Patents
Literature
393 results about "Field pattern" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
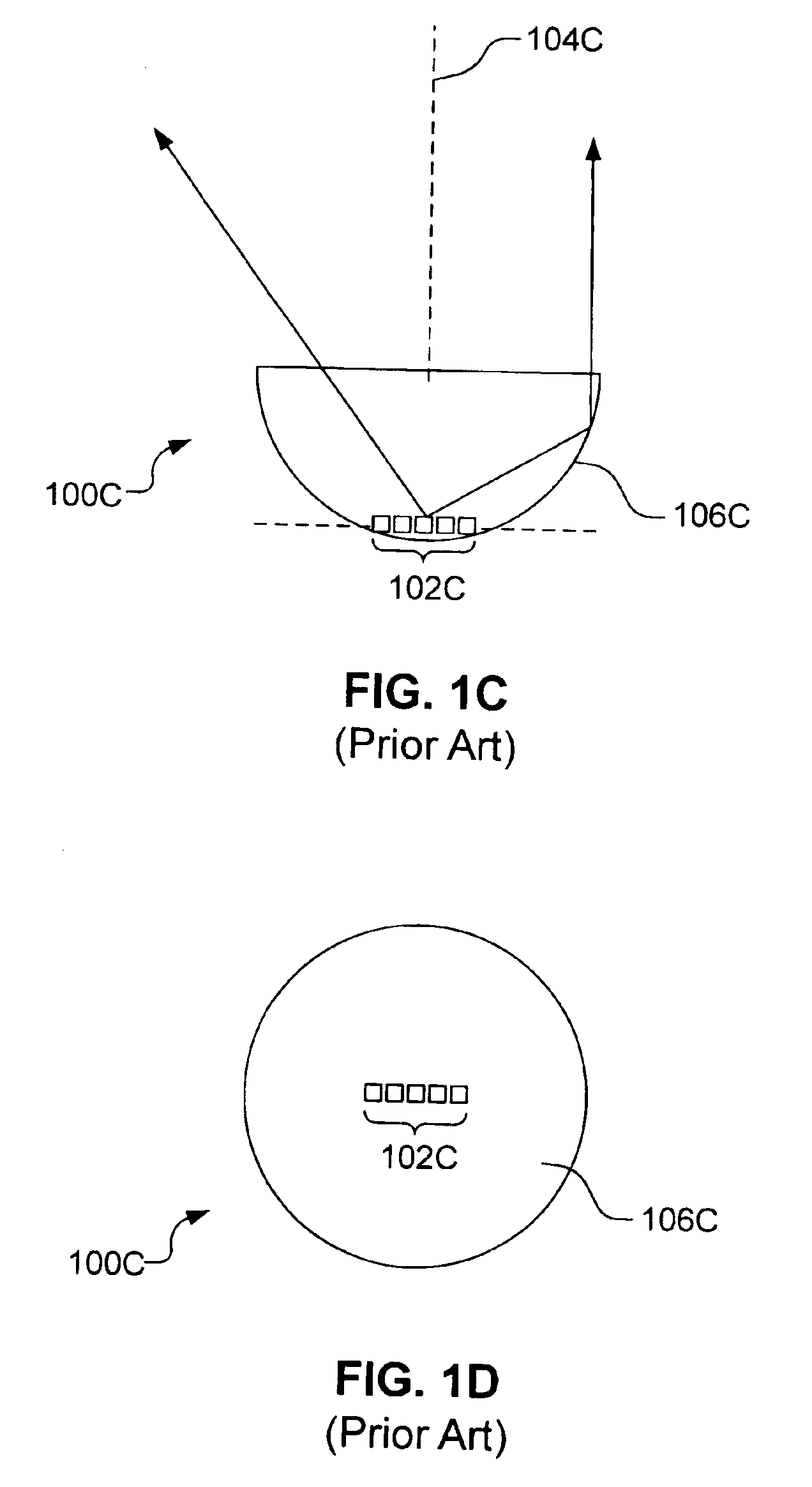
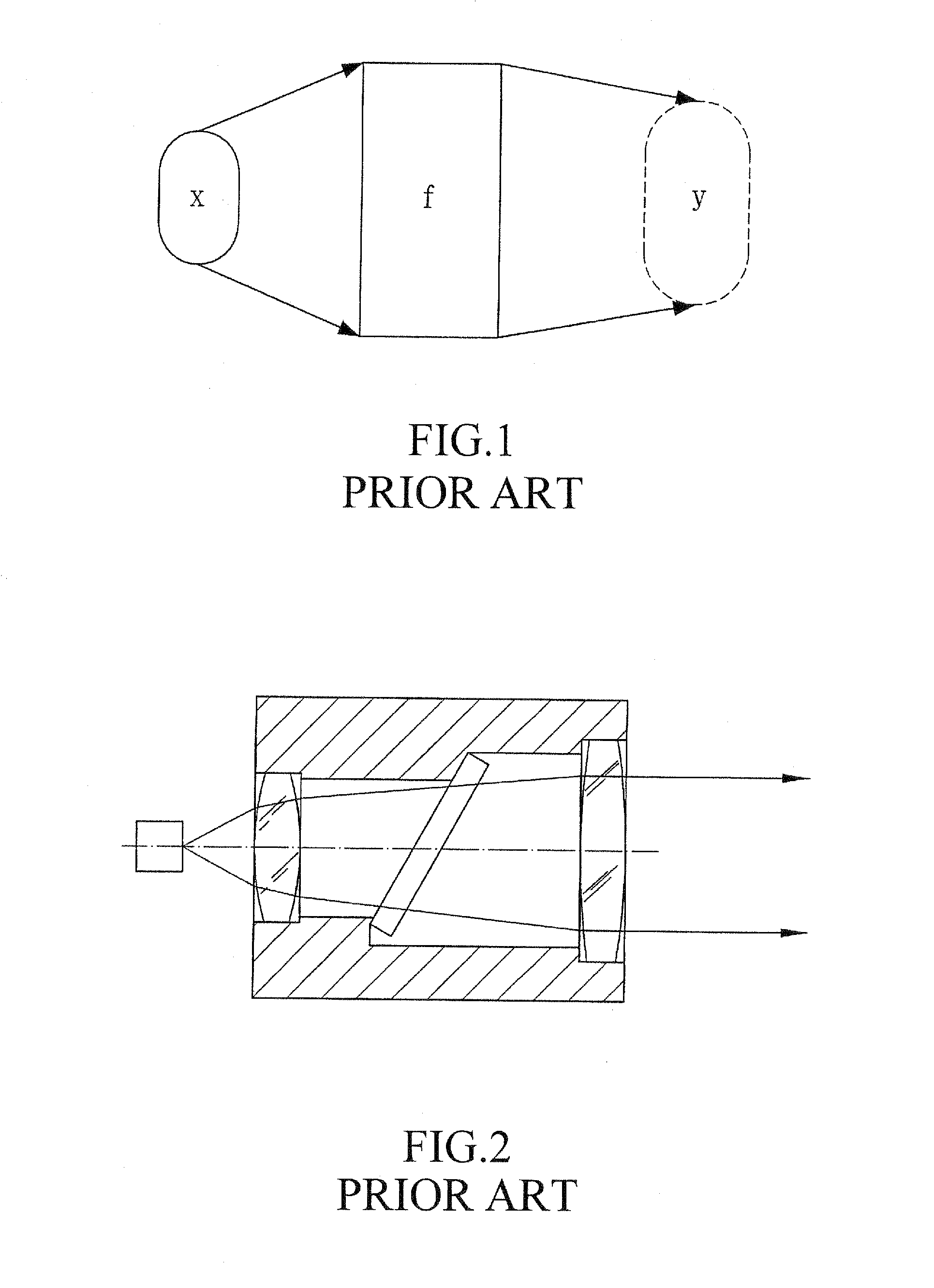
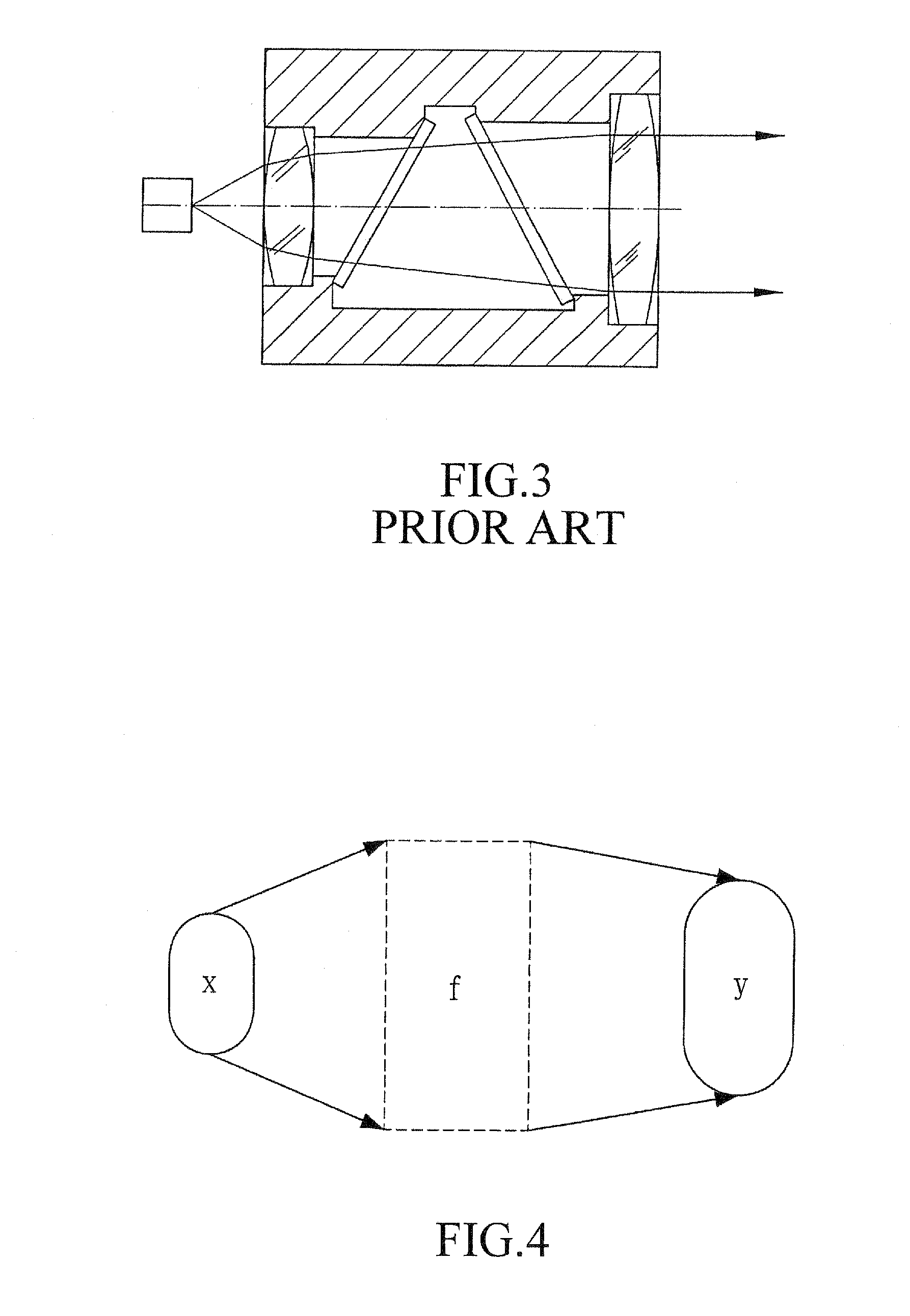
The far-field pattern of an antenna may be determined experimentally at an antenna range, or alternatively, the near-field pattern may be found using a near-field scanner, and the radiation pattern deduced from it by computation.
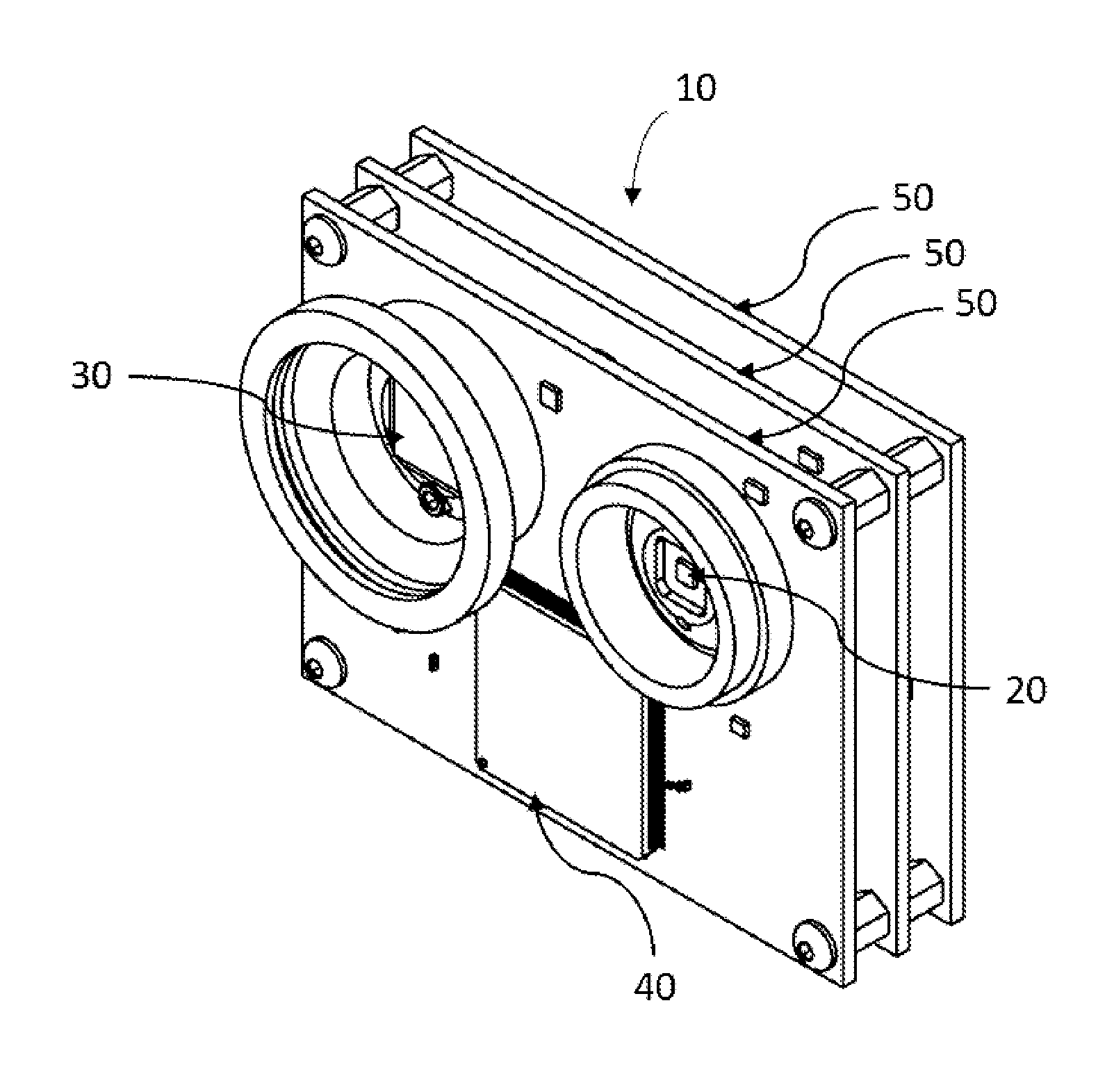
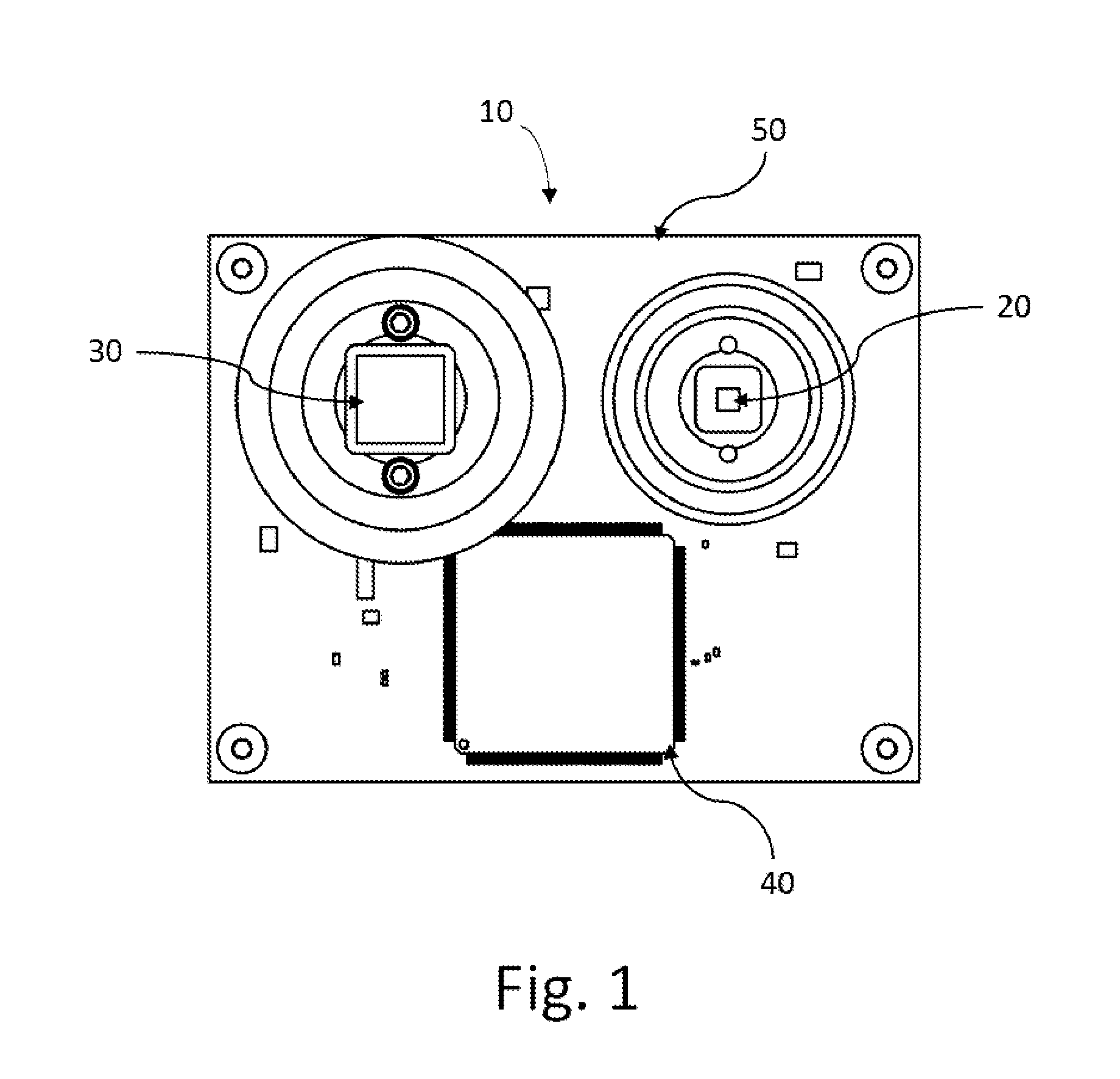
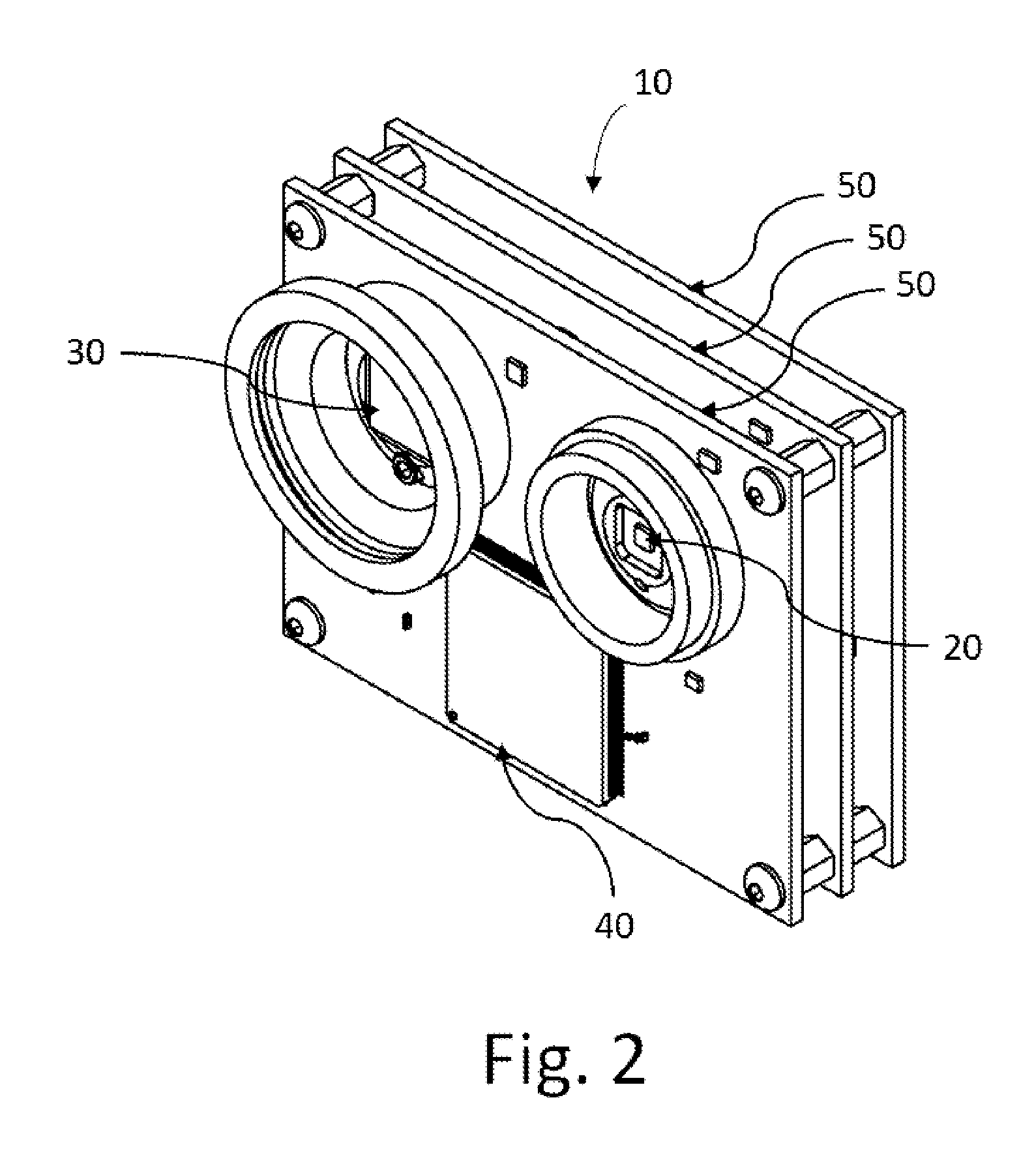
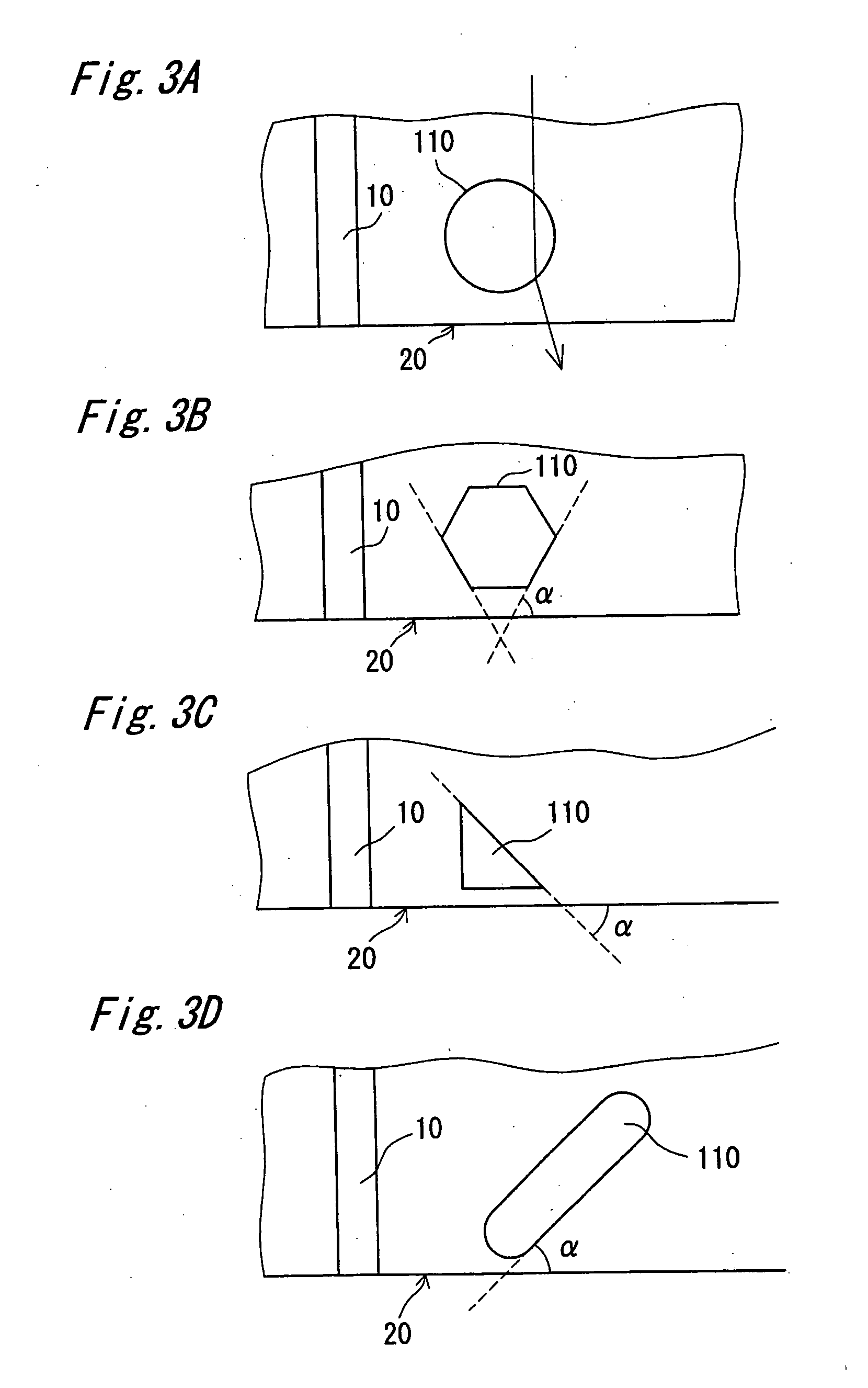
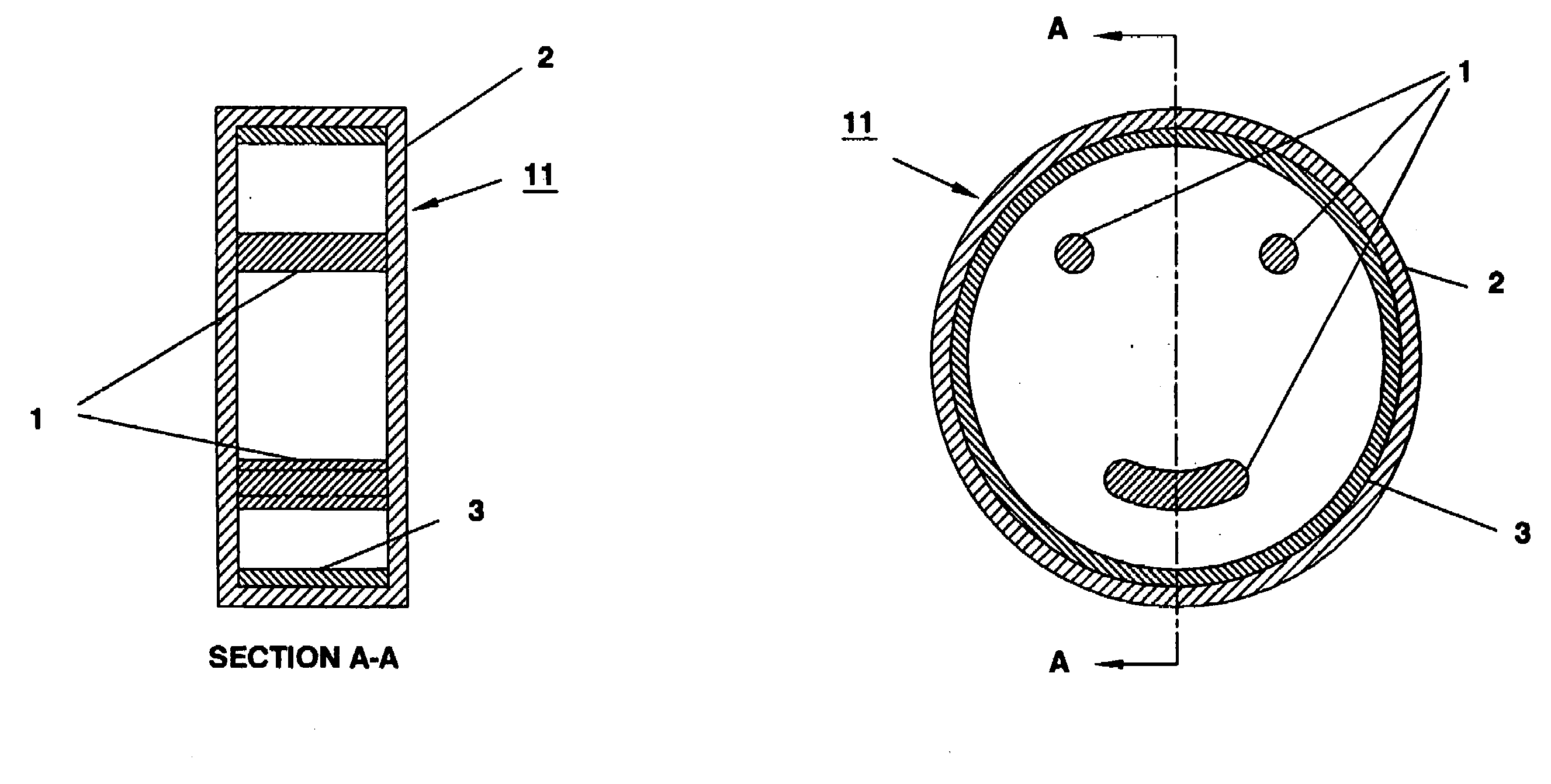
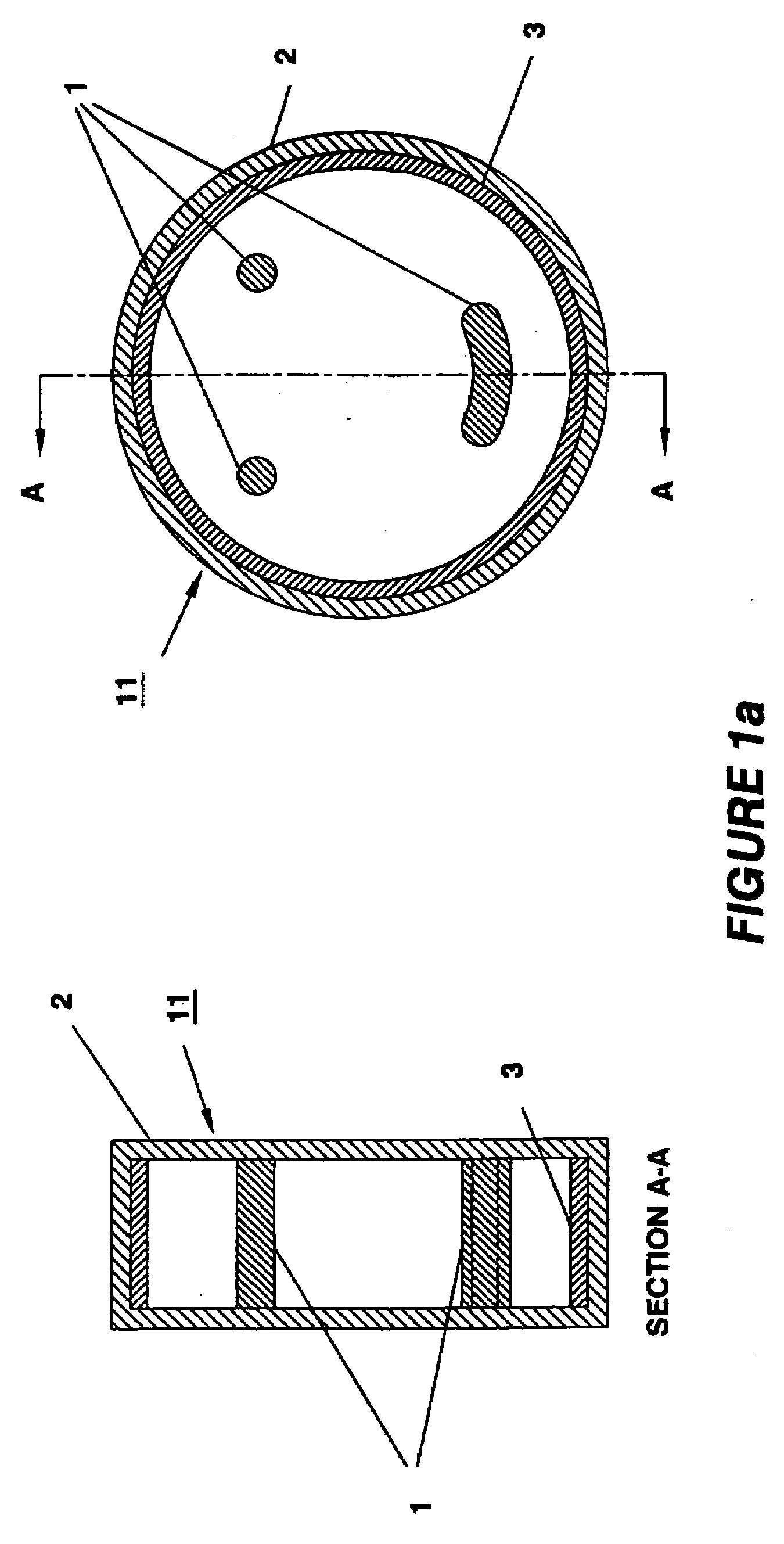
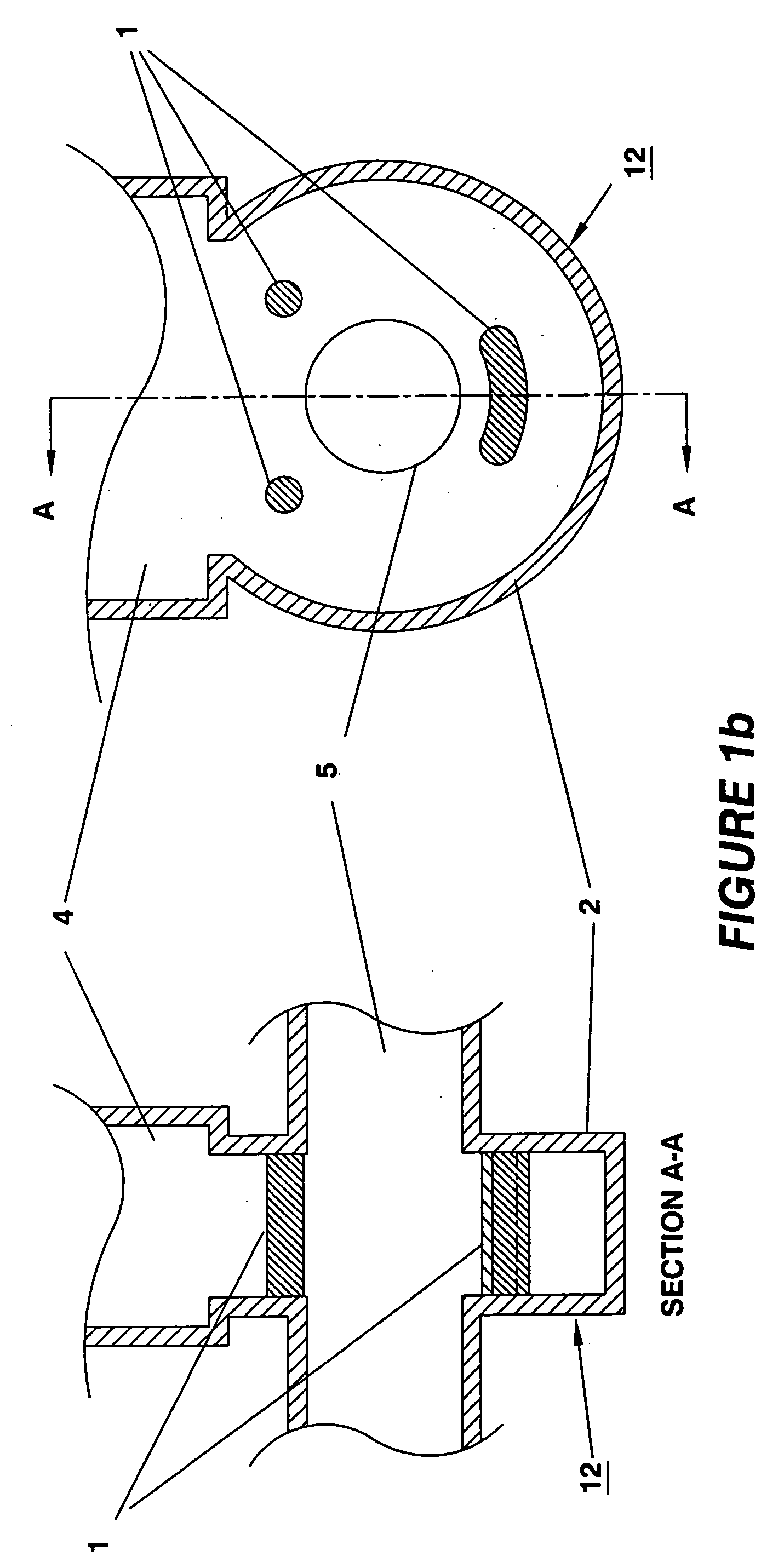
Apparatus and method for conformal mask manufacturing
ActiveUS20080160431A1Electric discharge tubesPhotosensitive materialsComputational physicsIrradiation
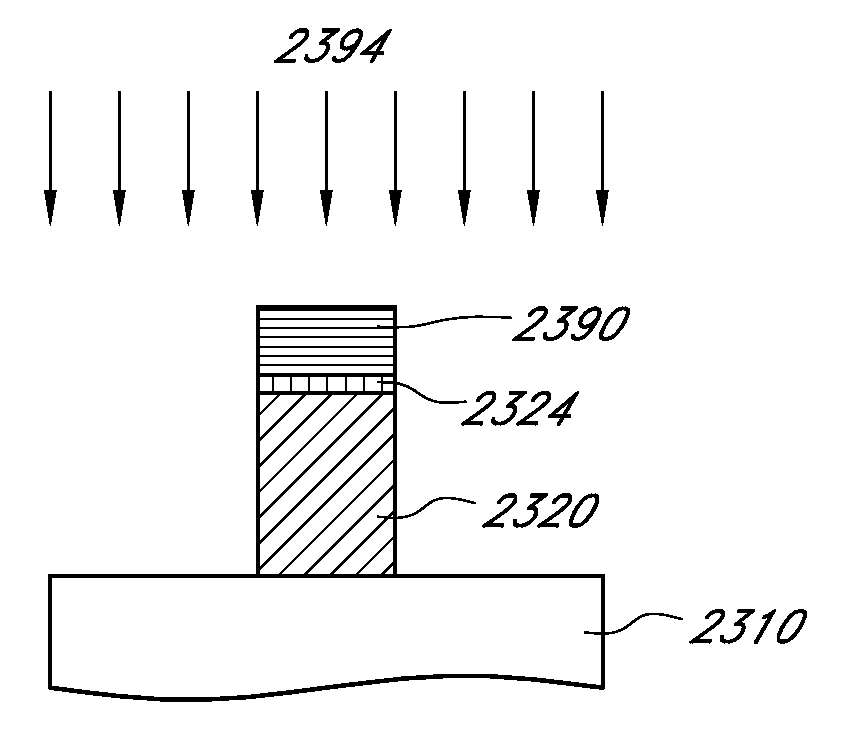
A manufacturing process technology creates a pattern on a first layer using a focused ion beam process. The pattern is transferred to a second layer, which may act as a traditional etch stop layer. The pattern can be formed on the second layer without irradiation by light through a reticle and without wet chemical developing, thereby enabling conformal coverage and very fine critical feature control. Both dark field patterns and light field patterns are disclosed, which may enable reduced or minimal exposure by the focused ion beam.
Owner:NEXGENSEMI HLDG INC
System and method for selective communication with RFID transponders
InactiveUS6848616B2Minimizing creationSmall sizeMemory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsTransceiverCoupling
A system having an RFID transceiver is adapted to communicate exclusively with a single RFID transponder located in a predetermined confined transponder target area. The system includes a magnetic coupling device comprising a magnetic flux generator responsive to a radio frequency input signal and a magnetic field pattern former. The pattern former is configured to collect flux produced by the flux generator and to form a field pattern in the location of the transponder target area. The system establishes, at predetermined transceiver power levels, a mutual magnetic coupling which is selective exclusively for a single transponder located in the transponder target area.
Owner:ZEBRA INVESTMENT HLDG CORP +1
Axial LED source
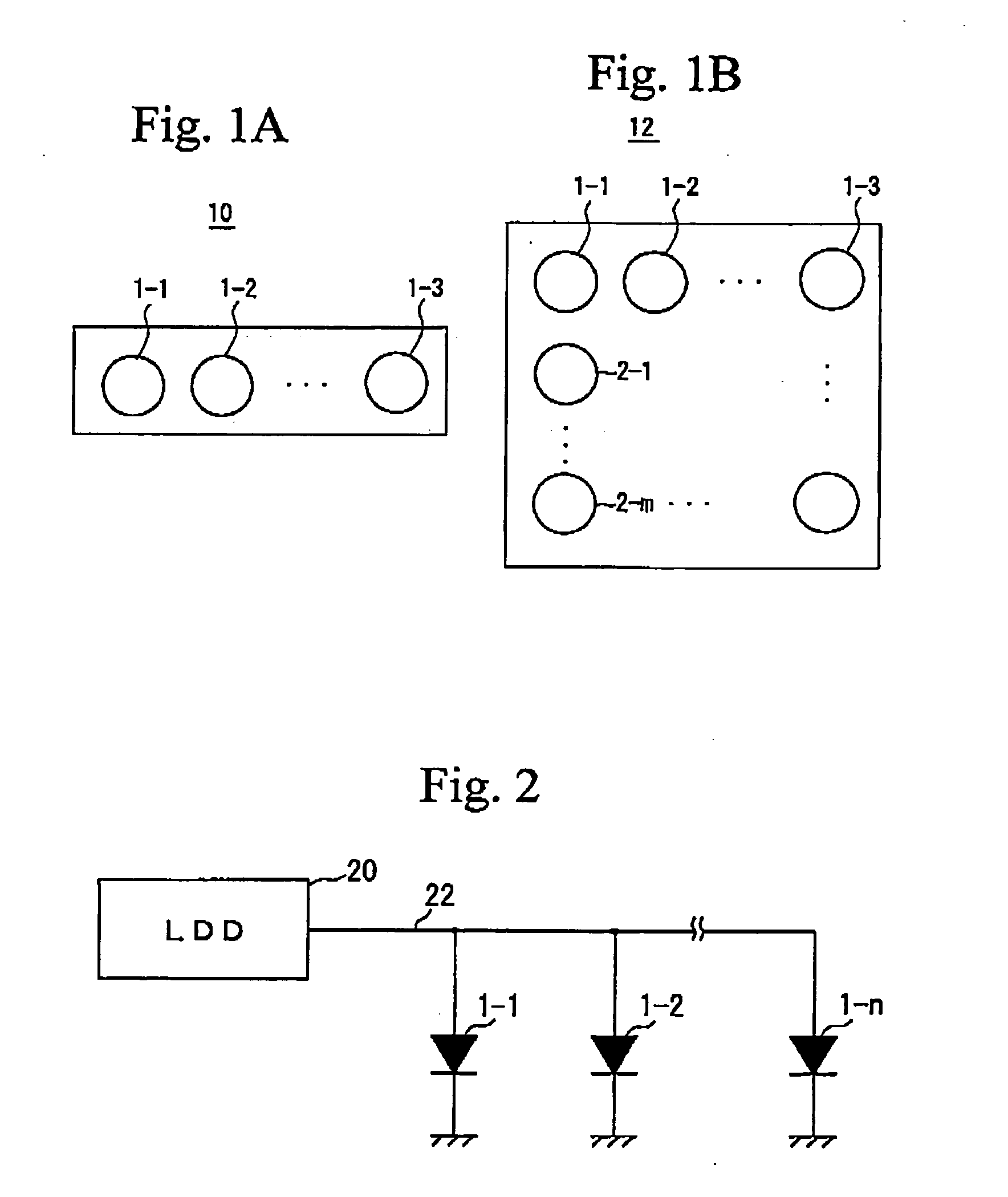
A lamp has LED sources that are placed about a lamp axis in an axial arrangement. The lamp includes a post with post facets where the LED sources are mounted. The lamp includes a segmented reflector for guiding light from the LED sources. The segmented reflector includes reflective segments each of which is illuminated primarily by light from one of the post facets (e.g., one of the LED sources on the post facet). The LED sources may be made up of one or more LED dies. The LED dies may include optic-on-chip lenses to direct the light from each post facet to a corresponding reflective segment. The LED dies may be of different sizes and colors chosen to generate a particular far-field pattern.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Solid state optical phased array lidar and method of using same
ActiveUS20150293224A1Instruments for comonautical navigationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical delay lineRadiation pattern
A lidar-based apparatus and method are used for the solid state steering of laser beams using Photonic Integrated Circuits. Integrated optic design and fabrication micro- and nanotechnologies are used for the production of chip-scale optical splitters that distribute an optical signal from a laser essentially uniformly to an array of pixels, said pixels comprising tunable optical delay lines and optical antennas. Said antennas achieve out-of-plane coupling of light.As the delay lines of said antenna-containing pixels in said array are tuned, each antenna emits light of a specific phase to form a desired far-field radiation pattern through interference of these emissions. Said array serves the function of solid state optical phased array.By incorporating a large number of antennas, high-resolution far-field patterns can be achieved by an optical phased array, supporting the radiation pattern beam forming and steering needed in solid state lidar, as well as the generation of arbitrary radiation patterns as needed in three-dimensional holography, optical memory, mode matching for optical space-division multiplexing, free space communications, and biomedical sciences. Whereas imaging from an array is conventionally transmitted through the intensity of the pixels, the optical phased array allows imaging through the control of the optical phase of pixels that receive coherent light waves from a single source.
Owner:QUANERGY SOLUTIONS INC
Ultra-wideband magnetic antenna
InactiveUS6091374AShort antennas for non-sinusoidal wavesAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesUltra-widebandElectrical conductor
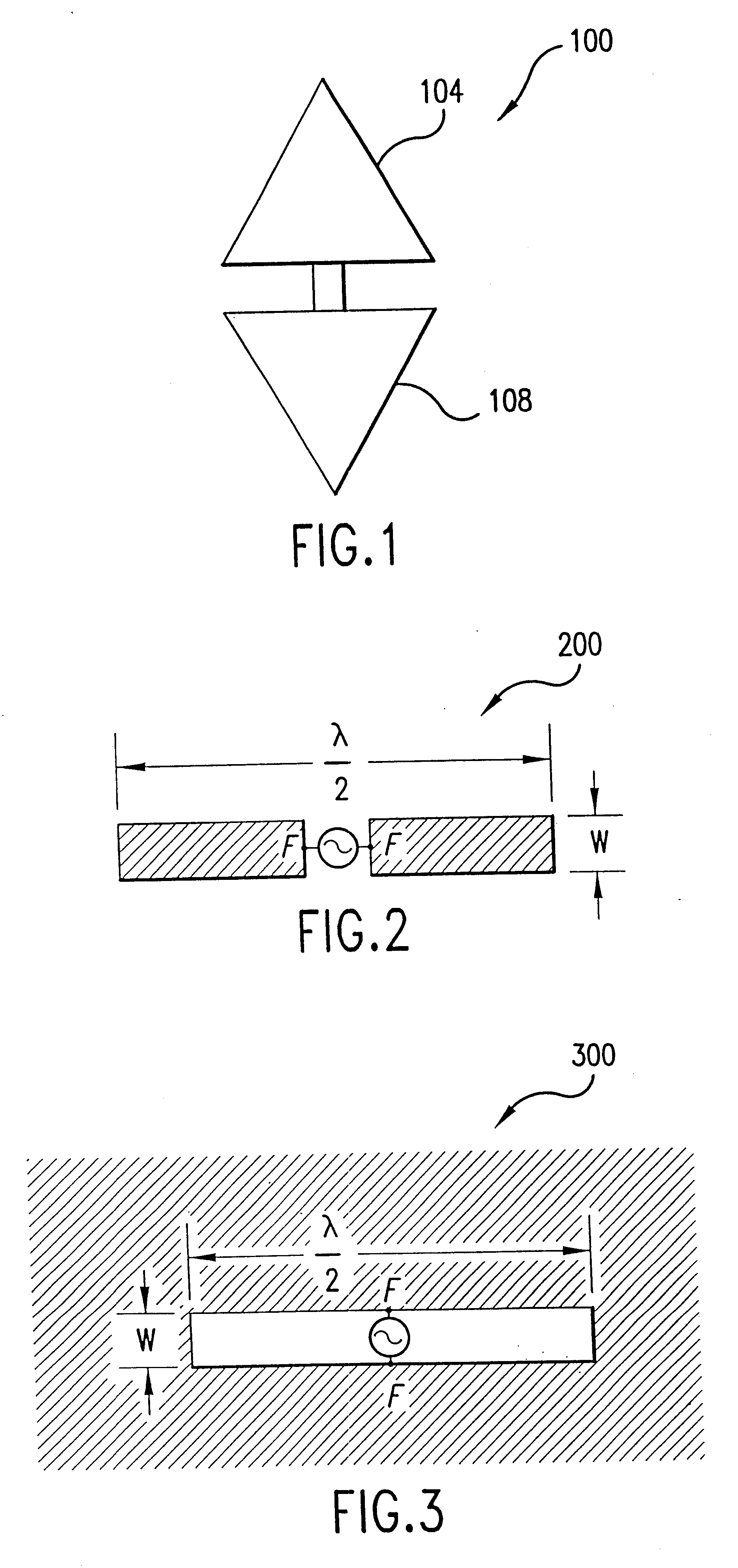
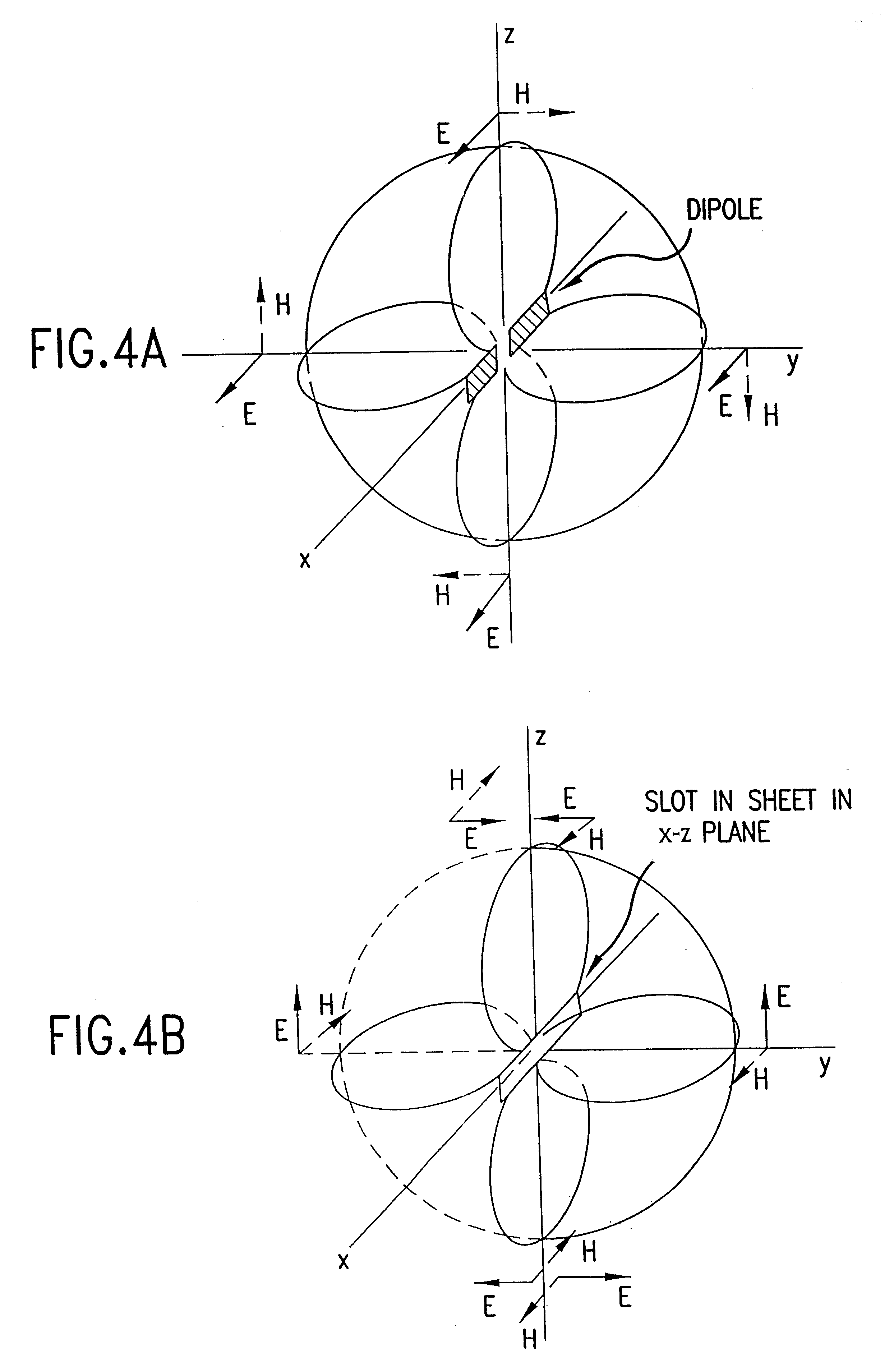
An ultra-wideband magnetic antenna includes a planar conductor having a first and a second slot about an axis. The slots are substantially leaf-shaped having a varying width along the axis. The slots are interconnected along the axis. A cross polarized antenna system is comprised of an ultra-wideband magnetic antenna and an ultra-wideband dipole antenna. The magnetic antenna and the dipole antenna are positioned substantially close to each other and they create a cross polarized field pattern. The present invention provides isolation between a transmitter and a receiver in an ultra-wideband system. Additionally, the present invention allows isolation among radiating elements in an array antenna system.
Owner:TIME DOMAIN
Ultra-wideband magnetic antenna
InactiveUS6400329B1Short antennas for non-sinusoidal wavesAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesUltra-widebandElectrical conductor
An ultra-wideband magnetic antenna includes a planar conductor having a first and a second slot about an axis. The slots are substantially leaf-shaped having a varying width along the axis. The slots are interconnected along the axis. A cross polarized antenna system is comprised of an ultra-wideband magnetic antenna and an ultra-wideband dipole antenna. The magnetic antenna and the dipole antenna are positioned substantially close to each other and they create a cross polarized field pattern. The present invention provides isolation between a transmitter and a receiver in an ultra-wideband system. Additionally, the present invention allows isolation among radiating elements in an array antenna system.
Owner:TIME DOMAIN
Antenna device and method for transmitting and receiving radio waves
InactiveUS6980782B1Easy to manufactureEasy to installResonant long antennasAntenna supports/mountingsResonanceInput impedance
An antenna device for transmitting and receiving radio frequency waves, installable in a communication device includes an antenna structure switchable between antenna configuration states. Each state is distinguished by a set of radiation parameters, such as resonance frequency, input impedance, bandwidth, radiation pattern, gain, polarization, and near-field pattern. A switching device selectively switches the structure between the states. The antenna device includes a first receiver which receives a first measured operation parameter indicative of quality of transmission of radio frequency waves by the antenna structure, and a second receiver which receives a second measured operation parameter indicative of quality of reception of radio frequency waves by the structure. The antenna device includes a controller which controls the switching device, and selective switching of the antenna structure between the states, based on the first and second measured operation parameters, to improved transmission and / or reception quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light source apparatus and optical communication module comprising it
ActiveUS20050226636A1Small sizeLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor laser optical deviceHigh densityMagnifying glass
A light source device for radiating a stimulated emission from a semiconductor laser to outside via a multiple scattering optical system, which system has a first region located adjacent to the semiconductor laser and a second region that abuts on the first region and reaches the outside. The first region contains scatterers at a higher density than the second region does. The light source device has an amount of near-field pattern speckles σPAR of 3×10−3 or more. The second region may have a lens portion as a magnifier for at least a principle part of a secondary planar light source formed at an interface between the first and second regions.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
System and method for capturing and positioning particles
InactiveUS20040262210A1Water/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsLaboratory glasswaresElectrical conductorImage resolution
A micro-electromagnet matrix captures and controls the movement of particles with nanoscale resolution. The micro-electromagnet matrix includes multiple layers of microconductors, each layer of microconductors being orthogonal to an adjacent layer or microconductors. The layers of microconductors are formed on a substrate and have insulating layers therebetween. The field patterns produced by the micro-electromagnet matrix enable precise manipulation of particles. The micro-electro-magnet matrix produces single or multiple independent field peaks in the magnetic field that are used to trap, move, or rotate the particles. The micro-electromagnet matrix also produces electromagnetic fields to probe and detect particles.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Alignment apparatus for x-ray imaging system
A method for aligning a radiation source with a portable image receiver in a radiographic imaging system generates a magnetic field with a predetermined field pattern and with a time-varying vector direction at a predetermined frequency from an emitter apparatus that is coupled to the radiation source, wherein the generated magnetic field further comprises a synchronization signal. Sensed signals from the magnetic field are obtained from a sensing apparatus that is coupled to the image receiver, wherein the sensing apparatus comprises three or more sensor elements, wherein at least two of the sensor elements are arranged at different angles relative to each other and are disposed outside the imaging area of the image receiver. An output signal is indicative of an alignment adjustment according to the amplitude and phase of the obtained sensed signals relative to the synchronization signal.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Semiconductor laser device
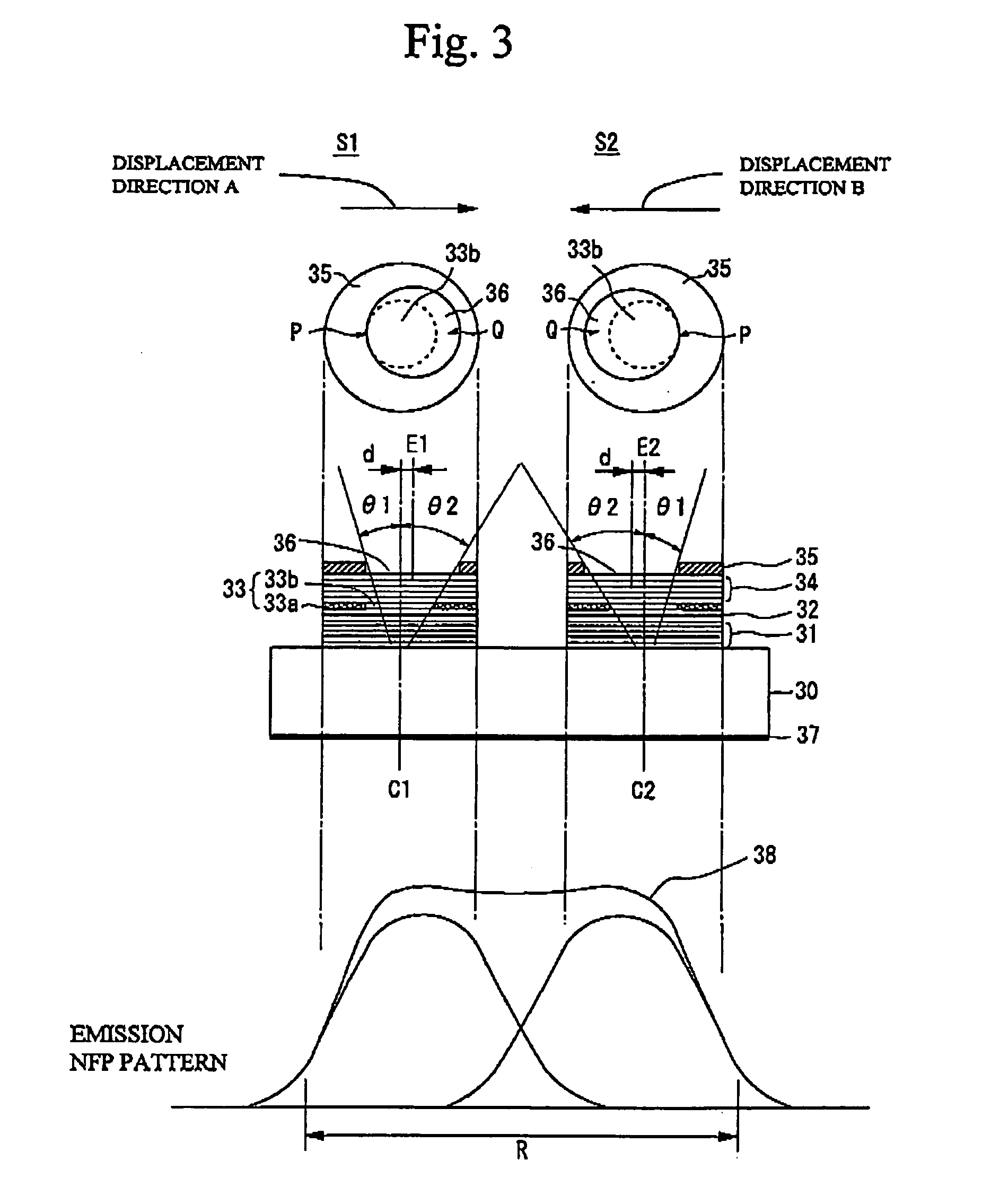
A semiconductor laser device having a far field pattern (FFP) with a Gaussian distribution that is less prone to ripples is provided. The semiconductor laser device comprises a semiconductor layer having a first conductivity type, an active layer, a semiconductor layer having a second conductivity type, a waveguide region formed by restricting current within a stripe-shaped region in the semiconductor layer of the second conductive type, and a resonance surface provided on an end face substantially perpendicular to the waveguide region. A plurality of recesses is formed at positions spaced from the waveguide region in the semiconductor layer of the second conductivity type in a region adjacent to the resonance surface.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
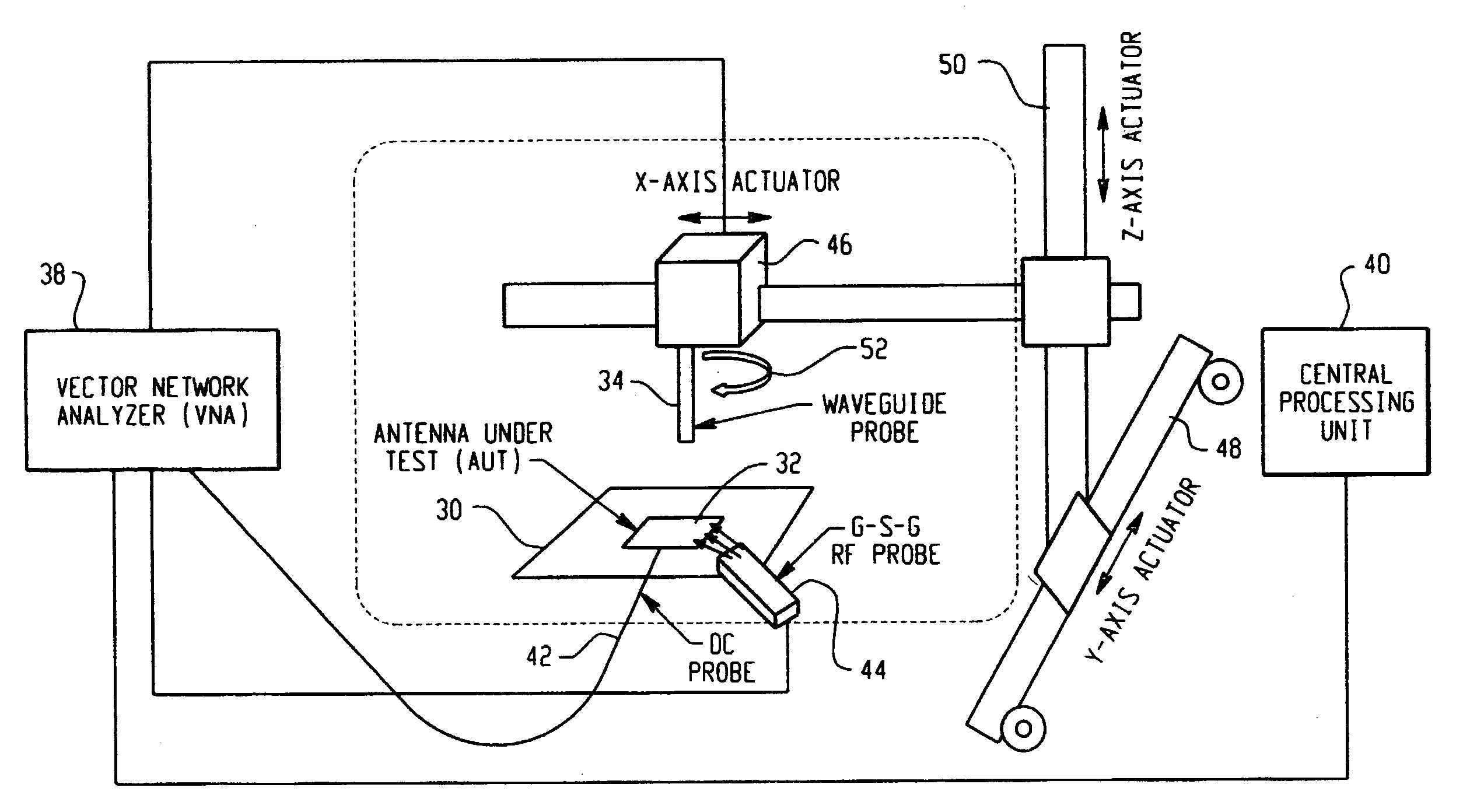
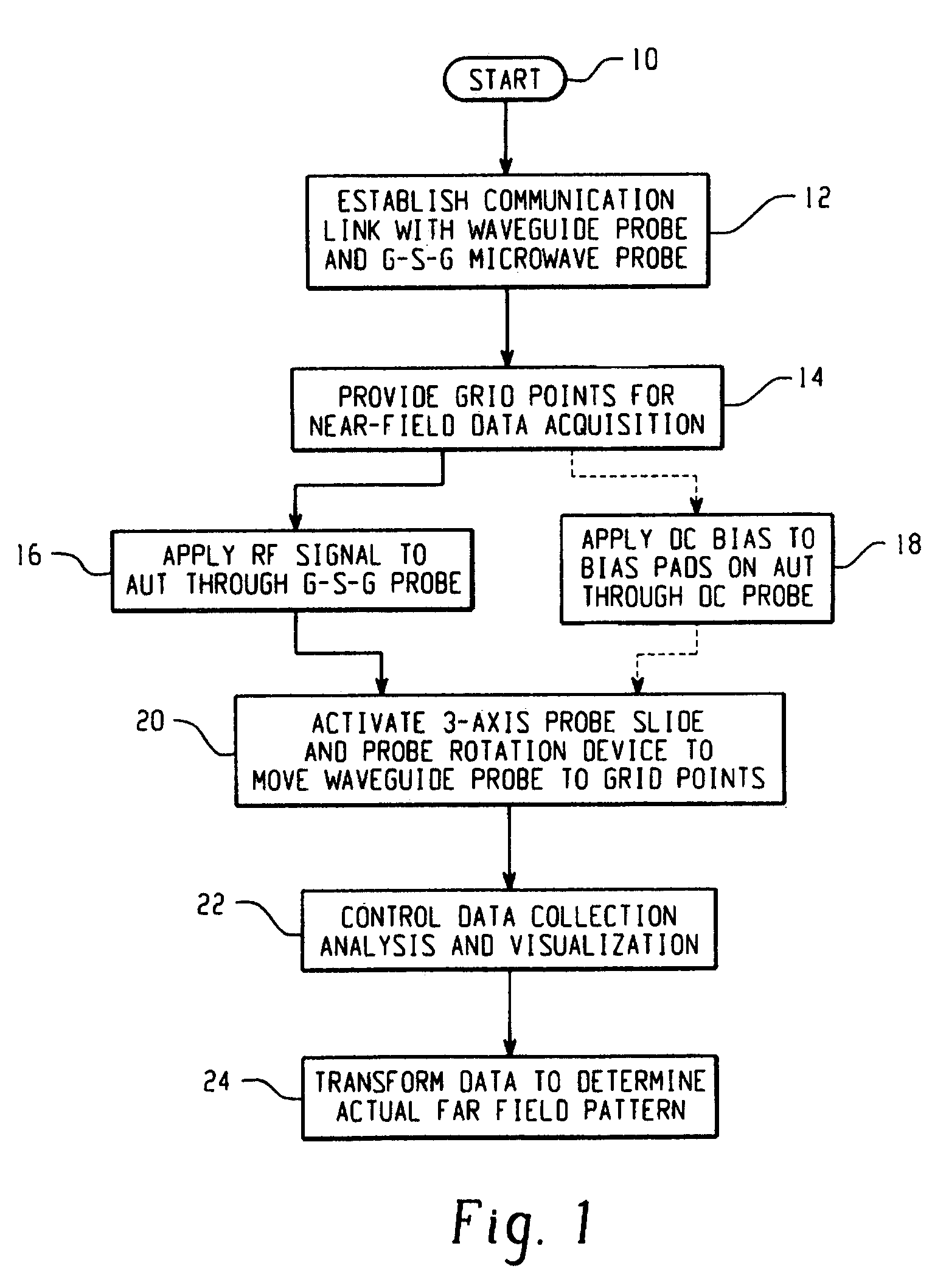
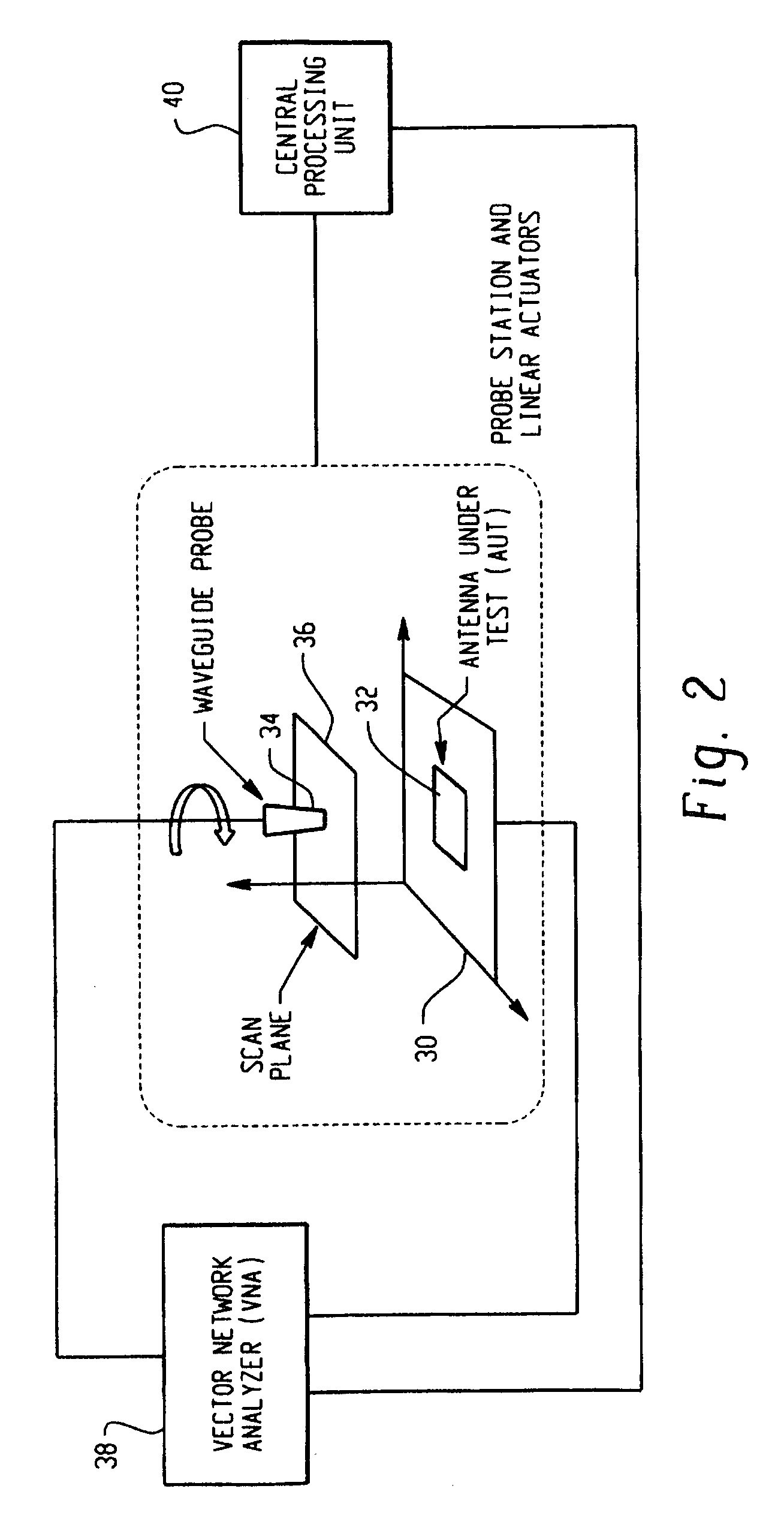
Antenna near-field probe station scanner
A miniaturized antenna system is characterized non-destructively through the use of a scanner that measures its near-field radiated power performance. When taking measurements, the scanner can be moved linearly along the x, y and z axis, as well as rotationally relative to the antenna. The data obtained from the characterization are processed to determine the far-field properties of the system and to optimize the system. Each antenna is excited using a probe station system while a scanning probe scans the space above the antenna to measure the near field signals. Upon completion of the scan, the near-field patterns are transformed into far-field patterns. Along with taking data, this system also allows for extensive graphing and analysis of both the near-field and far-field data. The details of the probe station as well as the procedures for setting up a test, conducting a test, and analyzing the resulting data are also described.
Owner:ADMINISTATOR OF NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE +1
System and method of interferentially varying electromagnetic near field patterns
InactiveUS20050205566A1Useful in treatmentAvoid radiationSurgical instrument detailsMicrowave therapyAbnormal tissue growthElectrical conductor
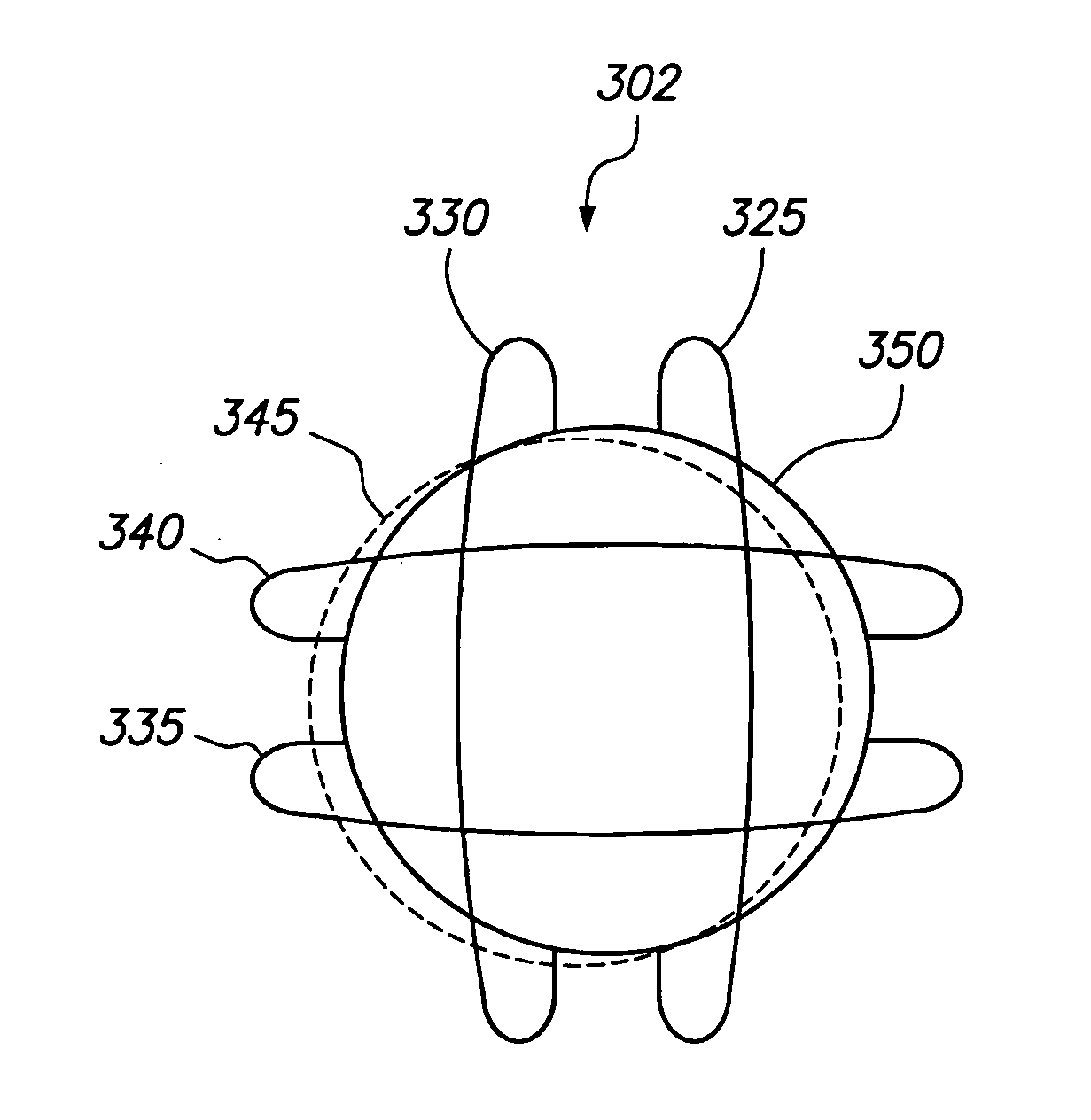
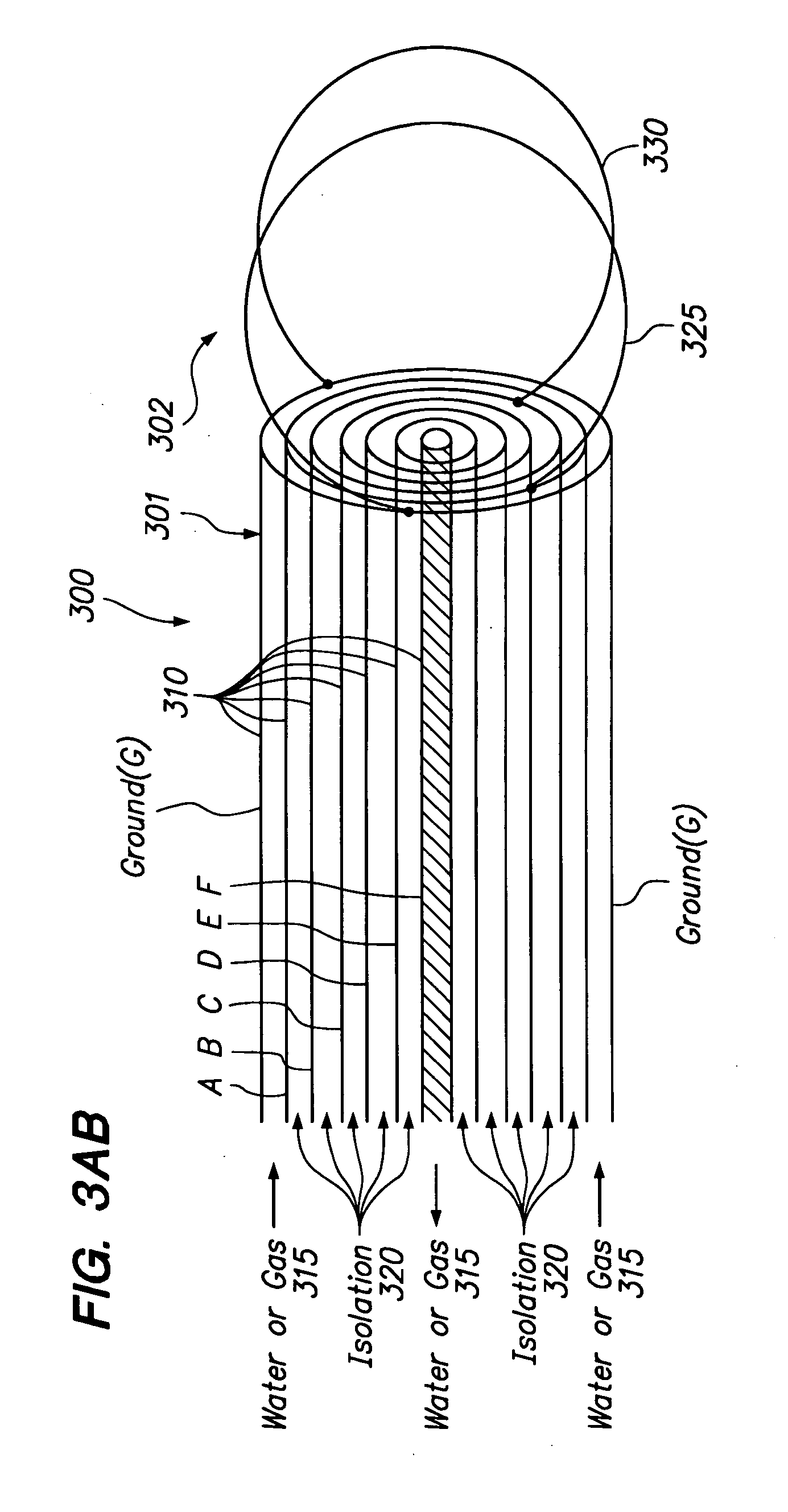
A system for ablating tissue using interferential electromagnetic fields, comprises tumor shape information; radiation tip shape and position information; a mathematical model for computing first frequency and phase information, second frequency and phase information, and mixing information based on the tumor shape information and on the radiation tip shape and position information. The system further comprises a first generator mechanism for generating a first tone based on the first frequency information and on the first phase information; a second generator mechanism for generating a second tone based on the second frequency information and on the second phase information; a mixer for mixing the first and second tones based on the mixing information; and a radiation tip for generating an interferential electromagnetic field pattern based on the first and second tones. The radiation tip may include radiation coils affixed to the distal end of a conduction member. The conduction member may include a set of nesting conductors for transmitting current to the radiation coils within the radiation tip, the current being selected based on the interferential electromagnetic field pattern desired. Also, using interferential electromagnetic field patterning, non-medical and / or non-cell-destroying systems, e.g., a tissue warmer, a faster microwave oven, an effective security gateway, and / or a safer cellular telephone, may be created.
Owner:SOLATRONIX
Surface emitting semiconductor laser array and optical transmission system using the same
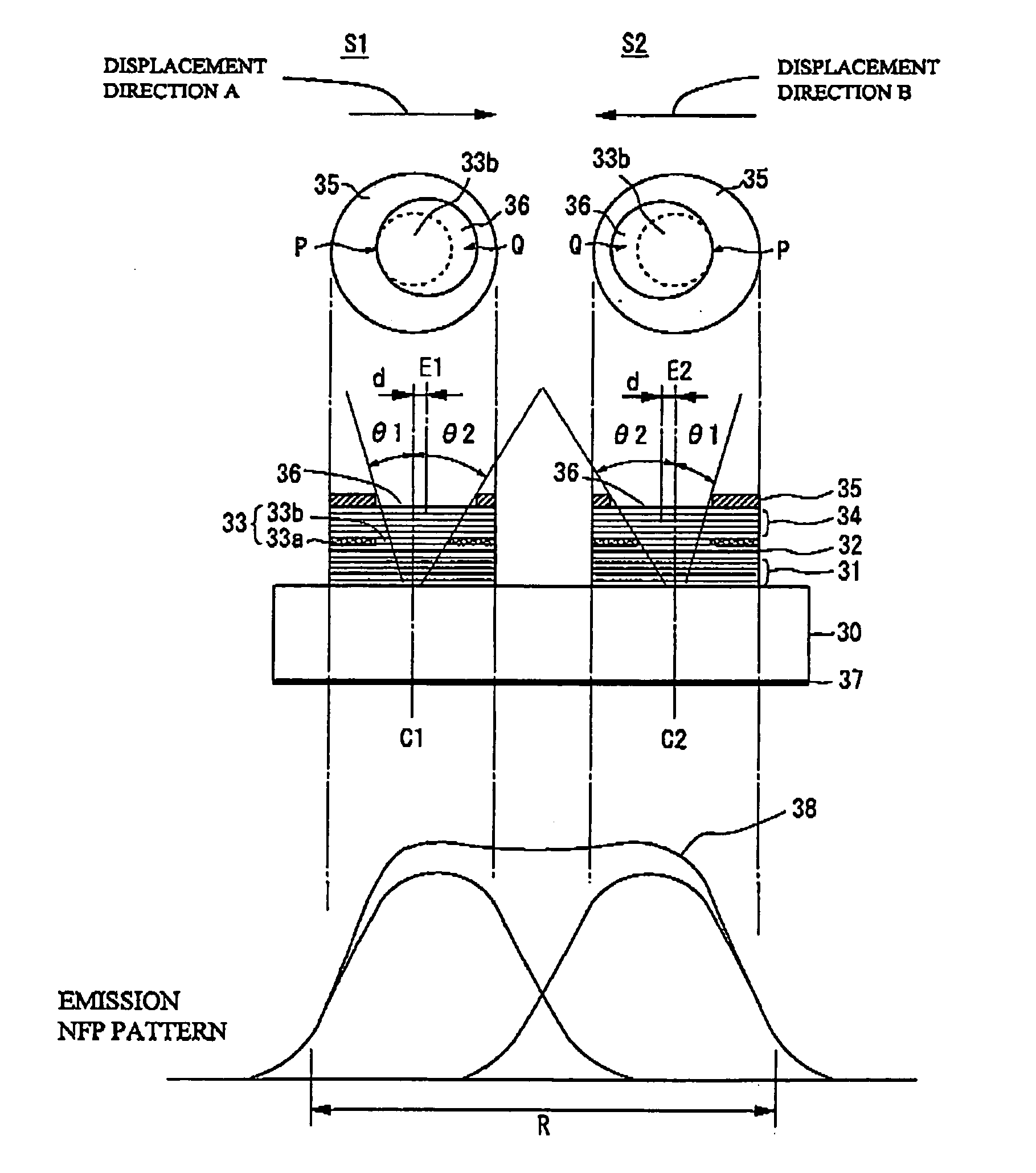
A surface emitting semiconductor laser array includes multiple light-emitting portions arranged in a one-dimensional or two-dimensional array, each of the light-emitting portions including, on a substrate, an active region and a current funneling portion between first and second reflection mirrors, and a light-emission aperture above the second reflection mirror, laser beams being simultaneously emitted from the multiple light-emitting portions. At least one of the multiple light-emitting portions has a near field pattern different from those of other light-emitting portions.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Collimation lens having freeform surface and design method thereof
InactiveUS20110270585A1Eliminate troubleReduce the amount requiredSpecial data processing applicationsLensCircular discSolution processed
A freeform surface included collimation lens is provided, which is designed through a freeform surface design process to provide an integrally-formed unitary structure. The design method includes a step of identifying an optic field pattern of light source, a step of performing graphic analysis of freeform surface tangential vector formula, a step of acquiring freeform surface control point, a step of constructing a three-dimensional model, and a step of performing geometric processing. Through these steps, tangential vectors of control points of each freeform surface are determined and an approximating process or an exact solution process is adopted to determine the coordinates of the points of the freeform surface. Three-dimensional modeling software is then employing to construct an ellipsoid collimation lens, which realizes an optic collimation performance of at least 88% when tested with a circular disk set at a distance of 200 meters and having a diameter of 35 meters.
Owner:NATIONAL CHANGHUA UNIVERSITY OF EDUCATION
Method and system for magnetically assisted statistical assembly of wafers
InactiveUS20030186469A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectretDielectric layer
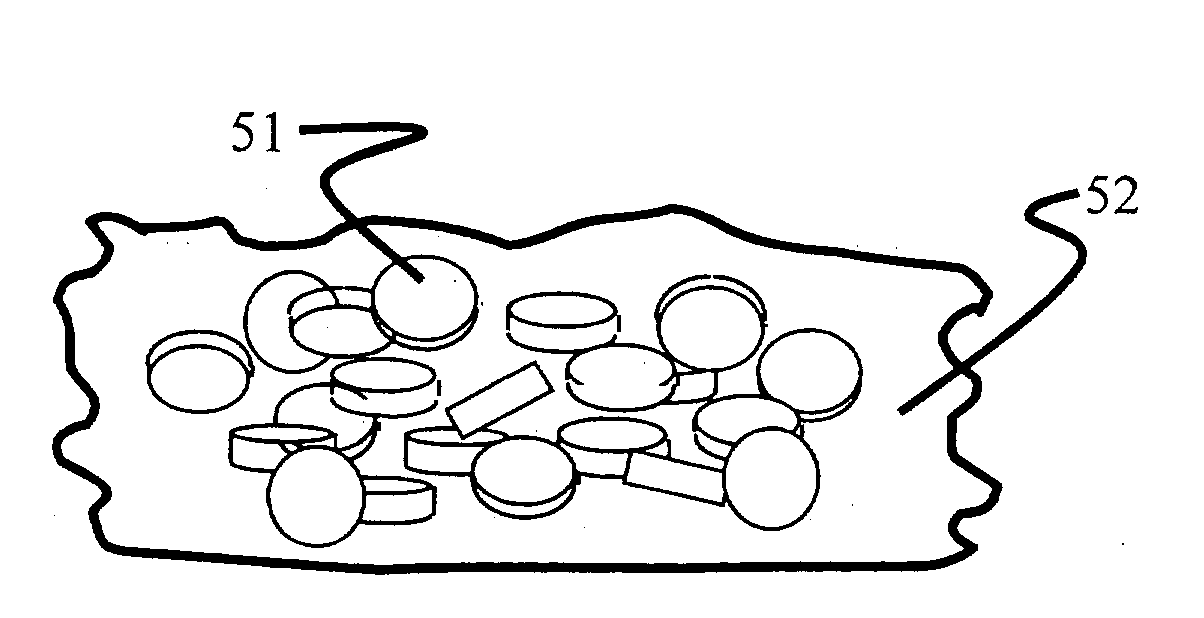
A wafer having heterostructure therein is formed using a substrate with recesses formed within a dielectric layer. A magnetized magnetic layer or a polarized electret material is formed at the bottom of each recess. The magnetized magnetic layer or a polarized electret material provides a predetermined magnetic or electrical field pattern. A plurality of heterostructures is formed from on an epitaxial wafer wherein each heterostructure has formed thereon a non-magnetized magnetic layer that is attracted to the magnetized magnetic layer formed at the bottom of each recess or dielectric layer that is attracted to the polarized electret material formed at the bottom of each recess. The plurality of heterostructures is etched from the epitaxial wafer to form a plurality of heterostructure pills. The plurality of heterostructure pills is slurried over the surface of the dielectric layer so that individual heterostructure pills can fall into a recess and be retained therein due to the strong short-range magnetic or electrical attractive force between the magnetized magnetic layer in the recess and the non-magnetized magnetic layer on the heterostructure pill or between the polarized electret material in the recess and the dielectric on the heterostructure pill. Any excess heterostructure pills that are not retained in a recess formed within the dielectric layer are removed and an overcoat is applied to form a substantial planar surface.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Antenna device for transmitting and/or receiving radio frequency waves and method related thereto
InactiveUS6954180B1Easy to controlEasy to manufacturePolarisation/directional diversityAntenna supports/mountingsResonanceInput impedance
An antenna device for transmitting and / or receiving electromagnetic radiation, installable in and connectable to a communication device, inlcudes an antenna structure switchable between a plurality of antenna configuration states. Each antenna configuration state is distinguished by a set of radiation parameters, such as resonance frequency, input impedance, bandwidth, radiation pattern, gain, polarization, and near-field pattern. Each of the plurality of antenna configuration states is adapted for use of the antenna device in the communication device in a respective predefined physical operation environment. A switching device selectively switches the antenna structure between the plurality of antenna configuration states.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Alignment apparatus for X-ray imaging system
A method for aligning a radiation source with a portable image receiver in a radiographic imaging system generates a magnetic field with a predetermined field pattern and with a time-varying vector direction at a predetermined frequency from an emitter apparatus that is coupled to the radiation source, wherein the generated magnetic field further comprises a synchronization signal. Sensed signals from the magnetic field are obtained from a sensing apparatus that is coupled to the image receiver, wherein the sensing apparatus comprises three or more sensor elements, wherein at least two of the sensor elements are arranged at different angles relative to each other and are disposed outside the imaging area of the image receiver. An output signal is indicative of an alignment adjustment according to the amplitude and phase of the obtained sensed signals relative to the synchronization signal.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
System and Method for Selective Communication with RFID Transponders
InactiveUS20050092838A1Minimizing creationSmall sizeMemory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsTransceiverCoupling
A system having an RFID transceiver is adapted to communicate exclusively with a single RFID transponder located in a predetermined confined transponder target area. The system includes a magnetic coupling device comprising a magnetic flux generator responsive to a radio frequency input signal and a magnetic field pattern former. The pattern former is configured to collect flux produced by the flux generator and to form a field pattern in the location of the transponder target area. The system establishes, at predetermined transceiver power levels, a mutual magnetic coupling which is selective exclusively for a single transponder located in the transponder target area.
Owner:ZIH CORP
Solid state optical phased array lidar and method of using same
ActiveUS10132928B2Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical delay lineRadiation pattern
A lidar-based apparatus and method are used for the solid state steering of laser beams using Photonic Integrated Circuits. Integrated optic design and fabrication micro- and nanotechnologies are used for the production of chip-scale optical splitters that distribute an optical signal from a laser essentially uniformly to an array of pixels, said pixels comprising tunable optical delay lines and optical antennas. Said antennas achieve out-of-plane coupling of light.As the delay lines of said antenna-containing pixels in said array are tuned, each antenna emits light of a specific phase to form a desired far-field radiation pattern through interference of these emissions. Said array serves the function of solid state optical phased array.By incorporating a large number of antennas, high-resolution far-field patterns can be achieved by an optical phased array, supporting the radiation pattern beam forming and steering needed in solid state lidar, as well as the generation of arbitrary radiation patterns as needed in three-dimensional holography, optical memory, mode matching for optical space-division multiplexing, free space communications, and biomedical sciences. Whereas imaging from an array is conventionally transmitted through the intensity of the pixels, the optical phased array allows imaging through the control of the optical phase of pixels that receive coherent light waves from a single source.
Owner:QUANERGY SOLUTIONS INC
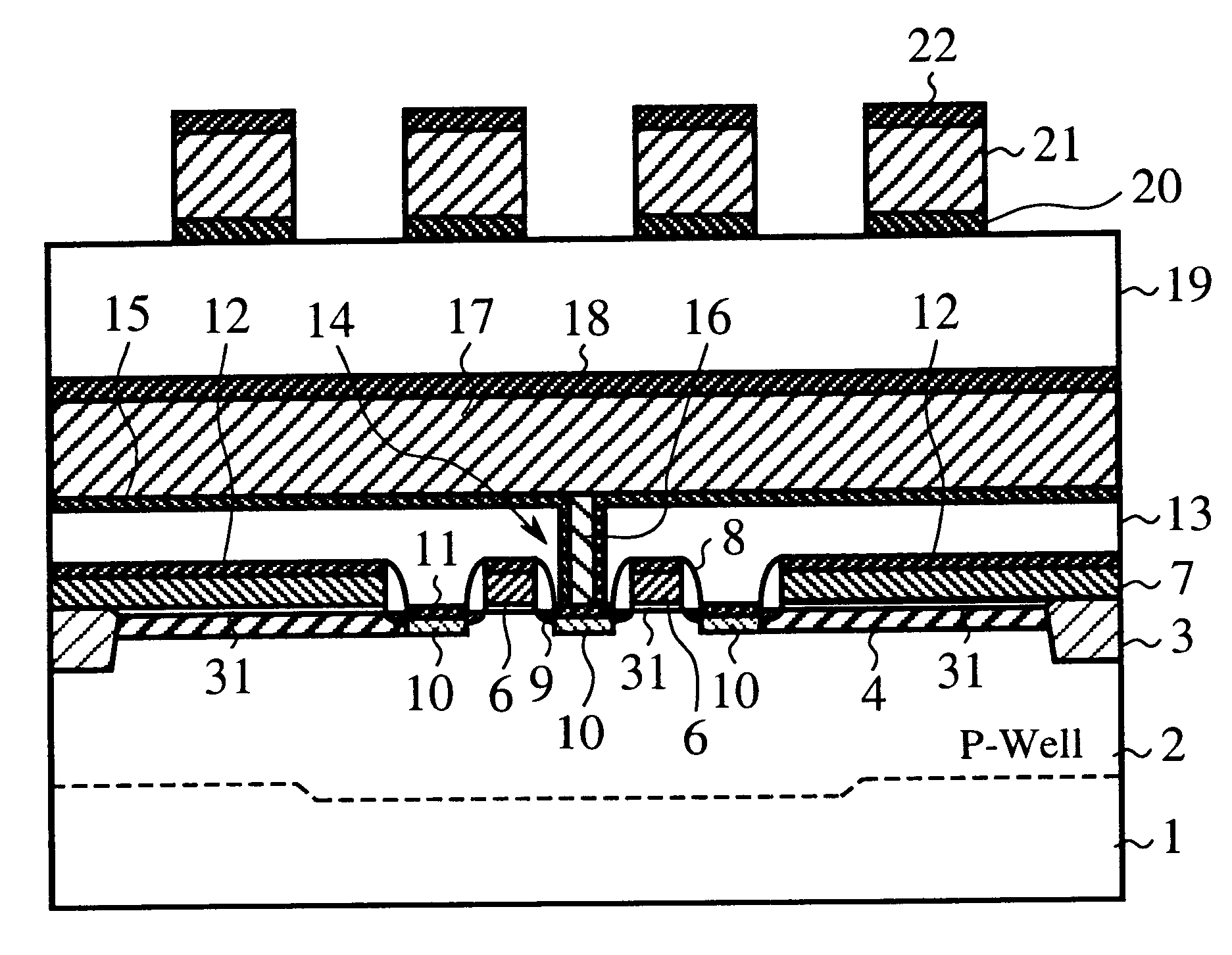
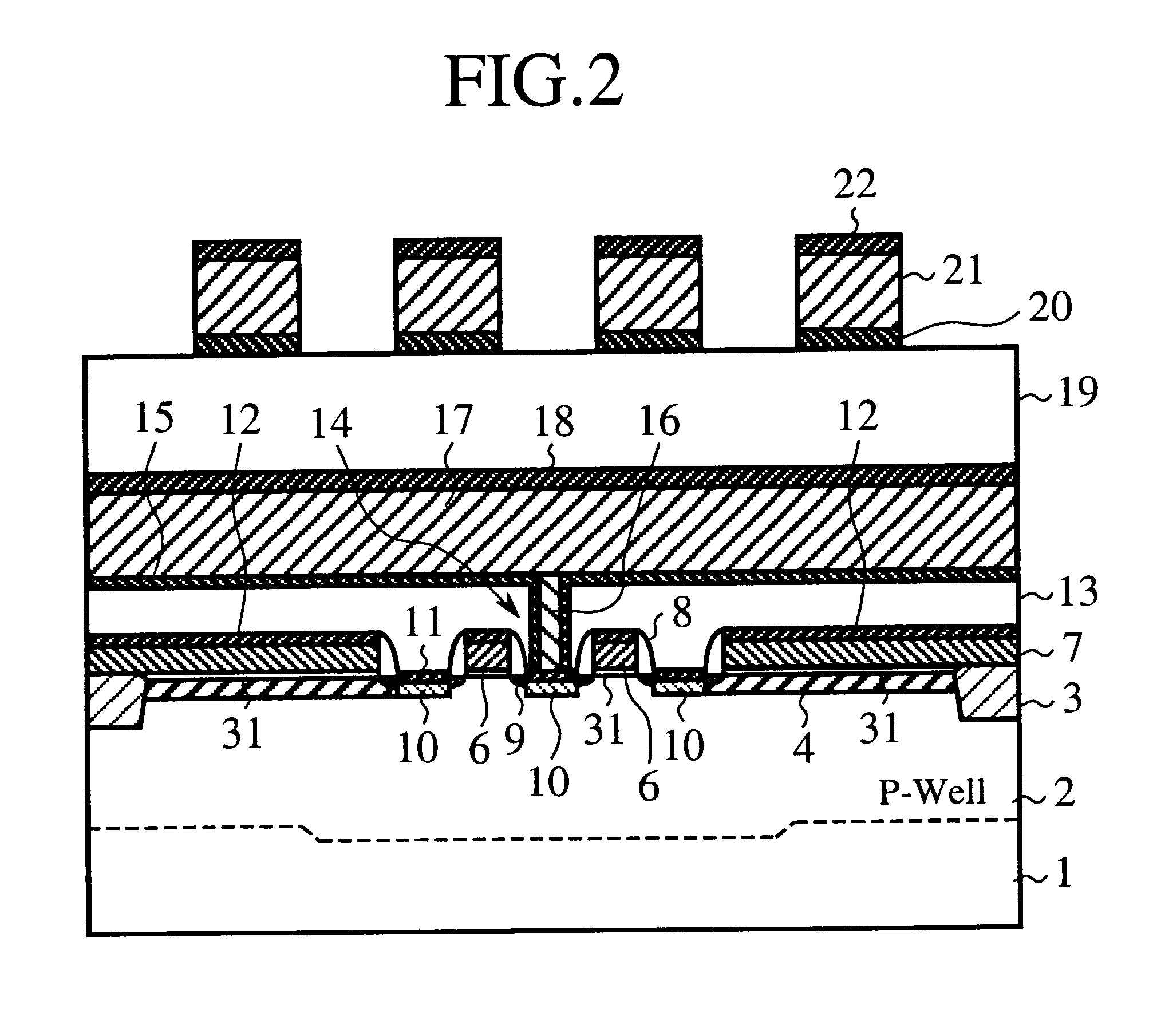
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and method of manufacturing the same, and cell size calculation method for DRAM memory cells
There is provided a semiconductor integrated circuit device comprising: a field placement creating a field pattern in an array form by closest packing on a first conductance-type semiconductor substrate, the field pattern including a plurality of memory cells which define an active area and a device isolation region of a field effect transistor, and which are arranged in a predetermined pitch in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, each memory cell having a pattern of a certain length-to-width size; a cell plate placement providing a capacitor structure between a second conductance-type diffusion region formed by an impurity implant to the active area and a cell plate electrode formed so as to cover part of the active area with a predetermined cell plate pattern through a capacitor dielectric, the cell plate pattern extending in the transverse direction with a certain length size; and a word line placement in which a word line pattern is arranged in the transverse direction of a vacant zone of the active area in which the cell plate electrode is not formed and serves as a gate electrode of the field effect transistor on the active area, the word line pattern being formed through a gate oxide at a predetermined interval, wherein the layout of a cell array of the memory cells is provided by a closest packing cell configuration.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
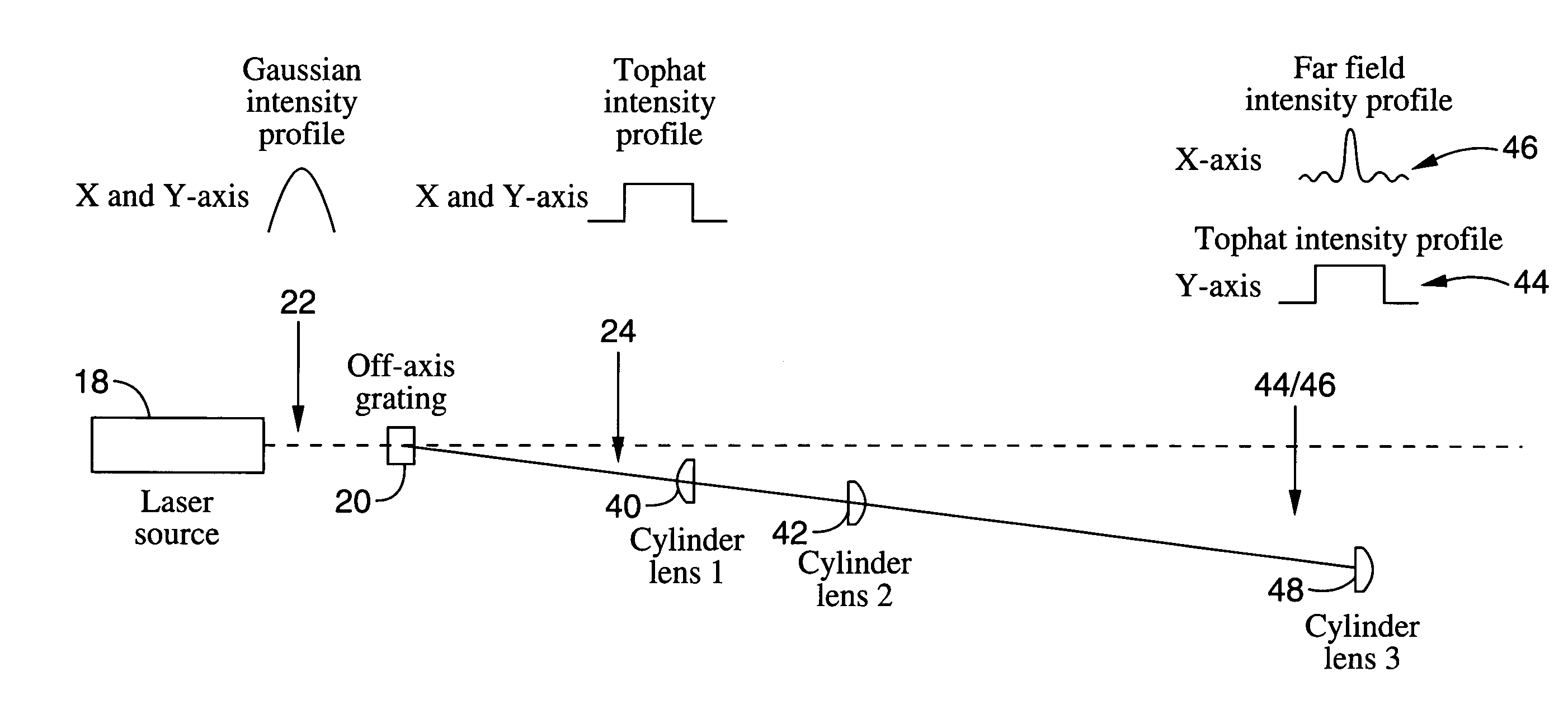
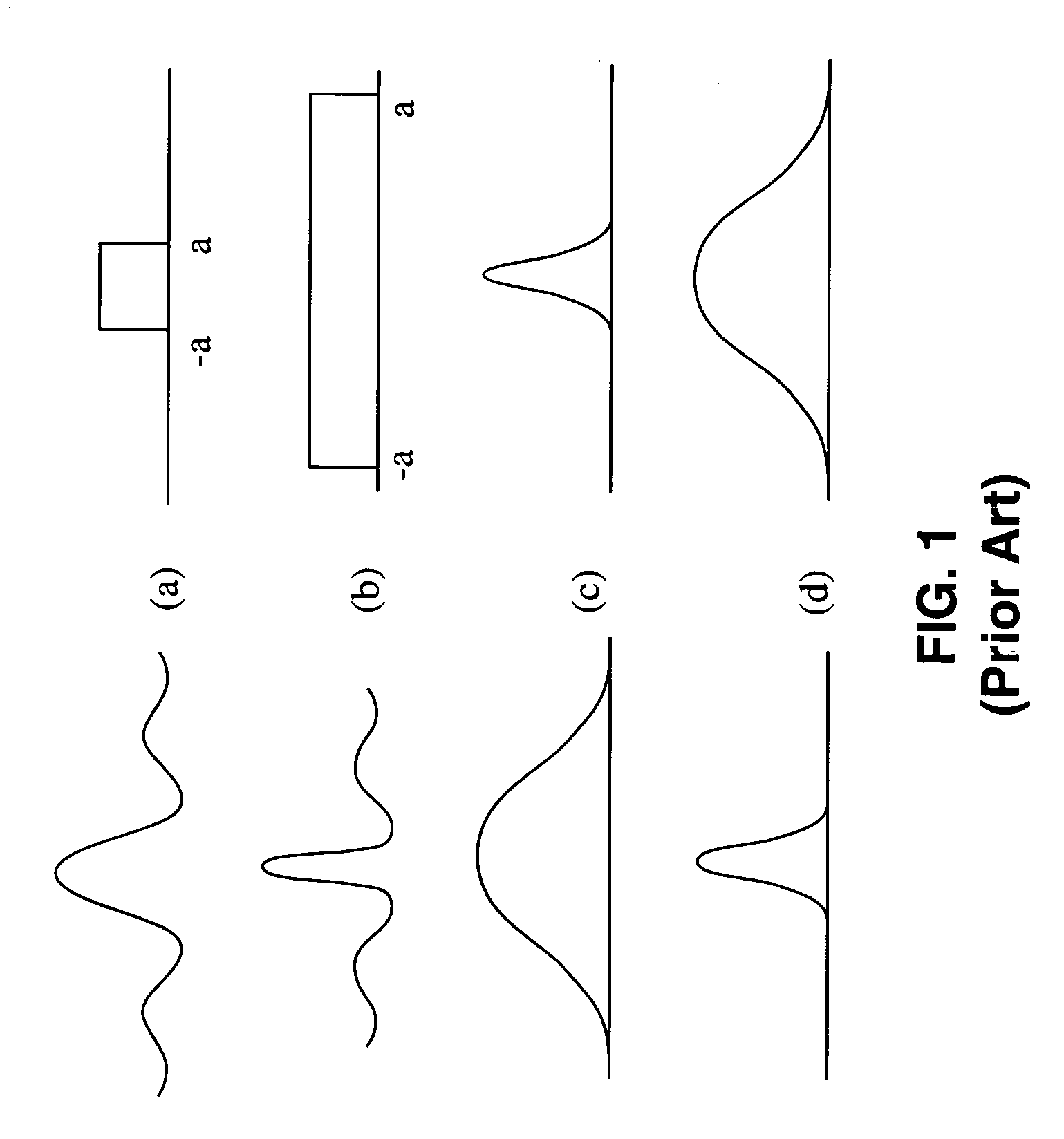
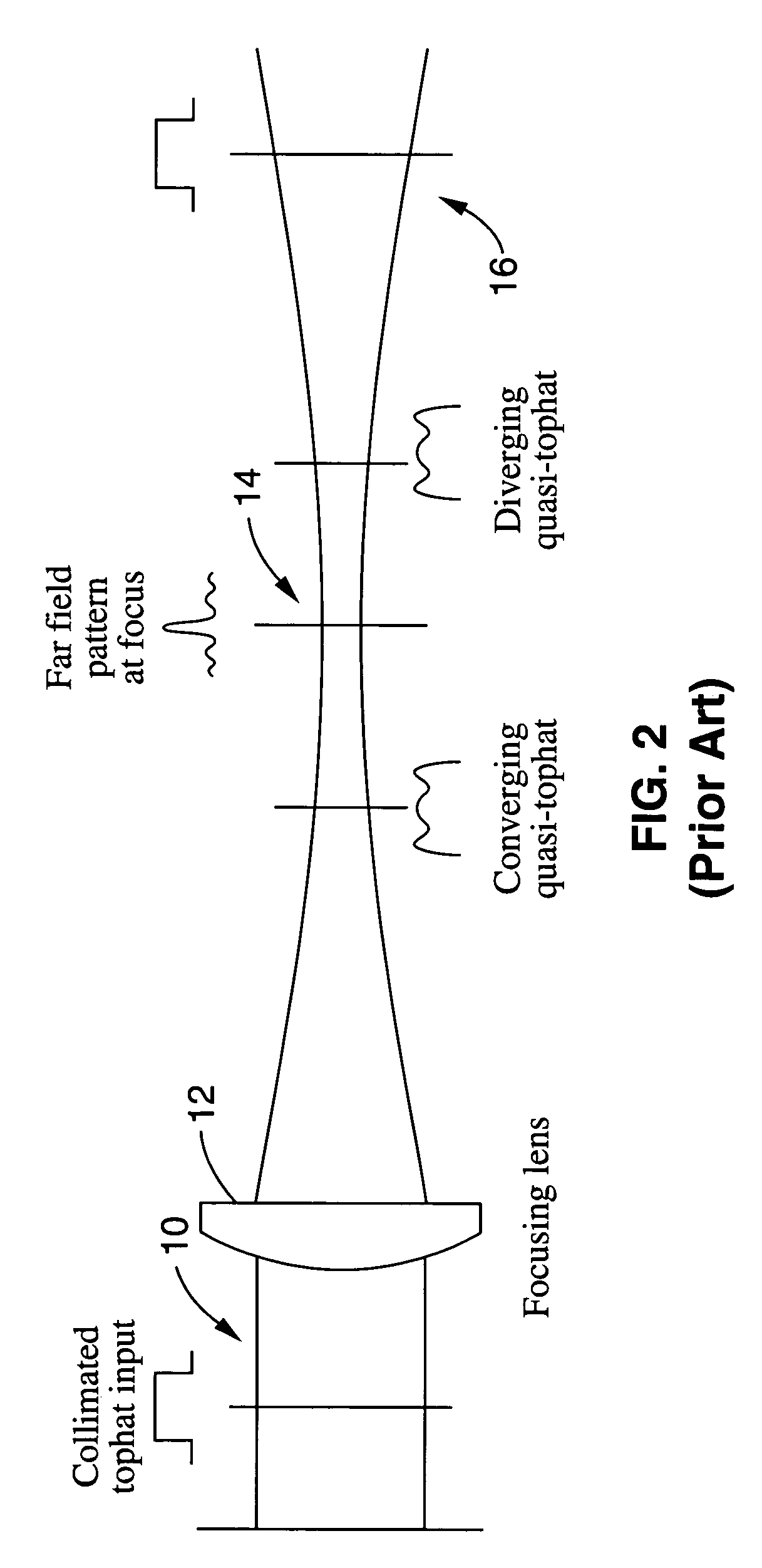
Method and apparatus for transformation of a gaussian laser beam to a far field diffraction pattern
InactiveUS6975458B1Optical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsGaussian beamFourier transform on finite groups
A method and apparatus for converting a Gaussian laser beam into a propagating far field diffraction pattern using an off-axis diffractive optic. This propagating far field pattern is focused by a lens to obtain a flattop intensity at the focal plane. The technique is based on the idea of Fourier transform pairs and produces a small spot diameter with a useable depth of field. A focused uniform intensity profile can be useful for many laser applications.
Owner:KANZLER KURT
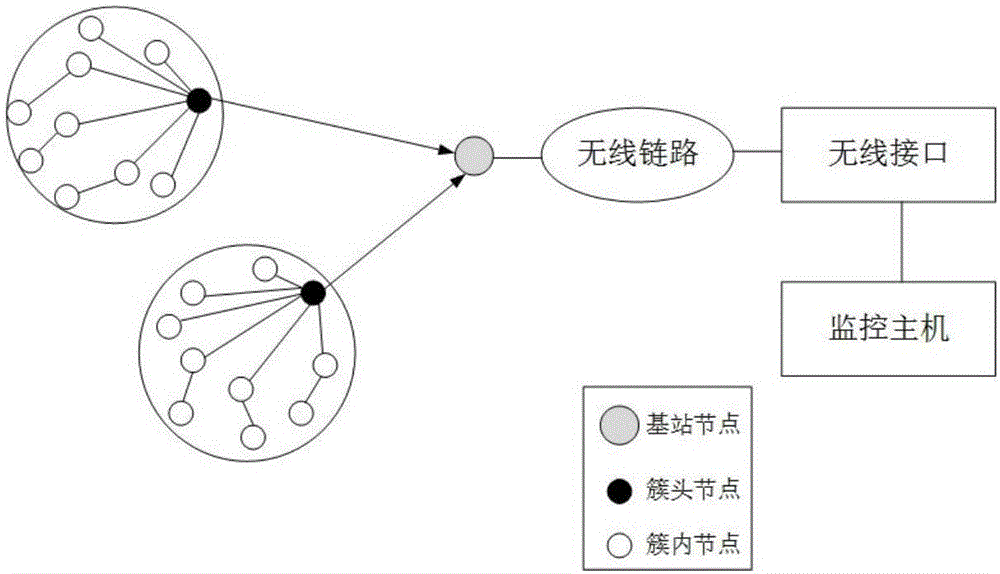
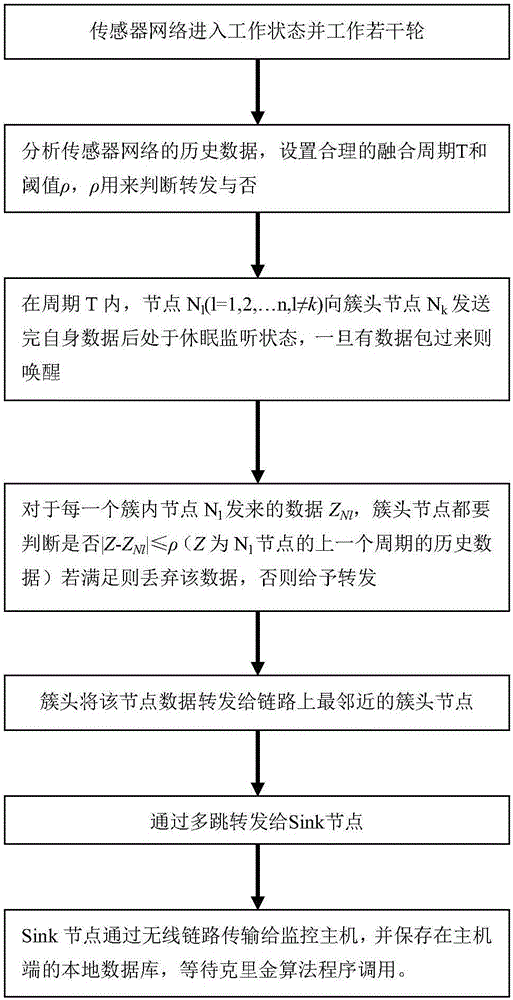
Wireless sensor network temperature monitoring method based on improved Kriging algorithm
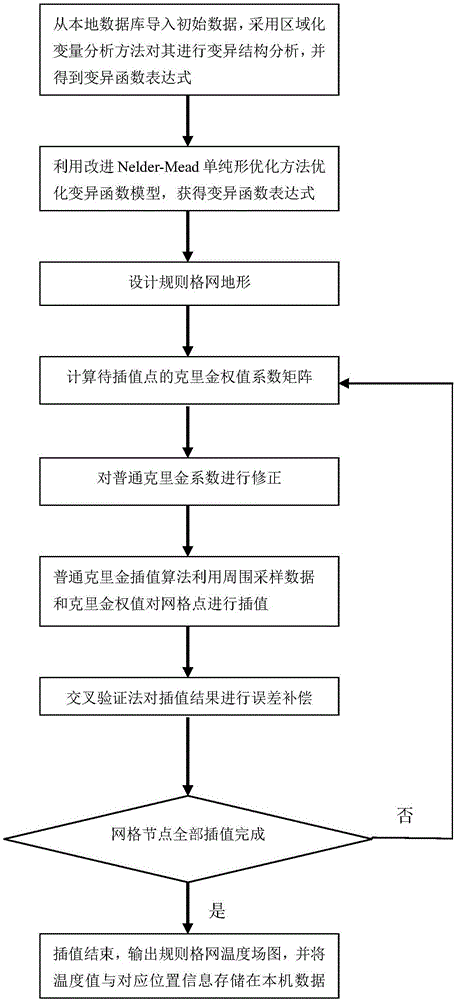
ActiveCN106714336AThe science of predicting outcomesEnergy saving life cycleThermometer detailsTransmission systemsTerrainStructure analysis
The invention discloses a wireless sensor network temperature monitoring method based on an improved Kriging algorithm. The wireless sensor network temperature monitoring method comprises the steps of: firstly, establishing a layer cluster type wireless sensor network topological structure, analyzing historical temperature data of a target region, setting a threshold value rho and a fusion cycle T, performing periodic fusion on in-cluster node data at a cluster head node based on the threshold value rho, acquiring initial temperature data, transmitting the initial temperature data to a monitoring host by means of a wireless link and saving the initial temperature data in a local database; importing the initial temperature data, and performing variable structure analysis on the initial temperature data to generate a variation function expression; and optimizing a variation function model by utilizing an improved Nelder-Mead simplex method, designing a regular grid terrain, performing temperature interpolation by adopting an ordinary Kriging algorithm, carrying out error correction, and outputting a regular grid temperature field pattern. The wireless sensor network temperature monitoring method optimizes the variation function model by utilizing the improved Nelder-Mead simplex method, corrects weights of the ordinary Kriging algorithm, performs error compensation on the interpolation result, and makes the interpolation result more scientific and closer to the actual situation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
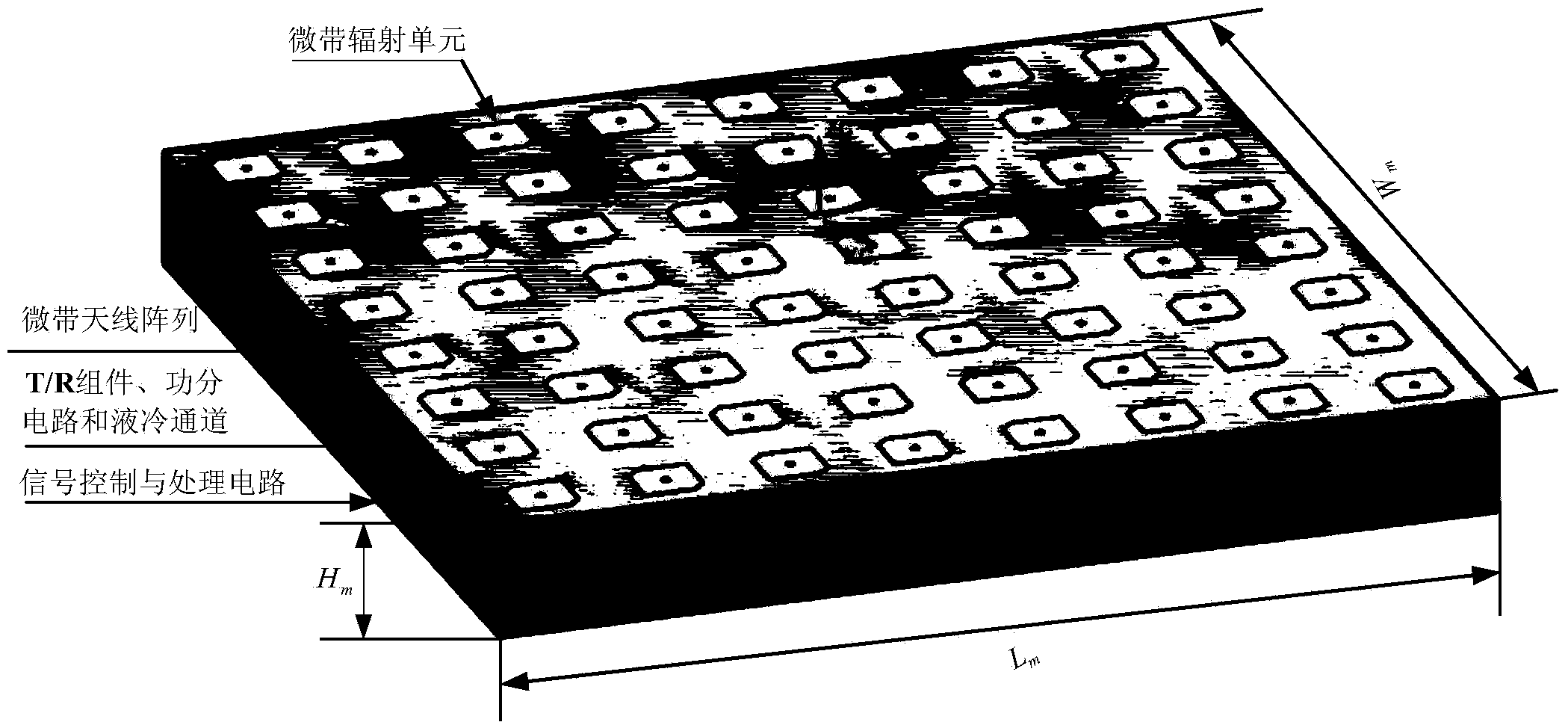
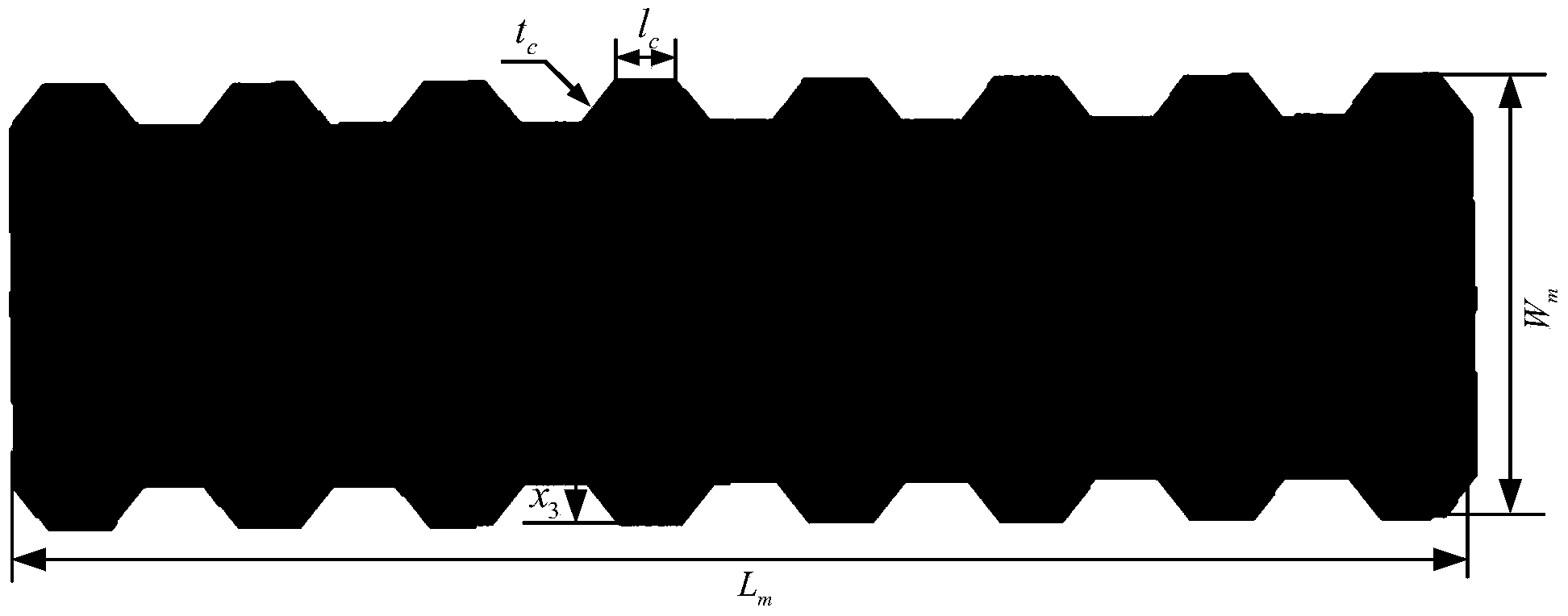
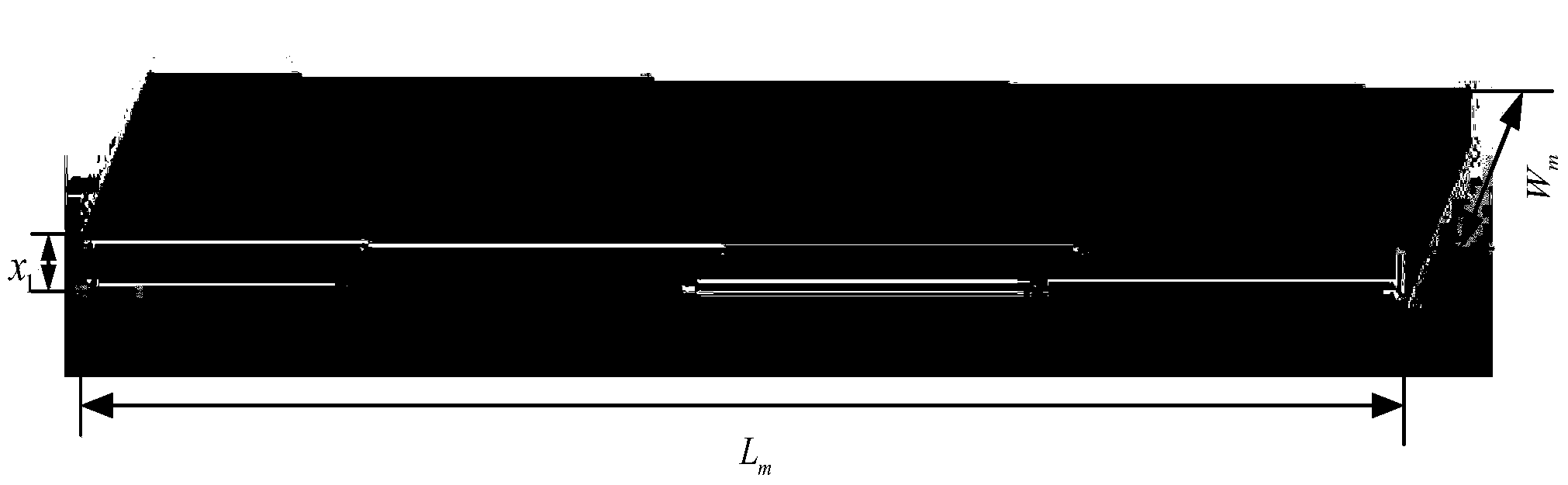
Data-driven design method integrating active interlayer microstrip antenna structure and electromagnetism and antenna
ActiveCN103353904ATo overcome the difficulty in realizing the design of electromechanical integrationRealize the structureSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemEngineeringRadio frequency
The invention discloses a data-driven design method integrating an active interlayer microstrip antenna structure and electromagnetism and an antenna, and solves the problem that the prior art can not realize the integrated design of the structure and electromagnetism. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, fixing the material, size, panel and cellular size of a radio frequency function layer according to electrical property indexes, secondly, obtaining front deformation data and stress data of the antenna structure through mechanical analysis, thirdly, preprocessing the front deformation data, so as to obtain the position error of each radiating element, fourthly, calculating a far-field pattern of an interlayer microstrip antenna according to a data-driven coupling model, fifthly, calculating and considering the wave-transparent performance influenced by the panel and cellular, sixthly, establishing an optimization design model integrating the interlayer microstrip antenna structure and electromagnetism, and seventhly, solving the optimization design model, so as to obtain an optimal integrating result. The method can realize the simultaneous optimal design of the active interlayer microstrip antenna structure and electromagnetism, shortens the development period, and improves force-electricity properties of products.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Rod-loaded radiofrequency cavities and couplers
InactiveUS20080068112A1Effective dampingResonatorsCoupling devicesParticle acceleratorAccelerated particle
This invention relates to radiofrequency (rf) cavities and couplers that comprise metallic or dielectric rods to provide specified concentration of field patterns for the operating modes in the interaction region, for applications in particle accelerators, pulsed rf power sources, amplifiers, mode converters and power couplers.
Owner:DULY RES
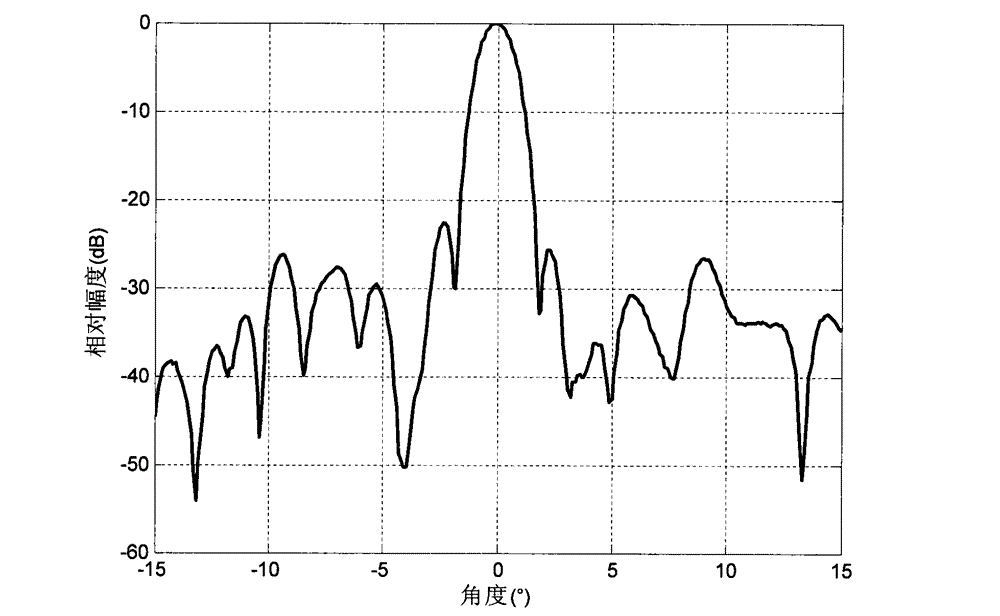
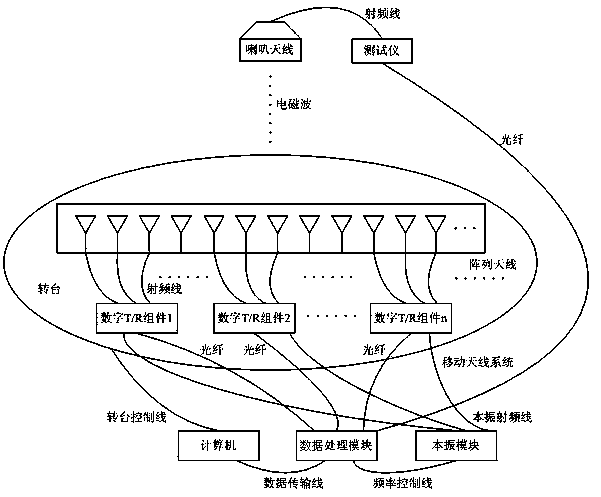
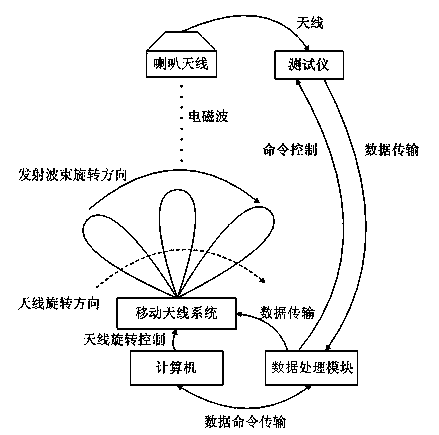
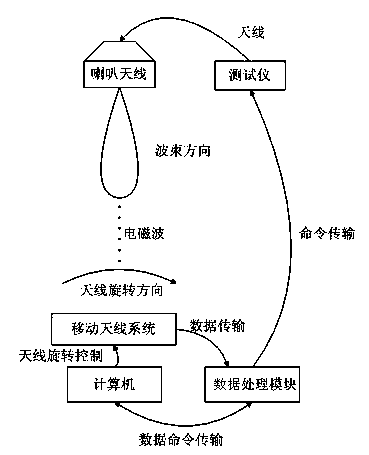
Method for measuring far-field pattern of phased-array antenna
The invention provides a method for measuring the far-field pattern of a phased-array antenna. Through the phase shift amount compensation of each array element of the phased-array antenna, the method achieves the measurement of the far-field pattern of the phased-array antenna within a limited distance. The method comprises the steps: selecting a microwave chamber with a rotary table, enabling a to-be-measured phased-array antenna to be installed on the rotary table, and enabling the to-be-measured phased-array antenna and a testing system antenna to remain separated by a preset distance; measuring and calculating the geometrical relation between each array element of the to-be-measured phased-array antenna and the testing system antenna; carrying out the phase shift compensation of each array element of the to-be-measured phased-array antenna according to the geometrical relation; enabling the to-be-measured phased-array antenna to rotate through the rotary table, and executing the measurement of the far-field pattern of the to-be-measured phased-array antenna. Therefore, the method can achieve the measurement of the far-field pattern of the phased-array antenna through carrying out the phase shift compensation of all array elements of the phased-array antenna under the condition that there is no near-field scanning system, compact field or far field.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
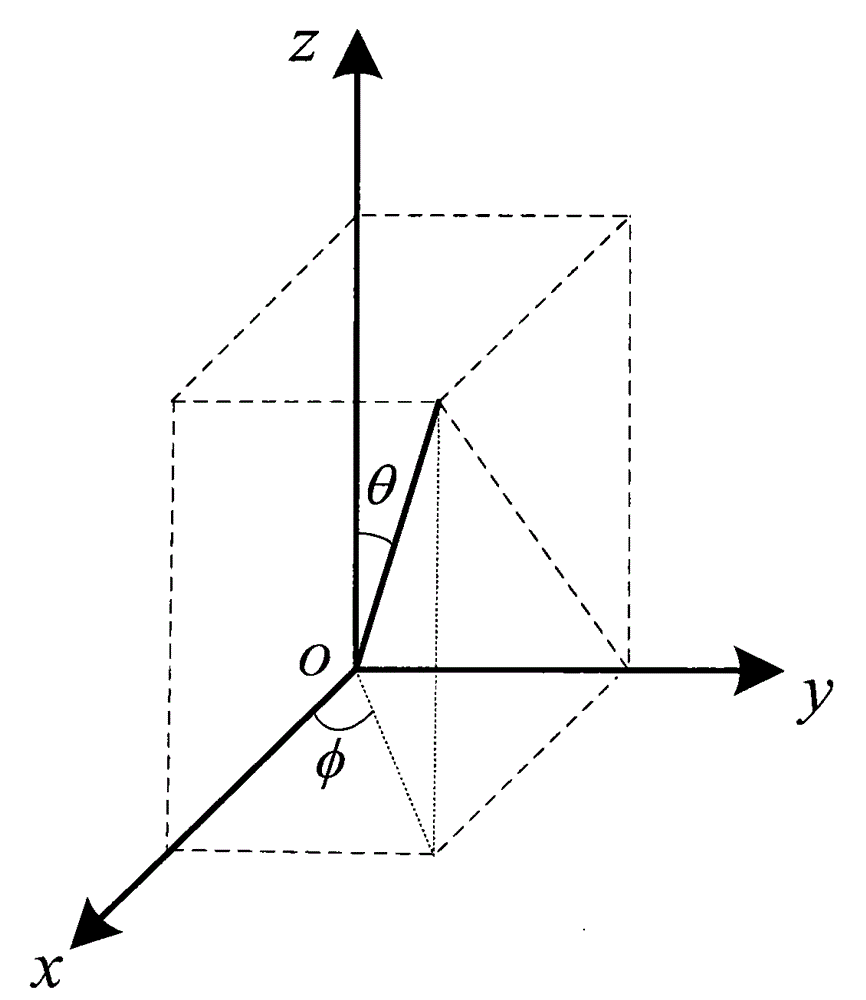
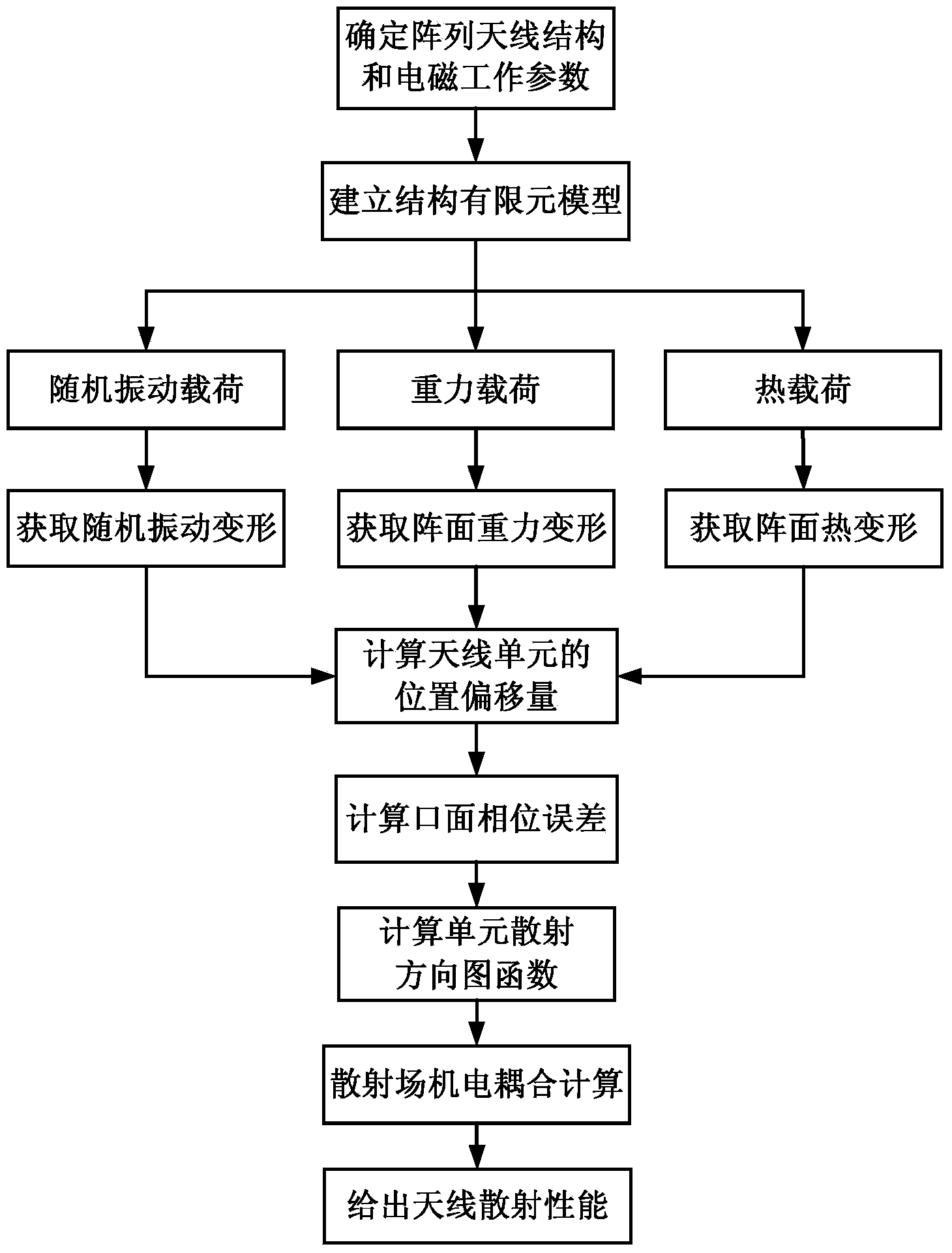
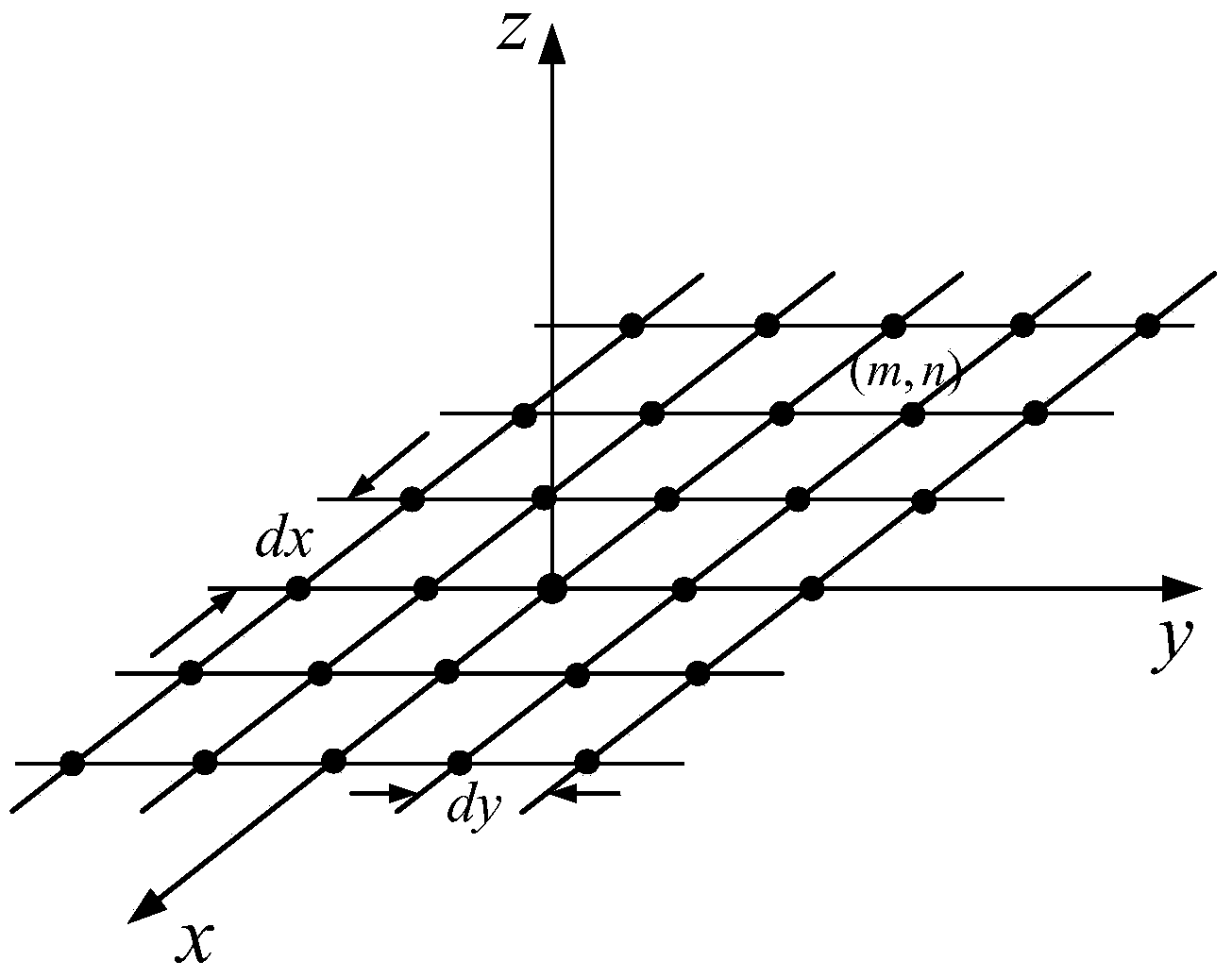
Deformed array antenna scattering performance analyzing method based on electromechanical coupling
ActiveCN104038295ASolve computing problemsShorten the development cycleTransmission monitoringElement modelPhase difference
The invention discloses a deformed array antenna scattering performance analyzing method based on electromechanical coupling. The deformed array antenna scattering performance analyzing method based on the electromechanical coupling includes that determining geometrical model parameters, material attributes and electromagnetic working parameters of an array antenna; building a finite element model of the antenna; determining constraint conditions and random vibration load, gravity load and thermal load environments of the finite element model, calculating the array surface deformation of the array antenna under the constraint conditions and load environments, and extracting the position offsets of antenna center nodes of the finite element model of the antenna under the conditions; accumulating to obtain the total position offset of the antenna; calculating the spatial phase difference of two adjacent antenna unit scatting fields in the array surface to obtain an aperture phase difference; calculating an antenna unit scattering pattern; calculating an array antenna scattering field pattern; analyzing the influence of the array structure deformation on the antenna scattering performance under the load environments. The deformed array antenna scattering performance analyzing method based on the electromechanical coupling is used for quantitatively evaluating the influence of the array surface structure deformation on the antenna scattering performance under the load environments and guiding the array antenna structure design, cooling design and scattering performance simulation analysis and evaluation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Radio frequency identification reader having antennas in different directions
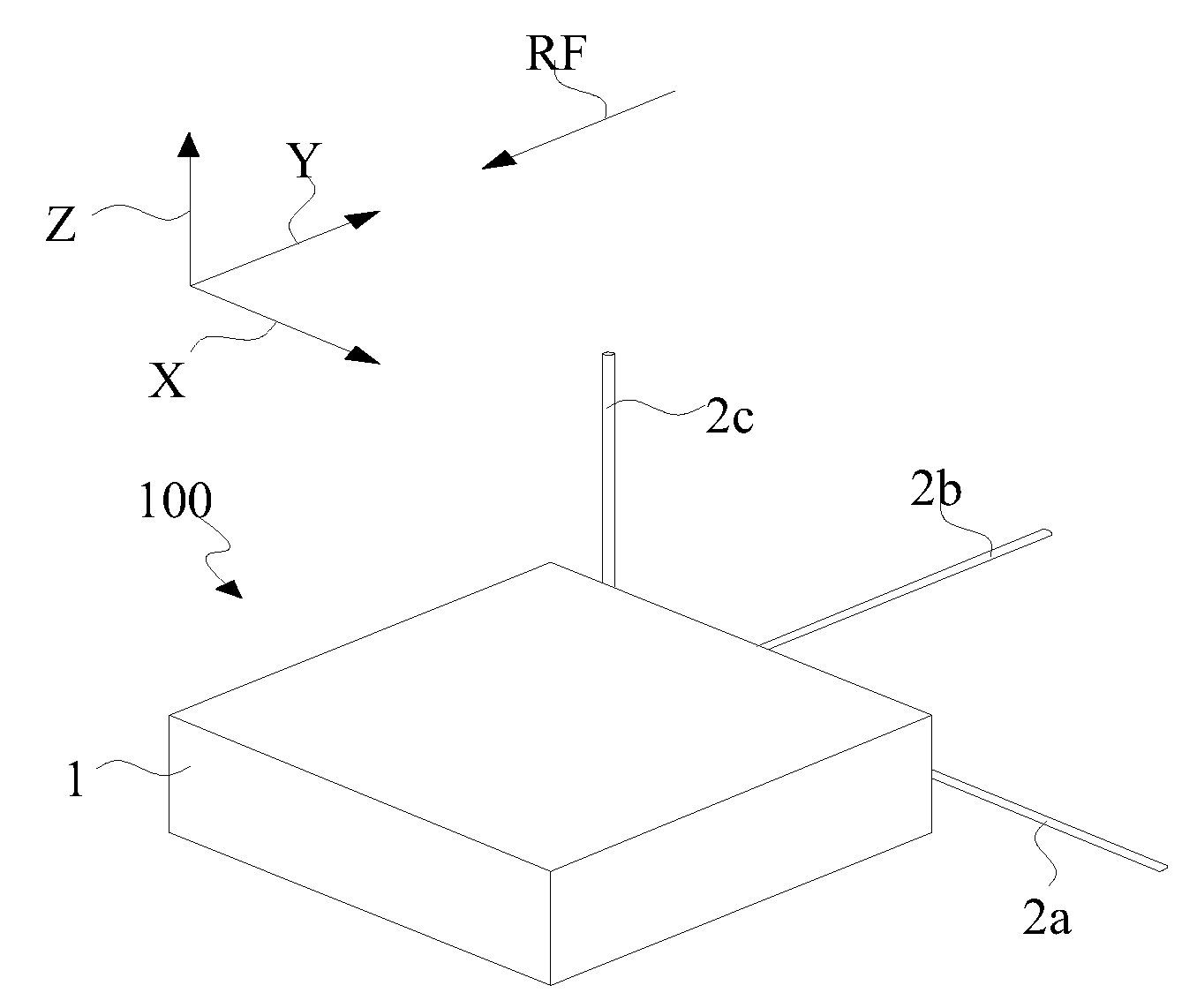
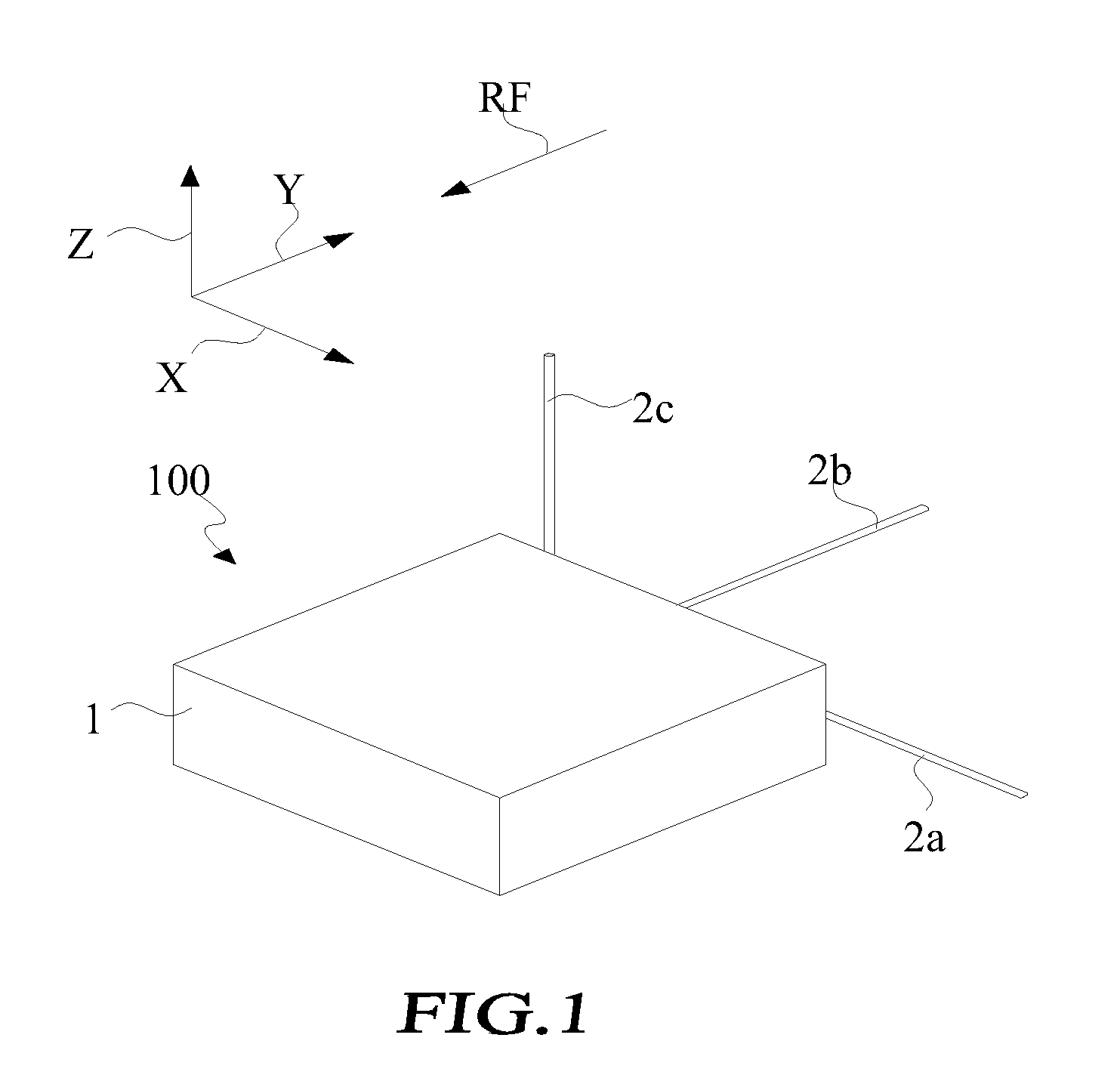
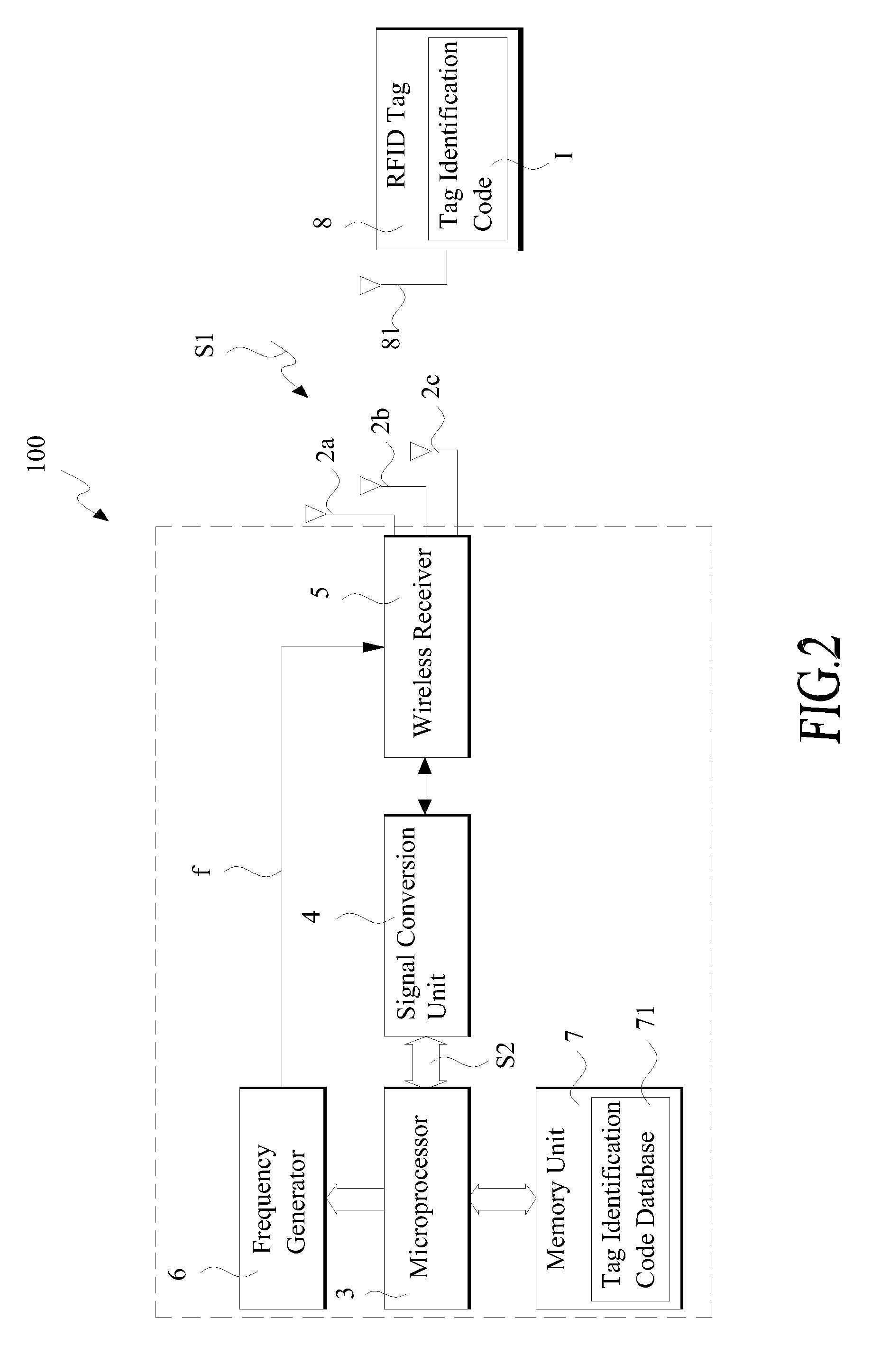
InactiveUS20100079245A1Lower performance requirementsImprove signal receptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsSensing record carriersCarrier signalEngineering
A radio frequency identification (RFID) reader includes a plurality of signal antennas, which are respectively arranged in directions that are not parallel to and co-linear with each other. Each of the signal antennas has a predetermined antenna field pattern and operates with a predetermined carrier wave frequency. A wireless receiver is connected to the signal antennas. A signal conversion unit is connected to the wireless receiver. A frequency generator generates the carrier wave frequency to the signal antenna. A microprocessor is connected to the signal conversion unit and the frequency generator.
Owner:MITAC TECH CORP
Electronic device capable of eliminating interference
The invention provides an electronic device capable of eliminating interference. The electronic device capable of eliminating interference comprises a first radio component, a second radio component, a quadrature coupler, a first two-way phase shifter and a second two-way phase shifter, wherein the first radio component and the second radio component work at the same frequency band and are used for emitting a first signal and a second signal respectively. The quadrature coupler is used for providing isolation between emission ports of the first radio component and the second radio component and avoiding internal interference when the first signal and the second signal are emitted at the same time. The quadrature coupler is further used for making the field pattern of the first signal and the field pattern of the second signal mutually orthogonal, wherein the first signal field pattern and the second signal field pattern which are mutually orthogonal and are obtained through radiation can restrain external disturbance signals. The first two-way phase shifter and the second two-way phase shifter are used for conducting phase adjustment on the first signal field pattern and the second signal field pattern which are obtained through radiation so as to control the radiation directions of the first signal field pattern and the second signal field pattern. According to the electronic device capable of eliminating interference, mutual interference which may be caused when radio components with the approximately same working band inside an electronic device work at the same time can be avoided, and the external disturbance signals are prevented from being received.
Owner:AMBIT MICROSYSTEMS (SHANGHAI) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com