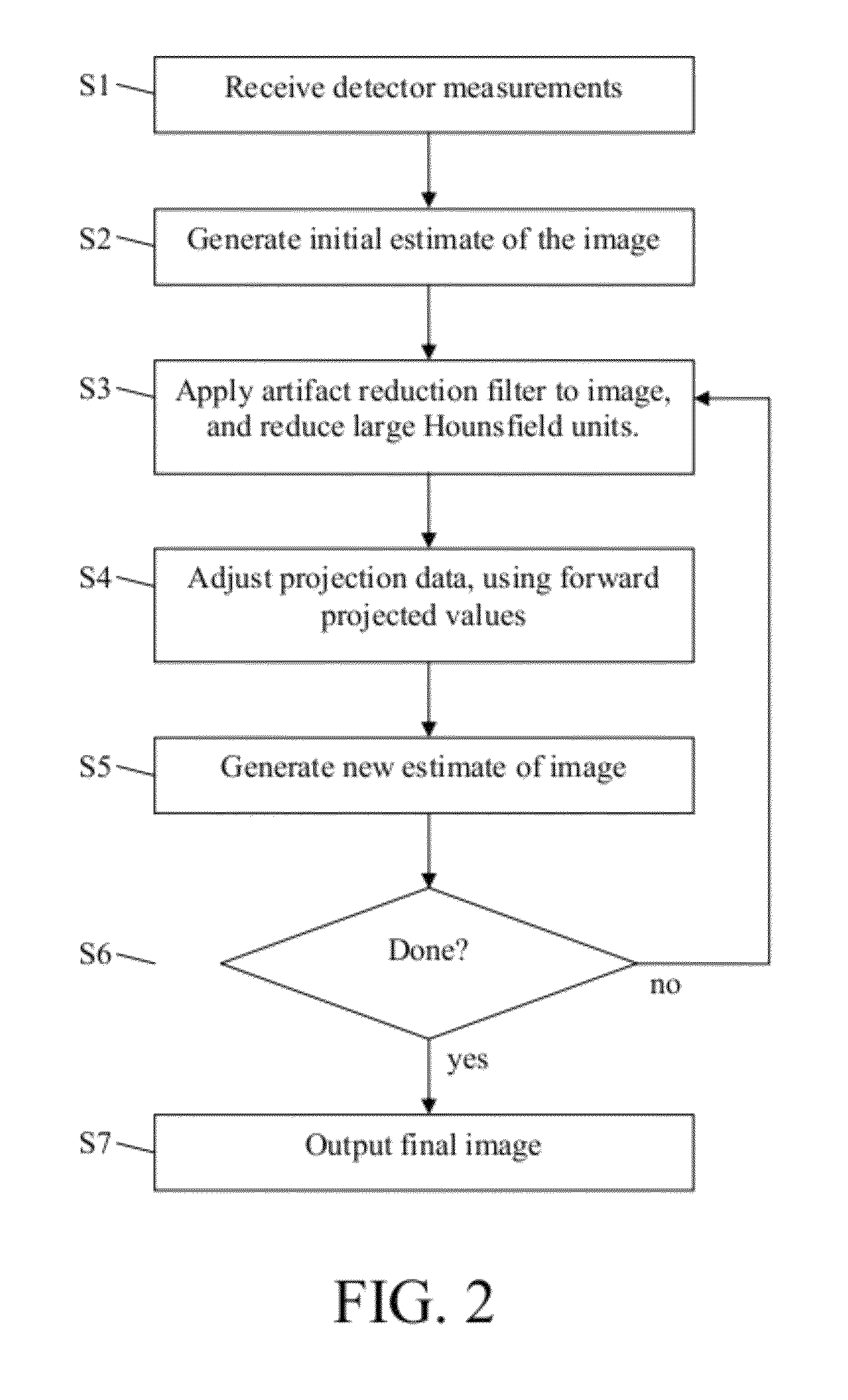
Iterative reduction of artifacts in computed tomography images using forward projection and an edge-preserving blur filter
ActiveUS8233586B1Reduce noiseReduce beam hardening artifactImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionFuzzy filterIterative method
We present an iterative method for reducing artifacts in computed tomography (CT) images. First, a filter is applied to the experimental projection data that adaptively expands the detector element size in regions with low photon counts, until the desired number of photons are detected. The initial image is then calculated using an existing reconstruction technique. In each iteration, artifacts and noise in the current image are reduced by using an edge-preserving blur filter. Metal pixels (determined from the initial image) are replaced with smaller values. The resulting image is forward projected. Rays that go through metal are replaced with the forward projected values. Rays that do not pass near metal are kept at the experimental values. Filtered backprojection is then performed on the new projection data to determine the updated image. Finally, after the last iteration, metal pixels are copied from the initial image.
Owner:BOAS FRANZ EDWARD
Automated management of user activity lists
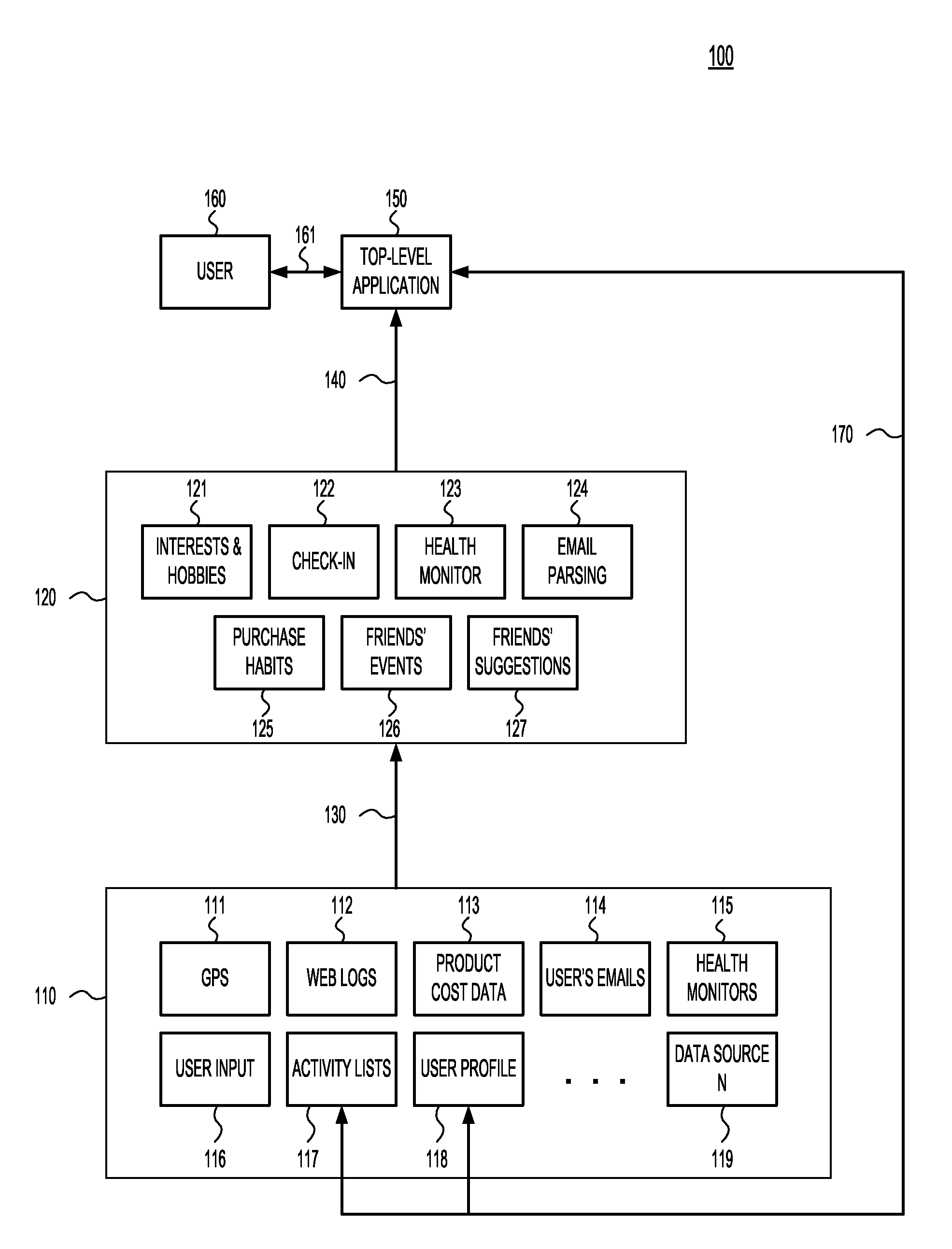
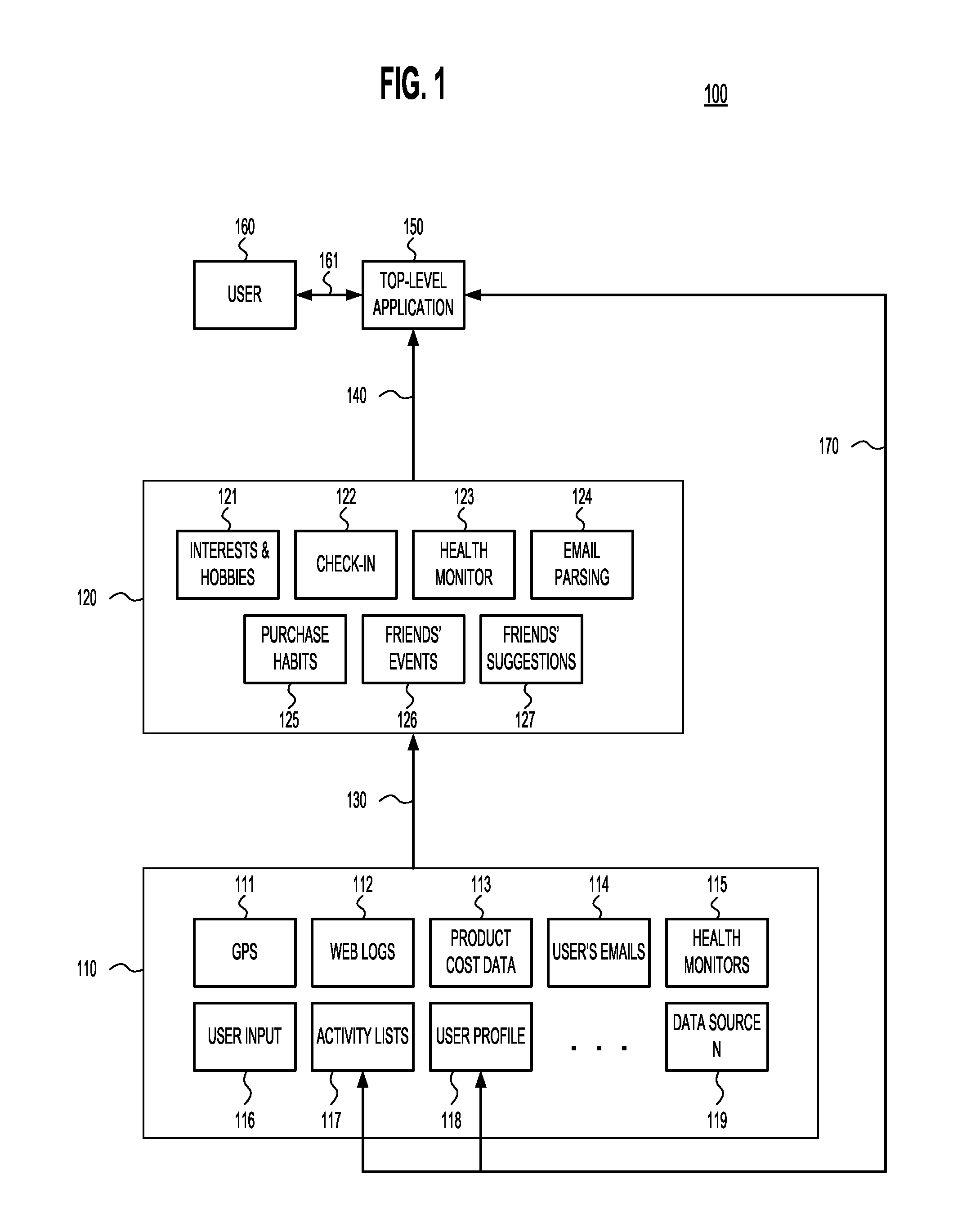
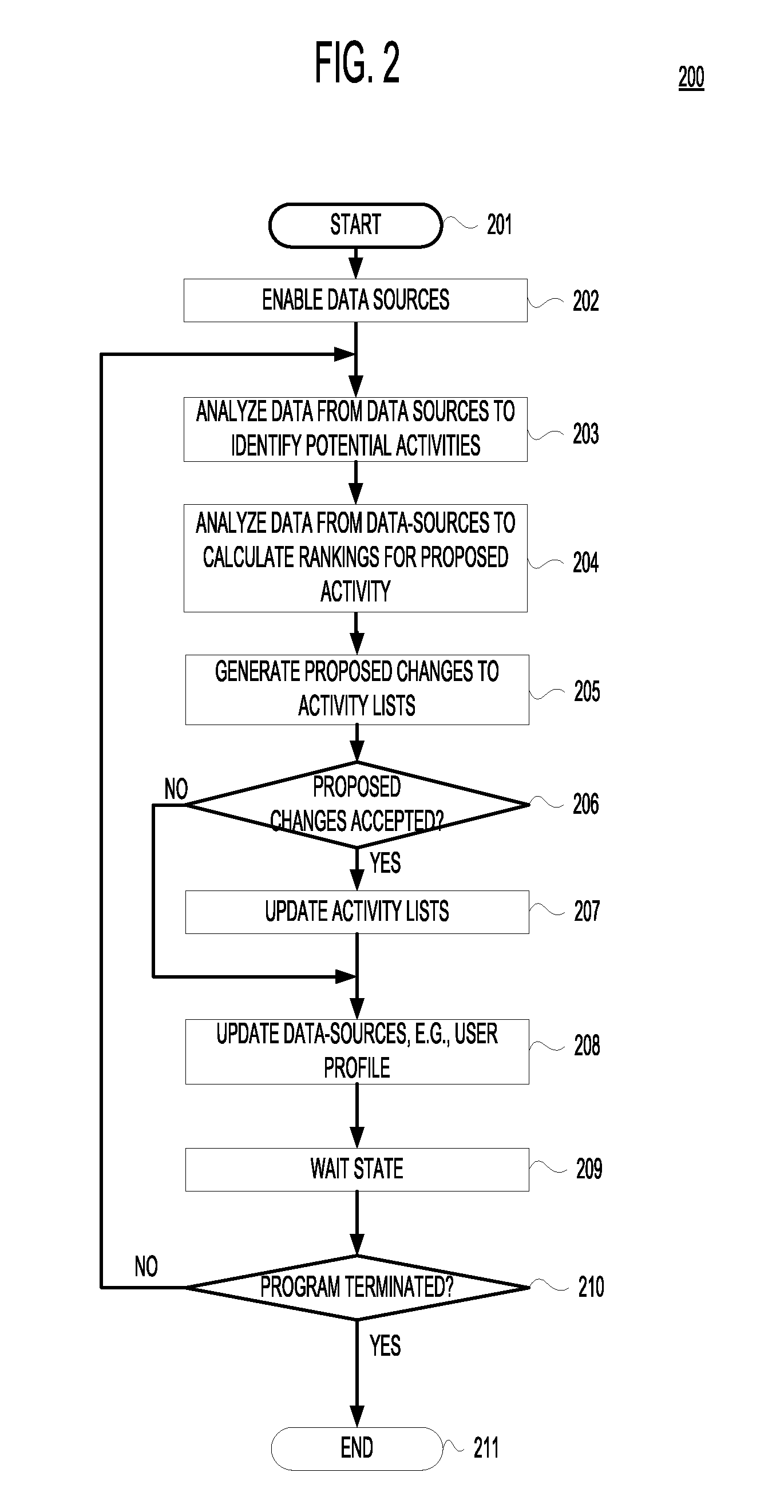
Embodiments of the present invention are iterative methods that: 1) analyze data from one or more electronic data-sources so as to a) identify or generate an activity (“proposed activity”) of potential importance to a given user, b) calculate one or more ranks that indicate the method's estimate of how important the activity is to the user, c) generate one or more proposed changes to the user's electronic lists of activities (“activity list”) to accommodate the identified activity and, d) determine if the proposed changes should be accepted or rejected; 2) if the proposed changes are accepted, apply the proposed changes to the activity lists, and; 3) update the data-sources in response to whether and how the proposed changes were accepted or rejected.
Owner:YARLAGADDA ANNAPURNA
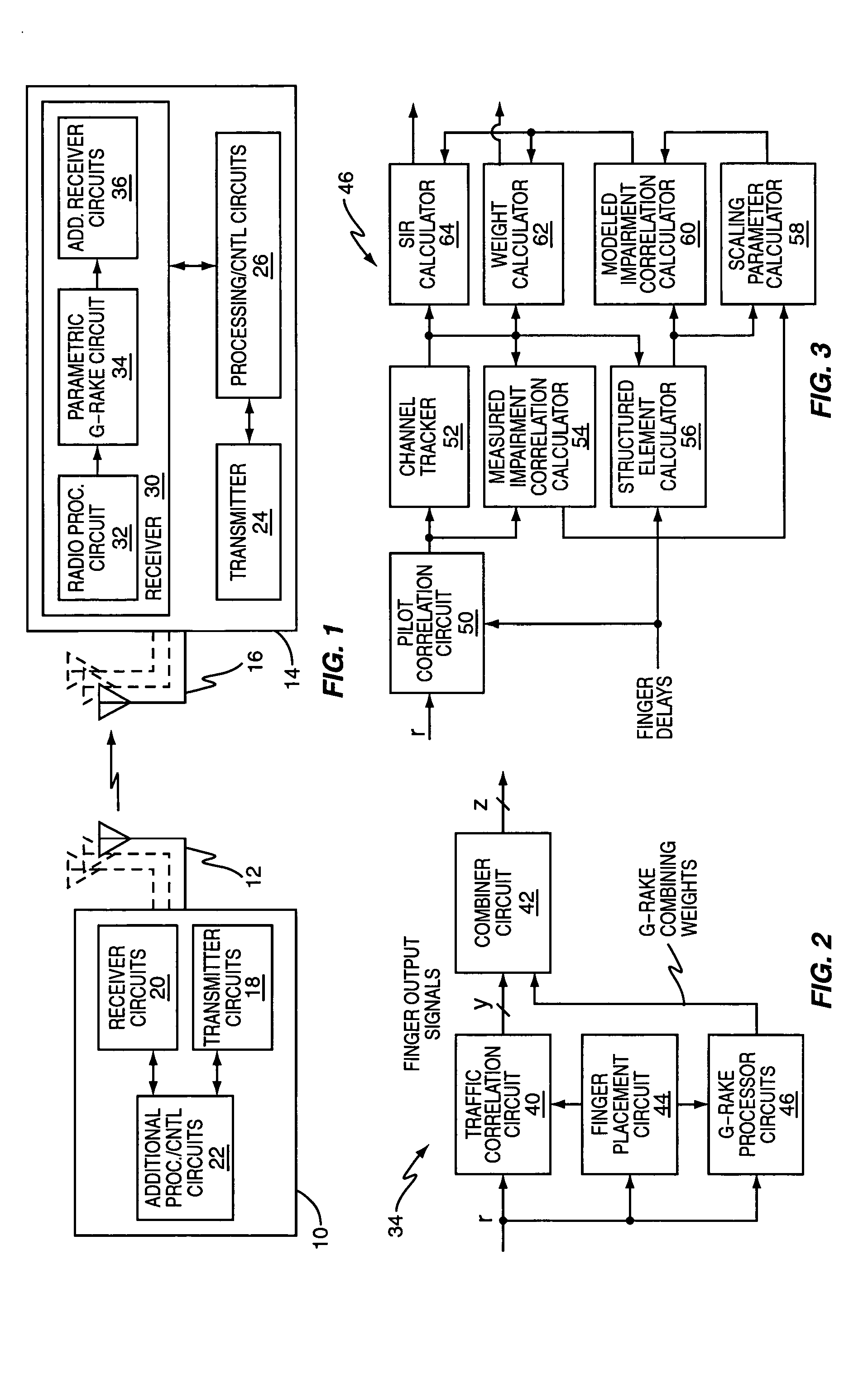
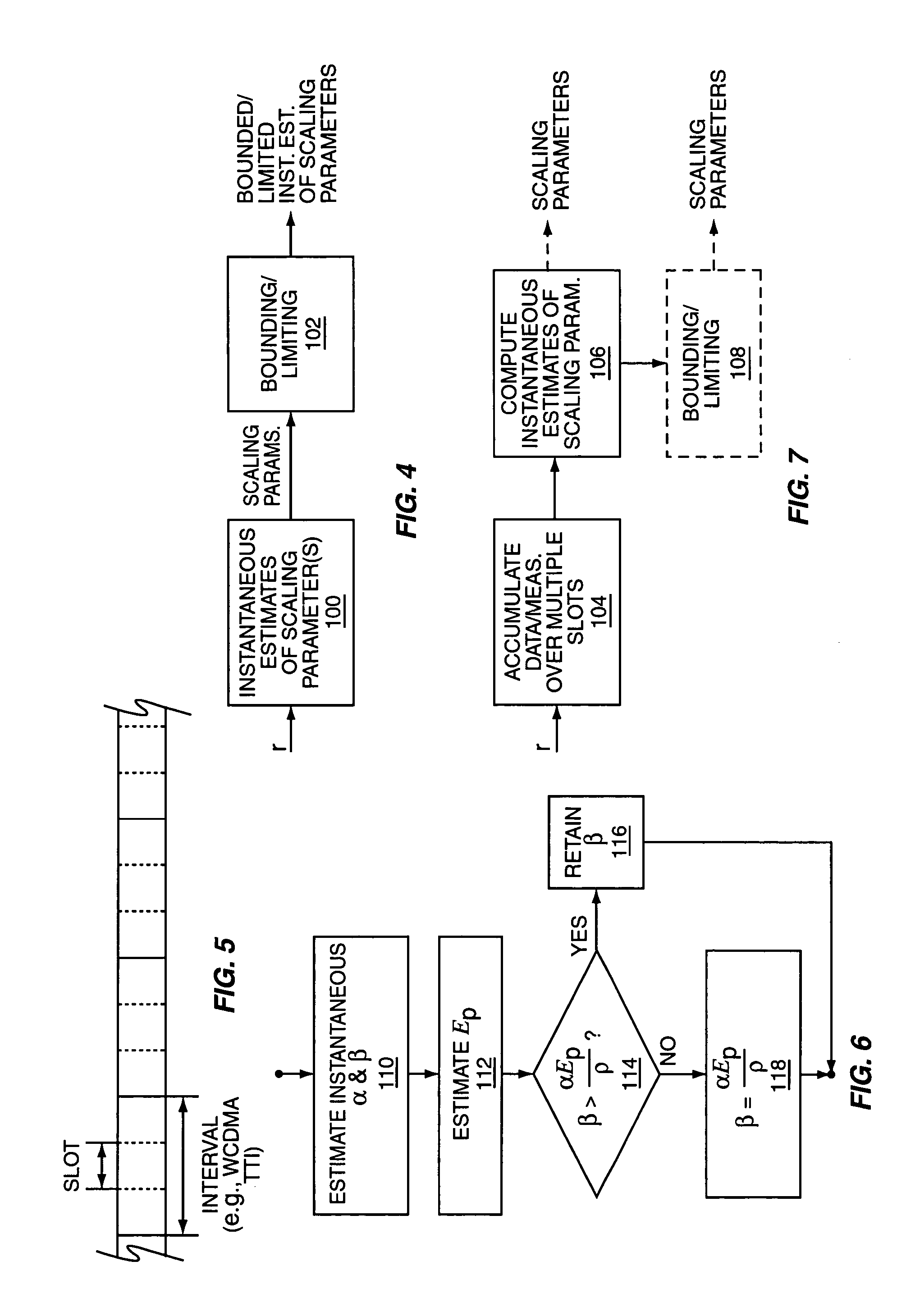
Method and apparatus for scaling parameter estimation in parametric generalized rake receivers
InactiveUS20060007990A1Spatial transmit diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverEngineering
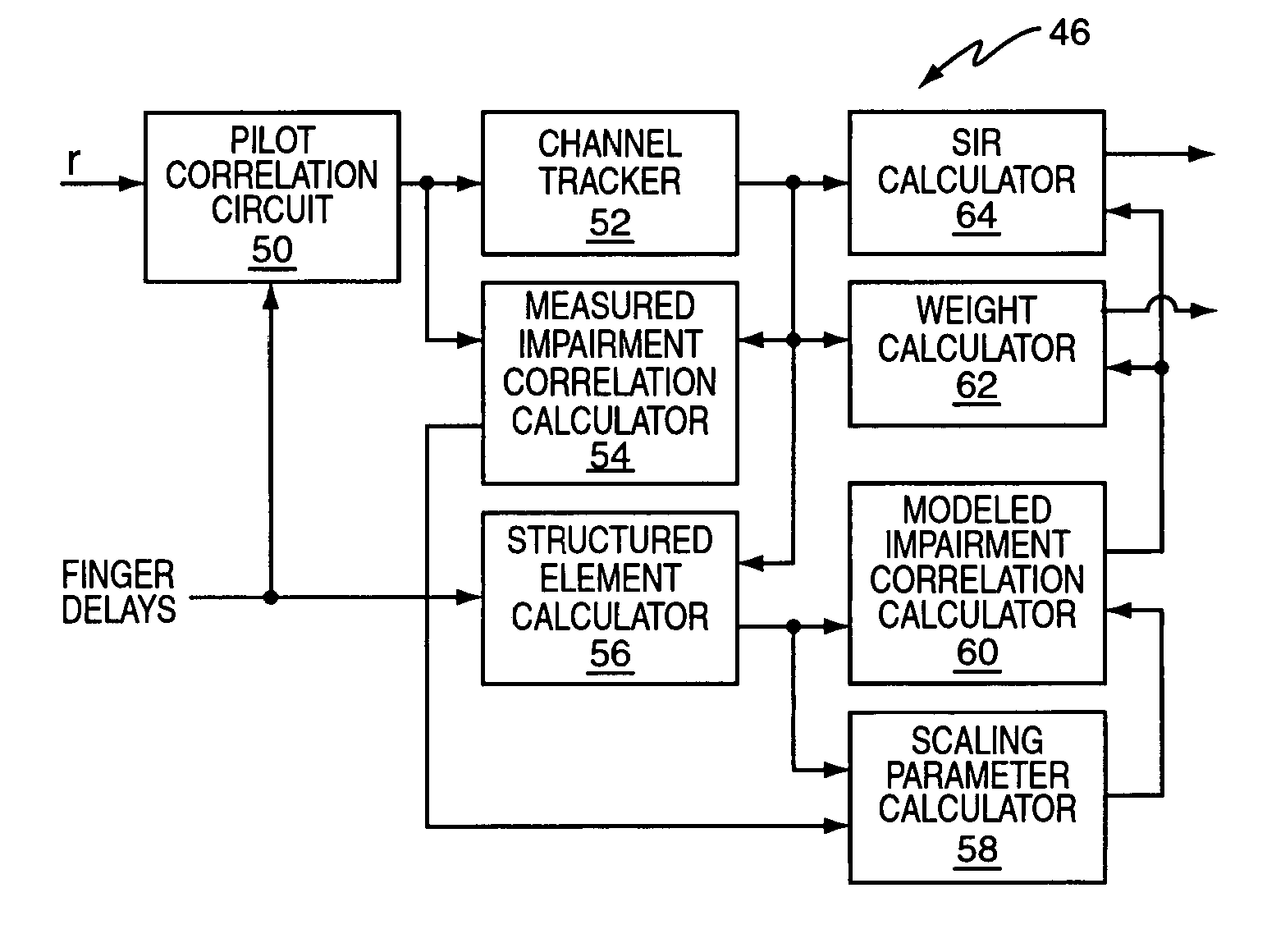
A wireless communication receiver, such as the receiver included in a wireless communication transceiver implemented in a base station or in a mobile station of a wireless communication network, includes a parametric G-RAKE receiver circuit and a method that compute parametric scaling parameters on a per transmission interval basis. In one embodiment, measured impairment correlations are obtained for an individual transmission slot and used to estimate instantaneous values of the scaling parameters. One or both of those instantaneous values are then constrained according to one or more defined limits. In other embodiments, multiple transmission slots are used to increase the number of measurements available to estimate the scaling parameters, with parameter constraining optionally applied. Further embodiments use iterative methods and / or solve for one parameter, and use the results to obtain the other parameter(s). One or more of these embodiments can be improved through the use of error correction / detection information.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
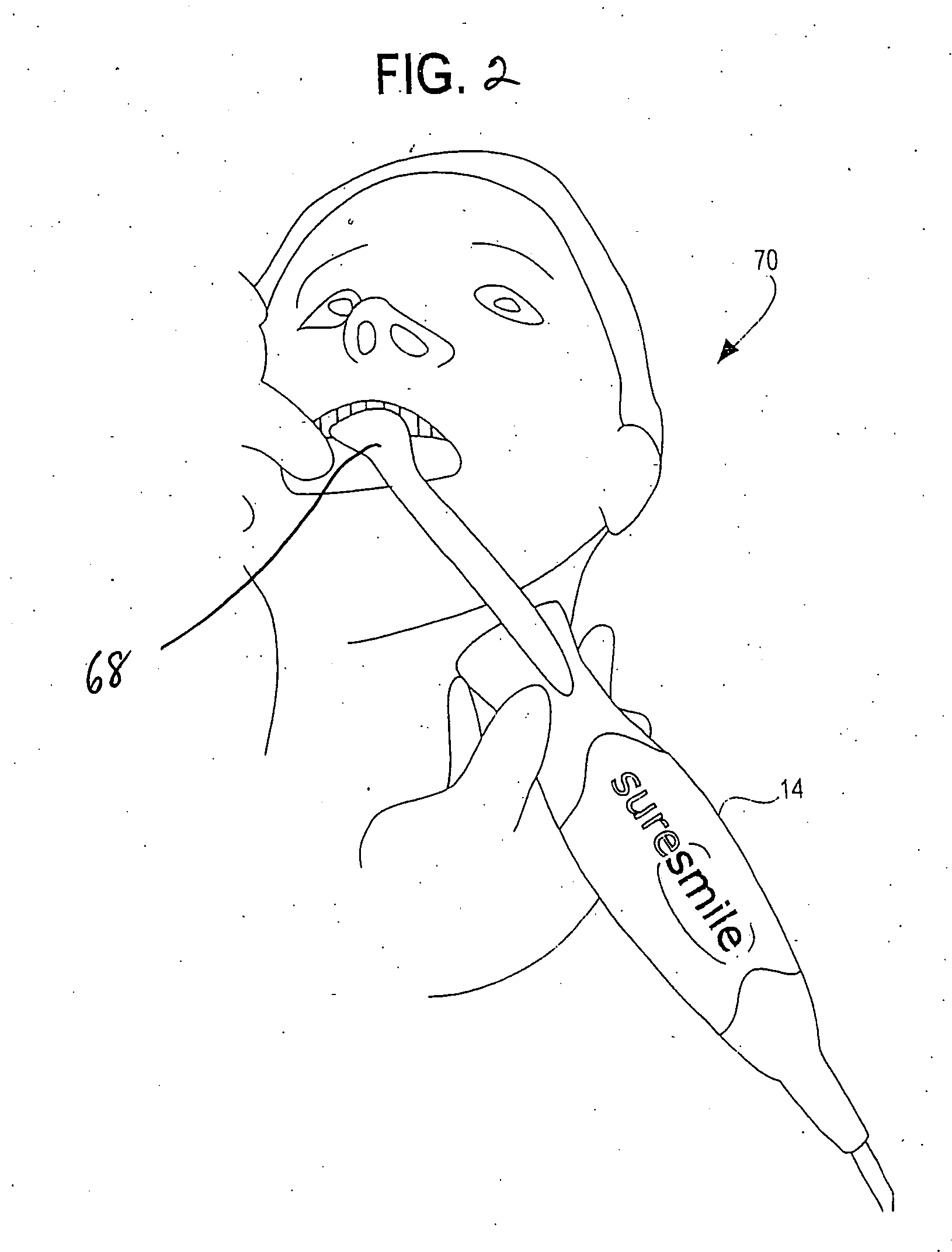
Method and system for finding tooth features on a virtual three-dimensional model
A method and system are disclosed for finding virtual tooth features on virtual three-dimensional models of the teeth of patients. The tooth features comprise marginal ridges, cusp tips, contact points, central groove and buccal groove. Tooth axes system plays a key role in identifying the tooth features. An iterative method is disclosed for improving the accuracy of the tooth axes system. A virtual three-dimension model preferably obtained by scanning the dentition of a patient forms the basis for determining the tooth features. Tooth features are derived for all categories of teeth including molars, premolars, canines and front teeth. Tooth features are very helpful and used in planning orthodontic treatment. The tooth features are determined automatically using the computerized techniques; and can be manually adjusted when necessary.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
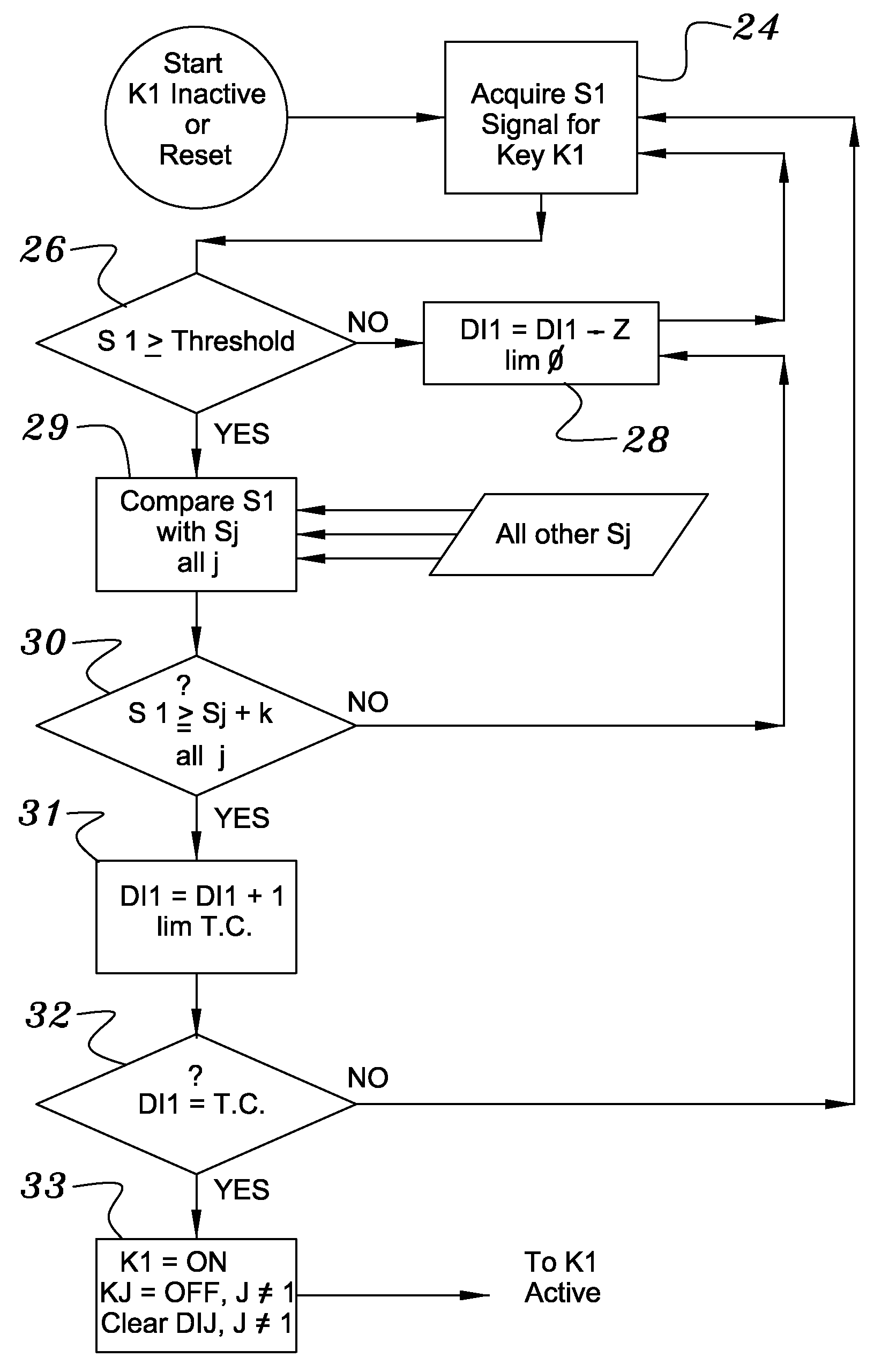
Capacitive keyboard with non-locking reduced keying ambiguity
ActiveUS7821425B2Reduce ambiguitySignal strength valueElectronic switchingDevice coding detailsEngineeringIterative method
Keyboards, keypads and other data entry devices can suffer from a keying ambiguity problem. In a small keyboard, for example, a user's finger is likely to overlap from a desired key to onto adjacent ones. An iterative method of removing keying ambiguity from a keyboard comprising an array of capacitive keys involves measuring a signal strength associated with each key in the array, comparing the measured signal strengths to find a maximum, determining that the key having the maximum signal strength is the unique user-selected key, and maintaining that selection until either the initially selected key's signal strength drops below some threshold level or a second key's signal strength exceeds the first key's signal strength.
Owner:NEODRON LTD
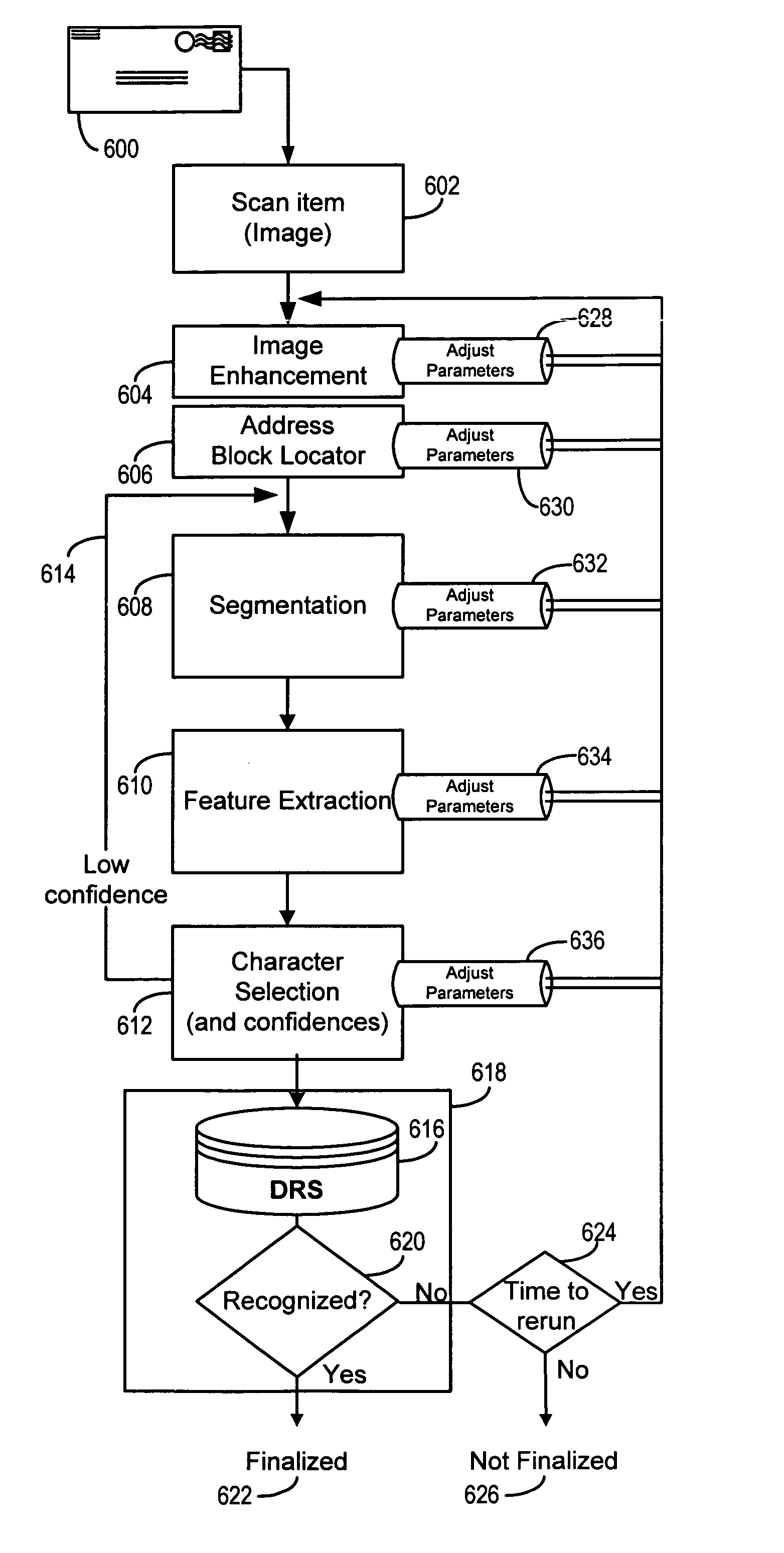
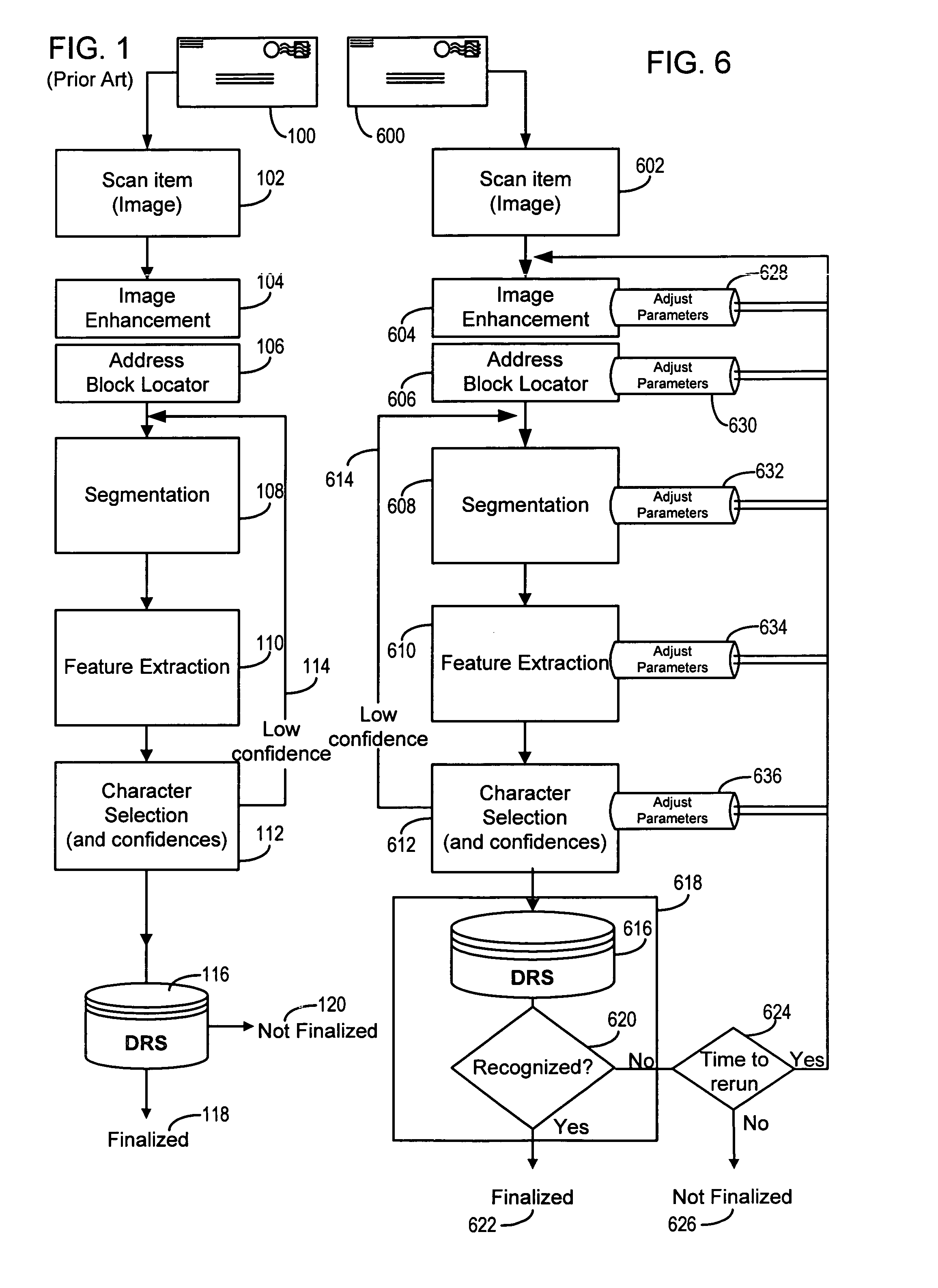
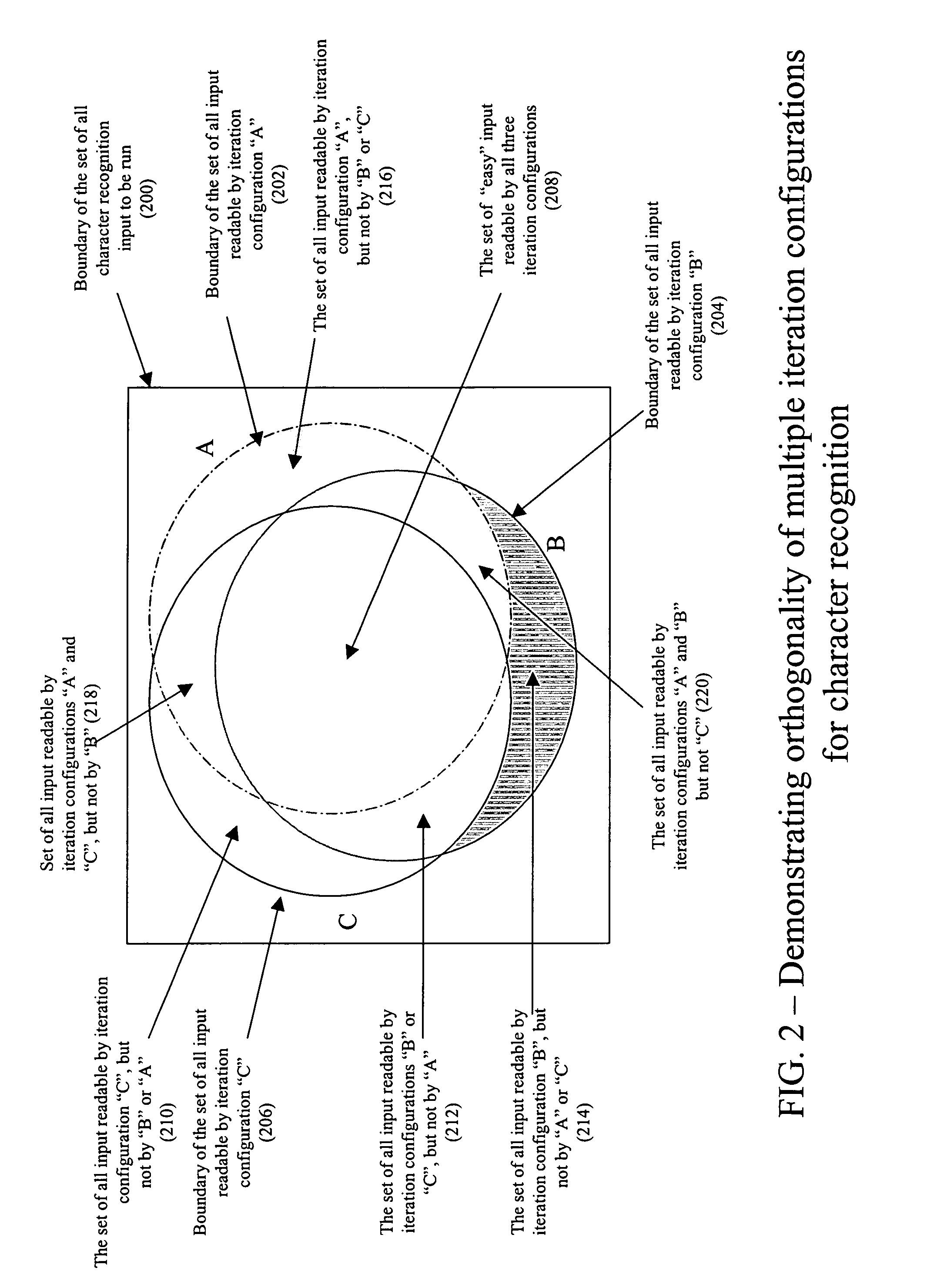
Orthogonal technology for character recognition
The present invention encompasses a self-orthogonal character recognition engine for executing an iterative method employing a database of predetermined character strings. The method receives a digital representation of a character string. It then generates a proposed result string by applying to the captured digital image a predetermined recognition routine including one or more recognition subroutines. Each recognition subroutine employs an initial parameter setting. Next, if the proposed result string does not match any of the predetermined character strings in the database, the initial parameter setting of a recognition subroutine is changed to a next setting. The recognition process is then repeated using the next parameter setting to generate and test a next result string. The process can be repeated iteratively until a result string is verified or the process times out.
Owner:MATTHEWS INT CORP
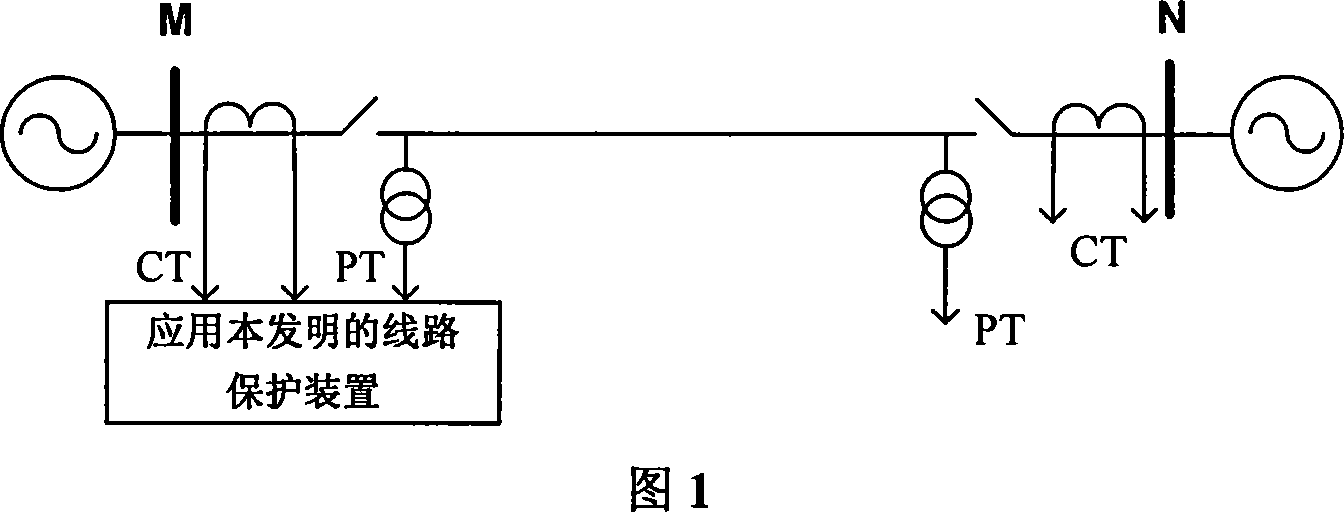
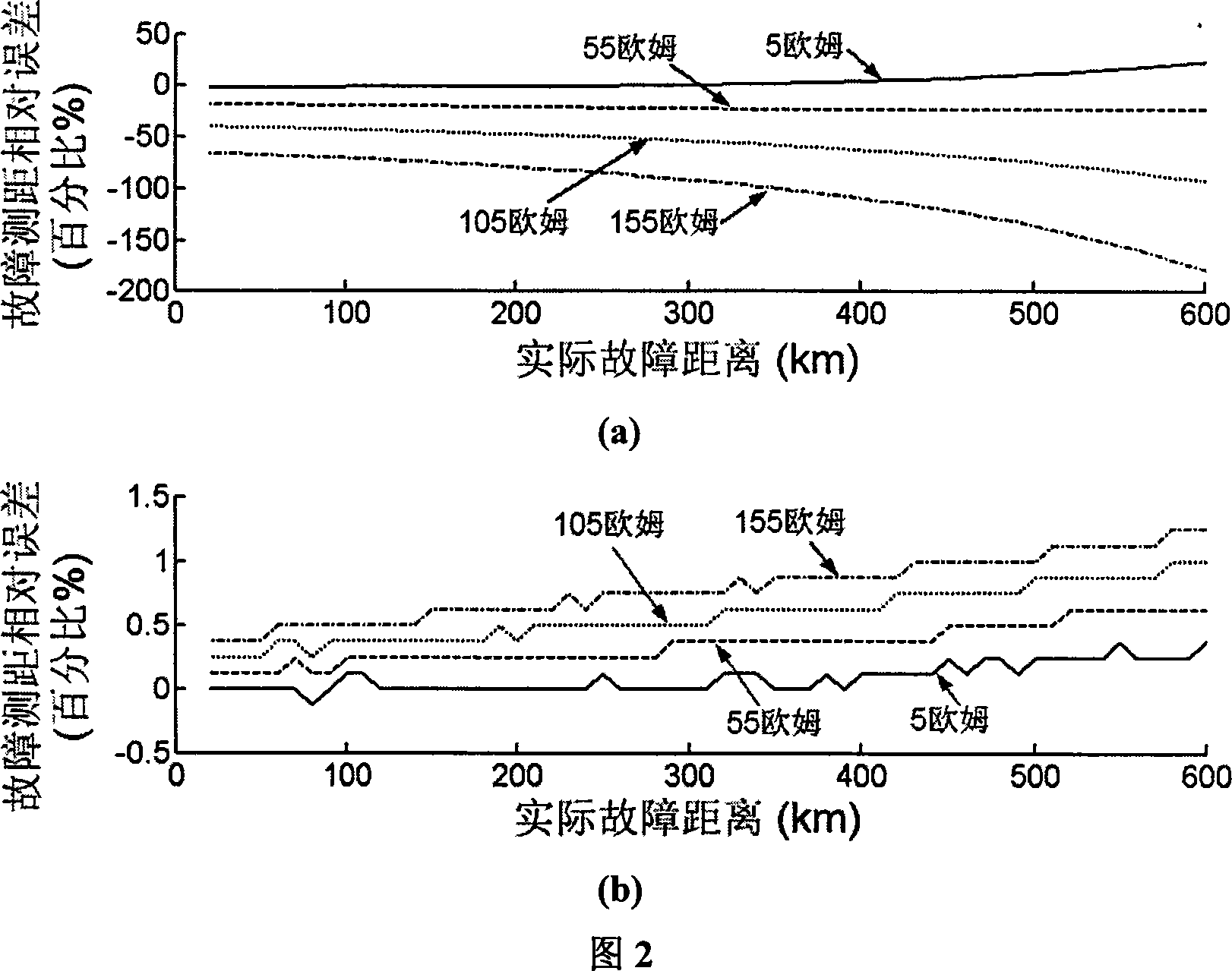
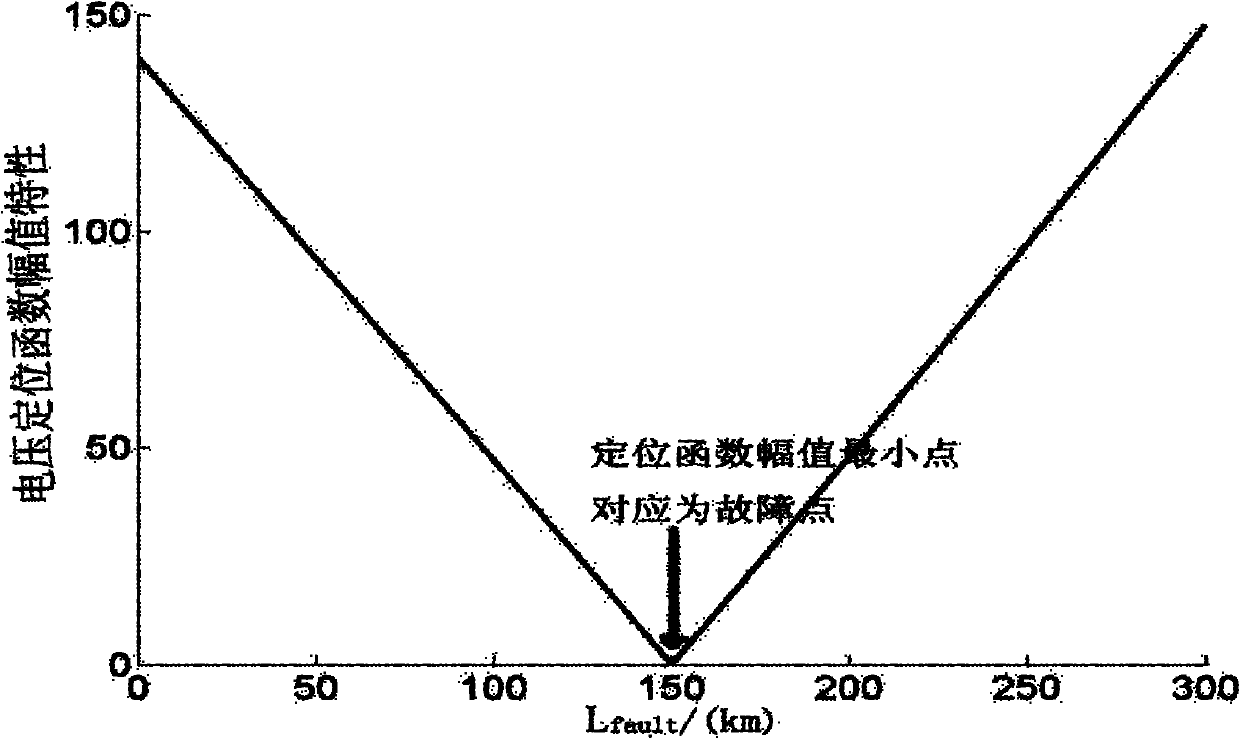
Distributing capacitance current and transition resistance influence resisting line one-end fault ranging method
ActiveCN101067641ADescribe physical propertiesThere is no non-convergence problemFault locationCapacitancePhase currents
The invention belongs to the electrical power system domain, specially relates to the line single end fault distance measuring method of the anti- distributed capacity electric current and the transition resistance influence. Including: surveys the transformer substation protection installment place fault phase voltage, the phase current, the zero sequence voltage, the zero sequence electric current and the negative sequence electric current as the input value; using the fault voltage cross zero time to measure the resistance characteristic which is not influence by transition resistance, from the protected line begin end start, computing the measure voltage real part computed value of the fault point voltage cross zero point time, compared with the measured value of the measure voltage real part, computing the error; and taking the delta-S as the step size, in turn computing the setting range which is protected by the send tripping signal, if cannot obtain the protect tripping signal, searching the total track length which is protected, taking the minimum point as the fault point. The invention method is not influenced by the distributed capacity electric current and transition resistance, does not have the false root problem of solving equation method and non convergence question of the iterative method, and has the very high practical value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Keyboard with reduced keying ambiguity
ActiveUS20040008129A1Electronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingProximity sensorAmbiguity
When an array of proximity sensors is used as a keyboard, it can provide an ambiguous output if a user's finger overlaps several keys or if liquid is spilled on the keyboard. This ambiguity is reduced by an iterative method that repeatedly measures a detected signal strength associated with each key, compares all the measured signal strengths to find a maximum, determines that the key having the maximum signal strength is the unique user-selected key and then suppresses or ignores signals from all other keys as long as the signal from the selected key remains above some nominal threshold value.
Code transformation
ActiveUS20090064091A1Simple processEasy to transformSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsComputerized systemTheoretical computer science
Owner:CSC TECH SINGAPORE PTE
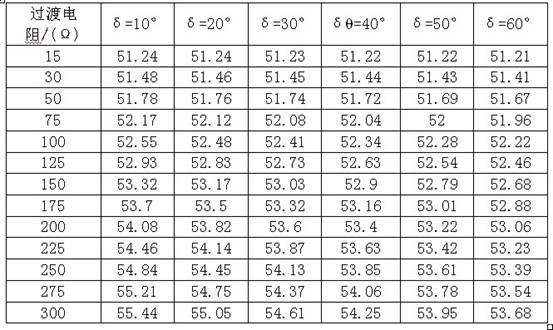
Line single-phase earth fault single-terminal location method based on positioning function amplitude characteristics
ActiveCN102200563AAvoid influenceThere is no false root problemFault locationPhase currentsCapacitance
The invention discloses a line single-phase earth fault single-terminal location method based on positioning function amplitude characteristics. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring fault phase voltage, fault phase current, fault phase negative-sequence current and zero-sequence current at a protection installation position of a transformer substation as input variables; with the origin of a protected line as a start point, calculating the positioning function amplitude of each point on a fault phase line one by one in a way that step length increases gradually till a trip signal setting range is reached; if protection trip signals cannot be obtained, searching all over the protected line, taking the point with the smallest positioning function amplitude as a fault pointand setting the distance between the point and the line protection installation position. The method is not influenced by distributed capacitance, or load current or transition resistance, does not have the problems of false root existing in the method of solving equation or non-convergence existing in the iteration method and achieves very high practical value.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
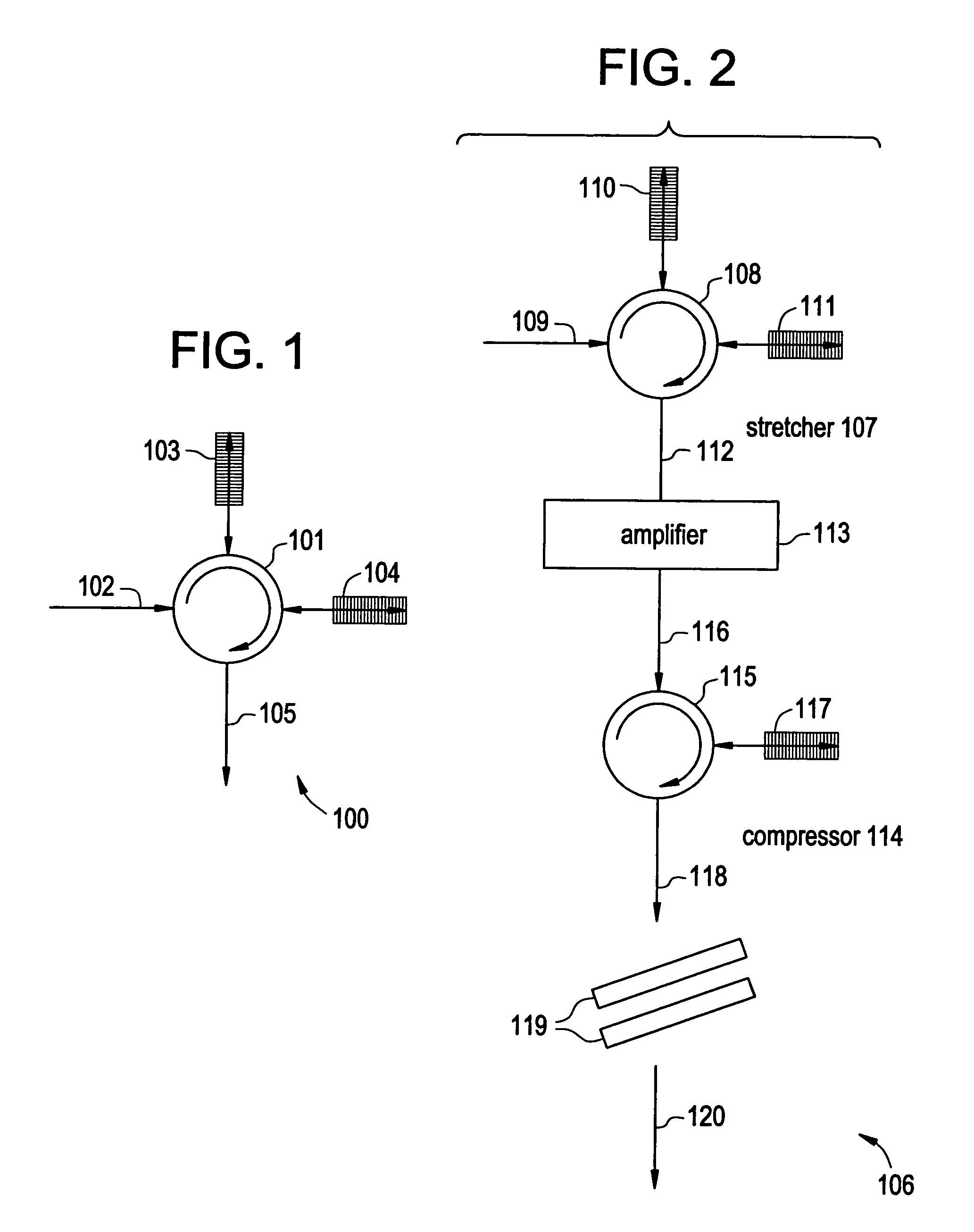
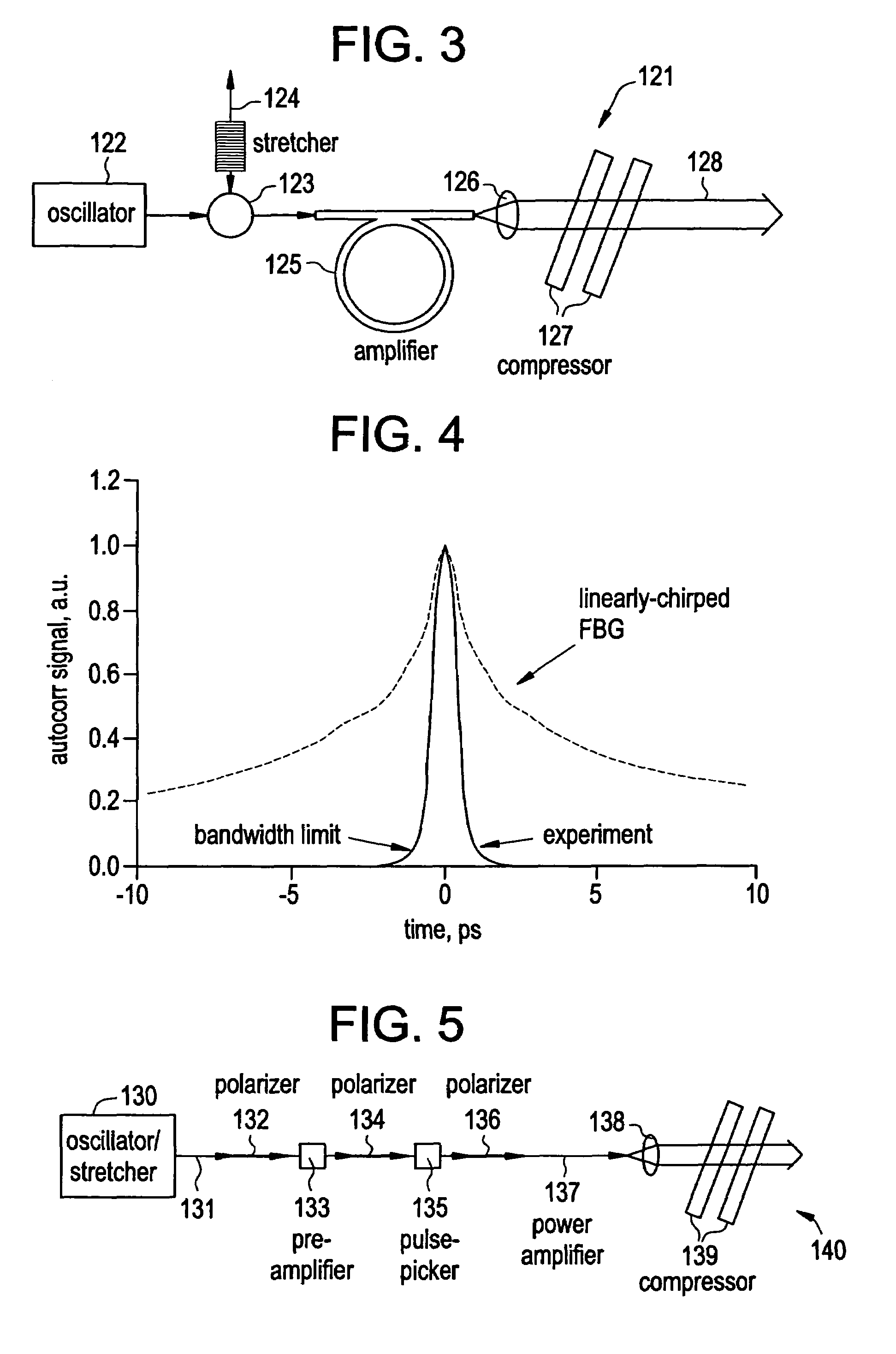
In-line, high energy fiber chirped pulse amplification system
InactiveUS7257302B2Accurately dispersion matchedBig ratioOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLaser arrangementsGratingHigh energy
By writing non-linear chirp into fiber Bragg gratings, greater control over dispersion compensation in CPA systems is obtained, such that, for example, the dispersion profile of the fiber Bragg grating and a bulk compressor may be matched. An iterative method of writing the fiber grating can reduce the group delay ripple to very low levels; and adaptive control of the fiber grating dispersion profile can further reduce these levels, while in addition offering greater acceptable yield in the manufacture of such gratings. Fiber Bragg gratings may be designed so as to provide customized pulse shapes optimized for various end uses, such as micromachining, for example, and may also be used to counteract gain-narrowing in a downstream amplifier.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
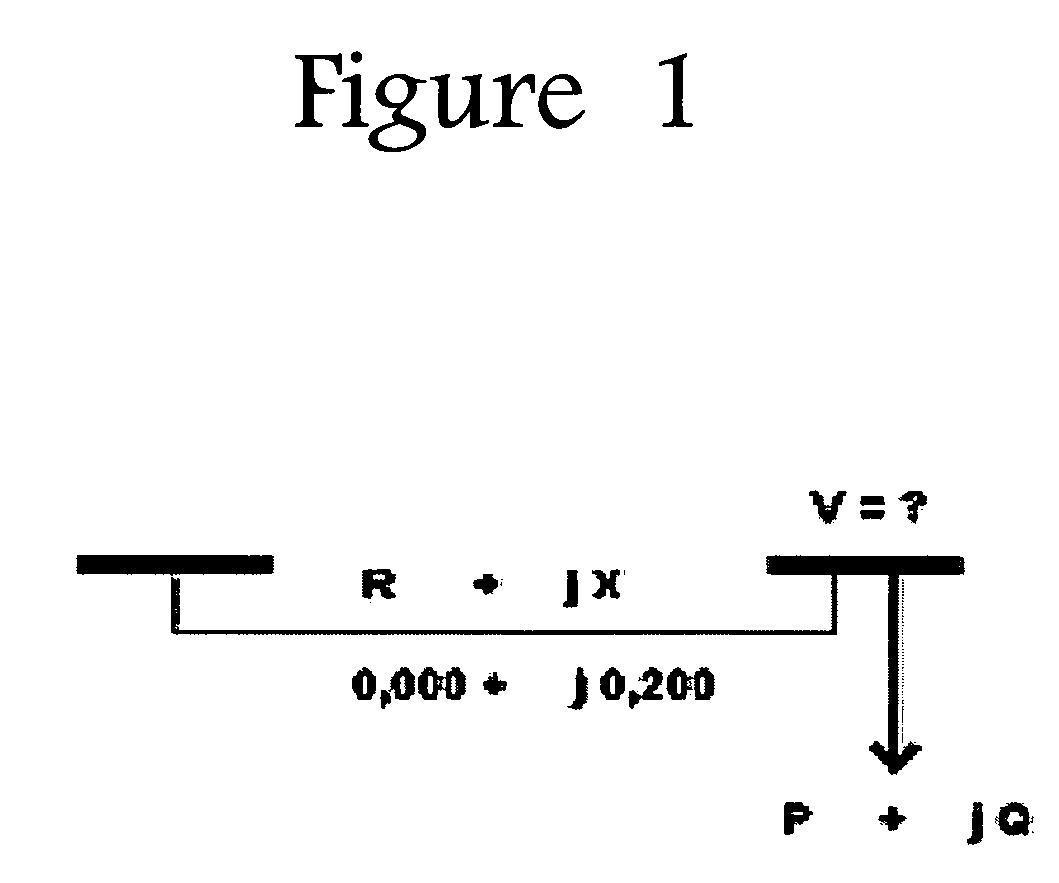
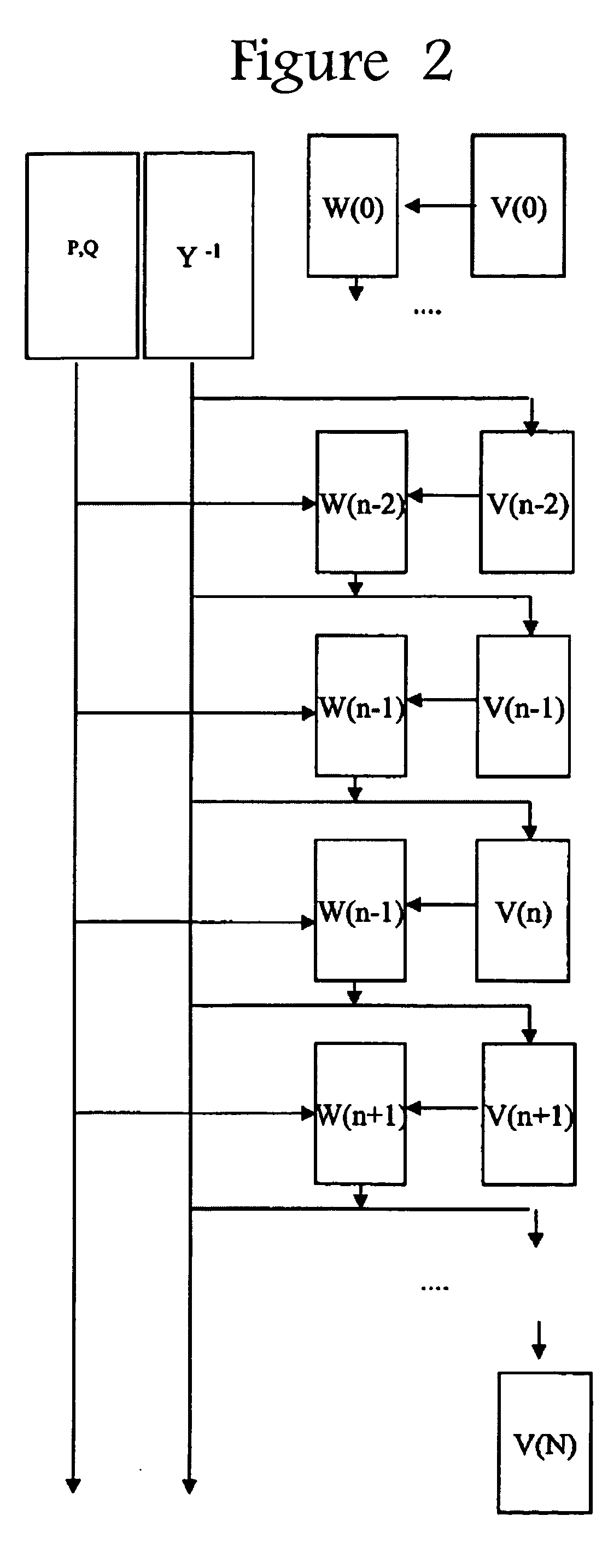
System and method for monitoring and managing electrical power transmission and distribution networks
ActiveUS20060111860A1Simple methodLevel controlTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesElectric power systemPower grid
A system and method for monitoring and managing electrical power transmission and distribution networks through use of a deterministic, non-iterative method using an holomorphic embedding and algebraic approximants for determining the real-time load flow in a power generating system having an electrical grid. Such method may be employed for real-time or off-line applications for electric power systems reliability assessment, and is capable of determining whether or not a physical solution to the load flow problem exists, or if the system is in a state of voltage collapse.
Owner:APLICACIONES & INFORMATICA AVANZADA
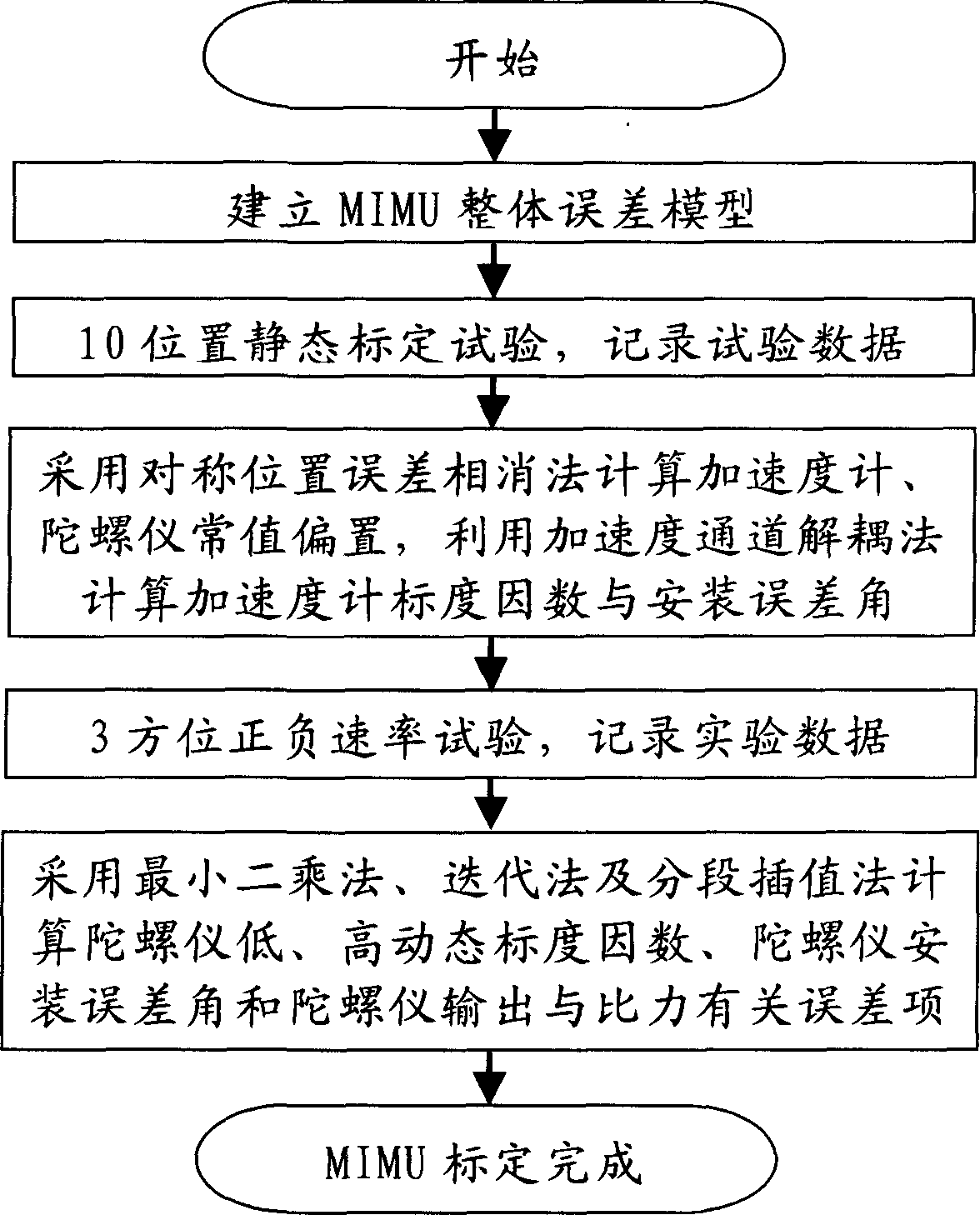
Microinertia measuring unit precisive calibration for installation fault angle and rating factor decoupling
InactiveCN1818555ASolve the errorSolving Scale Factor Coupling IssuesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
An accurate calibration method of micro inertia measuring unit by decoupling erection error angle (EEA)with scale factor includes setting up MIMU integral error model and separating couple between EEA of accelerometer and gyroscope and scale factor ,using position error canceling method to calculate out and to separate out scale factor and EEA of accelerometer as well as using least square method and iteration method to calculate out EEA of gyroscope and its relative error items in 10 position static calibration test and in 3 direction positive and negative rate test ,then using interpolation method to calculate out scale factor of gyroscope .
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
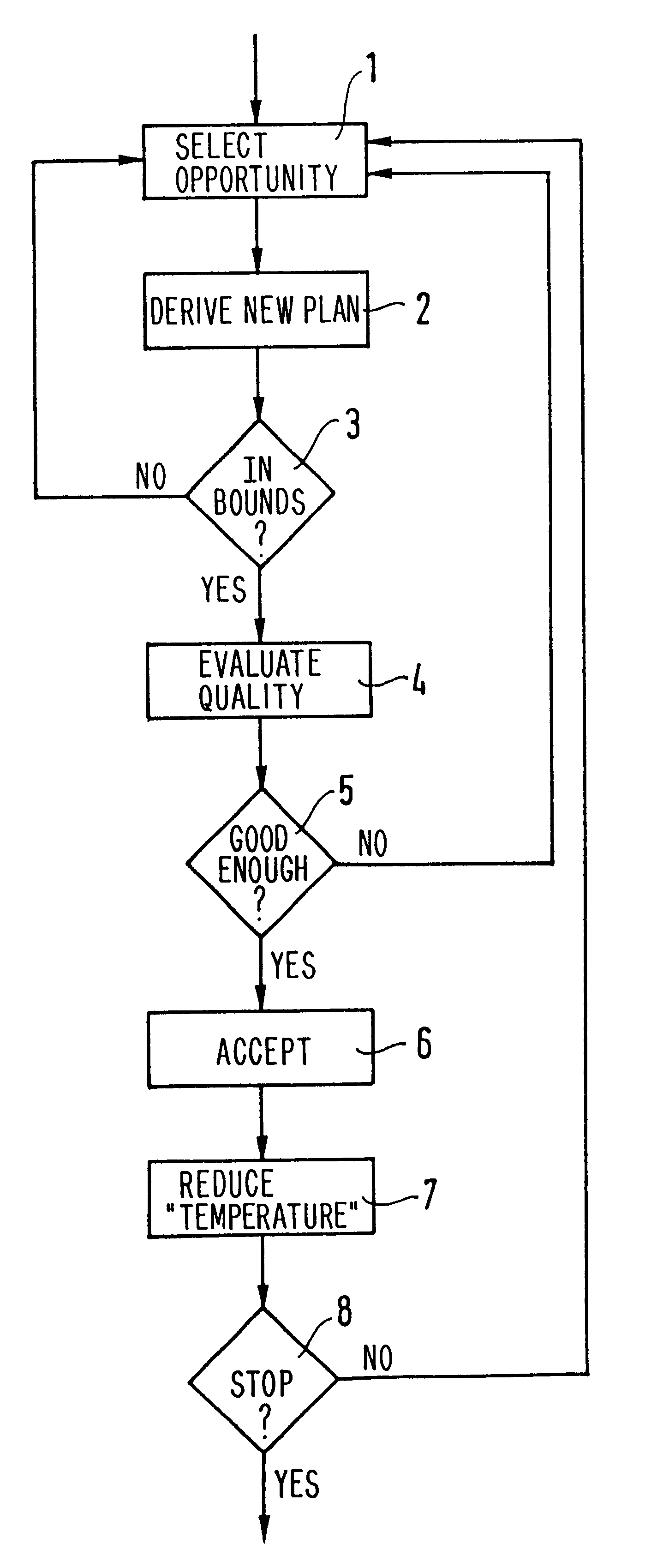
Method of planning satellite requests by constrained simulated annealing
InactiveUS6405186B1Improve planning qualityQuality improvementMathematical modelsArtificial satellitesProgram planningEngineering
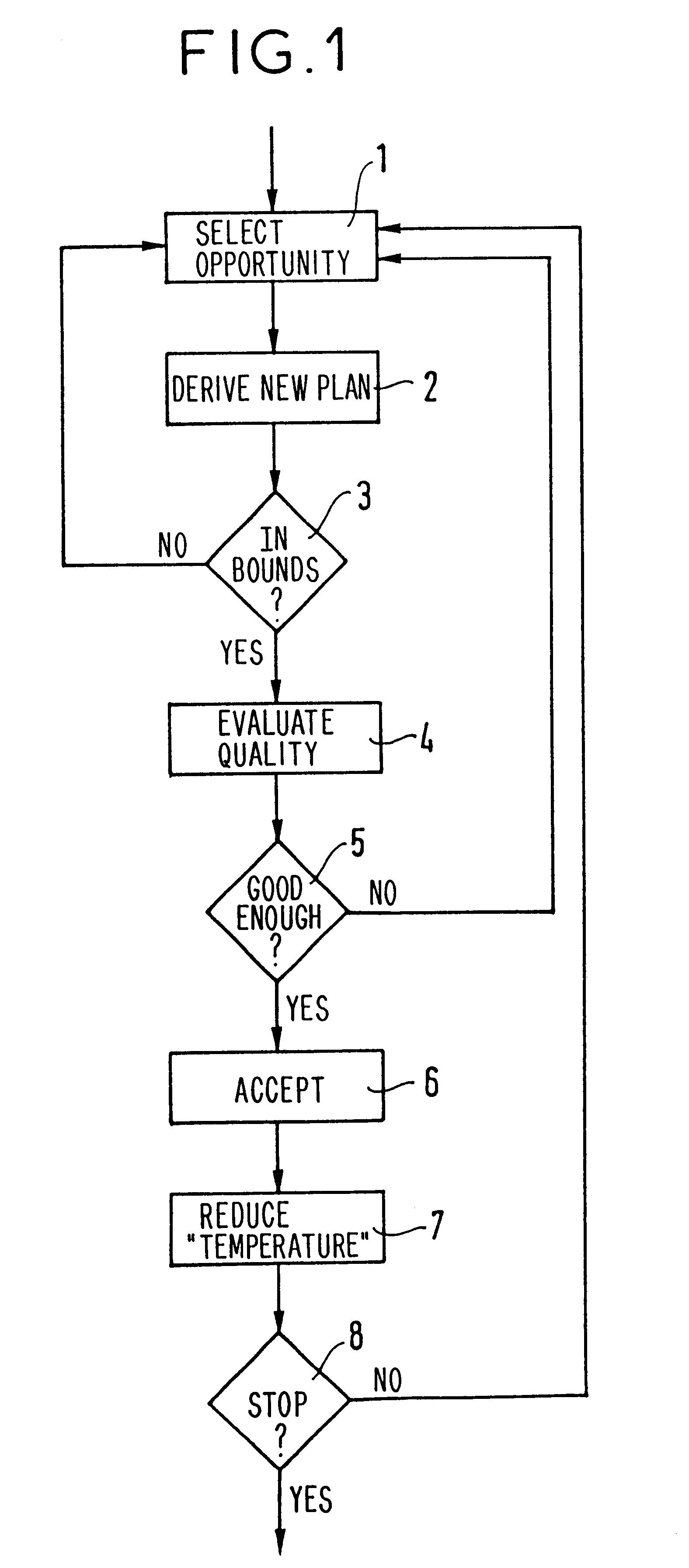
An iterative method enabling a request plan to be established for an observation satellite. A plan consists in a succession of requests which are associated with pluralities of opportunities for satisfying said requests. The plan must also comply with a plurality of constraints. Each iteration k of the iterative method is made up of the following steps:new opportunity is selected;a provisional plan is derived from the preceding plan k-1 as calculated in-the preceding iteration, and from the new opportunity;provisional plan is verified for compliance with said plurality of constraints;the quality of said provisional plan is evaluated; andit is determined whether the provisional plan should be confirmed as plan k as a function of the quality of said provisional plan and of the quality of said preceding plan k-1.In the method, it is decided whether or not to confirm the provisional plan by a probabilistic metaheuristic of the simulated annealing type, and by the rule for constructing the provisional plan as a function of the newly selected opportunity.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Stable adaptive filter and method
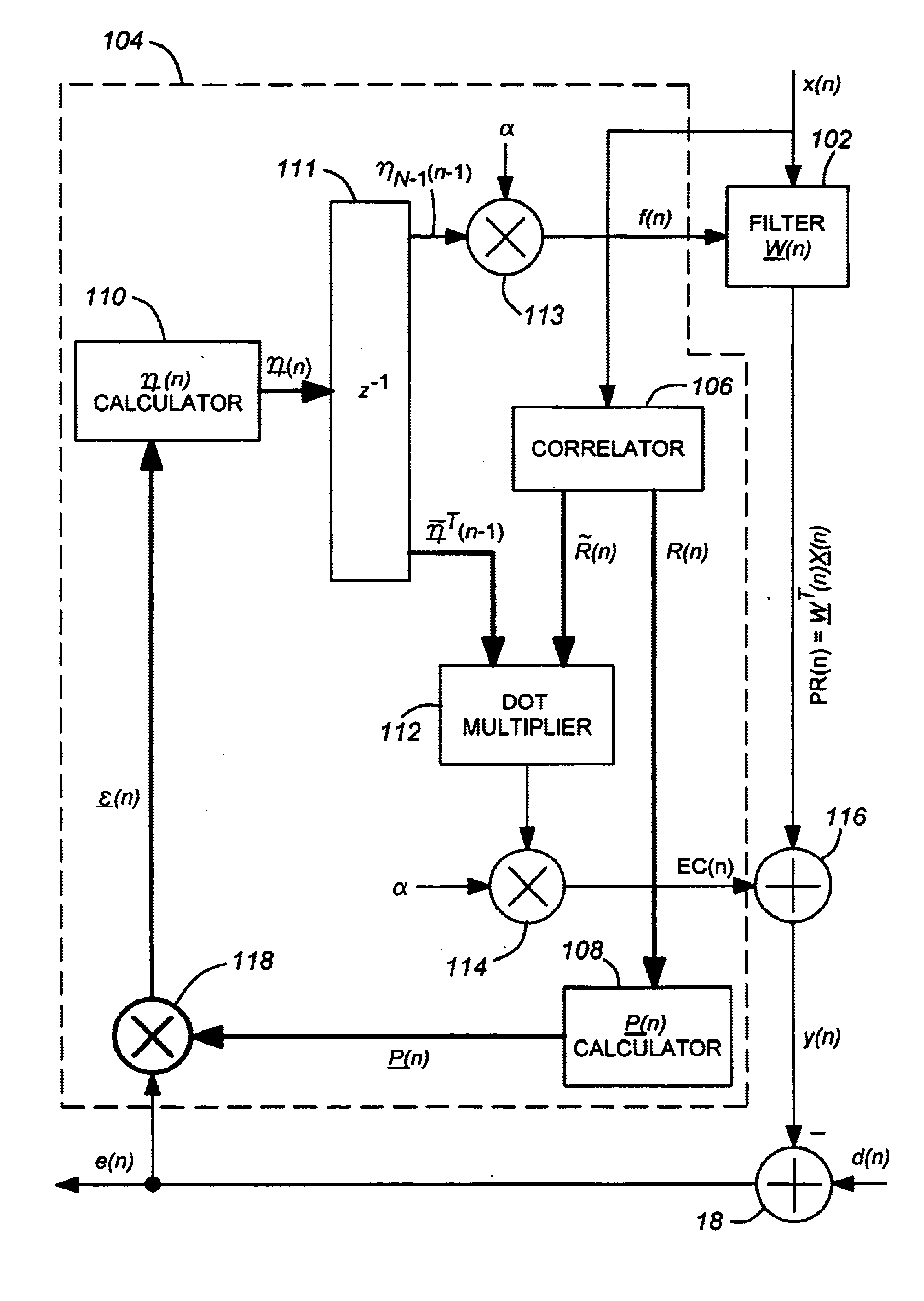
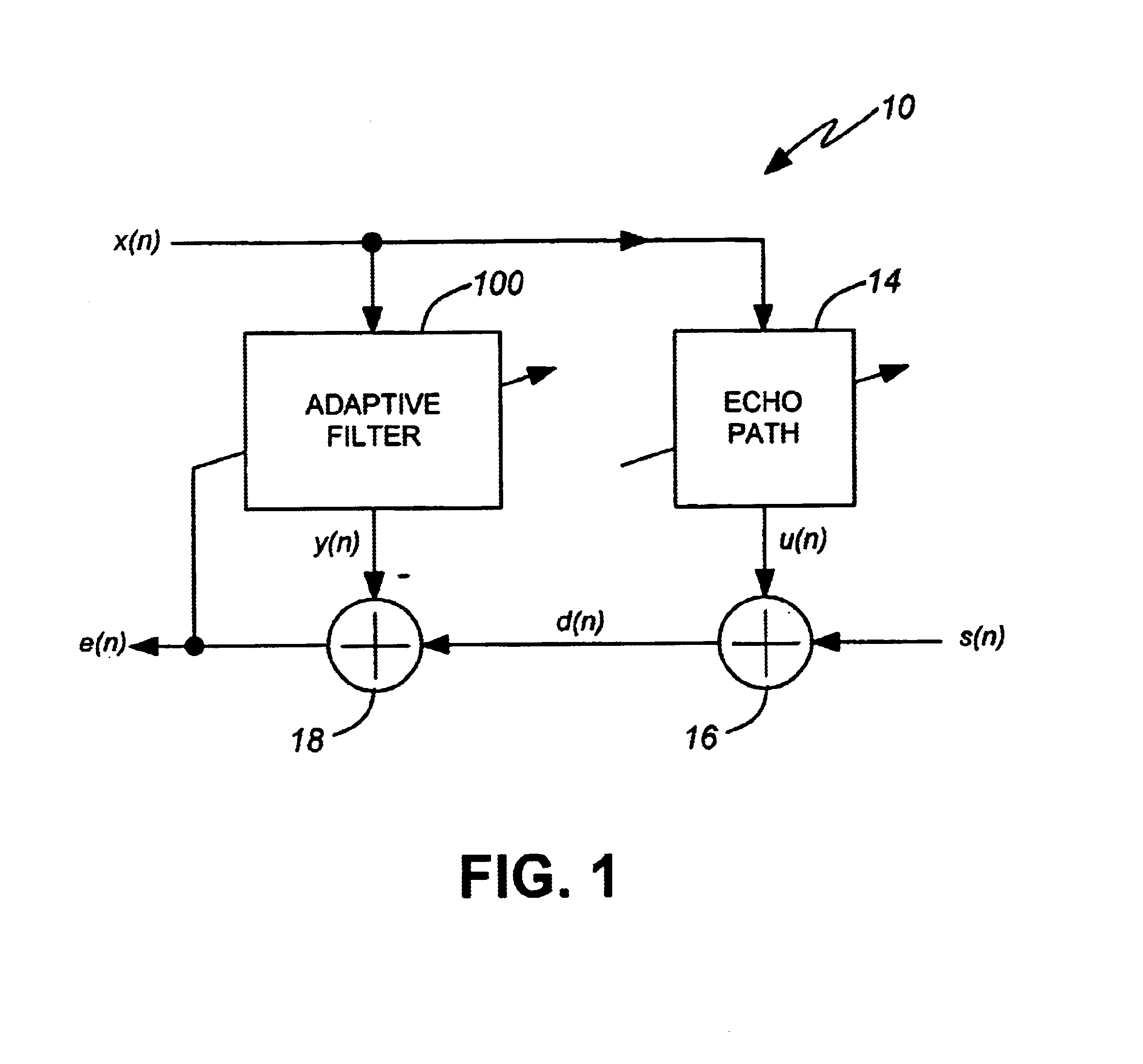
Stable adaptive filter and method are disclosed. The invention solves a problem of instability associated with Fast Affine Projection adaptive filters caused by error accumulation in an inversion process of an auto-correlation matrix. The Stable FAP uses a simplification of setting a normalized step size close to unity and reduces a problem of the matrix inversion to solving a system of linear equations whose solution coincides with a first column of the inverse auto-correlation matrix. The system of linear equations is then solved by one of descending iterative methods which provide inherent stability of operation due to intrinsic feedback adjustment. As a result, inevitable numerical errors are not accumulated, being corrected as the process goes on. In first and second embodiments of the invention the system of linear equation is solved by steepest descent and conjugate gradient methods respectively. Being immune to numerical errors, the invented method and filter are suitable for various DSP platforms, e.g., 16 and 24 bit fixed-point as well as floating point platform.
Owner:CIENA
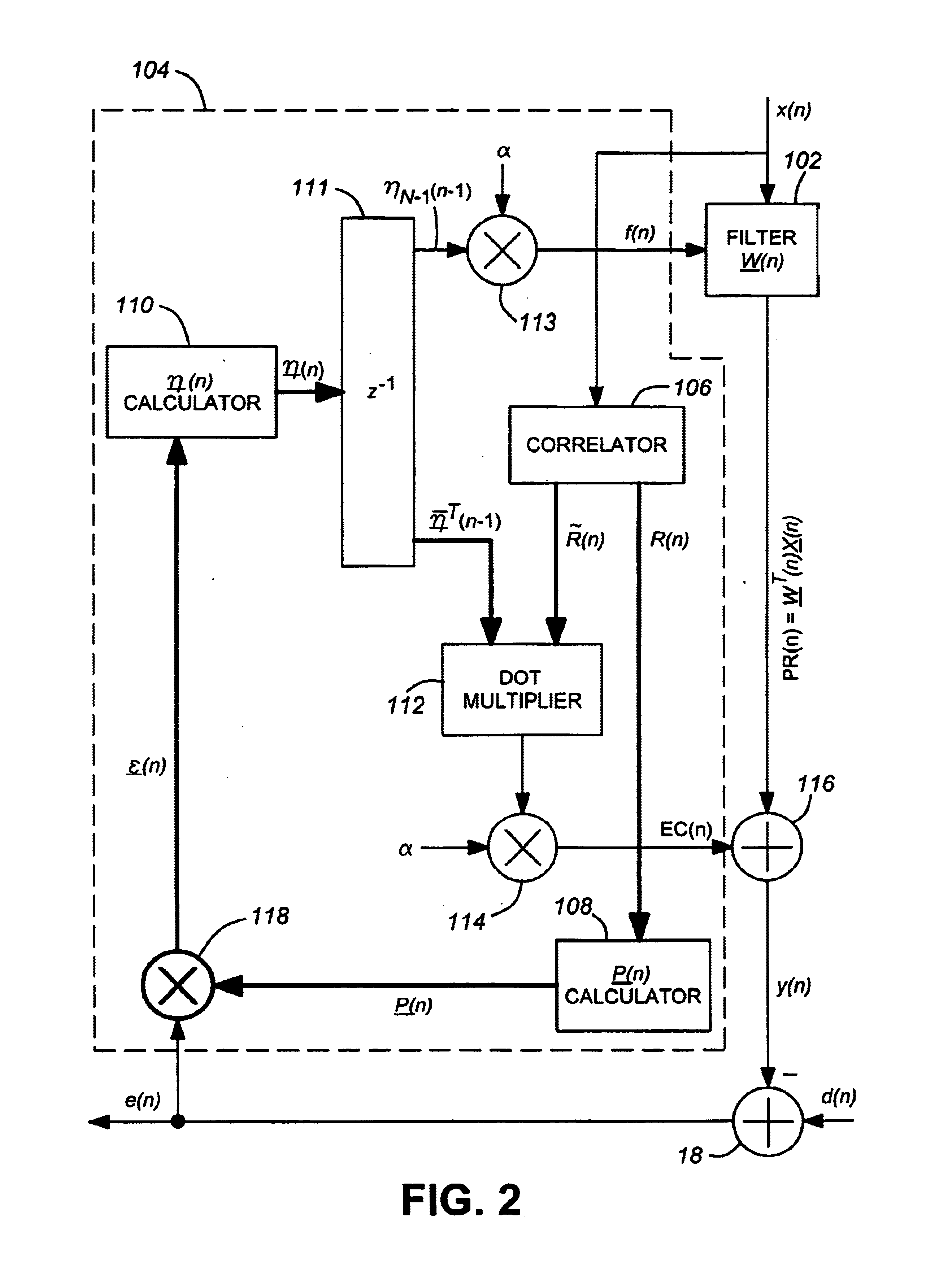
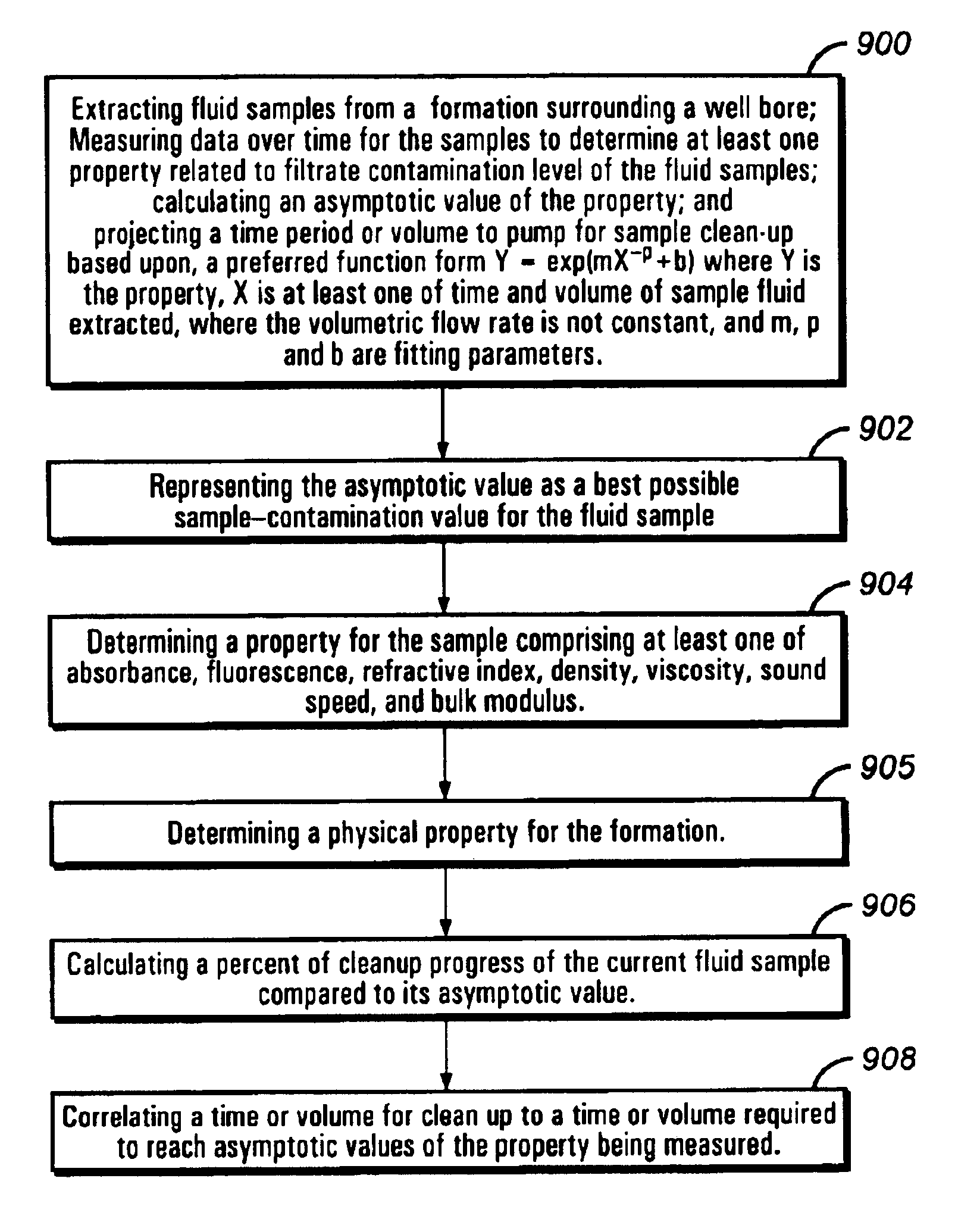
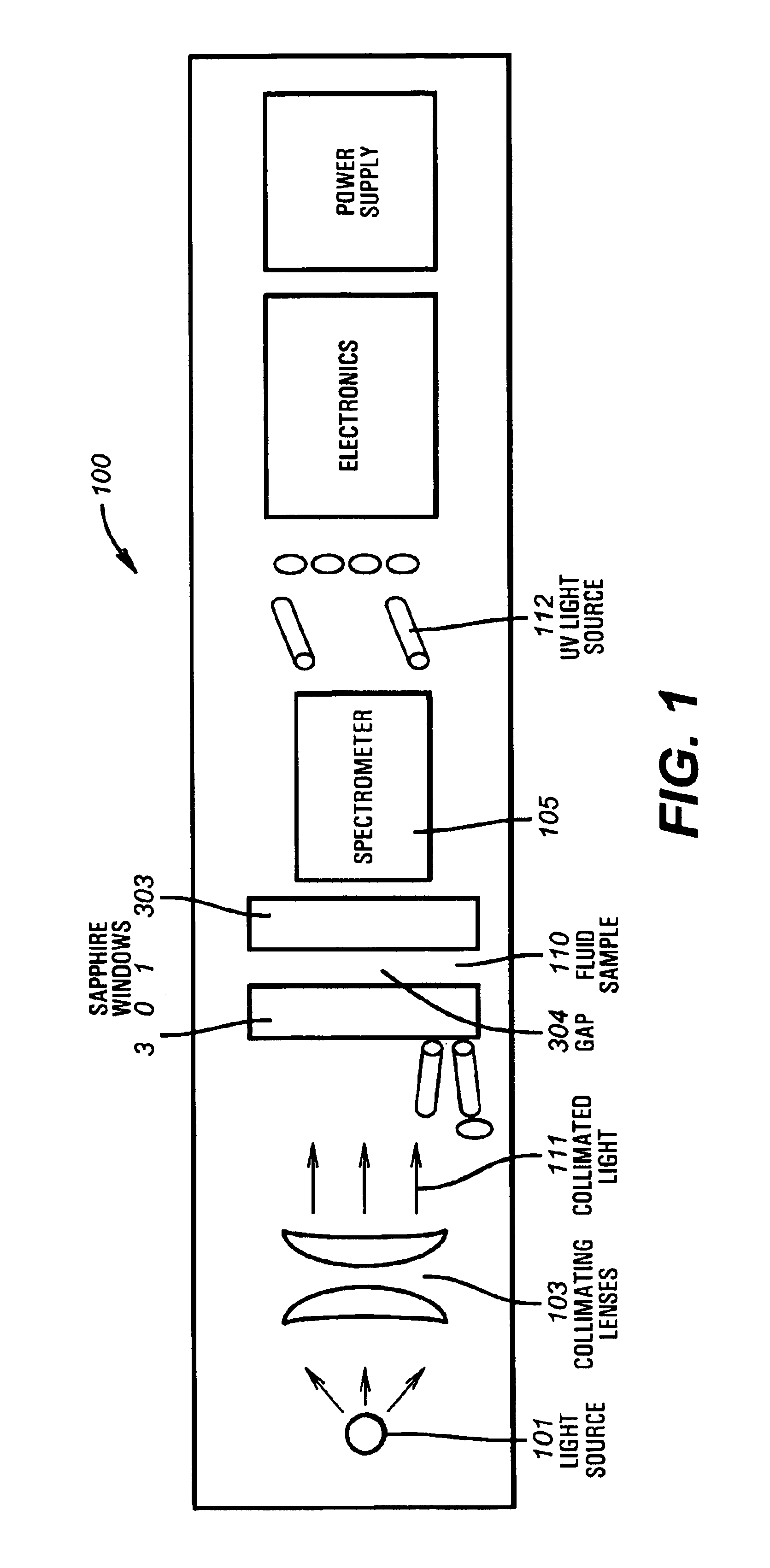
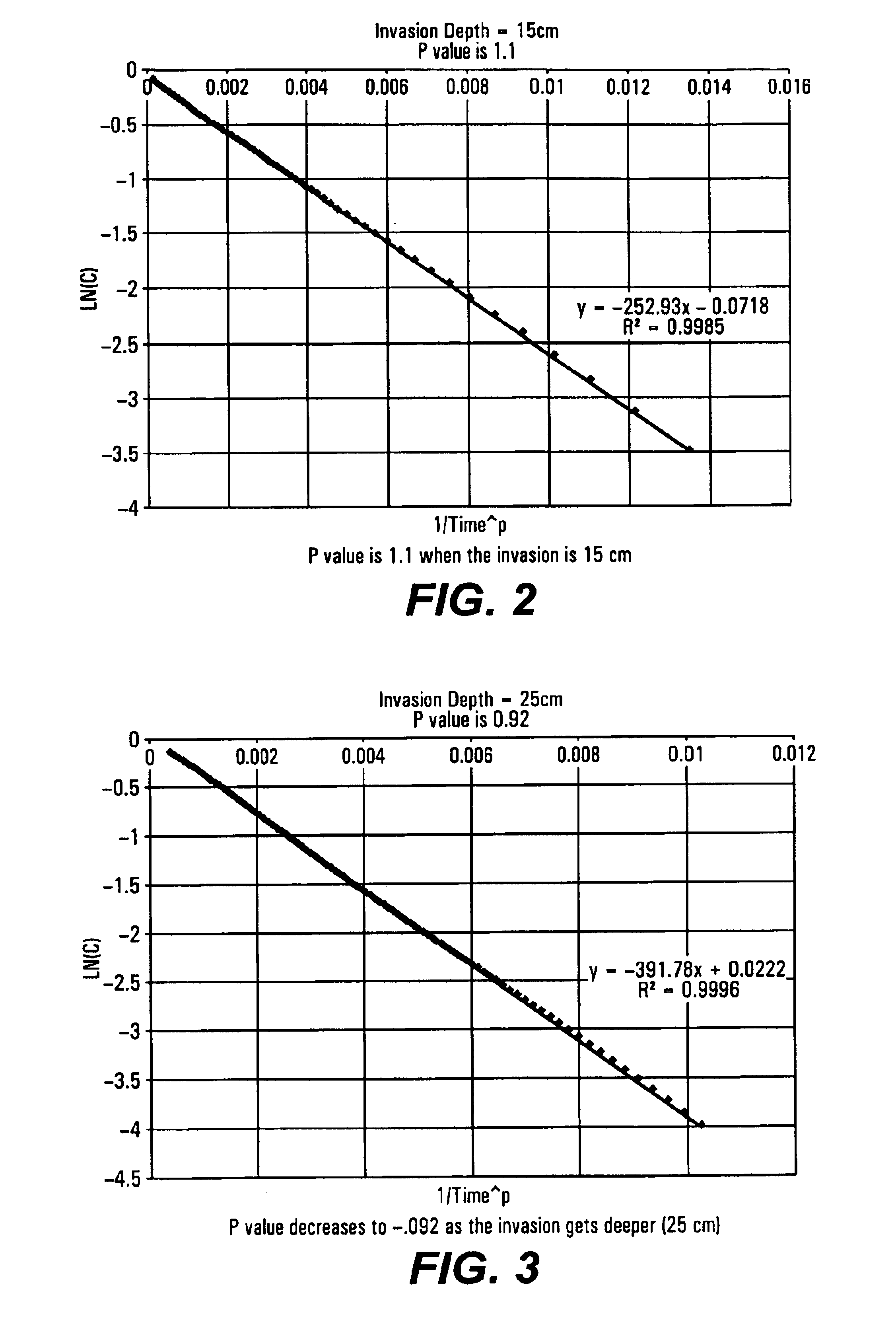
Method and apparatus for quantifying progress of sample clean up with curve fitting
InactiveUS6714872B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPhase-affecting property measurementsCurrent sampleRegression analysis
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and system for finding tooth features on a virtual three-dimensional model
A method and system are disclosed for finding virtual tooth features on virtual three-dimensional models of the teeth of patients. The tooth features comprise marginal ridges, cusp tips, contact points, central groove and buccal groove. Tooth axes system plays a key role in identifying the tooth features. An iterative method is disclosed for improving the accuracy of the tooth axes system. A virtual three-dimension model preferably obtained by scanning the dentition of a patient forms the basis for determining the tooth features. Tooth features are derived for all categories of teeth including molars, premolars, canines and front teeth. Tooth features are very helpful and used in planning orthodontic treatment. The tooth features are determined automatically using the computerized techniques; and can be manually adjusted when necessary.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
Method of decoding by message passing with scheduling depending on neighbourhood reliability
InactiveUS20090313525A1Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionDecoding methodsDependability
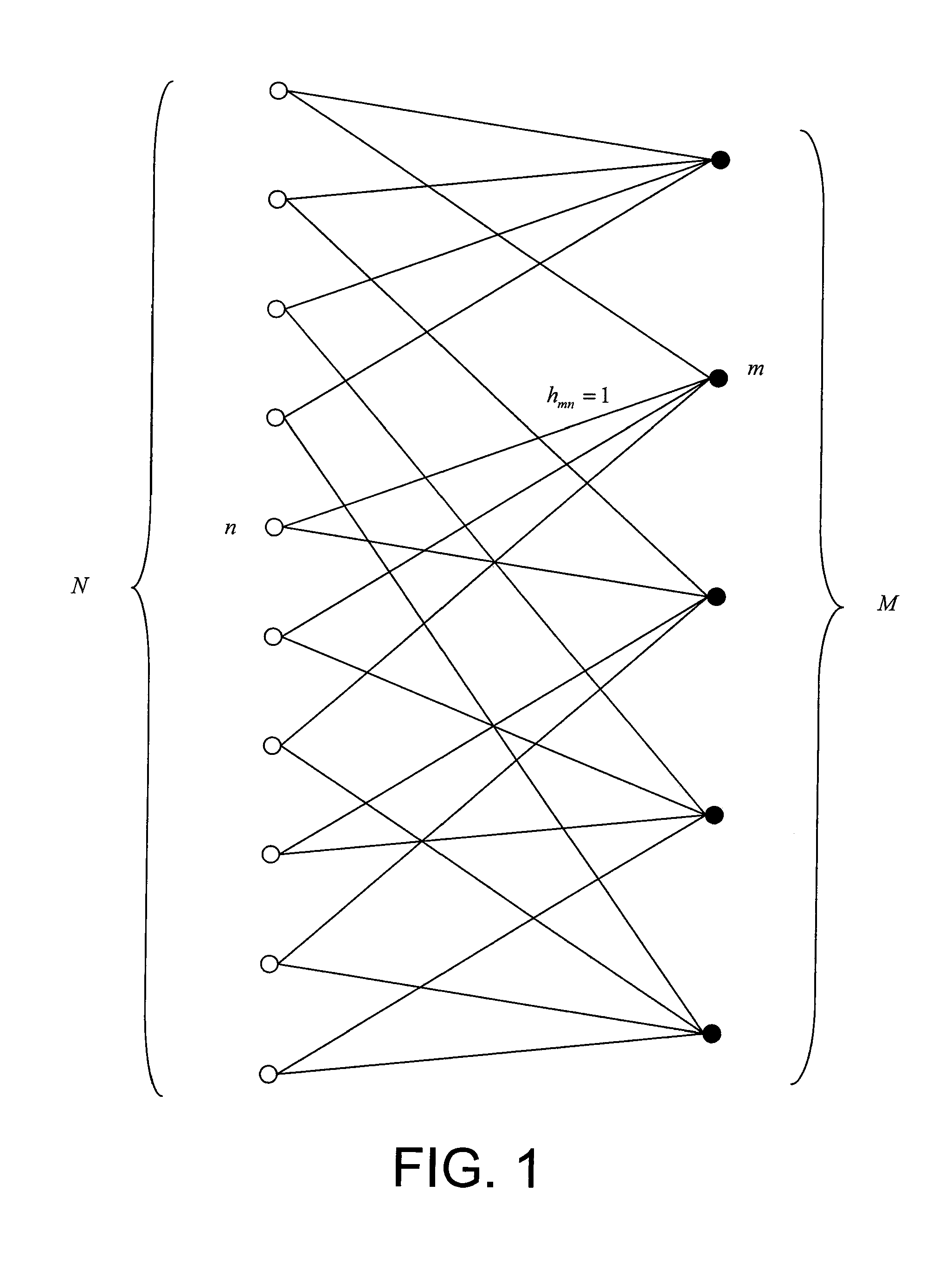
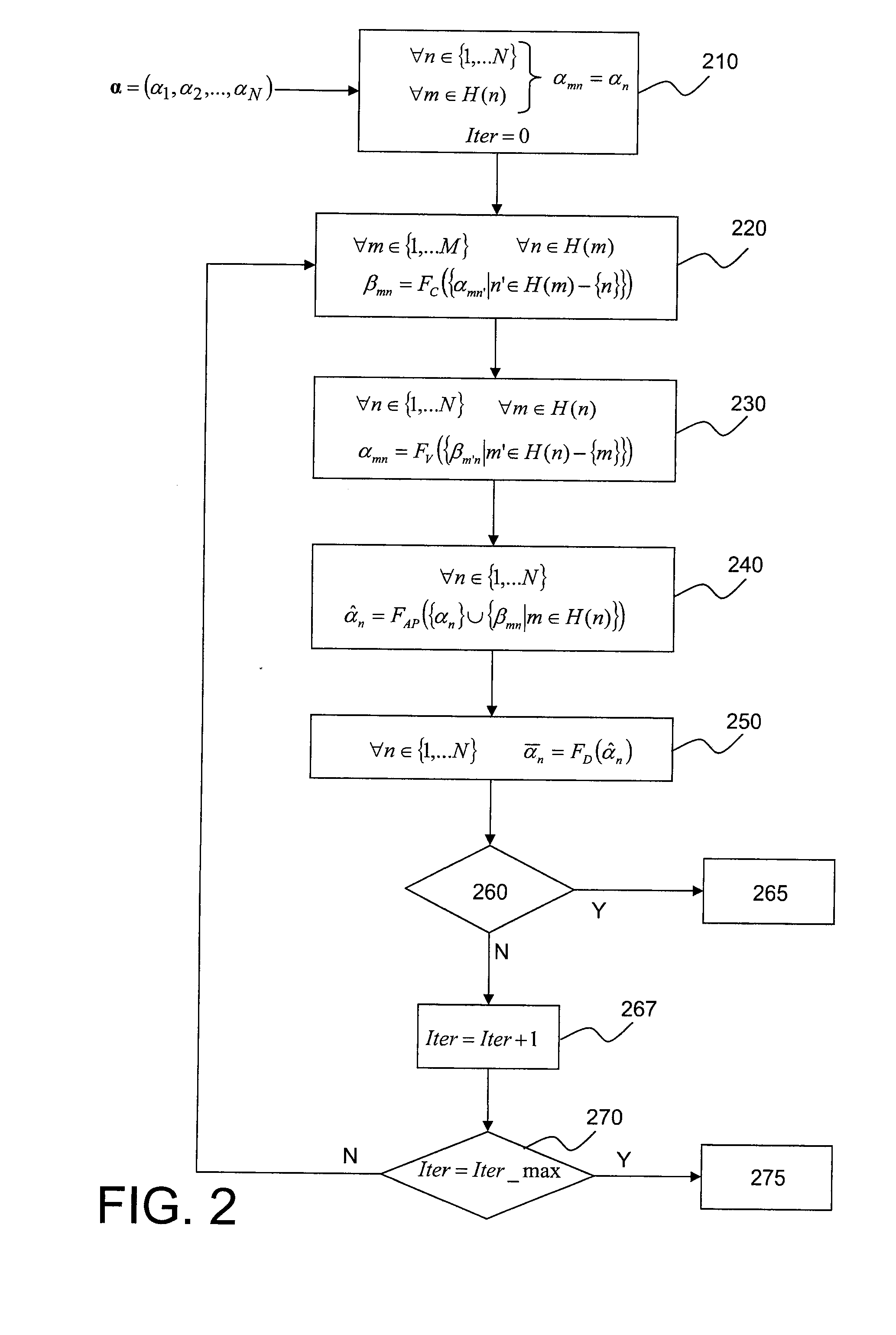
The invention relates to an iterative method by message passing for decoding of an error correction code that can be displayed in a bipartite graph comprising a plurality of variable nodes and a plurality of check nodes. For each iteration in a plurality of decoding iterations of said method:variable nodes or check nodes are classified (720) as a function of the corresponding degrees of reliability of decoding information available in the neighbourhoods (Vn(d),Vm(d)) of these nodes, a node with a high degree of reliability being classified before a node with a low degree of reliability;each node thus classified (725) passes at least one message (αmn,βmn) to an adjacent node, in the order defined by said classification.The invention also relates to a computer program designed to implement said decoding method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
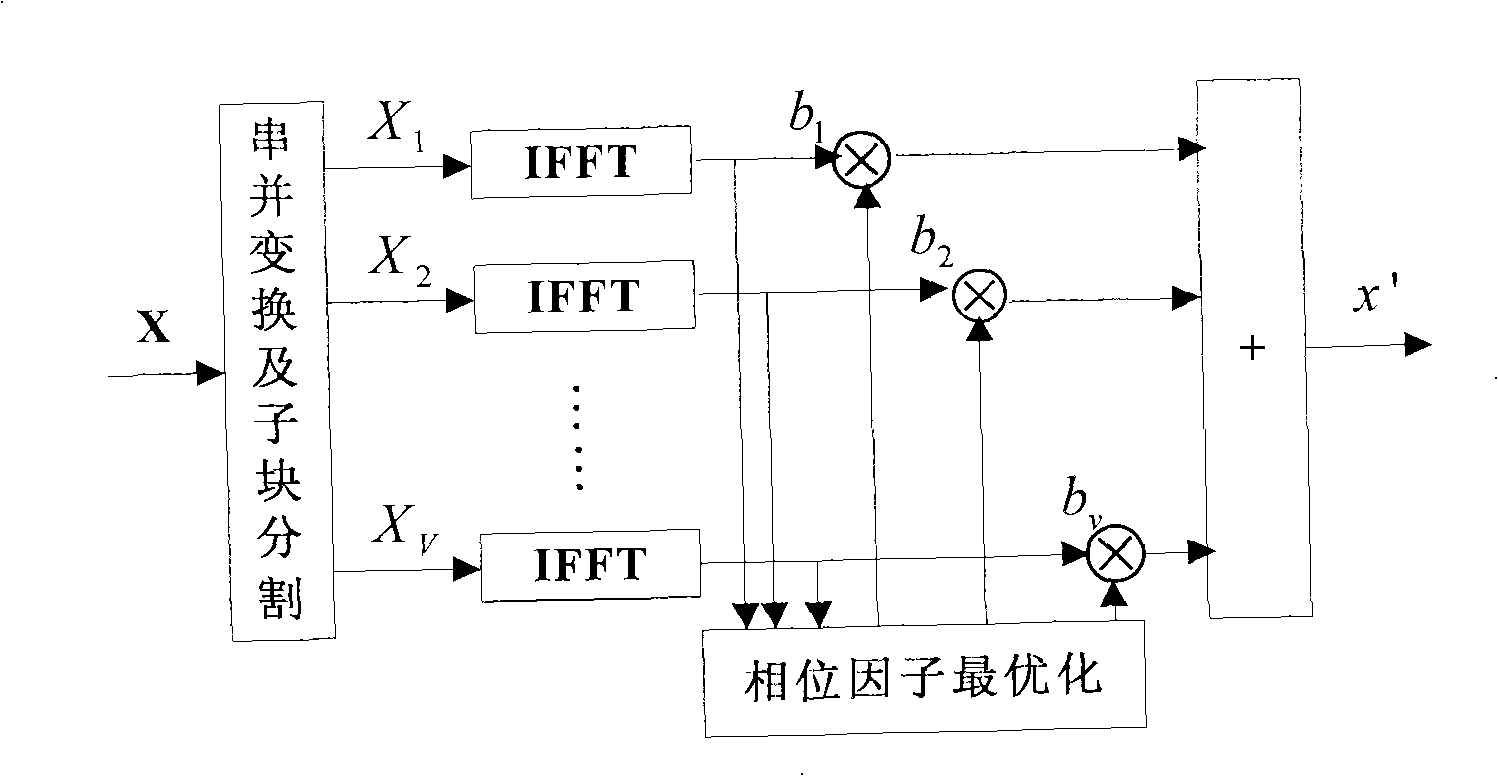
Improved iterative PTS method for lowering peak-average-ratio in OFDM system
InactiveCN101340417AReduce complexitySmall amount of calculationMulti-frequency code systemsRound complexityCommunications system
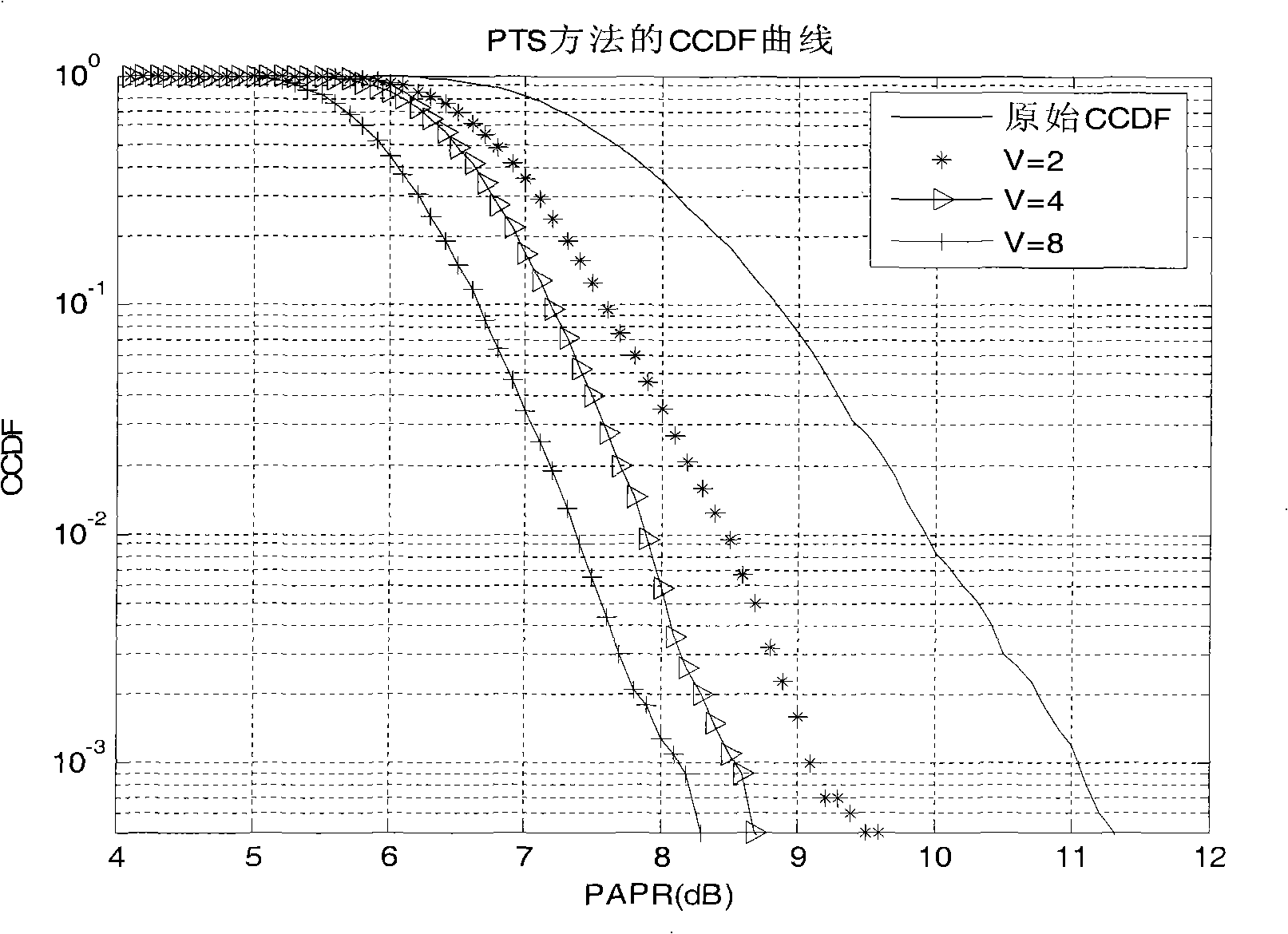
The invention relates to an improved iterative PTS method for reducing peak-to-average power ratio in an OFDM system, and the technical proposal is as follows: an improved iterative PTS algorithm is proposed by using an OFDM system model under a frequency selective fading channel, taking the reduction of the complexity of the traditional algorithm as a starting point and taking the traditional partial transfer sequence method PTS for reducing the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) as the basis. The improved iterative PTS method is characterized by comprising the following steps: a frame of input OFDM symbols is segmented into V subsequences which are not overlapped mutually, the minimum PAPR is calculated by summing various sub-blocks, sideband information is integrated and the combination with the minimum PAPR is selected for sending. The method can ensure the applicability of a wireless communication system under a wireless fading channel and reduce the PAPR of the OFDM system without the increase of the complexity of the system, thereby realizing balance between the applicability of the system and the complexity of the system, having no need of sending the sideband information additionally and improving the reliability of the system and the availability of the system.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com