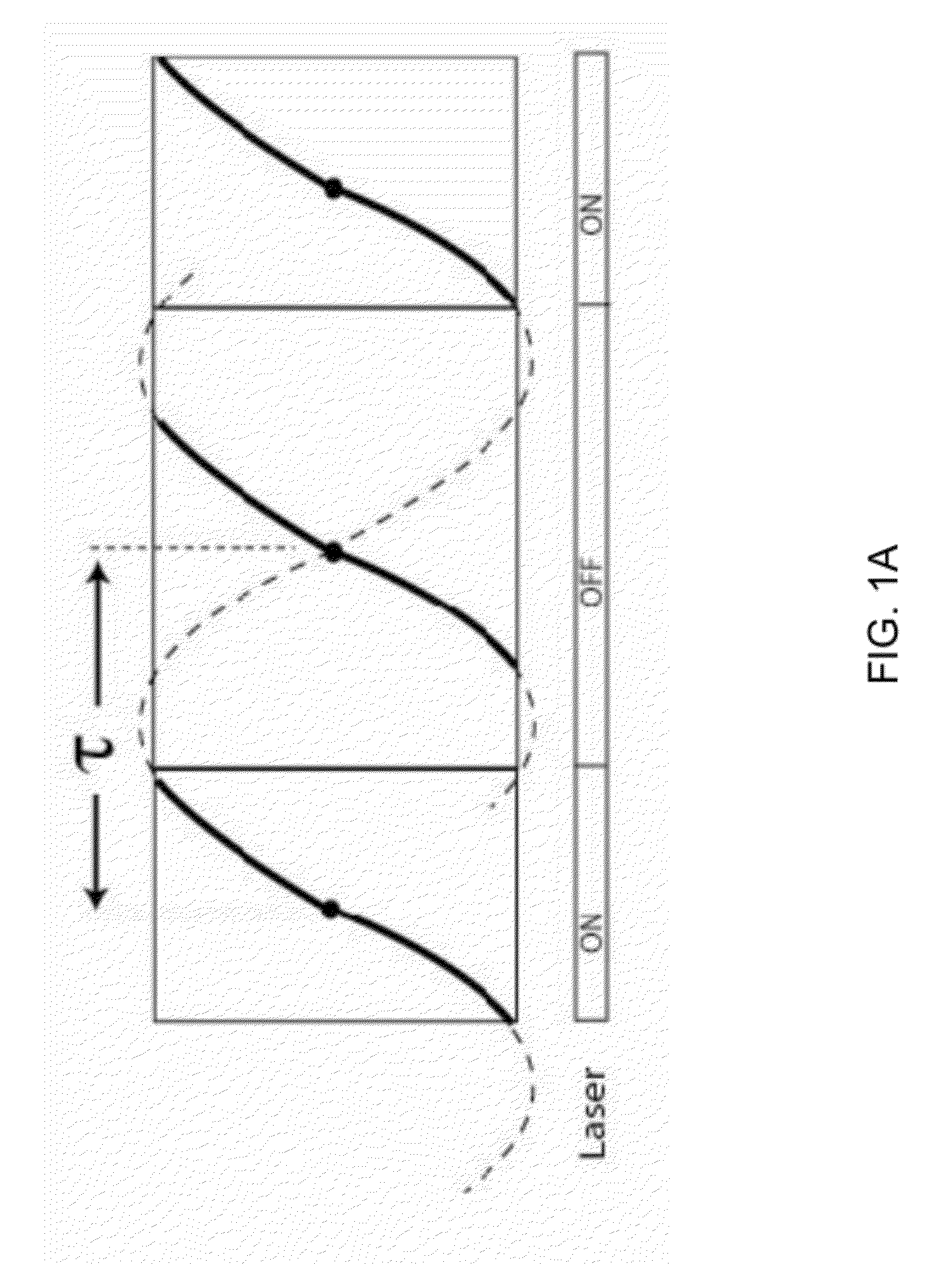
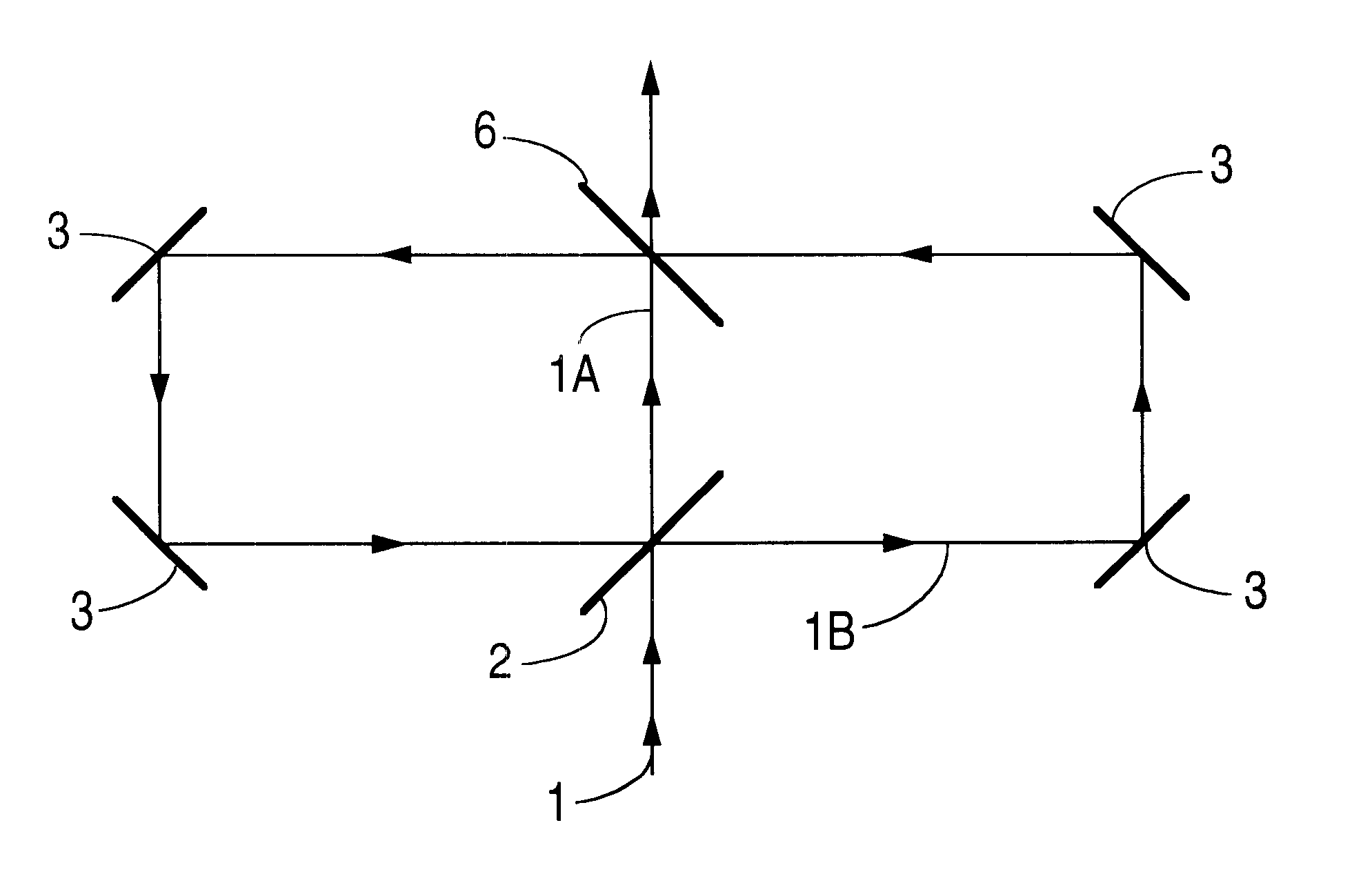
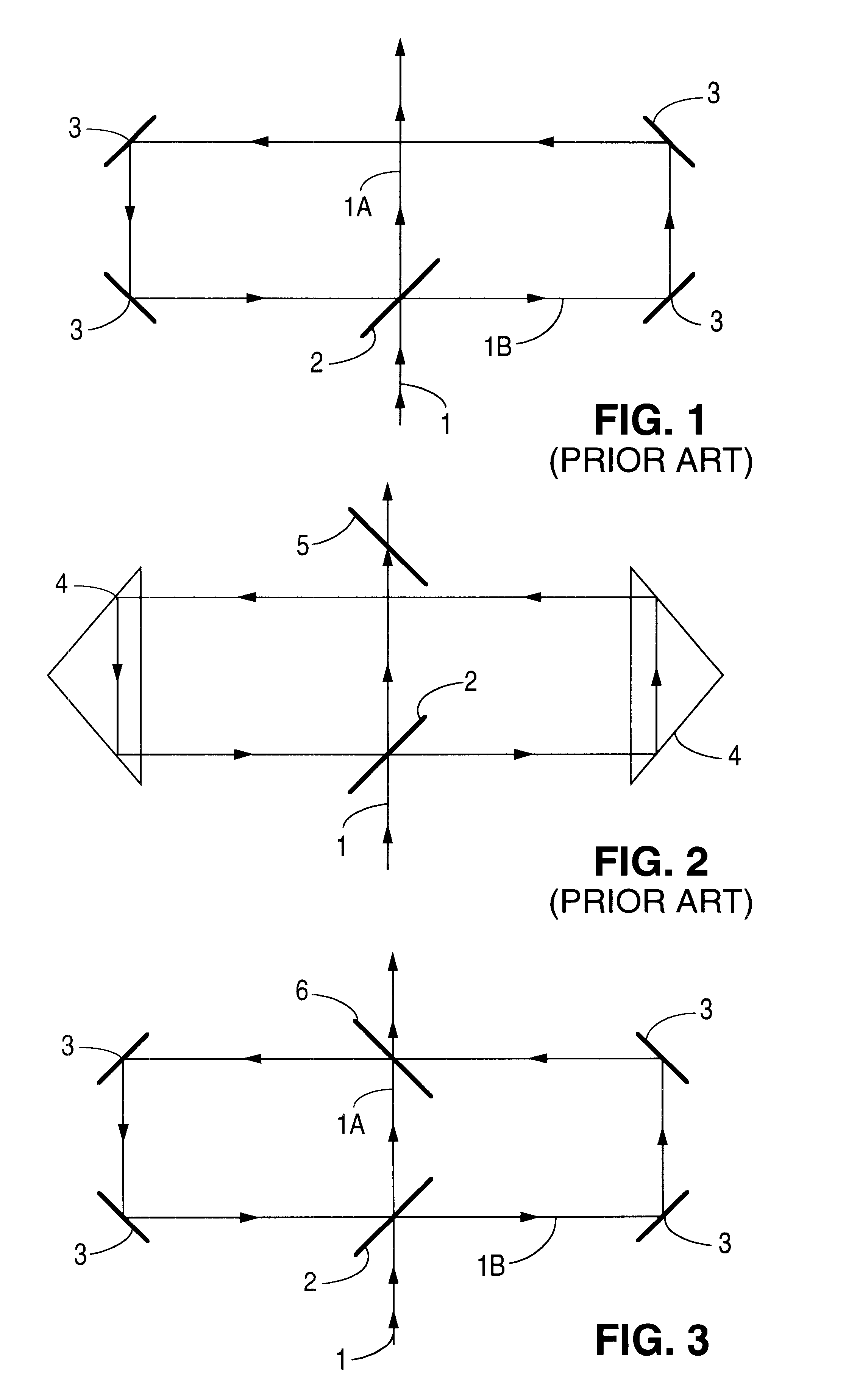
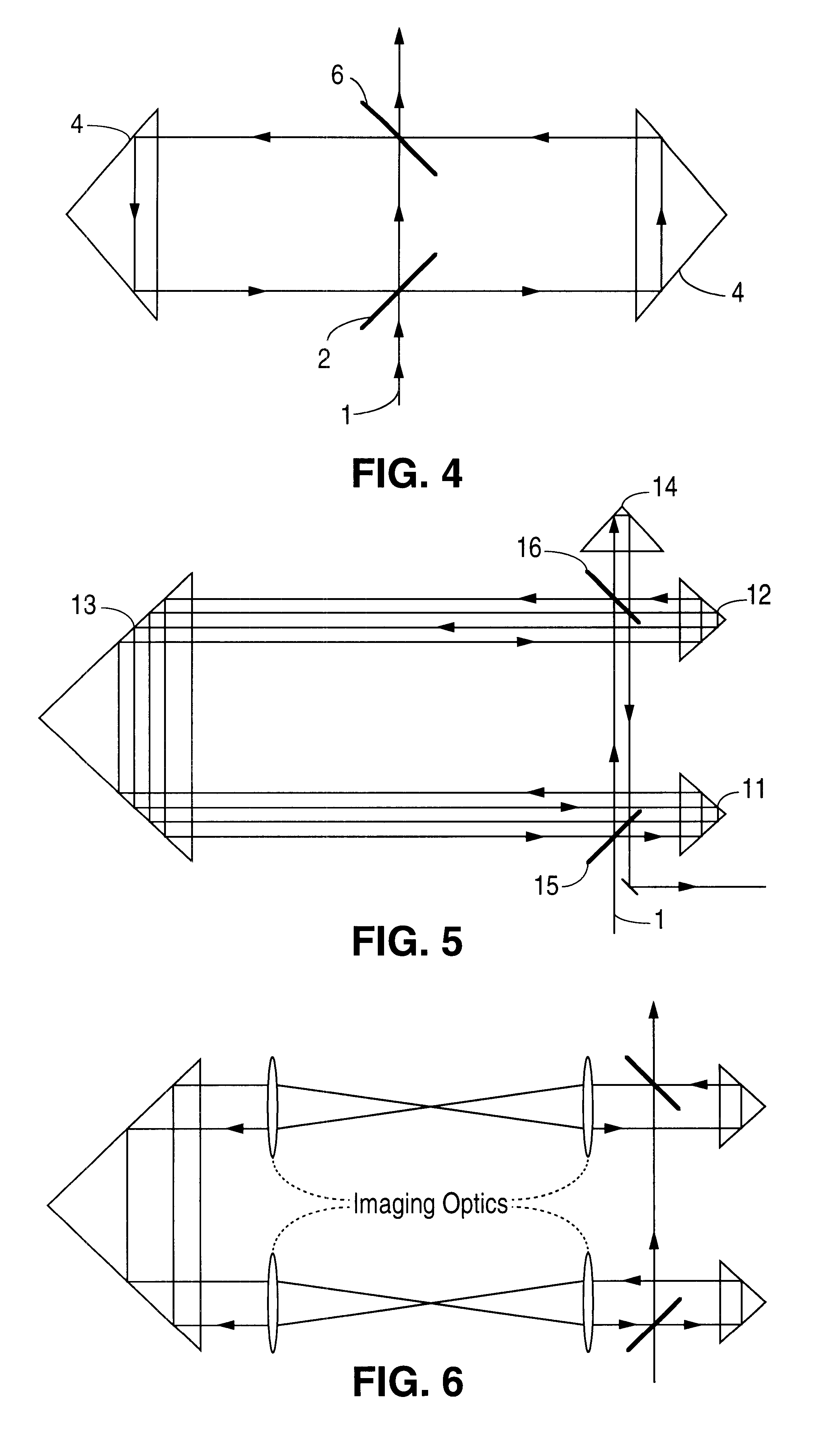
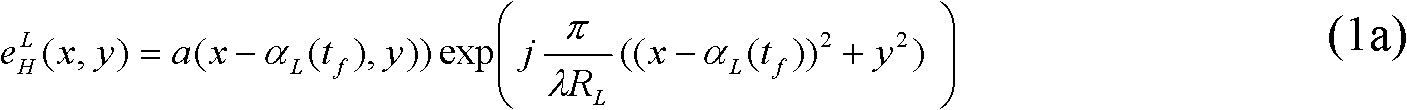Patents
Literature
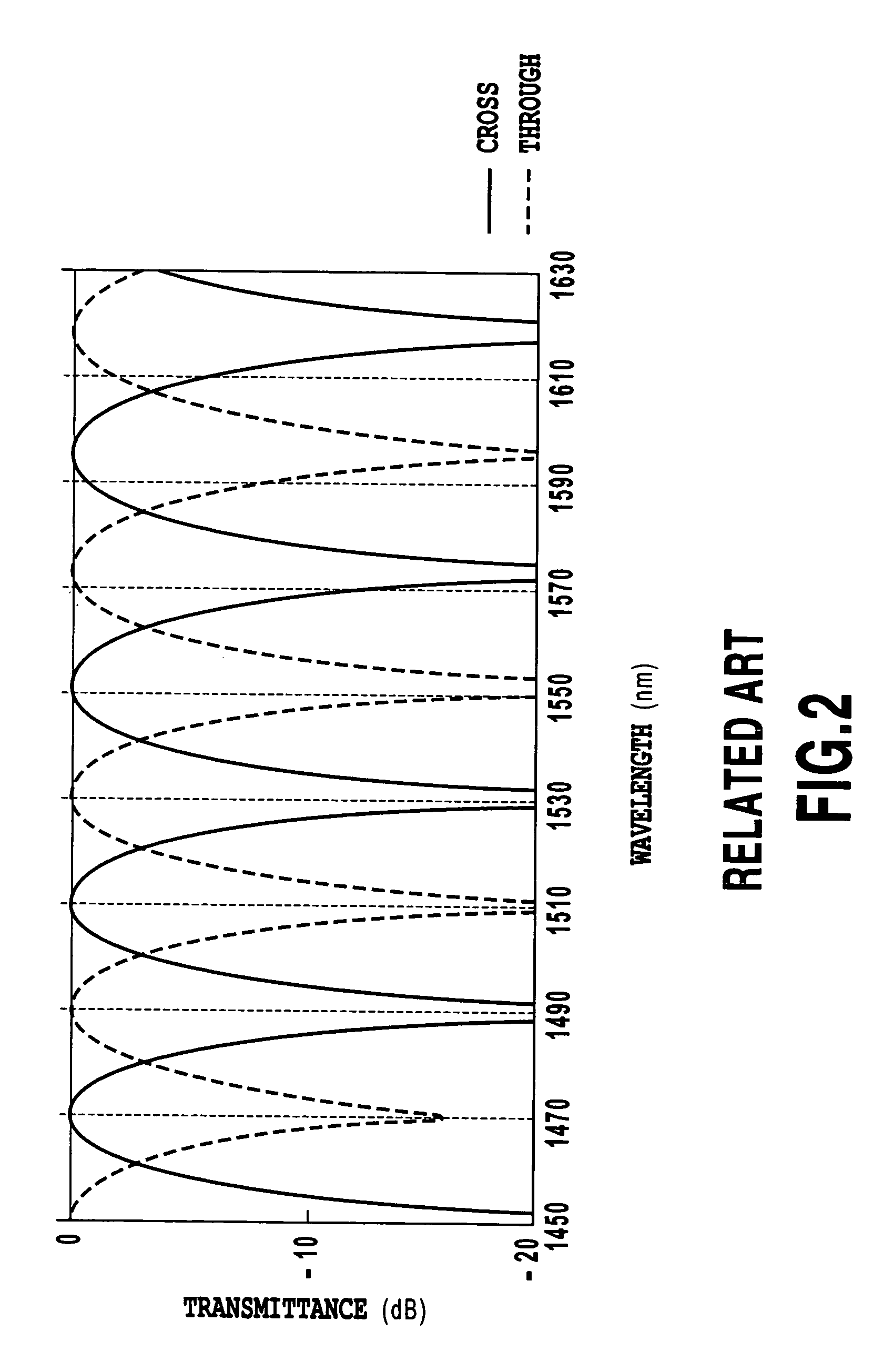
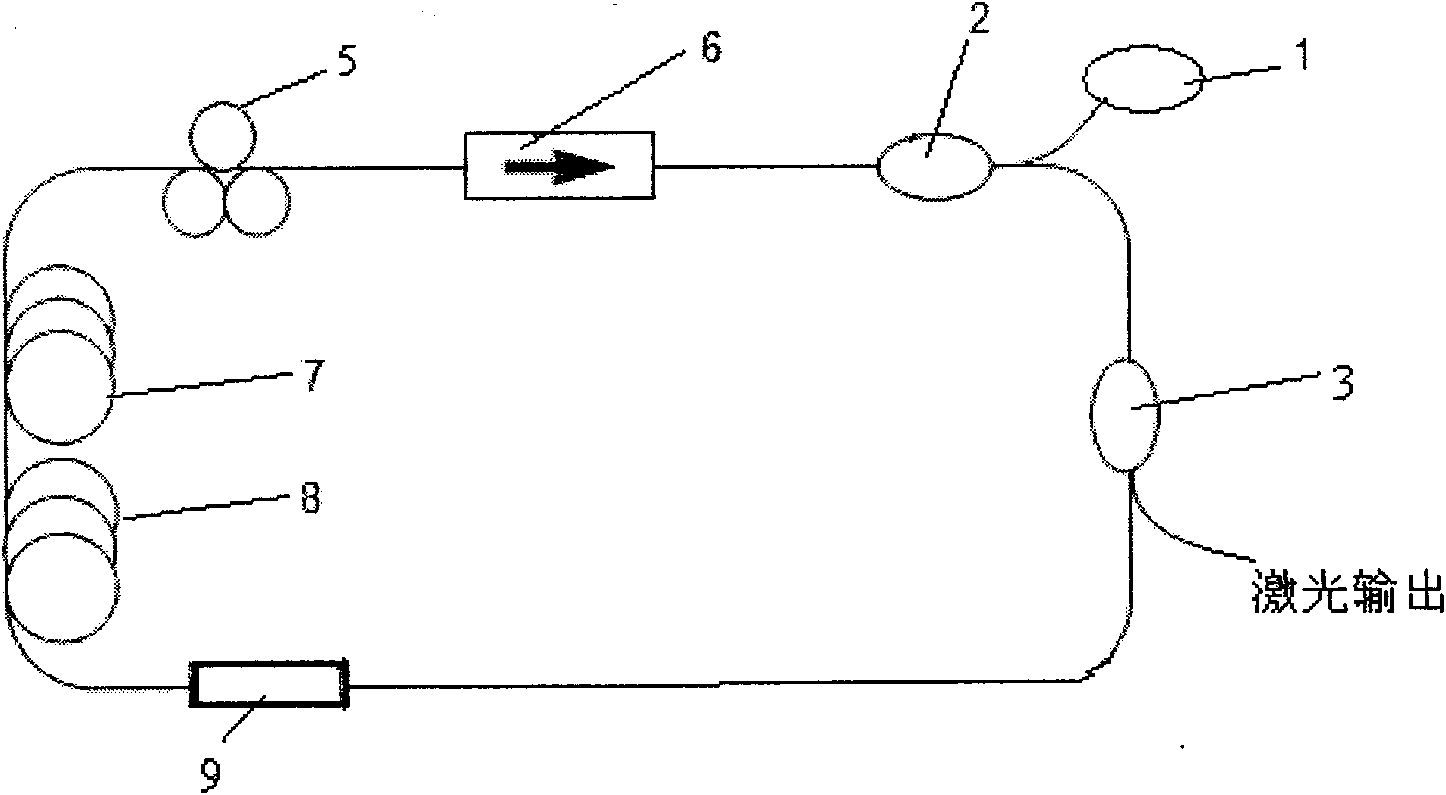
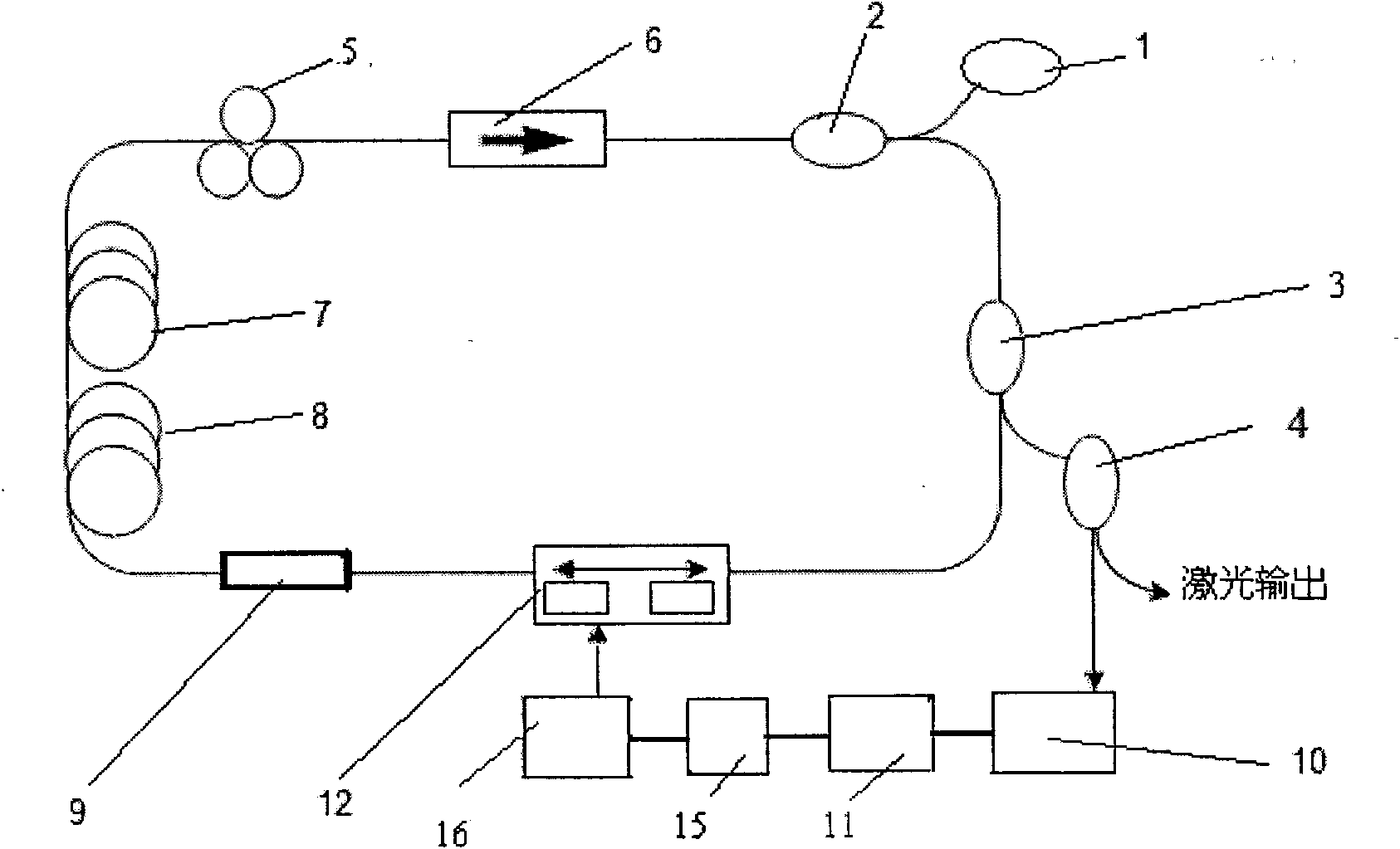
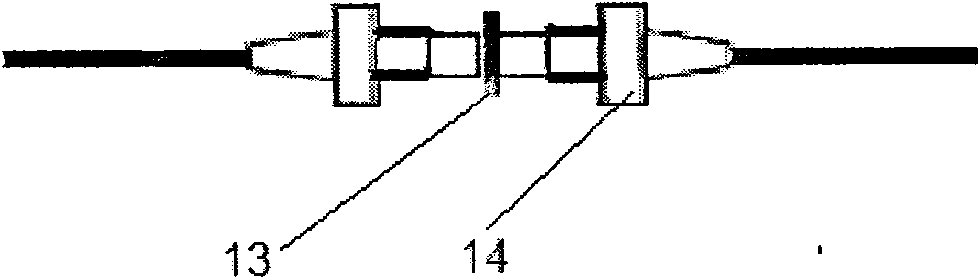
441 results about "Optical delay line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aspects of basic OCT engine technologies for high speed optical coherence tomography and light source and other improvements in optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS7061622B2Scattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringGratingAcousto-optics
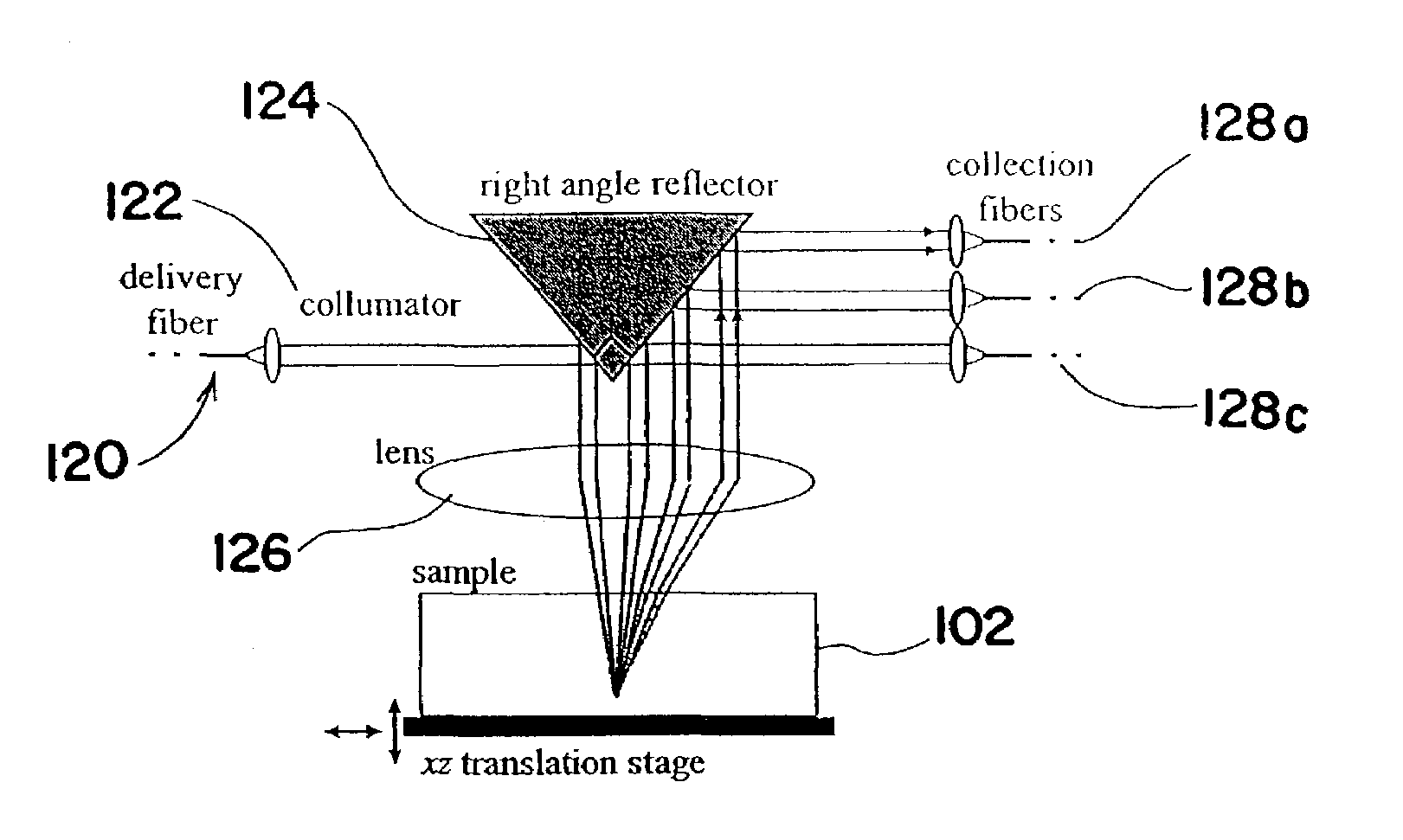
An optical coherence tomography (OCT) system including an interferometer provides illuminating light along a first optical path to a sample and an optical delay line and collects light from the sample along a second optical path remitted at several scattering angles to a detector. In one embodiment, illuminating light is directed along a number of incident light paths through a focusing lens to a sample. The light paths and focusing lens are related to the sample and to both the incident light source and the detector. In another embodiment, a focusing system directs light to a location in the sample. A transmission grating or acousto-optic modulator directs light from the sample at an angle representative of the wavelength of the incident light on the transmission grating or acousto-optic modulator.
Owner:UNIVERSITY HOSPITALS OF CLEVELAND CLEVELAND +1
Solid state optical phased array lidar and method of using same
ActiveUS20150293224A1Instruments for comonautical navigationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical delay lineRadiation pattern
A lidar-based apparatus and method are used for the solid state steering of laser beams using Photonic Integrated Circuits. Integrated optic design and fabrication micro- and nanotechnologies are used for the production of chip-scale optical splitters that distribute an optical signal from a laser essentially uniformly to an array of pixels, said pixels comprising tunable optical delay lines and optical antennas. Said antennas achieve out-of-plane coupling of light.As the delay lines of said antenna-containing pixels in said array are tuned, each antenna emits light of a specific phase to form a desired far-field radiation pattern through interference of these emissions. Said array serves the function of solid state optical phased array.By incorporating a large number of antennas, high-resolution far-field patterns can be achieved by an optical phased array, supporting the radiation pattern beam forming and steering needed in solid state lidar, as well as the generation of arbitrary radiation patterns as needed in three-dimensional holography, optical memory, mode matching for optical space-division multiplexing, free space communications, and biomedical sciences. Whereas imaging from an array is conventionally transmitted through the intensity of the pixels, the optical phased array allows imaging through the control of the optical phase of pixels that receive coherent light waves from a single source.
Owner:QUANERGY SOLUTIONS INC
Optical Buffering Methods, Apparatus, and Systems for Increasing the Repetition Rate of Tunable Light Sources
ActiveUS20120250028A1Reduce image qualityHigh optical losses—fromUsing optical meansCoupling light guidesEngineeringOptical communication
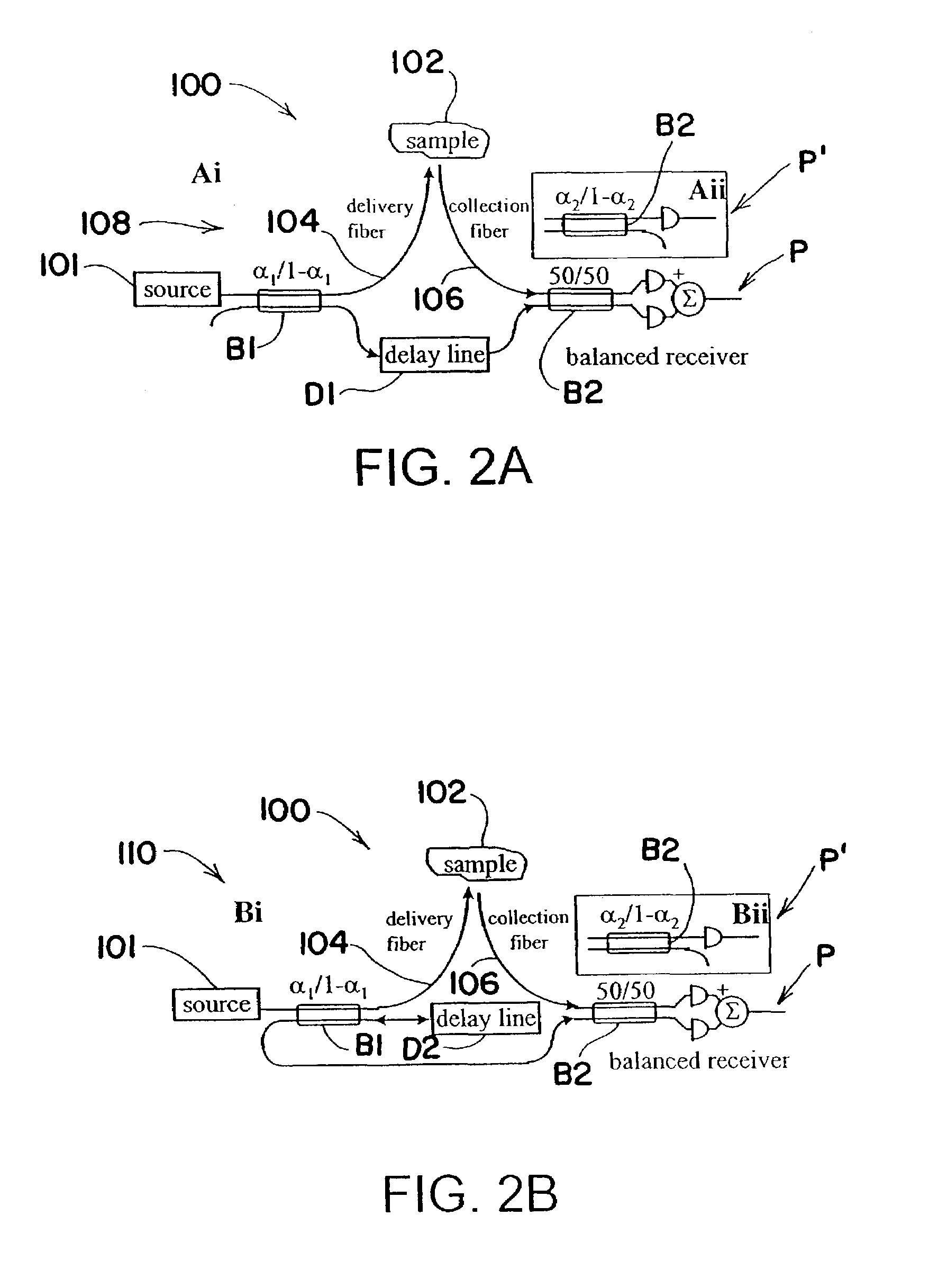
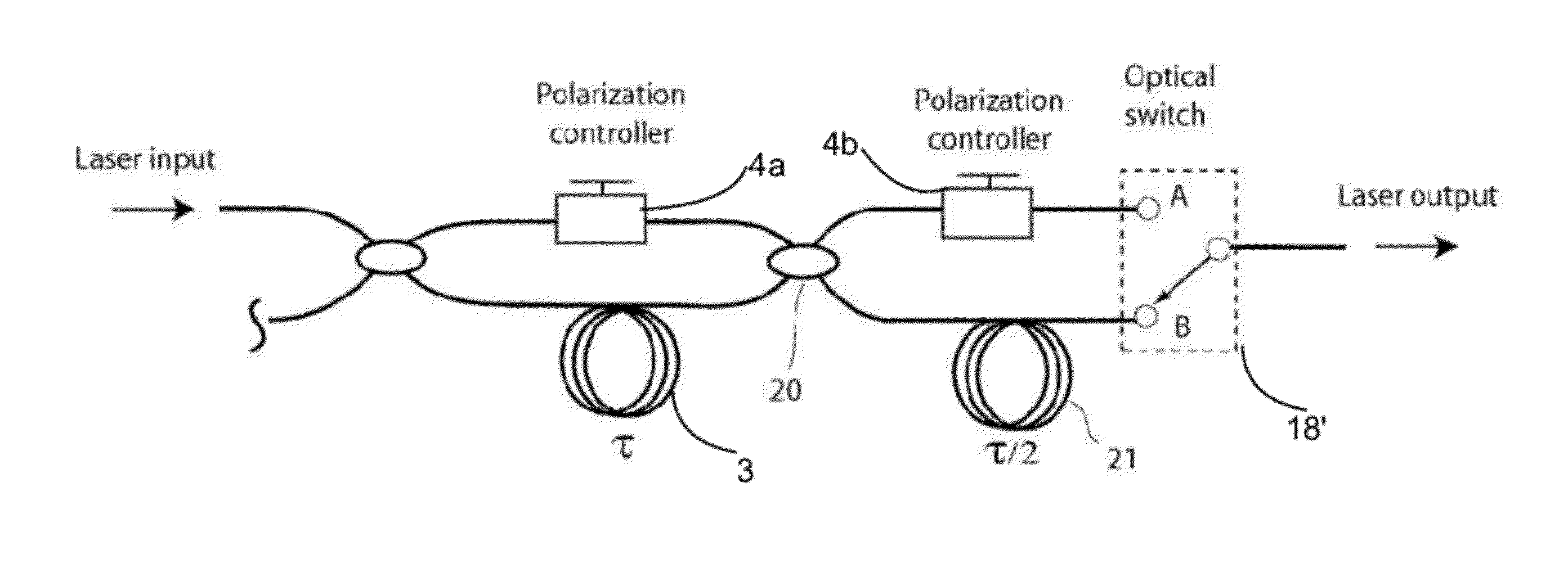
In one embodiment, the invention relates to an apparatus for increasing the repetition rate in a light source. The apparatus includes a first optical coupler comprising a first arm, a second arm and a third arm; a first mirror in optical communication with the second arm of the first optical coupler; and a first optical delay line having a first end in optical communication with the third arm of the first optical coupler and a second end in optical communication with a second mirror, wherein light entering the first arm of the first optical coupler leaves the first arm of the first optical coupler either delayed by an amount (τ) or substantially undelayed.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Optical pulse stretching and smoothing for ArF and F2 lithography excimer lasers
InactiveUS6389045B1Easy to stretchFlat shapeOptical resonator shape and constructionGenerators/motorsOptical reflectionLithographic artist
A method and apparatus are provided for temporally stretching and smoothing of the pulses of an output beam of excimer and lithography lasers. The method and apparatus are based upon providing an optical delay line or circuit having a plurality of optical reflectors and a plurality of beam recombiners or splitters so arranged as to divide the pulse into numerous portions which vary in their travel time through the circuit. As a result, the energy of the incident pulse is greatly stretched and smoothed.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Optical waveguide device with an adiabatically-varying width
Optical waveguide devices are disclosed which utilize an optical waveguide having a waveguide bend therein with a width that varies adiabatically between a minimum value and a maximum value of the width. One or more connecting members can be attached to the waveguide bend near the maximum value of the width thereof to support the waveguide bend or to supply electrical power to an impurity-doped region located within the waveguide bend near the maximum value of the width. The impurity-doped region can form an electrical heater or a semiconductor junction which can be activated with a voltage to provide a variable optical path length in the optical waveguide. The optical waveguide devices can be used to form a tunable interferometer (e.g. a Mach-Zehnder interferometer) which can be used for optical modulation or switching. The optical waveguide devices can also be used to form an optical delay line.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
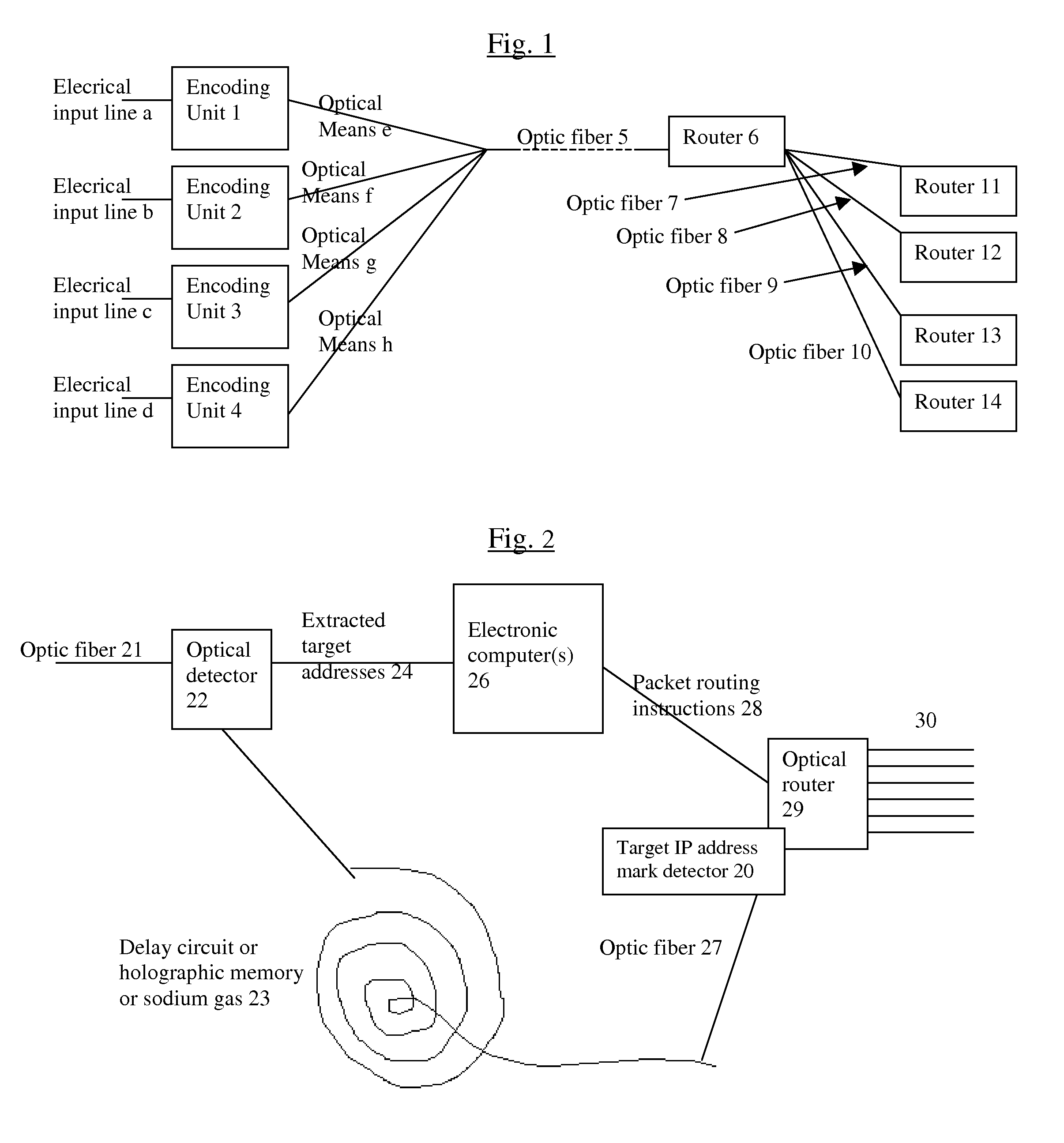
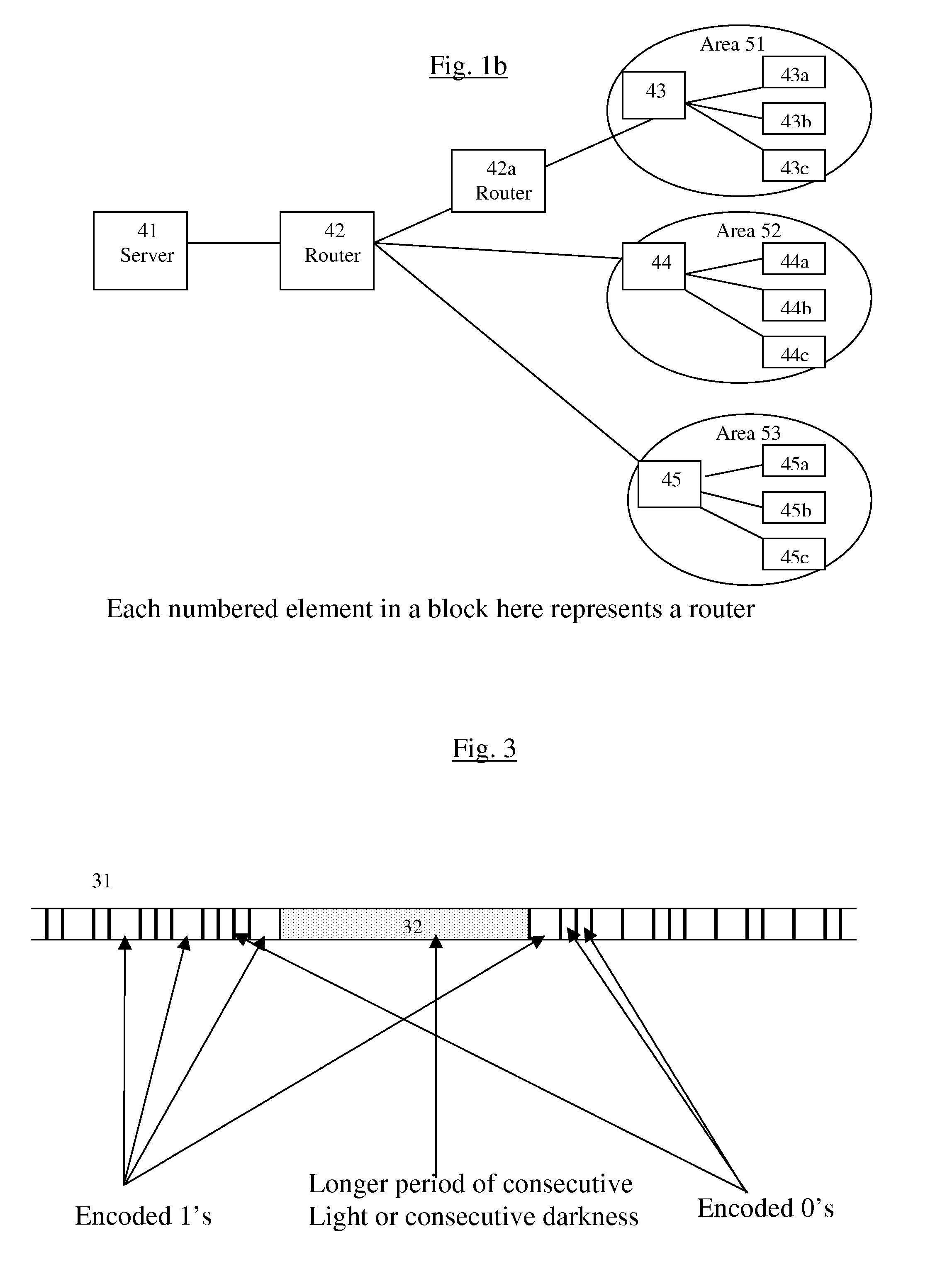
System and method for improving the efficiency of routers on the Internet and/or cellular networks and/or other networks and alleviating bottlenecks and overloads on the network
InactiveUS20080145050A1Simpler and flexible bufferingCheaply and easilyMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical delay lineIndividual data
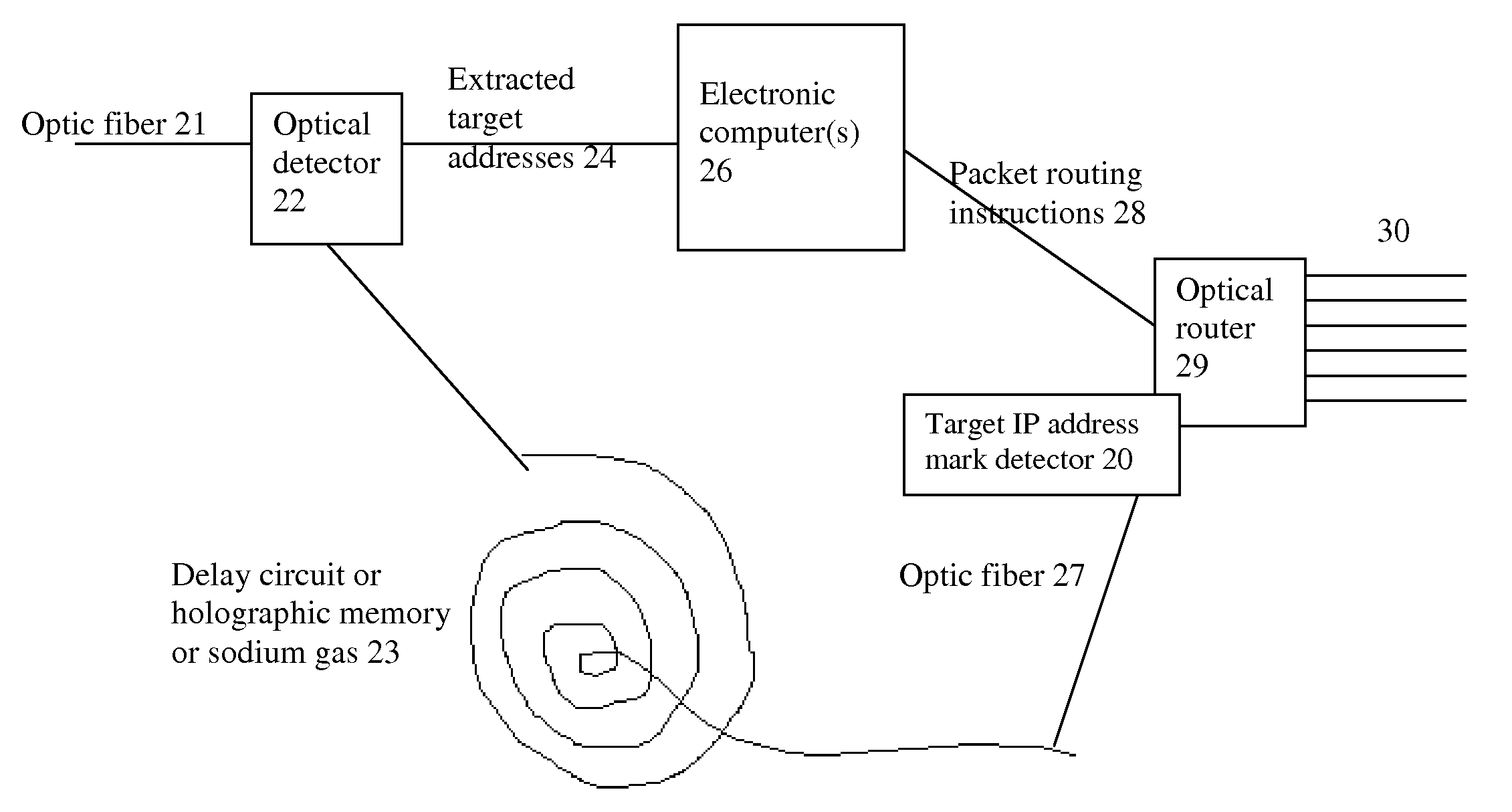
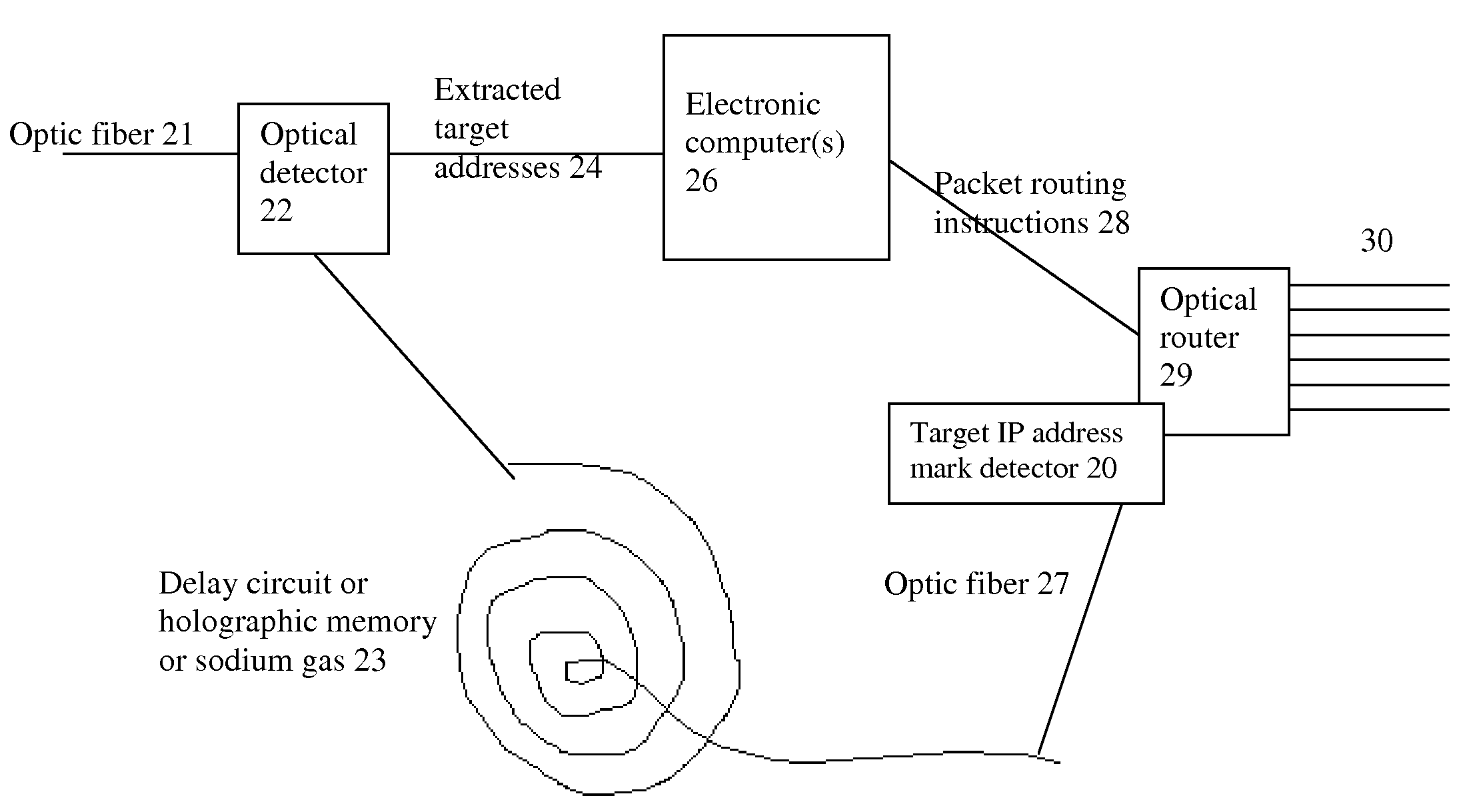
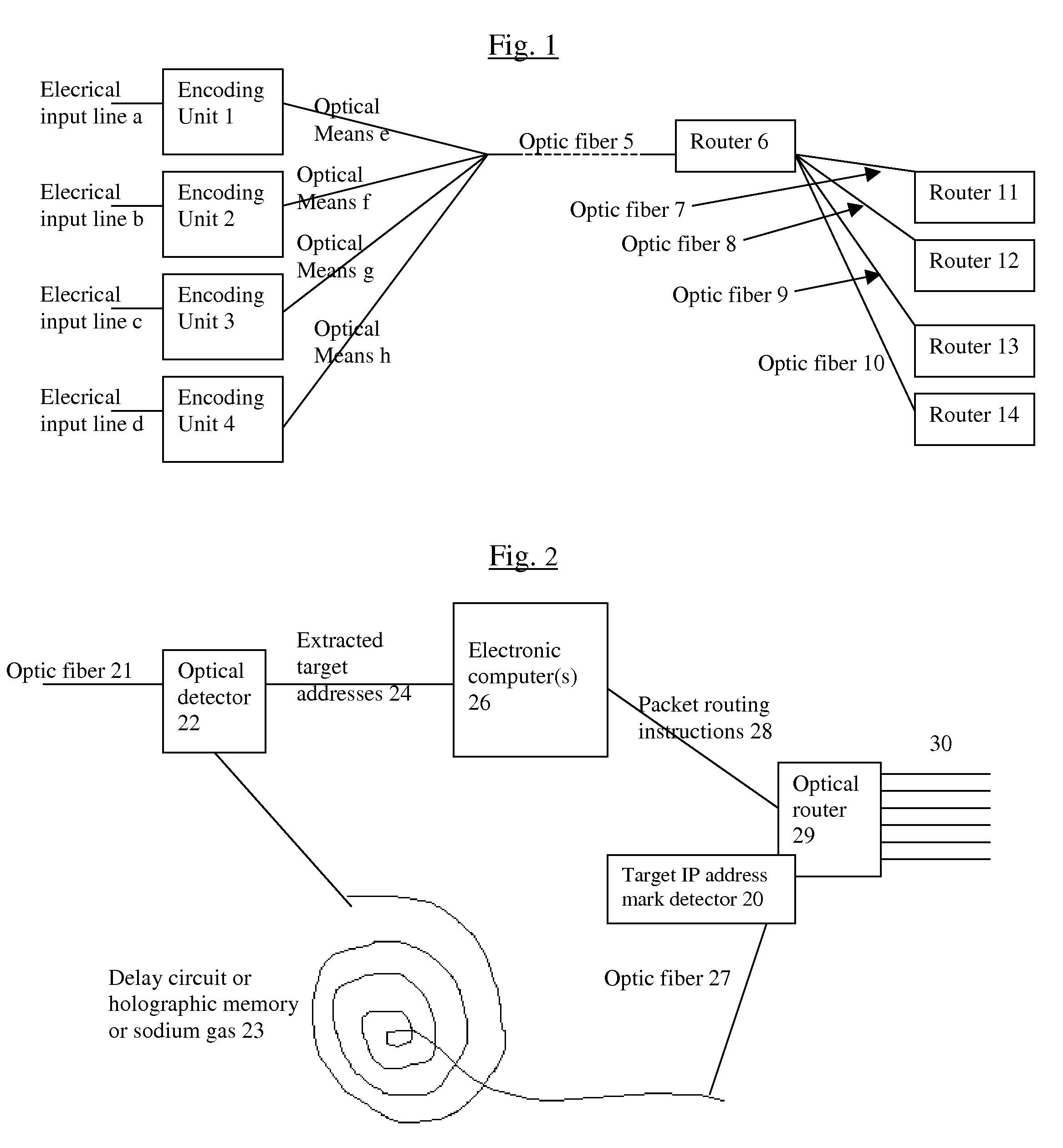
The biggest bottleneck in the Internet today is caused by the slow speed of routers, compared to the speeds that are achieved by optic fibers with DWDM (Dense Wave Division Multiplexing). Packet switching or something similar to it is needed not just for better utilization of the lines, but also because it is superior to circuit switching in many ways, such as better scalability as the Internet grows, better handling of traffic congestions, and better routing flexibility. But optical routers are currently unable to do packet switching except by translating the data to electronic data and then back, which is very inefficient. The present invention solves this problem by optically marking and detecting the packet headers or parts of them, translating at most only the headers or parts of them to electronics for making packet switching decisions, and keeping the rest of the packets in optical delay lines, and solving response-time problems in the router, so that the crude optical switches can execute the packet switching decisions at fast bit rates. This solution has very high scalability and becomes even more efficient when physical addresses are used. Another optimization described in this invention is improving routing efficiency and bandwidth utilization by grouping together identical data packets from the same source going to the same general area with a multiple list of targets connected to each copy of the data and sent together to the general target area. These grouped packets are then preferably broken down into smaller groups by the routers in the general target area and finally broken down to individual data packets for delivering to the final actual destinations. This optimization works best with Physical addresses, and can be very useful for example for optimizing the access to very popular sites such as for example Yahoo or CNN, and can be used also for example for more efficiently transferring streaming data, such as for example from Internet radio stations, or Internet TV stations which will probably exist in the next years. Another important optimization is a new architecture and principles for routing based on physical geographical IP addresses (such as for example based on GPS), in a way much more efficient than has been previously discussed in the literature that suggested using physical (geographical) addresses. This is preferably based on a hierarchy similar to a hierarchical road system, so that preferably the MAIN routers (and / or intermediary-level routers) are preferably also connected directly and preferably with high-bandwidth as peers between each other, without having to go through lower-level routers in order to reach their peers, so that once a higher-level router (and especially if it's one of the MAIN routers) decides to forward a packet (or a group of packets) to a higher-level peer, preferably the packets don't have to go through lower level routers. However, conversion from the current architecture to the new one can be done very easy, as shown in the description below.
Owner:BARHON MAYER BATYA
Apparatus and method for switching, modulation and dynamic control of light transmission using photonic crystals
ActiveUS7421179B1Reduce power consumptionLow heat generationNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guidePhotonicsSilicon oxide
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
System and method for improving the efficiency of routers on the internet and/or cellular networks and/or other networks and alleviating bottlenecks and overloads on the network
InactiveUS8073327B2Improving routing efficiency and bandwidth utilization efficiencyEfficient transferMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsIp addressThe Internet
Owner:BARHON MAYER BATYA
Solid state optical phased array lidar and method of using same
ActiveUS10132928B2Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical delay lineRadiation pattern
A lidar-based apparatus and method are used for the solid state steering of laser beams using Photonic Integrated Circuits. Integrated optic design and fabrication micro- and nanotechnologies are used for the production of chip-scale optical splitters that distribute an optical signal from a laser essentially uniformly to an array of pixels, said pixels comprising tunable optical delay lines and optical antennas. Said antennas achieve out-of-plane coupling of light.As the delay lines of said antenna-containing pixels in said array are tuned, each antenna emits light of a specific phase to form a desired far-field radiation pattern through interference of these emissions. Said array serves the function of solid state optical phased array.By incorporating a large number of antennas, high-resolution far-field patterns can be achieved by an optical phased array, supporting the radiation pattern beam forming and steering needed in solid state lidar, as well as the generation of arbitrary radiation patterns as needed in three-dimensional holography, optical memory, mode matching for optical space-division multiplexing, free space communications, and biomedical sciences. Whereas imaging from an array is conventionally transmitted through the intensity of the pixels, the optical phased array allows imaging through the control of the optical phase of pixels that receive coherent light waves from a single source.
Owner:QUANERGY SOLUTIONS INC
Chaos Brillouin optical coherence domain analysis distributed optical fiber sensing device and method
ActiveCN105136178AOvercoming resolutionOvercome the sensing distanceThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansPhotodetectorDisplay device
The invention relates to a distributed optical fiber sensing system, and in particular relates to a chaos Brillouin optical coherence domain analysis distributed optical fiber sensing device and method. According to the invention, the problems of unavailable spatial resolution and sensing distance combination, severely limited sensing distance and low spatial resolution of the existing distributed optical fiber sensing system are solved. The chaos Brillouin optical coherence domain analysis distributed optical fiber sensing device comprises a wide spectrum chaos semiconductor laser, a 1*2 optical fiber coupler, an optical scrambler, an optical isolator, a first optical amplifier, a variable optical delay line, a second optical amplifier, an optical circulator, a sensing optical fiber, a tunable optical filter, a broadband gain photodetector, a data acquisition device, a signal processing device and a display device. The device and the method, which are provided by the invention, are applicable to the field of distributed optical fiber sensing.
Owner:太原网讯同诚科技有限公司
Orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar
ActiveCN102435996AReduce the effects of phase interferenceBig optic toesElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh resolution imagingRadar systems
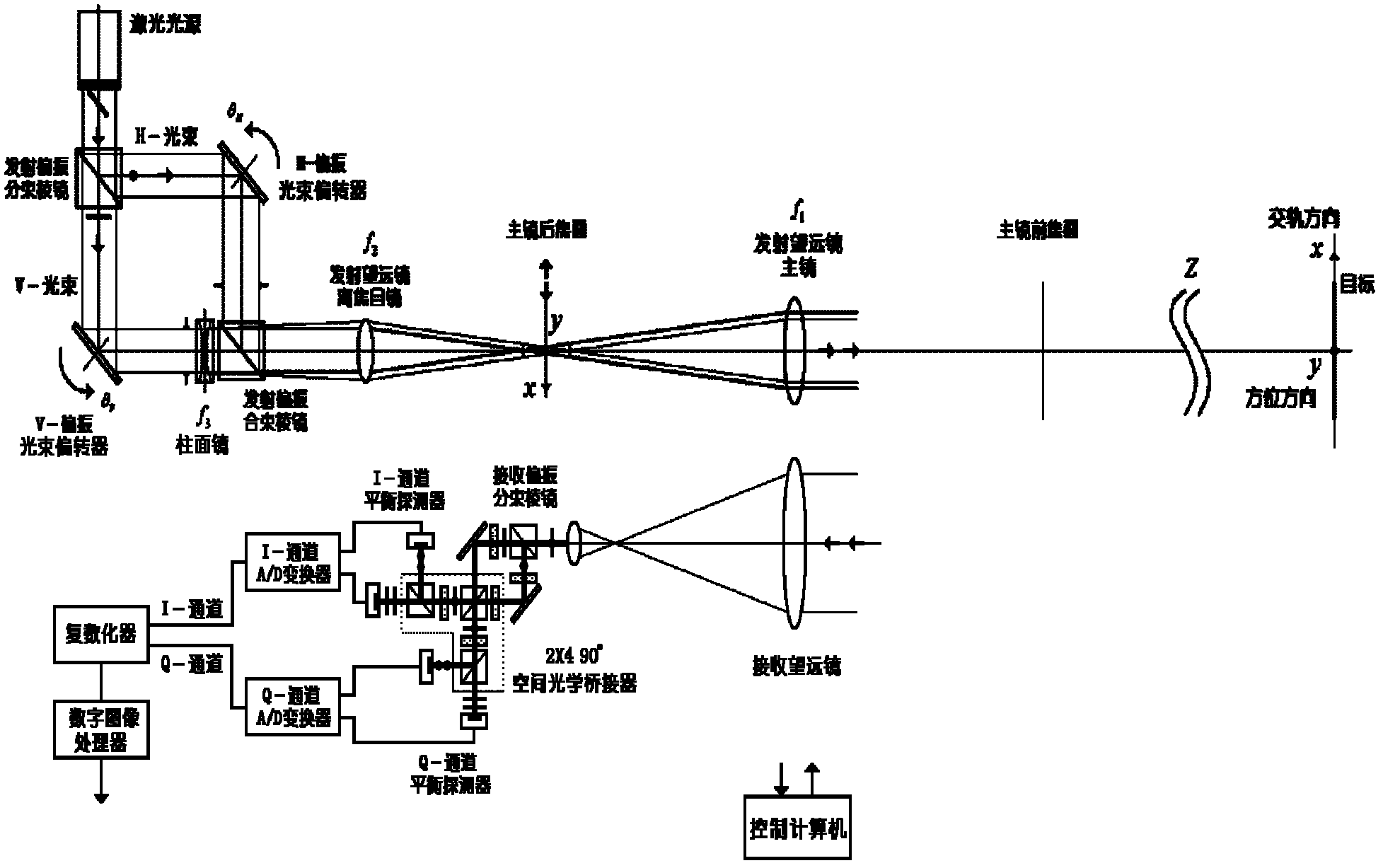
The invention relates to an orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar. The orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar comprises a laser light source, a transmission polarization beam splitter, a horizontal polarization optical path beam deflector, a horizontal polarization optical path transform lens, a vertical polarization optical path beam deflector, a vertical polarization optical path transform lens, a transmission polarization beam combiner, a transmitter telescope ocular, a transmitter telescope primary lens, a receiver telescope, a receiving polarization beam splitter, a 2 * 490 DEG optical bridge, an inphase channel balanced detector, an inphase channel A / D (analogue / digital) converter, a 90 DEG of phase shift channel balanced detector, a 90 DEG of phase shift channel A / D (analogue / digital) converter, a pluralizing processor, a digital image processor and a control computer. The orthoptic synthetic aperture laser imaging radar automatically eliminates phase changes and interference of atmosphere, motion platforms, optical radar systems and speckles, has high resolution imaging in larger optical footprint and larger receiving aperture, does not need optical delay lines, does not need real-time beat frequency signal phase synchronization, does not have shadows during imaging, and can be used for various lasers with single-module and single-frequency properties.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
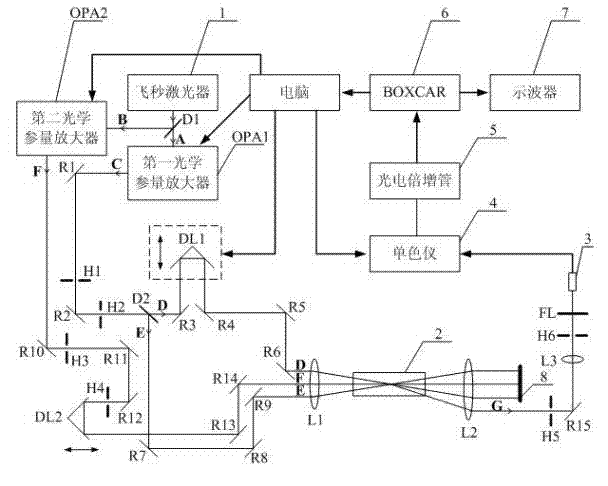
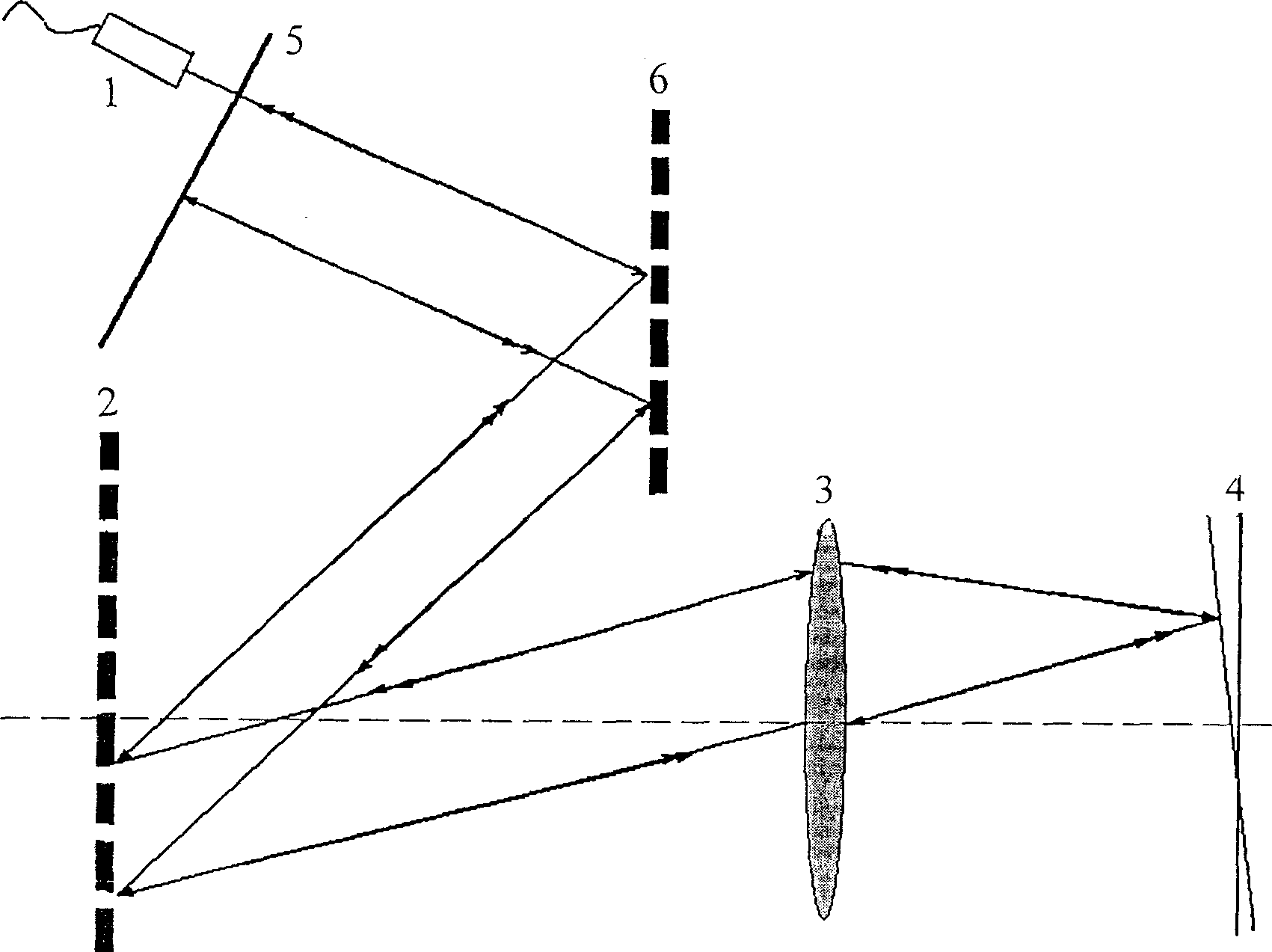
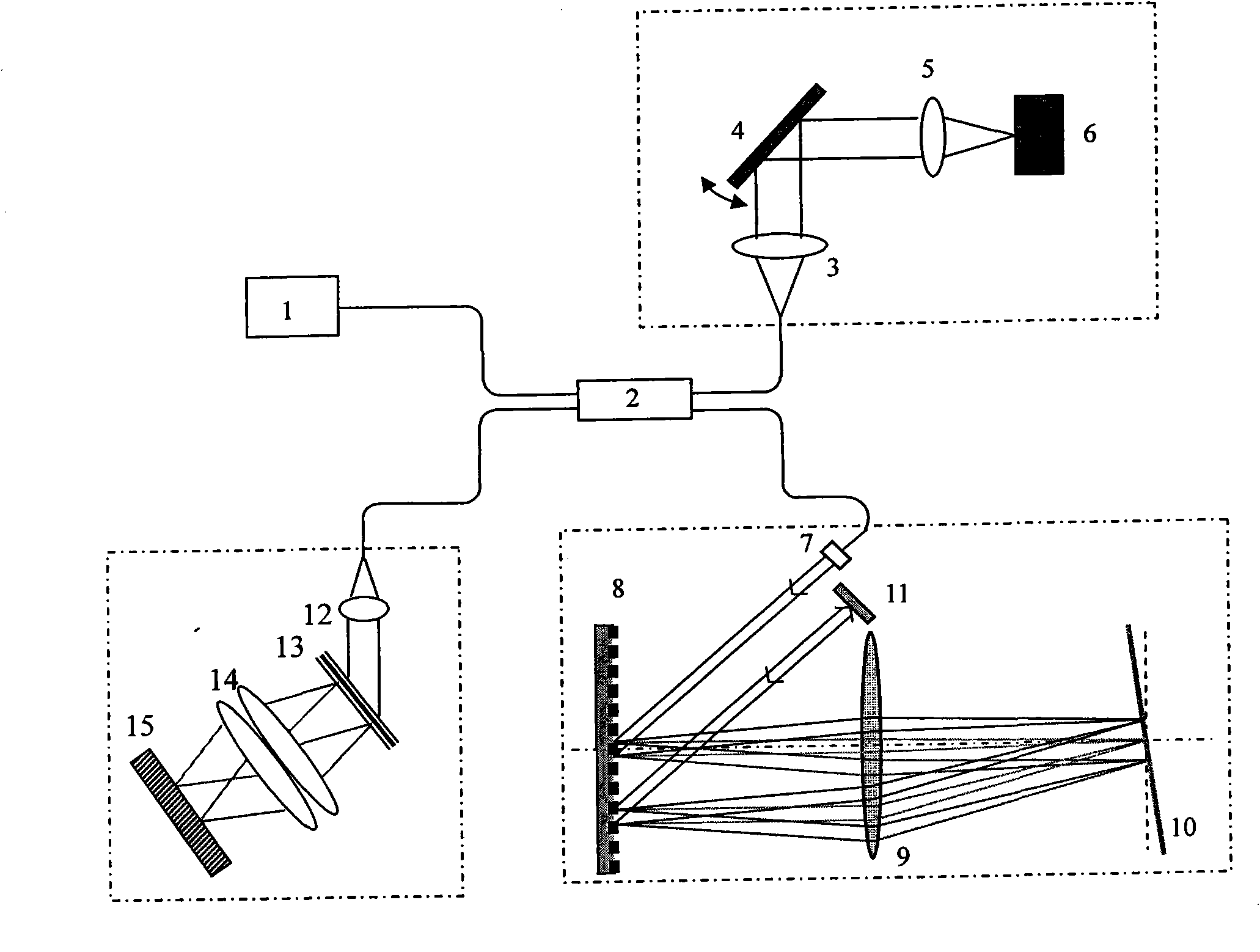
Normal-temperature normal-pressure femto-second CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Spectroscopy) time-resolved spectrum measuring system
InactiveCN101819064ASimple and fast operationImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringNonlinear opticsFemto second laser
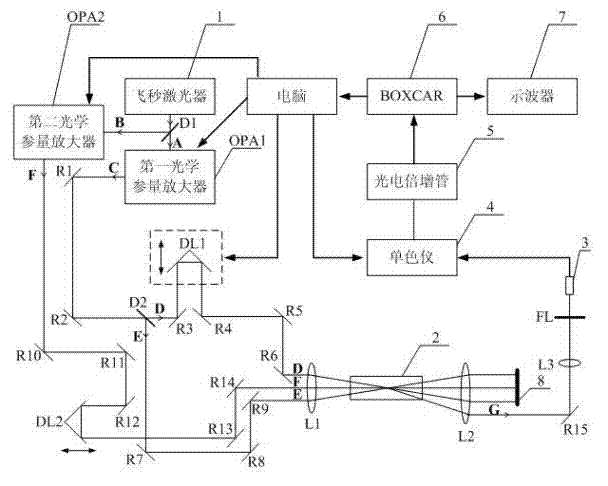
The invention relates to a normal-temperature normal-pressure femto-second CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Spectroscopy) time-resolved spectrum measuring system which relates to the technical field of nonlinear optics and solves the problem of multiple limiting factors of traditional femto-second CARS time-resolved spectrum measuring experiment. Beams output by a femto-second laser are adjusted through a series of reflectors and optical delay lines by the system to form three bundles of beams which have approximate energy and are respectively positioned on three peaks of a square on the vertical direction of the beams, the beams are focused to a sample pool and then emit a new beam along a specific angle, i.e. a CARS signal, the CARS signal is filtered through a filter plate, then received by a probe and input to a monochromator, the data acquisition of an electrical signal converted by a photomultiplier is carried out by utilizing BOCCAR, and the data are input to a computer for data processing. The invention can carry out femto-second CARS time-resolved spectrum measurement under the experimental conditions of normal temperature and normal pressure and is applicable for the femto-second CARS spectrum measurement of gas samples and liquid samples in a static sample pool.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Sub-millimeter spatial resolution distributed optical fiber sensing device and method
ActiveCN105136177AIncrease powerIncrease sensing distanceThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansLow speedPhotodetector
The invention relates to a distributed optical fiber sensing system, and specifically relates to a sub-millimeter spatial resolution distributed optical fiber sensing device and method. According to the invention, the problems of unavailable spatial resolution and sensing distance combination, seriously limited sensing distance and low spatial resolution of the existing distributed optical fiber sensing system are solved. The sub-millimeter spatial resolution distributed optical fiber sensing device comprises a chaos laser, a 1*2 optical fiber coupler, a high-speed electro-optic modulator, a microwave signal source, a first optical amplifier, an optical isolator, an optical scrambler, an variable optical delay line, a low-speed electro-optic modulator, a second optical amplifier, an optical circulator, a sensing optical fiber, a photodetector, a phase-lock amplifier, a signal generator, a data acquisition card and a computer. The device and the method, which are provided by the invention, are applicable to the field of distributed optical fiber sensing.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
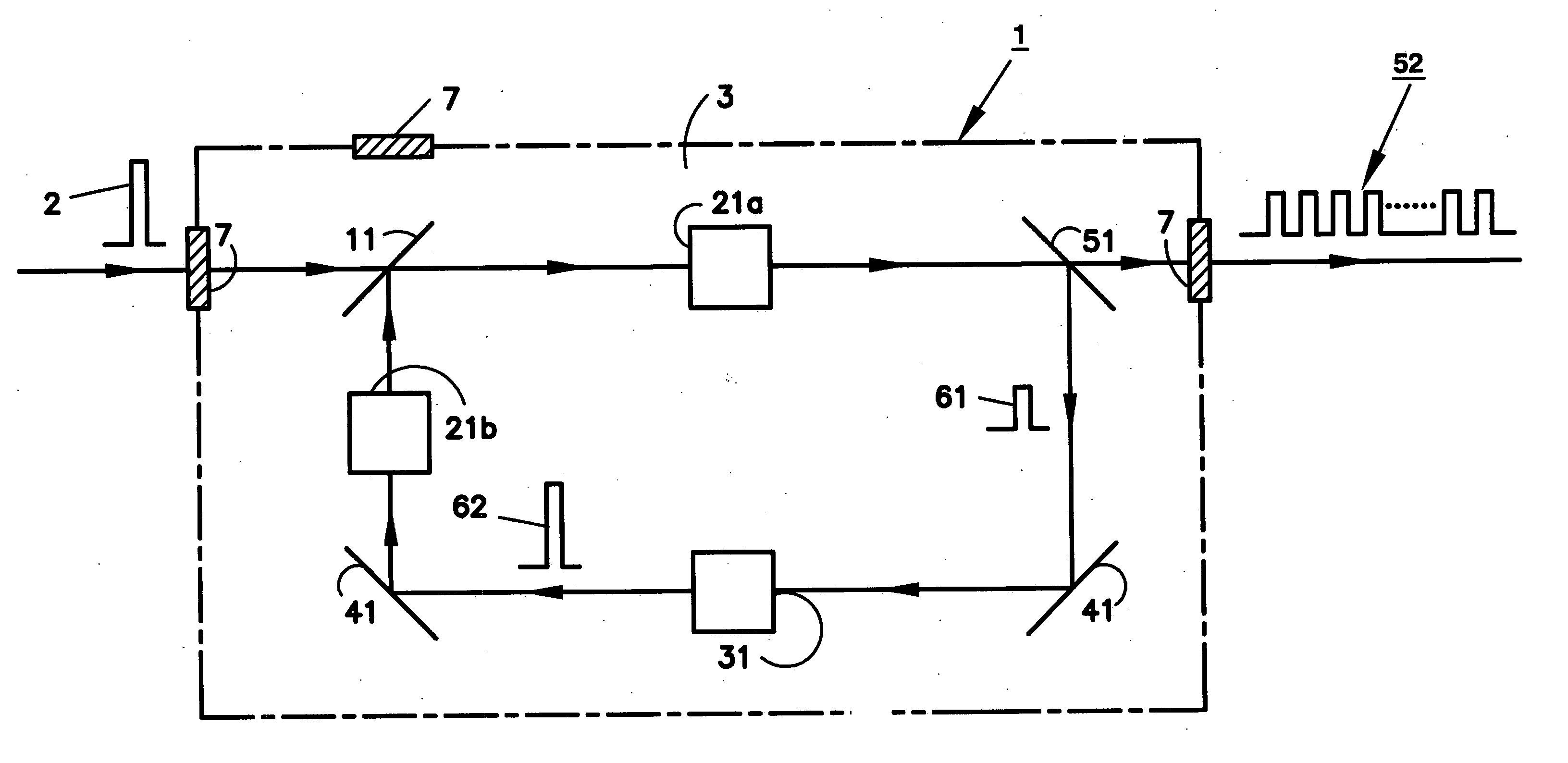
Laser pulse multiplier
ActiveUS20070047601A1Increase the number ofImproves electron production rateOptical resonator shape and constructionFibre transmissionTime structureOptoelectronics
A device for generating a plurality of laser pulses from a recirculating single laser pulse in an optical delay line that is capable of partially transmitting the trapped pulse out of the delay line. The energy of the partially reflected trapped pulse is restored before beginning another round trip in the delay line. The time structure of an output pulse train thus generated by the device comprises a sequence of macro pulses, each comprising a plurality of micro pulses.
Owner:DULY RES
Twin array Michelson optical fiber white light interference strain gage
InactiveCN101329168AGuaranteed real-timeSimplify complexityThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansPhotodetectorLight beam
The invention provides a white light interferometer strain gauge of twin array Michelson optical fibers, which consists of a broad-band light source, an photodetector, a coupler, a single-mode connecting optical fiber, an optical attenuator, an optical delay line and a sensing array that is composed of twin optical fiber sensors, wherein, broad-band light emitted by the broad-band light source is split by the coupler, one light beam is transmitted into an array that consists of an arm optical fiber sensor by the optical attenuator, the other light beam is transmitted into the array that consists of another arm optical fiber sensor by the optical delay line, and light signals that are returned by the two arms are transmitted into the photodetector for detection and analysis by the coupler. The white light interferometer strain gauge of the twin array Michelson optical fibers is characterized in that the white light interferometer strain gauge can realize the measurement of strain and temperature at the same time, reduces the influence of temperature to the measurement by utilizing the temperature compensation technique, and simultaneously, simplifies system complexity, lowers testing cost, ensures the real-time property of testing and improves testing reliability; furthermore, the white light interferometer strain gauge has simple structure, easy implementation, low cost and price and easy acquisition.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
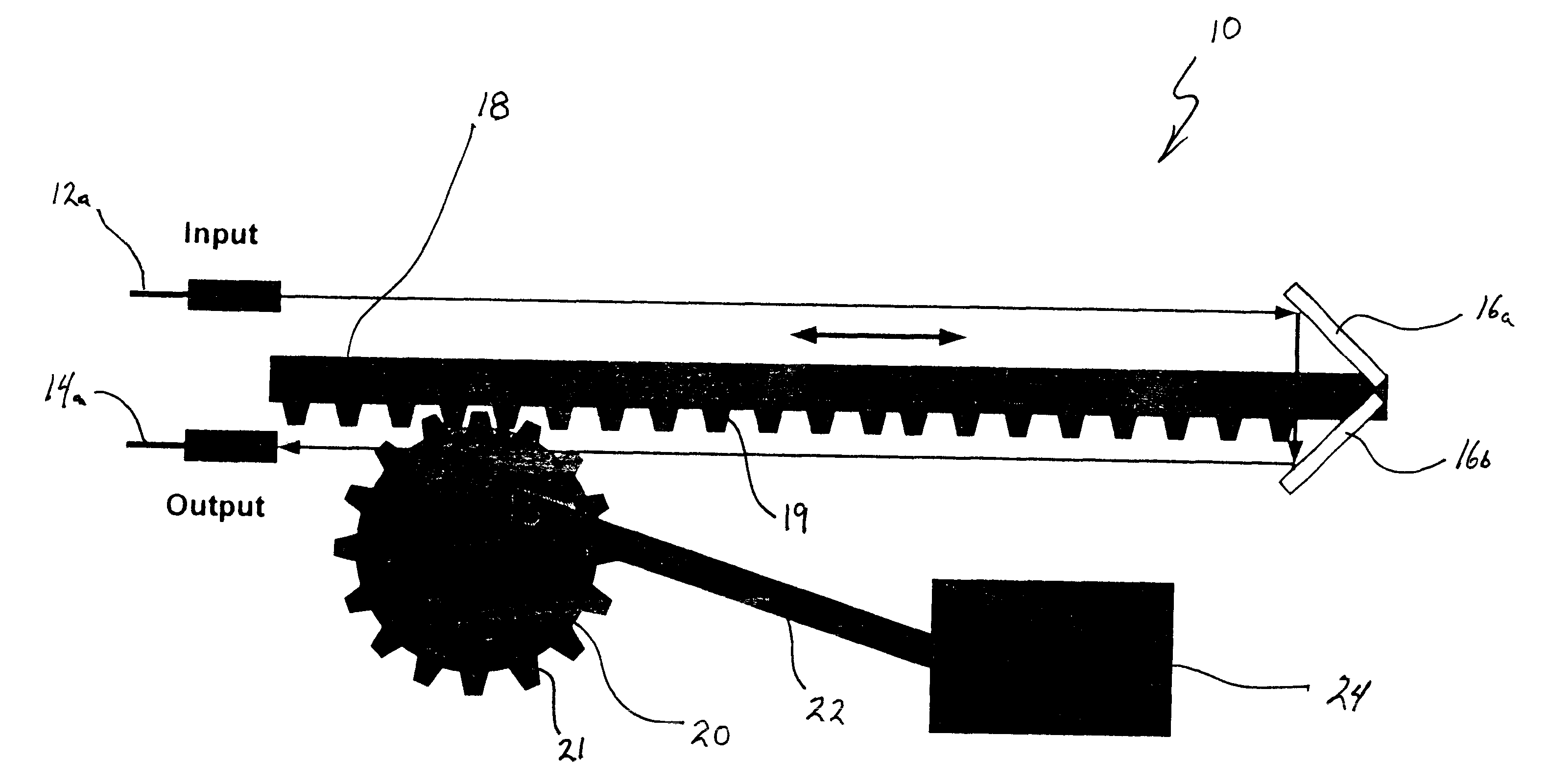
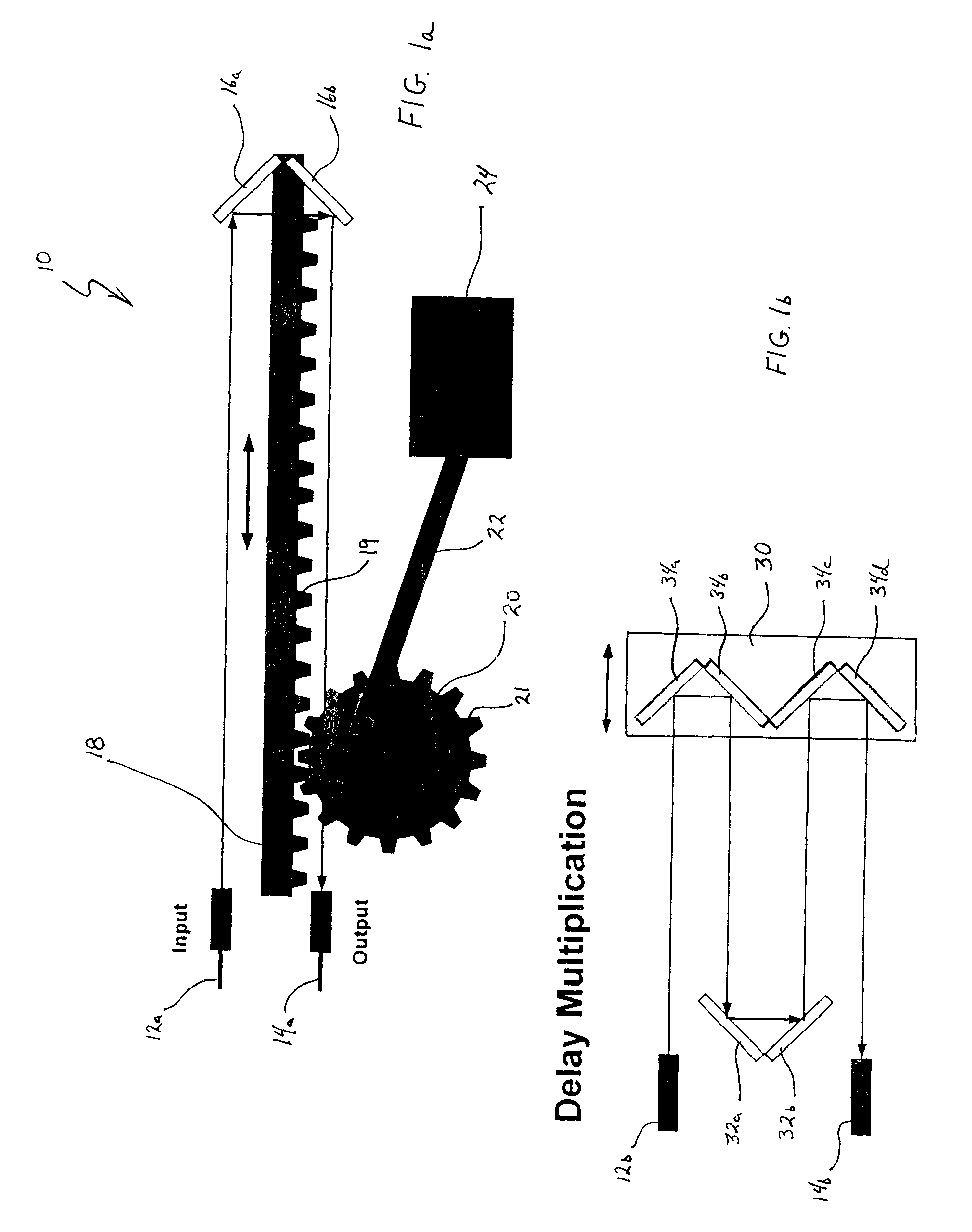
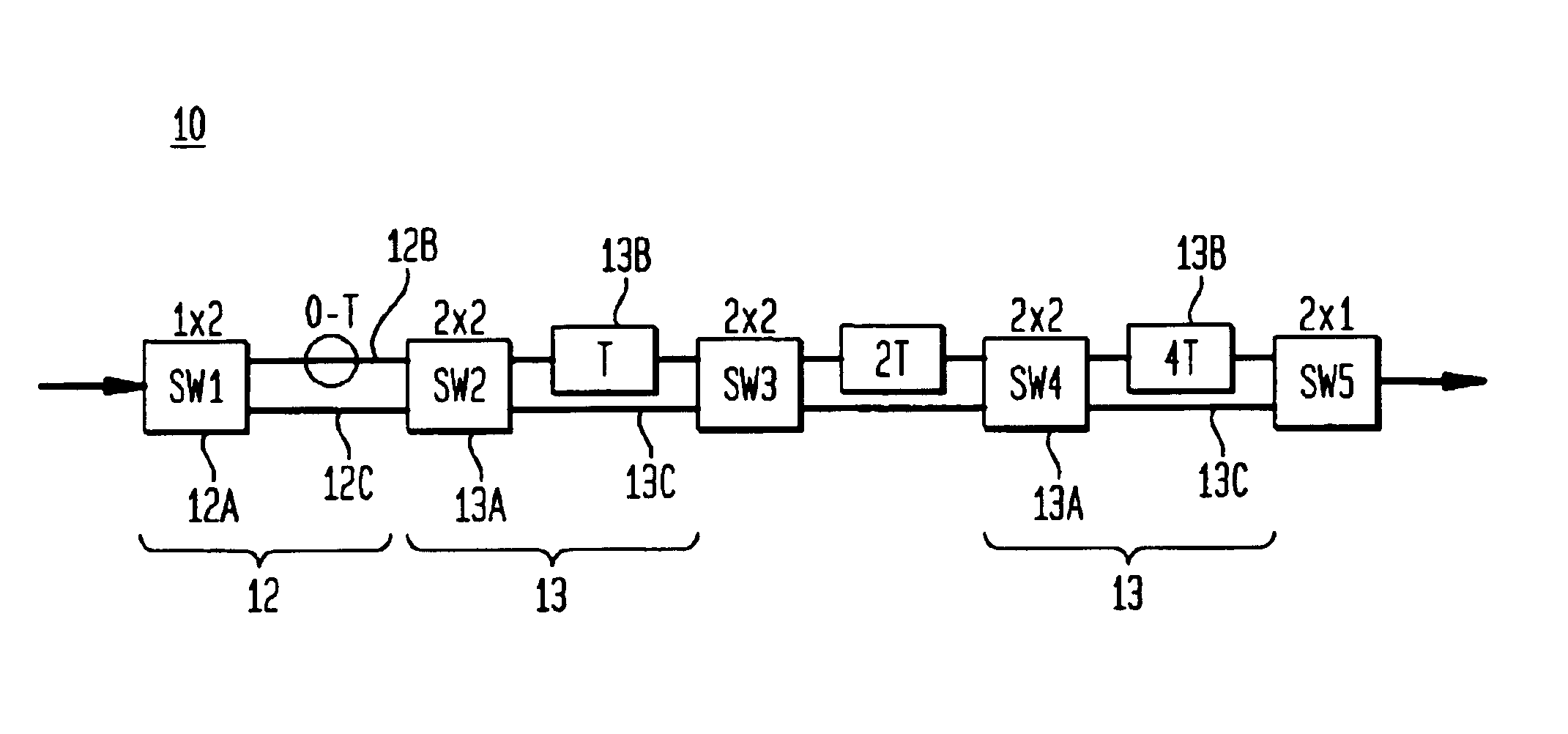
Mems variable optical delay lines
InactiveUS6356377B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSnap-action arrangementsEngineeringOptical delay line
A variable optical delay line using MEMS devices. A reflector on a micro machine linear rack is positioned and spaced from an input source and / or an output to receive and reflect input light waves toward the output. The distance between the reflector and the input and output is variable and thereby enables selective path delay compensation of the input light wave signals. Other disclosed embodiments utilize pivoting MEMS mirrors and selective adjustment of the mirror pivot angles to provide the selective path delay compensation required in a light wave system.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Small-size optical fiber femtosecond laser with wide repetition frequency tuning range
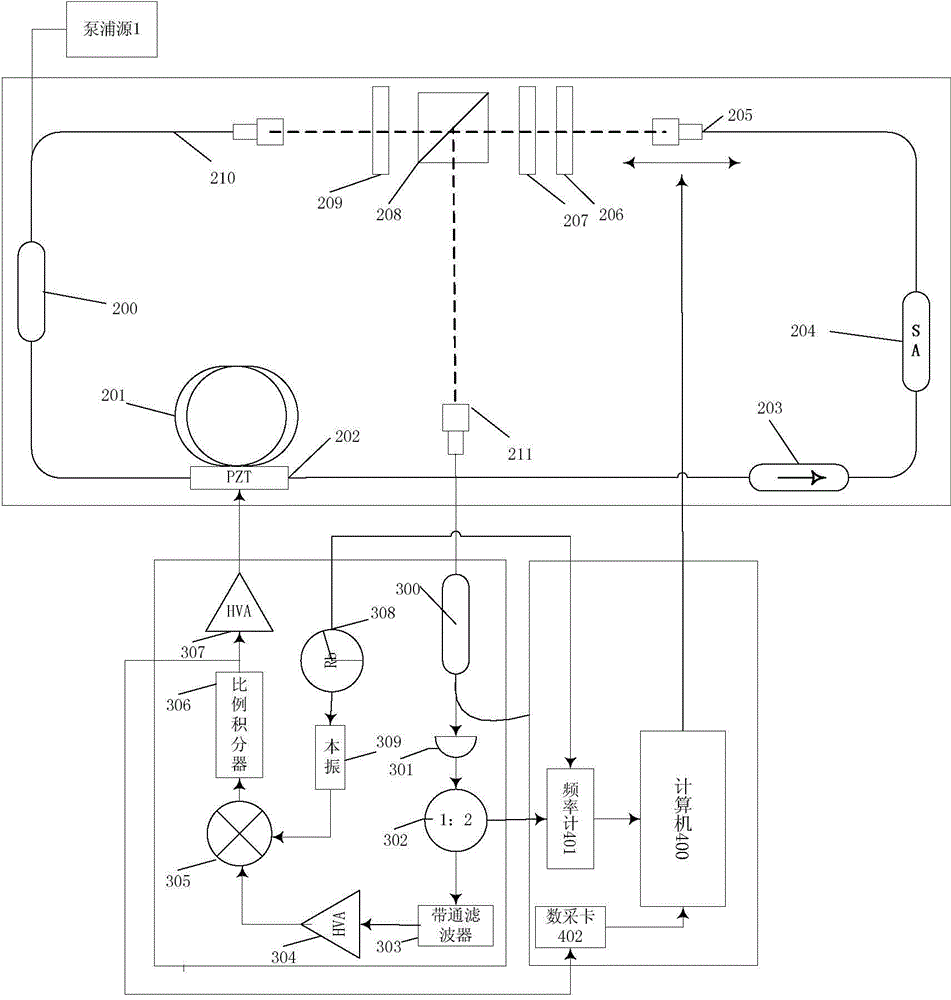
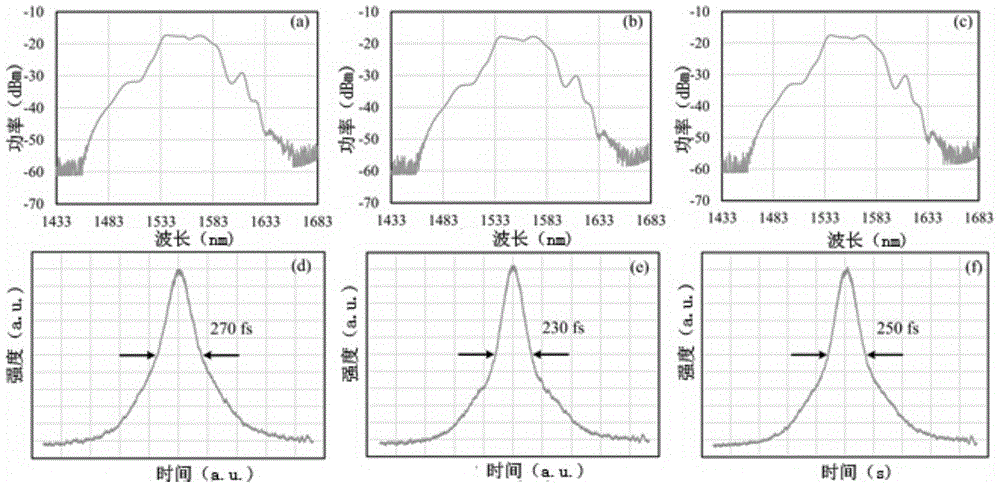
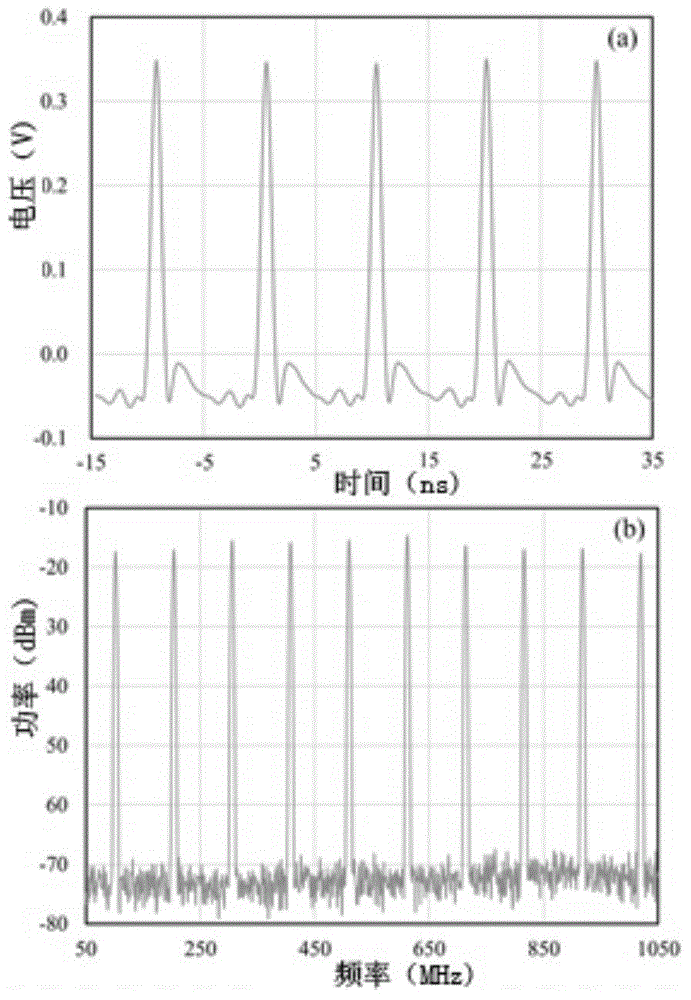
The invention provides a small-size optical fiber femtosecond laser with a wide repetition frequency tuning range. The small-size optical fiber femtosecond laser comprises a repetition frequency adjustable erbium-doped optical fiber laser based on a mixing mode-locking mechanism, a repetition frequency locking system and a computer control system, wherein the erbium-doped optical fiber laser is provided with an annular cavity, an automatically controlled optical delay line is added into the cavity, the repetition frequency of the laser can realize the large-range tuning, and in order to realize the repetition frequency stabilization, on one hand, piezoelectric ceramics are used for controlling the length of the gain optical fiber, so that the short period fluctuation of the repetition frequency is inhibited; on the other hand, the large-range long-period fluctuation of the repetition frequency can be compensated through regulating an optical delay line. The femtosecond laser has the advantages that the size is small, the stability is high, the repetition frequency tuning performance is realized, the repetition frequency can be controlled, and the like. The work potential in industrial environment is realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
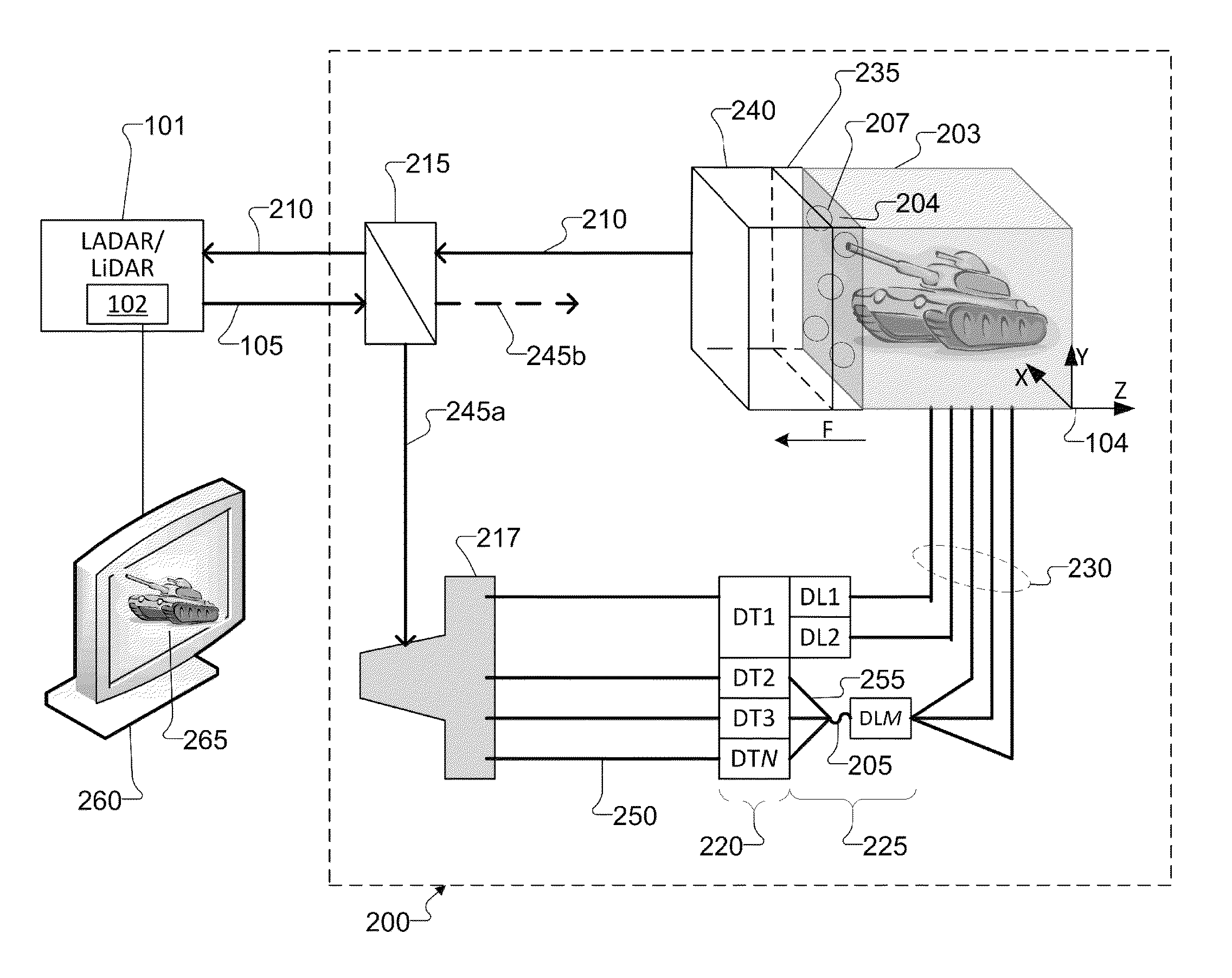
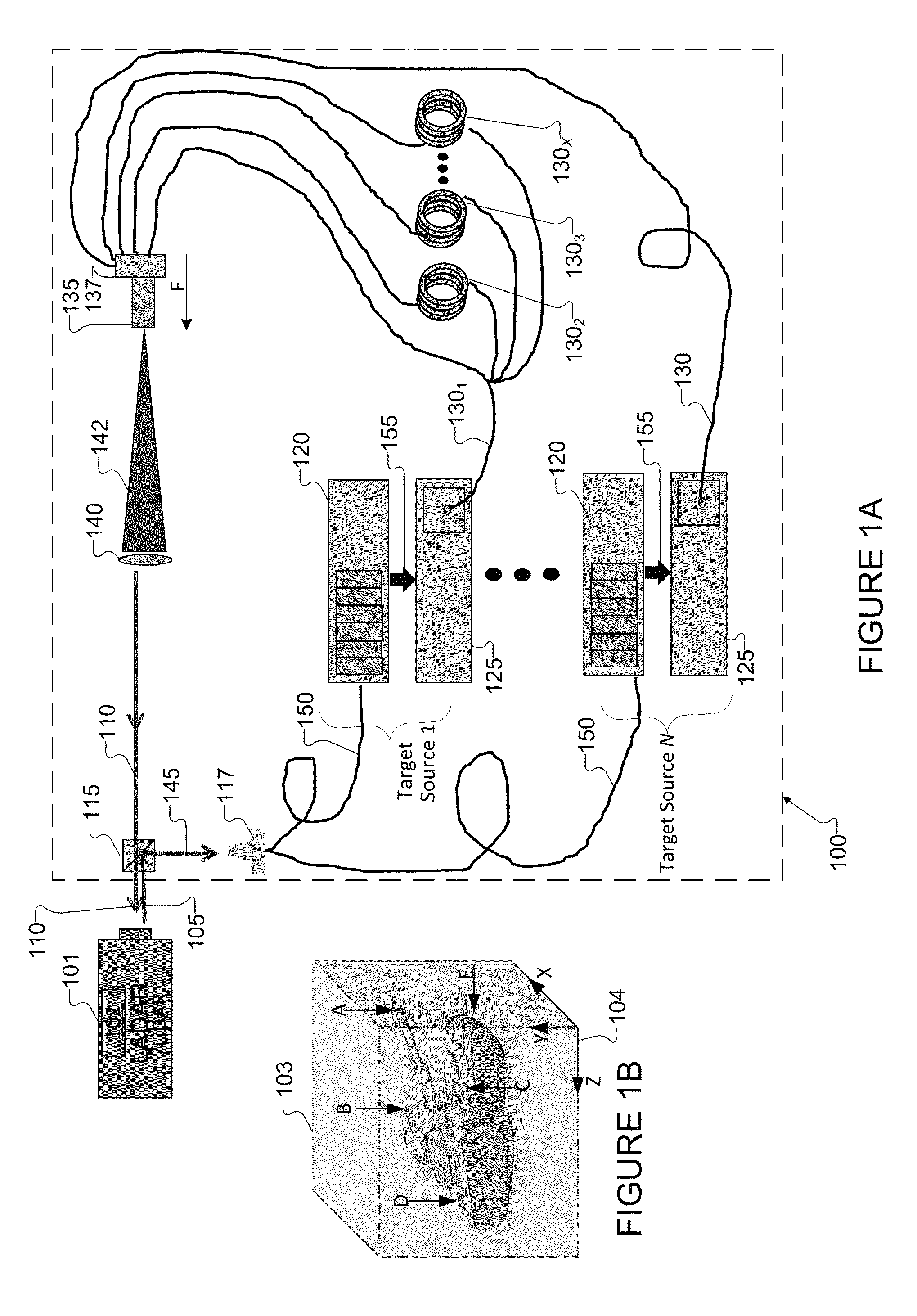
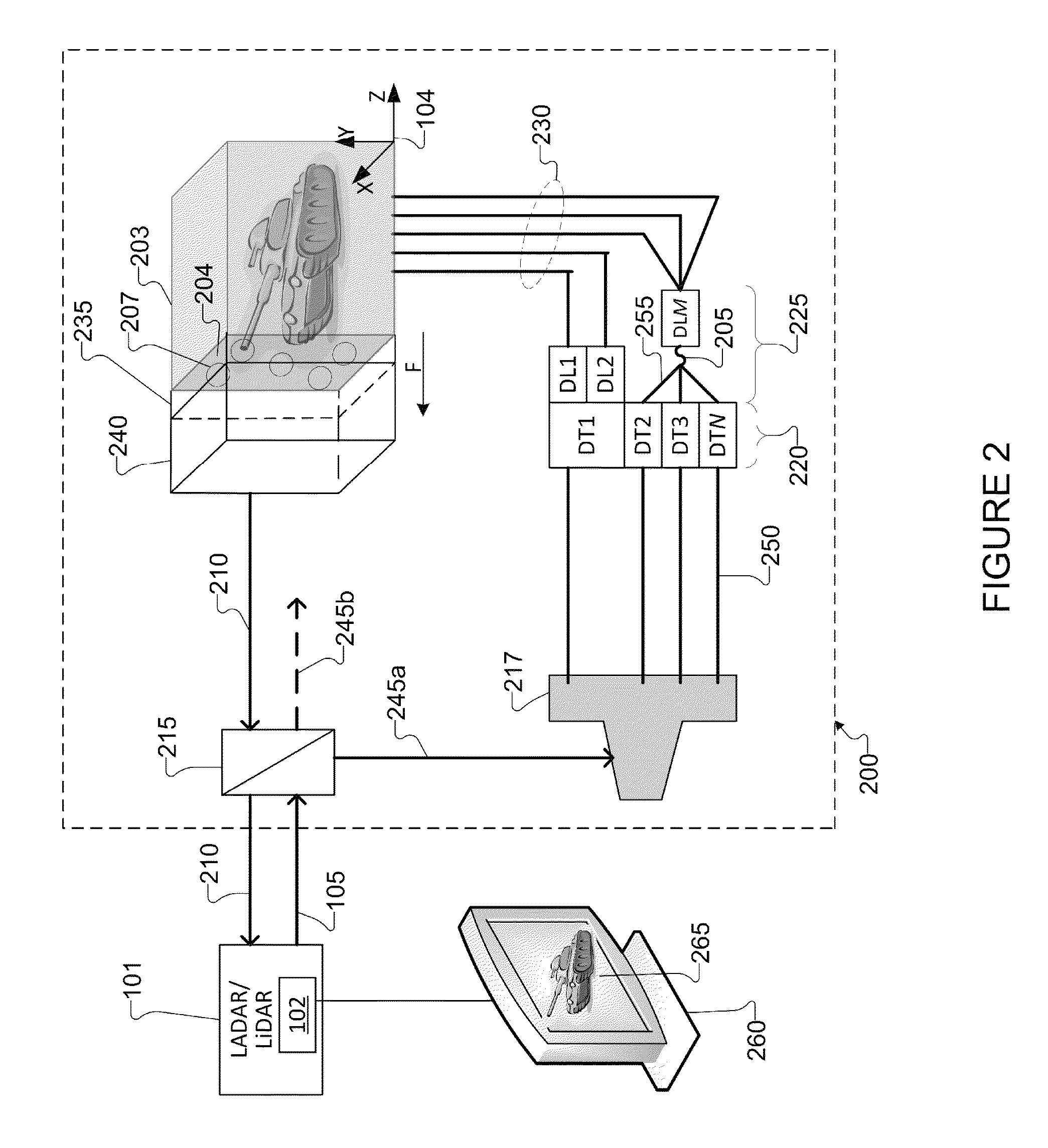
Portable programmable ladar test target
A method of testing a Laser Detection and Ranging (LADAR) or LIght Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) system includes receiving an input signal from the LADAR / LiDAR and triggering light / laser sources to output pulses. The method includes transmitting the light / laser pulses into a first end of two or more fiber optical delay lines. The method includes transmitting the pulses throughout a length of two or more fiber optical delay lines. The method includes after a delay time corresponding to the length of the fiber optical delay lines, transmitting the pulses out through a second end of the fiber optical delay lines arranged within a target plane. The pulses output yield a return signals transmission from the target plane to the LADAR / LiDAR. The return signal transmission is delayed by times for the light / laser pulses to traverse the length of the fiber optical delay lines.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
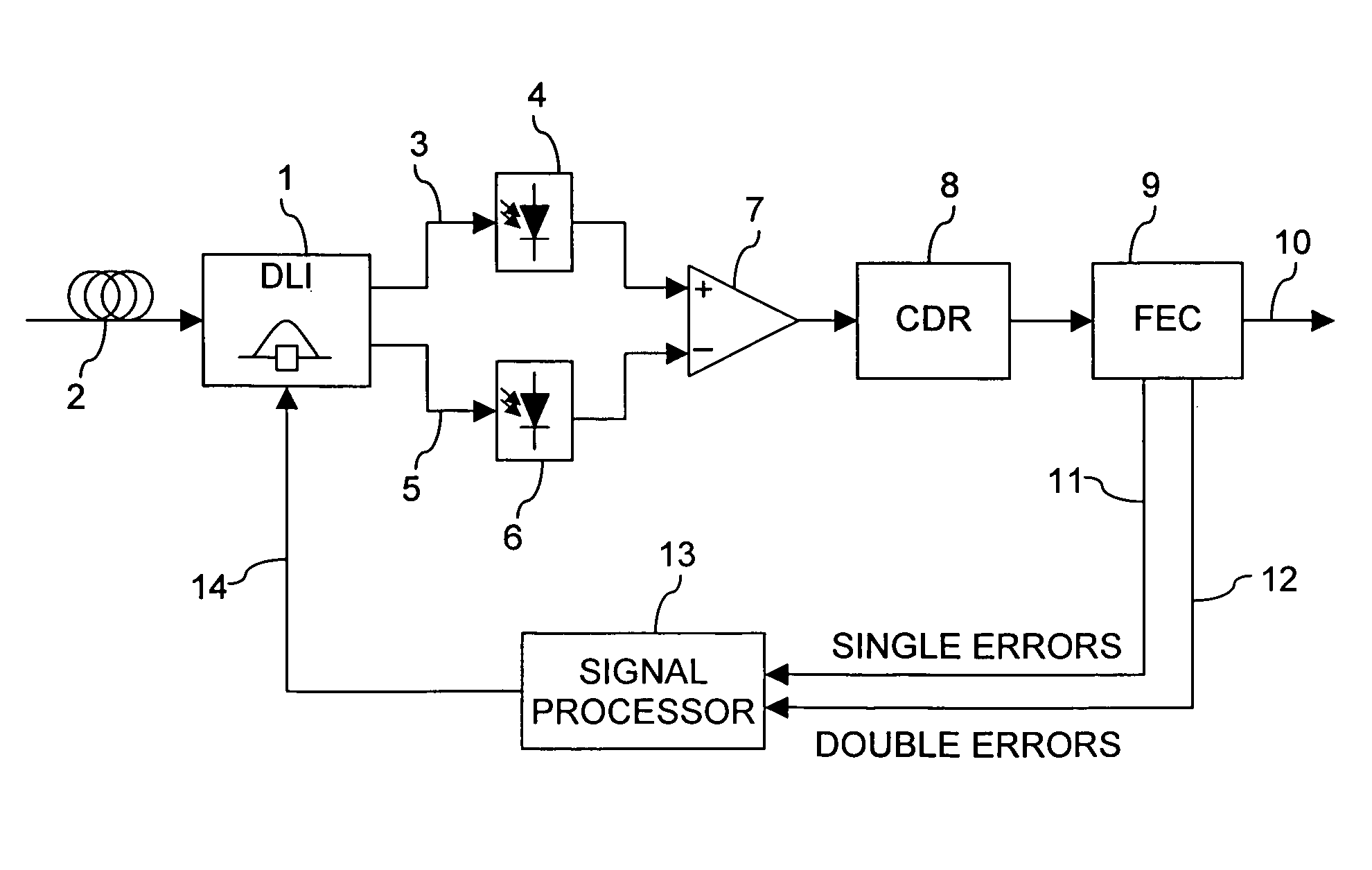
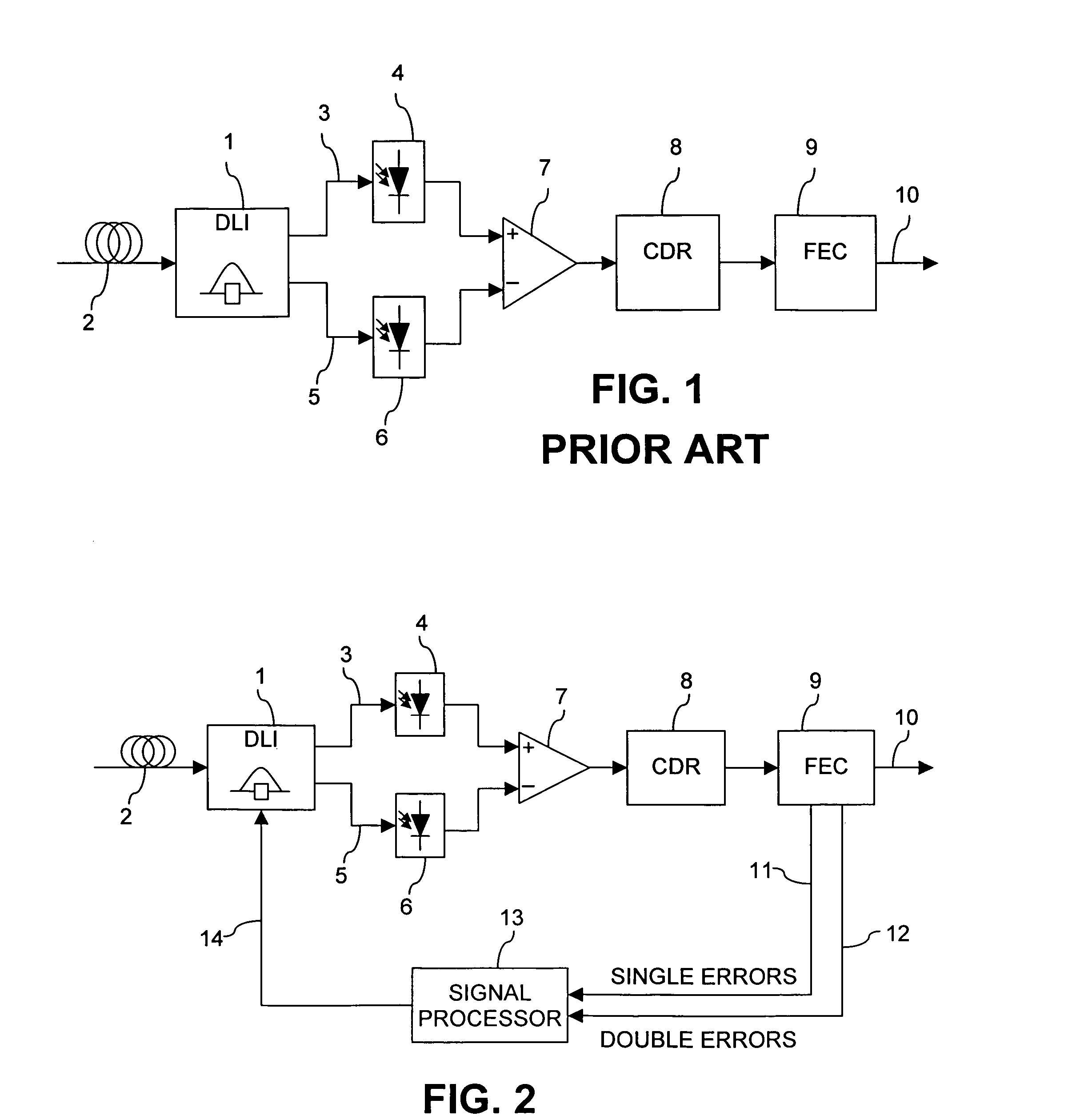
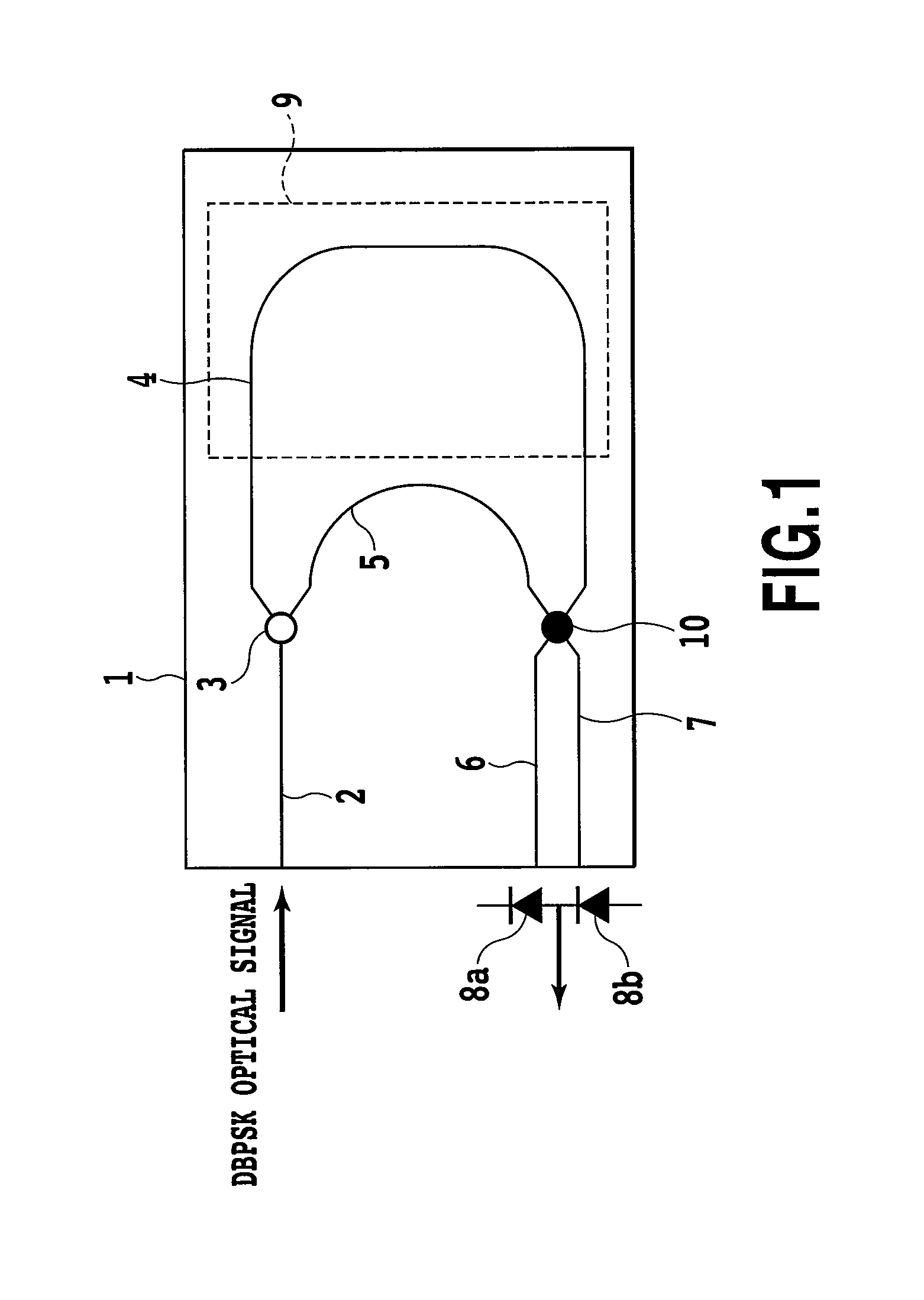
Control of delay line interferometer
ActiveUS7266311B2Low costCounting errorTransmission monitoringPhase-modulated carrier systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Phase shifted
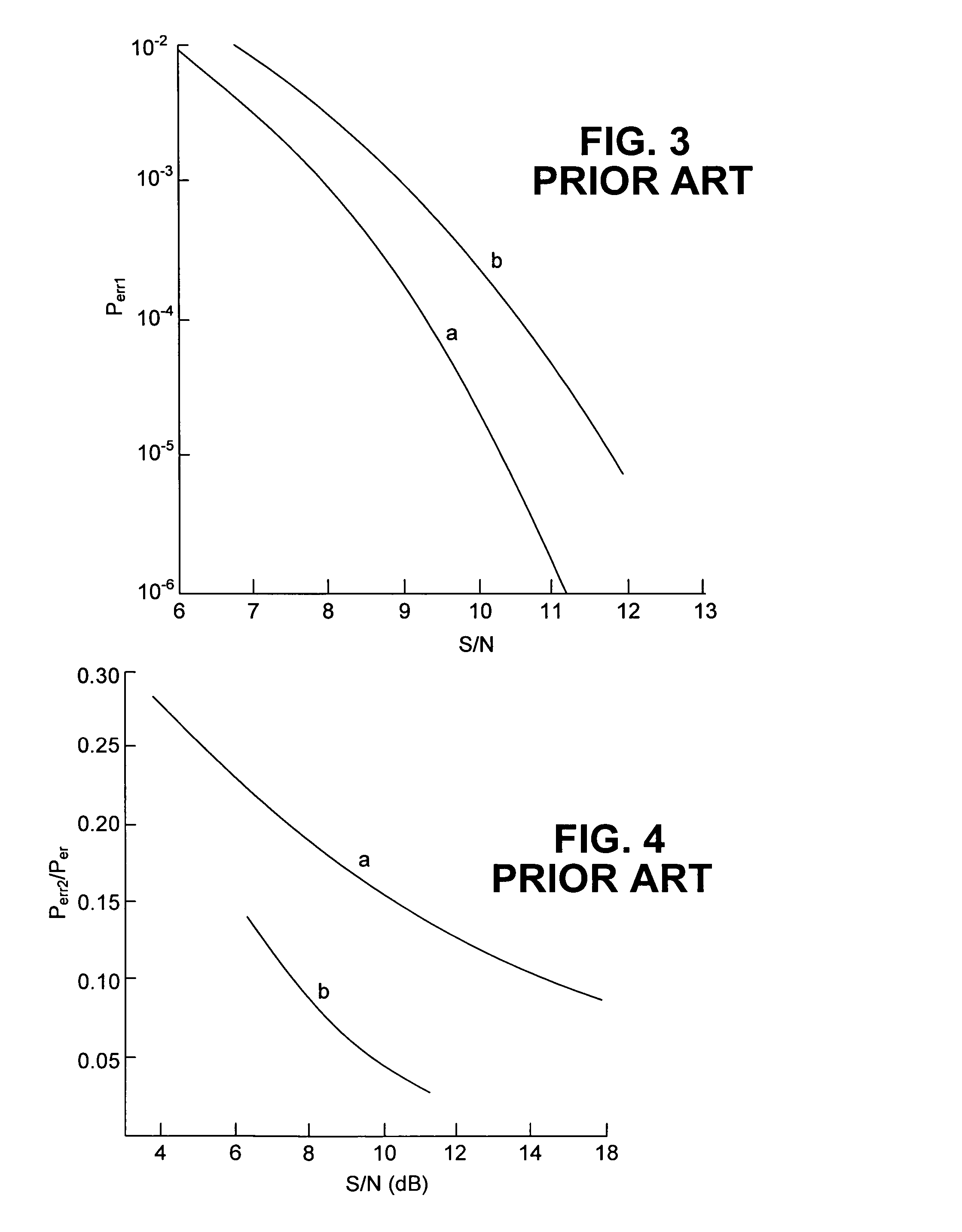
The delay setting of an optical delay line interferometer (DLI) used to decode differentially encoded phase shift keyed signals (DPSK or DQPSK) is controlled using a control signal representative of the ratio Perr2 / Perr1 of the rate of occurrence of double errors and the rate of occurrence of errors. The ratio Perr2 / Perr1, as the delay setting of the DLI is varied, exhibits a characteristic W-shaped structure consisting of a local maximum at the optimum value and two minima adjacent to the maximum, one on each side of it. This structure is present over a wide range of signal to noise ratio and residual dispersion.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
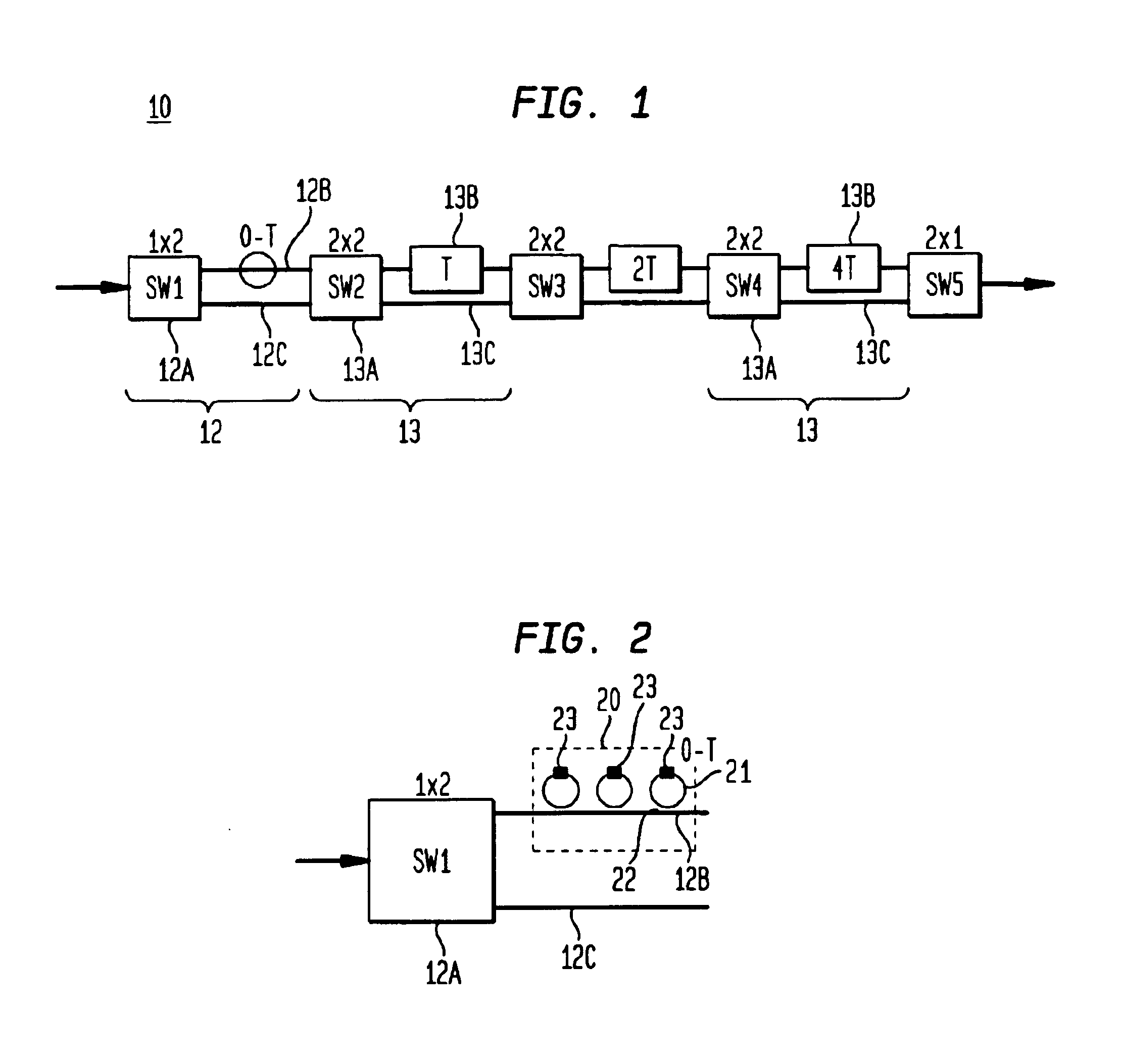
Compact optical delay lines
InactiveUS6956998B2High magnitudeIncrease the number ofTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCouplingWaveguide
The present invention provides an optical delay, for example, an optical delay line, having at least first and second waveguides, each waveguide having a first end at a first side of the device and a second end at a second side of the device, wherein the second end of the first waveguide is coupled to the second end of the second waveguide at a reflective coupling region, which reverts the direction of propagation of radiation in the device from propagating towards the second side of the device via the first waveguide to propagating towards the first side of the device via the second waveguide.
Owner:MAIN STREET VENTURES
Interference optical switch and variable optical attenuator
ActiveUS20060072866A1High extinction ratioLarge fabrication toleranceCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhase differenceOptical attenuator
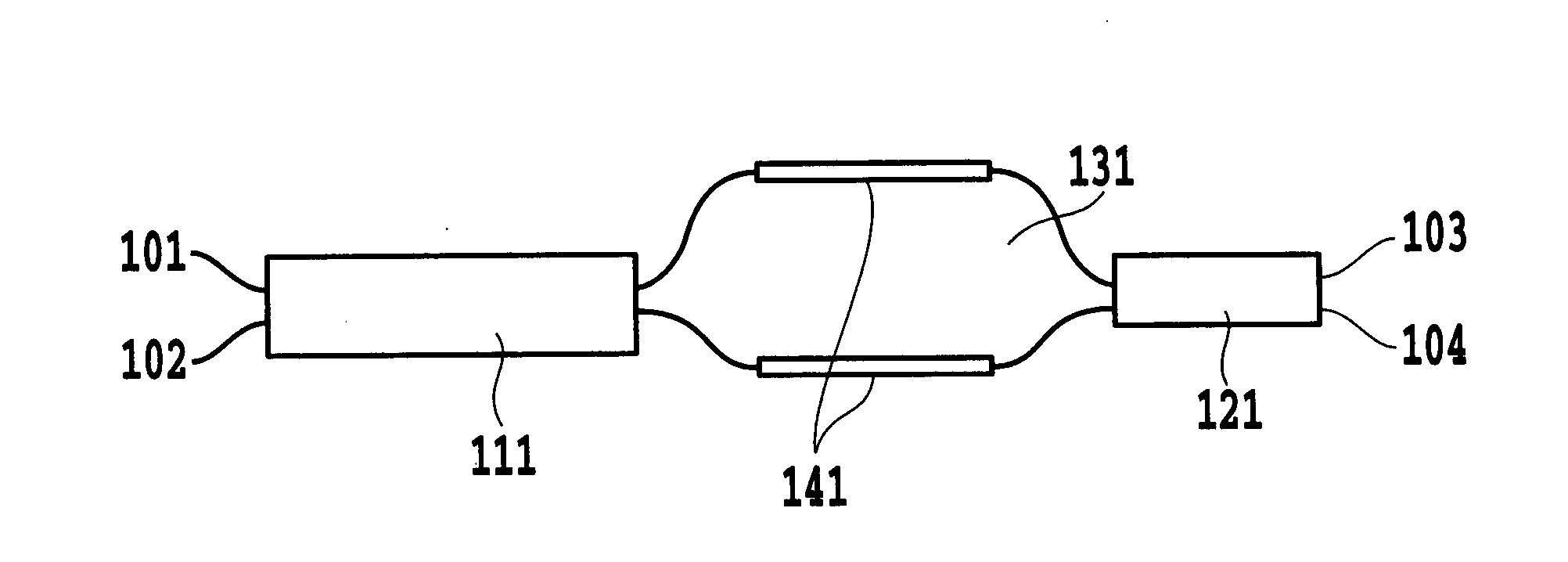
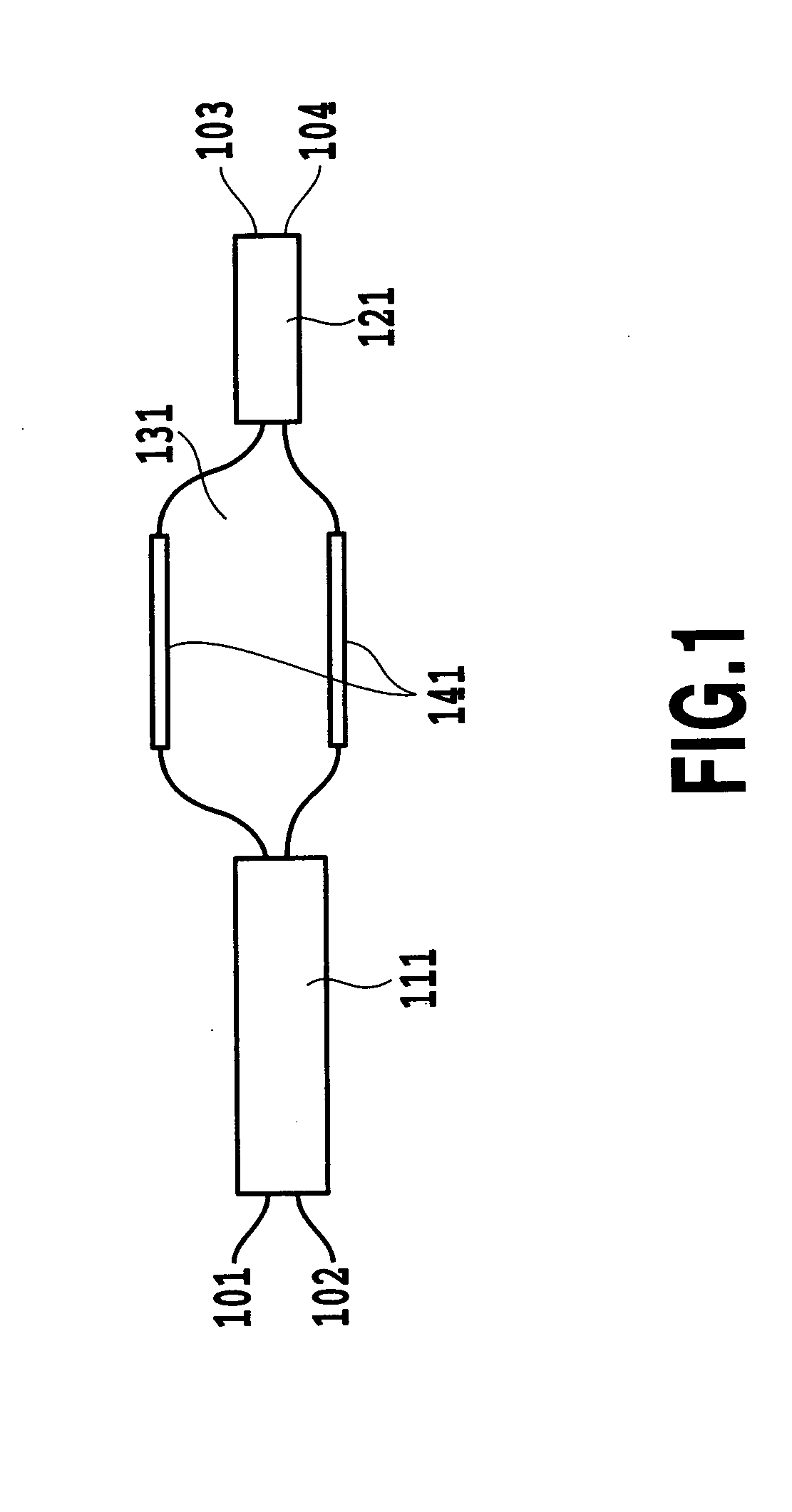
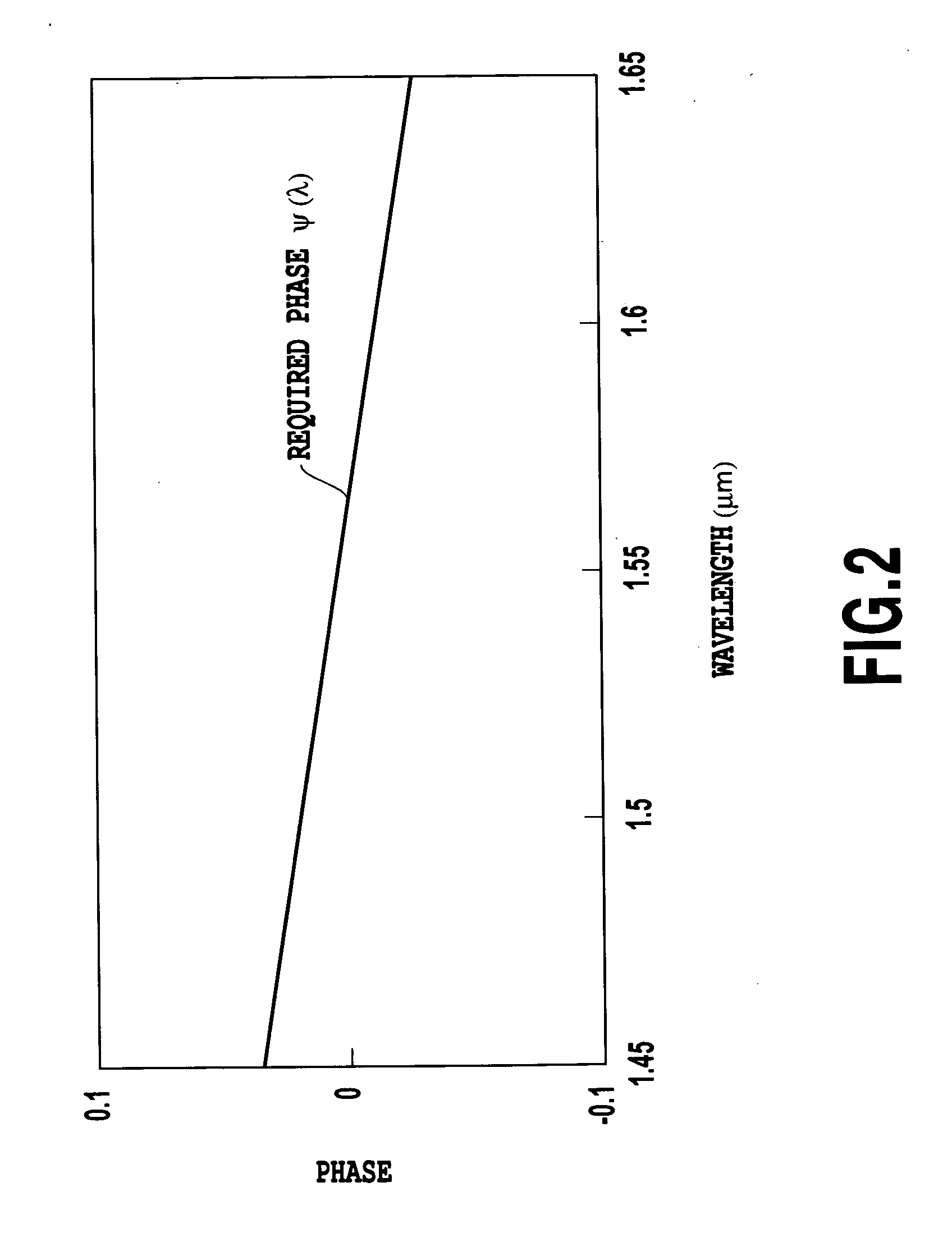
The present invention discloses an interferometer optical switch that can carry out switching over a broad band and has a high extinction ratio and large fabrication tolerance. The interferometer optical switch employs a phase generating coupler, the phase difference of the output of which has wavelength dependence, as at least one of the optical multi / demultiplexing device included in the interferometer optical switch. A wavelength insensitive interferometer optical switch is implemented by making the sum 2π{φ1(λ)+φΔL(λ)+φ2(λ)} constant regardless of the wavelength, where φ1(λ) is the phase produced by the first optical multi / demultiplexing device, 2πφΔL(λ) is the phase difference of the optical delay line with an optical path length difference of ΔL, and 2πφ2(λ) is the phase produced by the second optical multi / demultiplexing device.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
RF lightwave coding system for radar pulse compression
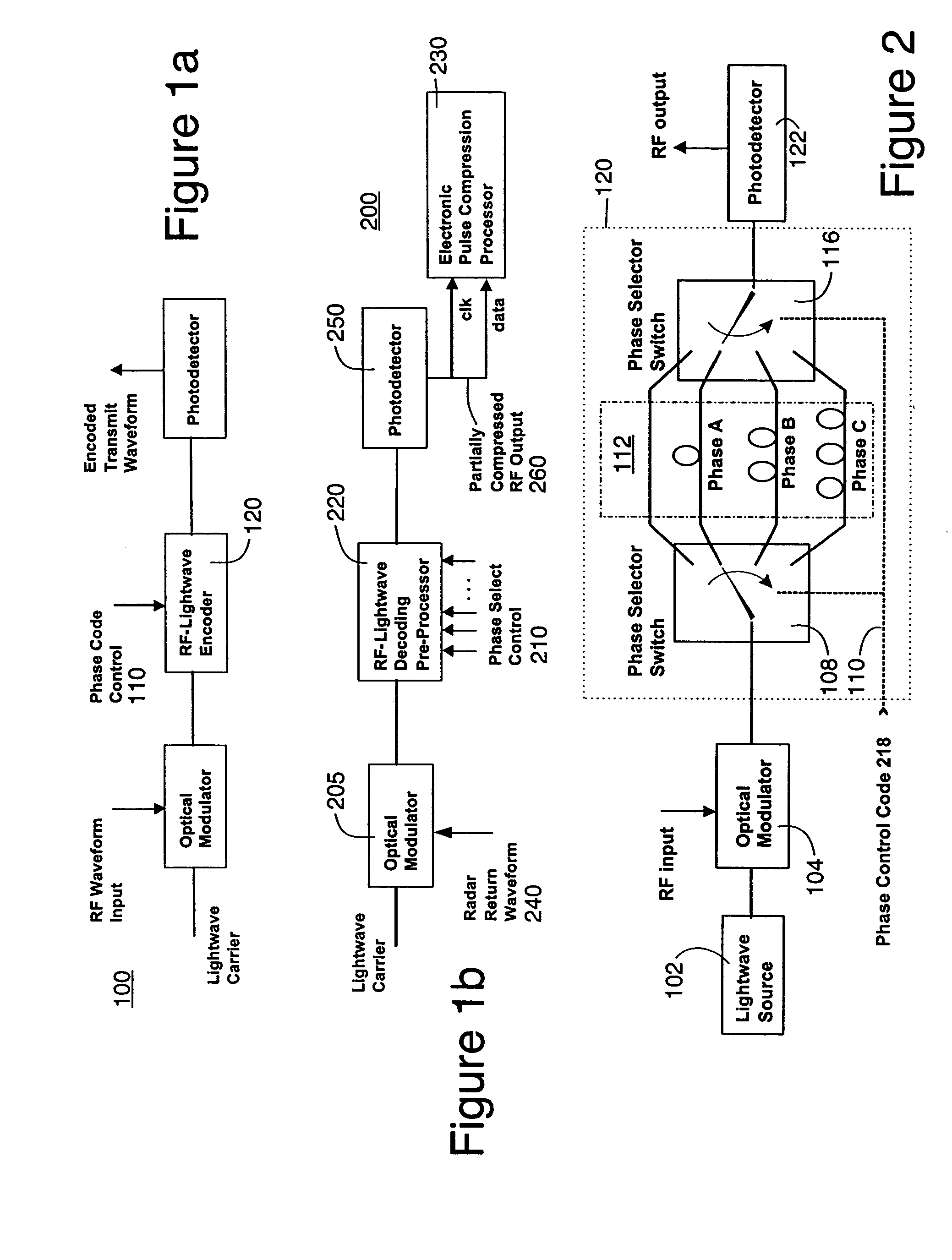
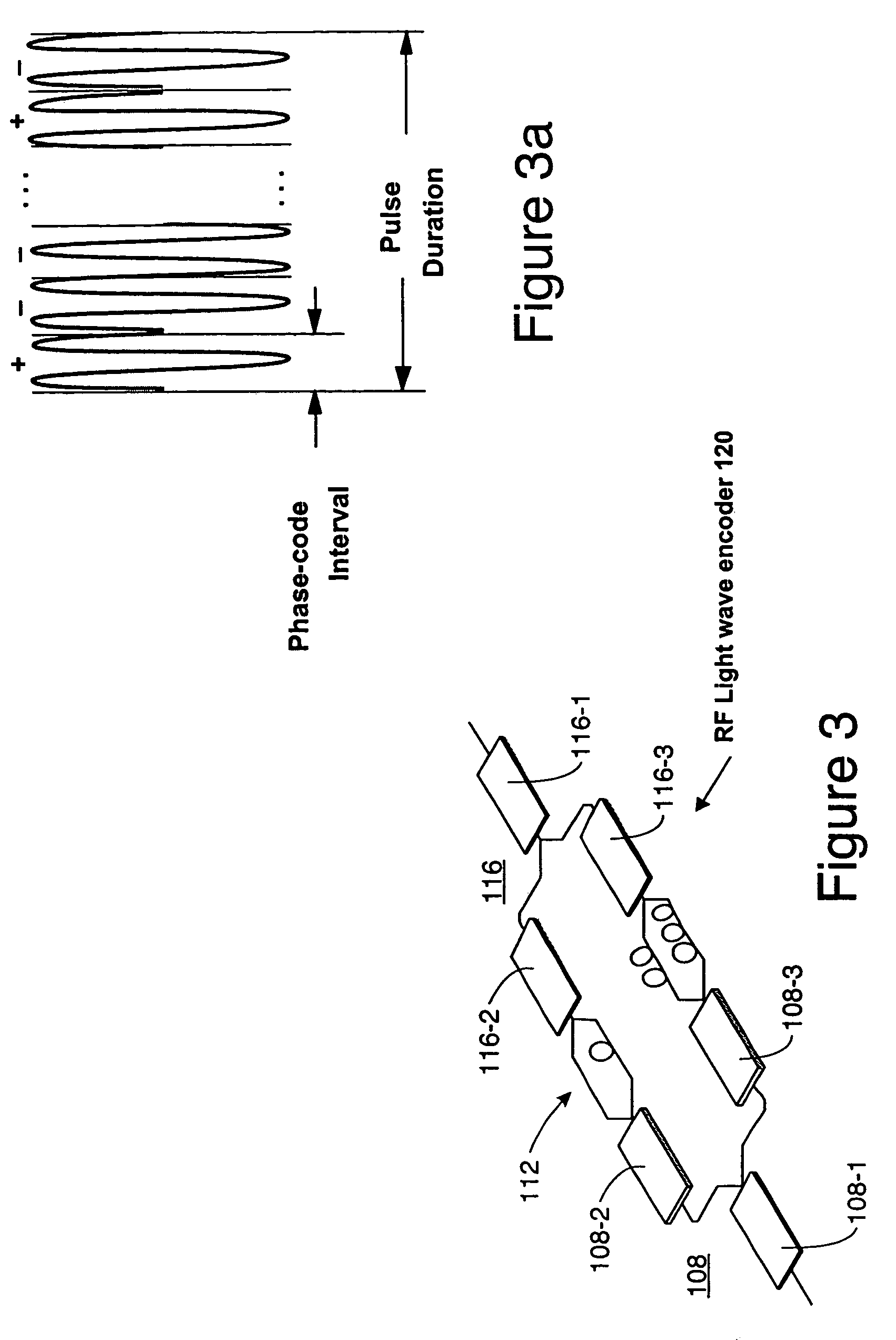
InactiveUS7053814B2Shorter compressed pulsesBig ratioRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase shiftedRadar
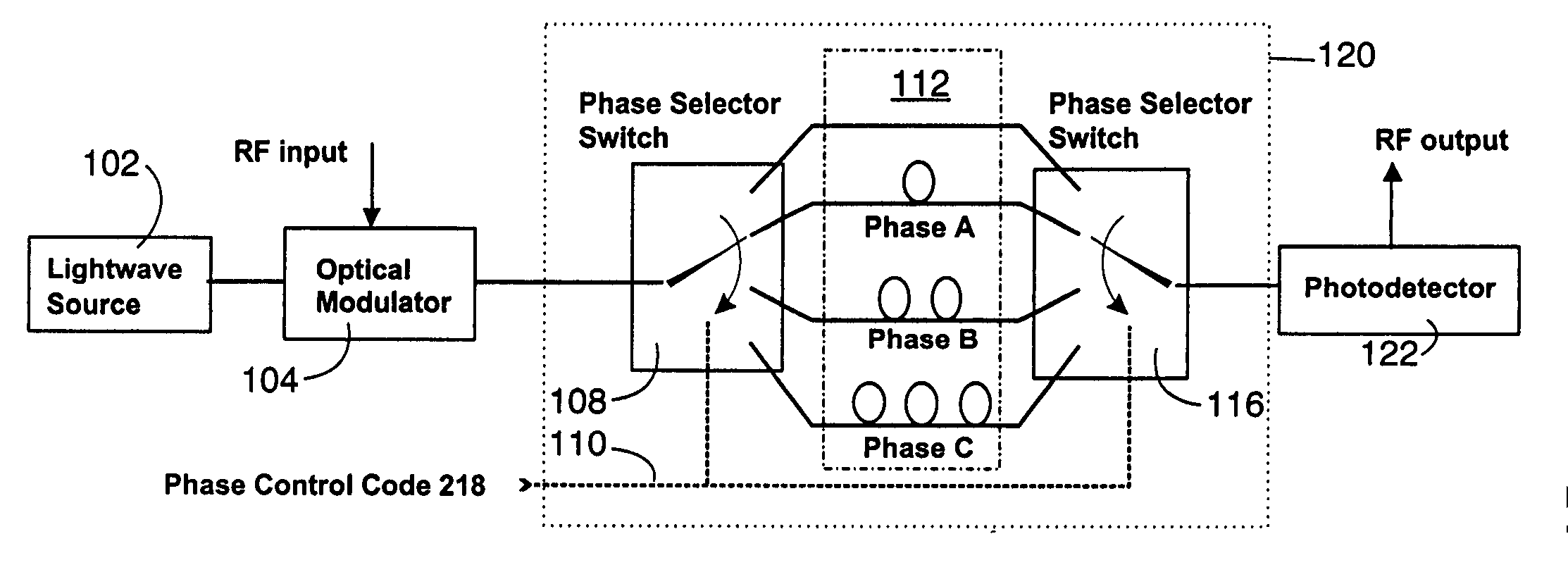
An apparatus for preparing a RF radar transmit waveform and for decoding RF return waveforms comprising: a RF-lightwave encoder and a decoding preprocessor to phase-encode the RF radar transmit waveform and partially decode the return signal, the encoder including switched optical delay lines for producing desired RF phase shifts, and the decoding preprocessor including a tapped optical delay line and optical delay lines that counteract the delays imposed by the delay lines of the encoder, wherein the RF-lightwave encoder and the decoders allow shorter compressed pulses and larger pulse-compression ratios to be achieved than can be obtained using conventional electronic approaches. Wideband transmit waveforms can be generated due to the use of the switched optical delay lines and, unlike prior art approaches, is not restricted to single-frequency waveforms. The taps can be weighted to accomplish objectives such as reduction of side lobes in the compressed pulse.
Owner:HRL LAB
Optical multi/demultiplexing circuit equipped with phase generating device
InactiveUS7085438B2Effect is exertedCoupling light guidesOptical multiplexMultiplexingPhase difference
An optical multi / demultiplexing circuit includes at least one phase generating optical coupler and an optical delay line coupled to the phase generating optical coupler. The phase generating optical coupler consists of at least one input and at least two outputs. At least one of the phase generating optical coupler has a wavelength dependent or frequency dependent output phase difference in the passband of the circuit so that it can change the transmittance characteristics of the optical multi / demultiplexing circuit.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
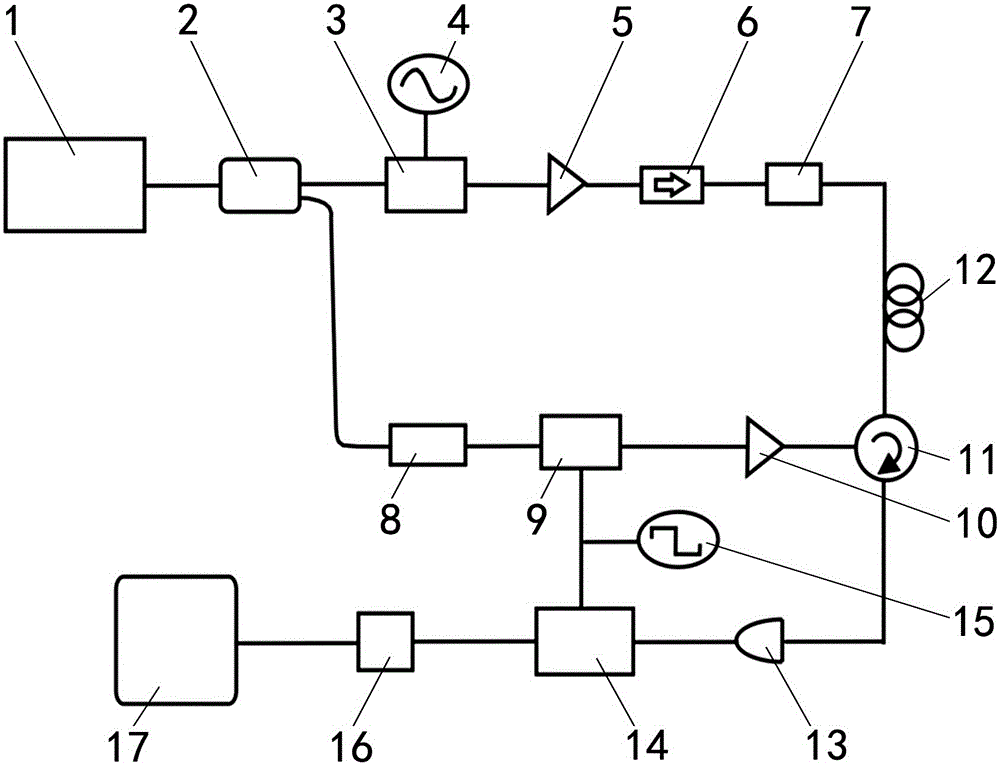
Passive mode-locking fiber laser delay feedback chaotization system based on graphene
InactiveCN101944990AImprove competitivenessGood development prospectsLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsMode locked fiber laserFiber coupler
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Real-time imaging optical coherent chromatography skin diagnostic device
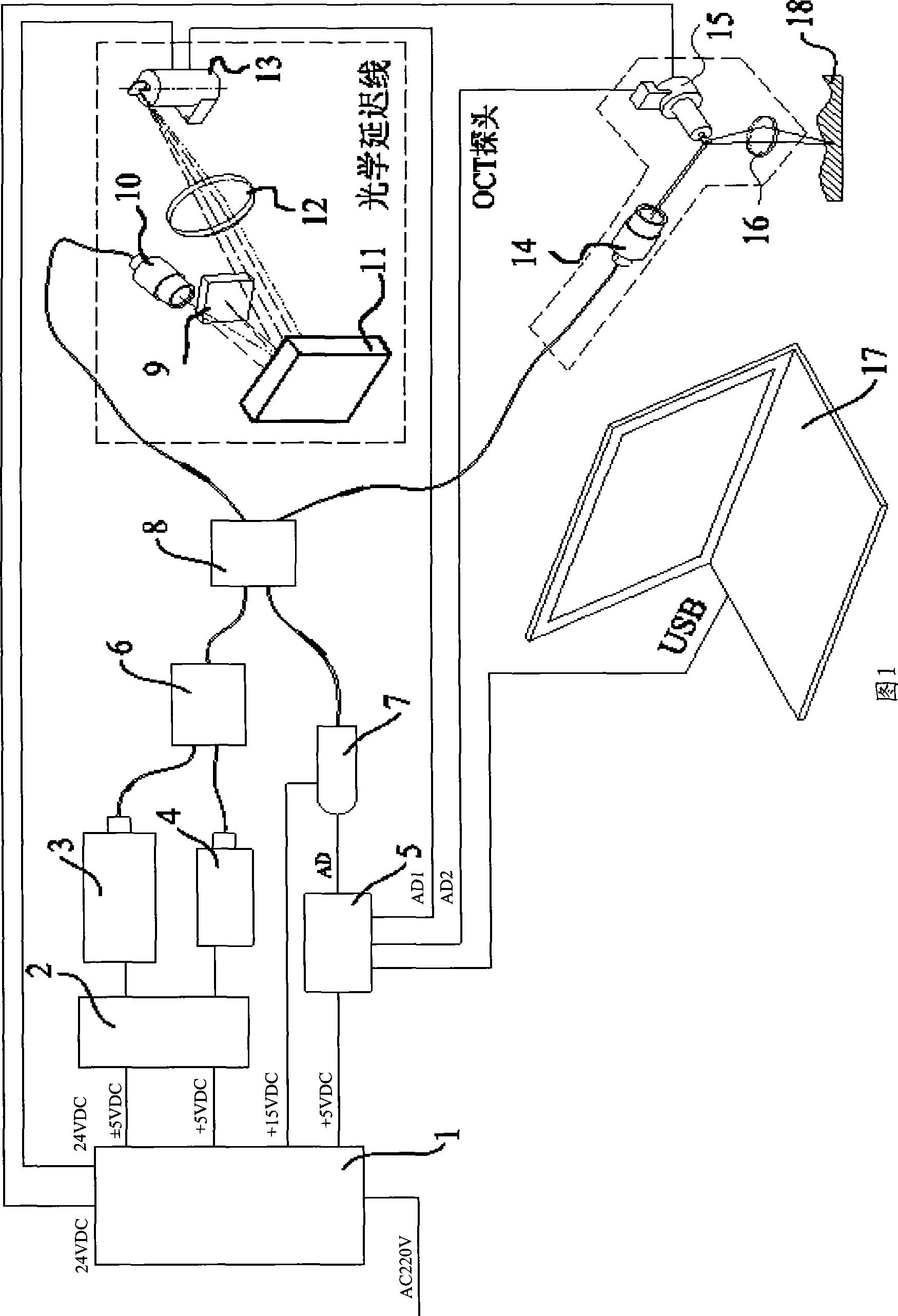
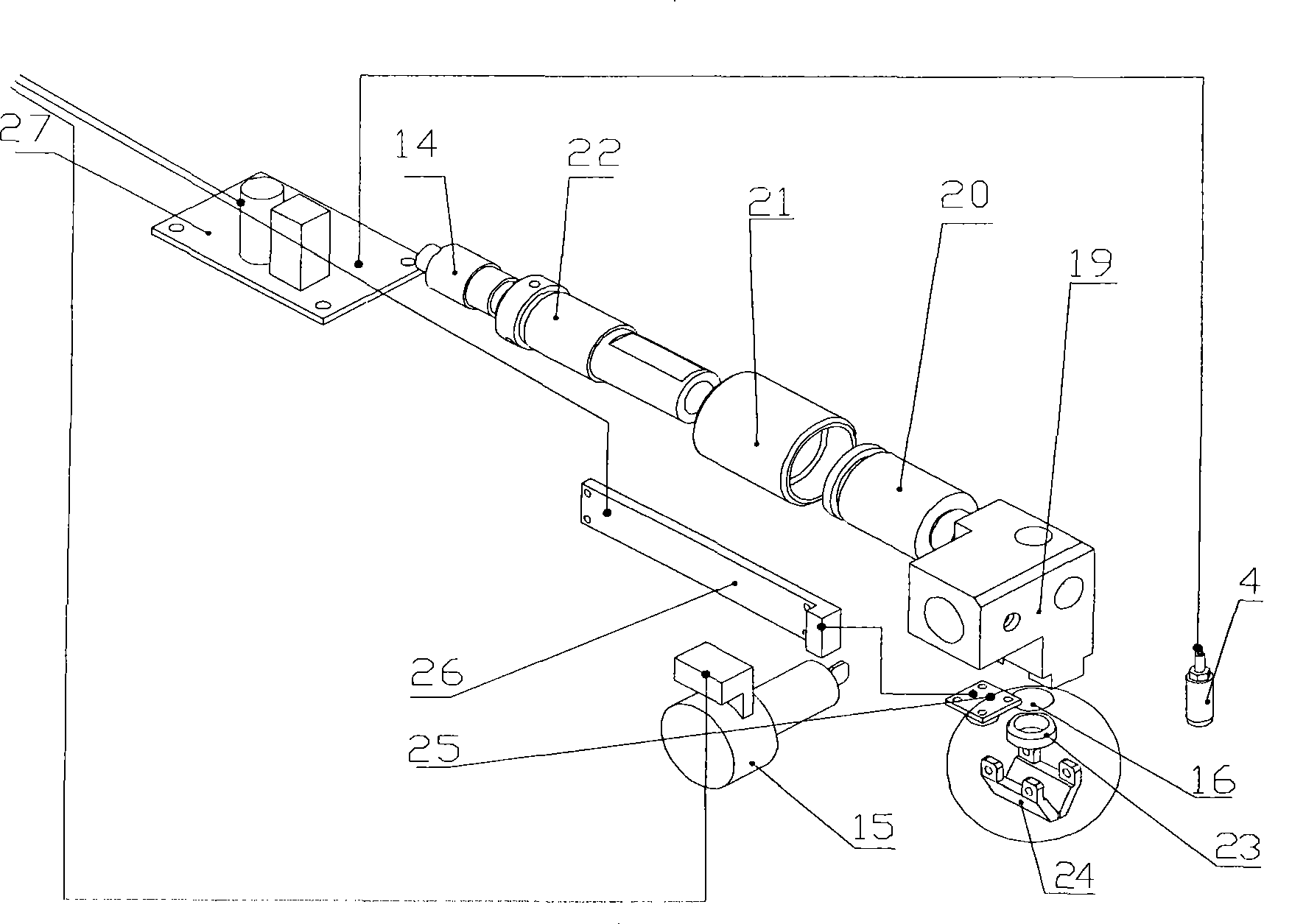
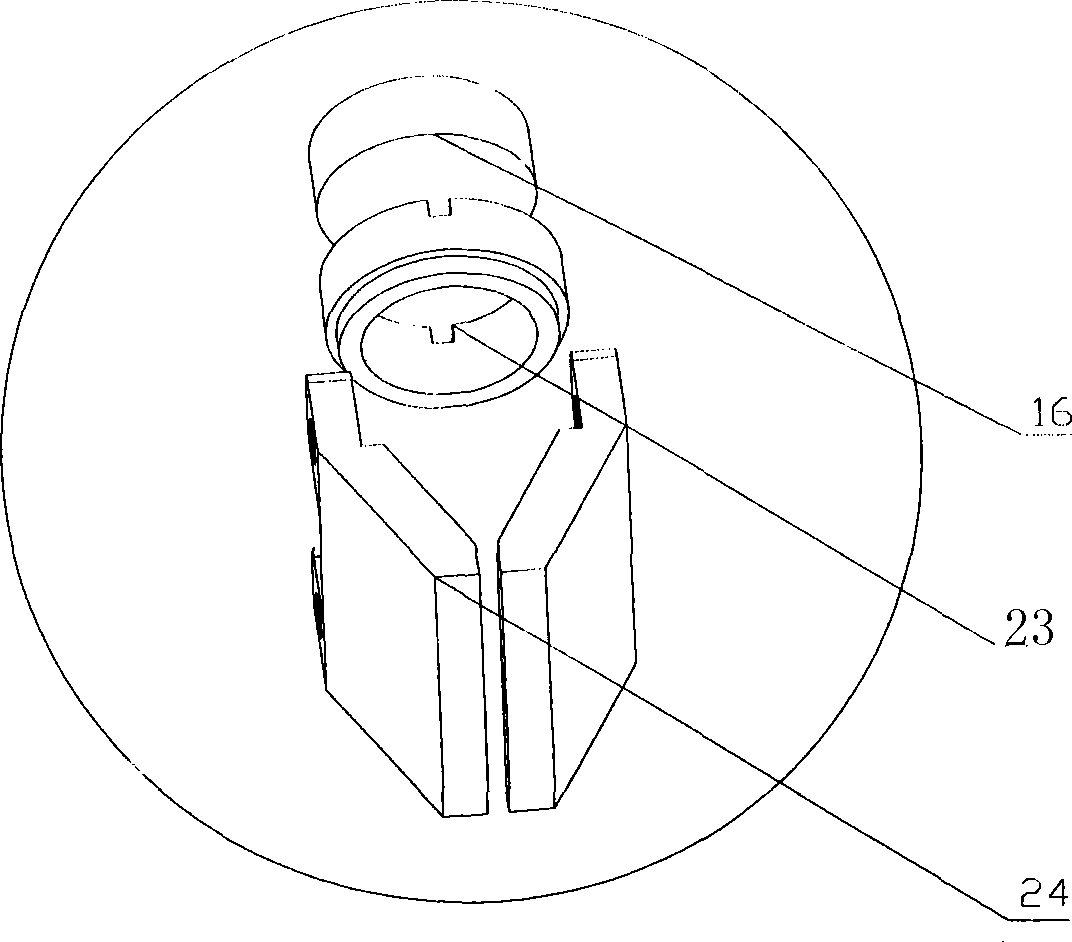
InactiveCN101458212AQuick scanHigh-resolutionPhase-affecting property measurementsRapid imagingDisplay device
The invention discloses real-time imaging skin diagnosis equipment by optical coherence tomography, and belongs to the field of optical imaging equipment. The equipment comprises a power supply, a light source control circuit, a light source, an indicating light source, a first optical fiber coupler, a second optical fiber coupler, an OCT probe, an optical delay line, a photo detector, a signal processing and control circuit, and a computation processing and display device. The imaging equipment takes the optical coherence tomography (OCT probe) as a core, processes signals rapidly by the signal processing and control circuit, and improves the imaging speed and image resolution by cooperating with the computation processing and display device; designs of a wideband light source and a duckbill-shaped probe applicable to skin scanning cause the equipment to be applicable to scanning human skin, and real-time and rapid imaging can be realized by cooperation of the signal processing and control circuit with the computation processing and display device.
Owner:BEIJING NEWRAYSING LASER TECH
Dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent chromatographic imaging
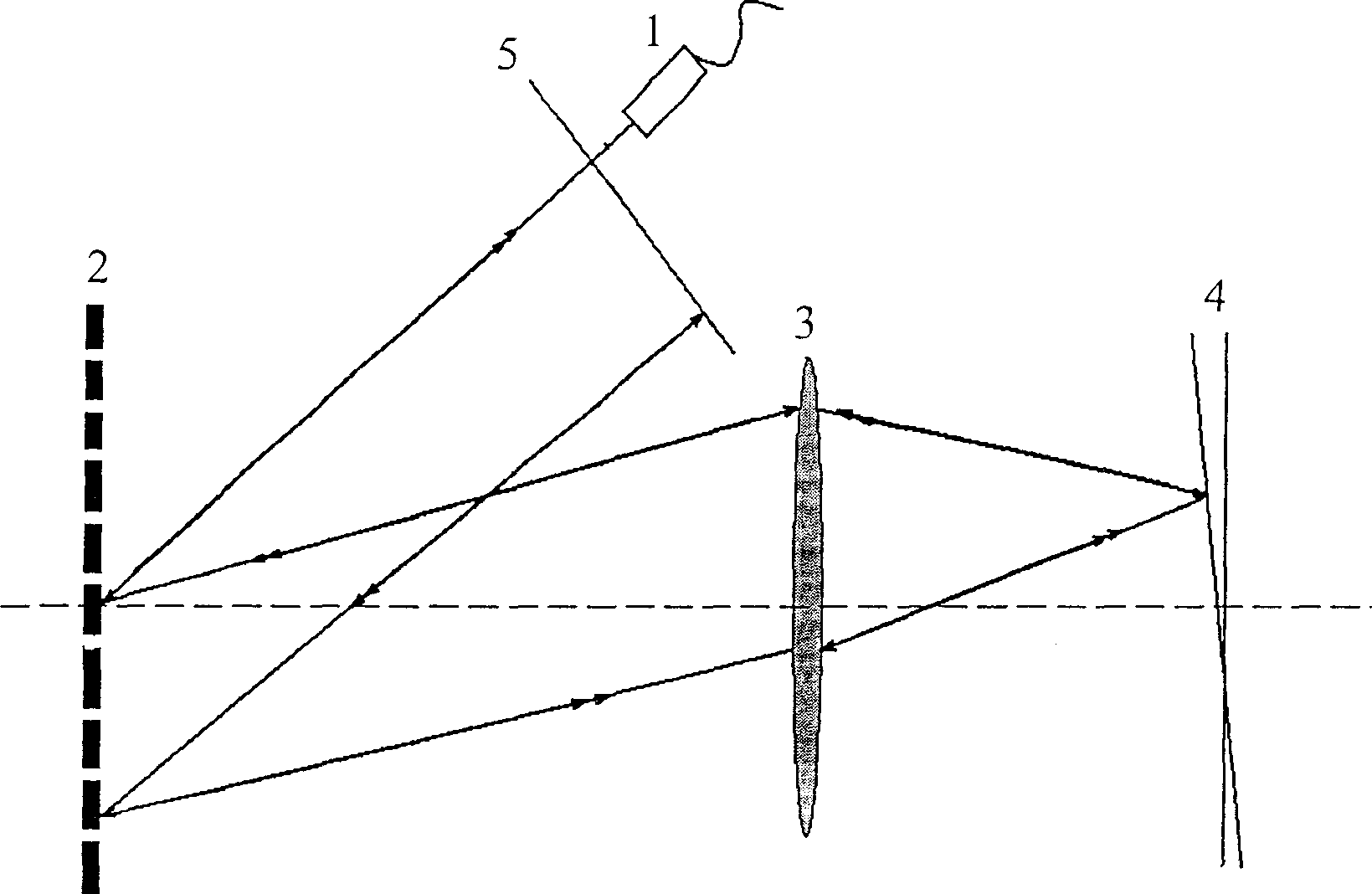
InactiveCN1887220ALarge dispersion adjustment rangeWide Compensation Spectral RangeSurgeryMaterial analysis by optical meansGratingPhase retardation
The present invention discloses dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent tomographic imaging (OCT). The system has one increased blazed grating parallelly set with the original blazed grating in a single grating fast scanning optical delay line, and thus one independently regulated variable of interval between two blazed gratings and capacity of generating group velocity dispersion and third-order dispersion in great varying range and arbitrary sign combination, so that the OCT system may obtain precise matching between the dispersion of the reference arm and the dispersion of the sample arm and longitudinal resolution approaching the theoretical calculated value. The double grating system has wide dispersion regulating range, wide compensation spectrum range and small residual dispersion other than the capacity of independently controlling phase delay and group delay, and possesses three functions of depth scan, phase modulation and dispersion compensation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
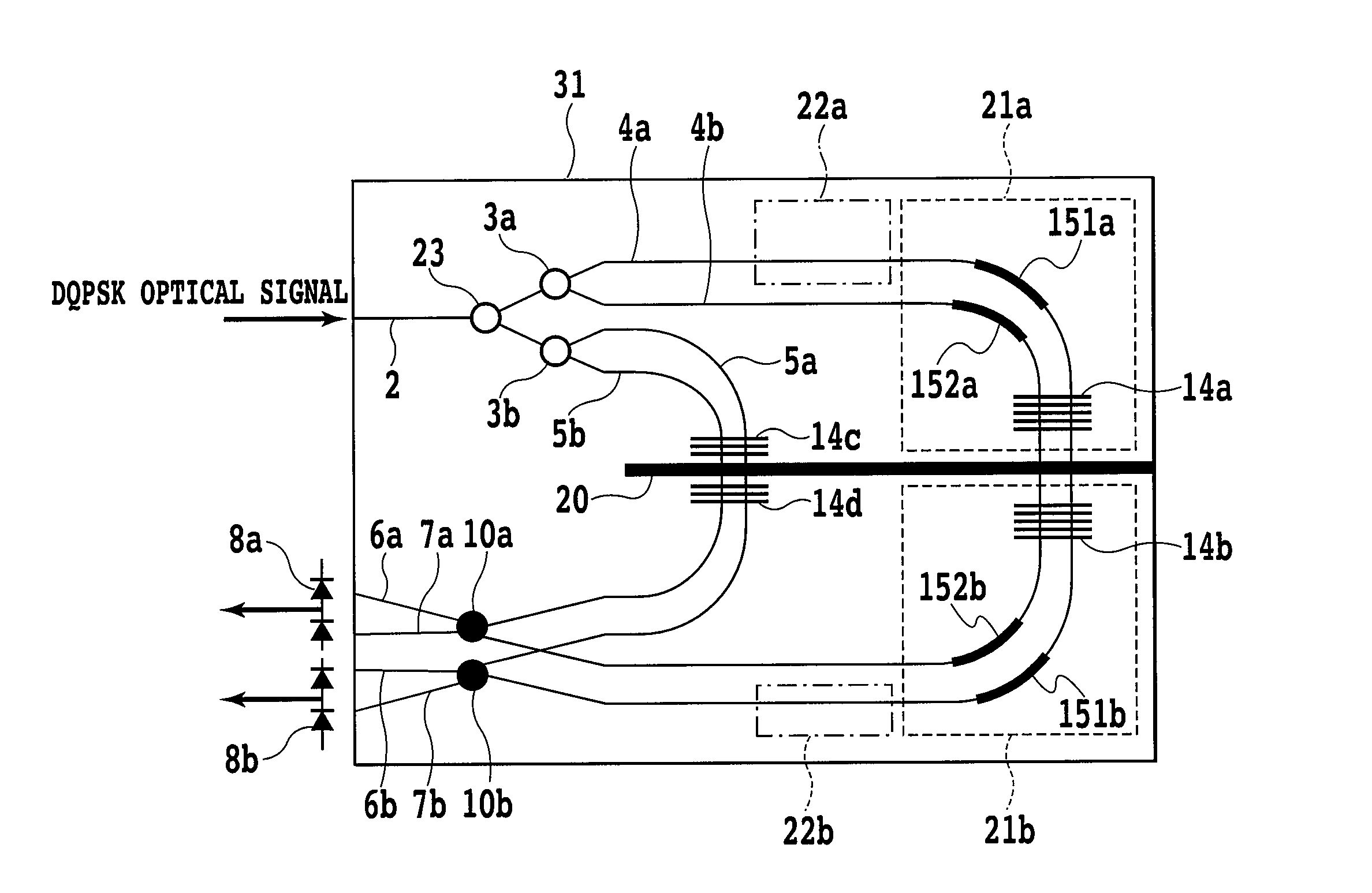
Optical delay line interferometer
ActiveUS7899279B2Eliminate dependenceSimple configurationLight demodulationElectromagnetic receiversDifferential phasePolarization coupling
A demodulator is provided for a multilevel differential phase shift keyed signal, capable of eliminating polarization dependence due to birefringence and polarization coupling-induced light resulting from a waveguide structure, and also, polarization dependence due to dynamic birefringence produced at the time of driving a variable phase adjuster. The demodulator is configured of an optical delay line interferometer of a waveguide interference type. The S / N ratio of a demodulated signal in the demodulator formed by the optical delay line interferometer can be also improved. Further, both the polarization dependence and the temperature dependence of the optical delay line interferometer can be reduced. The disposition of a polarization converter and groves filled with a temperature compensation material makes it possible to provide a circuit configuration suitable for eliminating the polarization dependence and the temperature dependence of the optical delay line interferometer.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
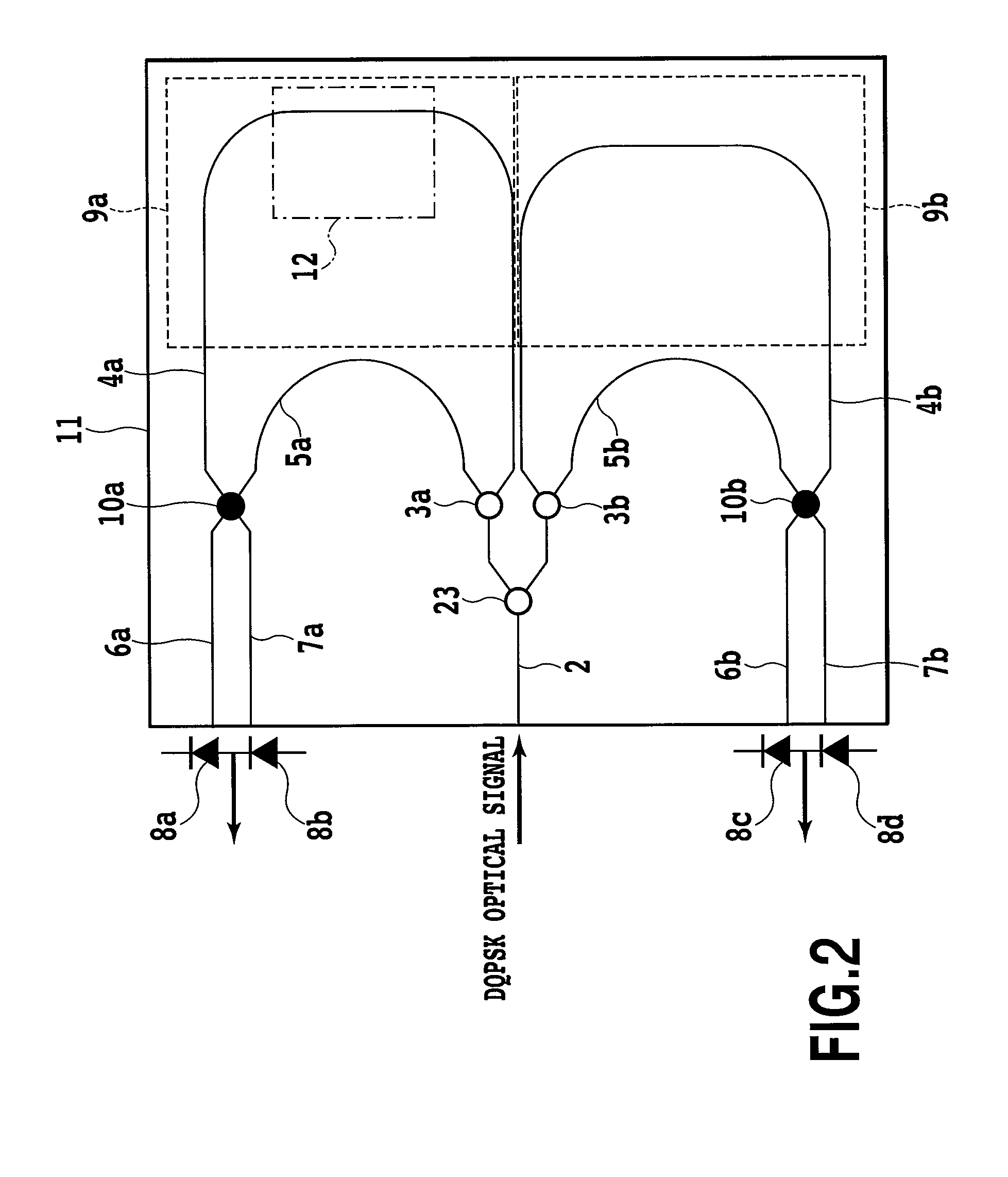
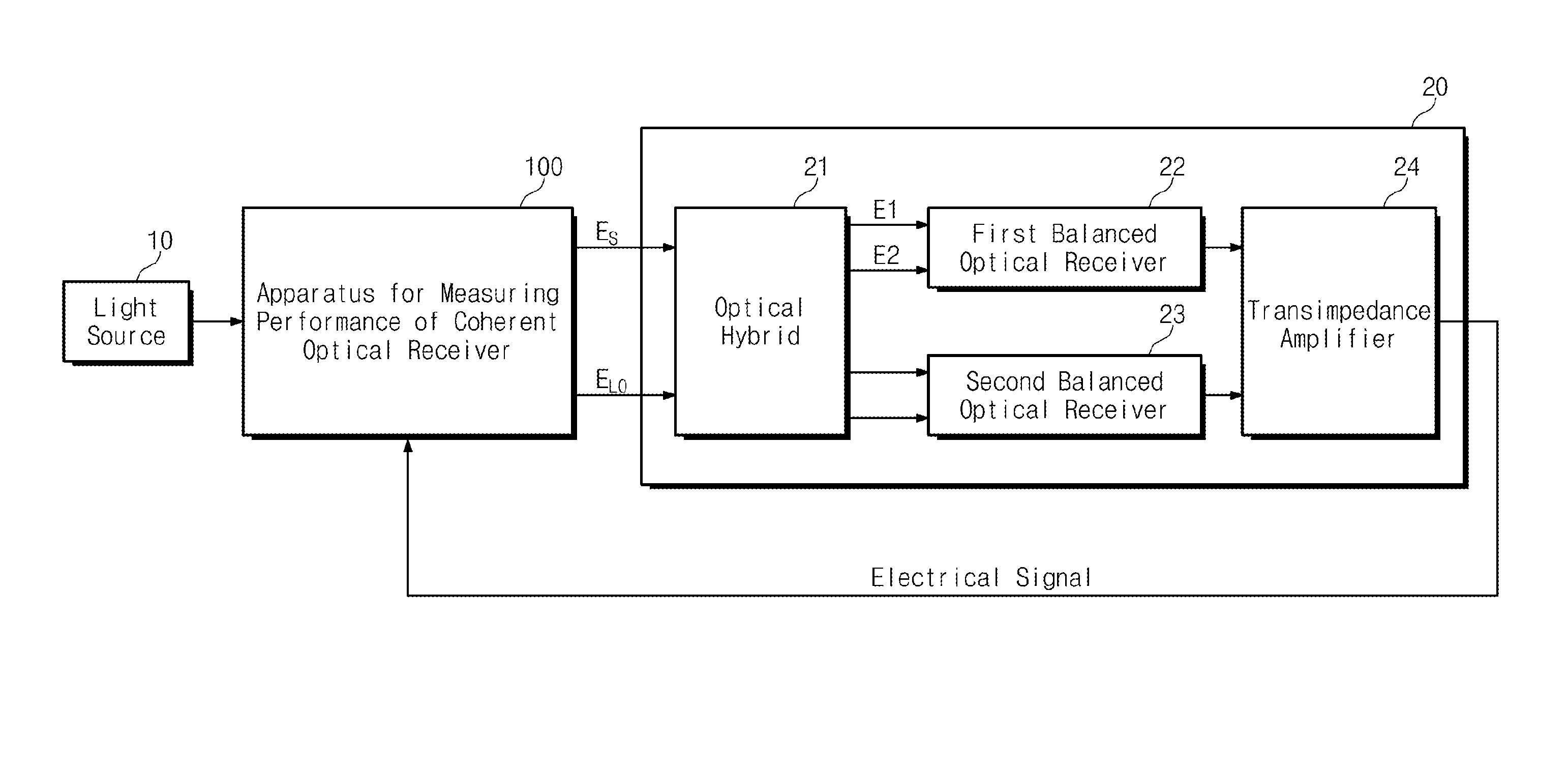
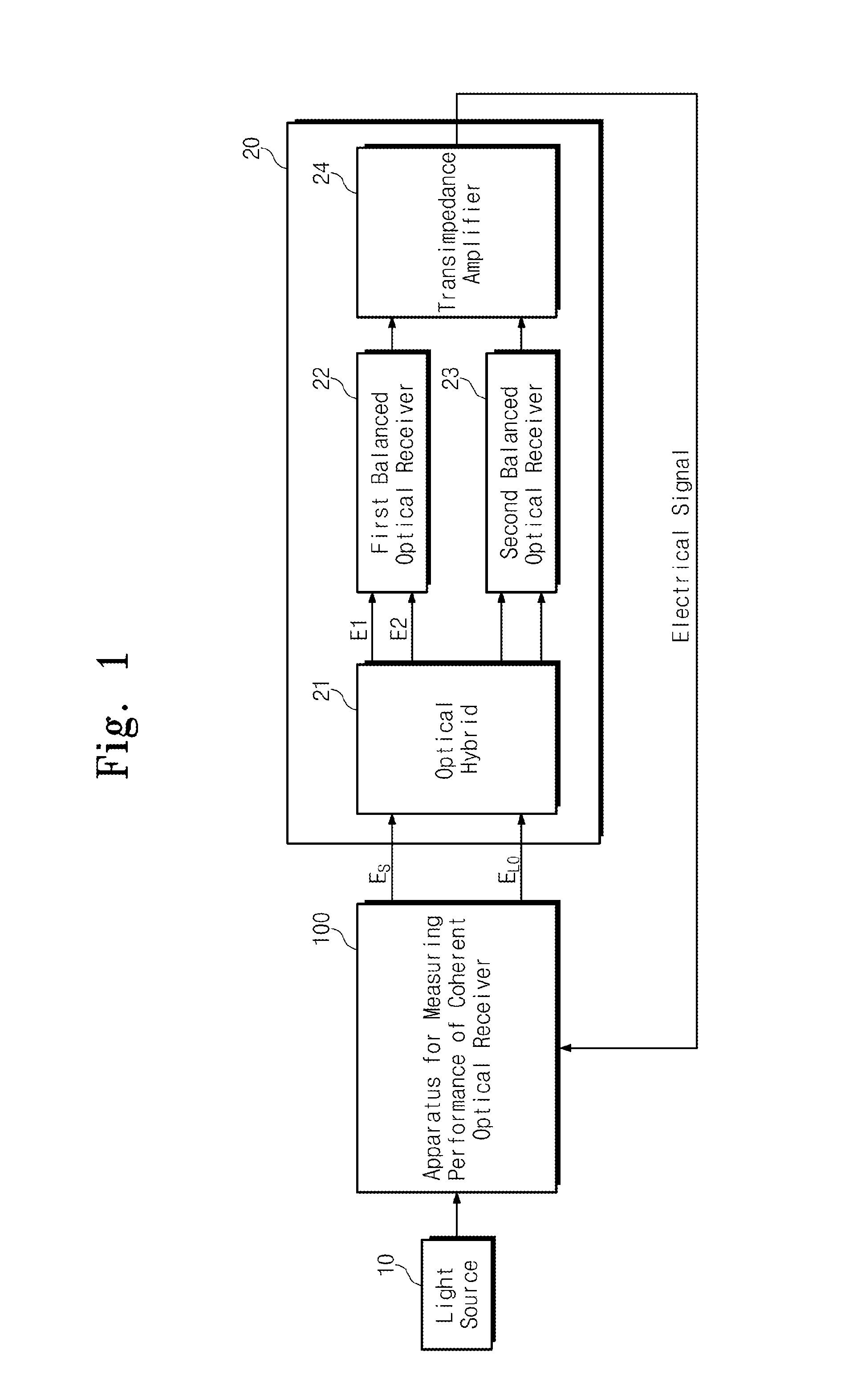
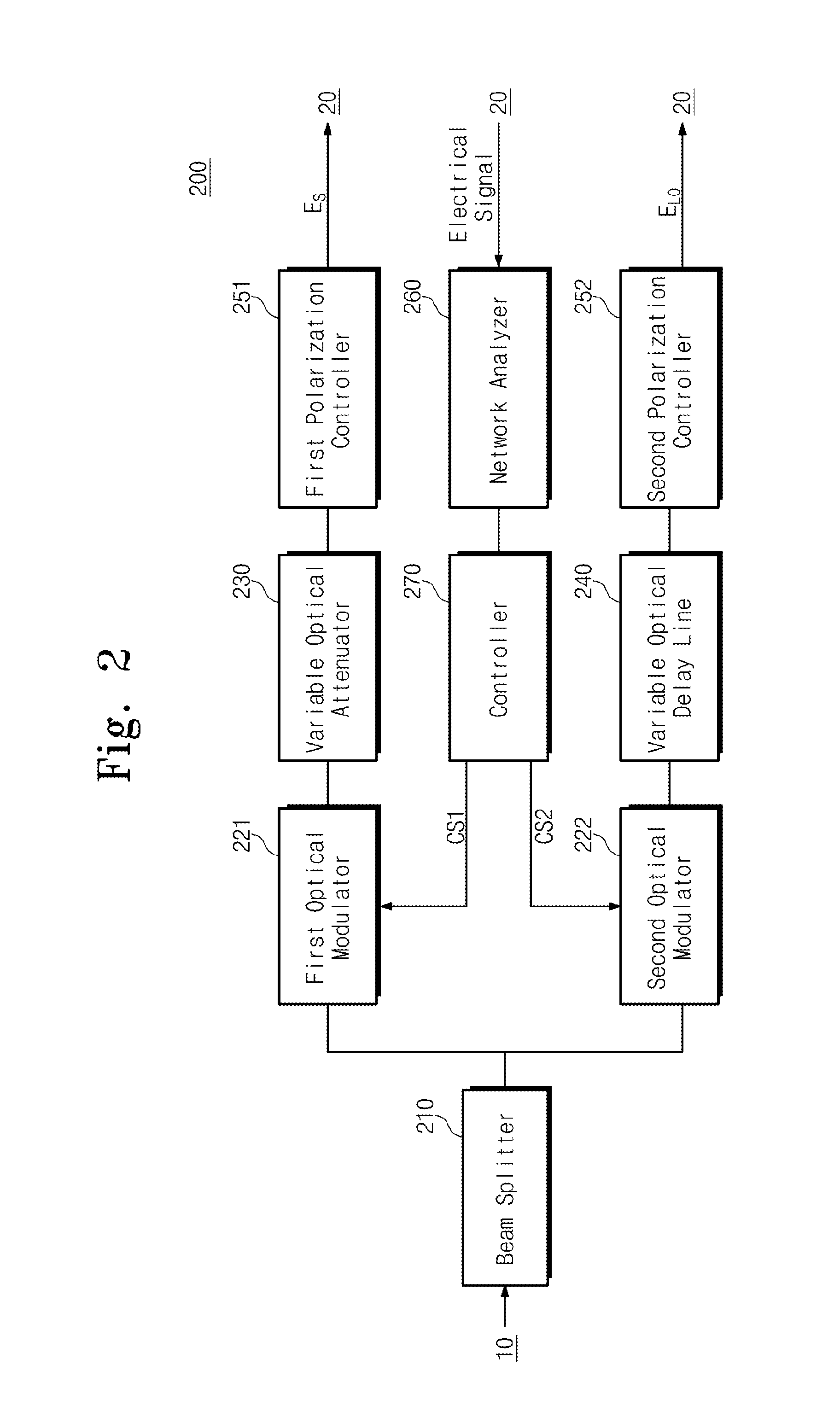
Apparatus for measuring performance of coherent optical receiver
An apparatus for measuring performance of a coherent optical receiver includes a beam splitter splitting light into first and second paths, a first optical modulator modulating the first path light, a variable optical attenuator controlling an optical power of the first optical modulator, a first polarization controller transmitting a signal controlling polarization of an output of the variable optical attenuator to the coherent optical receiver, a second optical modulator modulating the second path light, a variable optical delay line delaying time of an output of the second optical modulator, a second polarization controller transmitting a signal controlling polarization of an output of the variable optical delay line to the coherent optical receiver, a network analyzer measuring performance of the coherent optical receiver and controlling the optical modulators, and a controller transmitting a control signal to the optical modulators.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
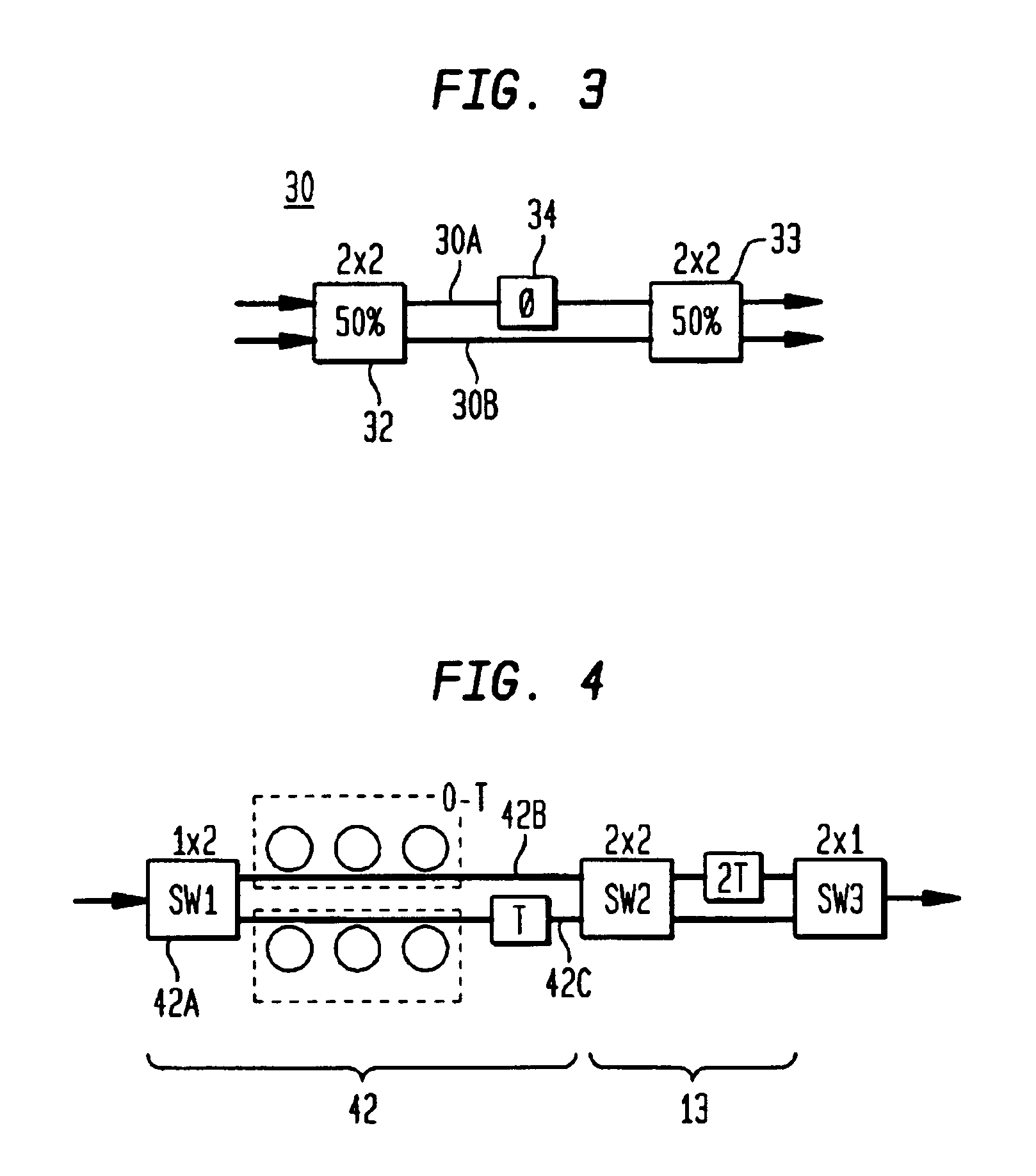
Compact solid-state variable optical delay line with a large continuous tuning range
In accordance with the invention, a variable delay line with continuous tuning comprises an optical path providing at least one continuous delay element coupled to a series of switchable binary fixed delays. The series of switchable delays can be configured to select a delay among a plurality of incremental delays, and the continuous delay can set a continuous delay in a range encompassing the delay increment of the binary series. In a preferred embodiment, the variable delay element comprises a tunable all pass filter (APF) with delay tunable from essentially 0 to a time T and the switchable binary fixed delays form a series (0,T), (0, 2T), (0, 4T), . . . , [0, (2n+1)], where n is an integer ≧0. The switches are preferably Mach-Zehnder switches. In an alternative embodiment, the continuous delay element comprises a suitable pair of APF arms. The path and all components can be fabricated as an integrated planar waveguide (solid state) device.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Mirror-image separation method and system based on group delay wavenumber carrier frequency
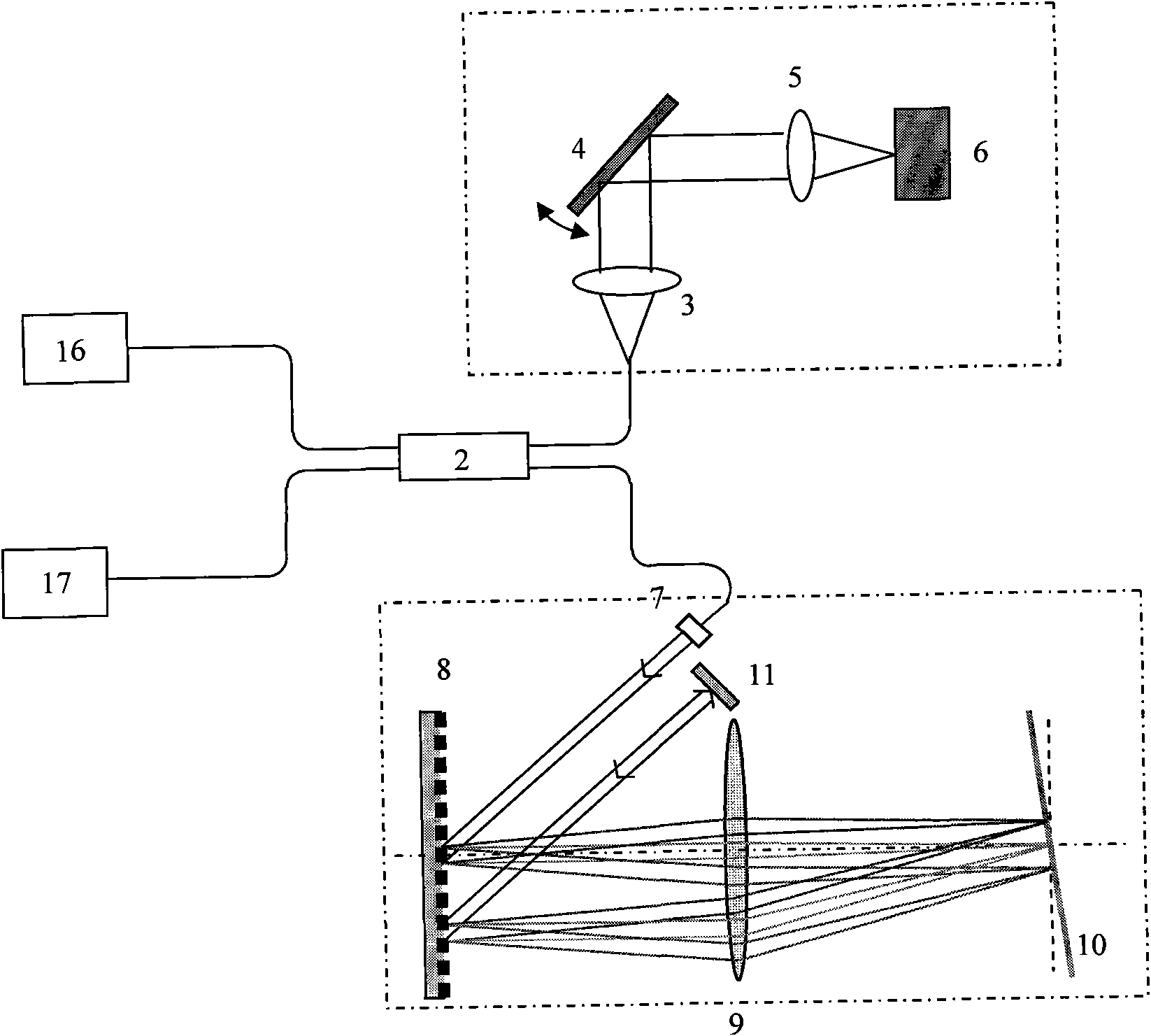
InactiveCN102028454AAchieve separationSensitivity drop is smallPhase-affecting property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical axisOptical pathlength
The invention discloses a mirror-image separation method and a system thereof based on group delay wavenumber carrier frequency; a grating-type optical delay line is arranged in a reference arm of a Fourier domain optical coherence tomography system, based on a specific angle between a reflecting mirror and an optical axis vertical plane in the optical delay line, an additional bit phasor linearly varied along with spectrum wavenumber is introduced in each spectrum component to realize a specific group delay in zero-phase delay of reference light. The reference light after group delay is converged with a sample light to form an interference spectrum of relative carrier frequency. An image reconstruction based on rapid Fourier conversion is executed to the interference spectrum, a conjugation mirror image thereof may deviate from a position when no carrier frequency exists, the equivalent offset is much greater than introduced additional optical path amount in each spectrum component so as to effectively separate a direct current component from the conjugation mirror image in the premise of guaranteeing the minimum flexibility reduction of the interference signal, thereby realizing the full range imaging of the Fourier domain optical coherence tomography. The method of the invention can be applied to a spectrum domain optical coherence tomography system and a sweep frequency optical coherence tomography system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com