Patents
Literature
708 results about "Subroutine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
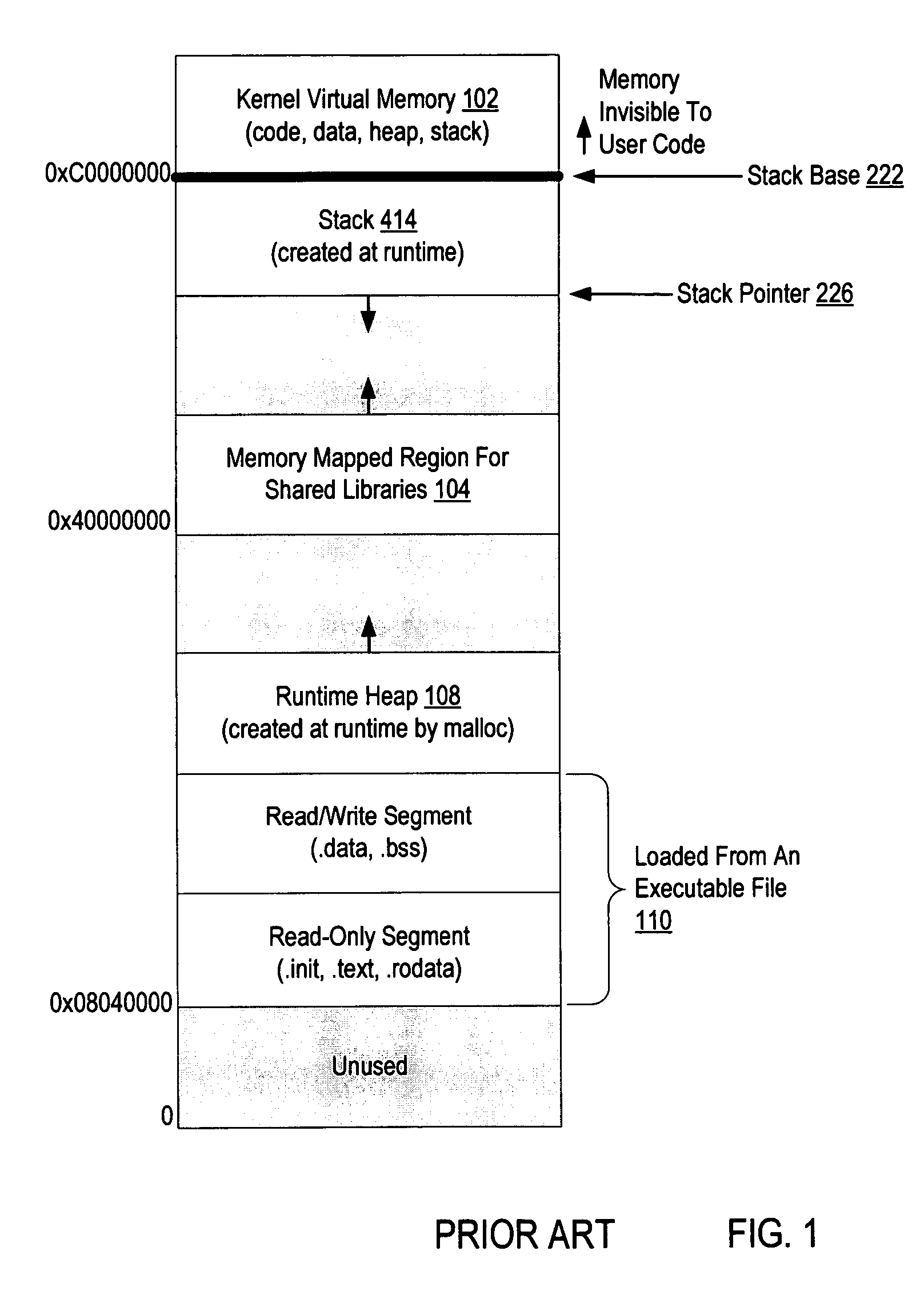
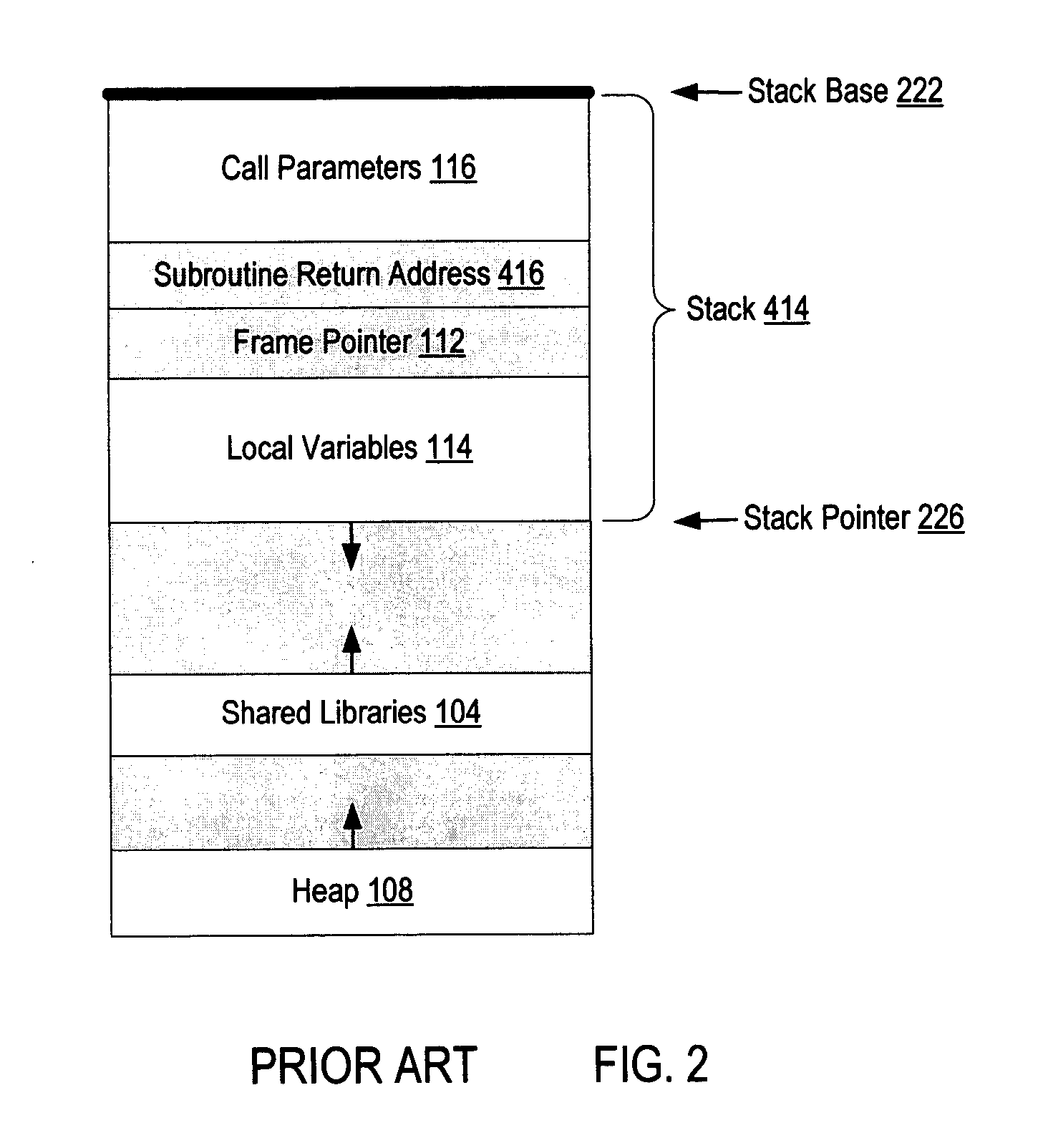
In computer programming, a subroutine is a sequence of program instructions that performs a specific task, packaged as a unit. This unit can then be used in programs wherever that particular task should be performed.
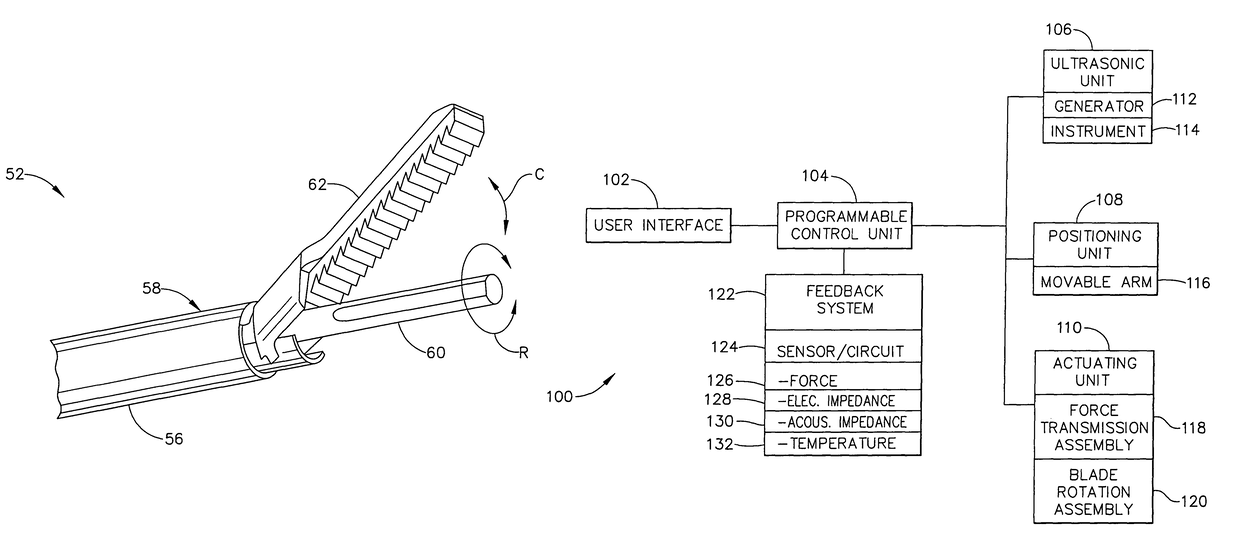
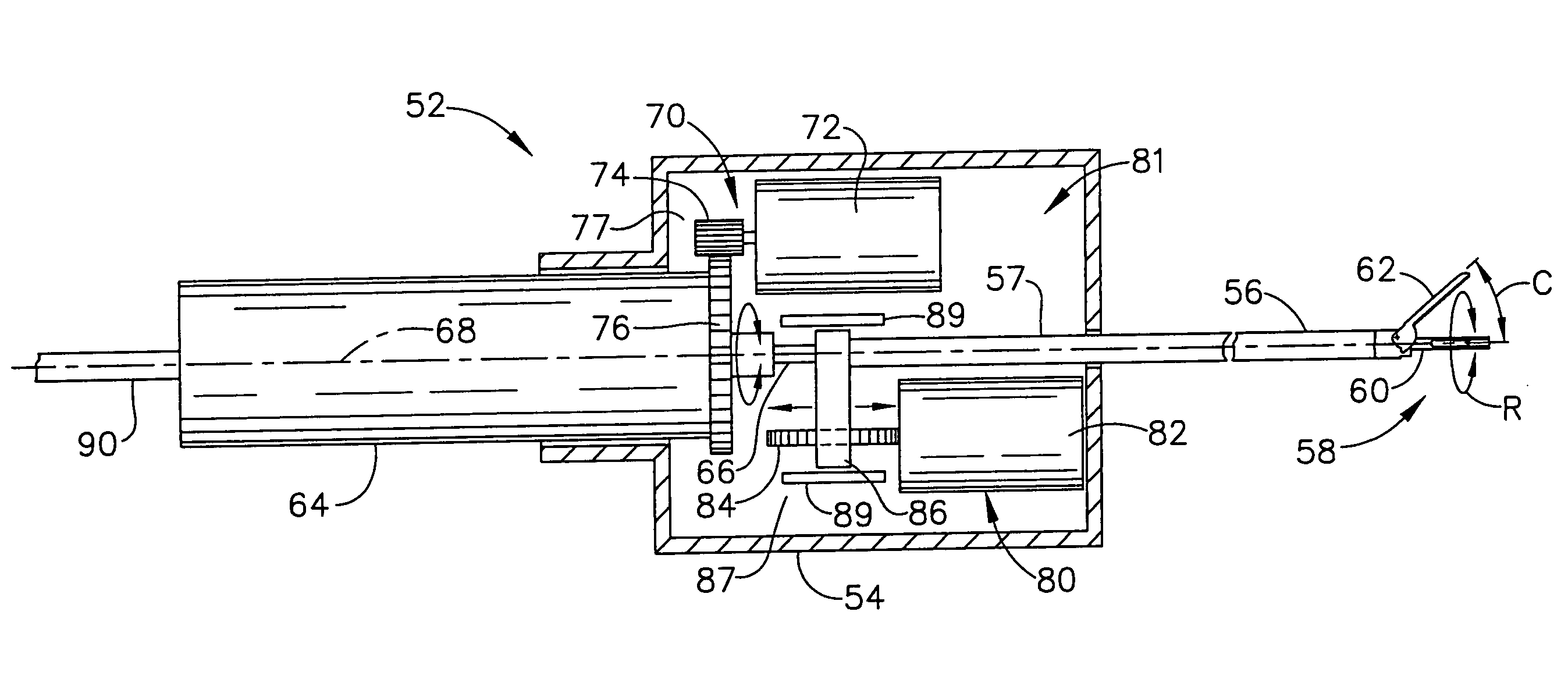
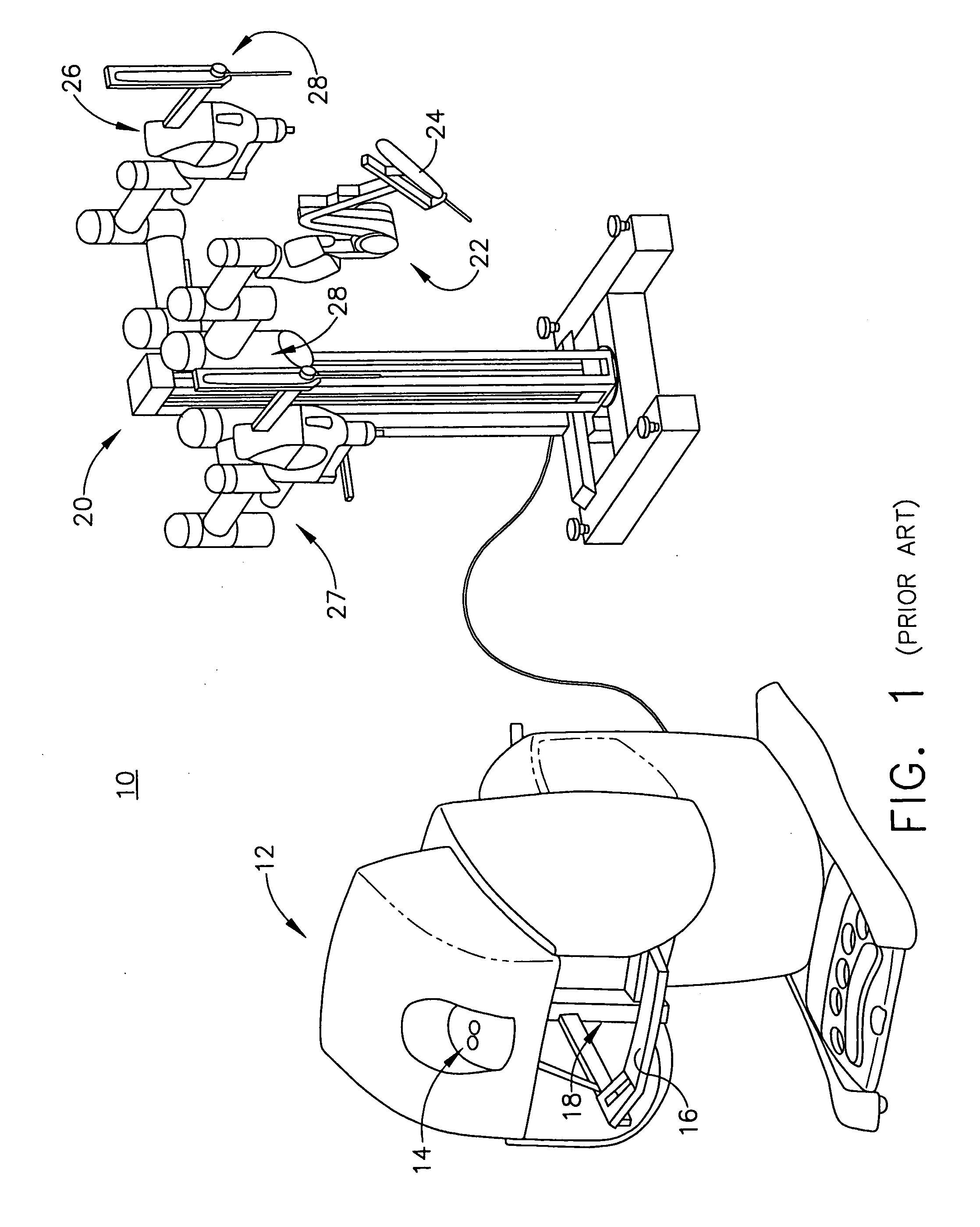
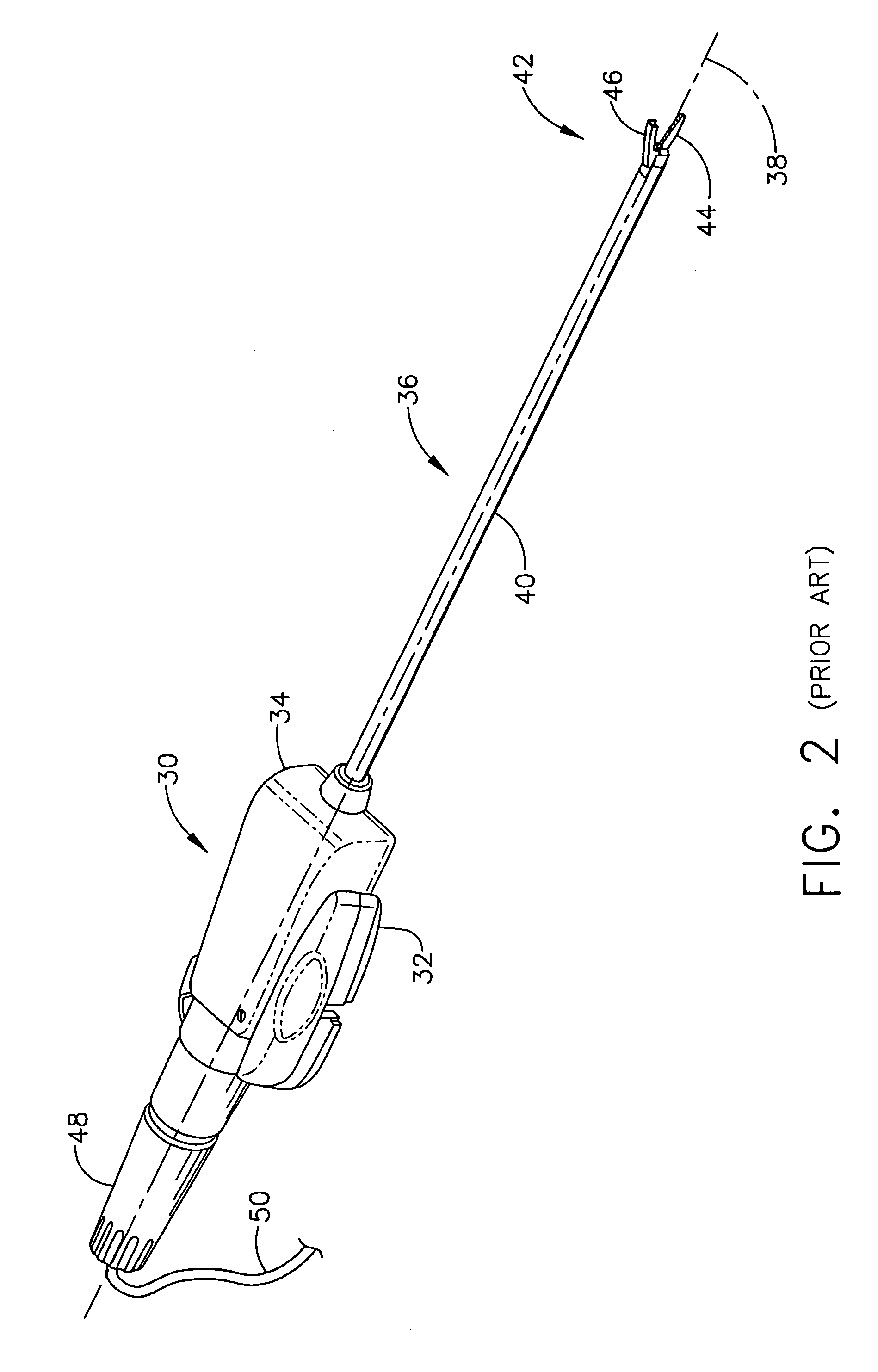
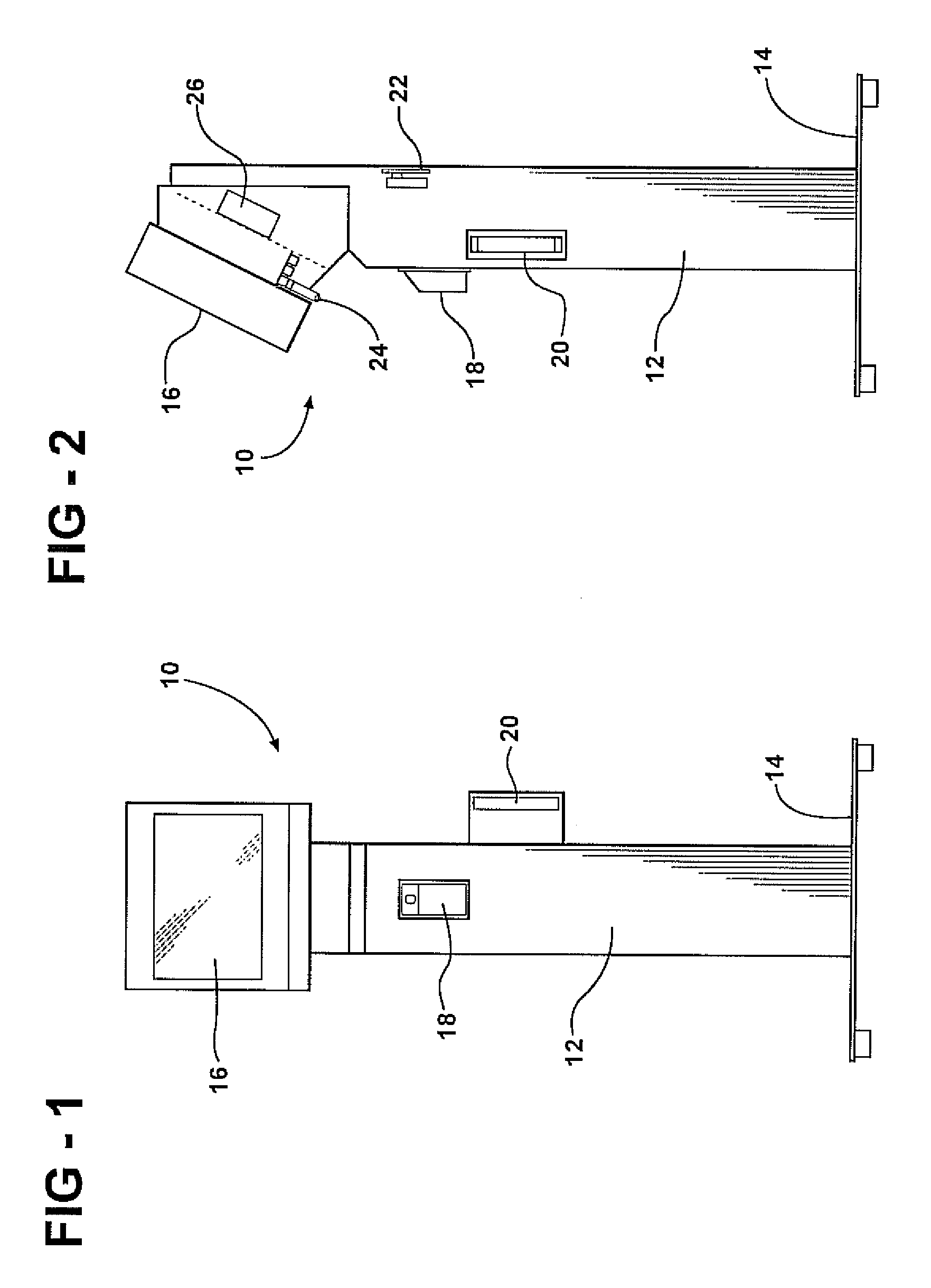
Ultrasonic surgical system and method
An ultrasonic surgical system has an ultrasonic unit including an instrument operatively connected to an ultrasonic generator, wherein the instrument has an ultrasonic end effector on the distal end of a shaft. The system further includes a positioning unit including a movable arm adapted for releasably holding the instrument, whereby an operator may direct the positioning unit to position the end effector at a surgical site inside a body cavity of a patient for performing a plurality of surgical tasks. The system further includes a control unit operatively connected to the ultrasonic and positioning units, wherein the control unit is programmable with a surgical subroutine for performing the surgical tasks. The system further includes a user interface operatively connected to the control unit for initiating an operative cycle of the surgical subroutine such that the surgical tasks are automatically performed during the operative cycle.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Ultrasonic surgical system and method
ActiveUS20070239028A1Automatically performUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSurgical operationSurgical site
An ultrasonic surgical system has an ultrasonic unit including an instrument operatively connected to an ultrasonic generator, wherein the instrument has an ultrasonic end effector on the distal end of a shaft. The system further includes a positioning unit including a movable arm adapted for releasably holding the instrument, whereby an operator may direct the positioning unit to position the end effector at a surgical site inside a body cavity of a patient for performing a plurality of surgical tasks. The system further includes a control unit operatively connected to the ultrasonic and positioning units, wherein the control unit is programmable with a surgical subroutine for performing the surgical tasks. The system further includes a user interface operatively connected to the control unit for initiating an operative cycle of the surgical subroutine such that the surgical tasks are automatically performed during the operative cycle.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
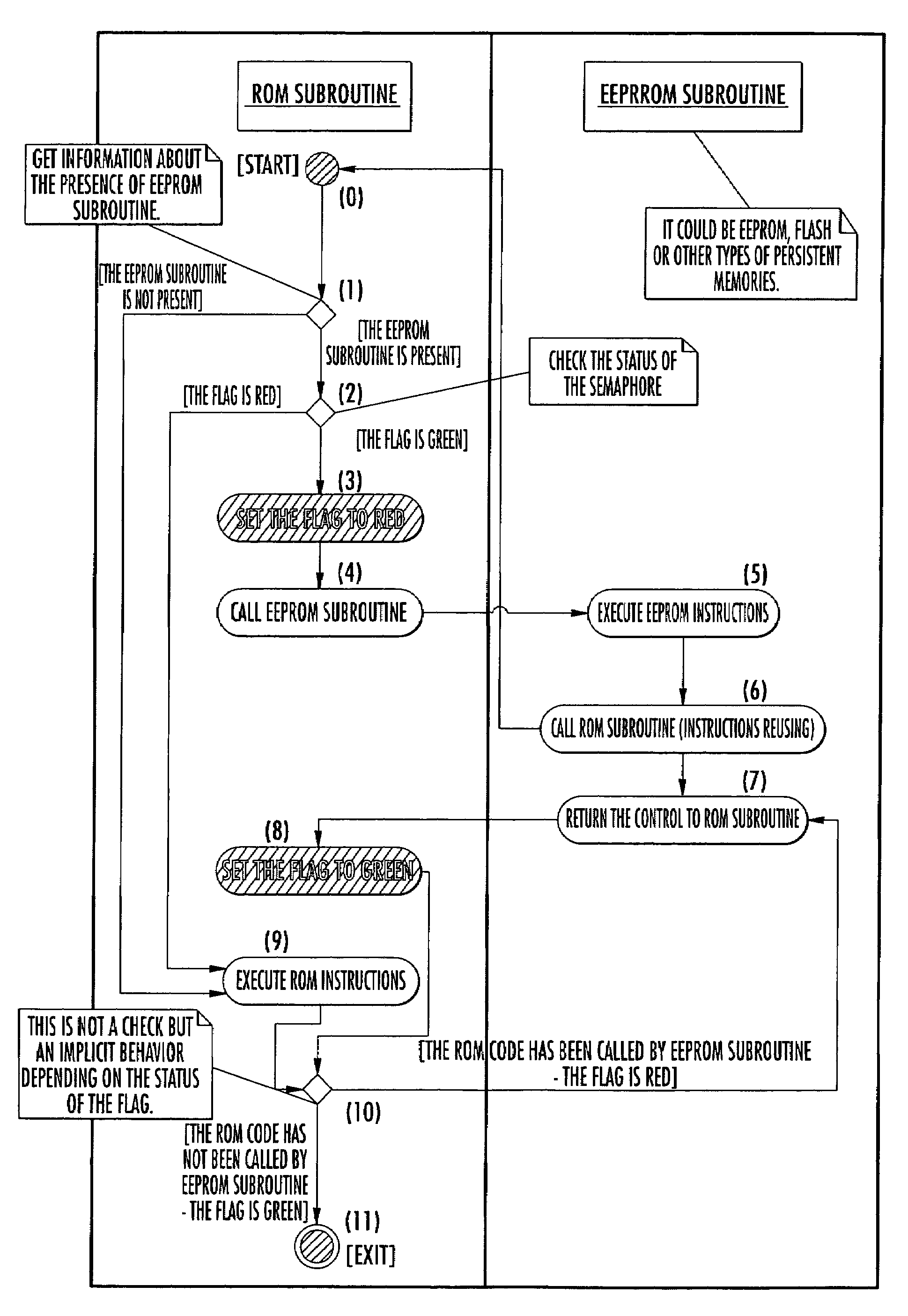
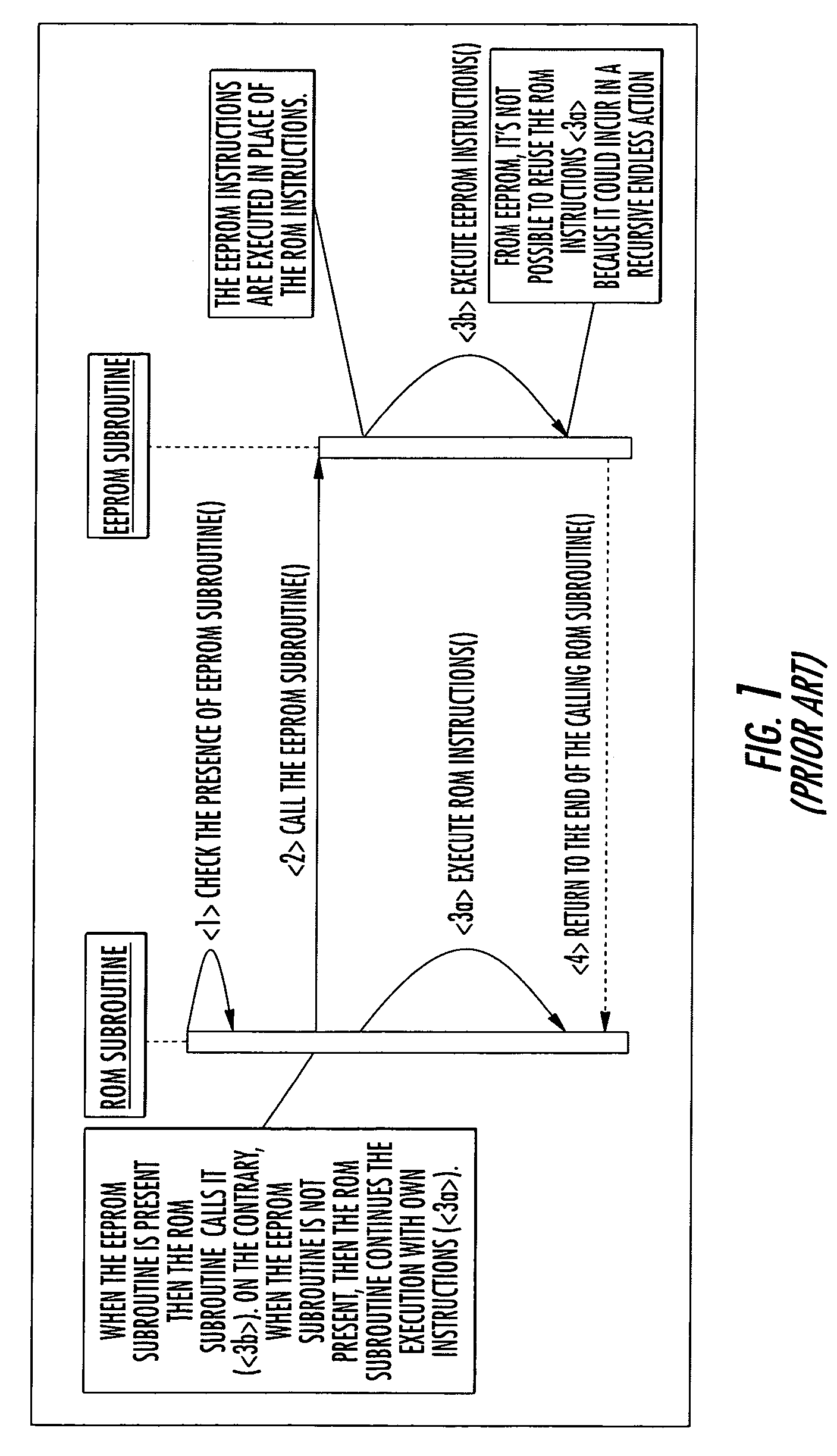
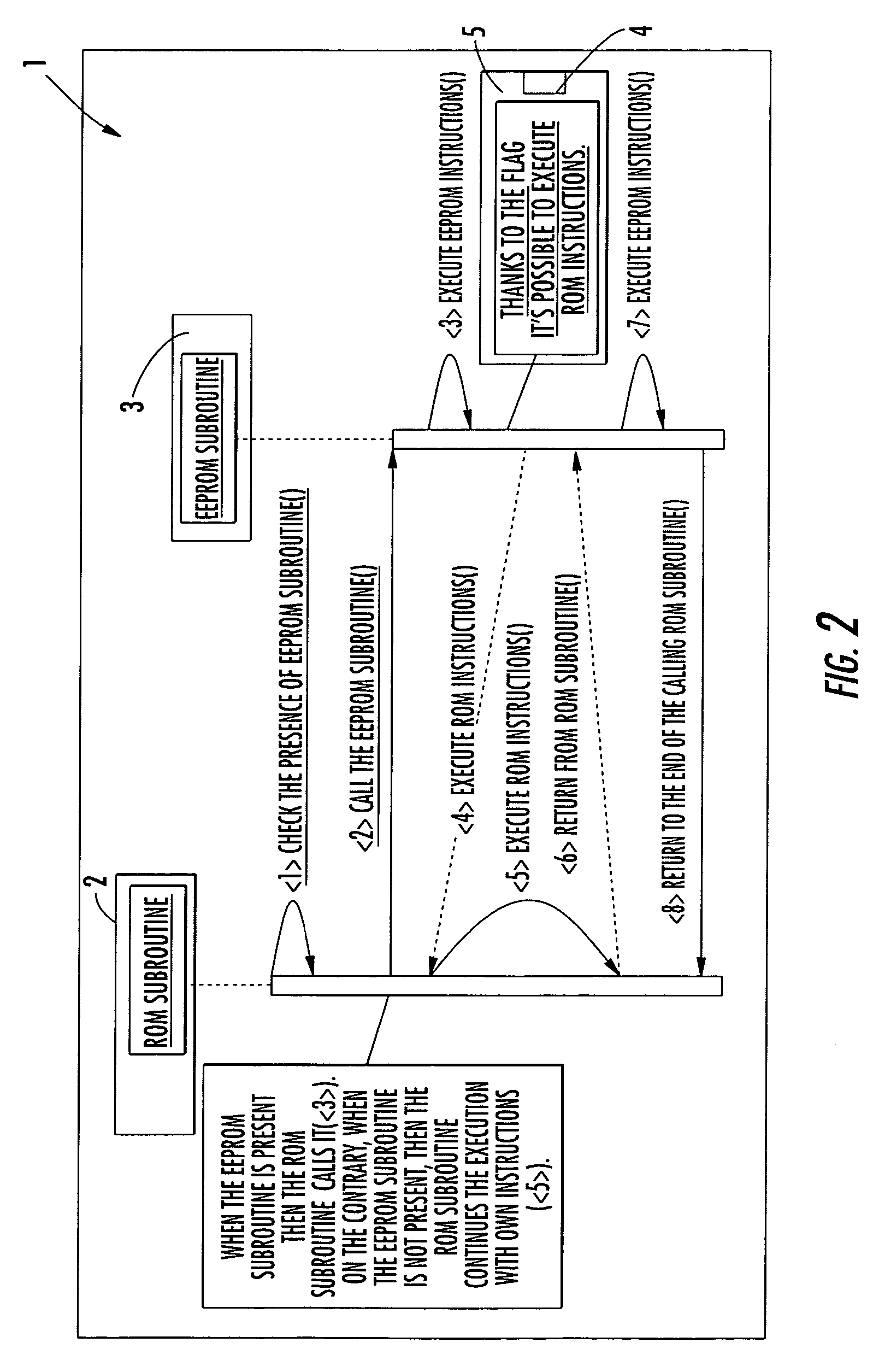
Method for patching ROM instructions in an electronic embedded system including at least a further memory portion
A mechanism for patching read only memory (ROM) instructions in an embedded system is provided. The embedded system includes non-volatile memory such as a ROM, a RAM and an EEPROM. In one configuration, the ROM contains application modules (subroutines) that are subordinate to a flag status. The flag status indicates to the subroutine whether to execute the ROM instructions in the ROM or the extended instructions in the EEPROM. The instructions in the EEPROM may be used to patch or to extend the behaviors masked in the ROM instructions. The extended instructions in the EEPROM may reuse the ROM instructions in the ROM without resulting in recursive actions.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
System for remote loading of objects or files in order to update software
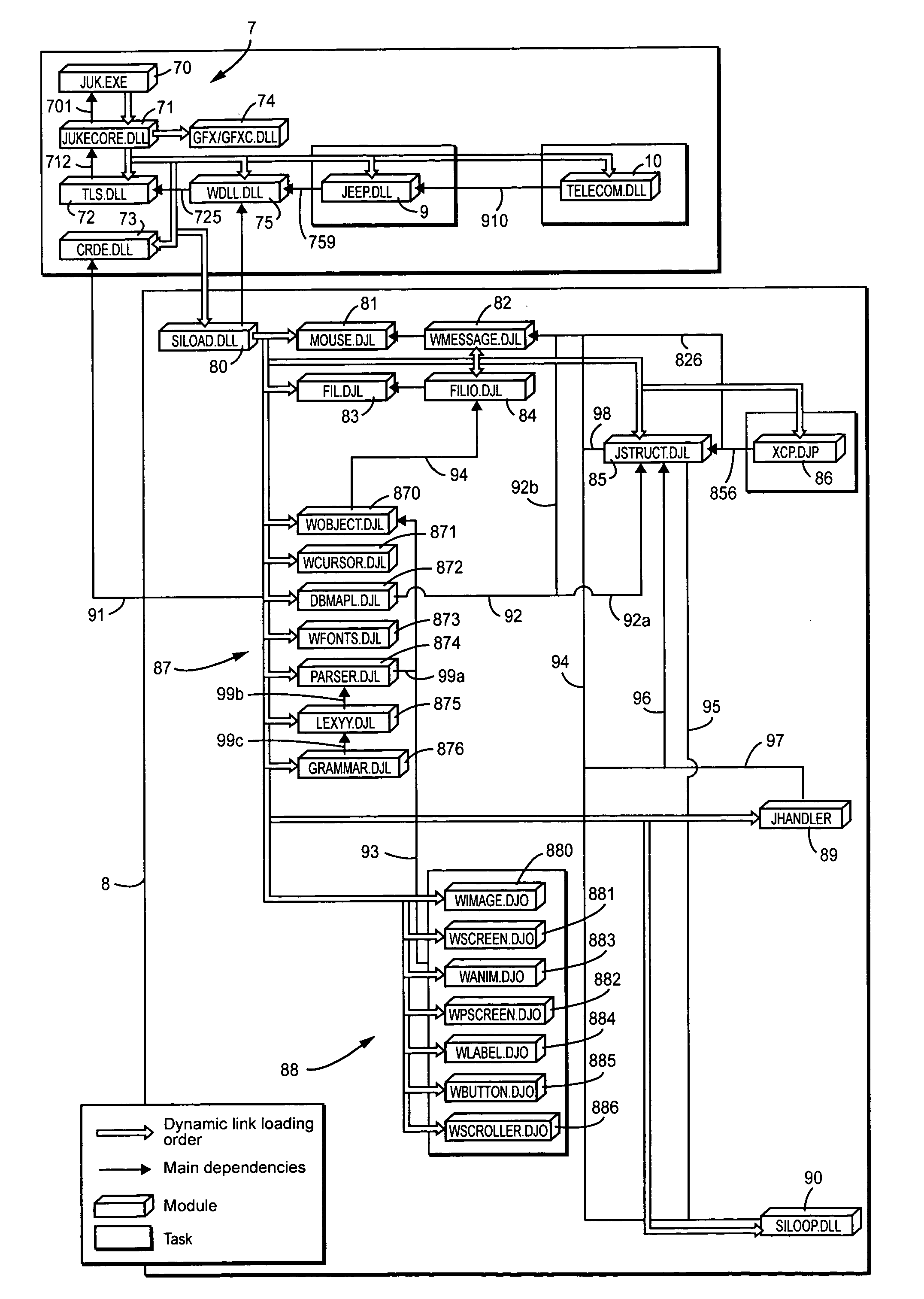
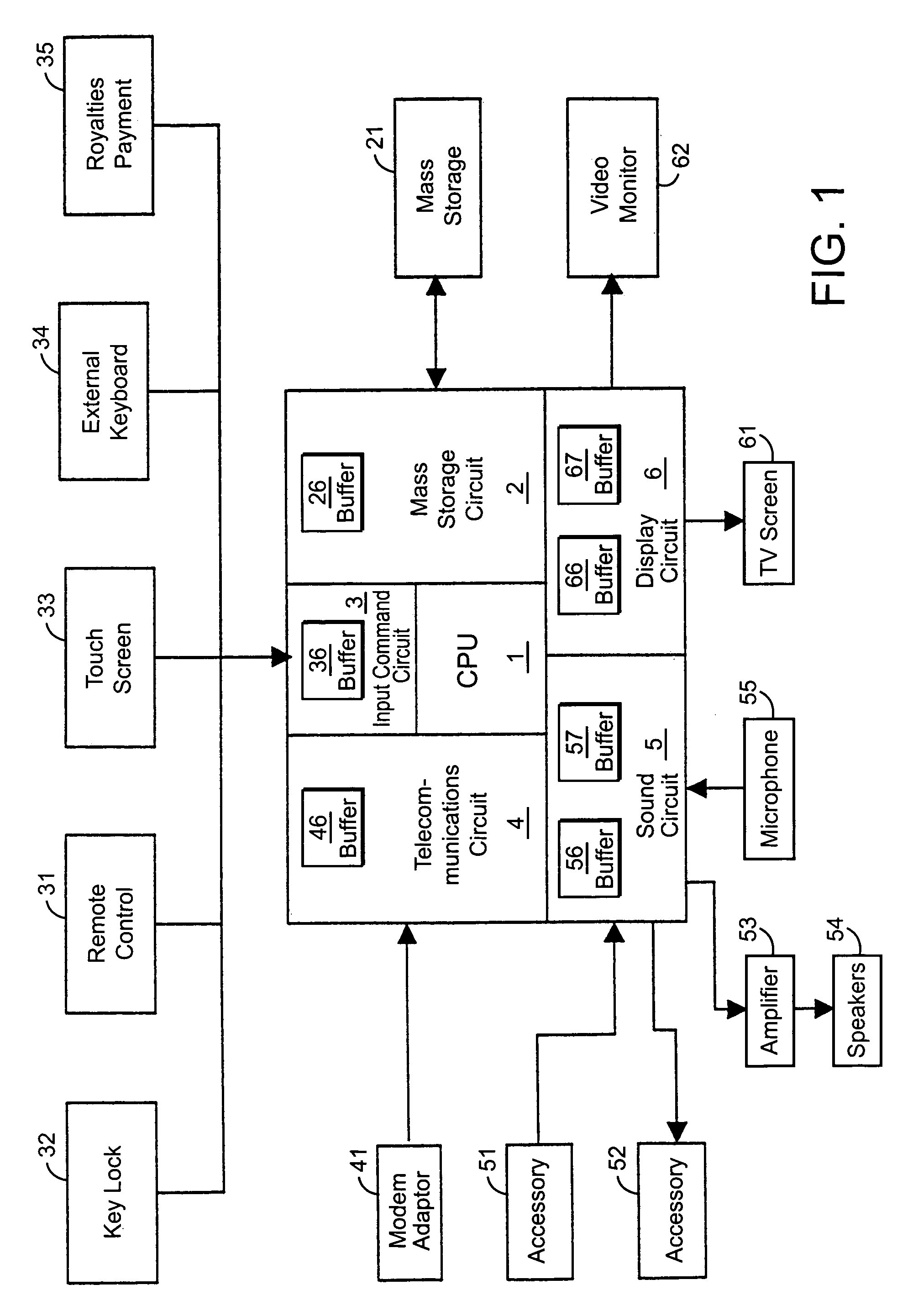
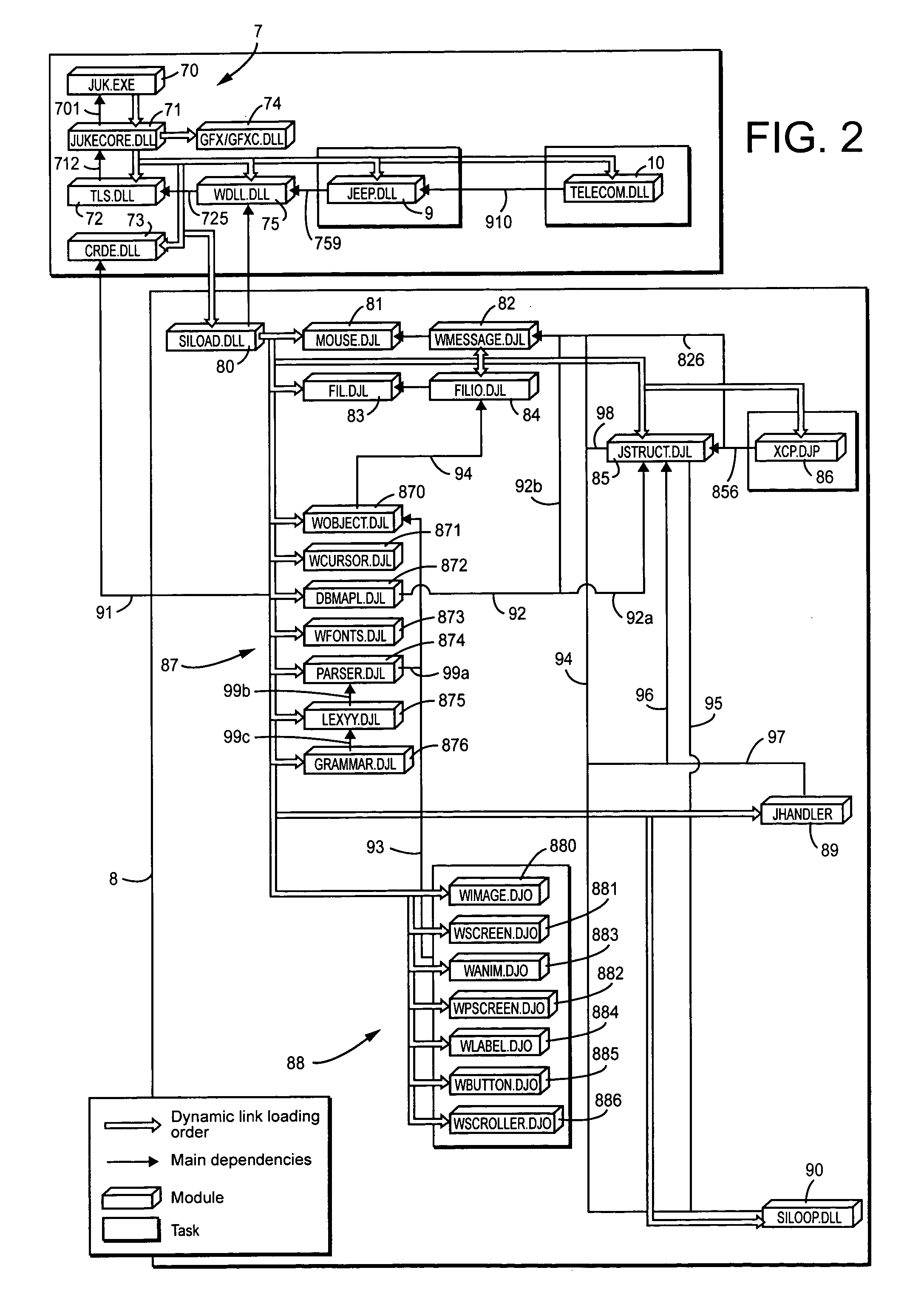
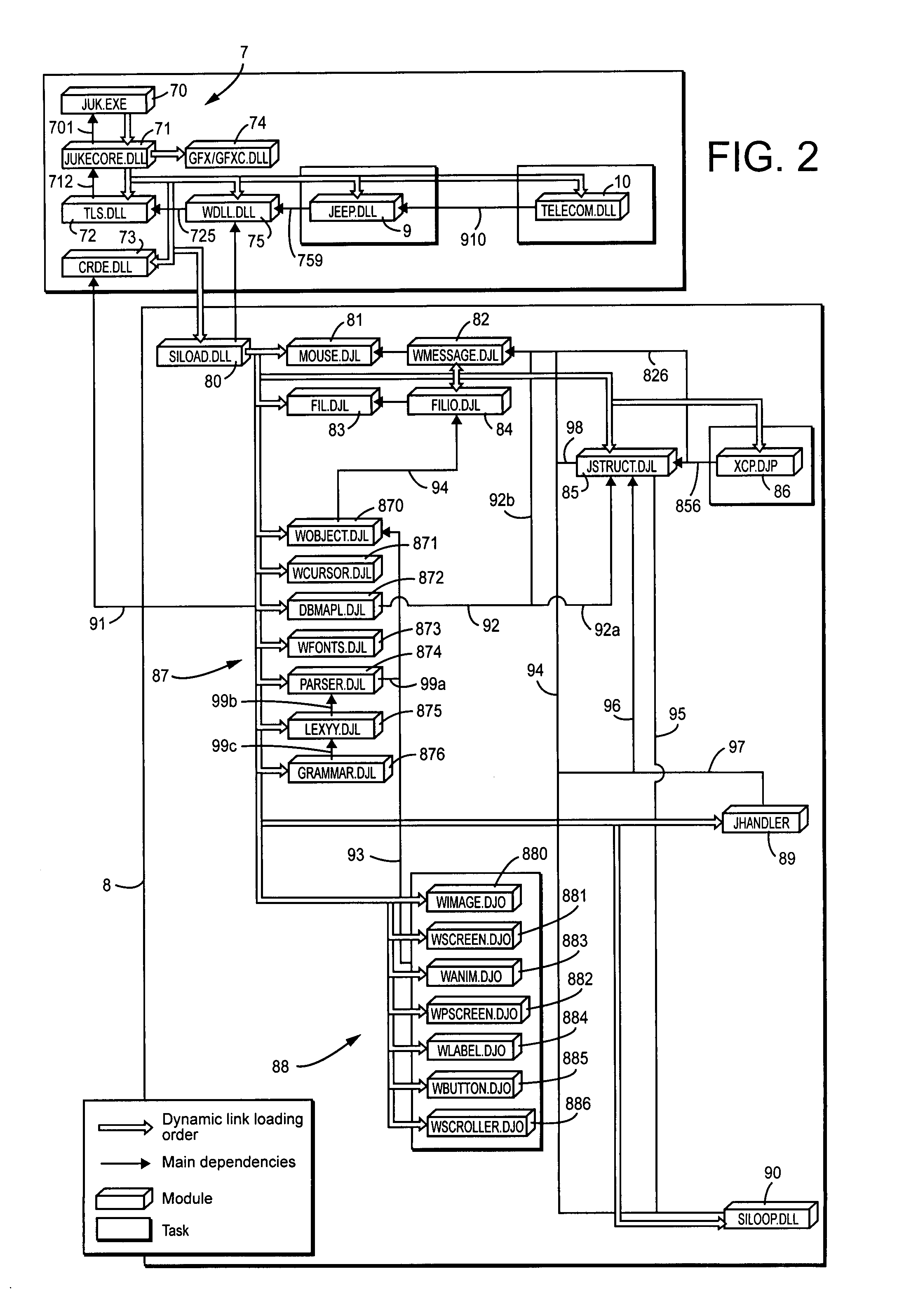
A system for remote loading of objects or files in order to update software includes operating system architecture that calls for different tasks to be broken down into software modules that are connected to one another by dynamic links or are composed of executable subroutines that have main dependence links to other parts of the operating system. Each of the modules is composed of object files or libraries that are represented by dynamic link libraries among themselves according to a number of dependence levels that are described in their respective attributes.
Owner:TOUCHTUNES MUSIC CORP
Integrated interactive software visualization environment
InactiveUS7174536B1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsBlock levelSubroutine
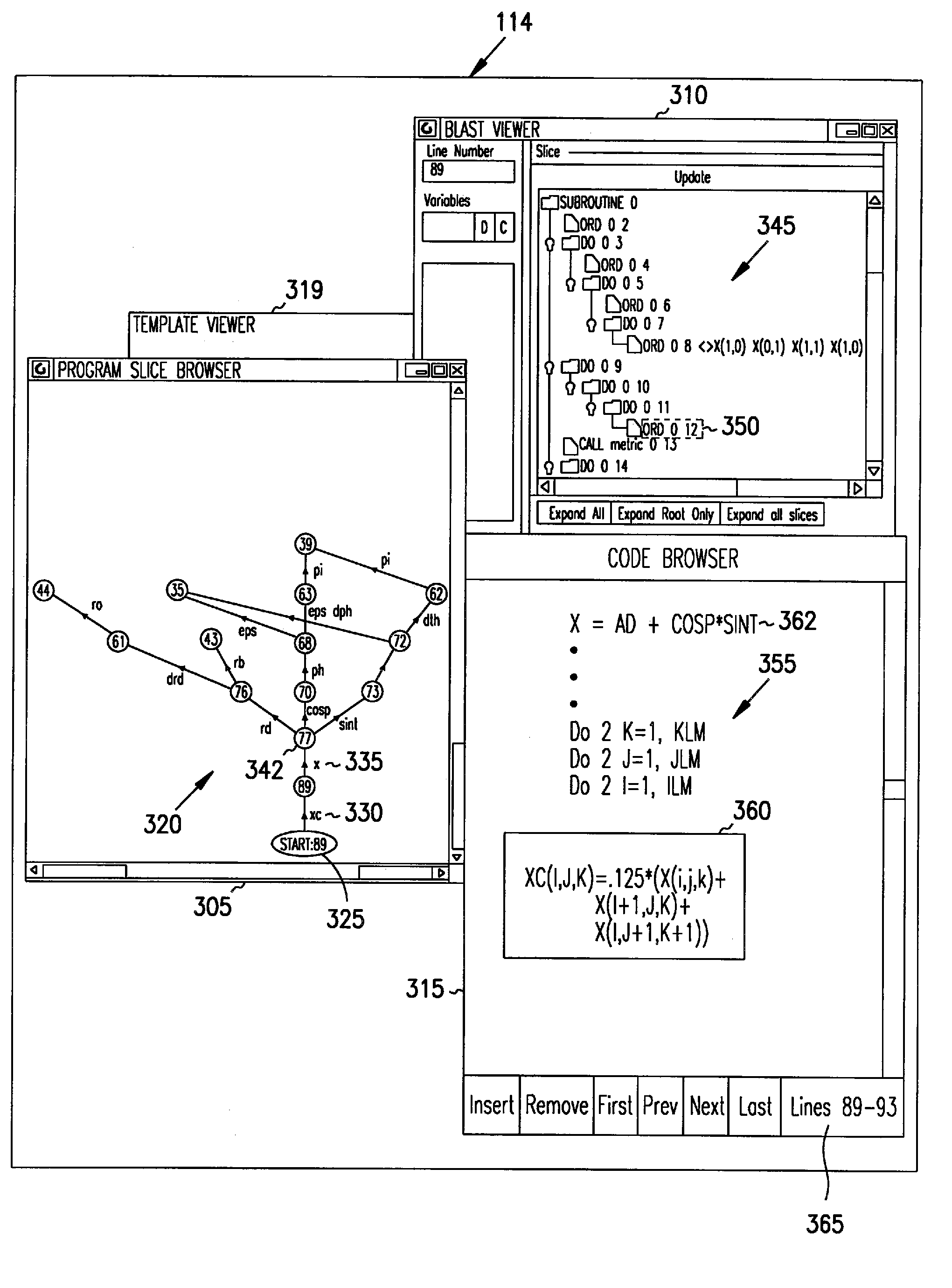
A method, system, apparatus, and program product for displaying a program slice diagram, which represents source code. The program slice diagram includes a directed graph that has multiple nodes and arcs connecting the nodes. Nodes can correspond to statements within a selected subroutine of the source code, variable references outside the subroutine, or calls made to other subroutines that are considered part of the program slice. Arcs represent data flow dependencies between the nodes. In another aspect, the invention encompasses a software environment for visualizing source code that includes a code browser, a block-level abstract syntax tree viewer, a program slice browser, and a template viewer. This software visualization environment is integrated, allows cross-referencing between its components, and is coupled with a performance visualization environment.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Video controller system with object display lists
InactiveUS20020145611A1Television system detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGraphicsScan line
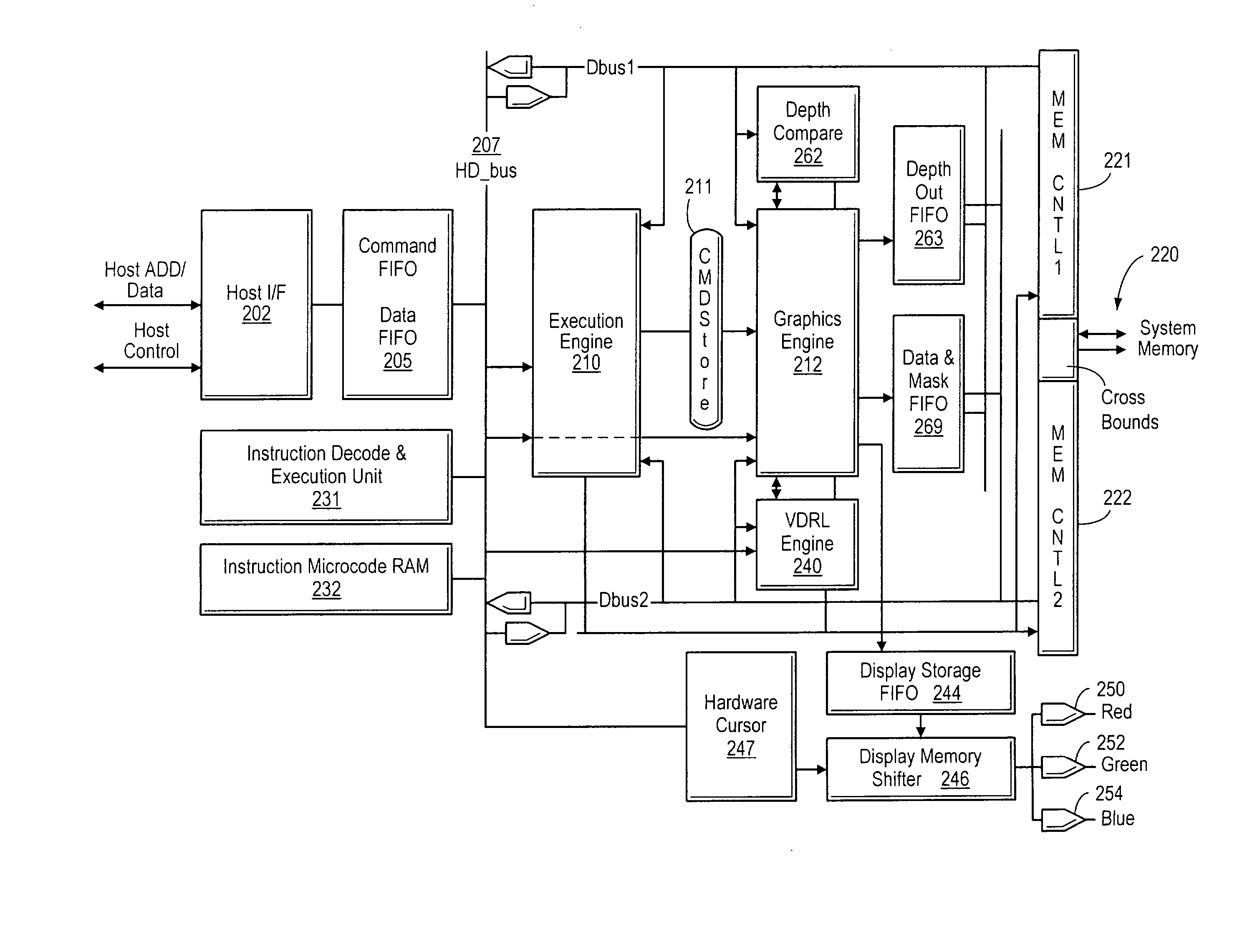
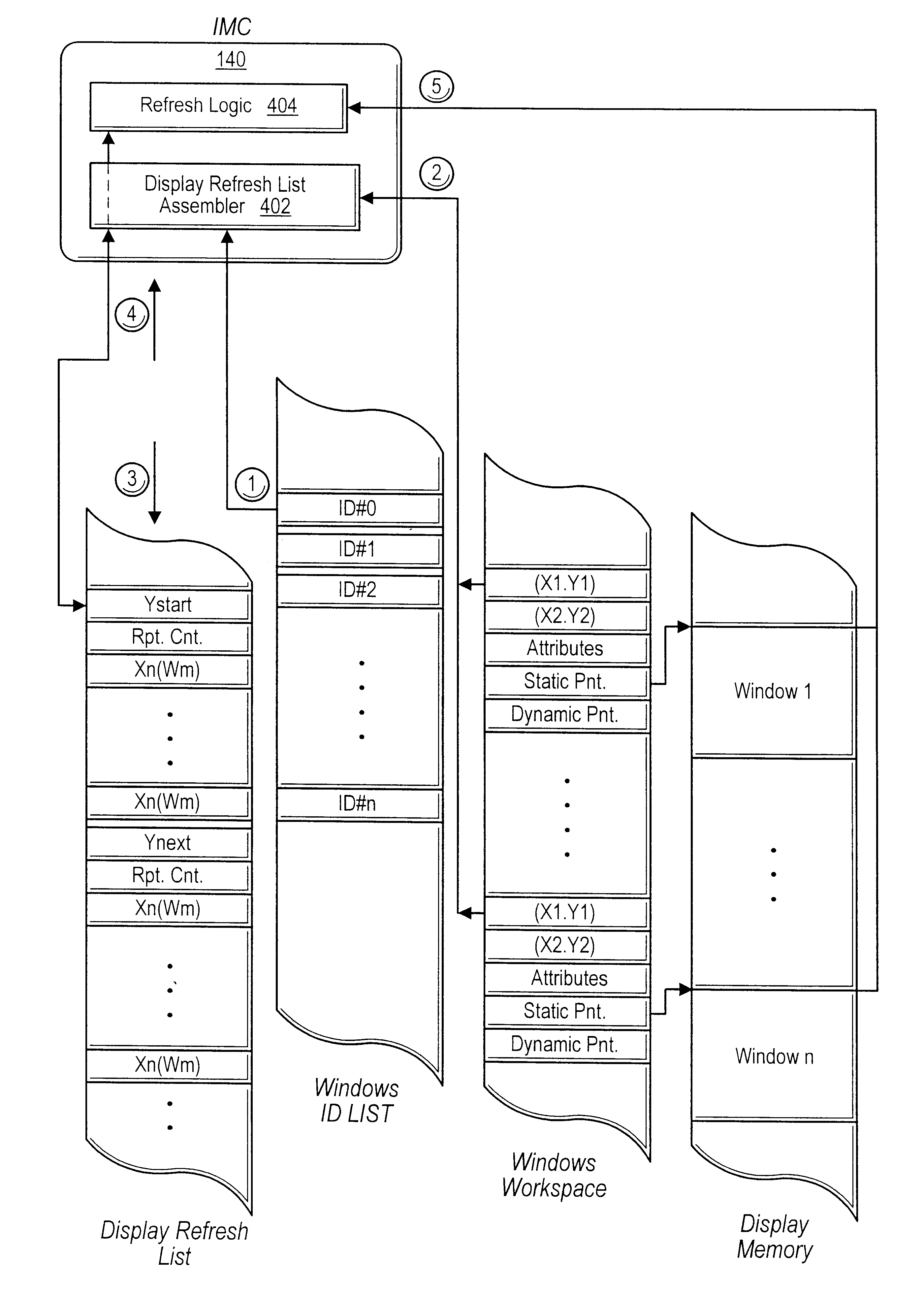
A graphics controller which performs display list-based video refresh operations that enable objects with independent frame rates to be efficiently assembled is disclosed. The graphics controller maintains a virtual display refresh list (VDRL) comprising a plurality of pointers to scan line segments in memory. The graphics controller also creates, maintains, and deletes draw display lists (DDLs) that comprise pointers to object display list subroutines (ODLs) that independently draw objects in memory. The ODLs may allocated one or more buffers in memory into which different frames of the objects are drawn. When an ODL has completed executing, the corresponding pointer in the DDL may be updated to point to the buffer location in memory that stores the newly completed object frame. The VDRL is maintained independently (and may be doubled-buffered) and is updated using the DDLs. Motion estimation may be performed by the graphics controller using the different frames of objects that are drawn into memory by the ODLs. The different object frames may also be animated by the graphics controller once they are drawn into memory. The object frames stored in memory may be compressed to conserve memory.
Owner:DIGIMEDIA TECH LLC
System for remote loading of objects or files in order to update software
InactiveUS8032879B2Saving informationVersion controlBootstrappingComputer moduleArchitecture of Integrated Information Systems
A system for remote loading of objects or files in order to update software includes operating system architecture that calls for different tasks to be broken down into software modules that are connected to one another by dynamic links or are composed of executable subroutines that have main dependence links to other parts of the operating system. Each of the modules is composed of object files or libraries that are represented by dynamic link libraries among themselves according to a number of dependence levels that are described in their respective attributes.
Owner:TOUCHTUNES MUSIC CO LLC
Apparatus and method for the treatment of sleep apnea, arrhythmia, and partial epilepsy
InactiveUS20050222503A1Pulse broadeningLow oxygenCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationPartial epilepsyMedicine
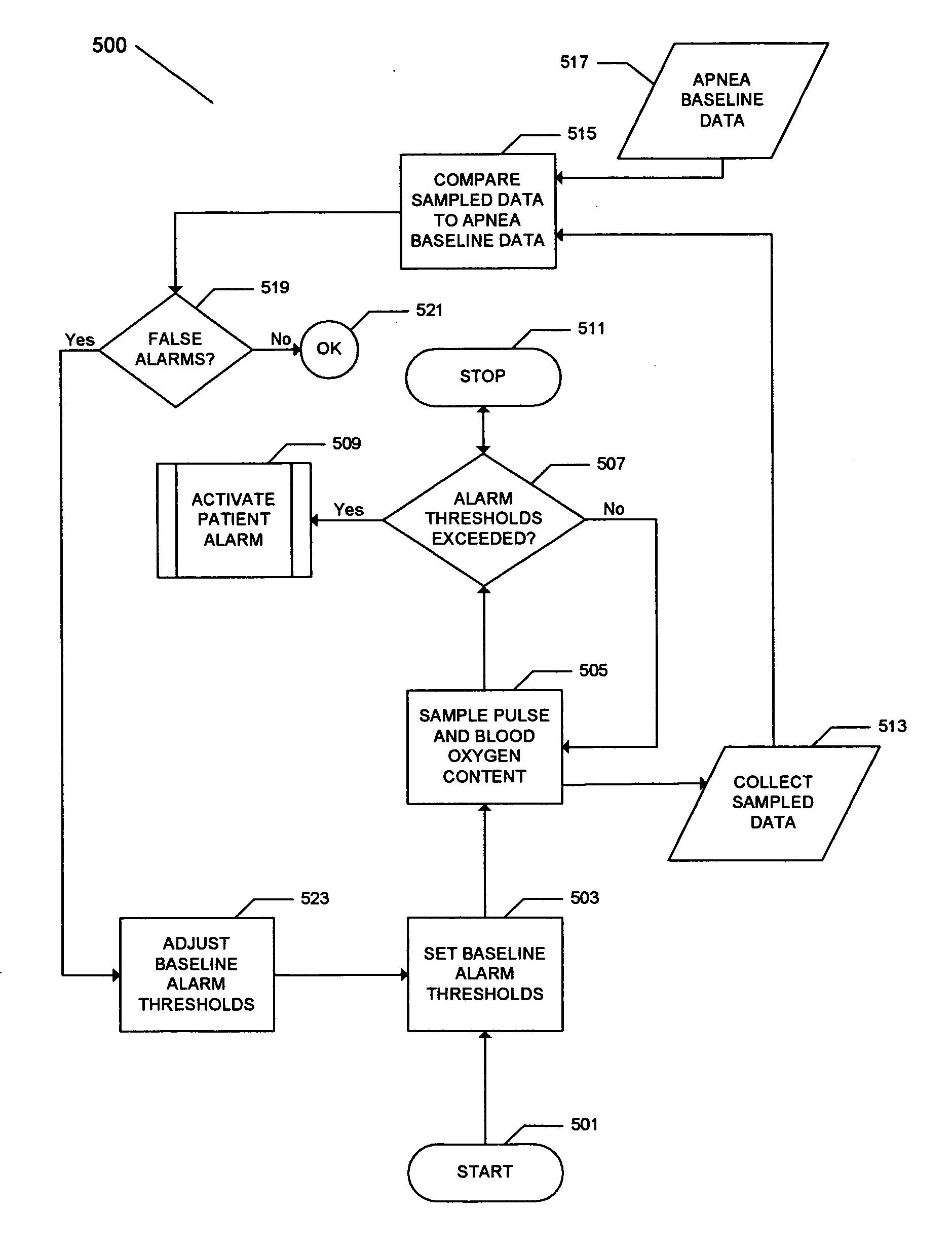
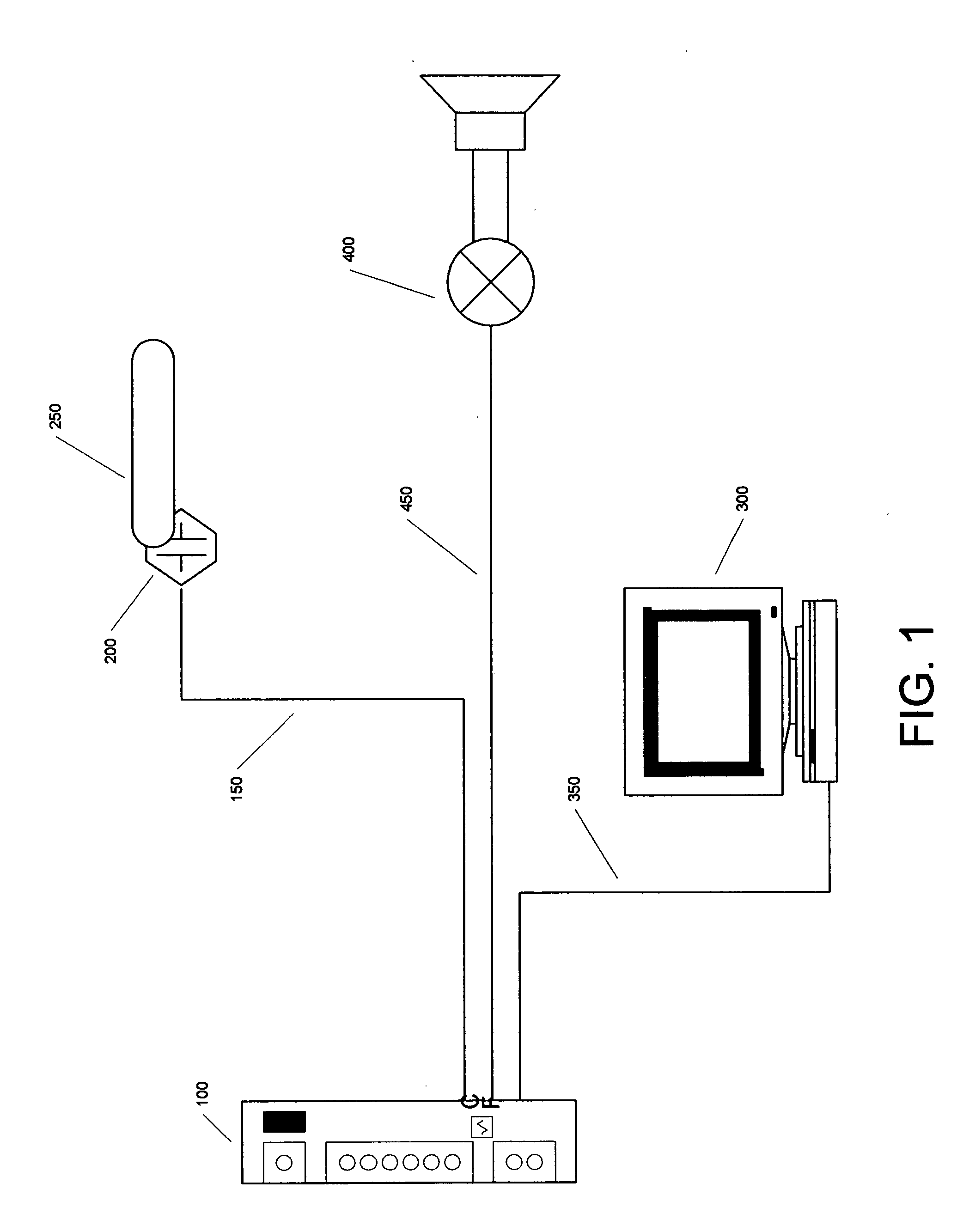
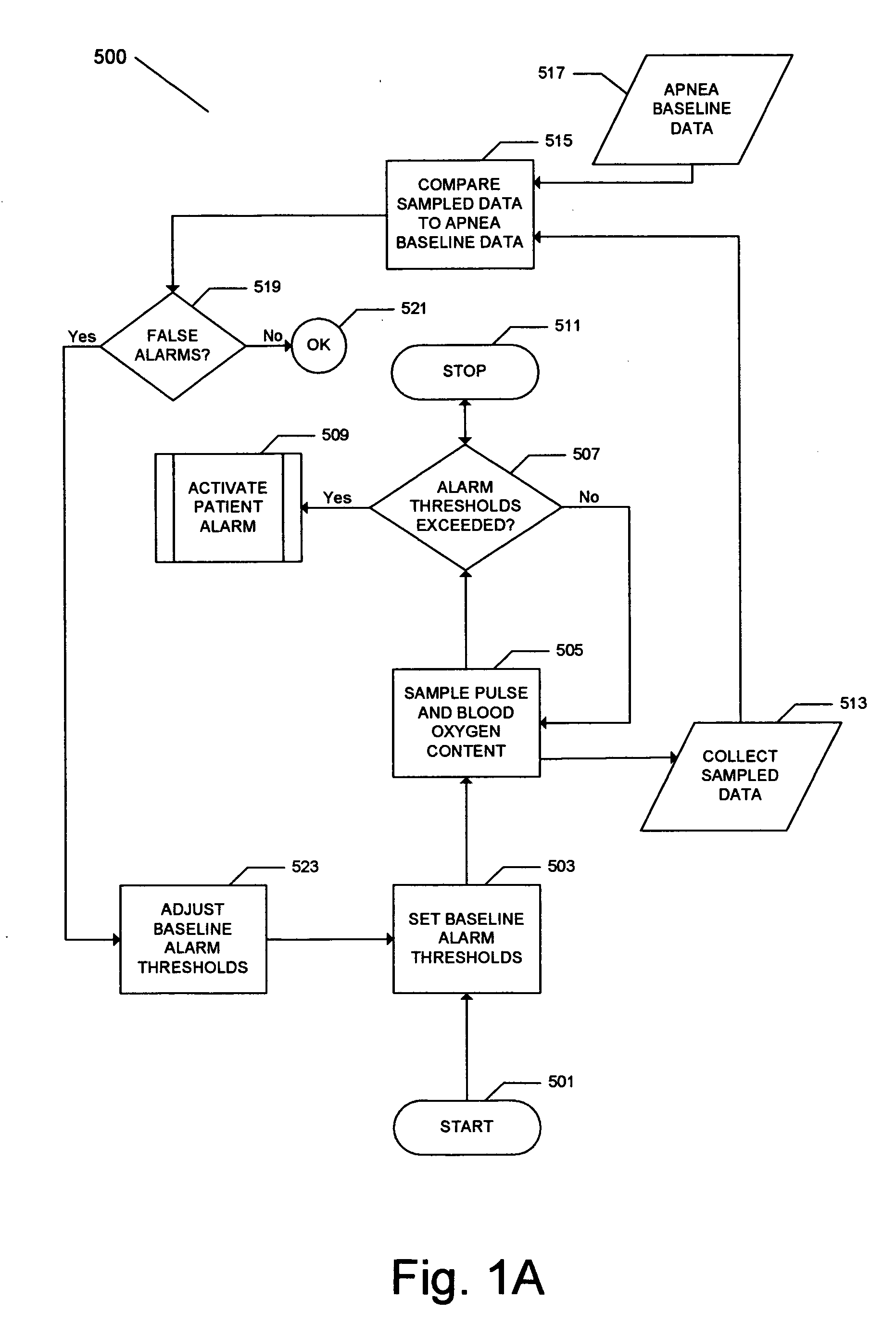
An apparatus to detect the onset of sleep apnea, and to provide an automated way to awaken the sleeping patient at the onset of sleep apnea. The apparatus may also contain a recording device or computer that captures blood oxygen levels and pulse rates throughout the period of sleep, and may contain computer programs, algorithms, subroutines or logic to determine the level of blood oxygen and pulse rate that indicates the onset of a sleep apnea event. The method of arousing the patient from sleep at the onset of a sleep apnea event will decrease or eliminate the occurrence of sleep apnea, arrhythmia, and partial epilepsy over time.
Owner:DUNLOP DAVID A +1
Method and system in a computer network for bundling and launching hypertext files and associated subroutines within archive files
InactiveUS6026437AReduce download timeImprove packaging efficiencyData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideApplication software
A method and system in a computer network for dynamically bundling and launching hypertext files within archive files, wherein the computer network includes at least one client connectable to one or more servers. Initially, an archive file is established within the computer network wherein particular subroutines are maintained. Thereafter, a particular hypertext file is associated with a selected subroutine maintained within the archive file. The particular hypertext file and the selected subroutine are subsequently bundled together within the archive file. Thereafter, the archive file is automatically transmitted to the client from a server maintained within the computer network, in response to a client request to download the hypertext file, such that the subroutine and the hypertext file are downloaded within a single selected archive file from the server, thereby reducing download time and increasing data packaging efficiency. The subroutine may be composed of an applet and the hypertext file may be based on an HTML file having tags which point to particular applets and data associated with the applets.
Owner:IBM CORP
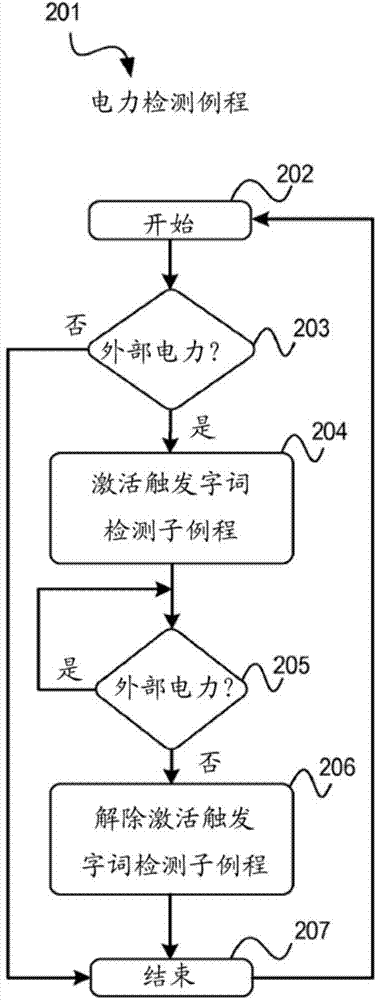
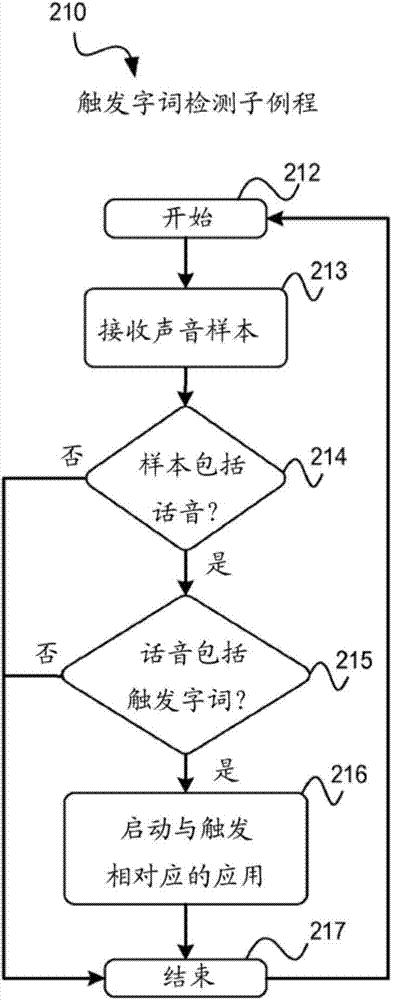
Systems and methods for continual speech recognition and detection in mobile computing devices
ActiveCN103930945AInfluence IgnoreContinuous operationSound input/outputSpeech recognitionElectric powerSubroutine
The present application describes systems, articles of manufacture, and methods for continuous speech recognition for mobile computing devices. One embodiment includes determining whether a mobile computing device is receiving operating power from an external power source or a battery power source, and activating a trigger word detection subroutine in response to determining that the mobile computing device is receiving power from the external power source. In some embodiments, the trigger word detection subroutine operates continually while the mobile computing device is receiving power from the external power source. The trigger word detection subroutine includes determining whether a plurality of spoken words received via a microphone includes one or more trigger words, and in response to determining that the plurality of spoken words includes at least one trigger word, launching an application corresponding to the at least one trigger word included in the plurality of spoken words.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
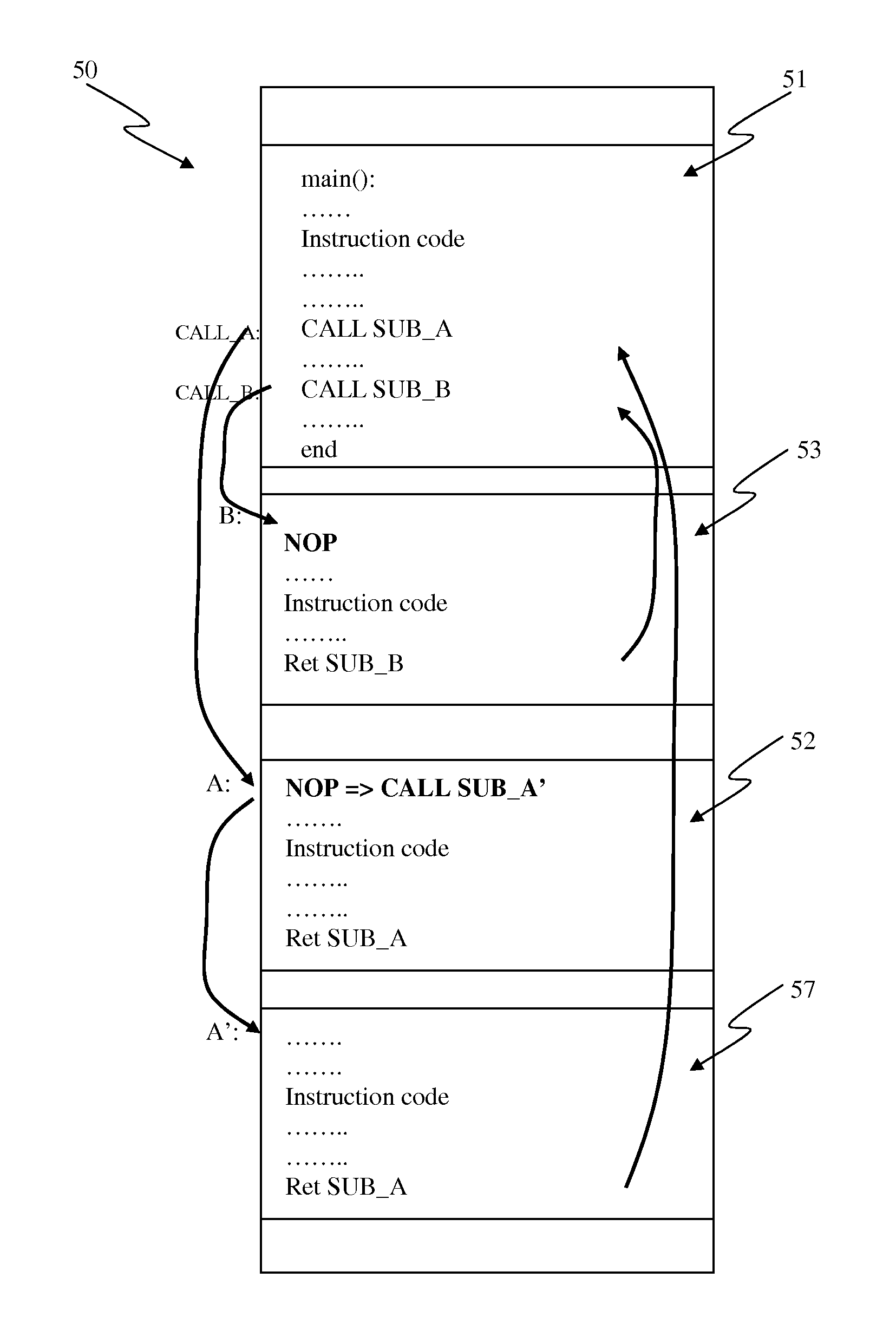
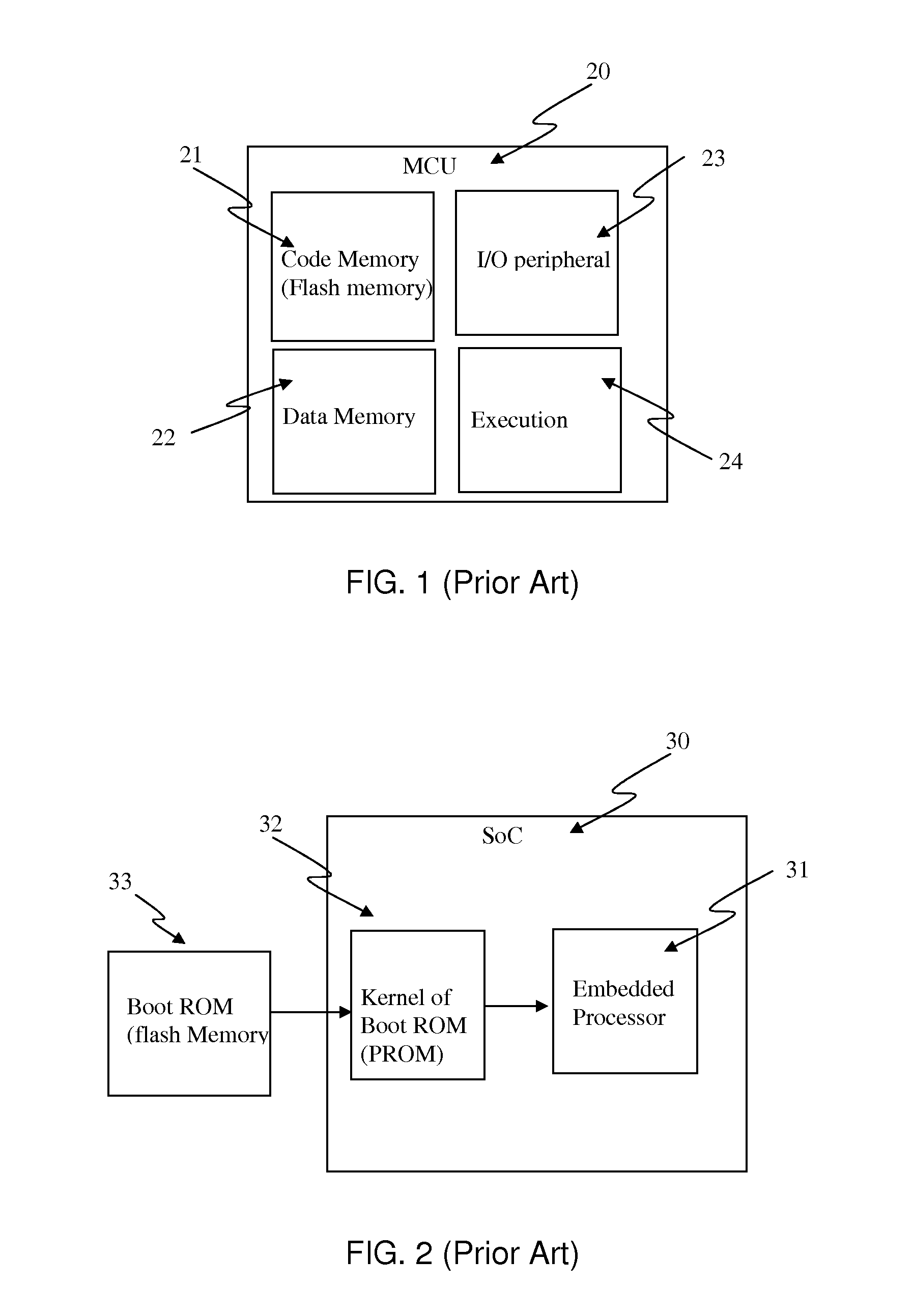
Method and System of Using One-Time Programmable Memory as Multi-Time Programmable in Code Memory of Processors
A method, device and system of using an One-Time-Programmable (OTP) memory as an Multiple-Time Programming (MTP) memory equivalent is disclosed. The use of OTP memory in this manner allows code to be updated one or more times and yet remain small in size and relatively easy to process (fabricate). The code can be program code for a processor, such as boot code, boot code kernel or other instruction code. According to one aspect, an OTP memory is able to functionally operate as if it were a MTP memory through intelligent use of NOPs, which are no operations. Subsequently, if a particular subroutine or function in the program code needs to be modified, an instruction (e.g., JUMP instruction) can be programmed into the NOP so that certain existing instructions can be bypassed and the execution of instructions of a new module can be performed.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
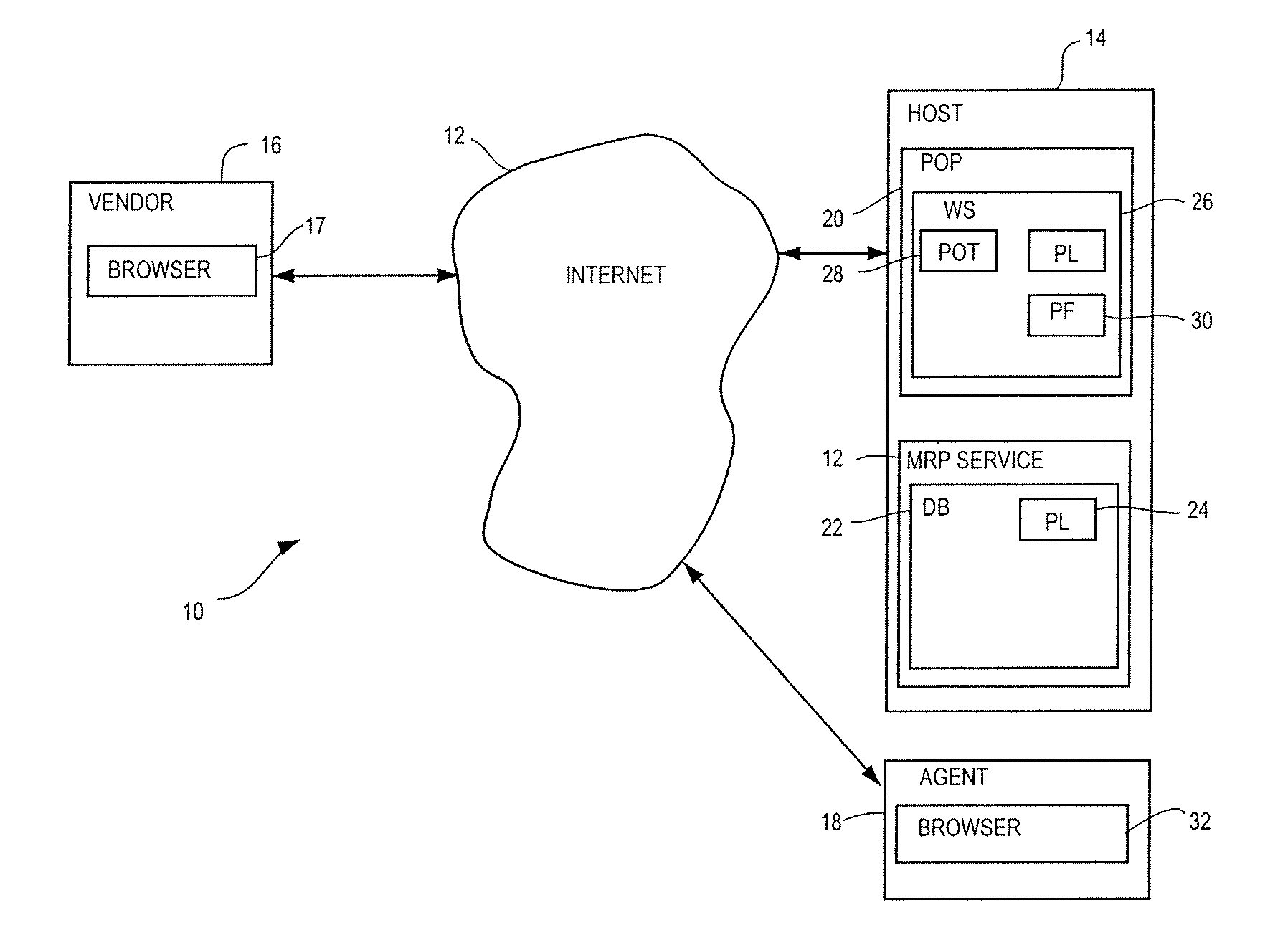
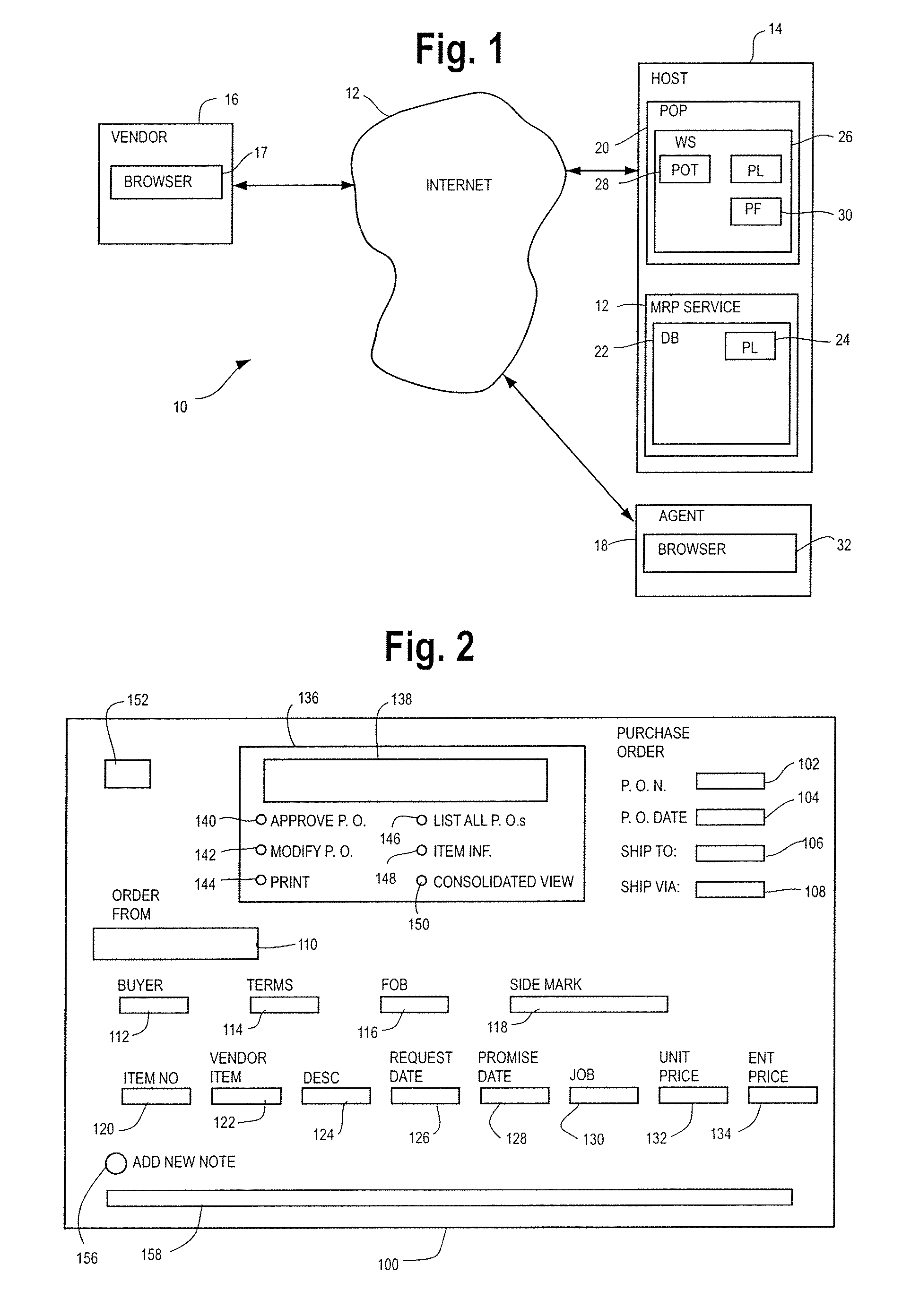
Method of Processing Orders
A method and apparatus are provided for processing orders by a host of an ordering organization, the orders being placed by the ordering organization with a vendor. The method includes the steps of an agent of the ordering organization accessing an order website and entering a plurality of order items and the host incorporating the order items and a change subroutine into a webpage. The method further includes the steps of an agent of the vendor retrieving the webpage from the host of the ordering organization, the agent of the ordering organization and agent of the vendor negotiating the conditions of the order and the change subroutine tracking and recording the agreed upon conditions.
Owner:SNIPERDYNE
Computationally efficent radar processing method and sytem for SAR and gmti on a slow moving platform
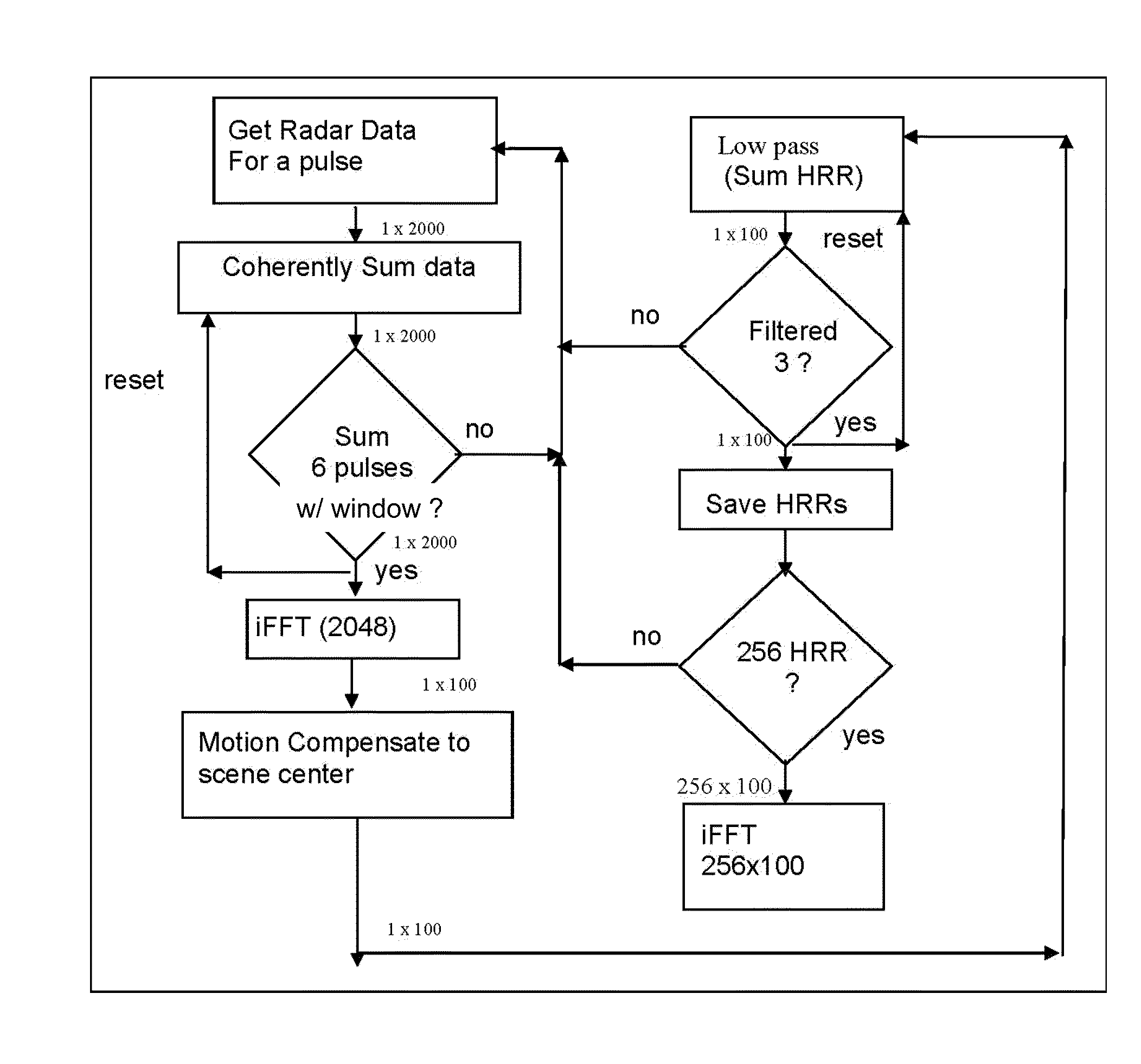
A method and system for processing radar data obtained from a platform which is subjected to non-uniform movement, the distance the platform travels during the formation of an image comprising an aperture; the system comprising software programming for performing a subroutine for building up an average pulse representing a single point on the aperture; the subroutine comprising the steps of inputting radar data from a radar antenna; passing the radar signal through low noise amplifier to reduce impact of electronic noise from the radar system; down converting the signal with a mixer to obtain a lower frequency; filtering out harmonics from the higher frequency range; sampling the radar data using an analog to digital converter at least at Nyquist down range frequency; based upon the IF of the radar; determining a scene center (center of SAR imagery) for the purpose of motion compensation; performing a two stage averaging scheme of the received signals with a variable window function; determining a window function based upon the velocity and acceleration of the platform and scene center; the window function comprising a first stage window; coherently averaging N pulses together to create an average pulse; performing an inverse Fourier transform; compensating to the scene center by multiplying by a complex exponential based upon both the GPS and inertial navigational system; summing the average pulses using low pass filter; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building up an average pulse a first predetermined number of times for a time period that is less than the Nyquist sample time interval; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building an average pulse for a predetermined number of times to generate a second predetermined number of average pulses; the software programming operating to perform a two dimensional inverse Fourier transform to obtain SAR image; outputting the SAR image on a display screen; and a display for displaying the outputted SAR image.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Biometric access control system
ActiveUS8207816B2Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsLocking mechanismControl system
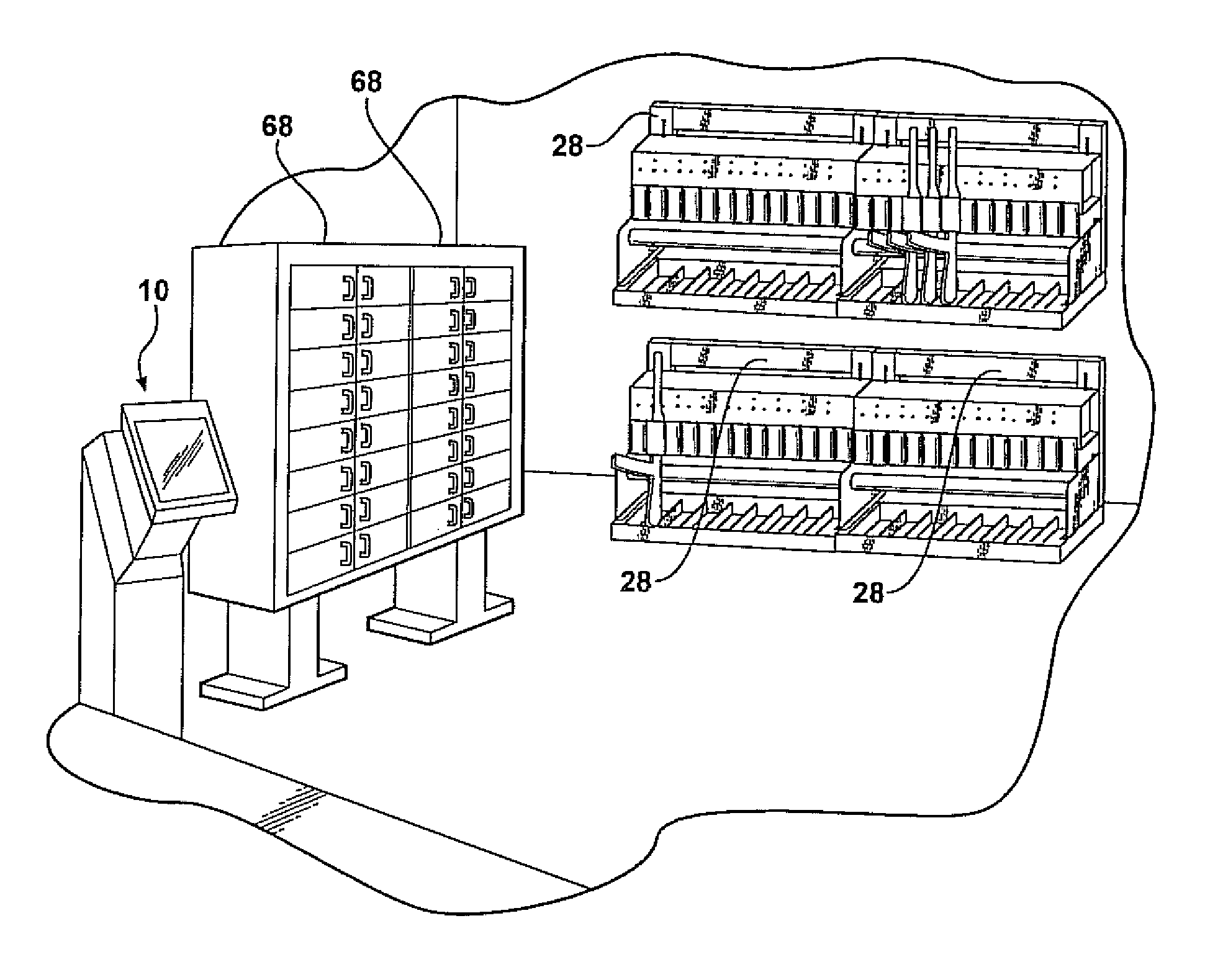
A biometric access control system for tracking critical assets and including an ID station incorporating a biometric input reader, an RFID antenna and reader and a wired or wireless (Bluetooth) communication device. A remotely positioned structure includes either or both of a rack or a locker for holding a plurality of the critical assets in individually locked fashion. A processor control built into the ID station operatively actuates each of a plurality of individual locking mechanisms incorporated into the rack structure or locker, in response to successive biometric and weapon selection inputs communicating with the processor, and for determining at least one of user identification and weapon release authorization prior to the processor actuating the locking mechanism to release the weapon. An associated computer writeable medium operates with the processor and establishes a series of subroutines for establishing user identification, weapons rating, selective weapon release / reentry and associated maintenance and record keeping log reports.
Owner:LAW ENFORCEMENT INTELLIGENT DEVICES
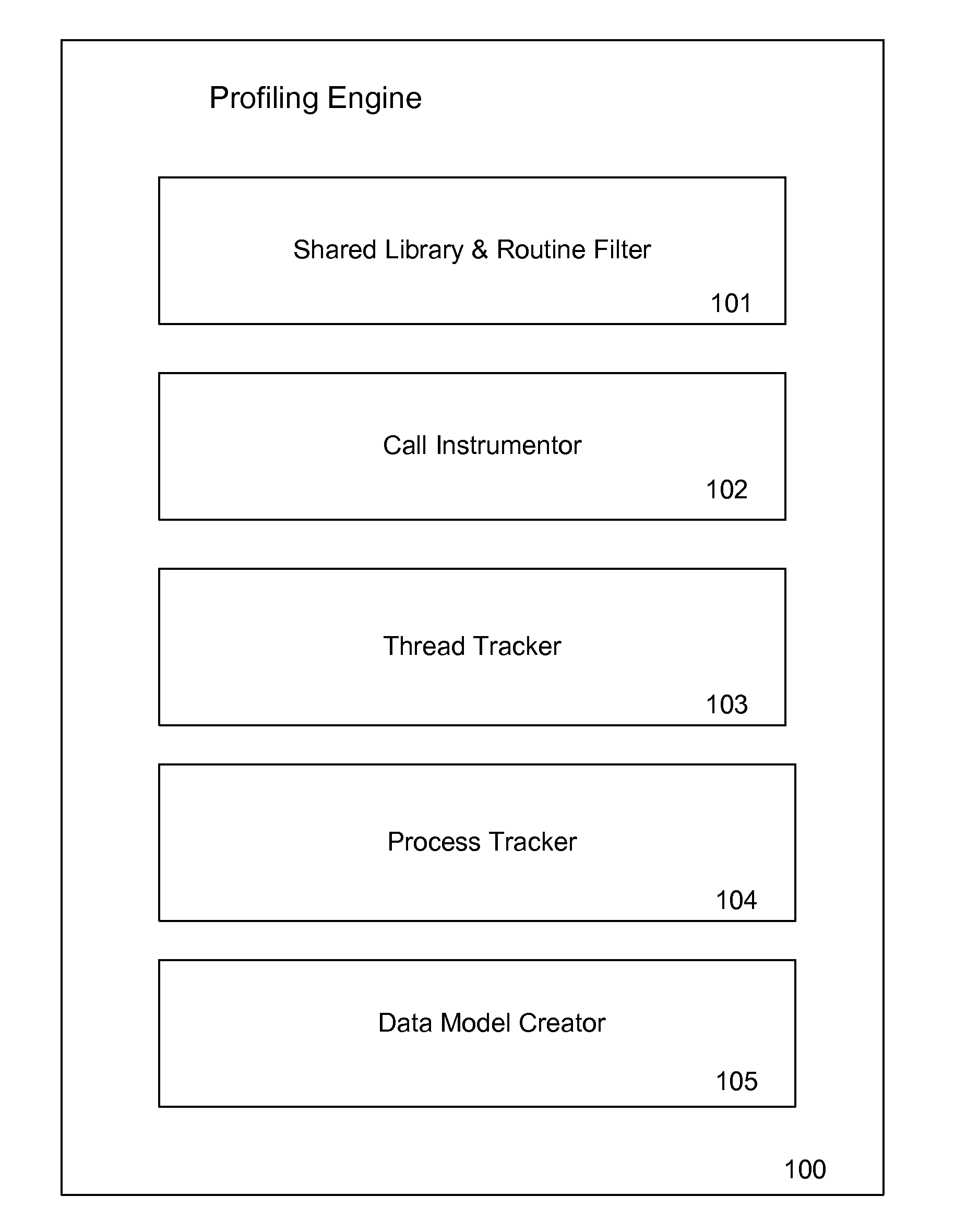
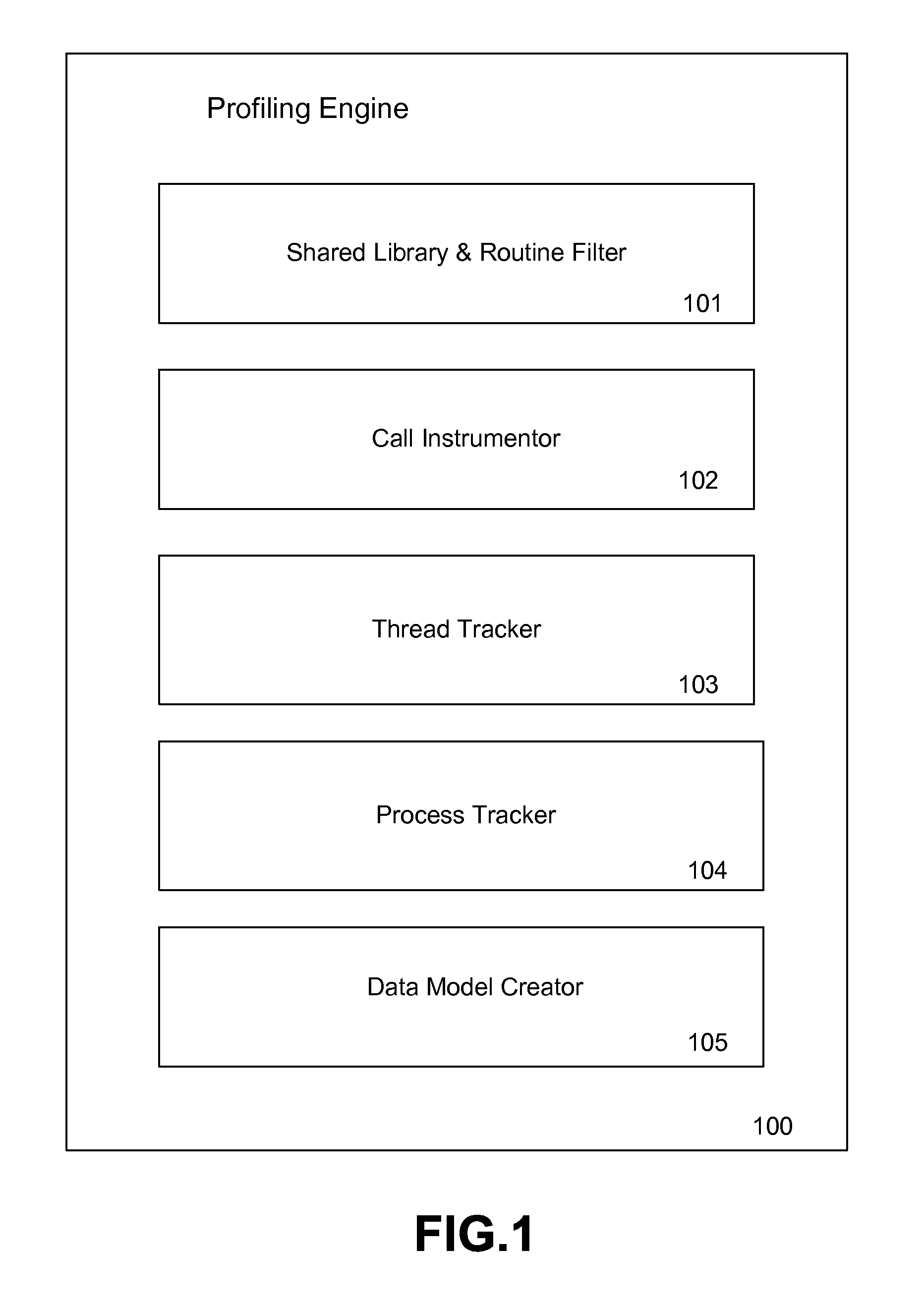
System and method for analyzing dynamic performance of complex applications
A system and method for monitoring the performance and execution flow of a target application and generating a corresponding data model are provided. The system and method comprise attaching to a thread or process of a target application and tracking the execution of subroutines using instrumentation commands. Data representing the execution flow of the various subroutines, subroutine calls, and their performance is gathered and used to generate data models representing the threads and processes of the application. The data models are optionally merged and / or pruned. A visualization of the data models is generated indicating relevant points of interest within the target application's execution flow.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Biometric access control system incorporating a touchscreen accessible and kiosk based id station operating in combination with multiple critical asset retaining racks and locers for permitting selective biometric input and processor driven/wireless release authorization, maintenance and inventory control of any plurality of critical assets and including an associated computer writeable medium operating with the id station for enabling asset release, reentry and associated inventory control
ActiveUS20080252414A1Quick ViewElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsLocking mechanismControl system
A biometric access control system for tracking critical assets and including an ID station incorporating a biometric input reader, an RFID antenna and reader and a wired or wireless (Bluetooth) communication device. A remotely positioned structure includes either or both of a rack or a locker for holding a plurality of the critical assets in individually locked fashion. A processor control built into the ID station operatively actuates each of a plurality of individual locking mechanisms incorporated into the rack structure or locker, in response to successive biometric and weapon selection inputs communicating with the processor, and for determining at least one of user identification and weapon release authorization prior to the processor actuating the locking mechanism to release the weapon. An associated computer writeable medium operates with the processor and establishes a series of subroutines for establishing user identification, weapons rating, selective weapon release / reentry and associated maintenance and record keeping log reports.
Owner:LAW ENFORCEMENT INTELLIGENT DEVICES
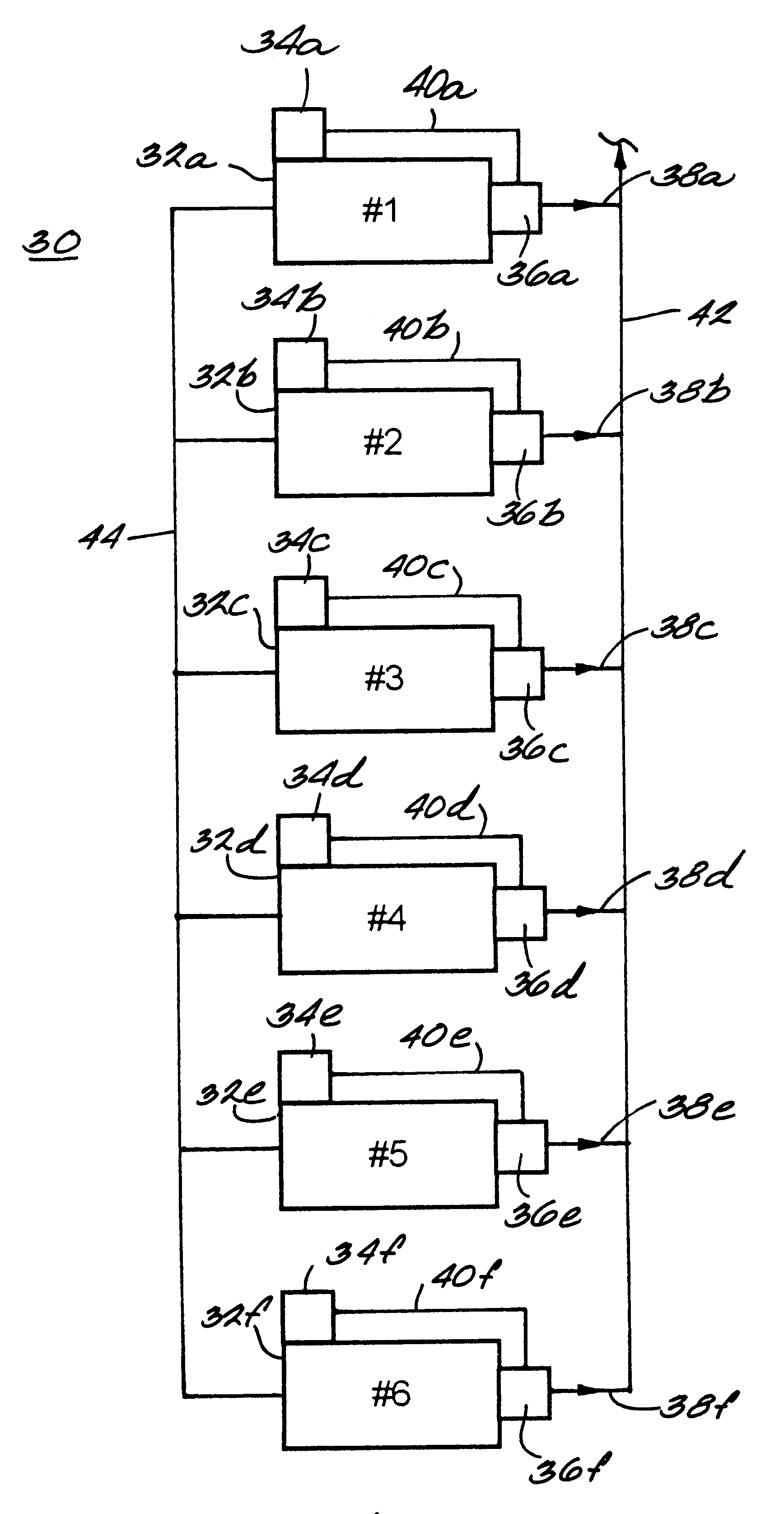
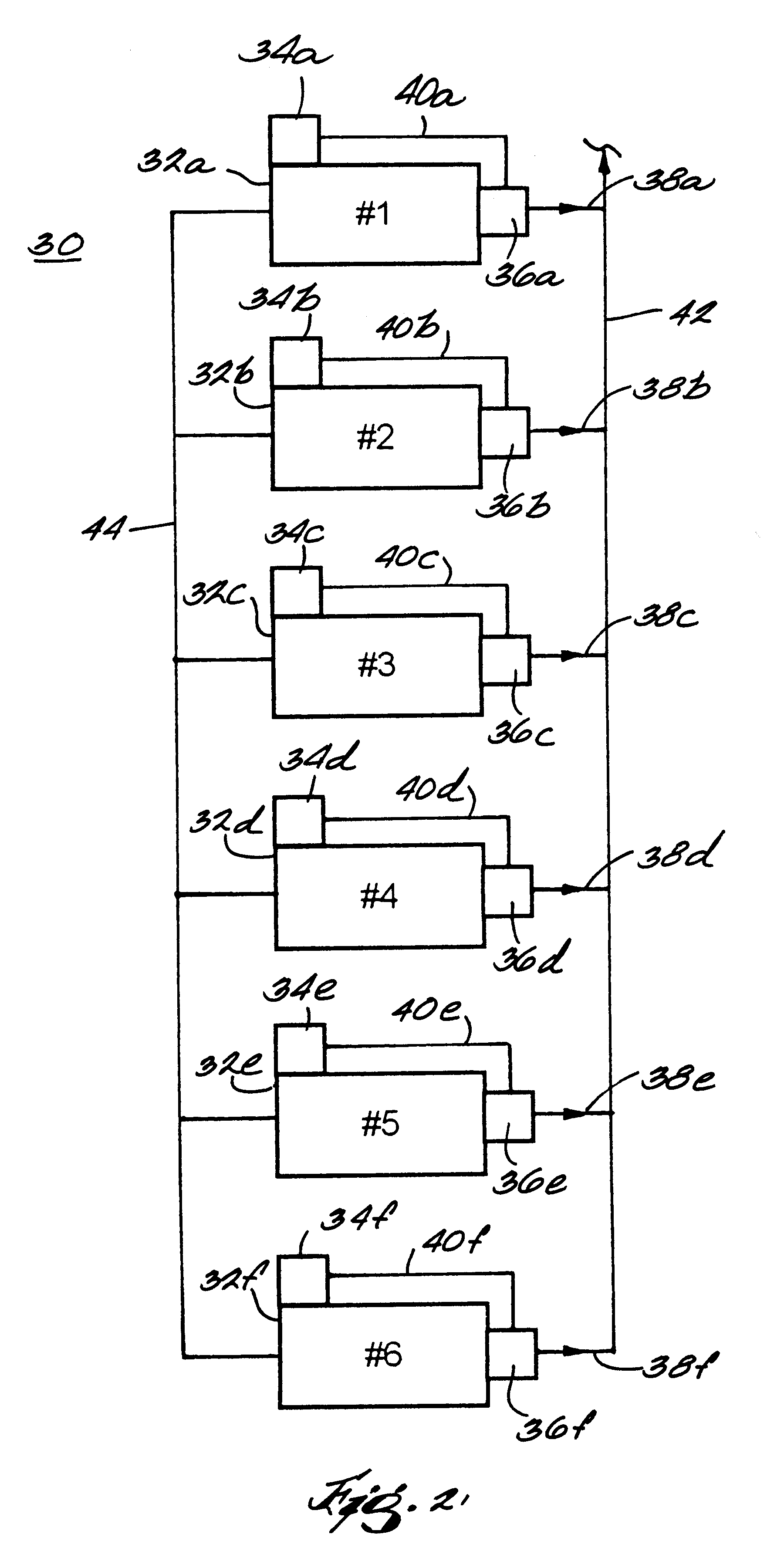
Method for controlling the operation of a compression system having a plurality of compressors
InactiveUS6233954B1Space heating and ventilation safety systemsSpace heating and ventilation control systemsCompressed fluidRanking
A fluid compression system includes a plurality of compressors, each compressor having a local controller for controlling operation thereof and a sensor for sensing the pressure of compressed fluid discharged therefrom. A method for controlling operation of the fluid compression system includes establishing a set point pressure threshold for loading and unloading each compressor, and assigning a ranking to each compressor for identifying a highest ranked compressor and a lowest ranked compressor, whereby the highest ranked compressor for the compression system initiates all commands for controlling all of the lower ranked compressors in the compression system. The method also includes commencing a loading subroutine including loading the highest ranked unloaded compressor, setting a load delay timer, sensing the pressure of the compressed fluid discharged from the highest ranked compressor, comparing the sensed discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor to the set point pressure threshold established for the highest ranked compressor, and transmitting a load command from the controller of the highest ranked compressor to the controller of the next highest ranked unloaded compressor if the sensed discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor remains less than or equal to the set point pressure threshold established for the highest ranked compressor, and the load delay timer equals zero. The loading subroutine is repeated until the discharge pressure of the highest ranked compressor is greater than the set point pressure threshold established therefor.
Owner:INGERSOLL RAND CO
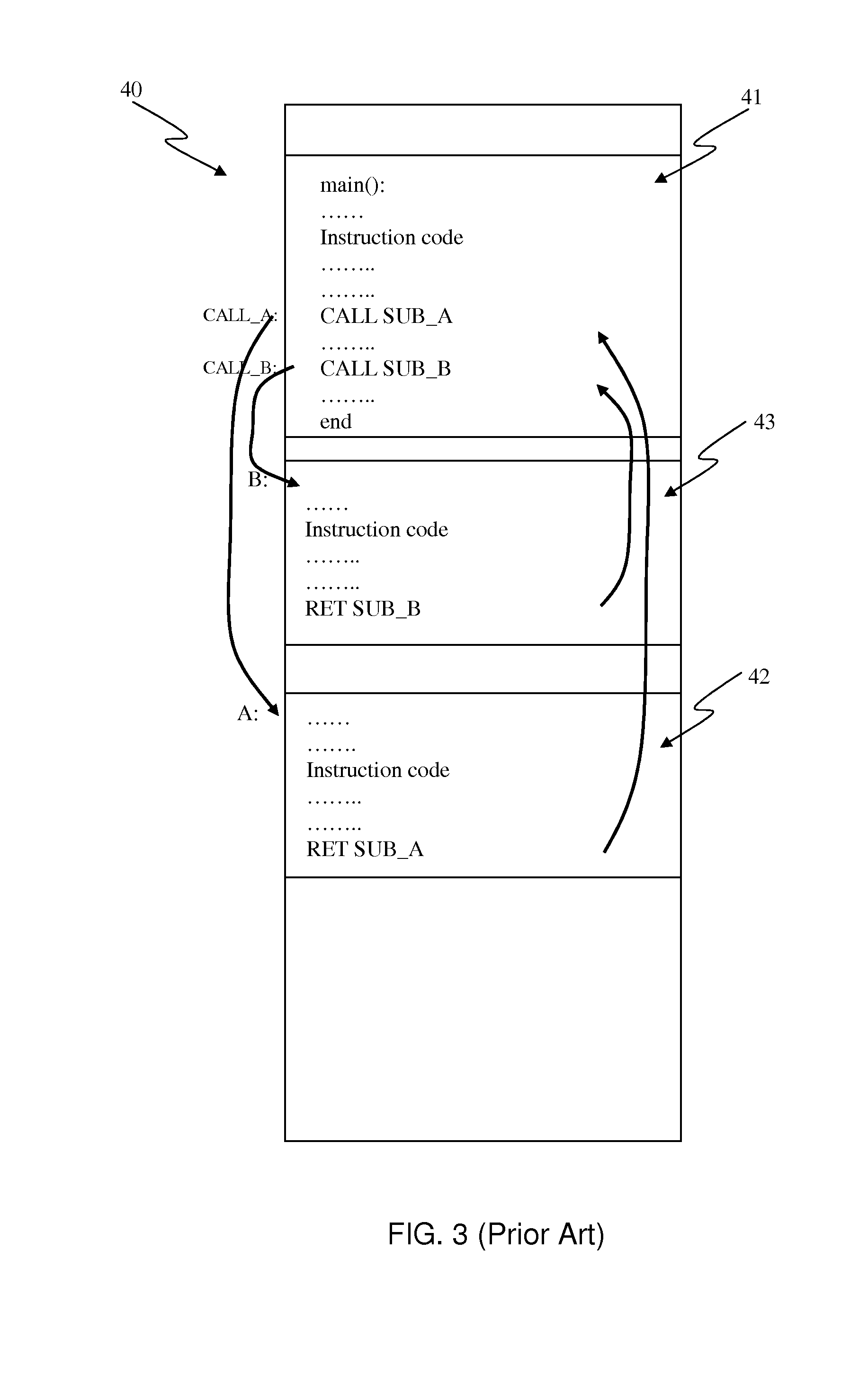
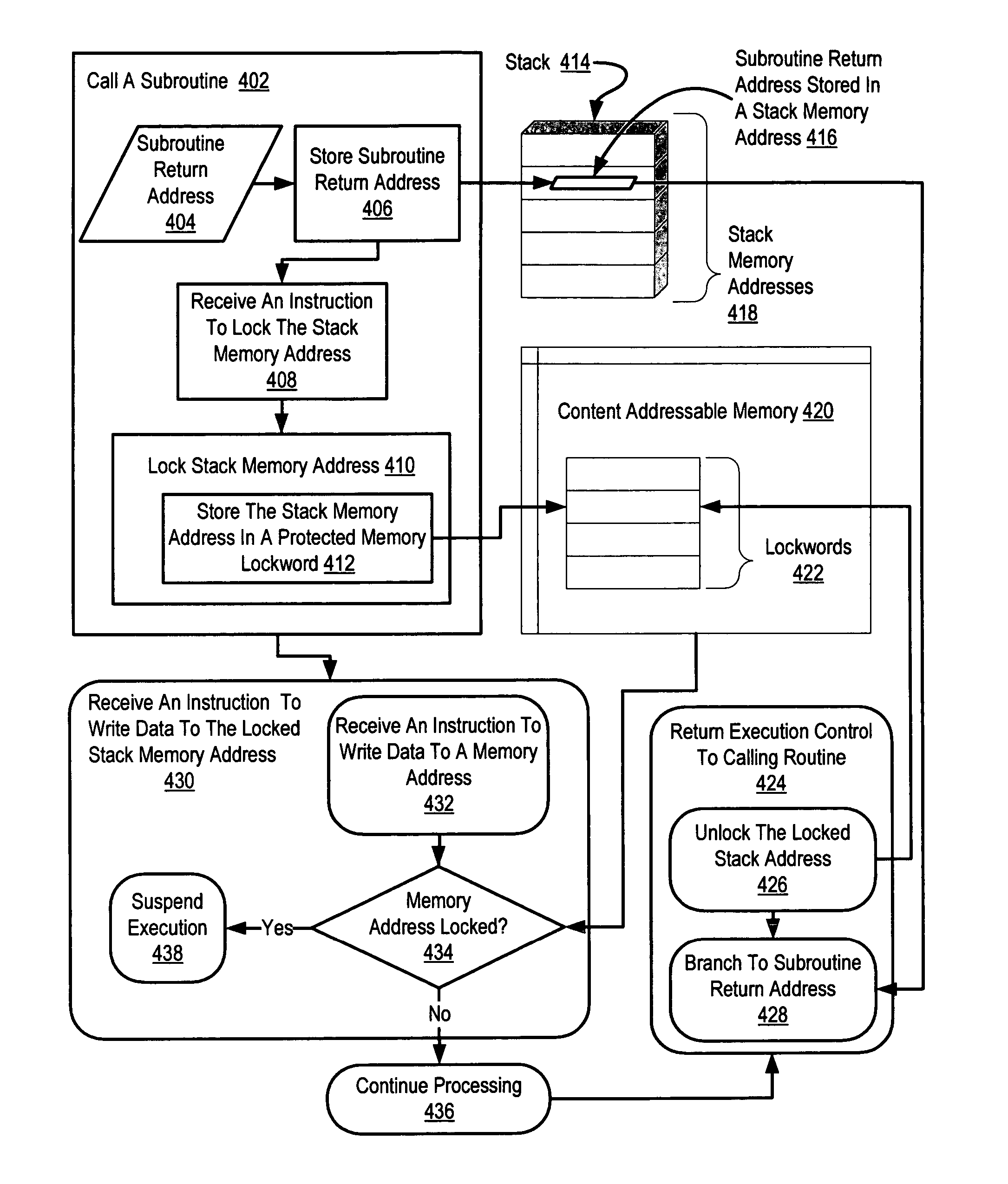
Write protection of subroutine return addresses
Exemplary methods, systems, and products are described that operate generally by moving subroutine return address protection to the processor itself, in effect proving atomic locks for subroutine return addresses stored in a stack, subject to application control. More particularly, exemplary methods, systems, and products are described that write protect subroutine return addresses by calling a subroutine, including storing in a stack memory address a subroutine return address and locking, by a computer processor, the stack memory address against write access. Calling a subroutine may include receiving in the computer processor an instruction to lock the stack memory address. Locking the stack memory address may be carried out by storing the stack memory address in a protected memory lockword. A protected memory lockword may be implemented as a portion of a protected content addressable memory.
Owner:IBM CORP
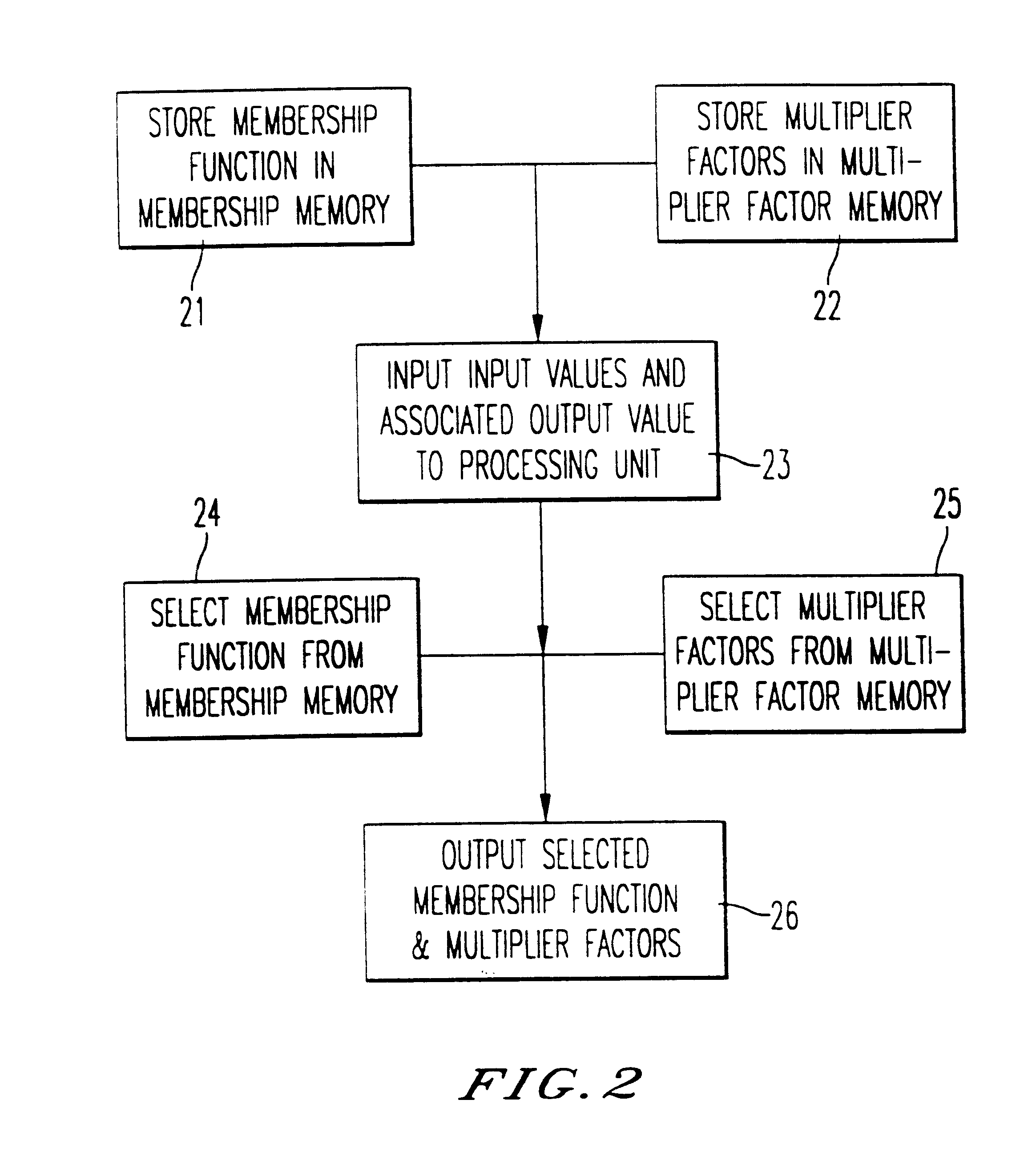
Stochastic encoder/decoder/predictor
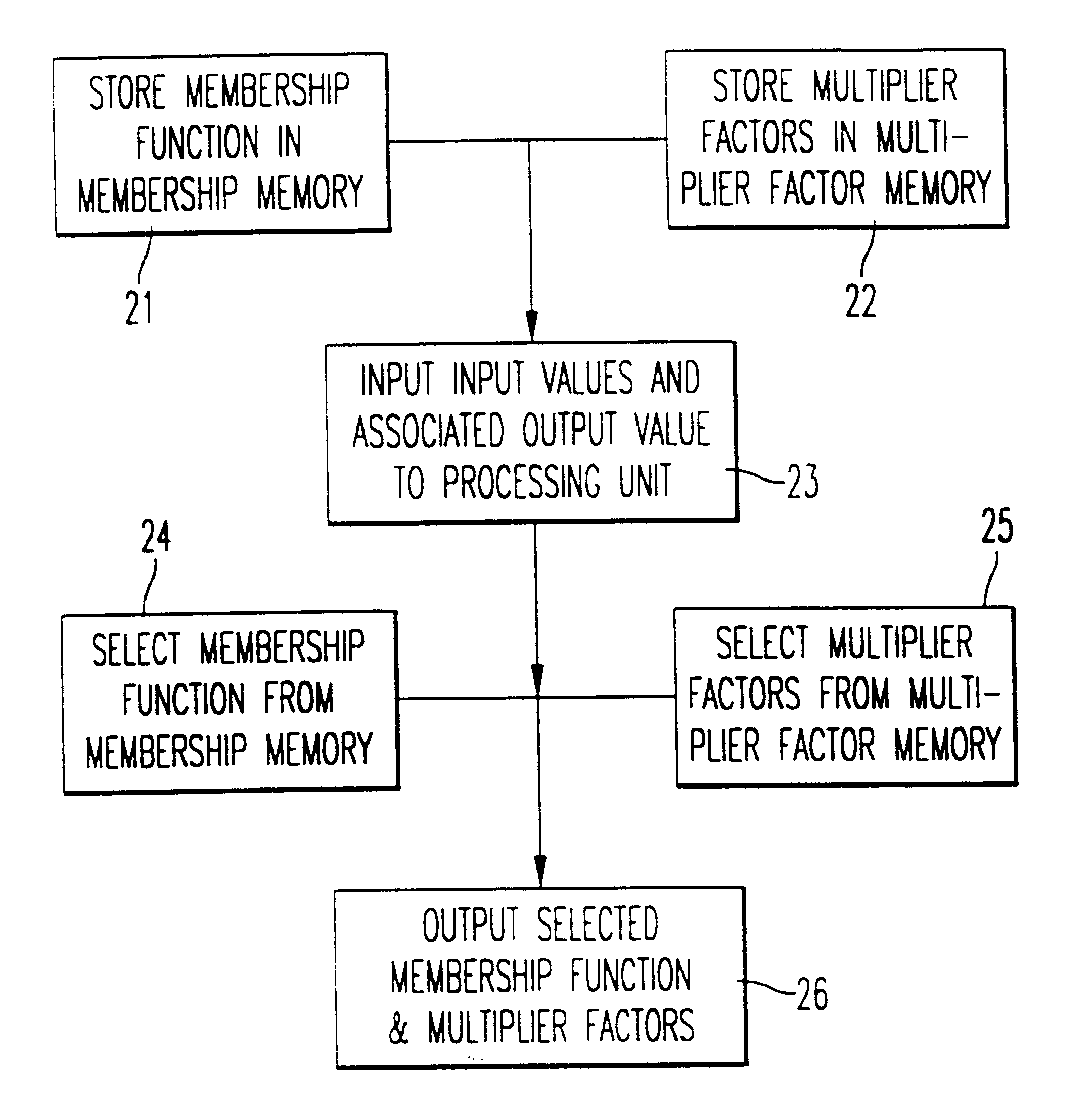
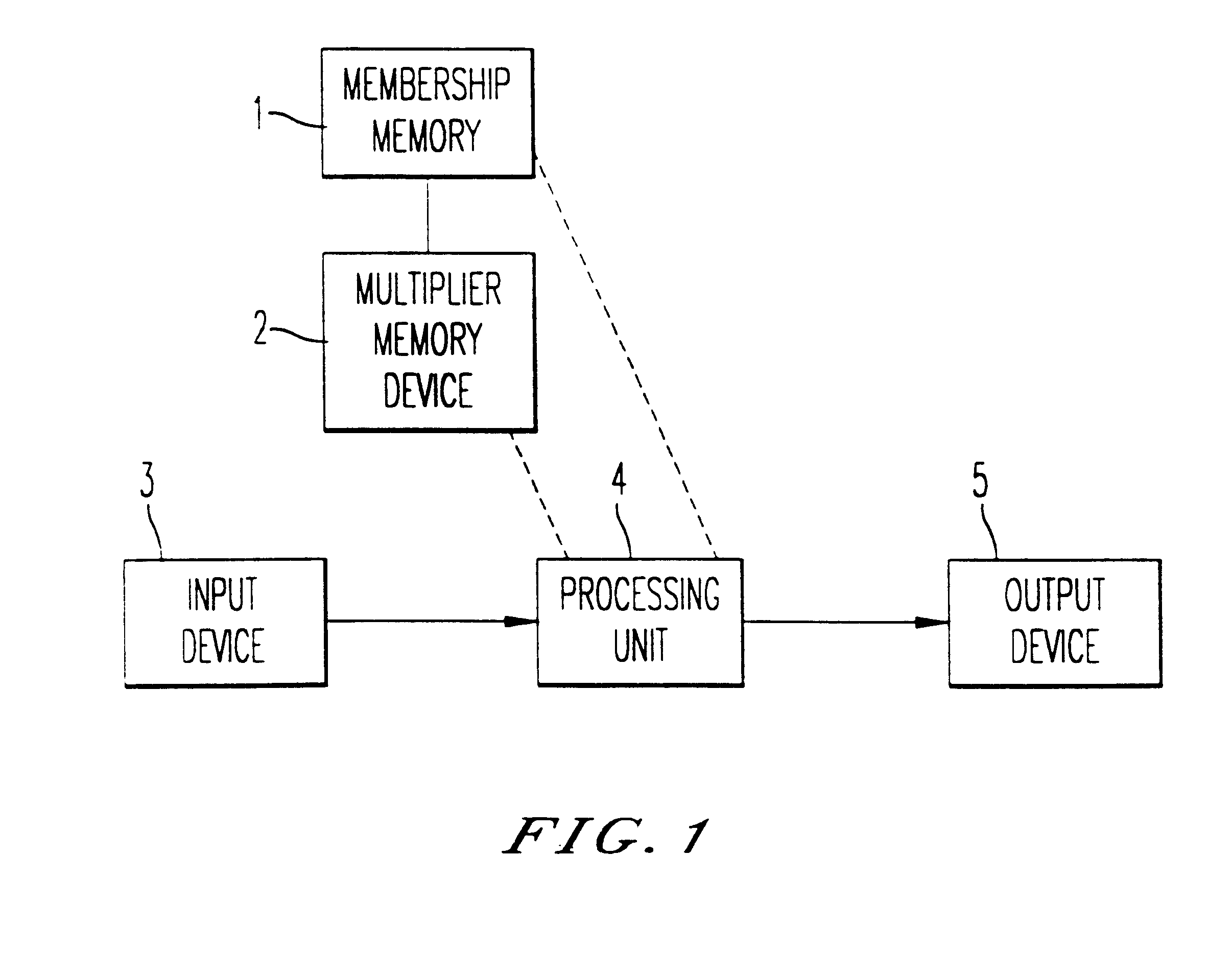
An artificial intelligence system is provided which makes use of a dual subroutine to adapt weights. Elastic Fuzzy Logic ("ELF") System is provided in which classical neural network learning techniques are combined with fuzzy logic techniques in order to accomplish artificial intelligence tasks such as pattern recognition, expert cloning and trajectory control. The system may be implemented in a computer provided with multiplier means and storage means for storing a vector of weights to be used as multiplier factors in an apparatus for fuzzy control.
Owner:IPU POWER MANAGEMENT
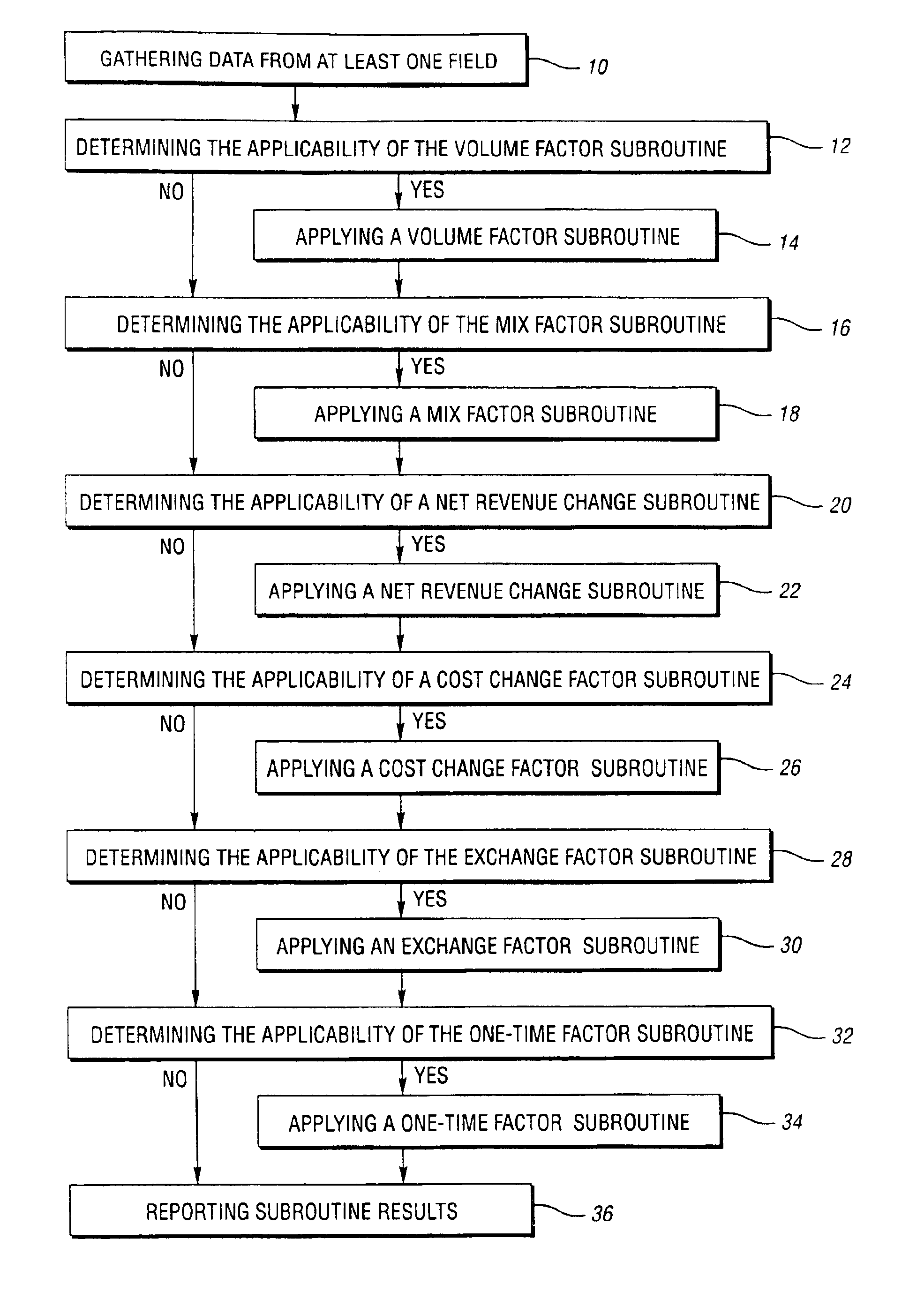
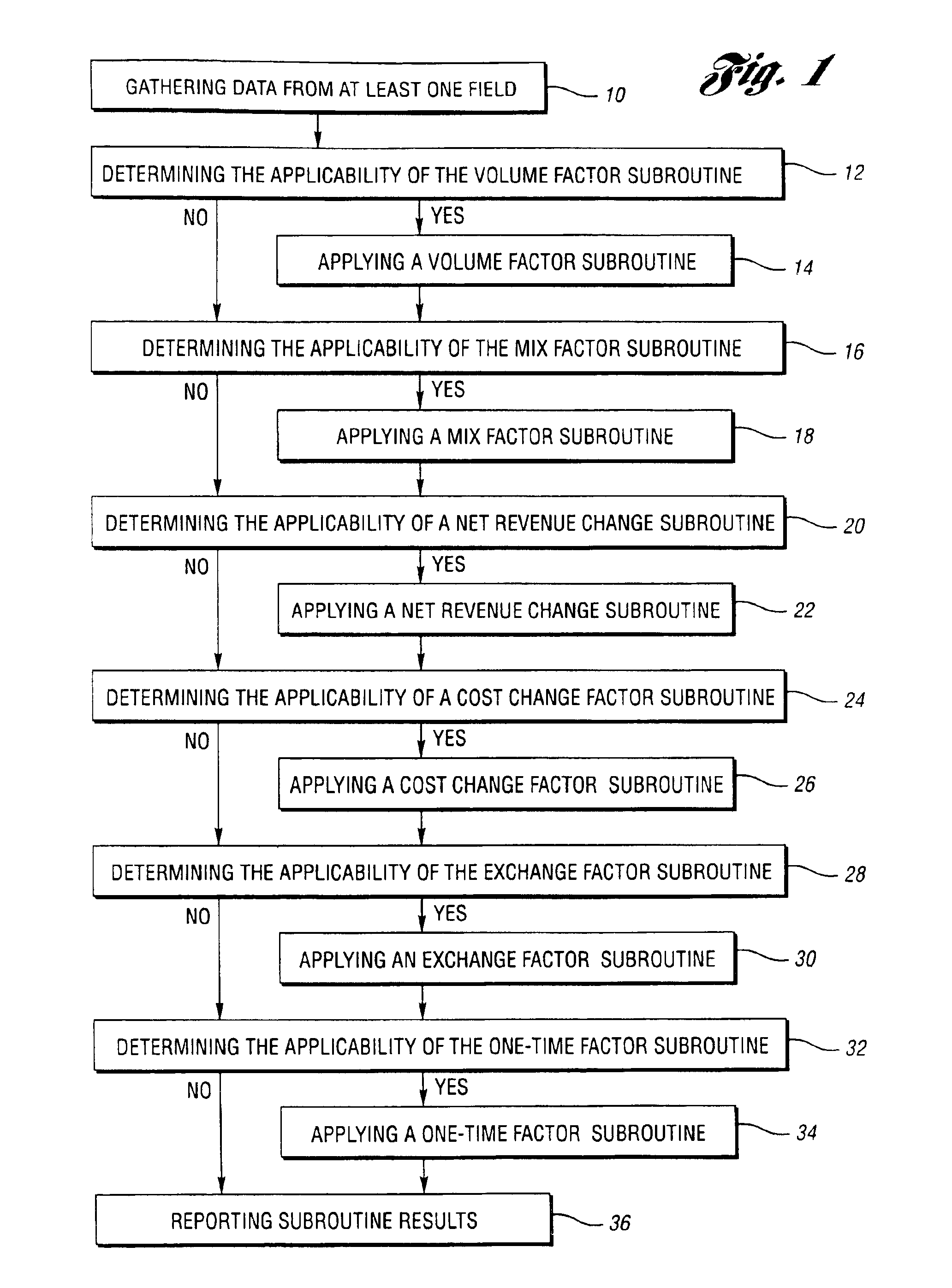
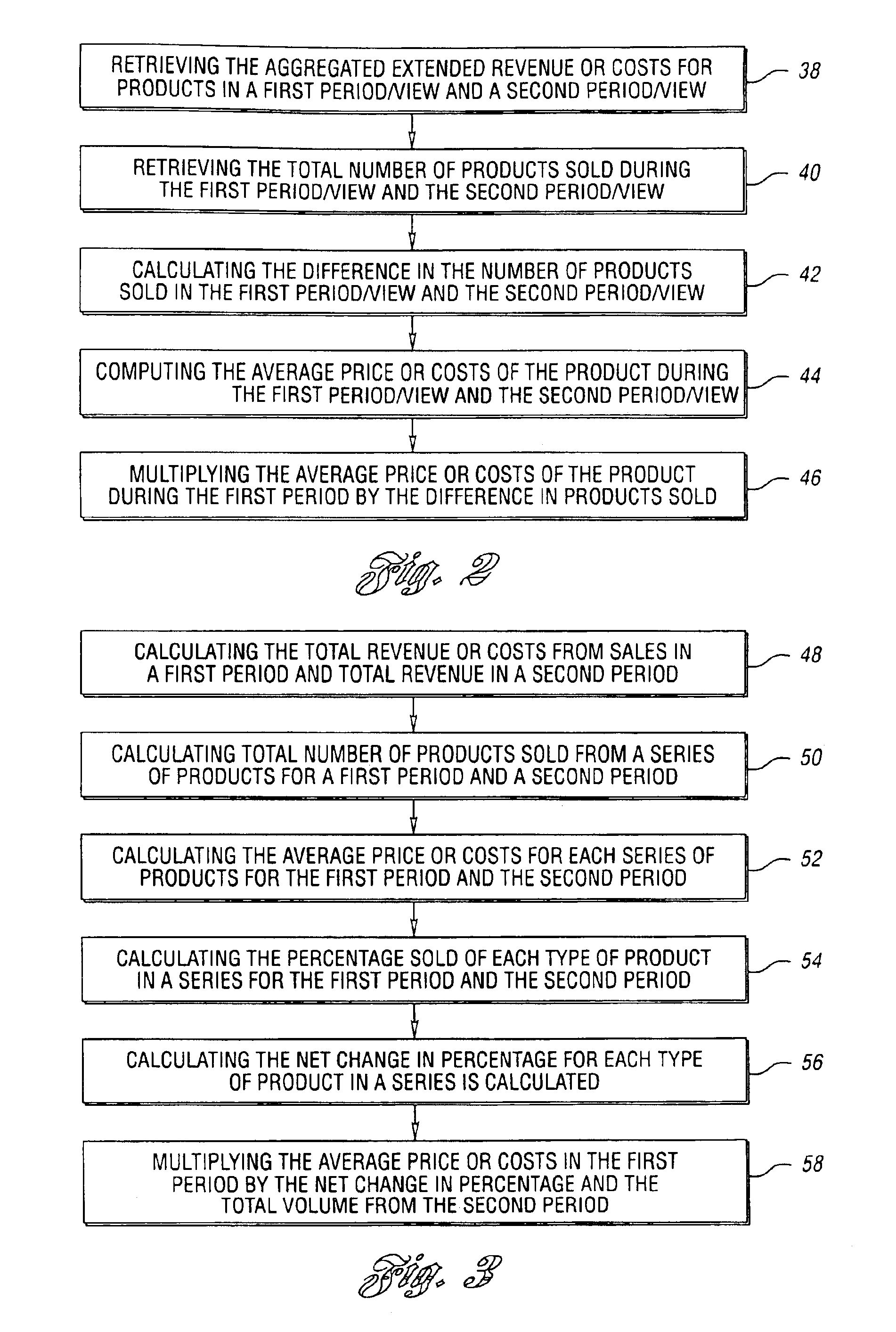
Automated method for analyzing and comparing financial data
An improved and automated method of analyzing data is provided. The method includes the steps of: gathering data from at least one field in financial statements from at least two different time periods or views; applying a volume variance subroutine against the gathered data; applying a mix variance subroutine against the gathered data; applying a net revenue change subroutine against the gathered data; applying a cost change subroutine against the gathered data; applying an exchange subroutine against the gathered data; applying a one-time subroutine against the gathered data; and reporting the results of the volume variance subroutine, the mix subroutine, the net revenue change subroutine, the cost change subroutine, the exchange subroutine, and the one-time subroutine.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
System and method for real time programmability of an engine control unit
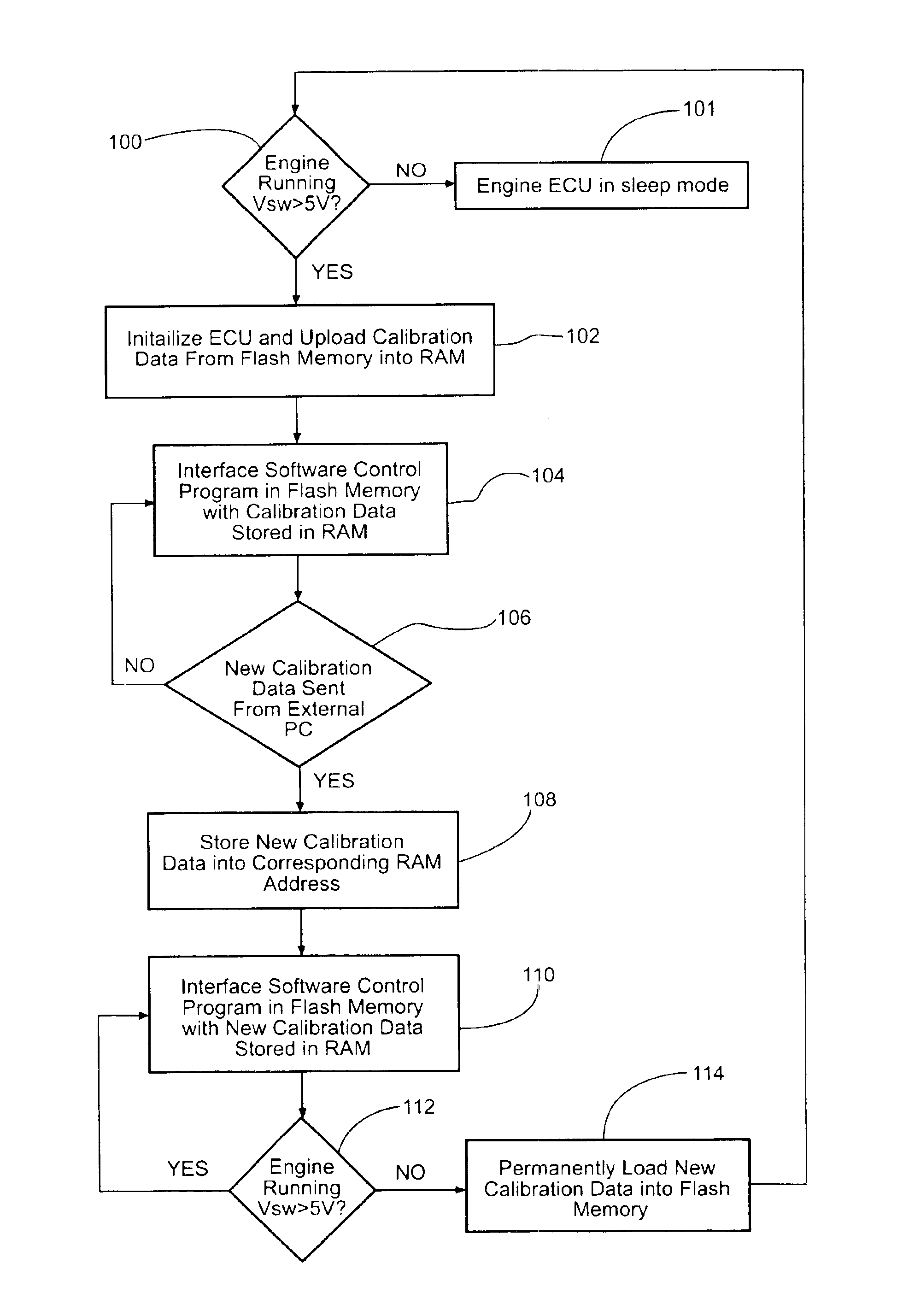
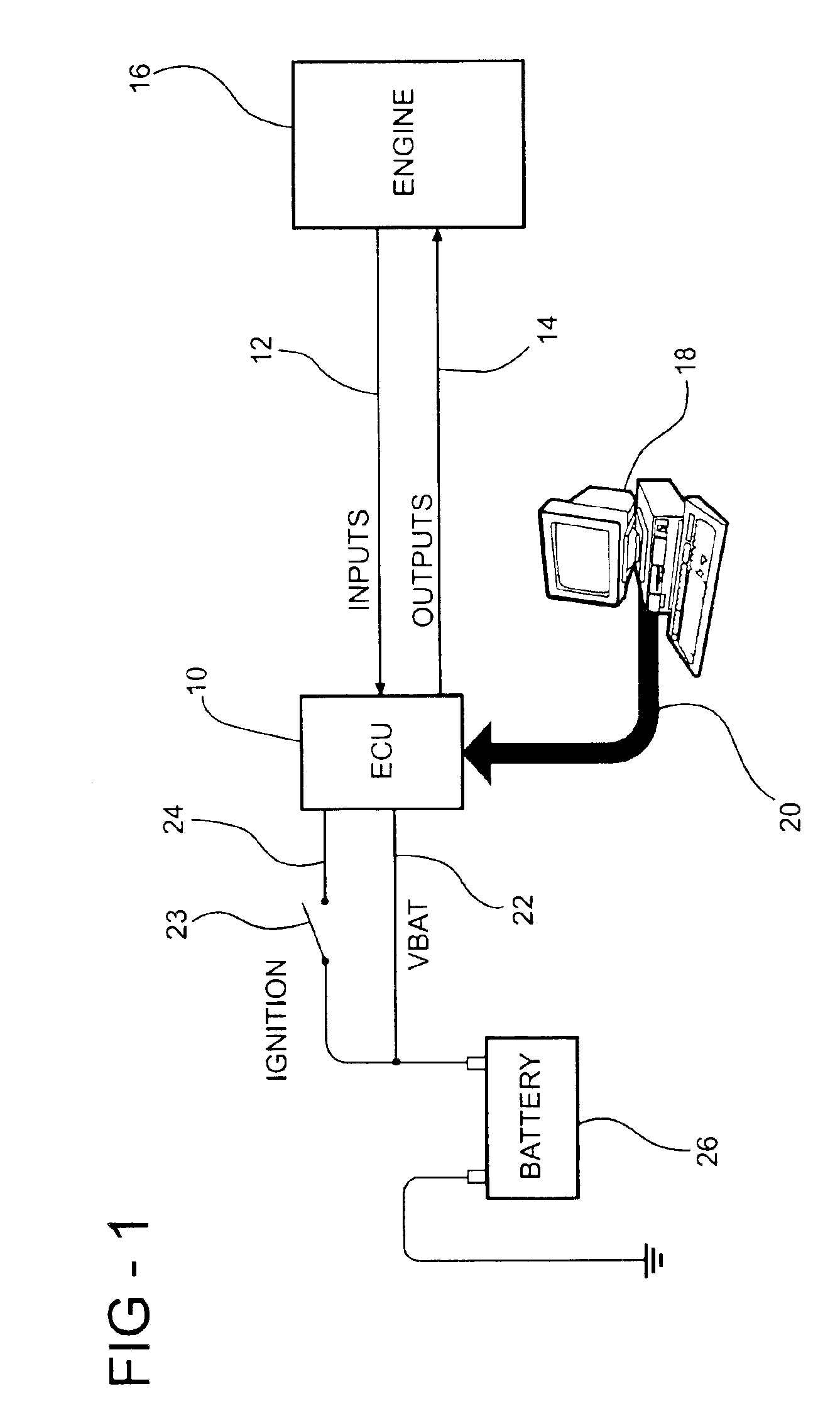
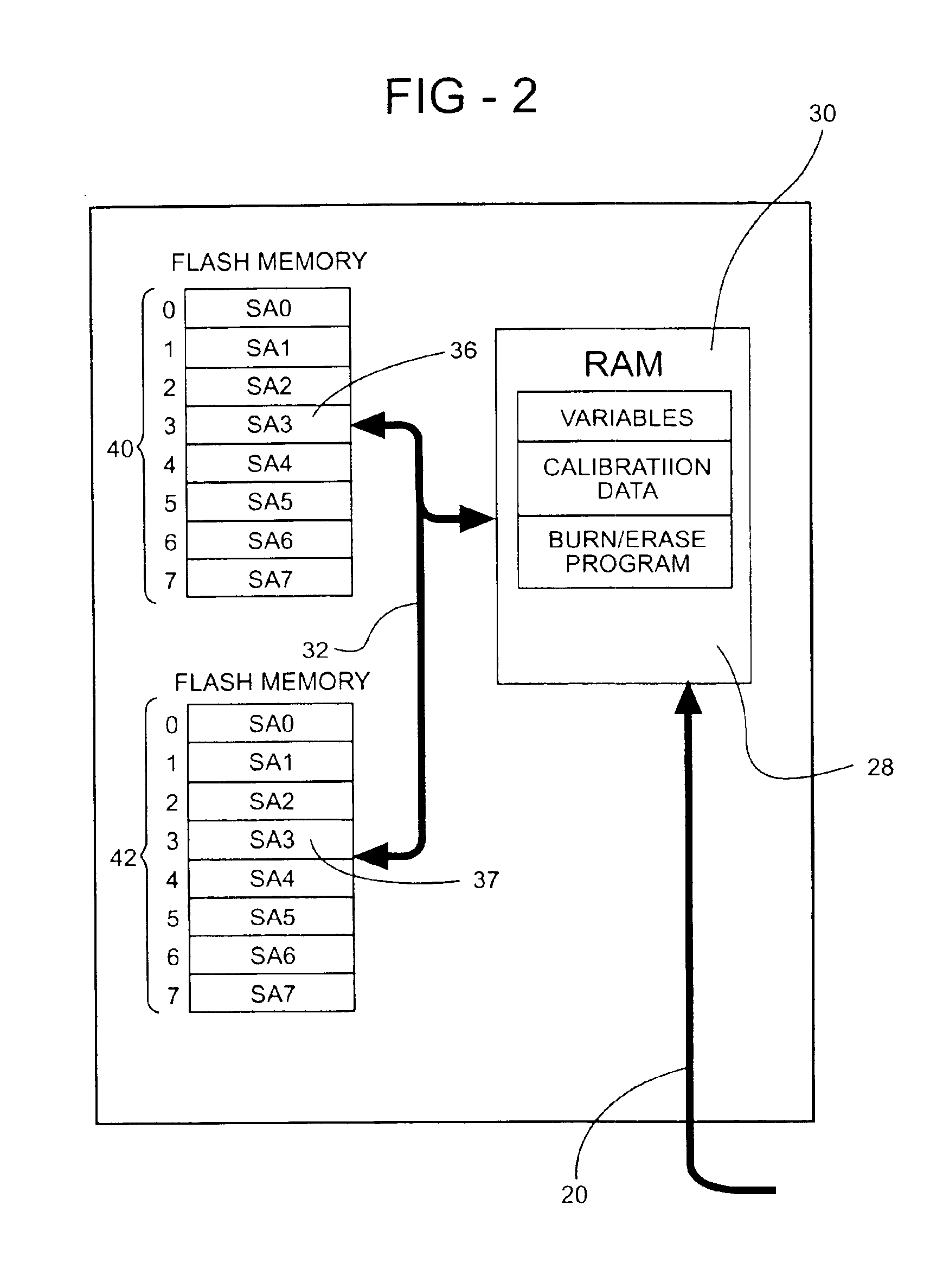
InactiveUS6928362B2Short amount of timeShorten development timeAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlComputer sciencePeripheral
A method for real time programmability of an engine electronic control unit (ECU). The present invention allows a user to update calibration data previously stored in memory in the engine ECU with new calibration data sent from an external device. The user can monitor the effects of the new calibration data on the engine instantaneously without having to wait for a period of time for the new calibration data to be permanently stored in the engine ECU's memory. To permanently store the new calibration data into the main memory, an erase / reprogram subroutine is uploaded from the main memory to a temporary memory. After the erase / reprogram subroutine is uploaded into the temporary memory location, the erase / reprogram subroutine will execute and permanently download the new calibration data into the main memory in response to a predetermined vehicle event.
Owner:MEANEY JOHN
Video controller system with screen caching
A graphics controller which performs display list-based video refresh operations and compresses assembled scan lines or portions thereof is disclosed. The graphics controller maintains a virtual display refresh list (VDRL) comprising a plurality of pointers to scan line segments in memory. The graphics controller may also create, maintain, and delete draw display lists (DDLs) that comprise pointers to object display list subroutines (ODLs) that independently draw objects in memory. The ODLs may allocated one or more buffers in memory into which different frames of the objects are drawn. When an ODL has completed executing, the corresponding pointer in the DDL may be updated to point to the buffer location in memory that stores the newly completed object frame. The VDRL is maintained independently (and may be doubled-buffered) and is updated using the DDLs. The video data assembled as the VDRL is executed is output to the display device. The video data may also be compressed and stored into memory. If the underlying graphics objects have not been changed since the previous screen refresh, the compressed video data in memory may be used in lieu of following the corresponding pointers in the VDRL.
Owner:INTERACTIVE SILICON
Determination of local variable type and precision in the presence of subroutines
InactiveUS6442751B1Accurate trackingData processing applicationsSoftware engineeringLocal variableComputer science
A method is provided for tracking the type of at least one local variable after calling a subroutine. The exemplary method associates each one of a plurality of branch instructions calling the subroutine with a first information, which indicates the type of value stored in the local variable when each one of the plurality of branch instructions is executed. The exemplary method associates at least one execution point-of-interest within the subroutine with a second information. The execution point-of-interest is any point within the subroutine where it may be necessary to ascertain the type of each local variable. The second information is a data structure indicating a change in type made to the local variable after entering the subroutine and before the execution point-of-interest. The exemplary method associates the execution point-of-interest with a return address for the subroutine. This return address enables the method to identify the point in the calling program from which the current subroutine was called. When a request is received to identify the type of the local variable at the execution point-of-interest in the subroutine, the exemplary method obtains a second map from the second information using the execution point-of-interest. The second map indicates the change in type of the local variable made within the subroutine. The method also obtains the return address associated with the execution point-of-interest, and obtains a first map from the first information using the return address. The first map indicates the type of value stored in the local variable when one of the branch instructions is executed to call the subroutine. Given the first and second maps, the exemplary method merges the first map with the second map to identify a current type for the local variable. In performing this merge, the method combines the type status of the local variable as modified by the subroutine with the type status of the local variable as it stood before calling the subroutine.
Owner:IBM CORP
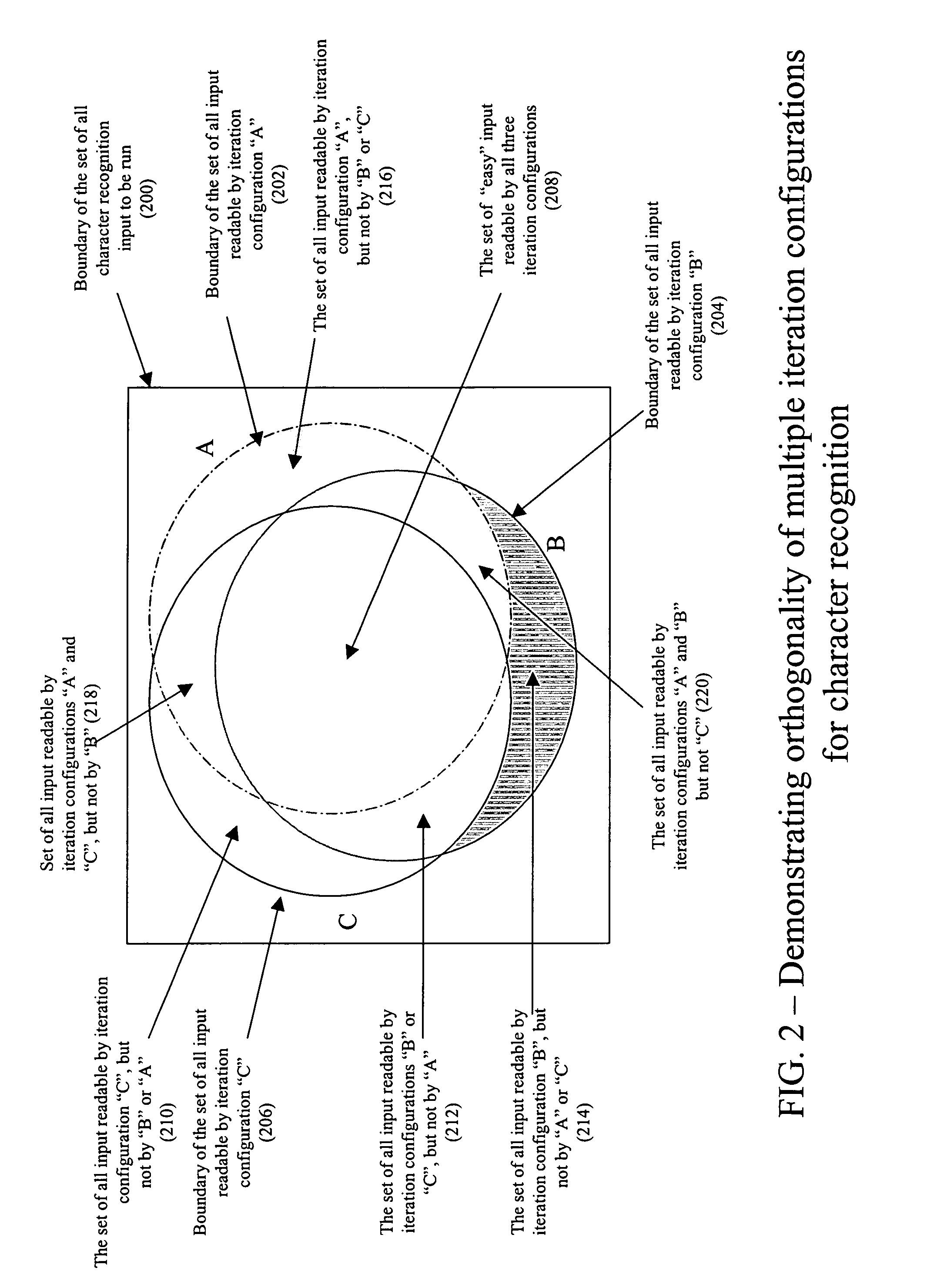
Orthogonal technology for character recognition
The present invention encompasses a self-orthogonal character recognition engine for executing an iterative method employing a database of predetermined character strings. The method receives a digital representation of a character string. It then generates a proposed result string by applying to the captured digital image a predetermined recognition routine including one or more recognition subroutines. Each recognition subroutine employs an initial parameter setting. Next, if the proposed result string does not match any of the predetermined character strings in the database, the initial parameter setting of a recognition subroutine is changed to a next setting. The recognition process is then repeated using the next parameter setting to generate and test a next result string. The process can be repeated iteratively until a result string is verified or the process times out.
Owner:MATTHEWS INT CORP
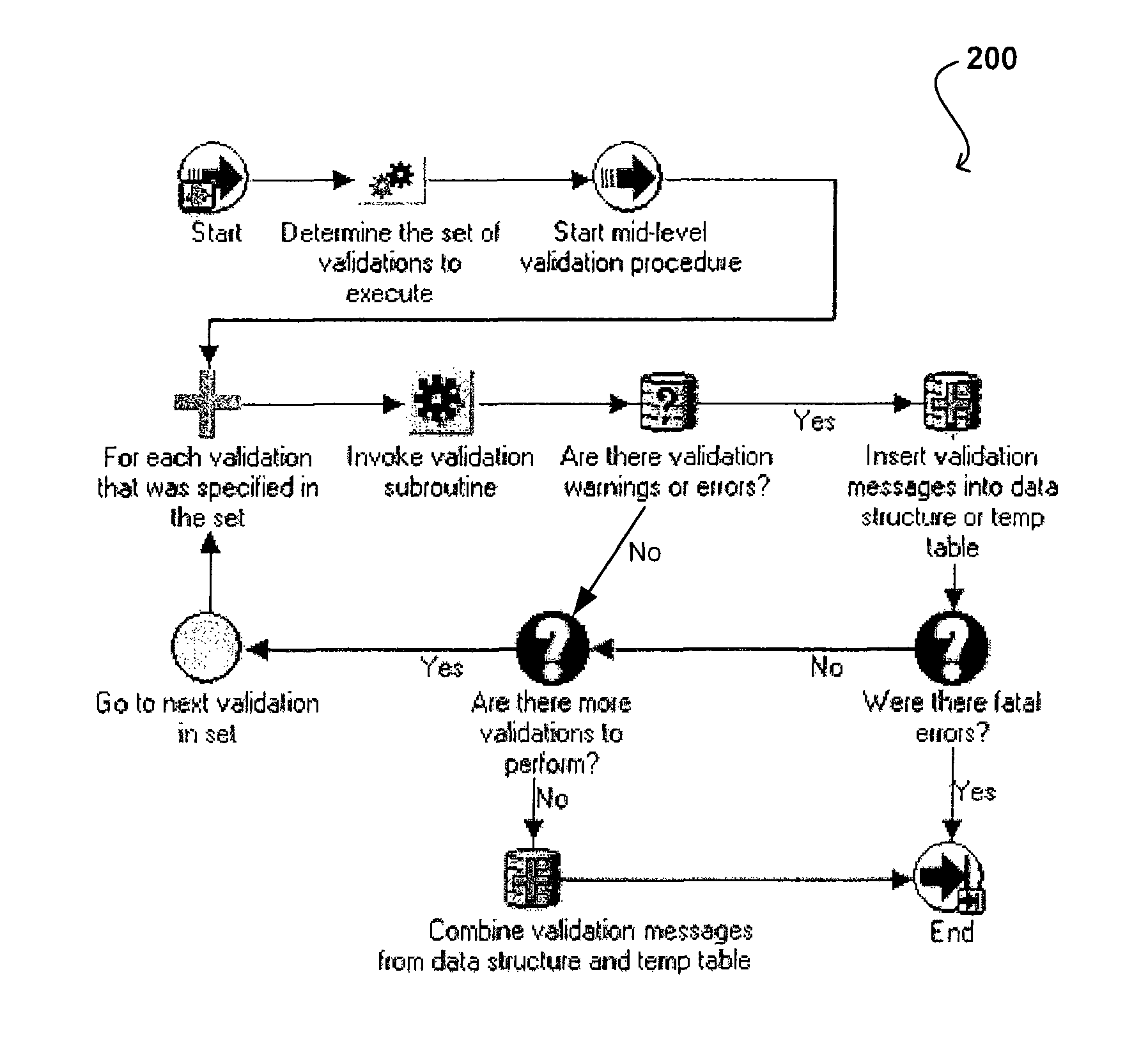
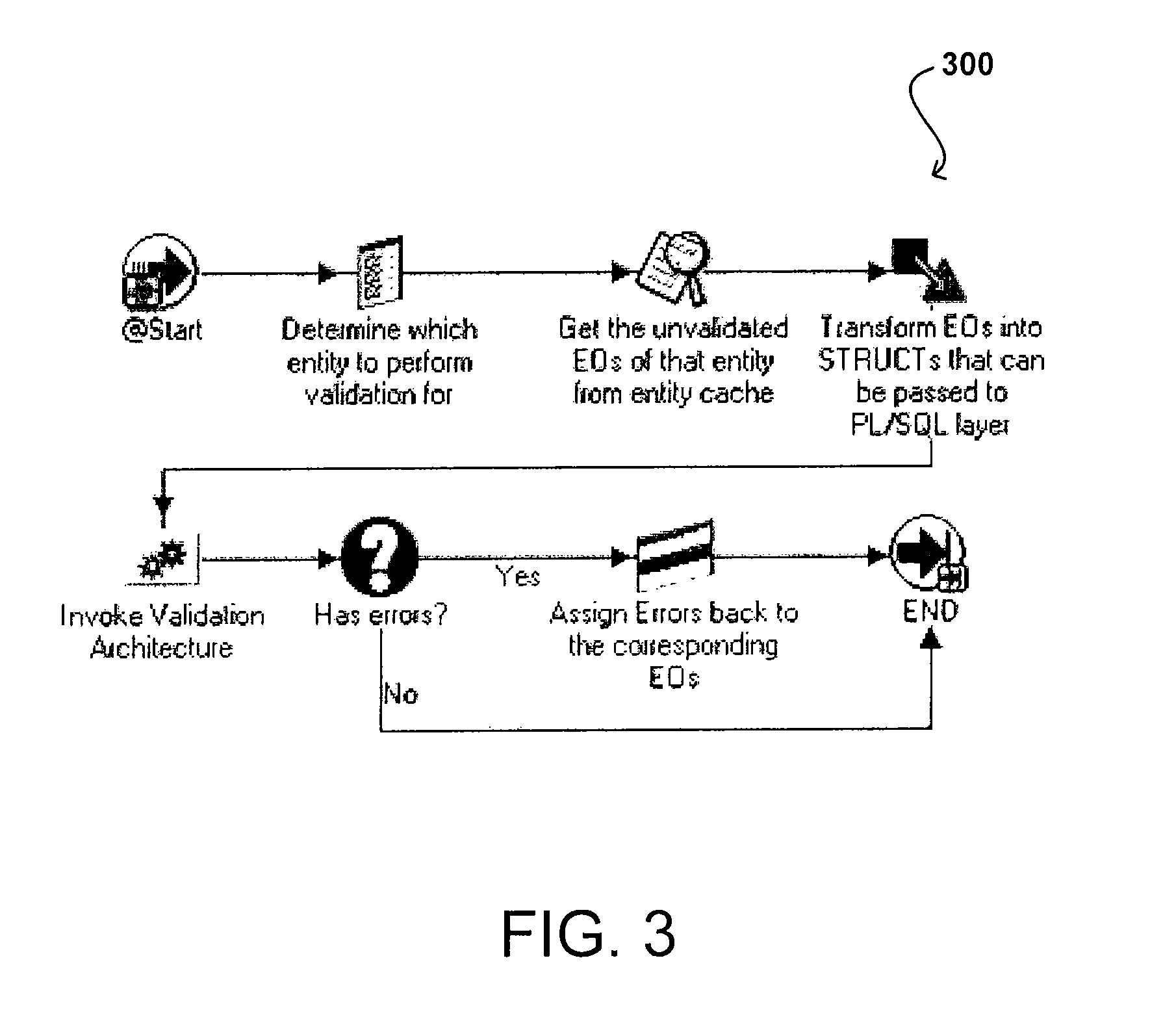
Architecture for data validation
ActiveUS8418142B2Easy to createSufficient flexibilitySoftware designSpecific program execution arrangementsData validationDuplicate code
A data validation architecture is provided that minimizes duplicate code and enables easy creation of new validations using a high-performance and scalable design. Such an architecture provides sufficient flexibility to disable certain validations when they are not applicable to the flow, interpret validation failures differently according to requirements of the calling application, and specify the type of document for which a particular validation is applicable. The architecture provides a standardized flow for performing data validation, specifying a set of required parameters for validation subroutines, as well as where validation results are to be stored for access by a calling program. Such an architecture also provides a framework for performing common processing required for most validation flows without restricting the flexibility of the validation subroutines.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
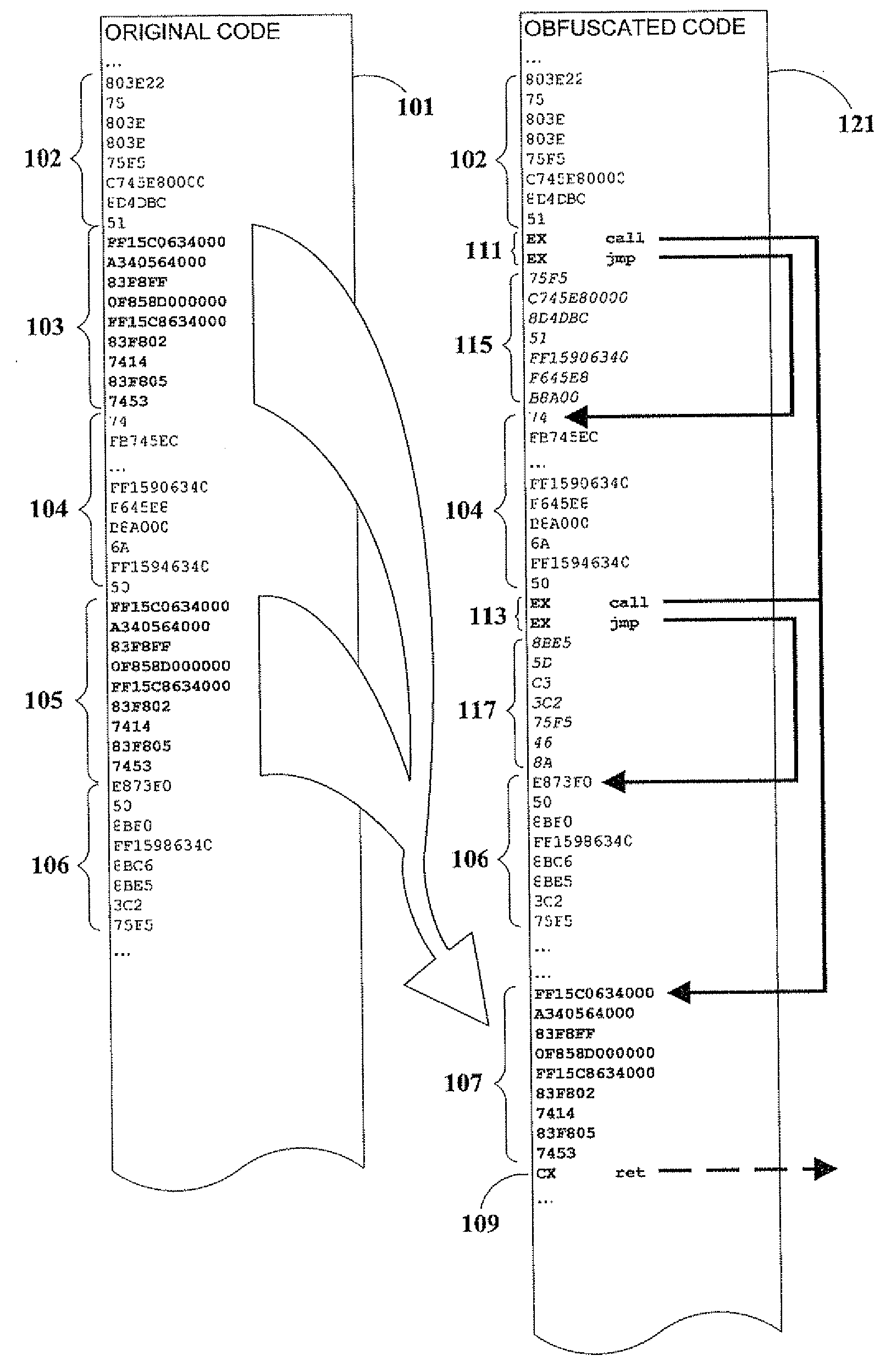
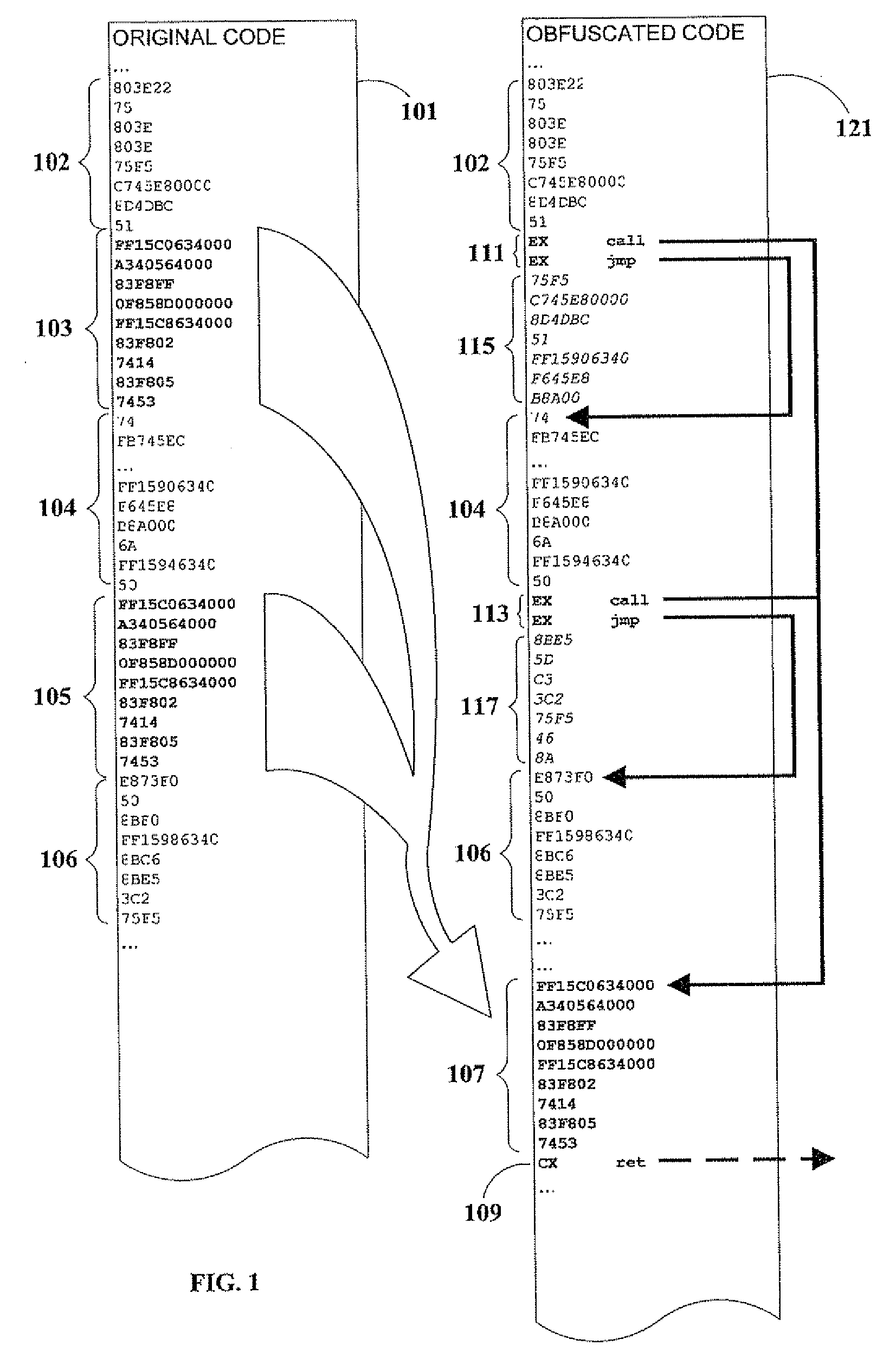
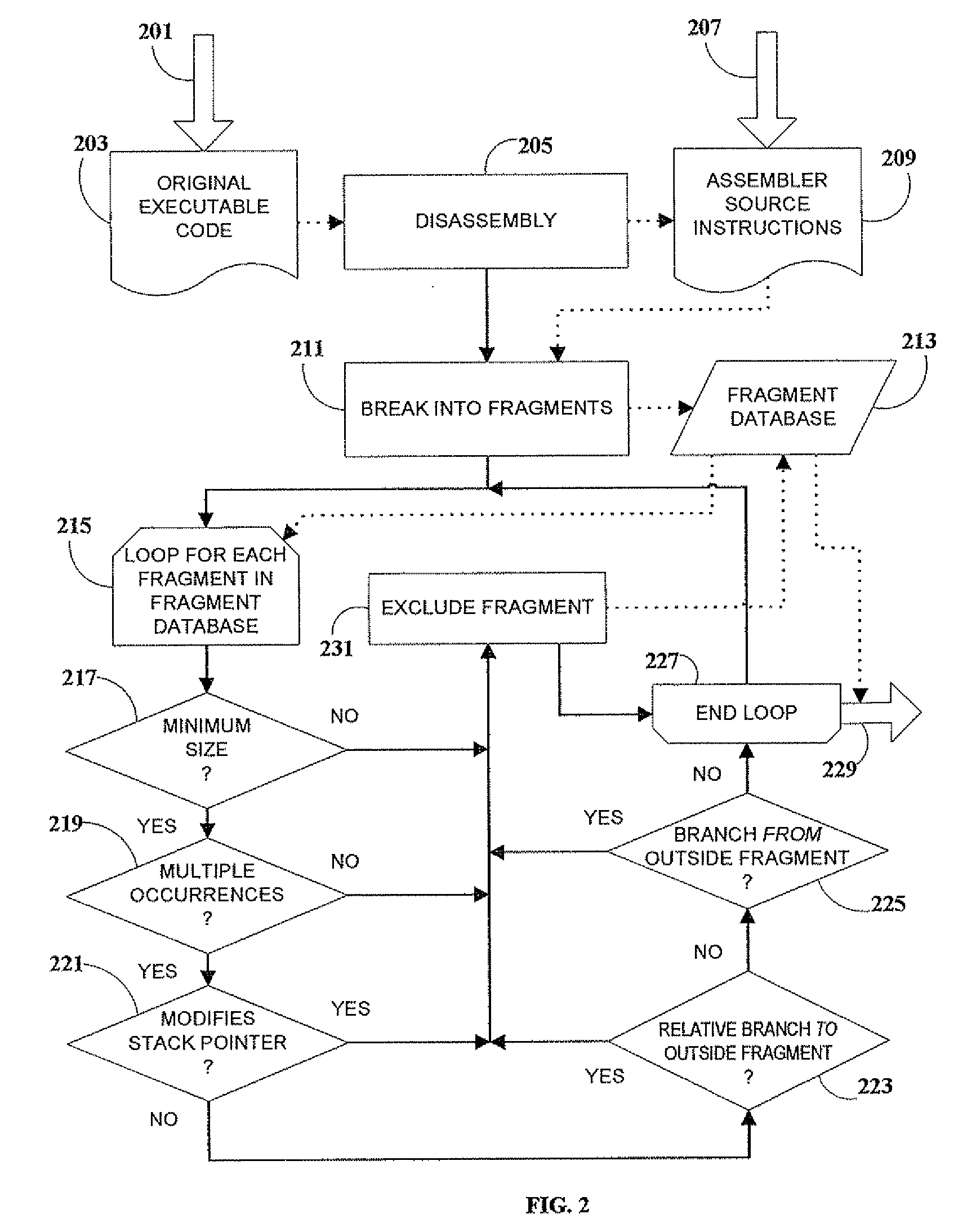
Code Obfuscation By Reference Linking
InactiveUS20090049425A1Improve efficiencyMinimize inflationProgram/content distribution protectionSpecific program execution arrangementsObfuscationDecoy
A method of obfuscating executable computer code to impede reverse-engineering, by interrupting the software's execution flow and replacing in-line code with calls to subroutines that do not represent logical program blocks. Embodiments of the present invention introduce decoy code to confuse attackers, and computed branching to relocated code so that actual program flow cannot be inferred from disassembled source representations.
Owner:SAFENET DATA SECURITY ISRAEL
Correction method and exposure apparatus
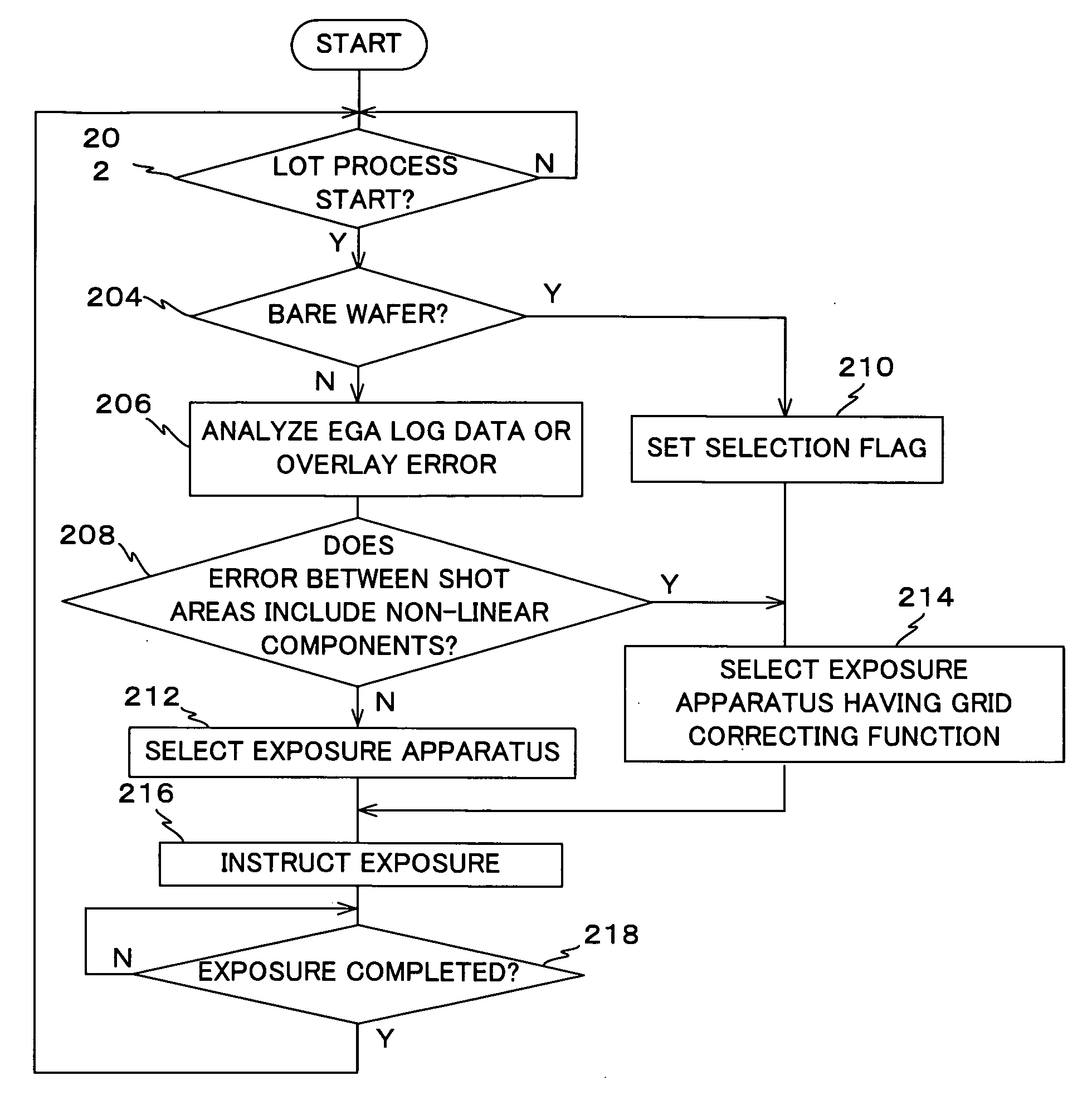
ActiveUS20090153817A1Short timePrecise functionPhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansLinear componentCorrection method
At Step 602, the grid of a wafer loaded into an exposure apparatus is approximated by a mathematical function fitting up to, for example, a cubic function, and at Step 612, the magnitude of a residual error between the position of a sample shot area obtained by the function and an actually measured position is compared with a predetermined threshold value. GCM measurement is performed in a mathematical function mode in a subroutine 616, or it is performed in a map mode in a subroutine 616, on the basis of the result of the comparison. In addition, it is determined whether to extract non-linear components from the wafer in each lot on the basis of a variation in the temperature of the wafer (Step 622) and a variation in random error between the wafers (Step 624).
Owner:NIKON CORP
Video controller system with object display lists
A graphics controller which performs display list-based video refresh operations that enable objects with independent frame rates to be efficiently assembled is disclosed. The graphics controller maintains a virtual display refresh list (VDRL) comprising a plurality of pointers to scan line segments in memory. The graphics controller also creates, maintains, and deletes draw display lists (DDLs) that comprise pointers to object display list subroutines (ODLs) that independently draw objects in memory. The ODLs may allocated one or more buffers in memory into which different frames of the objects are drawn. When an ODL has completed executing, the corresponding pointer in the DDL may be updated to point to the buffer location in memory that stores the newly completed object frame. The VDRL is maintained independently (and may be doubled-buffered) and is updated using the DDLs. Motion estimation may be performed by the graphics controller using the different frames of objects that are drawn into memory by the ODLs. The different object frames may also be animated by the graphics controller once they are drawn into memory. The object frames stored in memory may be compressed to conserve memory.
Owner:DIGIMEDIA TECH LLC
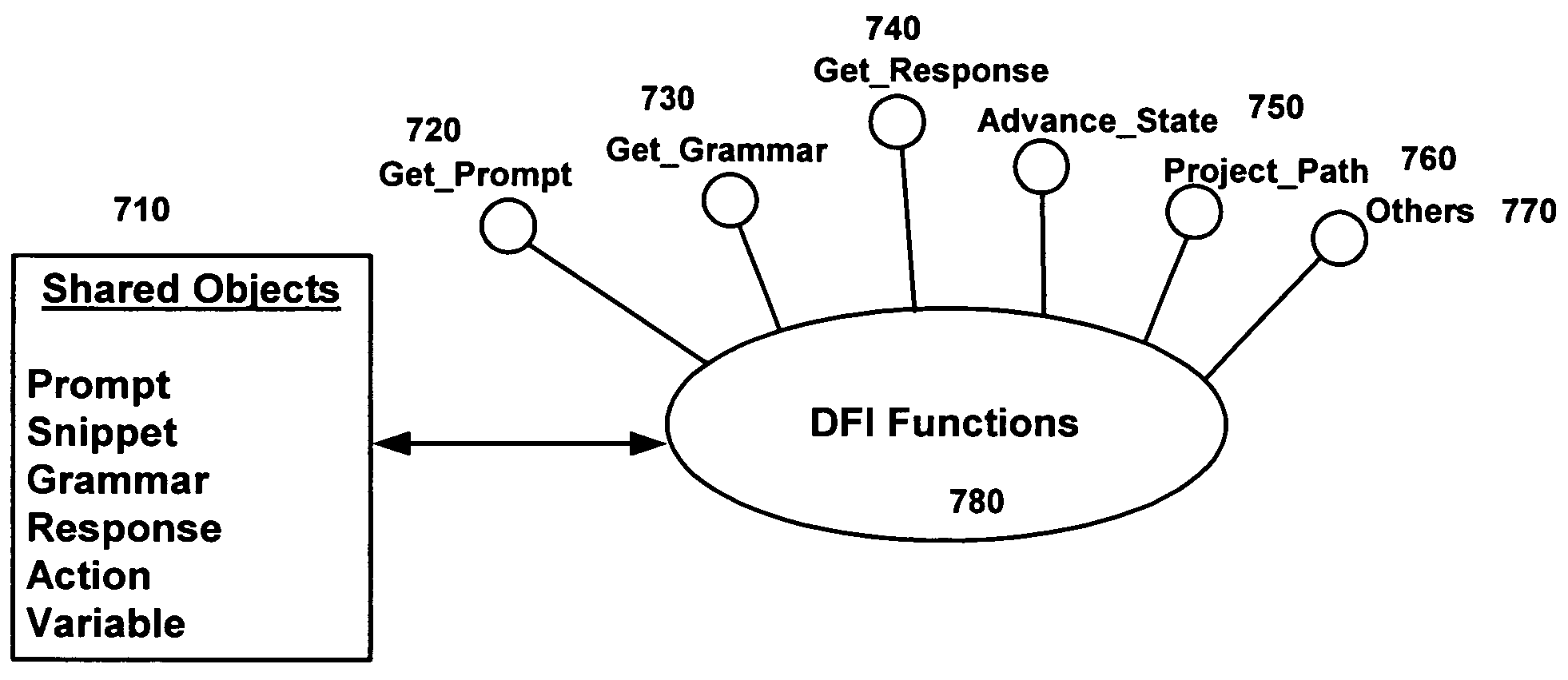
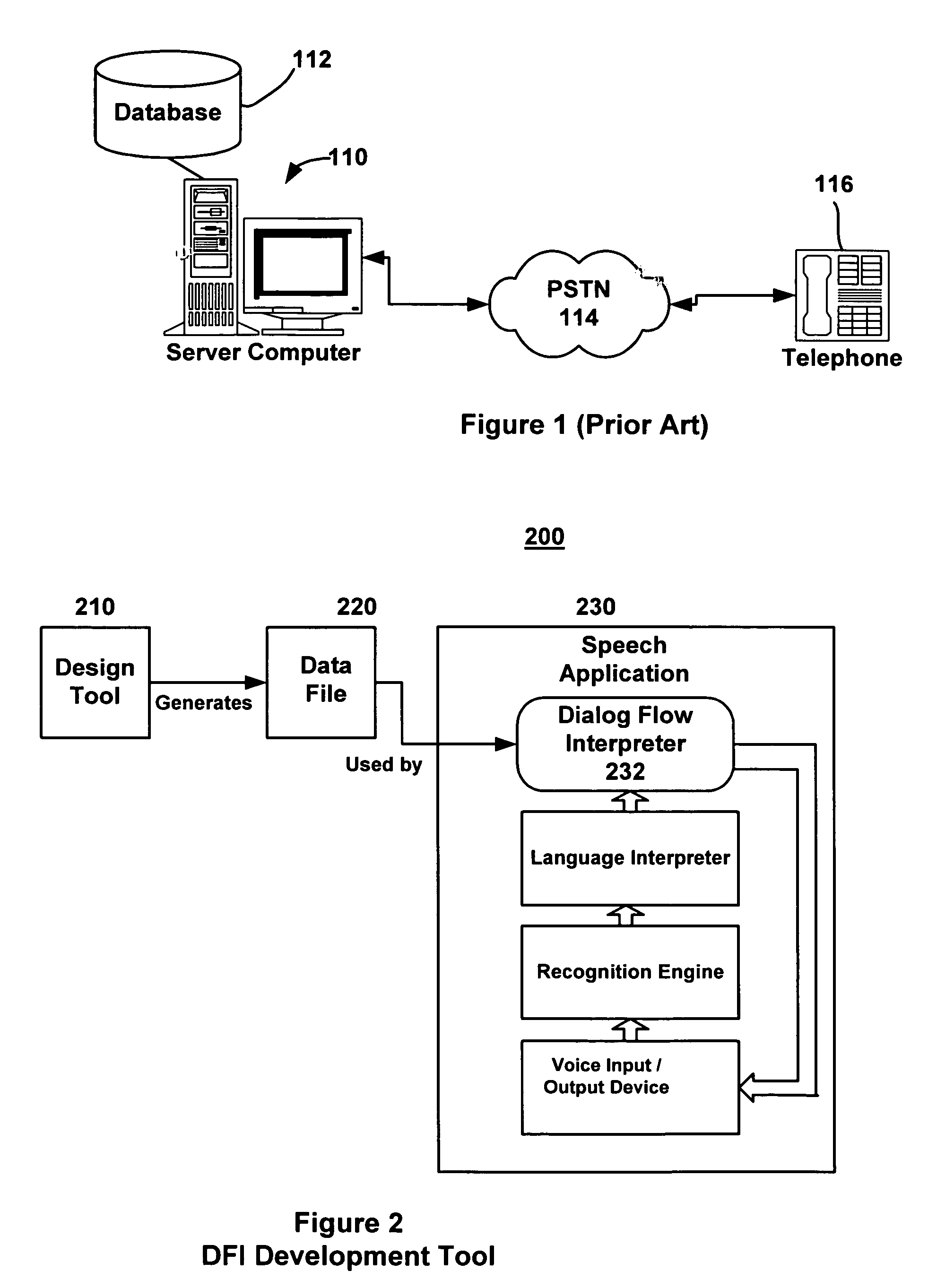
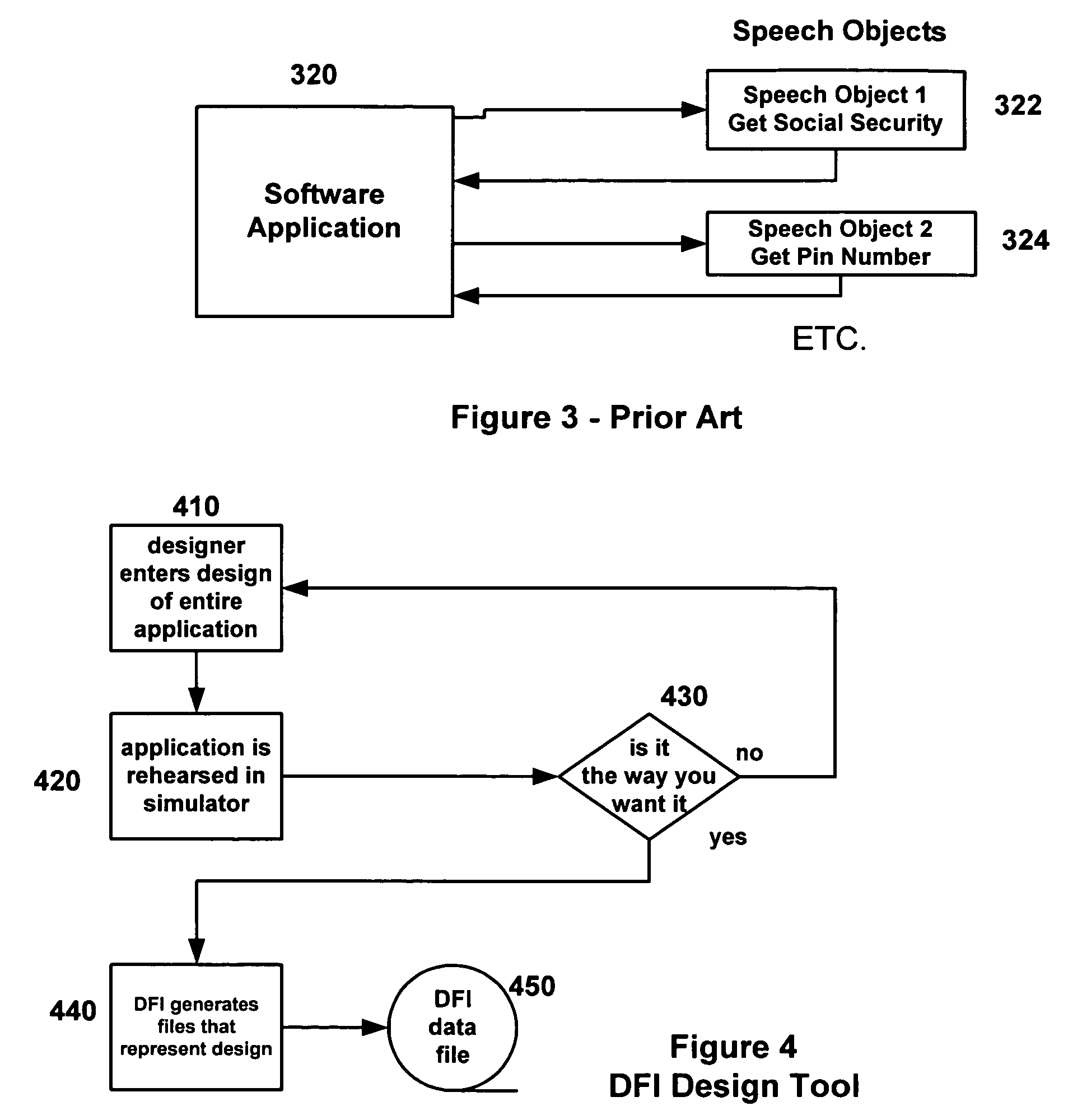
Dialogue flow interpreter development tool
InactiveUS7024348B1Easy to integrateEasy to changeSoftware engineeringSpeech recognitionSoftware developmentSubroutine
A computer software product is used to create applications for enabling a dialogue between a human and a computer. The software product provides a programming tool that insulates software developers from time-consuming, technically-challenging programming tasks by enabling the developer to specify generalized instructions to a Dialogue Flow Interpreter, which invokes functions to implement a speech application, automatically populating a library with dialogue objects that are available to other applications. The speech applications created through the DFI may be implemented as COM (component object model) objects, and so the applications can be easily integrated into a variety of different platforms. In addition, “translator” object classes are provided to handle specific types of data, such as currency, numeric data, dates, times, string variables, etc. These translator object classes have utility either as part of the DFI library or as a sub-library separate from dialogue implementation.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
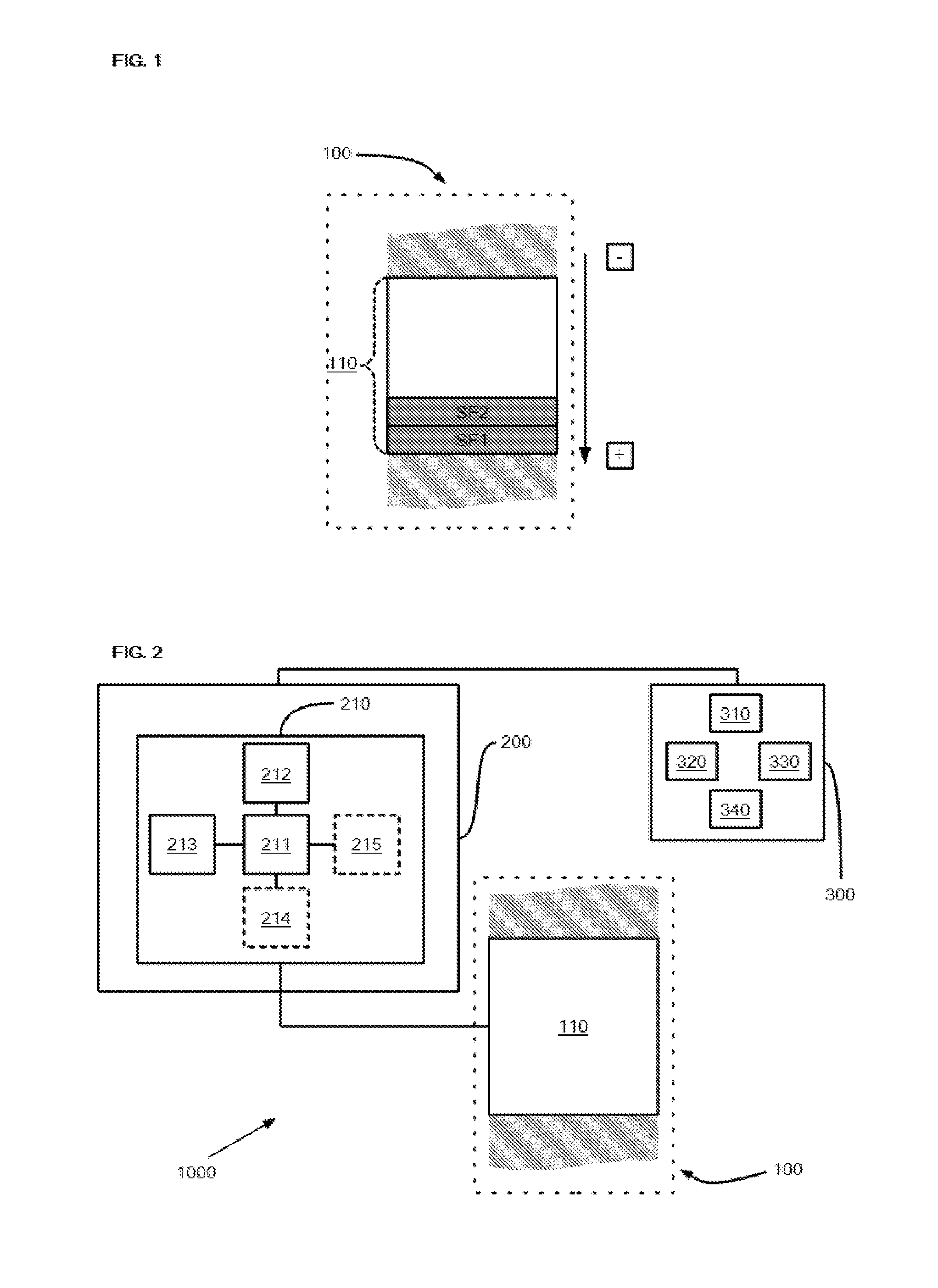
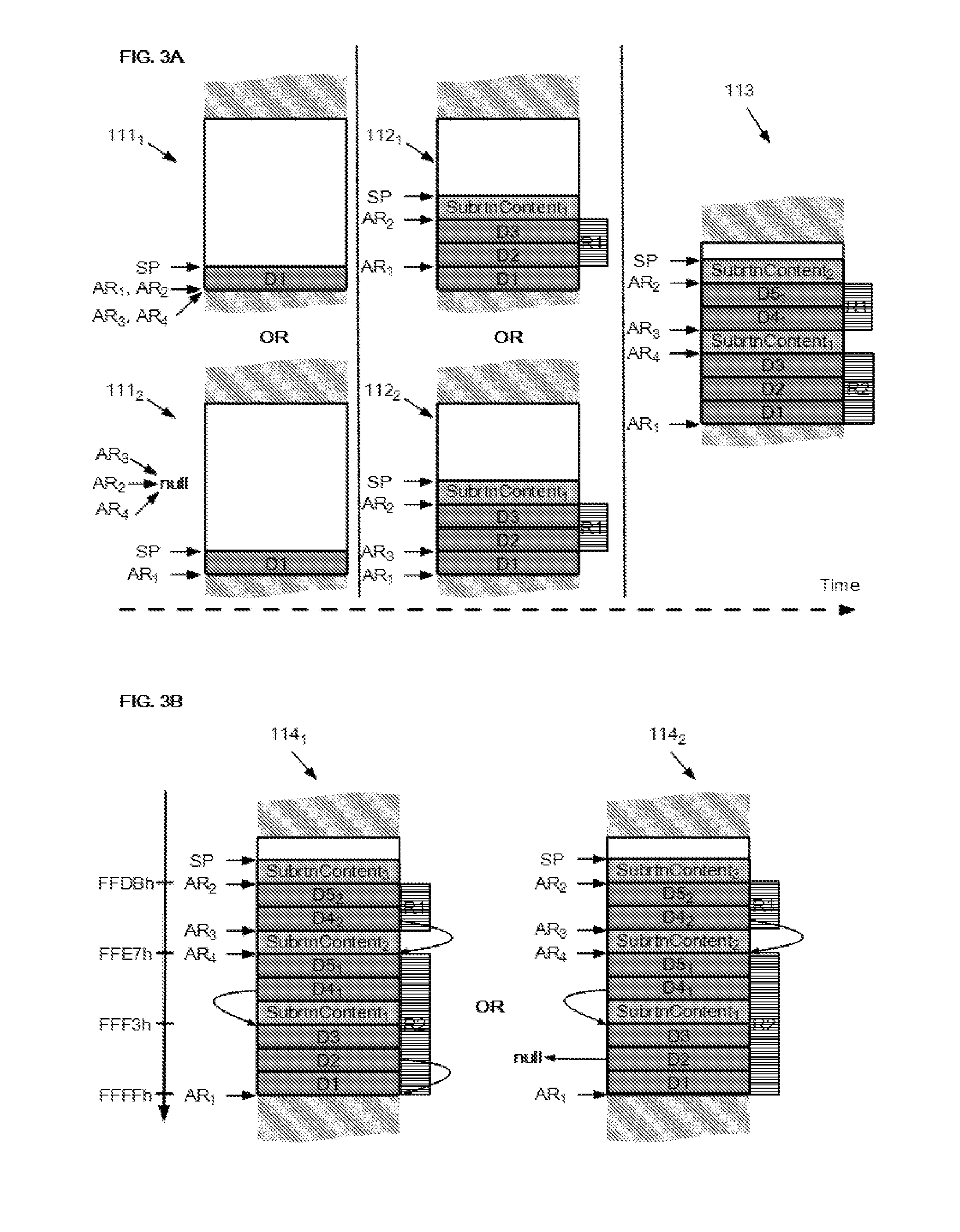
Dynamic subroutine stack protection
ActiveUS20150220453A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsSoftware engineeringProcessing element
A protection unit of a subroutine stack accessible by a CPU controlled by one main software program, for storing and removing stack frame(s), the stack protection unit being coupleable to the stack and the CPU, comprising:a processor coupled to a first and a second address register;wherein, when a first stack frame is stored onto the stack and the execution of the main software program is suspended by the CPU due to the execution of a subroutine;the processing unit is adapted to set one access rule based on the first and second address registers, preventing:the ongoing subroutine, from accessing a hardware-protected region of the stack, comprising at least one stack frame associated with a return address from which the main software program resumes execution after termination of the execution of the subroutine.A processor, a method and a computer program are also claimed.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com