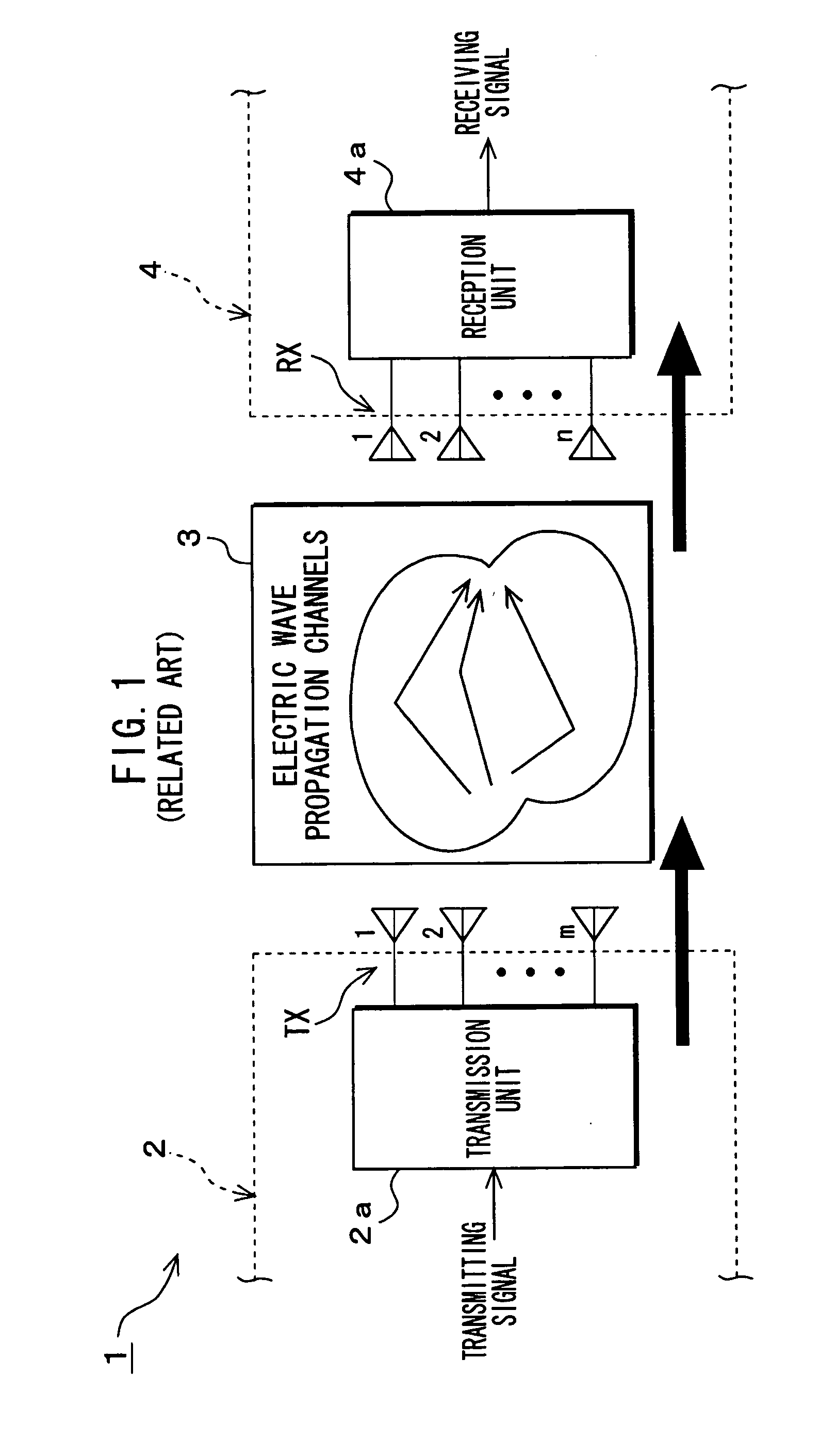
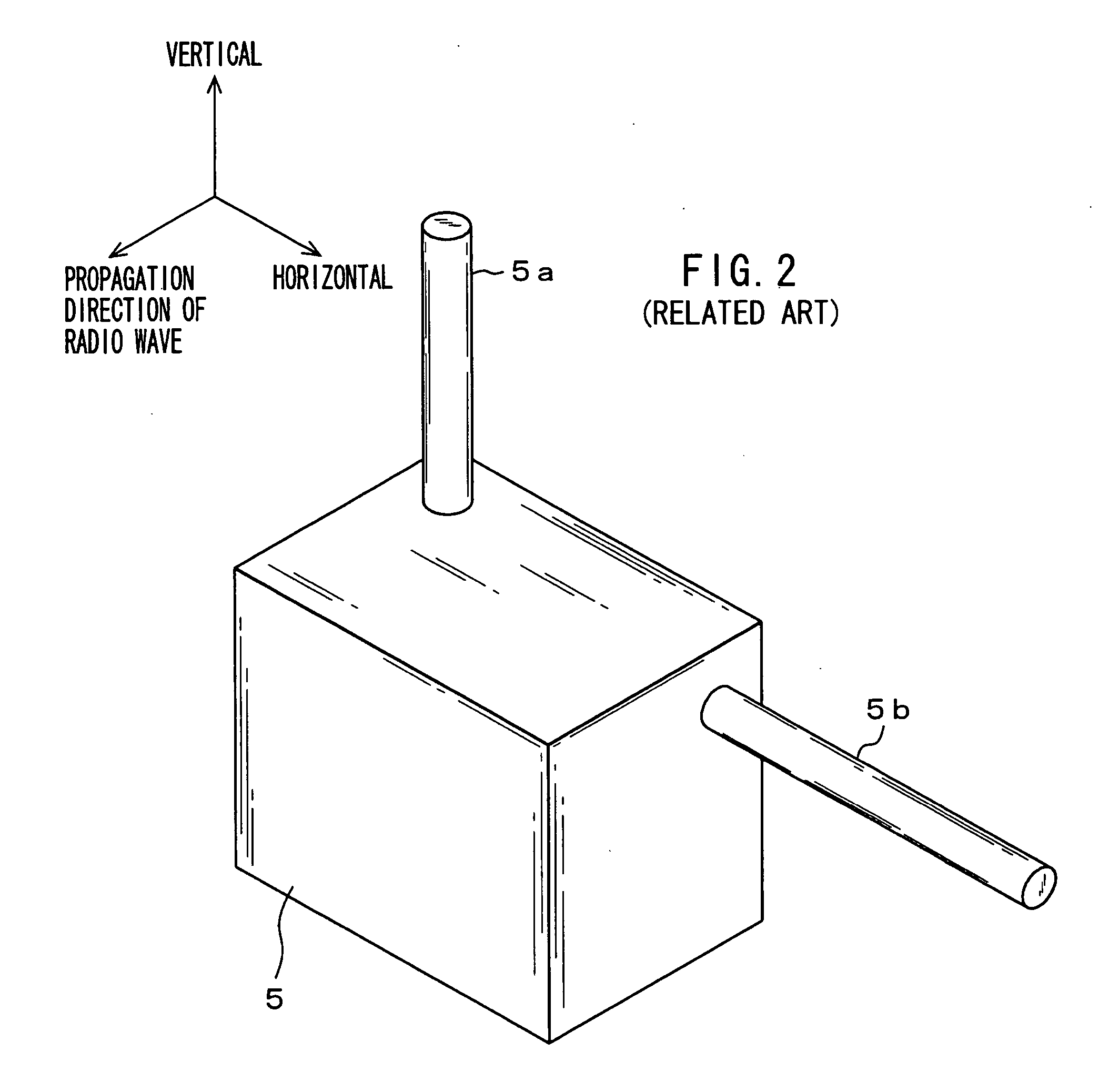
Patents
Literature
243 results about "Planar antennas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
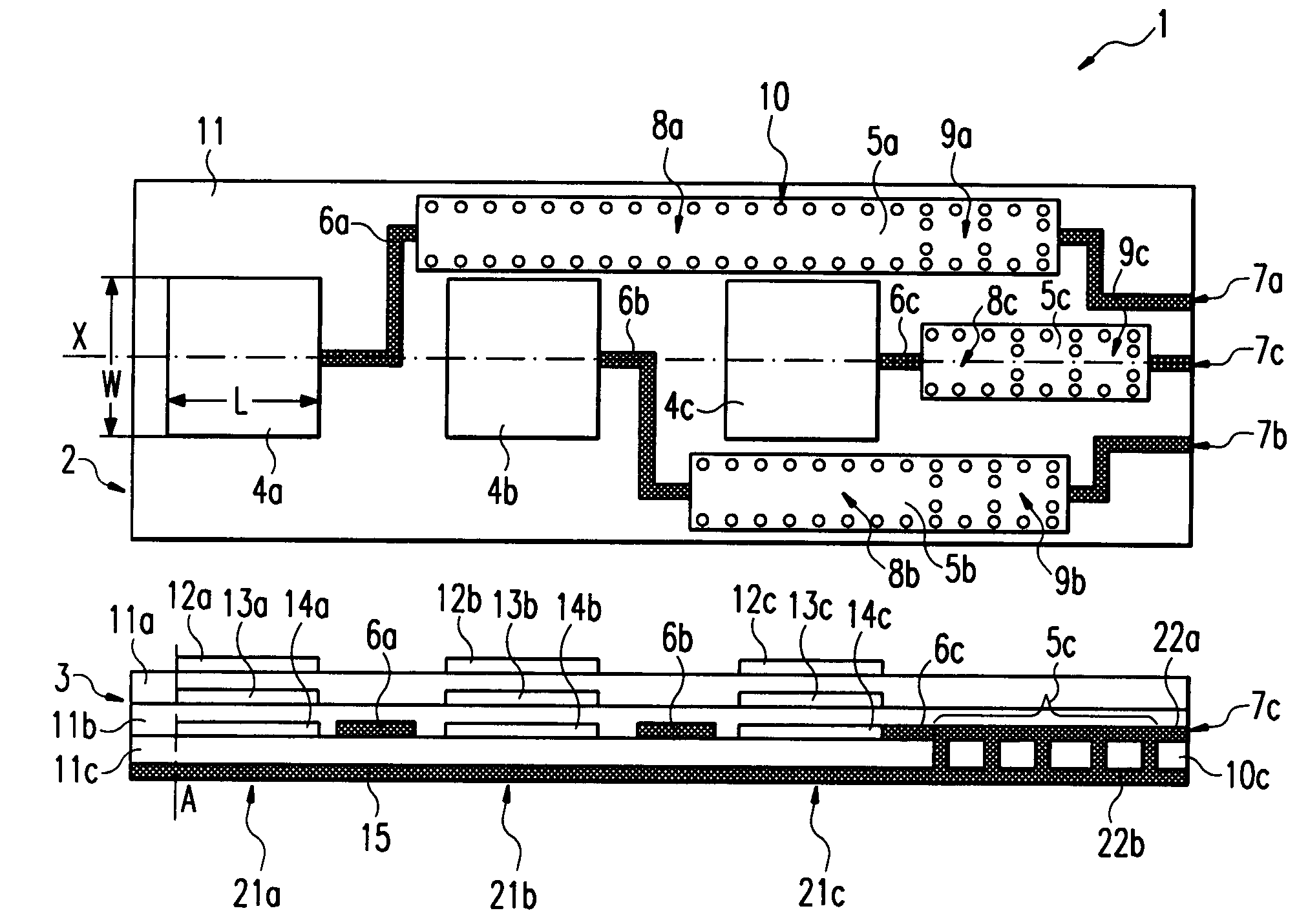
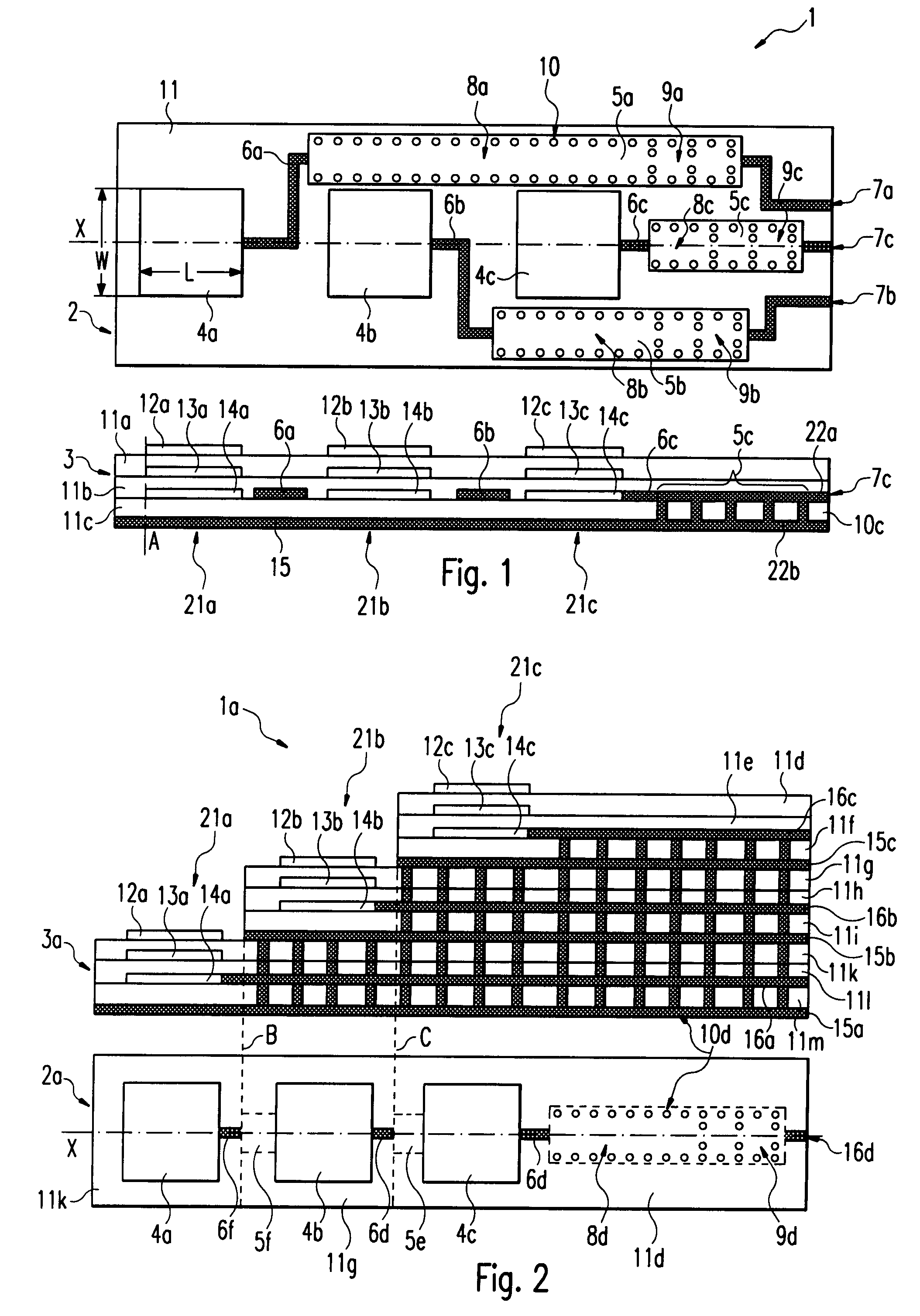
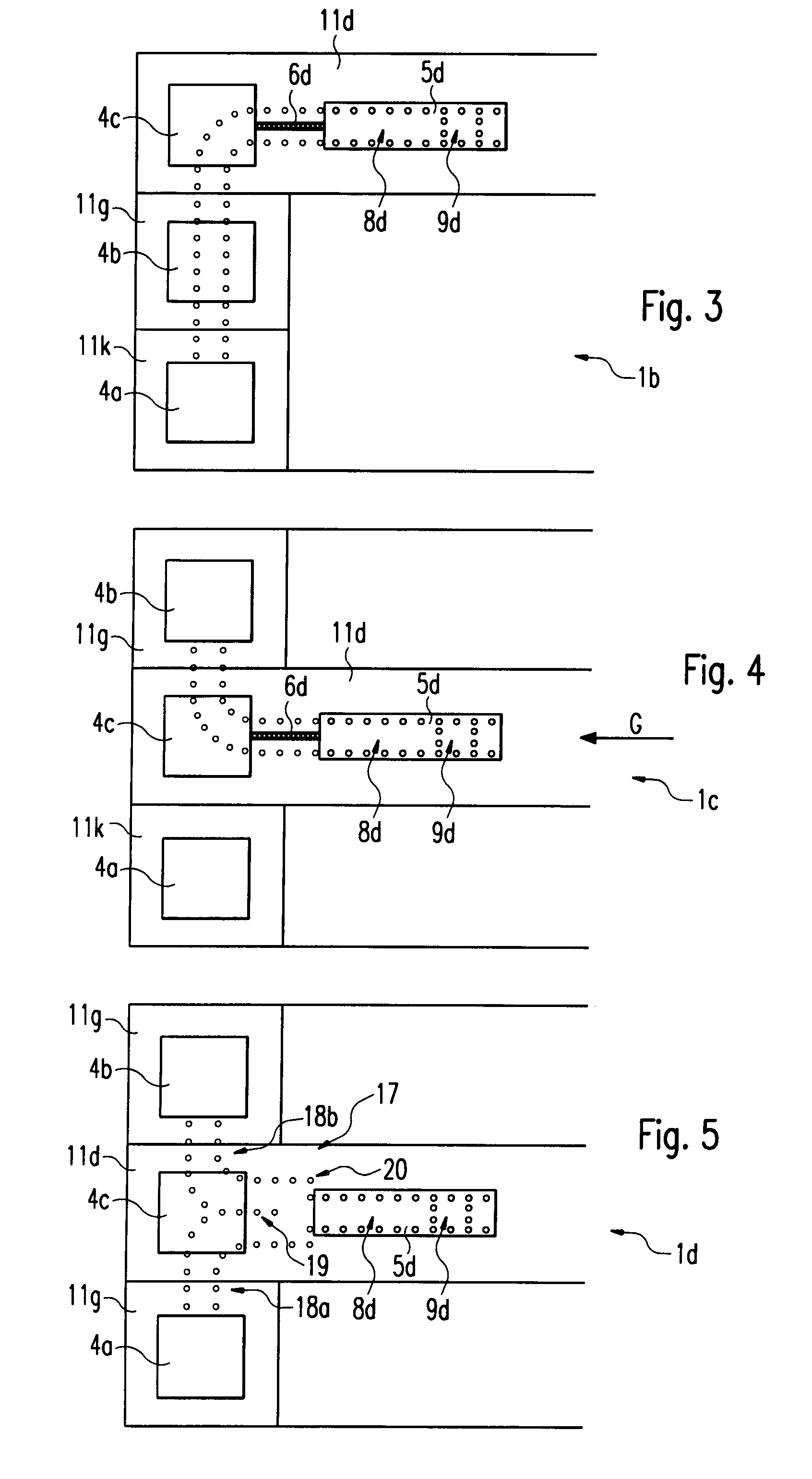
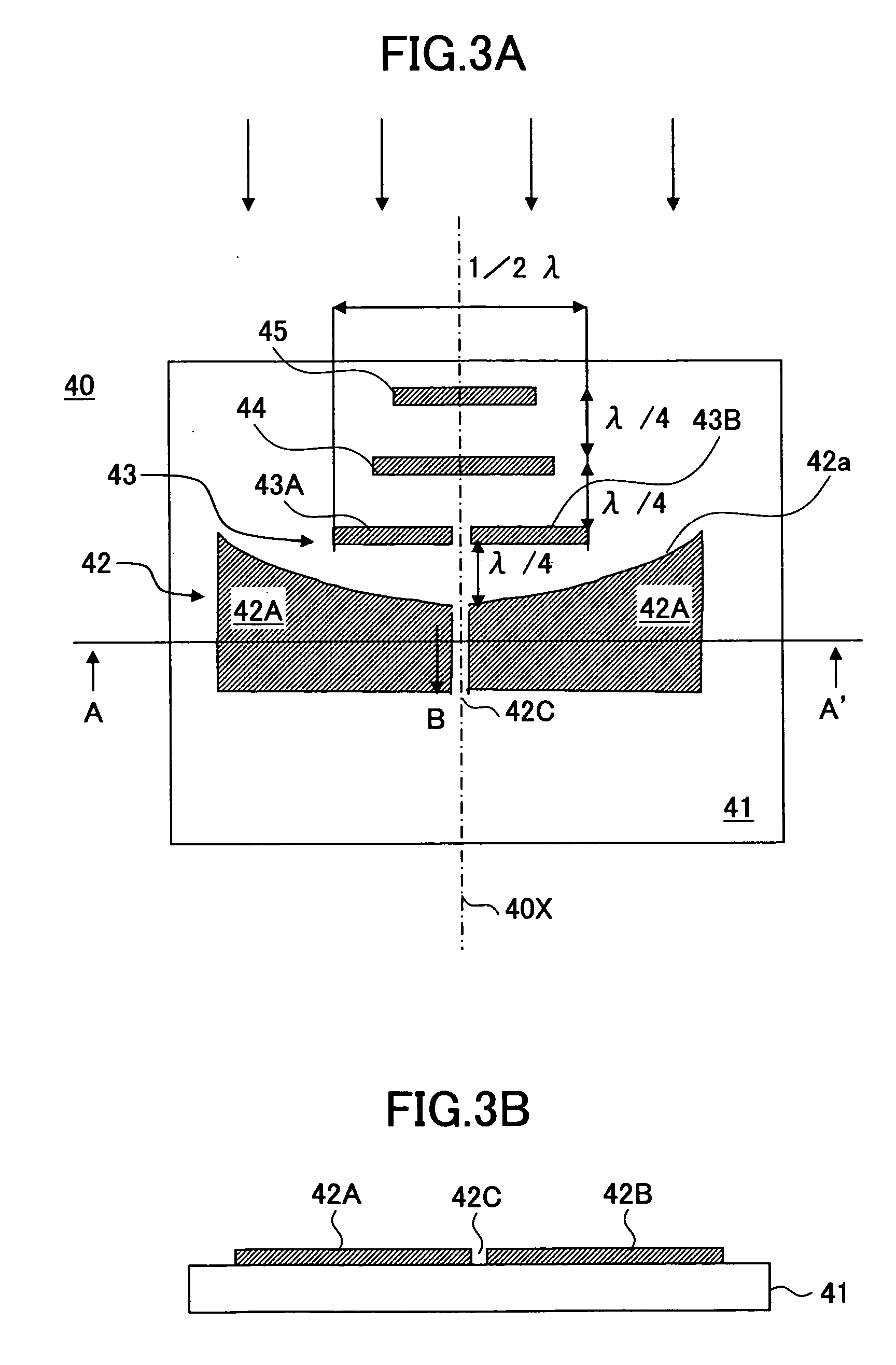
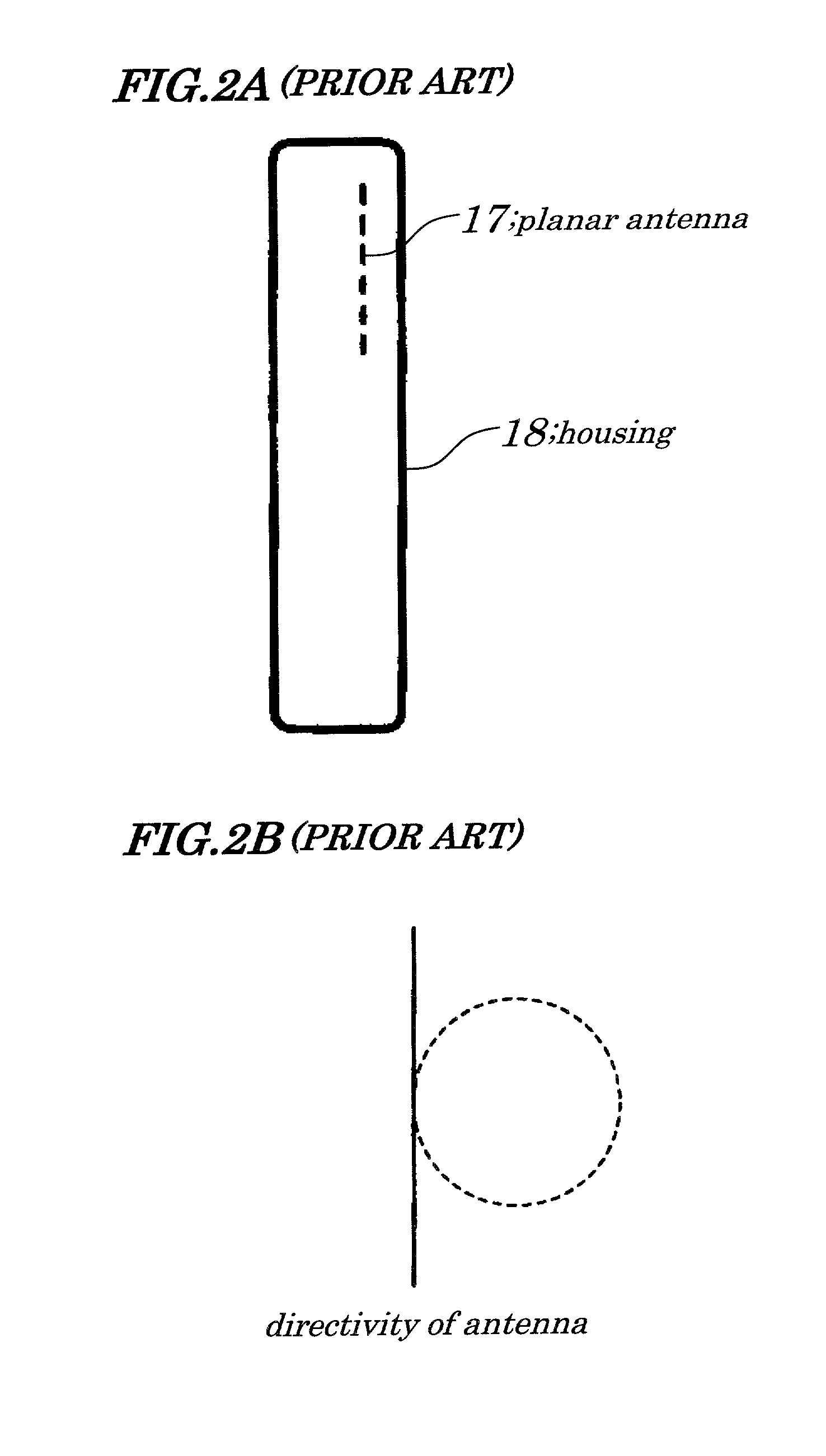
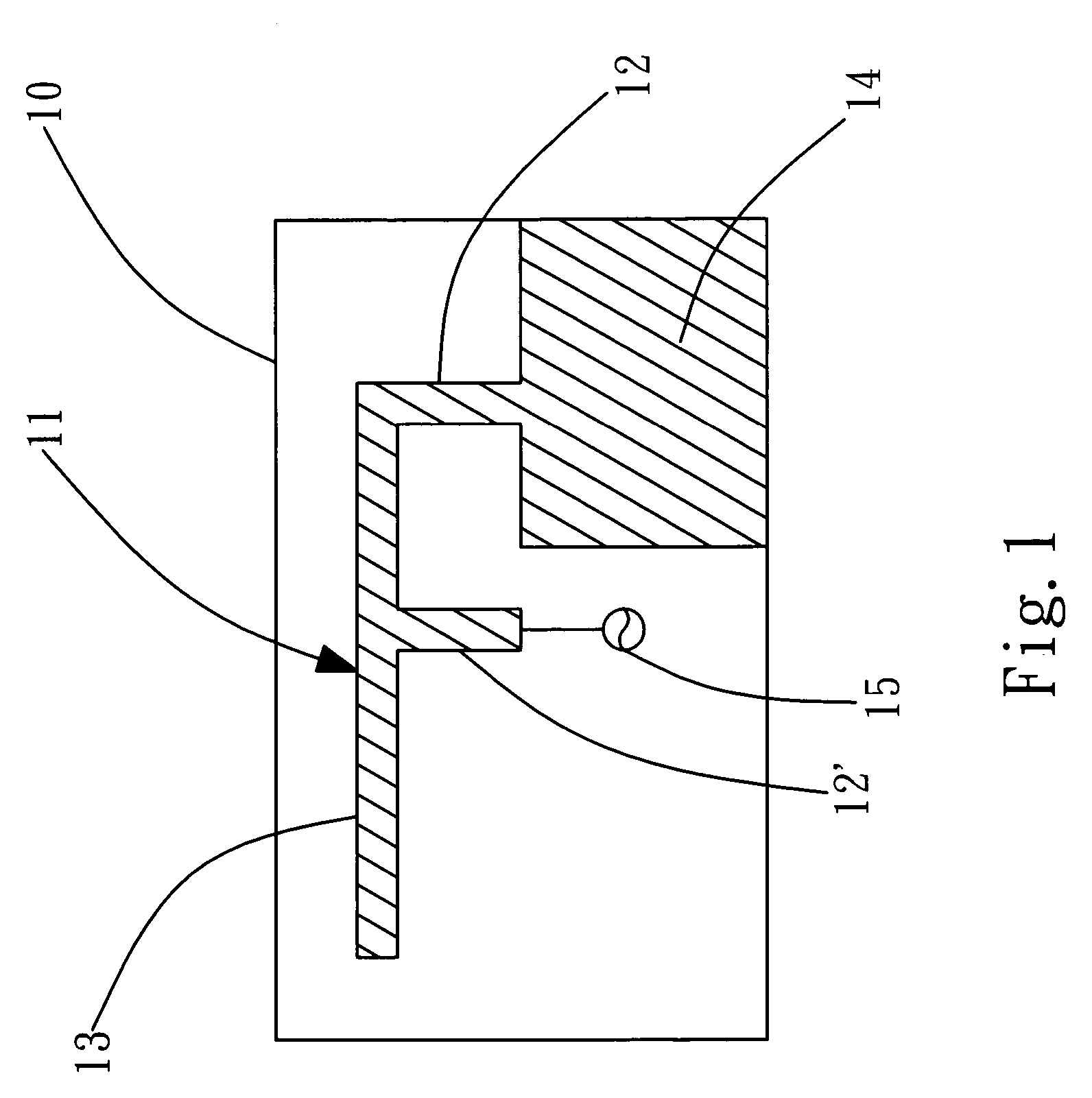
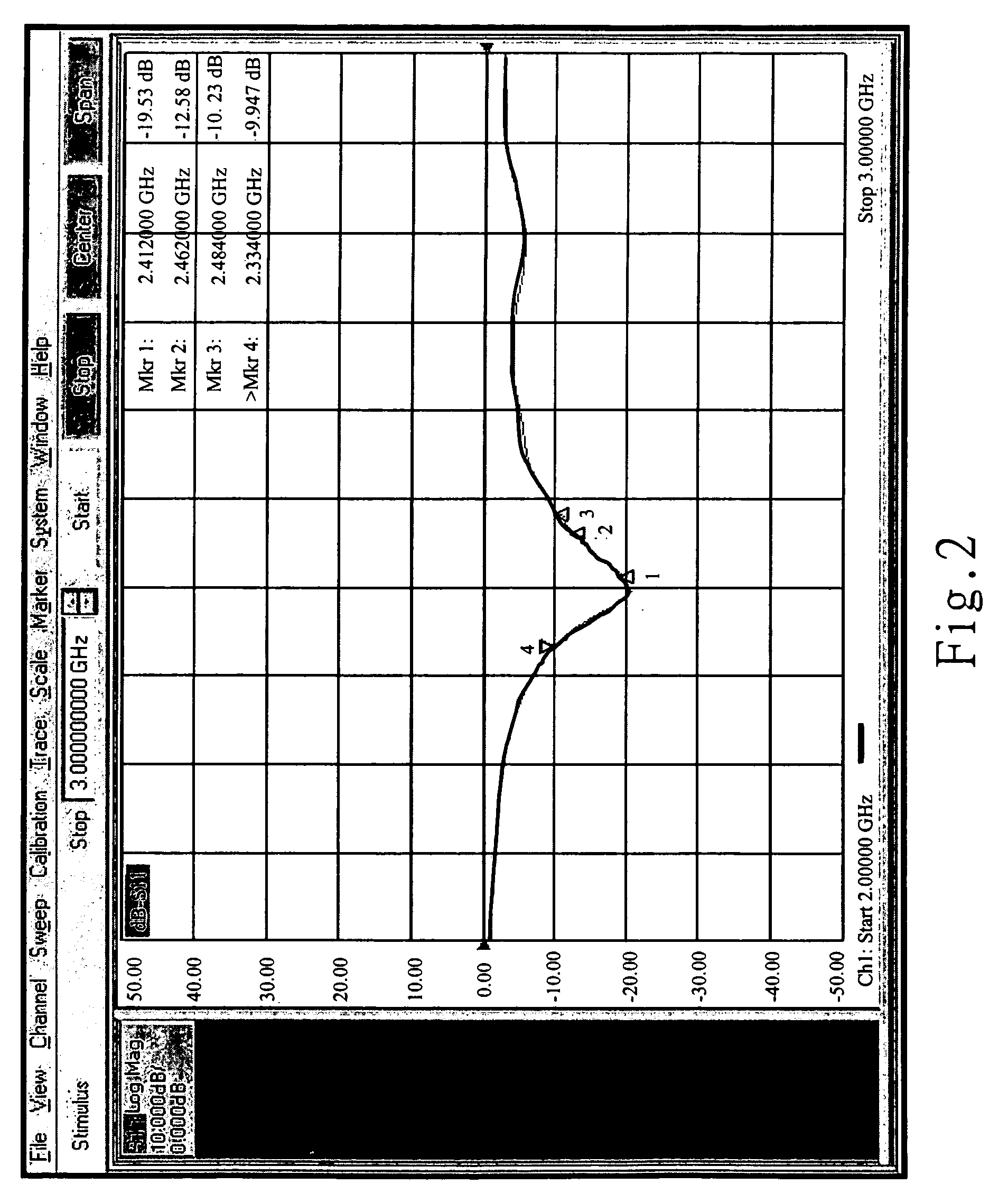
Dielectric covered planar antennas
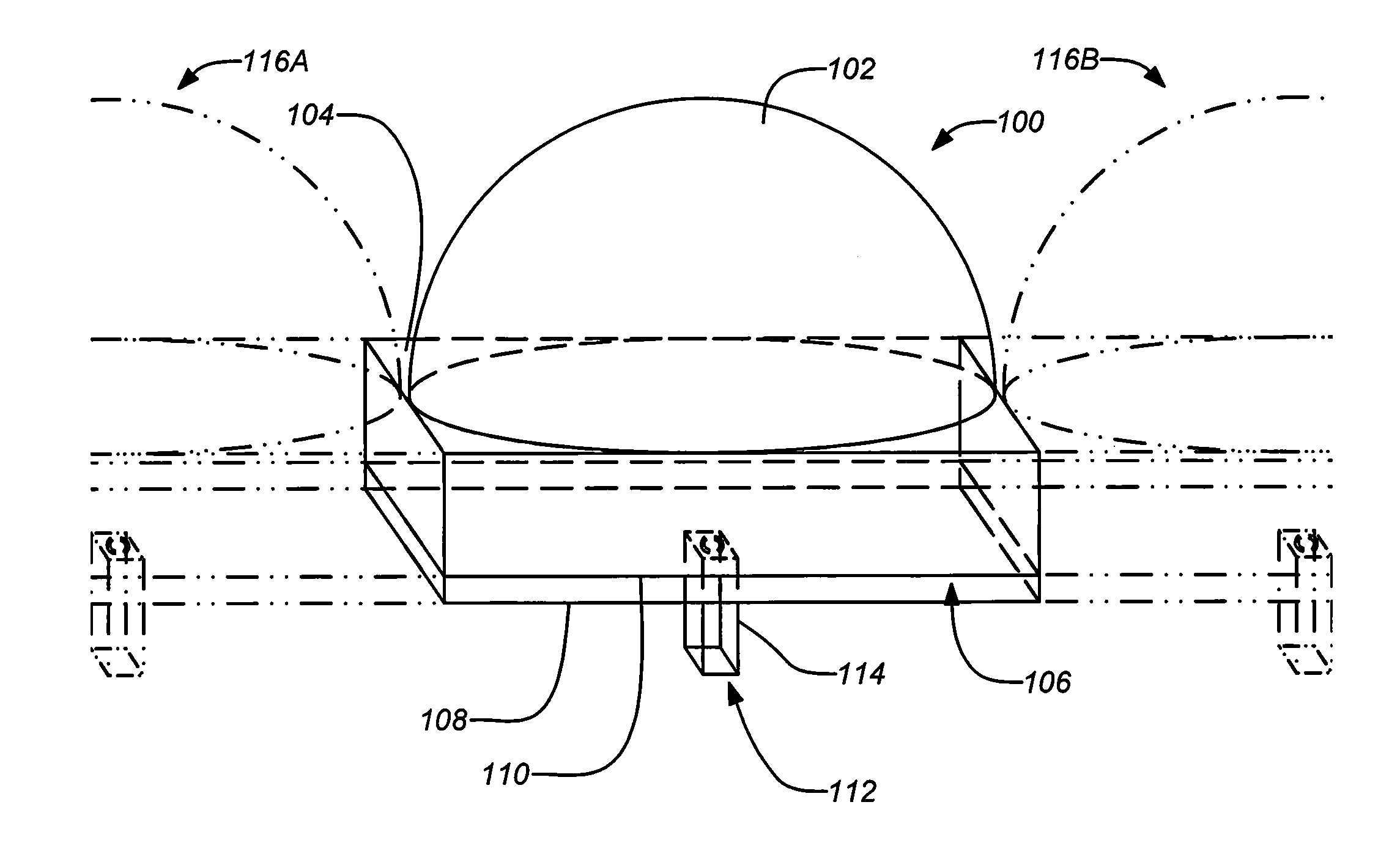
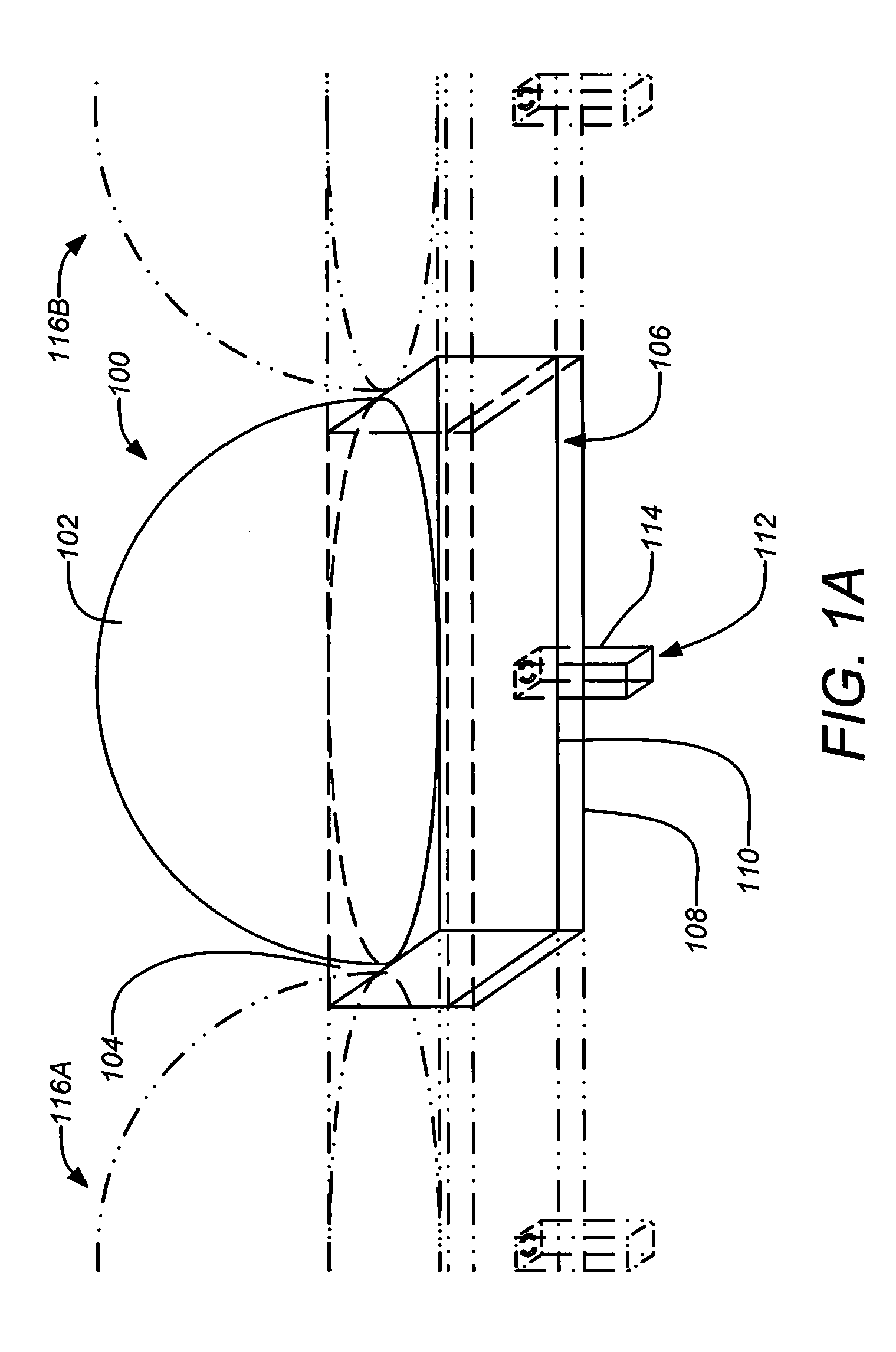
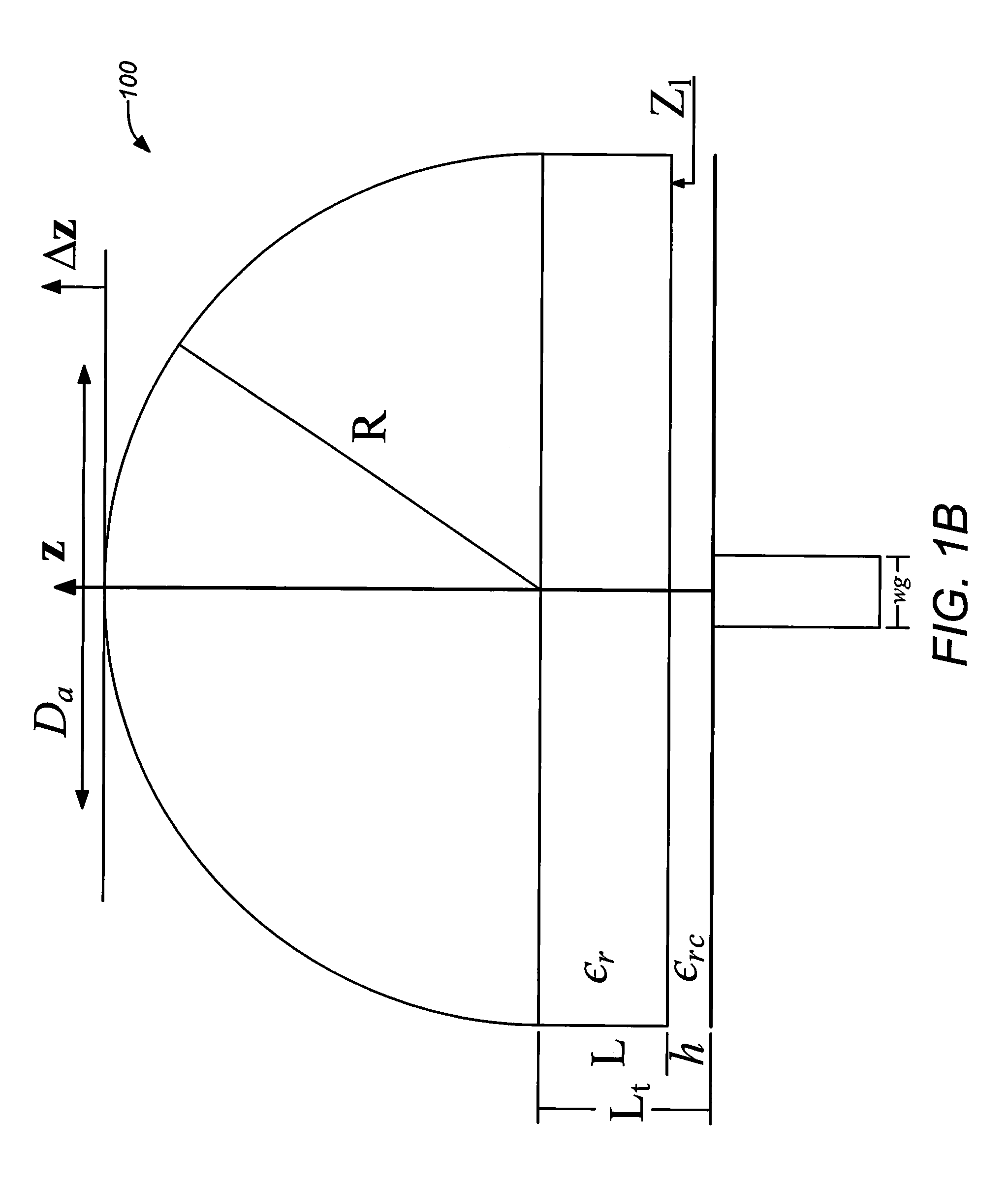
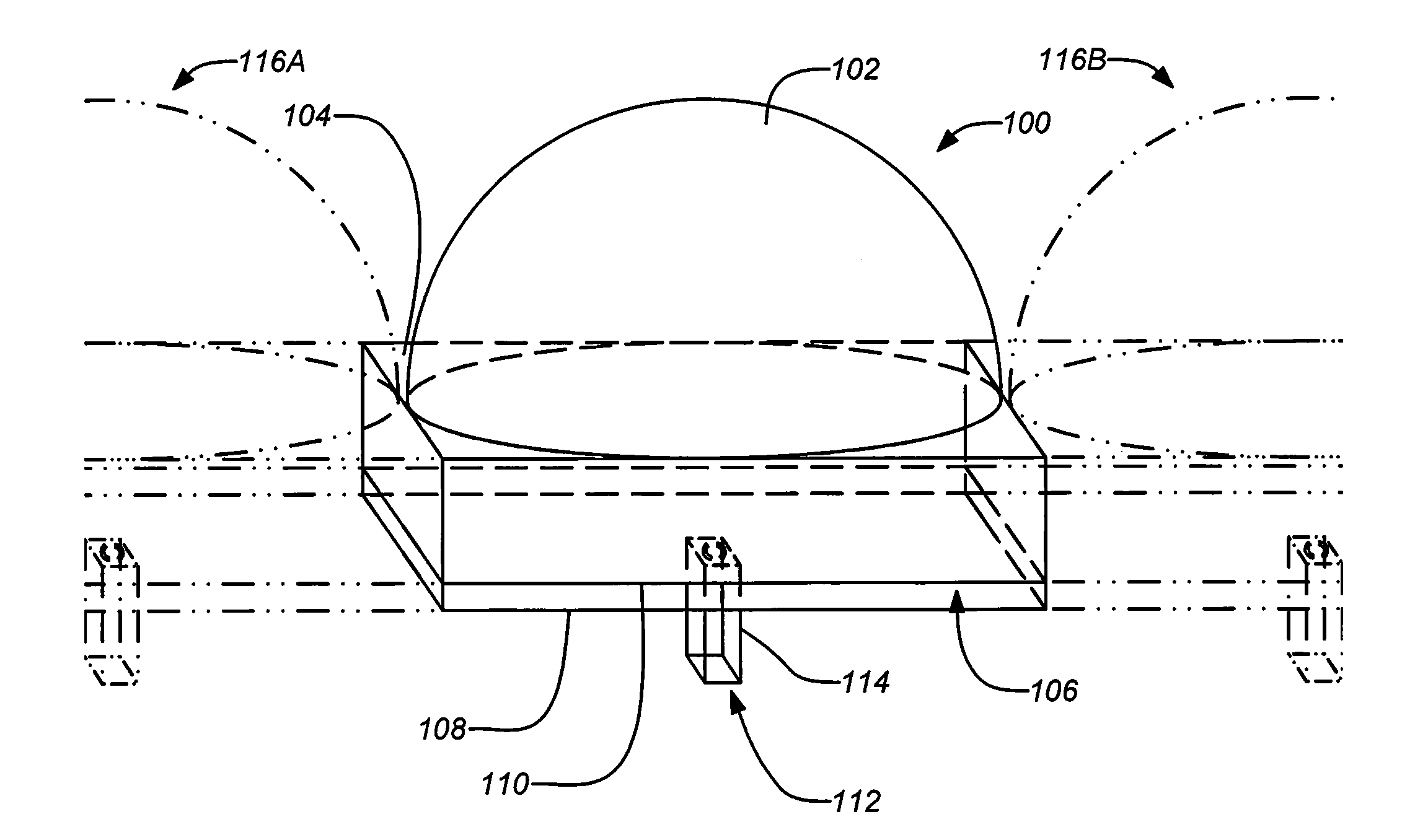
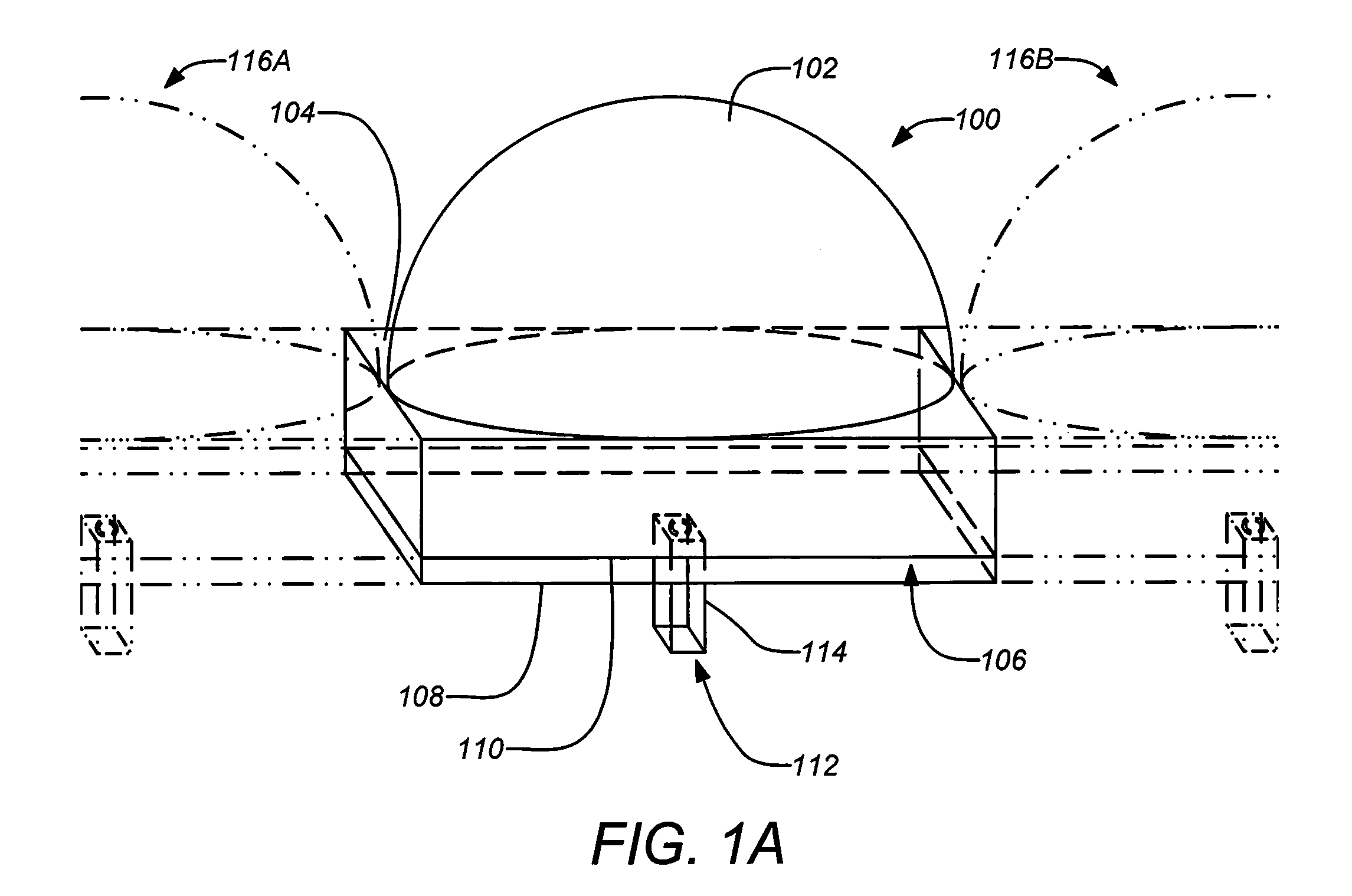
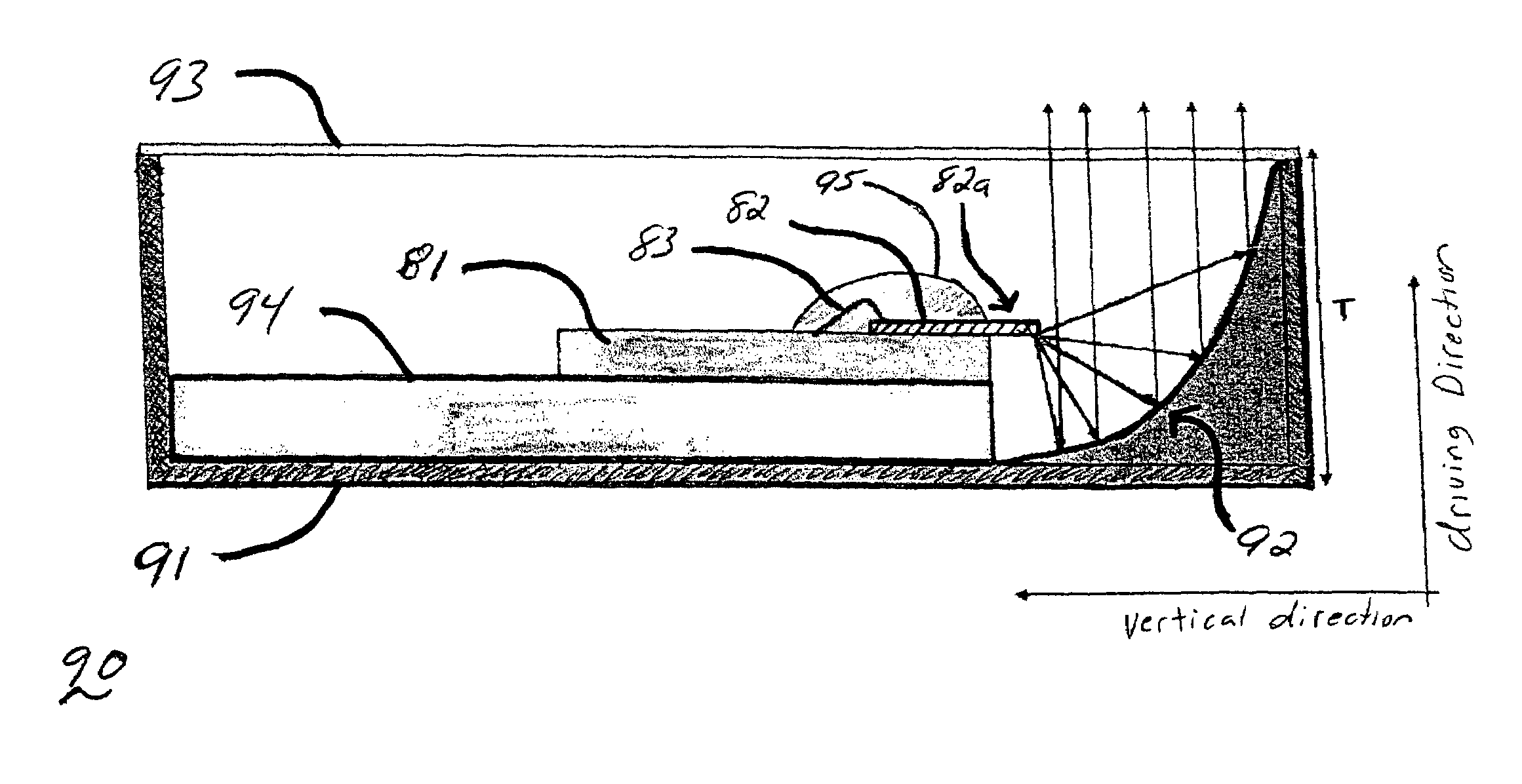
An antenna element suitable for integrated arrays at terahertz frequencies is disclosed. The antenna element comprises an extended spherical (e.g. hemispherical) semiconductor lens, e.g. silicon, antenna fed by a leaky wave waveguide feed. The extended spherical lens comprises a substantially spherical lens adjacent a substantially planar lens extension. A couple of TE / TM leaky wave modes are excited in a resonant cavity formed between a ground plane and the substantially planar lens extension by a waveguide block coupled to the ground plane. Due to these modes, the primary feed radiates inside the lens with a directive pattern that illuminates a small sector of the lens. The antenna structure is compatible with known semiconductor fabrication technology and enables production of large format imaging arrays.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
System, method and computer-accessible medium for depth of field imaging for three-dimensional sensing utilizing a spatial light modulator microscope arrangement
ActiveUS20150369660A1Efficiently modulate the intensity, phase, and/or polarization of incident radiationSolid-state devicesRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorPlanar antennas
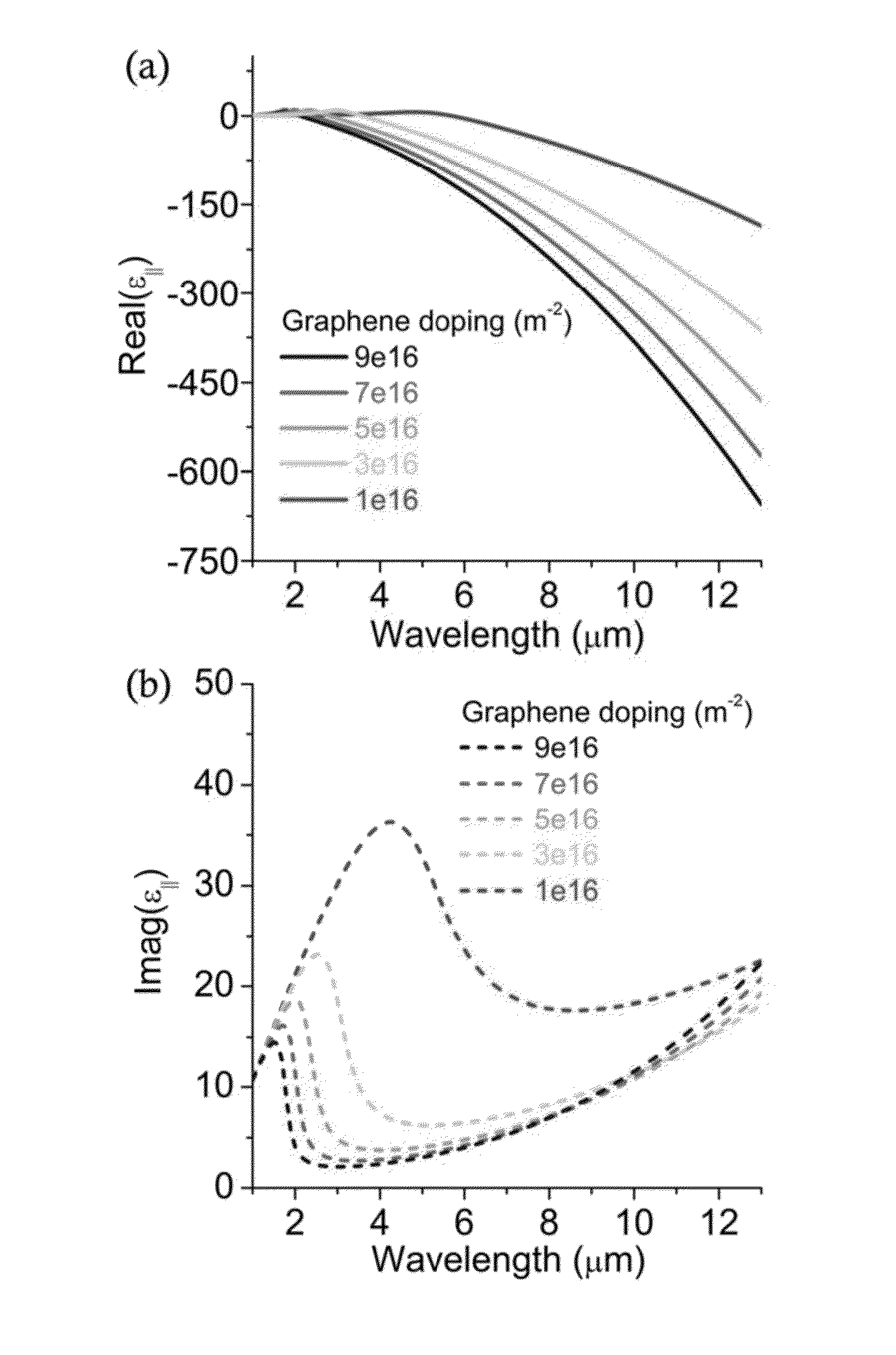
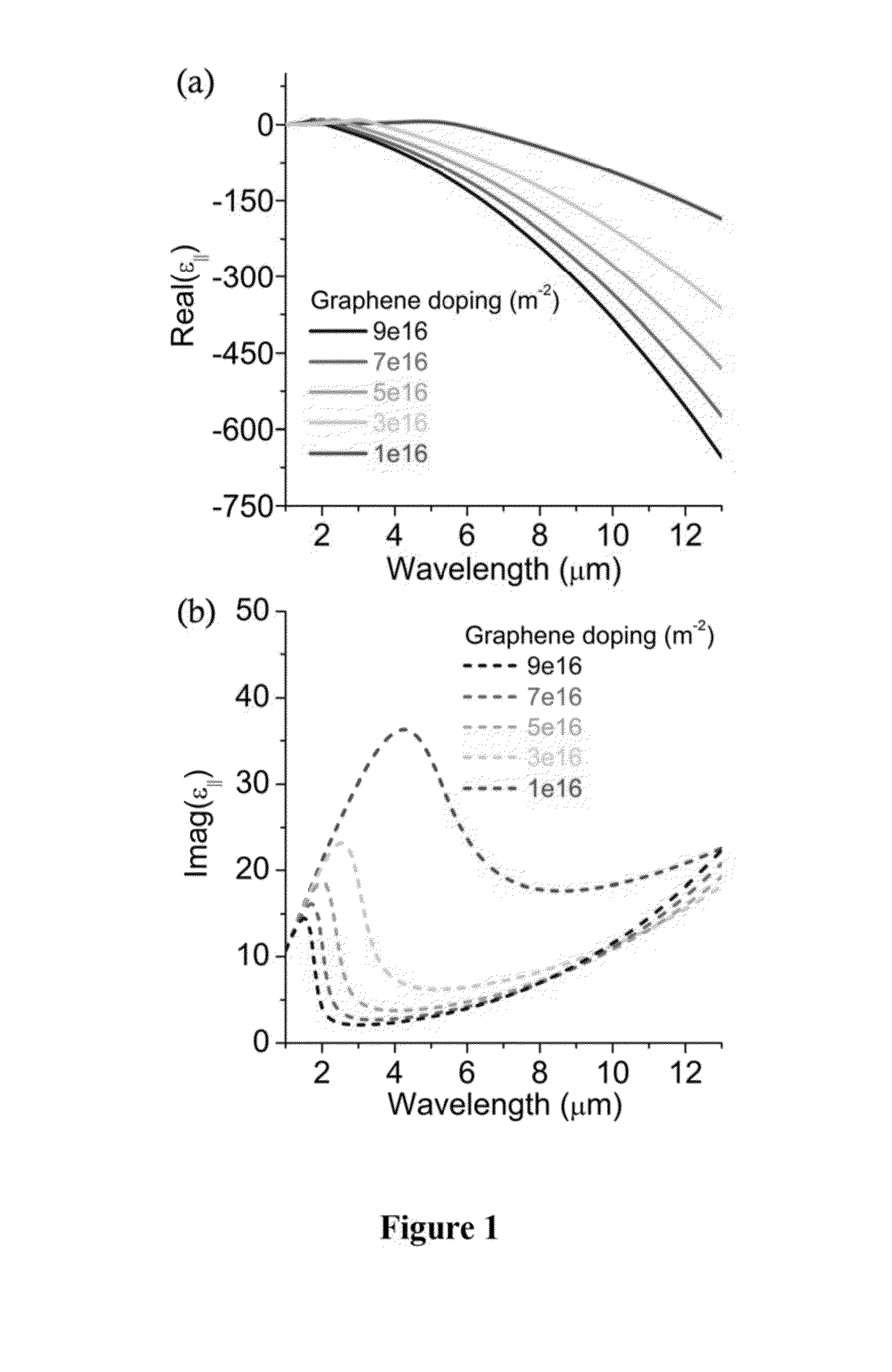
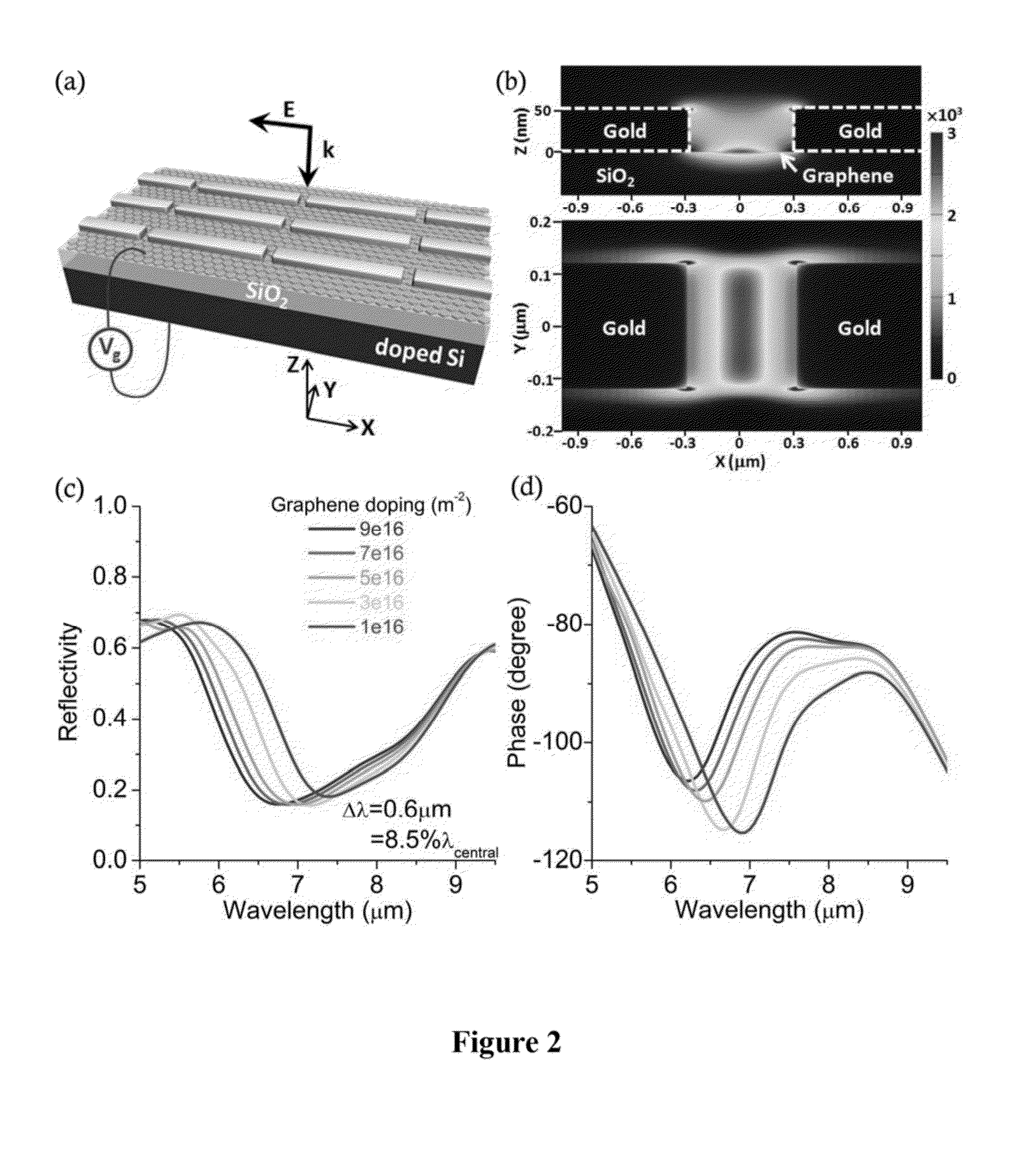
Exemplary embodiment can utilize the properties of tunable thin-film, material (e.g., graphene) to efficiently modulate the intensity, phase, and / or polarization of transmitted and / or reflected radiation, including mid-infrared (“mid-IR”) radiation. Exemplary embodiments include planar antennas comprising tunable thin-film material sections and metallic sections disposed in contact with the tunable thin-film material sections, each metallic section having a gap with at least one dimension related to a wavelength of the radiation, which in some embodiments may be less than the wavelength. The metallic layer may comprise rods arrange in one or more shapes, or one or more apertures of one or more shapes. Embodiments of the antenna may also comprise a substrate, which may be a semiconductor or conductor in various embodiments. Embodiments also include systems, computer-implemented methods, devices, and computer-readable media for effectuating desired modulation of incident radiation by, e.g., varying the doping level of the tunable thin-film material.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Apparatus and methods for packaging antennas with integrated circuit chips for millimeter wave applications
ActiveUS20070063056A1Highly-integratedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransceiverCommunications system
Apparatus and methods are provided for integrally packaging antennas with semiconductor IC (integrated circuit) chips to provide highly-integrated and high-performance radio / wireless communications systems for millimeter wave applications including, e.g., voice communication, data communication and radar applications. For example, wireless communication modules are constructed with IC chips having receiver / transmitter / transceiver integrated circuits and planar antennas that are integrally constructed from BEOL (back end of line) metallization structures of the IC chip.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Plasma processing method and plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20070077737A1High densityLow electron temperatureElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon filmEngineering
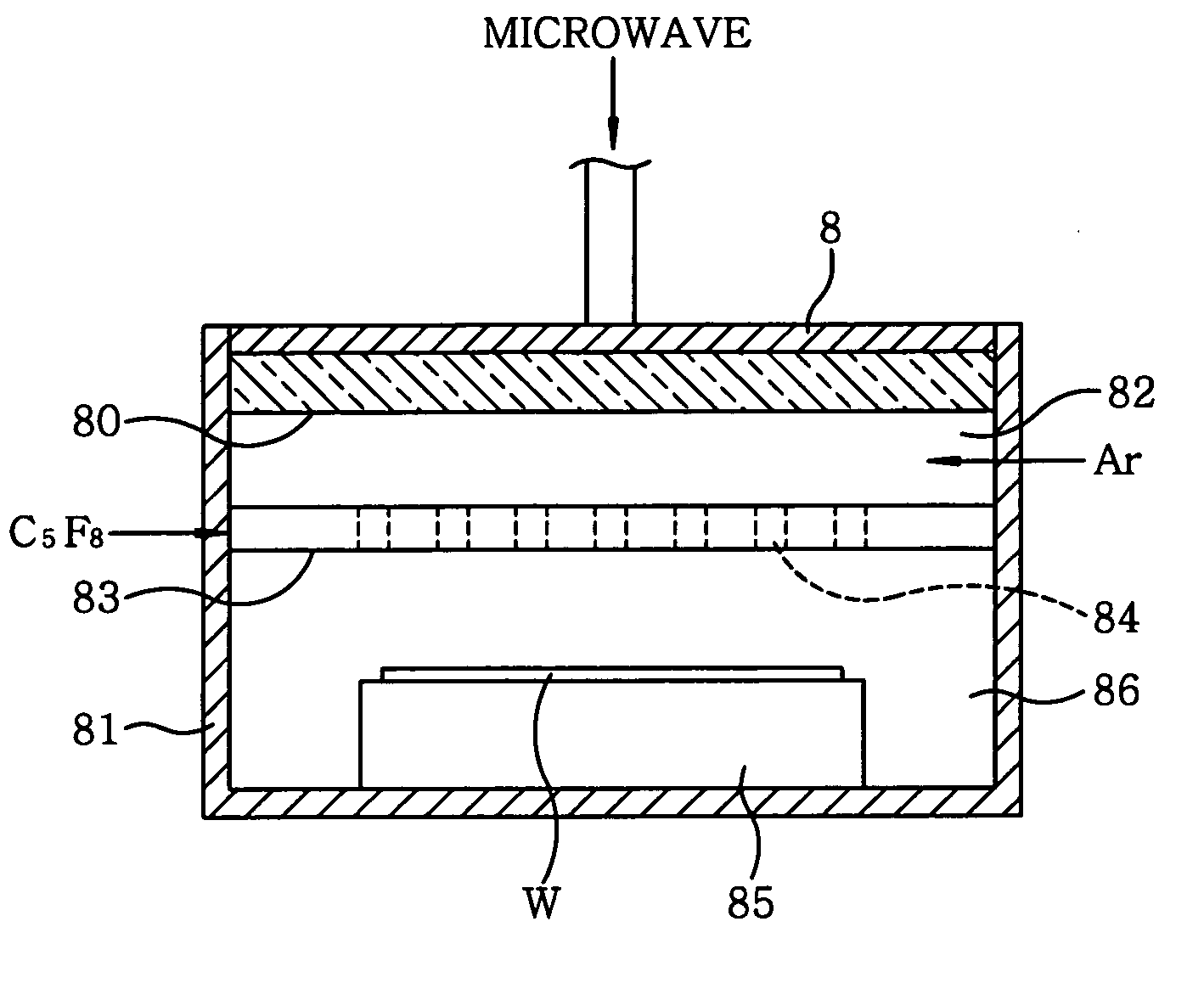
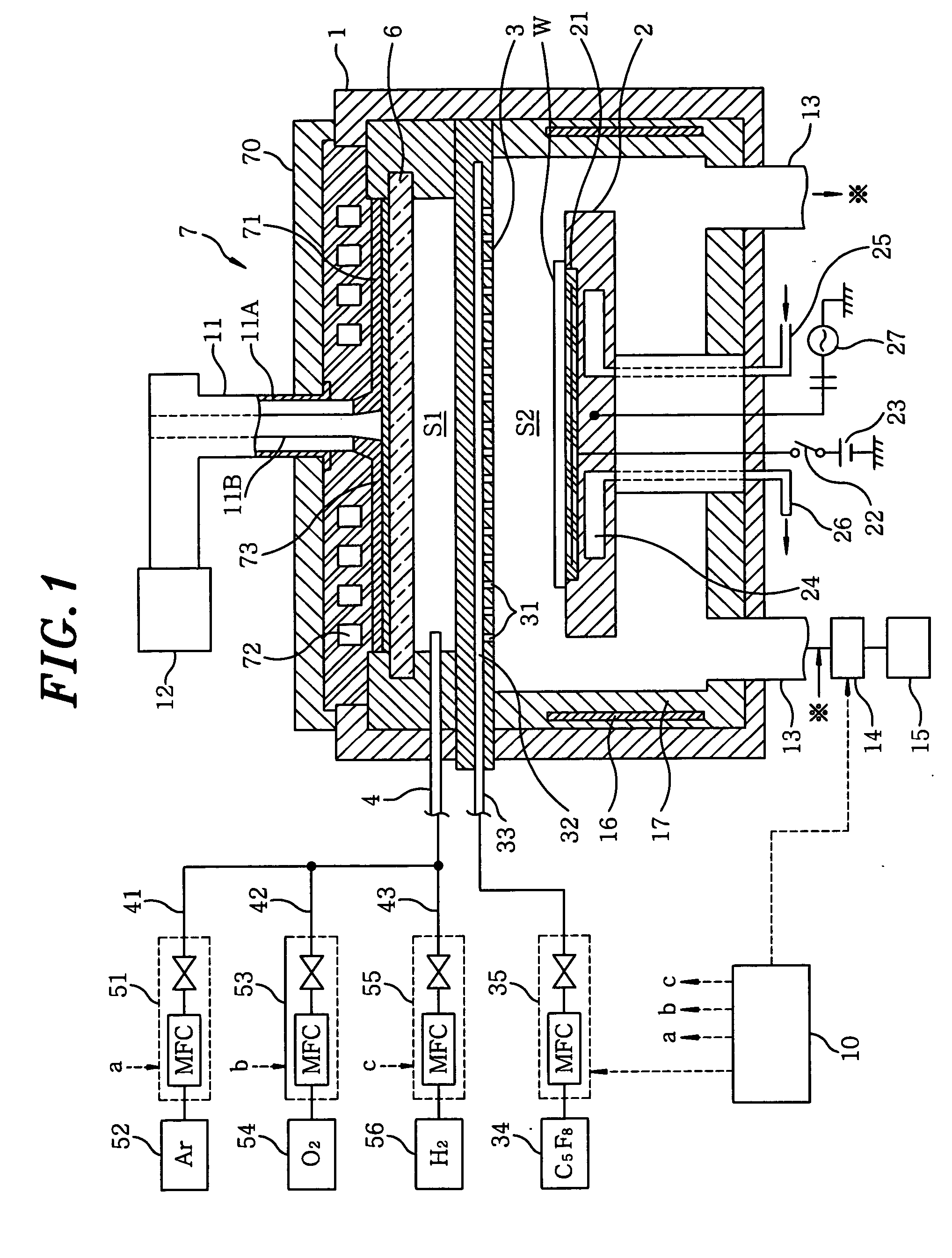
A microwave is radiated into a processing chamber (1) from a planar antenna member of an antenna (7) through a dielectric plate (6). With this, a C5F8 gas supplied into the processing chamber (1) from a gas supply member (3) is changed (activated) into a plasma so as to form a fluorine-containing carbon film of a certain thickness on a semiconductor wafer (W). Each time a film forming process of forming a film on one wafer is carried out, a cleaning process and a pre-coating process are carried out. In the cleaning process, the inside of the processing chamber is cleaned with a plasma of an oxygen gas and a hydrogen gas. In the pre-coating process, the C5F8 gas is changed into a plasma, and a pre-coat film of fluorine-containing carbon thinner than the fluorine-containing carbon film formed in the film forming process is formed.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Flexible substrate integrated waveguides
This invention relates to a device operable to guide electromagnetic waves in substrate integrated structures, said substrate integrated structures being made in one component. In detail planar antennas are part of said substrate integrated structures, which are connected to electromagnetic waveguides. This invention also allows 3D structures of the above mentioned components in a multilayer substrate.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
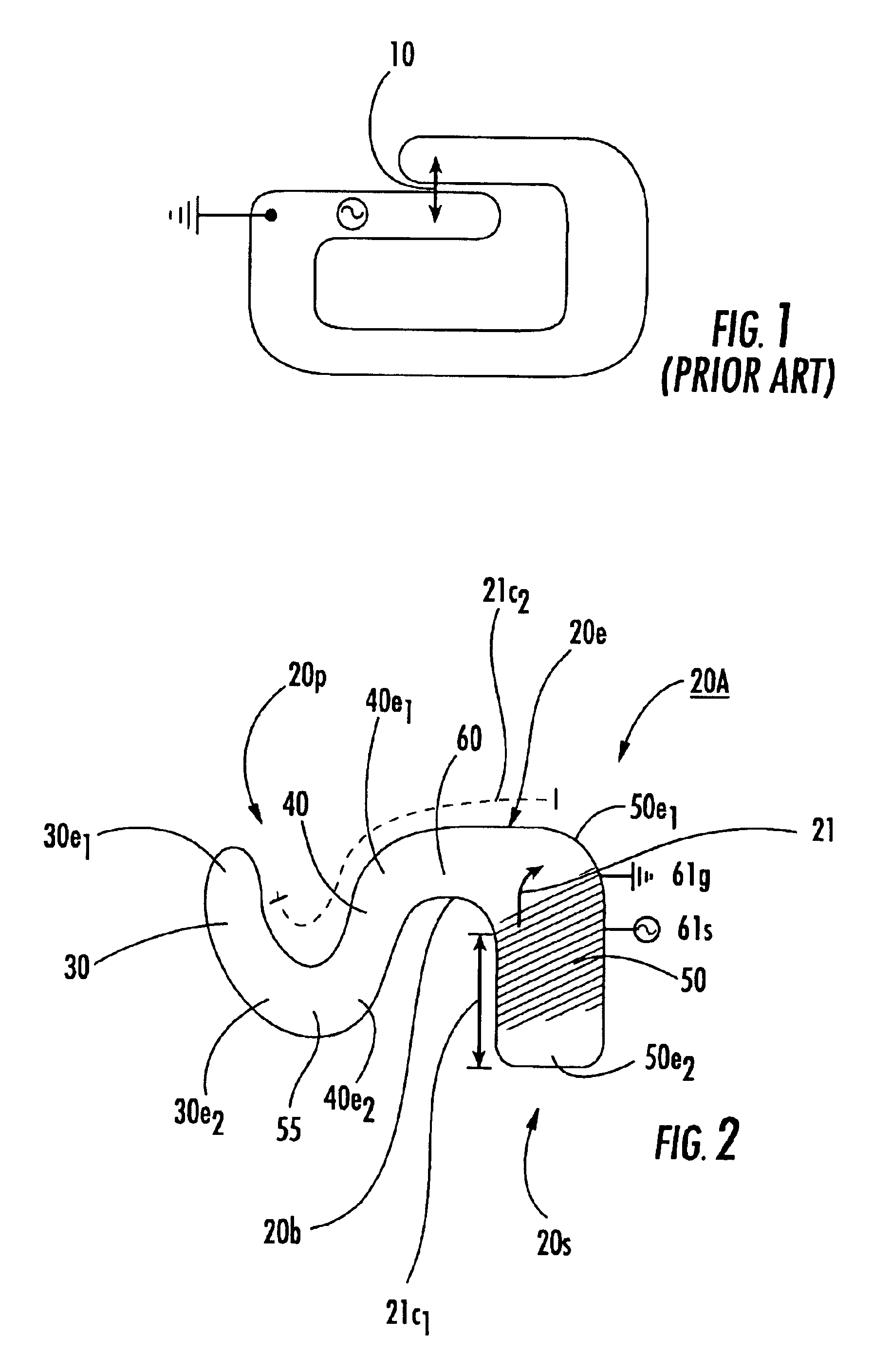
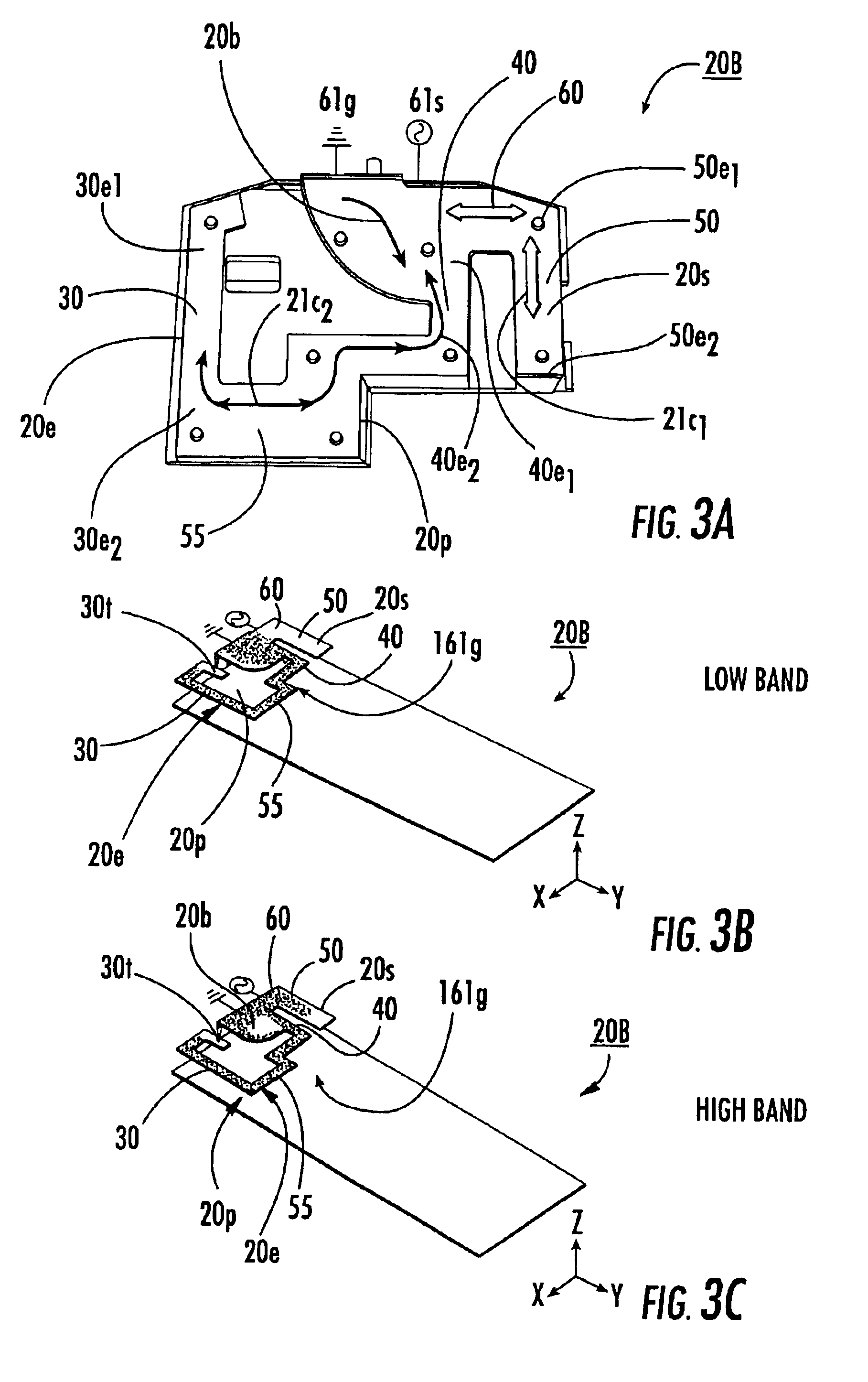
Multi-branch planar antennas having multiple resonant frequency bands and wireless terminals incorporating the same
InactiveUS6903686B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsPlanar antennasHeat spreader
A conductive element with a primary branch and a secondary branch are separated by a bend segment and the signal and ground feeds are positioned adjacent each other on a common portion of the conductive element. The frequencies in the high band may be at least about twice that of the frequencies in the low band. The branches and bend segment are constructed such that the primary branch radiates at both high and low band operation. The two branches combine to form a more efficient high band radiator.
Owner:SONY CORP
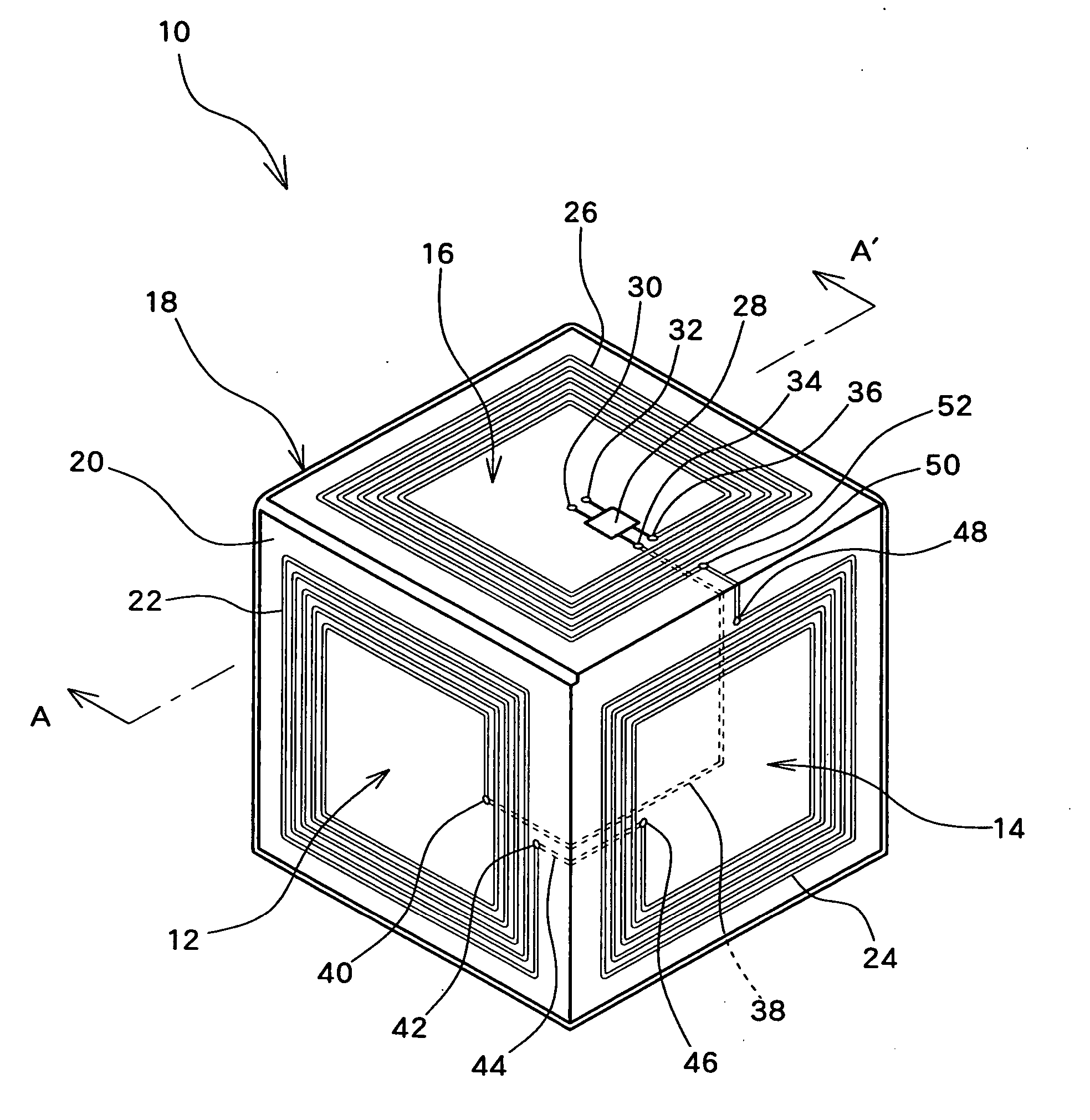
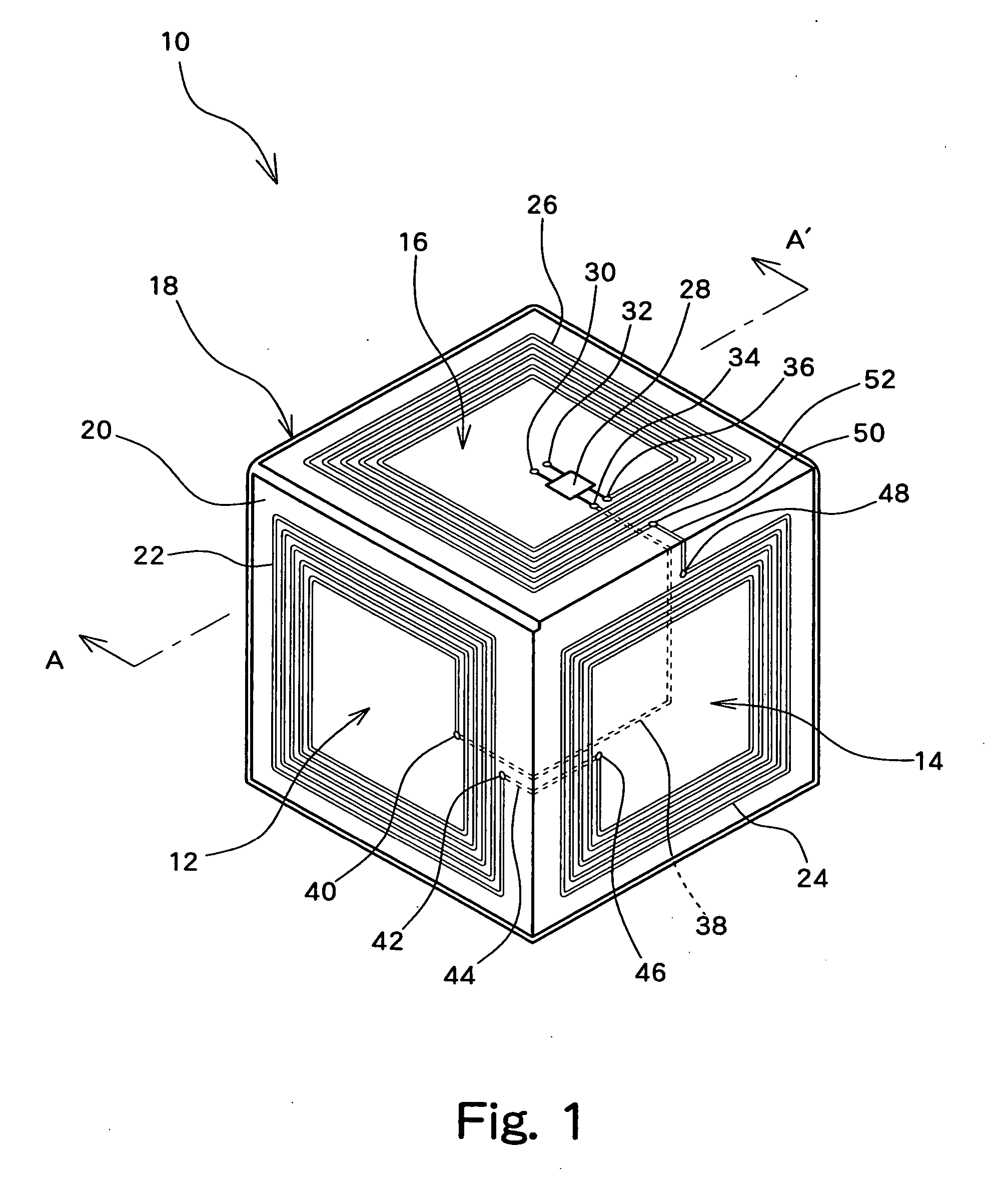
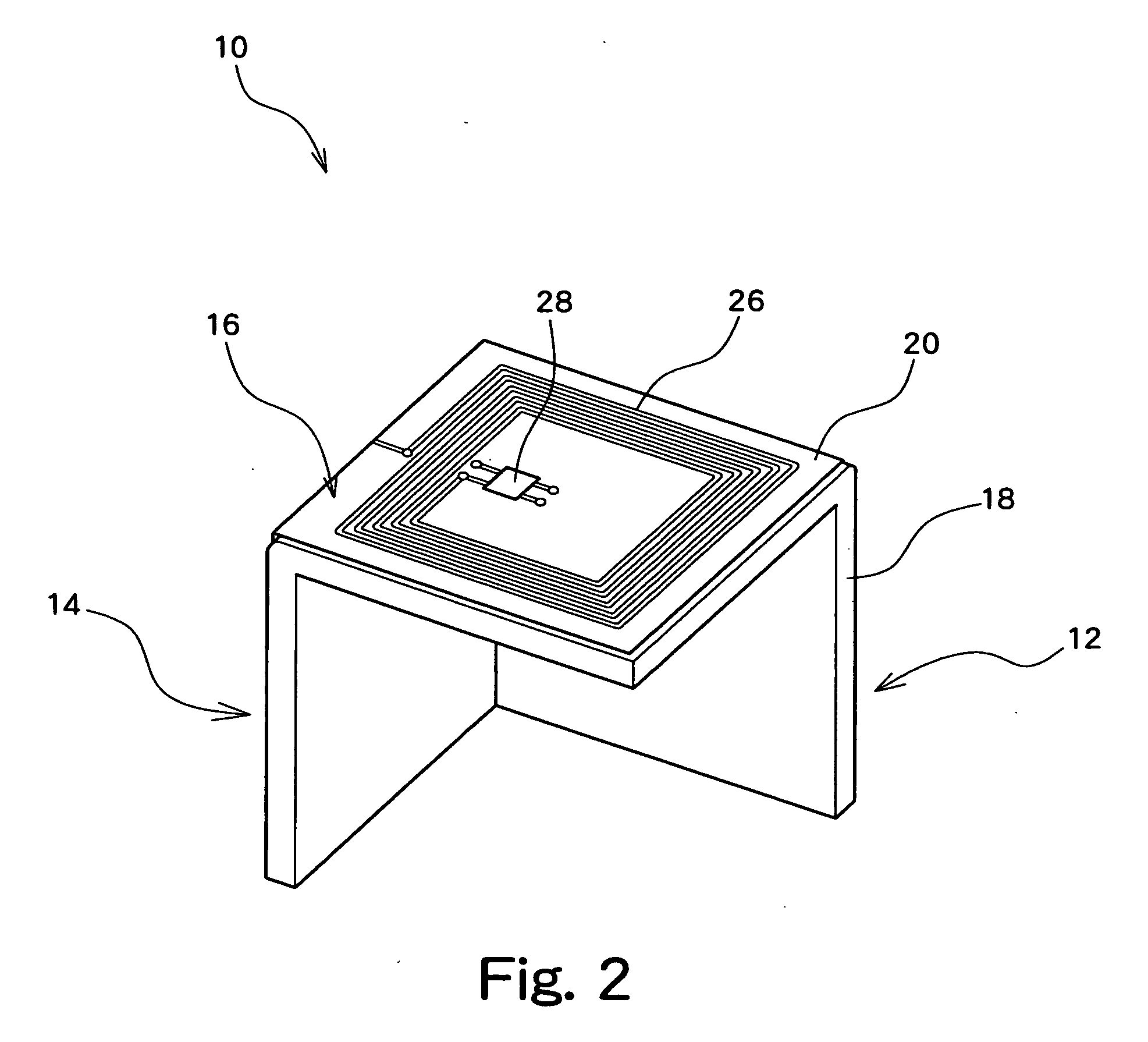
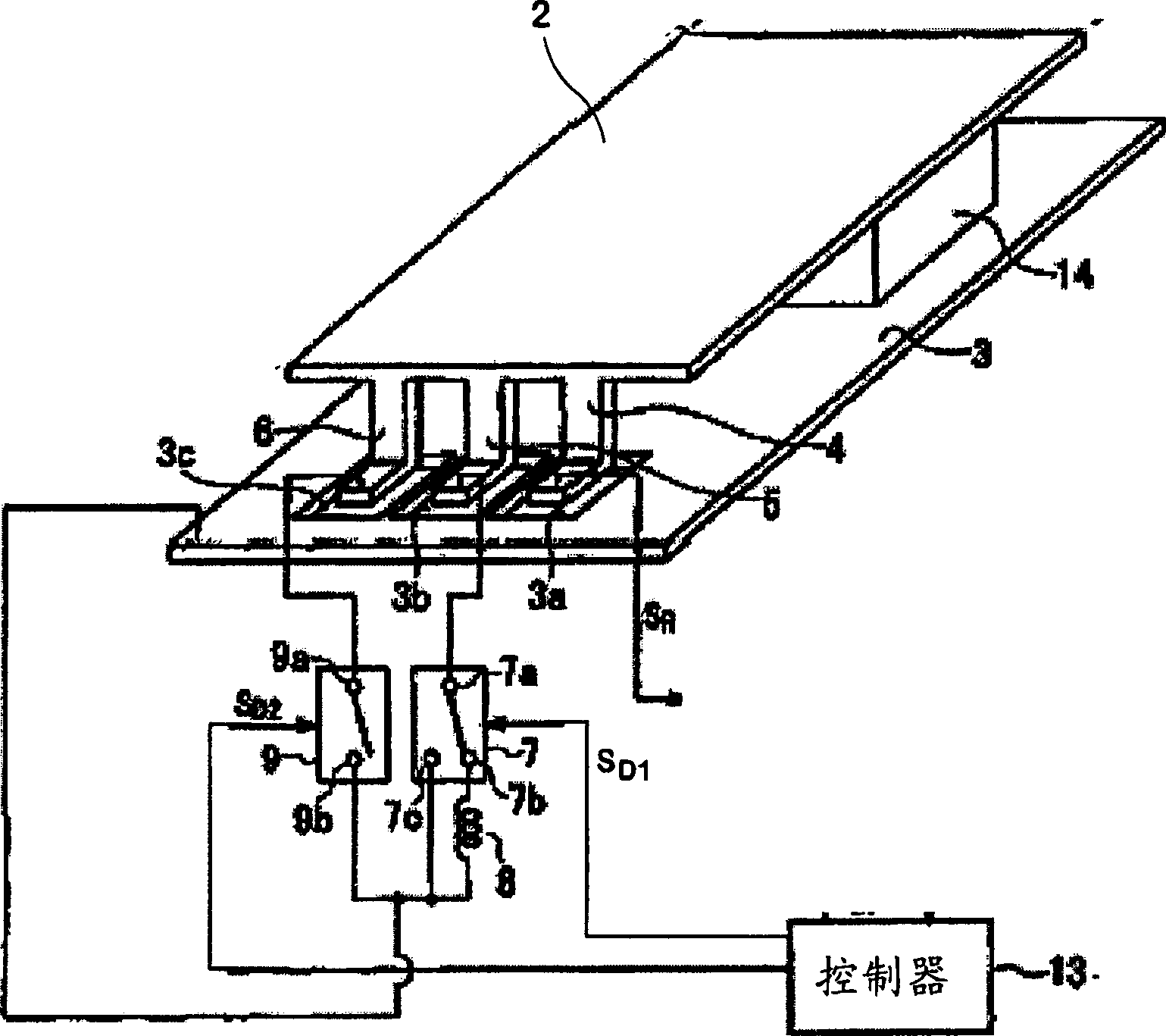
IC tag provided with three-dimensional antenna and pallet provided with the IC tag
InactiveUS20050242959A1Small sizeOutput power intensity can be increasedContainer decorationsLevel indicationsPlanar antennasEngineering
The IC tag comprises a three-dimensional antenna and an integrated circuit. The three-dimensional antenna is configured in such a manner that a plurality of planar antennas, each capable of performing emission and reception of radio waves by itself, are arranged at angles so as to be not parallel to each other. The integrated circuit is also connected to the three-dimensional antenna and performs transmission or reception of a signal via the three-dimensional antenna.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Mm-wave/IR monolithically integrated focal plane array
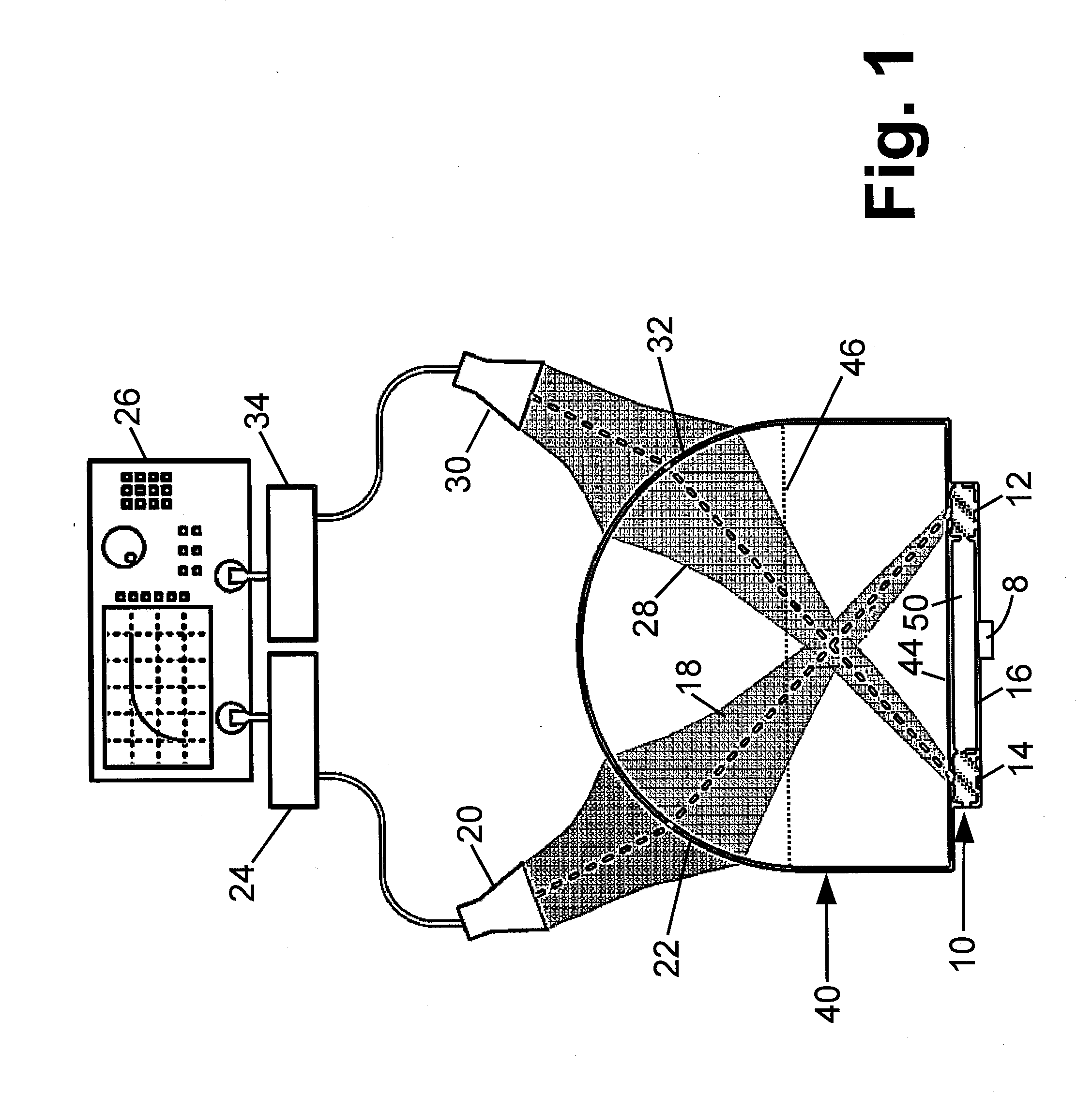
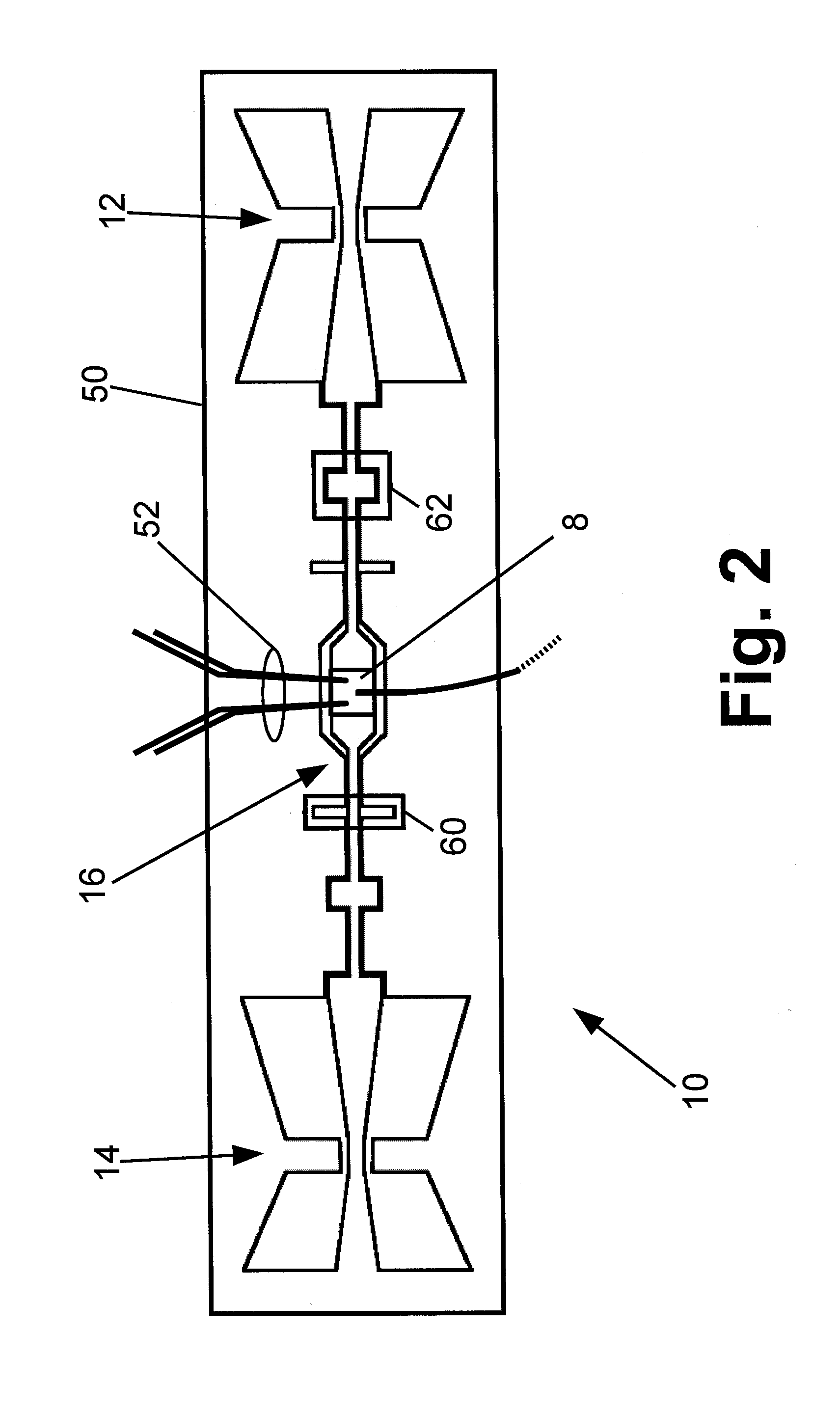
An integrated infrared and millimeter-wave monolithic focal plane sensor array having a substrate upon which an integrated array of infrared sensors and mm-wave sensors are provided at a first planar level on the same side of the substrate, and a planar antenna for receiving incident millimeter-wave radiation located at a second planar level located between the integrated array of sensors and the surface of the substrates for coupling the mm-wave radiation field to the mm-wave sensor. The antenna receiver of electromagnetic radiation, in one embodiment, is an antenna having a crossed bowtie configuration which efficiently couples the radiation field to the mm-wave sensor. The invention also is directed to a method of fabricating such a radiation sensor.
Owner:HRL LAB
Intrabody navigation system for medical applications
InactiveUS7555330B2Suppression of distortionEliminate needDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationFrequency spectrumPlanar antennas
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Antenna device, wireless communication apparatus using the same, and control method of controlling wireless communication apparatus
InactiveUS20070035463A1Suitable environmentAvoid interferenceIndividually energised antenna arraysPolarised antenna unit combinationsTelecommunications equipmentEngineering
Owner:SONY CORP
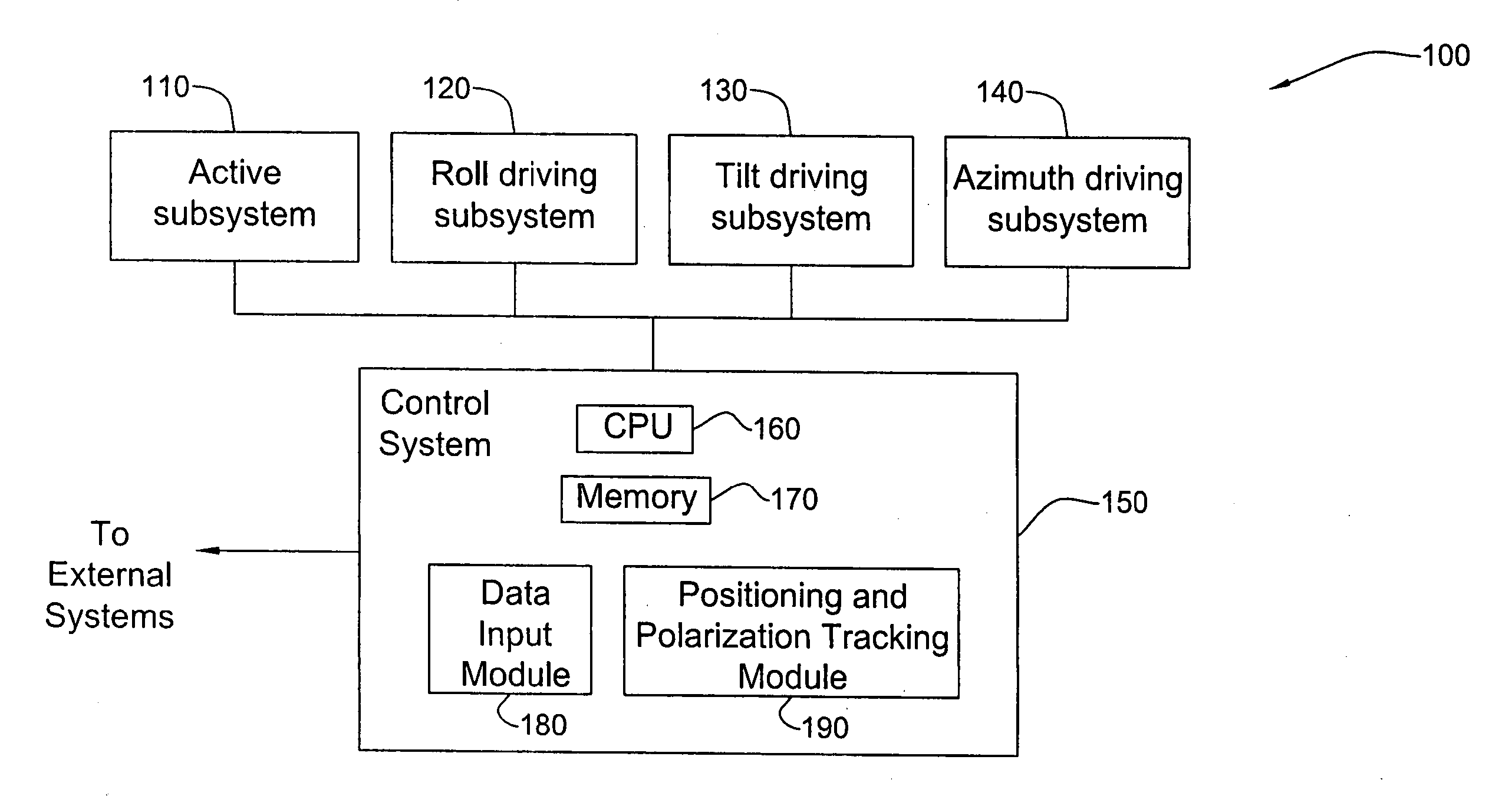
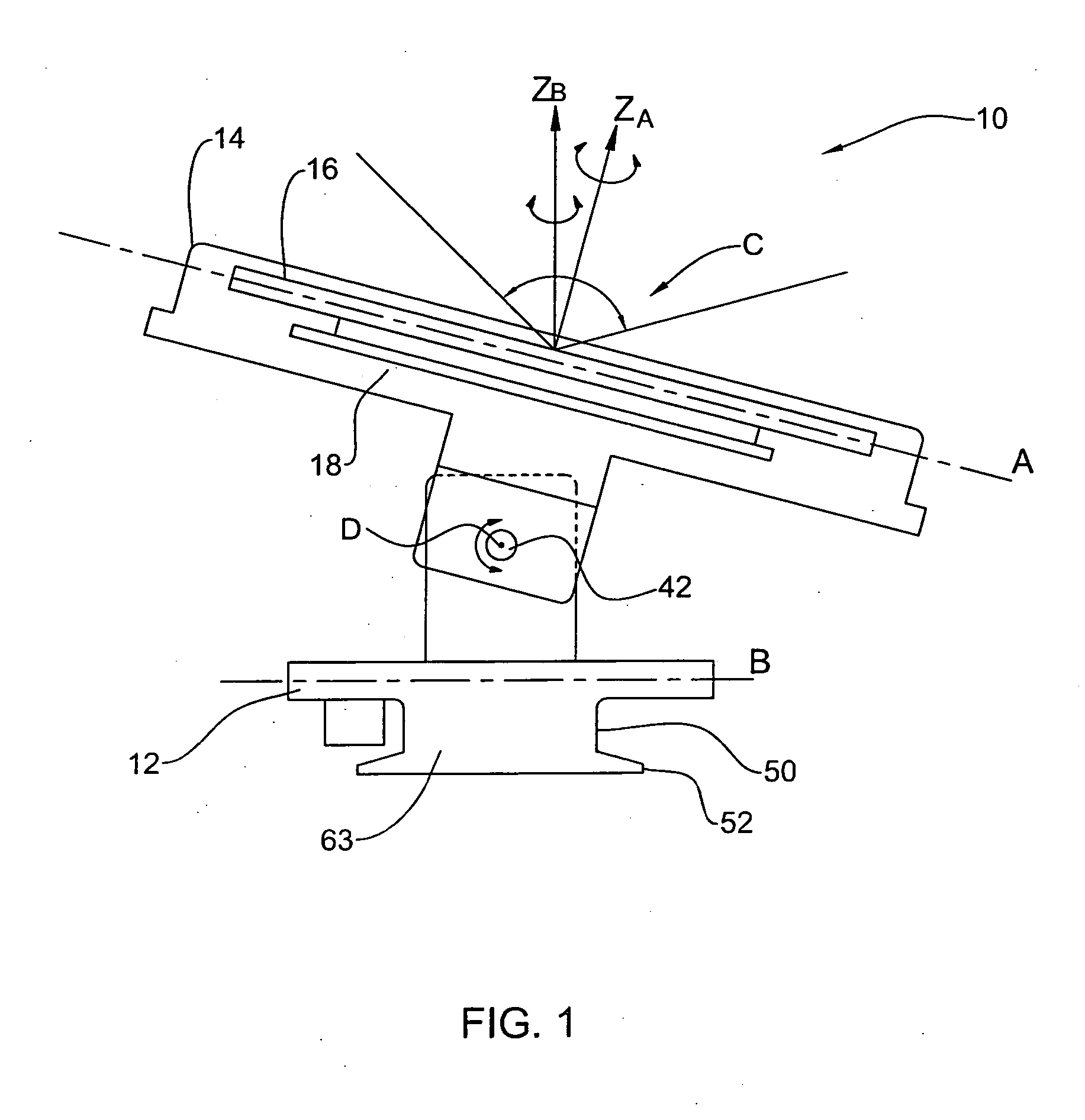
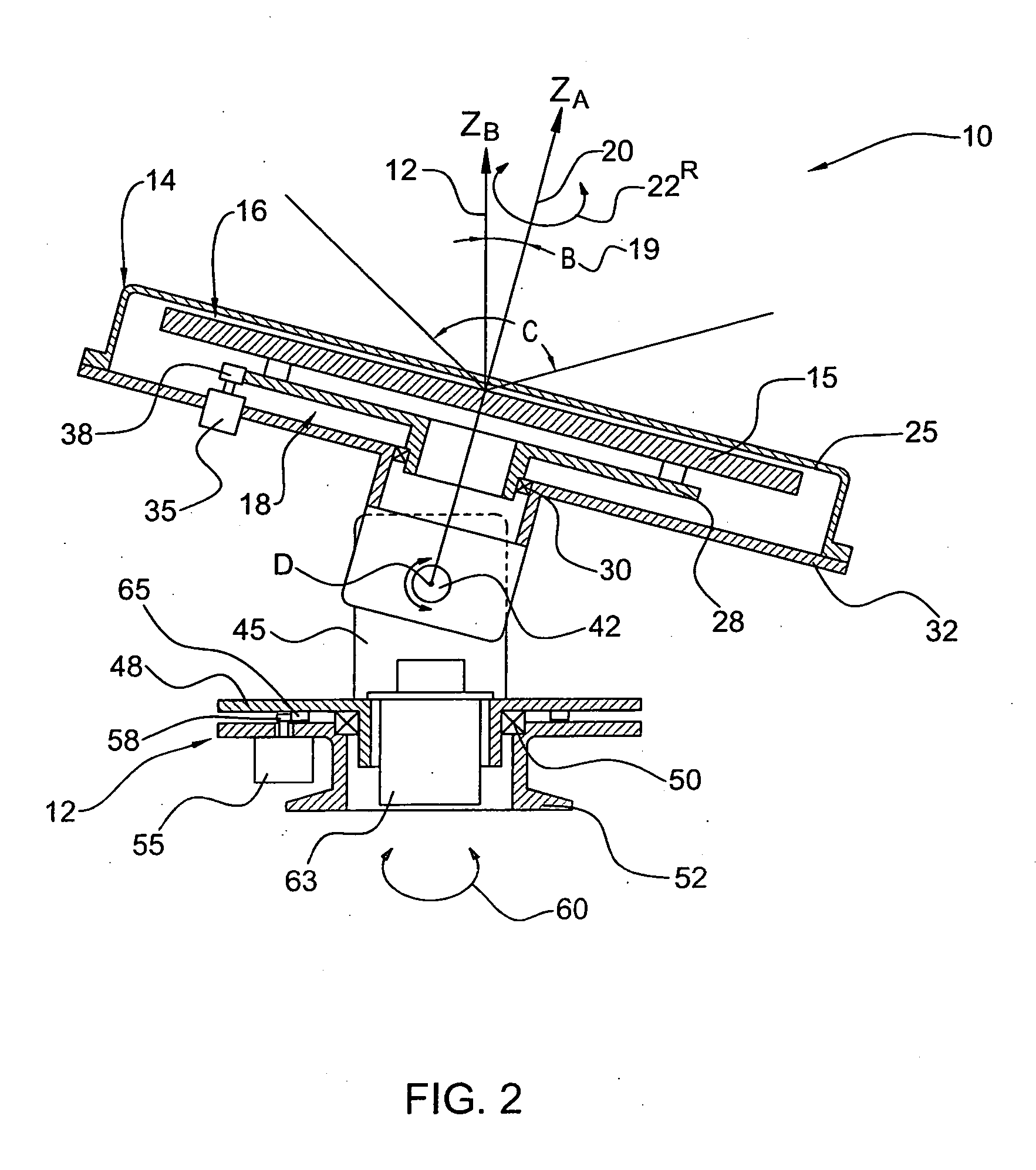
Phased array planar antenna and a method thereof
A phased array antenna system accommodating onto a platform for tracking a target moving relatively to the platform, the antenna system comprising a first planar active subsystem operable for receiving / transmitting an RF signal of a certain linear polarization direction and for selectively performing electronic scanning; a second, roll subsystem coupled to the active subsystem and operable for rotational movement of the active subsystem about a first axis perpendicular to a plane defined by the planar active subsystem; a third, elevation subsystem coupled to the second, roll subsystem and to a fourth azimuth subsystem, the azimuth subsystem defining a central axis of the antenna system and being operable for providing rotational movement of the first planar subsystem about the central axis, the elevation subsystem being configured to provide a certain angular orientation between the plane defined by the active subsystem and a plane defined by the azimuth subsystem, thereby allowing positioning the first planar active subsystem with respect to the target such that the linear polarization direction is substantially aligned with a linear polarization direction of RF radiation received and / or transmitted by the target.
Owner:ELTA SYST LTD
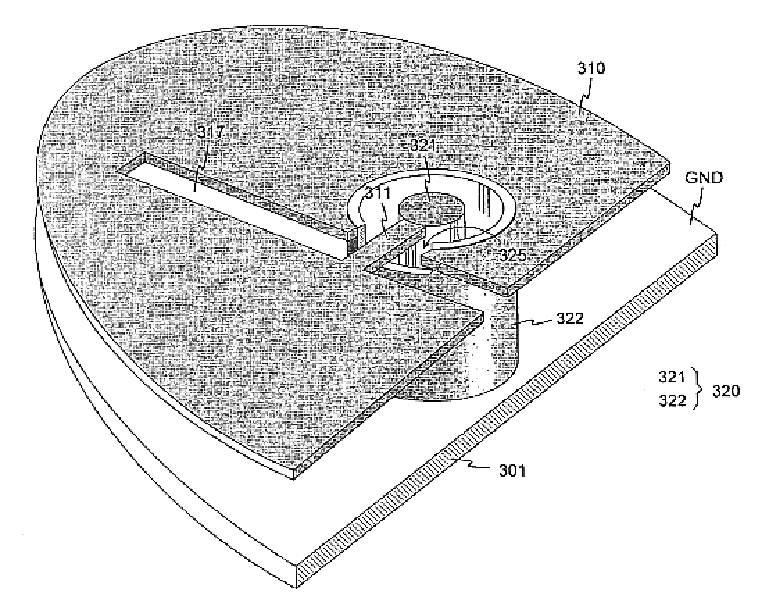
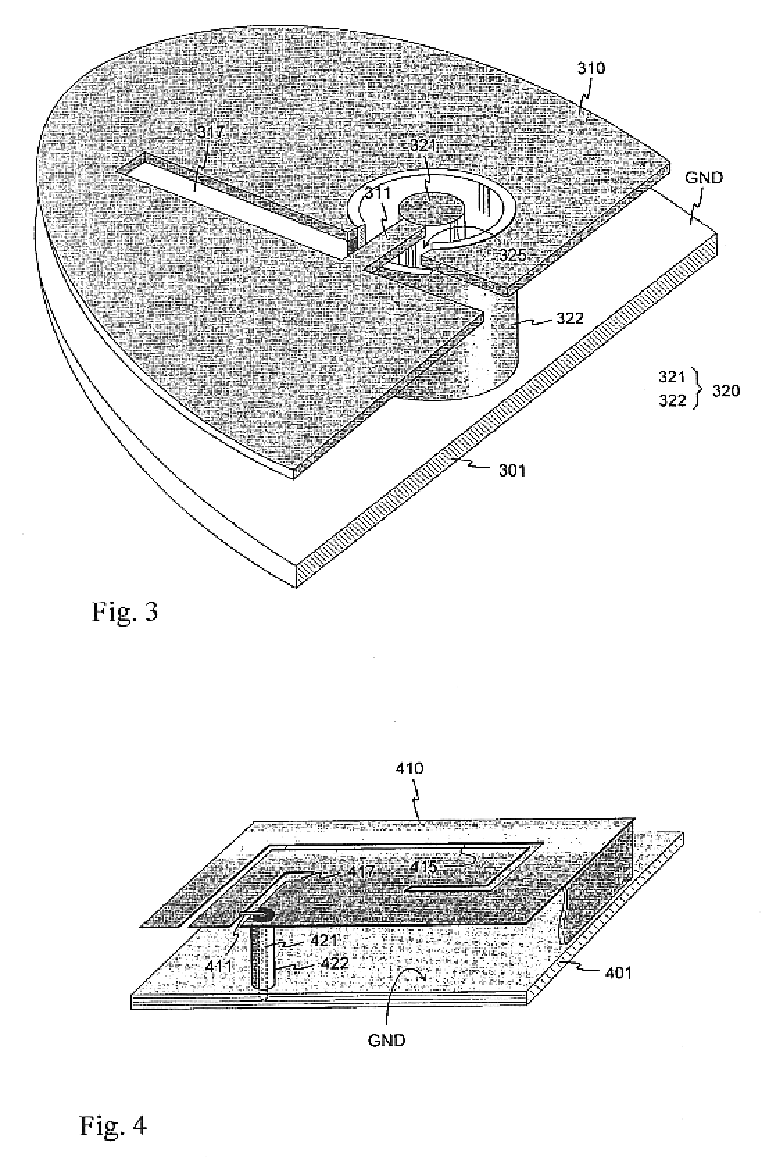
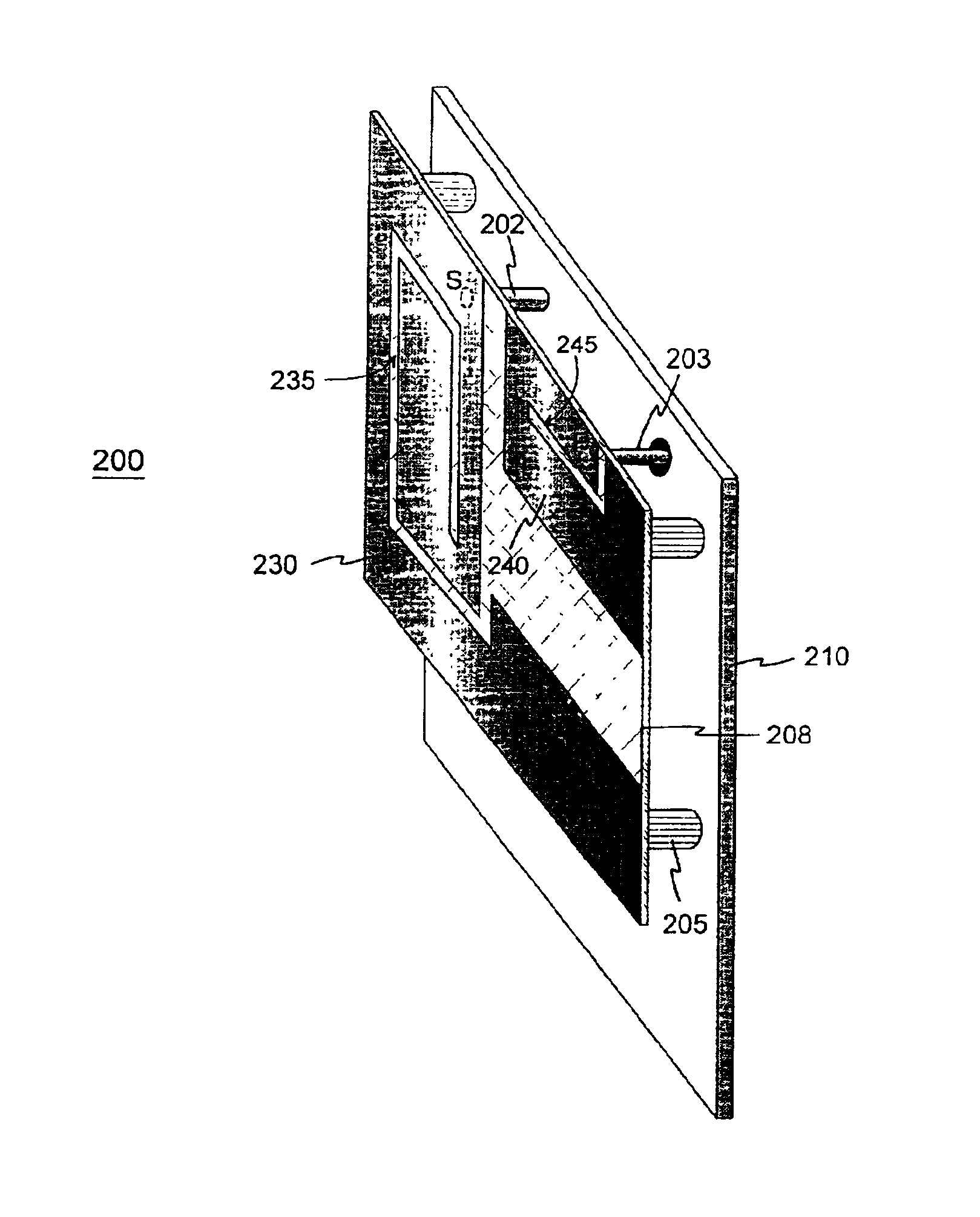
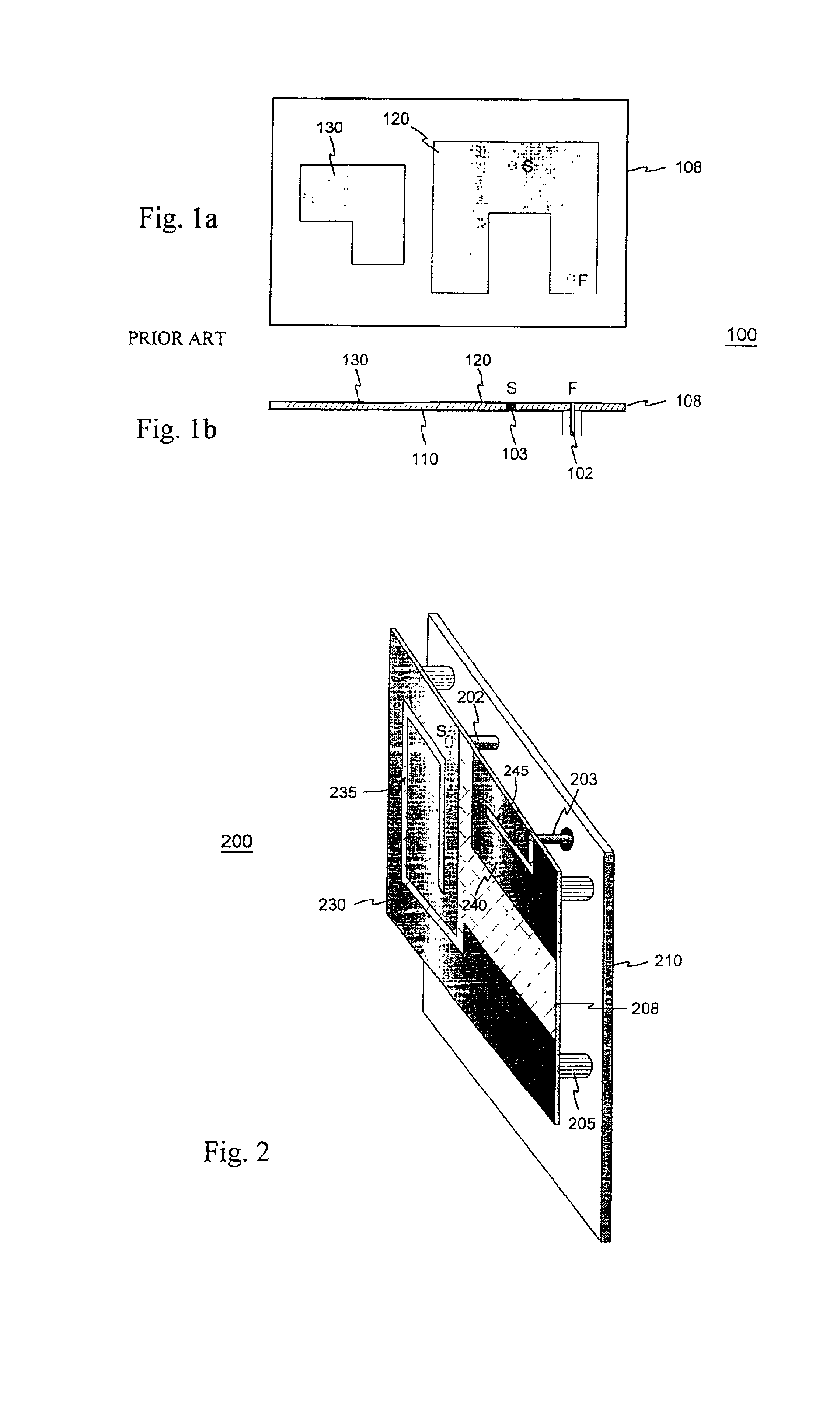
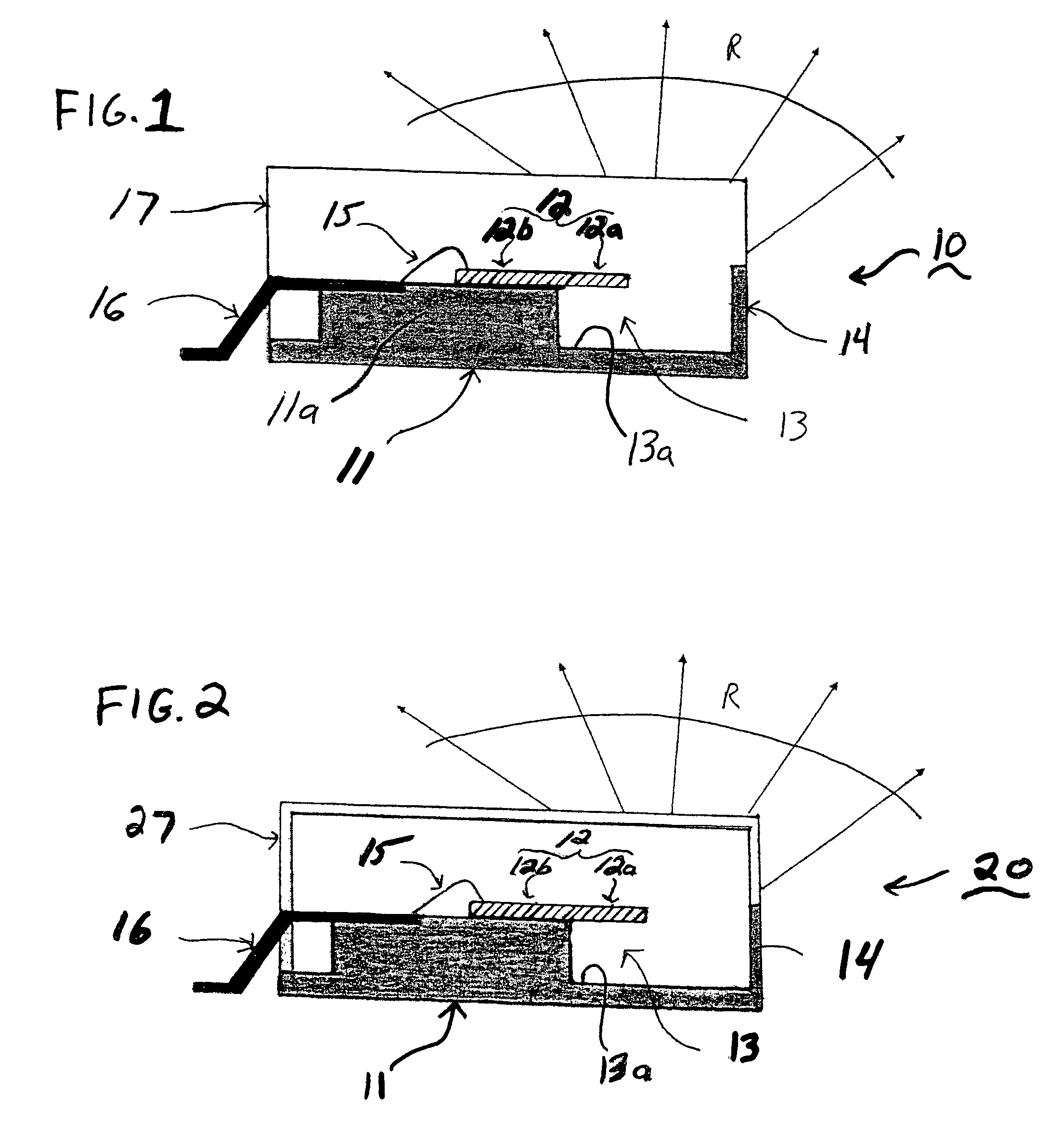
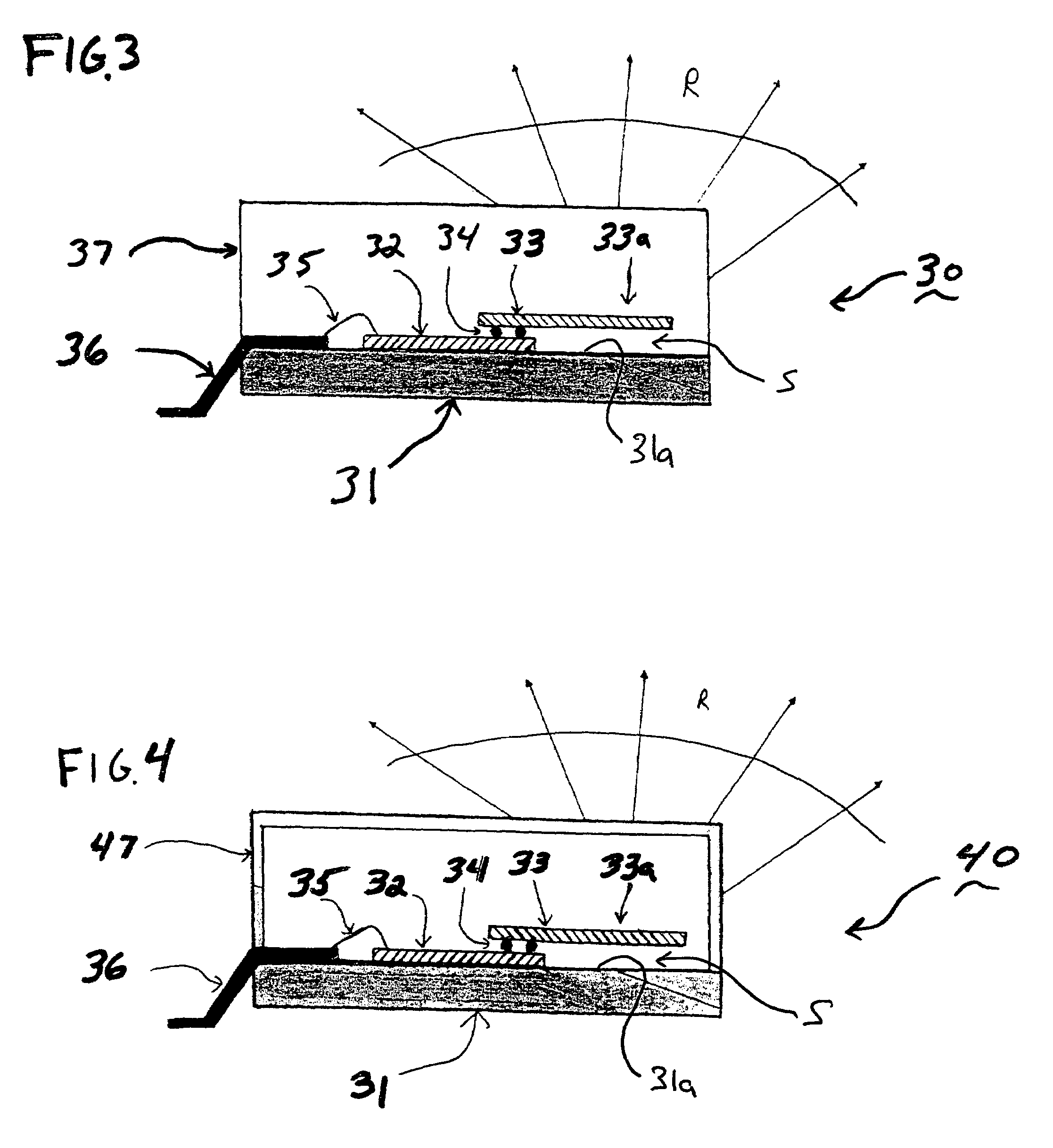
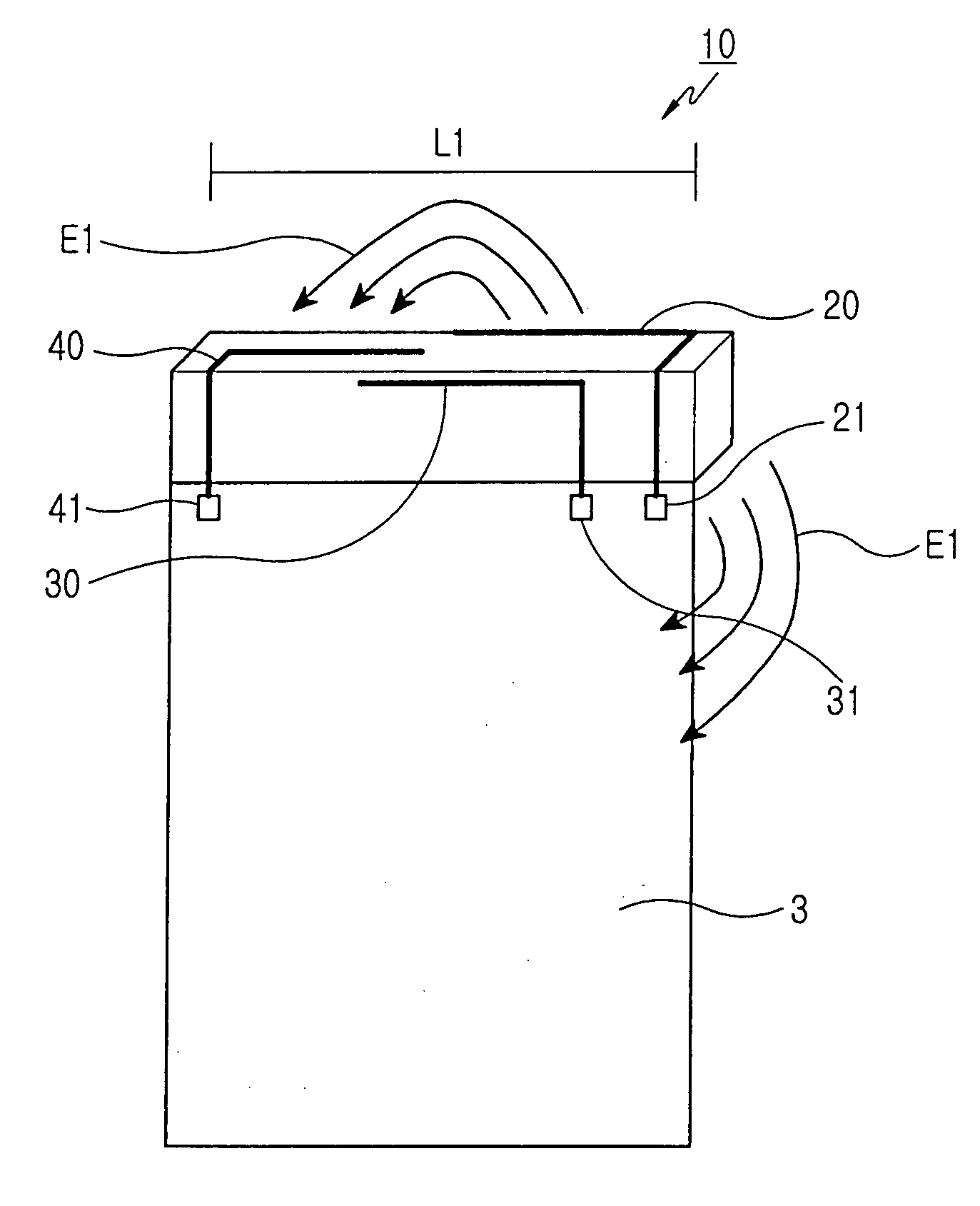
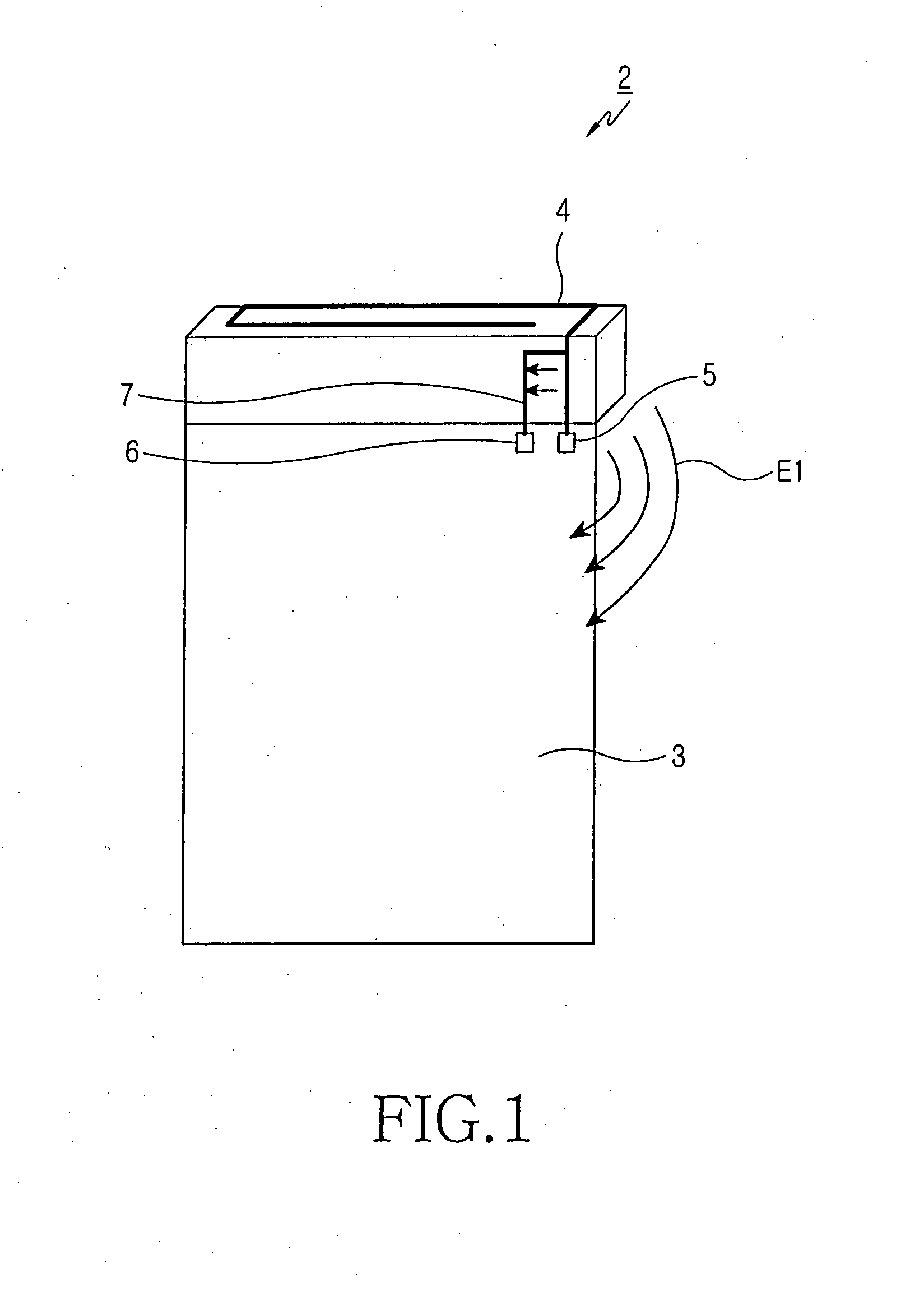
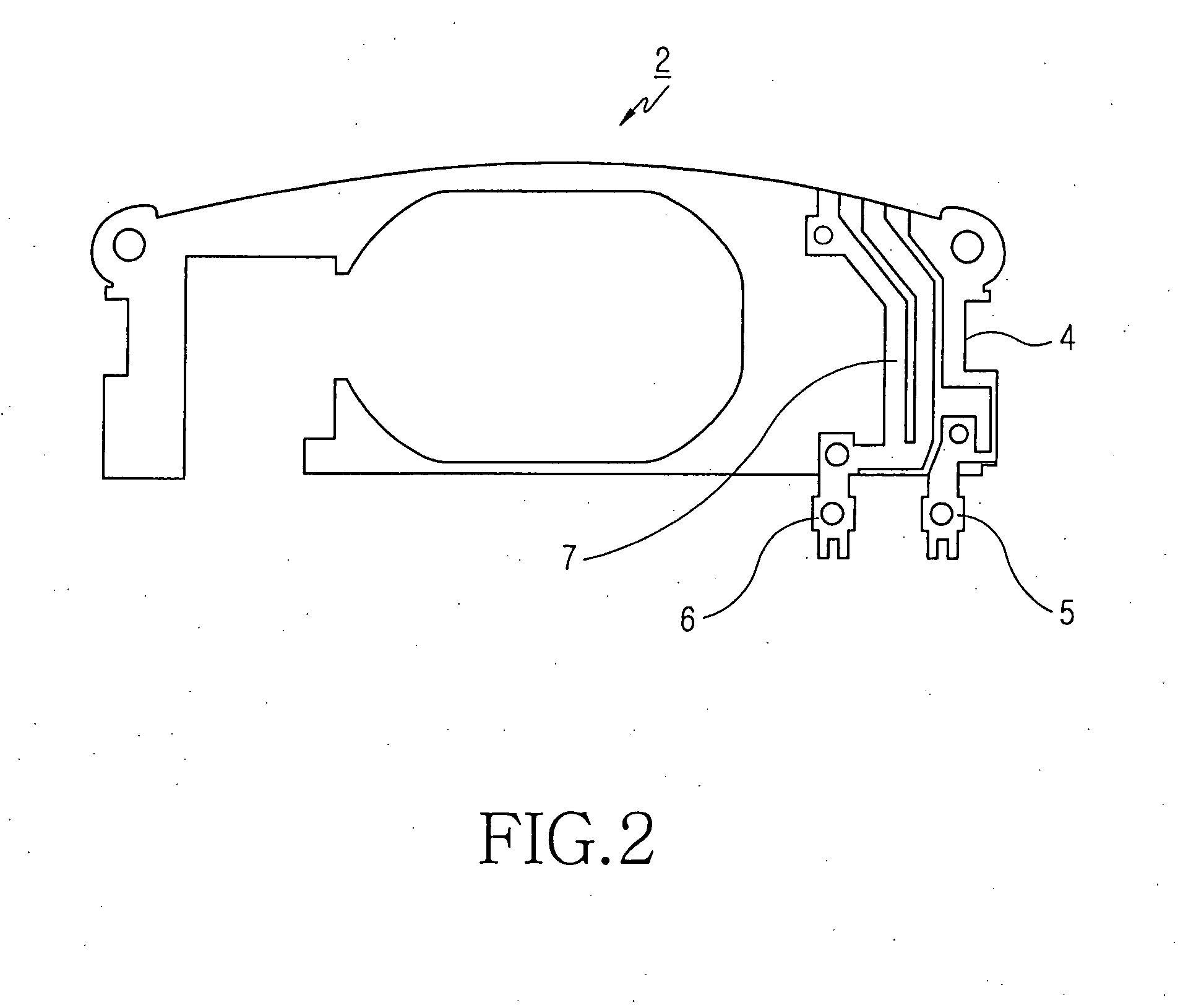
Planar antenna
InactiveUS6801166B2Simple and inexpensive to fabricateReduce the required powerSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorAntenna gain
Internal planar antenna especially applicable to mobile communication devices. A PIFA-type planar antenna is fed coaxially-like. This means that the feed conductor (321) of a radiating plane (310) is surrounded by a shield conductor (322) galvanically connected to the ground plane (GND) for the length between these planes. The shield conductor at the same time serves as a short circuit conductor for the antenna. The antenna is matched by means of a matching slot (317) going between the connection points of the feed and short circuit conductors, and / or of the shape of the short circuit conductor. A feed arrangement at issue increases antenna gain without increasing the SAR value of the antenna.
Owner:CANTOR FITZGERALD SECURITIES
Planar antenna structure
InactiveUS6922171B2Reliable dual resonanceWidebandSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention relates to planar antennas the structural components of which include a parasitic element. The antenna structure comprises a PIFA-type structure (230, 210, 202) to be placed inside the covers of a mobile station. The PIFA is fed parasitically e.g. through a conductive strip (240) placed on the same insulating board. The feed conductor (203) of the whole antenna structure is in galvanic contact with this feed element; a short-circuit point the feed element doesn't have. The feed element (240) also serves as an auxiliary radiator. The resonance frequencies of the antenna elements or their parts are arranged according to need so as to overlap, to be close to each other or to be relatively wide apart. The structure may also comprise a whip element in connection with the feed element. According to the invention, a relatively simple structure provides a reliable dual resonance and, hence, a relatively wideband antenna when the resonances are close to each other. Moreover, no polarization rotation takes place in the antenna radiation inside the frequency band realized through the dual resonance.
Owner:CANTOR FITZGERALD SECURITIES
Compact cellular phone
InactiveUS7031744B2Not easy to influenceMaintain transmission qualityCollapsable antennas meansSpatial transmit diversityPlanar antennasElectrical impedance
Owner:COLTERA
Planar antenna and radio apparatus
InactiveUS20060061513A1Easy constructionReduce areaRadiating elements structural formsSlot antennasRadio equipmentPlanar antennas
A planar antenna is formed of a circuit substrate and a slot line formed on the circuit substrate for guiding an electromagnetic wave in an axial direction thereof, the planar antenna emitting the electromagnetic wave at an end part of said slot line, wherein the end part has a curved shape forming a focal point at a location on an axis of the slot line with offset by a distance of about a quarter wavelength of the electromagnetic wave, and wherein there is provided a conductor pattern having a length of about a half of the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave at the focal point.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Loop antenna with a parasitic radiator
ActiveUS7728785B2Sacrificing radiation efficiencyLess sensitiveAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsElectromagnetic couplingPlanar antennas
It is an objective of the present invention to provide an antenna construction that allows the thickness of an antenna structure be lower than that of planar antennas according to prior art without sacrificing the radiation efficiency at the desired RF-bands as 900 MHz GSM and 1800 MHz / 1900 MHz DCS / PCS. A further object of the invention is to provide an antenna construction that is insensitive to changes in positions of electrically conductive objects in the vicinity. The objectives of the invention are achieved by a loop antenna structure equipped with an electrically conductive parasitic radiator that is electro-magnetically coupled with the antenna loop. Performance at the DCS / PCS bands can be further improved by using an electrically conductive tuner element that provides a stronger electromagnetic coupling between the antenna loop and the parasitic radiator.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
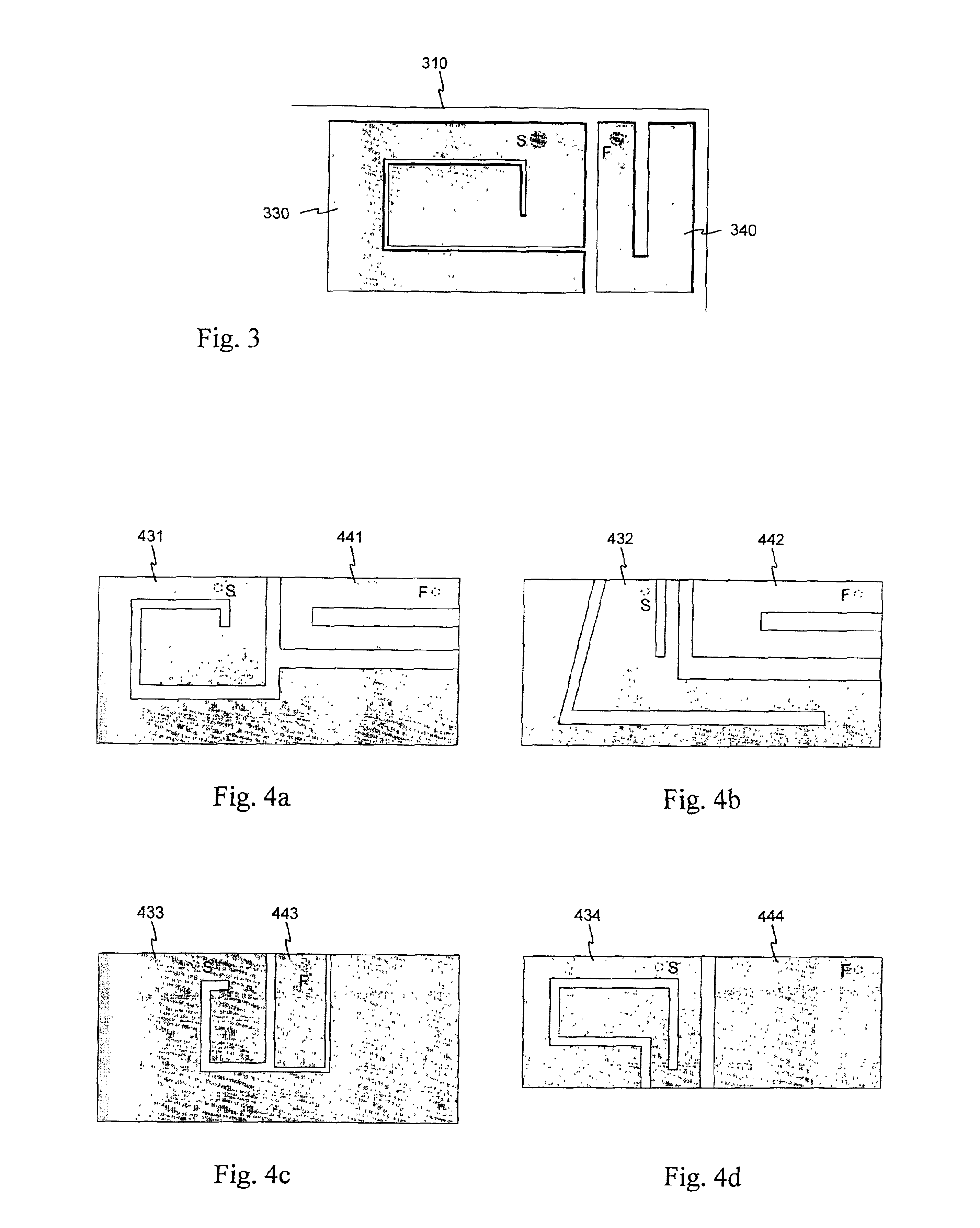
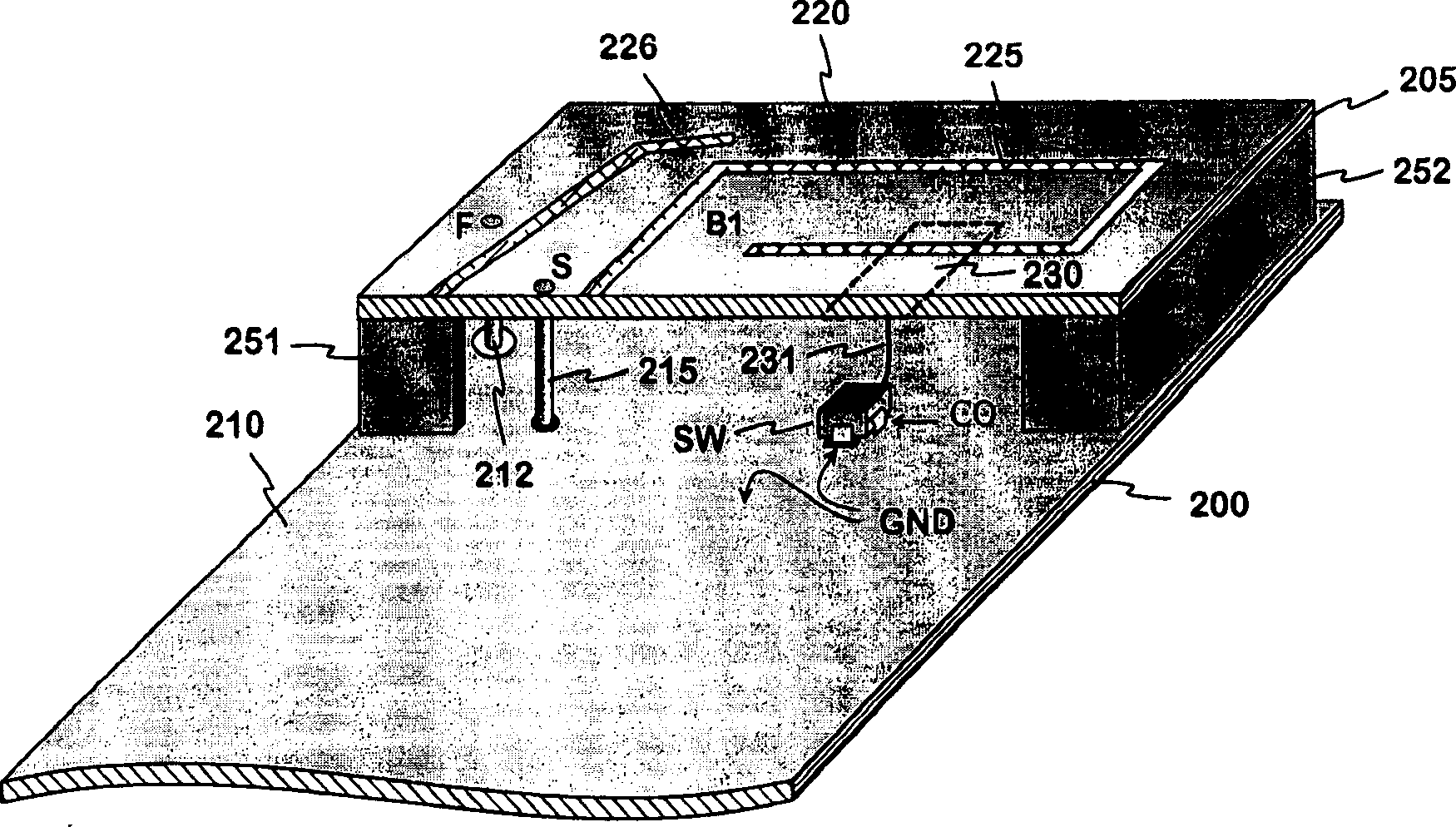
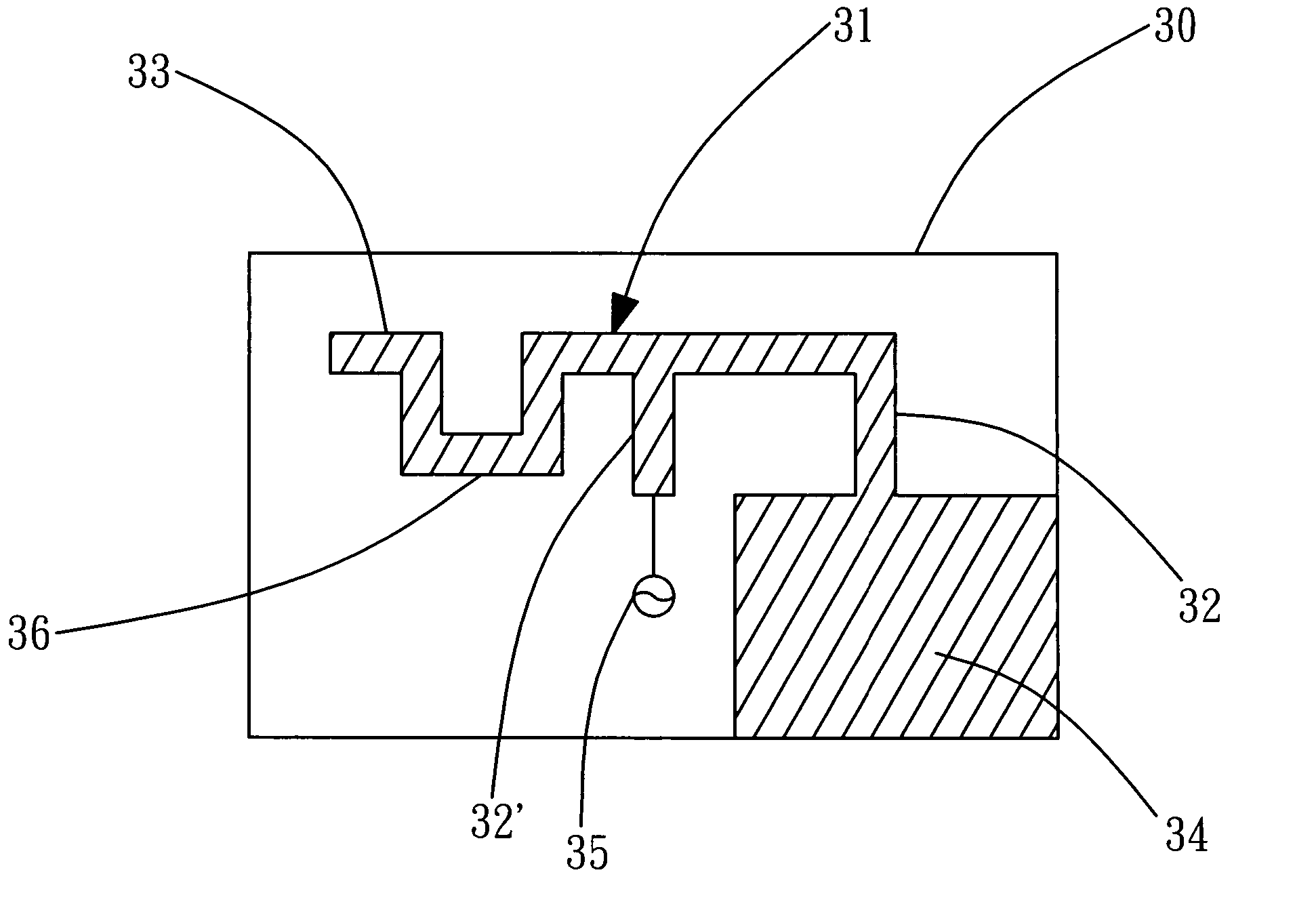
Internal antenna
InactiveCN1495966AExcellent electrical propertiesChange electrical lengthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna gainDual band antenna
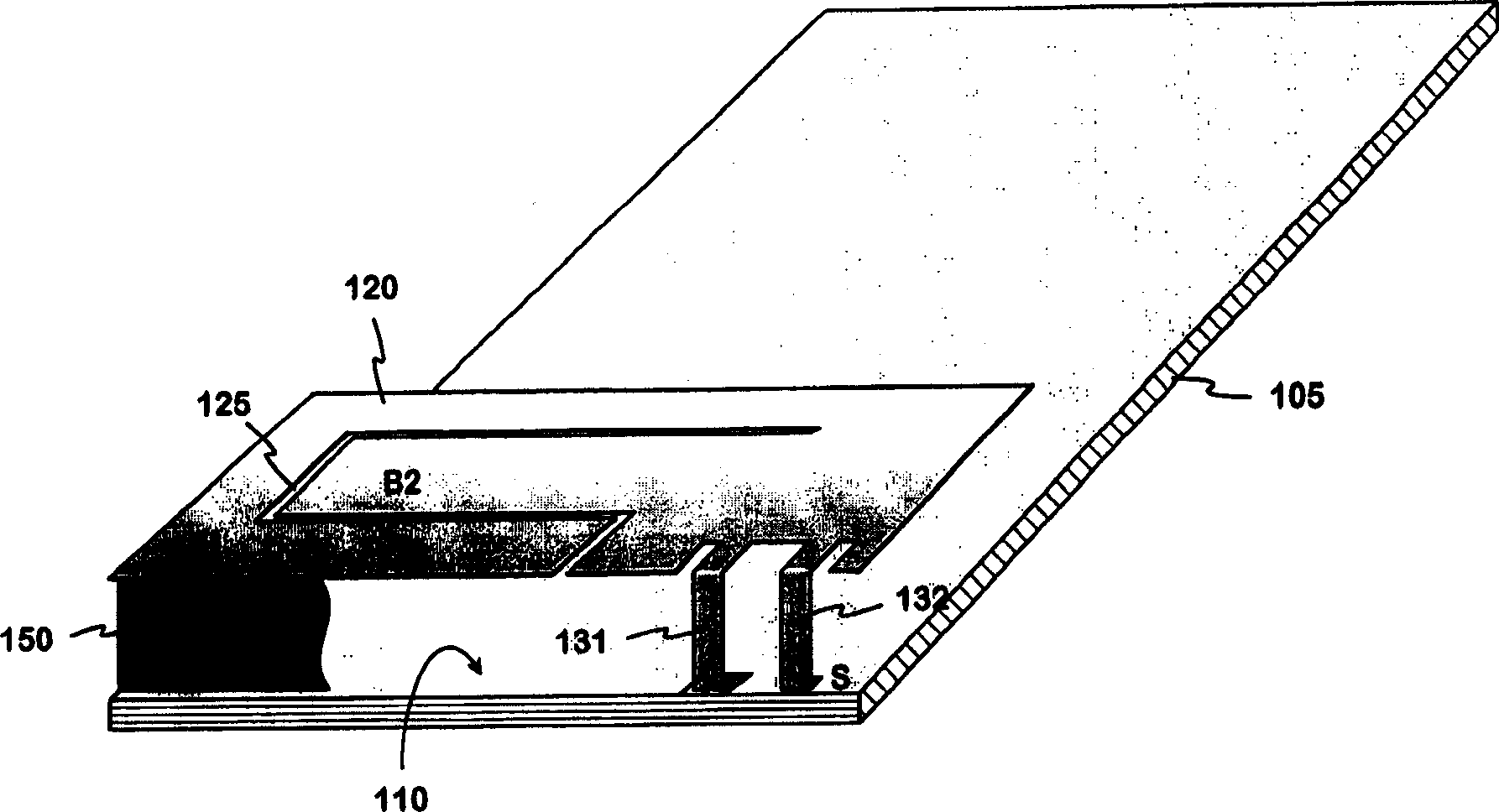
An internal planar antenna for small radio apparatuses, and a radio apparatus. The ground plane (310) of the planar antenna is shaped such that it improves the matching of the antenna. The shaping may be done by means of one or more slots (315, 316) in the ground plane. The slot suitably changes the electrical length of the ground plane as viewed from the short-circuit point (S) so that the ground plane will function as a radiator in an operating band of the antenna. Also the slot (331) in the ground plane can be arranged to function as an additional radiator in an operating band of the antenna. Antenna gain will increase as the matching is improved, and the upper band of a dual band antenna, for example, can be made broader.
Owner:L K PROD OY
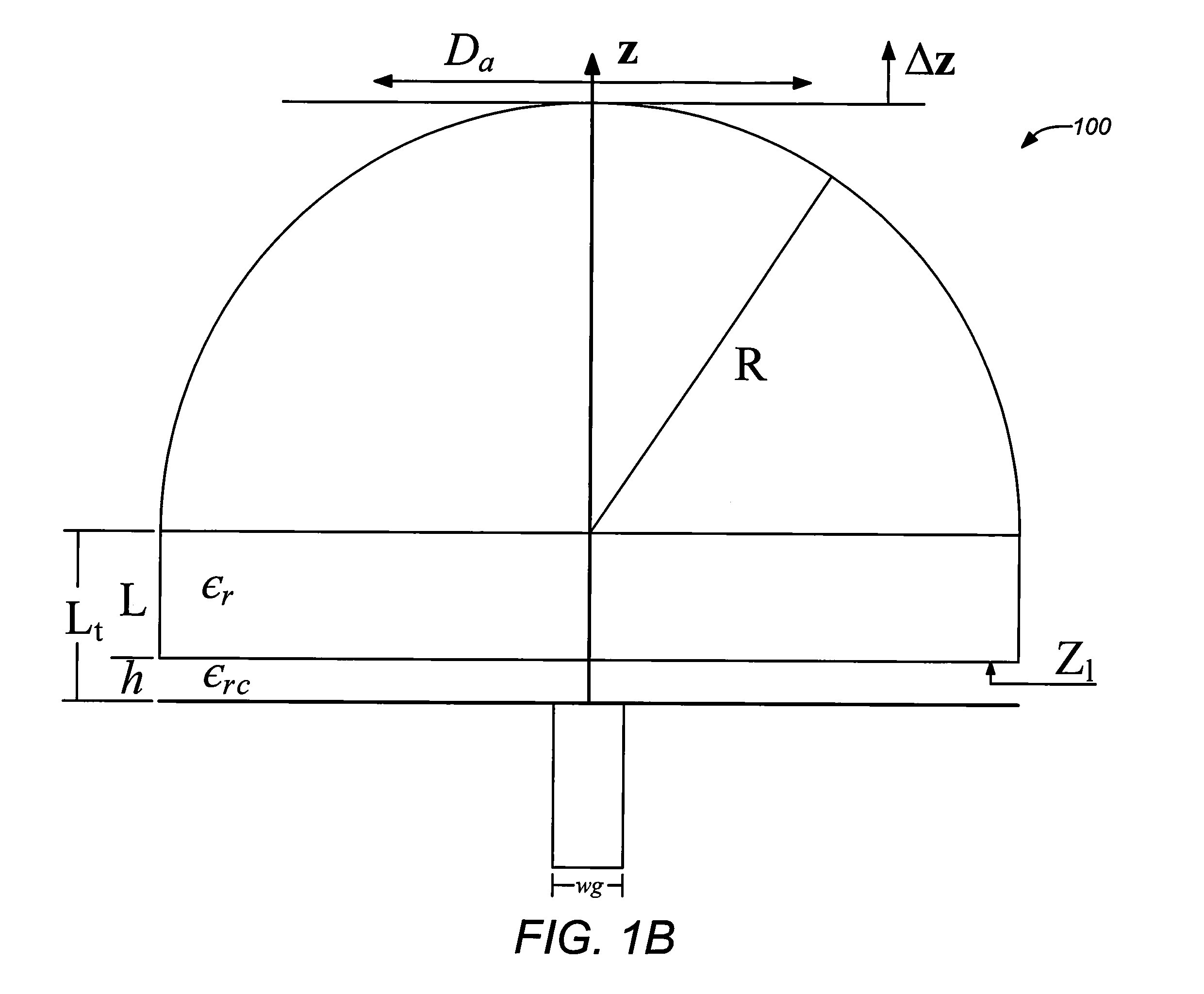
Dielectric covered planar antennas
An antenna element suitable for integrated arrays at terahertz frequencies is disclosed. The antenna element comprises an extended spherical (e.g. hemispherical) semiconductor lens, e.g. silicon, antenna fed by a leaky wave waveguide feed. The extended spherical lens comprises a substantially spherical lens adjacent a substantially planar lens extension. A couple of TE / TM leaky wave modes are excited in a resonant cavity formed between a ground plane and the substantially planar lens extension by a waveguide block coupled to the ground plane. Due to these modes, the primary feed radiates inside the lens with a directive pattern that illuminates a small sector of the lens. The antenna structure is compatible with known semiconductor fabrication technology and enables production of large format imaging arrays.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
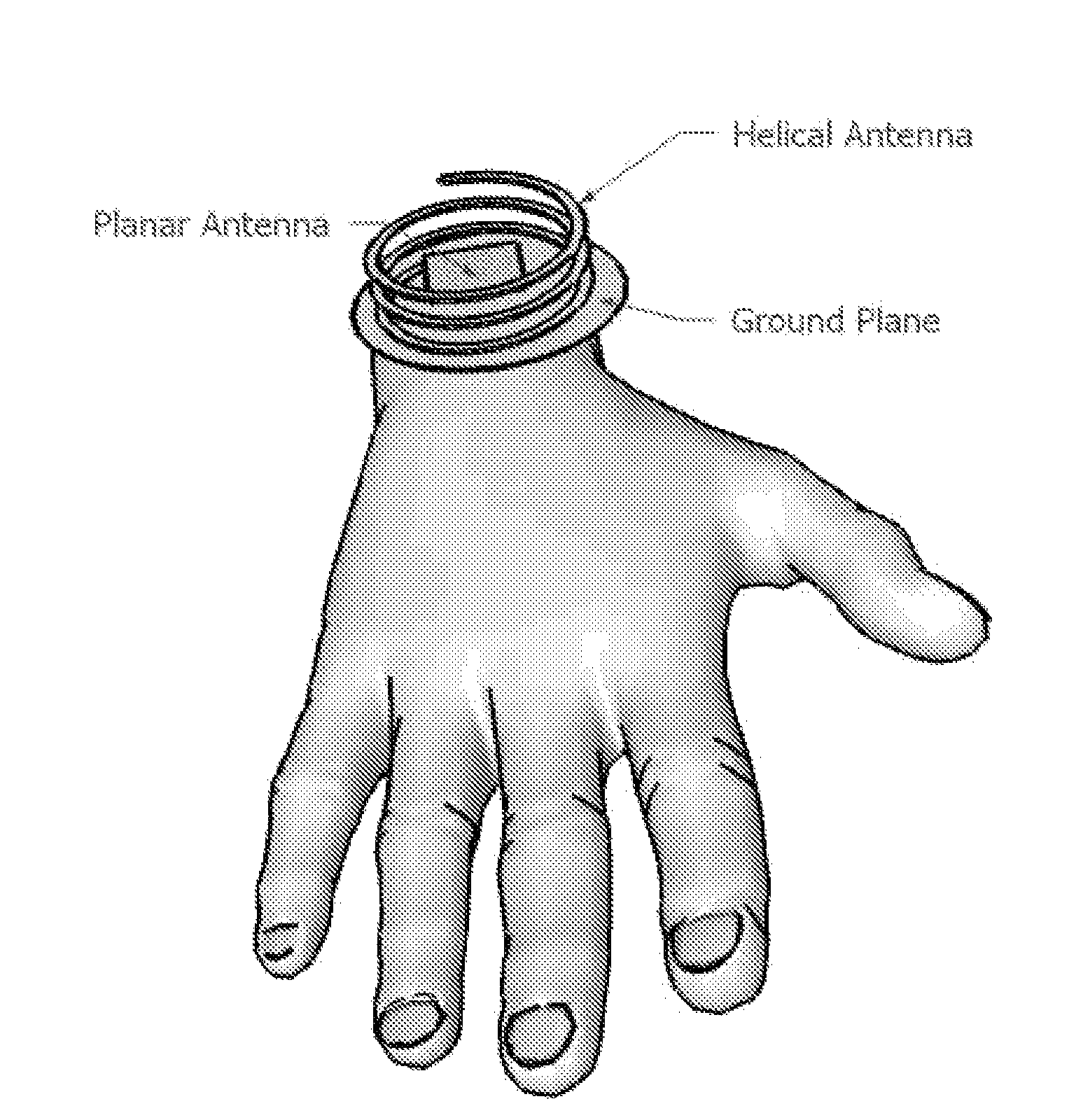
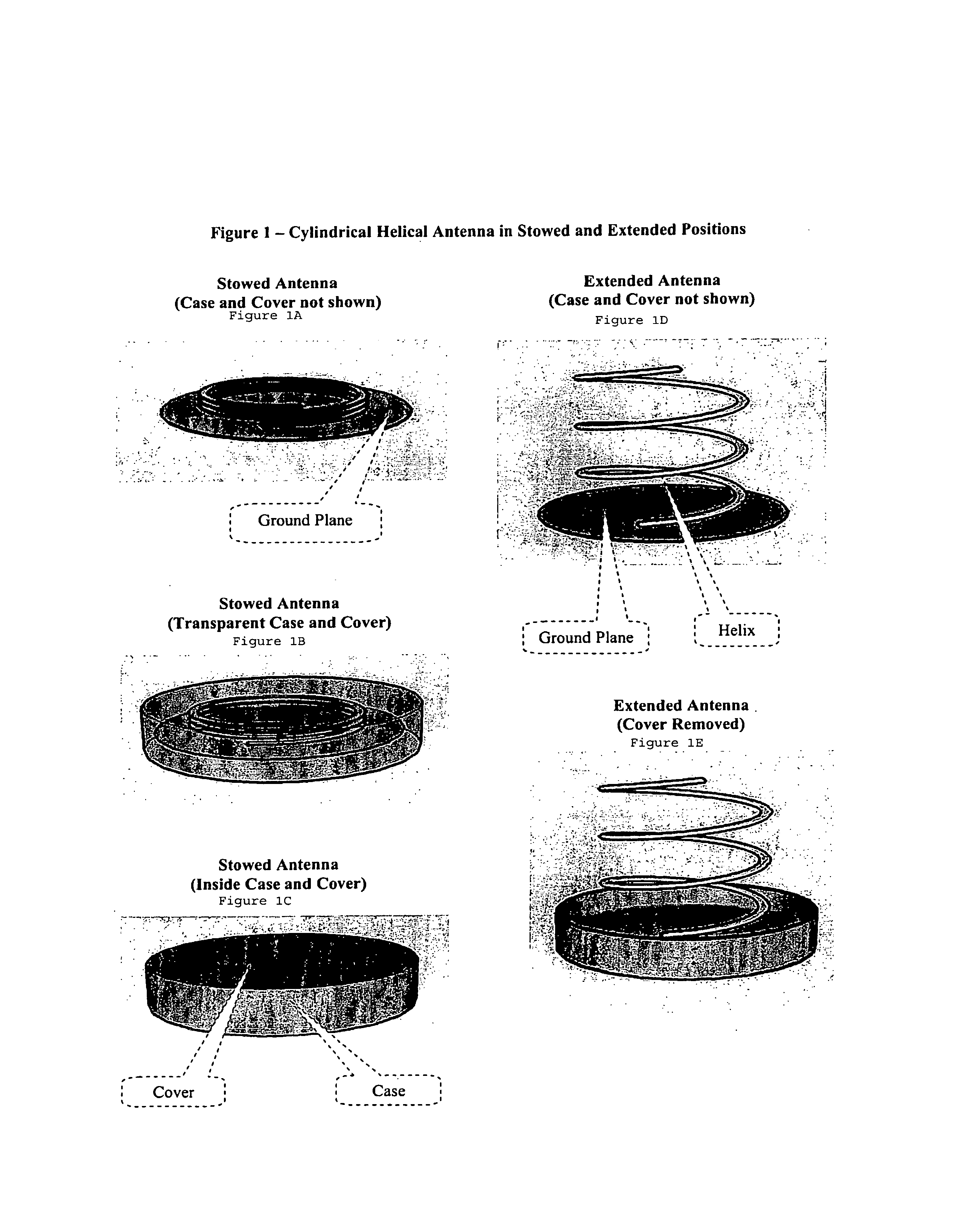
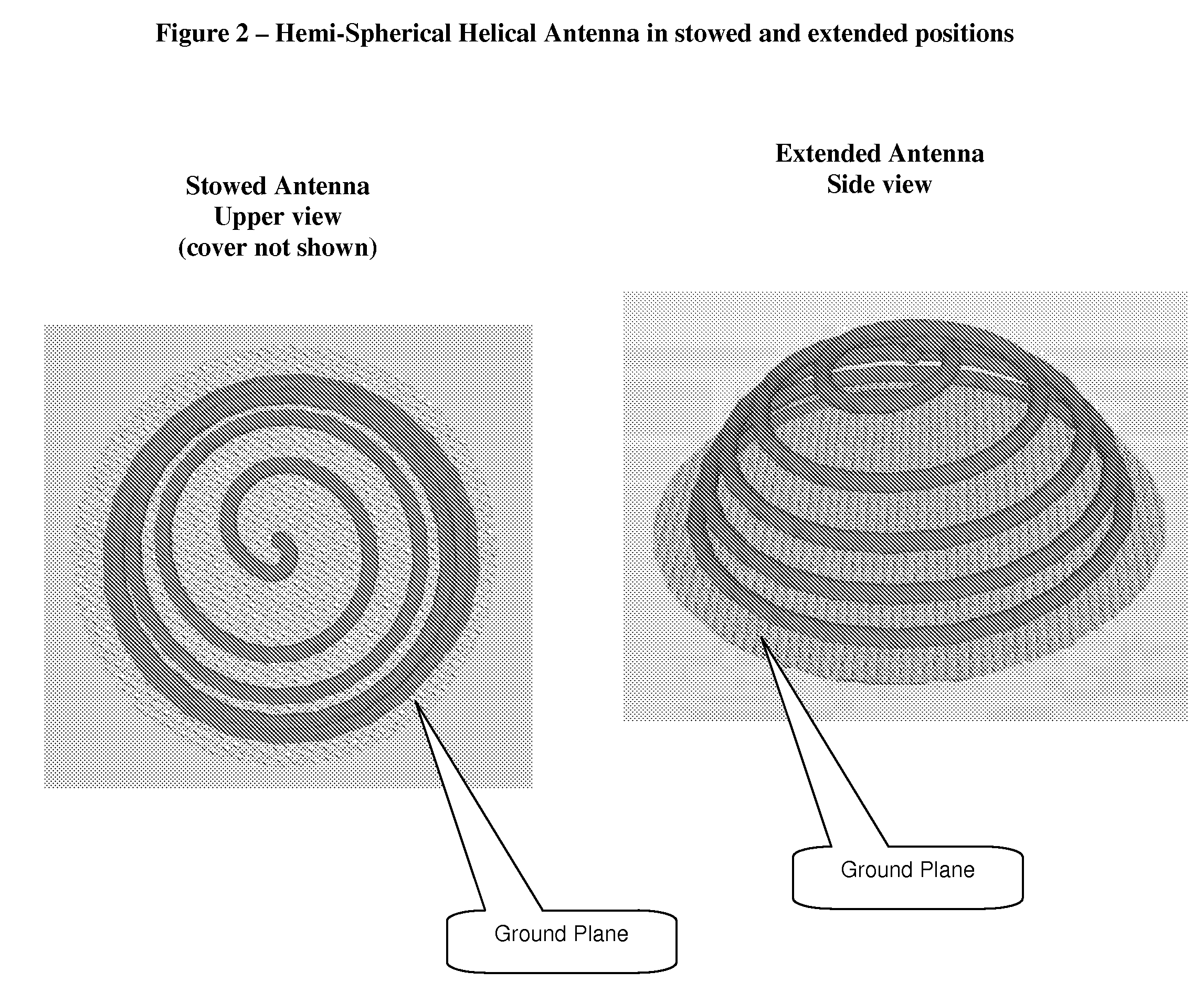
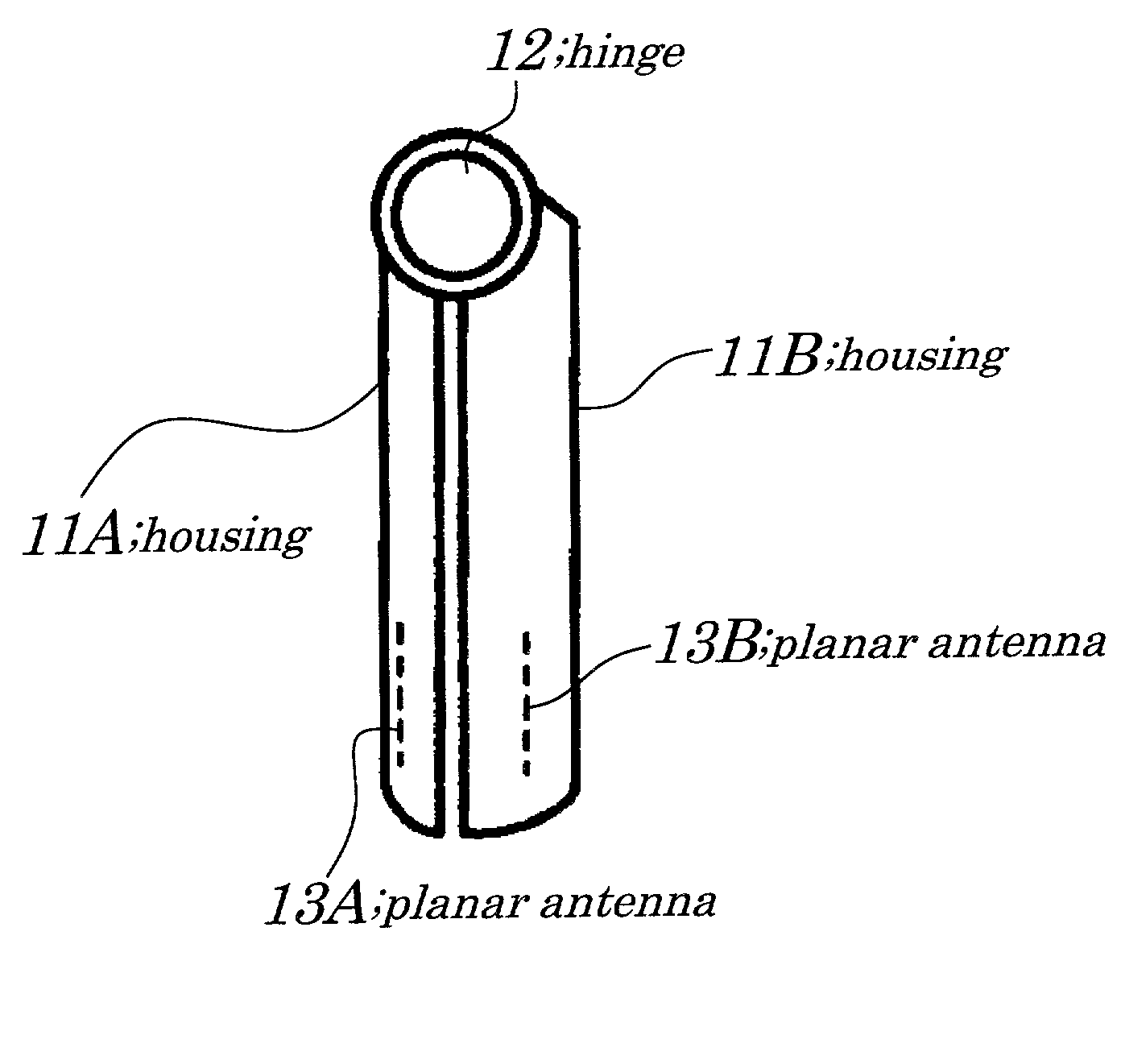
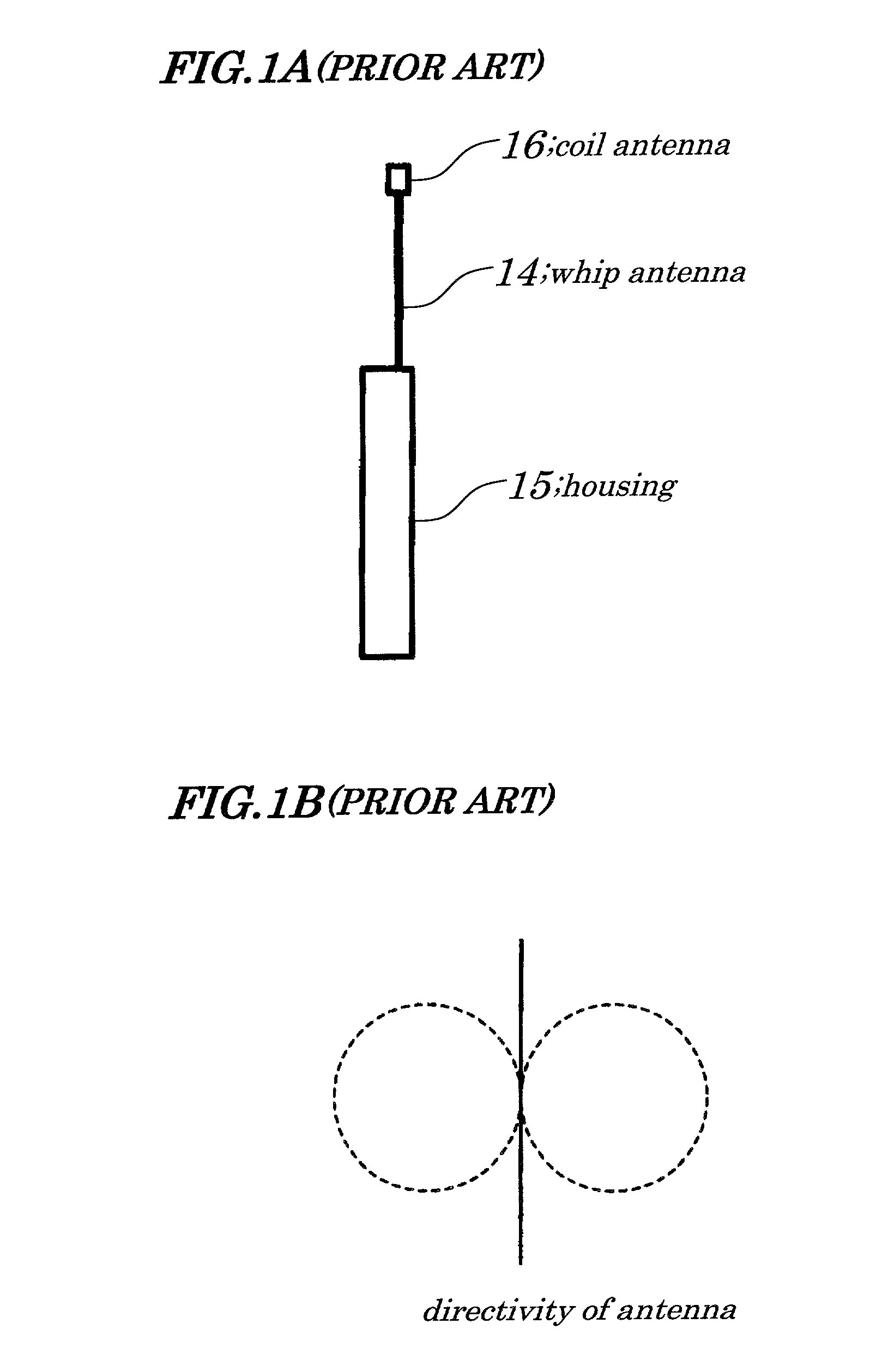
Extendable helical antenna for personal communication device
ActiveUS7586463B1Substantial electromagnetic decouplingOverall small sizeCollapsable antennas meansAntenna supports/mountingsGround planeHelical antenna
The present invention discloses a portable personal communication device with an extendable helical antenna. This helical antenna is made of an elastic conductive spring, configured to change its height over a ground plane and along the antenna axis, mainly having two positions: a stowed position where the antenna is pressed down between the ground plane and a rigid cover, achieving a low profile; and an operational position where the rigid cover is removed and the antenna is extended by its own spring force, to a higher height, improving antenna gain. Normally, a second planar antenna may be placed over the same ground plane, not exceeding the footprint of the helical antenna, thus utilizing a compactly small volume and yet achieving a considerable electromagnetic decoupling between the antennas, due to their different radiation patterns. According to one embodiment, these antennas are installed in a Personal Locator Beacon (PLB) for Search and Rescue (SAR) of people in distress, where the planar antenna is coupled to a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS, such as GPS) receiver, and the helical antenna is coupled to a VHF / UHF radio.
Owner:MOBIT TELECOM
Apparatus and methods for packaging antennas with integrated circuit chips for millimeter wave applications
ActiveUS7342299B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransceiverCommunications system
Apparatus and methods are provided for integrally packaging antennas with semiconductor IC (integrated circuit) chips to provide highly-integrated and high-performance radio / wireless communications systems for millimeter wave applications including, e.g., voice communication, data communication and radar applications. For example, wireless communication modules are constructed with IC chips having receiver / transmitter / transceiver integrated circuits and planar antennas that are integrally constructed from BEOL (back end of line) metallization structures of the IC chip.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
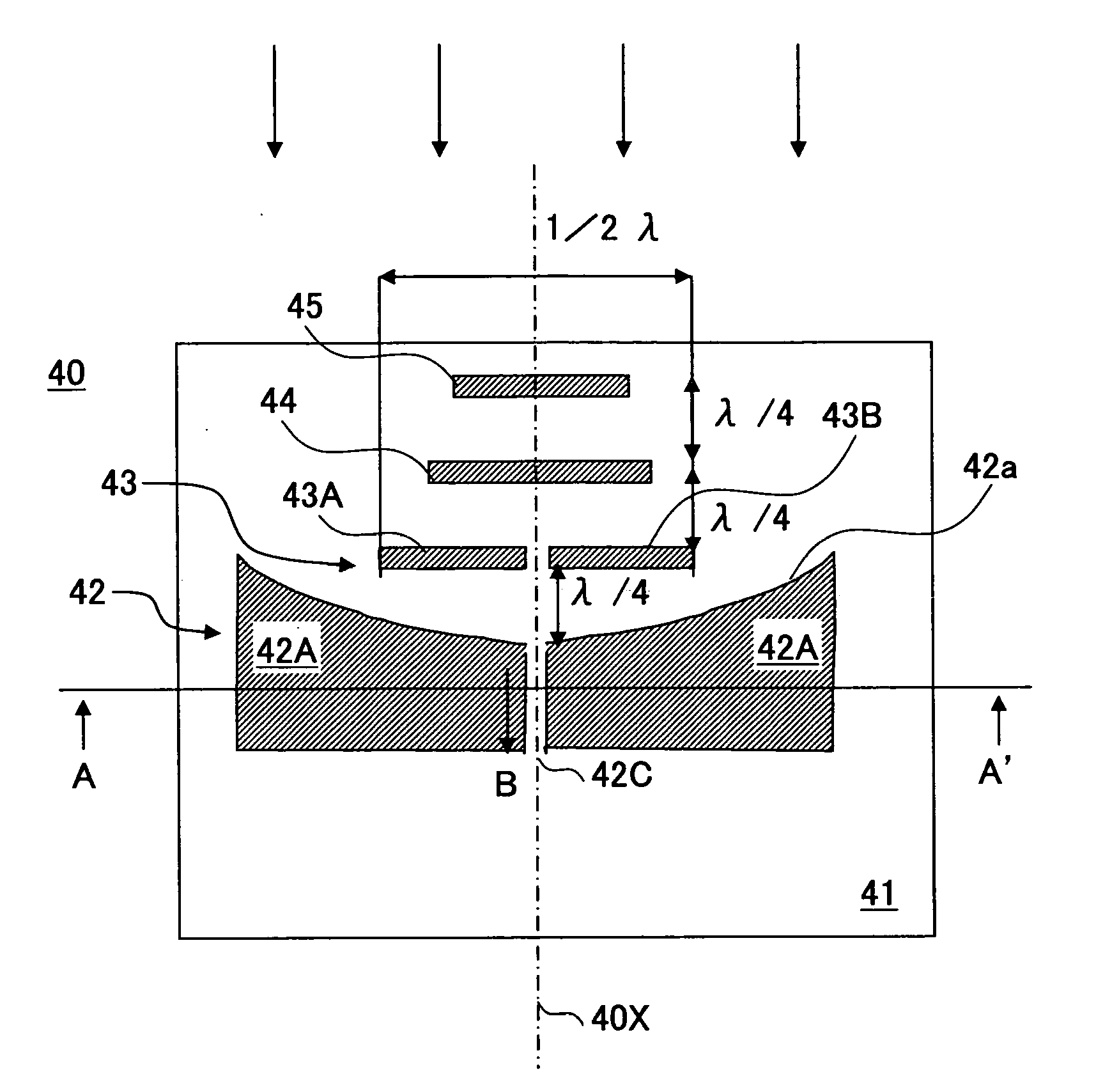
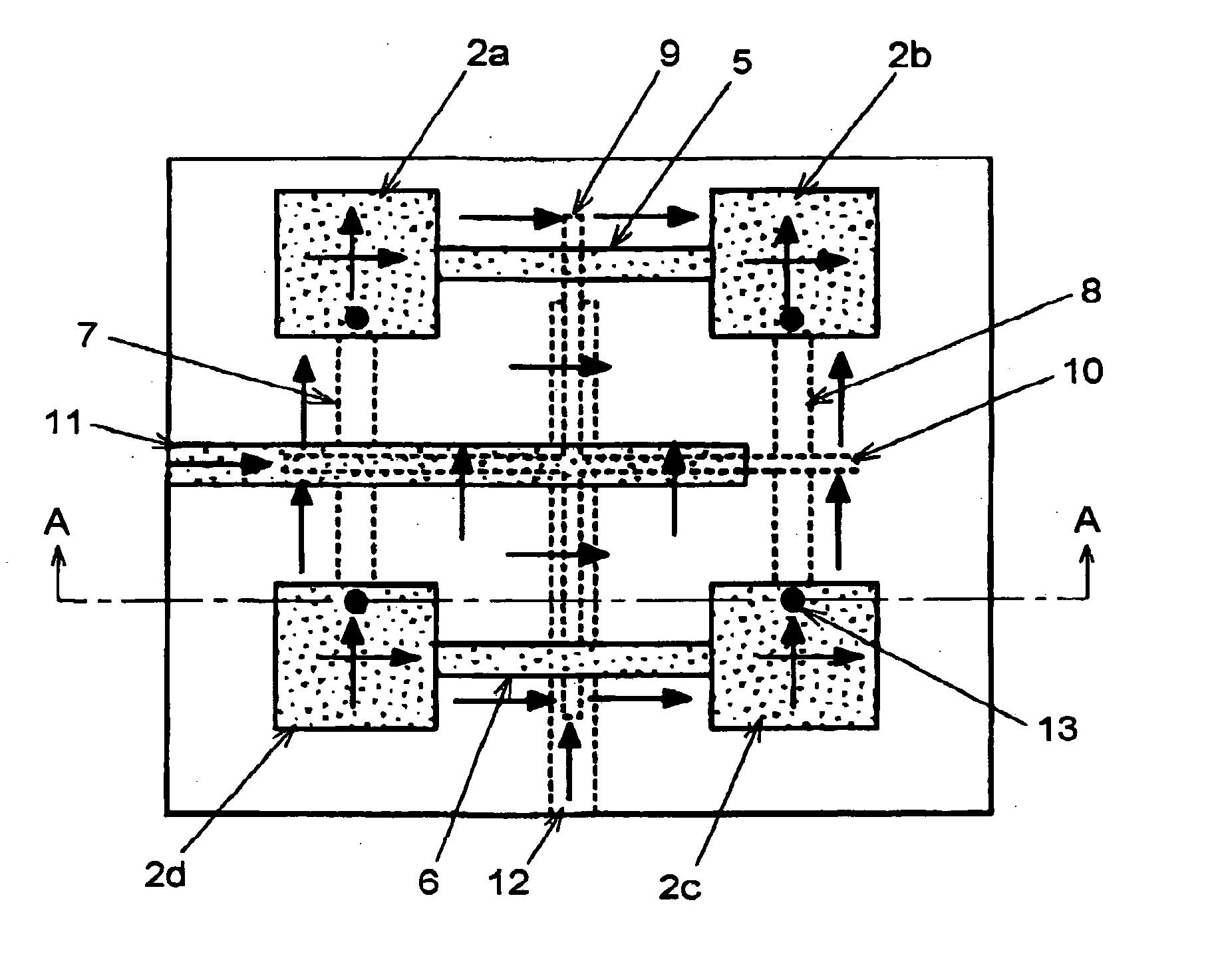
Planar array antenna
InactiveUS20050264451A1Easy wiringThe implementation process is simpleSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectromagnetic couplingElectrical conductor
A planar array antenna using a multi-layer substrate having an intermediate layer conductor in a laminated face comprises: four pieces of planar antenna elements disposed at each of geometrically square shaped apexes; first and second slot lines formed in the intermediate layer conductor, and intersecting each other; first to fourth microstrip lines formed along each side of geometrical squares so as to be coupled to each antenna element, and at the same time, electromagnetically coupled to first and second slot lines at both ends of these slot lines; and fifth and sixth microstrip lines, the top end sides thereof traversing the first and second slot lines, respectively, so as to be electromagnetically coupled to the first and second slot lines.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD +1
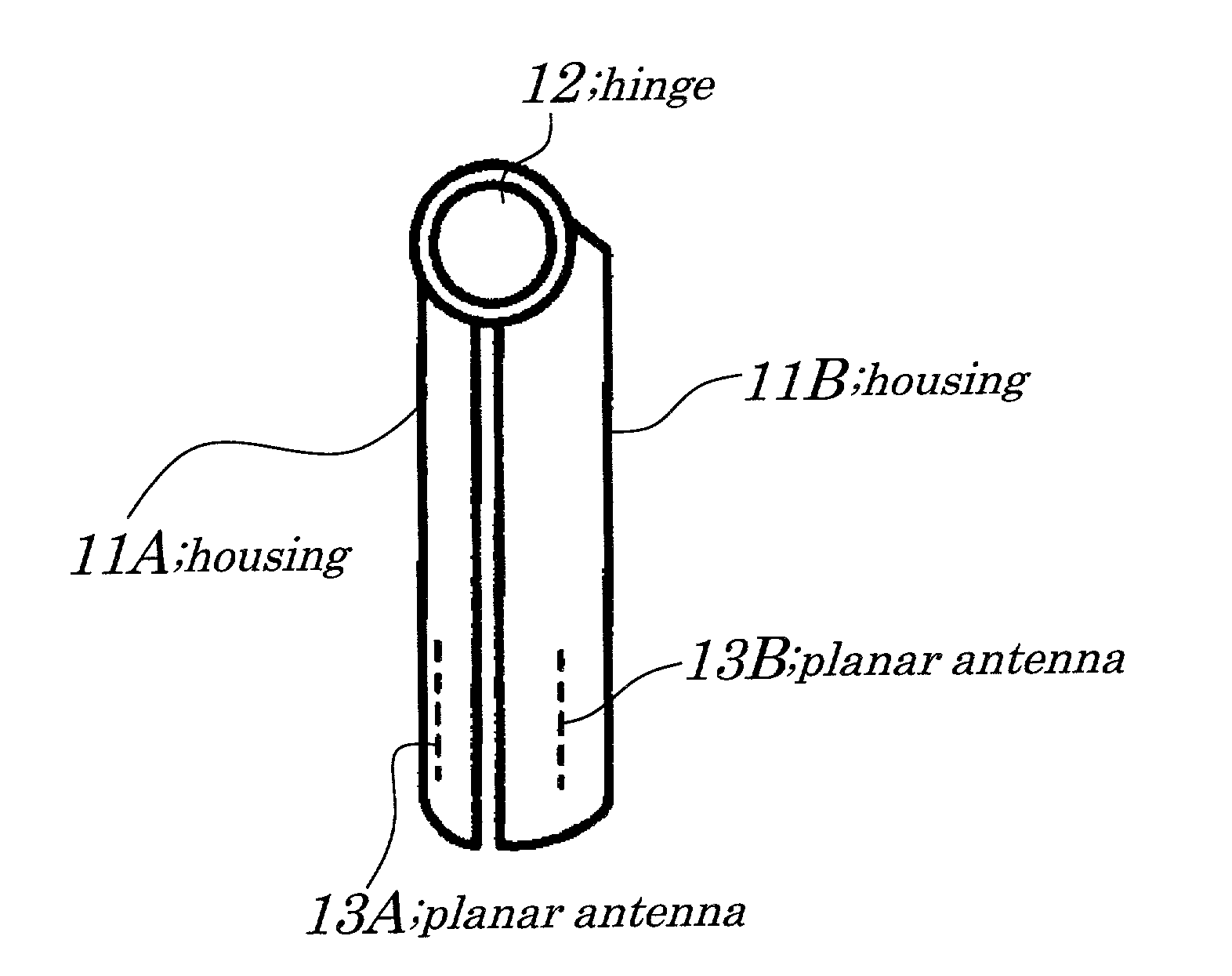
Compact cellular phone
InactiveUS20020068602A1Spatial transmit diversityCollapsable antennas meansPlanar antennasEngineering
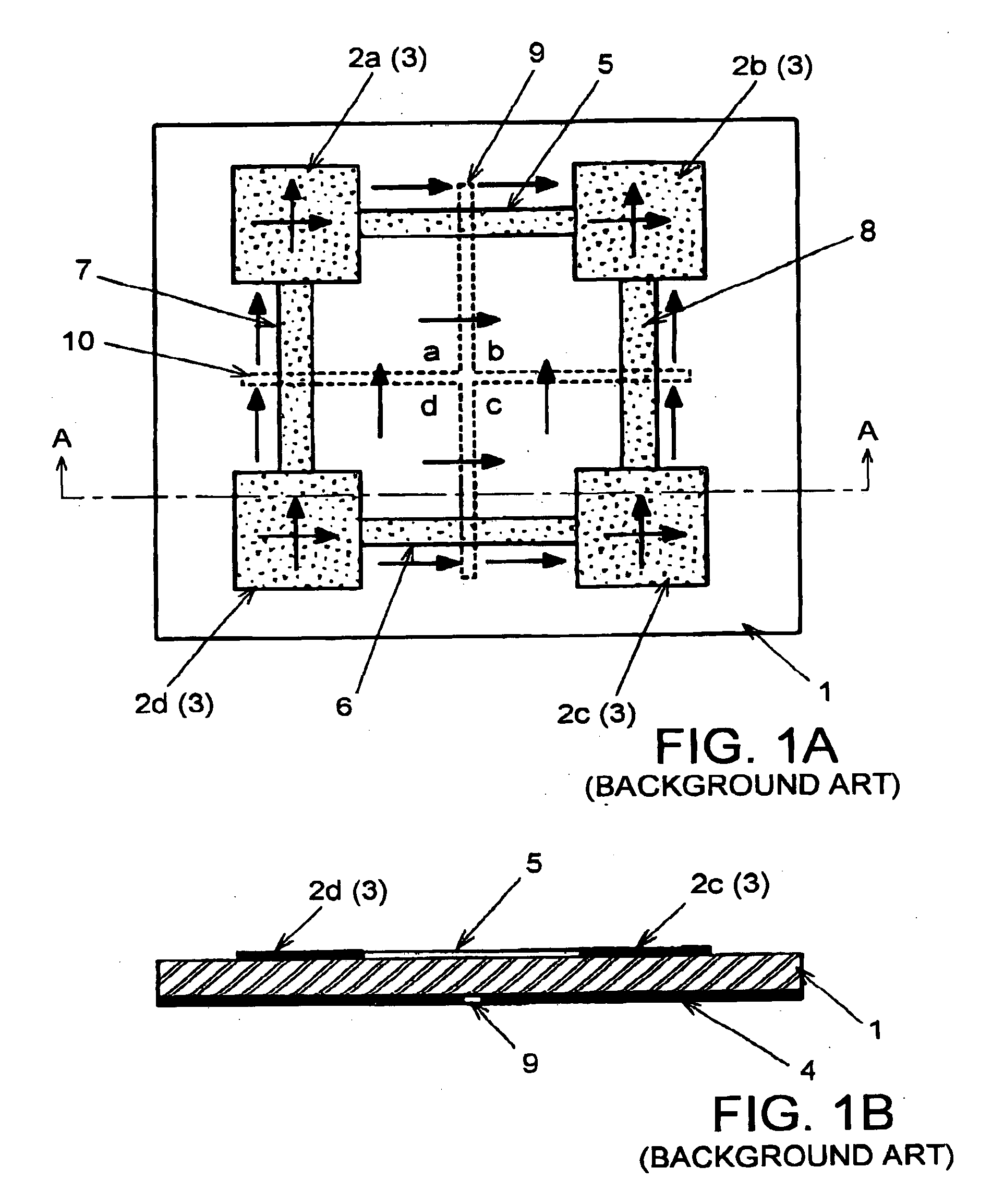
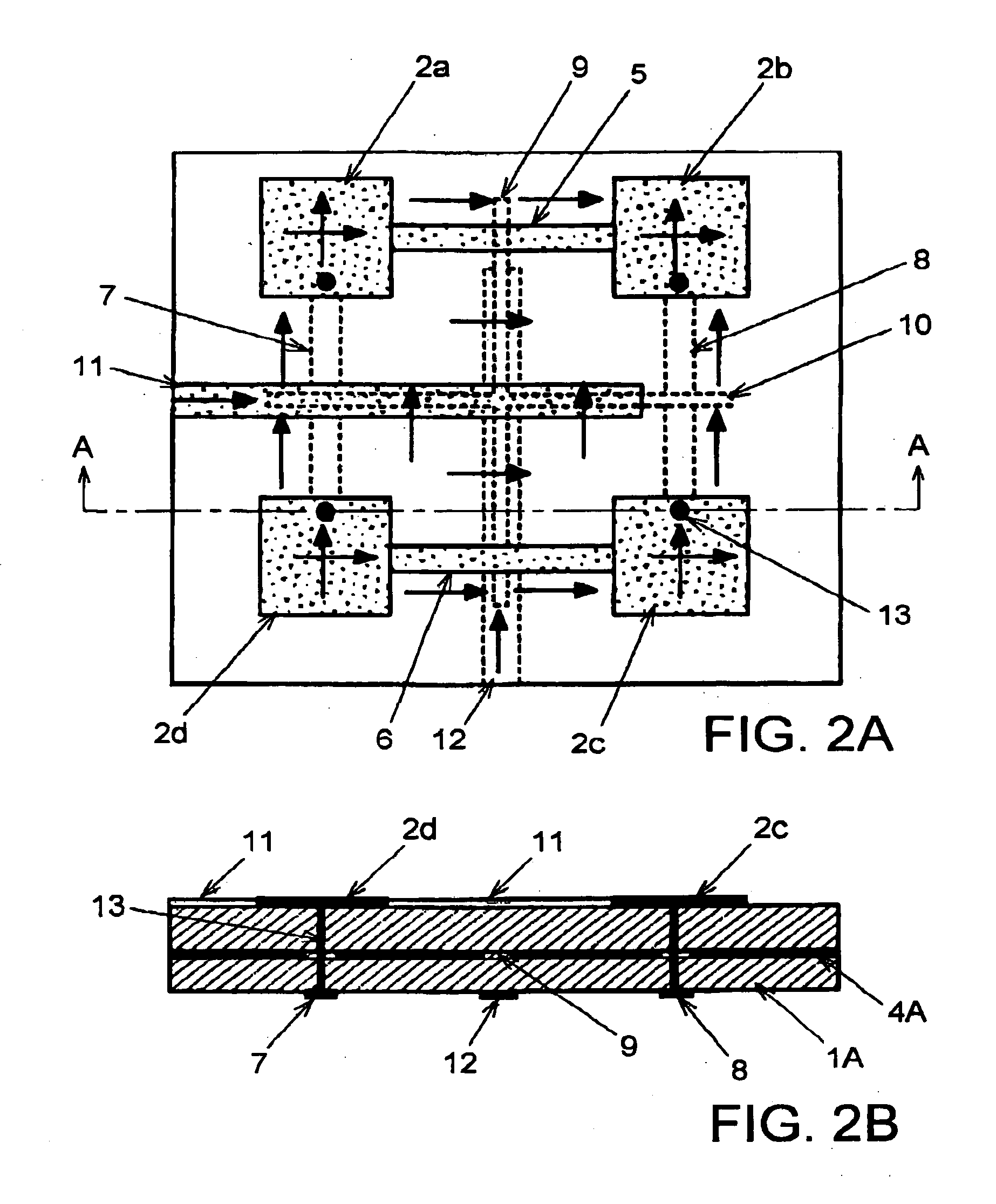
A compact cellular phone with a foldable configuration and two planar antennas having outward directivities are provided inside the compact cellular phone in the foldable configuration. An interval between the two planar antennas provided to a pair of housings is equal to or wider than a width of a human palm in a state in which the compact cellular phone is open. The two planar antennas are planar inverse F-type antennas or patch antennas and impedance around each of the two planar antennas is measured. Then, one of the two planar antennas, which has a preferred transmission characteristic, is selected and used.
Owner:COLTERA
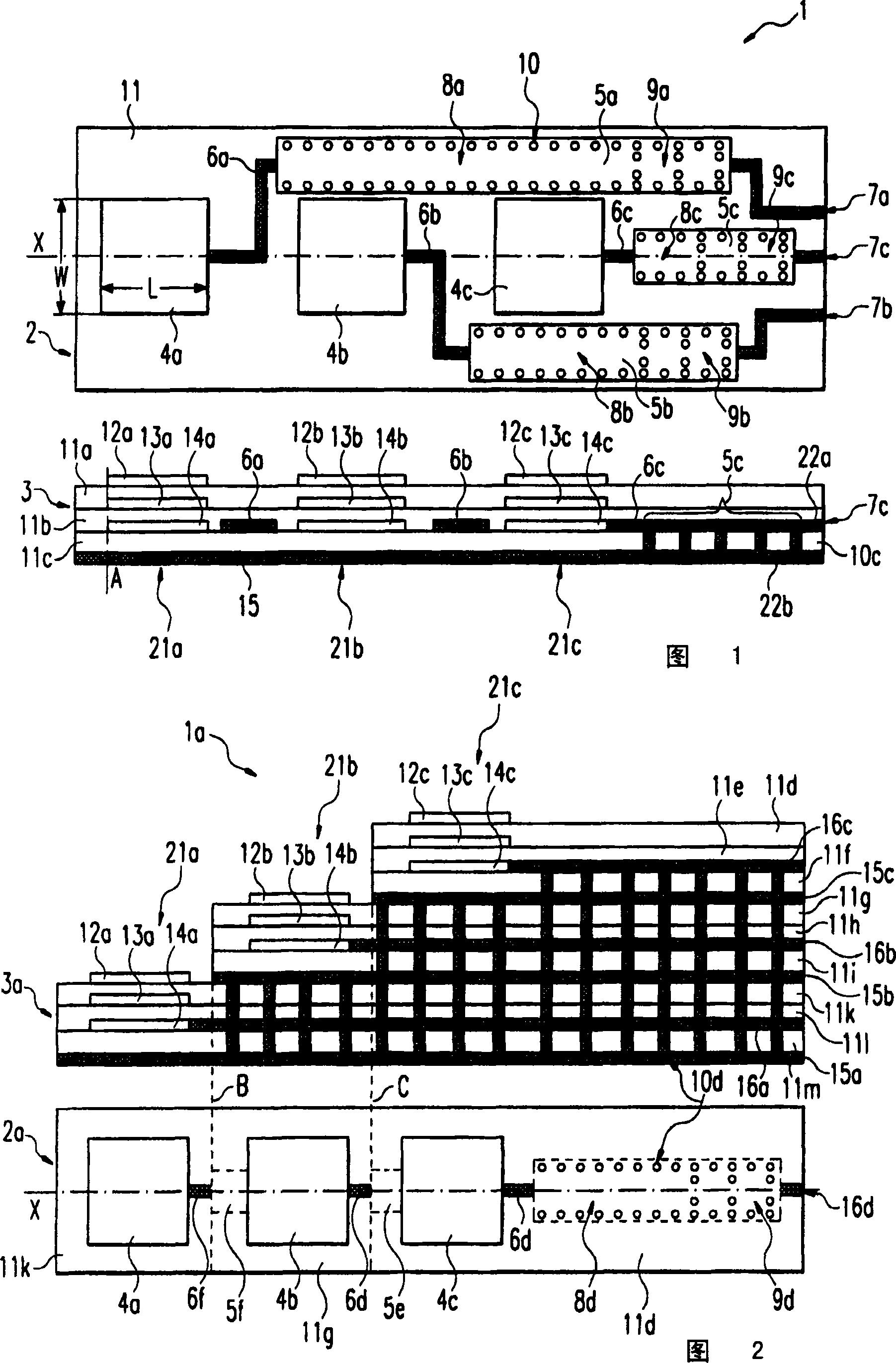
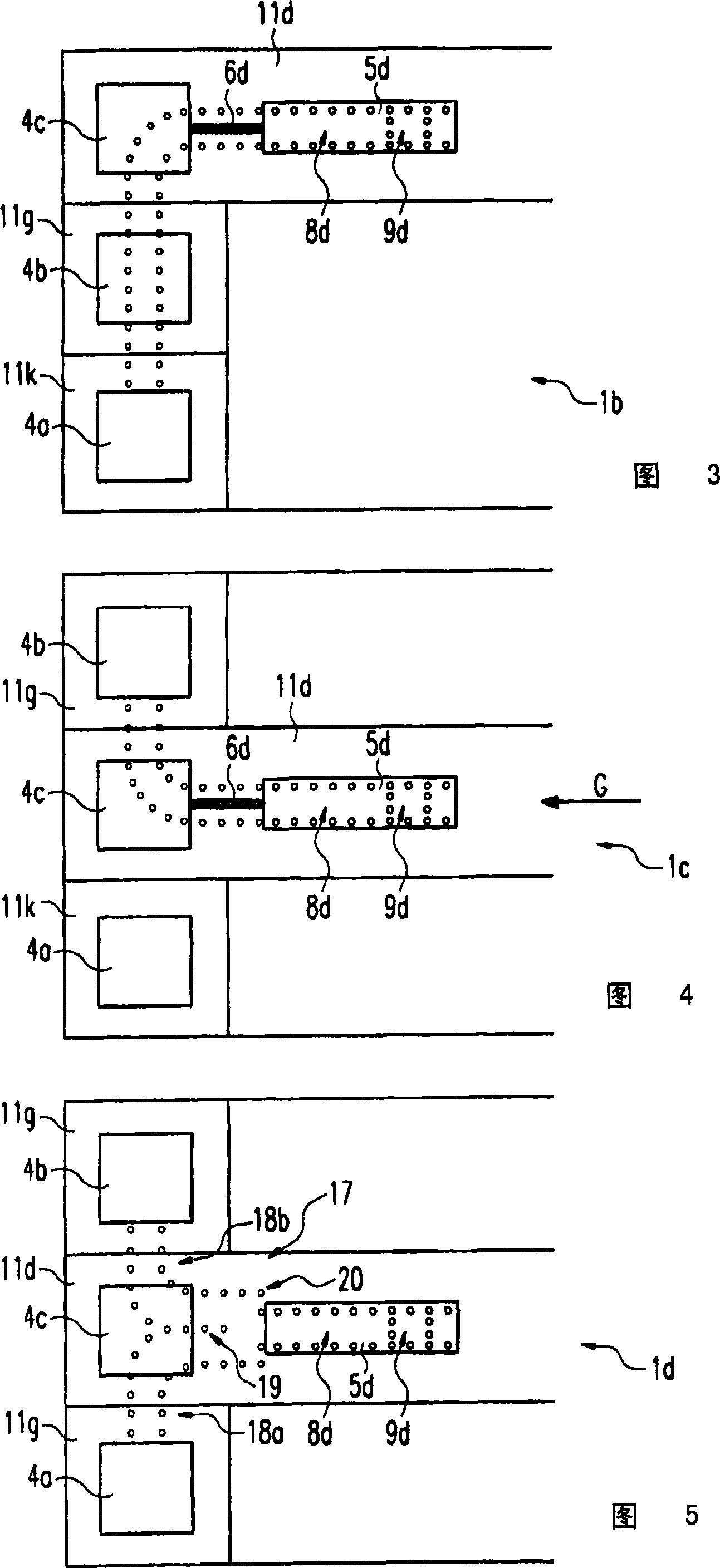
Method for the manufacture of a printed circuit and planar antenna manufactured with this printed circuit
InactiveUS7060418B2Reading method can be performed more quicklyEconomical and speedy applicationPhotomechanical apparatusRadiating elements structural formsElectrically conductiveEngineering
In a method for the manufacture of a printed circuit on a dielectric carrier (2), in a first step a circuit pattern (1) is applied with an electrically conductive ink and, in a second step, the circuit model is plated, the electrically conductive ink being applied by means of a method of gravure printing and the plating being done by electrolytic or chemical means.
Owner:MICROCONNECTIONS
Adjustable plane antenna
InactiveCN1492538ASize did not changeLow dissipation growthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsRadio equipmentElectromagnetic coupling
Owner:L K PROD OY
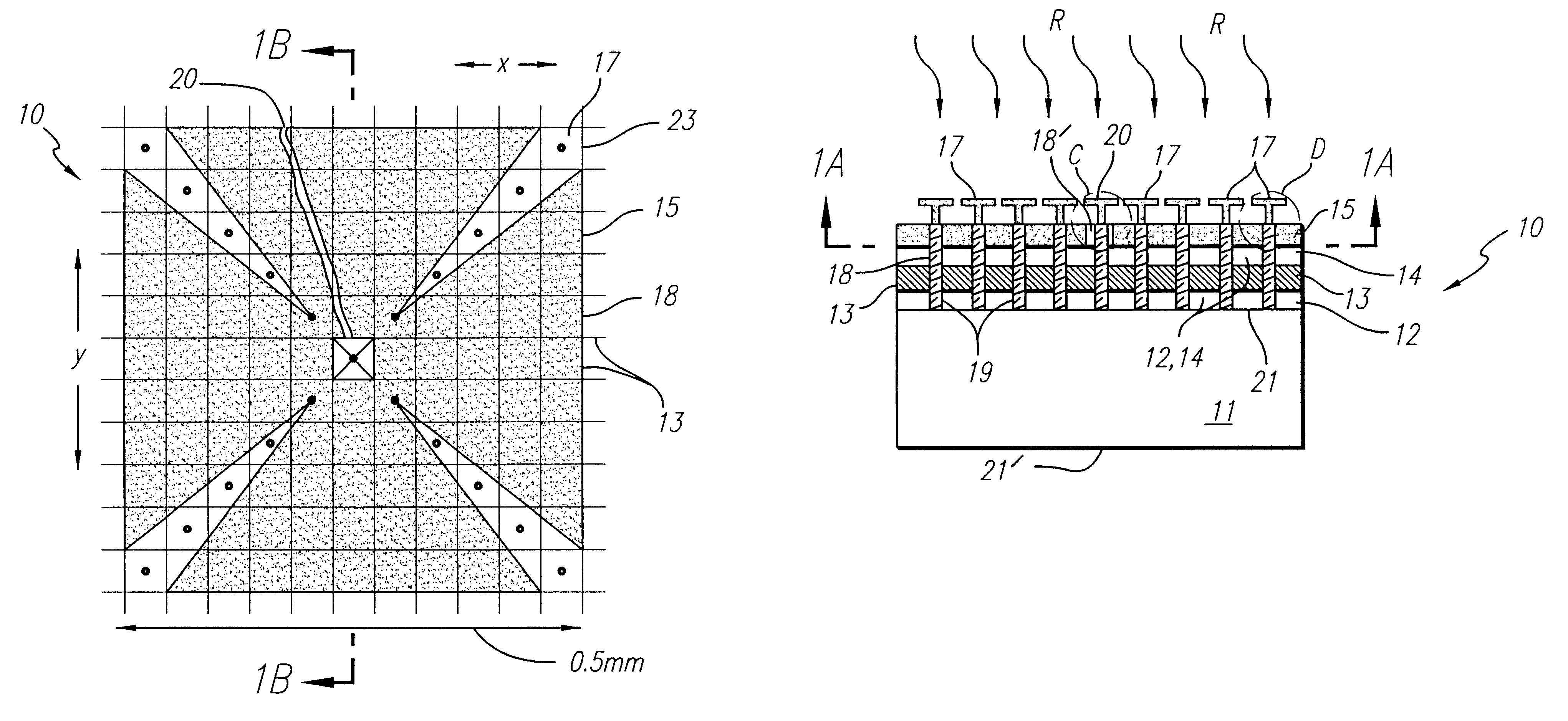
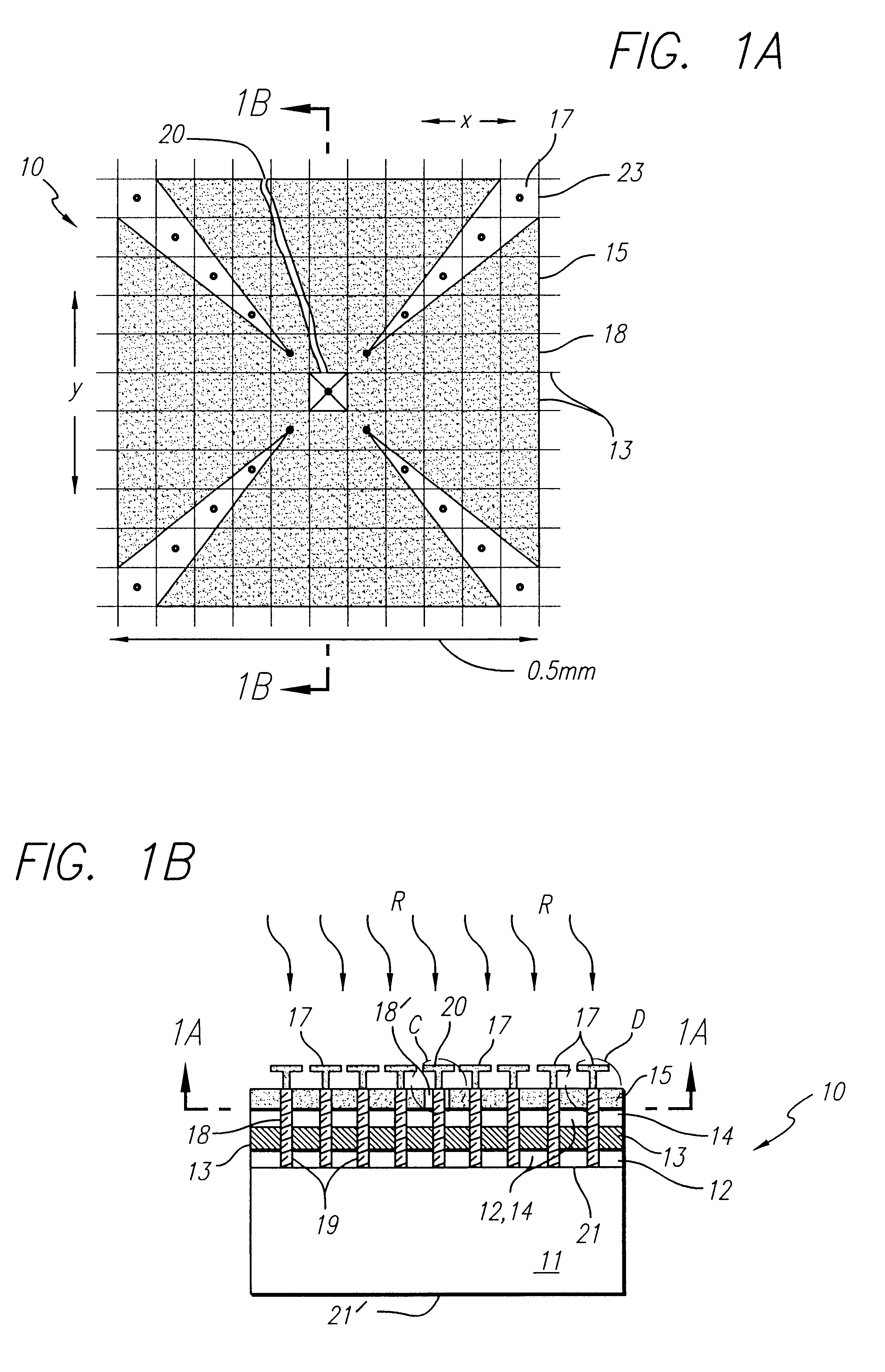
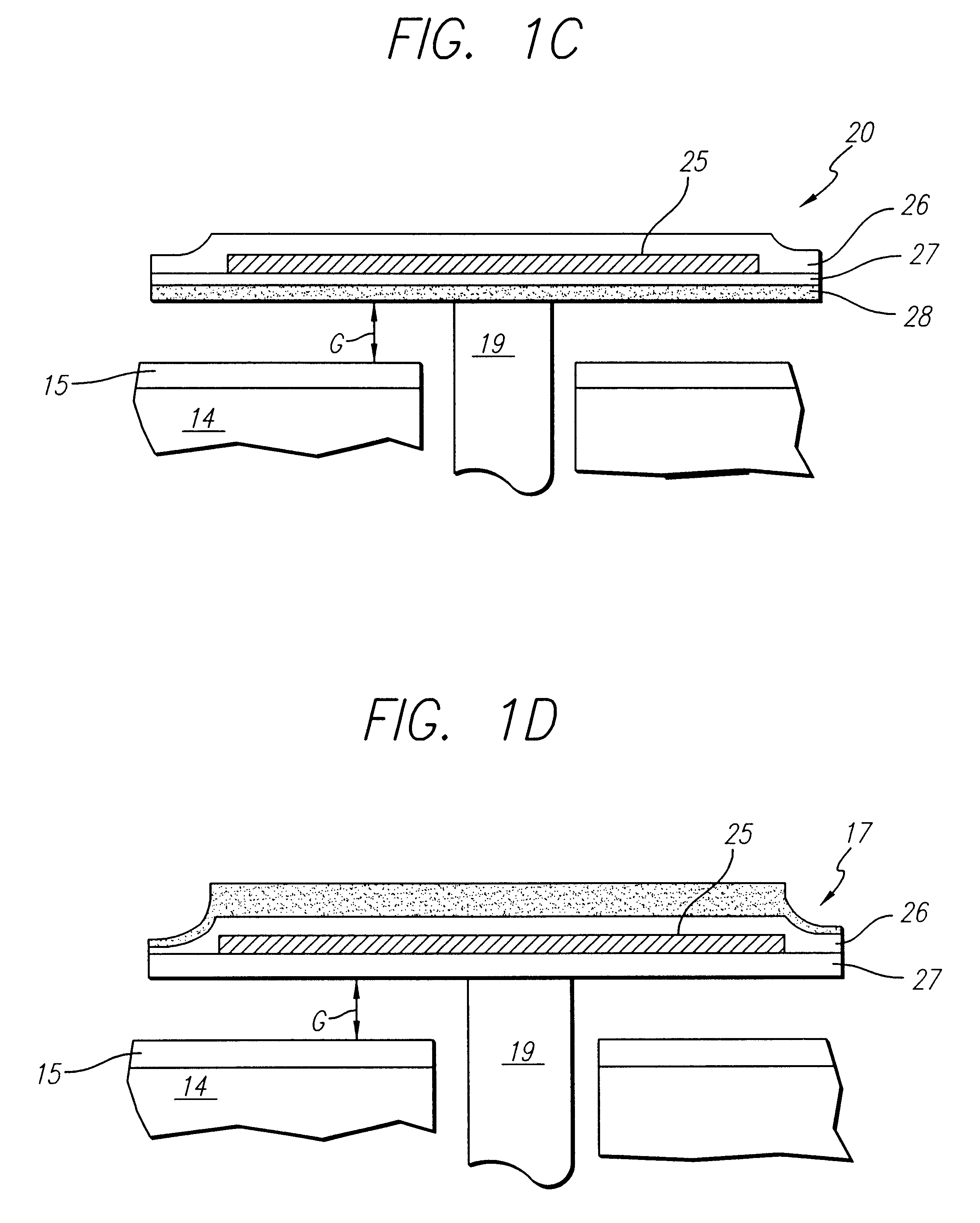
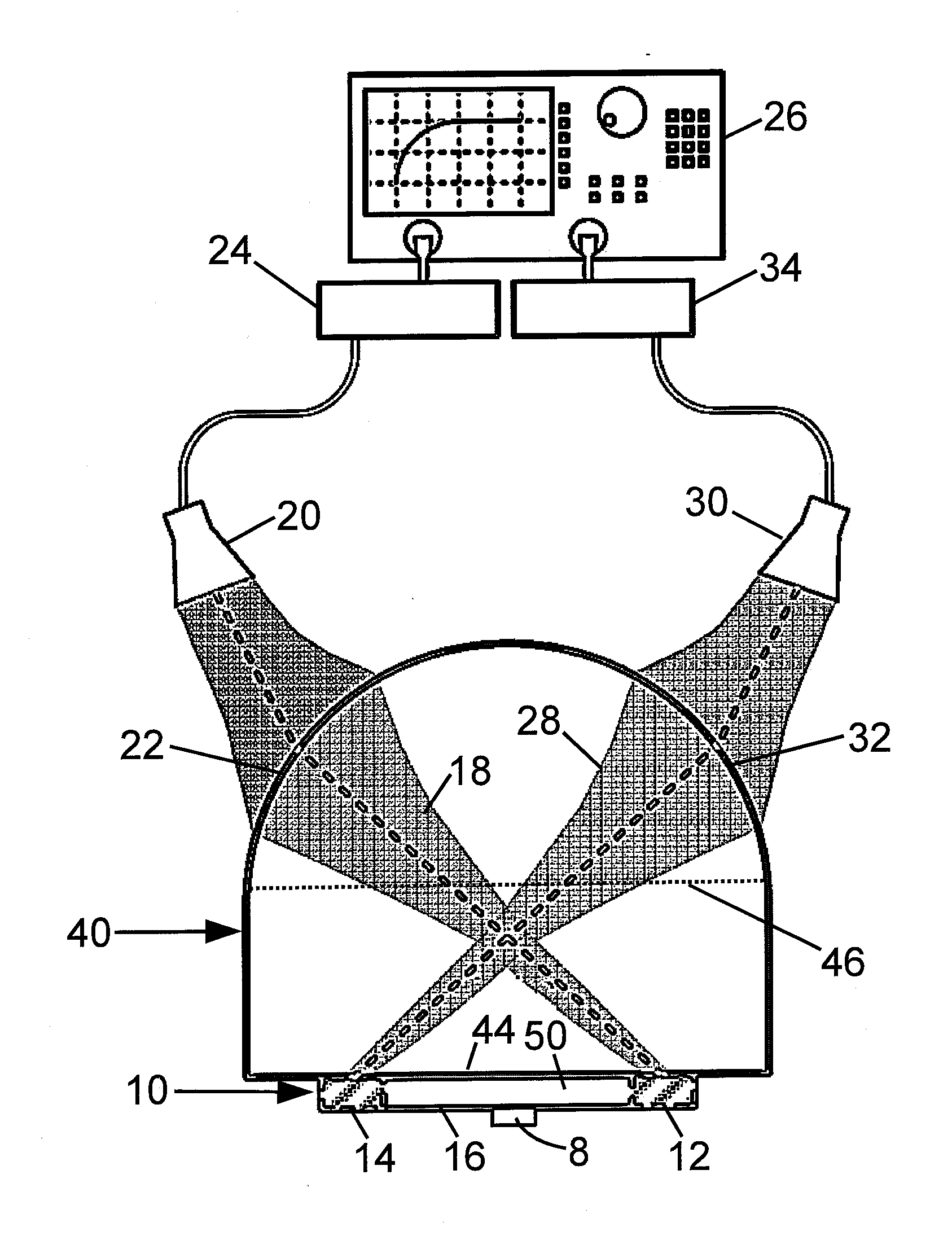
Non-contact probe measurement test bed for millimeter wave and terahertz circuits, integrated devices/components, systems for spectroscopy using sub-wavelength-size-samples
ActiveUS20150102225A1Radiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsMeasurement testSpectroscopy
A test fixture for characterizing a device-under-test (DUT) includes first and second planar antennas and a planar waveguide arranged to guide terahertz (THz) and / or millimeter wave (mmW) radiation between the first and second planar antennas. The planar waveguide is further configured to couple THz and / or mmW radiation guided between the first and second planar antennas with the DUT. A beam forming apparatus is arranged to transmit a probe THz and / or mmW radiation beam to the first planar antenna of the test fixture. An electronic analyzer is configured to wirelessly receive a THz and / or mmW signal emitted by the second planar antenna responsive to transmission of the probe THz and / or mmW radiation beam to the first planar antenna. The planar antennas may be asymmetrical beam-tilted slot antennas.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Millimeter-wave sensor system for parking assistance
InactiveCN107810430ALow costLower requirementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionIntegrated antennaWireless connectivity
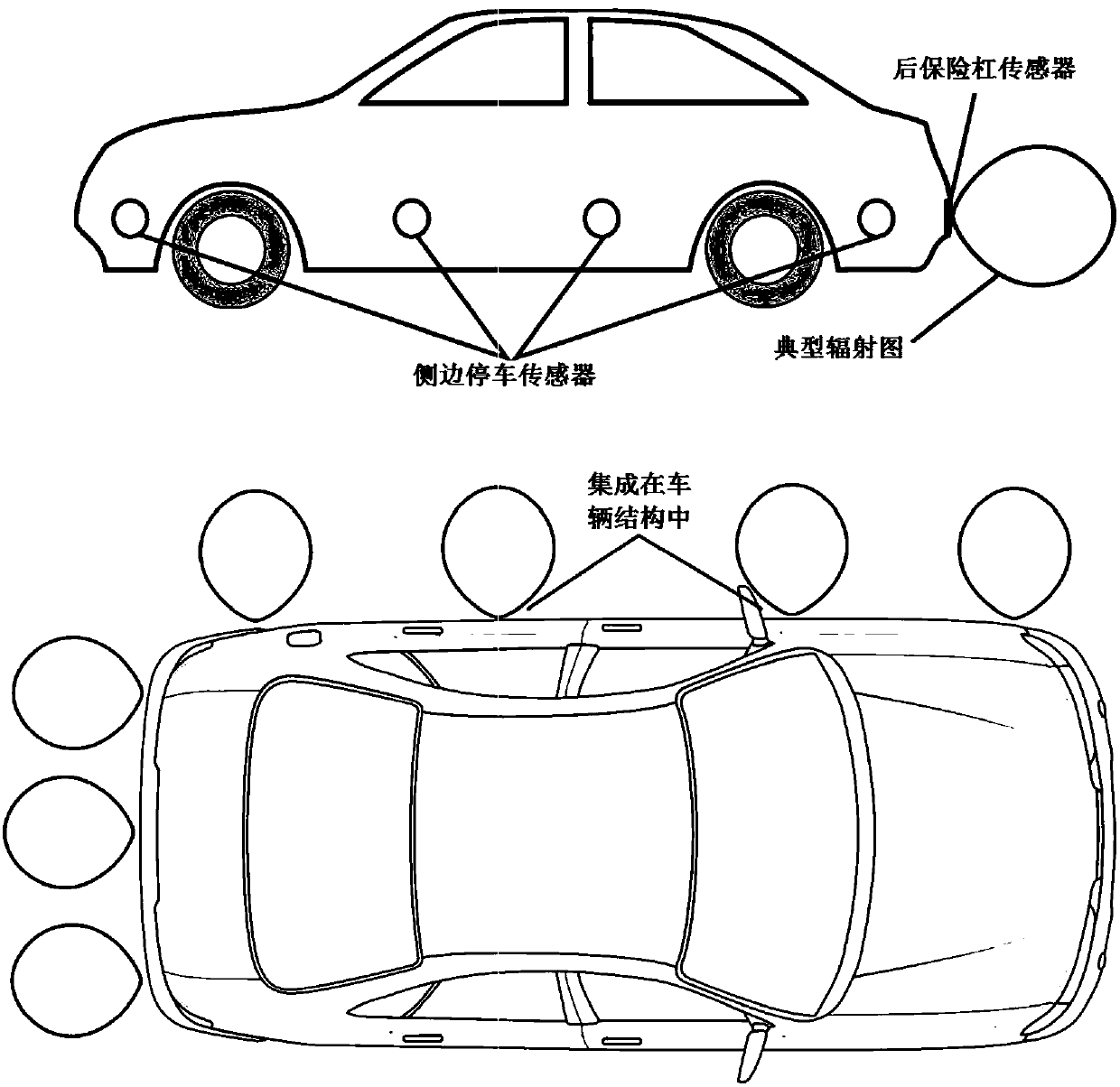
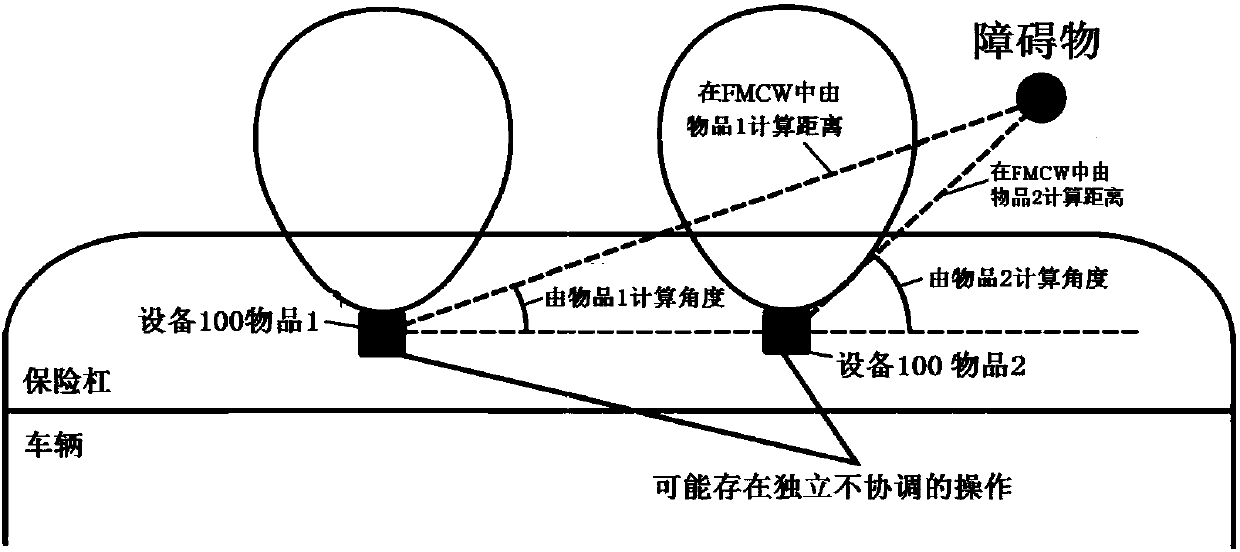
The present invention relates to a parking support Apparatus and Method of operation comprising of an mm-wave radar sensor, having an integrated mm-wave IC front end. The proposed Apparatus is capableof detecting the parking obstacle object distance and angle, having inherently low cost system topology, suitable as a replacement in functionality for the commonly used ultrasound sensors. The proposed apparatus topology consist of one transmitting and two planar antennae, mm-wave radar topology with one down conversion chain and one transmitter chain based on FMCW radar, CW radar and Doppler radar, analog combining circuitry and N mm-wave power detectors, where N takes integer values from 1 and larger. The specific proposed method of operation is adjusted to a dedicated application. A combination of more than one proposed apparatus enables smart observation of the parking area in front of the moving platform with wired or wireless connection to the information evaluation and control entity. The proposed apparatus topology with lower complexity consist of one transmit and two planar antennae, mm-wave radar topology without any down conversion chain and one transmitter chain based onCW radar operation, analog combining circuitry and N mm-wave power detectors, where N takes values from 1 to 3. The system operation topology allows full distance and obstacle angle calculation by theapparatus itself in one topology solution or to have the information being calculated, combining more sensors, using low complexity apparatus topologies, also proposed in this innovation. The integration of the proposed apparatus in the vehicle bumper is inherently possible and may be optically and functionally provided as an efficient replacement for ultrasound parking assist systems. The complete proposed sensor apparatus topologies with integrated antennae, mm-wave IC and digital processing parts may be realized in a module smaller than 1 x 1 x 0.5 cm and operating in the 77-81 GHz band.
Owner:NEWELL LAKE CO
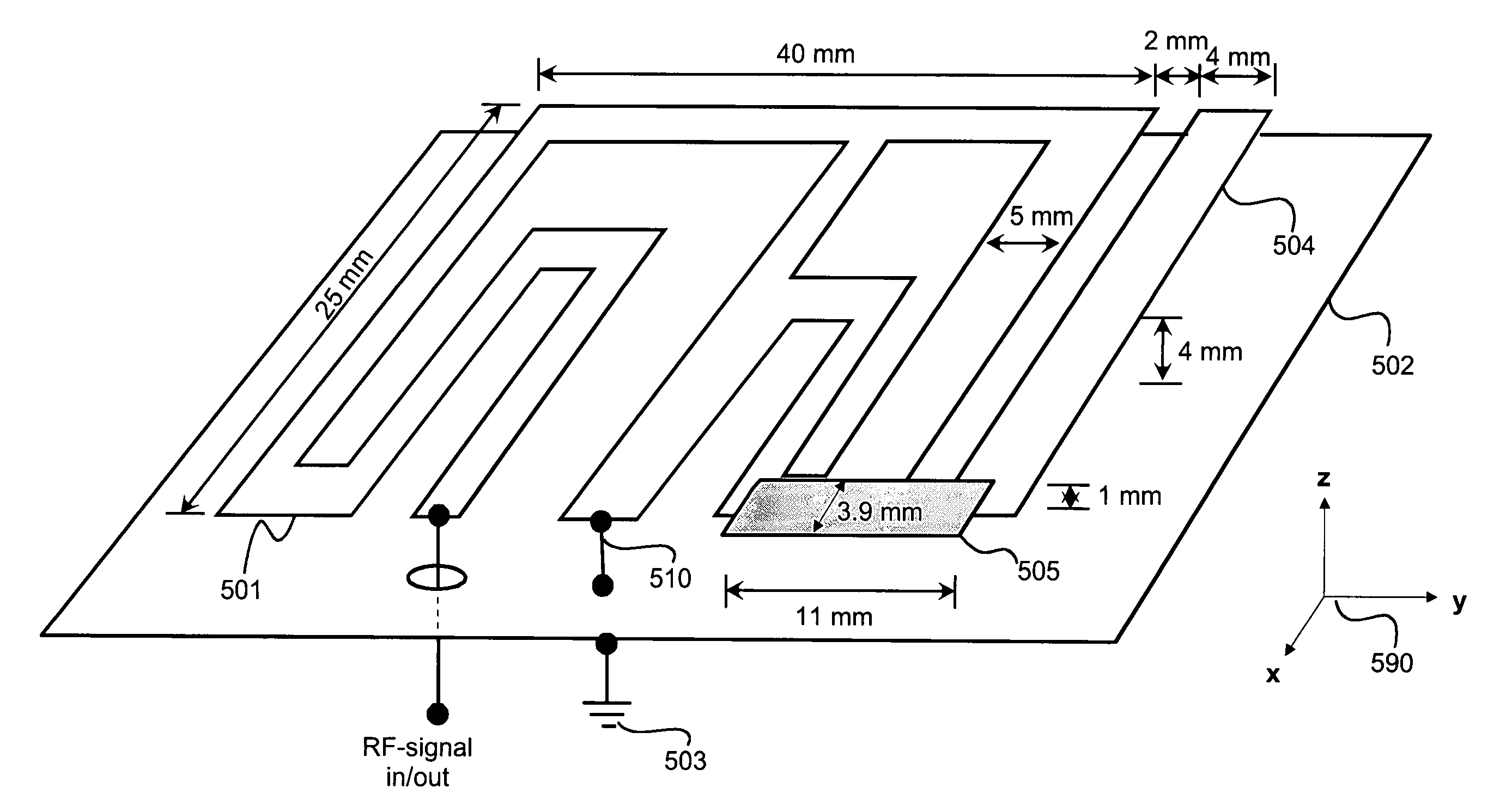
Omni-directional, multi-polarity, low profile planar antenna
ActiveUS8269672B2Excellent SWR (standing wave ratio)For signal receptionSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsHigh-definition televisionHigh definition tv
An omni-directional, multi-polarity, low profile planar antenna for receiving high definition television signals includes a dielectric substrate having a first side and a second side on which are respectively formed first and second conductive patterns. Each conductive pattern includes segments functioning as antenna elements which are arranged to form a first modified H-shaped pattern on the first side of the dielectric substrate, and a second modified H-shaped pattern on the second side of the dielectric substrate which is disposed substantially ninety degrees with respect to the first modified H-shaped pattern. Each of the H-shaped patterns includes an extended S-shaped segment.
Owner:VOXX INT CORP
Built-in type antenna apparatus for mobile terminal
InactiveUS20080129644A1Reduce SARImprove Radiation PerformanceElongated active element feedIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsPlanar antennasGround pattern
A built-in antenna apparatus for a mobile terminal is provided. The built-in antenna apparatus includes a first planar antenna having a first feeding point for providing a first radiation pattern, a second planar antenna having a second feeding point for providing a second radiation pattern, the second planar antenna being located adjacent to the first planar antenna, and a ground stub having a ground point for providing a ground pattern, the ground stub placed a distance apart from the first and the second planar antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Structure for inverted F plane antenna
InactiveUS20050264447A1Increased operating bandwidthImprove signal receptionRadiating elements structural formsElongated active element feedPlanar antennasSoftware engineering
The present invention is related to a structure for inverted F plane antenna, which is on a surface of a PCB by way of etching. The antenna comprises a pair of parallel sections constructed by a first parallel section, a second parallel section and a vertical section perpendicular to the two parallel sections, wherein the first parallel section connects to a grounding end of the PCB electrically, the second parallel section connects to a power end of the PCB, the vertical section has a bending portion with U shape to increase the length of receiving signals, therefore reflection signals may be highly decreased, and functions of receiving / emission stronger power are then achieved and receiving / emission band width is increased; further, under conditions of not extending the length of the vertical section and shrinking the volume of the antenna shall upgrade the convenience of the design.
Owner:CHUNG GUAN TECH
Flexible substrate integrated waveguides
This invention relates to a device operable to guide electromagnetic waves in substrate integrated structures, said substrate integrated structures being made in one component. In detail planar antennas are part of said substrate integrated structures, which are connected to electromagnetic waveguides. This invention also allows 3D structures of the above mentioned components in a multilayer substrate.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com