Patents
Literature
62 results about "Residual dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
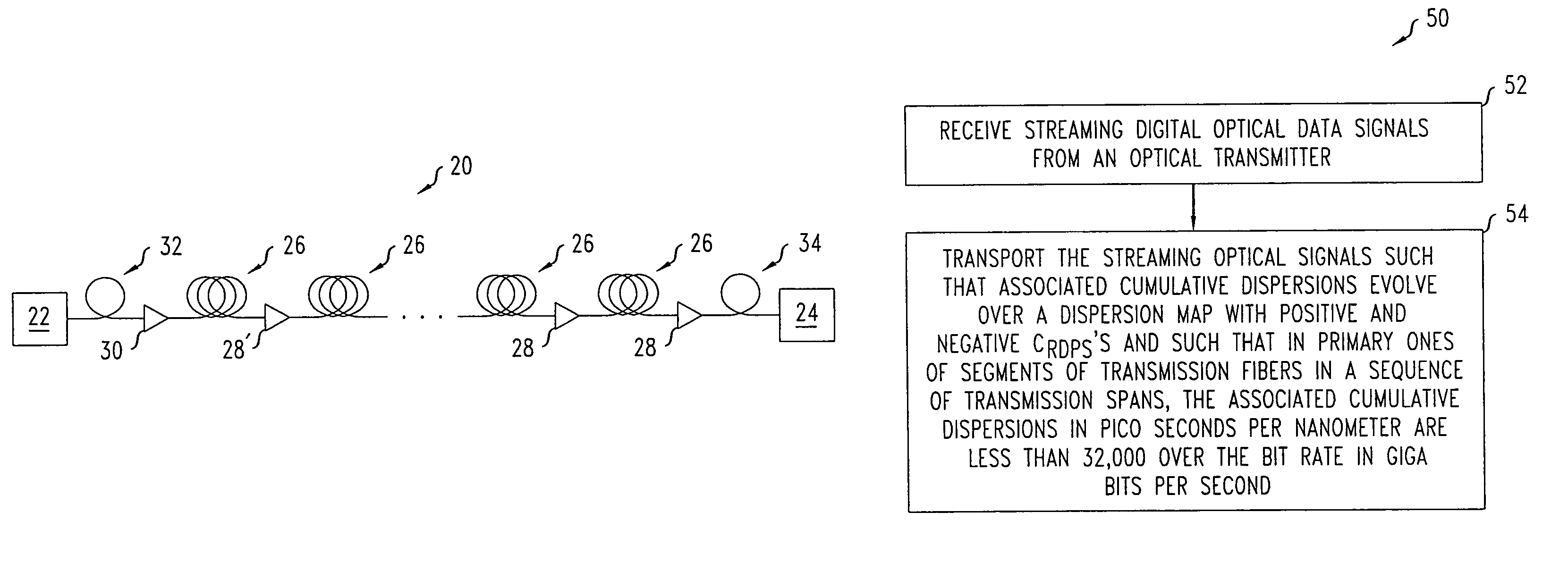
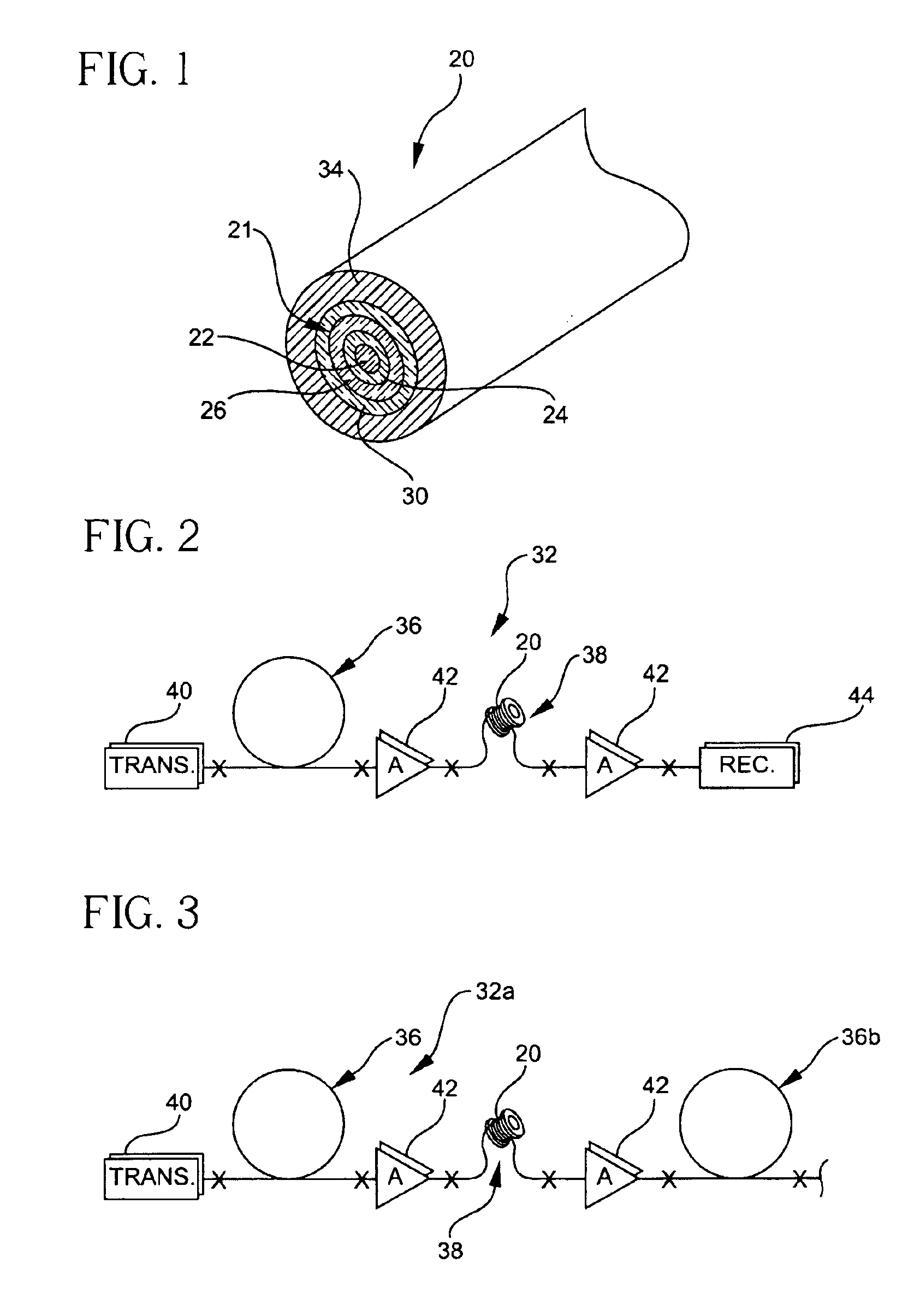
Method of adaptive signal degradation compensation
InactiveUS7099597B2Optimizes receive end pulse shapeMinimizes BER valueElectromagnetic transmittersSignal qualityTransport system
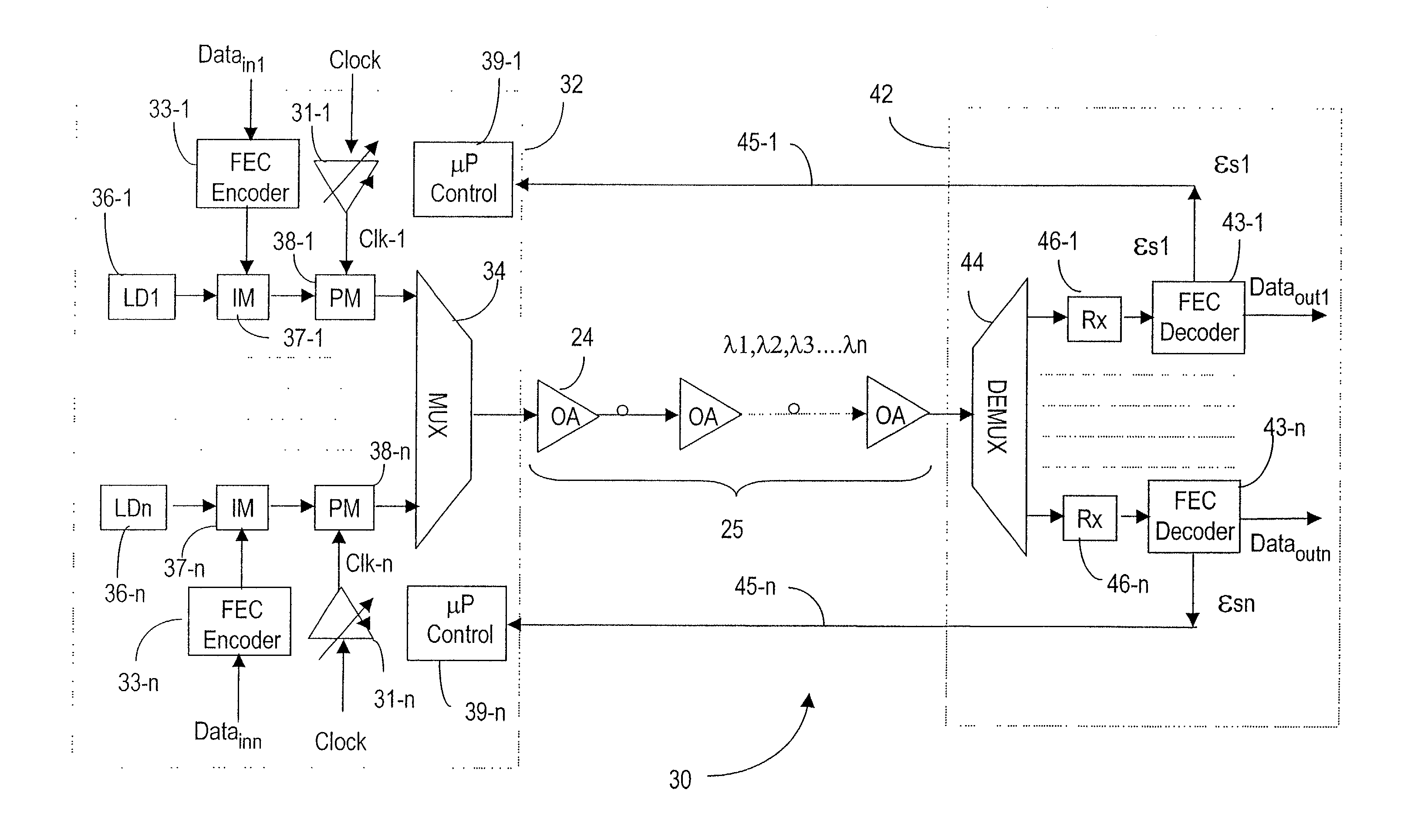
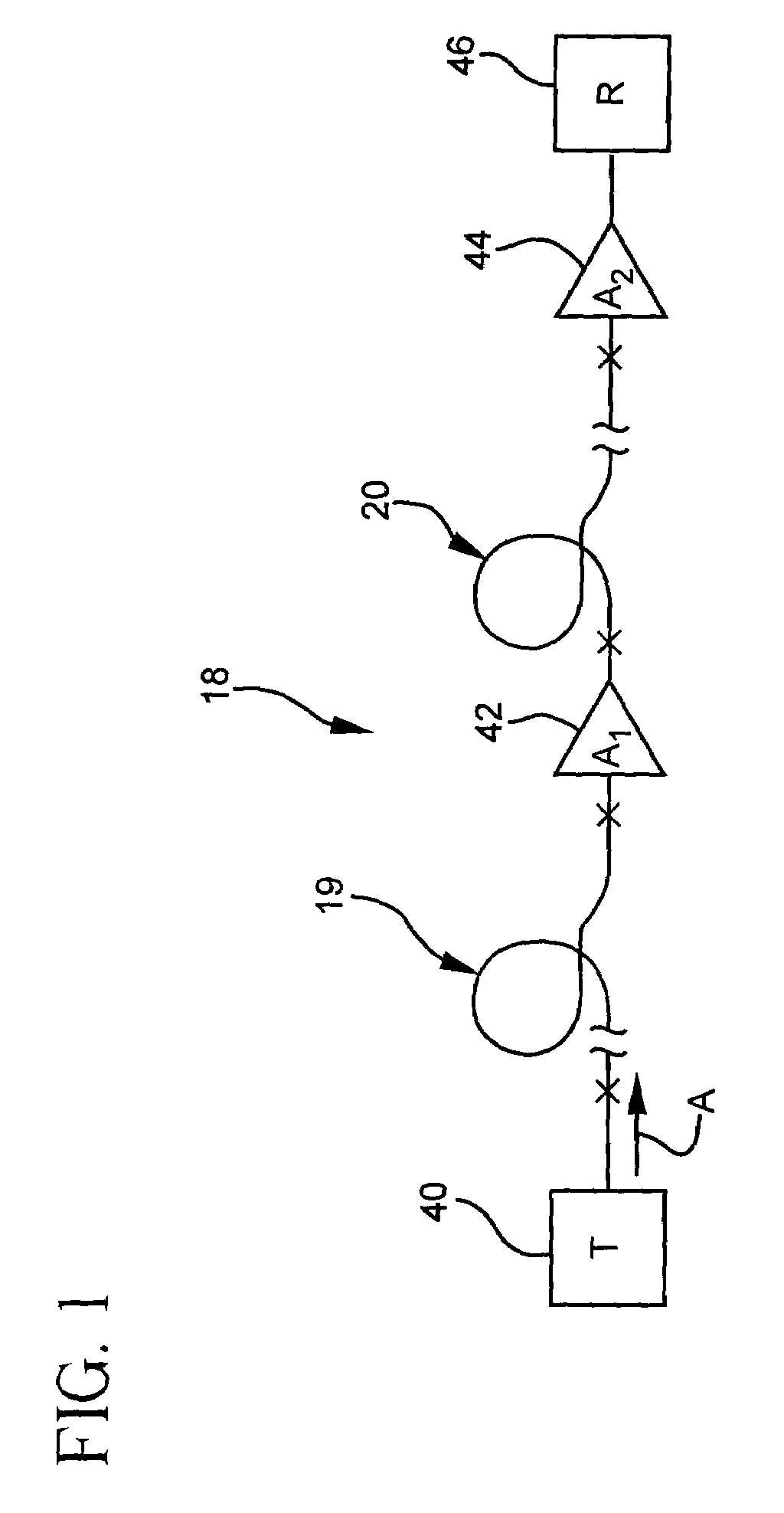
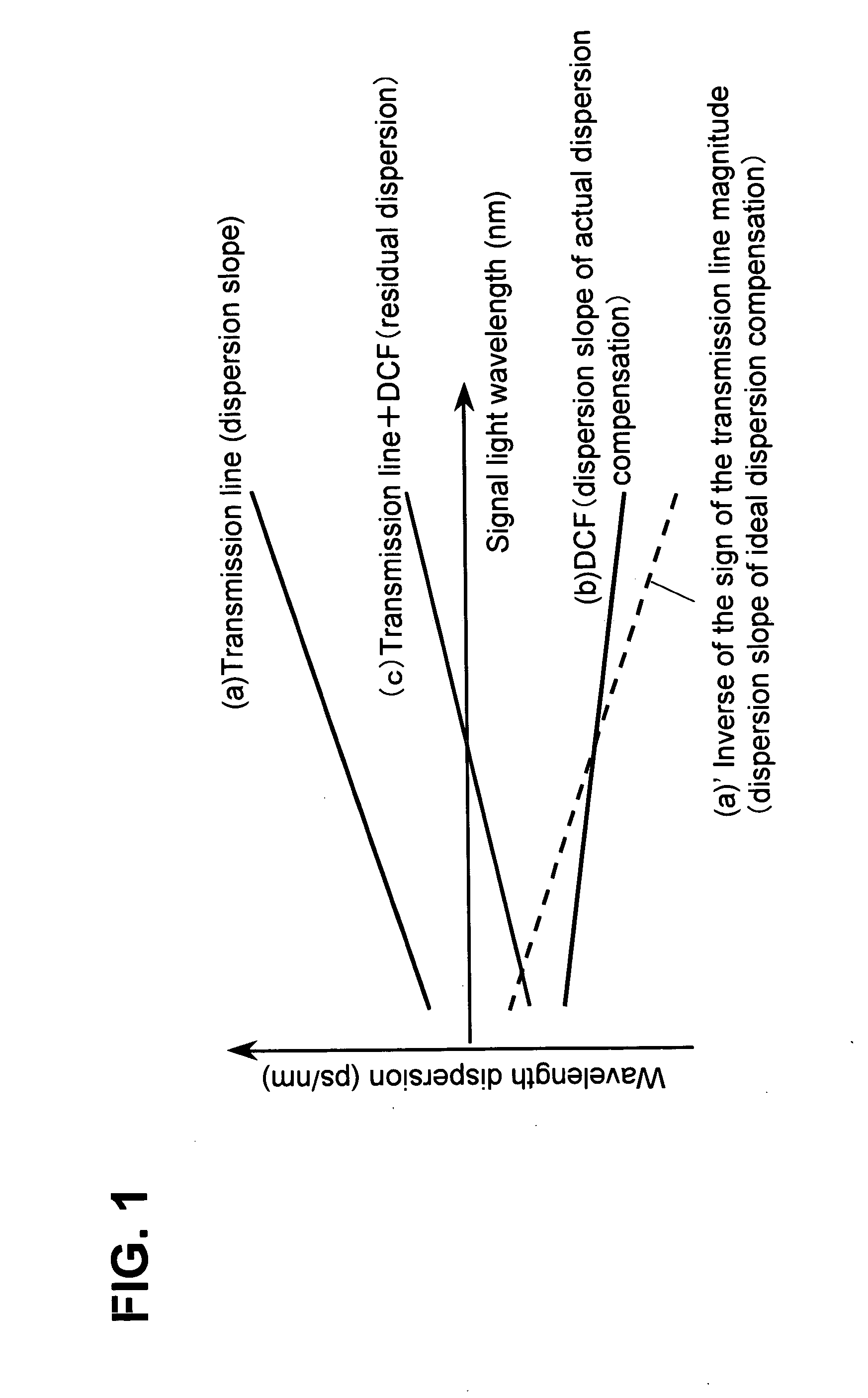
An iterative process is used to set the phase prechirp of a WDM optical transport system to a system's optimal level that maximizes the signal quality. A signal degradation factor takes into account linear and non-linear effects along the optical path and is used as a receive end feedback signal to control the phase prechirp level at the transmitter site. By using the FEC corrected errors rate as the feedback signal, optimization of signal quality is performed even when the system is running error free. By using an adaptive phase prechirp transmitter, signal degradation compensation can be also performed on a per wavelength basis to compensate for the residual dispersion slope and to allow optimization of individual channels independently of the net link dispersion value.This method provides more flexibility when using optical switching in core networks, as it allows path optimization to new physical link connectivity, without requiring any change to the optical components such that, significant signal degradation tuning range for a WDM optical transport system is provided.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
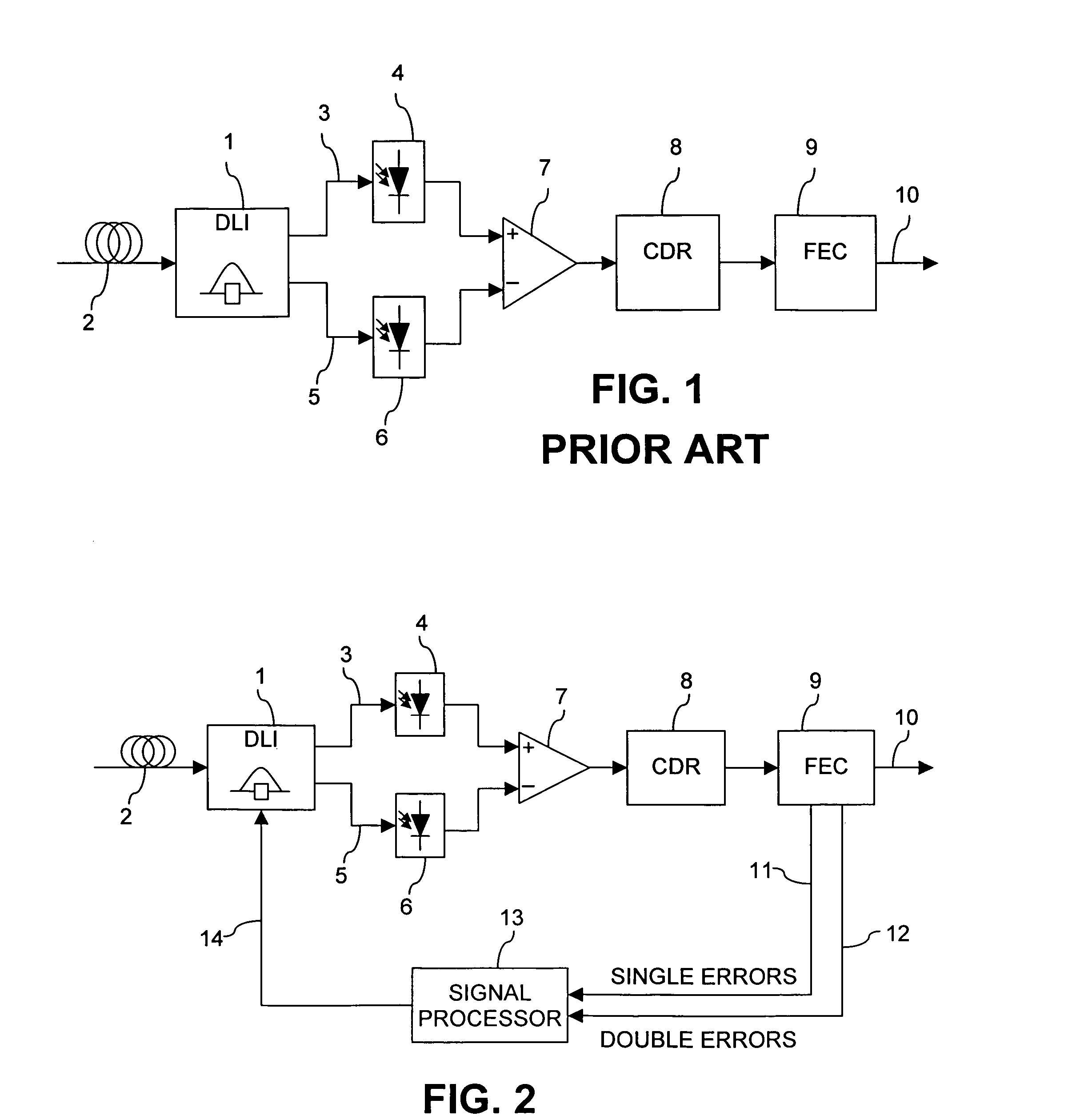
Control of delay line interferometer
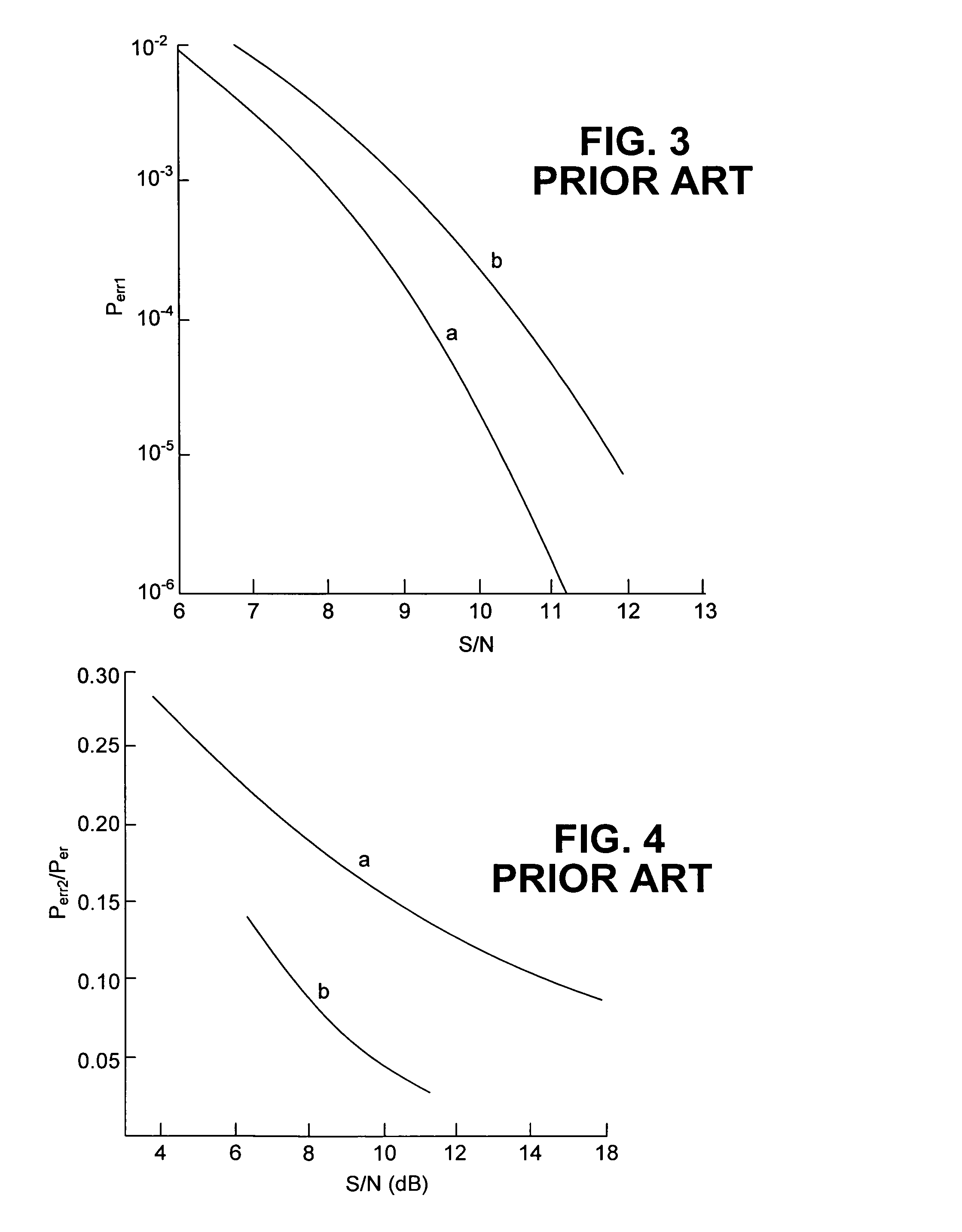
ActiveUS7266311B2Low costCounting errorTransmission monitoringPhase-modulated carrier systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Phase shifted
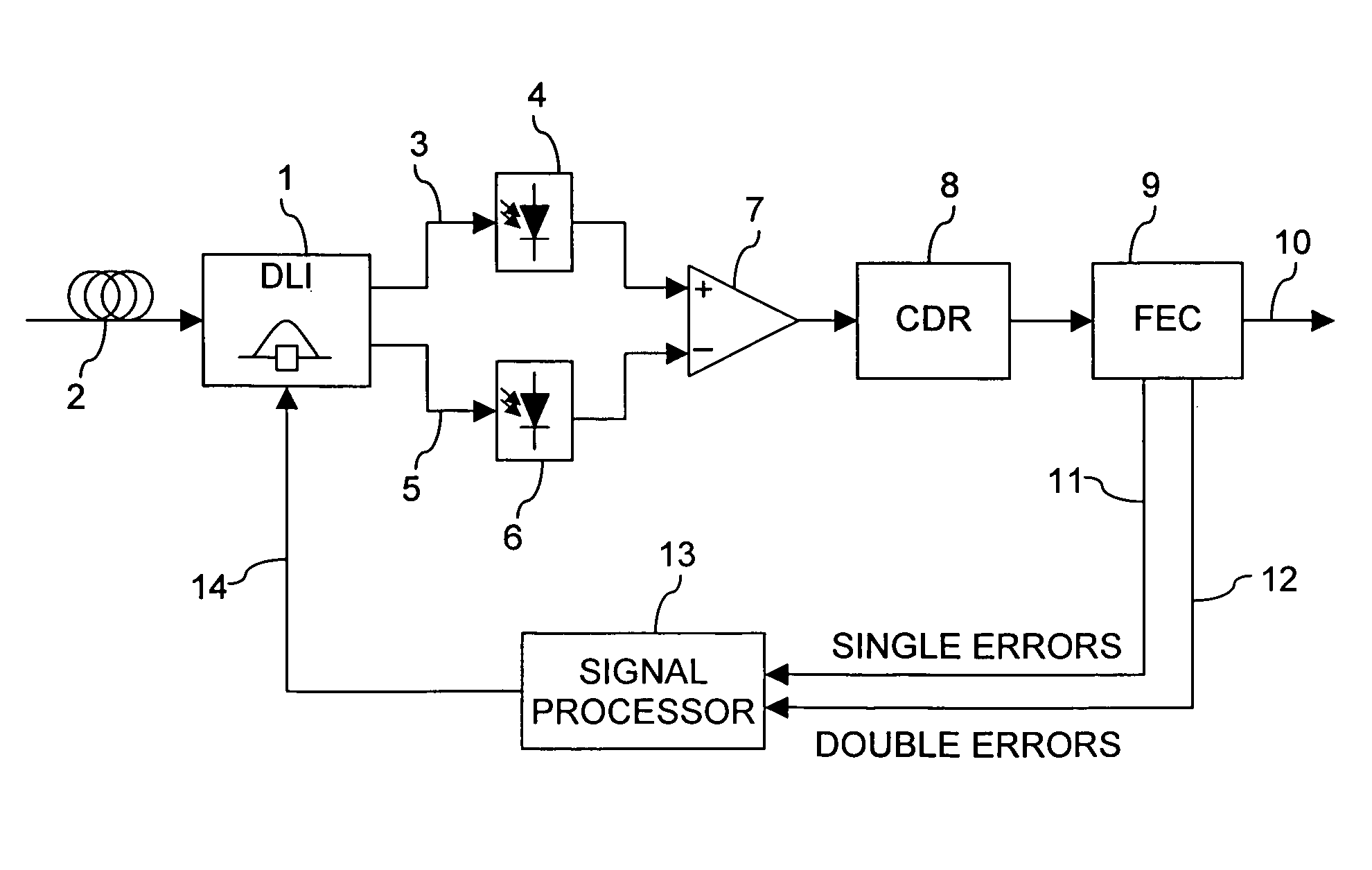
The delay setting of an optical delay line interferometer (DLI) used to decode differentially encoded phase shift keyed signals (DPSK or DQPSK) is controlled using a control signal representative of the ratio Perr2 / Perr1 of the rate of occurrence of double errors and the rate of occurrence of errors. The ratio Perr2 / Perr1, as the delay setting of the DLI is varied, exhibits a characteristic W-shaped structure consisting of a local maximum at the optimum value and two minima adjacent to the maximum, one on each side of it. This structure is present over a wide range of signal to noise ratio and residual dispersion.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
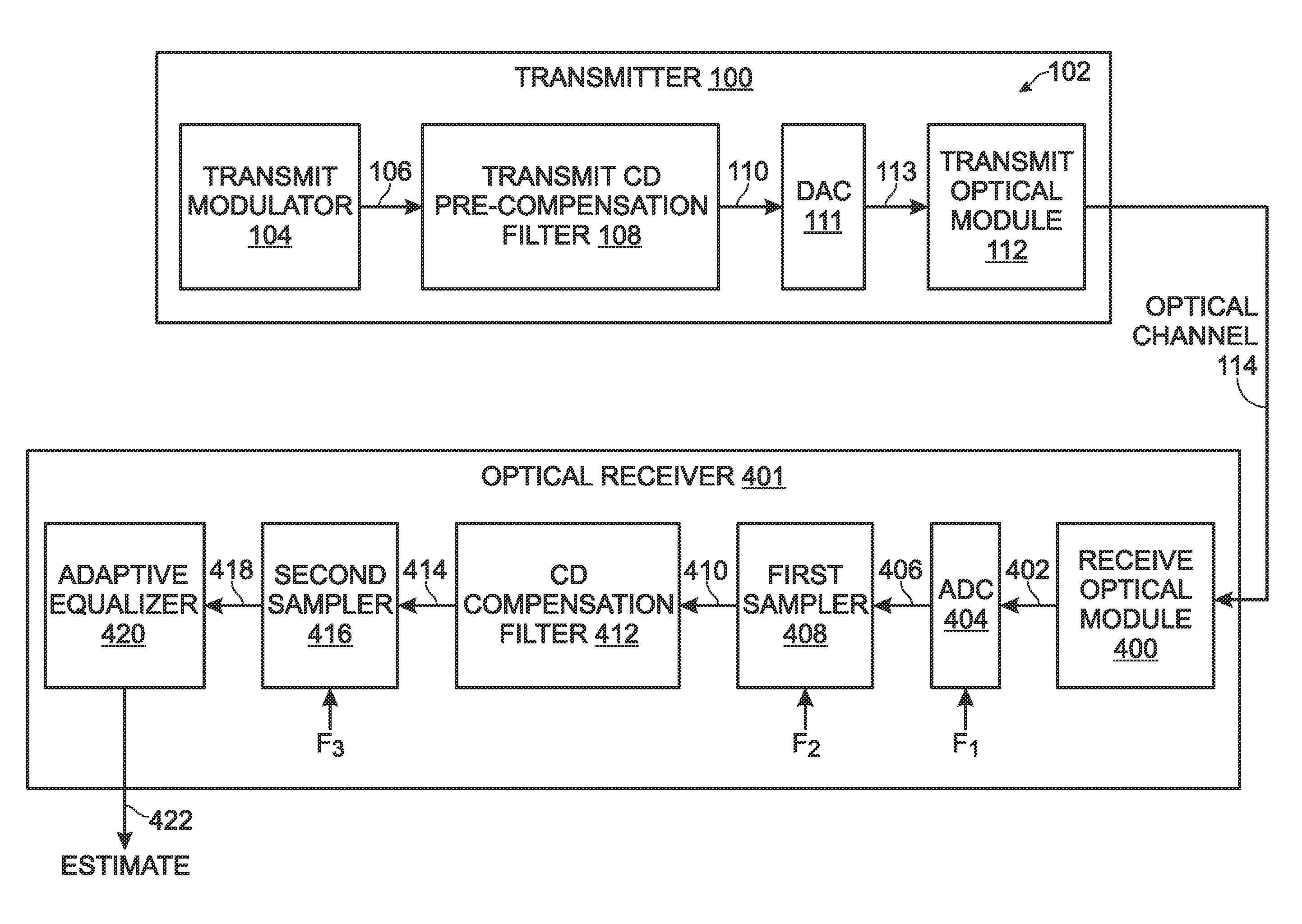
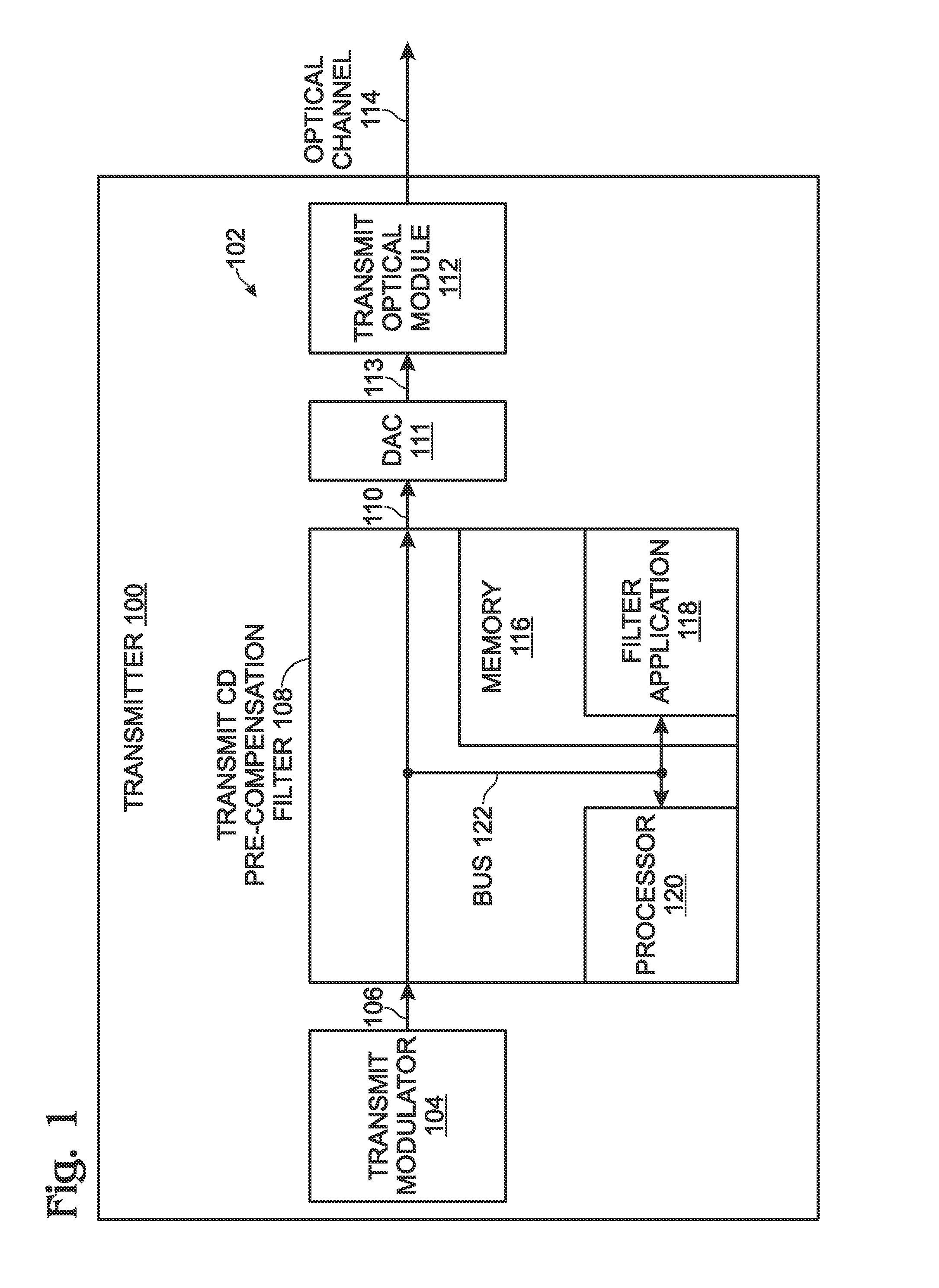
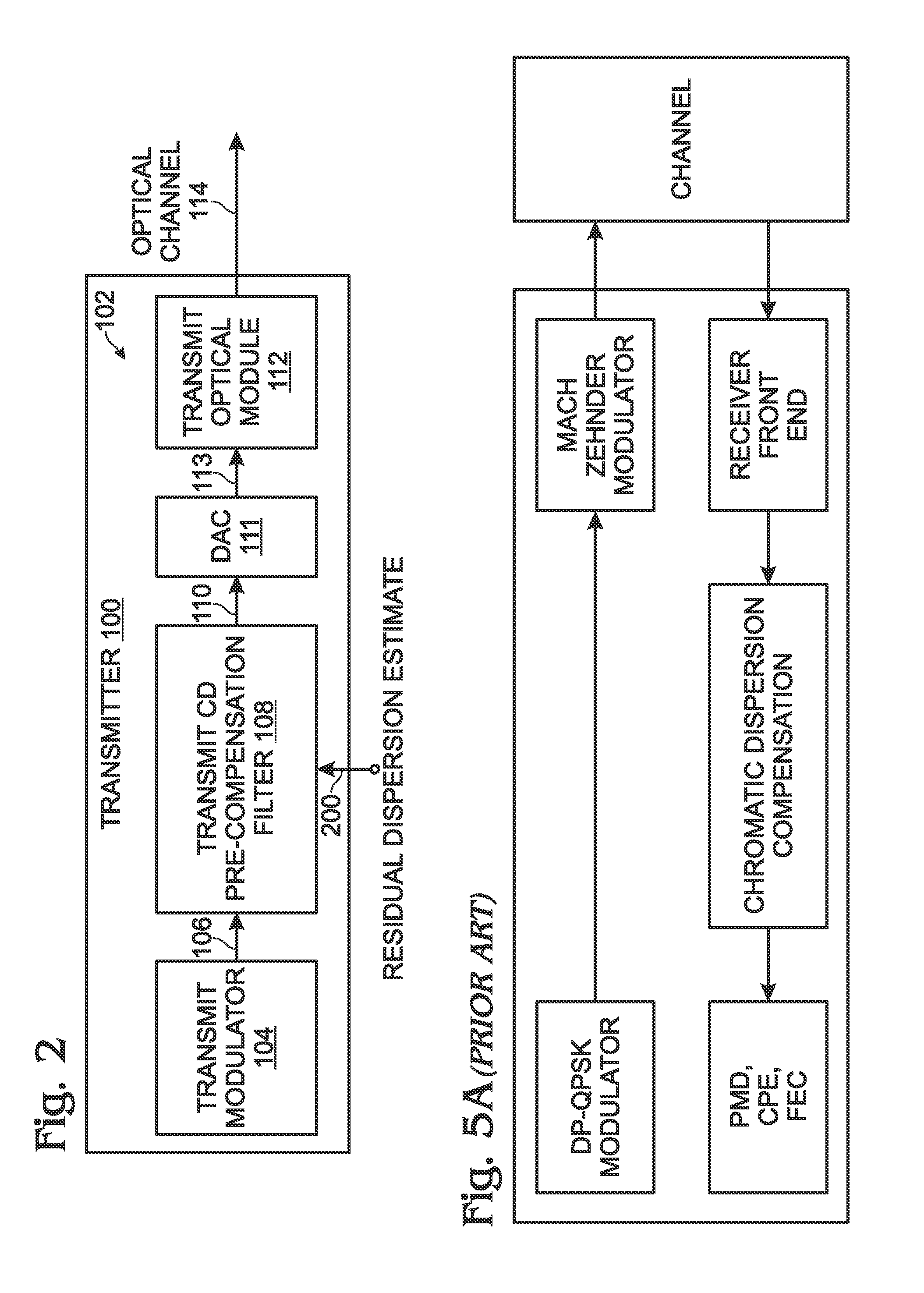
Chromatic dispersion pre-compensation
A method is provided for performing chromatic dispersion (CD) pre-compensation. The method generates an electronic signal at a transmitter, and uses a transmit CD compensation estimate to compute a CD pre-compensation filter. The transmit CD pre-compensation filter is used to process the electronic signal, generating a pre-compensated electronic signal. The pre-compensated electronic signal is converted into an optical signal and transmitted to an optical receiver via an optical channel. In one aspect, the transmitter generates a test electronic signal and the CD compensation estimate uses a first dispersion value to compute a first CD compensation filter. The transmitter accepts a residual dispersion estimate of the test optical signal from the first optical receiver CD compensation filter, generated from a (receiver-side) CD estimate, and then the transmit CD estimate can be modified in response to the combination of the first dispersion value and residual dispersion estimate.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
Dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent chromatographic imaging
InactiveCN1887220ALarge dispersion adjustment rangeWide Compensation Spectral RangeSurgeryMaterial analysis by optical meansGratingPhase retardation
The present invention discloses dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent tomographic imaging (OCT). The system has one increased blazed grating parallelly set with the original blazed grating in a single grating fast scanning optical delay line, and thus one independently regulated variable of interval between two blazed gratings and capacity of generating group velocity dispersion and third-order dispersion in great varying range and arbitrary sign combination, so that the OCT system may obtain precise matching between the dispersion of the reference arm and the dispersion of the sample arm and longitudinal resolution approaching the theoretical calculated value. The double grating system has wide dispersion regulating range, wide compensation spectrum range and small residual dispersion other than the capacity of independently controlling phase delay and group delay, and possesses three functions of depth scan, phase modulation and dispersion compensation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Low total excursion dispersion maps
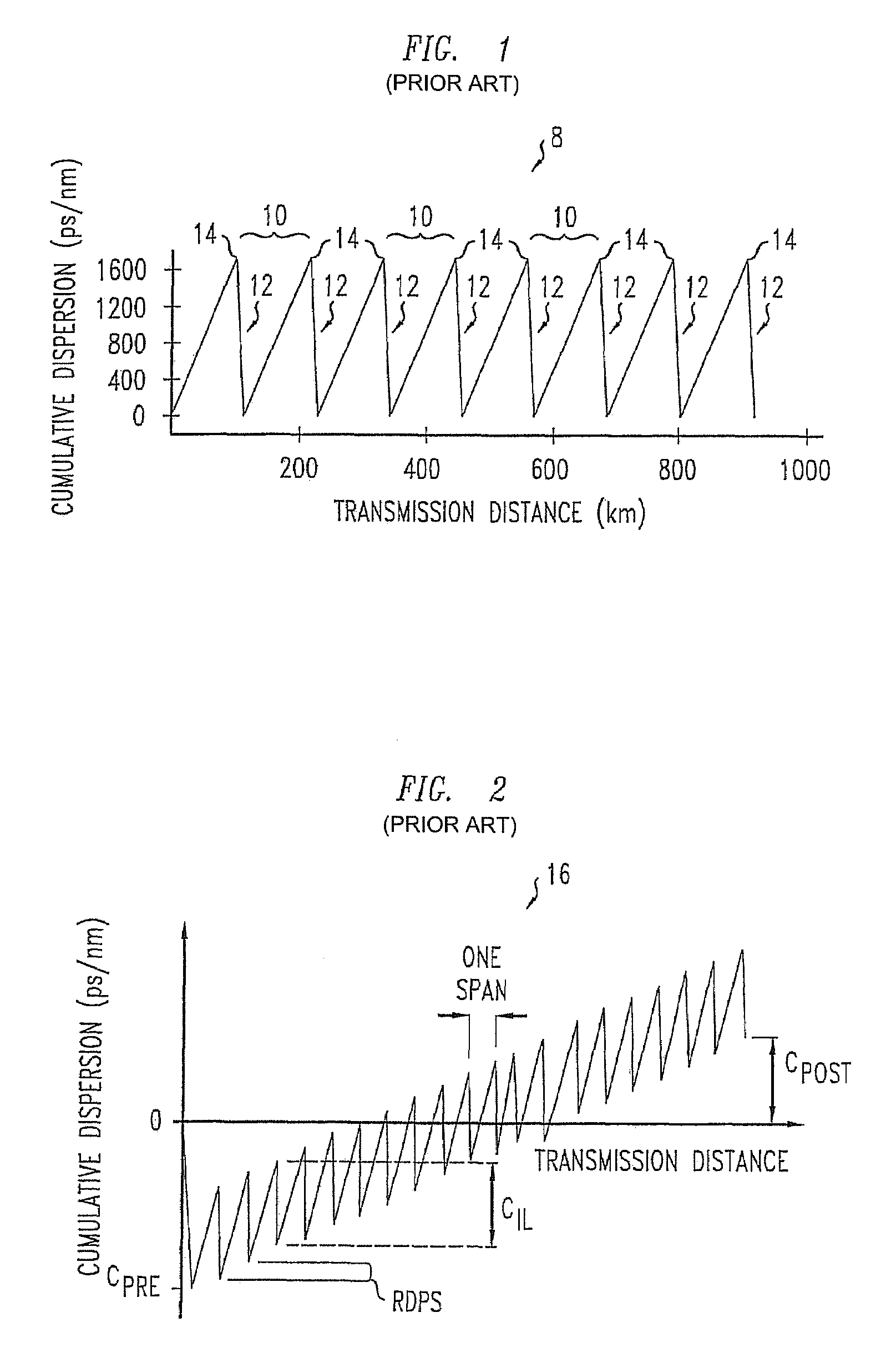
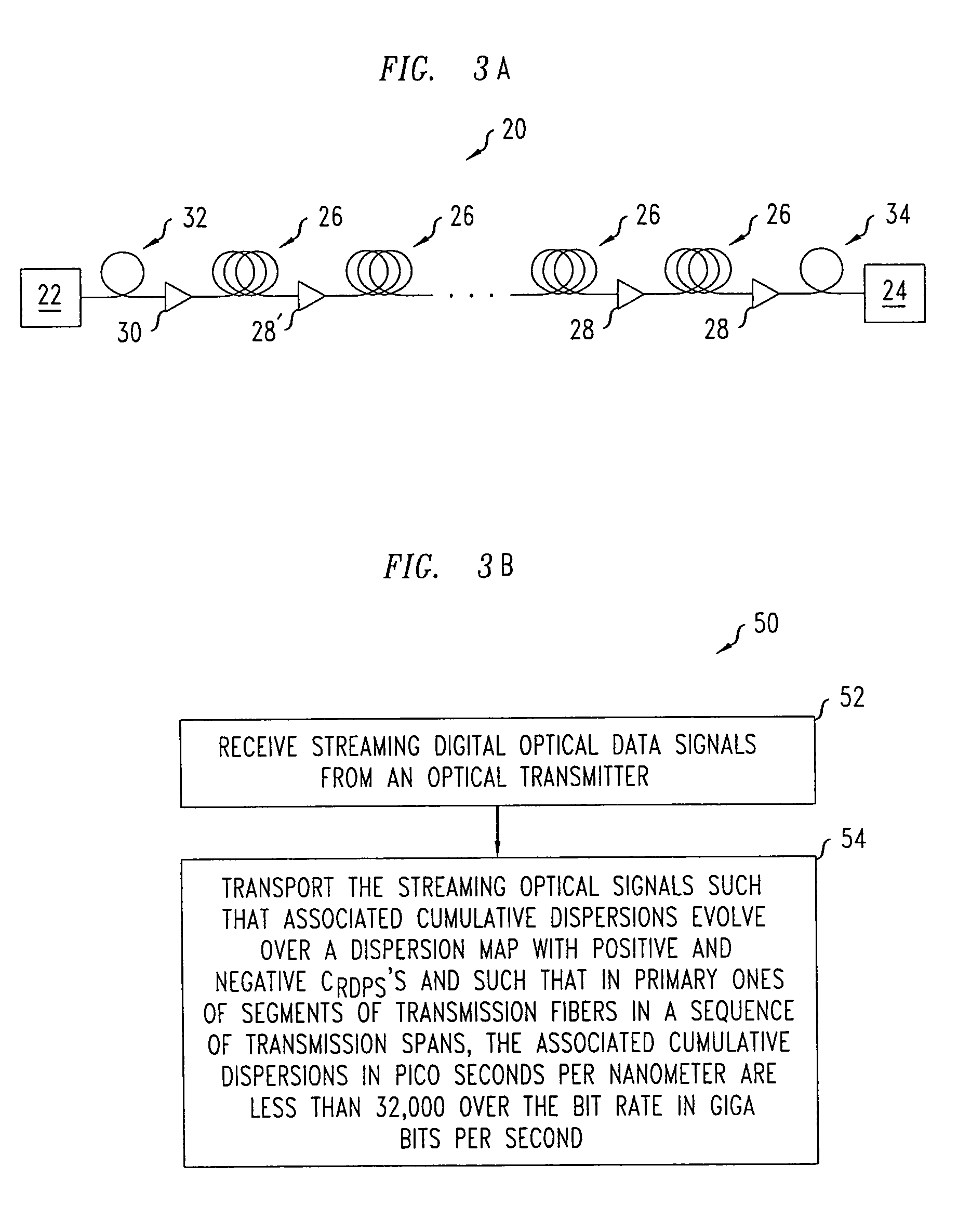
InactiveUS7280765B2Reduce pulse degradationIncrease power levelMultimode transmissionDigital dataData signal
A process optically transports digital data over an all-optical long-haul communication path. The process includes transporting digital optical data signals at a selected bit rate and a selected wavelength over a sequence of transmission spans. The sequence includes 70 percent or more of the spans of the long-haul all-optical communication path. Each span of the sequence has a primary local maximum optical power point for the wavelength on a transmission fiber and nearest to an input of the span. The transporting causes a cumulative dispersion of each signal to evolve such that residual dispersions per span are positive over some of the spans and are negative over other of the spans. At the primary local maximum power points, magnitudes of cumulative dispersions of the signals in pico seconds per nanometer remain at less than 32,000 times the inverse of the bit rate in giga bits per second.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
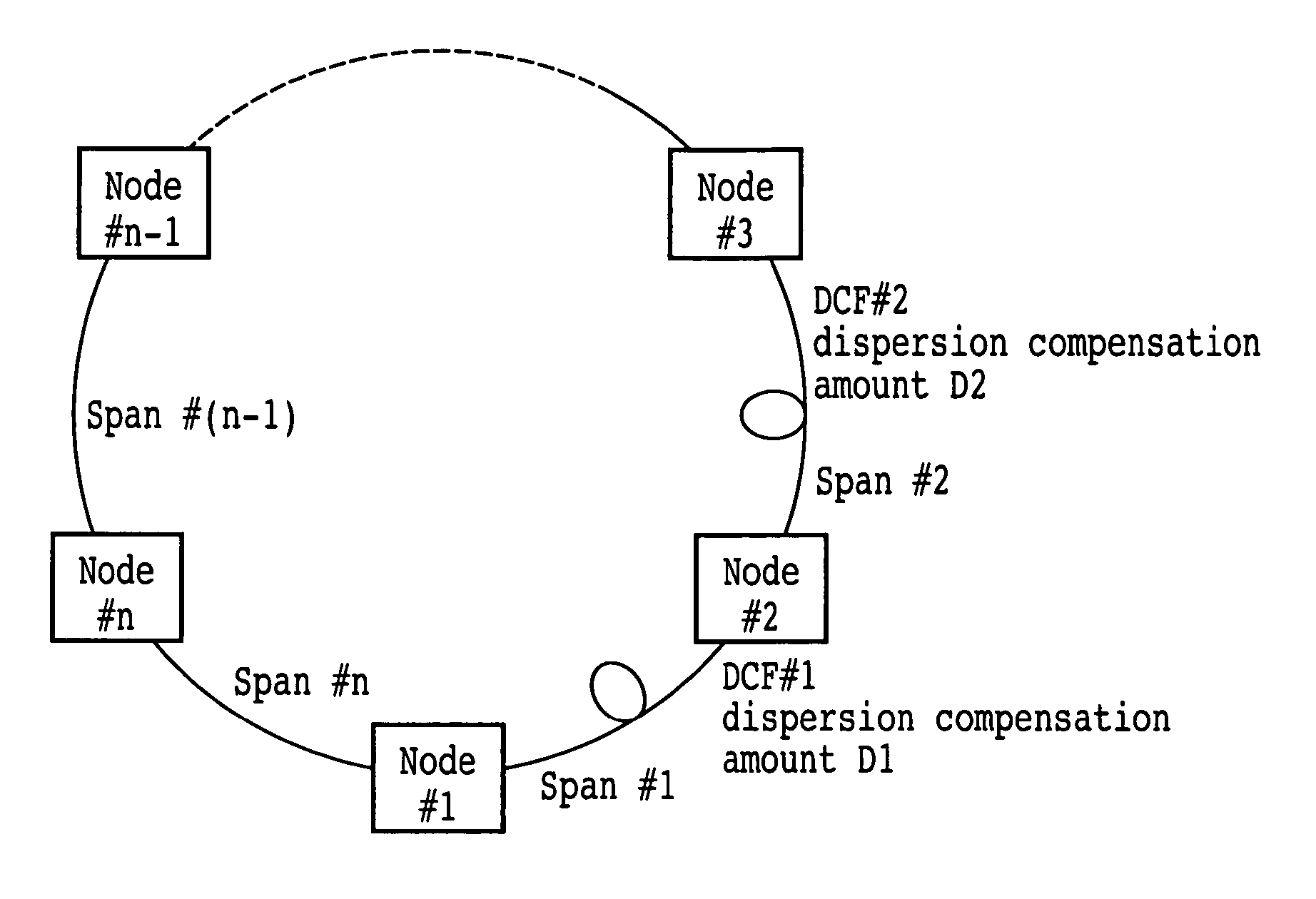
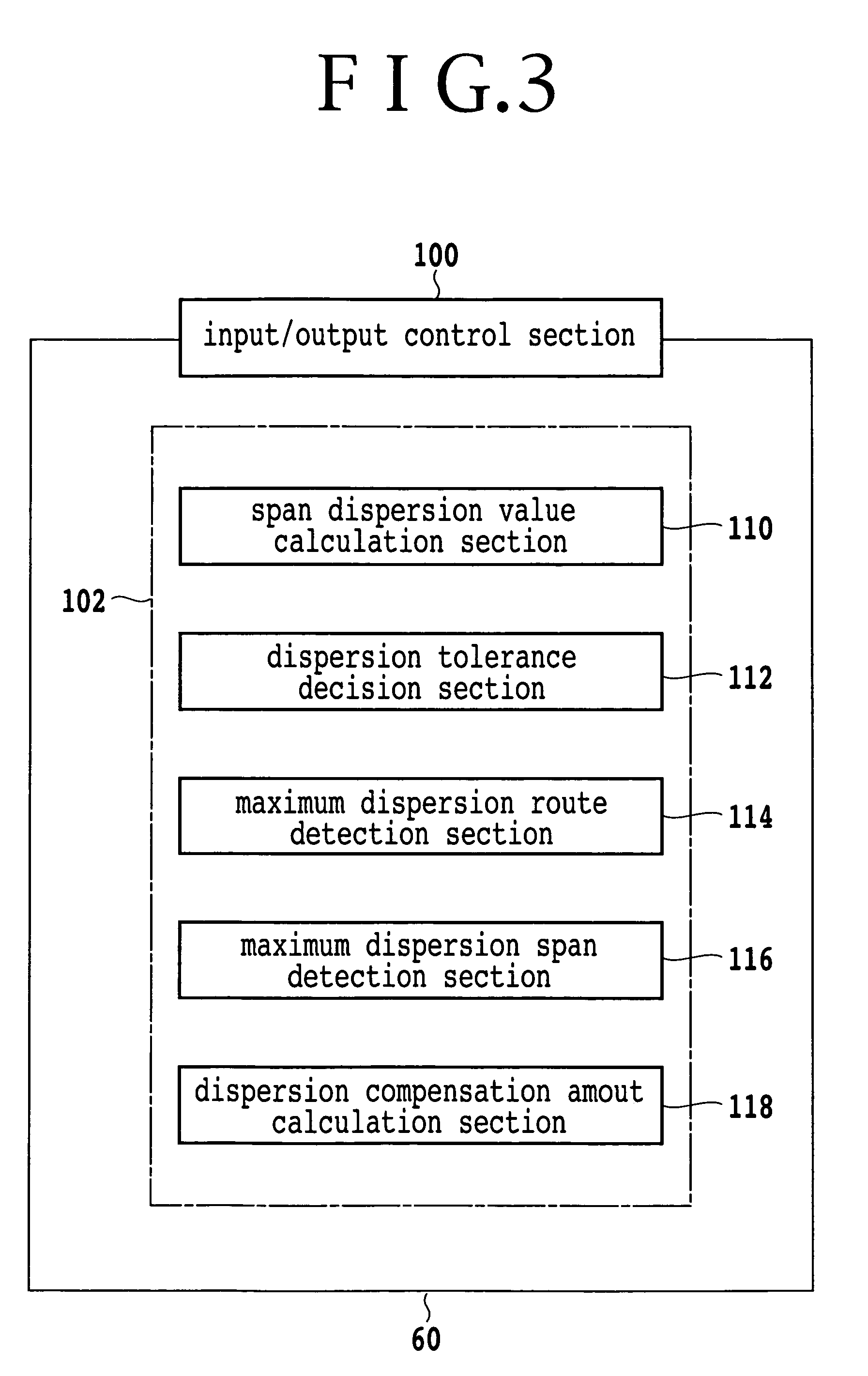
Optical transmission network, optical transmission apparatus, dispersion compensator arrangement calculation apparatus and dispersion compensator arrangement calculation method
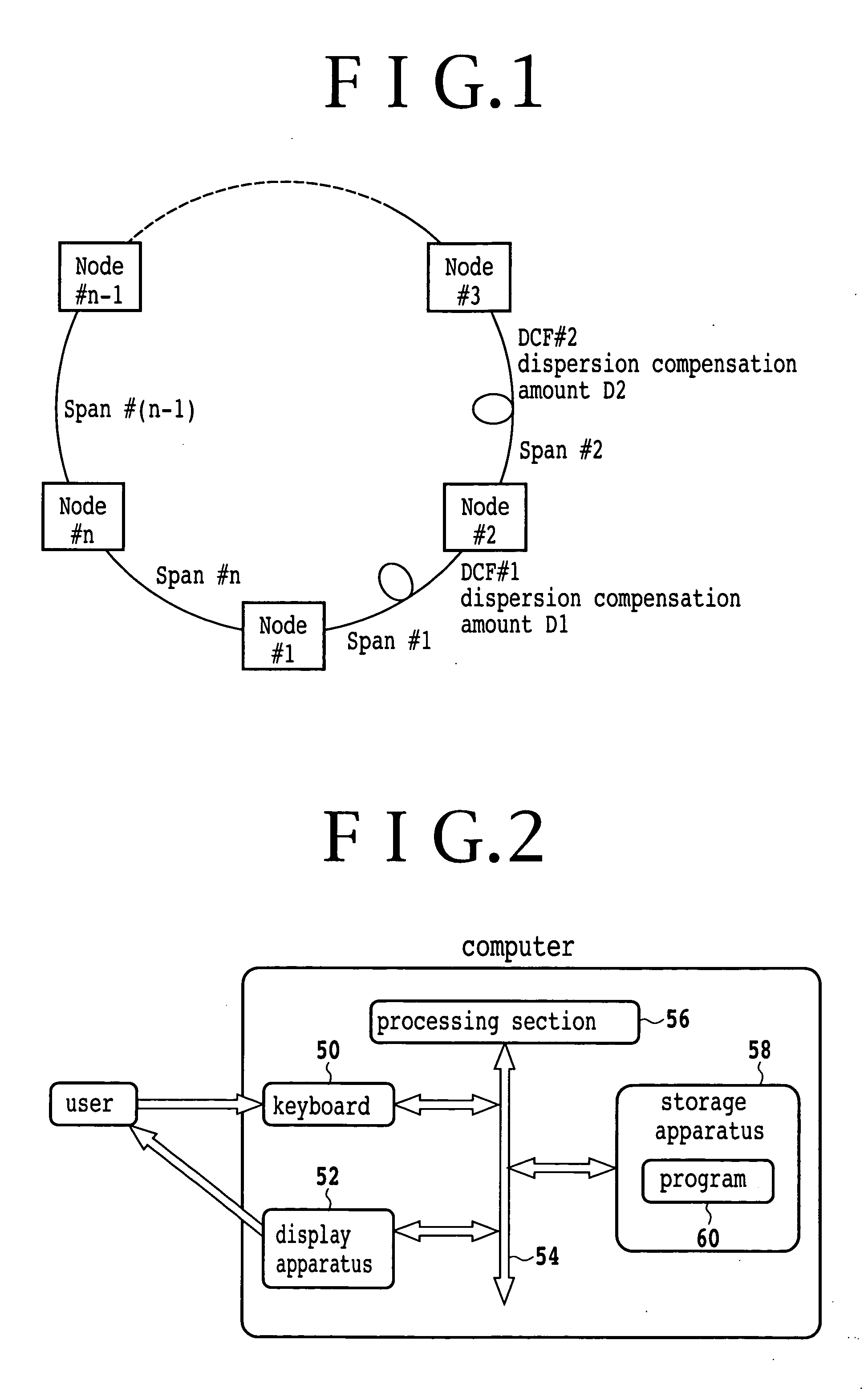
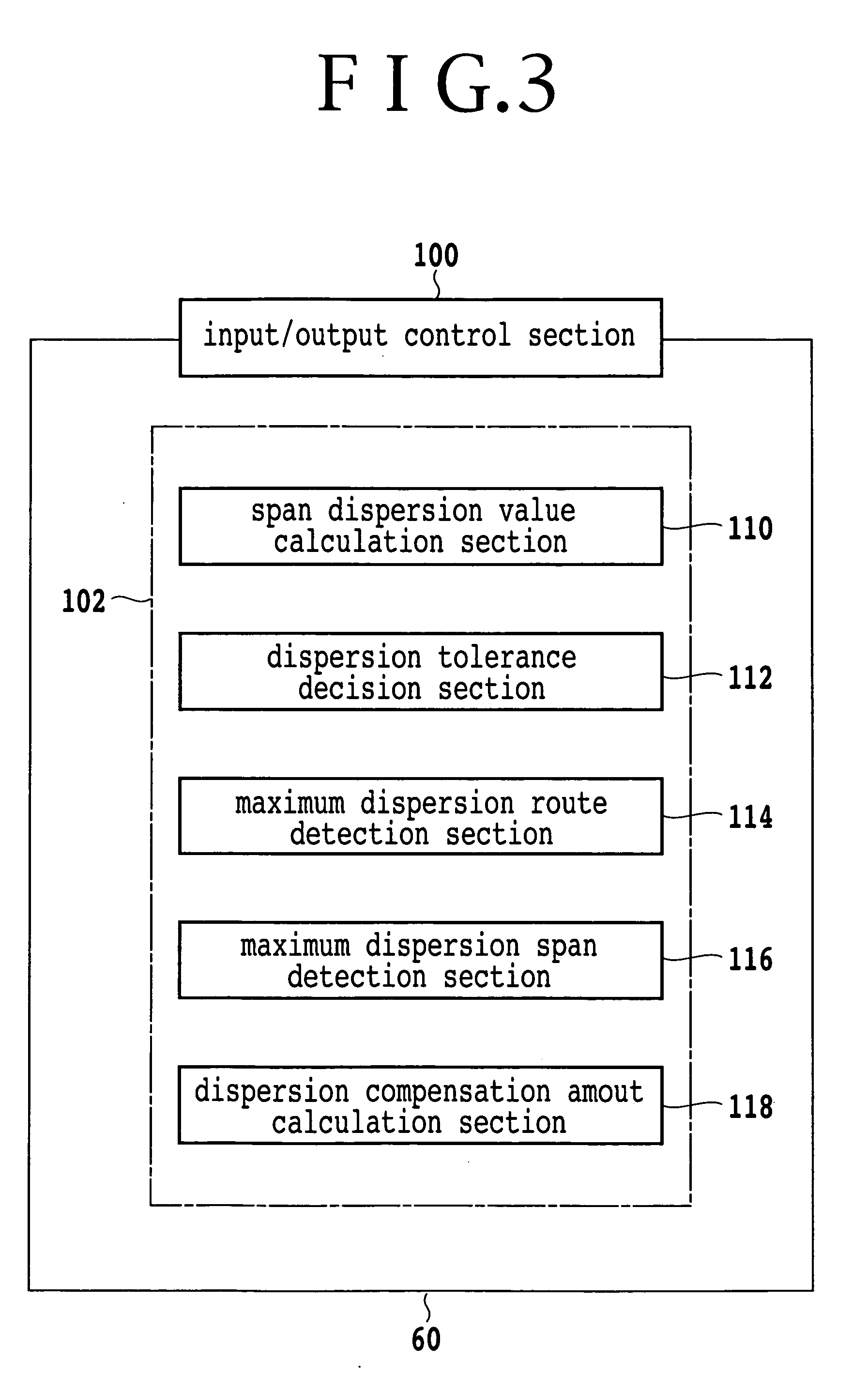
InactiveUS20050175279A1Reduce dispersion compensation amountReduce the amount of compensationRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringMechanical engineering
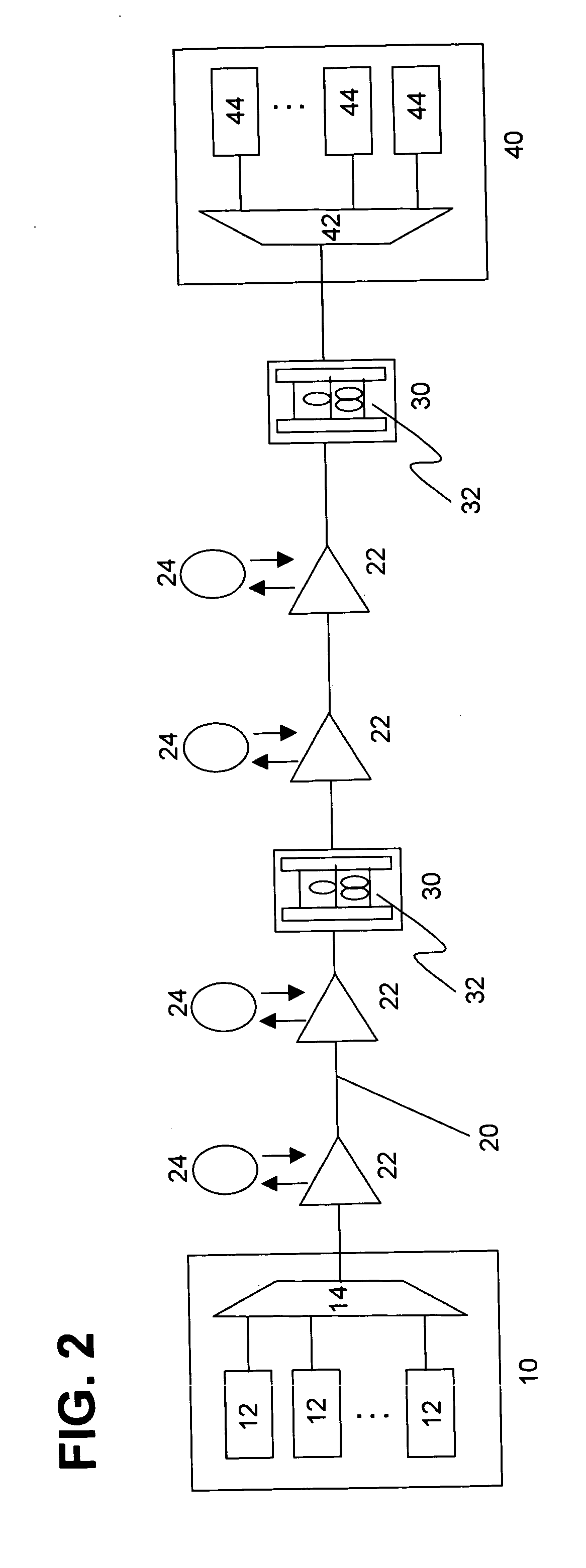
An optical transmission network includes a first dispersion compensator arranged in a maximum dispersion span having a maximum dispersion value and searched out from within a maximum dispersion route having a maximum dispersion value from among routes of non-regeneration intervals within which a dispersion value before dispersion compensation does not satisfy an upper limit of a dispersion tolerance, and a second dispersion compensator arranged in a maximum dispersion span having a maximum dispersion value searched out from within a maximum dispersion route having a maximum dispersion value from among the routes when a dispersion compensator is successively arranged until a route of a non-regeneration interval within which a dispersion value of a certain channel does not satisfy the dispersion tolerance does not remain any more based on the dispersion value after the dispersion compensation with respect to the searched out maximum dispersion span. The dispersion compensation amounts of the first and second dispersion compensators are such that, when the dispersion compensation amount of the maximum dispersion span in which the first and second dispersion compensators are arranged is successively increased, the span has a residual dispersion value equal to or higher than a fixed range and the maximum dispersion route which relates to the spans has a residual dispersion value which satisfies the dispersion tolerance or the span has a residual dispersion value which is within the fixed range.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
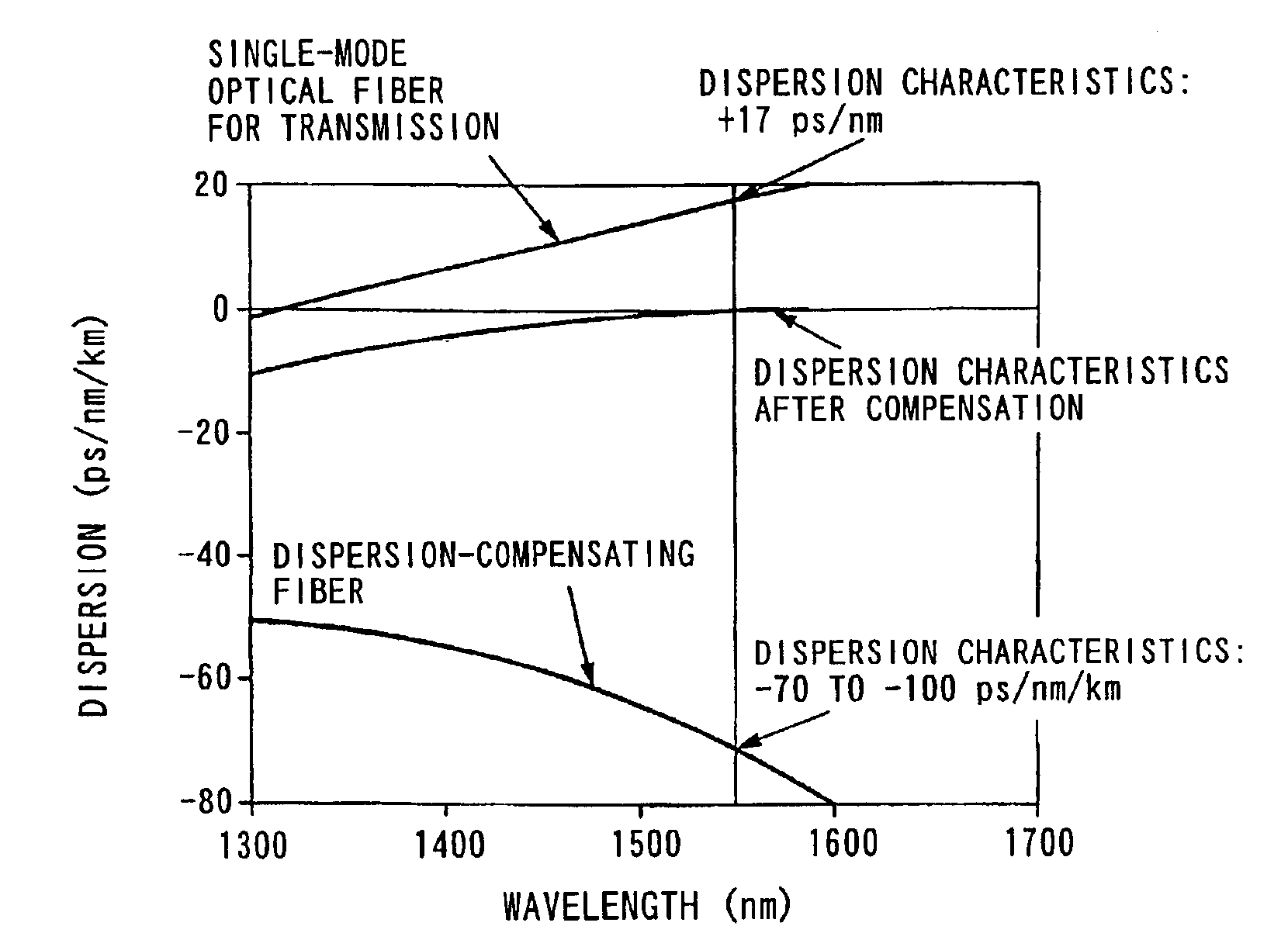
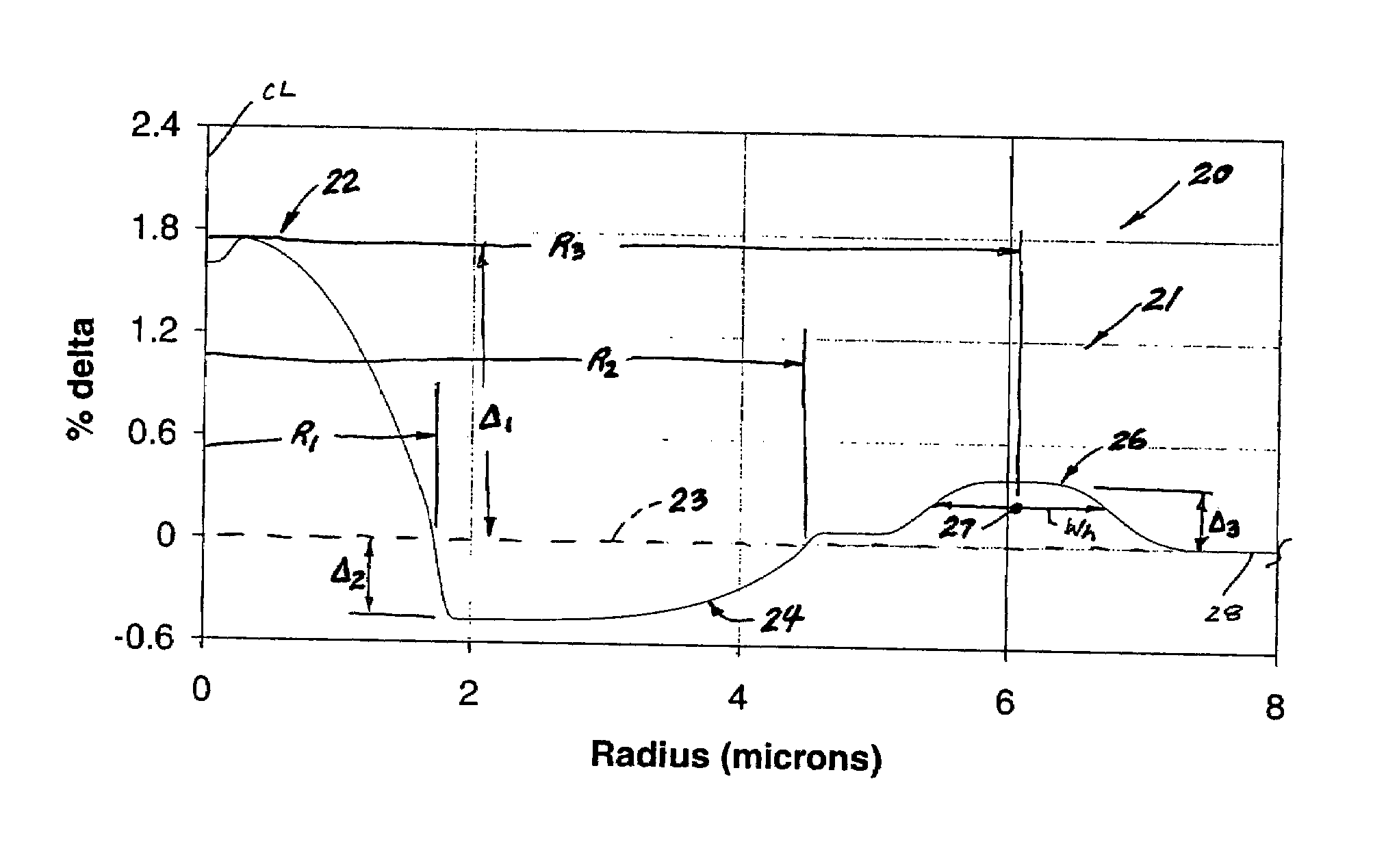
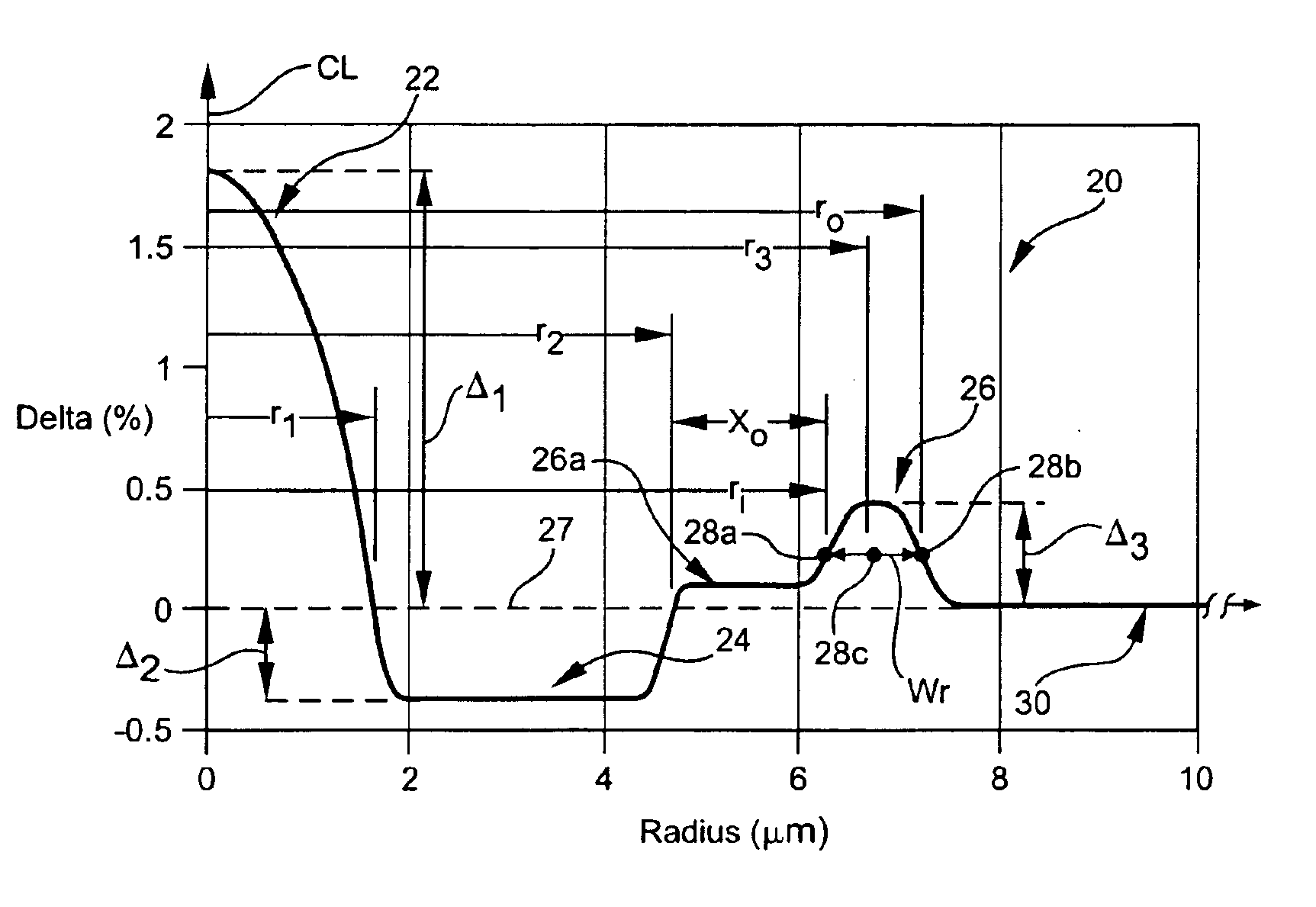
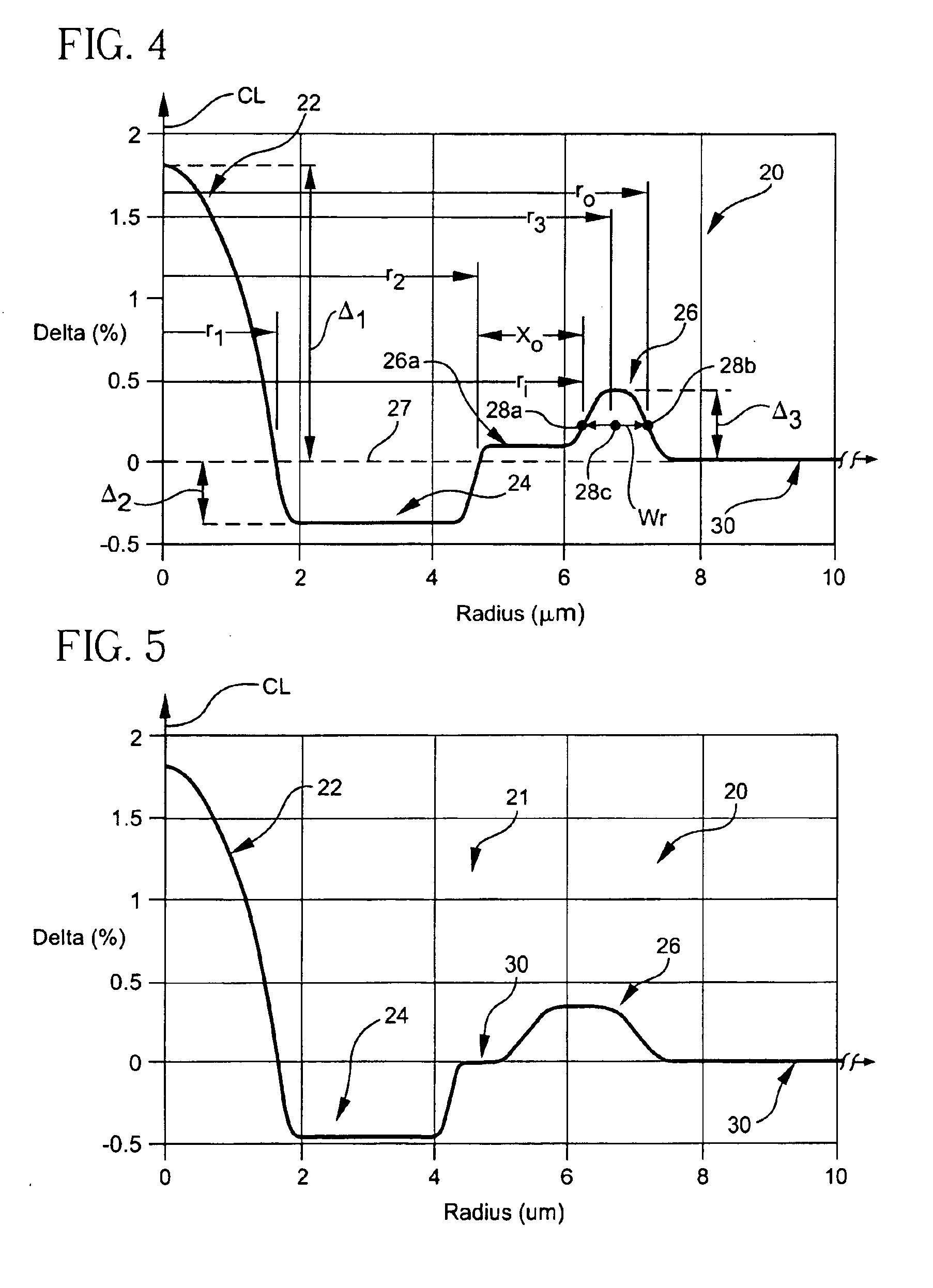
High figure of merit dispersion compensating fiber for standard single mode fiber and transmission system utilizing same
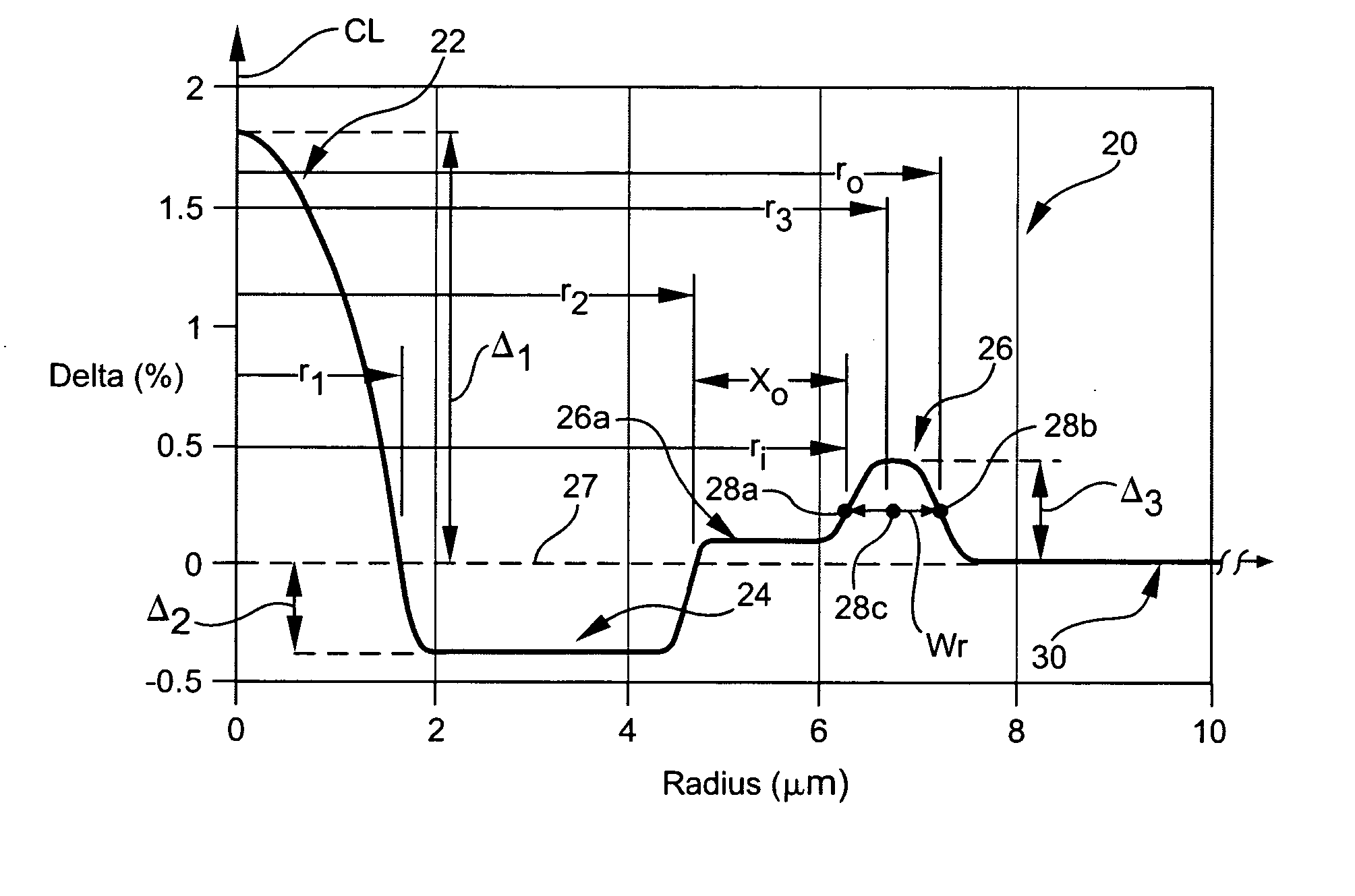
InactiveUS20050063655A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringFigure of merit
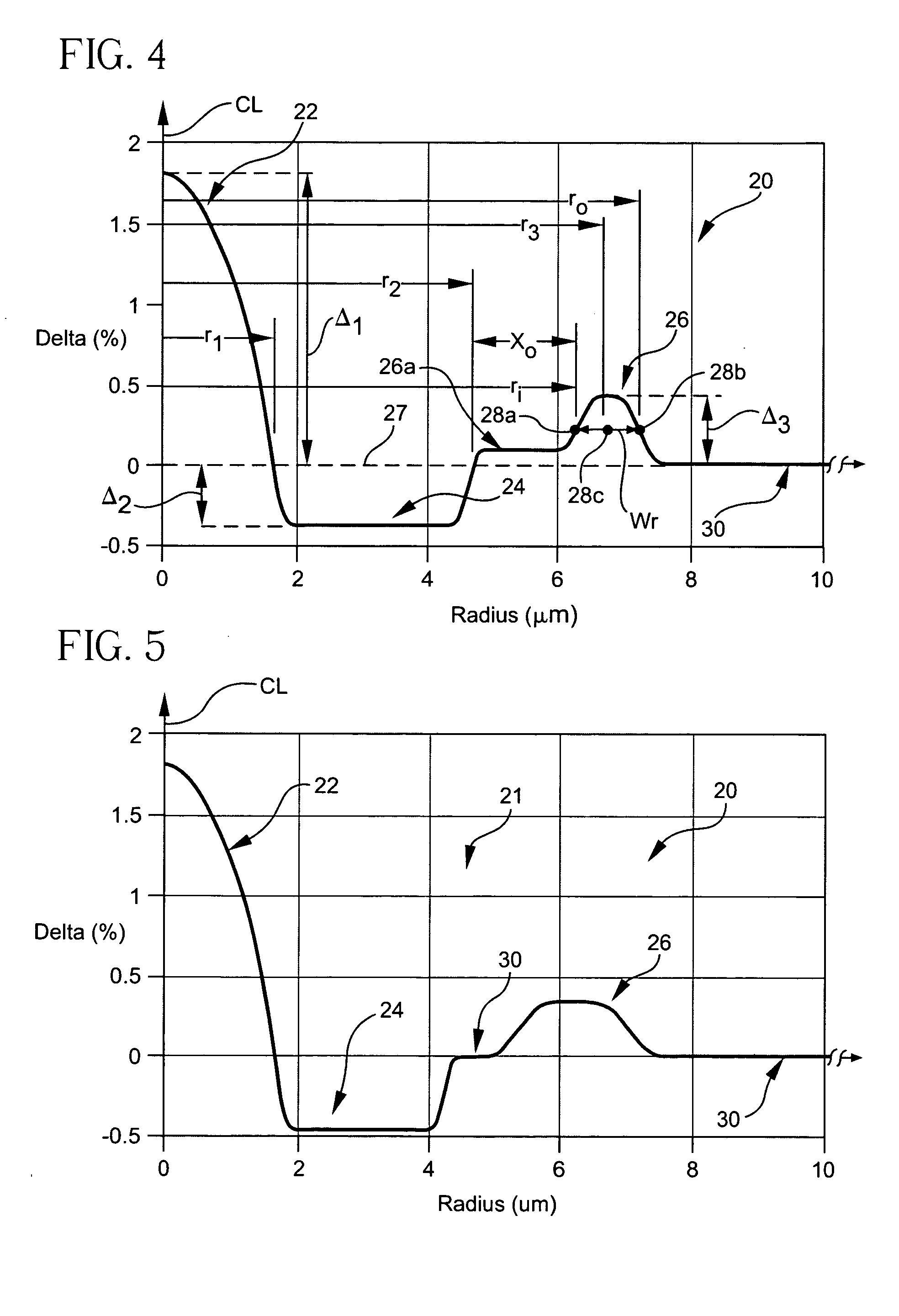
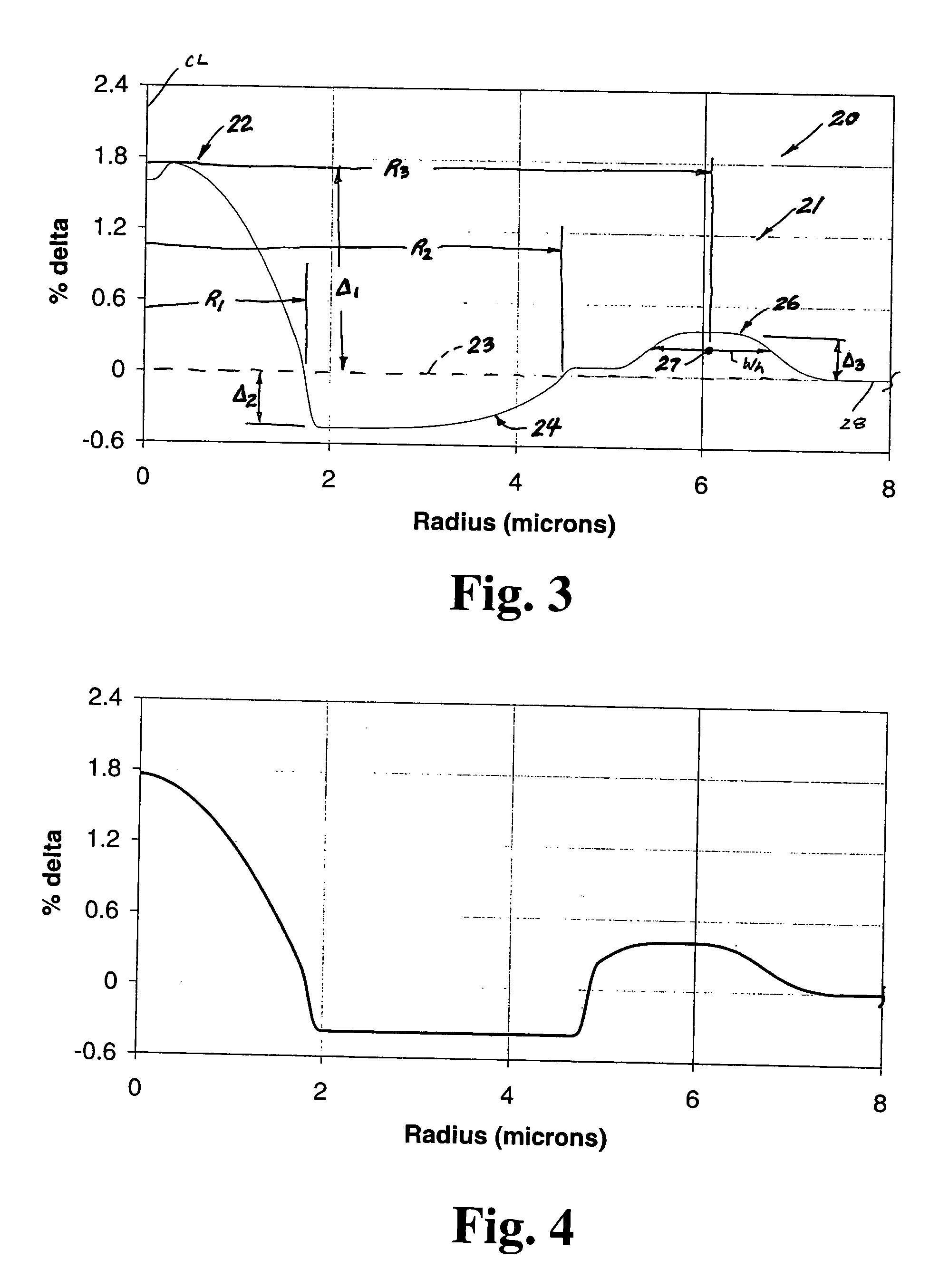
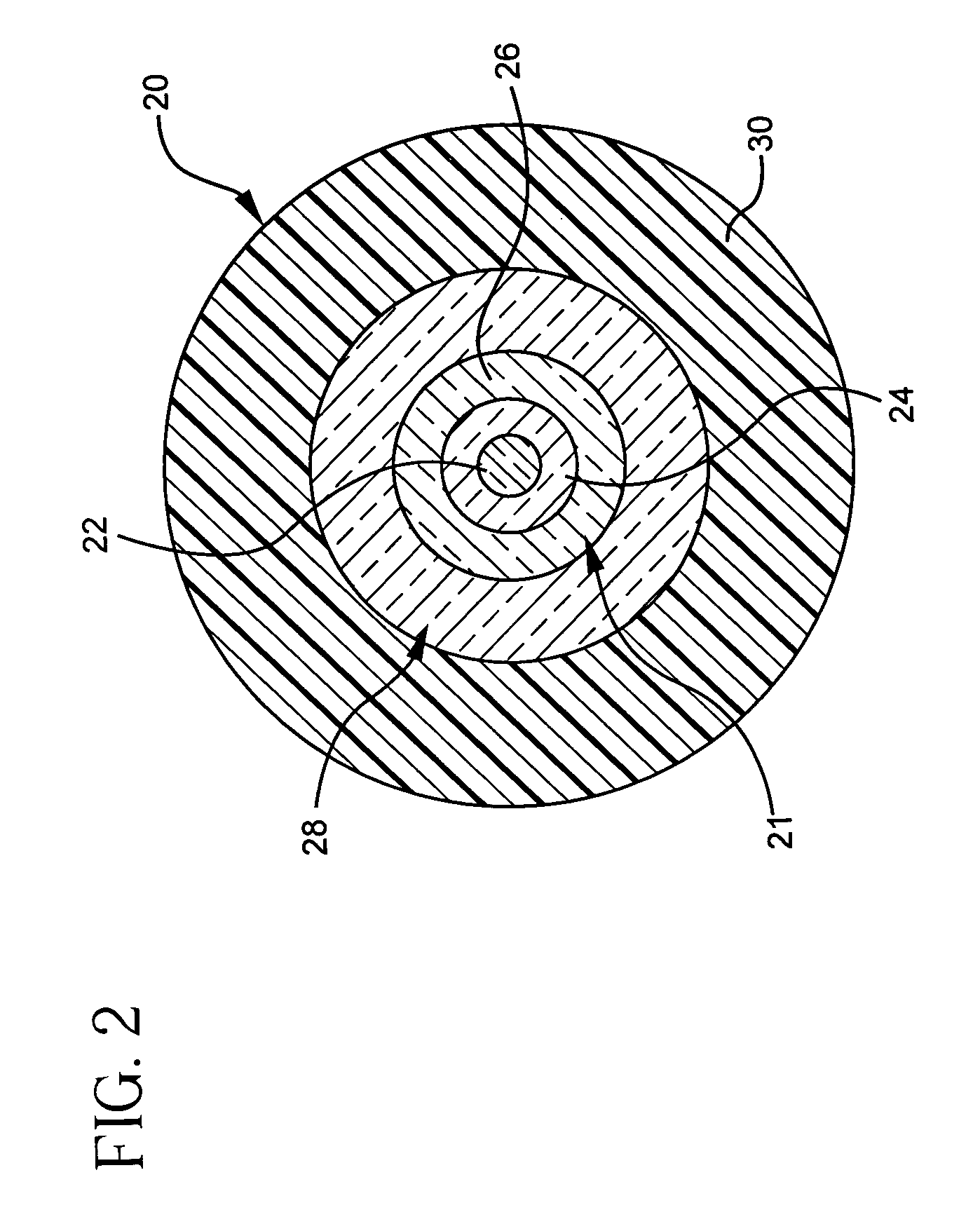
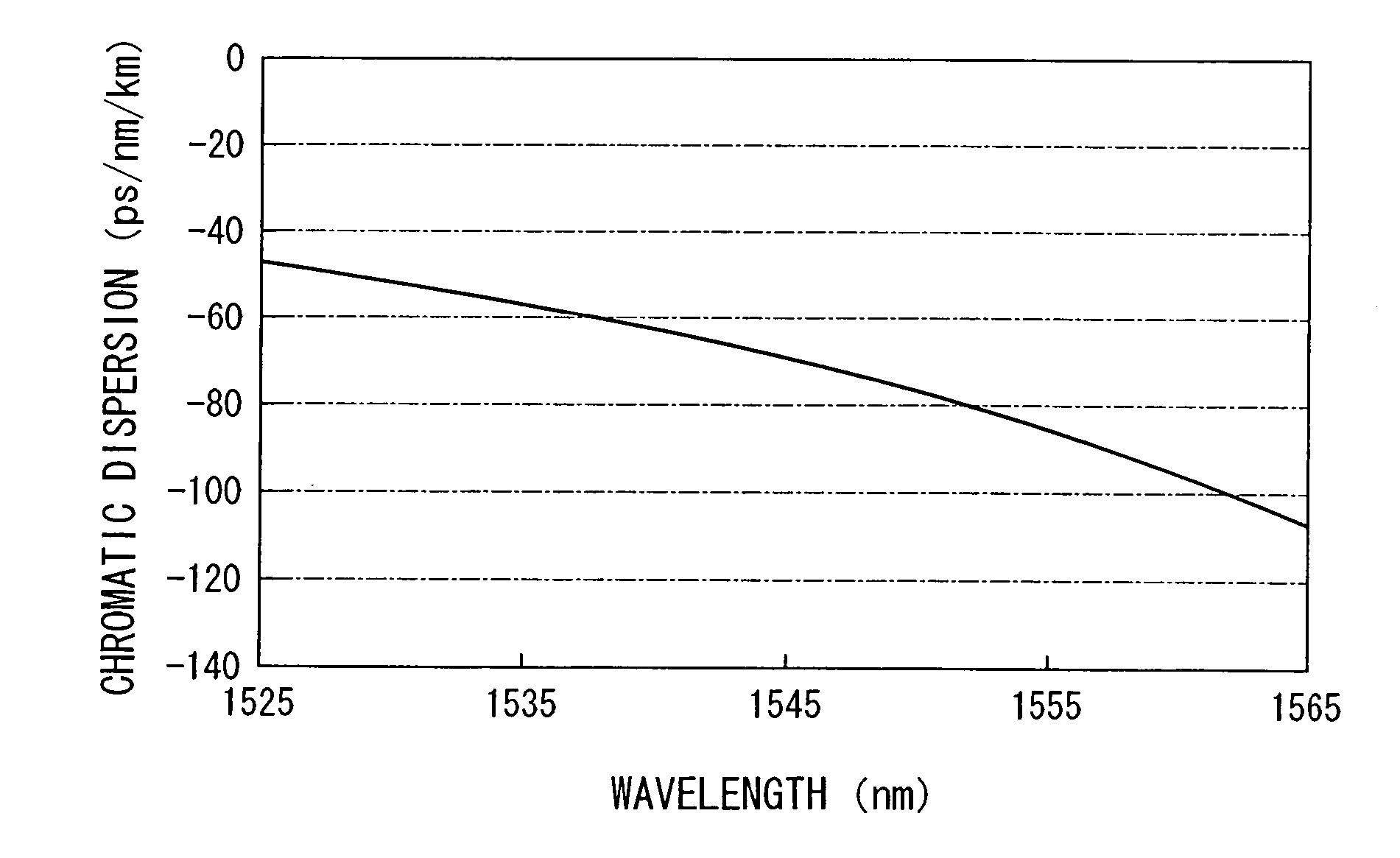
A dispersion compensating optical fiber that includes a segmented core having a central core segment, a moat segment, and a ring segment wherein the ring segment is preferably offset from the moat outer radius, r2, by a ring offset, Xo, greater than 0.4 μm. The refractive index profile is selected to provide a total dispersion at 1550 nm of between about −120 and −145 ps / nm / km, and a total dispersion slope at 1550 nm of between about −0.36 and −0.56 ps / nm2 / km. The refractive index profile is preferably further selected to provide a kappa, defined as the total dispersion at 1550 nm divided by the dispersion slope at 1550 nm, of between about 250 and 320 nm. Optical transmission systems including the present invention dispersion compensating optical fiber which have residual dispersion less than ± 15 ps / nm per 100 km of standard single mode transmission fiber are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method and system for compensating residual dispersion curvature
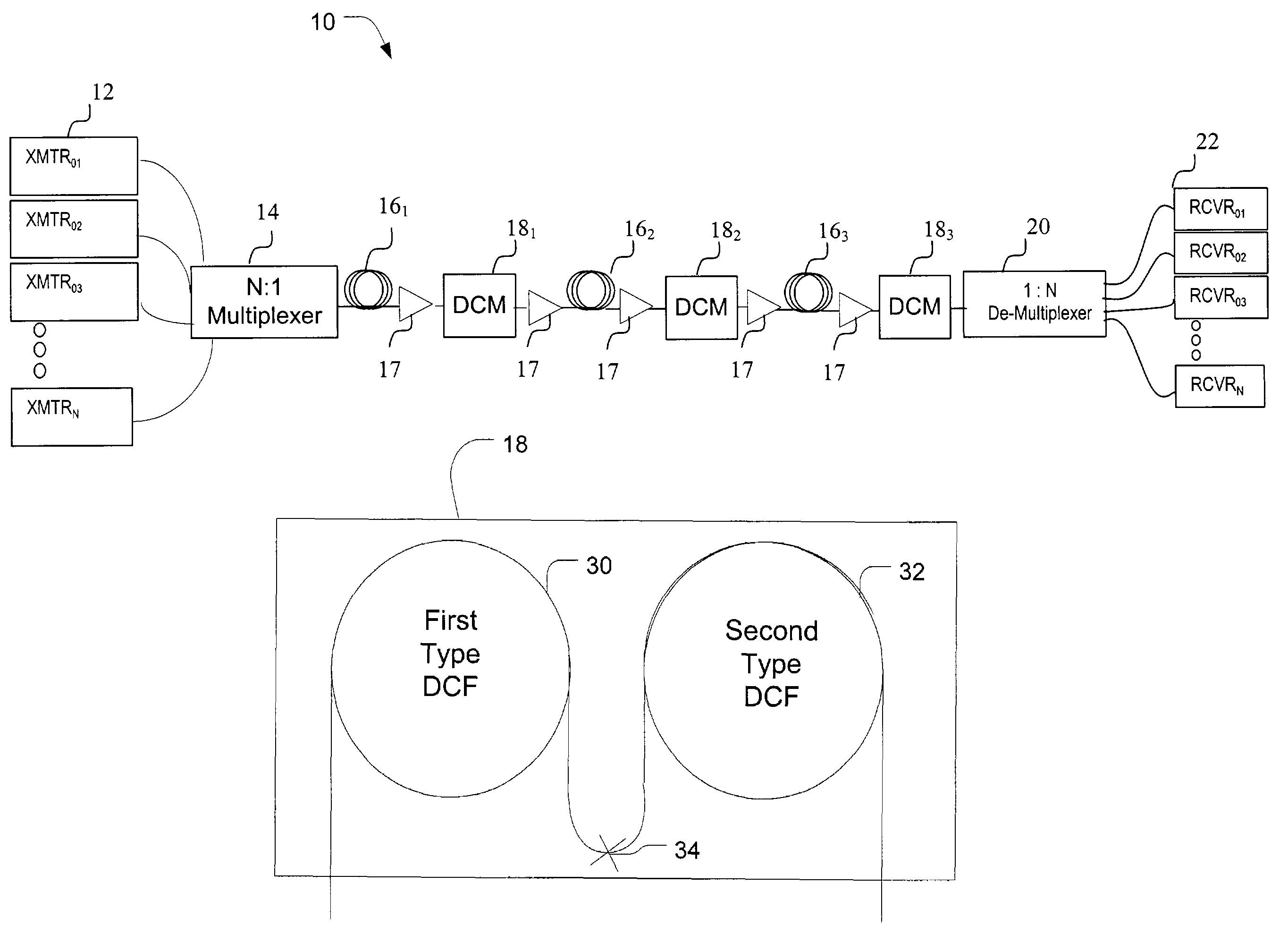
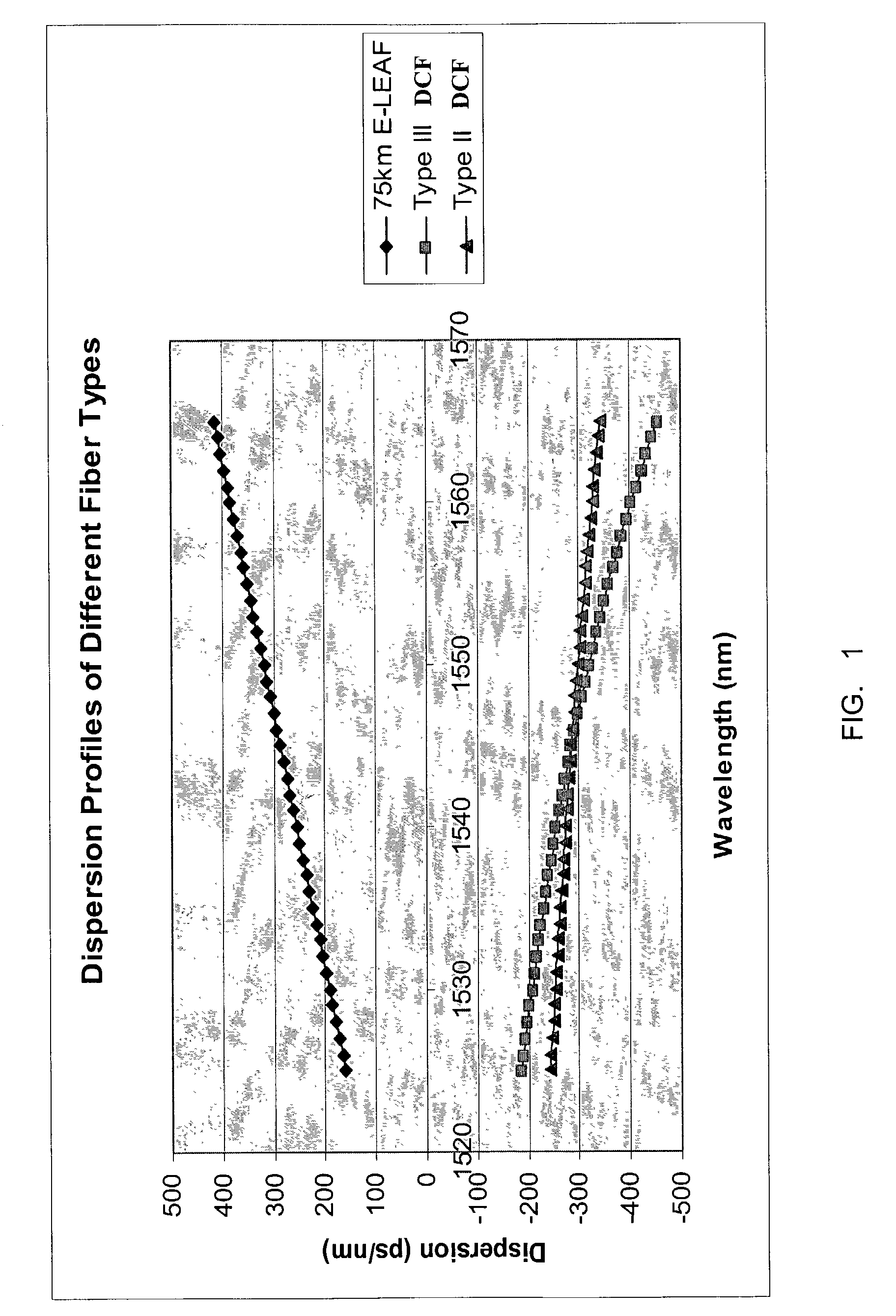
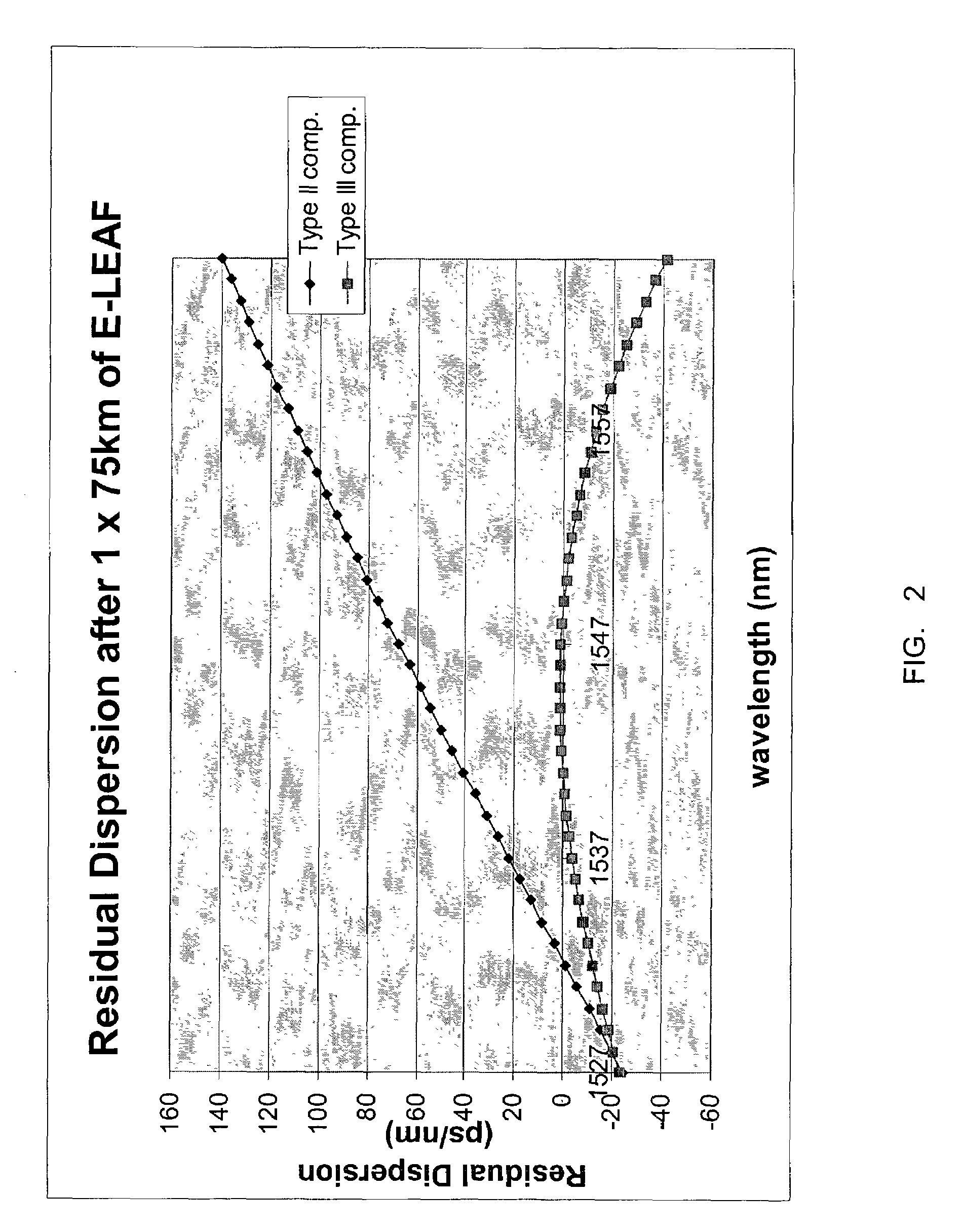
A method and system for compensating residual dispersion curvature in an optical communication network is disclosed. One embodiment employs two types of dispersion compensating fiber to reduce higher order terms in a residual dispersion profile. The two types of dispersion compensating fiber may be co-located in a dispersion compensation module positioned in each transmission fiber link. Alternatively, the two types of dispersion compensating fiber may be distributed across a span of the optical communication network.
Owner:CIENA
Wavelength dispersion compensation design method and a system thereof
InactiveUS20060193638A1Shorten design timeWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsEngineeringLength wave
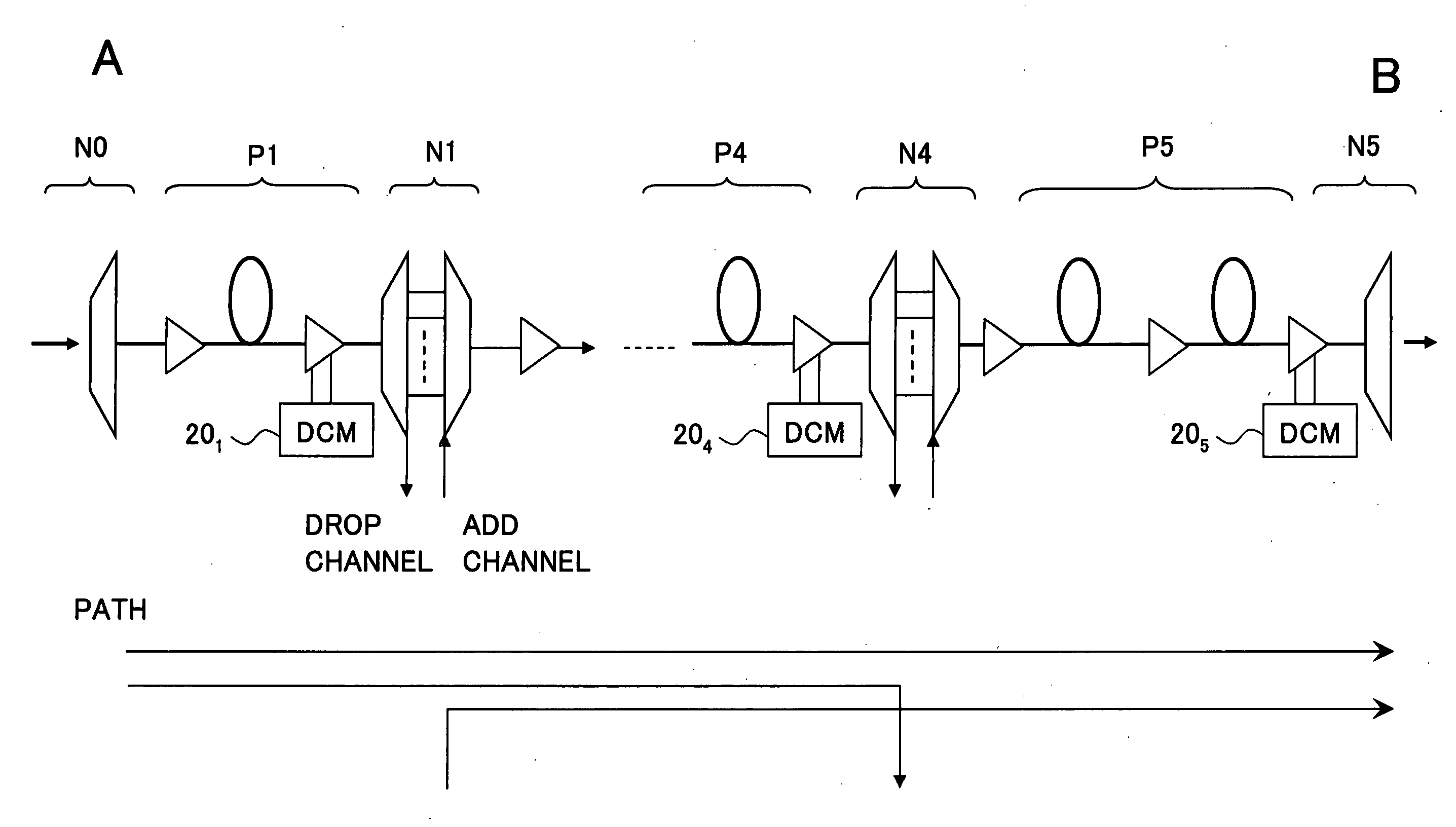
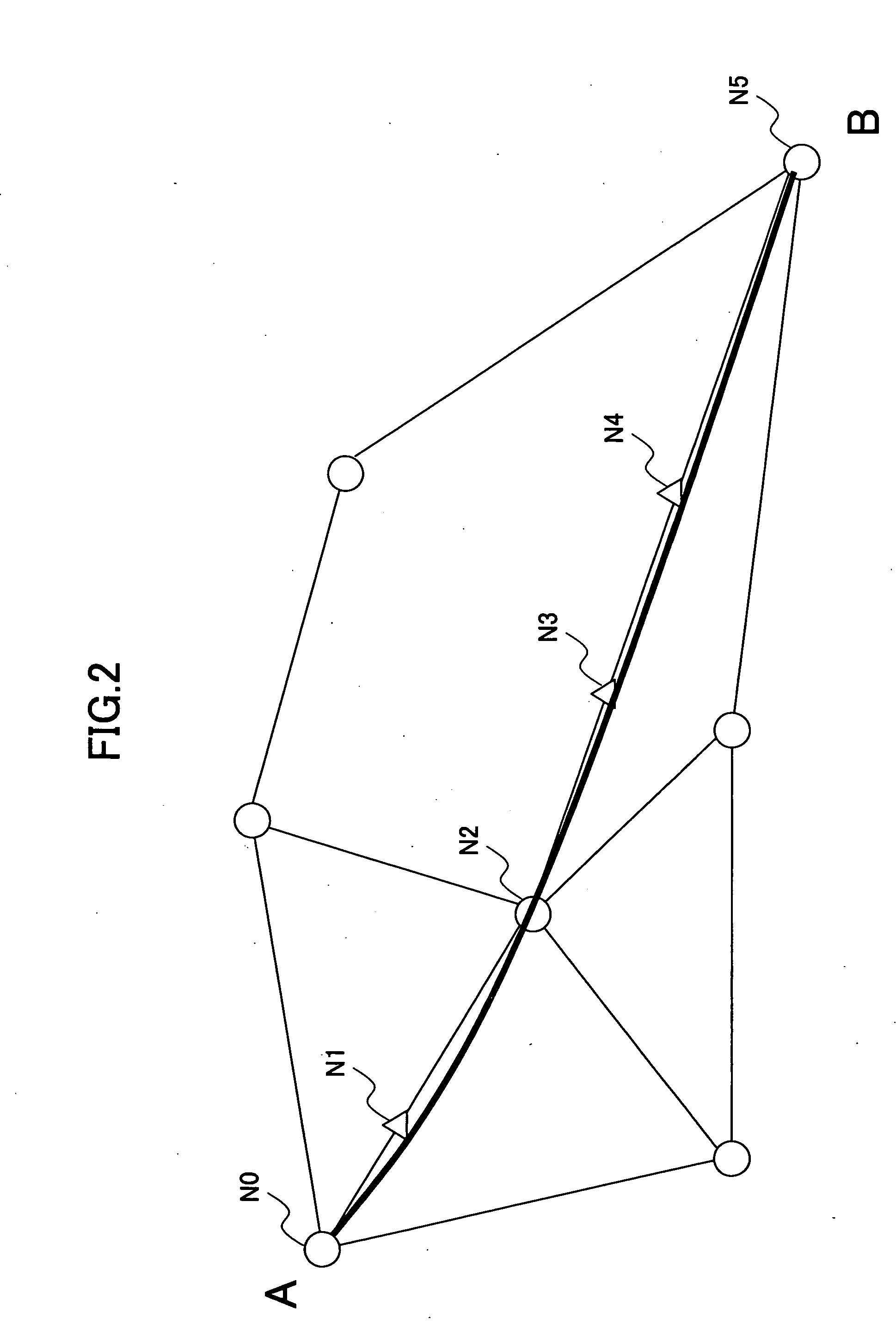
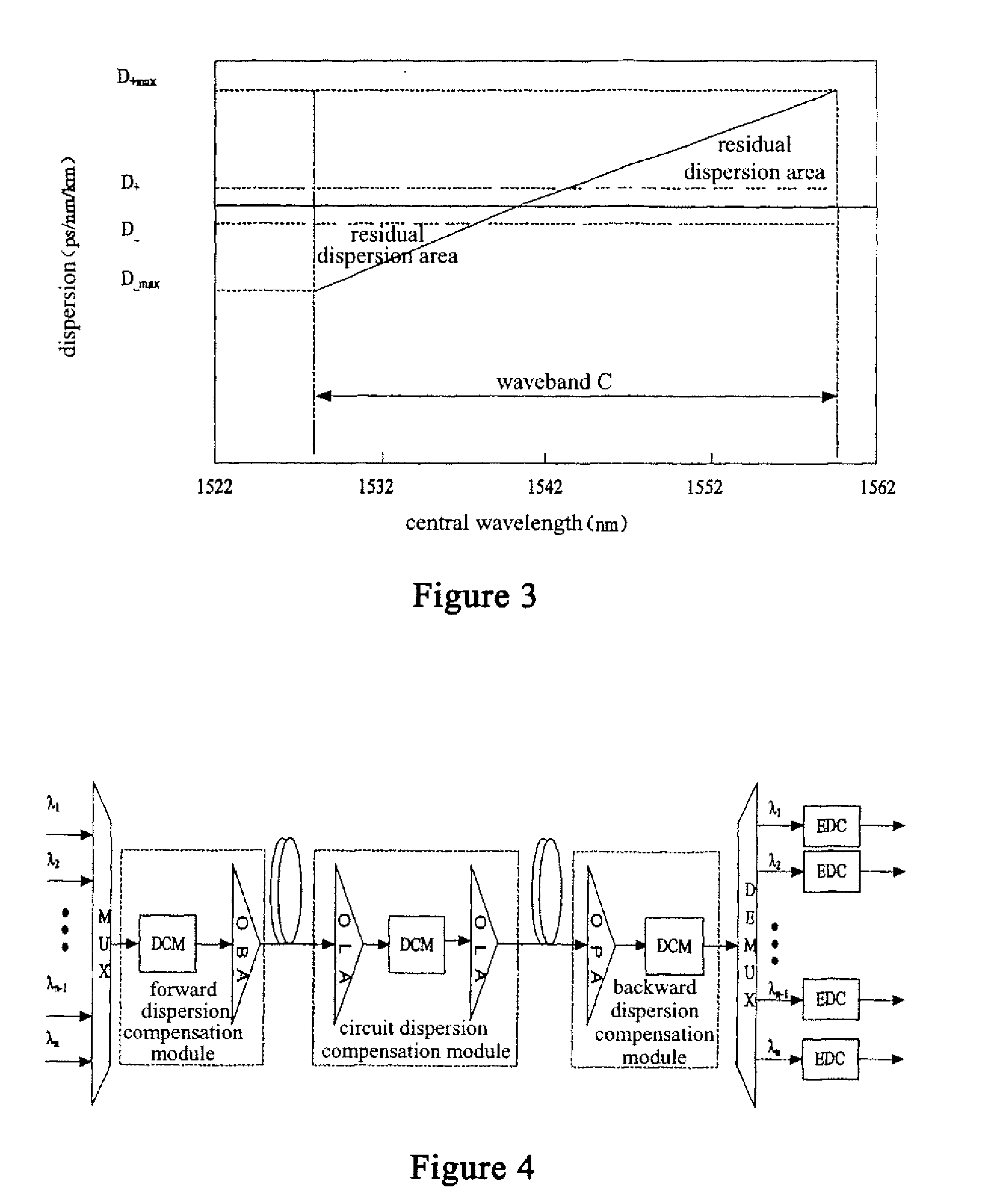
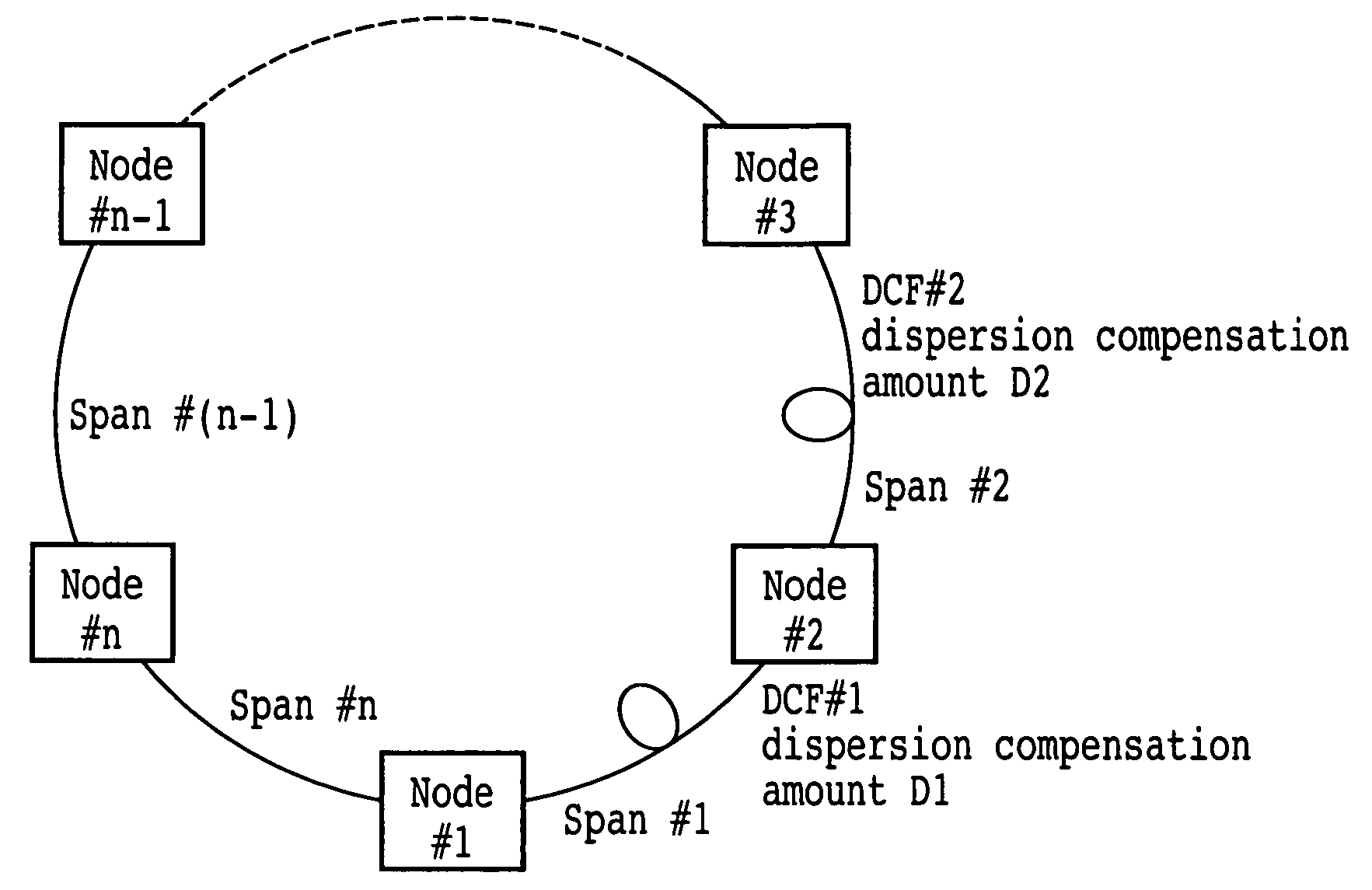
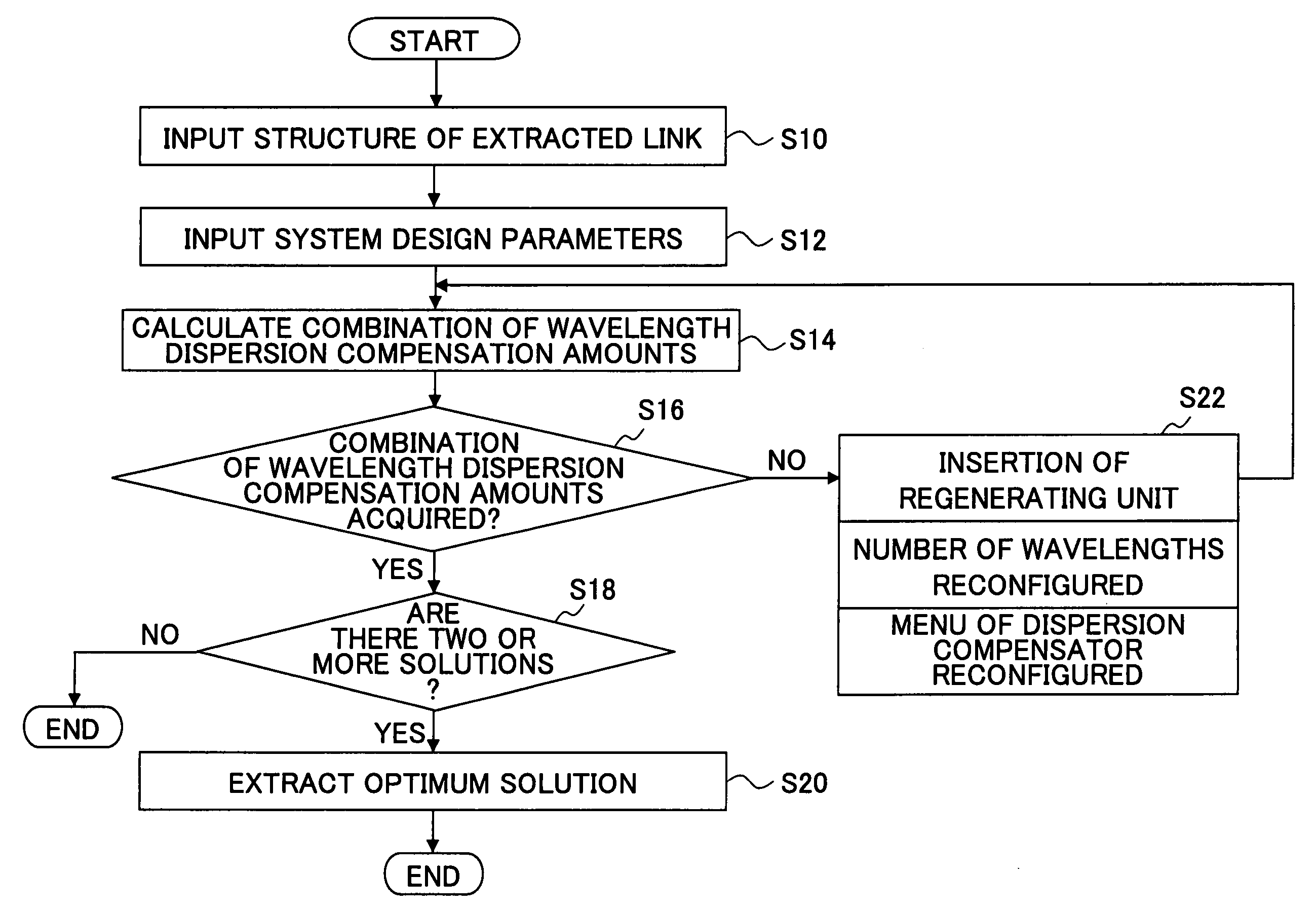
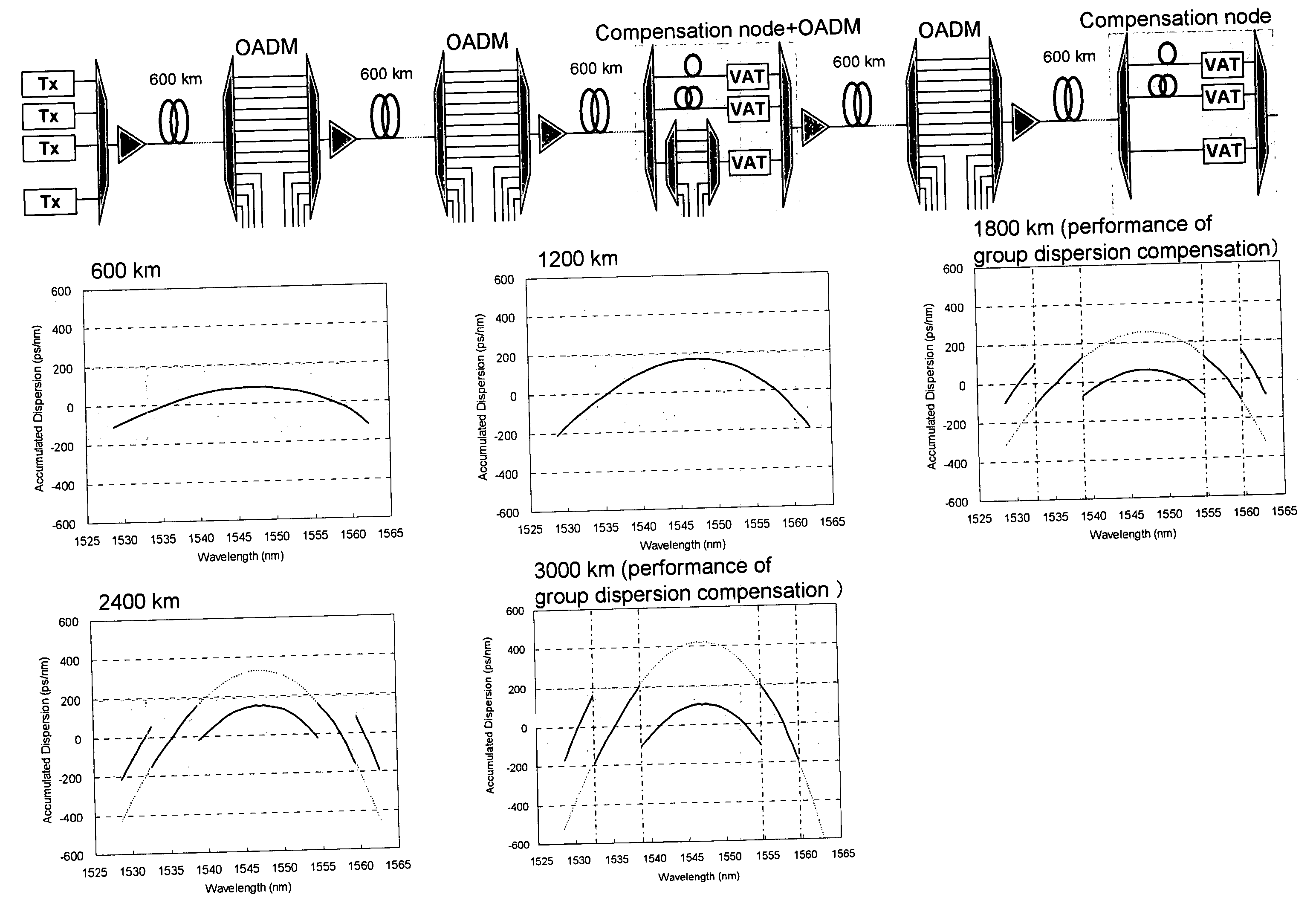
The present invention discloses a design method of wavelength dispersion compensation of a desired link that is extracted from an optical network, the link including two or more spans, and two or more nodes (N1, N4) that are equipped with an add / drop function, as shown in FIG. 2. All residual dispersion ranges of paths that reach corresponding nodes are adjusted to fall within predetermined tolerable residual dispersion ranges that are set up for all the paths of the link by adjusting wavelength dispersion compensators provided to each of the spans.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
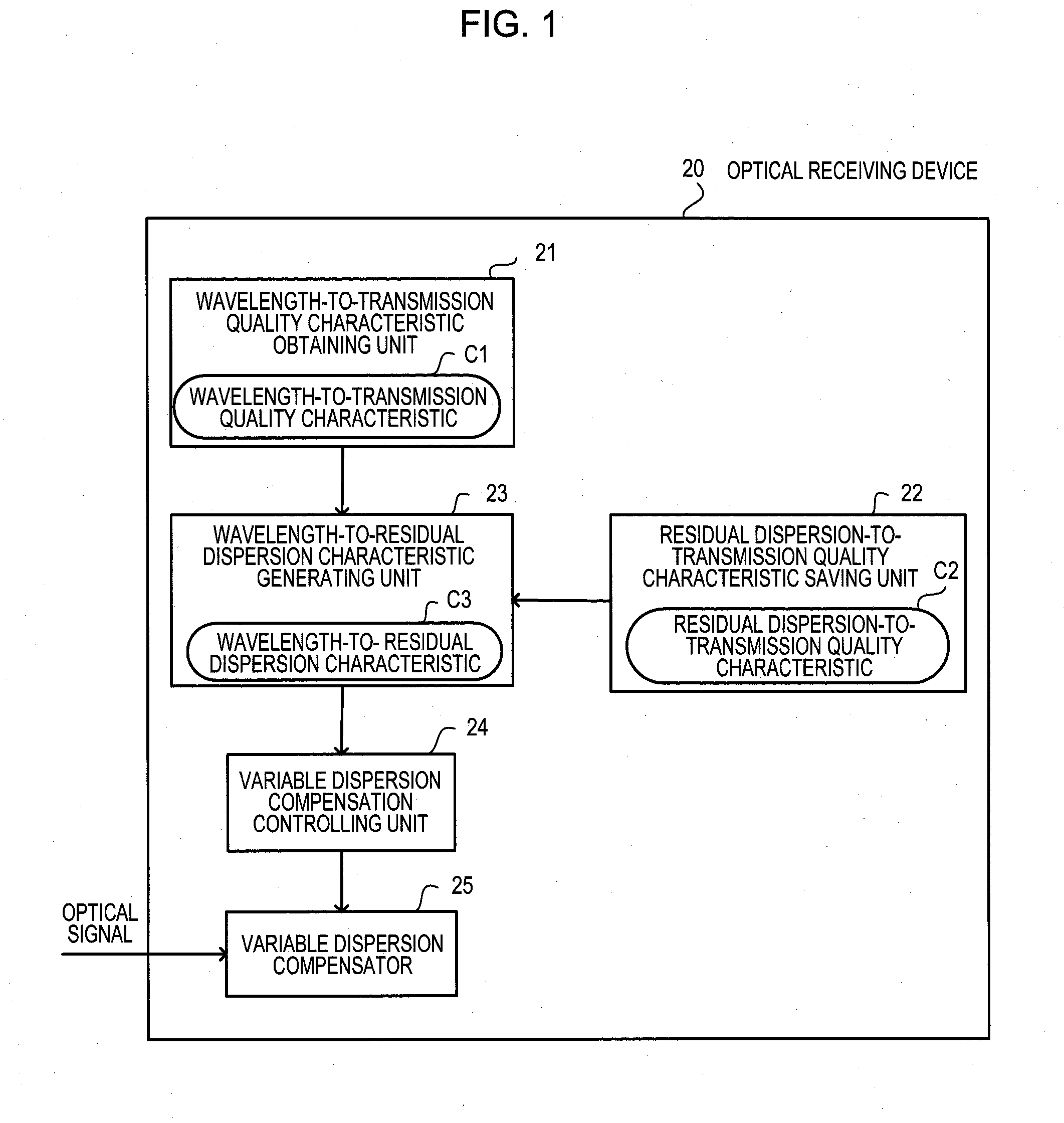
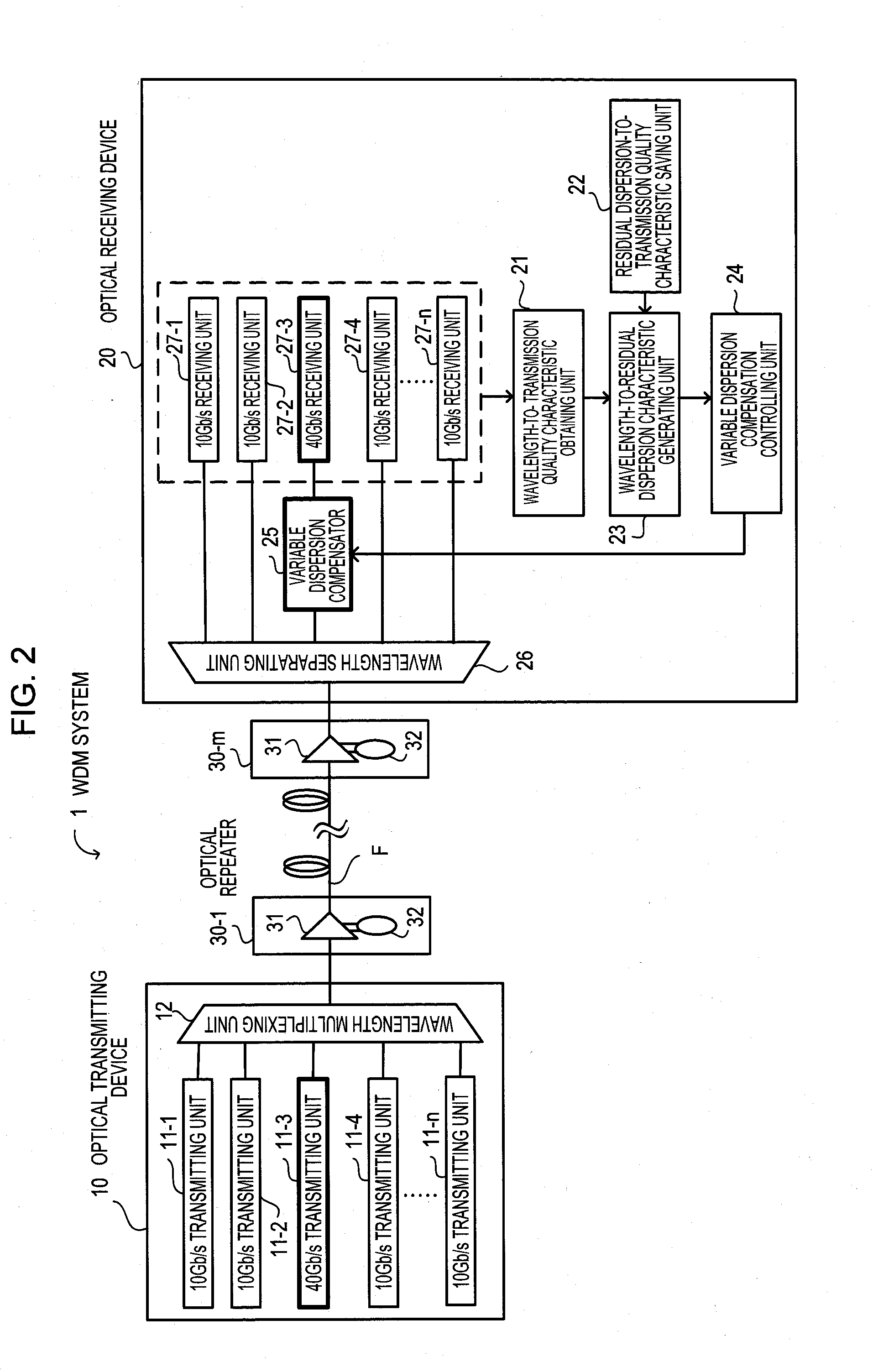
Optical receiving device and optical transmission system
InactiveUS20090097866A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringTransport systemEngineering
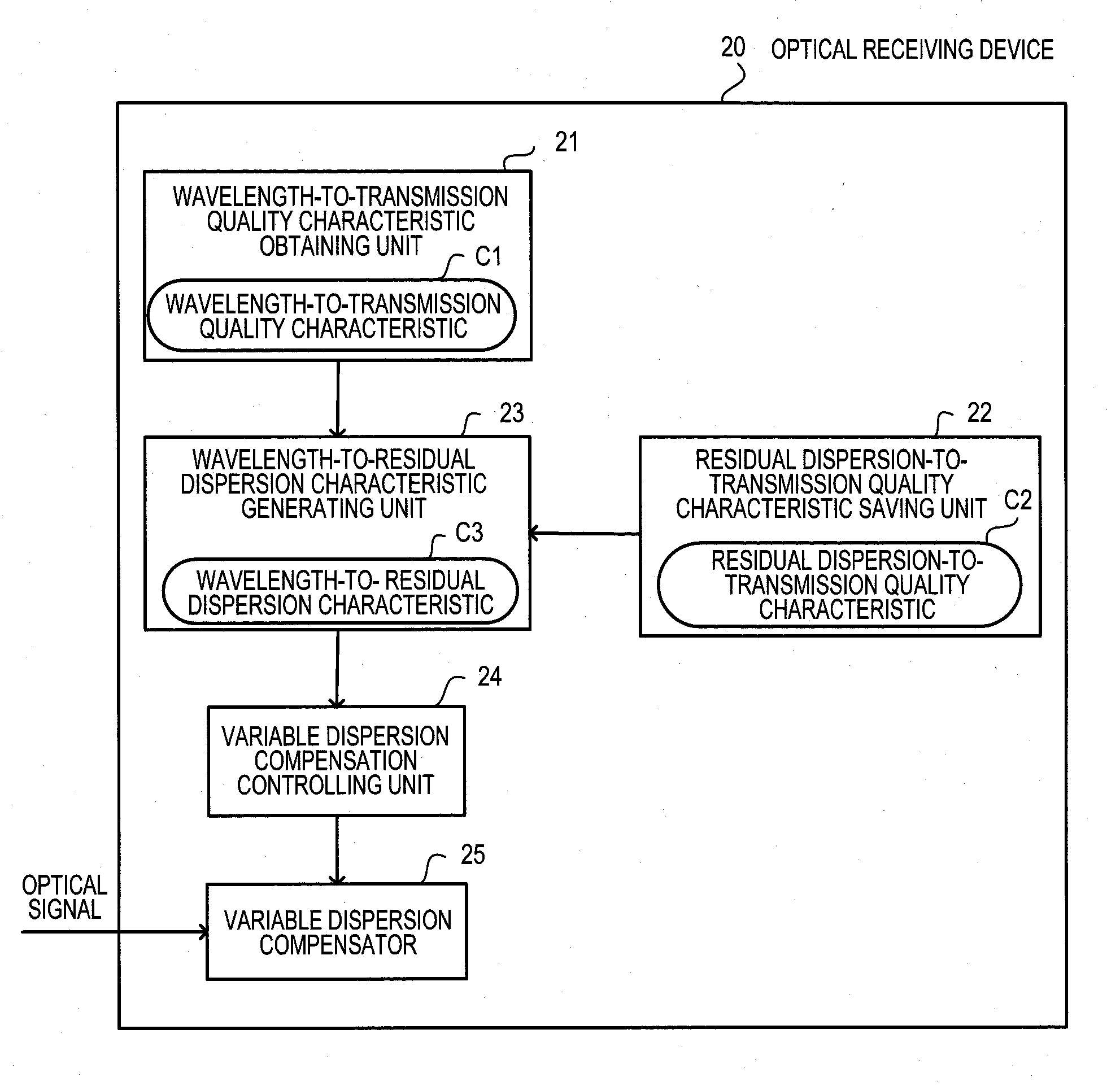
According to an aspect of an embodiment, an apparatus includes: a wavelength-to-transmission quality characteristic obtaining unit for obtaining a wavelength-to-transmission quality characteristic; a residual dispersion-to-transmission quality characteristic saving unit for saving a residual dispersion-to-transmission quality characteristic; a wavelength-to-residual dispersion characteristic generating unit for generating a wavelength-to-residual dispersion characteristic from a relationship between the wavelengths of the other channels and the residual dispersion based on the wavelength-to-transmission quality characteristic and the residual dispersion-to-transmission quality characteristic; a variable dispersion compensator for providing variable dispersion compensation to another channel,; and a variable dispersion compensation controlling unit for performing setting control on a dispersion compensation amount.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Wavelength division multiplexing system, method and device for its residual dispersion compensation
ActiveUS20090202248A1Large long distanceLarge toleranceWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationControl signalEngineering
The present invention provides a wavelength division multiplexing system and a method and device for its residual dispersion compensation, wherein the device for residual dispersion compensation of wavelength division multiplexing system comprises: a performance parameter detecting device for receiving and detecting performance parameter of receiving terminal optical signal and sending detecting result of the performance parameter to a central control device; the central control device for deciding a dispersion regulating mode of a tunable dispersion compensator according to the detecting result of the performance parameter and sending the dispersion regulating mode to a tunable dispersion compensator control device through control signaling; and the tunable dispersion compensator control device for receiving the control signaling sent by the central control device and adjusting dispersion compensation amount of the tunable dispersion compensator according to the control signaling in order to make residual dispersion of wavelength channels to satisfy requirements of dispersion tolerance of an optical receiver. Therefore, the present invention optimizes residual dispersion of each channel and solves the problem of transmission performance deterioration caused by residual dispersion of long distance optical transmission system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Electrical domain dispersion compensation method based on dispersion curve in WDM network
InactiveCN101447834AWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionElectricityDigital signal processing
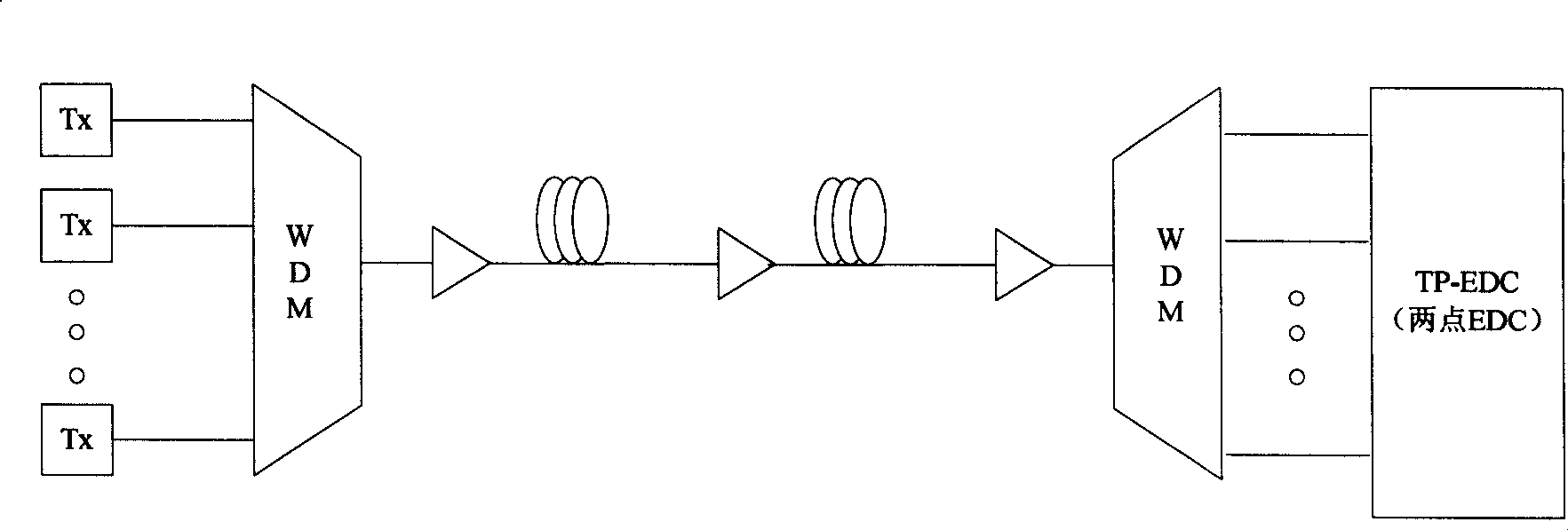
The invention relates to an electrical domain dispersion compensation method based on dispersion curves in the WDM network. Electronic dispersion compensation (EDC) technology belongs to a technology that the dispersion problem of optical transmission is treated by mature digital signal processing method. In the WDM system, a traditional one-to-one EDC equalizer is adopted. As more channels are used, the cost of the system is increased gradually; and in aspect of deployment, due to an EDC module, the difficulty of design is increased. TP-EDC receiver provided by the invention avoids the disadvantages. The receiver has function of all of the channels of dynamic equilibrium WDM system. The implementation method is simple, and the deployment is flexible. The method is applicable for the construction of brand new network and the interconnection between new and old optical-fiber networks. The method is also applicable in the environment of crossing a plurality of optical fibers. Due to the key technology of the method, the method is applicable in ROADM network environment, and the method can effectively solve the residual dispersion problem.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Optical transmission system
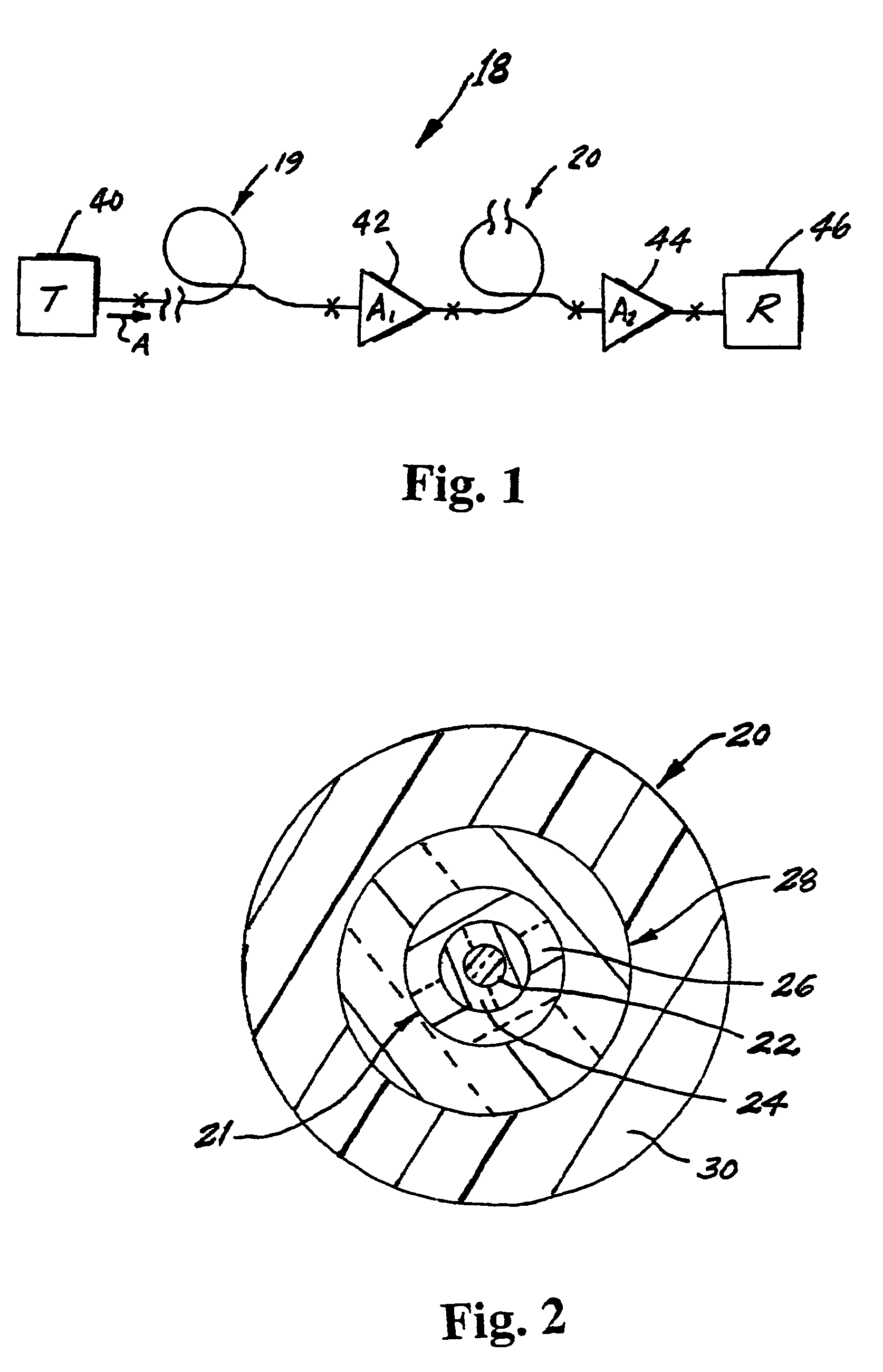
InactiveUS6876803B2Adequate dispersion compensationLow residual dispersionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesEngineeringTransmitter
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
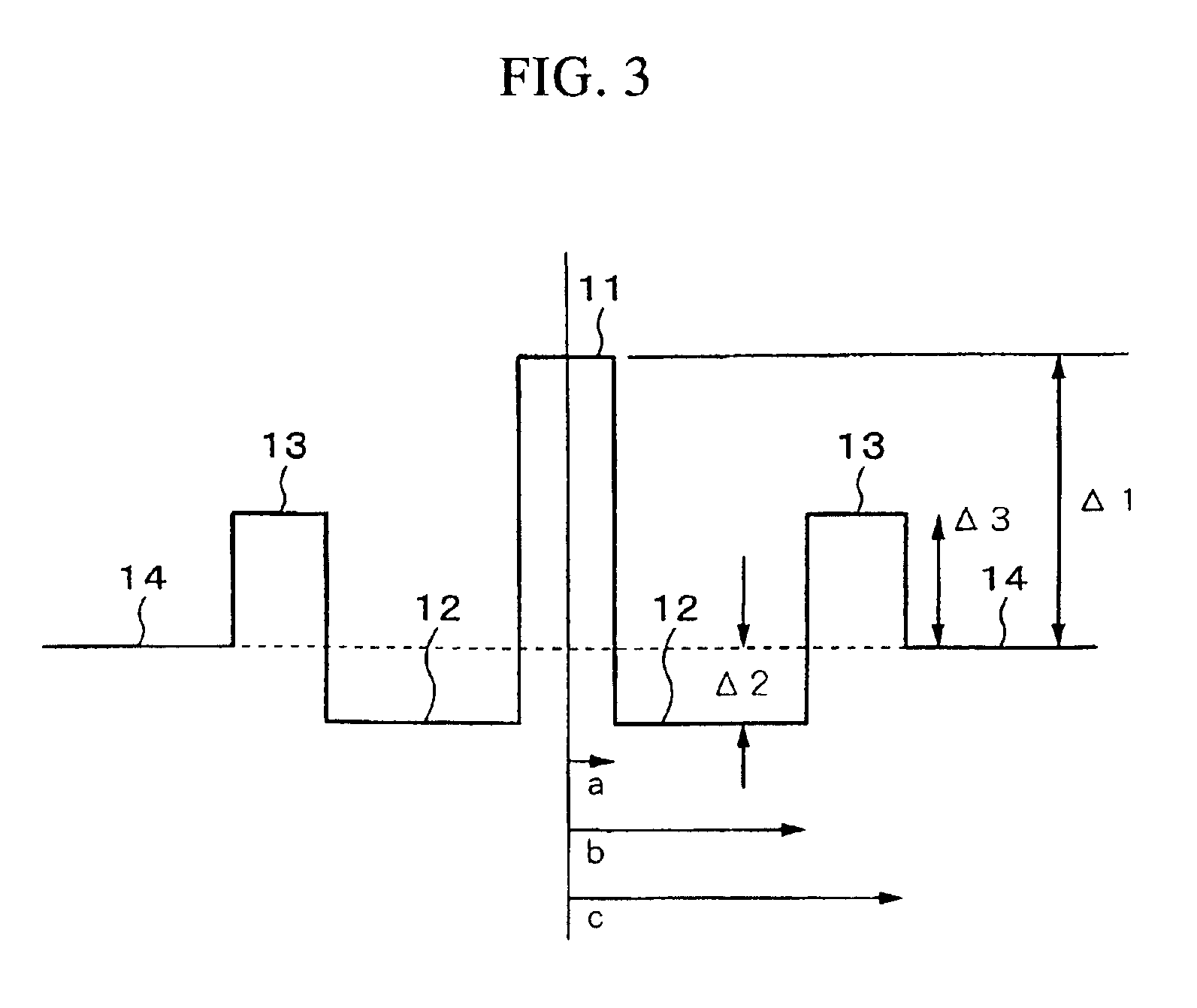
Large kappa dispersion compensating fiber and transmission system
InactiveUS6987918B1High kappaHigh effective areaOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingElectromagnetic transmissionEngineeringLength wave
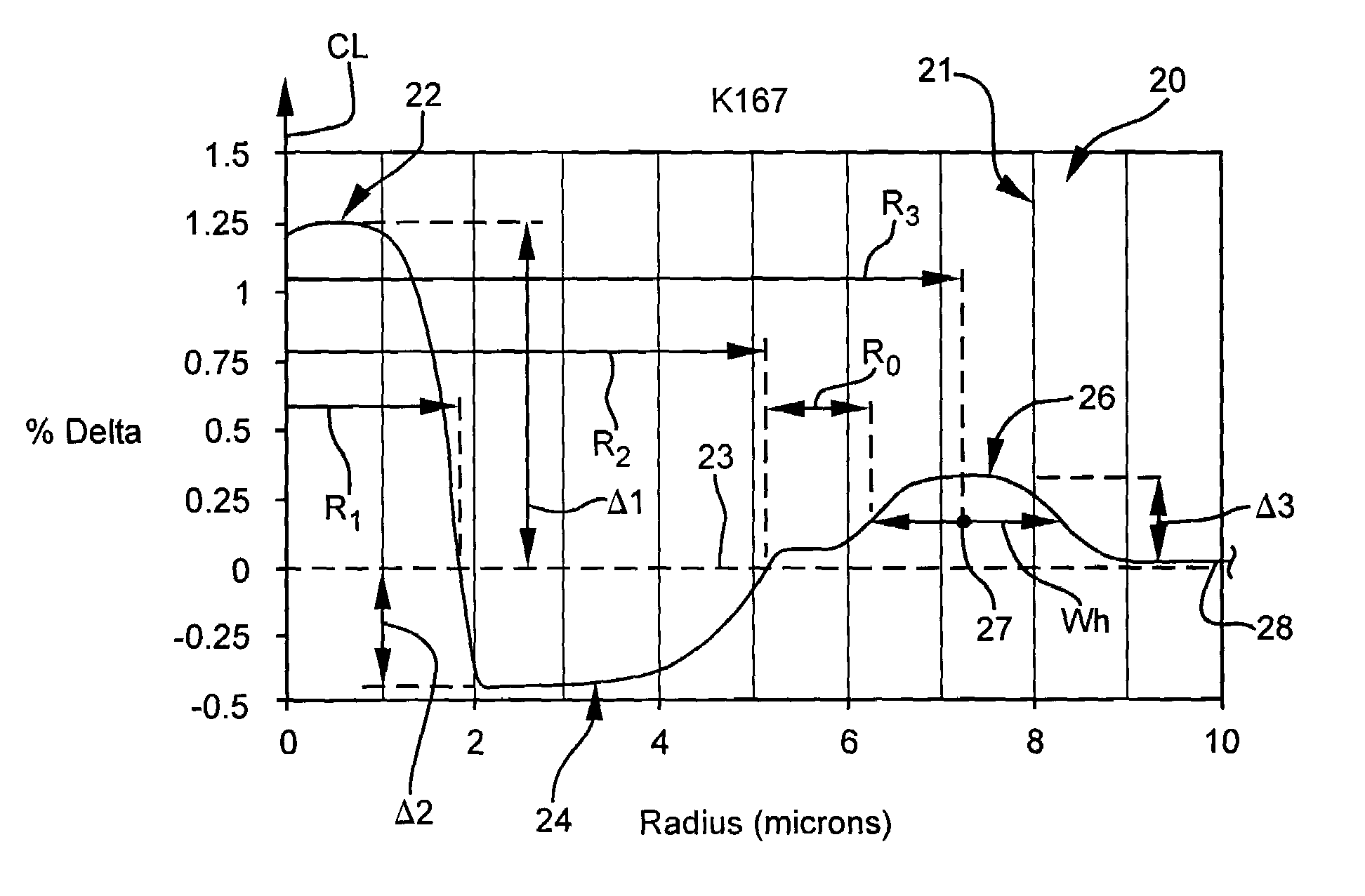
A dispersion compensation fiber for a moderate dispersion, low slope transmission fiber and transmission system including same. The dispersion compensating fiber has a refractive index profile having a central core with a core delta (Δ1), a moat surrounding the central core having a moat delta (Δ2), and a ring surrounding the moat having a positive ring delta (Δ3). The fiber's refractive index profile is selected to provide total dispersion less than −80 at 1550 nm and less than −90 ps / nm / km at 1600 nm, dispersion slope less than −0.18 ps / nm2 / km at 1550 and less than −0.10 ps / nm2 / km at 1600 nm / kappa between 250 and 450 at 1550 nm, and a kappa ratio (defined as kappa at 1600 nm / kappa at 1550 nm) of greater than 1.35. The dispersion compensating fiber, when used in a transmission system, may provide low average residual dispersion across the C, L, and C+L bands when such systems include moderate dispersion, low dispersion slope transmission fibers with a total dispersion between 4 and 8 ps / nm / km, and a dispersion slope less than 0.025 ps / nm2 / km at all wavelengths between 1525 and 1625 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
One-step continuous granulation preparation method for water absorbent granule
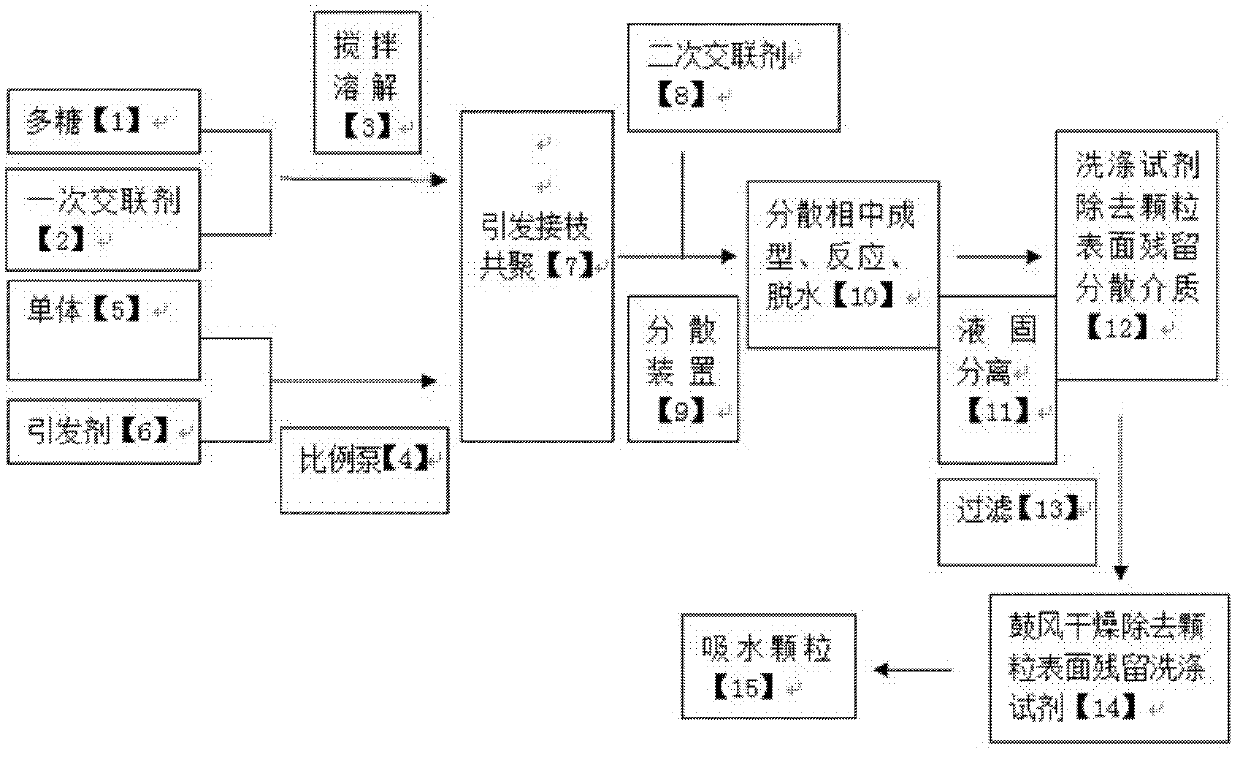
The invention discloses a one-step continuous granulation preparation method for a water absorbent granule, and the water absorbent granule consists of polysaccharide, monomer, initiator and cross-linking agents according to a certain proportion by weight. The method includes the following steps: (A) the polysaccharide and the primary cross-linking agent are added into a reactor and uniformly mixed under the condition of nitrogen protection until dissolution, the initiator and the monomer partially neutralized neutralizing alkali are added, and the temperature is controlled to initiate graft copolymerization reaction; (B) the secondary cross-linking agent is added, and after the reaction solution is uniformly mixed, granulation is fulfilled; (C) dispersion medium is filtered, the granulesare transferred into washing reagent, and the residual dispersion medium on the surfaces of the granules is washed off with the washing reagent; (D) the washing reagent is filtered, and a heating fanis used for removing the residual washing reagent on the surfaces of the granules; (E) the water absorbent granules are obtained. The method is easy, and is simple and convenient to operate. The water absorbent granules cannot be easily caked under the high-humidity condition, and the invention solves the problems that: in the conventional aqueous solution method for preparation, the granules aremostly powdery, the grain size is ununiform, and the drying time is overlong. The one-step continuous granulation preparation method is suitable for mass production.
Owner:WUHAN LICHENG BIOTECH
System And Method For Tunable Chromatic Dispersion Compensation
InactiveUS20100284701A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringAudio power amplifierData signal
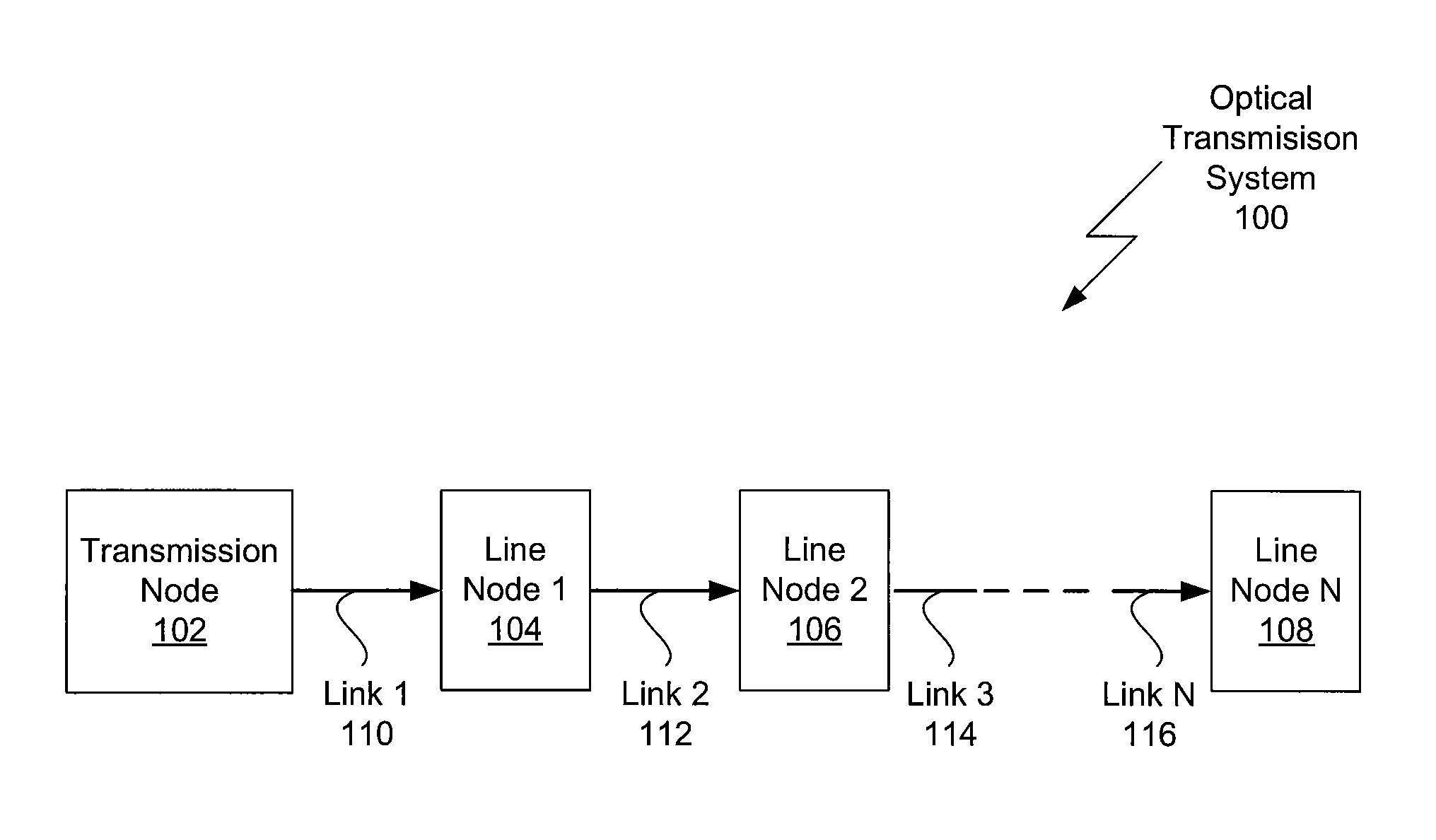
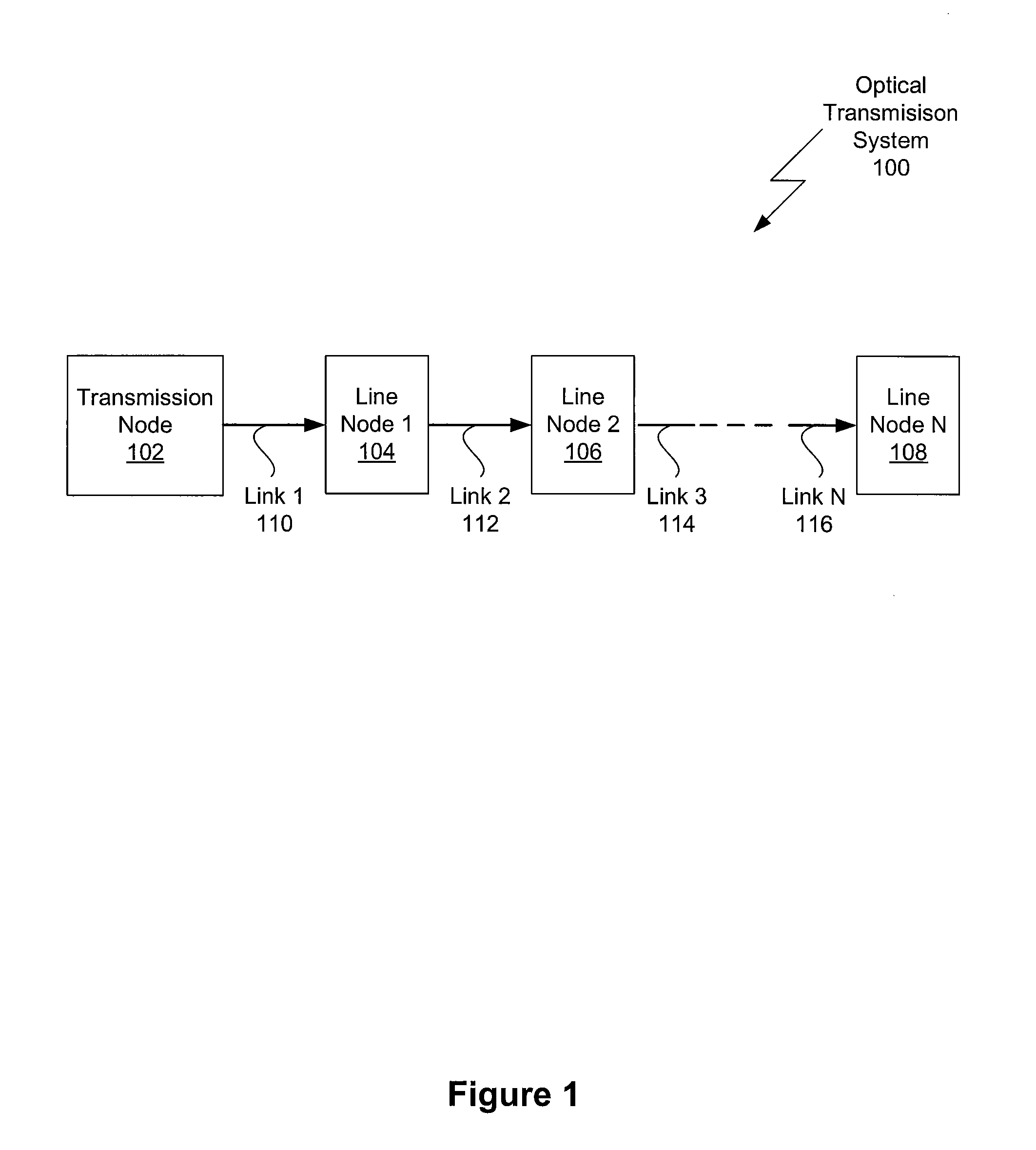
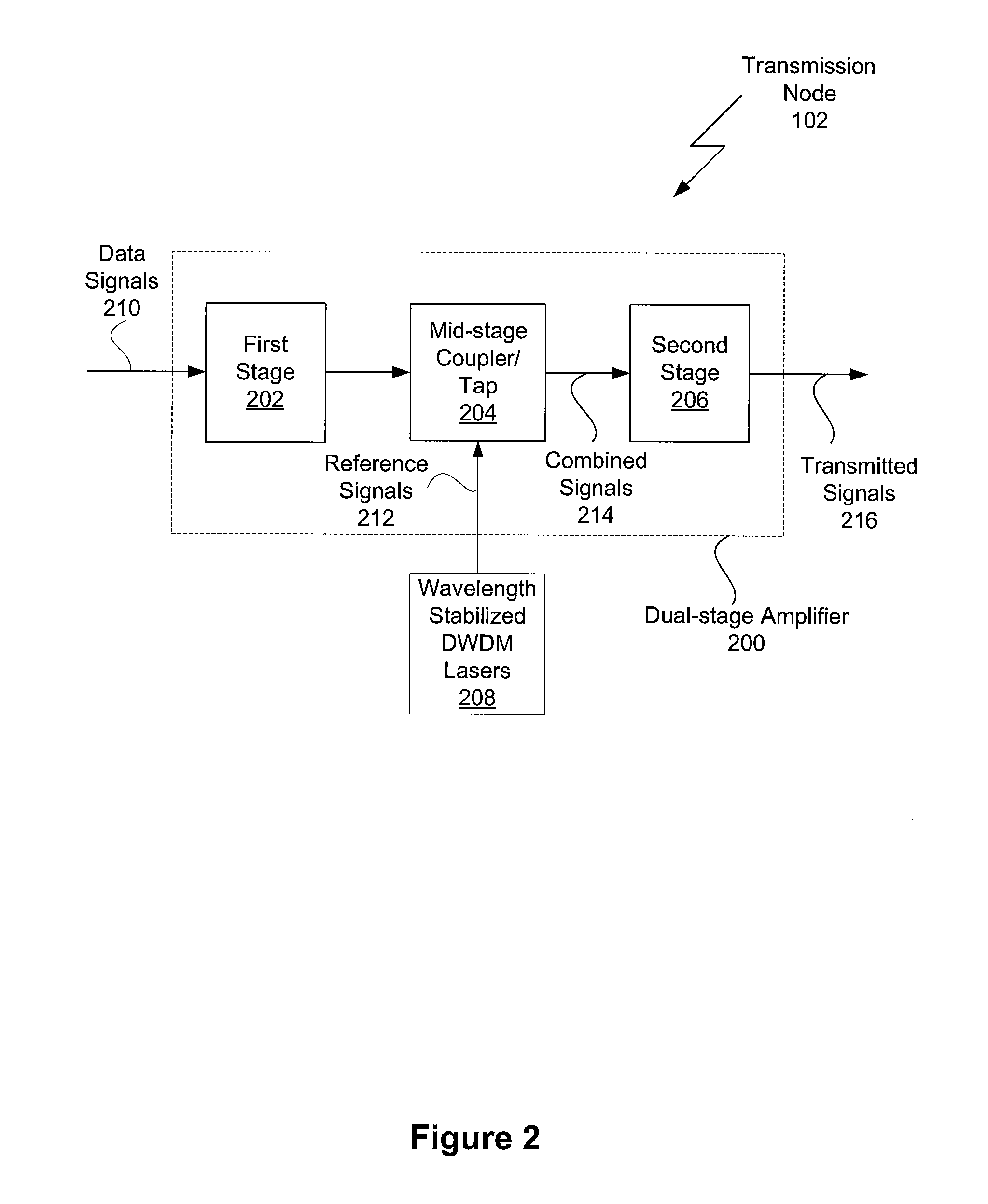
One embodiment sets forth a technique for measuring chromatic dispersion using reference signals within the operational range of amplifiers used to refresh data signals. One red / blue laser pair in the transmission node is used for measuring dispersion and chromatic dispersion compensation is added at each line node in the system. Since reference and data signals propagate through each amplifier, the reference signals used to measure chromatic dispersion receive the same dispersion compensation (and will have the same residual dispersion) as the data signals. Therefore, any residual dispersion in the data signals will manifest itself in downstream dispersion measurements and, thus, can be corrected. The tunable dispersion compensator in each line node may be set to compensate for the measured dispersion, thereby compensating for both the chromatic dispersion of the link connecting the current node to the prior node and any uncorrected residual dispersion from prior nodes.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Nonlinear device comprising a spectrally broadening fiber
InactiveUS7139478B2Improve system performanceTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsFrequency spectrumControl signal
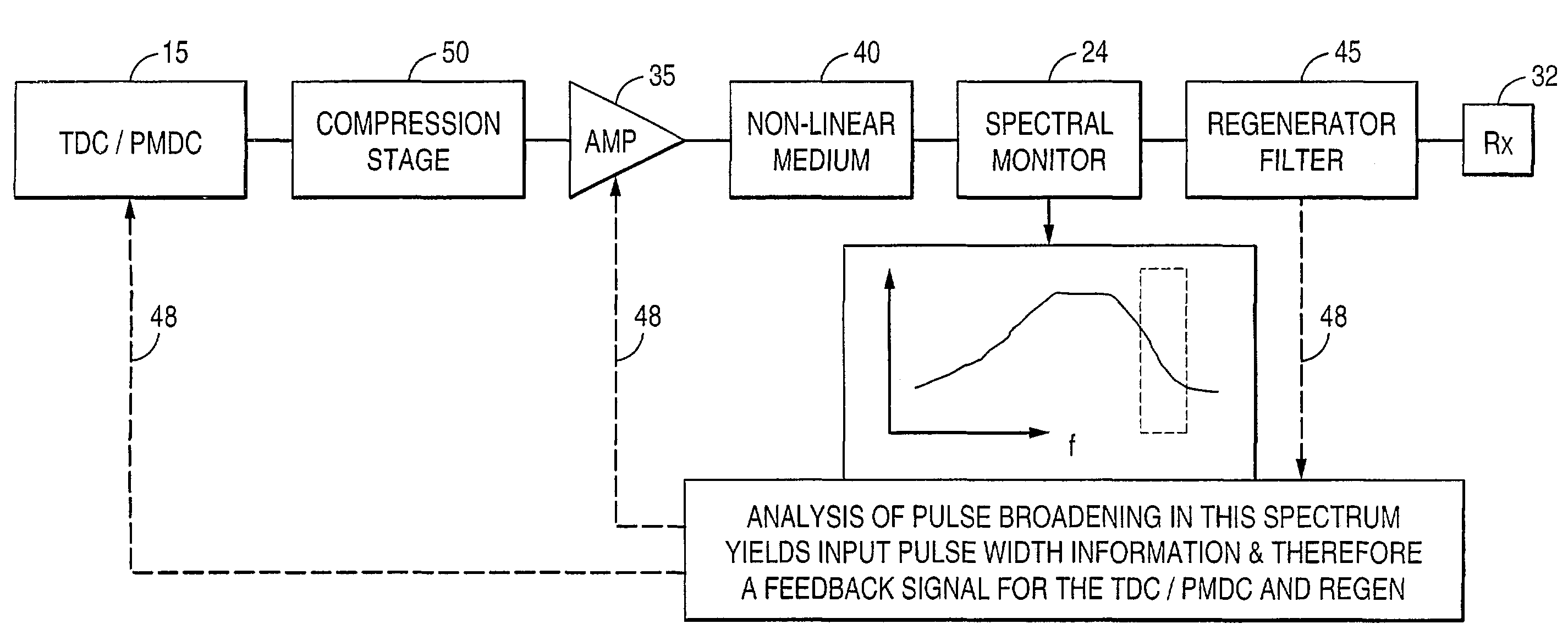
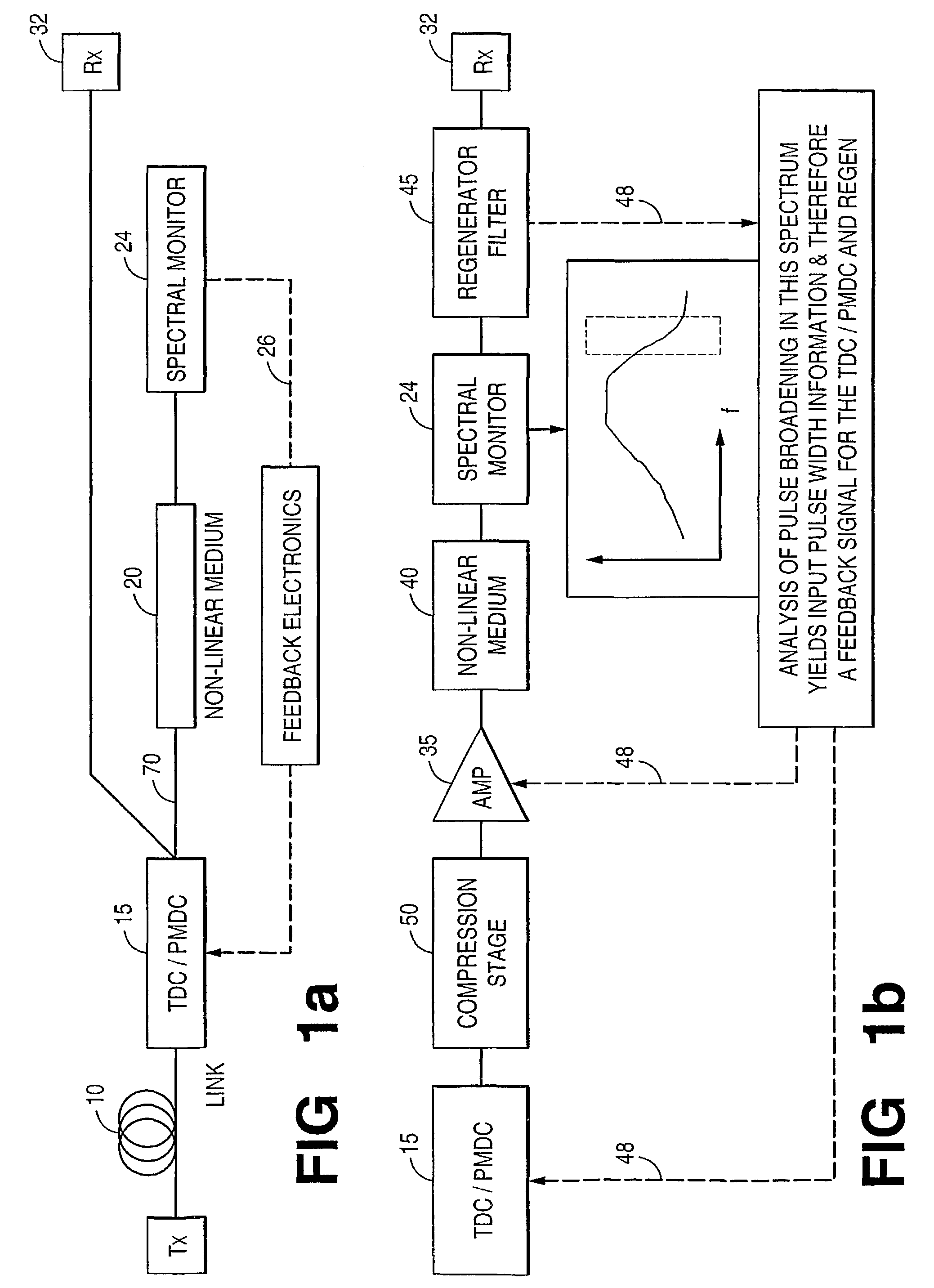
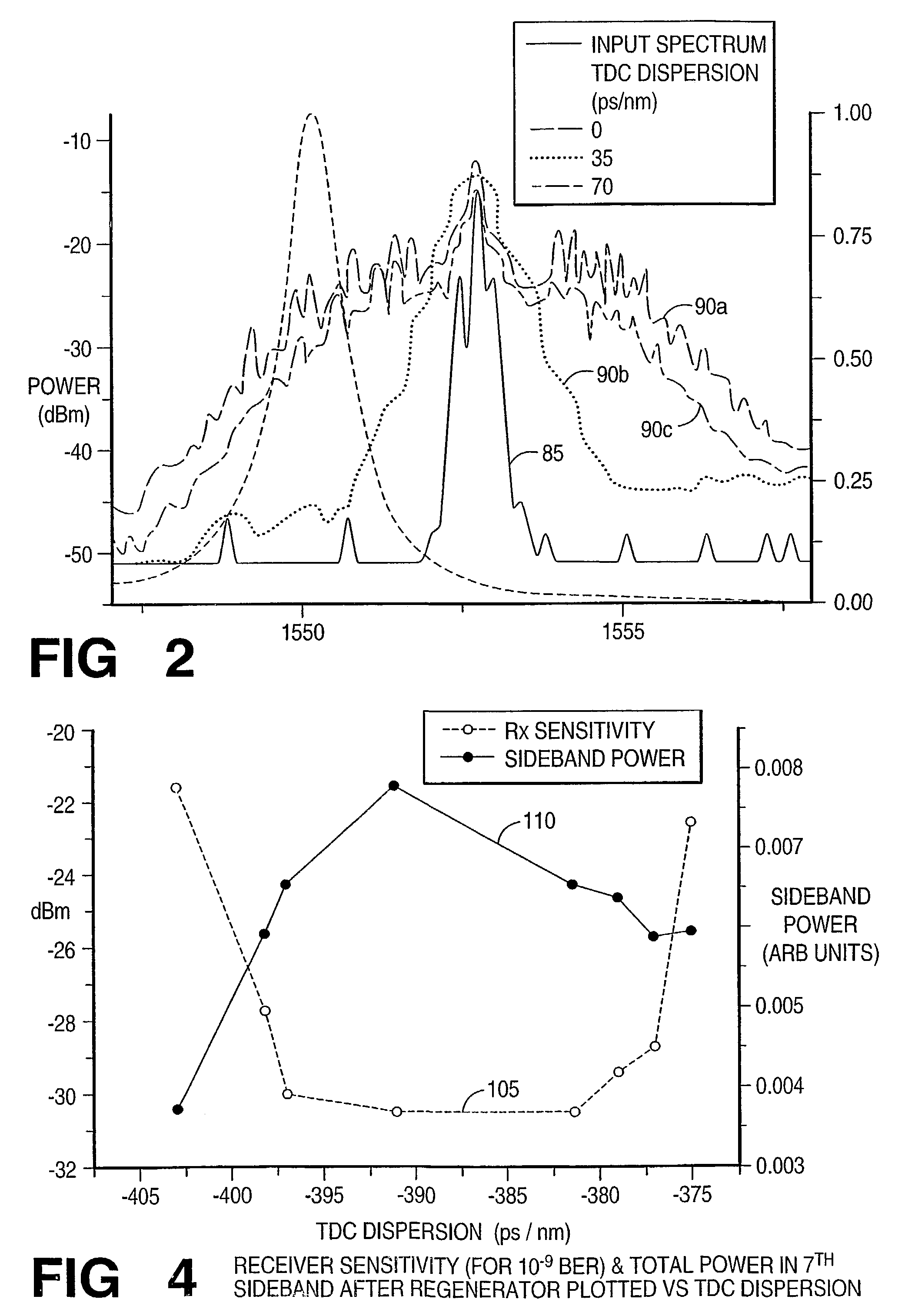
Embodiments of the invention include system for monitoring the effectiveness of pulse shaping in a nonlinear optical fiber (40). The spectral content of the pulse, after passing through the nonlinear fiber (40), provides an indication of how effectively the pulse was regenerated. A portion of the pulse exiting the nonlinear fiber is tapped off and its pulse energy is measured in at least one selected spectral region. The selected spectral region is one in which the pulse tends to gain energy when effective regeneration is taking place. The information concerning the effectiveness of pulse shaping in a nonlinear optical fiber is fed back to dynamically change the residual dispersion at the regenerator input. The spectral measurement leads to a control signal (48) to indicate a level of performance of the system, or to improve the performance of the system by adjusting an operational parameter.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Dispersion compensating fiber module, and optical fiber transmission line
InactiveUS7181115B2Small sizeReduce dispersionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesEngineeringLength wave
A dispersion compensating fiber module which, when connected to an optical fiber which exhibits, at a wavelength of 1.55 μm, a chromatic dispersion of between +2 and +6 ps / nm / km, a dispersion slope of between +0.075 ps / nm2 / km and +0.095 ps / nm2 / pm, and a relative dispersion slope of between 0.016 nm−1 and 0.024 nm−1, performs compensation so that the residual dispersion of the connected optical fiber is reduced, the dispersion compensating fiber module includes a dispersion compensating fiber and at least one optical fiber fused to the dispersion compensating fiber, in which the dispersion compensating fiber module exhibits at a wavelength of 1.55 μm, a relative dispersion slope of between 0.016 nm−1 and 0.026 nm−1; and in a wavelength range between 1.525 μm and 1.565 μm, a maximum residual dispersion difference, when converted per km of the transmission optical fiber, of less than or equal to 0.4 ps / nm / km.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
Optical transmission network, optical transmission apparatus, dispersion compensator arrangement calculation apparatus and dispersion compensator arrangement calculation method
InactiveUS6987903B2Reduce the amount of compensationRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringOptical Transport Network
An optical transmission network includes a first dispersion compensator arranged in a maximum dispersion span having a maximum dispersion value and searched out from within a maximum dispersion route having a maximum dispersion value from among routes of non-regeneration intervals within which a dispersion value before dispersion compensation does not satisfy an upper limit of a dispersion tolerance, and a second dispersion compensator arranged in a maximum dispersion span having a maximum dispersion value searched out from within a maximum dispersion route having a maximum dispersion value from among the routes when a dispersion compensator is successively arranged until a route of a non-regeneration interval within which a dispersion value of a certain channel does not satisfy the dispersion tolerance does not remain any more based on the dispersion value after the dispersion compensation with respect to the searched out maximum dispersion span. The dispersion compensation amounts of the first and second dispersion compensators are such that, when the dispersion compensation amount of the maximum dispersion span in which the first and second dispersion compensators are arranged is successively increased, the span has a residual dispersion value equal to or higher than a fixed range and the maximum dispersion route which relates to the spans has a residual dispersion value which satisfies the dispersion tolerance or the span has a residual dispersion value which is within the fixed range.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High figure of merit dispersion compensating fiber for standard single mode fiber and transmission system utilizing same
InactiveUS6925237B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringFigure of merit
A dispersion compensating optical fiber that includes a segmented core having a central core segment, a moat segment, and a ring segment wherein the ring segment is preferably offset from the moat outer radius, r2, by a ring offset, Xo, greater than 0.4 μm. The refractive index profile is selected to provide a total dispersion at 1550 nm of between about −120 and −145 ps / nm / km, and a total dispersion slope at 1550 nm of between about −0.36 and −0.56 ps / nm2 / km. The refractive index profile is preferably further selected to provide a kappa, defined as the total dispersion at 1550 nm divided by the dispersion slope at 1550 nm, of between about 250 and 320 nm. Optical transmission systems including the present invention dispersion compensating optical fiber which have residual dispersion less than + / −15 ps / nm per 100 km of standard single mode transmission fiber are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Dispersion compensating fiber for low slope transmission fiber and optical transmission line utilizing same
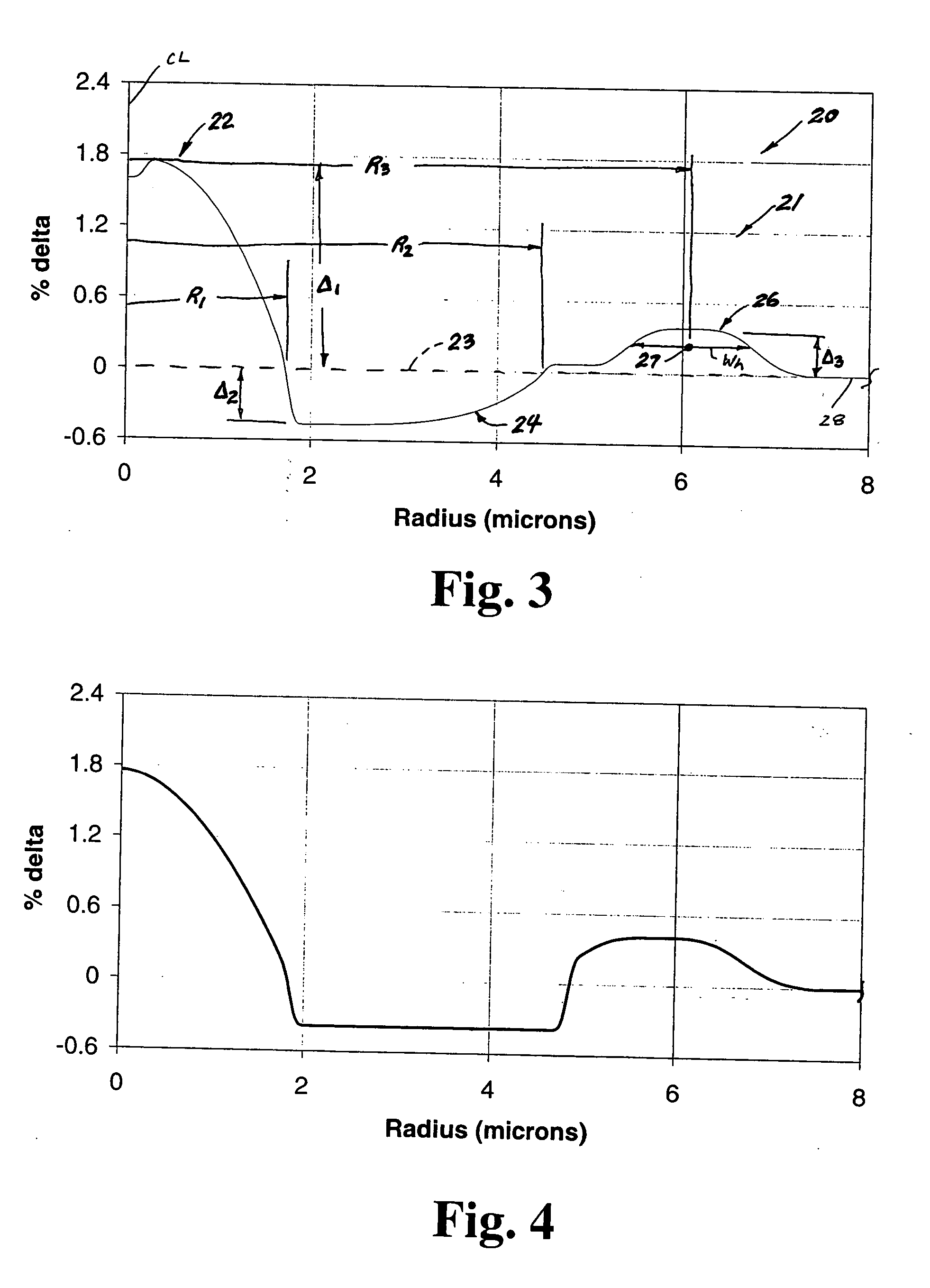
InactiveUS6975801B2High effective areaLow bend-lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringResidual dispersion
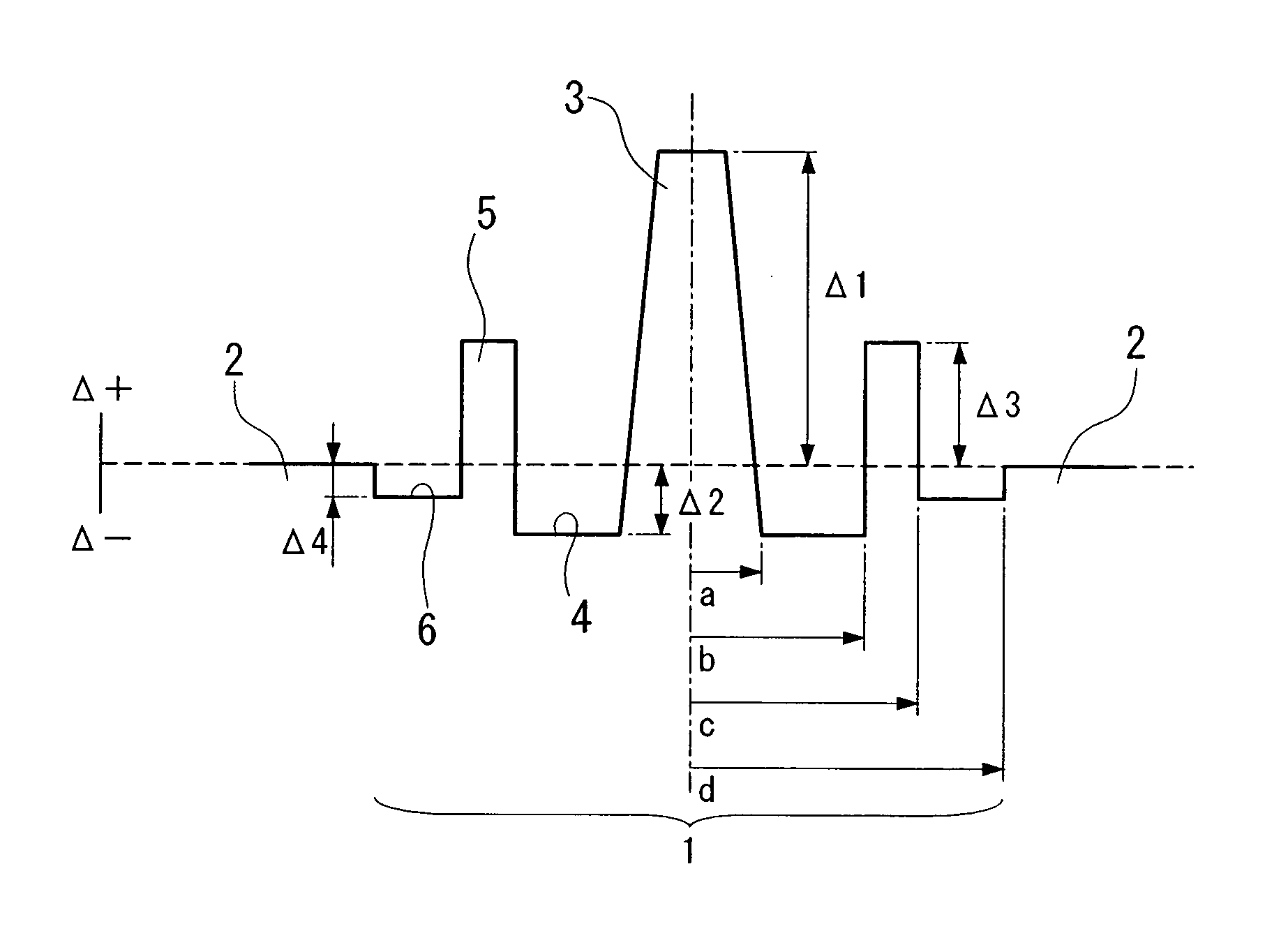
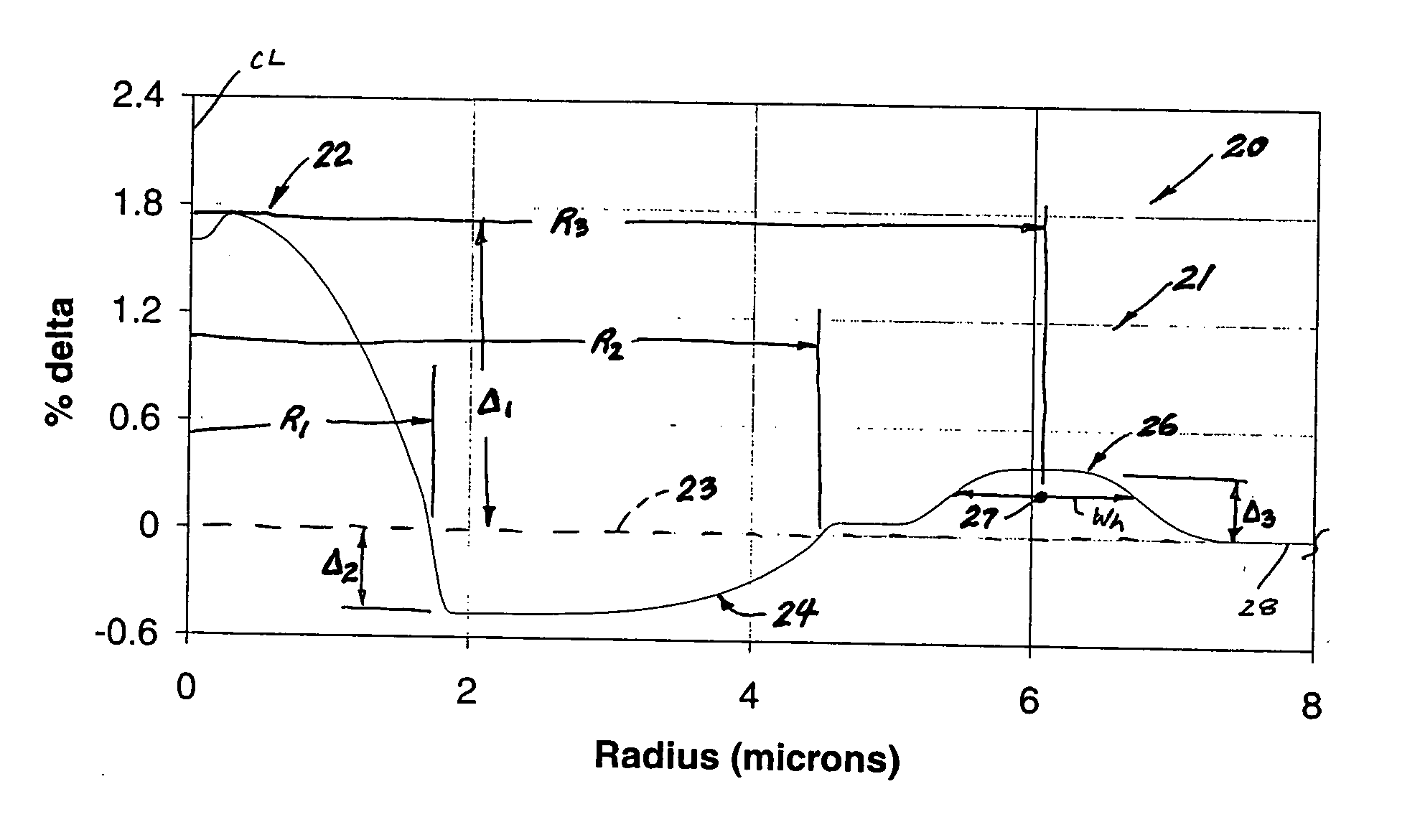
A Dispersion Compensation (DC) fiber for low slope transmission fiber (such as a NZDSF) and transmission line including same. The DC fiber has a refractive index profile having a central core with a core delta (Δ1) value less than 1.8%, a moat surrounding the central core having a moat delta (Δ2) value greater than −0.9%, and a ring surrounding the moat having a positive ring delta (Δ3). The DC fiber's refractive index profile is selected to provide total dispersion less than −40 and greater than −87 ps / nm / km, and kappa of greater than 165 and less than 270 nm, all at 1550 nm. The DC fiber, when used in a transmission line, may provide low average residual dispersion across the C, L, and C+L when such lines include transmission fibers with a total dispersion between 4 and 10 ps / nm / km and a dispersion slope less than 0.045 ps / nm2 / km at 1550 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Wavelength dispersion compensation design method and a system thereof
InactiveUS7382979B2Shorten design timeWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsEngineeringLength wave
The present invention discloses a design method of wavelength dispersion compensation of a desired link that is extracted from an optical network, the link including two or more spans, and two or more nodes (N1, N4) that are equipped with an add / drop function, as shown in FIG. 2. All residual dispersion ranges of paths that reach corresponding nodes are adjusted to fall within predetermined tolerable residual dispersion ranges that are set up for all the paths of the link by adjusting wavelength dispersion compensators provided to each of the spans.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Devices and methods for dynamic dispersion compensation
InactiveUS20060139740A1Not high insertion lossRapid responseLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingEngineeringBroadband
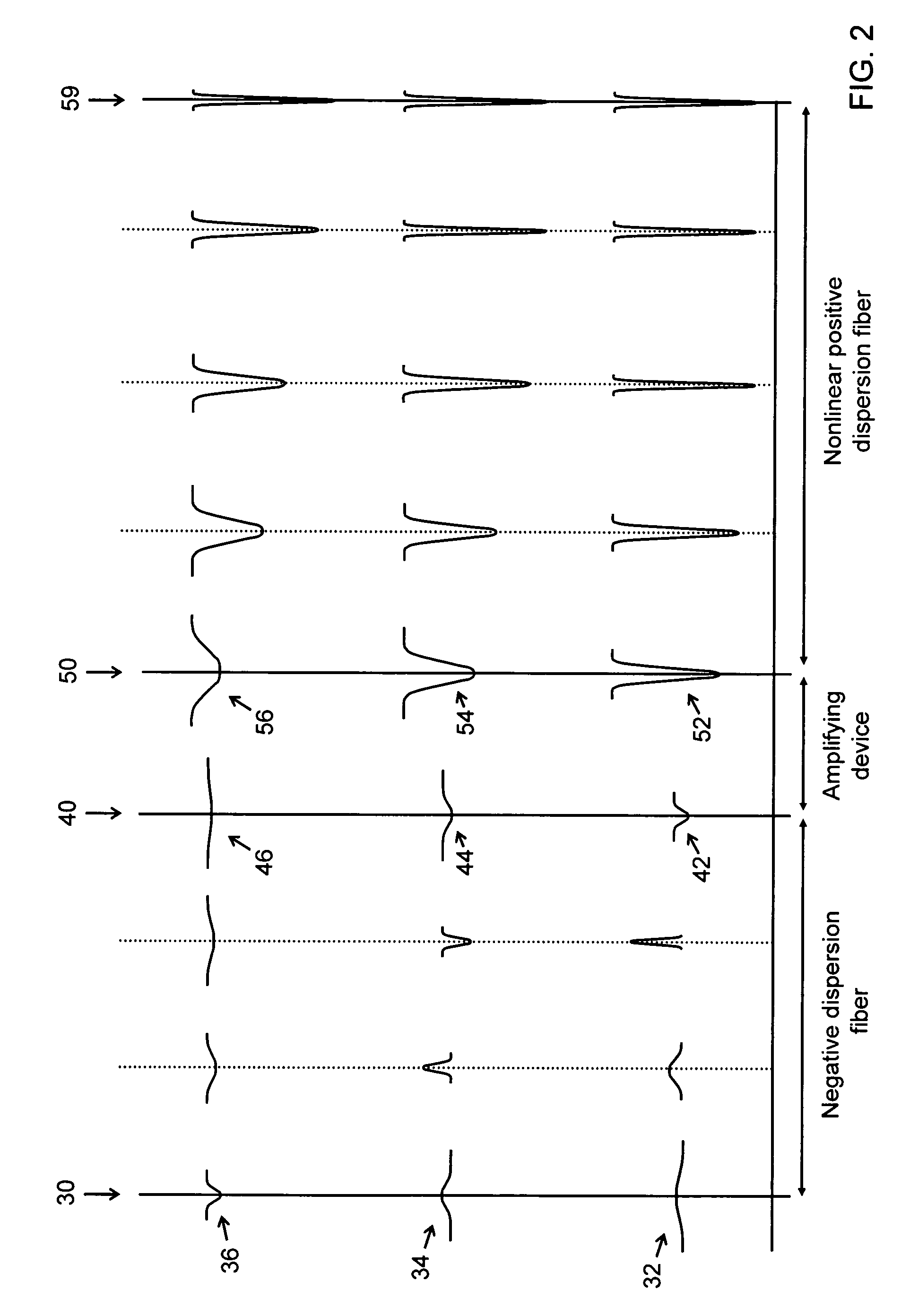
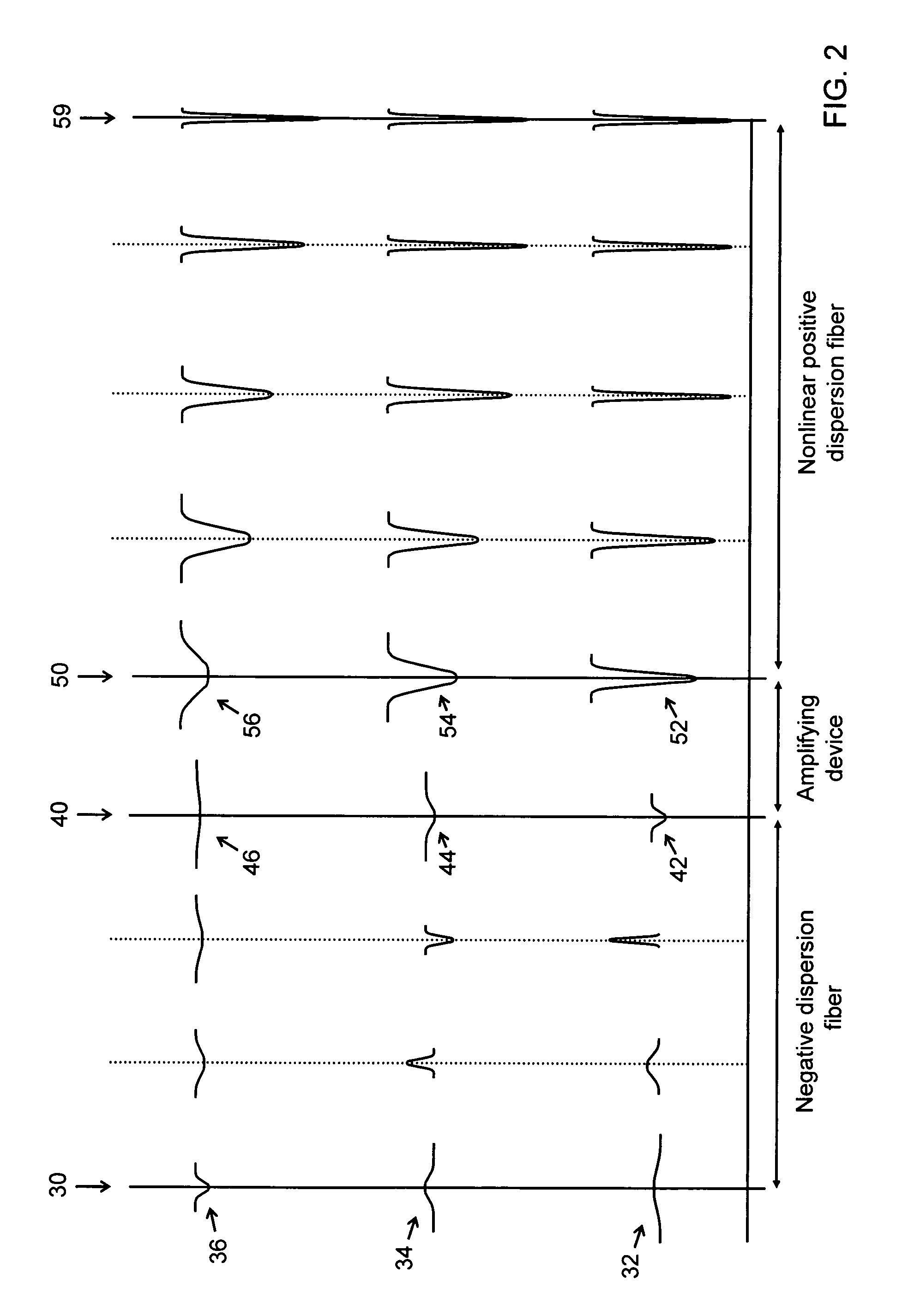
The present invention provides devices and methods for dispersion compensation. According to one embodiment of the invention, a dispersion compensating device includes a negative dispersion fiber having an input configured to receive the optical signal, the negative dispersion fiber having a length and dispersion sufficient to remove any positive chirp from each wavelength channel of the optical signal, thereby outputting a negatively chirped optical signal; an amplifying device configured to amplify the negatively chirped optical signal; and a nonlinear positive dispersion fiber configured to receive the negatively chirped optical signal. The devices of the present invention provide broadband compensation for a systems having a wide range of variable residual dispersions.
Owner:CORNING INC
Recycling method of silicon carbide
The invention discloses a recycling method of silicon carbide for recycling silicon carbide in silicon-containing mortar, wherein the silicon-containing mortar contains silicon carbide, silicon, impurities and dispersion. The method comprises the following steps: filtering the silicon-containing mortar to remove dispersion preliminarily and obtain silicon mud; heating silicon mud to volatilize residual dispersion and obtain silicon carbide / silicon mixture without impurities; placing the silicon carbide / silicon mixture in alkaline solution to dissolve silicon in the mixture; and removing alkaline solution with the dissolved silicon to obtain the purified silicon carbide. The invention has the following advantages: 1) the deterioration of dispersion in the silicon-containing mortar can be avoided; 2) organic solvent is not used for separating silicon carbide; and 3) the high speed centrifugation method is not required for separating silicon carbide.
Owner:HONG JING ENVIRONMENT
Dynamic dispersion detecting method and apparatus
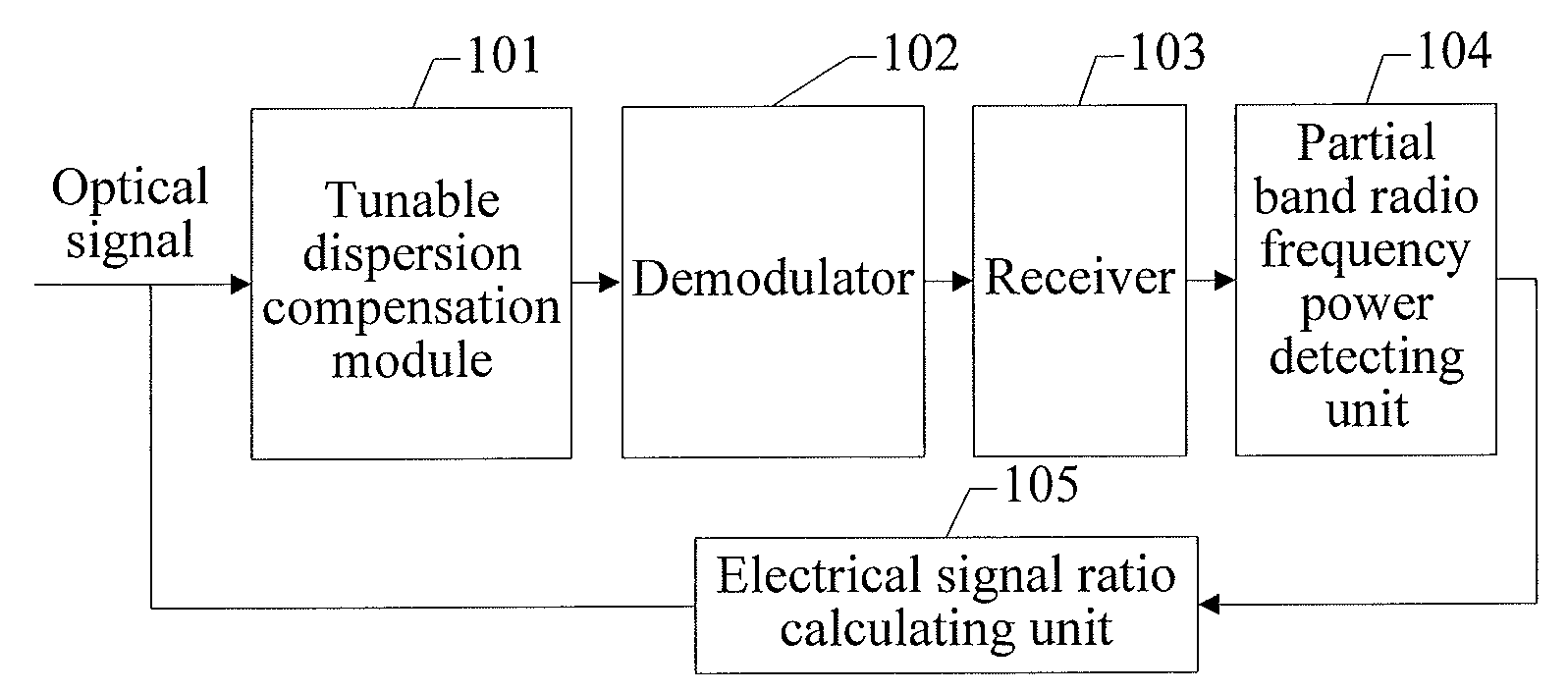
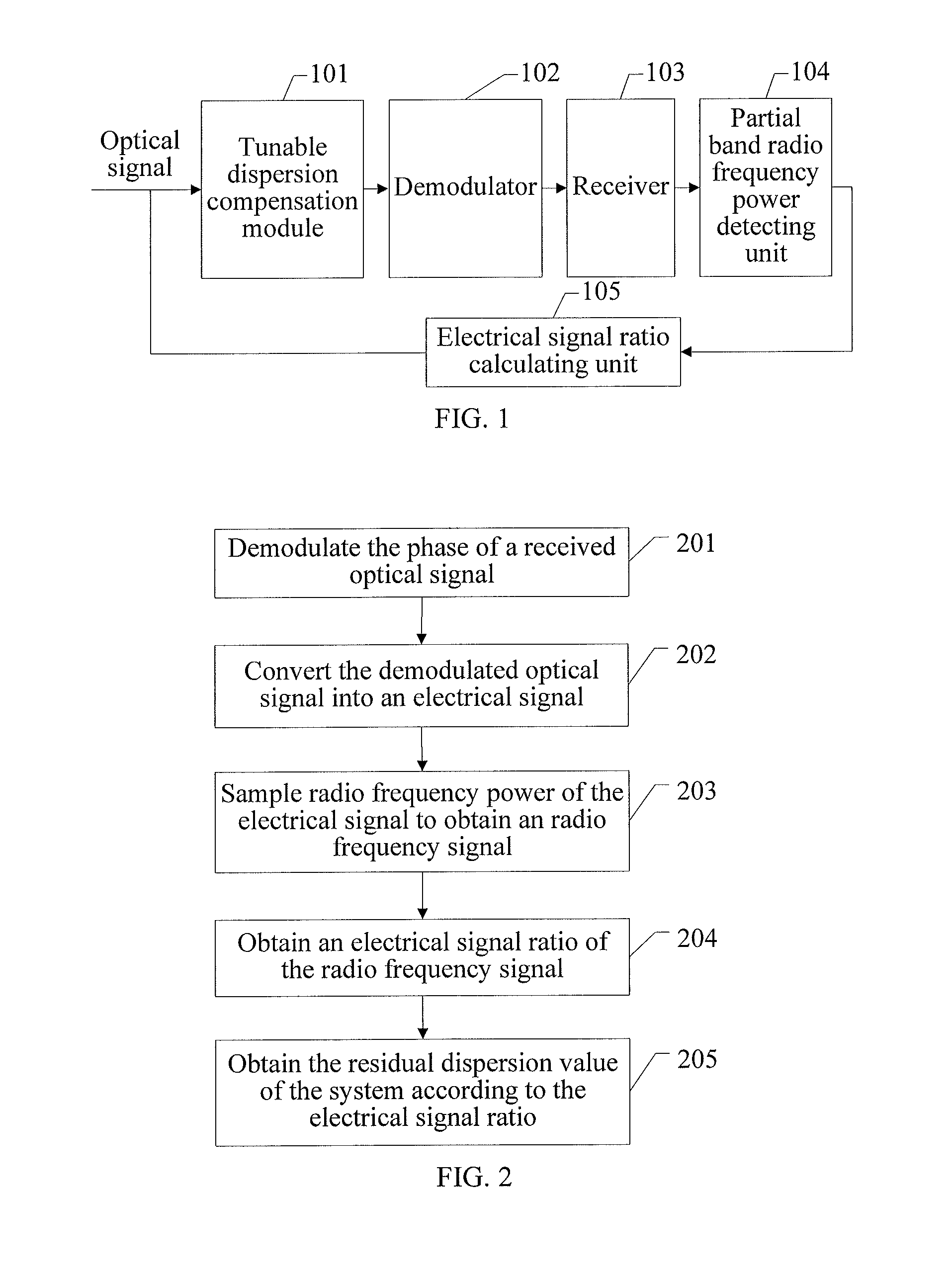
ActiveUS20120232819A1Improve accuracyCorrection for dispersionDigital variable/waveform displayDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectricityRadio frequency signal
A dynamic dispersion detecting method and apparatus are disclosed. The apparatus includes a tunable dispersion compensation module (101), a demodulator (102), a receiver (103), a partial band radio frequency power detecting unit (104), and an electrical signal ratio calculating unit (105). The method includes: demodulating a phase of a received optical signal; converting the demodulated optical signal into an electrical signal; sampling radio frequency power of the electrical signal to obtain an radio frequency signal; obtaining an electrical signal ratio of the radio frequency signal; and comparing a value of a currently detected electrical signal ratio with the values of the previously detected electrical signal ratios, tuning a dispersion compensation value according to a comparison result to find a peak electrical signal ratio, and obtaining a residual dispersion value of a system according to the peak electrical signal ratio.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Large kappa dispersion compensating fiber and transmission system
InactiveUS20050286849A1High kappaGood bend loss propertyOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingElectromagnetic transmissionEngineeringLength wave
A dispersion compensation fiber for a moderate dispersion, low slope transmission fiber and transmission system including same. The dispersion compensating fiber has a refractive index profile having a central core with a core delta (Δ1), a moat surrounding the central core having a moat delta (Δ2), and a ring surrounding the moat having a positive ring delta (Δ3). The fiber's refractive index profile is selected to provide total dispersion less than −80 at 1550 nm and less than −90 ps / nm / km at 1600 nm, dispersion slope less than −0.18 ps / nm2 / km at 1550 and less than −0.10 ps / nm2 / km at 1600 nm, kappa between 250 and 450 at 1550 nm, and a kappa ratio (defined as kappa at 1600 nm / kappa at 1550 nm) of greater than 1.35. The dispersion compensating fiber, when used in a transmission system, may provide low average residual dispersion across the C, L, and C+L bands when such systems include moderate dispersion, low dispersion slope transmission fibers with a total dispersion between 4 and 8 ps / nm / km, and a dispersion slope less than 0.025 ps / nm2 / km at all wavelengths between 1525 and 1625 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
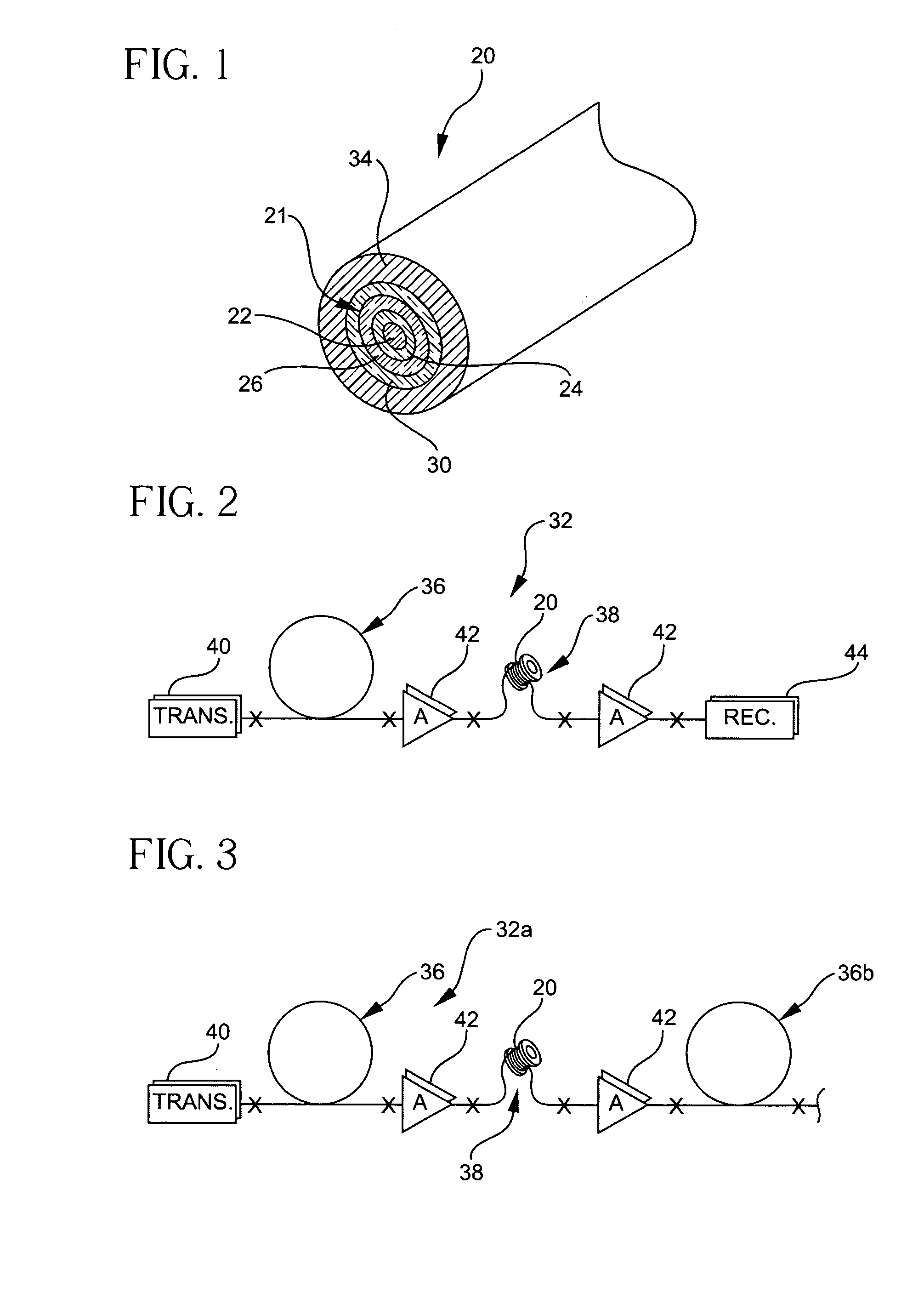
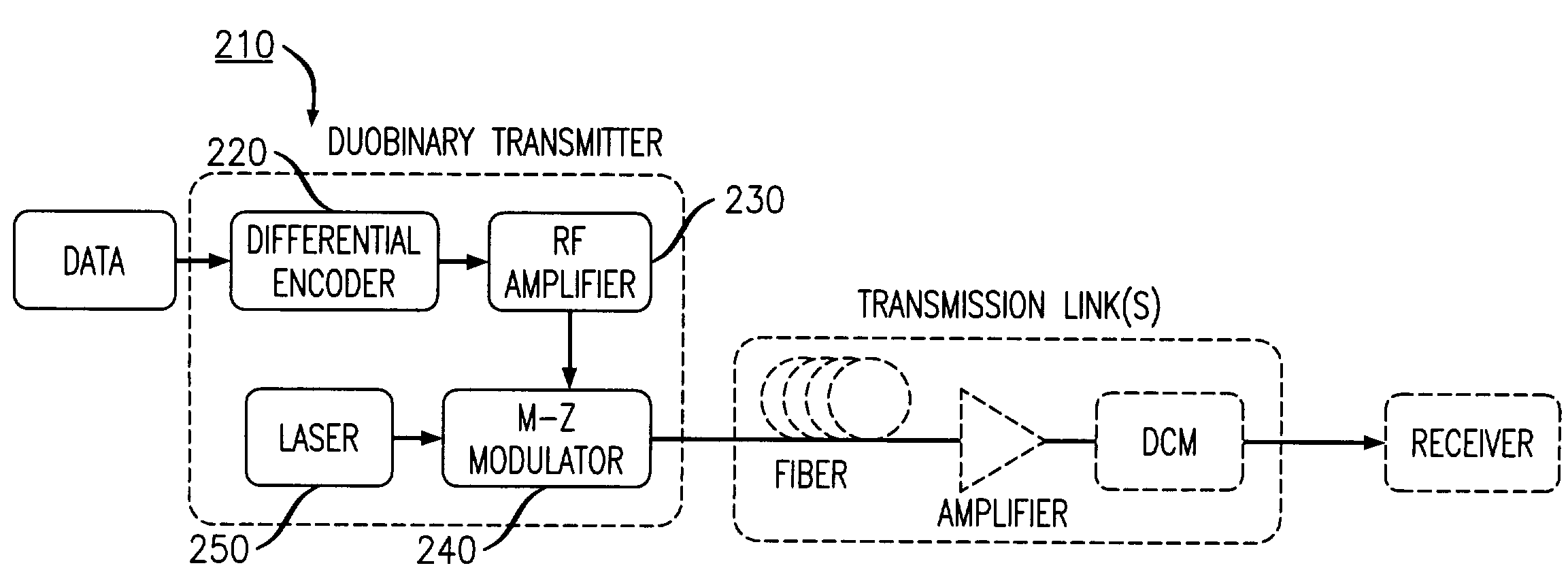
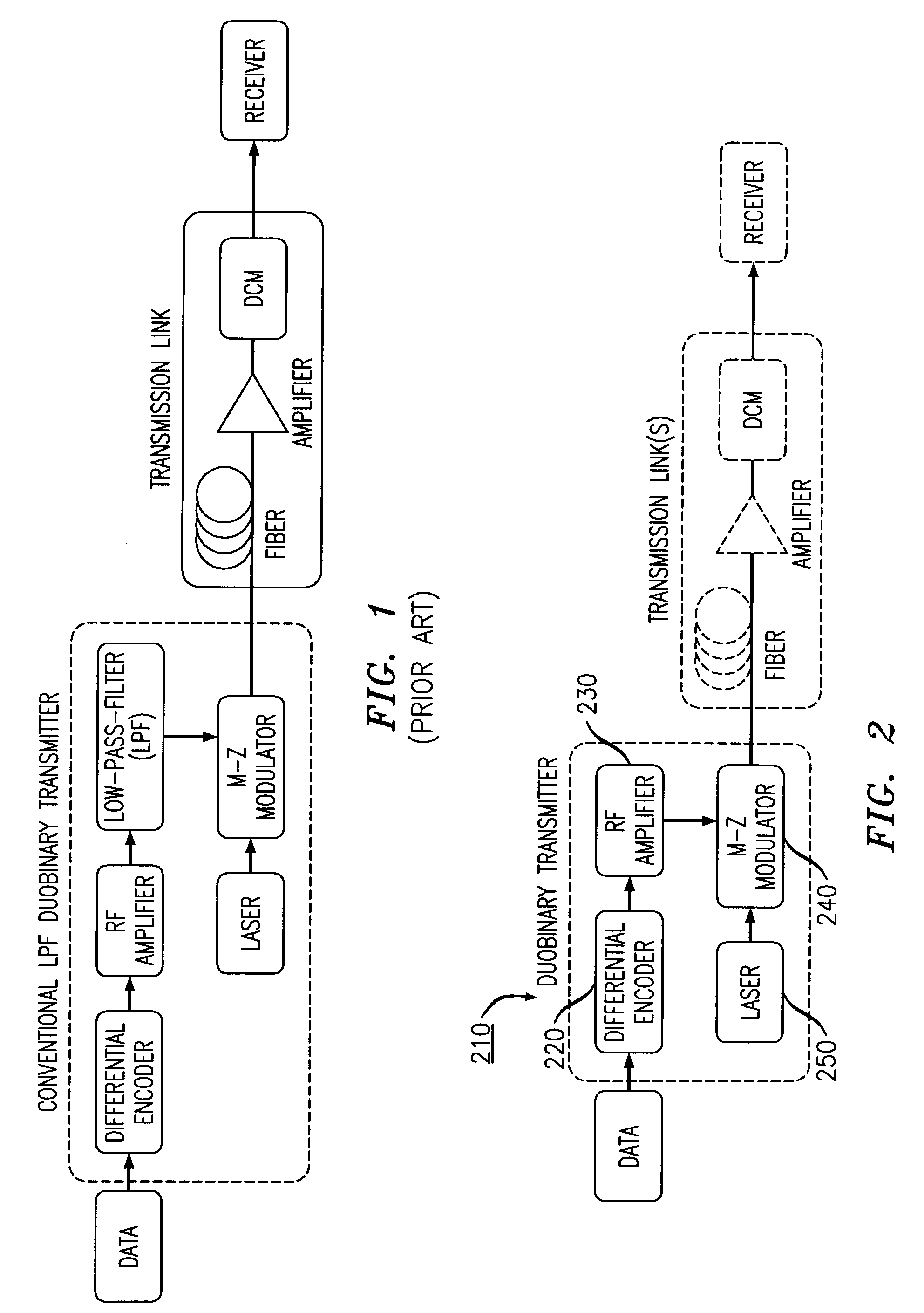
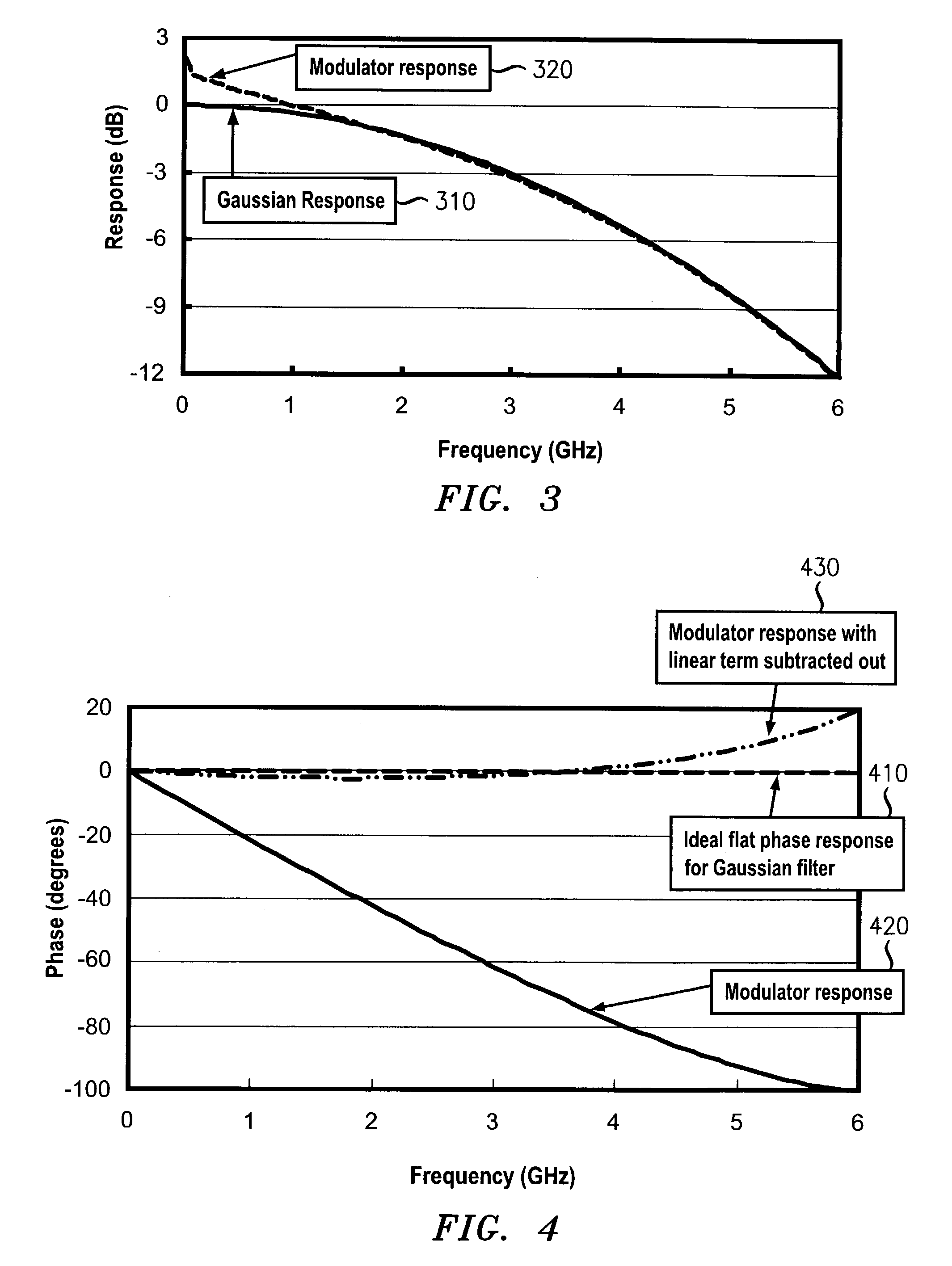
Apparatus and method for duobinary transmission
An apparatus and method are provided for transmitting an optical duobinary signal using a low bandwidth modulator having a bandwidth of less than about 60% of the transmission bit rate of the transmitter. The modulator is adapted to provide low pass filtering for low pass filtered duobinary transmission in an optical fiber transmission system having residual dispersion.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission system and wavelength dispersion compensation unit
ActiveUS20050213987A1Simple configurationResidual dispersion efficientlyWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationLength waveResidual dispersion
In the WDM optical transmission system, a high-slope dispersion compensator compensates wavelength dispersion produced in the optical transmission line. The high-slope dispersion compensator has a dispersion slope characteristic, by which a dispersion slope is substantially compensated over the wavelength bandwidth of the optical transmission line, and also a dispersion compensation characteristic, by which the residual dispersion produced after compensating the dispersion slope using the above dispersion slope characteristic becomes symmetrical with respect to a wavelength in the vicinity of the center of the wavelength bandwidth. To achieve the above compensation, a wavelength-multiplexed signal is divided into wavelength bandwidth groups, and the residual dispersion of the optical transmission line is compensated on a group-by-group basis for the wavelength bandwidth groups.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Dispersion compensating fiber module, and optical fiber transmission line
InactiveUS20050201700A1Increase costSmall sizeOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingElectromagnetic transmissionEngineeringLength wave
A dispersion compensating fiber module which, when connected to an optical fiber which exhibits, at a wavelength of 1.55 μm, a chromatic dispersion of between +2 and +6 ps / nm / km, a dispersion slope of between +0.075 ps / nm2 / km and +0.095 ps / nm2 / pm, and a relative dispersion slope of between 0.016 nm−1 and 0.024 nm−1, performs compensation so that the residual dispersion of the connected optical fiber is reduced, the dispersion compensating fiber module includes a dispersion compensating fiber and at least one optical fiber fused to the dispersion compensating fiber, in which the dispersion compensating fiber module exhibits at a wavelength of 1.55 μm, a relative dispersion slope of between 0.016 nm−1 and 0.026 nm−1; and in a wavelength range between 1.525 μm and 1.565 μm, a maximum residual dispersion difference, when converted per km of the transmission optical fiber, of less than or equal to 0.4 ps / nm / km.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Devices and methods for dynamic dispersion compensation
InactiveUS7079737B1Not high insertion lossRapid responseLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingEngineeringWavelength
The present invention provides devices and methods for dispersion compensation. According to one embodiment of the invention, a dispersion compensating device includes a negative dispersion fiber having an input configured to receive the optical signal, the negative dispersion fiber having a length and dispersion sufficient to remove any positive chirp from each wavelength channel of the optical signal, thereby outputting a negatively chirped optical signal; an amplifying device configured to amplify the negatively chirped optical signal; and a nonlinear positive dispersion fiber configured to receive the negatively chirped optical signal. The devices of the present invention provide broadband compensation for a systems having a wide range of variable residual dispersions.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com