Patents
Literature
611 results about "Non-linear effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enantioselective synthesis, a non-linear effect refers to a process in which the enantiopurity of the catalyst or chiral auxiliary does not correspond with the enantiopurity of the product produced. For example: a racemic catalyst would be expected to convert a prochiral substrate into a racemic product (a linear effect), but this is not always the case and a chirally enriched product can be produced instead (a non-linear effect).
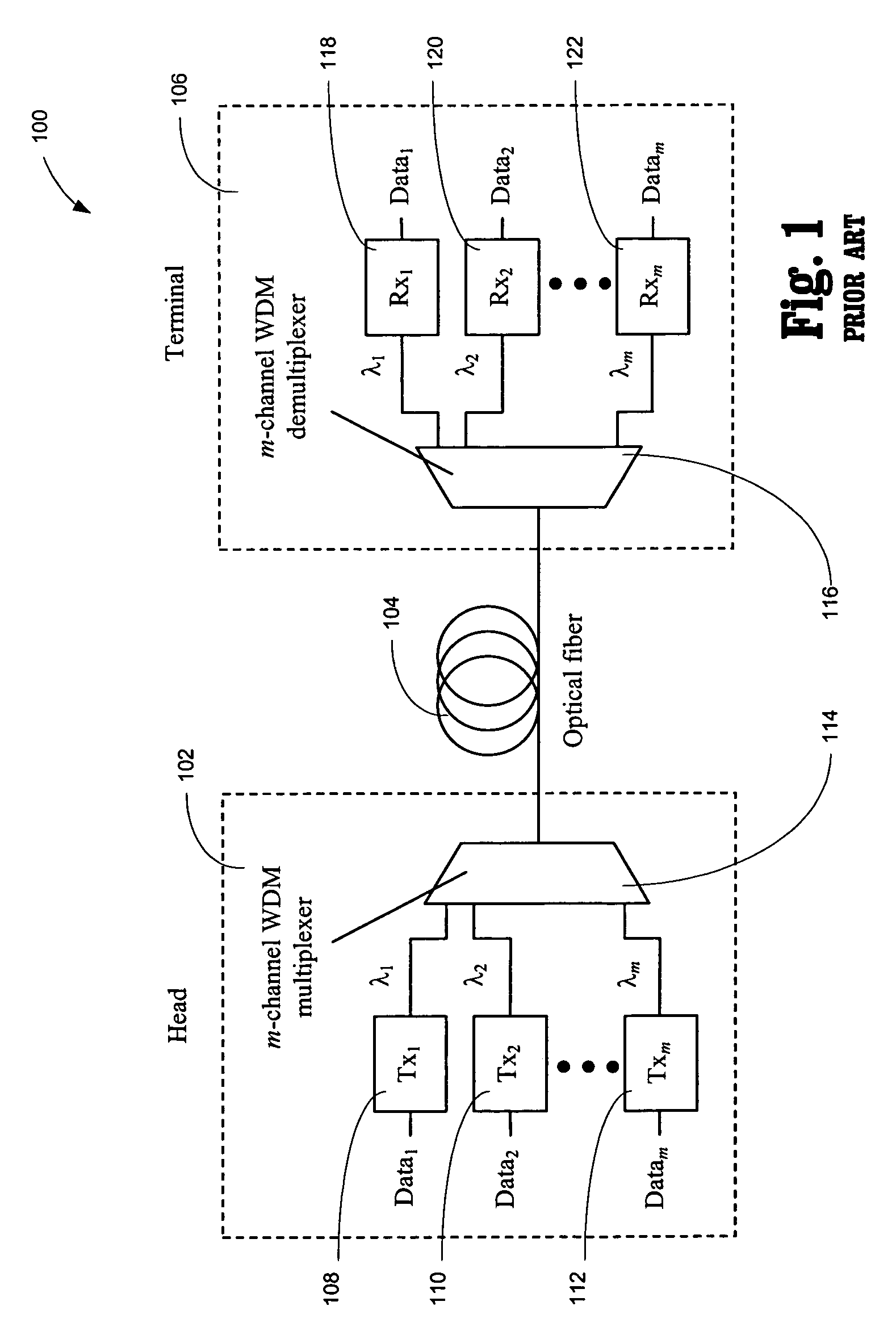
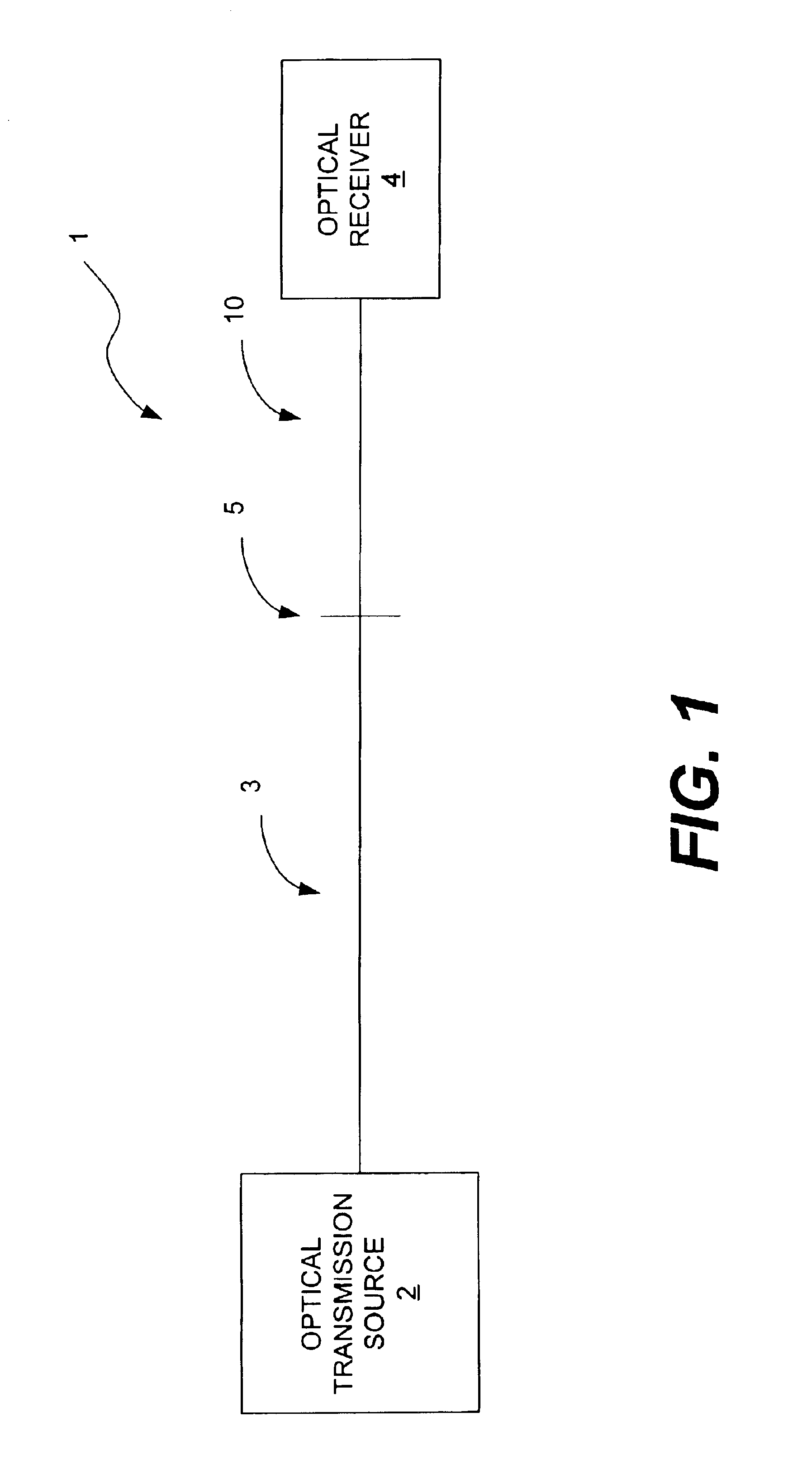
Super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber and communication system incorporating the same
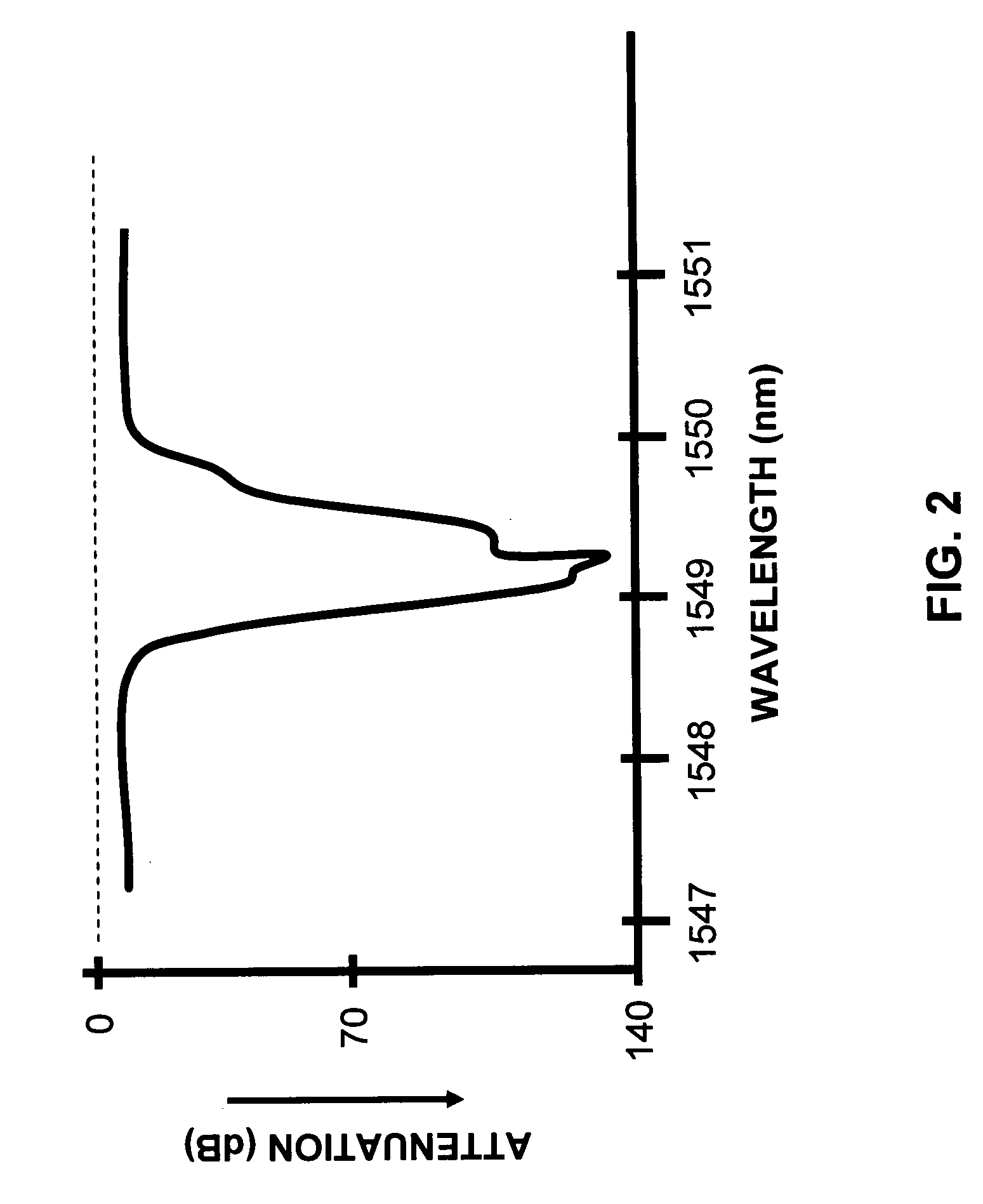
ActiveUS6904218B2Increase the effective areaLow cutoff wavelengthOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberUltrasound attenuation
A super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber that is suitable for communicating over a wide wavelength range and that, because of its large effective area, suppresses nonlinear effects that typically result from interaction between signal channels. The effective area, Aeff, of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is equal to or greater than approximately 80 μm2 at a wavelength window around 1310 nm. The cutoff wavelength of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is less than 1310 nm. Thus, the SLA fiber of the present invention has a very large effective area and a very low cutoff wavelength. In accordance with the present invention, a variety of SLA fibers are provided that all have very large effective areas and desirable transmission properties. The large effective areas of the SLA fibers of the present invention enable nonlinear effects to be suppressed, as well as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in analog transmission. The large effective areas also enable attenuation to be reduced. The result of suppressing nonlinear effects and reducing attenuation enable signals to be transmitted over long distances and over a broad bandwidth.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
BAW apparatus
ActiveUS7365619B2Reduce non-linearityAdd dimensionImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesHarmonicNon-linear effects
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Electrical domain compensation of non-linear effects in an optical communications system
ActiveUS7756421B2Reduce signalingCompensation DistortionElectromagnetic transmissionCommunications systemEngineering
Nonlinearity-induced signal distortions are compensated by processing an input communications signal, in the electrical domain prior to Electrical-to-optical conversion and transmission through an optical link of a communications system. According to the invention, a compensation operator is determined that substantially mitigates the nonlinearity-induced signal distortions imparted to an optical signal traversing the communications system. The input communications signal is then input to the compensation operator to generate a predistorted electrical signal. This predistorted electrical signal is then used to modulate an optical source to generate a corresponding predistorted optical signal for transmission through the optical communications system. With this arrangement, arbitrary nonlinearity-induced signal distortions imparted by the optical link can be compensated in such a manner that a comparatively undistorted optical signal is obtained at the receiving end of the optical link.
Owner:CIENA
Line fiber for WDM optical fiber transmission systems
InactiveUS6396987B1Increasing channel data rateLow costOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWdm transmission systemsTransport system
The invention provides a monomode optical fiber having, at a wavelength of 1550 nm: an effective section area greater than or equal to 60 mum2; chromatic dispersion close to 8 ps / (nm.km); a chromatic dispersion slope of absolute value less than 0.07 ps / (nm2.km). In the range of wavelengths used in a WDM transmission system, typically 1530 nm to 1620 nm, the fiber has chromatic dispersions greater than 7 ps / (nm.km), thereby making it possible to limit non-linear effects. The invention also provides a WDM optical fiber transmission system using such a fiber as a line fiber. The small slope of its chromatic dispersion is an advantage in such a system.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
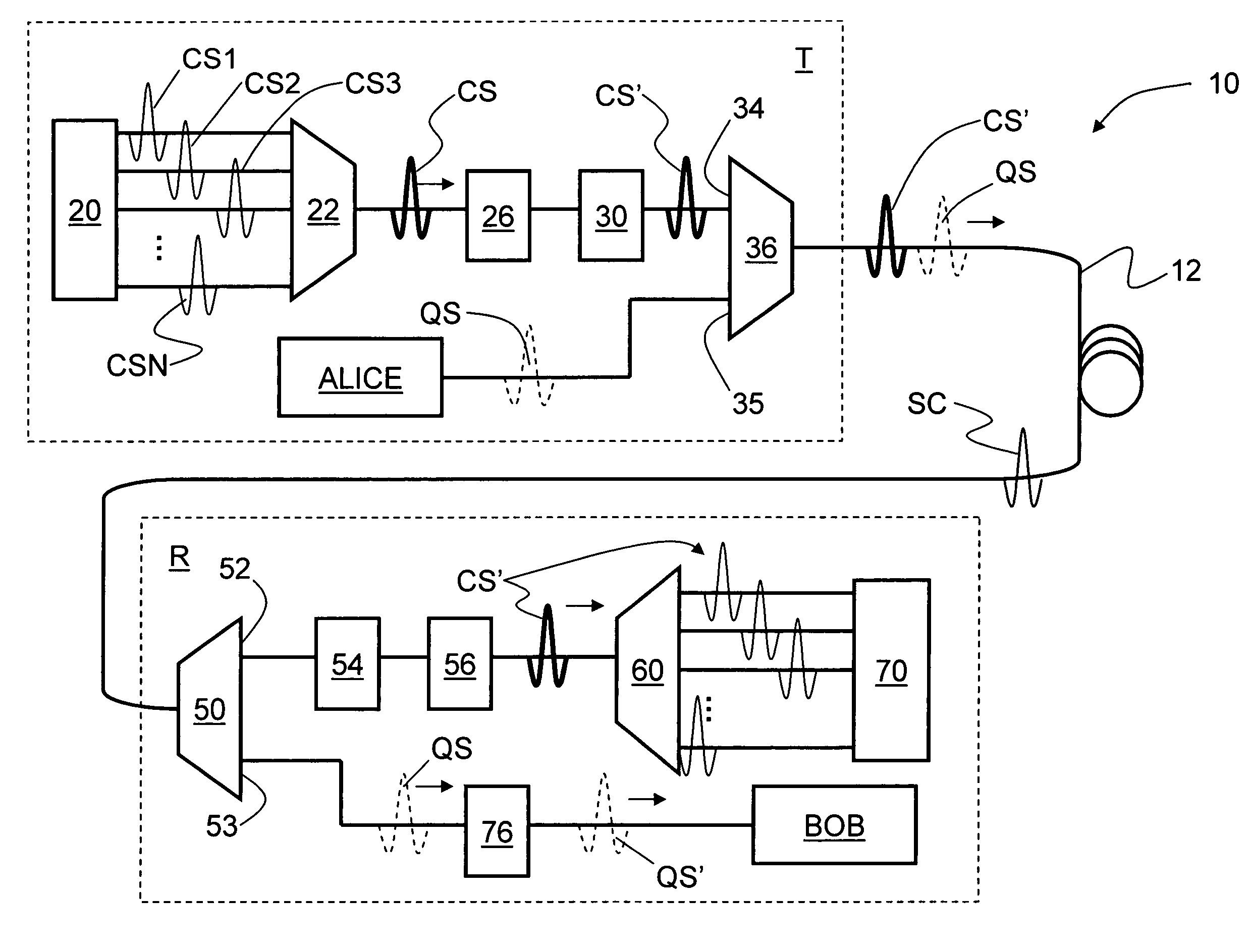
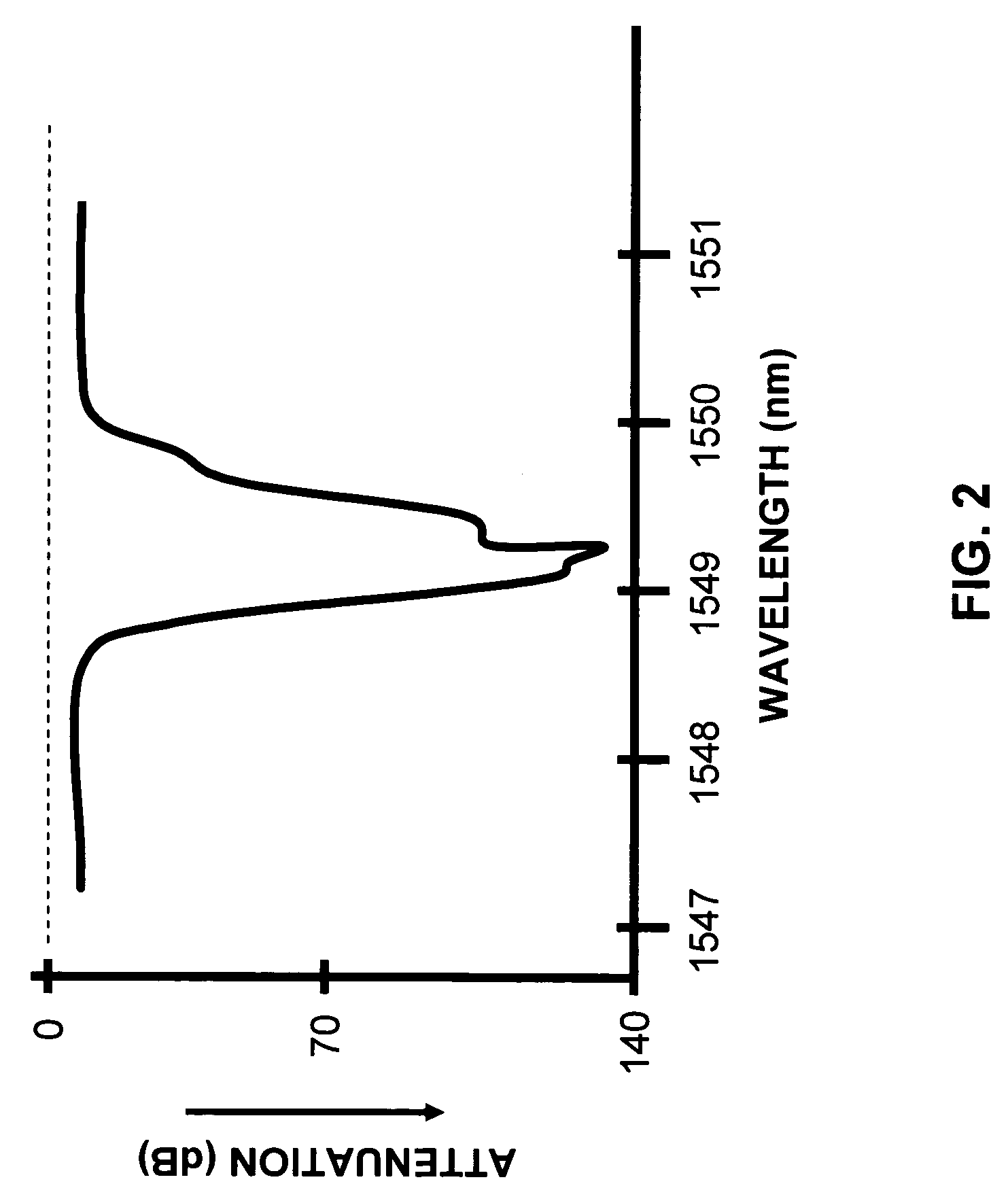
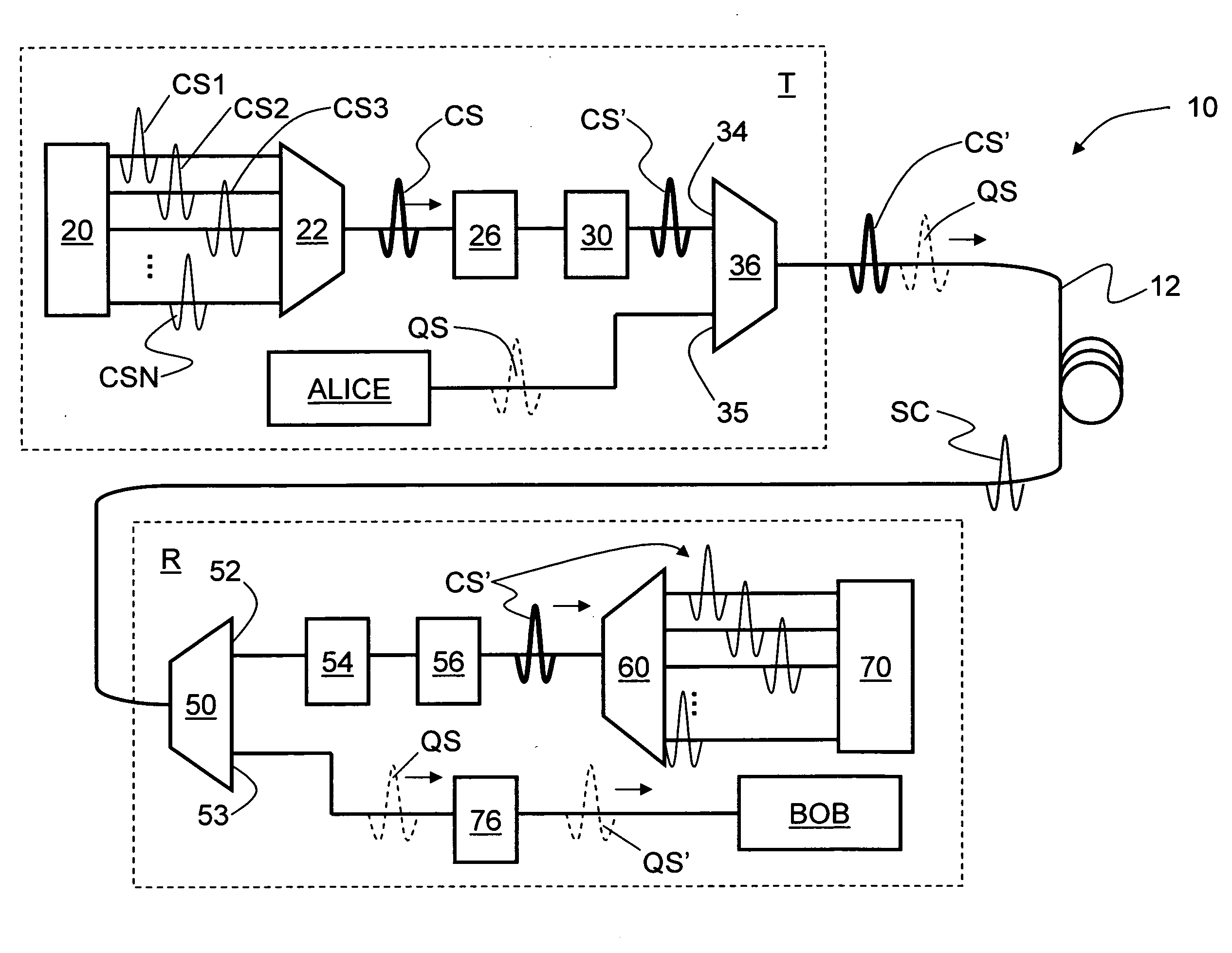
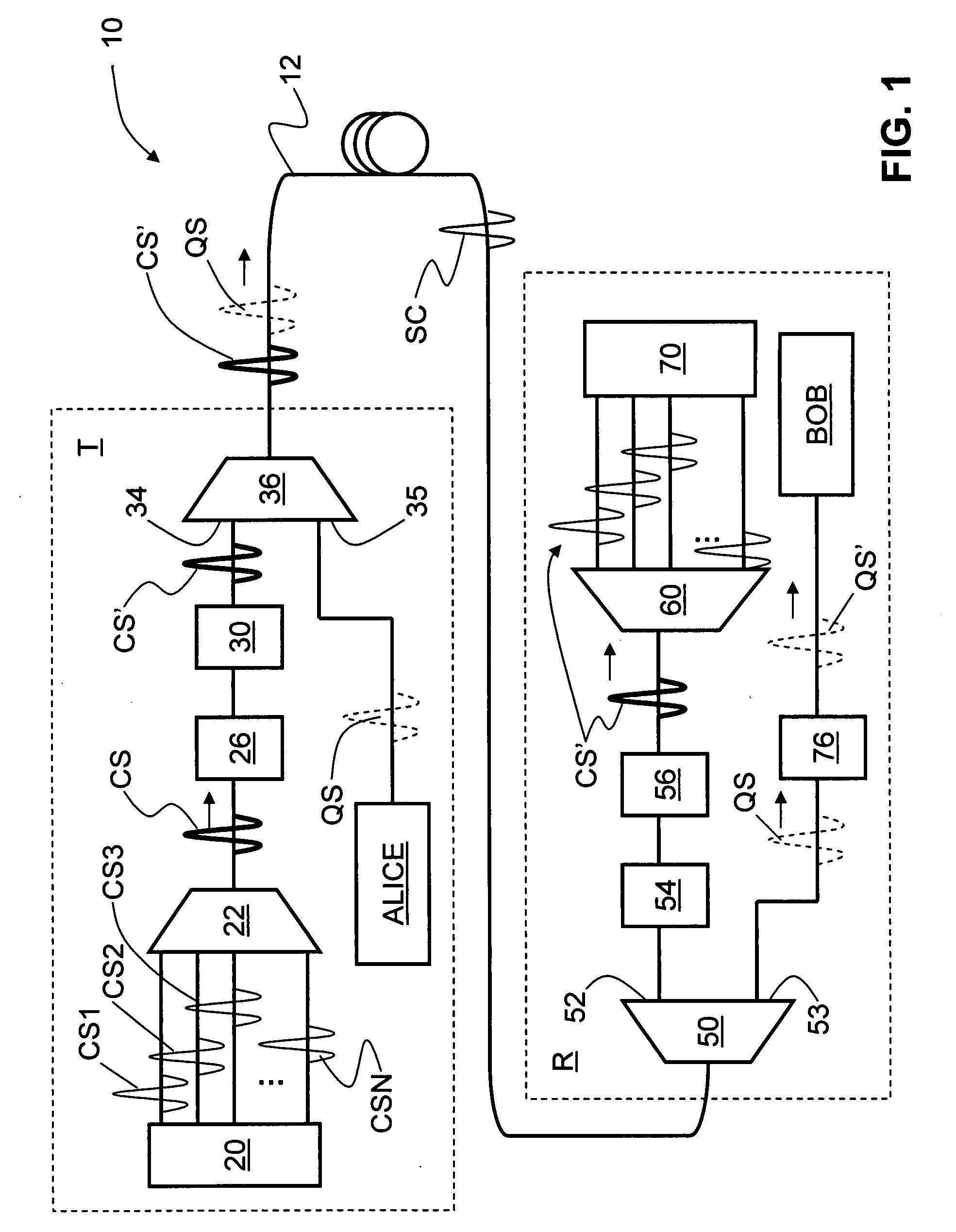
Systems and methods for transmitting quantum and classical signals over an optical network
ActiveUS7248695B1Reduce Optical NoiseKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationMultiplexingLength wave
Systems and methods for transmitting quantum and classical signals over an optical network are disclosed, wherein the quantum signal wavelength either falls within the classical signal wavelength band, or is very close to one of the classical signal wavelengths. The system includes a deep-notch optical filter with a blocking bandwidth that includes the quantum signal wavelength but not any of the classical signal wavelengths. The deep-notch optical filtering is applied to the classical signals prior to their being multiplexed with the quantum signals to prevent noise generated by the classical signals from adversely affecting transmission of quantum signals in the transmission optical fiber. Narrow-band filtering is also applied to the quantum signals prior to their detection in order to substantially exclude spurious non-quantum-signal wavelengths that arise from non-linear effects in the optical fiber. The present invention allows for the quantum and classical signals to have wavelengths within just a few nanometers of one another, which has benefits for both classical and quantum signal transmission on a common transmission optical fiber.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
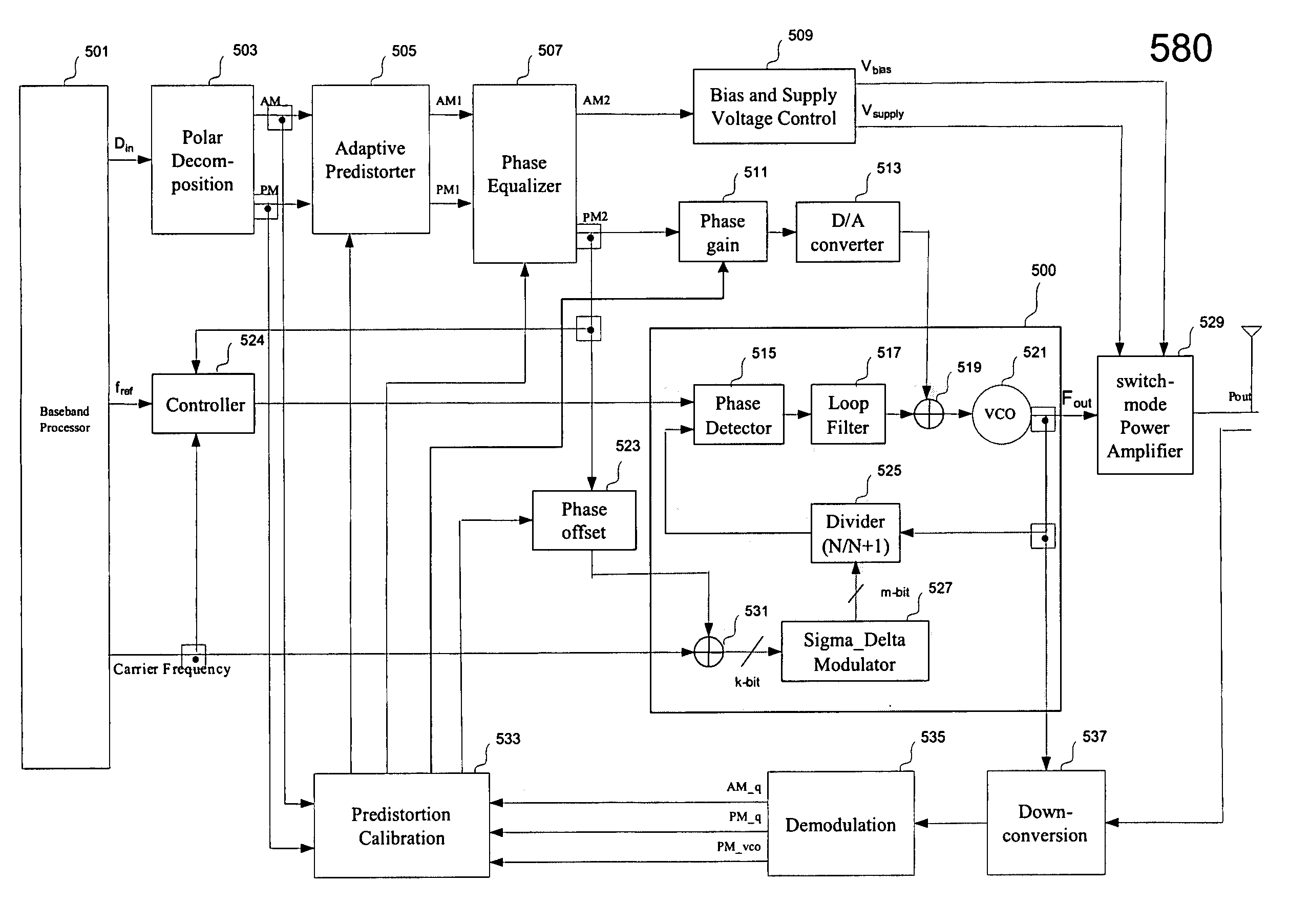
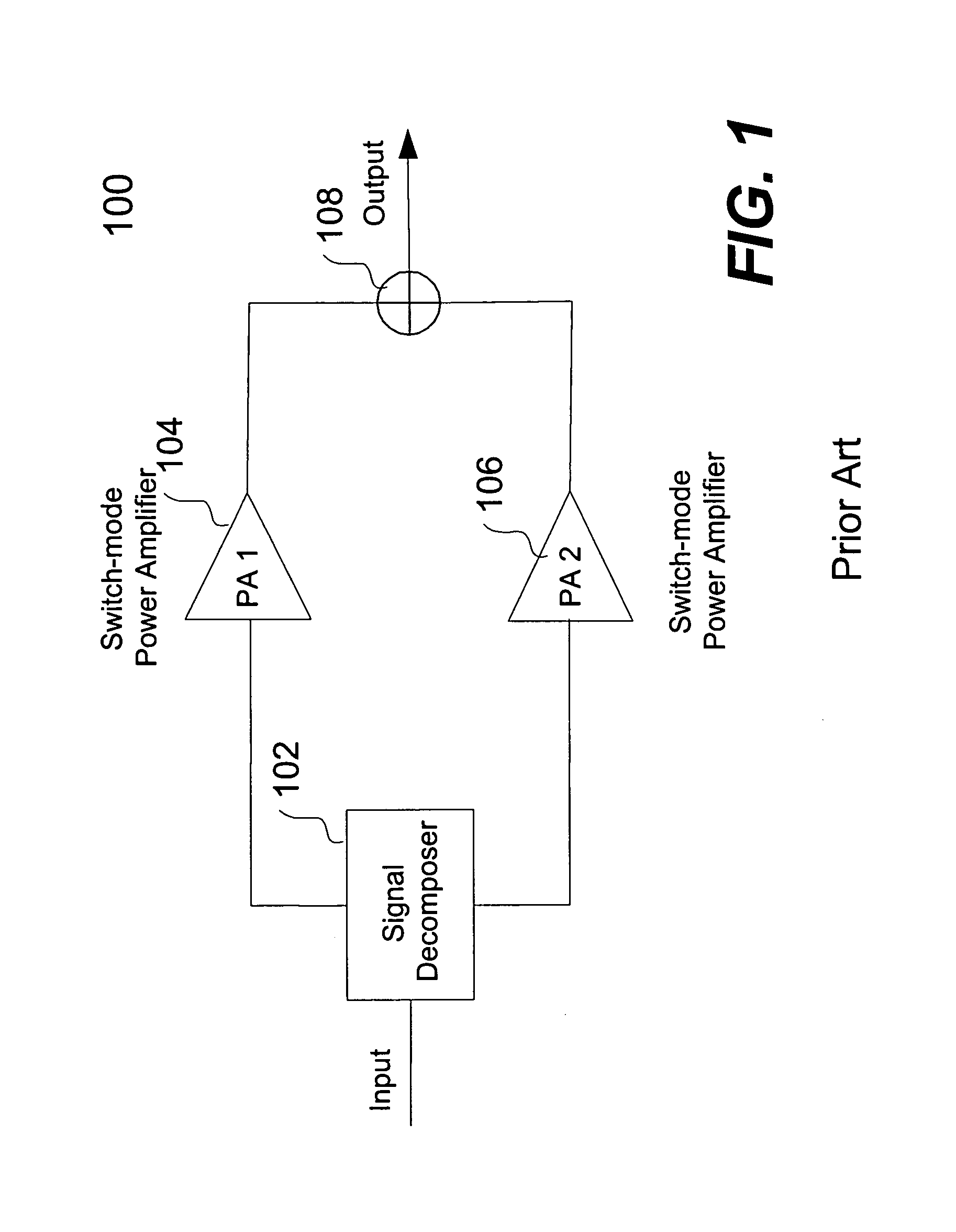
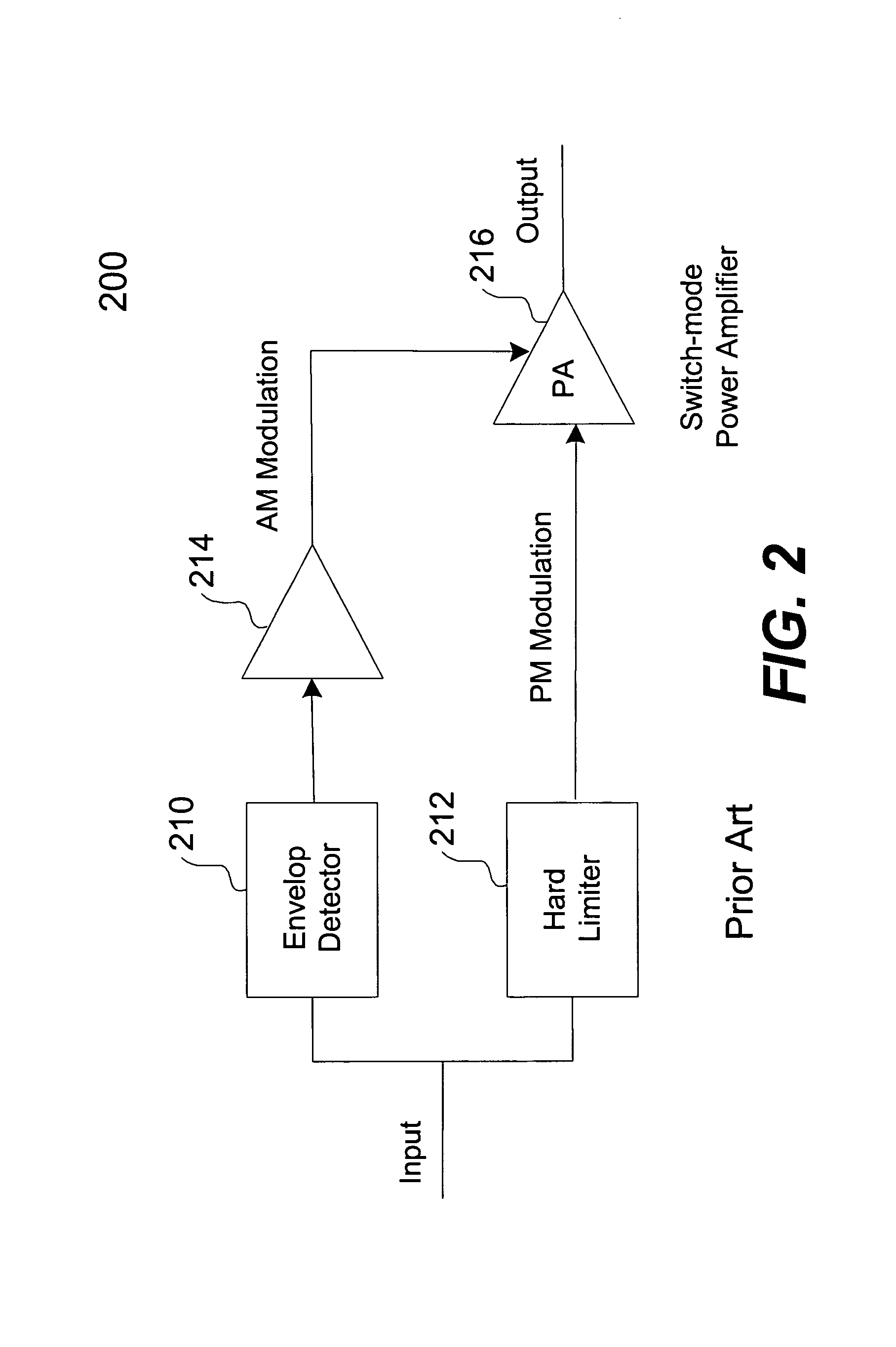
Direct modulation of a power amplifier with adaptive digital predistortion
InactiveUS7346122B1Timing mismatchLow costModulated-carrier systemsPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierRadio frequency
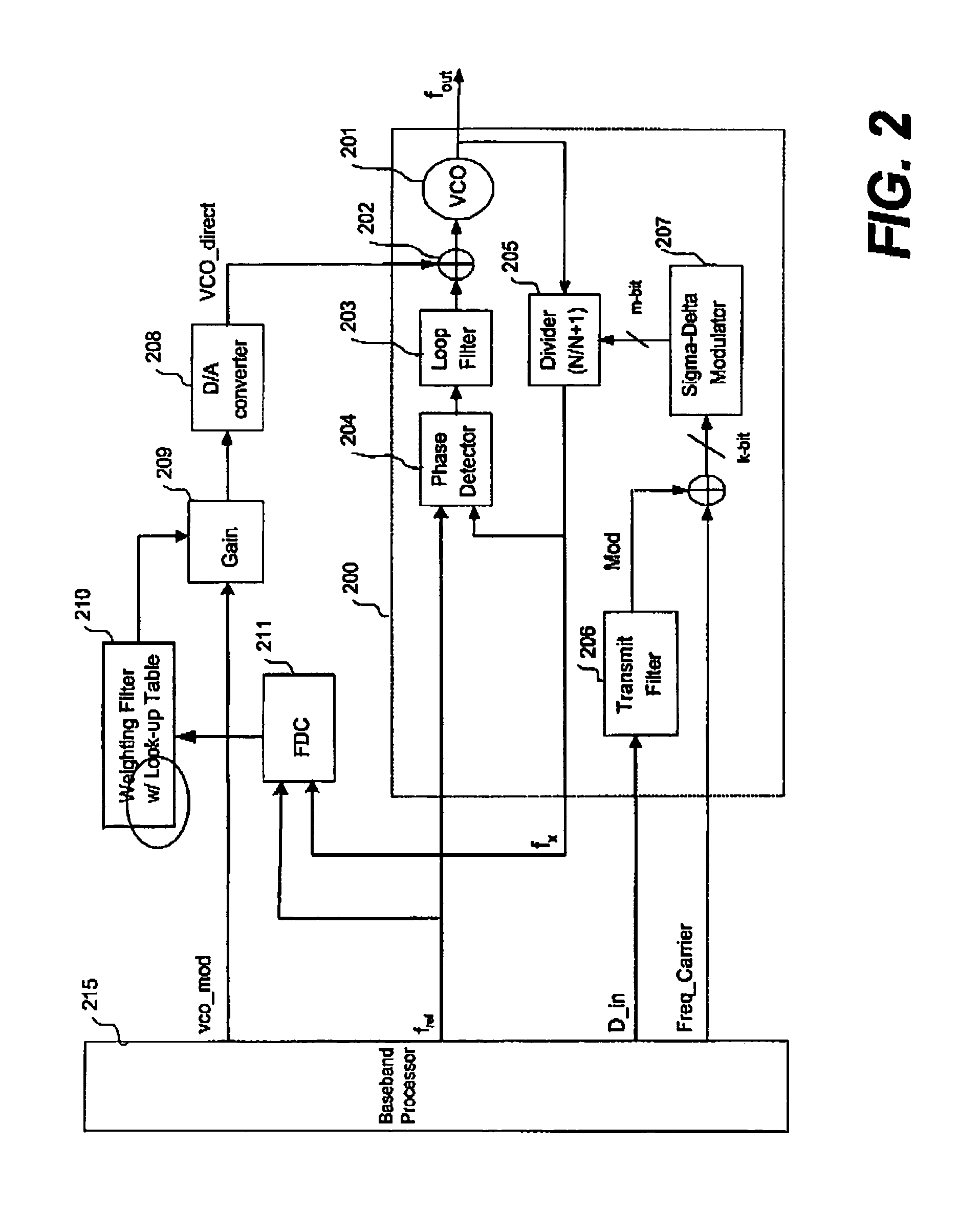
Techniques for direct modulation of a switching-mode power amplifier with adaptive digital predistortion are disclosed. A baseband digital modulated signal is decomposed into an amplitude signal and a phase signal in polar coordinates. The amplitude signal is used to modulate supply voltages of the power amplifier. The phase signal is used to modulate a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) of a phase-locked loop (PLL), which generates a phase-modulated radio-frequency (RF) carrier coupled to the input of the power amplifier. The digital predistortion is implemented by using a feedback demodulator, which regenerates the baseband amplitude and phase information from the output of the power amplifier. The VCO drift and other non-linear effects of the power amplifier are compensated. High power efficiency and high linearity for different modulation standards are achieved.
Owner:CAO WEIXUN
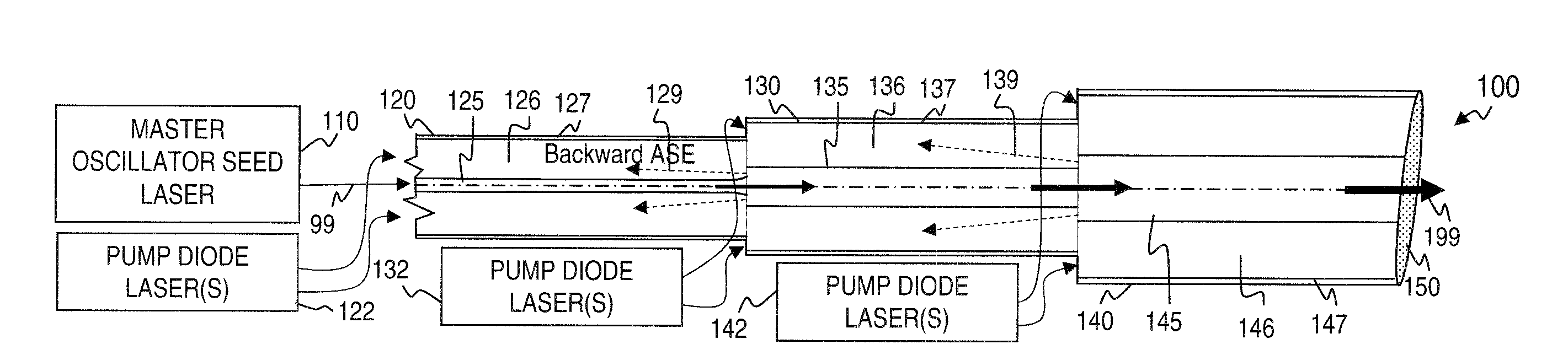
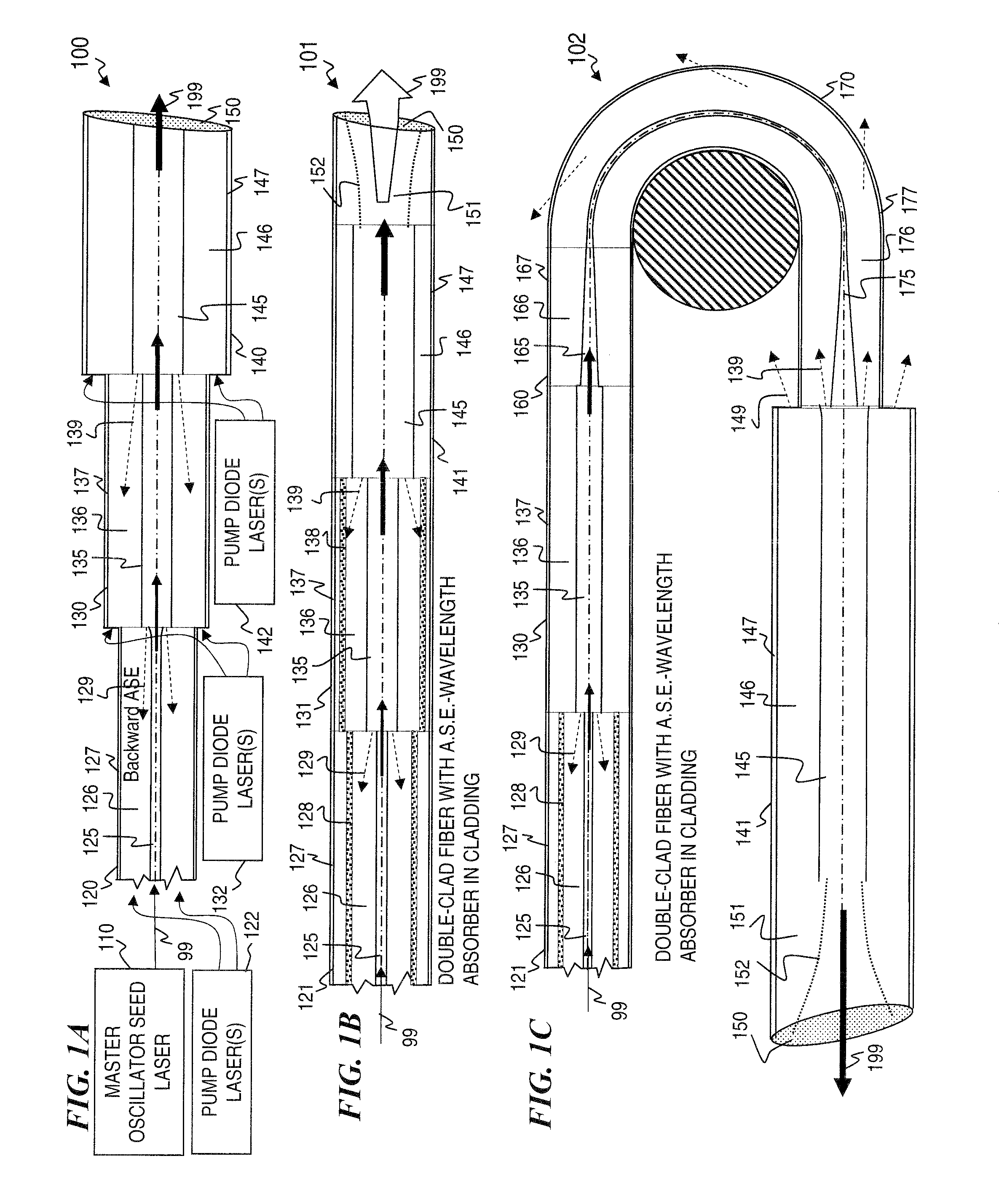
Method and apparatus for optical gain fiber having segments of differing core sizes
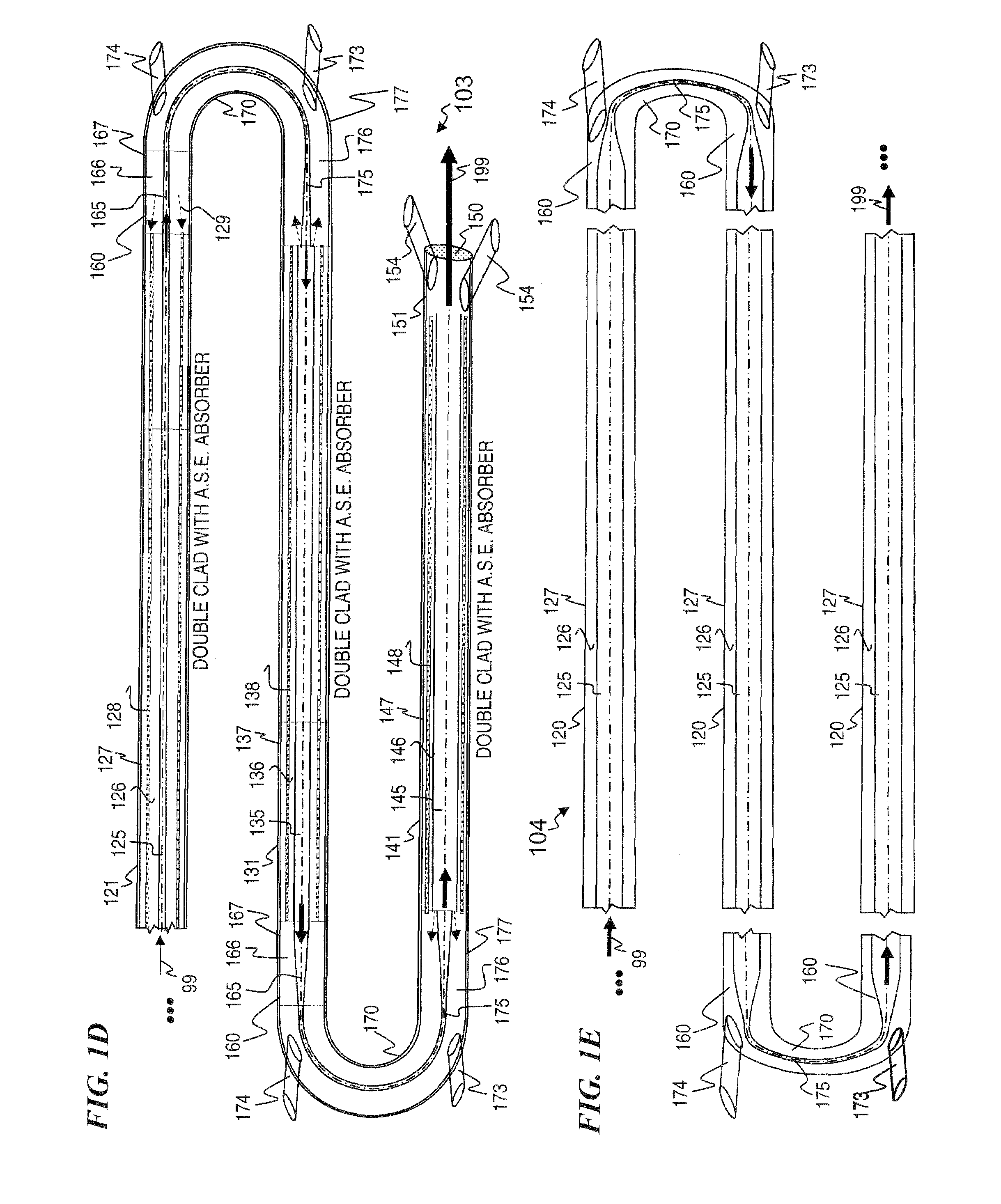
ActiveUS7768700B1Enhanced energy extractionReduce the amount requiredLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiberBandpass filtering
Apparatus and method for amplifying laser signals using segments of fibers of differing core diameters and / or differing cladding diameters to suppress amplified spontaneous emission and non-linear effects such as four-wave mixing (FWM), self-phase modulation, and stimulated Brillouin and / or Raman scattering (SBS / SRS). In some embodiments, different core sizes have different sideband spacings (spacing between the desired signal and wavelength-shifted lobes). Changing core sizes and providing phase mismatches prevent buildup of non-linear effects. Some embodiments further include a bandpass filter to remove signal other than the desired signal wavelength and / or a time gate to remove signal at times other than during the desired signal pulse. Some embodiments include photonic-crystal structures to define the core for the signal and / or the inner cladding for the pump. Some embodiments include an inner glass cladding to confine the signal in the core and an outer glass cladding to confine pump light in the inner cladding.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Plating processes utilizing high intensity acoustic beams
InactiveUS6368482B1Improve the plating processIncrease choiceCellsRadiation applicationsLight beamAcoustic wave
A system and a method for selective plating processes are disclosed which use directed beams of high intensity acoustic waves to create non-linear effects that alter and improve the plating process. The directed beams are focused on the surface of an object, which in one embodiment is immersed in a plating solution, and in another embodiment is suspended above a plating solution. The plating processes provide precise control of the thickness of the layers of the plating, while at the same time, in at least some incidents, eliminates the need for masking.
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S AS REPRESENTED BY THE +1
High pass modulation of a phase locked loop
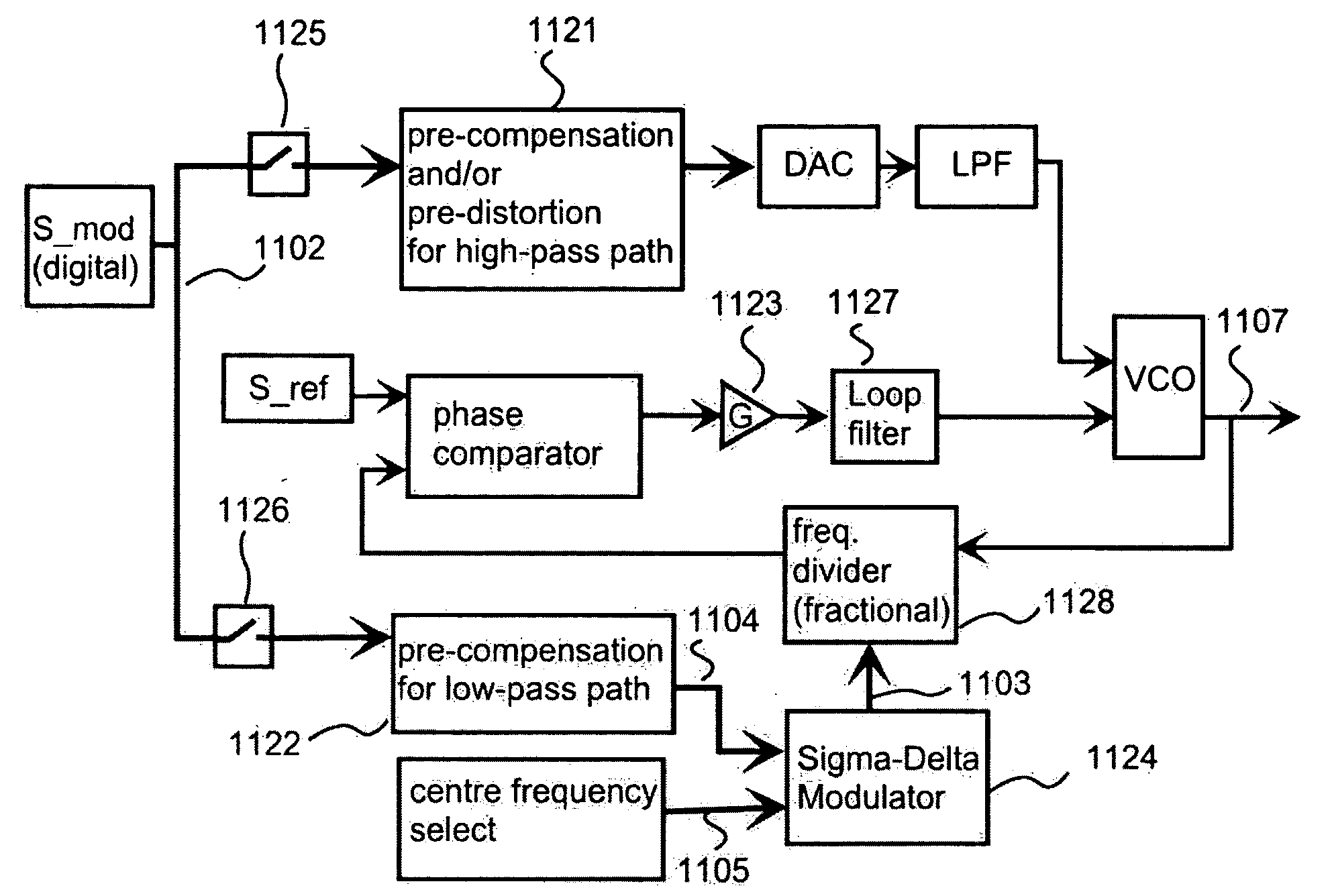
ActiveUS20070036238A1Drawback and limitationCompensation effectModulated-carrier systemsAngle modulationDigital signal processingRadio frequency
A radio frequency modulator based on direct frequency / phase modulation of output signal of a controllable oscillator (724) that is a part of a phase locked loop (PLL) provides a direct modulator that is able to operate over a wide frequency range with a flat frequency response. A modulation signal is digitally processed (721, 730) before injection to a high-pass path of a direct modulator. Applicability of digital signal processing is based on the fact that the modulation signal is a base band signal. Therefore, the modulation signal (702) occupies such a band in the frequency domain so that a sufficient ratio of a sampling rate to an upper edge frequency of the modulation signal can be achieved. Digital processing is used for compensating an effect of non-flat high-pass PLL transfer function and / or to perform pre-distortion of the input signal of a controlled oscillator to compensate an effect of non-linearity of a controlled oscillator.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
BAW apparatus
ActiveUS20060290446A1Improve linearityReduce and eliminate generation of harmonicImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesHarmonicNon-linear effects
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Direct modulation of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) with adaptive gain control
InactiveUS7015738B1Reduce output noiseWide bandwidthPulse automatic controlAngle modulationLoop filterDigital analog converter
Techniques for direct modulation of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) with adaptive digital gain control for wideband wireless applications are disclosed. A digital adaptive gain control loop is used to directly modulate the VCO, and a phase-locked loop (PLL) to track the frequency drift and other nonlinear effects of the VCO. As the PLL is applied to track the carrier frequency without passing the modulation signal into the PLL loop filter, the PLL can be implemented with a narrow loop bandwidth. The wideband frequency modulated signal is directly up-converted to the radio frequency (RF) signal by directly modulating the VCO through a digital-to-analog converter which is digitally controlled by an adaptive gain control loop. Thus, both wide bandwidth and low output noise for a frequency synthesizer and modulator can be achieved.
Owner:CAO WEIXUN
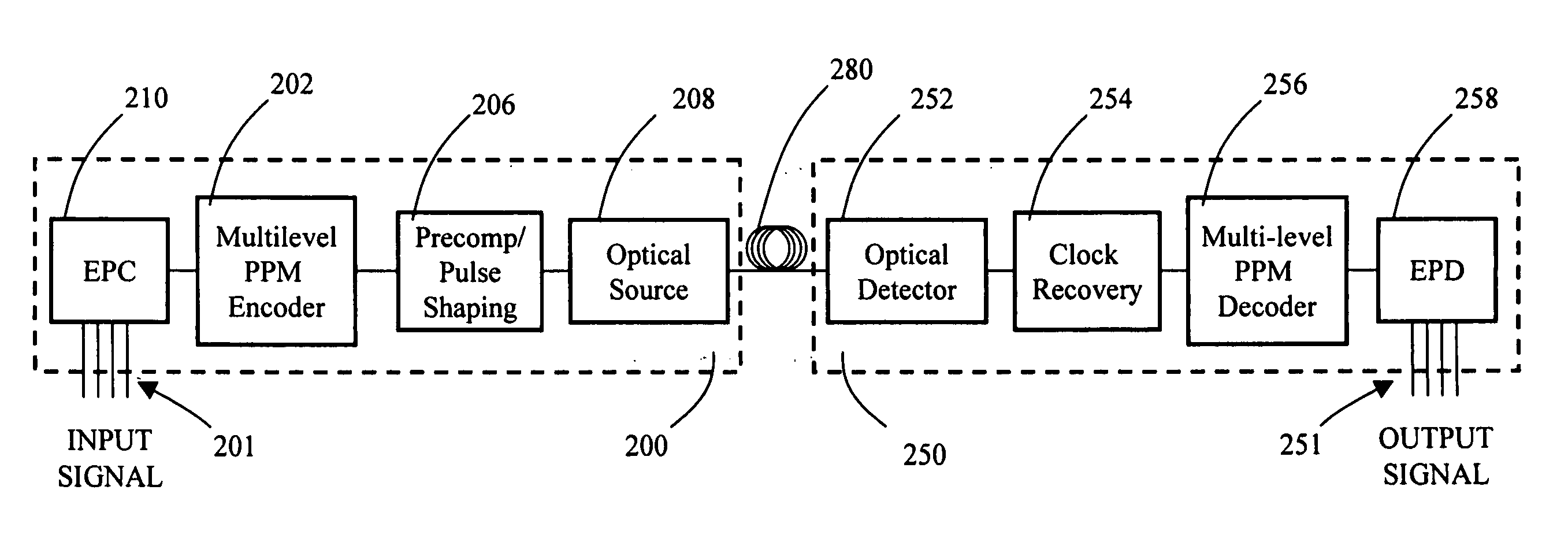
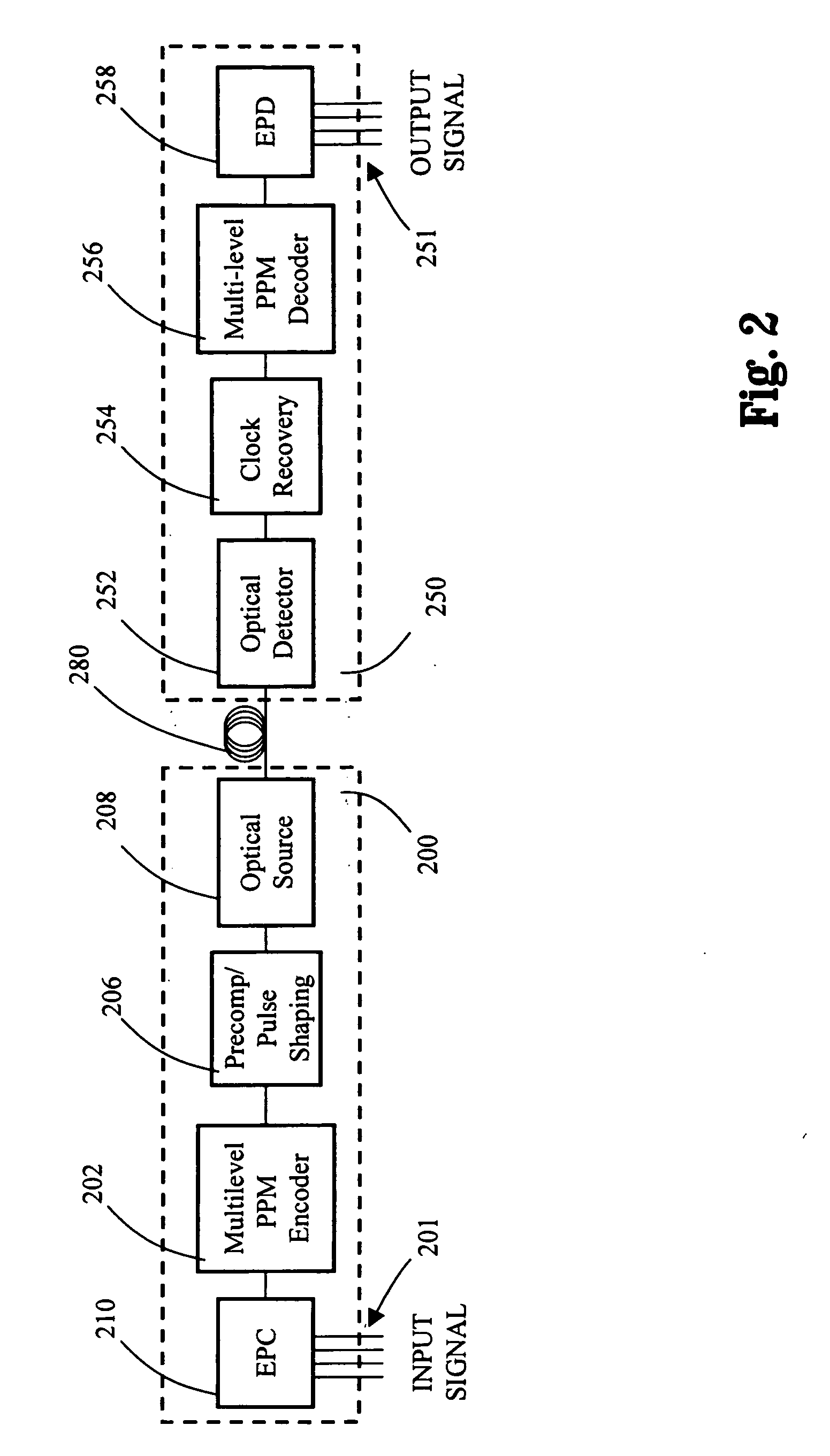
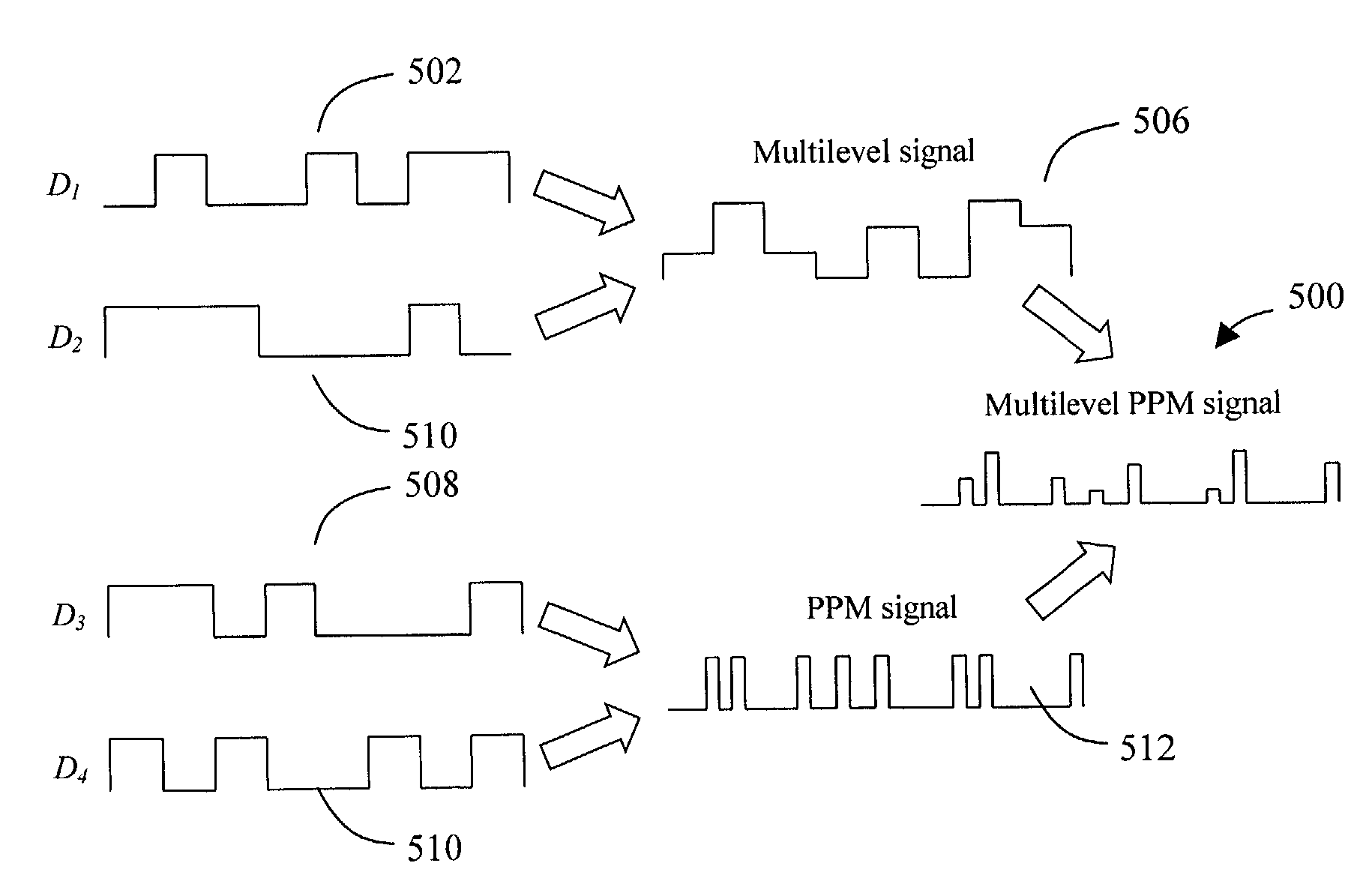
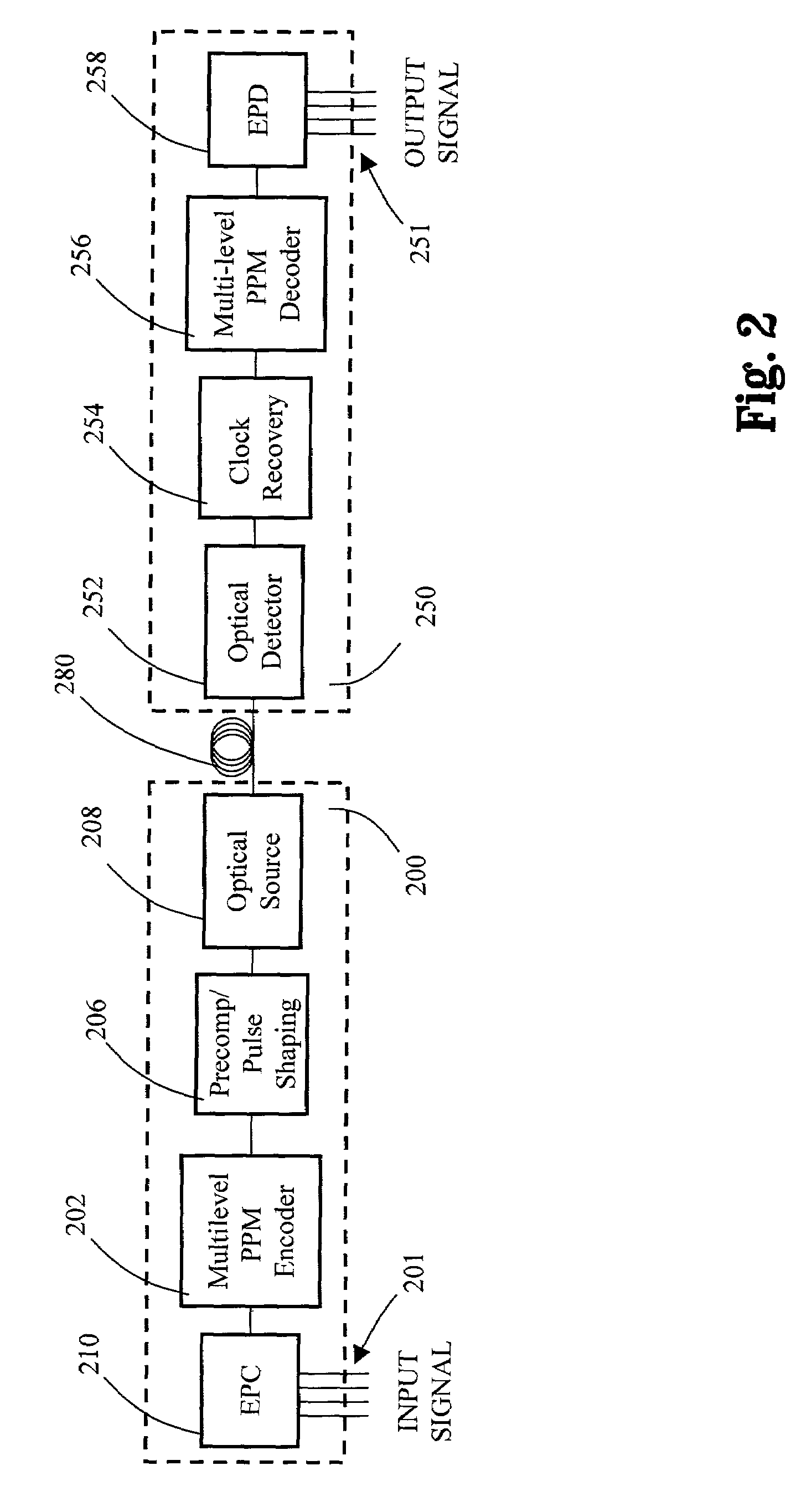
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS20070092265A1Increasing aggregate data rateReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
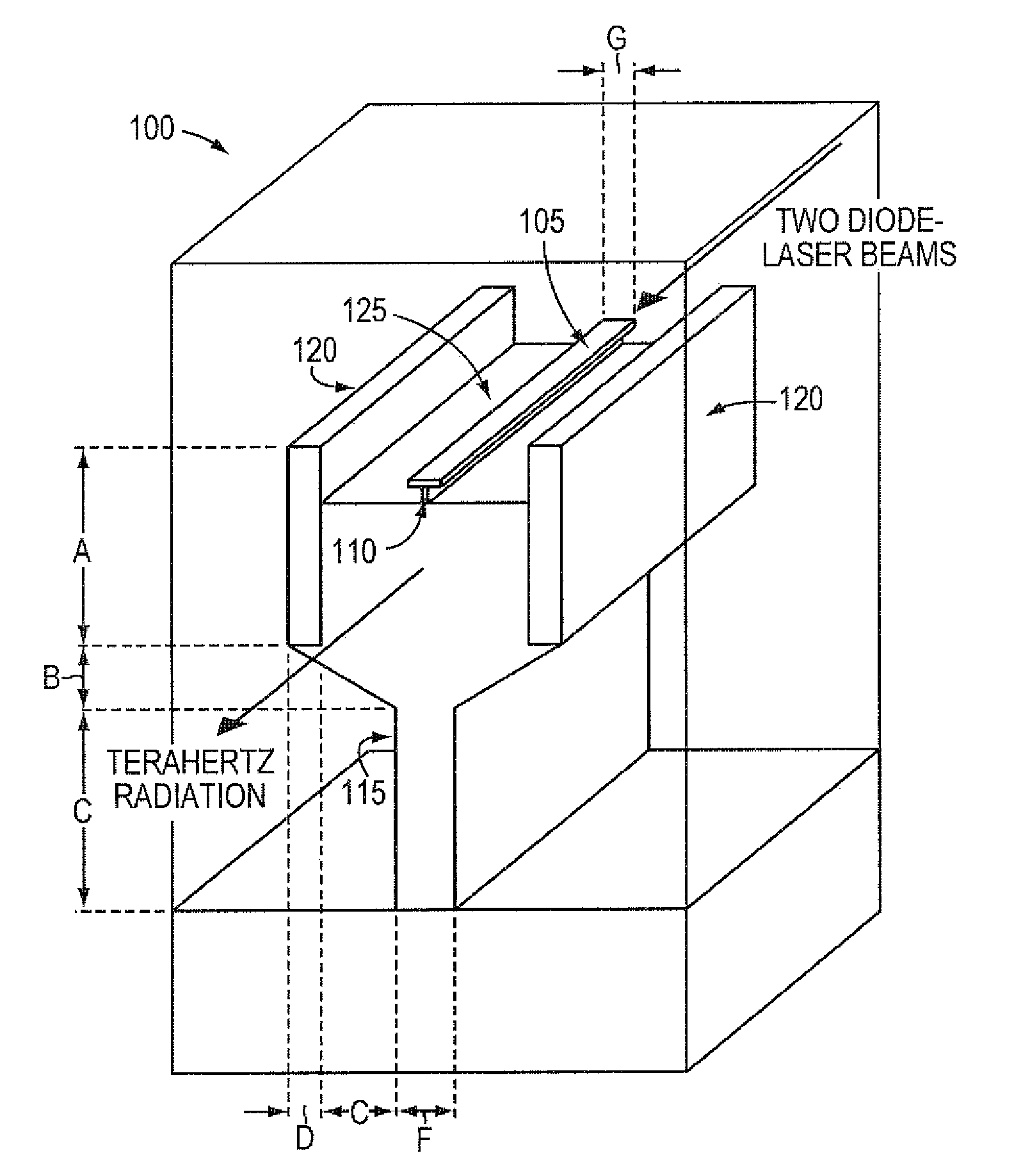
Low loss terahertz waveguides, and terahertz generation with nonlinear optical systems
InactiveUS7480434B2Solid masersOptical waveguide light guideTerahertz radiationNear infrared radiation
A silicon based source for radiation in the 0.5-14 Terahertz regime. This new class of devices will permit continuously tunable, milli-Watt scale, continuous-wave, room temperature operation, a substantial advance over currently available technologies. The Silicon Terahertz Generator (STG) employs a silicon waveguide for near infrared radiation, situated within a metal waveguide for Terahertz radiation. A nonlinear polymer cladding permits two near-infrared lasers to mix, and through difference frequency generation produces Terahertz output. The small dimensions of the design greatly increase the optical fields, enhancing the nonlinear effect. The design can also be used to detect Terahertz radiation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
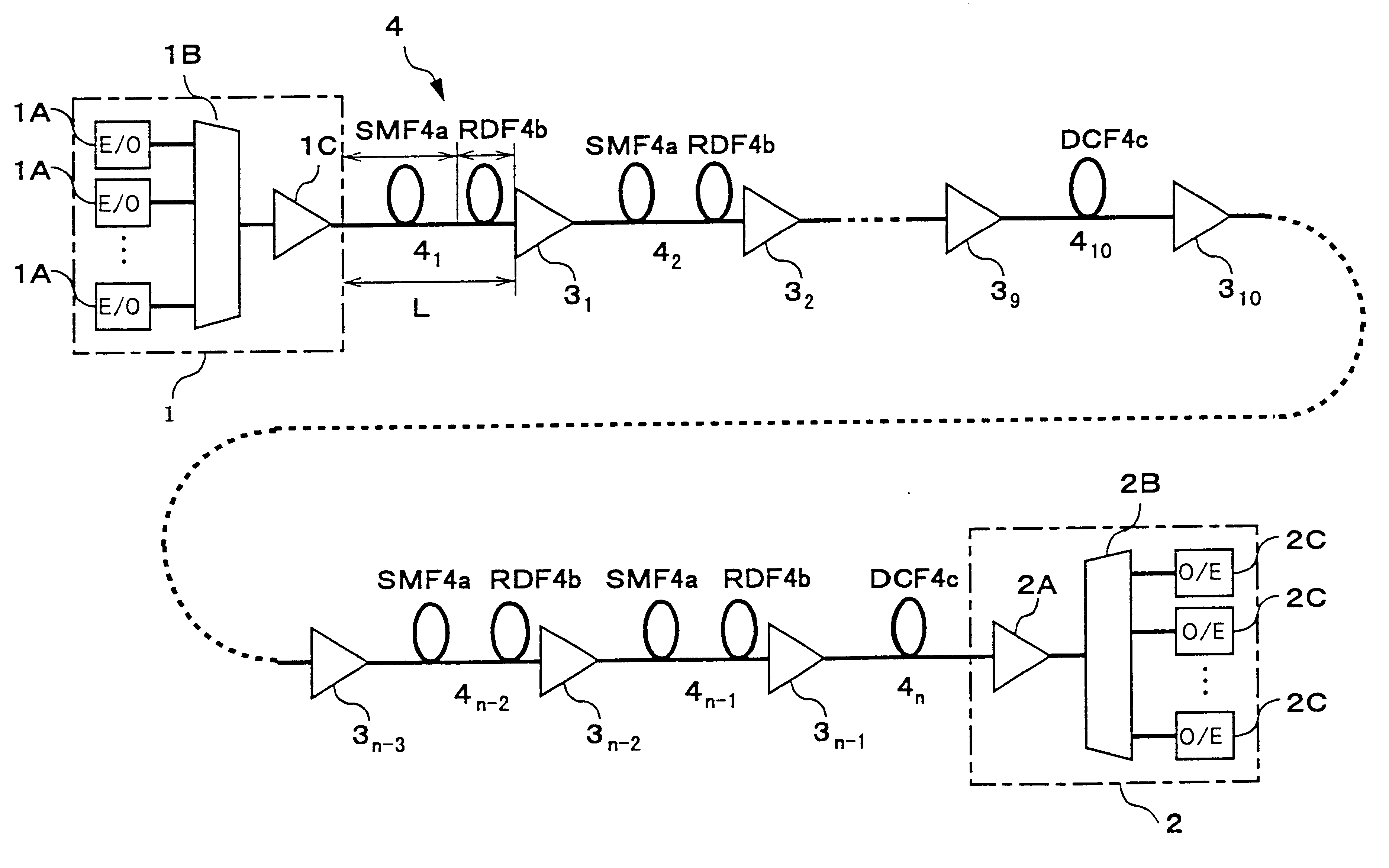
Wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission system
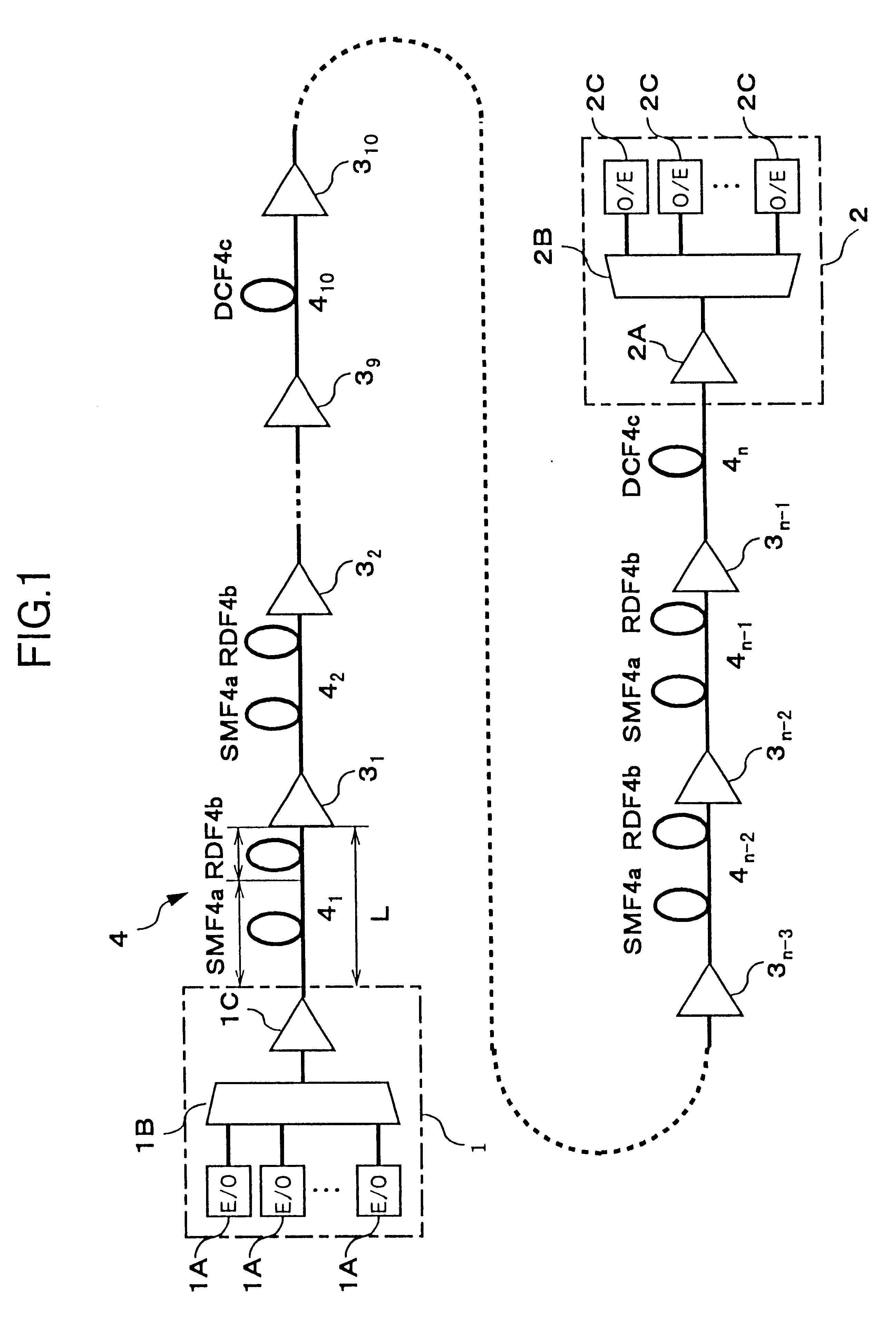
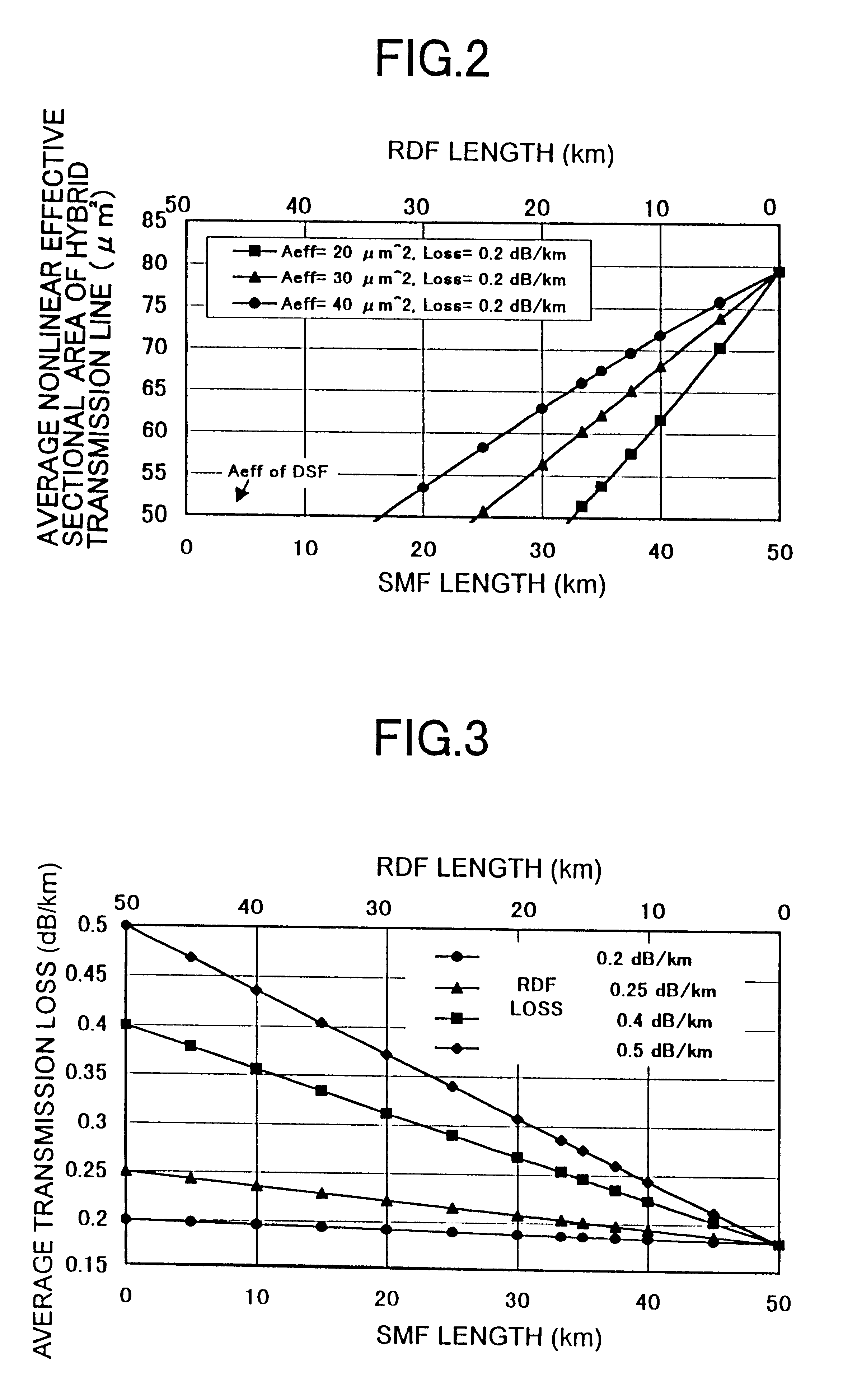
An object of the present invention is to provide a WDM optical transmission system with an excellent transmission characteristic by employing a hybrid transmission line which is formed by combining under optimal conditions an optical fiber having positive wavelength dispersion, and an optical fiber having negative wavelength dispersion. According to the WDM optical transmission system, an optical transmitter station, optical amplifiers, and an optical receiver station are interconnected over an optical fiber transmission line. The optical fiber transmission line has an inter-repeater segment formed with a hybrid transmission line composed of a 1.3 mum zero-dispersion SMF and an RDF, and an inter-repeater segment formed with a DCF for compensating for cumulative wavelength dispersion generated in the hybrid transmission line. As the conditions for setting the hybrid transmission line, a ratio of the length of the RDF to the length of the inter-repeater segment must be 20% or more and 40% or less. Consequently, an influence due to a nonlinear effect or transmission loss in the hybrid transmission line can be minimized to thereby improve a transmission characteristic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method of optical signal transmission with reduced degradation by non-linear effects
InactiveUS6323993B1Laser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemEngineering
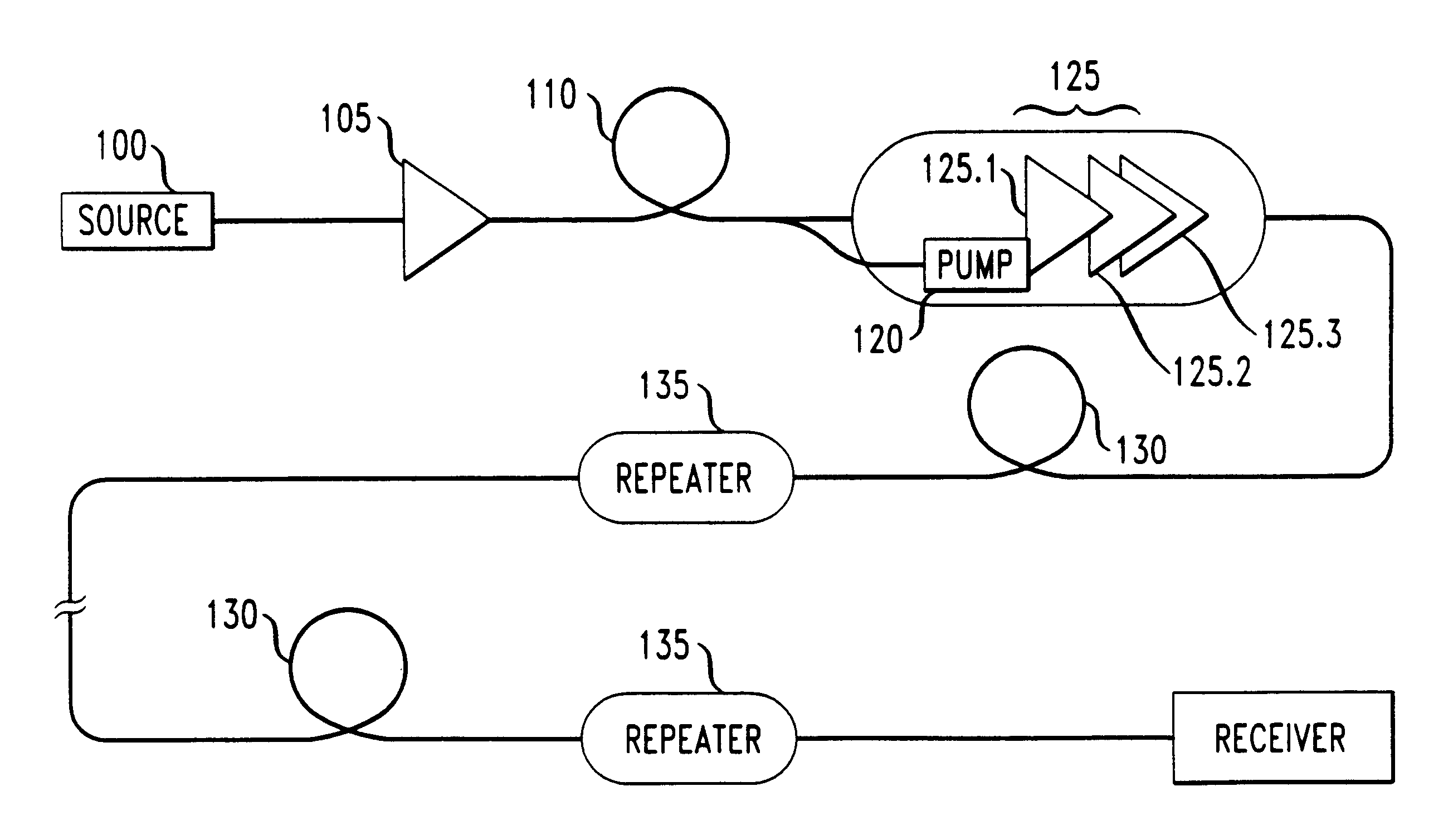
In an optical communication system, the signal power level injected into each of one or more optical fiber spans is reduced so as to suppress undesired non-linear effects. This reduction in injected signal level is made possible by remotely pumped amplification in the spans that are affected.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Methods and devices of quantum encoding on dwdm (ROADM) network and fiber optic links .
InactiveUS20110206204A1Reduce signal to noise ratioReduce probabilityPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPhoton polarization
The invention solves the following complicated problems. Elaboration of the procedure for secret key extraction from the lower layer optic signal even in a presence of noise in fiber-optic cable. The realization of the quantum protection amplification scheme to clean states of the entangling polarized photons against noise in optical channels, especially in case of use Einstein-Podolsky-Rozen method with single photon source for transmitting and measuring secret keys photon polarization in ROADM network. The development of a system for code key transmission that satisfies requirements of fortuitousness and privacy along with speed enlargement of the key generation in ROADM network. The achievement of the acceptable optical fiber amplification without losing its behavior and the protocol determination, which will allow to detect and correct bit errors in fiber optic cable and ROADM network, caused by linear and nonlinear effects. The development of quantum encoding systems for telecommunication topologies.
Owner:SYCHEV DMITRY IVANOVICH MR +2
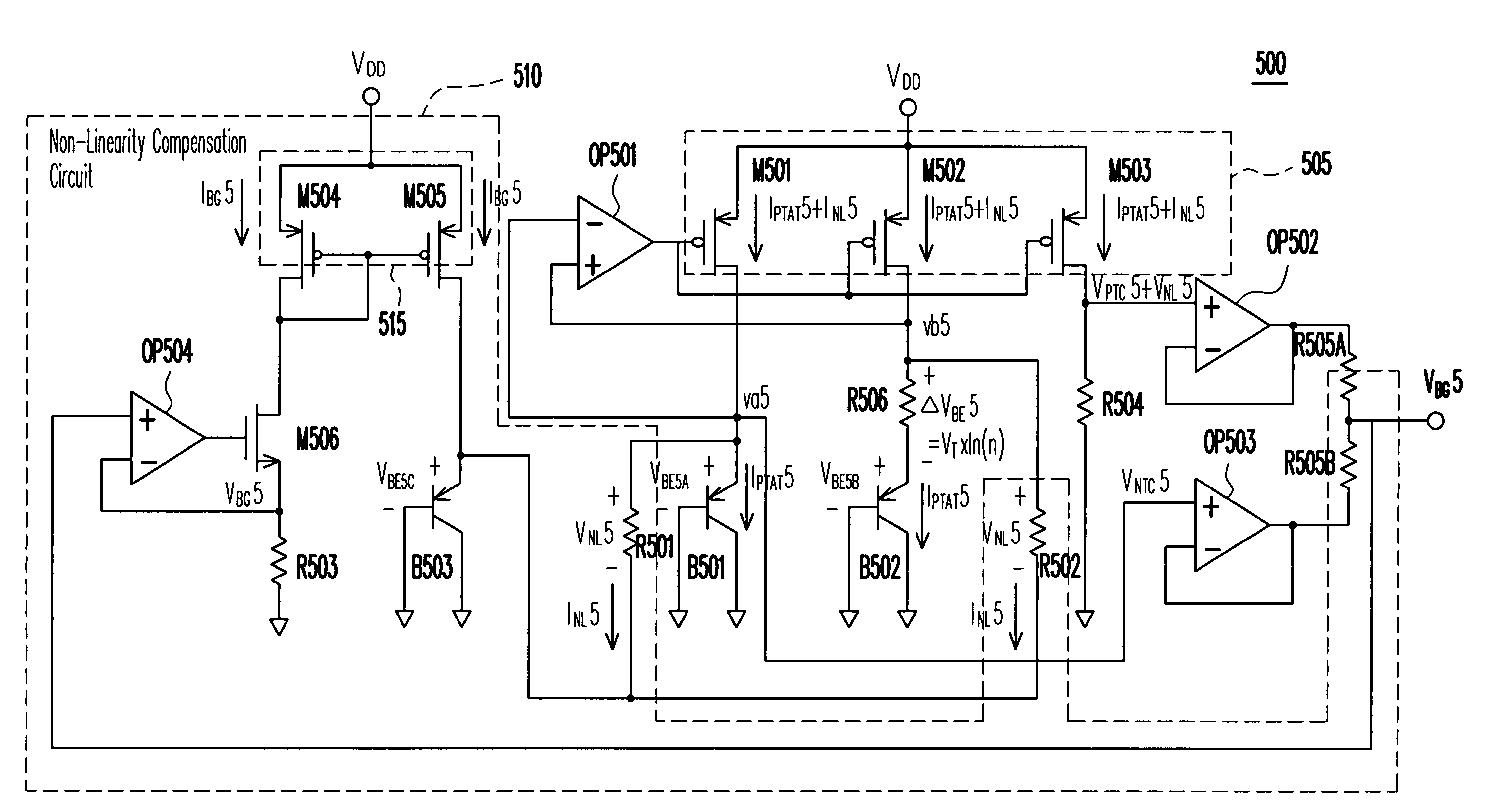
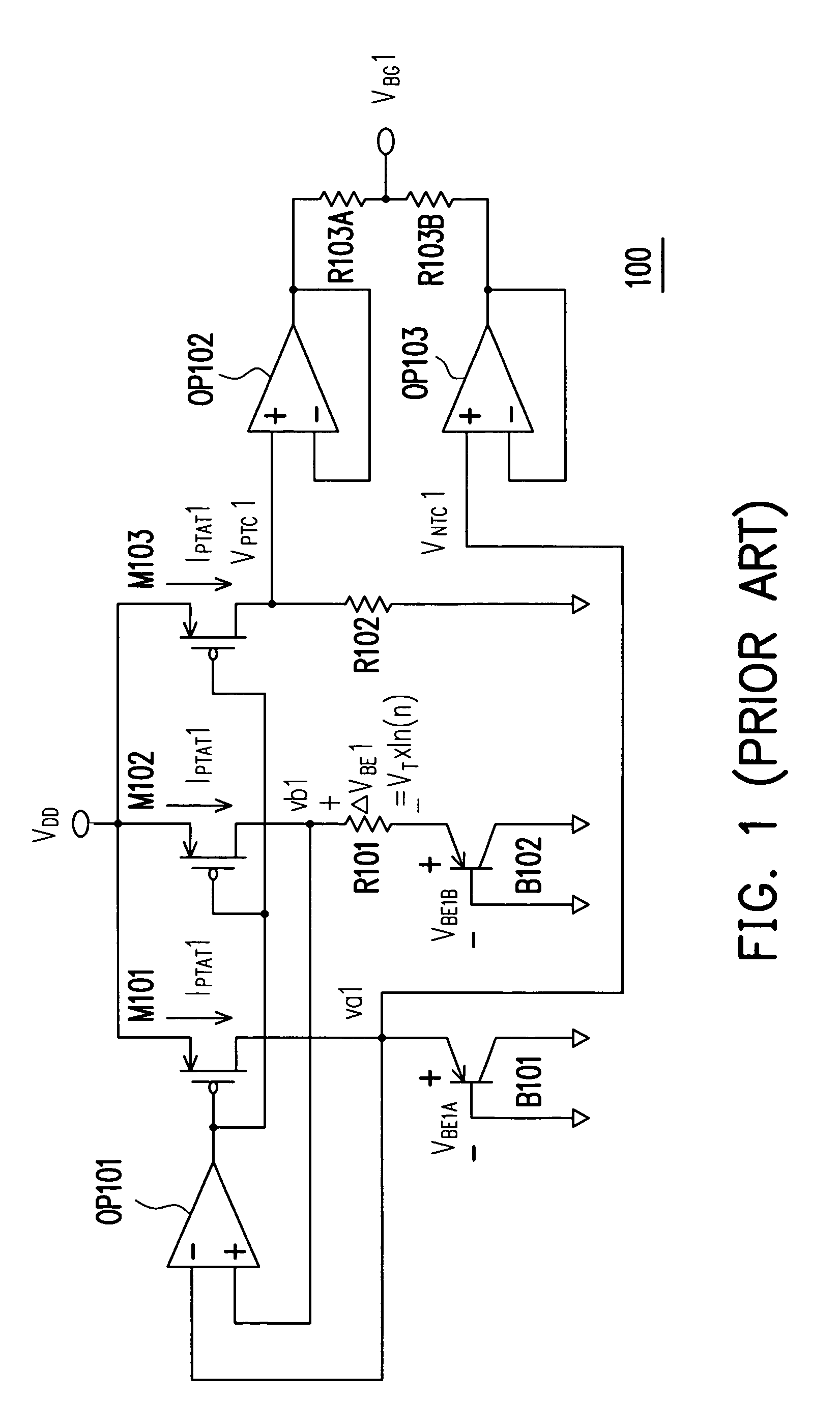
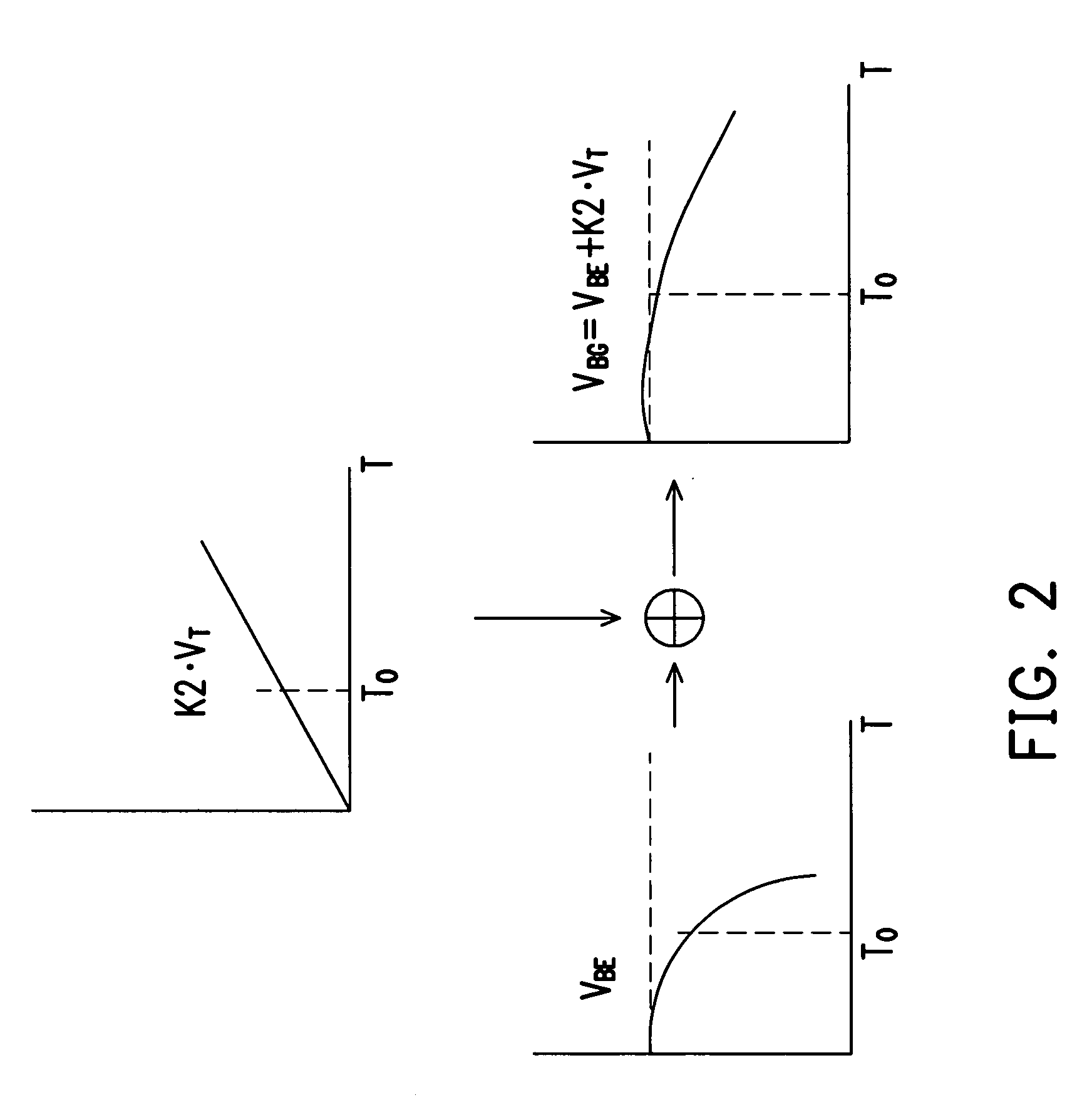
Non-linearity compensation circuit and bandgap reference circuit using the same
InactiveUS7411380B2High precisionLow costPower supply linesElectric variable regulationEngineeringReference circuit
A non-linearity compensation circuit and a bandgap reference circuit using the same for compensating non-linear effects of a reference voltage are provided. In the non-linearity compensation circuit, the reference voltage is transformed into a temperature independent current. A current mirror mirrors the temperature independent current for biasing a bipolar junction transistor (BJT). Further, two resistors are used for estimating a non-linear voltage, so as to compensate the reference voltage.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS7149256B2Reduce transmit powerIncreasing aggregate data rateAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
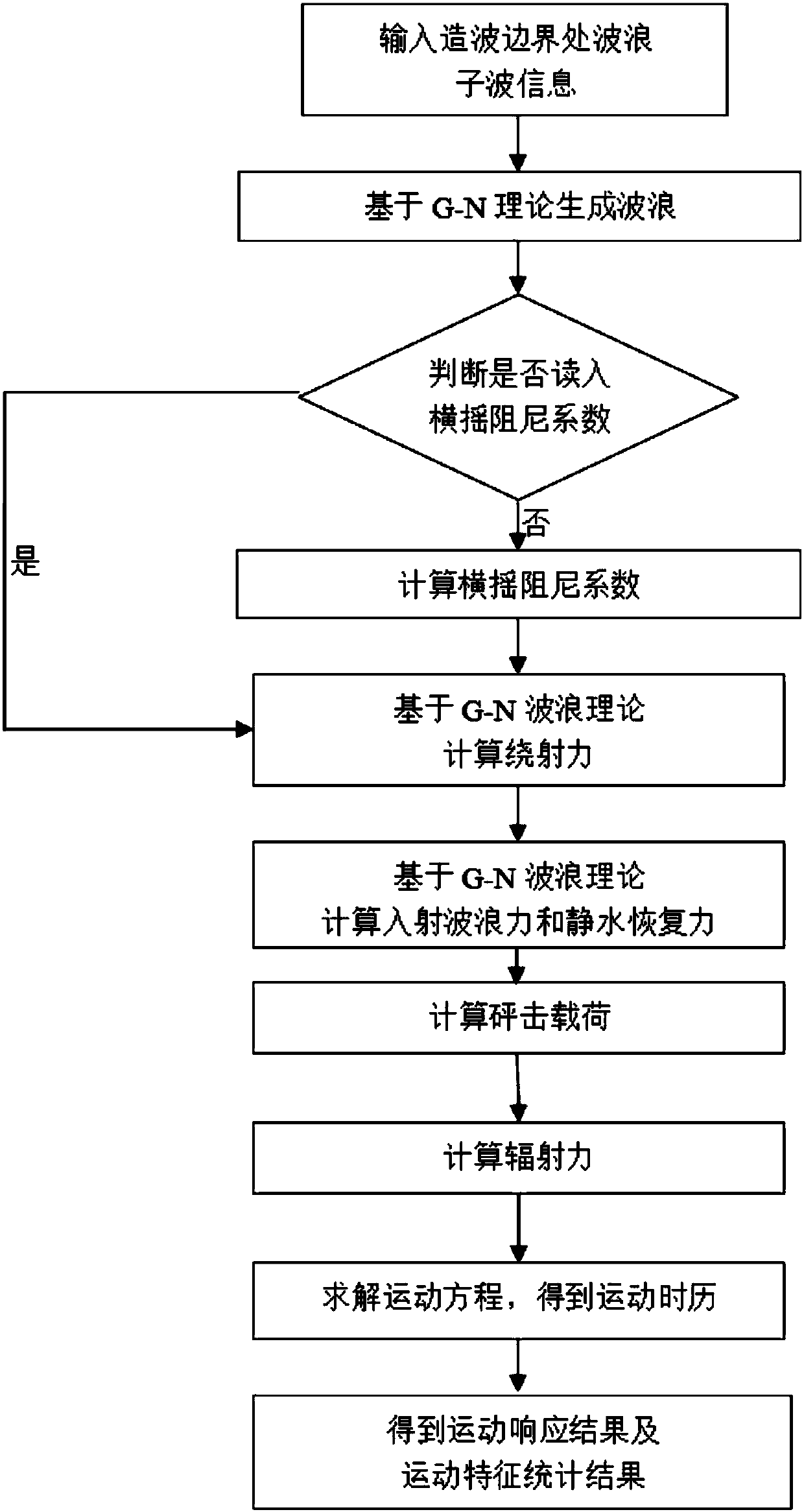
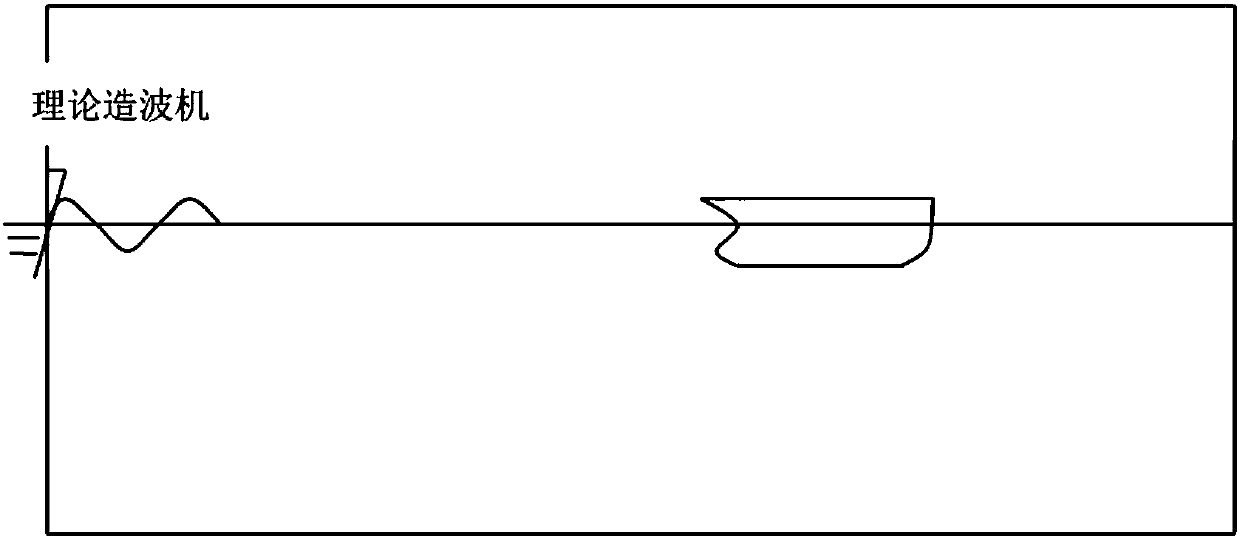
G-N wave model-based forecast method for large-amplitude motion of ship in severe sea condition
The invention discloses a G-N wave model-based forecast method for a large-amplitude motion of a ship in a severe sea condition, and belongs to the technical field of ship motion forecast. Through nonlinear simulation of the motion of the ship in waves, a nonlinear effect of an incident wave force and a hydrostatic restoring force of a ship body is considered, and an incident wave pressure on thewet surface of the ship body is calculated. A fluid pressure is solved based on a G-N wave theory, so that the incident wave force and a hydrostatic pressure are obtained; a radiation force and a diffraction force are solved by adopting an impulse response function method, wherein the wave surface of the diffraction force is obtained by a G-N wave model; and consistency correction can be performedin calculation. The large-amplitude motion of the ship is forecast by adopting a weak nonlinear motion equation based on coupling of three freedom degrees including heaving, pitching and rolling; RAOis calculated for analyzing motion characteristics of the ship; a simulated motion response time history significant valve, a motion extremum value and oscillation statistics are analyzed by utilizing a wave-by-wave analysis theory; and the motion of the ship body can be forecast more accurately.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
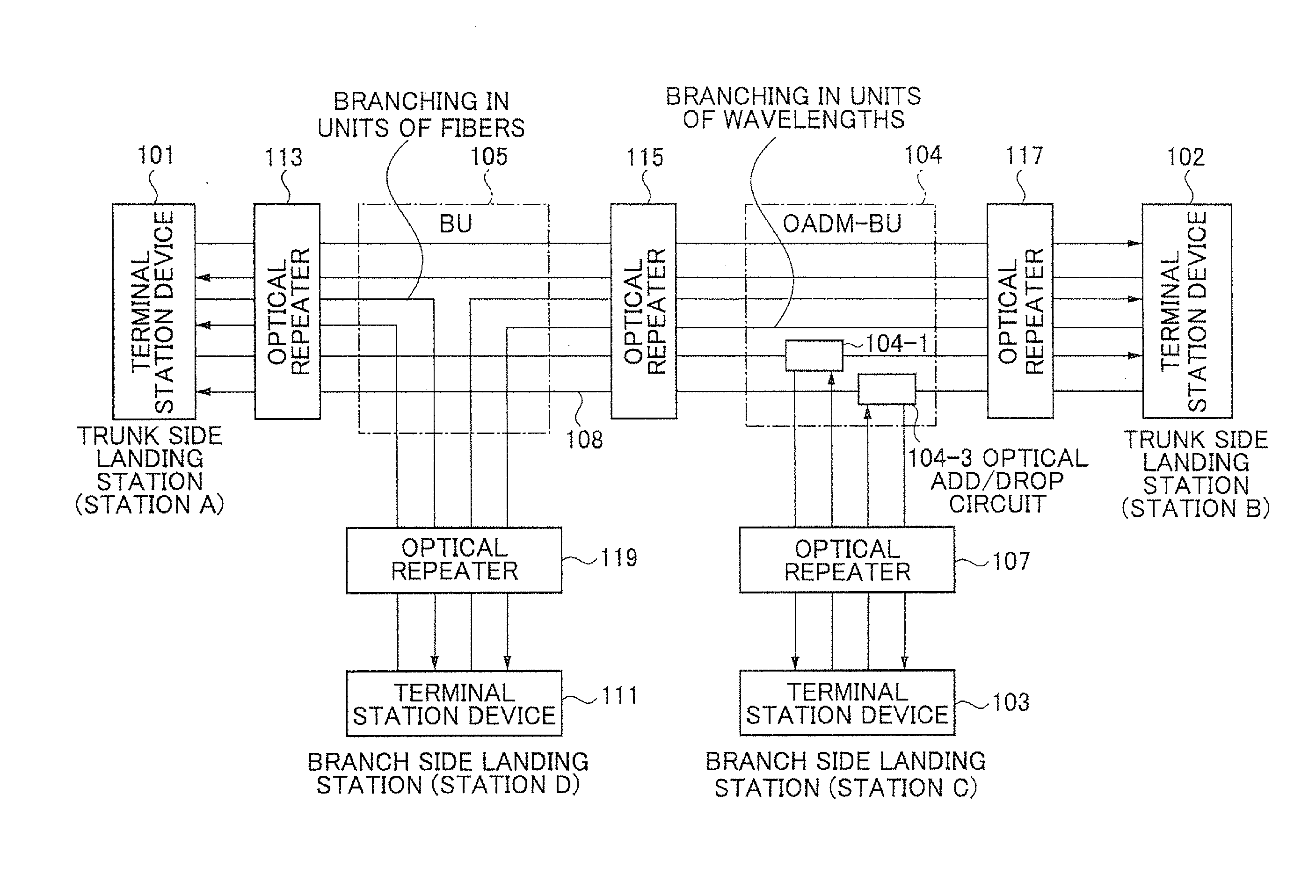
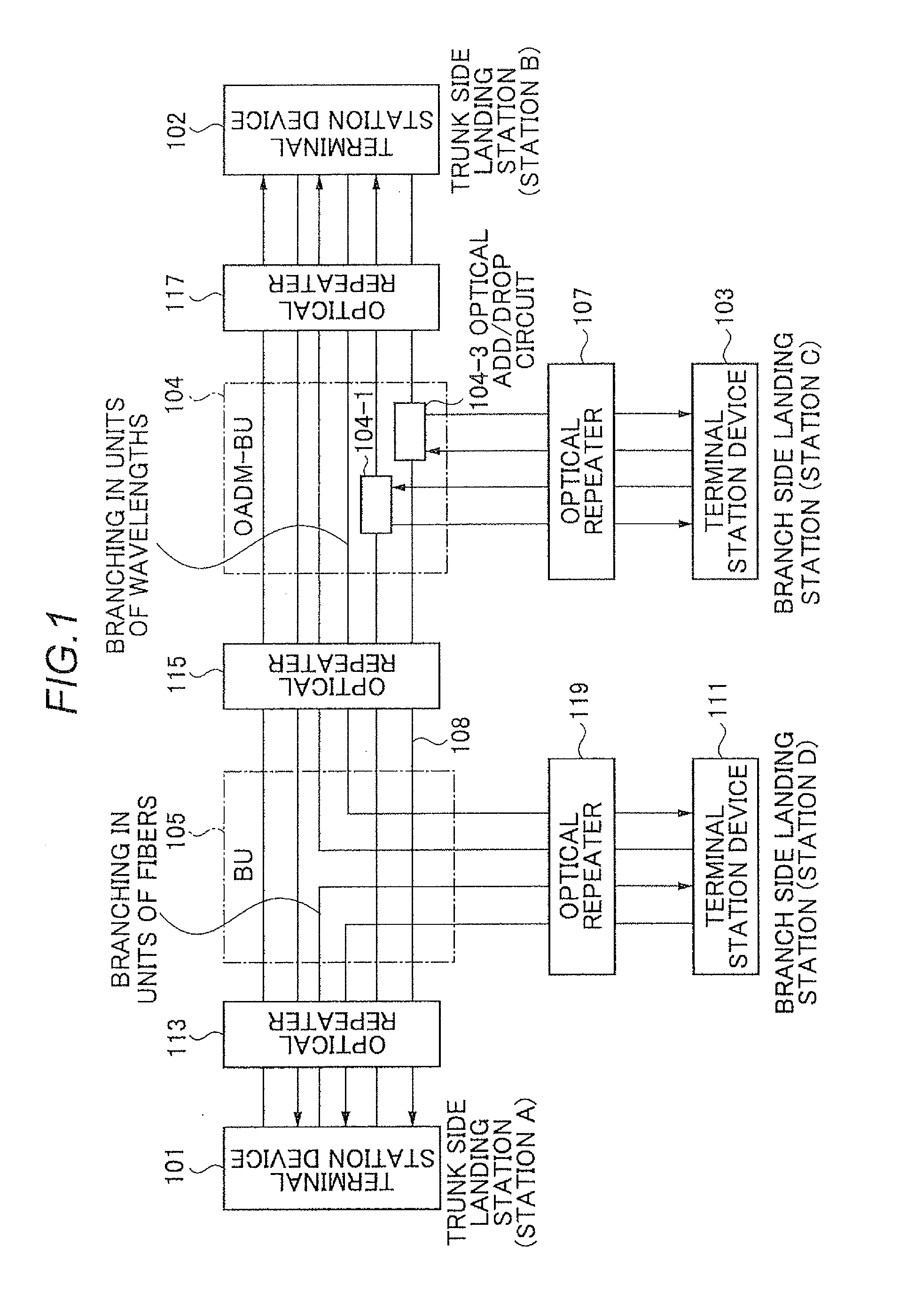
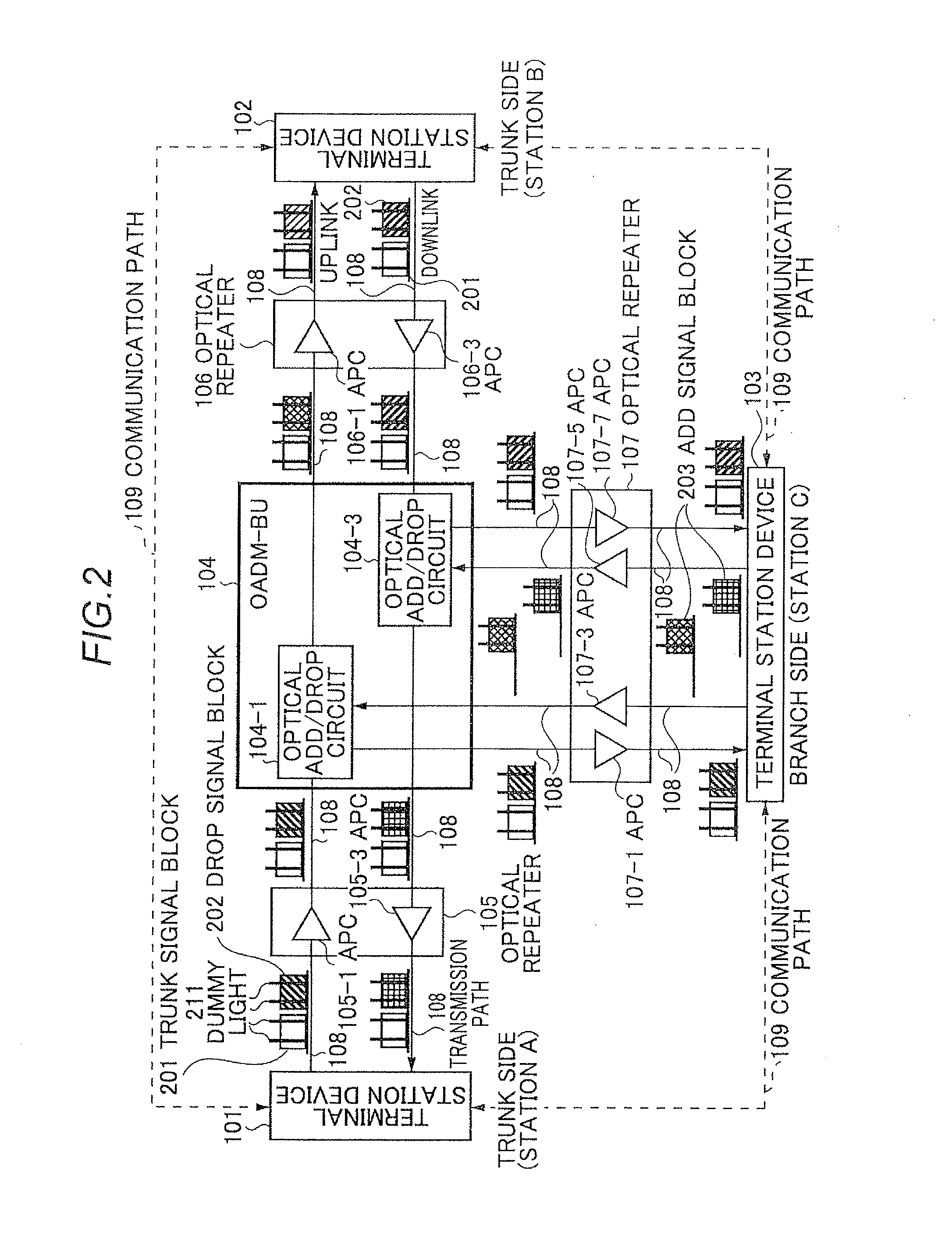
Optical signal level adjustment system, information analysis/control signal generation apparatus in the same system, and information analysis/control signal generation method
ActiveUS20110311216A1Increase in channel power can be preventedAvoiding characteristicLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsChannel powerInformation analysis
The present invention enables to prevent transmission characteristics from deteriorating due to the nonlinear effect in the transmission path caused by an increase in the channel power when a cable disconnection occurs. An optical signal level adjustment method comprises the steps of: obtaining, based on one or more optical signal disconnections which are detected per wavelength block and each of which is detected by a signal disconnection detection section included in each of terminal station devices, a location at which the optical signal disconnection has occurred, a combination of a terminal station device and a wavelength block, and a dummy light adjustment amount, said combination being required to be subjected to adjustment of transmission dummy light, said combination and said dummy light adjustment amount corresponding to the location; and transmitting, to the terminal station device which is required to be subjected to adjustment of the transmission dummy light, a control signal for adjusting the intensity of the dummy light in the obtained wavelength block by the dummy light adjustment amount.
Owner:NEC CORP
Systems and methods for transmitting quantum and classical signals over an optical network
Systems and methods for transmitting quantum and classical signals over an optical network are disclosed, wherein the quantum signal wavelength either falls within the classical signal wavelength band, or is very close to one of the classical signal wavelengths. The system includes a deep-notch optical filter with a blocking bandwidth that includes the quantum signal wavelength but not any of the classical signal wavelengths. The deep-notch optical filtering is applied to the classical signals prior to their being multiplexed with the quantum signals to prevent noise generated by the classical signals from adversely affecting transmission of quantum signals in the transmission optical fiber. Narrow-band filtering is also applied to the quantum signals prior to their detection in order to substantially exclude spurious non-quantum-signal wavelengths that arise from non-linear effects in the optical fiber. The present invention allows for the quantum and classical signals to have wavelengths within just a few nanometers of one another, which has benefits for both classical and quantum signal transmission on a common transmission optical fiber.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
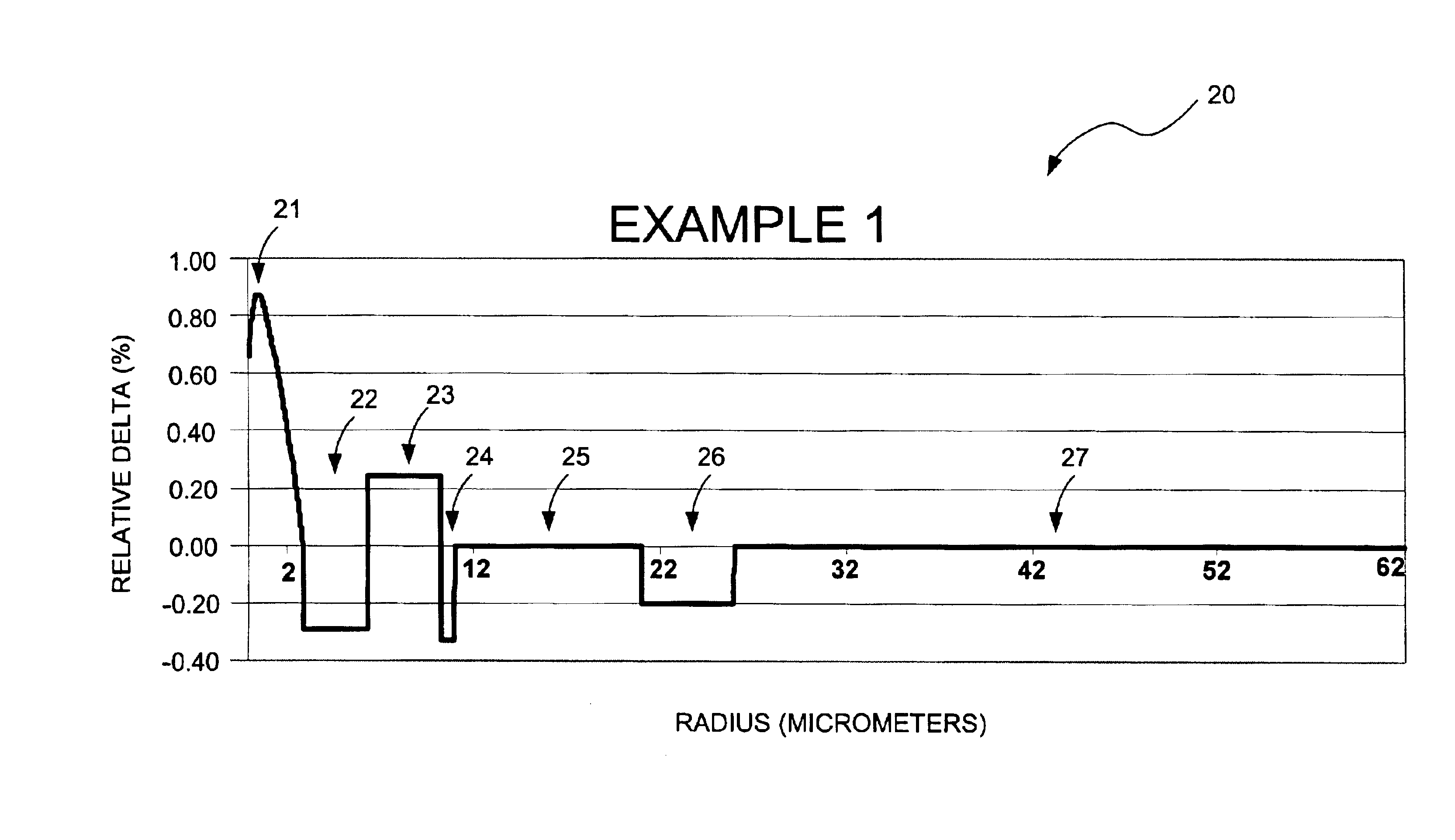
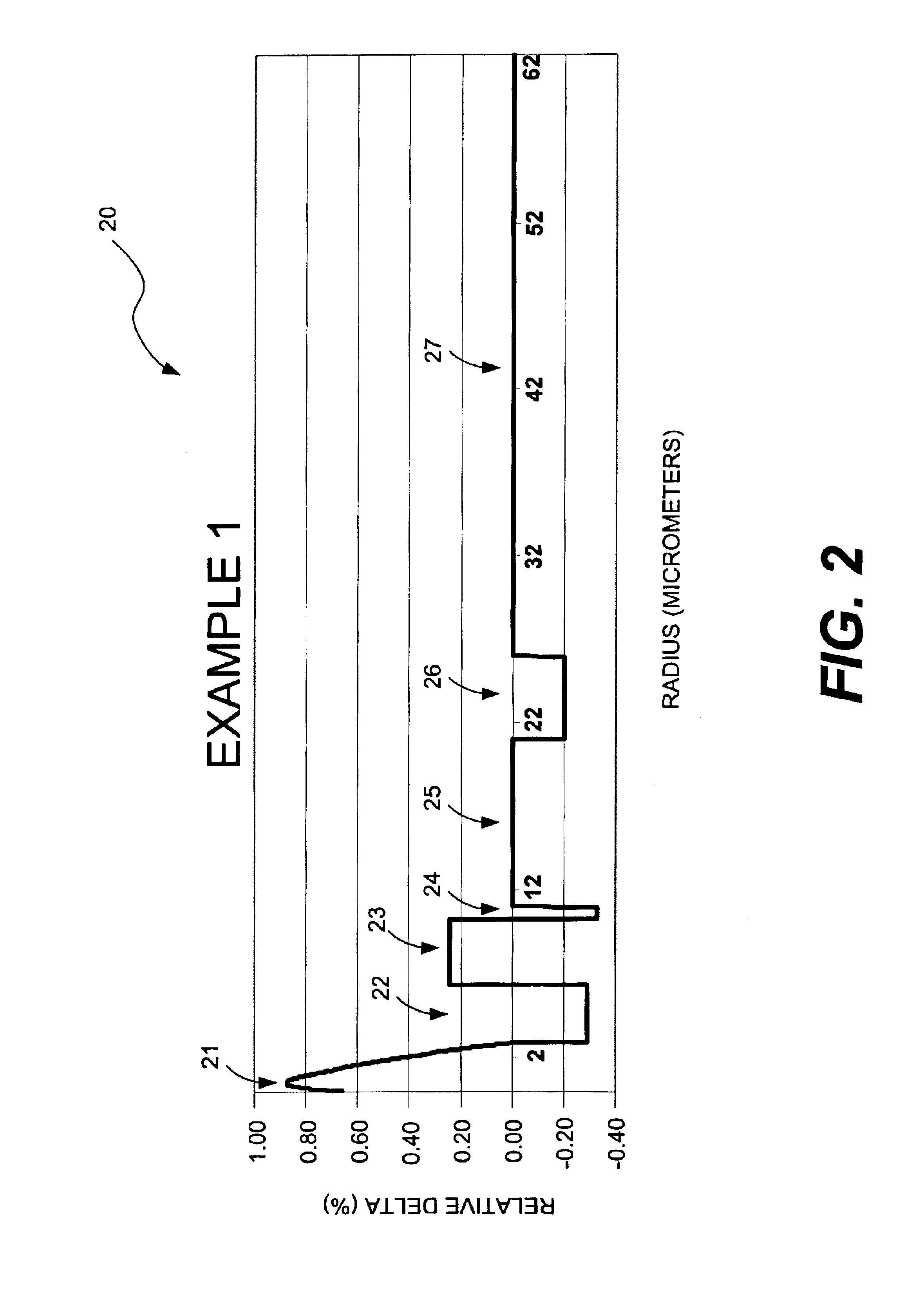
Large-effective-area inverse dispersion compensating fiber, and a transmission line incorporating the same
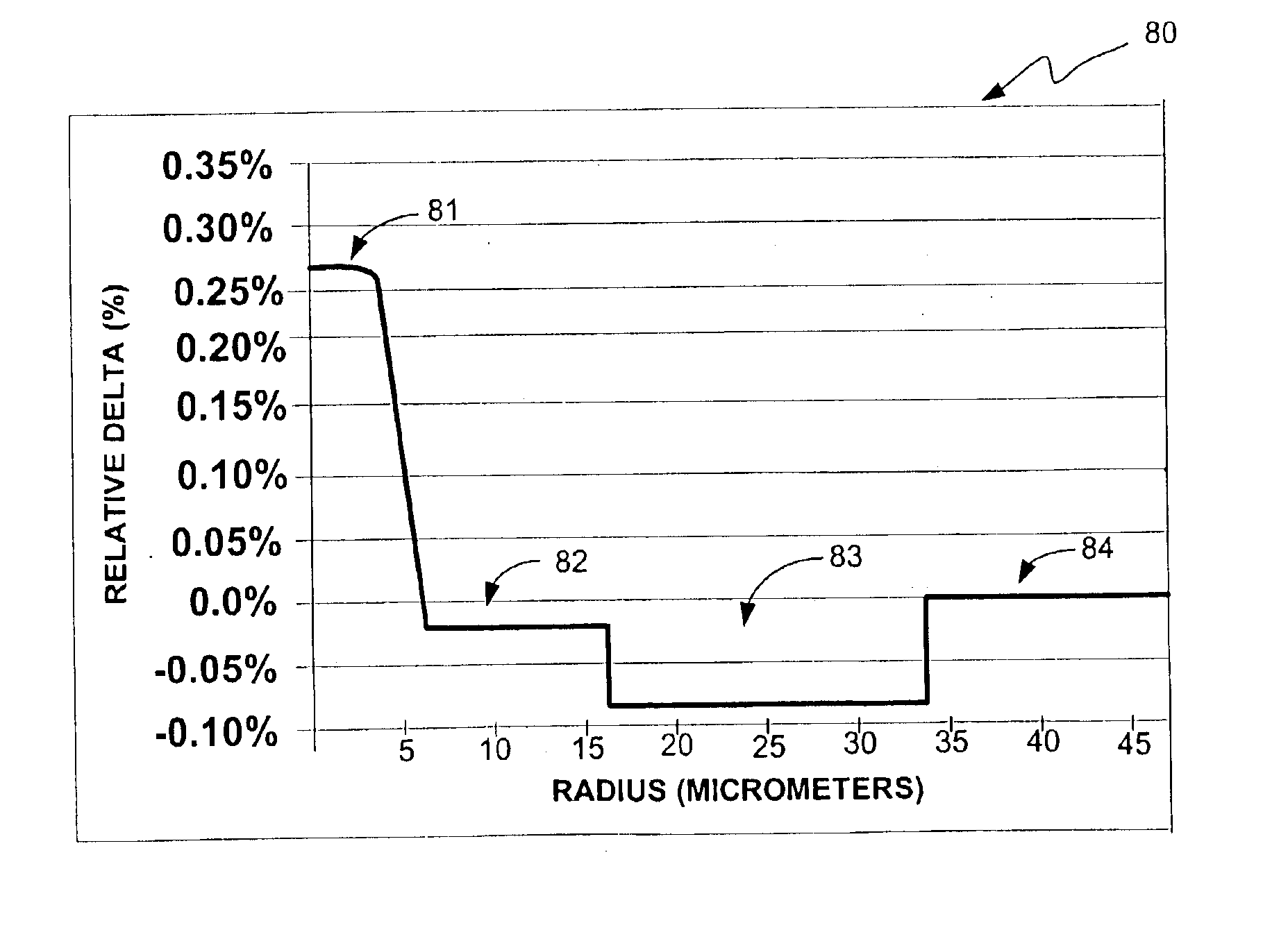
ActiveUS6959137B2Negative dispersionReduce nonlinear effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingElectromagnetic transmissionMicrometerEngineering
An inverse dispersion fiber having a large effective area and a transmission system that incorporates the fiber for providing dispersion and dispersion slope compensation in a transmission fiber. The large-effective-area inverse dispersion optical fiber (IDF) has a negative dispersion and a negative dispersion slope. The effective area, Aeff, of the IDF preferably is greater than approximately 31 micrometers squared (μm2) at a transmission wavelength of approximately 1550 nm. The large-effective-area IDF is suitable for use with super-large-effective-area (SLA) transmission fiber for compensating dispersion in the SLA transmission fiber while reducing nonlinear effects between wavelength channels and cabling loss, which is especially advantageous in transoceanic and long-haul terrestrial systems. These nonlinear effects are inversely related to the effective area of the fiber (i.e., nonlinearities˜1 / Aeff). Thus, an increase in the effective area of the fiber translates into a decrease in nonlinear interactions, which increases bandwidth capabilities and limits signal degradation. Furthermore, the large-effective-area IDF of the present invention has very desirable transmission properties. The present invention also provides a transmission system comprising at least one of the large-effective-area IDF optical fibers of the present invention. Furthermore, Aeff can be made large without having to increase the ratio, Ra, of the diameter of the core to the diameter of the trench region.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
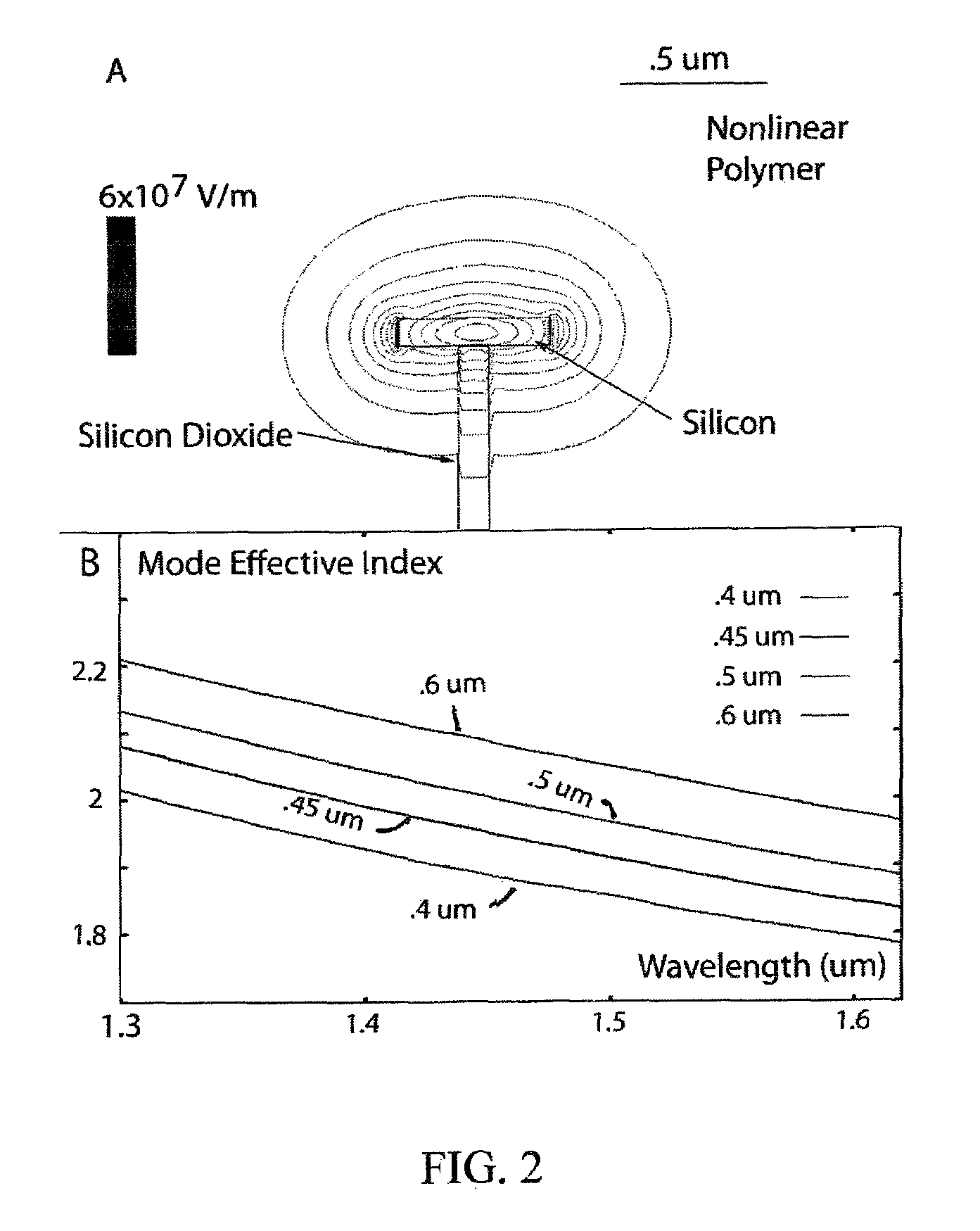
High-nonlinearity micro-ring waveguide optical device
InactiveCN103576413AEnhance nonlinear effectsLower the thresholdNon-linear opticsRidge waveguidesLogic gate
The invention relates to a micro-ring waveguide optical device capable of realizing all-optical signal processing by utilizing a high-nonlinearity effect, and aims to overcome the defect that nonlinear coefficients are insufficient when a conventional micro ring performs all-optical signal processing. The provided micro-ring waveguide optical device comprises a straight waveguide and a parallel growth micro ring on a substrate, wherein the micro ring is an annular resonant cavity; the ridge waveguide part of the micro ring adopts a parallel slot structure instead of a single ridge waveguide structure; and the straight waveguide is coupled with the micro ring. According to the micro-ring waveguide optical device, one parallel slot micro-ring waveguide structure is innovated; and when light is coupled into the parallel slot micro-ring waveguide structure, the slot waveguide structure can well limit a light field, the light intensity of resonance light is enhanced greatly due to the resonance effect of the micro ring, accordingly, various nonlinear effects of the micro ring are enhanced, the threshold value is reduced, the efficiency is improved, and the device can be applied to the all-optical signal processing fields such as optical frequency comb, wavelength conversion, logic gate, format conversion and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Exposure apparatus with laser device
InactiveUS7212275B2Improve maintainabilityNarrow spectral widthActive medium materialPhotomechanical exposure apparatusNonlinear optical crystalOptical fiber amplifiers
A laser apparatus that includes a laser light generation section, an optical amplification section, a wavelength conversion section and a suppressing section is provided. The laser light generation section includes a single wavelength oscillatory laser and generates pulsed light having a single wavelength within a wavelength range ranging from about 1.51 to 1.59 μm. The optical amplification section includes an optical fiber amplifier and is optically connected to the laser light generation section to amplify the pulsed light. The wavelength conversion section includes a nonlinear optical crystal and is optically connected to the optical amplification section to perform wavelength conversion of the amplified pulsed light into ultraviolet light. The suppressing section suppresses expansion of a wavelength width of light originated in a nonlinear effect of an optical element between the single wavelength oscillatory laser and the wavelength conversion section.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Polarization related outputting multiple wavelength and passive mode locking optical fiber laser
InactiveCN101483307AGuaranteed one-way operationEnhance nonlinear effectsActive medium shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The present invention discloses a polarization relevant output multi-wavelength and passive mode-locking optical fiber laser which belongs to laser and light communication field. A ring laser cavity includes Er-doped fiber that is taken as gain medium; a 980nm / 1550nm wavelength-division multiplexer is used to couple pumping laser of 980nm into the Er-doped fiber; a polarization relevant isolator with tail optical fiber on two ends guaranties the laser work in one way, meanwhile plays the role of a polarizer; two polarization controllers respectively on two side of the polarization relevant isolator are used to control polarization state, a 10dB coupler with 10% of the terminal port used to output optical signal and 90% of the optical signal stays in the cavity for cycle. A segment of long single mode fiber is inserted in the laser cavity and used to increase nonlinear effect inside the laser cavity; a piece of polarization maintaining optical fiber and a polarization relevant isolator constitute a birefraction optical fiber periodicity filter; the optical fiber laser is provided with two different output modes, namely mode locking pulse output and multi- wavelength continuous wave output, and can adjust polarization and switch between the two output modes.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Optical signal waveform shaping apparatus
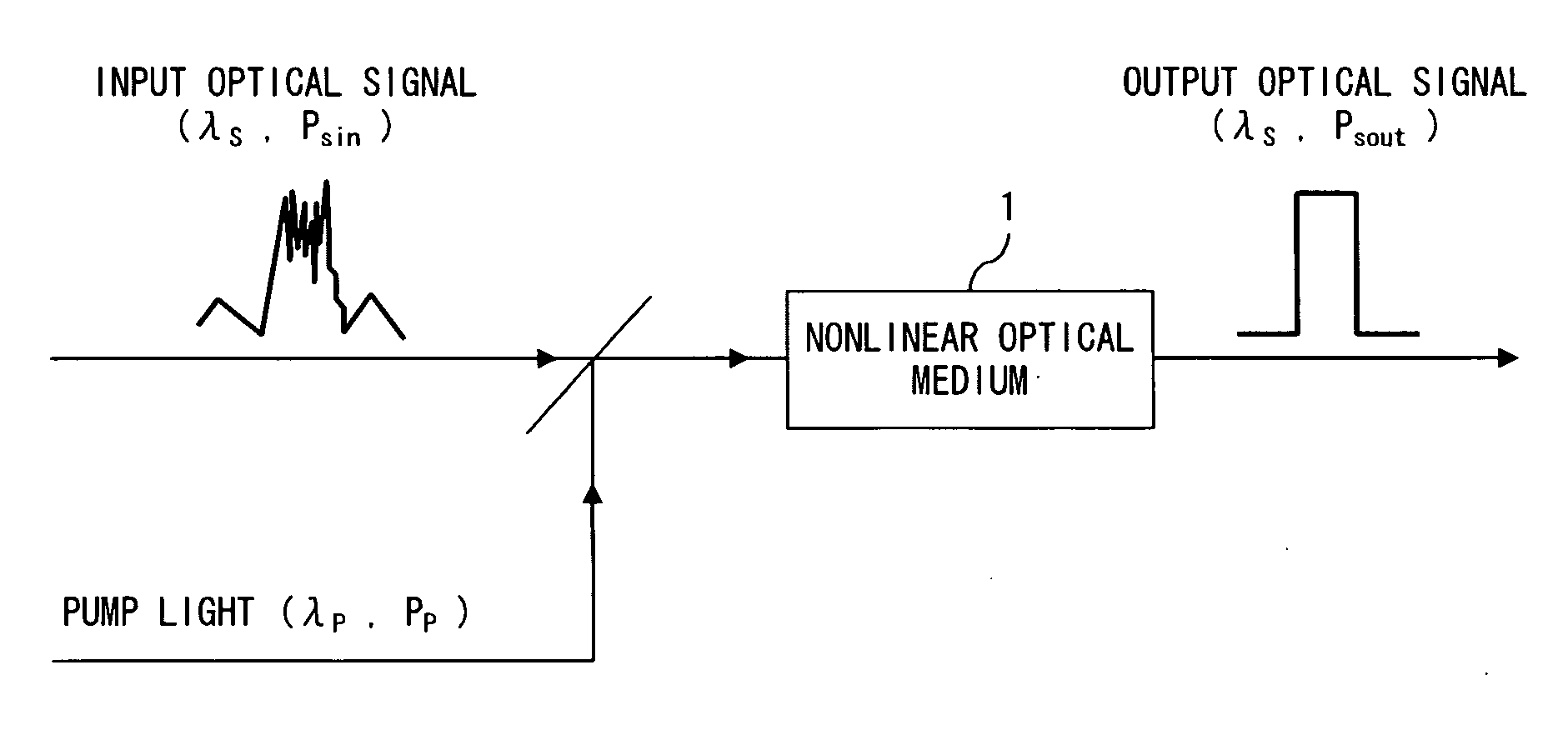
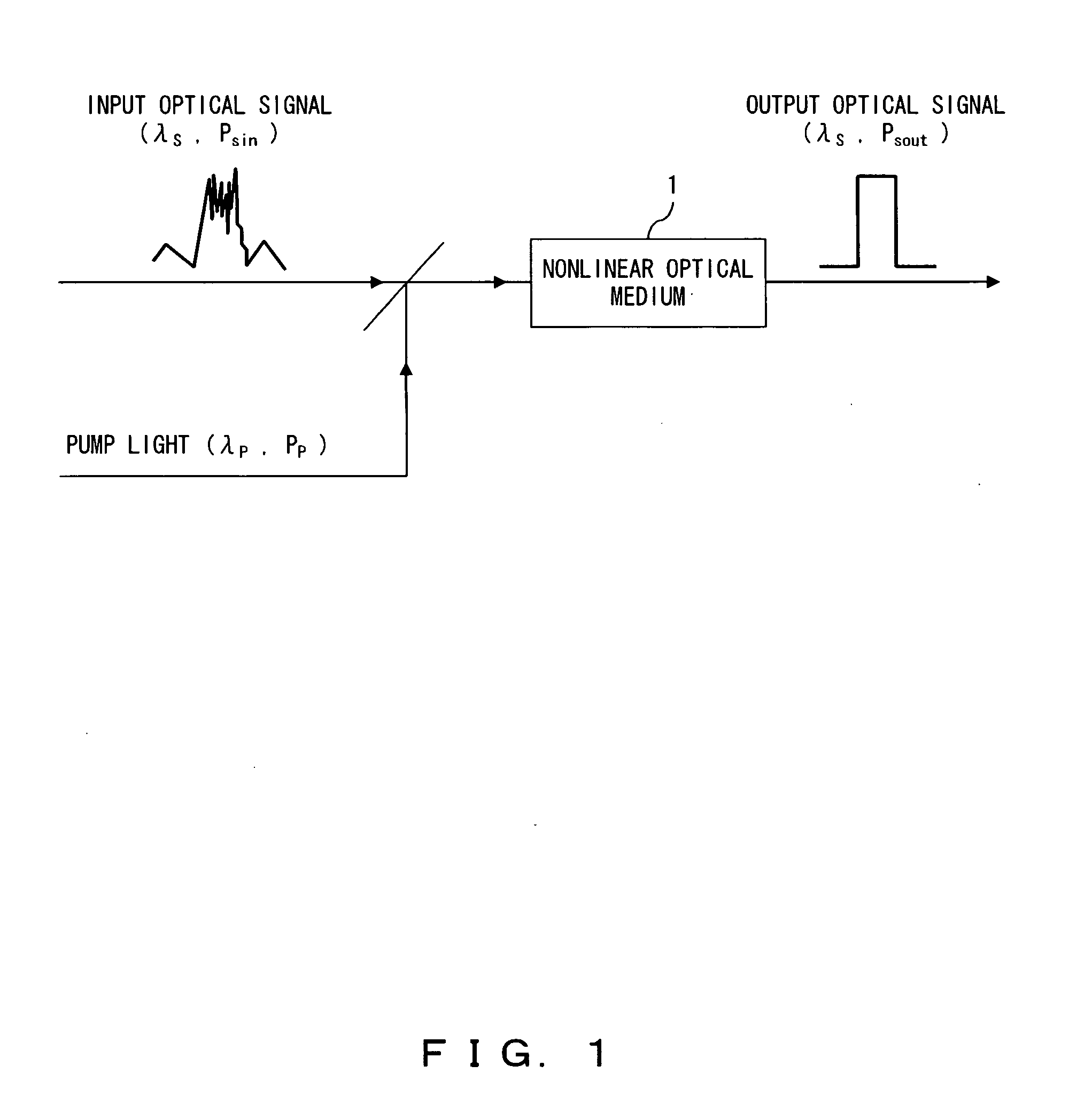
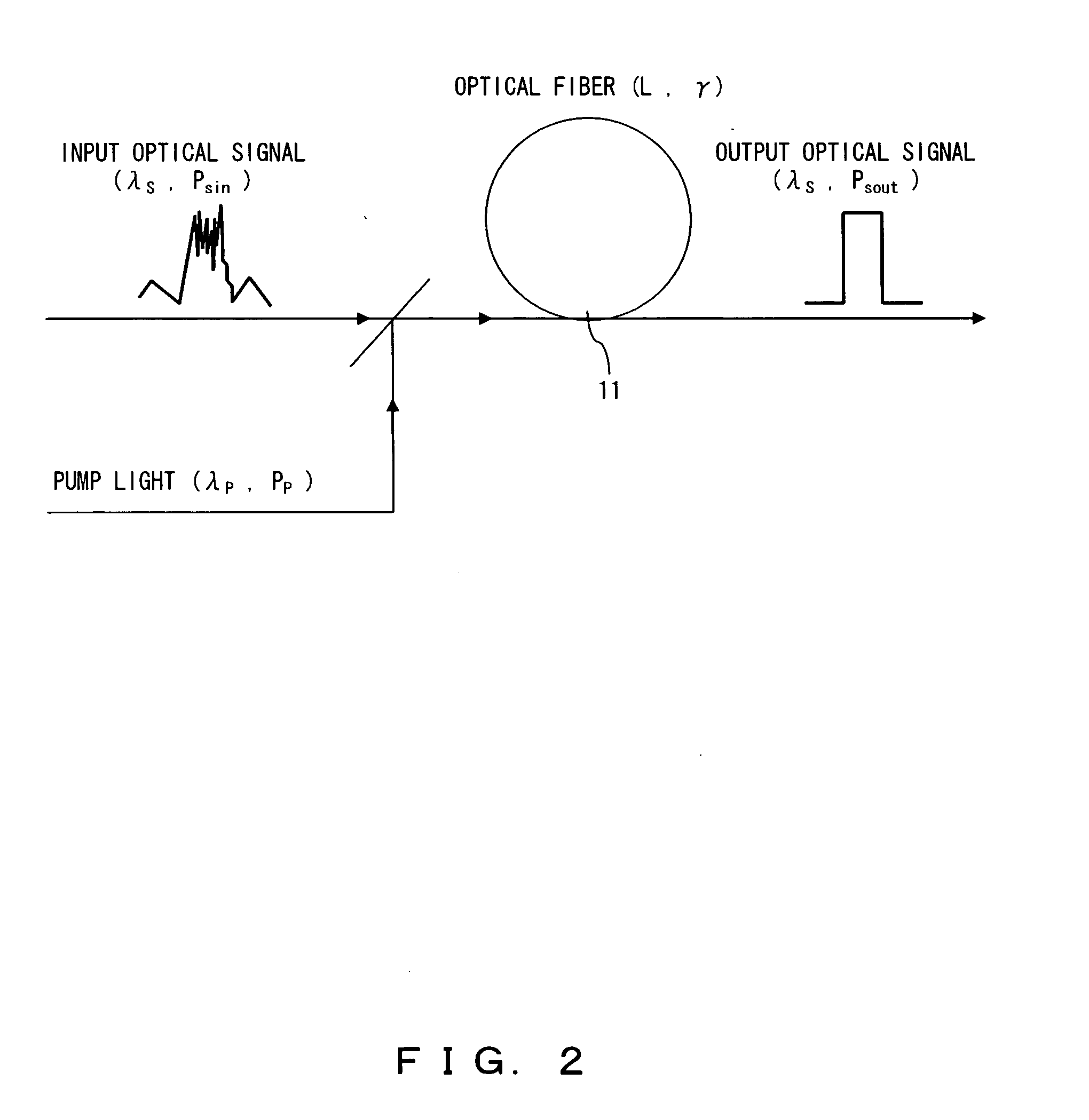
InactiveUS20070230518A1Suppresses “ 1 ” level noiseSuppress noiseLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionPower controllerWaveform shaping
An optical signal and pump light are input to a nonlinear optical medium. In the nonlinear optical medium, the optical signal is amplified with a nonlinear effect caused by the pump light. A monitor circuit monitors parametric gain in the nonlinear optical medium. A first power controller increases input power of the optical signal so that the gain reaches saturation. A second power controller controls input power of the pump light so as to obtain a desired gain.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Dispersion compensation method and fiber transmission system
InactiveUS20090175629A1Reduce nonlinear effectsDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersEngineeringFiber-optic communication
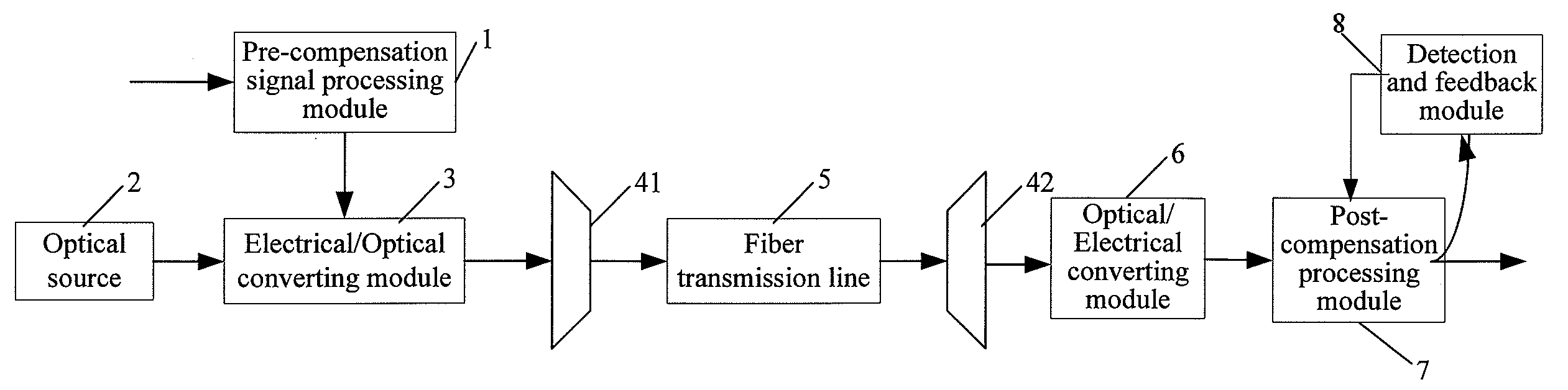
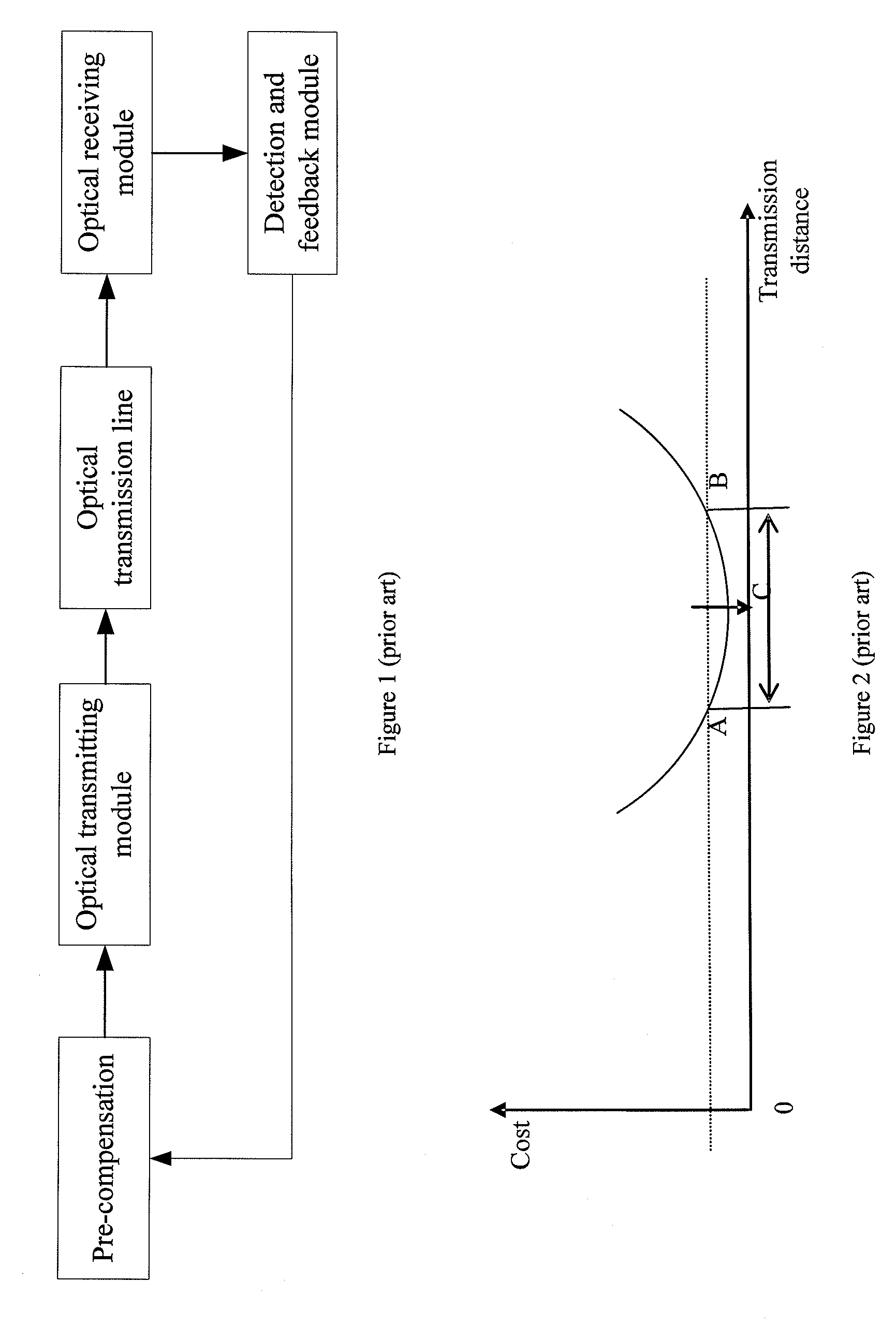
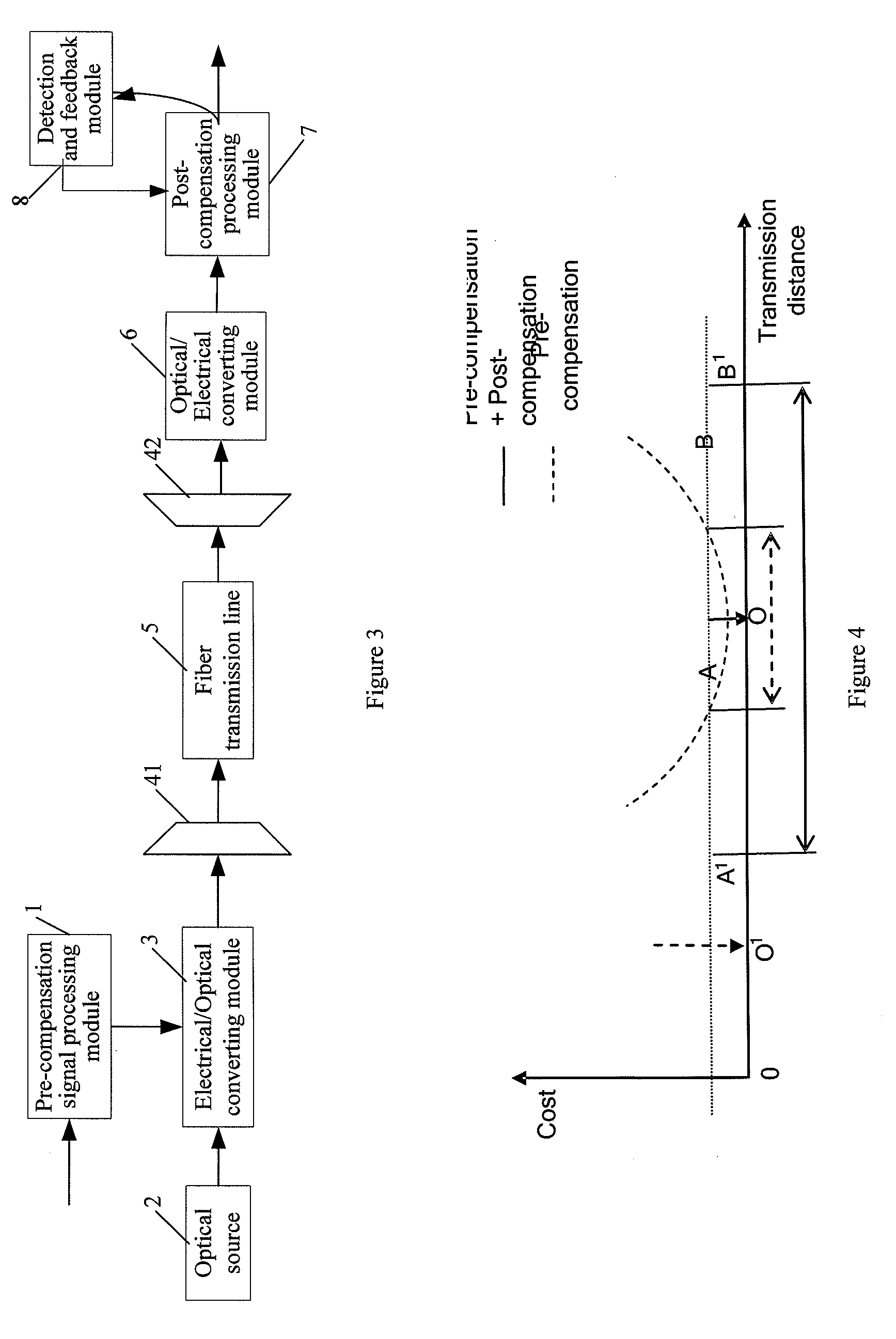
A dispersion compensation method and a fiber transmission system are disclosed, pertaining to the field of fiber communications. The dispersion compensation method includes: after performing electrical pre-compensation processing on a digital transmit signal, the transmitting end controls the electrical / optical converting module to output a distorted optical signal; after receiving the optical signal, the receiving end performs post-compensation processing after converting the optical signal into an electrical signal, or converts the optical signal into an electrical signal after performing post-compensation processing on the optical signal. The fiber transmission system includes: a pre-compensation signal processing module, an optical source, an electrical / optical converting module, a fiber transmission line, an optical / electrical converting module, and a post-compensation processing module. With the technical solution of the present disclosure, the non-linear effect may be suppressed, and a flexible dispersion compensation solution may be provided for a dynamically configurable network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
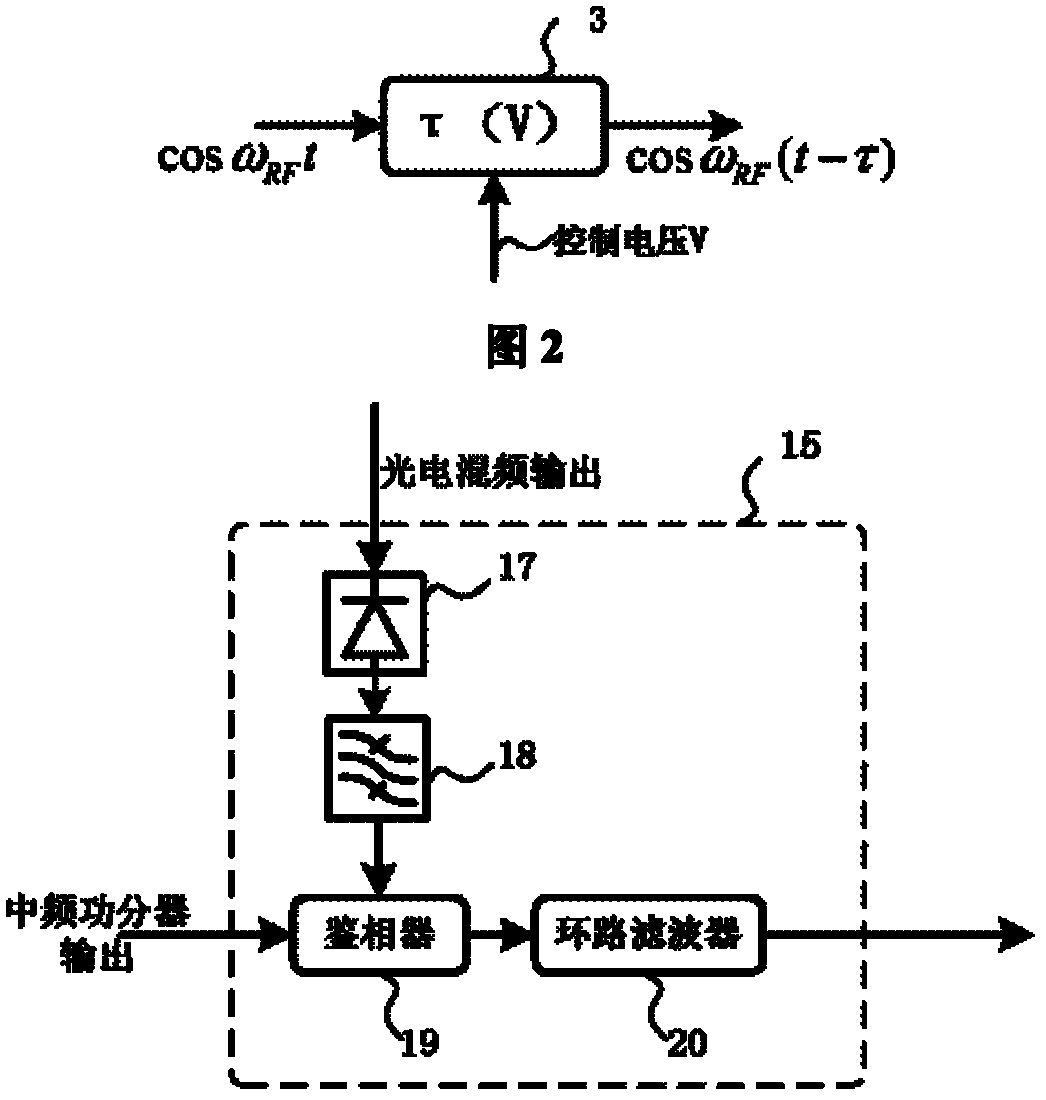
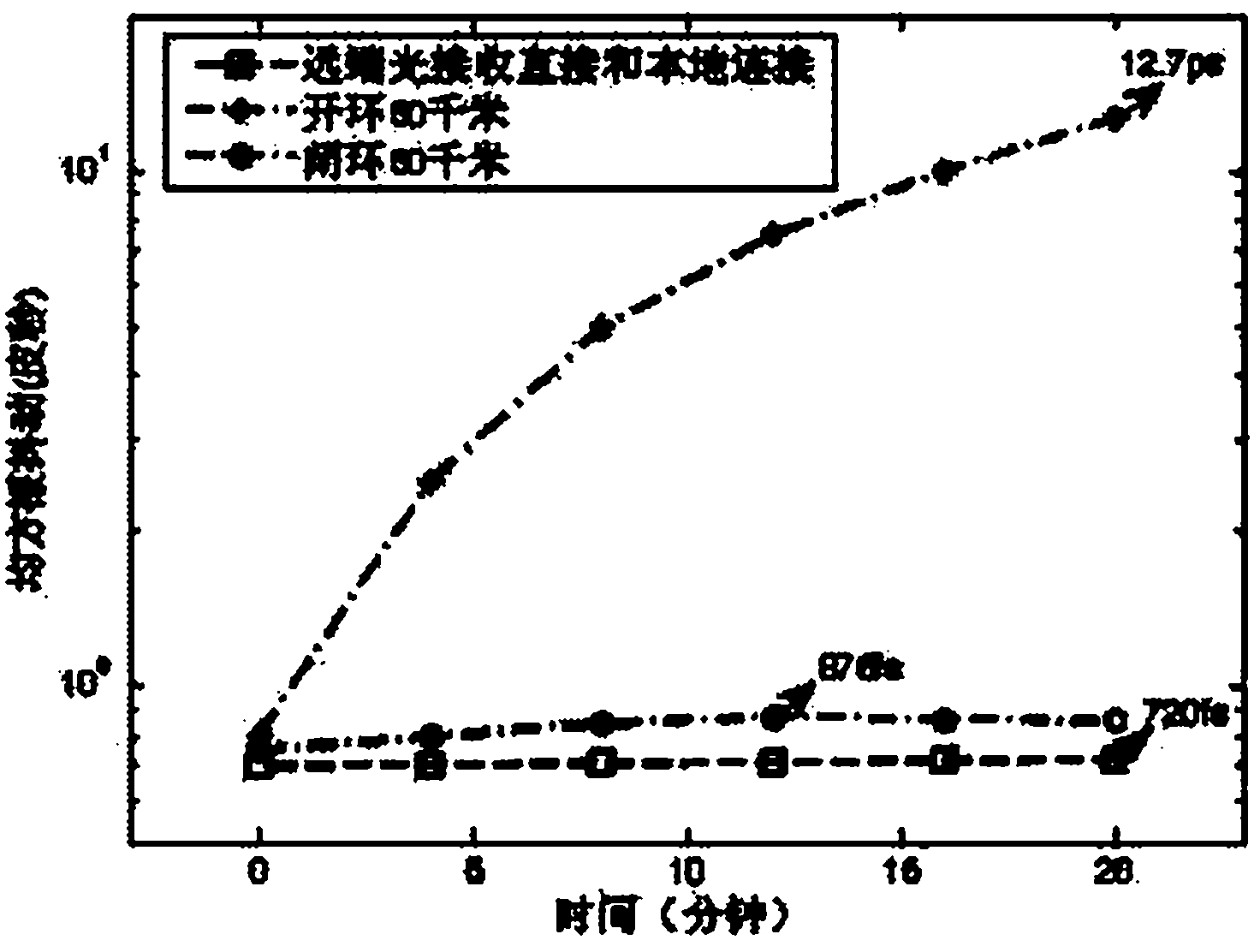
Delay-locked-loop-based remote microwave signal phase-stabilized optical fiber transmission device
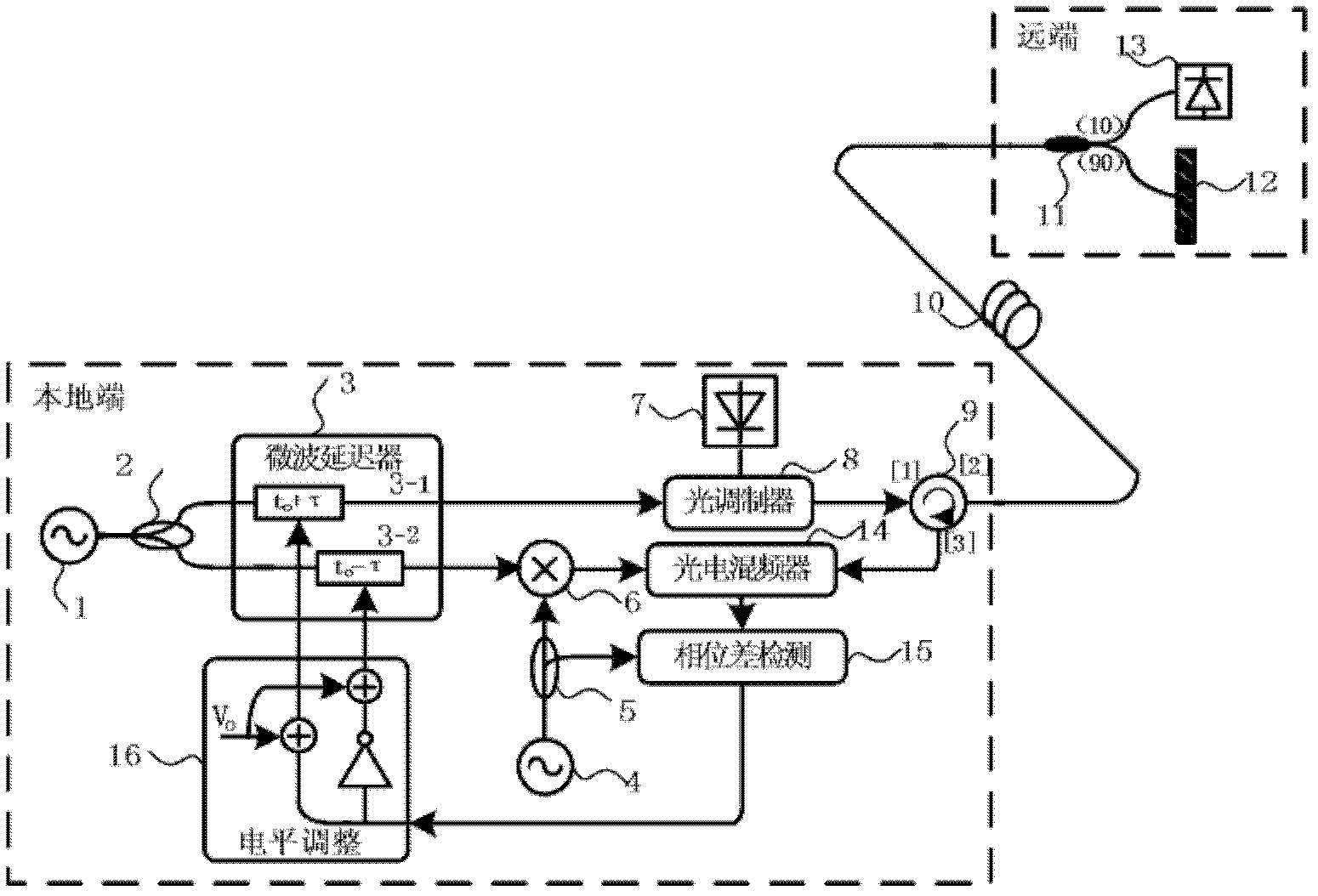
InactiveCN102215104ALow signal to noise ratioAvoid disadvantages such as phase polarity ambiguityFibre transmissionSynchronising arrangementPhase differenceDelay-locked loop
The invention discloses a delay-locked-loop-based remote microwave signal phase-stabilized optical fiber transmission device, which realizes the phase synchronization of a local microwave signal and a remote microwave signal by utilizing a delay-locked loop. The device realizes optoelectronic heterodyne mixing by utilizing the nonlinear effects of an optoelectronic modulator for phase detection, drives and controls a microwave delayer by feeding a phase difference signal back, performs phase change on the microwave signals, compensates microwave signal phase disturbance caused by the delay change of a transmission link, keeps a phase synchronism relationship between the local microwave signal and the remote microwave signal, solves the problem of phase asynchronism between the local microwave signal and the remote microwave signal, fulfills the aim of phase-stabilized transmission of the microwave signals, adopts noncoherent correction, and has the advantages of wide dynamic range, high stability and the like, besides a long phase-stabilized transmission distance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
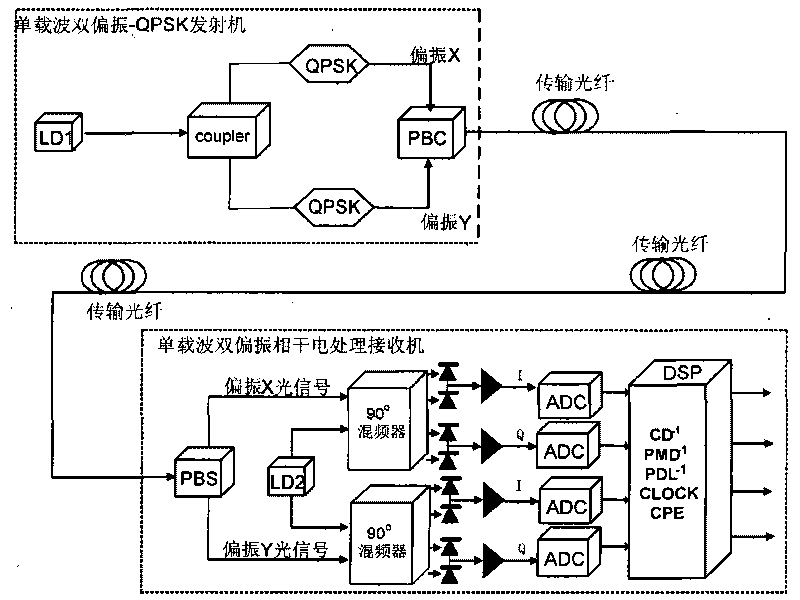
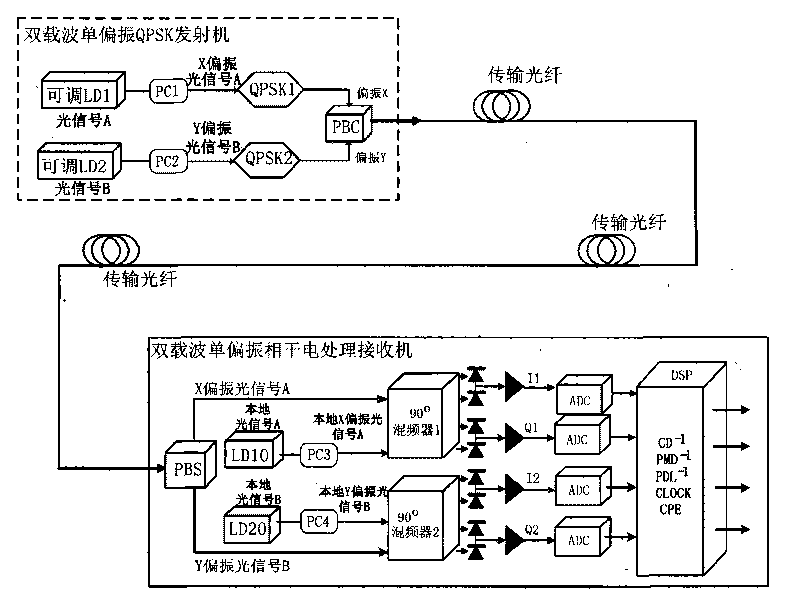
Optical signal transmission processing method, sending device and system
ActiveCN101729187AIncrease nonlinear toleranceLong transmission distancePolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversNonlinear toleranceLength wave
The embodiment of the invention relates to the field of communication transmission, and discloses an optical signal transmission processing method, an optical signal sending device and an optical signal transmission system. The optical signal sending device comprises a sending end optical signal generating device, a first polarization controller, a second polarized controller, a first quarternaryphase-shift keying modulator, a second quarternary phase-shift keying modulator and a polarization beam combiner, wherein the sending end optical signal generating device is used for generating an optical signal A and an optical signal B with different wavelengths; the first polarization controller is used for carrying out polarization control for the optical signal A and generating an X polarization optical signal A; the second polarized controller is used for carrying out polarization control for the optical signal B and generating a Y polarization optical signal B; the first quarternary phase-shift keying modulator is used for modulating the X polarization optical signal A; the second quarternary phase-shift keying modulator is used for modulating the Y polarization optical signal B; and the polarization beam combiner is used for combining the modulated X polarization optical signal A and the modulated Y polarization optical signal B into a dual-carrier single-polarization optical signal. The invention enables the nonlinear effect in an optical fiber to be inhabited, enhances the nonlinear tolerance limit and the fiber feeding power of the optical signal transmission system andextends the transmission distance.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
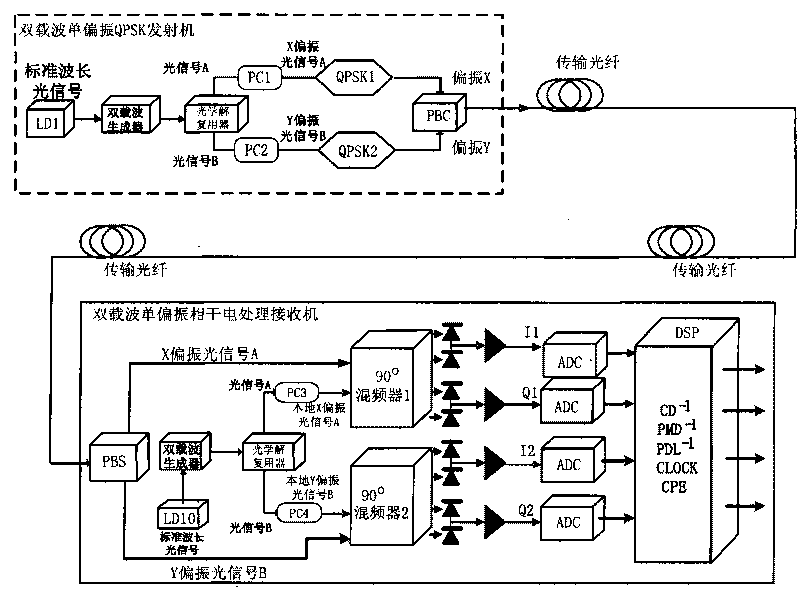
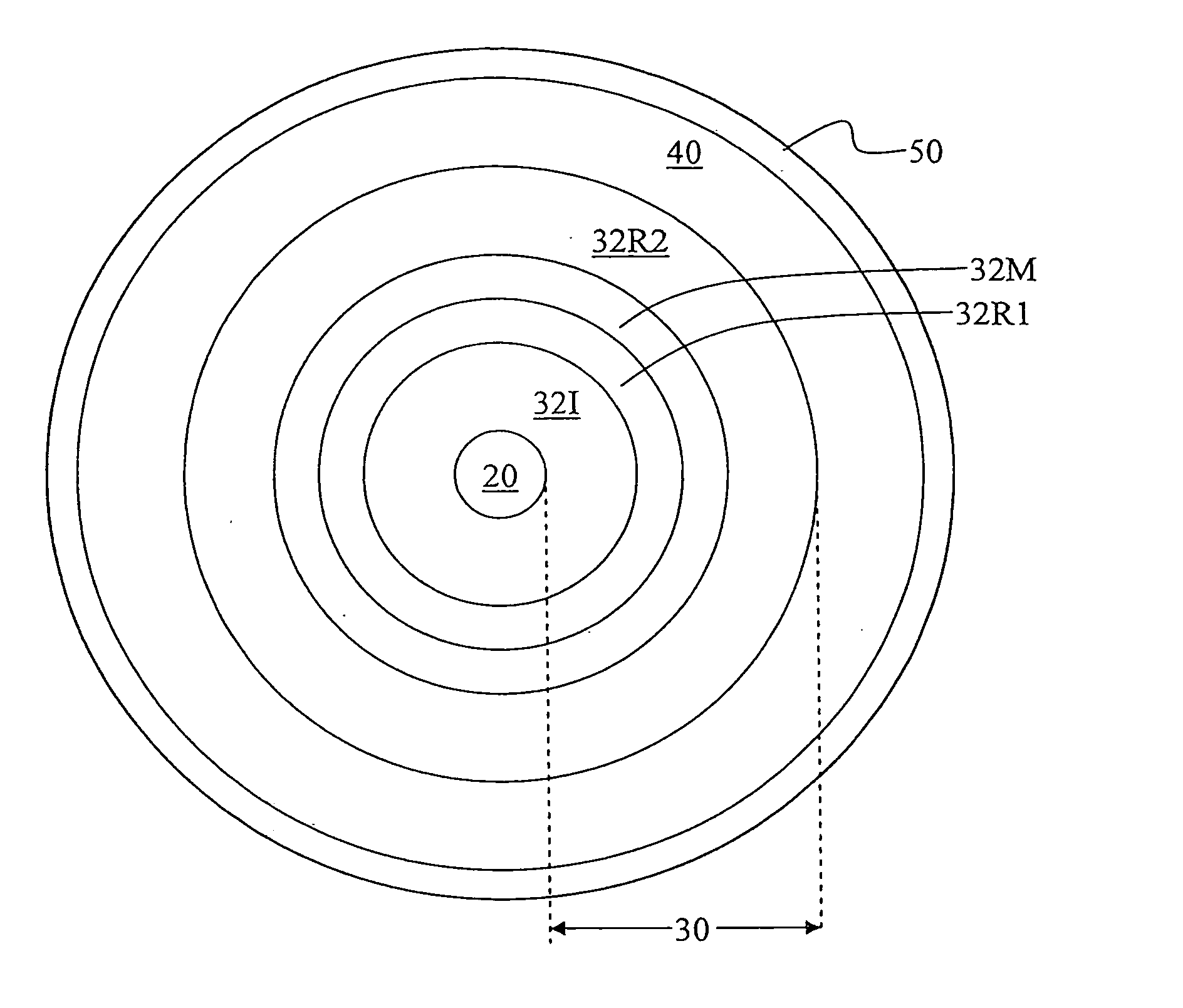
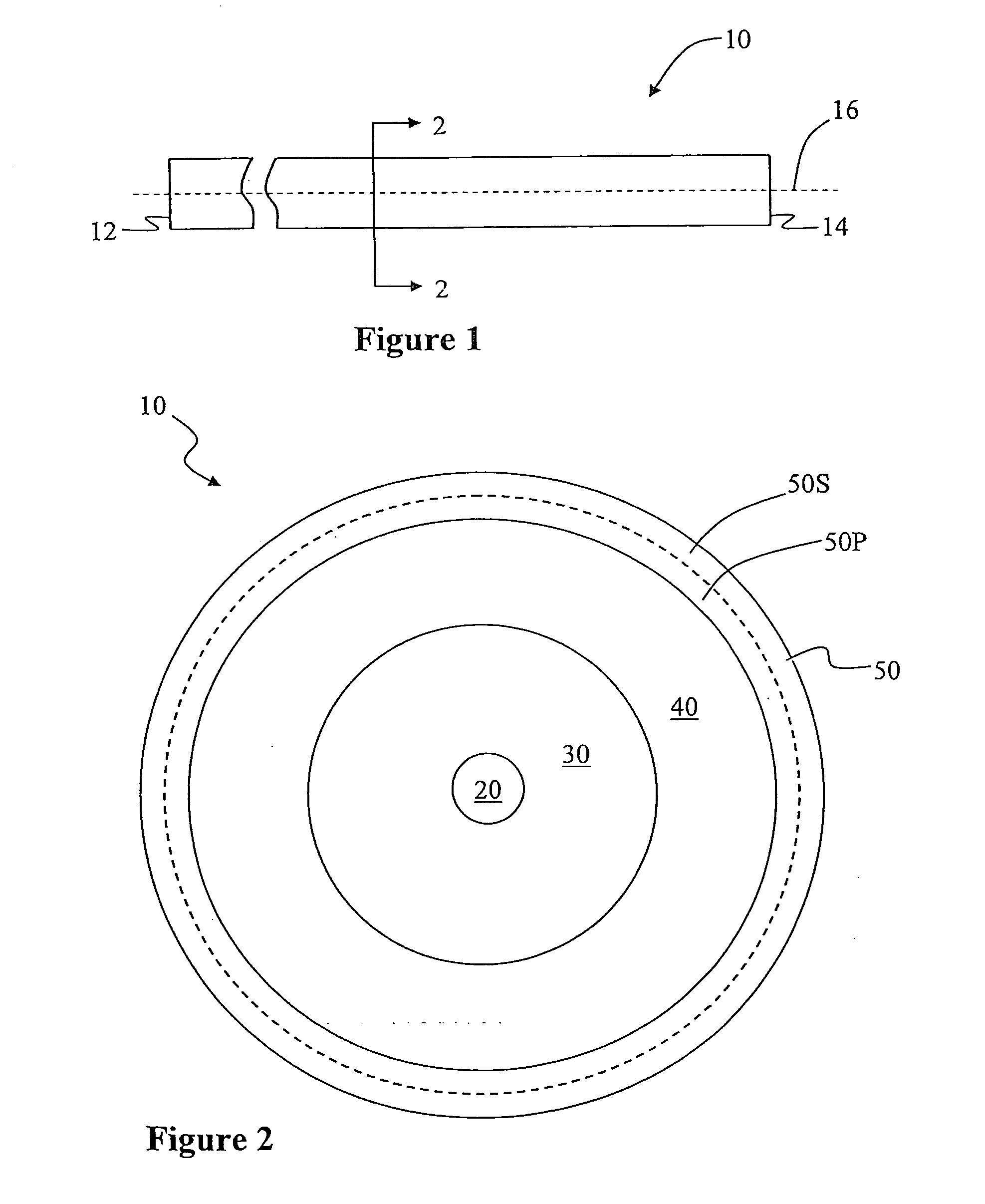
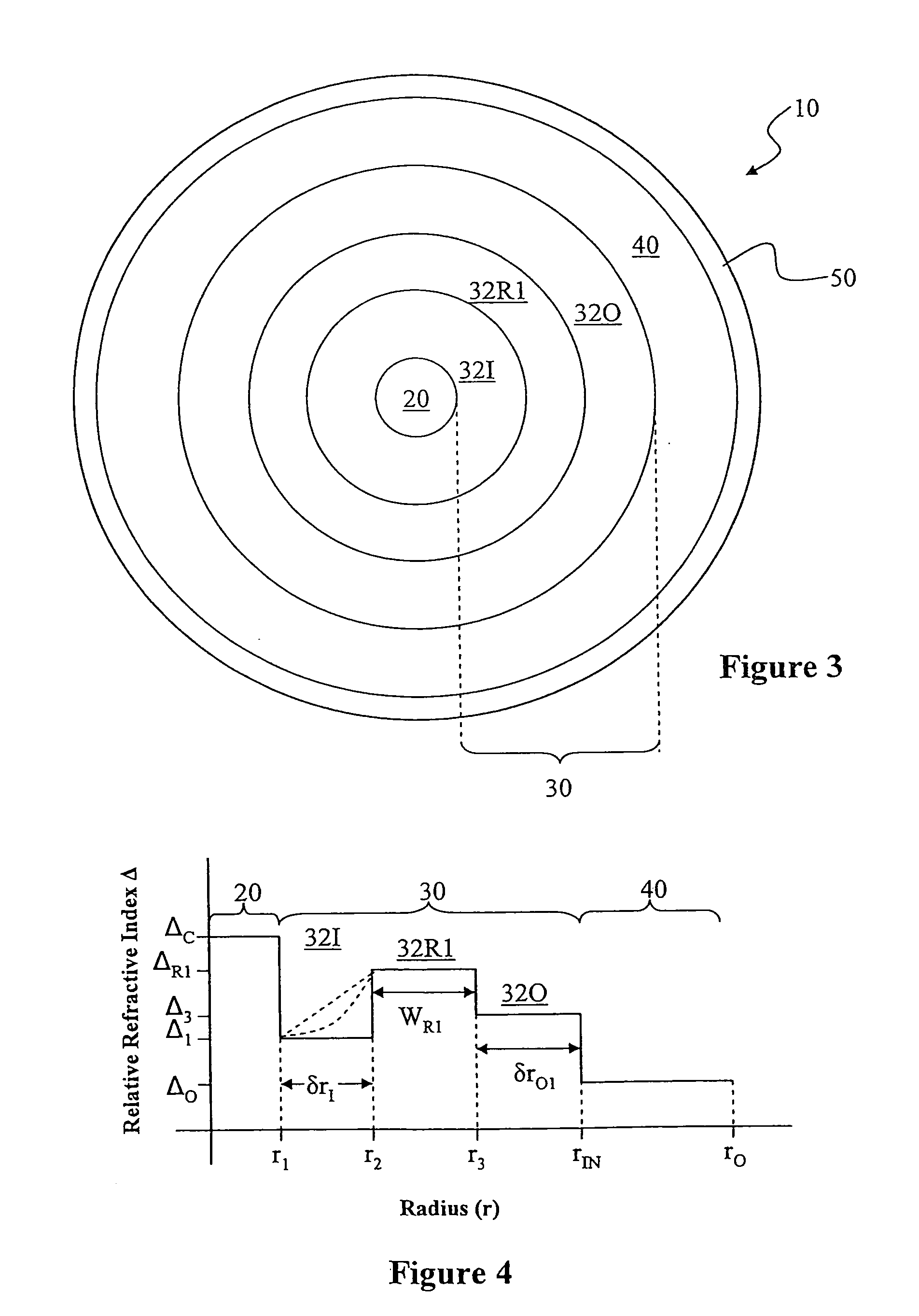
Large Mode Area Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20100195194A1Reduce nonlinear effectsIncrease optical powerLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with polarisationRelative attenuationUltrasound attenuation
A large-mode-area (LMA) optical fiber (10) that operates as a single-mode optical fiber. The optical fiber includes a core region (20) surrounded by an inner cladding (32), which in turn is surrounded by an outer cladding (40). The inner cladding includes at least one up-doped ring region (32R1). The ring region is configured to form a large attenuation differential between the higher-order modes and the fundamental mode so only that the fundamental mode remains traveling in the optical fiber. If necessary, the optical fiber can include a bend (10B) having a select “resonant” bend diameter (DB) that increases the relative attenuation of the fundamental and higher-order modes. The optical fiber supports an effective mode field diameter (MFD) of up to 40 μm to 50 μm. As a result, detrimental non-linear effects are suppressed, which allows the optical fiber to carry substantially more optical power than conventional LMA optical fibers. The LMA optical fiber is thus eminently suited for a number of optical-fiber-based applications calling for high optical power, such as fiber lasers and pump sources for wavelength conversion.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com