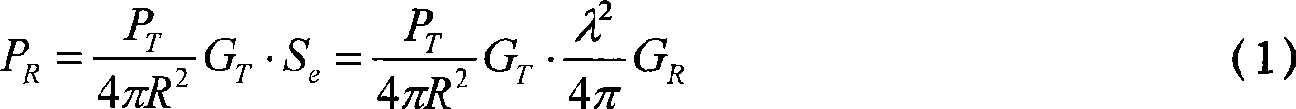Patents
Literature
1625 results about "Radiation field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
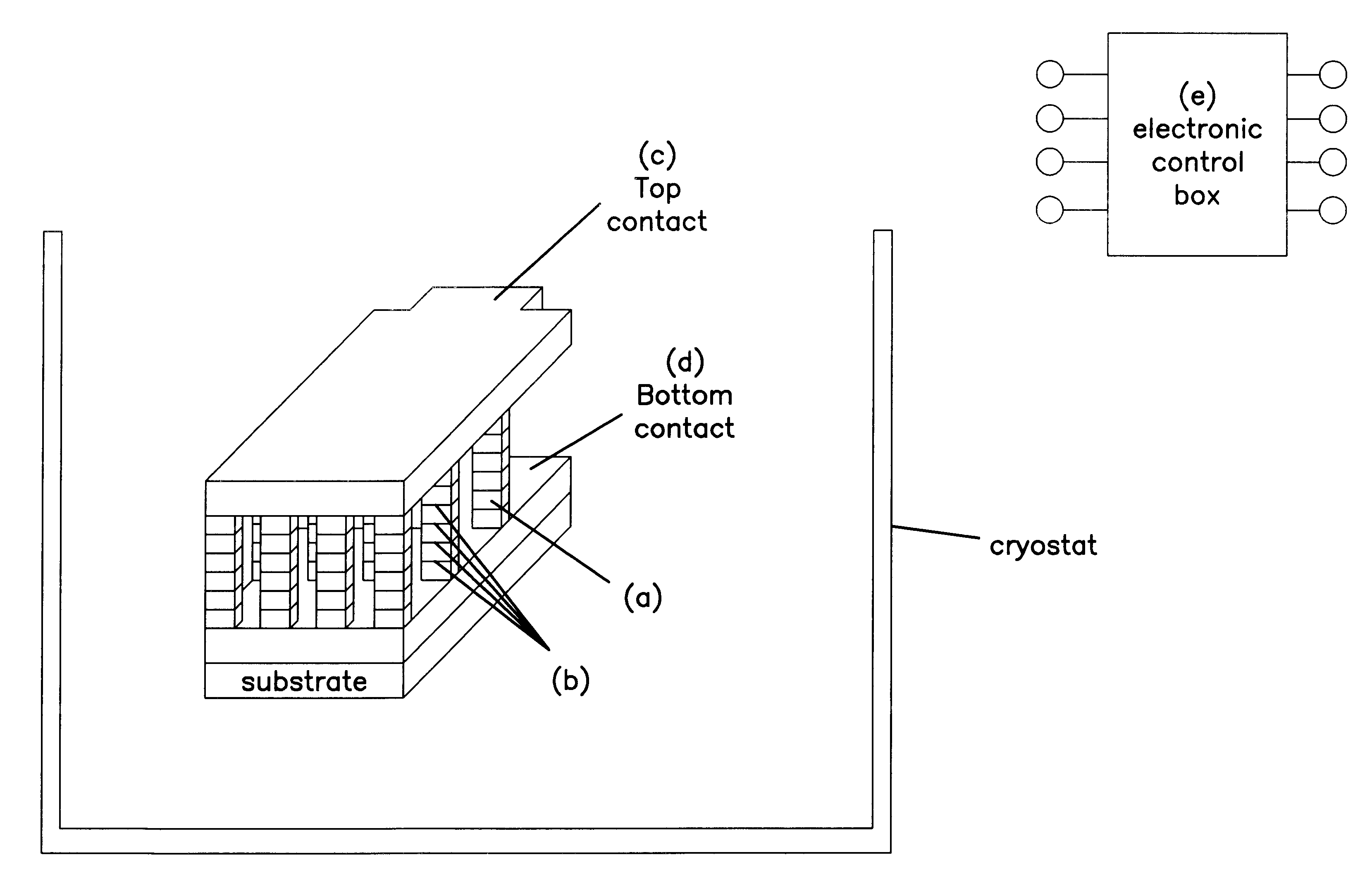
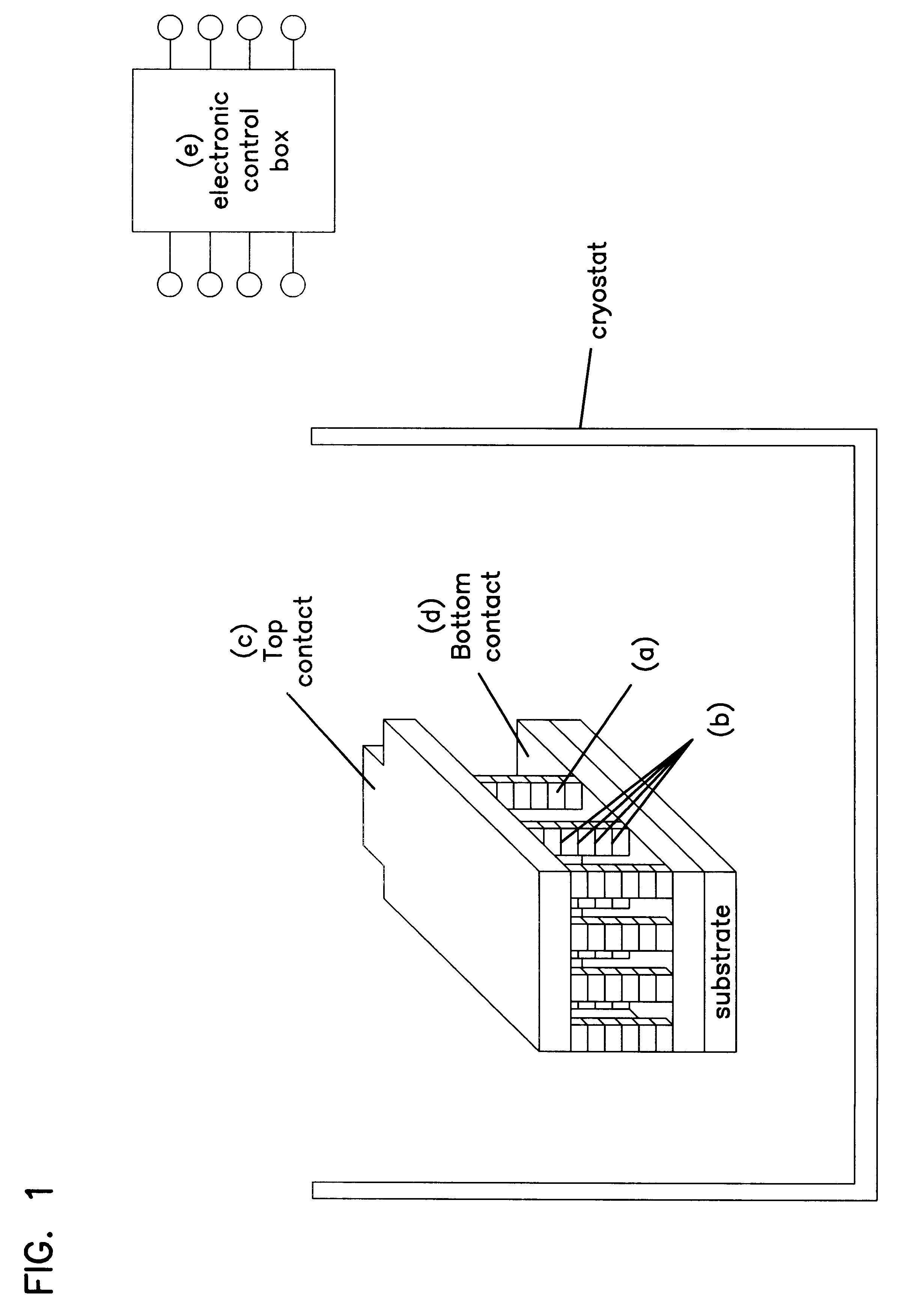
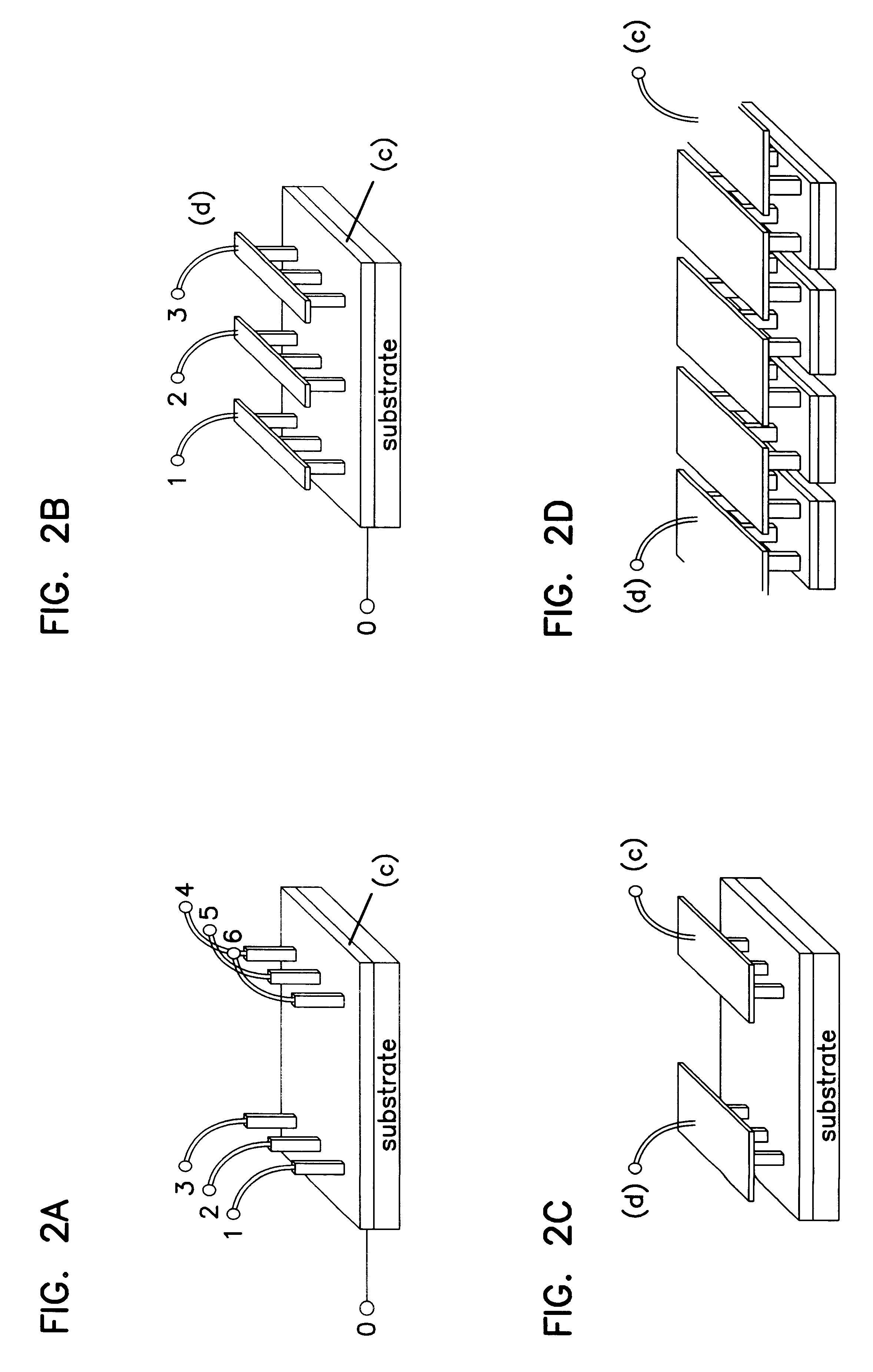
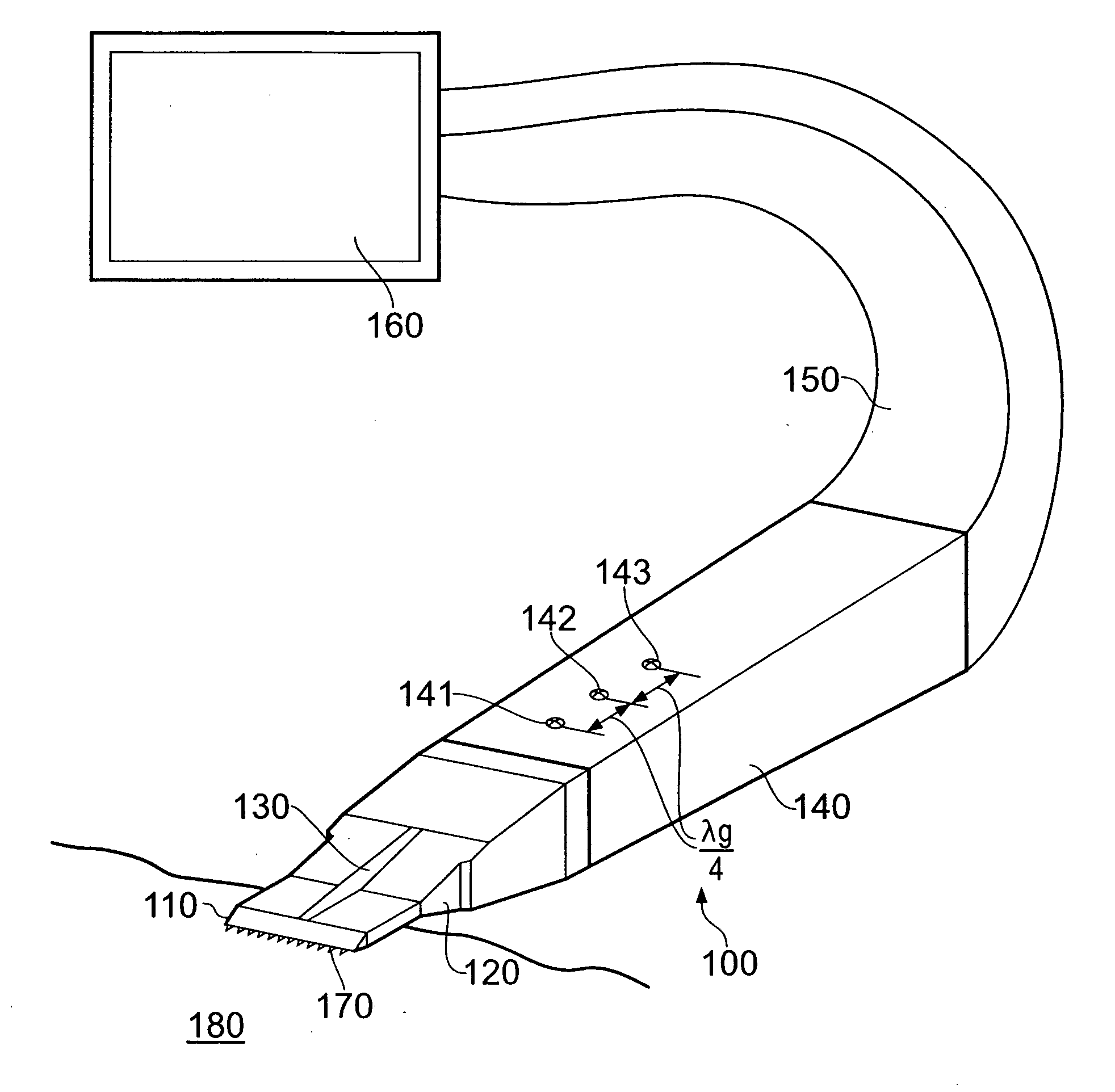
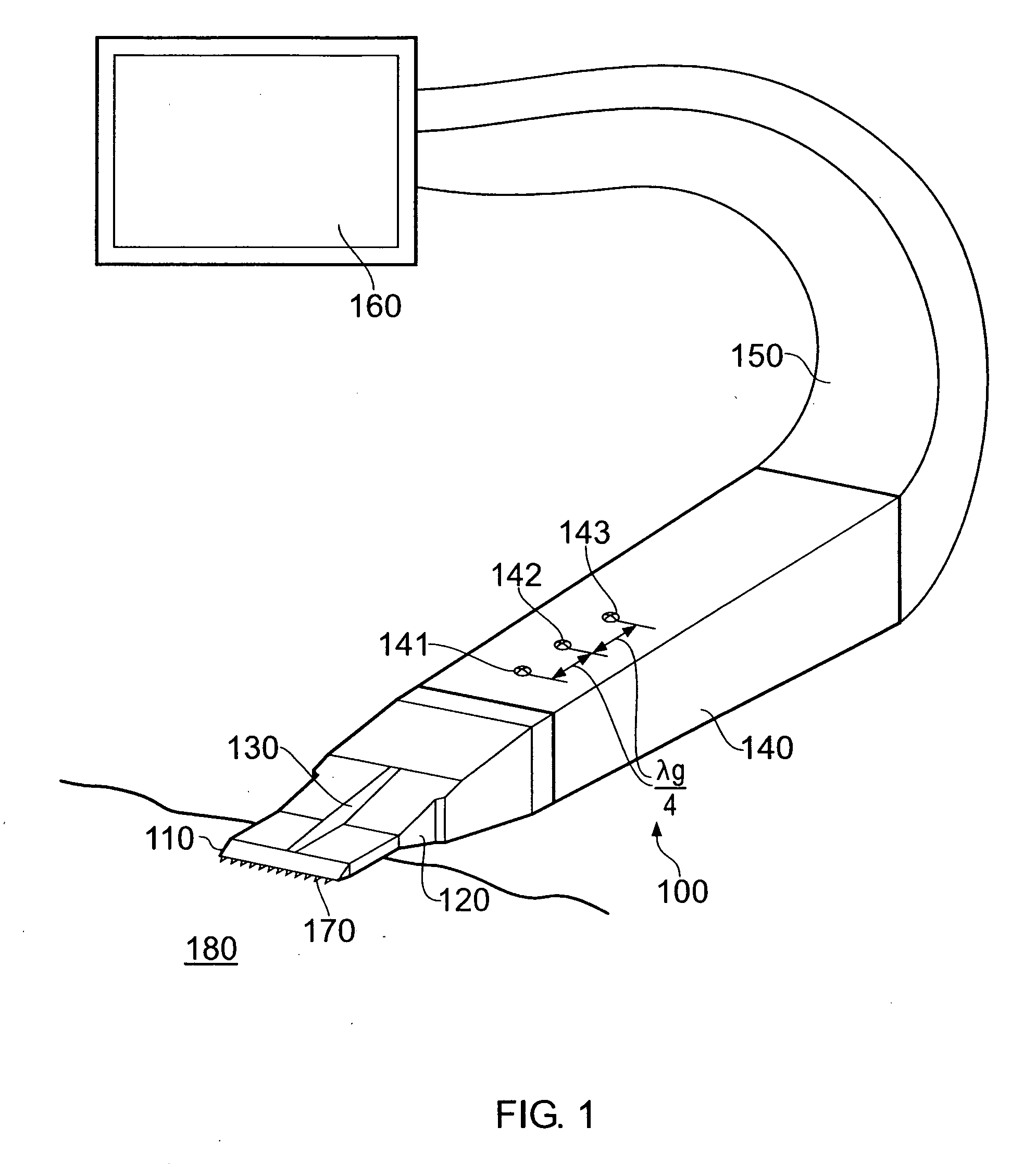
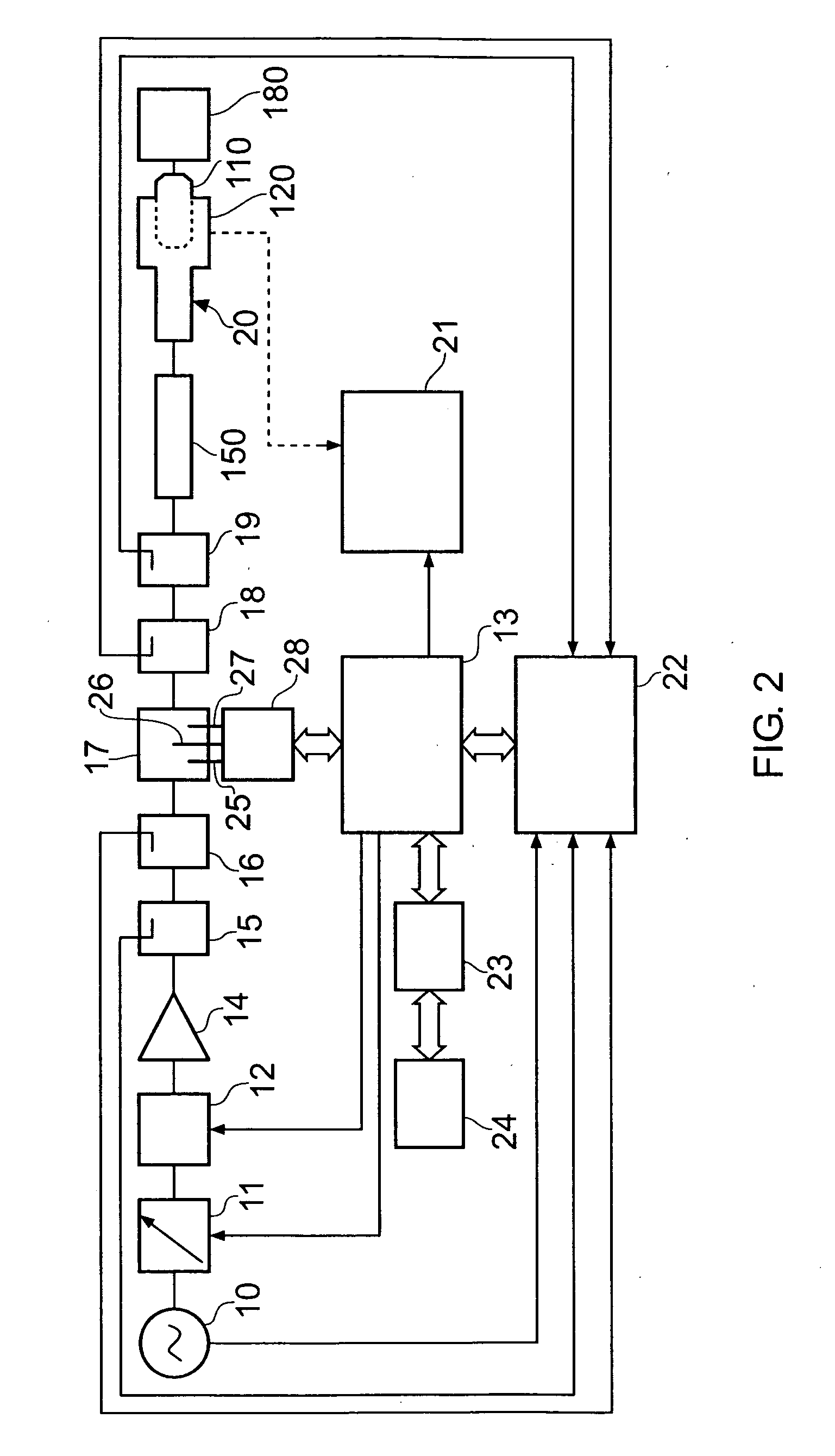
Method and apparatus for wireless powering and recharging
InactiveUS6127799ABatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingRf fieldMicrowave
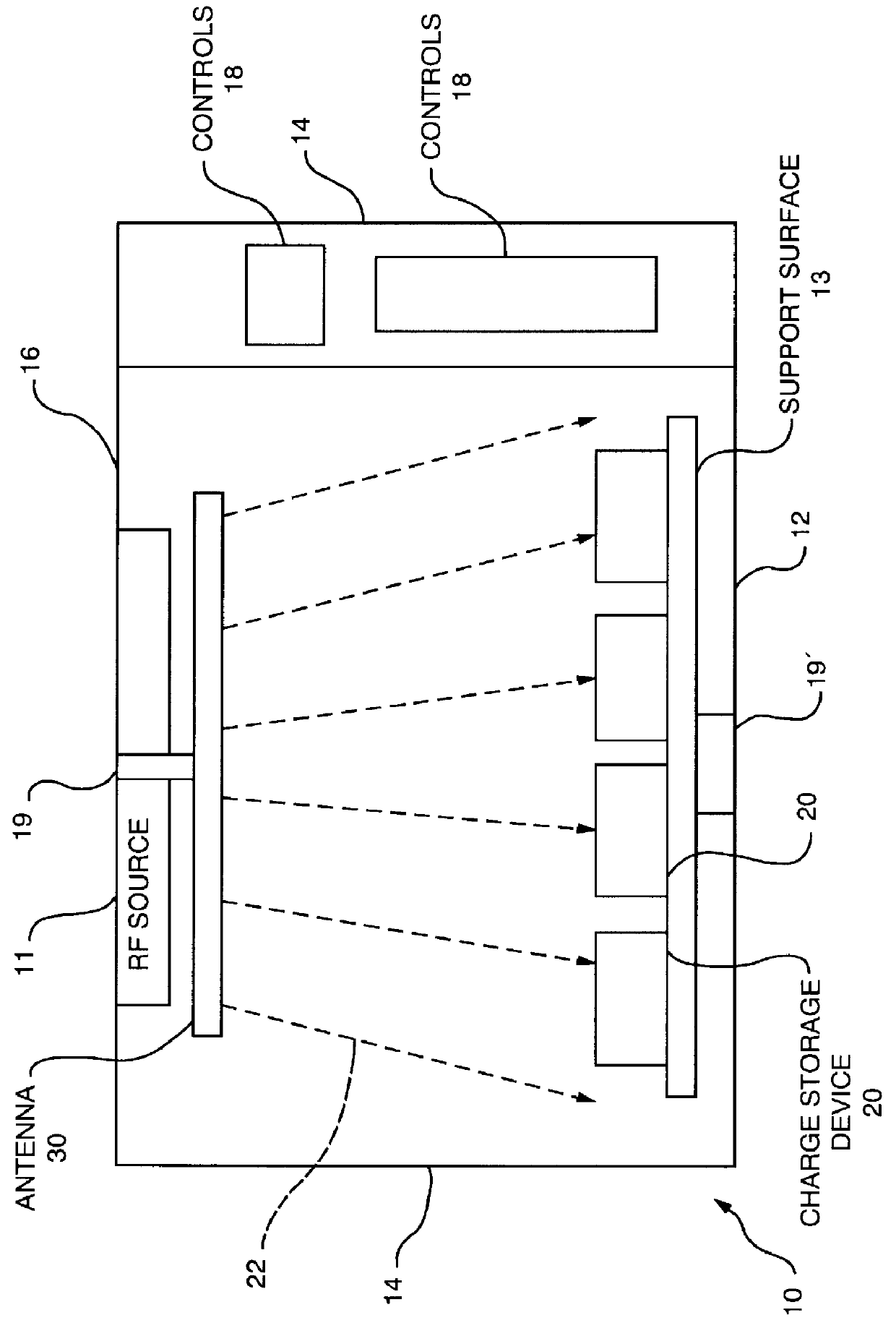
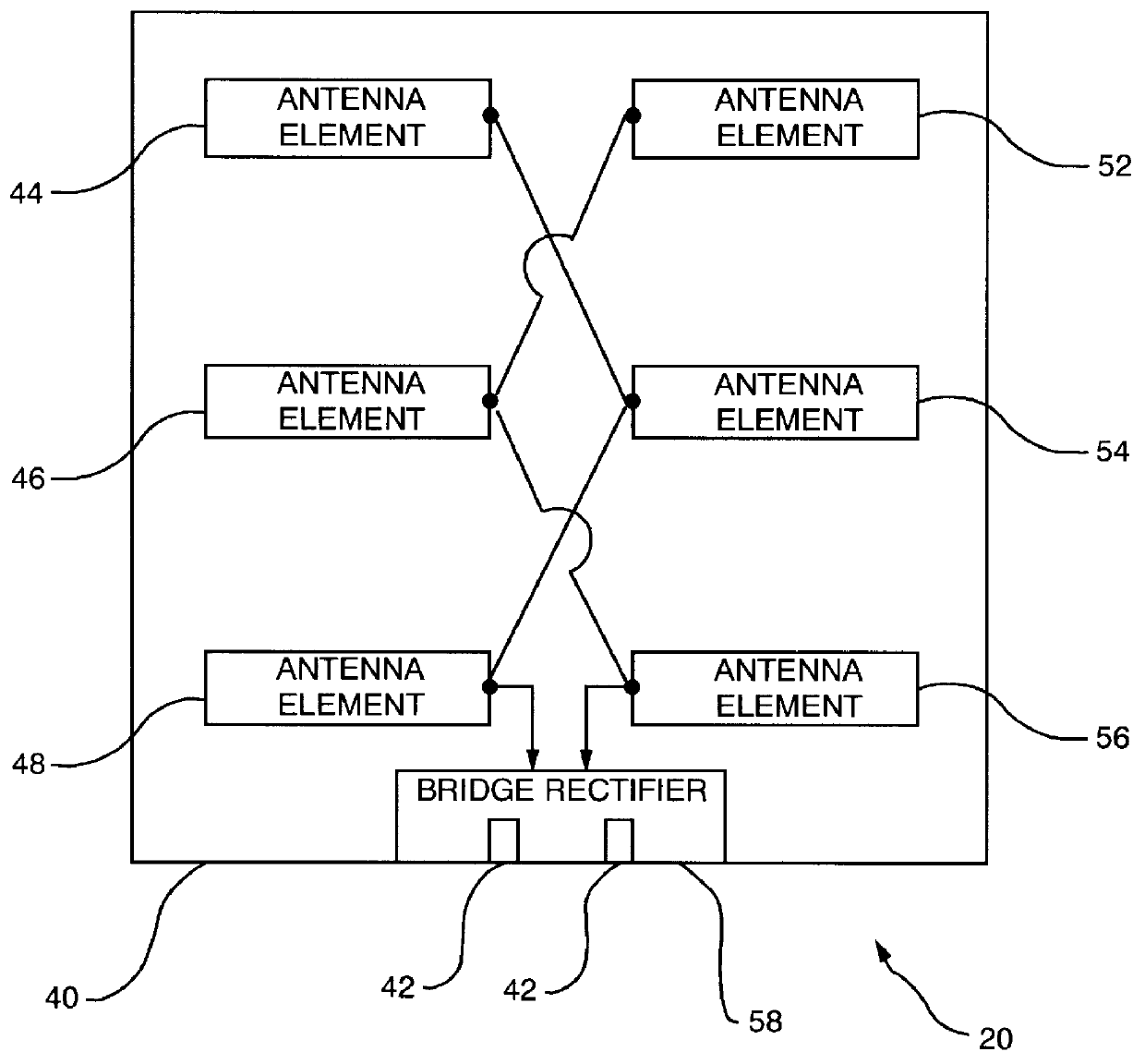
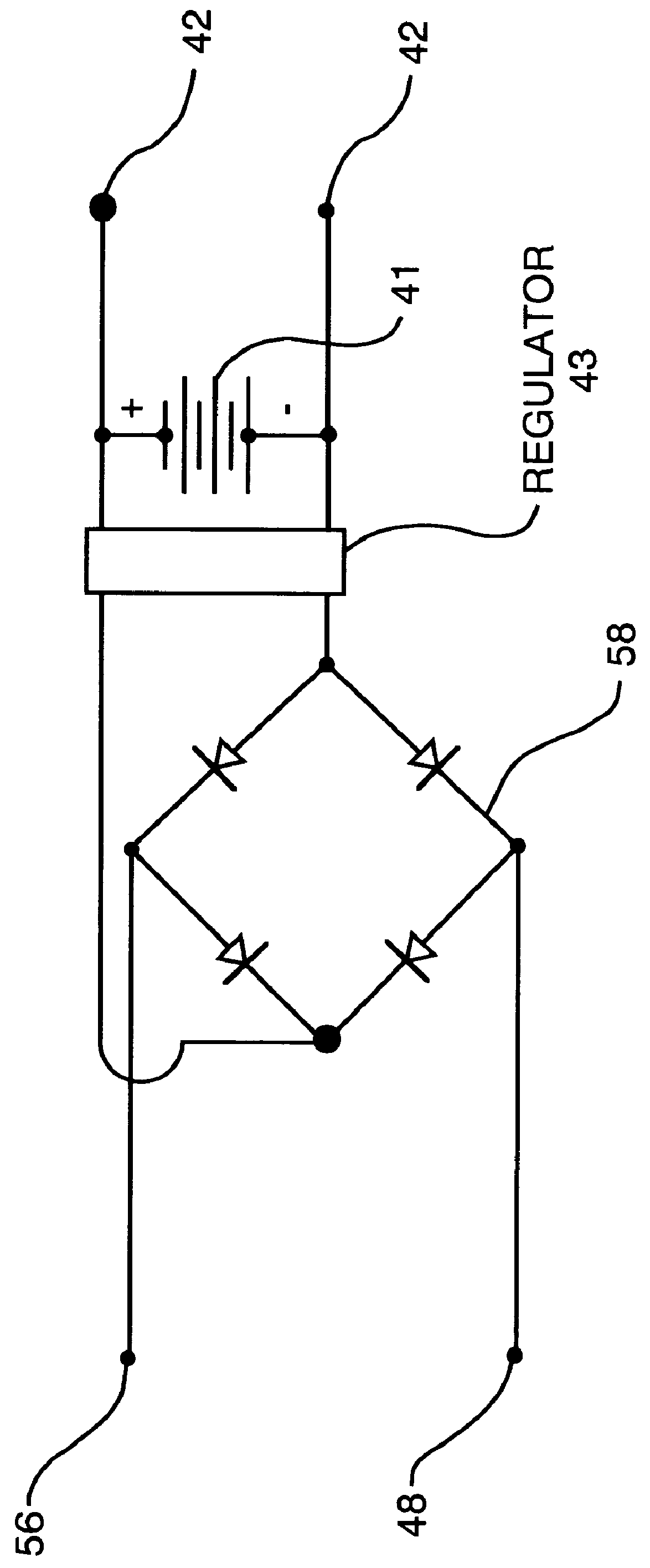
An arrangement is provided for charging a charge storage device by placing the charge storage device in an RF or microwave radiation field. One or more antennas which receive the radiated RF electromagnetic field are placed on the charge storage device. Rectifiers connected to the antennas rectify the received RF electromagnetic field an produce a DC output current which is used to charge the charge storage device. The charge storage device may be a battery or a capacitor and may form an integral part of an electronic device. The same RF field that charges the charge storage device can also be employed to communicate data to transponders which may be associated with computing devices.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Device and method for spatially resolved photodetection and demodulation of modulated electromagnetic waves
InactiveUS7060957B2Low lighting powerExtend integration timePrismsSolid-state devicesPulse radiationData acquisition
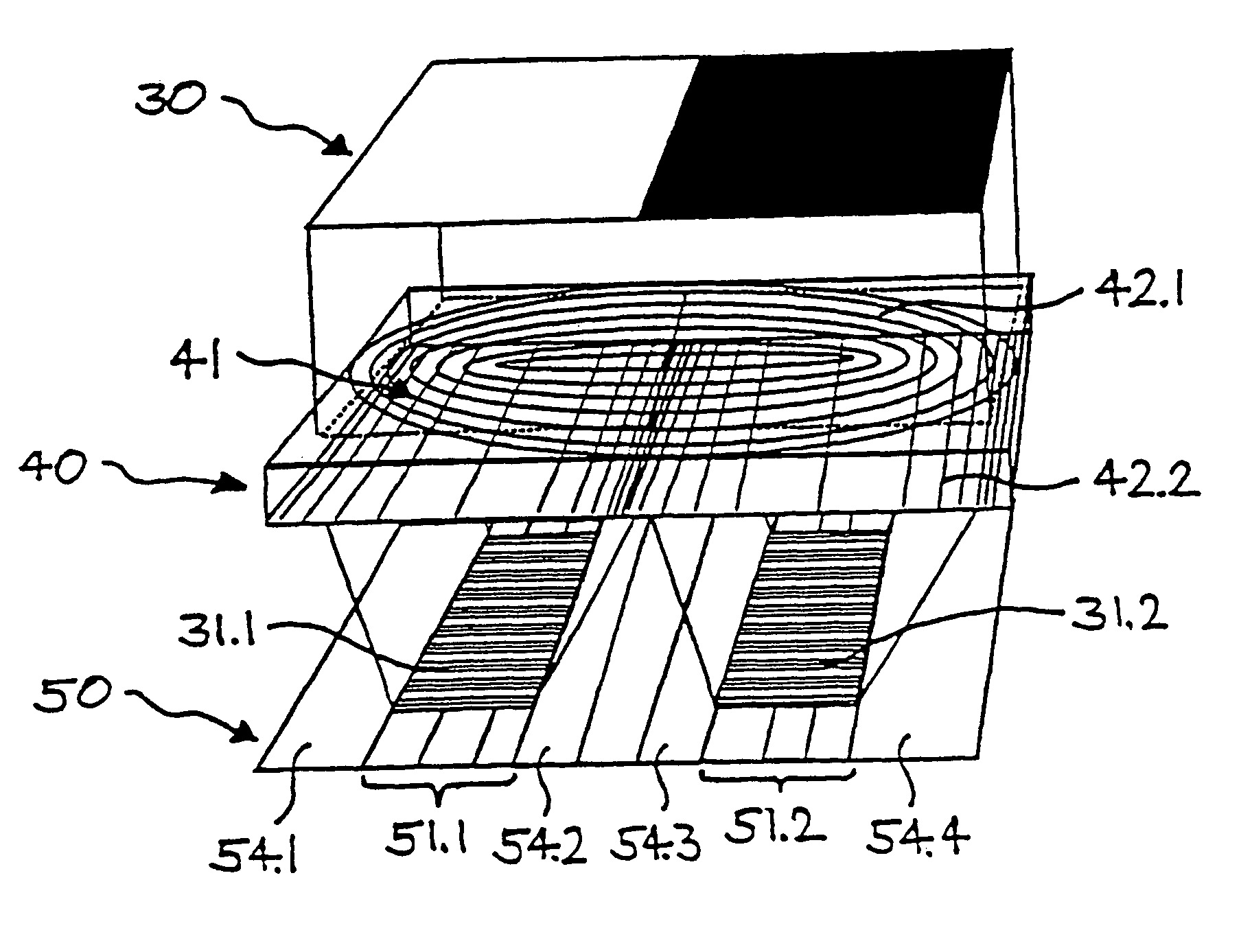
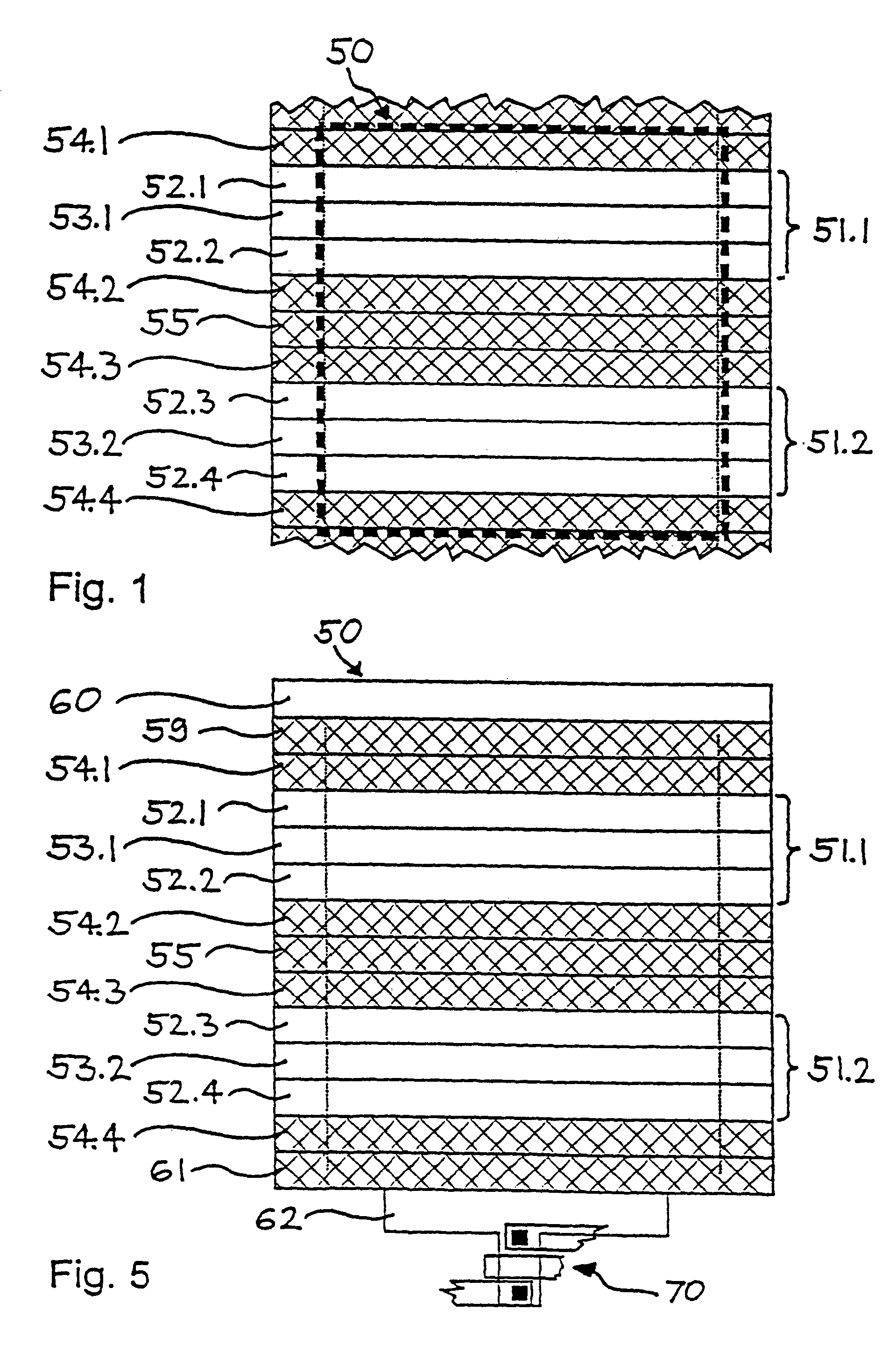
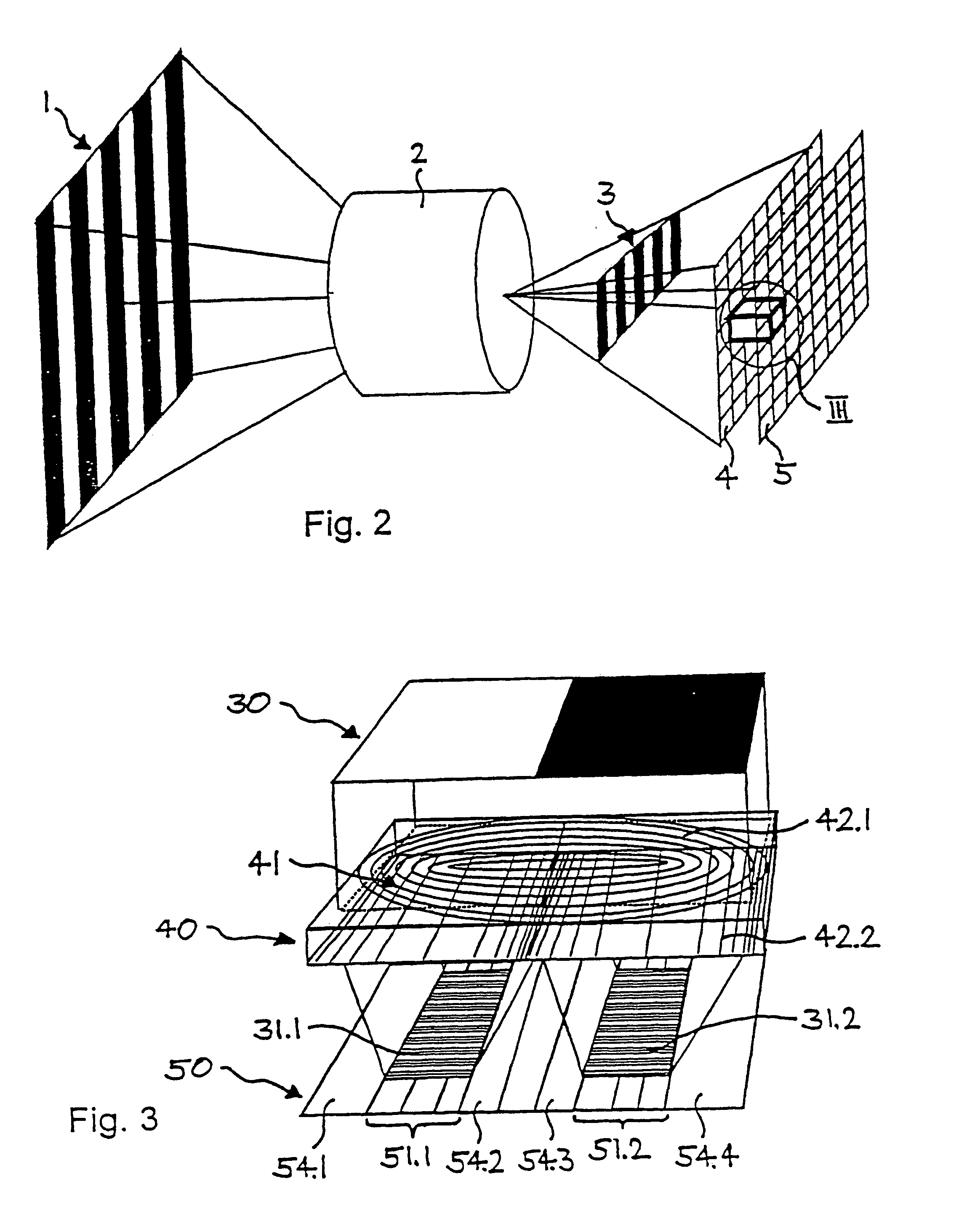
A device and method for spatially resolved photodetection and demodulation of temporally modulated electromagnetic waves makes it possible to measure phase, amplitude and offset of a temporally modulated, spatially coded radiation field. A micro-optical element (41) spatially averages a portion (30) of the scene and equally distributes the averaged intensity on two photo sites (51.1.51.2) close to each other. Adjacent to each of these photo sites (51.1) are two storage areas (54.1, 54.2) into which charge from the photo site can be moved quickly (with a speed of several MHz to several tens or even hundreds of MHz) and accumulated essentially free of noise. This is possible by employing the charge-coupled device (CCD) principle. The device combines a high optical fill factor, insensitivity to offset errors, high sensitivity even with little light, simultaneous data acquisition, small pixel size, and maximum efficiency in use of available signal photons for sinusoidal as well as pulsed radiation signals. The device and method may be used in a time-of-flight (TOF) range imaging system without moving parts, offering 2D or 3D range data.
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Nanodosimeter based on single ion detection
InactiveUS7081619B2Time-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFluenceDosimeter
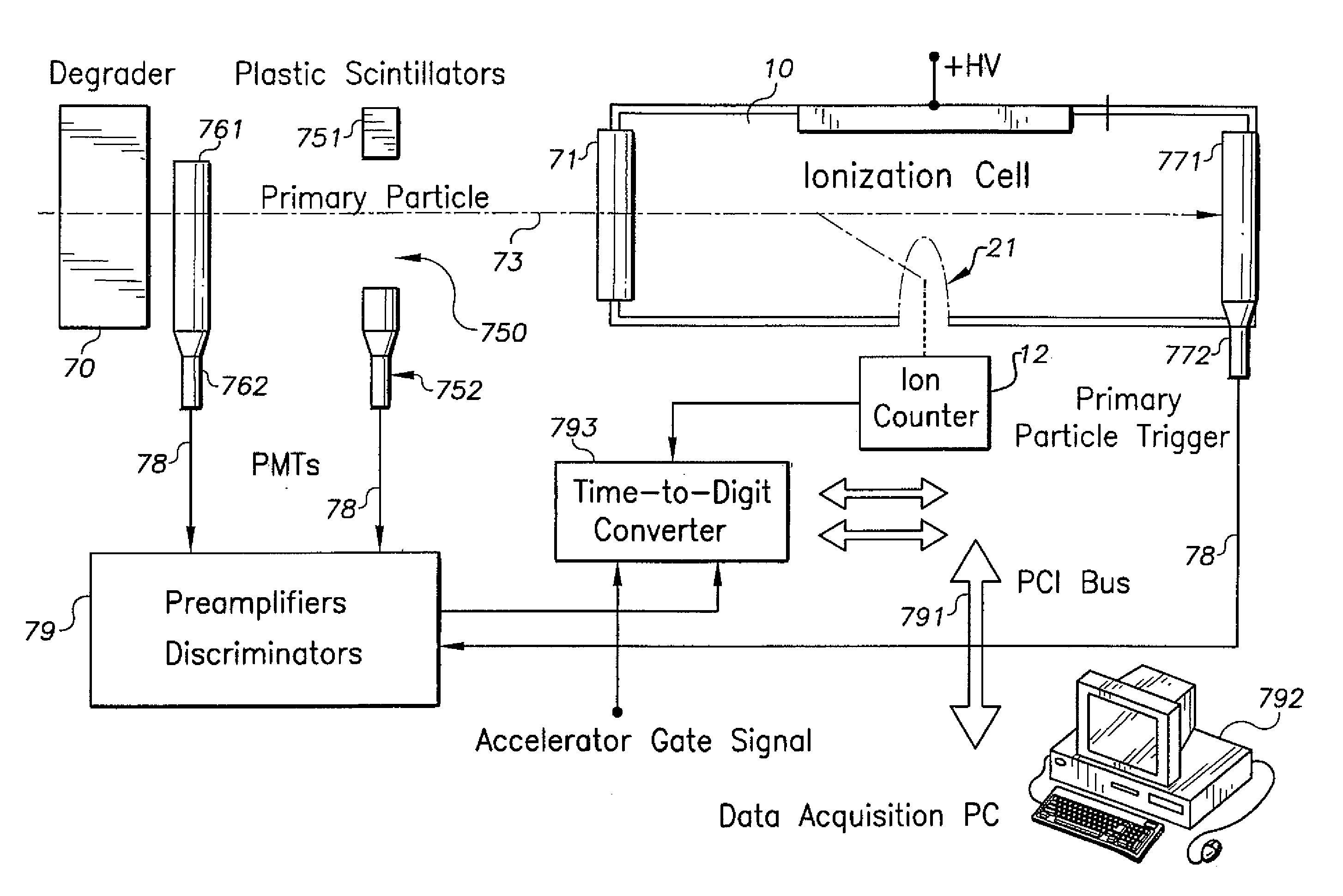
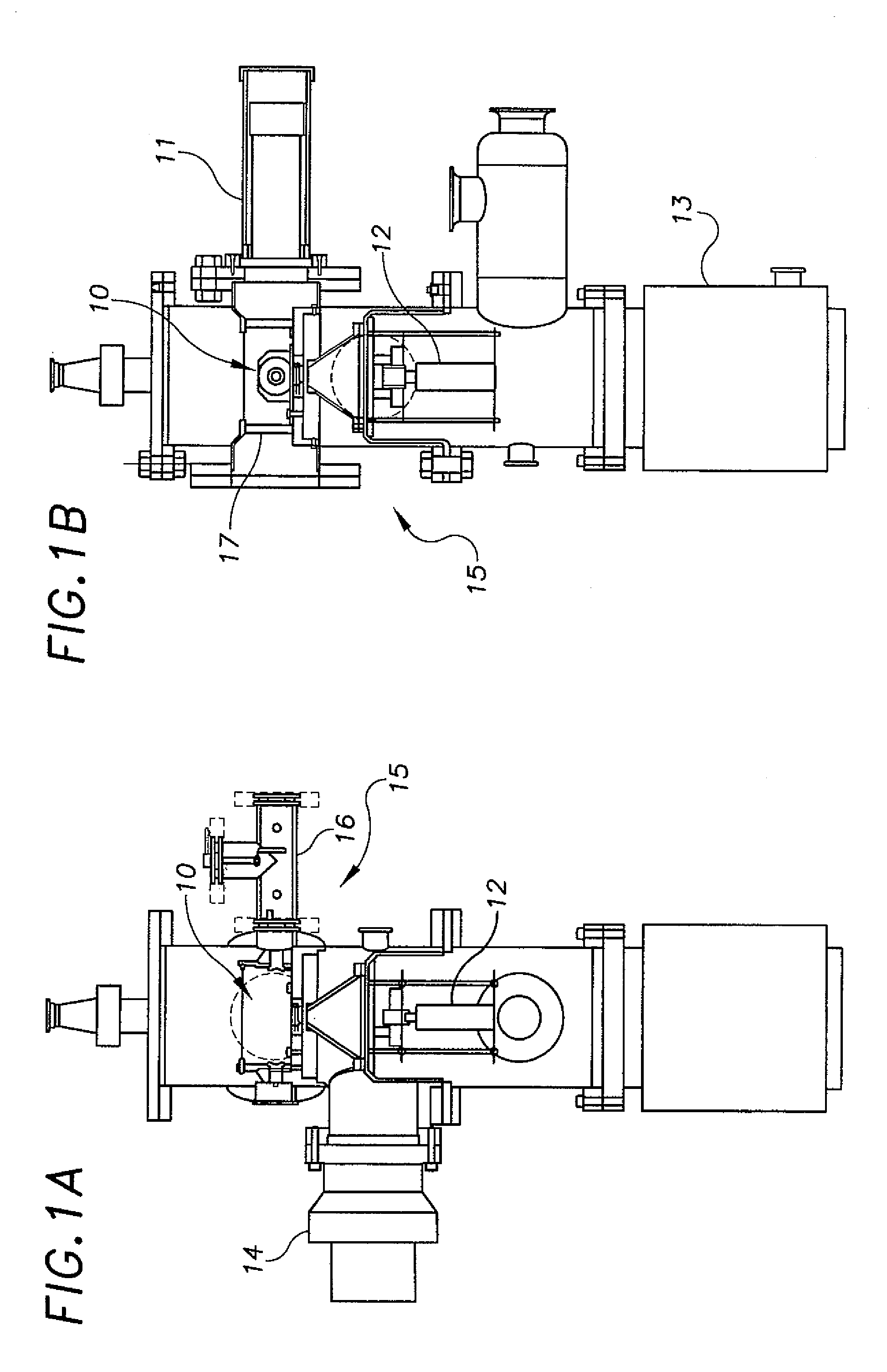
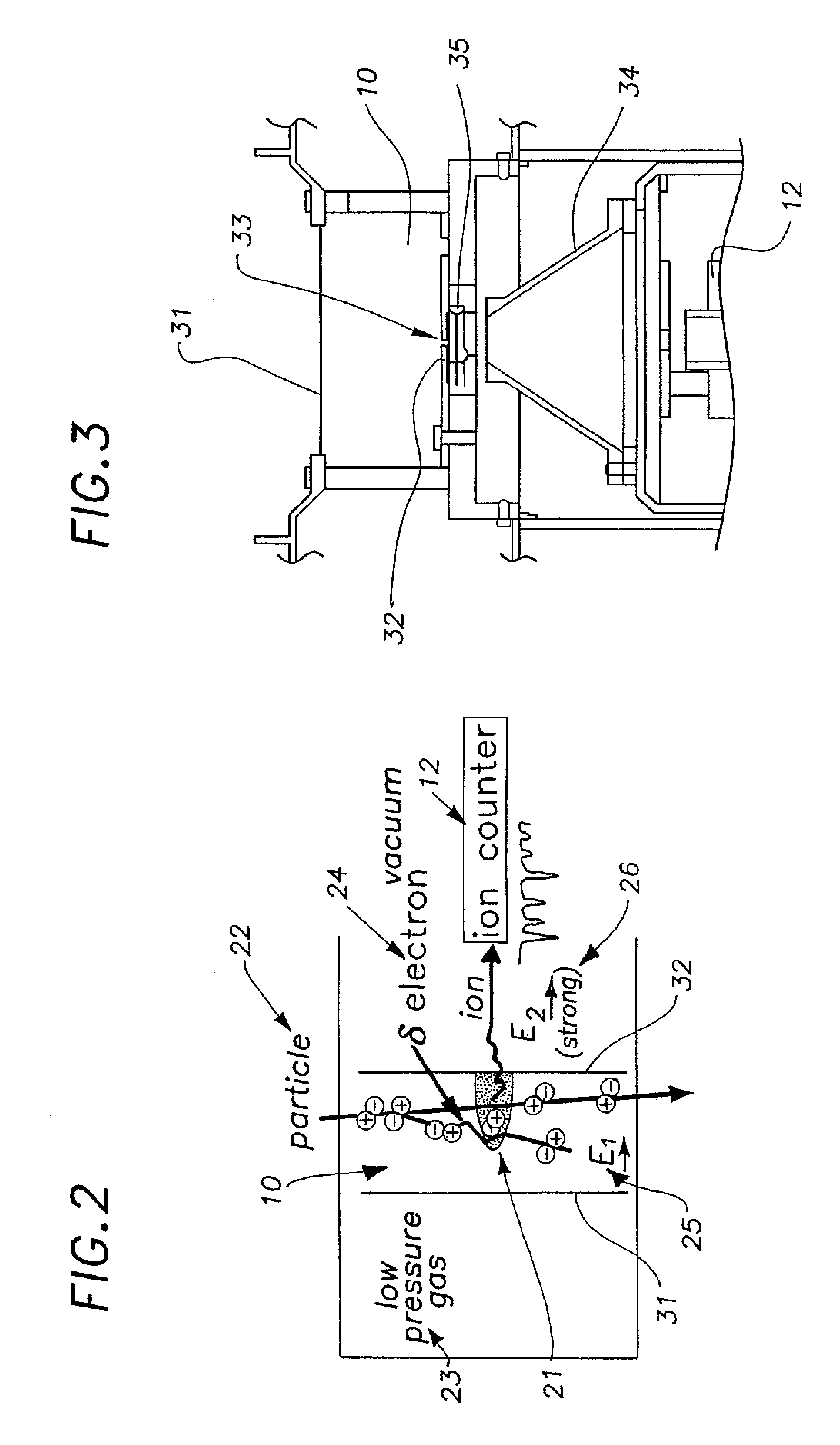
A nanodosimeter device (15) for detecting positive ions induced in a sensitive gas volume by a radiation field of primary particle, comprising an ionization chamber (10) for holding the sensitive gas volume to be irradiated by the radiation field of primary particles; an ion counter system connected to the ionization chamber (10) for detecting the positive ions which pass through the aperture opening and arrive at the ion counter (12) at an arrival time; a particle tracking system for position-sensitive detection of the primary particles passing through the sensitive gas volume; and a data acquisition system capable of coordinating the readout of all data signals and of performing data analysis correlating the arrival time of the positive ions detected by the ion counter system relative to the position sensitive data of primary particles detected by the particle tracking system. The invention further includes the use of the nanodosimeter for method of calibrating radiation exposure with damage to a nucleic acid within a sample. A volume of tissue-equivalent gas is radiated with a radiation field to induce positive ions. The resulting positive ions are measured and compared with a determination of presence or extent of damage resulting from irradiating a nucleic acid sample with an equivalent dose of radiation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY +1
Architecture and method of coupling electromagnetic energy to thermal detectors
InactiveUS6329655B1Antenna supports/mountingsSolid-state devicesSensing applicationsElectromagnetic shielding
A radiation sensor. The inventive sensor has a two-level detector structure formed on a substrate in which a thermal detector element is suspended over the substrate as a microbridge structure. A receiver of electromagnetic radiation is provided on the same side of the substrate in a manner that efficiently couples the radiation field to the thermal detector element. The thermal detector element has a sandwich structure including a heater metal layer, a dielectric layer, and a thin film thermo-resistive material. The thermal detector element is suspended out of physical contact with the receiver. In one embodiment, the receiver is an antenna having a crossed bowtie configuration that efficiently couples the radiation field to the detector element. The inventive radiation sensors are especially useful for mm-wave and microwave sensing applications. The sensor can be used individually or in linear or two-dimensional arrays thereof. The invention also is directed to a method of fabricating such a radiation sensor.
Owner:HRL LAB +1
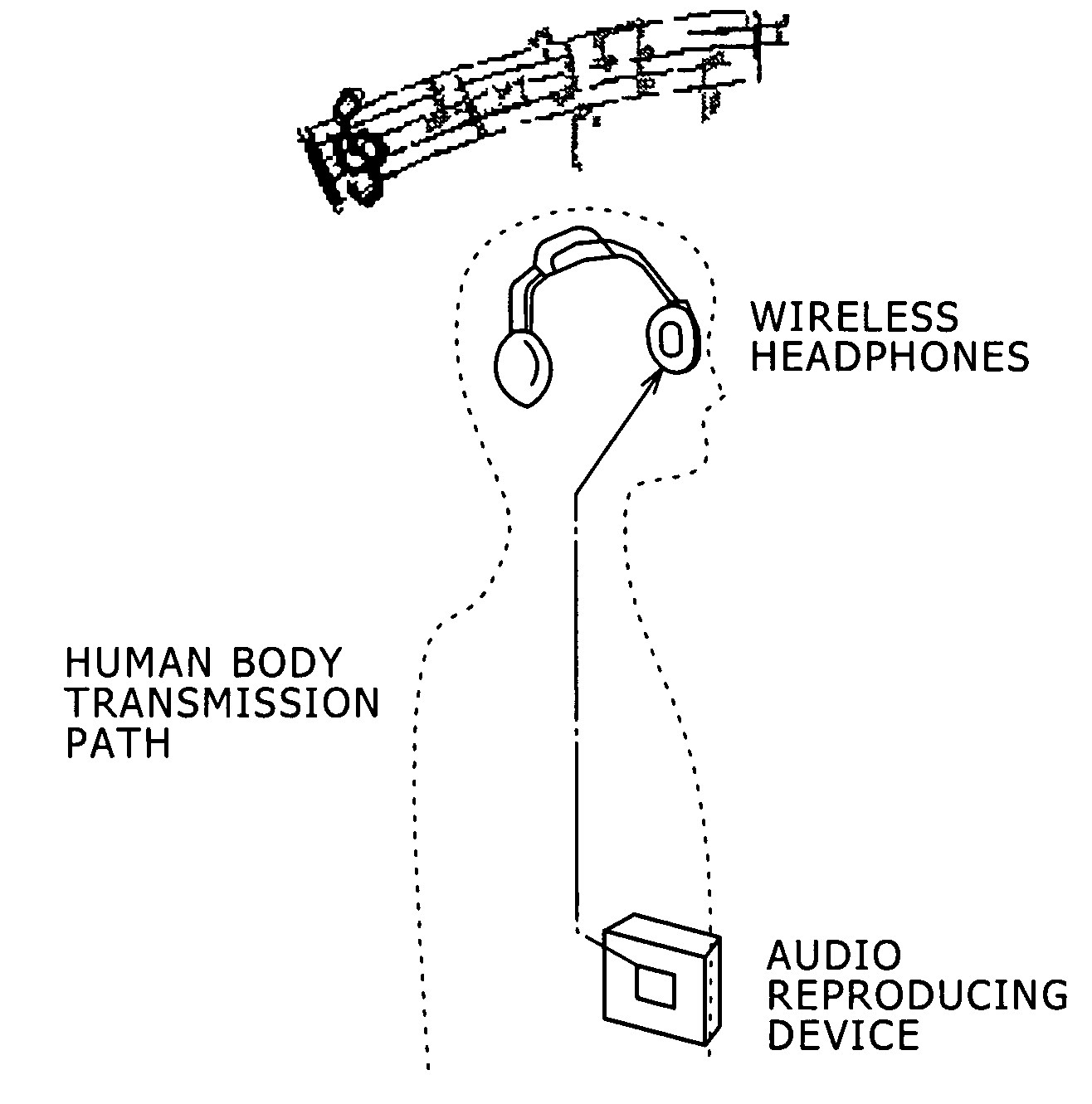
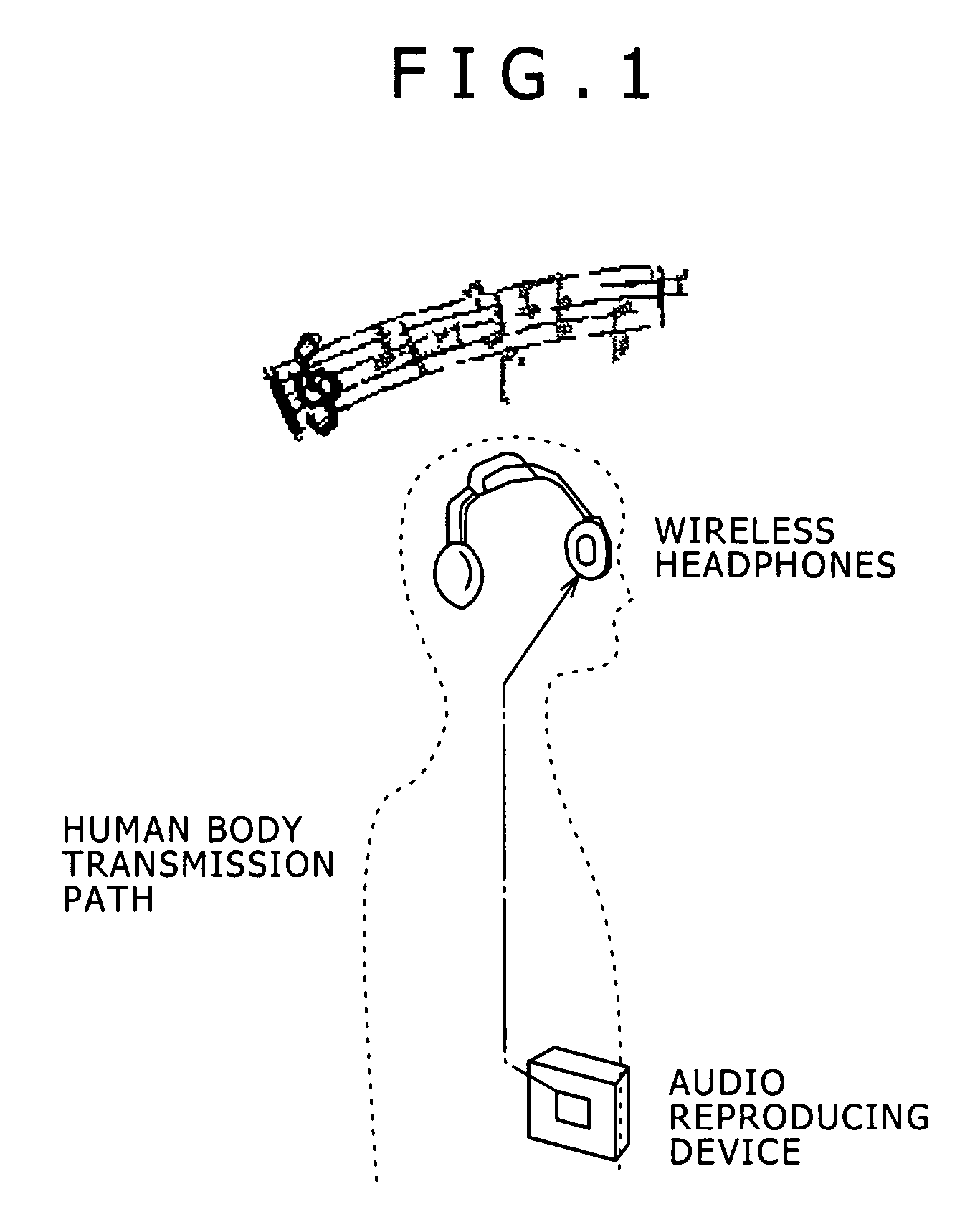
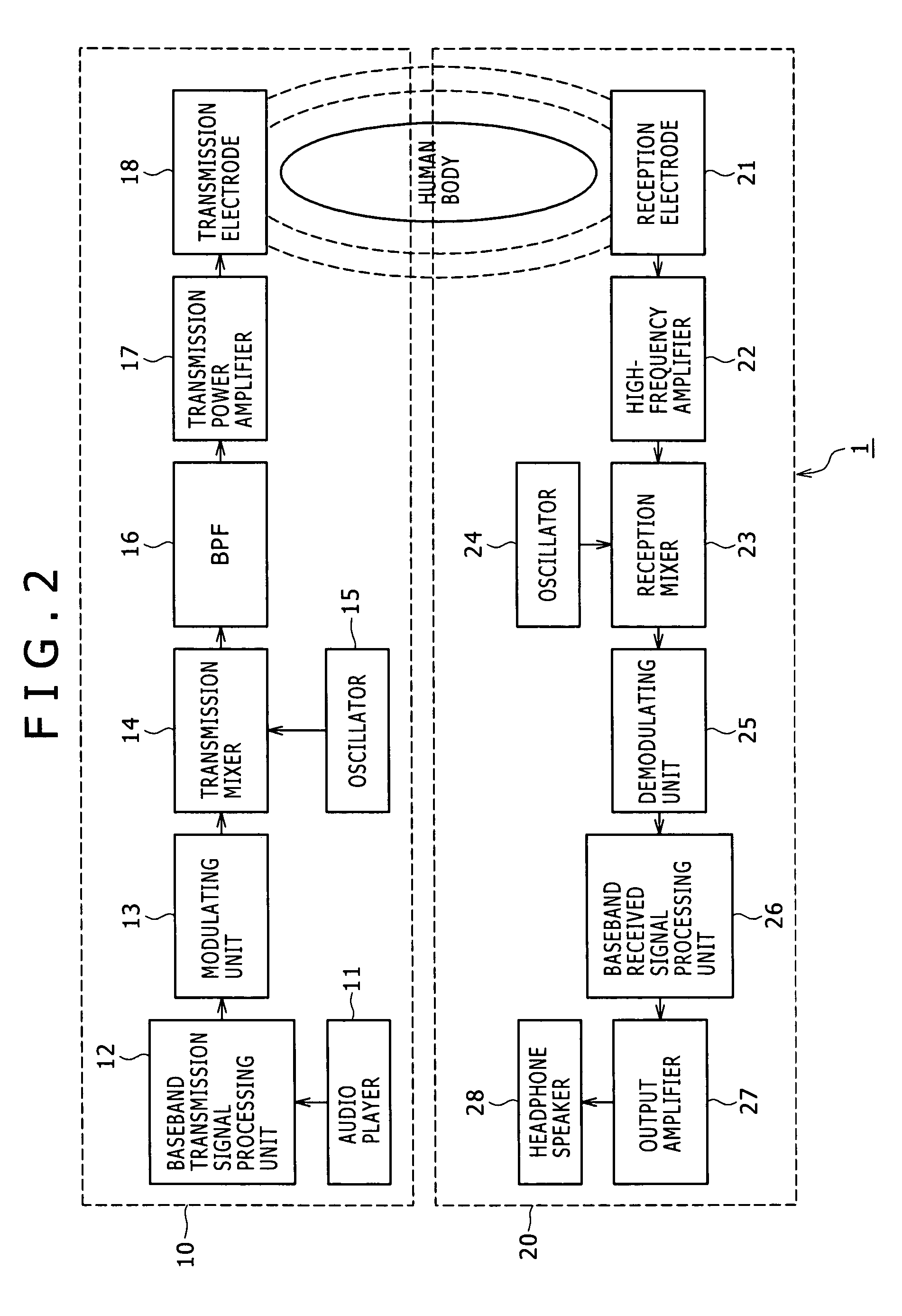
Human body communication system and communication device
InactiveUS20060252371A1Facilitate communicationNear-field transmissionResonant long antennasHuman bodyCommunications system
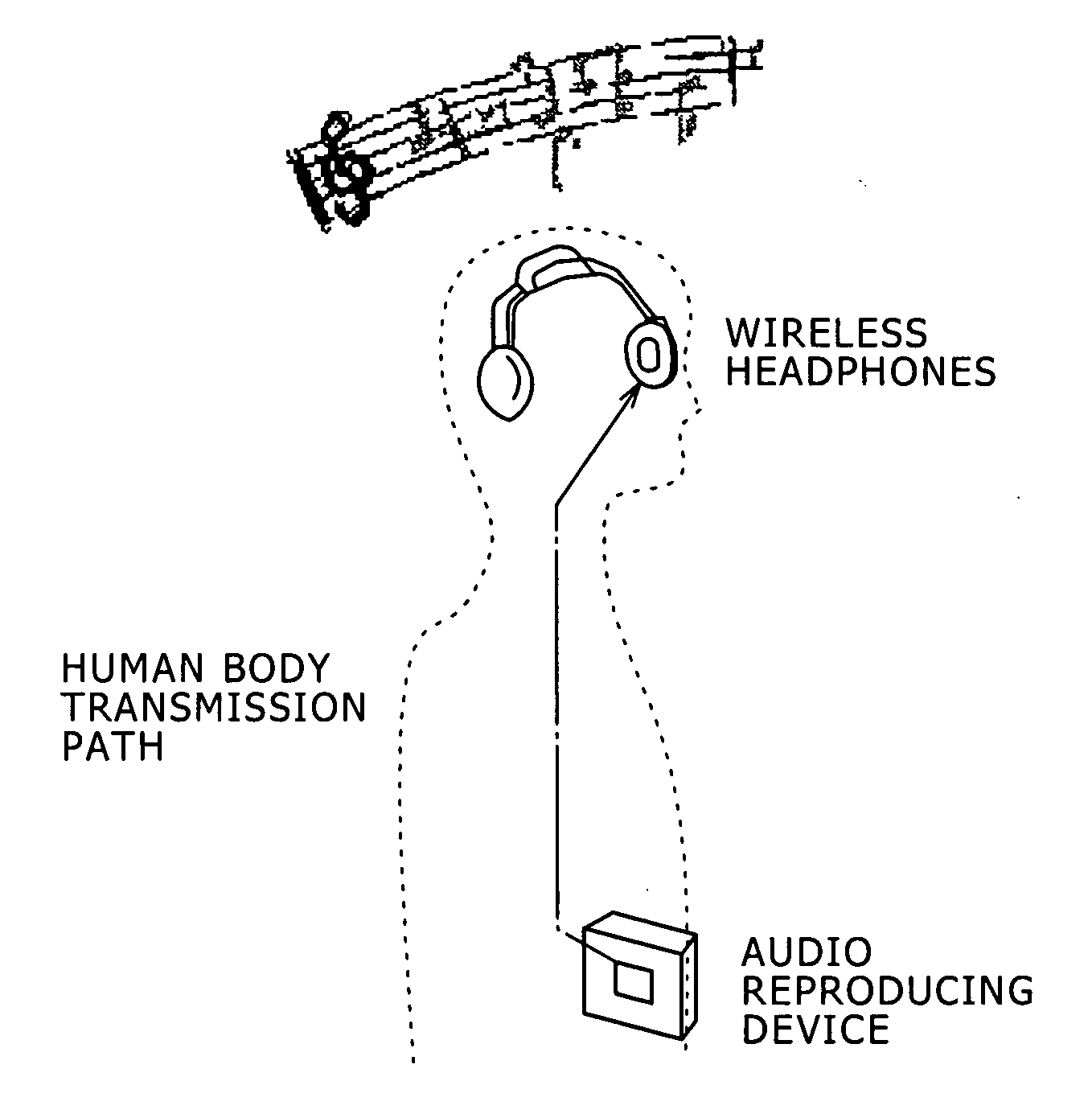
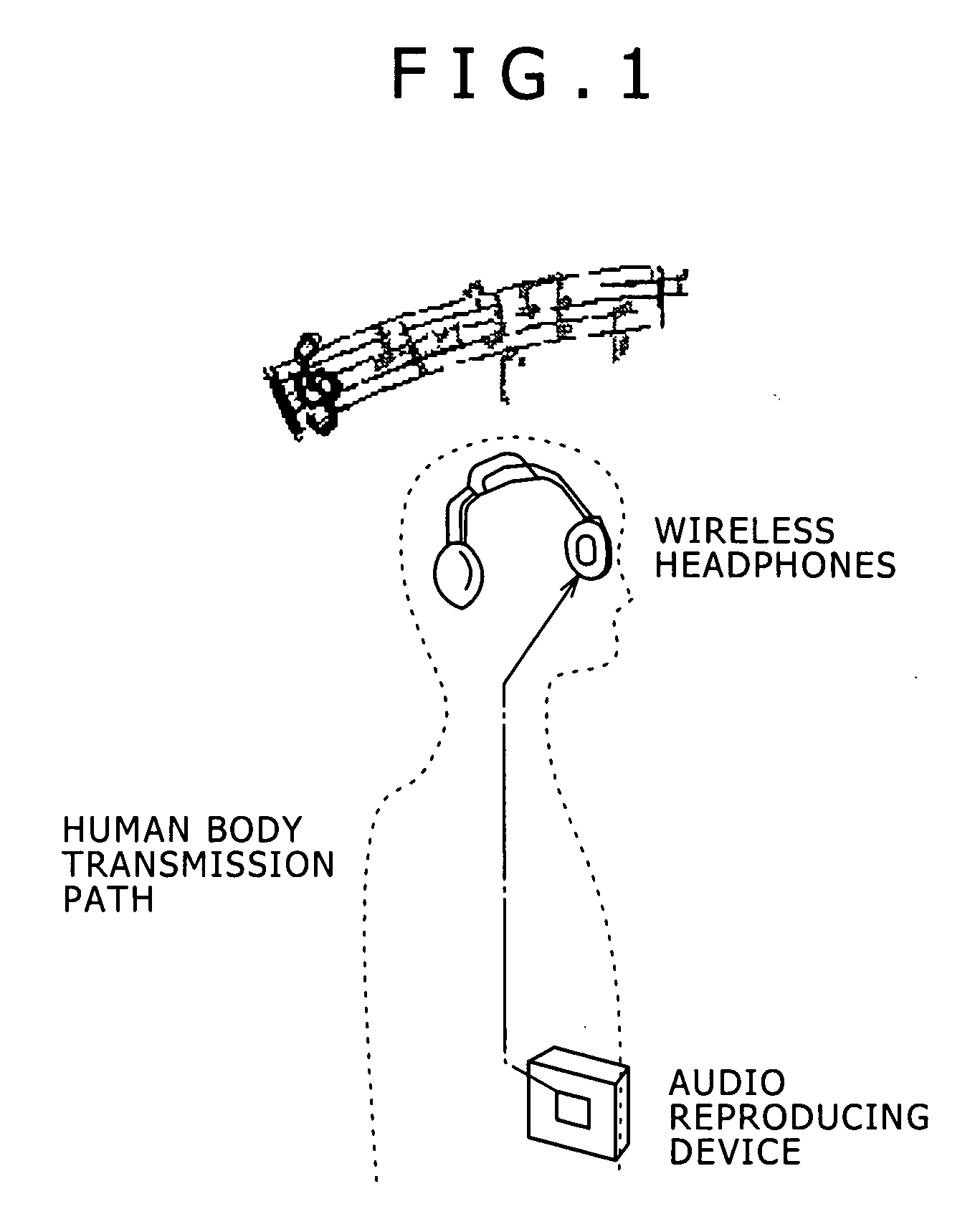
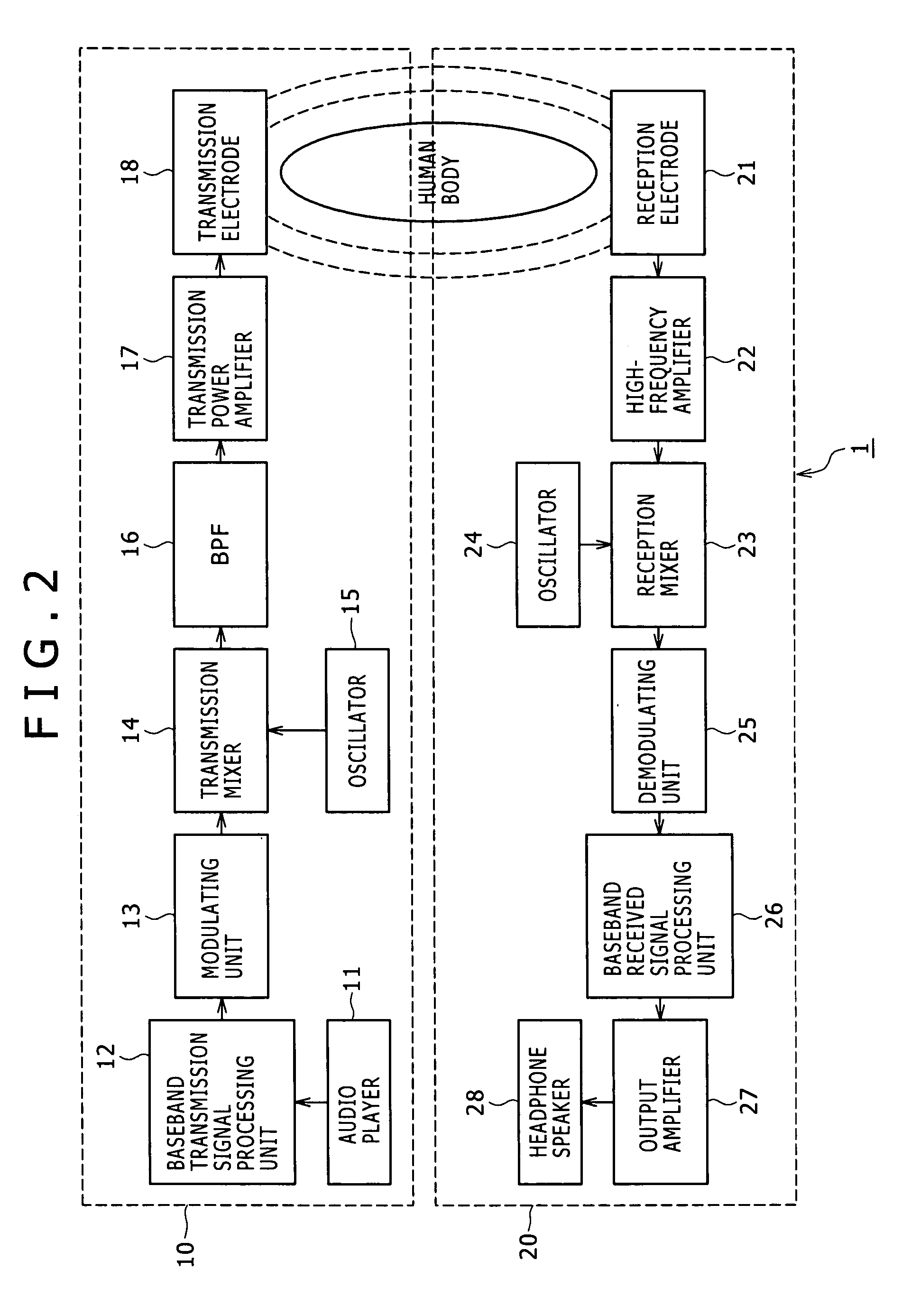
Disclosed herein is a human body communication system for communicating data via an electric field formed by intervention of a human body, the human body communication system including: a transmitter for generating the electric field by transmitting a potential difference signal corresponding to transmission data from a transmitting electrode; and a receiver for receiving the data by reading the potential difference signal in the electric field by a receiving electrode; wherein the transmitter and the receiver use the potential difference signal in a frequency band such that a quasi-electrostatic field formed within the human body is dominant over a radiation field formed outside the human body when the transmitting electrode and the receiving electrode are each disposed in very close vicinity to the human body.
Owner:SONY CORP
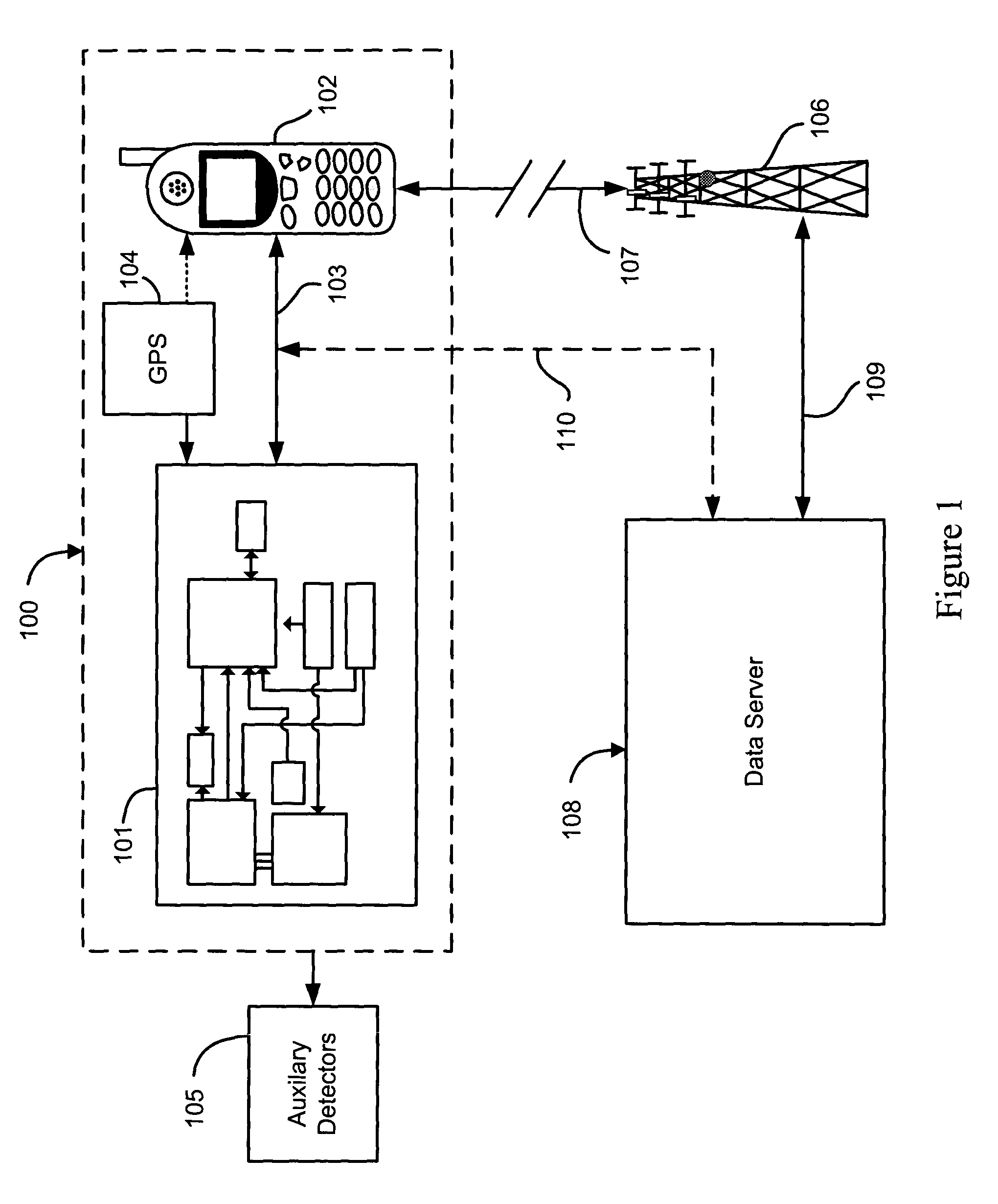
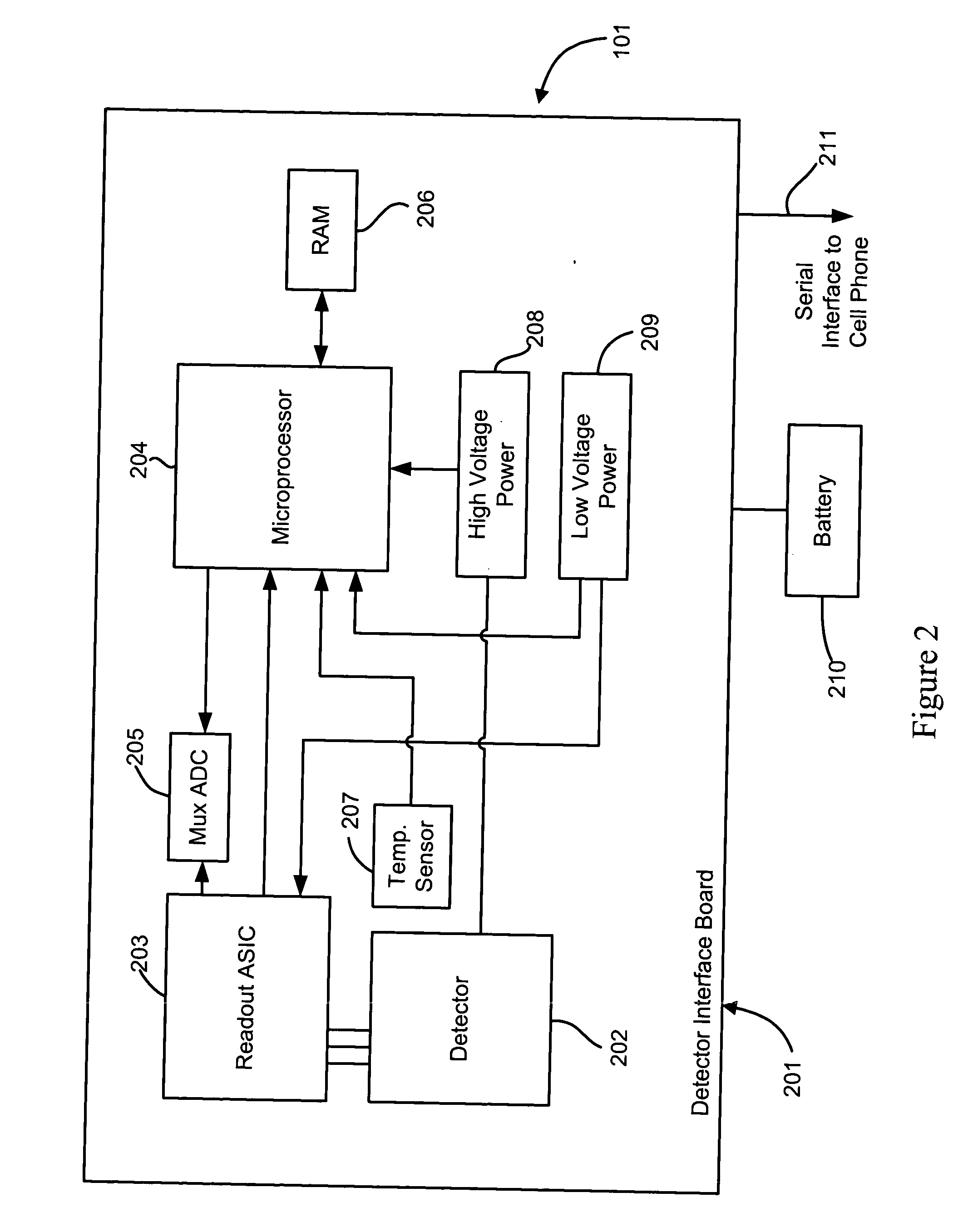
Cellular telephone-based radiation sensor and wide-area detection network
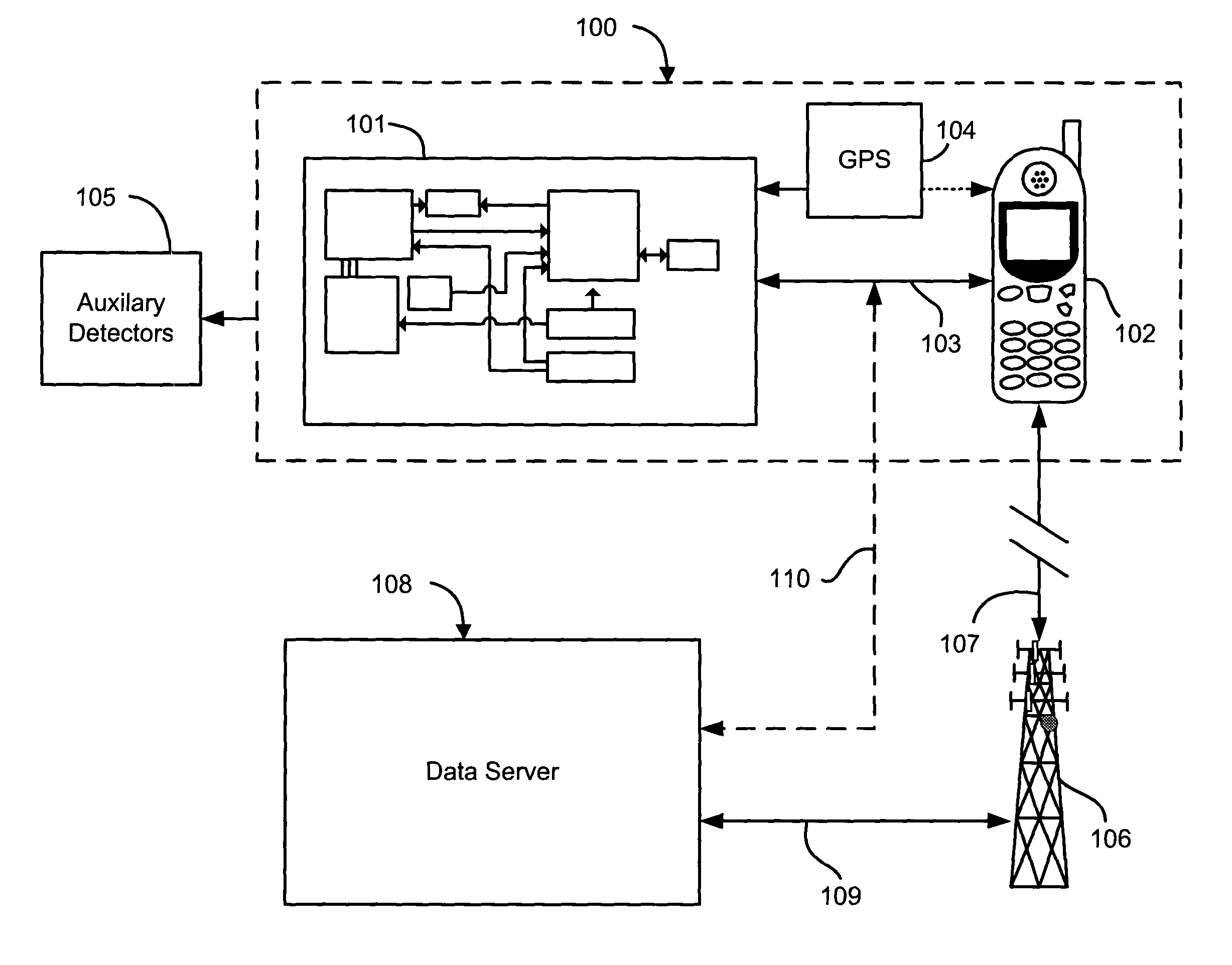
A network of radiation detection instruments, each having a small solid state radiation sensor module integrated into a cellular phone for providing radiation detection data and analysis directly to a user. The sensor module includes a solid-state crystal bonded to an ASIC readout providing a low cost, low power, light weight compact instrument to detect and measure radiation energies in the local ambient radiation field. In particular, the photon energy, time of event, and location of the detection instrument at the time of detection is recorded for real time transmission to a central data collection / analysis system. The collected data from the entire network of radiation detection instruments are combined by intelligent correlation / analysis algorithms which map the background radiation and detect, identify and track radiation anomalies in the region.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Mm-wave/IR monolithically integrated focal plane array
An integrated infrared and millimeter-wave monolithic focal plane sensor array having a substrate upon which an integrated array of infrared sensors and mm-wave sensors are provided at a first planar level on the same side of the substrate, and a planar antenna for receiving incident millimeter-wave radiation located at a second planar level located between the integrated array of sensors and the surface of the substrates for coupling the mm-wave radiation field to the mm-wave sensor. The antenna receiver of electromagnetic radiation, in one embodiment, is an antenna having a crossed bowtie configuration which efficiently couples the radiation field to the mm-wave sensor. The invention also is directed to a method of fabricating such a radiation sensor.
Owner:HRL LAB
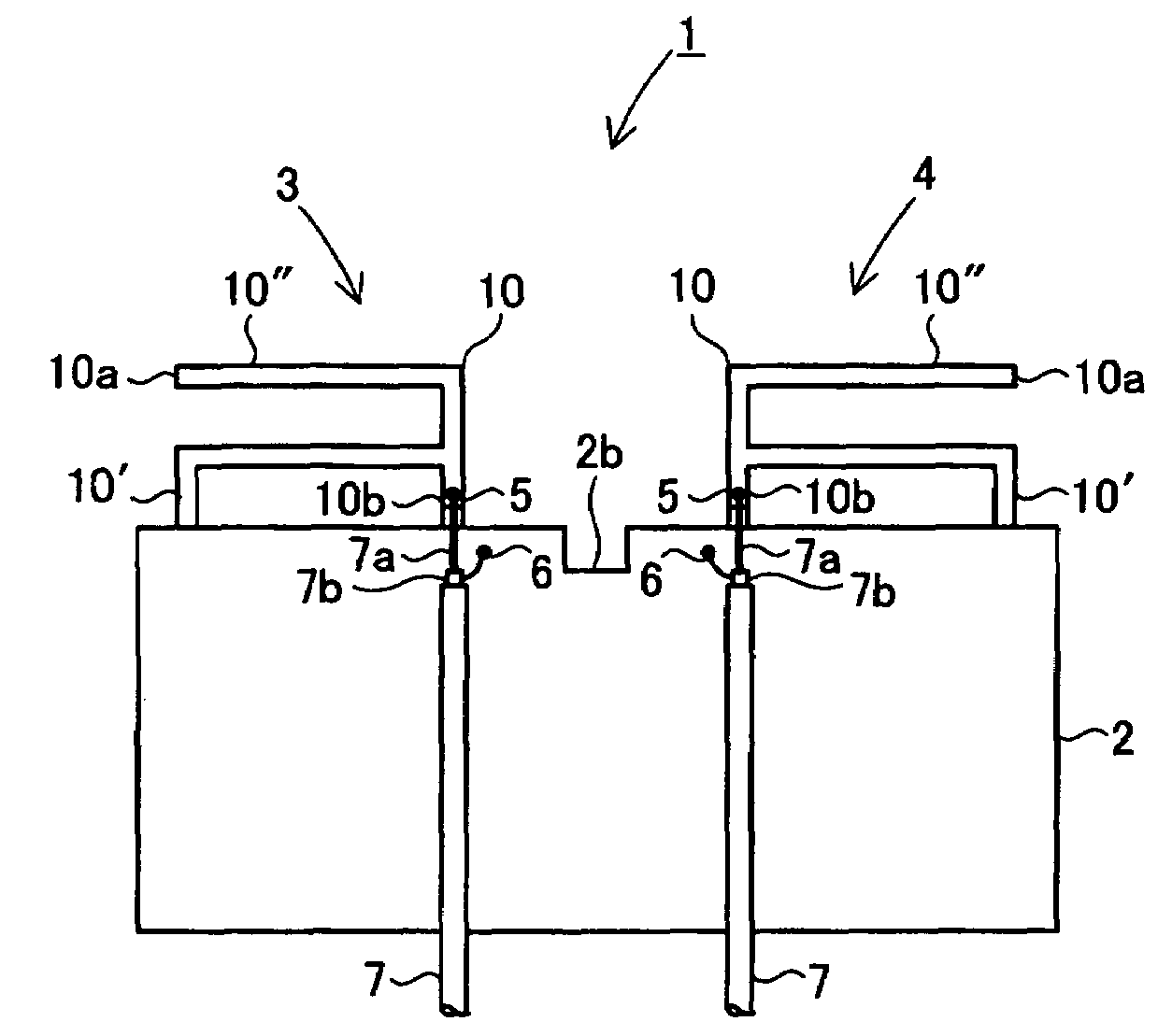
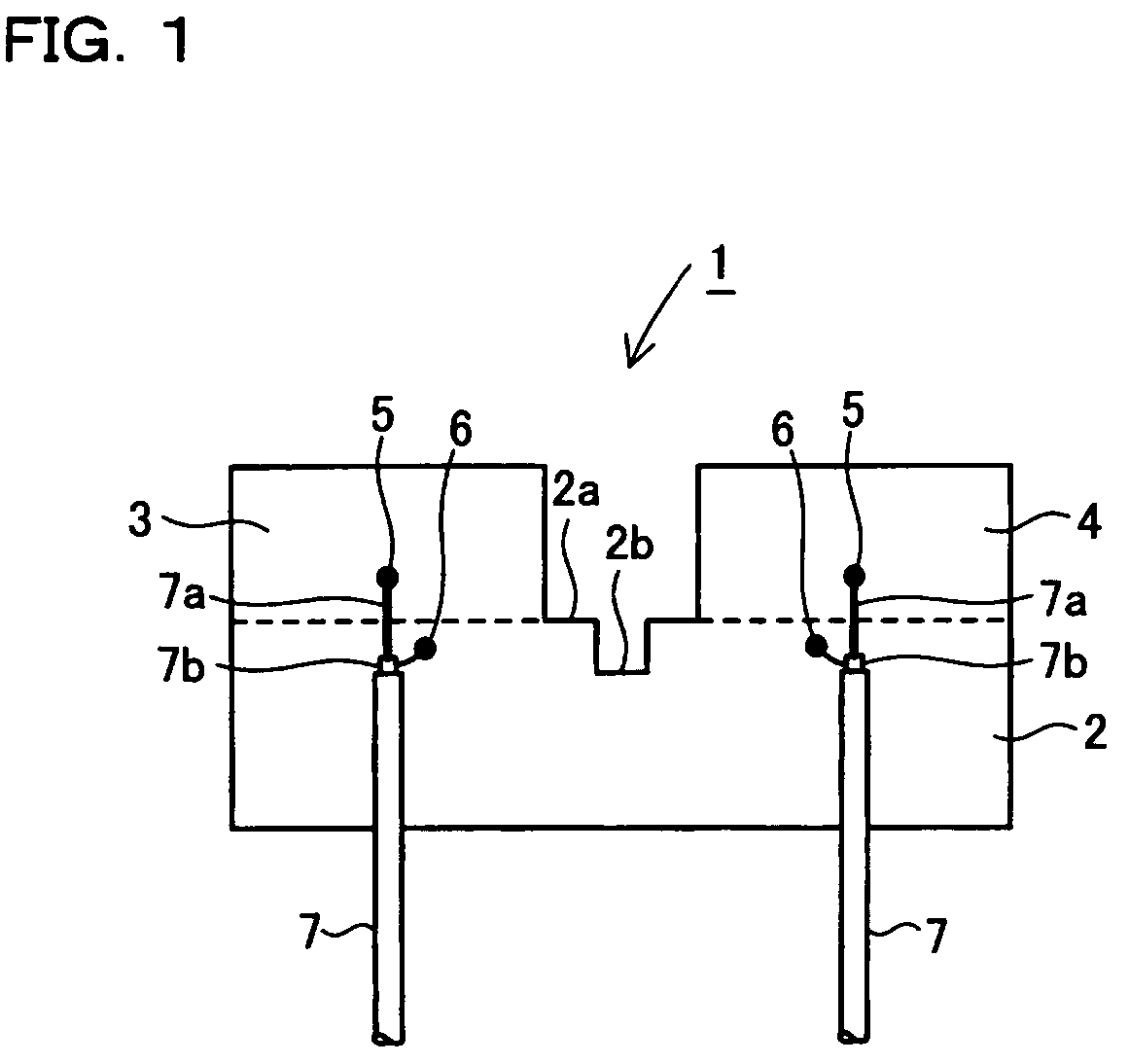
Planar antenna with multiple radiators and notched ground pattern
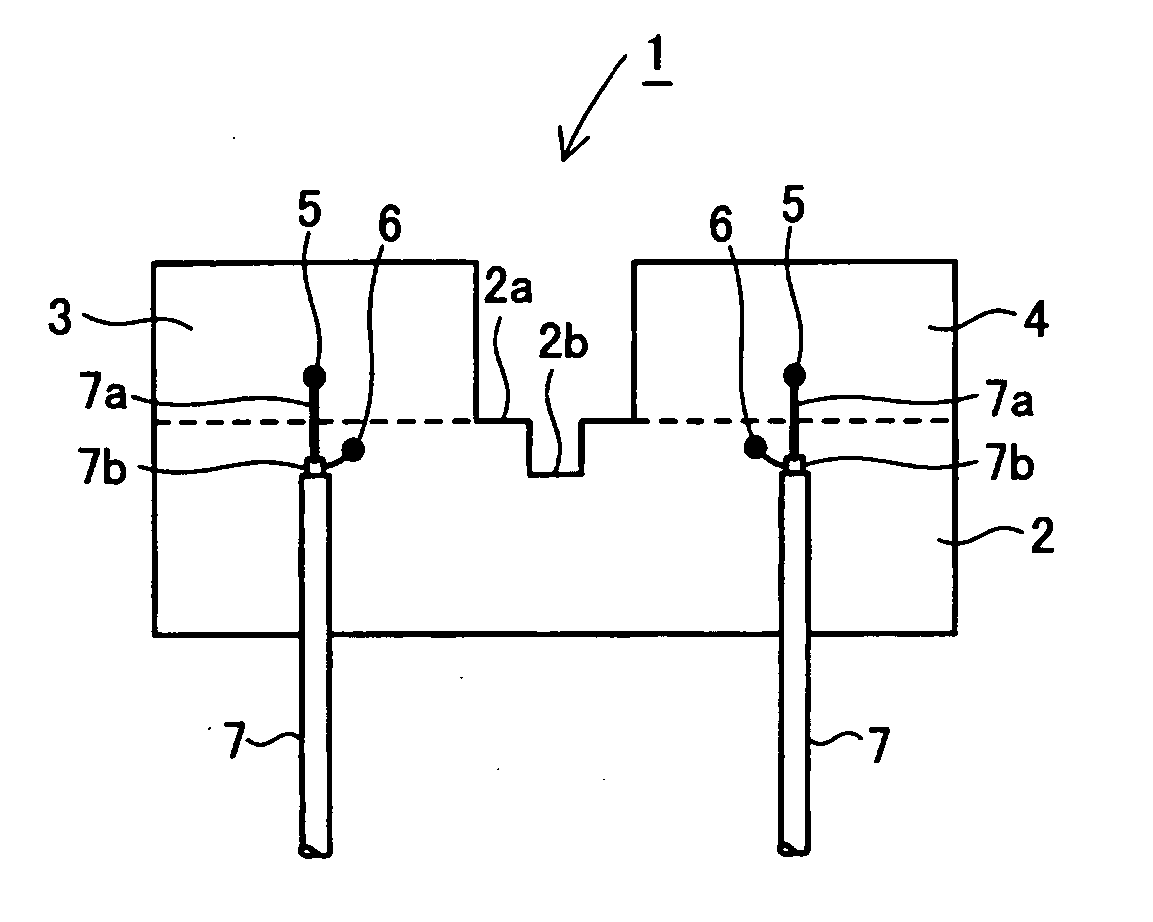
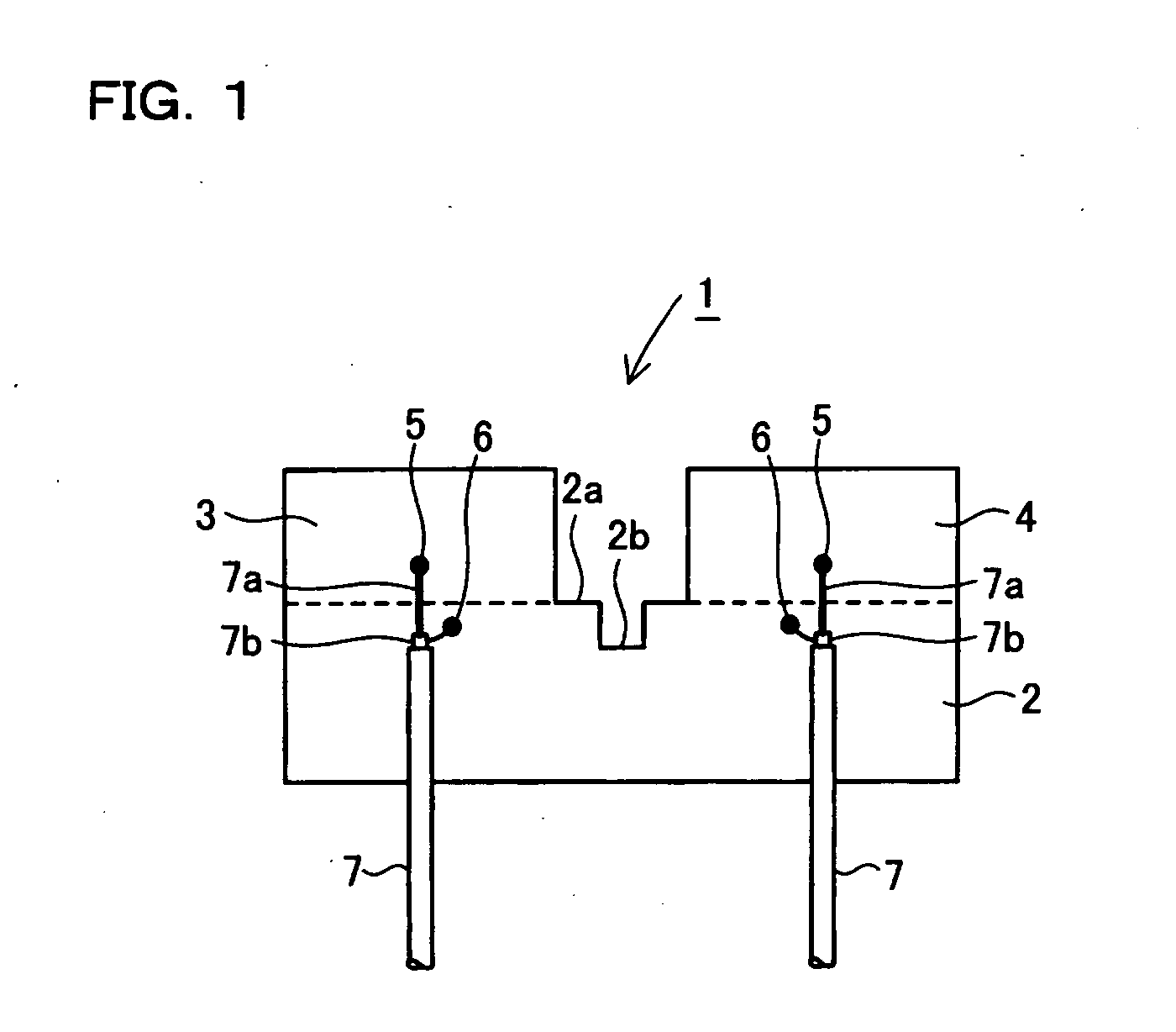
ActiveUS20070001911A1Reduce electromagnetic interactionCoupling degree can not be increasedSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringRadiation field
An antenna consisting of a single small and lightweight package, where each radiating element operates independently with reduced interference among the radiating elements. An integrated multi-element planar antenna includes a ground pattern 2 with a notch 2b formed at an end 2a, first radiating element 3 placed on one side of the notch 2b and equipped with a feeder 5, and second radiating element 4 placed on the other side of the notch 2b and equipped with a feeder 5. For example, inverted F antennas are used as the first radiating element 3 and second radiating element 4. The first radiating element 3 and second radiating element 4 are placed symmetrically about the notch 2b such that separation distance will be the largest at locations where their radiation fields are the highest.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
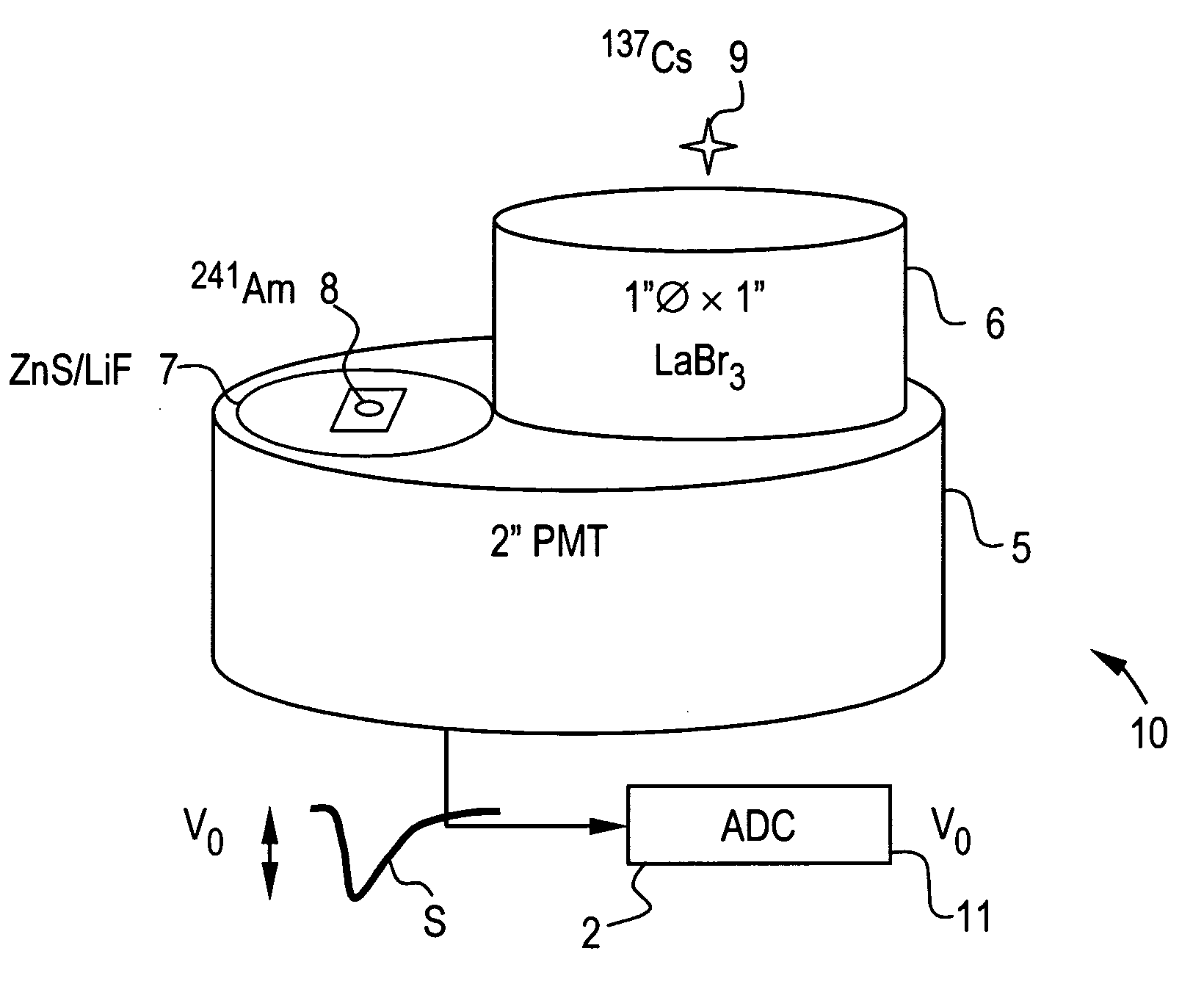
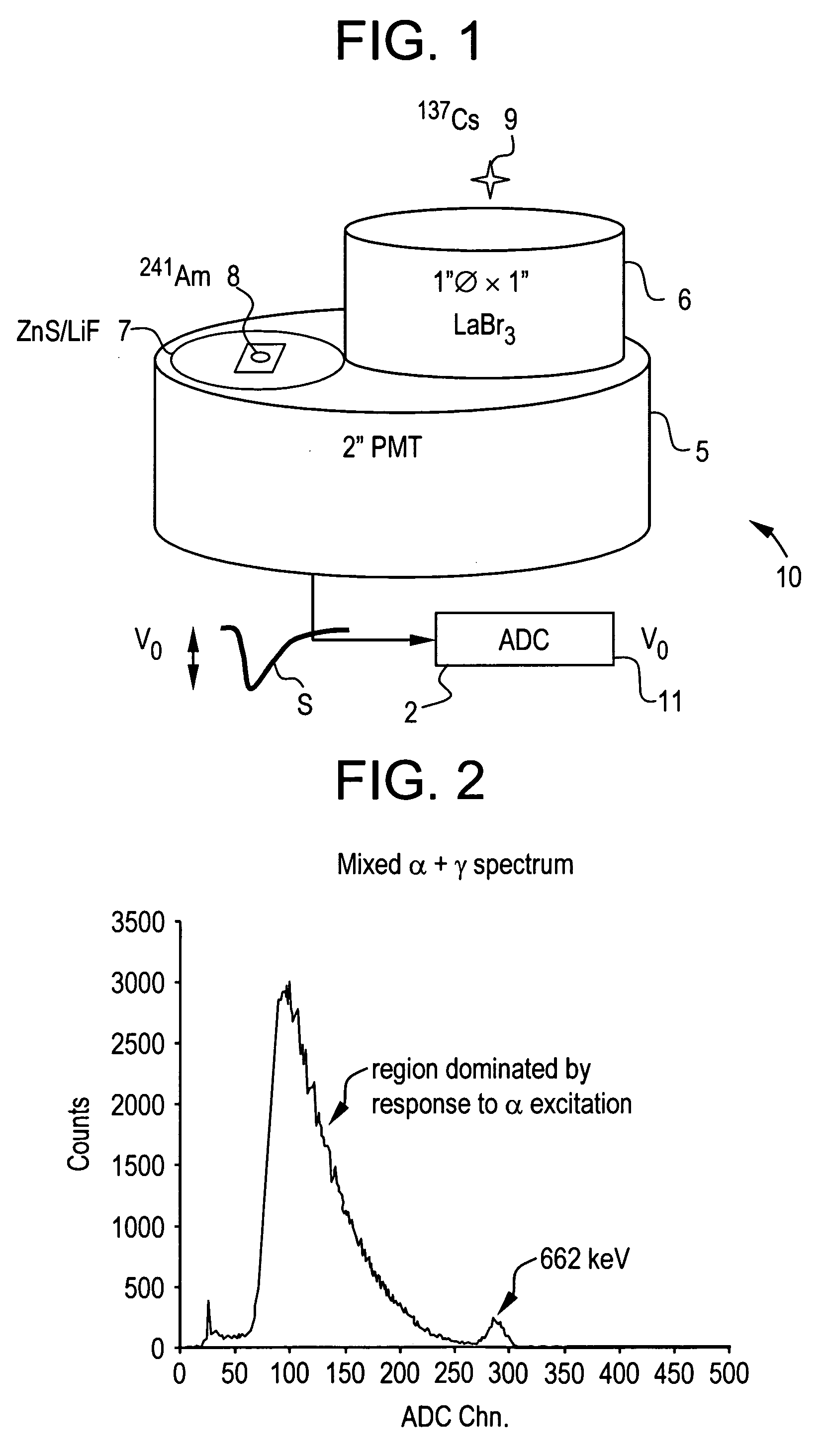
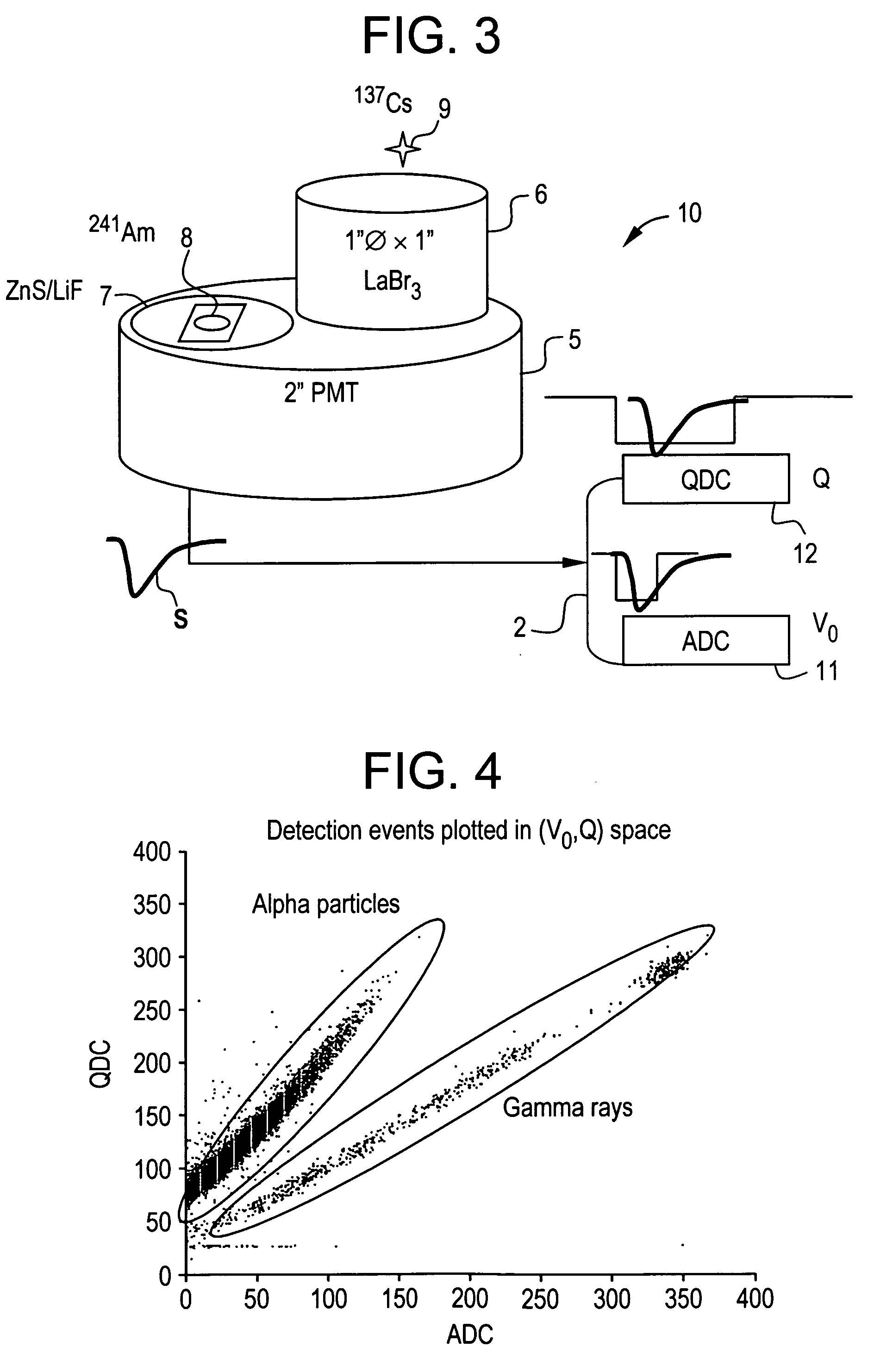
Pulse shape discrimination method and apparatus for high-sensitivity radioisotope identification with an integrated neutron-gamma radiation detector
InactiveUS20070290136A1Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacteristic energyGamma energy
A method and apparatus for discriminating the types of radiation interacting with an integrated radiation detector having of a pulse-mode operating photosensor which is optically coupled to a gamma-ray scintillator sensor and a neutron scintillator sensor and uses an analog to digital converter (ADC) and a charge to digital converter (QDC) to determine scintillation decay times and classify radiation interactions by radiation type. The pulse processing provides for, among other things, faithful representation of the true energy spectrum of the gamma radiation field and allows for radioisotope identification by searching for the presence of characteristic energy lines in the gamma energy spectrum. The pulse shape discrimination method ensures that the high sensitivity and resolution of the isotope identification function is not affected during operation in mixed neutron-gamma fields.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
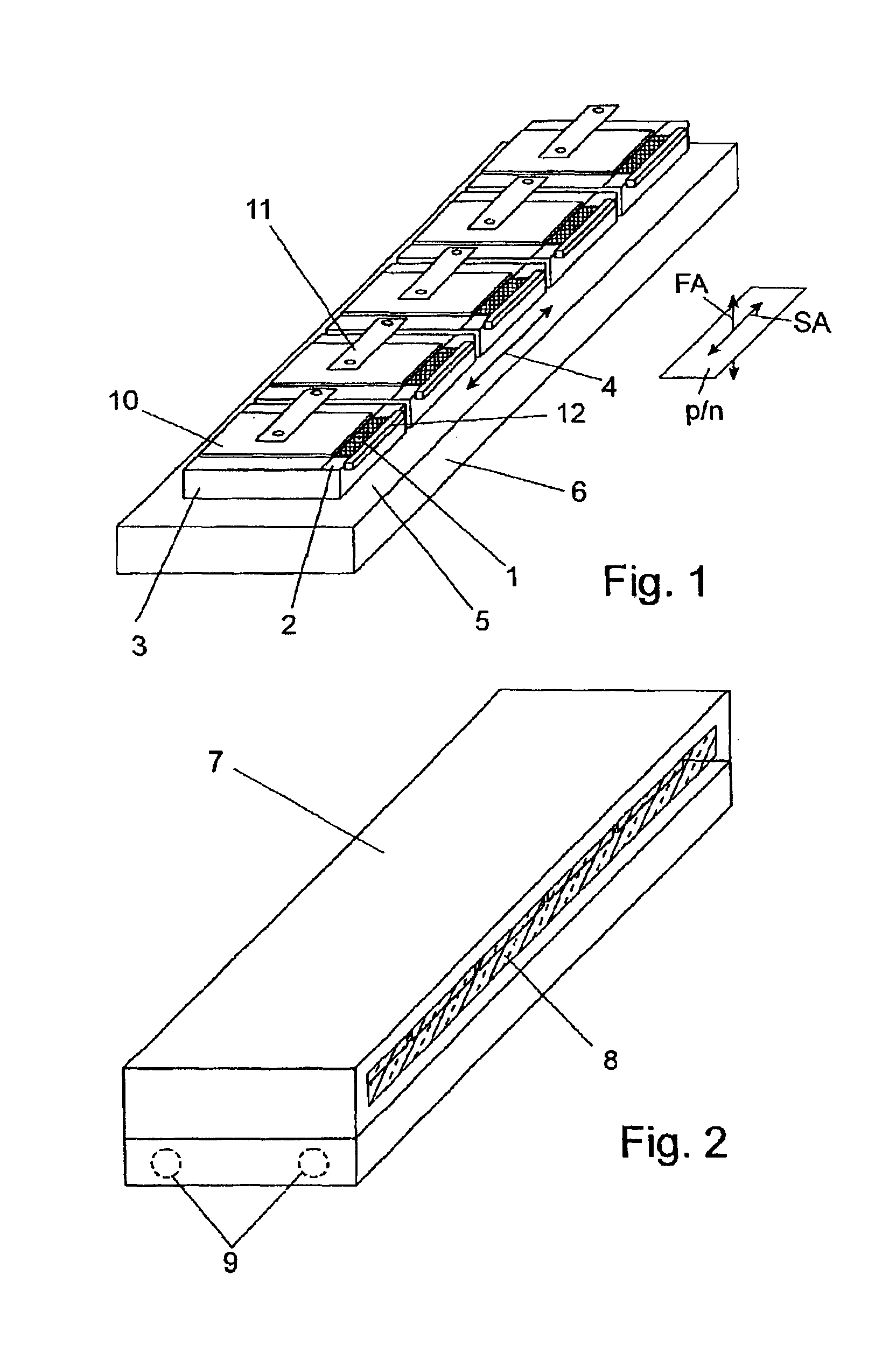
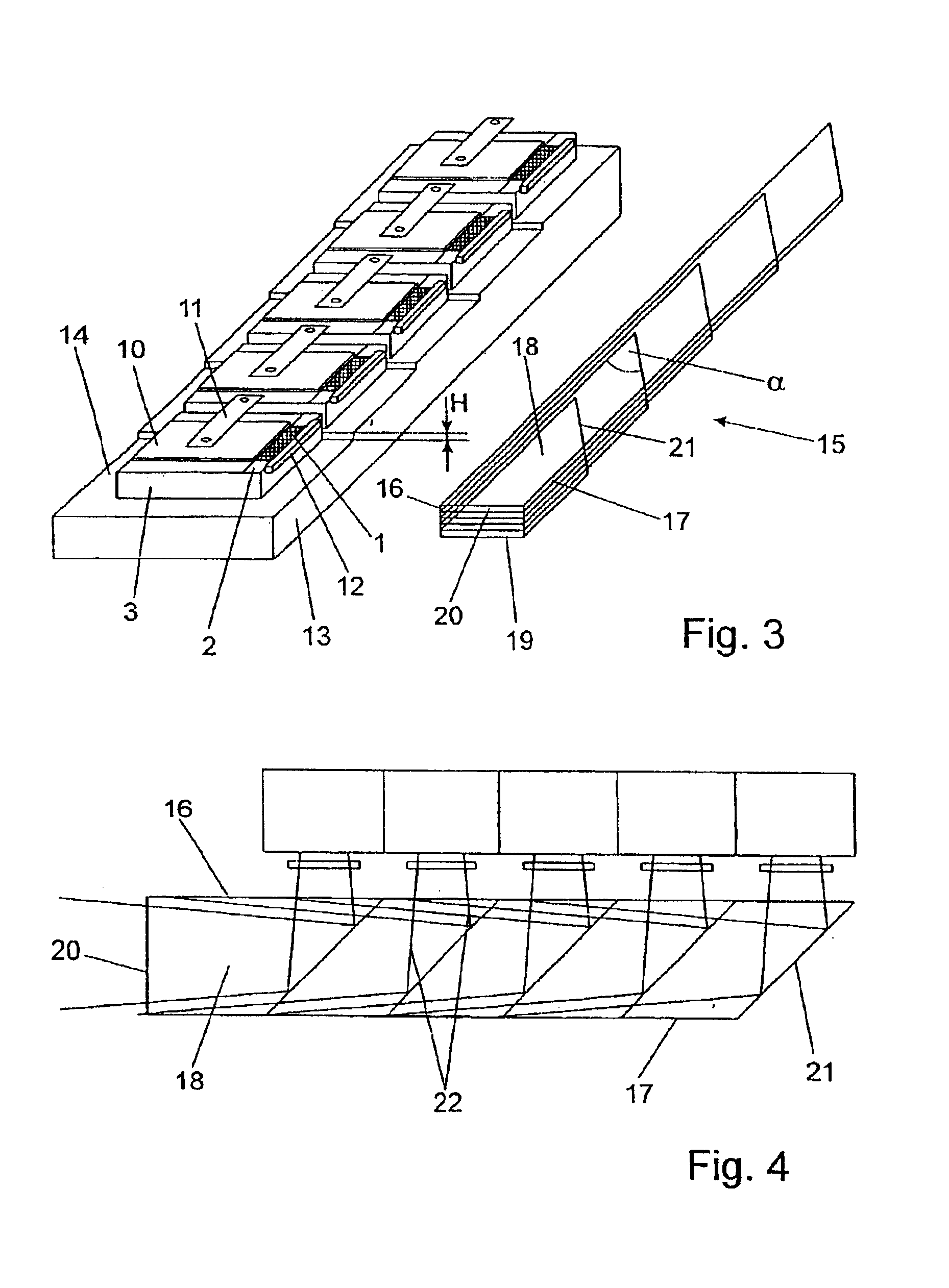
Diode laser arrangement with a plurality of diode laser arrays
InactiveUS6898222B2Promote homogenizationSemiconductor laser arrangementsExcitation process/apparatusLaser arrayRadiation field
A diode laser arrangement is disclosed wherein a radiation source is designed which can be scaled with respect to power such that different types of cooling can be applied and the configuration of the radiation field is suitable for adapting to different tasks in a simple manner. For this purpose, every diode laser is connected to a thermal contact surface of a separate, heat-spreading carrier which is fastened to a cooling surface of a common cooling element so as to be electrically insulated. The carriers are arranged adjacently in such a way that the line-shaped emission regions of the diode lasers are adjacent in series and the p-n junction planes extend parallel to the thermal contact surfaces. The diode laser arrangement is particularly suitable as a pump light source.
Owner:JENOPTIK LASERDIODE
Planar antenna with multiple radiators and notched ground pattern
ActiveUS7289068B2Reduce electromagnetic interactionCoupling degree can not be increasedSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringRadiation field
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
X-ray pixel beam array systems and methods for electronically shaping radiation fields and modulation radiation field intensity patterns for radiotherapy
ActiveUS8306184B2X-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationElectron sourceLight beam
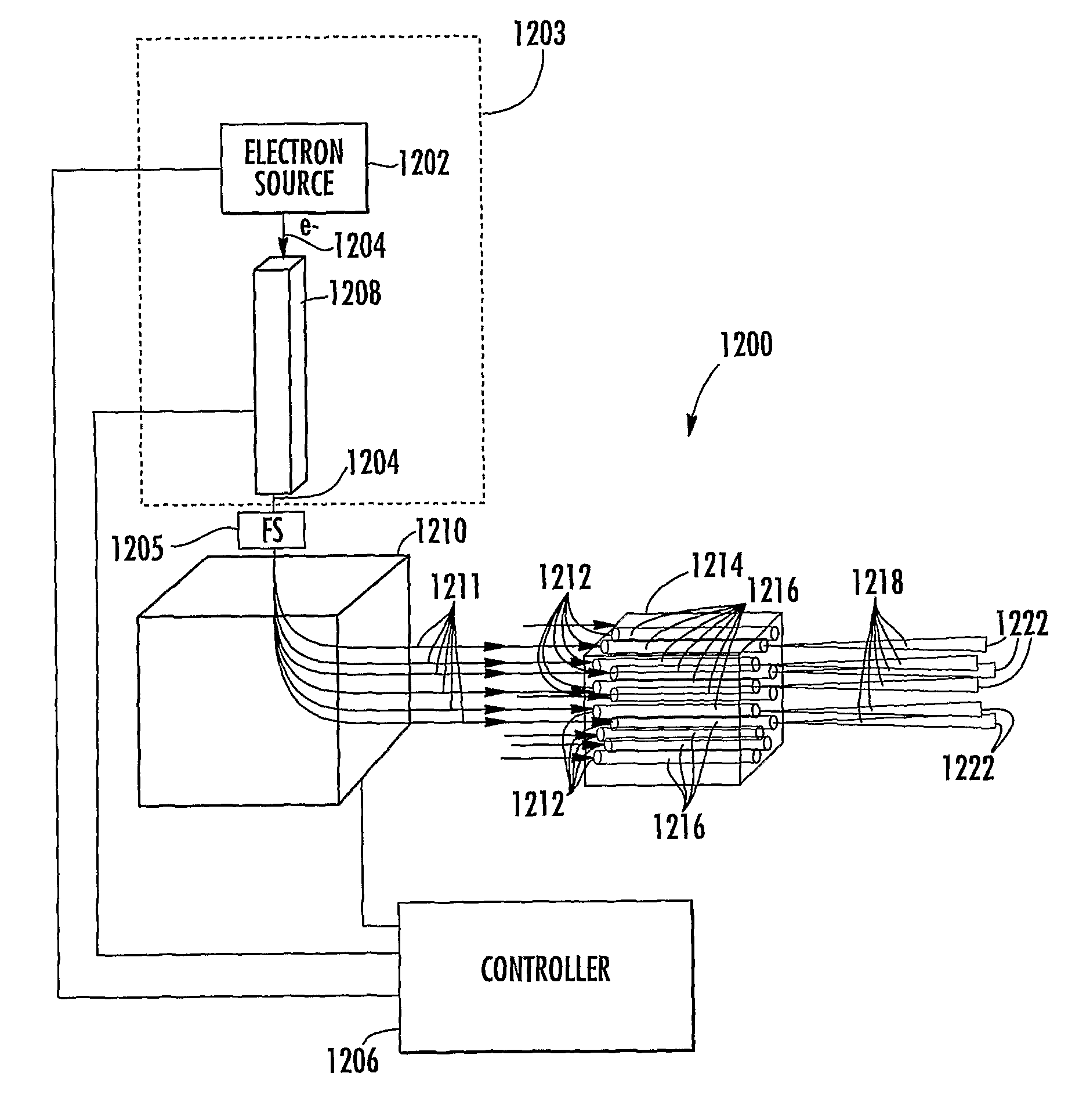
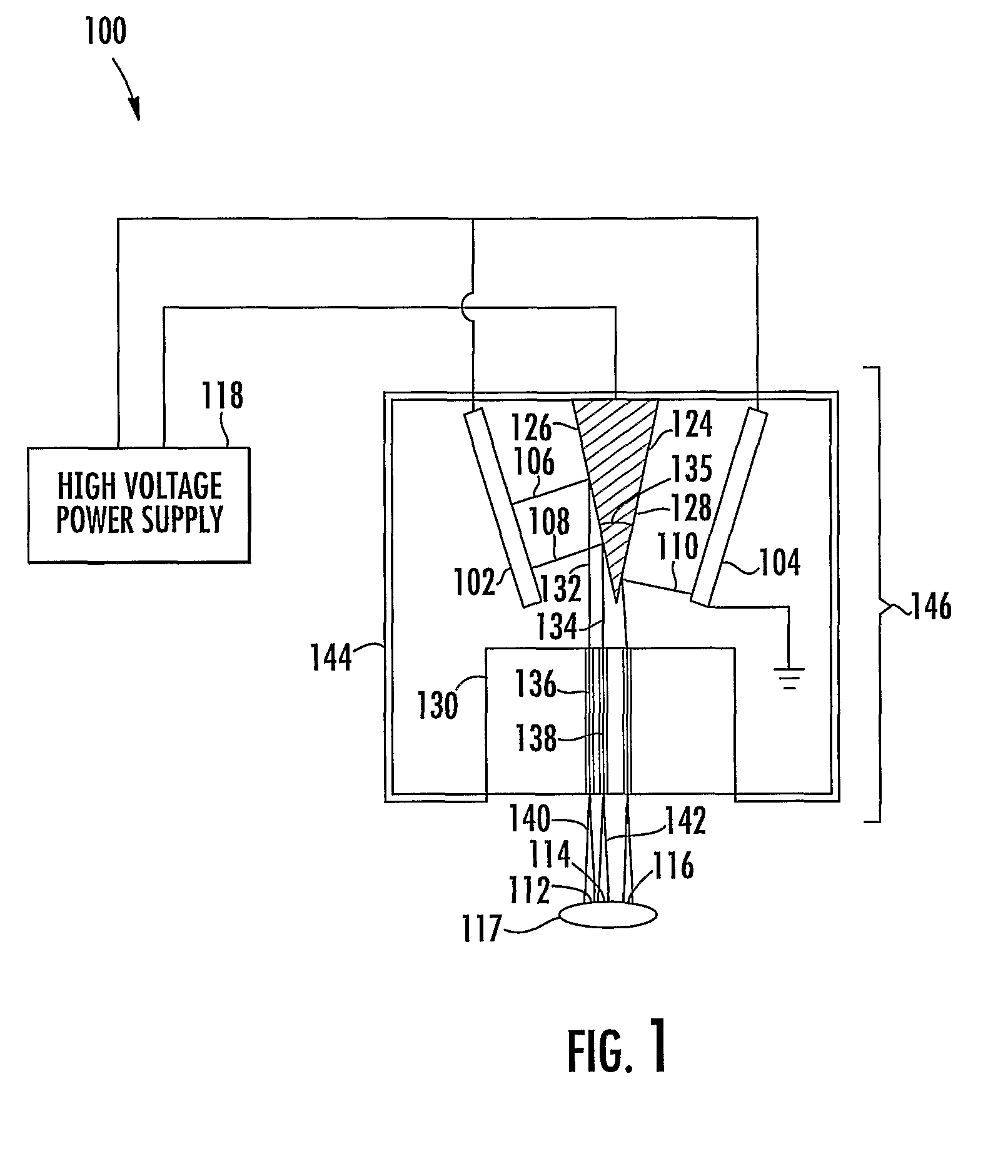
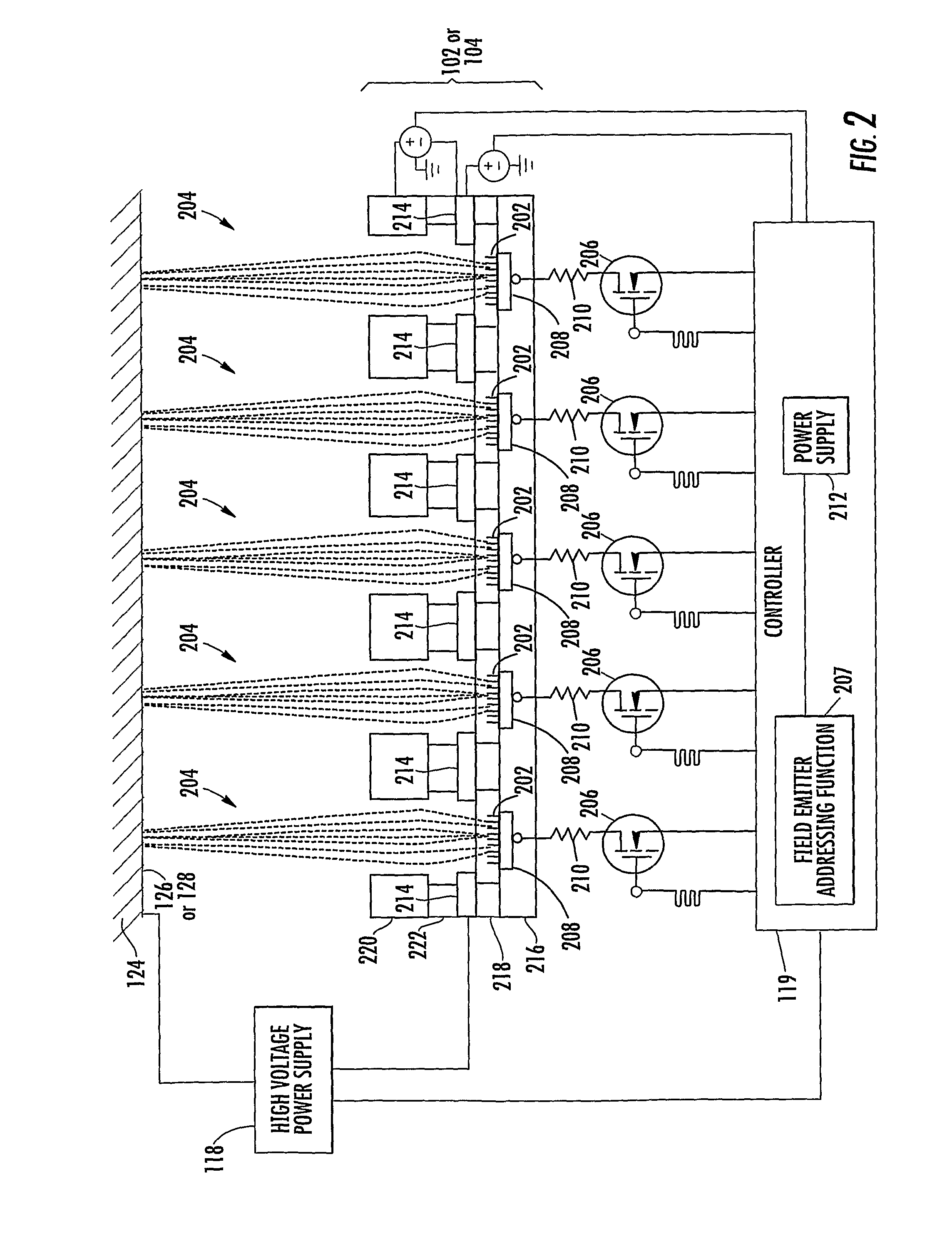
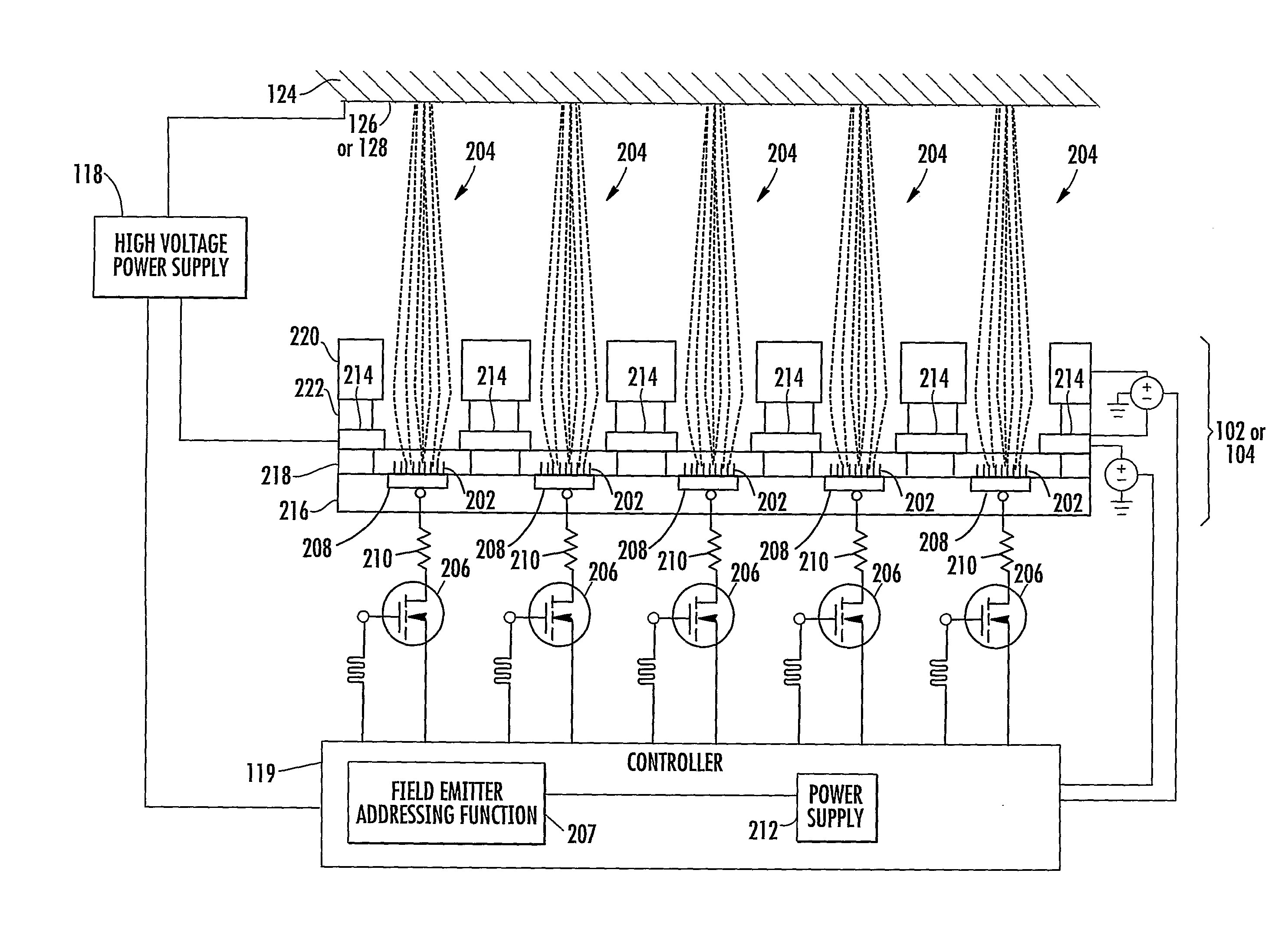
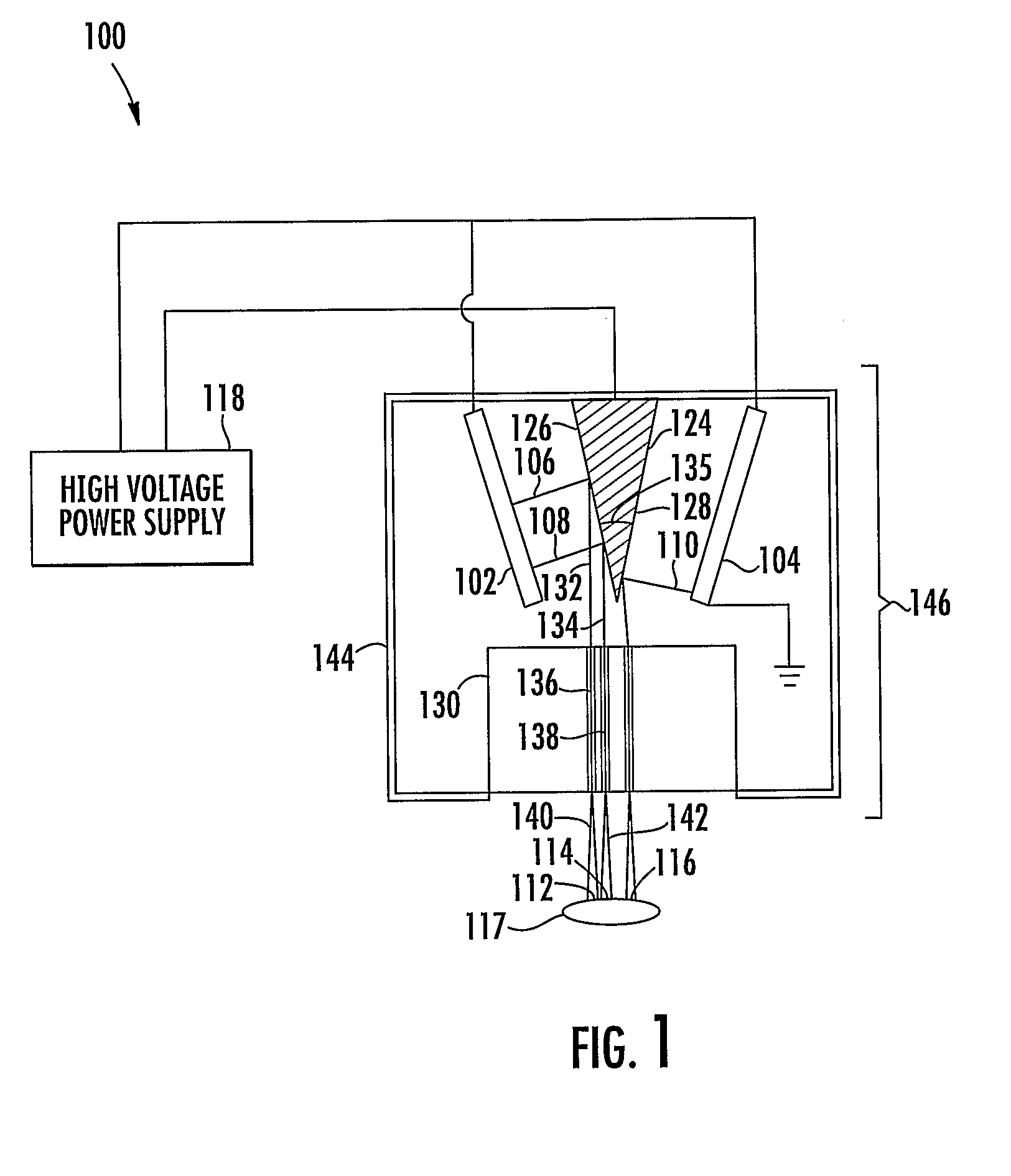
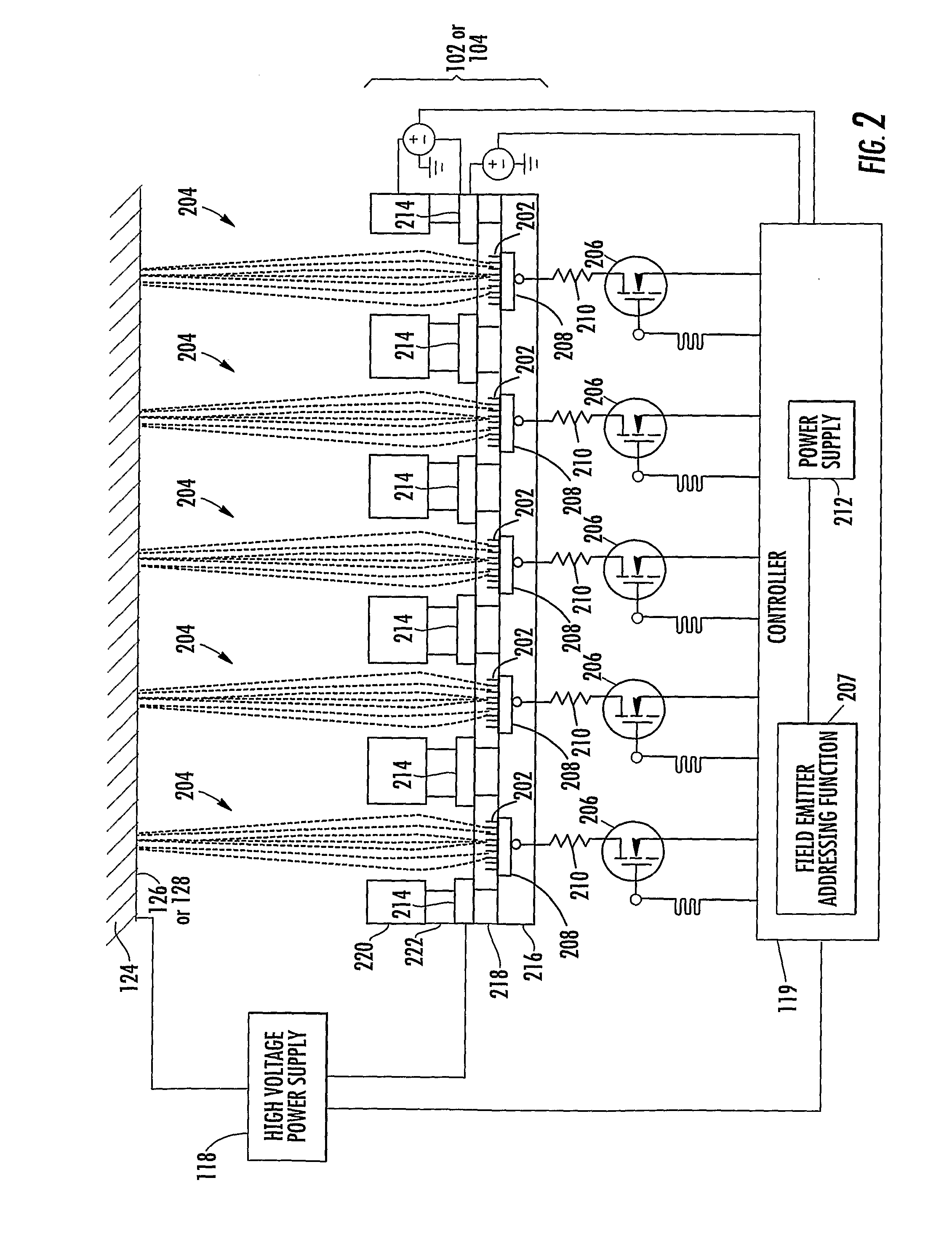
X-ray pixel beam array systems and methods for electronically shaping radiation fields and modulating radiation field intensity patterns for radiotherapy are disclosed. One exemplary pre-clinical system may include addressable electron field emitters (102, 104) that are operable to emit a plurality of electron pixel beams (106, 108, 110). Each electron pixel beam may correspond to an x-ray target (124) and x-ray pixel beam collimation aperture (136, 138) to convert a portion of energy associated with the electron pixel beam to a corresponding x-ray pixel beam (140, 142). Further, the x-ray pixel beam array collimator (130) forms a one-to-one correspondence between individual electron pixel beam and its corresponding x-ray pixel beam. One exemplary clinical system may include a high-energy electron source (1203), an n-stage scanning system (1210), x-ray pixel beam targets (1212), and an x-ray pixel beam array collimator (1214). A controller (1206) may sequentially direct electron beam pulses to predetermined x-ray pixel targets and produce an electronically controlled radiation field direction, pattern; and intensity pattern.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
X-ray pixel beam array systems and methods for electronically shaping radiation fields and modulation radiation field intensity patterns for radiotherapy
ActiveUS20100260317A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray tube with very high currentSoft x rayElectron source
X-ray pixel beam array systems and methods for electronically shaping radiation fields and modulating radiation field intensity patterns for radiotherapy are disclosed. One exemplary pre-clinical system may include addressable electron field emitters (102, 104) that are operable to emit a plurality of electron pixel beams (106, 108, 110). Each electron pixel beam may correspond to an x-ray target (124) and x-ray pixel beam collimation aperture (136, 138) to convert a portion of energy associated with the electron pixel beam to a corresponding x-ray pixel beam (140, 142). Further, the x-ray pixel beam array collimator (130) forms a one-to-one correspondence between individual electron pixel beam and its corresponding x-ray pixel beam. One exemplary clinical system may include a high-energy electron source (1203), an n-stage scanning system (1210), x-ray pixel beam targets (1212), and an x-ray pixel beam array collimator (1214). A controller (1206) may sequentially direct electron beam pulses to predetermined x-ray pixel targets and produce an electronically controlled radiation field direction, pattern; and intensity pattern.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
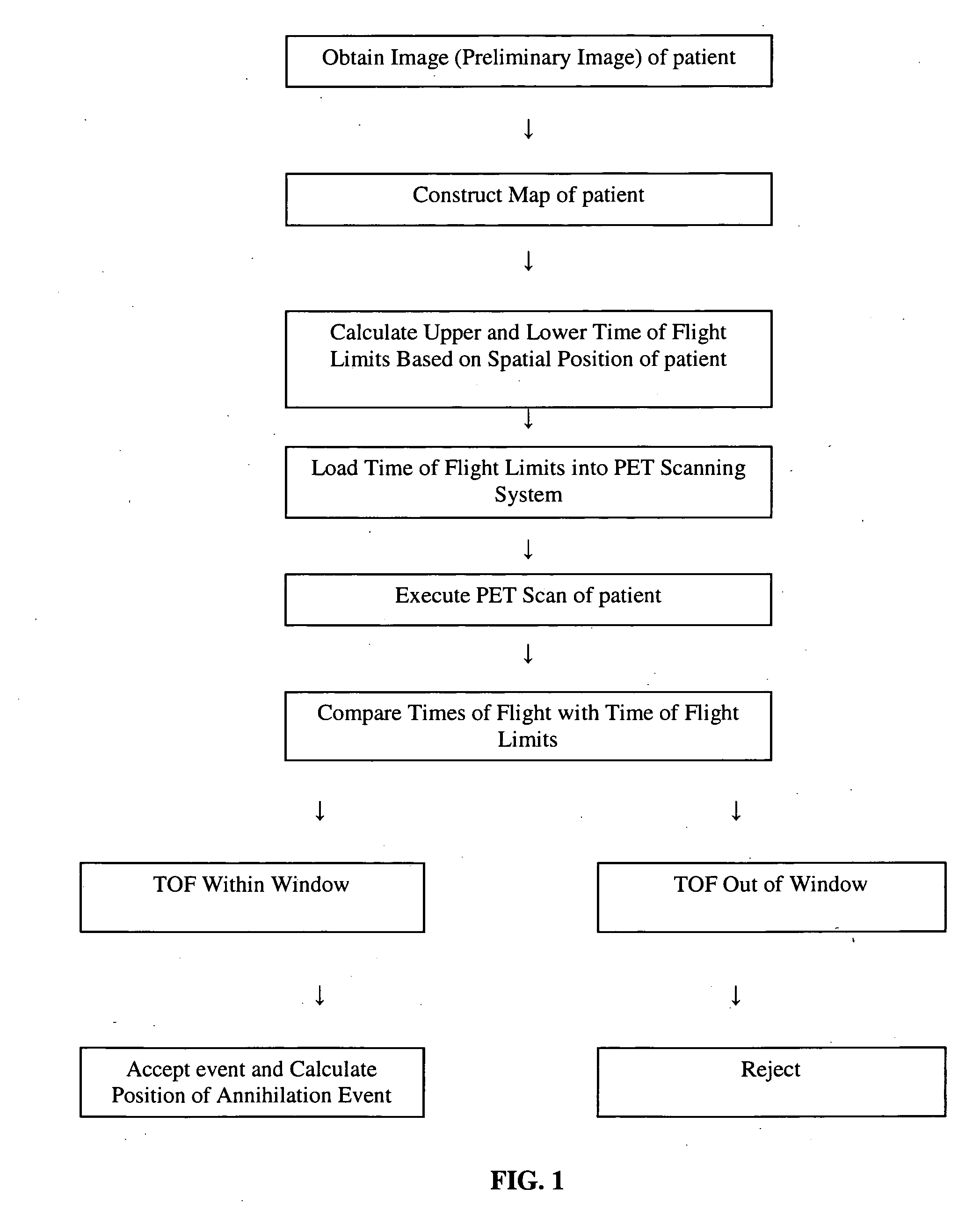
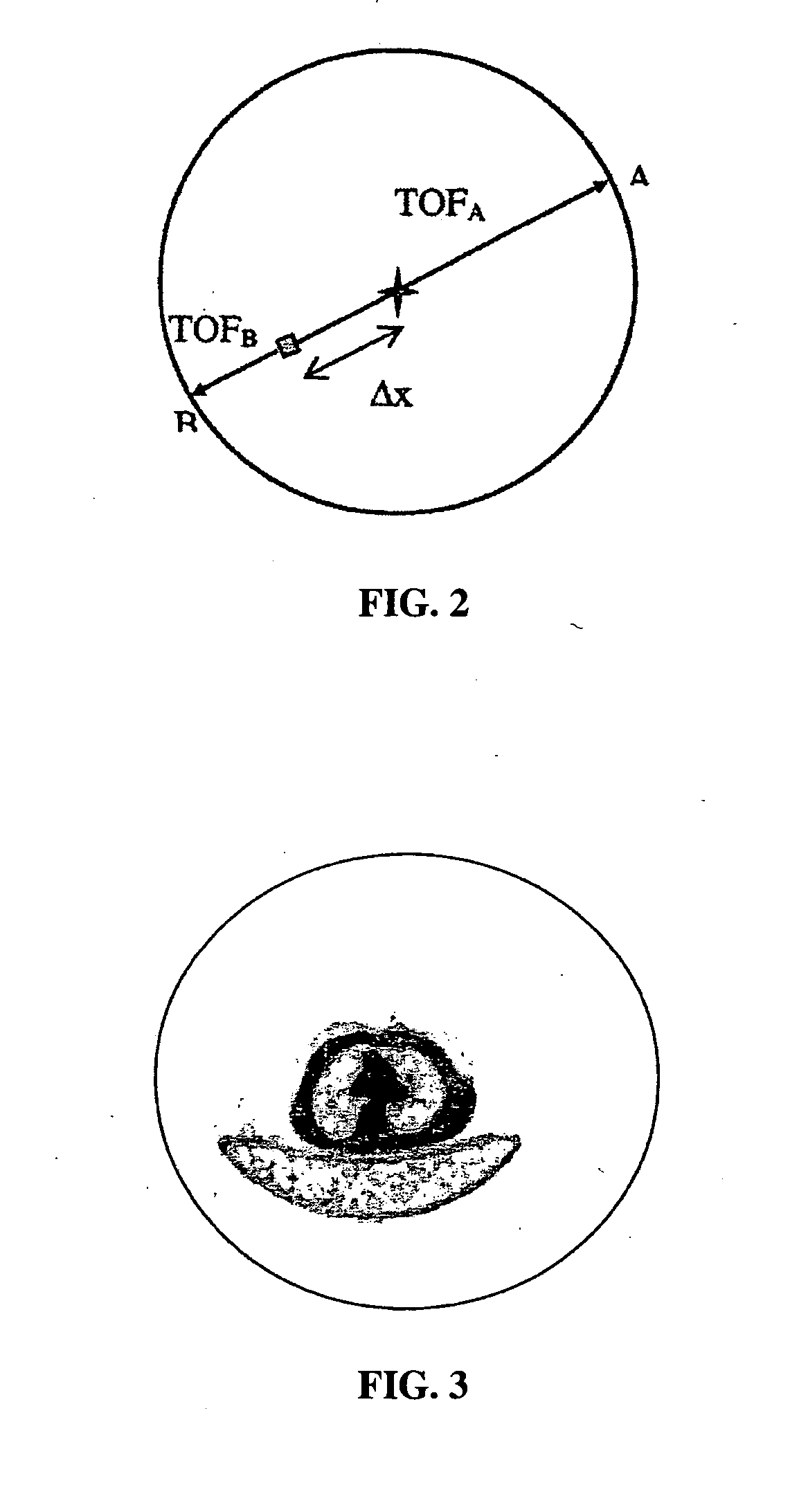
Method for reducing an electronic time coincidence window in positron emission tomography
ActiveUS20070106154A1Shorten the timeReducing random coincidencesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsGamma photonRadiation field
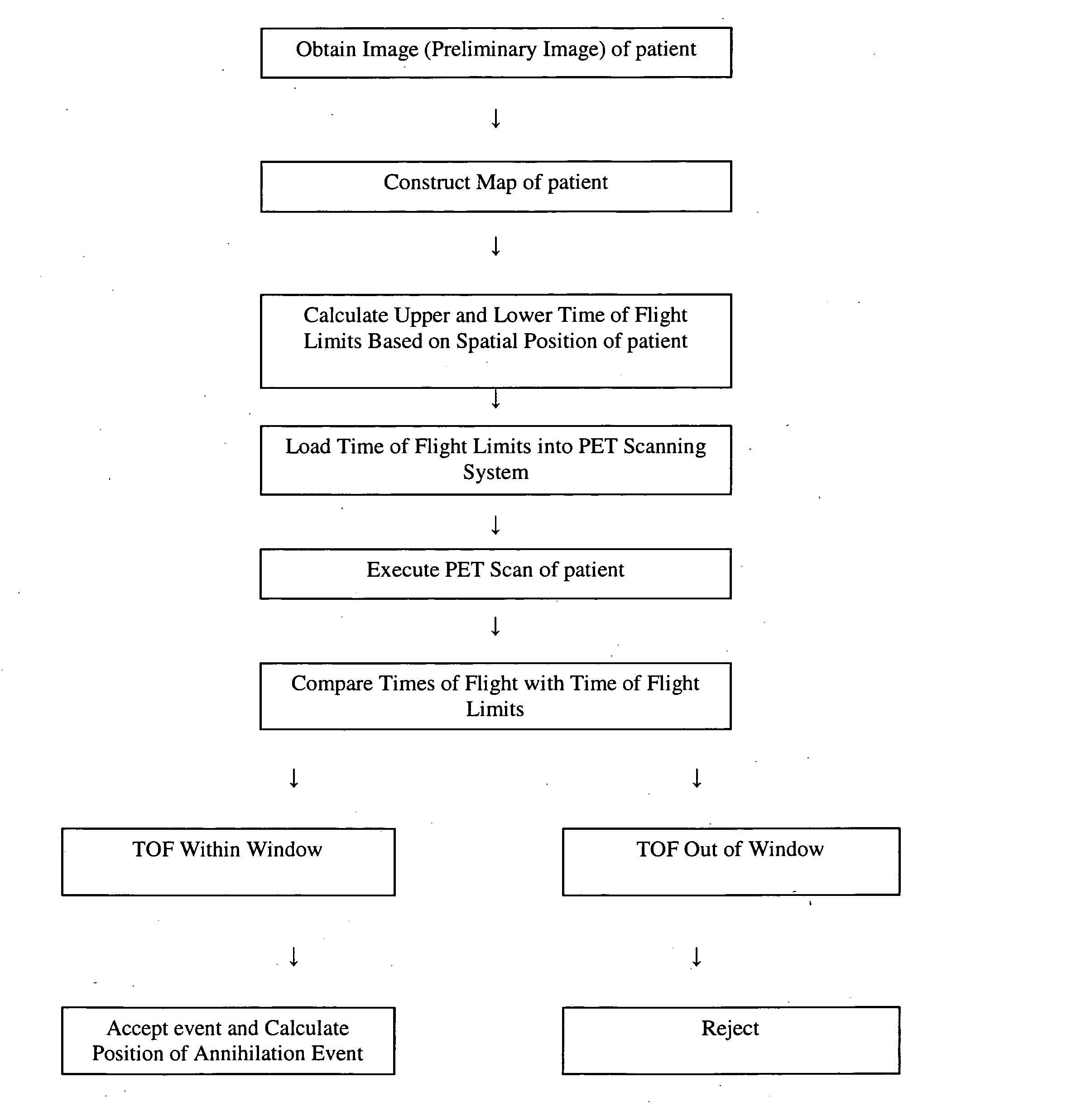
A method for acquiring PET images with reduced time coincidence window limits includes obtaining a preliminary image of a patient within a radiation field of view (FOV), determining the spatial location of the patient within the FOV based on the preliminary image, calculating a different time coincidence window based on the spatial location of the patient for each possible pair of oppositely disposed detectors, scanning the patient with a PET scanning system to detect a pair of gamma photons produced by an annihilation event, determining whether the detection of the pair of gamma photons occurs within the time coincidence window, accepting the detected event only if the detection of the gamma photons occurs within the time coincidence window, calculating the spatial location of accepted annihilation event, and adding the calculated spatial location of the annihilation event to a stored distribution of calculated annihilation event spatial locations representing the distribution of radioactivity in the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
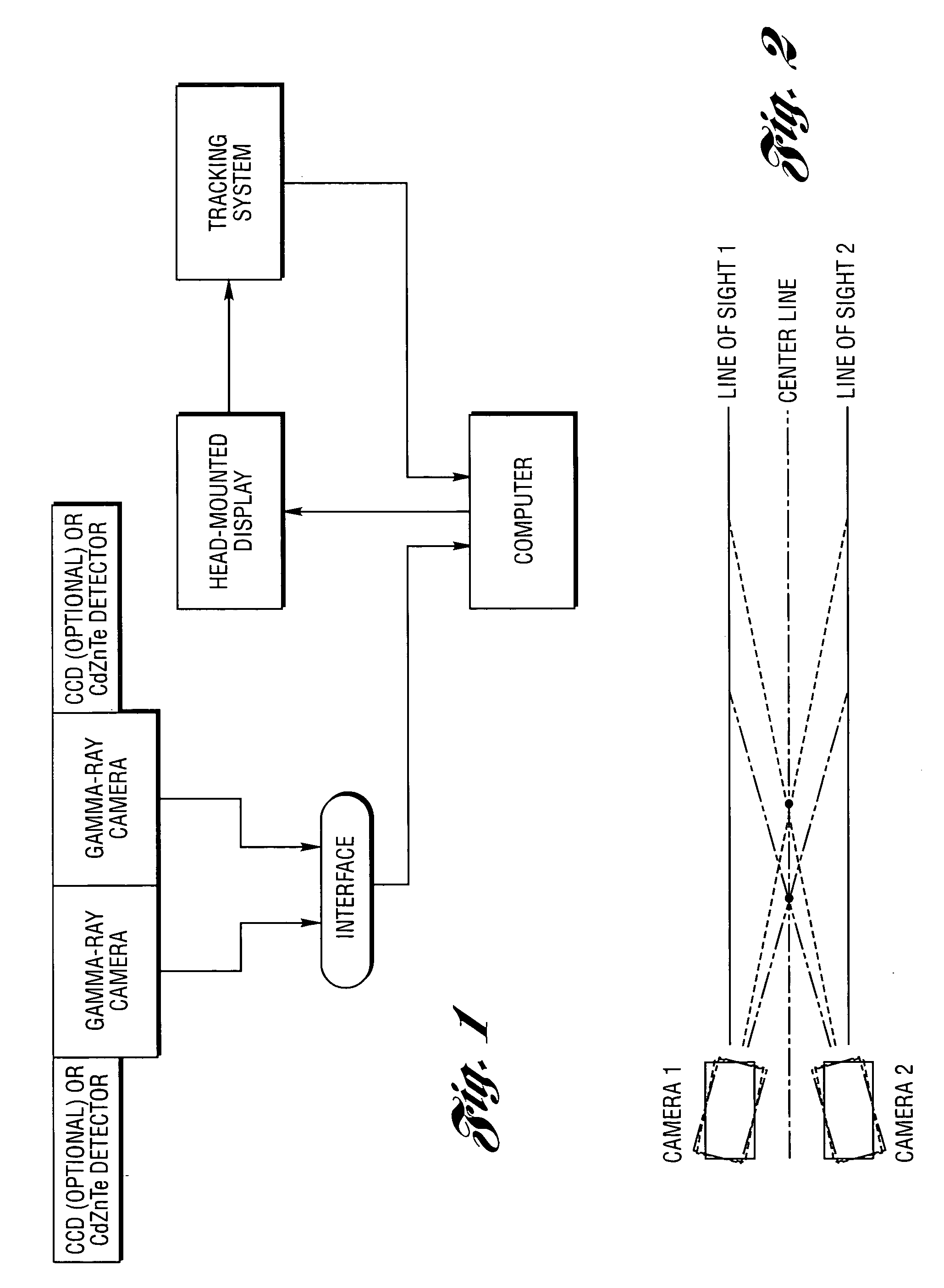
Method and system for high-speed, 3D imaging of optically-invisible radiation and detector and array of such detectors for use therein
InactiveUS20050017181A1Reduce exposureStrong applicationElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesHuman exposureSpectroscopy
A high-speed, three-dimensional, gamma-ray imaging method and system as well as a detector and array of such detectors for use therein are provided which characterize radioactivity distributions in nuclear and radioactive waste and materials facilities by superimposing radiation images on a view of the environment using see-through display screens or shields to provide a stereoscopic view of the radiation. The method and system provide real-time visual feedback about the locations and relative strengths of radioactive sources. The method and system dynamically provide continuous updates to the displayed image illustrating changes, such as source movement. A pair of spaced gamma-ray cameras of a detector subsystem function like “gamma eyes”. A pair of CCD cameras may be coupled to the detector subsystem to obtain information about the physical architecture of the environment. A motion tracking subsystem is used to generate information on the user's position and head orientation to determine what a user “sees”. The invention exploits the human brain's ability to naturally reconstruct a 3D, stereoscopic image from 2D images generated by two “imagers” separated by a known angle(s) without the need for 3D mathematical image reconstruction. The method and system are not only tools for minimizing human exposure to radiation thus assisting in ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) planning, but also are helpful for identifying contamination in, for example, laboratory or industrial settings. Other optically-invisible radiation such as infrared radiation caused by smoldering fires may also be imaged. Detectors are manufactured or configured in curvilinear geometries (such as hemispheres, spheres, circles, arcs, or other arrangements) to enable sampling of the ionizing radiation field for determination of positional activity (absolute or relative amounts of ionizing radiation) or spectroscopy (energy distributions of photons). More than one detector system may be used to obtain three-dimensional information. The detector systems are specifically suitable for direct visualization of radiation fields.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Fibre Optic Dosimeter
InactiveUS20090014665A1Reduces and prevents entryReduce and prevent detectionX-ray spectral distribution measurementElectrical apparatusDosimeterLight pipe
A dosimeter (100) for radiation fields is described. The dosimeter includes a scintillator (1) a light pipe (2) having a first end in optical communication with the scintillator (1) and a light detector (6). The light pipe (2) may have a hollow core (3) with a light reflective material about the periphery of the hollow core (3). The dosimeter (100) may further include a light source (61) that generates light for use as a calibrating signal for a measurement signal and / or for use to check the light pipe (2).
Owner:THE UNIV OF SYDNEY
Radiotherapy planning method and device, radiotherapy dose determining method and device and radiotherapy quality guaranteeing method and device
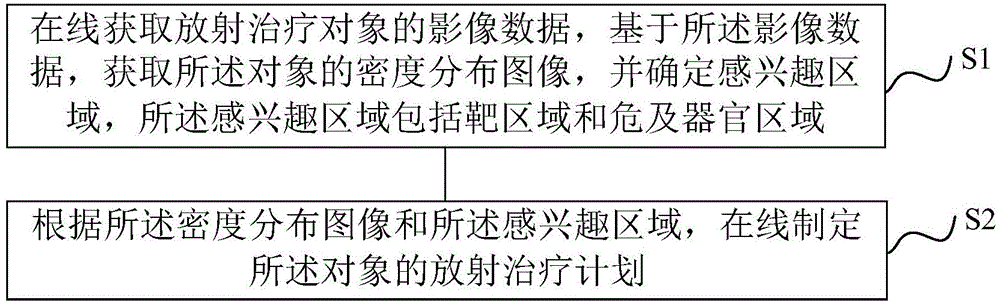
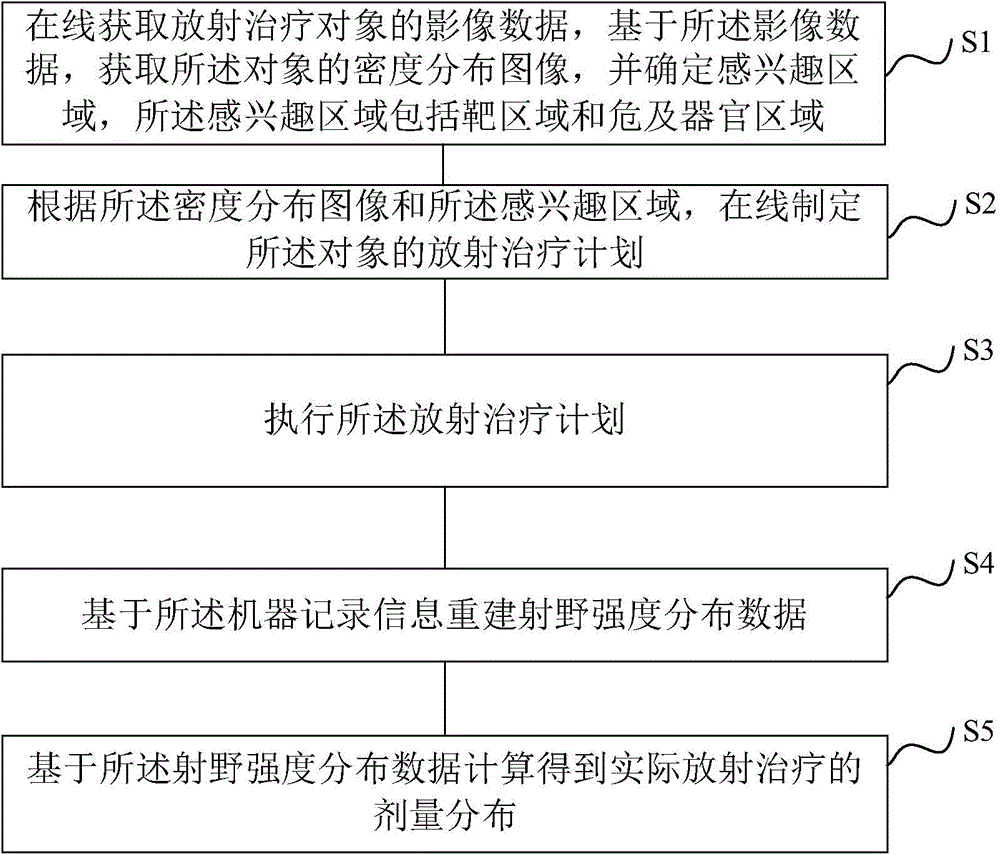
ActiveCN104548372AHigh precisionReduce repetitive setup errorsRadiation therapyObject basedDensity distribution
The invention discloses a radiotherapy planning method and device, a radiotherapy dose determining method and device and a radiotherapy quality guaranteeing method and device. The radiotherapy dose determining method includes the steps of online obtaining image data of a radiotherapy object, obtaining a density distribution image of the object based on the image data, determining a region of interest, and online making a radiotherapy plan of the object according to the density distribution image and the region of interest; executing the radiotherapy plan; rebuilding radiation field intensity distribution data based on information recorded by machines; carrying out calculation based on the radiation field intensity distribution data to obtain practical radiotherapy dose distribution. As the online-obtained image data are adopted, the accuracy of the image data is improved; as the radiation field intensity distribution data are rebuilt based on the information recorded by the machines, the dose distribution accuracy is higher. In the radiotherapy quality guaranteeing method, when deviation exists between the practical dose distribution result and a main plan dose, a sub-plan is modified, it is guaranteed that the use total dost is coincident with the plan dose, and the radiotherapy quality is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Polygonal radiation module having radiating members without light guiding board
A polygonal radiation module having radiating members without a light guiding board for a backlight module or a lighting device includes a polygonal optical plate with a rising area having a rising surface defined at a center thereof, a plurality of radiating members, and a diffusion plate. The radiating members surrounding a periphery of the optical plate possess radiant half-intensity angles of the radiation below 15 degrees for respectively forming optic axial directions thereof. Whereby, the optic axial directions of the radiating members face to the rising surface, and radiation fields are individually generated as pivoted by the optic axial directions to cast at the rising surface. Thus, an even radiating surface caused by a diffusion of light source from the diffusion plate could be preferably obtained even if no light guiding board is applied.
Owner:SOUTHERN TAIWAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
4 dimensional magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7382129B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correlationVoxel
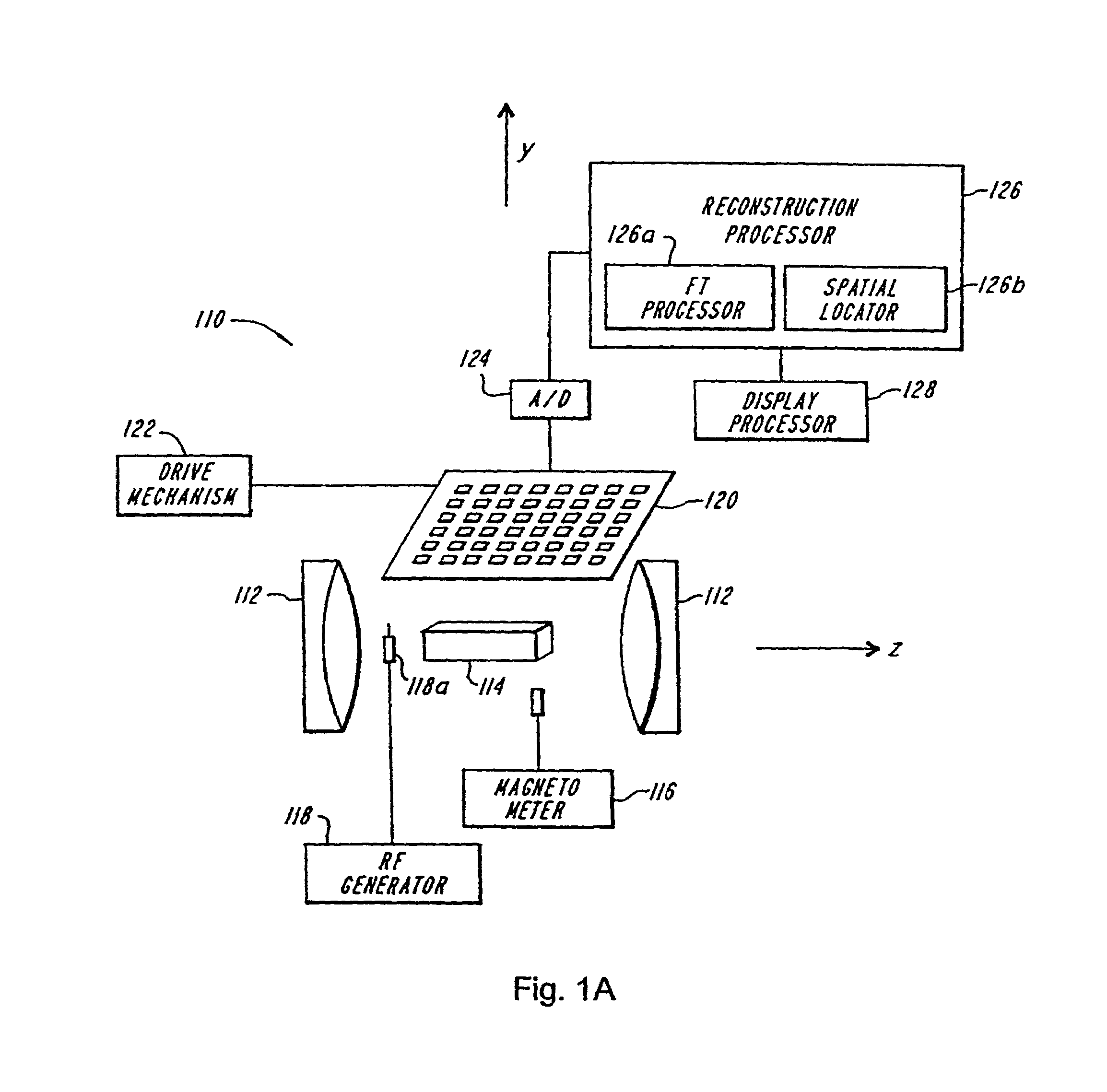
Provided are apparatus and methods for forming a multidimensional image of inanimate or animate objects which utilize a magnetization source (112) to magnetize a volume of an object to be imaged, a radiation source (118) for applying a radiation field to the object to be imaged, an output signal detector (120) for producing output signals in response to the secondary radiation at a plurality of spatial locations outside of the object as a function of time, processors (126, 126a and 126b) for determining a plurality of Fourier components, for associating the Fourier components due to each voxel (14) by phase, and for converting each set of components into a voxel location, and an image processor (128) for producing an image.
Owner:MILLS RANDELL L
Josephson junction array device, and manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6348699B1Generation of microwave power is considerably enhancedIncrease generationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMicrowaveImpedance matching
Owner:OXXEL OXIDE ELECTRONICS TECH
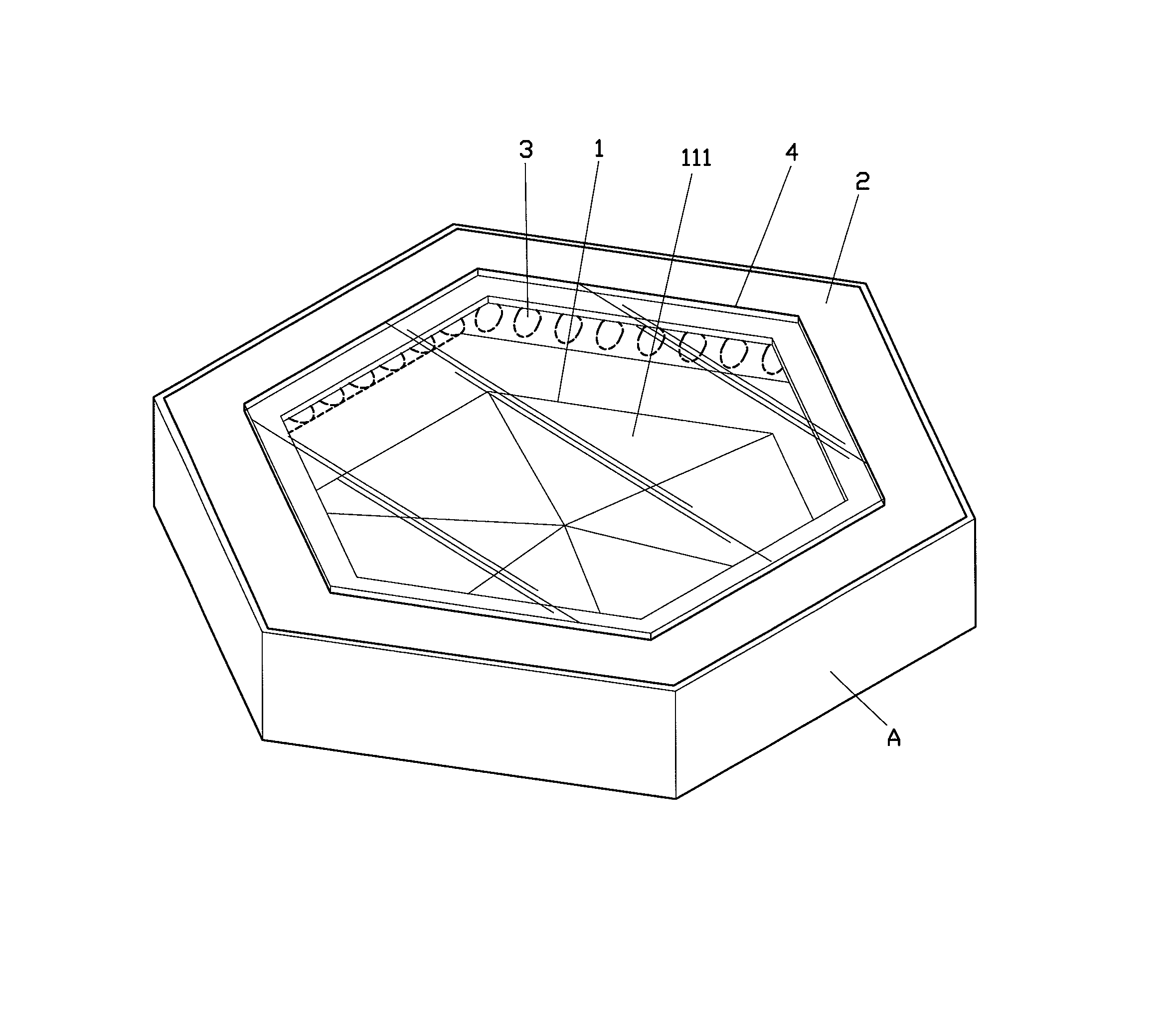
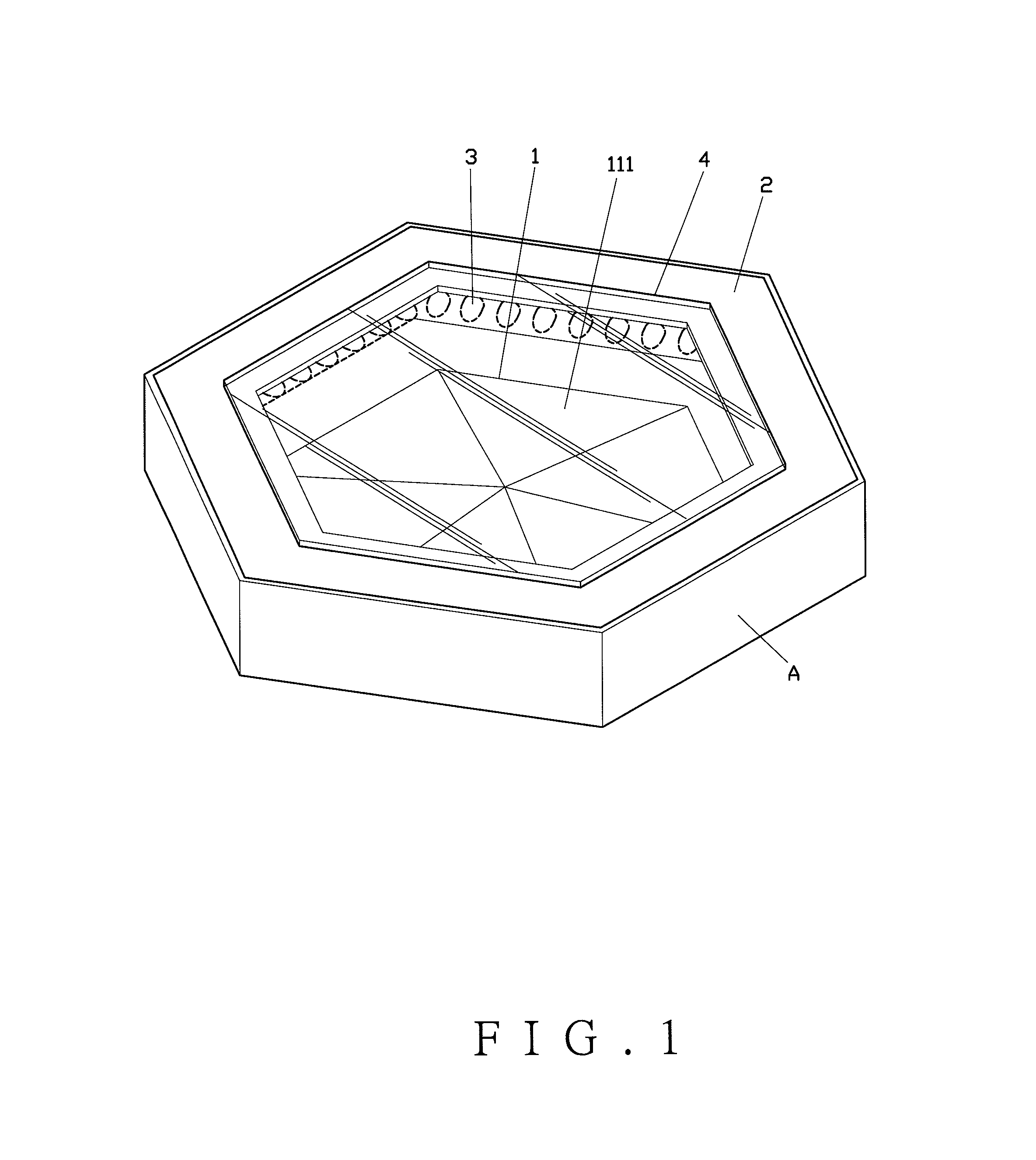
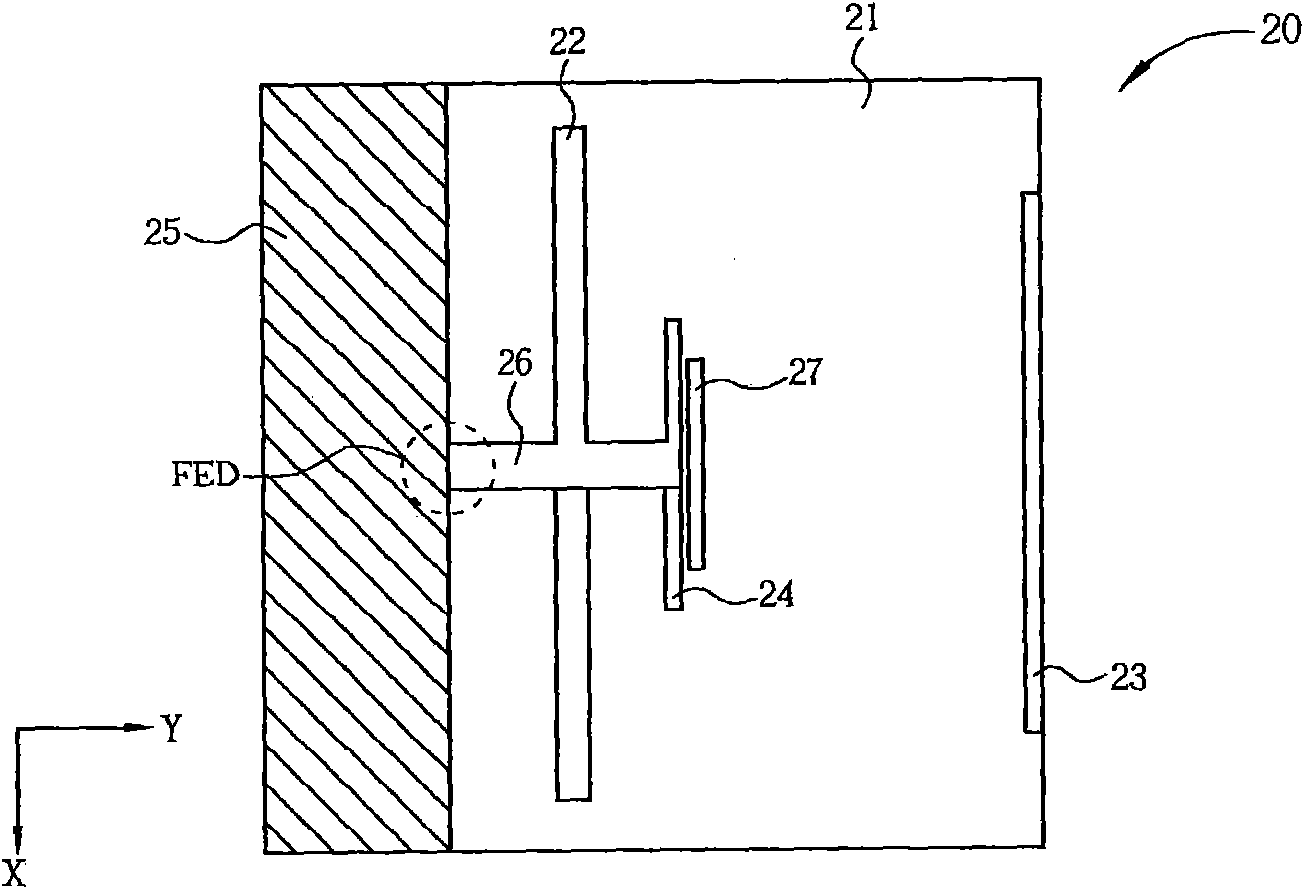
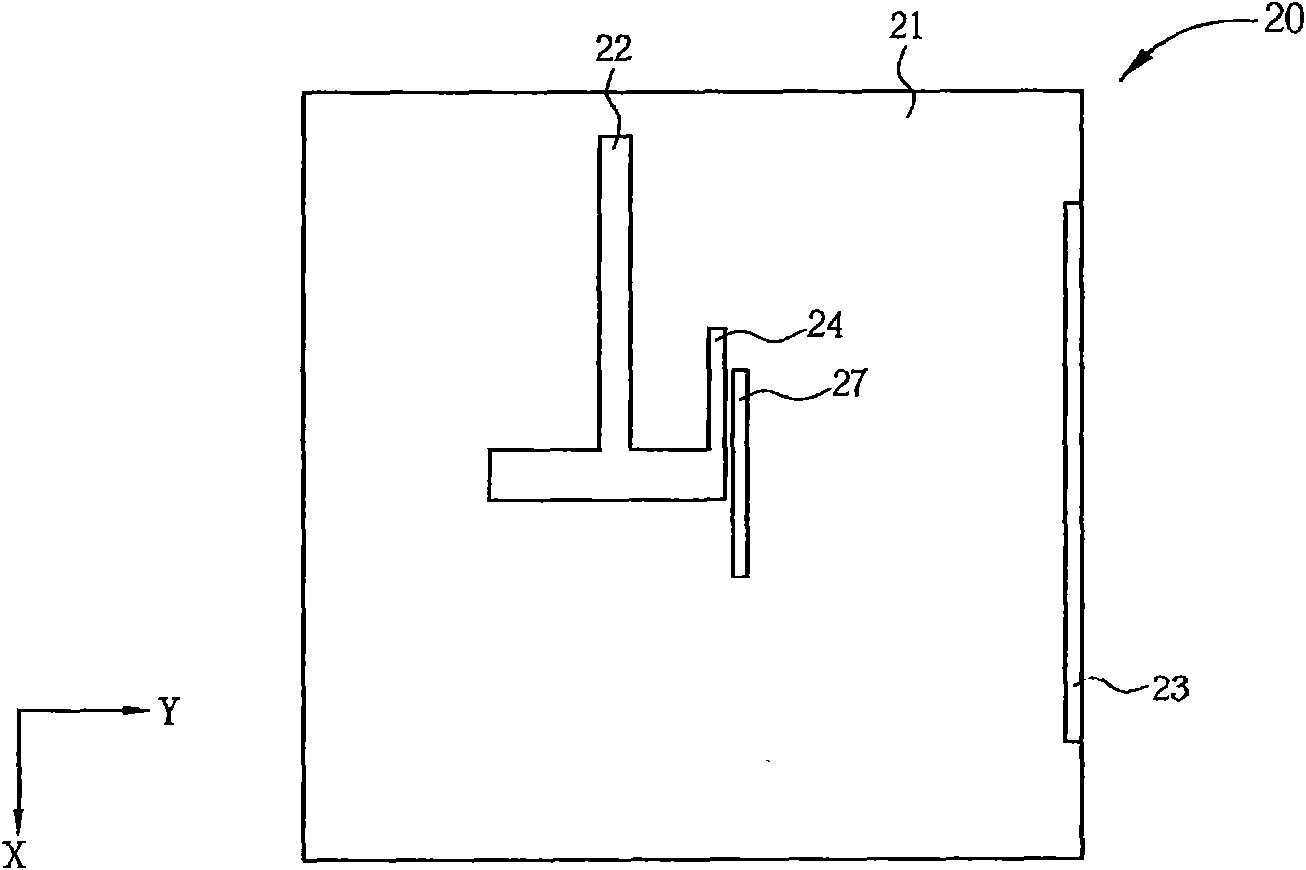
Double-frequency printing type yagi antenna
The invention discloses a double-frequency printing type yagi antenna which comprises a substrate, a first driver, a first director, a second driver and a reverberator. The first driver is formed on the substrate, and is used for generating a radiation field type of a first waveband. The first director is formed at one side of the first driver on the substrate, and is used for guiding the radiation field type of the first waveband to the first direction. The second driver is formed between the first driver and the first director on the substrate, and is used for generating the radiation field type of the second waveband. The reverberator is formed at one side of the first driver on the substrate, and is used for reverberating the first waveband and the second waveband at the radiation field type to the first direction.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
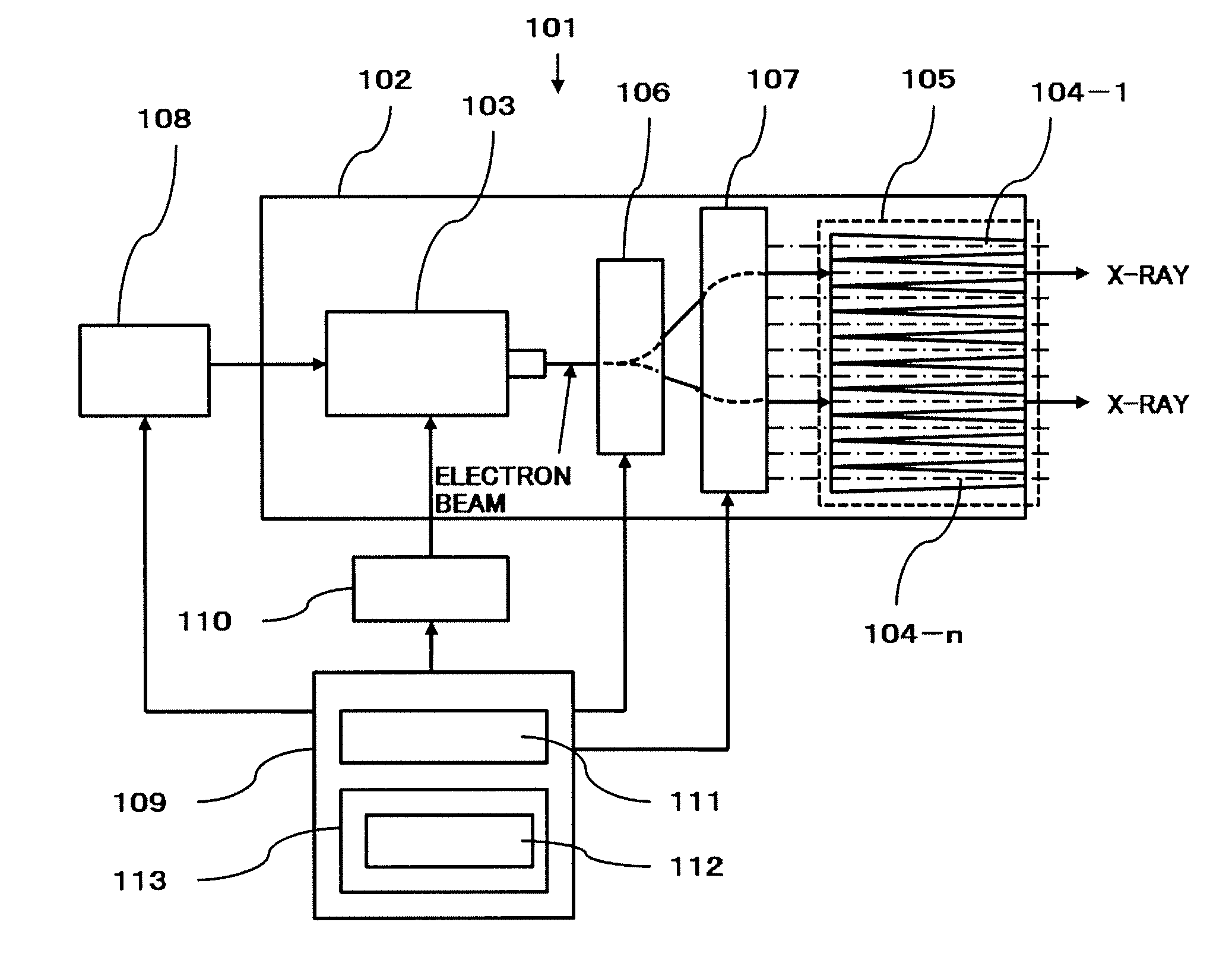
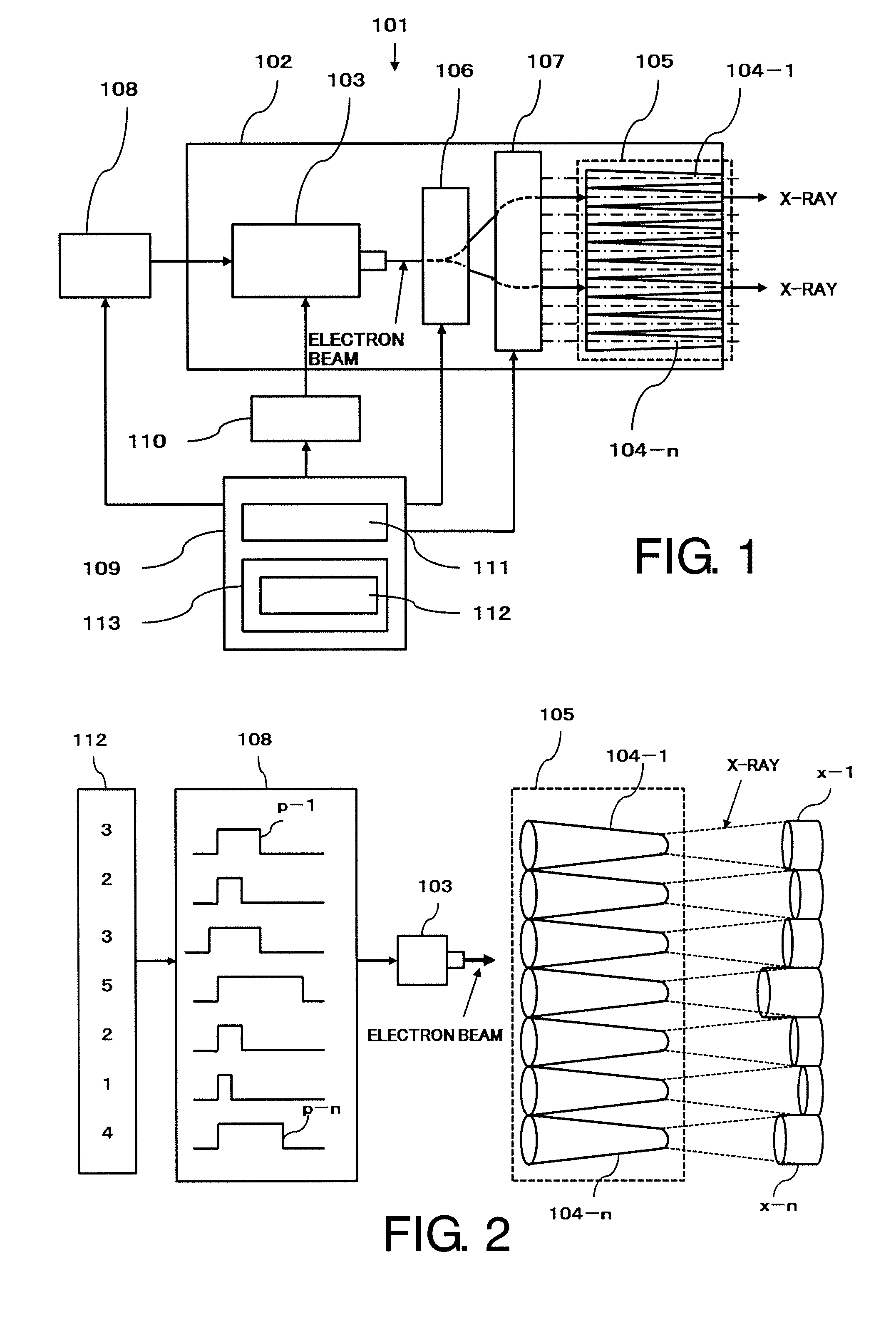
X-ray generator
InactiveUS20090154650A1Reduce the burden onShorten treatment timeX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingRadiation fieldHigh energy
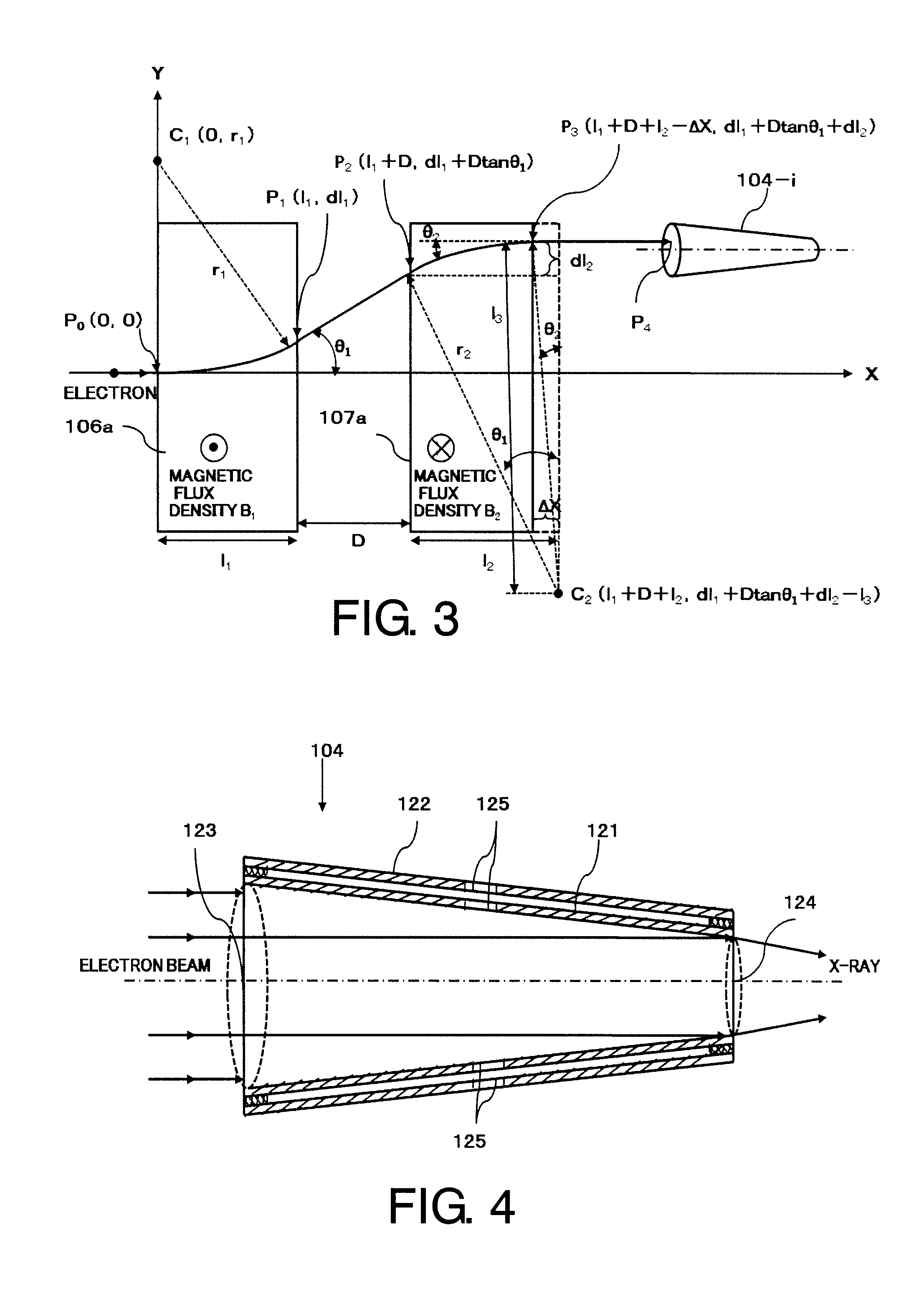
The electron beam corresponding to radiation intensity data 112 is output from an electron source 103 by supplying high energy pulse p-1 through p-n corresponding to the radiation intensity data 112 of the radiation field to electron source 103 from power source 108. This electron beam is deflected to be incident in parallel to the medial axis of the X-ray target tube by a deflection means comprising electromagnets, X-ray beam x-1 through x-n which electron beam collides to the inner wall of X-ray target tube 104-1 through 104-n, and have desired intensity is irradiated.
Owner:AET
Real-time three-dimensional radiation therapy apparatus and method
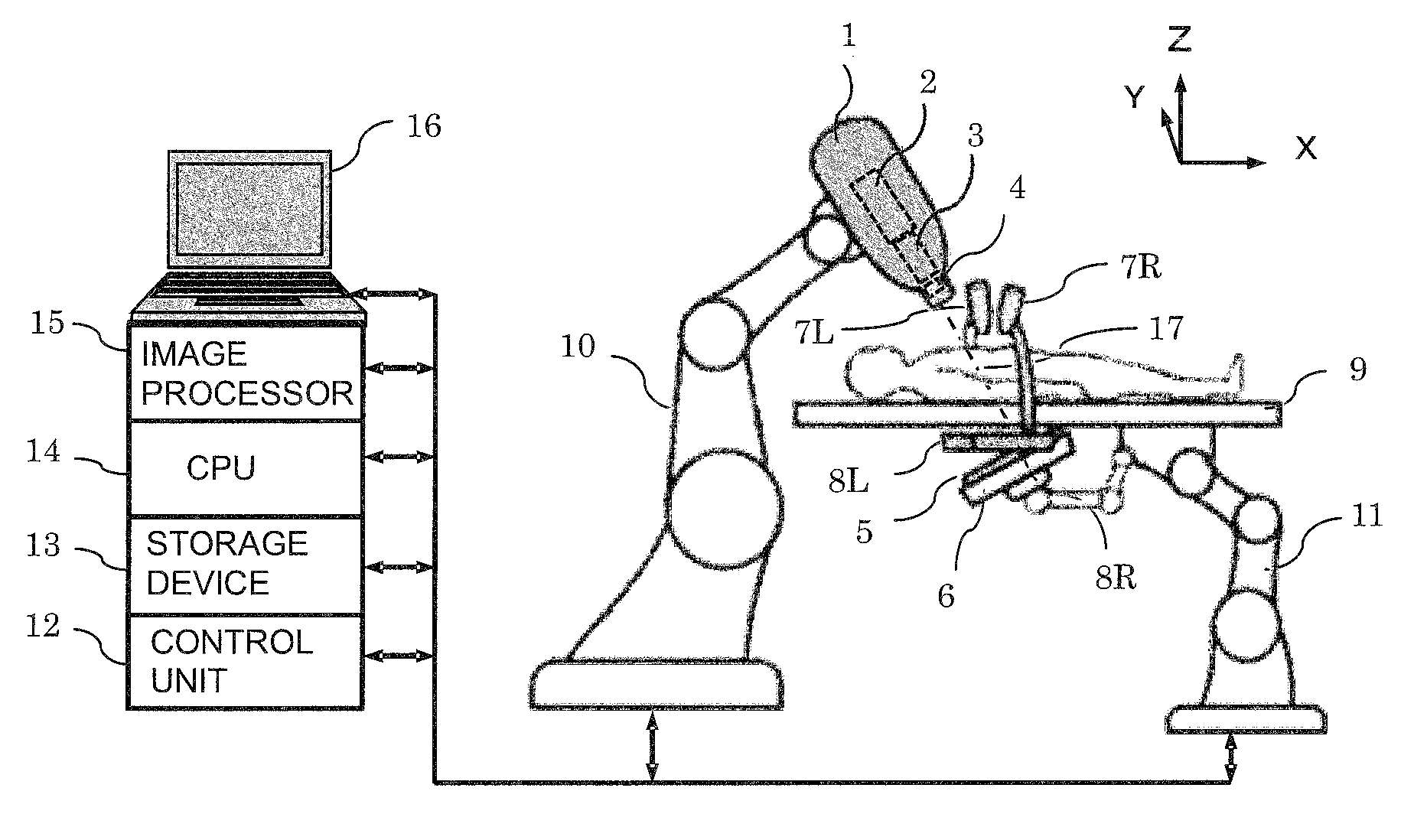
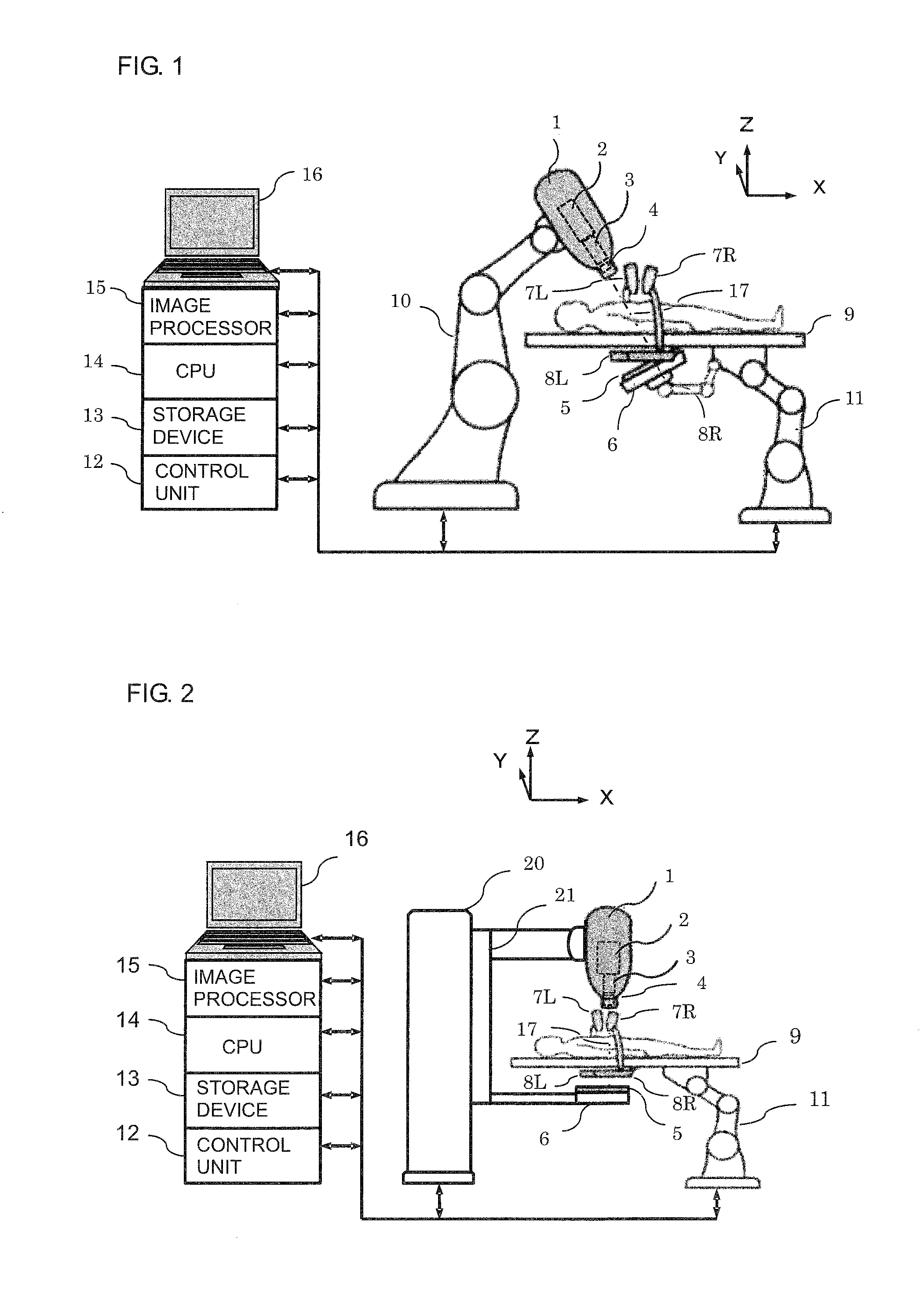
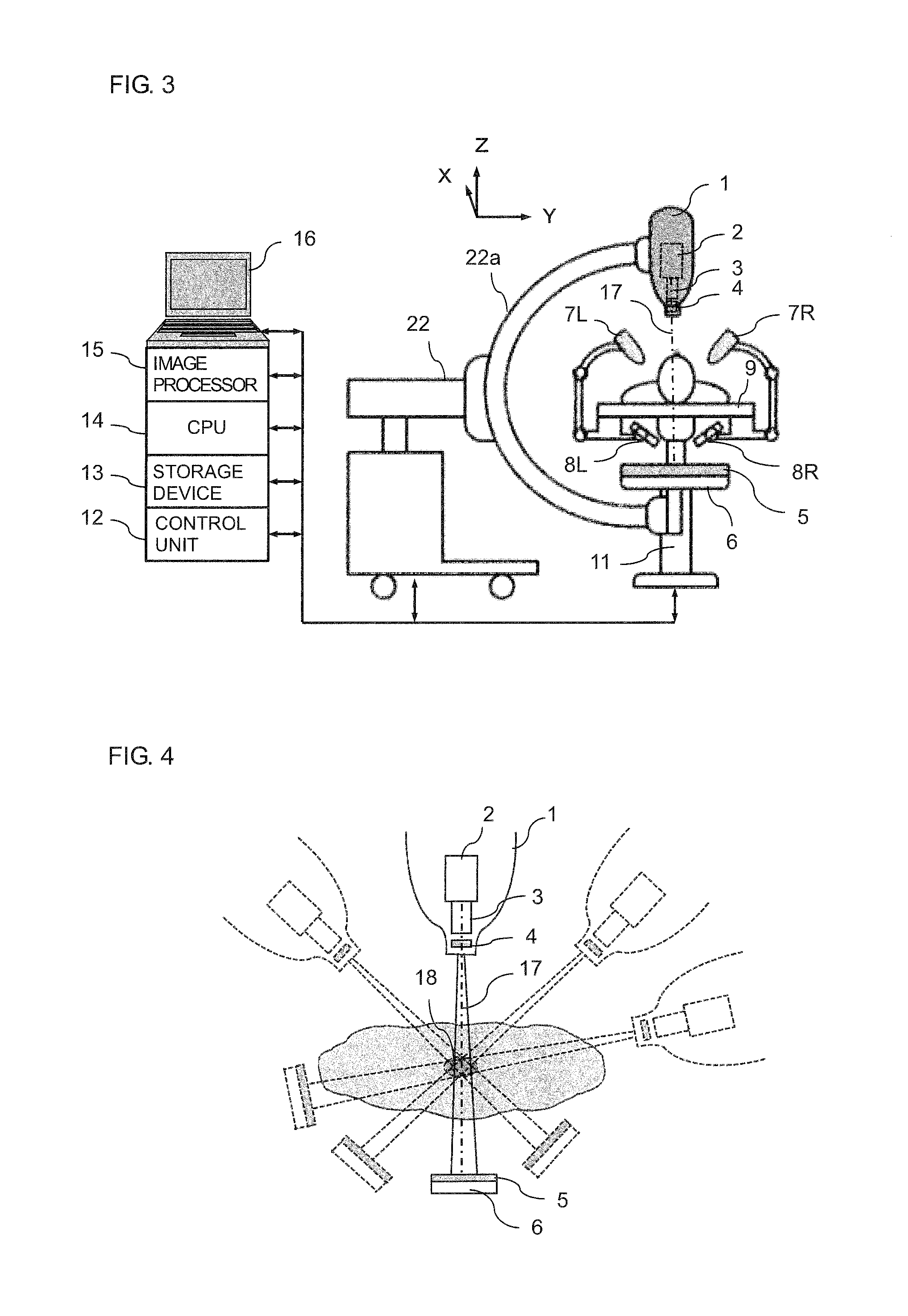
InactiveUS9149656B2High precisionIncrease speedMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment targetsX-ray
A radiation therapy apparatus including a robot supporting a robot head; a therapeutic radiation source attached to the robot head; a collimator for adjusting a radiation field shape of therapeutic radiation radiated from the therapeutic radiation source; a first therapeutic radiation detector attached to the robot head; a couch configured to support a patient lying supine thereon; a second therapeutic radiation detector for detecting the therapeutic radiation, disposed opposite the first therapeutic radiation detector with the couch disposed therebetween; at least two X-ray sources and detectors for position detection of a marker and / or a treatment target; an image processor for reconstructing an image of the treatment target; and a CPU that computes the intensity, irradiation direction, dose, and dose distribution of the therapeutic radiation, and dose absorbed by the treatment target, radiation field shape, and position of the treatment target in real time for feedback to a next irradiation.
Owner:ACCUTHERA
Surgical antenna
ActiveUS20100030207A1Ensure efficient flowPrevents tissue charringIncision instrumentsSurgical instruments for heatingTransformerImpedance matching
A surgical instrument (100) (e.g. scalpel) is disclosed which has an antenna arranged to emit a substantially uniform microwave radiation field (e.g. having a frequency of 5-100 GHz) at an edge of a cutting element (110) (e.g. blade). The emitted radiation can cauterise tissue e.g. broken blood vessels simultaneously with cutting. The antenna may be integral with the cutting element, e.g. a metallised piece of ceramic attachable at an end of a waveguide (120, 150) to receive radiation therefrom. The cutting element (110) can include a quarter wave transformer to couple power efficiently from the waveguide (120). The instrument can be used with impedance matching apparatus to control the energy delivered into the tissue. Also disclosed is an invasive ablation probe (e.g. insertable through a catheter) having a plurality of radiating elements whose emitted field combine to give a uniform effect at an insertion end of the probe.
Owner:CREO MEDICAL LTD
Human body communication system and communication device
InactiveUS7664476B2Facilitate communicationResonant long antennasNear-field transmissionHuman bodyCommunications system
Disclosed herein is a human body communication system for communicating data via an electric field formed by intervention of a human body, the human body communication system including: a transmitter for generating the electric field by transmitting a potential difference signal corresponding to transmission data from a transmitting electrode; and a receiver for receiving the data by reading the potential difference signal in the electric field by a receiving electrode; wherein the transmitter and the receiver use the potential difference signal in a frequency band such that a quasi-electrostatic field formed within the human body is dominant over a radiation field formed outside the human body when the transmitting electrode and the receiving electrode are each disposed in very close vicinity to the human body.
Owner:SONY CORP
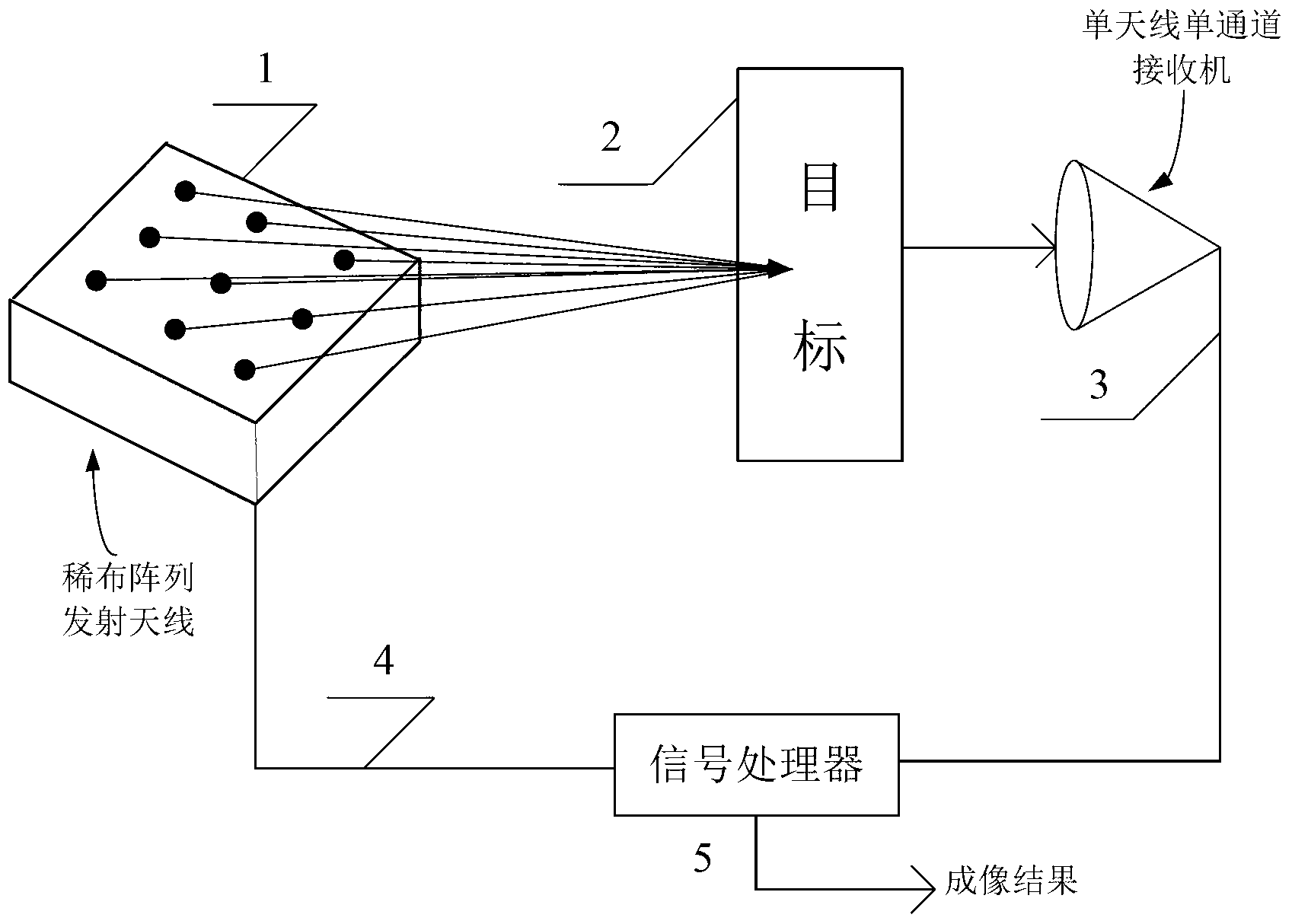
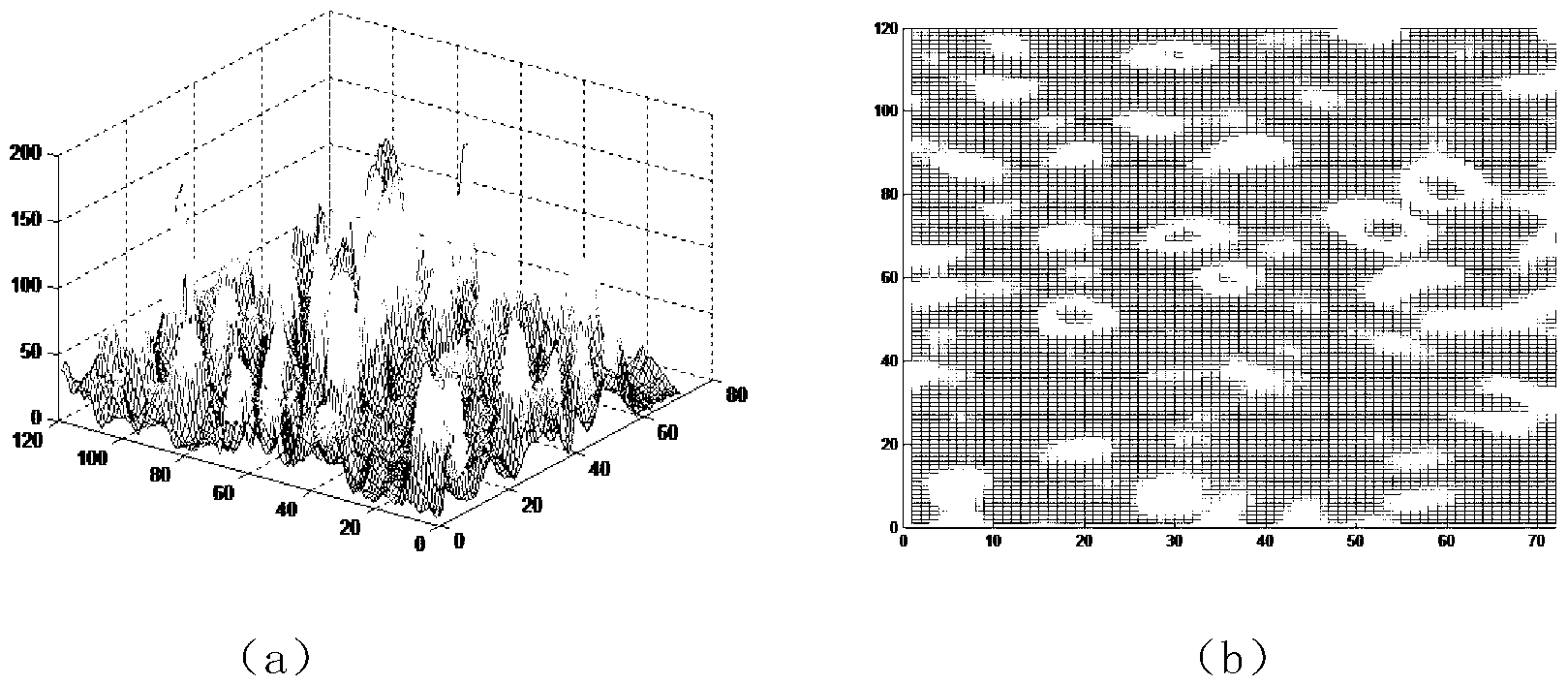
Microwave related imaging system and imaging method based on thinned array
InactiveCN103235298AReduce usageReduce complexityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionThinned arrayAmbiguity
The invention discloses a microwave related imaging system and a microwave related imaging method based on a thinned array, which mainly aim to solve the problems of poor imaging effect and low resolution when non-radial relative movement does not exist between a radar antenna and a target in the prior art. The system comprises a transmitting antenna (1), a target (2), a receiver (3) and a signal processor (5), wherein the transmitting antenna (1) is formed by a thinned array antenna; different microwave coded signals are transmitted by all array elements, so as to form a microwave radiation field in space through incoherent superposition; the target (2) is irradiated through the microwave radiation field, so as to generate target scattering echoes; the microwave radiation field (4) on the surface of the target (2) is stored; the target scattering echoes are received by the receiver (3) through a single antenna and a single channel; and the target scattering echoes received by the receiver (3) and the pre-stored microwave radiation field (4) are processed by the signal processor (5), so as to obtain the imaging of the target. By using the system and the method, super-resolution imaging of the target without ambiguity can be realized when the non-radial relative movement does not exist between the radar antenna and the target, and the system and the method can be used for super-resolution imaging of the target by an airborne forward-looking radar and a ball-borne radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Near-field real-time calibration method for human body millimeter wave imaging safety inspection system
InactiveCN102135610ARadiation field disturbance is smallReduce disturbanceWave based measurement systemsTime delaysRadiation field
The invention discloses a near-field real-time calibration method for a human body millimeter wave imaging safety inspection system, and the calibration system comprises a switch array, an antenna array, a metal calibration line, an amplitude and phase consistency calibration module and a relative time delay calibration module. The antenna array is used for measuring a reference signal, the amplitude and phase consistency calibration module is used for calibrating amplitude and phase consistency, and the relative time delay calibration module is used for calibrating relative time delay, thereby completing the near-field real-time calibration method for the human body millimeter wave imaging safety inspection system. In the method, the metal line is adopted for performing near-field calibration on the imaging system, and the disturbance of the structure of the metal calibration line on a radiation field of the antenna array is small, so that the calibration repeatability is good, and the calibration precision can be ensured. The calibration method can complete calibration by only performing measurement on an air target region once, a calibration reflector does not need to be placed, the calibration time is less than imaging measurement time, and real-time calibration can be performed on a working clearance of the system at any time.
Owner:中国航天科工集团第二研究院二〇三所
Electromagnetic radiation sensitivity testing method for increasing test precision
ActiveCN101520482AAccurate detectionMeet the test conditionsElectrical testingElectric field sensorCoupling
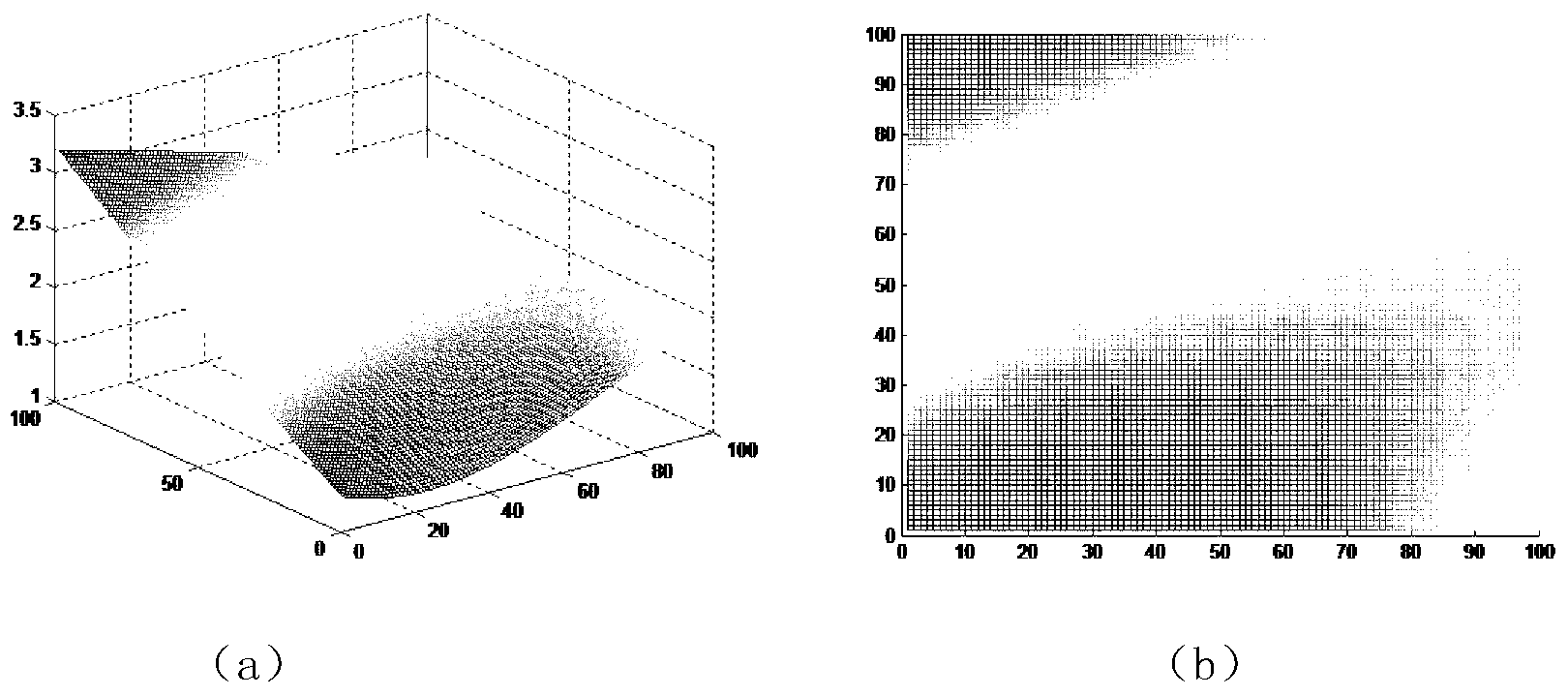
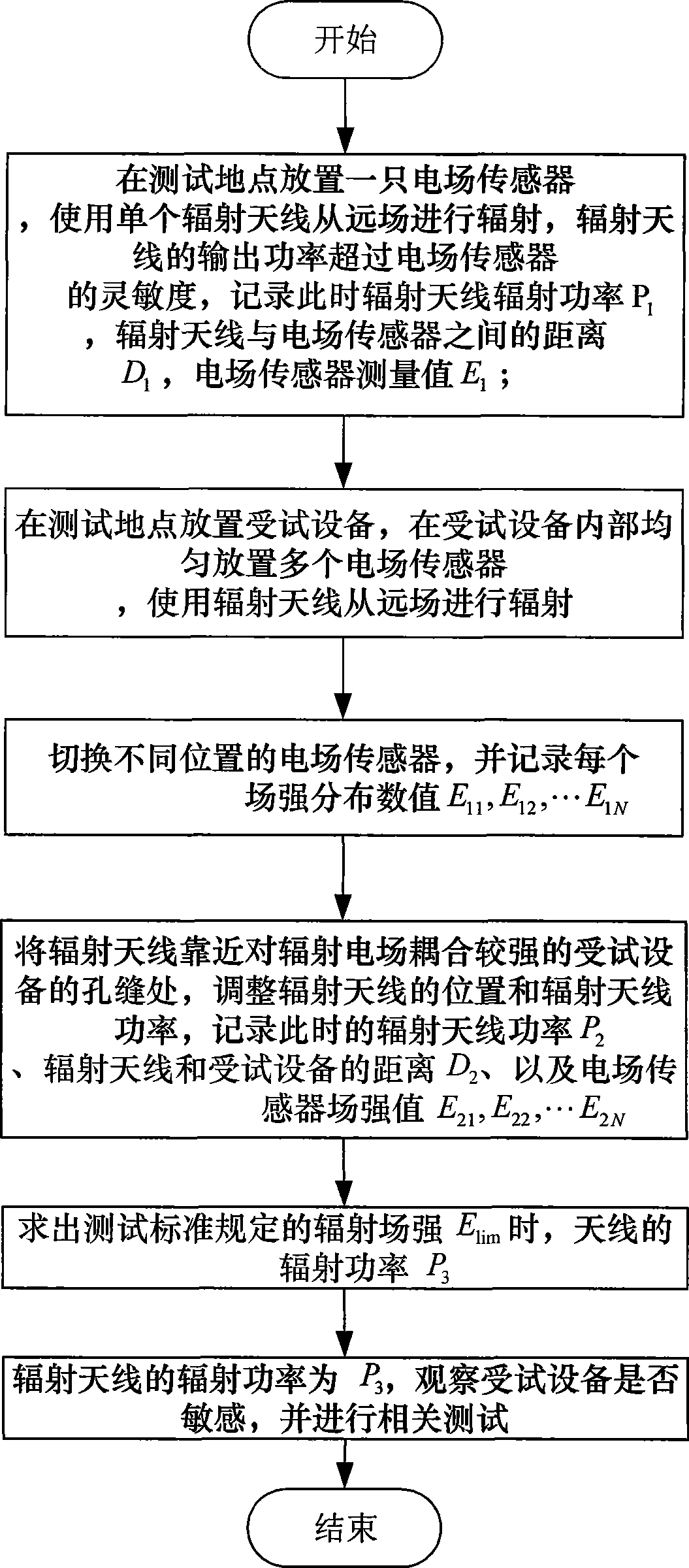
The invention discloses an electromagnetic radiation sensitivity testing method for increasing test precision, which comprises six steps: a single radiating antenna is used for radiating from a far field, and the radiating power of the antenna, the field intensity value of electric-field sensors and the distance between the antenna and the electric-field sensors are measured; a tested device is placed, and a plurality of electric-field sensors are arranged; the values of the electric-field sensors are recorded at the moment; the radiating antenna is approached to the tested device, the difference of the field intensity value at the moment and the field intensity measured in the last step is from 0dB to 6 dB, and the values of the electric-field sensors are recorded at the moment; the power of the radiating antenna is calculated in standard field intensity; and a sensitivity test is carried out. The invention gives out satisfying conditions between the radiation field intensity Elim prescribed by a testing standard and the radiation power P of the radiating antenna, utilizes an antenna theory to calculate the satisfying conditions between the power of the radiating antenna and the measuring field intensity value of a testing point when an internal coupling field of the tested device reaches the testing requirement and gives out a quantized calculating method, thereby increasing the precision of the electromagnetic radiation sensitivity test, and ensuring that a testing result is accurate and can repeatedly appear.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and system to reconstruct treatment dose to a patient from integrated exit-transit images of radiation fields taken during treatment
A method and system to compute the dose to a patient (2) given a captured integrated exit-transit image (5) of the radiation rays (4) traveling from the source of x-rays (1) through the patient (2) to the imaging device (3) to product the exit-transit image (5). Each radiation field image (5) is transformed (6,8,10,12) to multiple images (7,9,11,13) for each phantom thickness (26) that was measured with the imaging device (3) for a range of field sizes (21). Given the water equivalent path (22) through the patient for a ray (4) reaching a pixel (15, 16), the final pixel value (19) is interpolated from the images (9, 11) that bracket the water equivalent path through the patient (22).
Owner:LIFELINE SOFTWARE INC
Gamma nuclide identification method
ActiveCN105607111AThe principle is simpleEasy to implementX-ray spectral distribution measurementGamma energyRadiation field
The invention provides a gamma nuclide fast identification method in a complex radiation field, comprising the following steps: measuring a radiation field to get a gamma energy spectrum; deducting a comprehensive background from the gamma energy spectrum and reducing the noise of the gamma energy spectrum to get a net energy spectrum; determining potential nuclides according to the peak positions in the net energy spectrum; calculating the total net peak area of each potential nuclide; standardizing the total net peak area of each potential nuclide to get the standardized total net peak area of the potential nuclide; deducting a Compton scattering background from the standardized total net peak area of each potential nuclide to get the pure peak area value of each potential nuclide; calculating the total probability value and the probability standard threshold of each potential nuclide in the radiation field; and calculating the existence probability of each potential nuclide. According to the invention, multiple times of background deduction calculation and standardization are performed on the measured energy spectrum data, and a nuclide can be identified and the existence probability of the nuclide can be calculated quickly based on the total probability value calculated based on the probability statistics principle and the standard threshold calculated by a standard source.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com