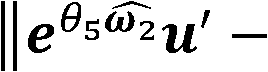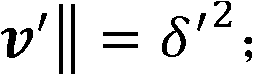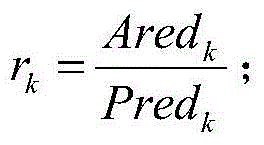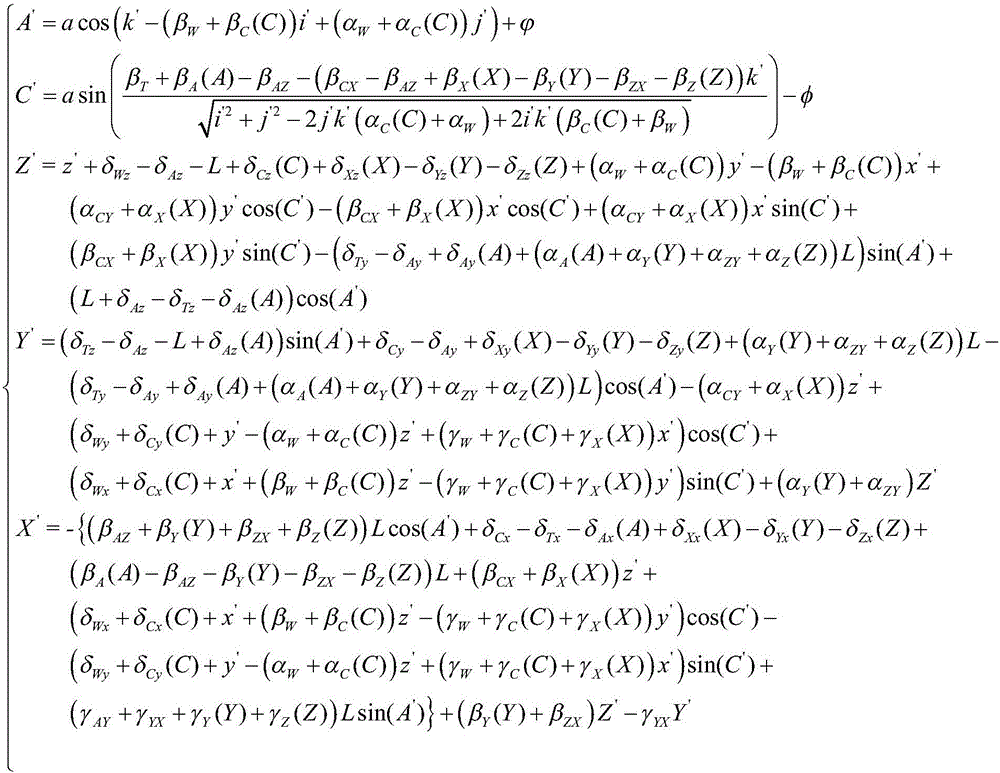Patents
Literature
674 results about "Inverse kinematics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
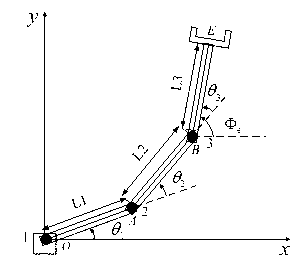
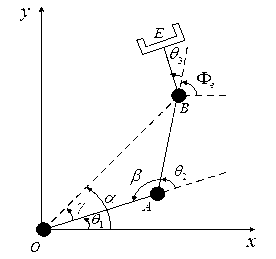
Inverse kinematics is the mathematical process of recovering the movements of an object in the world from some other data, such as a film of those movements, or a film of the world as seen by a camera which is itself making those movements. This is useful in robotics and in film animation.
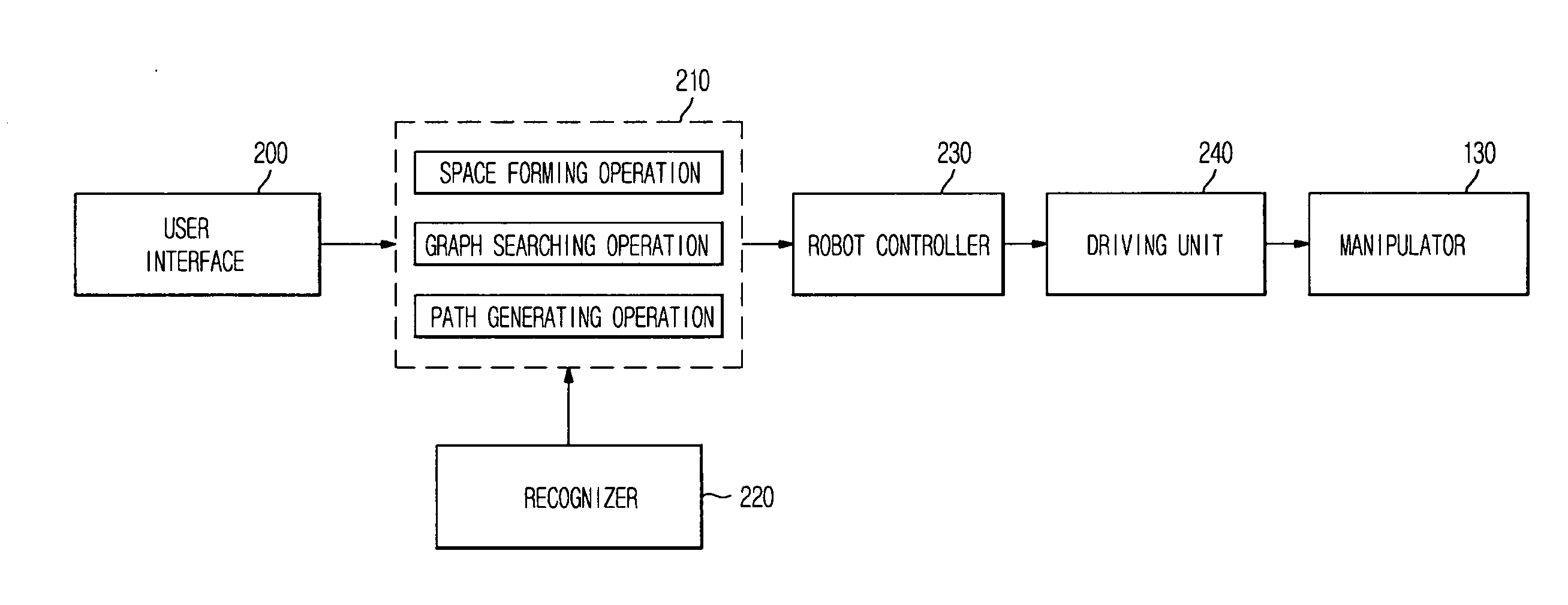
Method and apparatus to plan motion path of robot
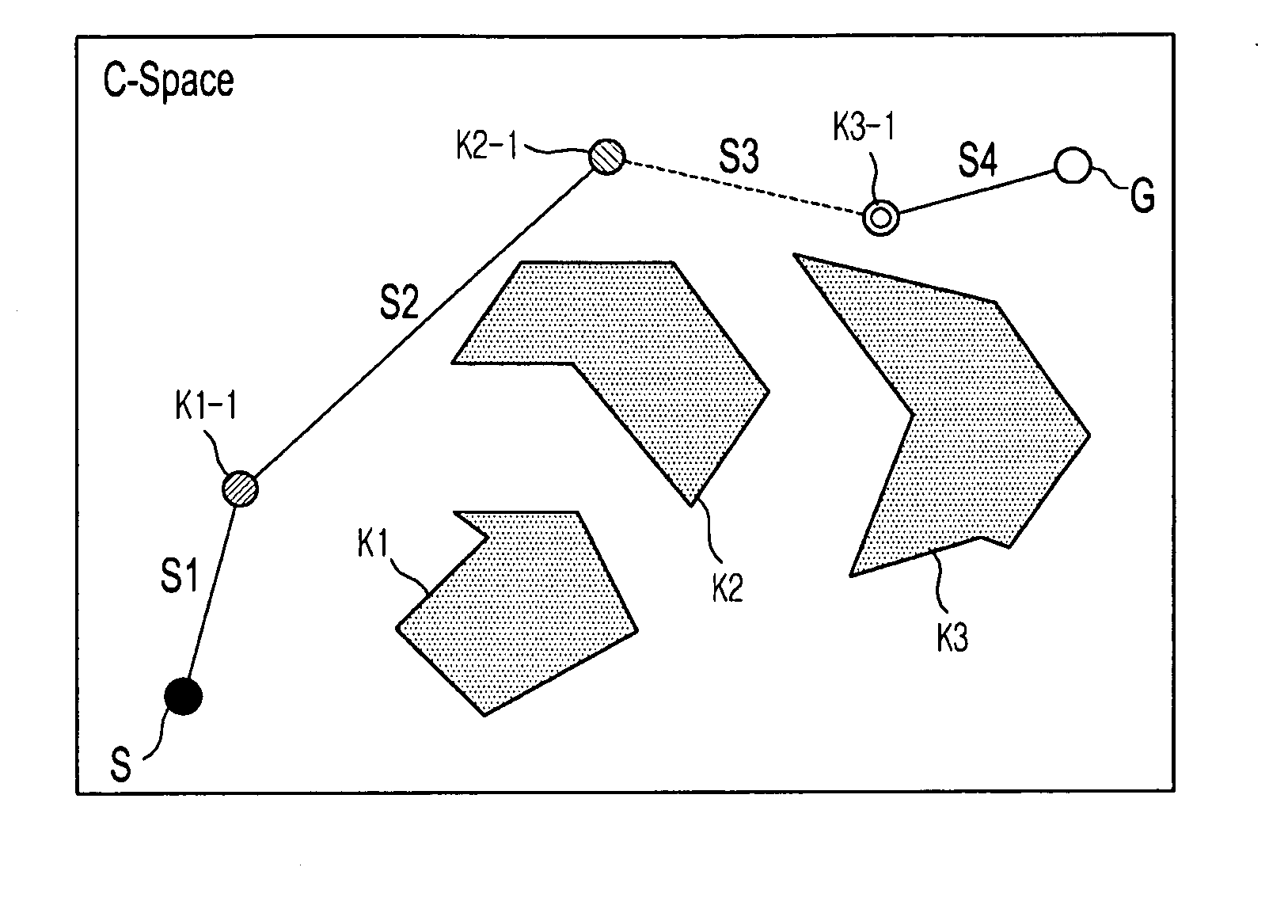
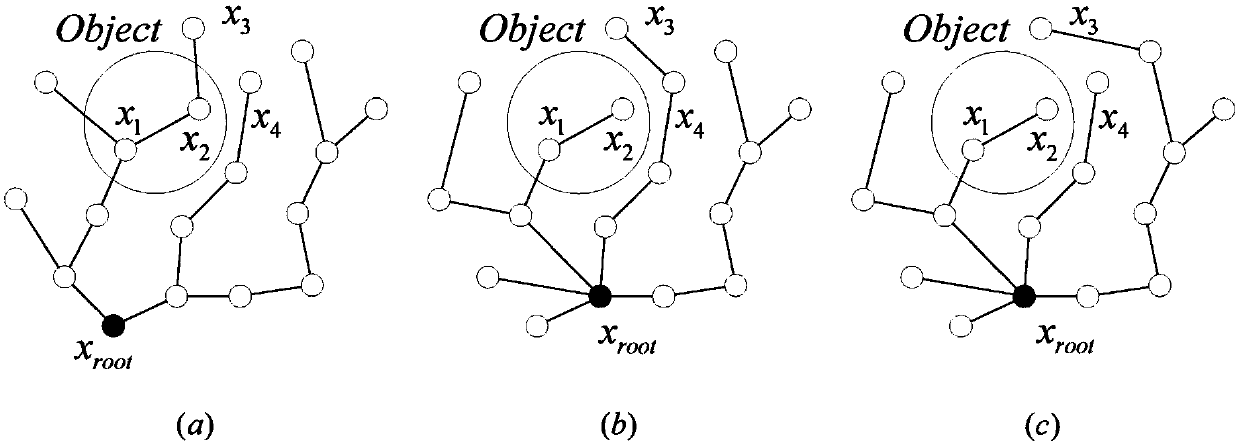
ActiveUS20110035087A1Reduce probabilitySolution can be rapidly obtainedProgramme-controlled manipulatorInstruments for road network navigationAlgorithmRandom tree
A suitable waypoint is selected using a goal score, a section from a start point to a goal point through the waypoint is divided into a plurality of sections based on the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, and trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections using a Best First Search & Rapidly Random Tree (BF-RRT) algorithm so as to generate a path. By this configuration, a probability of local minima occurring is decreased compared with the case where the waypoint is randomly selected. In addition, since the trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections each having the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, the solution may be rapidly obtained. A time consumed to search for an optimal motion path may be shortened and path plan performance may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
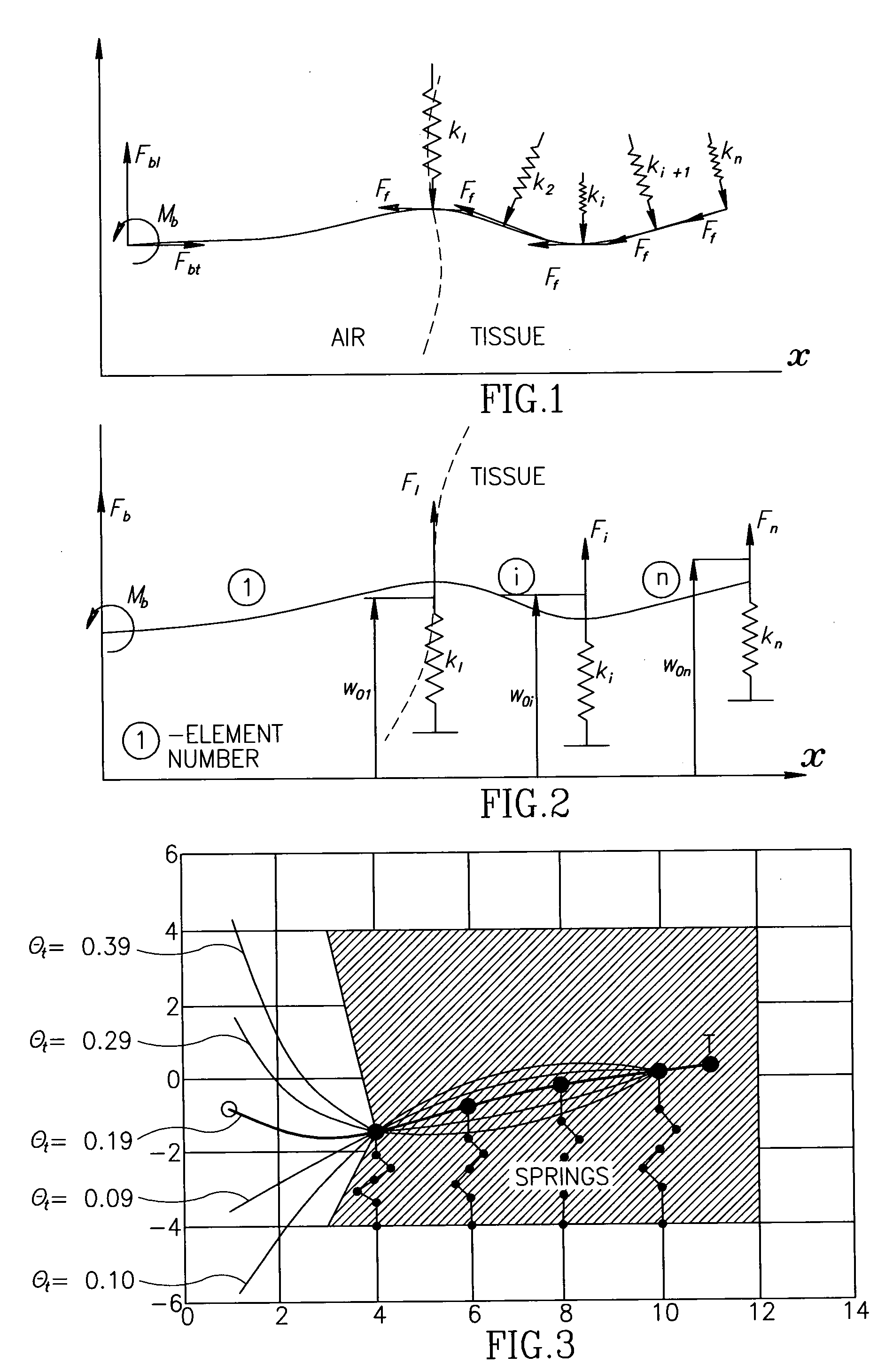
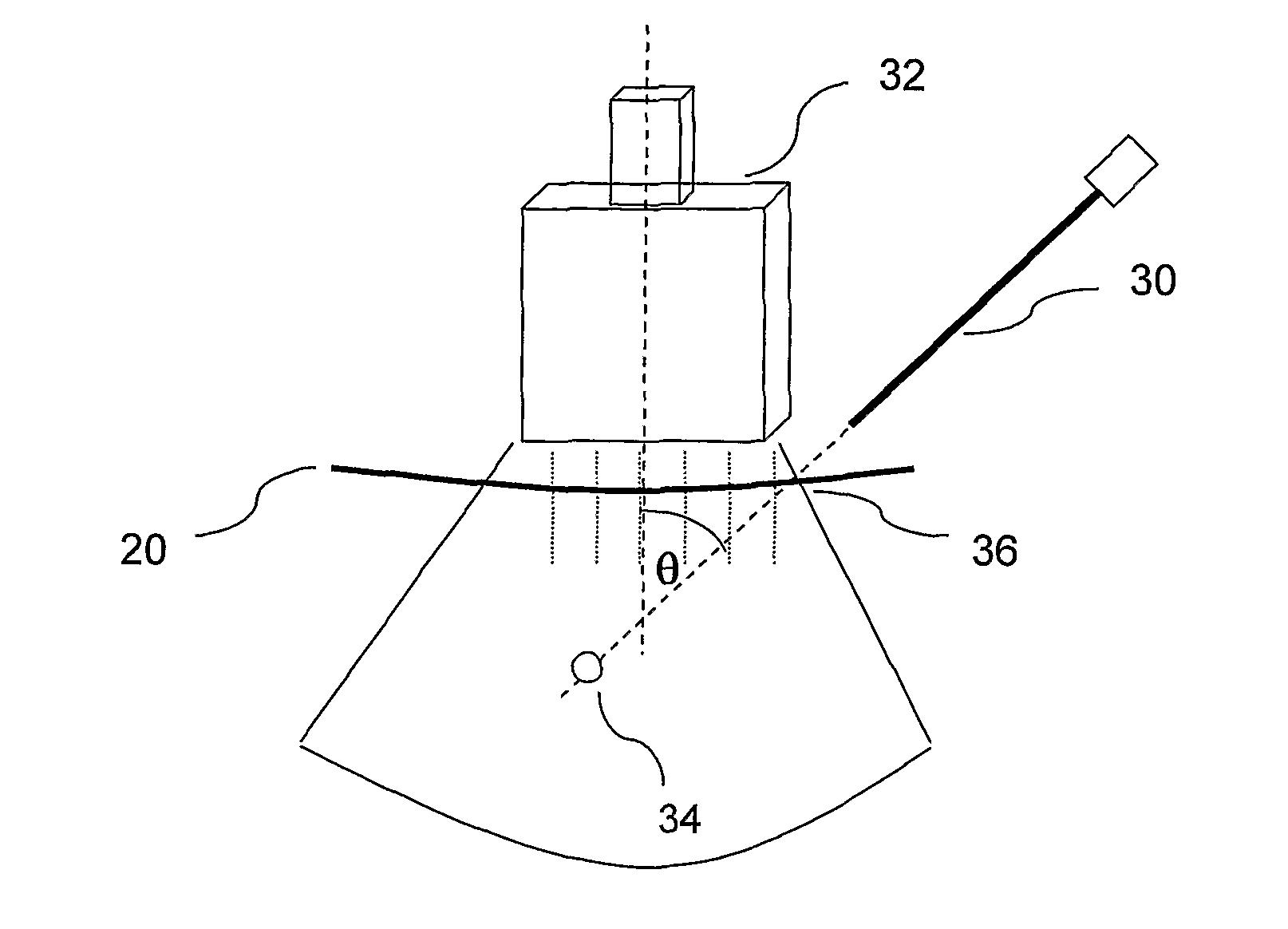
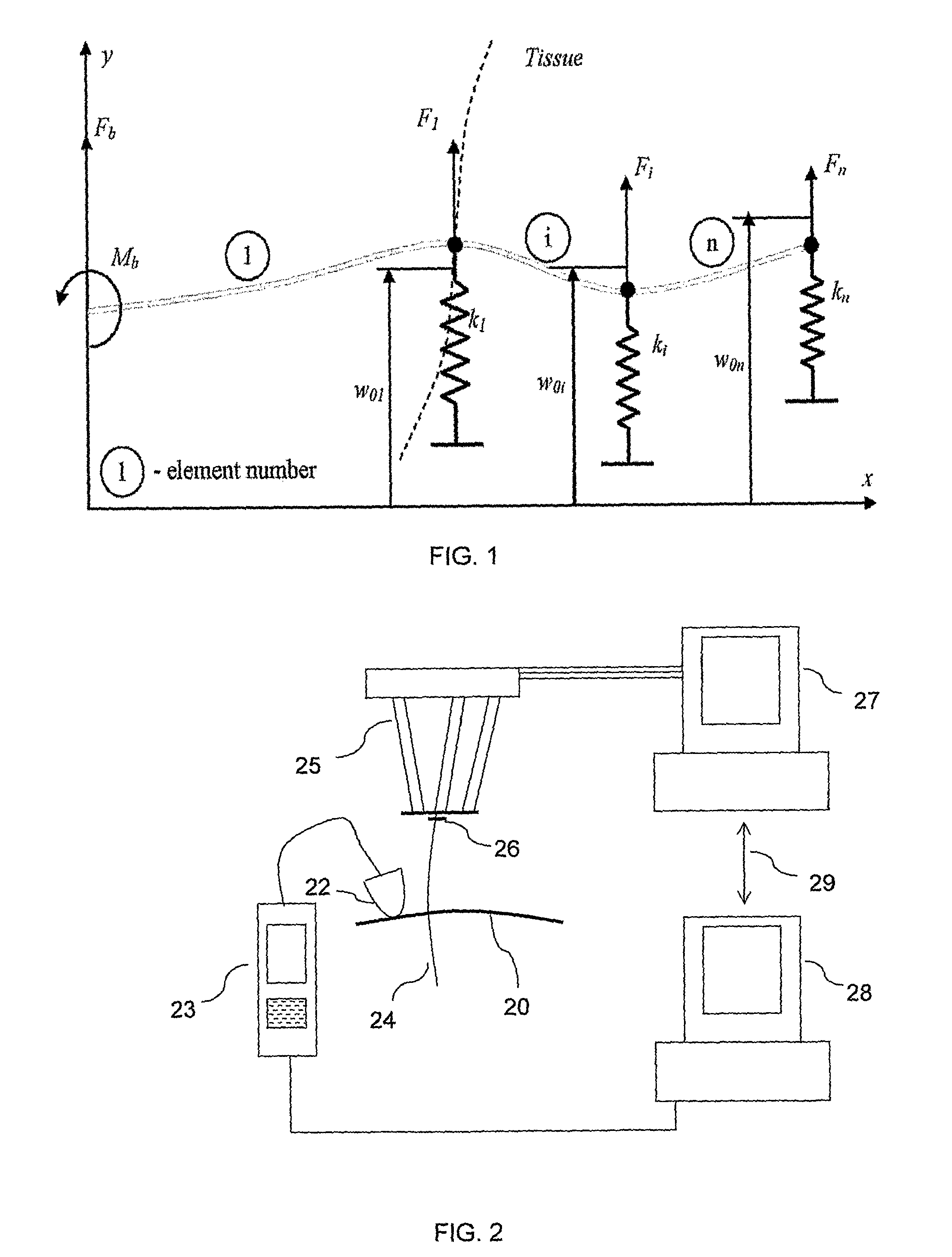
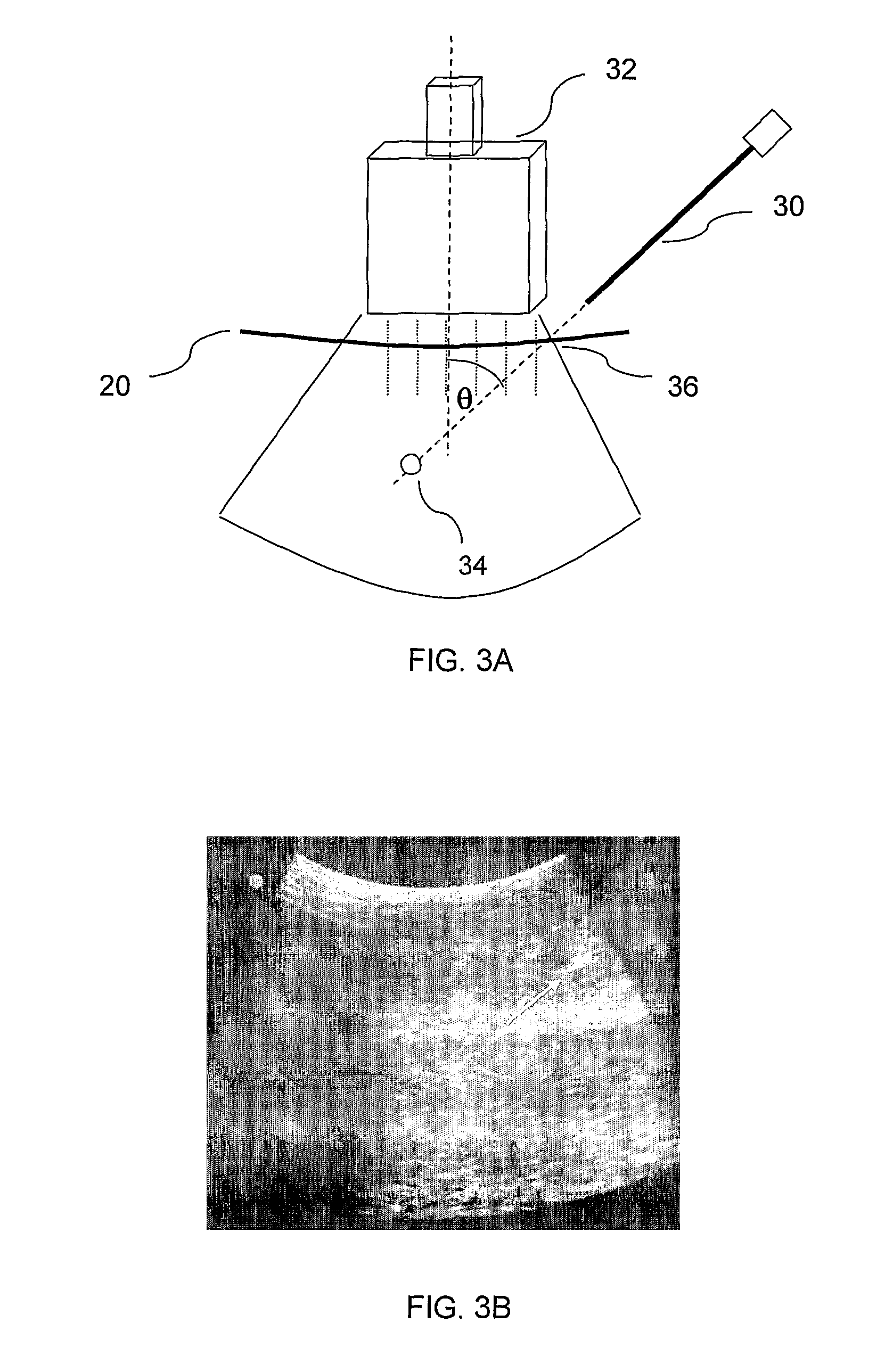
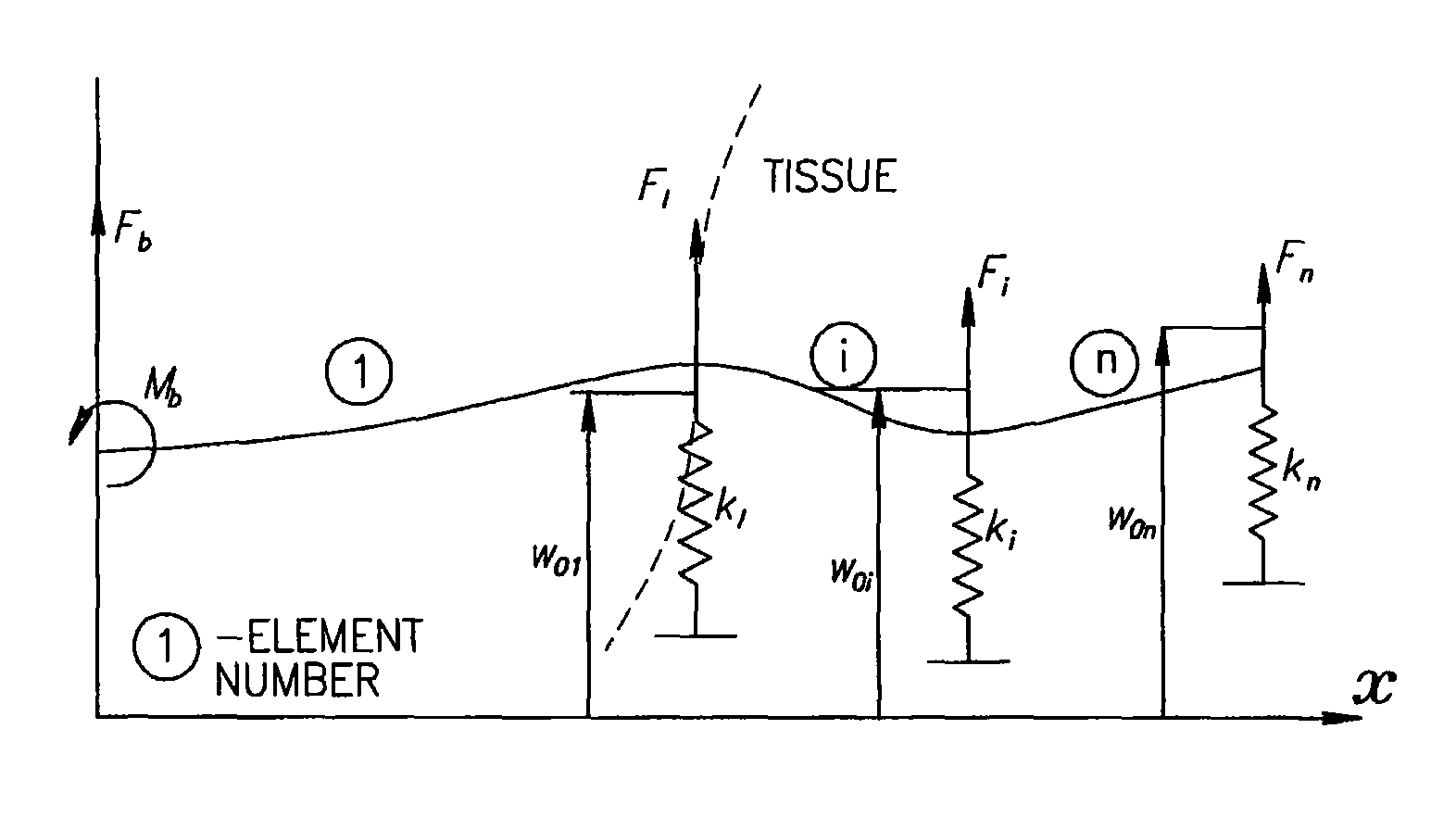
Controlled steering of a flexible needle
ActiveUS20090149867A1Avoid obstaclesReduce in quantitySurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsStiffness coefficientRobotic systems
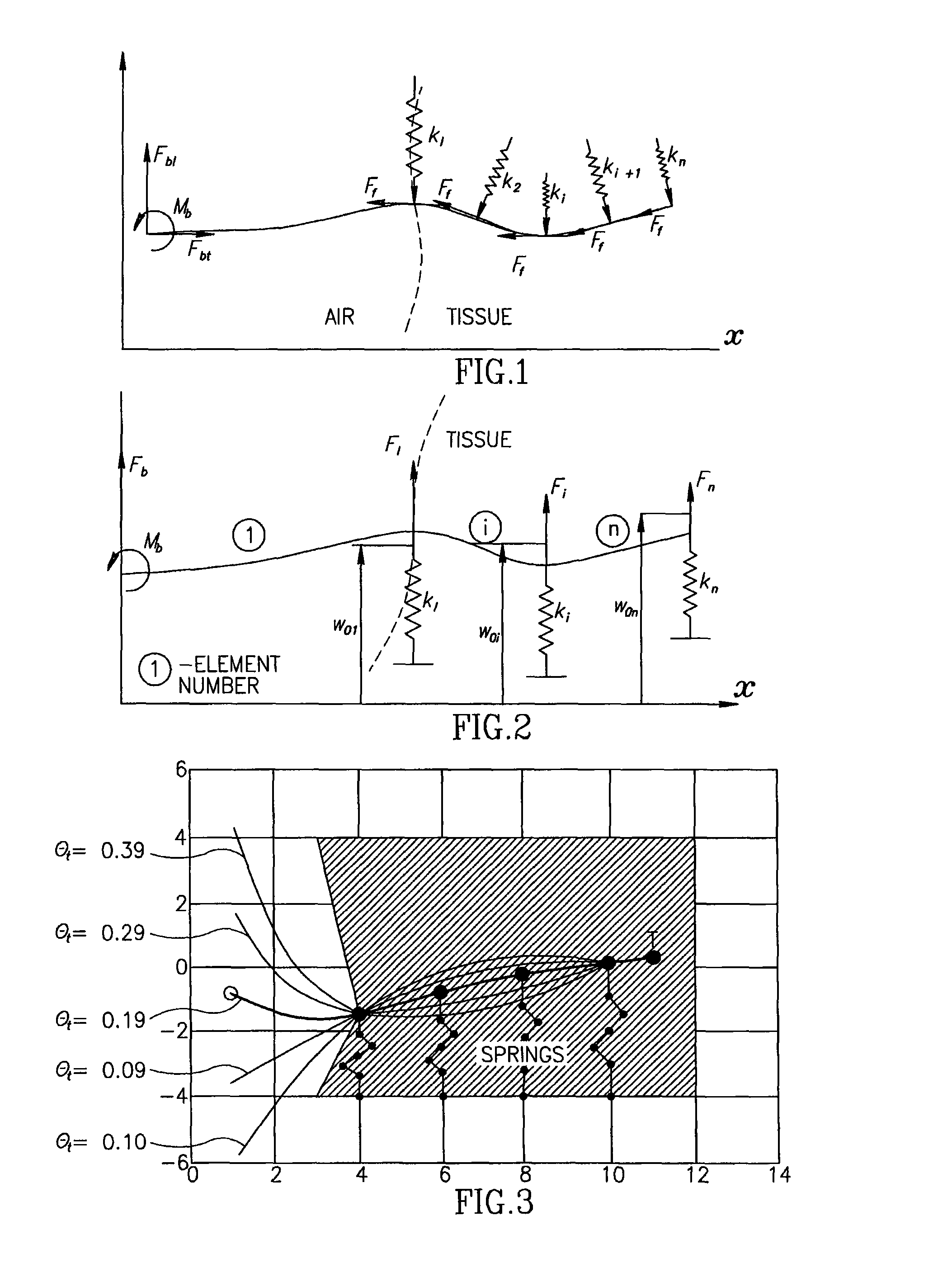
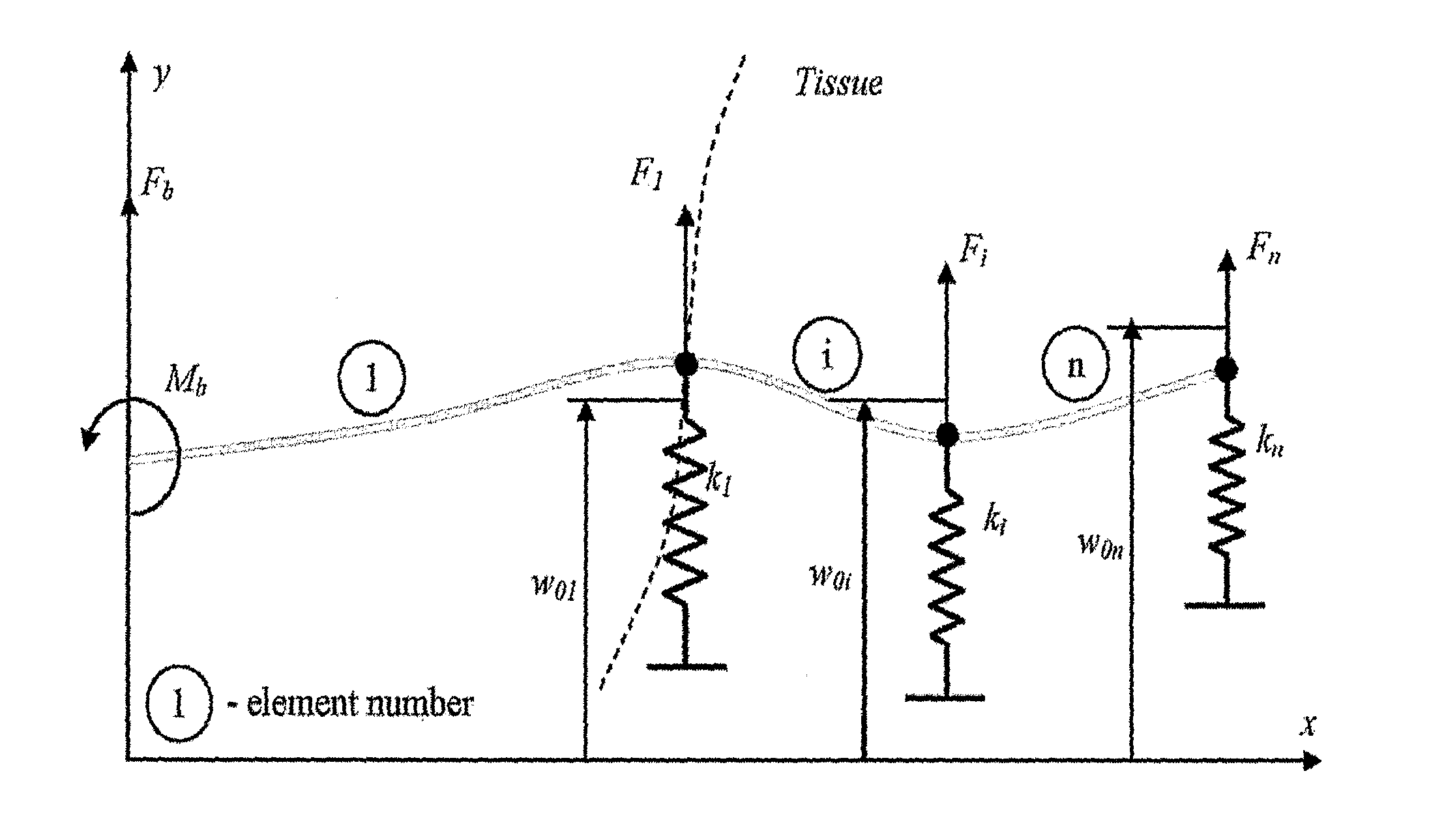
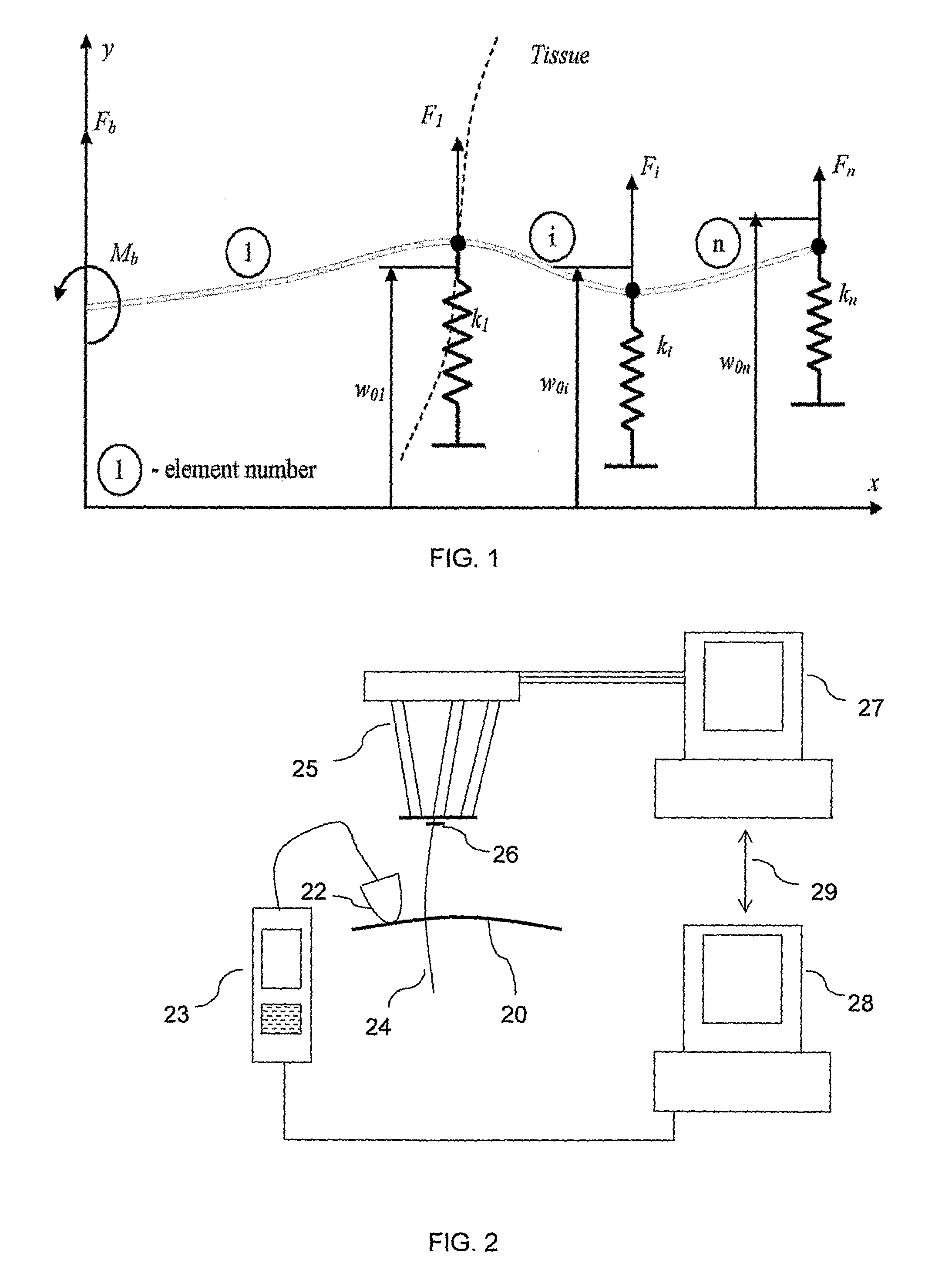
A robotic system for steering a flexible needle during insertion into soft-tissue using imaging to determine the needle position. The control system calculates a needle tip trajectory that hits the desired target while avoiding potentially dangerous obstacles en route. Using an inverse kinematics algorithm, the maneuvers required of the needle base to cause the tip to follow this trajectory are calculated, such that the robot can perform controlled needle insertion. The insertion of a flexible needle into a deformable tissue is modeled as a linear beam supported by virtual springs, where the stiffness coefficients of the springs varies along the needle. The forward and inverse kinematics of the needle are solved analytically, enabling both path planning and correction in real-time. The needle shape is detected by image processing performed on fluoroscopic images. The stiffness properties of the tissue are calculated from the measured shape of the needle.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Individualizable convenience system for drivers
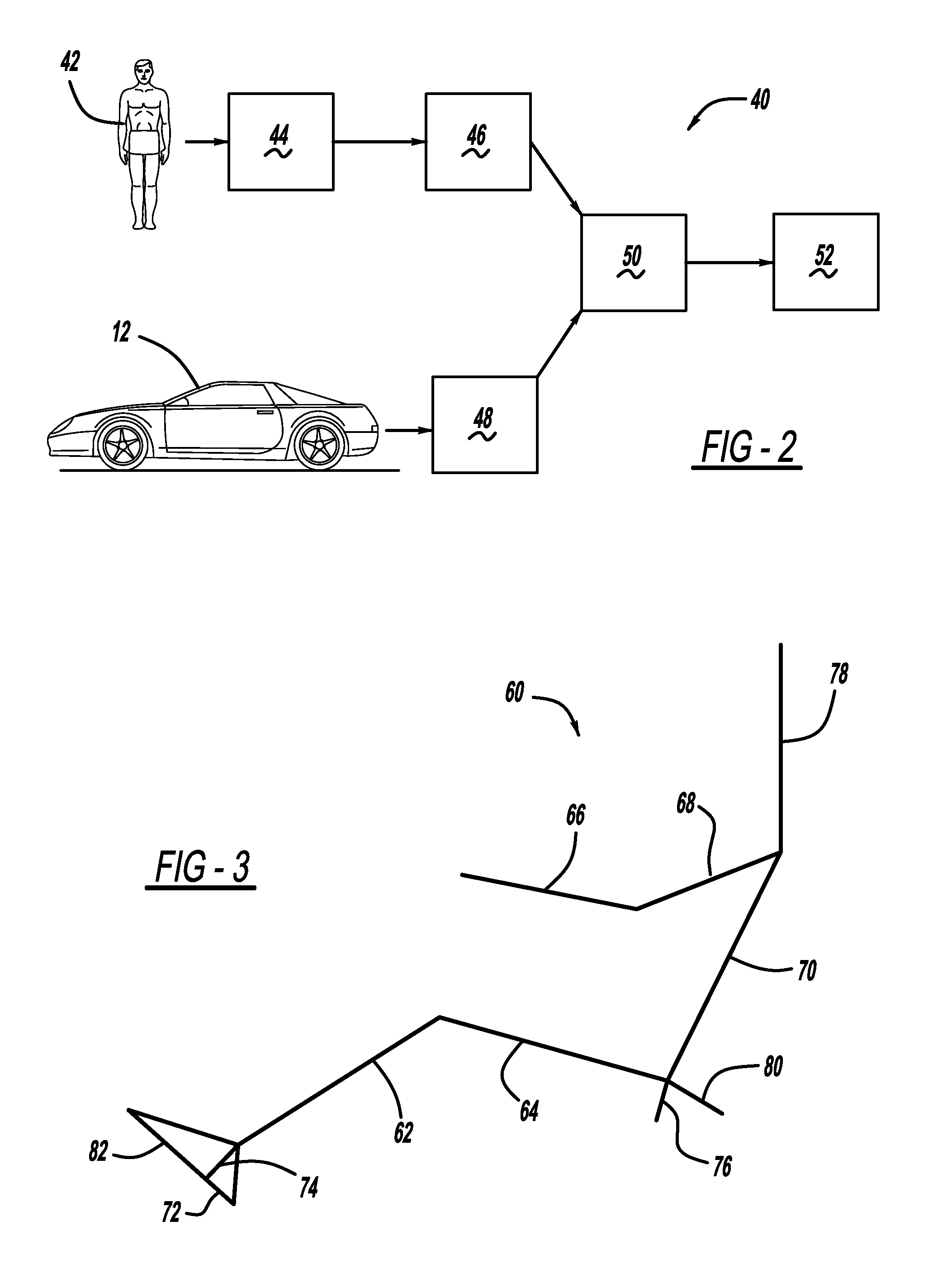
A method and system for automatically adjusting a driver seat, steering wheel, pedals, mirrors, and other components of a vehicle, based on information about the size of the driver. The method uses basic information about the driver's size—including standing height, sitting height, and gender—in a model which estimates all anthropometric data for the driver. The anthropometric data for the driver—including upper and lower arm and leg lengths, torso length, and other dimensions—is used in inverse kinematic calculations to determine optimal positions and orientations for the adjustable components of the vehicle's cockpit. The method then pre-adjusts the components before the driver enters the vehicle, and makes compatible adjustments to the mirrors and other components if the driver adjusts the driver seat.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Redundant manipulator motion planning method
InactiveCN101804627AImprove computing efficiencyStrong real-timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorAngular velocityEngineering
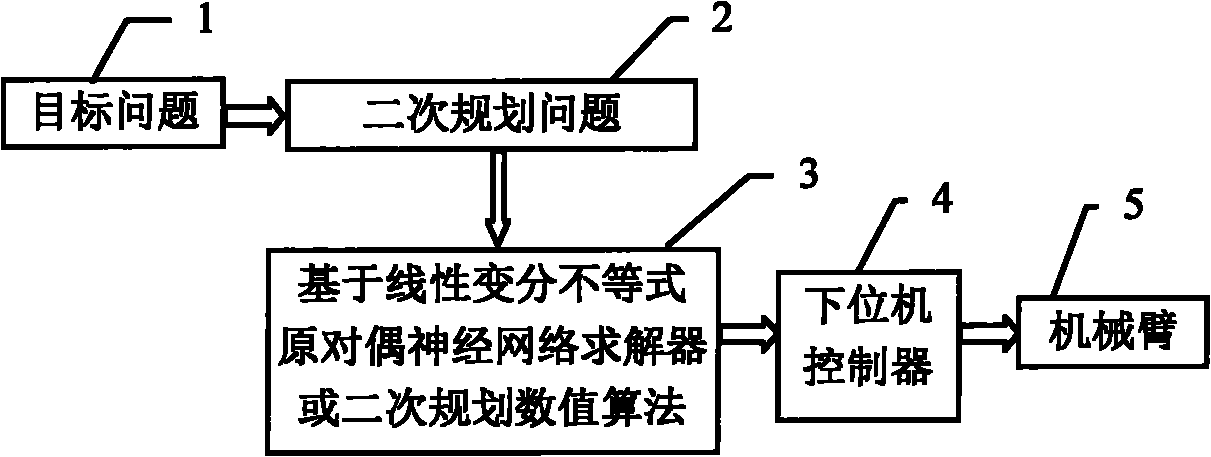
The invention provides a redundant manipulator motion planning method which comprises the following steps that: (1) an upper computer analyzes the inverse kinematics of a manipulator on a velocity layer through quadratic optimization, the designed minimum performance index can be velocity norm, repetitive motion or kinetic energy and is bound by a velocity jacobian equation, an inequation and a joint angular velocity limit, and the angular velocity limit changes with a joint angle; (2) the quadratic optimization of step (1) is optimized into a quadratic programming problem; (3) the quadratic programming problem in step (2) is calculated by a linear variational inequation primal-dual neural network solver or a numerical method; and (4) the calculation result in step (3) is transmitted to a lower computer controller to drive the manipulator to move. The redundant manipulator motion planning method is based on the primal-dual neural network of the linear variational inequation, has global exponential convergence, does not involve matrix inversion and other complicated operations, greatly improves the calculation efficiency, and simultaneously has strong real-time performance, and can adapt to the changes to the joint angular velocity limit.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Robot action based on human demonstration
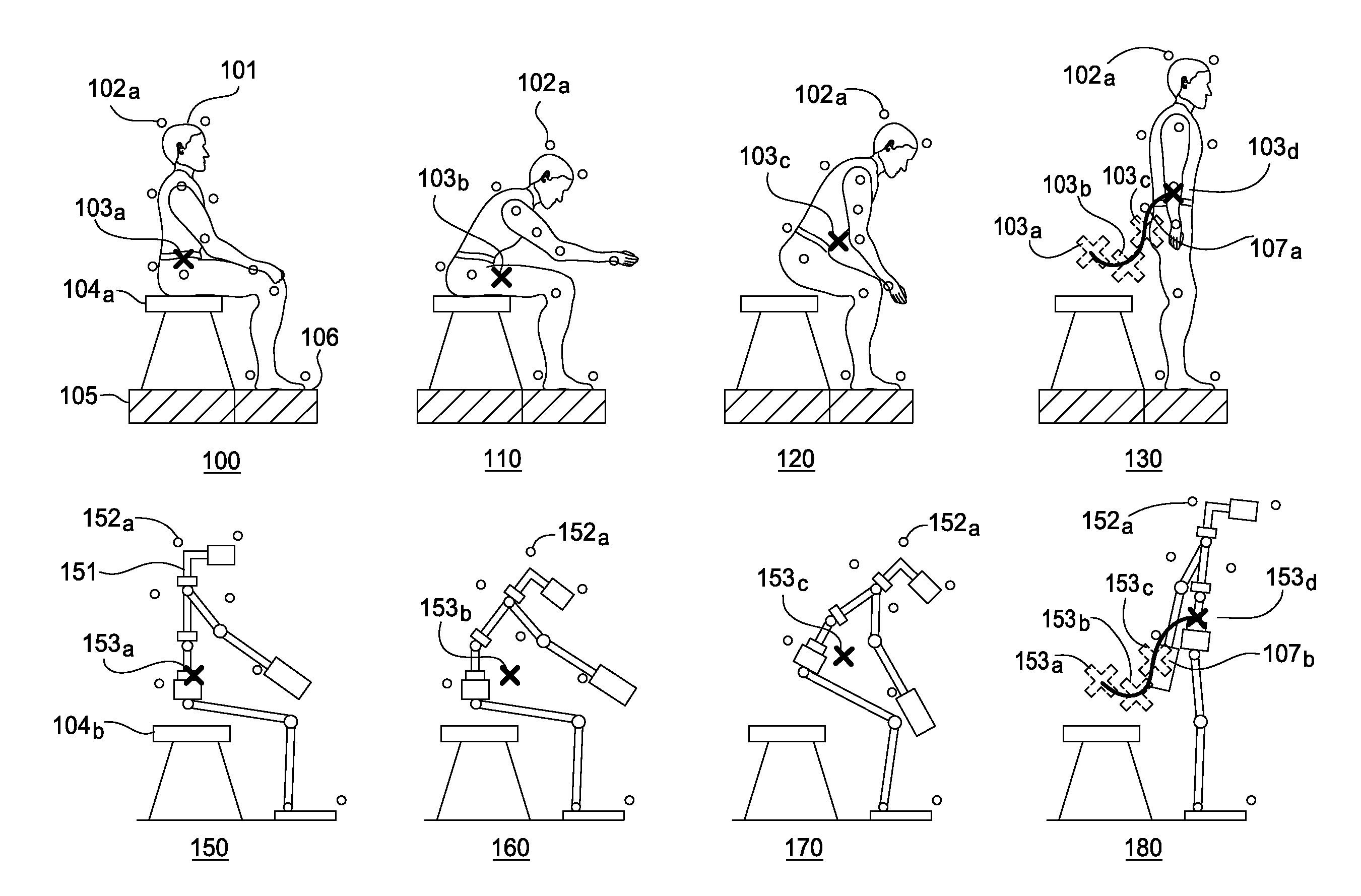
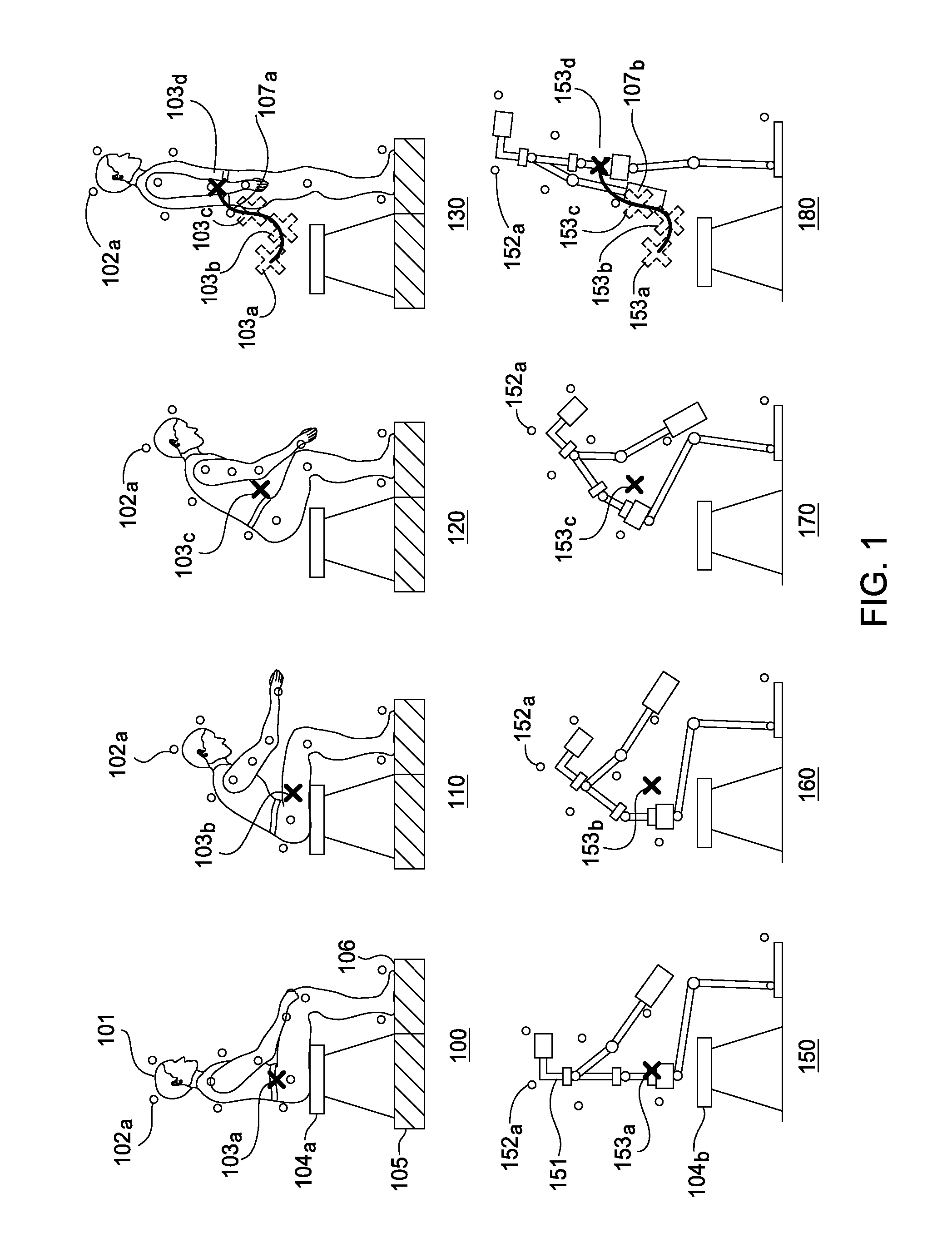
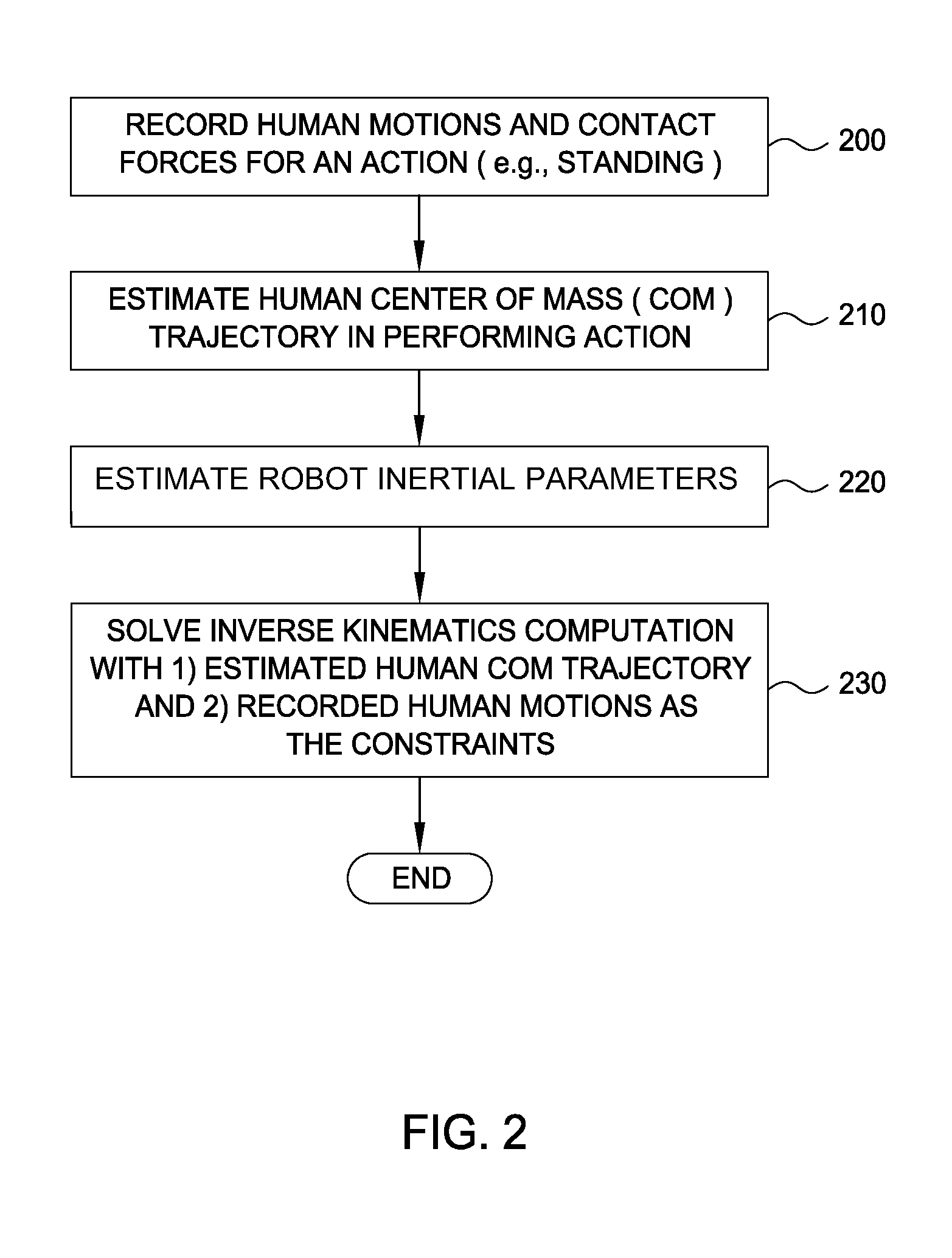
Embodiments of the invention provide an approach for reproducing a human action with a robot. The approach includes receiving data representing motions and contact forces of the human as the human performs the action. The approach further includes approximating, based on the motions and contact forces data, the center of mass (CoM) trajectory of the human in performing the action. Finally, the approach includes generating a planned robot action for emulating the designated action by solving an inverse kinematics problem having the approximated human CoM trajectory as a hard constraint and the motion capture data as a soft constraint.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Genetic-algorithm-based trajectory planning optimization method for mobile mechanical arm
The invention relates to a genetic-algorithm-based trajectory planning optimization method for a mobile mechanical arm. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps of first establishing a forward kinematic model and an inverse kinematic model of a multi-degree-of-freedom mobile mechanical arm; then fitting a joint trajectory by adopting a composite curve of a quartic polynomial mathematical model and a quintic polynomial mathematical model, and calculating solutions of the corresponding mathematical models according to a linear constraint equation; next selecting a trajectory optimization target according to the principles of shortest motion time, minimum spatial motion distance and less than or equal to maximum set joint torque of the mobile mechanical arm; and finally globally optimizing the optimization target by utilizing a genetic algorithm to obtain an optimal trajectory curve of an end actuator of the mechanical arm. According to the method, the trajectory planning efficiency and the tracking accuracy of the mechanical arm are improved, and the problems of real-time trajectory planning of the mobile mechanical arm and trajectory planning optimization and control of the mechanical arm in an uncertain environment are also solved; and the trajectory planning optimization method for the mobile mechanical arm is effective.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
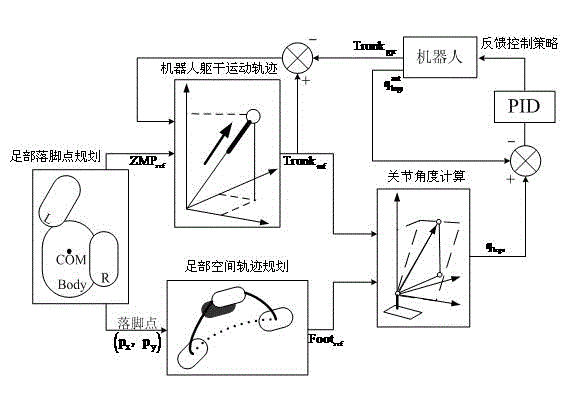
Closed-loop control-based humanoid robot omnidirectional walking method
The invention provides a closed-loop control-based humanoid robot omnidirectional walking method, which comprises foot stance planning, robot body movement track, foot space track planning, joint angle calculation and feedback control policy. The method comprises the following steps of planning the stances of the feet of the robot in a two-dimensional space, and calculating a zero moment point (ZMP) value of the robot; establishing a bilinear inverted pendulum model with prediction control according to the ZMP value, and obtaining a reference pose of the robot body; performing cubic spline interpolation on the planned stances to obtain the best moving track of every two stances in a three-dimensional space so as to obtain a foot stance pose; and calculating angles of joints of the robot according to the reference poses of the body and the feet by using inverse kinematics knowledge. In the walking process of the humanoid robot, the omnidirectional walking of the robot is realized through closed-loop control. Compared with the prior art, the robot walking method has the advantages of high robustness and high stability.
Owner:DEEPBLUE ROBOTICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
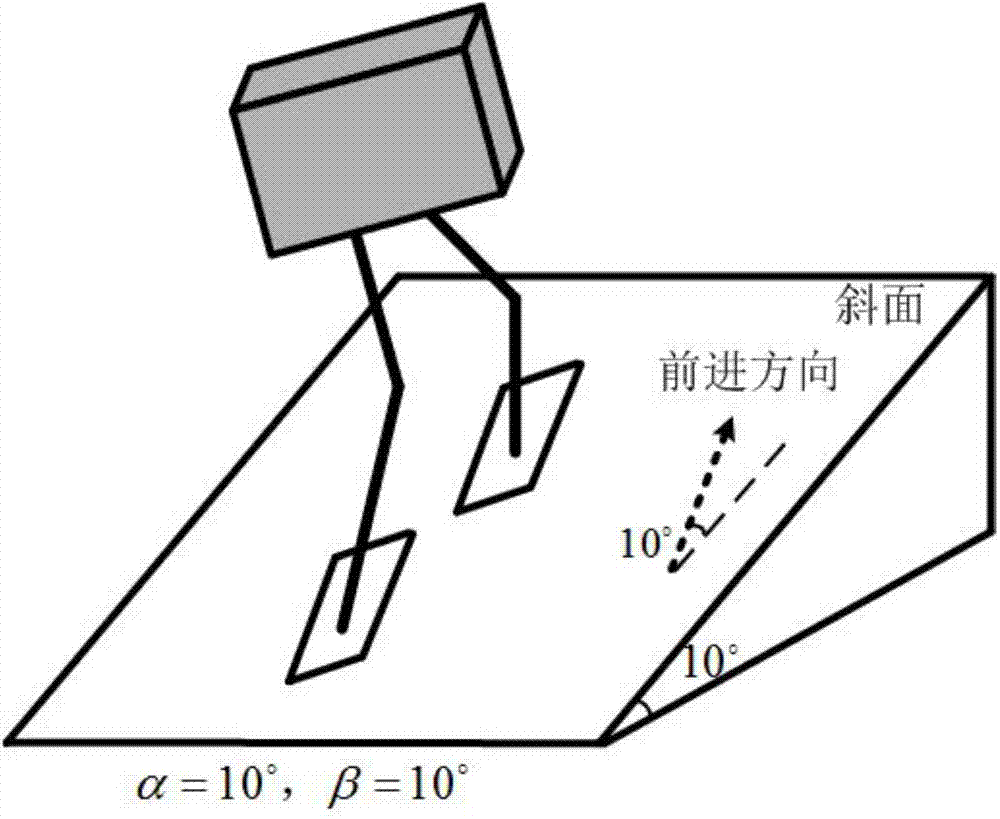
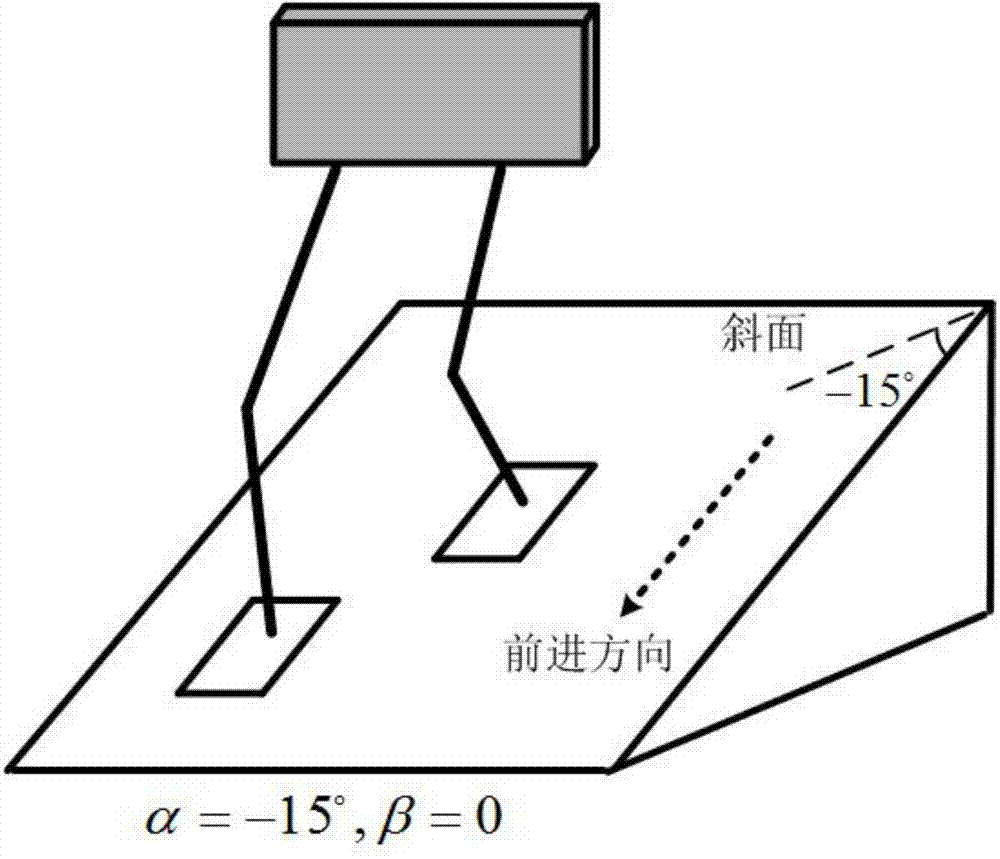
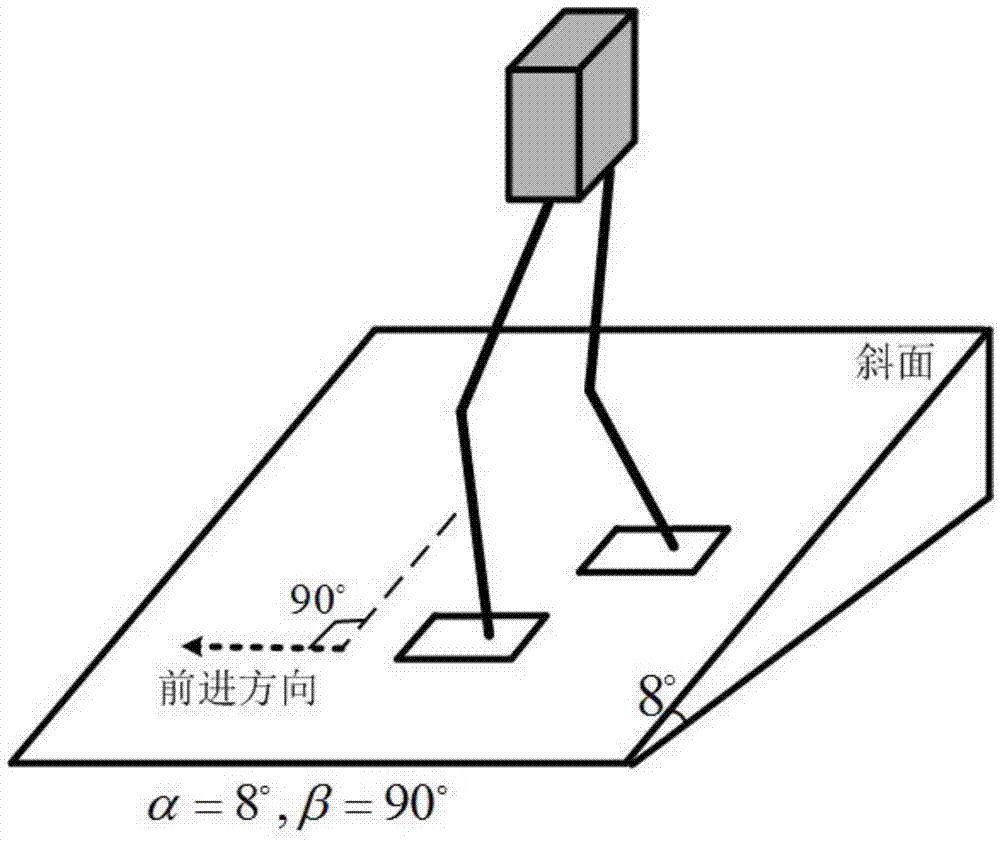
Gait planning method for walking of biped robot along slope
ActiveCN104331081AImprove environmental adaptabilityMovement coordination and natureAttitude controlCoronal planeDecomposition
The invention discloses a gait planning method for walking of a biped robot along a slope, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The method contains two core theories, namely, non-orthogonal decomposition and synthesis of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum and gait planning based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum. The method comprises the steps of gait parameter configuration, non-orthogonal decomposition of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum, foot trajectory planning based on three times of spline interpolation, centroid trajectory planning of a sagittal plane and a coronal plane based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum, non-orthogonal synthesis of the centroid trajectories of the sagittal plane and the coronal plane, and solving of joint trajectories of a robot based on inverse kinematics. By adopting the method of the invention, stable walking of a biped robot along all directions of a slope can be effectively achieved. The method is universal, simple in algorithm and high in practicality.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Ultrasound guided robot for flexible needle steering
ActiveUS8663130B2Absence of hazardMore availabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasound imagingRobotic systems
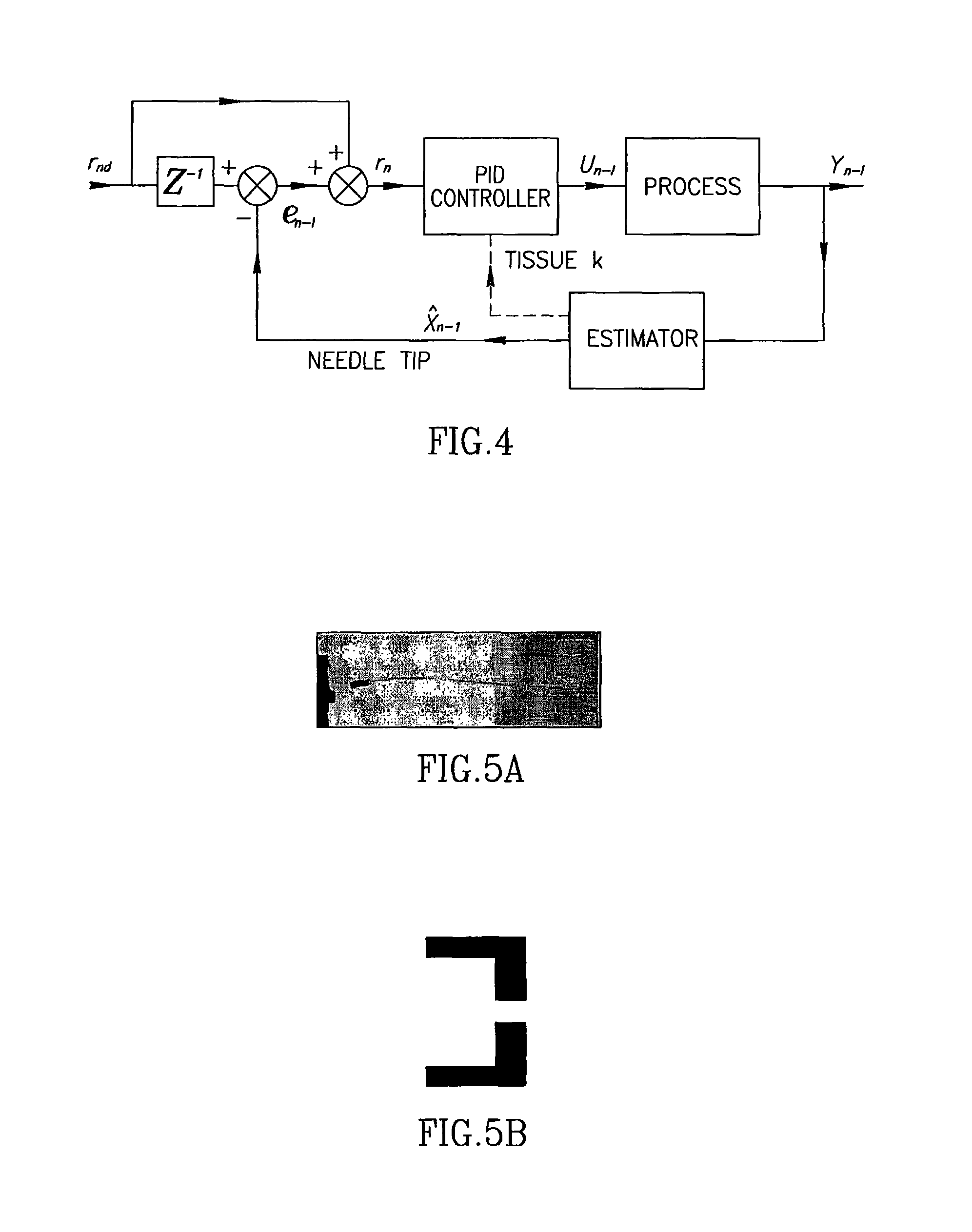
A robotic system for flexible needle steering under ultrasound imaging. A robot is used to steer the needle along a predetermined curved trajectory by maneuvering the needle base. The needle tip position is detected by an ultrasound sensor and the tracking error of the needle tip from a predetermined needle path is input to a controller which solves the inverse kinematic based on the needle position, and the needle and tissue properties. The control algorithm uses a novel method to detect the elastic properties of the tissue by analyzing tissue motion at the region in front of the needle tip. The inverse kinematic solution may be performed on a model of the needle as a flexible beam having laterally connected virtual springs to simulate lateral forces exerted by the tissue elasticity. The system is able to direct the needle to a target within the tissue while circumventing forbidden regions.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Controlled steering of a flexible needle
ActiveUS8348861B2Reduce in quantitySurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsStiffness coefficientRobotic systems
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method and system for gesture recognition
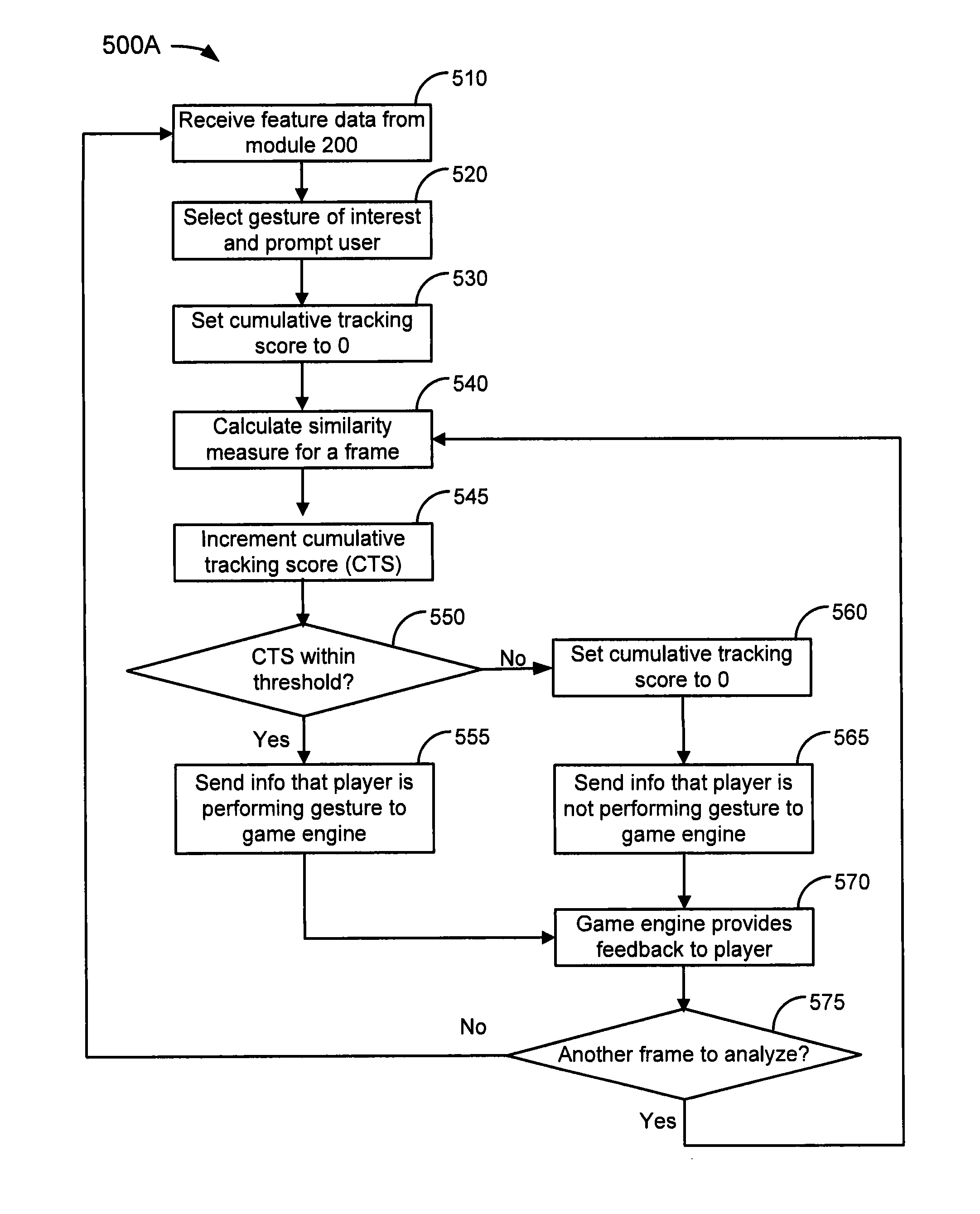
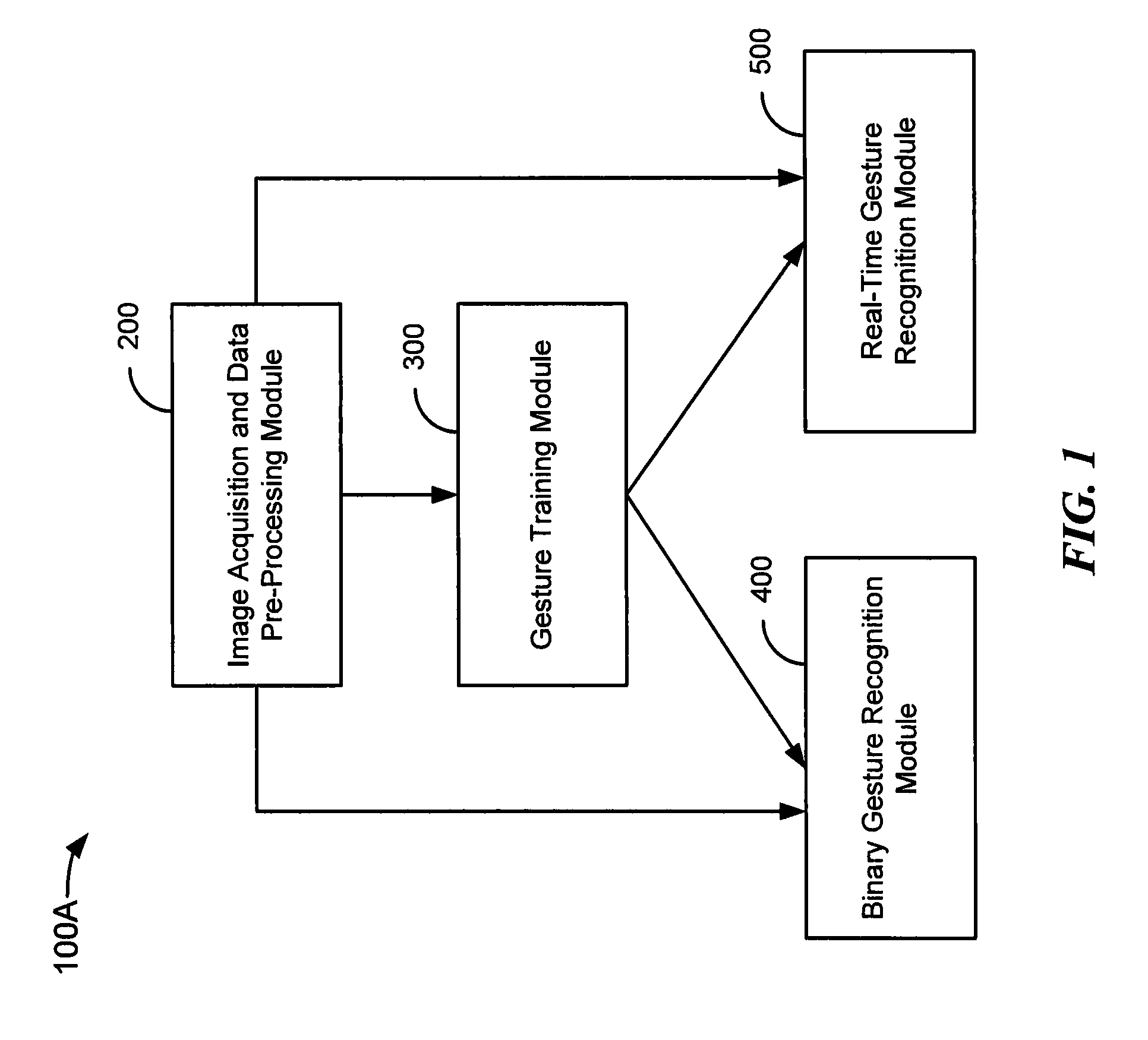
ActiveUS8824802B2Computationally efficientEfficient smoothingColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsMethod of imagesComputer vision
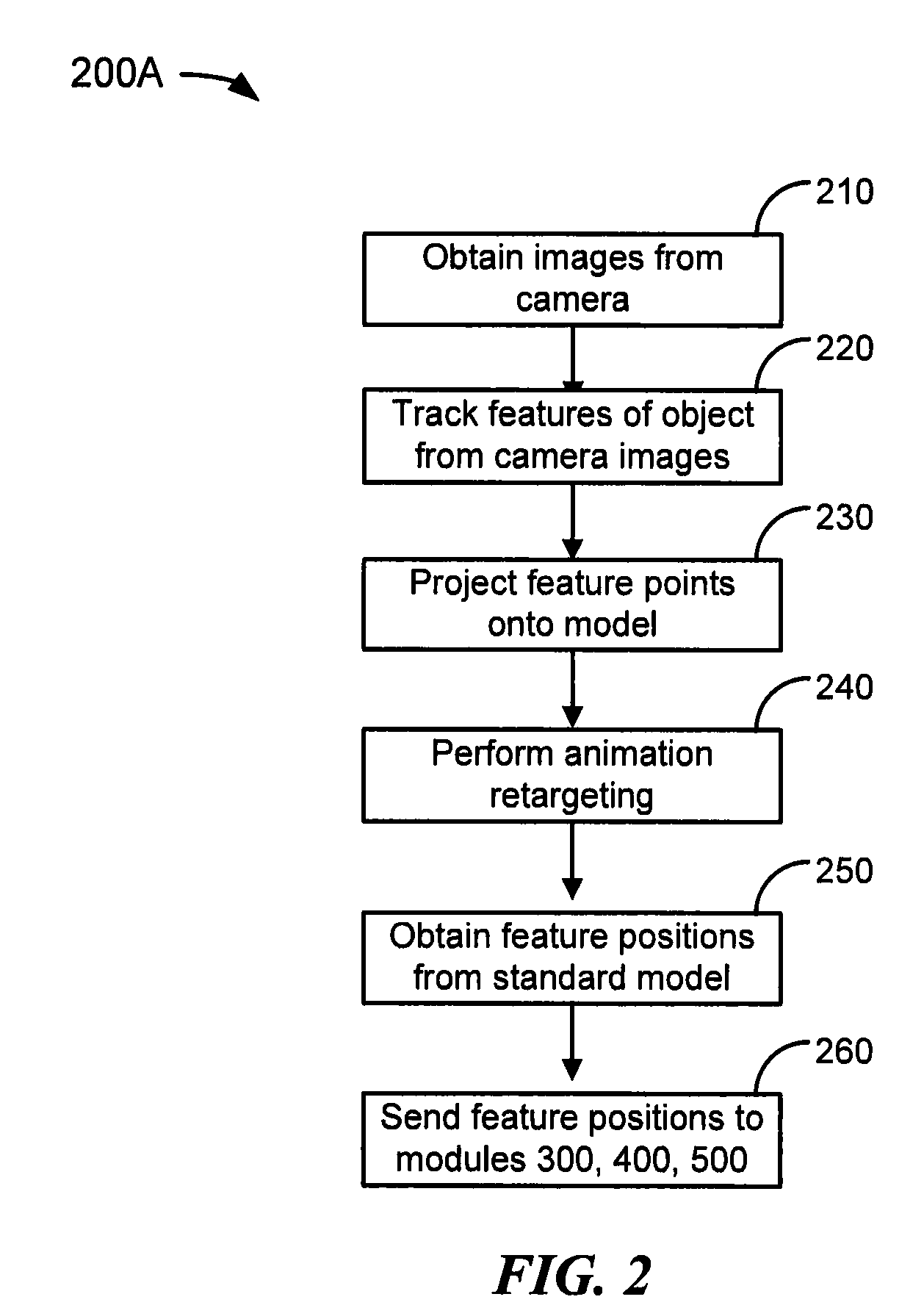
A method of image acquisition and data pre-processing includes obtaining from a sensor an image of a subject making a movement. The sensor may be a depth camera. The method also includes selecting a plurality of features of interest from the image, sampling a plurality of depth values corresponding to the plurality of features of interest, projecting the plurality of features of interest onto a model utilizing the plurality of depth values, and constraining the projecting of the plurality of features of interest onto the model utilizing a constraint system. The constraint system may comprise an inverse kinematics solver.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Ultrasound guided robot for flexible needle steering
ActiveUS20110112549A1Absence of radiation hazardLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasound imagingRobotic systems
A robotic system for flexible needle steering under ultrasound imaging. A robot is used to steer the needle along a predetermined curved trajectory by maneuvering the needle base. The needle tip position is detected by an ultrasound sensor and the tracking error of the needle tip from a predetermined needle path is input to a controller which solves the inverse kinematic based on the needle position, and the needle and tissue properties. The control algorithm uses a novel method to detect the elastic properties of the tissue by analyzing tissue motion at the region in front of the needle tip. The inverse kinematic solution may be performed on a model of the needle as a flexible beam having laterally connected virtual springs to simulate lateral forces exerted by the tissue elasticity. The system is able to direct the needle to a target within the tissue while circumventing forbidden regions.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method of six-DOF industrial robot passing singular region
InactiveCN103909522APass smoothlySolve the unstable operationProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringSacroiliac joint
The invention discloses a method of a six-DOF industrial robot passing a singular region. The method includes the steps of 1, planning a motion curve of the six-DOF industrial robot in the Cartesian space; 2, subjecting coordinates and attitudes of interpolation points in the motion curve to inverse kinematic solution so as to obtain angular displacements, angular velocities and angular acceleration joint variables of joints of the six-DOF industrial robot at the interpolation points; 3, setting the singular region for the six-DOF industrial robot, calculating the joint variables of the interpolation points, judging whether the interpolation points are in the singular region or not, and if yes, further judging the type of singular configuration; 4, allowing the six-DOF industrial robot to pass the singular region. The method has the advantages that the method is simple and feasible and the problem that at present, the six-DOF industrial robot moves unstably due to abrupt change in the joint angular velocity when the six-DOF industrial robot encounters the singular region is well solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
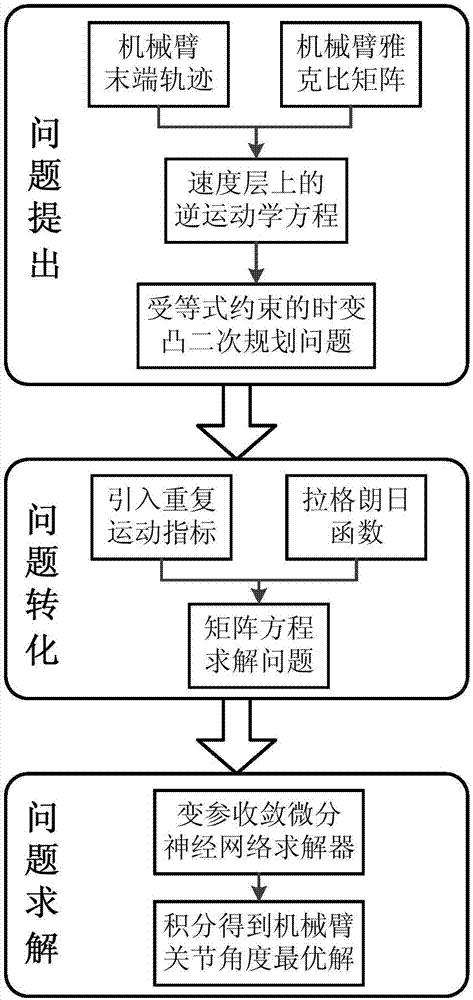
Repetitive movement planning method for redundancy mechanical arm
ActiveCN106945041AAddressing non-repetitive motion problemsImprove real-time performanceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRepetitive movementsPlanning method
The invention discloses a repetitive movement planning method for a redundancy mechanical arm based on a variable-parameter convergence differential neural network. The repetitive movement planning method includes the following steps that firstly, a redundancy mechanical arm inverse kinematics equation is established on a speed layer through the track of the tail end of the redundancy mechanical arm; secondly, the inverse kinematics problem in the first step is designed as a time-varying convex quadratic programming problem constrained by the equation; thirdly, a repetitive movement index is introduced in the time-varying convex quadratic programming problem; fourthly, the time-varying convex quadratic programming problem in which the repetitive movement index is introduced is converted into a time-varying matrix equation through a lagrangian function; fifthly, the time-varying matrix equation is solved through the variable-parameter convergence differential neural network; and sixthly, integration is conducted on the optimal solution, obtained in the fifth step, on the speed layer of the redundancy mechanical arm, and the optimal solution of the joint angle is obtained. By means of the repetitive movement planning method for the redundancy mechanical arm based on the variable-parameter convergence differential neural network, the variable-parameter convergence differential neural network is adopted for solving the repetitive movement of the redundancy mechanical arm, and the beneficial effects of the high calculating efficiency, high real-time performance and good robustness are achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Control method, equipment, system and construction machinery for multi-joint mechanical arm support
ActiveCN103147577AReduce shockIncrease flexibilityUnderground chambersMechanical machines/dredgersDiscrete programmingEngineering
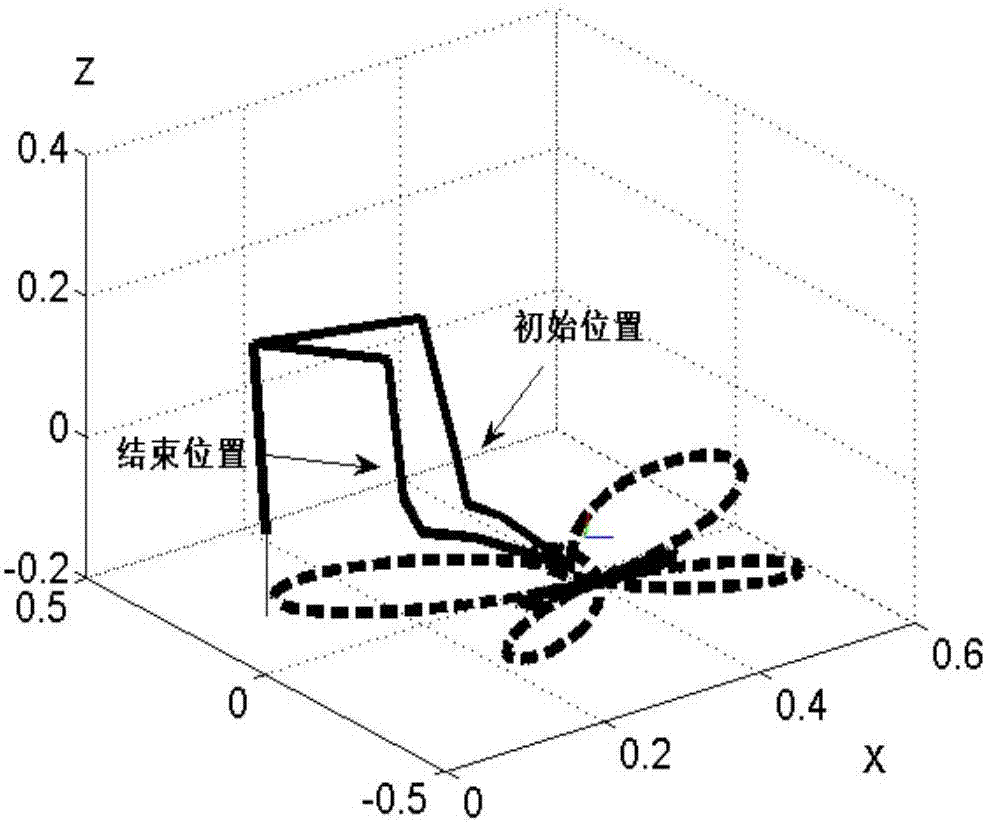
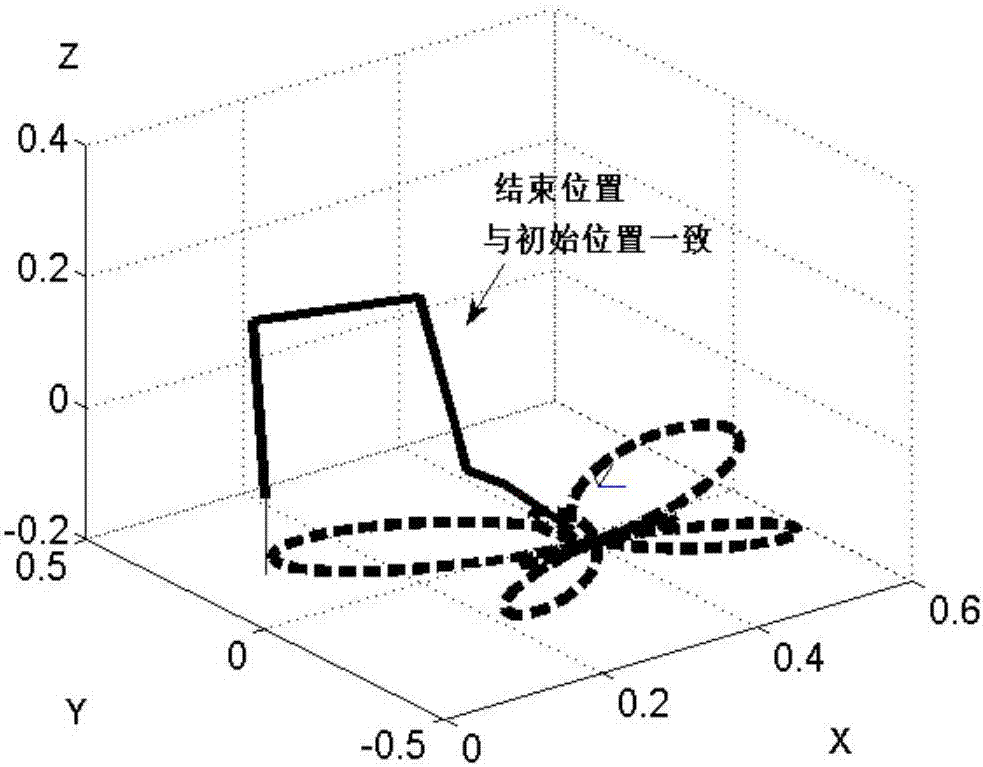
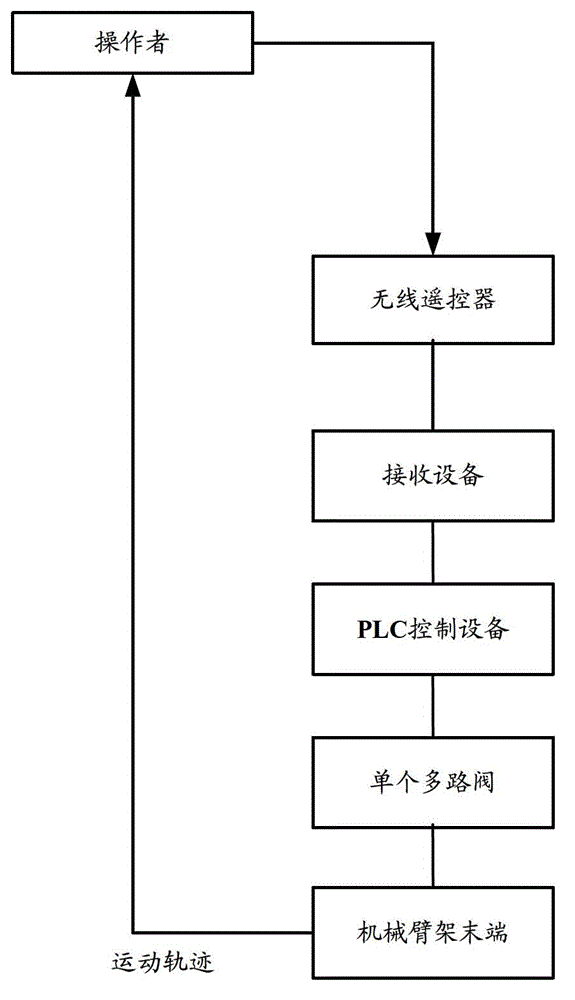
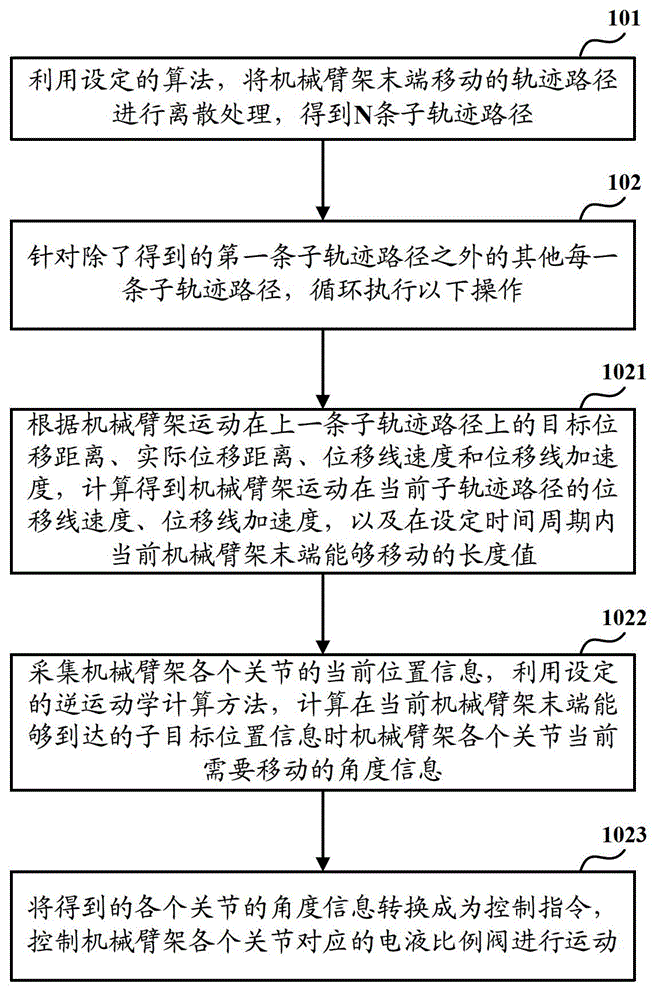
The invention discloses a control method, equipment, a system, and construction machinery for a multi-joint mechanical arm support. The control method mainly comprises the steps that a moving track path of the tail end of the mechanical arm support is divided into a plurality of sub track paths; aiming at each sub track path, the length value that the tail end of the mechanical arm support can move within a set duration, and current position information of each joint of the mechanical arm support is collected to calculate the required moving angle information of each joint of the mechanical arm support under the position information of subgoals capable of being reached by the tail end of the mechanical arm support; the obtained angle information of each joint in converted into control instructions, so that each joint of the mechanical arm support is controlled to move; the track path of the tail end of the mechanical arm support is subjected to discrete programming; and aiming at the sub track paths after programming, the moving angle information of each other joint of the mechanical arm support are determined according to the inverse kinematic principle. Therefore, the operation stability of the tail end of the arm support is guaranteed sufficiently, and the control precision for the tail end of the multi-joint mechanical arm support is improved.
Owner:ZOOMLION HEAVY IND CO LTD
Method for quick solution of six-degree-of-freedom humanoid dexterous arm inverse kinematics
InactiveCN102509025AImprove computing efficiencyHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringShoulder joint capsule
The invention discloses a method for quick solution of six-degree-of-freedom humanoid dexterous arm inverse kinematics. The method includes: firstly, setting up a six-degree-of-freedom human arm simulated joint structural model, solving an elbow joint angle and two joint angles of the shoulder joint according to a planar relation formed by the shoulder center, the elbow center, the wrist center and the neck center of the dexterous arm and the tail end position of the dexterous arm, and further solving three joint angles of the wrist joint by the aid of the dexterous arm tail-end posture relation; and calculating position error of a dexterous arm target link to prove effectiveness of the solution of the inverse kinematics by means of a positive kinematic model. Compared with a numerical solving method for robot inverse kinematics, the method for quick solution of six-degree-of-freedom humanoid dexterous arm inverse kinematics is high in precision and quick in speed, and can be used for humanoid dexterous arm operational tasks having high requirements on precision and instantaneity.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
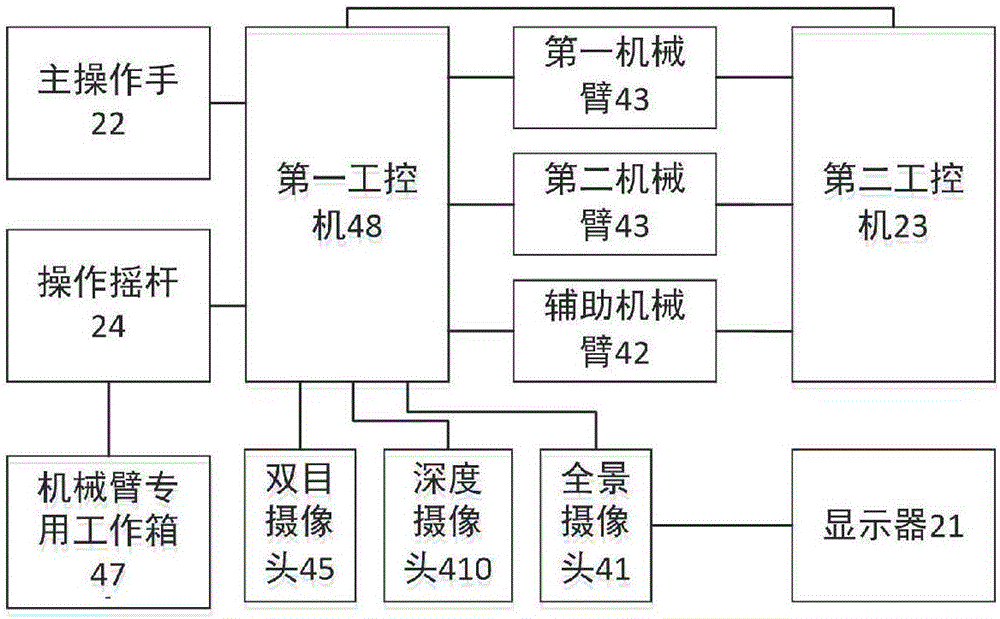
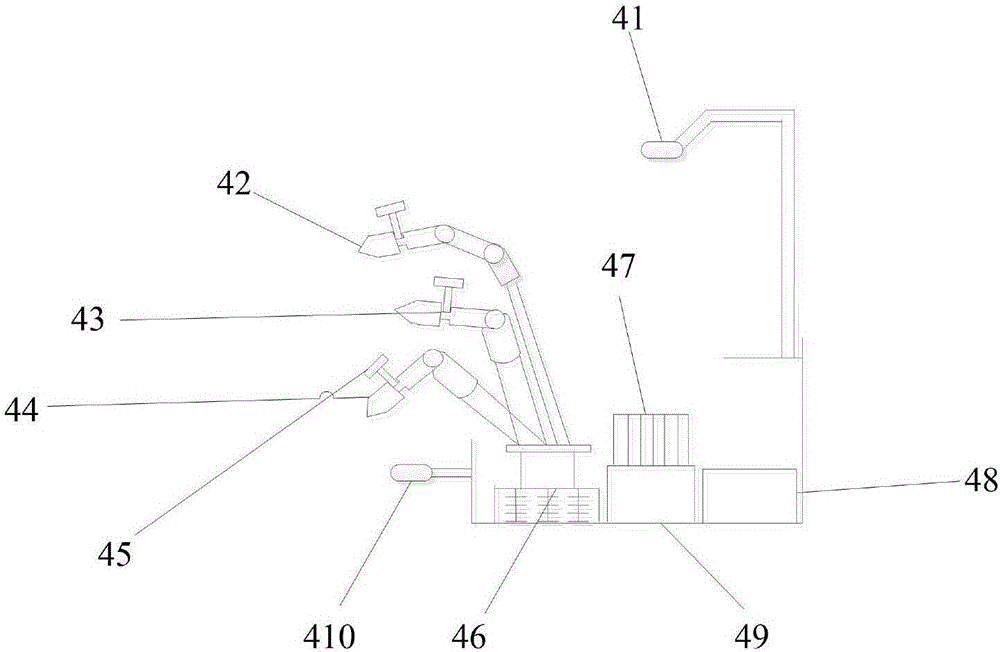
Hot-line work robot control system based on dual mechanical arms and auxiliary arm
ActiveCN106493708AImprove reliabilityImprove convenienceProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemEngineering
The invention provides a hot-line work robot control system based on dual mechanical arms and an auxiliary arm. The first mechanical arm, the second mechanical arm and the auxiliary mechanical arm each carry a binocular camera; the binocular cameras are used for acquiring operation scene images of the mechanical arms and sending the operation scene images to a data process and control system; the data process and control system plans a mechanical arm spatial path according to the operation scene images; according to a specific method, the tail end positions of the mechanical arms and an operation target position are converted into a same reference coordinate system, and the coordinate difference between the tail end positions of the mechanical arms and the operation target position under the same reference coordinate system is acquired; and according to the coordinate difference, the angle expected value of each joint of the mechanical arms is solved out through an inverse kinematic computing method. According to the hot-line work robot control system based on the dual mechanical arms and the auxiliary arm, based on a method in which binocular vision is combined with coordinate conversion, the mechanical arms are autonomously controlled to complete the hot-line work target of a distribution line, the labor intensity of operation personnel is relieved, and safety is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
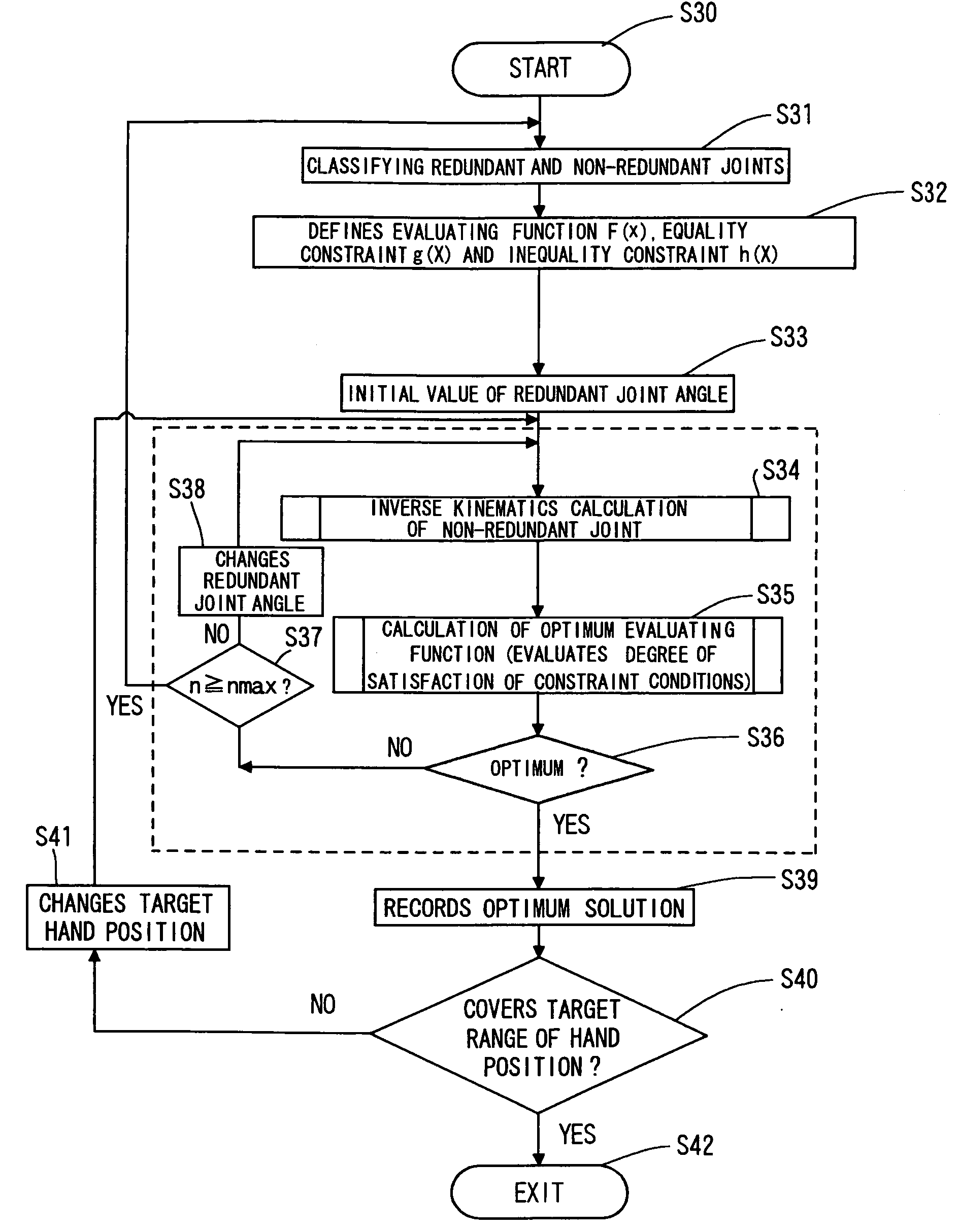
Method of controlling redundant manipulator
InactiveUS20050143860A1Increase speedProgramme-controlled manipulatorData processing applicationsManipulatorInverse kinematics
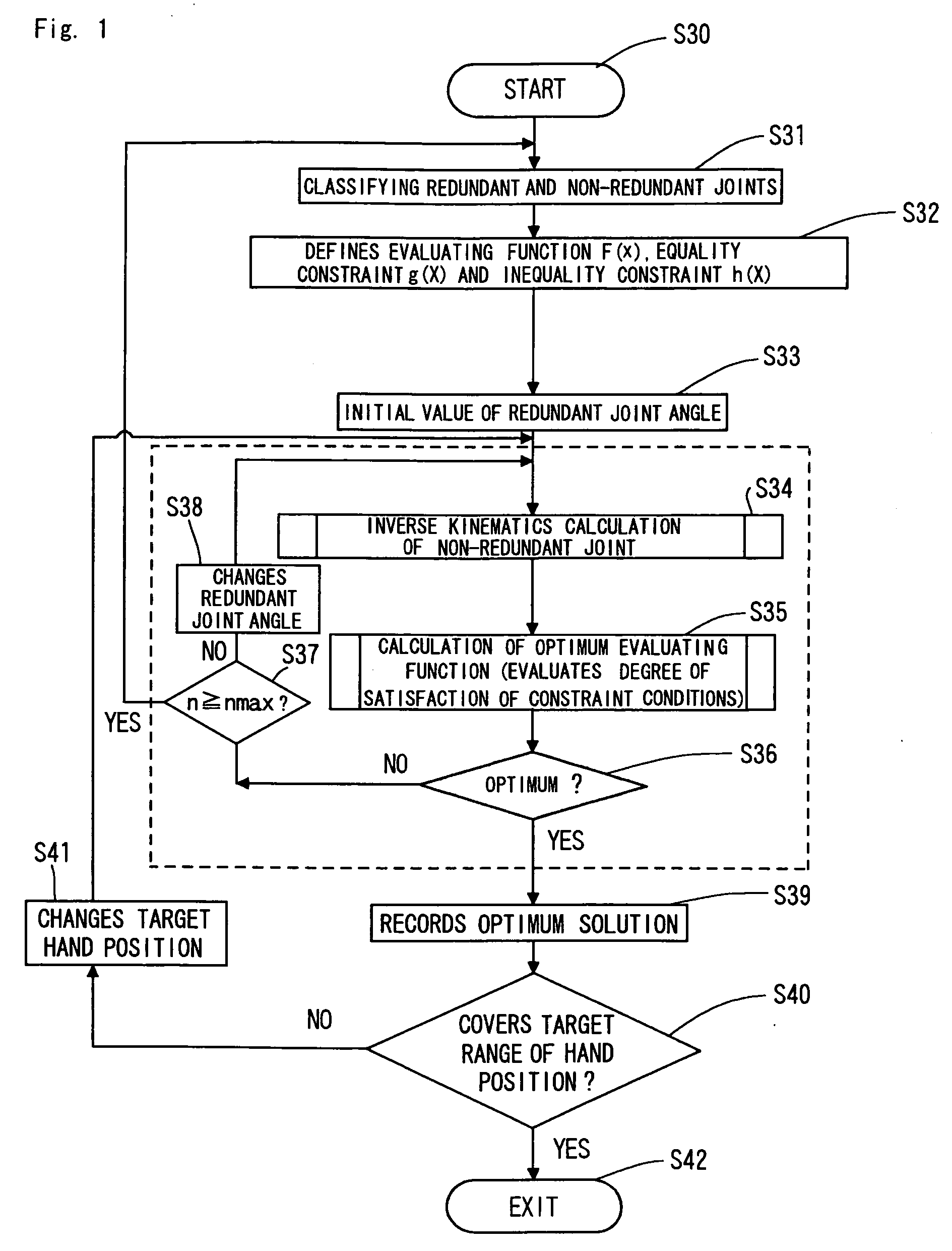
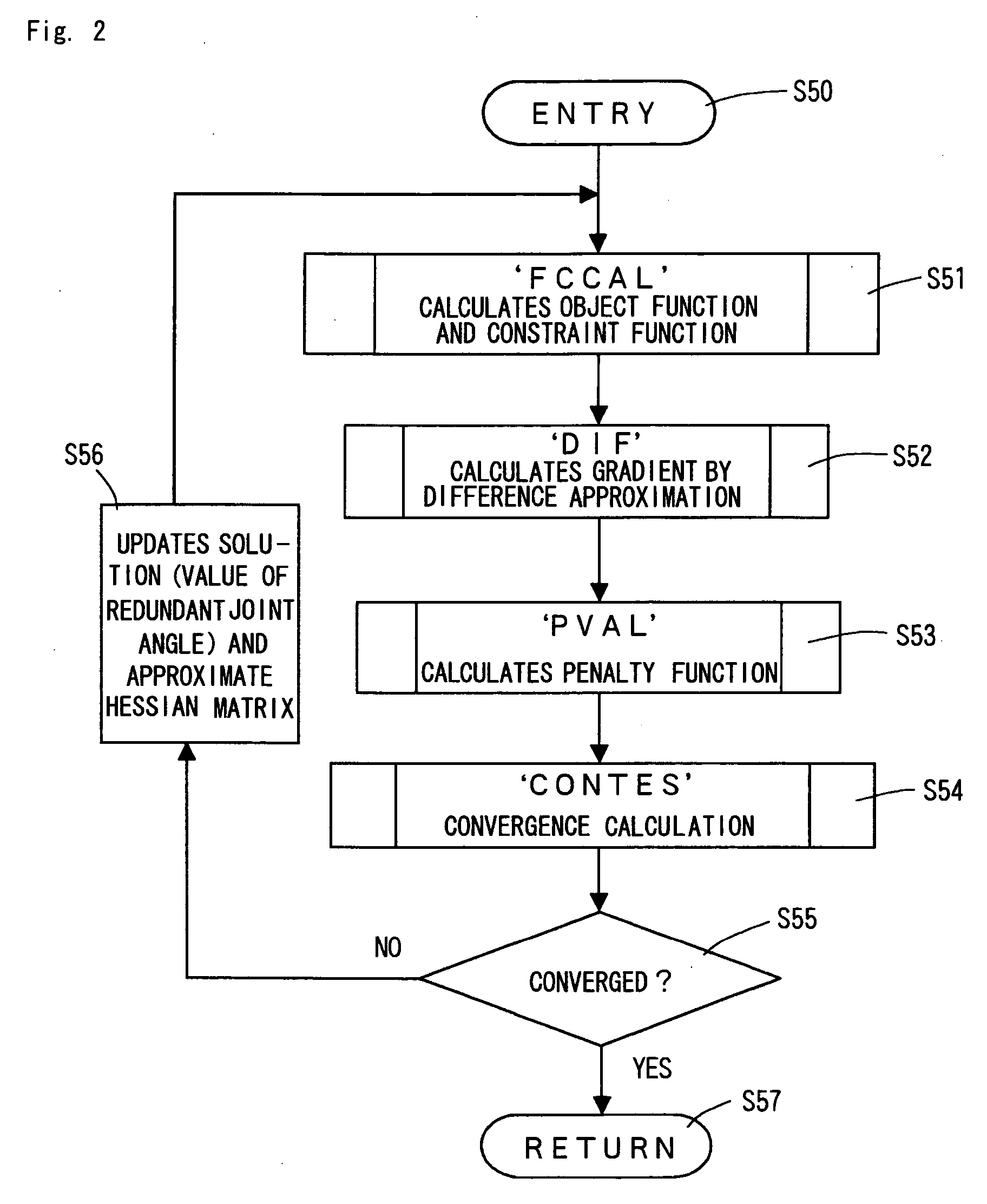
A method of controlling a redundant manipulator for assigning one or more redundant joints from a plurality of joints and obtaining the solution to an inverse kinematics problem at high-speed. The joints are arbitrarily classified into redundant joints and non-redundant joints, and an initial value is set for the joint angle of the classified redundant joint as a parameter. Then based on an evaluating function or a constraint condition defined by the joint angle of the redundant joint provided as a parameter and the joint angle of the non-redundant joint, which is determined by the inverse kinematics calculation according to the change of the parameter, an optimum solution of a set of joint angles is determined, and until the optimum solution covers the target range of the hand position, the procedure to determine the optimum solution is repeated with relaxing the constraint conditions.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Inverse kinematics solution method for six-degree-of-freedom serial robot
ActiveCN102637158AAvoid problems with rank less than orderIngenious ideaComplex mathematical operationsRobot kinematicsTabu search
The invention discloses an inverse kinematics solution method for a six-degree-of-freedom serial robot. The inverse kinematics solution method comprises the steps of: establishing a connecting rod coordinate system and setting variables theta 1, theta 2, theta 3, theta 4, theta 5 and theta 6; setting an initial configuration; solving theta 4, theta 5 and theta 6 by utilizing a geometric method; and eliminating theta 1, theta 2 and theta 3 by utilizing an algebra elimination method and introducing a tabu search algorithm when solving a non-orthogonal spheroid or the terminal structure of the non-orthogonal spheroid, thereby solving out corresponding numerical solutions. The inverse kinematics solution method is smart in conception and utilizes the geometric method and the algebra elimination method for comprehensive solution, thereby avoiding the problem that the rank of an equation determinant of coefficient is smaller than order caused by arbitrary establishing of equations and correctly obtaining the analytic solutions of six axes efficiently; and for complex-structure trigonometric function relationship, a linear equation in two unknowns can be effectively transformed to a linear equation with one unknown by the elimination method in the use of the geometric method, and therefore a unique corresponding analytic solution is obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU CRP ROBOT TECH CO LTD
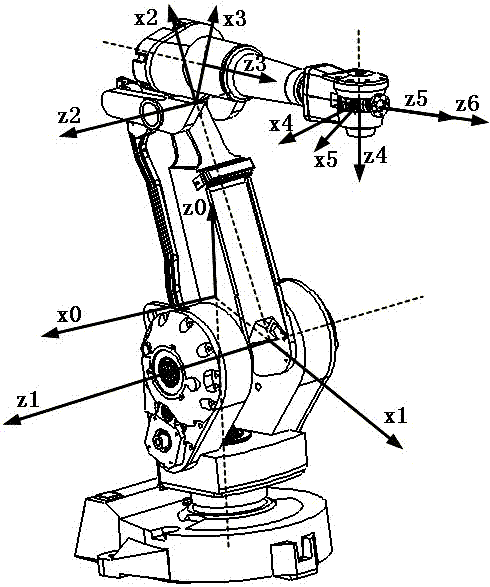
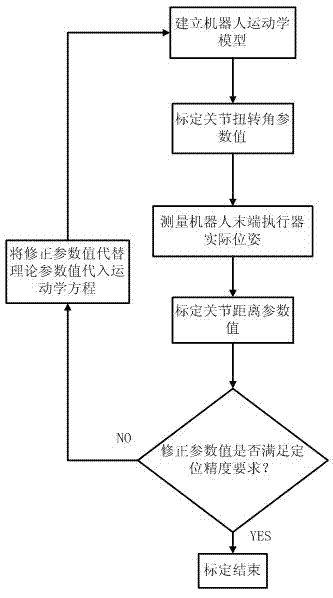
Industrial robot positioning precision calibration method
InactiveCN102692873AImprove absolute positioning accuracyImprove performanceAdaptive controlKinematics equationsEngineering
The invention relates to an industrial robot positioning precision calibration method used for improving robot absolute positioning precision. The method comprises the steps that: a robot kinetics model is established; a rotary joint equation is established by using a circumferential method; joint torsion angle parameter values are calculated; the actual pose of a robot end is measured accurately by utilizing a laser tracker; D-H algorithm inversion kinetics equation is improved to obtain geometrical structural parameters; calibration of joint distance parameter values and calibration of joint offset are realized, and thereby first calibration is completed. Error correction is carried out on D-H parameters based on first calibration results, and if positioning precision can not meet requirements, second calibration can be carried out by substituting parameter correction values, instead of theoretical parameter values, into the kinetics equation. Absolute positioning precision of the robot is improved with the calibration method, which is proved in experiments. According to the invention, the calibration method is advantaged in that the method is simple and practical and introduces small external errors.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
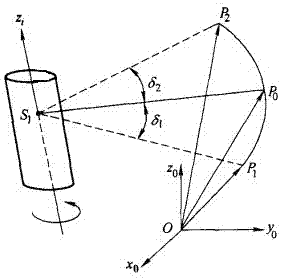
Robot precision compensation method for variable-parameter error recognition
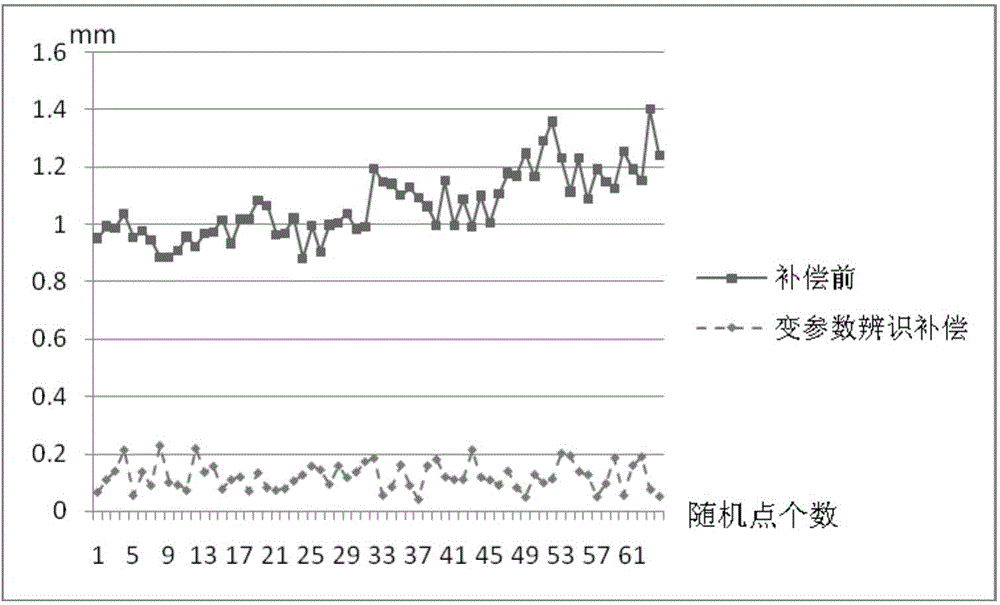
ActiveCN104535027AImprove absolute positioning accuracyFind global convergent solutionNavigational calculation instrumentsLaser trackerInverse kinematics
The invention discloses a robot precision compensation method for variable-parameter error recognition and belongs to the technical field of robot inverse calibration. A variable-parameter error module is provided, errors of pose points of a robot in different spaces are sampled through a laser tracker, a plurality of points which are closest to an expected pose point are sought in the near area range according to the space where the expected pose point is located, and an improved Levenberg-Marquardt damp iterative least square method algorithm is used for solving the global convergent solution of the parameter error corresponding to the expected pose point, and therefore the practical parameter of the expected pose point is solved. The pose point at which the robot should arrive practically is solved through the practical parameter of the expected pose point and through inverse kinematics of the expected pose point, and the absolute positioning precision compensation of the robot at the pose point is achieved. The robot precision compensation method can obviously improve the absolute positioning precision of the robot and can be applied to the field where the requirement for robot precision is high.
Owner:江苏航鼎智能装备有限公司
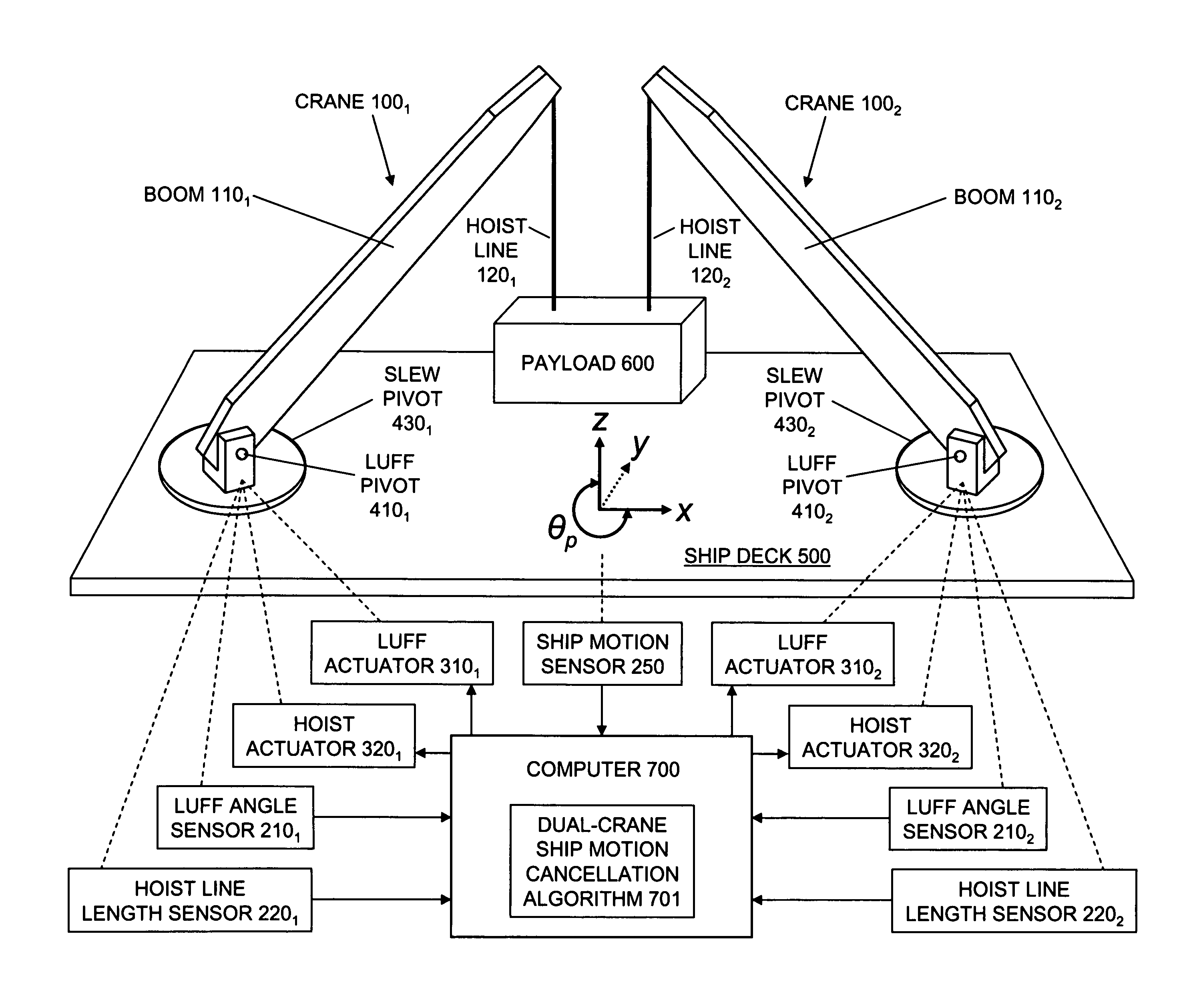
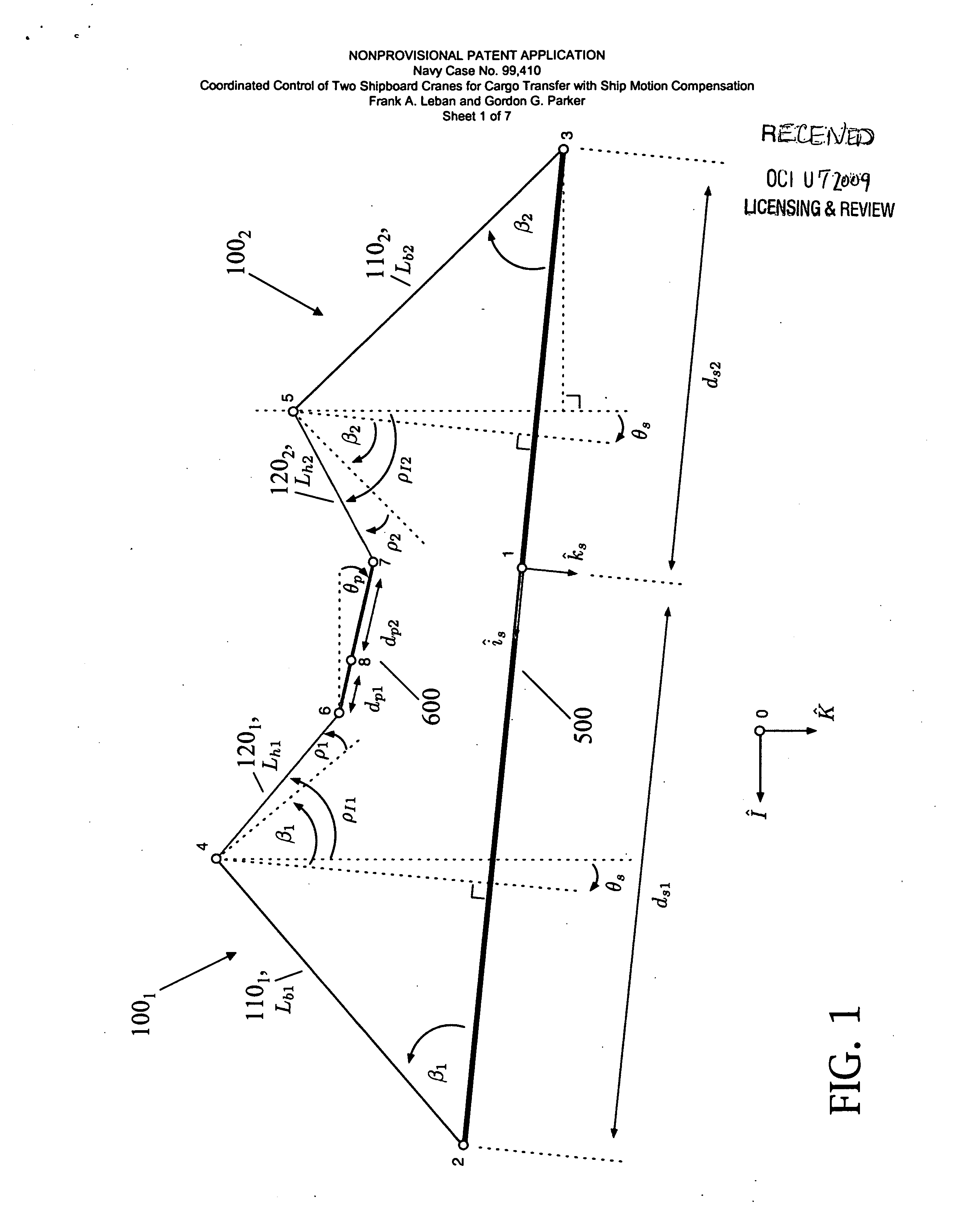
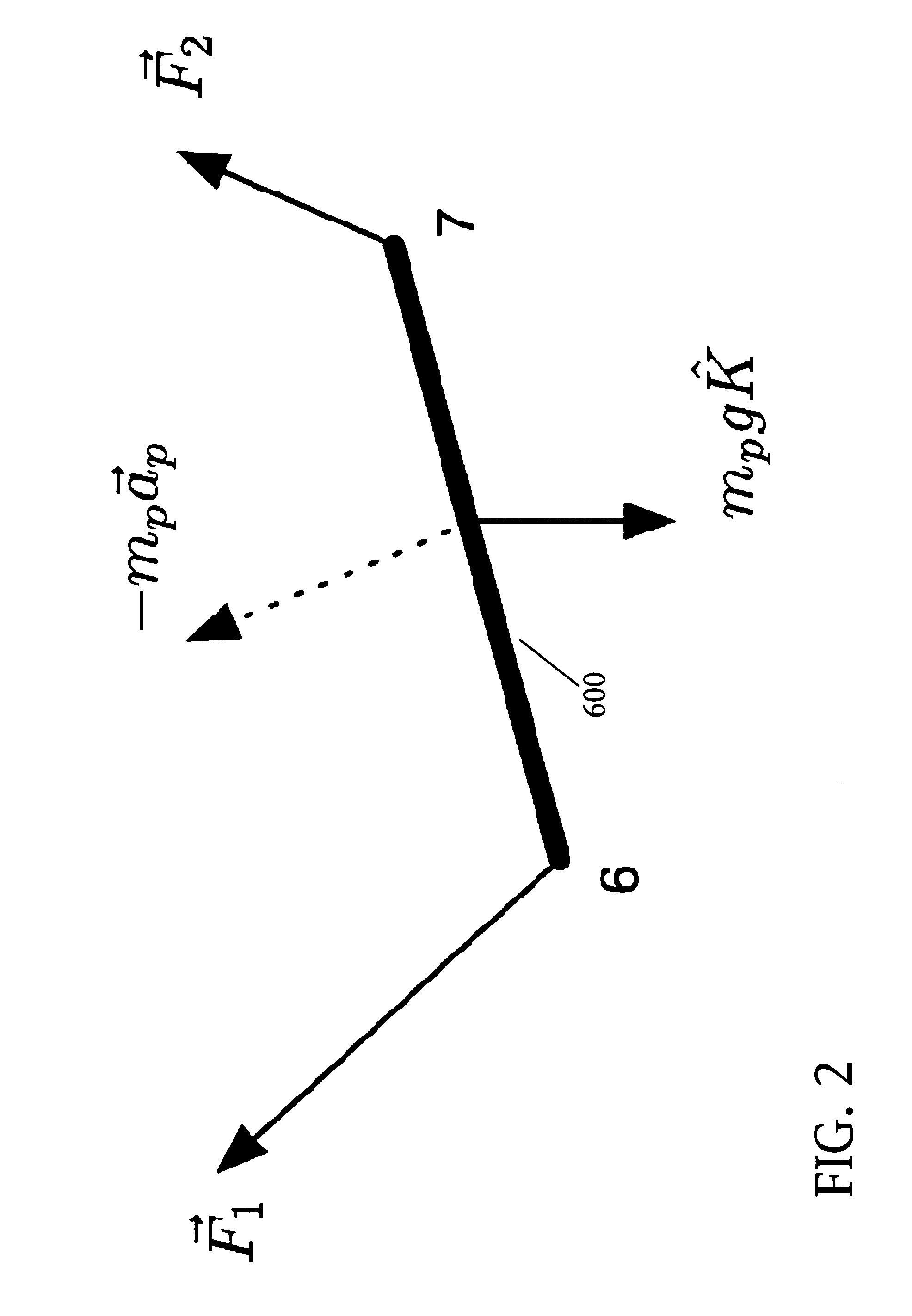
Coordinated control of two shipboard cranes for cargo transfer with ship motion compensation
The present invention is typically embodied to exert active control of two same-shipboard cranes performing joint lifting of a payload. Sensory signals indicative of ship motion, and of luff angle and hoist line length of both cranes, are transmitted to a computer. The sensory signals are processed by the computer using a ship motion cancellation algorithm, which solves for values of the respective luff angles and hoist line lengths of both cranes, such values achieving static equilibrium (e.g., zero motion horizontally, vertically, and rotationally in the same vertical geometric plane) of the suspended payload. Inverse kinematic control signals in accordance with the mathematical (e.g., minimum norm) solutions are transmitted by the computer to respective luff angle actuators and hoist line length actuators of both cranes so that the suspended payload tends toward steadiness. Inventive control thus acts on a continual basis to significantly reduce pendulation during the two-crane lifting operation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
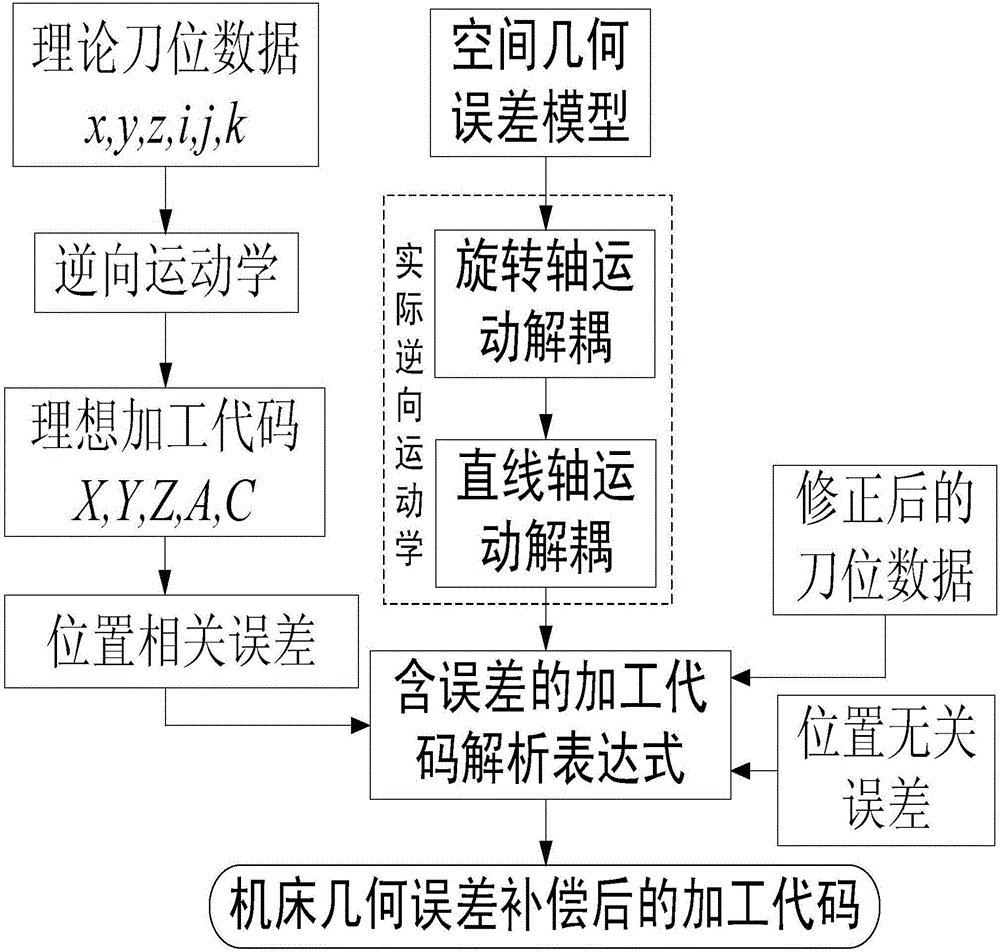
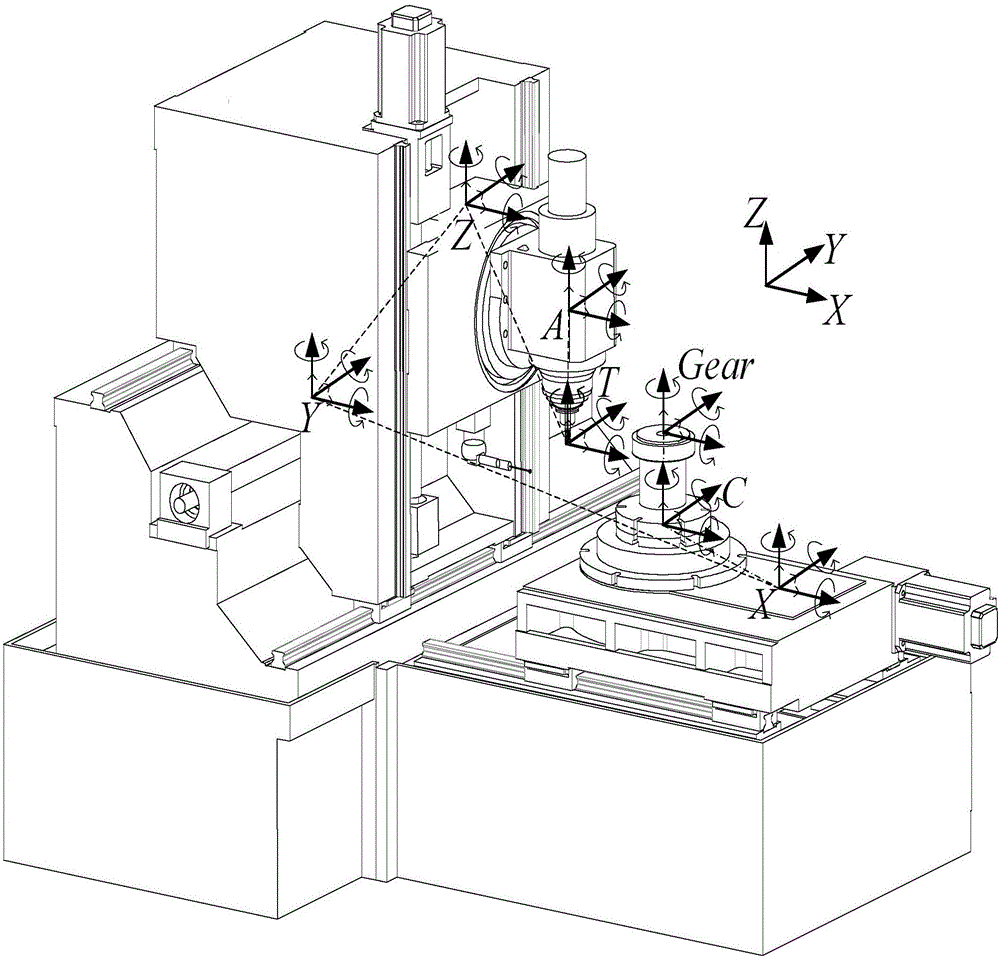
Method for actually compensating for geometrical errors of five-axis numerical control tooth manufacturing machine tool through inverse kinematics
ActiveCN106325207AImprove computing efficiencyProgramme controlComputer controlCutter locationAnalytical expressions
The invention provides a method for actually compensating for geometrical errors of a five-axis numerical control tooth manufacturing machine tool through the inverse kinematics. The method includes the steps of building a space geometrical error model containing position unrelated errors and position related errors on the basis of a homogeneous coordinate transformational matrix, and deducing a processing code analytical expression containing the geometrical errors from the space geometrical error model according to the characteristics of the homogeneous coordinate transformational matrix. Theoretical cutter location data is modified by 12 pose deviations (6 static pose deviations and 6 movement pose deviations) of a cutter relative to a workpiece. The geometrical errors of the machine tool can be compensated for by substituting the position unrelated errors, the position related errors and the modified cutter location data into the processing code analytical expression for compensating for the geometrical errors of the machine tool, and meanwhile the12 pose deviations of the cutter relative to the workpiece are modified. The error compensation method is simple in compensation process, easy to understand, small in calculation amount, high in compensation efficiency and wide in application range, and the basic compensation concept of the method is suitable for numerical control machine tools of various types.
Owner:NANJING GONGDA CNC TECH
Tele-operative surgical systems and methods of control at joint limits using inverse kinematics
ActiveUS10188471B2Highly configurableProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRemote surgeryRange of motion
Devices, systems, and methods for controlling manipulator movements at joint range of motion limits are provided. In one aspect, methods include locking one or more joints of the manipulator when the one or more joints hit a respective joint limit by modifying an input into a Jacobian of the manipulator when calculating joint movement of a master control using inverse kinematics to provide improved, more intuitive force feedback through the master control. In some embodiments, scaling and weighting between different joint movements is applied within the inverse kinematics. In another aspect, methods include applying a constraint within the inverse kinematics so that calculated movement of the joints approach joint movements of an identical kinematic chain with applied loads within an isolated physical system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method for uniquely solving inverse kinematics numerical value of joint type mechanical arm
ActiveCN109895101AOvercoming the requirement of full rankSimple modeling methodProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoints typesEngineering
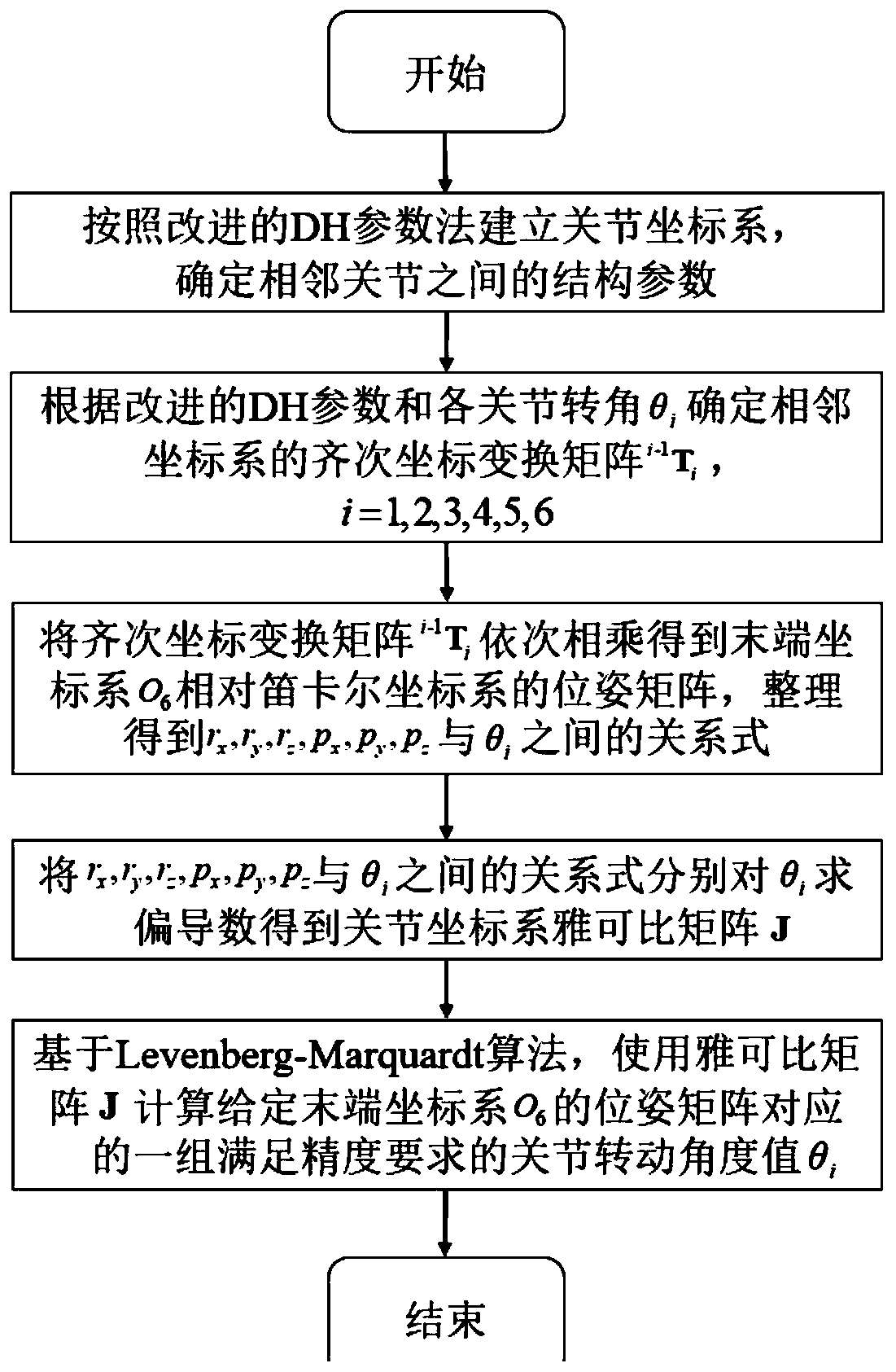
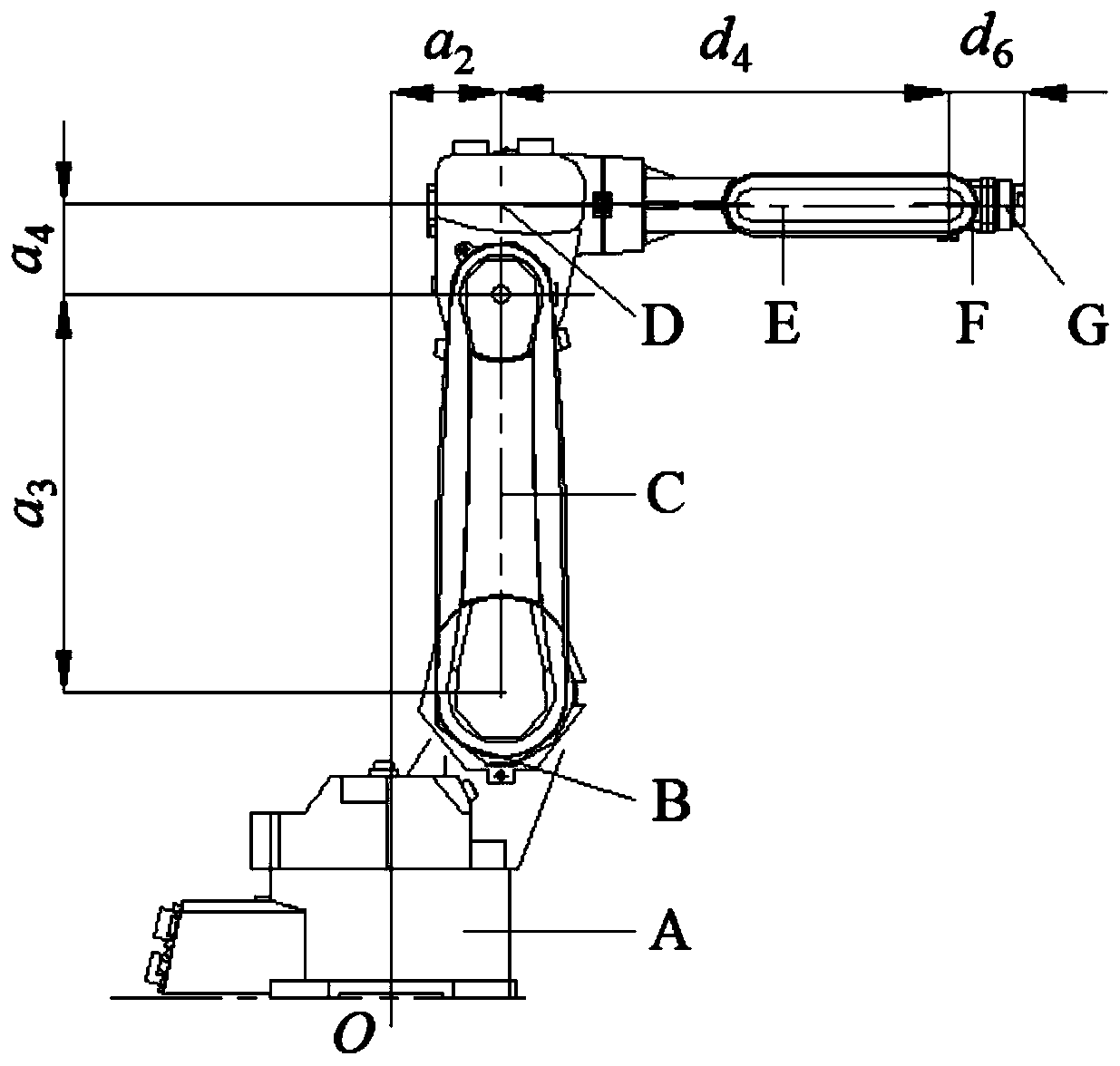
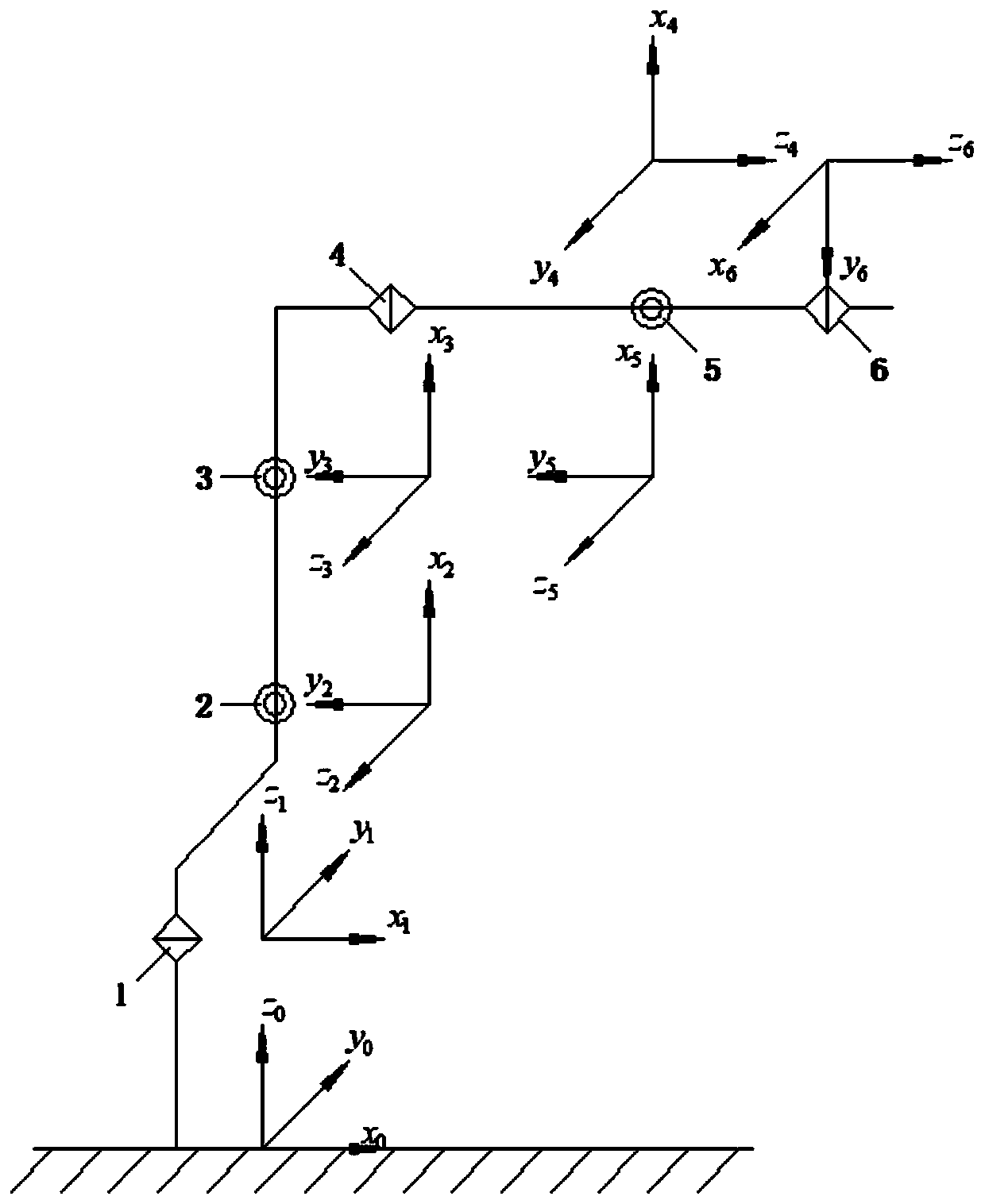
The invention discloses a method for uniquely solving the inverse kinematics numerical value of the joint type mechanical arm, belongs to the technical field of modern intelligent manufacturing, relates to the technical field of industrial robots, relates to a method for uniquely solving the inverse kinematics numerical value of a joint type six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm with shoulder joints facing forward. According to the method, a mechanical arm joint coordinate system is built according to an improved DH parameter method, four structural geometrical parameters between adjacent joints of the mechanical arm are determined, a homogeneous coordinate transformation matrix of two adjacent coordinate systems is calculated. For a given pose matrix of a tail end coordinate system O6, animproved newton iteration method, namely a Levenberg marquardt iterative algorithm is adopted, the inverse kinematics solution of the joint coordinate system is calculated by using a jacobian matrix J, and the six joint rotation angle values theta i which correspond to the pose matrix and meet the precision requirement are obtained. The method overcomes the requirement that a traditional newton iteration method needs to fully rank the jacobian matrix j, the modeling method is simple, clear and effective, the method has the characteristics of being high in solving precision, high in solving speed and simple and feasible in solving process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Redundancy dual-mechanical-arm multi-index coordinate exercise planning method
ActiveCN106426164AMeet the needs of different tasksImprove work efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematics equationsPerformance index
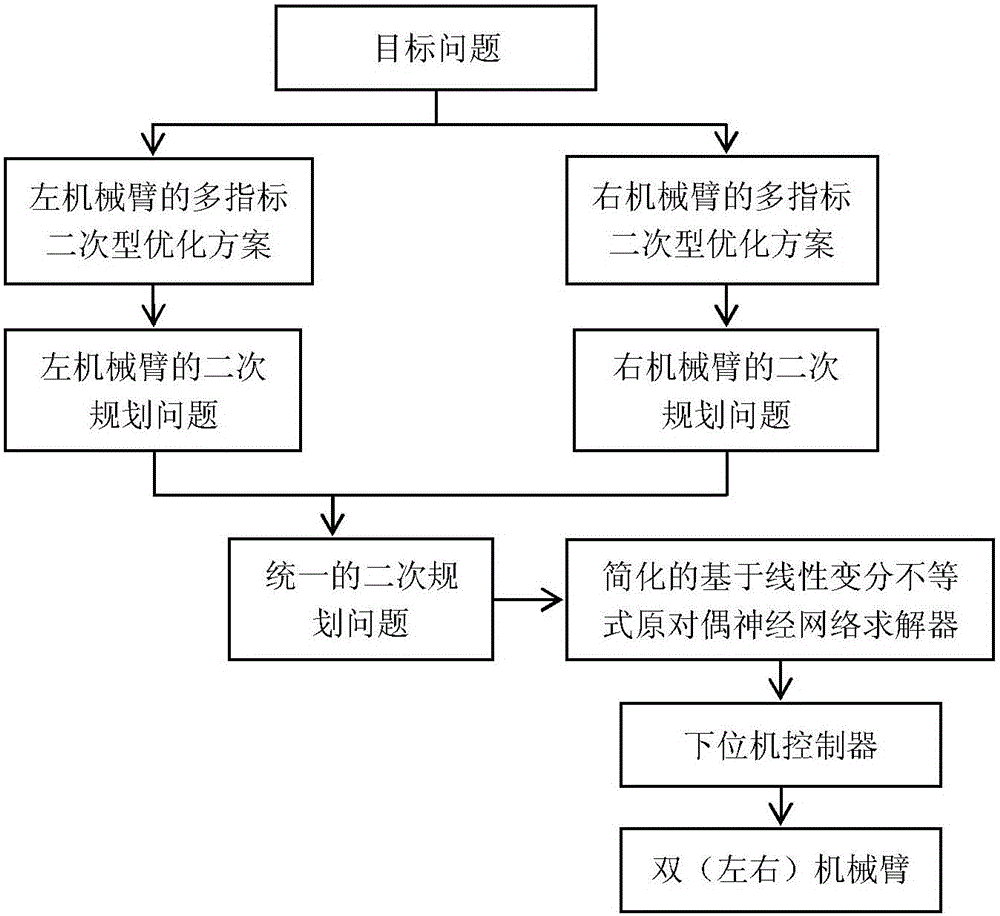
The invention discloses a redundancy dual-mechanical-arm multi-index coordinate exercise planning method. The method includes the steps that (1) based on a target problem, quadric form prioritization schemes are adopted for an upper computer to conduct inverse kinematics analysis on double mechanical arms on the speed layer, designed performance indexes are formed by the weighted array of three indexes including a minimum velocity two-norm, repeating motion and a minimum velocity infinite norm, and the performance indexes are limited to the kinematical equations, the joint angle extremities and the joint angle velocity extremities of the double mechanical arms correspondingly; (2) the quadric form prioritization schemes of the double mechanical arms in the step (1) are converted into standard quadratic programming problems; (3) the quadratic programming problems of the double mechanical arms in the step (2) are unified into one quadratic programming problem; (4) the unified quadratic programming problem in the step (3) is solved with a simplified original dual neural network solver based on the linear variational inequality; and (5) a solving result in the step (4) is transmitted to a lower computer controller to drive the double mechanical arms to move.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Dynamic obstacle avoidance path planning method of seven-degree-of-freedom redundant mechanical arm based on fast random search tree
ActiveCN109571466AAvoid the problem of target state uncertaintyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputation complexityDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a dynamic obstacle avoidance path planning method of a seven-degree-of-freedom redundant mechanical arm based on a fast random search tree. The dynamic obstacle avoidance pathplanning method of the seven-degree-of-freedom redundant mechanical arm based on the fast random search tree comprises the steps of offline planning and online planning, the offline planning uses an analytic solution method of inverse kinematics of a redundant mechanical arm to determine an optimal target state to be regarded as a target node to construct a search tree, the online planning is to extend and rewire the search tree according to the current environment, a path from the target node to a root node is obtained in real time, when the mechanical arm moves, the root node of the tree changes, and if the target node is blocked by an obstacle, the target node is switched, and a new path is searched to avoid the dynamic obstacle. According to the dynamic obstacle avoidance path planningmethod of the seven-degree-of-freedom redundant mechanical arm based on the fast random search tree, through the offline planning and the online planning, the problem that RRT* cannot be used for theredundant mechanical arm real-time obstacle avoidance due to the high computational complexity of the RRT* is solved, by updating the root node and the target node of the search tree in real time, the problem that the target node in the dynamic environment is unreachable is solved, and a collision-free path is planned for the mechanical arm in real time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus to plan motion path of robot
ActiveUS20110035050A1Improve performanceEfficiently escapeProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEngineeringManipulator
If a manipulator of a robot falls in local minima when expanding a node to generate a path, the manipulator may efficiently escape from local minima by any one of a random escaping method and a goal function changing method or a combination thereof to generate the path. When the solution of inverse kinematics is not obtained due to local minima or when the solution of inverse kinematics is not obtained due to an inaccurate goal function, an optimal motion path to avoid an obstacle may be efficiently searched for. The speed to obtain the solution may be increased and thus the time consumed to search for the optimal motion path may be shortened.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
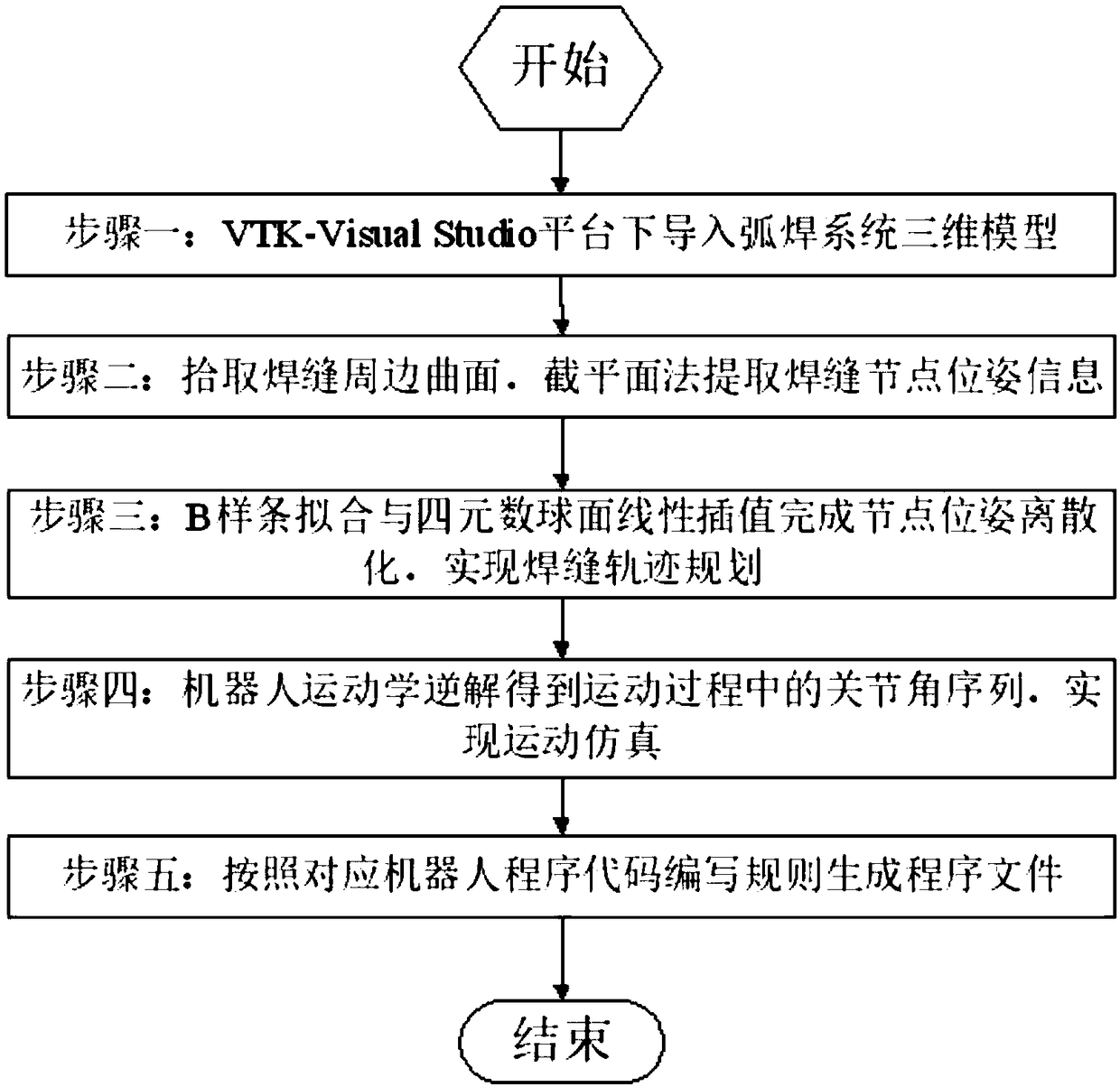
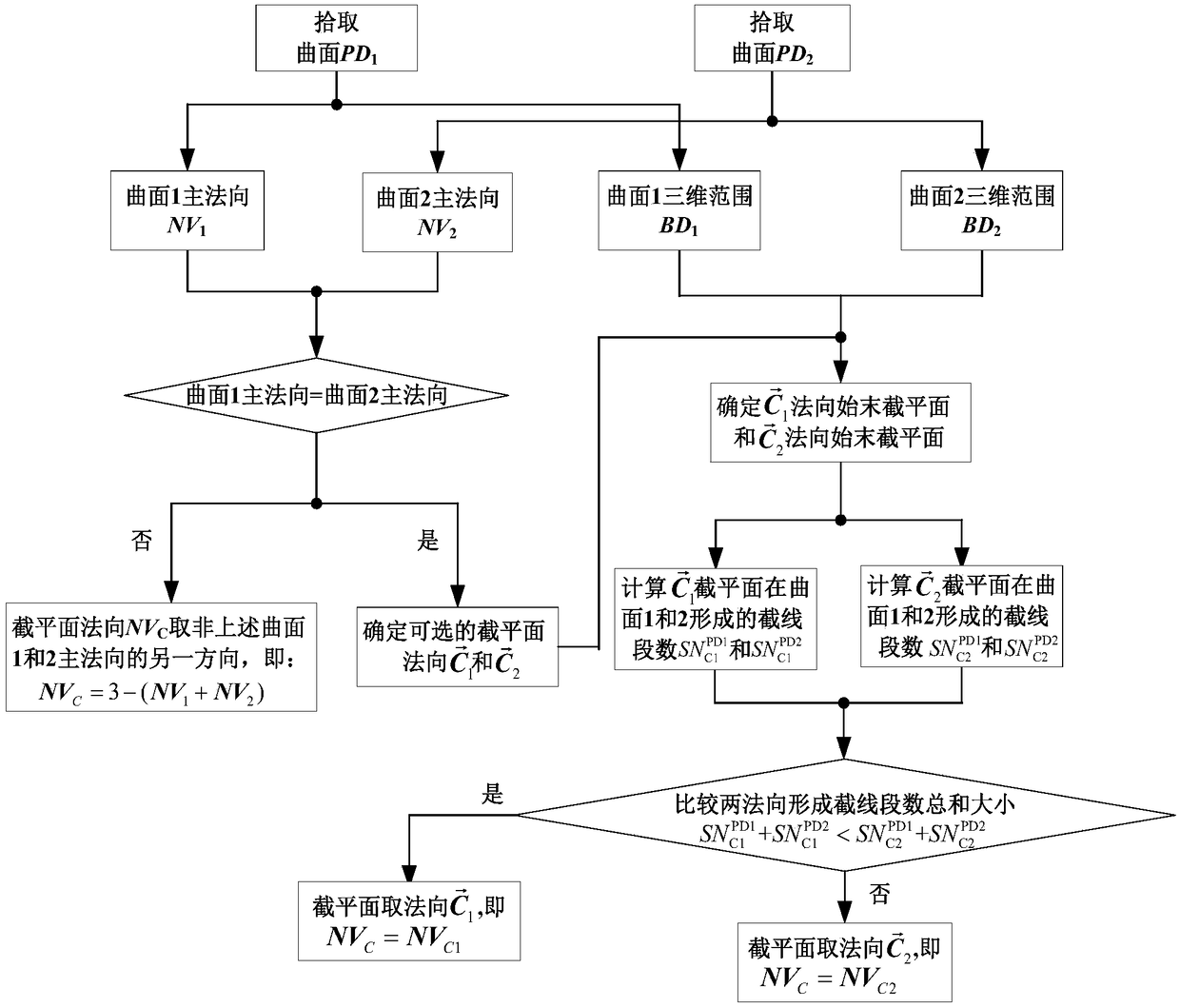
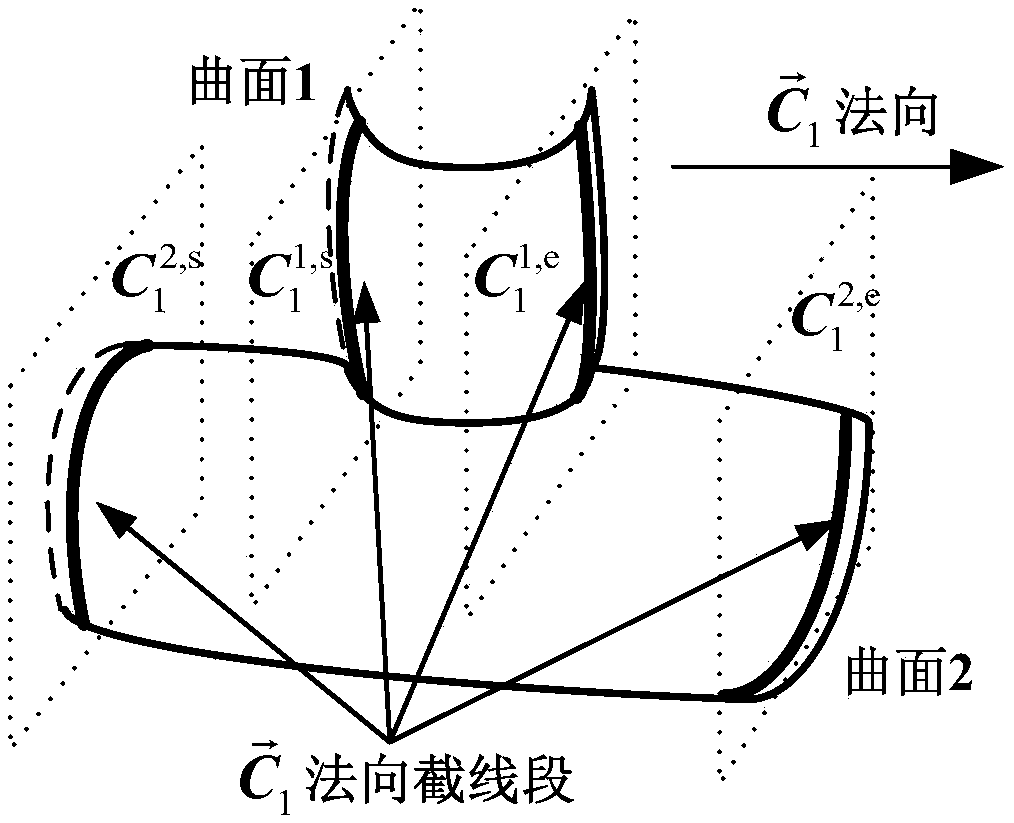
Industrial robot space intersecting curve welding offline programming method
ActiveCN109226937AQuick buildMeet the generality of modelingProgramme-controlled manipulatorWelding accessoriesEngineeringDiscretization
The invention discloses an industrial robot space intersecting curve welding offline programming method. The method comprises the steps that firstly, an arc welding robot and a welding workpiece three-dimensional model are guided in, two peripheral hook faces of a welding line are formed through mouse pickup, a cut plane set is created inside a workpiece coordinate system, and node pose information of the welding line is extracted; according to the node pose, position and posture discretization are achieved along the curve of the welding line, and then welding line trajectory planning is achieved through coordinate conversion; then, a joint angle sequence needed in the robot motion process is obtained through robot inverse kinematics, and motion simulation is achieved; finally, according to language rules written by corresponding robot motion control program codes, a corresponding program file is generated. By adopting an open source VTK visual tool magazine, offline programming independent development is achieved, the method does not dependent on third party CAD software, the track of the welding line can be generated only through mouse picking, no complex external data computingor guiding-in process is needed, the man-machine interaction is good, and the needed robot program can be rapidly generated.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
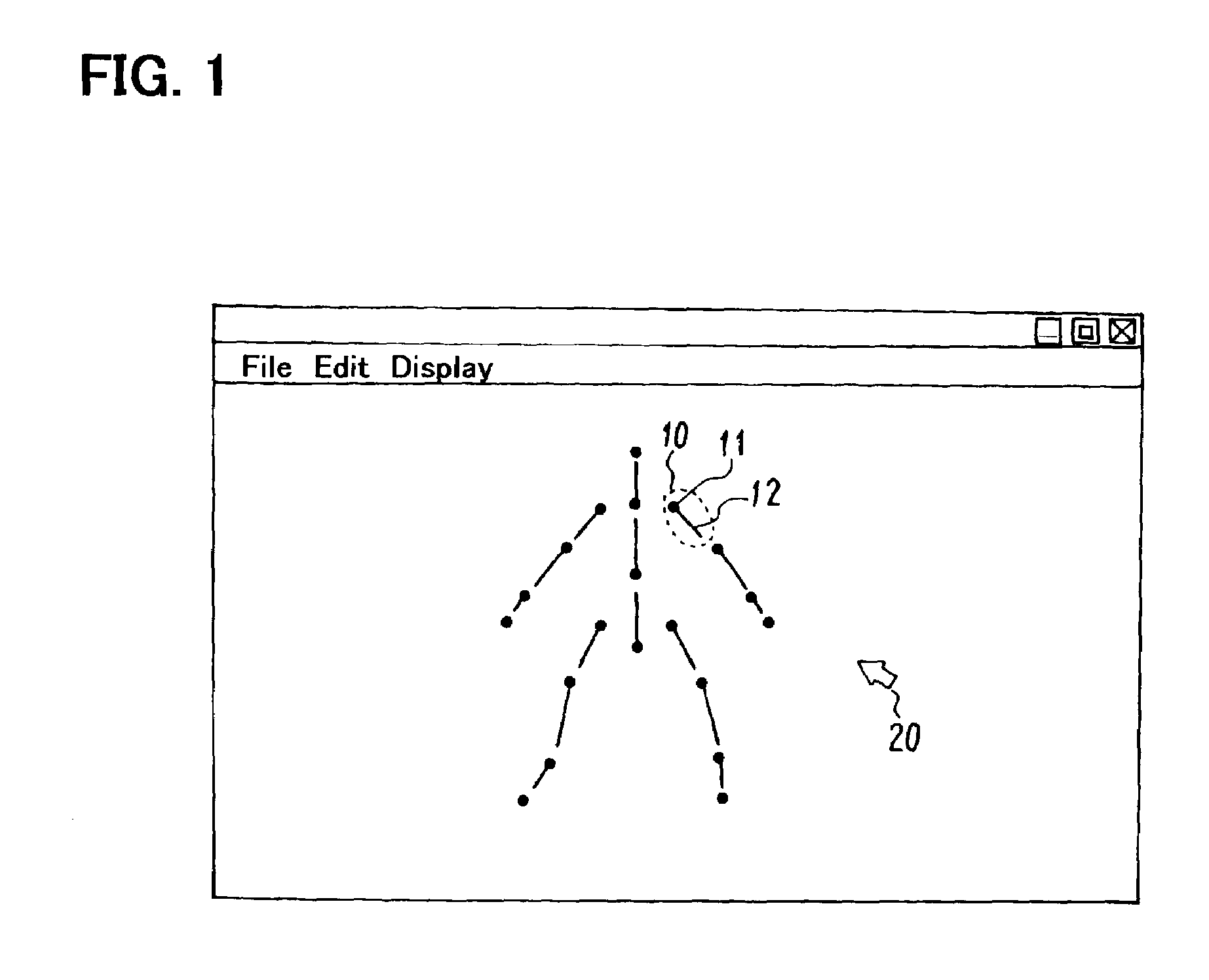
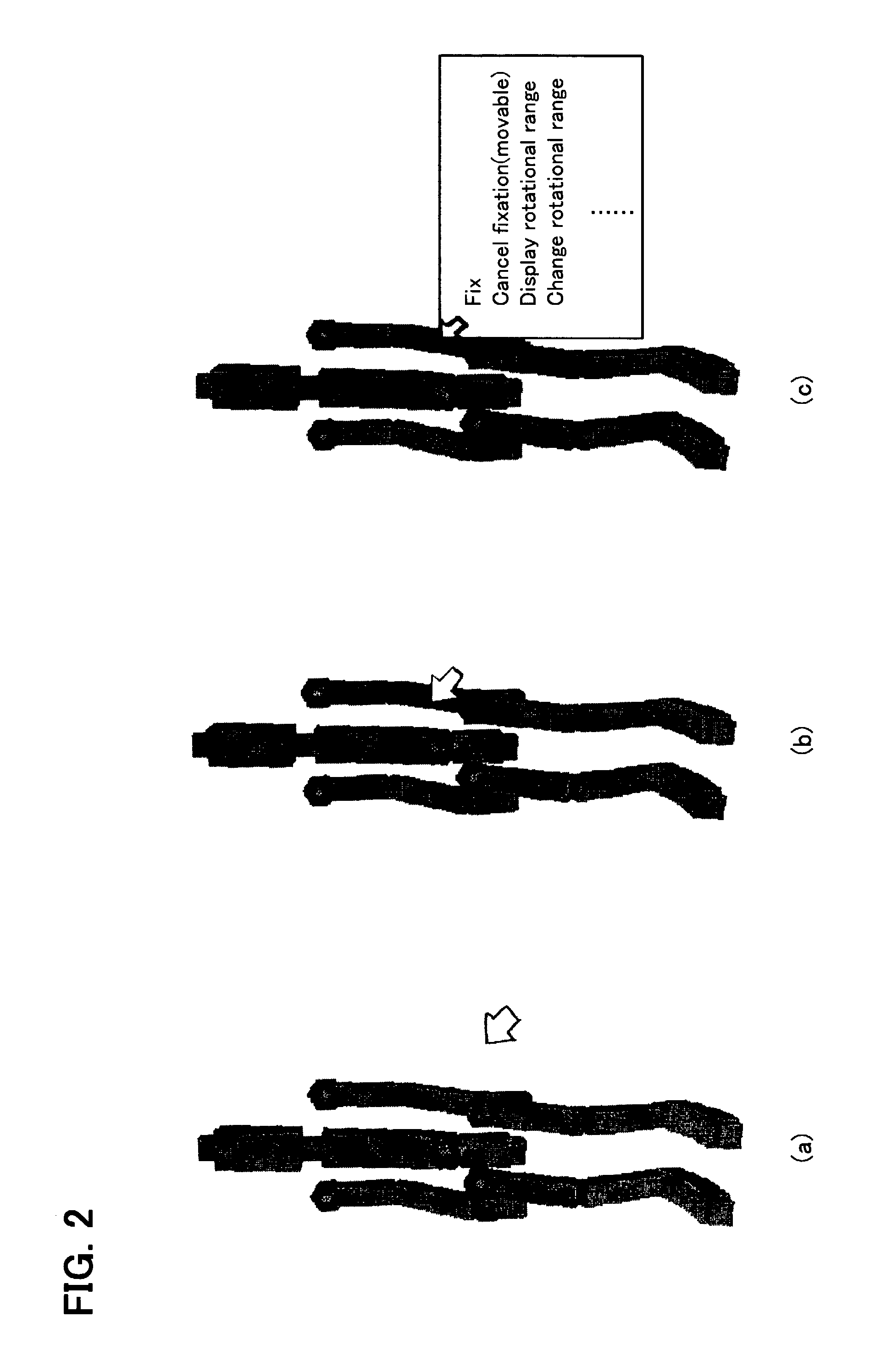
Animation creation program
InactiveUS7106334B2Simpler and easer operationEasy to operateAnimation3D-image renderingHumanoid robot naoAnimation
The present invention provides an animation creation program whereby the posture of a structure comprising a plurality of links can be determined by means of a simpler and easer operation. In accordance with the movement of one link in the structure comprising a plurality of links, the animation creation program of the present invention automatically determines the spatial positions of the other links of the structure so that the structure retains a posture that is as natural as possible. The animation creation program of the present invention uses, for example, inverse kinematics computation that is a computation method for controlling a human-type robot (humanoid) and is based on a matrix known as a Jacobian and the inverse matrix thereof which is known as the Singularity-Robust Inverse (SR-Inverse). By using this computation method in an animation creation program, in the creation of an animation of a structure comprising a plurality of links, it is possible, when moving one link of a structure displayed on a screen, to automatically determine the positions of the other links of the structure so that the posture of the structure as a whole does not become unnatural, and to create an animation of the structure comprising a plurality of links by means of a simpler and easer operation.
Owner:SEGA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com