Patents
Literature
666 results about "Return-to-zero" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
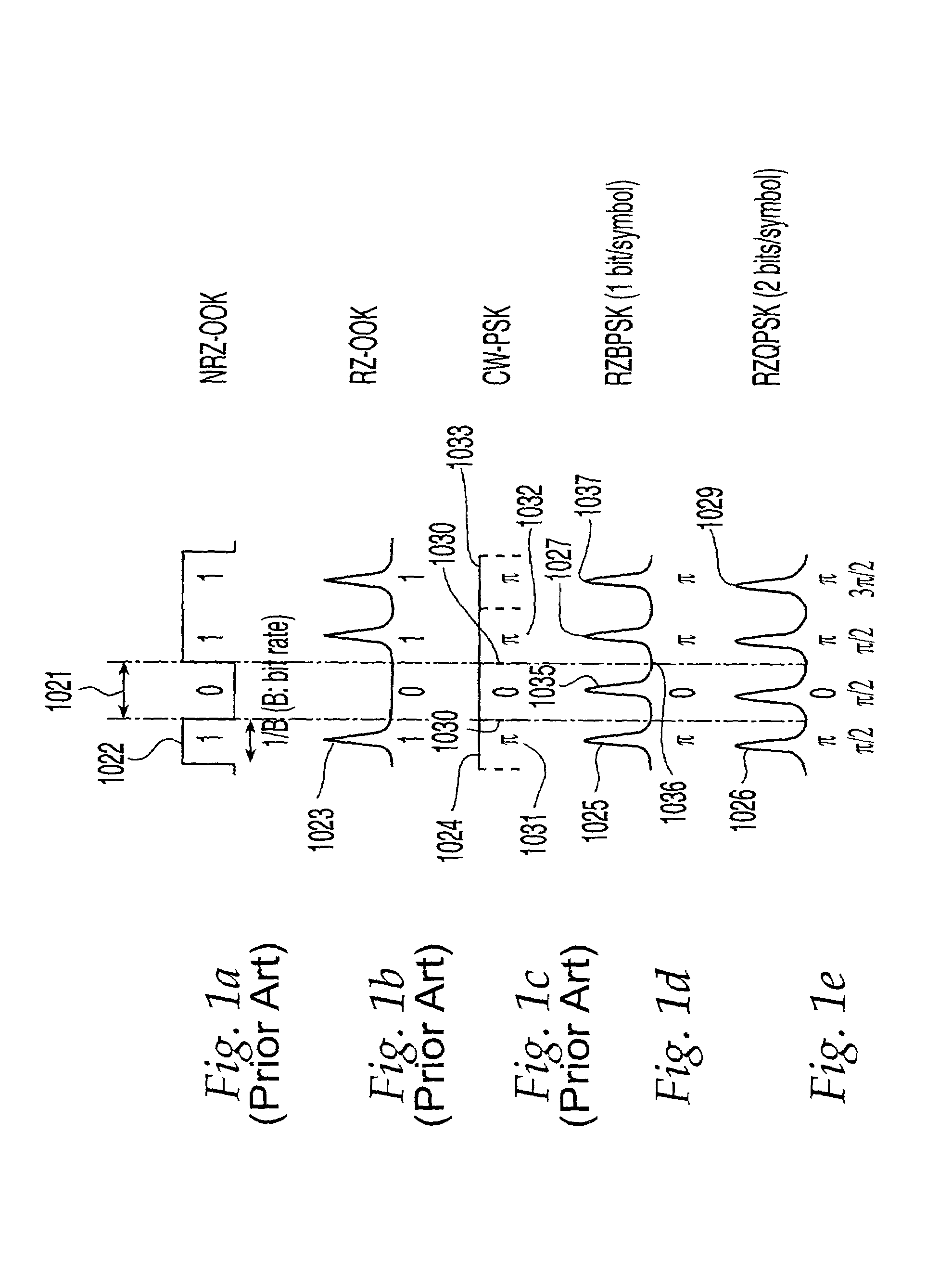
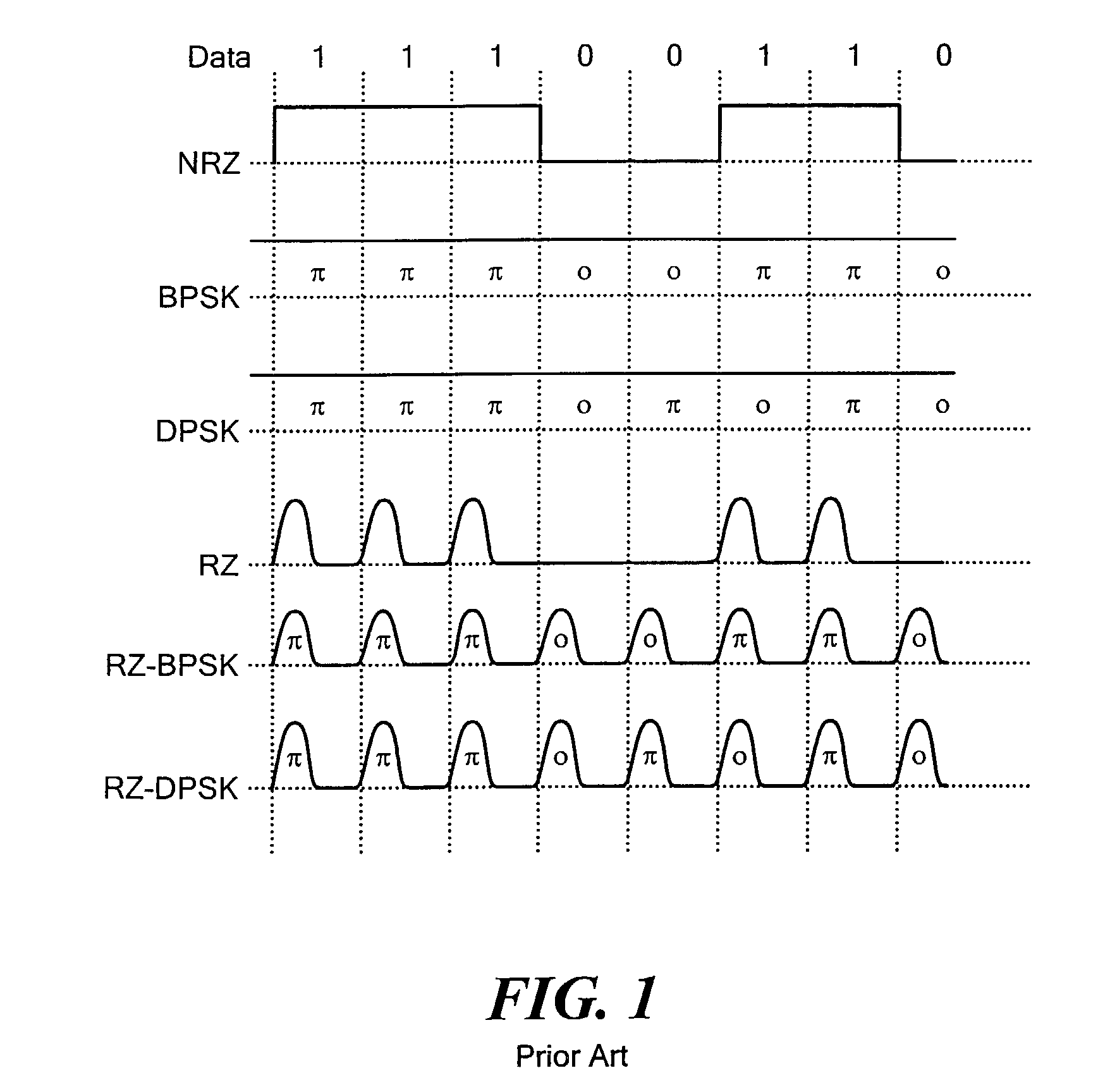
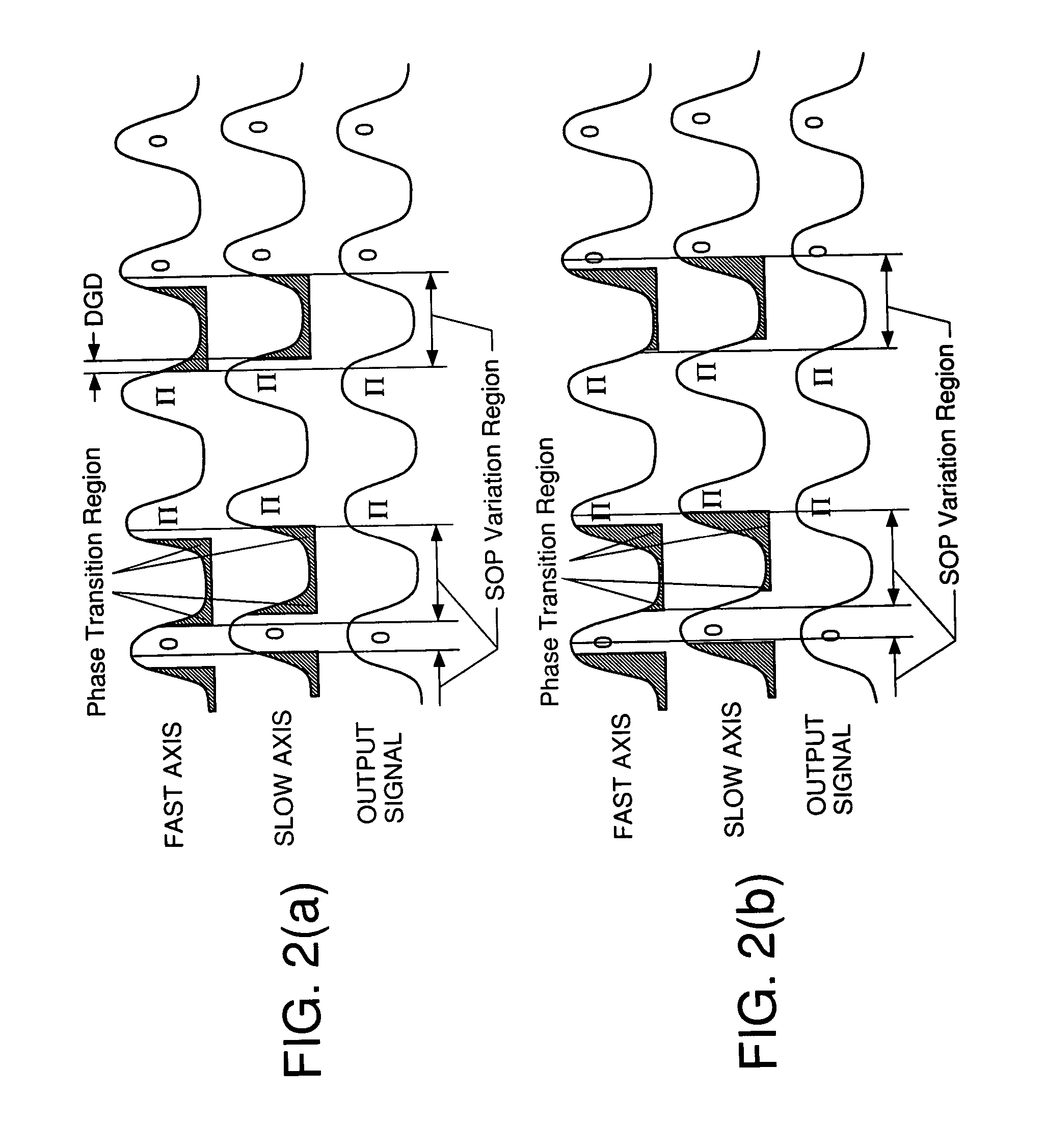
Return-to-zero (RZ or RTZ) describes a line code used in telecommunications signals in which the signal drops (returns) to zero between each pulse. This takes place even if a number of consecutive 0s or 1s occur in the signal. The signal is self-clocking. This means that a separate clock does not need to be sent alongside the signal, but suffers from using twice the bandwidth to achieve the same data-rate as compared to non-return-to-zero format.
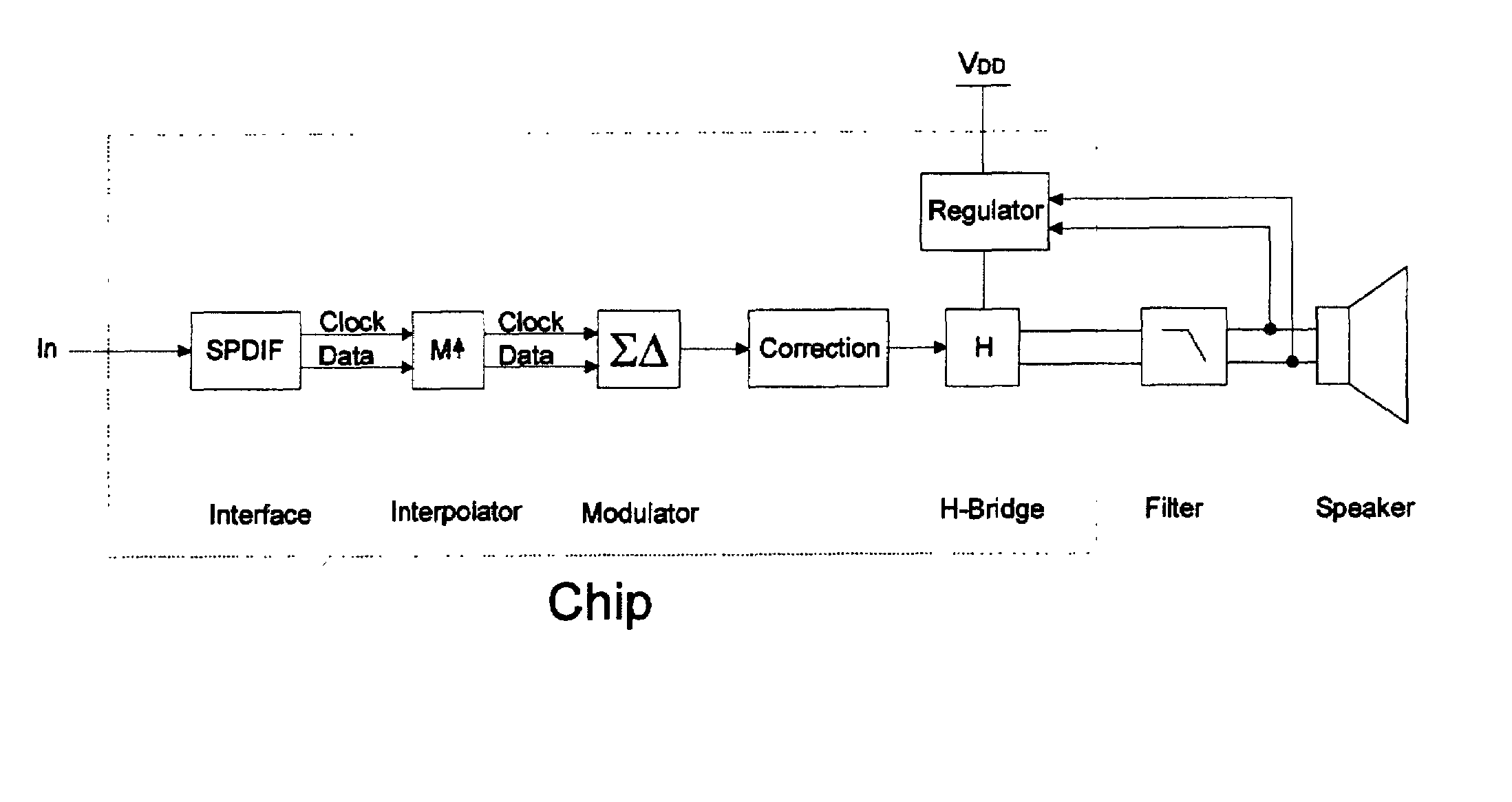
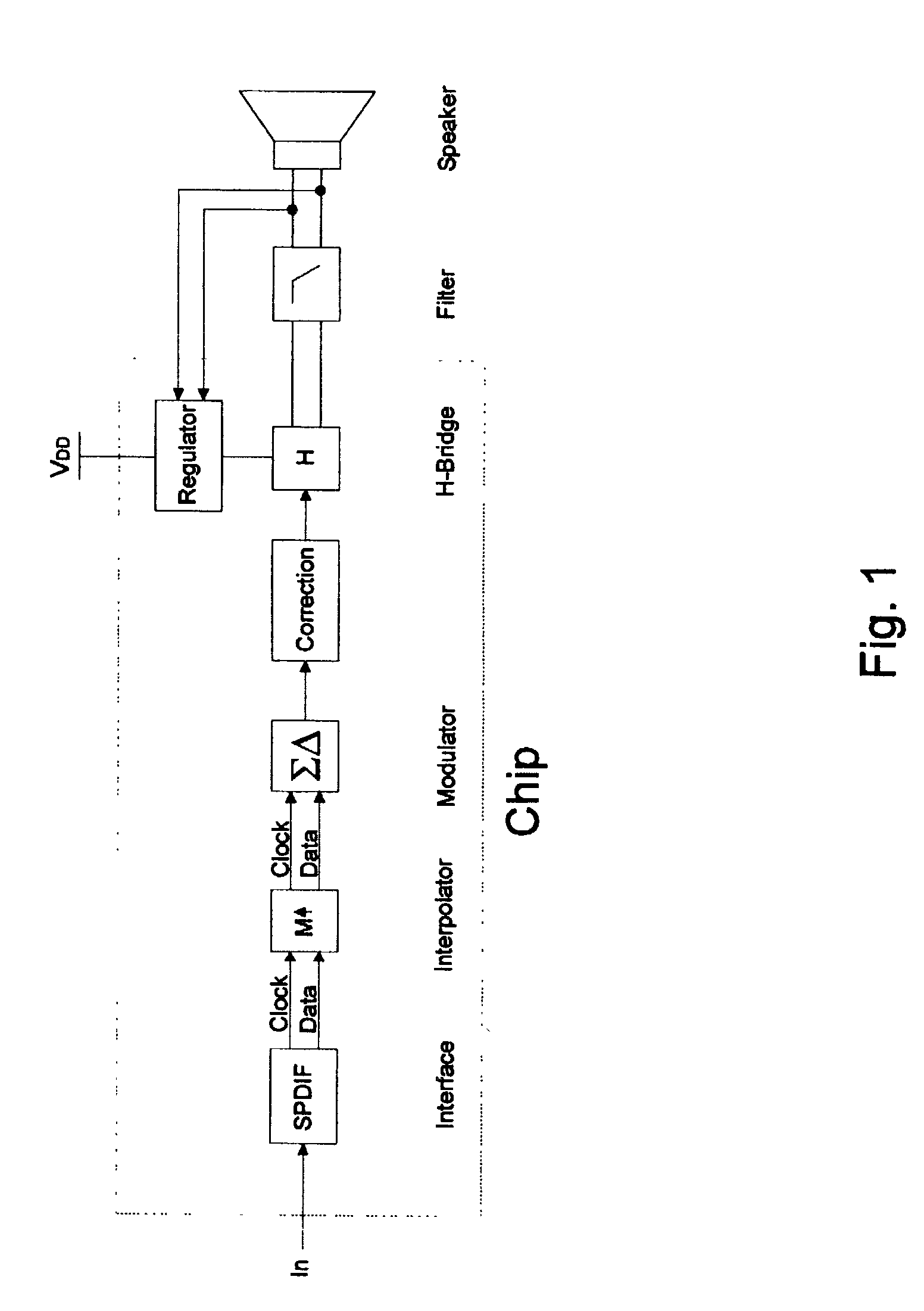
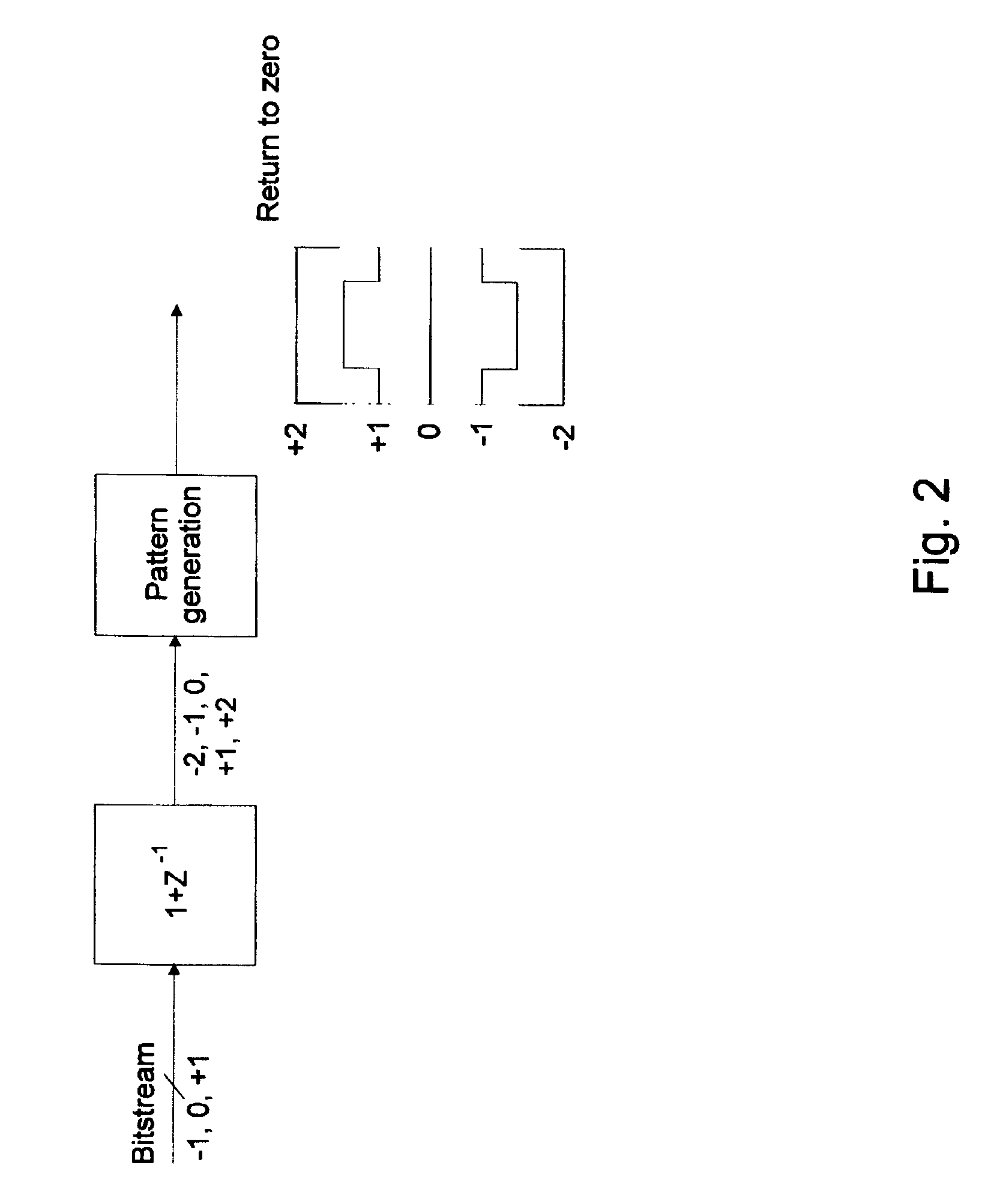
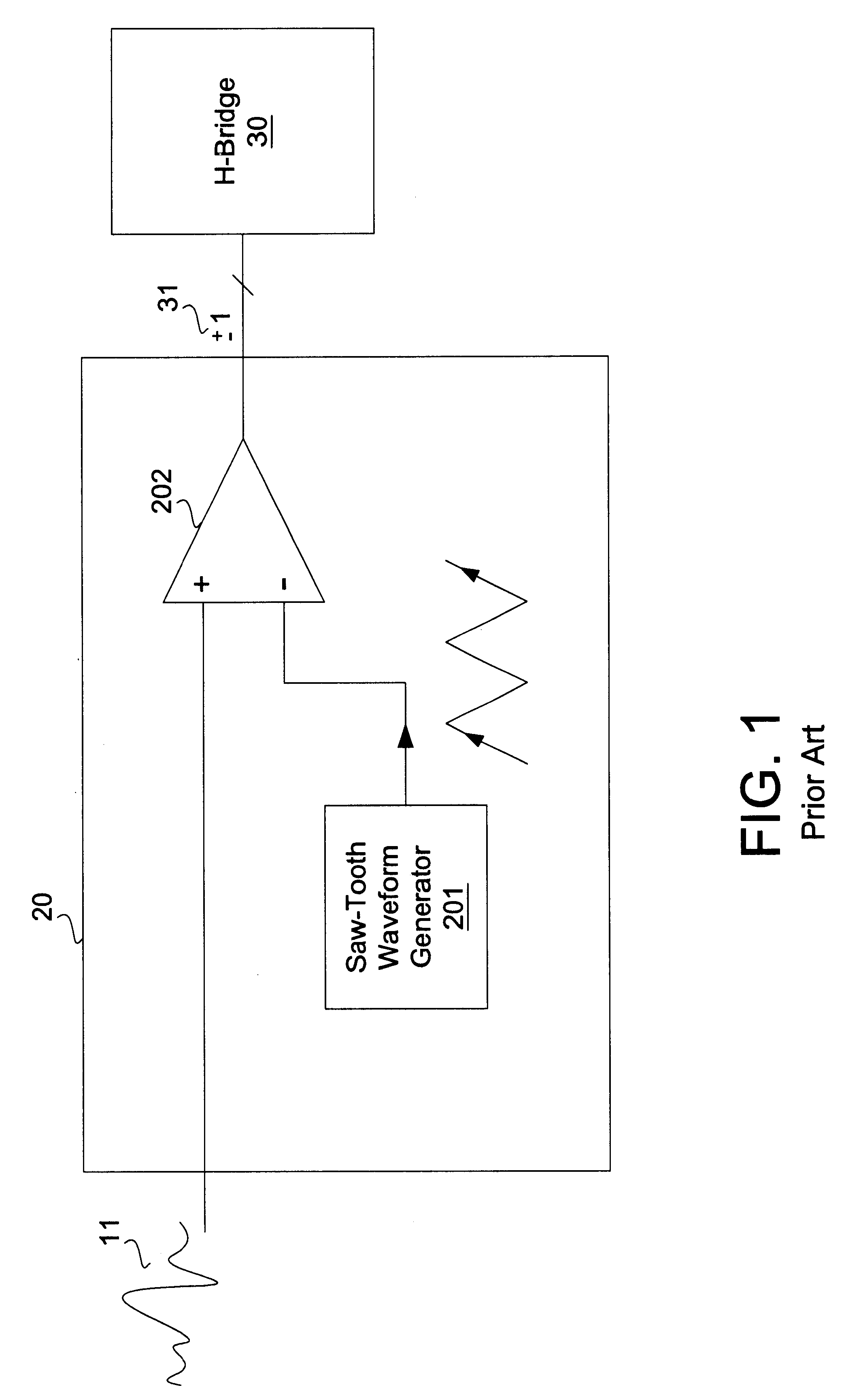
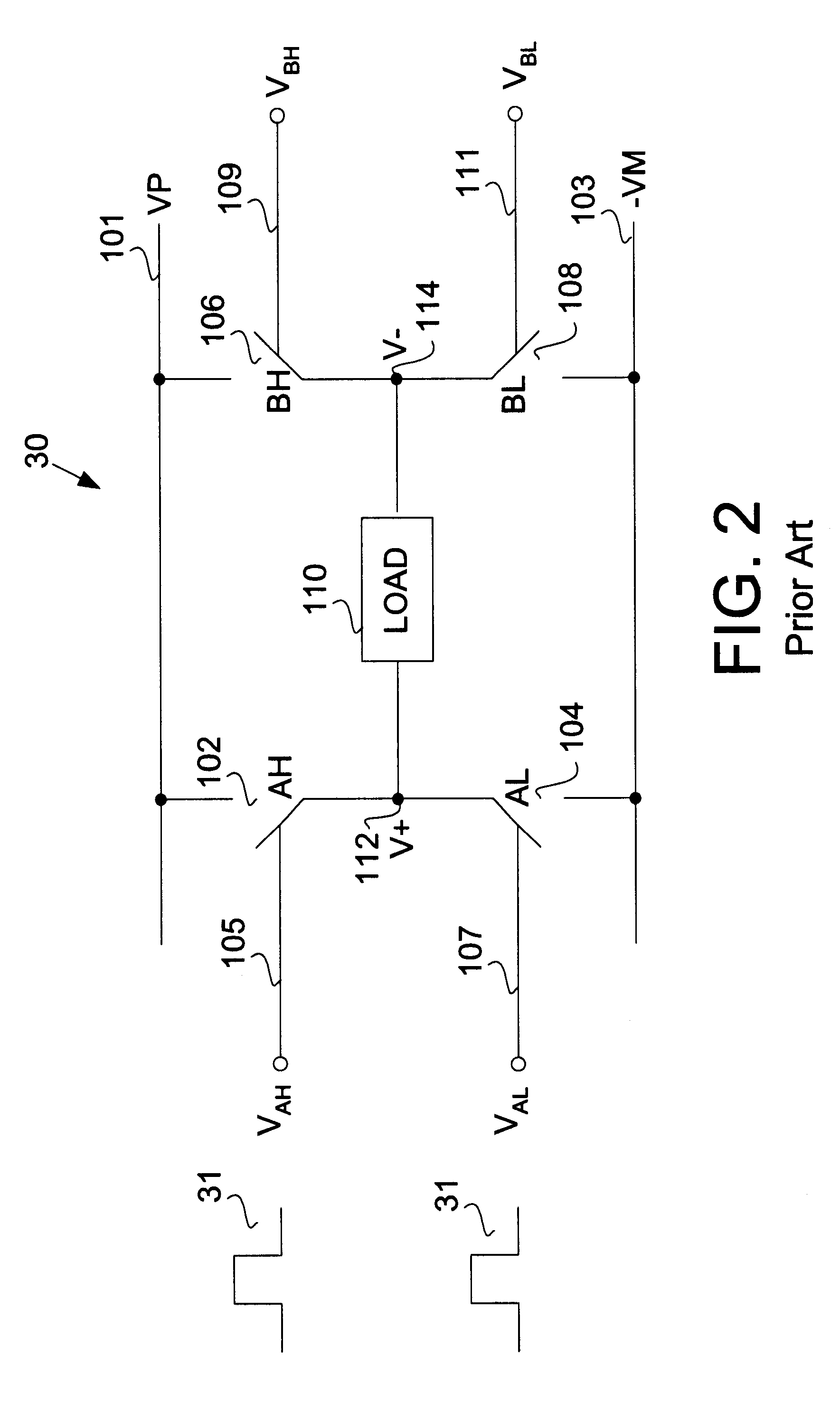
High efficiency driver for miniature loudspeakers
ActiveUS7336794B2Digitally weighted transducing elementsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsThree levelReturn-to-zero
In a first aspect the present invention provides a compact high efficiency driver suitable for driving a loudspeaker, such as a miniature loudspeaker for mobile phones or hearing aids. The driver comprising an interface for receiving an input signal, a three-level modulator, and a three-level H-bridge. The interface may be adapted to receive a digital input signal. In a preferred embodiment of the driver the H-bridge is controlled by a correction circuit which is operated by a Return-To-Zero scheme. In a further preferred embodiment the driver comprises a supply voltage step-up circuit for increasing a voltage supplied to the H-bridge. In a second aspect the present invention provides a miniature loudspeaker assembly having a built-in driver. In a third aspect the present invention provides a mobile device with a built-in miniature loudspeaker assembly.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
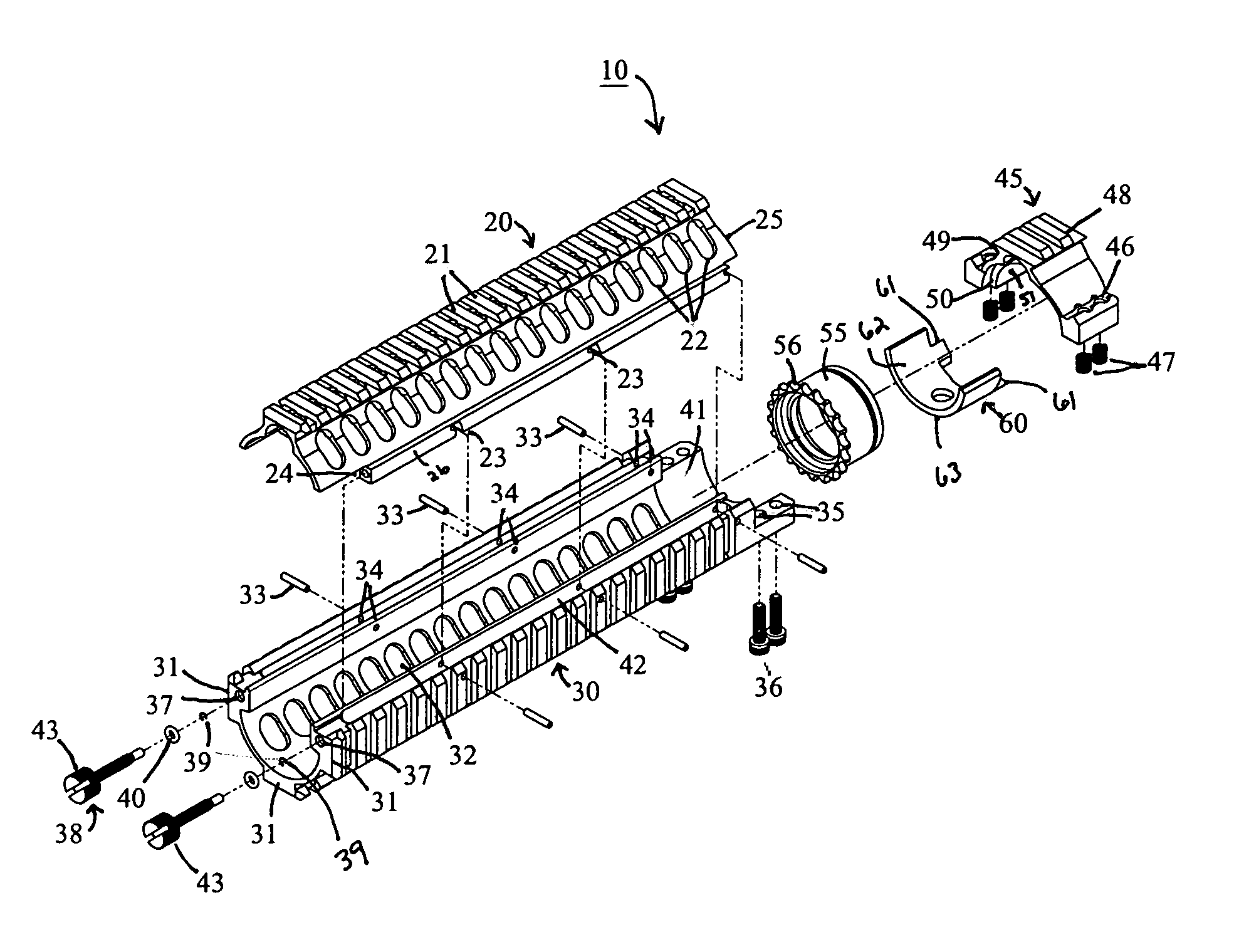
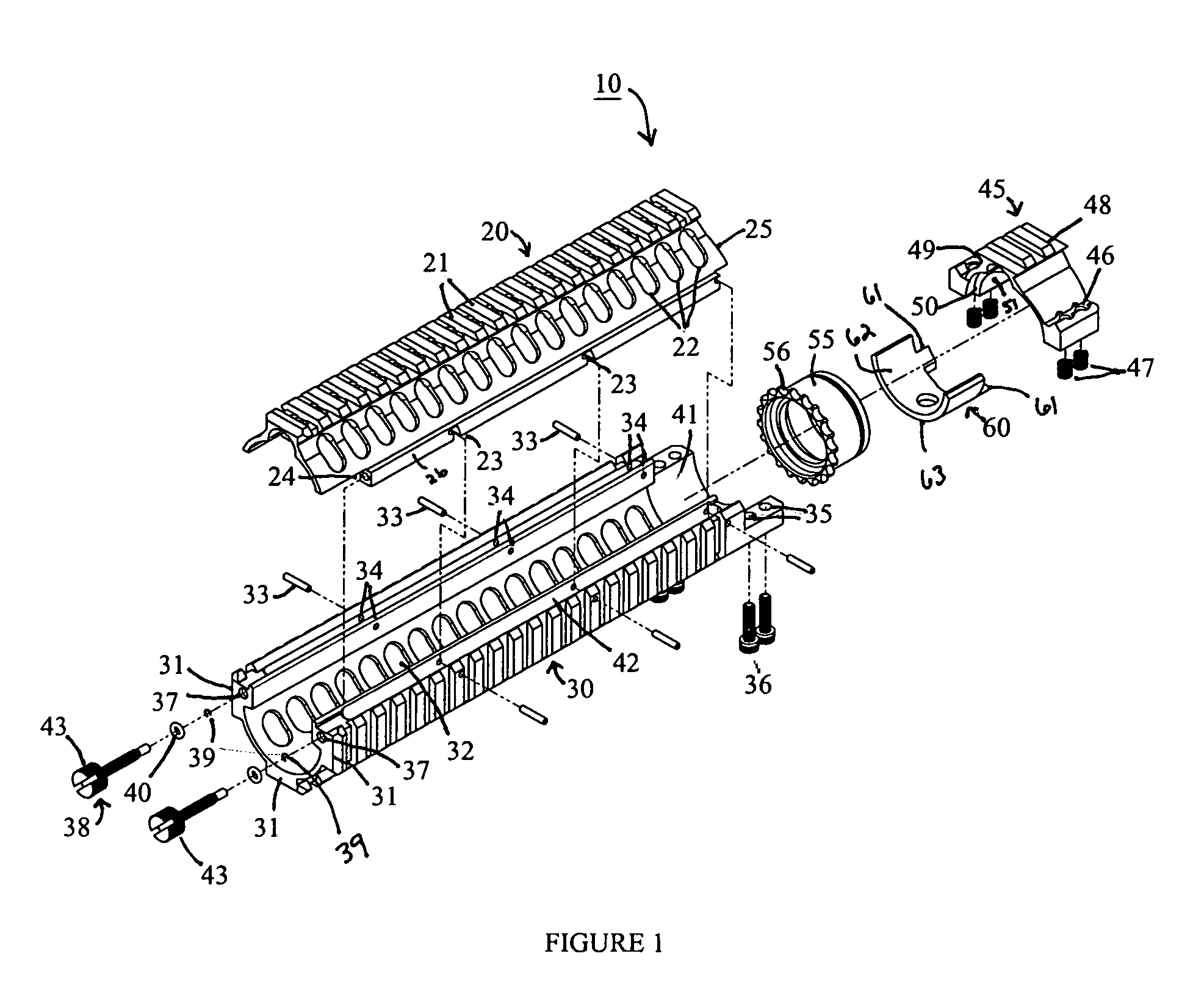
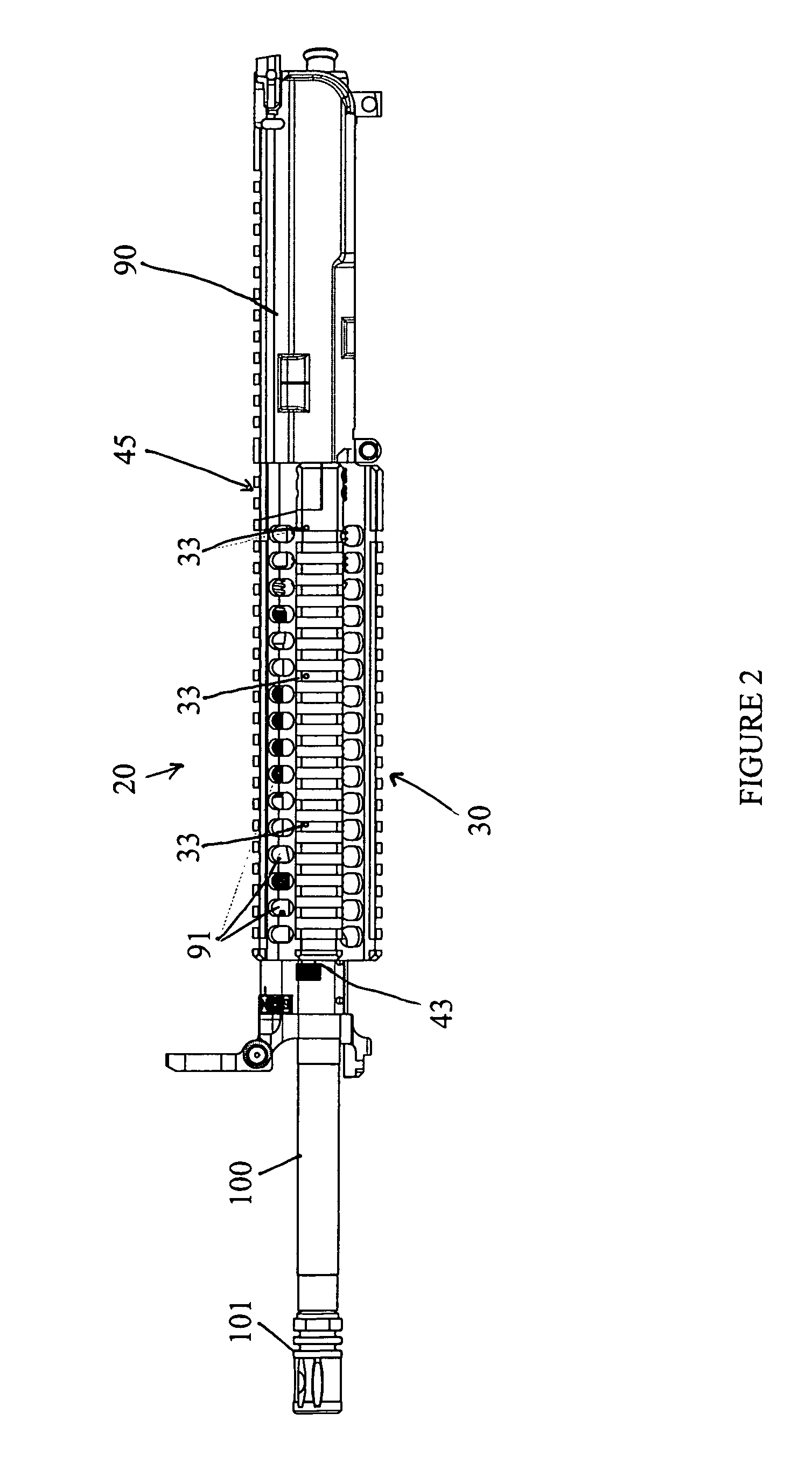
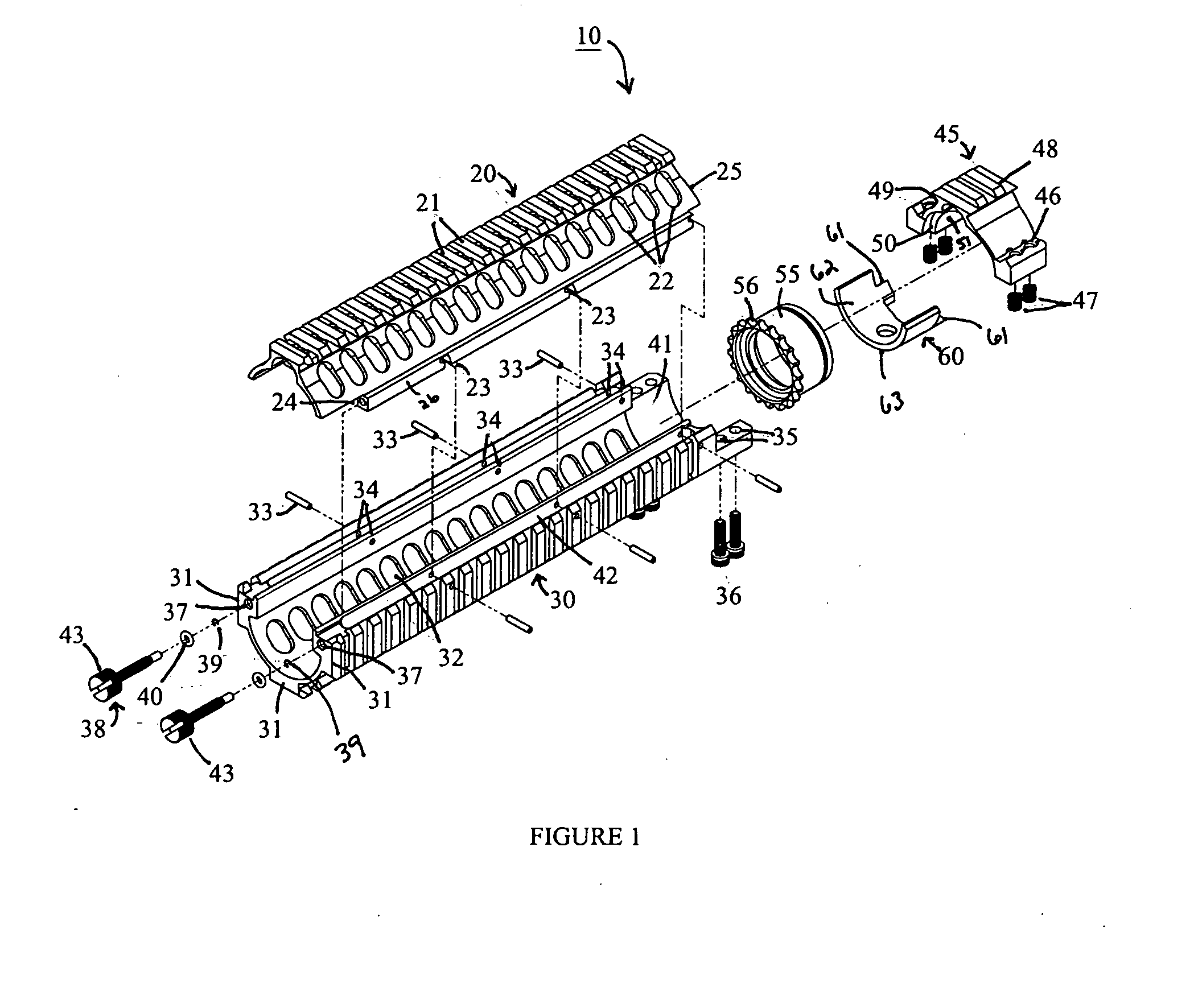
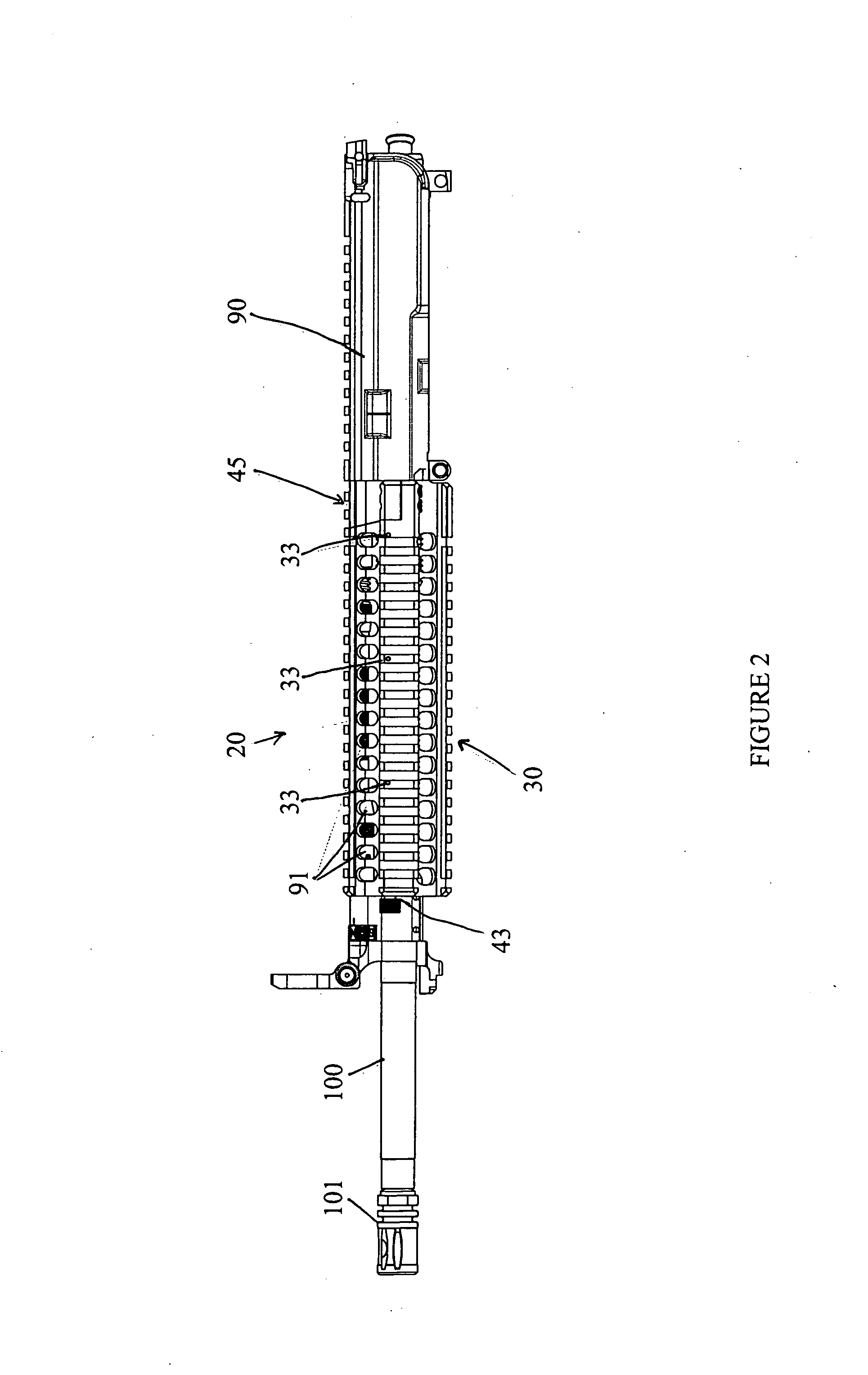
Top opening, modular top rail, multi-rifle adaptable free float rail adaptor system (ARM-R)
An improved Rail Adaptor System / Rail Accessory System (RAS) which attaches to a firearm. The rail is top opening, modular, and free floats the barrel. Provided is a rigid, lightweight, strong platform for mounting firearm accessories. Heat transmission from the barrel assembly to the user is limited. The user is also protected from ventilated gases originating from the operating system. A quick detachable top rail section is provided so that that gas system may be easily accessed. This removable top section of the rail is what makes this device unique because the RAS may be installed without removing the barrel, gas system, front sight base, flash hider or the barrel nut. The herein described RAS is adaptable to a wide variety of firearms with the use of conversion parts. The top rail “returns to zero” on reinstallation allowing the remounting of various optics and electronic gun sites without the need to realign them.
Owner:LWRC INTERNATIONAL
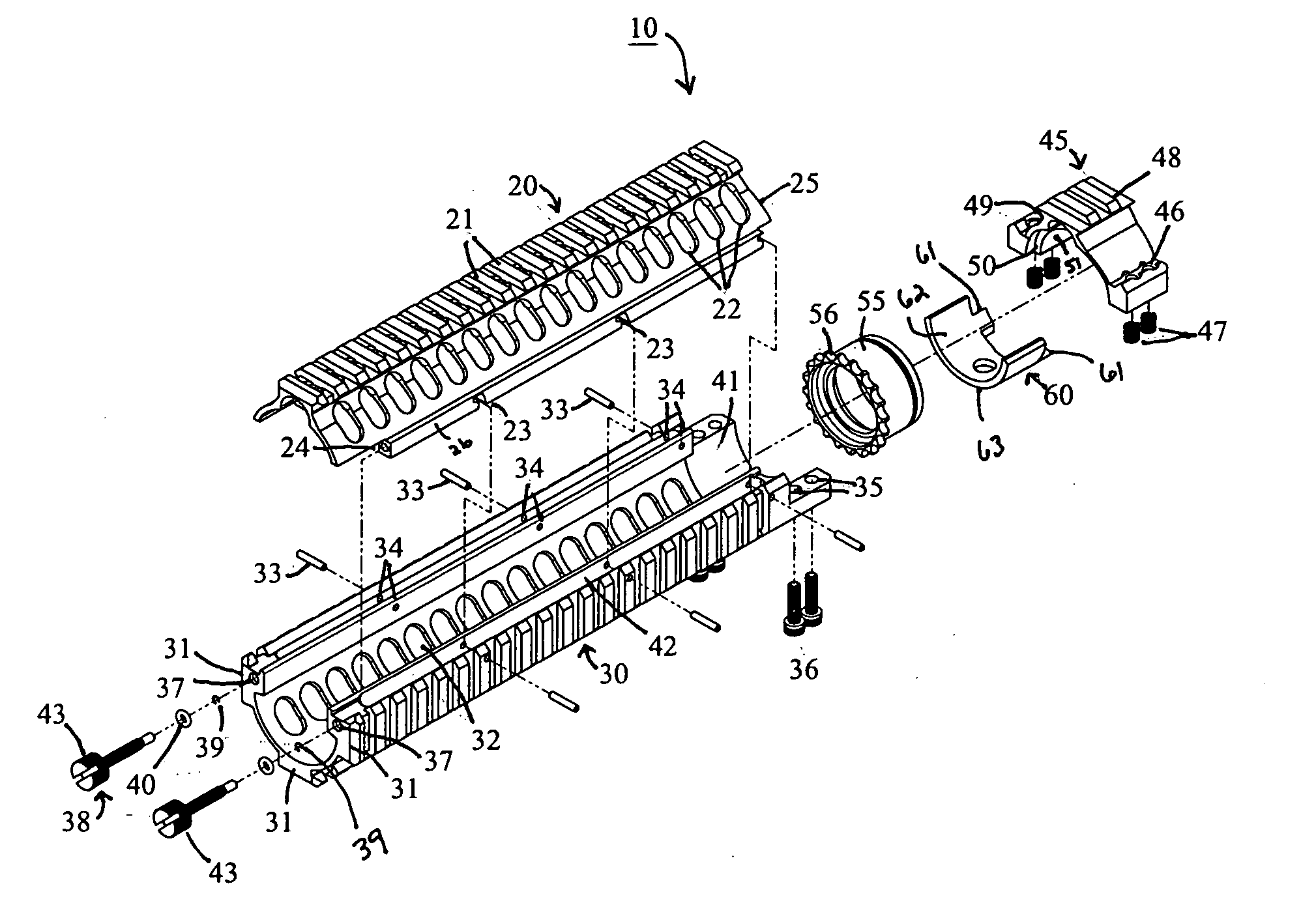
Top opening, modular top rail, multi-rifle adaptable free float rail adaptor system (arm-r)
ActiveUS20120042557A1Minimizing transferImprove ventilationCartridge extractorsWeapon cleaningReturn-to-zeroHeat transmission
An improved Rail Adaptor System / Rail Accessory System (RAS) which attaches to a firearm. The rail is top opening, modular, and free floats the barrel. Provided is a rigid, lightweight, strong platform for mounting firearm accessories. Heat transmission from the barrel assembly to the user is limited. The user is also protected from ventilated gases originating from the operating system. A quick detachable top rail section is provided so that that gas system may be easily accessed. This removable top section of the rail is what makes this device unique because the RAS may be installed without removing the barrel, gas system, front sight base, flash hider or the barrel nut. The herein described RAS is adaptable to a wide variety of firearms with the use of conversion parts. The top rail “returns to zero” on reinstallation allowing the remounting of various optics and electronic gun sites without the need to realign them.
Owner:LWRC INTERNATIONAL
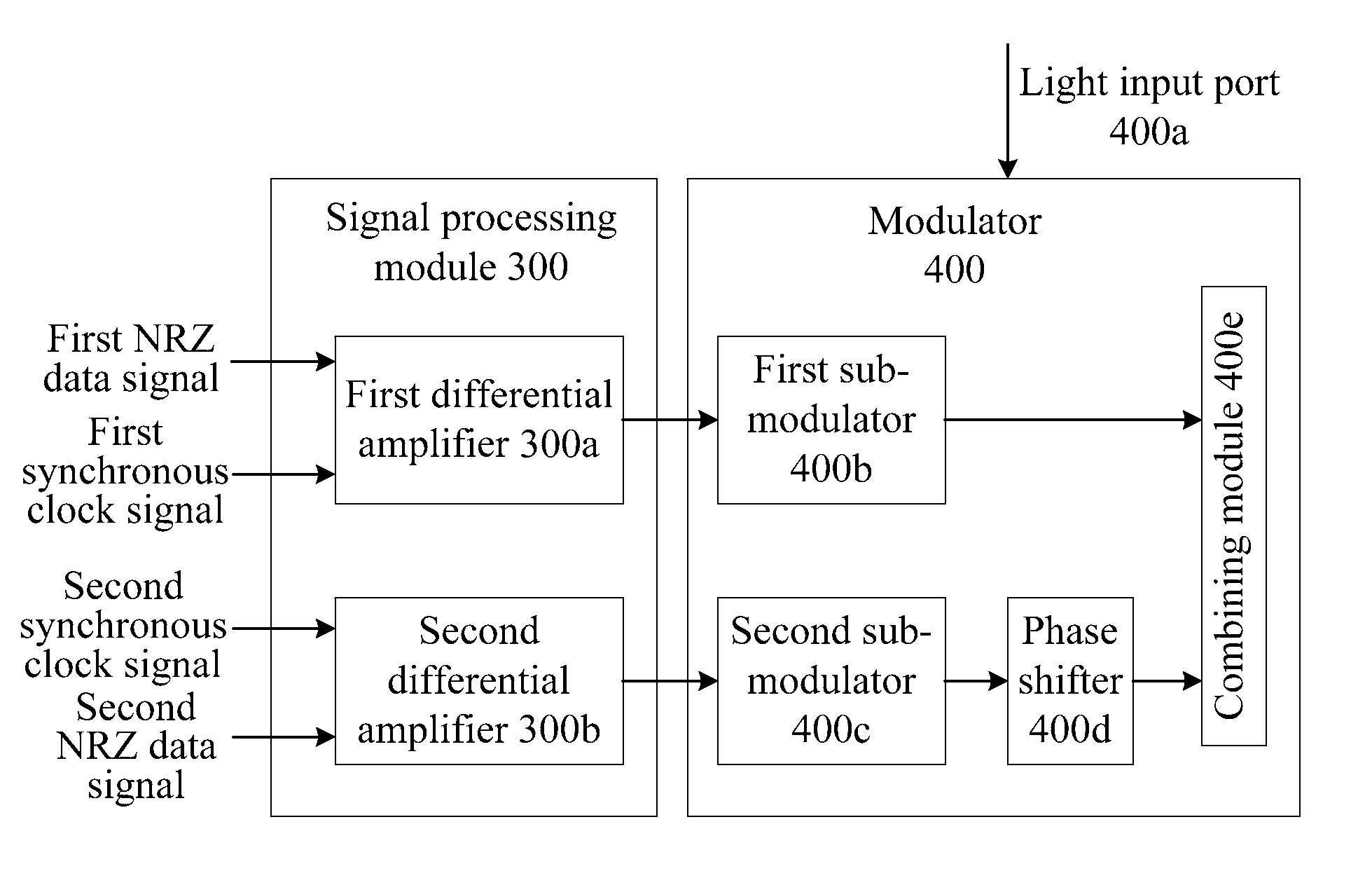
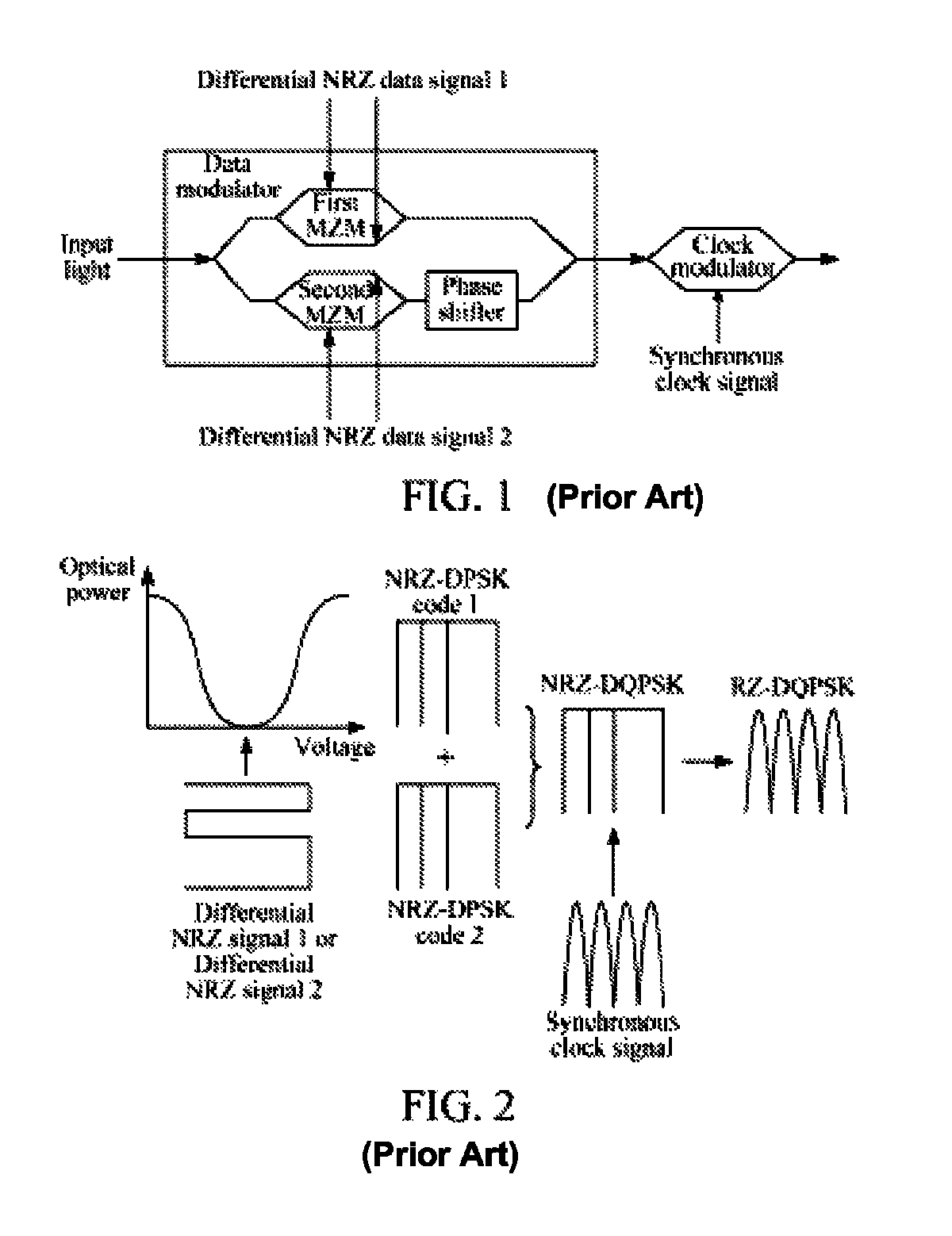
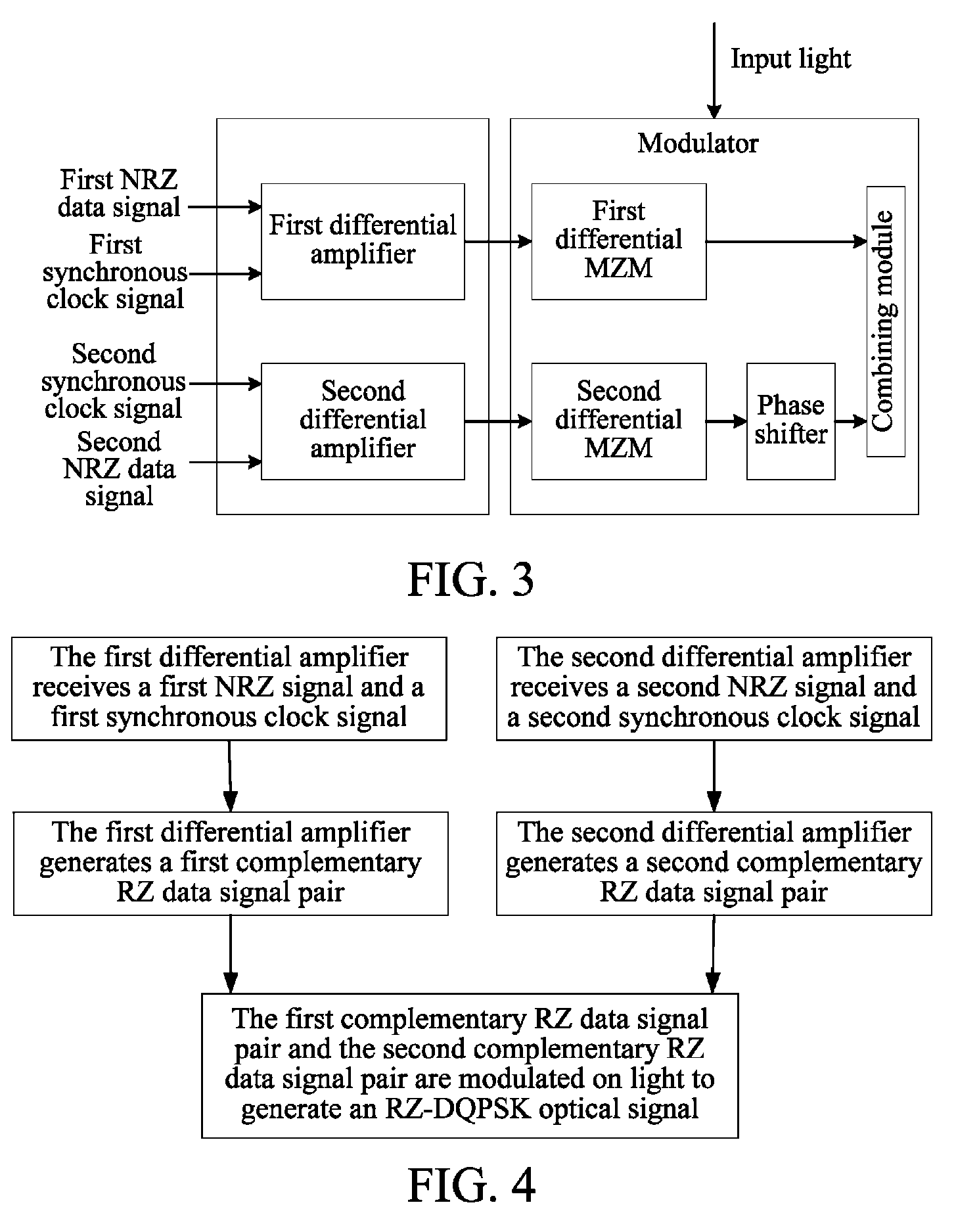
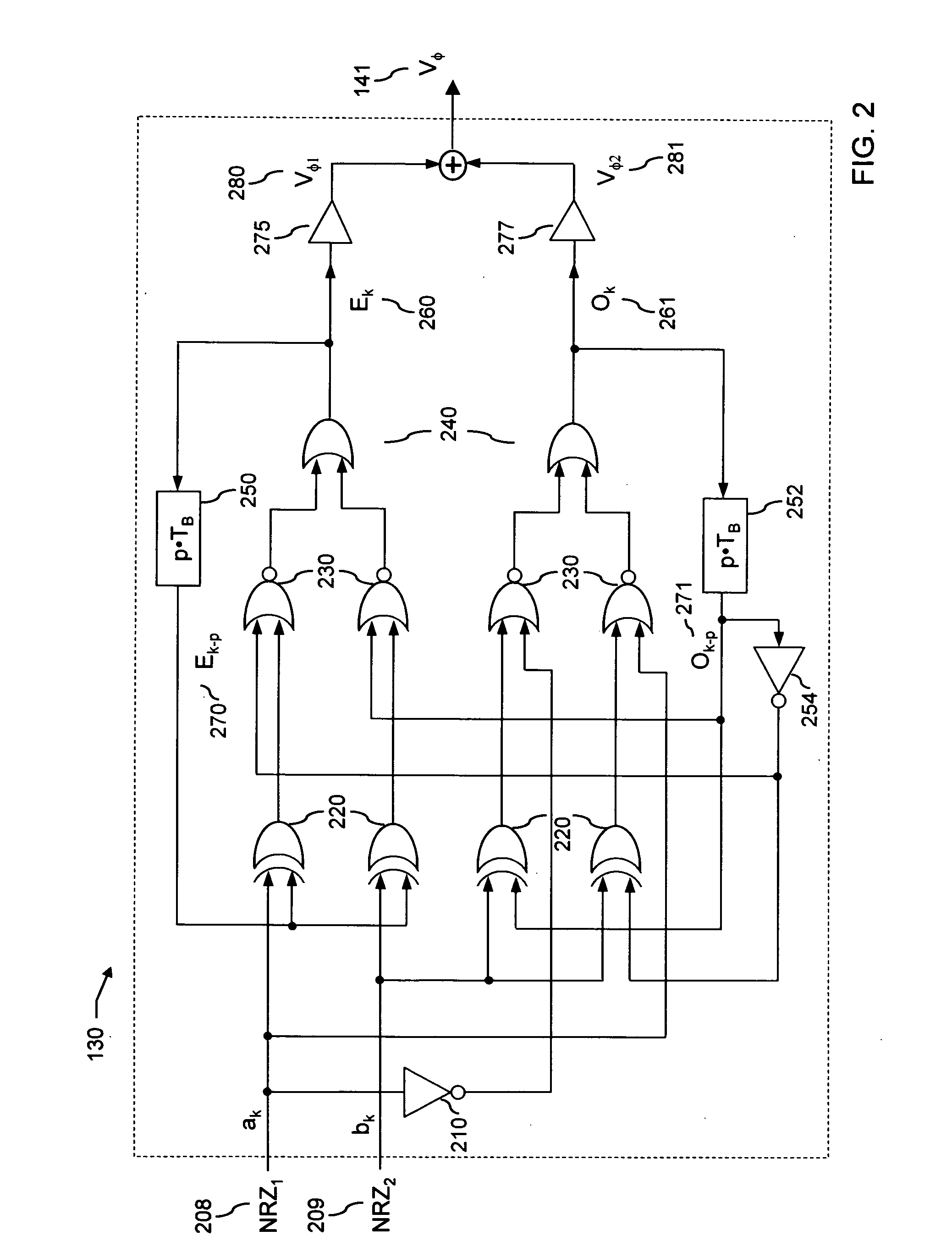
Method and device for generating optical signals
ActiveUS8831440B2Simple structureLow costElectromagnetic transmittersOptical NRZ to RZ conversionReturn-to-zeroSoftware engineering
The method includes: receiving a first Non Return to Zero (NRZ) data signal and a synchronous clock signal, and performing Return to Zero (RZ) processing to generate a first complementary RZ data signal pair; receiving a second NRZ data signal and a synchronous clock signal, and performing RZ processing to generate a second complementary RZ data signal pair; and modulating the first complementary RZ data signal pair and the second complementary RZ data signal pair on light to generate an RZ-Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (RZ-DQPSK) optical signal. Through the method and device, RZ processing are performed on the NRZ data signals to generate the complementary RZ data signal pairs, and the complementary RZ data signal pairs are modulated on the light, thereby reducing the cost and the insertion loss of the entire device, lowering the requirements for input optical power and reducing the complexity of loop circuit control.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
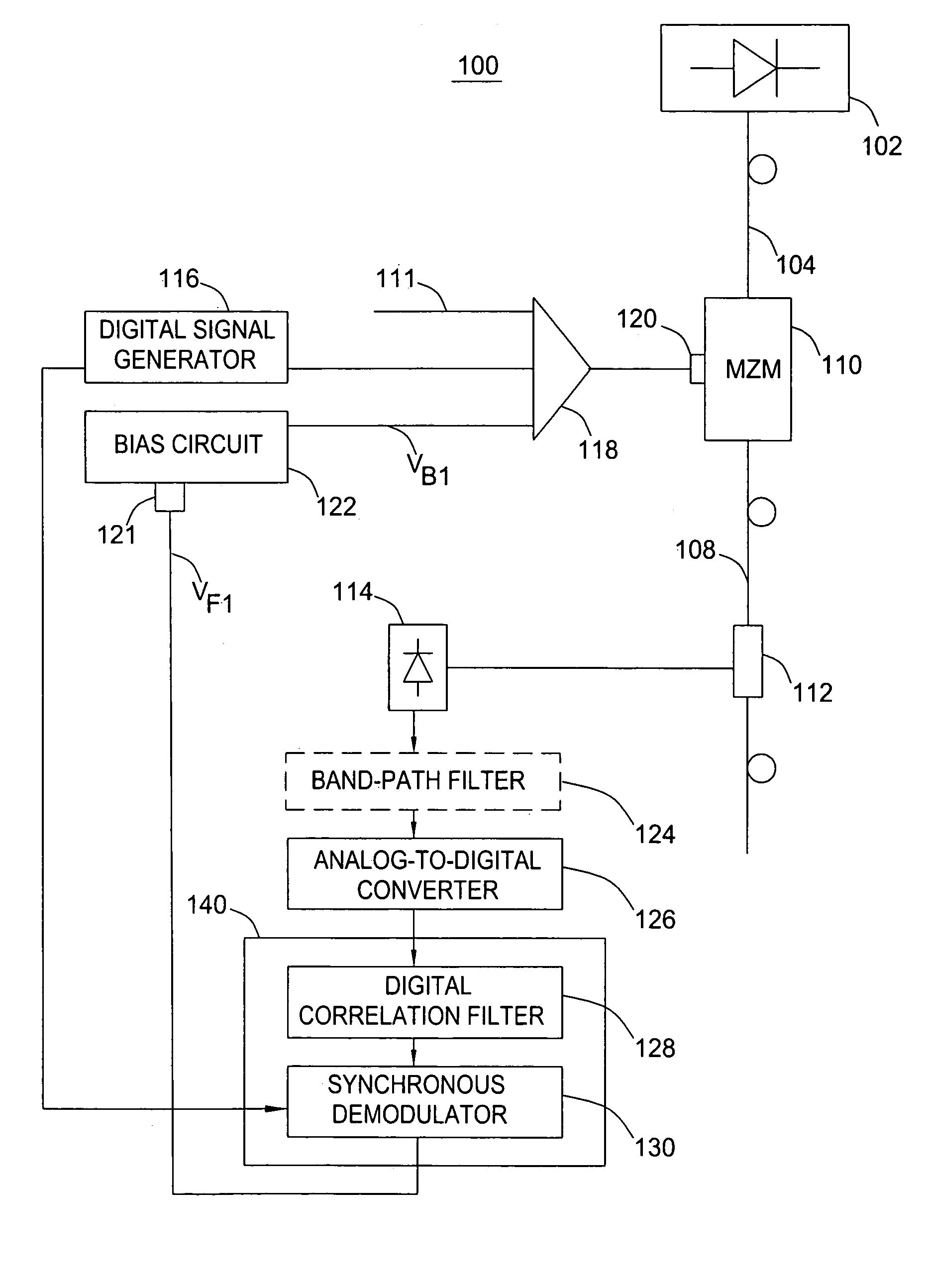
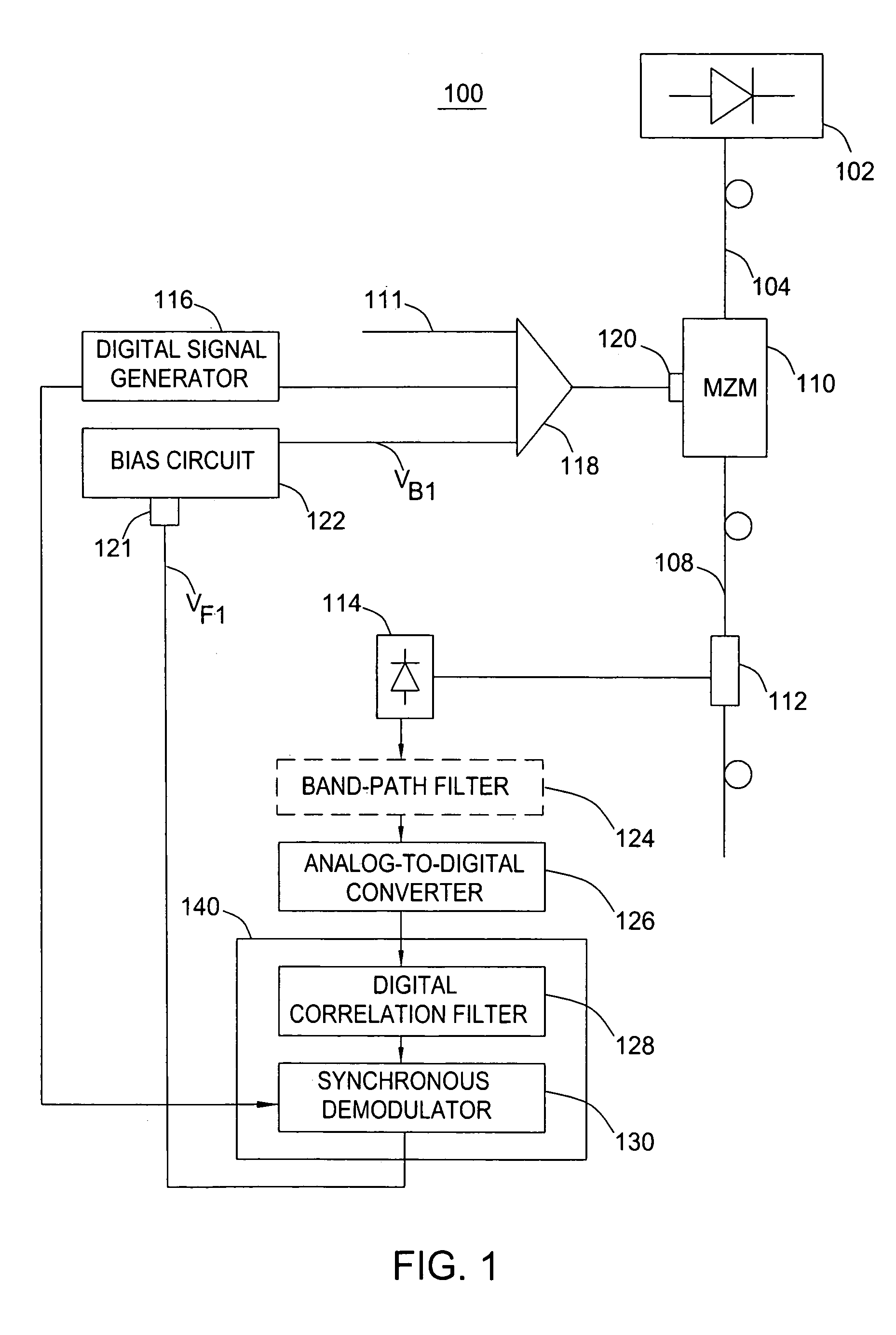
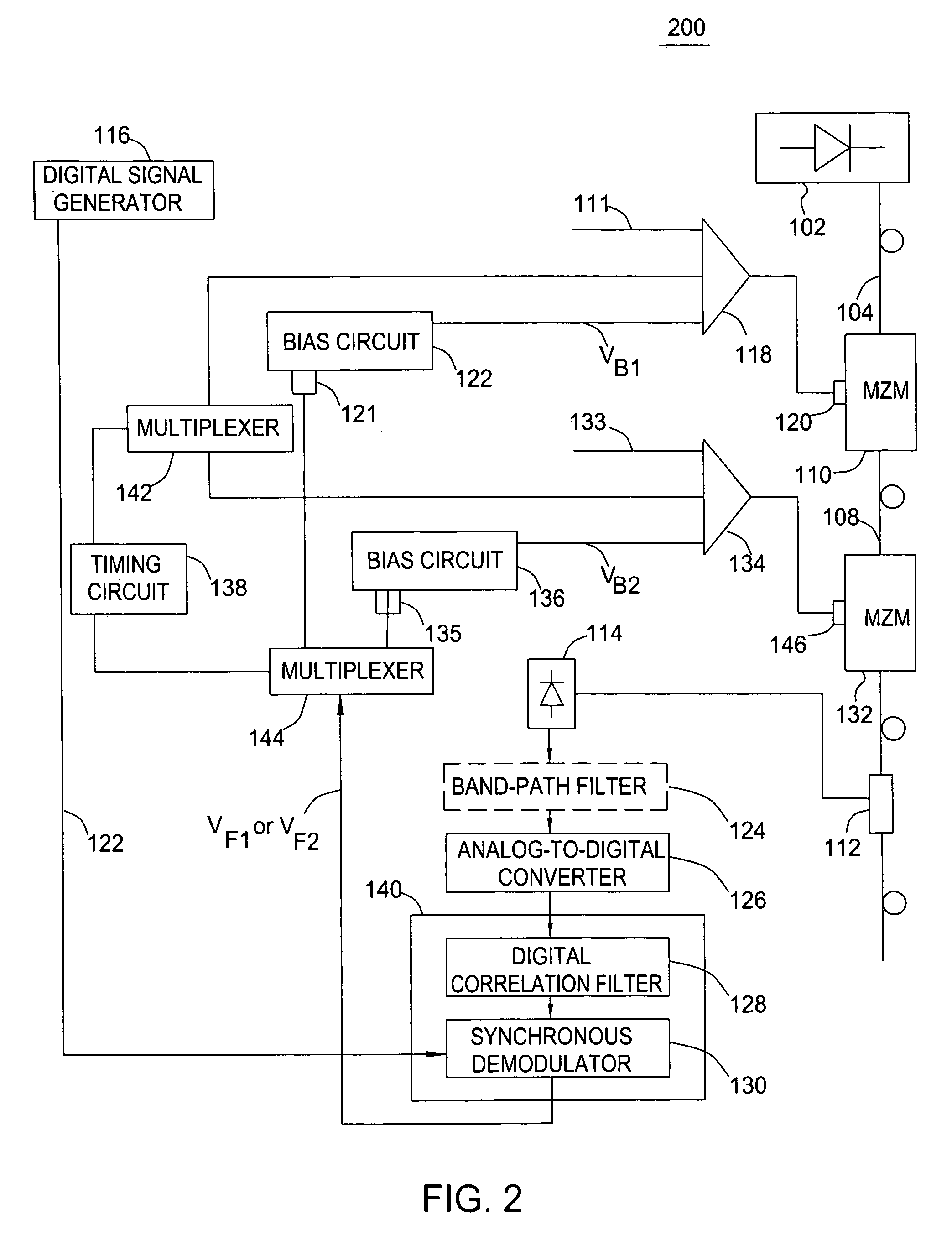
Method and apparatus for controlling a bias voltage of a Mach-Zehnder modulator
A method and apparatus for controlling a bias voltage of a Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) use a digital pilot signal and a digital correlation technique to produce a feedback signal for adjusting the bias voltage to the quadrature bias point. Embodiments of the invention include apparatuses performing a non-return-to-zero (NRZ), return-to-zero (RZ), or carrier suppressed RZ (CSRZ) high-speed optical modulation.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
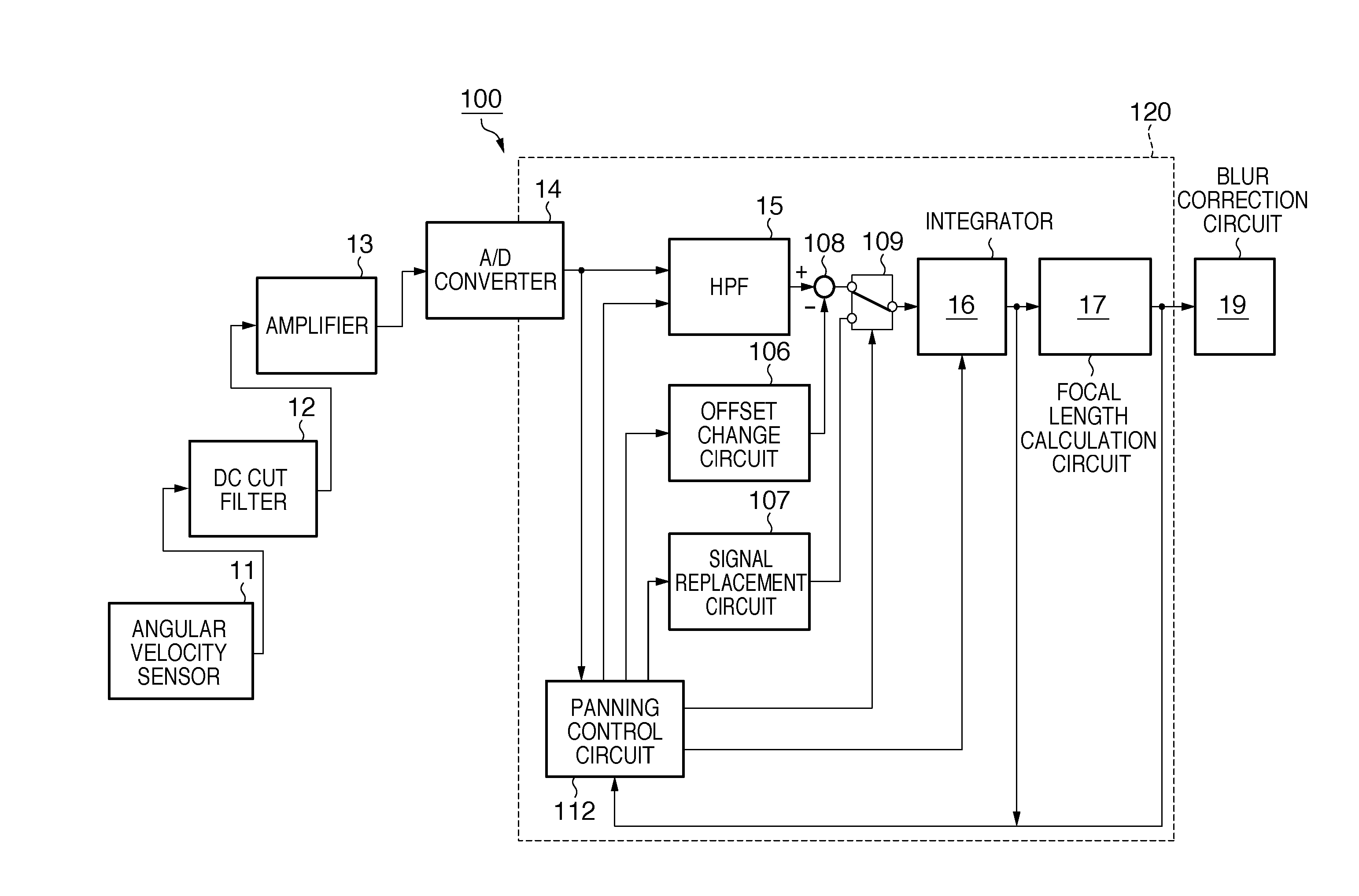
Blur correction apparatus and image capturing apparatus
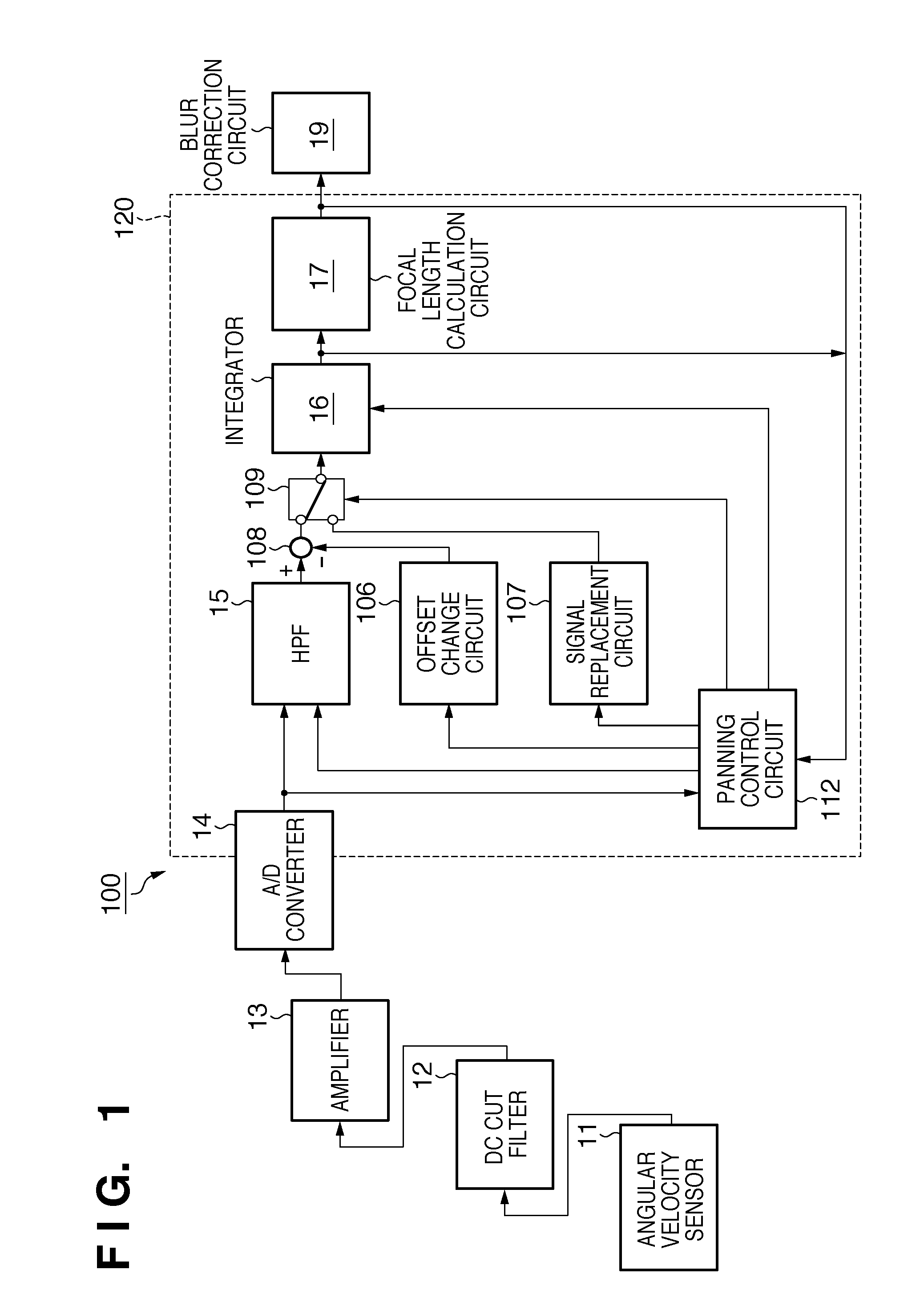
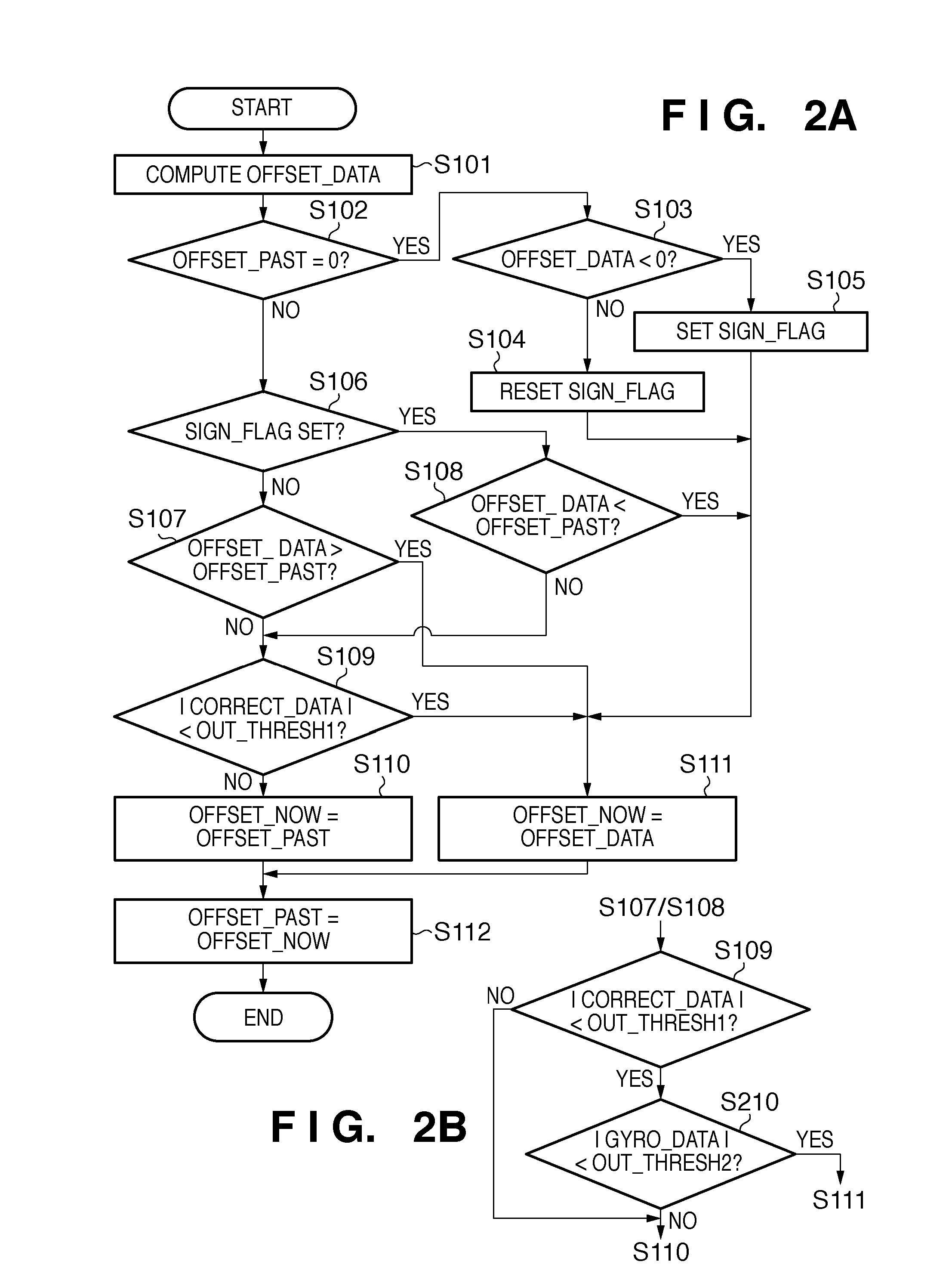
ActiveUS20110013031A1Prevent degradationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsReturn-to-zeroComputer science
Upon detecting the start of a panning operation, an adder-subtracter applies an offset from an offset change circuit to the output of an HPF (High-Pass Filter) representing the shake amount of an image capturing apparatus to decrease the shake amount. The offset value is set to be larger as the value of shake correction data output from a focal length calculation circuit is closer to the correction limit of a blur correction circuit. Upon detecting the end of the panning operation, the offset value is returned to zero. This invention provides a blur correction apparatus capable of suppressing degradation of a blur correction effect even when in a panning state.
Owner:CANON KK
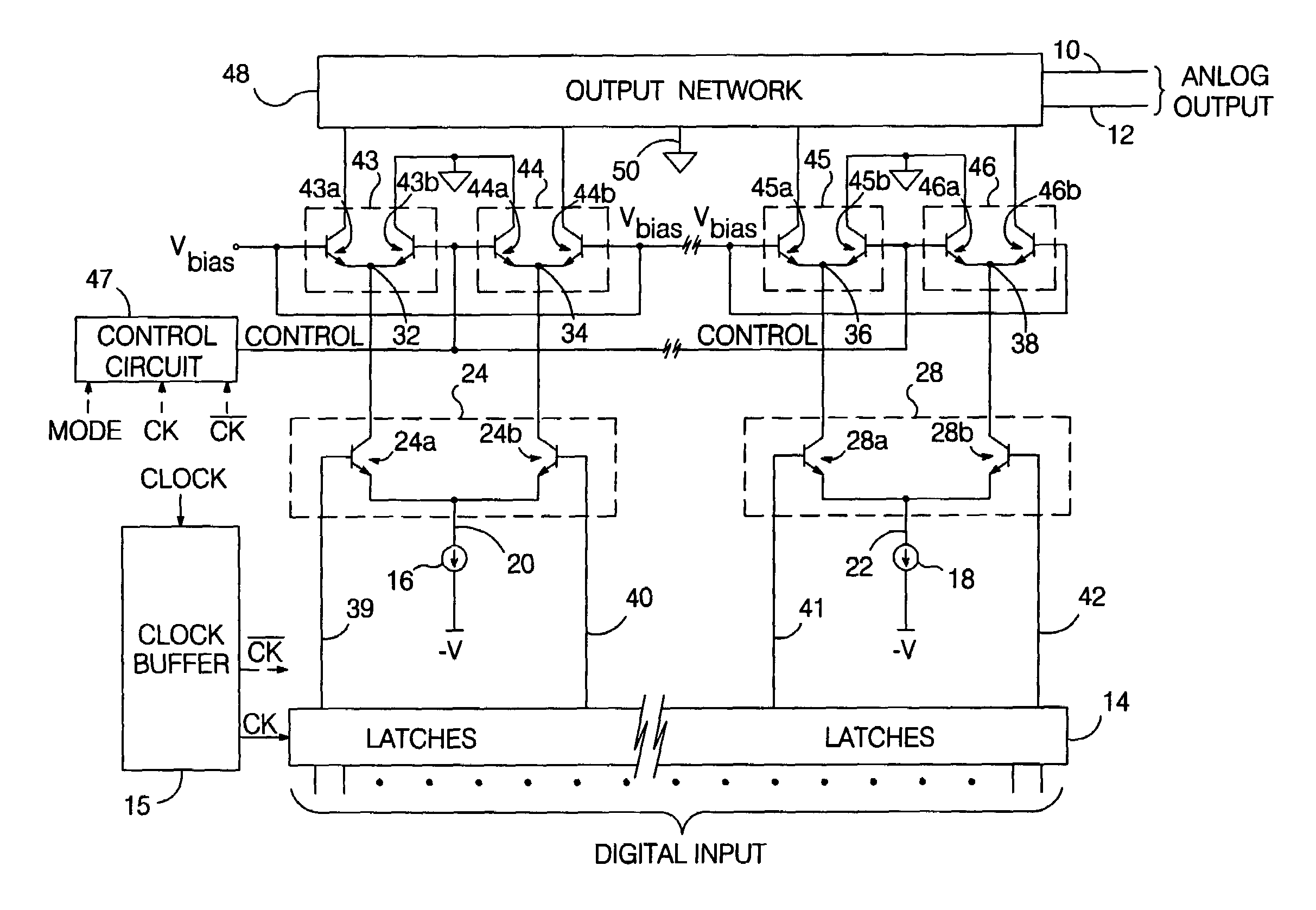
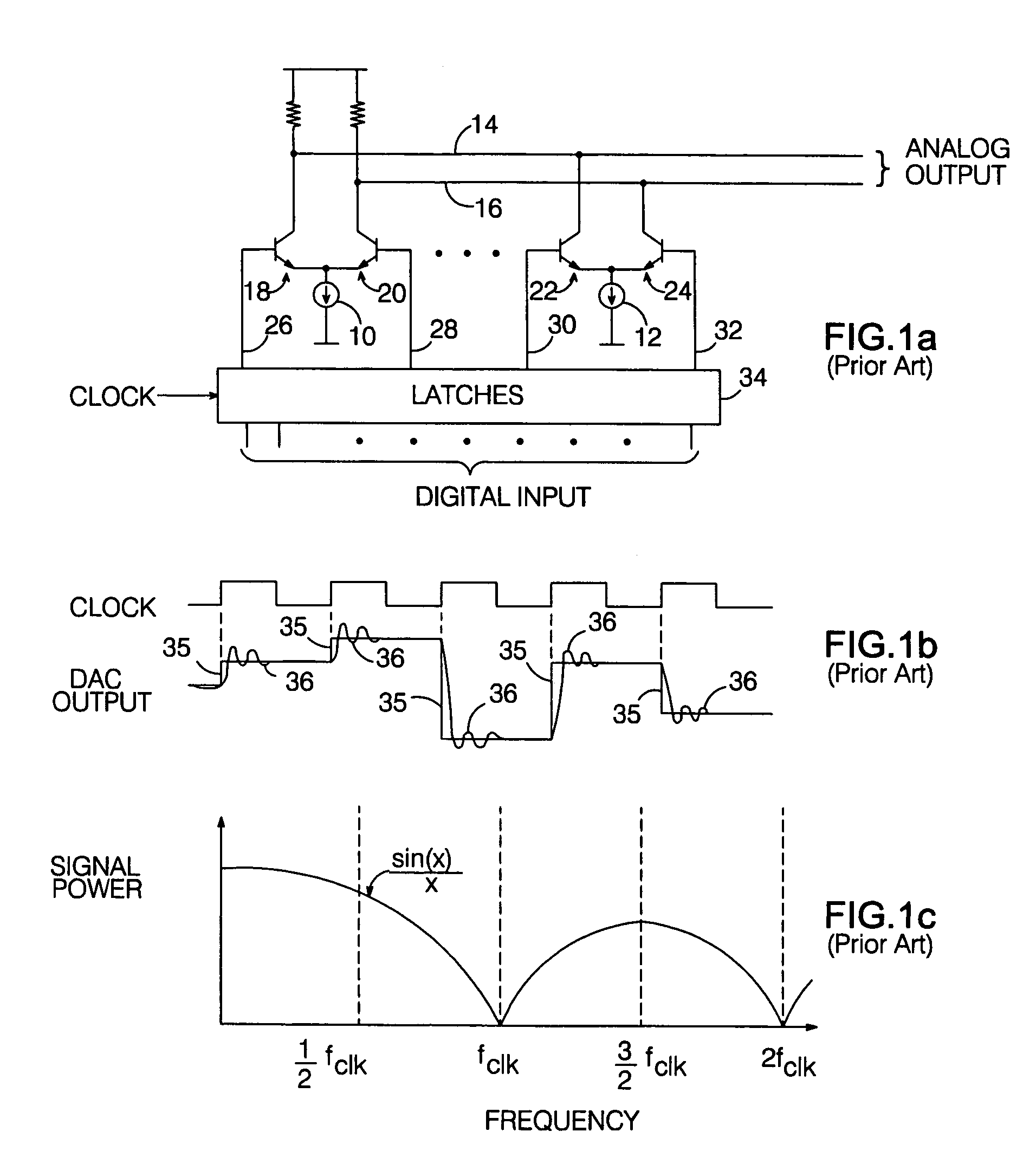
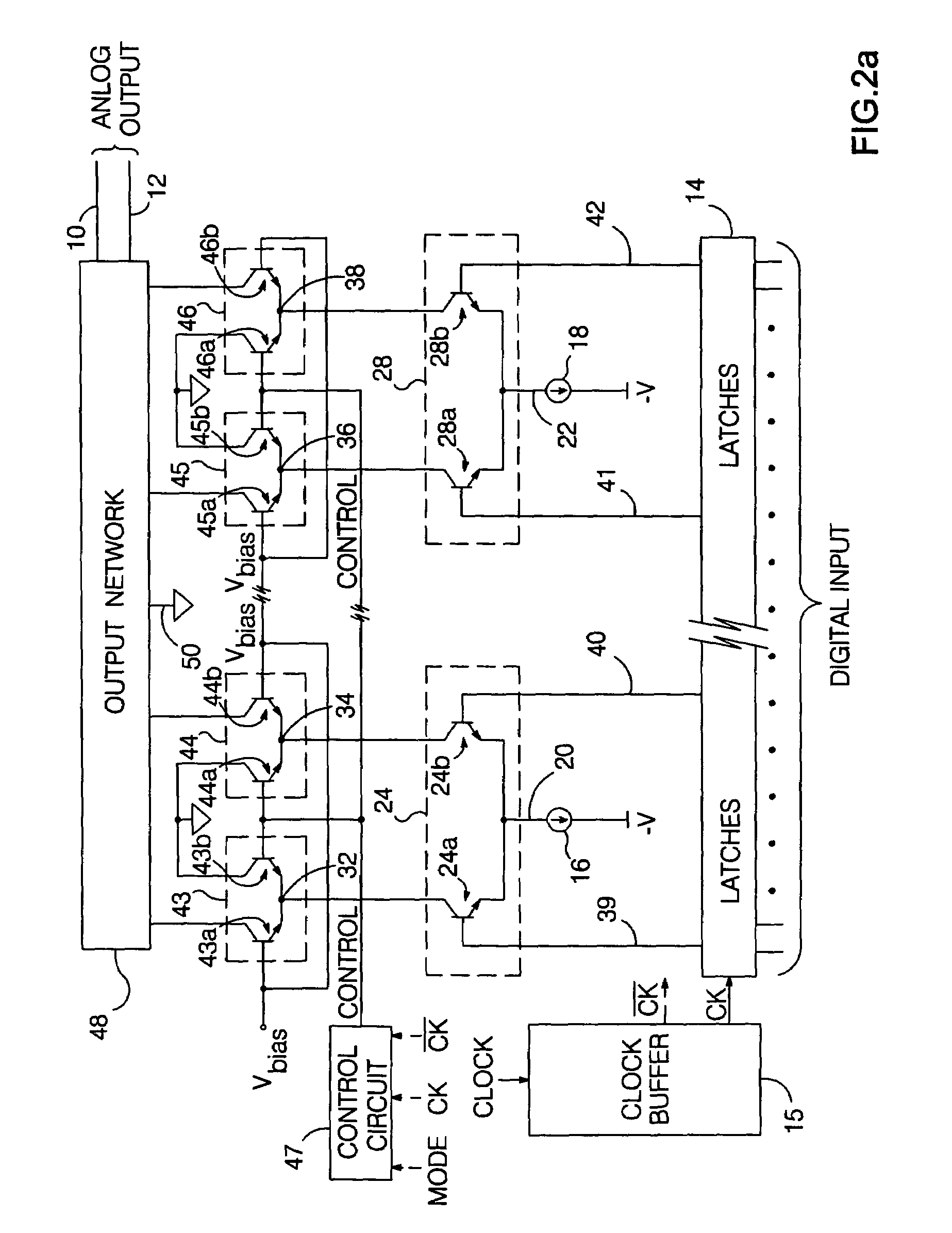
Return-to-zero current switching digital-to-analog converter
InactiveUS7042379B2Increased frequency rangeReduce noiseElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsReturn-to-zeroControl signal
A “return-to-zero” (RZ) current switching DAC includes an analog output node for which a “zero” potential has been defined. The outputs of a plurality of current sources are selectively directed to respective intermediate nodes in response to respective control signals, which are varied in synchronization with a clock signal CK. A plurality of RZ circuits are connected between respective intermediate nodes and the analog output node. In a preferred embodiment, each RZ circuit directs the current applied to a respective intermediate node to ground or to the analog output node in synchronization with CK. An output network pulls the analog output node to the “zero” potential when currents applied to the intermediate nodes are directed to ground.
Owner:OTROSANI ASSET MGMT L L C
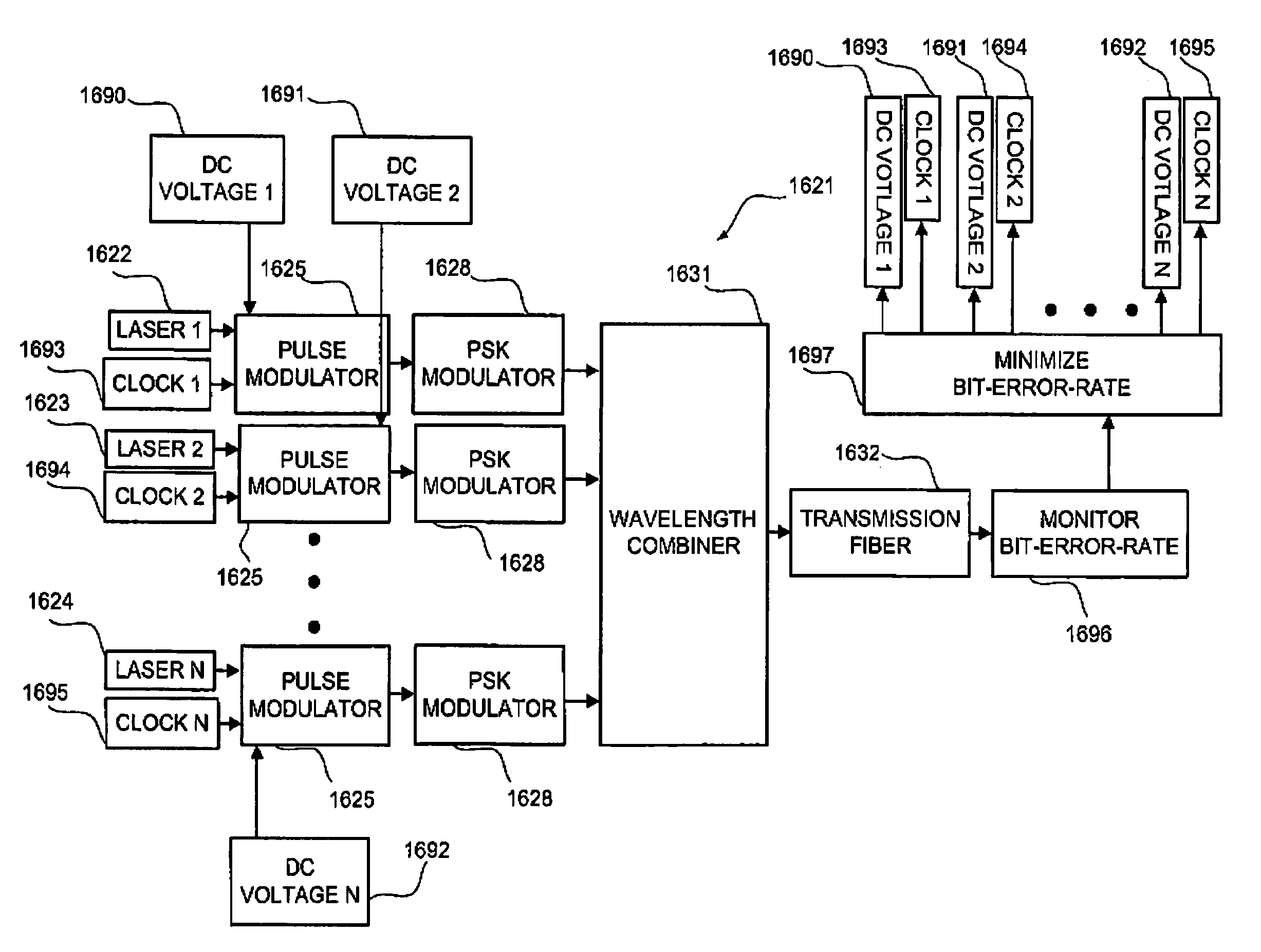
Method and system for mitigating nonlinear transmission impairments in fiber-optic communications systems
InactiveUS7224906B2Time-division optical multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansFiberReturn-to-zero
The present invention relates to a method for transmitting data. An optical pulse stream comprising a plurality of return-to-zero optical pulses is prepared by modulating a phase of light output by an optical source to thereby encode data from a data source. The light of the optical pulse stream has a wavelength. The optical pulse stream is transmitted along an optical fiber of an optical network. Optical pulse streams of the invention enhance transmission performance at least in part by reducing noise at the receiver caused by fiber non-linearities.
Owner:CELIGHT
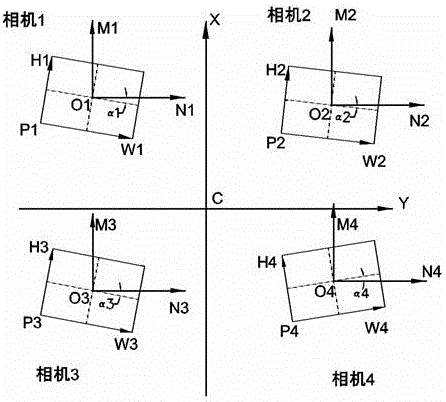
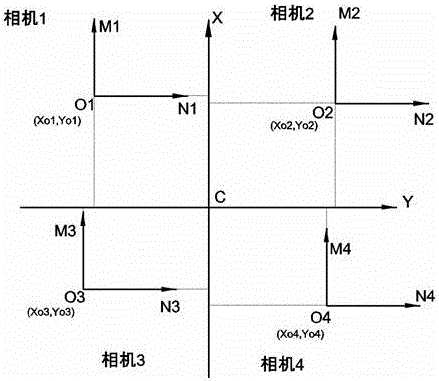
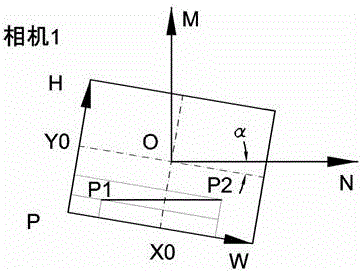
Multi-camera calibration and alignment fitting method
ActiveCN106127722AAvoid errorsDerivation is simpleImage enhancementImage analysisReturn-to-zeroComputer vision
The invention discloses a multi-camera calibration and alignment fitting method. A posture of a target object is observed by using a first camera group; a posture of a fitting object is observed by using a second camera group; and rotating coordinate systems of the two camera groups coincide. A calibration process comprises a first calibration stage, a second calibration stage and a third calibration stage. In the first calibration stage, internal parameters and a camera mounting angle of each camera in the camera groups are calibrated; in the second calibration stage, the position, in an output coordinate system of each camera in the camera groups, of a rotating center of a correction platform is calibrated and the rotating coordinate systems are established according to the condition that the rotating center of the correction platform is a fixed point after returning to zero; and in the third calibration stage, mapping and calibration are performed: the first camera group is mapped and calibrated by the second camera group according to the condition that the rotating coordinate systems of the first camera group and the second camera group coincide.
Owner:SHENZHEN VISION DRAGON INTELLIGENT SENSOR CO LTD
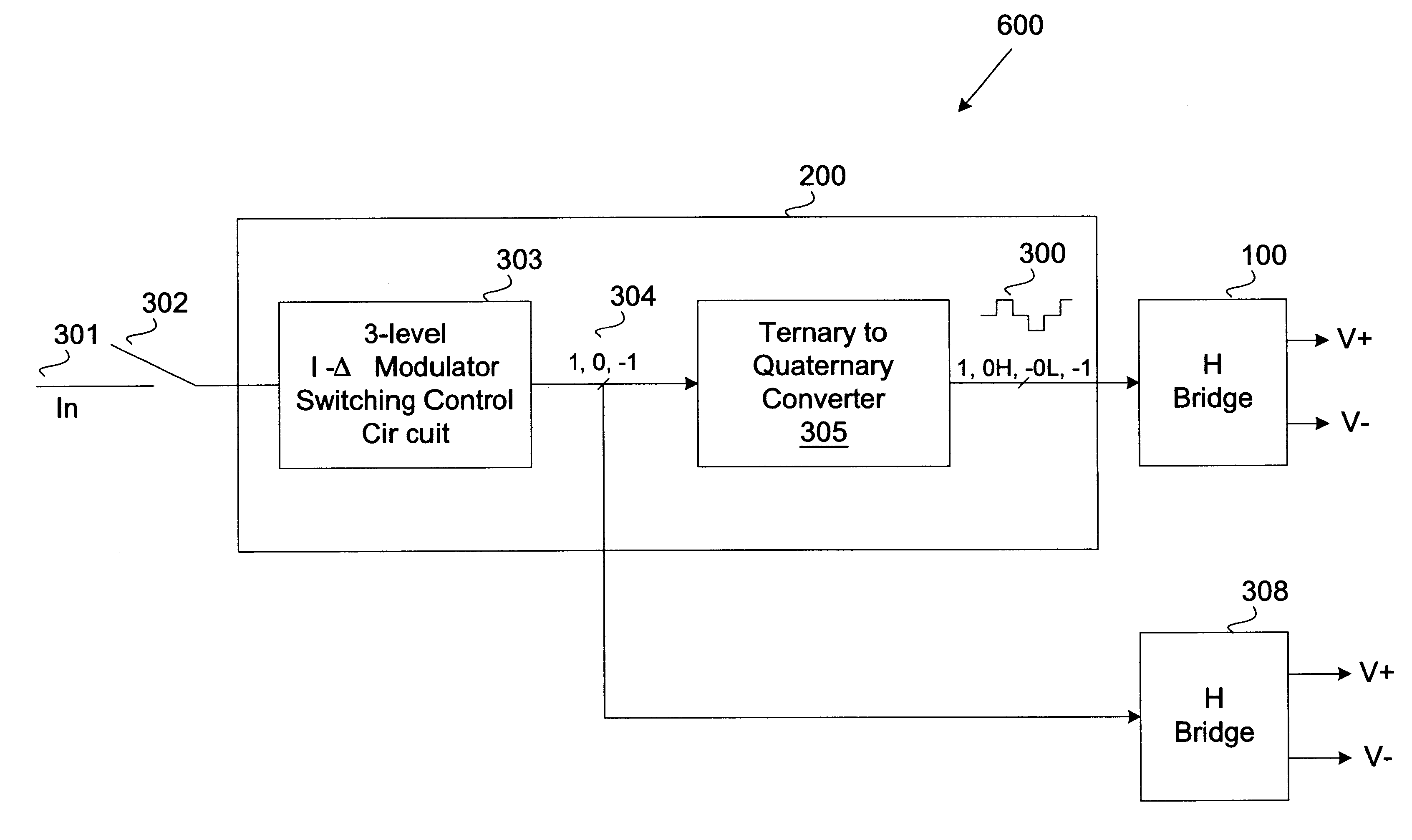
Switching amplifier incorporating return-to-zero quaternary power switch
Invention resides in a switching amplifier having a quaternary input control signal that provides quaternary levels (1, 0H, -1, and 0L) which is coupled to an H-bridge amplifier to provide error cancellation in switching amplifier output signal. The quaternary control signal alternates from a zero state at a high level ("0H") to a zero state at a low level ("0L") between each non-zero state (+1 or -1). In a preferred embodiment, a three-level sigma-delta modulator is provided for greater operational efficiency for ease of detecting zero states and minimizing power. The three-level sigma-delta modulator receives and converts an amplifier input signal into a ternary output signal that is then coupled to a ternary-to-quaternary converter to generate the quaternary control signal to provide as input to the H-bridge.
Owner:RALPH CHANG JONG
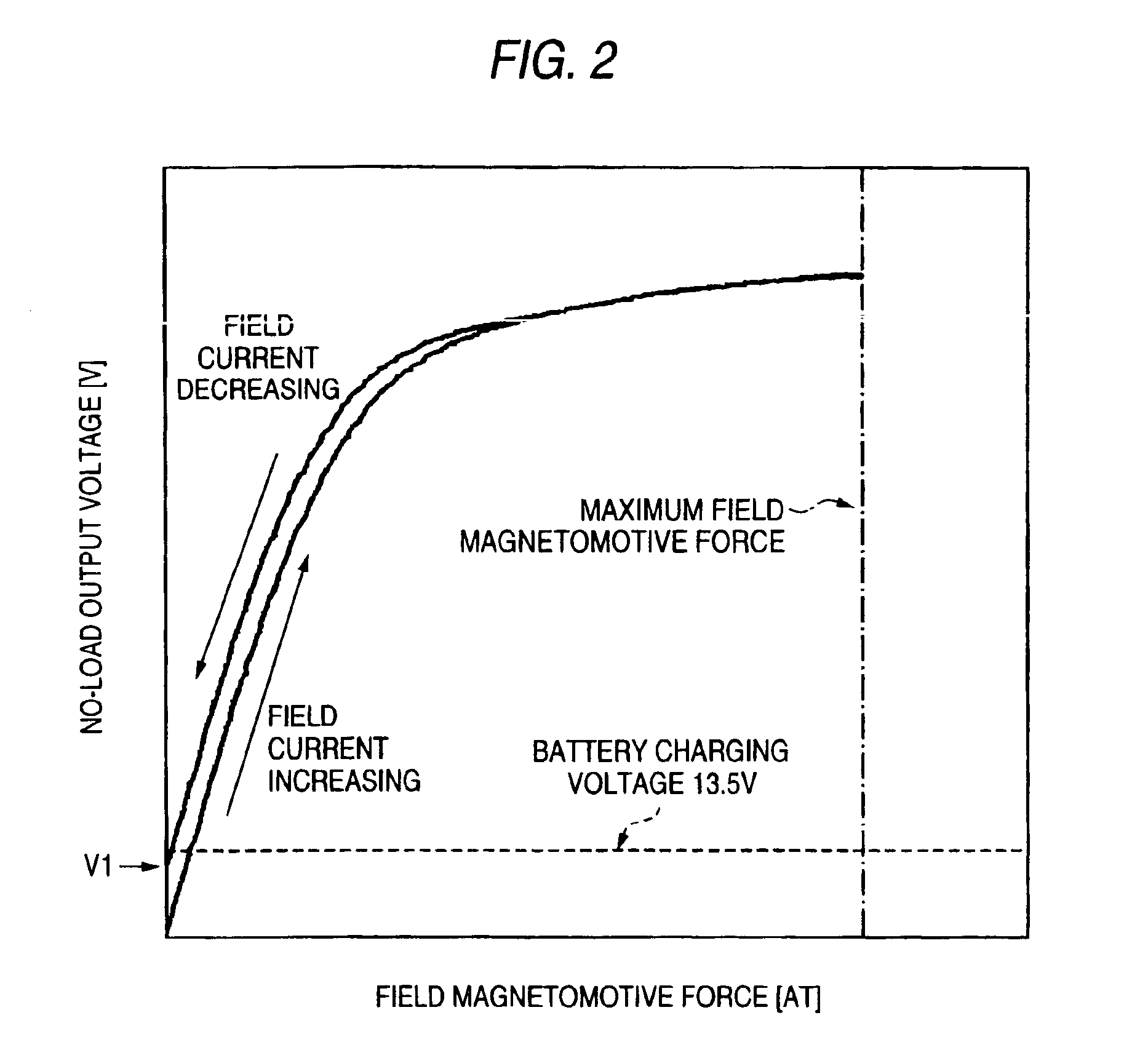
Rotary electric machine for vehicle and control device thereof
The rotary electric machine includes an armature core constituting a stator having an armature coil for charging a vehicle battery with its output voltage; rotor cores disposed inside the armature core with a predetermined gap therebetween and made up of magnetic pole parts formed as claw poles so that adjacent magnetic poles are different and cylindrical parts carrying a field coil; and permanent magnets provided in the magnetic circuit of the rotor cores for supplying magnetic flux along with the field coil to the armature core. The magnetizing force of the permanent magnets with respect to the armature core is set so that at a predetermined speed the output voltage of the armature coil immediately after a field current passed through the field coil is returned to zero from the maximum magnetizing force exerted by the field current does not exceed the charging voltage of the battery.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Faucet filter with sight glass
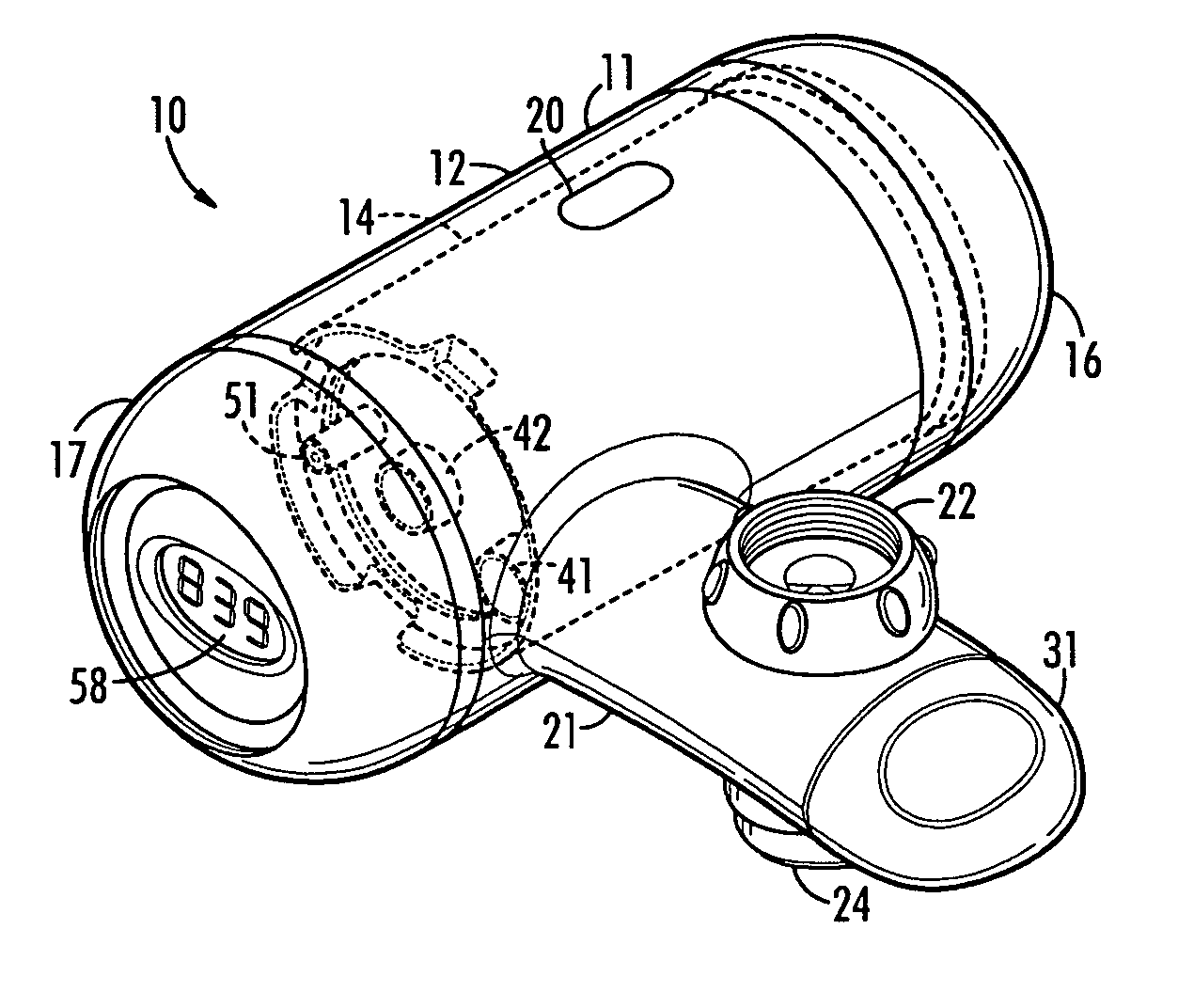
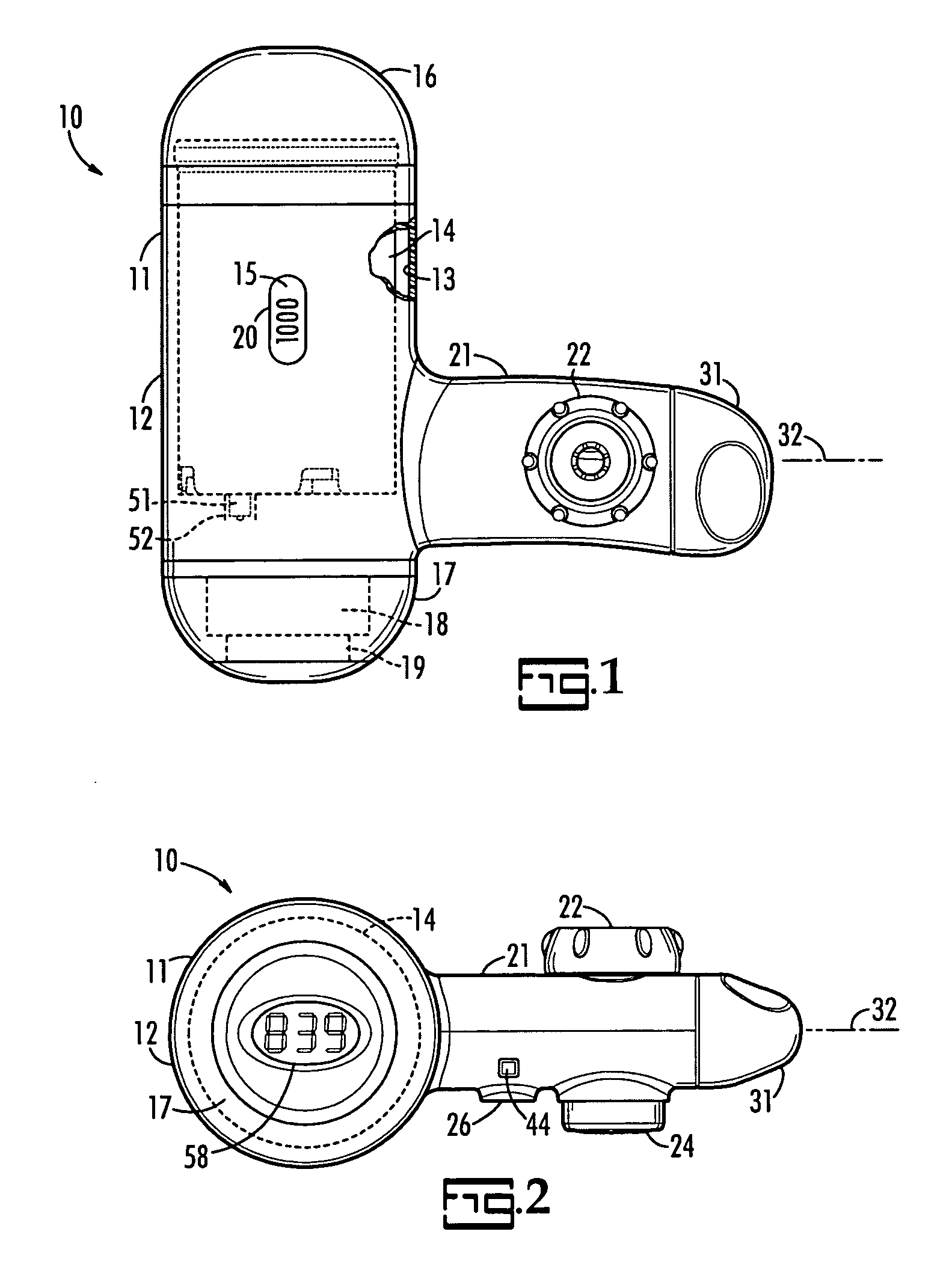
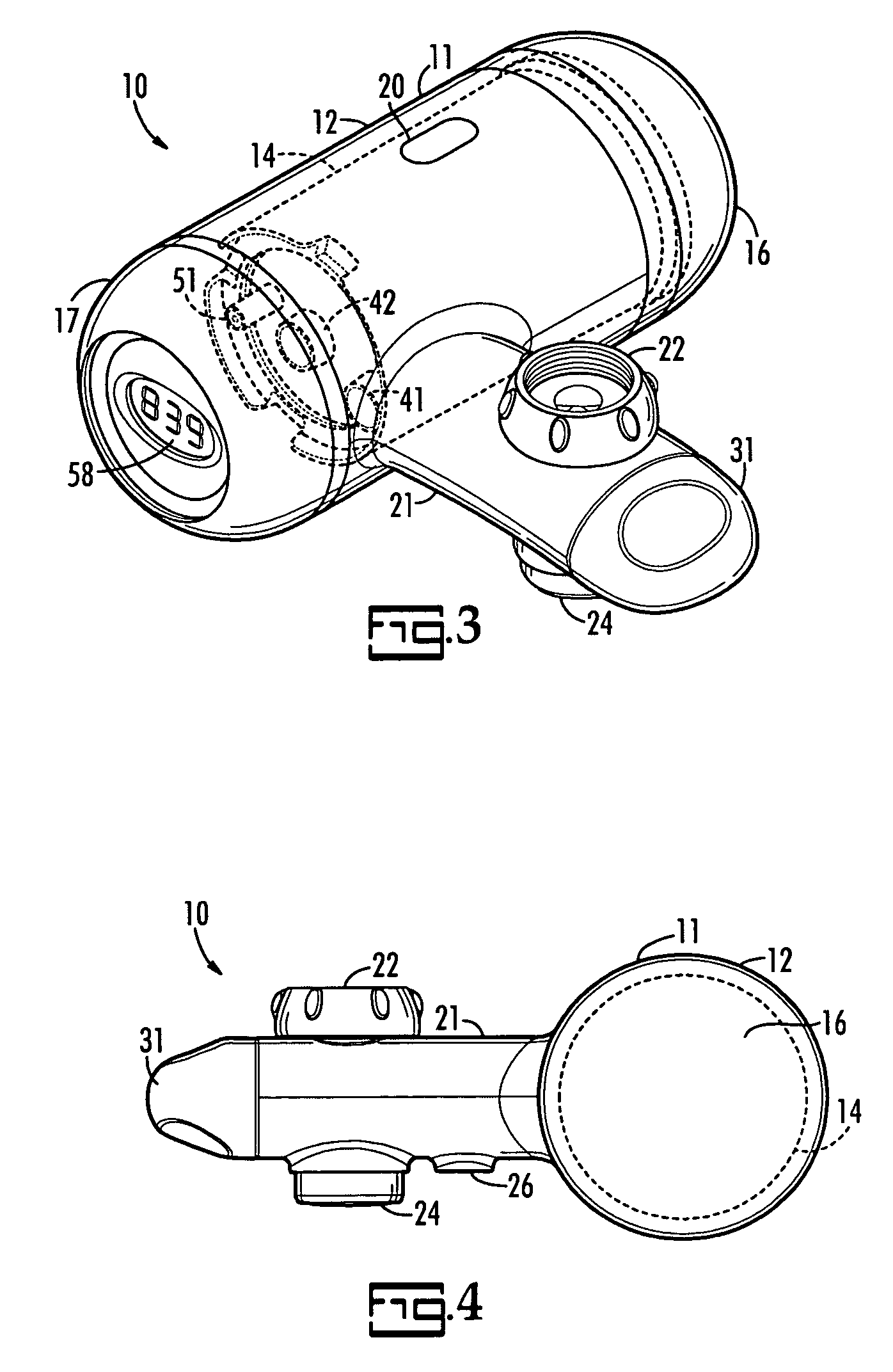
ActiveUS20060207920A1Increase capacityEconomic flexibilityWater treatment parameter controlSettling tanks feed/dischargeReturn-to-zeroFiltration
A faucet mounted filter device includes a horizontally disposed cylindrical part for housing a replaceable filter cartridge and a horizontally disposed arm part extending radially from the cylindrical part which has a connector on its upper side for releasable connection to a downwardly discharging water faucet. A window is provided in the cylindrical part through which the water filtration capacity gallonage is visible. A built in microprocessor with a counter delivers data to a read-out at the front end of the cylindrical part which displays the gallonage of water filtered by the filter cartridge. A sensor connected to the microprocessor senses flow of filter water and installation and removal of the cartridge causes the counter to start counting and to return to zero, respectively.
Owner:PROTECT PLUS
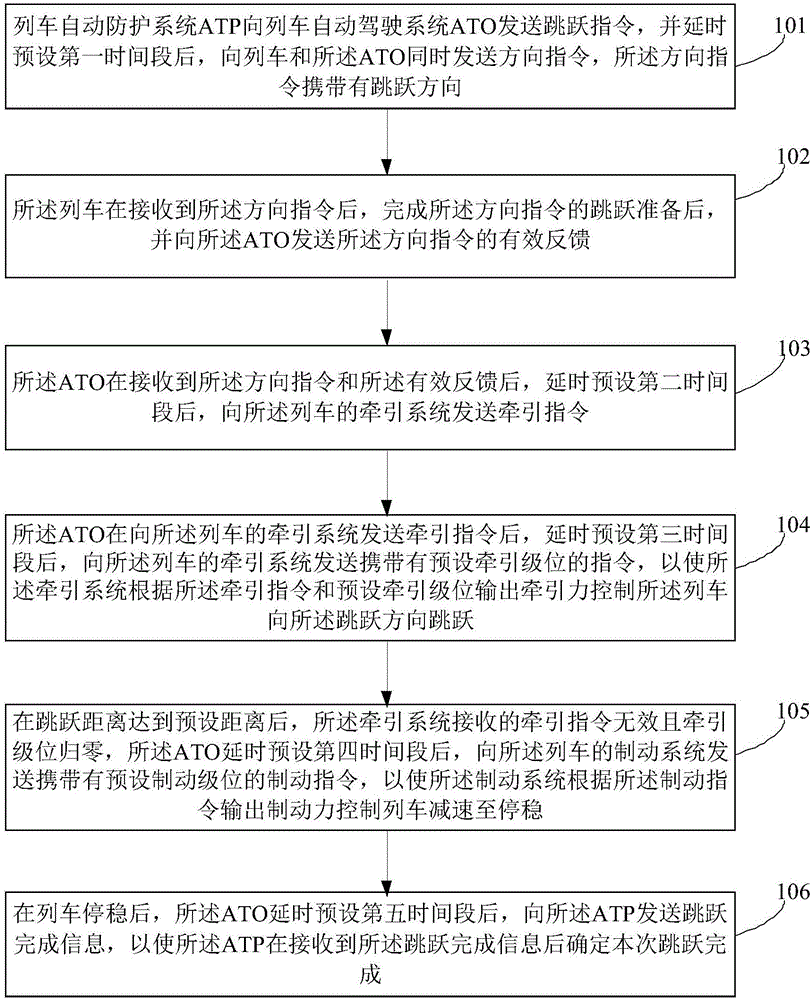
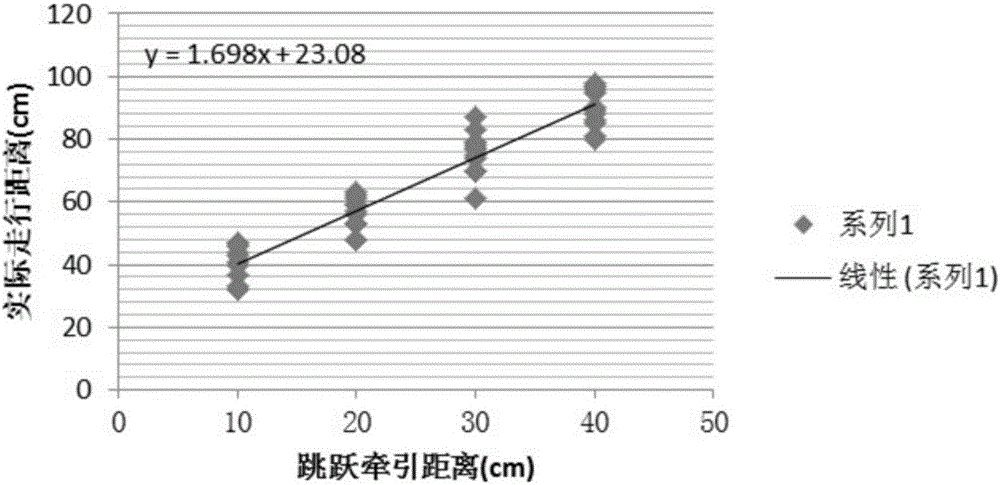
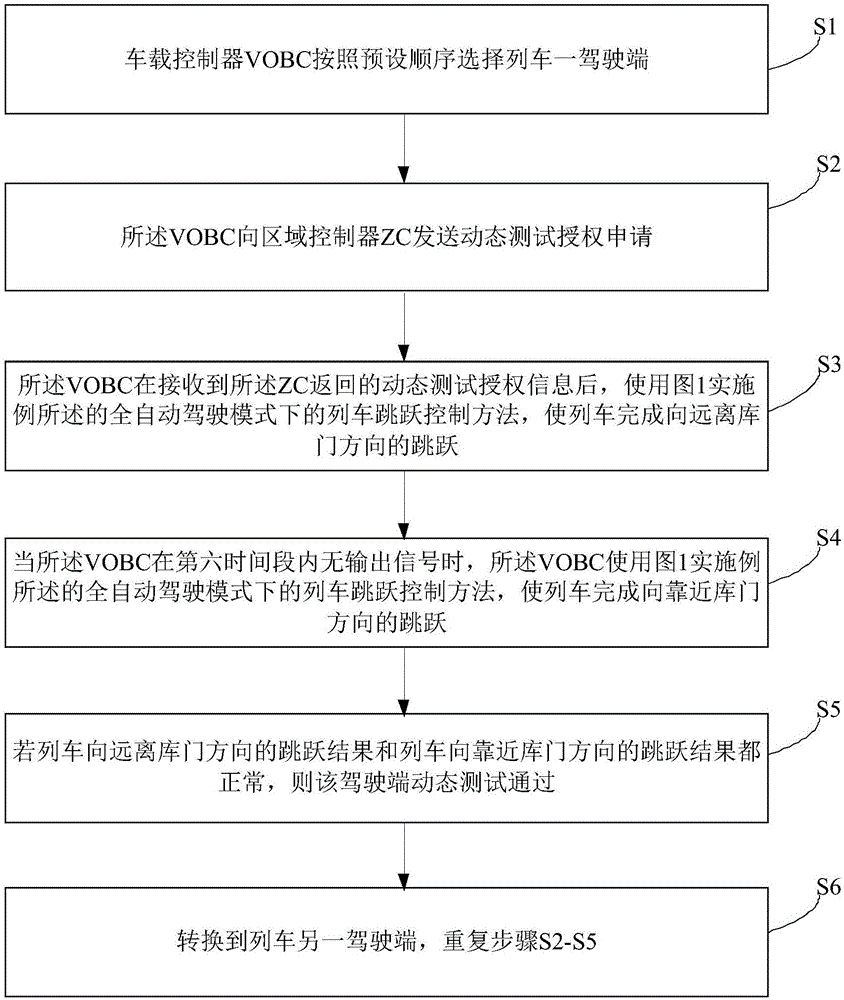
Train jump control method, dynamic testing method and jump benchmark parking method under FAM (Full Automatic Mode)
ActiveCN106347331AAccurate parkingDynamic testing is accurateAutomatic initiationsRailway signalling and safetyReturn-to-zeroTraction system
The invention provides a train jump control method, a dynamic testing method and a jump benchmark parking method under an FAM (Full Automatic Mode). The jump control method comprises the following steps: an ATP transmits a jump instruction to an ATO, delays for T1 and then synchronously transmits a direction instruction to the train and the ATO; the train receives the direction instruction, then finishes jump preparation and transmits an effective feedback of the direction instruction to the ATO; the ATO receives the direction instruction and the effective feedback, delays for T2 and transmits a traction instruction to a train traction system; the ATO delays for T3, then transmits an instruction carrying a preset traction level to the train traction system, enables the train traction system to output a traction force and enables the train to jump; after jump distance reaches preset distance, the traction instruction is ineffective, and the traction level returns to zero; the ATO delays for T4, then transmits a braking instruction carrying a preset braking level to a train braking system, enables the train braking system to output a braking force, and enables the train to slow down and stably stop; after the train stably stops, the ATO delays for T5, then transmits jump finishing information to the ATP, and enables the ATP to determine the finishing of the jump. Based on the jump control method of the train, a dynamic testing result is more accurate, and jump benchmark parking is more precise.
Owner:TRAFFIC CONTROL TECH CO LTD
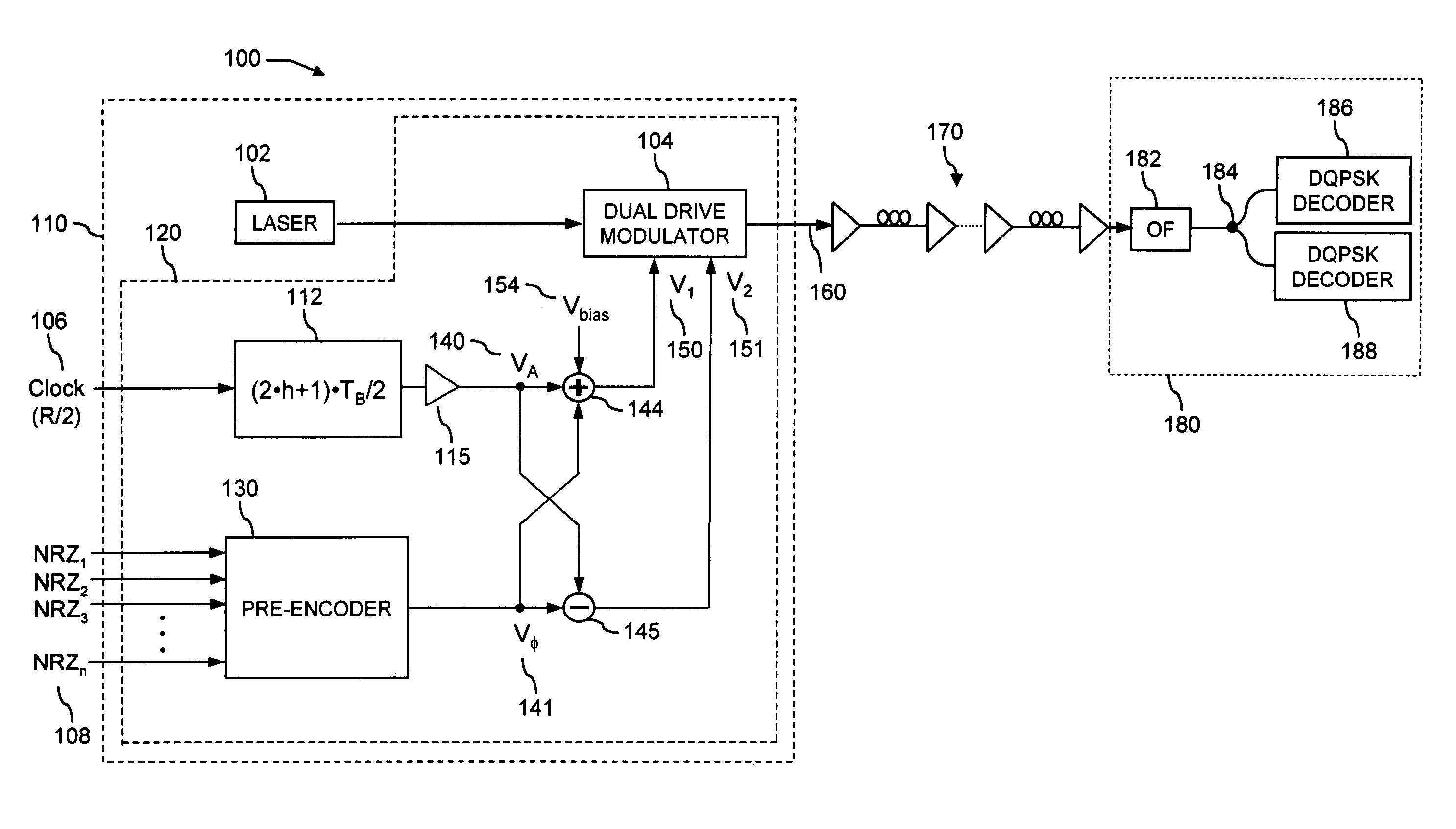
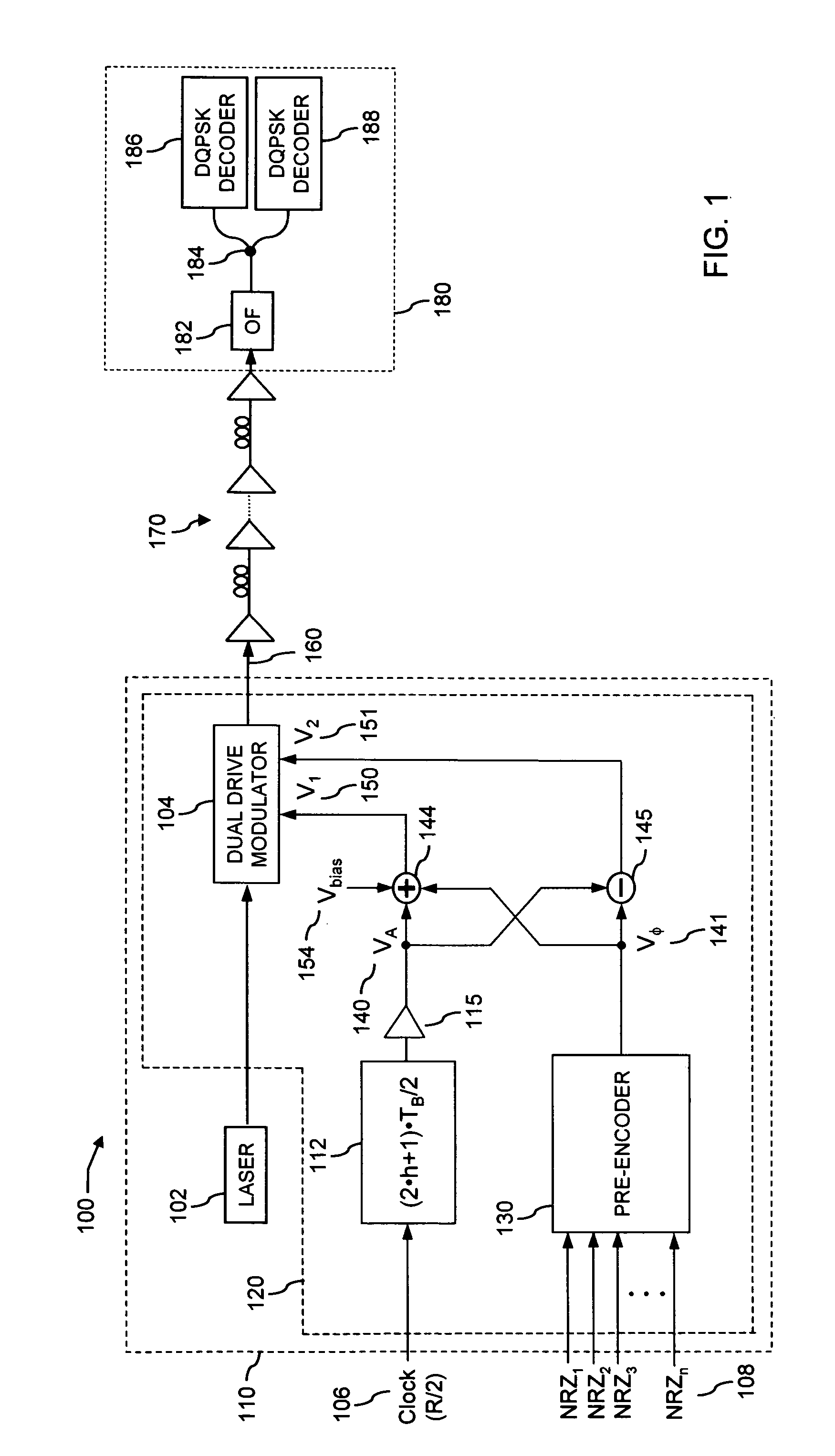
Optical return-to-zero phase-shift keying with improved transmitters
InactiveUS20070009269A1Improve spectral efficiencyElectromagnetic transmittersReturn-to-zeroPhase shifted
An apparatus and a method for transmitting at least a digital optical signal with return-to-zero phase-shift keying, employing a single optical modulator with dual-drive design, the said encoded optical signal having improved spectral efficiency and performances, and being generated by transmitters with simplified scheme; an optical communication system comprising the said apparatus, a transmission line and an apparatus to receive the said optical signal.
Owner:ZITELLI MARIO
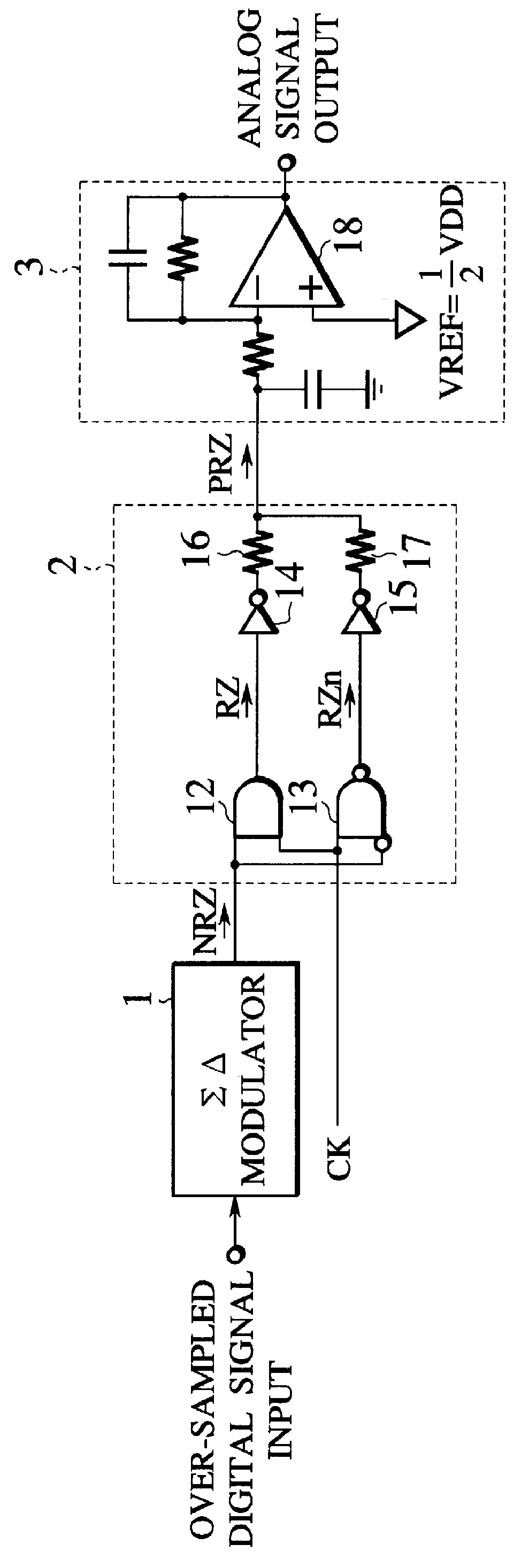
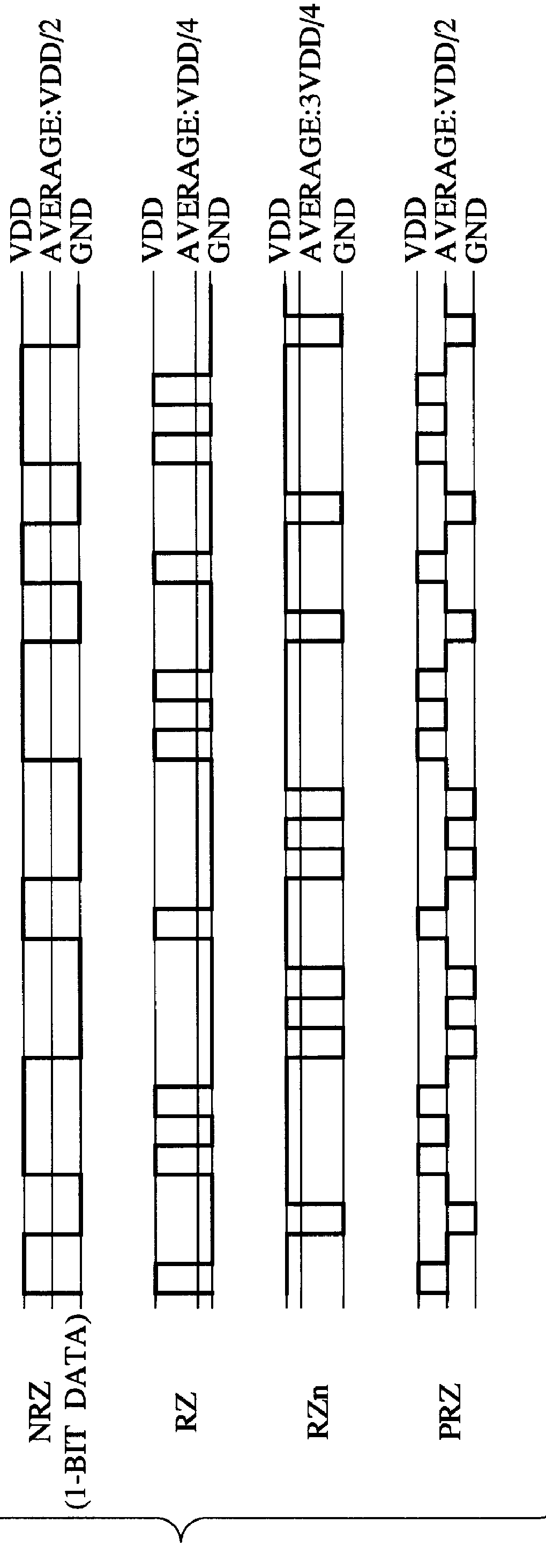
D/A converter
There is provided an over-sampling D / A converter which has a mute function for fixing an average DC potential of an analog output signal to a predetermined potential, and comprises a SIGMA DELTA modulator for receiving a multibit digital signal to which a DC offset value is added and then outputting a one-bit non-return-to-zero signal, a signal generator for receiving the non-return-to-zero signal and the clock signal, then generating a return-to-zero signal which is a logical multiplication of the non-return-to-zero signal and the clock signal and a complementary signal of the return-to-zero signal which is a logical addition of the non-return-to-zero signal and an inverted signal of the clock signal, and then adding the return-to-zero signal to the complementary signal of the return-to-zero signal to thus output a polar-return-to-zero signal, and an analog filter for receiving the polar-return-to-zero signal and then outputting an analog signal. Accordingly, because an average DC potential of an output signal at the time of the mute operation-ON is set substantially equal to the average DC potential of the output signal at the time of the mute operation-OFF, variation in the average DC potential in the output signal due to ON / OFF of the mute operation can be prevented. As a result, generation of audible click noises can be prevented.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Light receiving circuit and signal processing method
ActiveUS20100284703A1Improve reception performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansAmplifiers controlled by lightAudio power amplifierDifferential phase
A light receiving circuit includes: a 1-bit delay interferometer; two photodiodes; and a demodulating circuit for converting current signals of the photodiodes into voltages to thereby demodulate signals that have been modulated by return-to-zero differential phase shift keying, the demodulating circuit including a differential transimpedance amplifier, in which the differential transimpedance amplifier includes a level adjusting circuit that has a function of adjusting levels of a positive phase signal and a negative phase signal of two feedback closed loops.
Owner:NEC CORP
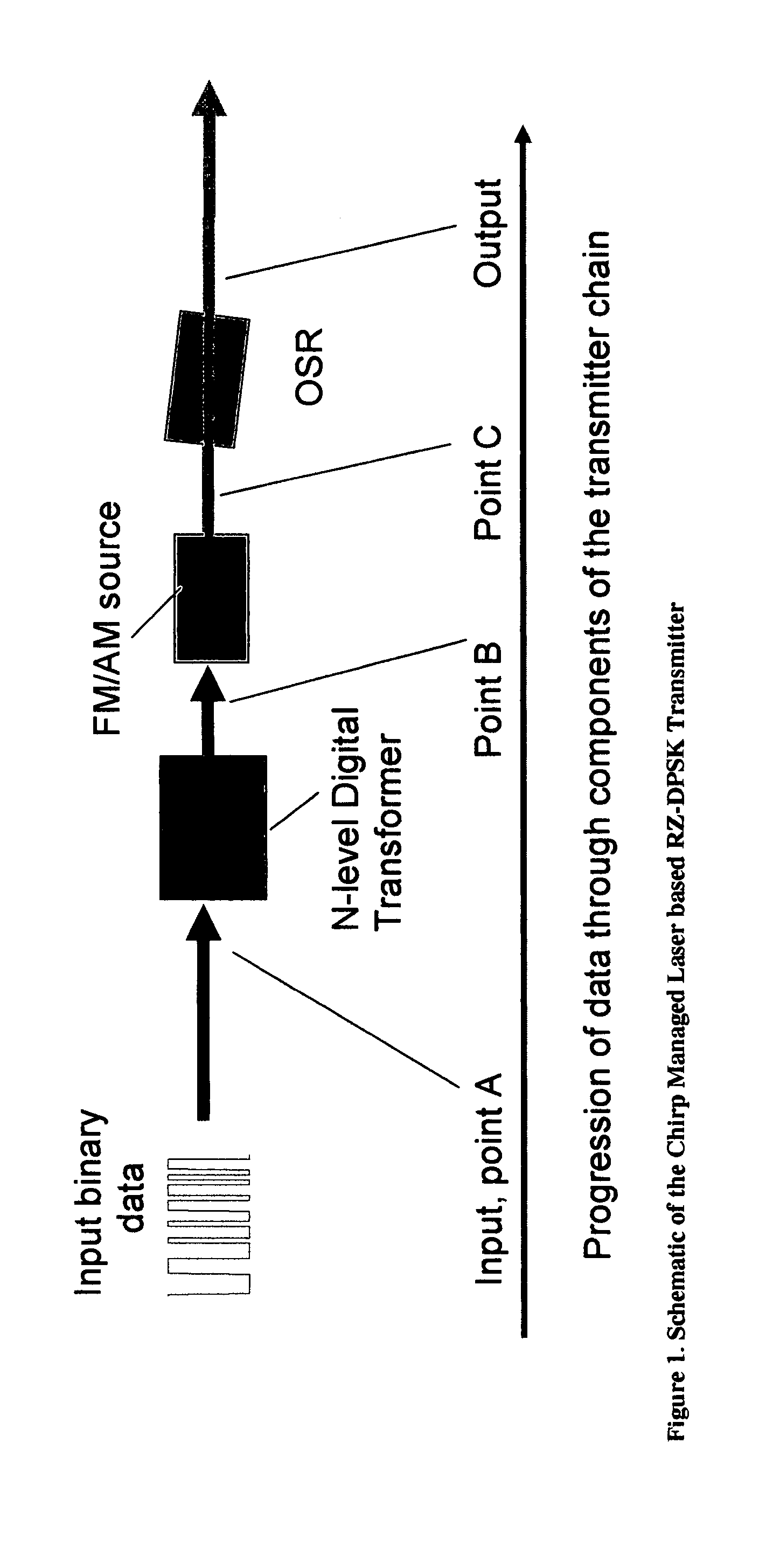
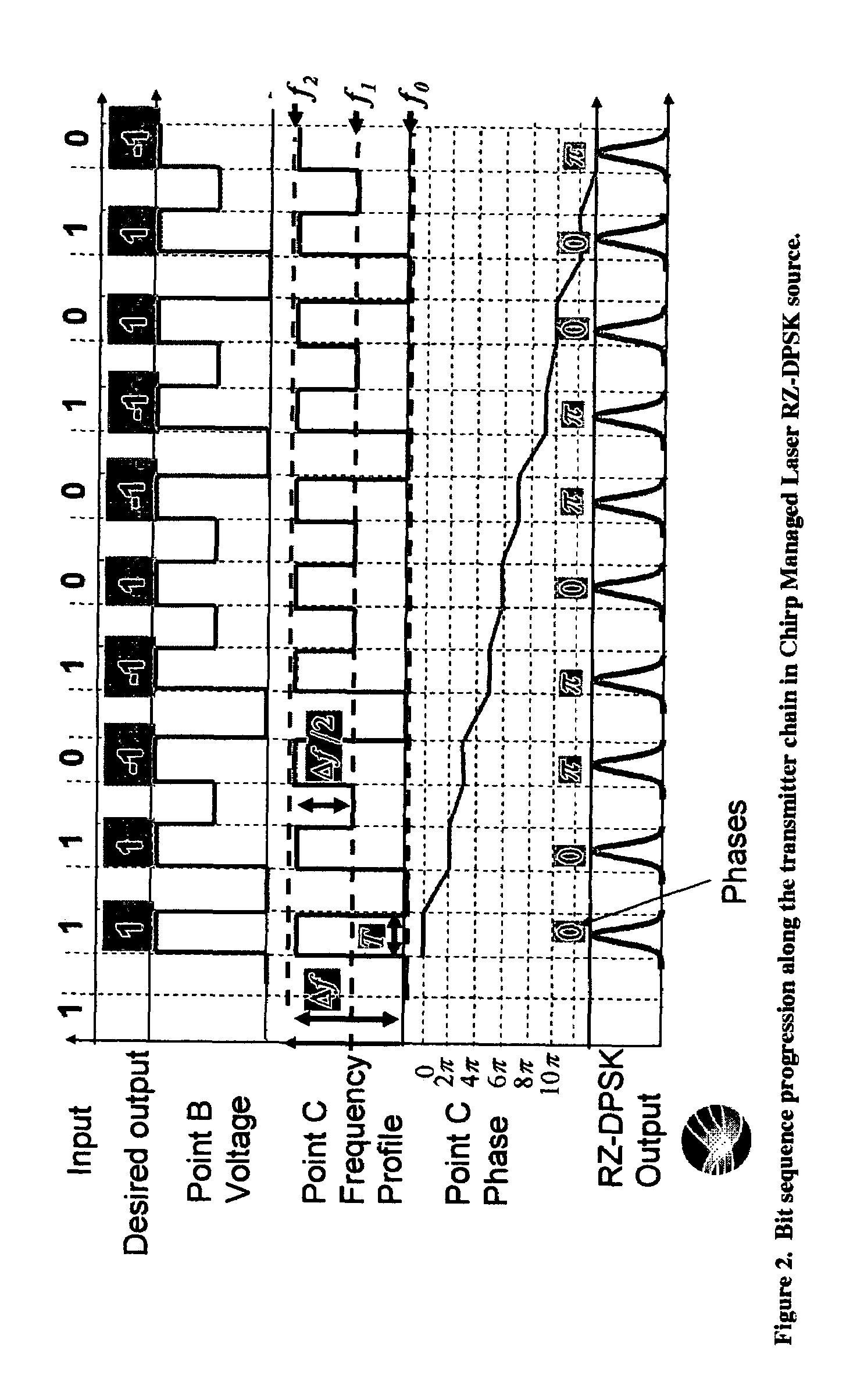
Versatile compact transmitter for generation of advanced modulation formats
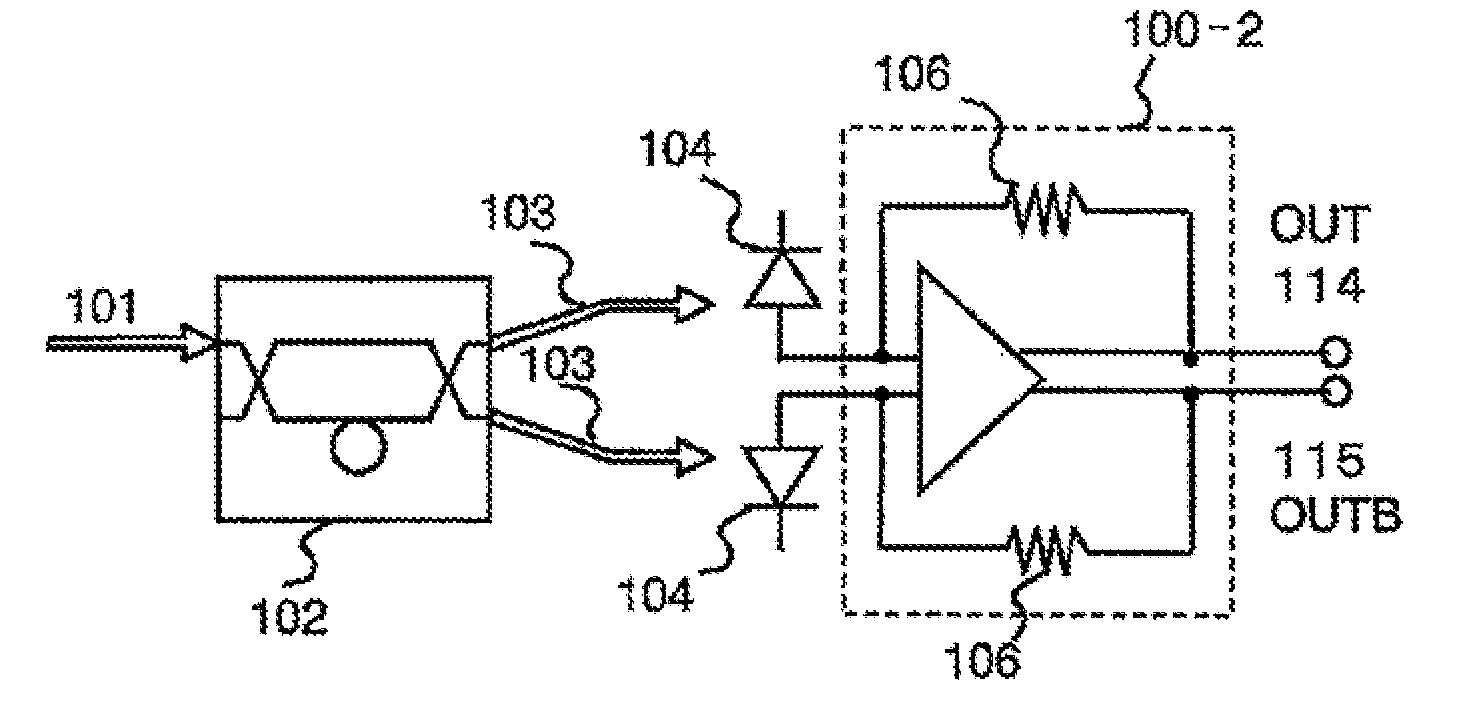
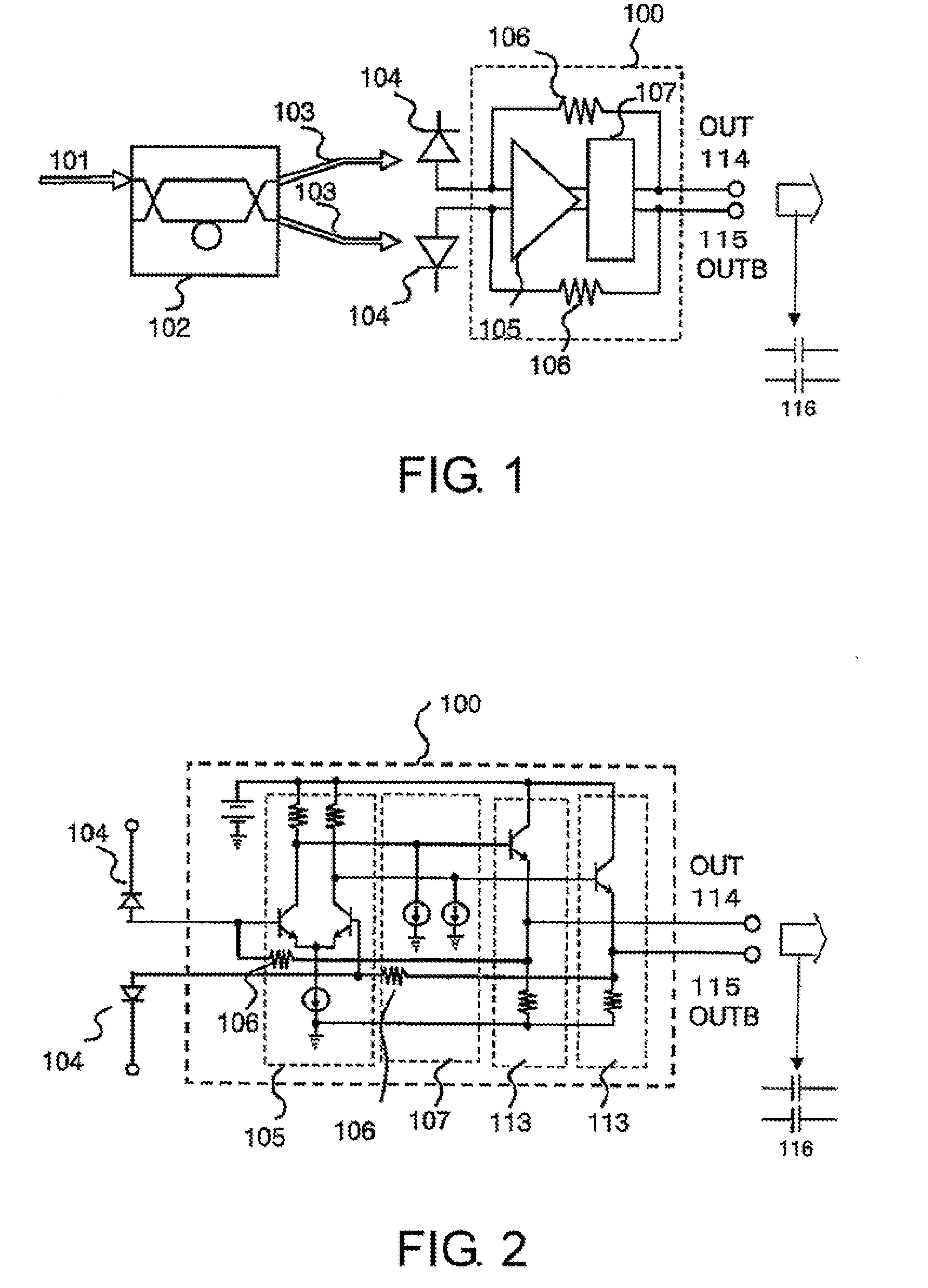
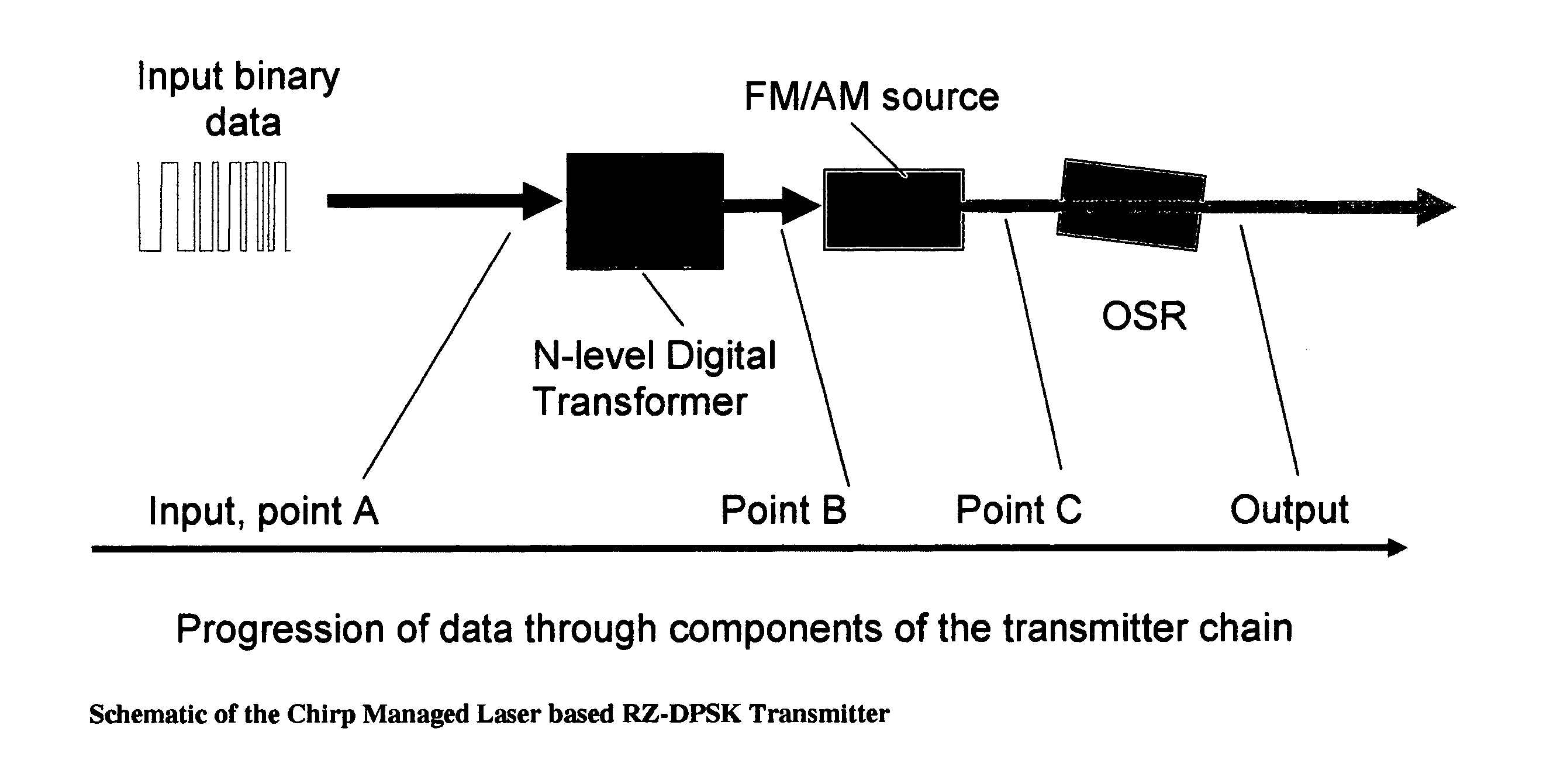
InactiveUS7474859B2Electromagnetic transmittersOptical NRZ to RZ conversionReturn-to-zeroPhase shifted
A system for generating a return-to-zero differentially-phase-shift-keyed (RZ-DPSK) optical signal comprising:a driver comprising an N-level digital multilevel transformer (DMT) configured to receive a two level digital electrical signal representing 1s and 0s and output a N-level electrical signal, wherein N>2;an FM source configured to receive the N-level electrical signal output by the driver and generate an optical frequency modulated signal; andan optical spectrum reshaper (OSR) configured to receive the optical frequency modulated signal output by the FM source and generate the desired RZ-DPSK optical signal. A method for generating a return-to-zero differentially-phase-shift-keyed (RZ-DPSK) optical signal, the method comprising:(1) receiving a two level digital electrical signal representing 1s and 0s and outputting a N-level electrical signal, wherein N>2;(2) receiving the N-level electrical signal output and generating an optical frequency modulated signal; and(3) receiving the optical frequency modulated signal and generating the desired RZ-DPSK optical signal.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
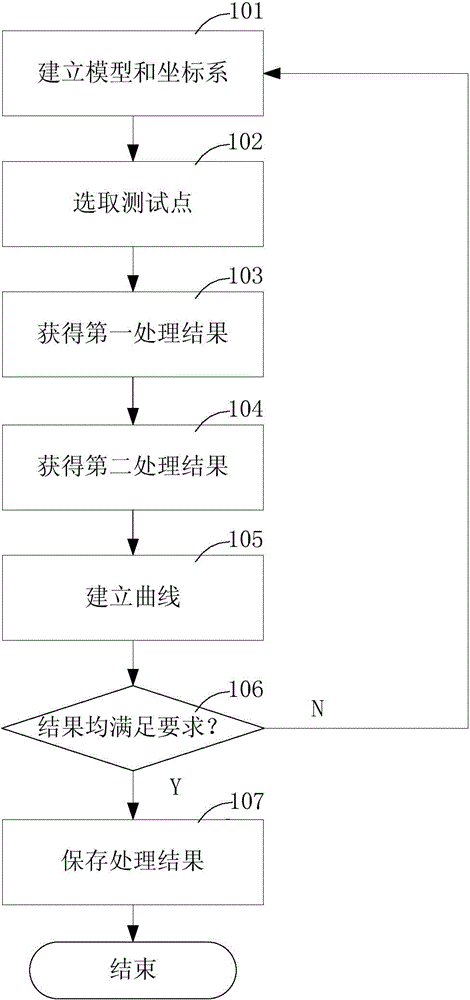
CAE (computer aided engineering)-based car body rigidity analysis method
InactiveCN104573174AReduce workloadThe result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsReturn-to-zeroWorkload
The invention relates to the technical field of computer aided engineering (CAE), in particular to a CAE (computer aided engineering)-based car body rigidity analysis method used for analyzing the bending rigidity and the torsional rigidity of a front longitudinal beam, a threshold and a rear longitudinal beam of the car body. The CAE-based car body rigidity analysis method comprises the following steps: establishing a finite element mesh model of the car body and a coordinate system; carrying out a simulation test by applying load and constraints; obtaining a processing result, and generating a curve; then, judging whether the processing result meets requirements; if the processing result meets the requirements, storing the processing result, and otherwise, establishing a finite element mesh model of the car body again to conveniently carry out a simulation test. In the method, the displacement and the torsion angle of a node are analyzed by the finite element mesh model of the car body to carry out rigidity analysis instead of calculating by selecting the node by experience, and therefore the result is more accurate; an analysis result is automatically obtained, the workload of engineers is lightened, and project development time is saved; the result can be returned to zero to make the result to be normalized, the result has high compatibility, and comparison and analysis can be conveniently carried out.
Owner:BRILLIANCE AUTO
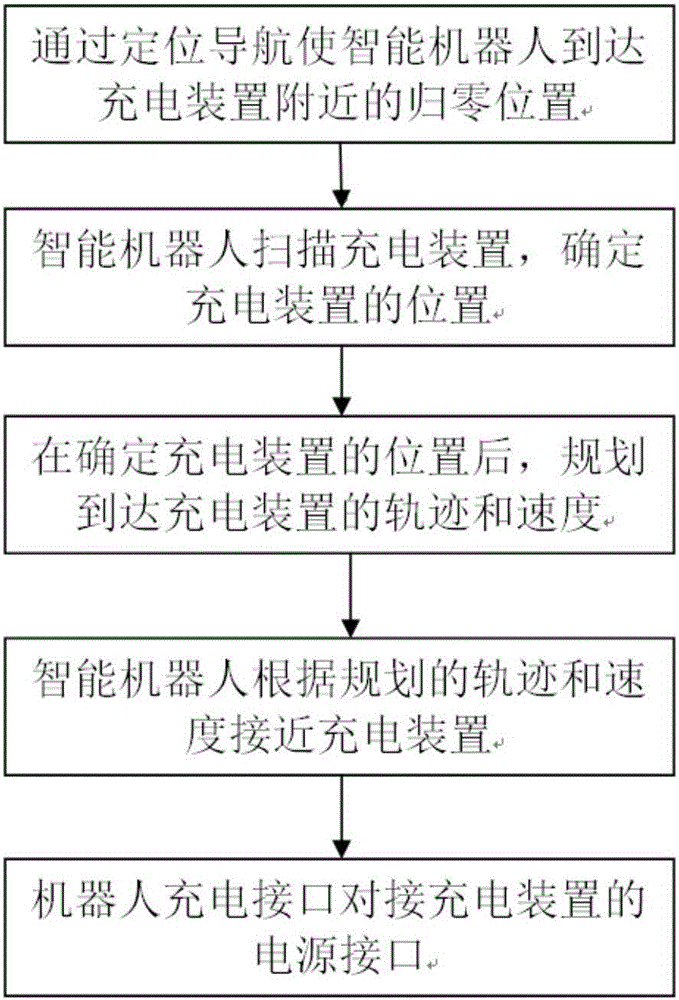
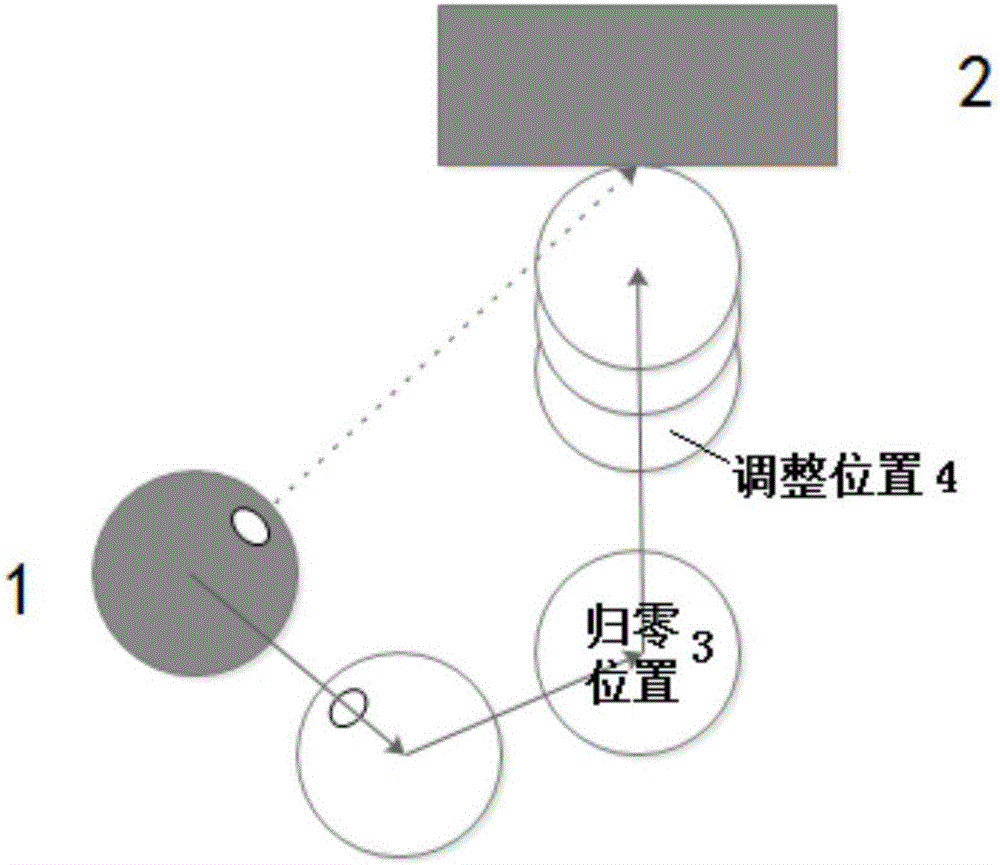
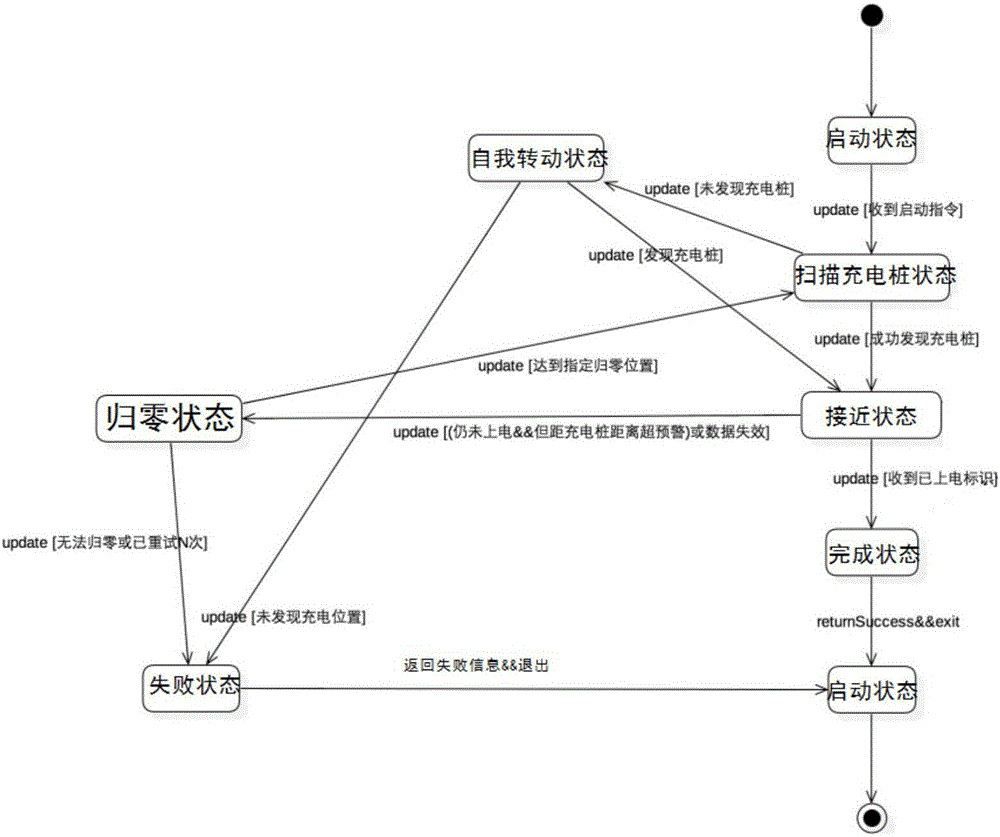
Automatic charging method for intelligent robot
ActiveCN105739501AImprove docking success rateLow docking timeBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerReturn-to-zeroButt joint
The invention provides an automatic charging method for an intelligent robot, which comprises the following steps that: 1, the intelligent robot reaches the return-to-zero position near a charging device through the navigation and positioning; 2, the intelligent robot scans the charging device and determines the position of the charging device; 3, after the position of the charging device is determined, a track and a speed through which the charging device is reached are programmed; 4, the intelligent robot approaches the charging position according to the programmed track and speed; and 5, a charging interface of the robot is in butt joint with a power supply interface of the charging device. According to the method, the control mechanism adapted to various actual states is introduced in a re-charging process for the accuracy and safety considerations, so that the robot can make emergency response and adjustment adaptable to various abnormal states.
Owner:北京云迹科技股份有限公司
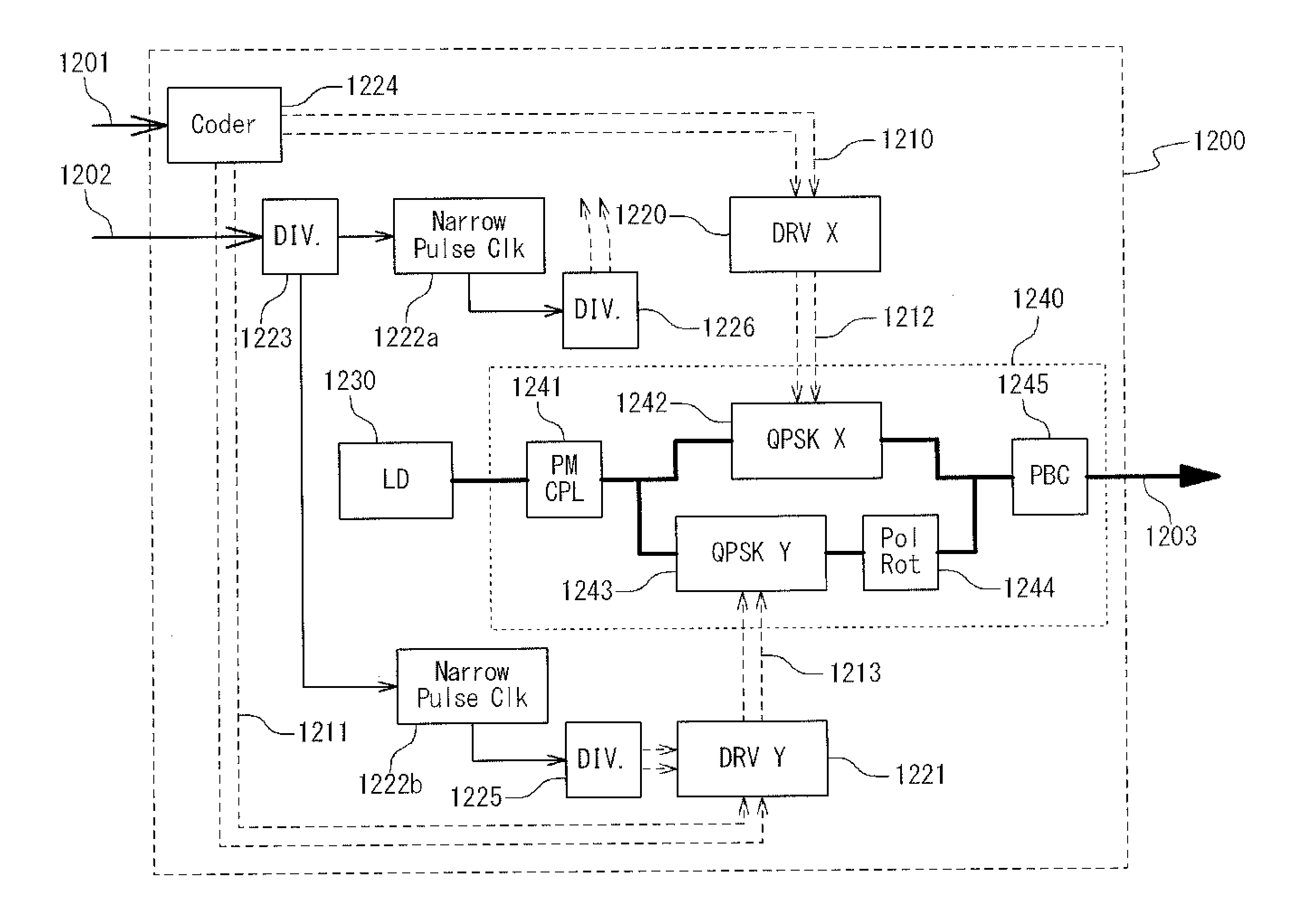
Apparatus for pseudo-return-to-zero modulation
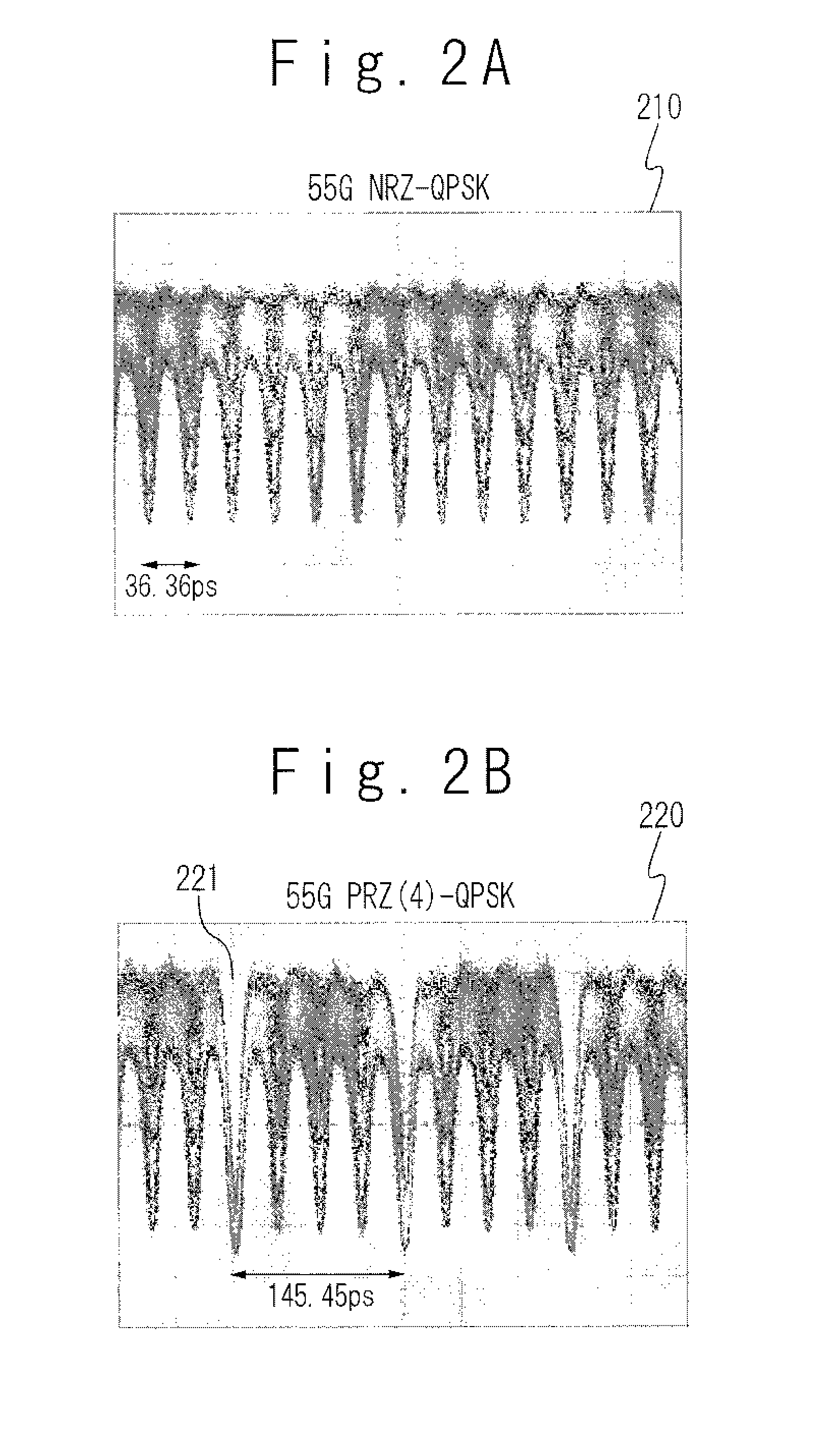
A Pseudo-Return-to-Zero modulator is provided with a narrow pulse clock generator, a modulator driver, and an optical modulator. The narrow pulse clock generator generates a narrow pulse clock of order n, where one of levels occupies half a symbol period and the other level occupies (n−1) plus half a symbol period, n being equal to or more than two. The modulator driver generates an electrical signal in response to binary data and the narrow pulse clock. The optical modulator modulates an optical carrier in response to the electrical signal so that the modulated optical carrier is in a PRZ(n) format.
Owner:NEC CORP
Double-axis synchronous movement control device and method based on feedback of laser displacement sensor
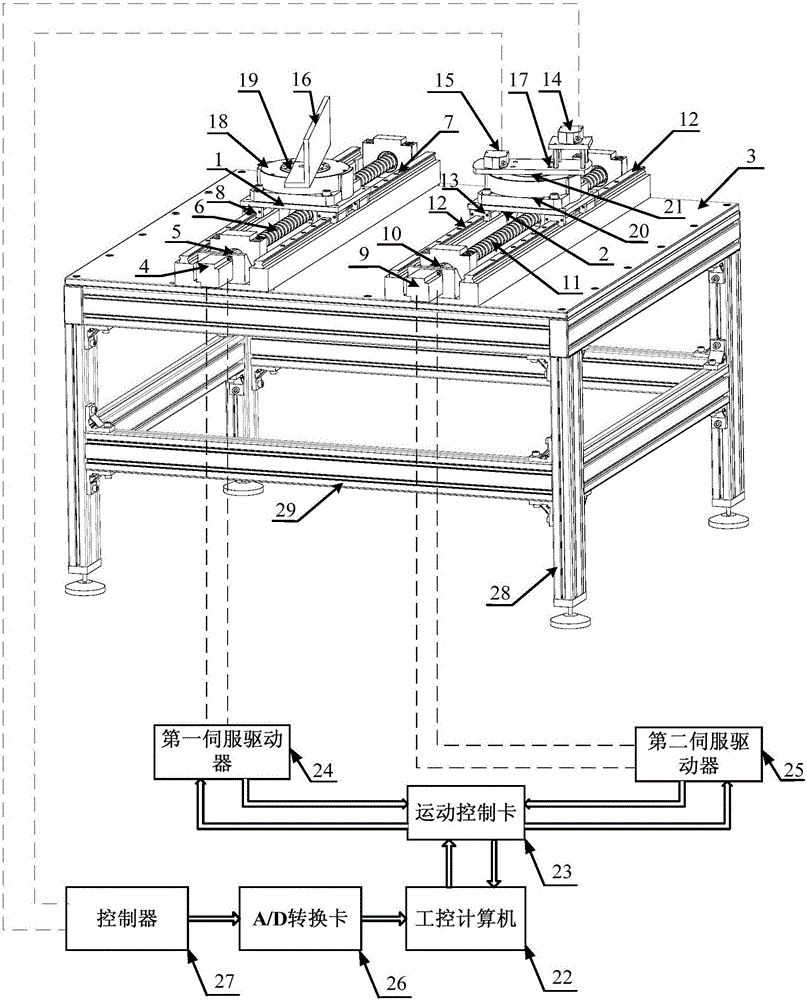
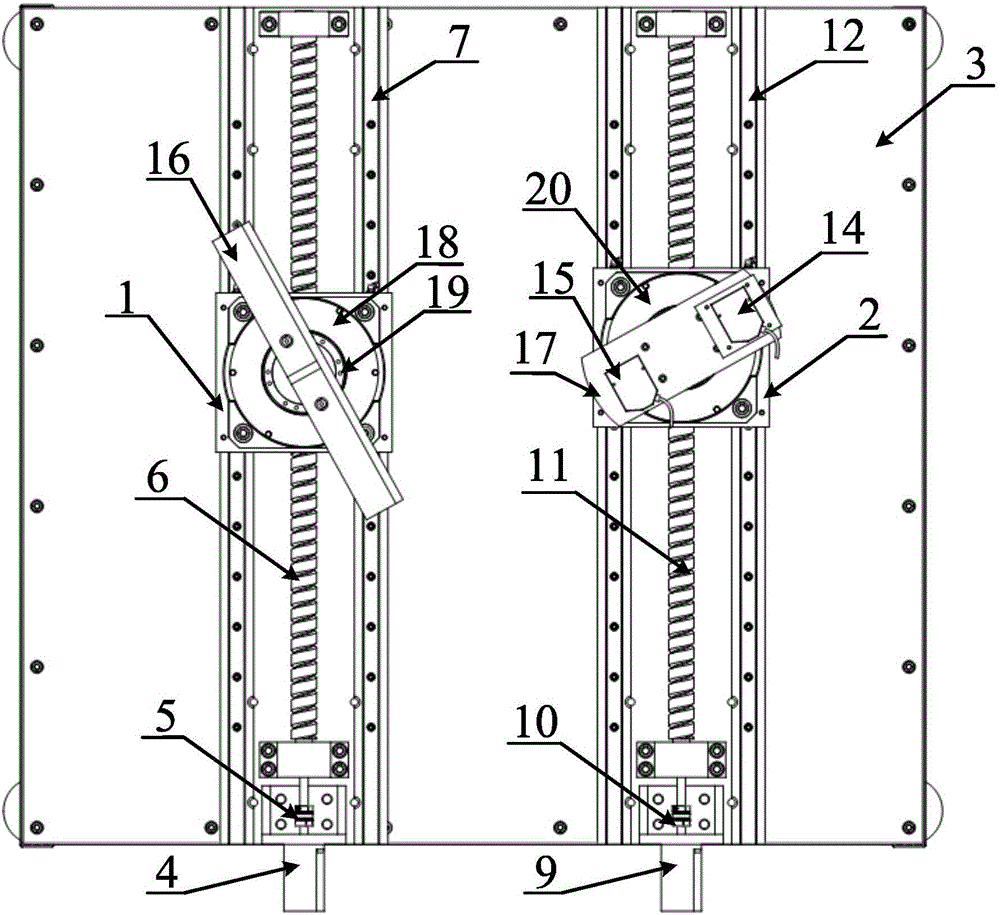
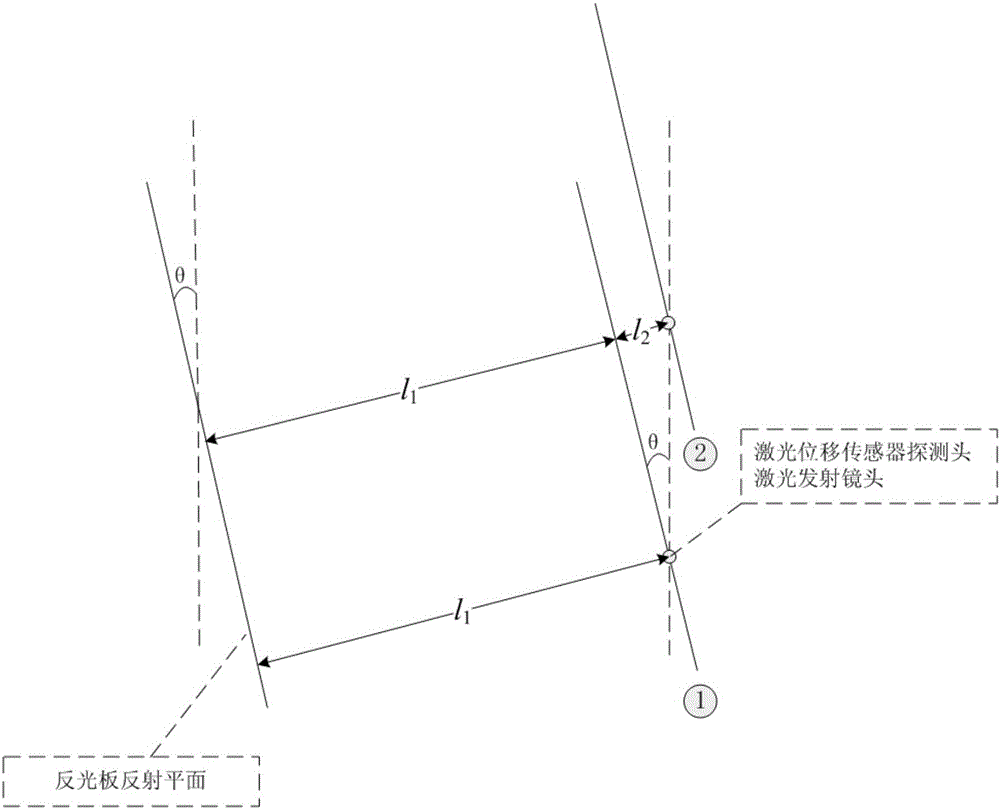
ActiveCN106125774AHigh measurement accuracyHigh sampling frequencyControl using feedbackLong path laserReturn-to-zero
The invention discloses a double-axis synchronous movement control device and method based on the feedback of a laser displacement sensor, and the device comprises a double-axis synchronous movement control device body, a displacement detection system, and a control module. The double-axis synchronous movement control device body comprises a first drive mechanism, a second drive mechanism, a first linear movement platform, a second linear movement platform, and an experiment table. The displacement detection system comprises a long-distance laser displacement sensor, a high-precision laser displacement sensor, a reflecting plate, a workbench, a first dividing plate, and a second dividing plate. The control module is connected with the first drive mechanism, the second drive mechanism, the long-distance laser displacement sensor and the high-precision laser displacement sensor. The device enables the movement range of the double-axis synchronous movement control to be enlarged, breaks the limits of a conventional fixed-type detection device, does not need to return to zero, achieves the synchronous movement stably, accurately and quickly, and can quickly recover the synchronization when interference appears and the movement is not synchronous.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Control of an optical modulator for desired biasing of data and pulse modulators
ActiveUS7394992B2Sacrificing performanceStable and accurate operating pointTransmission monitoringElectromagnetic transmittersData streamPulse modulator
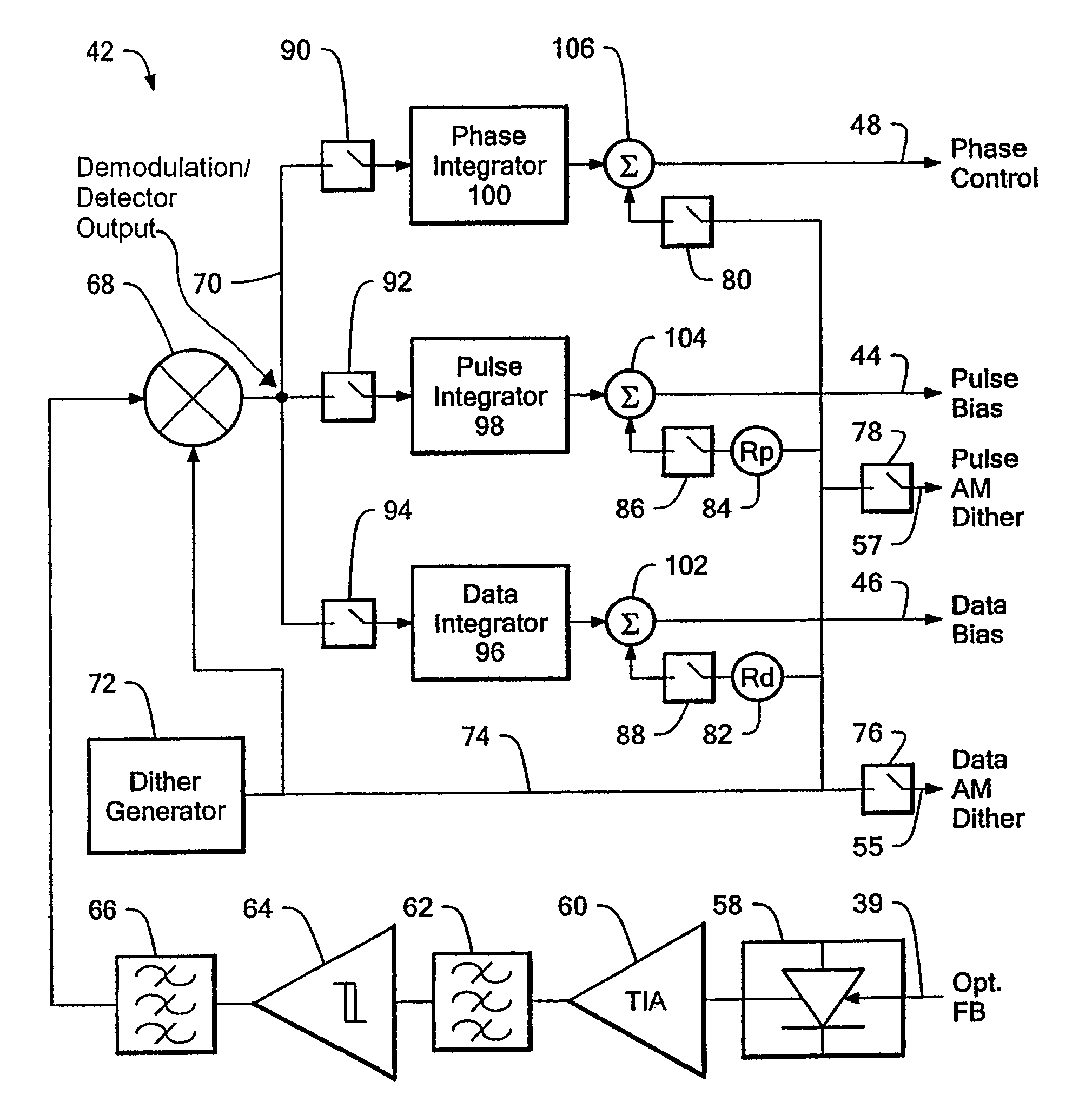
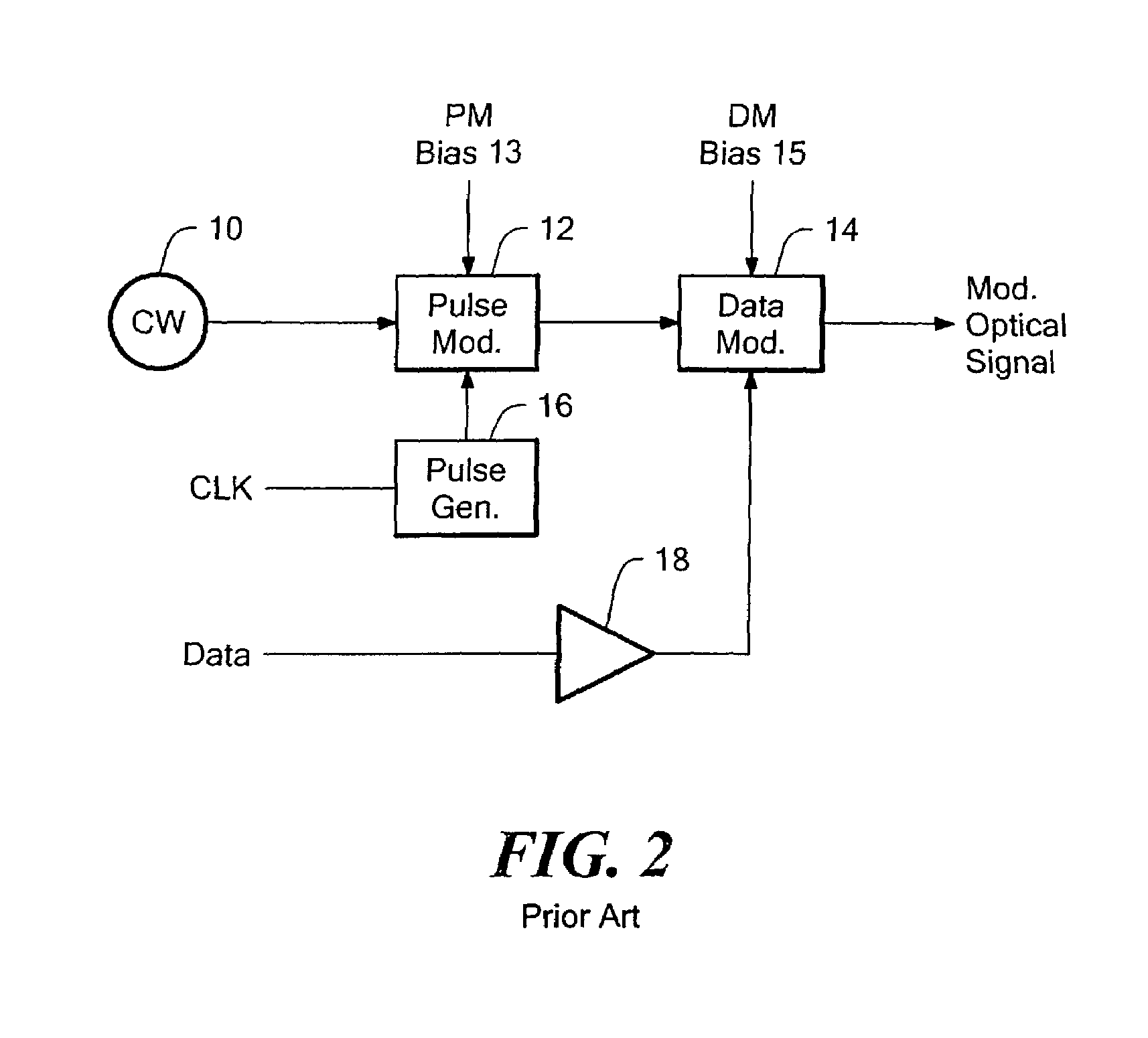
In an optical transmitter, continuous wave light from a laser passes through a data modulator (DM) for non-return-to-zero (NRZ) encoding of a data stream and through a pulse modulator to add return-to-zero encoding to the modulated optical signal. A modulator controller monitors the output optical signal power, optimizes the bias setting for the DM and the PM, and optimizes the phase relationship between the pulse and data components of the modulated optical signal. For each optimization, a low amplitude and low frequency dither signal is injected at appropriate points in the modulator. A single photo detector and electrical receiver are used in a multiplexed fashion to monitor the optical output signal and derive separate feedback signals. Remaining control circuitry forces a null in a respective residual dither component in the optical output signal to maintain the desired bias level or phase alignment.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPTICS INC
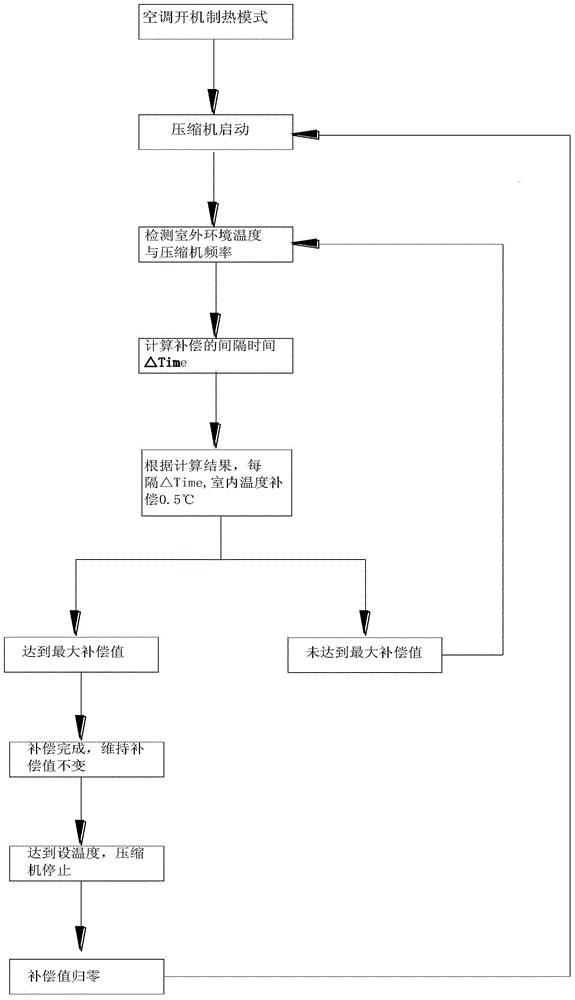
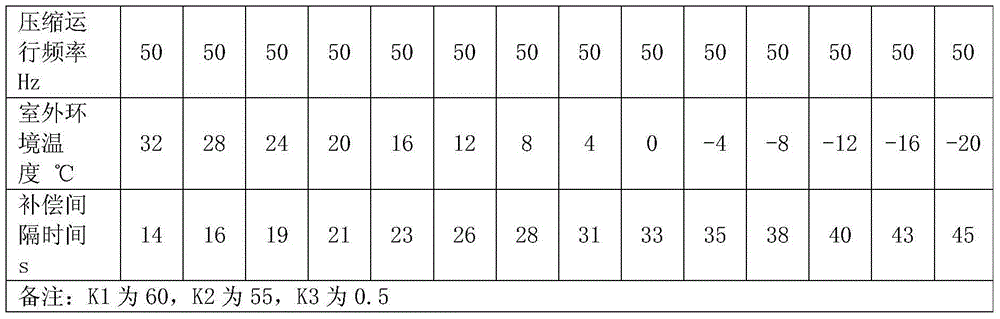
Control method for indoor temperature compensation during heating operation of variable frequency air conditioner
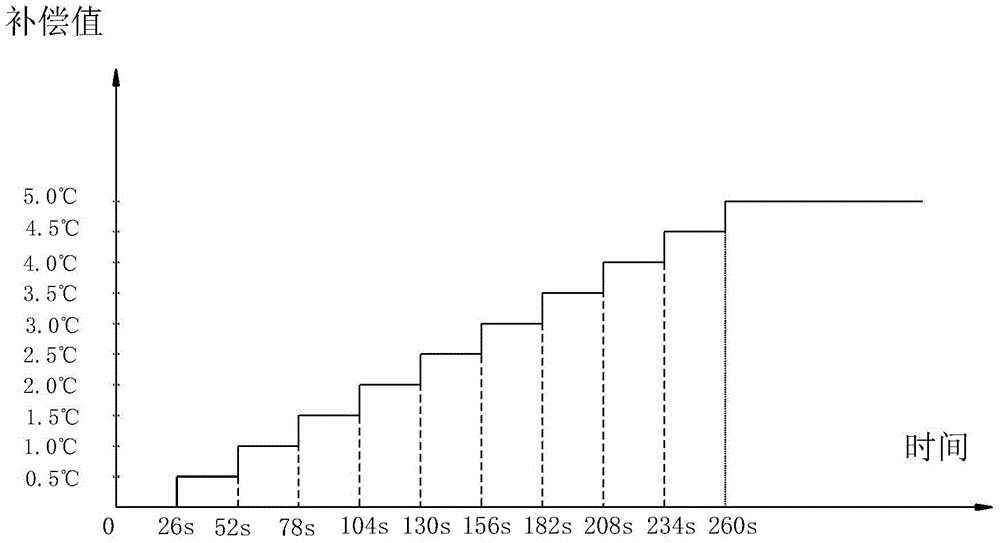
ActiveCN104654528AComply with heat loadAccurate temperature controlMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsTemperature controlReturn-to-zero
The invention discloses a control method for indoor temperature compensation during heating operation of a variable frequency air conditioner. After a compressor is started, sectional cumulative compensation is adopted to cumulate an indoor temperature compensation value according to set interval time and a set temperature compensation step value until to a set indoor temperature total compensation value; the compressor stops when the indoor temperature reaches the set temperature, and the compensation value is returned to zero; the compensation is restarted after the indoor temperature is lower than the set temperature and the compressor is restarted. By using the sectional cumulative compensation method, the temperature in a room can be reflected more really. Thus, the frequency calculation of the compressor conforms to real room heat load well, so the temperature control of the air conditioner is more accurate and the comfort of a user can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN MEGMEET ELECTRICAL CO LTD
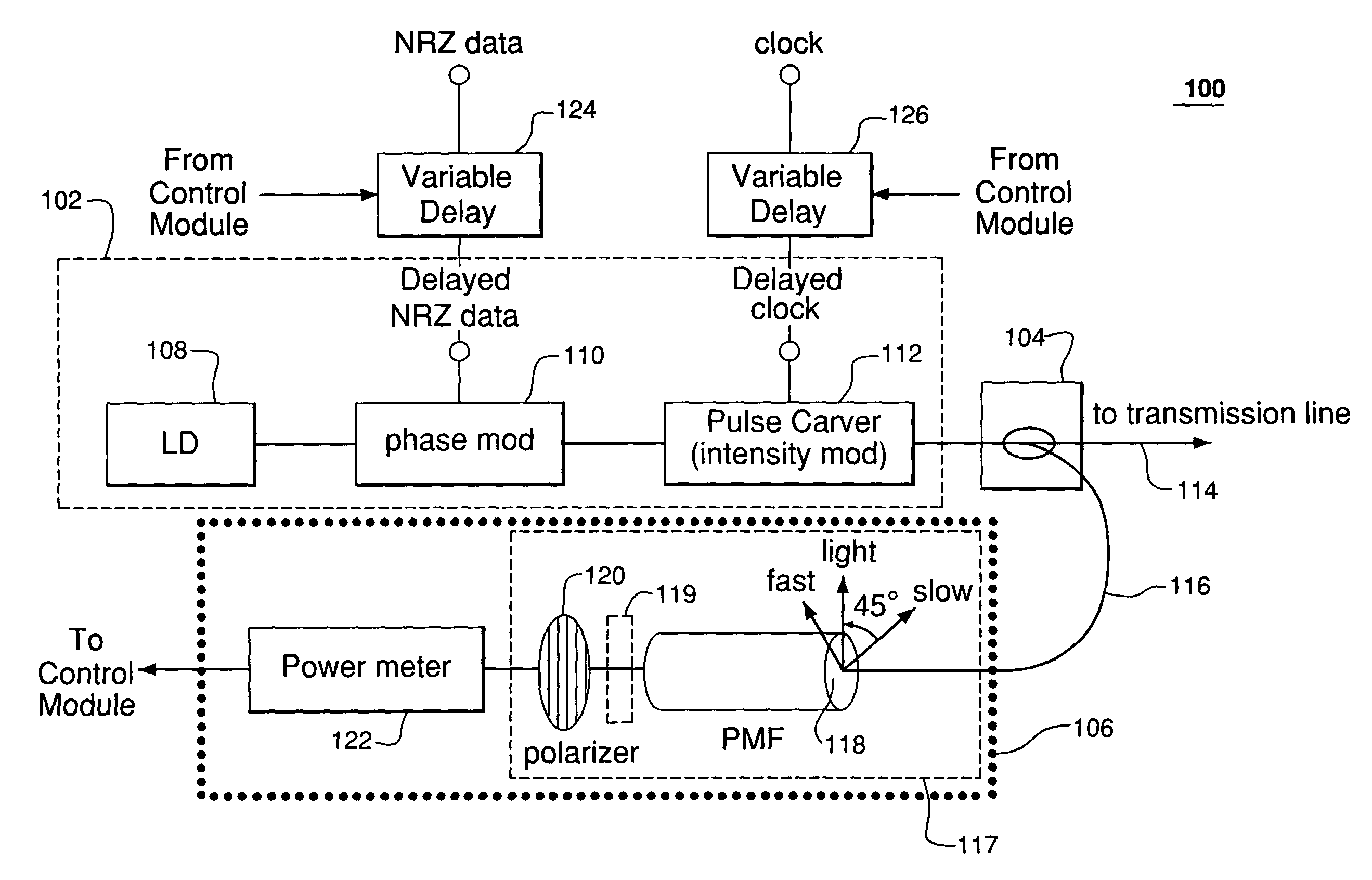
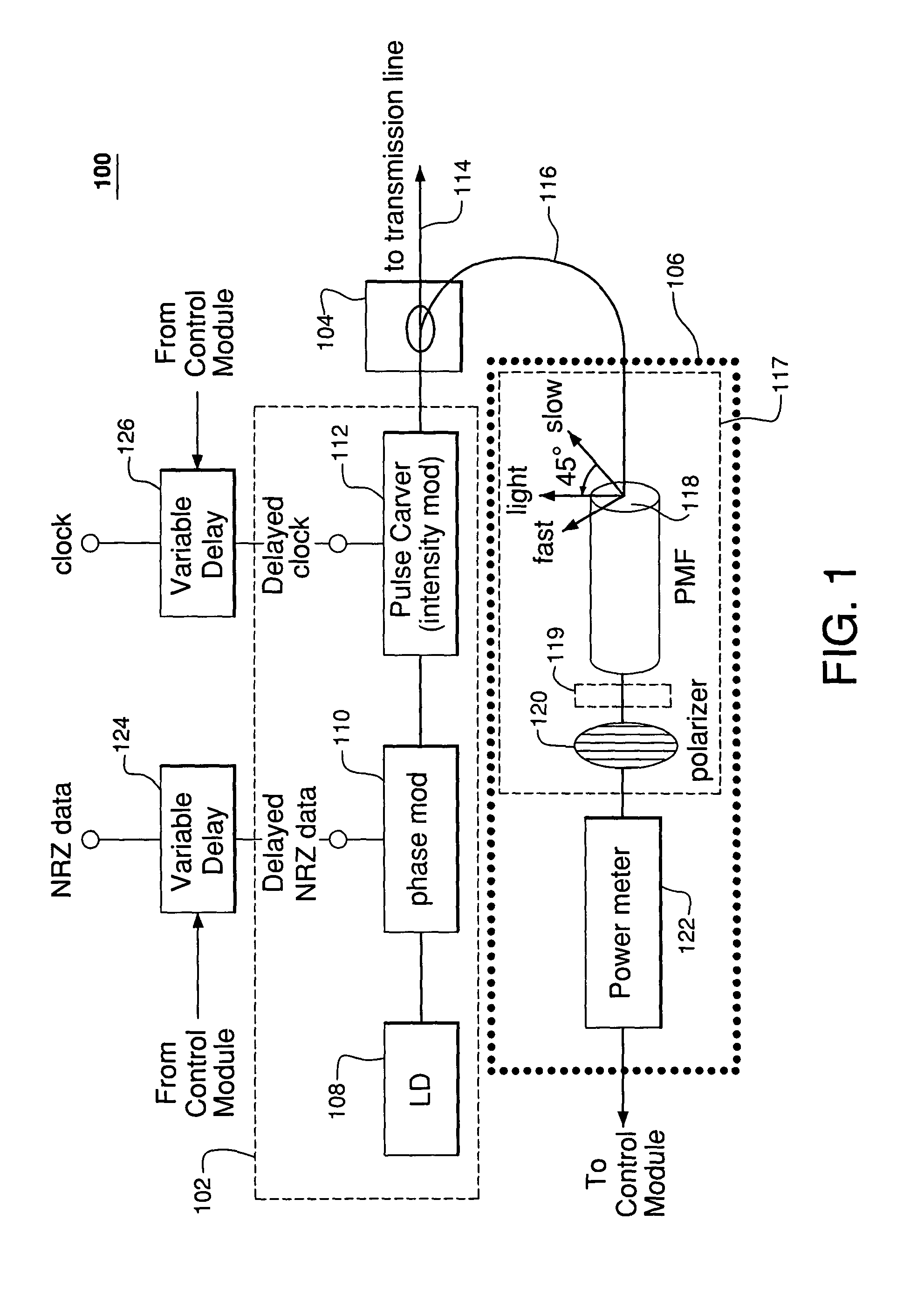
Monitoring alignment between pulse carvers and phase modulators in optical systems
Timing alignment between a pulse carver (i.e., intensity modulator) and a phase modulator, e.g., in a return-to-zero (RZ) differential phase-shift keying (DPSK) optical transmitter, is monitored by filtering a signal from the transmitter and measuring the power of the filtered signal. In certain embodiments, the filter has a birefringent device (such as a polarization-maintaining fiber) and a polarizer. The polarizer may be a rotating polarizer with a rotating quarter-wave plate in front of it. In other embodiments, the filter is a periodic filter such as a Mach-Zehnder interferometer or an etalon filter. Regardless, the measured power may be used to generate control signals used to variably delay the signals that drive the phase modulator and / or the pulse carver to compensate for detected misalignment. The measured power may also be used to monitor the bit-error-rate degradation caused by timing misalignment between the pulse carver and the phase modulator.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Rotary Vector Gear for Use in Rotary Steerable Tools
A rotary vector gear for controlling longitudinal axis offset about a central longitudinal axis is disclosed. The device uses single rotary motion through a rotary vector gear to produce hypotrochoidic offset similar to a flower petal and is capable or ready return to zero offset. The device may be used in downhole rotary steerable oil and gas drilling tools and in computer controlled milling machines for providing controlled offset.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method for testing liquid absorption rate of battery diaphragm
InactiveCN103512821AAccurate measurementEasy to operateWeighing by absorbing componentReturn-to-zeroOperability
The invention relates to the field of battery detection and discloses a method for testing the liquid absorption rate of a battery diaphragm. The method comprises the following steps: (1) intercepting a diaphragm sample; (2) measuring the volume of the diaphragm sample, and recording the volume as V1; (3) putting a container filled with an electrolyte on an electronic scale, making the reading return to zero, fixing a circular ring by using a fine line, and recording reading of the scale as M1 after the circular ring is completely immersed and suspended in the electrolyte; (4) fixing the diaphragm sample on the circular ring, repeating the step (3), and recording reading of the scale as M2 within 1-180 minutes; and (5) substituting a formula L=(rhoV1+M1-M2) / V1 of the liquid absorption rate, and calculating the liquid absorption rate L. The method has the advantages of simplness in operation, accurate test result, simple equipment, high operability, low test cost and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN SENIOR TECH MATERIAL
Method and system for 80 and 160 gigabit-per-second QRZ transmission in 100 GHz optical bandwidth with enhanced receiver performance
InactiveUS20060228118A1High receptionHigh transmissionPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberFir system
Owner:TERADVANCE COMM
Configurable pulse amplitude modulation clock data recovery
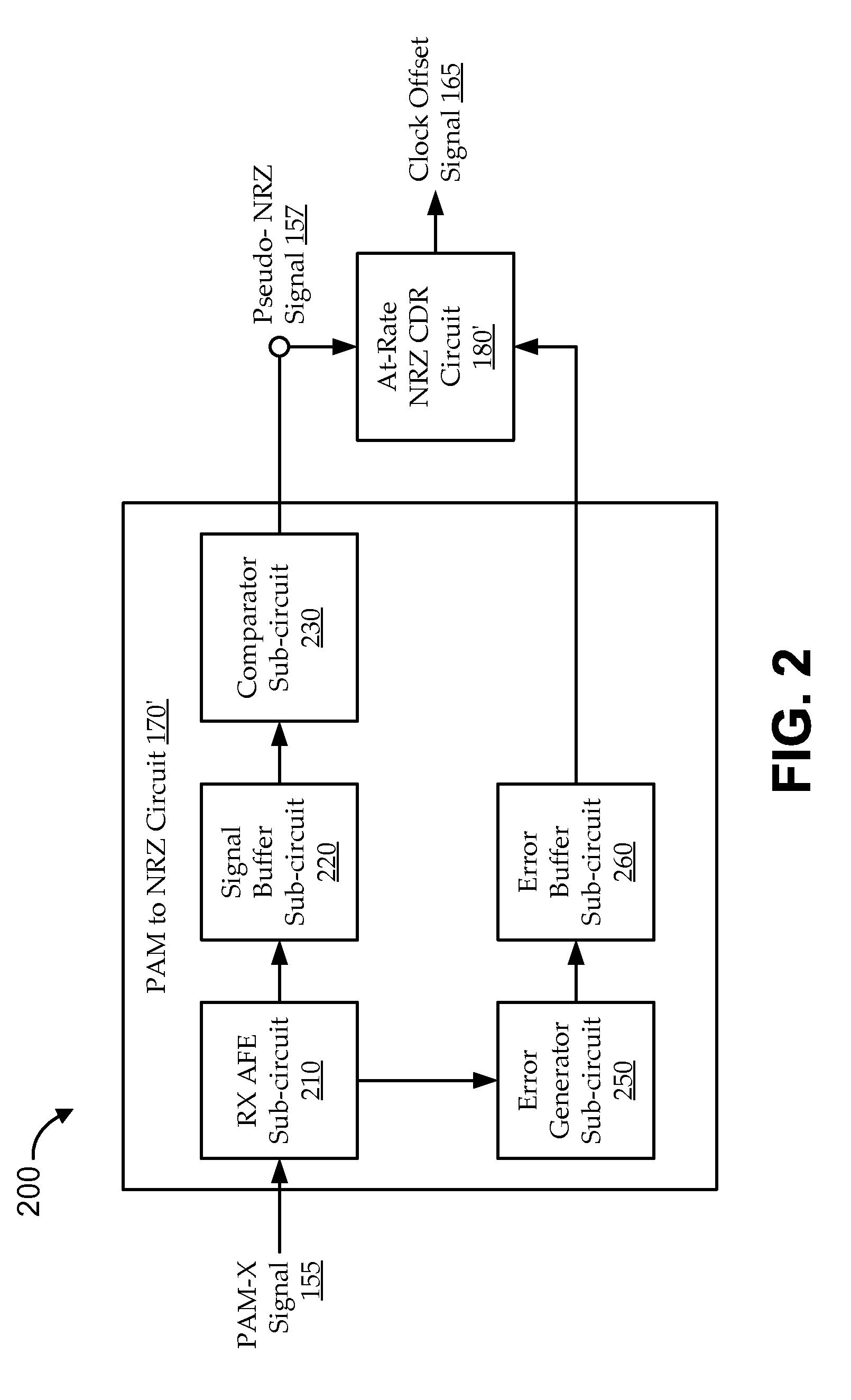
ActiveUS9184906B1Facilitate dual-mode signalingReduce workloadSynchronisation error correctionSynchronisation error detectionReturn-to-zeroDual mode
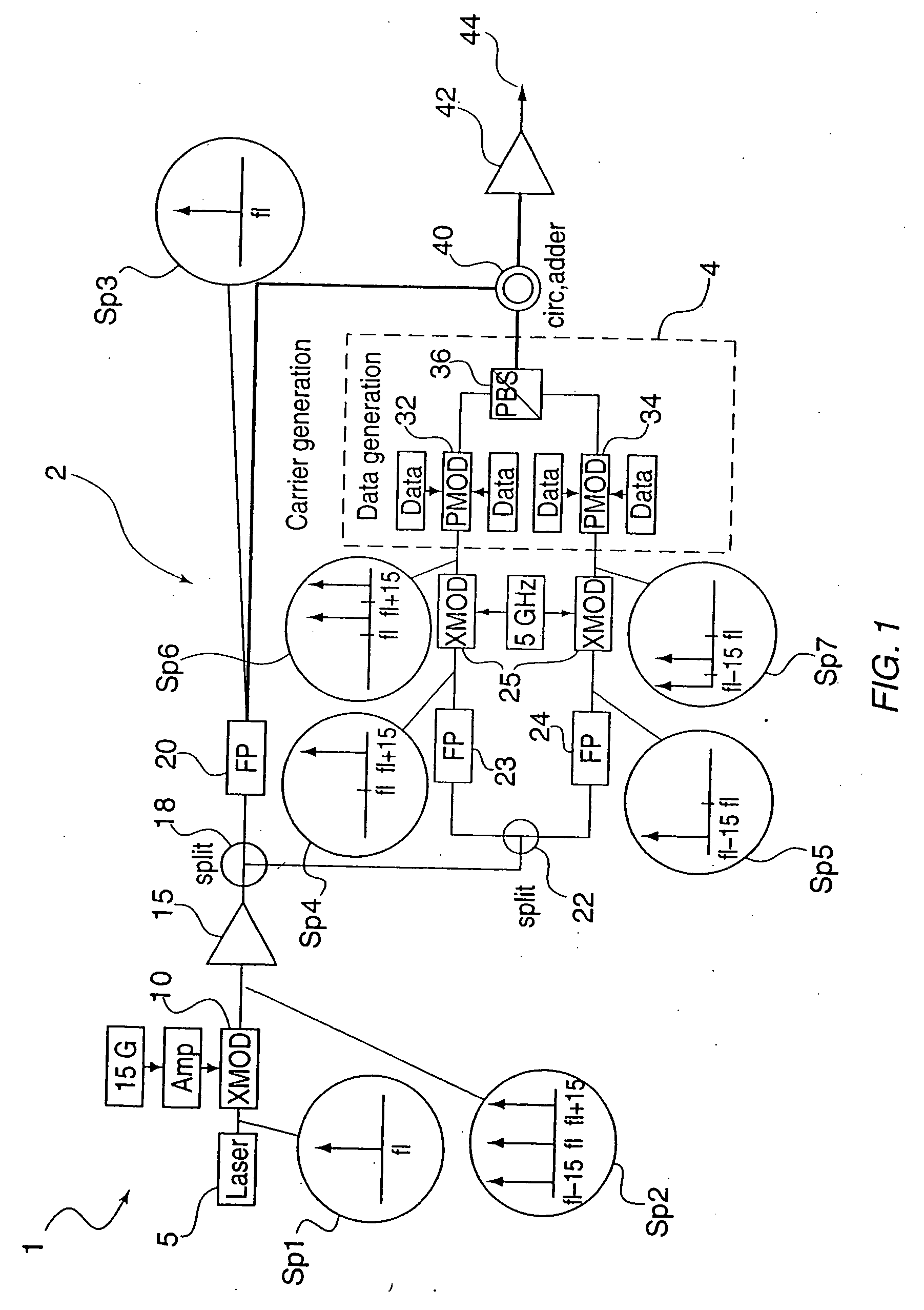
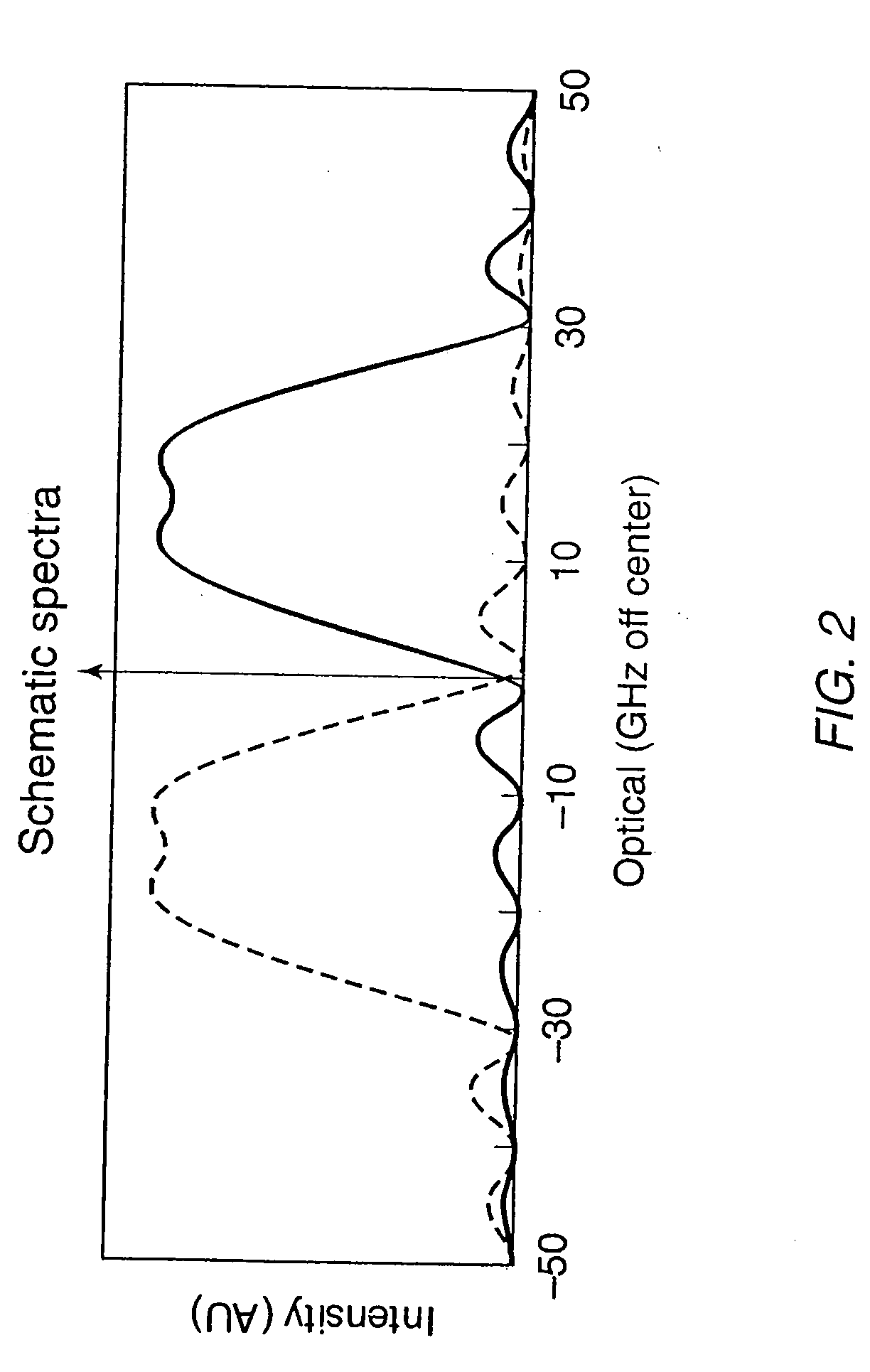
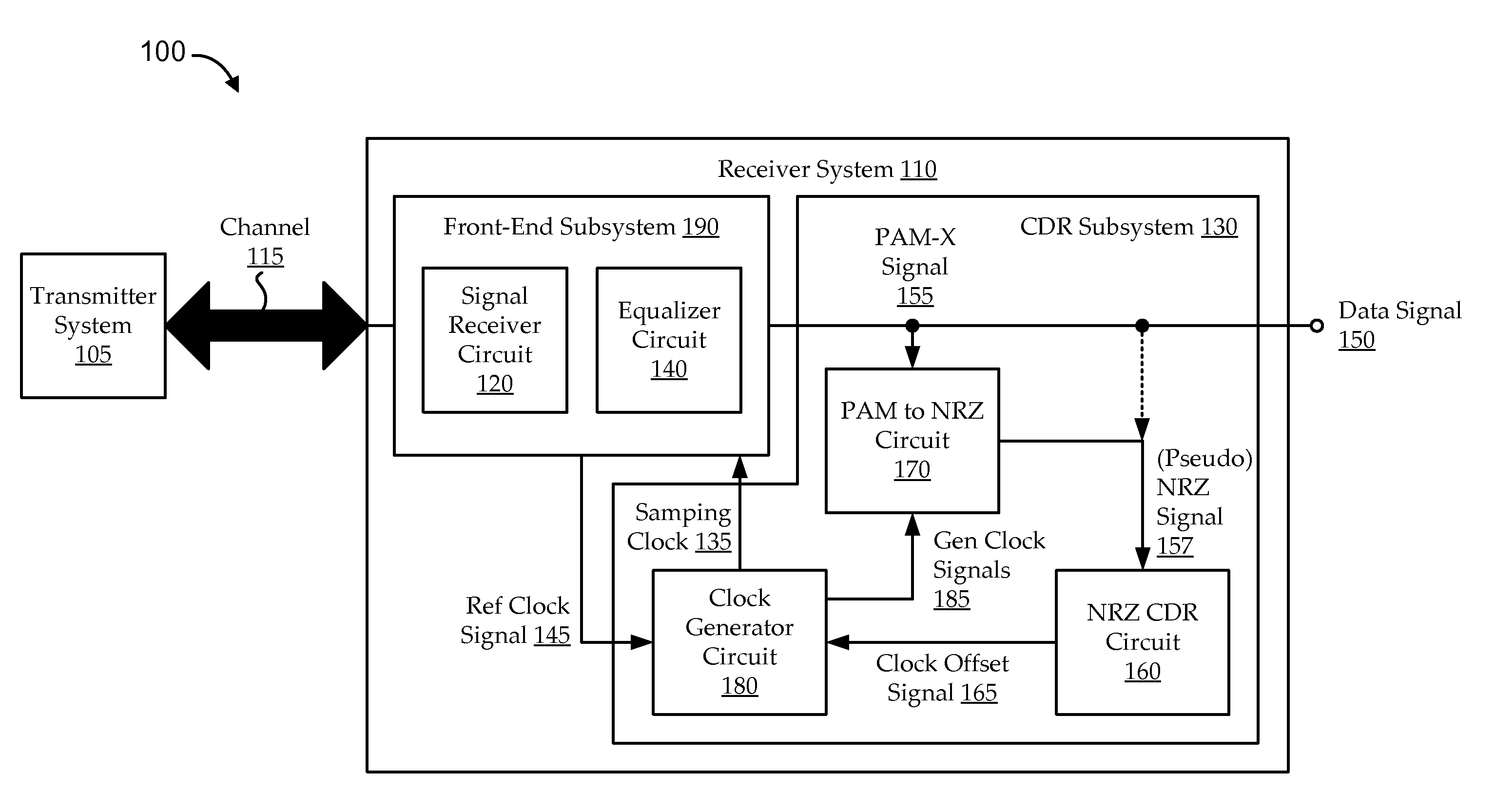
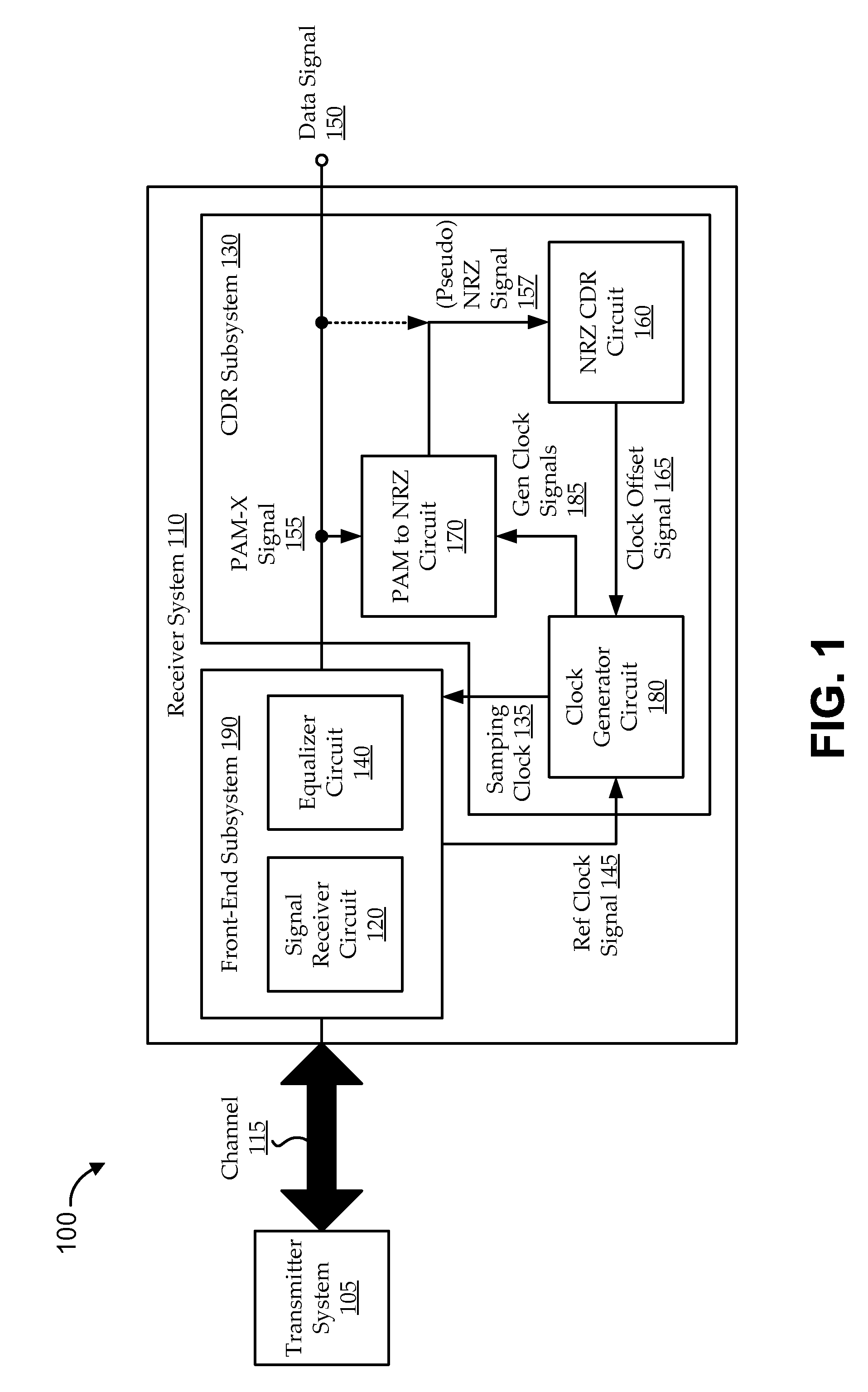
Embodiments include systems and methods for using generalized pulse amplitude modulation (PAM-X) signaling with an at-rate not-return-to-zero (NRZ) clock data recovery (CDR) system. Some implementations include dual-mode signaling for an at-rate CDR (e.g., using standard NRZ signaling at lower operating frequencies and pseudo-NRZ signaling derived from PAM-X signaling at higher operating frequencies. Embodiments derive an apparent direction of signal transition from PAM-X signaling. The direction can be used to calculate pseudo-NRZ values. For example, when the PAM-X signal transitions in an upward direction, a pseudo-current NRZ value and a pseudo-previous NRZ value of ‘−1’ and ‘+1’ can be generated, respectively. An at-rate NRZ CDR can use the pseudo-NRZ values and a derived error value to make an offset determination. The offset determination can then be used to offset a generated clock signal in the CDR system.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
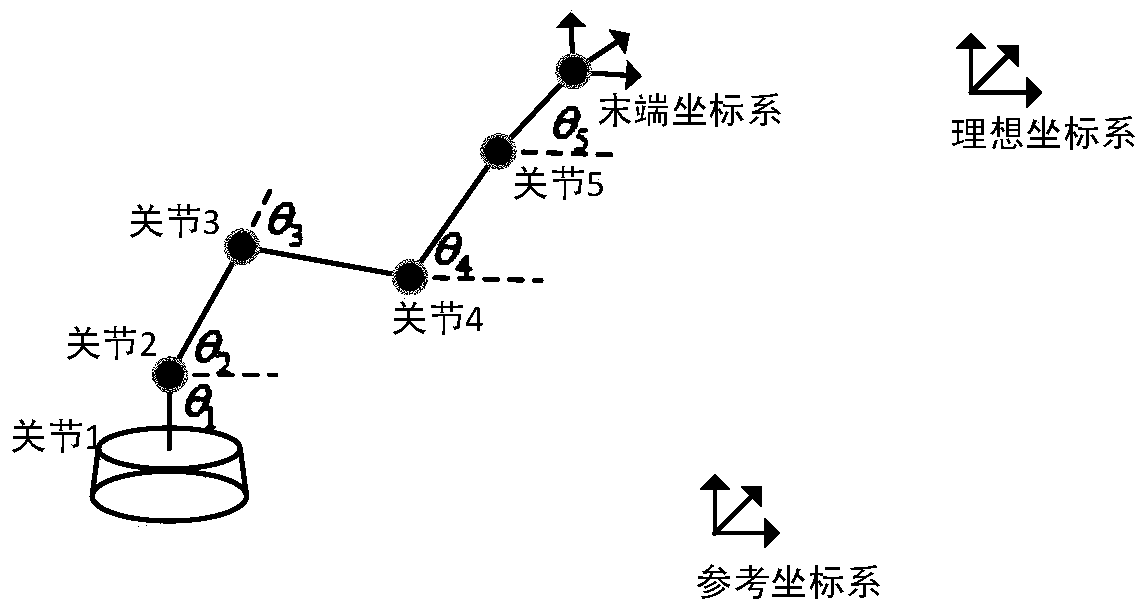
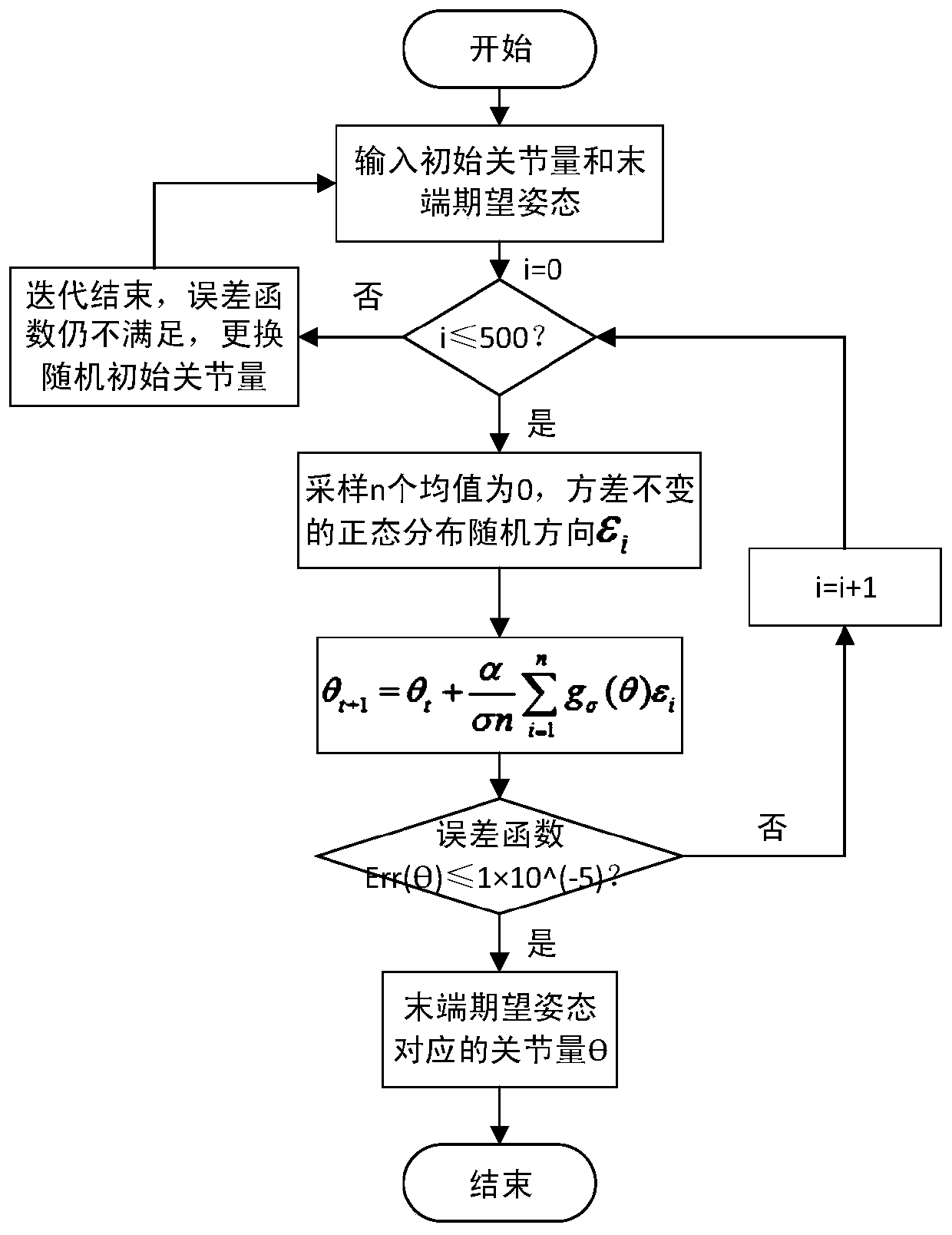
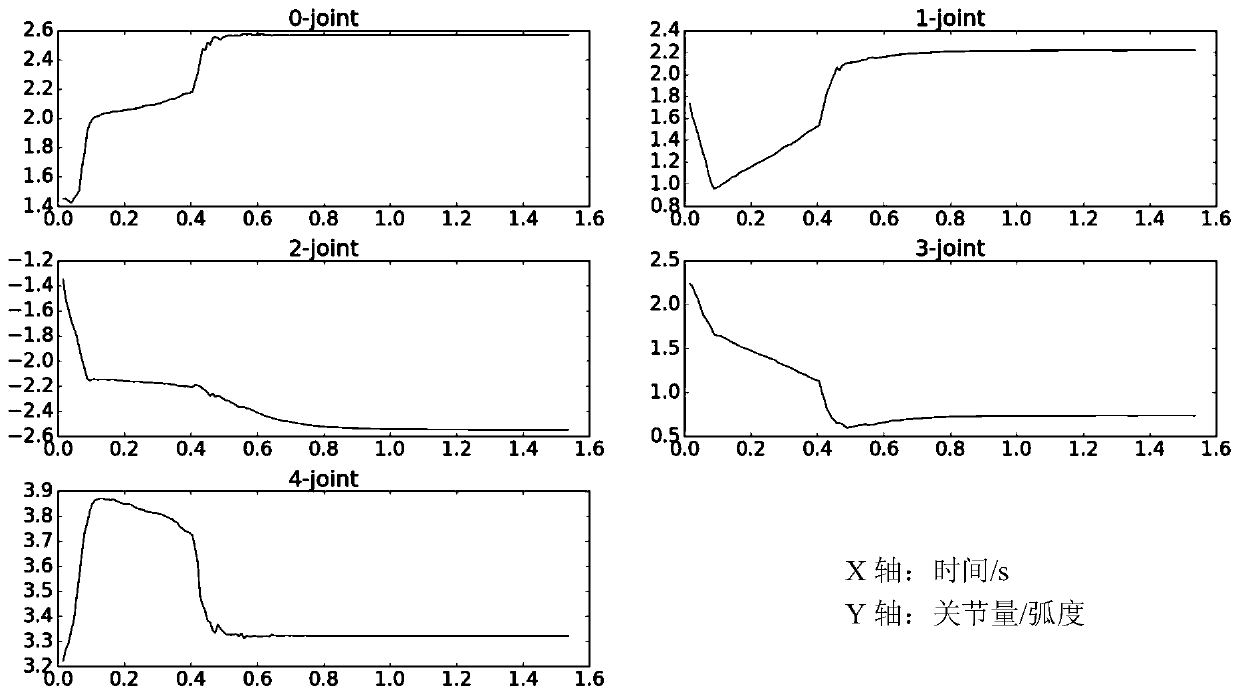
Five-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm inverse kinematics solving method
ActiveCN110434851ASolve the situation where inverse kinematics has no solutionHigh speedProgramme-controlled manipulatorReturn-to-zeroDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a five-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm inverse kinematics solving method. The method comprises the following steps that 1) a positive kinematics model is established accordingto mechanical arm D-H parameters; 2) a mechanical arm tail end pose error function model is established; 3), the tail pose error function is minimized based on an evolutionary strategy algorithm; 4),an mechanical arm inverse kinematics equation is iterated within an error function allowable error; and 5), if iteration is over, the error function is not returned to zero or allowable error, and the equation is returned to the step 2 to replace the initial joint value and re-calculate is carried out. The method provided by the invention can effectively solve the problem that the mechanical arminverse kinematics is unsolved due to unfilled rank of jacobian matrix during mechanical arm inverse kinematics iteration solving. The mechanical arm inverse kinematics solving method has high speed and extremely high precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Static target segmentation method based on Gauss background model
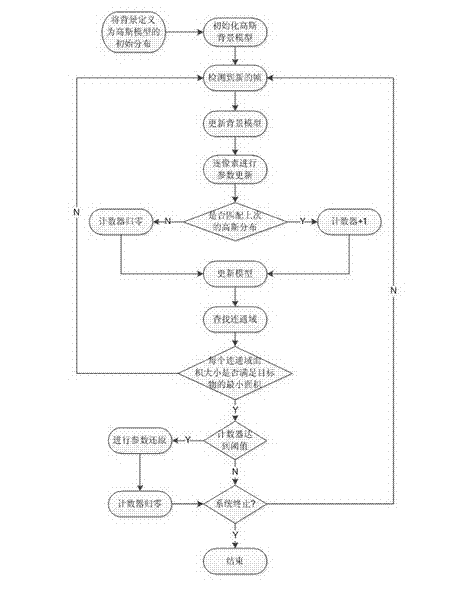
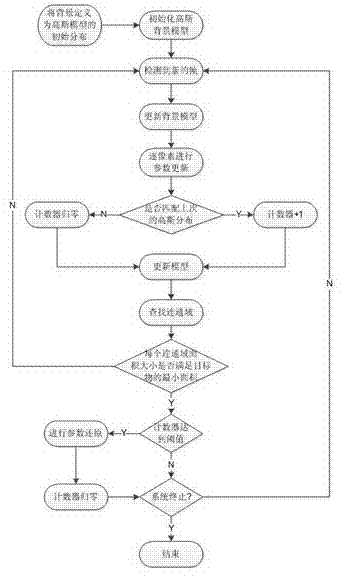
InactiveCN102509073AImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionReturn-to-zero
The invention relates to a static target segmentation method based on a Gauss background model. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, building a Gauss mixed model according to a first frame or pre-loading background, and loading parameter thresholds of the required parts; when a new frame enters, scanning pixel by pixel and matching with a background model; if distribution which is the same with a previous frame is matched, adding one, otherwise returning to zero; then carrying out parameter updating according to a matching result, sorting updated distributions, and selecting a corresponding generated background model according to the thresholds; filtering a smaller foreground part by finding a connected domain, so as to eliminate interference of noise and complicated background, and carrying out parameter restoration pixel by pixel according to an accumulated value of a counter at the foreground part. By applying the method provided by the invention, the Gauss background model can effectively identify a static object which enters into a background for a long time, and sensitivity identification to luminosity and learning capability of the Gauss background model can be maintained.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com