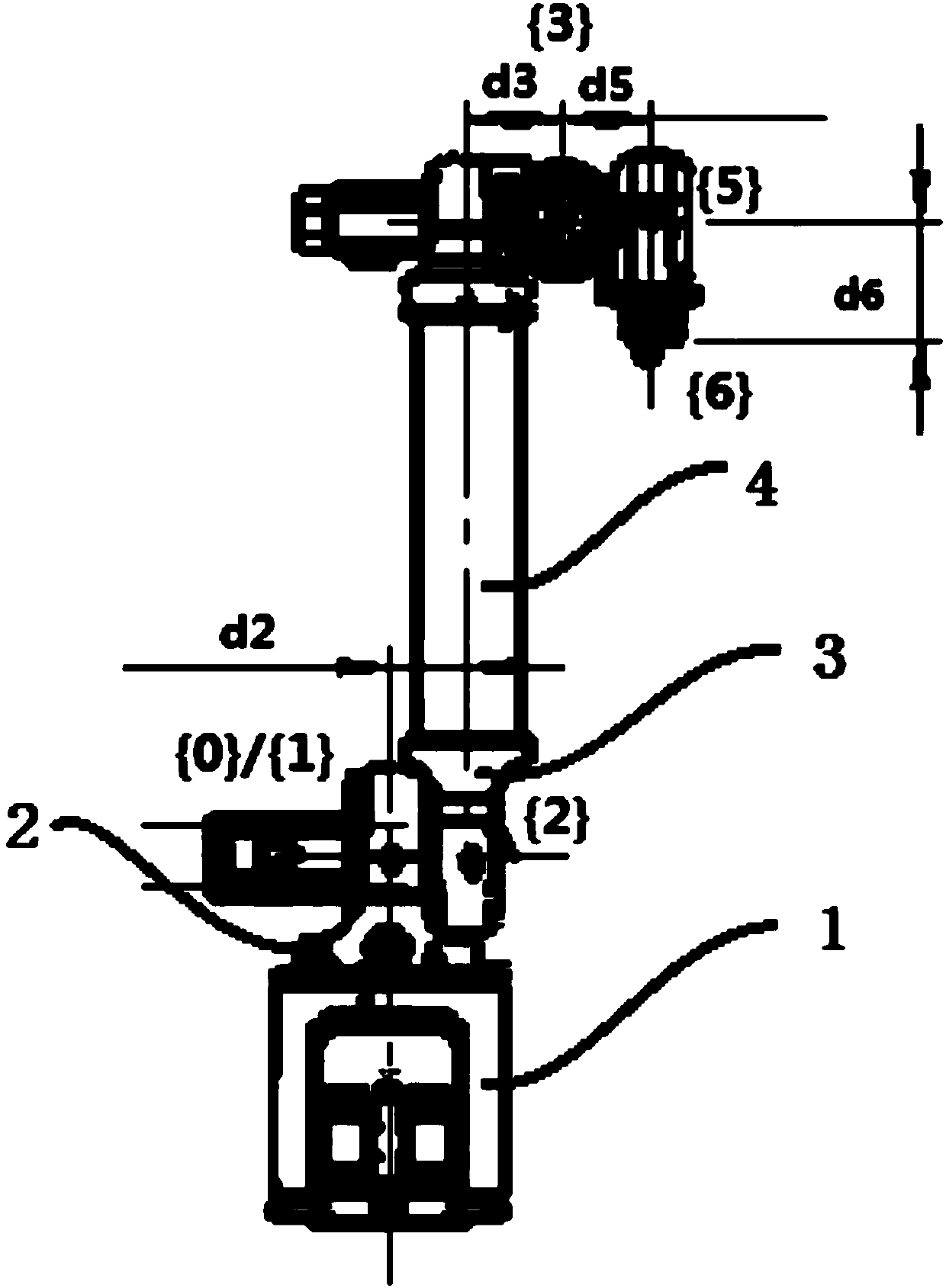
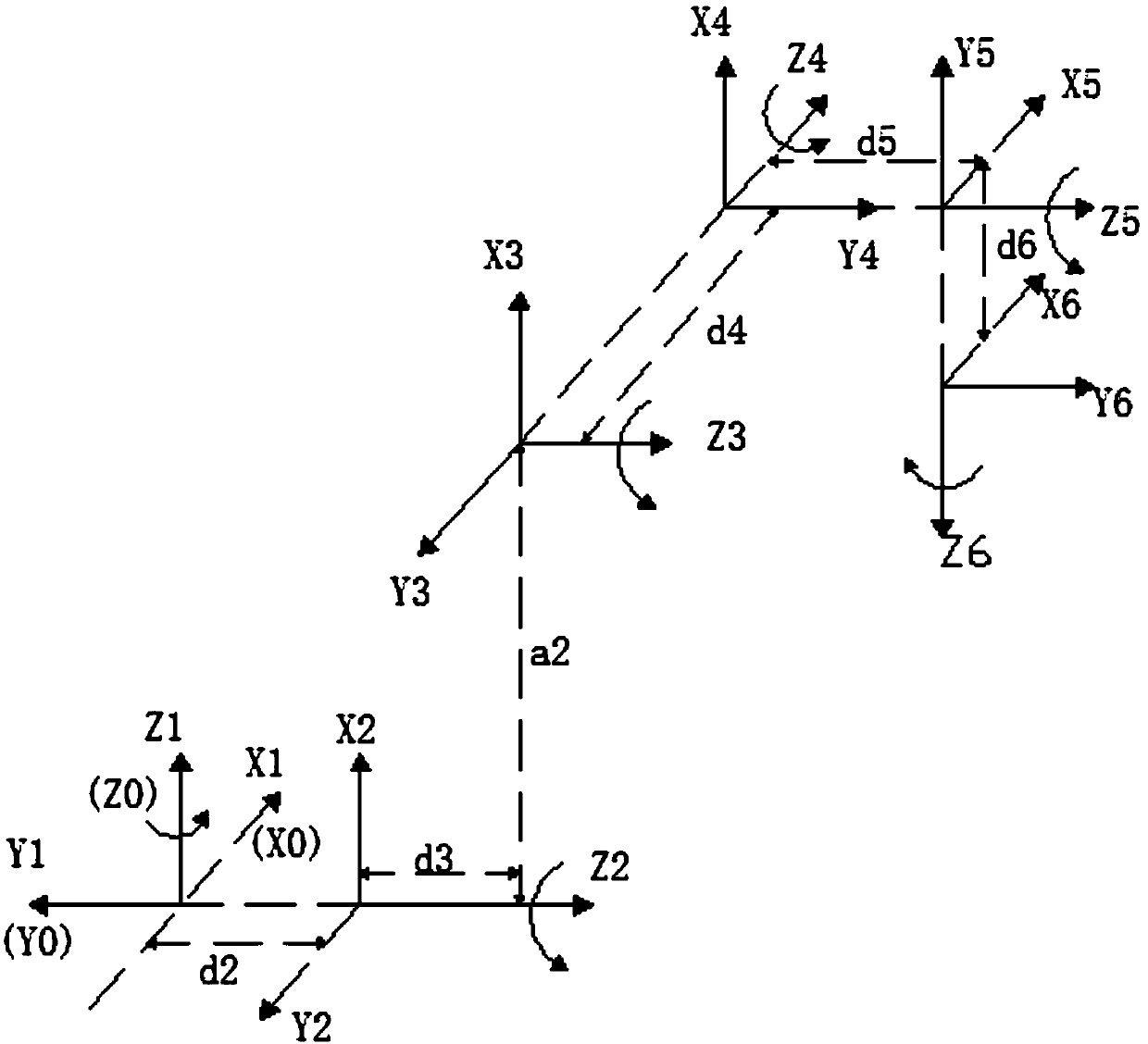
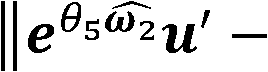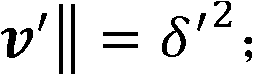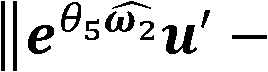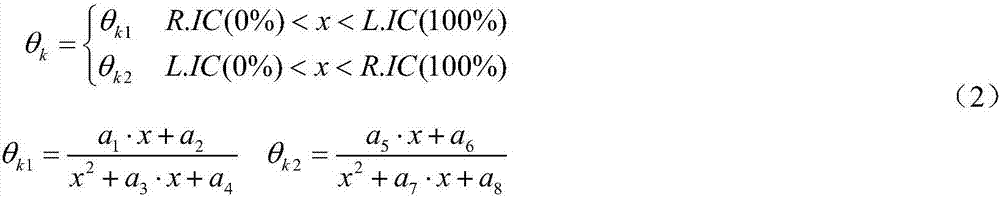Patents
Literature
319 results about "Robot kinematics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
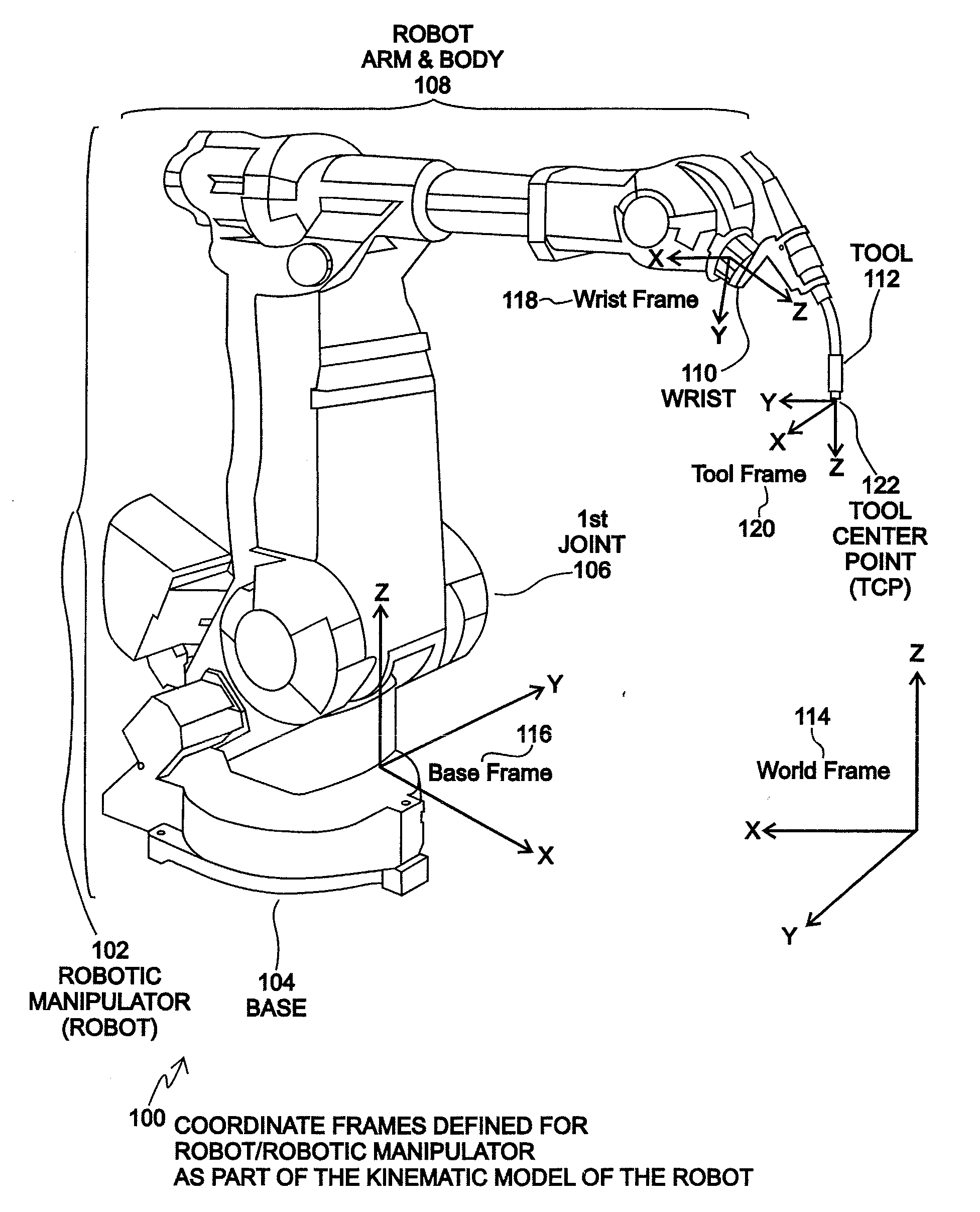
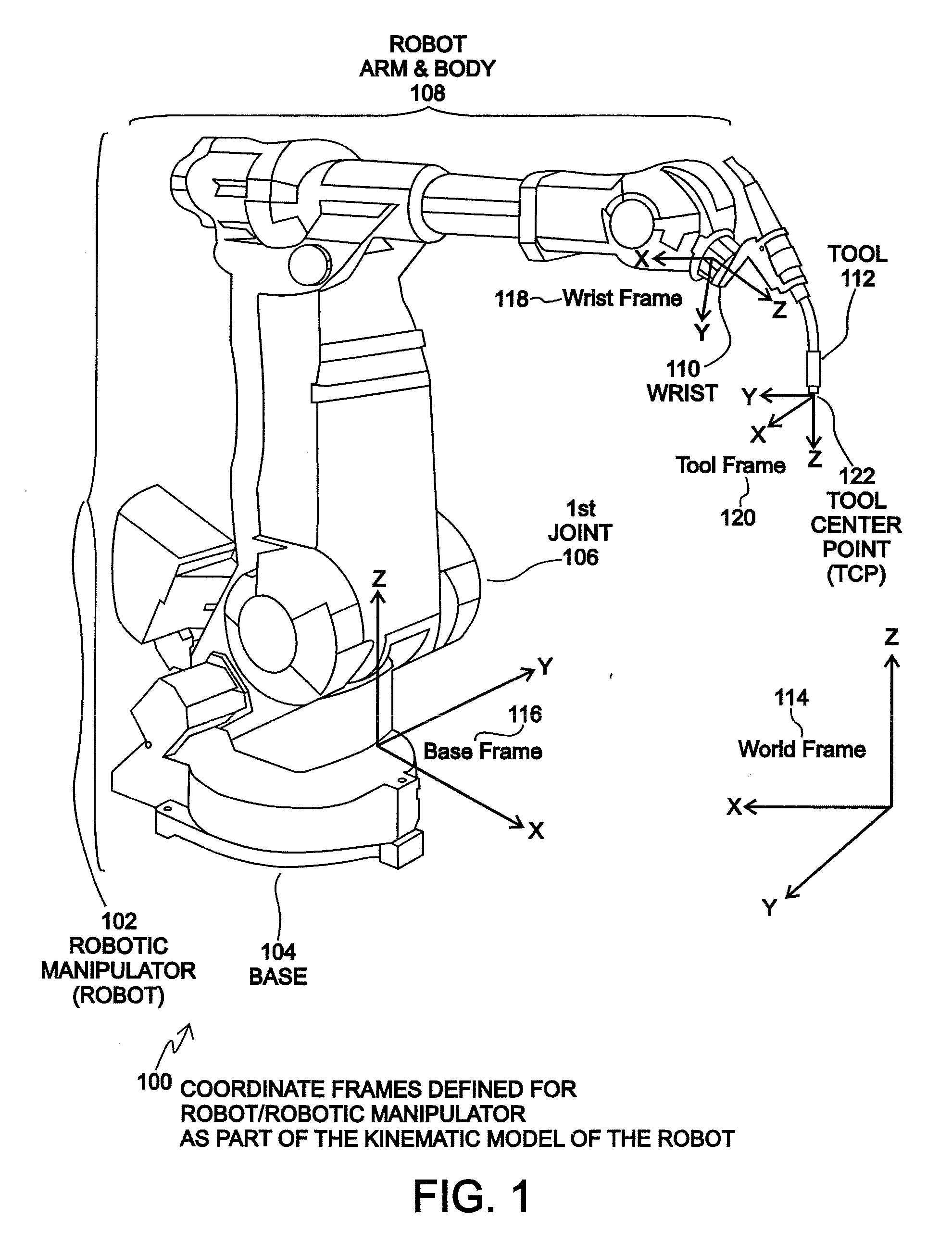
Robot kinematics applies geometry to the study of the movement of multi-degree of freedom kinematic chains that form the structure of robotic systems. The emphasis on geometry means that the links of the robot are modeled as rigid bodies and its joints are assumed to provide pure rotation or translation.
Method and system for finding a tool center point for a robot using an external camera
Disclosed is a method and system for finding a relationship between a tool-frame of a tool attached at a wrist of a robot and robot kinematics of the robot using an external camera. The position and orientation of the wrist of the robot define a wrist-frame for the robot that is known. The relationship of the tool-frame and / or the Tool Center Point (TCP) of the tool is initially unknown. For an embodiment, the camera captures an image of the tool. An appropriate point on the image is designated as the TCP of the tool. The robot is moved such that the wrist is placed into a plurality of poses. Each pose of the plurality of poses is constrained such that the TCP point on the image falls within a specified geometric constraint (e.g. a point or a line). A TCP of the tool relative to the wrist frame of the robot is calculated as a function of the specified geometric constraint and as a function of the position and orientation of the wrist for each pose of the plurality of poses. An embodiment may define the tool-frame relative to the wrist frame as the calculated TCP relative to the wrist frame. Other embodiments may further refine the calibration of the tool-frame to account for tool orientation and possibly for a tool operation direction. An embodiment may calibrate the camera using a simplified extrinsic technique that obtains the extrinsic parameters of the calibration, but not other calibration parameters.
Owner:RIMROCK AUTOMATION
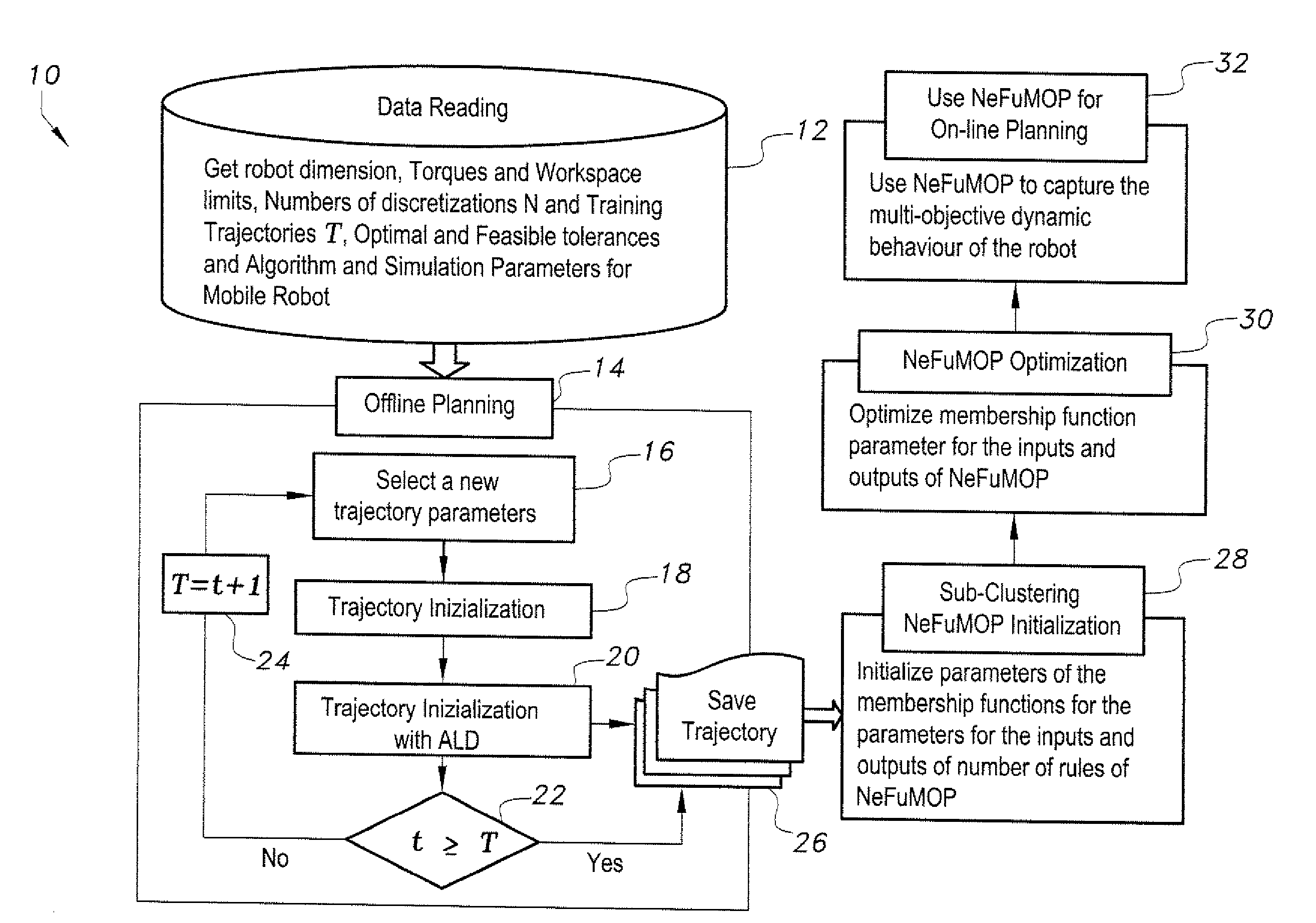
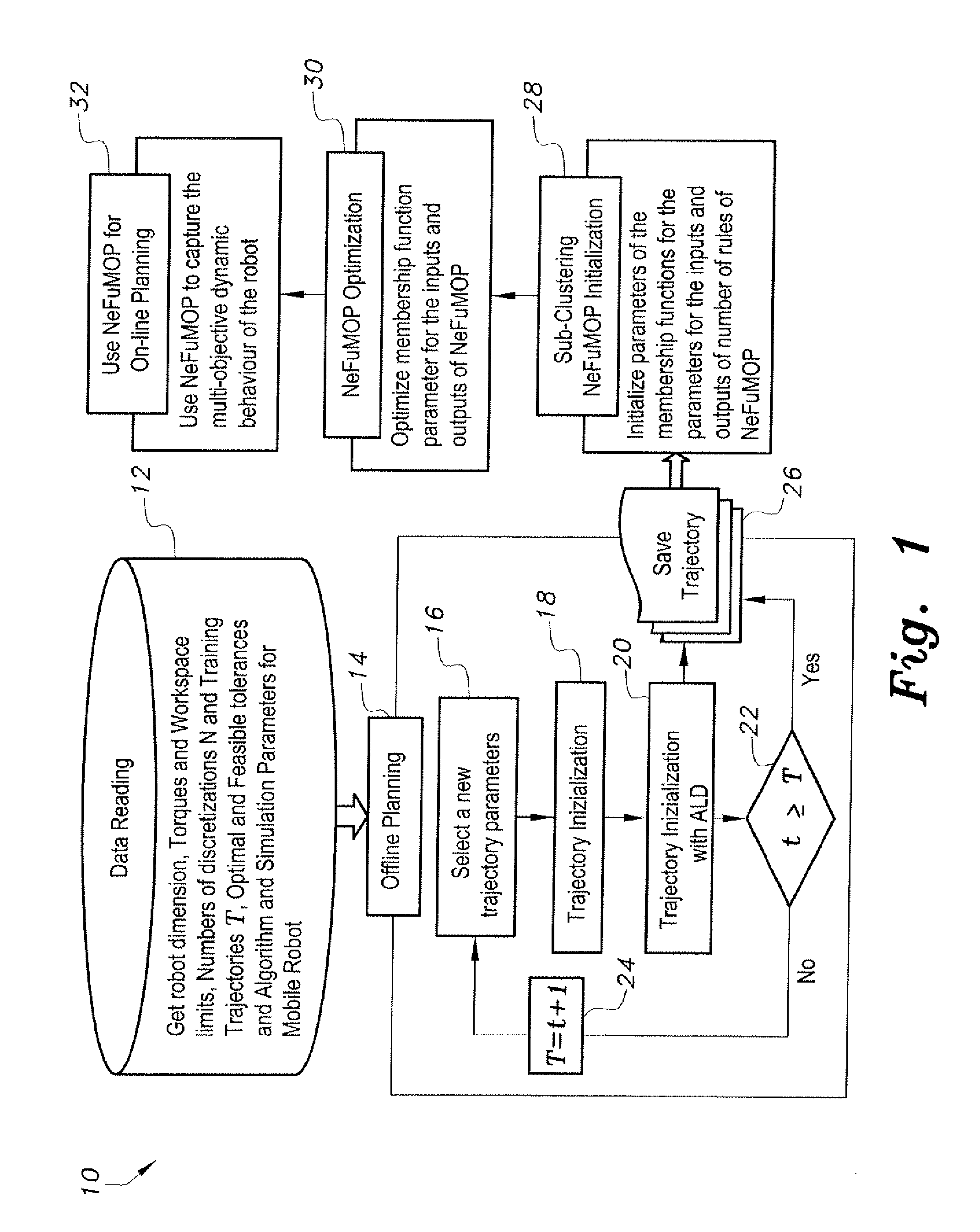
Parallel kinematic machine trajectory planning method
InactiveUS20120290131A1Minimize timeMinimizing energyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlData setParallel kinematics
The parallel kinematic machine (PKM) trajectory planning method is operable via a data-driven neuro-fuzzy multistage-based system. Offline planning based on robot kinematic and dynamic models, including actuators, is performed to generate a large dataset of trajectories, covering most of the robot workspace and minimizing time and energy, while avoiding singularities and limits on joint angles, rates, accelerations and torques. The method implements an augmented Lagrangian solver on a decoupled form of the PKM dynamics in order to solve the resulting non-linear constrained optimal control problem. Using outcomes of the offline-planning, the data-driven neuro-fuzzy inference system is built to learn, capture to and optimize the desired dynamic behavior of the PKM. The optimized system is used to achieve near-optimal online planning with a reasonable time complexity. The effectiveness of the method is illustrated through a set of simulation experiments proving the technique on a 2-degrees of freedom planar PKM.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
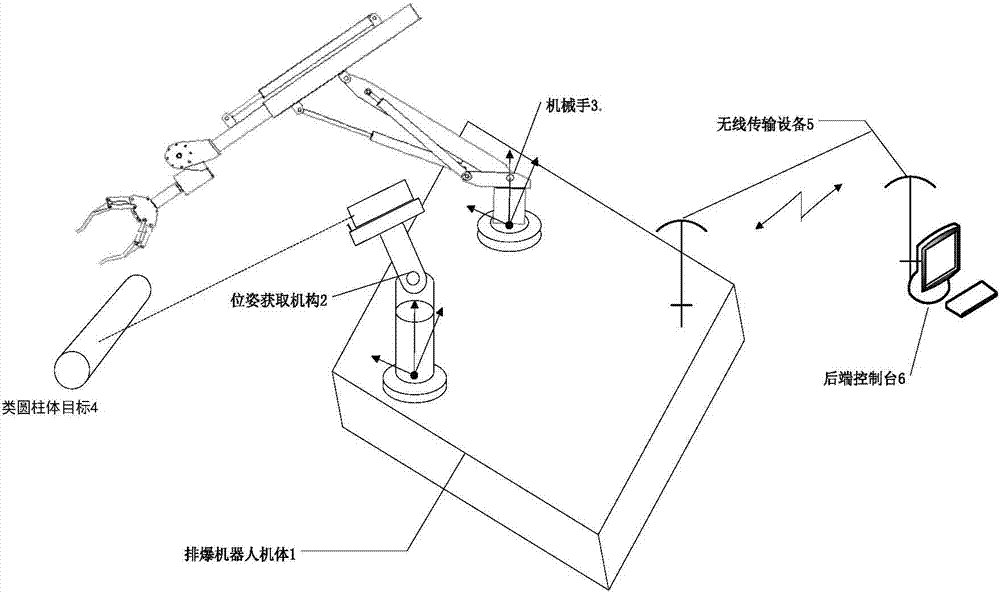
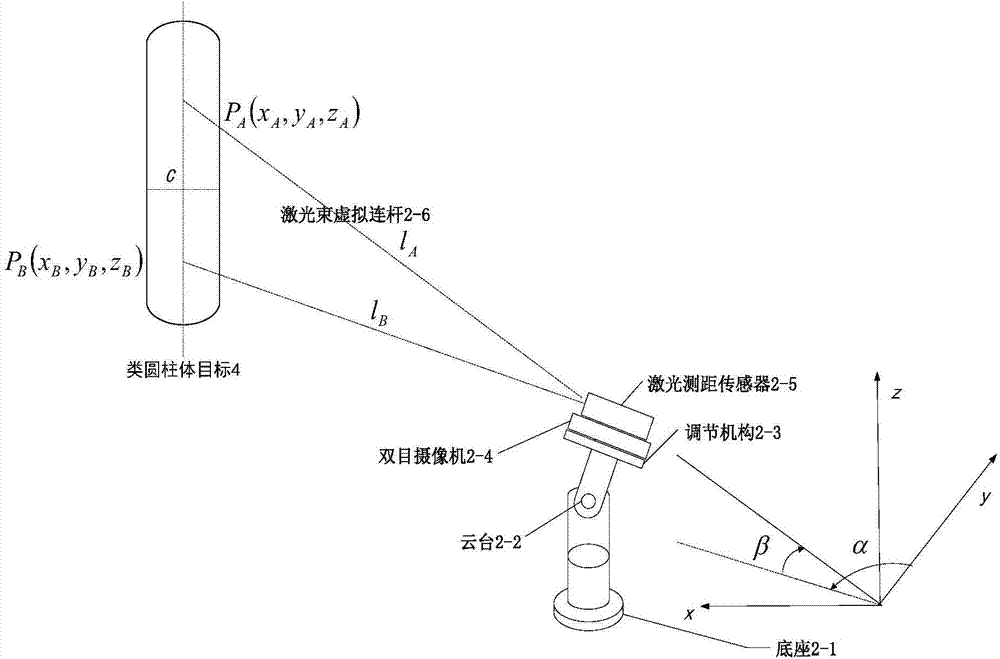
Target capturing system and method of explosive ordnance disposal robot
InactiveCN103522291ADegree of reductionReduce fatigueProgramme-controlled manipulatorLaser rangingInformation processing
The invention provides a target capturing system and method of an explosive ordnance disposal robot. The system comprises a gesture acquiring mechanism, an information processing unit, a manipulator and a robot body. The gesture acquiring mechanism is used for measuring a length value of a laser beam irradiating to a target article from a laser distance sensor, acquiring an rotary angel and pitch angle of the laser beam through rotary and pitch motions of a holder, and further acquiring three-dimensional coordinates of laser spots of the laser beam on the target article by establishing a robot kinematic equation. The information processing unit is used for calculating the gesture of the manipulator corresponding to the target article according to coordinate information of the target on a gesture acquiring mechanism base and corresponding position relations between the gesture acquiring mechanism and the manipulator. The manipulator is used for capturing the target based on gesture information of the target corresponding to the manipulator. The robot body is used for fixing the manipulator and the gesture acquiring mechanism. The laser distance sensor is fixed on the holder and can rotate and pitch with the holder synchronically.
Owner:ORDNANCE TECH RES INST OF THE GENERAL ARMAMENT DEPT PLA
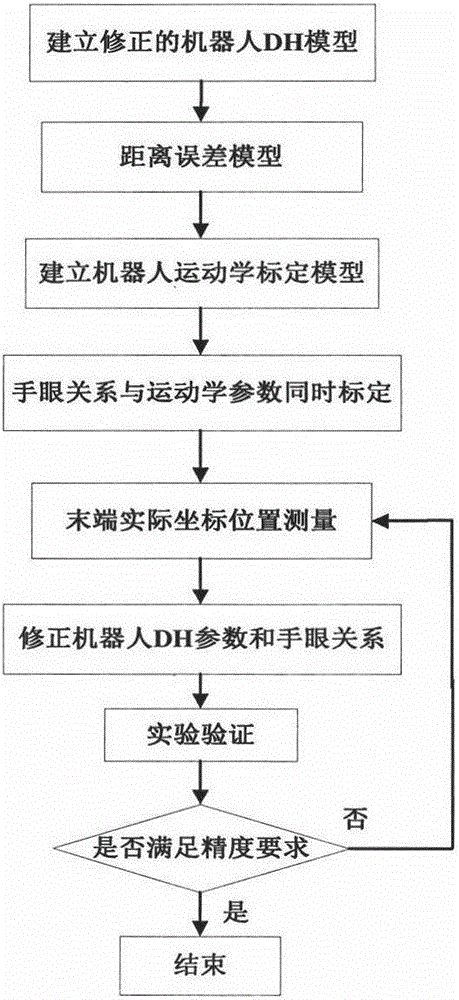
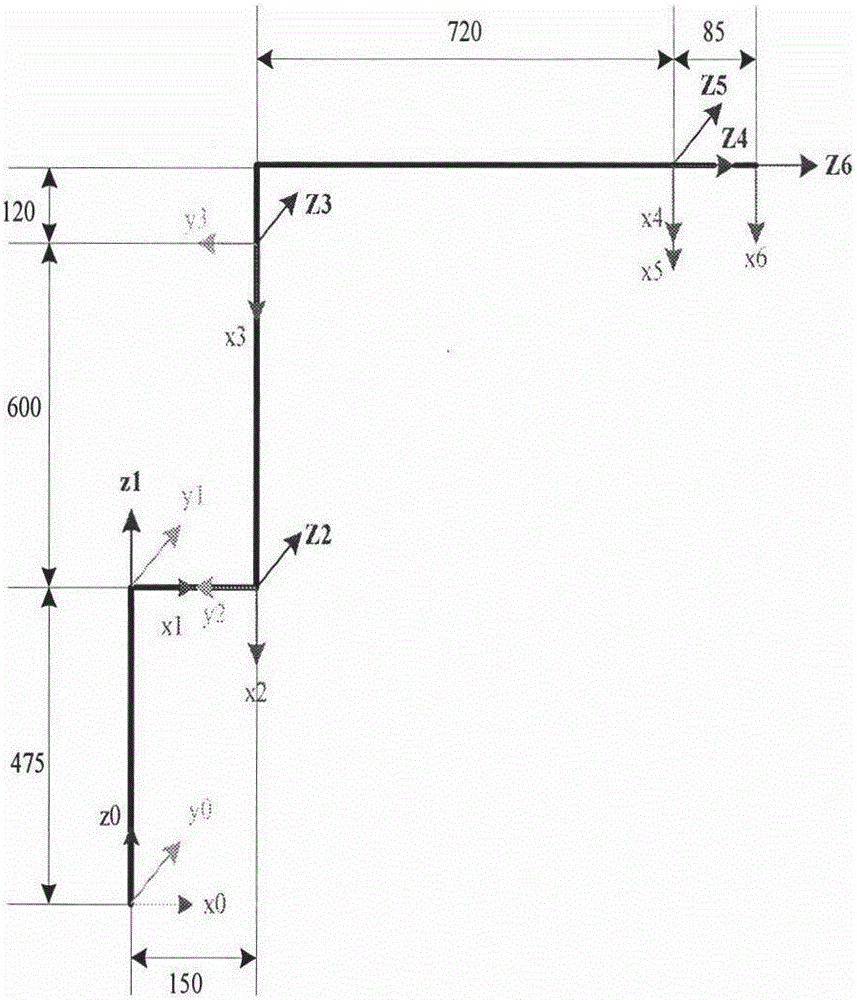
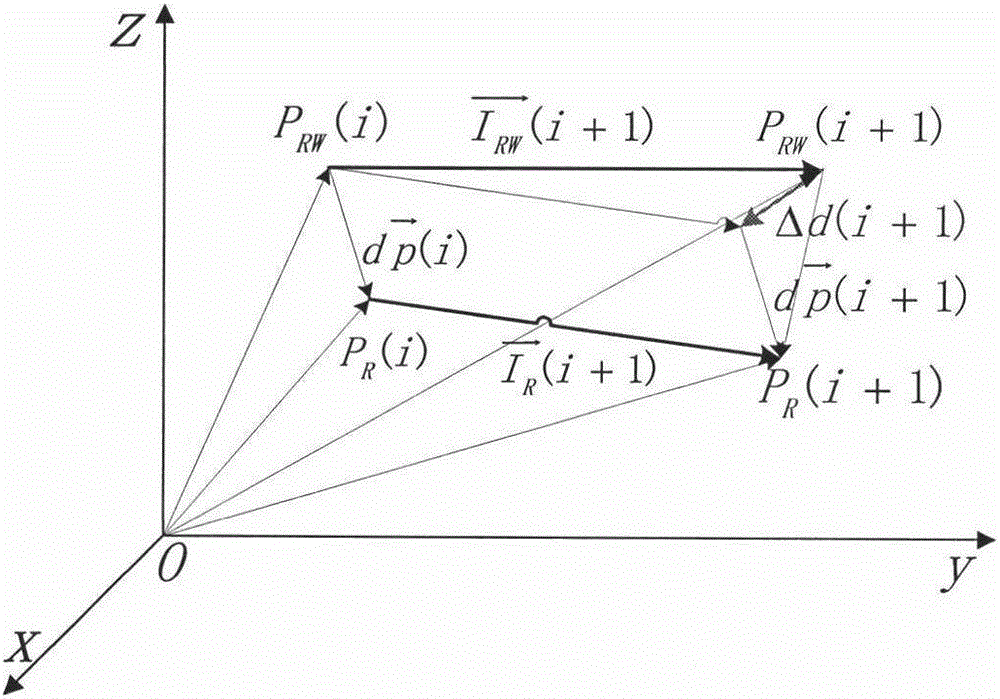
Robot kinematics calibration method based on vision measurement and distance error model
InactiveCN105773609ASimple kinematic calibration methodKinematic calibration method is practicalProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsSimulation
The invention discloses a robot kinematics calibration method based on vision measurement and a distance error model. The method includes the steps that a corrected robot D-H model is established; the distance error model is established; a robot kinematics calibration model is established; simultaneous calibration of a hand-eye relation and kinematics parameters is performed; measurement of an actual coordinate position of a tail end is performed; robot D-H parameters are corrected; and experimental verification is conducted. The robot kinematics calibration method based on vision measurement and the distance error model and provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple, efficient and fast; a non-contact measurement mode of vision detection is adopted; meanwhile, repetitive errors of hand-eye calibration are considered, and the calibration model is simplified through a mode of an equidistance model; and accordingly, the positioning precision and distance precision of an industrial robot can be greatly improved, the robot kinematics calibration method is universally suitable for series connection joint-type robots, and certain practical significance is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Inverse kinematics solution method for six-degree-of-freedom serial robot
ActiveCN102637158AAvoid problems with rank less than orderIngenious ideaComplex mathematical operationsRobot kinematicsTabu search
The invention discloses an inverse kinematics solution method for a six-degree-of-freedom serial robot. The inverse kinematics solution method comprises the steps of: establishing a connecting rod coordinate system and setting variables theta 1, theta 2, theta 3, theta 4, theta 5 and theta 6; setting an initial configuration; solving theta 4, theta 5 and theta 6 by utilizing a geometric method; and eliminating theta 1, theta 2 and theta 3 by utilizing an algebra elimination method and introducing a tabu search algorithm when solving a non-orthogonal spheroid or the terminal structure of the non-orthogonal spheroid, thereby solving out corresponding numerical solutions. The inverse kinematics solution method is smart in conception and utilizes the geometric method and the algebra elimination method for comprehensive solution, thereby avoiding the problem that the rank of an equation determinant of coefficient is smaller than order caused by arbitrary establishing of equations and correctly obtaining the analytic solutions of six axes efficiently; and for complex-structure trigonometric function relationship, a linear equation in two unknowns can be effectively transformed to a linear equation with one unknown by the elimination method in the use of the geometric method, and therefore a unique corresponding analytic solution is obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU CRP ROBOT TECH CO LTD
High-compliance method for guiding robot to cooperatively work by people
ActiveCN109848983ACompliantReal-time communicationProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsRobot kinematics
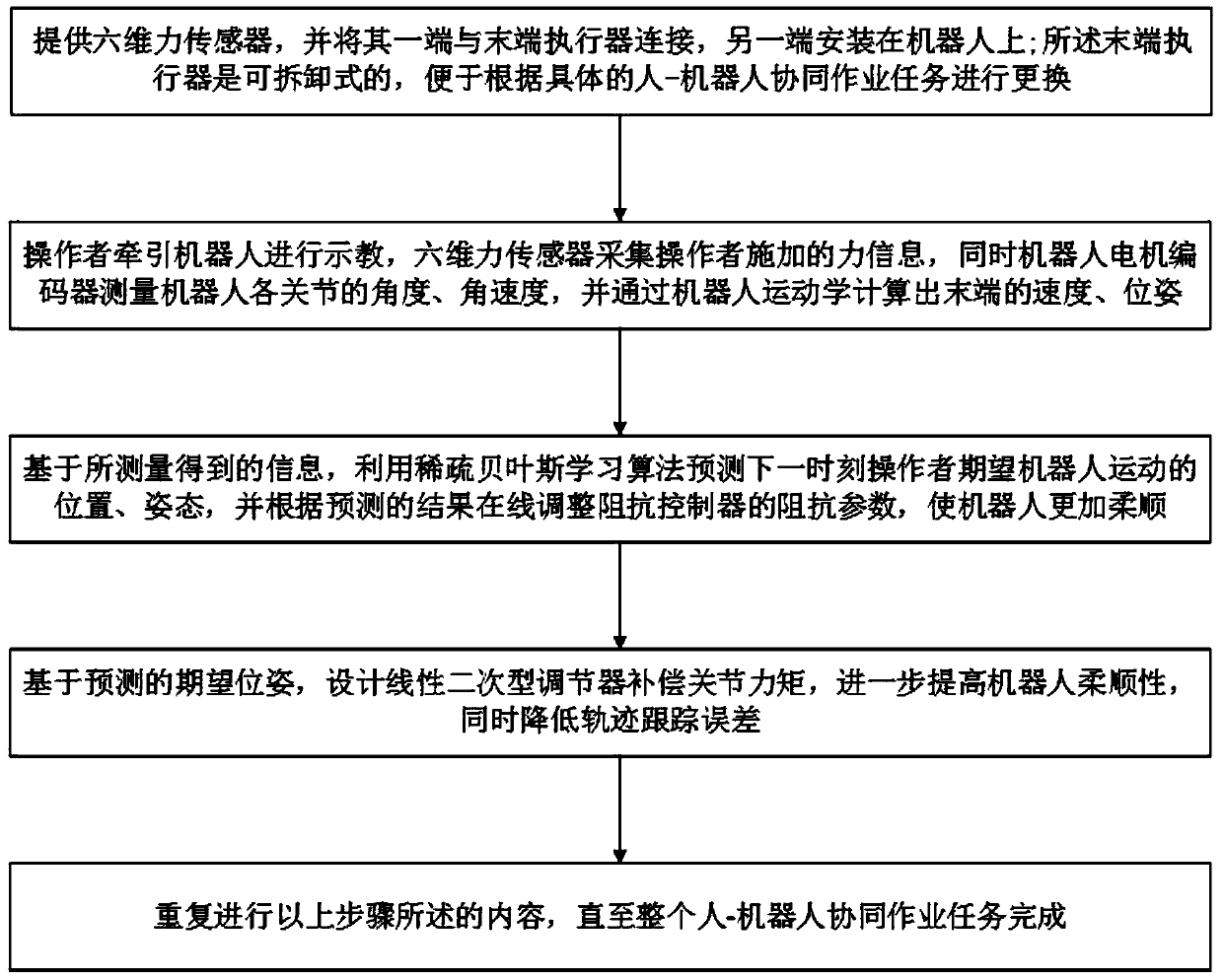
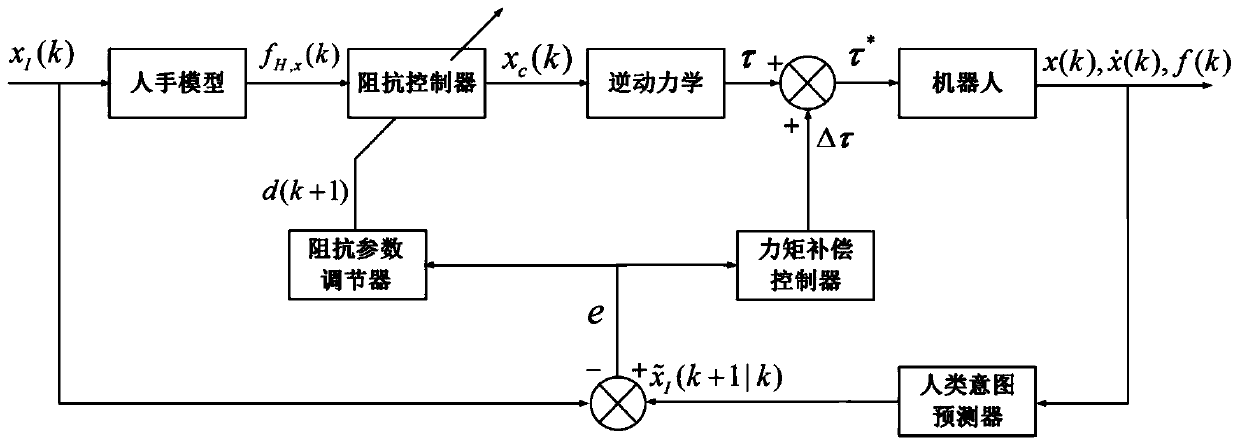
The invention belongs to related technical field of intelligent sensing, and discloses a high-compliance method for guiding a robot to cooperatively work by people. The method comprises the followingsteps: (1) a human-computer cooperation system is provided; (2) the robot is towed for demonstration; a six-dimensional force sensor and a motor encoder of the human-computer cooperation system respectively measure information of force applied by operators and the angle and the angle speed of each joint of the robot; and a computer obtains the terminal speed and pose of the robot through robot kinematics calculation; and (3) the robot motion position and pose desired by the operators at the next time are predicted by adopting a sparse bayesian learning algorithm based on the information obtained in the step (2); and the torque of each joint is compensated through online adjustment of impedance parameters of an impedance controller according to the predicting result and design of a linear secondary adjuster. The method improves the compliance and the demonstration precision of the robot, and reduces the demonstration difficulty of the operators.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
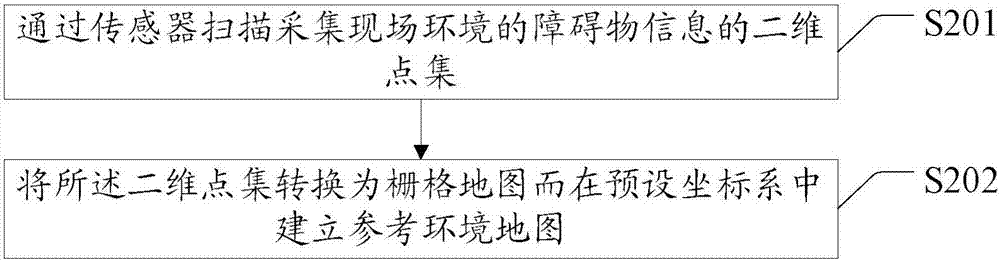
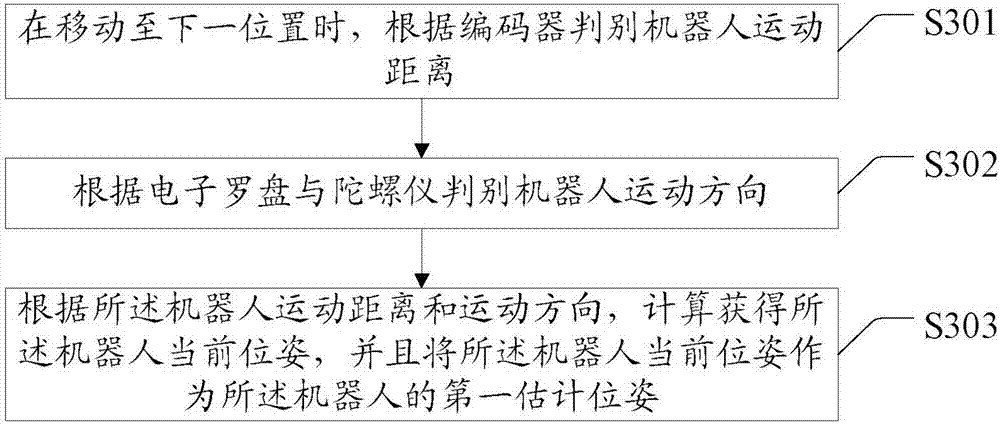
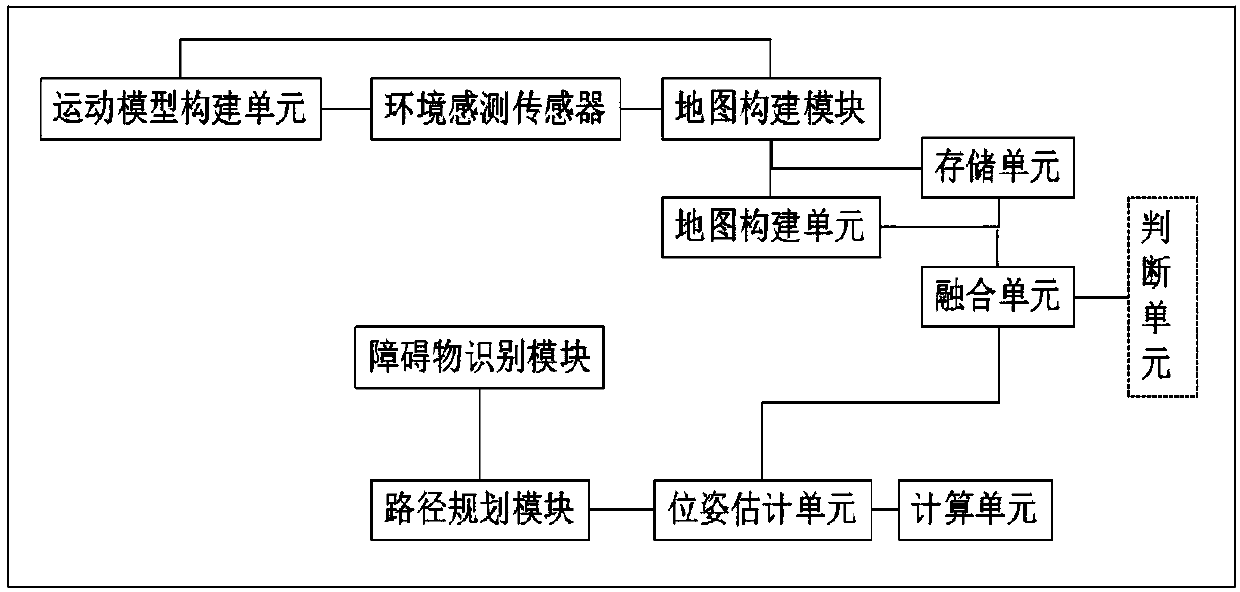
Synchronous positioning and map establishment method and equipment
InactiveCN107167148ABuild fast and preciseHigh positioning accuracyInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsKinematicsRobot kinematics
The invention discloses a synchronous positioning and map establishment method and equipment. The synchronous positioning and map establishment method comprises the following steps: loading a preset robot kinematic model which is established according to the structure of a robot; scanning an environment by using an sensor, and establishing a reference environment map in a preset coordinate system; when moving to a next position, estimating a first estimated posture of the robot through an inertial navigation system; scanning by using the sensor so as to obtain an updated environment map, acquiring a second estimated posture and a new reference environment map according to the updated environment map, the reference environment map and the first estimated posture; acquiring an updated posture according to the first estimated posture and the second estimated posture; and updating the posture of the robot according to the updated posture. The synchronous positioning and map establishment method has the effects that convenience and precision of synchronous positioning and map establishment are improved.
Owner:ANKE SMART CITY TECH PRC
Kinematic calibration system and method for industrial robot
The invention discloses a kinematic calibration system and method for an industrial robot. The kinematic calibration system comprises measurement targets placed in a working area, a robot and an end effector arranged on the robot, as well as a computer, wherein the computer is provided with a first receiving module for reading joint angle data of the robot, a second receiving module for reading detection data of three displacement sensors, a first computation module for computing the nominal coordinate positions of the measurement targets according to data of both the first receiving module and the second receiving module, and a second computation module for computing compensation data of the robot according to the difference between the nominal distance of the measurement targets and the actual distance. The kinematic calibration system can not only correct kinematic parameters of the robot to improve the absolute positioning accuracy of operation but also calibrate the relative position relationship between a workpiece and a base of the robot, is very low in cost and simple and convenient to operate, and can be widely applied to middle and small-sized enterprises.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
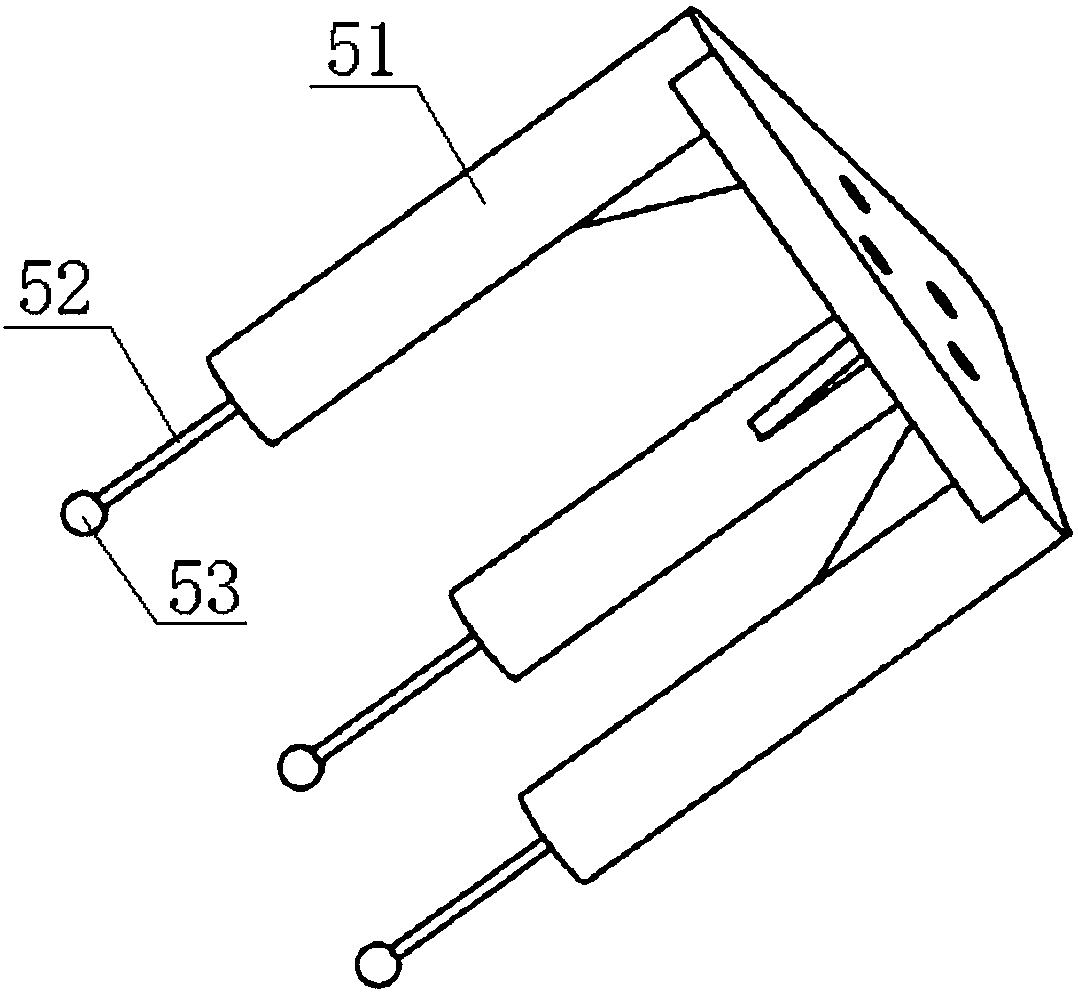
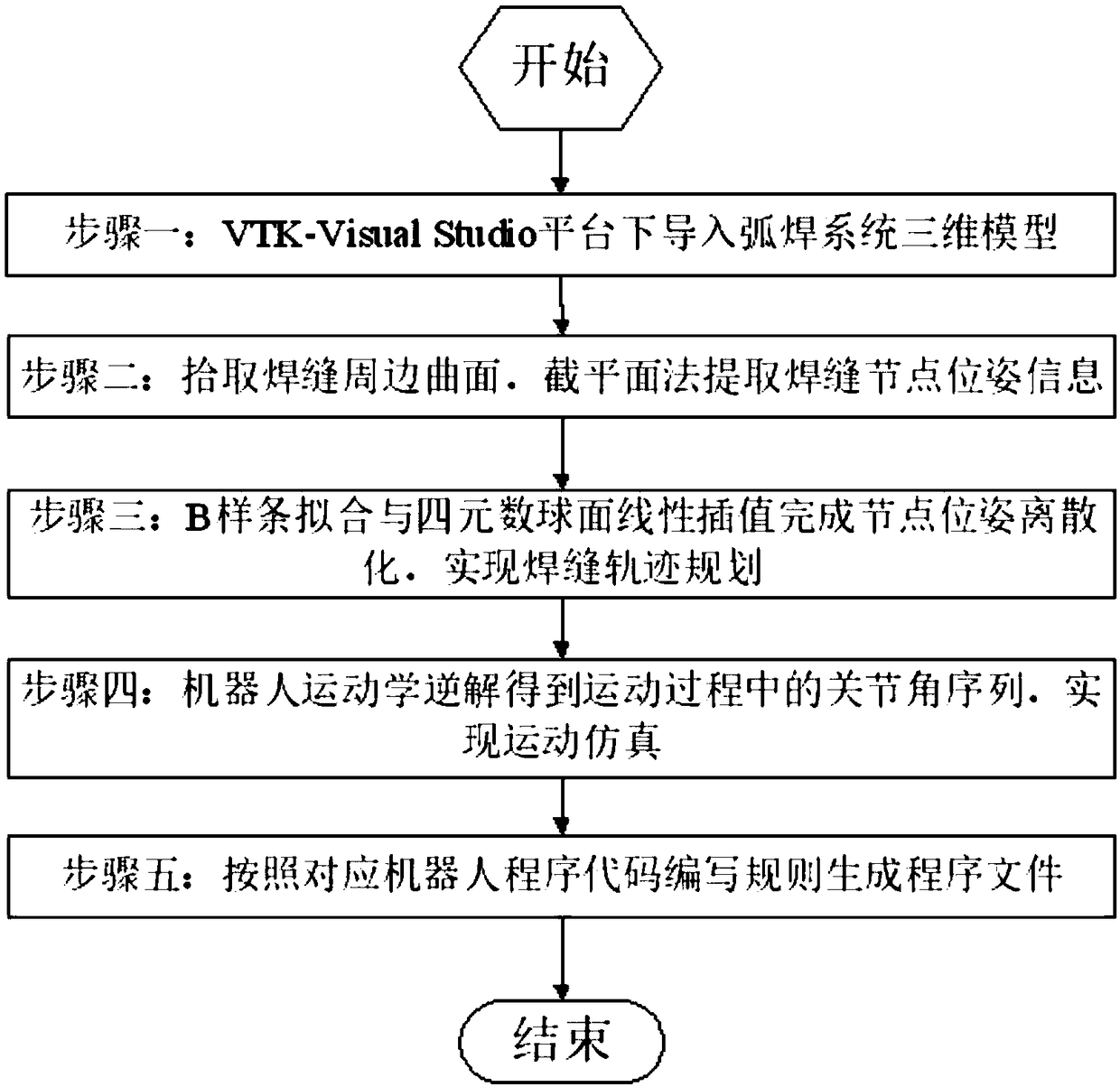
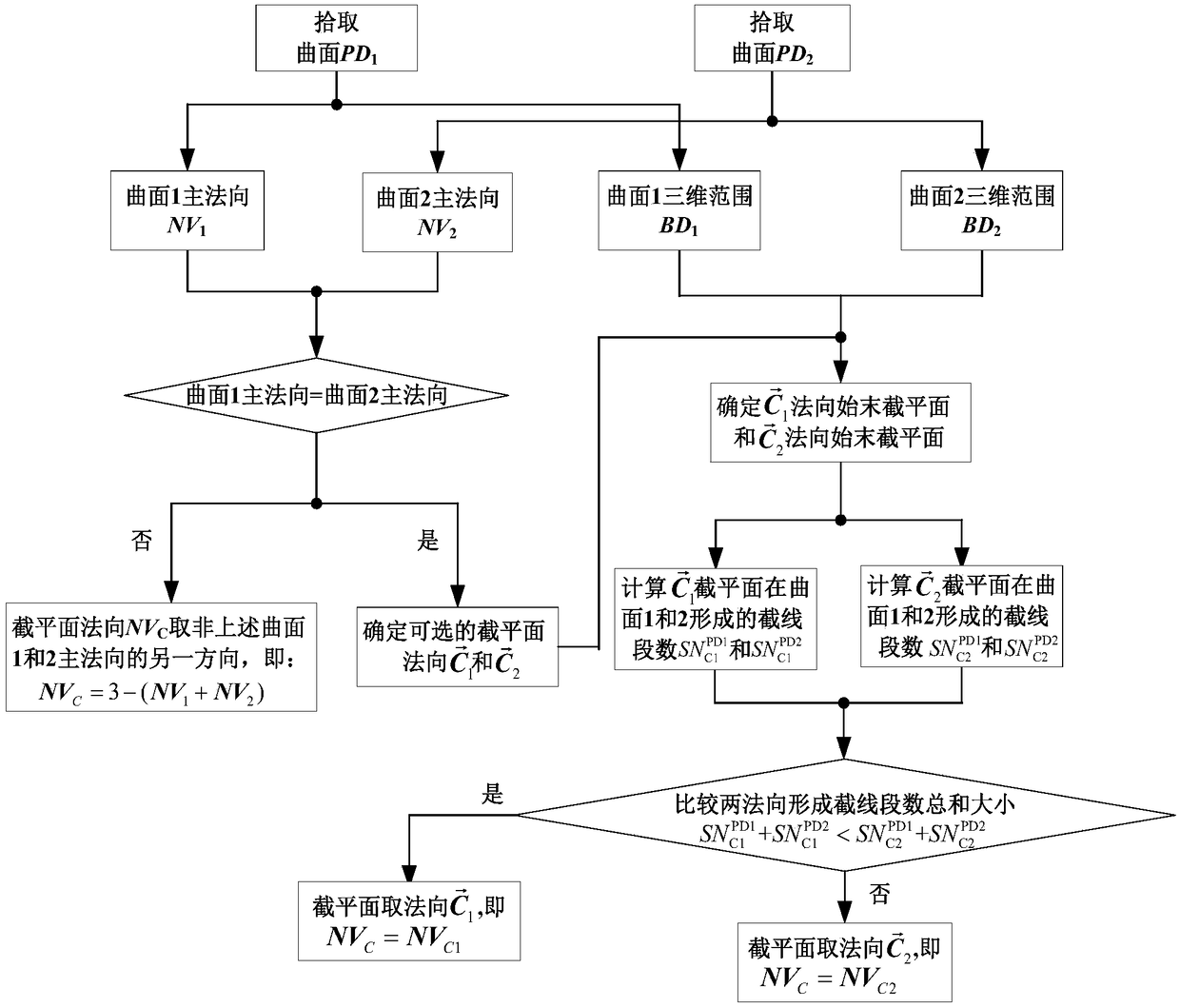
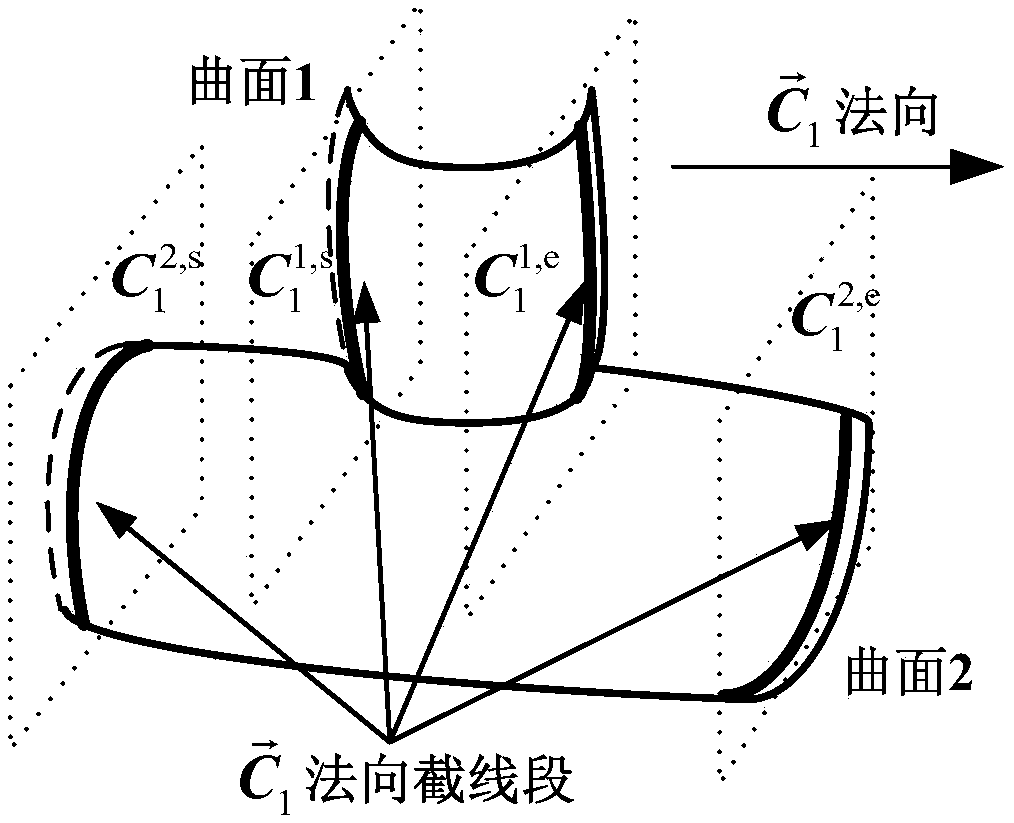
Industrial robot space intersecting curve welding offline programming method
ActiveCN109226937AQuick buildMeet the generality of modelingProgramme-controlled manipulatorWelding accessoriesEngineeringDiscretization
The invention discloses an industrial robot space intersecting curve welding offline programming method. The method comprises the steps that firstly, an arc welding robot and a welding workpiece three-dimensional model are guided in, two peripheral hook faces of a welding line are formed through mouse pickup, a cut plane set is created inside a workpiece coordinate system, and node pose information of the welding line is extracted; according to the node pose, position and posture discretization are achieved along the curve of the welding line, and then welding line trajectory planning is achieved through coordinate conversion; then, a joint angle sequence needed in the robot motion process is obtained through robot inverse kinematics, and motion simulation is achieved; finally, according to language rules written by corresponding robot motion control program codes, a corresponding program file is generated. By adopting an open source VTK visual tool magazine, offline programming independent development is achieved, the method does not dependent on third party CAD software, the track of the welding line can be generated only through mouse picking, no complex external data computingor guiding-in process is needed, the man-machine interaction is good, and the needed robot program can be rapidly generated.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
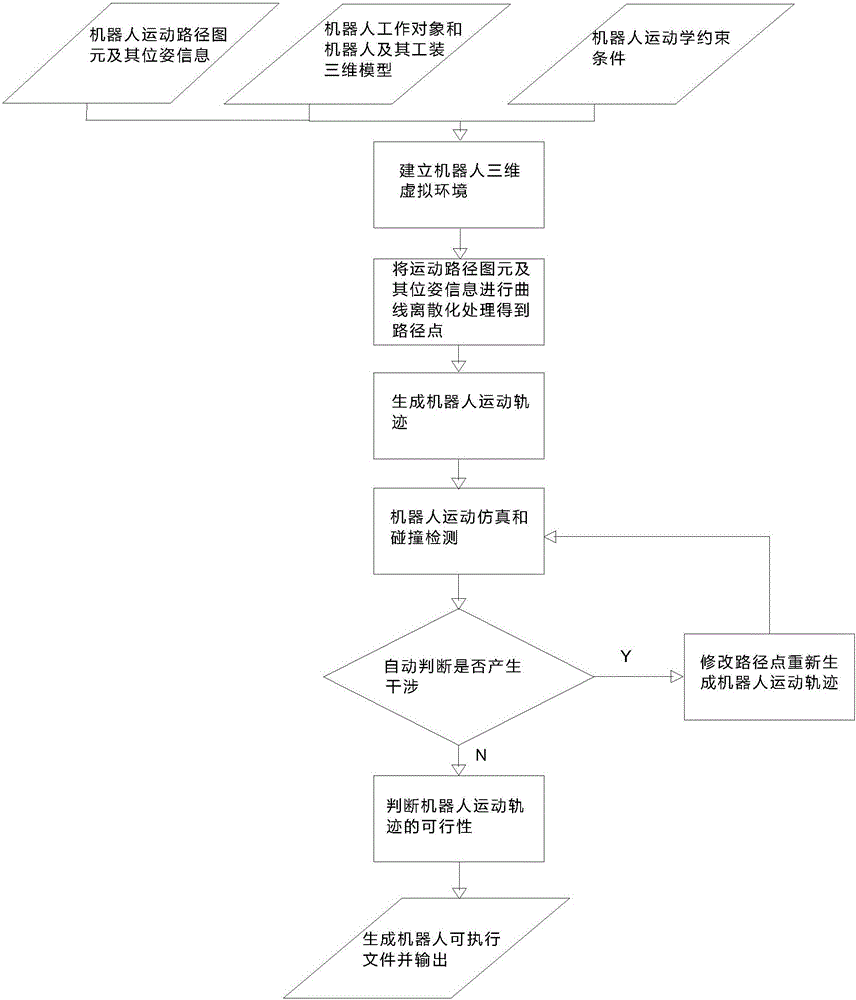
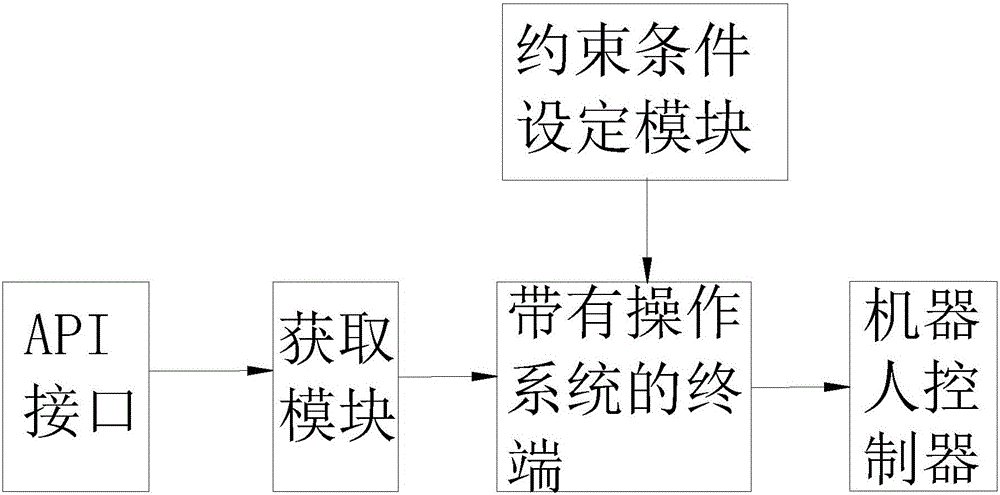
Robot off line programming system and method
InactiveCN105945942ARealize motion controlRealize automatic programmingProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsOperational systemCollision detection
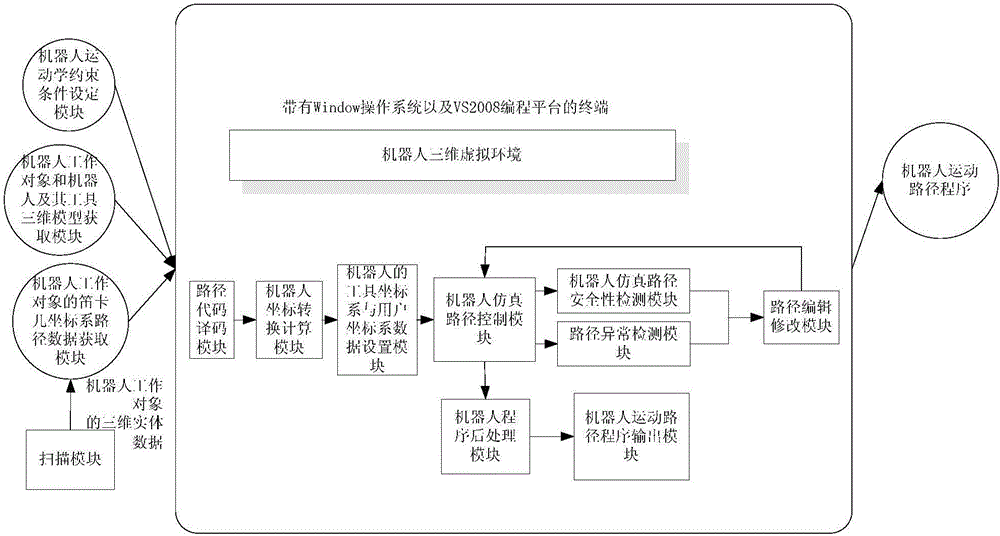
The invention discloses a robot off line programming system and method. The robot off line programming method includes: importing a robot kinematic constraint condition, a three-dimensional model of a working object of a robot, three-dimensional models of the robot and a tooling thereof into a robot three-dimensional virtual environment; performing curve discretization on extracted robot motion path graph primitives and pose information thereof, extracting path points, and generating a robot motion path; performing robot motion simulation and collision detection; modifying the path points according to a given definition on basis of the result of robot motion simulation and collision detection, generating a new robot motion path and pose, and displaying the new robot motion path and pose in an operation system; acquiring a feasibility result and generating a robot executable file; and communicating with the robot, importing the robot executable file into a robot controller, and realizing robot motion control. The robot off line programming system and method can effectively simplify operations, and improve the efficiency of robot programming work.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for simply and easily calibrating industrial robot
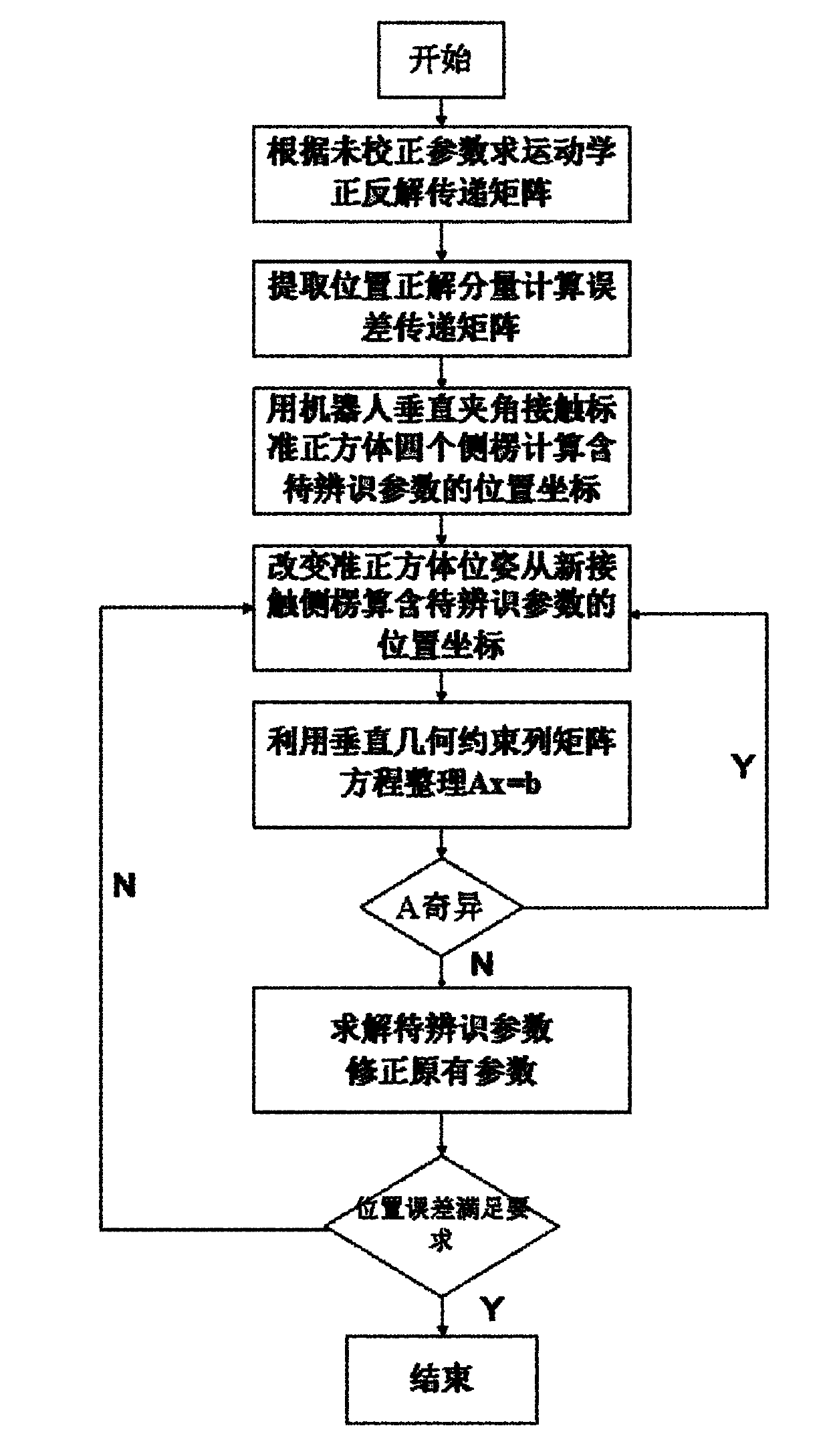
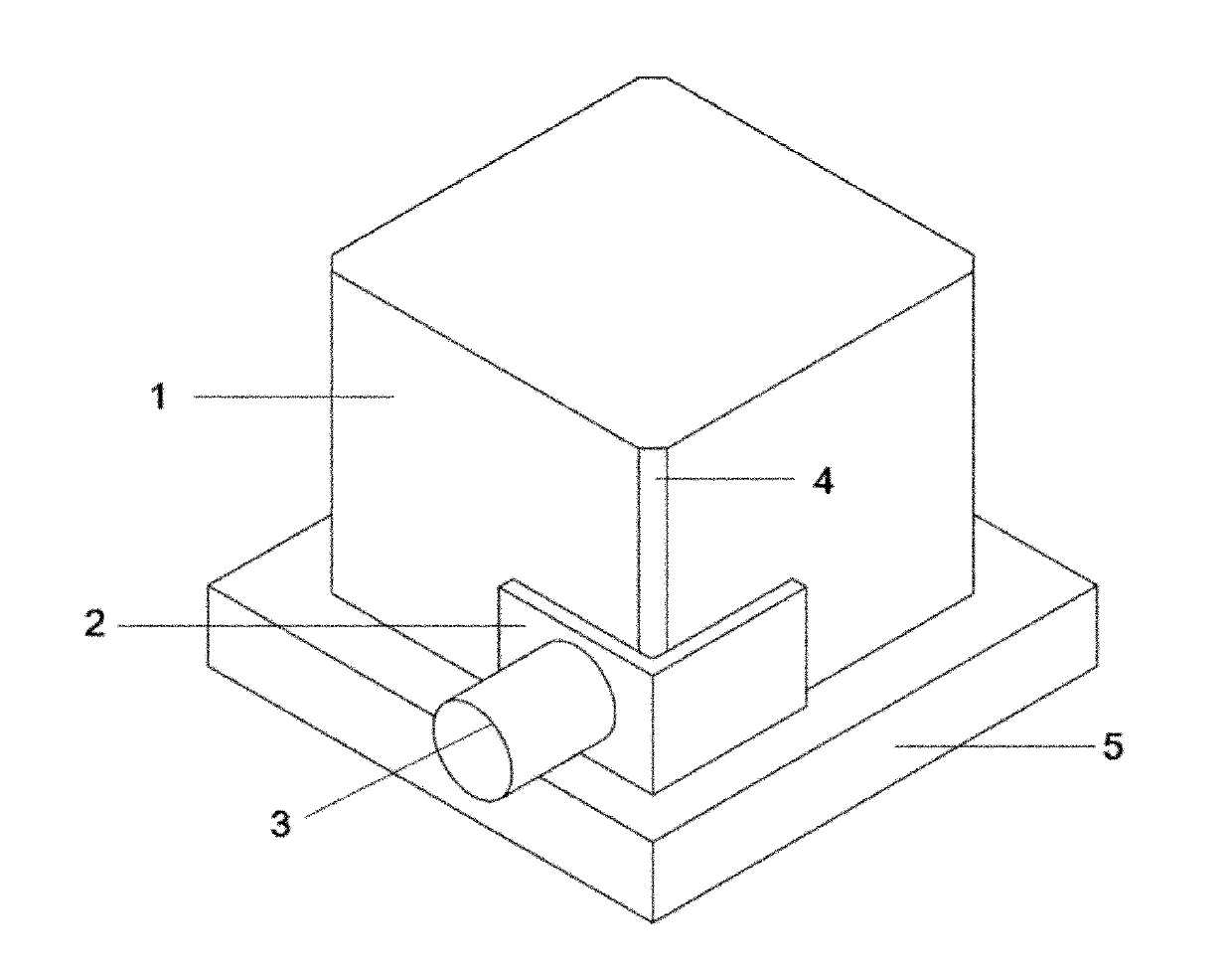
The invention relates to a method for simply and easily calibrating an industrial robot. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing an industrial robot kinematics model, and solving a robot kinematics pose transfer matrix; extracting a robot end position component, and calculating an error transfer matrix; operating a robot end clamp to contact four side edges of a standard cube, reading a code disc number of each joint of the robot, and calculating a position coordinate; changing the pose of the standard cube, reading the code disc number of each joint of the robot again, calculating the position coordinate, and repeating the step for many times; and listing position coordinate matrix equations with an identification parameter, and arranging the position coordinate matrix equations in a manner of Ax=b, wherein A is of a matrix type, x is a column vector with the identification parameter, and b is the column vector, and if A is not strange, a parameter to be identified is solved, and the original parameter is corrected by using the identification result. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of convenience, practicability, lower cost, more simpleness on operations, capability of reaching a higher precision, and unnecessity of buying high-precision equipment, such as a high-precision laser instrument and a vidicon.
Owner:SHENYANG SIASUN ROBOT & AUTOMATION
Robot motion path off-line programming method and system
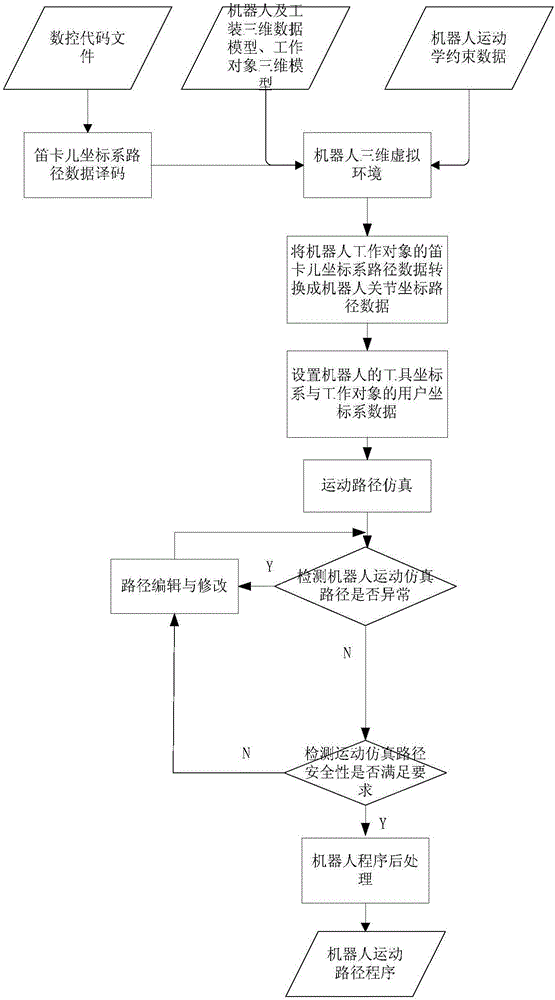
InactiveCN104942808AEasy to operateImprove work efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorNumerical controlJoint coordinates
The invention discloses a robot motion path off-line programming method and system. Robot kinematics constraint conditions, a robot, a robot tooling three-dimensional model, a robot work object three-dimensional model and a numerical control code file are loaded in a robot three-dimensional virtual environment; Cartesian coordinate system path data of a robot work object are acquired through the numerical control code file, and the Cartesian coordinate system path data of the robot work object are converted into robot joint coordinate path data; robot motion path simulation is performed, the abnormal condition and security of the robot joint coordinate path data are detected, edited and modified, and the robot joint coordinate path data are converted into corresponding robot motion path programs on the condition that no abnormal condition occurs and the security meets the conditions. According to the robot motion path off-line programming method and system, robot complex motion curve path programming can be achieved, and the advantages of being easy to operate, high in working efficiency and the like are achieved.
Owner:GSK CNC EQUIP
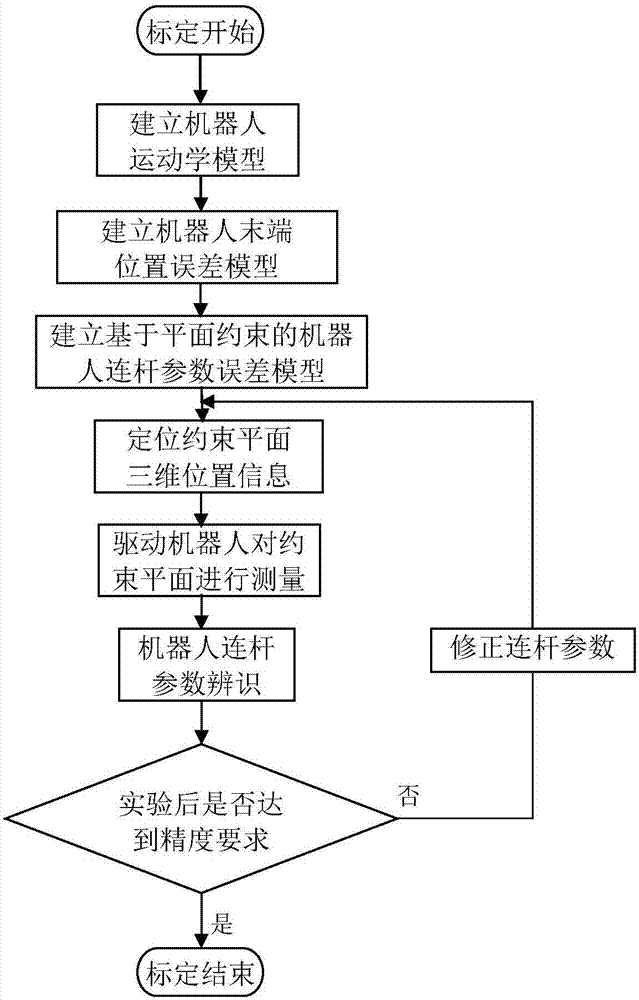
Robot self-calibration method based on vision-assisted positioning
The invention relates to a robot self-calibration method based on plane constraint and vision-assisted positioning. The robot self-calibration method based on plane constraint and vision-assisted positioning is used for obtaining real connection rod parameters of a robot. Firstly, a robot kinematic model combining a D-H method and a MD-H method is established; secondly, a robot terminal position error model is established; thirdly, a robot connection rod parameter error model based on plane constraint is established; fourthly, images, of a constraint plane, in a left camera and a right camera are obtained through binocular vision, target point information in each image is extracted, the three-dimensional position information of the constraint plane under a basic coordinate system of the robot is positioned through three-dimensional matching; the position information is input into a robot control system, and the robot is driven to measure the constraint plane; and finally the measured data are substitute into the plane constraint error model, the real geometric connection rod parameters of the robot are recognized, and after correction, measurement of the constraint plane and recognition are repeatedly conducted until a precision requirement is met. The robot self-calibration method based on plane constraint and vision-assisted positioning has the advantages of being low in cost and high in precision and efficiency.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Wheel type moving robot track tracking method based on fast terminal sliding mode
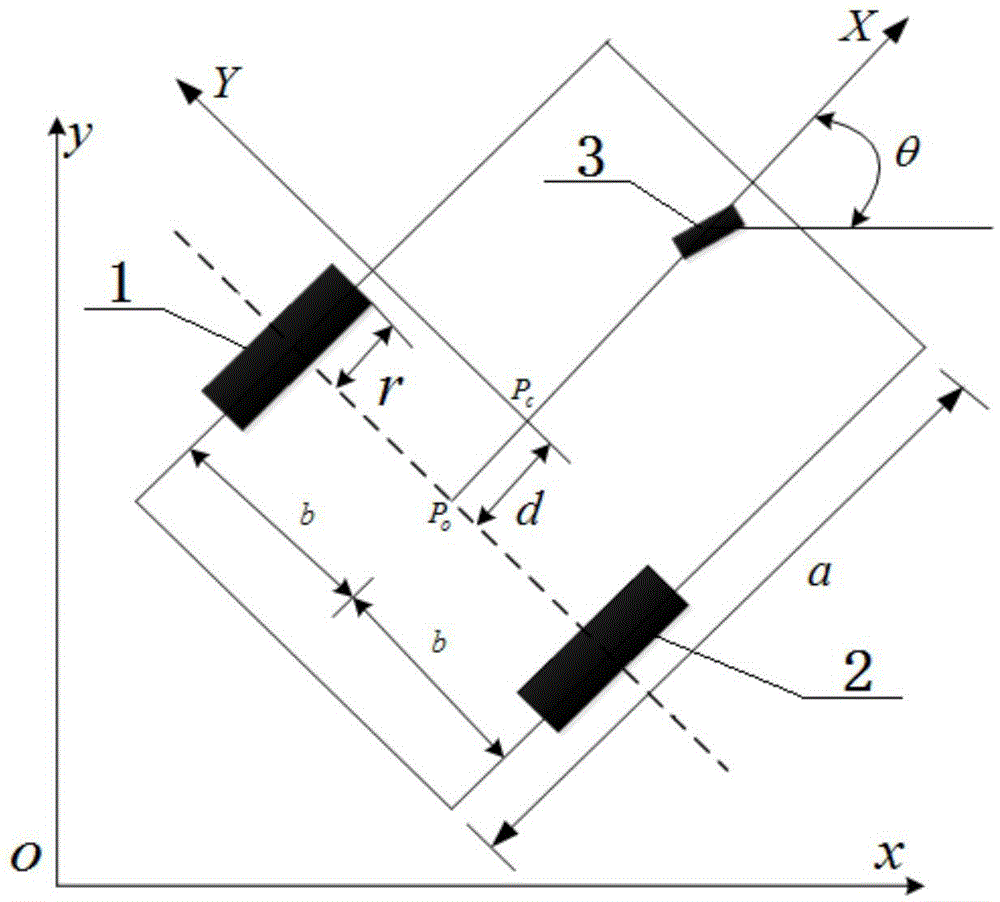
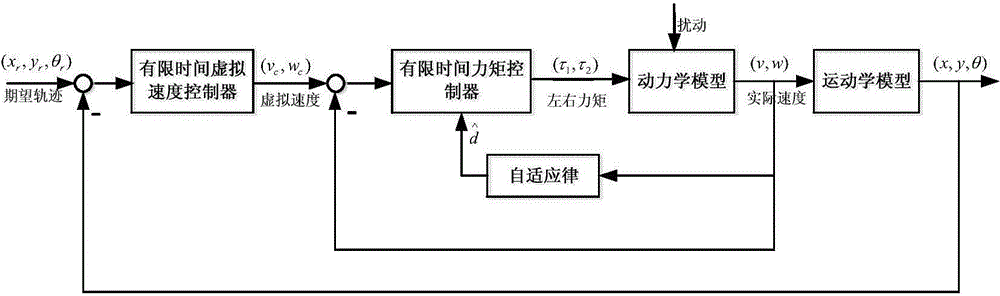
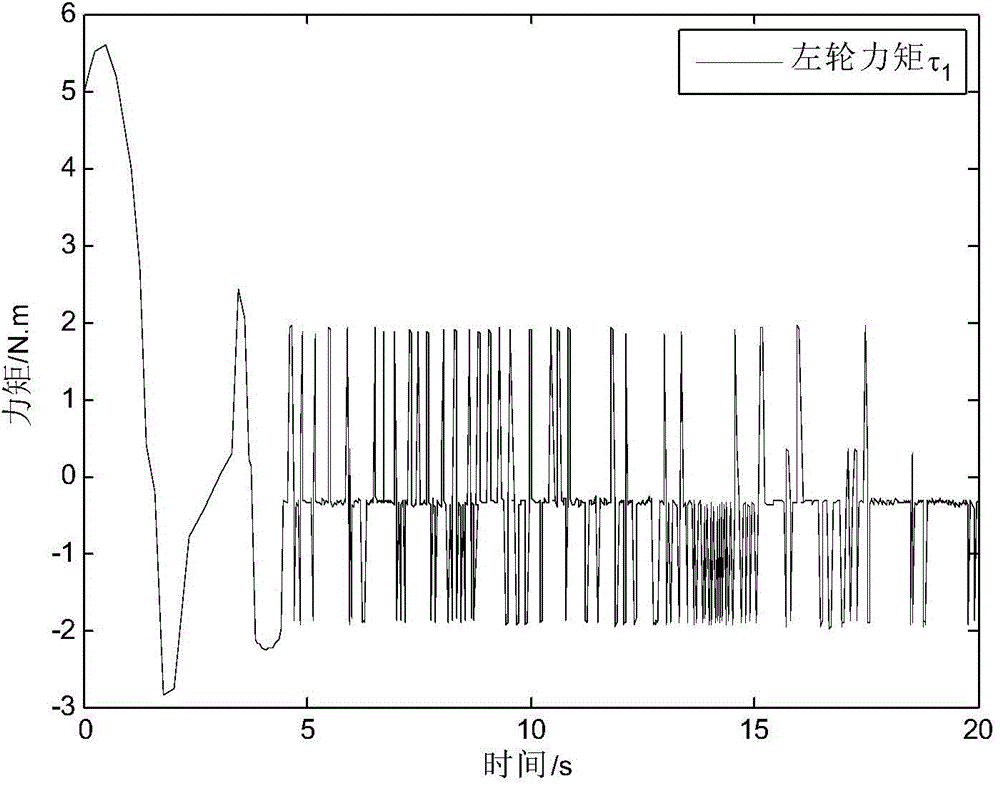
ActiveCN104932506AEasy to trackImprove robustnessPosition/course control in two dimensionsTracking modelAngular velocity
The invention discloses a wheel type moving robot track tracking method based on a fast terminal sliding mode. The wheel type moving robot track tracking method comprises steps of (1) establishing a kinematic model of the wheel type moving robot and an expectation track model and establishing an error model according to the kinematic model and the expectation track model, (2) introducing an appropriate sliding mode surfaces s1, s2, designing a virtual feedback amount according to the error model <~ > theta e<->, (3) obtaining a linear speed deviation signal <~ > Upsilon and a angular velocity deviation signal <~ >Omega, (4) constructing the wheel type moving robot kinematic model and substituting the linear speed deviation signal <~ > Upsilon and the angular velocity deviation signal <~ >Omega into the kinematic model, and designing a left-and-right-wheel torque controller Tau, an unknown parameter estimator <^>Phi and an external interference disturbance estimator. The wheel type moving robot track tracking method based on a fast terminal sliding mode can track the expectation track in the limited time under the disturbance complicated working condition of the unknown parameters and the external disturbance, has a good tracking effect and has a strong robustness for the unknown parameters and the external disturbance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
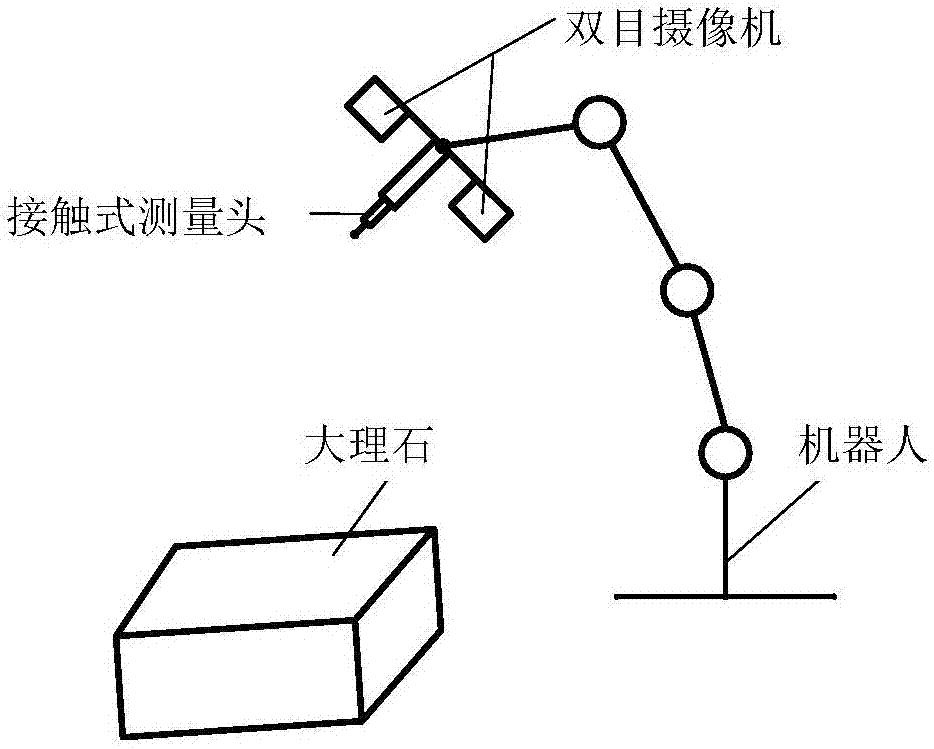
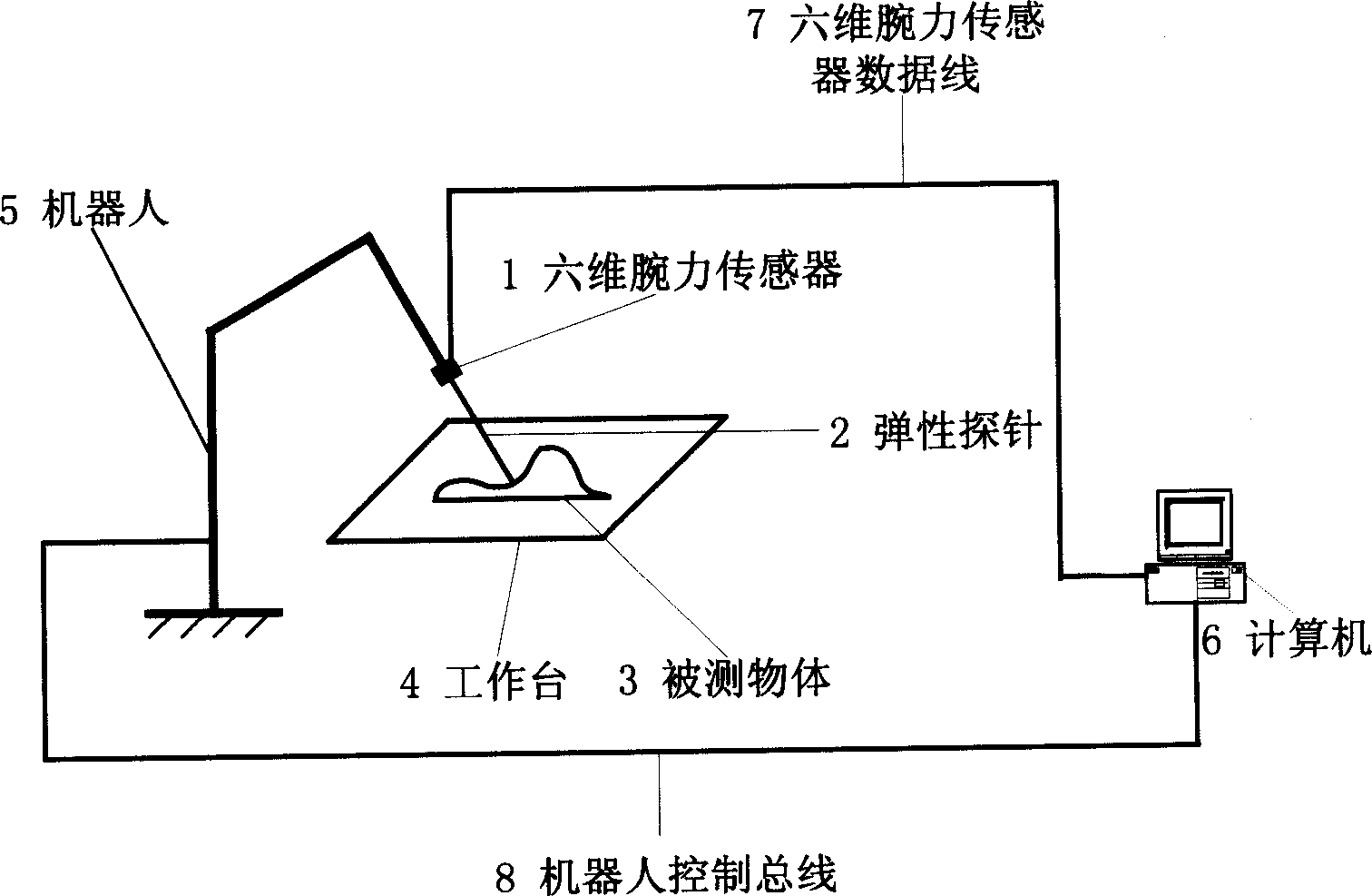
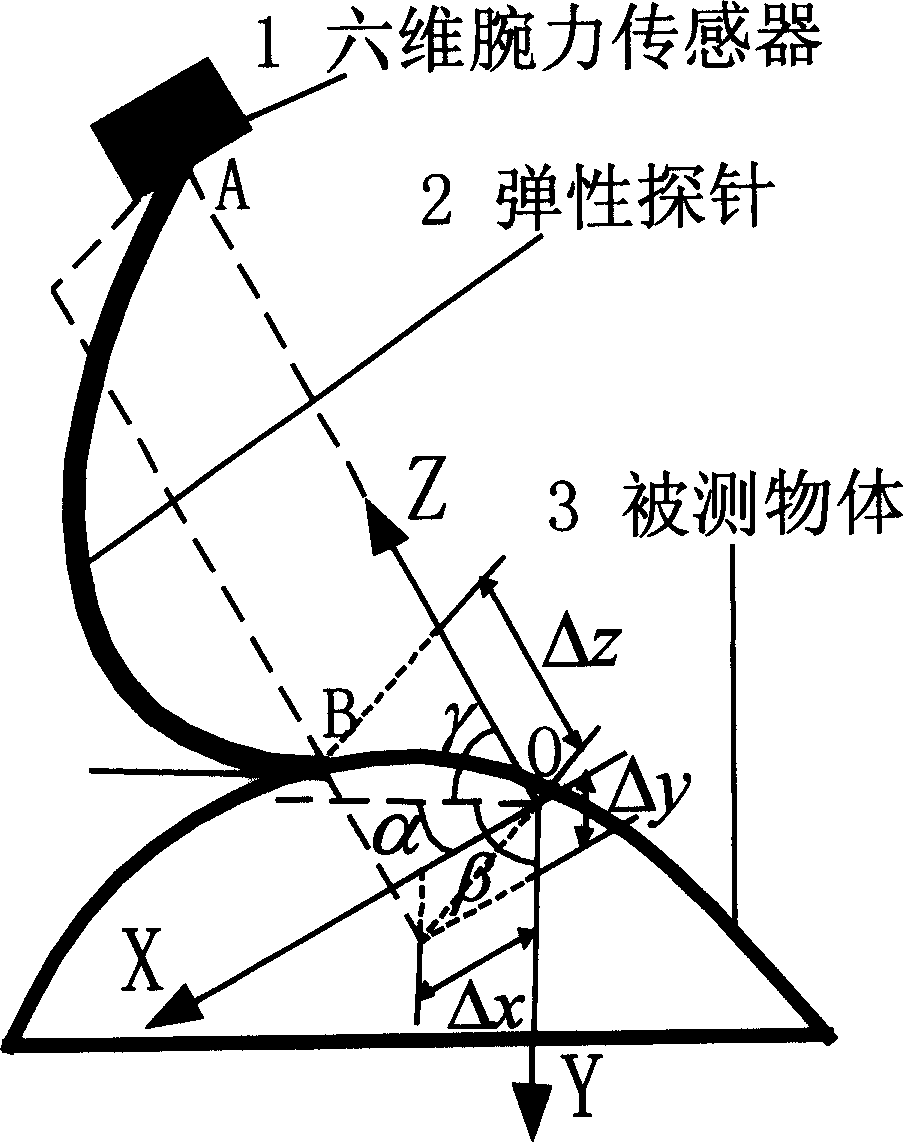
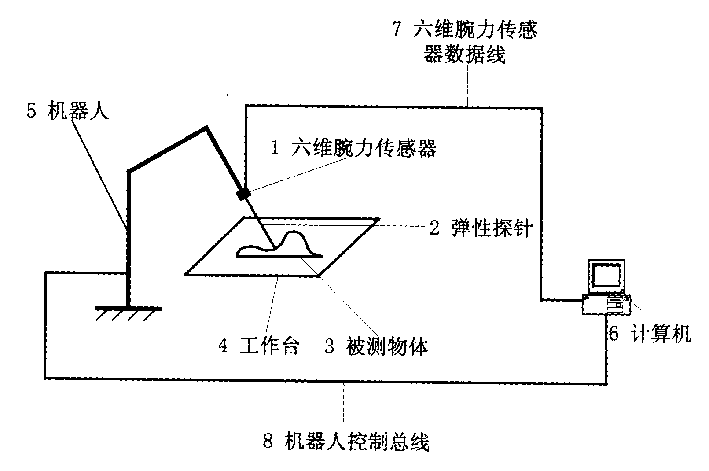
Contact type object position and gesture measurer
InactiveCN1512134AAvoid uncertaintyAvoid errorsMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsElectric/magnetic contours/curvatures measurementsMeasurement deviceVisual perception
The present invention belongs to automatic precise measurement device for replacing traditional binocular visual detection device, and is especially the detection of workpiece surface shape or object position and gesture with robot arm, six-dimensional wrist force sensor and elastic probe. The technological scheme includes obtaining the ideal coordinates in tool coordinate system of point on some object by means of the stress information of probe on the object surface, coordinate transforming to obtain the coordinates of the point in robot-based coordinate system, controlling the motion of robot terminal end via six-dimensional wrist force sensor information for well contact and shift of the probe on the measured surface to obtain serial coordinate information of points on the object surface and determine the position, gesture or surface geometric shape of the object in the robot-based coordinate system. Meanwhile, the robot may be also replaced with a video camera.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
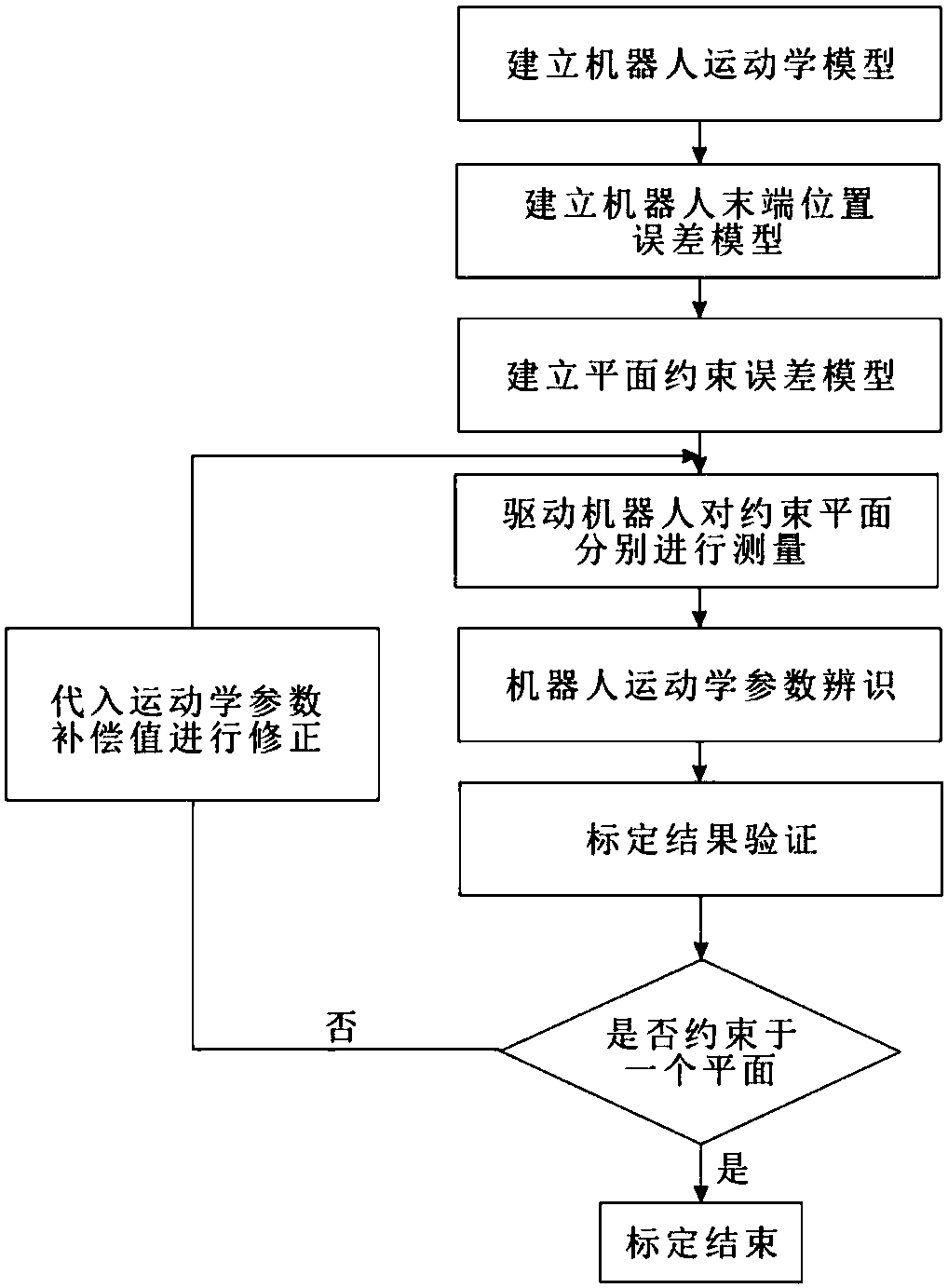
Plane constraint error model and robot self-calibration method
The invention discloses a plane constraint error model and a robot self-calibration method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, establishing a robot kinematics model; 2, establishing a robot tail end position error model; 3, establishing the plane constraint error model; 4, driving a robot to measure the constraint plane; 5, identifying kinematics parameters of the robot; and 6, verifying the calibration result. The plane constraint error model and the self-calibration method have the beneficial effects that firstly, cost is low, wherein one calibration block with relatively high precision is needed, and cost not exceeds one thousand while the advanced measuring equipment tends to be tens of thousands or more millions in cost; secondly, a plane accurate spatial equation can be obtained, compared with a traditional plane constraint calibration method, the calibration precision is improved; thirdly, compared with a traditional plane constraint error model, the error model is greatly simplified; and fourthly, the calibration block can be placed in the working space of the robot in any posture, and the difficulty of calibration experiments is reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Markerless tracking of robotic surgical tools
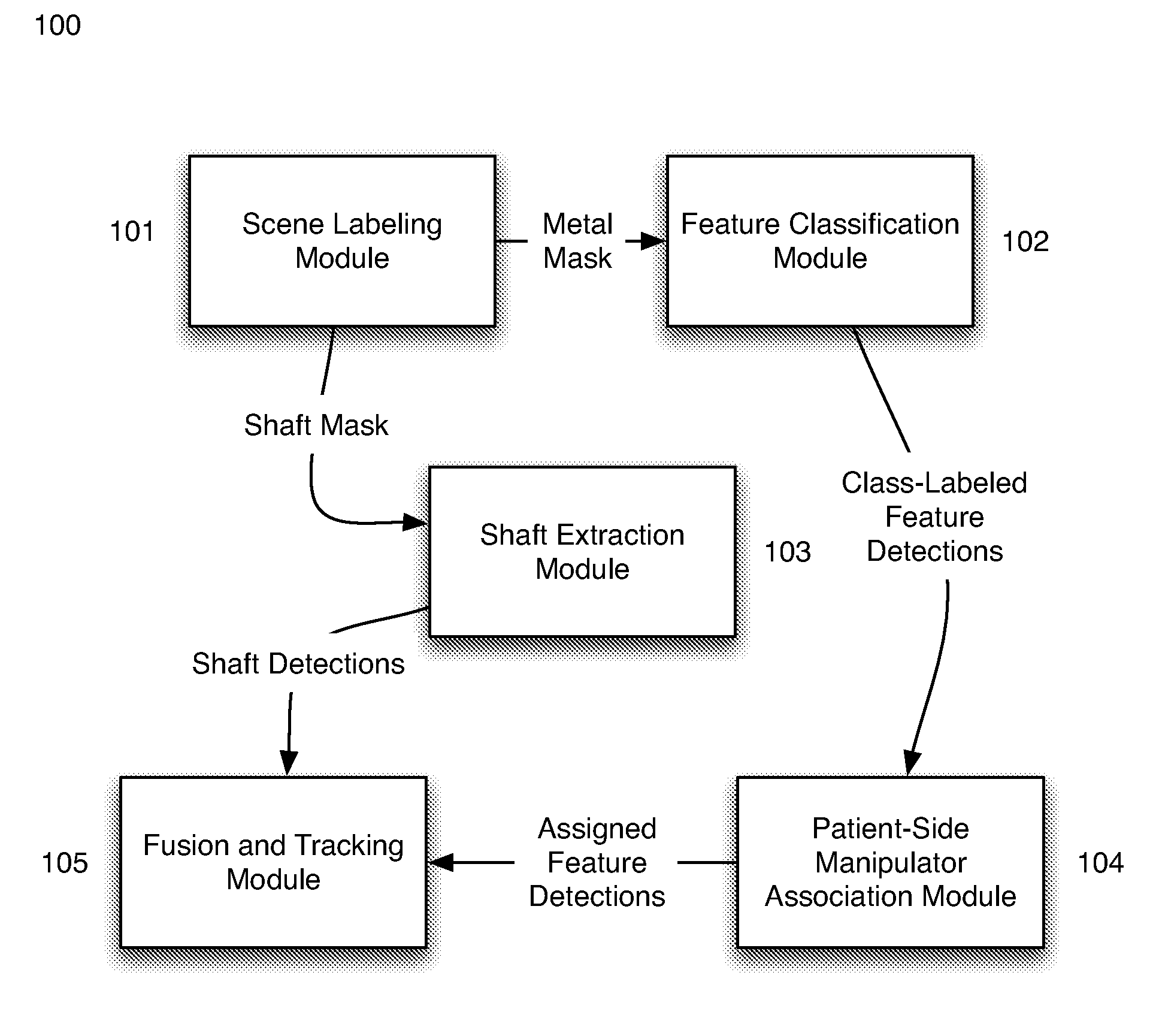
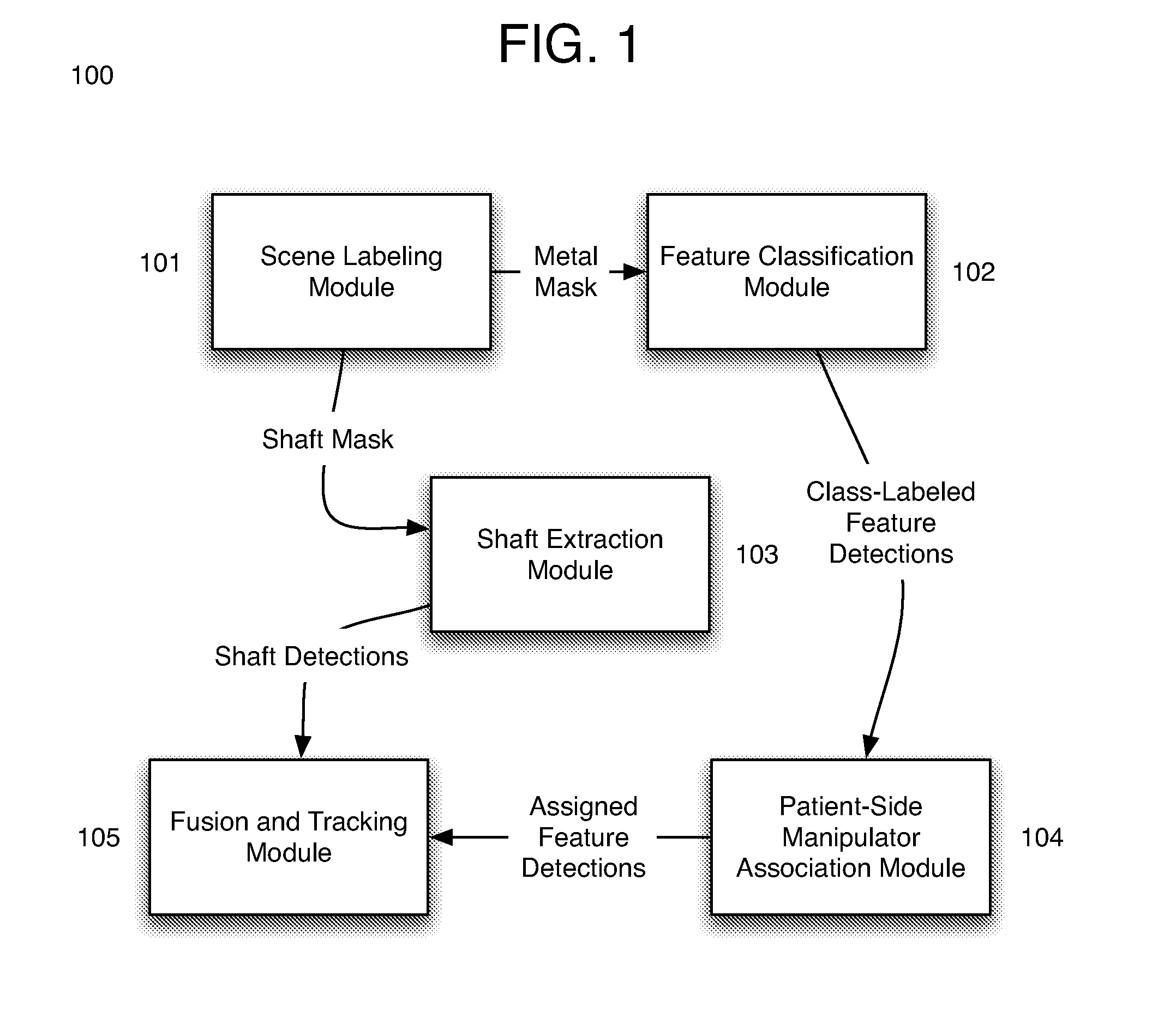
Appearance learning systems, methods and computer products for three-dimensional markerless tracking of robotic surgical tools. An appearance learning approach is provided that is used to detect and track surgical robotic tools in laparoscopic sequences. By training a robust visual feature descriptor on low-level landmark features, a framework is built for fusing robot kinematics and 3D visual observations to track surgical tools over long periods of time across various types of environments. Three-dimensional tracking is enabled on multiple tools of multiple types with different overall appearances. The presently disclosed subject matter is applicable to surgical robot systems such as the da Vinci® surgical robot in both ex vivo and in vivo environments.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
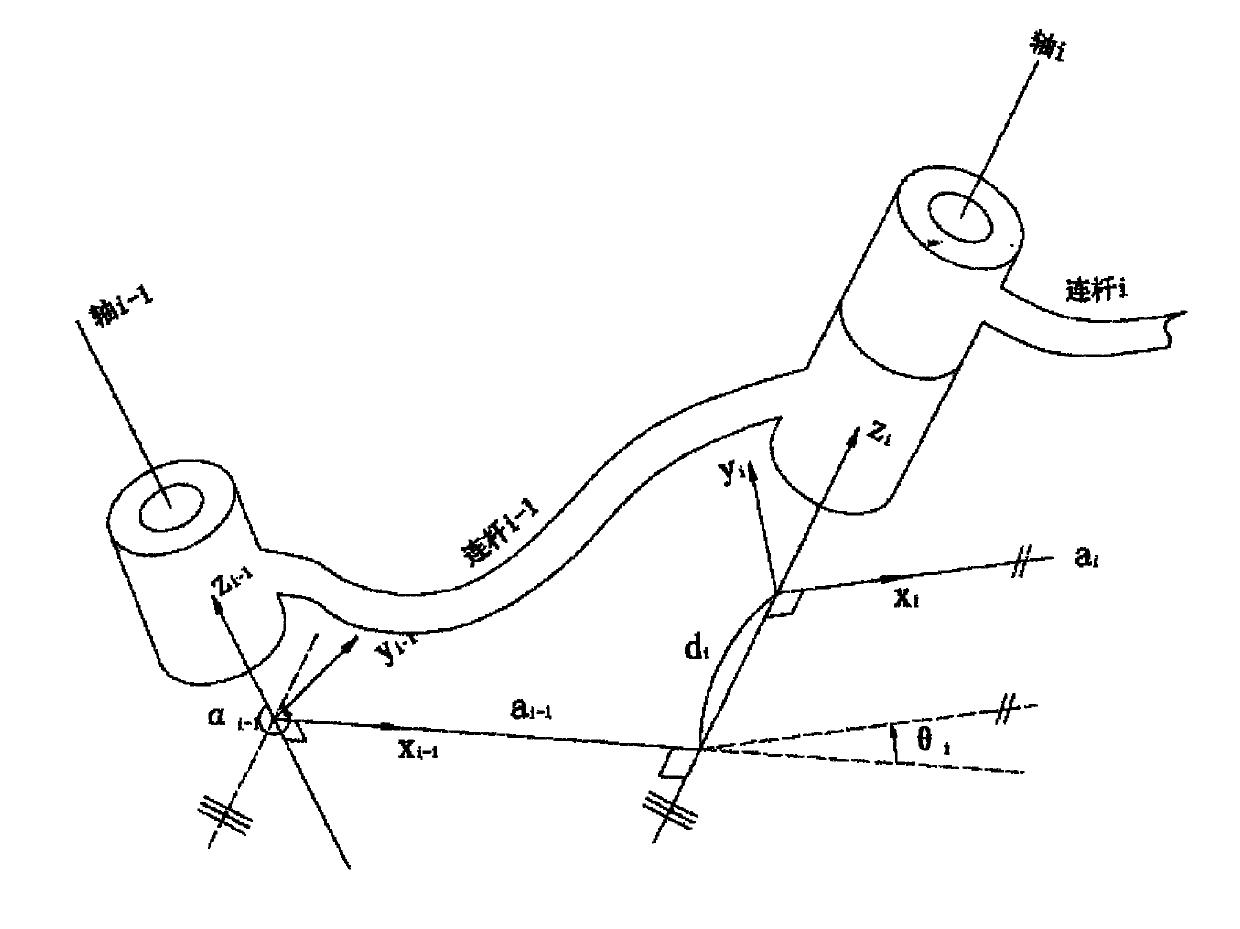
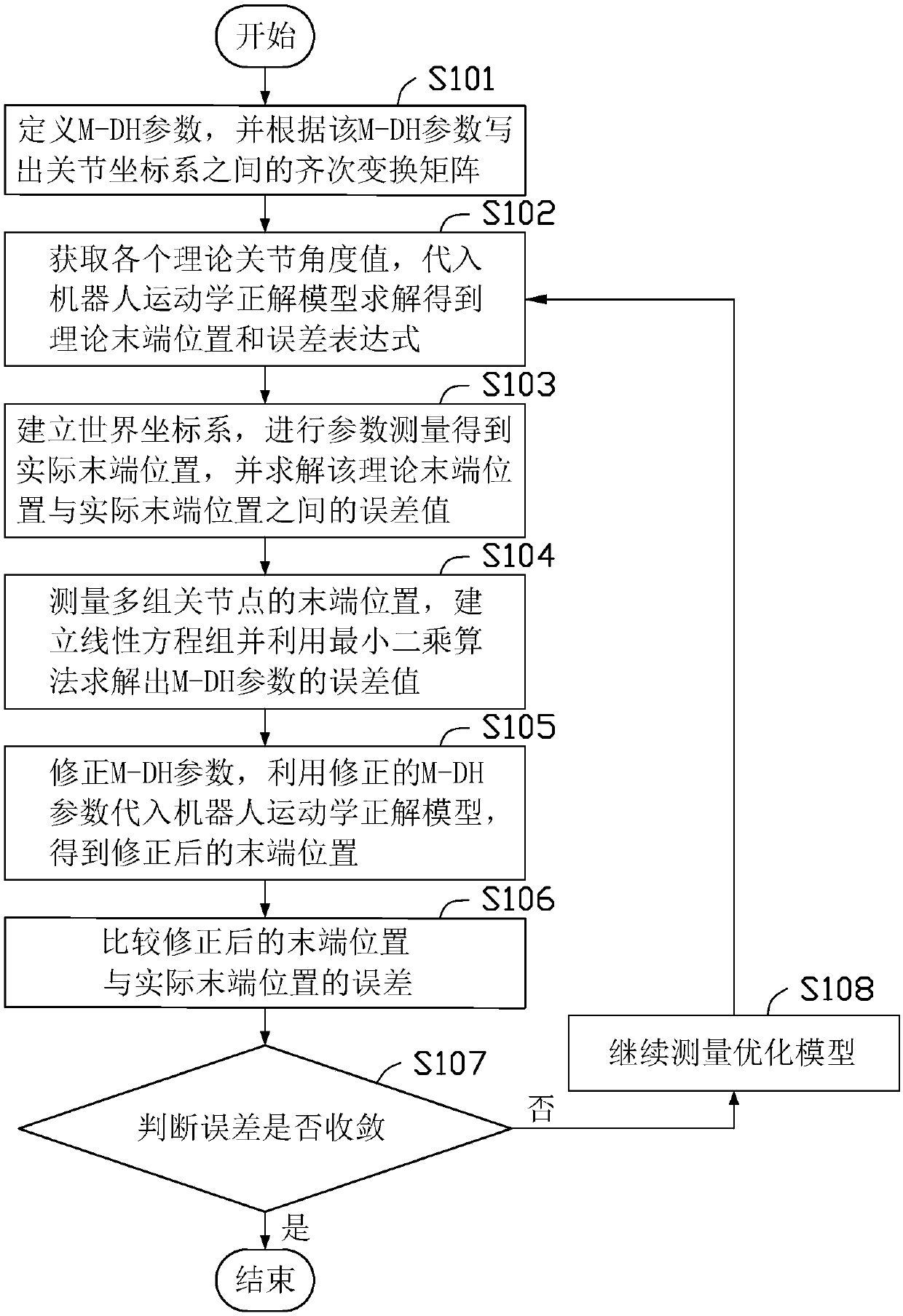
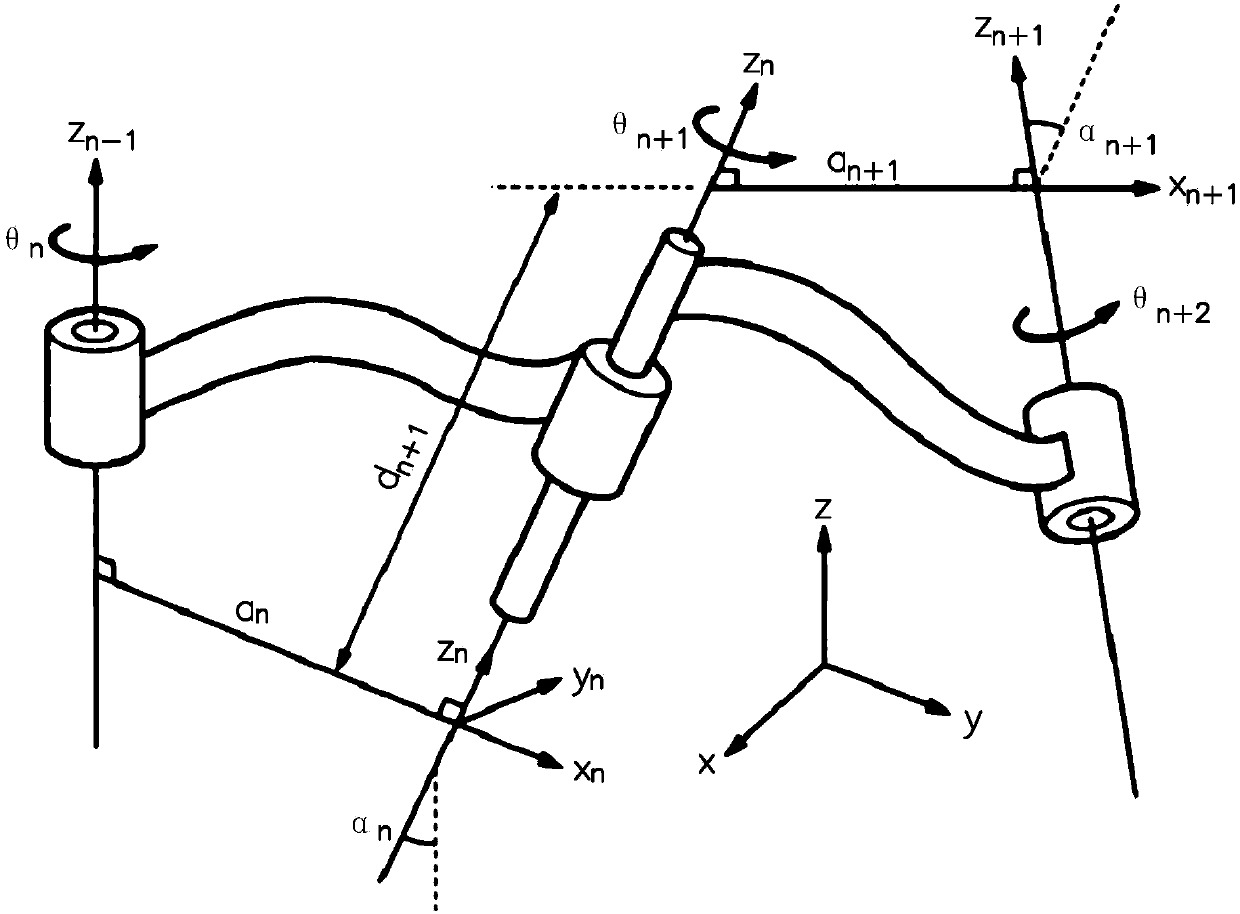
Parameter measurement and identification method and device of mechanical arm, terminal, and storage medium
InactiveCN108527373AHigh precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorMeasurement deviceJoint coordinates
The invention provides a parameter identification method of a mechanical arm. The parameter identification method of the mechanical arm comprises the steps of defining an M-DH parameter, and writing out a homogeneous transformation matrix between joint coordinate systems; acquiring each theoretical joint angle value, substituting into a robot kinematics forward analysis model, and solving to obtain a theoretical terminal position and an error expression; measuring a practical terminal position, and solving an error value between the theoretical terminal position and the practical terminal position; measuring terminal positions of multiple groups of joint points, building a system of linear equations, and utilizing a least squares algorithm for solving an error value of the M-DH parameter;correcting the M-DH parameter, and utilizing the corrected M-DH parameter to obtain a corrected terminal position; and judging whether an error between the corrected terminal position and the practical terminal position is converged or not, and if yes, finishing the flow. The invention further provides a parameter measurement method and a parameter measurement device of the mechanical arm, a parameter identification device of the mechanical arm, a terminal device and a storage medium. By utilizing the embodiment of the invention, the parameter identification accuracy can be improved.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
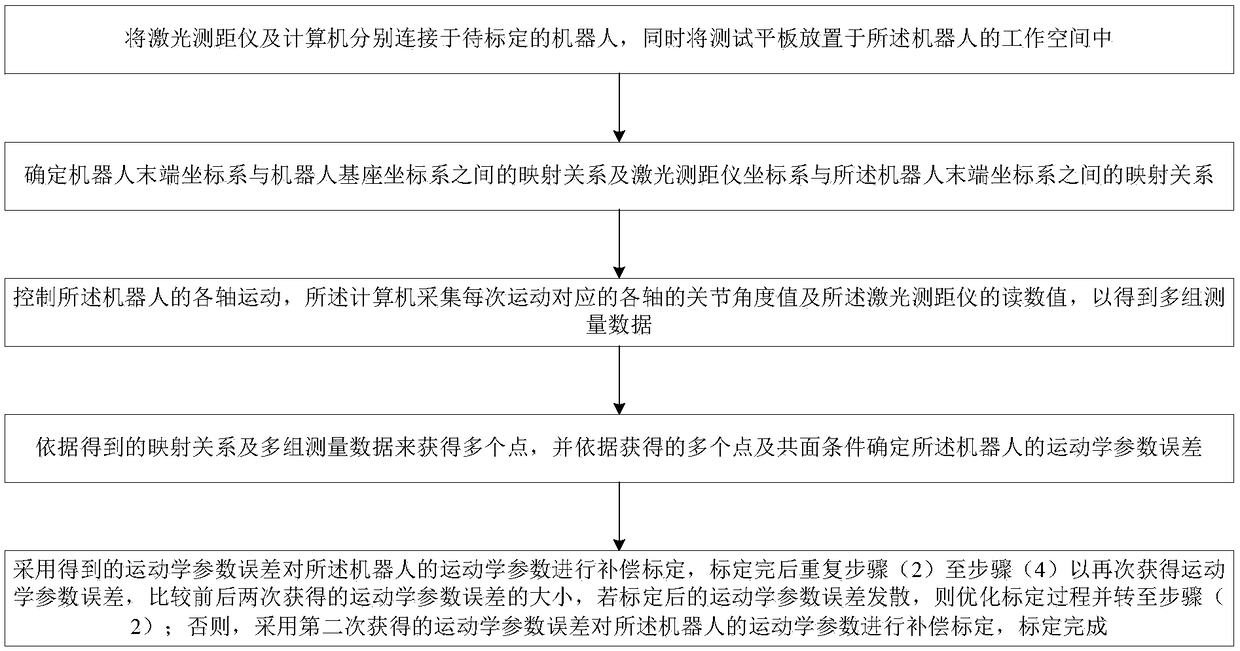
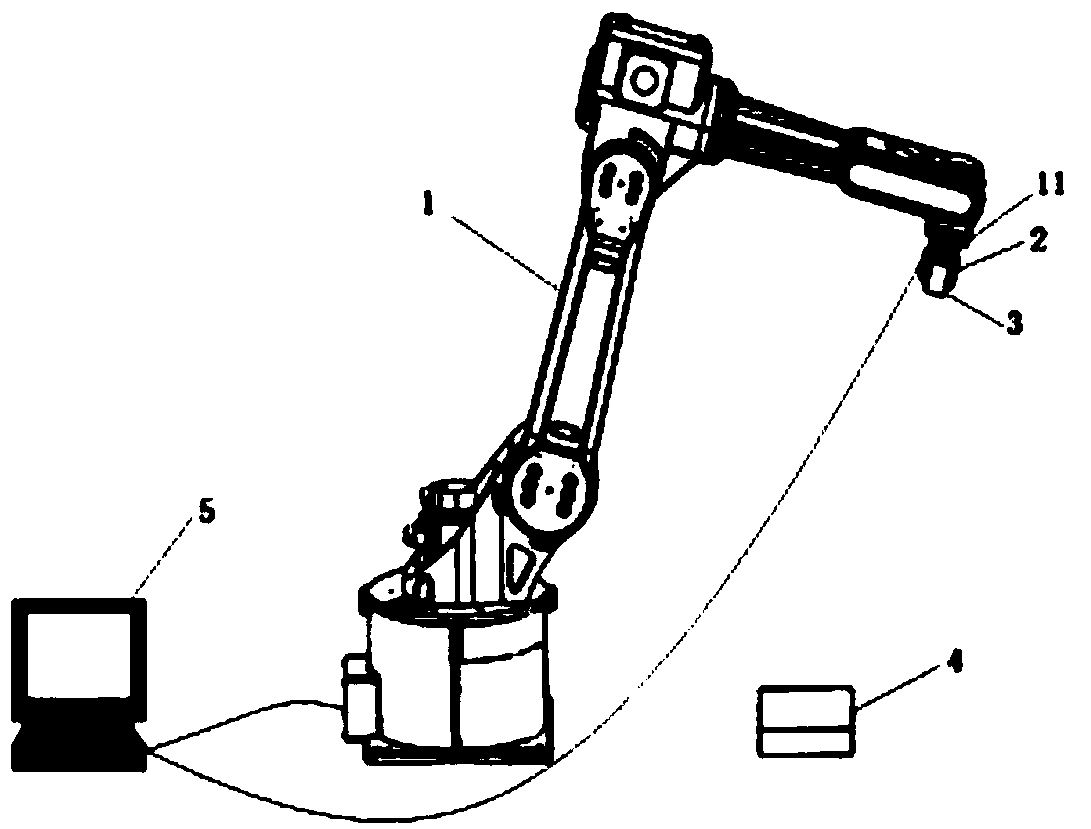
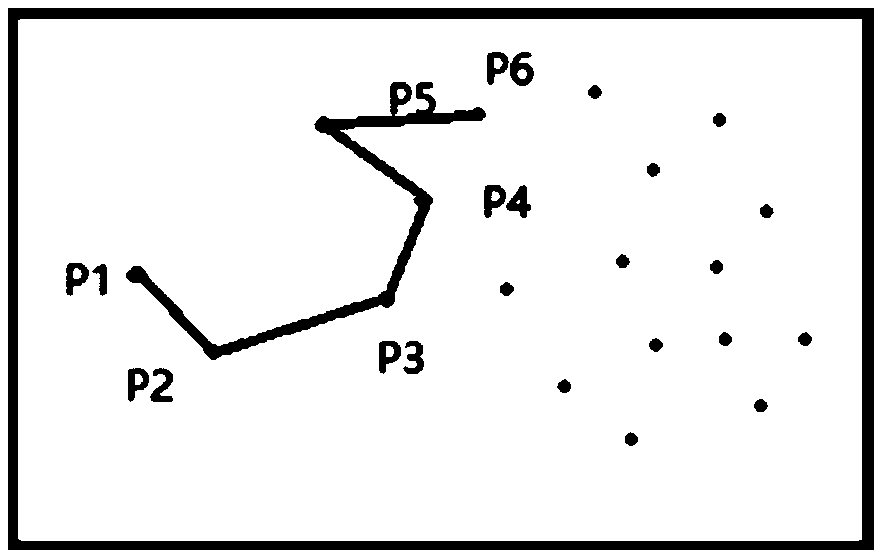
Robot kinematics parameter calibration method based on laser range finder
ActiveCN109304730ASimple structureEasy to installUsing optical meansManipulatorLaser rangingKinematics
The invention belongs to the technical field of information measurement, and discloses a robot kinematics parameter calibration method based on a laser range finder. The method comprises the followingsteps that the laser range finder is connected to a to-be-calibrated robot, and a test flat plate is placed in the working space of the robot; (2) a mapping relation between a robot tail end coordinate system and a base coordinate system of the roboy and the mapping relation between a laser range finder coordinate system and the robot tail end coordinate system of the robot are determined; (3) ajoint angle value corresponding to each time of movement of the robot and a reading value of the laser range finder are gathered; (4) a plurality of points are obtained, and a kinematic parameter error is determined according to a coplane condition; and (5) compensation calibration is carried out on the kinematics parameters of the robot, the kinematics parameter error is acquired again after thecalibration is completed, the kinematics parameter error is compared with the value of the last time, and then calibration completion or re-calibration is determined. According to the method, the measuring efficiency is high, the operation is simple, the implementation is easy, and the accuracy is high.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method and equipment for synchronous positioning and map establishing
ActiveCN107917712AImprove build conveniencePrecise positioningNavigational calculation instrumentsDesign optimisation/simulationKinematicsRobot kinematics
The invention discloses a method and equipment for synchronous positioning and map establishing. The method and the equipment are applied to robots. The map establishing method comprises the followingsteps: loading a preset robot dynamitic model; scanning an environment by using an environment sensor, establishing an initial global map in a preset coordinate system, expressing the initial globalmap by a plurality of geometric prototypes, storing the geometric prototypes in a same sequence, and marking with storage serial numbers; when being moved to a current position, scanning by using theenvironment sensor so as to obtain a current partial map, expressing the current partial map by using a plurality of geometric prototypes, storing the geometric prototypes in a sequence identical to that of the initial global map, marking with storage serial number, and combining according to comparison of the geometric prototype storage serial numbers of the current partial maps and the initial global map so as to obtain an updated global map; and according to the current partial maps, the initial global map and the updated global map, estimating a current posture of a robot. The calculationamount of map establishment is effectively simplified, and the storage space is effectively reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU AGV ROBOT CO LTD
Curve welding seam welding technology based on line structured light
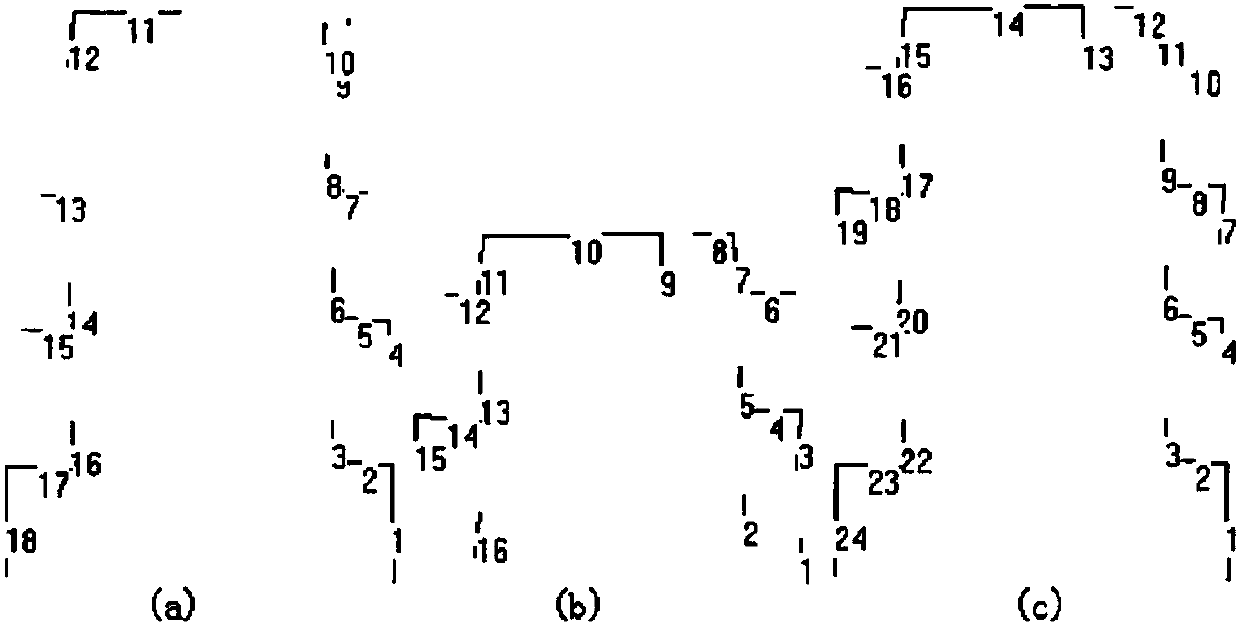
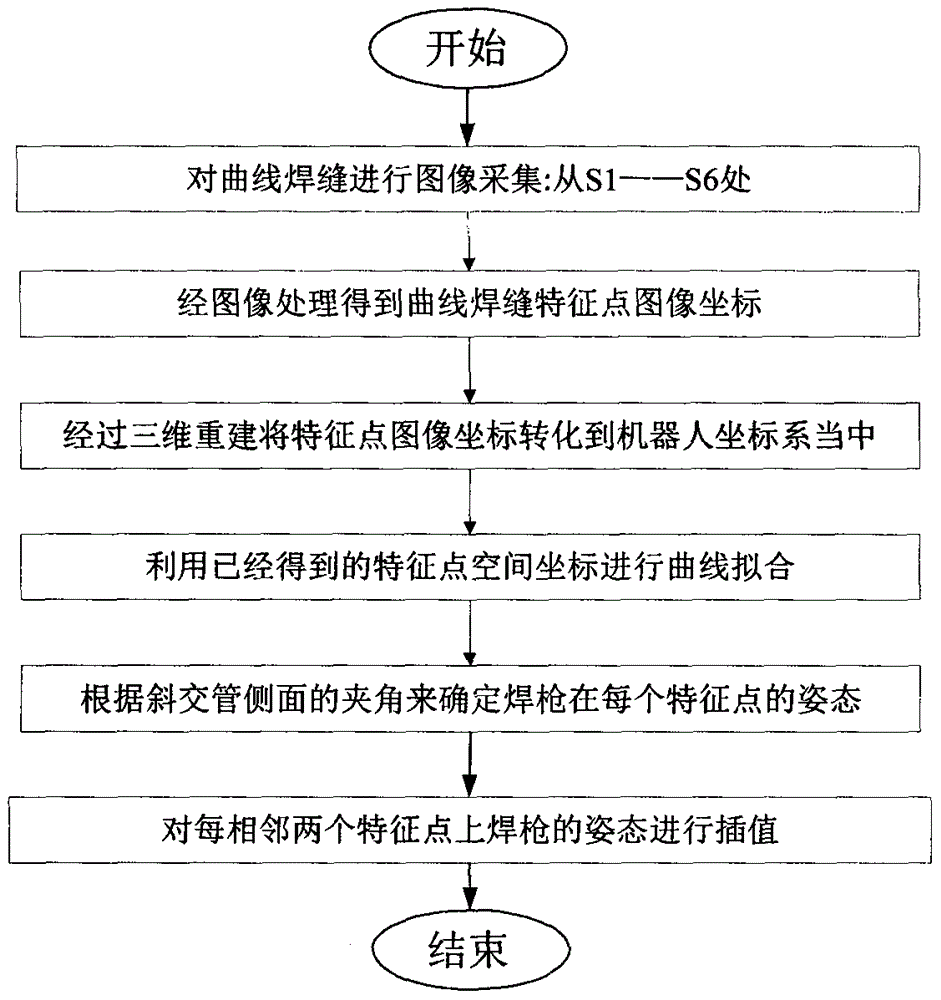
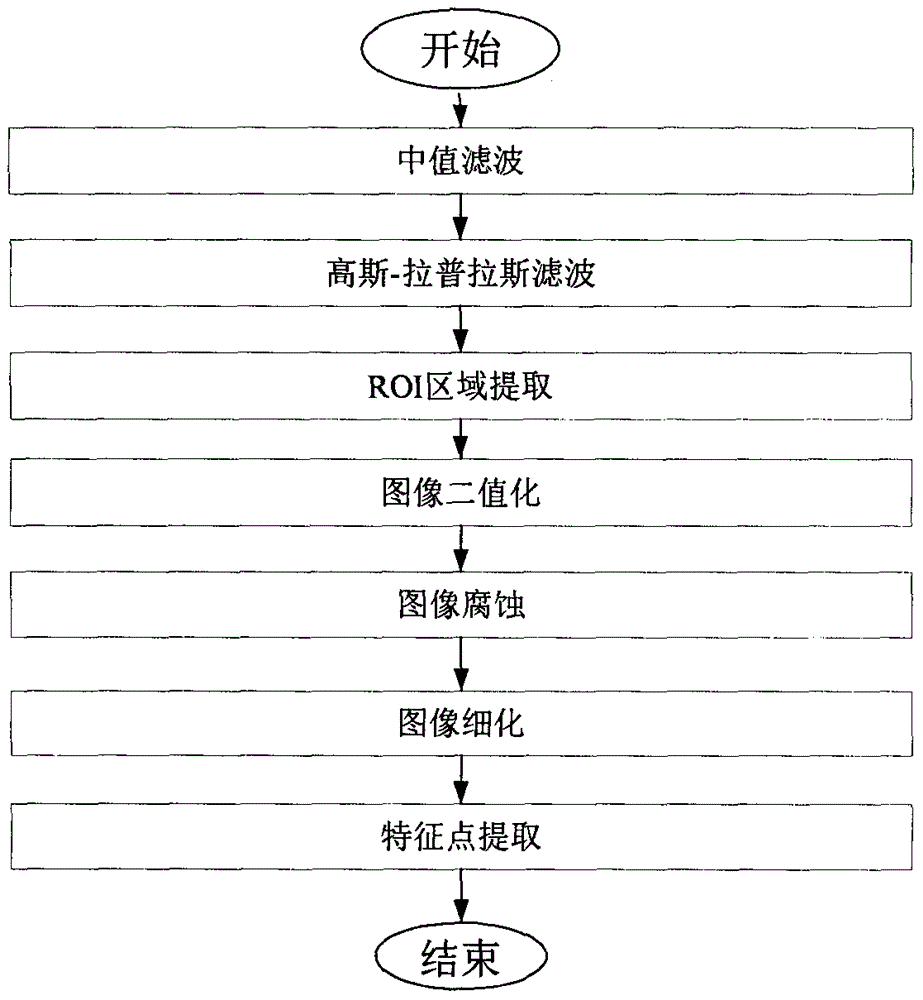
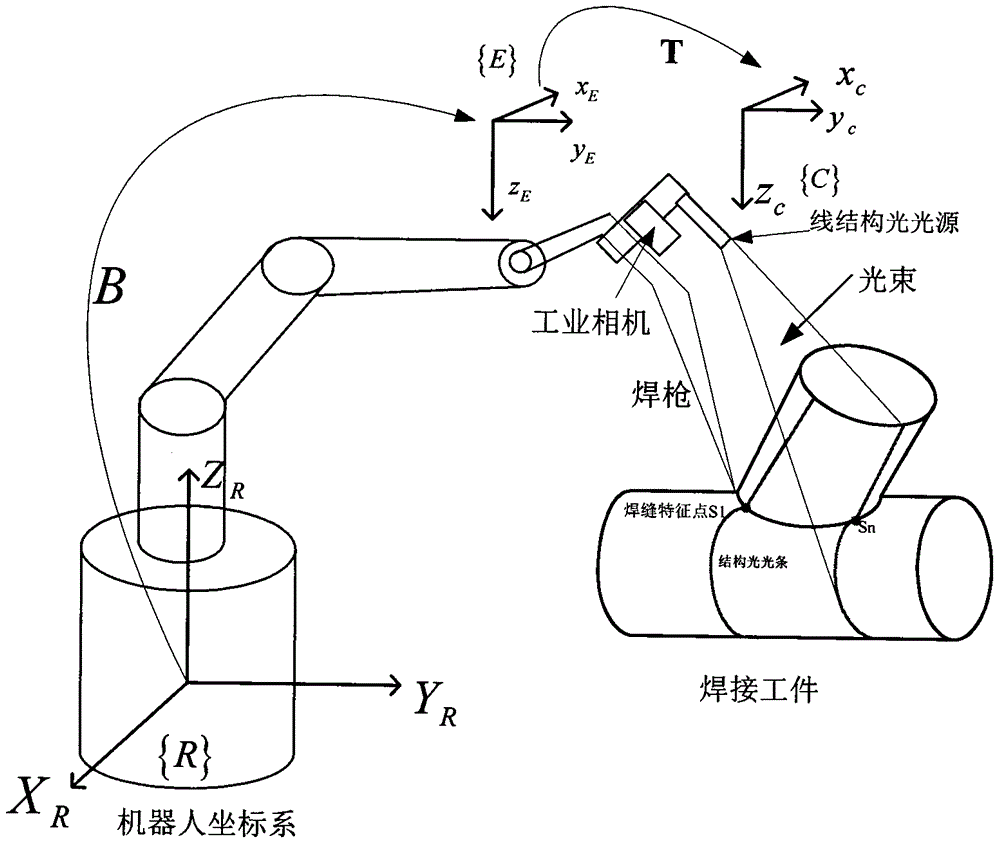
InactiveCN106425181AAchieving identifiabilityAchieve weldingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesTracking modelEngineering
The invention discloses a curve welding seam welding technology based on line structured light and oriented to an oblique crossed tube. According to the method, machine version and robot kinematics are combined very well, so that the problems that the process of obtaining curve welding seam feature points is not flexible, and a curve track model are difficult to establish are solved. The curve welding seam welding technology comprises the following steps of: firstly, controlling a six-degree-of-freedom robot, enabling a robot end to drive an industrial camera to shoot a curve welding seam image with the line structured light; and then, carrying out a series of image pre-treatment and feature point extraction work to obtain space coordinates of all feature points of a curve welding seam, and fitting through a B sample curve, and finally obtaining a smooth space curve. Besides, the gesture of a welding gun can be changed in real time according to included angles at the two sides of a workpiece when the welding gun is used for welding a curve, so that the welding process and welding requirements are improved better.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Global path planning method
InactiveCN109798909AConvenience and precision in motion controlBreakpoint reductionInstruments for road network navigationRobot kinematicsPath plan
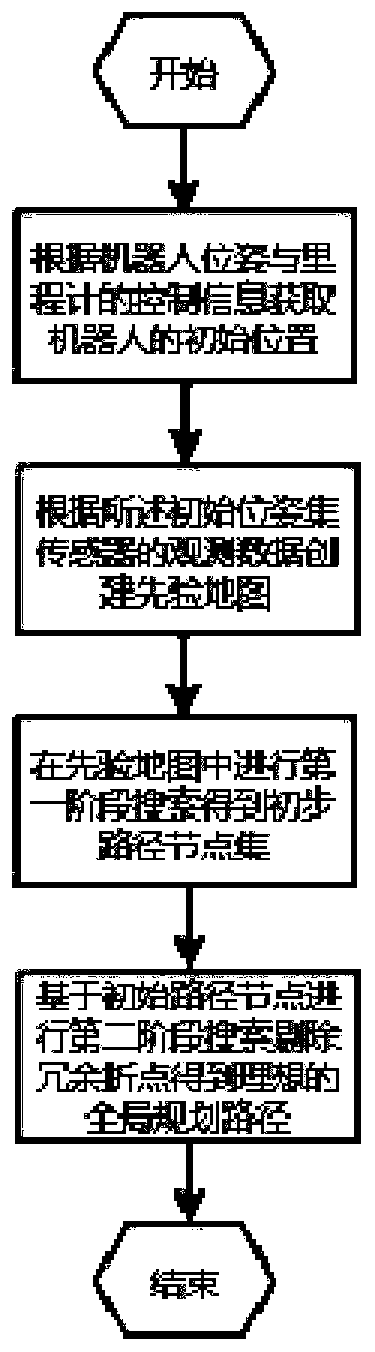
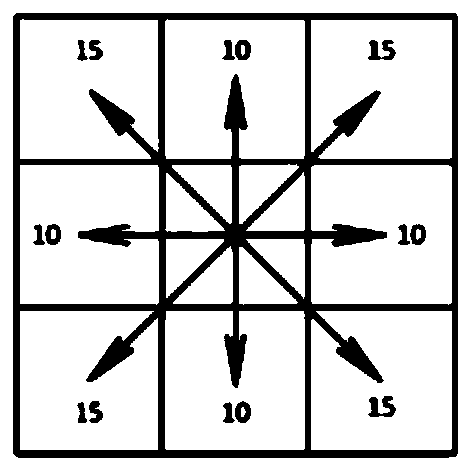
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots and discloses a global path planning method. Aiming at the problem of difficulty in robot control due to large quantity of turning points in robot path planning in the prior art, the global path planning method is provided and includes steps: adding an angle constraint function a(n) in an original A* algorithm cost function, completing first stage searching in global path planning through the improved A* algorithm cost function to work out a robot movement angle constrained preliminary global path, wherein n refers to a current node of a robot state; extracting a result of the first stage searching, performing second stage searching, rejecting redundancy turn points in the path to obtain a final global path according with a robot kinematic principle. By adding of the angle constraint function and adoption of two-stage searching to plan the global path according with the robot kinematic principle, the turn points in the path are sharply reduced, and the smooth and short global path is achieved under the condition of guarantee of timeliness.
Owner:南京达特智能科技有限公司
Inverse kinematics calculation method of six-freedom-degree wrist-biased serial robot
ActiveCN107685330ASmall amount of calculationFast convergenceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobot kinematicsComputer science
The invention discloses an inverse kinematics calculation method of a six-freedom-degree wrist-biased serial robot. According to the method, an analytical solution of inverse kinematics of the six-freedom-degree wrist-unbiased serial robot serves as an approximate solution and an iteration starting point of the inverse kinematics of the six-freedom-degree wrist-unbiased serial robot, an inverse kinematics value solution of the six-freedom-degree wrist-biased serial robot meeting the precision is calculated through constant iterationapproach, and the convergence rate is high. Compared with a traditional calculation method, the calculation amount is small, the computation quantity of a robot controller is decreased, and the real-timeliness is improved.
Owner:FOSHAN HUASHU ROBOTICS CO LTD +1
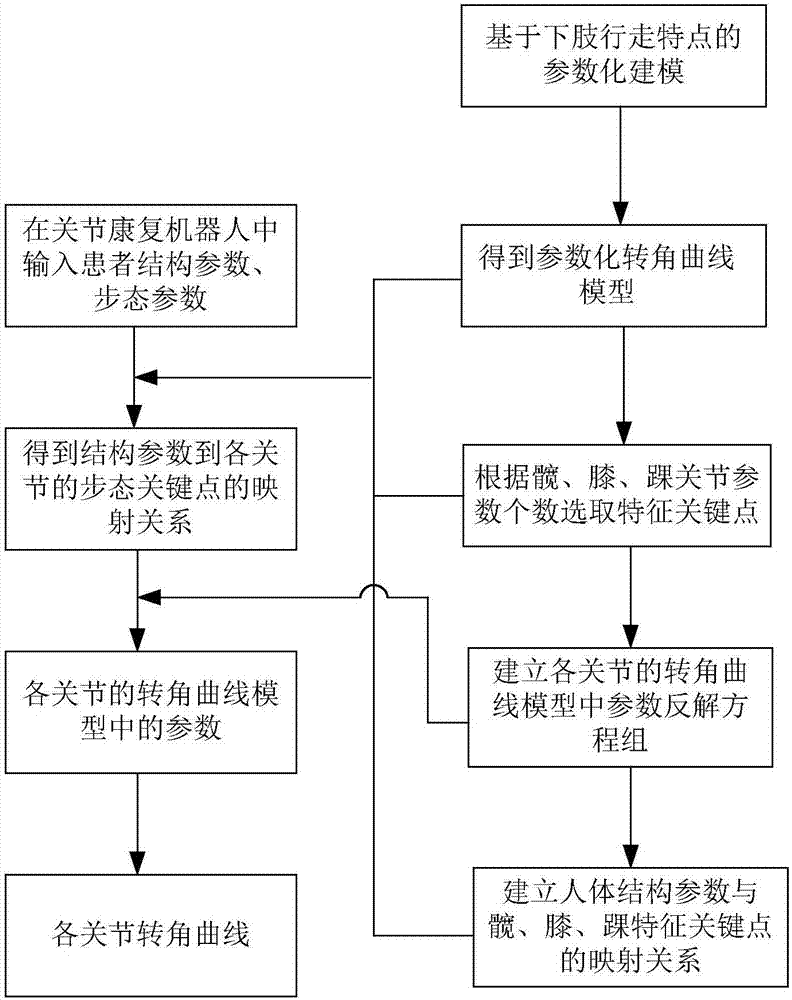
Lower limb rehabilitation robot gait planning method based on lower limb walking characteristics
ActiveCN107273611AIn line with the law of lower limb movementRealize motion trajectory customizationWalking aidsDesign optimisation/simulationHuman bodyGait
The invention provides a lower limb rehabilitation robot gait planning method based on lower limb walking characteristics. Firstly, parameterized modeling is performed based on the lower limb walking characteristics, wherein parameterized mathematic models of the lower limb hips, knees and ankle turn angles of the human body are established, and the forms of function curves of the models and required parameter number are determined; secondly, a mathematic inverse solution equation set of curve parameters is established; thirdly, the linear and nonlinear mapping relation of human body structure parameters and characteristic key point positions is found; finally, human body structure parameters are measured, the characteristic key points of a patient are found according to the mapping relation between the human body structure parameters and the characteristic key points, the curve parameters are inversely solved to obtain a specific curve expression, kinematic positions and corresponding lower angles of a robot are solved according to the specific structure and configuration of the lower limb rehabilitation robot to generate a joint movement instruction corresponding to the robot. The lower limb rehabilitation robot gait planning method conforms to a human body lower limb movement rule and can also reveal the mechanism of human body lower limb movements.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
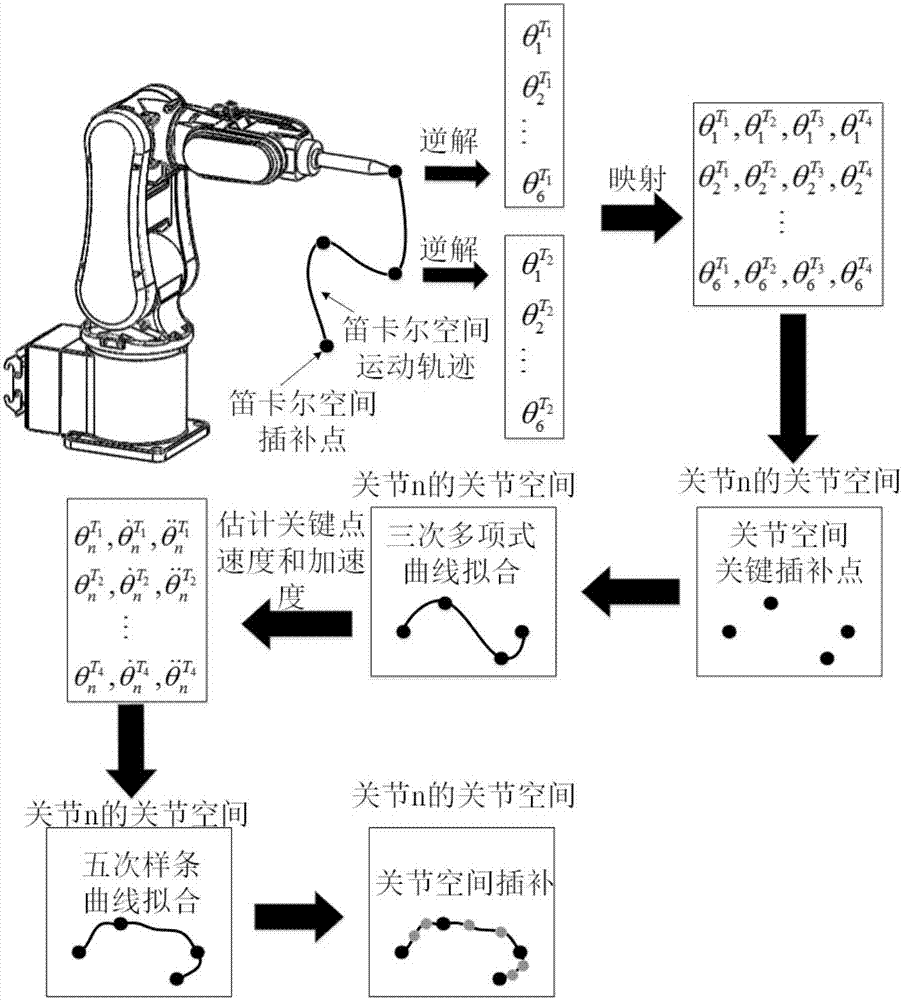
Method for planning smooth joint space trajectory of robot
ActiveCN106863306ASave resourcesLighten the computational burdenProgramme-controlled manipulatorCurve fittingRobot kinematics
The invention discloses a method for planning the smooth joint space trajectory of a robot. The method comprises the steps: first, by the inverse algorithm of robot kinematics, realizing the mapping from robot Cartesian space motion trajectory to joint space motion trajectory, and obtaining joint space key interpolation points; then, according to the maximum speed constraint of each joint of a robot, adjusting the Cartesian interpolation period; estimating the angular speed and the angular acceleration of the joint space key interpolation points with the help of cubic polynomial curves, and providing conditions for quintic spline curve fitting on the next step; finally, starting from the first joint space key interpolation point, using adjacent two joint space key interpolation points to construct quintic spline curves as the joint space motion trajectory, and then conducting joint space interpolation. The method solves the problem that the joint space motion trajectory of the robot is not smooth.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
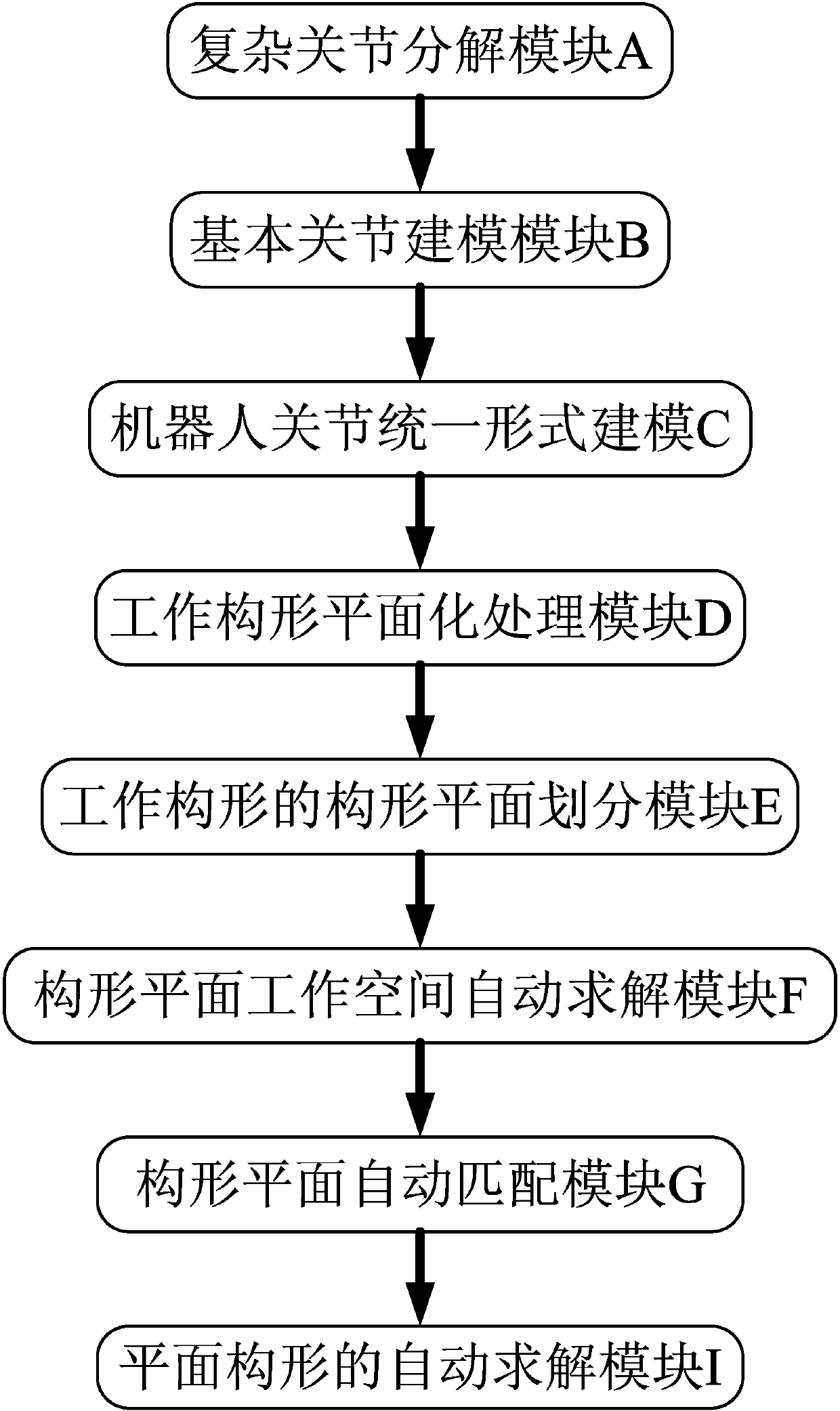
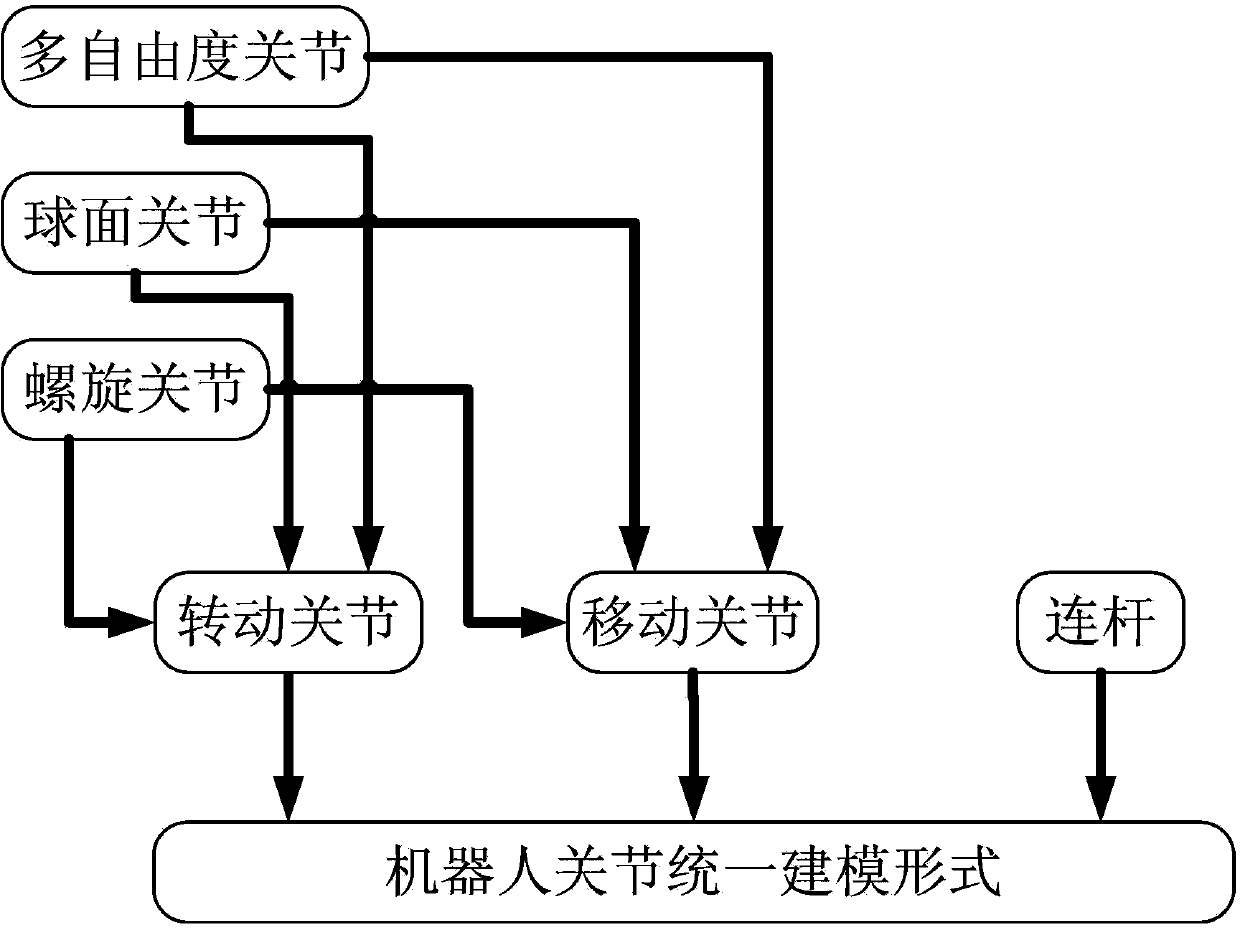
General calculation method for inverse kinematics of serial robots
ActiveCN103390101AMeet the actual needs of motion controlQuick solveSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationRobot kinematics
The invention discloses a general calculation method for inverse kinematics of serial robots. The general calculation method comprises the following steps of classifying and simplifying a plurality of types of robot moving joints to establish a uniform robot moving joint kinematic model; performing two-dimensional processing on robot working configuration according to a planar processing method, classifying and dividing formed planar configurations on the basis and respectively establishing automatic planar configuration working space calculation methods; and performing configuration plane matching on any robot configuration to solve the inverse kinematics of the serial robots. The method overcomes the defects of the limitation and specificity for solving the robot configuration by the traditional analytic method, and solves the problems of non-instantaneity and low accuracy of a general iterative method, can quickly and accurately solve the inverse kinematics of the robots, and meets the requirement for calculating the general robot kinematics and the actual requirement on robot motion control.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
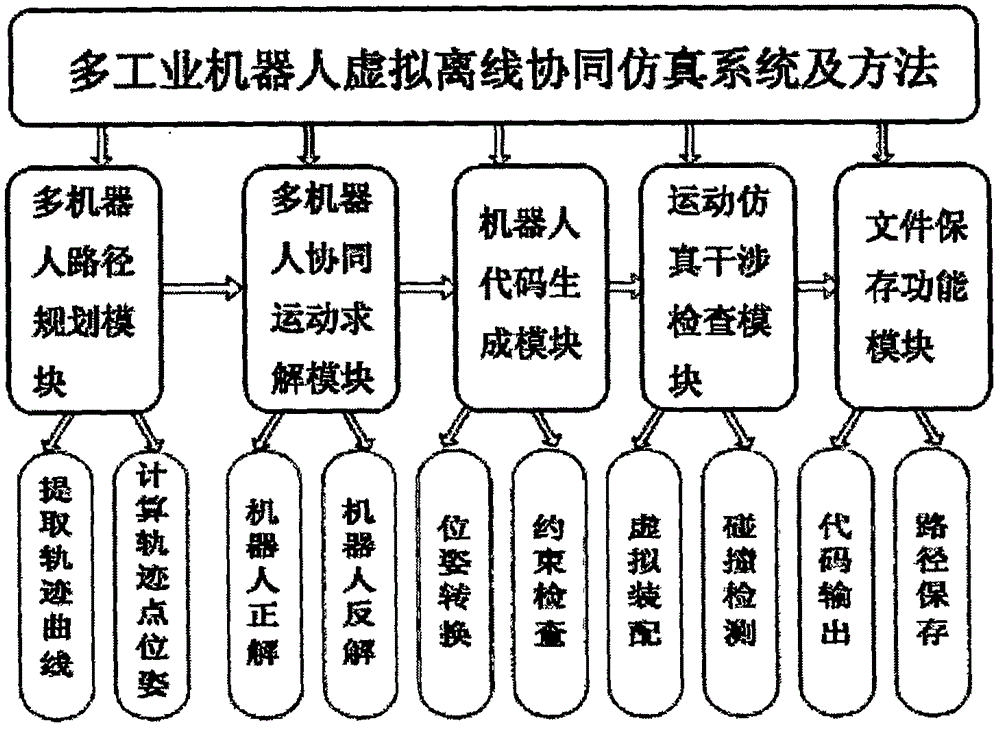
Multi-industrial-robot virtual offline co-simulation system and method
InactiveCN106444739AImprove development efficiencyIncrease productivityPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesKinematicsRobot kinematics
The invention discloses a multi-industrial-robot virtual offline co-simulation system and method. The system comprises a multi-robot path planning module, a multi-robot co-movement solving module, a robot code generating module, a movement simulation interference checking module and a file saving functional module. The method comprises the steps of: 1, constructing a multi-robot virtual workstation; 2, extracting an actual machining path of robots by using workpiece numerical simulation; 3, performing robot kinematics analysis; 4, performing discrete processing on the whole path, and simulating the movement in three-dimensional software by virtual assembly; 5, outputting movement control programs of the robots in the whole movement process according to code formats of different robots; 6, repeating step 4, performing interference checking, and if interference and collision occur, performing safety prompt; and 7, saving necessary information required in the whole co-movement process. The system and the method improve the development efficiency, reduce the technical threshold, and improve the production efficiency of enterprises.
Owner:鹿龙 +1
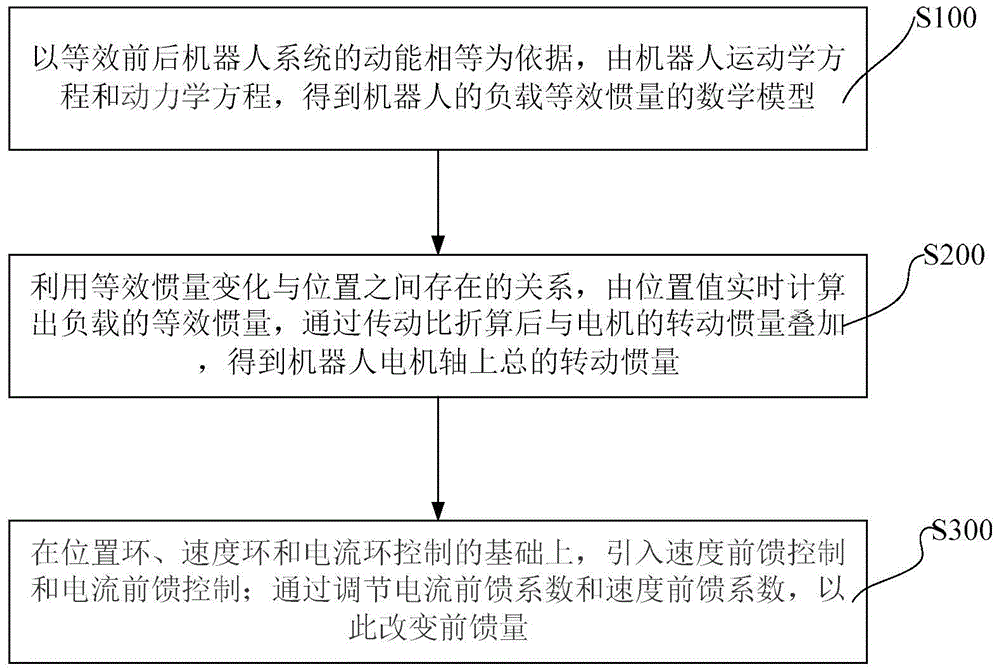
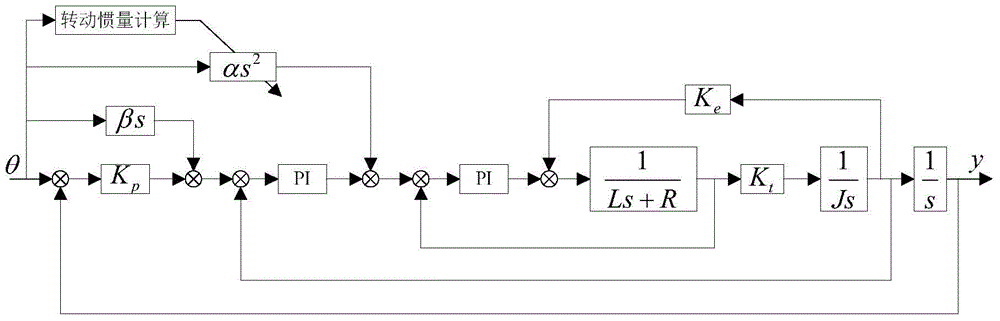
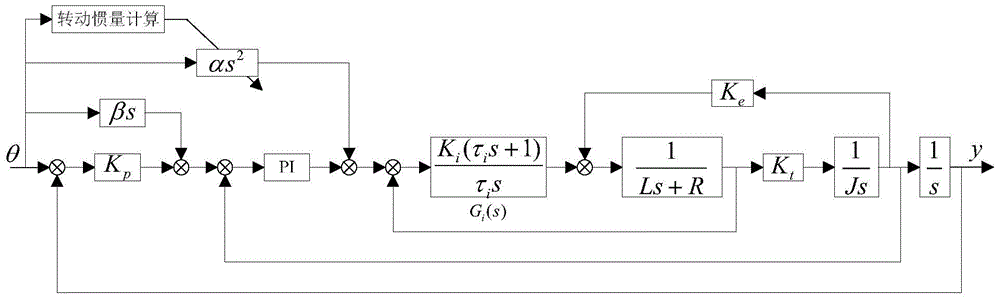
Feed-forward control method for robot servo system
ActiveCN105676896AImprove the effect of servo controlReduce running timeSpeed/accelaration control using electric meansKinematicsElectric machinery
The invention discloses a feed-forward control method for a robot servo system. The method comprises following steps: analyzing the robot kinematics and dynamics; deducing a mathematical expression of a load equivalent inertia J([theta]) of the robot based on the assumption that kinetic energies before and after equivalence are equal to each other; by use of the relation between the equivalent inertia change and positions, the load equivalent inertia J([theta]) which is calculated in real time with a position value[theta] is converted with a transmission ratio and then is accumulated with a rotational inertia JM of an electrical motor to obtain a total rotational inertia J of a motor shaft; finally, adjusting a current feed-forward coefficient [alpha] by use of the total rotational inertia J of the motor shaft to change the feed-forward value and therefore the servo control effect is increased. By use of the method, there is no need to identify the rotational inertia of the robot load; feed-forward control is adopted to eliminate the influence of inertia change on system dynamic performance; the method is simple and convenient to apply.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
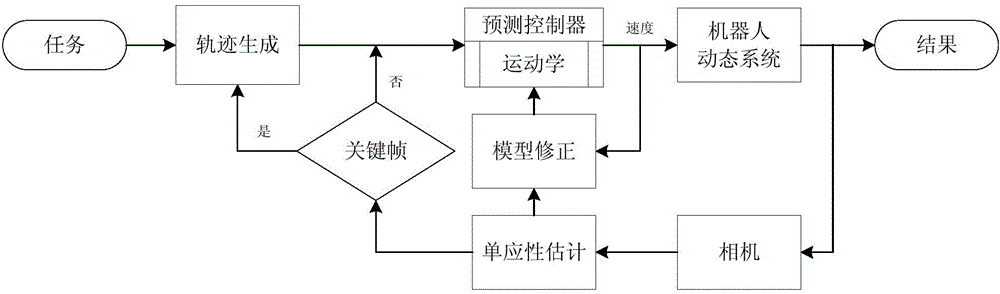
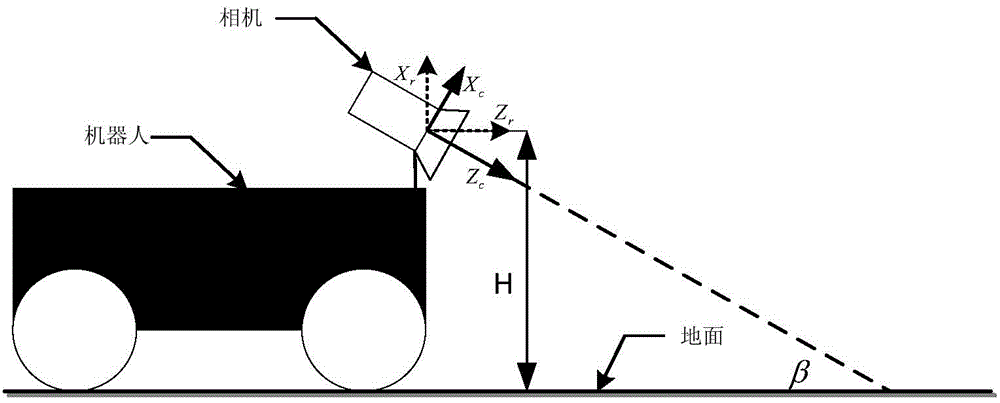
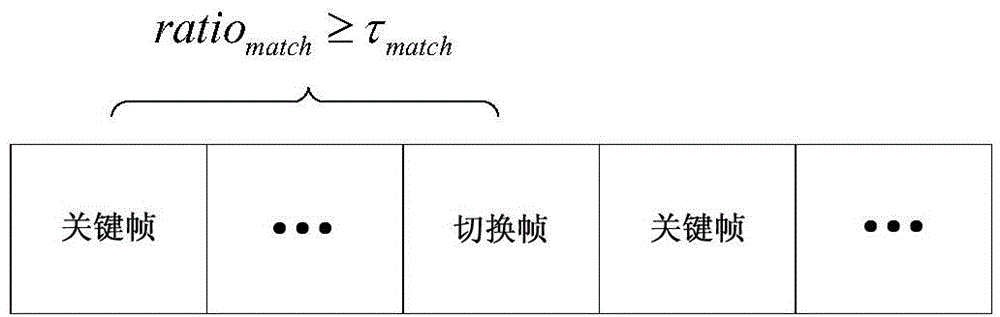
Mobile robot visual servo control method based on key frame strategy
InactiveCN104808590AOvercoming the low precision problemOvercome field of view constraintsNumerical controlRelational modelCharacteristic space
The invention discloses a mobile robot visual servo control method based on a key frame strategy, which comprises the steps of 1) planning a moving path for a robot according to given conditions; 2) converting physical trajectory tracking in a visual navigation task and posture adjustment under the condition that a target is visible into a trajectory in an image feature space; 3) defining image features based on a homography relation between a current image frame and a key frame, and expressing movement conditions of the robot implicitly by the image features; and establishing a mutual relation model of visual control systems based on a robot kinematic model and a camera model, and designing and predicting a controller tracking trajectory. According to the invention, no training is required to be carried out on the robot on a given trajectory in advance, the target is not required to be continuously visible in the movement process, and the navigation accuracy of the robot is ensured to a certain degree.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
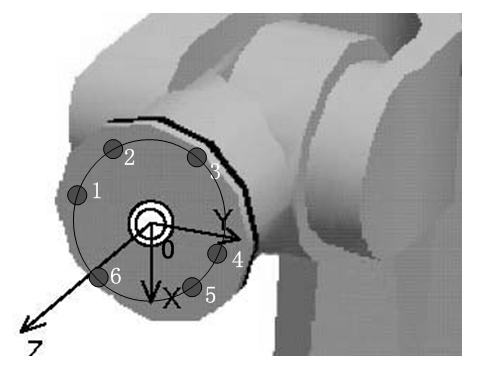
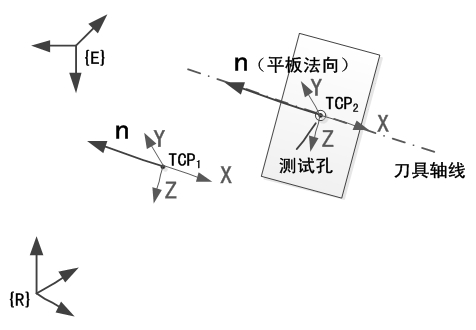
Indirect measurement method based tool parameter calibration method for high-precision drilling robot
ActiveCN102601684AImprove calibration accuracySolve the unmeasurableMeasurement/indication equipmentsKinematicsRobot kinematics
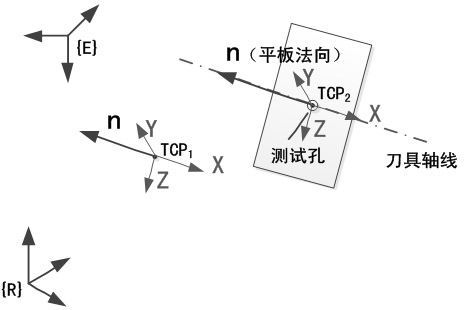
The invention discloses an indirect measurement method based tool parameter calibration method for a high-precision drilling robot, which relates to two TCPs (tool center points), wherein one TCP can be determined by directly measuring while the other TCP is a virtual tool point on the axis of a tool of a drilling device. A calibration flat plate is drilled to fix the position of the virtual tool point when the tail end of the robot is controlled to reach a certain position, and a robot kinematic model is used for determining parameters of the virtual tool point. Procedures which are difficulty in guaranteeing of precision of point alignment and the like during tool parameter calibration of a traditional robot are avoided, so that calibration precision is improved. Application range of the method is widened, the problem that the virtual tool point cannot be measured is solved, the whole calibration process can be programmed to be fixed, and corresponding program parameters can be modified for adaption even productive tasks change, so that application of the method in industrial fields can be facilitated.
Owner:南京航浦机械科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com