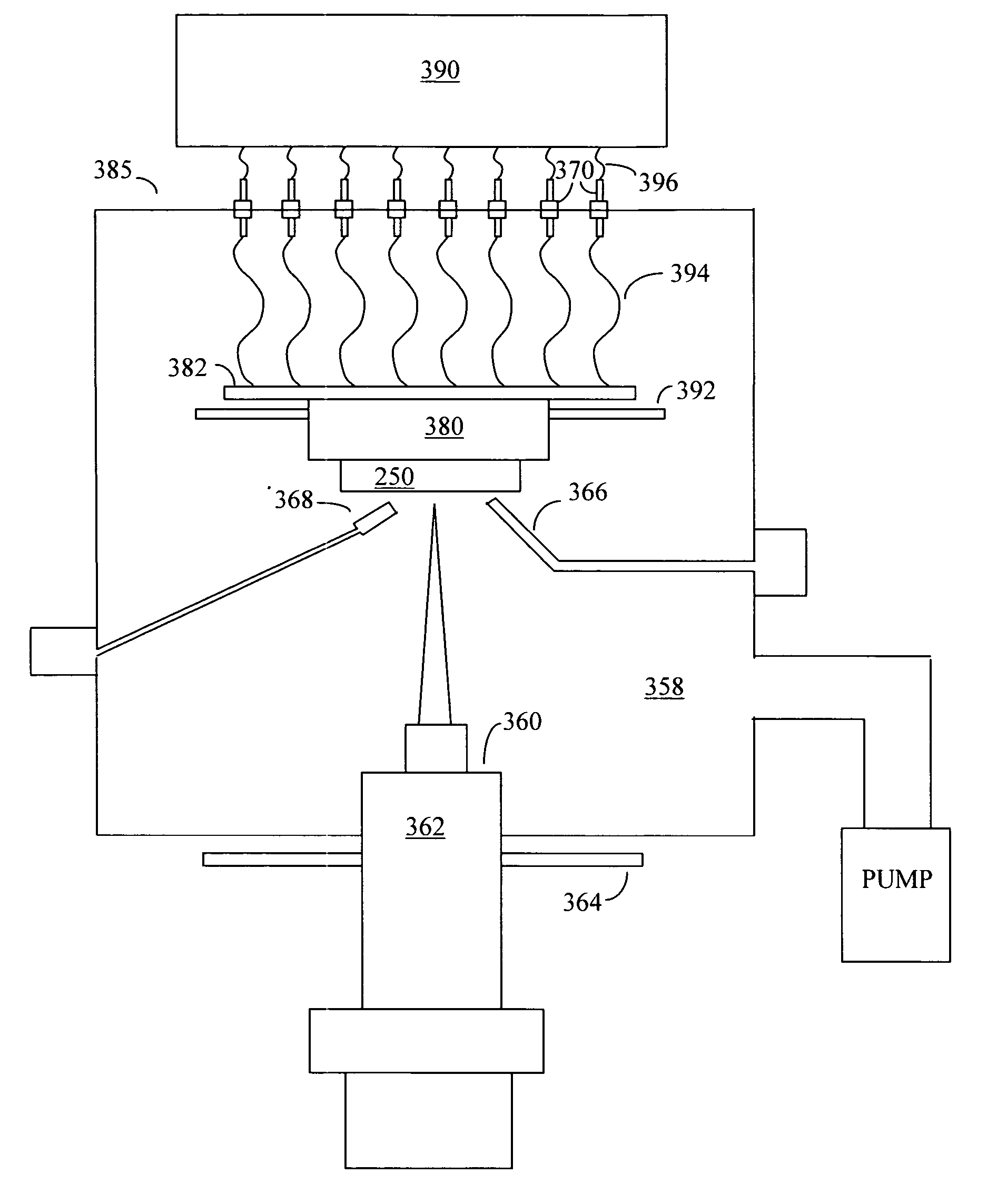
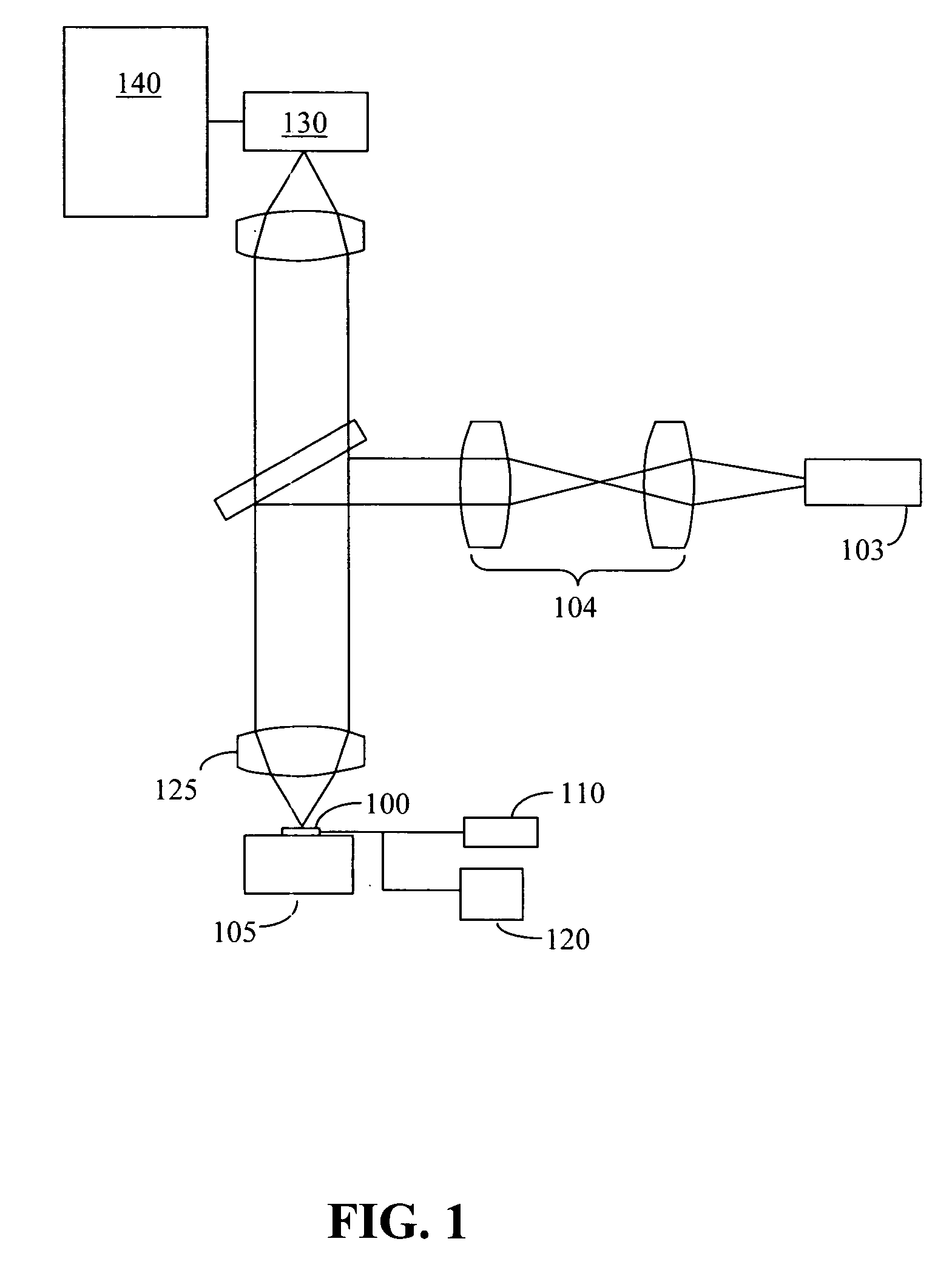
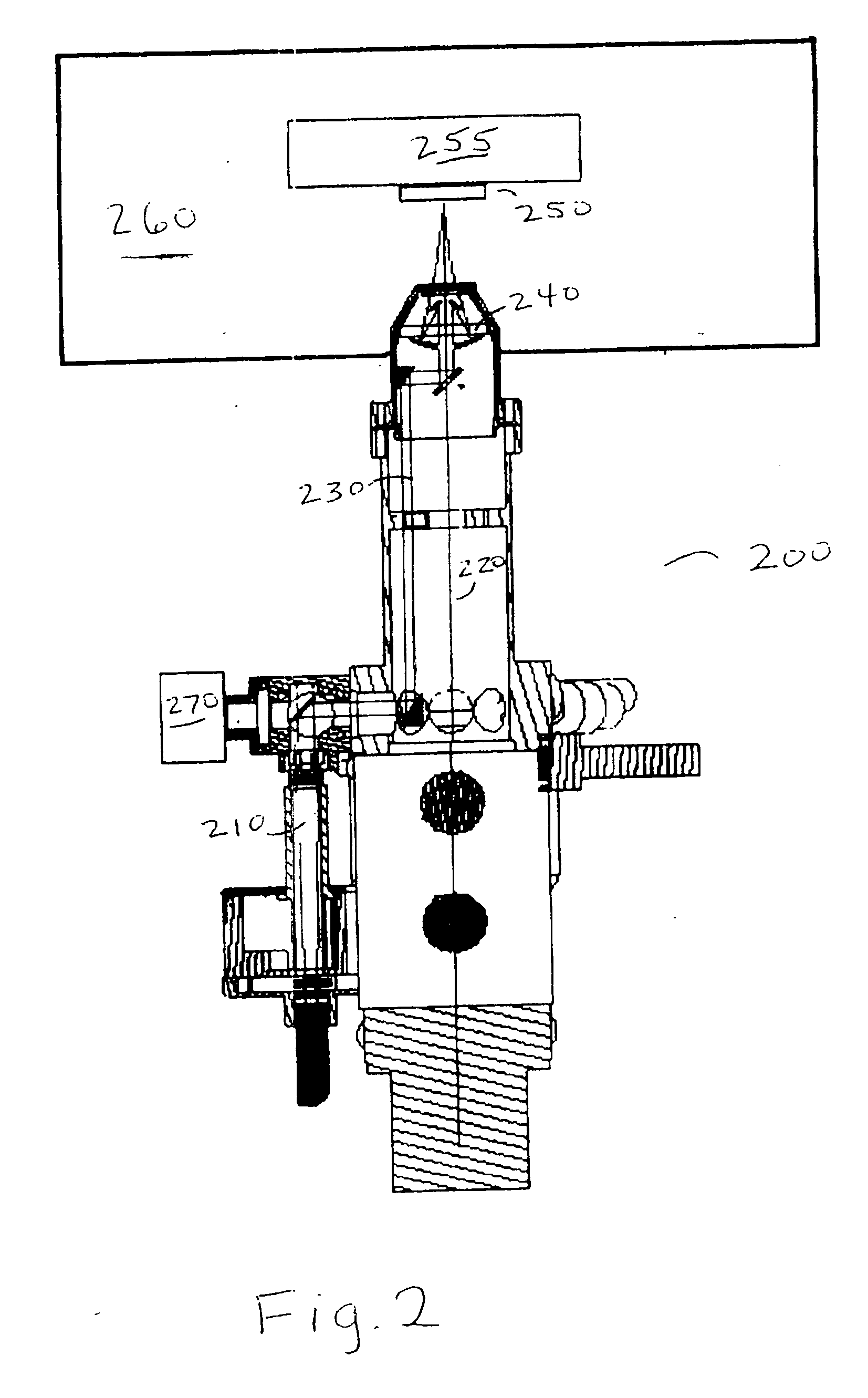
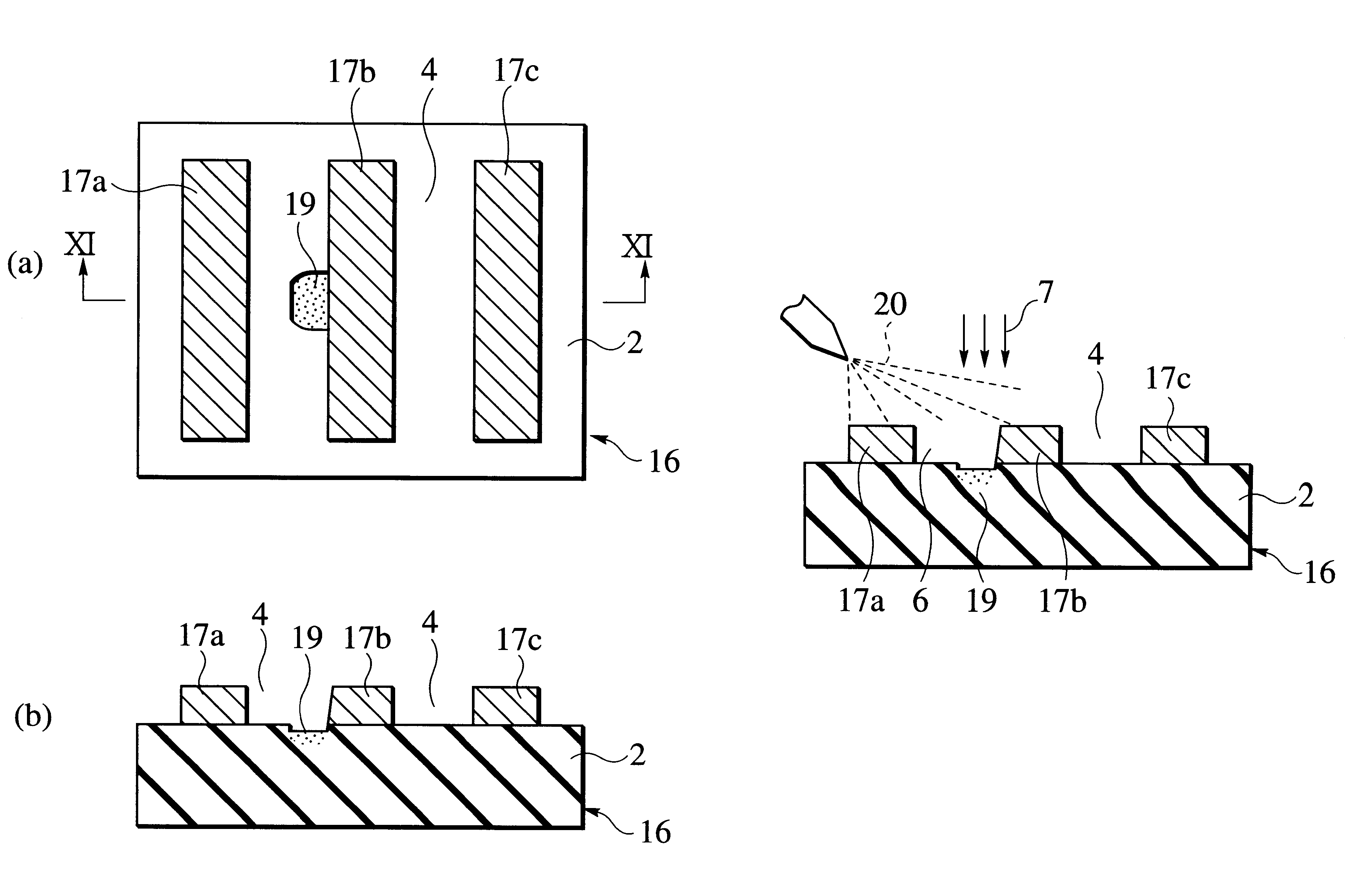
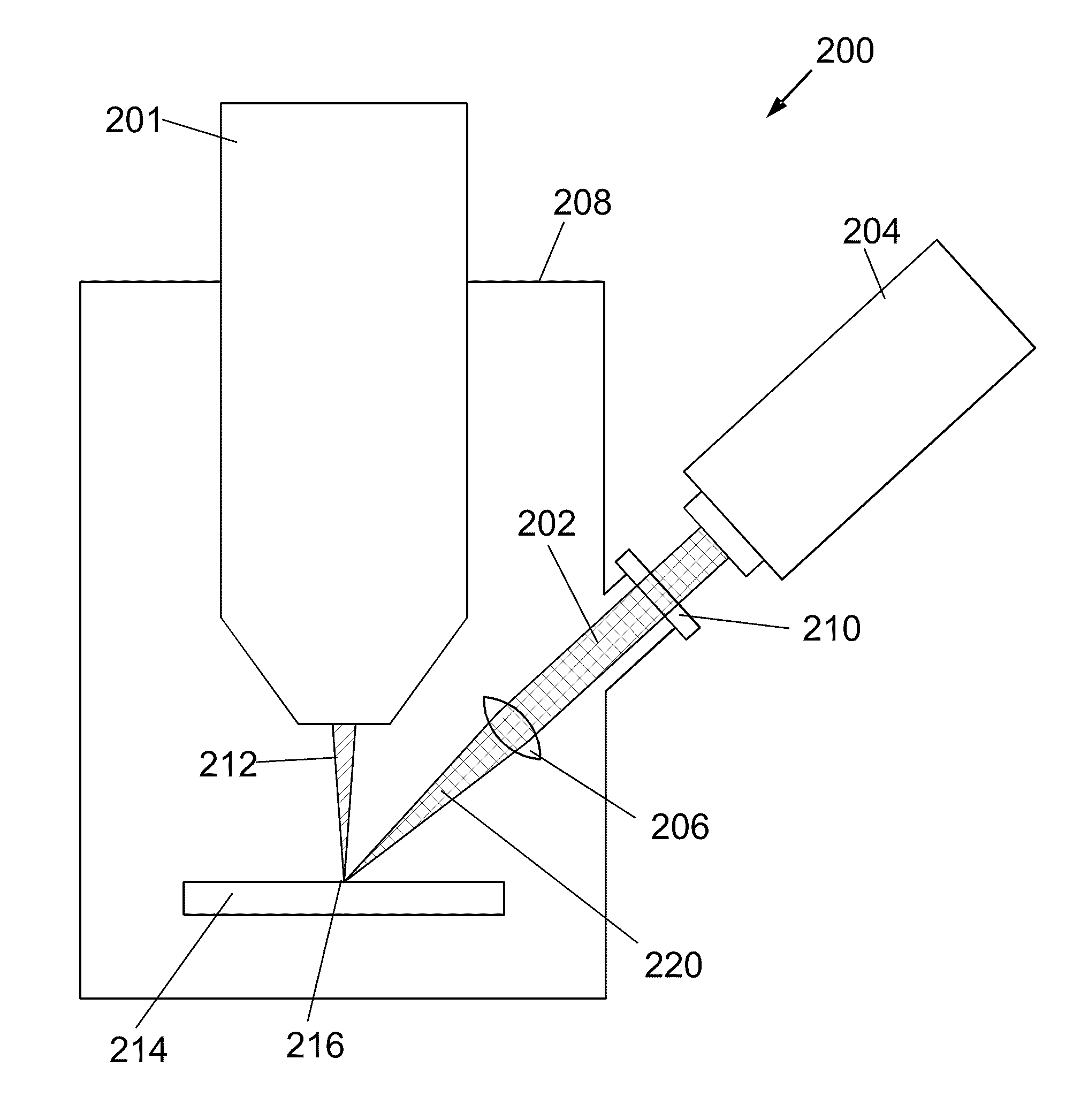
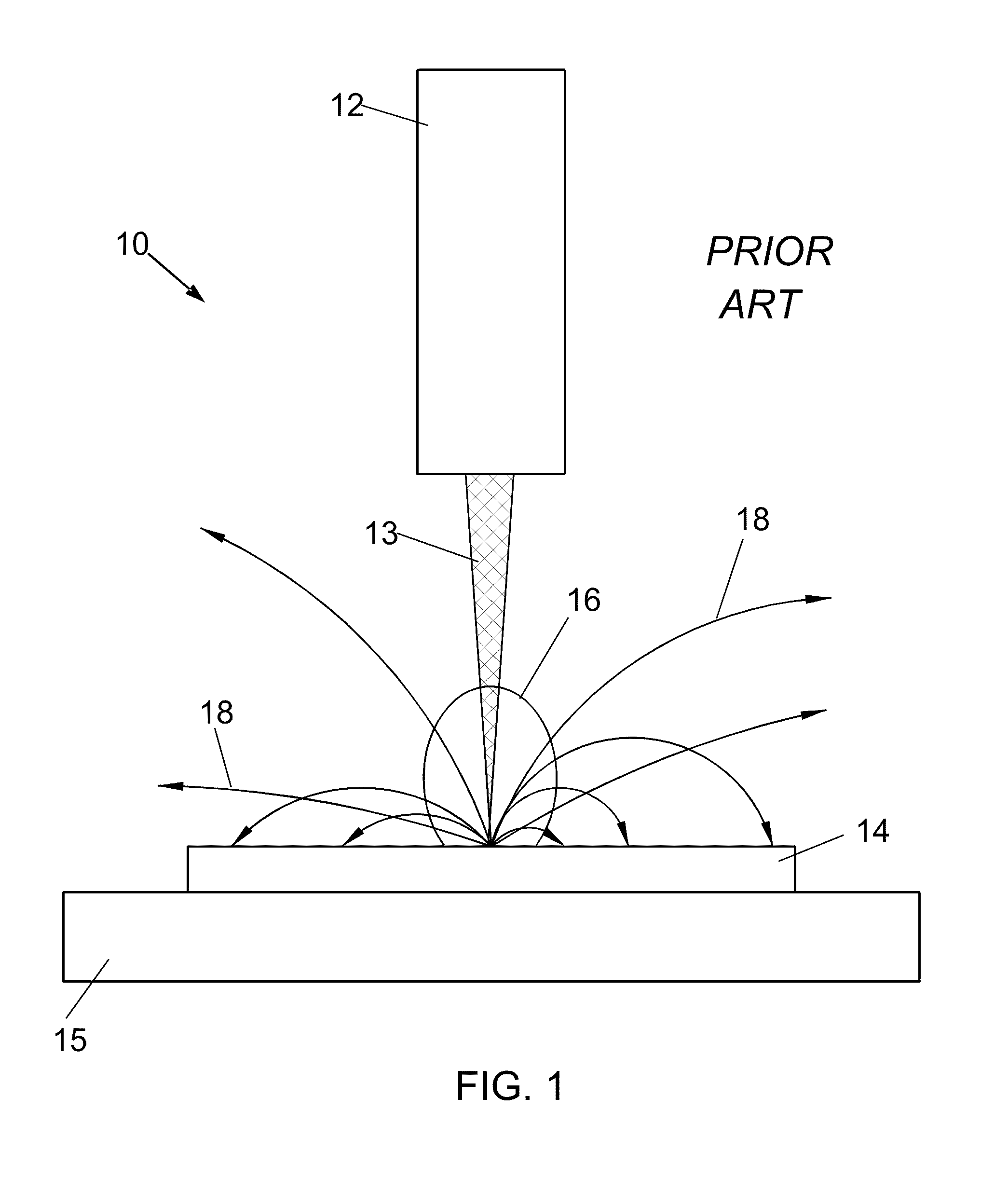
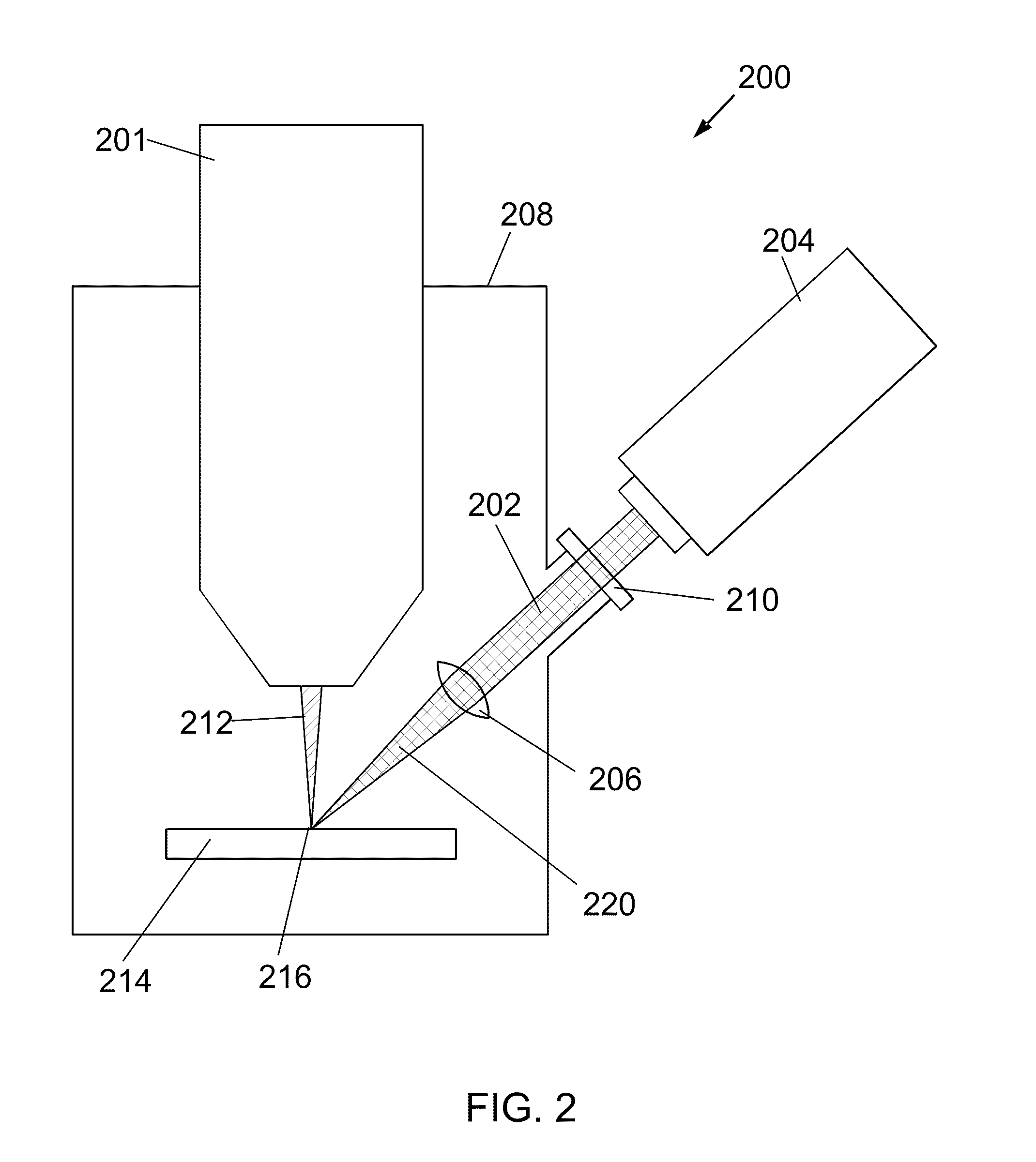
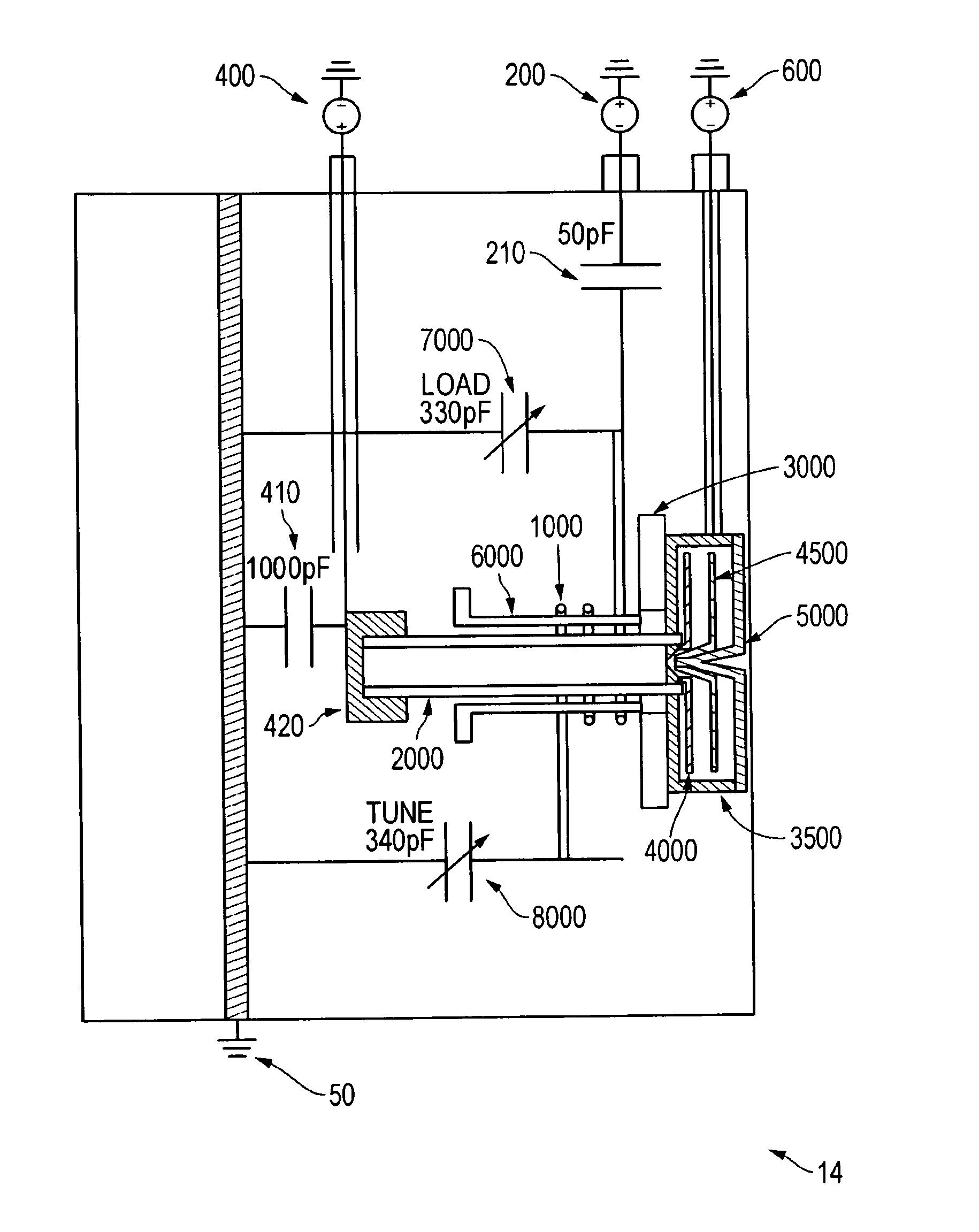
Patents
Literature
1255 results about "Focused ion beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
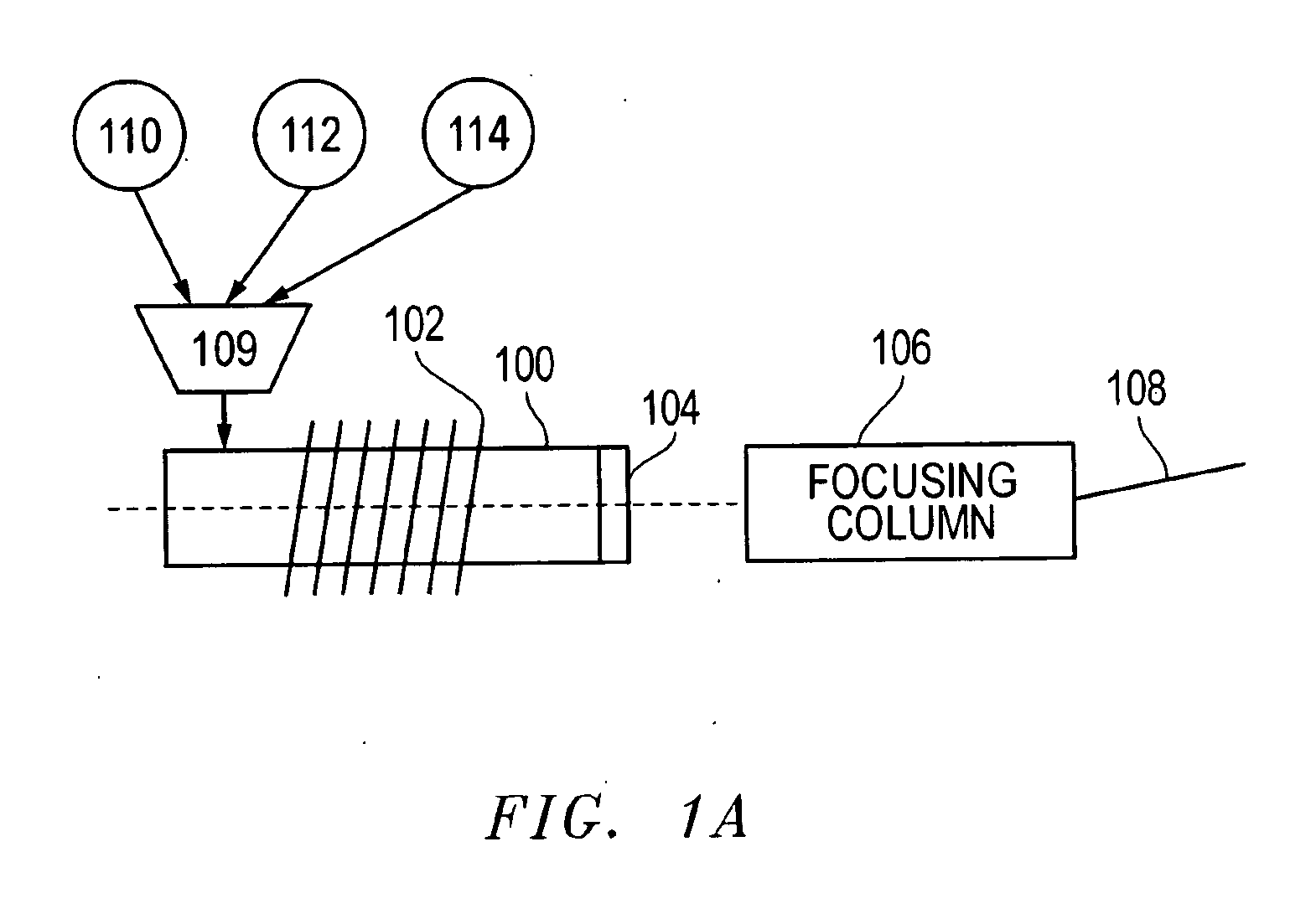
Focused ion beam, also known as FIB, is a technique used particularly in the semiconductor industry, materials science and increasingly in the biological field for site-specific analysis, deposition, and ablation of materials. A FIB setup is a scientific instrument that resembles a scanning electron microscope (SEM). However, while the SEM uses a focused beam of electrons to image the sample in the chamber, a FIB setup uses a focused beam of ions instead. FIB can also be incorporated in a system with both electron and ion beam columns, allowing the same feature to be investigated using either of the beams. FIB should not be confused with using a beam of focused ions for direct write lithography (such as in proton beam writing). These are generally quite different systems where the material is modified by other mechanisms.
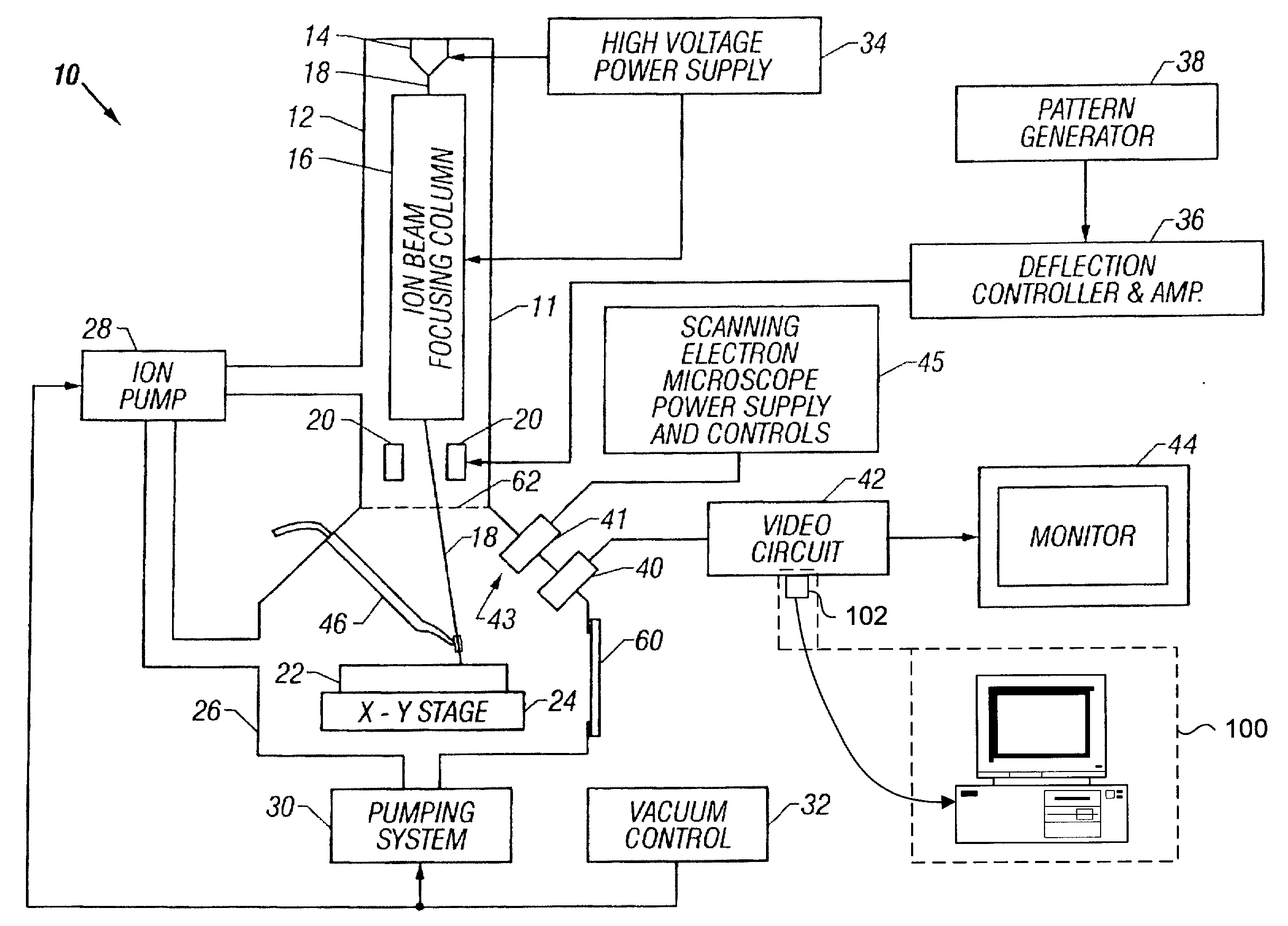
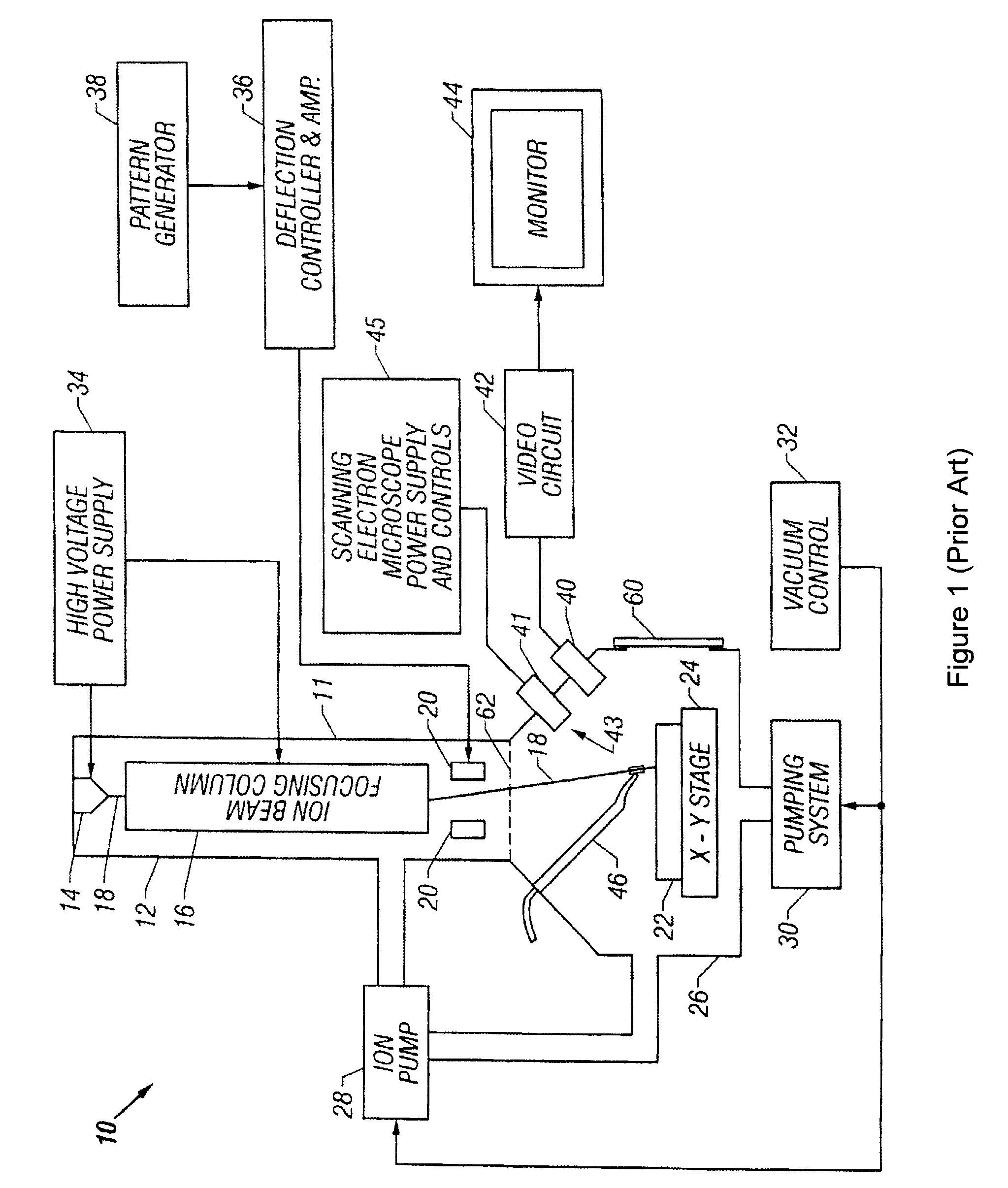
Apparatus and method for conformal mask manufacturing
ActiveUS20080160431A1Electric discharge tubesPhotosensitive materialsComputational physicsIrradiation
A manufacturing process technology creates a pattern on a first layer using a focused ion beam process. The pattern is transferred to a second layer, which may act as a traditional etch stop layer. The pattern can be formed on the second layer without irradiation by light through a reticle and without wet chemical developing, thereby enabling conformal coverage and very fine critical feature control. Both dark field patterns and light field patterns are disclosed, which may enable reduced or minimal exposure by the focused ion beam.
Owner:NEXGENSEMI HLDG INC
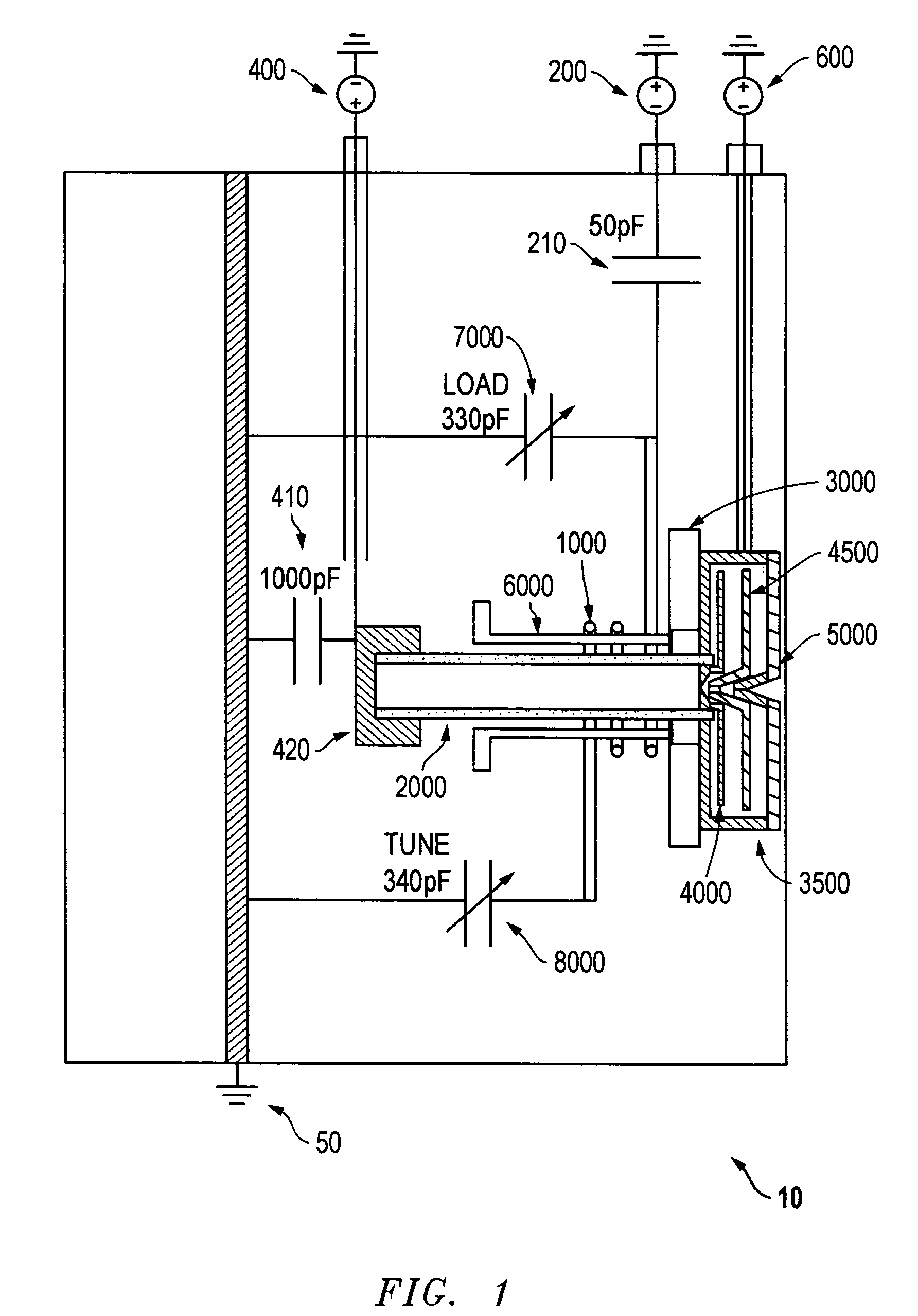
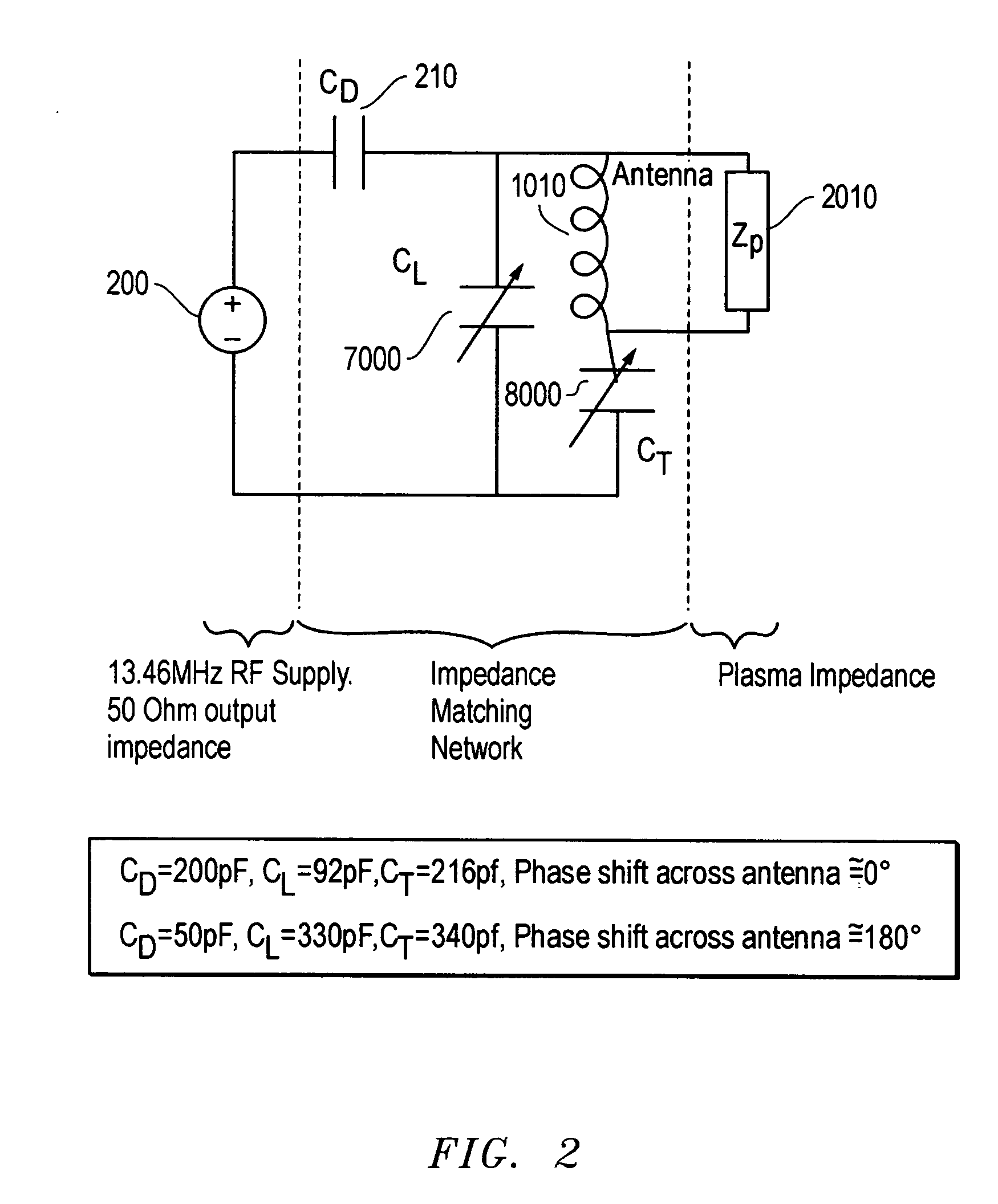
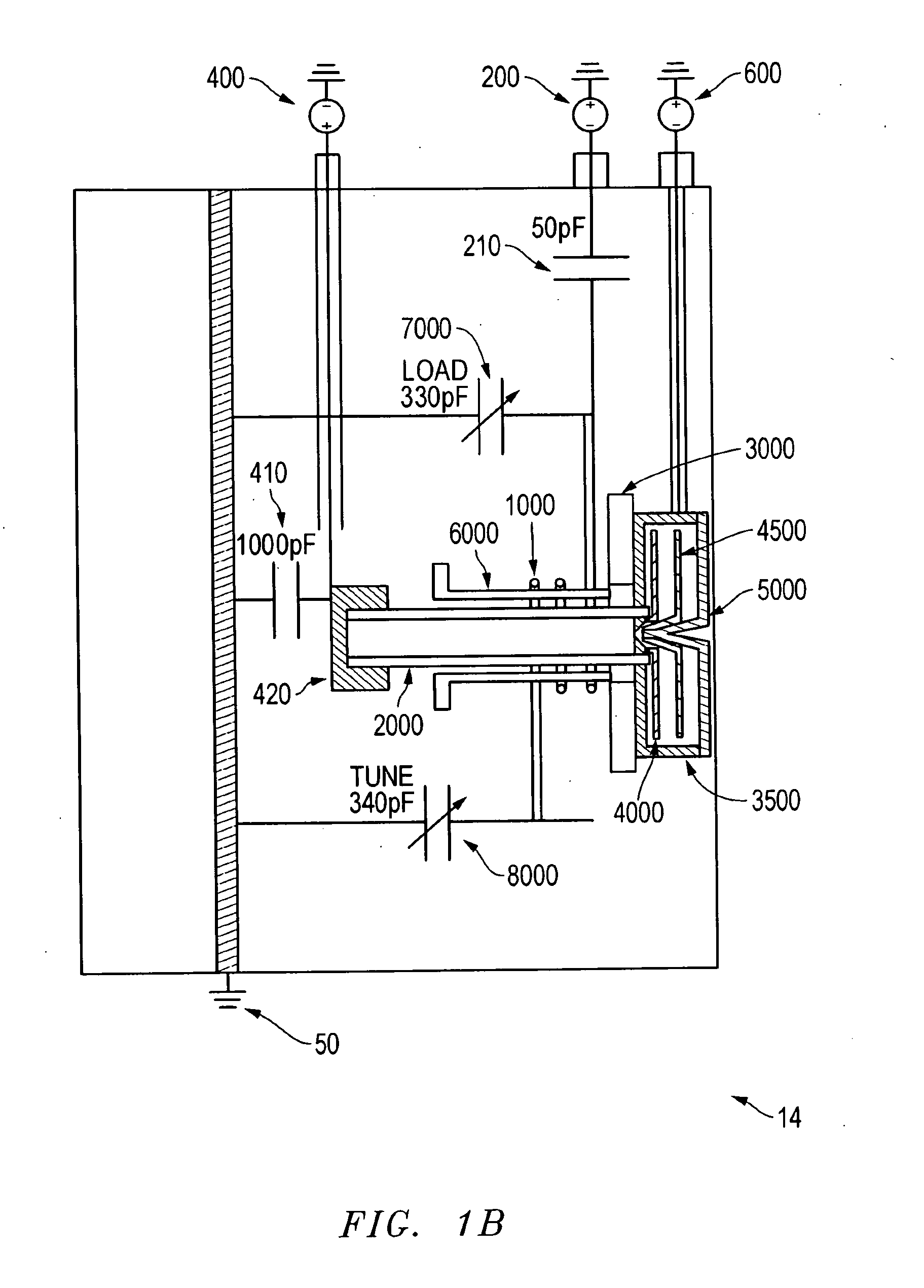
Magnetically enhanced, inductively coupled plasma source for a focused ion beam system
ActiveUS7241361B2Increase ion densityEliminate plasma potential modulationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationIon beamCombined use
The present invention provides an inductively coupled, magnetically enhanced ion beam source, suitable to be used in conjunction with probe-forming optics to produce an ion beam without kinetic energy oscillations induced by the source.
Owner:FEI CO
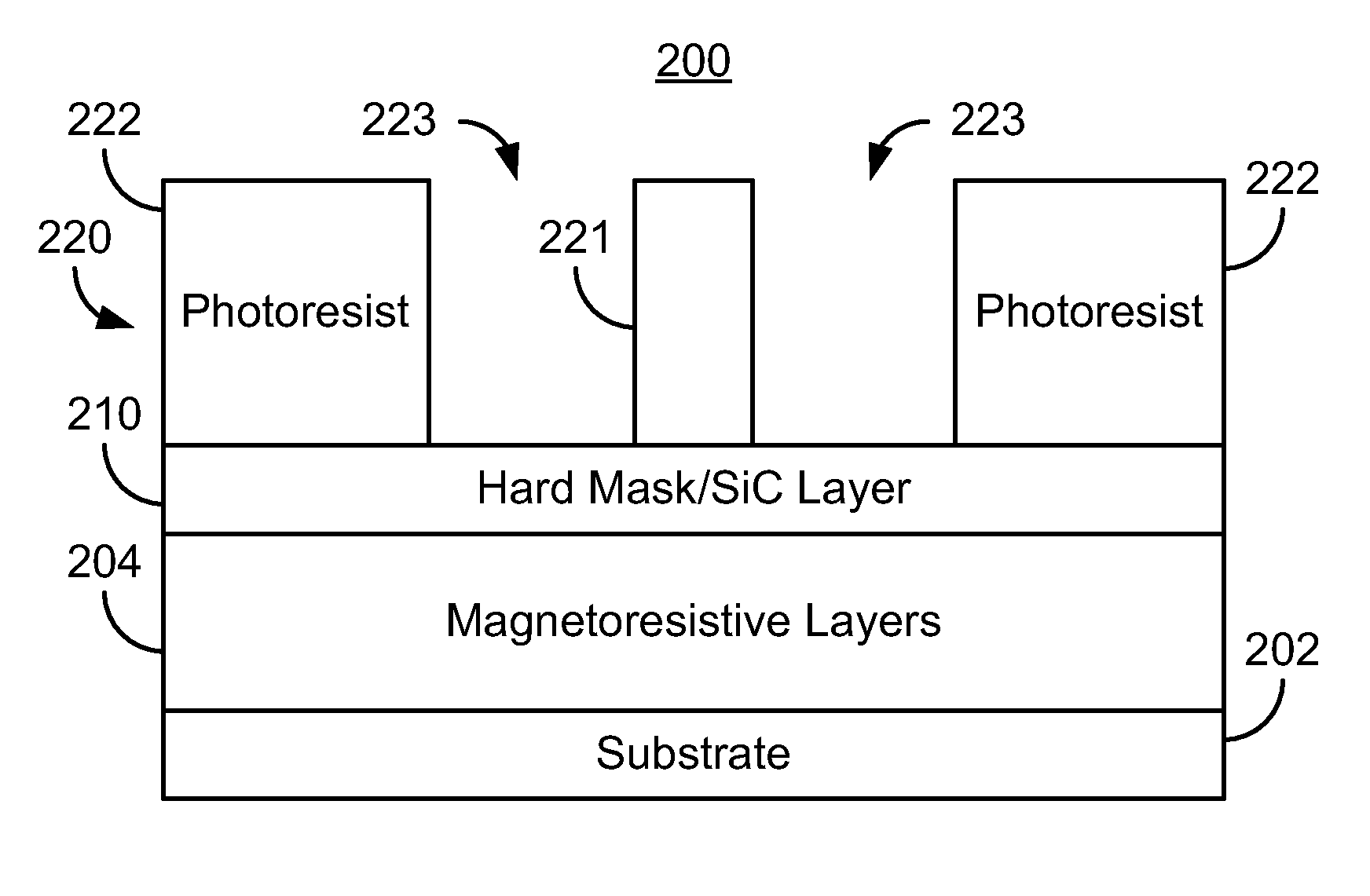
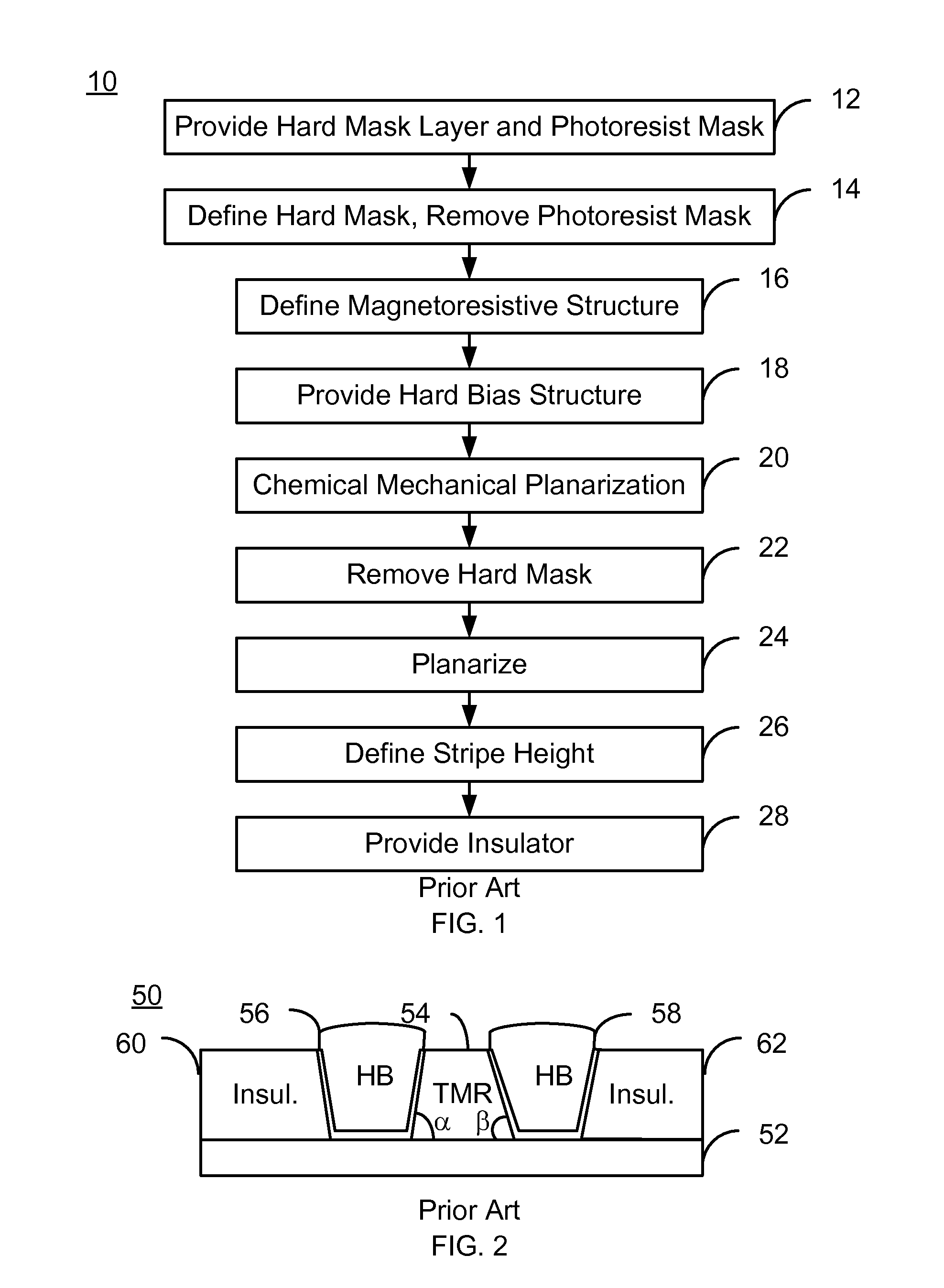
Method and system for providing a magnetic recording transducer using an ion beam scan polishing planarization
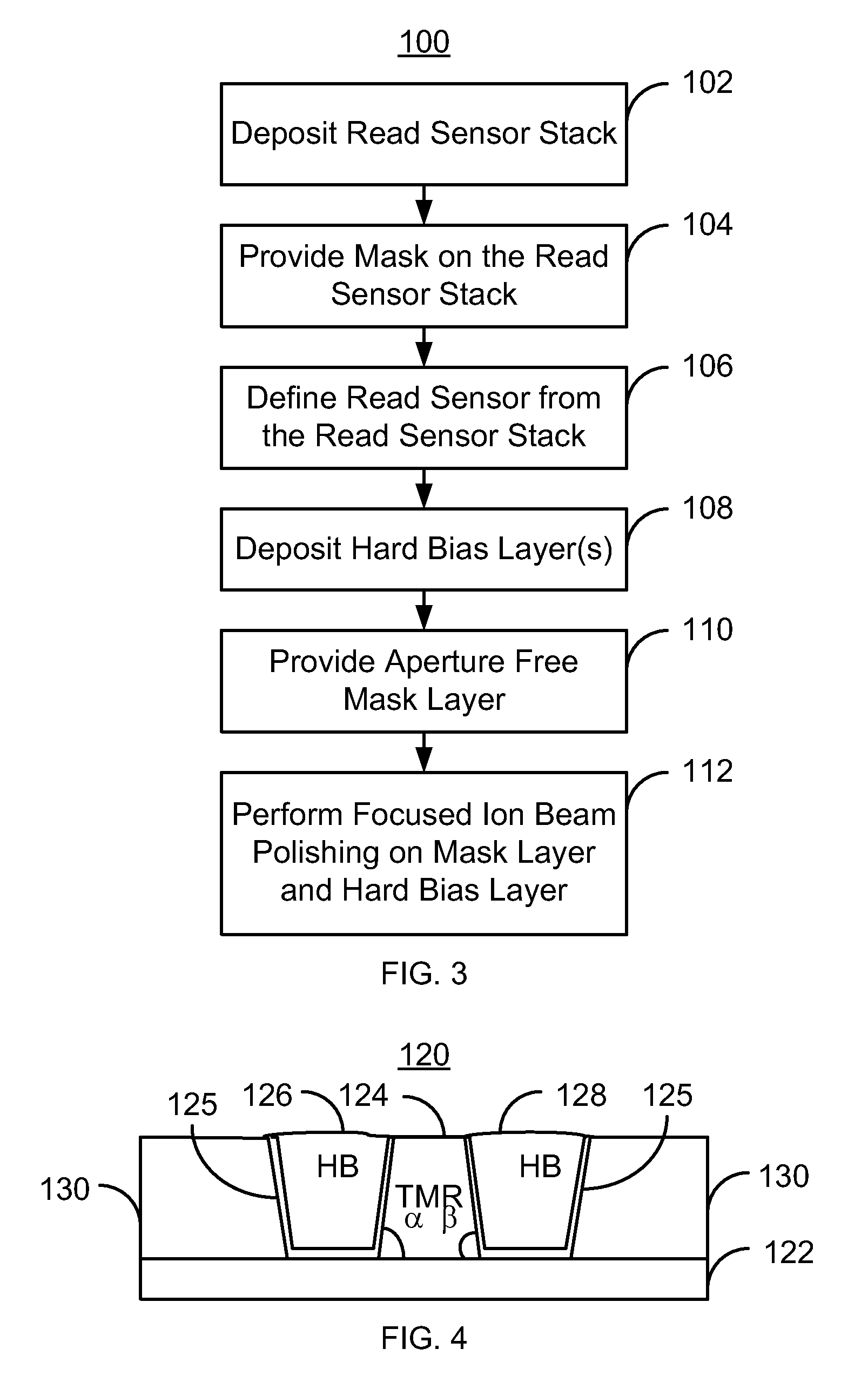
A method and system for fabricating a read sensor on a substrate for a read transducer is described. A read sensor stack is deposited on the substrate. A mask is provided on the on the read sensor stack. The mask has a pattern that covers a first portion of the read sensor stack corresponding to the read sensor, covers a second portion of the read sensor stack distal from the read sensor, and exposes a third portion of the read sensor stack between the first and second portions. The read sensor is defined from the read sensor stack. A hard bias layer is deposited. An aperture free mask layer including multiple thicknesses is provided. A focused ion beam scan (FIBS) polishing step is performed on the mask and hard bias layers to remove a portion of the mask and hard bias layers based on the thicknesses.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
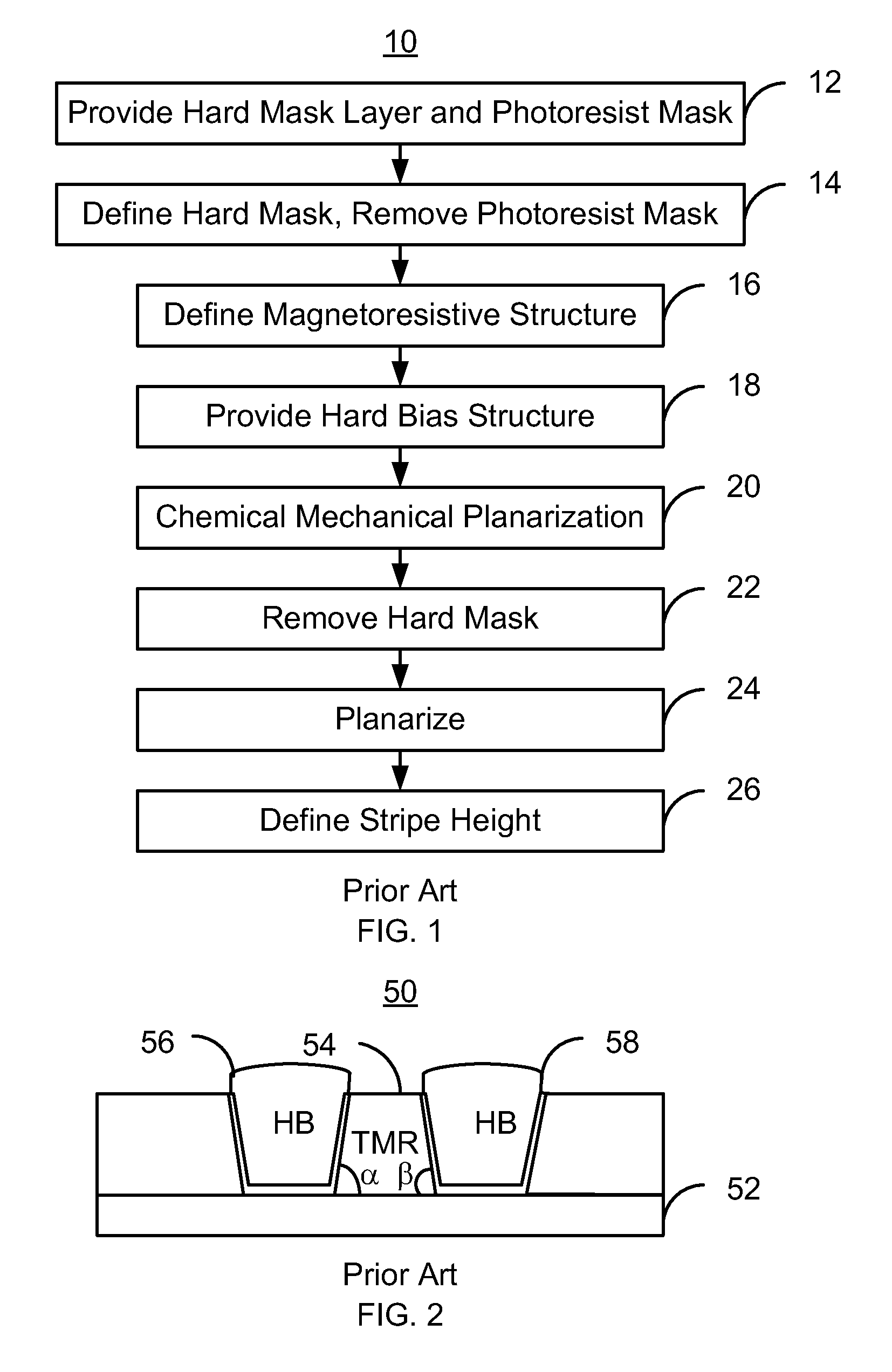
Method and system for providing a read sensor in a magnetic recording transducer using focused ion beam scan polishing
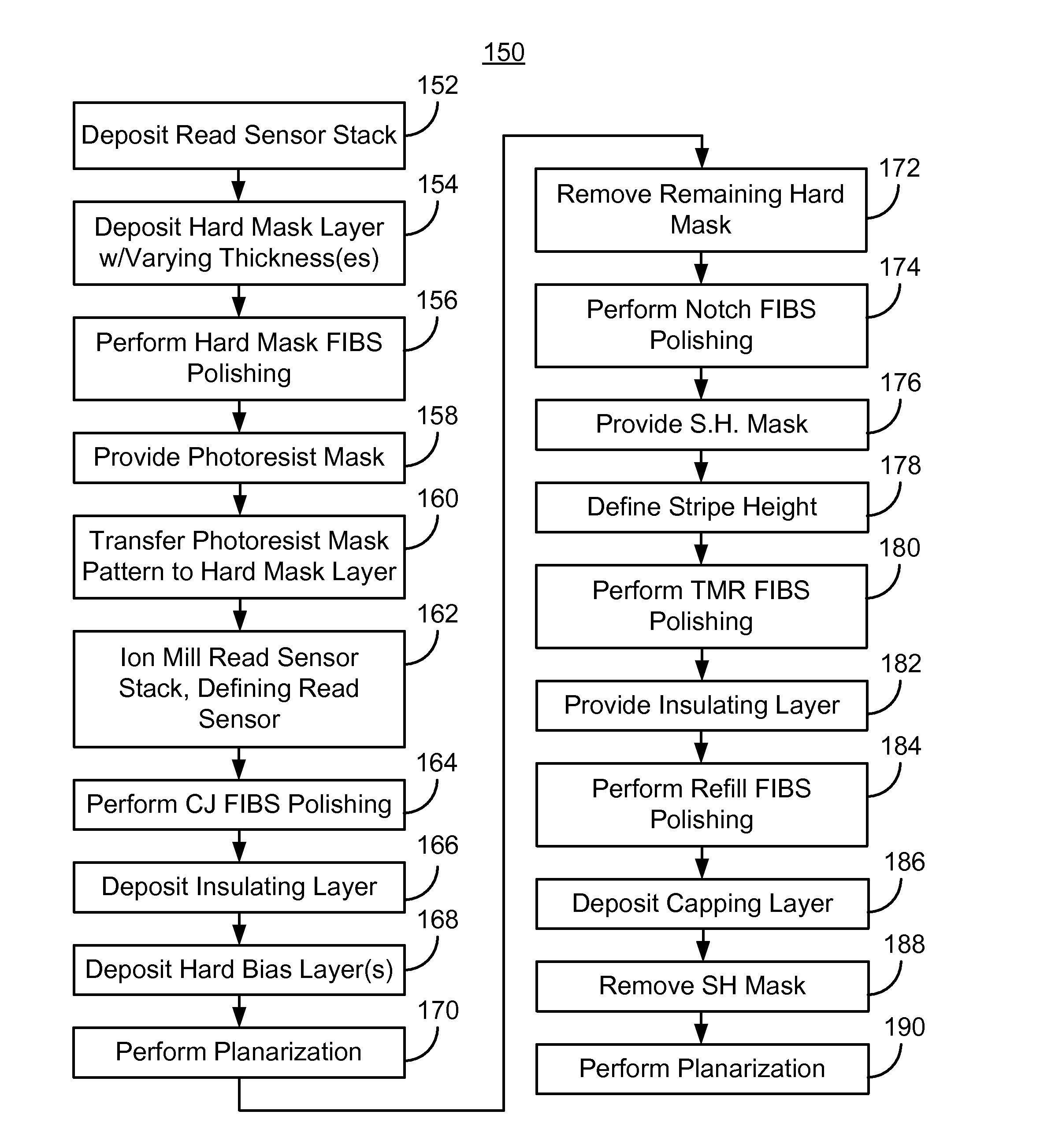
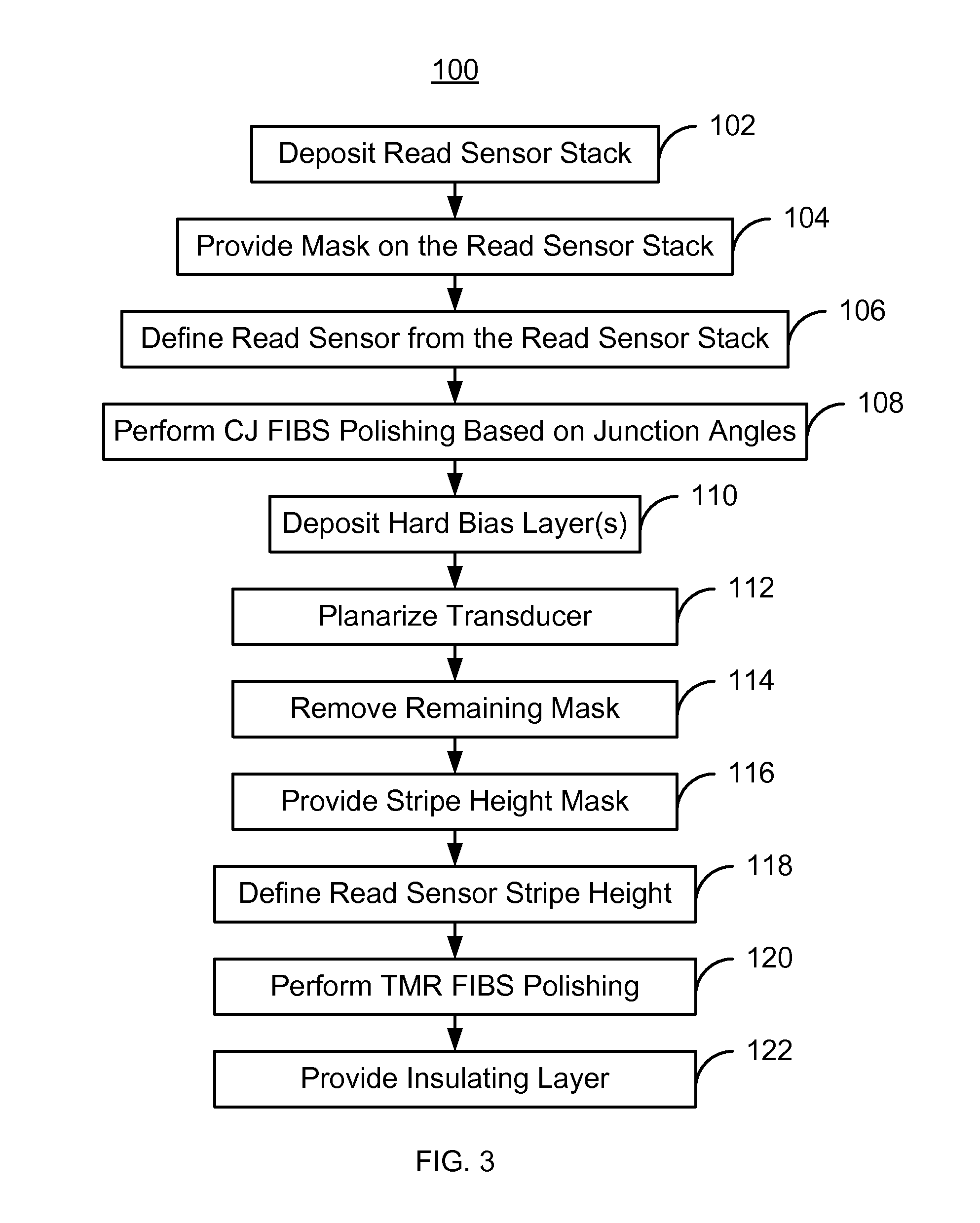
InactiveUS8480911B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoftware engineeringIon beam
A read sensor for a read transducer is fabricated. The read transducer has field and device regions. A read sensor stack is deposited. A mask covering part of the stack corresponding to the read sensor is provided. The read sensor having inboard and outboard junction angles is defined from the stack in a track width direction. A critical junction (CJ) focused ion beam scan (FIBS) polishing that removes part of the read sensor based on the junction angles is performed. A hard bias structure is deposited and the transducer planarized. A remaining portion of the mask is removed. A stripe height mask covering part of the read sensor and hard bias structure in a stripe height direction is provided. The read sensor stripe height is defined. A tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) FIBS polishing that removes part of the stack in the field region is performed. An insulating layer is provided.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
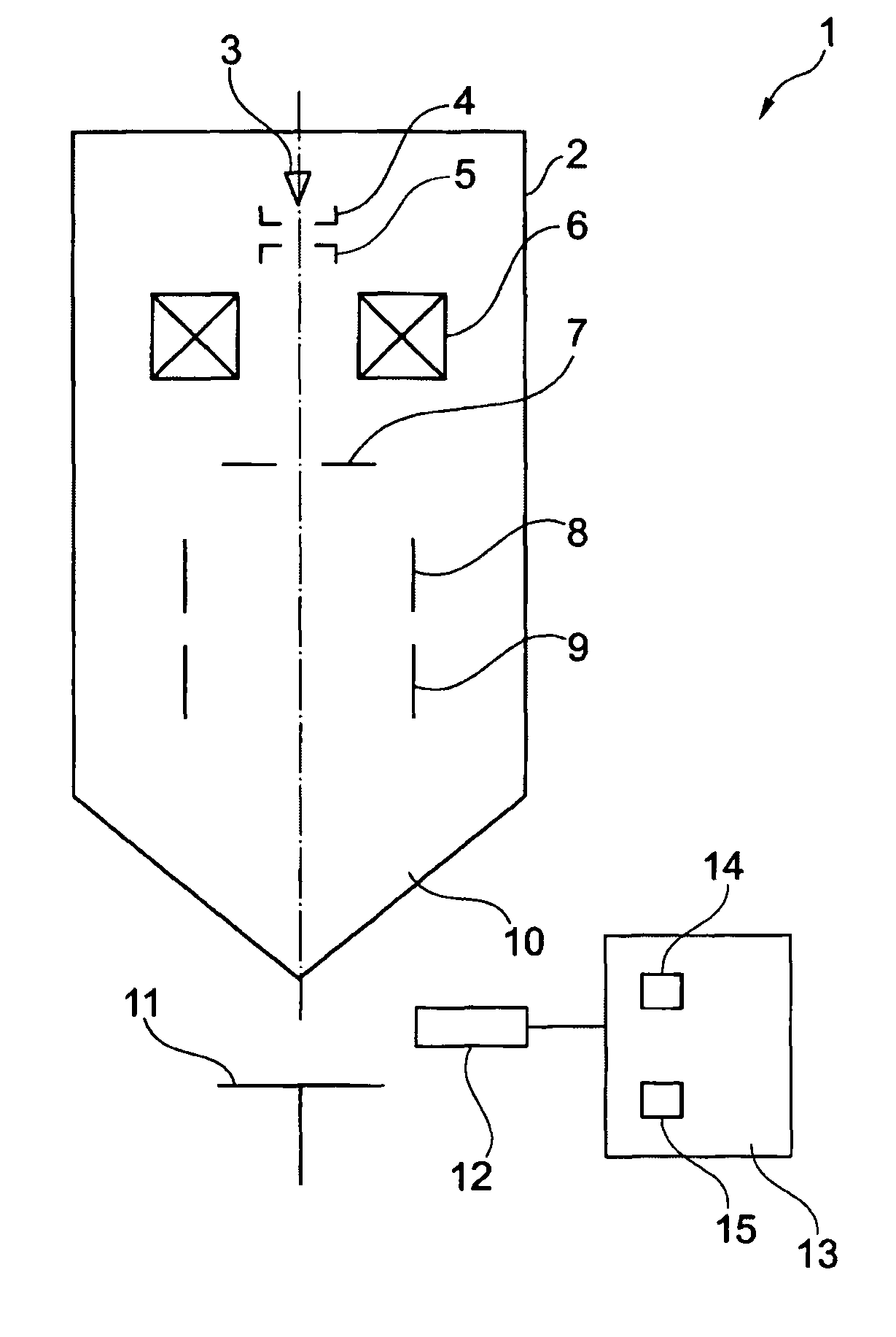
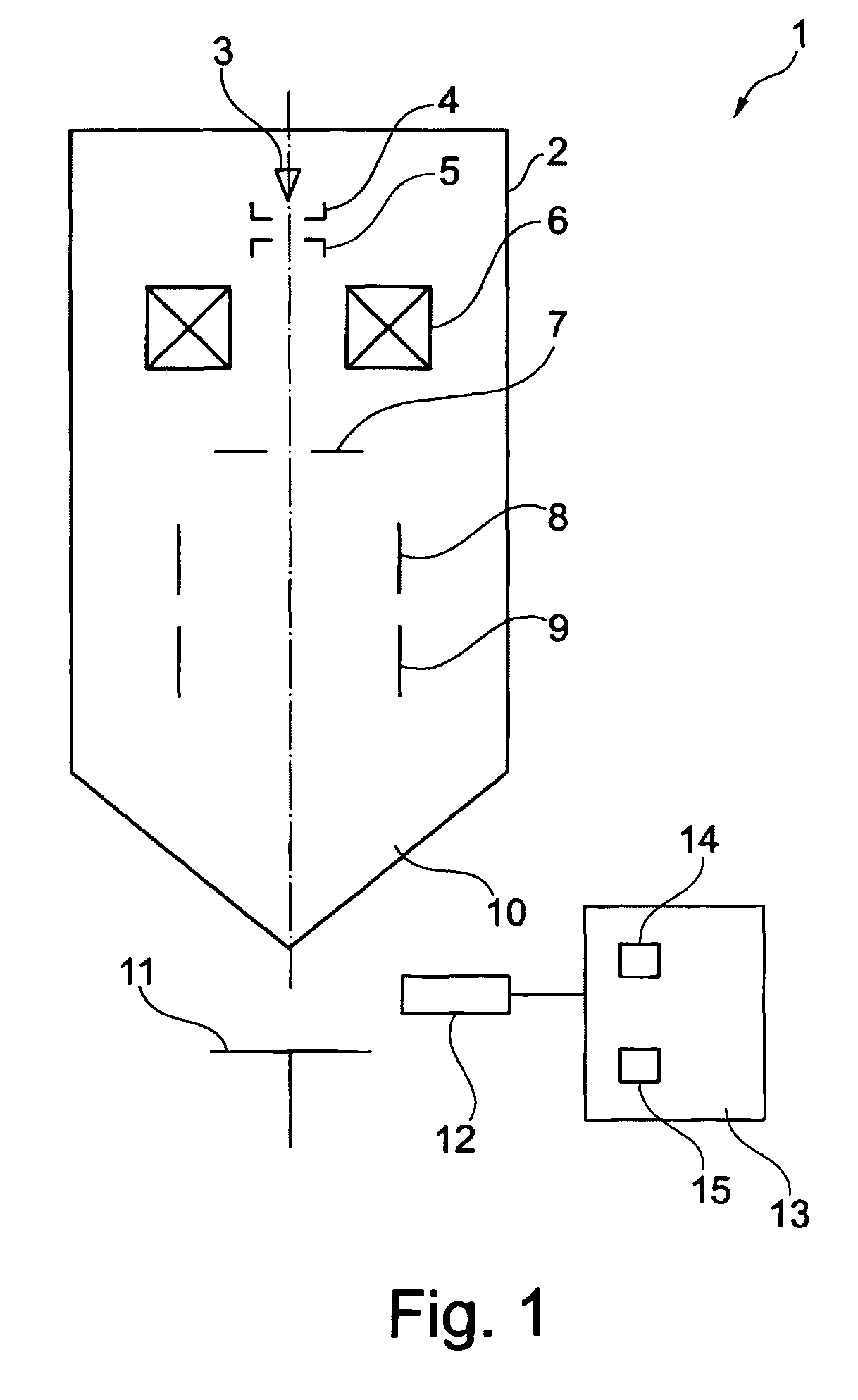
Device and method for analyzing an organic sample
ActiveUS8263933B2Easy to analyzeHigh resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A device and method for analyzing an organic sample provide high spatial resolution. A focused ion beam is directed onto the organic sample. Fragments detached from the sample are examined using mass spectroscopy.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190103131A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion characteristicAvoid it happening againDisposition/mounting of recording headsMagnetic materials for record carriersIn planeX-ray
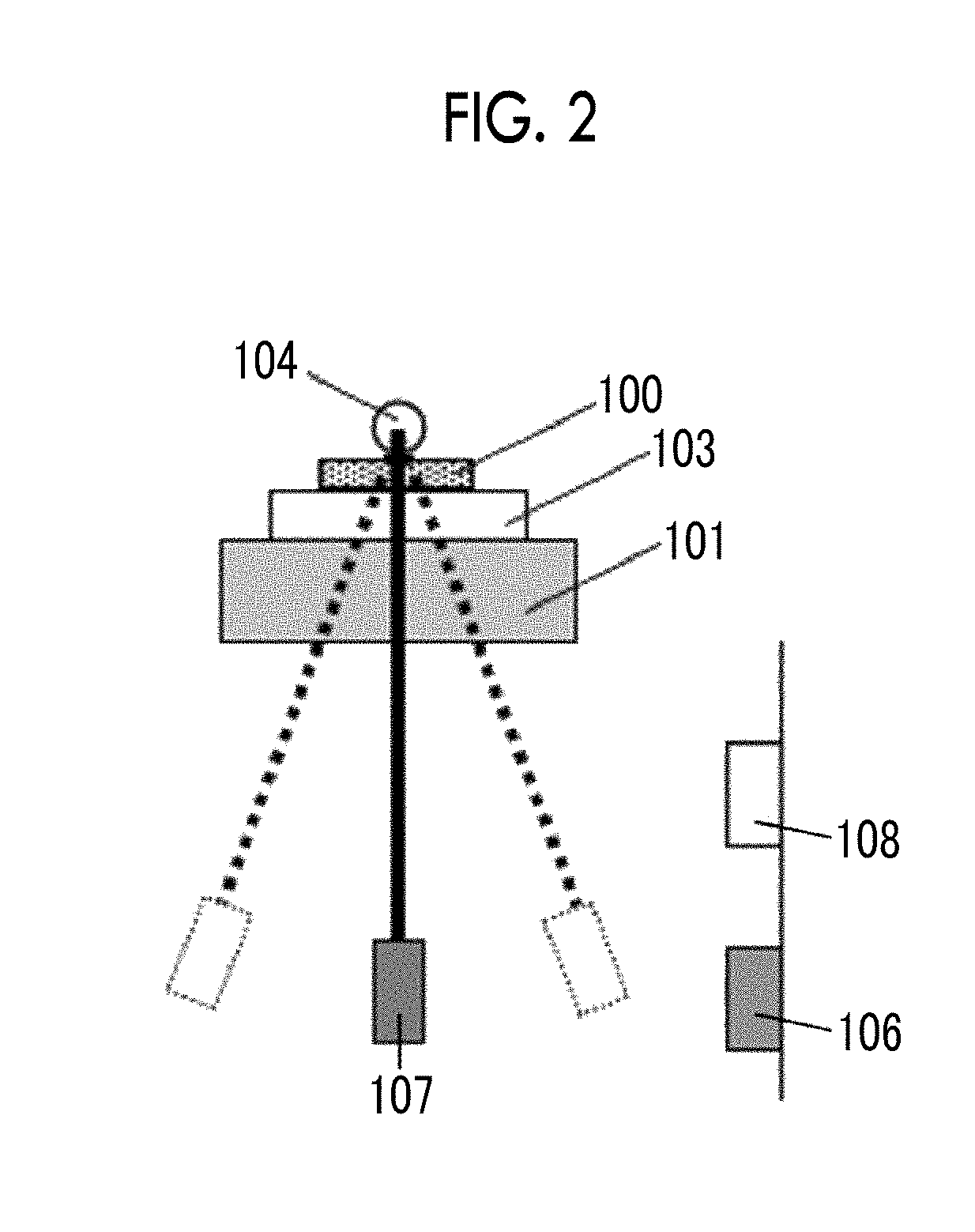
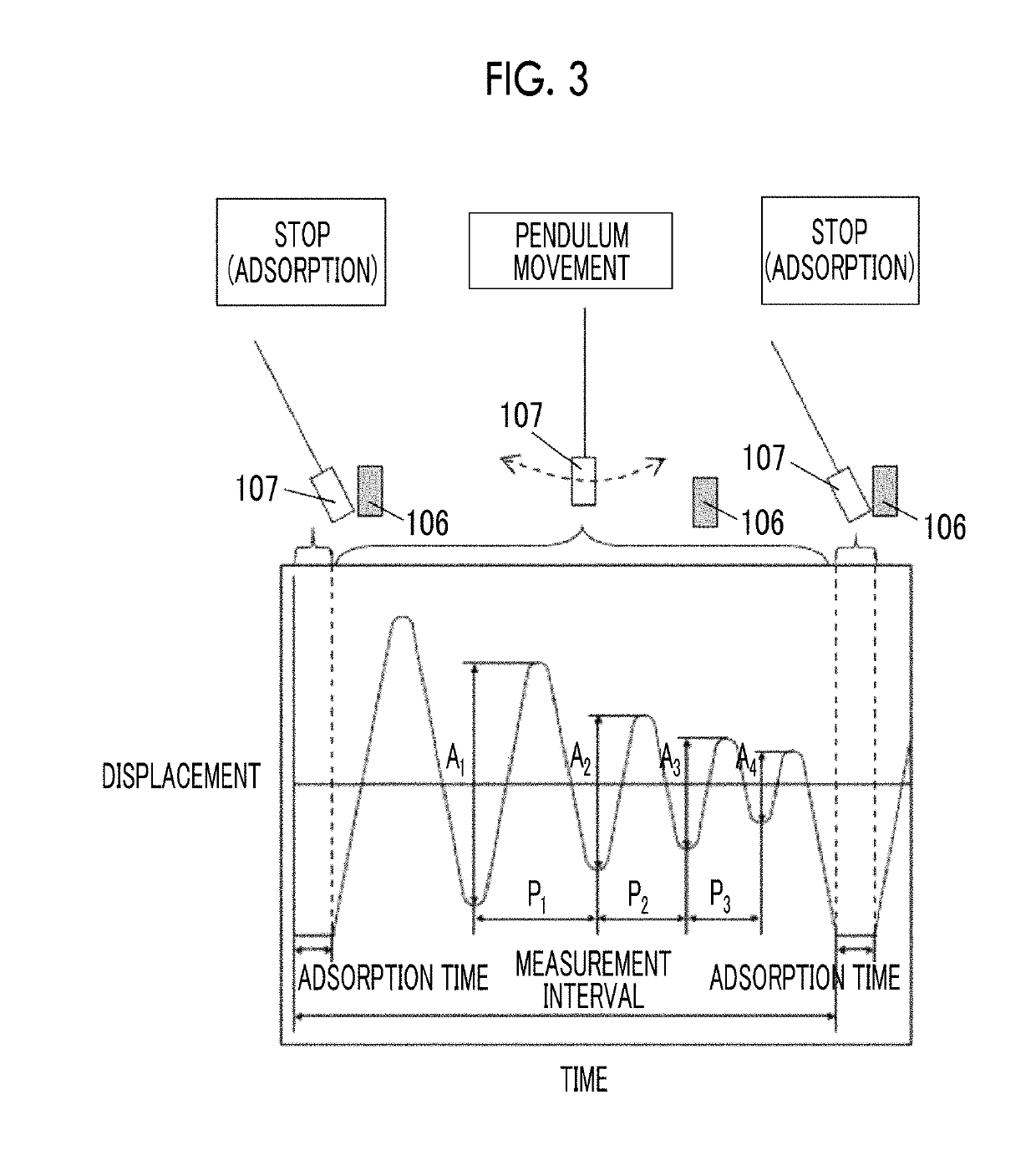
Provided are a magnetic recording medium, in which a magnetic layer includes ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, a binding agent, and an oxide abrasive, an intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic recording medium is 0.65 to 1.00, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm, and a magnetic recording and reproducing device including this magnetic recording medium.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Lift-out probe having an extension tip, methods of making and using, and analytical instruments employing same
InactiveUS7009188B2Extended service lifeEfficient removalMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesIon beamConductive materials
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190103133A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion characteristicAvoid it happening againMaterials with ironBase layers for recording layersIn planeX-ray
Provided are a magnetic recording medium, in which a magnetic layer includes a ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, a binding agent, an oxide abrasive, an intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio is 0.65 to 1.00, one or more kinds of component selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide is contained in a magnetic layer side portion on the non-magnetic support, a C—H derived C concentration of the magnetic layer is 45 atom % to 65 atom %, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm, and a magnetic recording and reproducing device including this magnetic recording medium.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190103135A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion characteristicAvoid it happening againManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageIn planeX-ray
Provided are a magnetic recording medium, in which a magnetic layer includes a ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, a binding agent, and an oxide abrasive, an intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic recording medium is 0.65 to 1.00, a contact angle with respect to 1-bromonaphthalene measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is 50.0° to 55.0°, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm, and a magnetic recording and reproducing device including this magnetic recording medium.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190103134A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion characteristicAvoid it happening againMaterials with ironProtective coatings for layersIn planeX-ray
Provided are a magnetic recording medium, in which a magnetic layer includes ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder, a binding agent, and an oxide abrasive, an intensity ratio Int(110) / Int(114) obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic recording medium is 0.65 to 1.00, a coefficient of friction measured regarding a base portion of a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.30, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm, and a magnetic recording and reproducing device including this magnetic recording medium.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20190103130A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion characteristicAvoid it happening againDisposition/mounting of recording headsMagnetic materials for record carriersMagnetic tapeViscoelasticity
Provided are a magnetic tape, in which a magnetic layer includes a ferromagnetic powder, a binding agent, and an oxide abrasive, ΔSFD in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape calculated by Expression 1, ΔSFD=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C., is equal to or smaller than 0.50, a logarithmic decrement acquired by a pendulum viscoelasticity test performed regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.050, and an average particle diameter of the oxide abrasive obtained from a secondary ion image obtained by irradiating the surface of the magnetic layer with a focused ion beam is 0.04 μm to 0.08 μm, and a magnetic recording and reproducing device including this magnetic tape.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
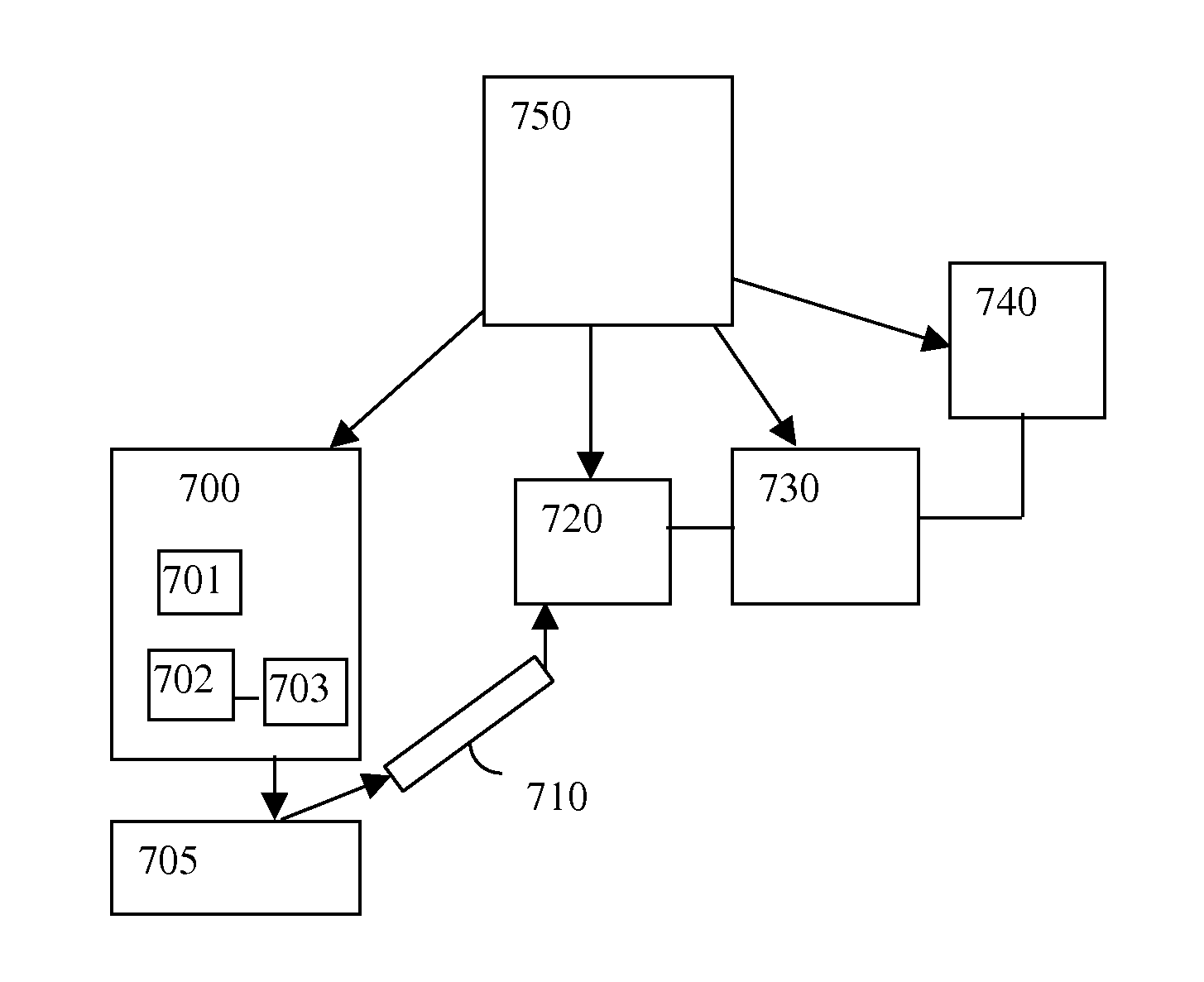
Integration of photon emission microscope and focused ion beam
InactiveUS20060012385A1Vacuum gauge using ionisation effectsFault location by increasing destruction at faultPhoton emissionIon beam
An integrated FIB / PEM apparatus and method for performing failure analysis on integrated circuits. In-situ failure analysis is enabled by integrating Photon Emission Microscopy into a Focused Ion Beam system, thereby improving throughput and efficiency of Failure Analysis. An iterative method is described for identifying and localizing fault sites on the circuit.
Owner:DCG SYST
Method for repairing pattern defect, photo mask using the method, and semiconductor device manufacturing method employing the photo mask
InactiveUS6335129B1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon beamThin layer
A new method for repairing pattern defect on a photo mask is provided. The method includes the steps of: (a) determining the irradiation area of the focused ion beam (FIB) directed towards a defect, by narrowing the irradiation area by a predetermined distance inwardly from the edge of the defect; (b) focusing the FIB onto its irradiation area to remove a part of the pattern film material of the defect from its top surface and thus leave a thin layer on a mask substrate; and (c) removing the thin layer by using a laser beam. The defect may be an isolated pattern or a pattern extended continuously from an edge of the normal pattern. Further, the photo mask repaired by the method, and a manufacturing method of semiconductor devices employing the repaired photo mask are proposed. The photo mask may include a phase shift mask.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
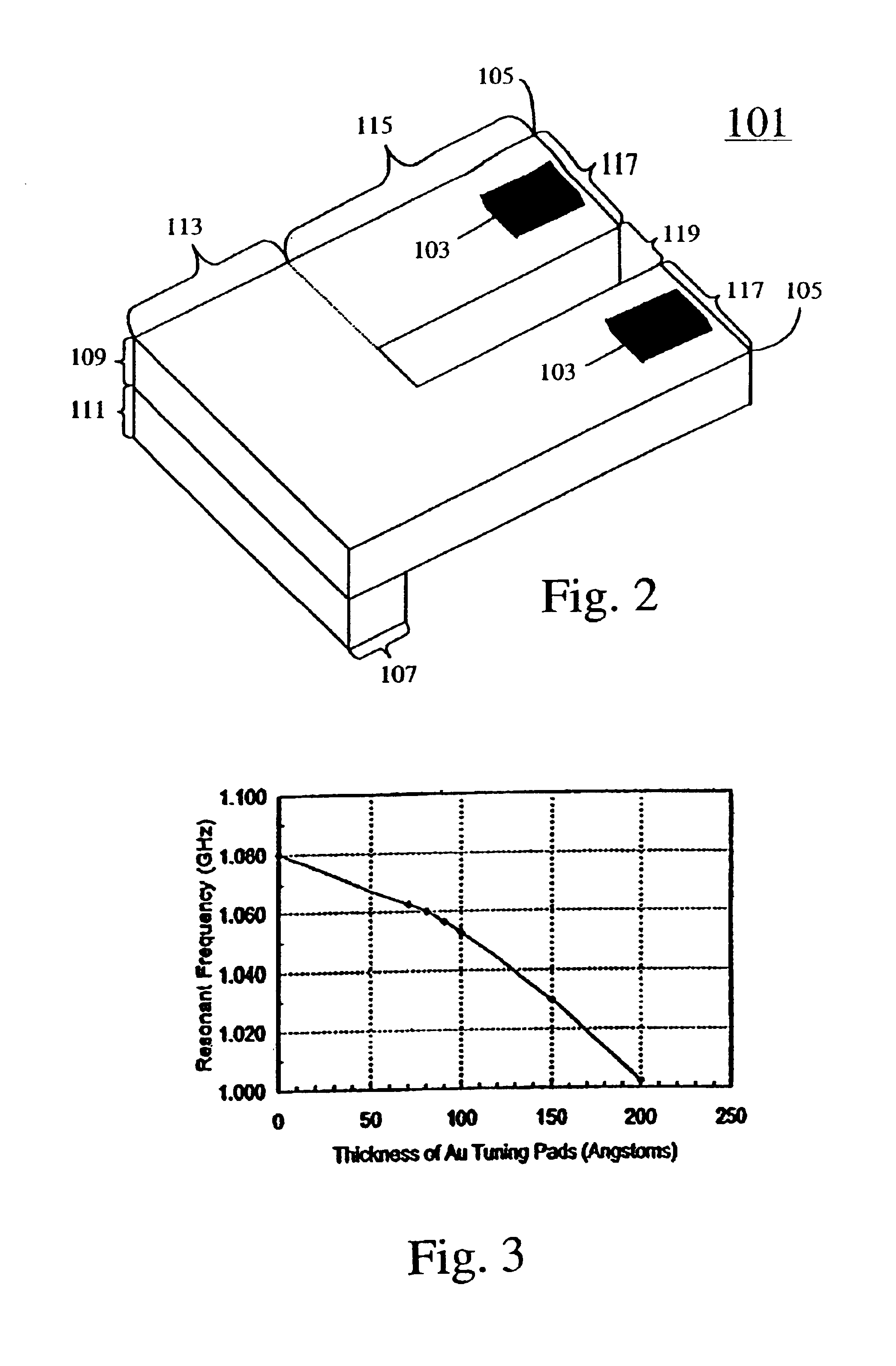
Micro electrical mechanical system (MEMS) tuning using focused ion beams
InactiveUS6922118B2Quality improvementChange the resonant frequencyCellsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesIon beamActive layer
A method for tuning an electro-mechanical device such as a MEMS device is disclosed. The method comprises operating a MEMS device in a depressurized system and using FIB micromachining to remove a portion of the MEMS device. Additionally, a method for tuning a plurality of MEMS devices by depositing an active layer and then removing a portion of the active layer using FIB micromachining. Also, a method for tuning a MEMS device and vacuum packaging the MEMS device in situ are provided.
Owner:HRL LAB
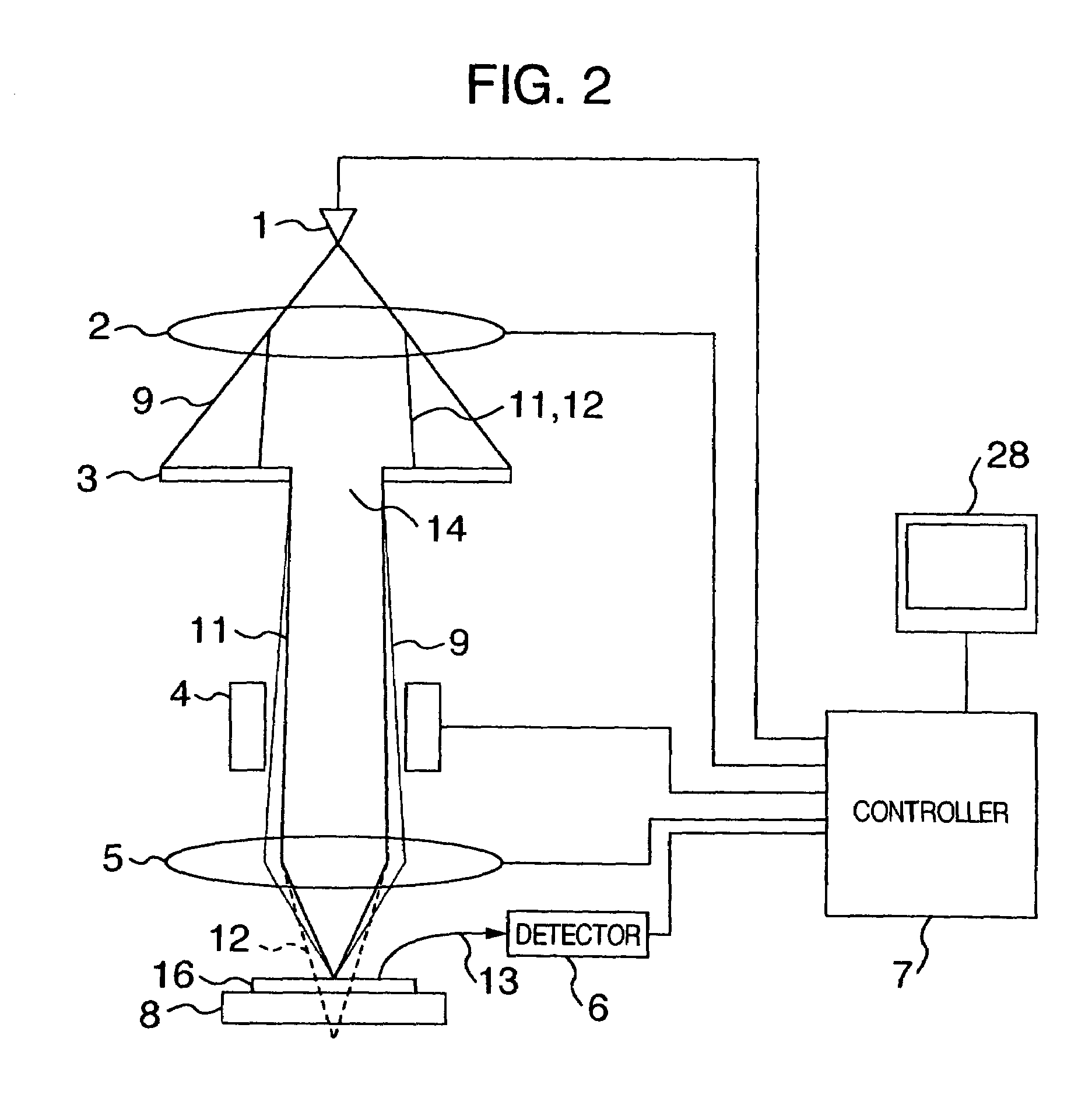
Focused ion beam system with coaxial scanning electron microscope
InactiveUS6900447B2Enhance the imageStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIon beamLight beam
A system including co-axial focused ion beam and an electron beam allows for accurate processing with the FIB using images formed by the electron beam. In one embodiment, a deflector deflects the electron beam onto the axis of the ion beam and deflects secondary particles collected through the final lens toward a detector. In one embodiment, a positively biased final electrostatic lens focuses both beams using the same voltage to allow simultaneous or alternating FIB and SEM operation. In one embodiment, the landing energy of the electrons can be varied without changing the working distance.
Owner:FEI CO
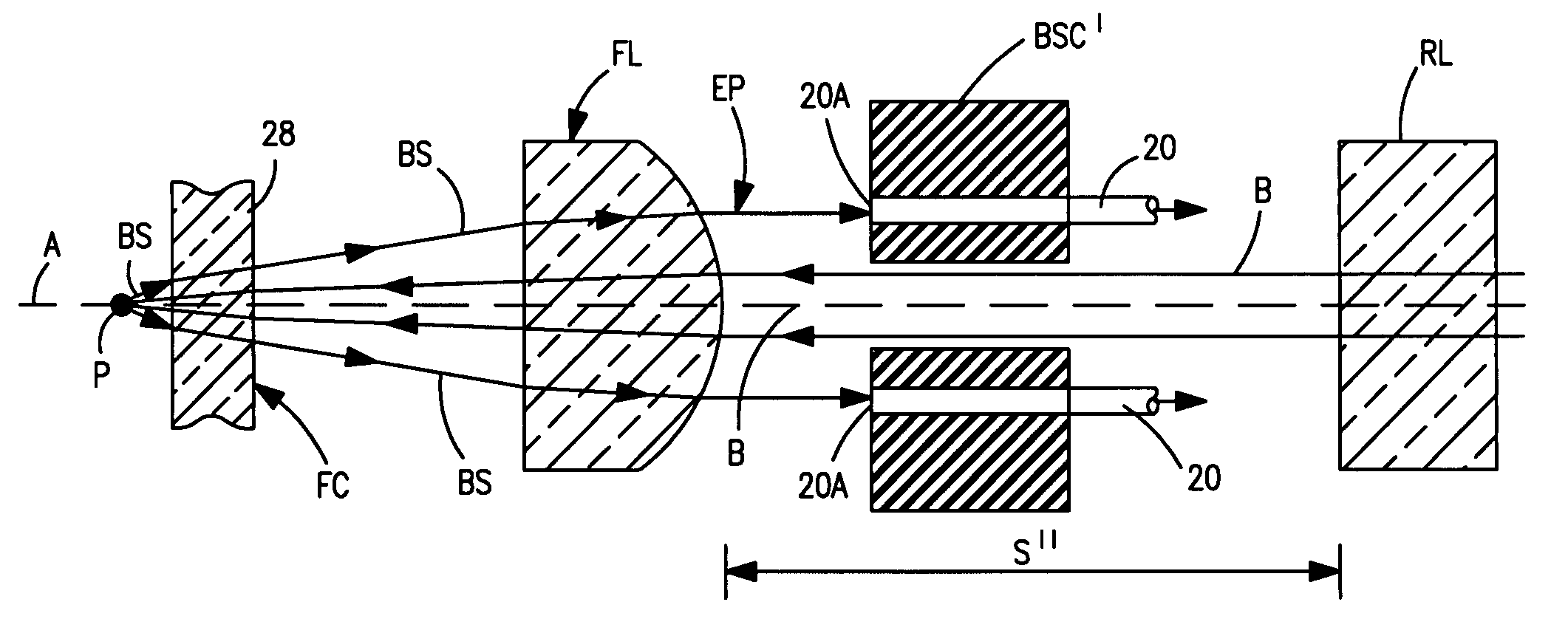
Magnetically enhanced, inductively coupled plasma source for a focused ion beam system
ActiveUS20050183667A1Eliminate plasma potential modulationIncrease ion densityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationIon beamCombined use
The present invention provides an inductively coupled, magnetically enhanced ion beam source, suitable to be used in conjunction with probe-forming optics to produce an ion beam without kinetic energy oscillations induced by the source.
Owner:FEI CO
Multi-source plasma focused ion beam system
ActiveUS20090309018A1Facilitates sequentially and simultaneouslyReduce necessityStability-of-path spectrometersVacuum evaporation coatingIon beamInductance
The present invention provides a plasma ion beam system that includes multiple gas sources and that can be used for performing multiple operations using different ion species to create or alter submicron features of a work piece. The system preferably uses an inductively coupled, magnetically enhanced ion beam source, suitable in conjunction with probe-forming optics sources to produce ion beams of a wide variety of ions without substantial kinetic energy oscillations induced by the source, thereby permitting formation of a high resolution beam.
Owner:FEI CO
FIB based open via analysis and repair
ActiveUS7786436B1Accurate locationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceIon beam
An improved method, apparatus, and control / guiding software for localizing, characterizing, and correcting defects in integrated circuits, particularly open or resistive contact / via defects and metal bridging defects, using FIB technology. An apparatus for identifying an abnormal discontinuity in a contact / via in an integrated circuit comprising a focused ion beam system to scan the ion beam over the contact / via to do remove or deposit via material, a detector to collect a secondary particle signal from the contact / via material that gets removed, a sub-system for storing the secondary particle signal from the contact / via in time as well as x-y scan position, a sub-system for correlating secondary particle signals and identifying discontinuities in the correlated secondary particle signals, a sub-system for optimizing the display of the abnormal discontinuity; and a computer to implement software aspects of the system.
Owner:DCG SYST
Method and apparatus for processing a micro sample
InactiveUS6927391B2Reduce resolutionGood for observationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementHigh fluxIon beam
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Manufacturing method for compound of metal and resin
The invention provides a manufacturing method for a compound of metal and resin. The method comprises the following steps of: providing a metal component; degreasing, deoiling and cleaning the metal component; etching the metal component by using a focused ion beam to form a nano hole dot matrix on the surface of the metal component; embedding the metal component into a forming mould and heating the metal component to 100-350 DEG C; and injecting molten crystalline thermoplastic resin into the mould and cooling, wherein the resin invades nano holes on the surface of the metal component to be combined with the metal component.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
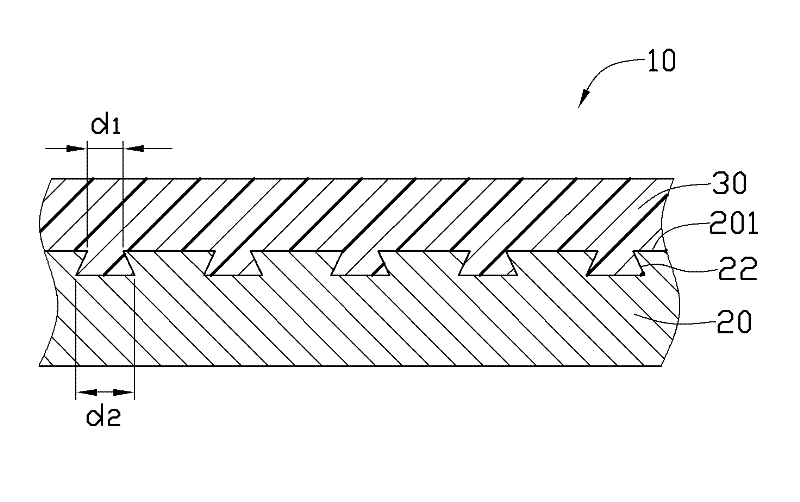
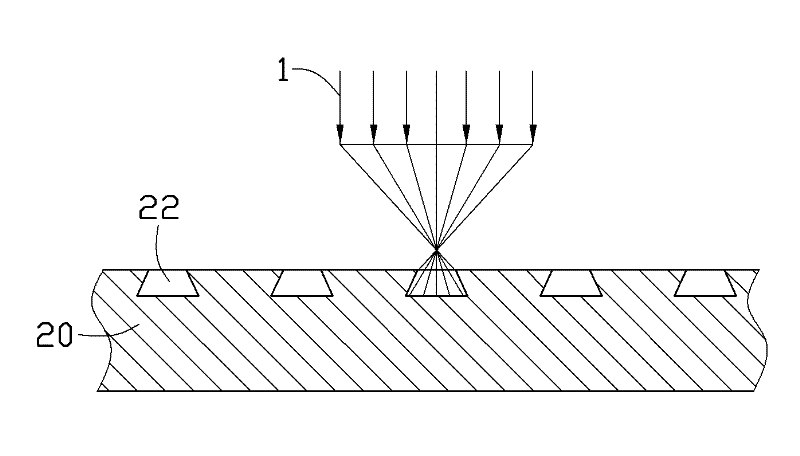
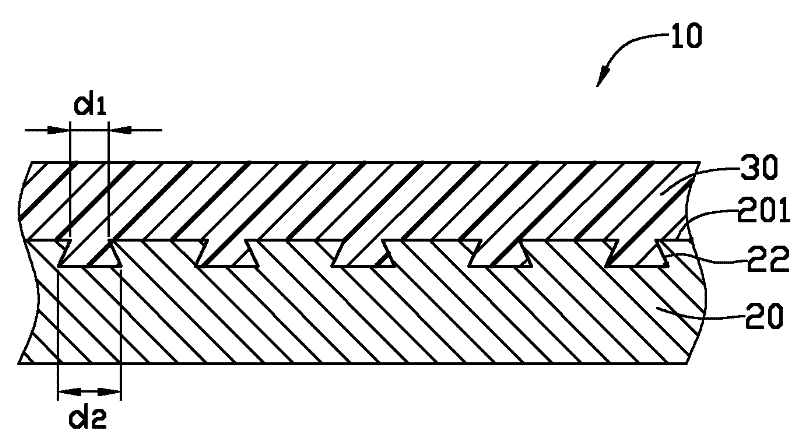
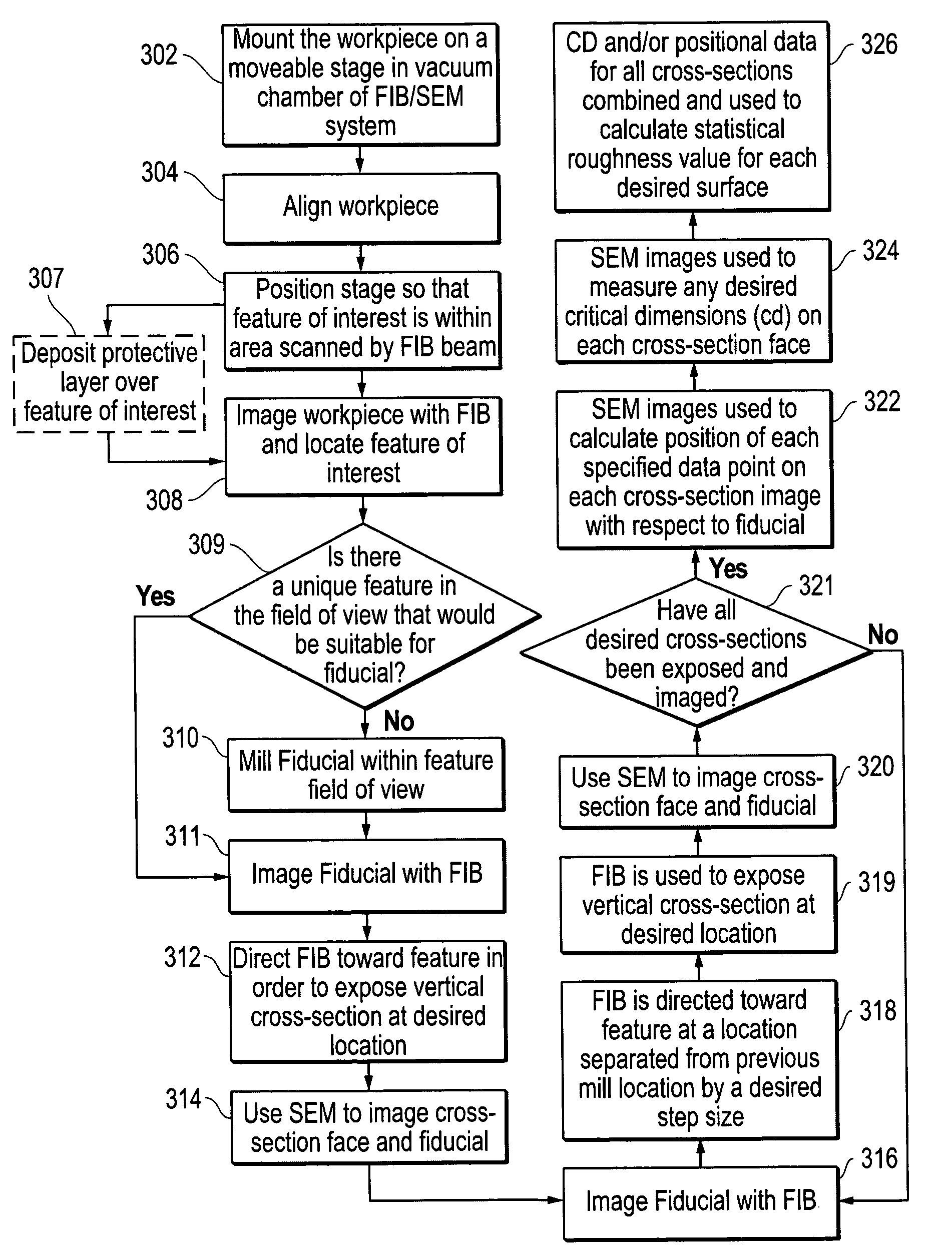
Method of measuring three-dimensional surface roughness of a structure
InactiveUS7348556B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesIon beamSurface roughness
An improved method of measuring the three-dimensional surface roughness of a structure. A focused ion beam is used to mill a succession of cross-sections or “slices” of the feature of interest at pre-selected intervals over a pre-selected measurement distance. As each cross-section is exposed, a scanning electron microscope is used to measure the relevant dimensions of the feature. Data from these successive “slices” is then used to determine the three-dimensional surface roughness for the feature.
Owner:FEI CO
Repetitive circumferential milling for sample preparation
ActiveUS7442924B2Increase ratingsShorten the timeParticle separator tubesRecord information storageIon beamLight beam
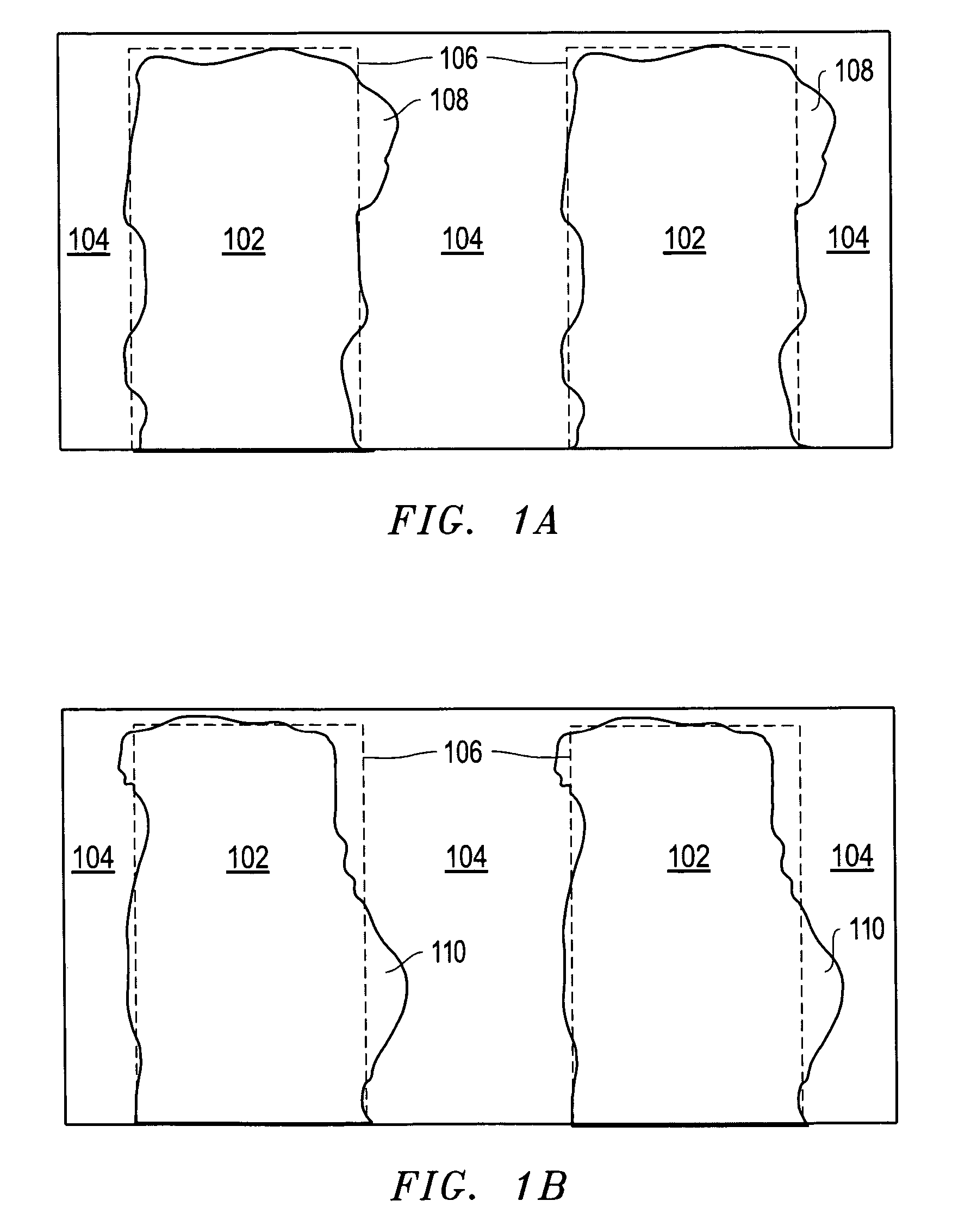
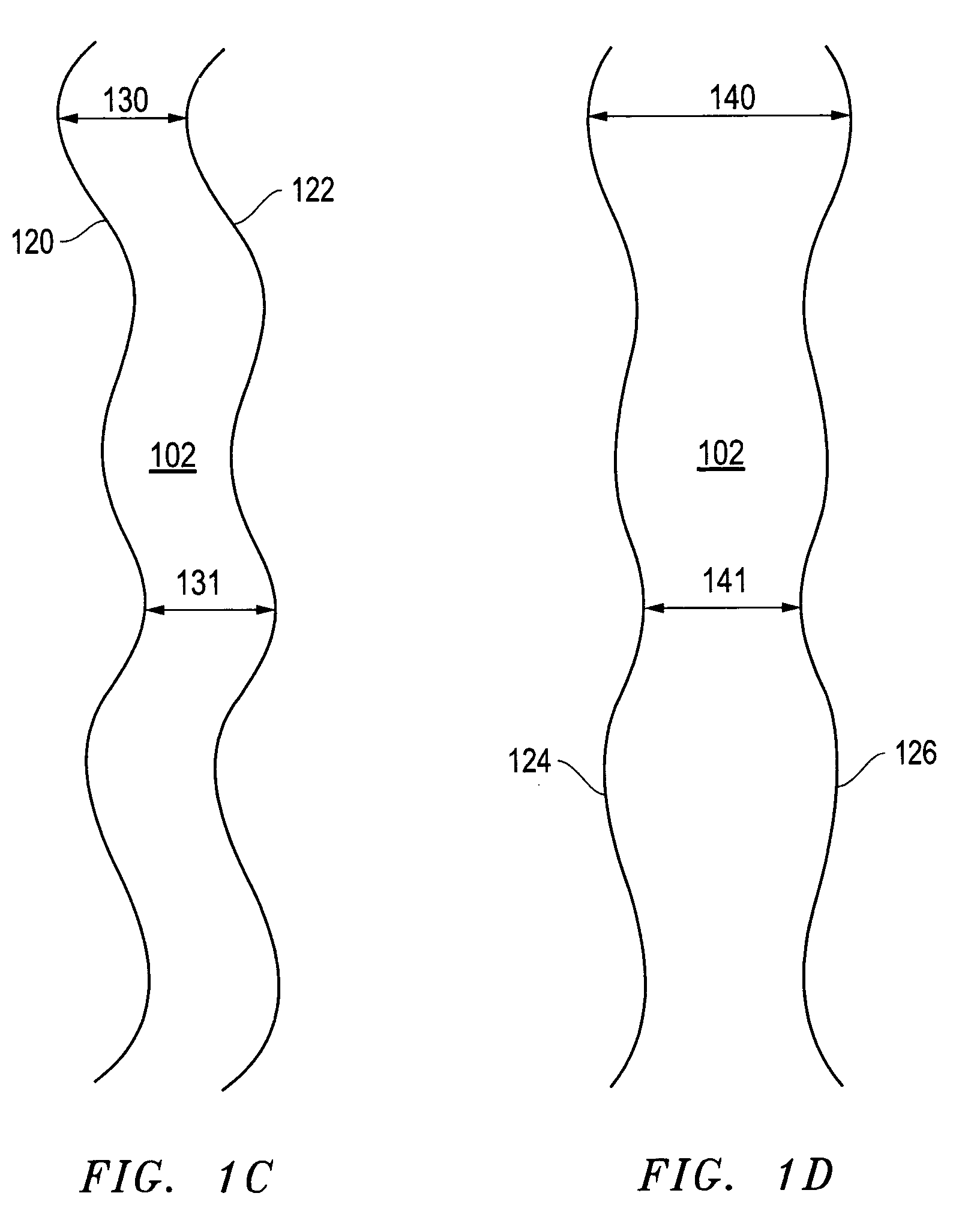
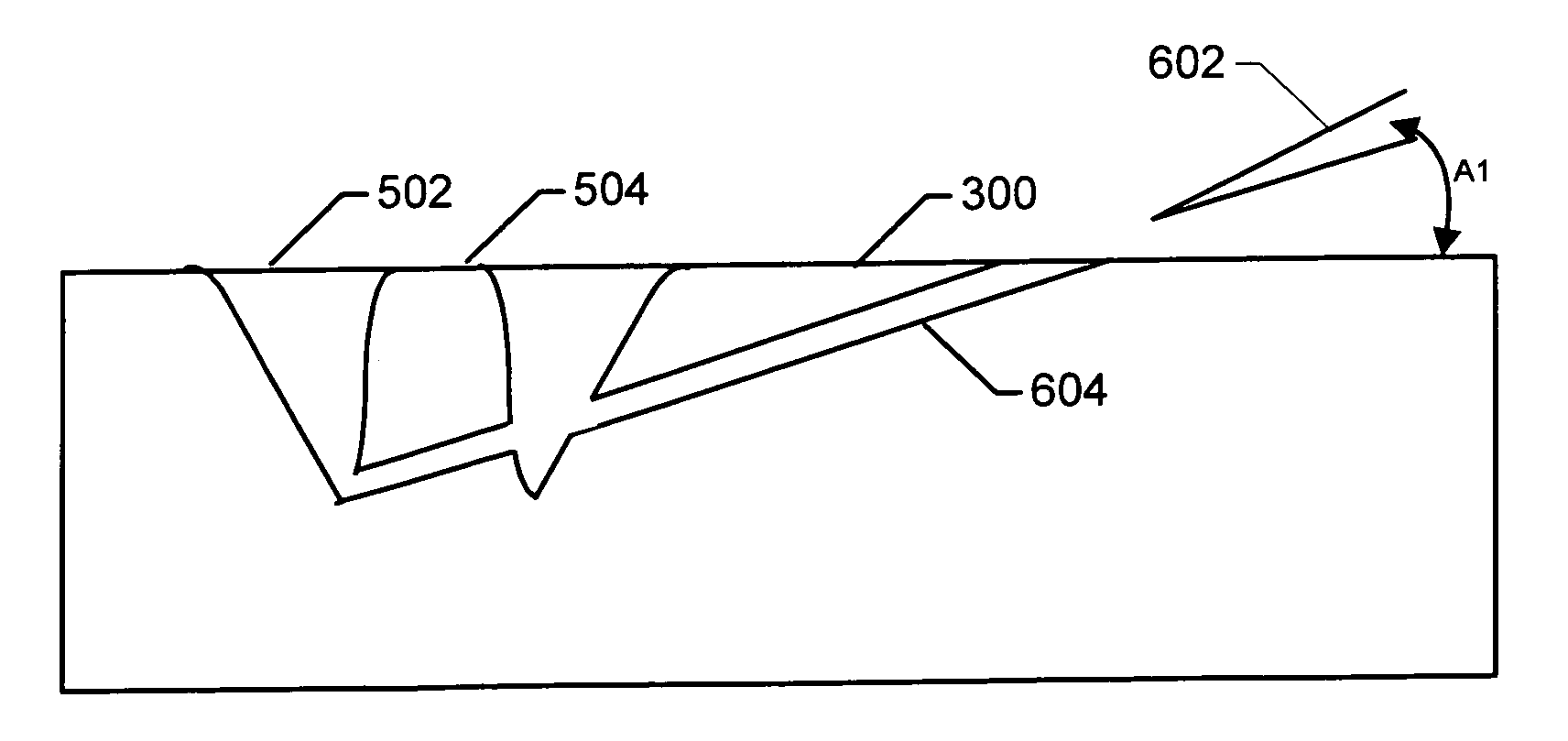
A method of sample extraction entails making multiple, overlapping cuts using a beam, such as a focused ion beam, to create a trench around a sample, and then undercutting the sample to free it. Because the sidewalls of the cut are not vertical, the overlapping cuts impinge on the sloping sidewalls formed by previous cuts. The high angle of incidence provides a greatly enhanced mill rate, so that making multiple overlapping cuts to produce a wide trench can requires less time than making a single, deep cut around the perimeter of a sample.
Owner:FEI CO
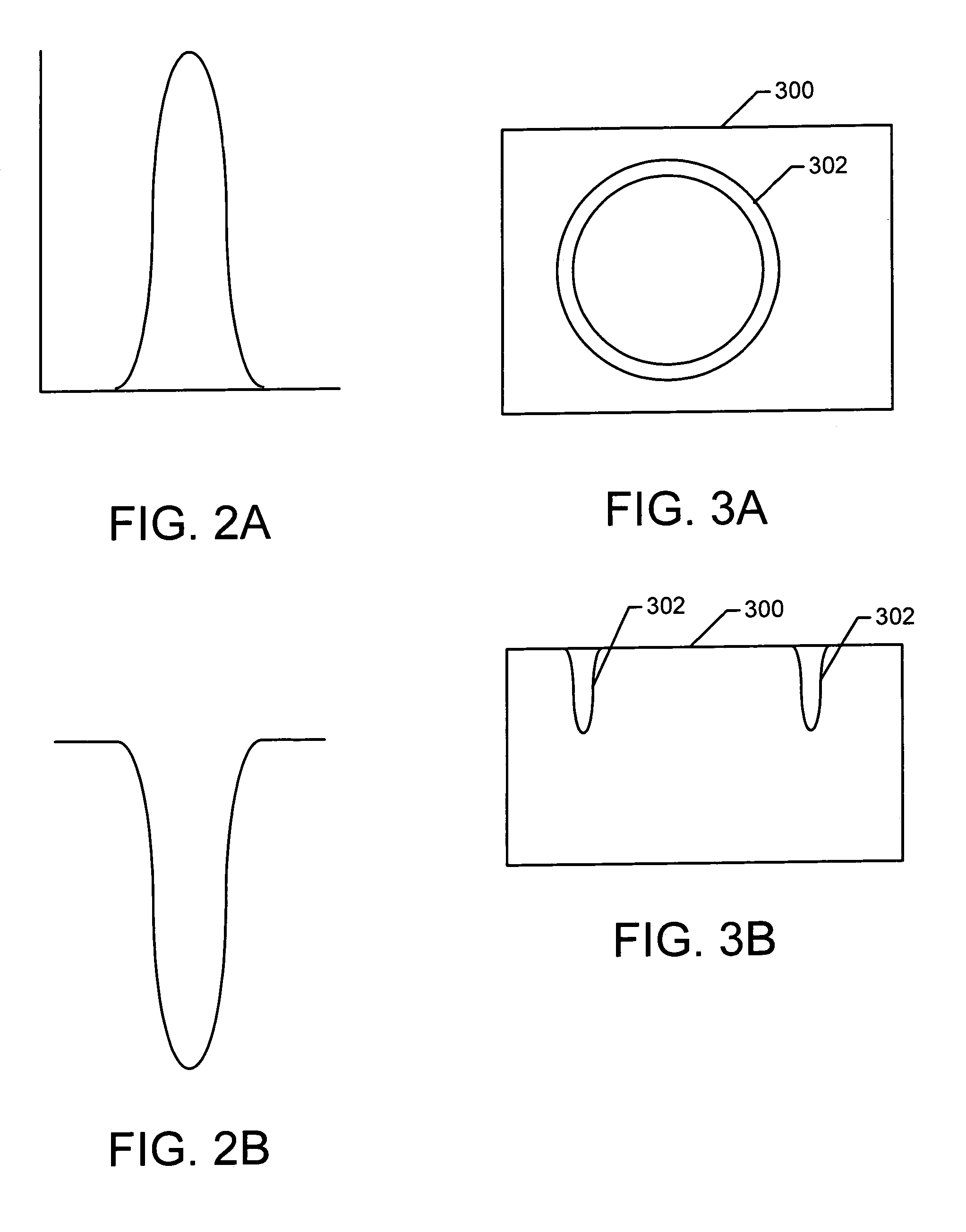
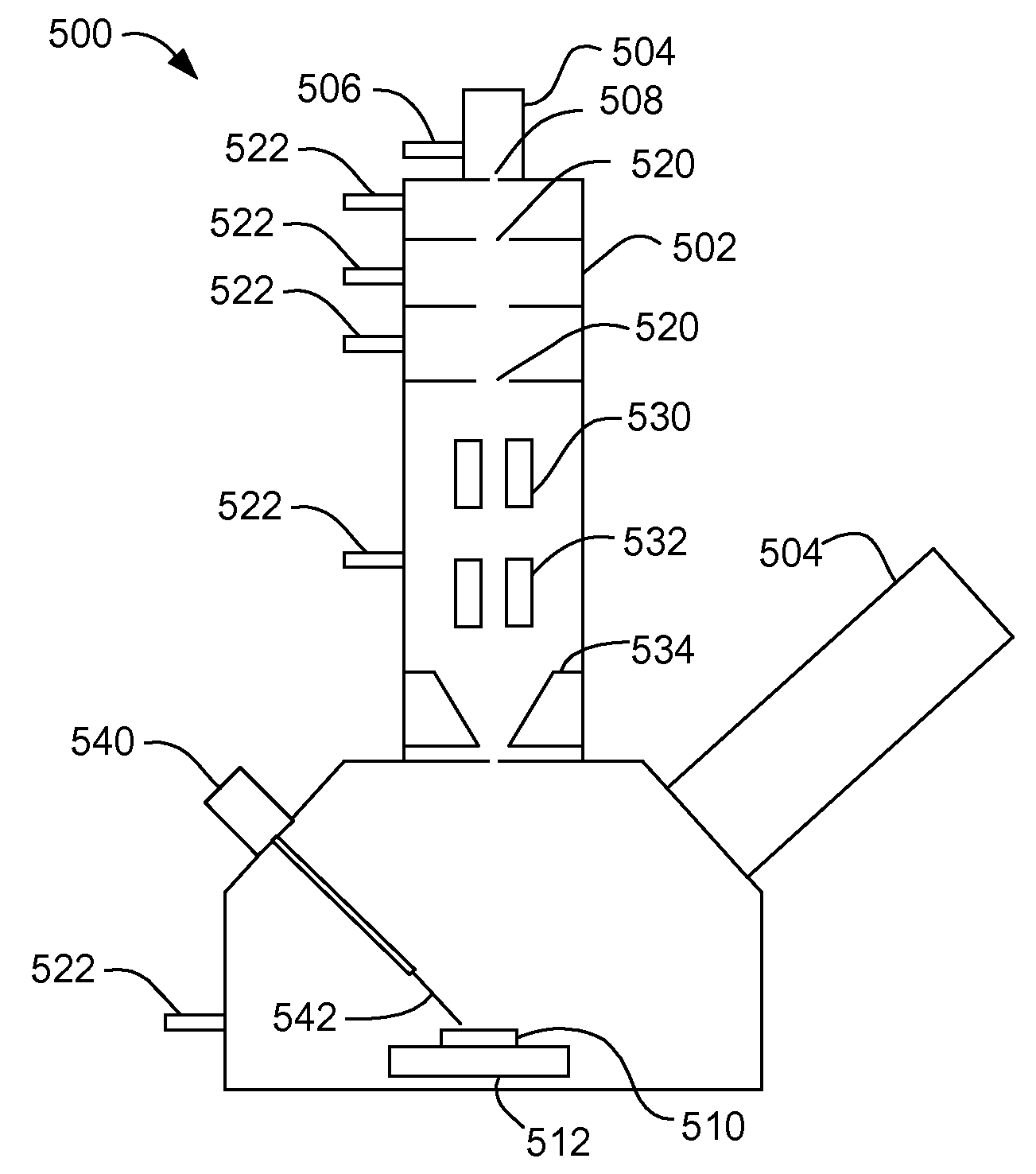
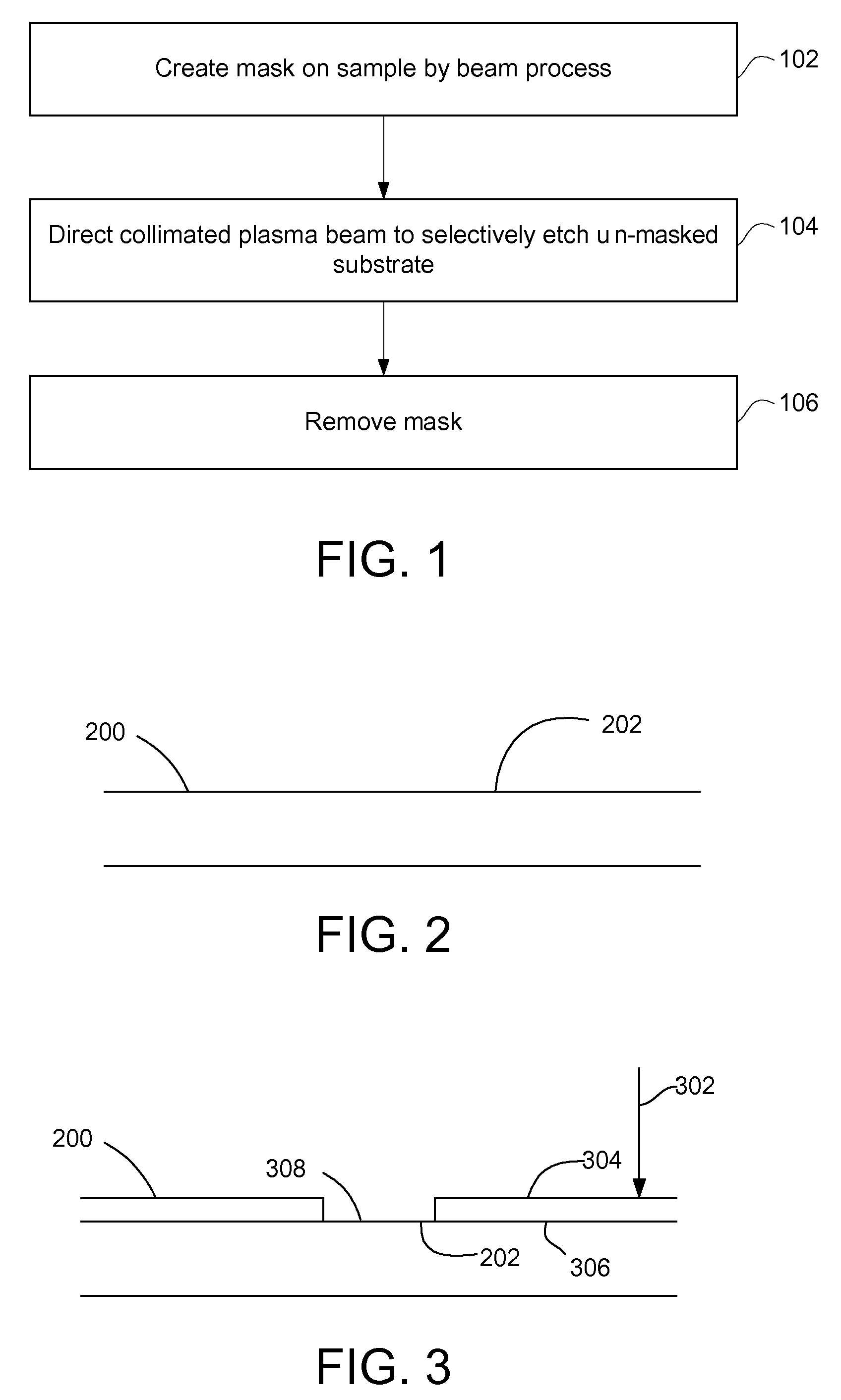
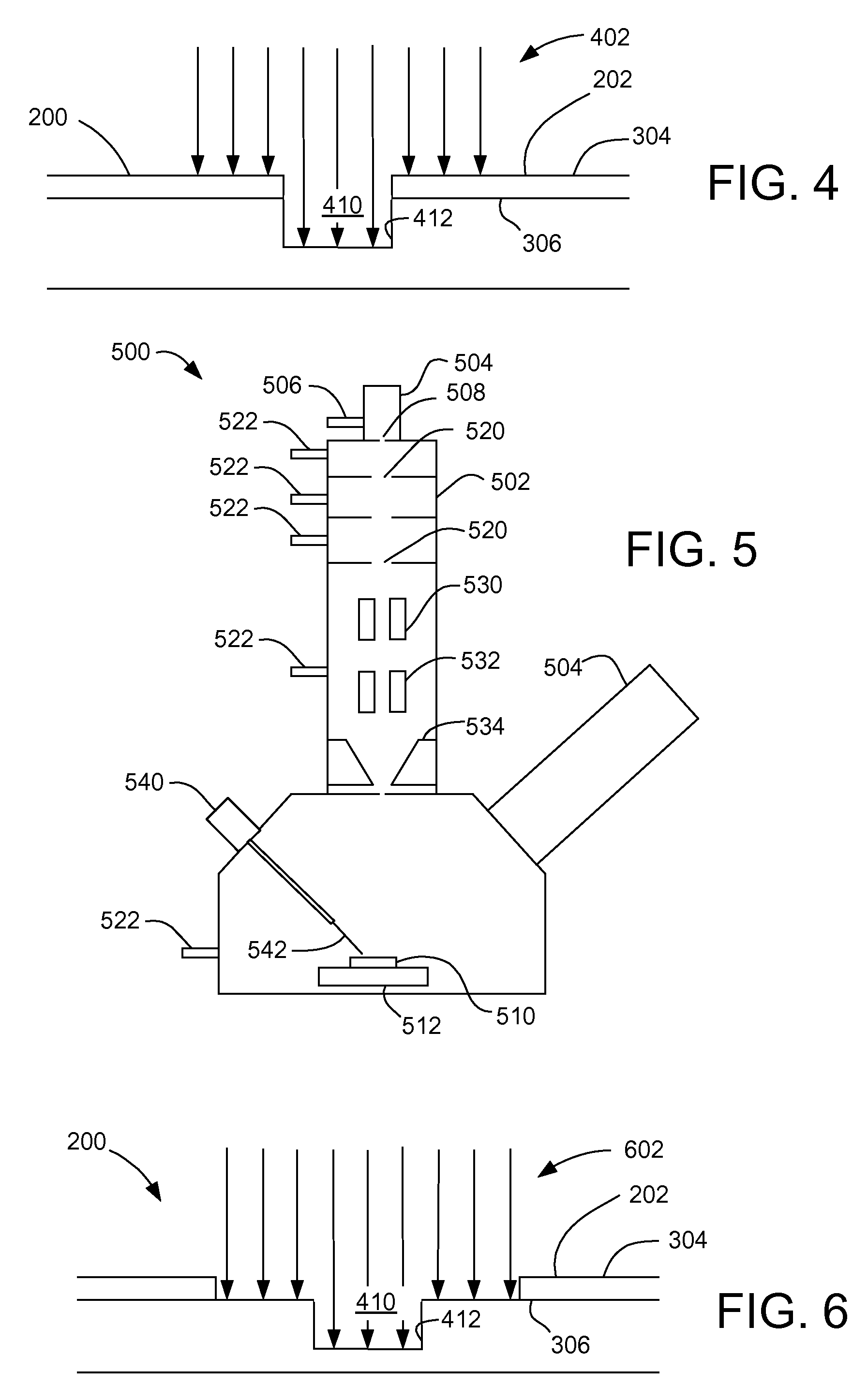
High resolution plasma etch
A method for fabrication of microscopic structures that uses a beam process, such as beam-induced decomposition of a precursor, to deposit a mask in a precise pattern and then a selective, plasma beam is applied, comprising the steps of first creating a protective mask upon surface portions of a substrate using a beam process such as an electron beam, focused ion beam (FIB), or laser process, and secondly etching unmasked substrate portions using a selective plasma beam etch process. Optionally, a third step comprising the removal of the protective mask may be performed with a second, materially oppositely selective plasma beam process.
Owner:FEI CO
System and Method for Focused Ion Beam Data Analysis
ActiveUS20090135240A1Increase changeFacilitate cognitionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSamplingGraphicsIon beam
A system and method for improving FIB milling endpointing operations. The methods involve generating real-time images of the area being milled and real-time graphical plots of pixel intensities with an increased sensitivity over native FIB system generated images and plots. The images and plots are generated with raw signal data obtained from the native FIB system. More specifically, the raw signal data is processed according to specific algorithms for generating images and corresponding intensity graphs which can be reliably used for accurate endpointing. In particular, the displayed images will display more visual information regarding changes in milled material, while the intensity graphs will plot aggregate pixel intensity data on a dynamically adjusting scale to dramatically highlight relative changes in milled material.
Owner:DCG SYST
Back-scatter detection in flow cytometers
ActiveUS7075647B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioSmall sizeMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamOptical flow
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Ion beam apparatus and sample processing method
InactiveUS7084399B2Improve throughputHigh positioning accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesHigh fluxImage resolution
For the sake of realizing high throughput and high processing position accuracy in an ion beam apparatus, two kinds of ion beams for processing are prepared of which one is a focusing ion beam for high image resolution and an edge processing ion beam of large beam current for permitting a sectional edge portion to be processed sharply, whereby high processing position accuracy can be ensured even with a large current ion beam.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Charged particle guide
ActiveUS7135678B2Reduce wearIncrease generationThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCharged particle detectorsSecondary electrons
A charged particle guide adapted to be coupled with a charged particle detector, such as a secondary electron detector. The charged particle guide, in one example, comprising two wires extending from the charged particle detector toward a source of charged particles, such as secondary electrons emitted from an IC upon application of a focused ion beam. Upon application of a bias voltage, the charged particle guide introduces a collecting electric field that attracts charged particles and directs the charged particles to the charged particles detector.
Owner:DCG SYST
Combination Laser and Charged Particle Beam System
ActiveUS20110248164A1Avoid saturationThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersHigh resolution imagingMaterial removal
A combined laser and charged particle beam system. A pulsed laser enables milling of a sample at material removal rates several orders of magnitude larger than possible for a focused ion beam. In some embodiments, a scanning electron microscope enables high resolution imaging of the sample during laser processing. In some embodiments, a focused ion beam enables more precise milling of the sample. A method and structure for deactivating the imaging detectors during laser milling enables the removal of imaging artifacts arising from saturation of the detector due to a plasma plume generated by the laser beam. In some embodiments, two types of detectors are employed: type-1 detectors provide high gain imaging during scanning of the sample with an electron or ion beam, while type-2 detectors enable lower gain imaging and endpoint detection during laser milling.
Owner:FEI CO
Multi-source plasma focused ion beam system
ActiveUS8076650B2Facilitates sequentially and simultaneouslyReduce necessityParticle separator tubesVacuum evaporation coatingLight beamIon beam
The present invention provides a plasma ion beam system that includes multiple gas sources and that can be used for performing multiple operations using different ion species to create or alter submicron features of a work piece. The system preferably uses an inductively coupled, magnetically enhanced ion beam source, suitable in conjunction with probe-forming optics sources to produce ion beams of a wide variety of ions without substantial kinetic energy oscillations induced by the source, thereby permitting formation of a high resolution beam.
Owner:FEI CO
Dual beam system
ActiveUS20100301211A1Simple operating systemThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDual beamImage resolution
A dual beam system provides for operation of a focused ion beam in the presence of a magnetic field from an ultra-high resolution electron lens. The ion beam is deflected to compensate for the presence of the magnetic field.
Owner:FEI CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com