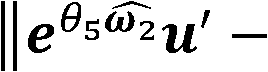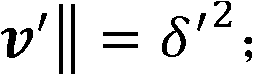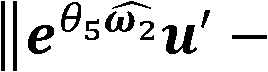Inverse kinematics solution method for six-degree-of-freedom serial robot
A technology of robot kinematics and degrees of freedom, applied in the direction of complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve problems such as small determinants of equation coefficients and inability to obtain corresponding analytical solutions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, taking The Unimation PUMA 560 robot as an example, establish a link coordinate system, put the robot link into the coordinate system, set the fixed end as the base coordinate, and set the rotation angles of the subsequent six joint axes as variables θ 1 , θ 2 , θ 3 , θ 4 , θ 5 , θ 6 ; and write the Denavit-Hartenberg parameter table as follows:
[0049] Connecting rod parameters of PUMA560 robot
[0050]
[0051] The rotation angle value of the known initial configuration is denoted as θ s , let G(θ t ) is the rigid body transformation of the inertial coordinate system when the robot is in the initial configuration, then each joint constructs a unit motion screw, and G(θ i ) represents the rotational motion of the i-th joint, at this time all other joints except the i-th joint are fixed in the initial configuration;
[0052] The structural feature of the Unimation PUMA 560 robot is that the first three axes control t...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the Kawasaki EE10 robot structure is taken as an example to illustrate the application of the tabu search method. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that when the wrist to be controlled by the robot is a non-orthogonal spherical wrist or a non-orthogonal aspheric wrist Structure, that is, when the axes of the last three joints of the robot linkage do not intersect at one point, it is very difficult to directly use the geometric method and algebraic elimination method to obtain the kinematic inverse solution, so the tabu search method is introduced in the calculation process. Its steps include:
[0075] (1) Establish the link coordinate system: put the robot link into the coordinate system, the fixed end is the base coordinate, and the rotation angles of the subsequent six joint axes are respectively set to the variable θ 1 , θ 2 , θ 3 , θ 4 , θ 5 , θ 6 ;
[0076] (2) Hypothesis θ 6 is a known value, use geometr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com