Patents
Literature
314results about How to "Reduce nonlinear effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber and communication system incorporating the same
ActiveUS6904218B2Increase the effective areaLow cutoff wavelengthOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberUltrasound attenuation
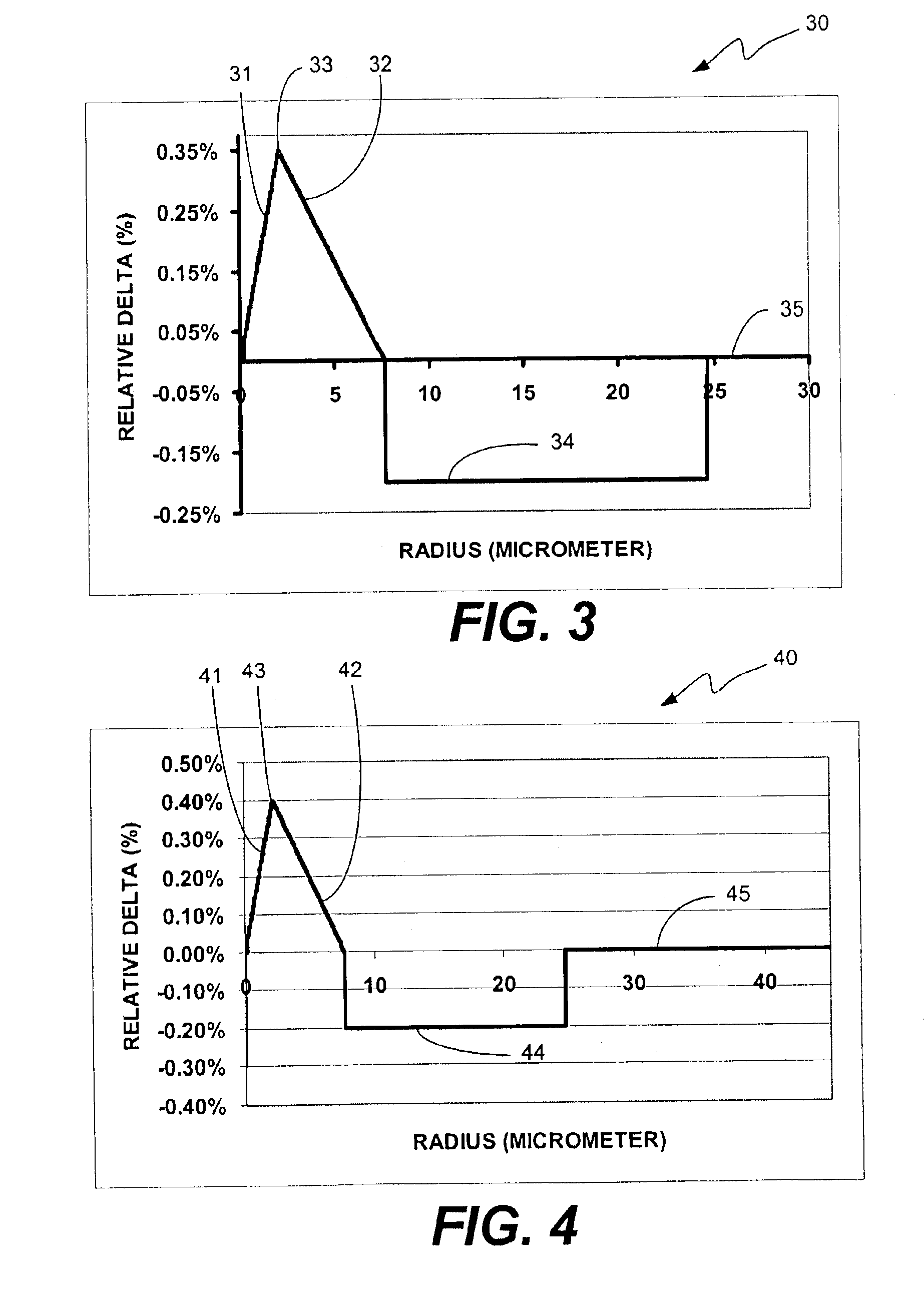
A super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber that is suitable for communicating over a wide wavelength range and that, because of its large effective area, suppresses nonlinear effects that typically result from interaction between signal channels. The effective area, Aeff, of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is equal to or greater than approximately 80 μm2 at a wavelength window around 1310 nm. The cutoff wavelength of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is less than 1310 nm. Thus, the SLA fiber of the present invention has a very large effective area and a very low cutoff wavelength. In accordance with the present invention, a variety of SLA fibers are provided that all have very large effective areas and desirable transmission properties. The large effective areas of the SLA fibers of the present invention enable nonlinear effects to be suppressed, as well as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in analog transmission. The large effective areas also enable attenuation to be reduced. The result of suppressing nonlinear effects and reducing attenuation enable signals to be transmitted over long distances and over a broad bandwidth.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Optical fiber
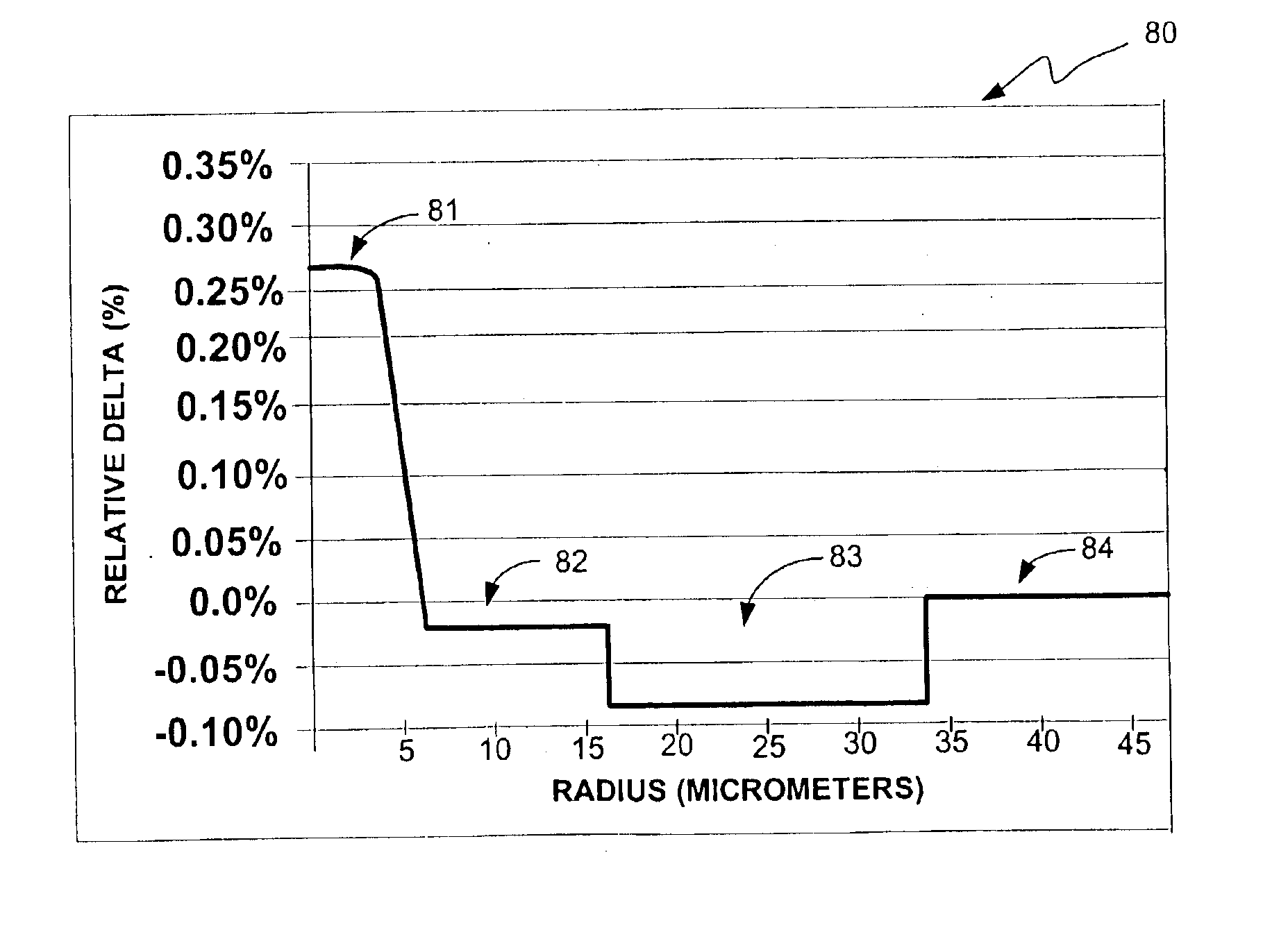
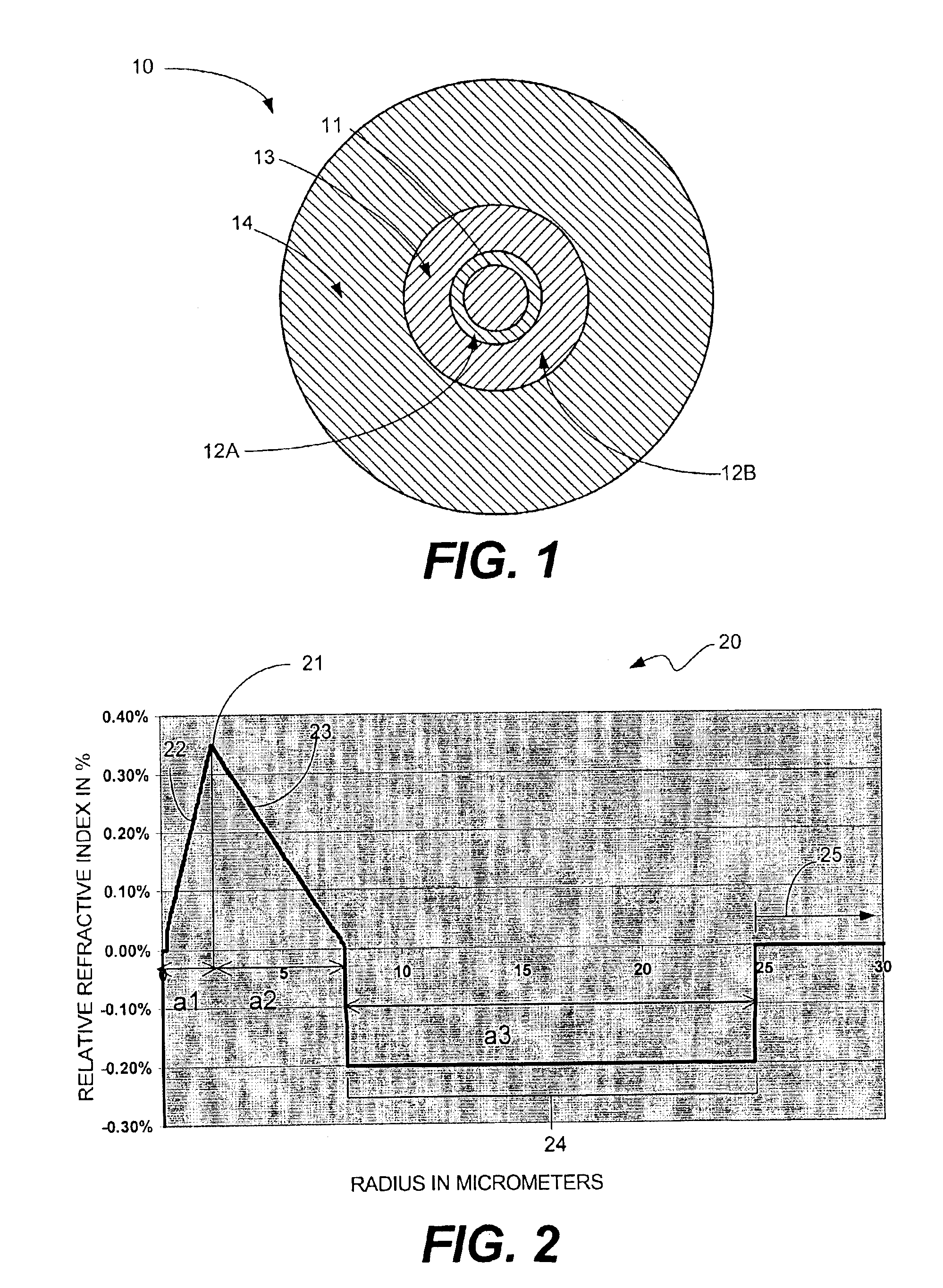
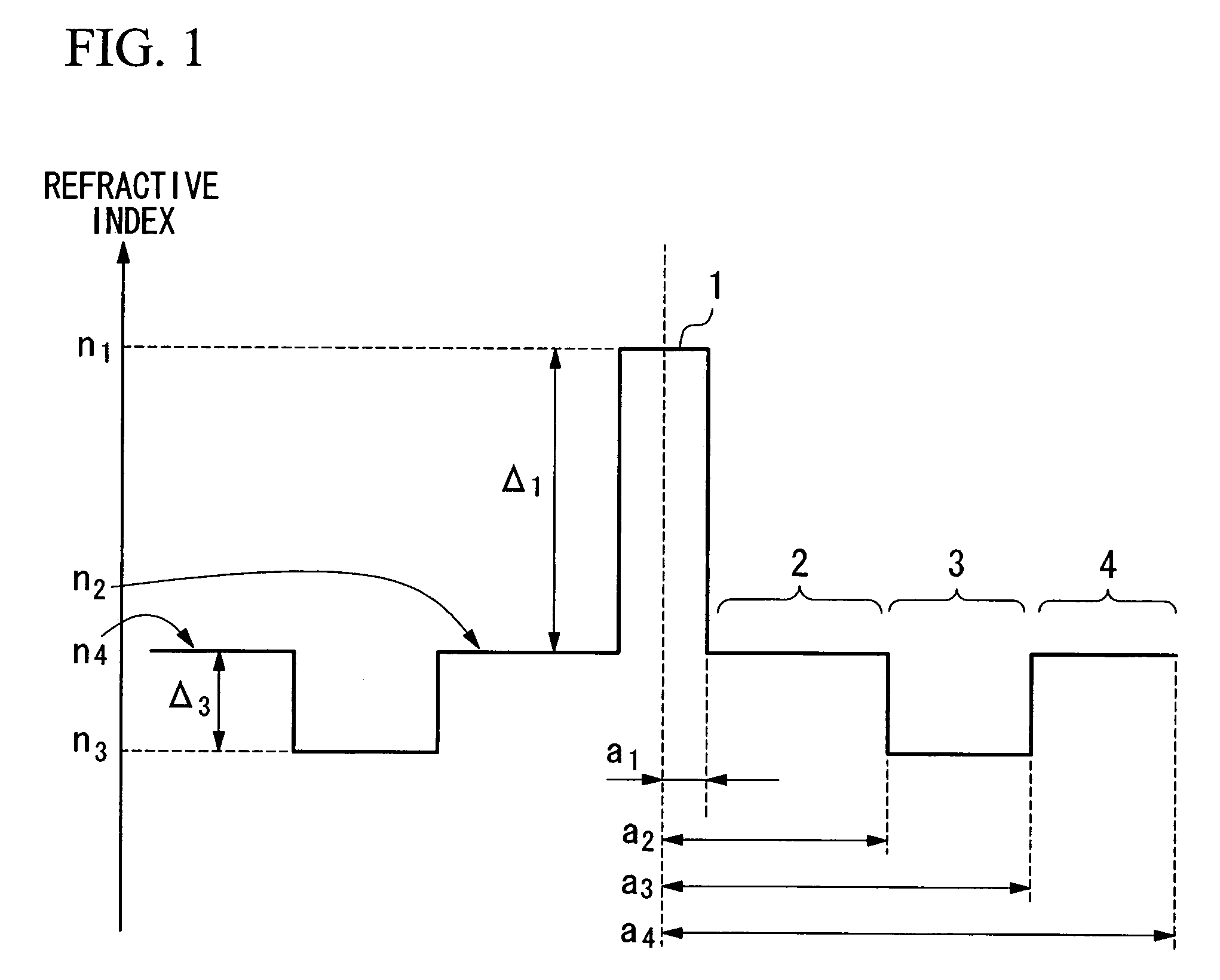
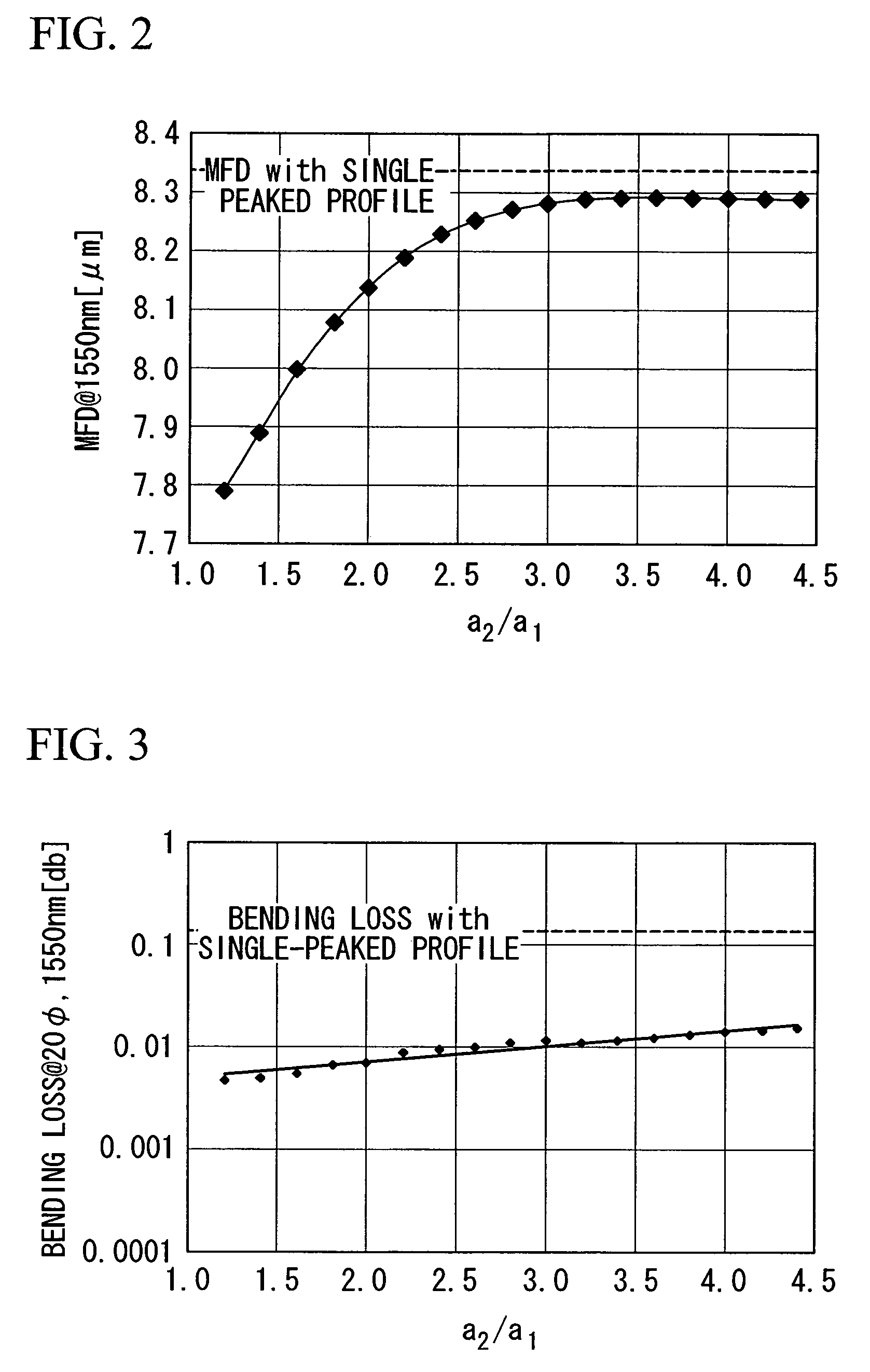
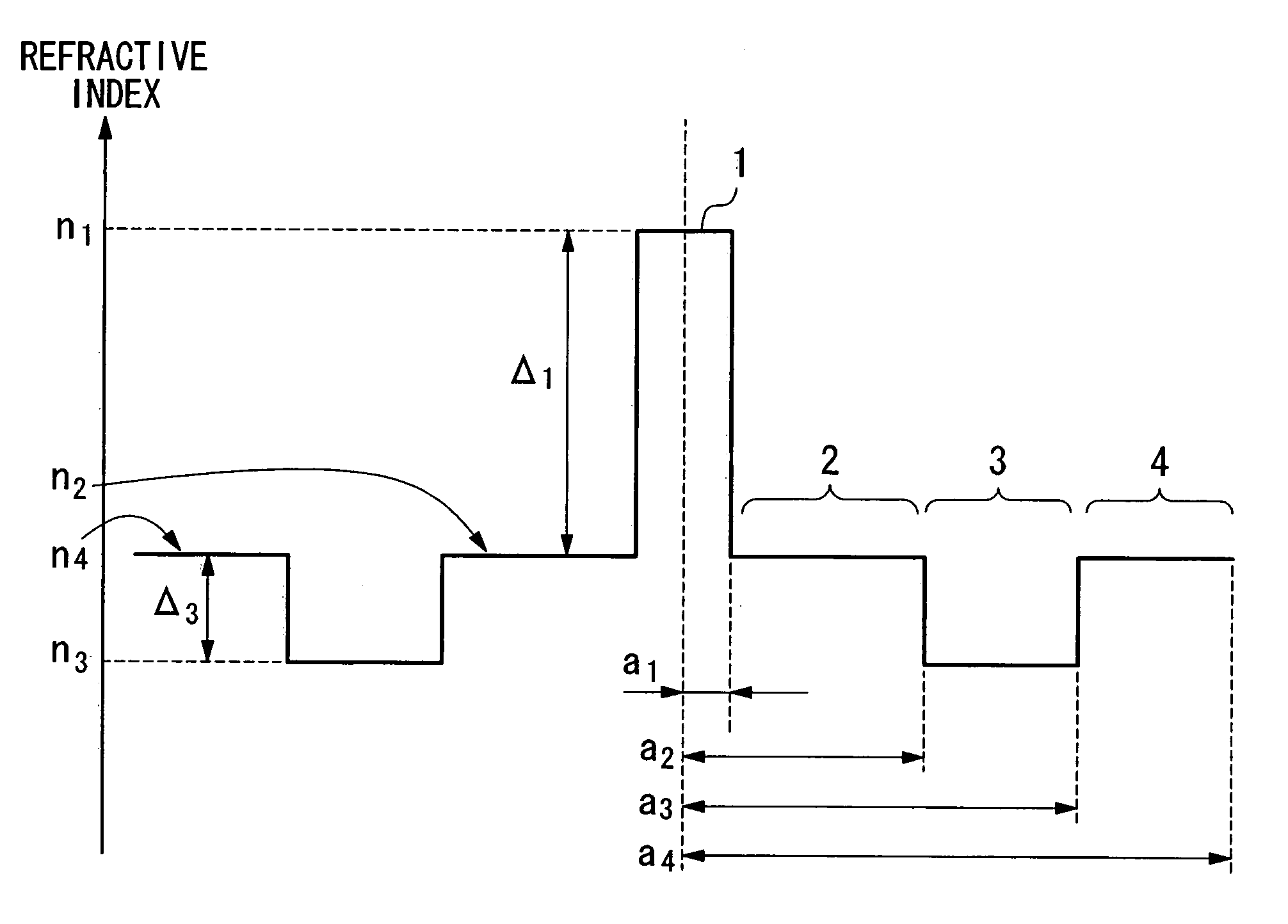
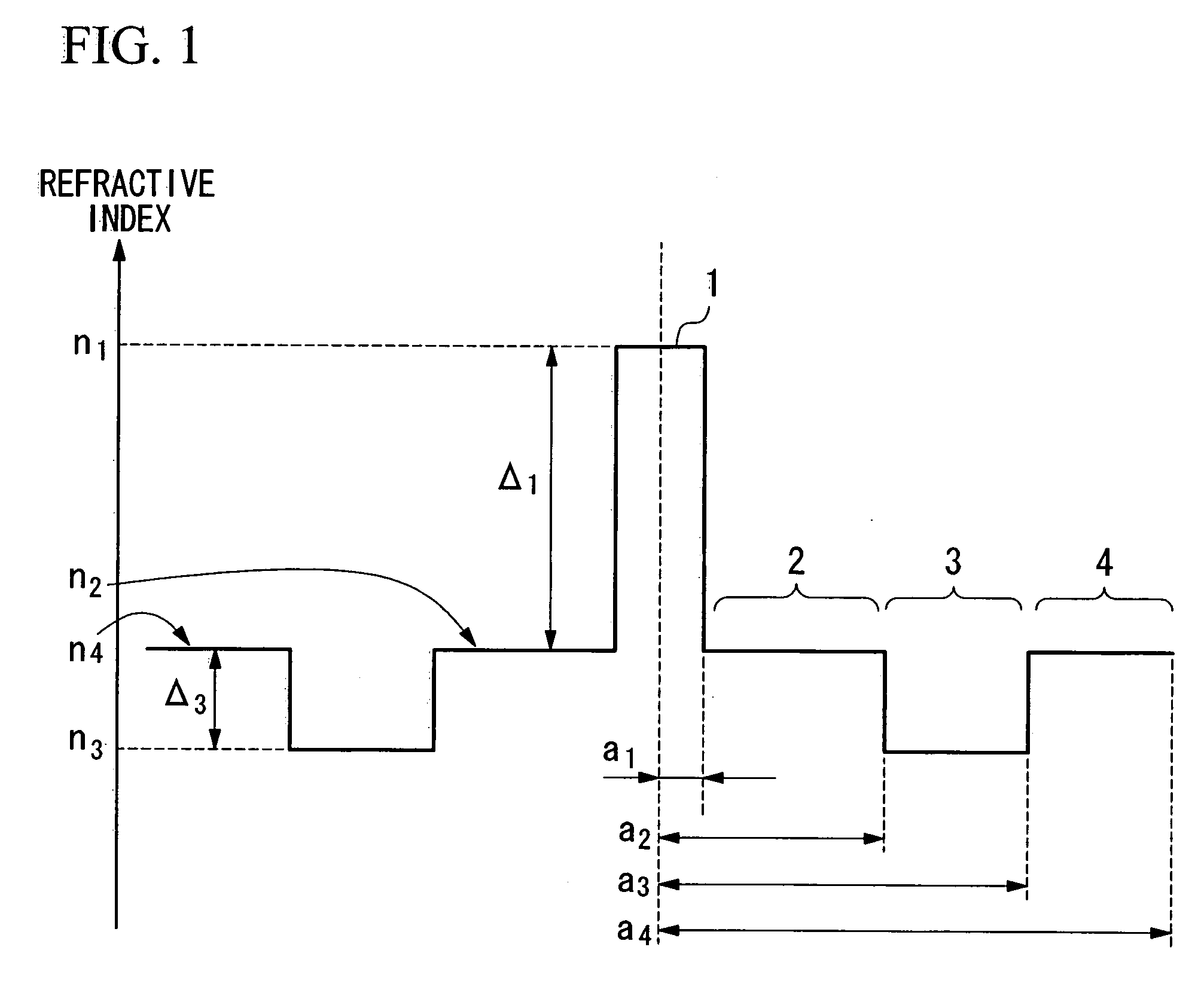
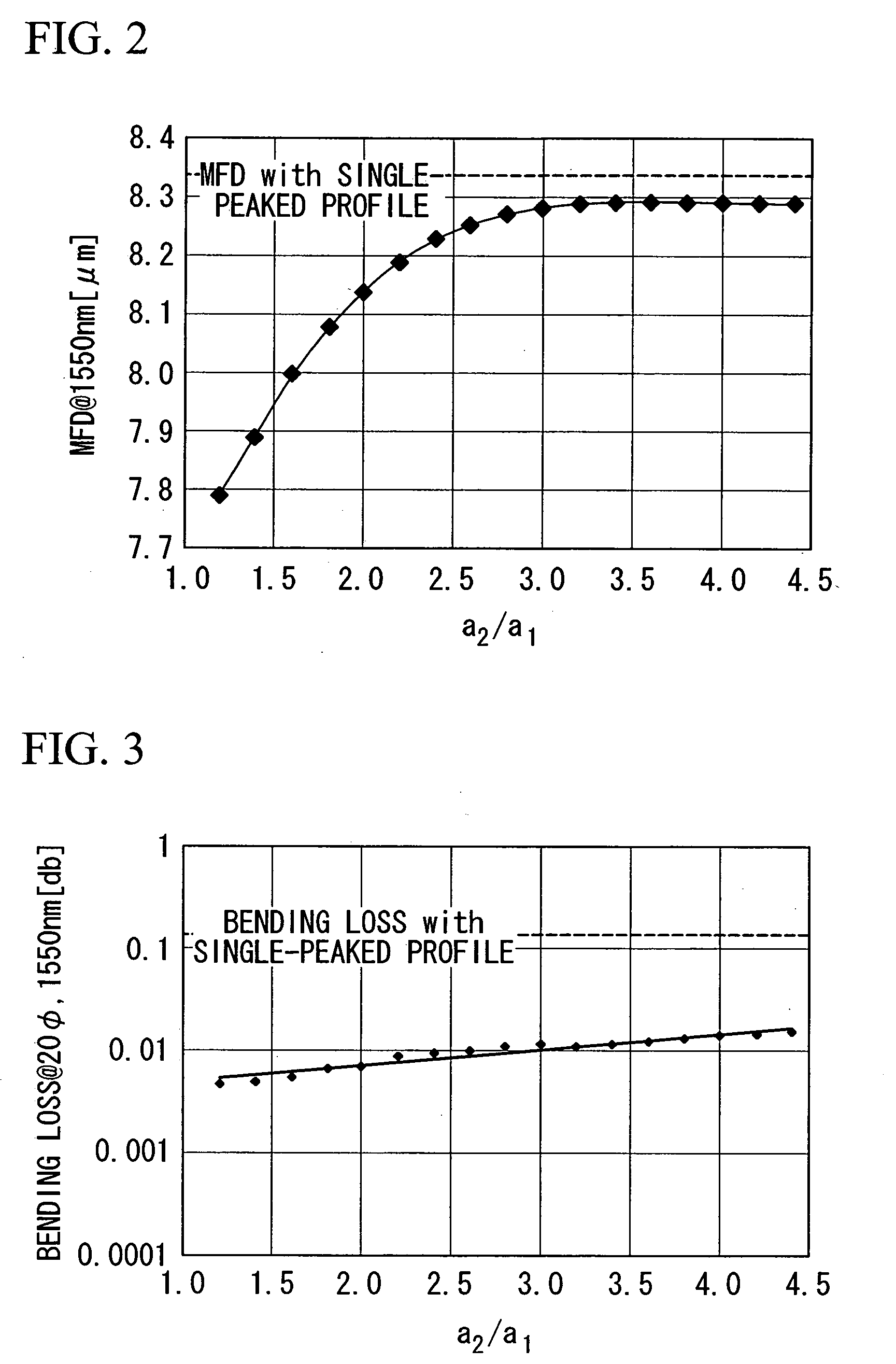
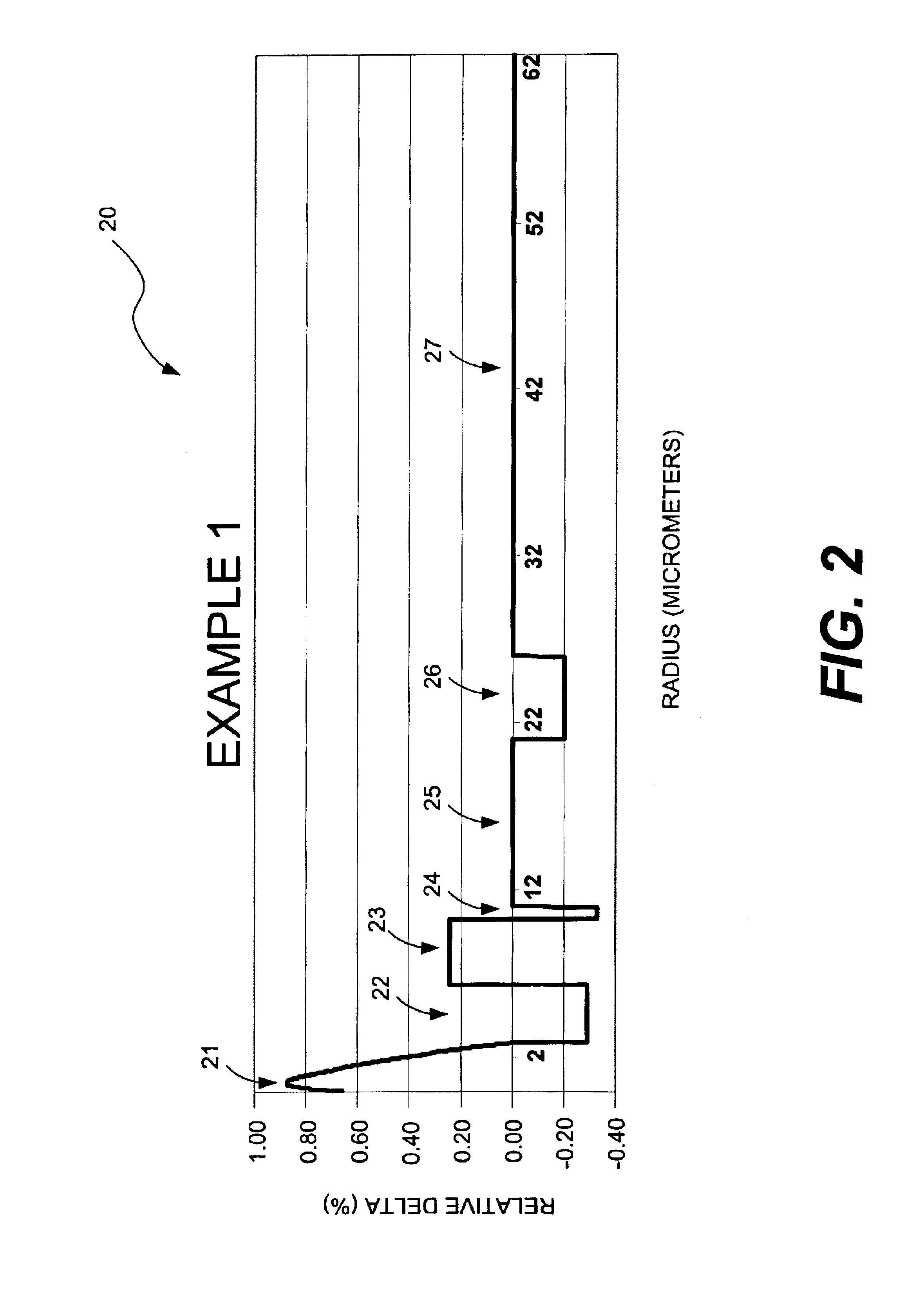
ActiveUS7164835B2Lower refractive indexReduce dispersionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideRelative refractive indexMaterials science
An optical fiber includes: a core at a center; a first cladding layer; a second cladding layer; and a third cladding layer. A maximum refractive index of the core is greater than any of maximum refractive indices of the first cladding layer, the second cladding layer, and the third cladding layer, and the maximum refractive index of the second cladding layer is smaller than any of the maximum refractive indices of the first and the third cladding layer. Additionally, a ratio of a2 / a1 is not less than about 2.5 and not more than about 4.5, where a1 represents the radius of the core, and a2 represents the radius of an outer periphery of the first cladding layer, and a relative refractive index difference of the core with respect to a maximum refractive index of the third cladding layer is not less than 0.20% and not more than 0.70%.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
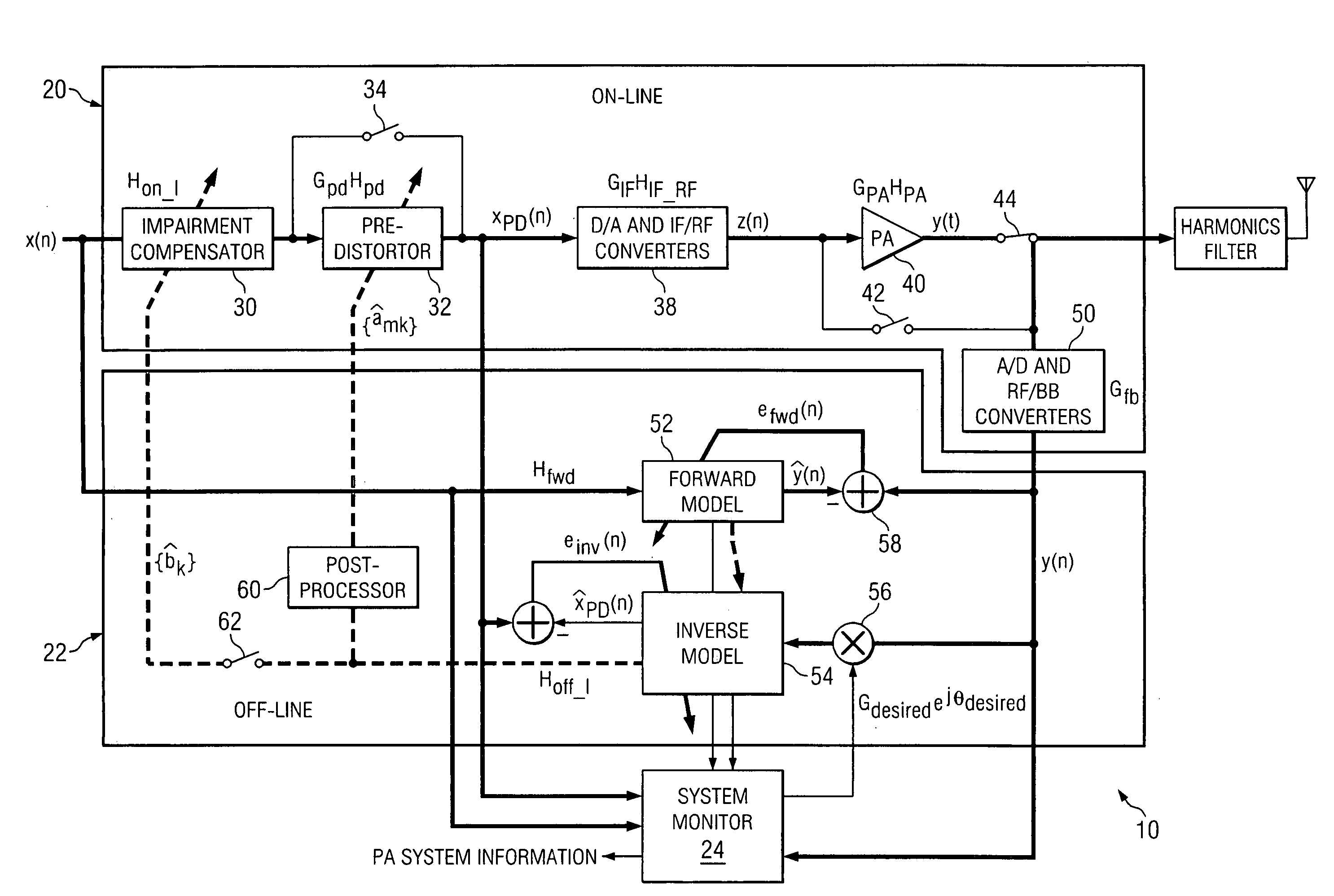
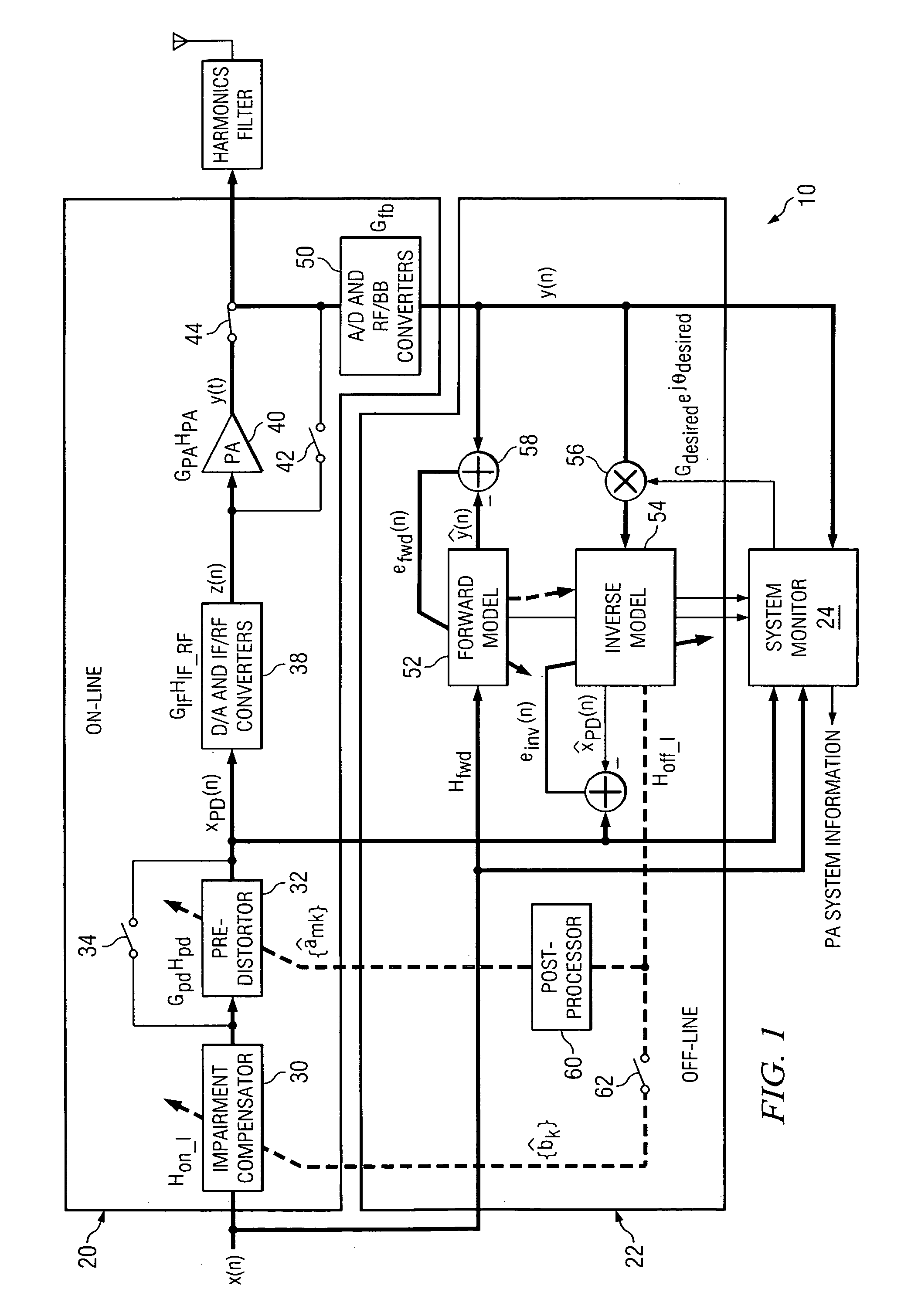
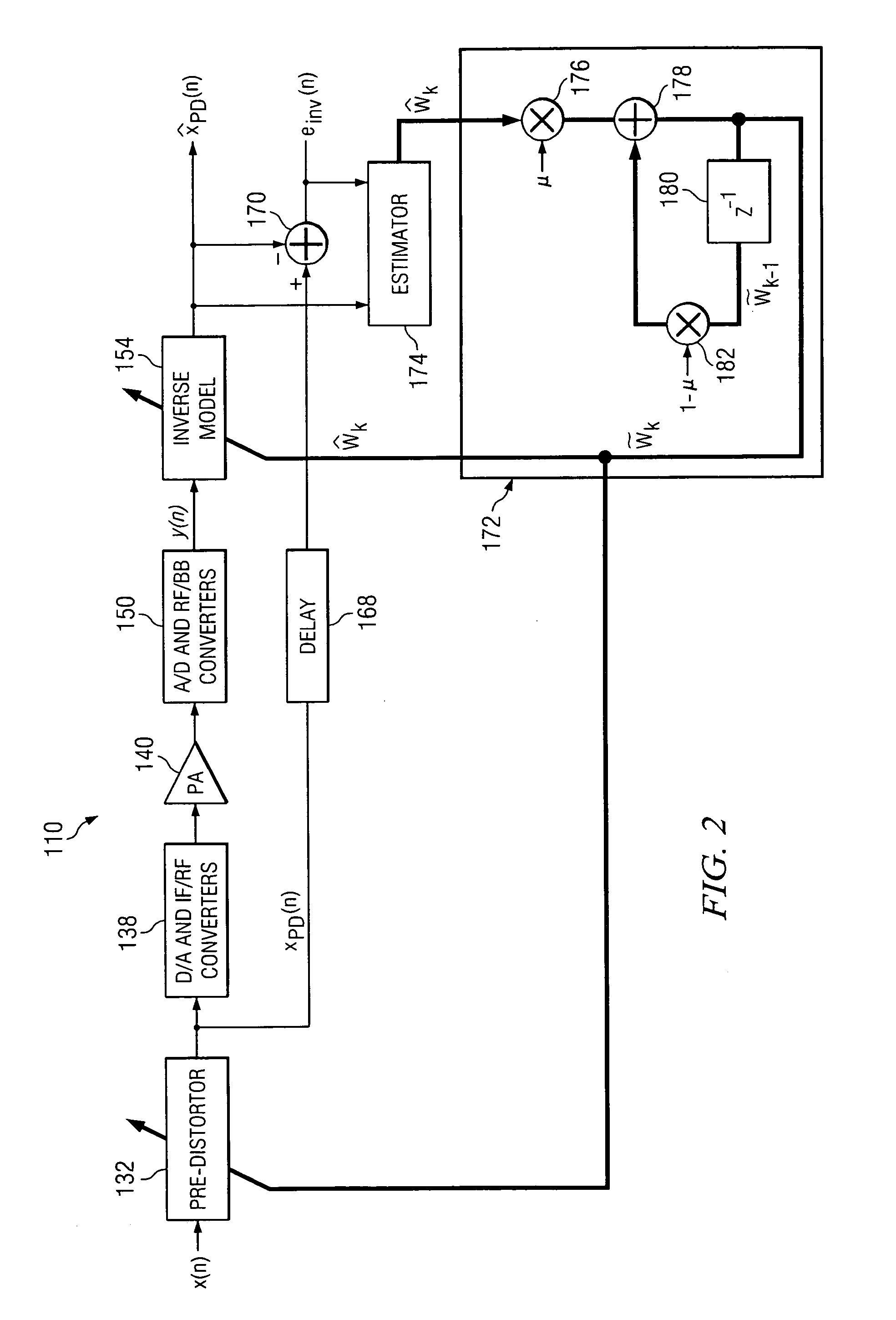
Performing remote power amplifier linearization
ActiveUS20060012426A1Reduce effectReduce nonlinear effectsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsLinearizationPower amplifier linearization
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Optical fiber
ActiveUS20060039665A1Improve transmission performanceReduce nonlinear effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideOptoelectronicsRelative refractive index
An optical fiber includes: a core at a center; a first cladding layer; a second cladding layer; and a third cladding layer. A maximum refractive index of the core is greater than any of maximum refractive indices of the first cladding layer, the second cladding layer, and the third cladding layer, and the maximum refractive index of the second cladding layer is smaller than any of the maximum refractive indices of the first and the third cladding layer. Additionally, a ratio of a2 / a1 is not less than about 2.5 and not more than about 4.5, where a1 represents the radius of the core, and a2 represents the radius of an outer periphery of the first cladding layer, and a relative refractive index difference of the core with respect to a maximum refractive index of the third cladding layer is not less than 0.20% and not more than 0.70%.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
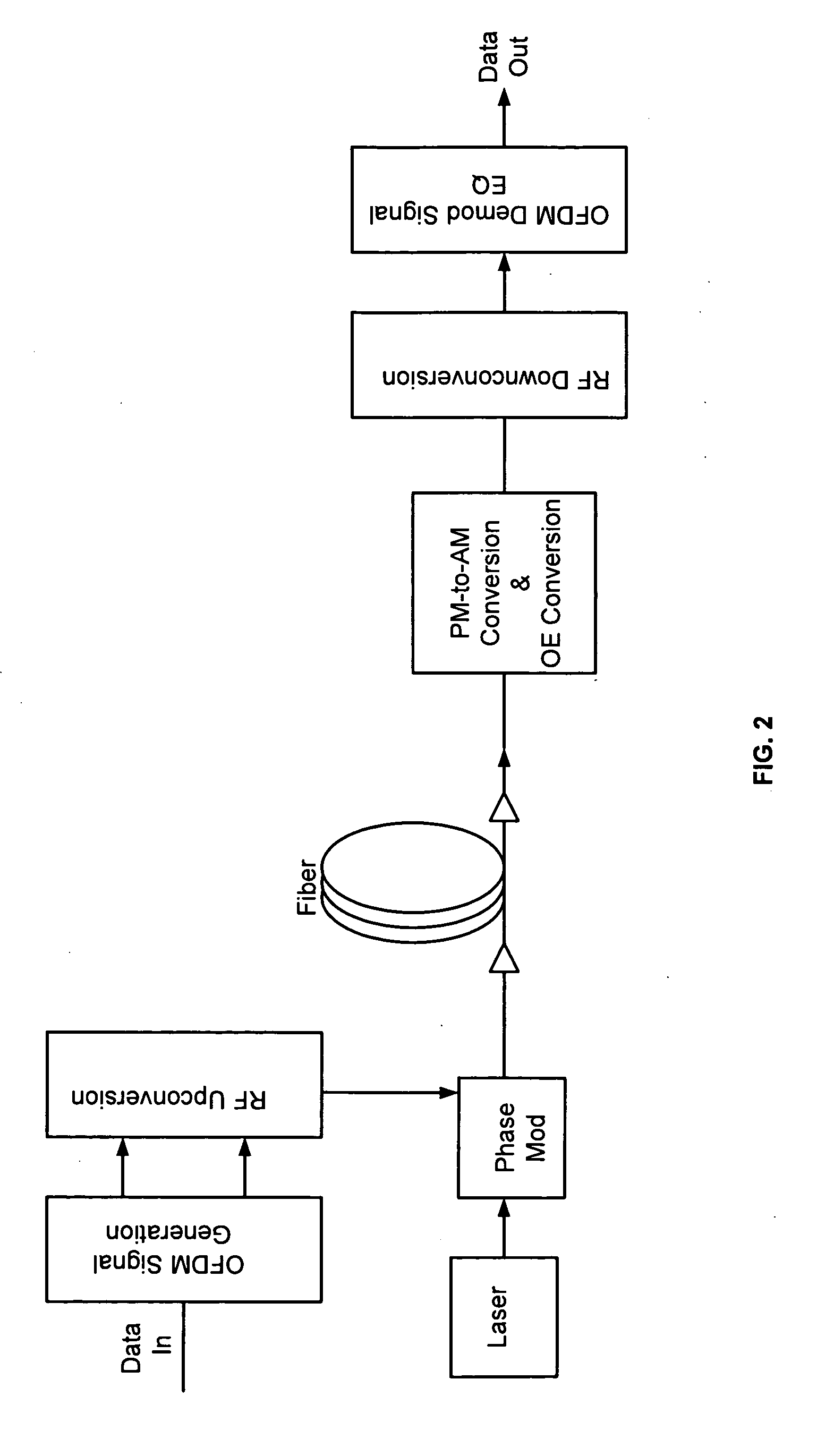
Non-linearity compensation in an optical transmission
ActiveUS20100247099A1Reduce nonlinear effectsImprove signal qualityModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsDigital signal processingOptical power
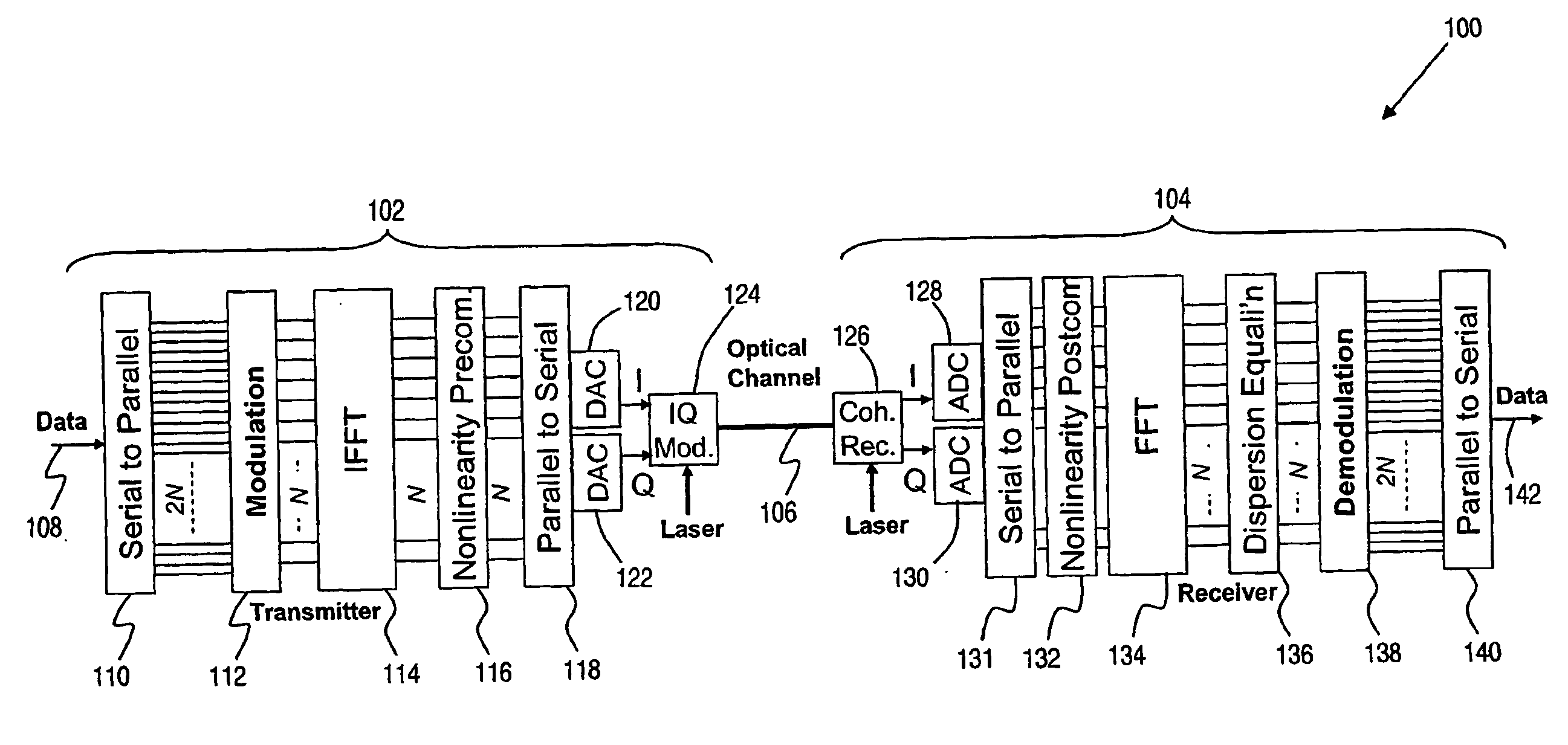
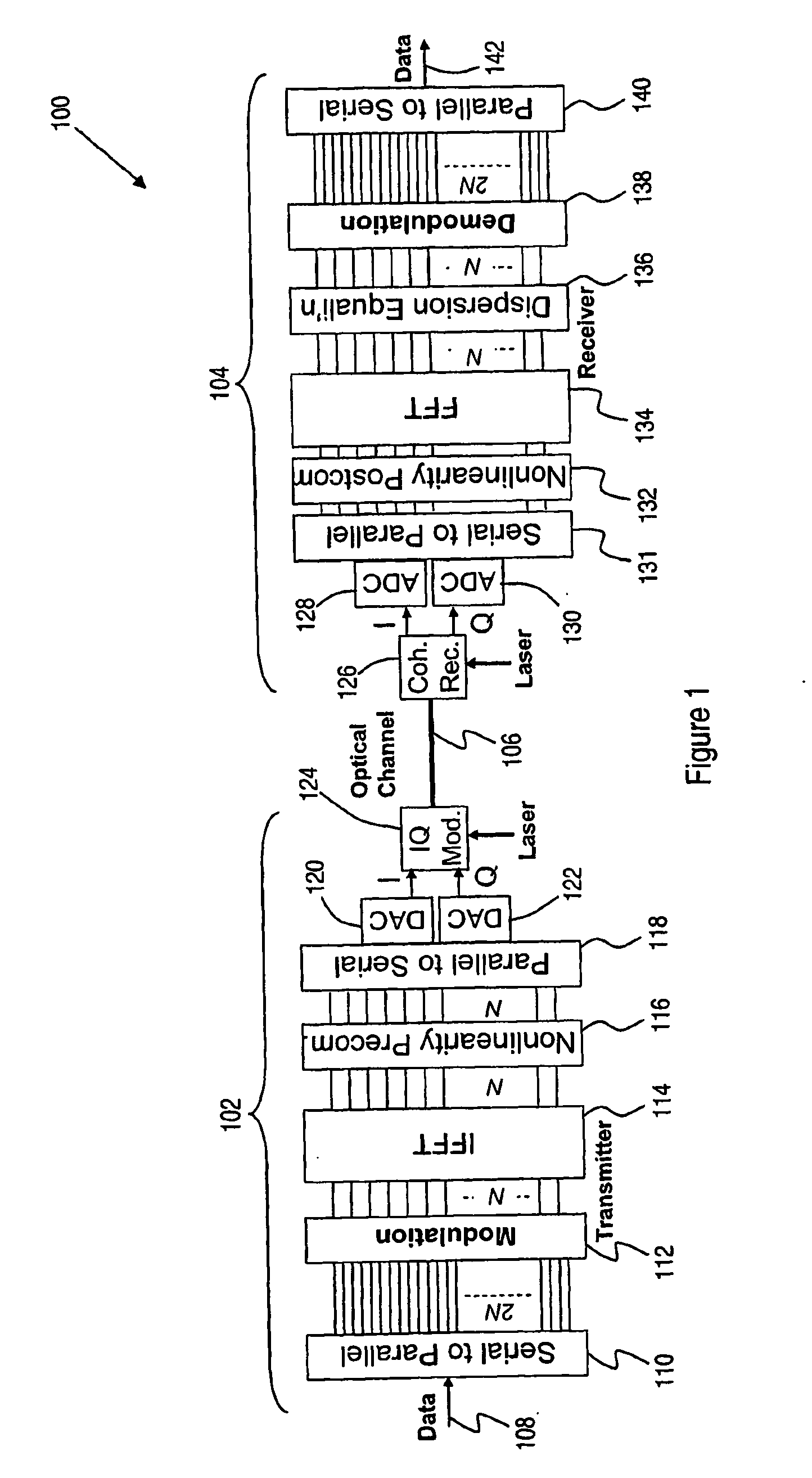
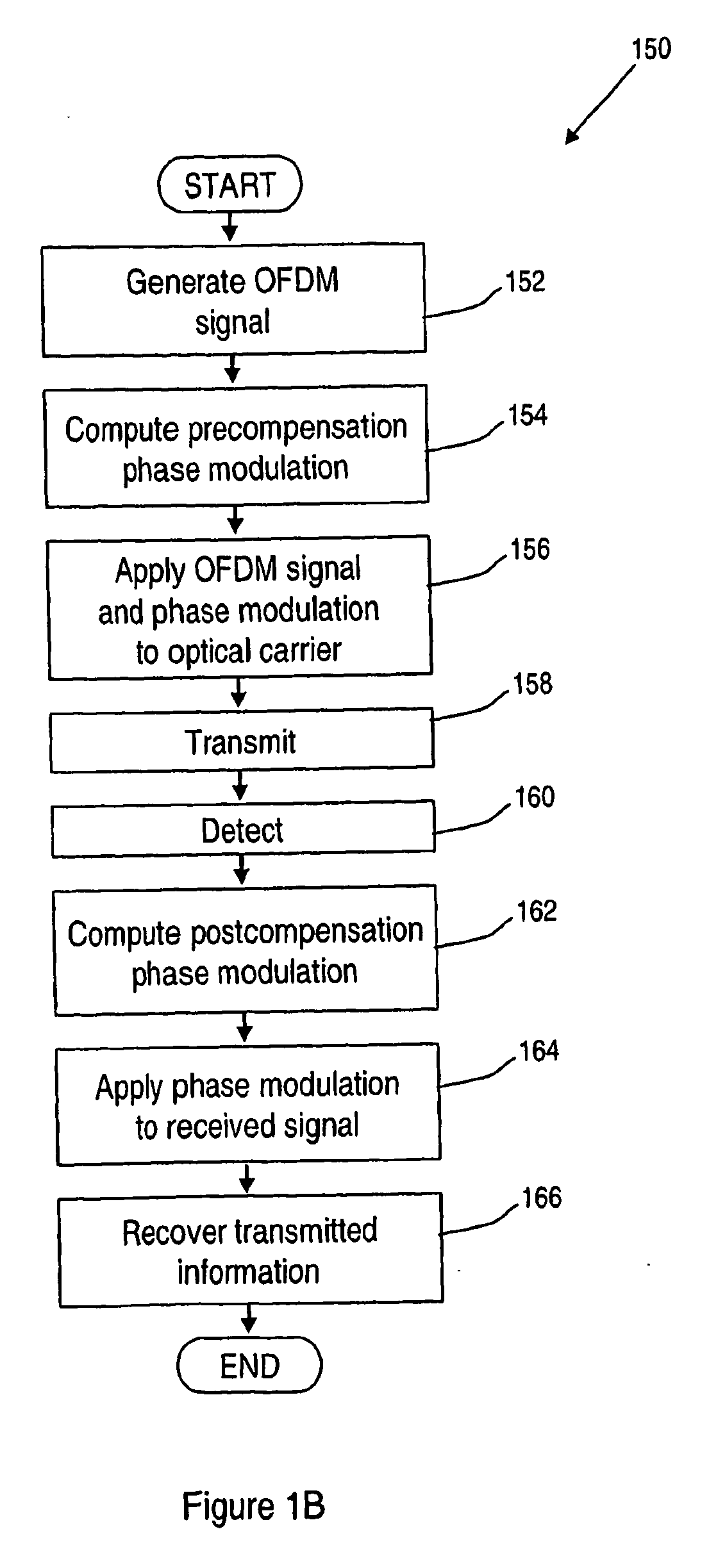
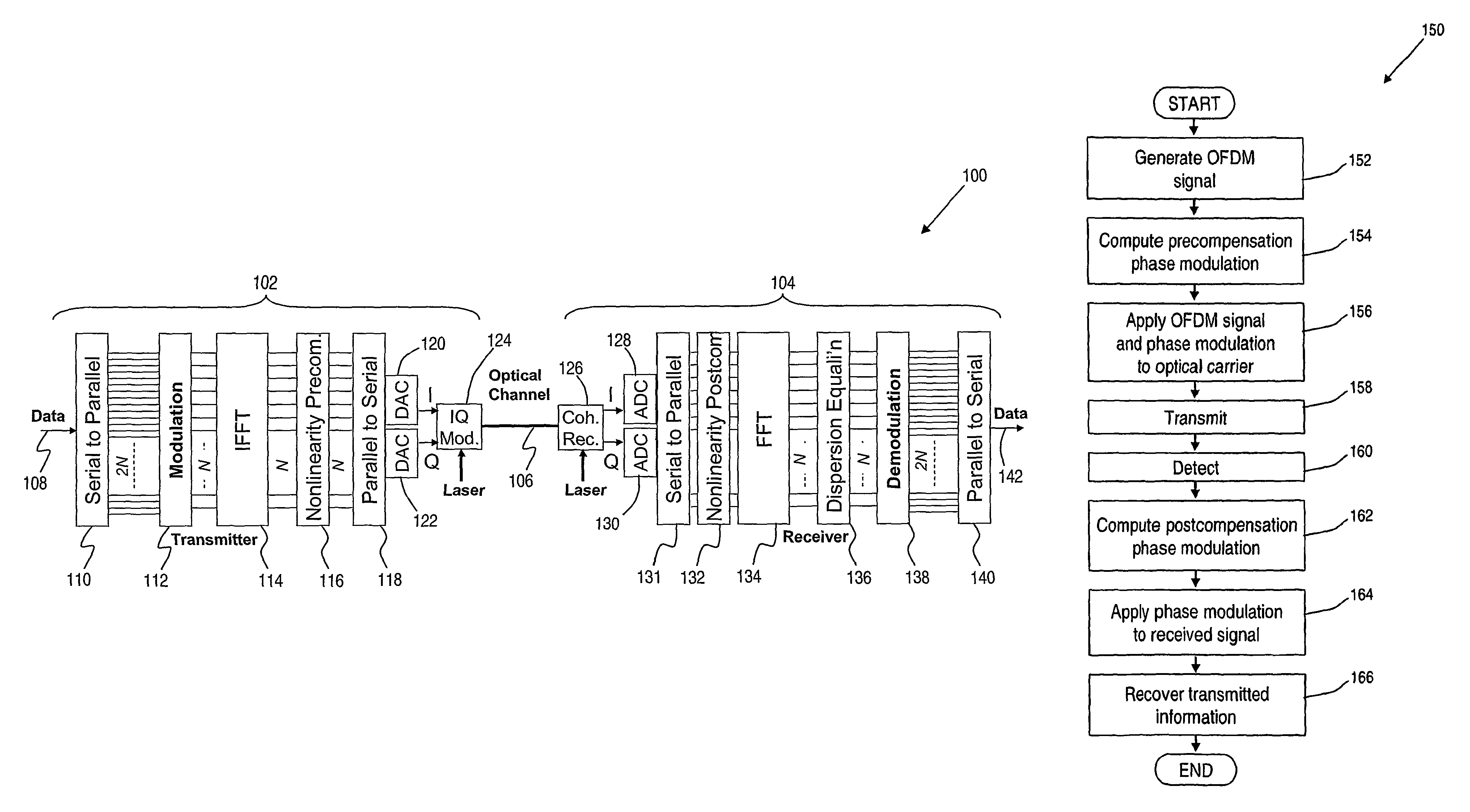
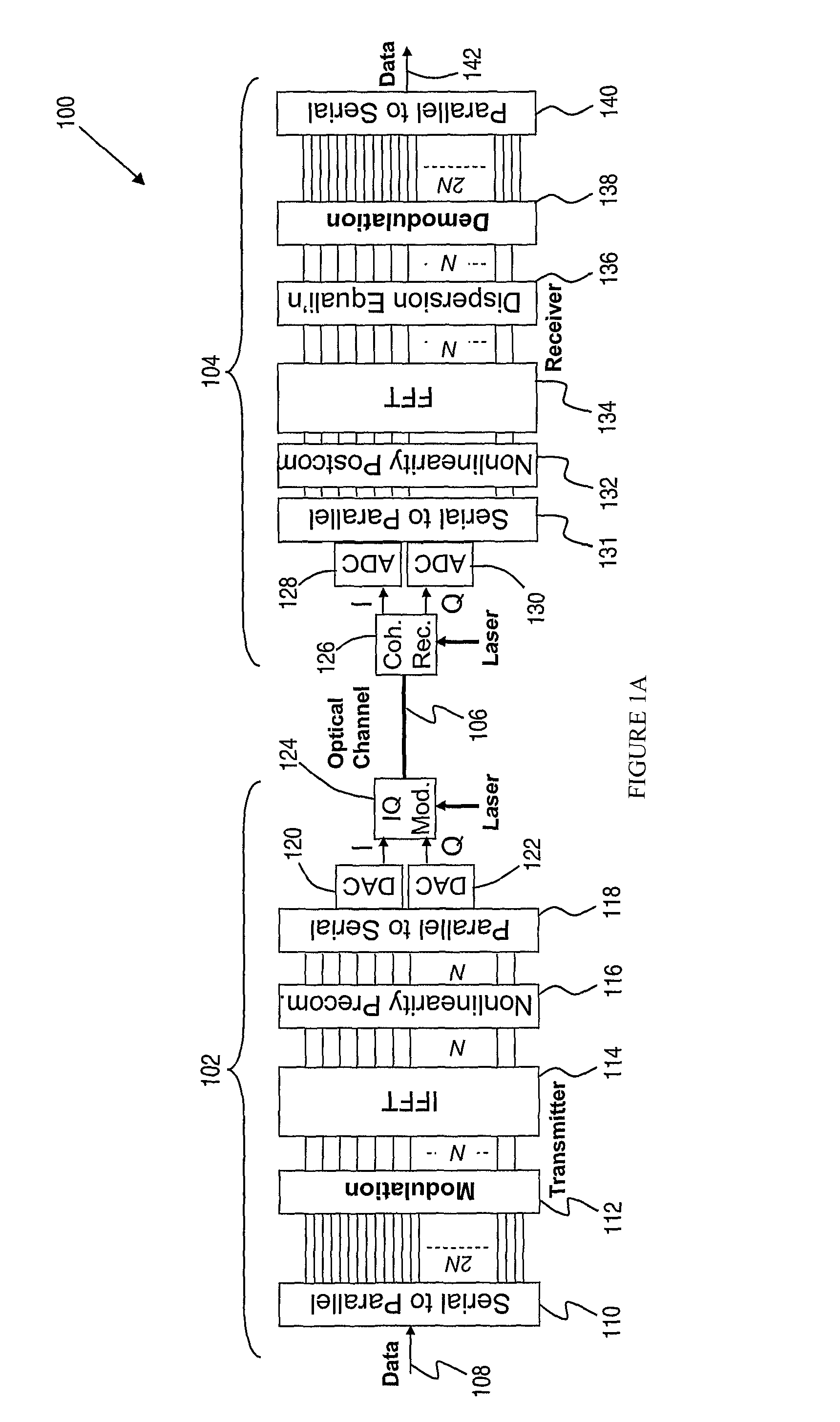
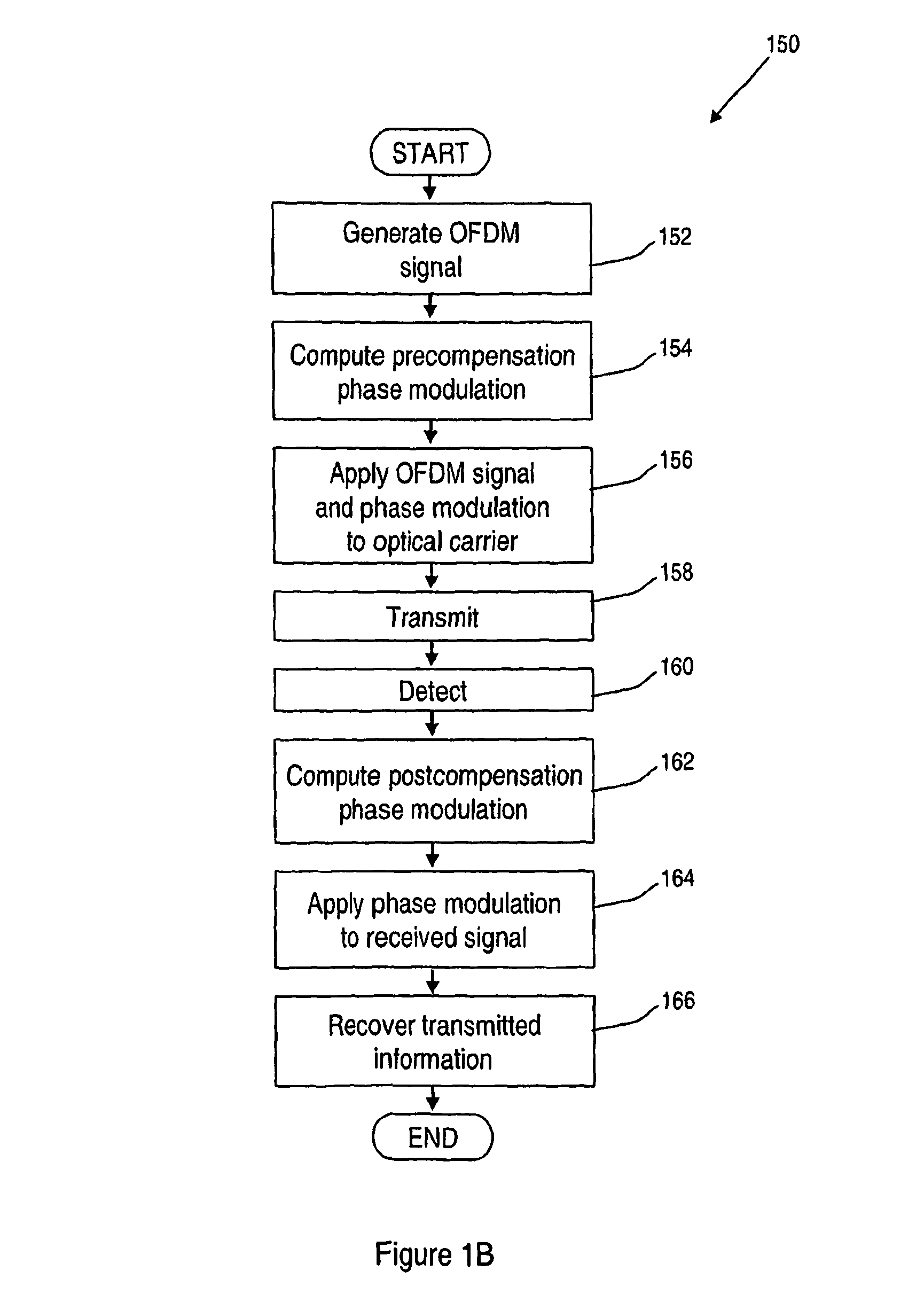
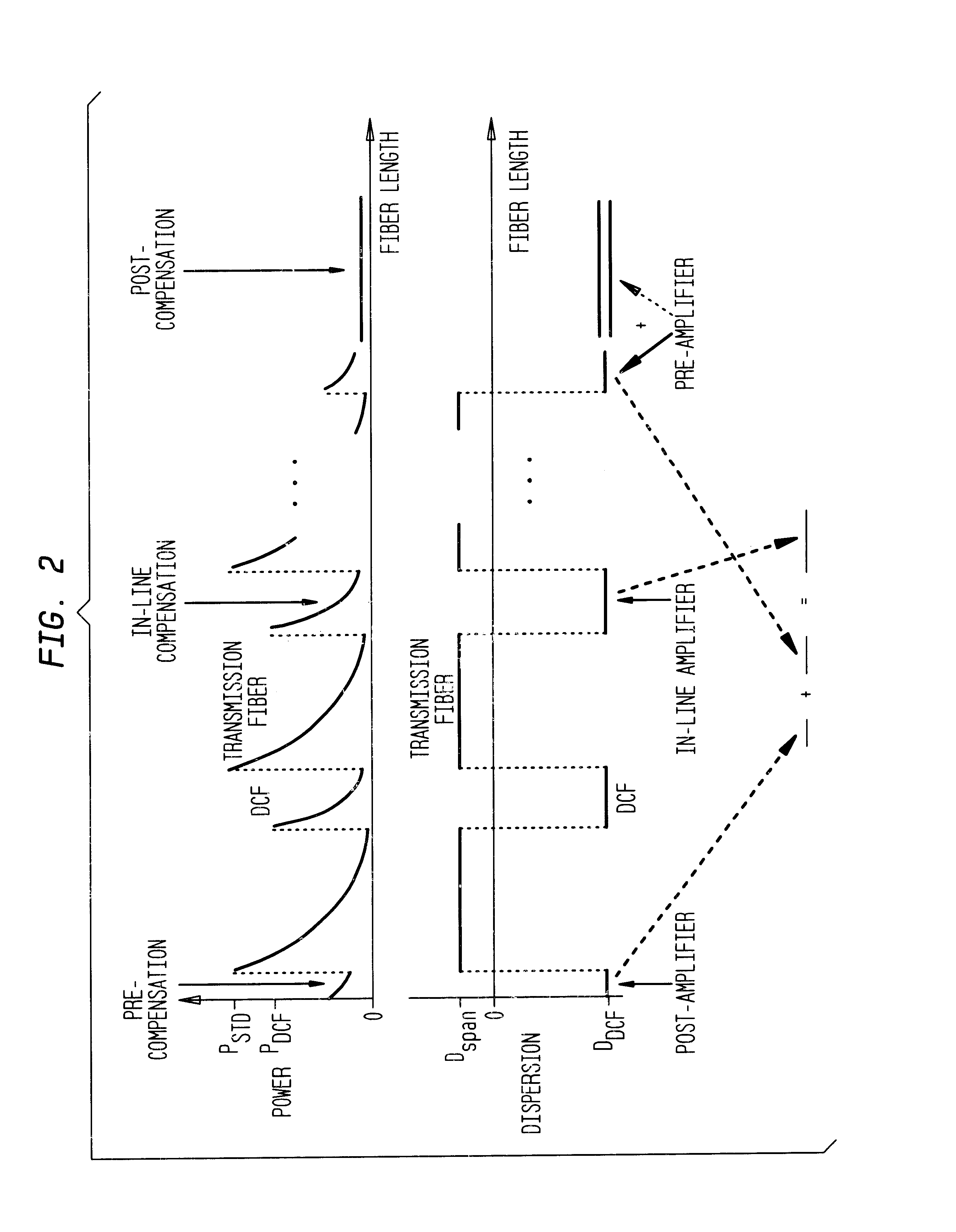
A method of transmitting information over a non-linear optical channel includes the step (152) of generating an information-bearing signal, preferably an OFDM signal, which includes a plurality of closely-spaced sub-carriers in the frequency domain. A time-varying phase modulation is determined (154), which is a first function, and preferably a linear function, of the transmitted optical power corresponding with the information-bearing signal. The information-bearing signal and the time-varying phase modulation are applied (156) to an optical source in order to generate a corresponding transmitted optical signal having substantially the stated transmitted optical power characteristic. The first function of transmitted optical power is selected so as to mitigate the effect of the non-linearity of the optical channel upon the transmitted optical signal. In alternative arrangements, a time-varying phase modulation, being a second function of optical power, is computed (162) and applied (164) to a signal received following transmission through a non-linear optical channel. The two alternative arrangements provide, respectively, for pre-compensation and post-compensation of non-linear propagation effects that may be carried out entirely within the electrical domain, for example using digital signal processing techniques.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
Dynamically balanced capacitive pick-off accelerometer
ActiveUS20050268719A1Reducing nonlinearity effect causeImprove the level ofAcceleration measurement using interia forcesCapacitor with electrode distance variationAccelerometerDevice form
A Micro Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) acceleration sensing device formed of a silicon substrate having a substantially planar surface; a pendulous sensing element having a substantially planar surface suspended in close proximity to the substrate planar surface; a flexure suspending the sensing element for motion relative to the substrate planar surface, the flexure having a both static geometric centerline and a dynamic centerline that is offset from the static geometric centerline; and a metal electrode positioned on the substrate surface for forming a capacitor with the pendulous sensing element, the metal electrode being positioned as a function of the dynamic centerline of the flexure.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Large-effective-area inverse dispersion compensating fiber, and a transmission line incorporating the same
ActiveUS6959137B2Negative dispersionReduce nonlinear effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingElectromagnetic transmissionMicrometerEngineering
An inverse dispersion fiber having a large effective area and a transmission system that incorporates the fiber for providing dispersion and dispersion slope compensation in a transmission fiber. The large-effective-area inverse dispersion optical fiber (IDF) has a negative dispersion and a negative dispersion slope. The effective area, Aeff, of the IDF preferably is greater than approximately 31 micrometers squared (μm2) at a transmission wavelength of approximately 1550 nm. The large-effective-area IDF is suitable for use with super-large-effective-area (SLA) transmission fiber for compensating dispersion in the SLA transmission fiber while reducing nonlinear effects between wavelength channels and cabling loss, which is especially advantageous in transoceanic and long-haul terrestrial systems. These nonlinear effects are inversely related to the effective area of the fiber (i.e., nonlinearities˜1 / Aeff). Thus, an increase in the effective area of the fiber translates into a decrease in nonlinear interactions, which increases bandwidth capabilities and limits signal degradation. Furthermore, the large-effective-area IDF of the present invention has very desirable transmission properties. The present invention also provides a transmission system comprising at least one of the large-effective-area IDF optical fibers of the present invention. Furthermore, Aeff can be made large without having to increase the ratio, Ra, of the diameter of the core to the diameter of the trench region.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
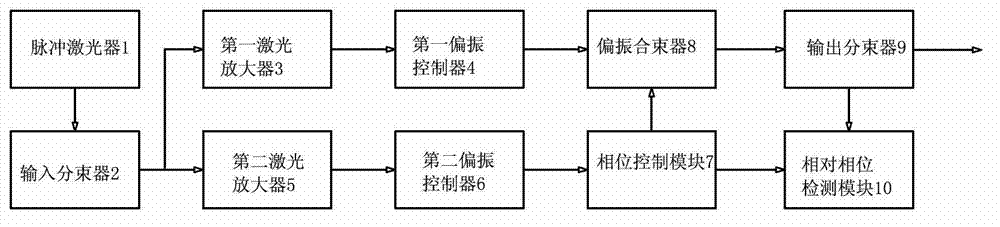
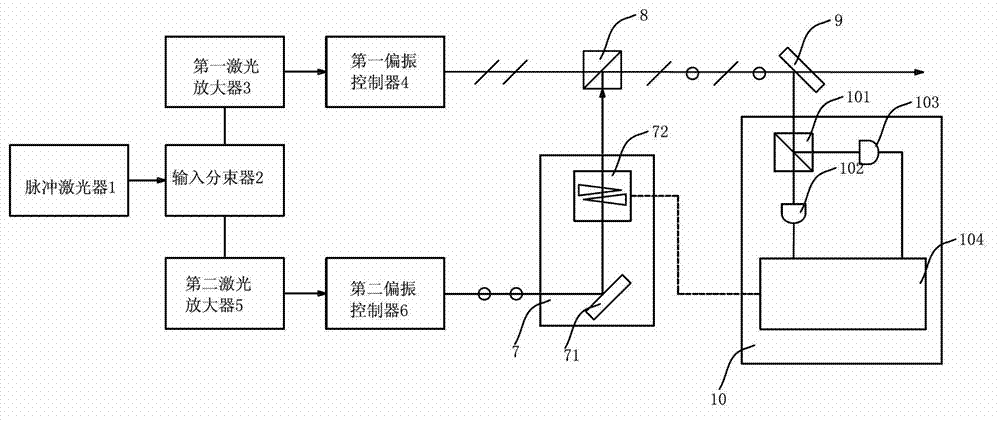
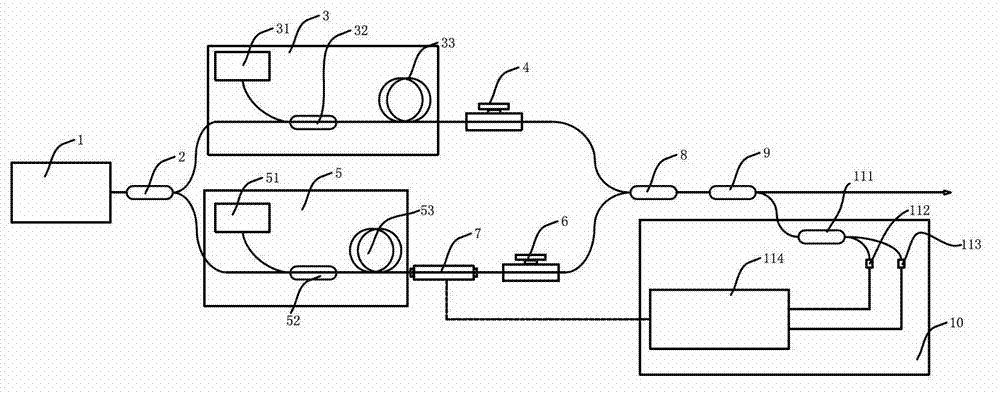
Polarization beam-combination device for pulsed laser
InactiveCN103033944AAchieve coaxial synthesisHigh synthesis efficiencyLaser detailsCoupling light guidesBeam splitterOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a polarization beam-combination device for a pulsed laser. The polarization beam-combination device comprises the pulsed laser, an input beam splitter, n laser amplifiers and n-1 polarization coherent beam-combination units. The pulsed laser outputs a beam of seed light. The input beam splitter divides the seed light into n sub-seed light beams. The n laser amplifiers respectively carry out power amplification to the n sub-seed light beams. The n-1 polarization coherent beam-combination units carry out pairwise polarization in-phase beam-combination for n-1 times to n laser beams output by the n laser amplifiers. N is a natural number which is bigger than or equal to two. An output end of the polarization beam-combination device is connected with an output beam splitter. A hard light output end of the output beam splitter is used as an output end of the polarization coherent beam-combination units. Light output from a low light output end of the output beam splitter shoots into a relative phase detection module of a drive phase control module, and the relative phase detection module enables phase positions of two laser beams to be consistent. Through adoption of a polarization detection method, the polarization beam-combination device detects the relative phase positions of the two laser beams, and is capable of achieving coaxial combination of a plurality of coherent light beams, high in combined efficiency and good in beam quality.
Owner:广东华快光子科技有限公司
Dispersion shifted optical fiber
InactiveUS6091873AReduce nonlinear effectsReduce dispersionOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDispersion-shifted fiberWdm transmission systems
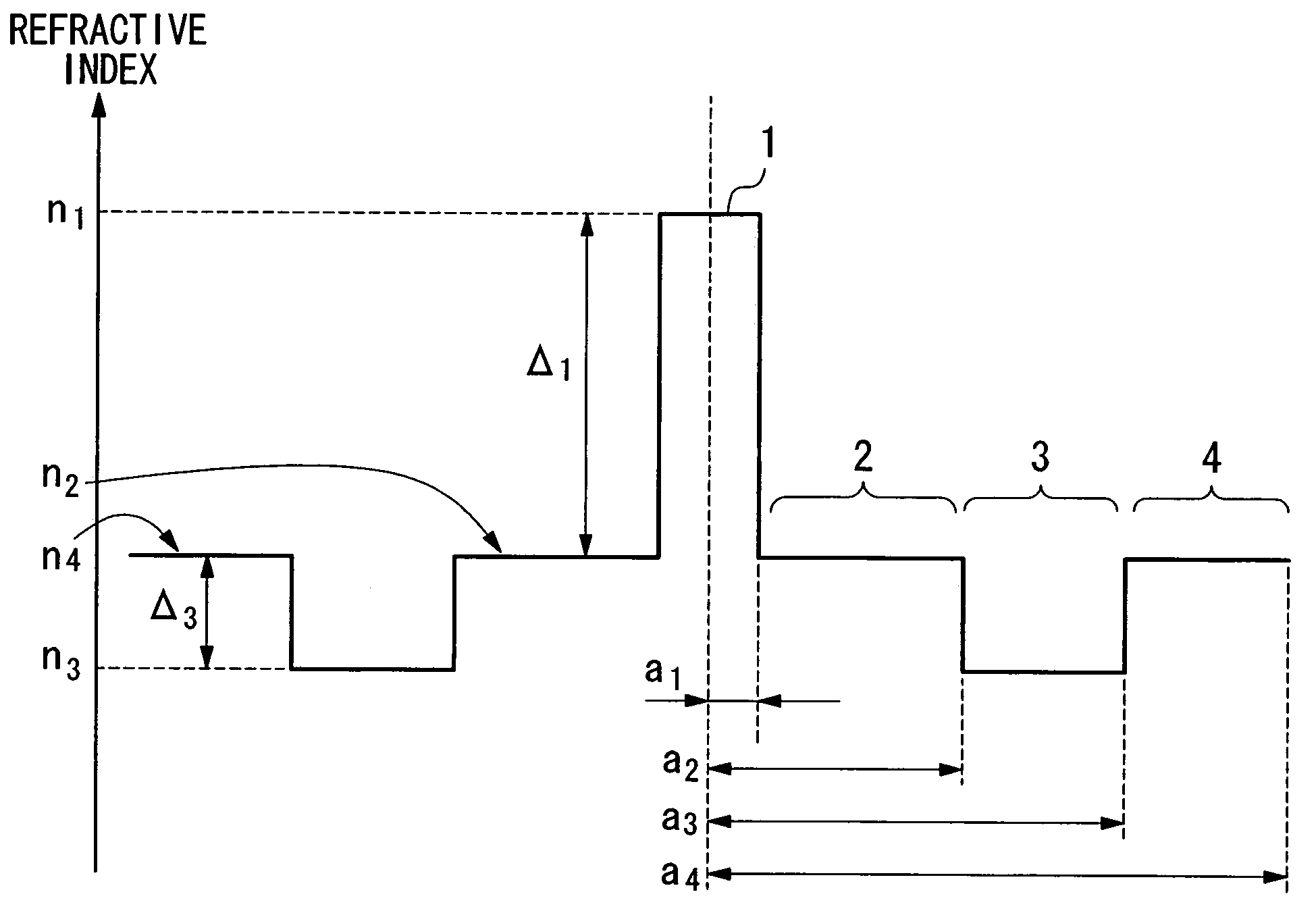
A dispersion-shifted optical fiber (DS-fiber) is structured so that it has nearly zero chromatic dispersion in the 1.55 mu m wavelength band and, at the same time, achieves both reduced non linear effects and low dispersion slope. In particular, dispersion slope is reduced to a level sufficient for the fiber to be used for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) applications. The properties of the fiber are developed such that chromatic dispersion in the 1.55 mu m band is nearly zero but not zero, effective cross section area is 45 DIFFERENCE 70 mu m2, bending loss is 0.1 DIFFERENCE 100 dB / m, dispersion slope is 0.05 DIFFERENCE 0.08 ps / km / nm2, and the cutoff wavelength is such that transmission is always single-mode transmission within the 1.55 mu m band. Such a DS-fiber has sufficiently large effective cross section area Aeff, low bending loss and small dispersion slope to make the fiber suitable for use in WDM transmission systems.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
Non-linearity compensation in an optical transmission
ActiveUS8112001B2Reduce nonlinear effectsImprove signal qualityModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsDigital signal processingOptical data transmission
A method of transmitting information over a non-linear optical channel includes the step (152) of generating an information-bearing signal, preferably an OFDM signal, which includes a plurality of closely-spaced sub-carriers in the frequency domain. A time-varying phase modulation is determined (154), which is a first function, and preferably a linear function, of the transmitted optical power corresponding with the information-bearing signal. The information-bearing signal and the time-varying phase modulation are applied (156) to an optical source in order to generate a corresponding transmitted optical signal having substantially the stated transmitted optical power characteristic. The first function of transmitted optical power is selected so as to mitigate the effect of the non-linearity of the optical channel upon the transmitted optical signal. In alternative arrangements, a time-varying phase modulation, being a second function of optical power, is computed (162) and applied (164) to a signal received following transmission through a non-linear optical channel. The two alternative arrangements provide, respectively, for pre-compensation and post-compensation of non-linear propagation effects that may be carried out entirely within the electrical domain, for example using digital signal processing techniques.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
Gas differential absorption laser radar based on non-coherent light source
ActiveCN106769952AEasy to achieve eye safetyLittle effect of turbulenceWave based measurement systemsColor/spectral properties measurementsFrequency spectrumPeak value
The invention discloses a gas differential absorption laser radar based on a non-coherent light source. The laser radar uses a non-coherent light source, laser of two operating wavelengths is filtered by a filtering technology, one operating wavelength is positioned on the peak value of a gas absorption line, the other operating wavelength deviates from the gas adsorption line, and the differential adsorption detection of an atmosphere gas ingredient can be realized through the detection of the atmosphere echo signal of two beams of laser. A time division multiplexing technology is adopted, only one detector is used for finishing the measurement of reference laser and signal light, and a system integration level is improved. According to the gas differential absorption laser radar, the gas (such as water vapour, CO2, HCN, CO and the like), which is positioned in a non-coherent light source frequency spectrum range, of the gas adsorption line can be realized. A non-coherent detection technology, a wavelength division multiplexing technology and the time division multiplexing technology are adopted to realize the detection of gas ingredients, and the gas differential absorption laser radar has the advantages of high system integration degree, all fiber linking, compact structure, low construction cost, relatively safe human eyes and the like.
Owner:南京泰爱信科技有限公司
Dry wind tunnel system
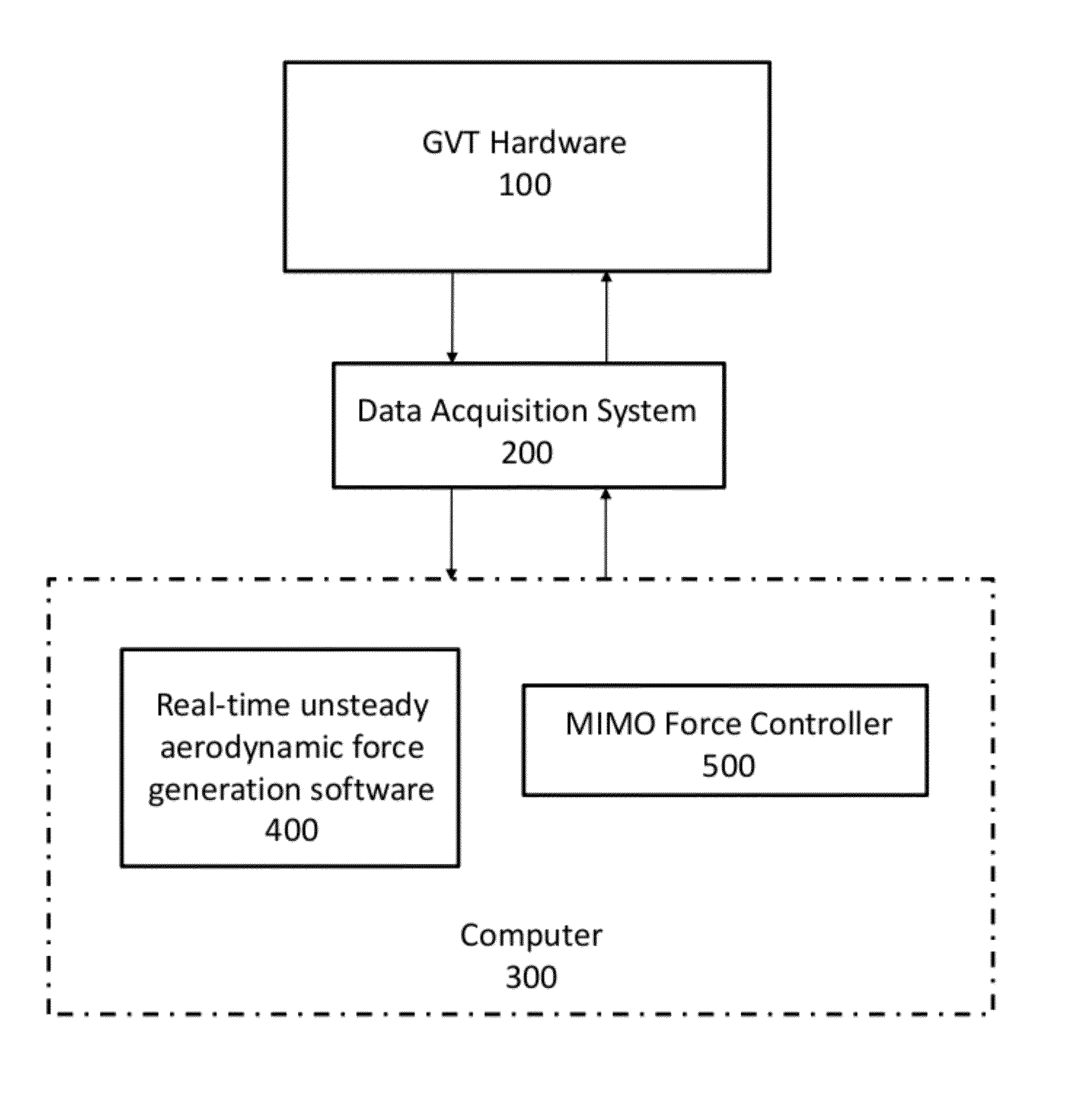
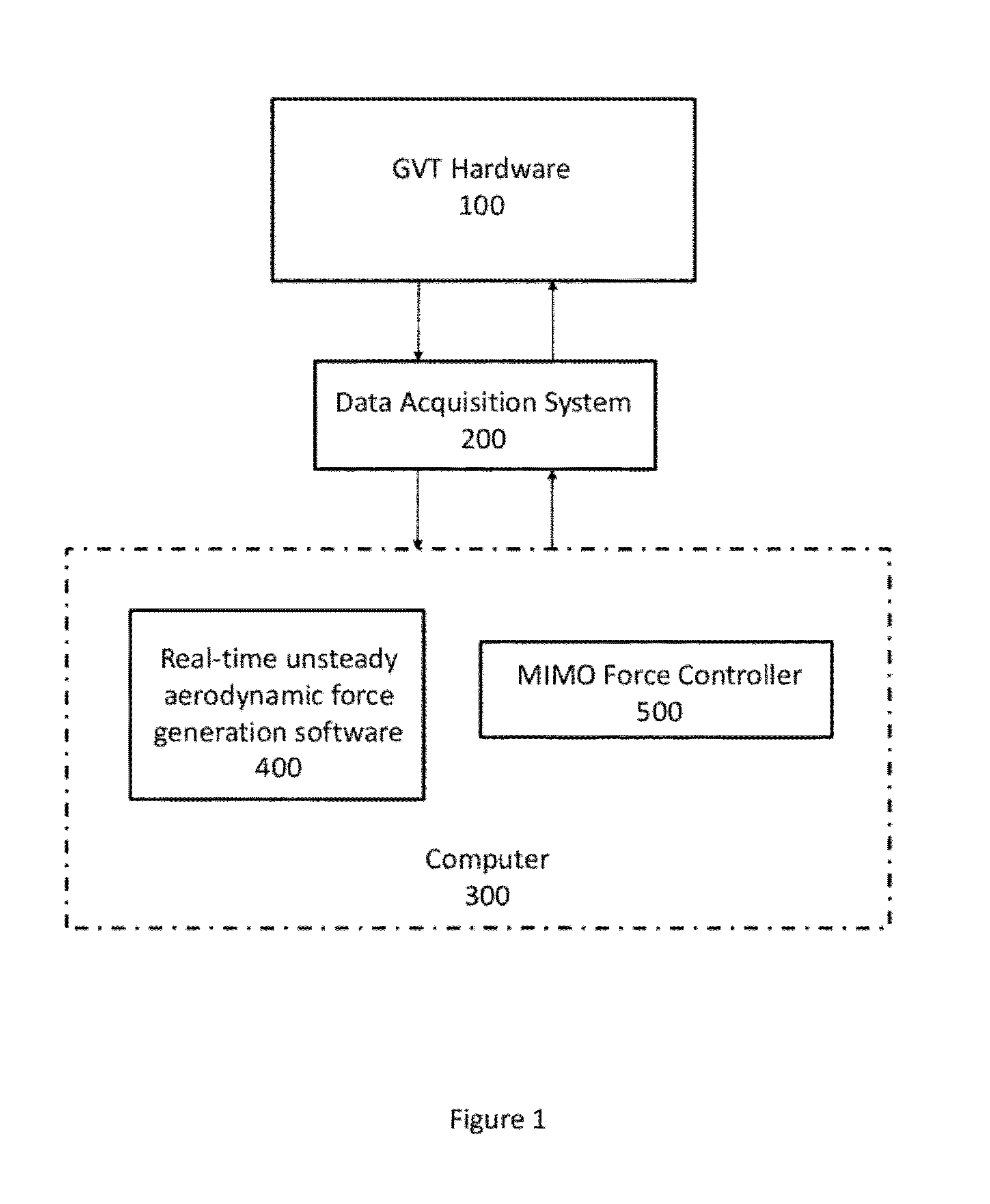
ActiveUS8393206B1Accurate calculationTesting is lowAerodynamic testingVibration testingFlight vehicleEngineering
This invention is a ground flutter testing system without a wind tunnel, called Dry Wind Tunnel (DWT) System. The DWT system consists of a Ground Vibration Test (GVT) hardware system, a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) force controller software, and a real-time unsteady aerodynamic force generation software, that is developed from an aerodynamic reduced order model (ROM). The ground flutter test using the DWT System operates on a real structural model, therefore no scaled-down structural model, which is required by the conventional wind tunnel flutter test, is involved. Furthermore, the impact of the structural nonlinearities on the aeroelastic stability can be included automatically. Moreover, the aeroservoelastic characteristics of the aircraft can be easily measured by simply including the flight control system in-the-loop. In addition, the unsteady aerodynamics generated computationally is interference-free from the wind tunnel walls. Finally, the DWT System can be conveniently and inexpensively carried out as a post GVT test with the same hardware, only with some possible rearrangement of the shakers and the inclusion of additional sensors.
Owner:ZONA TECH
Large Mode Area Optical Fiber
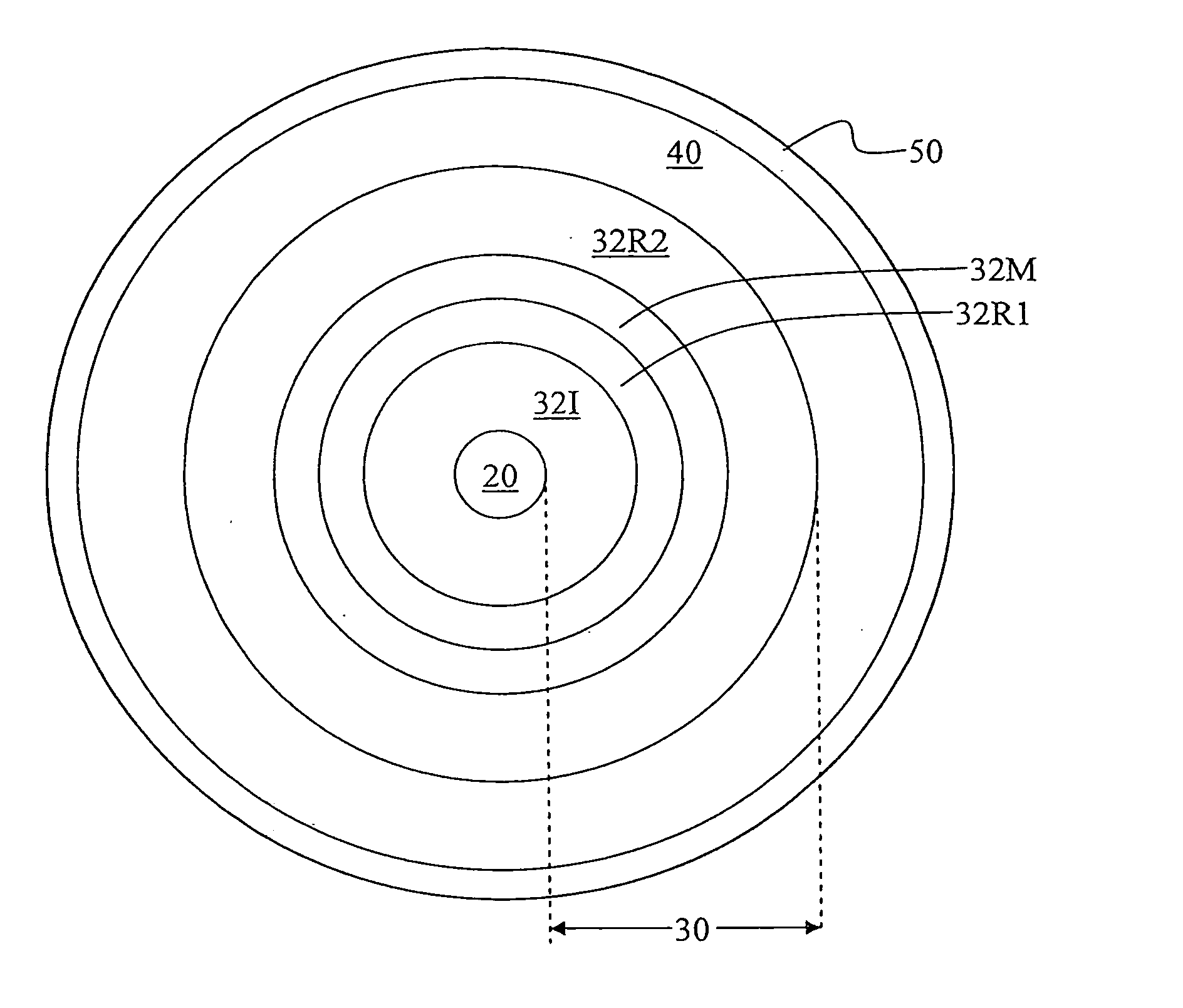
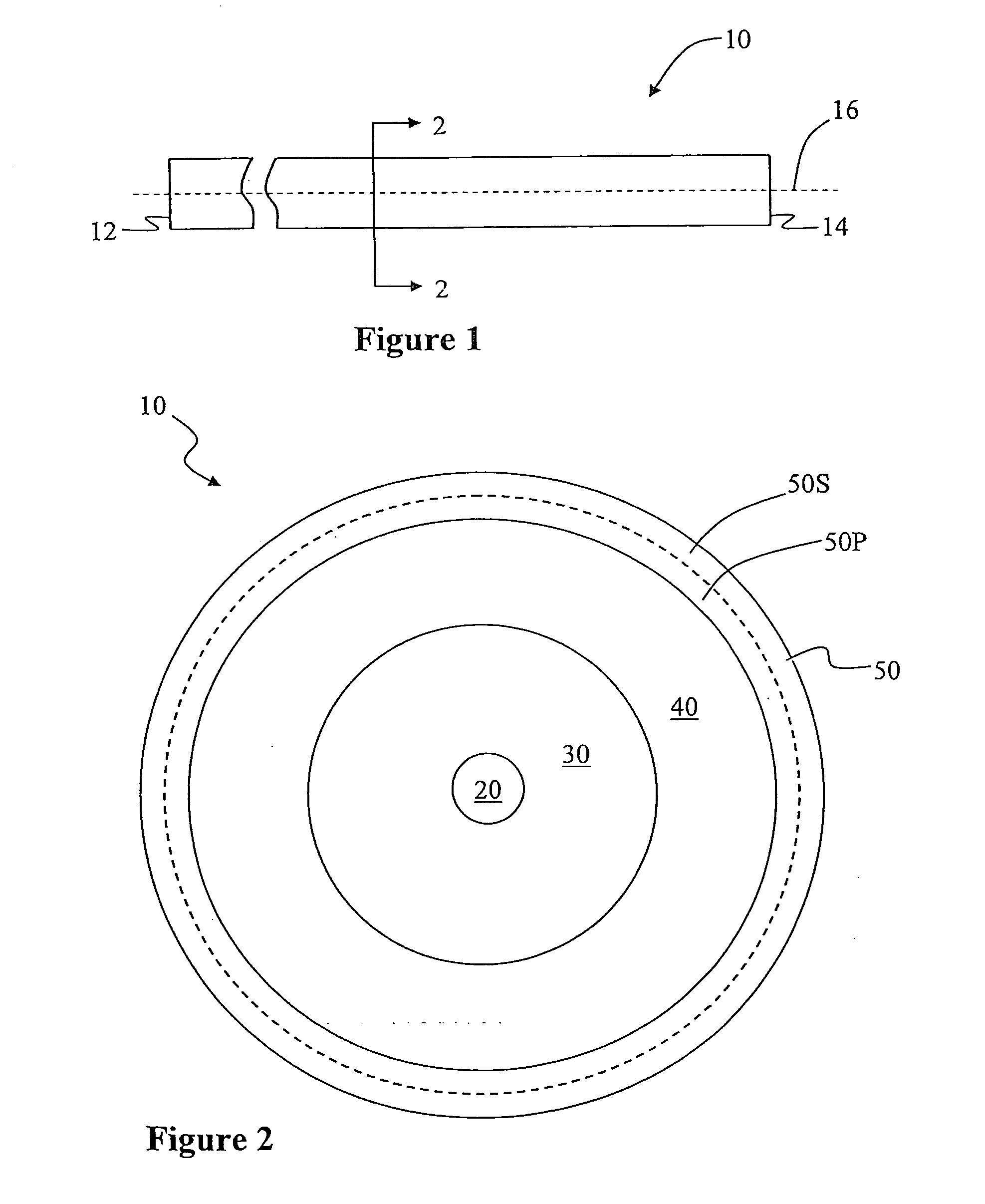
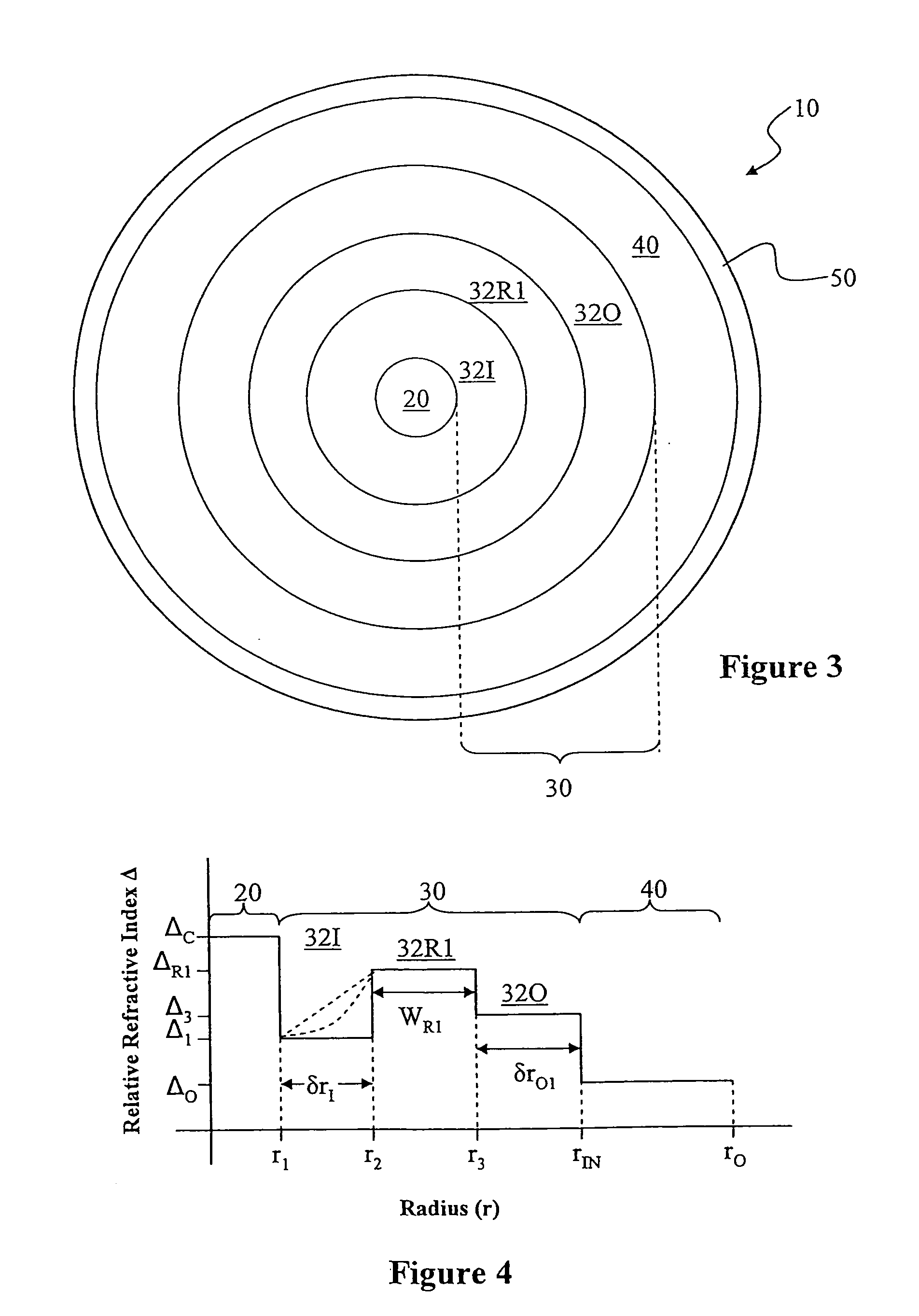
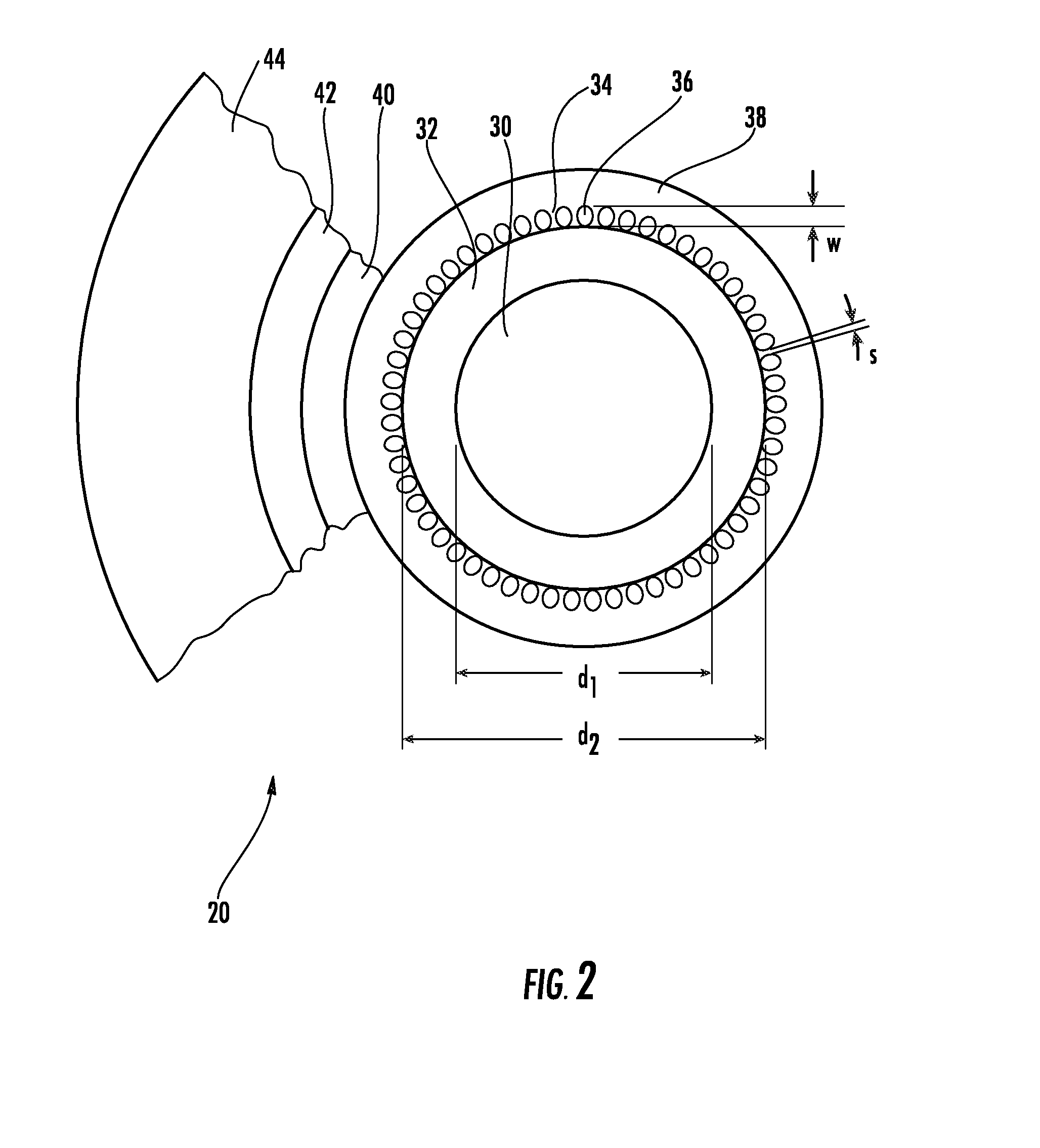
ActiveUS20100195194A1Reduce nonlinear effectsIncrease optical powerLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with polarisationRelative attenuationUltrasound attenuation
A large-mode-area (LMA) optical fiber (10) that operates as a single-mode optical fiber. The optical fiber includes a core region (20) surrounded by an inner cladding (32), which in turn is surrounded by an outer cladding (40). The inner cladding includes at least one up-doped ring region (32R1). The ring region is configured to form a large attenuation differential between the higher-order modes and the fundamental mode so only that the fundamental mode remains traveling in the optical fiber. If necessary, the optical fiber can include a bend (10B) having a select “resonant” bend diameter (DB) that increases the relative attenuation of the fundamental and higher-order modes. The optical fiber supports an effective mode field diameter (MFD) of up to 40 μm to 50 μm. As a result, detrimental non-linear effects are suppressed, which allows the optical fiber to carry substantially more optical power than conventional LMA optical fibers. The LMA optical fiber is thus eminently suited for a number of optical-fiber-based applications calling for high optical power, such as fiber lasers and pump sources for wavelength conversion.
Owner:CORNING INC
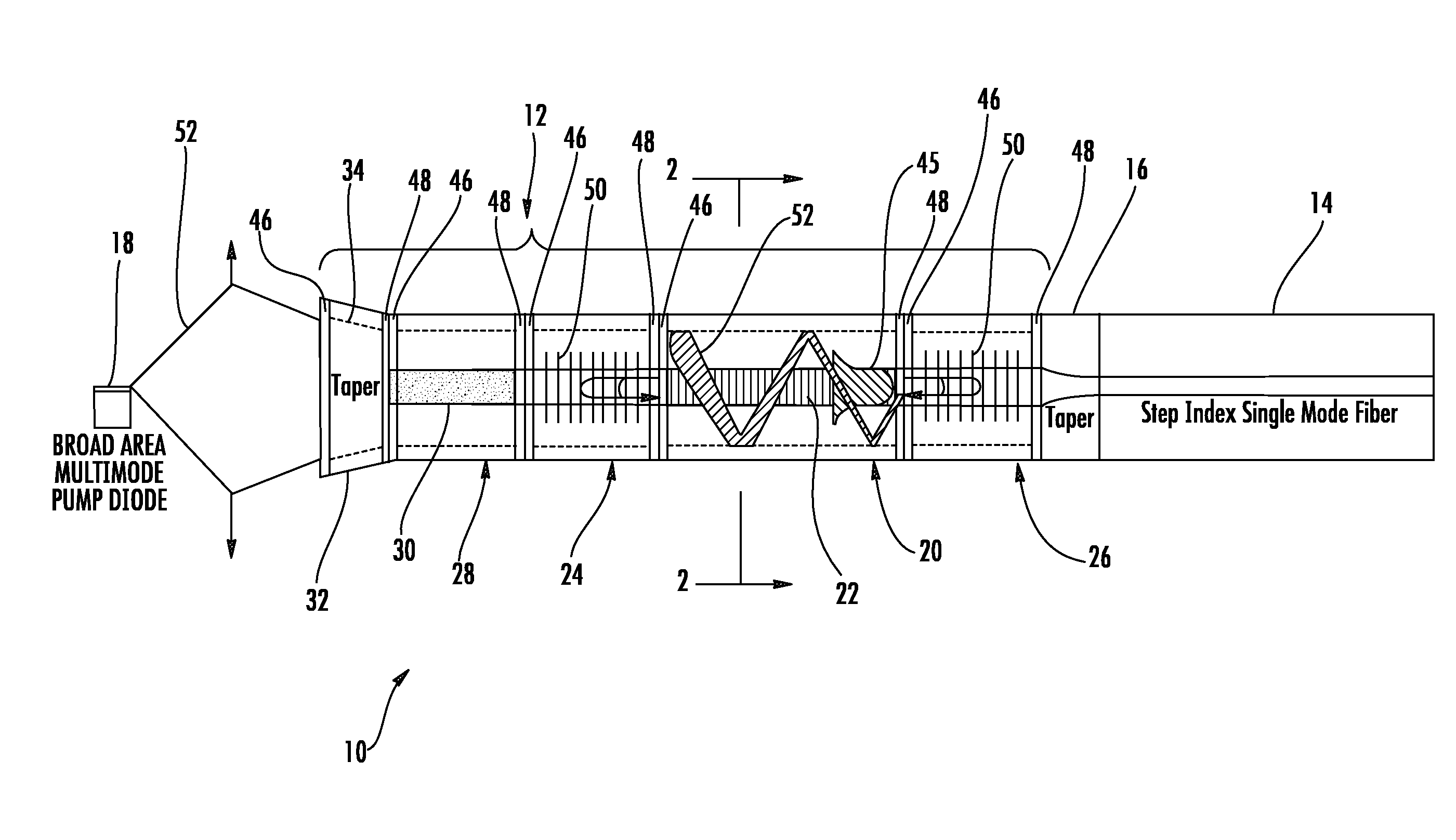
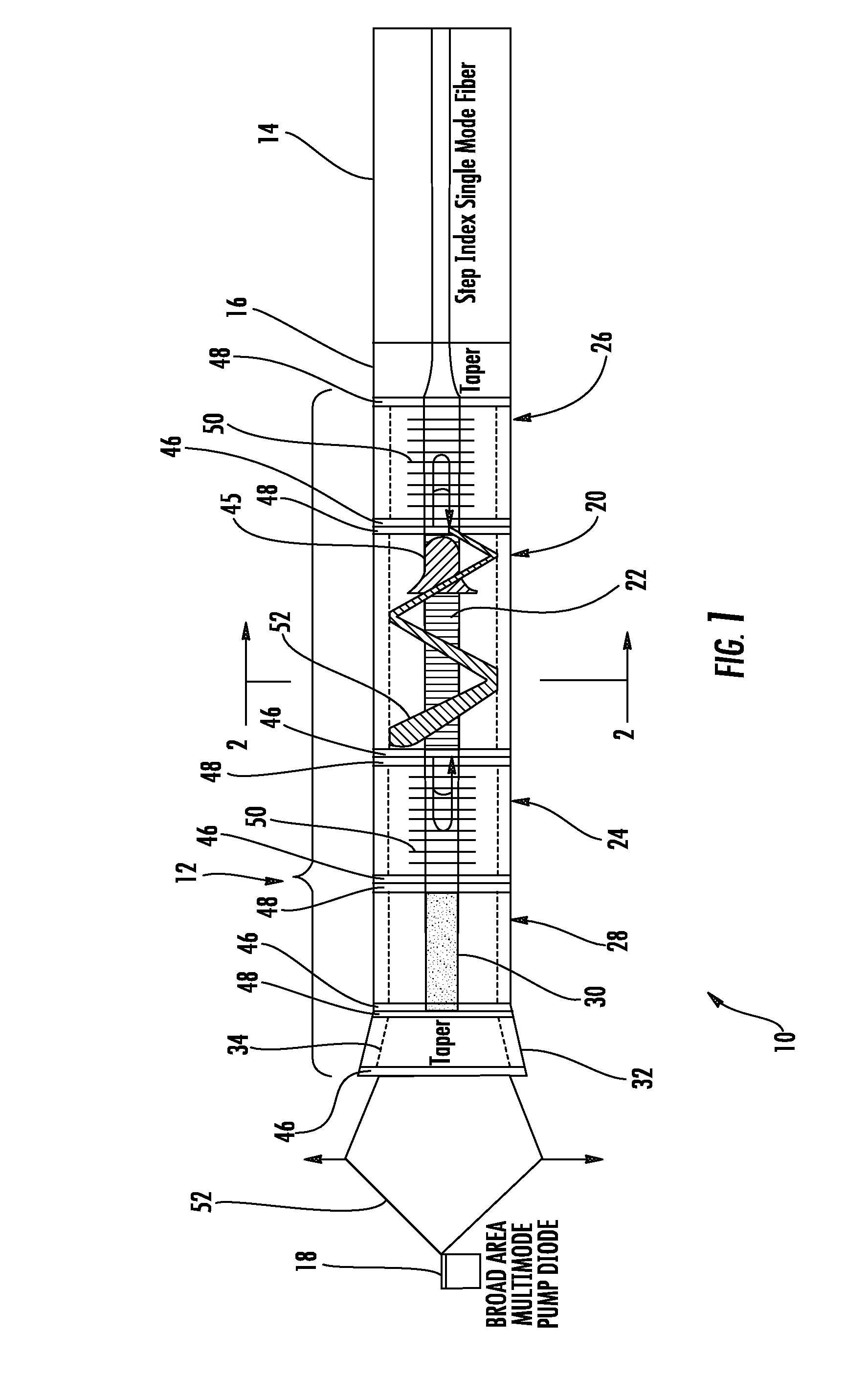
Fiber laser with large mode area fiber
InactiveUS20080144673A1Reduce nonlinear effectsHigh gainLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor lasersGratingFiber Bragg grating
A single-mode fiber laser includes a single mode holding, large mode area optical fiber assembly having a large mode area core, a first cladding and a second cladding. The optical fiber assembly has several unique sections including a gain section having a ytterbium-doped core, first and second reflective sections including fiber Bragg gratings that define a lasing cavity, and an absorptive section also having a ytterbium-doped core, the absorptive section having an output end coupled to an input end of said first reflective section. A broad area, multi-mode diode pump source is configured to pump multi-mode light into a tapered input section and cladding-pump the gain section. The gain section absorbs the multi-mode pump light and emits single-mode light. The absorptive section absorbs emissions at the operating wavelength and prevents operating emissions from reflecting back into said pump source.
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
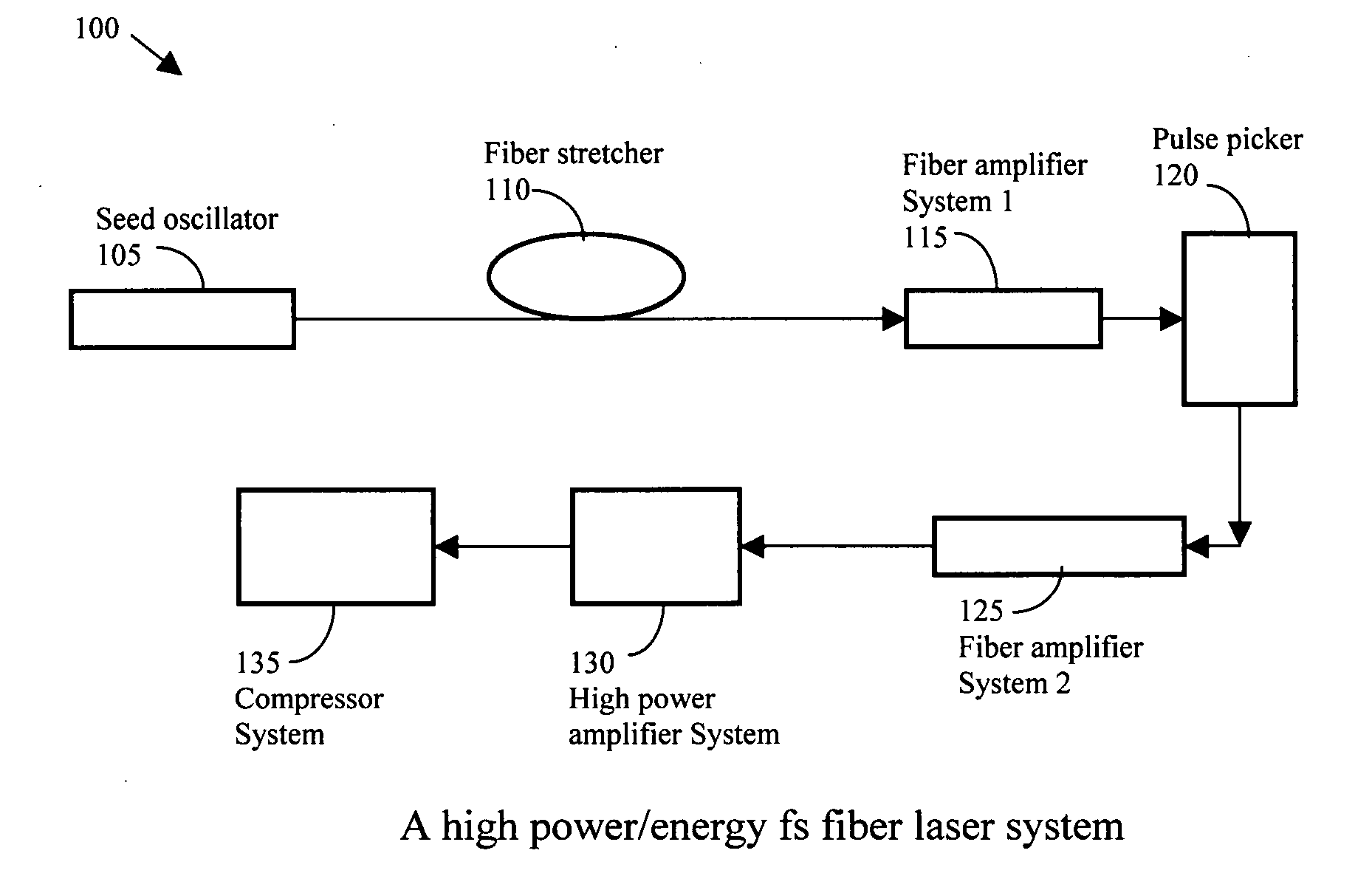
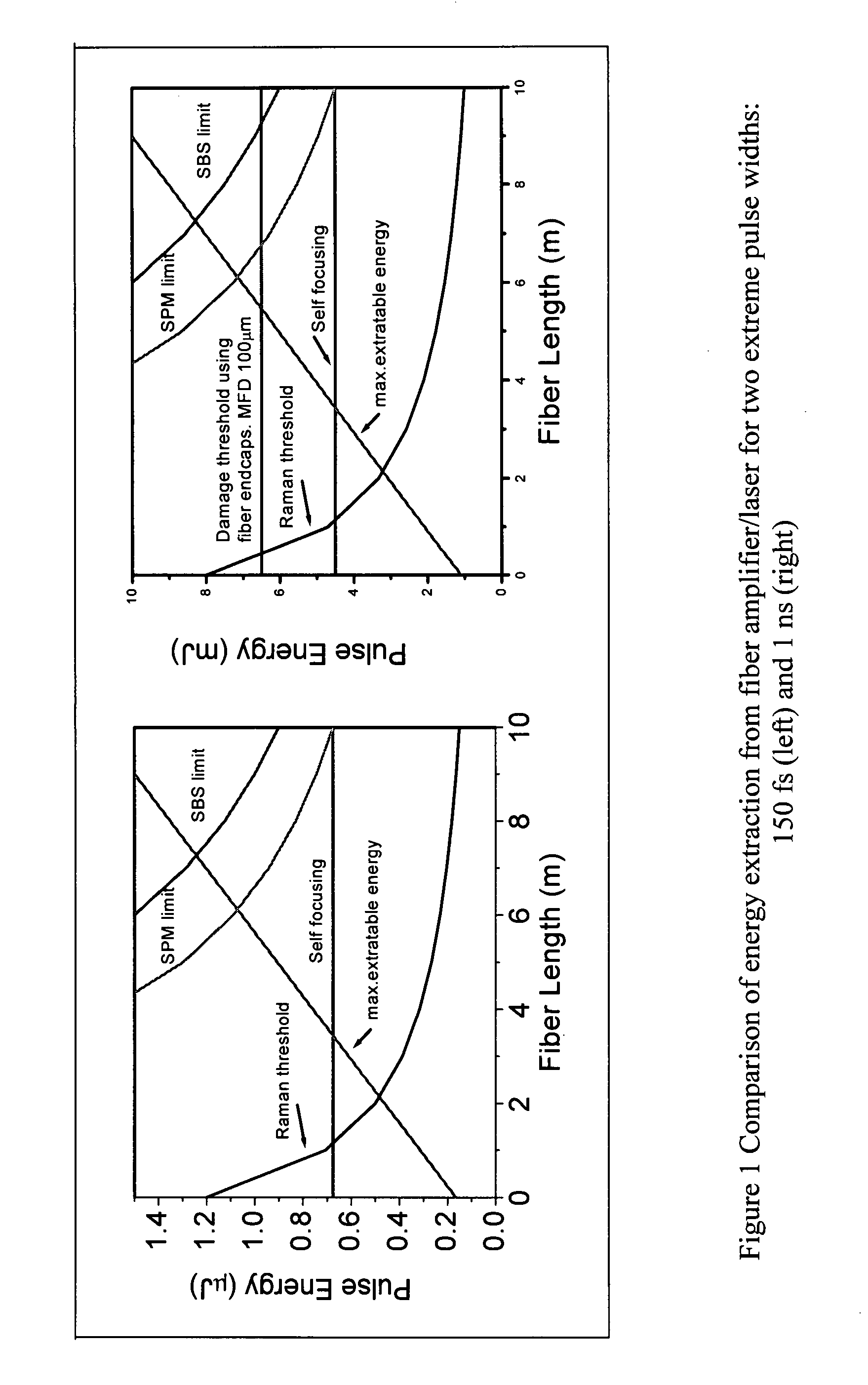
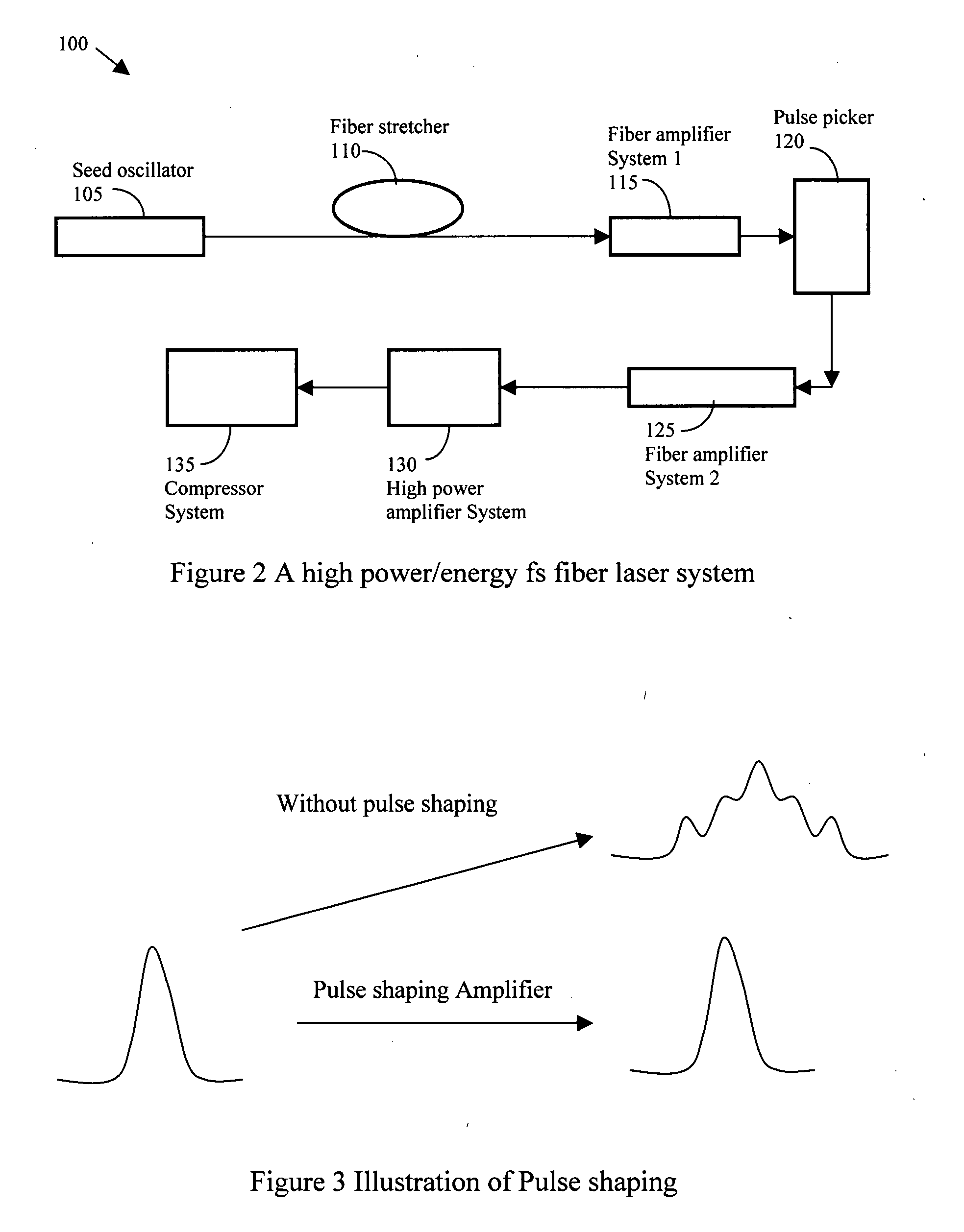
High energy short pulse fiber laser achieved by combining pulse shaping, polarization shaping and spectral shaping
InactiveUS20080089366A1Reduce nonlinear effectsLaser using scattering effectsSpectral shapingMultistage amplifier
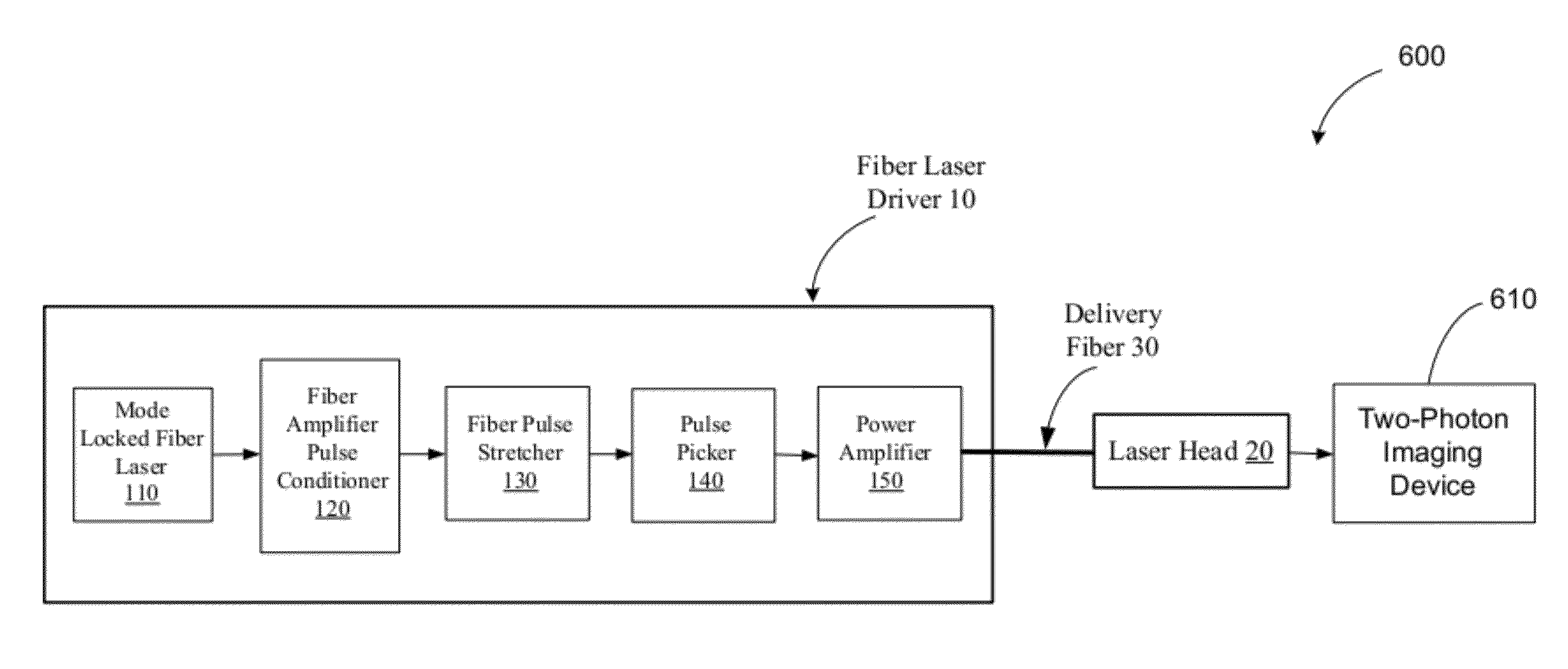
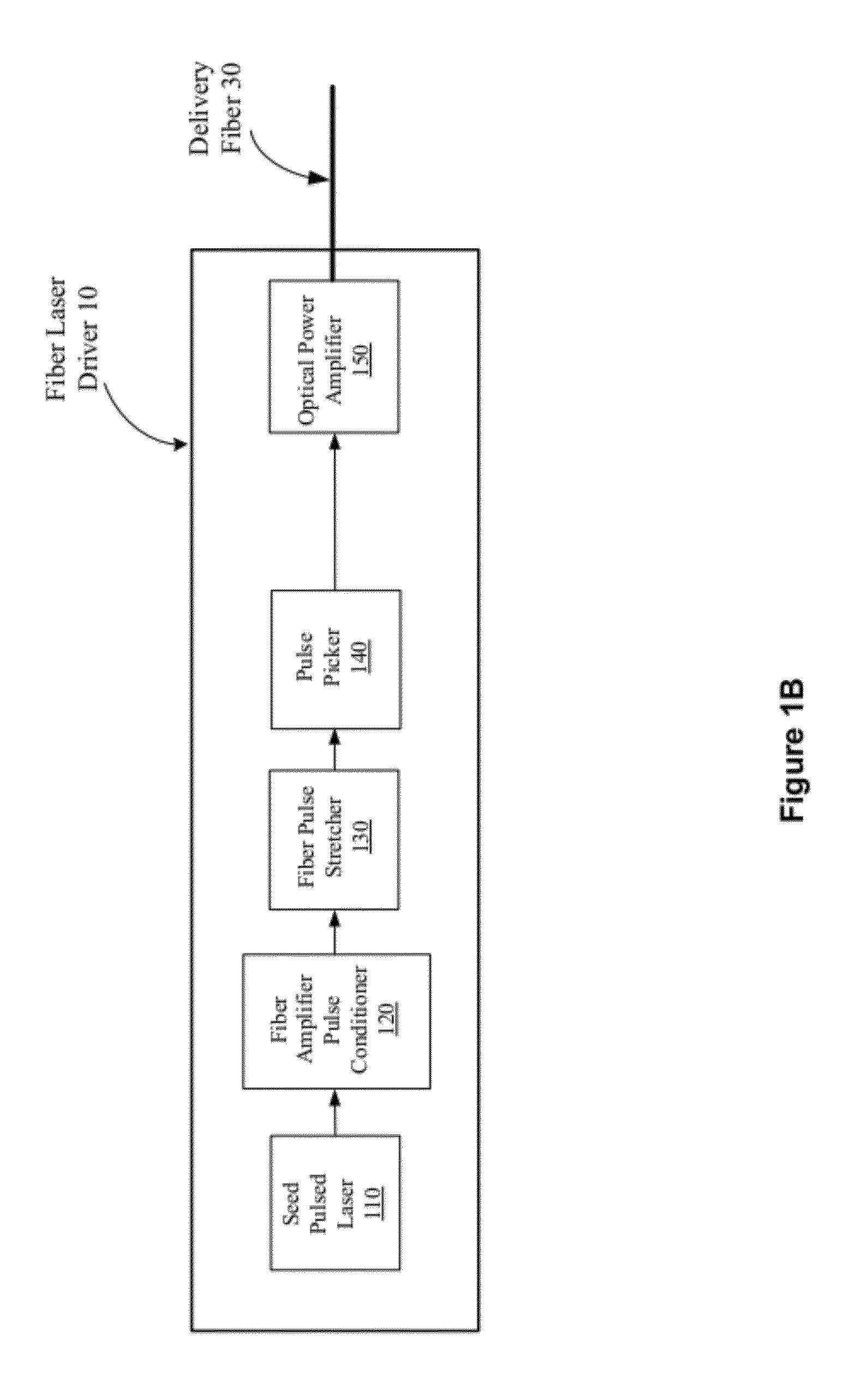
A fiber laser system includes a fiber mode-locking oscillator, a fiber stretcher, a multistage amplifier chain, a pulse picker, and a compressor wherein at least a device for performing a pulse shaping, a spectral shaping and a polarization shaping and a combination thereof is implemented in the fiber mode-locking oscillator, the fiber stretcher, the multistage amplifier chain, the pulse picker, and the compressor for managing and reducing nonlinear effects in the fiber laser system. The combinations of pulse shaping, spectral shaping and polarization shaping in different stages of the fiber laser system enables the fiber laser system to generate a short pulse of <200 fs and a high energy laser in a range between 1 uJ to over mJ and an average power from 1 W to 100 W.
Owner:POLARONYX
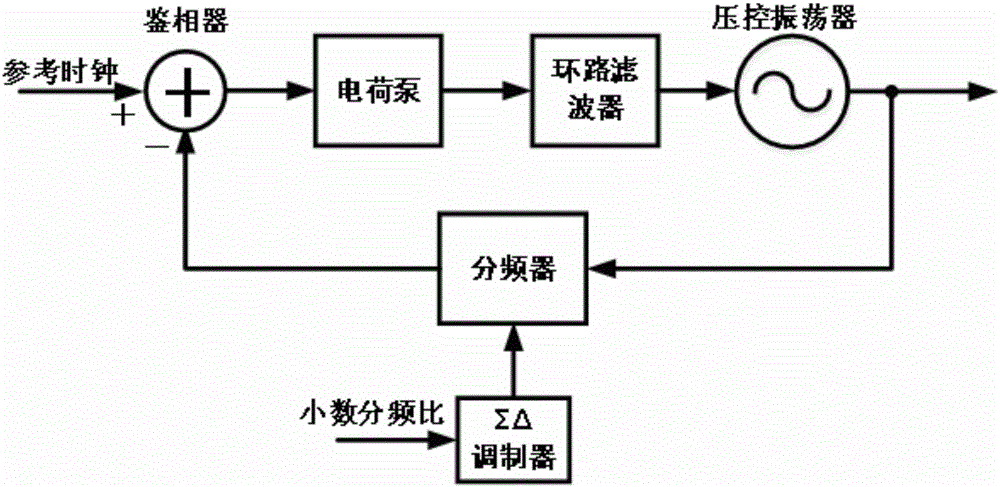
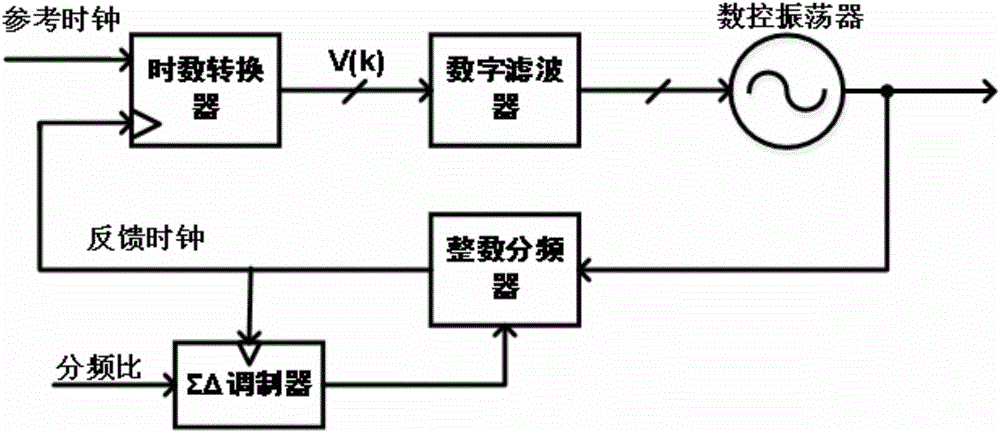
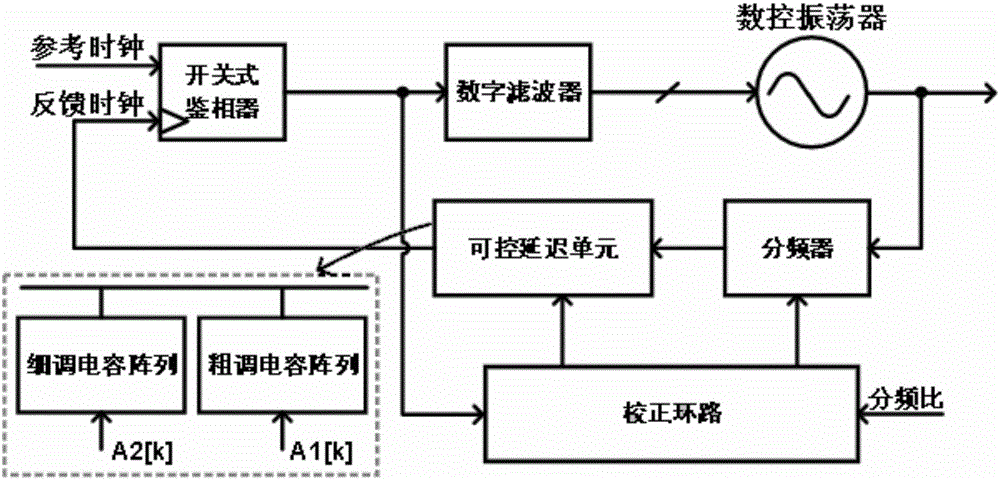
All-digital fractional-N phase-locked loop structure
ActiveCN106209093ASmall coverageShorten the effective lengthPulse automatic controlDigital control oscillatorEngineering
The invention provides an all-digital fractional-N phase-locked loop structure comprising a time-digital converter TDC, a digital filter DLF, a digital-controlled oscillator DCO, a digital-controlled phase interpolator DPI, a sigmadelta modulator SDM, an integer frequency divider DIV and a feedforward correction module. Conversion from digital control signals to phase information is completed by using the digital-controlled phase interpolator DPI, and the nonlinearity brought by the DPI can be eliminated by using the feedforward correction means. According to the structure, the complexity of the circuit design can be reduced, and the problems of high power consumption, complex design and poor noise in the existing structure can also be solved so that the structure is suitable for the field of high-performance and low-power-consumption wireless communication.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
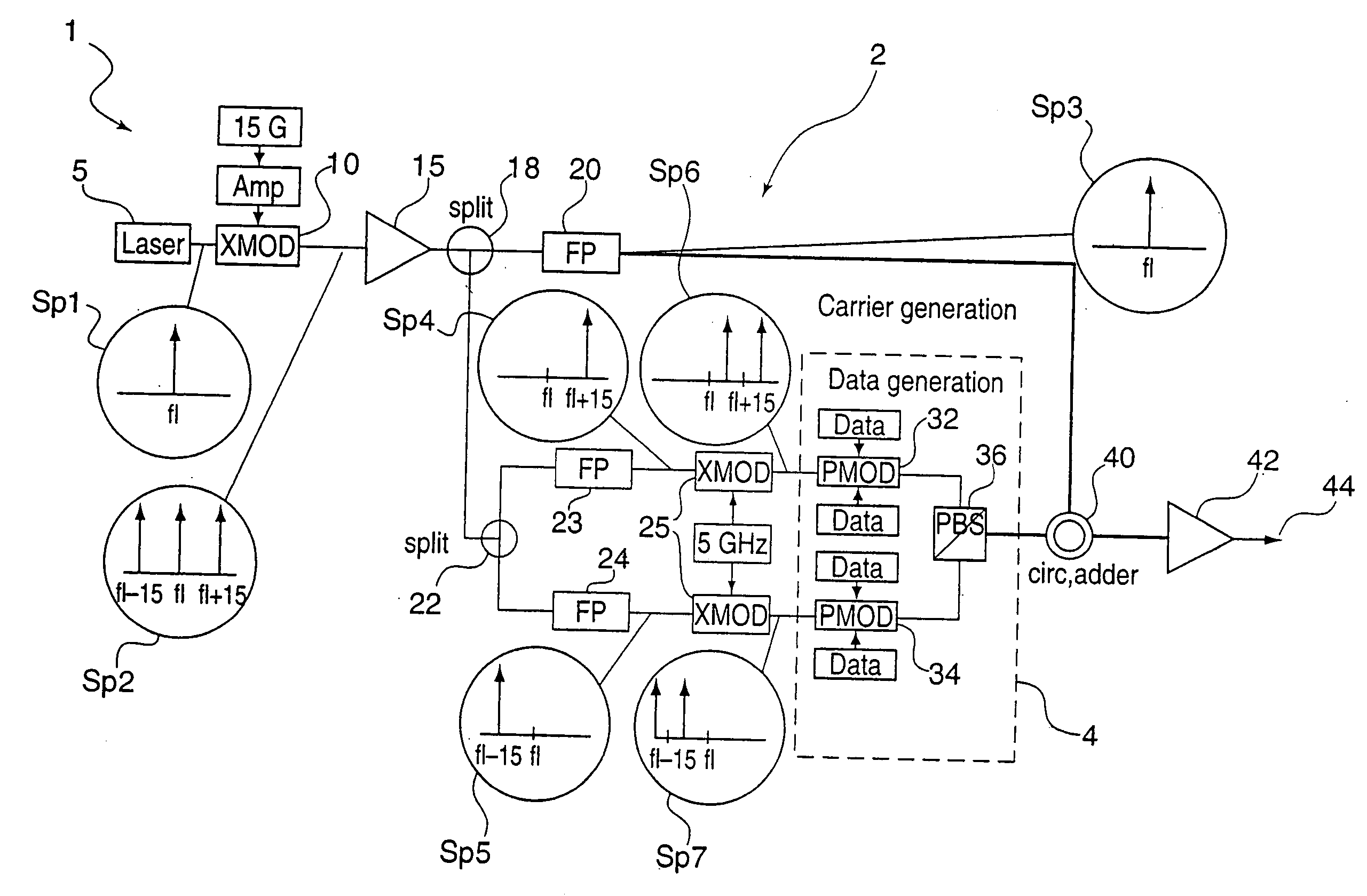
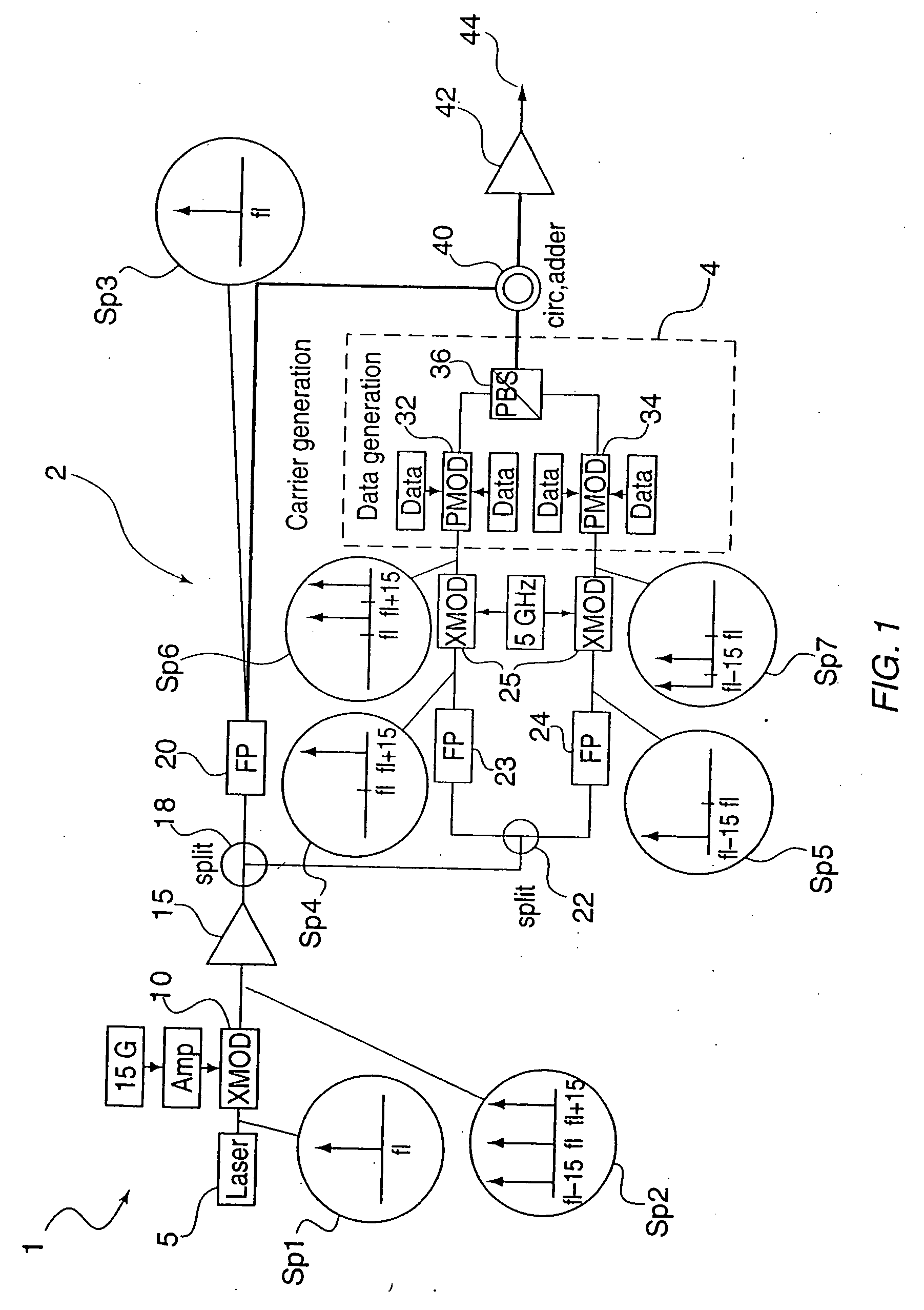
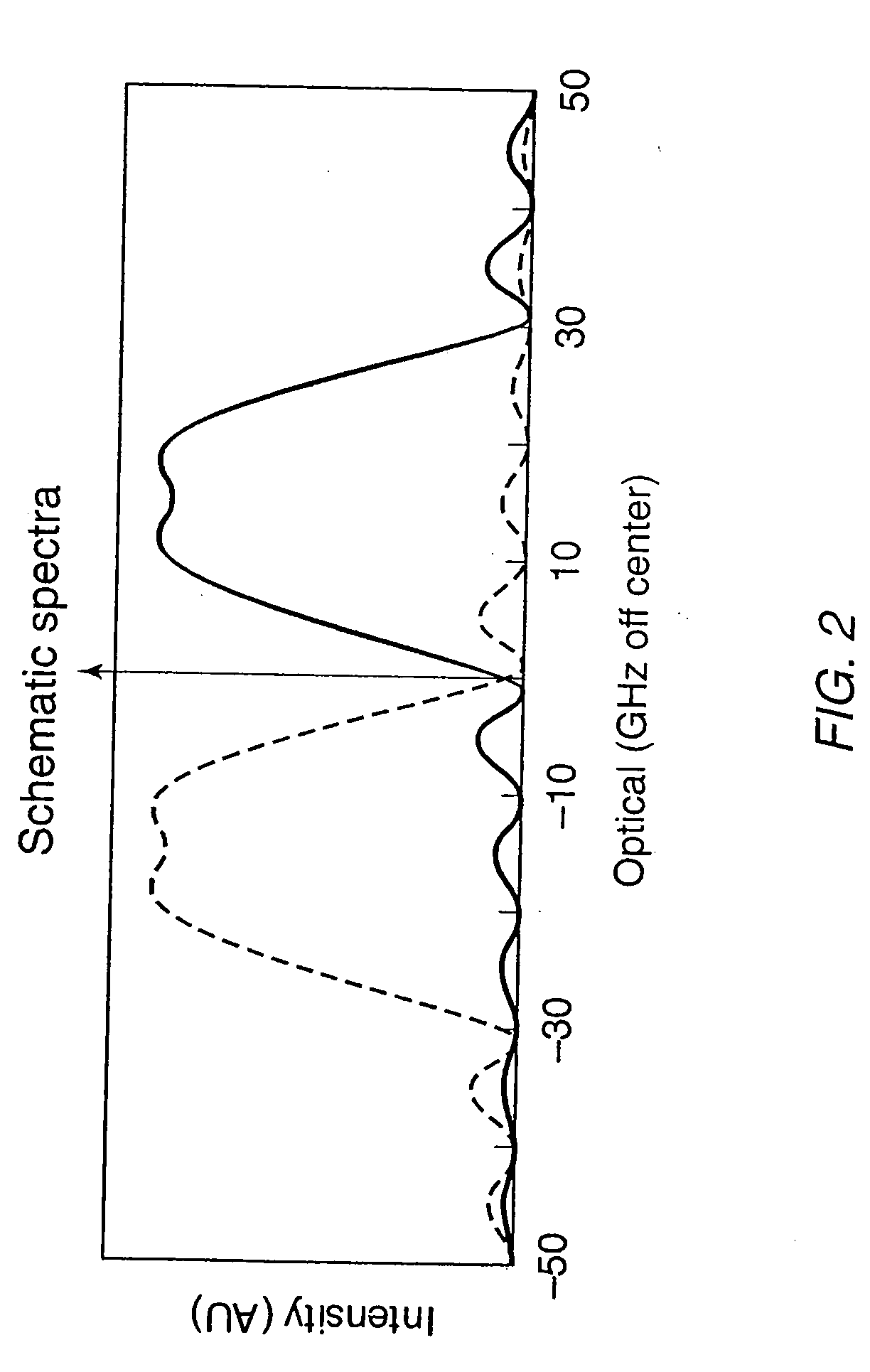
Method and system for 80 and 160 gigabit-per-second QRZ transmission in 100 GHz optical bandwidth with enhanced receiver performance
InactiveUS20060228118A1High receptionHigh transmissionPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberFir system
Owner:TERADVANCE COMM
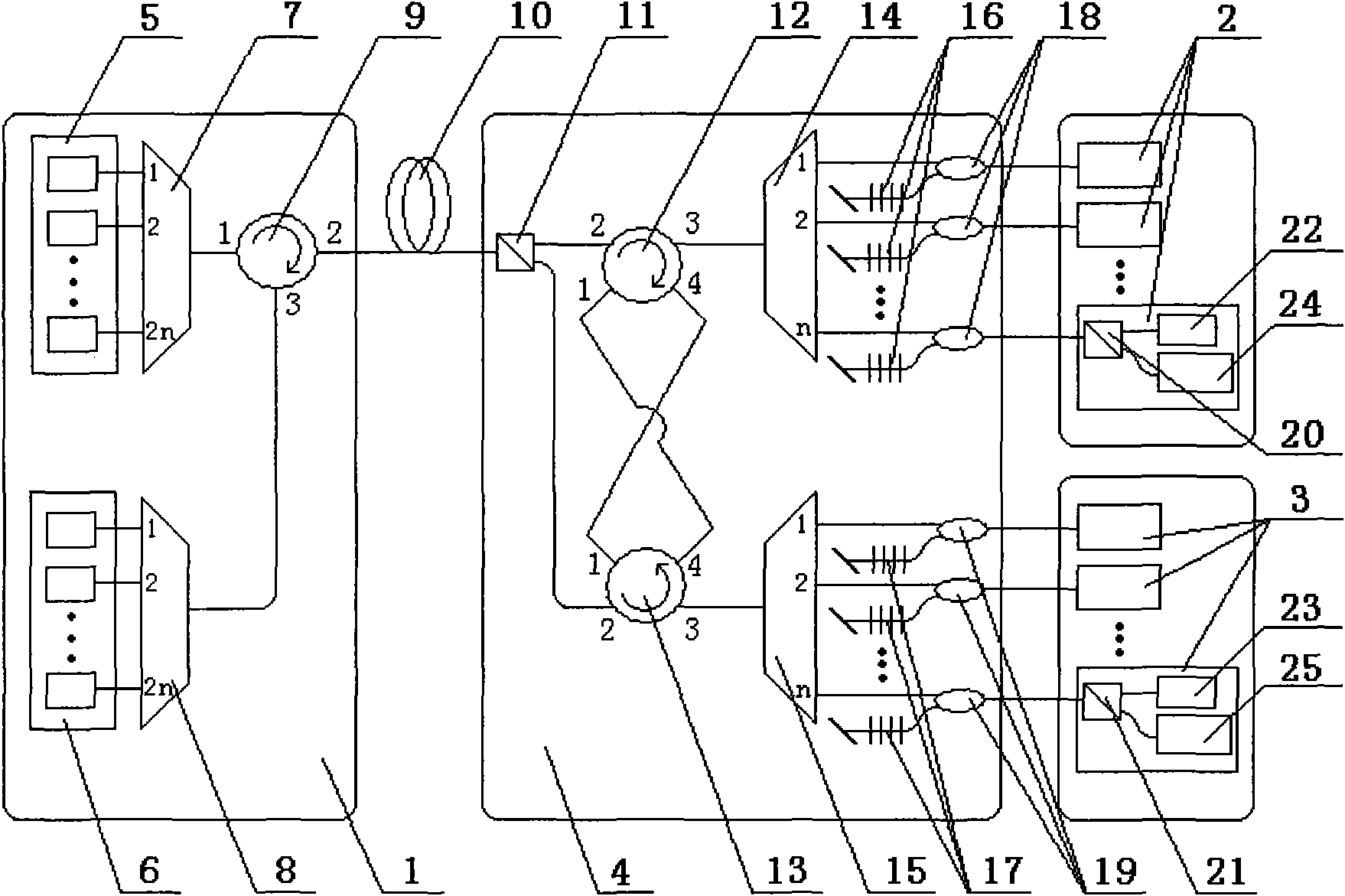
System for realizing wavelength reuse of self-injection wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network and method thereof
InactiveCN101557540AIncrease profitReduce light intensityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberWavelength reuse
The invention relates to a system for realizing wavelength reuse of a self-injection wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network and a method thereof. The system is formed by an optical line terminal OLT connected with remote nodes RN through a feed fiber, and the remote nodes RN connected with a plurality of optical network units ONU, wherein 2n optical network units ONU are divided into a group I of the optical network units ONU and a group II of optical network units ONU, and the number of the optical network units ONU in each group is the same, while uplink signals and downlink signals of two groups of the optical network units ONU are just opposite and do not have interaction with each other; the remote nodes are connected with the two groups of the optical network units ONU respectively and realize downlink signal separation, uplink signal combination and generation and return of seed light of the two groups of the optical network units ONU. The method realizes wavelength reuse by the system, divides the usable wave band into a wave band A and a wave band B, wherein the group I of the optical network units ONU carries the uplink signal and the seed light thereof by the wavelength of the wave band A, carries the downlink signal by the wavelength of the wave band B, while the group II of the optical network units ONU are just the opposite, thereby reusing the uplink signal and the downlink signal of the group I of the optical network units ONU by the group II of the optical network units ONU, not only avoiding that the seed light and the downlink signal cannot be separated by the optical network units ONU due to the fact that the seed light and the downlink signal are in the same wave band and are aliased with each other, but also realizing doubling of the number of the optical units ONU supported by the system and the wavelength utilization ratio.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Filter comprising acoustically coupled resonators
ActiveUS20050212620A1Excessive power densityAcoustic length is increasedPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksResonatorFilter element
A component operating with surface-proximal acoustic waves, in particular a filter with novel structure, has interdigital transducers arranged in serial and parallel branches, which are acoustically coupled with one another in different configurations. The component provides a loss-poor filter with simultaneously space-saving arrangement of the filter elements.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
High-power optical fiber laser
PendingCN107732641AReduce nonlinear effectsAvoid mutual harmOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionGratingRed laser
The invention discloses a high-power optical fiber laser. The laser structurally comprises a residual light collector, a red light / signal light beam combiner, a red light laser, a reverse cladding light mode stripper, a forward pumping pump source module, a forward pumping / signal beam combiner, a high-reflection grating, doped optical fiber, a low-reflection output grating, a reverse pumping / signal beam combiner, a reverse pumping pump source module, a forward cladding light stripper, and output optical fiber with an antireflection film end cap. Based on a linear fabry-perot resonance cavity structure, the forward pumping pump source module and the reverse pumping pump source module, with different wavelengths, provided with narrow-band protection filters are adopted, the forward pumping / signal beam combiner and the reverse pumping / signal beam combiner pump doped optical fiber from the front end and the back end of the doped optical fiber through the high-reflection grating and the low-reflection output grating at the same time, so that multi-kilowatt-class power stable output of the optical fiber laser is achieved, and mutual damage of residual pumping light on two sides to a pumpsource chip is avoided.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
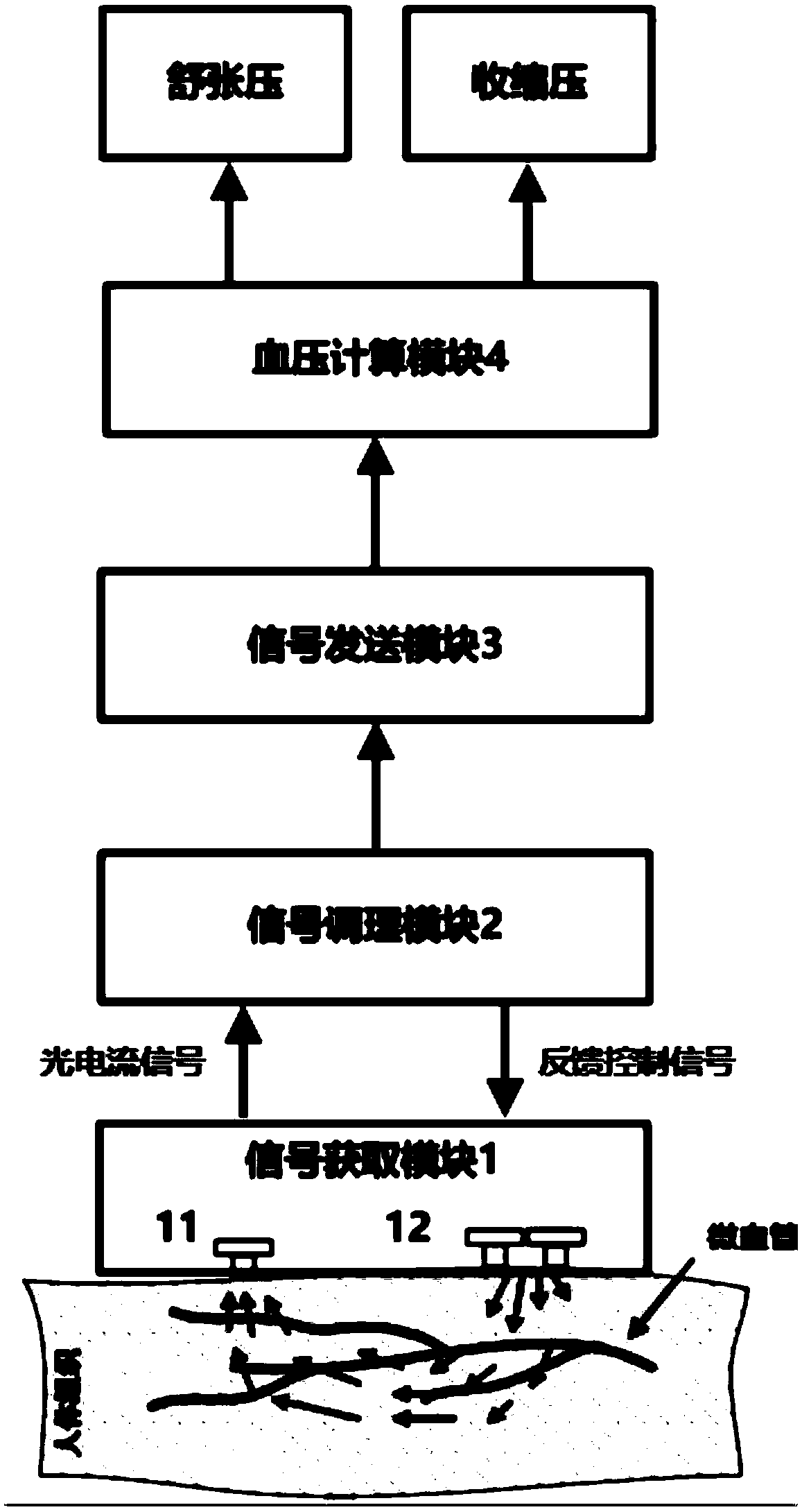
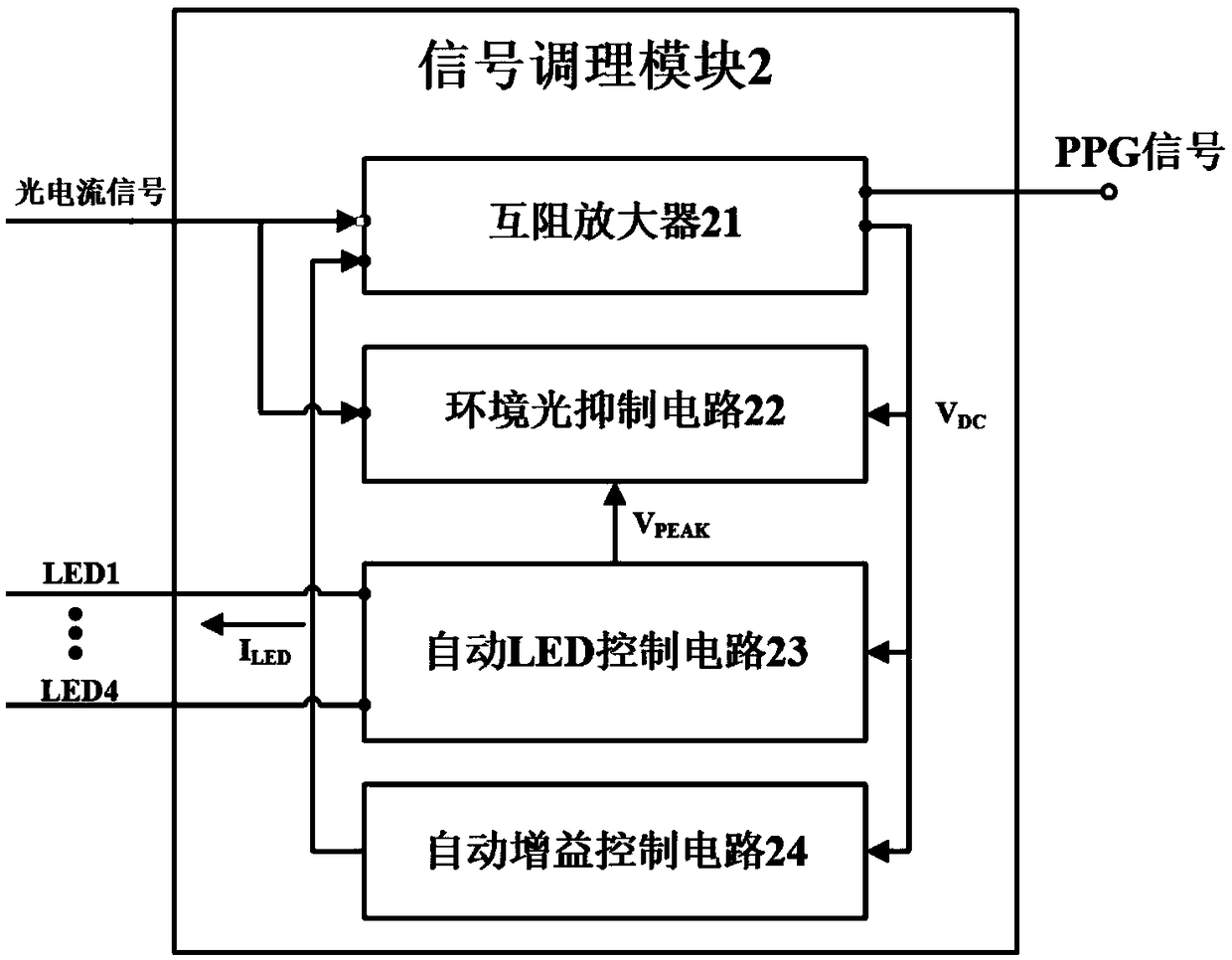
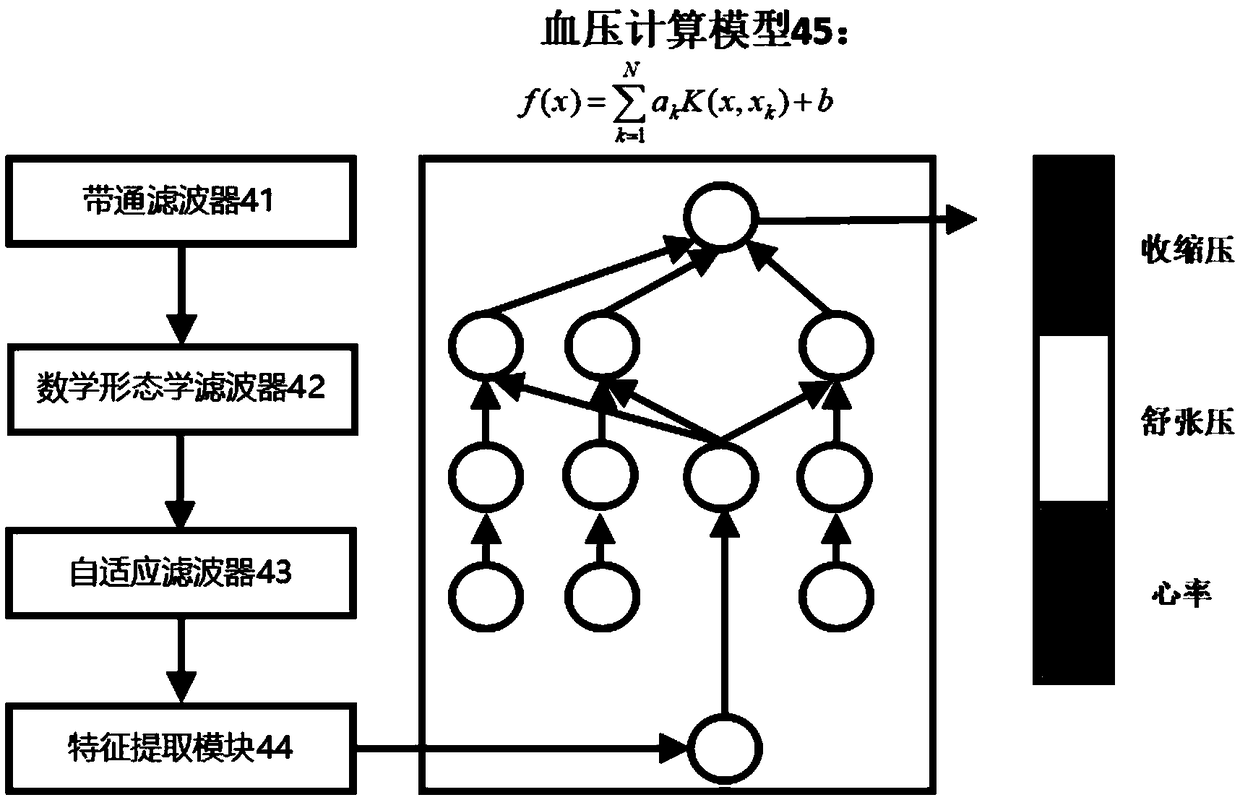
Real-time blood pressure monitoring device based on one-channel PPG signal
InactiveCN108652605AReal-time reflection of blood pressure statusReduce power consumptionEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsEngineeringPhotocurrent
The invention discloses a real-time blood pressure monitoring device based on a one-channel PPG signal. A signal acquisition module illuminates human body tissues and detects the intensity of the reflected light, and outputs a photocurrent signal; a signal modulation module modulates the photocurrent signal and feeds back and controls a light source emitter to obtain PPG voltage signals; a signalsending module samples the PPG voltage signals and sends the PPG voltage signals to a blood pressure calculation module; and the blood pressure calculation module performs filter pre-processing on thePPG voltage signals, and extracts characteristic values into a blood pressure calculation model for calculation to obtain real-time blood pressure and heart rate values. The real-time blood pressuremonitoring device is based on the real-time and continuity of the PPG signals, carries out all-weather blood pressure monitoring, reflects the diurnal variation of blood pressure, diagnoses early hypertension, assists in the identification of primary, secondary and complex hypertension, and has important significance in guiding rational medicine use. The real-time blood pressure monitoring devicehas obvious advantages in device power consumption, monitoring real-time performance and measurement accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fourier transform infrared spectrometer
InactiveUS20060238768A1Reduce the impactReduce impactRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryA d converterAnalog-to-digital converter
A method and apparatus for measuring radiometric signals. An infrared energy signal is directed through a sample and combined with a selected signal to reduce the effect of analog-to-digital converter nonlinearity. The combined signal is processed to, for example, accurately and repeatably identify the types of and concentration of molecules within the sample.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
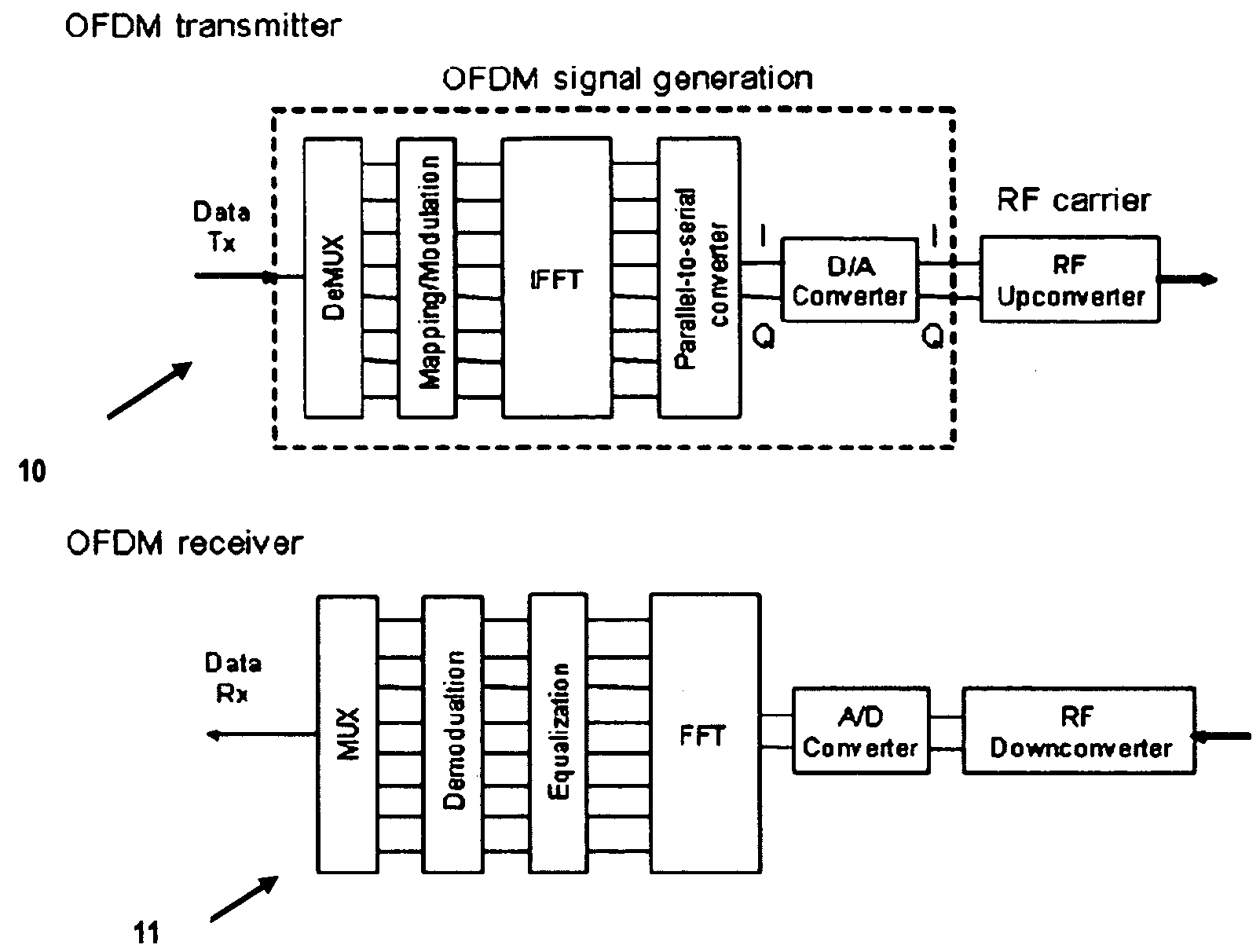
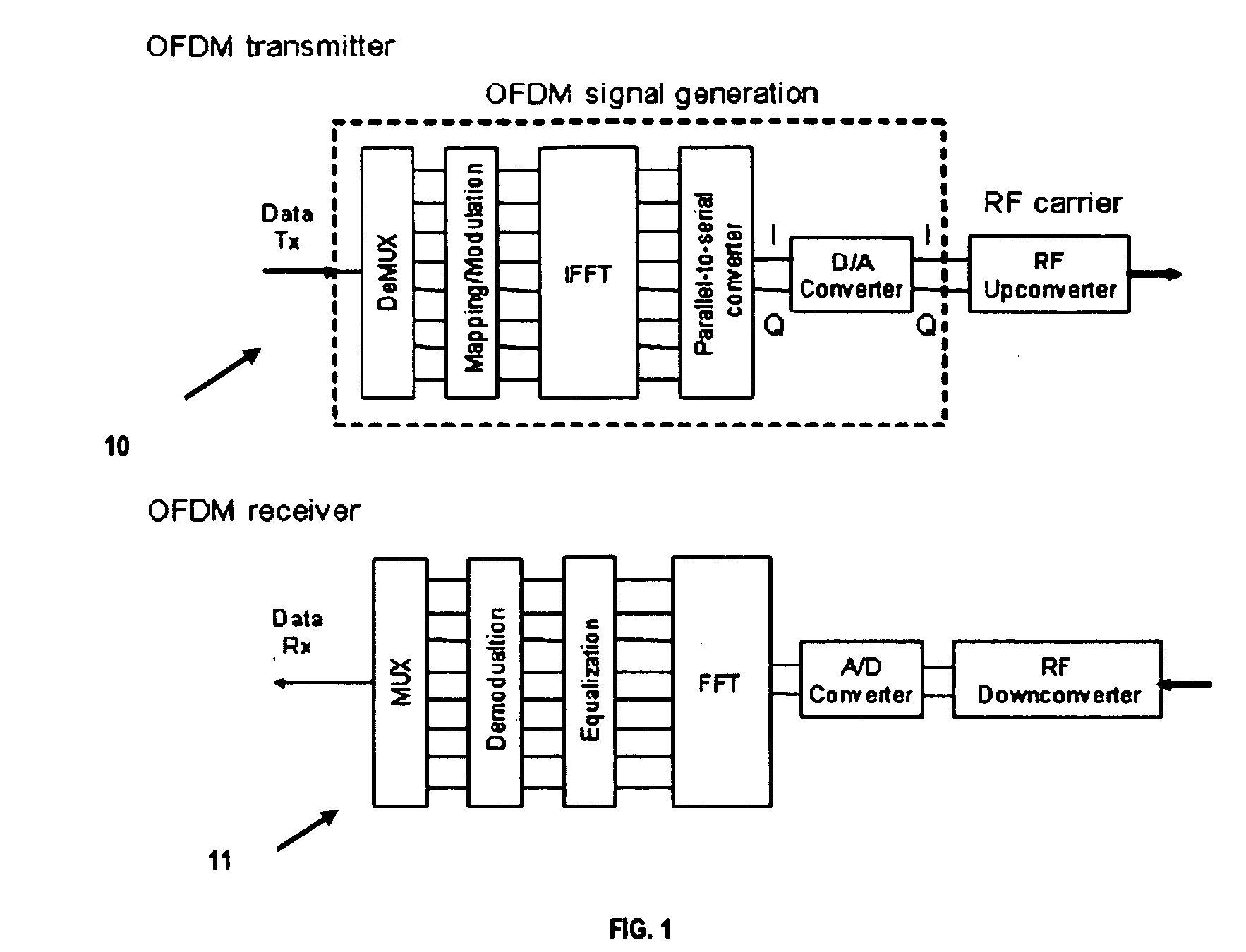
Phase Modulation Of An Optical Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Signal
InactiveUS20100027994A1Reduce effectIncrease of intensity and phase noiseModulated-carrier systemsOptical multiplexCarrier signalPhase modulation
A method includes generating an optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing OFDM signal with in-phase and quadrature-phase components; varying an RF carrier according to the in-phase and quadrature-phase components; and modulating a phase of a lightwave carrier according to the varied RF carrier to generate an optical OFDM signal with equalized amplitude.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
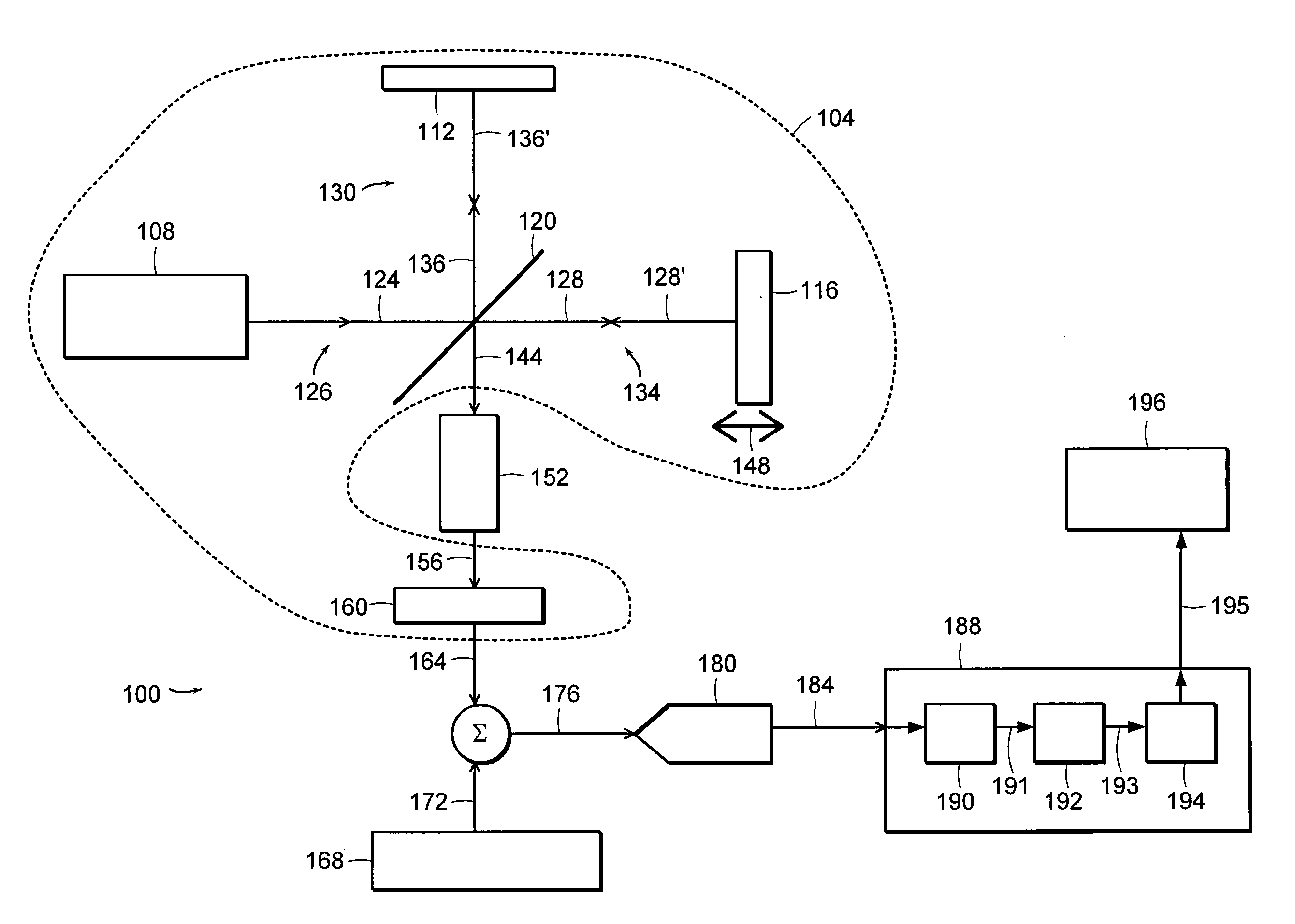
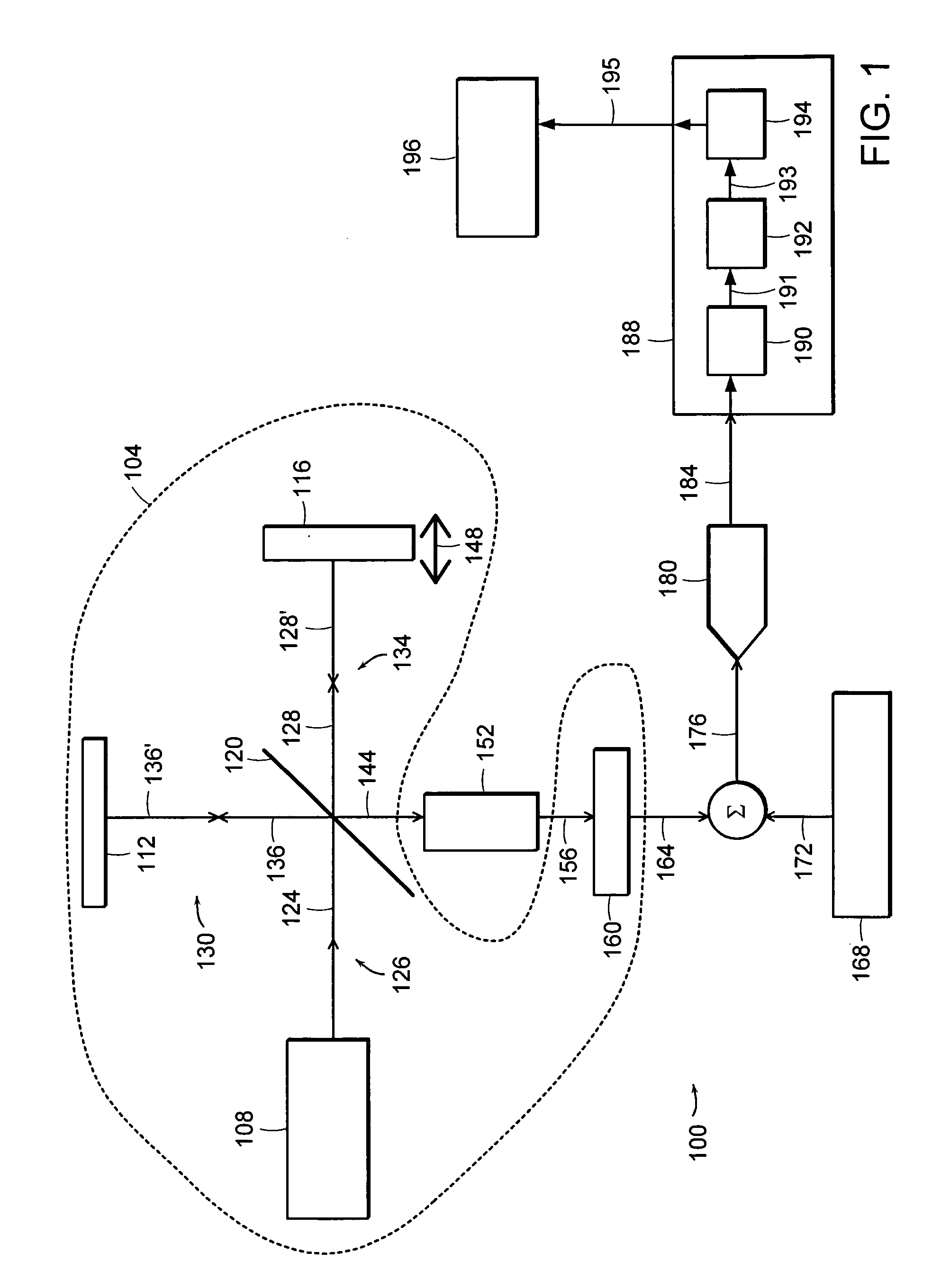
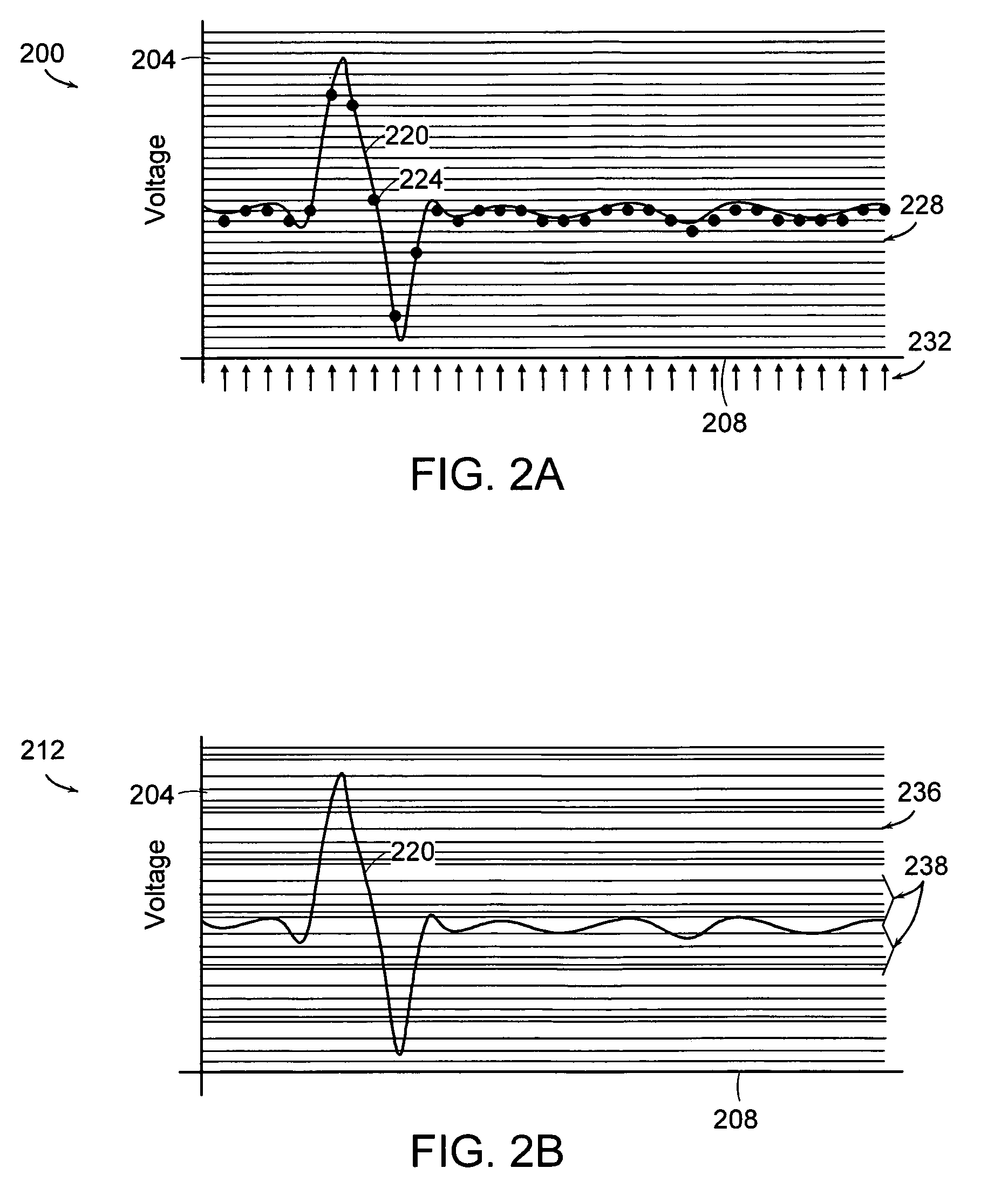
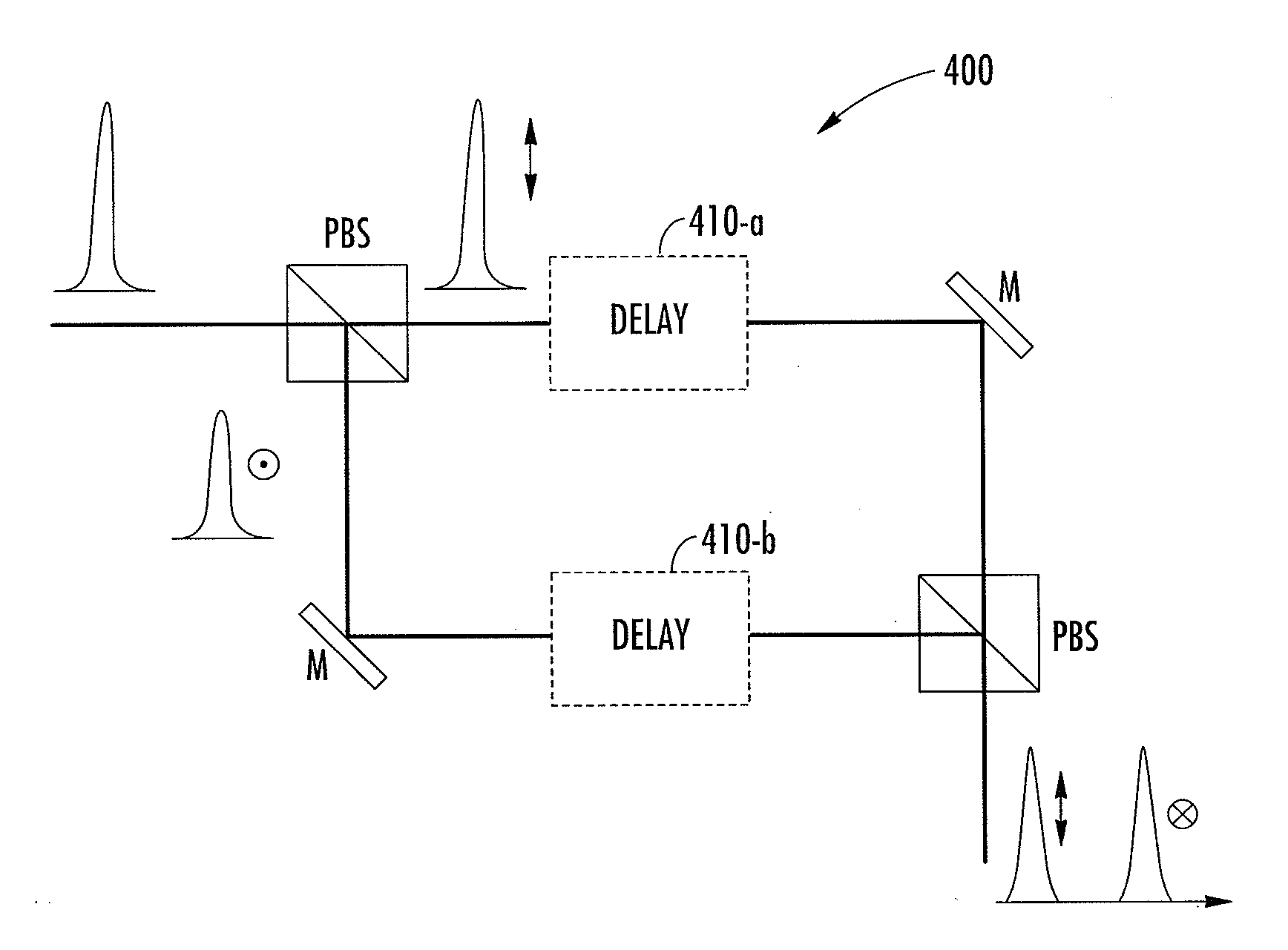
Optical pulse source with increased peak power
ActiveUS20120230353A1Reduce nonlinear pulse distortionAvailable power of pulsedLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionFiberSpectroscopy
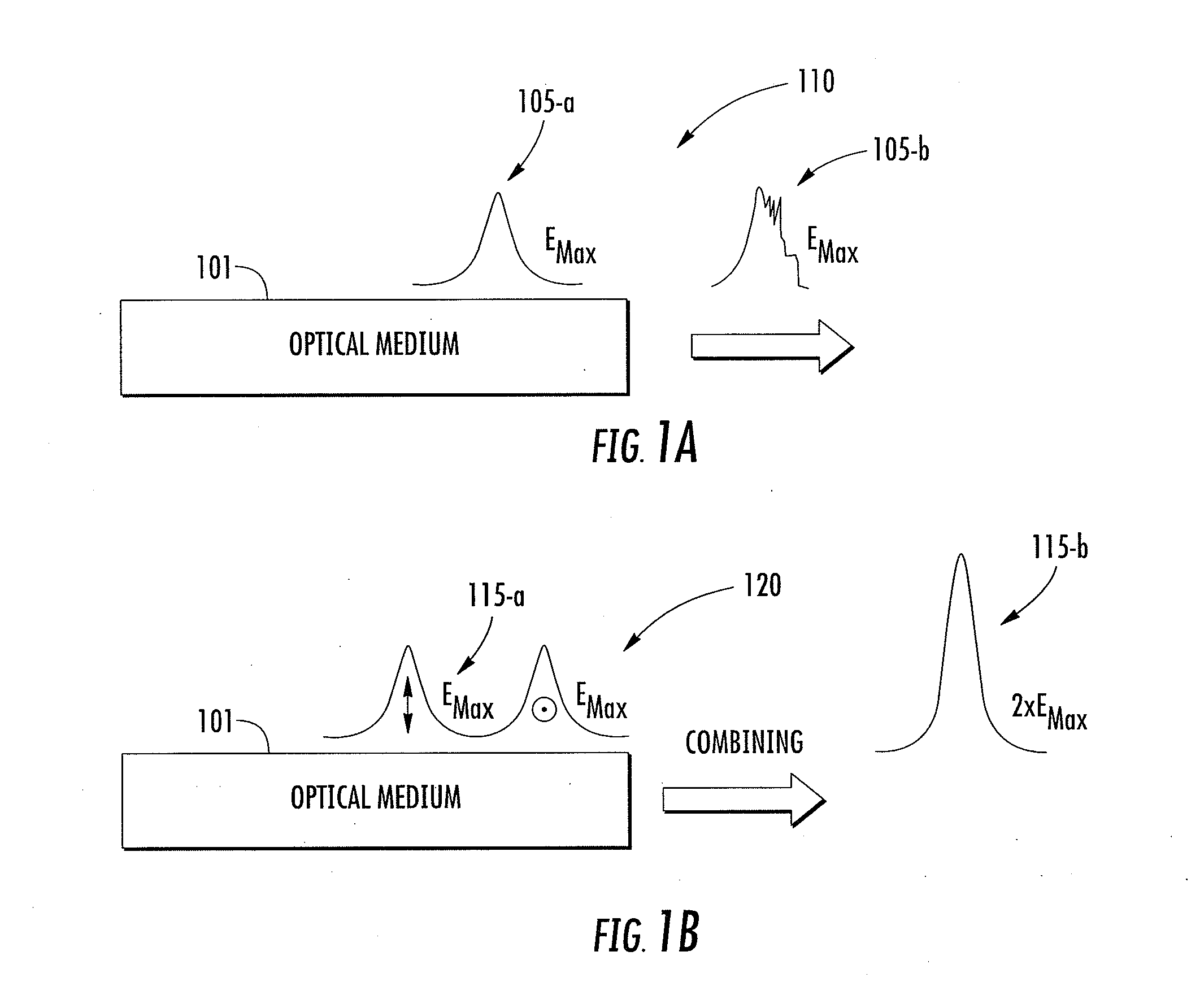
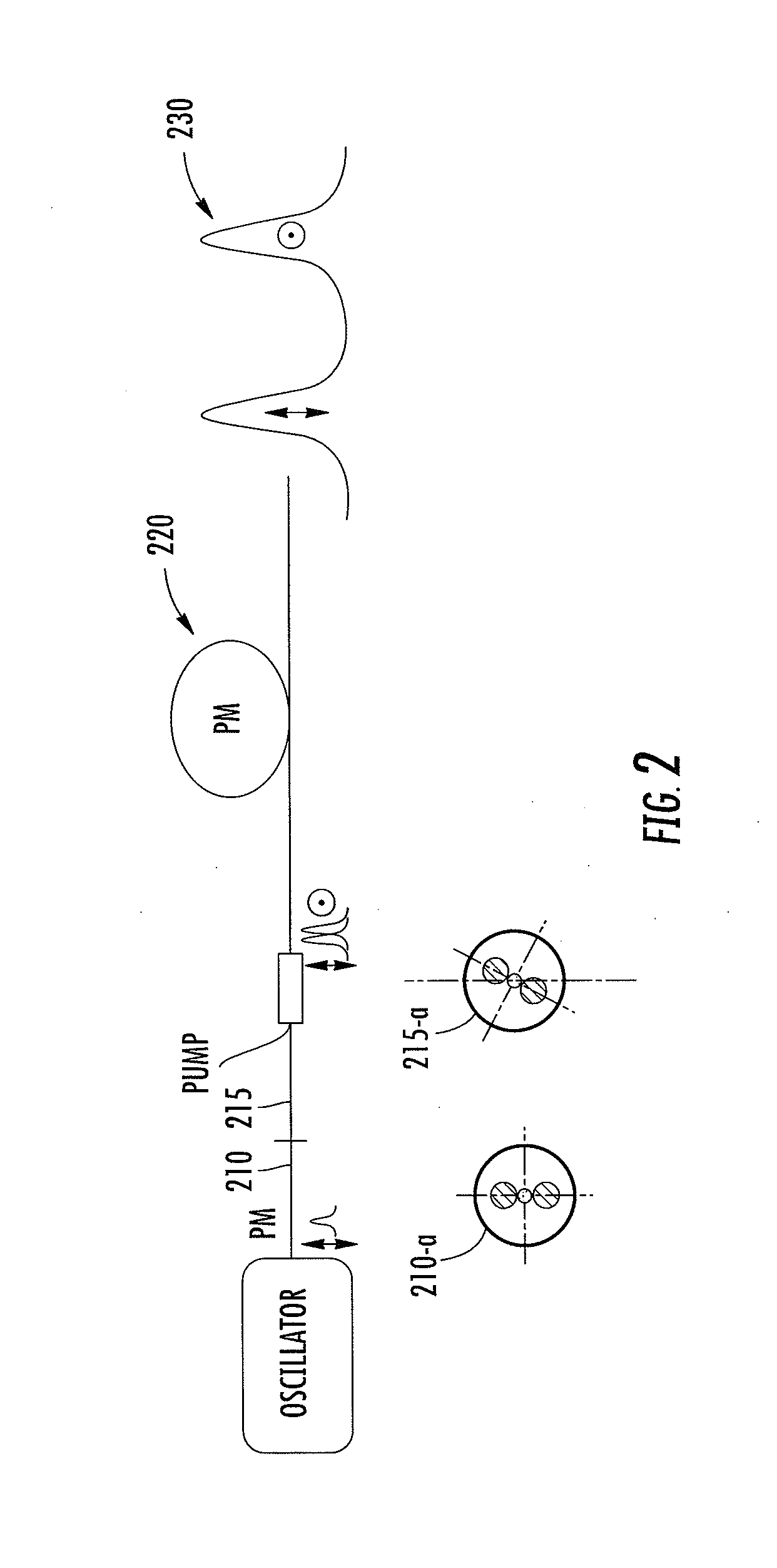
In at least one embodiment time separated pulse pairs are generated, followed by amplification to increase the available peak and / or average power. The pulses are characterized by a time separation that exceeds the input pulse width and with distinct polarization states. The time and polarization discrimination allows easy extraction of the pulses after amplification. In some embodiments polarization maintaining (PM) fibers and / or amplifiers are utilized which provides a compact arrangement. At least one implementation provides for seeding of a solid state amplifier or large core fiber amplifier with time delayed, polarization split pulses, with capability for recombining the time separated pulses at an amplifier output. In various implementations suitable combinations of bulk optics and fibers may be utilized. In some implementations wavelength converted pulse trains are generated. A method and system of the present invention can be used in time domain applications utilizing multiple beam paths, for example spectroscopy.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Modulation format with low sensitivity to fiber nonlinearity
InactiveUS6606176B1Solve narrow bandwidthImprove performanceElectromagnetic transmittersReturn-to-zeroFrequency spectrum
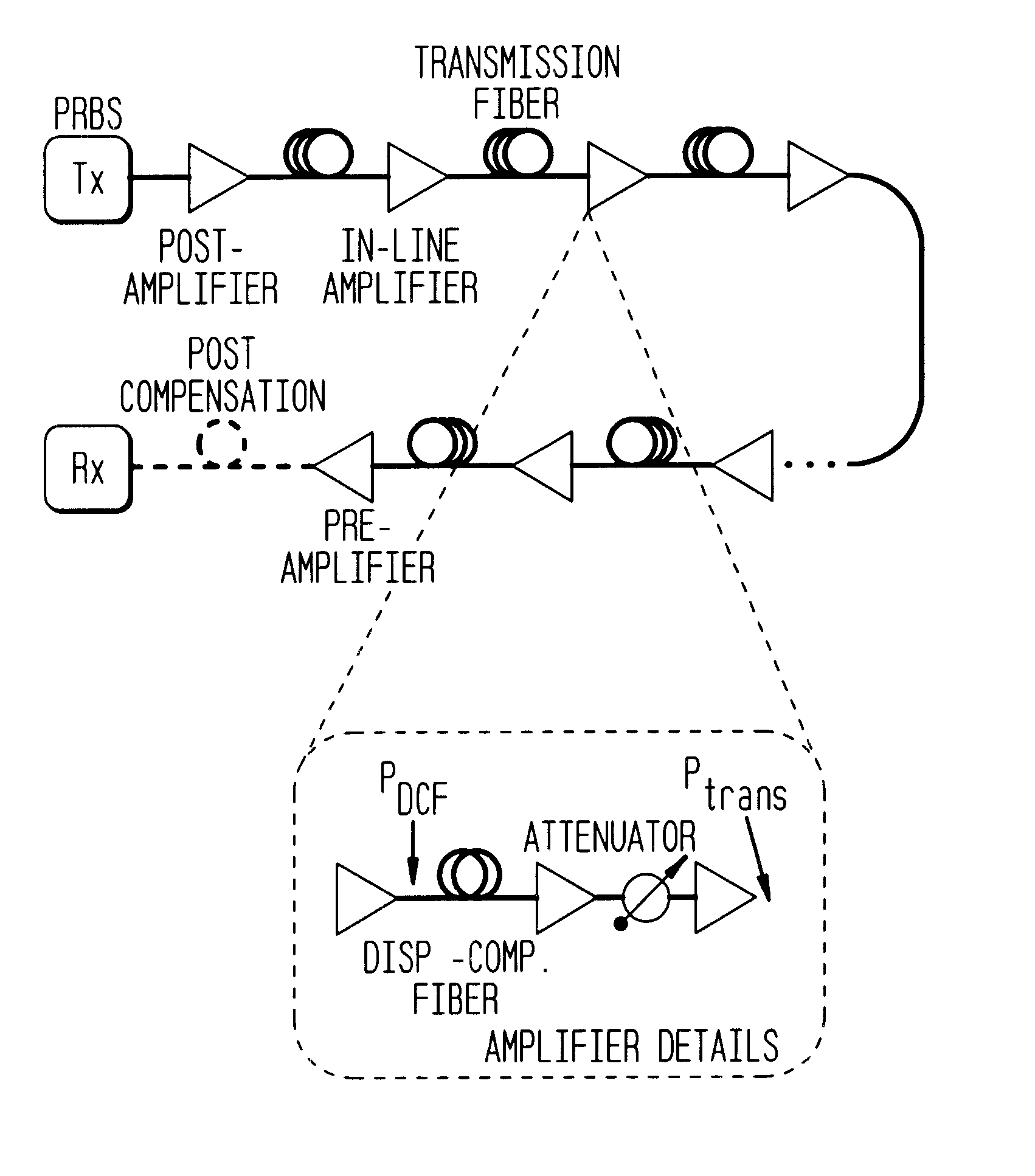
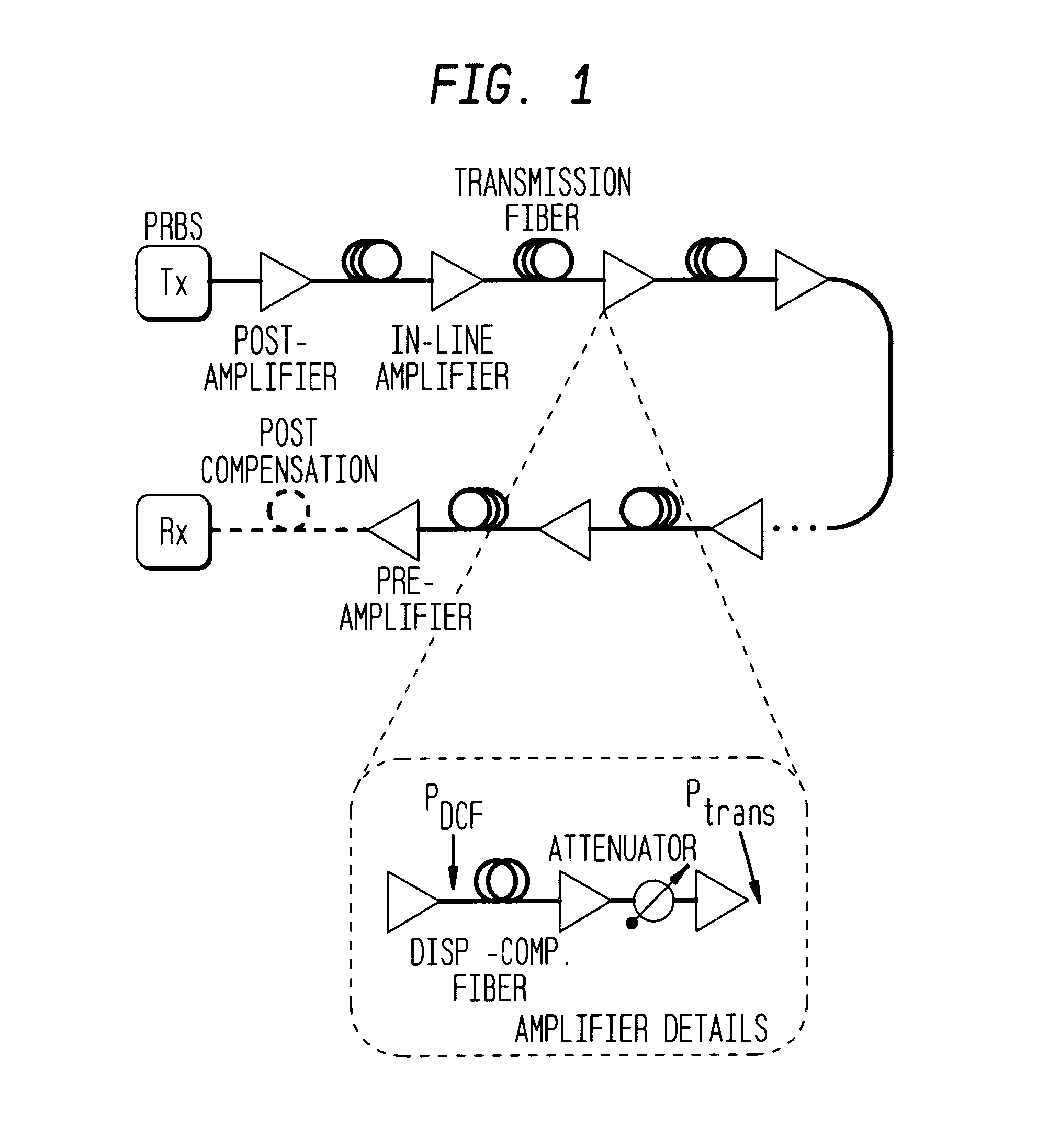
A method for modulating fiber optic transmissions with a low sensitivity to fiber non-linearity utilizes short pulses (typically shorter than 20 ps), and bit rates of 10 Gb / s and higher, to improve performance relative to heretofore known nonlinear transmission with Return-to-Zero (RZ) format implementations. At a base bit rate of 40 Gb / s, a distance determination for achieving 100% cumulative dispersion compensation is made, and a predetermined amount of pre-dispersion compensation is applied based on a determined distance using lower duty cycles for transmission. Higher bit rates (i.e., higher than 40 Gb / s) broaden the spectral bandwidth of the transmission and can result in no pre-dispersion compensation or negative distance pre-dispersion compensation of the same sign as the transmission fiber.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Dynamic gain balancing method and optical transmission system therewith
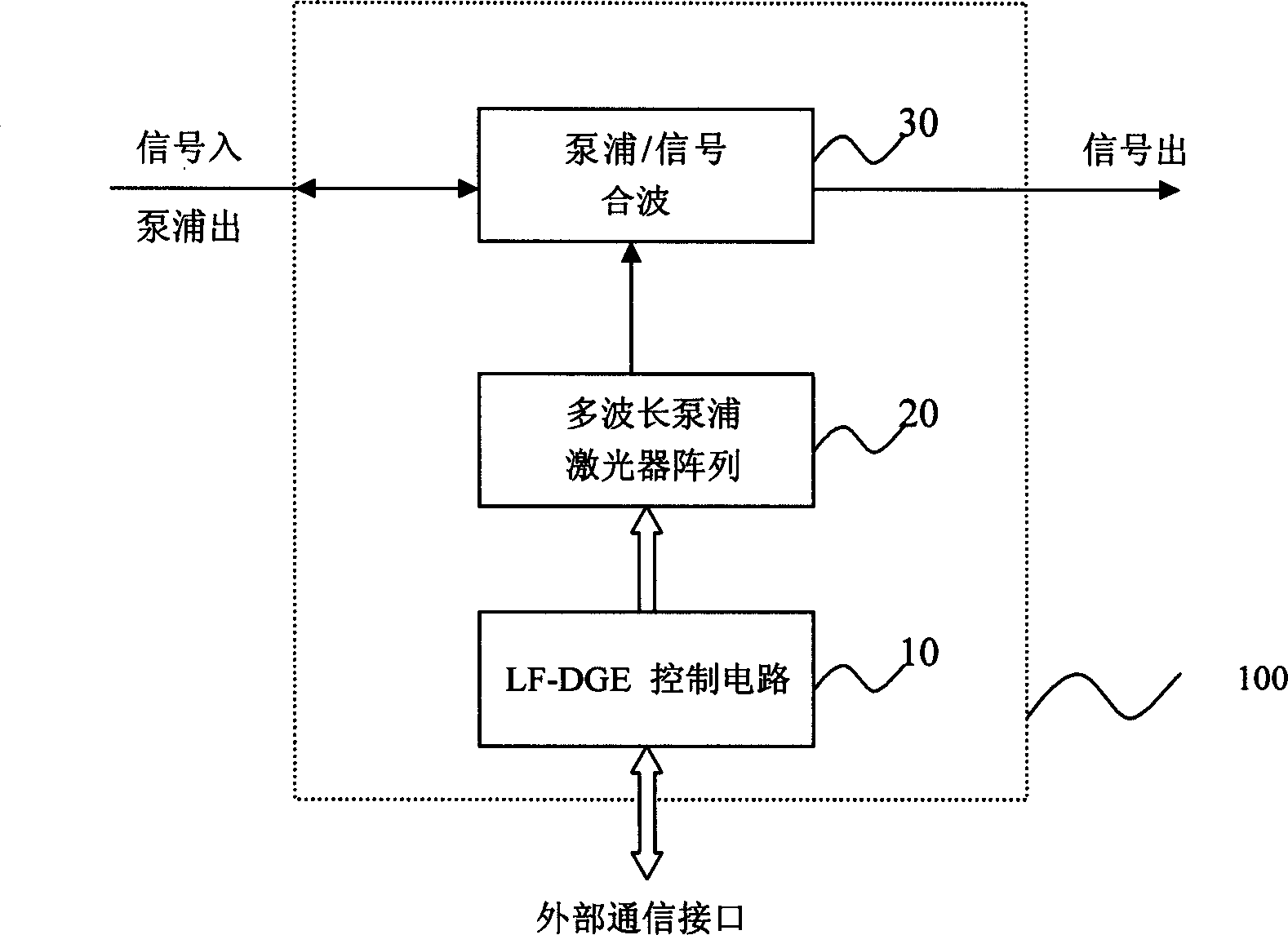
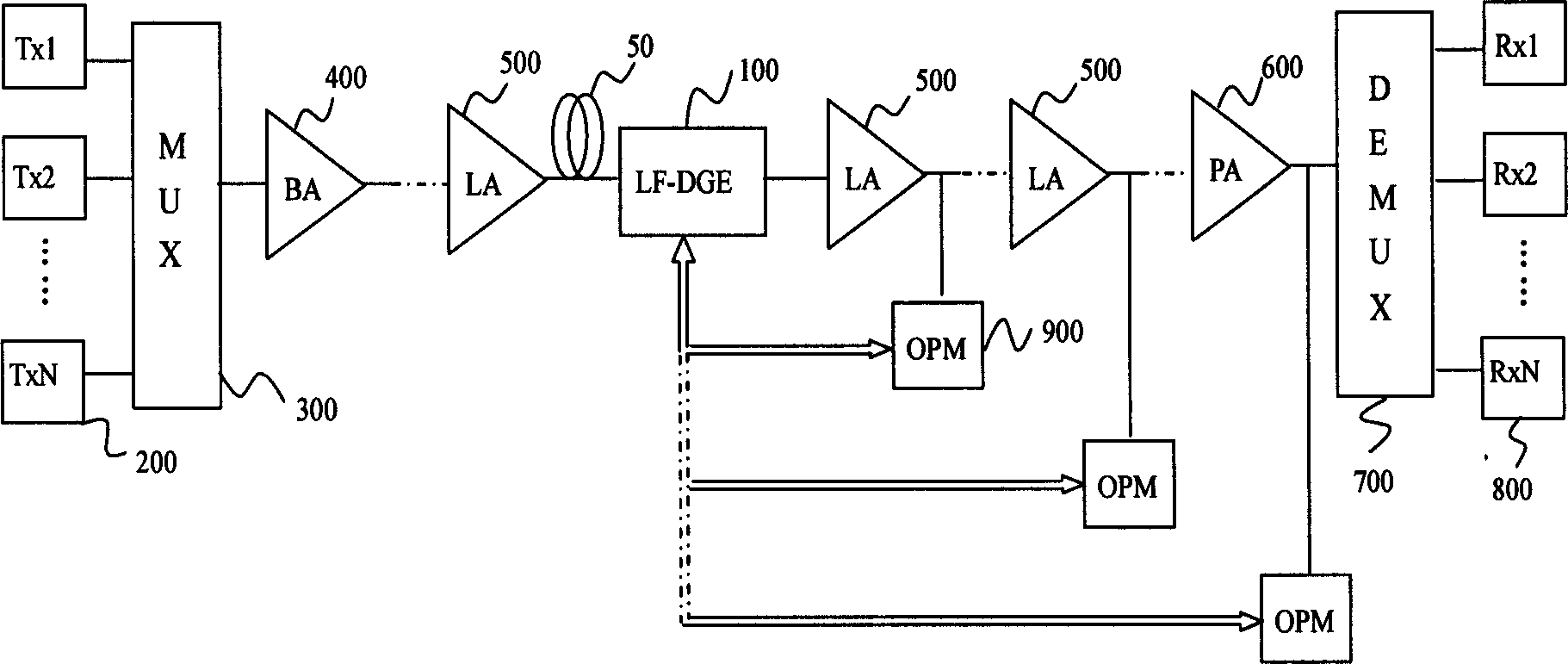
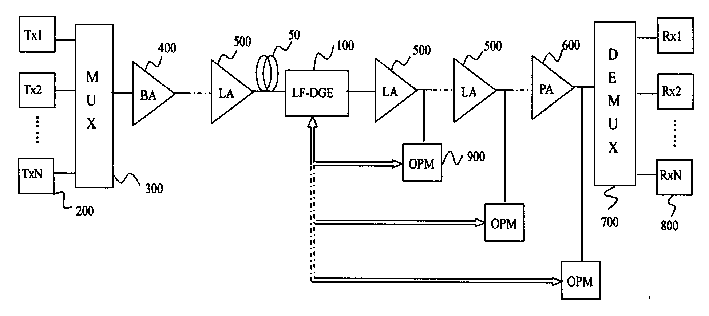
InactiveCN1490970AReduce nonlinear effectsImprove OSNRWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionTransport systemAudio power amplifier
A method protecting wavelength channel used in denseness wavelength division multiplex system of multiway multiplex system and its device, the feature is: in the dense wavelength division multiplex system, the multiplexer (MUX) adds and connects appending multiplexer, the outputting light signal of the multiplex ( MUX ) and the output of backup optics turnable unit (OTU) combine to output through the appending multiplexer, the appending multiplexer and relevant demultiplexer (DEMUX) take optics turnable unit (OTU) as backup protecting unit for system wavelength channel, the above statement demultiplexer ( DEMUX ) can add and connect appending demultiplexer to receive the signal from appending multiplexer, the appending multiplexer and appending demultiplexer take the optics turnable unit (OTU) as backup protecting unit for system wavelength channel. This invention has high utilization for wavelength resources.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Fiber lasers for producing amplified laser pulses with reduced non-linearity
ActiveUS20120217375A1Shorten fiber lengthMinimize nonlinear effectSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansGratingFiber Bragg grating
Owner:CALMAR OPTCOM
Portable laser deruster
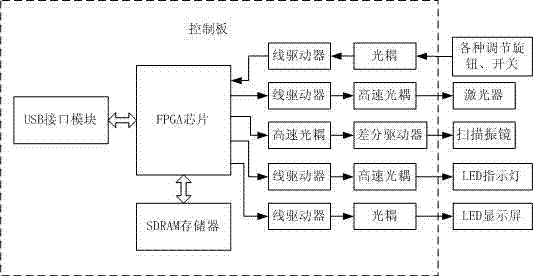
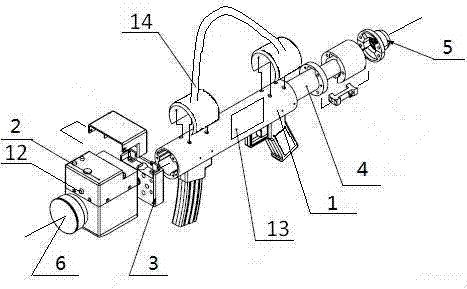
ActiveCN103878486AReduce pollutionHigh precisionLaser beam welding apparatusGalvanometerOptoelectronics
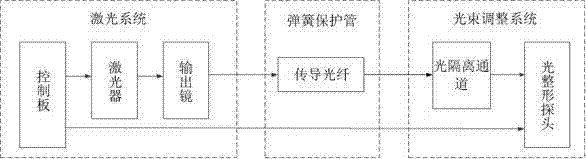
The invention discloses a portable laser deruster. The portable laser deruster comprises a laser system, a light beam adjusting system and a conductive fiber. The laser system is connected with the light beam adjusting system through the conductive fiber. The laser system comprises a main case, a laser device, a control plate and an output mirror, wherein the main case is provided with straps, and the laser device is located in the main case. The corresponding output end of the control plate is connected with a data interface of the laser device. The output end of the laser device is provided with the output mirror. The light beam adjusting system comprises an optical isolation channel and an optical reshaping probe. The optical isolation channel comprises an optical channel shell and an isolation sleeve, wherein the optical channel shell is provided with a handle, and the isolation sleeve is arranged in the optical channel shell. A clamping ring is arranged at one end of the optical channel shell, and the other end of the optical channel shell is connected with the optical reshaping probe. A beam expansion mirror, a scanning galvanometer and a light condensation system are sequentially arranged in the optical reshaping probe in the direction from the junction between the optical reshaping probe and the optical channel shell. The light condensation system comprises a mirror bracket, an F-Q field lens ring and an F-Q lens. The portable laser deruster has the advantages of being simple in structure, convenient to use, safe, and stable, thereby being beneficial to field operation.
Owner:ORDNANCE TECH RES INST OF THE GENERAL ARMAMENT DEPT PLA
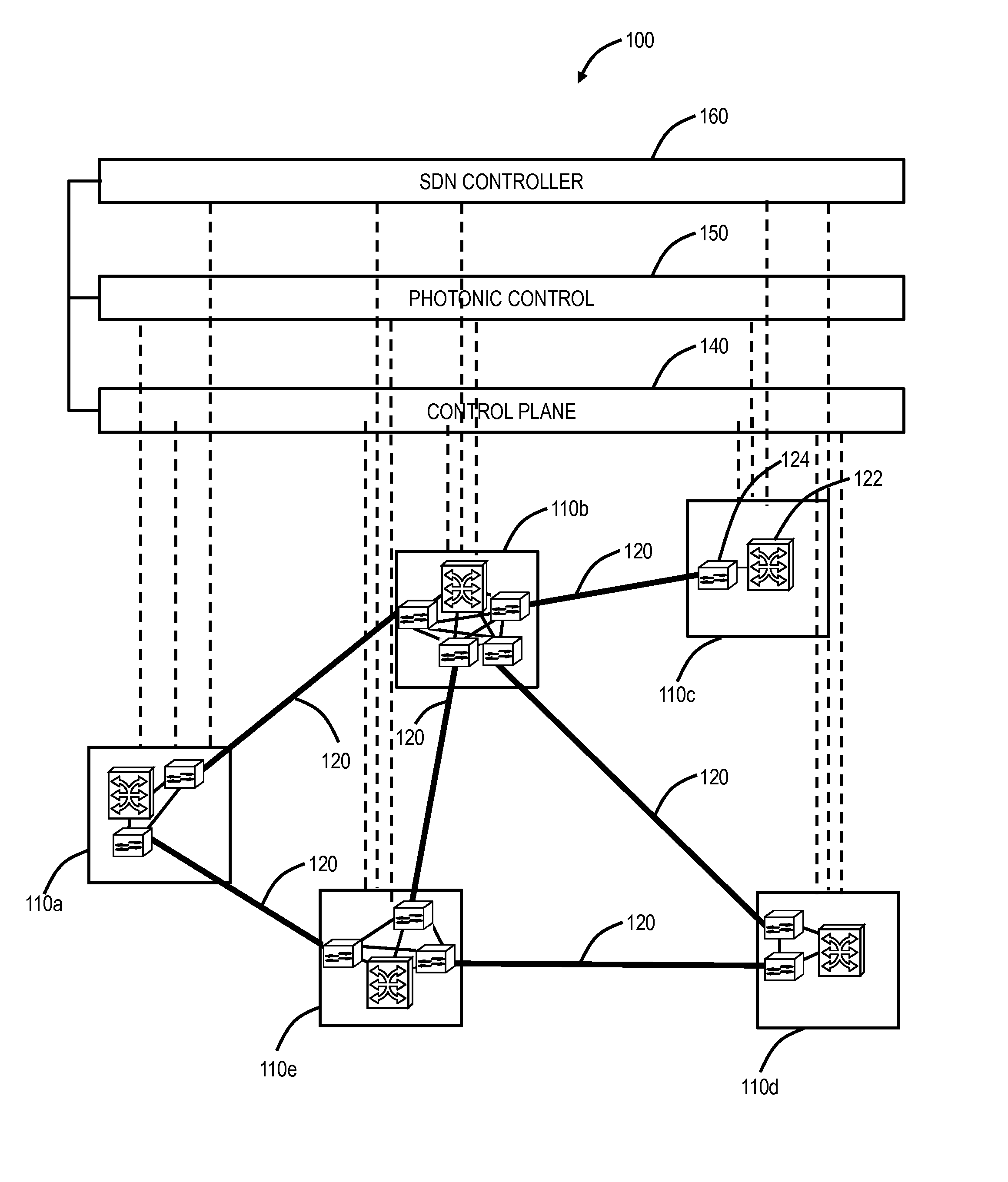
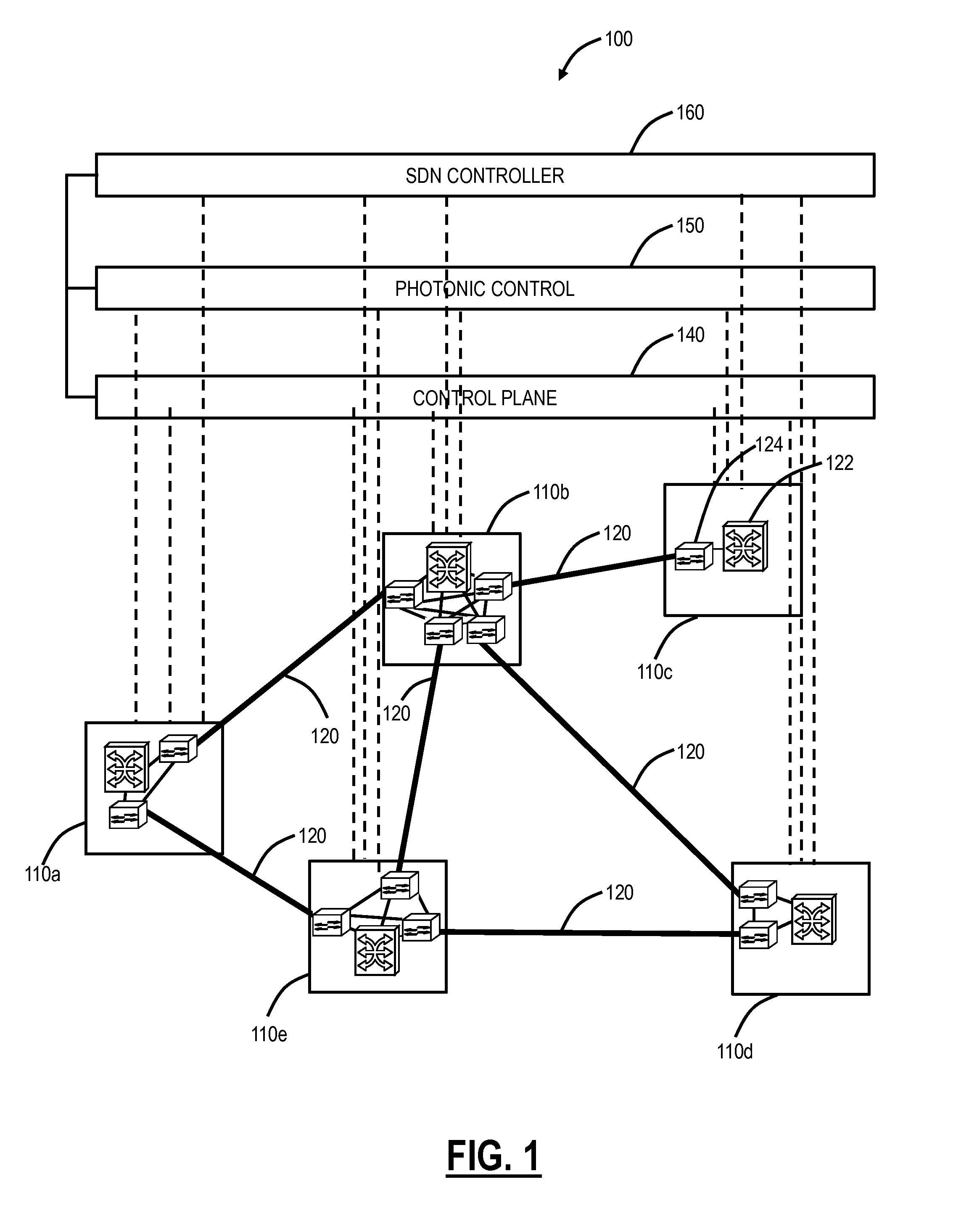
Margin-based optimization systems and methods in optical networks to unblock superchannels
ActiveUS20150333864A1Reduce marginOptimize capacityWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignalling characterisationOptimization systemEdge based
Systems and methods of increasing the supportable capacity from a first point to a second point in an optical network, include identifying a first optical signal that occupies a first portion of optical spectrum from the first point to the second point; identifying a second optical signal that occupies a second portion of the optical spectrum from the first point to the second point, wherein the second portion is adjacent to the first portion; adjusting the second optical signal to minimize part of or remove all of the second portion that is adjacent to the first optical signal to provide a freed up portion of the second portion; and adjusting the first optical signal to occupy some or all of the freed up portion.
Owner:CIENA
Tunable ytterbium-doping double-clad fiber mode-locked laser
InactiveCN103022860AFilter bandwidth adjustableLarge wavelength tuning rangeActive medium shape and constructionFiberGrating
The invention discloses a tunable ytterbium-doping double-clad fiber mode-locked laser which belongs to the technical field of lasers. The tunable ytterbium-doping double-clad fiber mode-locked laser is in an annular cavity structure, takes a large-core diameter double-clad ytterbium-doping fiber as a gain medium and works on a total positive dispersion area. The tunable ytterbium-doping double-clad fiber mode-locked laser realizes the mode locking self-starting and stably carries out mode locking by dint of a nonlinear polarization rotation technology and a spectrum filter, is adjustable in filtering bandwidth because the spectrum filter comprises a grating and a slit with adjustable width, has a tuning function and can continuously tune the center wavelength of an output pulse within a gain bandwidth range. The tunable ytterbium-doping double-clad fiber mode-locked laser disclosed by the invention realizes the total positive dispersion mode locking of the large-core diameter double-clad fiber by adopting nonlinear polarization rotation and a spectrum filter technology, obtains the ultrashort-pulse laser output supporting high power and high single-pulse energy, is continuously tunable in center wavelength and is convenient to operate and large in tuning range by composing the spectrum filter by adopting the grating and the slit.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com