Patents
Literature
338 results about "Heat spreading" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermographic Test Method and Testing Device for Carrying Out the Test Method
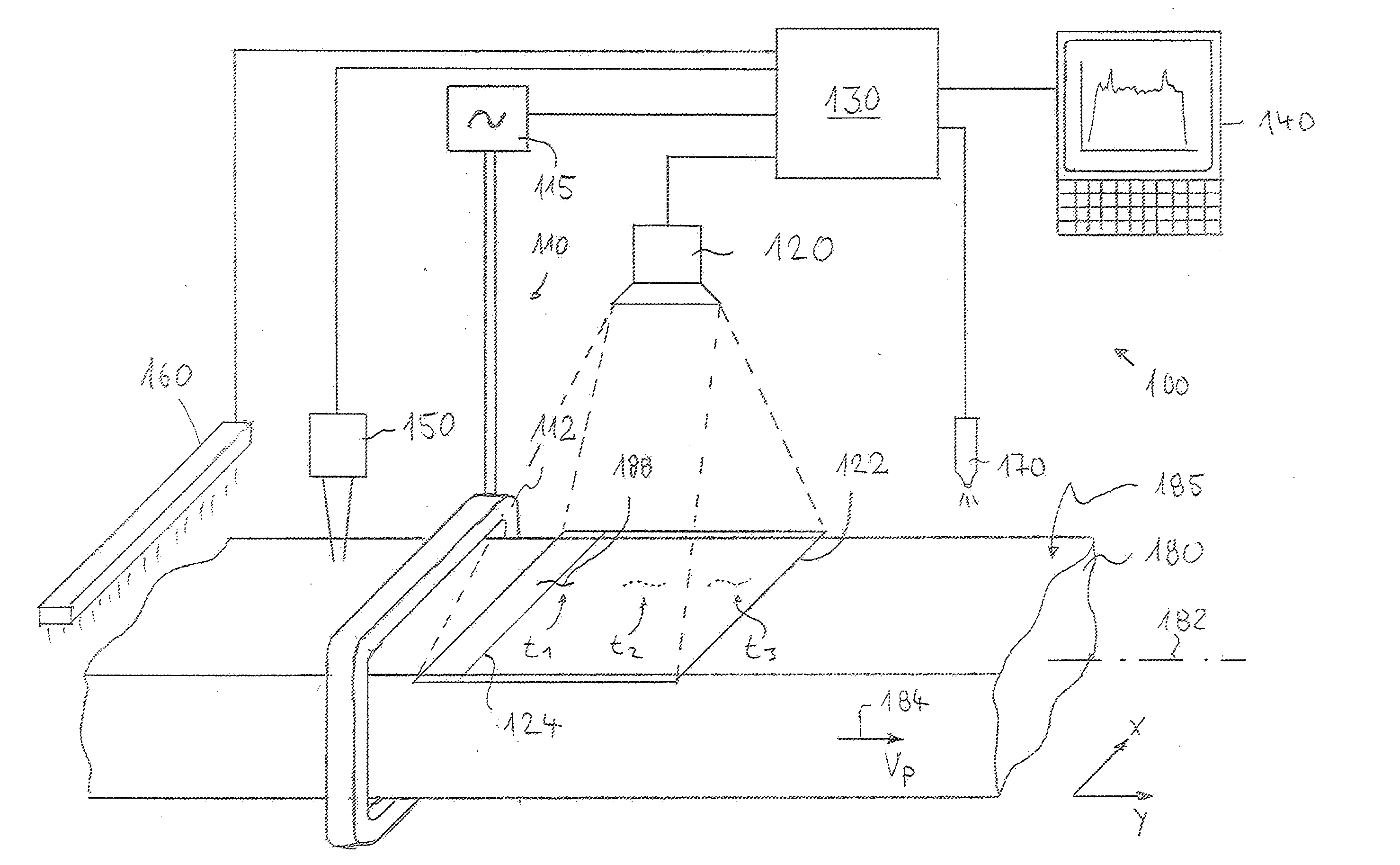
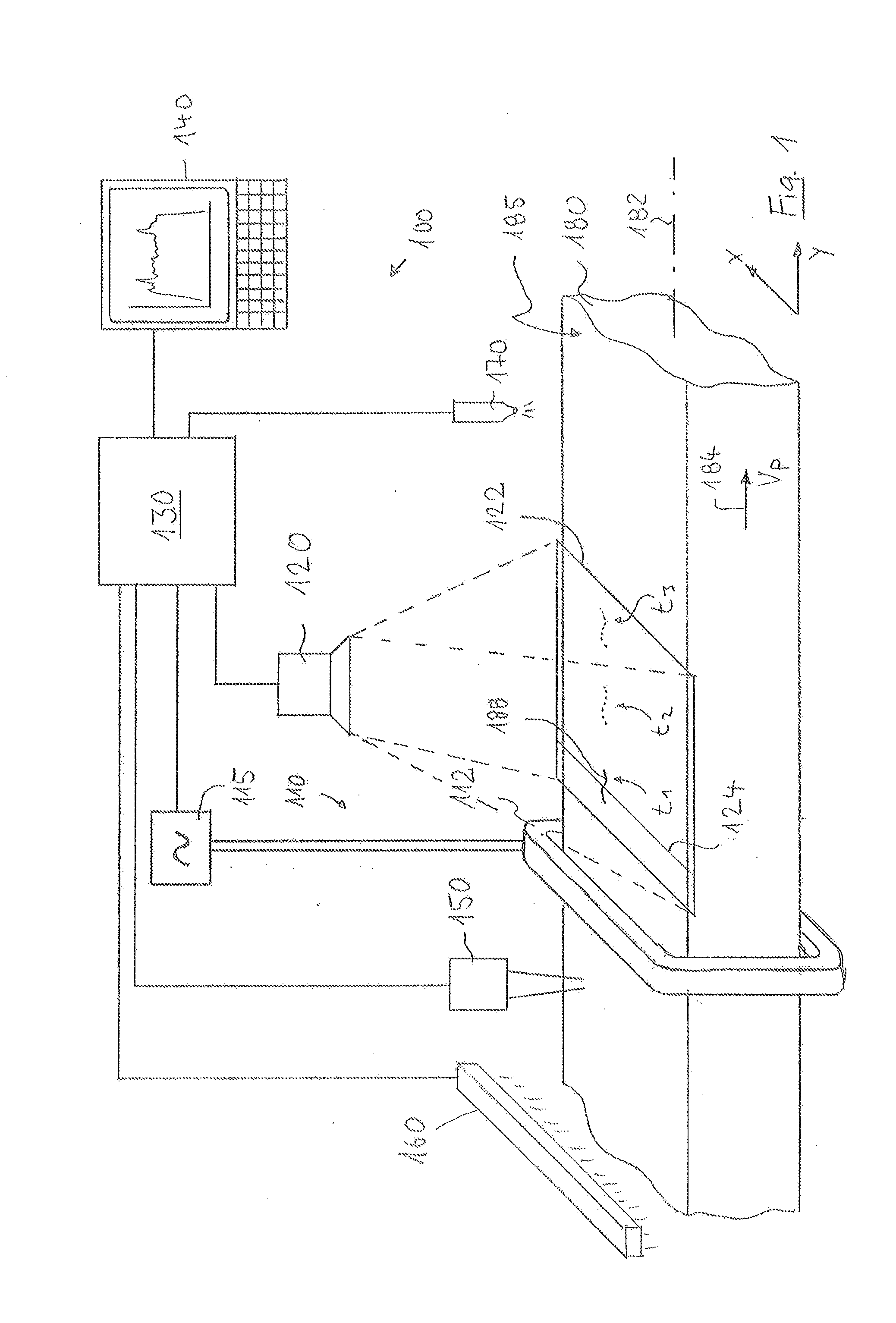
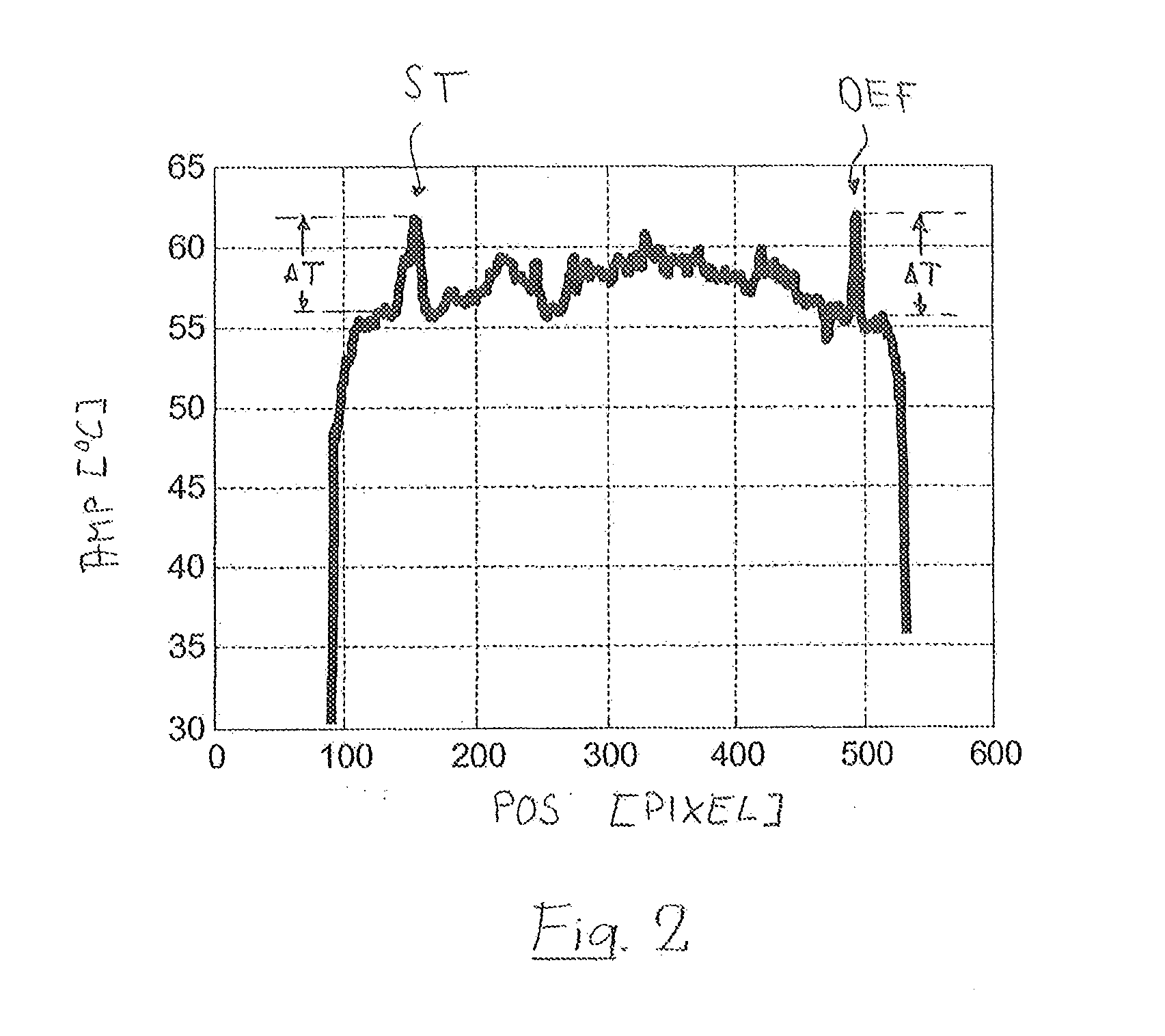
A thermographic test method locally resolves detection and identification of defects near the surface in a test object. A surface area of the test object is heated up. A series of thermographic images following one after another at a time interval is recorded within a heat propagation phase, each image representing a local temperature distribution in a surface region of the test object recorded by the image. Positionally correctly assigned temperature profiles are determined from the images, each positionally correctly assigned temperature profile being assigned to the same measuring region of the test object surface. Variations over time of temperature values are determined from the temperature profiles for a large number of measuring positions of the measuring region. These variations are evaluated on the basis of at least one evaluation criterion indicative of the heat flow in the measuring region.
Owner:INSTITUT DR FORSTER
3-d integrated semiconductor device comprising intermediate heat spreading capabilities
InactiveUS20100052134A1Effective coolingIncreased volume packing densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
In a three-dimensional chip configuration, a heat spreading material may be positioned between adjacent chips and also between a chip and a carrier substrate, thereby significantly enhancing heat dissipation capability. Furthermore, appropriately sized and positioned through holes in the heat spreading material may enable electrical chip-to-chip connections, while responding thermally conductive connectors may extend to the heat sink without actually contacting the corresponding chips.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Gallium nitride materials including thermally conductive regions
InactiveUS20020117695A1Effective distributionAmount of heat is generatedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGallium nitrideSilicon
The invention includes providing gallium nitride materials including thermally conductive regions and methods to form such materials. The gallium nitride materials may be used to form semiconductor devices. The thermally conductive regions may include heat spreading layers and heat sinks. Heat spreading layers distribute heat generated during device operation over relatively large areas to prevent excessive localized heating. Heat sinks typically are formed at either the backside or topside of the device and facilitate heat dissipation to the environment. It may be preferable for devices to include a heat spreading layer which is connected to a heat sink at the backside of the device. A variety of semiconductor devices may utilize features of the invention including devices on silicon substrates and devices which generate large amounts of heat such as power transistors.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
High Efficiency Concentrating Photovoltaic Module Method and Apparatus
InactiveUS20090223555A1Low cost per watt of electricityReduce the amount requiredPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationThermal expansionEngineering
A Concentrating Photovoltaics (CPV) module includes a metal frame, a plurality of Fresnel lenses, a secondary reflective or refractive concentrator, multi-junction solar cells with up to 40% efficiency and a novel heat spreading material. The Fresnel lenses and the secondary concentrator focus the sun over 500 times to maximize the amount of photons collected by the solar cells and converted to electricity. A newly designed soft board material provides coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) matched carrier for the solar cells and an efficient electrical connectivity method. The carrier board is attached to a specially formulated heat spreader made of graphite. At 40% the weight of aluminum and 18% the weight of copper, this specially formulated material offers thermal heat conductivity that is superior to copper. The combination of the above creates CPV modules with the highest efficiency and lowest cost per Watt.
Owner:STALIX
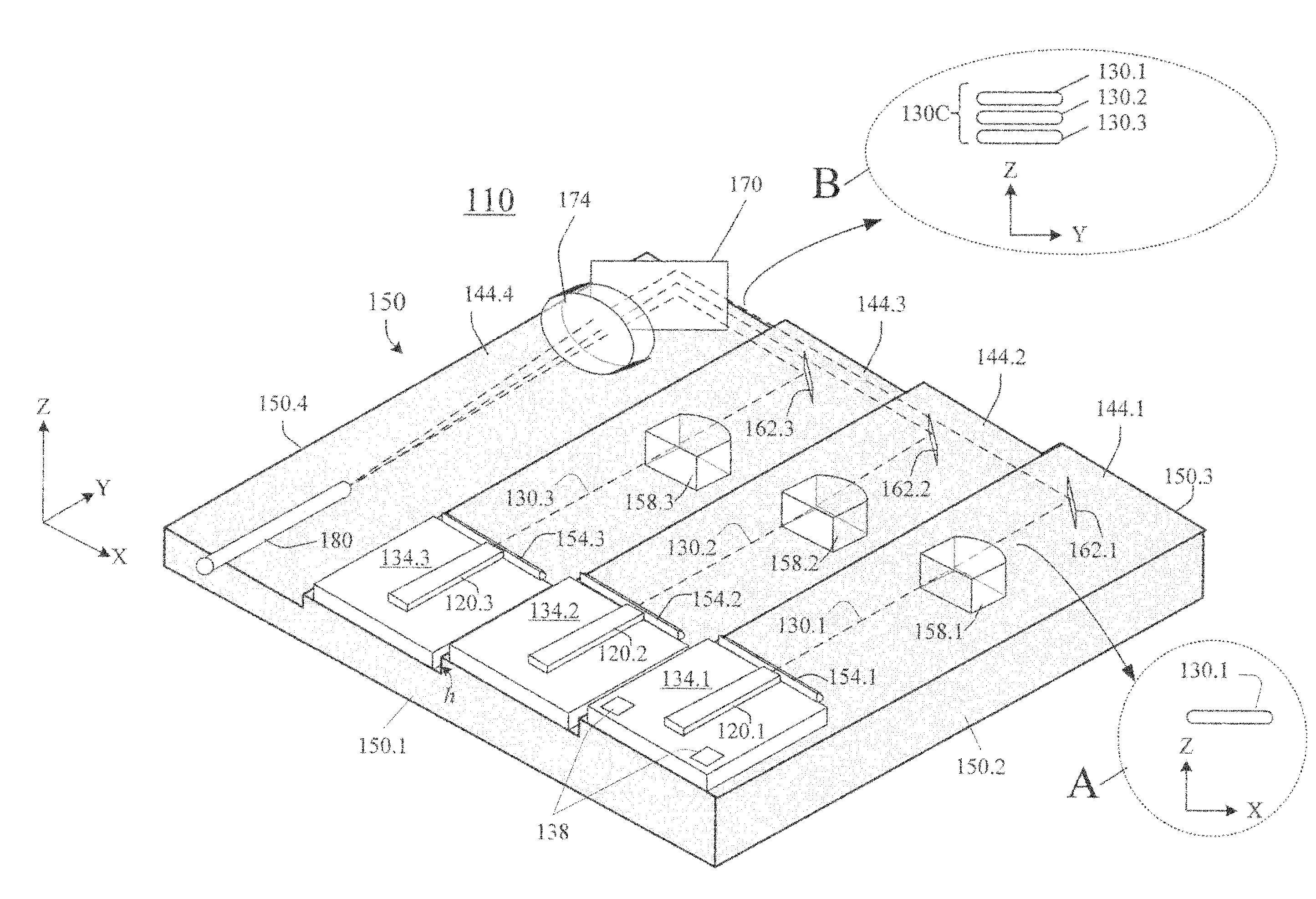
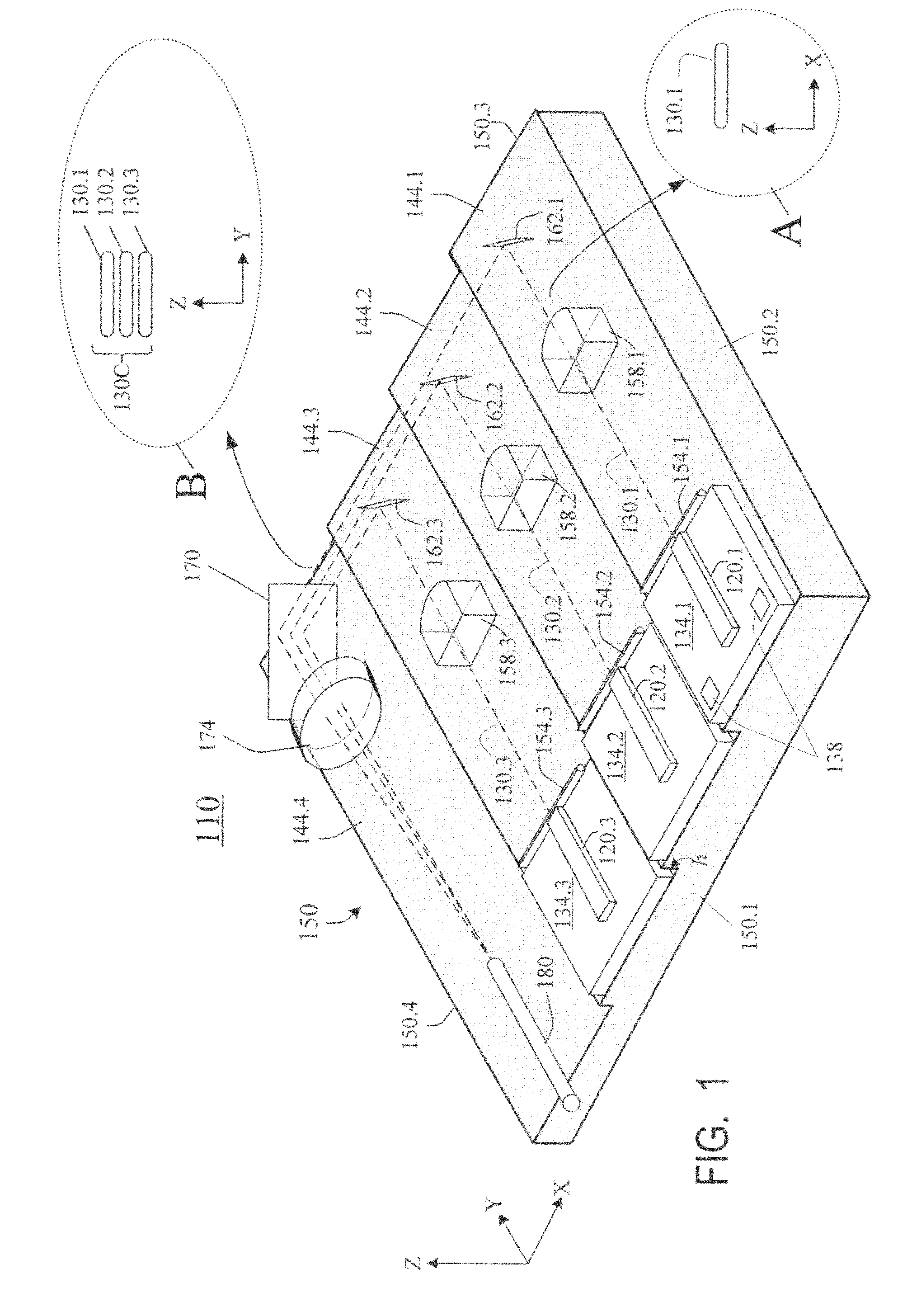
Laser diode assemblies
InactiveUS20090245315A1Reduce misalignmentReduce in quantitySemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLight beamLaser beams
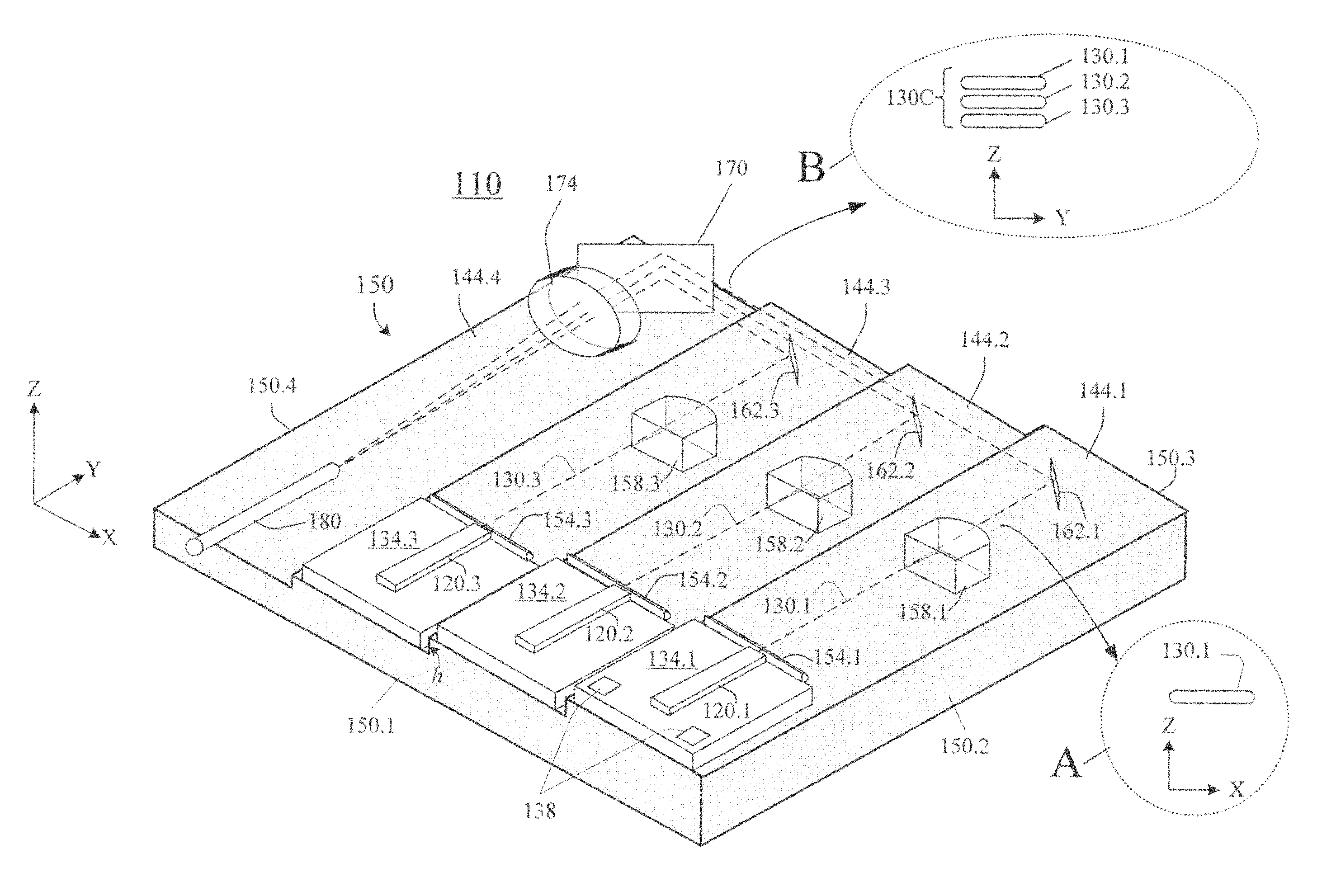
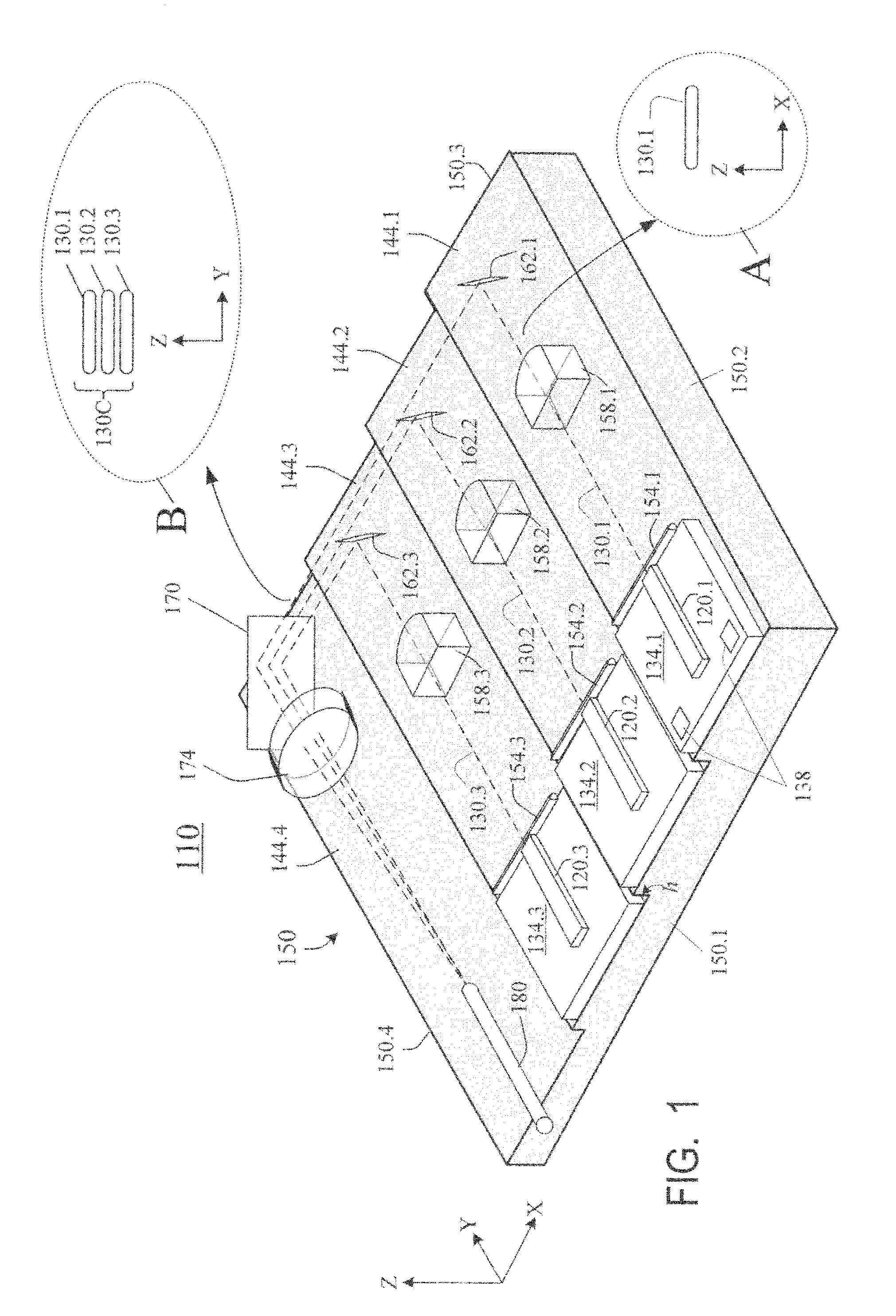
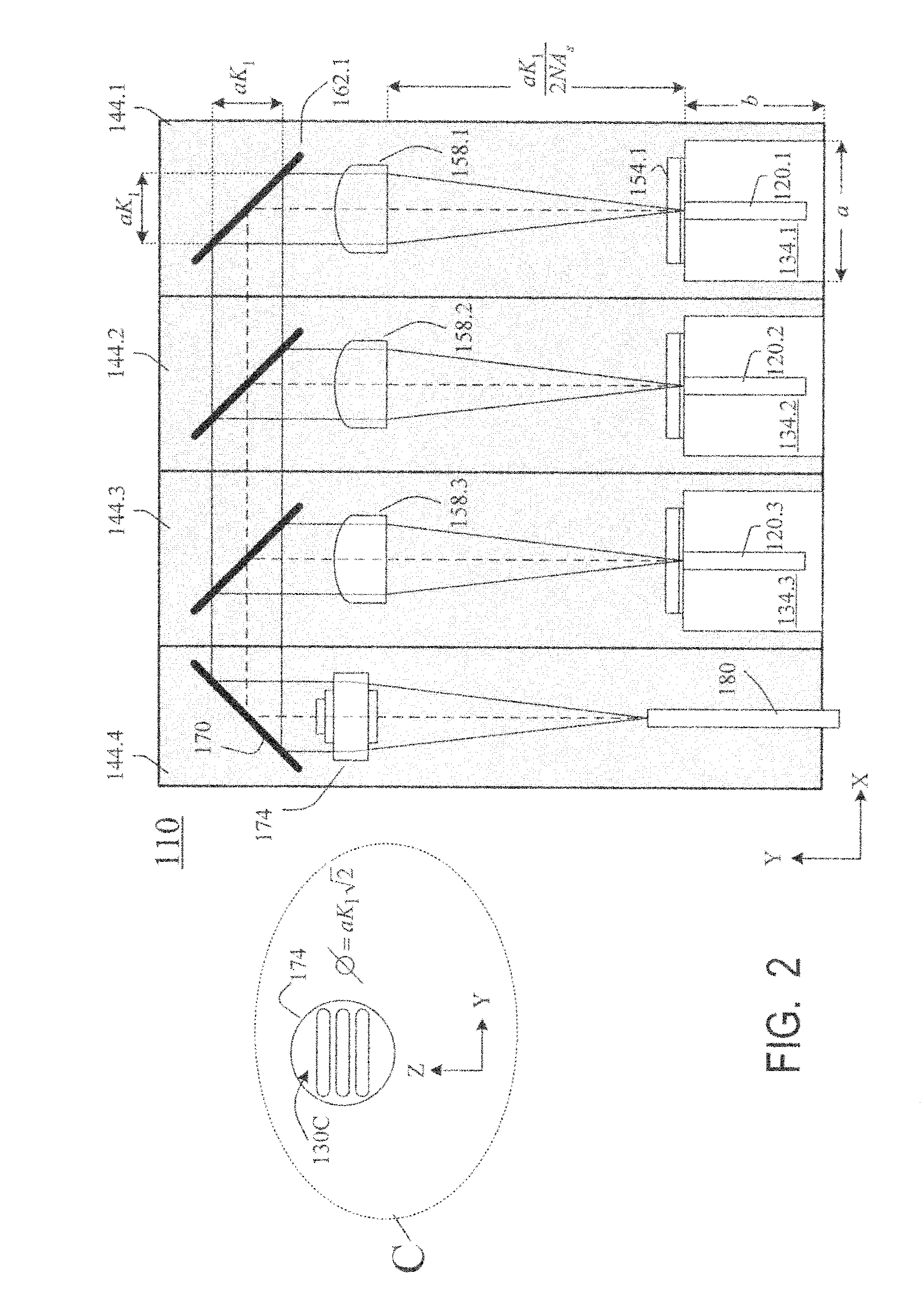
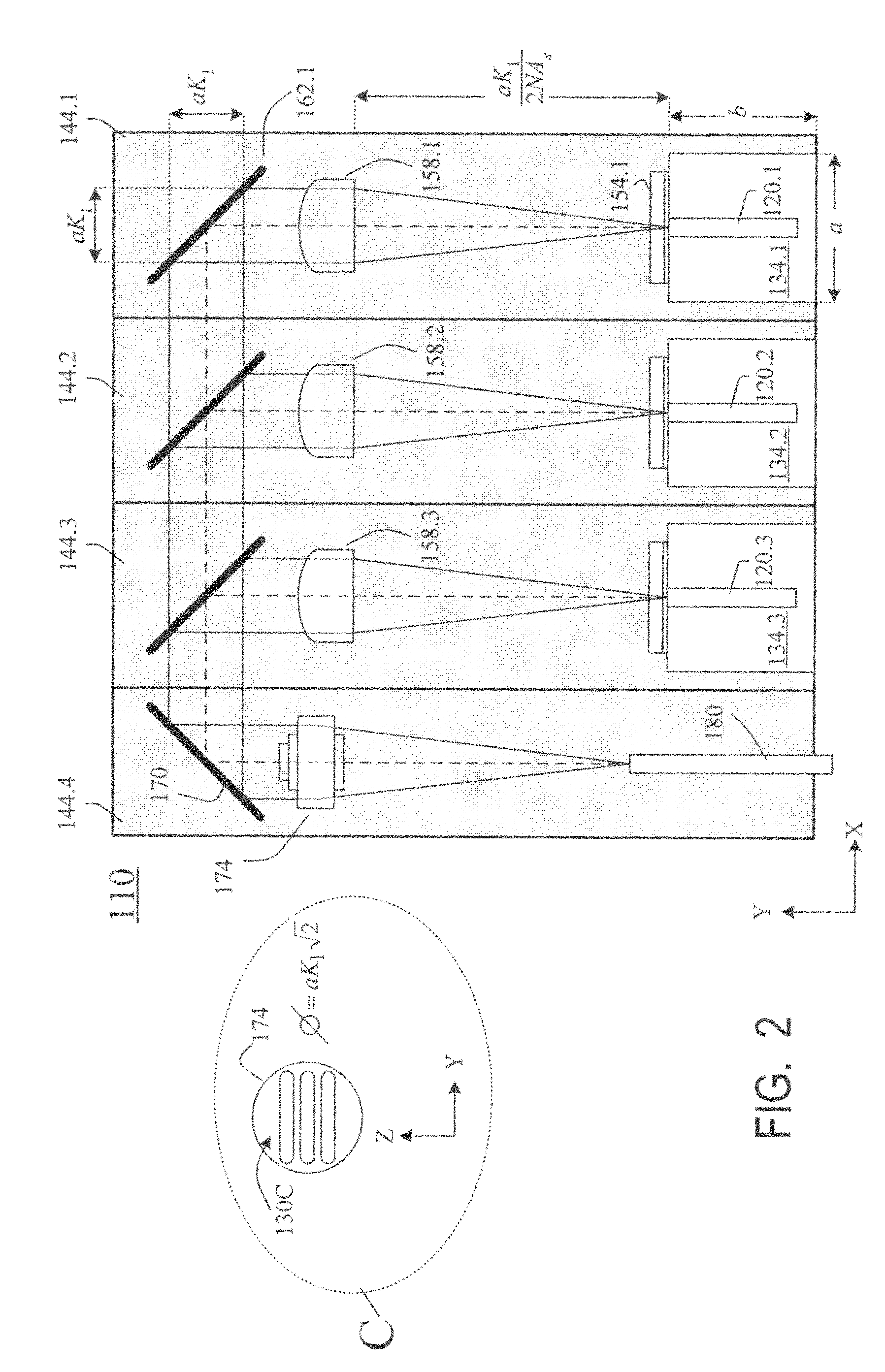
Laser diodes (120) emit laser beams along a vertical YZ plane at different distances from the YZ plane. The beams are collimated in their fast and slow axes, and are redirected by turning mirrors (162) to form a beam stack (130C) traveling along the XZ plane. The beam stack is turned by about 90°, then converged by a focusing lens (174) into an optical fiber (180). A compact assembly is thus provided. Each laser diode (120.i), its collimating optics (154.i, 158.i, i=1, 2, . . . ) and its turning mirror (162.i) are rigidly attached to a flat, heat-spreading surface (144.i) and thus remain aligned with each other in thermal cycling.
Owner:FAYBISHENKO VICTOR
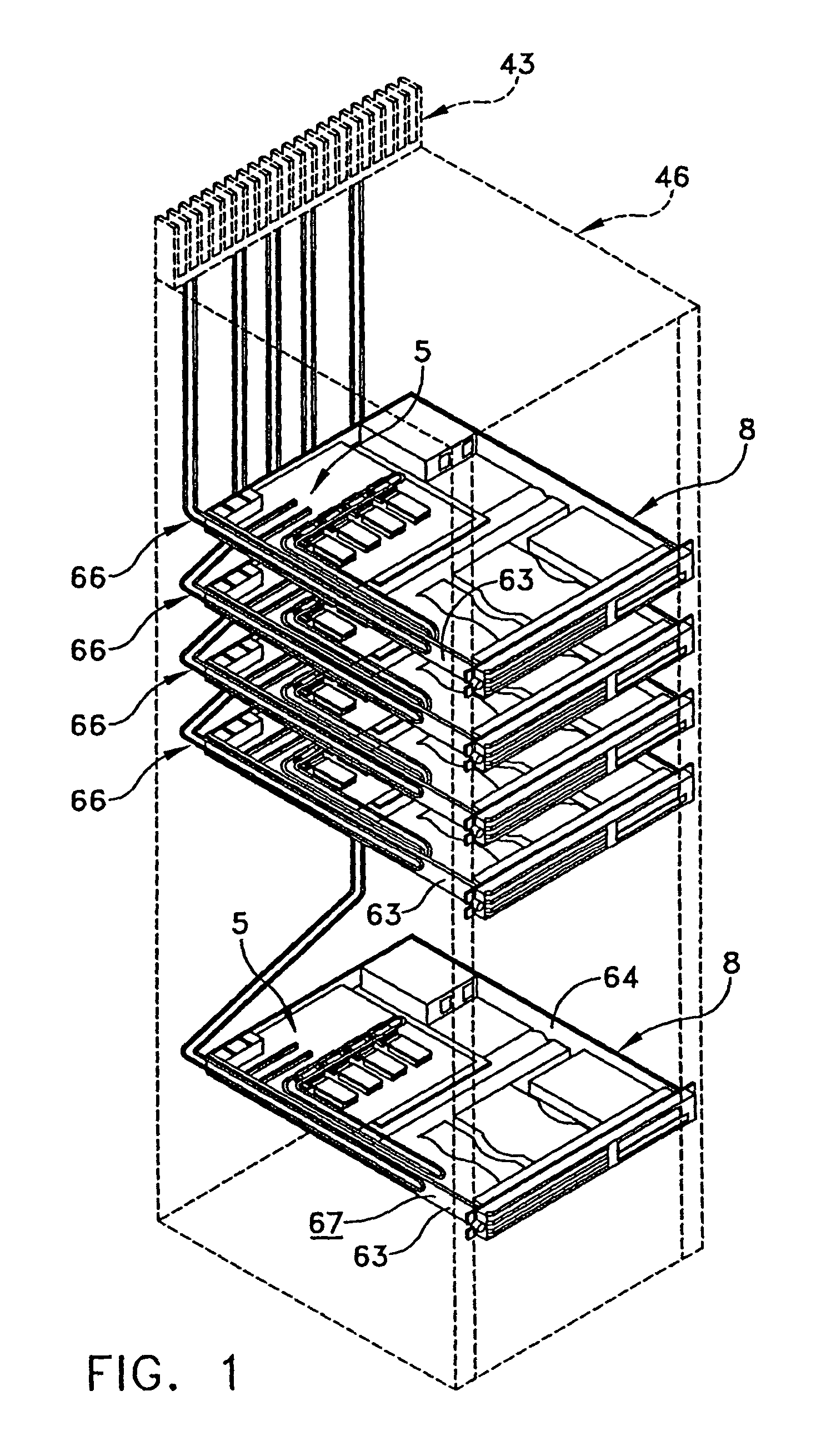
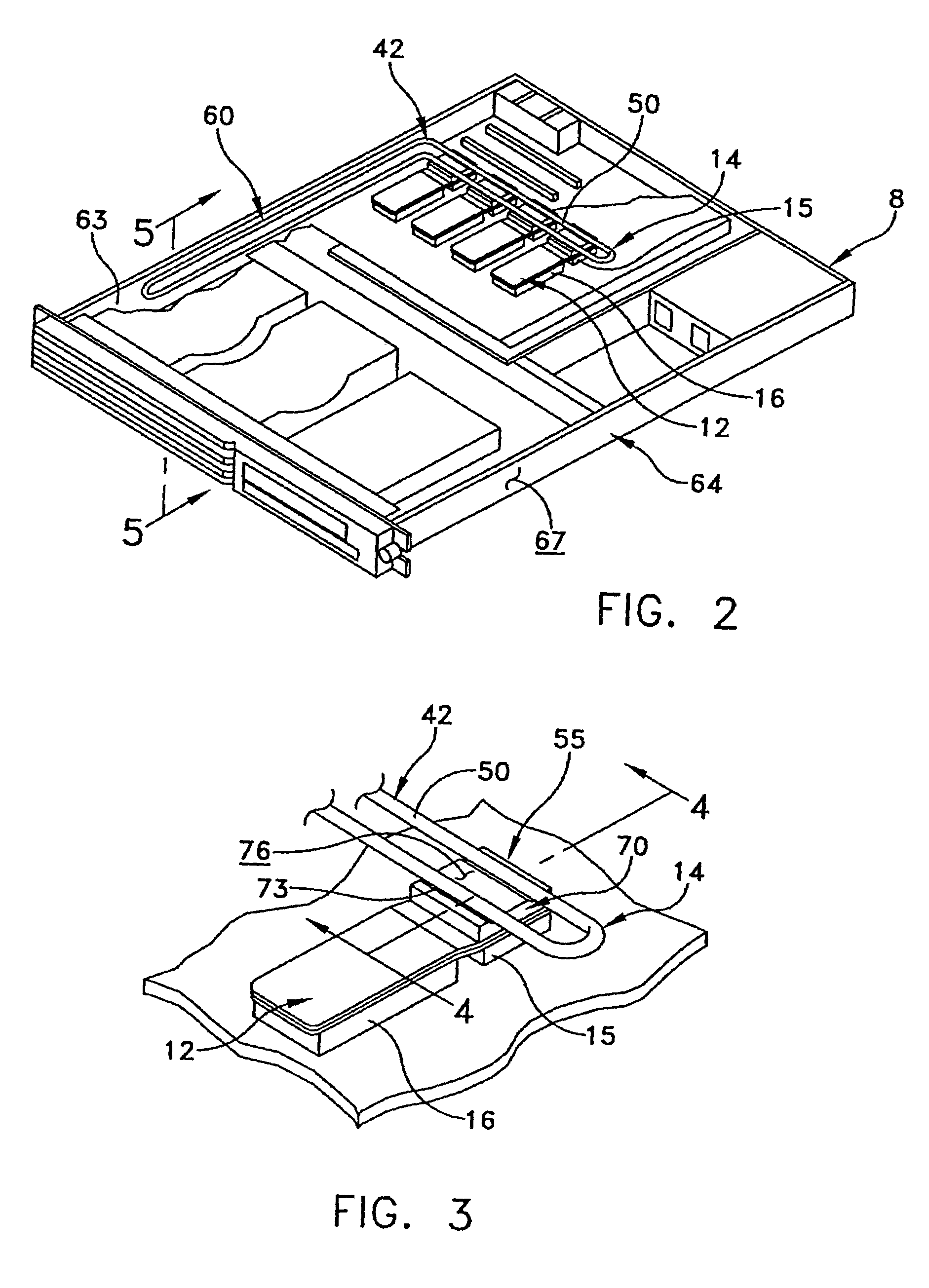
Thin multi-chip flex module
InactiveUS7796399B2Engagement/disengagement of coupling partsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPin arrayRigid frame
A multichip module comprises a multilayer substrate circuit having conductive patterns on its surface(s) to which microelectronic device(s) are attached. The conductive patterns include a series of electrical contacts adjacent to one edge of the substrate. The substrate is bonded to two rigid frames, one on each opposite surface. Each substrate has a series of castellations on one edge that are aligned and electrically connected to the respective contacts on the substrate, preferably by soldering. The castellations can serve as a self-aligning mechanism when the module is brought into contact with a low-profile pin array, and the module may be held in place on a motherboard by guide rails in a socket that engages the edges perpendicular to the castellated edge of the module. The module may further be provided with protective heat spreading covers.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS ASSEMBLY TECH
Methods and Apparatus for Improved Heat Spreading in Solid State Lighting Systems
ActiveUS20080089069A1Reduce weightEfficient transferLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLED lamp
A solid state lighting subassembly or fixture includes an anisotropic heat spreading material. A heat spreading layer may be placed between a light emitting diode (LED) and luminaire or reflector and serves to spread heat laterally away from the LED. Low profile, low weight heat spreading may be utilized both to retrofit existing light fixtures with. LEDs or to replace existing incandescent and fluorescent fixtures with LED based fixtures.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Thin multi-chip flex module
A flexible circuit comprises a folded dielectric sheet having conductive patterns on its surface(s) to which microelectronic device(s) are attached. The dielectric sheet is folded 180° about a selected axis and a bond layer joins the two halves over a portion of their respective surface areas so that a remaining portion of their areas remain unbonded and a bifurcated structure is thereby formed. Electrical contacts are provided on the unbonded or bifurcated portions of the flexible sheets. The flex may be attached to a rigid frame and provided with protective heat spreading covers. The folded flex design is particularly suitable for reel-to-reel manufacturing.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS ASSEMBLY TECH
Thermal management system and method for electronics system
InactiveUS6972365B2Lighting and heating apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal energySemiconductor chip
A thermal energy management system is provided having a heat spreading device that is operatively engaged with at least one semiconductor chip and a thermal bus operatively engaged with the heat spreading device so as to transport thermal energy from the heat spreading device to a heat sink. The heat spreading device includes a heat pipe and the thermal bus includes a loop thermosyphon. A second thermal bus may be operatively engaged with the first thermal bus so as to transport thermal energy from the first thermal bus to a heat sink. The second thermal bus may also include a loop thermosyphon. A method of managing thermal energy in an electronic system is also provided that includes spreading thermal energy generated by one or more devices over a surface that is relatively larger than the devices, thermally coupling an evaporator portion of a loop thermosyphon to the surface, and thermally coupling a condensing portion of the loop thermosyphon to a thermal energy sink, e.g., a second loop thermosyphon, convection fin, or cold plate.
Owner:THERMAL
Laser diode assemblies
InactiveUS7733932B2Reduce misalignmentReduce in quantitySemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser cooling arrangementsLight beamLaser beams
Laser diodes (120) emit laser beams along a vertical YZ plane at different distances from the YZ plane. The beams are collimated in their fast and slow axes, and are redirected by turning mirrors (162) to form a beam stack (130C) traveling along the XZ plane. The beam stack is turned by about 90°, then converged by a focusing lens (174) into an optical fiber (180). A compact assembly is thus provided. Each laser diode (120.i), its collimating optics (154.i, 158.i, i=1, 2, . . . ) and its turning mirror (162.i) are rigidly attached to a flat, heat-spreading surface (144.i) and thus remain aligned with each other in thermal cycling.
Owner:FAYBISHENKO VICTOR
LED illumination device
InactiveUS7918580B2Ensure adequate heatingControl areaNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceEngineeringHeat spreader
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Integrated circuit mounting for thermal stress relief useable in a multi-chip module
InactiveUS20070090522A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhysicsHeat spreading
Disclosed is a mounting structure for mounting an IC on a substrate, and particularly useful in a Multi-Chip Module (MCM). The mounting structure intervenes between the IC and the MCM substrate, and promotes heat dissipation from the IC. The mounting structure is insulative, and preferably comprises a direct bond to copper (DBC) board. A heat spreading region to which the IC is affixed is formed on a surface of the mounting structure with bond pad areas are around the heat spreading region. The other side of the mounting structure is mounted to the substrate, which also has bond pads. Bond pads on the IC are connected to the bond pad areas on the mounting structure, and the bond pad areas on the mounting structure are further coupled to the bond pads on the substrate. Each of these connections is preferably made by wirebonding. Thermal vias can be used in the mounting structure and / or in the substrate to further promote heat dissipation.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
Semiconductor package and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS6515356B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipSemiconductor package
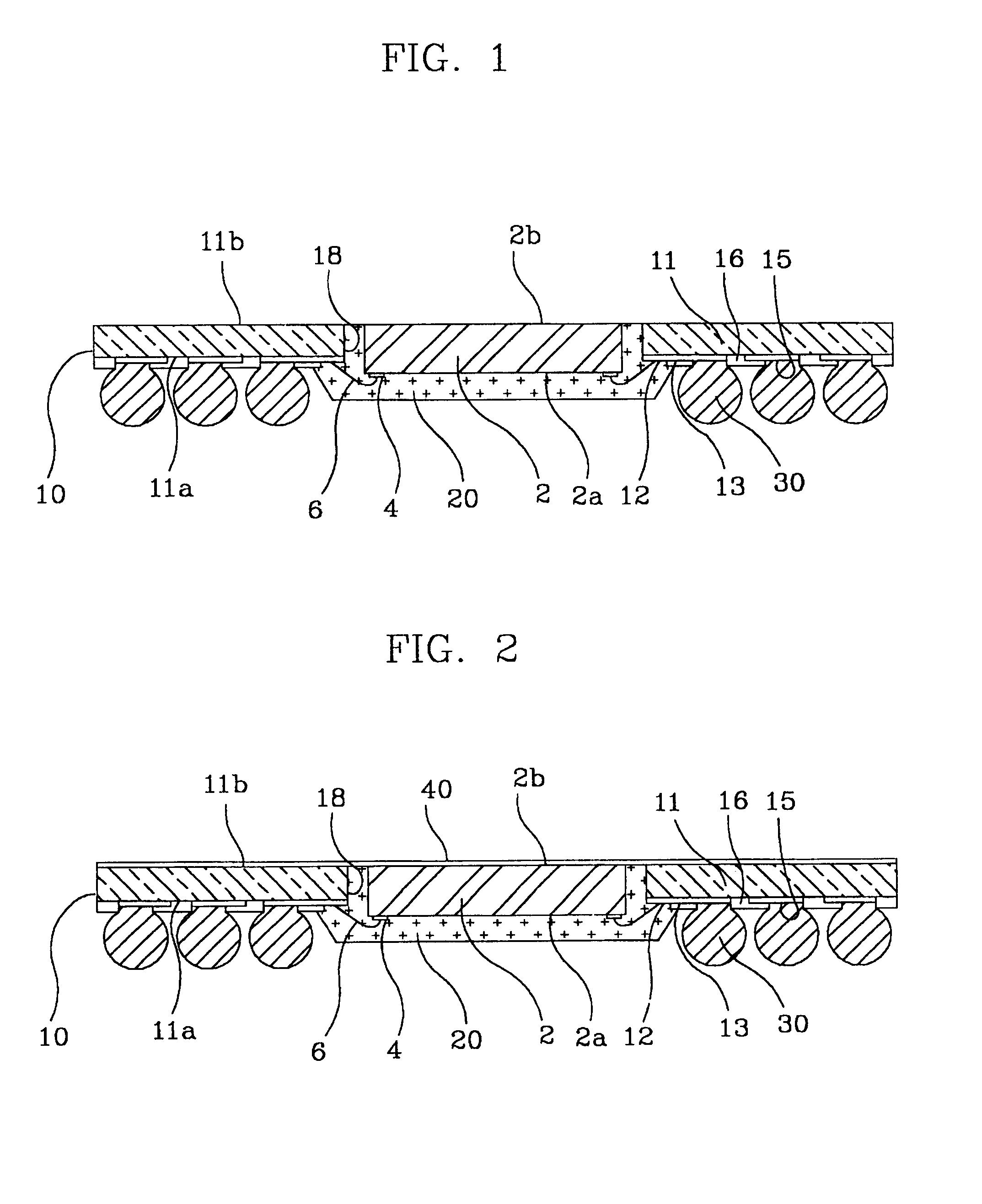
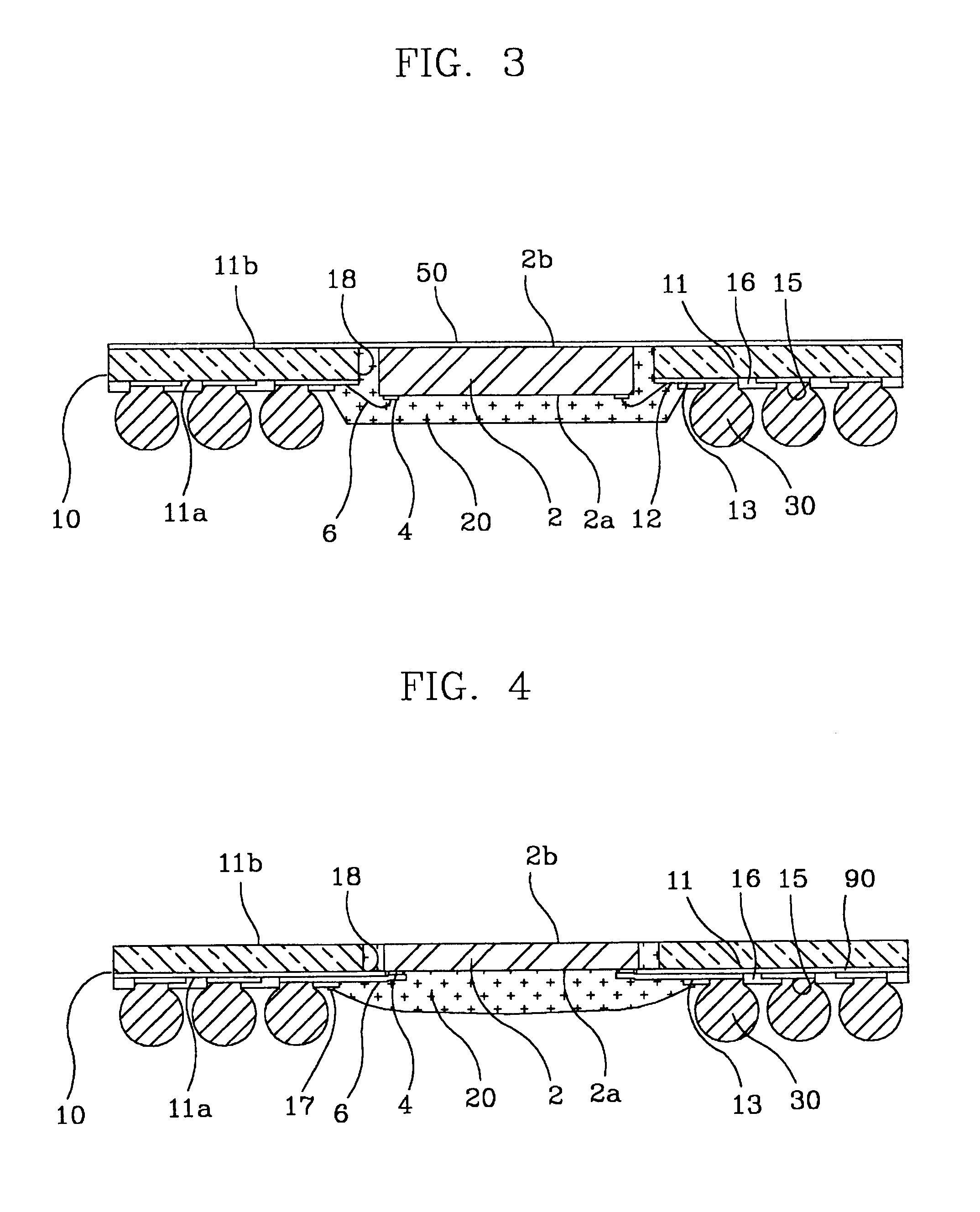
There is provided a semiconductor package and method for fabricating the same. An embodiment of the semiconductor package includes: a semiconductor chip having a first face and a second face, the first face having a plurality of input / output pads formed thereon; a circuit board composed of a resin film having a first face and a second face, a circuit pattern layer including a plurality of bond fingers and ball lands, and a cover coat covering the circuit pattern layer and selectively exposing the plurality of bond fingers and ball lands, the circuit pattern layer being formed on the first face of the resin film, the circuit board having a through hole at the center the semiconductor chip being placed in the through hole; electrical connection means for electrically connecting the input / output pads of the semiconductor chip to the bond fingers of the circuit board; an encapsulant for encapsulating the semiconductor chip, connection means and a part of the circuit board; and a plurality of conductive balls fused to the circuit board. Accordingly, the semiconductor package becomes very thin and its heat spreading performance is improved.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
Diode laser arrangement with a plurality of diode laser arrays
InactiveUS6898222B2Promote homogenizationSemiconductor laser arrangementsExcitation process/apparatusLaser arrayRadiation field
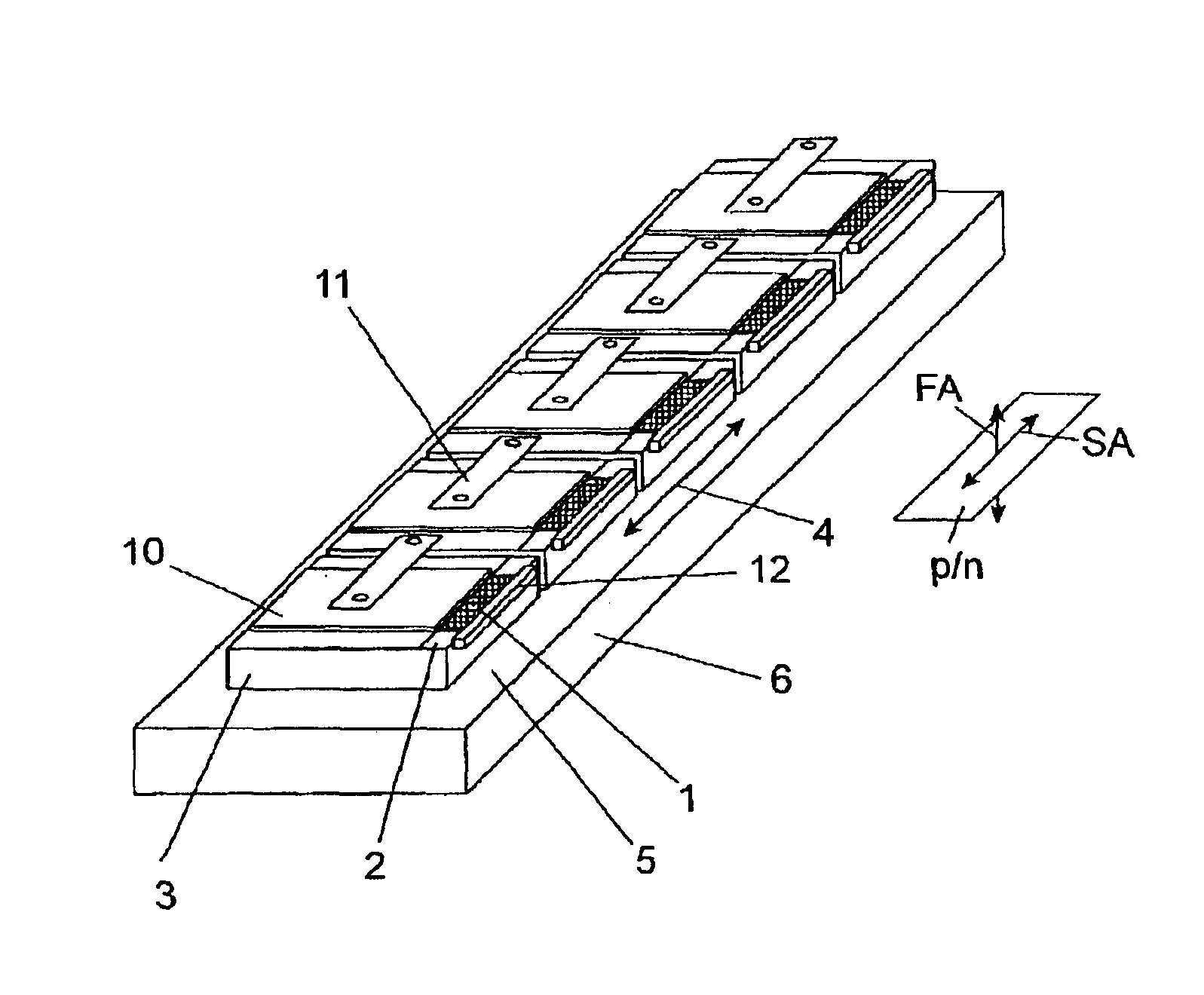
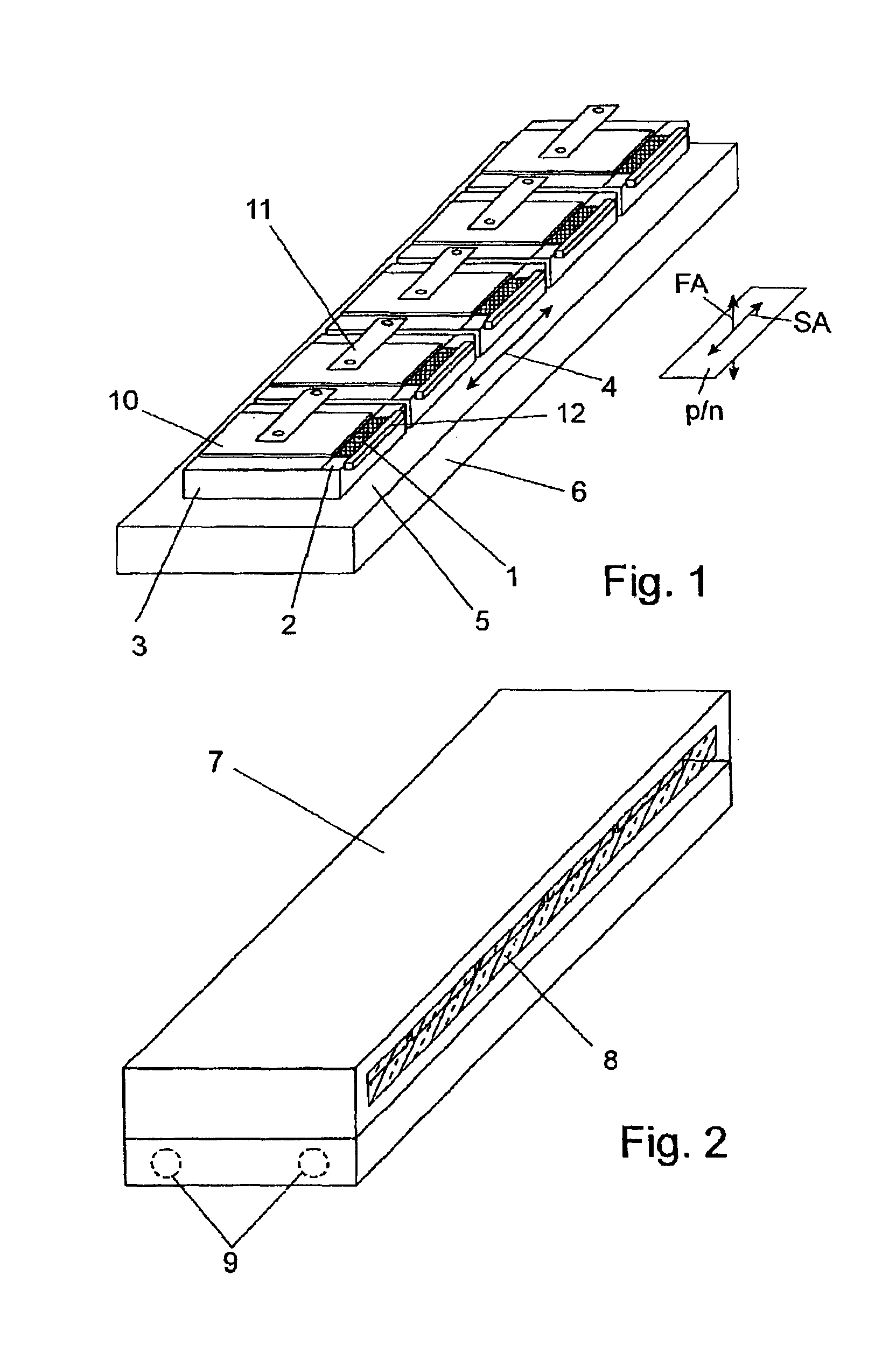
A diode laser arrangement is disclosed wherein a radiation source is designed which can be scaled with respect to power such that different types of cooling can be applied and the configuration of the radiation field is suitable for adapting to different tasks in a simple manner. For this purpose, every diode laser is connected to a thermal contact surface of a separate, heat-spreading carrier which is fastened to a cooling surface of a common cooling element so as to be electrically insulated. The carriers are arranged adjacently in such a way that the line-shaped emission regions of the diode lasers are adjacent in series and the p-n junction planes extend parallel to the thermal contact surfaces. The diode laser arrangement is particularly suitable as a pump light source.
Owner:JENOPTIK LASERDIODE
Multibeam arrays of optoelectronic devices for high frequency operation
ActiveUS7949024B2Increase powerReduces parasitic impedance characteristicSemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser cooling arrangementsContact padDevice form
A VCSEL array device formed of a monolithic array of VCSELs and short circuited mesas is disclosed. The VCSELs can be spaced symmetrically or asymmetrical, in a manner to improve power or speed, or in phase and in parallel. The VCSELs are connected to a first metal contact pad formed on a heat-spreading substrate. The short-circuited mesas are formed alongside the VCSELs and are bonded to and form a short circuit to a second metal contact pad on the grounding substrate. Each VCSEL is encompassed by a thick metal heat sink to increase the height of VCSEL mesas. The structure of the heat sink, the VCSELs and the shorting mesas reduce parasitic impedance thereby increasing output power and high frequency response. The VCSELs and shorting mesas can be packaged as a coplanar waveguide in a ground-signal-ground configuration that improves signal modulation characteristics.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Insulating structure having combined insulating and heat spreading capabilities
InactiveUS20050270746A1Reduce heatPreventing and delaying transfer of heatDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention provides an insulating structure comprising an insulating material and a heat spreading material. The invention further provides a portable electronic device comprising at least one heat generating component, an enclosure, and an insulating structure, wherein the insulating structure comprises an insulating material and a heat spreading material.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Methods and apparatus for improved heat spreading in solid state lighting systems
ActiveUS7794114B2Efficient transferMore cost-effective retrofittingLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceEngineering
A solid state lighting subassembly or fixture includes an anisotropic heat spreading material. A heat spreading layer may be placed between a light emitting diode (LED) and luminaire or reflector and serves to spread heat laterally away from the LED. Low profile, low weight heat spreading may be utilized both to retrofit existing light fixtures with LEDs or to replace existing incandescent and fluorescent fixtures with LED based fixtures.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
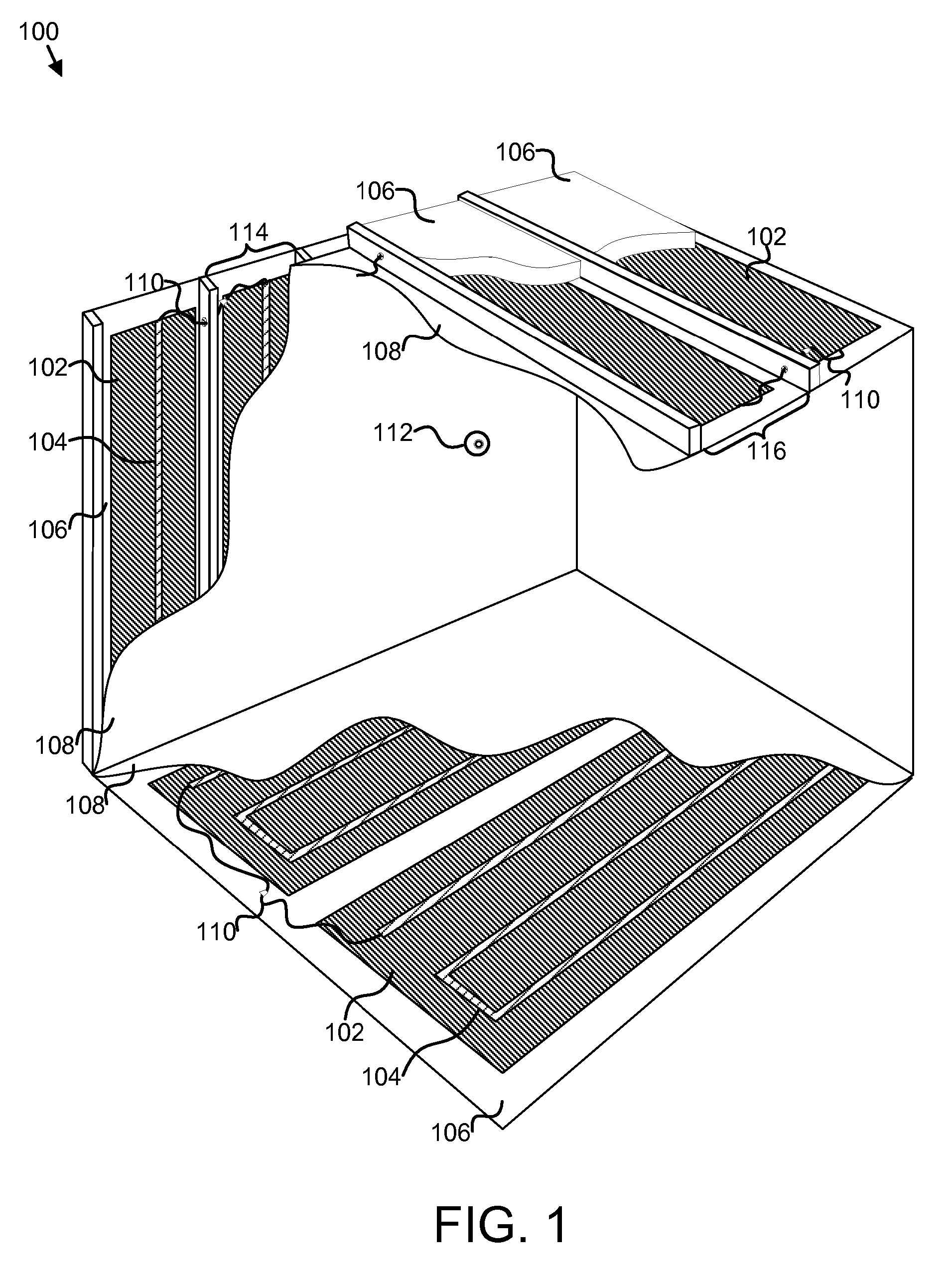
Uniform Heat Distribution in Resistive Heaters For Anti-Icing and De-Icing
ActiveUS20160221680A1Prevent freezingImprove protectionWindingsDe-icing equipmentsElectrical resistance and conductanceAdhesive
The concept of the present invention describes configurations to provide uniform heat distribution of resistive heaters. This configuration allows successful anti-icing and deicing with relatively low applied power. One aspect involves the use of a thin film heater applied just underneath the topcoat to efficiently direct all heat to the surface, allowing anti-icing and de-icing with minimal power. This can be accomplished by employing a hybrid electrode interface, using a metal foil or metal braid that is attached to the aircraft surface with a structural adhesive that has been smoothed along the edges with metal-filled adhesive. Another aspect of the present invention uses an array of heater cells created as a single sheet and a heat spreading material, provided underneath or overtop of the heater cells.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Multibeam array of top emitting vcsel elements
ActiveUS20130272330A1Improving illumination propertyIncrease capacitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersElectrical connectionCoplanar waveguide
A top emitting VCSEL array may be coupled to a separate heat spreading superstrate that may be positioned above the apertures of the array and that may be able to transmit the emitted beams through the heat spreading superstrate. The VCSEL devices in the array may be controlled by an electrical connection to a pattern of conductive elements positioned in close contact with, but electrically isolated from, the heat spreading superstrate. The conductive elements may electrically control one or more of the VCSEL devices to enable sectional control of the light output. The elements may also be arraigned in a ground-signal-ground or coplanar waveguide configuration to improve the frequency response of the array.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Multibeam Arrays of Optoelectronic Devices for High Frequency Operation
ActiveUS20100303113A1Increase powerReduces parasitic impedance characteristicSemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser cooling arrangementsContact padDevice form
A VCSEL array device formed of a monolithic array of VCSELs and short circuited mesas is disclosed. The VCSELs can be spaced symmetrically or asymmetrical, in a manner to improve power or speed, or in phase and in parallel. The VCSELs are connected to a first metal contact pad formed on a heat-spreading substrate. The short-circuited mesas are formed alongside the VCSELs and are bonded to and form a short circuit to a second metal contact pad on the grounding substrate. Each VCSEL is encompassed by a thick metal heat sink to increase the height of VCSEL mesas. The structure of the heat sink, the VCSELs and the shorting mesas reduce parasitic impedance thereby increasing output power and high frequency response. The VCSELs and shorting mesas can be packaged as a coplanar waveguide in a ground-signal-ground configuration that improves signal modulation characteristics.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
High efficiency concentrating photovoltaic module with reflective optics
InactiveUS20100012171A1Low costImprove solar conversion efficiencyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationElectricityThermal expansion
A Concentrating Photovoltaics (CPV) module includes light weight housing, a number of Cassegrain type reflective solar concentrators, a number of multi-junction solar cells and a novel heat spreading system. The primary and secondary reflectors focus the sun over 500 times to maximize the amount of photons collected by the solar cells and converted to electricity. A newly designed soft board material provides coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) matched carrier for the solar cells and an efficient electrical connectivity method. The carrier board is attached to a specially formulated heat spreader that is specially formulated to conduct heat longitudinally away from the solar cells. The combination of the above creates CPV modules with the highest efficiency and lowest cost per Watt.
Owner:AMMAR DANNY F
Thermally efficient computer incorporating deploying CPU module
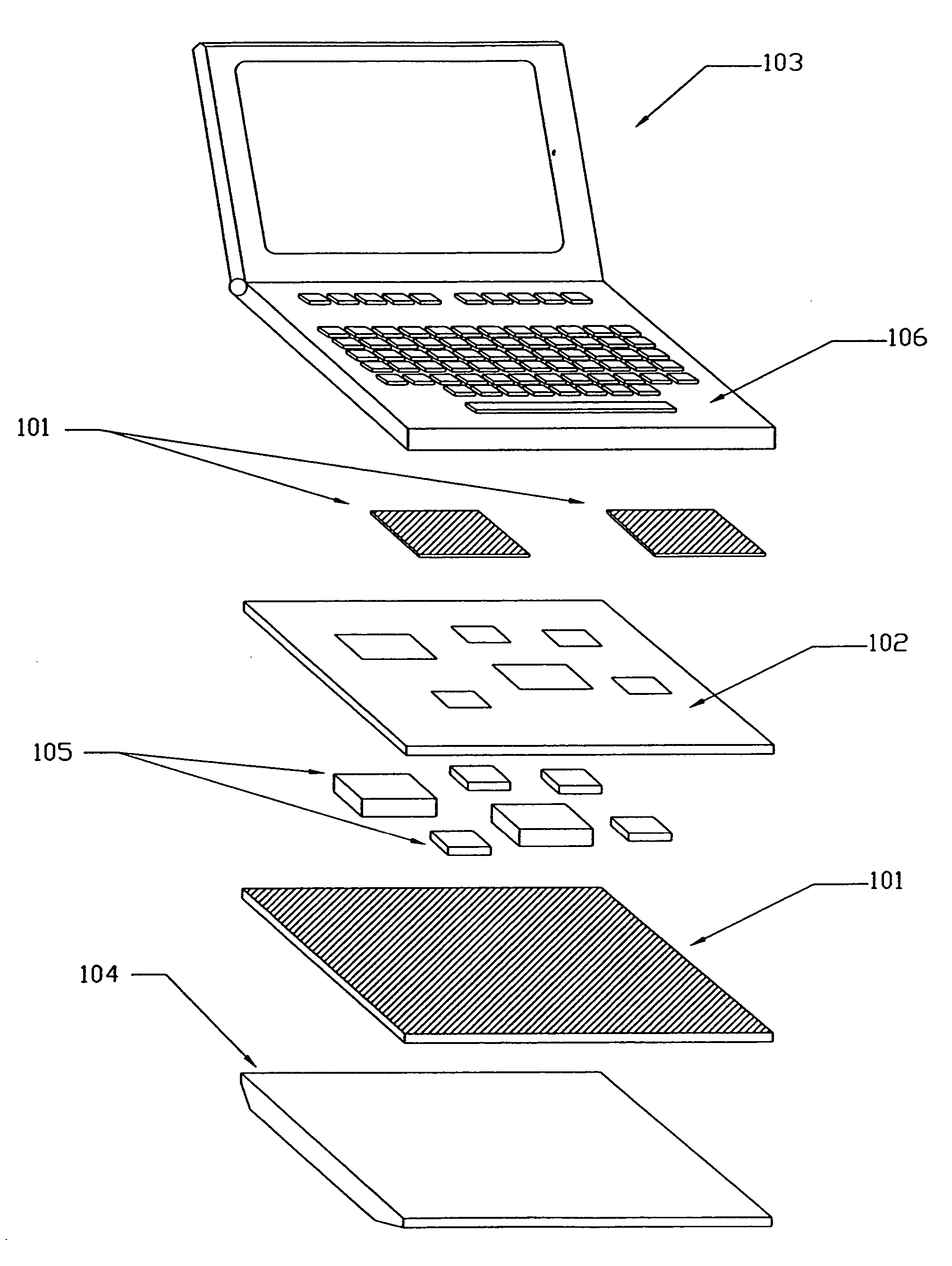
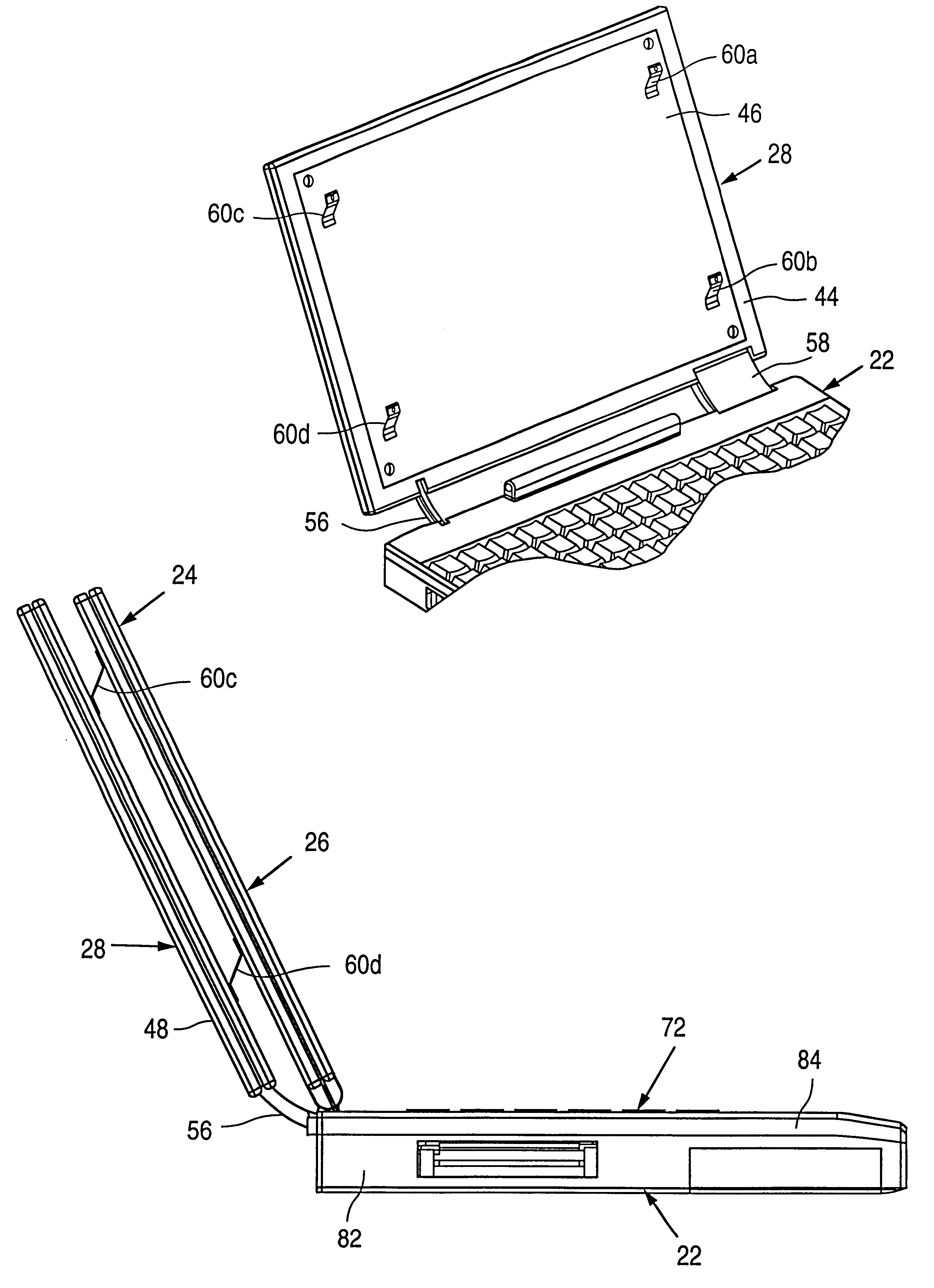
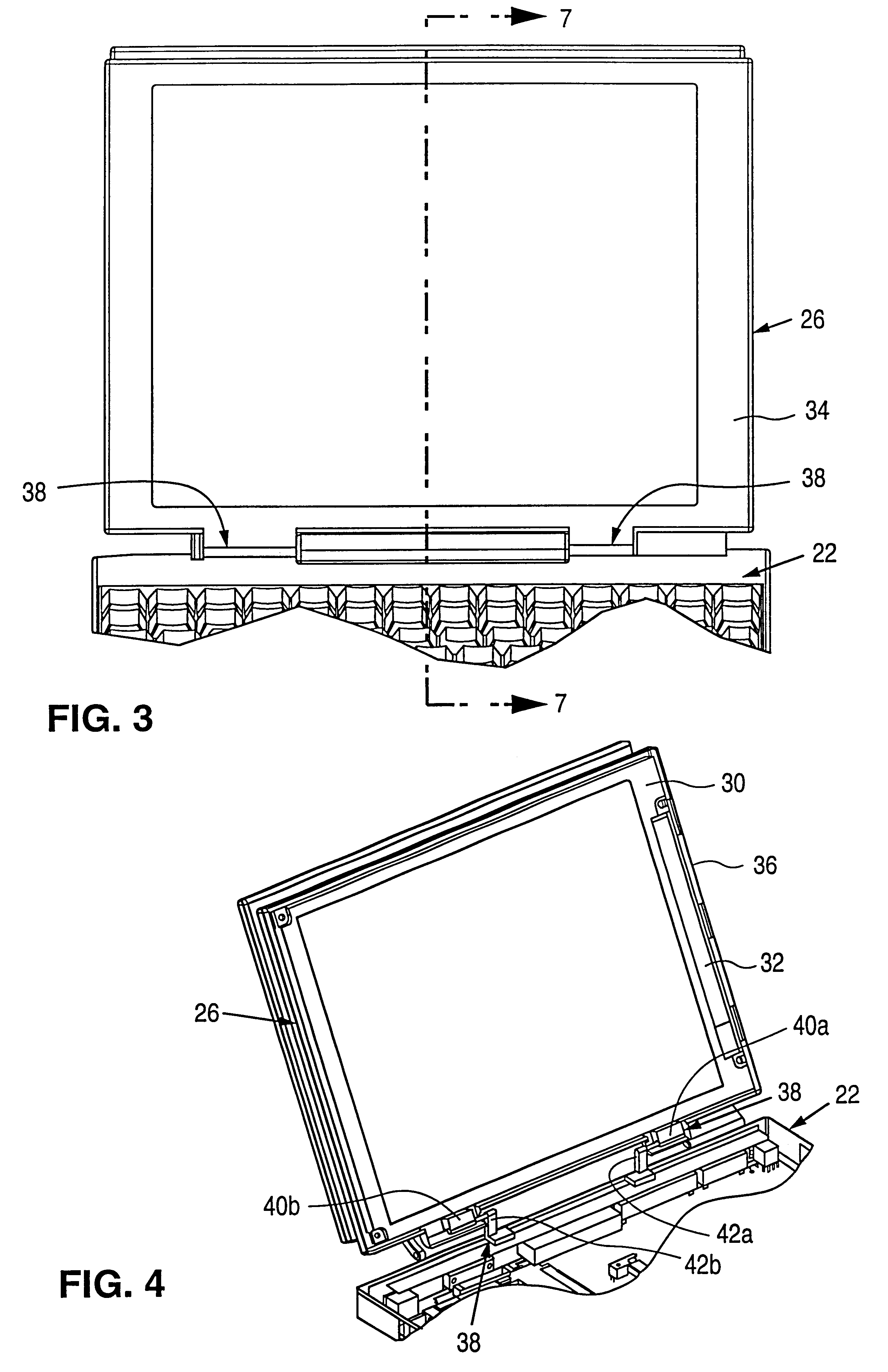
InactiveUS6243261B1Easy to separateImprove cooling effectDetails for portable computersCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsFlexible circuitsFlat panel display
A portable computer with a base (22) containing media, batteries, and keyboard, with the a CPU 52 and main PCB 50 located in a planar CPU module (28) separate from and behind the flat-panel display module (26), mechanically connected to the display module (26) with a deployment mechanism, and functionally connected to the display module (26) and base (22) by a base flexible circuit (78). The CPU module contains a heat-spreading front cover 46 facing the display module 26, and thermally connected to hot components on the main PCB 50. The translating mechanism operates such that when the display module (26) is closed, the CPU module (28) is adjacent to the display module (26), and when the display module (26) is open, the CPU module (28) is positioned with a gap between the it and the display module (26).
Owner:SPECULATIVE
Lateral heat spreading layers for epi-side up ridge waveguide semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS7061022B1Reduce thermal resistanceMaximum device performanceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsRidge waveguidesWaveguide
Disclosed are a semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same comprising a substrate, a mesa region adjacent to the substrate, an electroplated metal layer, for reducing the thermal resistance of the device, surrounding the mesa region, an insulator layer separating a side portion of the mesa region from the electroplated metal layer, a heat sink, a bonding layer adjacent to the heat sink, and a second metal layer in between the substrate and the heat sink, wherein the substrate is adjacent to the bonding layer, and wherein the electroplated metal layer dimensioned and configured to have a thickness of at least half a thickness of the mesa region; and to laterally spread heat away from the mesa region. The mesa region comprises a first cladding layer adjacent to the substrate, an active region adjacent the first cladding layer, and a second cladding layer adjacent to the active region.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Heat spreading circuit assembly
InactiveUS7889502B1Improve cooling effectDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsEngineeringDielectric layer
A circuit assembly including a substrate which has a dielectric layer, a heat spreader layer located at a first surface of the substrate, a heat generating component located at a second surface of the substrate, and a thermal pathway in thermal connection between the heat spreader layer and the heat generating component.
Owner:NEOGRAF SOLUTIONS LLC
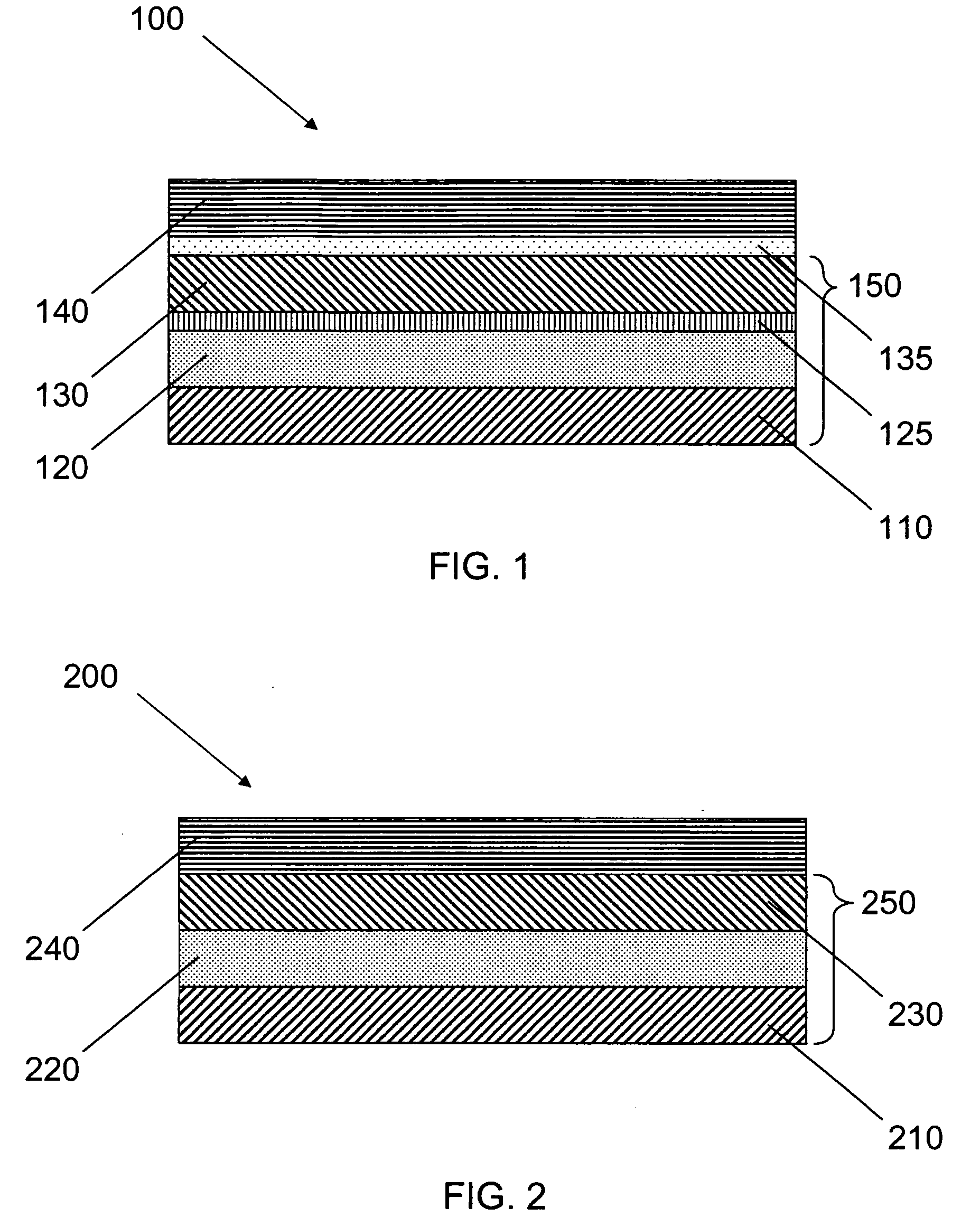
Wide bandgap semiconductor layers on SOD structures
InactiveUS20060113545A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBroadbandOpto electronic
Multi-layered structures containing GaN on SOD (silicon / diamond / silicon) substrates are described. The unique substrate / epilayer combination can provide electronic materials suitable for high-power and opto-electronic devices without commonly observed limitations due to excess heat during device operation. The resulting devices have built-in thermal heat spreading capability that result in better performance and higher reliability.
Owner:SP3 +1
LED illumination device
InactiveUS20090323342A1Ensure adequate heatingControl areaLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceEngineeringHeat spreader
An LED illumination device includes a light source and a heat sink. The heat sink includes an elongated base and a plurality of fins extending from the base. The base has a heat-absorbing surface and an opposite heat-spreading surface. The fins extend upwardly from the heat-spreading surface. The light source is attached to the heat-absorbing surface, whereby heat generated by the light source is removed by the heat sink. The heat-absorbing surface is one of a convex surface and a concave surface, whereby light emitted from the light source is diverged or converged towards objects.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Heat spreading thermal interface structure
InactiveUS7078109B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted electric component incorporationMetal alloyInterface layer
The thermal interface structure of the present invention is suited for use in a non-referenced die system between a heat source and heat sink spaced up to 300 mils apart and comprises a plurality of layers including a core body of high conductivity metal or metal alloy having opposite sides, a soft thermal interface layer disposed on one side of the core body for mounting against the heat sink and a thin layer of a phase change material disposed on the opposite side of the core body for mounting against the heat source wherein the surface area dimension (footprint) of the core body is substantially larger than the surface area of the heat source upon which the phase change material is mounted to minimize the thermal resistance between the heat source and the heat sink and wherein said soft thermal interface layer is of a thickness sufficient to accommodate a variable spacing between the heat source and the heat sink of up to 300 mils.
Owner:LAIRD TECH INC
Modular radiant heating apparatus
ActiveUS20060289000A1Improve protectionRoof coveringDomestic stoves or rangesThermal isolationCoupling
The radiant heating apparatus is disclosed, having a planar electrical heating element, a planar heat spreading layer, a finishing layer, a thermal isolation layer, and an electric power coupling. The planar electrical heating element converts electrical energy to heat energy. The planar heat spreading layer is in contact with the planar electrical heating element, and draws the heat energy out of the planar electrical heating element and distributes the heat energy. The finishing layer is disposed to one side of the planar heat spreading layer. The thermal isolation layer is disposed to an opposite side of the planar heat spreading layer as the finishing layer. Heat from the planar heat spreading layer conducts away from the thermal isolation layer and toward the finishing layer. The electric power coupling is connected to the electrical heating element to supply electrical power.
Owner:GREENHEAT IP HLDG LLC
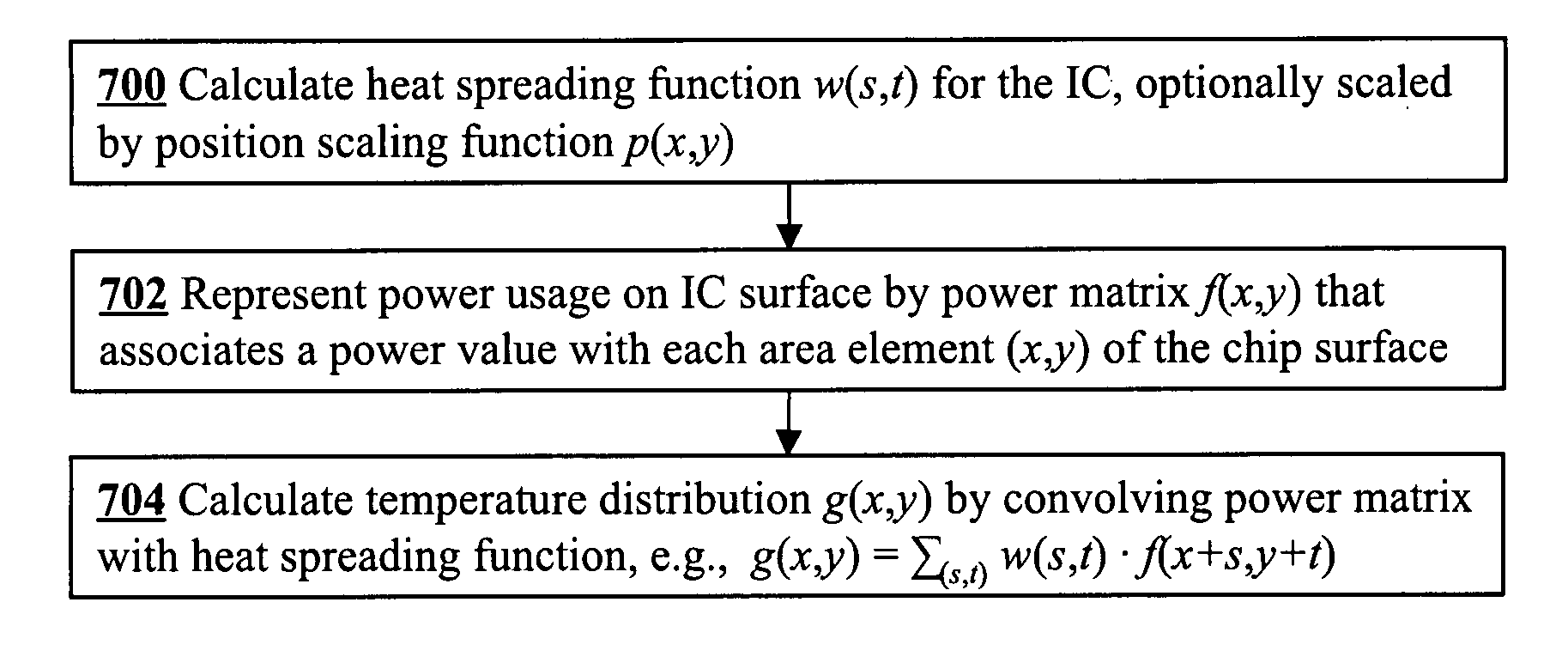
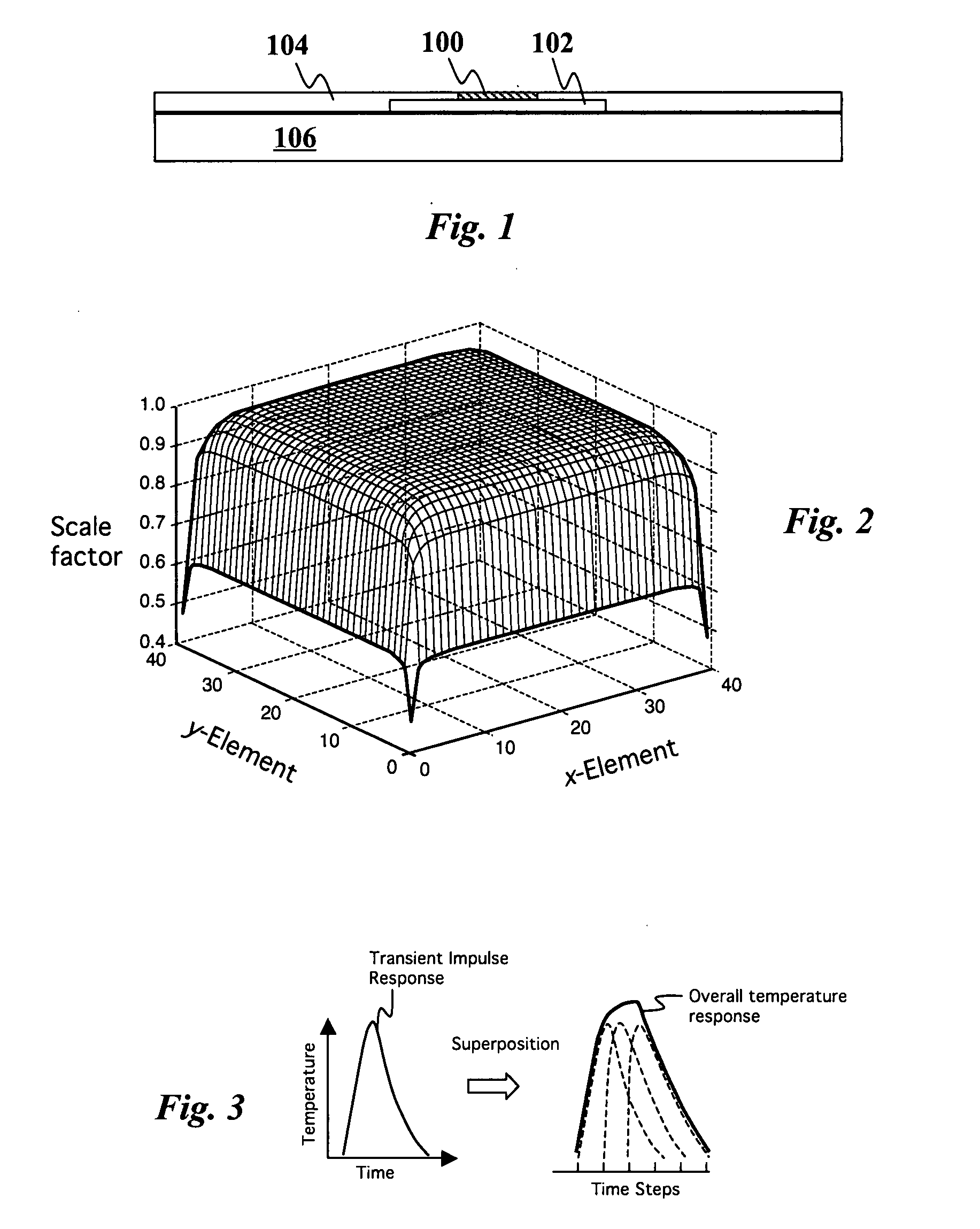
Efficient method to predict integrated circuit temperature and power maps
InactiveUS20080026493A1Fast and accurate methodMinimizes localized heatingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty computer hardwareElement analysisDiffusion function
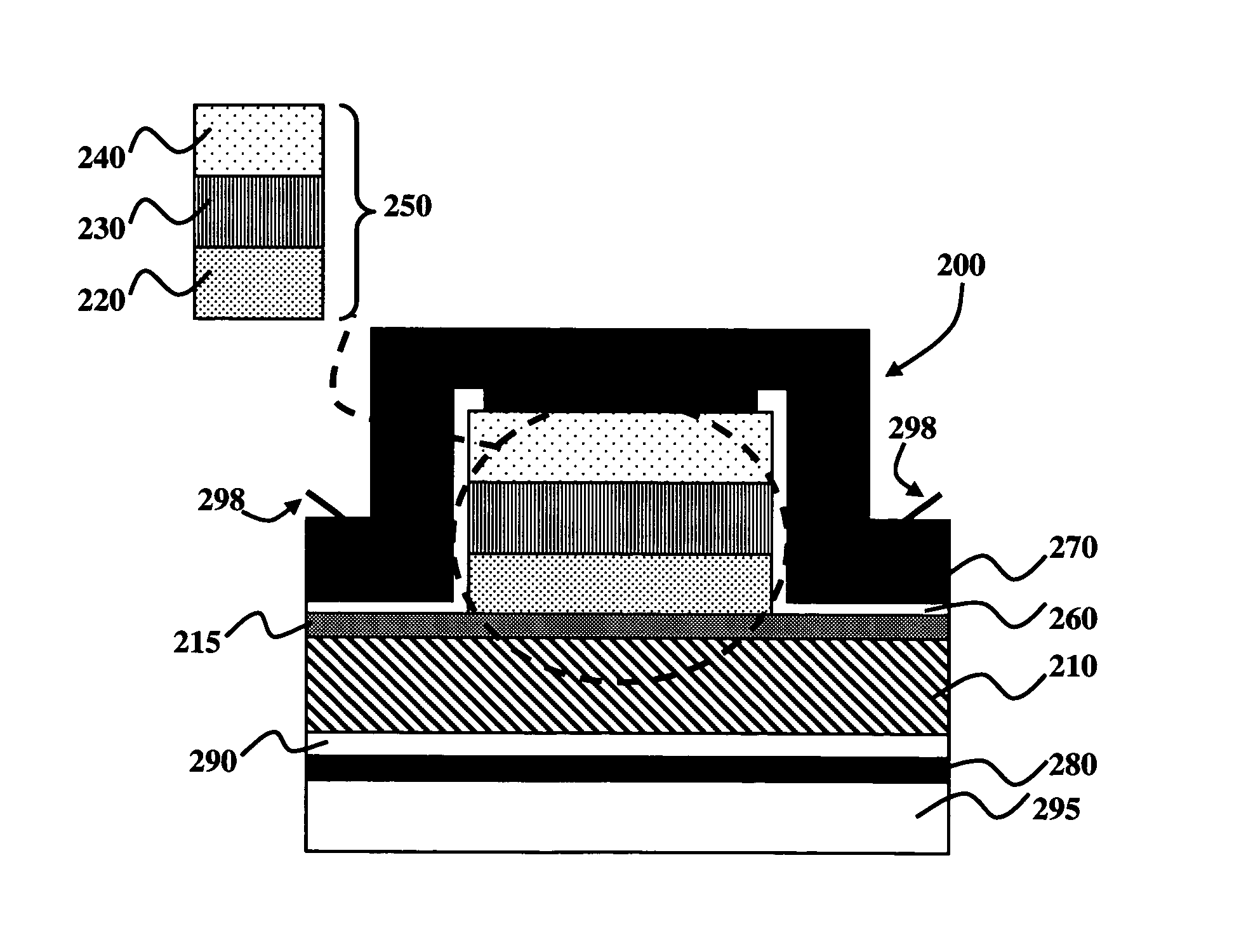
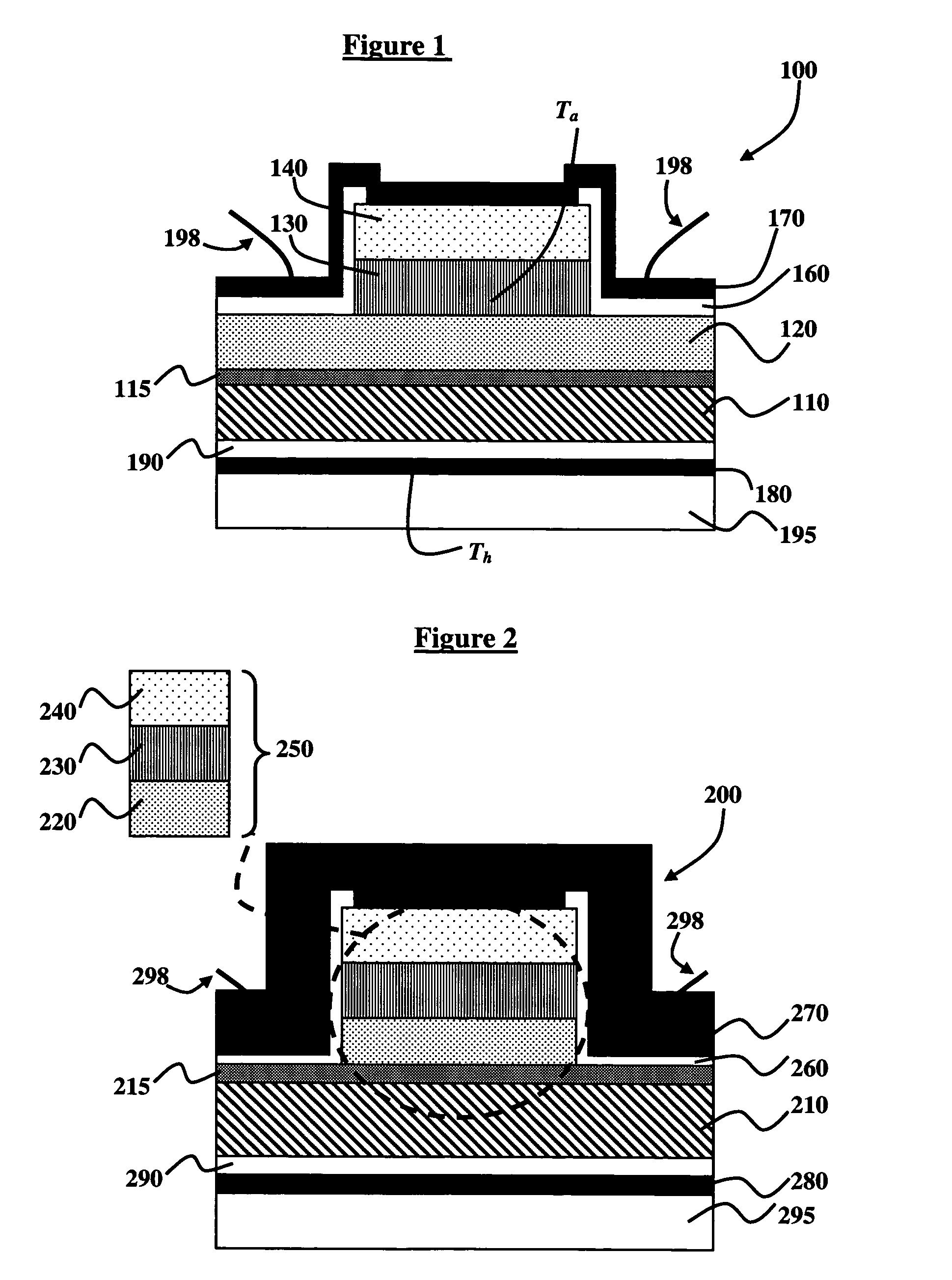
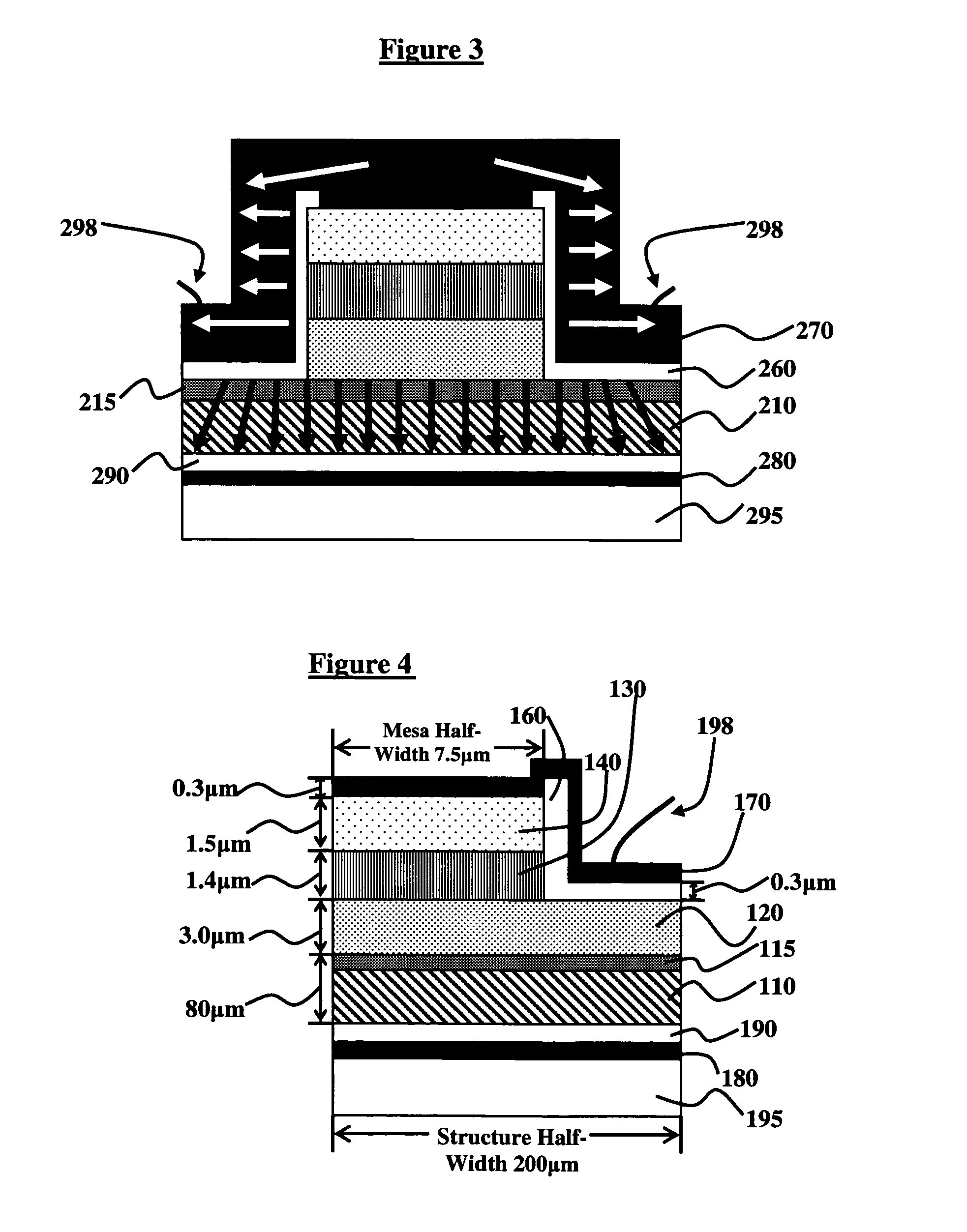
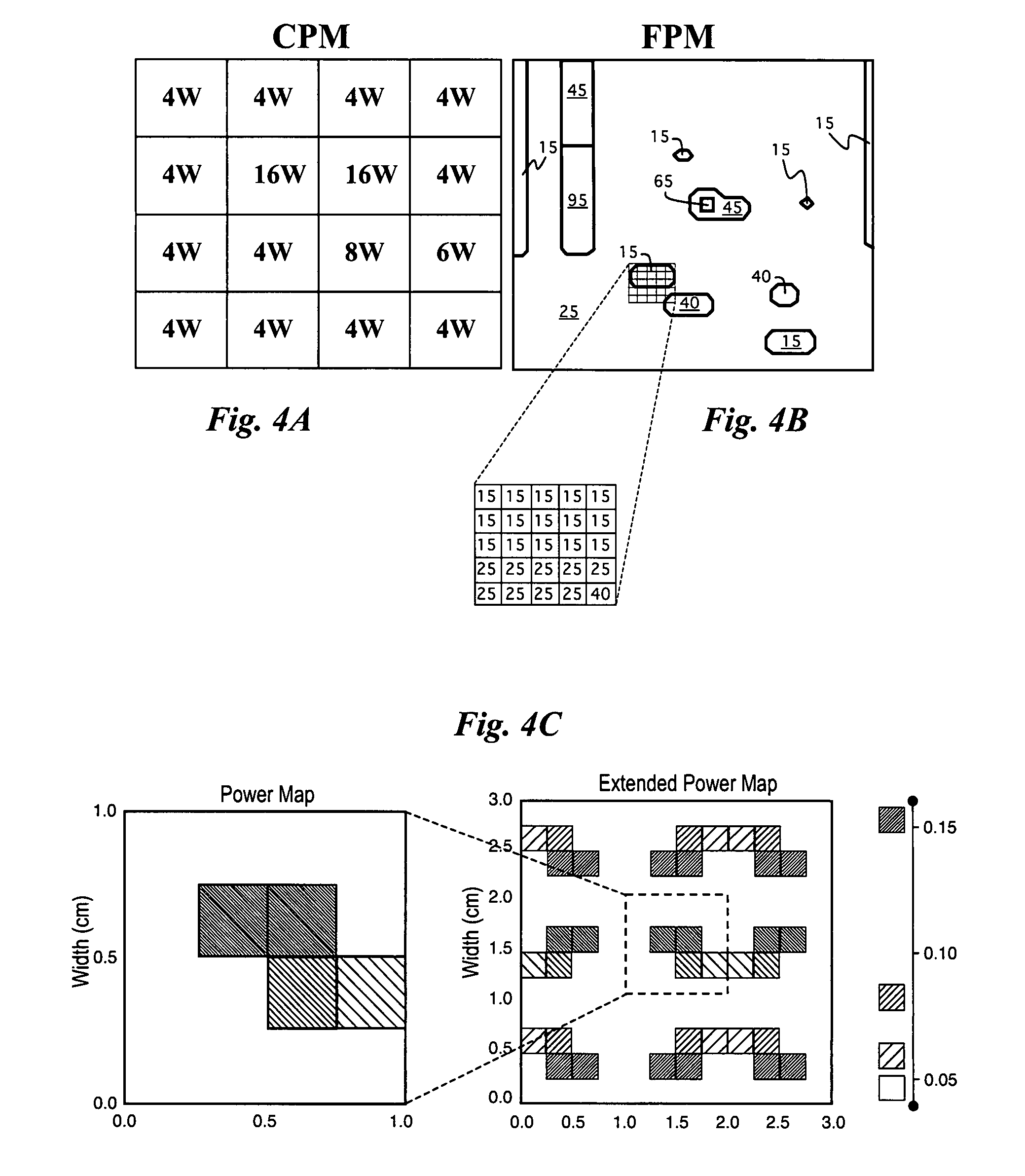
The temperature distribution associated with a design of an integrated circuit is calculated by convoluting a surface power usage represented by a power matrix with a heat spreading function. The heat spreading function may be calculated from a simulation of a point source on the integrated circuit using a finite element analysis model of the integrated circuit or other techniques. To account for spatial variations on the chip, the heat spreading function may be made dependent on position using a position scaling function. Steady-state or transient temperature distributions may be computed by using a steady-state or transient heat spreading function. A single heat spreading function may be convolved with various alternative power maps to efficiently calculate temperature distributions for different designs. In an inverse problem, one can calculate the power map from an empirically measured temperature distribution and a heat spreading function using various de-convolution techniques. While the forward problem is analogous to image blurring, the inverse problem is analogous to image restoration.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
Modular radiant heating apparatus
An apparatus, system, and method provide radiant heat. A planar electrical heating element converts electrical energy to heat energy. A planar heat spreading layer is in contact with the planar electrical heating element, drawing the heat energy out of the planar electrical heating element and distributing the heat energy. A finishing layer is disposed to one side of the planar heat spreading layer. A thermal isolation layer is disposed to an opposite side of the planar heat spreading layer as the finishing layer. Heat from the planar heat spreading layer conducts away from the thermal isolation layer and toward the finishing layer. An electric power coupling is connected to the electrical heating element to supply electrical power.
Owner:GREENHEAT IP HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com