Patents
Literature
1123 results about "Image representation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
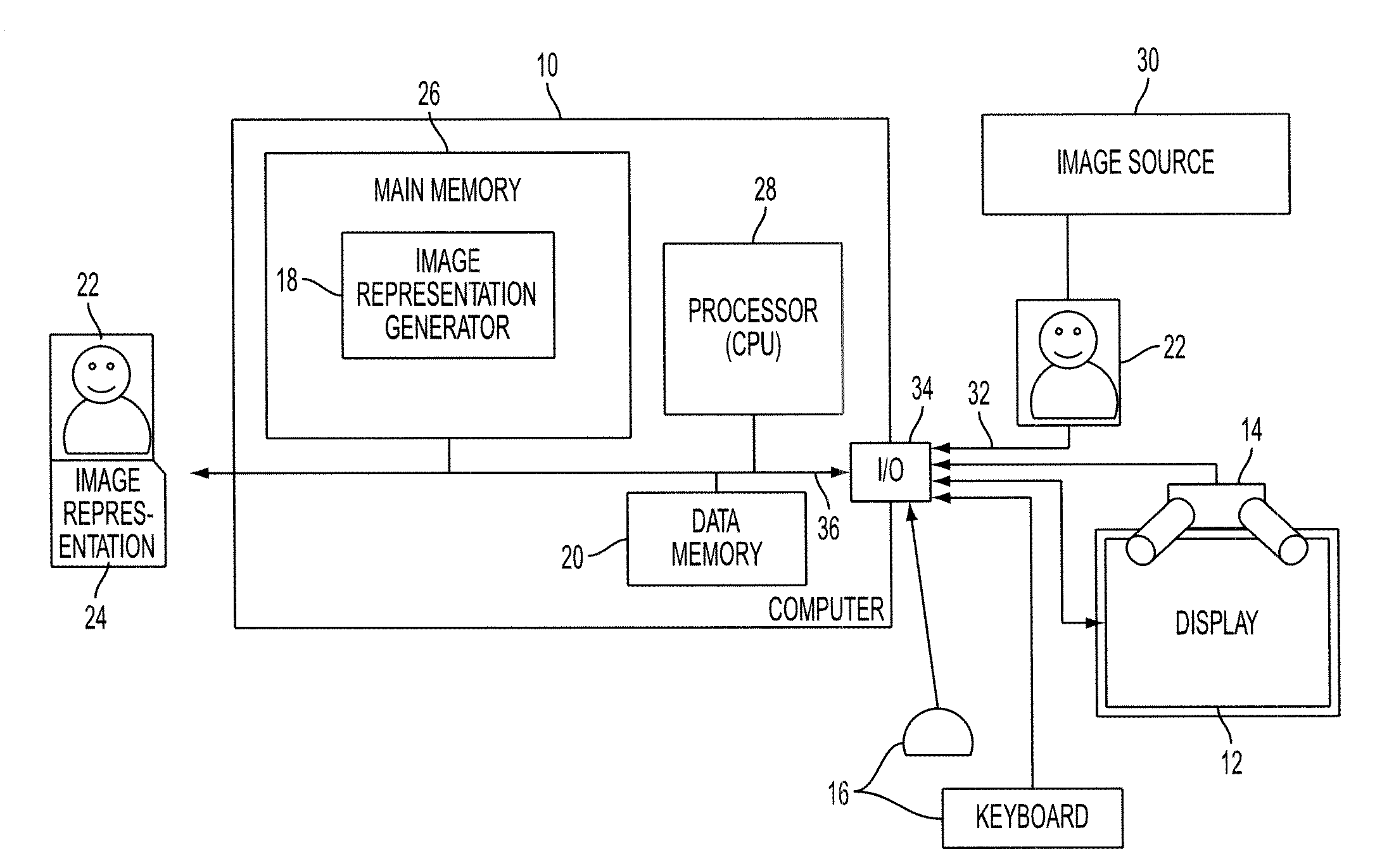
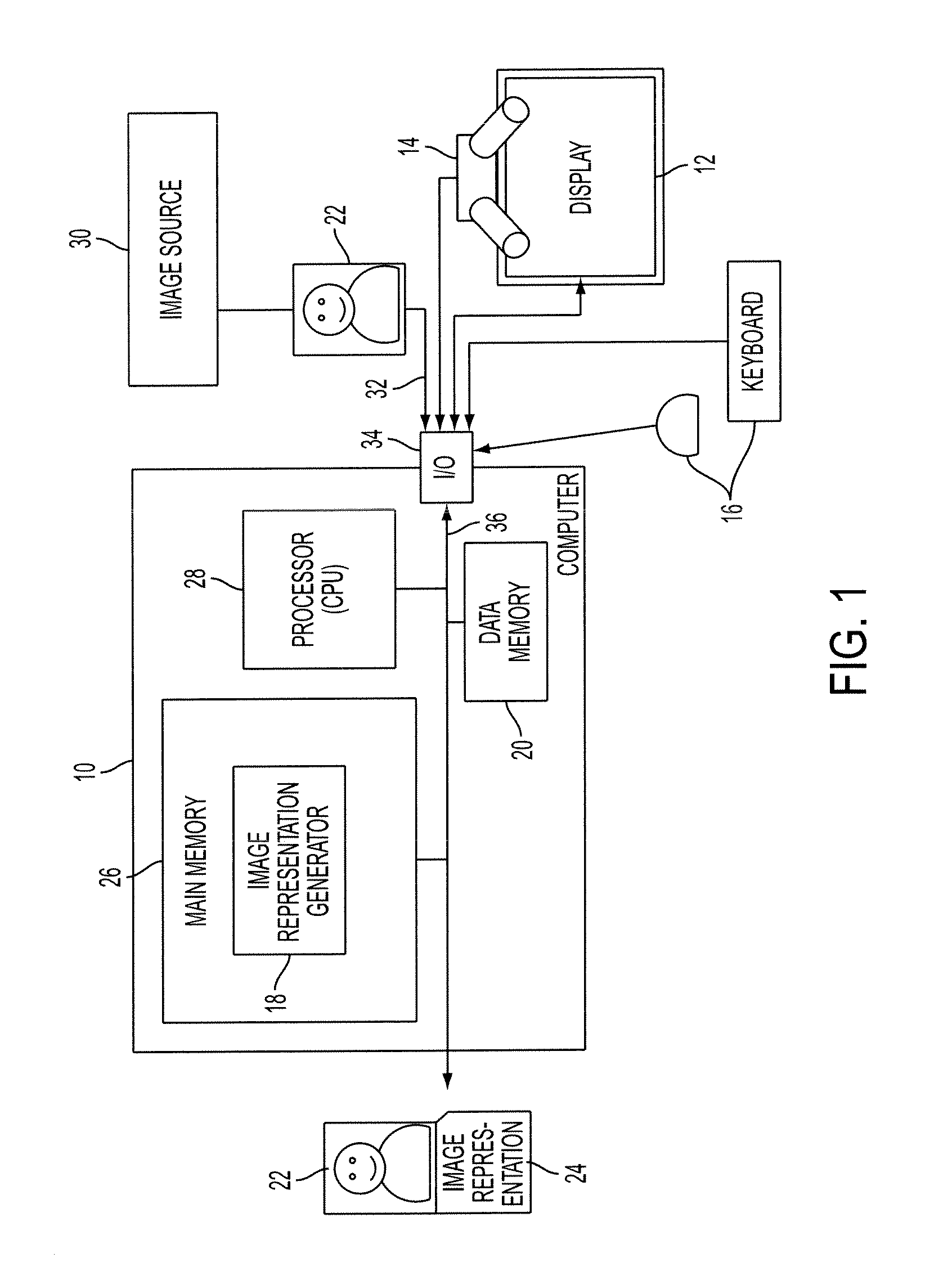
Image-level representation is a (numerical) way to represent an image without a direct pixel representation. For example, one could represent an image by its histograms of luminance and chroma values, or by its Fourier transform, or by any other statistical measure. Such a representation helps compare images or detect specific features.
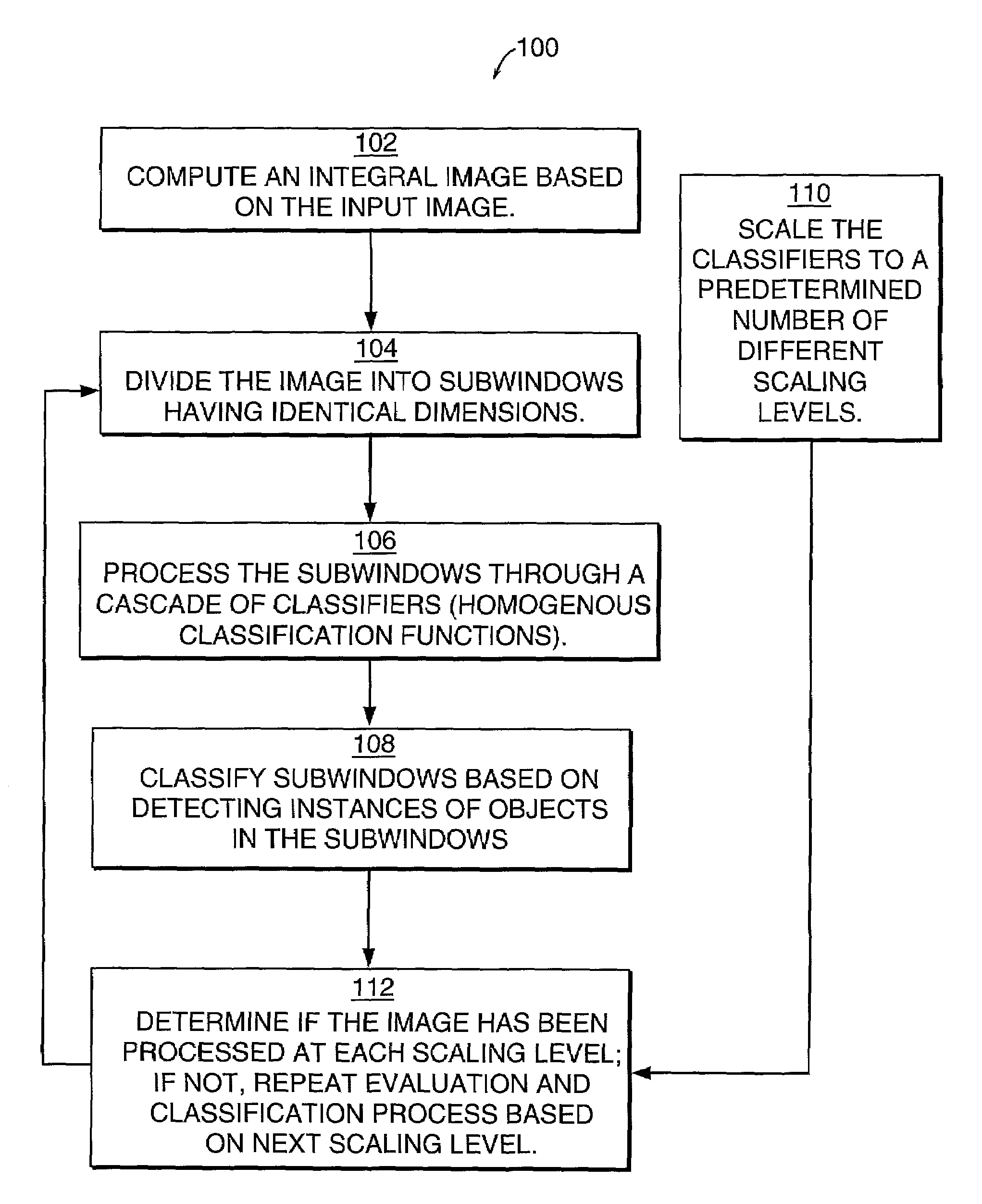
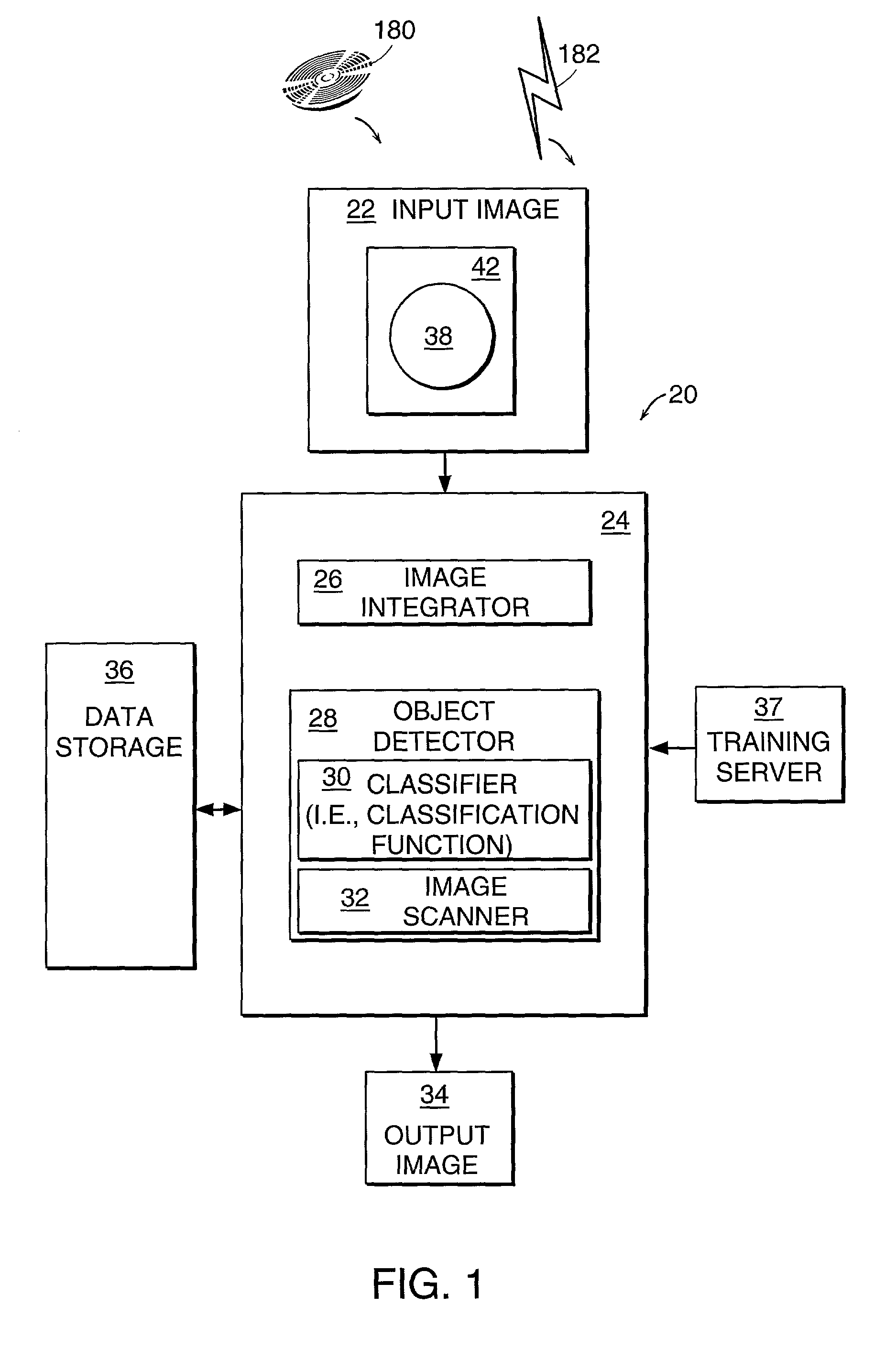
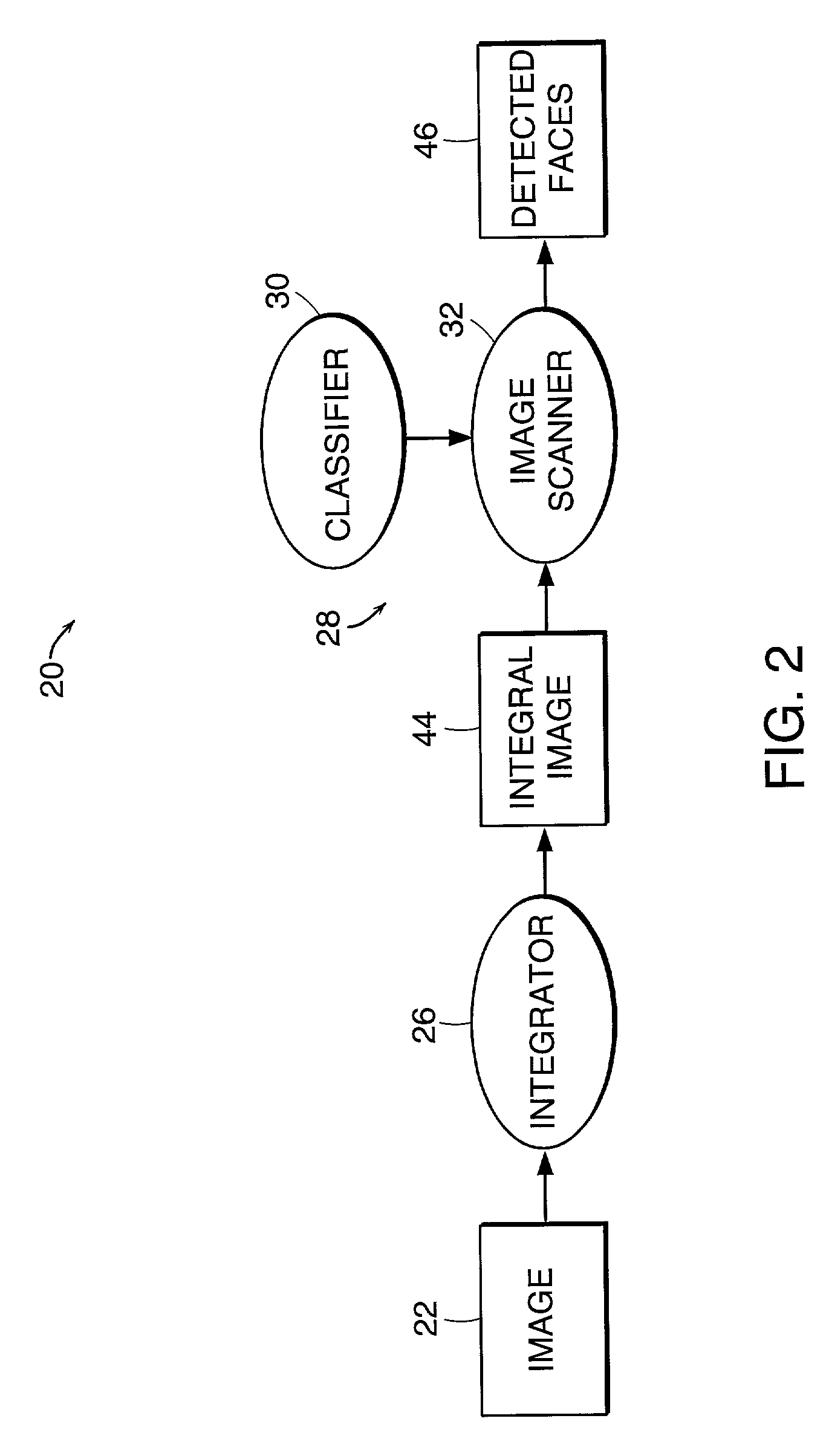
Method and system for object detection in digital images
InactiveUS7099510B2Powerful and efficientComputationally efficientCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsRadiologyDigital image
An object detection system for detecting instances of an object in a digital image includes an image integrator and an object detector, which includes a classifier (classification function) and image scanner. The image integrator receives an input image and calculates an integral image representation of the input image. The image scanner scans the image in same sized subwindows. The object detector uses a cascade of homogenous classification functions or classifiers to classify the subwindows as to whether each subwindow is likely to contain an instance of the object. Each classifier evaluates one or more features of the object to determine the presence of such features in a subwindow that would indicate the likelihood of an instance of the object in the subwindow.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
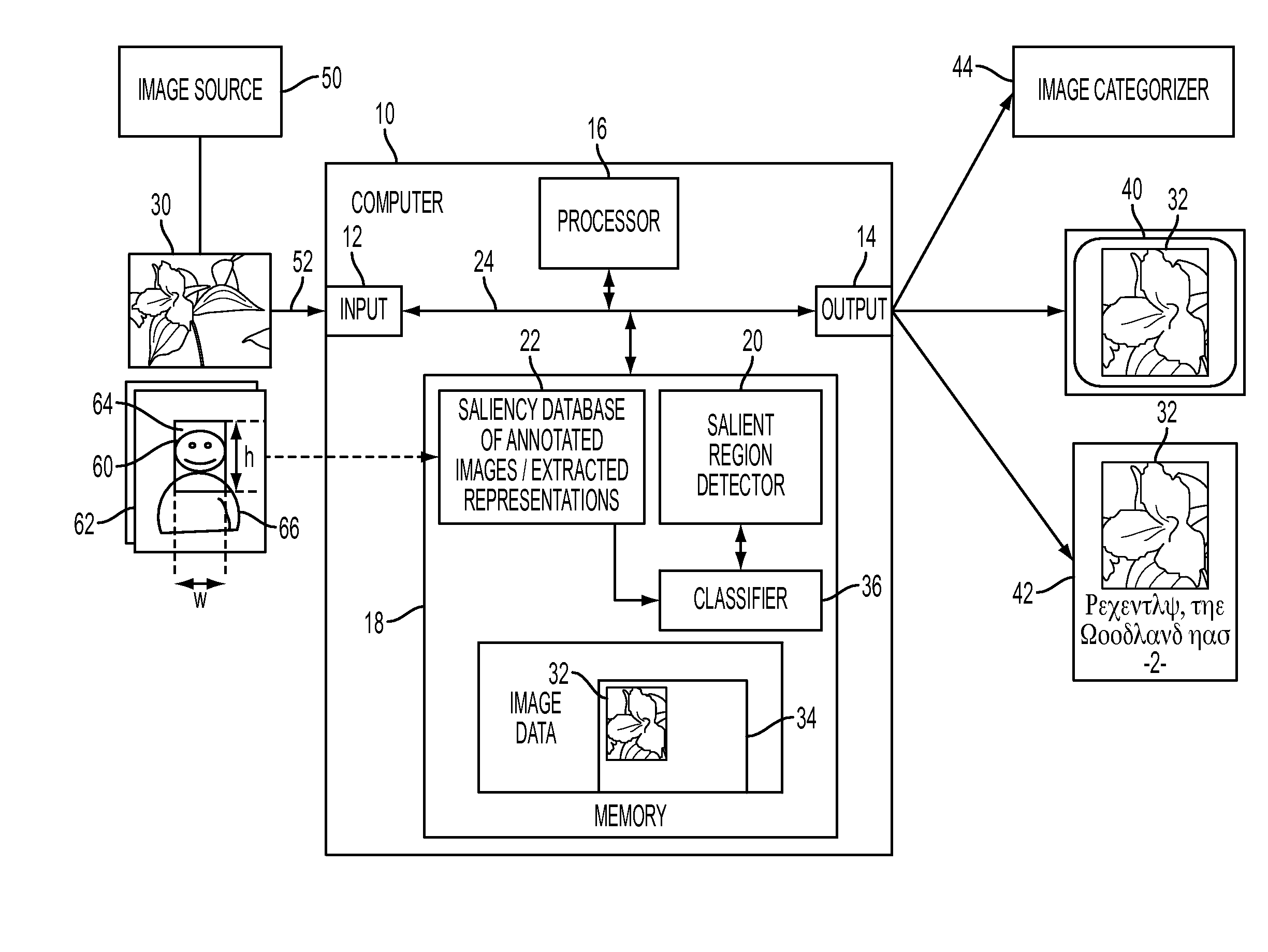
Framework for image thumbnailing based on visual similarity
ActiveUS20100226564A1Still image data indexingCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionVisual perception
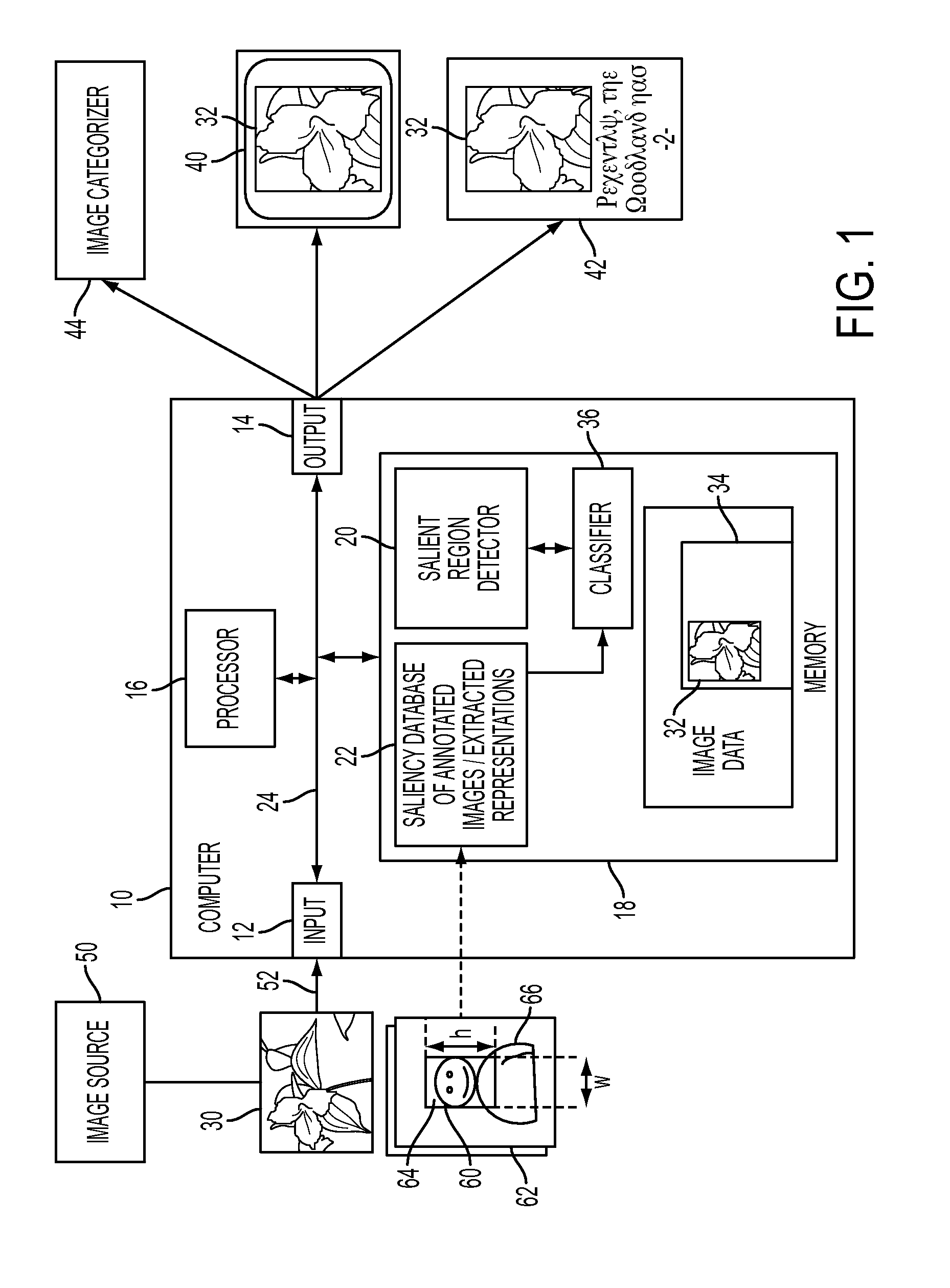
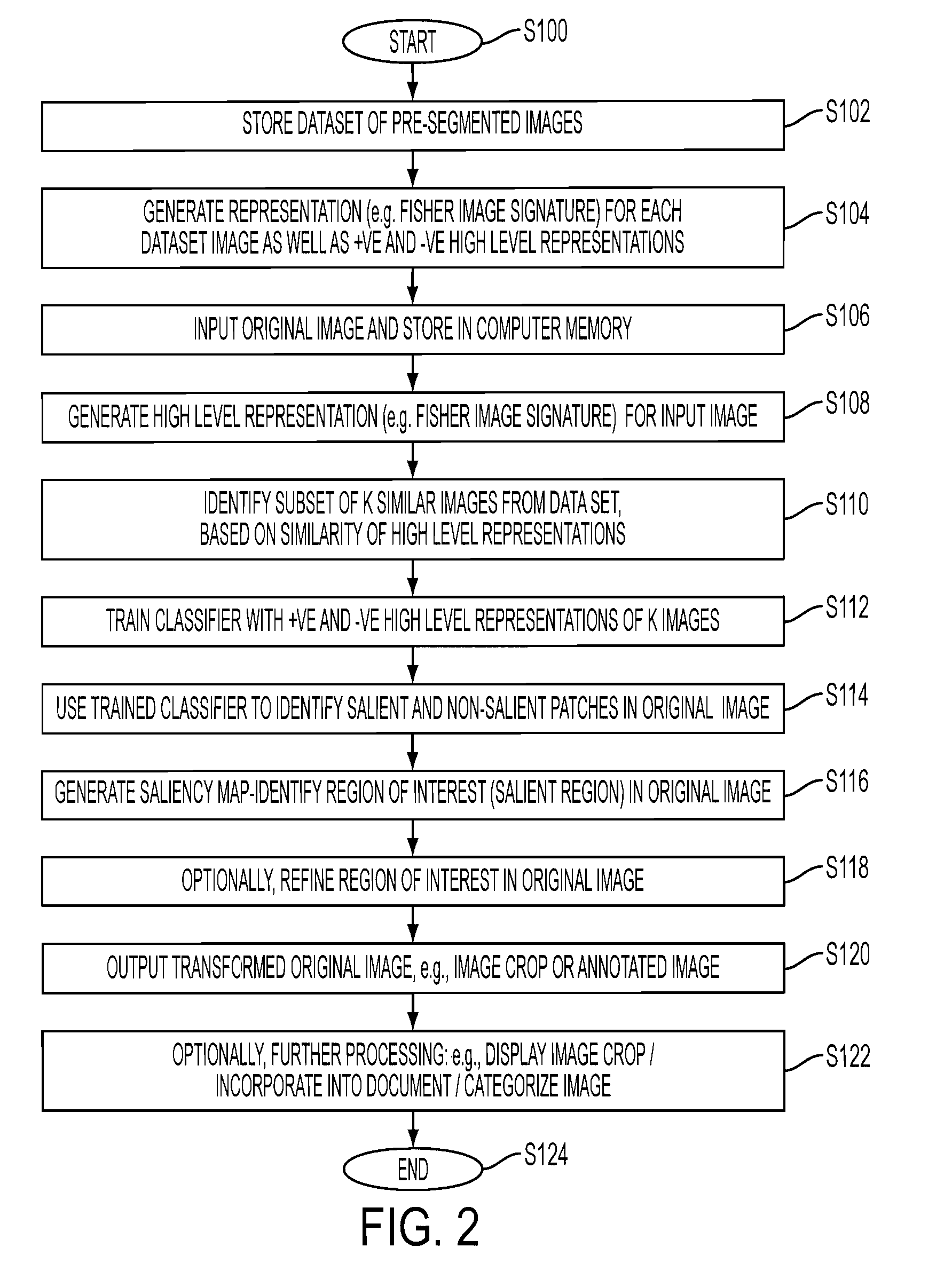
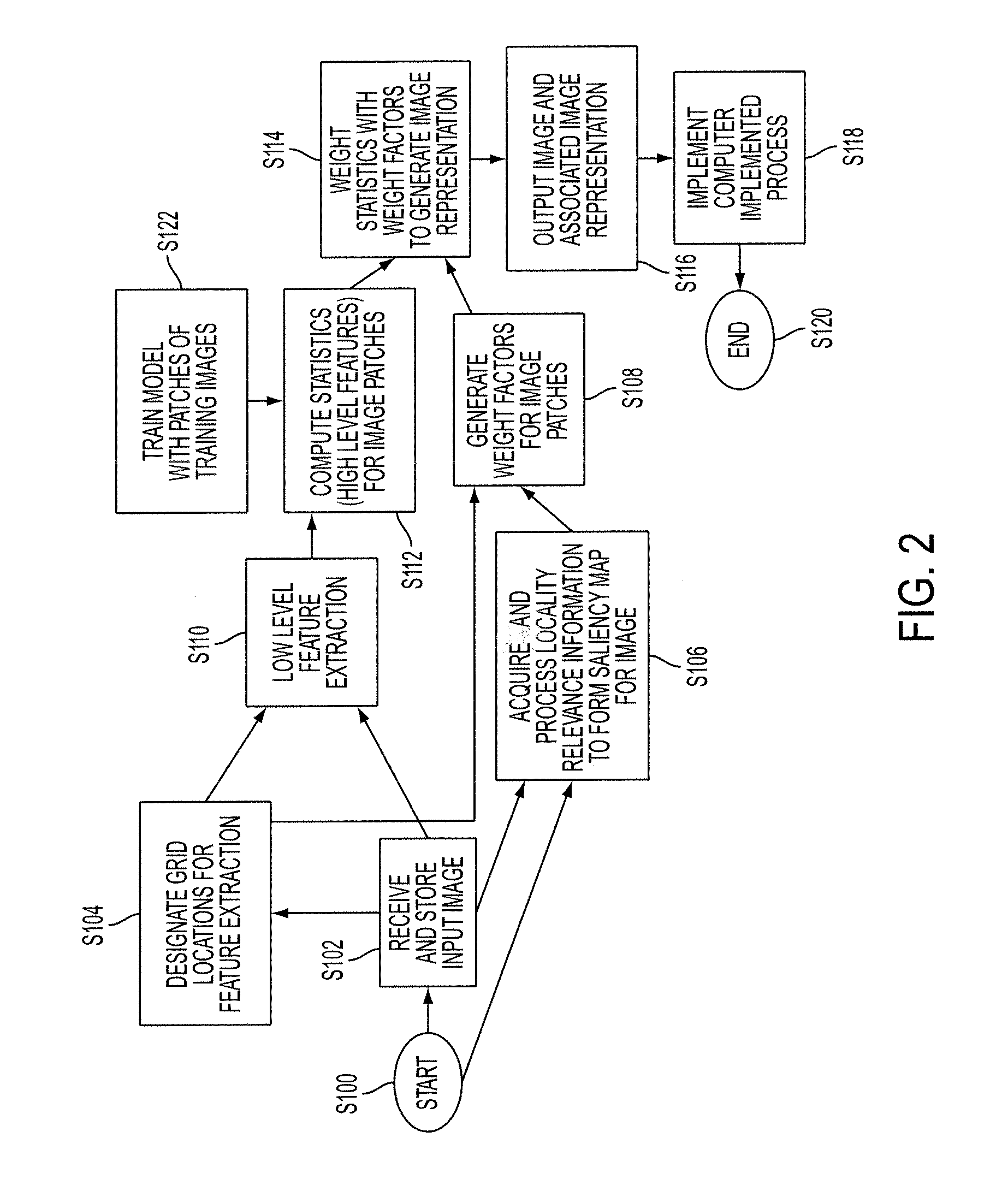
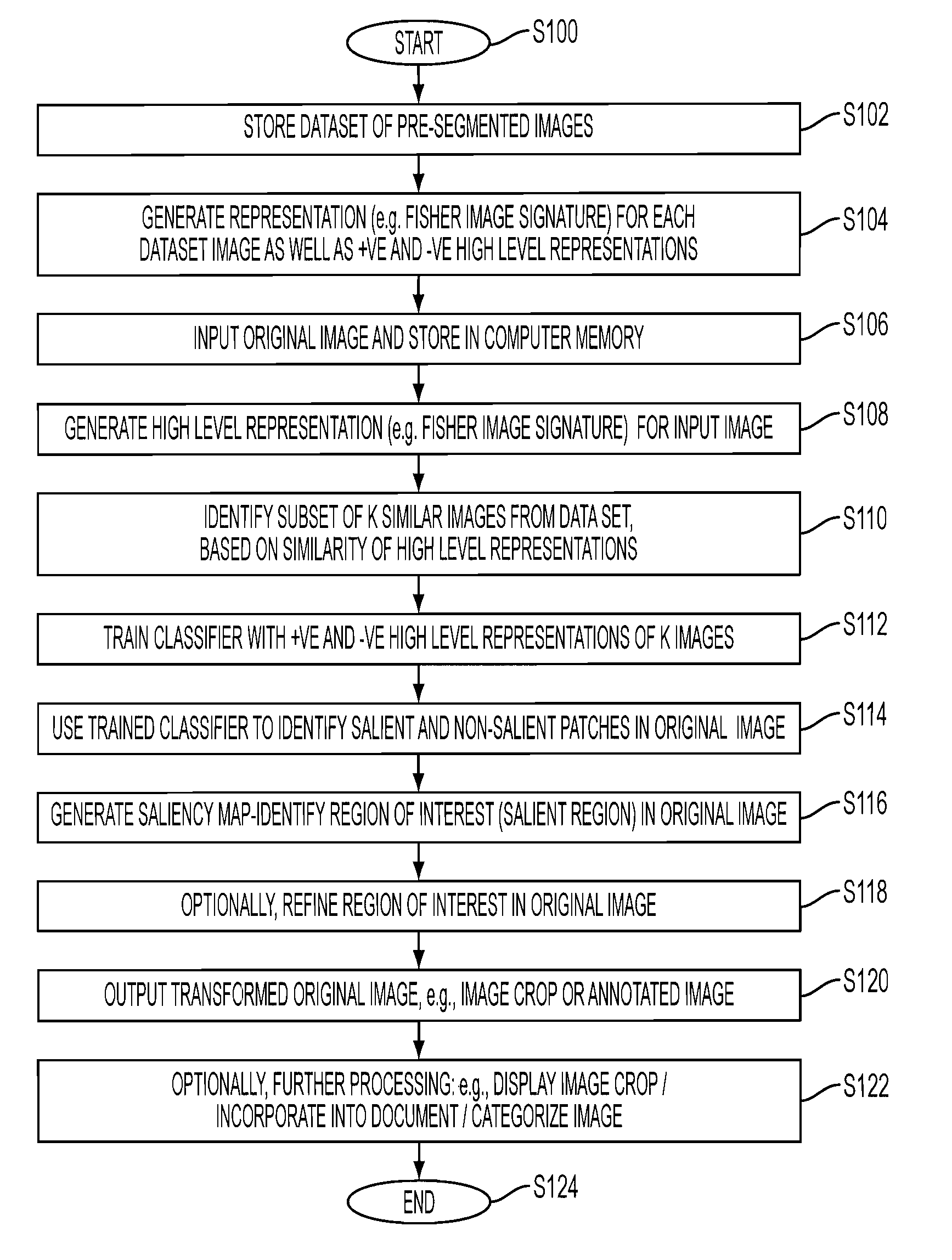
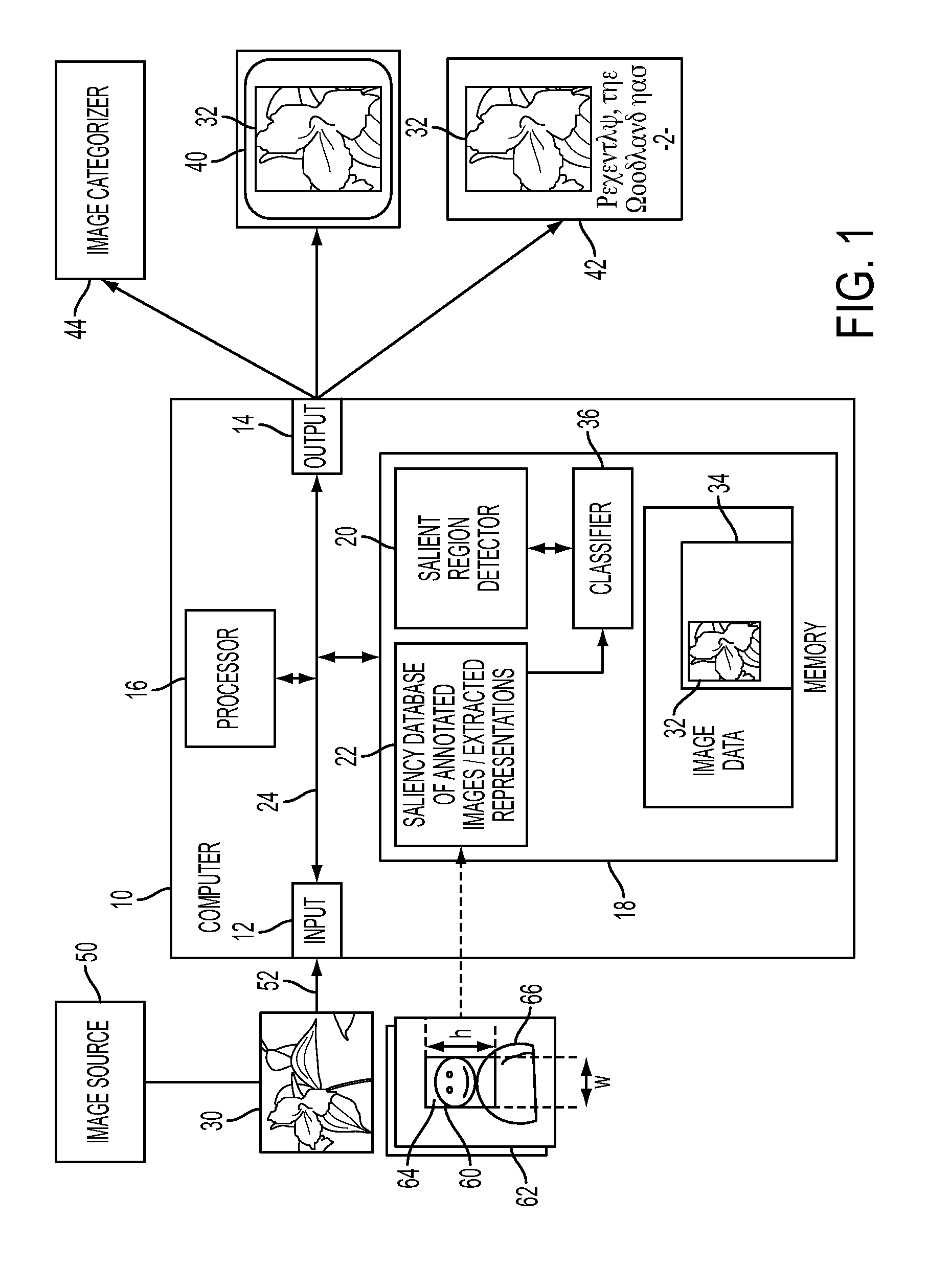
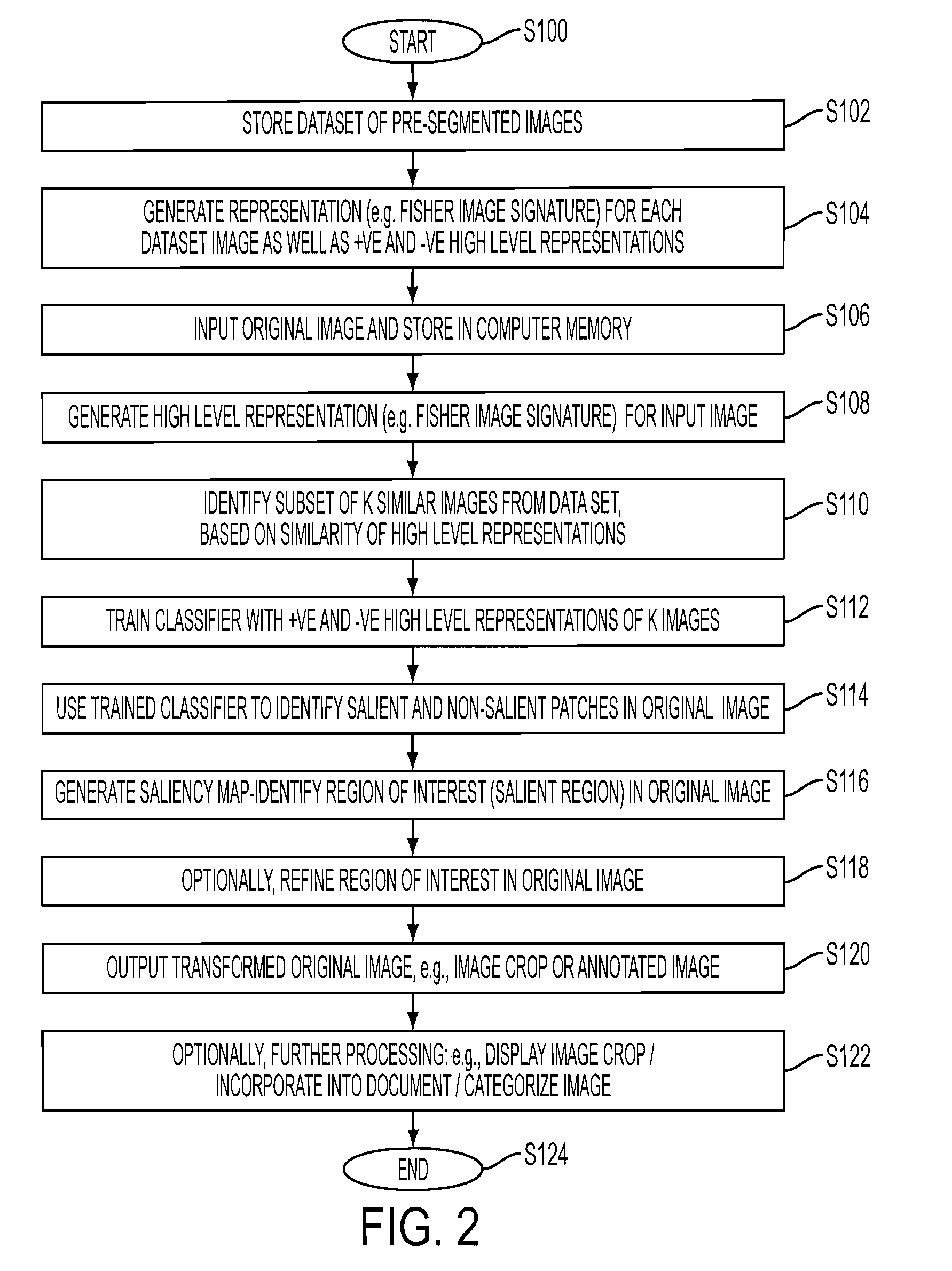
An apparatus and method for detecting a region of interest in an image are disclosed. Image representations for a set of images that have been manually annotated with regions of interest are stored, along with positive and negative representations of each image which are similarly derived to the image representations except that they are based on features extracted from patches within the region of interest and outside it, respectively. For an original image for which a region of interest is desired, the stored information for K similar images is automatically retrieved and used to train a classifier. The trained classifier provides, for each patch of the original image, a probability of being in a region of interest, based extracted features of the patch (represented, for example, as a Fisher vector), which can be used to determine a region of interest in the original image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Thermographic Test Method and Testing Device for Carrying Out the Test Method
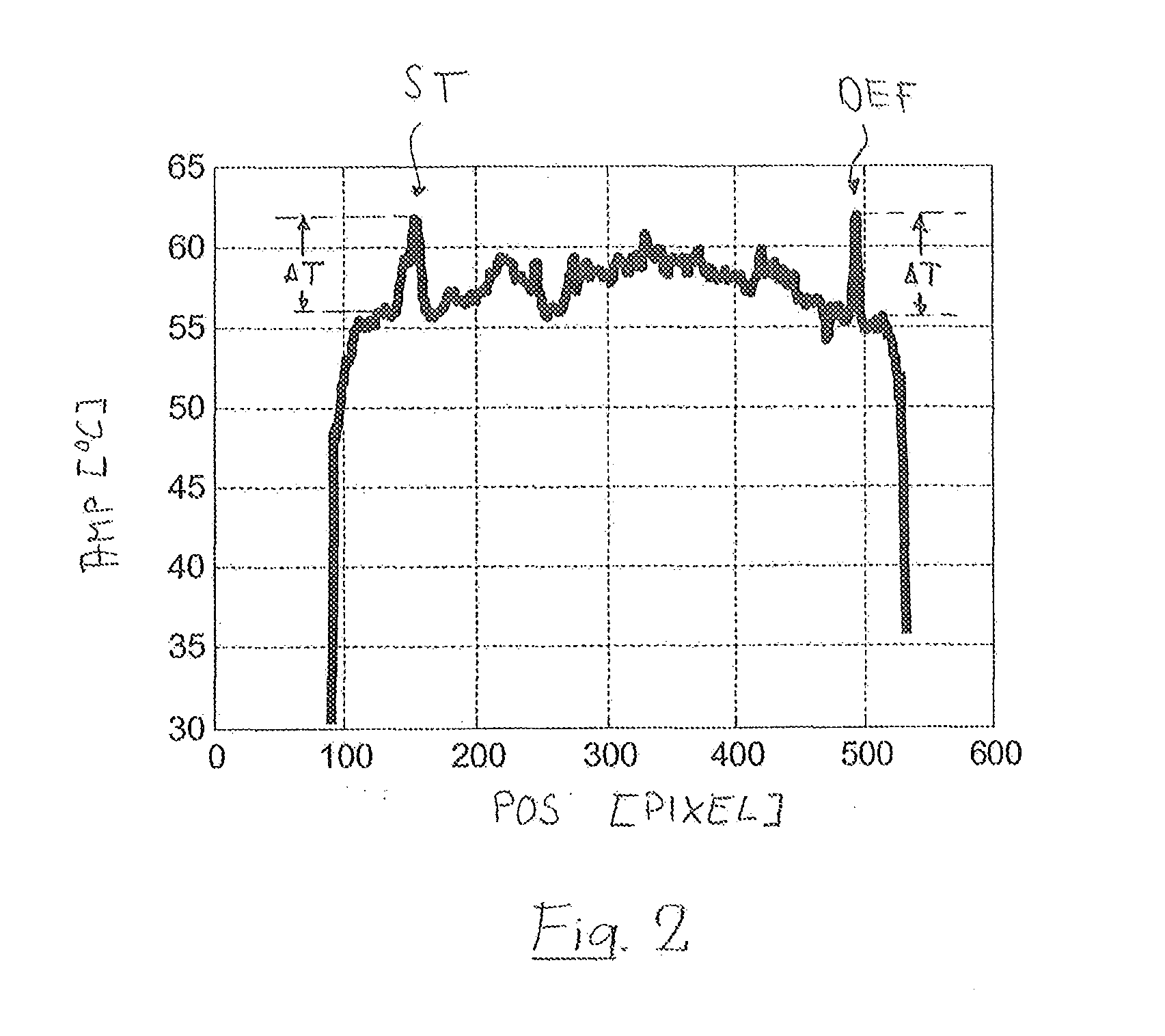
A thermographic test method locally resolves detection and identification of defects near the surface in a test object. A surface area of the test object is heated up. A series of thermographic images following one after another at a time interval is recorded within a heat propagation phase, each image representing a local temperature distribution in a surface region of the test object recorded by the image. Positionally correctly assigned temperature profiles are determined from the images, each positionally correctly assigned temperature profile being assigned to the same measuring region of the test object surface. Variations over time of temperature values are determined from the temperature profiles for a large number of measuring positions of the measuring region. These variations are evaluated on the basis of at least one evaluation criterion indicative of the heat flow in the measuring region.
Owner:INSTITUT DR FORSTER
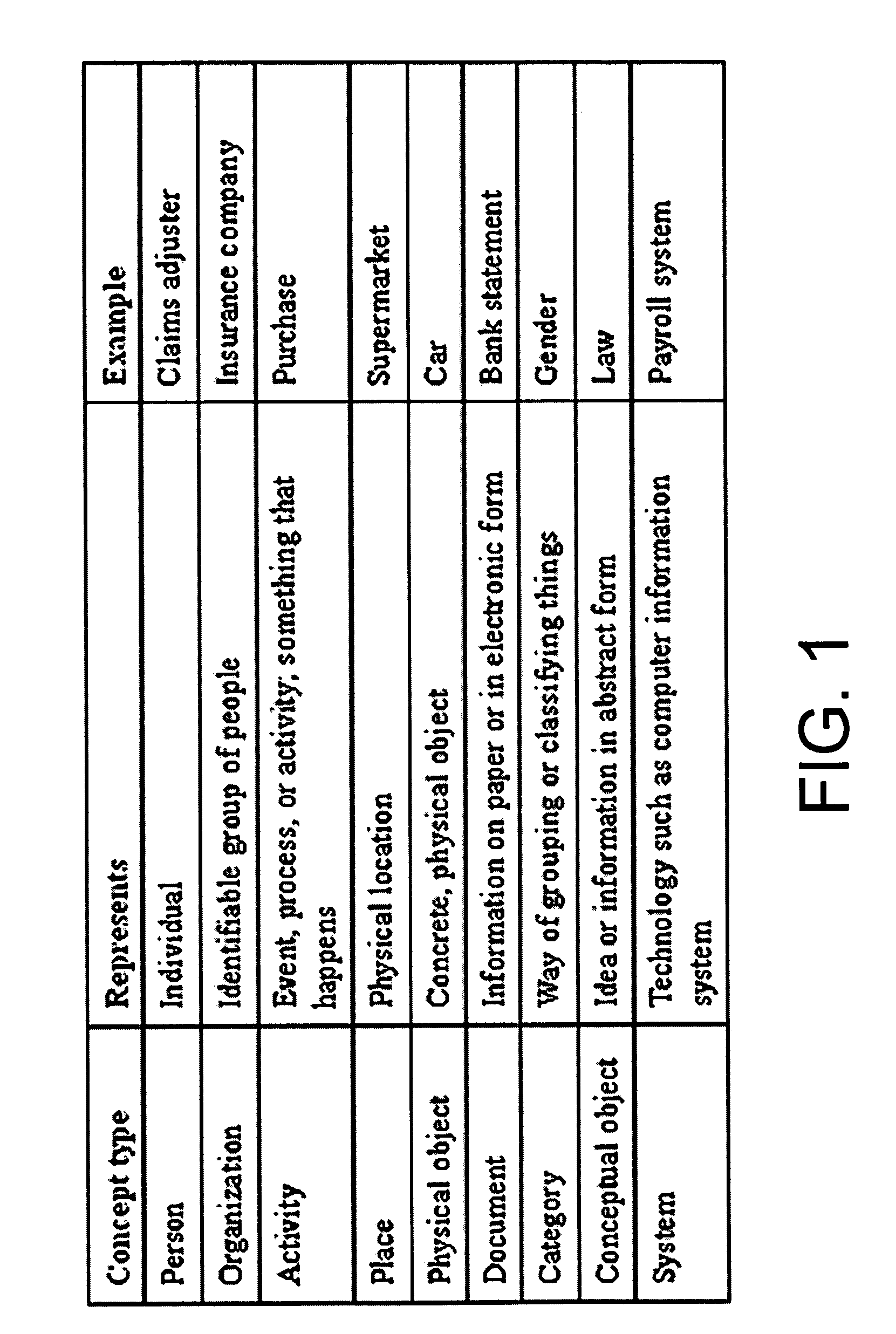
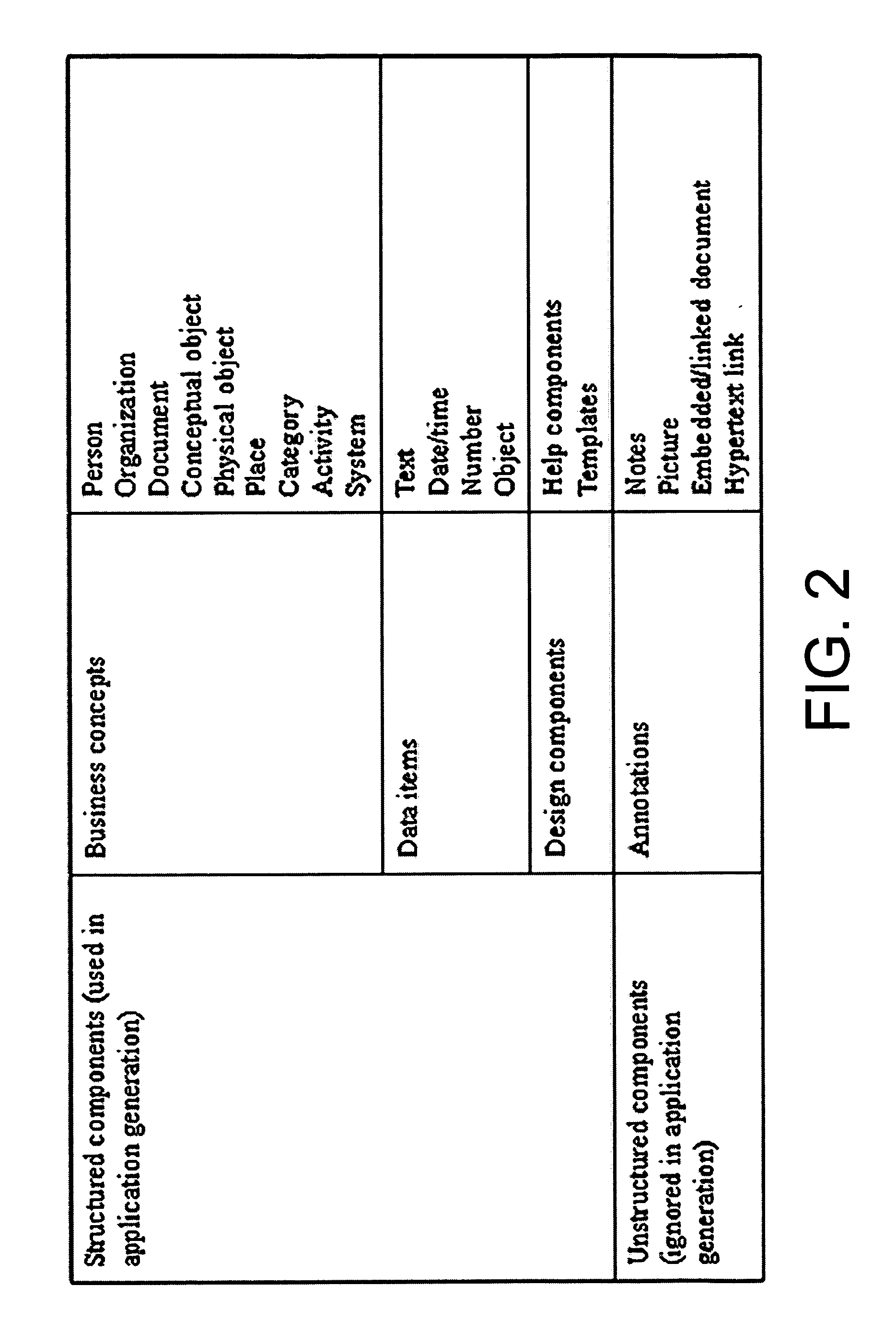
Systems and methods for software based on business concepts
InactiveUS20050289524A1Many taskEasy to understandSoftware designOffice automationSoftware systemPaper document
Business concept definitions may be utilized with software applications, components, tools, and system software. The business concepts definitions are each associated with archetypal definitions, which may also be known as innate concepts. These archetypal definitions may include a person, an organization, a system, a place, an activity, a document, a conceptual object, a physical object, and a category. The business concept definitions may also be represented by an image on a user interface, where the images may be selectable by a user. These business concept definitions may be manipulated and modified. Indeed, certain relationships may be denoted between business concept definitions through the positioning of the images on a user interface. Because these business concept definitions are associated with archetypal definitions, which may be intuitive for users, application definitions using these business concept definitions may be easily created by a user without programming skills.
Owner:MCGINNES SIMON
Clothing visualization
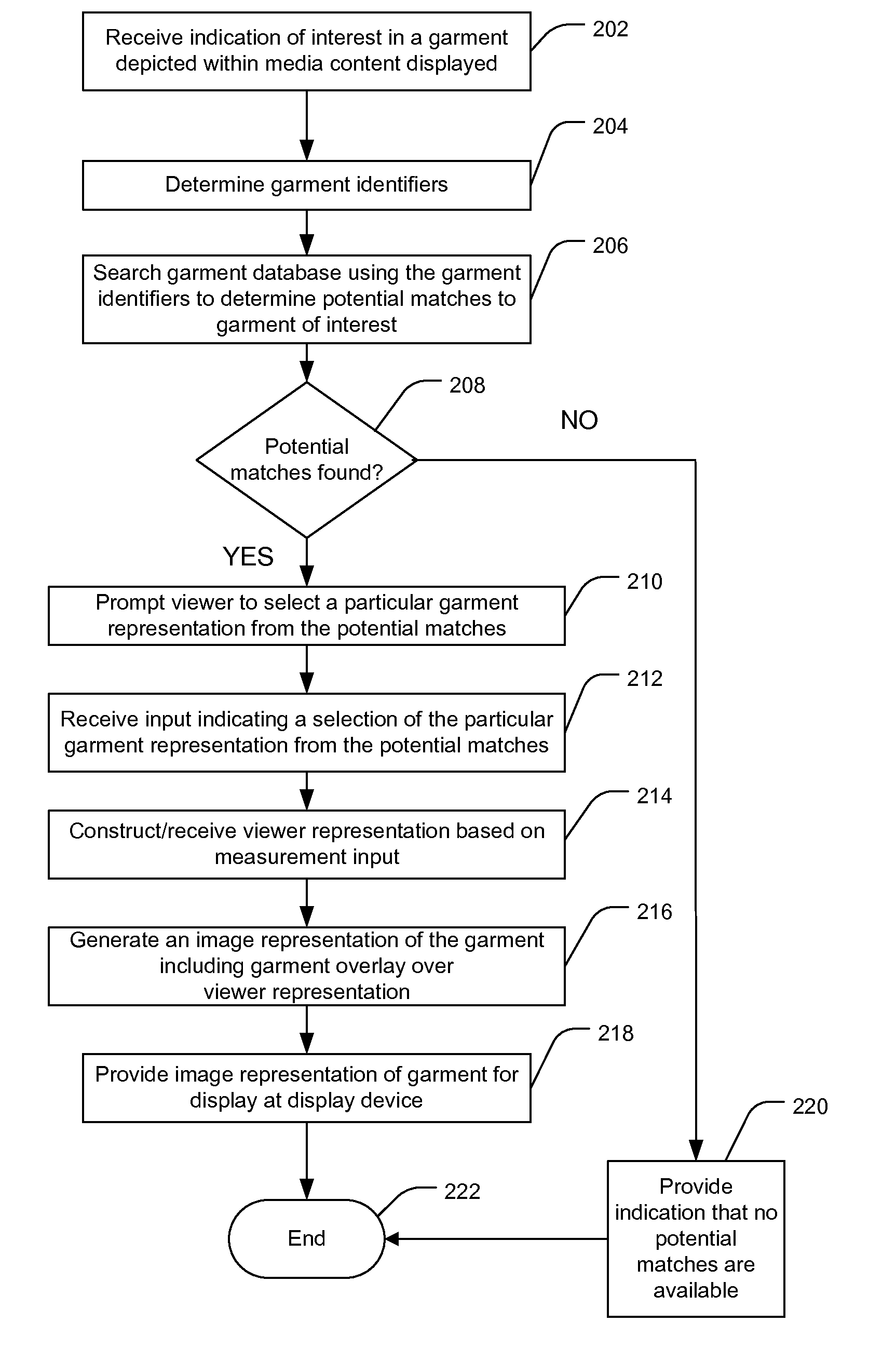
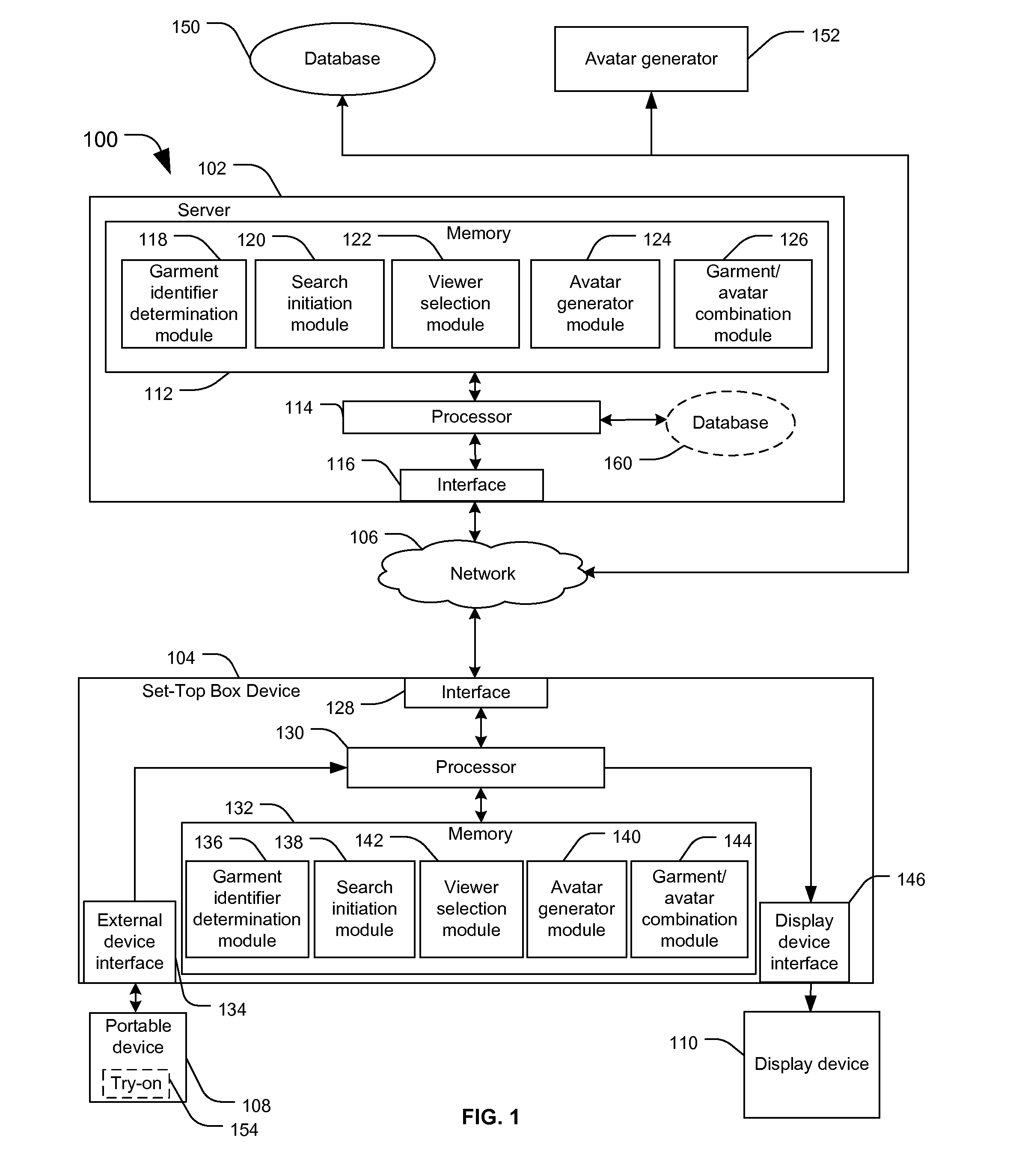
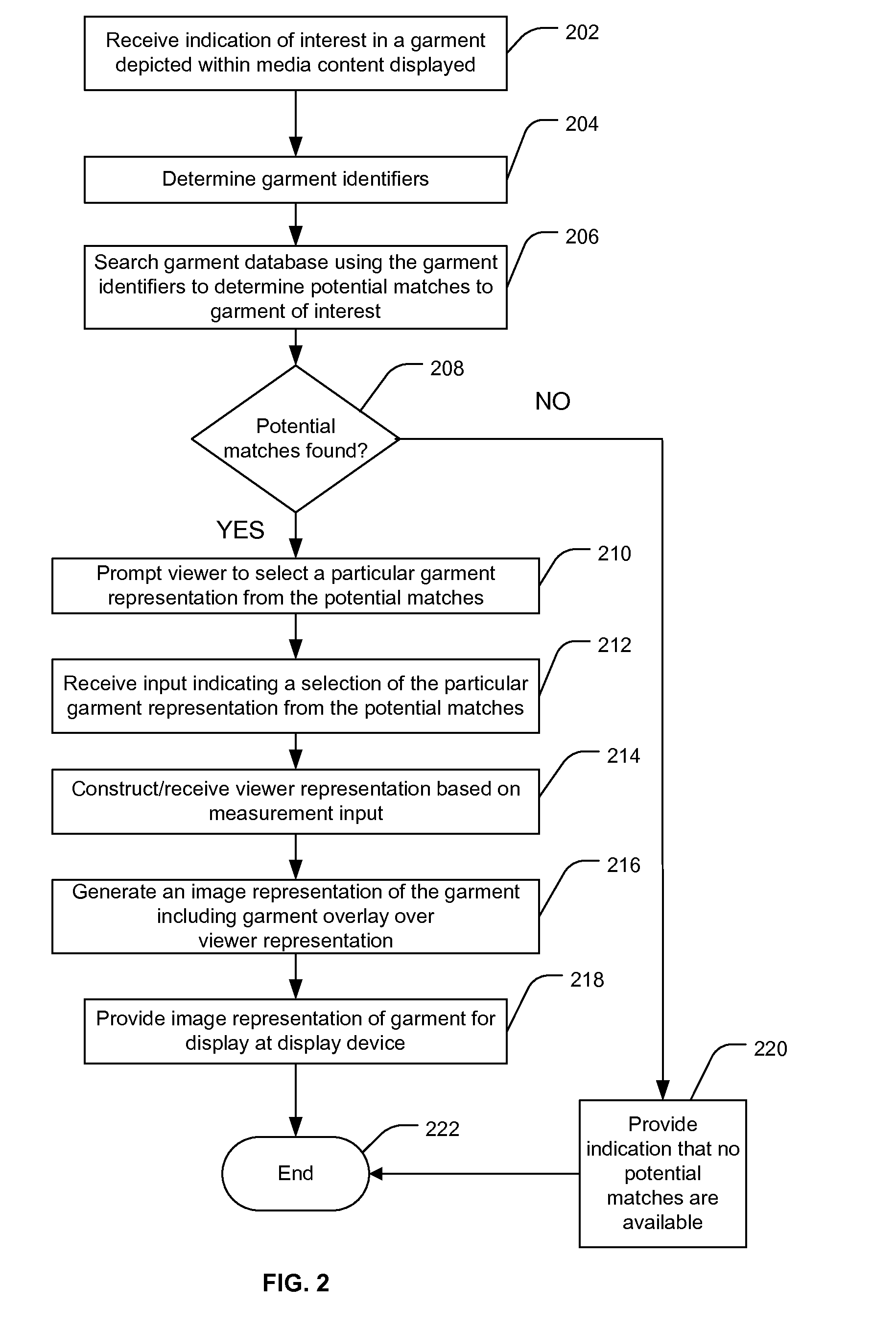
A method includes receiving an indication of interest in a garment depicted within media content displayed at a video display and determining, based on the media content, one or more garment identifiers associated with the garment. The method includes after determining the one or more garment identifiers, generating an image representation including a garment overlay and a viewer representation, the garment overlay at least partially covering the viewer representation. The viewer representation is generated based at least partially upon measurement input associated with the viewer. The garment overlay is based at least partially on the one or more garment identifiers and at least partially on the measurement input.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
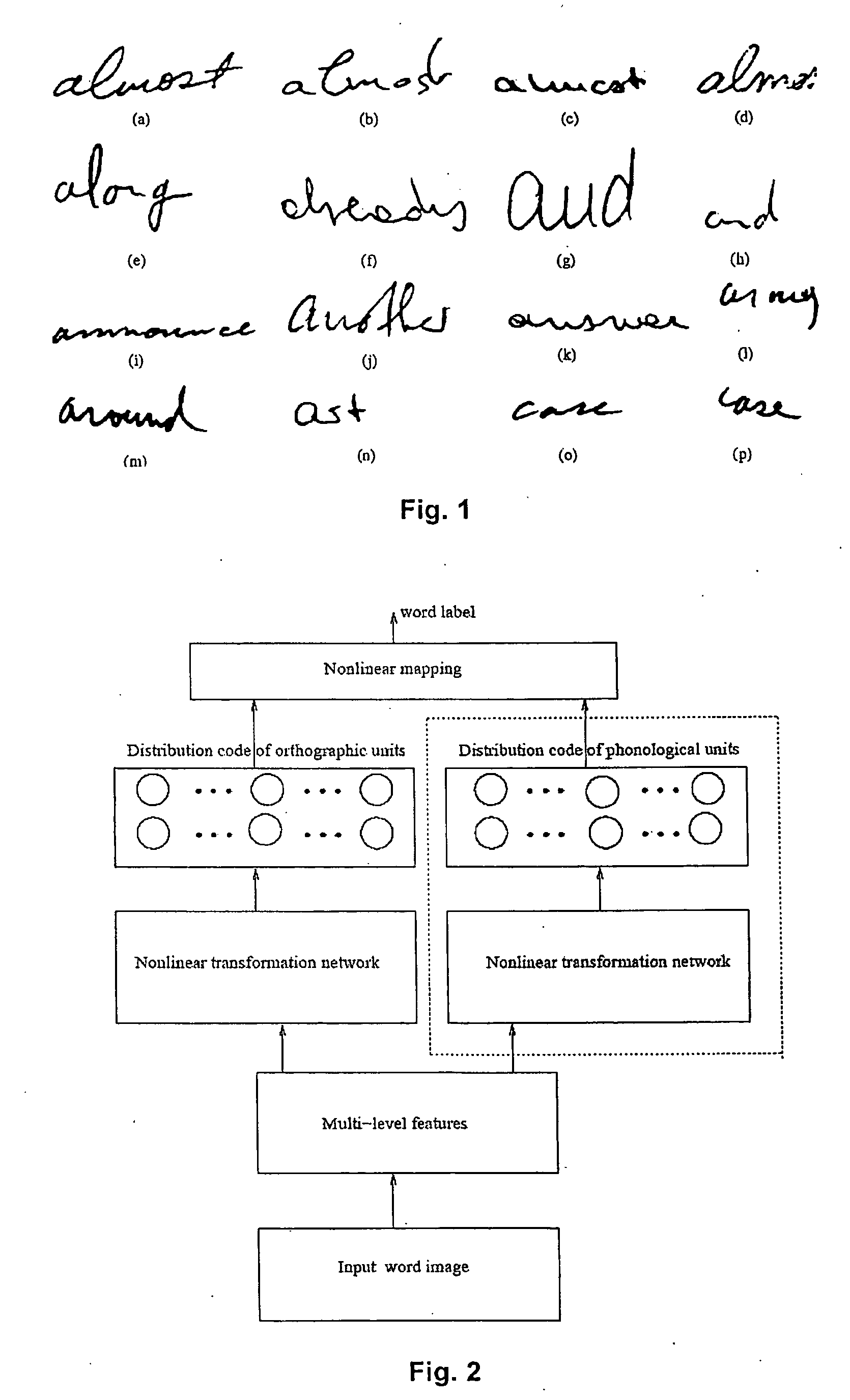
Handwritten word recognition based on geometric decomposition
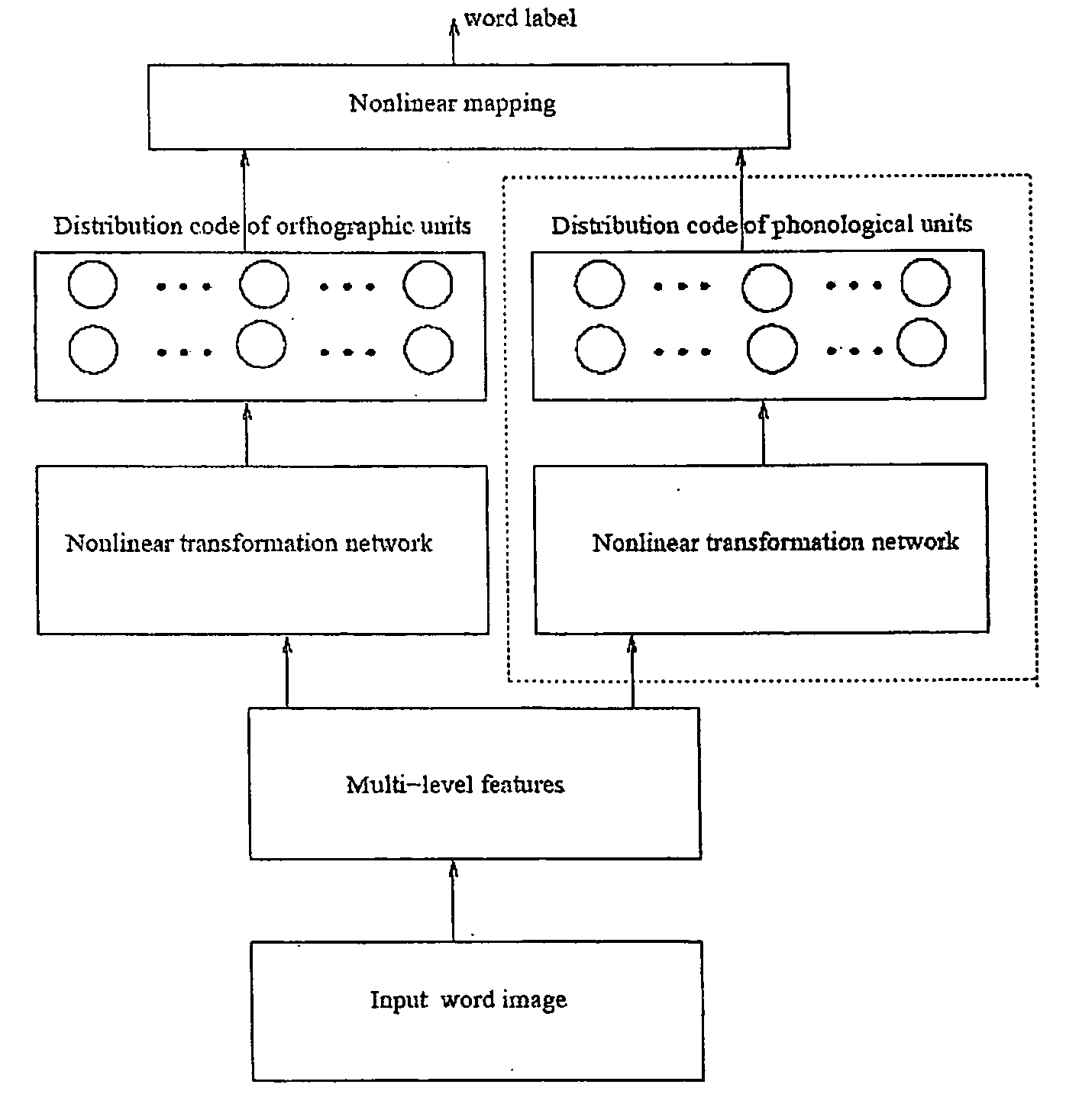
A method of recognizing a handwritten word of cursive script comprising providing a template of previously classified words, and optically reading a handwritten word so as to form an image representation thereof comprising a bit map of pixels. The external pixel contour of the bit map is extracted and the vertical peak and minima pixel extrema on upper and lower zones respectively of this external contour are detected. Feature vectors of the vertical peak and minima pixel extrema are determined and compared to the template so as to generate a match between the handwritten word and a previously classified word. A method for classifying an image representation of a handwritten word of cursive script is also provided. Also provided is an apparatus for recognizing a handwritten word of cursive script. This apparatus comprises a template of previously classified words, a reader for optically reading a handwritten word, and a controller being linked thereto for generating a match between the handwritten word and the previously classified words. Two algorithms are provided for respectively correcting the skew and slant of a word image.
Owner:IMDS SOFTWARE
Mirror having a portion in the form of an information provider
In a mirror with a non-reflective portion provided within its reflective mirror surface as an information provider the portion is transparent and is backed by a display. The display has a moving image or has a colored image representation. Preferably at least one loudspeaker is connected to the display behind the mirror surface. That loudspeaker can also be connected to an input device.
Owner:MIRROR IMAGE INC
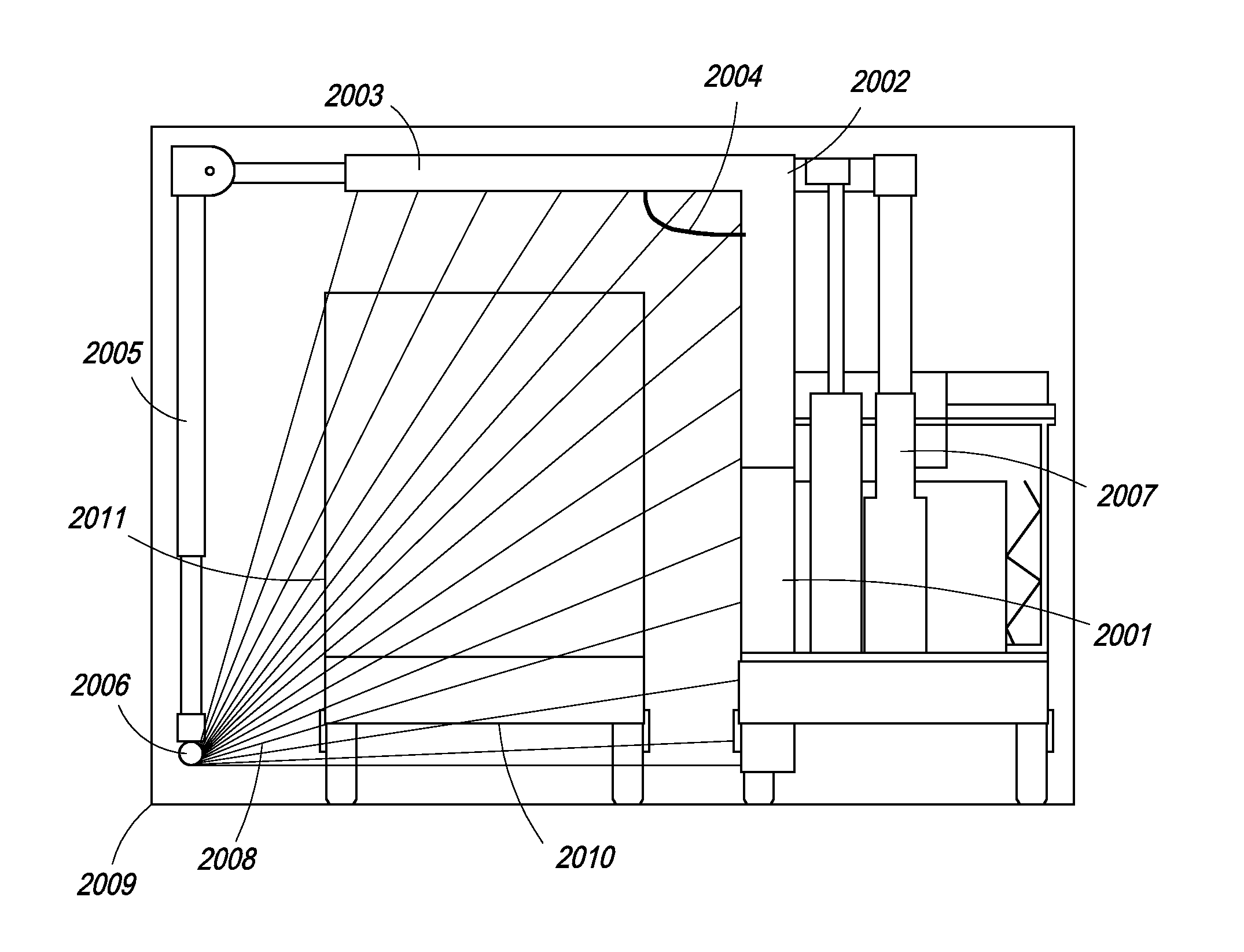
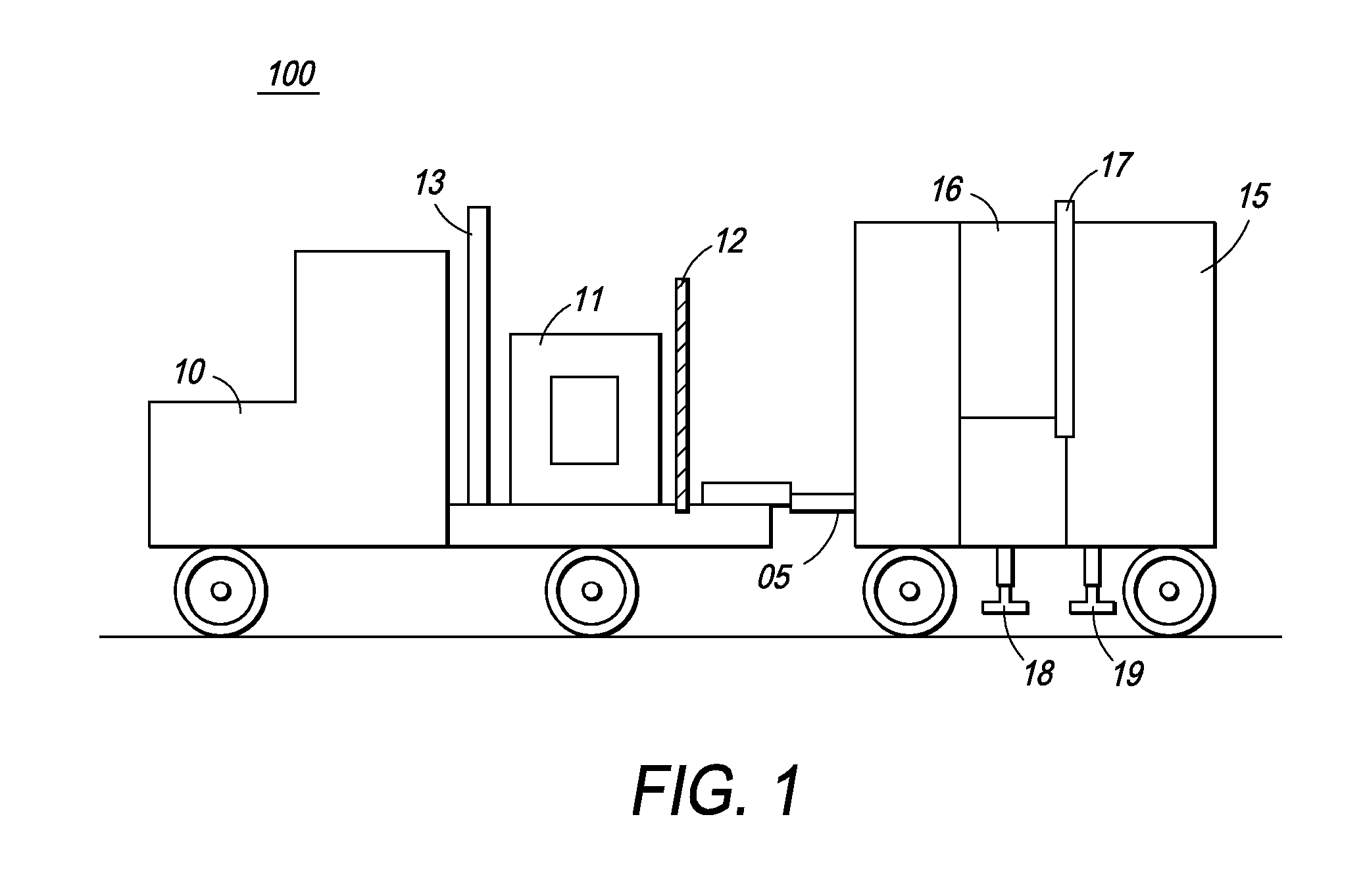
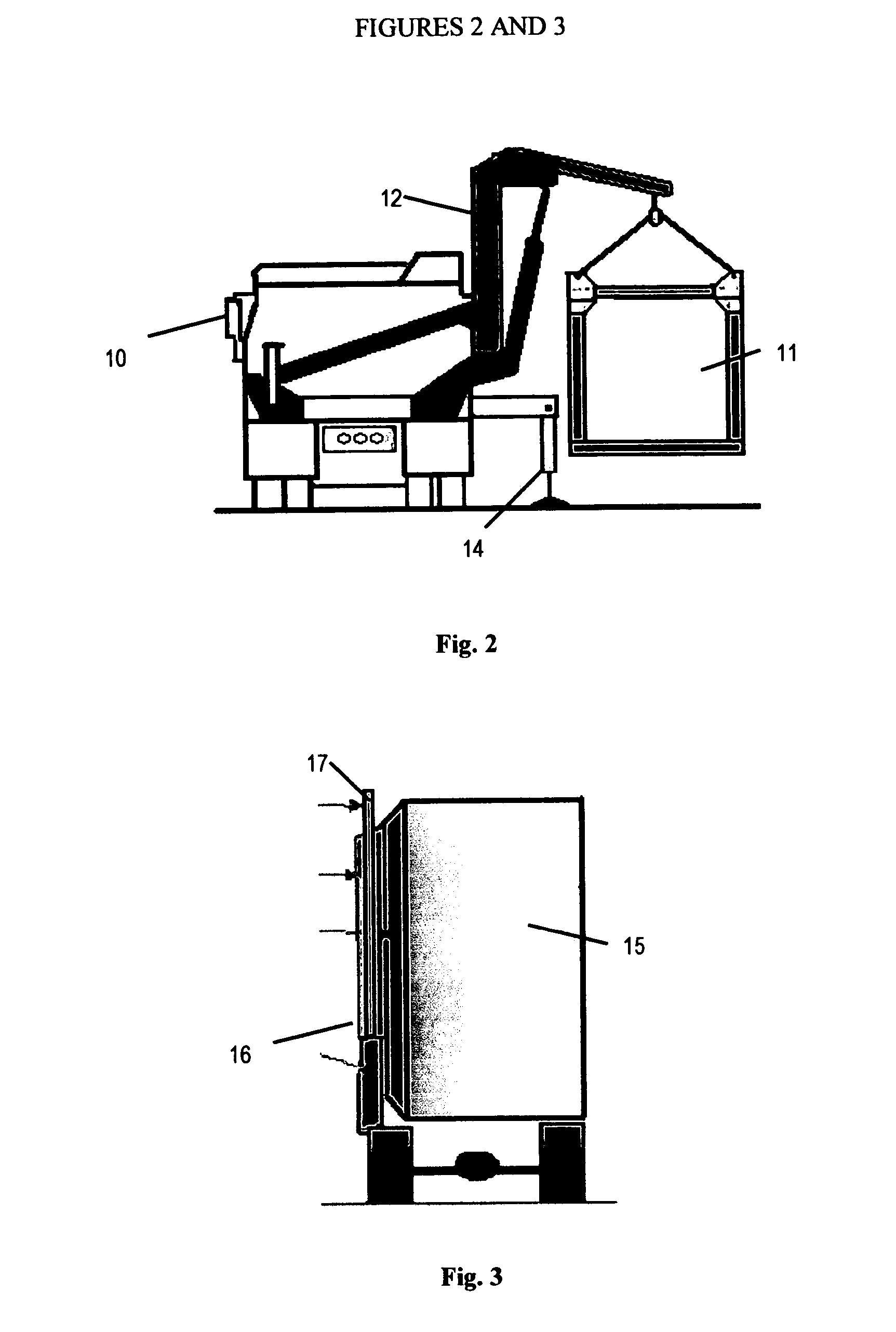
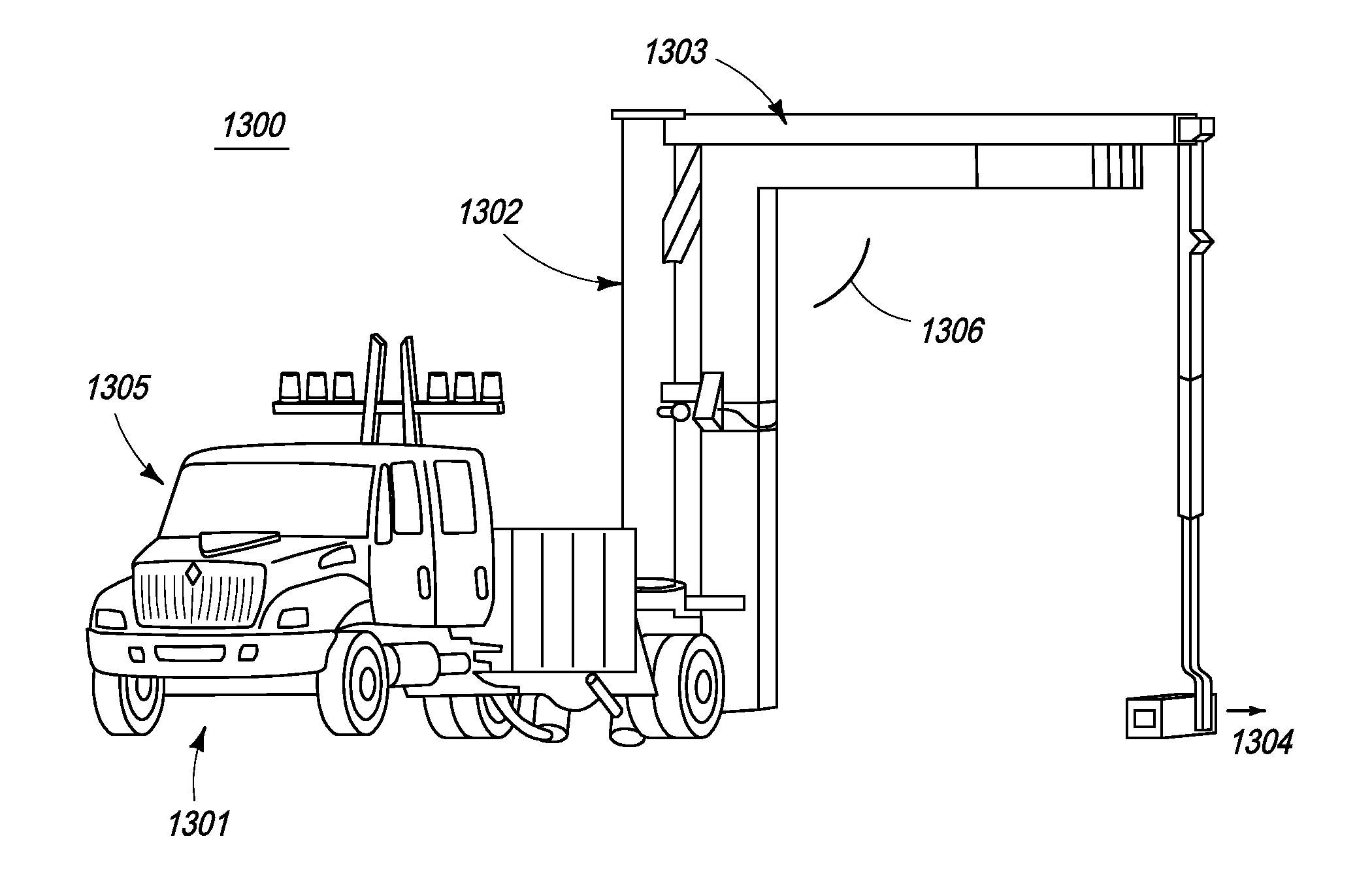
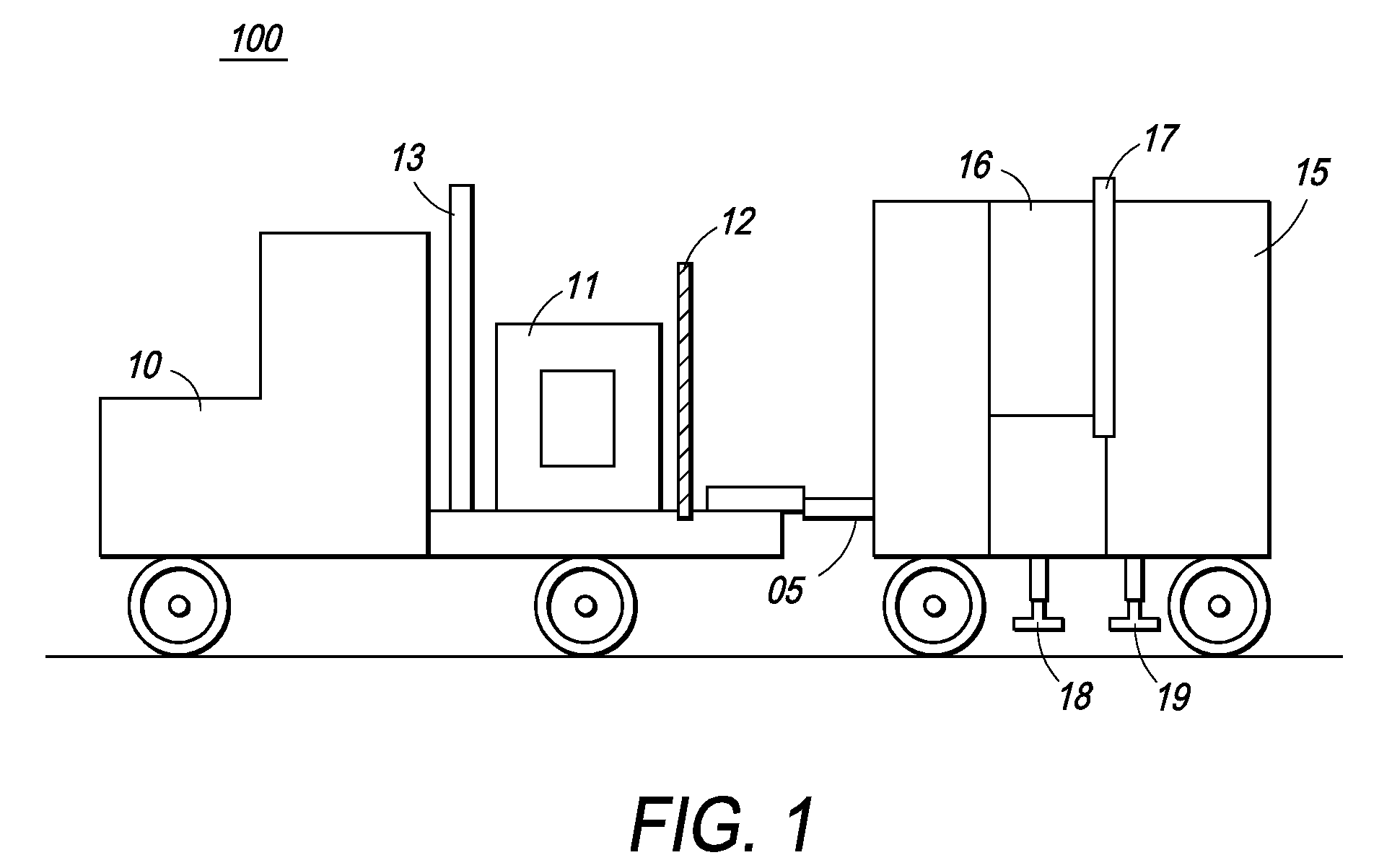
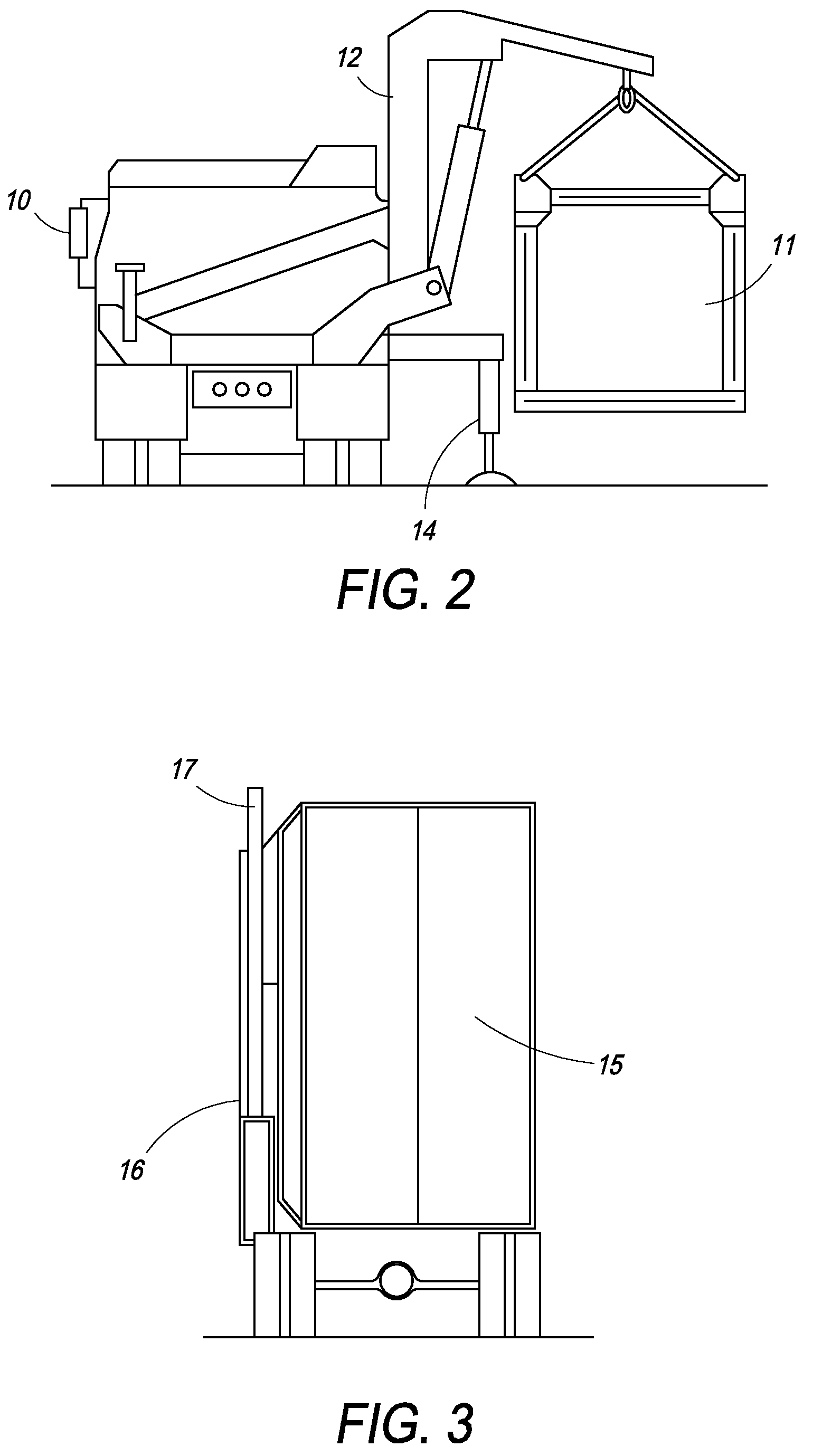
Single boom cargo scanning system
InactiveUS7322745B2Rapidly deployableCost-effectively and accurately on uneven surfaceRadiation/particle handlingParticle suspension analysisMobile vehicleDetector array
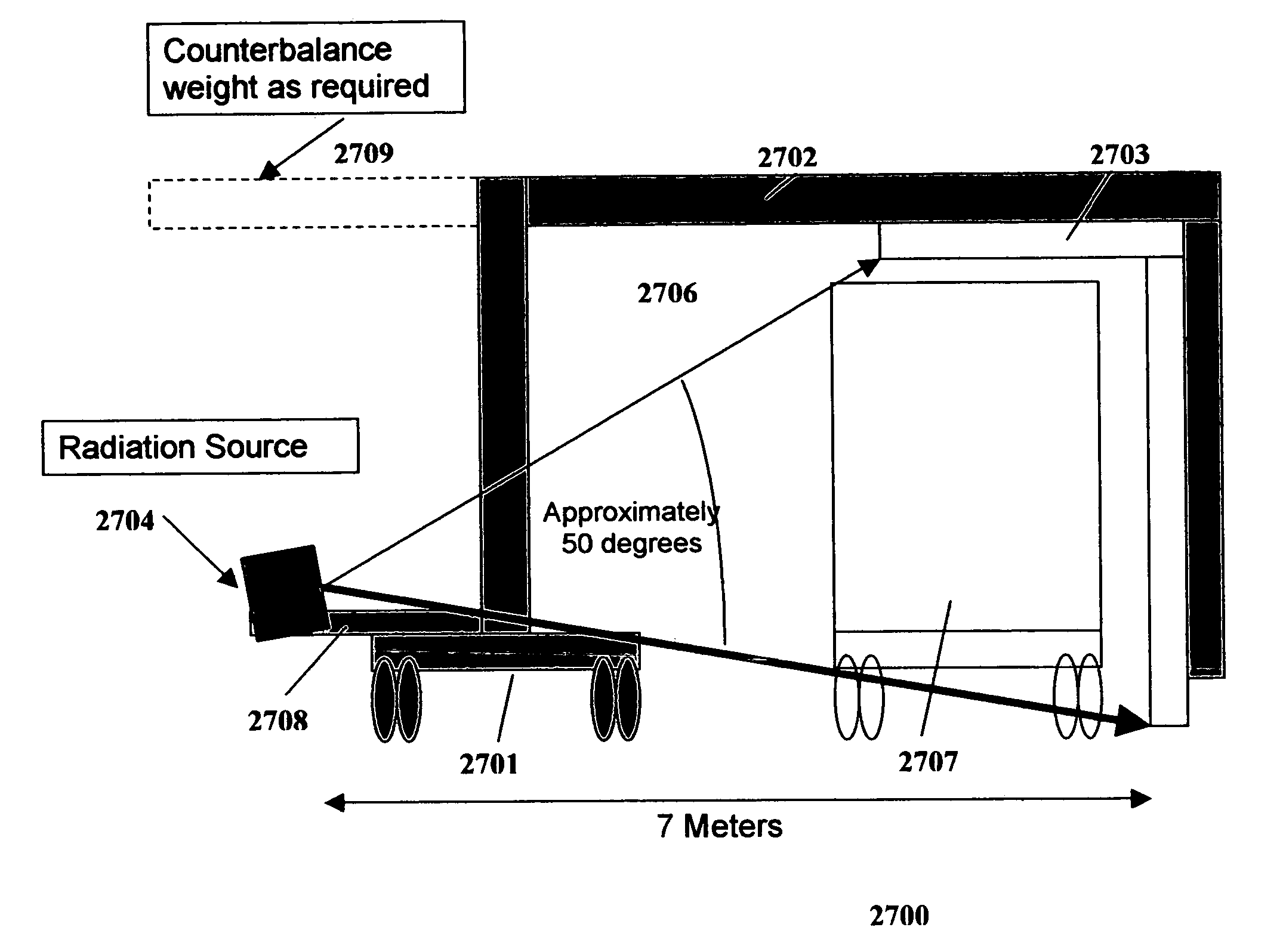
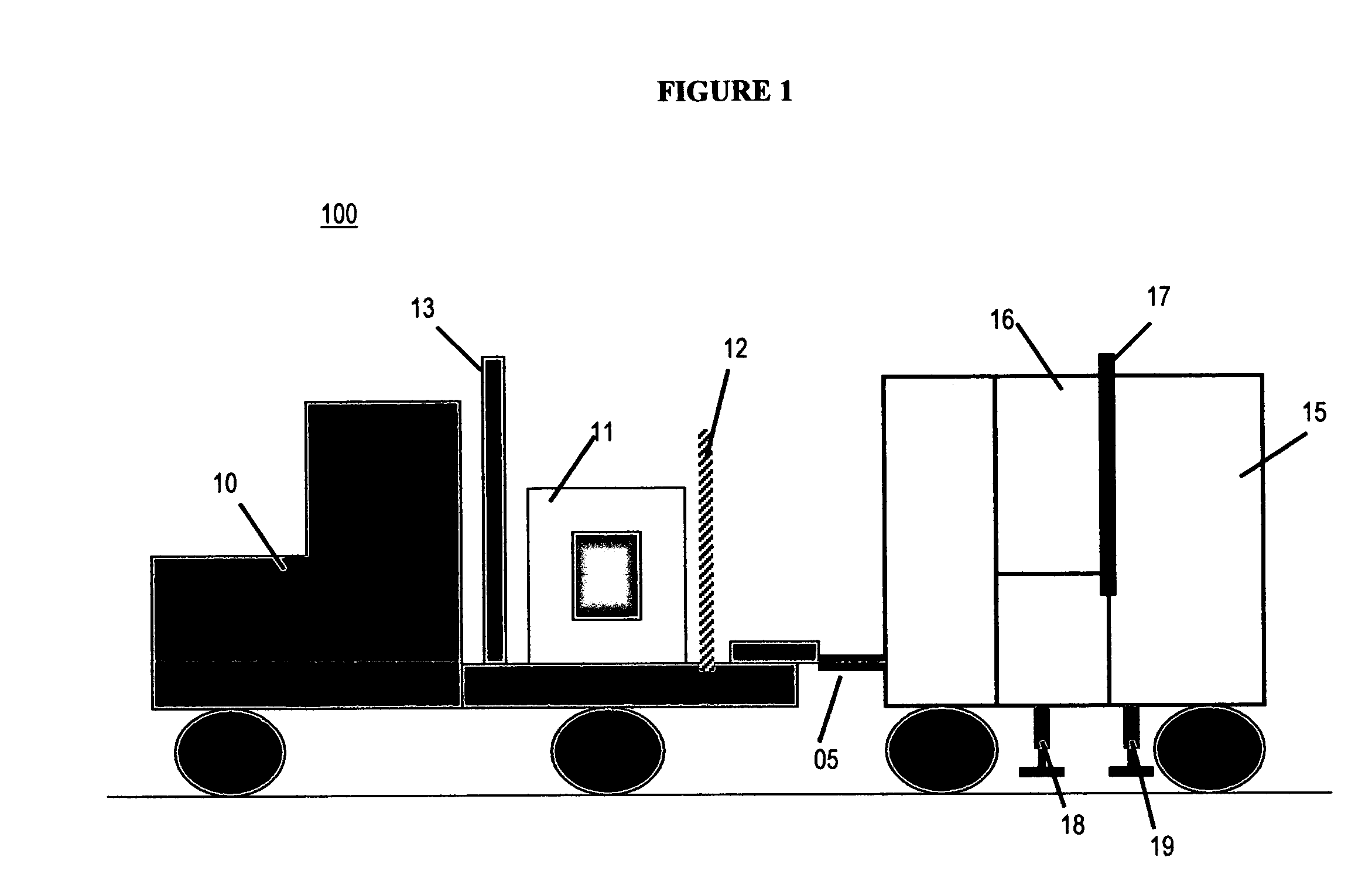
The inspection methods and systems of the present invention are mobile, rapidly deployable, and capable of scanning a wide variety of receptacles cost-effectively and accurately on uneven surfaces. The present invention is directed toward a portable inspection system for generating an image representation of target objects using a radiation source, comprising a mobile vehicle, a detector array physically attached to a movable boom having a proximal end and a distal end. The proximal end is physically attached to the vehicle. The invention also comprises at least one source of radiation. The radiation source is fixedly attached to the distal end of the boom, wherein the image is generated by introducing the target objects in between the radiation source and the detector array, exposing the objects to radiation, and detecting radiation.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
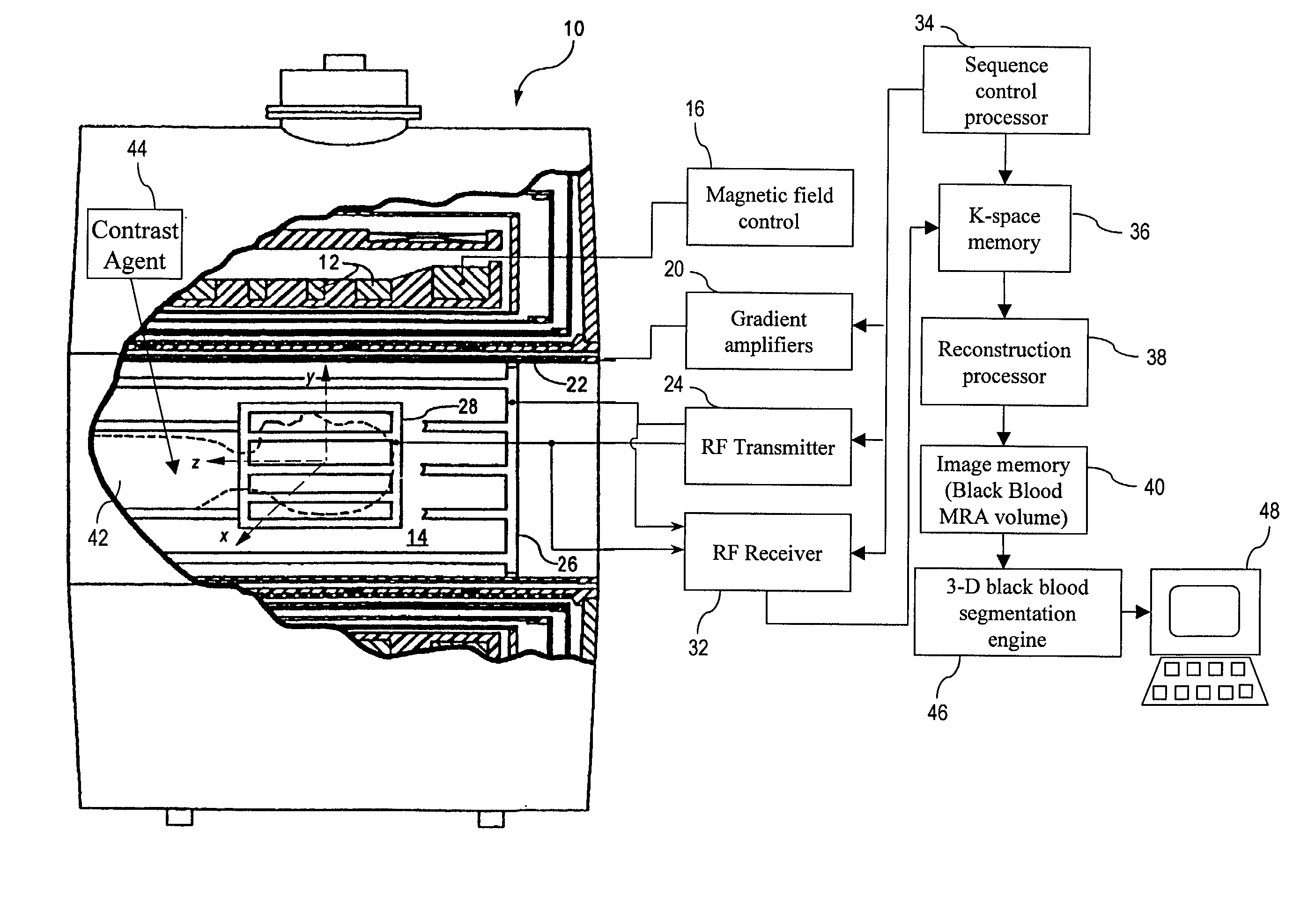
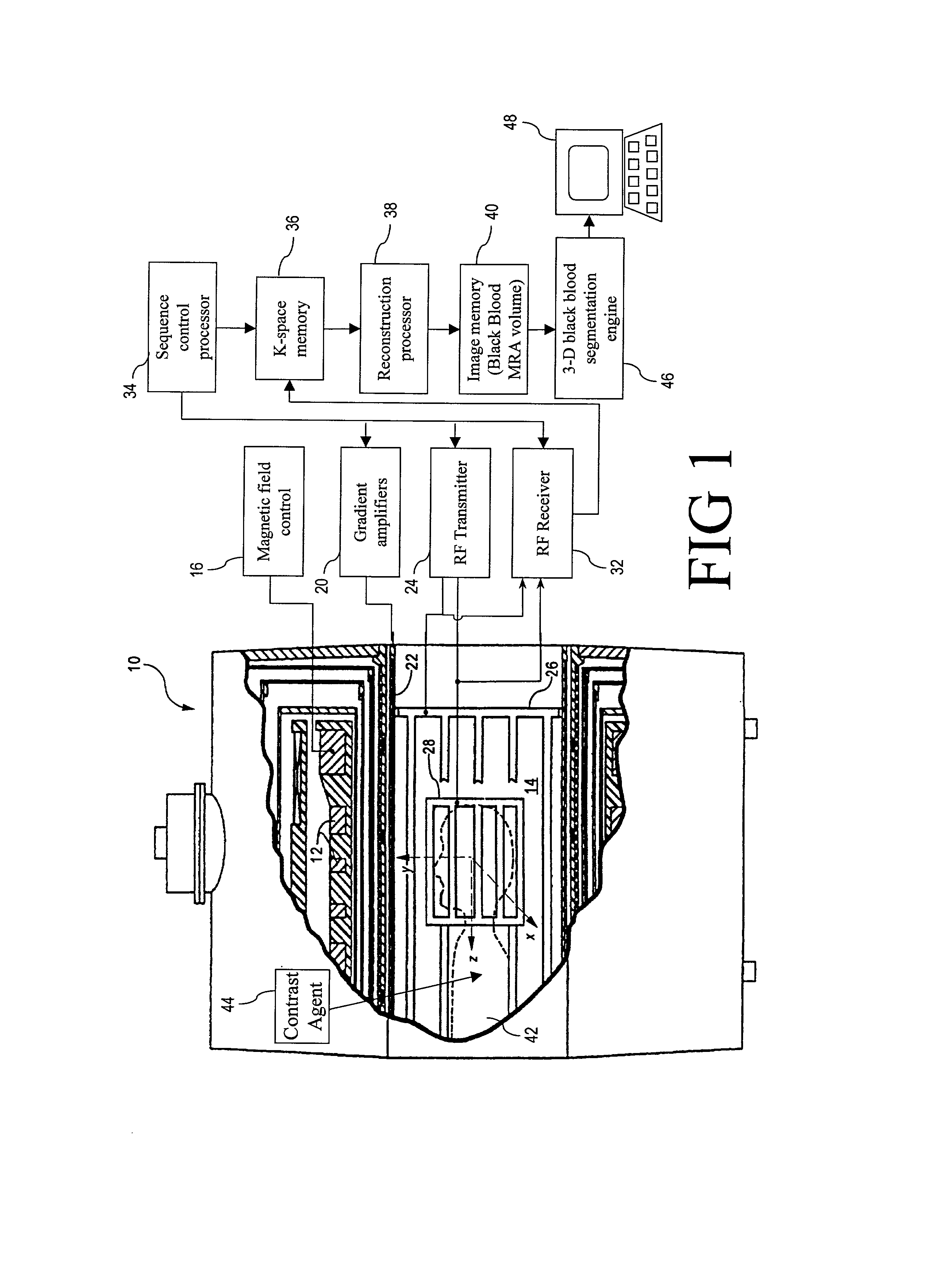
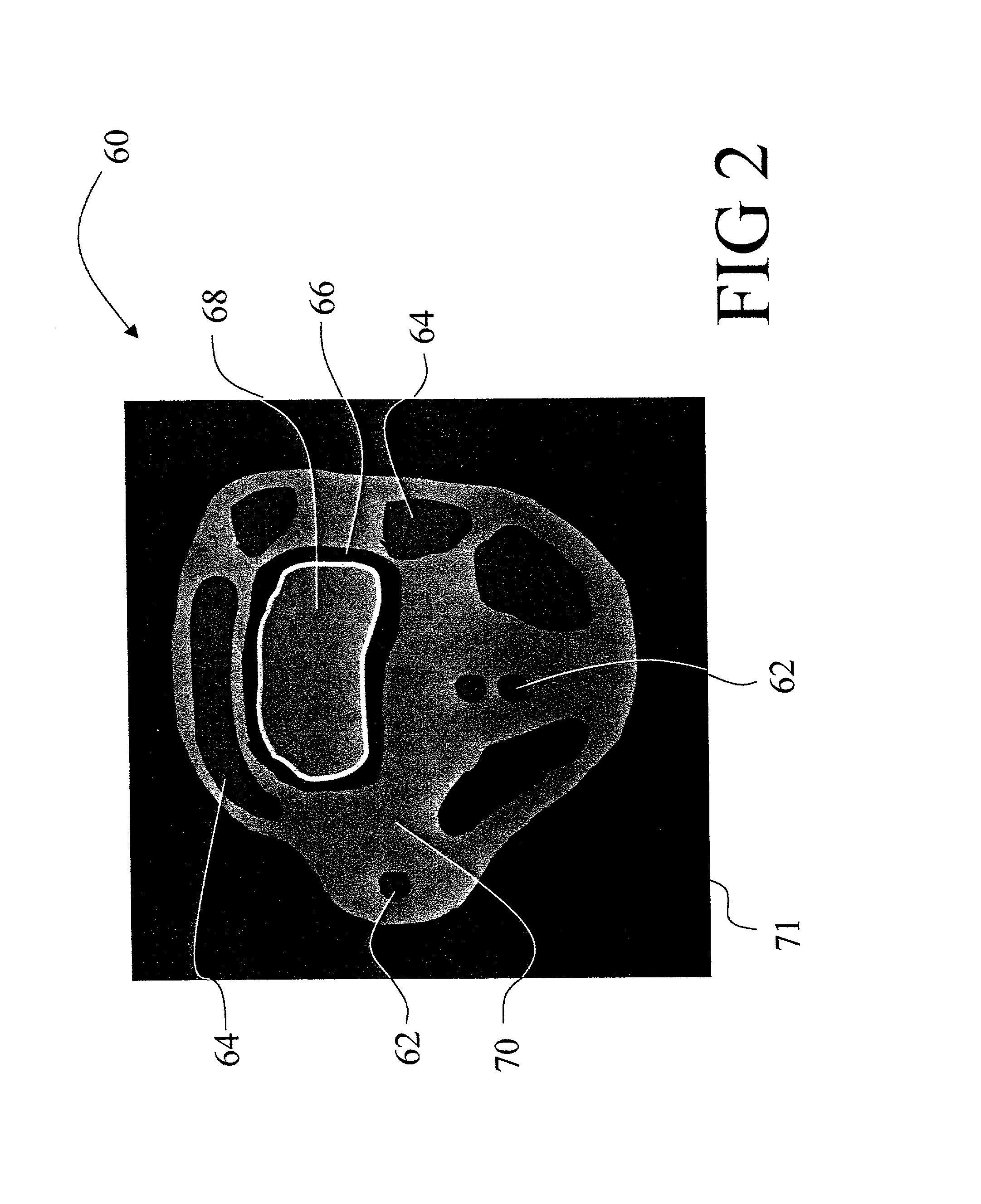
Black blood angiography method and apparatus
InactiveUS7020314B1Structural interferenceRemove non-vascular contrastImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionBlack bloodBlood Vessel Tissue
To produce a black body angiographic image representation of a subject (42), an imaging scanner (10) acquires imaging data that includes black blood vascular contrast. A reconstruction processor (38) reconstructs a gray scale image representation (100) from the imaging data. A post-acquisition processor (46) transforms (130) the image representation (100) into a pre-processed image representation (132). The processor (46) assigns (134) each image element into one of a plurality of classes including a black class corresponding to imaged vascular structures, bone, and air, and a gray class corresponding to other non-vascular tissues. The processor (46) averages (320) intensities of the image elements of the gray class to obtain a mean gray intensity value (322), and replaces (328) the values of image elements comprising non-vascular structures of the black class with the mean gray intensity value.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Modeling images as sets of weighted features
ActiveUS20100189354A1Character and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPosition dependentDigital image
An apparatus, method, and computer program product are provided for generating an image representation. The method includes receiving an input digital image, extracting features from the image which are representative of patches of the image, generating weighting factors for the features based on location relevance data for the image, and weighting the extracted features with the weighting factors to form a representation of the image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Framework for image thumbnailing based on visual similarity
Owner:XEROX CORP
Dynamic computed tomography imaging using positional state modeling
InactiveUS7058440B2Improves temporalImprove spatial resolutionElectrocardiographyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData segmentData set
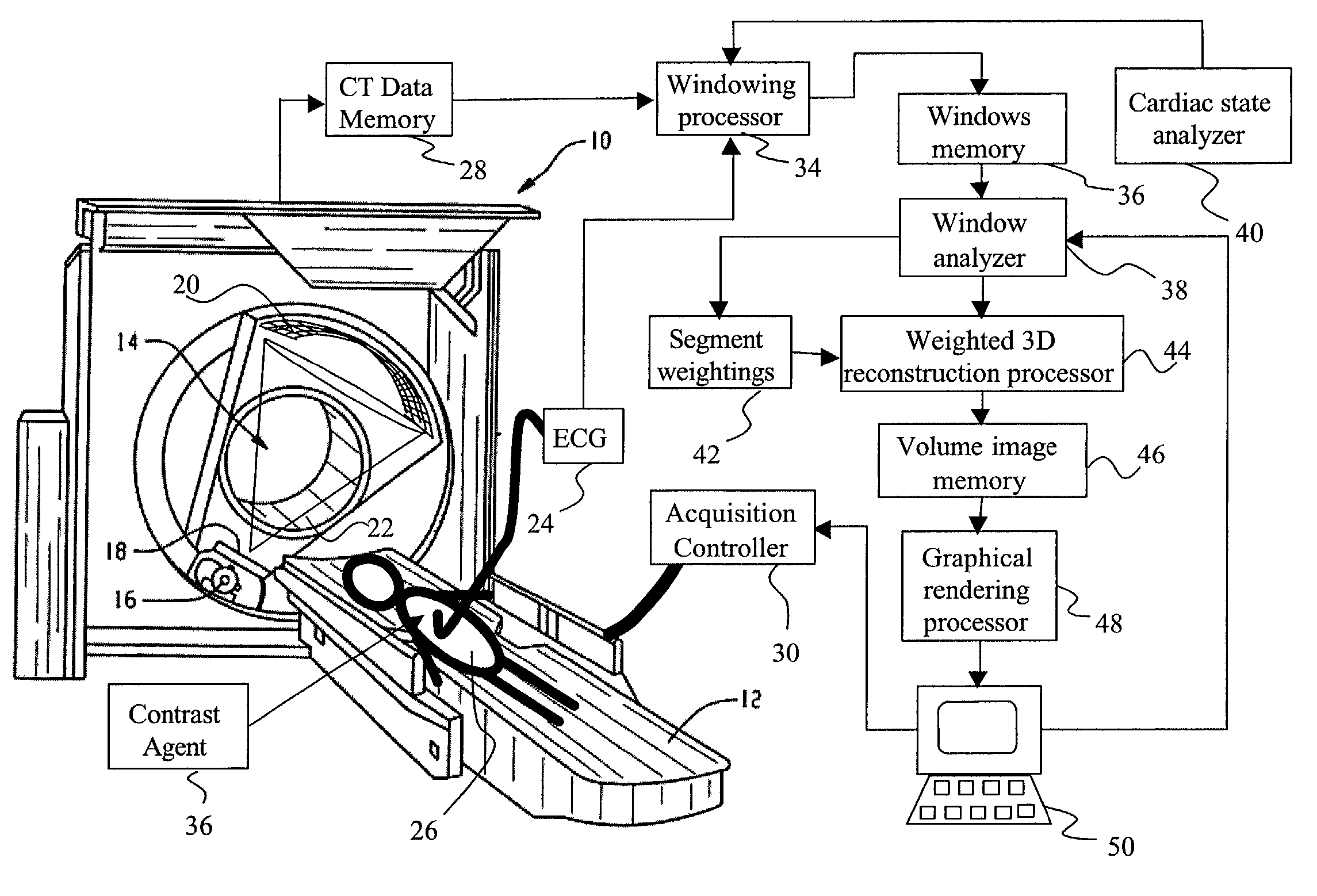
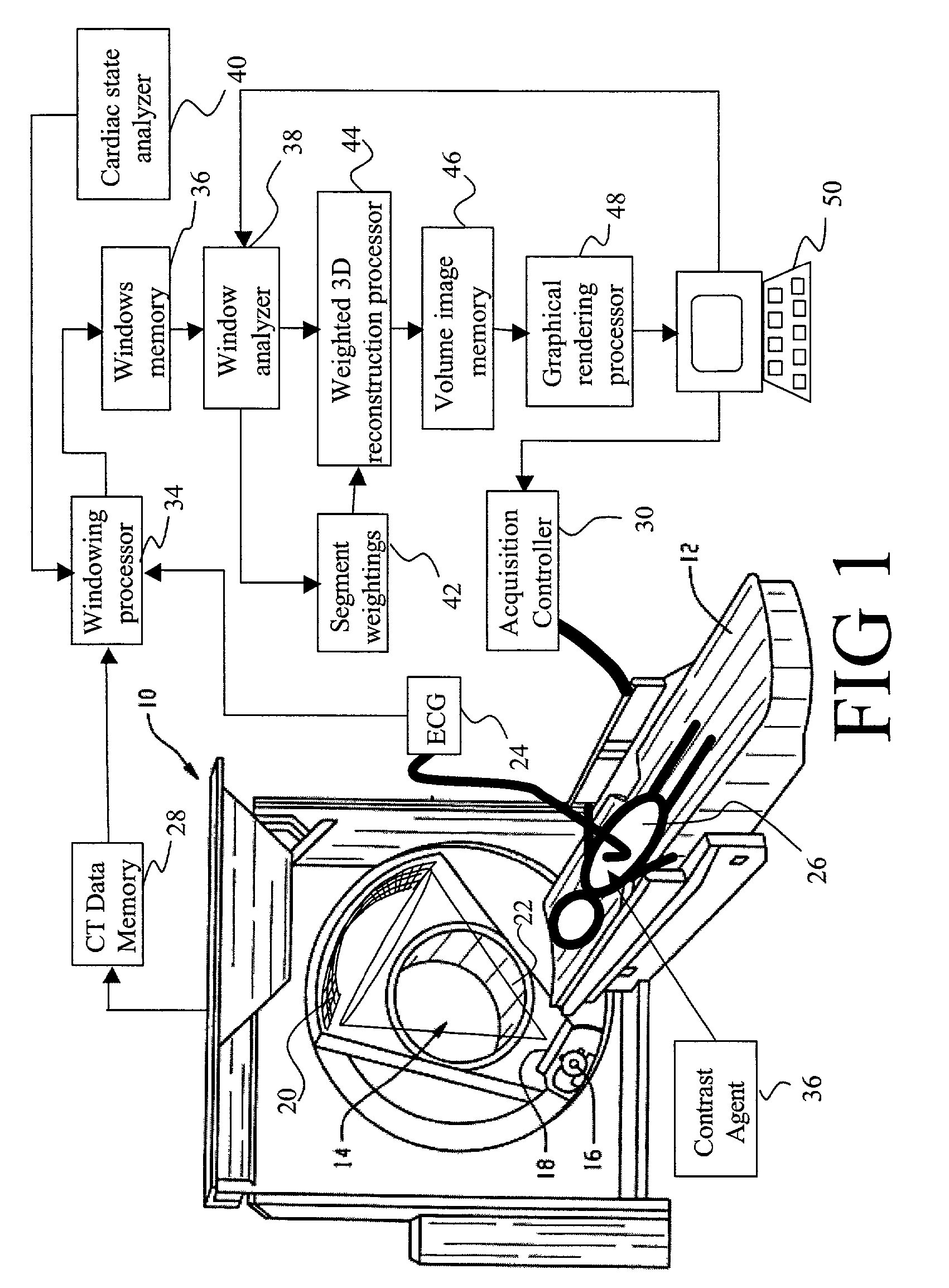
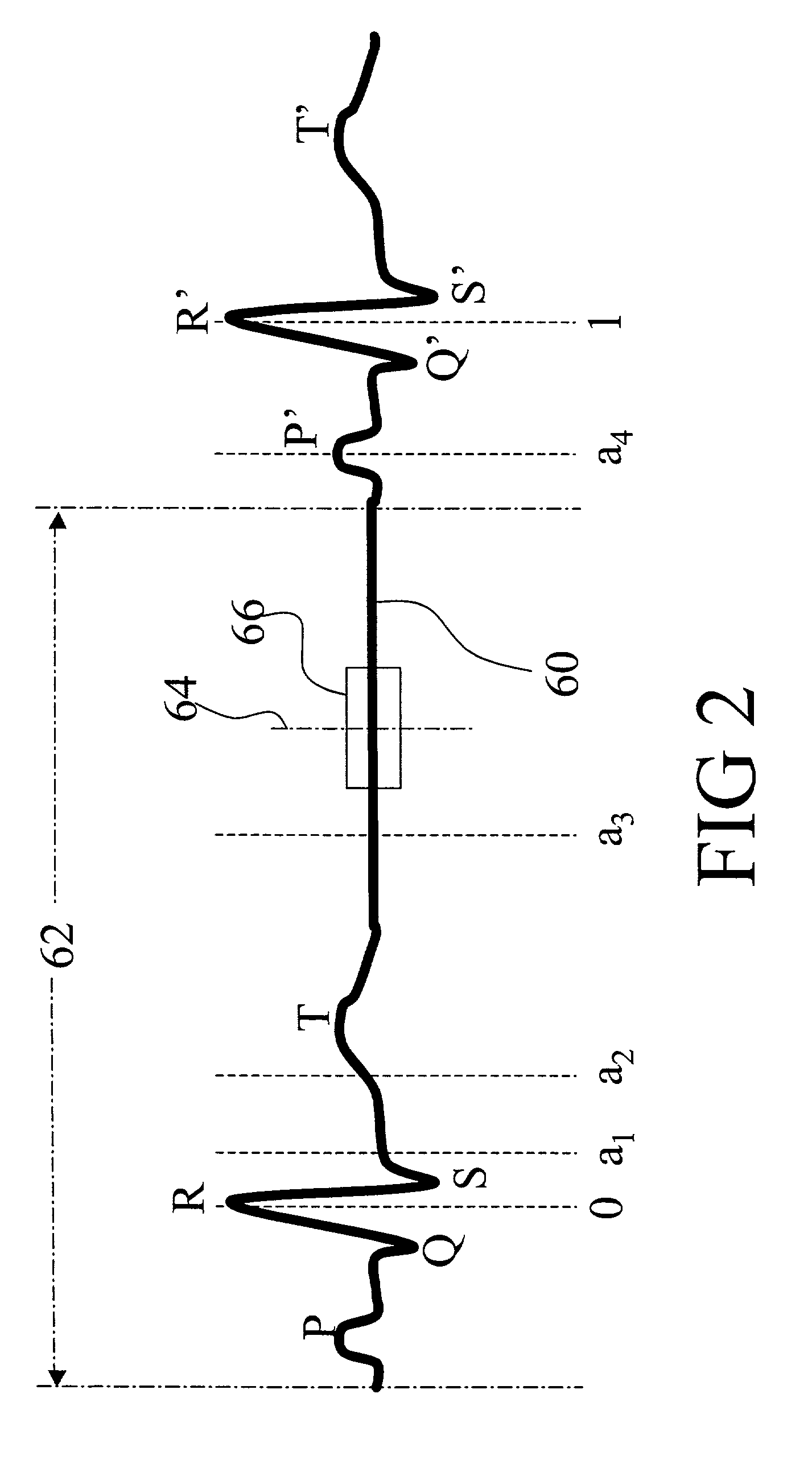
An apparatus for computed tomography (CT) imaging of a cyclically moving organ includes a positional state monitor (24, 40) that monitors a positional state of the cyclically moving organ such as the heart. A cone-beam CT scanner (10) acquires image data at least within a plurality of time windows. Each time window is centered about an occurrence of a selected positional state of the organ. A window analyzer (38) selects a data segment within each time window such that the data segments combine to form a complete data set covering a selected angular range. A reconstruction processor (44) reconstructs the selected data segments into an image representation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Multimode image capturing and decoding optical reader
InactiveUS7111787B2Easily searchable databaseUseful in detectionVisual representatino by photographic printingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareEngineering
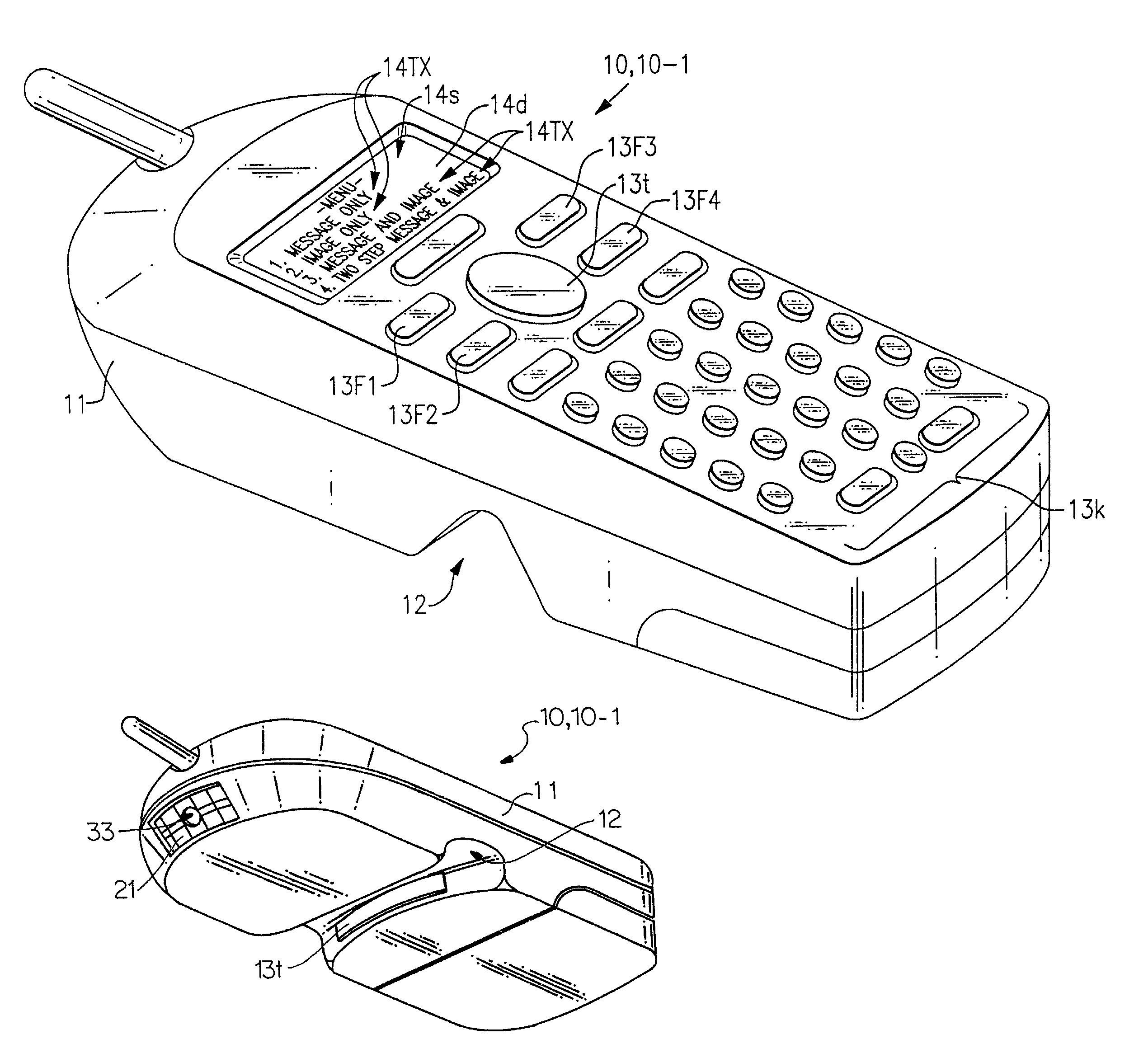
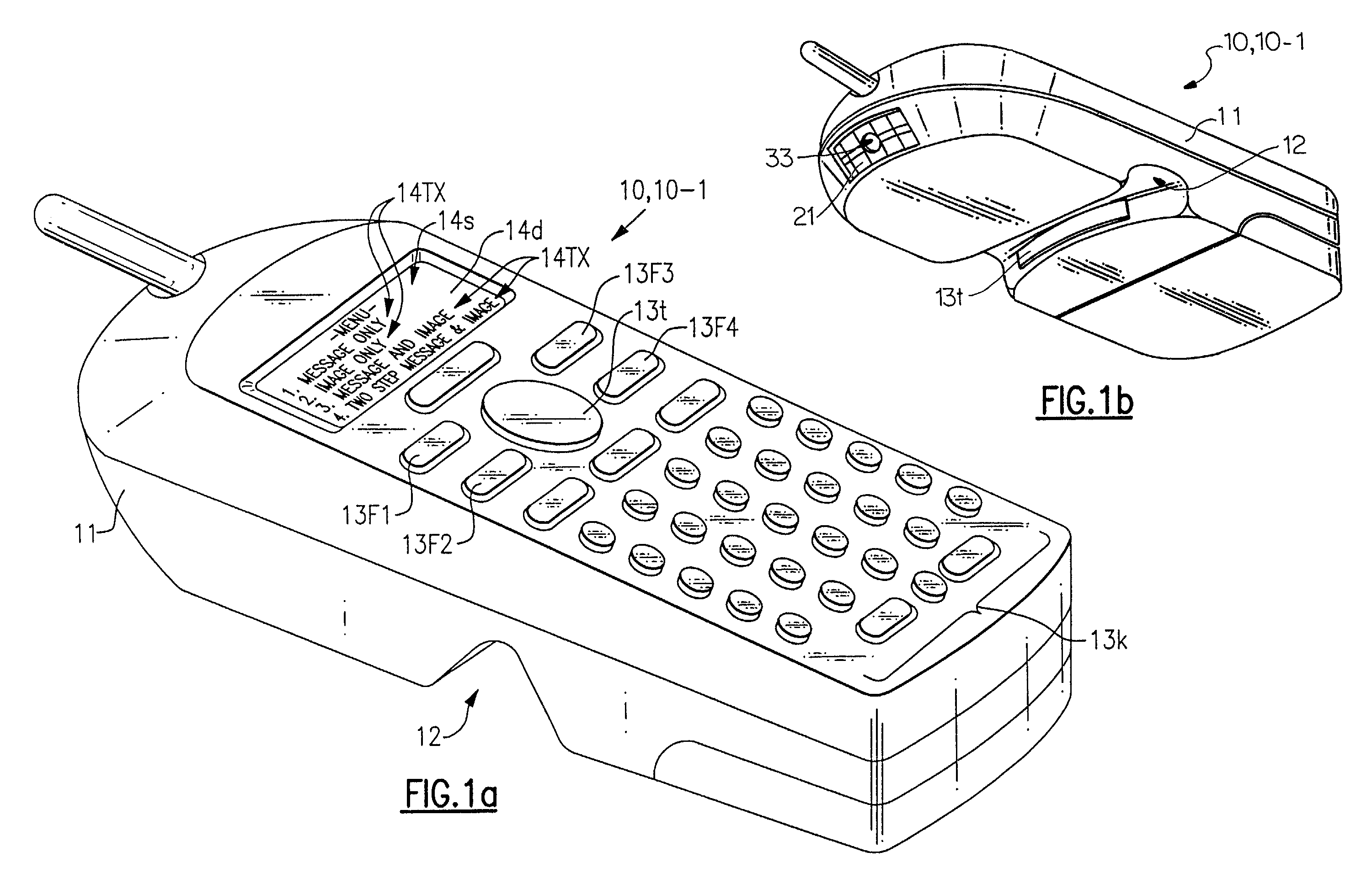
The present invention is an imaging device which can be equipped with decode functionality and which can be configured to operate in at least one of four user selected modes. In a first, “message only” mode, the device stores into a designated memory location a decoded-out message corresponding to a decodable indicia. In a second, “image only” mode, the device stores into a designated frame storage memory location an image representation of a scene. In a third, “omage plu message” mode the device stores into a designated frame storage memory location an image representation comprising a representation of a decodable symbol and into the same or other memory location the decoded-out message decoded from the decodable indicia, or data corresponding to the same. In the fourth, “two-step message and image” mode, the device is controlled to capture an image a first time for decoding a decodable indicia and a second time for capturing an image that is associated with the decoded-out message corresponding to the decodable indicia.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
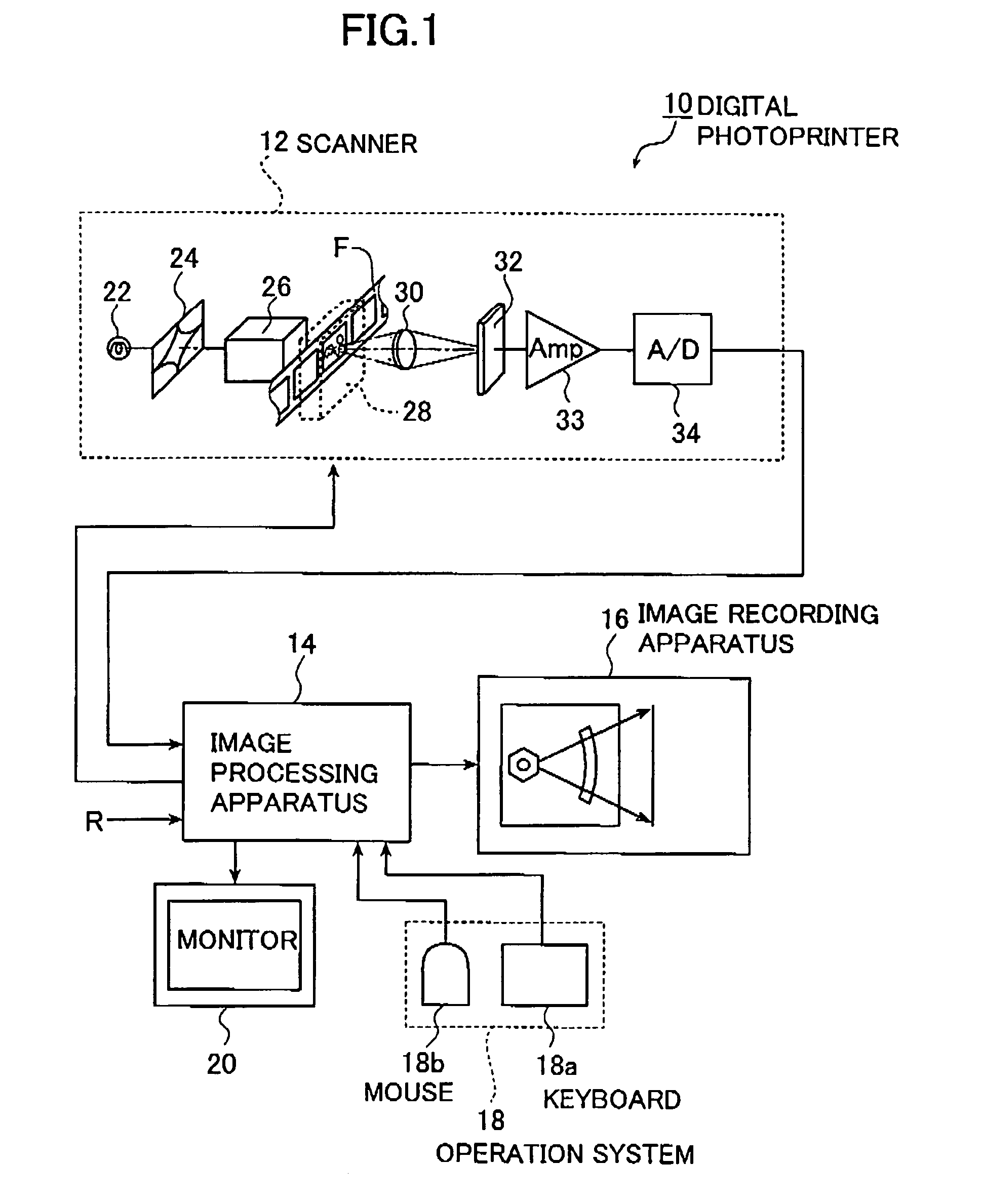
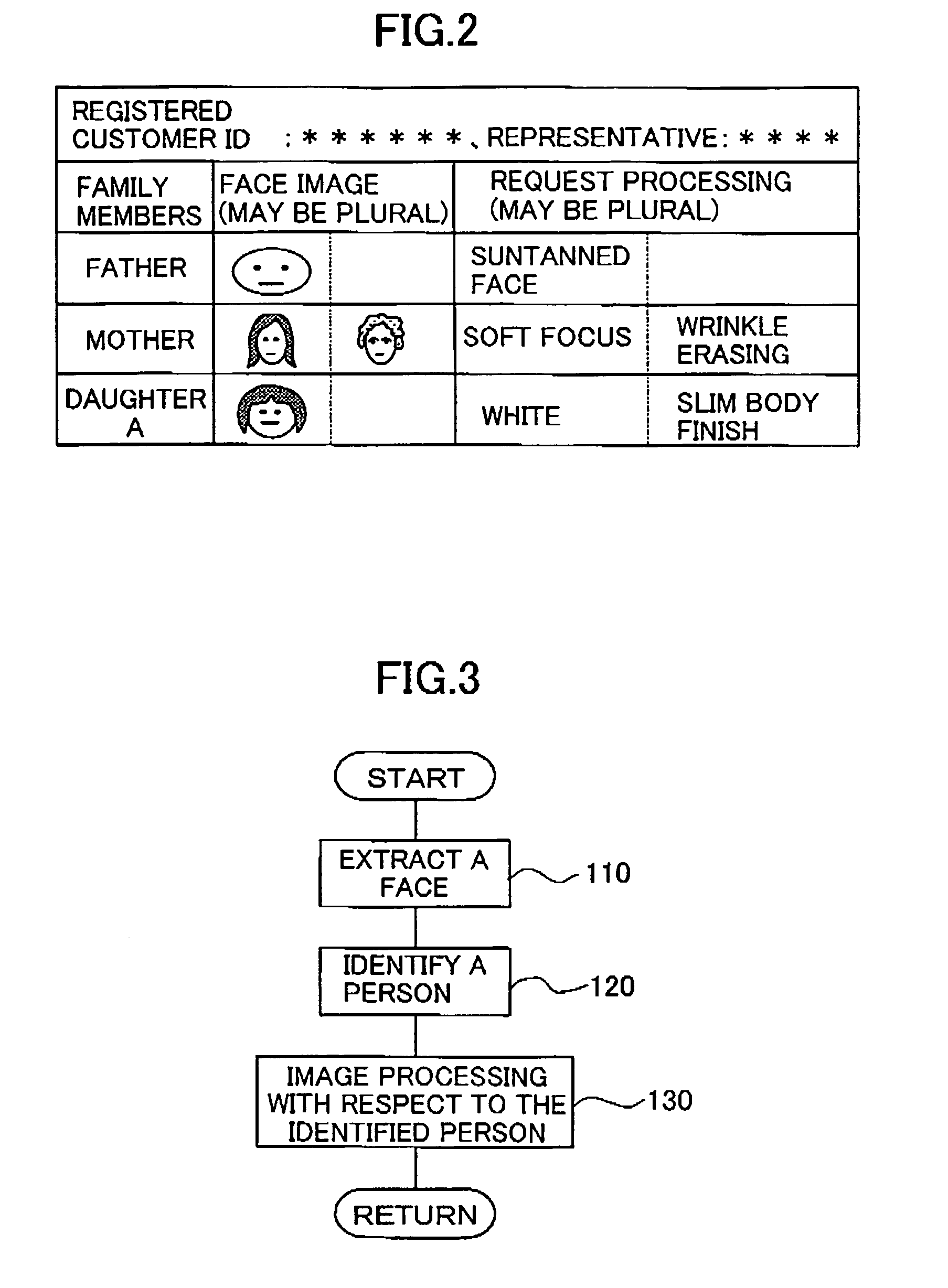
Image processing method using conditions corresponding to an identified person
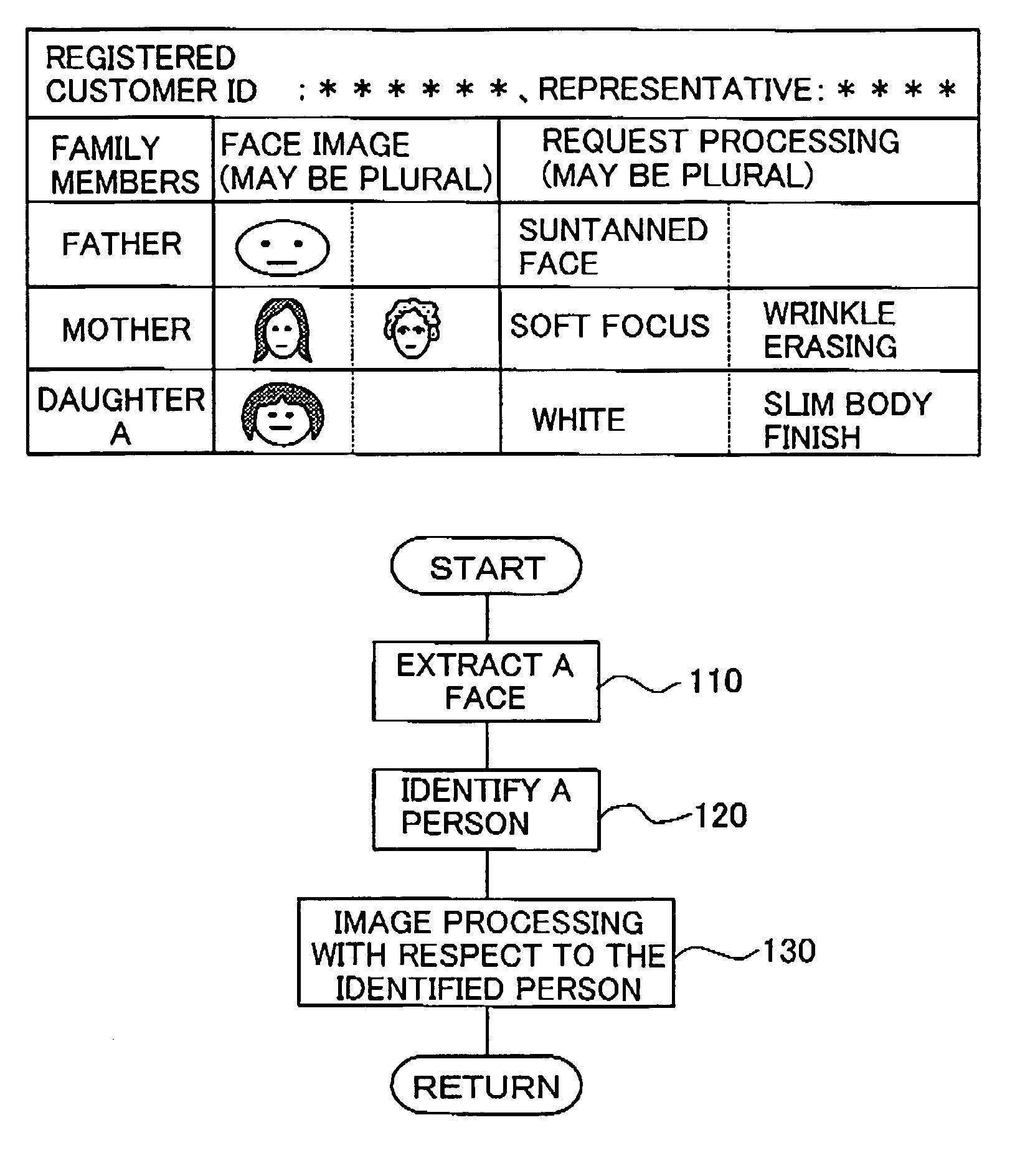
InactiveUS7106887B2Remove unnatural feelingEasy to correctAcquiring/recognising facial featuresImaging processingImage processing software
The image processing method applies image processing to an inputted image data. The method registers predetermined image processing conditions for each specific person in advance, extracts a person in the inputted image data, identifies the extracted person to find if the extracted person is the specific person and selects image processing conditions corresponding to the identified specific person to perform the image processing based on the selected image processing conditions. Amusement aspect in photography and image representation can be enhanced, and even inexperienced or unskilled persons in personal computer or image processing software can correct images.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
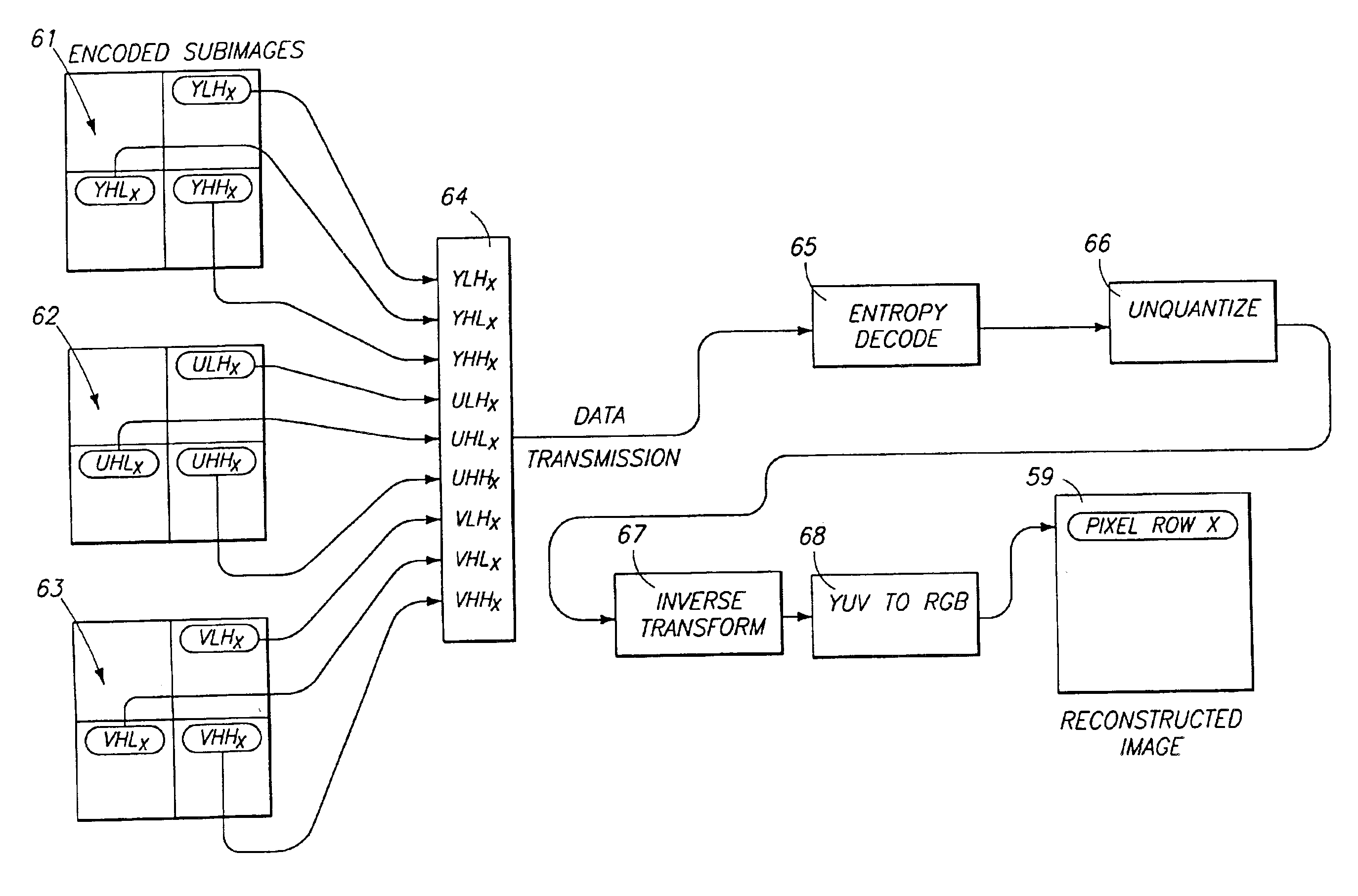
Progressive image transmission using discrete wavelet transforms
InactiveUS6847468B2Convenient previewImprove the level ofDigitally marking record carriersGeometric image transformationDecompositionImage transfer
Disclosed herein is a method of storing and of progressively transferring a still image so that it can be conveniently previewed during the transfer and so that a user can terminate the transfer at an early stage if the image turns out to be undesirable. The methods of the invention include transforming the image into a plurality of decomposition levels using a discrete wavelet transform. Each decomposition level comprises a plurality of subimages which allow reconstruction of an image representation of the still image. The decomposition levels are transmitted beginning with a base decomposition level providing a low level of image resolution and then proceeding with decomposition levels providing increasingly higher levels of image resolution. Within each decomposition level, rows of the various subimages are arranged or interlaced together in contiguous blocks, so that all data for a single row, at a single decomposition level, is transmitted together. At the receiving end of the transfer, the row blocks are reconstructed and displayed as they are received. The invention enables the initial display of a low resolution image which is gradually updated and sharpened, on a row-by-row basis, until a desired high resolution is achieved. The user may terminate the transfer at any point.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Authentication of identification documents
InactiveUS7016516B2Commercial value is not compromisedMaximization of identification signal energyTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsDocumentationComputer science
Security of photographic identification documents is enhanced by providing machine-readable information that may be correlated to other information pertaining to the individual represented by the image, such other information being, for example, printed on the document adjacent to the photograph.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP (FORMERLY DMRC CORP)
Method for autostereoscopically producing three-dimensional image information from scanned sub-pixel extracts and device for carrying out said method
ActiveUS20090278936A1Television system detailsStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
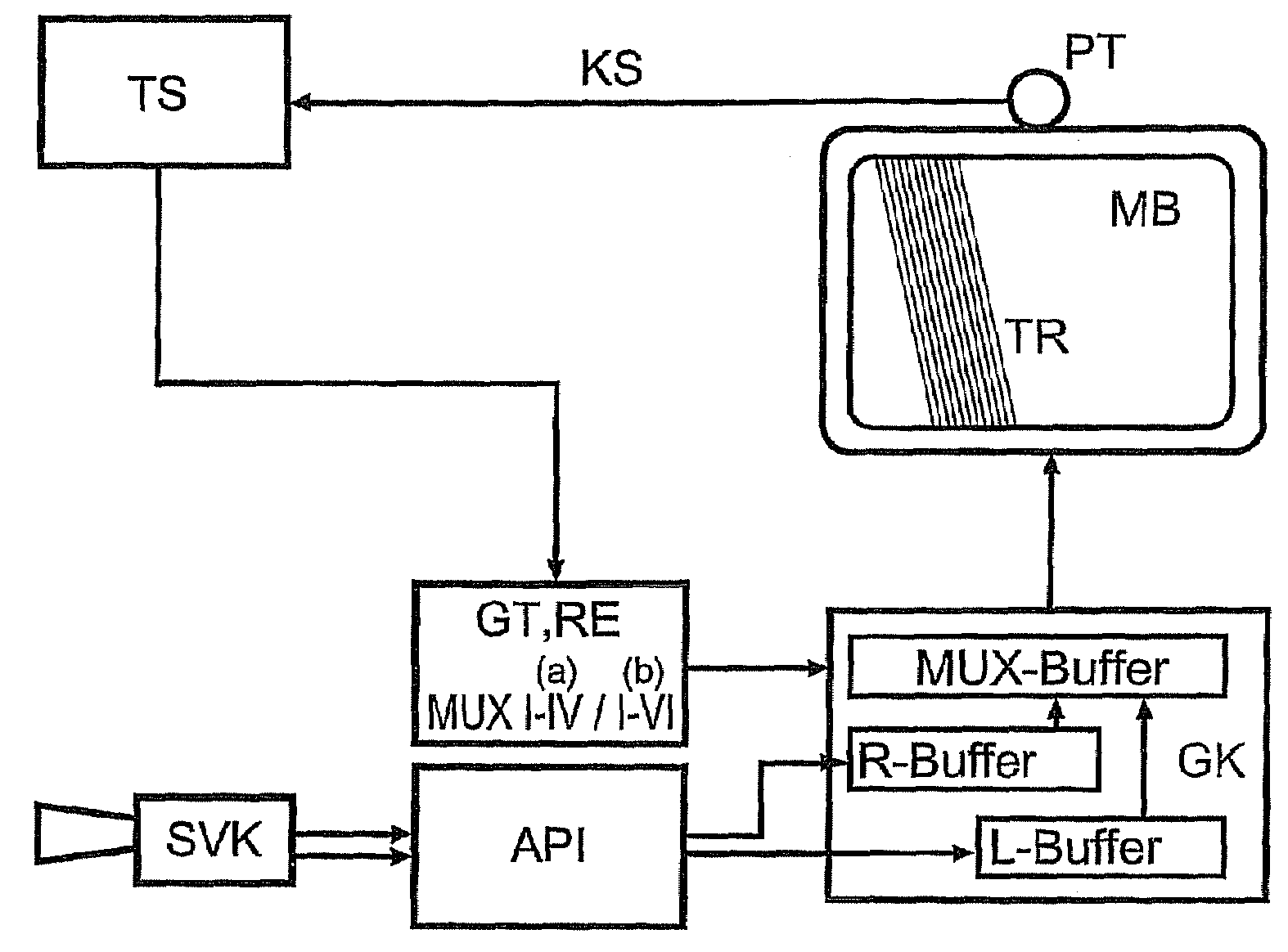
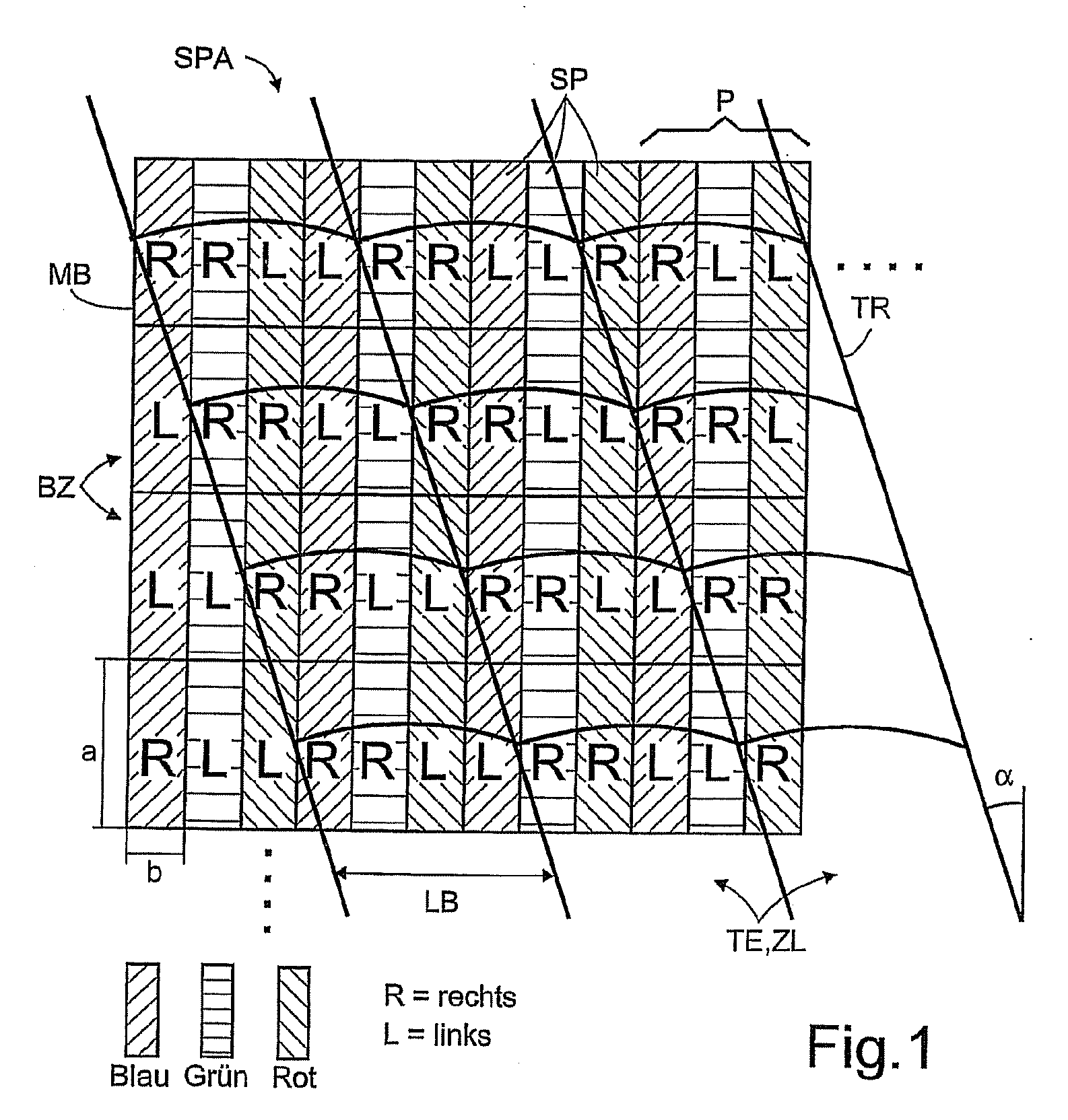
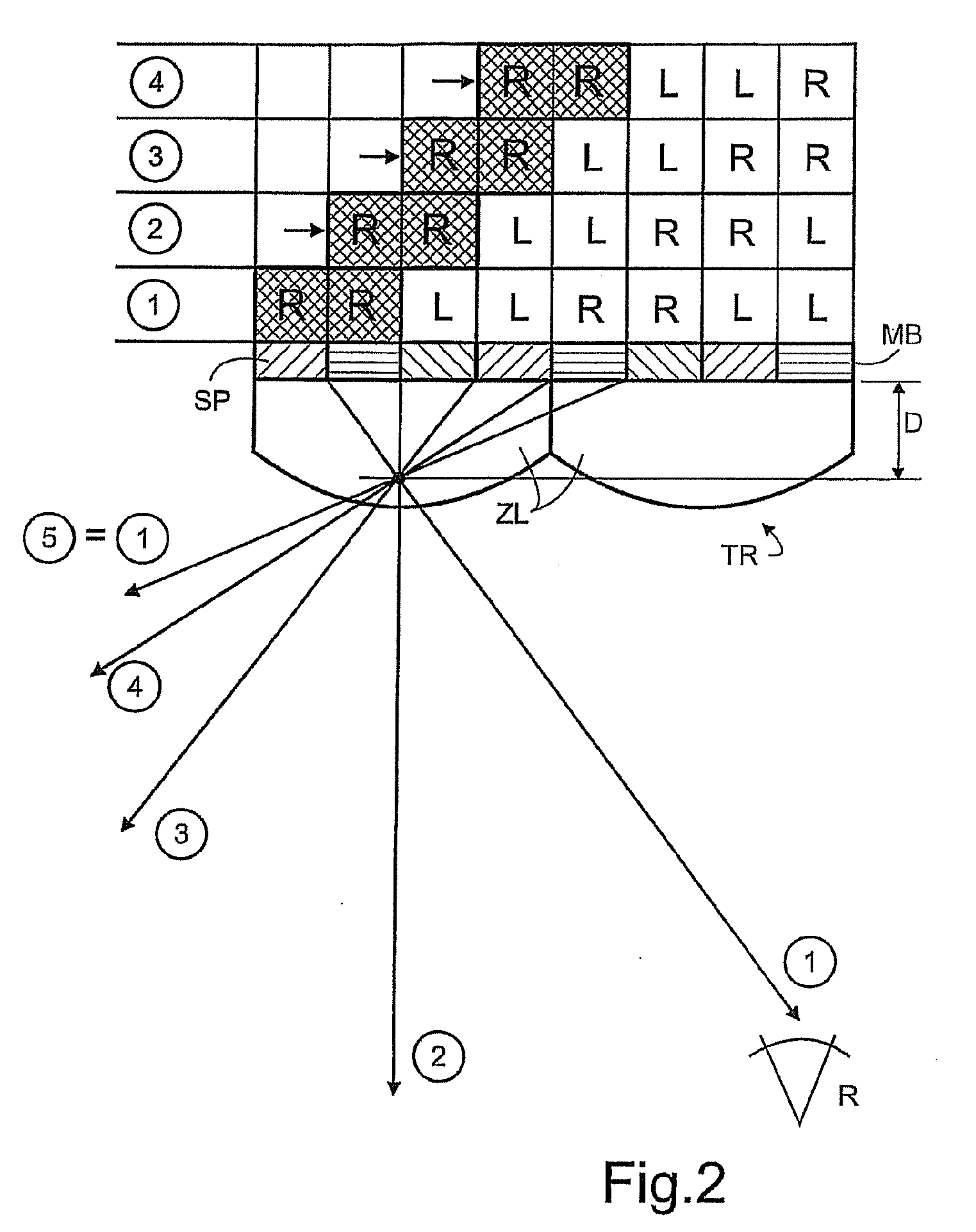
A method for autostereoscopically producing three-dimensional image information from scanned subpixel extracts uses a multiplex track method (MTV) having a separating raster (TR) obliquely extended with respect to a matrix screen (MB) and an electronic tracking (TS) of viewing areas ibased on two separated image views (L, R), that adjacently disposes two or three subpixels (SP) of each pixel (P) of the two image views (L, R) in the actual subpixel extraction (SPA), continuously and alternatingly preserving each subpixel address and disposes said subpixels (SP) in an overlapping manner on each other with an offset, whereby the resolution loss effects the subpixels (SP) only. The crosstalk resulting from the inclination of the separating raster (TR) is reduced by a special structure of the subpixel extraction (SPA), wherein the resolution homogenisation in two directions of the screen is simultaneously preserved. The formation of the actual subpixel extraction (SPA) is carried out according to multiplex schemes (MUXi) predetermined according to an observer actual position. One or several observers can be electronically tracked subject to the distance thereof from the matrix screen (MB), and the image representation can be adapted therefor.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Multidirectional selective plane illumination microscopy
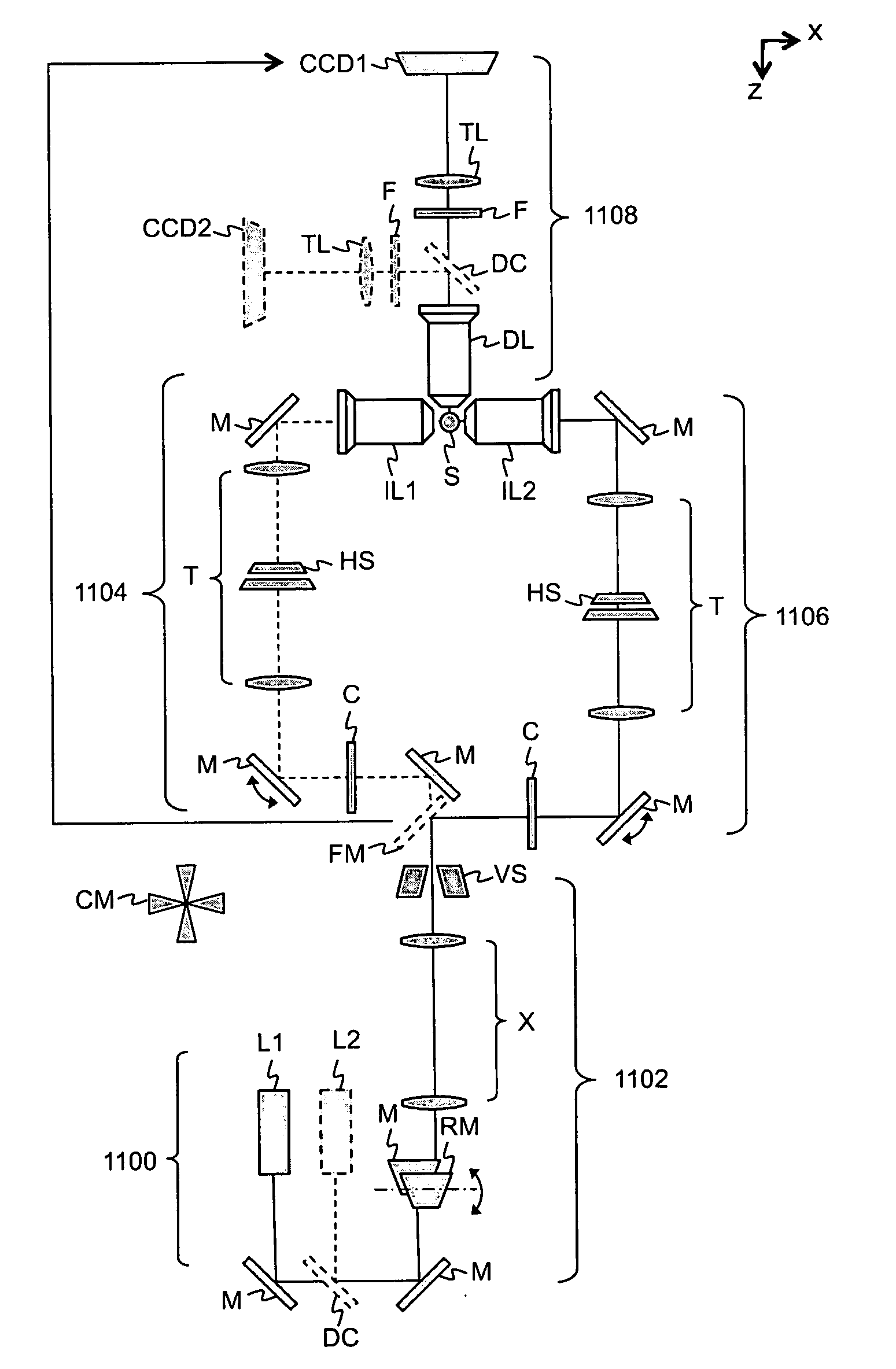
ActiveUS20110115895A1Improve imagingColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsWavefrontMicroscope
A method and device for multi-directional selective plane illumination microscopy is provided. A detector focal plane is alternately illuminated with at least two counter-propagating, coplanar light sheets, and an image of a specimen cross-section positioned in the focal plane is detected while only one light sheet illuminates the specimen. The wavefront of the illumination beams may be deformed with adaptive optics using feedback from light transmitted through the specimen. Multiple images of the specimen cross-section may be detected at different times and specimen positions and orientations to produce multi-view image stacks which may be processed using image fusion to produce a reconstructed image representation of the specimen. Additionally, the direction of propagation of the alternating light sheets may be pivoted in the focal plane while detecting the image.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
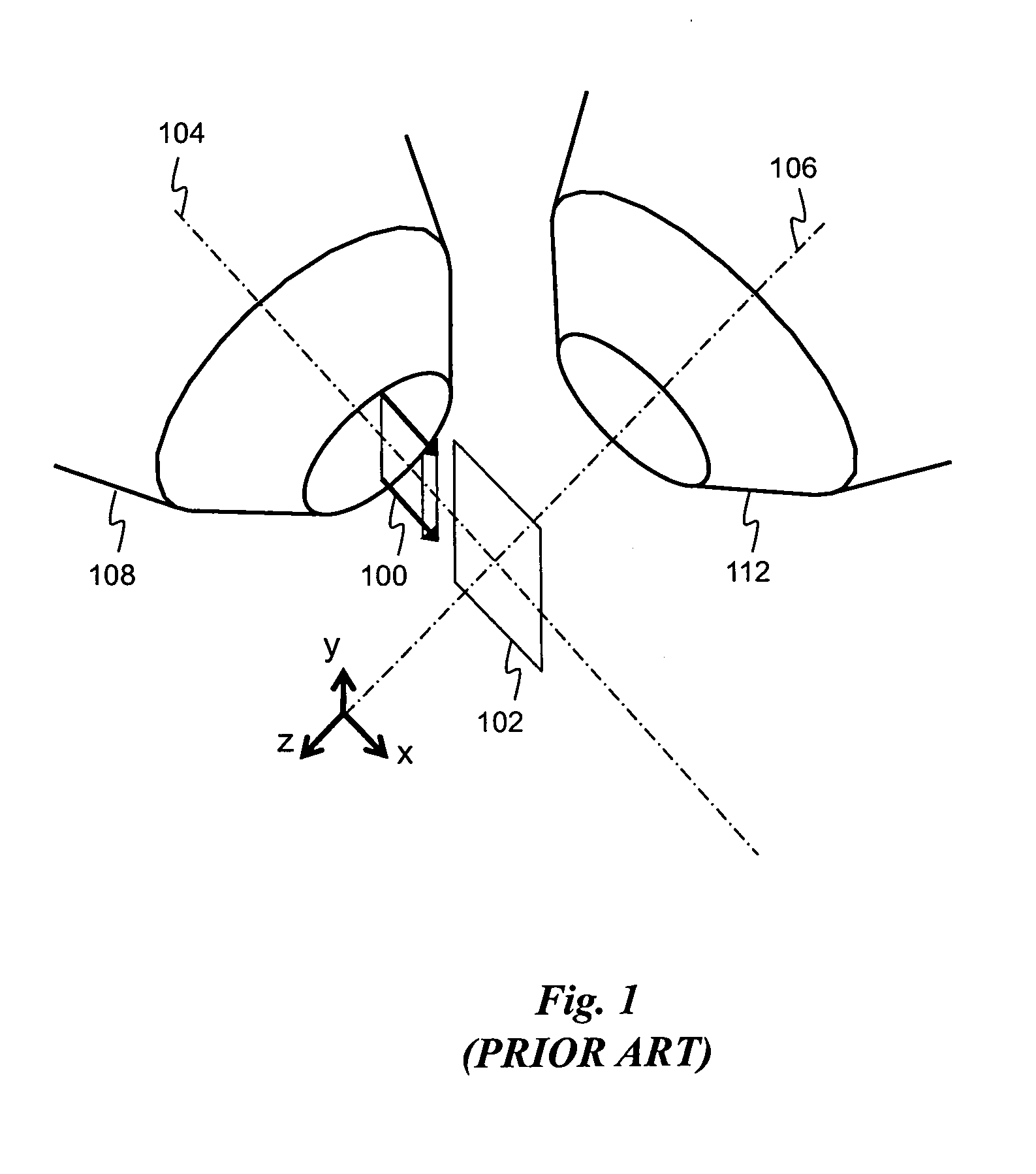
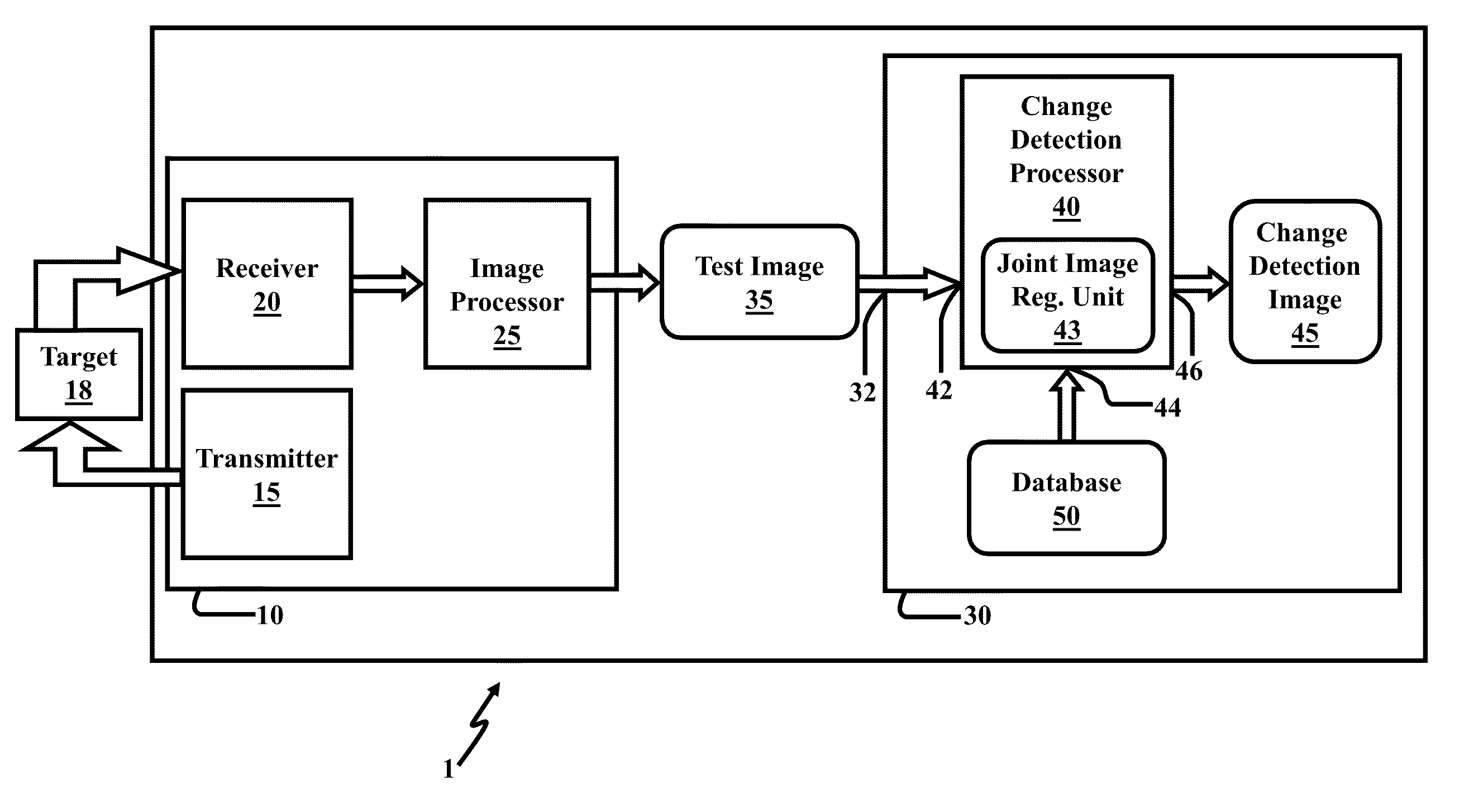
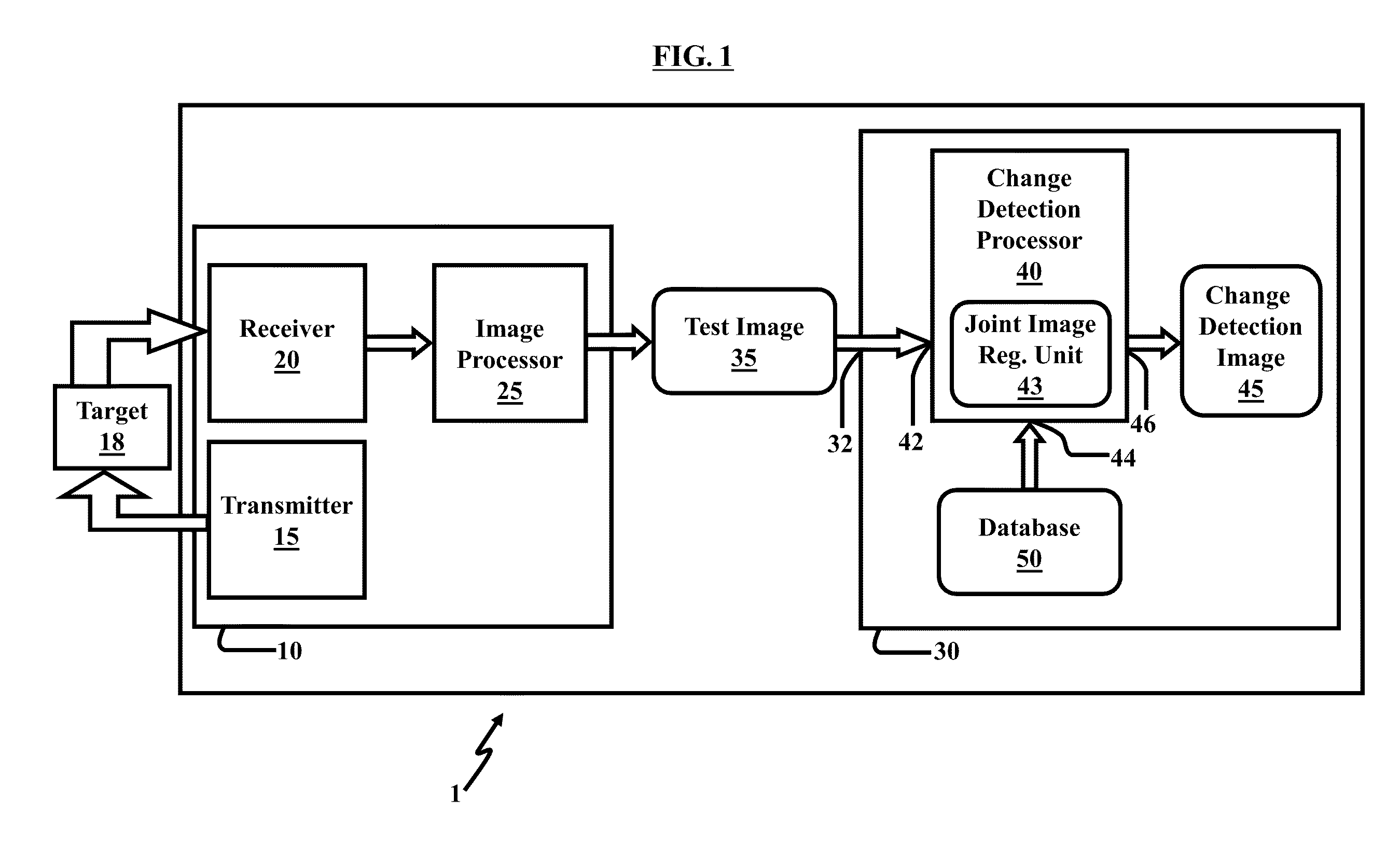
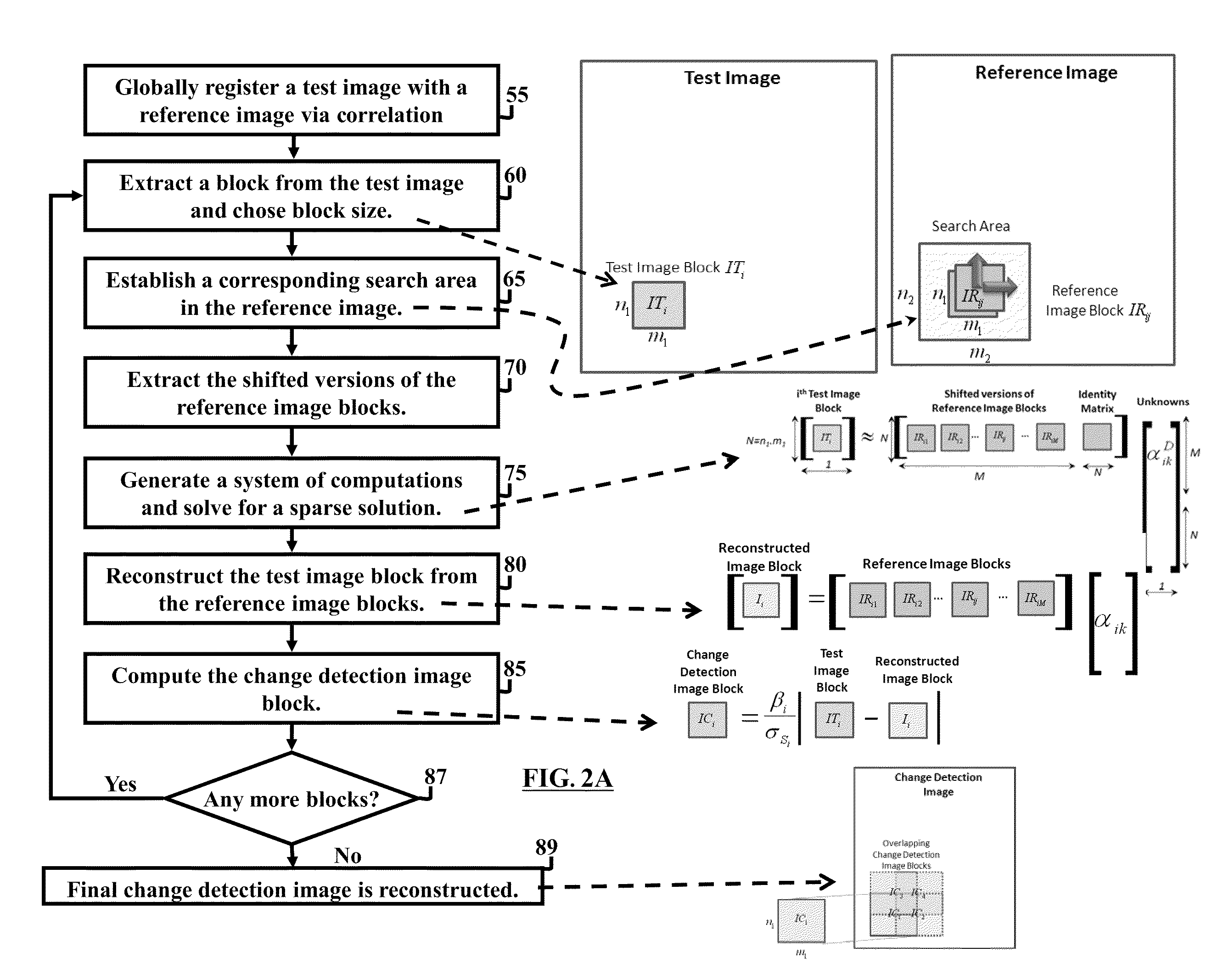
Method and system for image registration and change detection
InactiveUS20110222781A1Maximize correlationMinimize the differenceImage enhancementImage analysisLinearityImage registration
A system and method for detecting changes by comparing images which cover the same physical area but are collected at different times, the system comprising: at least one input for inputting an image of a target area; the image of the target area having signatures representing outstanding features; at least one processor operating to divide the image of a target area into a plurality of target subimages; at least one memory comprising reference data comprising reference subimages taken at or near the target area at various times, the at least one processor operating to determine a sparse image representation from the reference data; the sparse image representation of the target data being a linear combination of reference data from corresponding reference subimages stored in the at least one memory; the at least one processor operating to compare the target image to the sparse image representation and to match signatures from the target image to the sparse image representation to register the images and perform change detection.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Single boom cargo scanning system
InactiveUS7369643B2Rapidly deployableCost-effectively and accurately on uneven surfaceX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMobile vehicleDetector array
The inspection methods and systems of the present invention are mobile, rapidly deployable, and capable of scanning a wide variety of receptacles cost-effectively and accurately on uneven surfaces. The present invention is directed toward a portable inspection system for generating an image representation of target objects using a radiation source, comprising a mobile vehicle, a detector array physically attached to a movable boom having a proximal end and a distal end. The proximal end is physically attached to the vehicle. The invention also comprises at least one source of radiation. The radiation source is fixedly attached to the distal end of the boom, wherein the image is generated by introducing the target objects in between the radiation source and the detector array, exposing the objects to radiation, and detecting radiation.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
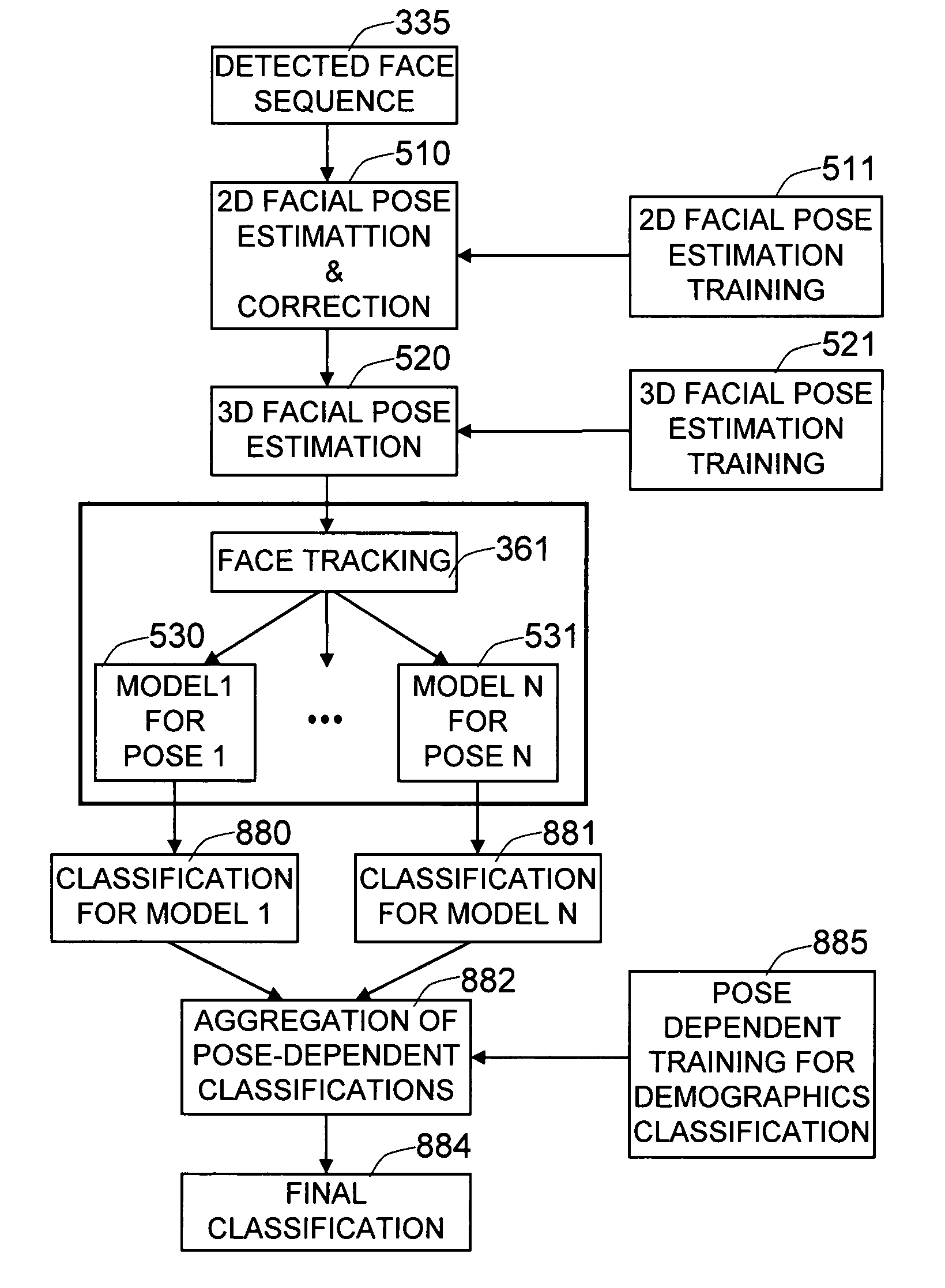
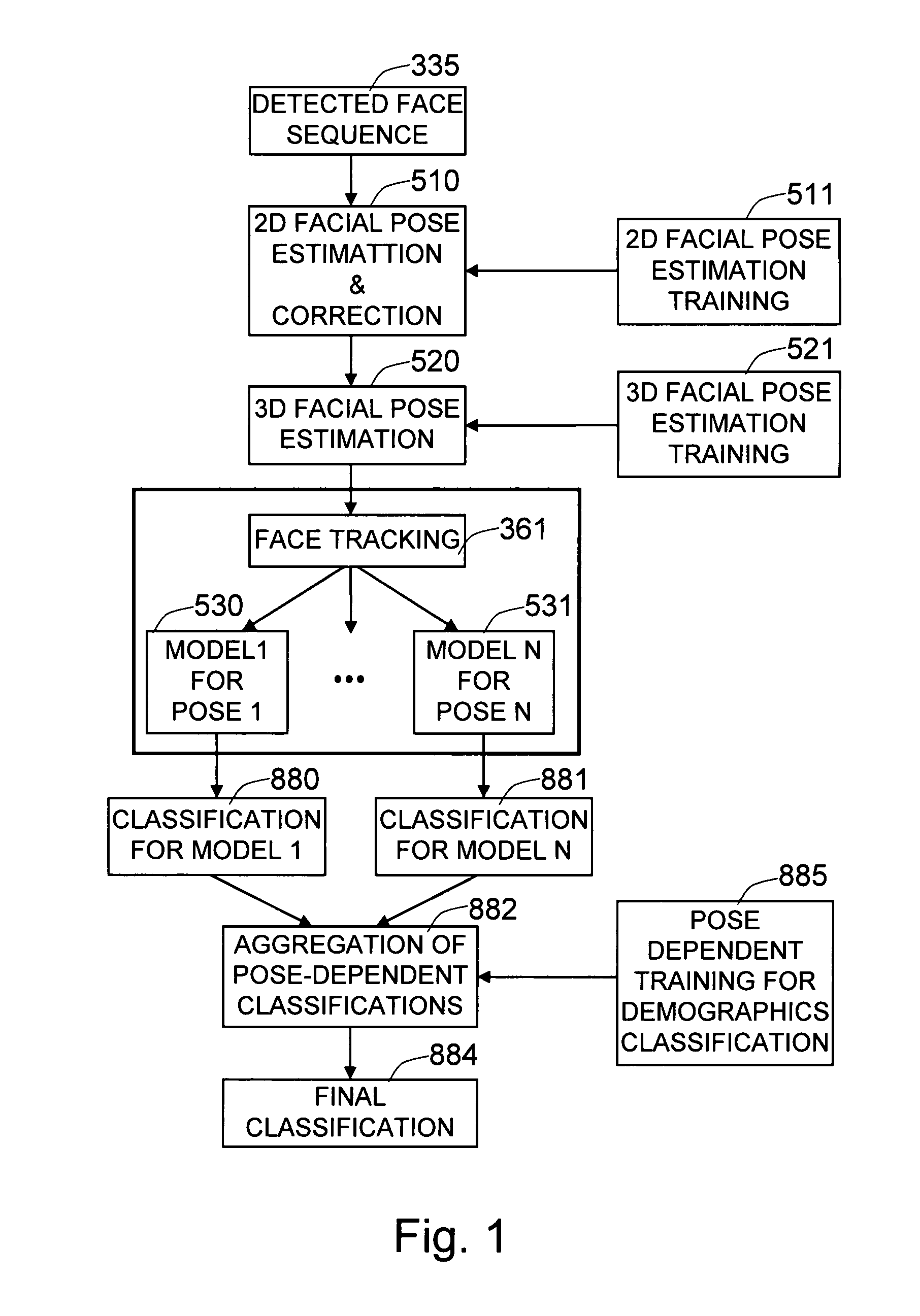
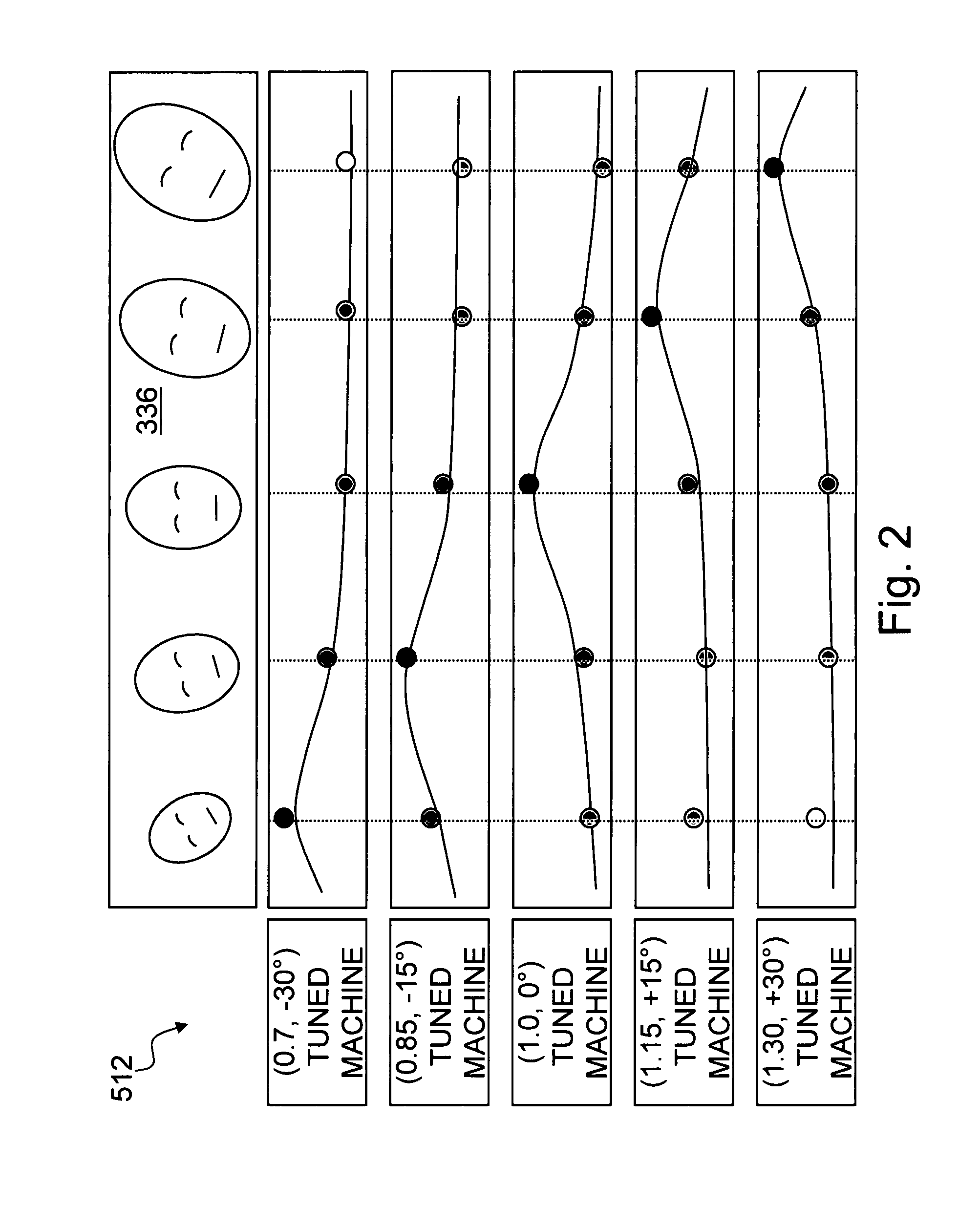
Method and system for robust demographic classification using pose independent model from sequence of face images
ActiveUS7848548B1Improve accuracyEffective estimateCharacter and pattern recognitionLearning basedFacial appearance
The invention provides a face-based automatic demographics classification system that is robust to pose changes of the target faces and to accidental scene variables, by using a pose-independent facial image representation which comprises multiple pose-dependent facial appearance models. Given a sequence of people's faces in a scene, the two-dimensional variations are estimated and corrected using a novel machine learning based method. We estimate the three-dimensional pose of the people, using a machine learning based approach. The face tracking module keeps the identity of the person using geometric and appearance cues, where multiple appearance models are built based on the poses of the faces. Each separately built pose-dependent facial appearance model is fed to the demographics classifier, which is trained using only the faces having the corresponding pose. The classification scores from the set of pose-dependent classifiers are aggregated to determine the final face category, such as gender, age, and ethnicity.
Owner:VIDEOMINING CORP
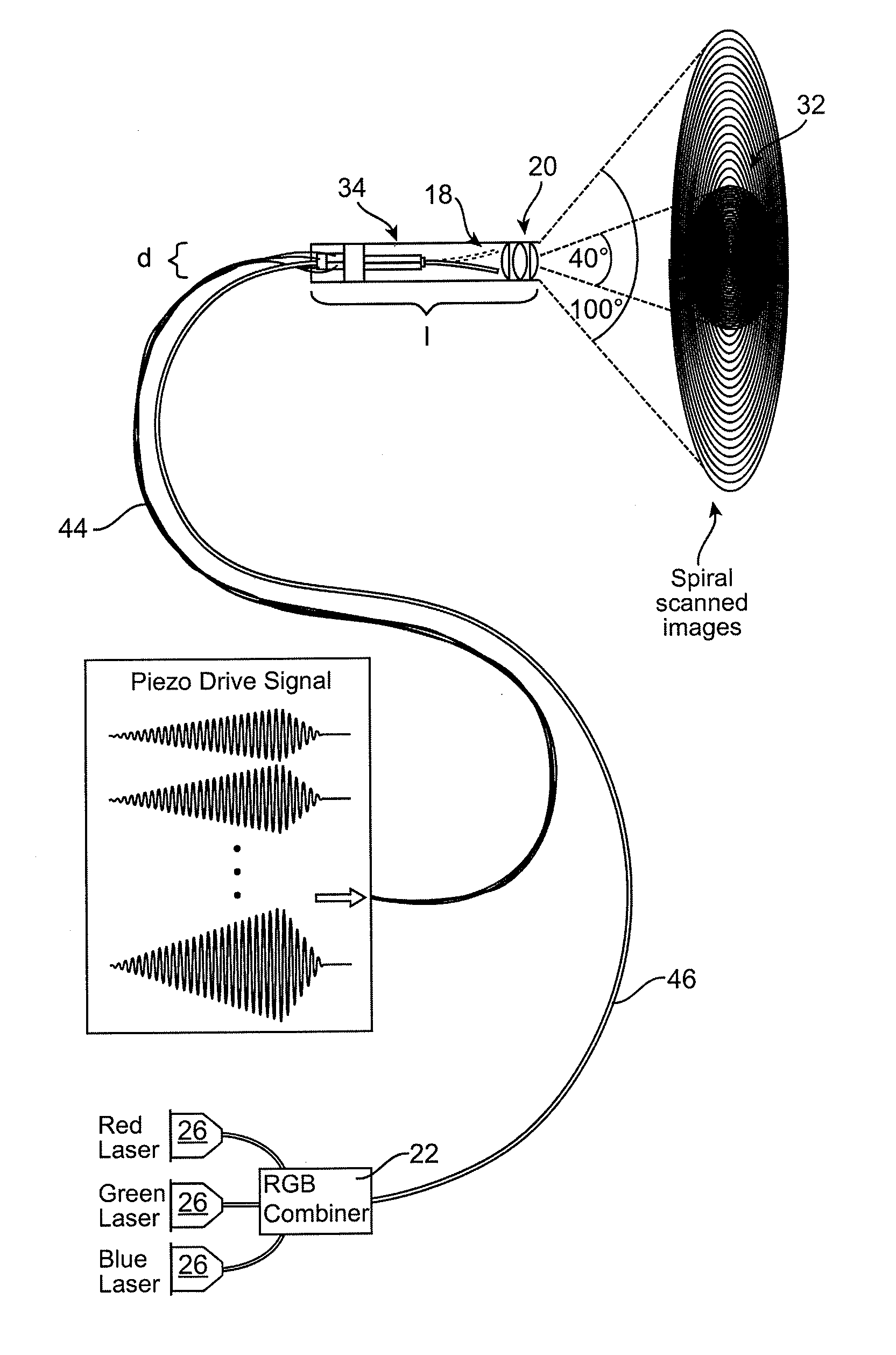
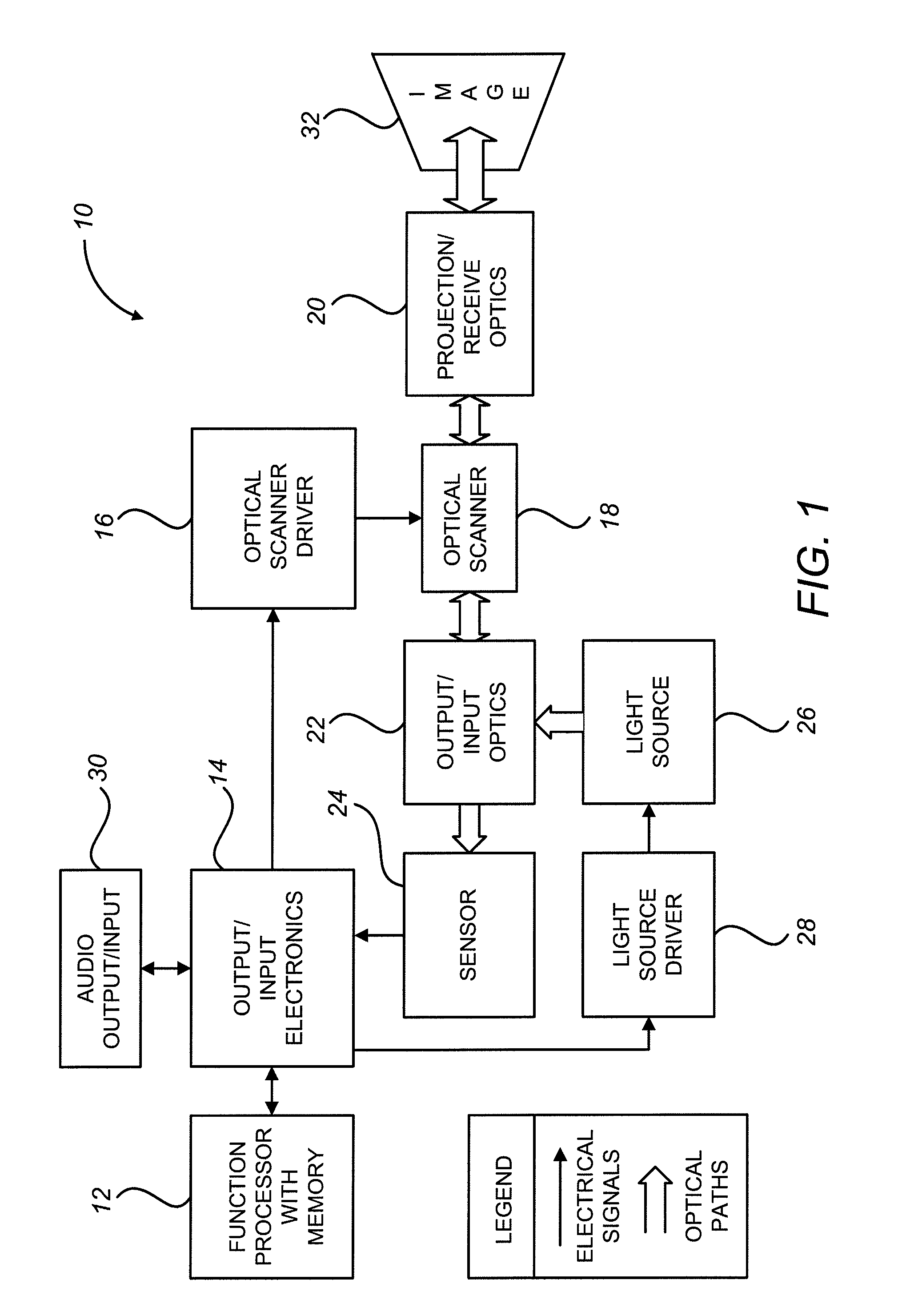
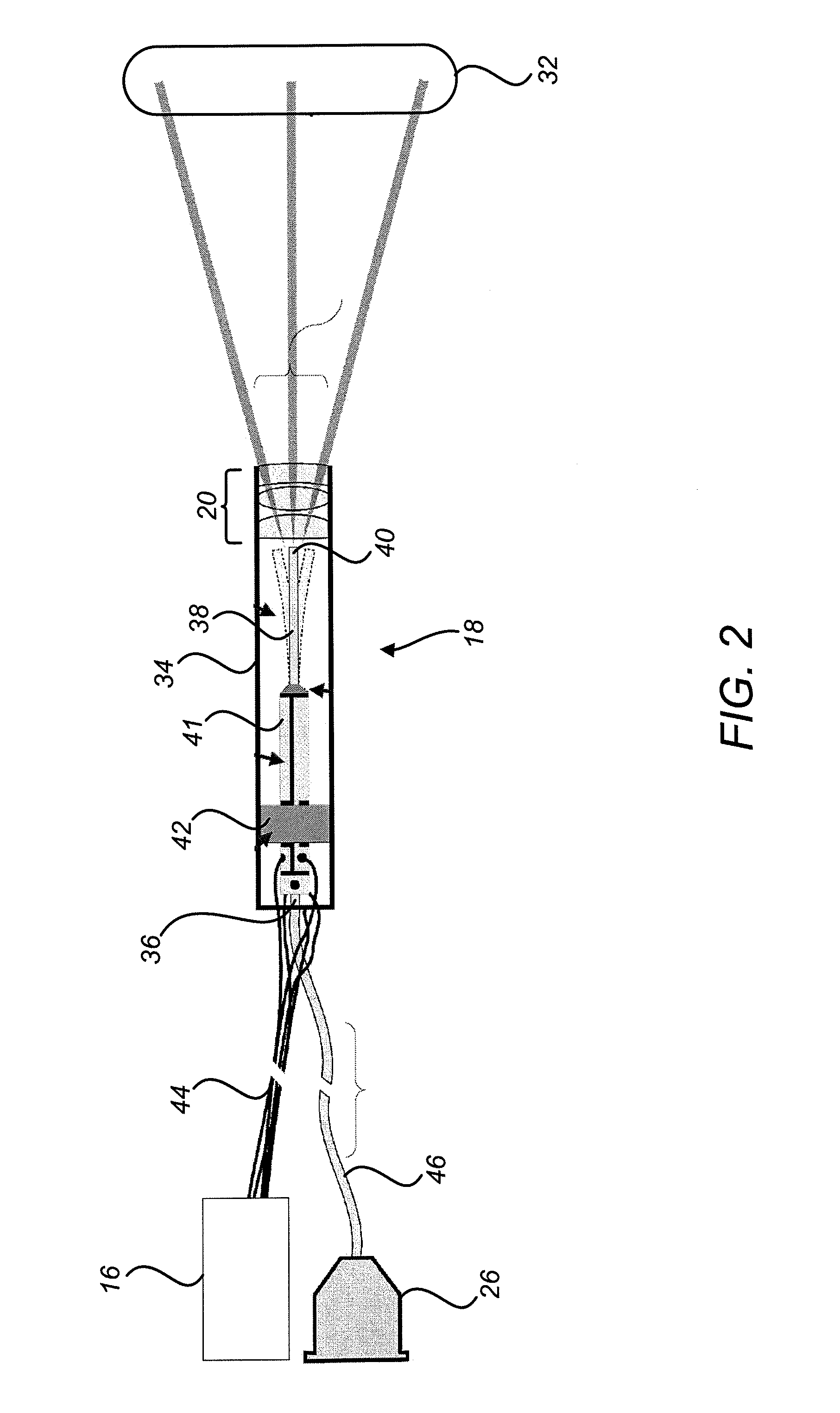
Scanning laser projection display devices and methods for projecting one or more images onto a surface with a light-scanning optical fiber
Image projection devices, high-speed fiber scanned displays and related methods for projecting an image onto a surface and interfacing with the projected image are provided. A method for projecting one or more images and obtaining feedback with an optical input-output assembly is provided. The input-output assembly comprising a light-scanning optical fiber and a sensor. The method includes generating a sequence of light in response to one or more image representations and a scan pattern of the optical fiber, articulating the optical fiber in the scan pattern, projecting the sequence of light from the articulated optical fiber, and generating a feedback signal with the sensor in response to reflections of the sequence of light.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Self-contained mobile inspection system and method
InactiveUS7486768B2Rapidly deployableCost-effectively and accurately on uneven surfaceHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation beam directing meansMobile vehicleDetector array
The inspection methods and systems of the present invention are mobile, rapidly deployable, and capable of scanning a wide variety of receptacles cost-effectively and accurately on uneven surfaces. The present invention is directed toward a portable inspection system for generating an image representation of target objects using a radiation source, comprising a mobile vehicle, a detector array physically attached to a movable boom having a proximal end and a distal end. The proximal end is physically attached to the vehicle. The invention also comprises at least one source of radiation. The radiation source is fixedly attached to the distal end of the boom, wherein the image is generated by introducing the target objects in between the radiation source and the detector array, exposing the objects to radiation, and detecting radiation.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
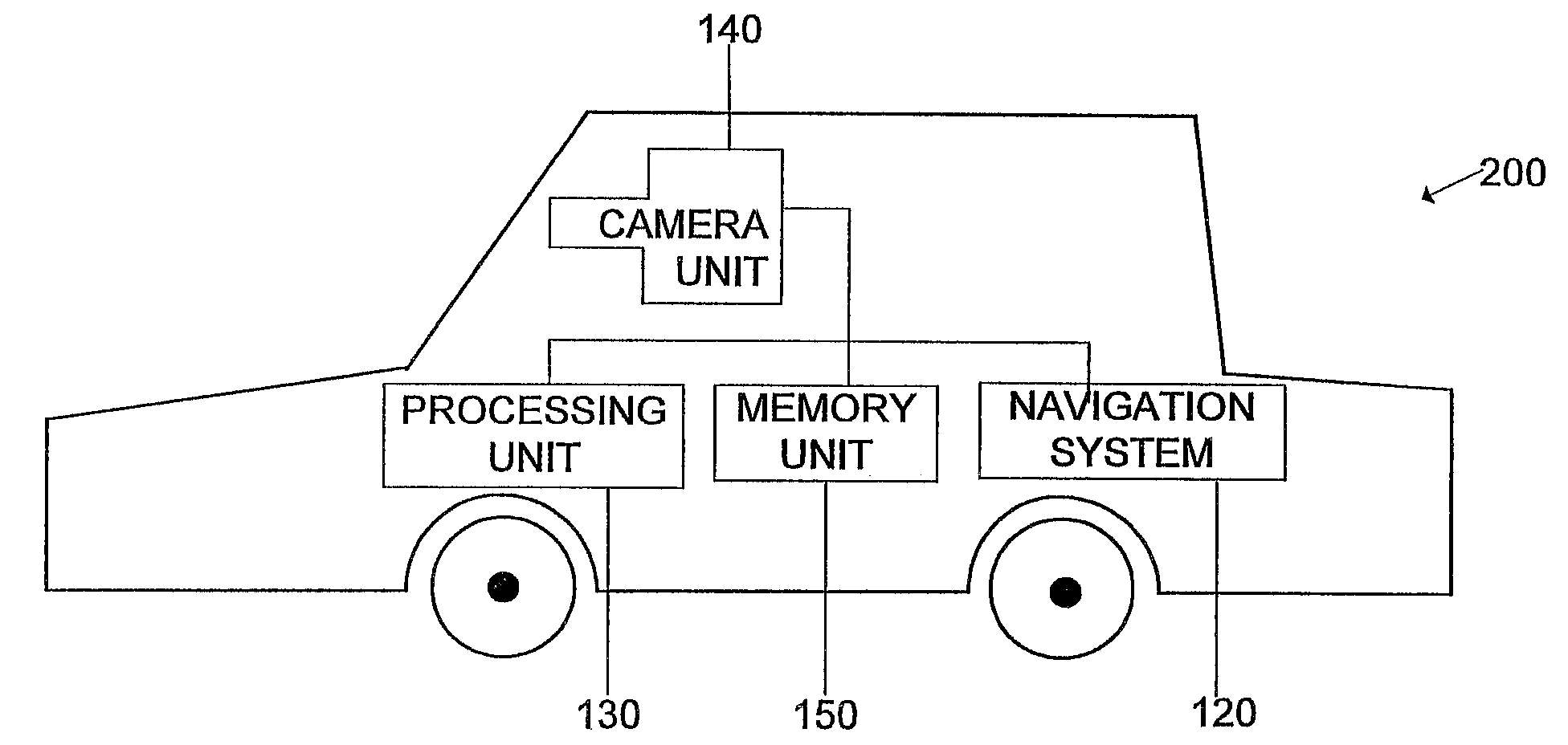
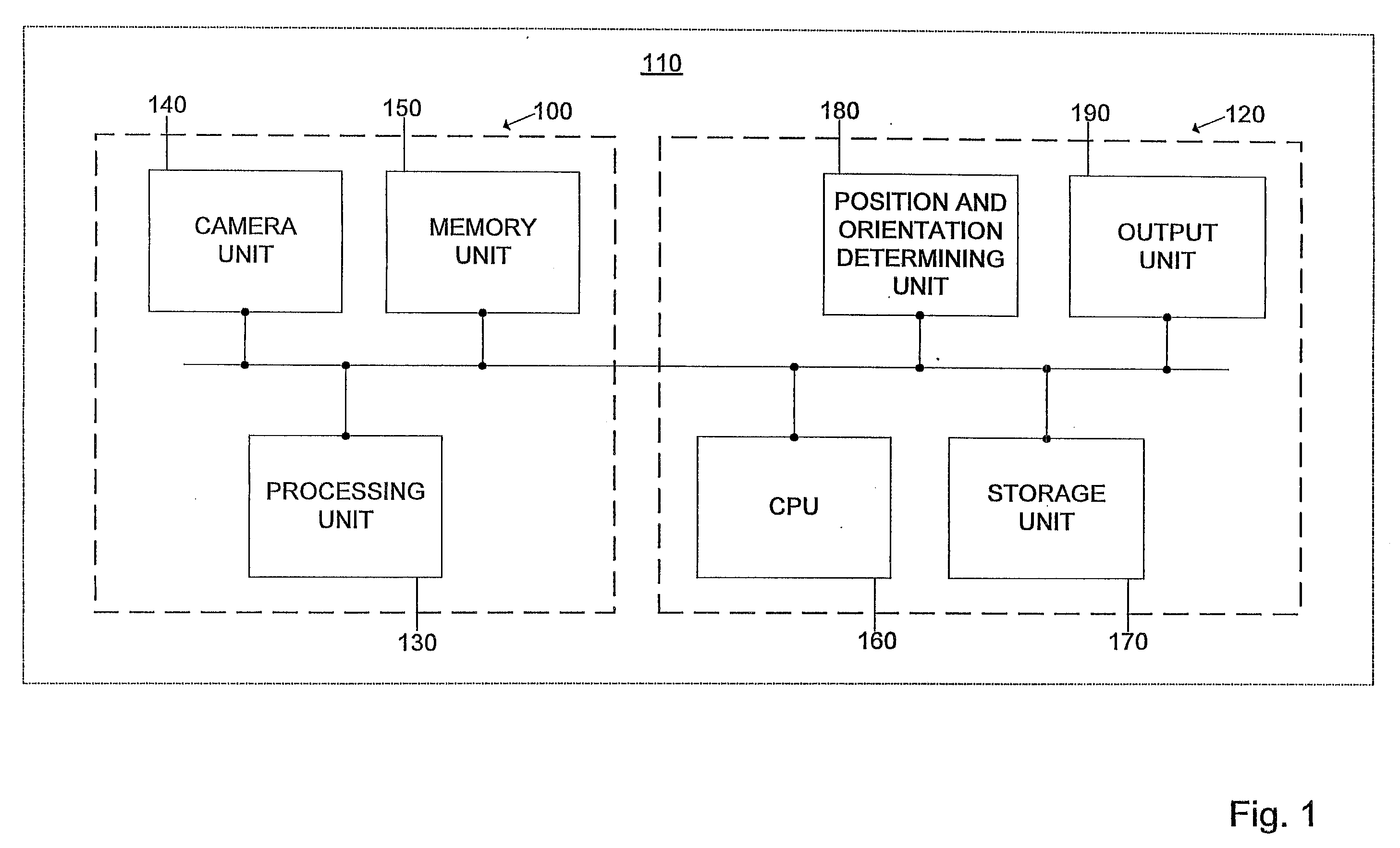
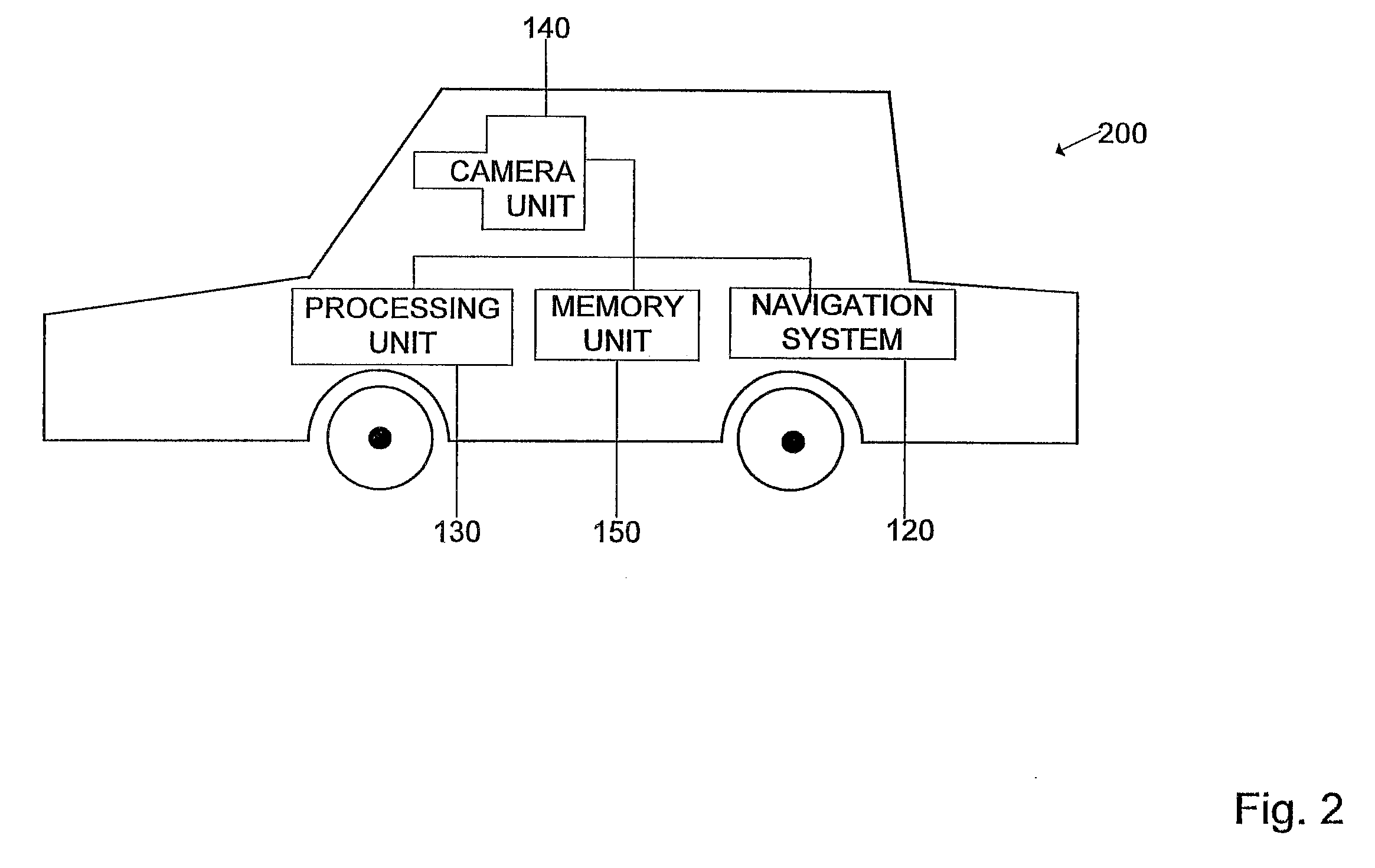
Image recongition system
ActiveUS20080056535A1Facilitate recognition of objectAccurate identificationInstruments for road network navigationImage analysisImaging dataImage identification
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Methods and apparatus for encoding a shared drawing memory
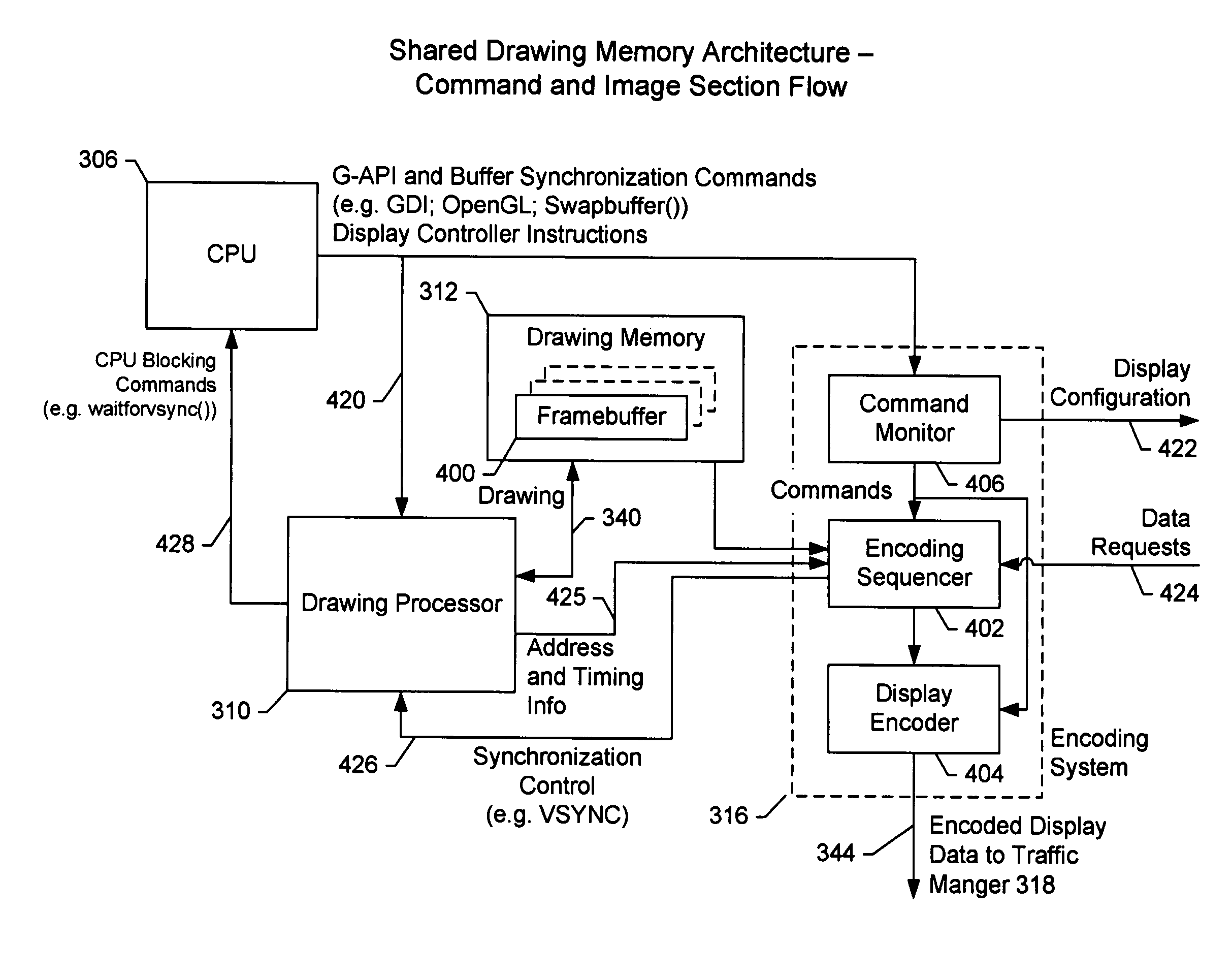
ActiveUS7747086B1Efficient communicationReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesImage codingDisplay deviceComputer science
A display encoding system is disclosed. The display encoding system includes at least one processor, an encoding circuit, the encoding circuit having a structure separate from the structure of the processor(s), a communication connection to a computer network, a drawing memory, a traffic manager, and a memory access circuit. The processor(s) are configured to execute drawing commands, access the drawing memory via the memory access circuit to store image representation(s) in the drawing memory. The encoding circuit is configured to access the drawing memory to encode at least a portion of the image representation(s) stored in the drawing memory based on the executed drawing commands. The traffic manager is configured to transmit the encoded image over the communication connection to at least one display device.
Owner:TERADICI CORP
Cargo scanning system
InactiveUS7783004B2Cost-effectively and accurately on uneven surfaceRapidly deployableX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationDetector arrayTranslational energy
The present invention is directed to a portable inspection system for generating an image representation of target objects using a radiation source. A detector array having a first configuration and a second configuration is connected to a housing and at least one source of radiation. The radiation source is capable of being transported to a site by a vehicle and of being positioned separate from the housing. The radiation source is housed in a radiation source box and movable within the radiation source box using an actuator. The actuator is operably connected to the radiation source and provides a translational energy that moves the radiation source between an operational position and a stowed position.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
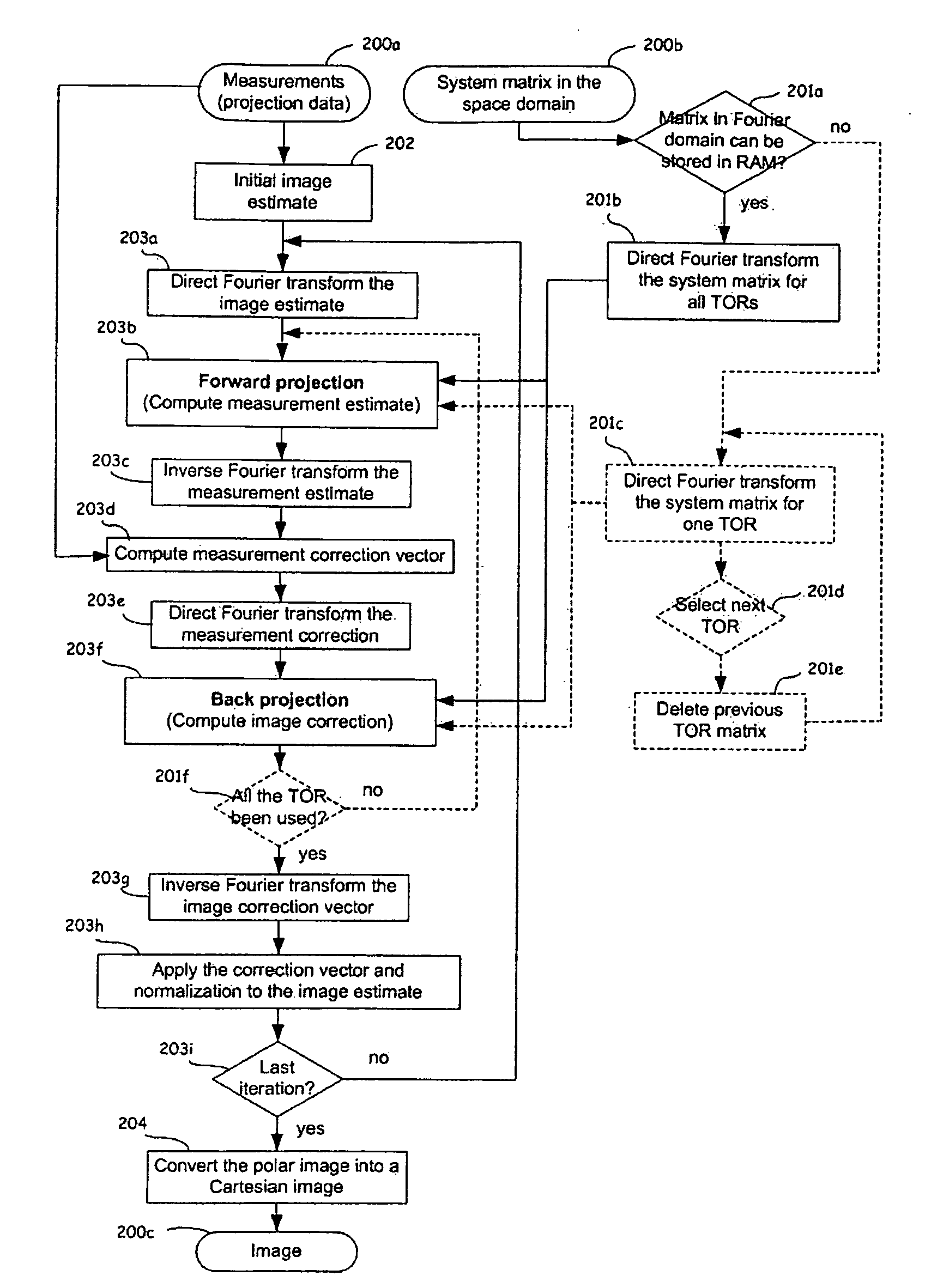
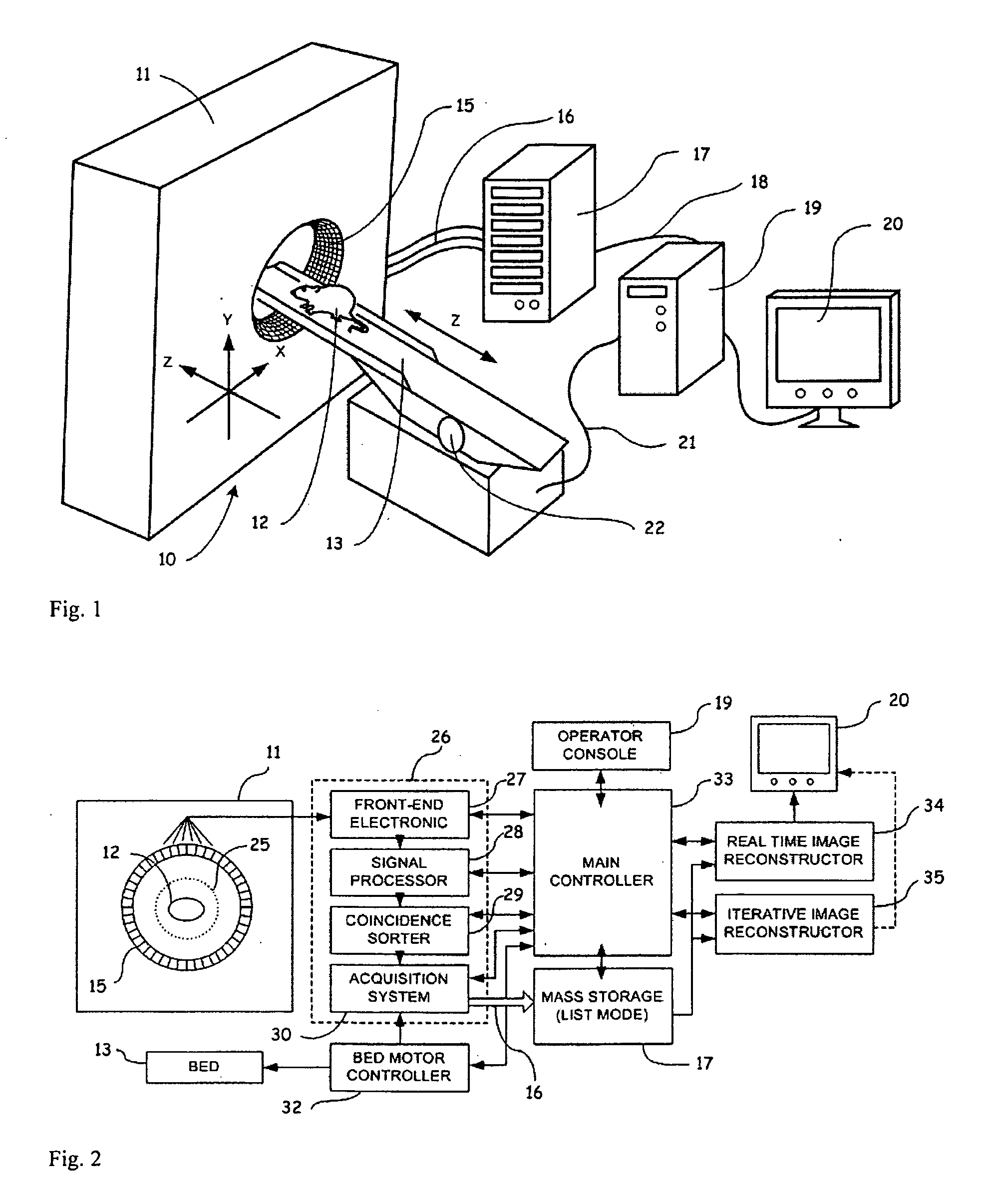
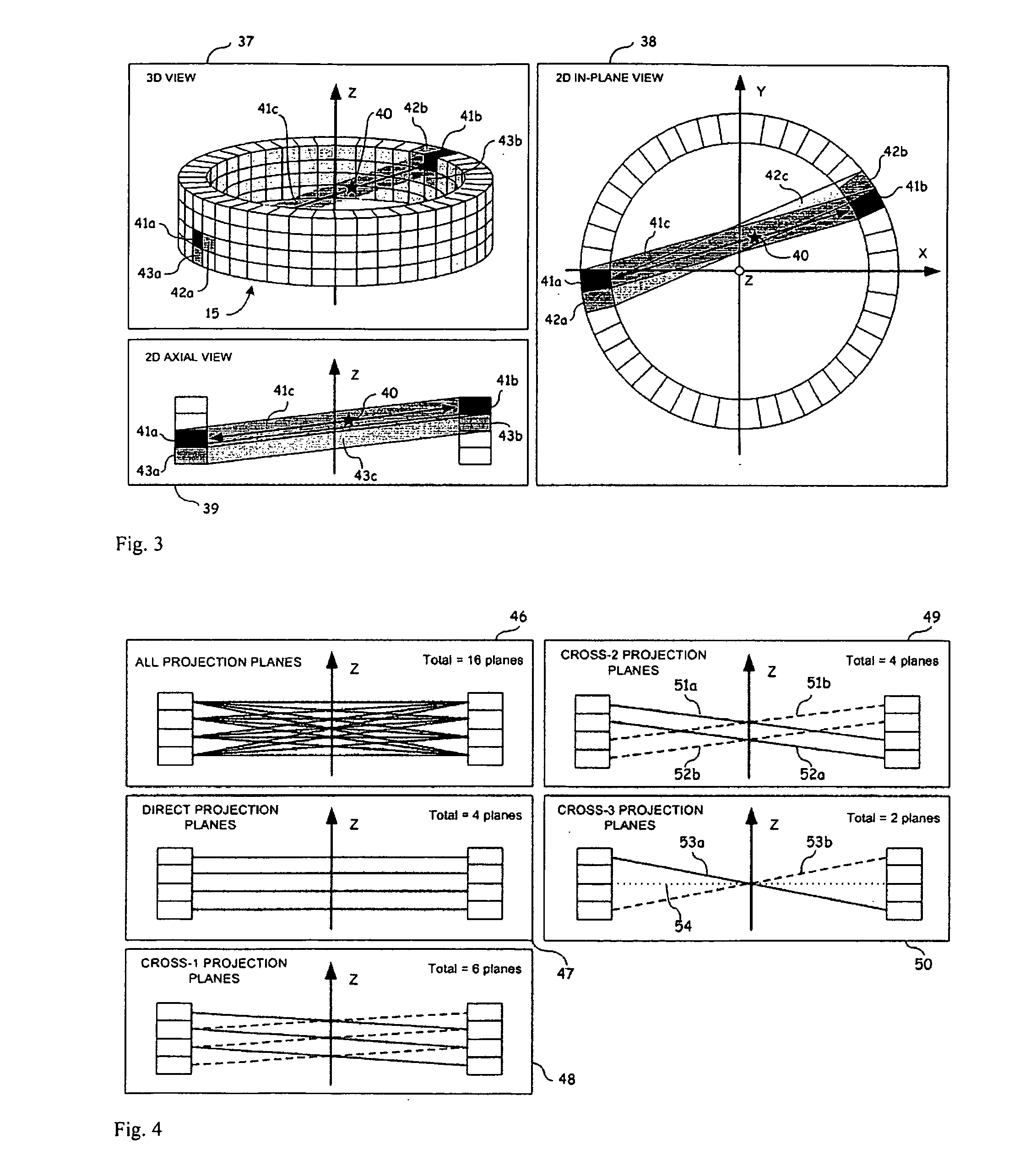
Image Reconstruction Methods Based on Block Circulant System Matrices
InactiveUS20090123048A1Minimized in sizeFast computerReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIn planeLines of response
An iterative image reconstruction method used with an imaging system that generates projection data, the method comprises: collecting the projection data; choosing a polar or cylindrical image definition comprising a polar or cylindrical grid representation and a number of basis functions positioned according to the polar or cylindrical grid so that the number of basis functions at different radius positions of the polar or cylindrical image grid is a factor of a number of in-plane symmetries between lines of response along which the projection data are measured by the imaging system; obtaining a system probability matrix that relates each of the projection data to each basis function of the polar or cylindrical image definition; restructuring the system probability matrix into a block circulant matrix and converting the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; storing the projection data into a measurement data vector; providing an initial polar or cylindrical image estimate; for each iteration; recalculating the polar or cylindrical image estimate according to an iterative solver based on forward and back projection operations with the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; and converting the polar or cylindrical image estimate into a Cartesian image representation to thereby obtain a reconstructed image.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
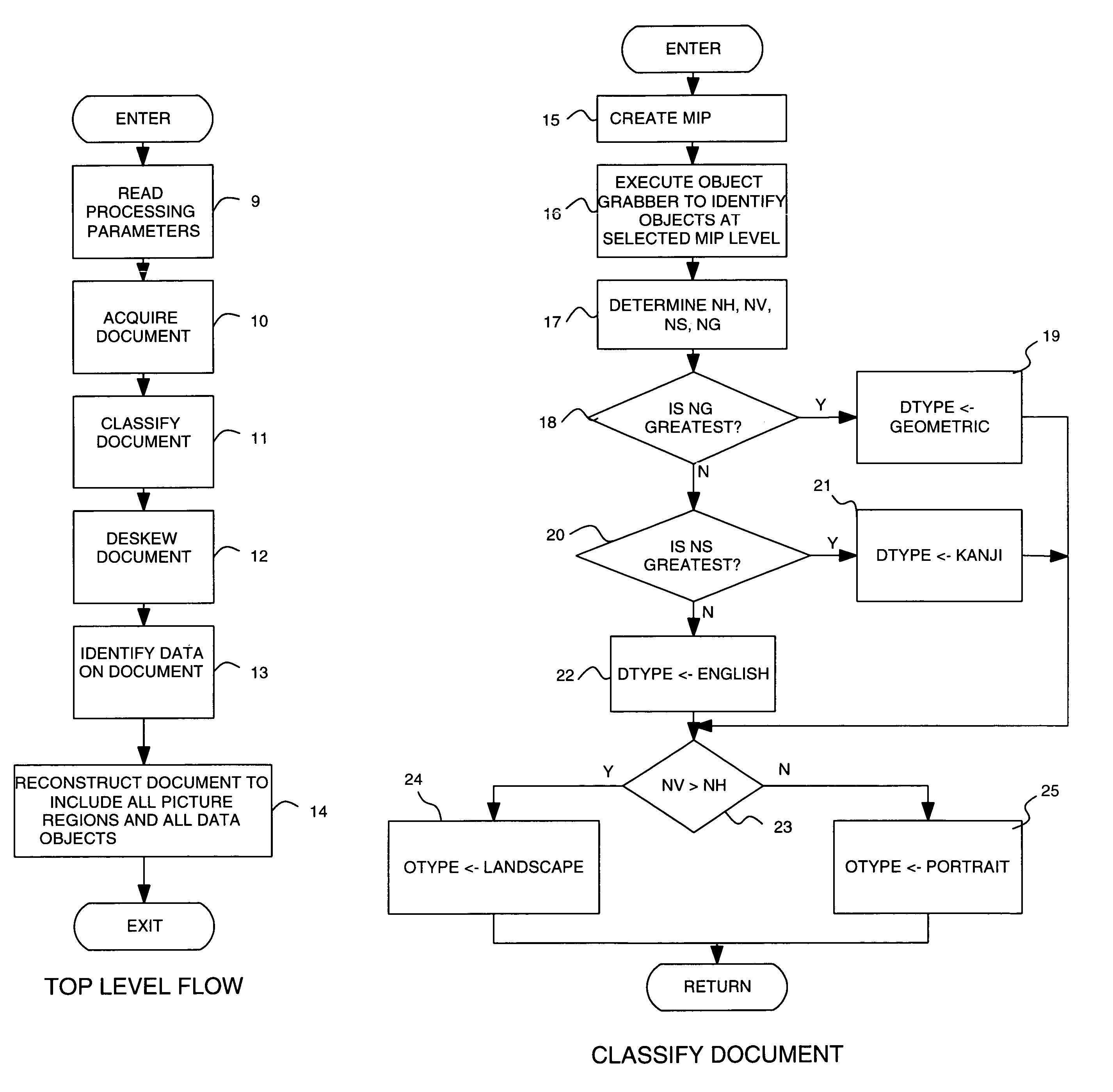
Method and apparatus for automatic cleaning and enhancing of scanned documents
InactiveUS7016536B1Fast informationFast noiseImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionDocument preparation
A method and apparatus are provided for removing noise from a first digital representation of data images and noise images of a document, including digitally scanning the document so as to produce the first digital representation of all the images of the document, including the data images and the noise images. After de-skewing the image representation, objects are built from a reduced-resolution representation of the scanned representation. Objects identified as picture objects are included in a mask which is logically ANDed with the de-skewed representation of the scanned document. All objects are added to an object list and initially marked as noise. Objects identified as text objects or geometric objects are marked as data objects. Objects identified as picture objects are included in a mask which is logically ANDed with the de-skewed representation to eliminate all other objects. Objects marked as data objects are added to that representation to provide the de-skewed, de-speckled representation of the scanned document.
Owner:GTX EURO LTD
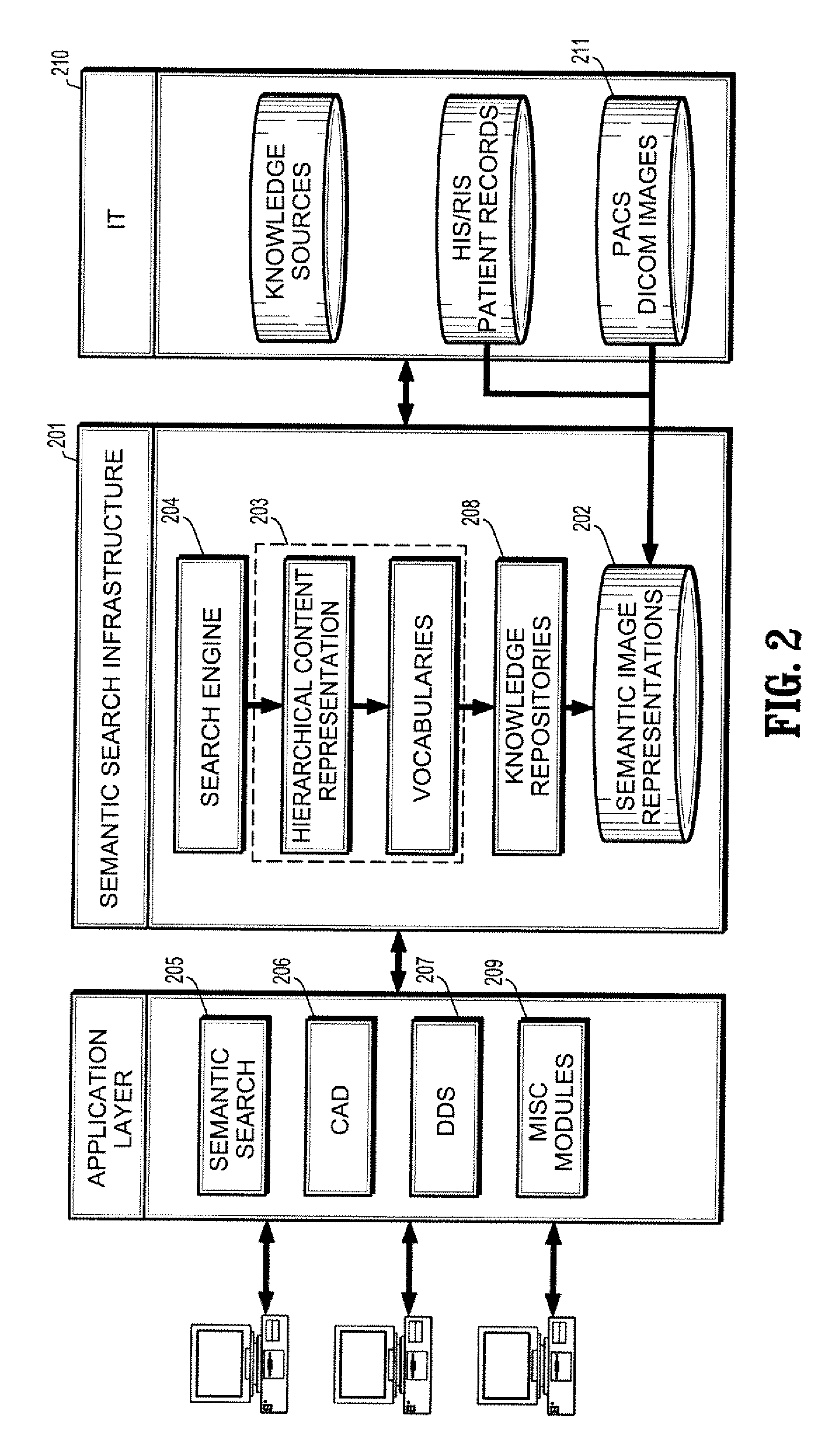
Scalable Semantic Image Search
InactiveUS20080027917A1Digital data information retrievalKnowledge representationSemantic searchSyntax
A computer-implemented system for searching a plurality of images for an image of interest including a database of semantic image representations corresponding to the plurality of images, wherein the semantic image representations link a semantic model of clinical properties, a syntactic model of high level image properties and an image vocabulary of low level image properties, a set of queries associated with the semantic image representations, and a semantic search engine, embodied as computer readable code executed by a processor, for receiving a search query, selecting at least one of the set of queries based on the search query, and searching the plurality of images for the image of interest by comparing the plurality of images against the semantic image representations associated with a selected query.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
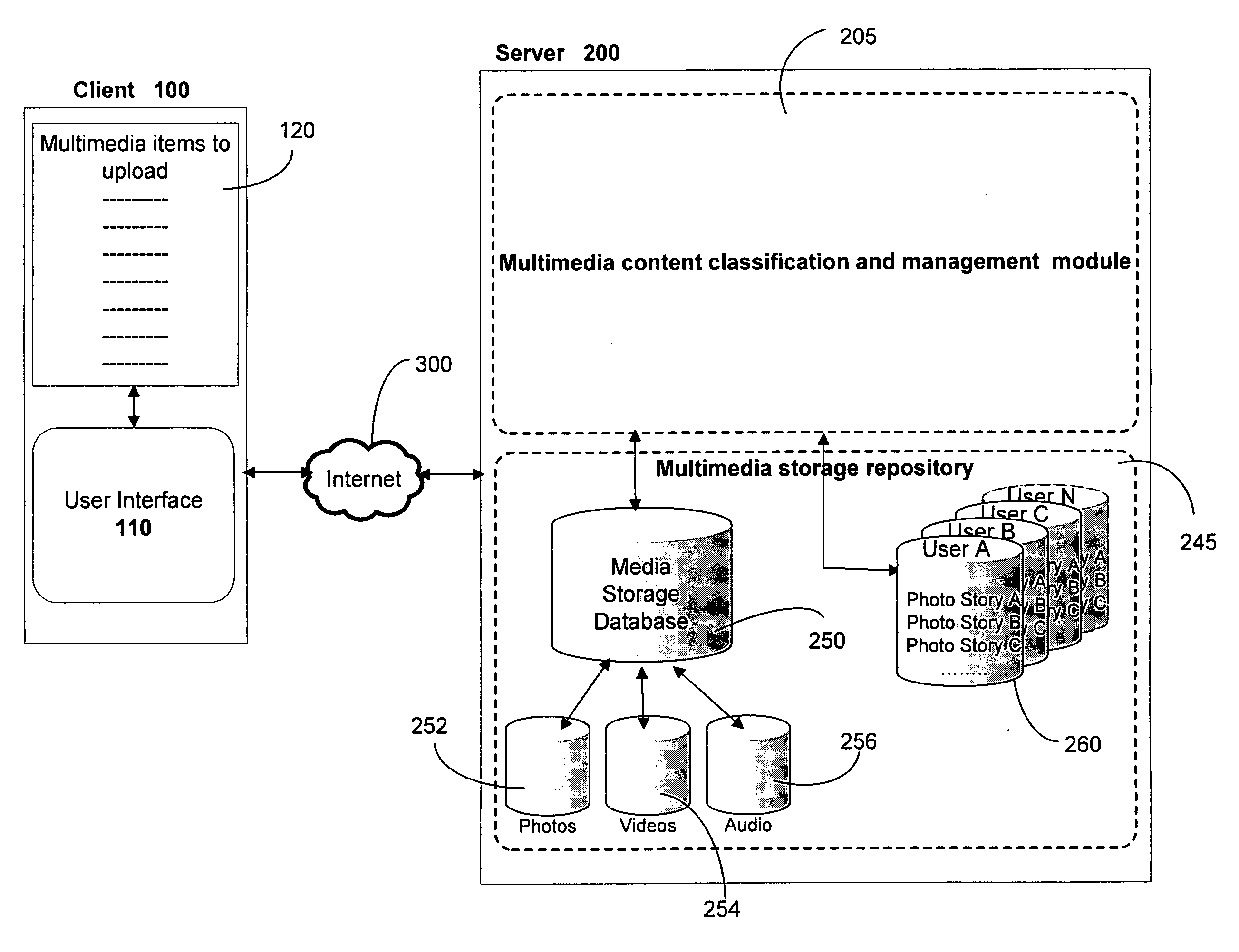
Context Aware Image Representation
ActiveUS20100332958A1More attentionGood flexibilityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsInformative contentContext based
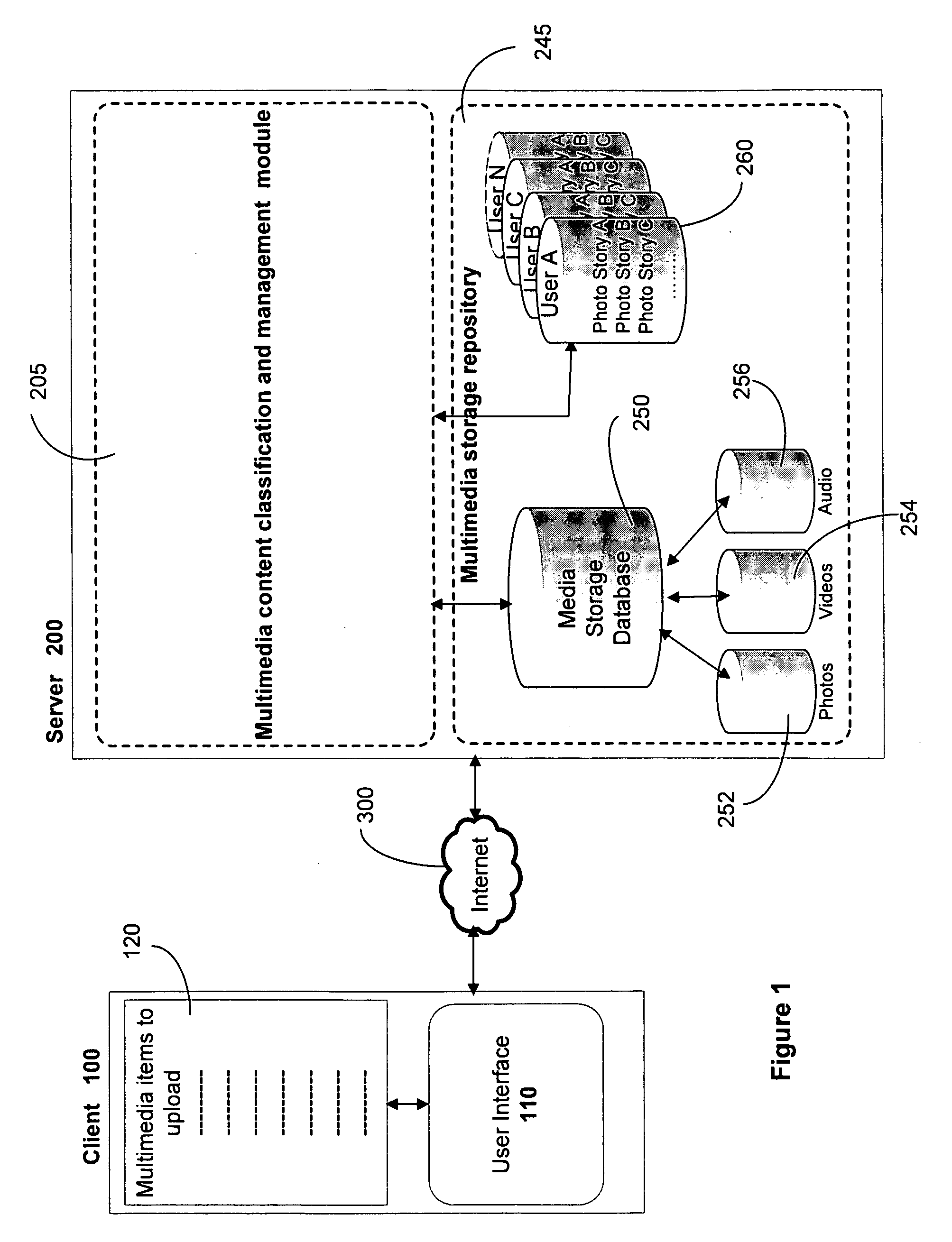
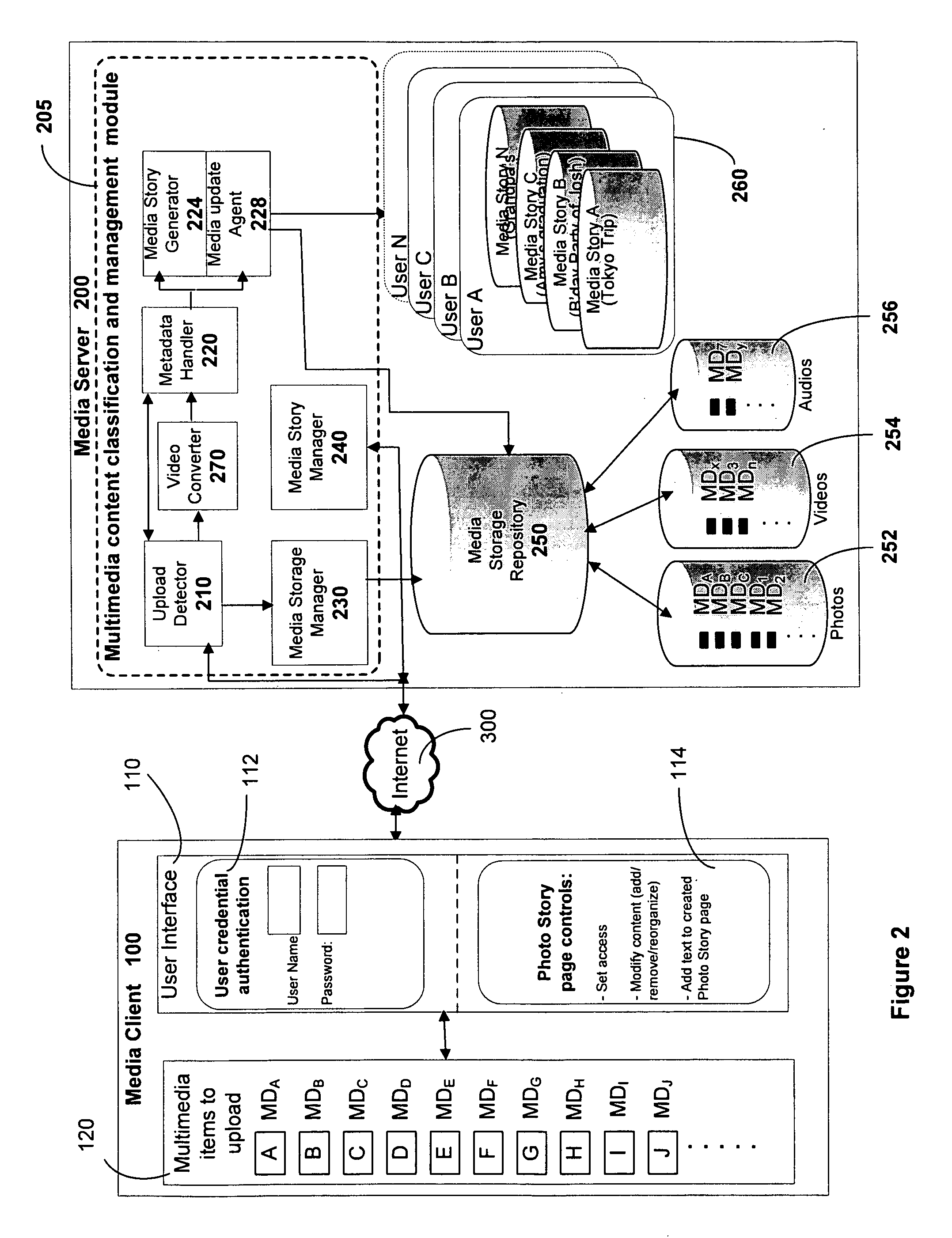
Methods and system for rendering context aware multimedia content include identifying a plurality of multimedia content that is uploaded for rendering. The uploaded multimedia content is examined to determine metadata associated with each of the plurality of multimedia contents. Contextual information associated with the metadata is identified and a grouping of the multimedia content into a plurality of groups is performed based on the contextual information. Each of the plurality of groups is then integrated into one or more photo stories. The photo stories are defined and rendered as content rich documents.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com