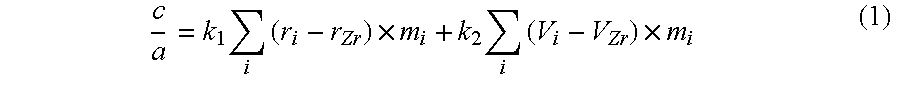Patents
Literature
11568results about How to "Low thermal conductivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
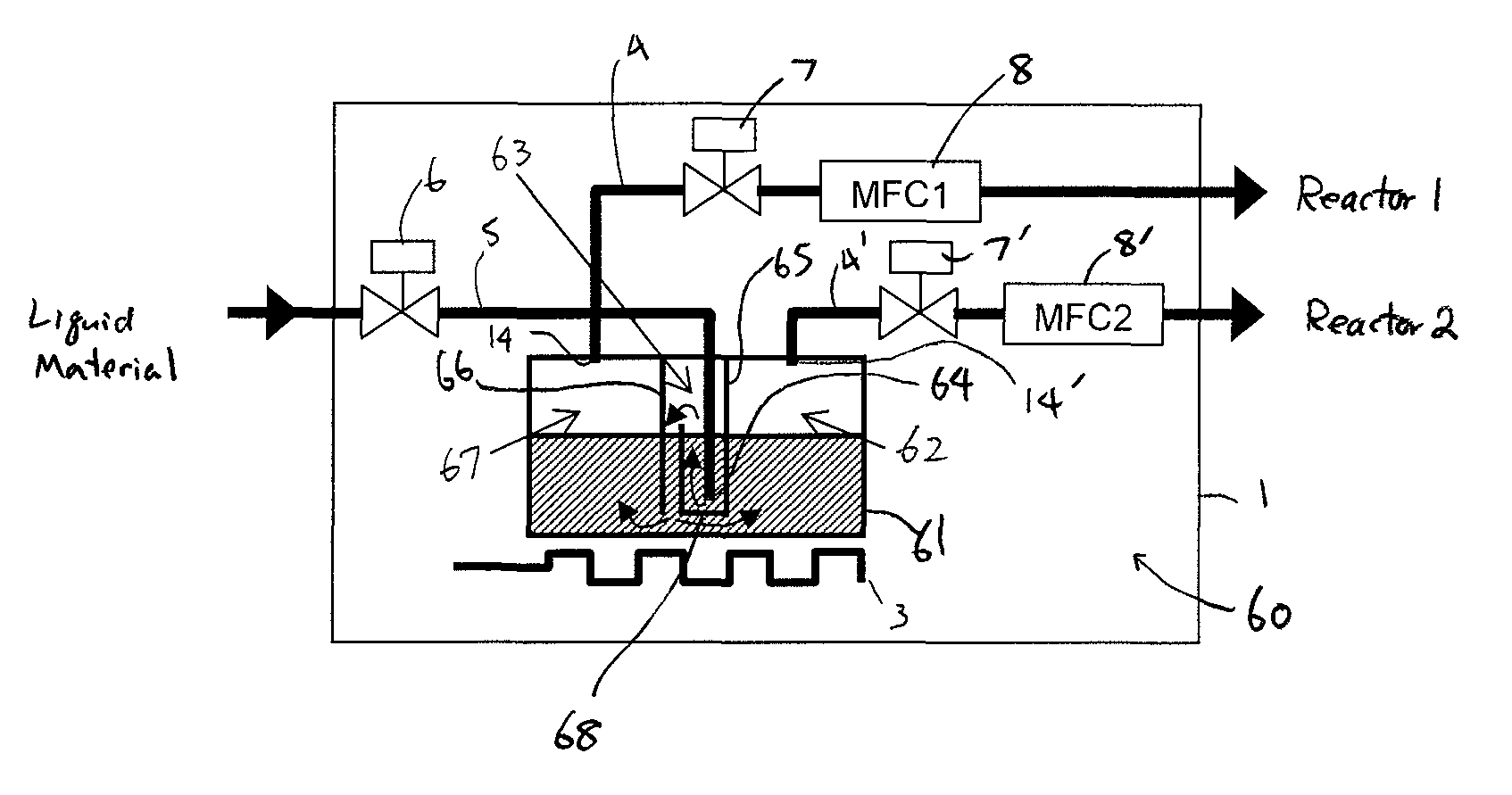
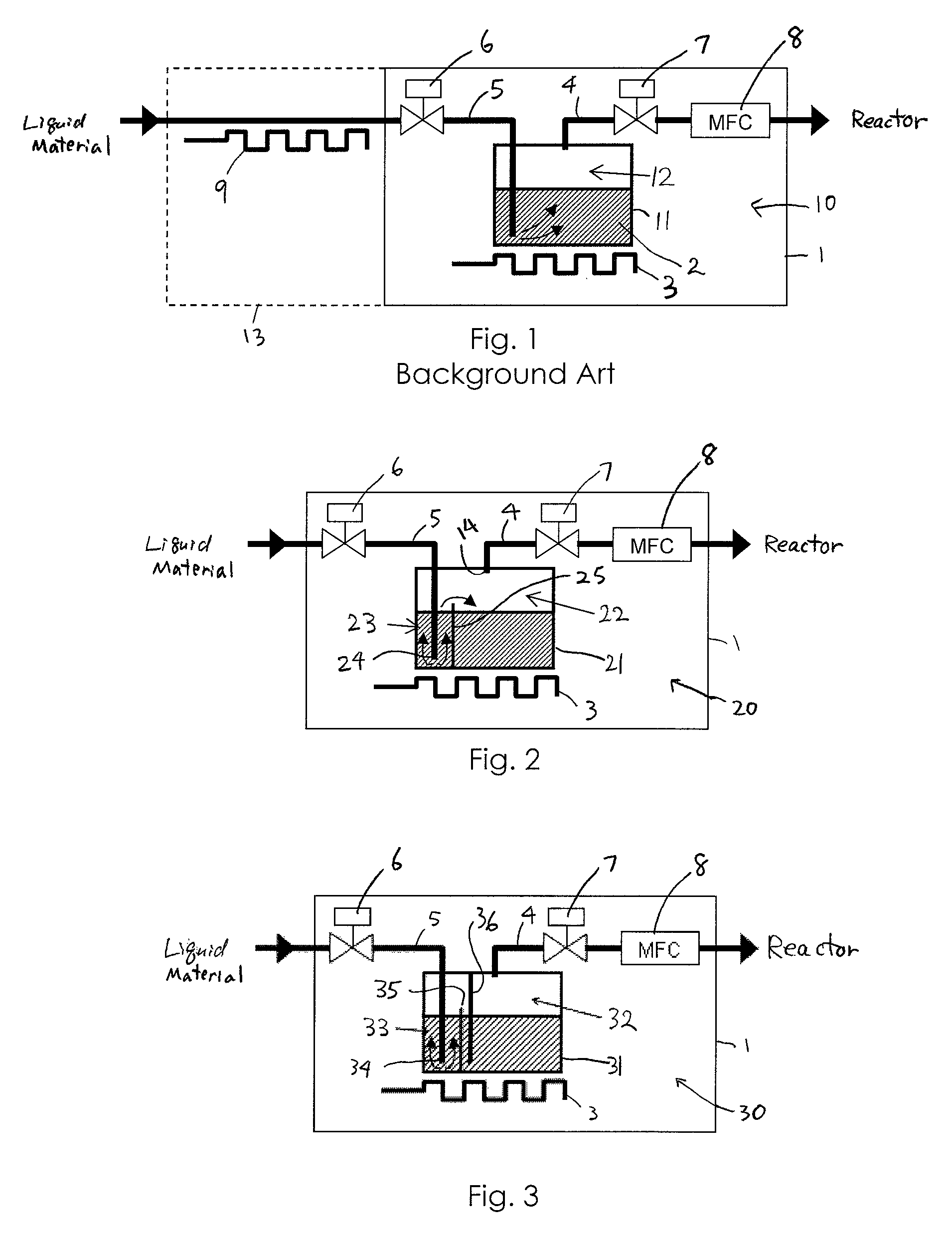
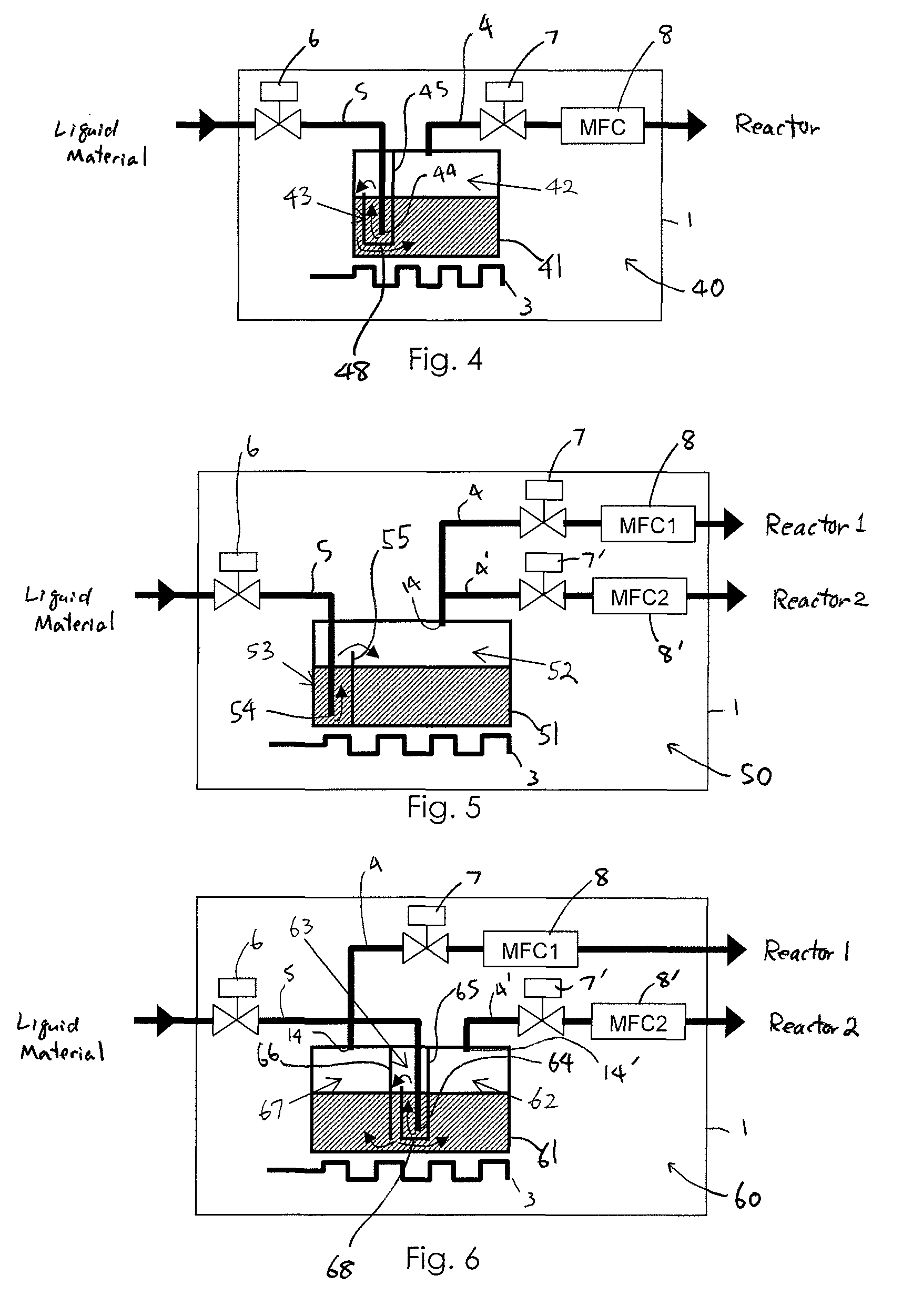
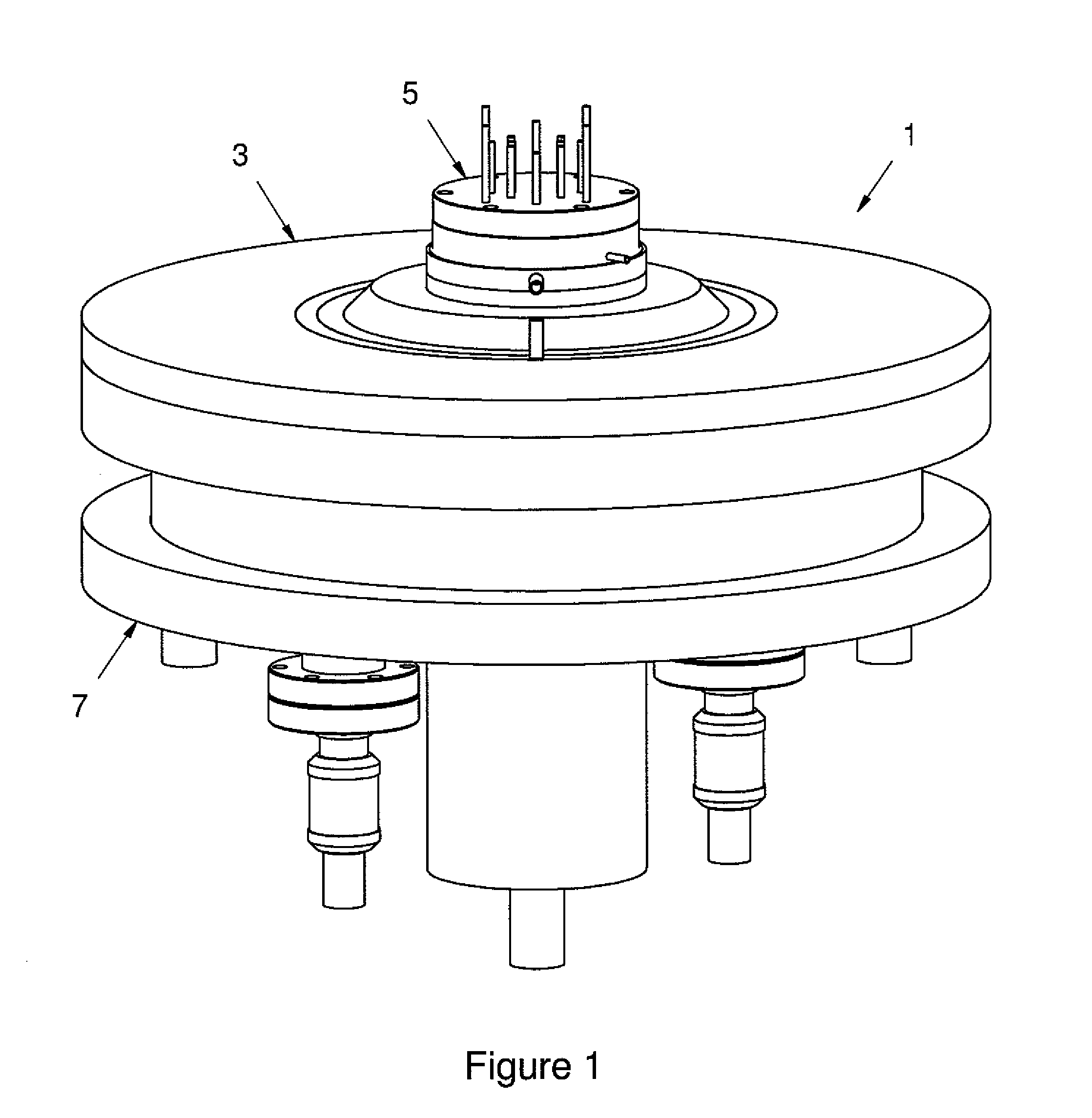
Liquid material vaporization apparatus for semiconductor processing apparatus
ActiveUS7833353B2Reduce the temperatureInhibition is effectiveSteam generation heating methodsSpray nozzlesVaporizationEngineering
A liquid material vaporization apparatus for a semiconductor processing apparatus includes: a vaporization tank; an inner partition wall disposed in the tank for dividing the interior of the tank into a charging compartment and a vaporization compartment which are liquid-communicatable with each other over an upper edge of the inner partition wall. A liquid material charged in the charging compartment overflows over the upper edge of the inner partition wall toward the vaporization compartment to store and vaporize the liquid material in the vaporization compartment.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
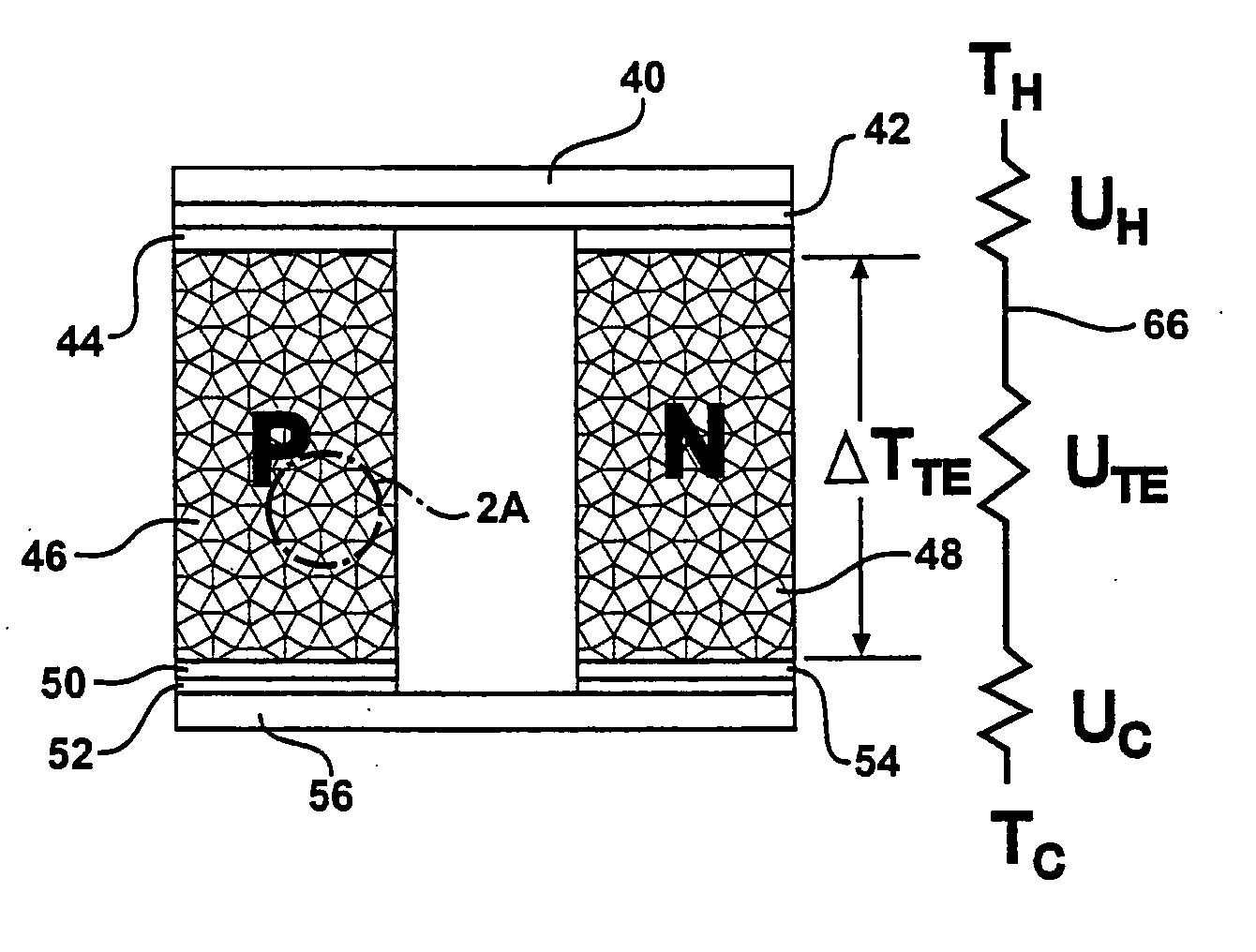
Nanostructured bulk thermoelectric material
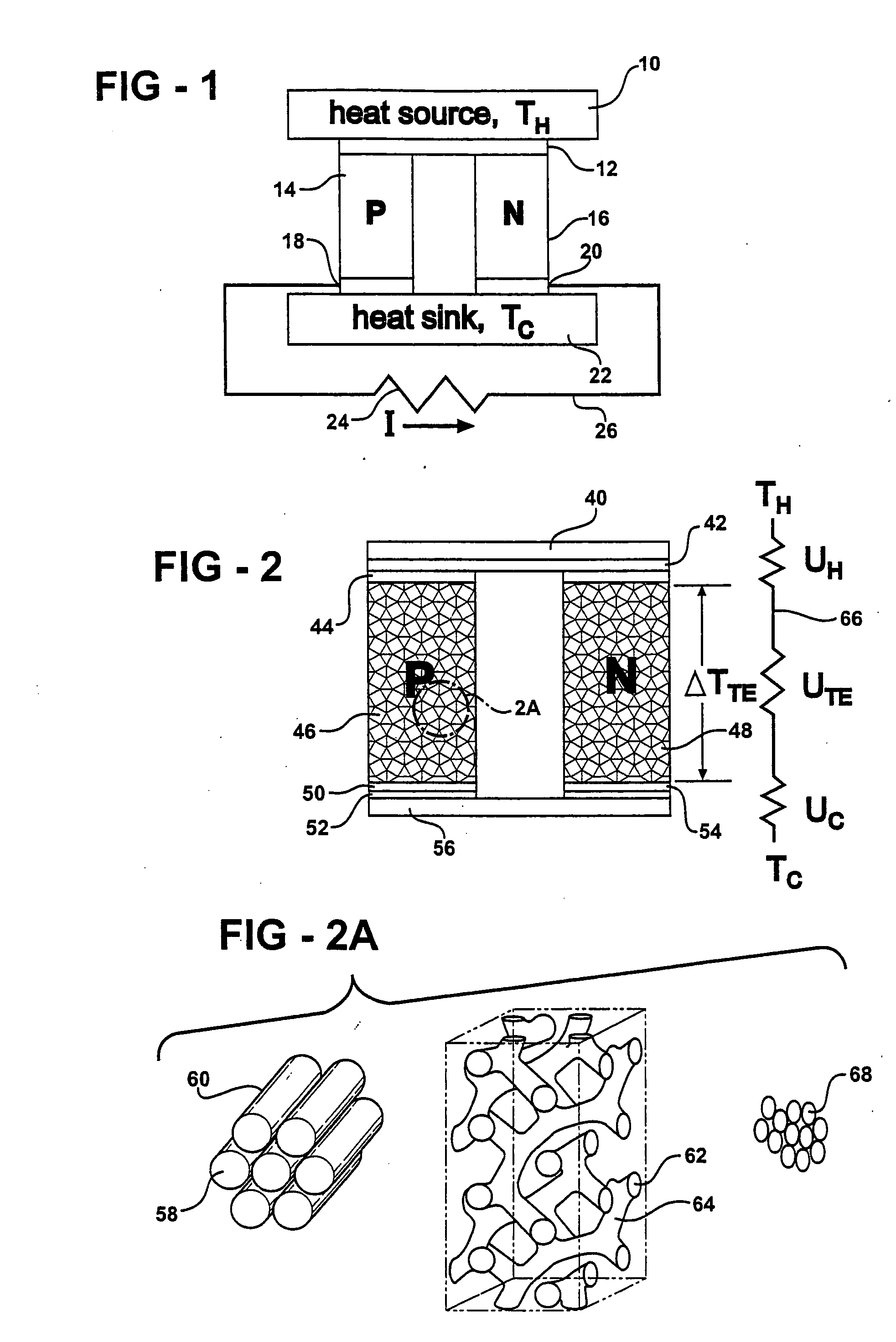
ActiveUS20060118158A1High quality factorImprove mechanical propertiesThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric materialsNanowire
A thermoelectric material comprises two or more components, at least one of which is a thermoelectric material. The first component is nanostructured, for example as an electrically conducting nanostructured network, and can include nanowires, nanoparticles, or other nanostructures of the first component. The second component may comprise an electrical insulator, such as an inorganic oxide, other electrical insulator, other low thermal conductivity material, voids, air-filled gaps, and the like. Additional components may be included, for example to improve mechanical properties. Quantum size effects within the nanostructured first component can advantageously modify the thermoelectric properties of the first component. In other examples, the second component may be a thermoelectric material, and additional components may be included.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD +1
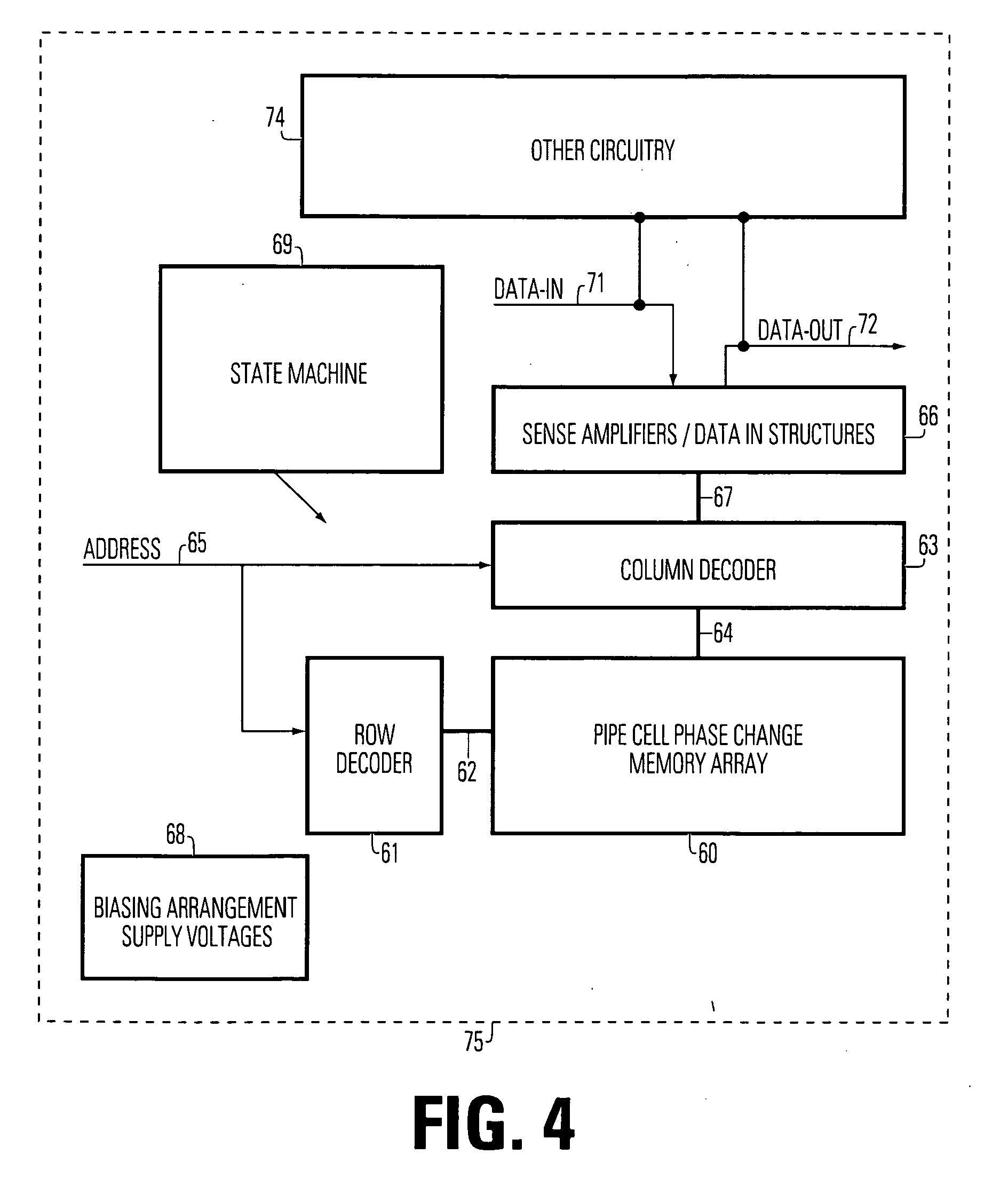
Method of manufacturing a pipe shaped phase change memory
InactiveUS20070111429A1Low thermal conductivityLower average currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryEngineering
A manufacturing method for a pipe-shaped memory cell device includes forming a bottom electrode having a top surface; forming a fill layer over the electrode, with a via having sides, extending from a top surface of the fill layer to the top surface of the bottom electrode; forming a conformal layer of programmable resistive material within the via, the conformal layer contacting the electrode and extending along the sides of the via to the top surface; and forming a top electrode in contact with the conformal layer over the fill layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
LED light fixture
InactiveUS20070247842A1Low thermal conductivityLower resistancePlanar light sourcesCeilingsInfraredElectricity
A light fixture using LEDs includes a lower skin layer possessing heat transfer properties. A circuit board is affixed to the lower skin layer, and a single LED, or a plurality of LEDs, is electrically connected to the circuit board. The single LED, or plurality of LEDs, when electrically activated, emits light through substantially around a vertical axis. The light fixture also includes a core possessing heat transfer properties that is in thermal contact with the LED and has an interior cavity for the LED. The core is affixed to the lower skin layer, and an upper skin layer, containing a window or windows over the LED or LEDs, is affixed to the core. The LEDs may be white, infrared, ultraviolet, and / or colored and may be mounted on a printed circuit board or individually.
Owner:INTEGRATED ILLUMINATION SYST
Thermocouple vacuum gauge
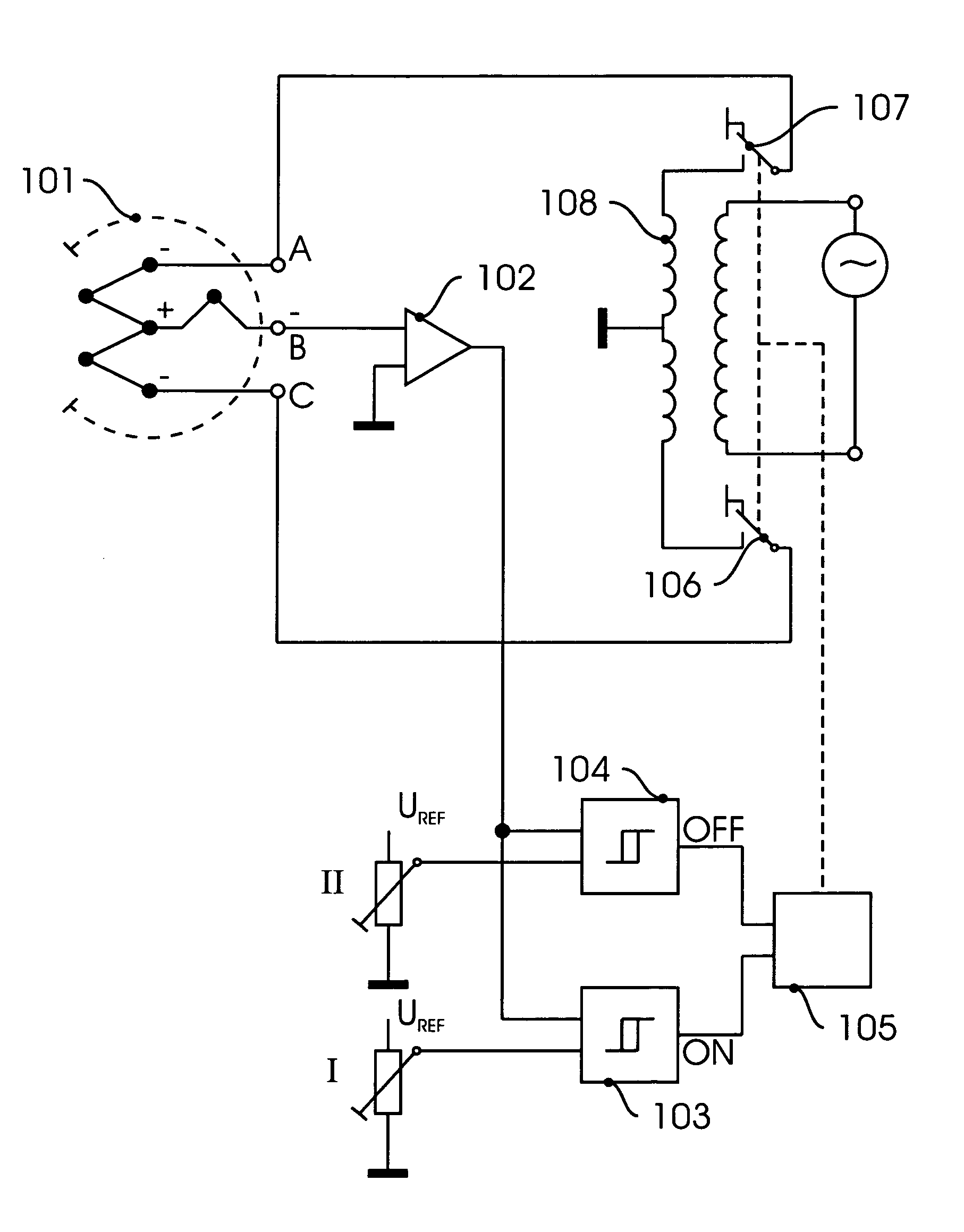
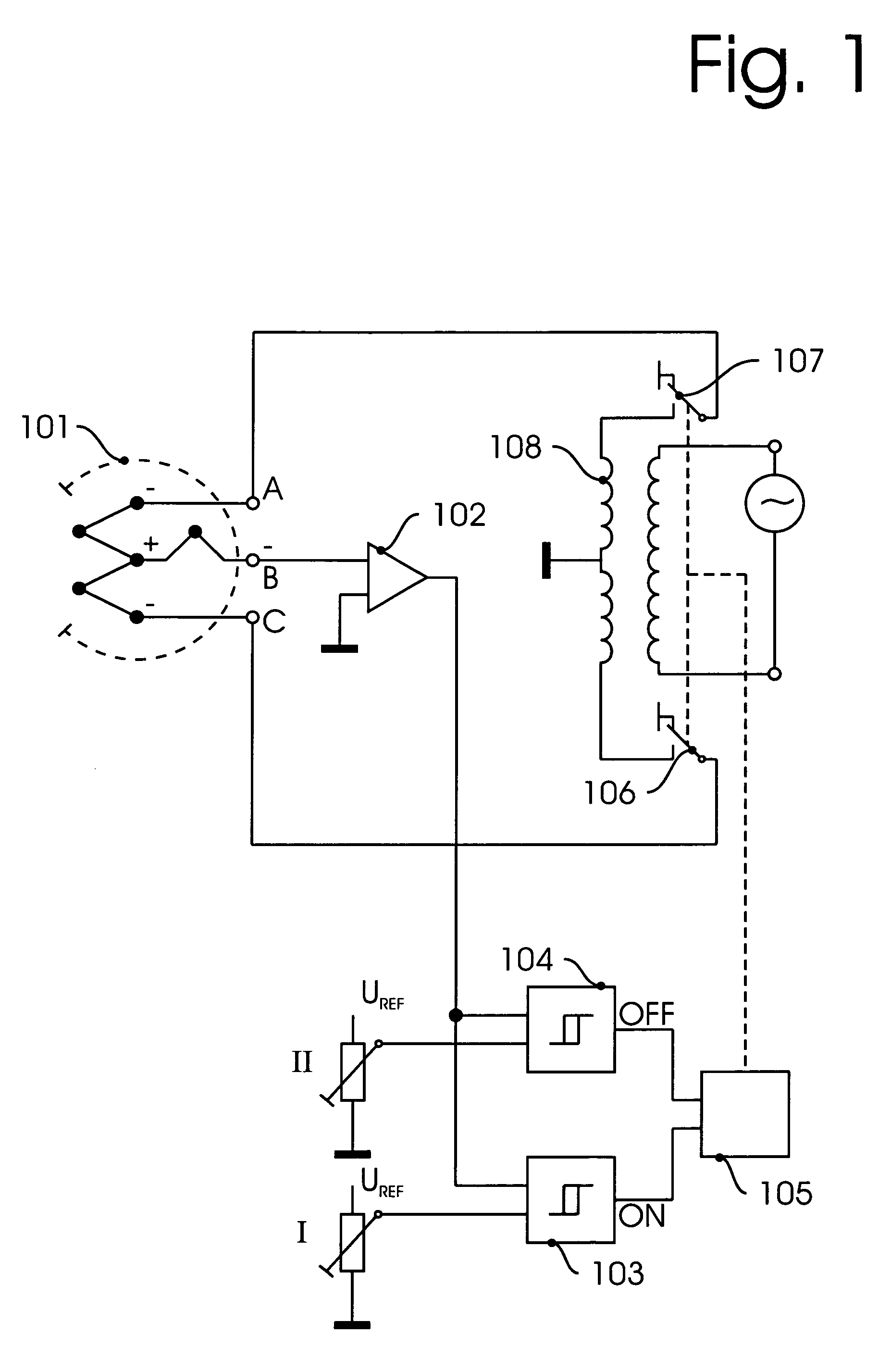
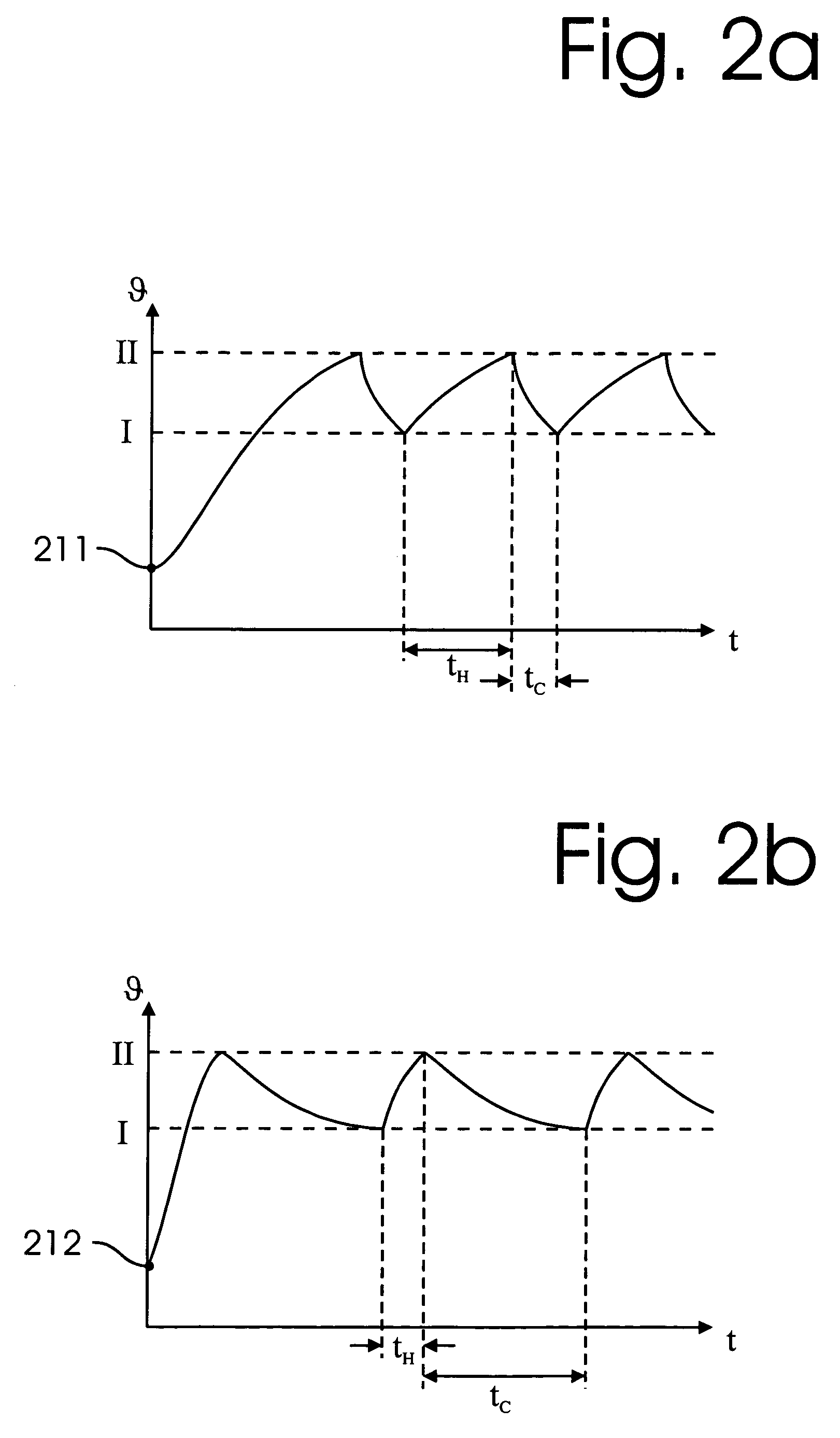
InactiveUS8047711B2Reduce heatLow thermal conductivityThermometer detailsVacuum gauge using heat conductivity variationHeating timeEngineering
A thermocouple vacuum sensor is provided, the thermocouple being surrounded by a gas or mixture of gases the pressure of which is to be measured. Cyclically the thermocouple is heated until its temperature reaches an upper temperature threshold. The thermocouple is subsequently cooled until its temperature reaches a lower temperature threshold. The heating time required to heat the thermocouple from the lower to the upper temperature threshold is measured. The cooling time required to cool the thermocouple from the upper temperature threshold to the lower temperature threshold may also be measured. The pressure surrounding the thermocouple may then be determined as a function of either the heating time, or the cooling time, or both.
Owner:HEINZ PLOECHINGER
Chemical vapor deposition reactor
InactiveUS8778079B2Improve the deposition effectOptimize geometrySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid transferring devicesGas phaseProcess engineering
Owner:VALENCE PROCESS EQUIP
Precision surface treatments using dense fluids and a plasma
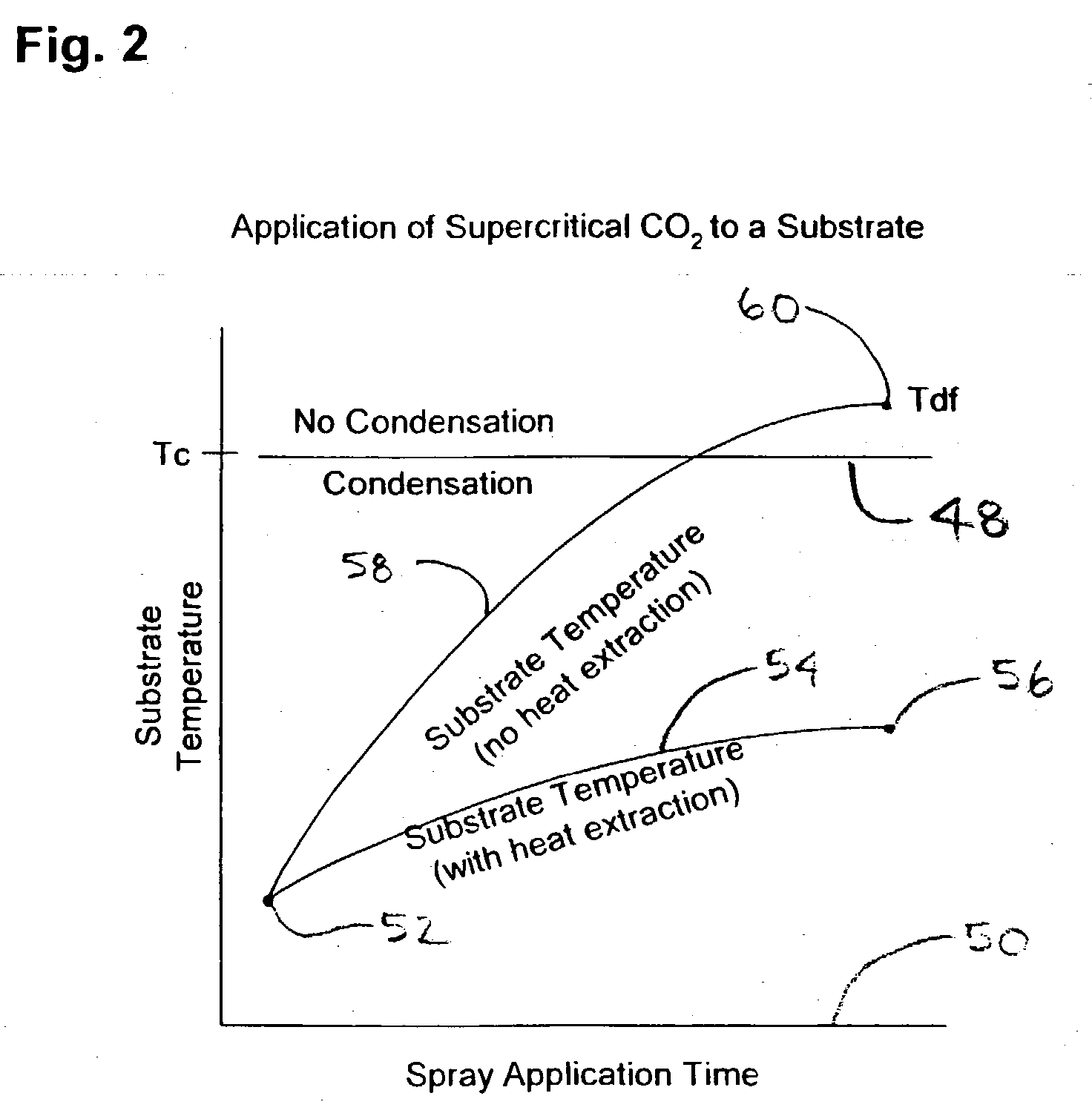
InactiveUS20040003828A1Reduce the temperatureEasy to separateElectric discharge tubesElectrostatic cleaningSolventSolid phases
The present invention is a method, process and apparatus for selective cleaning, drying, and modifying substrate surfaces and depositing thin films thereon using a dense phase gas solvent and admixtures within a first created supercritical fluid antisolvent. Dense fluids are used in combination with sub-atmospheric, atmospheric and super-atmospheric plasma adjuncts (cold and thermal plasmas) to enhance substrate surface cleaning, modification, precision drying and deposition processes herein. Moreover, conventional wet cleaning agents such as hydrofluoric acid and ammonium fluoride may be used with the present invention to perform substrate pre-treatments prior to precision drying and cleaning treatments described herein. Finally, dense fluid such as solid phase carbon dioxide and argon may be used as a follow-on treatment or in combination with plasmas to further treat a substrate surface.
Owner:JACKSON DAVID P
Aerogel-foam composites
InactiveUS20090029147A1Increase flexibilityMaintain good propertiesSolar heat devicesSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceMonolith
The invention provides reinforced aerogel monoliths as well as reinforced composites thereof for a variety of uses. Compositions and methods of preparing the monoliths and composites are also provided. Application of these materials in transparent assemblies is also discuss.
Owner:ASPEN AEROGELS
Structures and Methods of a Bistable Resistive Random Access Memory
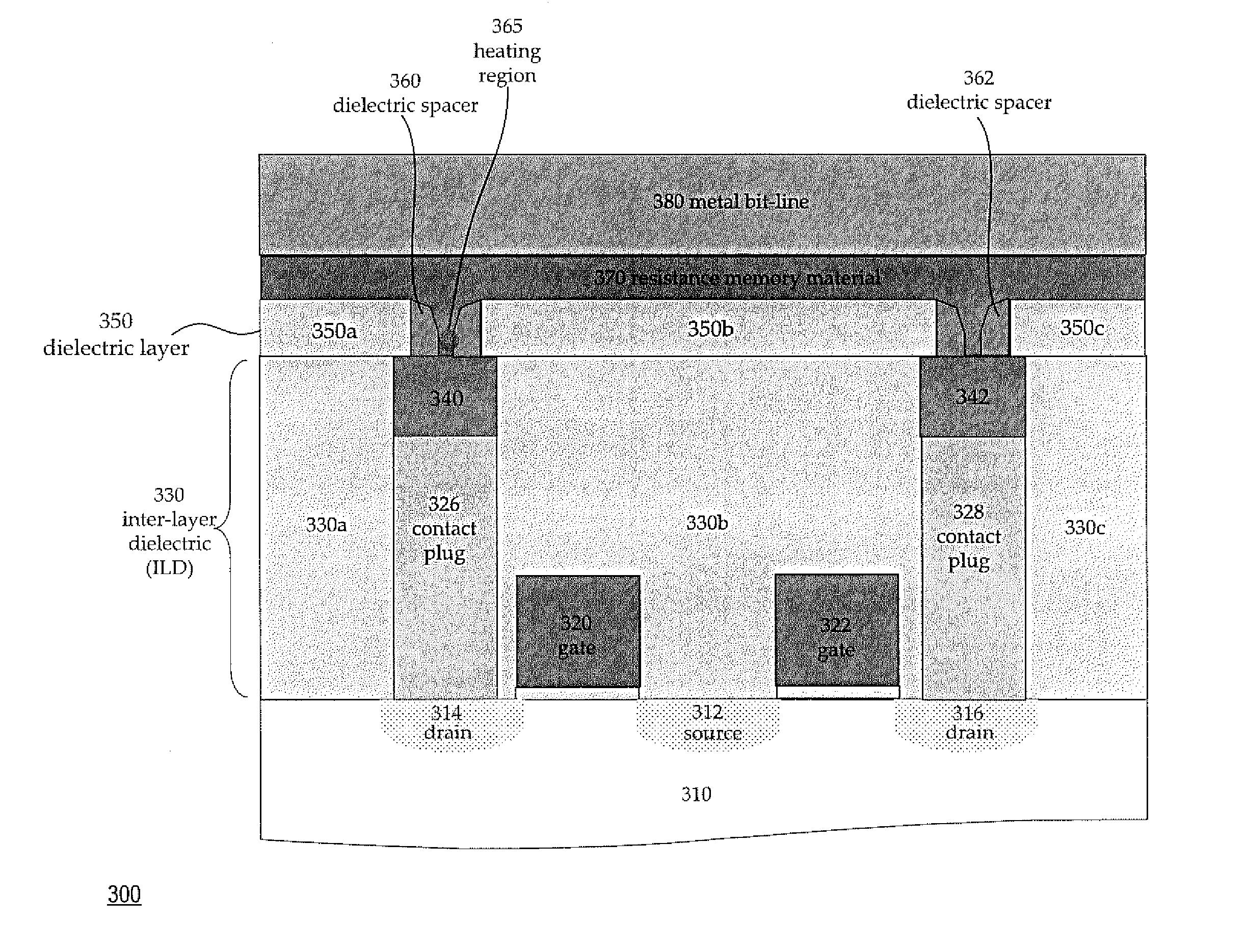
ActiveUS20070257300A1Reduce heat dissipationReduce heatTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
Structures and methods to form a bistable resistive random access memory for reducing the amount of heat dissipation from electrodes by confining a heating region in the memory cell device are described. The heating region is confined in a kernel comprising a programmable resistive memory material that is in contact with an upper programmable resistive memory member and a lower programmable resistive memory member. The lower programmable resistive member has sides that align with sides of a bottom electrode comprising a tungsten plug. The lower programmable resistive member and the bottom electrode function a first conductor so that the amount of heat dissipation from the first conductor is reduced. The upper programmable resistive memory material and a top electrode function as a second conductor so that the amount of heat dissipation from the second conductor is reduced.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
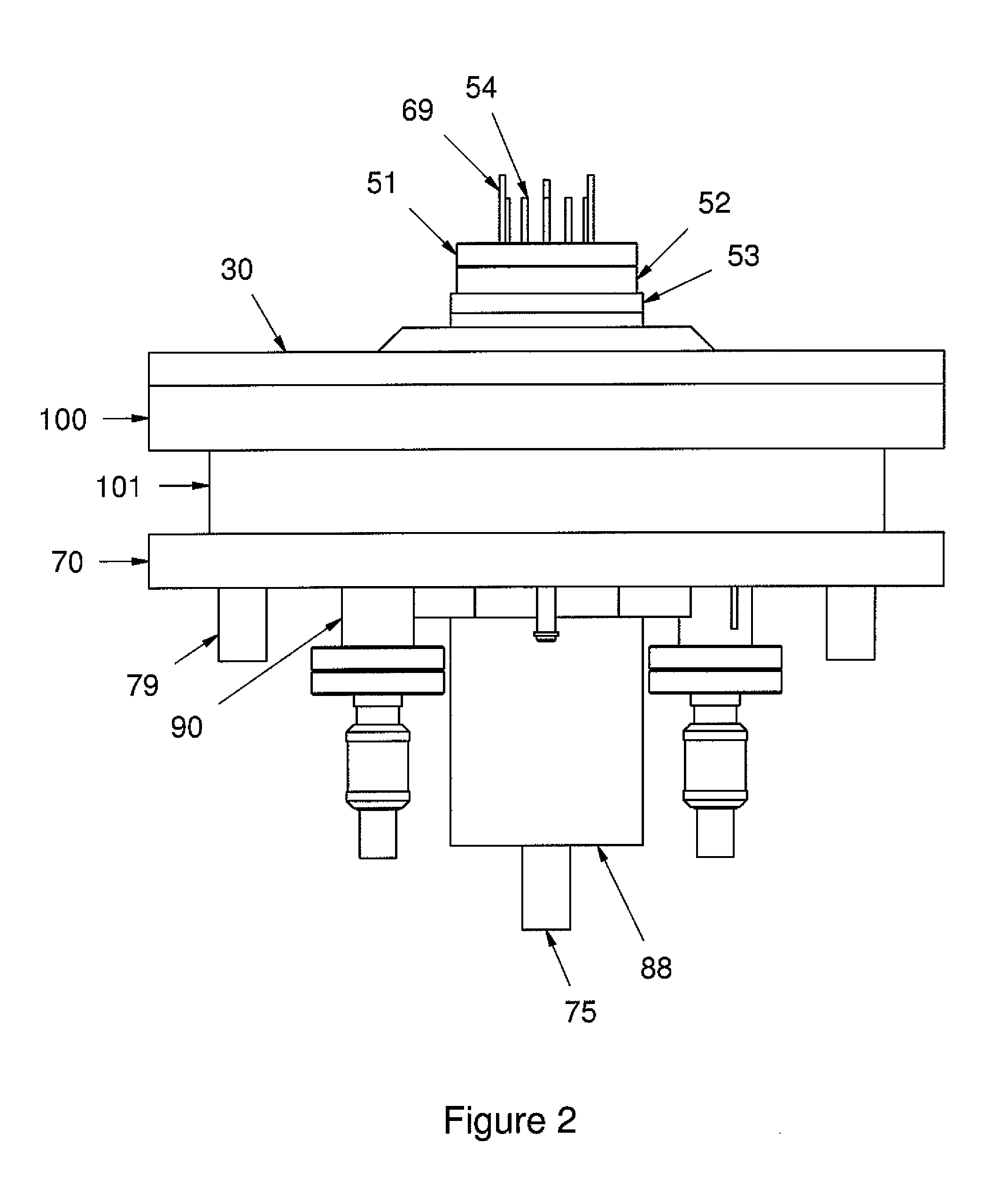
Chemical vapor deposition reactor
InactiveUS20120111271A1Improve the deposition effectOptimize geometrySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid transferring devicesGas phaseProcess engineering
A CVD reactor, such as a MOCVD reactor conducting metalorganic chemical vapor deposition of epitaxial layers, is provided. The CVD or MOCVD reactor generally comprises a flow flange assembly, adjustable proportional flow injector assembly, a chamber assembly, and a multi-segment center rotation shaft. The reactor provides a novel geometry to specific components that function to reduce the gas usage while also improving the performance of the deposition.
Owner:VALENCE PROCESS EQUIP
Aerogel/PTFE composite insulating material
ActiveUS20050100728A1Increase flexibilityHigh strengthDigital data processing detailsAdhesive articlesInto-structureMaterials science
A material comprising aerogel particles and a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) binder is formed having a thermal conductivity of less than or equal to 25 mW / m K at atmospheric conditions. The material is moldable or formable, having little or no shedding of filler particles, and may be formed into structures such as tapes or composites, for example, by bonding the material between two outer layers. Advantageously, composites may be flexed, stretched, or bent without significant dusting or loss of insulating properties.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
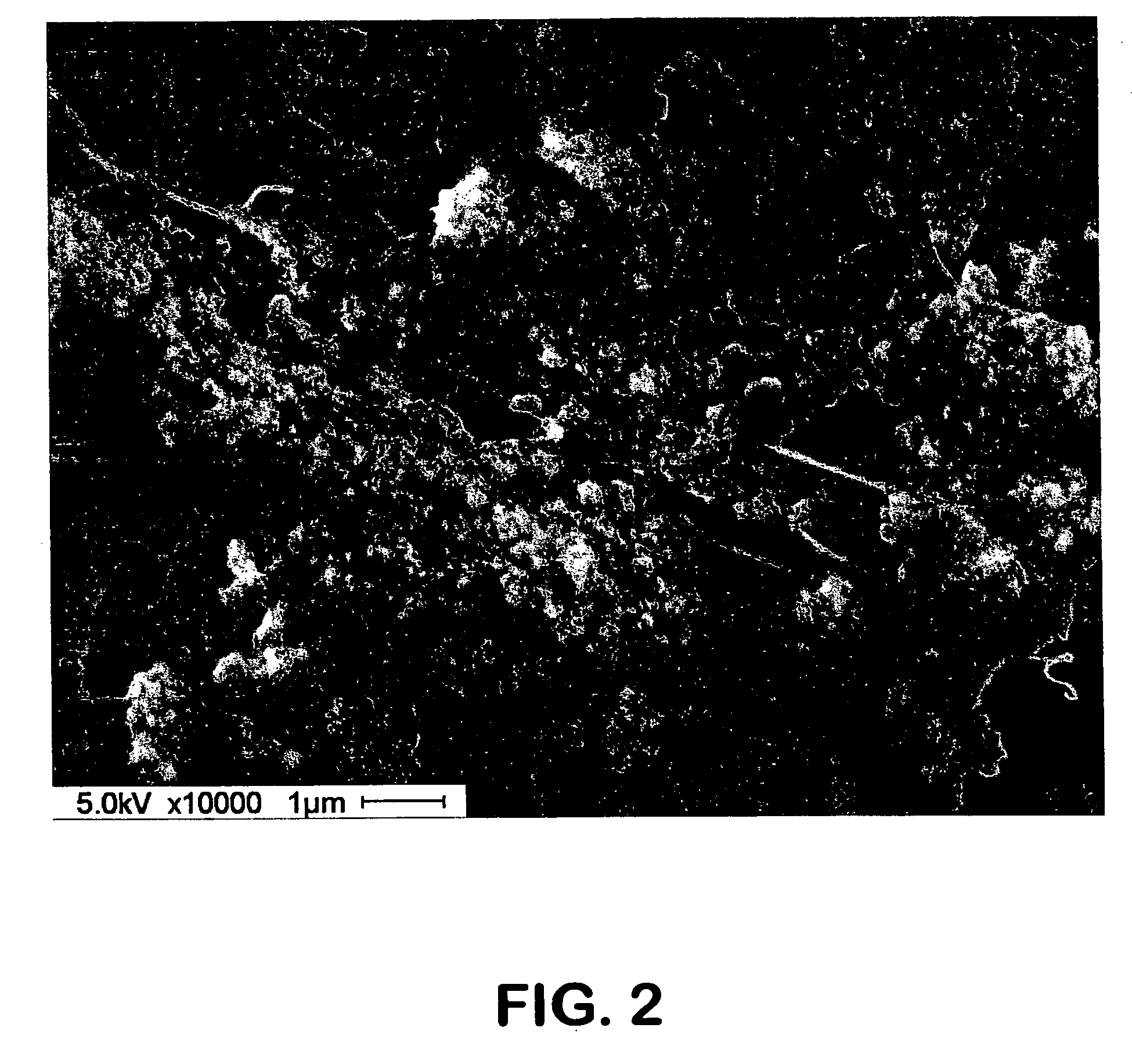
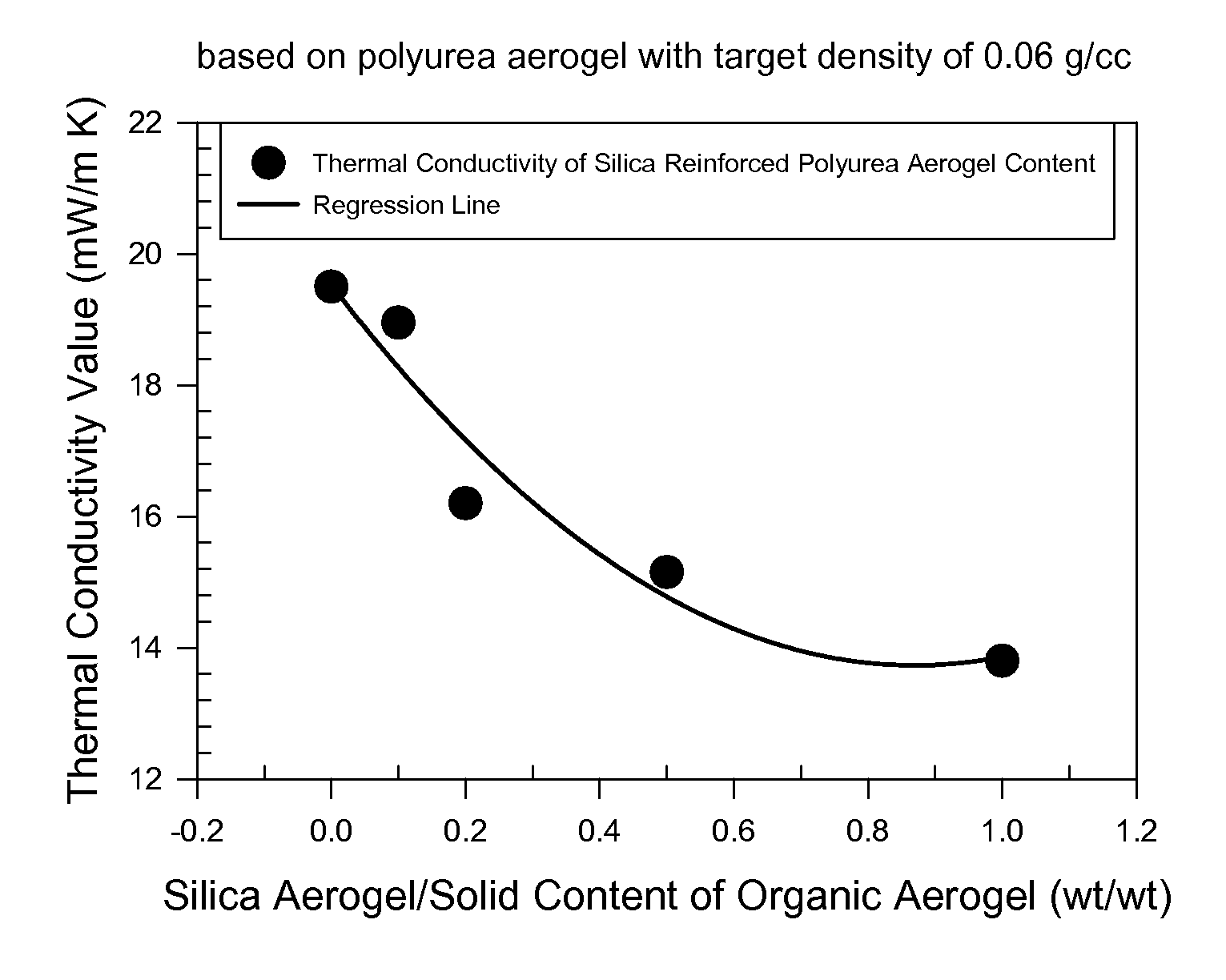
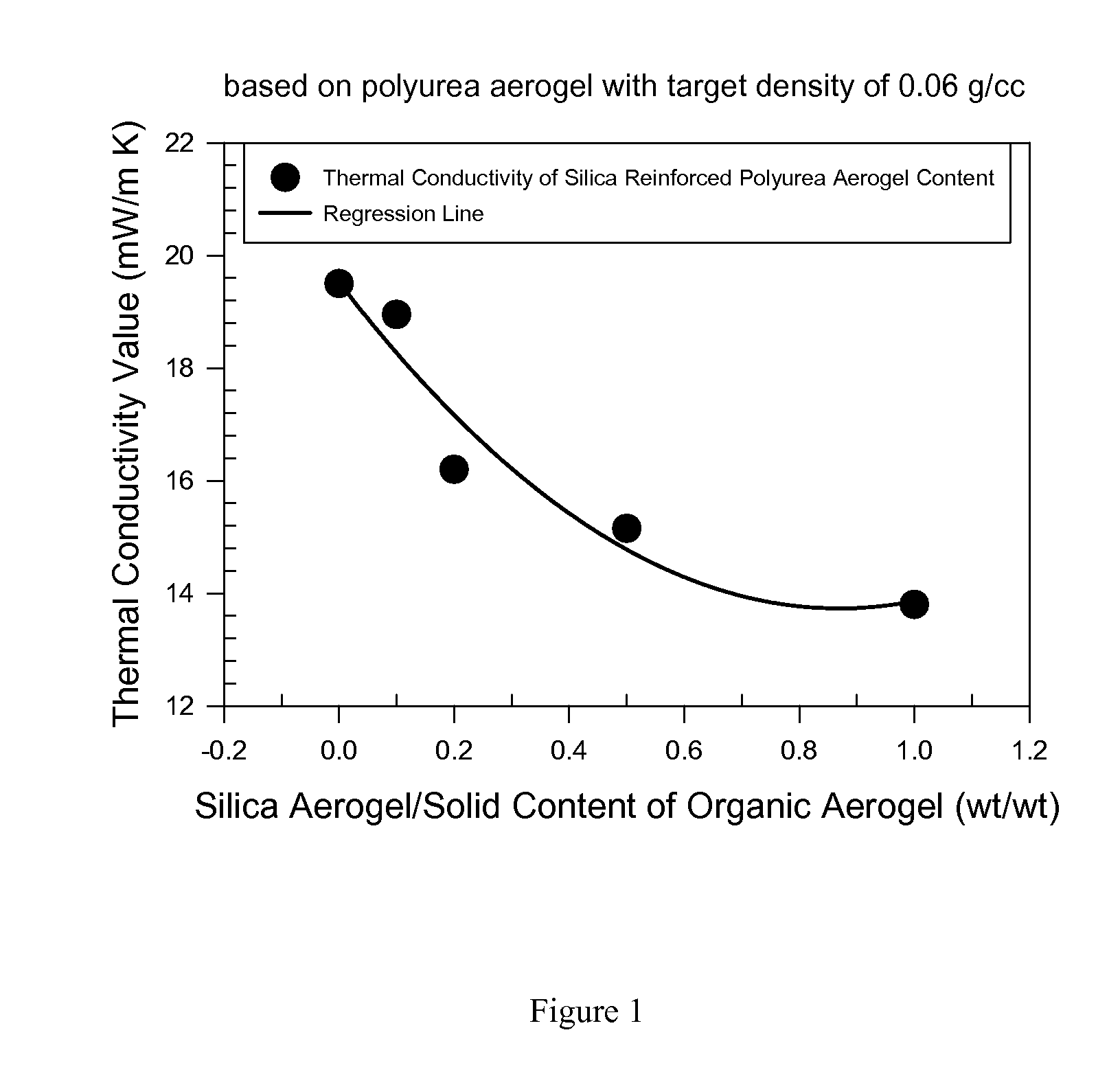
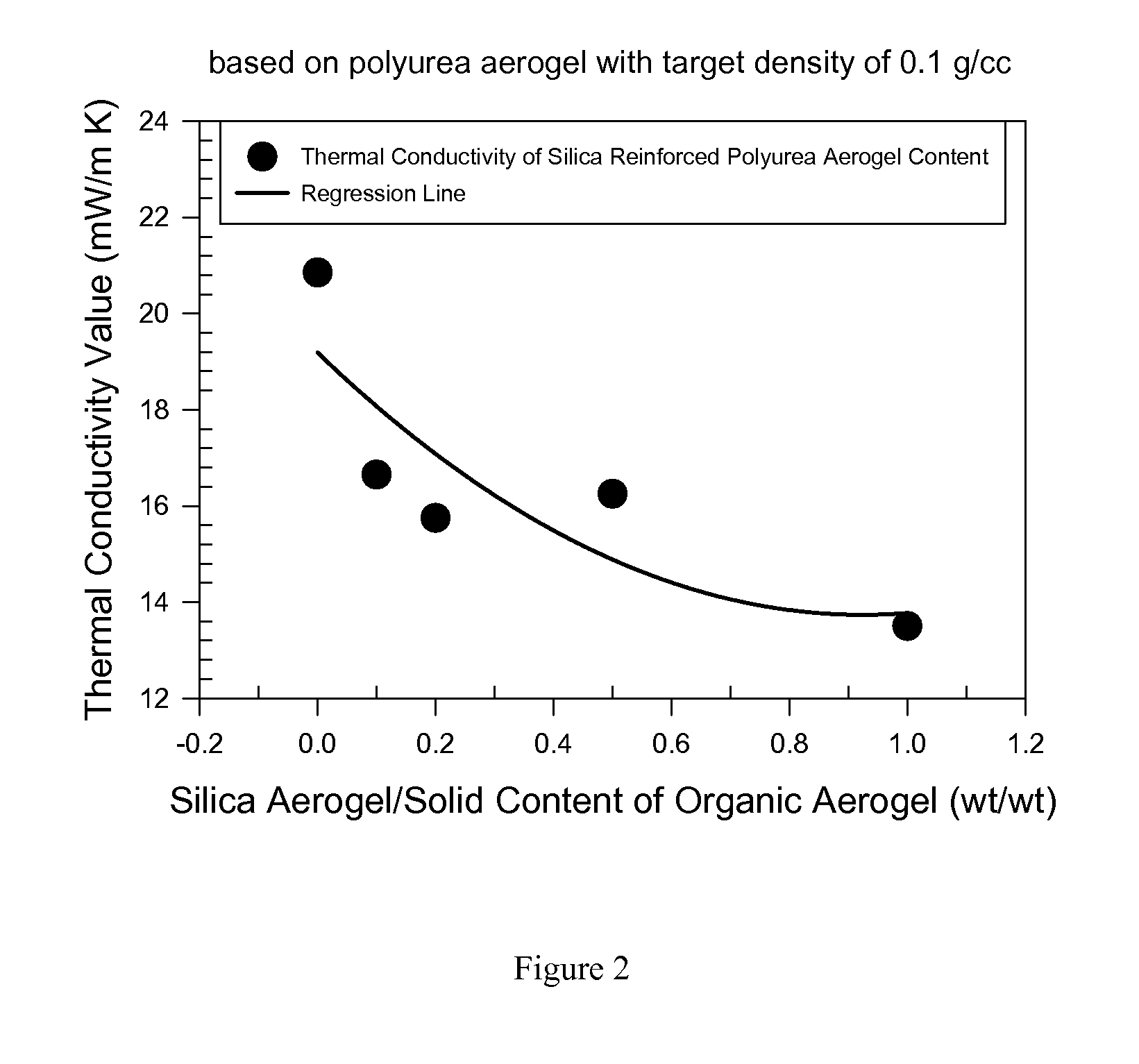
Organic aerogels reinforced with inorganic aerogel fillers
Composites comprising organic aerogel matrix and inorganic aerogel fillers are described. The methods of manufacturing such composite aerogels are also described. Inorganic aerogels fillers are demonstrated to improve the thermal performance of organic aerogels. Composite aerogels with various organic aerogels and inorganic aerogel fillers are described.
Owner:ASPEN AEROGELS INC
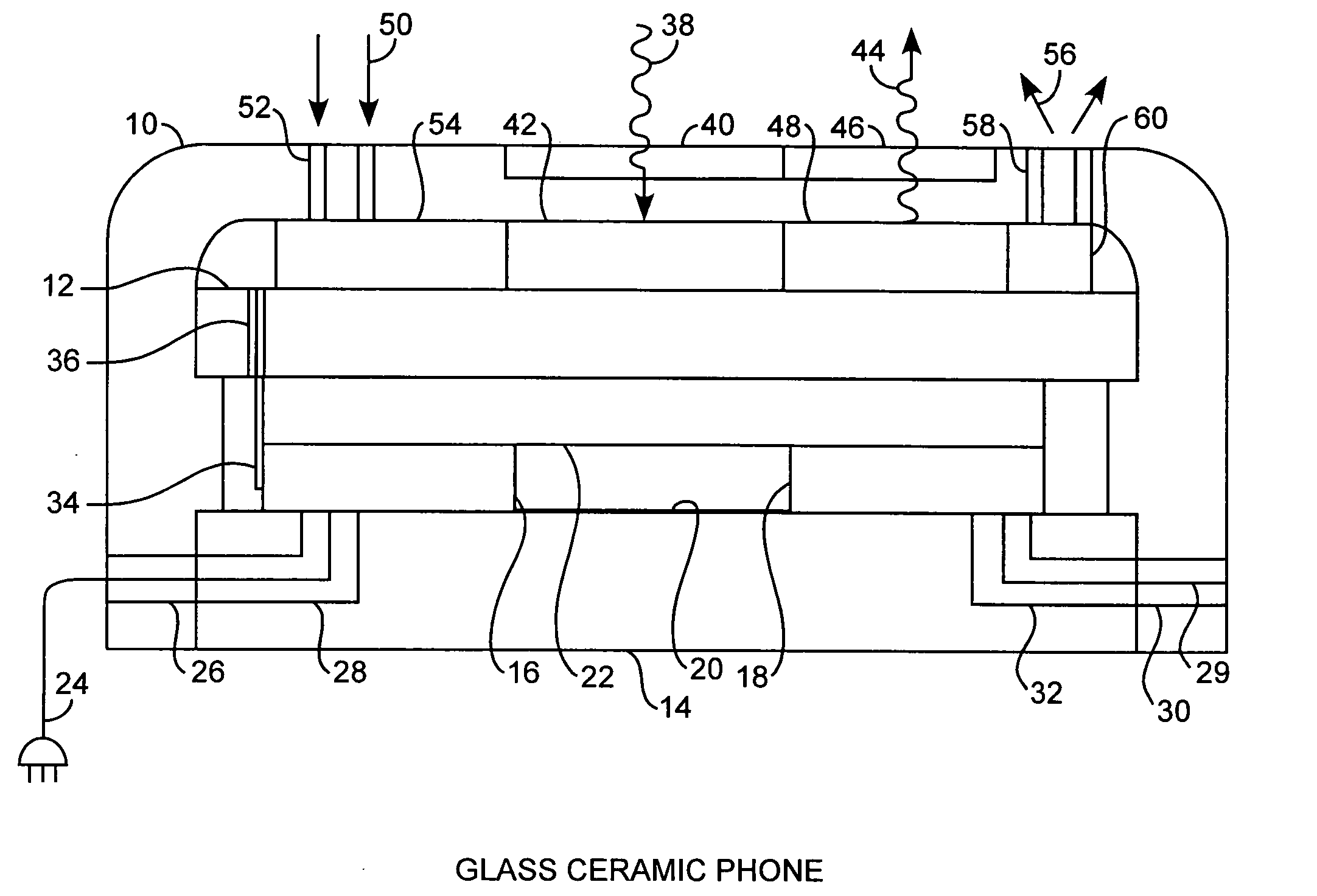
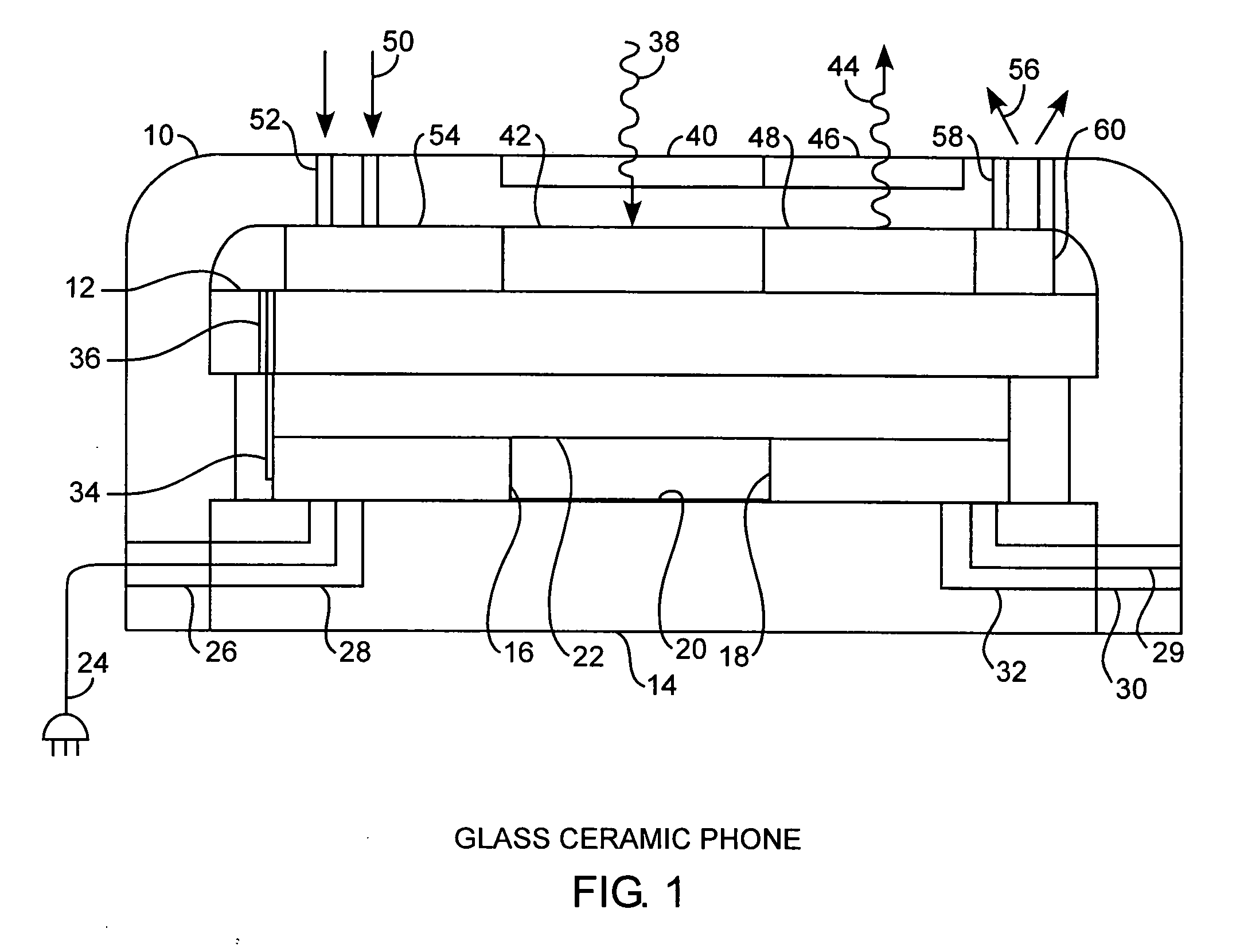
Integrated glass ceramic systems
ActiveUS20050135724A1Enhance dielectric propertyAdditional strengthCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCosmonautic power supply systemsOpto electronicElectricity
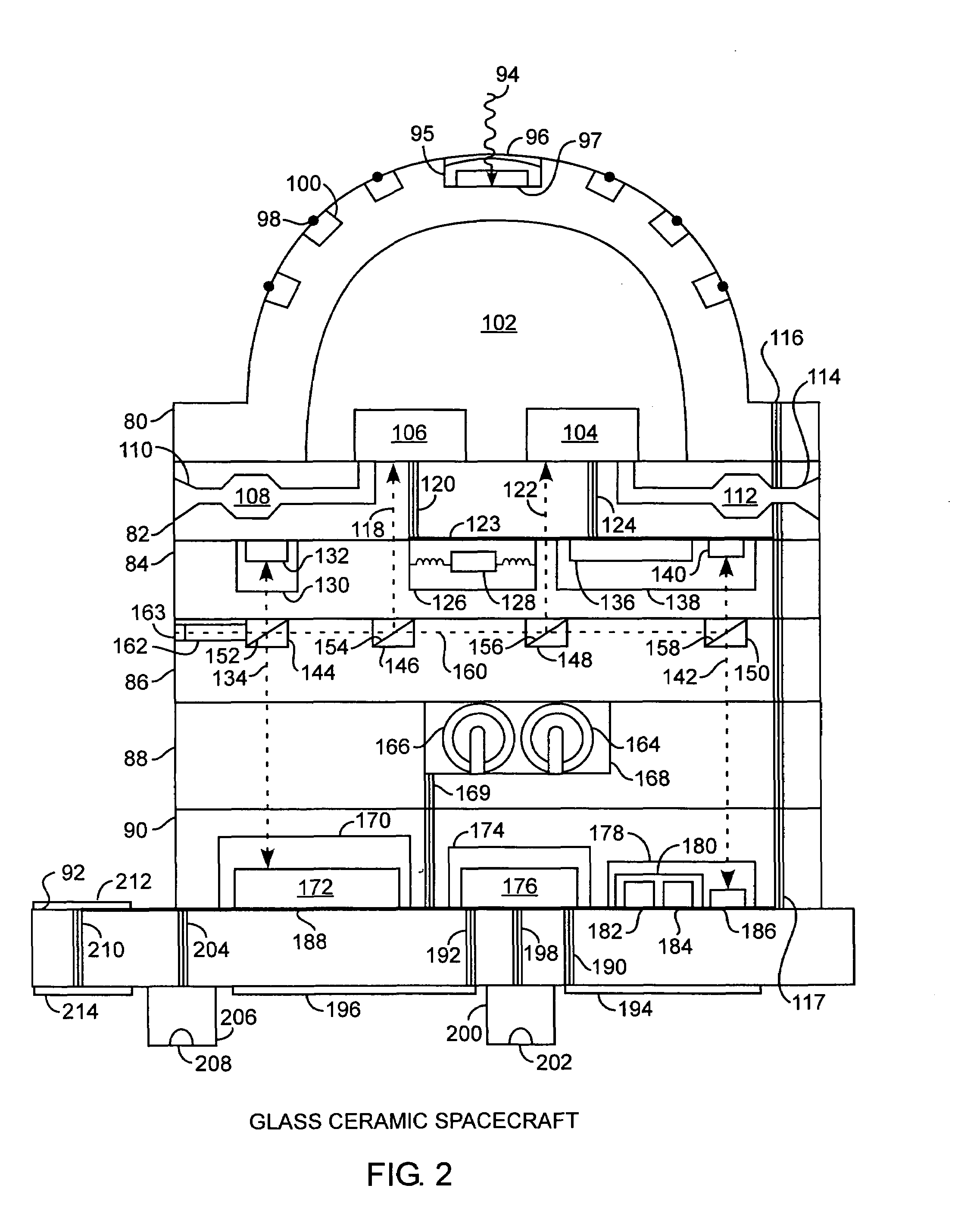
Integrated glass ceramic spacecraft include a plurality of glass ceramic components including molded, tempered, annealed, and patterned glass ceramic components coupled together for forming a support structure or frame or housing through which is communicated optical signals through an optical communications grid and electrical signals through an electrical communications grid, with the optical communications grid and electrical communication grid forming a composite electrooptical communications grid for spacecraft wide intercommunications. The support structure multifunctions as a frame, a housing, a support, a thermal control system, and as part of an electrooptical communications grid while encapsulating a plurality of optical, electronic, electrical, and MEMS devices between which is communicated the electrical and optical signals over the electrooptical communication grid.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
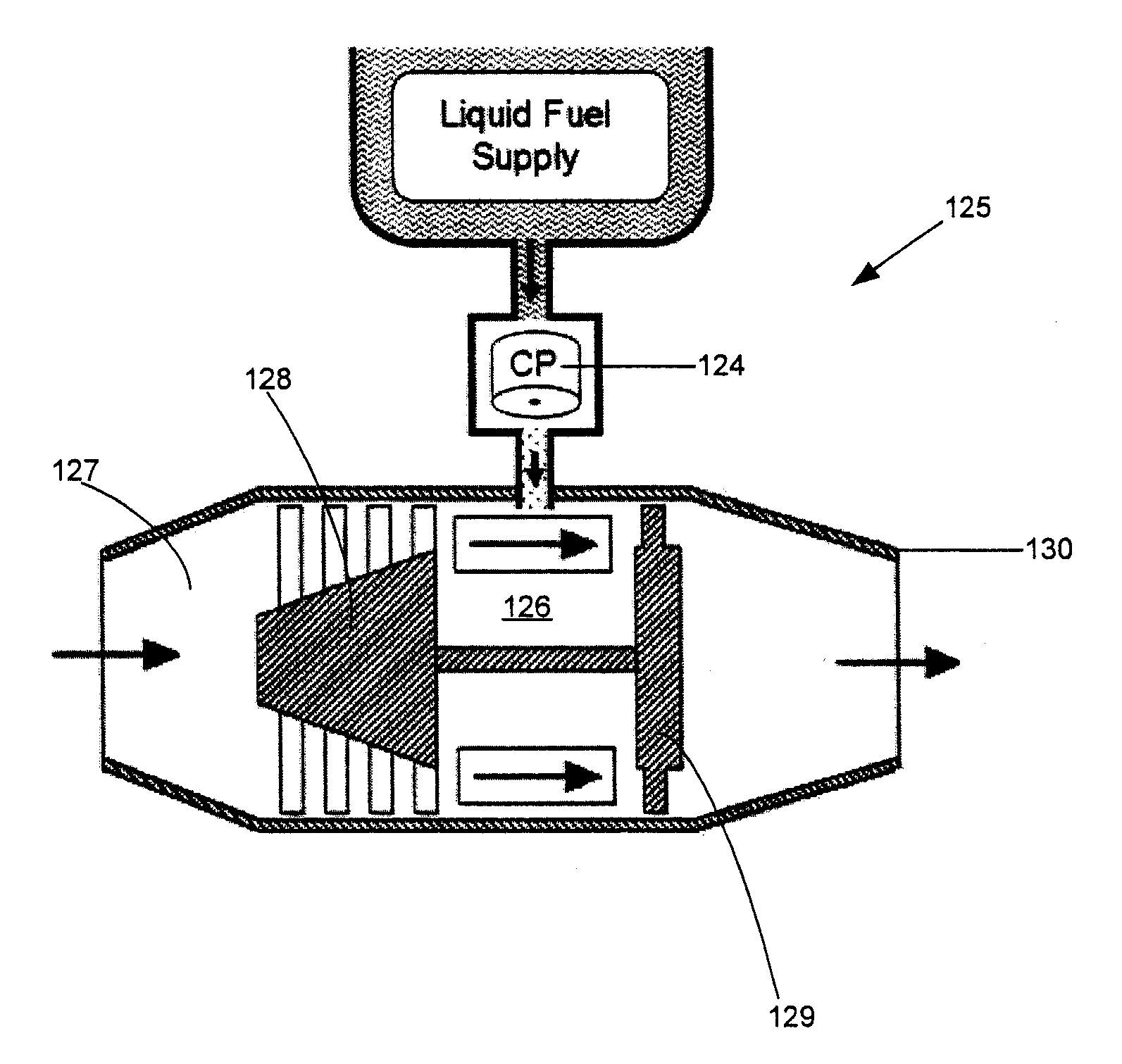
Localized surface volatilization
InactiveUS6909840B2Improved vaporizationIncrease vapor pressureDomestic stoves or rangesLiquid heating fuelElectrical resistance and conductanceProduct gas
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for rapid flash-like volatilization of high and low vapor pressure components from liquid or solid emanators which is in contact with a point or localized heat source. Vaporization is promoted by a geometrically small electrically resistive heating element with variable activation for pulsed or cyclic heating of an emanating surface containing the volatile components. The apparatus is primarily directed towards the treatment of residential air for fragrancing, odor elimination, treatment of insects or pests, air sanitization, air and surface antibacterial or antimicrobial treatment, or other ambient air or surface modification by way of gas or vapor distribution.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
Stimulating production from oil wells using an RF dipole antenna
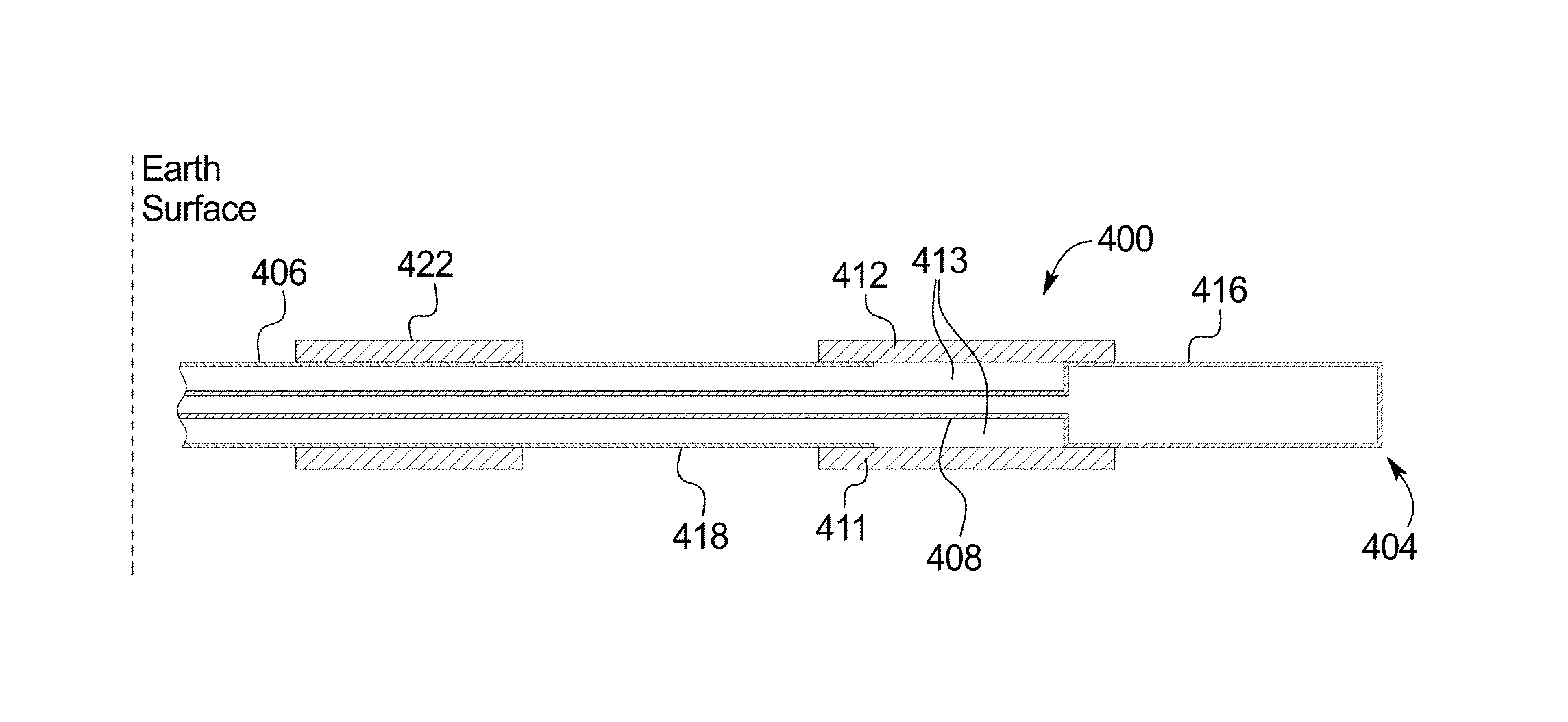
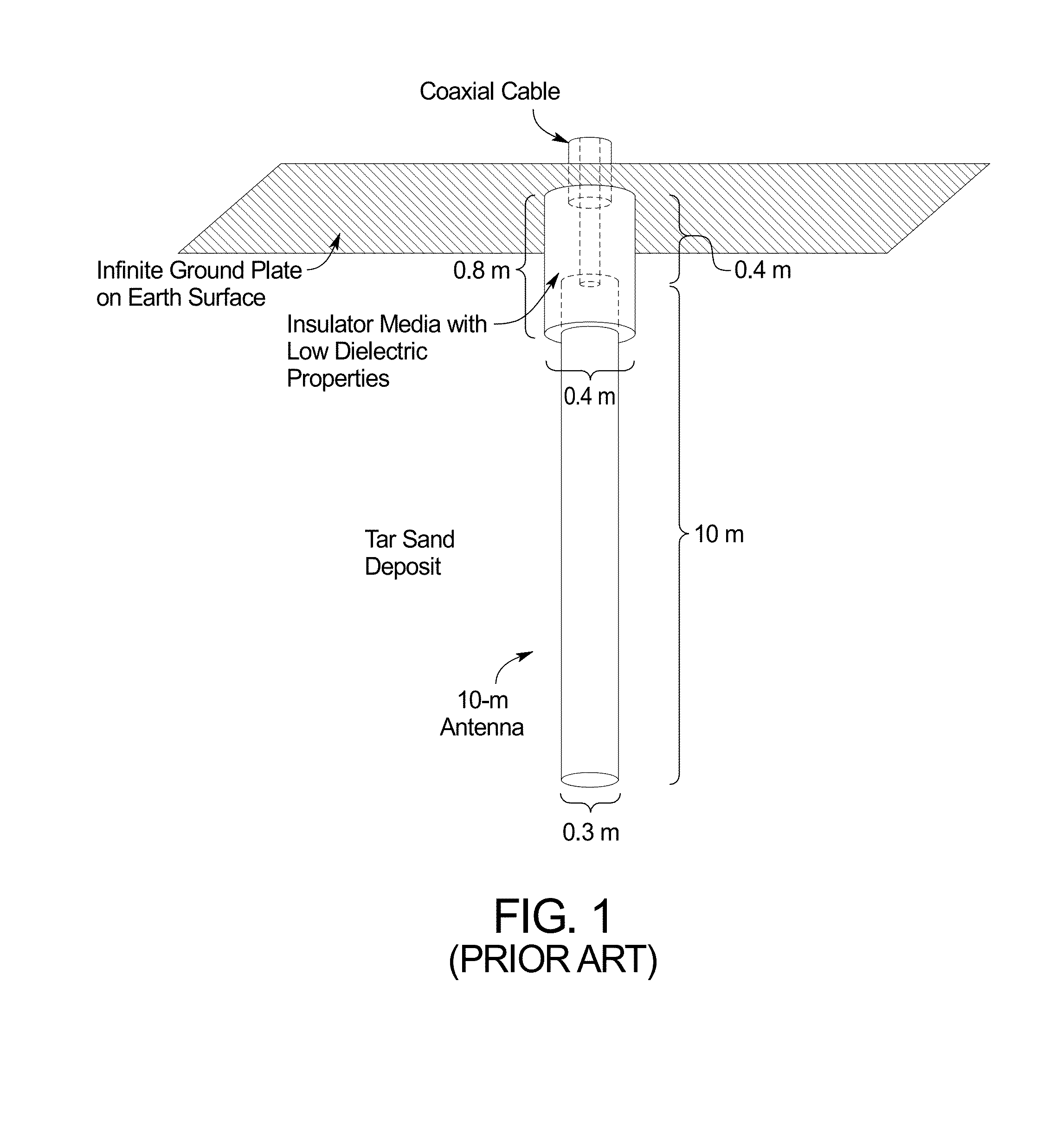
ActiveUS20140152312A1Reduced effectivenessLow thermal conductivityFluid removalDetection using electromagnetic wavesRf fieldElectrical conductor
A system emplaced in a subsurface formation configured to produce radio frequency (RF) fields for recovery of thermally responsive constituents includes coaxially disposed inner and outer conductors connected at an earth surface to an RF power source. The inner and outer conductors form a coaxial transmission line proximate said earth surface and a dipole antenna proximate said formation. The inner conductor protrudes from the outer conductor from a junction exposing a gap between the conductors to a deeper position within the formation. The RF power source is configured to deliver, via the conductors, RF fields to the formation. The system also includes at least one choke structure attached to said outer conductor at a distance at least ¼ wavelength above said junction. The choke structure is configured to confine a majority of said RF fields in a volume of said formation situated adjacent to said antenna.
Owner:PYROPHASE INC
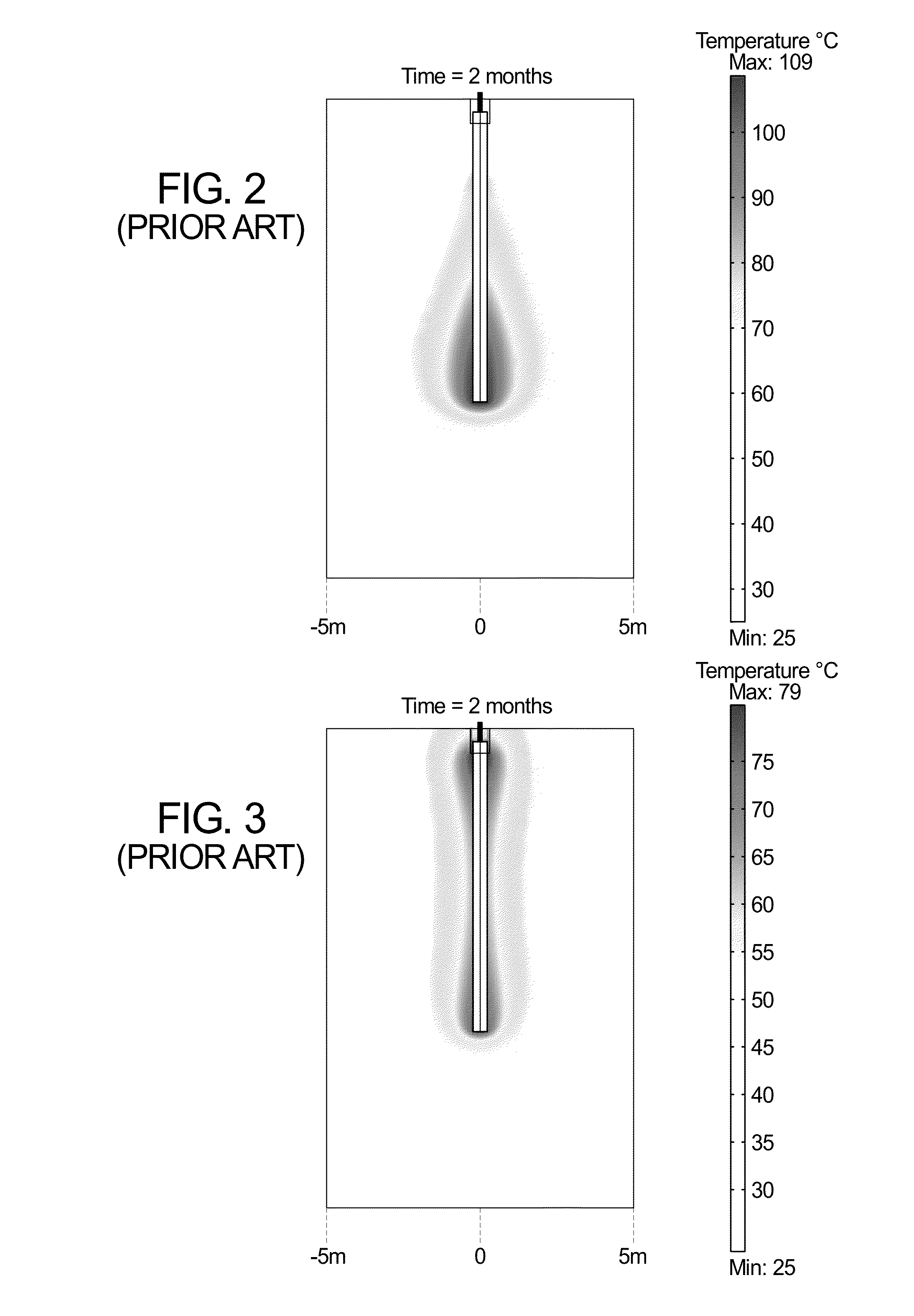
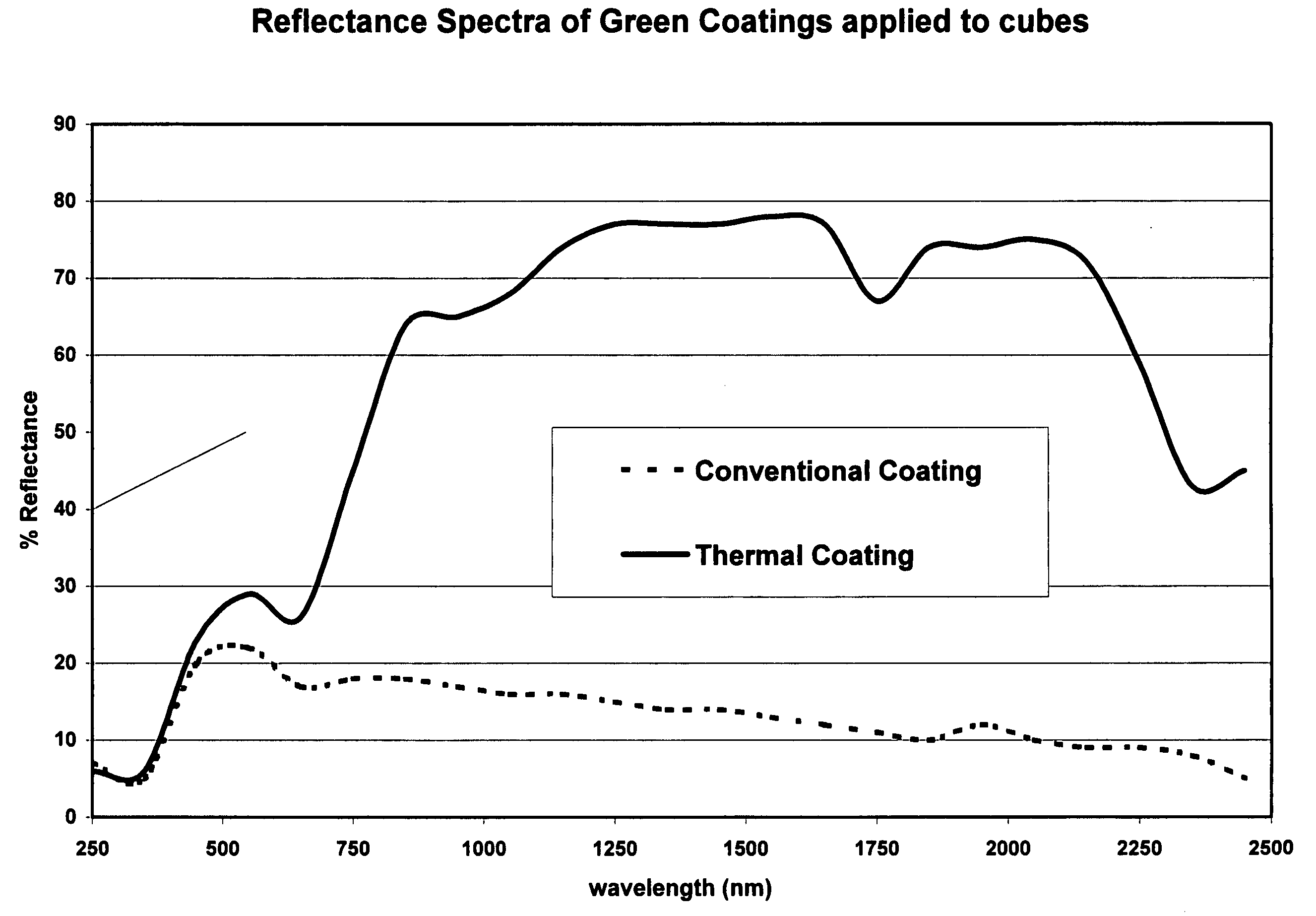
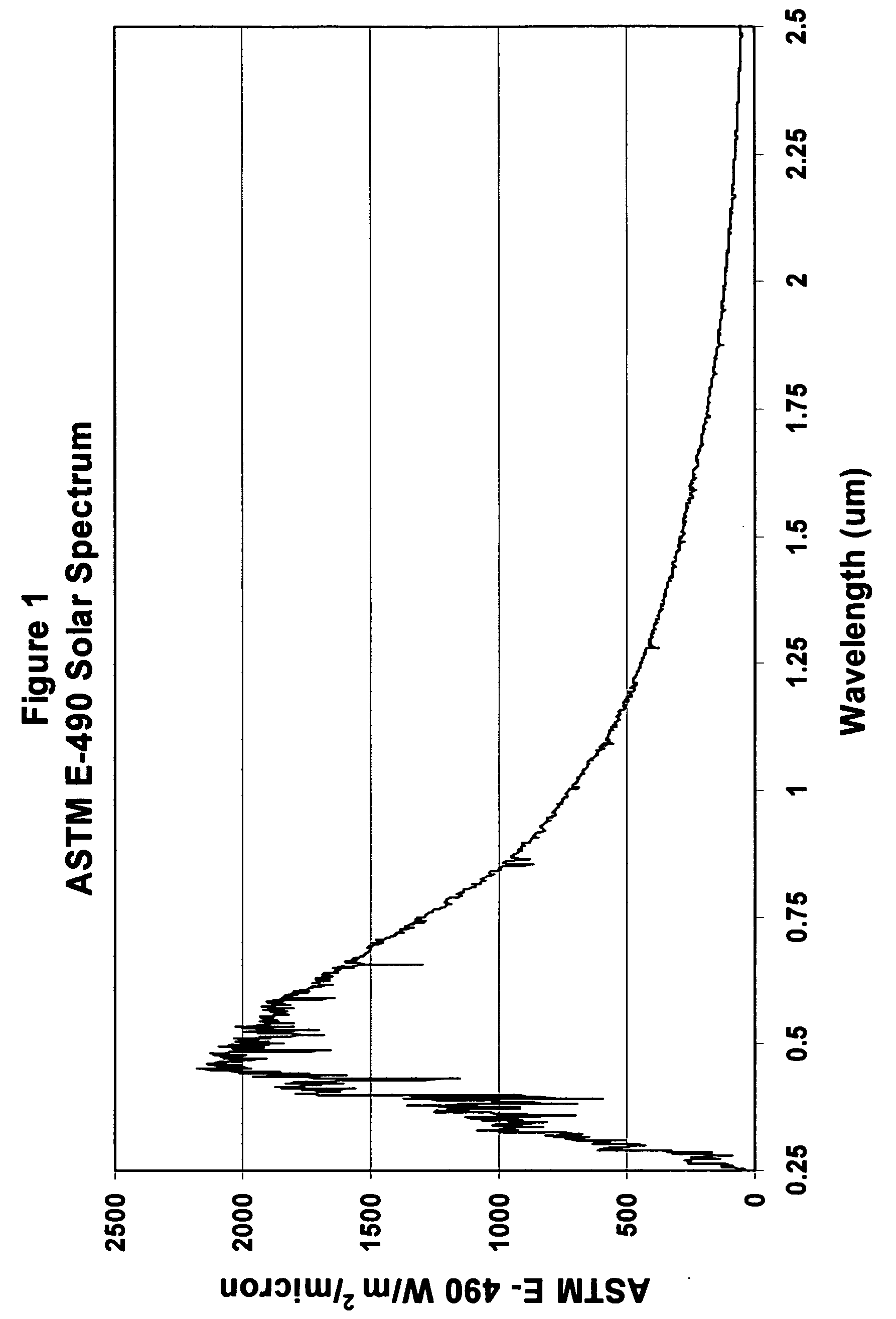
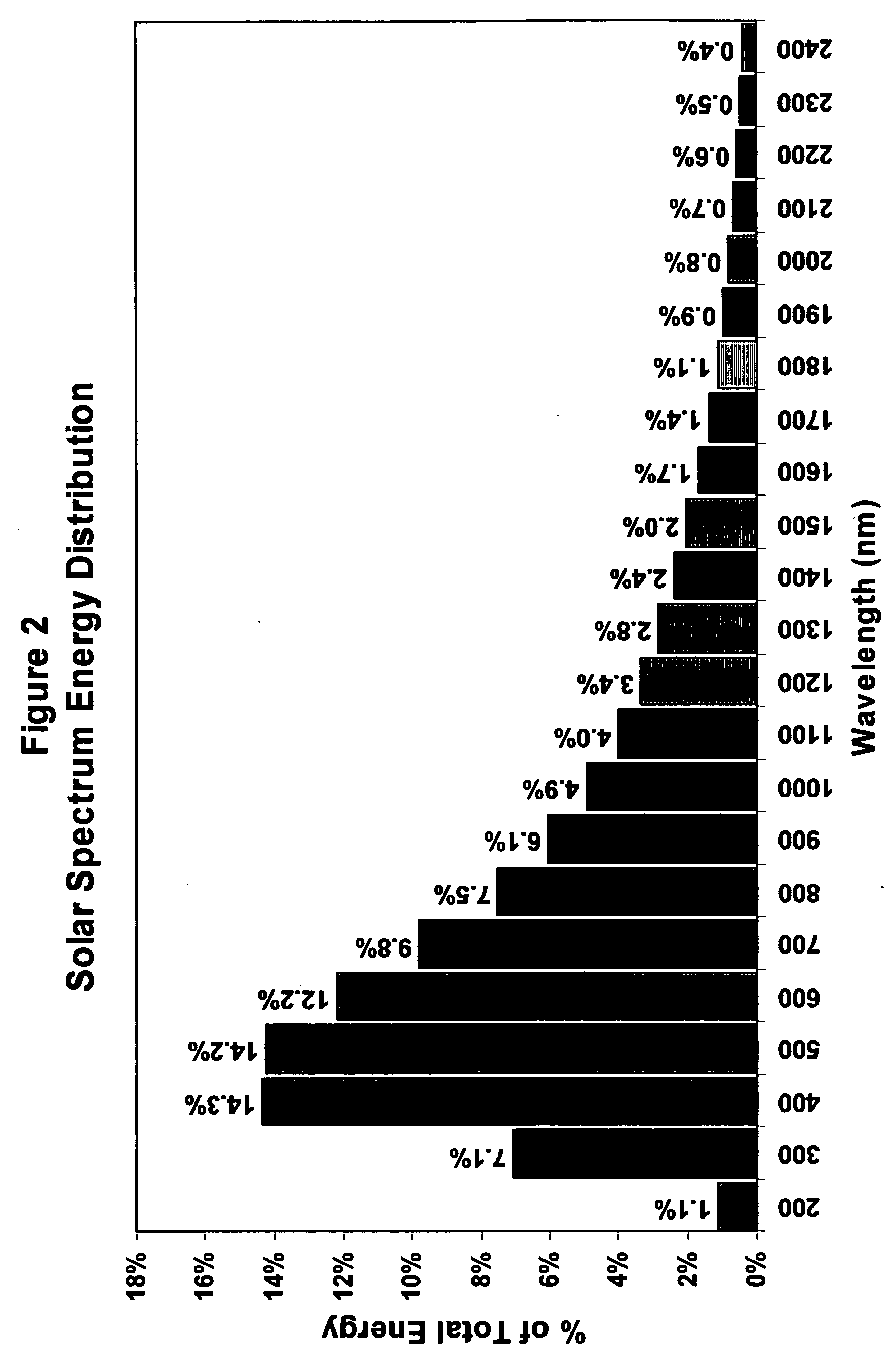
Composition of a thermaly insulating coating system
InactiveUS20050126441A1High infrared reflectivityLow thermal conductivityPigmenting treatmentCeramic layered productsCoating systemSolar spectra
A composition for a Coating System (paint) which forms an insulating material being designed to both reflect infrared radiation and have reduced thermal conductivity. The coating system may be either a single Thermal Coating or may be a Thermal Coating used in combination with a Thermal Primer. The Thermal Coating is formulated using conventional techniques and a resin used in paint manufacture, but utilizes primary pigments and extender mineral pigments which preferentially reflect in the infra red area of the solar spectrum. A method of characterizing particulate materials for their infra red reflectivity is described, which provides a means for preferential selection of particulate additives based on their relative visible light and infrared reflectivity. Additionally the incorporation of hollow micro-spheres is desired to reduce thermal conductivity. The Thermal Primer is designed to provide adhesion between the Thermal Coating and the substrate on which it is applied and uses conventional techniques to achieve those properties. However it has been found advantageous to incorporate hollow micro-spheres with low thermal conductivity, such as glass, ceramic or polymeric micro-spheres and / or an extender pigment with low thermal conductivity such as calcined clay to further reduce heat flow through the Coating System.
Owner:ANTHONY DAVID SKELHORN
Two-terminal nanotube devices and systems and methods of making same
ActiveUS20080012047A1Minimize flow of heatImprove conductivityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceNanotube
A two terminal switching device includes first and second conductive terminals and a nanotube article. The article has at least one nanotube, and overlaps at least a portion of each of the first and second terminals. The device also includes a stimulus circuit in electrical communication with at least one of the first and second terminals. The circuit is capable of applying first and second electrical stimuli to at least one of the first and second terminal(s) to change the relative resistance of the device between the first and second terminals between a relatively high resistance and a relatively low resistance. The relatively high resistance between the first and second terminals corresponds to a first state of the device, and the relatively low resistance between the first and second terminals corresponds to a second state of the device.
Owner:NANTERO
Devices and methods for acoustic shielding
InactiveUS20120111339A1Easy to storeReduce delivery acoustic energyUltrasound therapyRestraining devicesAcoustic energyNose
Acoustic shielding system and method for protecting and shielding non-targeted regions or tissues that are not intended to be treated by ultrasonic procedures from acoustic energy using a shield. In some embodiments, the shield comprises multiple layers made of one or more materials with one or more acoustic impedances. In some embodiments a multilayered shield includes materials with relatively different acoustic impedance levels. In some embodiments, the shield includes active components such as energy diversion devices, heating, cooling, monitoring, and / or sensing. In some embodiments, the shield is configured to protect an eye, mouth, nose or ear while allowing the ultrasound to treat the surrounding tissue. One embodiment of an eye shield is configured to fit under at least one eyelid and over a portion of the eye.
Owner:ULTHERA INC
Gallium nitride materials including thermally conductive regions
InactiveUS20020117695A1Effective distributionAmount of heat is generatedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGallium nitrideSilicon
The invention includes providing gallium nitride materials including thermally conductive regions and methods to form such materials. The gallium nitride materials may be used to form semiconductor devices. The thermally conductive regions may include heat spreading layers and heat sinks. Heat spreading layers distribute heat generated during device operation over relatively large areas to prevent excessive localized heating. Heat sinks typically are formed at either the backside or topside of the device and facilitate heat dissipation to the environment. It may be preferable for devices to include a heat spreading layer which is connected to a heat sink at the backside of the device. A variety of semiconductor devices may utilize features of the invention including devices on silicon substrates and devices which generate large amounts of heat such as power transistors.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Double temperature sensor
ActiveUS20080170600A1Easy to manufactureTolerances of the heat transfer coefficient can be minimizedThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectricityHeat flux
A double temperature sensor is provided for measuring a near-surface temperature of the ambient air and the temperature of the skin surface (9). A heat flux insulation block (4) is made of an insulation material in one piece as a housing. Two temperature sensor elements (2, 3) with respective electric connections (6) belonging to them are arranged in the heat flux insulation block (4) one on top of another at spaced locations from one another and near the surface.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Thermal solution for electronic devices
InactiveUS6982874B2Reduces and eliminates heat flowLow thermal conductivityMagnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal solutionEngineering
A thermal solution for an electronic device, which is positioned between a heat source and an external surface of the electronic device and / or another component of the electronic device, where the thermal solution facilitates heat dissipation from the heat source while shielding the external surface and / or second component from the heat generated by the heat source.
Owner:NEOGRAF SOLUTIONS LLC
Instrument for electrosurgical tissue treatment
InactiveUS20080021447A1Efficient ionizationLess heatSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesEngineeringLow temperature plasma
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to create a relatively low-temperature plasma for ablation of tissue adjacent to, or in contact with, the plasma. In one embodiment, an electrosurgical probe or catheter is positioned adjacent the target site so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into contact with, or close proximity to, a target tissue in the presence of electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to non-thermally generate a plasma adjacent to the active electrode(s), and to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. The high frequency voltage generates electric fields around the active electrode(s) with sufficient energy to ionize the conductive fluid adjacent to the active electrode(s). Within the ionized gas or plasma, free electrons are accelerated, and electron-atoms collisions liberate more electrons, and the process cascades until the plasma contains sufficient energy to break apart the tissue molecules, causing molecular dissociation and ablation of the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Light source device
InactiveUS20090303713A1Low thermal conductivityPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceElectricityLight-emitting diode
A light source device includes a circuit member, a heat dissipation component, an optical component and light emitting diode assemblies. The circuit member defines spaced through holes. The light emitting diode assemblies have a first side and a second side opposite to the first side. Each light emitting diode assembly passes through a corresponding through hole and is electrically connected to the circuit member. The heat dissipation component contacts the first side, is spaced from the circuit member, and is configured to dissipate heat generated by the light emitting diode assemblies. The optical component contacts the second side, and is configured to distribute light emitted from the light emitting diode assemblies.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
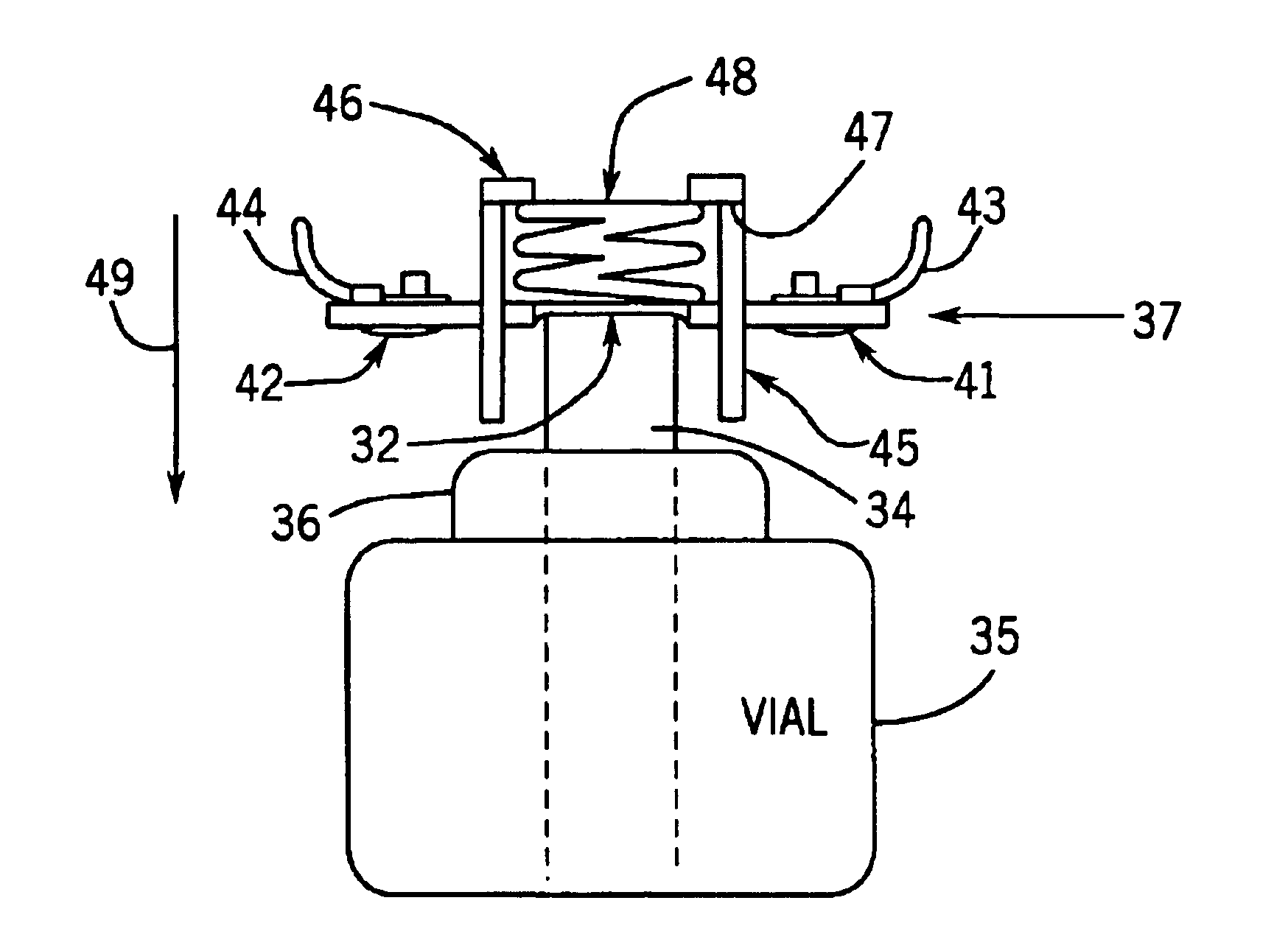
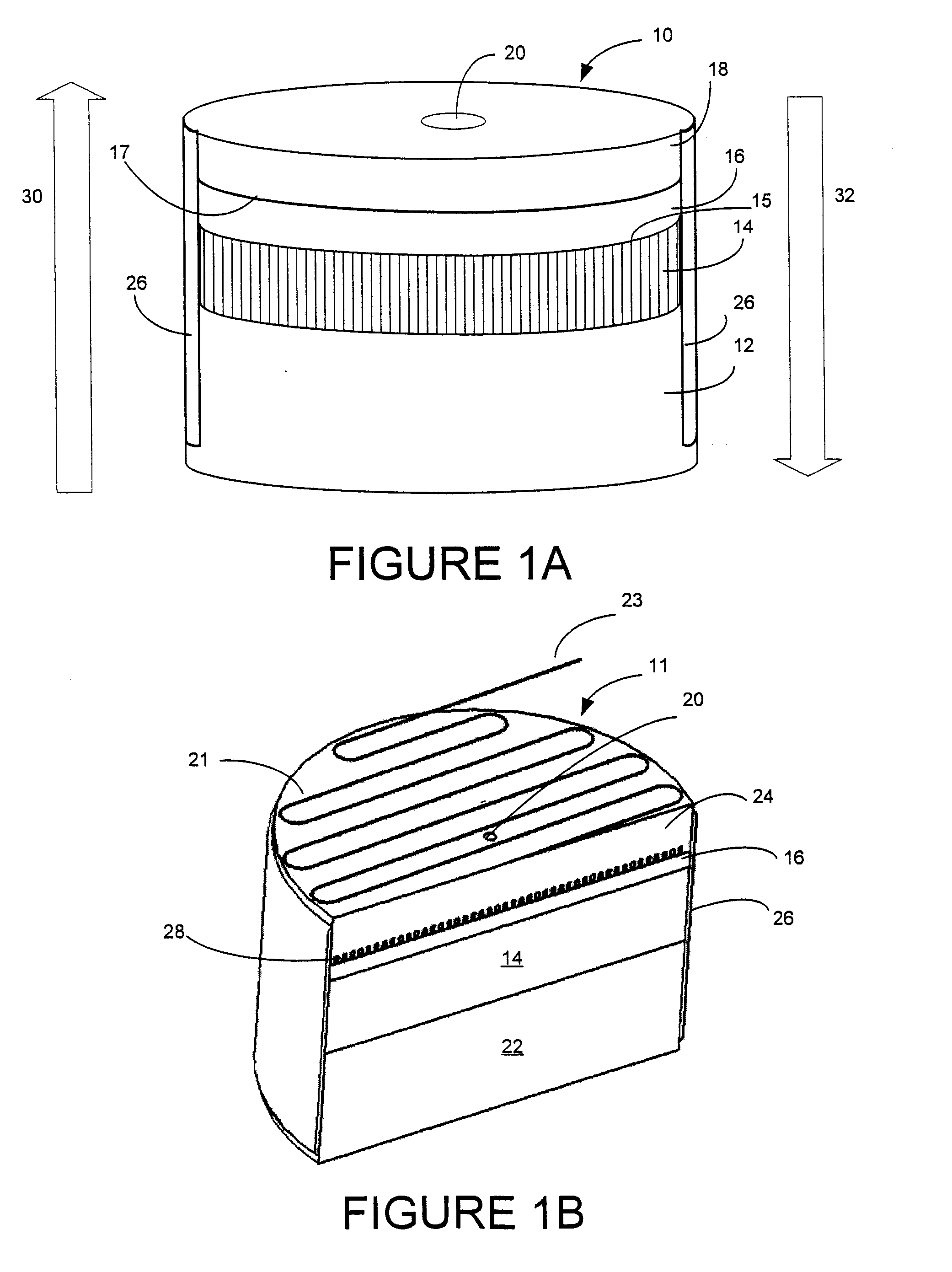
Capillary Pumps for Vaporization of Liquids
InactiveUS20090324206A1Improve permeabilityIncrease ratingsReactant parameters controlMixing methodsVaporizationEngineering
A capillary pump is provided for producing pressurized and unpressurized vapor emissions from liquid feed. In its simplest form, the capillary pump incorporates a liquid feed intake, a porous vaporization component, and a heat transfer component. Additional components, such as an insulator component, a feed pre-heat component, a liquid feed reservoir and / or delivery system, an integrated or associated heater component, a vapor collection chamber, a heat distribution component, an orifice component and / or vapor release component, may also be associated with or integrated in the improved capillary pumps. Capillary pump arrays are provided, and numerous applications for capillary pumps are disclosed.
Owner:VAPORE
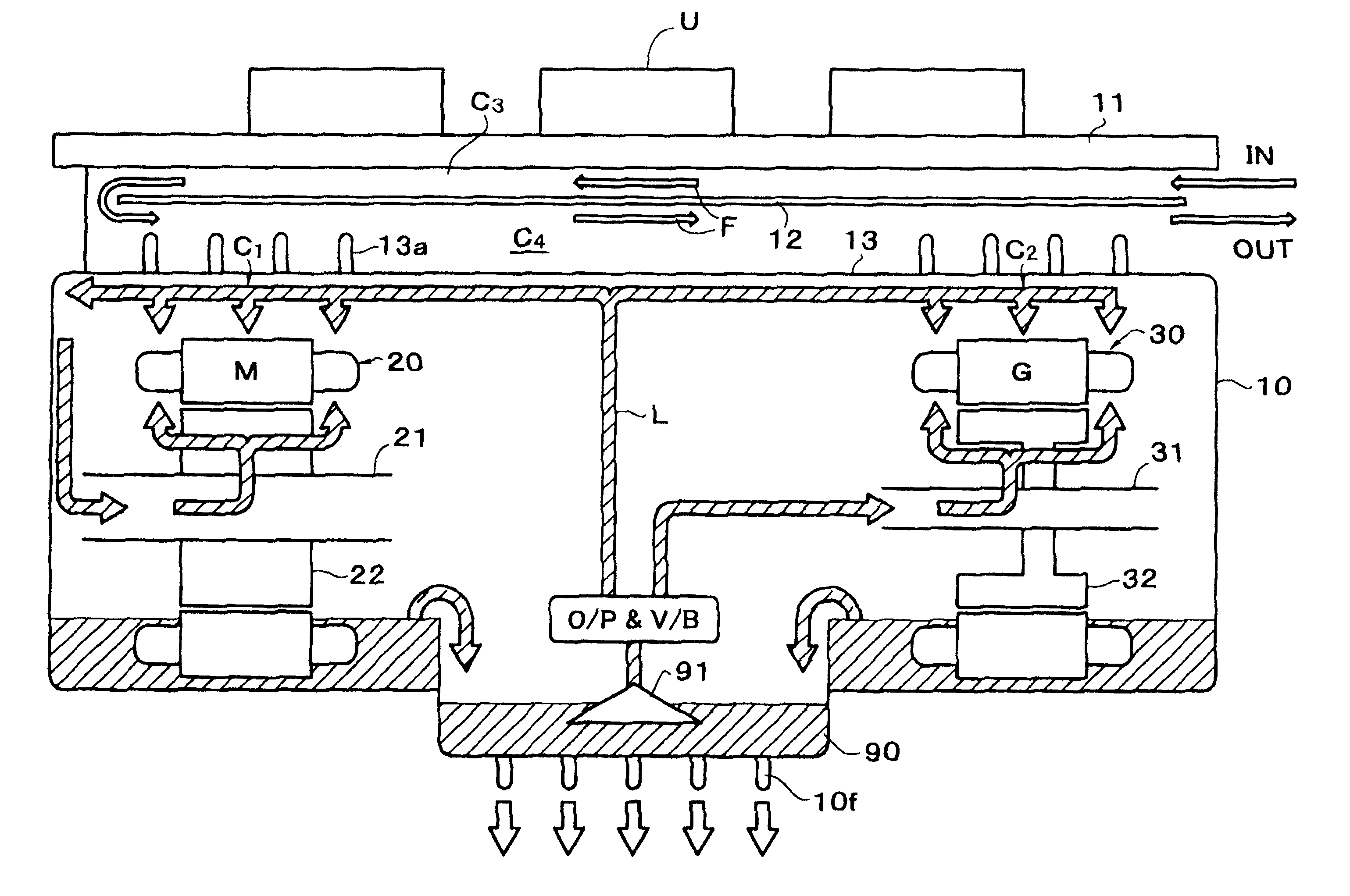
Drive unit with coolant flow through a space separating an inverter from a casing housing an electric motor
InactiveUS6201365B1Avoid contactLow thermal conductivityPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingElectric motor speed/torque regulationEngineeringCoolant flow
A drive unit which uses an electric motor as a power source and has an integrated inverter, with a cooling circuit for the electric motor and the inverter. The drive unit includes a drive unit case, the electric motor housed within the case, and the inverter fixed to the case. A coolant flow passage is provided between the drive unit case and the inverter. The inverter is fixed to the drive unit case through a panel wall, and a partition divides the coolant flow passage into chambers which are coextensive in parallel. As a result, the coolant which flows through the coolant flow passage acts as a two-stage heat shield, barring the heat generated by the electric motor from being transmitted to the inverter.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
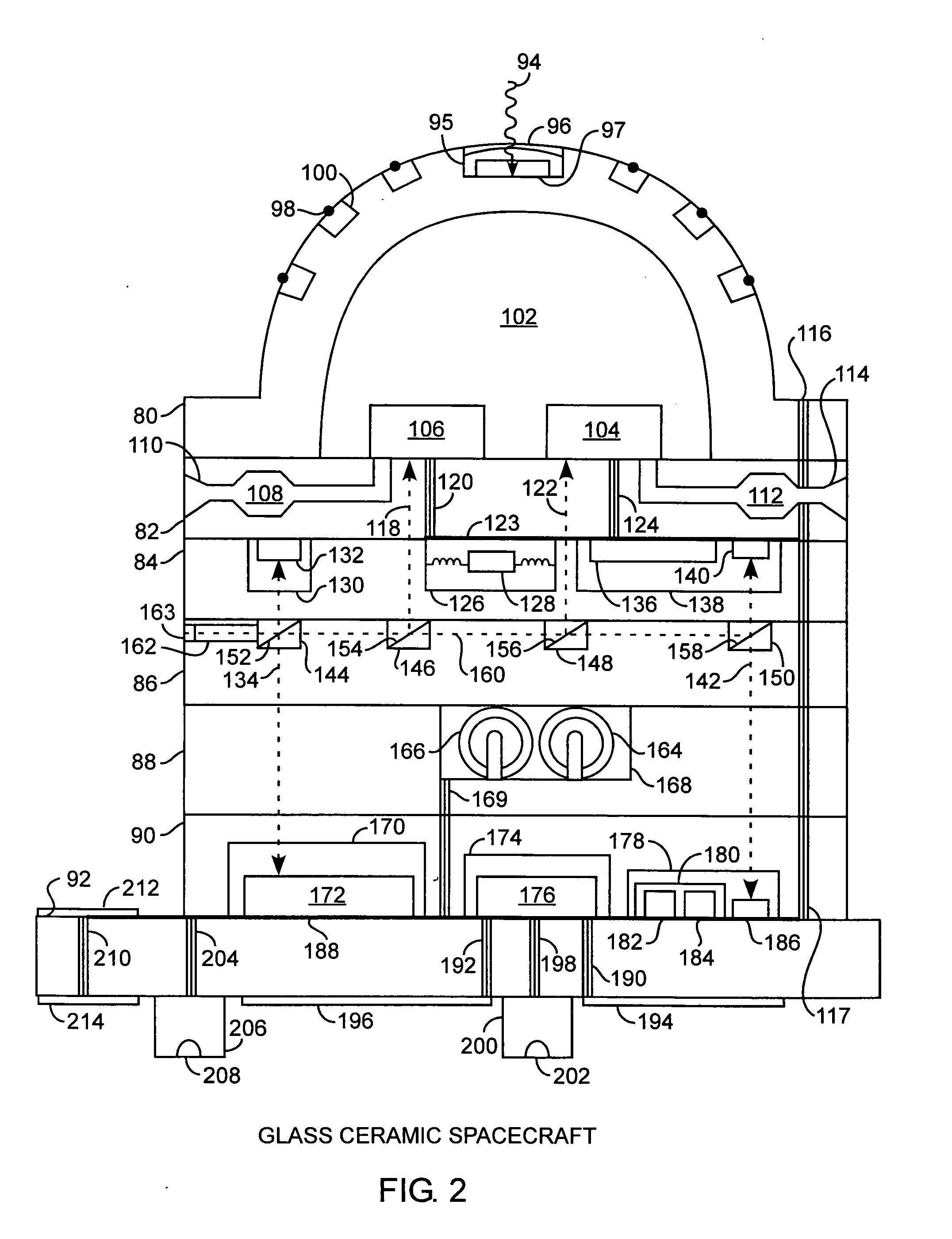
Integrated glass ceramic systems
ActiveUS6952530B2Improve structural strengthLow thermal conductivityCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCosmonautic power supply systemsElectricityOptical communication
Integrated glass ceramic spacecraft include a plurality of glass ceramic components including molded, tempered, annealed, and patterned glass ceramic components coupled together for forming a support structure or frame or housing through which is communicated optical signals through an optical communications grid and electrical signals through an electrical communications grid, with the optical communications grid and electrical communication grid forming a composite electrooptical communications grid for spacecraft wide intercommunications. The support structure multifunctions as a frame, a housing, a support, a thermal control system, and as part of an electrooptical communications grid while encapsulating a plurality of optical, electronic, electrical, and MEMS devices between which is communicated the electrical and optical signals over the electrooptical communication grid.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Aerogel containing blanket
ActiveUS20060125158A1Low thermal conductivityEvenly distributedNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberSlurry
A process of producing a blanket is described and can involve forming an aqueous slurry of hydrophobic aerogels, fibers, and at least one wetting agent, drying the aqueous slurry to form a substantially dried product, and calendaring the substantially dried product to form the blanket. The blanket can be used in a variety of applications, including windows.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Thermal barrier coatings with protective outer layer for improved impact and erosion resistance
InactiveUS6875529B1Improve erosion resistanceImprove impact resistanceMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingBond coatMetallic substrate
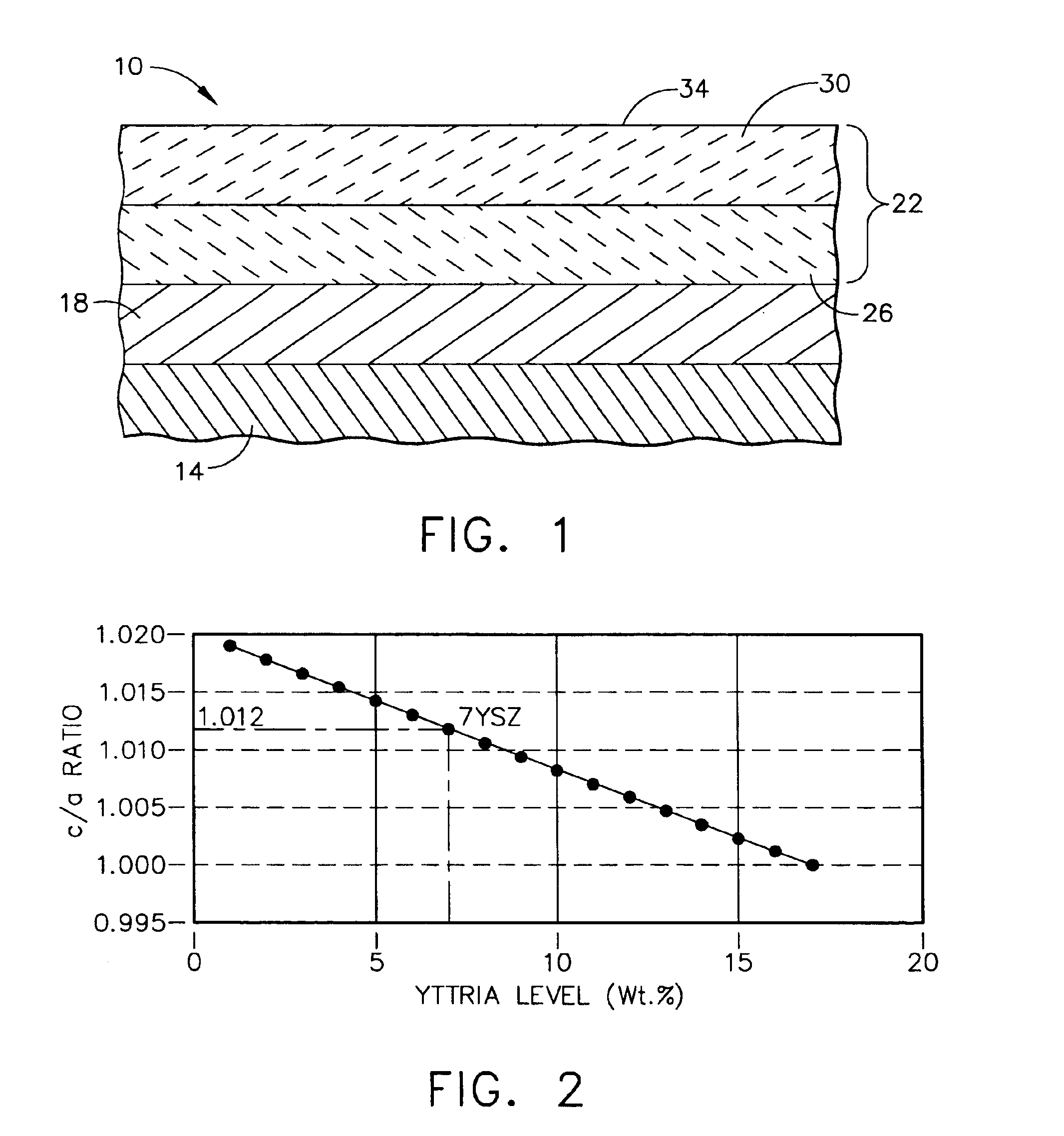
A reduced thermal conductivity thermal barrier coating having improved impact and erosion resistance for an underlying metal substrate of articles that operate at, or are exposed to, high temperatures. This coating comprises an inner layer nearest to the underlying metal substrate comprising a ceramic thermal barrier coating material, as well as a protective outer layer adjacent to and overlaying the inner layer and having an exposed surface. The outer layer has a thickness up to about 5 mils (127 microns) sufficient to impart impact and erosion resistance to the thermal barrier coating, and comprises a zirconia-containing ceramic composition having a c / a ratio of the zirconia lattice in the range of from about 1.011 to about 1.016 and stabilized in the tetragonal phase by a stabilizing amount of a stabilizing metal oxide selected from the group consisting of yttria, calcia, ceria, scandia, magnesia, india, ytterbia and mixtures thereof. This coating can be used to provide a thermally protected article having a metal substrate and optionally a bond coated layer adjacent to and overlaying the metal substrate. The thermal barrier coating can be prepared by forming the inner layer comprising the ceramic thermal barrier coating material, followed by forming on the inner layer the protective outer layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for electrosurgical tissue treatment
InactiveUS7572251B1Reduce ionic strengthFacilitate initiationCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsEngineeringLow temperature plasma
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to create a relatively low-temperature plasma for ablation of tissue adjacent to, or in contact with, the plasma. In one embodiment, an electrosurgical probe or catheter is positioned adjacent the target site so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into contact with, or close proximity to, a target tissue in the presence of electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to non-thermally generate a plasma adjacent to the active electrode(s), and to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. The high frequency voltage generates electric fields around the active electrode(s) with sufficient energy to ionize the conductive fluid adjacent to the active electrode(s). Within the ionized gas or plasma, free electrons are accelerated, and electron-atoms collisions liberate more electrons, and the process cascades until the plasma contains sufficient energy to break apart the tissue molecules, causing molecular dissociation and ablation of the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Thermal solution for portable electronic devices
InactiveUS7292441B2Reduces and eliminates heat flowLow thermal conductivityMagnetic/electric field screeningDigital data processing detailsThermal solutionEngineering
A thermal solution for a portable electronic device, which is positioned between a heat source and another component of the electronic device, where the thermal solution facilitates heat dissipation from the heat source while shielding the second component from the heat generated by the heat source.
Owner:NEOGRAF SOLUTIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com