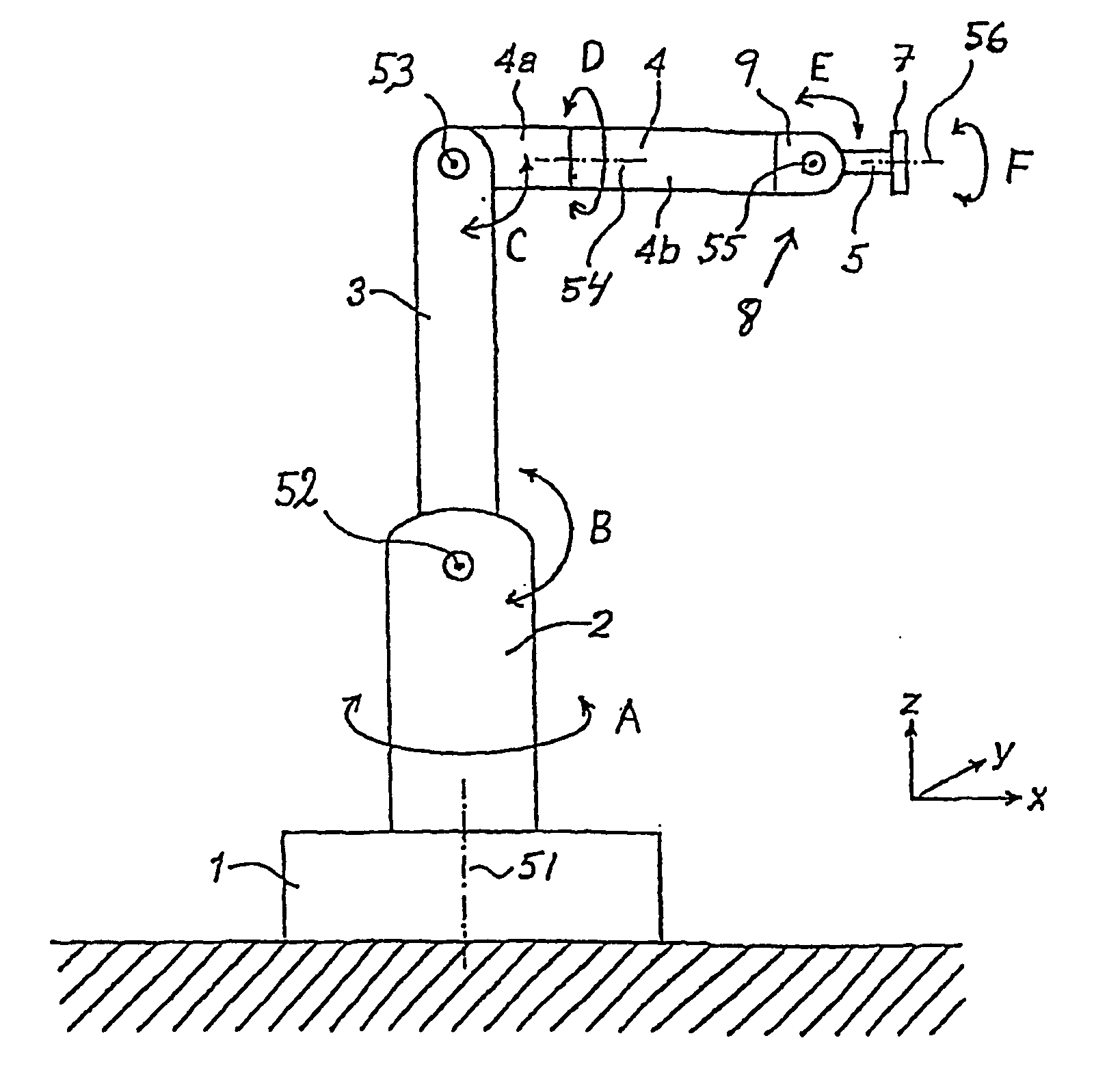
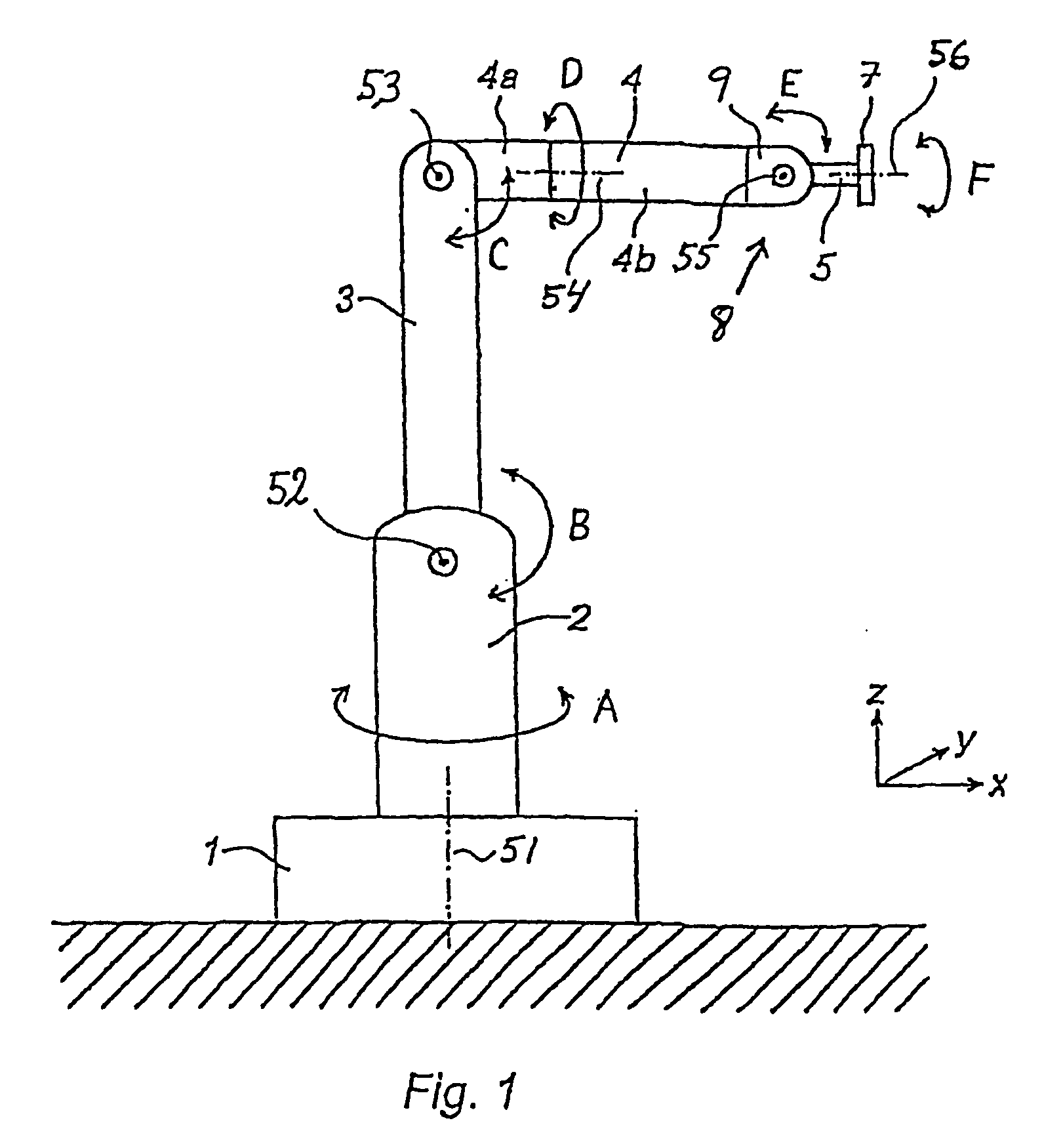
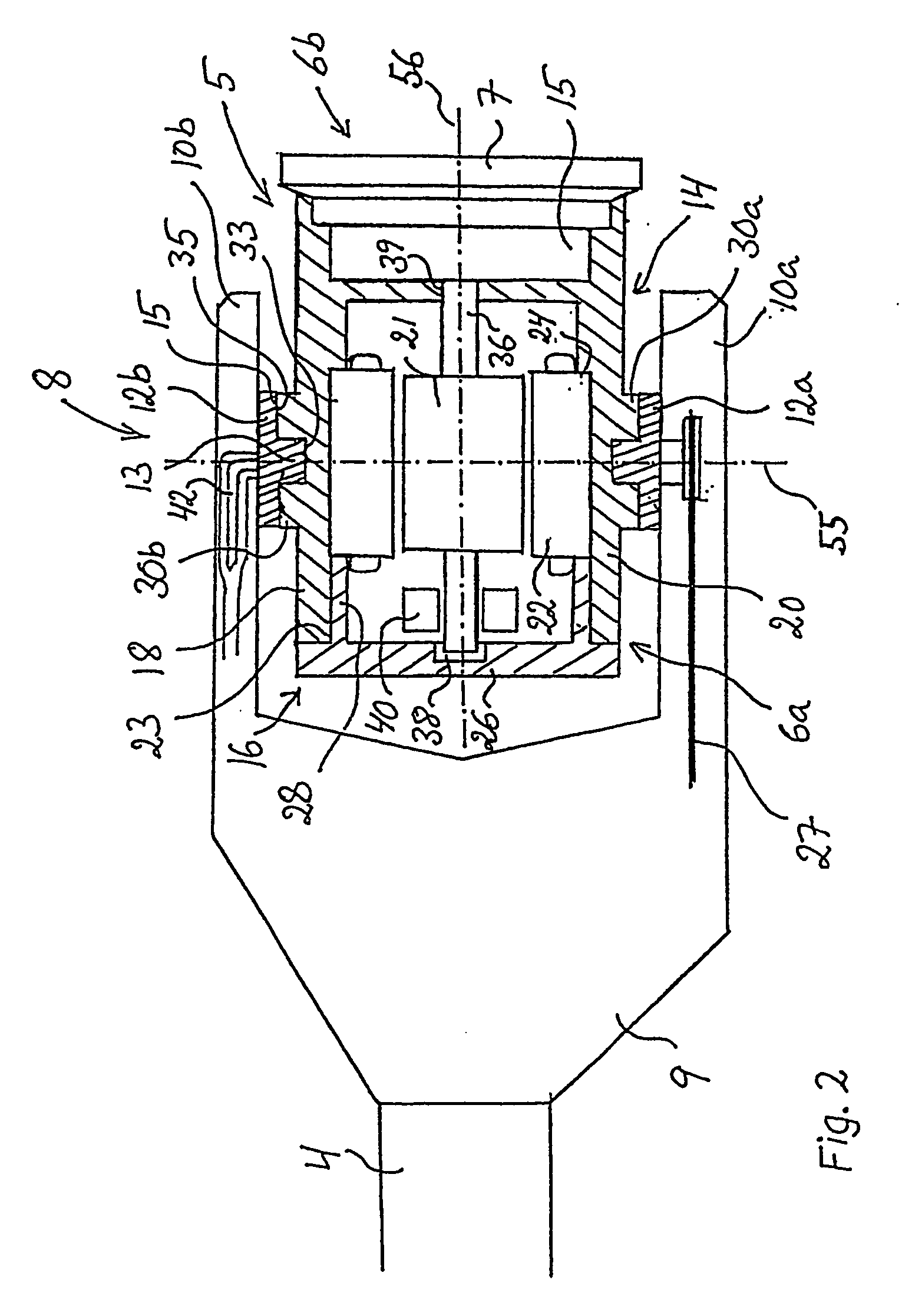
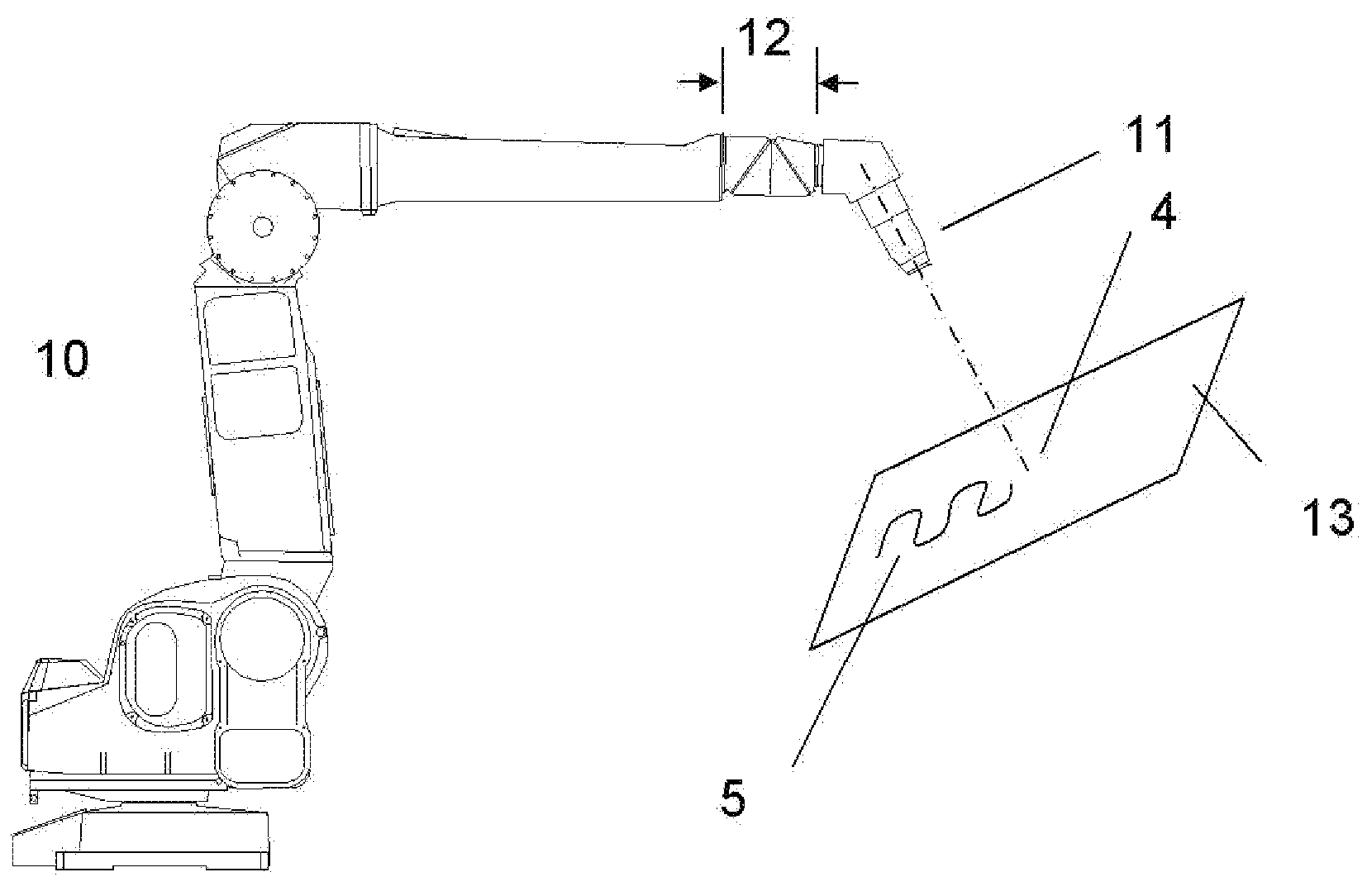
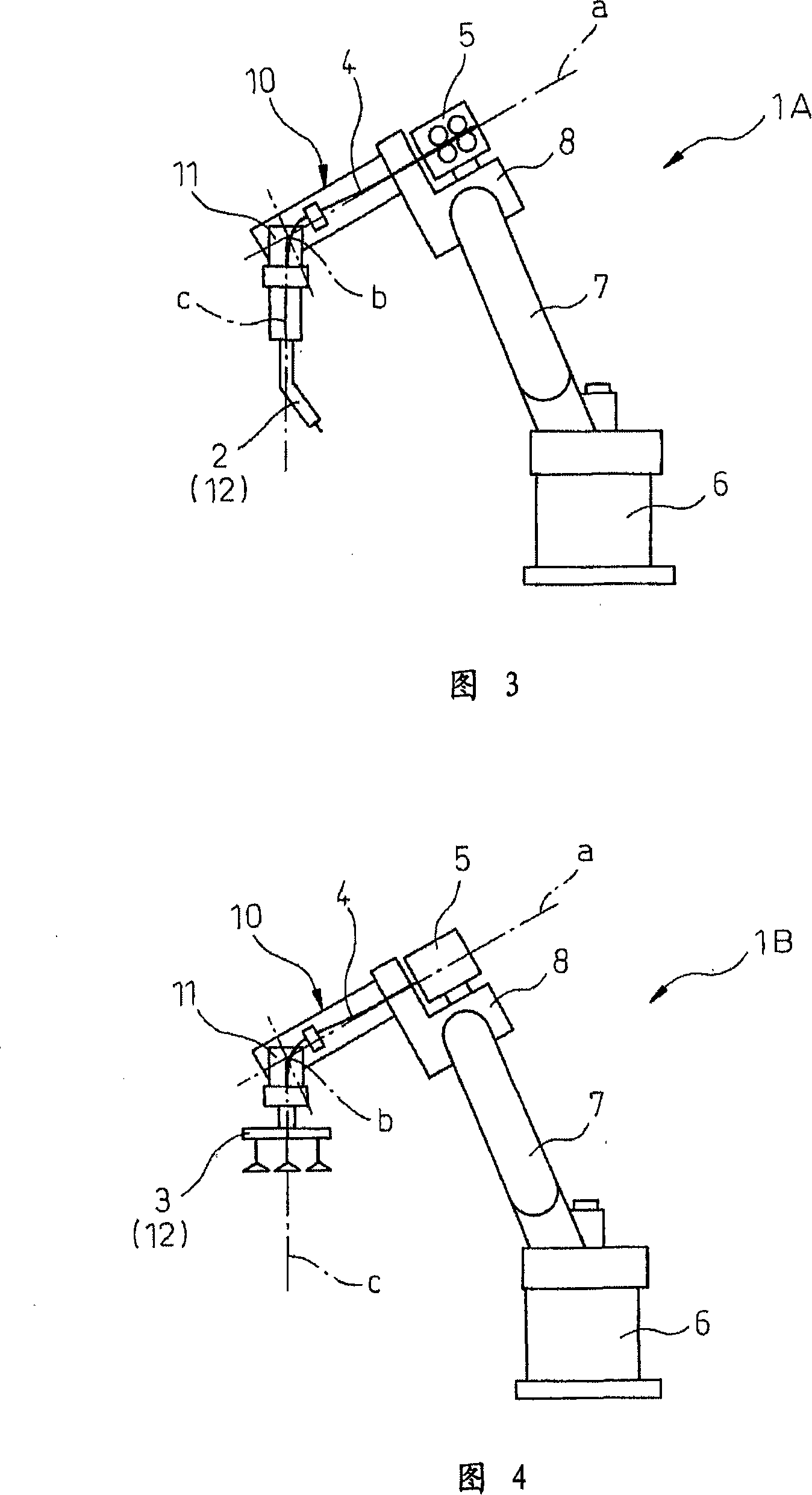
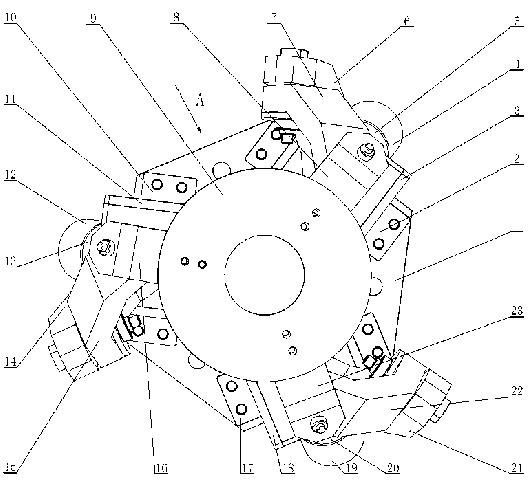
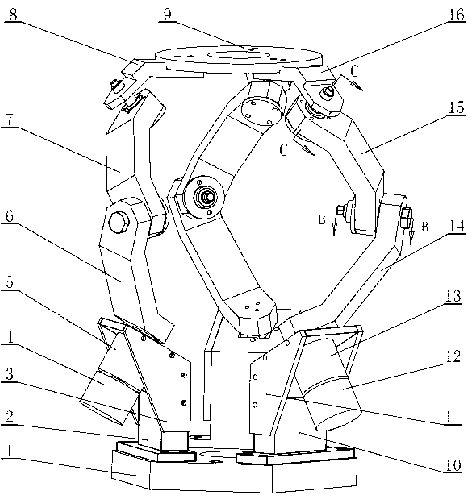
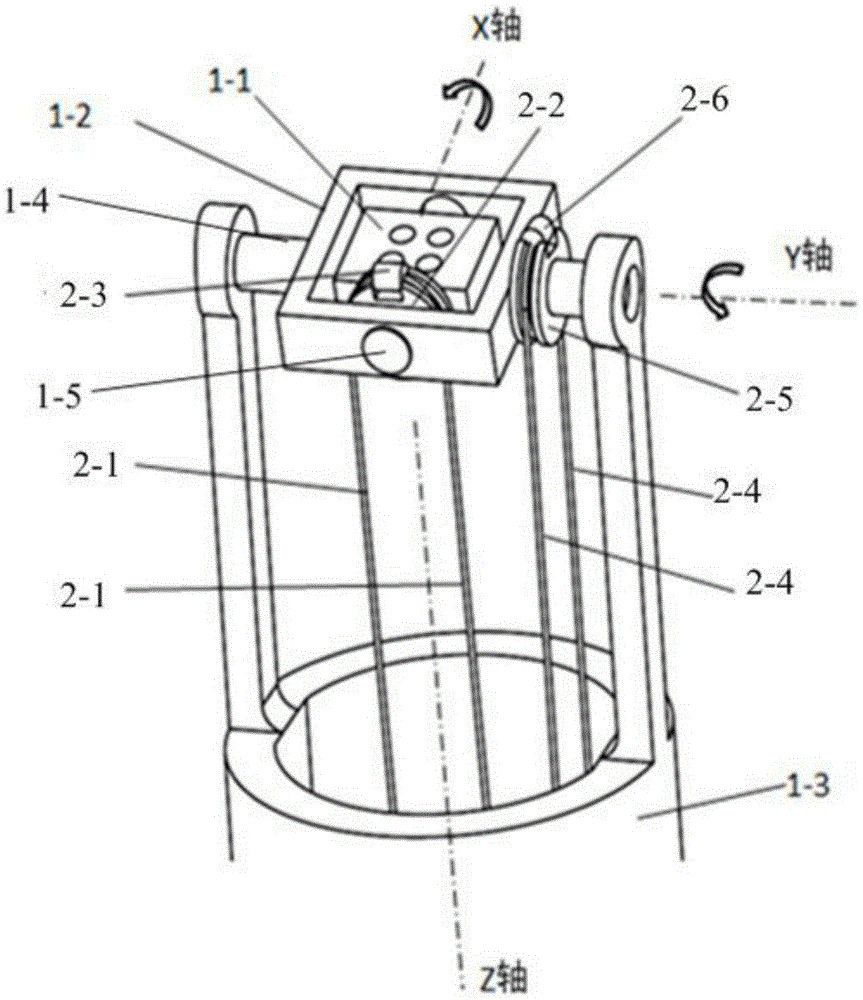
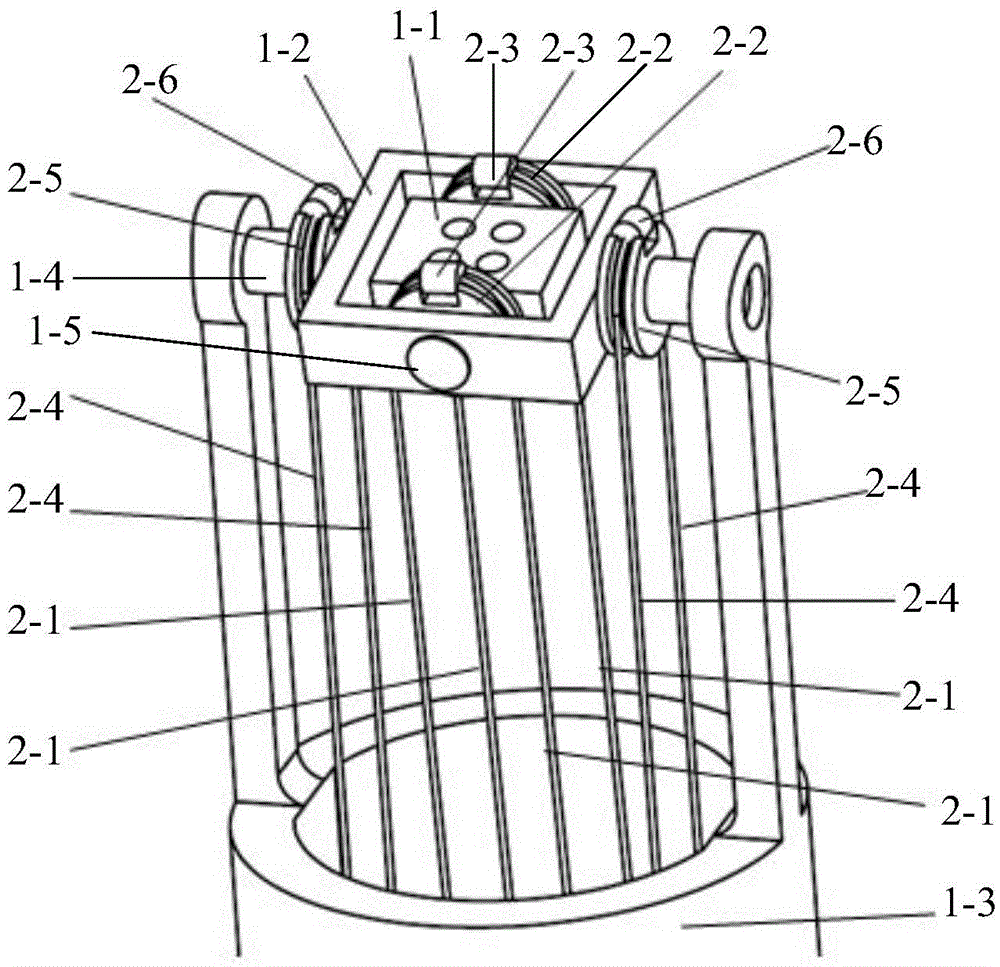
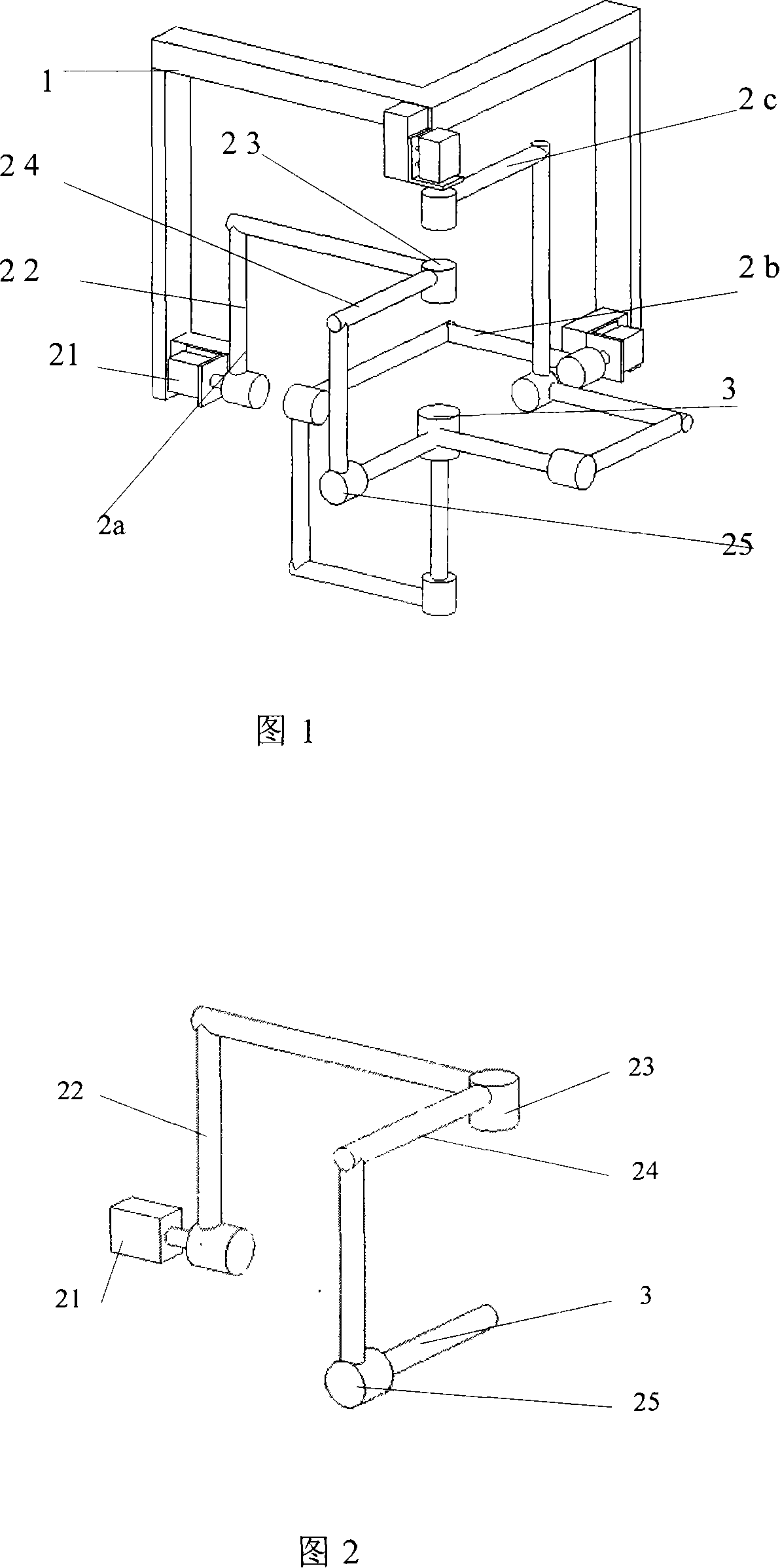
Patents
Literature
228 results about "Robot wrist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
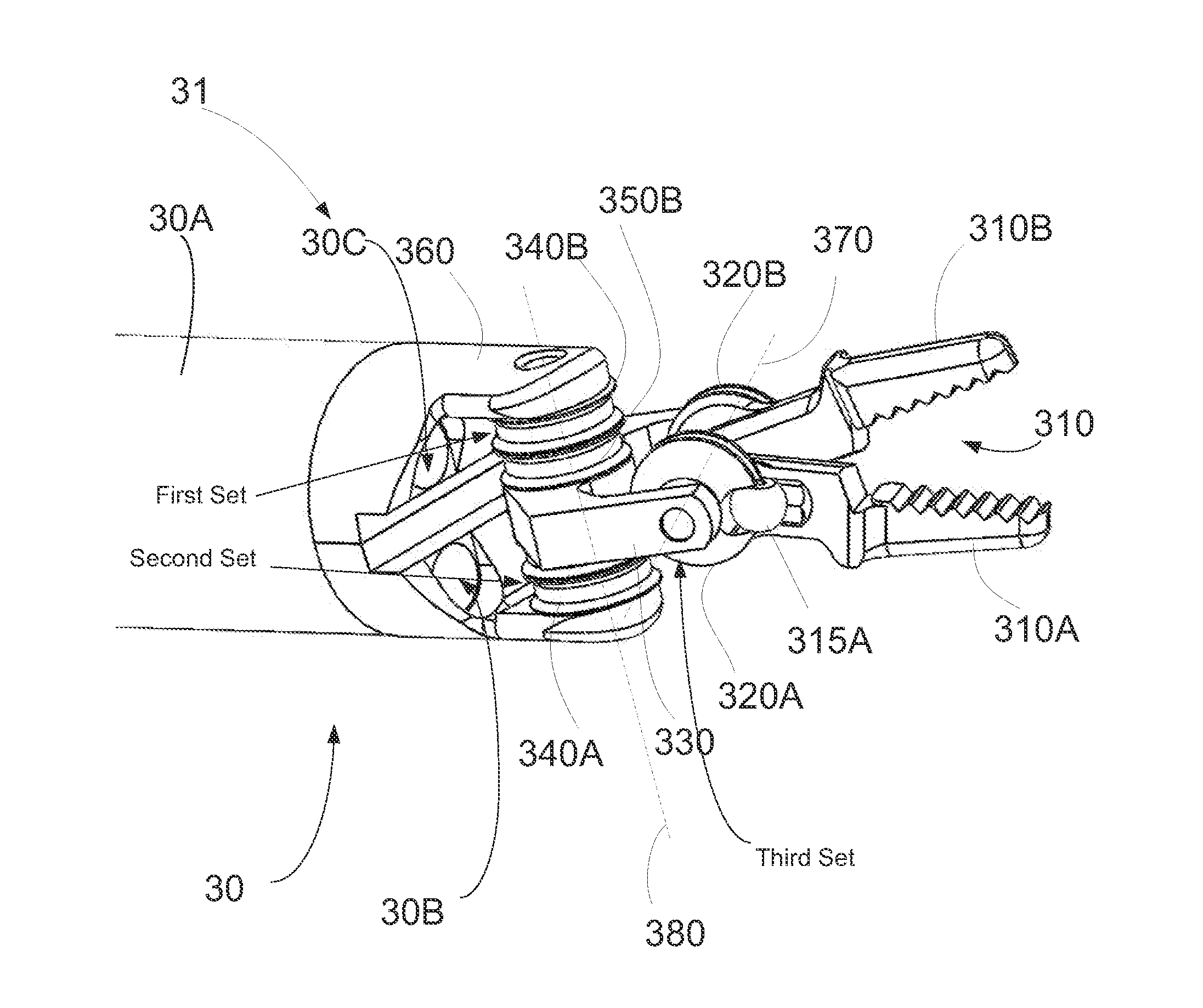
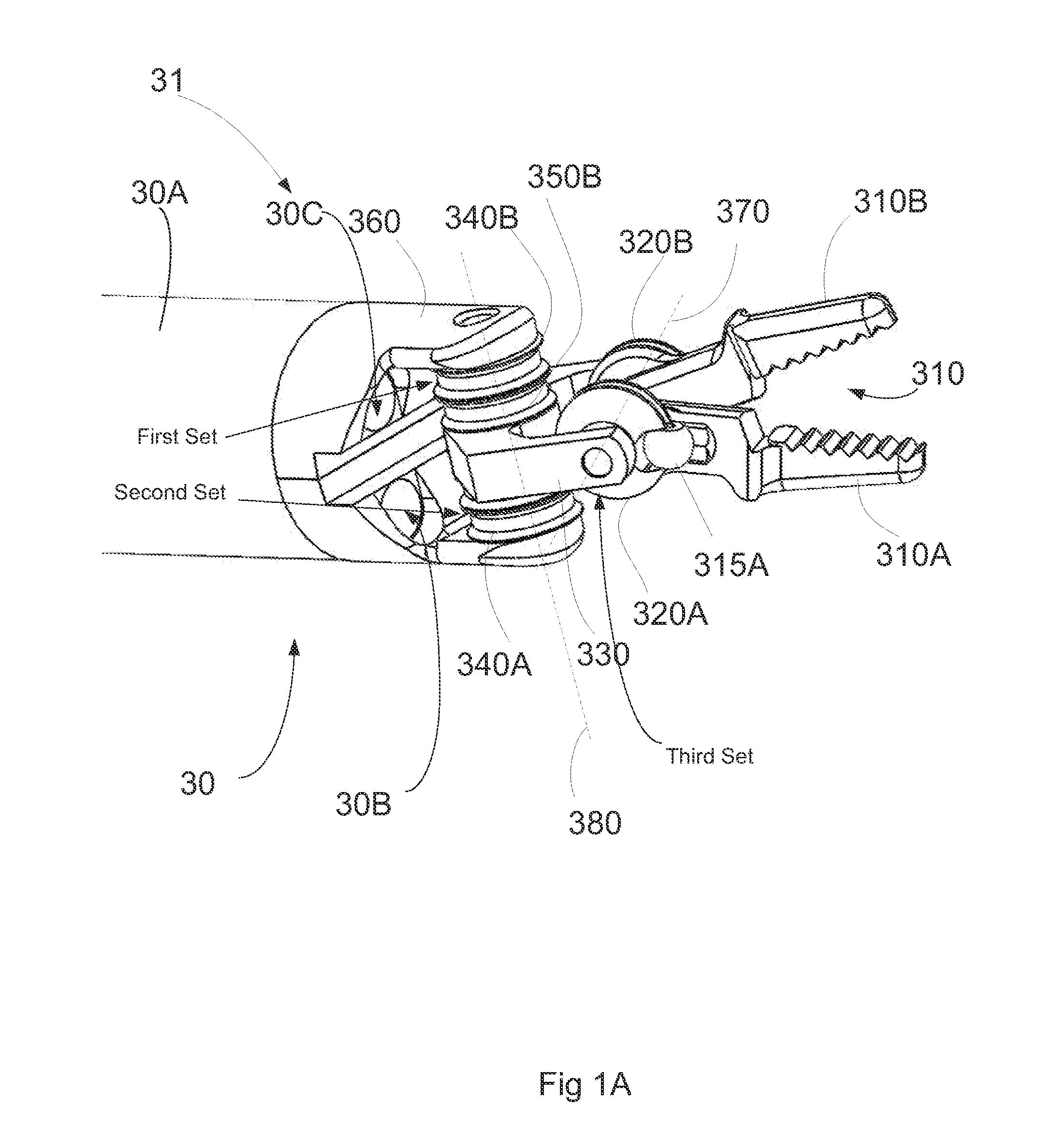
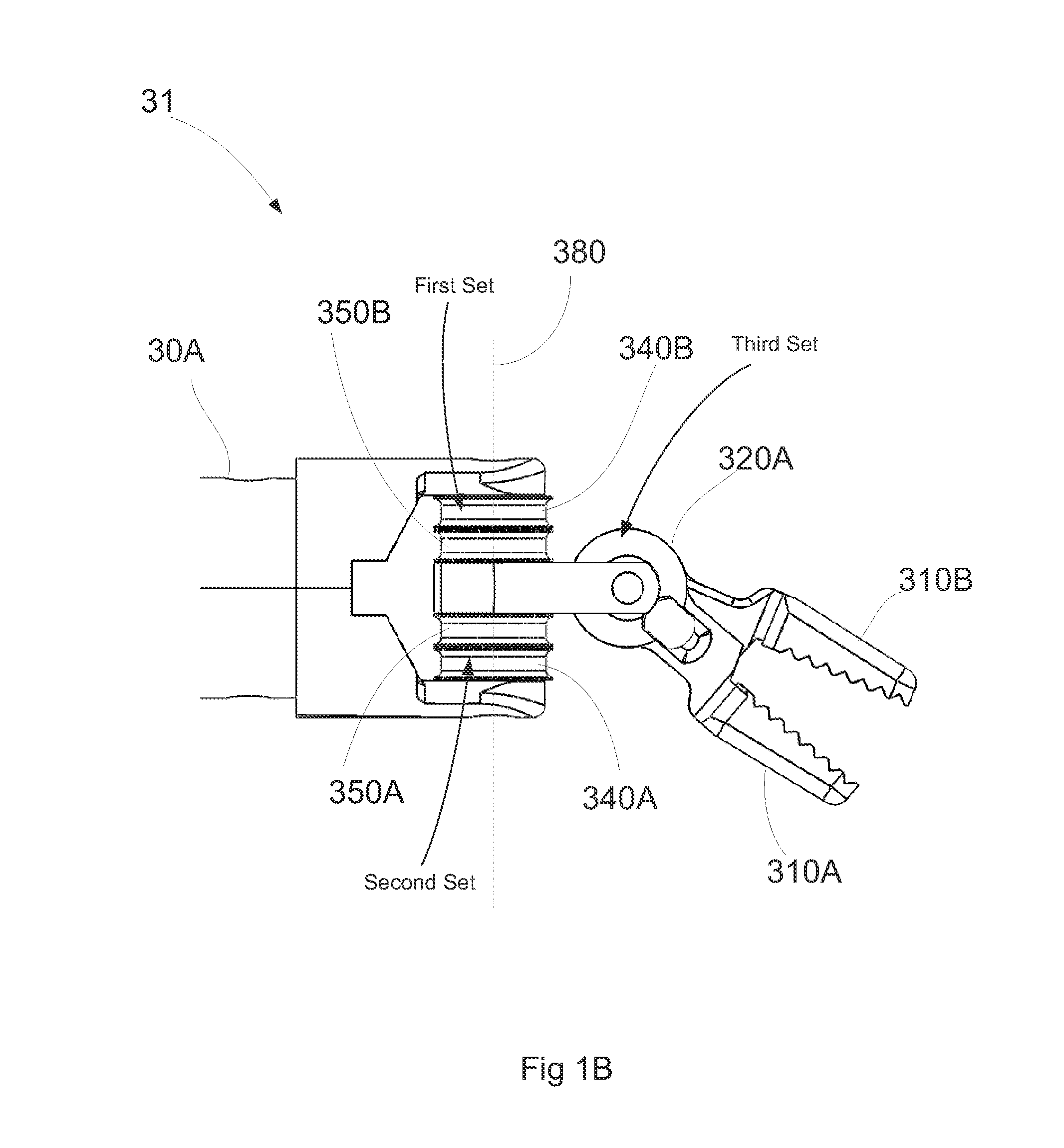
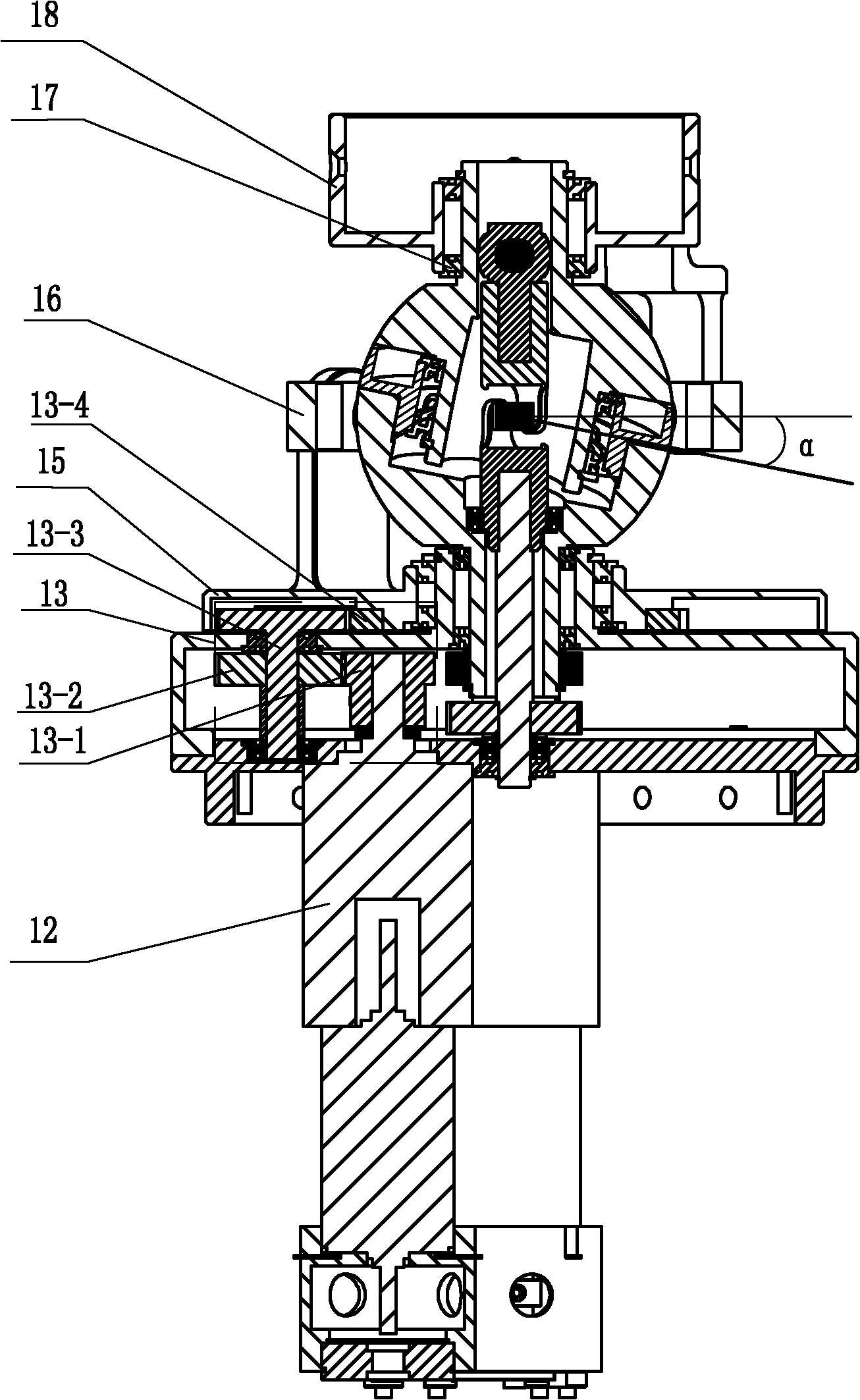
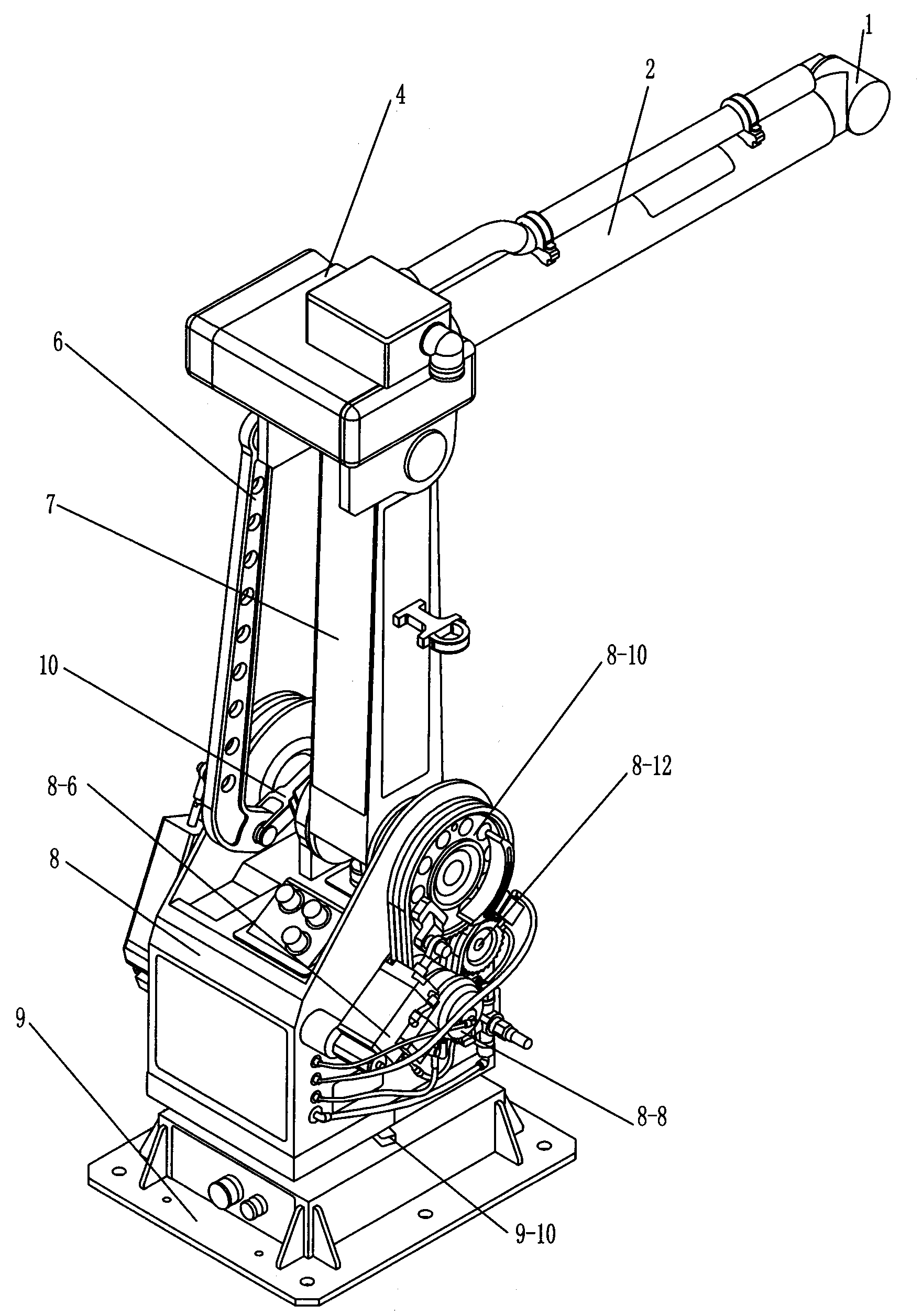
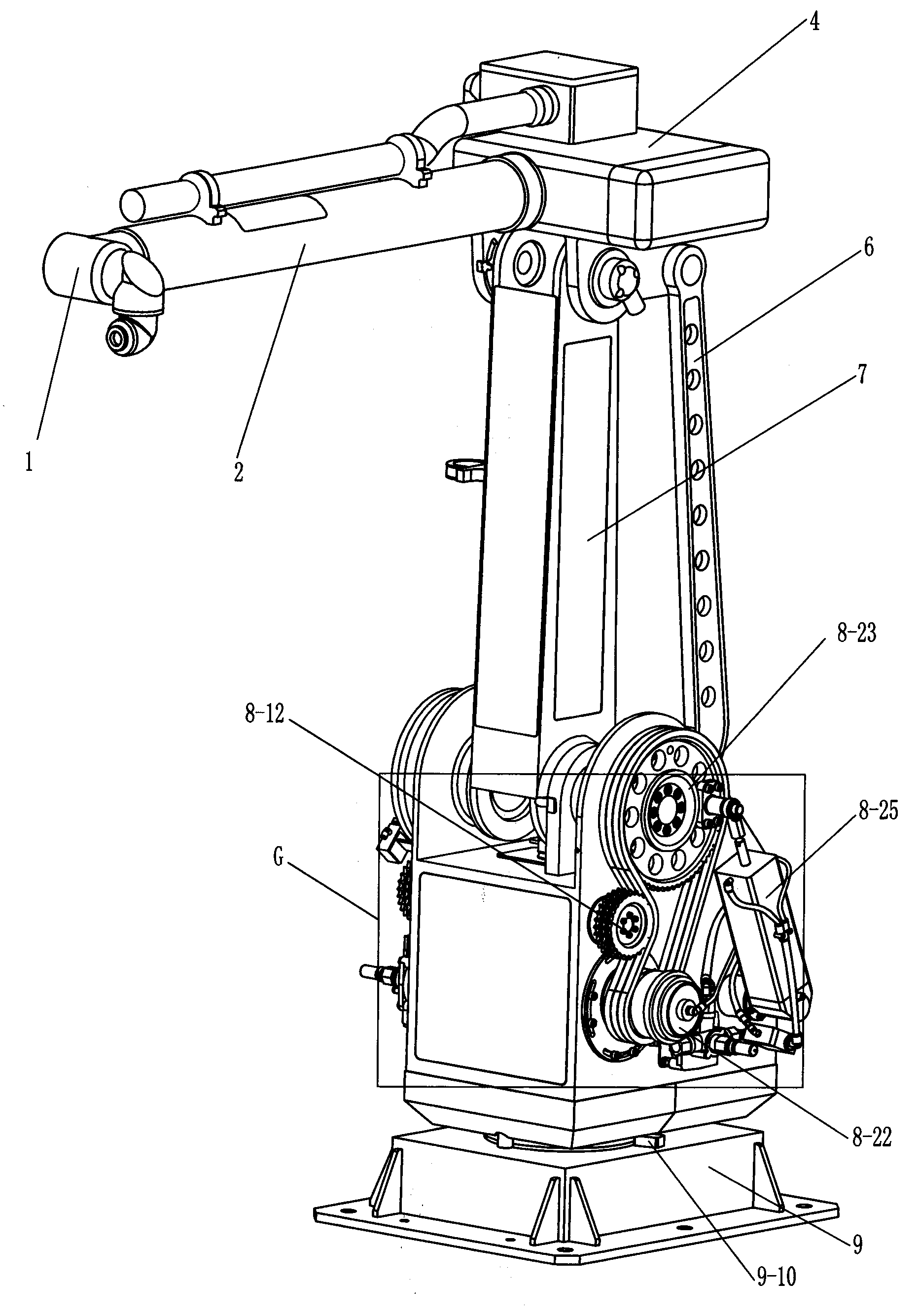
Compact robotic wrist
A surgical tool includes a tool shaft, and end effector and a wrist that couples the end effector to the tool shaft. The tool includes a drive mechanism configured to effect movement of one or both of the wrist and the end effector in yaw and pitch via independent actuation of four independent cable ends of two or more independent cables that extend between the drive mechanism and the wrist.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
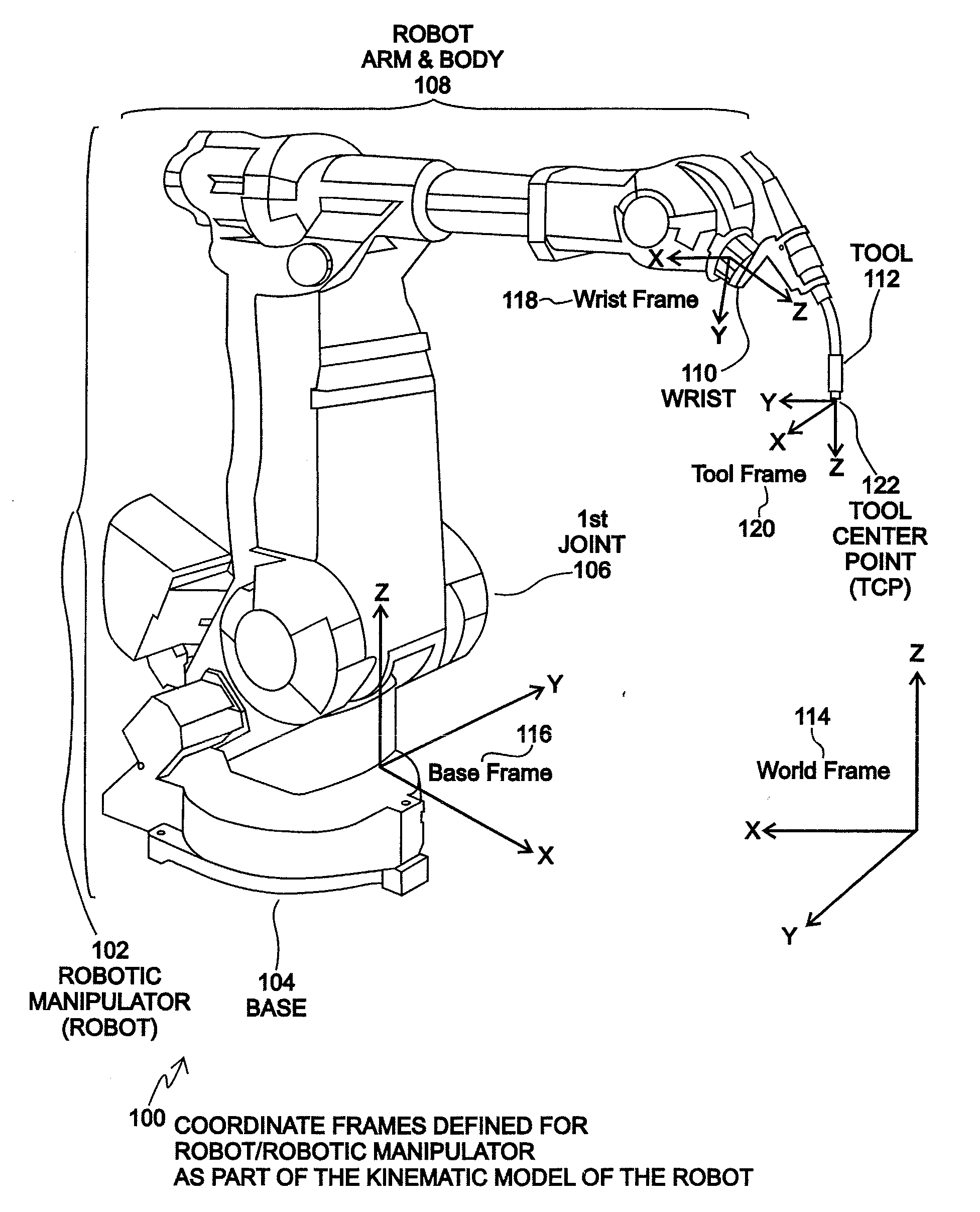
Method and system for finding a tool center point for a robot using an external camera
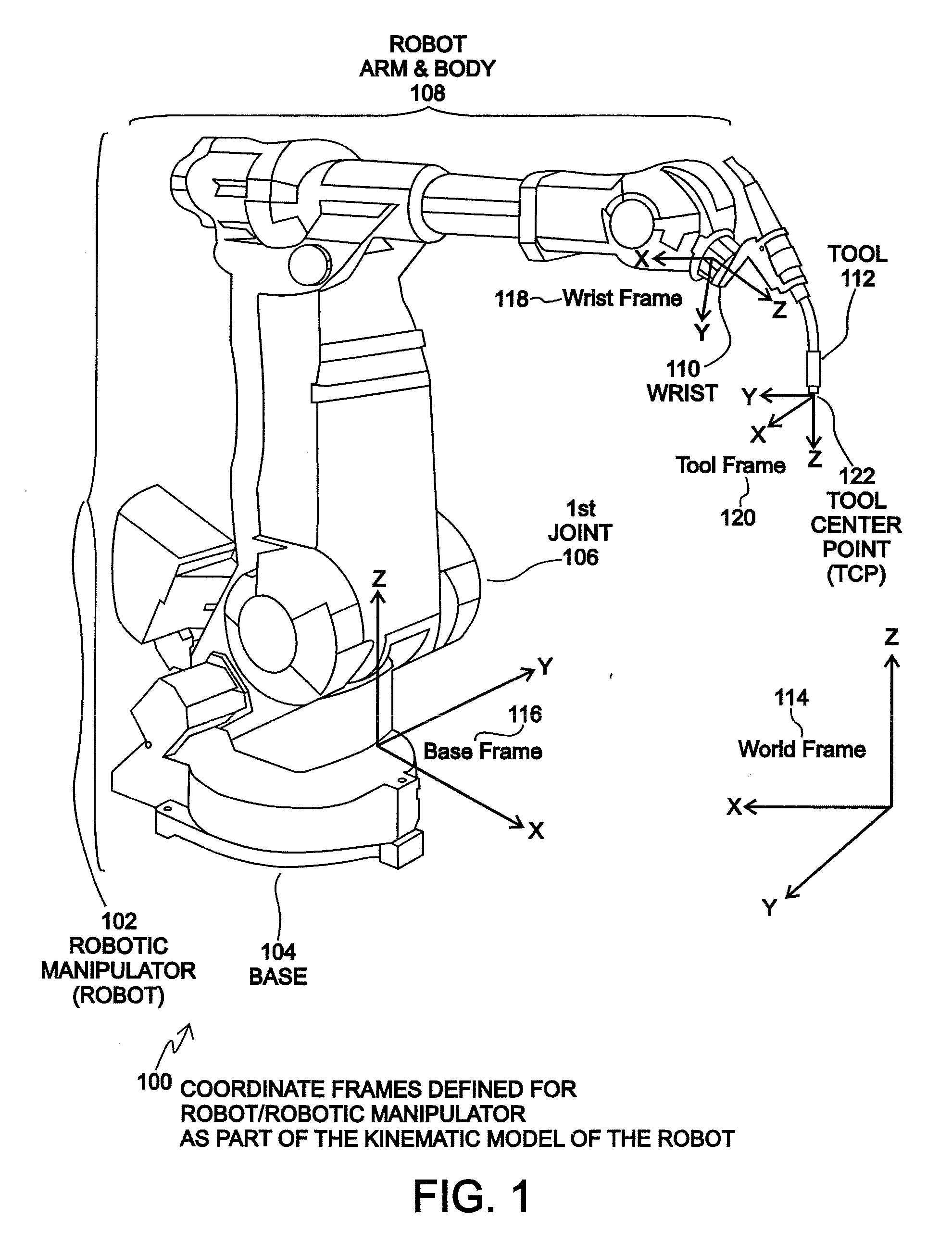
Disclosed is a method and system for finding a relationship between a tool-frame of a tool attached at a wrist of a robot and robot kinematics of the robot using an external camera. The position and orientation of the wrist of the robot define a wrist-frame for the robot that is known. The relationship of the tool-frame and / or the Tool Center Point (TCP) of the tool is initially unknown. For an embodiment, the camera captures an image of the tool. An appropriate point on the image is designated as the TCP of the tool. The robot is moved such that the wrist is placed into a plurality of poses. Each pose of the plurality of poses is constrained such that the TCP point on the image falls within a specified geometric constraint (e.g. a point or a line). A TCP of the tool relative to the wrist frame of the robot is calculated as a function of the specified geometric constraint and as a function of the position and orientation of the wrist for each pose of the plurality of poses. An embodiment may define the tool-frame relative to the wrist frame as the calculated TCP relative to the wrist frame. Other embodiments may further refine the calibration of the tool-frame to account for tool orientation and possibly for a tool operation direction. An embodiment may calibrate the camera using a simplified extrinsic technique that obtains the extrinsic parameters of the calibration, but not other calibration parameters.
Owner:RIMROCK AUTOMATION
Compact robotic wrist
ActiveUS20150209965A1Avoid excessive occlusionImprove abilitiesJointsDiagnosticsEngineeringRobot wrist
An integrated multiaxial wrist and grasper system for use in a robotic tool can yaw, pitch and grasp via actuation of four independent cable ends of four cables. The tool includes a drive mechanism that effects movement of the multiaxial wrist and grasper via actuation of the cables that extend between the drive mechanism and the wrist.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
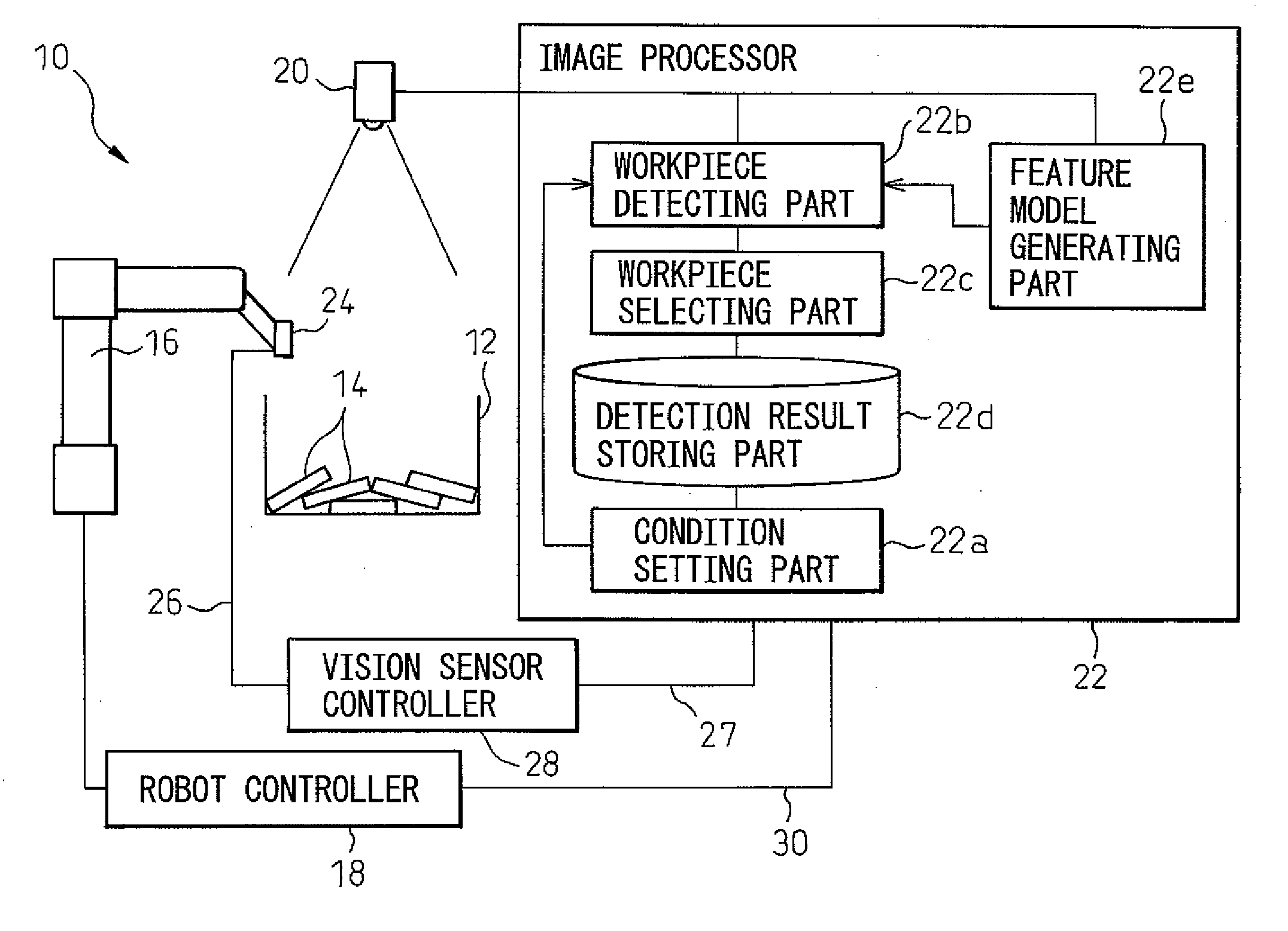
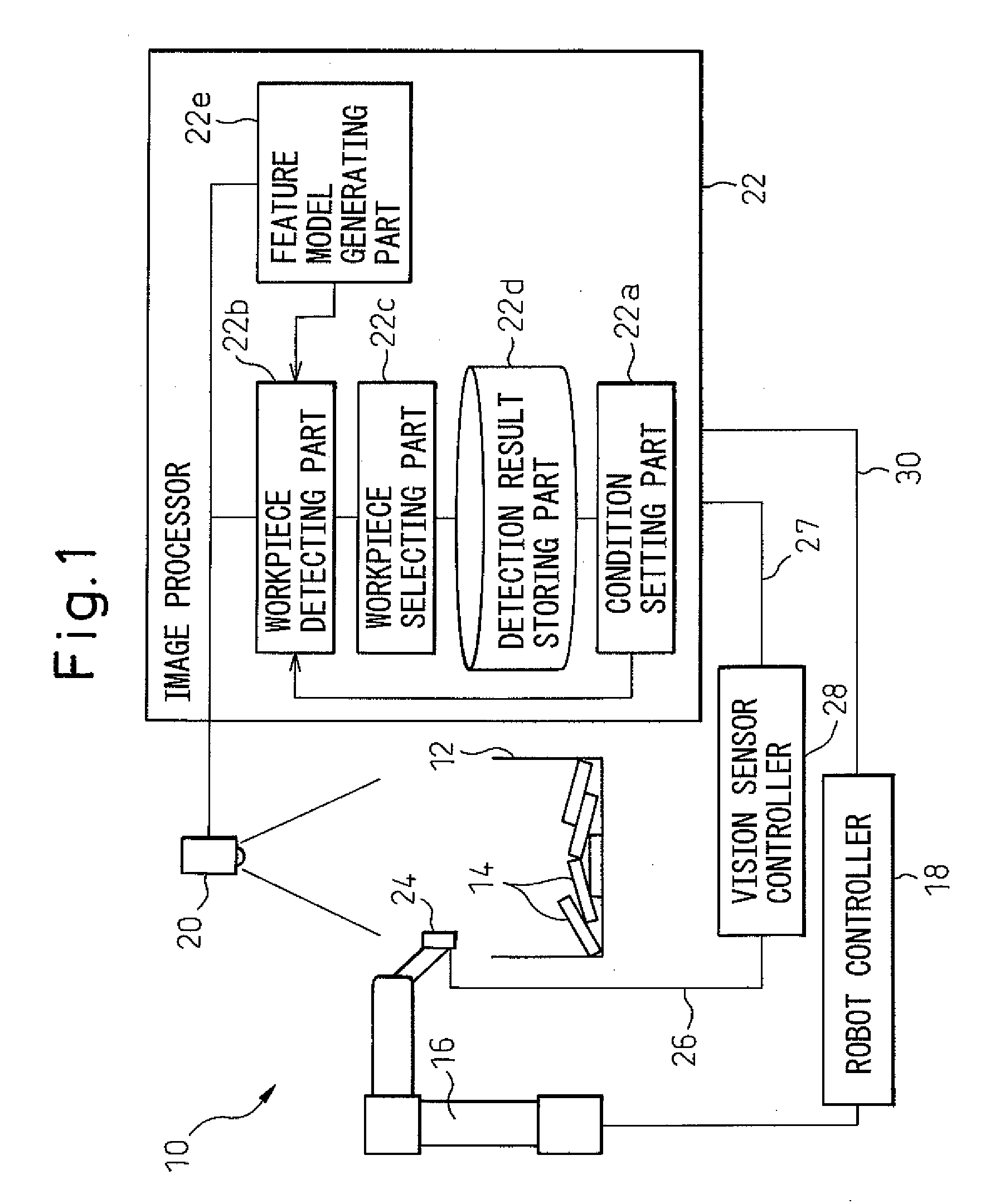
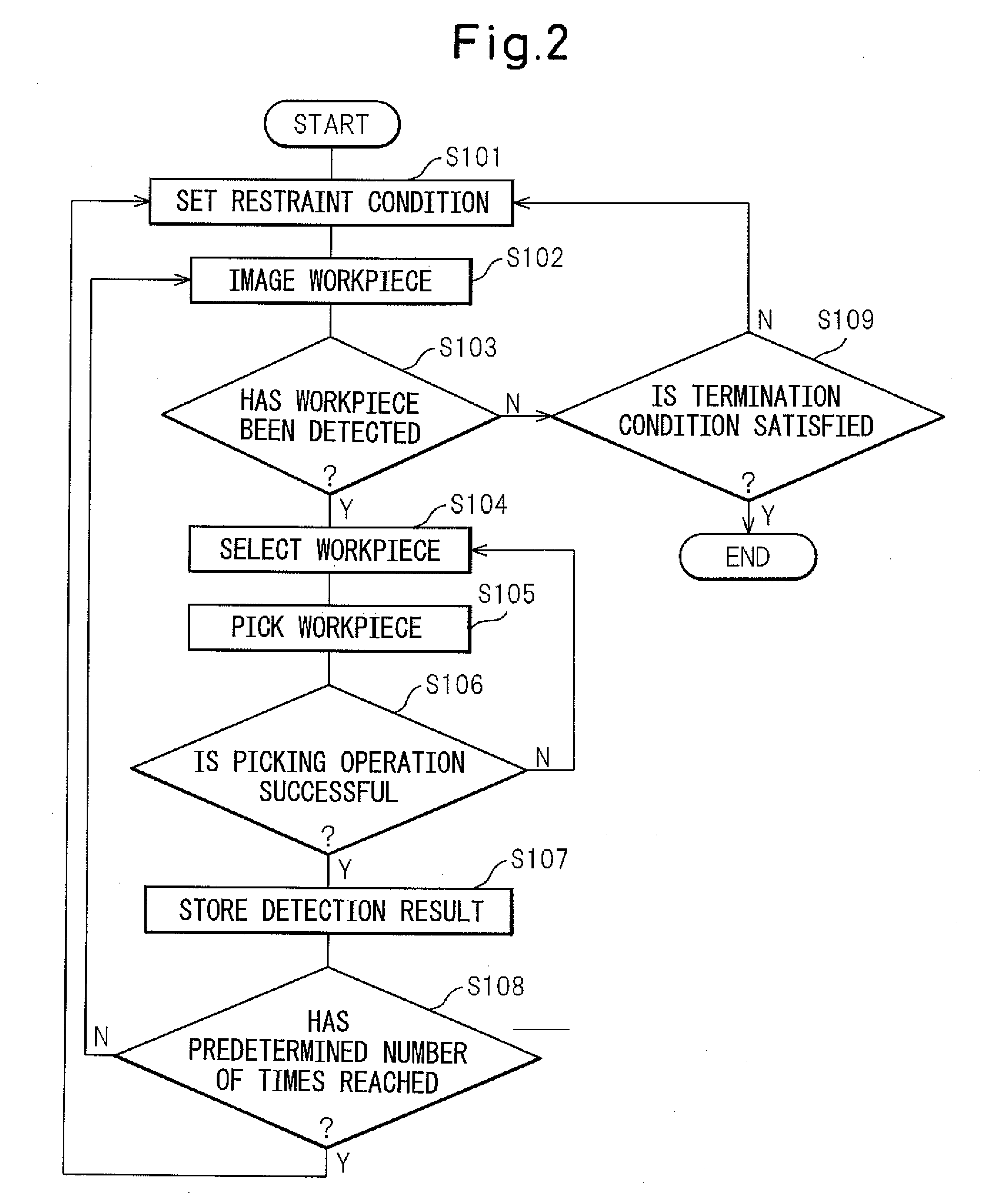
Workpiece picking device
ActiveUS20070177790A1Small sizeAccurate detectionProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorThree dimensional visionRobot controller
A workpiece picking device capable of correctly detecting the size of a workpiece. The picking device has a robot capable of picking the same kind of workpieces contained in a work container, a robot controller for controlling the robot, a video camera positioned above the work container so as to widely image the workpieces and an image processor for processing an image obtained by the video camera. The three-dimensional position and posture of each workpiece is measured by a three-dimensional vision sensor arranged on a wrist element of the robot.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Two-degree-of-freedom robot wrist
InactiveCN101927498AHighly integratedSimple structureProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsGear wheelDrive shaft
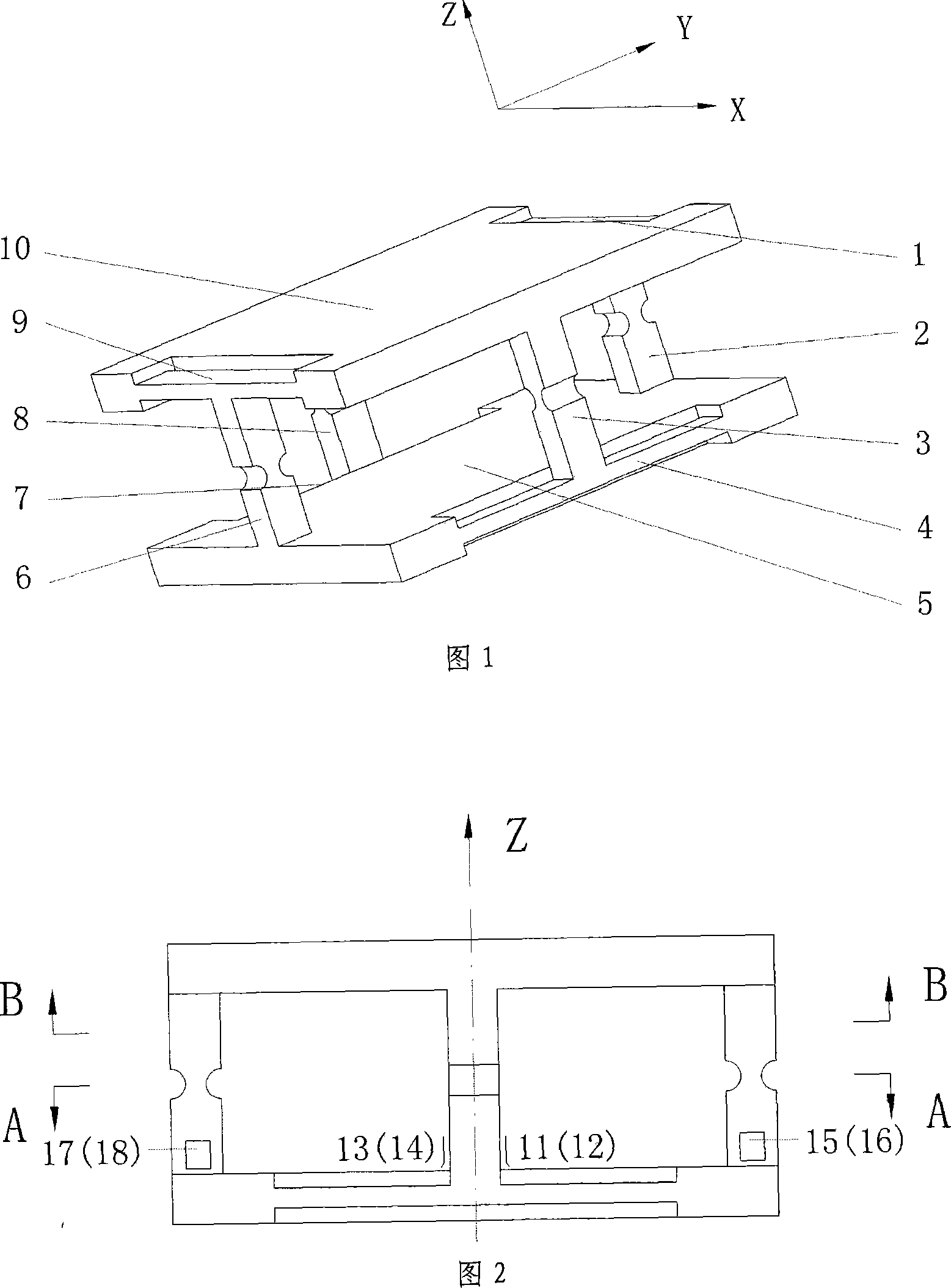
The invention discloses a two-degree-of-freedom robot wrist, which relates to a robot wrist and aims to solve the problems of complex structure, heavy weight, high control difficulty and low integration level existing in the conventional robot wrist. One of two input bases of a torque sensor is connected with a first driven bevel gear of a differential mechanism while the other is sleeved on a driven shaft of the differential mechanism; a support block is arranged on a bracket bottom plate of a support bracket; the differential mechanism is supported by the support block and two support arms of the support bracket; a driving frame is connected with the support bracket through a pre-tightening mechanism; first and second drivers are fixed on the driving frame and have opposite transmission directions; the first and second drivers are in transmission connection with first and second driving half shafts of the differential mechanism through first and second toothed belt transmission mechanisms; first and second position sensors are arranged on the first driving half shaft of the differential mechanism; and a tail end circuit board is fixedly arranged on an output base of the torque sensor. The robot wrist has the advantages of simple structure, light overall weight, easy control, high integration level and wrist pitching and deflection degrees of freedom.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist
InactiveCN102029614AEasy to adjust directionAchieve large-angle rotationJointsSpherical spaceThree degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist and relates to a robot wrist. The three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist solves the problems of complex structure, low integrated level, large own weight and coupling motion of the three-degree-of-freedom robot wrist. In the three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist, an upper semisphere shaft is rotationally connected with an interface of an end effector; an upper semisphere is rotationally connected with a lower semisphere; the contact surface of the upper semisphere and the lower semisphere is an offset inclined plane; the angle between the offset inclined plane and the horizontal plane is 10 to 25 degrees; an upper semisphere motor and a speed reducing mechanism are fixedly connected with a universal joint shaft through an upper semisphere gear transmission mechanism; the universal joint shaft is fixedly connected with the upper semisphere shaft through an internal universal joint; the upper semisphere shaft is rotationally connected with the interface of the end effector; a lower semisphere motor and the speed reducing mechanism are fixedly connected with a lower semisphere shaft through a lower semisphere gear transmission mechanism; a rotation motor and the speed reducing mechanism are fixedly connected with a turnplate through a rotation gear transmission mechanism; and the turnplate is in transmission connection with the interface of the end effector through an external universal joint. The three-degree-of-freedom spherical space robot wrist is applied to aerospace robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
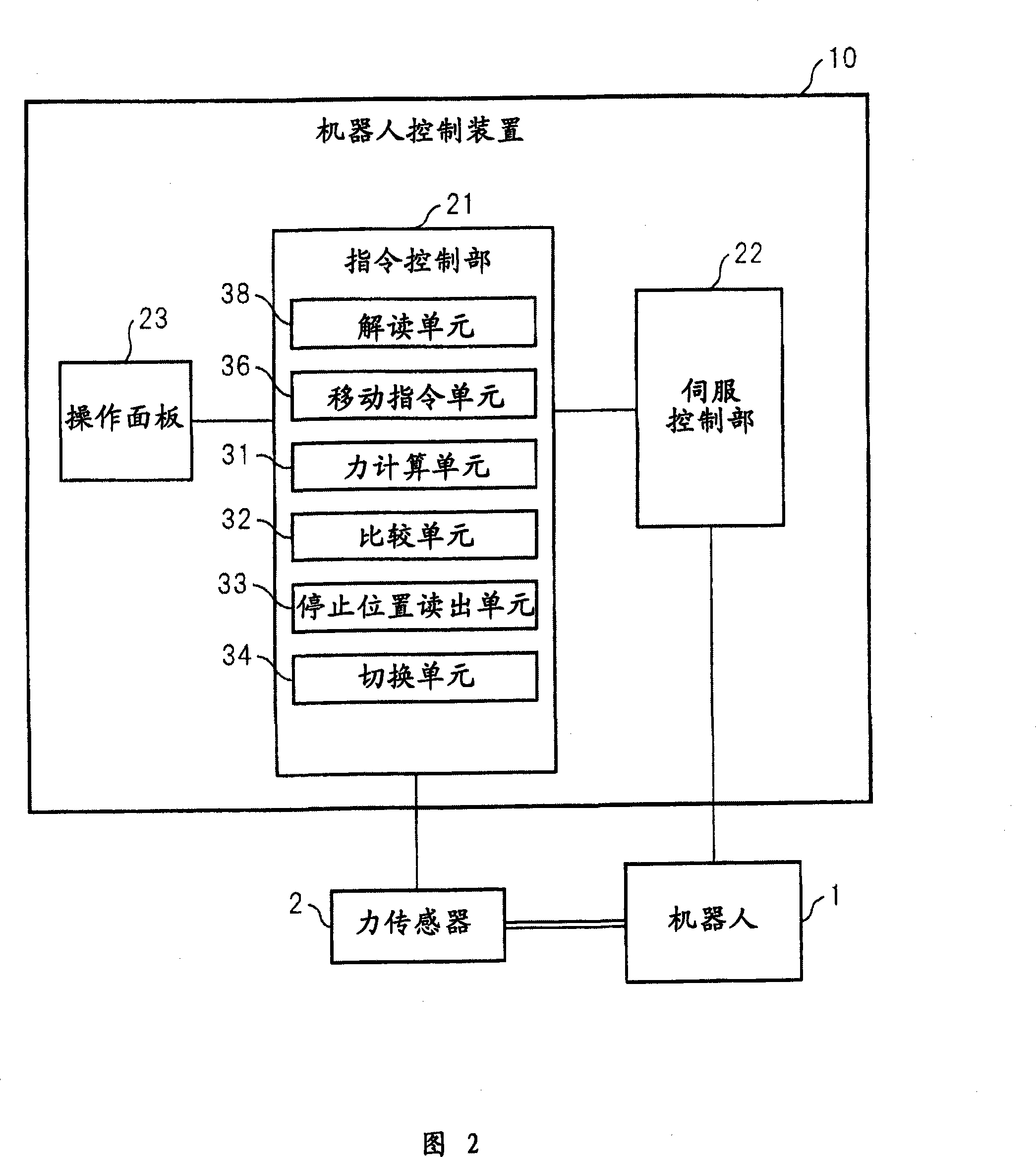
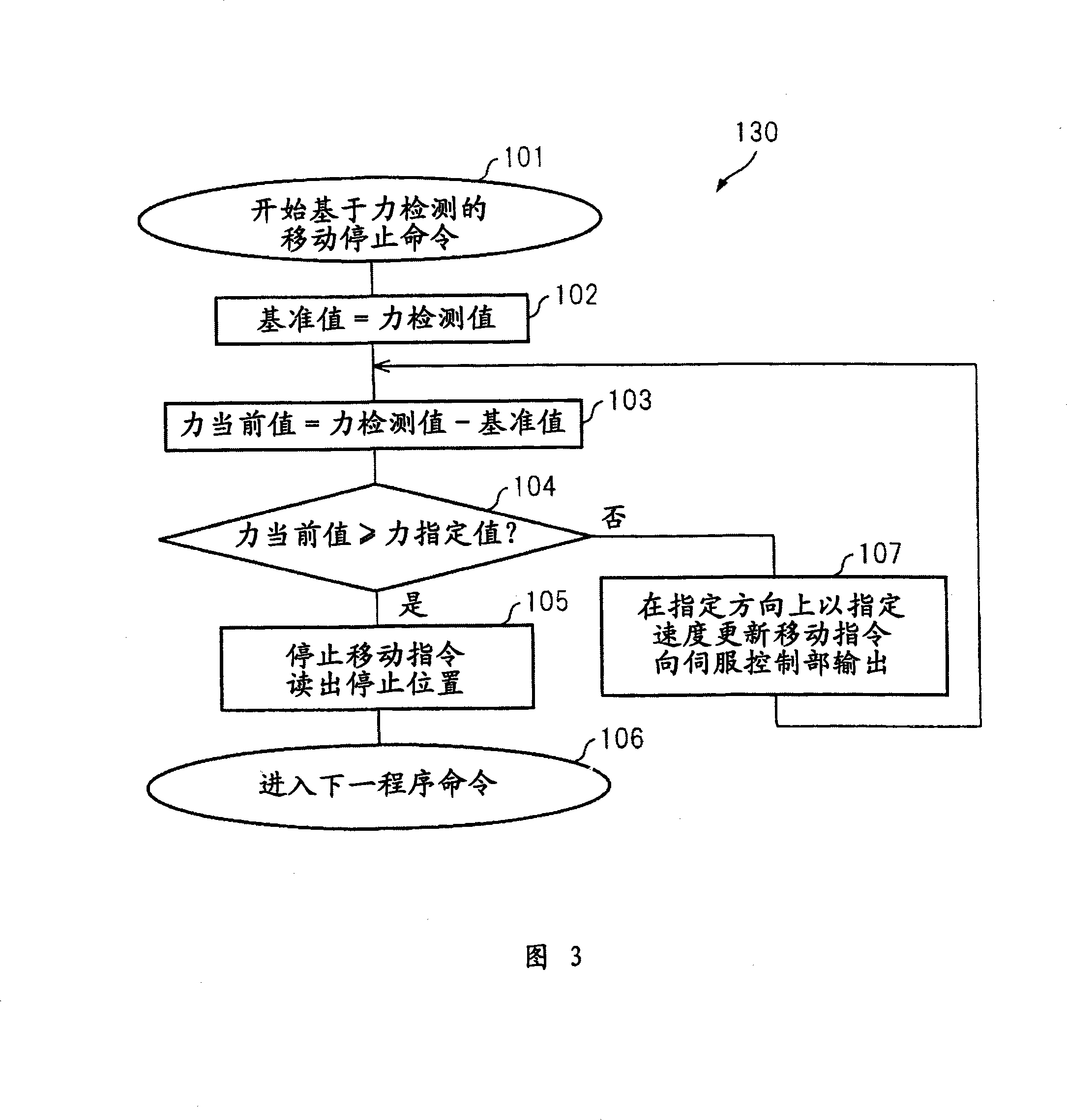
Robot control device
InactiveCN101239467AHigh precisionProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorInstruction unitRobot control
The present invention relates to a robot control device, which has a designated speed adjustment unit that adjusts the designated speed included in the program to be lower than the designated speed, and further includes: an interpretation unit that interprets the speed based on the detection value of the force sensor attached to the wrist of the robot. The movement stop command that stops the movement of the robot; the movement instruction unit generates a movement instruction that causes the robot to move in the direction specified by the program at the specified speed contained in the program, and the specified speed adjustment unit does not work; the force calculation unit generates the movement command when the robot starts to move The detection value of the force sensor is used as a reference value, and the change from the reference value is calculated as the current value of the force; the comparison unit, during the movement of the robot, repeatedly calculates the current value of the force calculated by the force calculation unit within a predetermined period and the predetermined force designation value comparison. When the force current value exceeds the specified force value, the movement command unit stops the robot. This makes it possible to detect an external force on the robot with high sensitivity and stop the robot with high precision.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Articulated robot wrist
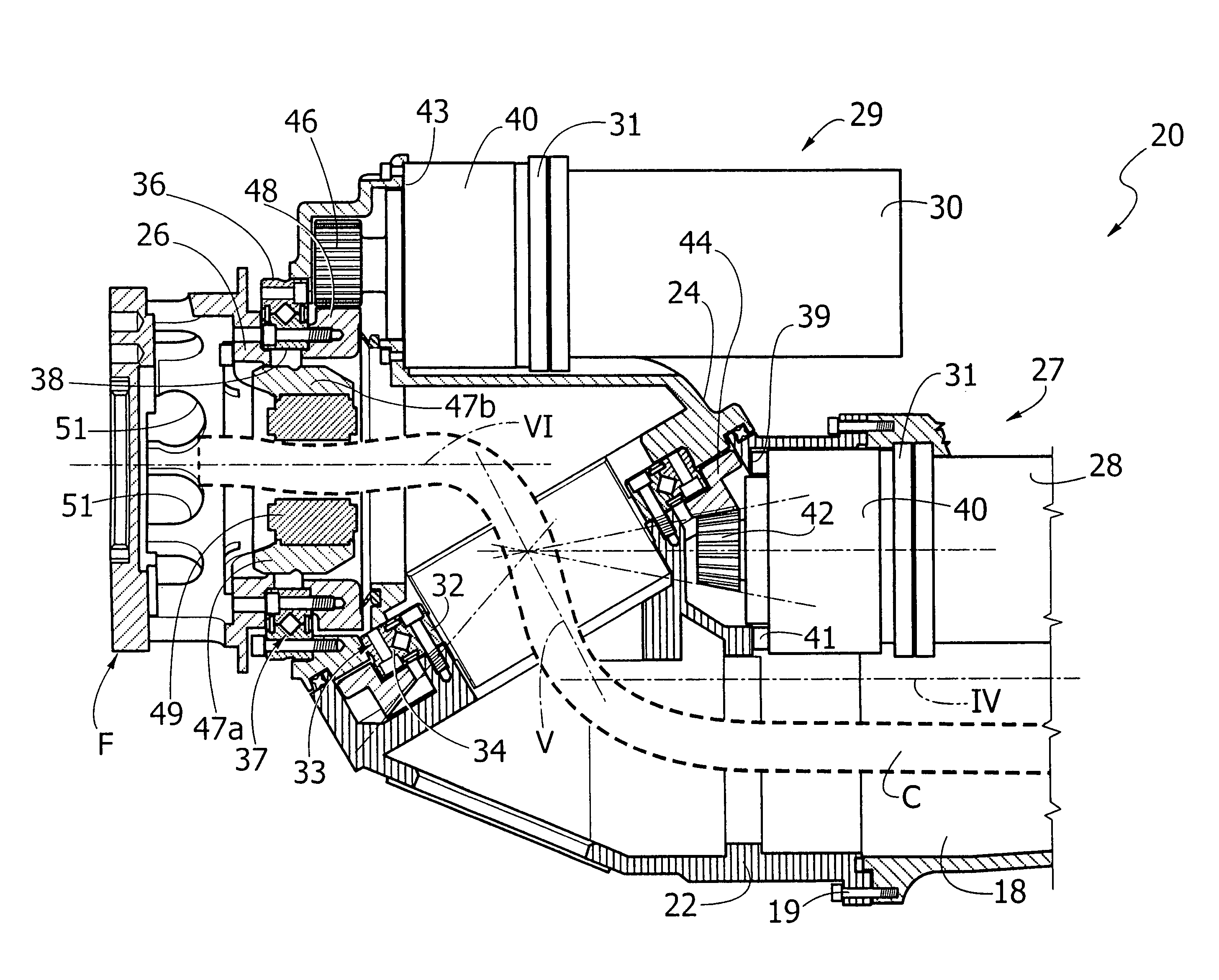
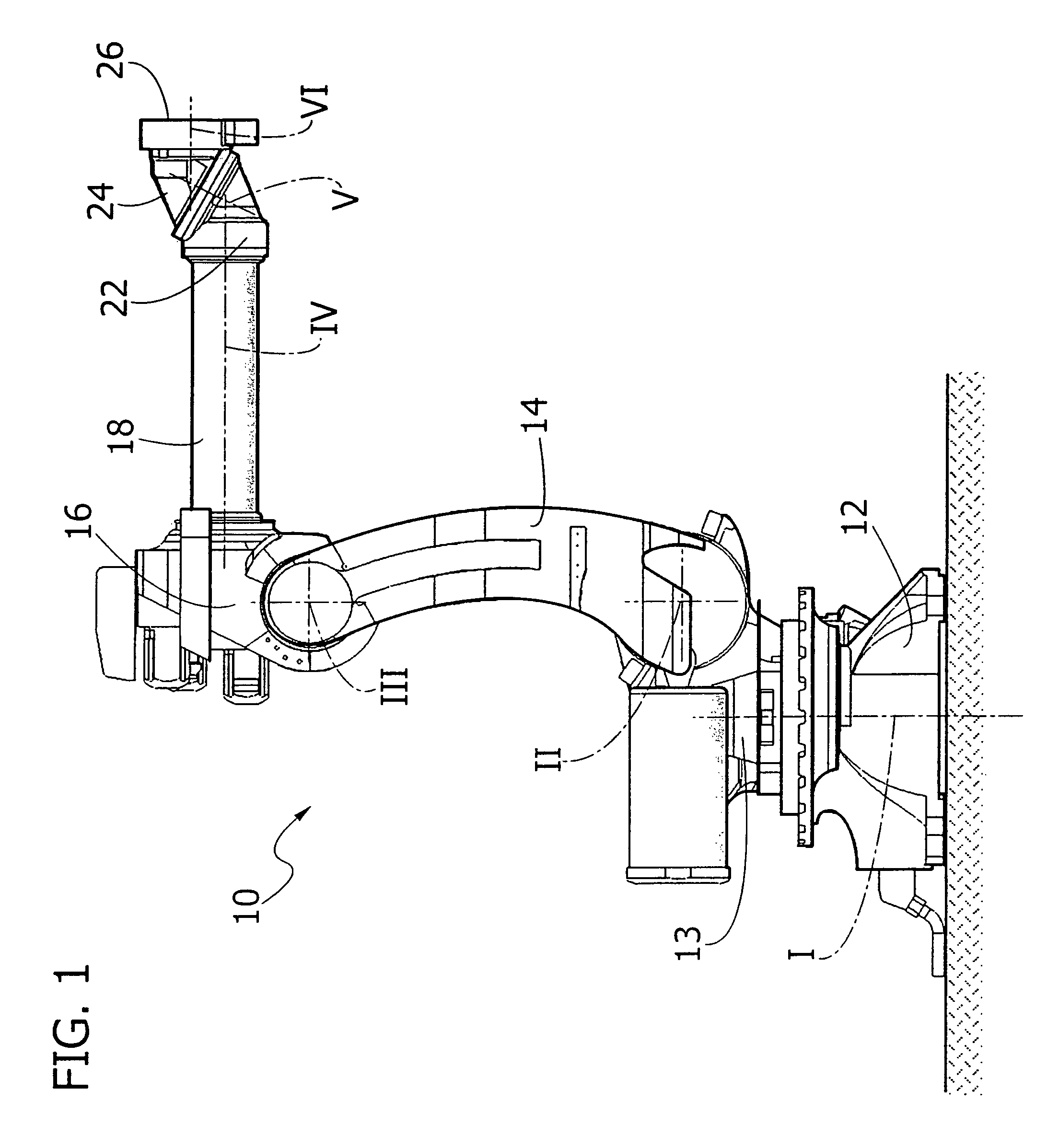
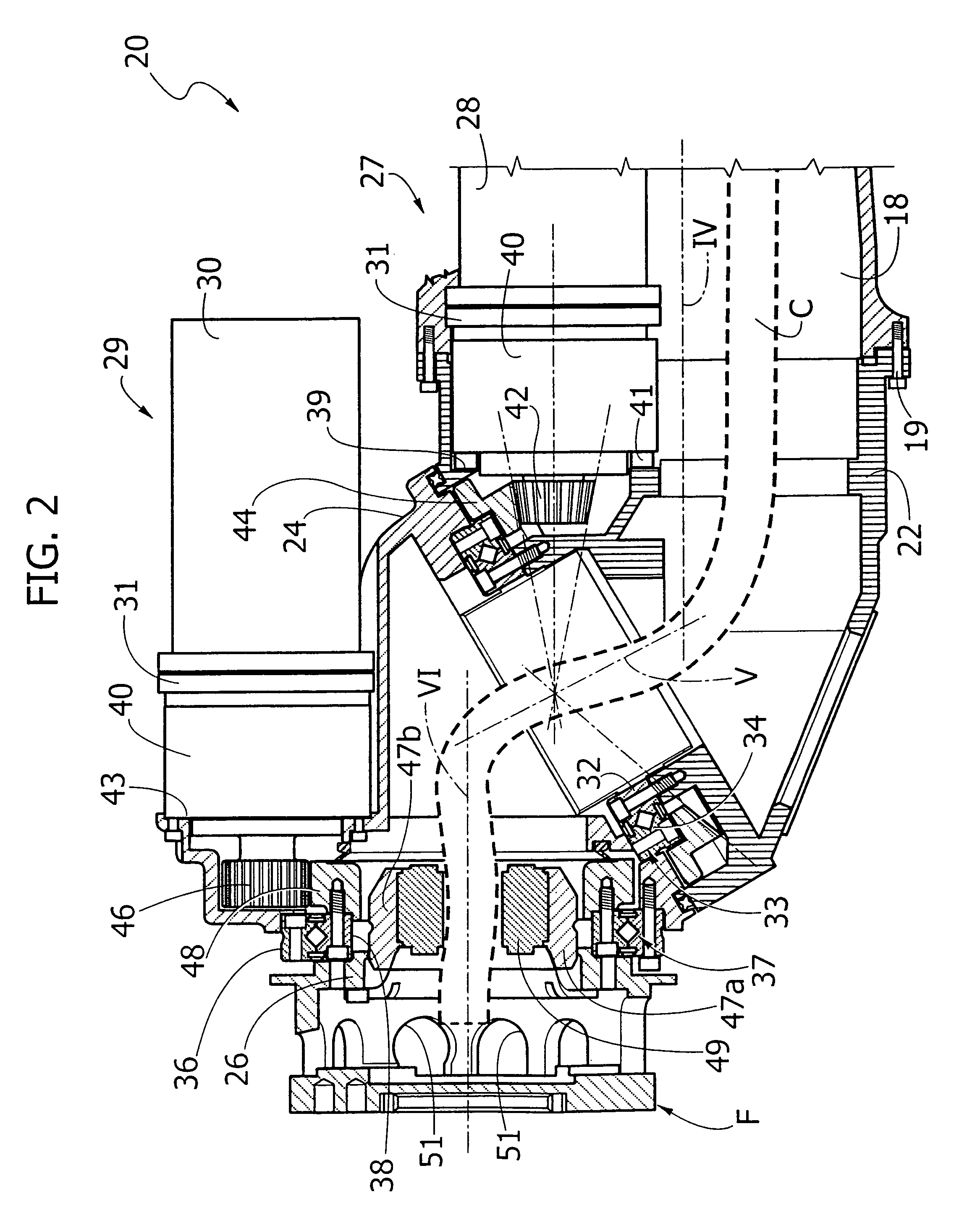
An articulated robot includes a wrist carrying a flange for attachment of an apparatus to be carried by the robot. The wrist comprises a first support mounted on a robot component that is rotatable about a first axis, a second support rotatably mounted on the first support about a second axis inclined with respect to the first axis, and a third support rotatably mounted on the second support about a third axis, inclined with respect to the second axis. A first motor carried by the first support drives the rotation of the second support, and a second motor carried by the second support drives the rotation of the third support, which ends with the flange for attachment of the apparatus to be carried by the robot.
Owner:COMAU SPA
Methods and apparatus for a robot wrist assembly
ActiveUS20080063504A1Extend your lifeLow thermal conductivityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention provides methods, apparatus, and systems for a wrist assembly including a housing having a cap and a bottom, at least one pivot at least partially enclosed in the housing and adapted to be coupled to a robot arm, and a belt coupled to the pivot and adapted to rotate the pivot about a bearing. The bottom of the housing is adapted to reflect heat away from the at least one pivot and the bearing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Articulated robot wrist
Described herein is an articulated robot wrist, comprising: a first support, which is to be mounted on a robot component that is rotatable about a first axis; a second support, mounted on said first support in a rotatable way about a second axis inclined with respect to said first axis; a first motor, carried by said first support, the shaft of which is connected in rotation to said second support via a first gear transmission; a third support, mounted on said second support in a rotatable way about a third axis, inclined with respect to said second axis; and a second motor, carried by the second support, the shaft of which is connected in rotation to said third support via a second gear transmission.
Owner:COMAU SPA
Managing structure for umbilical member of industrial robot
InactiveUS20060101936A1Easy to changeAvoid high pressureMechanical apparatusJointsRobotic systemsReduction drive
A managing structure, for an umbilical member for a work tool of a robot, capable of stabilizing the motion of the umbilical member during the operation of a wrist of the robot and making the work of modifying the system of the robot easier. The umbilical member is introduced into an opening formed at the back of a base of a forearm. The umbilical member extends through a hollow portion of a speed reducer and is drawn from a first opening formed on the side of a first wrist element. A cable for welding current and a tube for supplying shield gas, constituting the umbilical member, are directly connected to a welding torch rotatable about a third axis. A welding wire is guided and fed by a feed roller of a wire feeder and, then, is connected to the welding wire with the cable and the tube. The feed roller is driven by a motor contained within the first wrist element.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Robot wrist comprising a drive unit incorporated in a tilt
InactiveUS20060182595A1Small sizeReduce weightProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsControl theoryRobot wrist
A robot wrist for an industrial robot. A wrist housing and a wrist part, designated a tilt, are journalled at the wrist housing. The tilt is rotatable relative to the wrist housing about an axis of rotation and includes a drive unit including a motor with a motor housing. A shell part of the motor housing is designed to connect the tilt to the wrist housing.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method For Controlling A Robot Tool Center Point
InactiveUS20090074979A1Uniform thicknessCarry-out quicklyProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlProgram planningEngineering
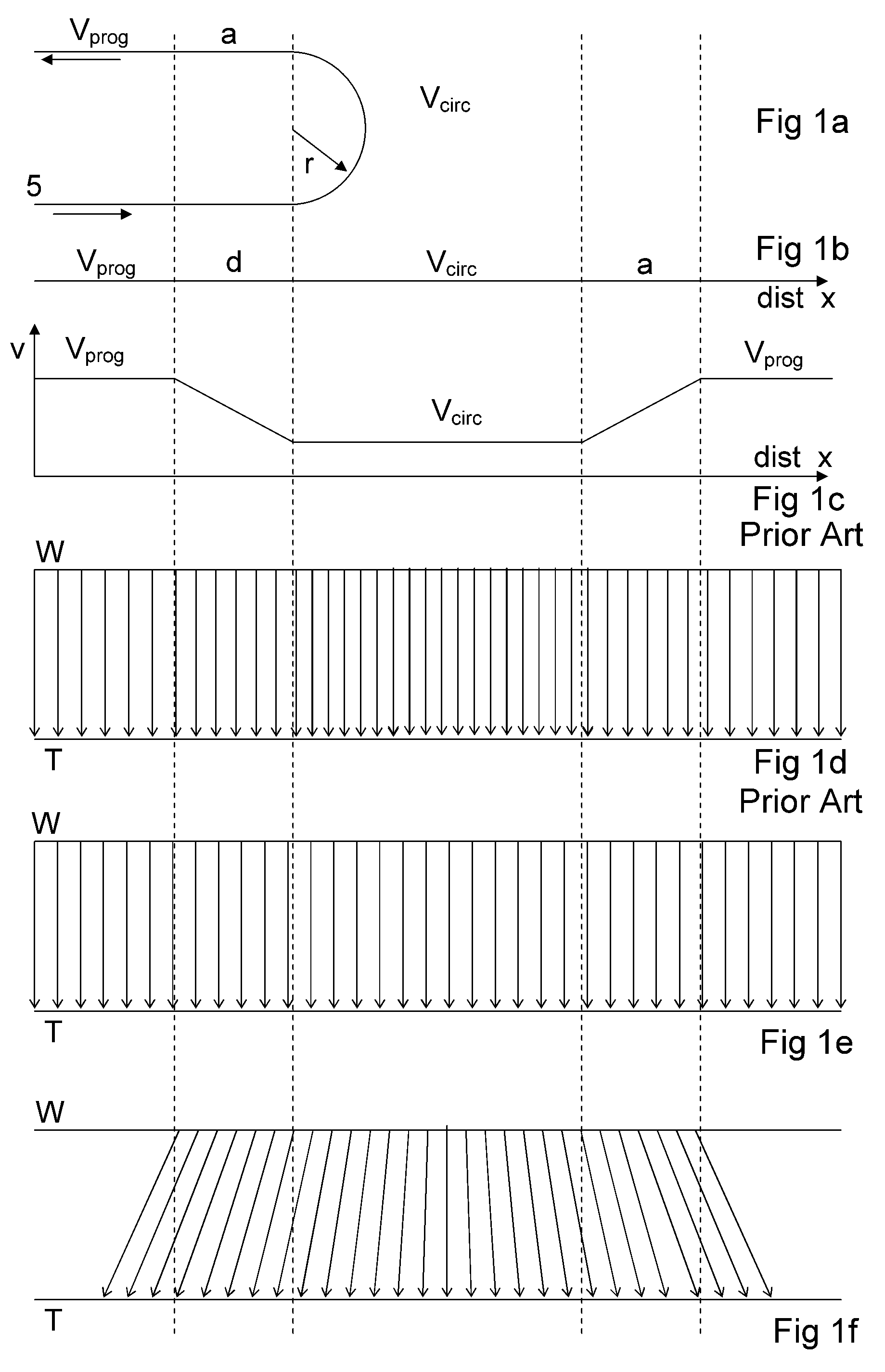
A method for controlling a painting system including an industrial robot or manipulator arm arranged with a wrist section and carrying a paint applicator arranged on the robot wrist is described. Paint is applied by the applicator to a substantially circular or elliptical area on the surface, the center of the area being defined as a Tool Center Point. The wrist section is arranged capable of moving and orienting the paint applicator. In the method, the paint applicator is moved by the manipulator arm so that the Tool Center Point moves along a planned path so coating a part of the surface. The planned path may include one or more bends. The path taken by the robot wrist may be controlled to follow a different path from the path taken by the Tool Center Point. A system and a computer program for carrying out the method are also described.
Owner:ABB AS
Wrist driving structure for industrial robot
ActiveCN101121264ASmall footprintOccupy space to achieveProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusGear driveGear wheel
A wrist driving structure for an industrial robot having: a first wrist element supported in cantilever fashion rotatably about a first axis; a second wrist element pivotally supported in cantilever fashion at a distal end side of the first wrist element with a proximal end as a supporting point about a second axis intersecting the first axis; a third wrist element supported in cantilever fashion at a distal end side of the second wrist element rotatably about a third axis intersecting the second axis; two driving motors provided in the first wrist element for driving the second wrist element and the third wrist element, respectively; and two gear sets for reducing a rotational speed of the two driving motors in predetermined reduction ratios. Each of the gear sets has a driving gear driven by one of the two driving motors and a driven ring gear which meshes with the driving gear. Two driven ring gears of the two gear sets are disposed coaxially with the second axis. Two driving gears of the two gear sets are positioned parallel to each other at both sides of the second axis.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Three-freedom-degree parallel robot wrists with aligning mechanisms
The invention relates to three-freedom-degree parallel robot wrists with aligning mechanisms. Each three-freedom-degree parallel robot wrist comprises a base, a mobile platform, three movement branched chains with the aligning mechanisms, three spherical pair structures and three power sources, wherein the three movement branched chains with the aligning mechanisms are movably connected with the mobile platform respectively; the three power sources directly drive the movement branched chains to enable the mobile platform to do three-freedom-degree movement; and particularly, as each aligning mechanism is arranged in the middle of each movement branched chain of each robot wrist, the positions of axial lines of three revolute pairs in the middle are adjusted conveniently, and the axial lines of the revolute pairs are enabled to intersect at one point as required, so that processing and assembling errors are reduced, and operation accuracy of each robot wrist is improved. The three-freedom-degree parallel robot wrists are easy in processing and assembling, flexible in movement, compact in structure and good in rigidity, and can be applied to parallel robots, micro-motion robots and other robots.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for automatically tracking unilateral sewing laser visual sense paths of composite material three-dimensional structural member
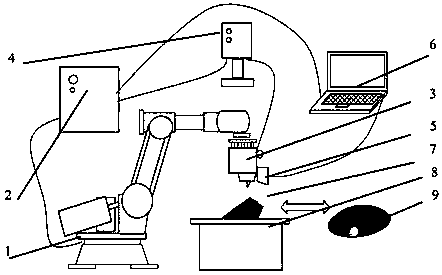
ActiveCN109591011ARapid positioningImprove calibration efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorProgramme-controlled sewing machinesLaser lightVisual perception
The invention discloses a method for automatically unilateral sewing laser visual sense paths of a tracking composite material three-dimensional structural member. The method comprises the following steps of performing demarcating with a three-stripe laser light source visual tracking system and performing real-time extraction on robot operation paths. According to the method disclosed by the invention, an eye-in-hand manner is adopted; laser stripes of a laser seam tracker are projected to the surface of a three-dimensional target, and corresponding three-dimensional position information is obtained, so that the relative pose relationship between the wrist of a robot and the laser visual sense system is determined; and the shape of a space curved surface character workpiece is matched bya laser visual system in a real-time manner, and the working path of the robot is extracted for tracking calculation. Compared with a conventional plane target, the method can effectively improve thedemarcating efficiency and the demarcating accuracy; the working plane of a three-stripe laser light source can be demarcated at the same time, and on the other side, the quick positioning of the space curved surface character workpiece and tracking requirement of unilateral sewing paths can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Frame type decoupling six component sensor and use method
The invention relates to a frame-type decoupling six-component sensor and an application method thereof, which belong to the field of industrial robots. The sensor comprises a fixed platform and a floating platform, wherein, cross beams are respectively arranged on the left and the right ends of the floating platform and are respectively connected with the fixed platform through a longitudinal beam to form a T-shaped beam; and cross beams are respectively arranged on the front and the back sides of the fixed platform and are respectively connected with the floating platform through a longitudinal beam to form an reversed T-shaped beam. The invention can achieve measurement and decoupling of spatial six-component forces, and has the advantages of simple structure, small size, high rigidity, high sensitivity, high accuracy, etc. The invention can be used in the field of robot wrist force sensors, wind tunnel balances, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Robot system
ActiveCN102189552AContact will notEfficient use ofProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsControl theory
Increased security of robot operation, efficient use of the floor space in a factory or the like, and simplified facilities are achieved. A process includes defining, in a memory, arm-occupied regions including robot arms and a workpiece and a tool attached to a robot wrist, a virtual safety protection barrier with which the arms are not allowed to come into contact, and a movable range of each robot axis; estimating the coasting angle of each robot axis for which the axis will coast when the robot is stopped due to an emergency stop during execution of a command for moving the robot to a next target position, from an actually measured amount of coasting and the like; determining a post-coasting predicted position of the robot by adding the coasting angles of the axes to the next target position; checking whether or not the arm-occupied regions at the post-coasting predicted position will come into contact with the virtual safety protection barrier, or whether or not the robot axes are within the movable ranges; and performing control to cause the robot to stop moving immediately upon detection of abnormality.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
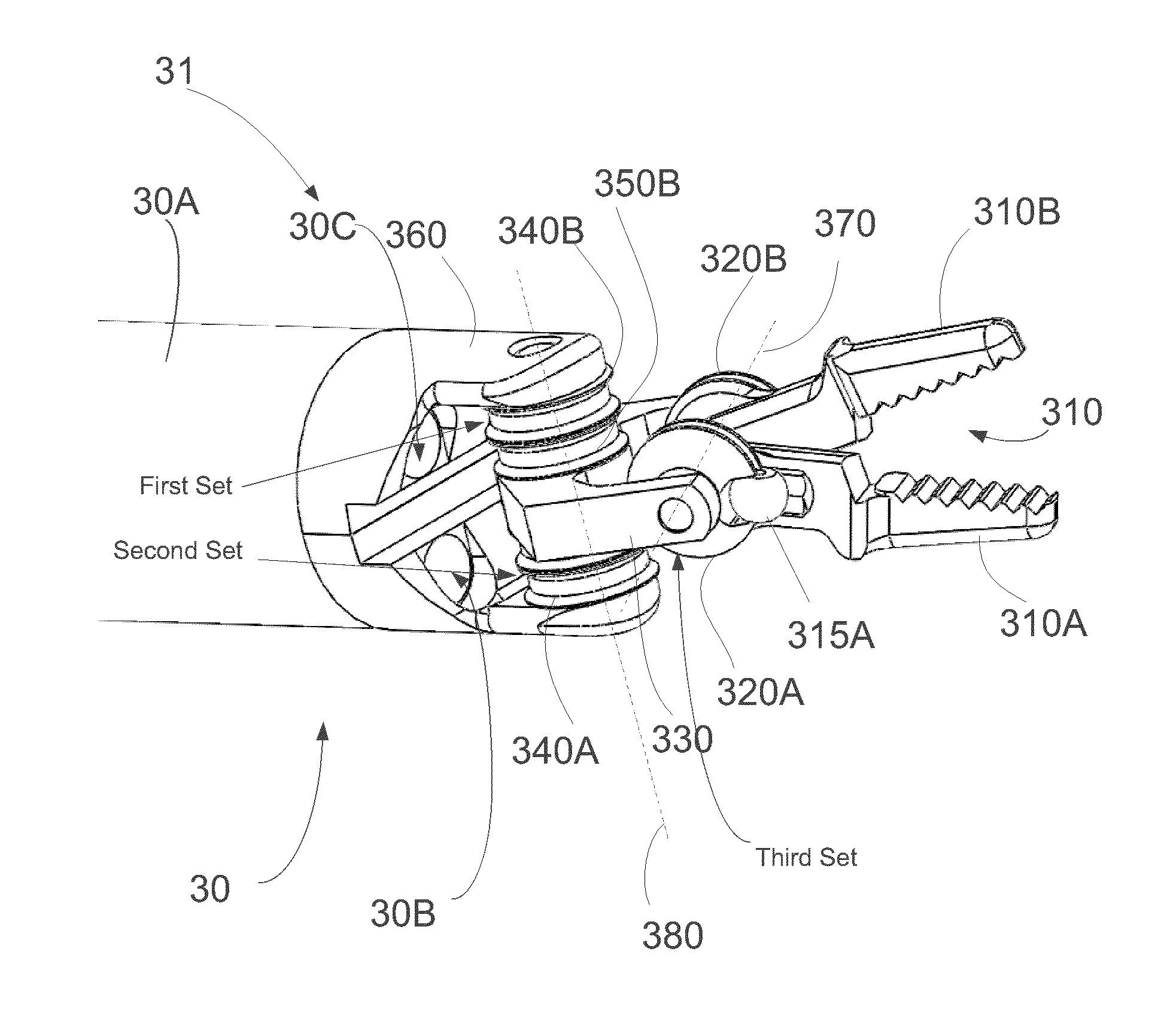
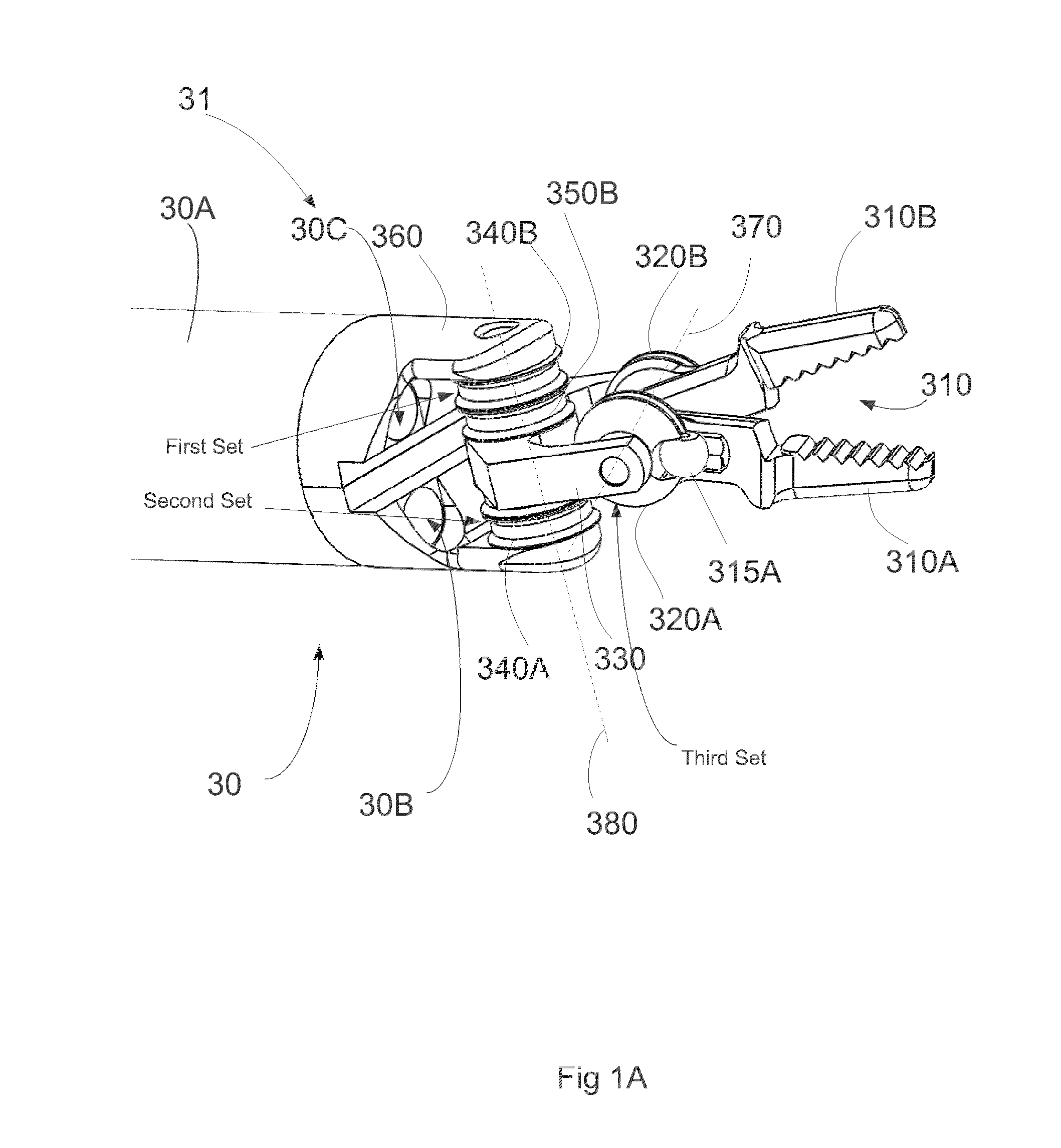
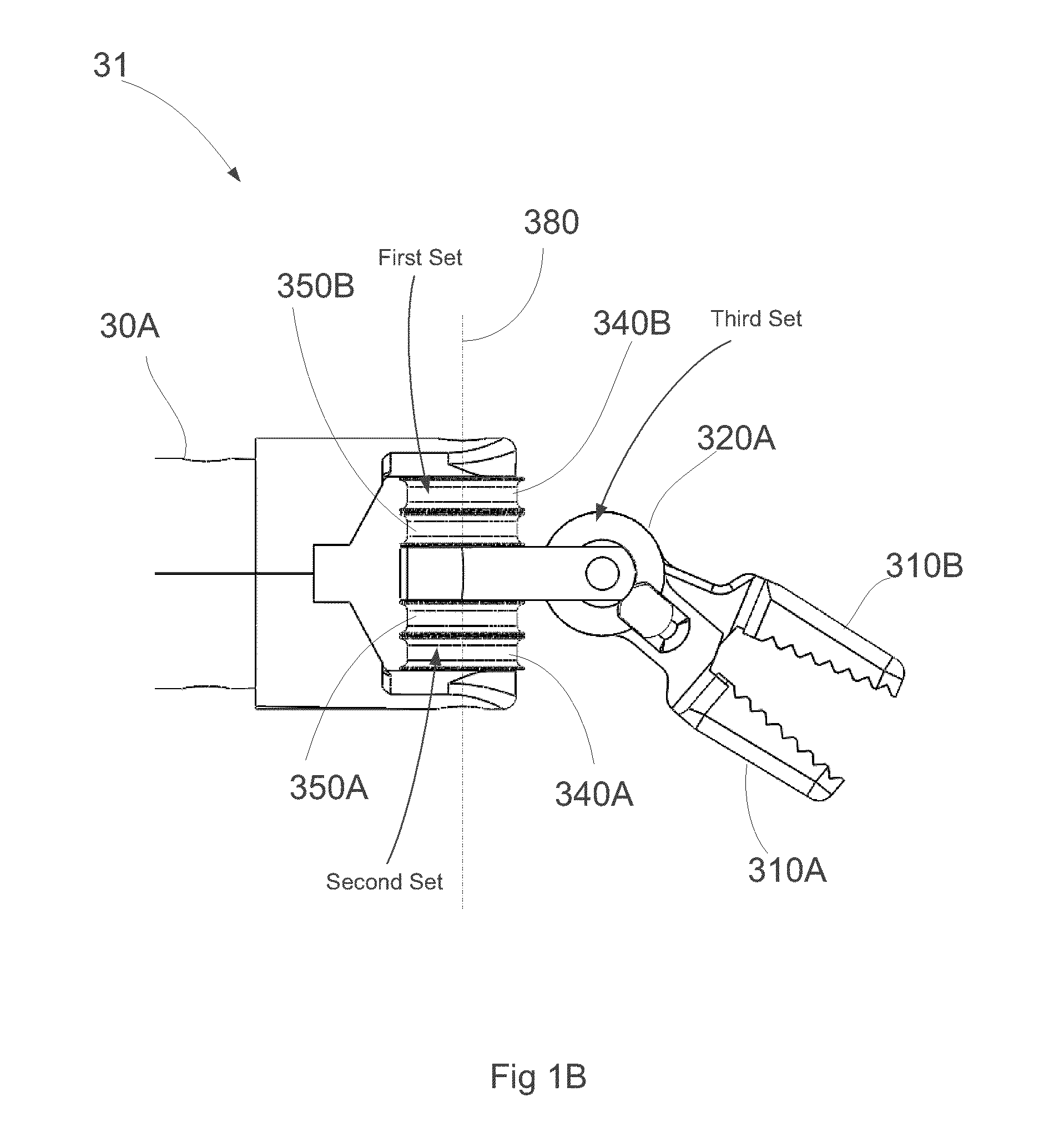
Wrist of robot and surgical robot
The invention provides a wrist of a robot and the surgical robot. The wrist of the robot comprises a substrate, a hooke joint structure, a first transmission mechanism, a second transmission mechanism and a driving mechanism. The hooke joint structure is arranged on the substrate, and used for fixing a surgical instrument. The driving mechanism drives the first transmission mechanism and the second transmission mechanism to move, and the first transmission mechanism and the second transmission mechanism drive the hooke joint structure to rotate at the first freedom degree and the second freedom degree respectively. At least one of the first transmission mechanism and the second transmission mechanism is a linear transmission mechanism and used for linearly driving the hooke joint structure to move. The rotation of each freedom degree is independently controlled to be driven by the first transmission mechanism and the second transmission mechanism. At least one of the first transmission mechanism and the second transmission mechanism is the linear transmission mechanism and used for linearly driving the hooke joint structure to move. Due to the fact that linear driving can be precisely controlled, control precision is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT MEDBOT (GRP) CO LTD
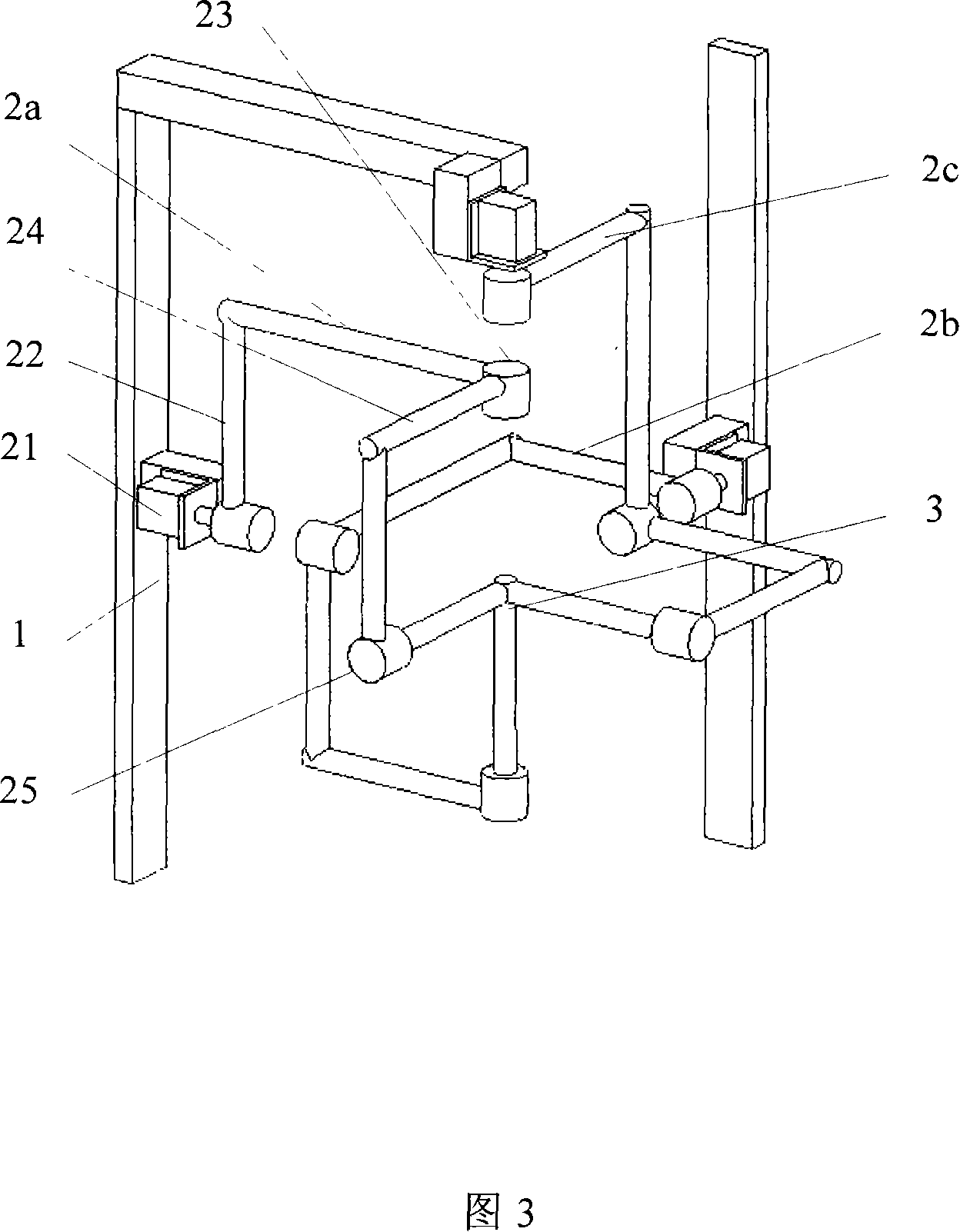
Movement decoupling spherical surface rotating paralleling mechanism can be used as the robot wrist joint
InactiveCN101116971ASimple structureEasy to installProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsMotor driveKinematic pair
The invention discloses a kinematic decoupling spherical rotation parallel mechanism that can be used as a robot wrist, comprising a rack (1), a movable platform (3) and three kinematic branch chains (2a), (2b) and (2c) which are fixed between the rack and the movable platform and are in the same structural type. Each kinematic branch chain comprises three revolute pairs and rods among the three revolute pairs, primary pairs of the three revolute pairs are distributed via positive crossing and the axes of all kinematic pairs converge to one point. Rotation motors of the three kinematic branch chains drive to realize that the movable platform rotates around the sphere surface of the axes convergence point of the rotation pairs and outputs. The initial end of each kinematic branch chain is motor-driven. The parallel mechanism relating to the invention has the advantages such as kinematic decoupling, simple in structure, easy to control and low in cost, and can be used in the fields such as robot wrist, shoulder joint, satellite positioning and advanced manufacturing.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
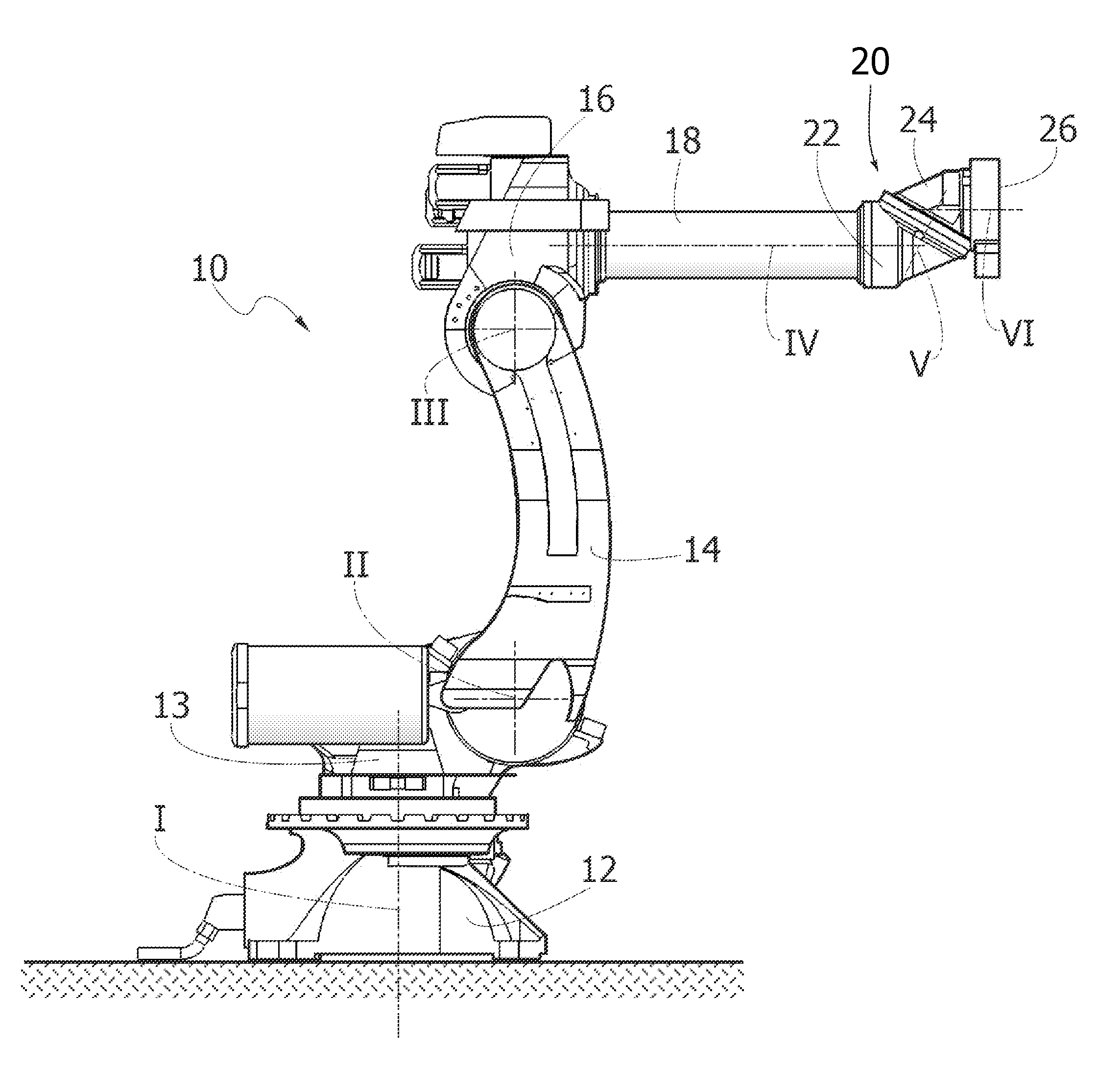
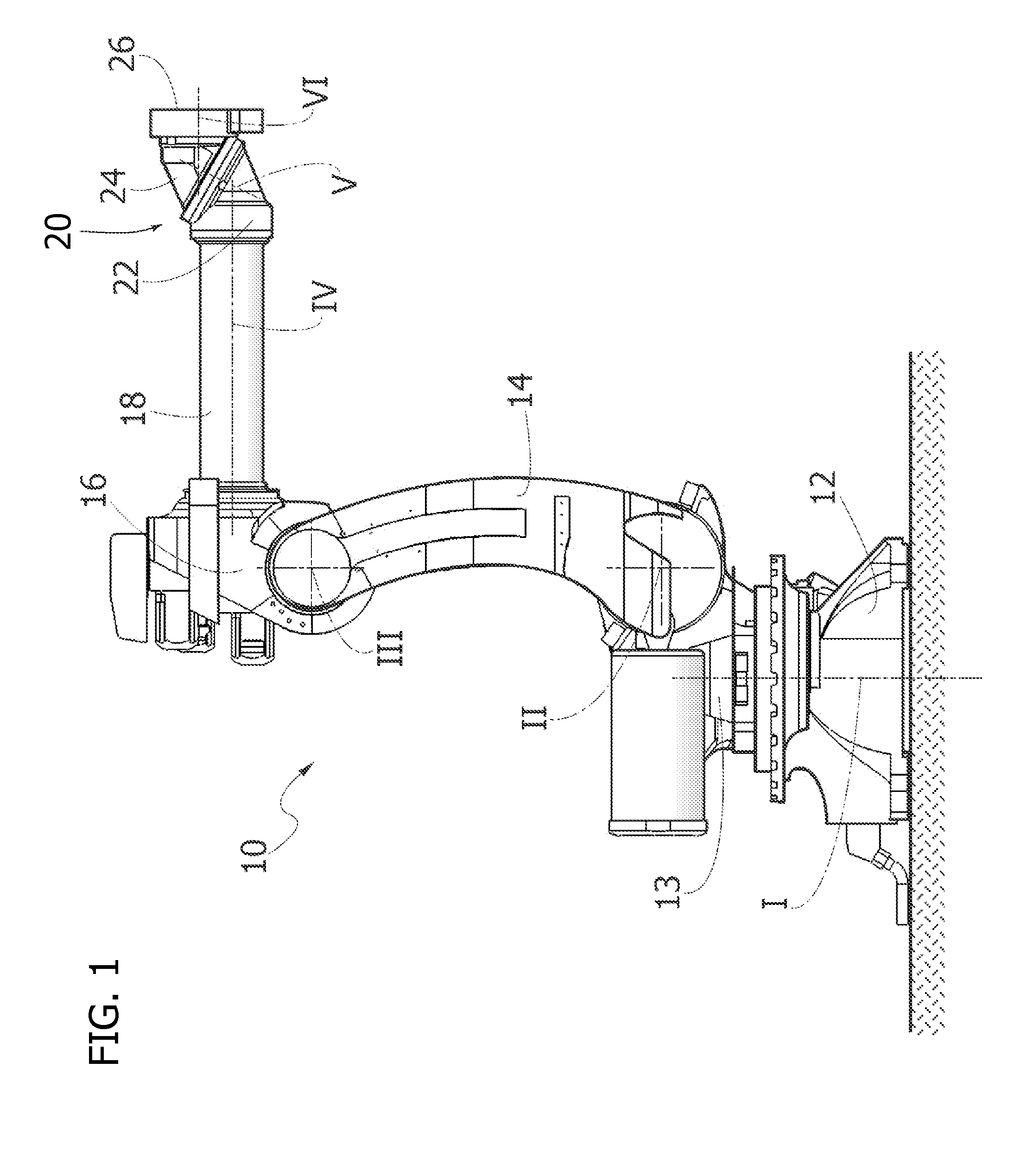
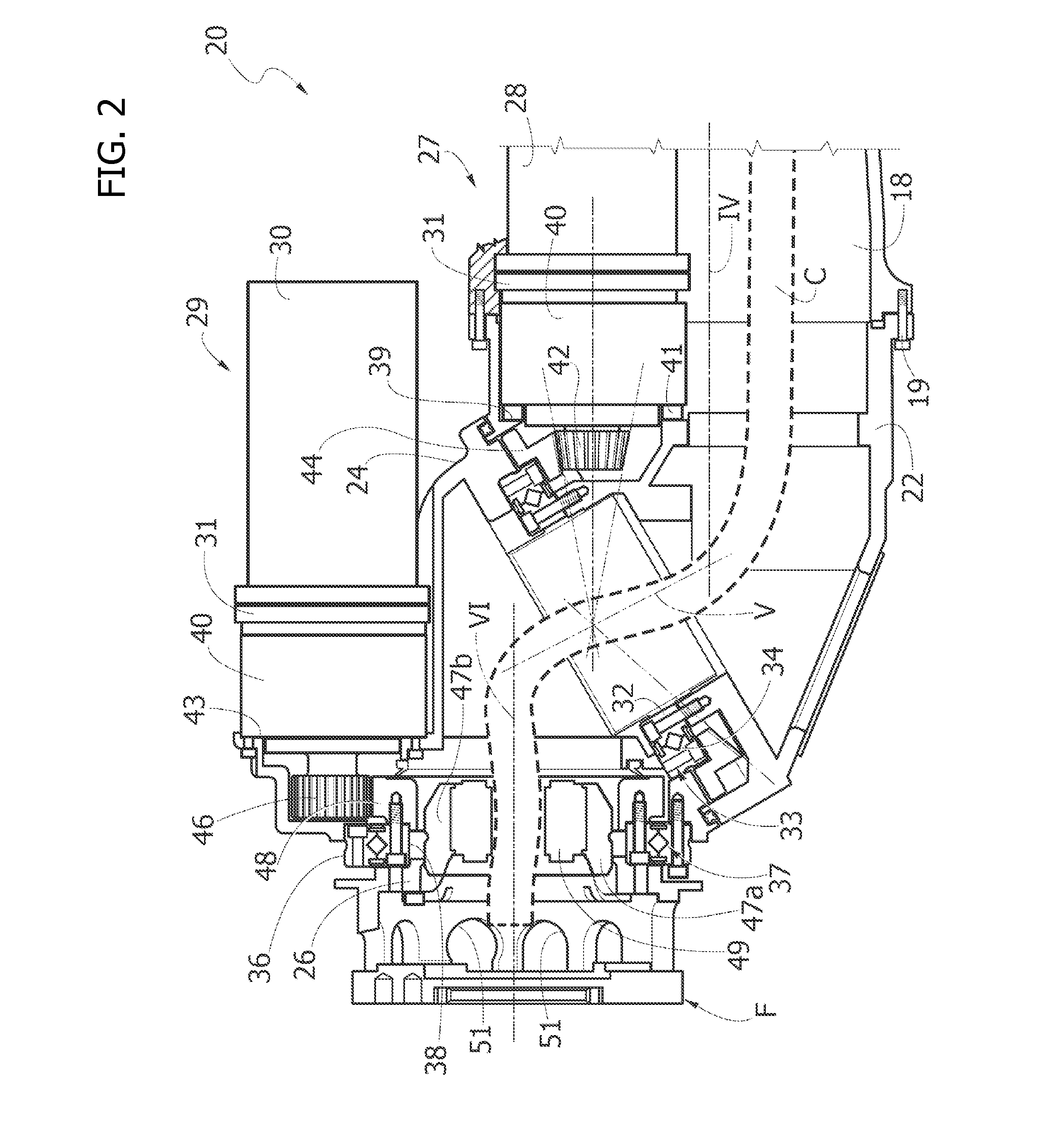
Multi-Axis Industrial Robot With Integrated Tool
InactiveUS20150108099A1Easy to useMinimal numberResistance electrode holdersMechanical apparatusMulti axisControl theory
An industrial robot including a robot chain of elements, a robot wrist bearing a tool (100) and a continuous internal passage through which one or more cables and / or pipes for the power supply and / or the fluid supply to the tool. The cables and pipes continue without interruption through the passage and through a flange of the robot up to respective connections of said tool, whereby the cables and pipes are arranged completely inside the robot and inside the tool, without the need to provide separate cables and pipes of the tool connected to the cables and the pipes of the robot at the flange of the robot.
Owner:COMAU SPA
3D laser printing system and method based on robot
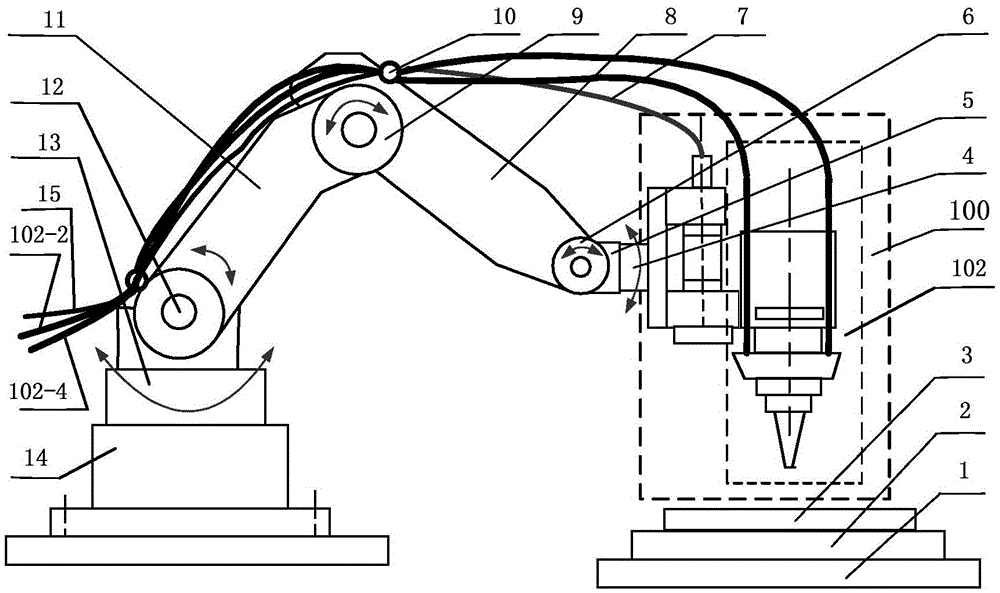
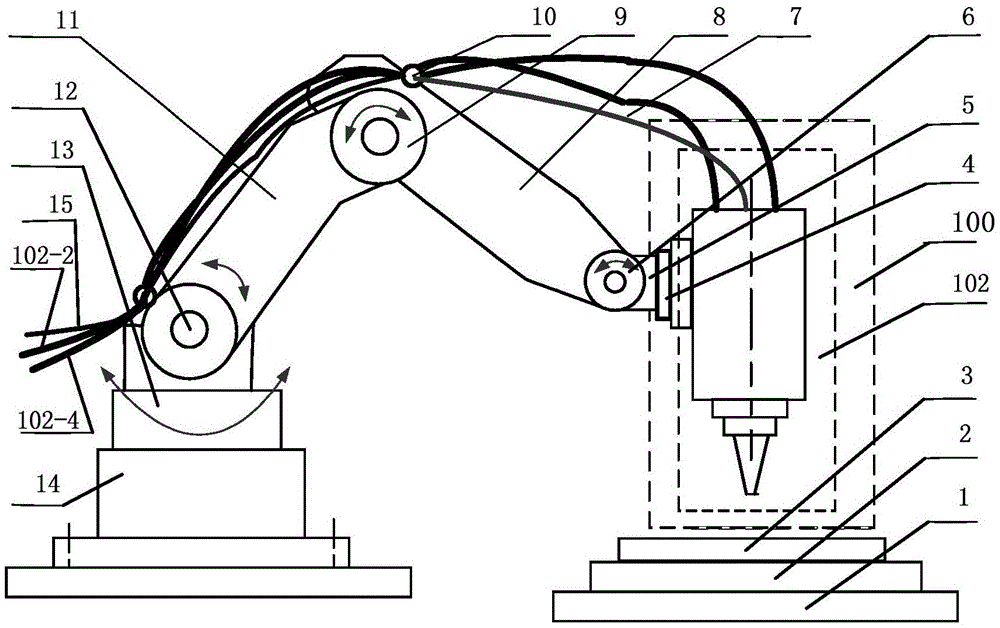
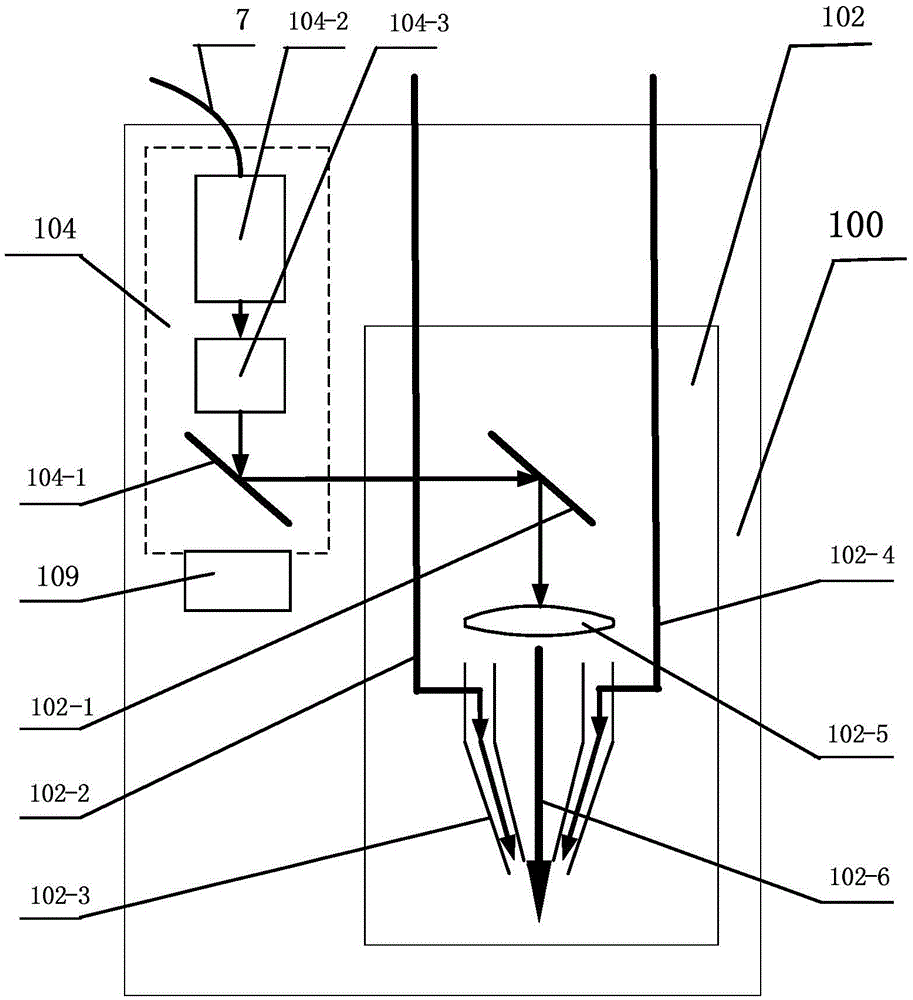
InactiveCN105499573AImprove processing efficiencyRealize processing and manufacturingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyShielding gasEngineering
The invention relates to a 3D laser printing system and method based on a robot. A mechanical arm is utilized for driving a laser printing head unit for 3D printing, and comprises a machine base, a horizontal rotating disc, an arm joint, an upper arm, an elbow joint, a lower arm, a wrist joint, a robot wrist, a connecting disc, a protection gas supply pipeline, and a powder supply pipeline connected with a powder stock bin. The connecting disc is connected with the laser printing head unit, the connecting disc drives the laser printing head unit to rotate, and the protection gas supply pipeline and the powder supply pipeline are fixed to the upper arm and the lower arm through fixing rings. The end of the protection gas supply pipeline and the end of the powder supply pipeline are connected with the laser printing head unit. The 3D laser printing system and method have the advantages that metal parts, especially stainless steel alloy parts, in any shape can be directly machined and manufactured, and the machining and manufacturing efficiency of the metal parts, especially the stainless steel alloy parts, in the complex shapes is greatly improved. Adopted metal powder is directly sprayed according to the shapes of the parts, and little powder is left, and can be recycled and reused.
Owner:CANGZHOU DWAYA LASER TECH CO LTD
Professional glaze spraying six-axis robot
A professional glaze spraying six-axis robot belongs to the technical field of robot, and solves the problems of expensiveness, complicated operation and difficult maintenance of a foreign glaze spraying robot system in domestic application. The robot wrists are connected to a fourth, fifth and sixth axis motor through wrist transmission chains; the robot wrists, small arms and a fourth, fifth and sixth shaft seat assembly are orderly connected; the upper part of a big arm assembly is connected with the fourth, fifth and sixth shaft seat assembly through a bearing shaft seat one, and the part is connected with second and third axis large chain wheel assemblies; a second axis motor assembly drives the second large chain wheel assembly to rotate; a second axis cylinder assembly is fixed on a second and third axis box bodies and the second axis large chain wheel assembly; upper part of a third axis driving connecting rod through a bearing two is connected with the fourth, fifth and sixth shaft seats assemblies, and the lower part is connected with a third axis drive bracket through a bearing three; the third axis driving bracket is connected with the third large chain wheel assemblies; and the third axis motor assembly through a chain two drives the third large chain wheel assemblies to rotate. The invention is special for glaze spraying.
Owner:杭州钱江机器人有限公司
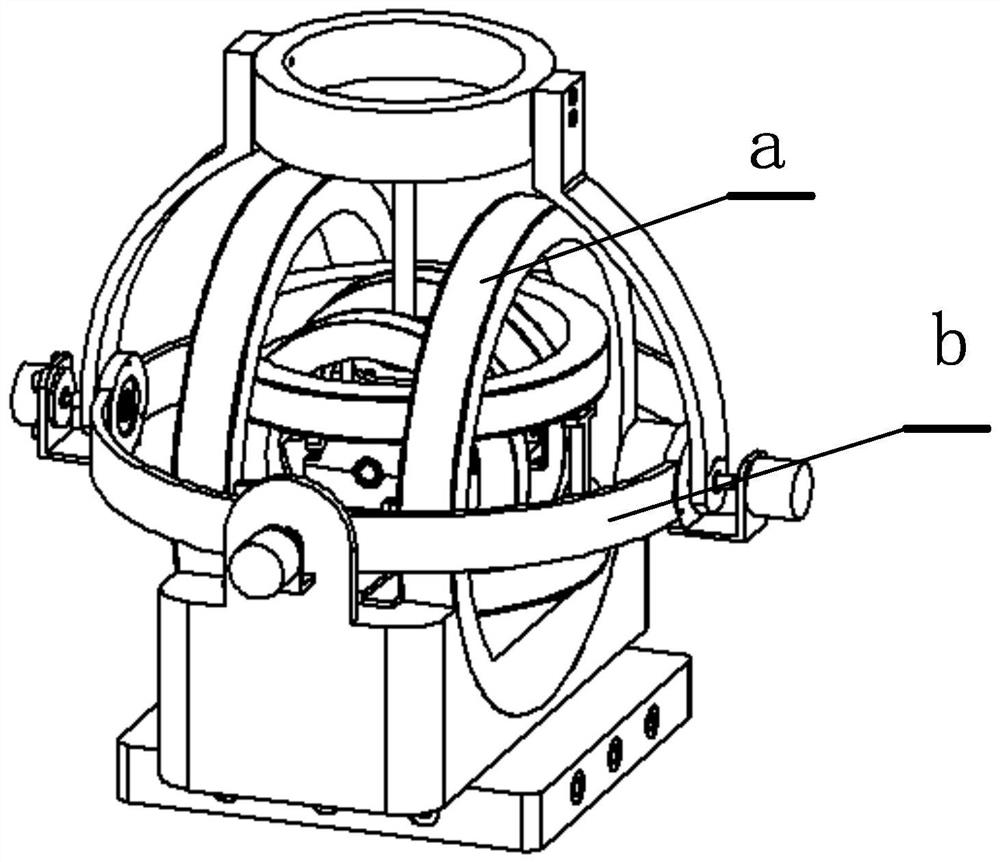
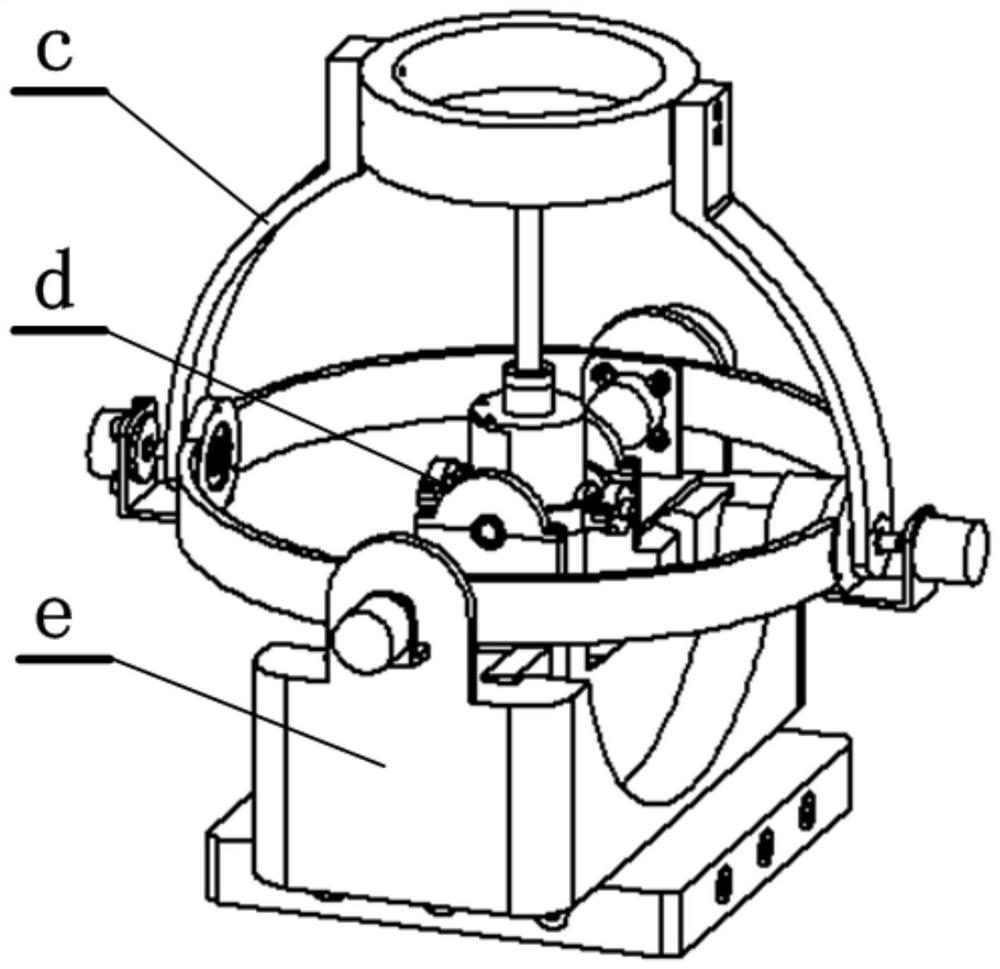
Electromagnetic driving two-degrees of freedom spherical robot wrist and control method thereof
ActiveCN111604935AEasy to adjustNested compactProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsResponse sensitivityEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of automation engineering and relates to an electromagnetic driving two-degrees of freedom spherical robot wrist and a control method thereof. The electromagnetic driving two-degrees of freedom spherical robot wrist is a high-integration driving spherical wrist device, the two output ends of an internal universal joint and an external universal joint passing through the same rotating center are coaxially connected, and a radial magnetizing permanent magnet in a servo mechanism is directly driven by a coaxial servo magnetic moment in a space universal rotary magnetic field to realize side-sway and pitching two-degrees of freedom rotation. The electromagnetic driving two-degrees of freedom spherical robot wrist overcomes the defects of a complicated driving machinery wrist, the wrist driving system is simple and light in structure, high in transmission efficiency, static and dynamic performance and control and response speed, can solve the modeling problem of the existing spherical electromagnetic driving joint three-dimensional complicated magnetic field, realize precise modeling of the spherical electromagnetic driving joint magnetic field and precise decoupling of electromagnetic coupling and mechanical coupling, and remarkably improves the response sensitivity and positioning precision of electromagnetic driving spherical joint control.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Power transmission device for driving robot wrist and power transmission device
InactiveUS20060213307A1Good rotation balanceHigh strengthProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsGear wheelEngineering
The power transmission device includes an internal gear and an external gear that is inscribed in the internal gear and engages with the internal gear, and can transmit an input power to an attachment. The power transmission device further includes: an inner pin for bringing out a relative rotation component between the internal gear and the external gear; and an output flange connected to the inner pin. In this configuration, the inner pin and the output flange are integrally formed as one member, and a mounting hole for connecting the output flange to the attachment is formed in a surface of the output flange that is opposite to the inner pin.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
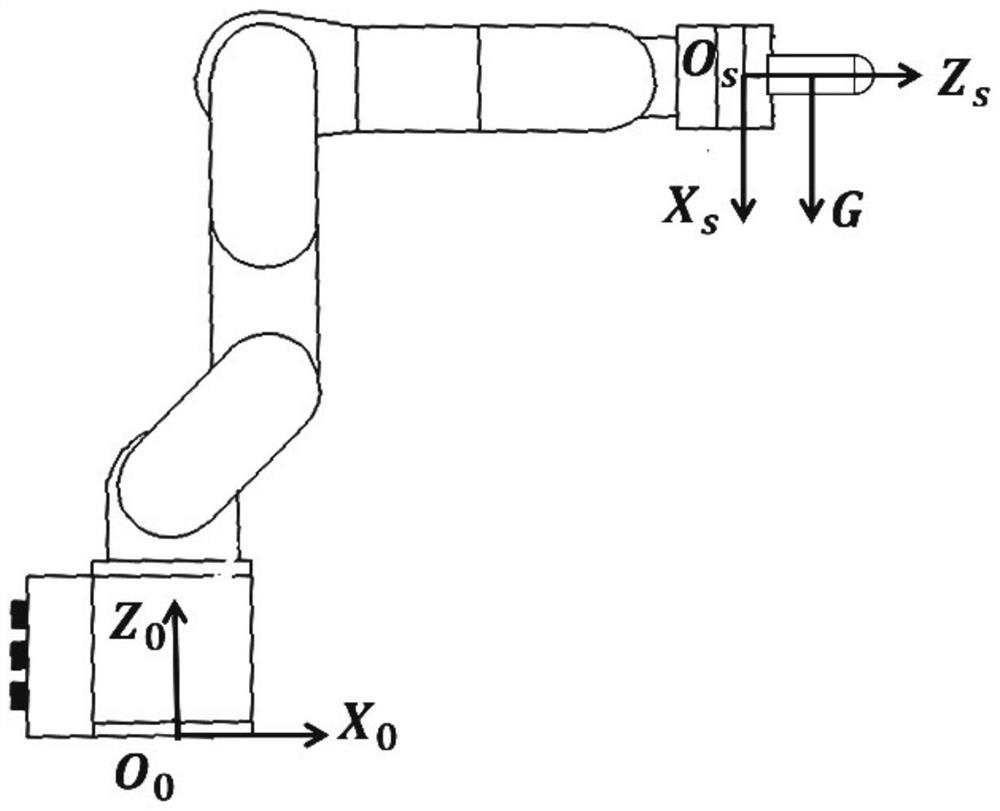
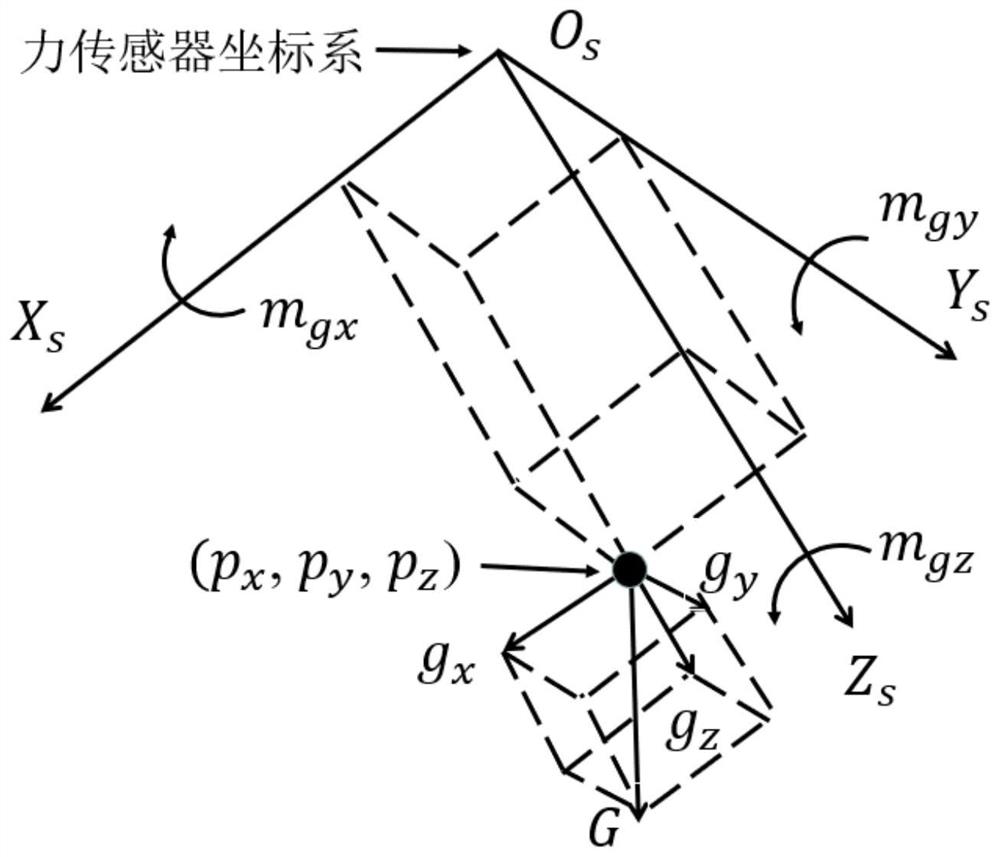
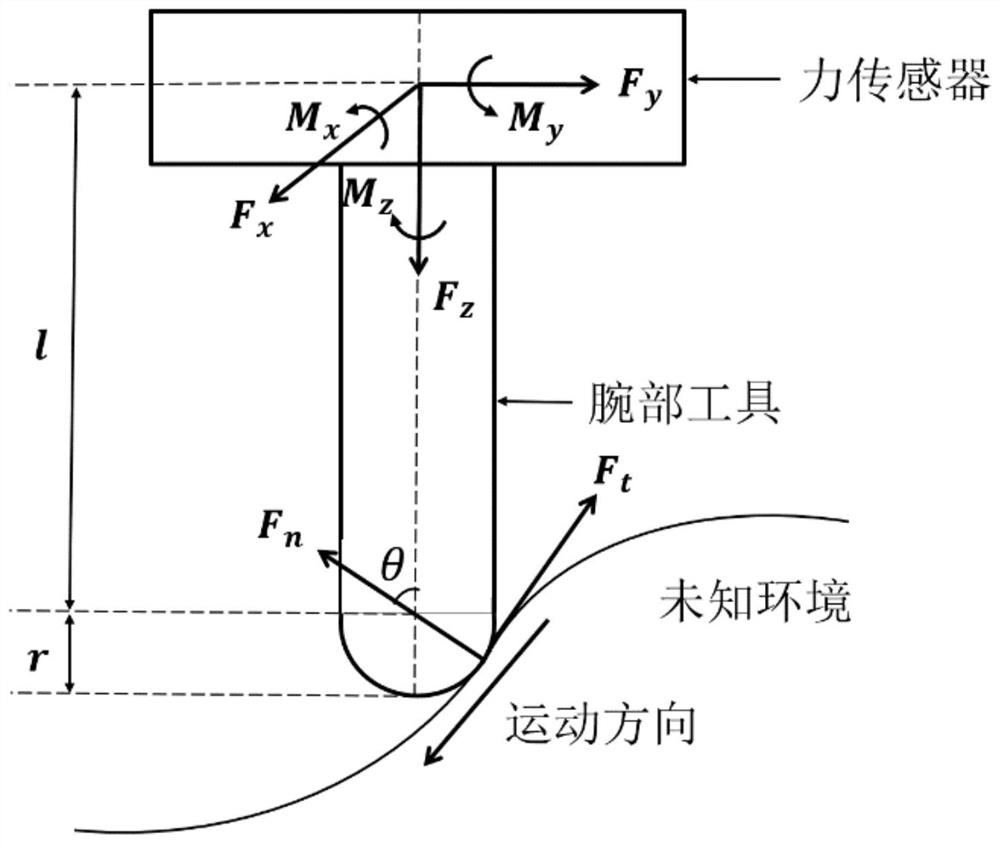
Six-degree-of-freedom robot force control method for unknown environment
PendingCN111624941AHigh measurement accuracyAccurate force perception informationNumerical controlSimulationMachine
The invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom robot force control method for an unknown environment and belongs to the field of compliance control of robot motion. The method comprises the followingspecific steps: firstly, acquiring zero data of a force sensor, the gravity of a robot wrist tool and barycentric coordinates, and determining true force and moment generated when the robot wrist tool is in contact with the environment; secondly, determining the position control direction and the force control direction of the movement of the tail end of the robot according to the true force andthe moment generated when the wrist tool of the robot is in contact with the environment; and finally, acquiring a reference trajectory of robot motion, determining an impedance control model, and completing force control operation of the robot. According to the invention, the measurement precision of the force sensor is improved through the on-line calibration of the force sensor, accurate forceperception information is provided for the force control operation of the robot, the impedance control strategy is adopted to control the motion trail of the robot, the conversion between force control and position control is stable, and the adaptability and robustness are better.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
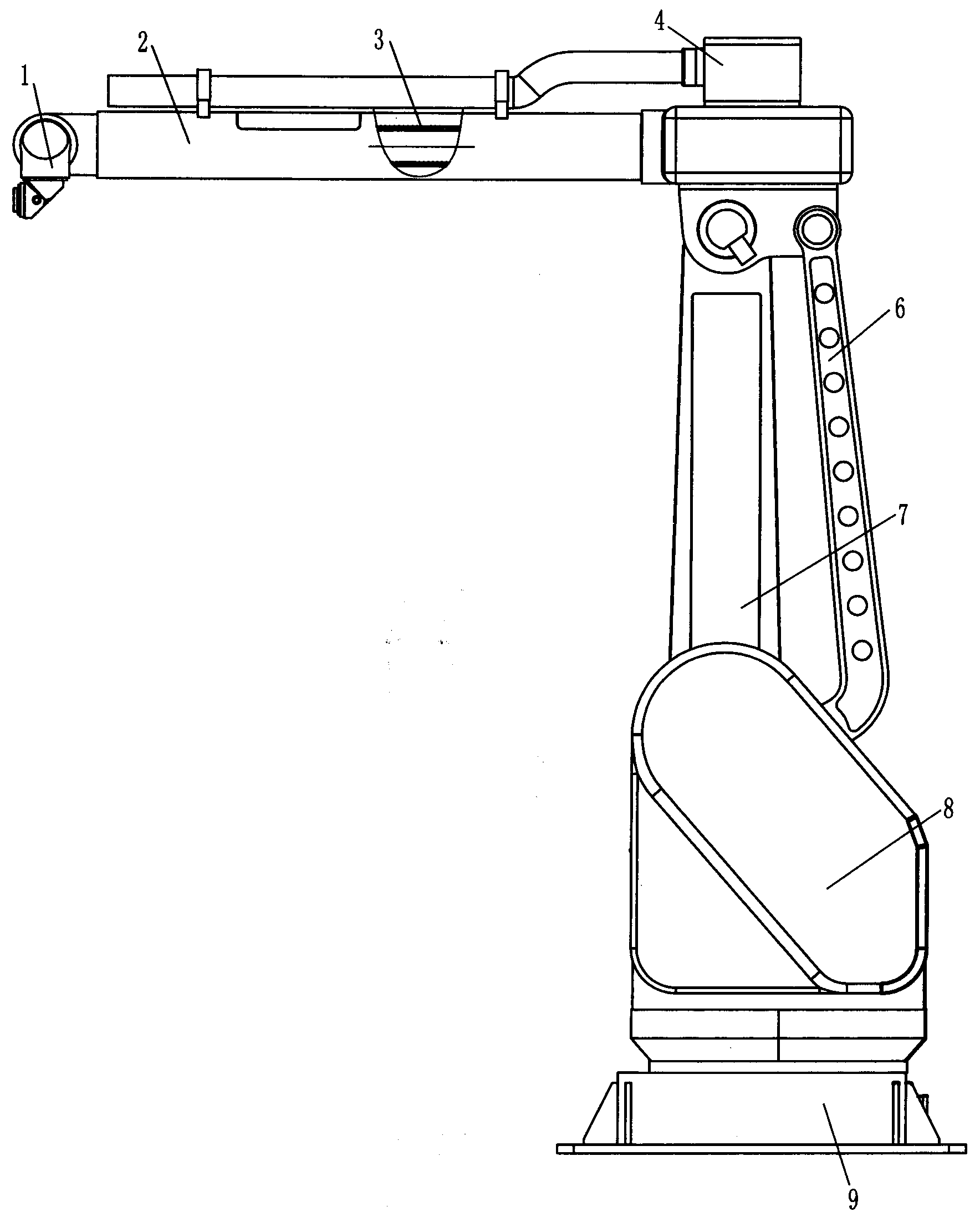
Six-axis industrial robot wrist capable of swinging spatially
The invention discloses a six-axis industrial robot wrist capable of swinging spatially. The six-axis industrial robot wrist comprises an arm, a swinging arm connected to the front end of the arm in a pivoted mode and a rotary hand connected to the front end of the swinging arm in a pivoted mode; the rotary hand comprises a spatial swinging mechanism connected to the front end of the swinging arm in a pivoted mode, the spatial swinging mechanism comprises a horizontal bottom plate, a first threaded rod, a second threaded rod, a horizontal moving body, a telescopic rod and a sphere support, wherein the first threaded rod and the second threaded rod are installed on the horizontal bottom plate in a sliding mode, the horizontal moving body is connected to the first threaded rod and the second threaded rod in a threaded mode, the bottom end of the telescopic rod is movably connected to the horizontal moving body, the top end of the telescopic rod is fixedly connected to a sphere, and the sphere support is fixed to the horizontal bottom plate. The first threaded rod and the second threaded rod are arranged longitudinally and transversely respectively, the sphere is movably installed on the sphere support, and the execution tail end of the rotary hand is installed on the sphere. According to the technical scheme, horizontal longitudinal and transverse movement of the horizontal moving body is converted into free swinging motion of the execution tail end of the rotary hand, and therefore the robot wrist can be operated more flexibly and adapt to various complicated technological requirements.
Owner:江苏汇能激光智能科技有限公司
Wrist device for three degree of freedom (TDOF) underactuated robot
InactiveCN102009414ALess joint degrees of freedomReduce volumeJointsUnderactuated robotsThree degrees of freedom
The invention relates to a wrist device for a three degree of freedom (TDOF) underactuated robot. The device comprises a static platform, a movable platform, three branches and two drive power sources, wherein the static platform is hinged with the movable platform through the three branches, and two of the three branches are connected with the two drive power sources respectively; and under driving of the two drive power sources, the movable platform performs three degree of freedom motion through transmission of the three branches.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
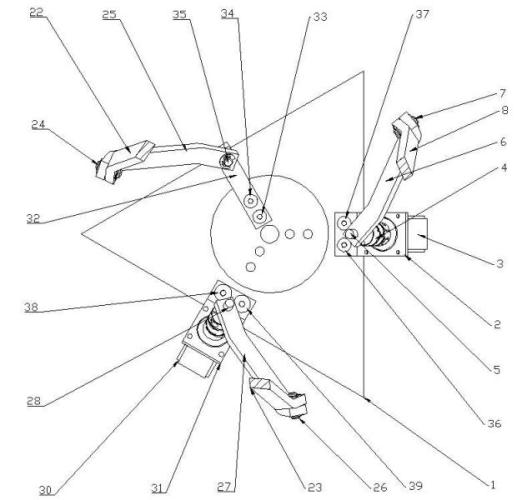
Side lifting and bottom supporting type carrying manipulator for transferring box and carrying method
InactiveCN105397825AFully automatedIncrease productivityGripping headsStacking articlesSurface layerEngineering
The invention discloses a side lifting and bottom supporting type carrying manipulator for a transferring box and a carrying method. The manipulator comprises a base, an inserting and bottom supporting mechanism, a side lifting mechanism and a pressing and edge hooking mechanism, wherein the inserting and bottom supporting mechanism, the side lifting mechanism and the pressing and edge hooking mechanism are correspondingly arranged on the base. The carrying method comprises the following steps: lifting one side of the transferring box through the side lifting mechanism so as to form an inclined gap in the bottom part of the transferring box; inserting the inserting and bottom supporting mechanism into the inclination gap and supporting to bottom part of the transferring box; hooking one side, relative to the side lifting mechanism, on the transferring box, through the pressing and edge hooking mechanism, and synchronously compressing the top surface of the transferring box, so as to fix the upper surface, the lower surface, the left surface and the right surface of the transferring box; then driving robot wrists to move to carry the transferring box. The carrying manipulator and the carrying method are specifically designed according to the properties of the general transferring box; each transferring box can be grasped from a surface layer of a stack and then carried to a specified place. Therefore, a plastic transferring box can be automatically removed from the stack, and an existing manual carrying manner is replaced, and as a result, the production efficiency can be effectively improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG TECHN COLLEGE OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC ENG
Wrist driving mechanism for robot
ActiveUS7028578B2Improve wrist driving mechanismSolve the lack of spaceMechanical apparatusJointsThree degrees of freedomDrive shaft
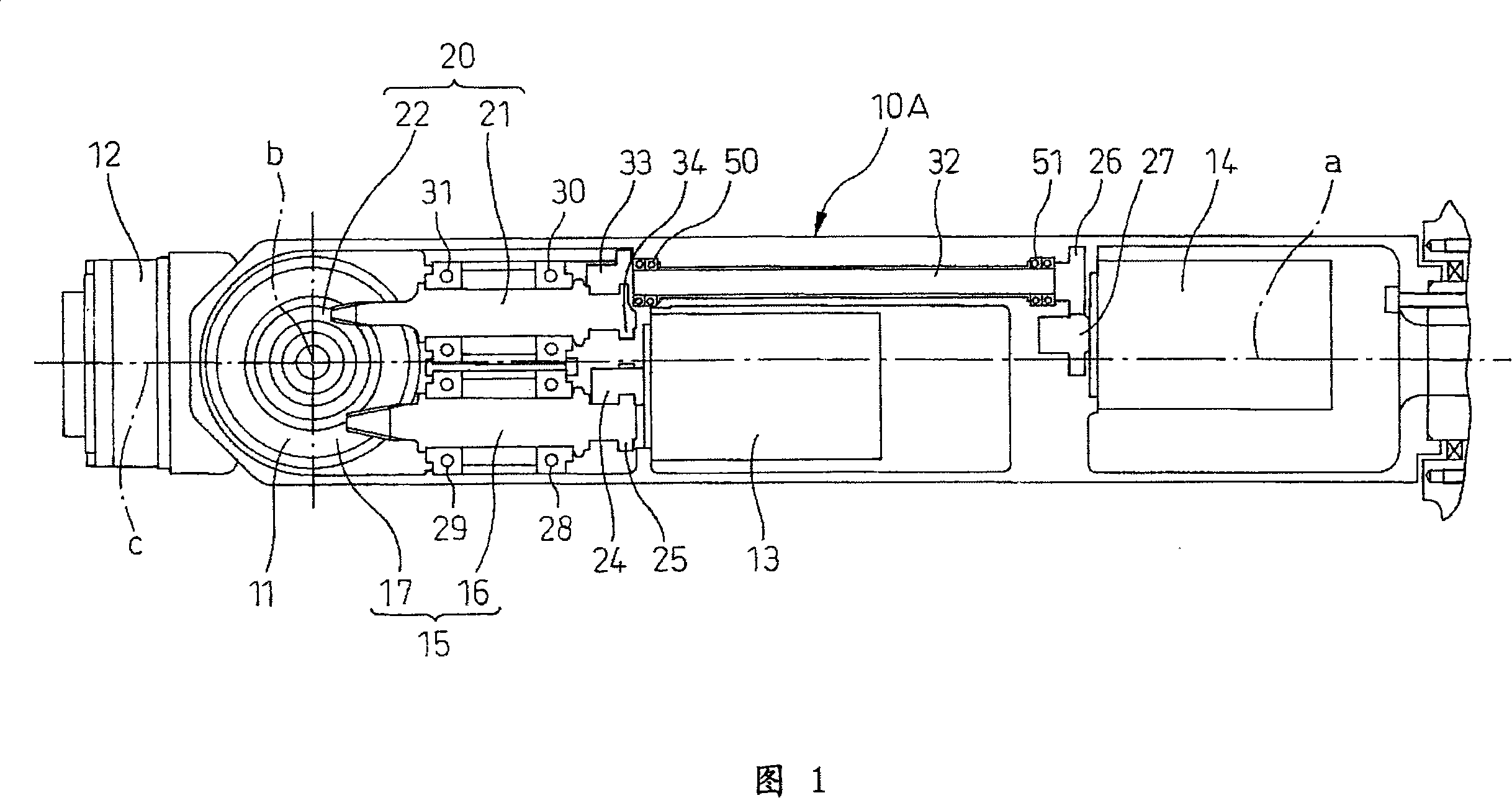
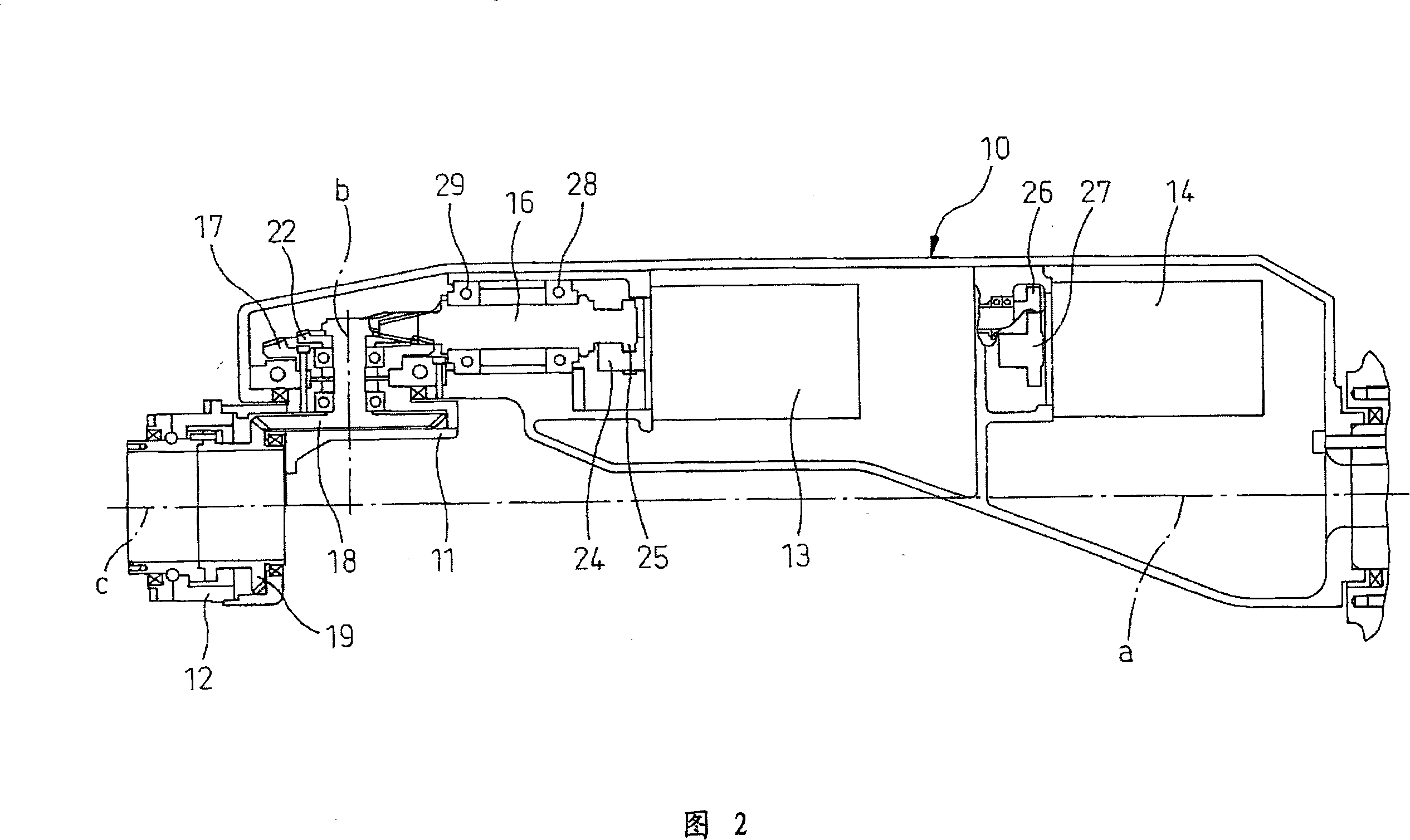
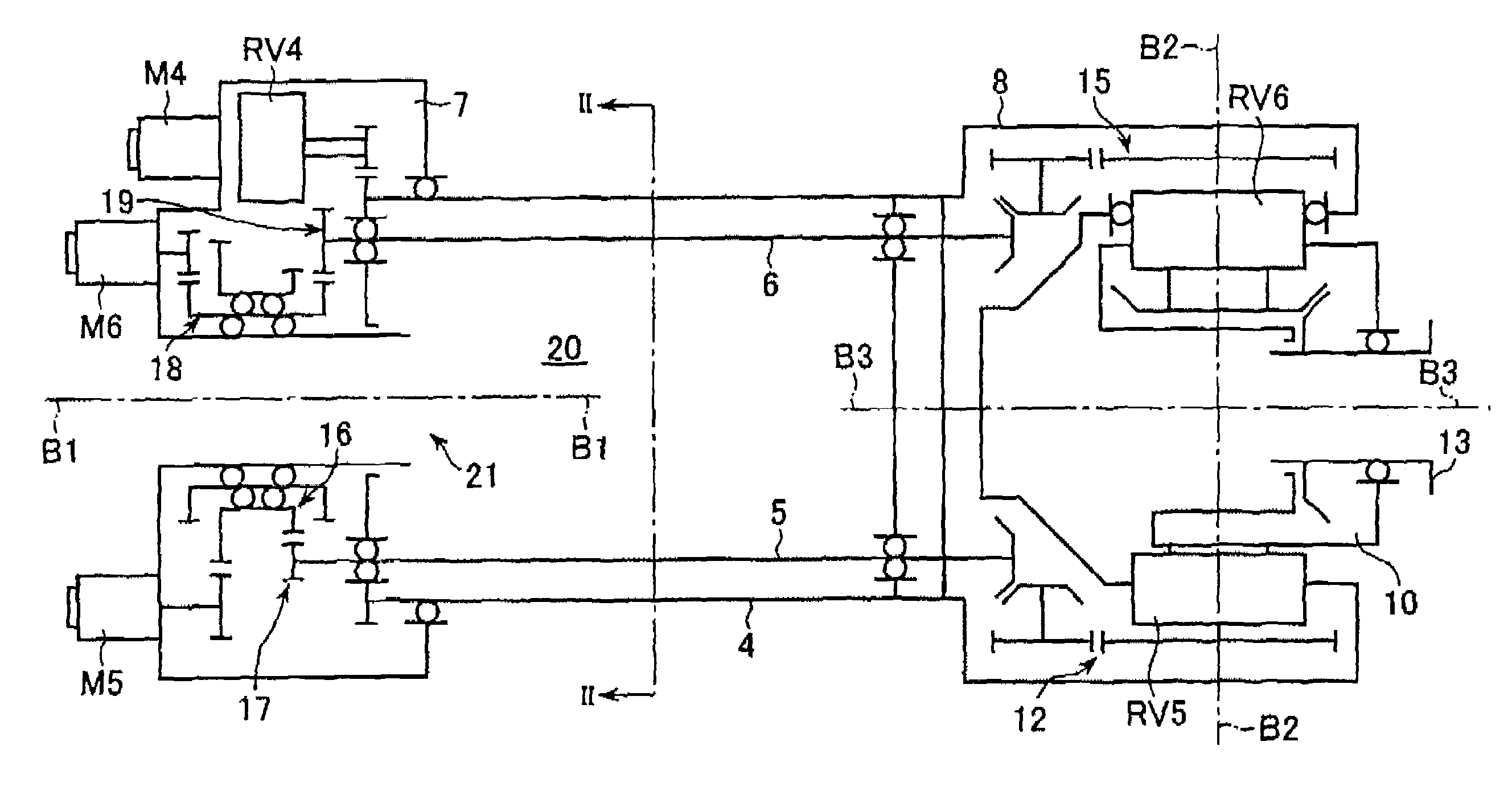
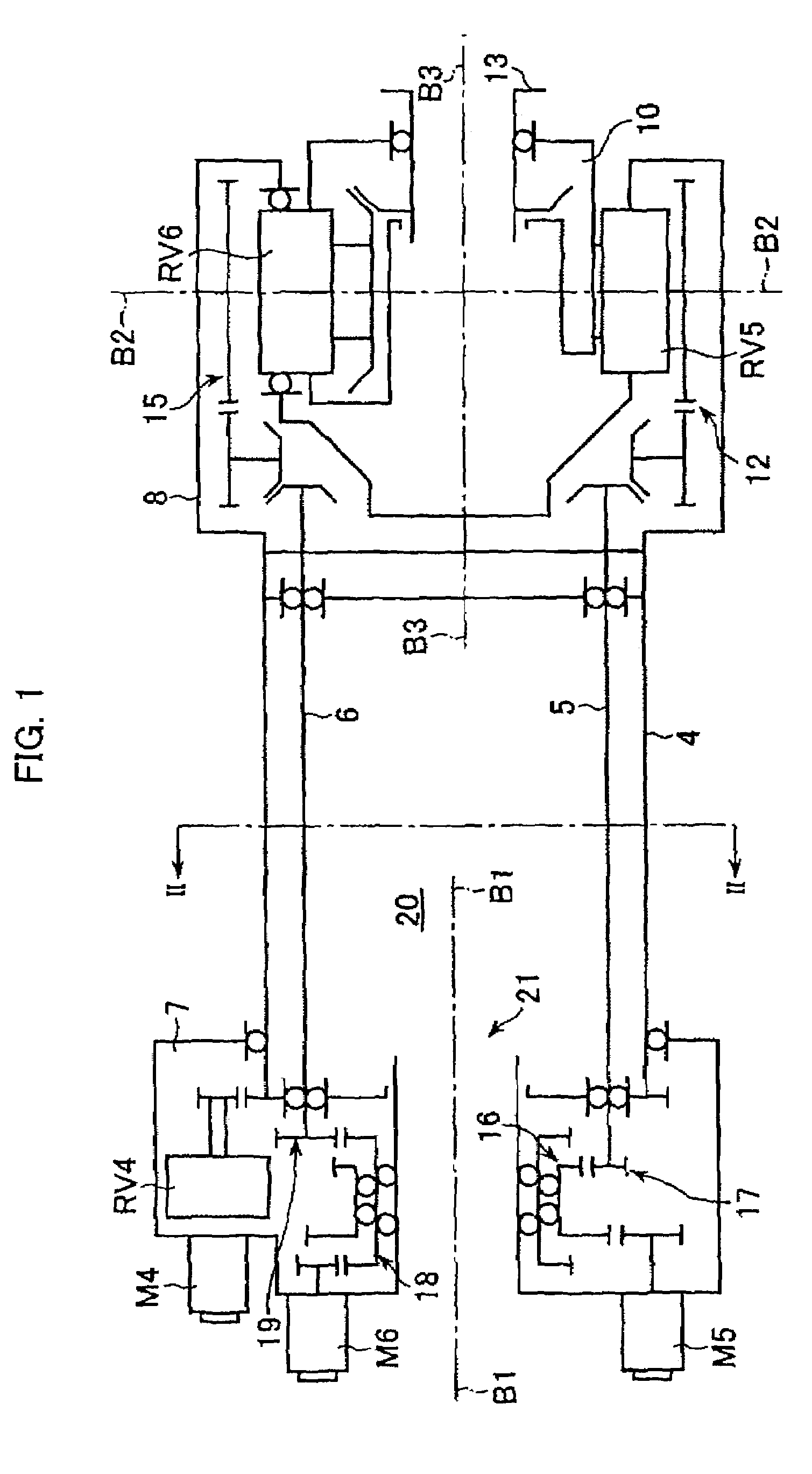
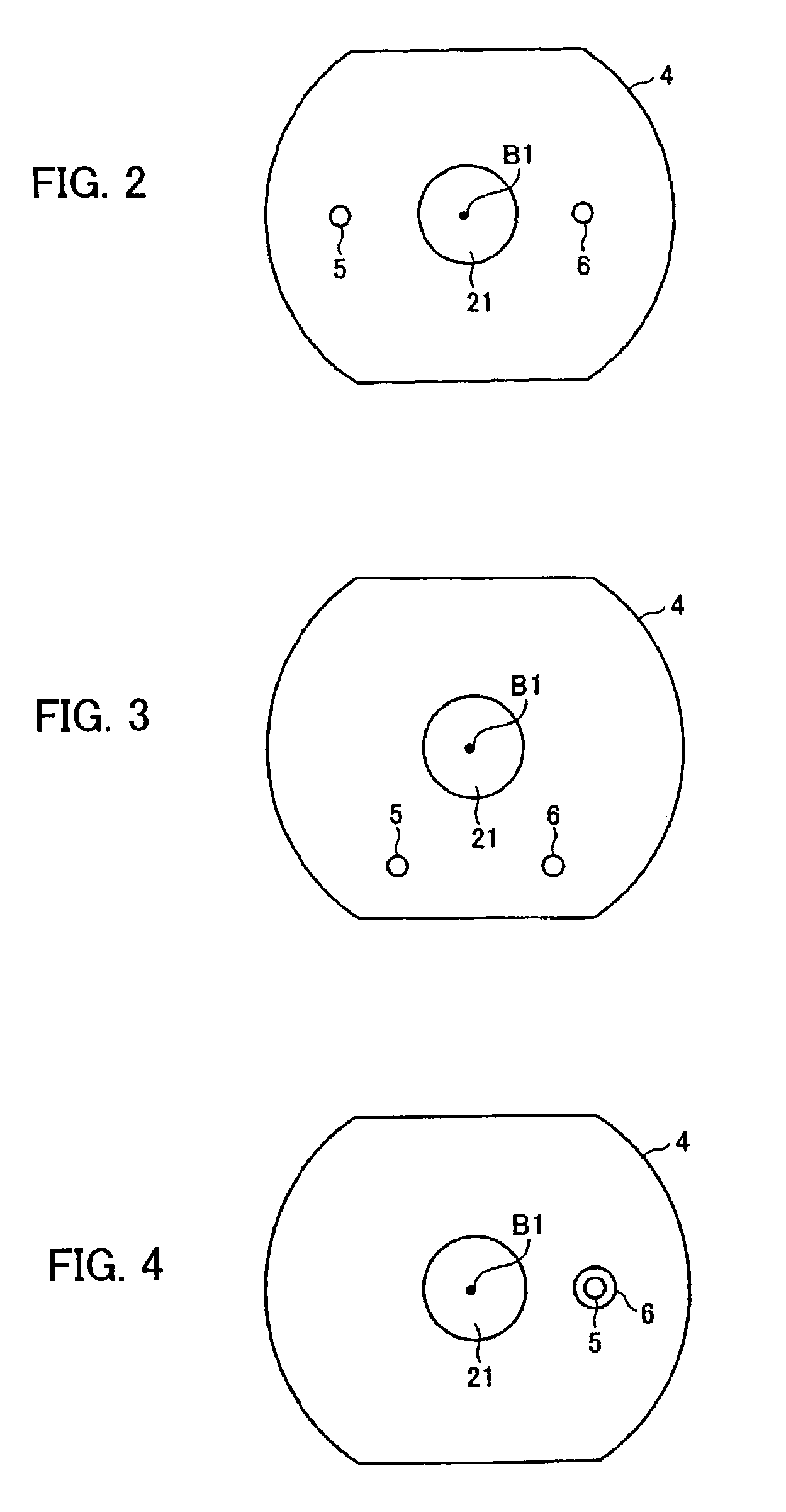
A wrist driving mechanism capable of arranging a large amount of cables and pipes in a robot arm. A robot wrist mechanism having three degrees of freedom is driven by first, second and third drive shafts for transmitting driving forces of first, second and third motors M4, M5 and M6, respectively. The first drive shaft is a hollow shaft for transmitting a rotational driving force from the motor M4 to a first wrist element supported rotatably around the first axis B1. The second and third drive shafts are arranged eccentrically with the first axis B1 in an inner space of the first drive shaft. The second drive shaft transmits a rotational driving force from the motor M5 to a second wrist element supported rotatably around the second axis B2, and the third drive shaft transmits a rotational force from the motor M6 to a third wrist element supported rotatably around the third axis B3. A first gear and a third gear as planet gears and a second gear and a fourth gear as sun gears are provided for avoiding complication of structure due to the eccentric arrangement of the second and third drive shafts.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com