Patents
Literature
351 results about "High-definition television" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
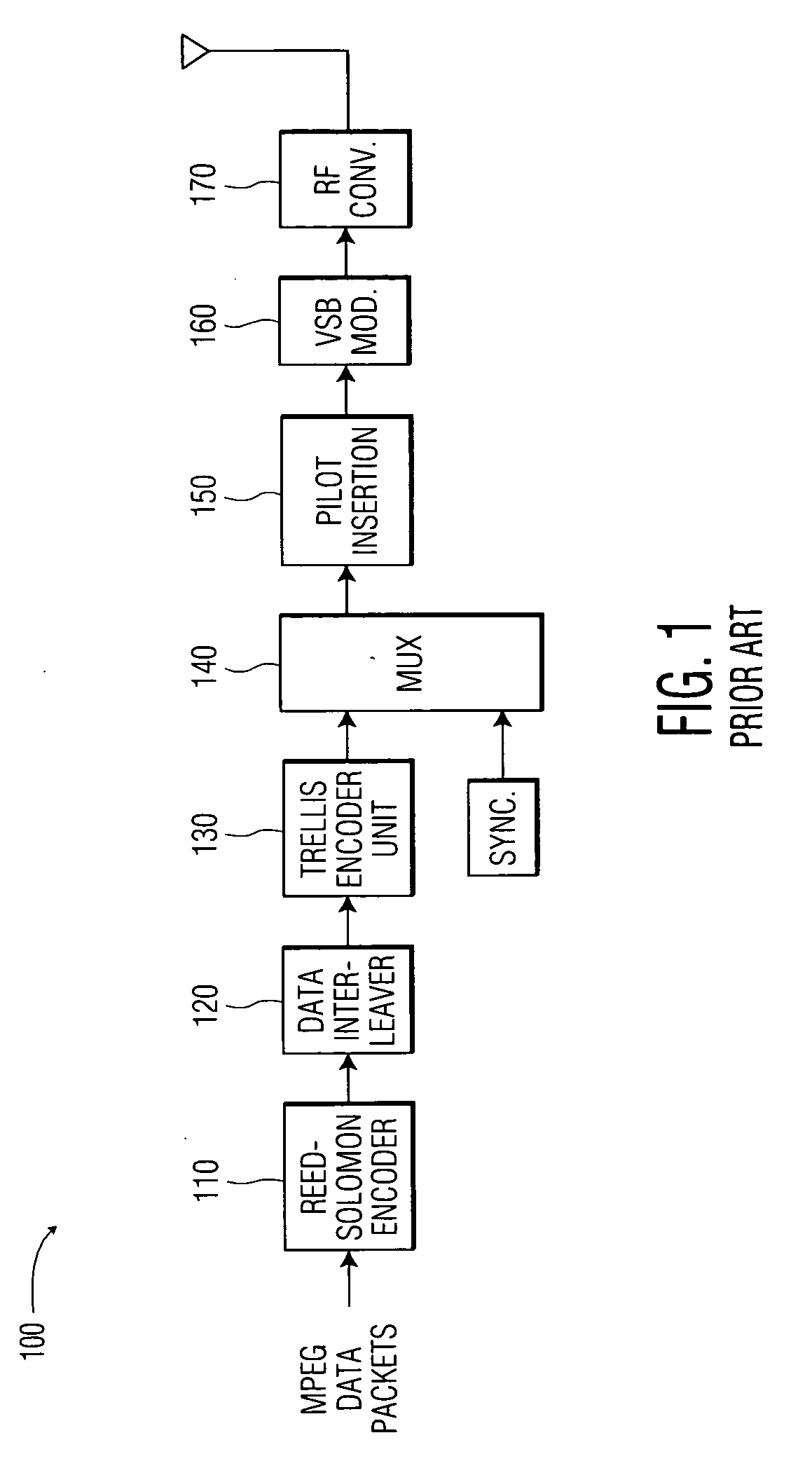
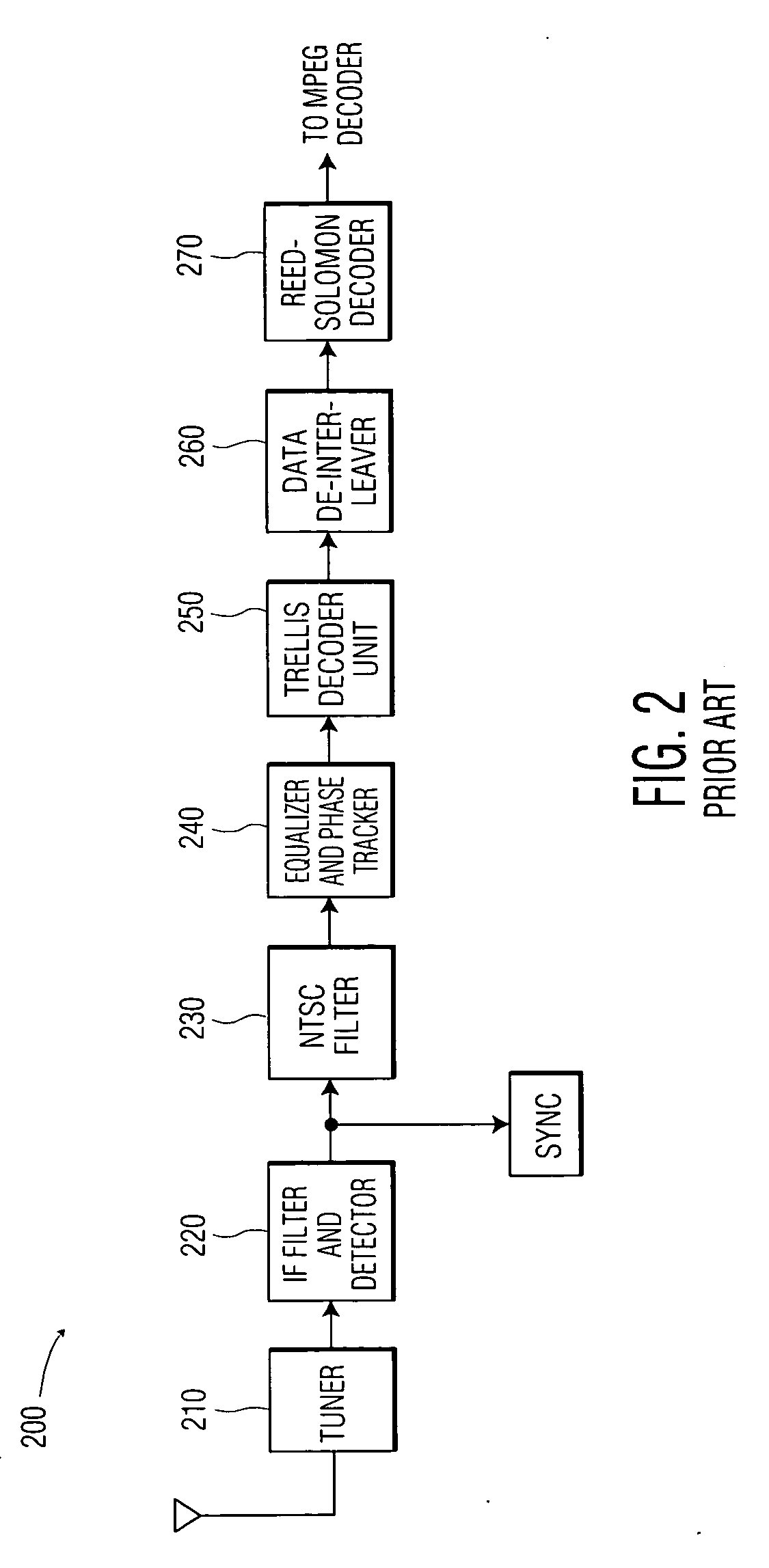
High-definition television (HDTV) is a television system providing an image resolution that is of substantially higher resolution than that of standard-definition television. This can be either analog or digital. HDTV is the current standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television, Blu-rays, and streaming video.
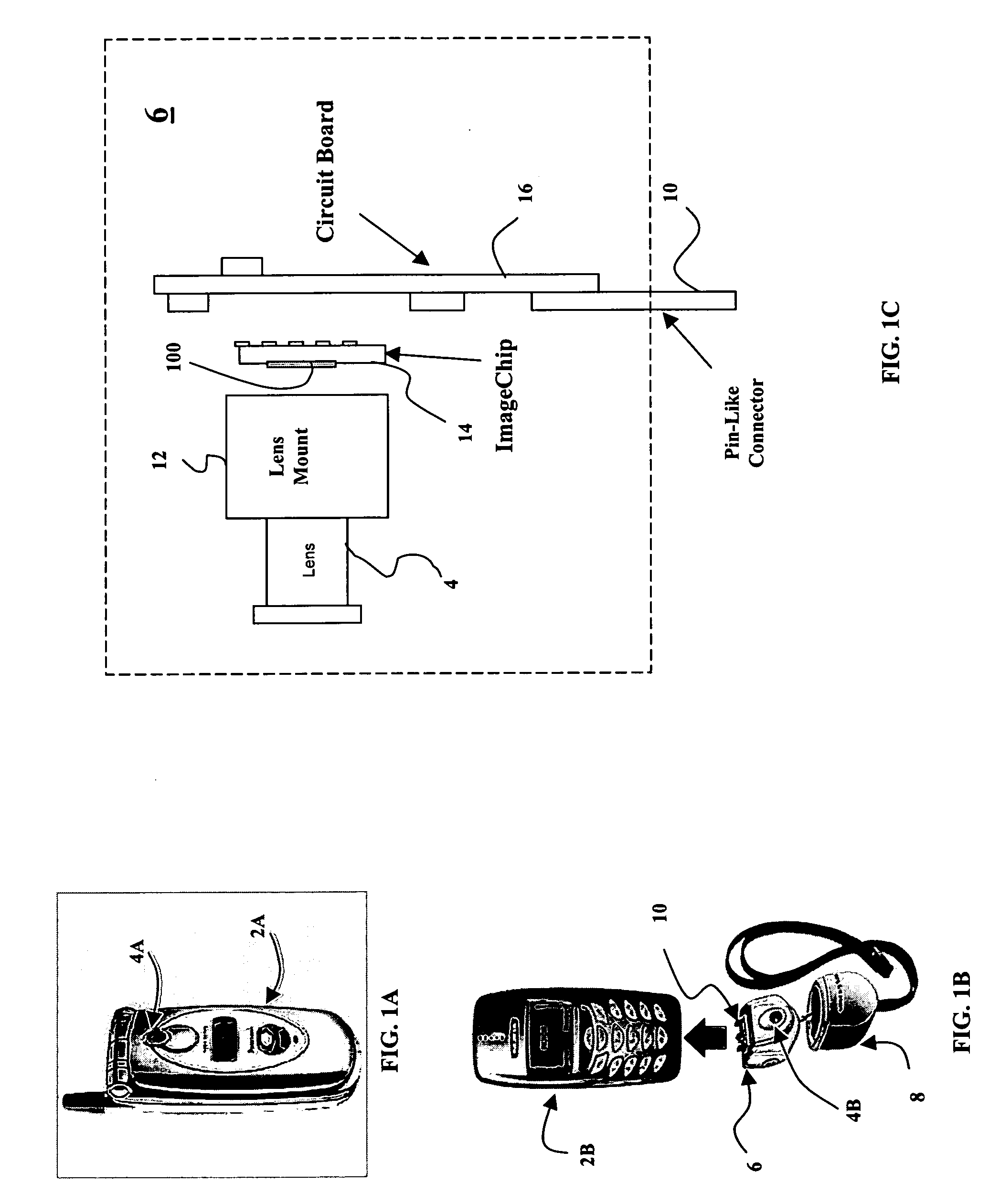
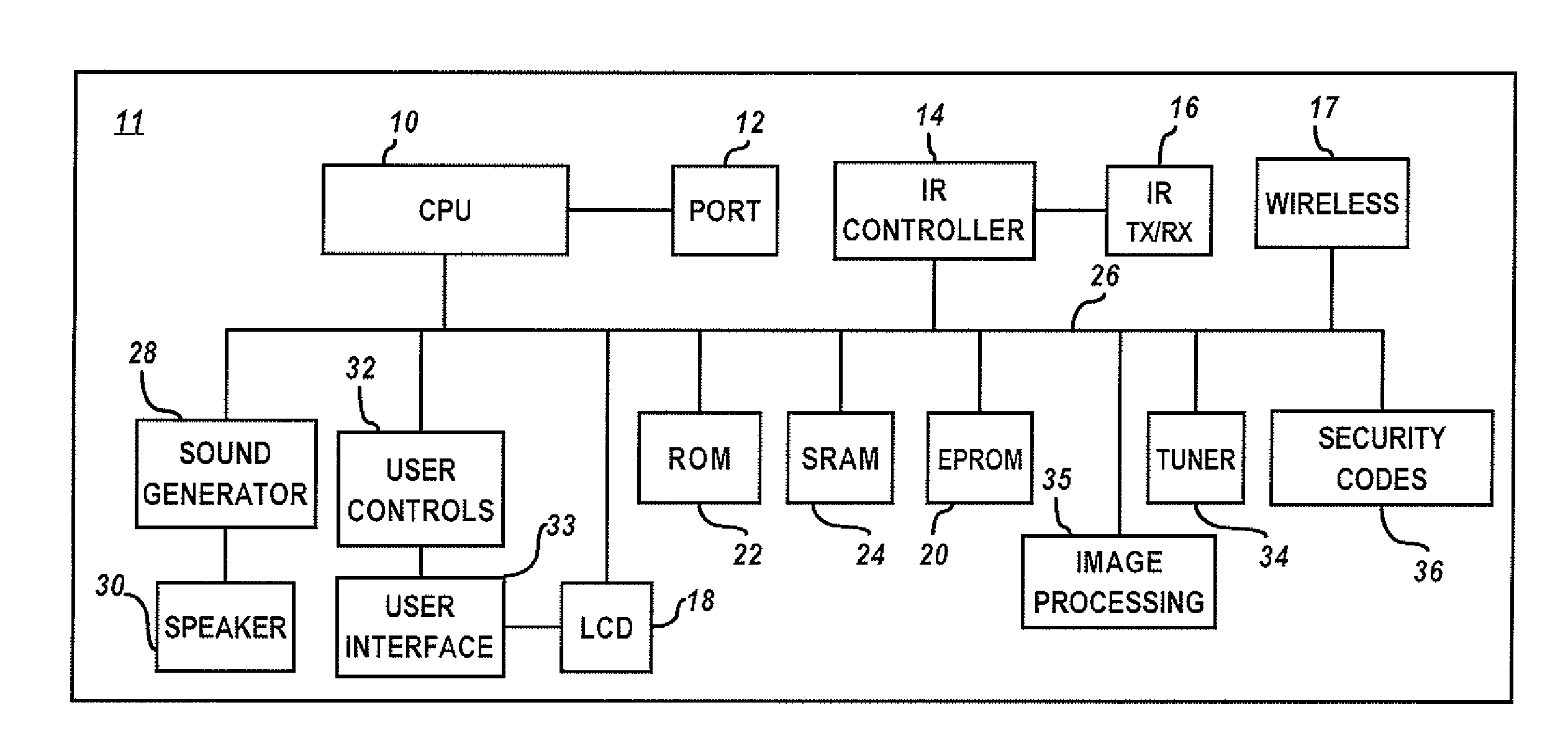
Optical information processing equipment and semiconductor light emitting device suitable therefor
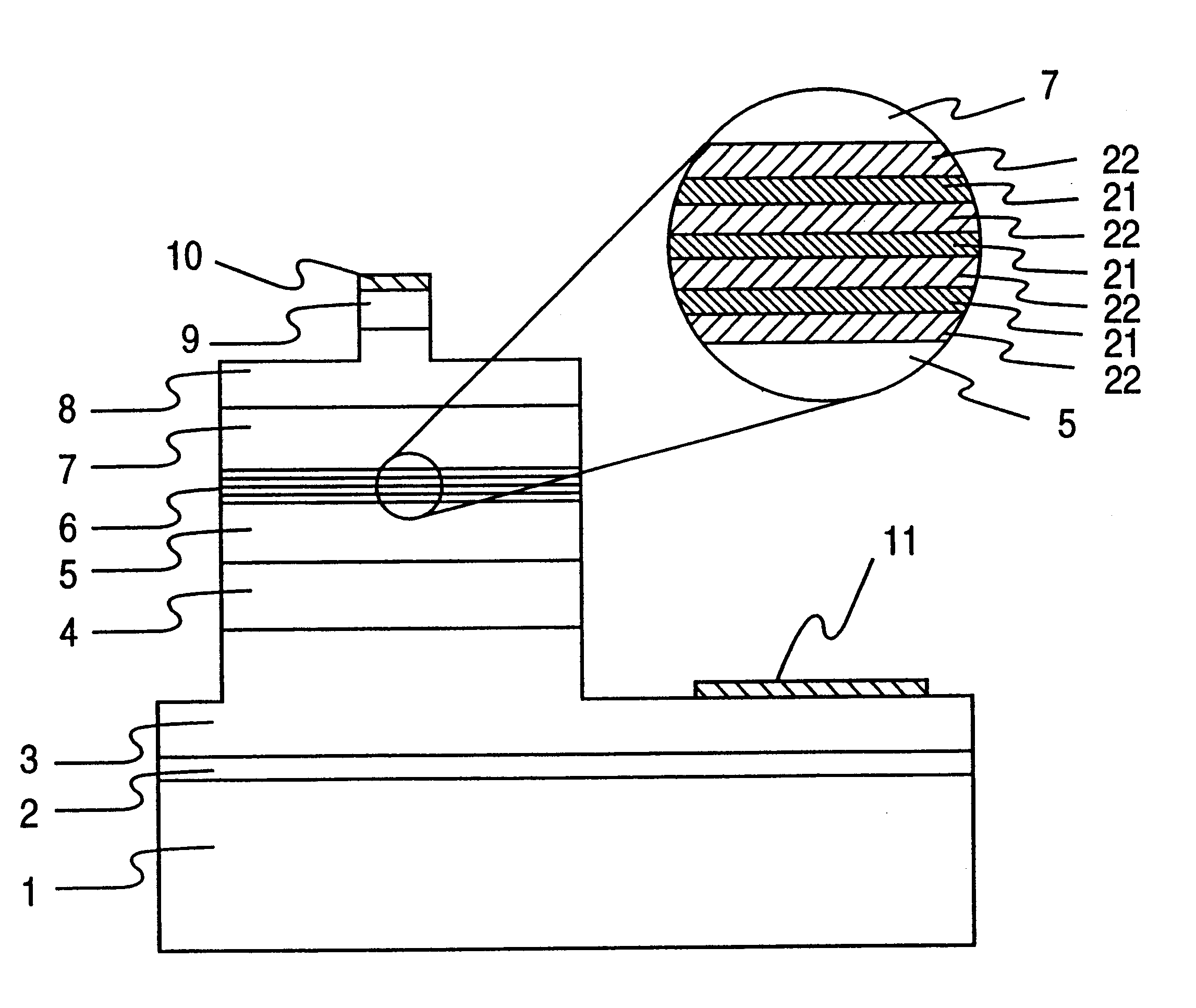
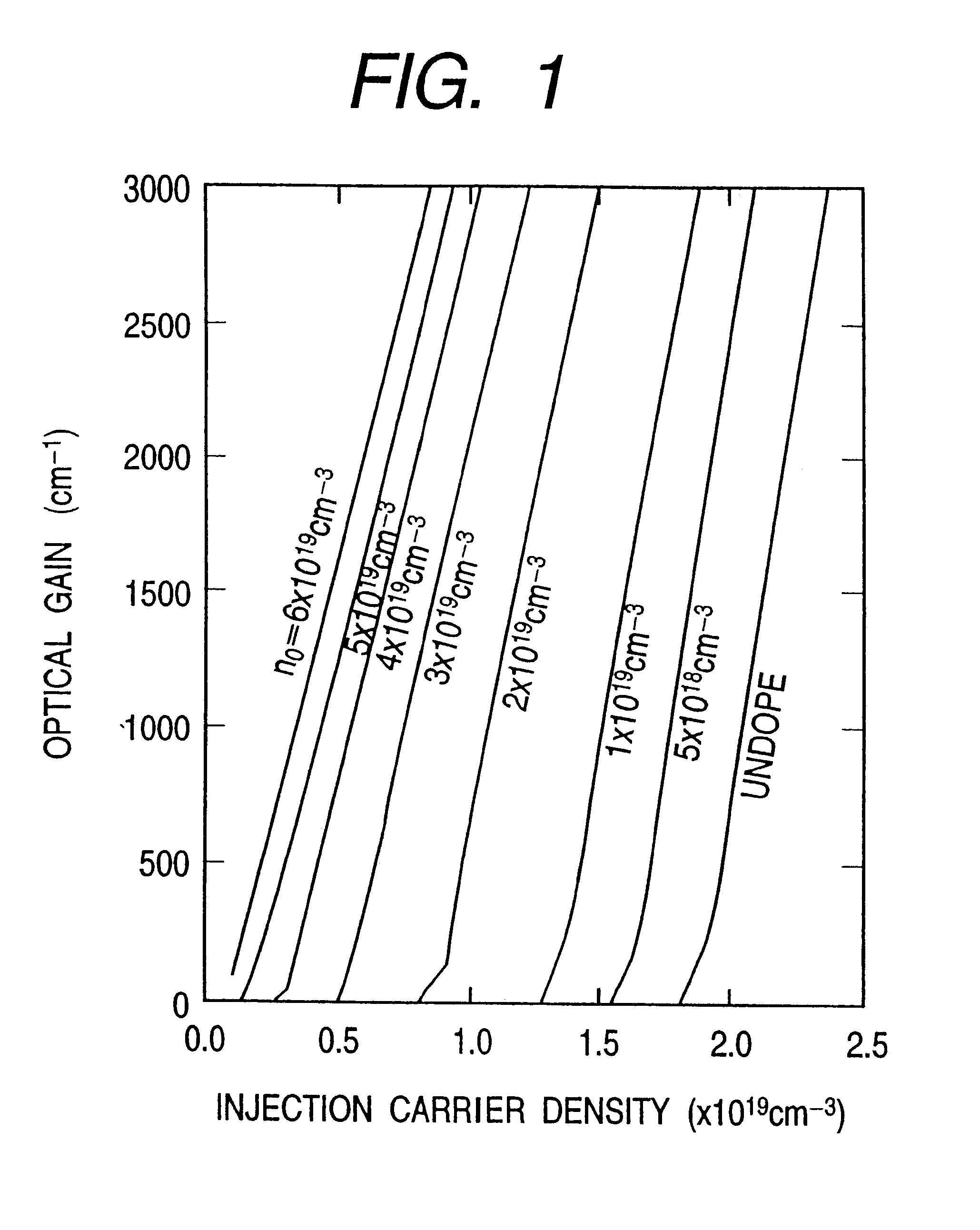
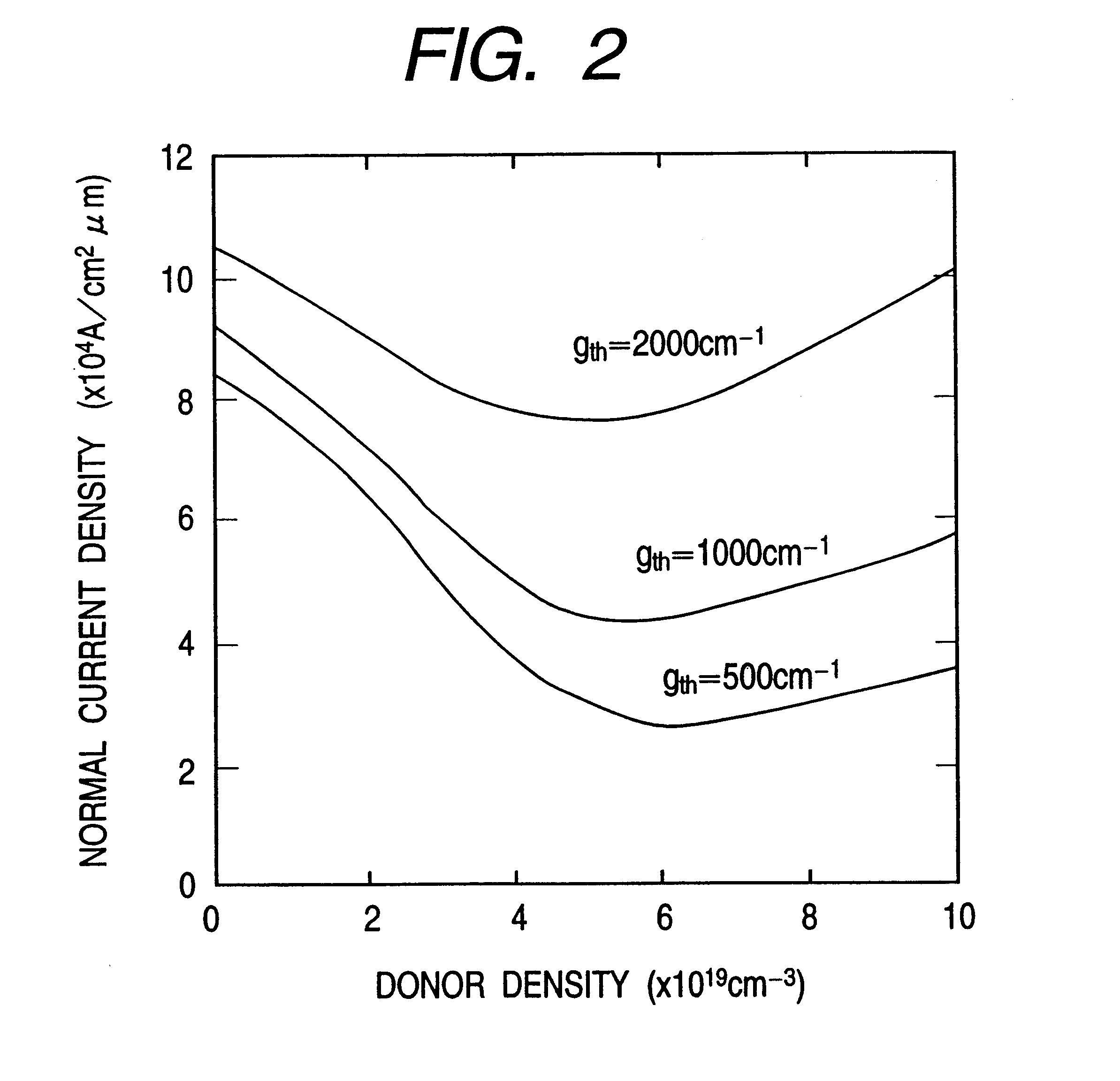
An information processor of a high reliability and a high recording density, and a blue color, blue-violet color and violet color based semiconductor light emitting device operable at a low threshold current density, used for the same, are provided. An optical information processor of a high reliability and a high recording density enables a moving picture, such as a high-definition television picture, to be recorded and reproduced satisfactorily. A barrier layer in a quantum-well active layer of a semiconductor light emitting device is doped with n-type impurities at a high density. Alternatively, the face orientation of a quantum-well active layer of a semiconductor light emitting device is a plane inclined from the (0001) plane, whereby the threshold current value of the semiconductor light emitting device can be decreased. The semiconductor light emitting device is typified by a gallium nitride based compound semiconductor laser device.
Owner:USHIO OPTO SEMICON
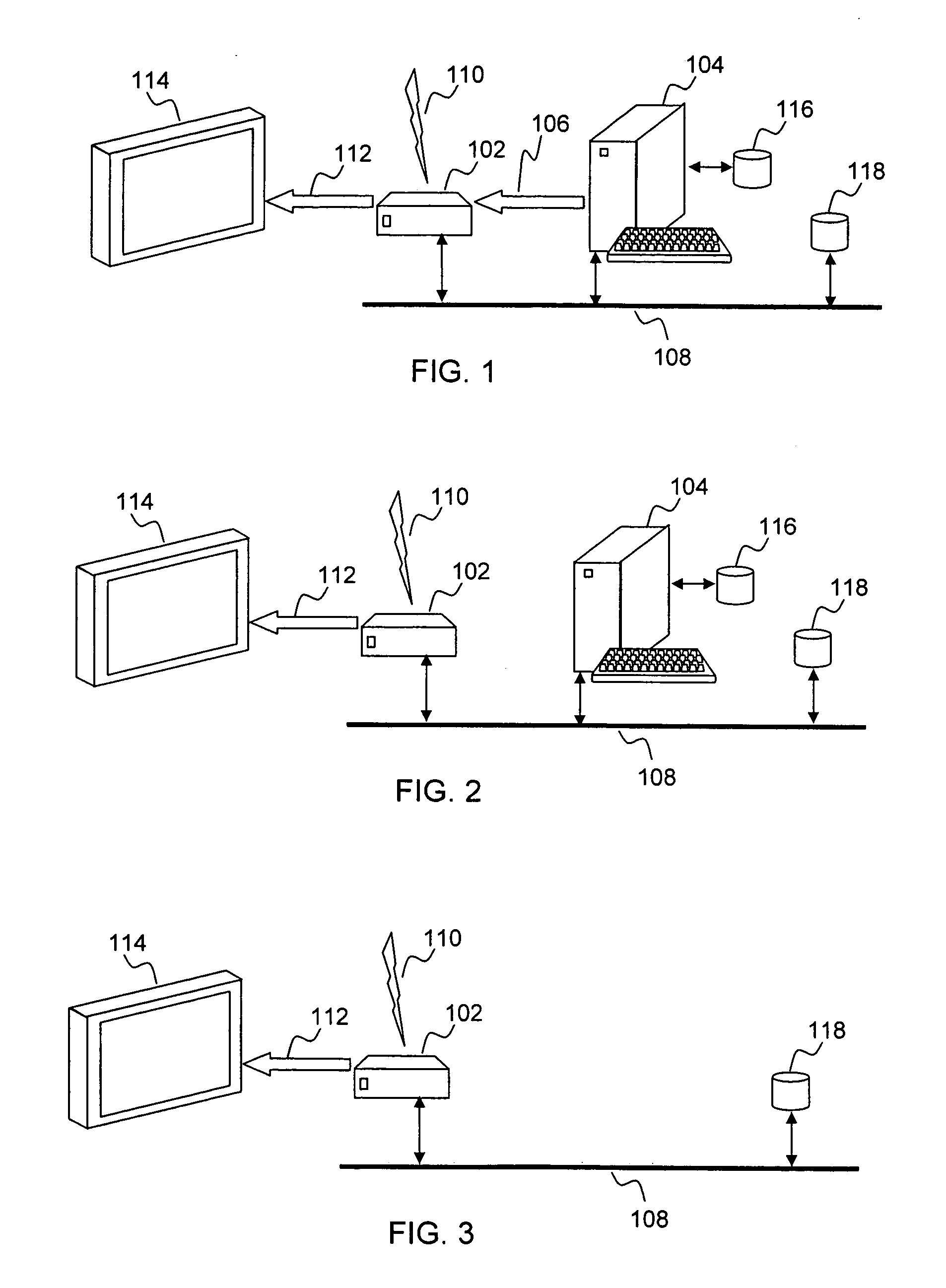
Secure integrated media center
InactiveUS20050125357A1Safe storageTelevision system detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionHard disc driveHigh definition tv
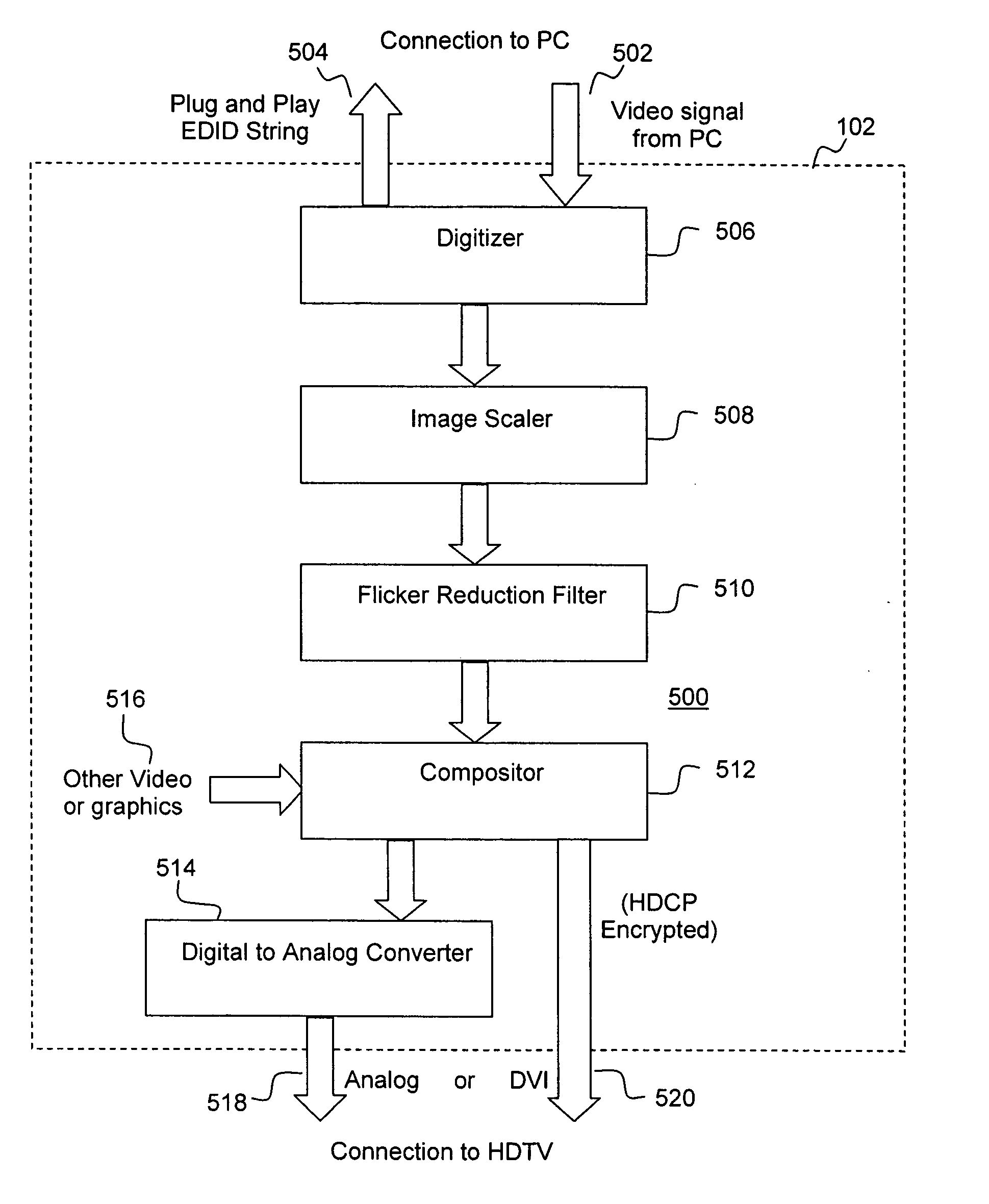
A set-top media system is disclosed which can be combined with an open architecture personal computer (PC) to provide a feature-rich secure integrated media center while meeting security rules of most major conditional access and content protection industry rules such as Cable Labs DFAST and PHILA agreements; and DTLA agreements for 5C-DTCP for IEEE1394, USB, and IP. The set-top media center and PC share common resources such as high definition display, remote control, hard disk drive, and other external unsecure storage devices. All media content is available seamlessly using a PC user interface, including controlled-content media such as high definition TV, within a PC desktop window. All controlled-content media is manipulated and managed within the set-top media system in a seamless manner. A novel mechanism is disclosed to allow controlled-content media to be stored on unsecure devices in encrypted form while overcoming the disk cloning attack problem for move operations.
Owner:SAADAT ABBAS SASAN +1
Multi-Hop Ultra Wide Band Wireless Network Communication
InactiveUS20070104215A1Avoid bandwidth reservation conflictImprove utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionFrequency spectrumCommunication device
A wireless communication system is provided that has at least three nodes arranged in a multi-hop ultra wide band (UWB) communication network such that communications from a first node destined for a third node pass through a second node. Each of the devices in the system includes a radio and a media access control (“MAC”) module that is configured to establish multi-hop UWB wireless communications between the three or more wireless communication devices that enables high bandwidth applications such as Voice Over Internet Protocol (“VoIP”); multiplayer gaming; Wireless High Definition Television; and Internet Protocol Television (“IPTV”) among others. The MAC module is configured to avoid bandwidth reservation conflicts so that network performance does not degrade as the number of hops or the number of nodes in the wireless communication system increases. The MAC also facilitates utilization of multiple channels to maximize the available spectrum and is further configured to dynamically switch between channels to maximize throughput and meet or exceed quality of service (“QoS”) requirements such that QoS is guaranteed and network resources are efficiently utilized.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
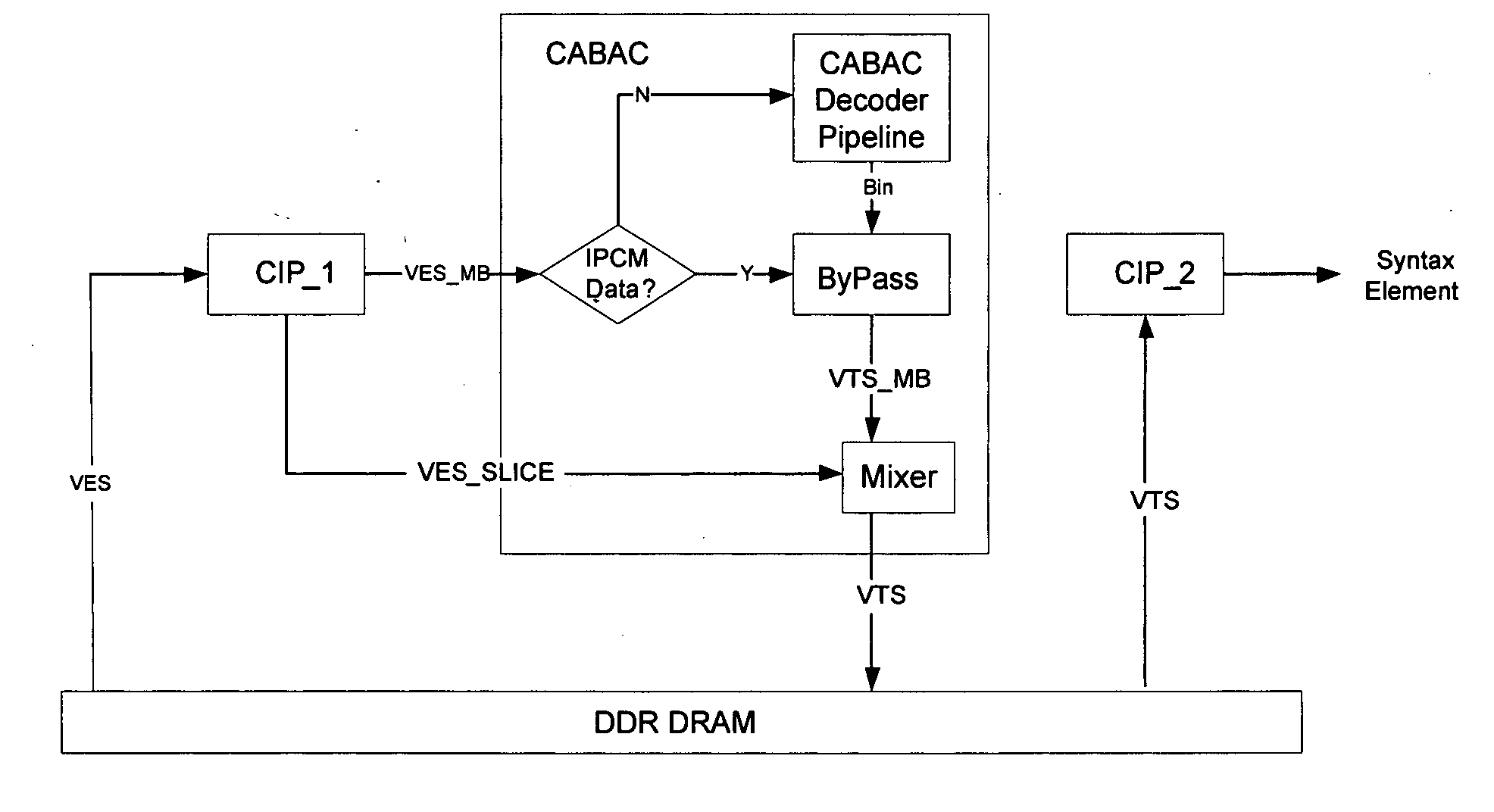
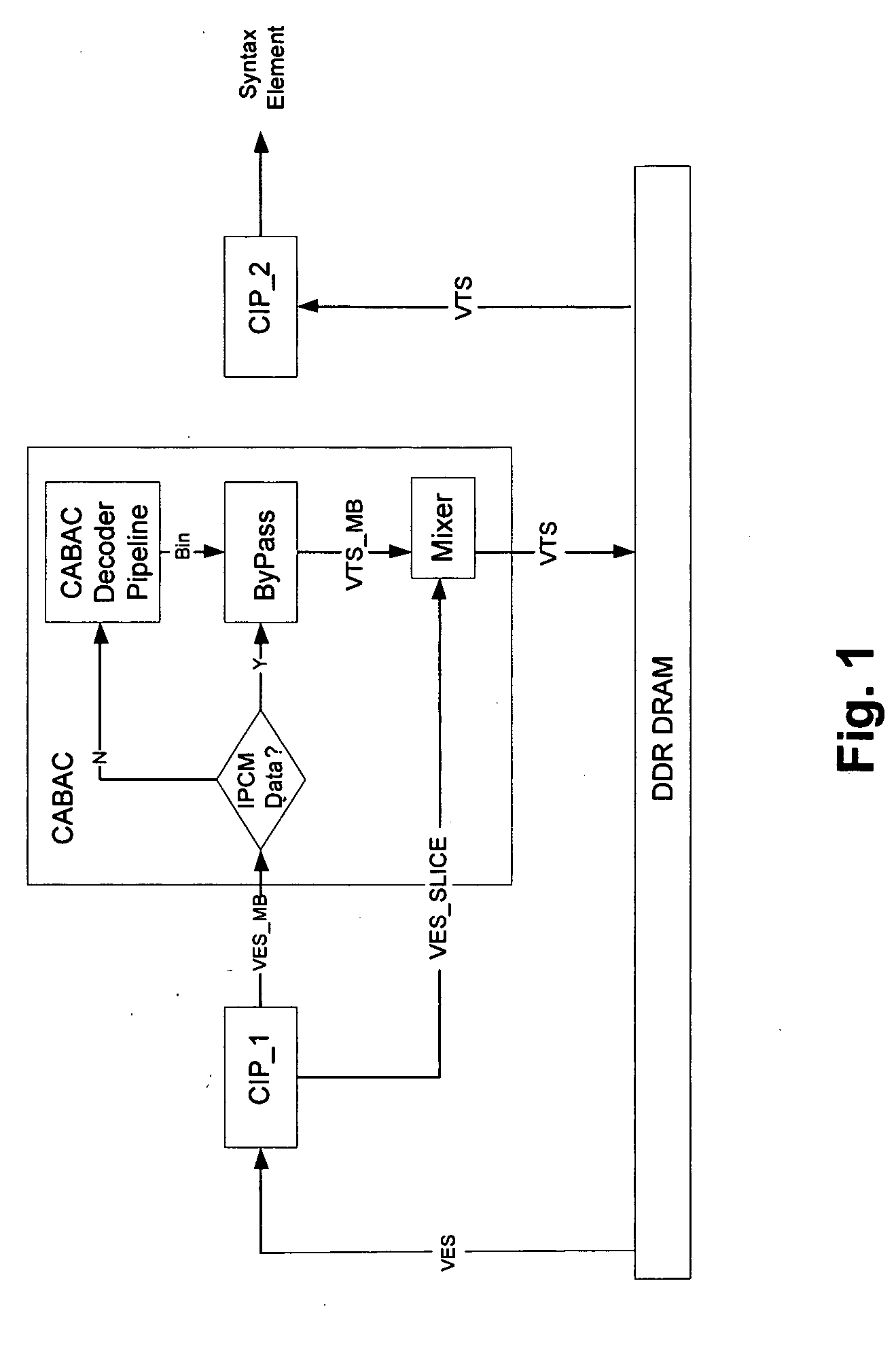
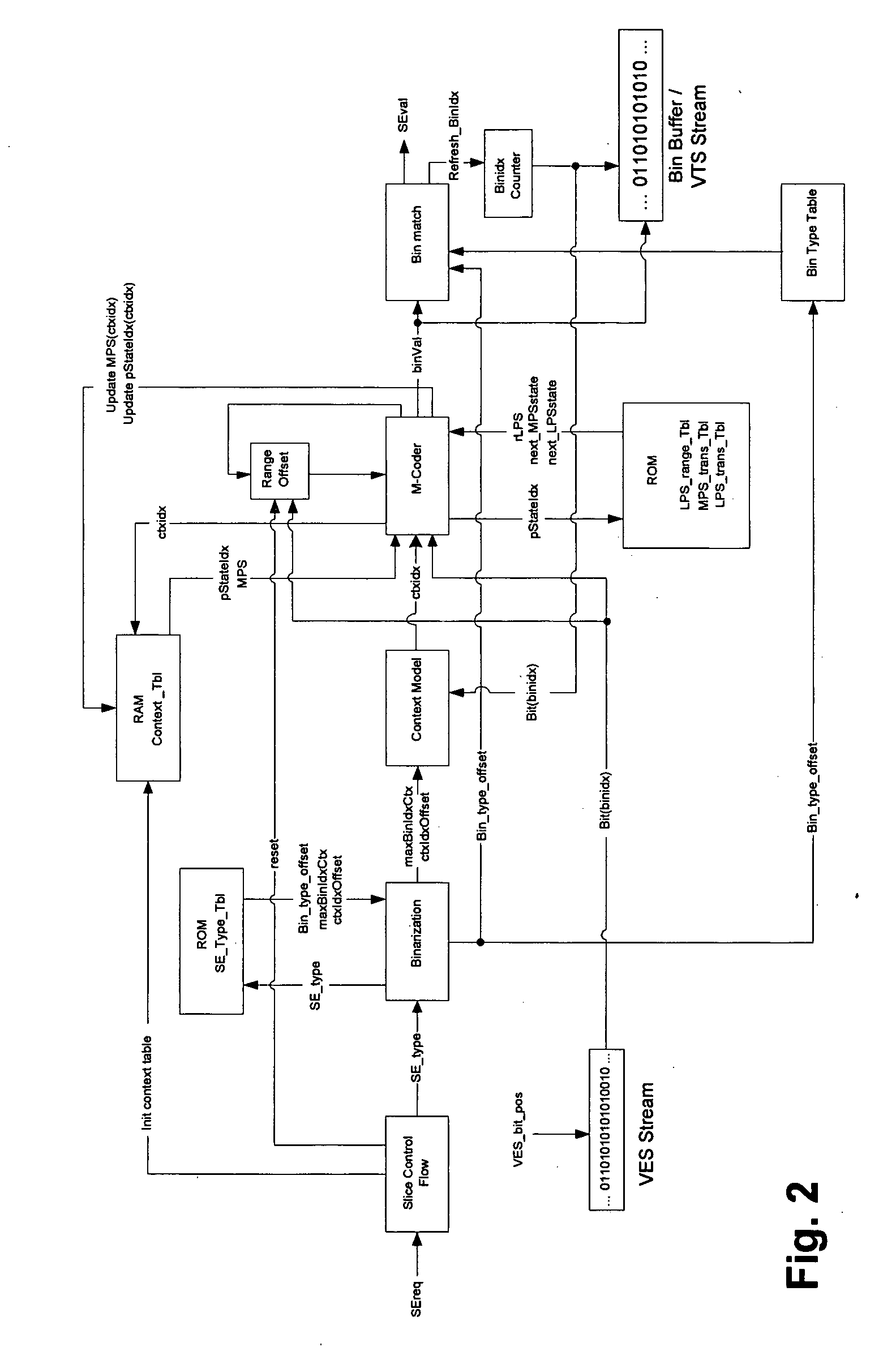
Two pass architecture for H.264 CABAC decoding process
InactiveUS20060126744A1Eliminate dependenciesHigh performance throughputColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionHigh-definition televisionComputer architecture
An architecture capable of stream parsing of the H.264 Content Based Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding (CABAC) format is disclosed. The architecture employs a two pass dataflow approach to implement the functions of CABAC bit parsing and decoding processes (based on the H.264 CABAC algorithm). The architecture can be implemented, for example, as a system-on-chip (SOC) for a video / audio decoder for use high definition television broadcasting (HDTV) applications. Other such video / audio decoder applications are enabled as well.
Owner:MICRONAS
Equalization and decision-directed loops with trellis demodulation in high definition TV
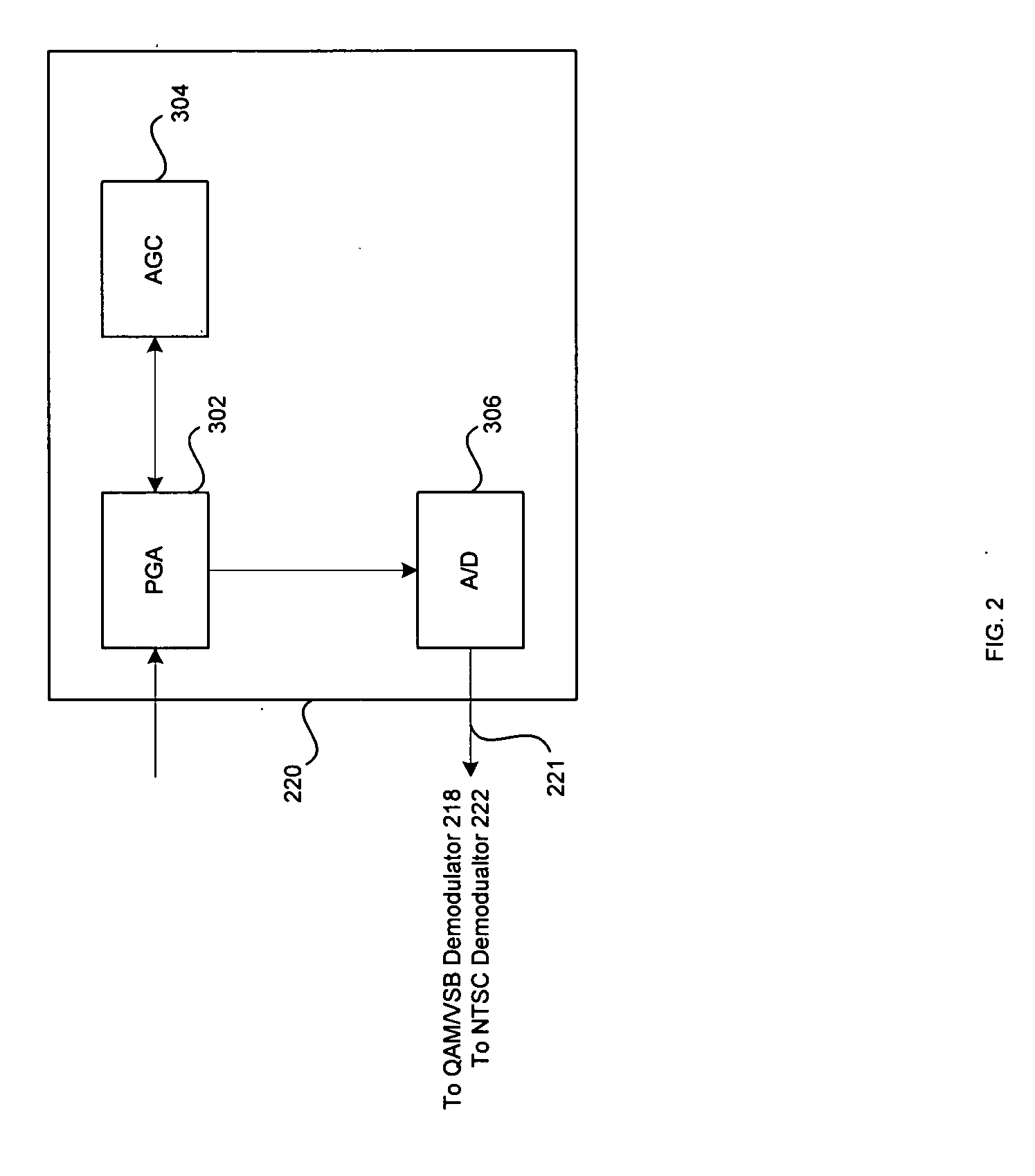
InactiveUS7474695B2Improve reliabilityIncrease delay timeTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksHigh definition tvHigh-definition television
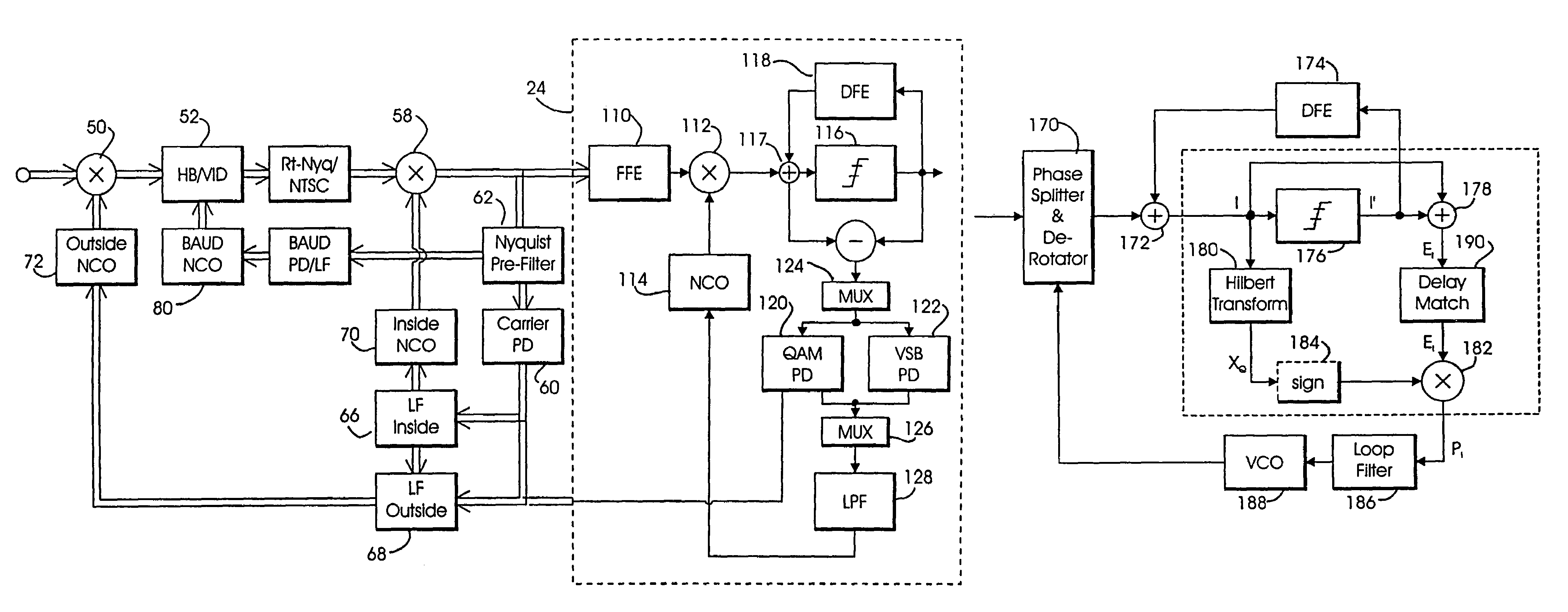
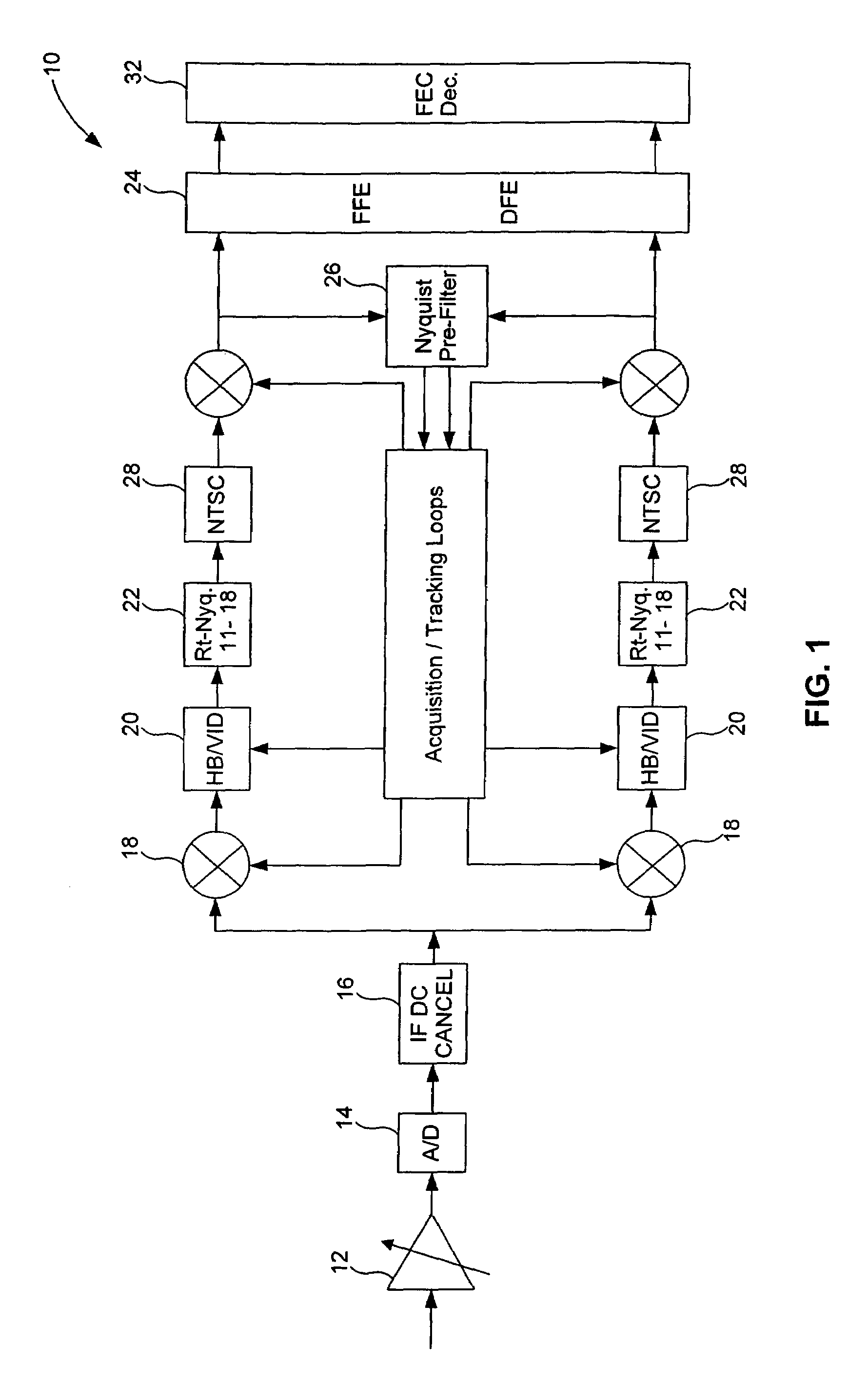
Improved decision feedback equalizer and decision directed timing recovery systems and methods suitable for use in connection with a dual mode QAM / VSB receiver system are disclosed. A trellis decoder operates in conjunction with a decision feedback equalizer circuit on trellis coded 8-VSB modulated signals. The trellis decoder includes a 4-state traceback memory circuit outputting a maximum likelihood decision as well as a number of intermediate decisions based upon the maximum likelihood sequence path. Any number of decisions, along the sequence, may be provided as an input signal to timing recovery system loops, with the particular decision along the sequence chosen on the basis of its delay through the trellis decoder. Variable delay circuitry is coupled to the other input of the timing recovery system loops in order to ensure that both input signals bear the same timestamp. Final decisions are output from the trellis decoder to a DFE in order to enhance the DFE's ability to operate in low SNR environments. A decision sequence estimation error signal is also generated and used to drive the tap updates of both the DFE and an FFE portion of the equalizer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
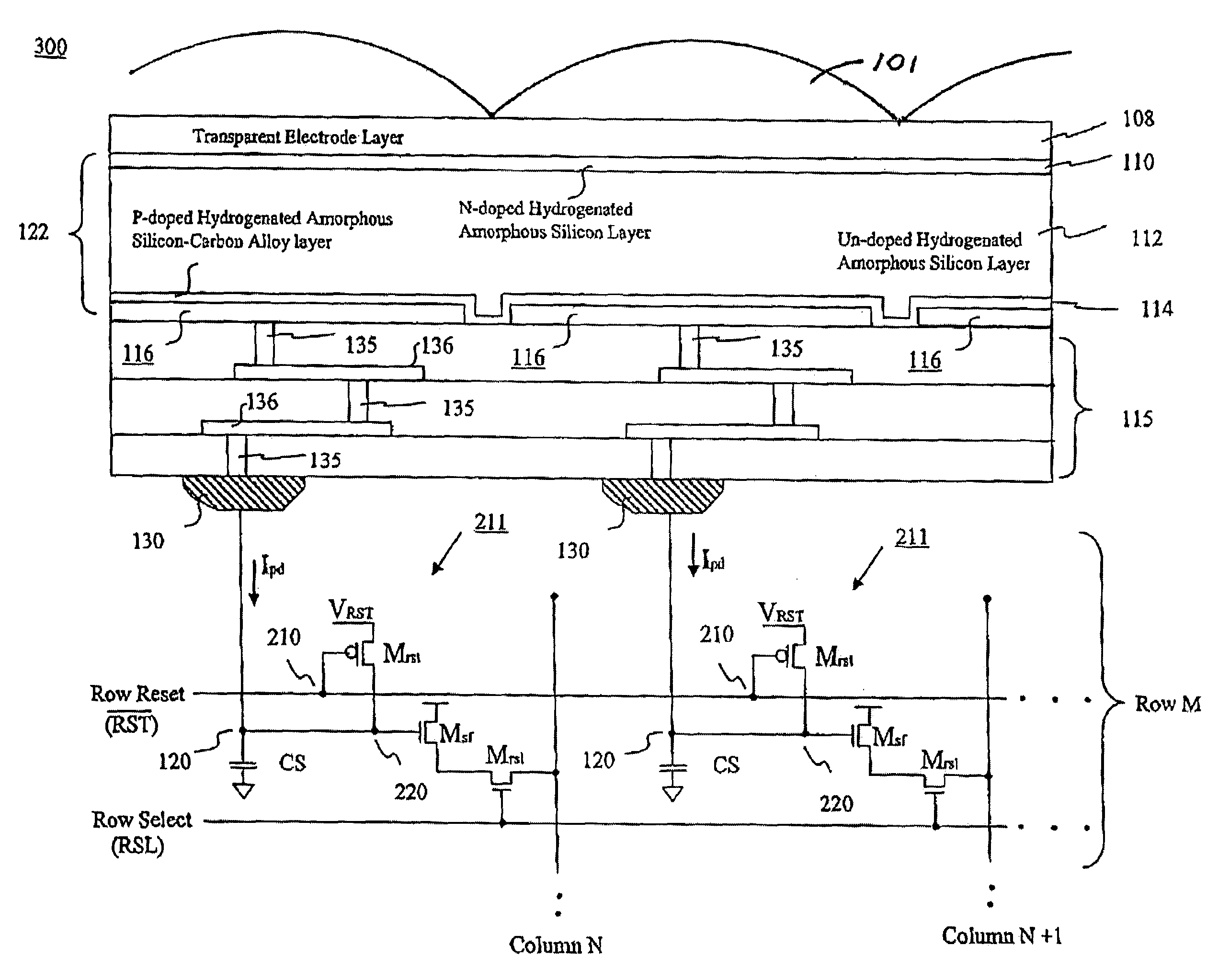
MOS or CMOS sensor with micro-lens array
InactiveUS20060249765A1Small pixelsMinimize and eliminate pixel to pixel crosstalkSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesCMOS sensorHigh-definition television
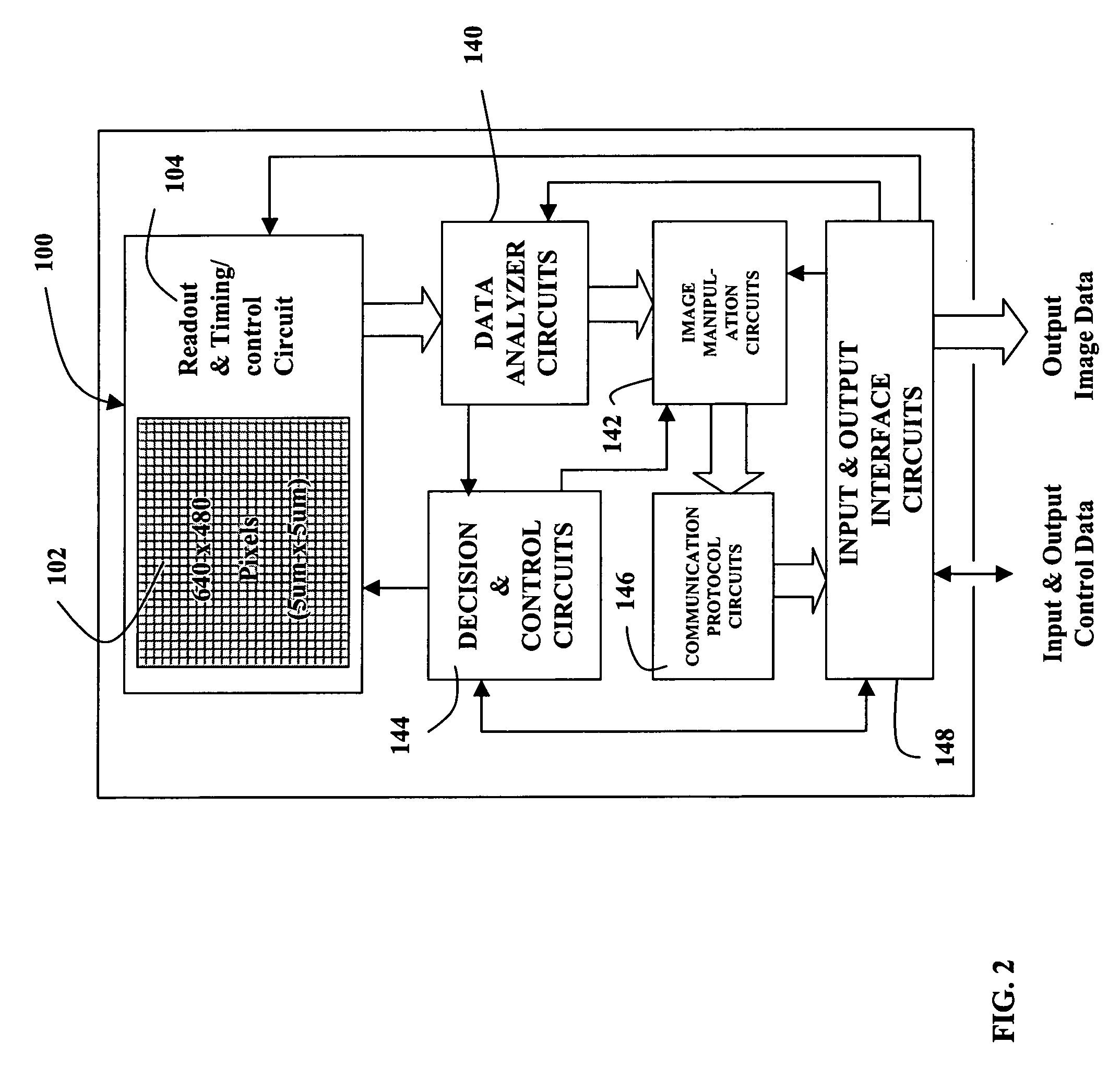
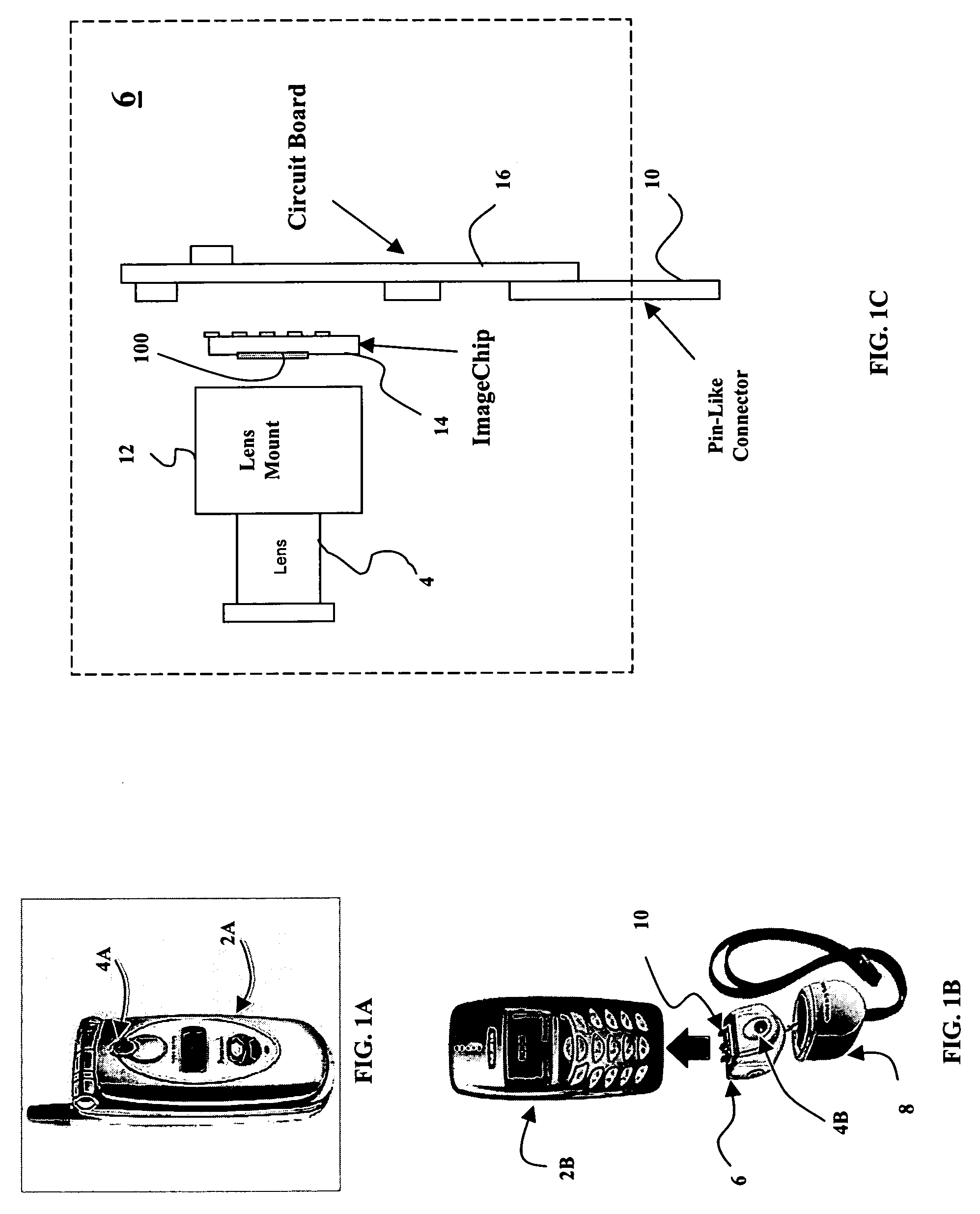
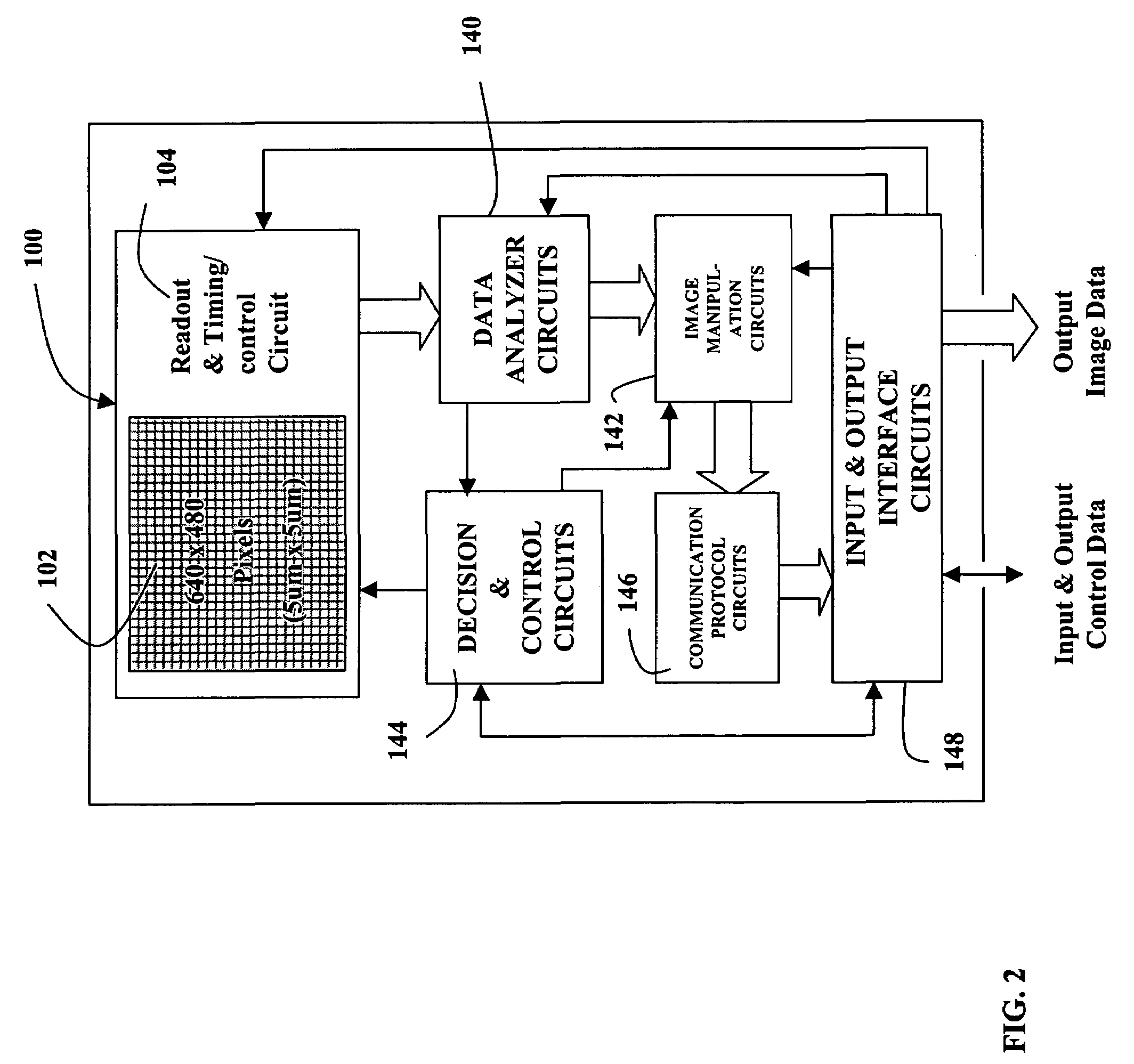
A MOS or CMOS sensor with a multi-layer photodiode layer covering an array of active pixel circuits. The multi-layer photodiode layer of each pixel is fabricated as continuous layers of charge generating material on top of the MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits so that extremely small pixels are possible with almost 100 percent packing factors. The sensor includes special features to minimize or eliminate pixel to pixel crosstalk. A micro-lens array with a micro-lens positioned above each pixel directs light illuminating the pixel toward the central portion of the pixel and away from its edges. Also, preferably carbon is added to doped amorphous silicon N or P bottom layer of the multi-layer photodiode layer to increase the electrical resistivity in the bottom layer to further discourage crosstalk. In preferred embodiments each of the pixels define a tiny surface area equal to or larger than about 3.24 square microns and smaller than or equal to about 25 square microns. Detailed descriptions are provided for two general types of sensors. The first type has a pixel count of about 0.3 to 1.9 million pixels and are especially suited for sues such as cell phone cameras. The second type with pixel count of between about 1.9 million pixels to more than 5 million pixels is especially suited for high definition television cameras.
Owner:E PHOCUS
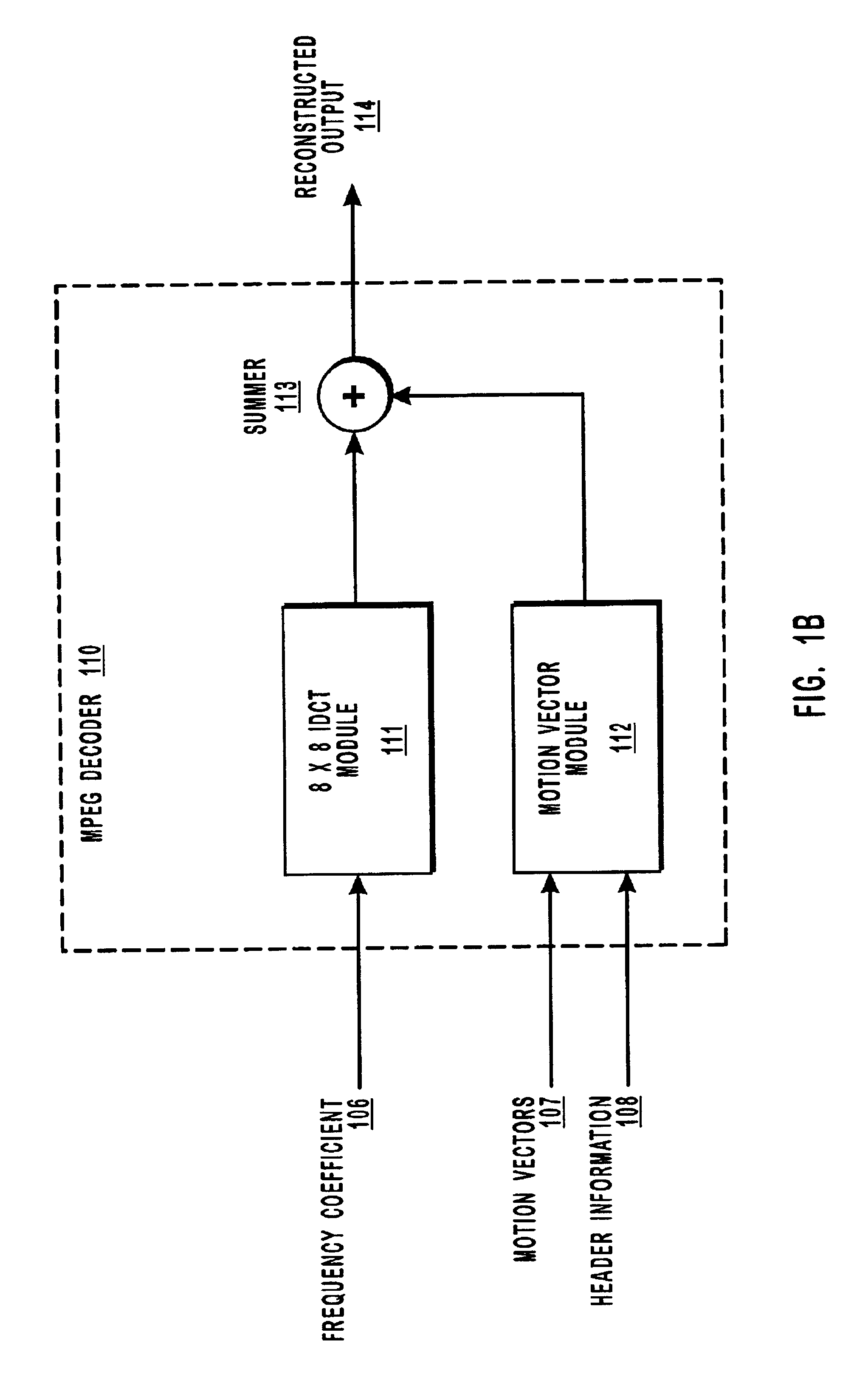
Systems and methods for MPEG subsample decoding
InactiveUS6850571B2Television system detailsGeometric image transformationHigh-definition televisionHigh definition tv
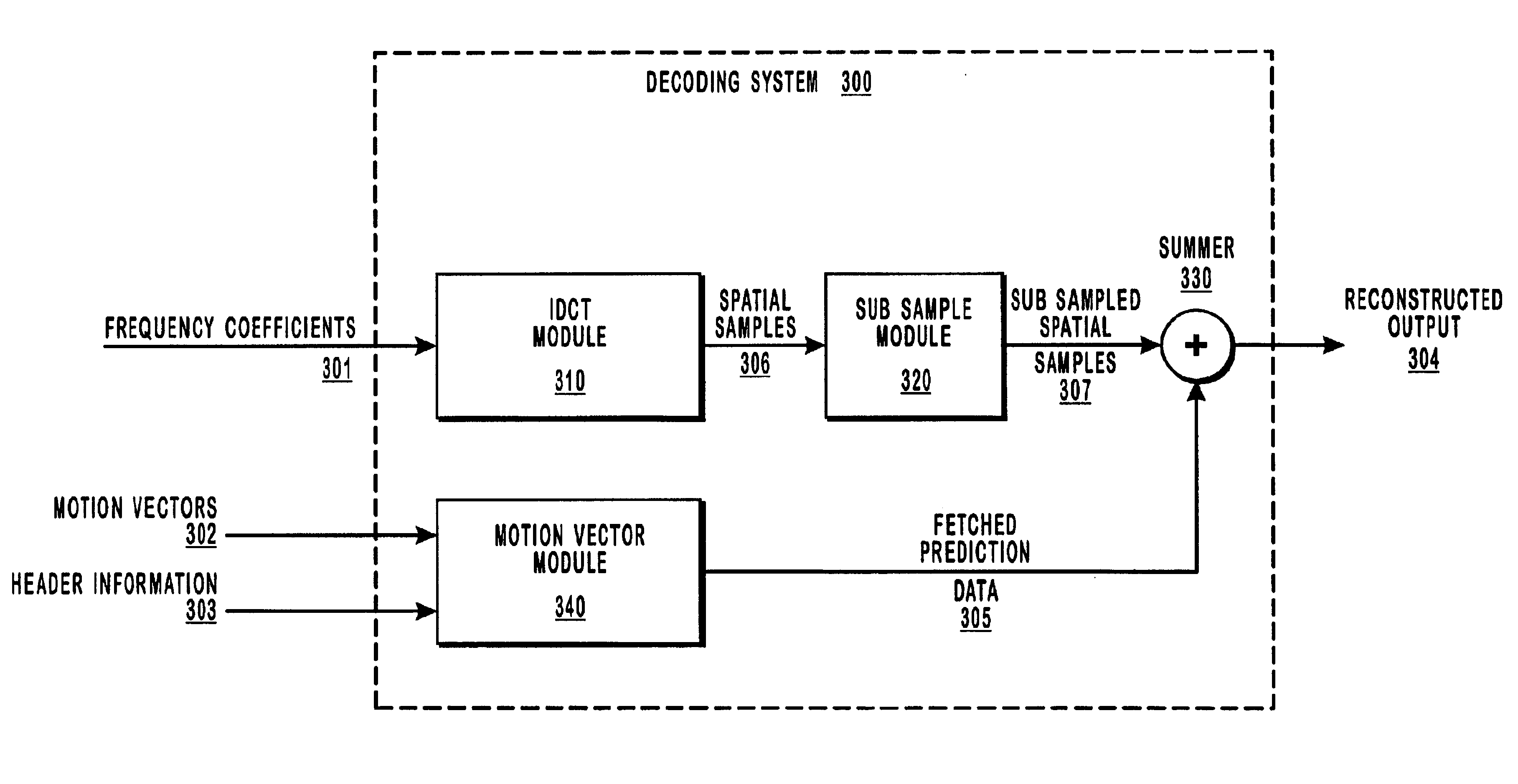
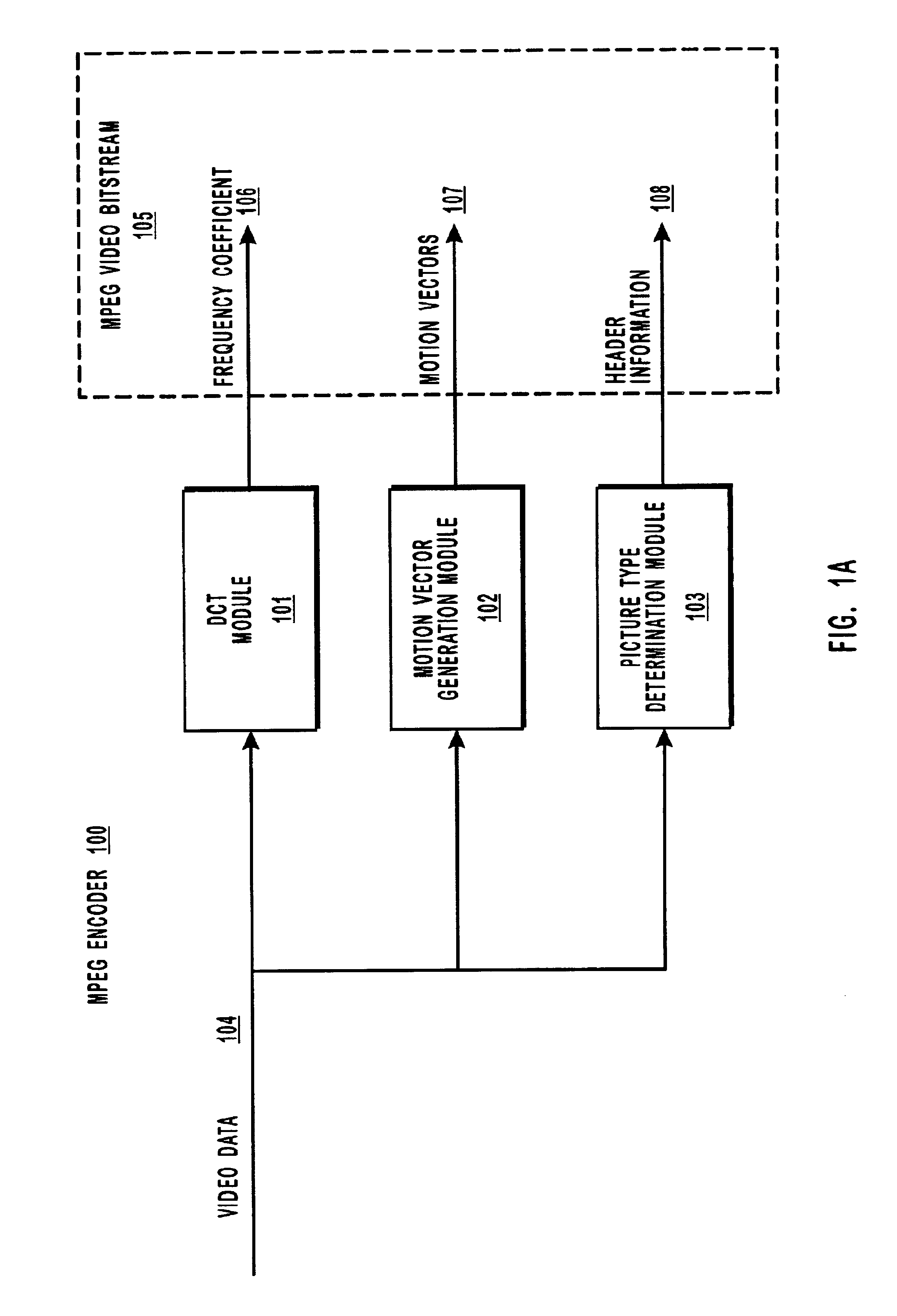
Decimating MPEG or other video data by subsampling the output of an inverse discrete cosine transform (IDCT) module. The decimation process is useful for reducing the volume of data that must be processed to display images on a display device, particularly when the volume of video data received at the decoder is greater than the amount needed to take advantage of the resolution of the display device. For example, high definition television data can be decimated for display on a standard television display device or in a picture-in-picture window, thereby reducing the amount of processing resources needed at the decoder and reducing the size of the frame buffers. Subsampling the output of the IDCT module reduces the volume of data and, for relatively static or constant pans, there is not a significant compounded loss of image quality as successive frames are decoded.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
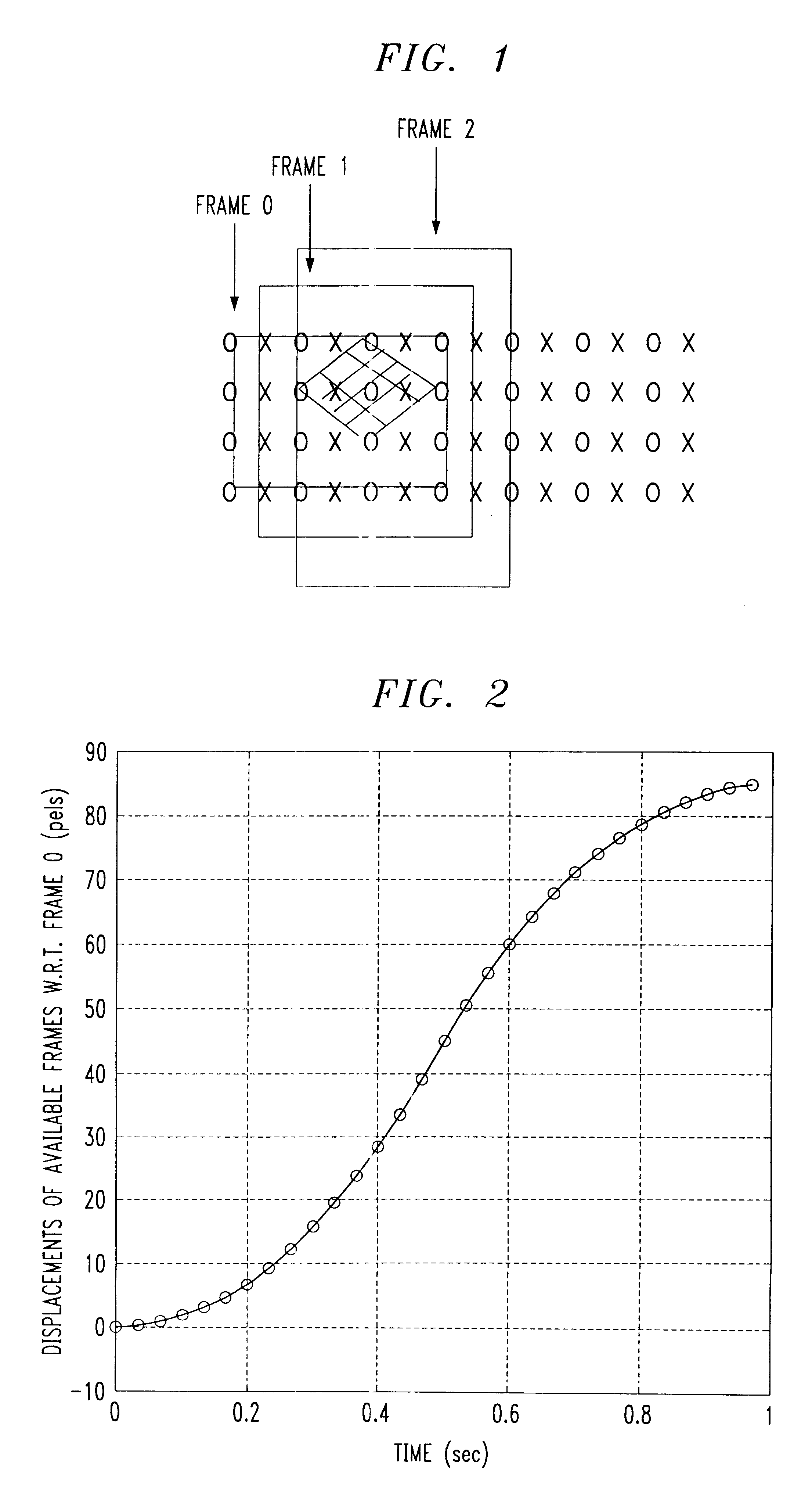
Motion compensation image interpolation-frame rate conversion for HDTV
InactiveUS6229570B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesHigh-definition televisionComputer graphics (images)
A process for up-converting an existing video source signal having a low frequency (frames / second) to a high frequency signal for use with High Definition Television (HDTV). The process samples the existing frames in the existing video signal and calculates integer displacements of pels within the existing frames. A polynomial curve fit is then performed on the displacements to obtain estimates of horizontal and vertical displacements of each block in each existing frame. Based on the alignment of the blocks within a sampling grid on each frame, the blocks are segregated into groups. The block groups are then used to interpolate missing or required frames of the high frequency signal in a piecemeal manner by utilizing blocks of a particular block group to estimate a corresponding block in a frame of the high frequency signal.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Multifunction display system
InactiveUS20100026912A1Television system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoHigh-definition television
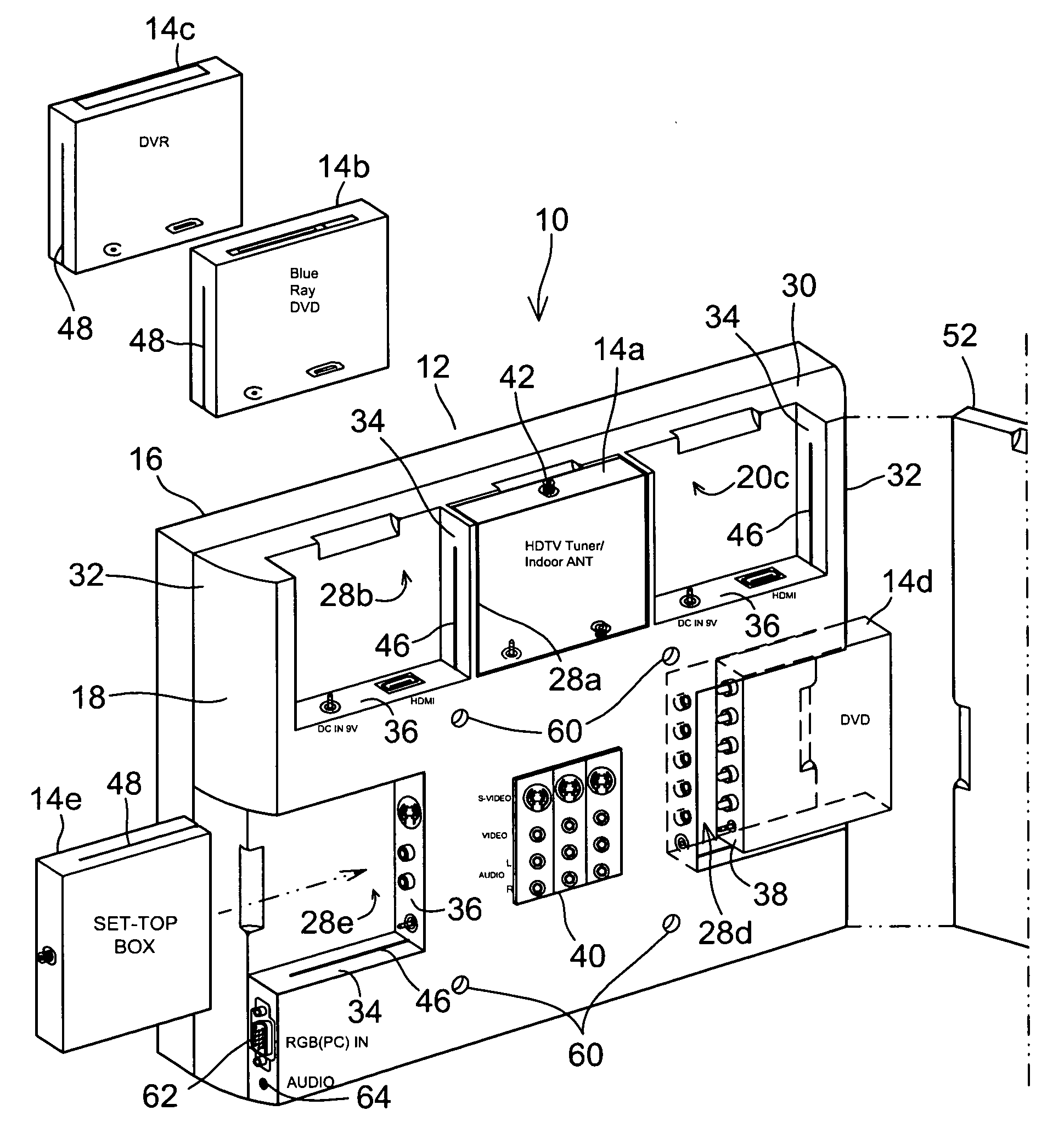
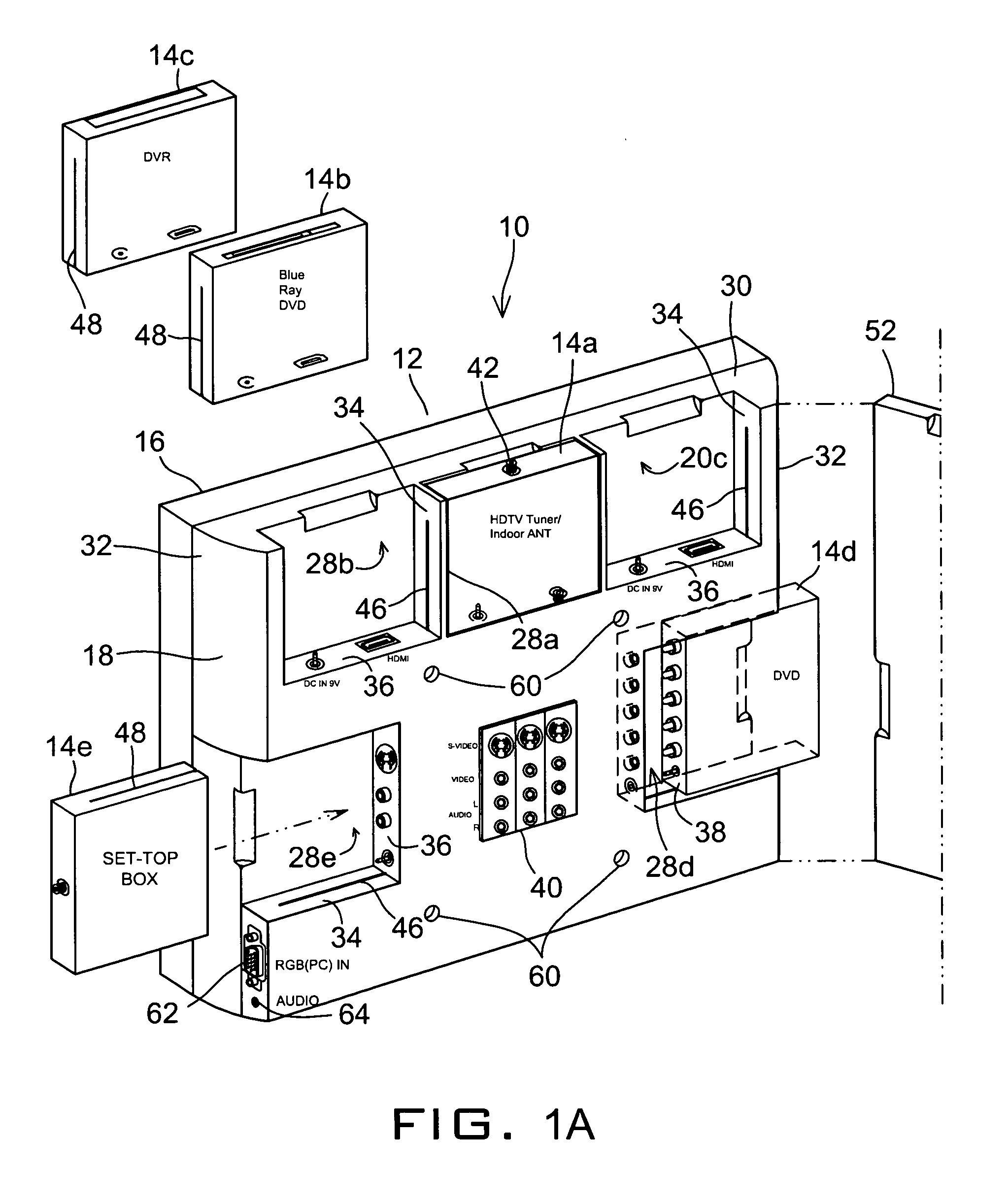
A multifunction display system is provided comprising a flat panel display screen; an electronic controller receiving video signal from an input and generating an output signal for displaying on the display screen; a power supply providing power to display screen and the electronic controller; a housing securing the display screen, the electronic controller and the power supply, wherein the housing includes a front shell and a rear shell that join together at a meeting line along a periphery of the display screen. The rear shell of the housing is a designed panel to receive multiple devices of specialized media playing capabilities in standardized boxes including but not limited to a regular or HD television tuner, a DVD and optical disc player, a digital video recorder, a hard drive player or an IPTV Divx player, mini PC and Internet and / or receiver router.
Owner:HO SOLOMON
Method of combining dispersed light sources for projection display
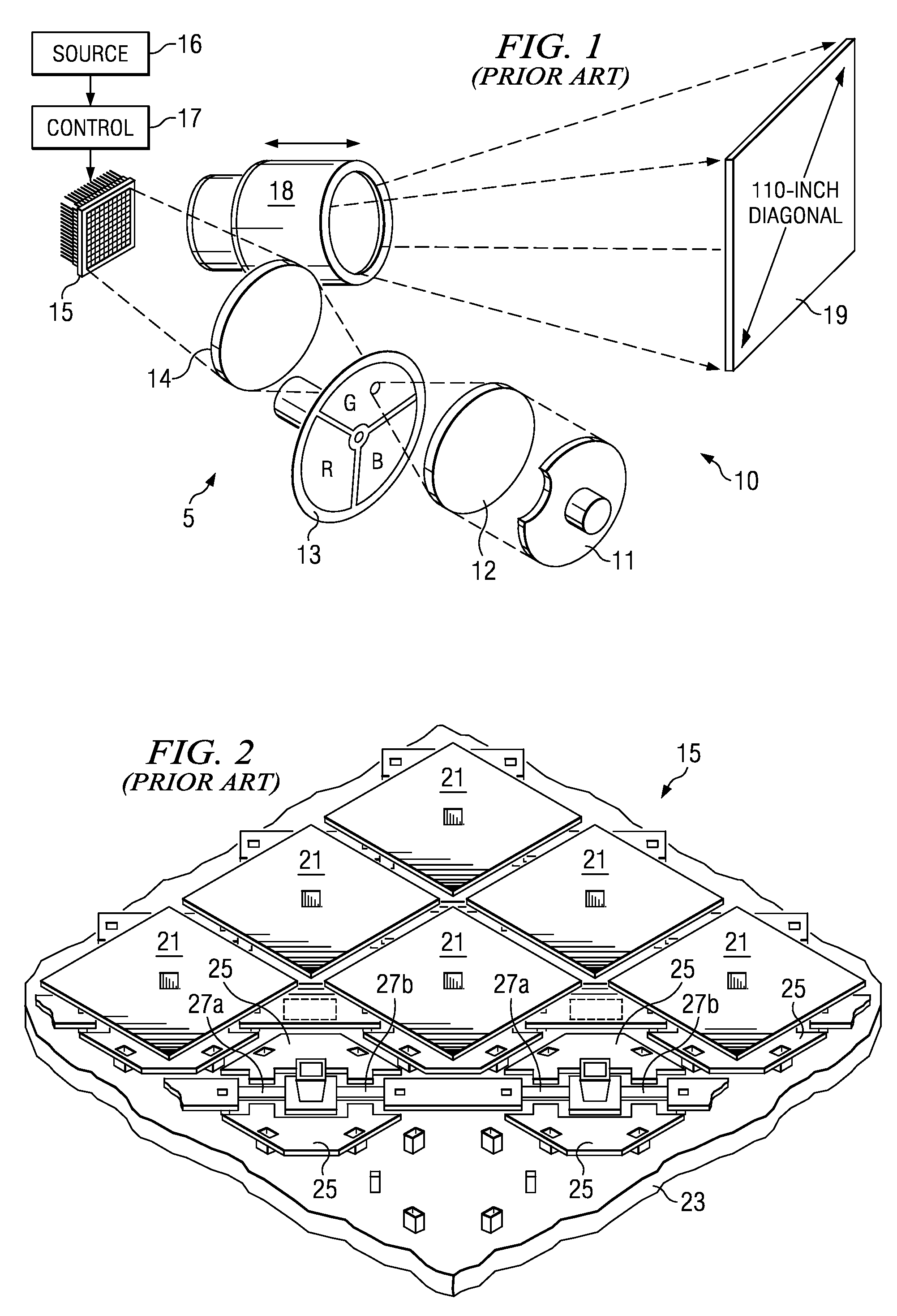
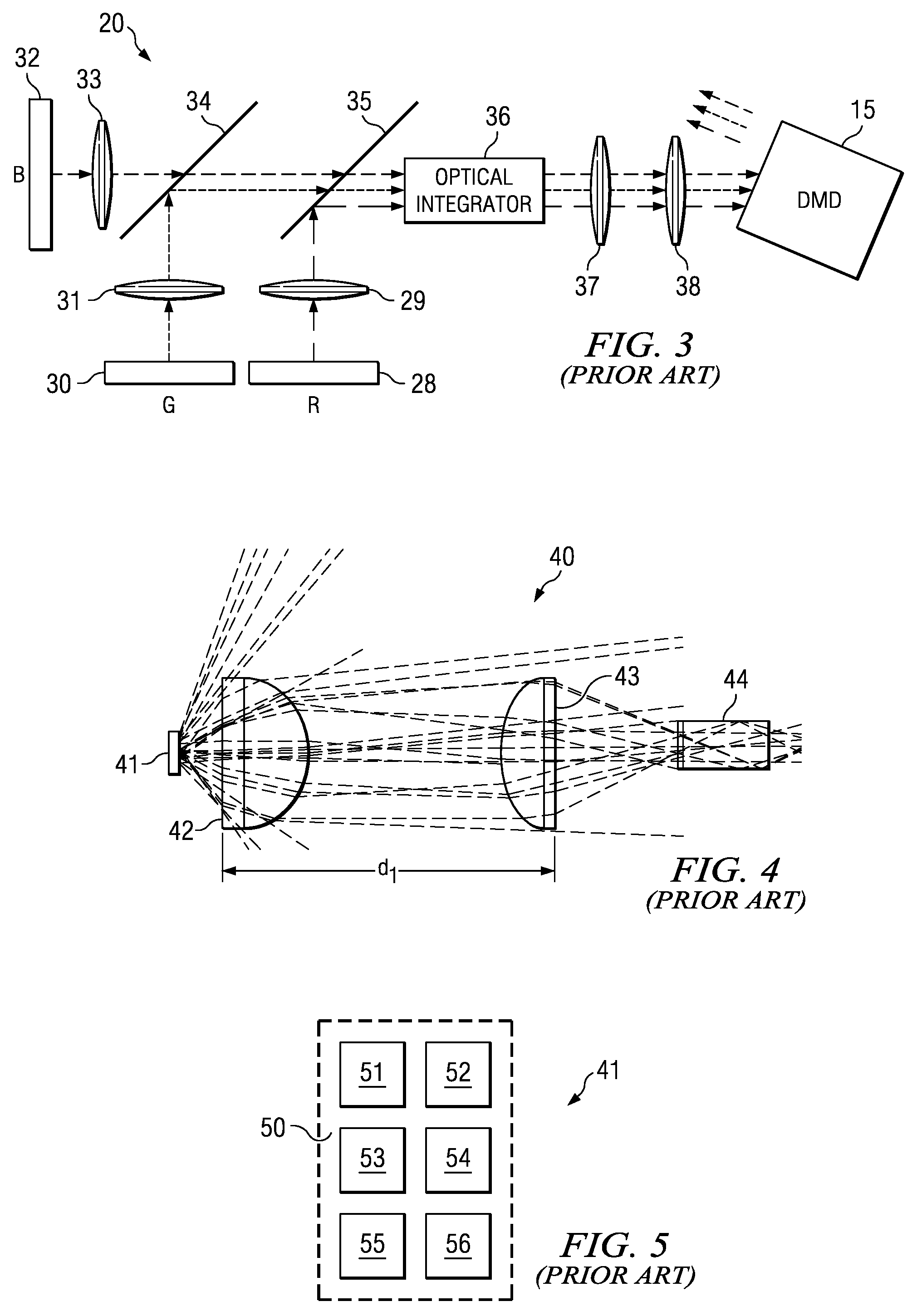
ActiveUS7537347B2Technical advantageGood for arrayingShow cabinetsImpedence networksHigh definition tvHigh-definition television
A method and system for combining light emitted by dispersed light sources for use in a projection display or similar system. A plurality of elongated and tapered light integrators are placed side by side forming an array, each having at their small input end a light source, such as an LED. Light collimated by each light integrator is further collimated by a convex lens disposed immediately at the output end of the light integrator. From the convex lenses, the light falls upon an array integrator, preferably a fly-eye type integrator, and passes through it to a second array integrator. Light emerging from the second array integrator is then passed through one or more relay lenses and falls upon a light modulator, such as a digital mircomirror device (DMD). The modulated light beam then passes through a projection lens and onto a visual image display screen. The display screen may, for example, be the screen of a high definition television (HDTV).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
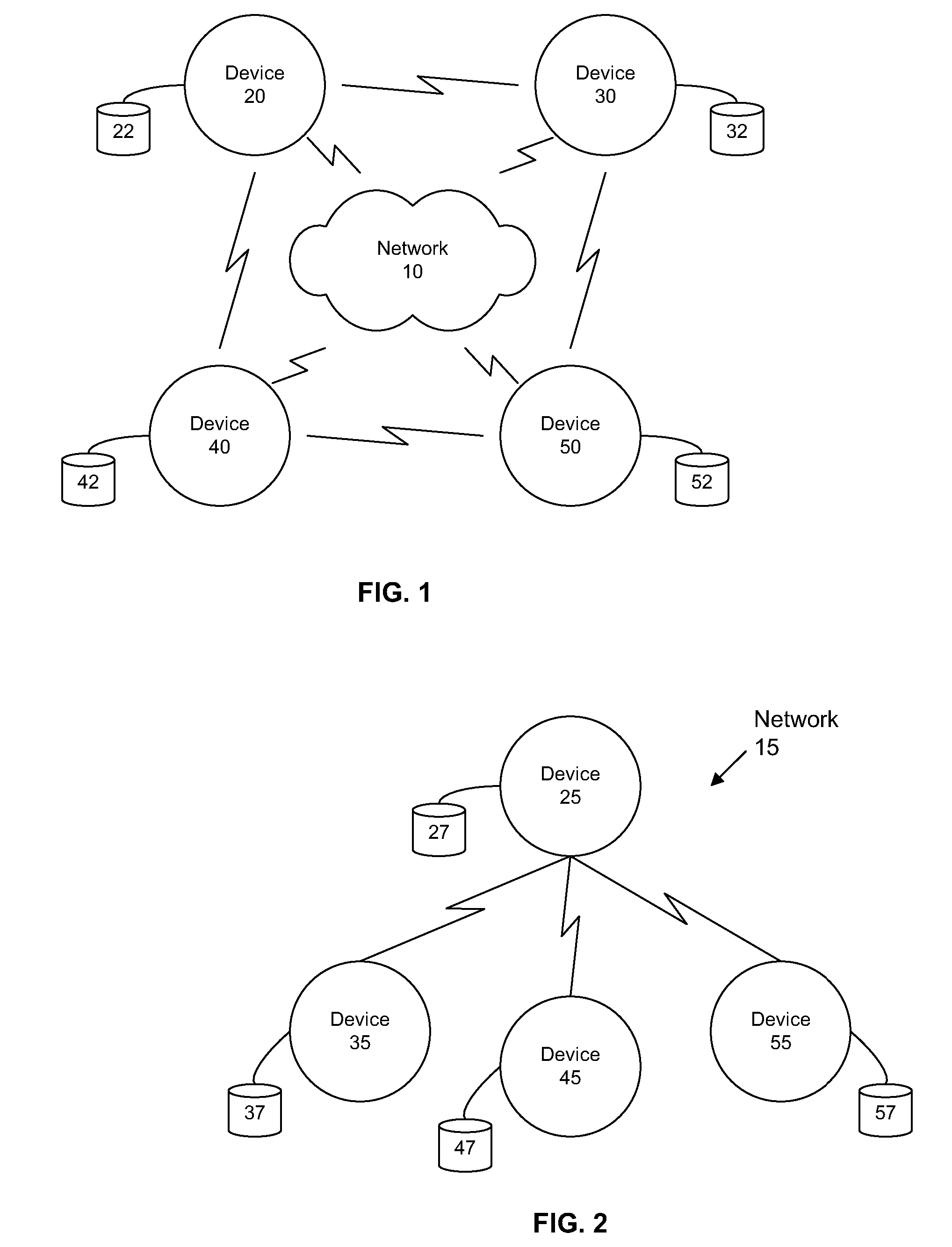
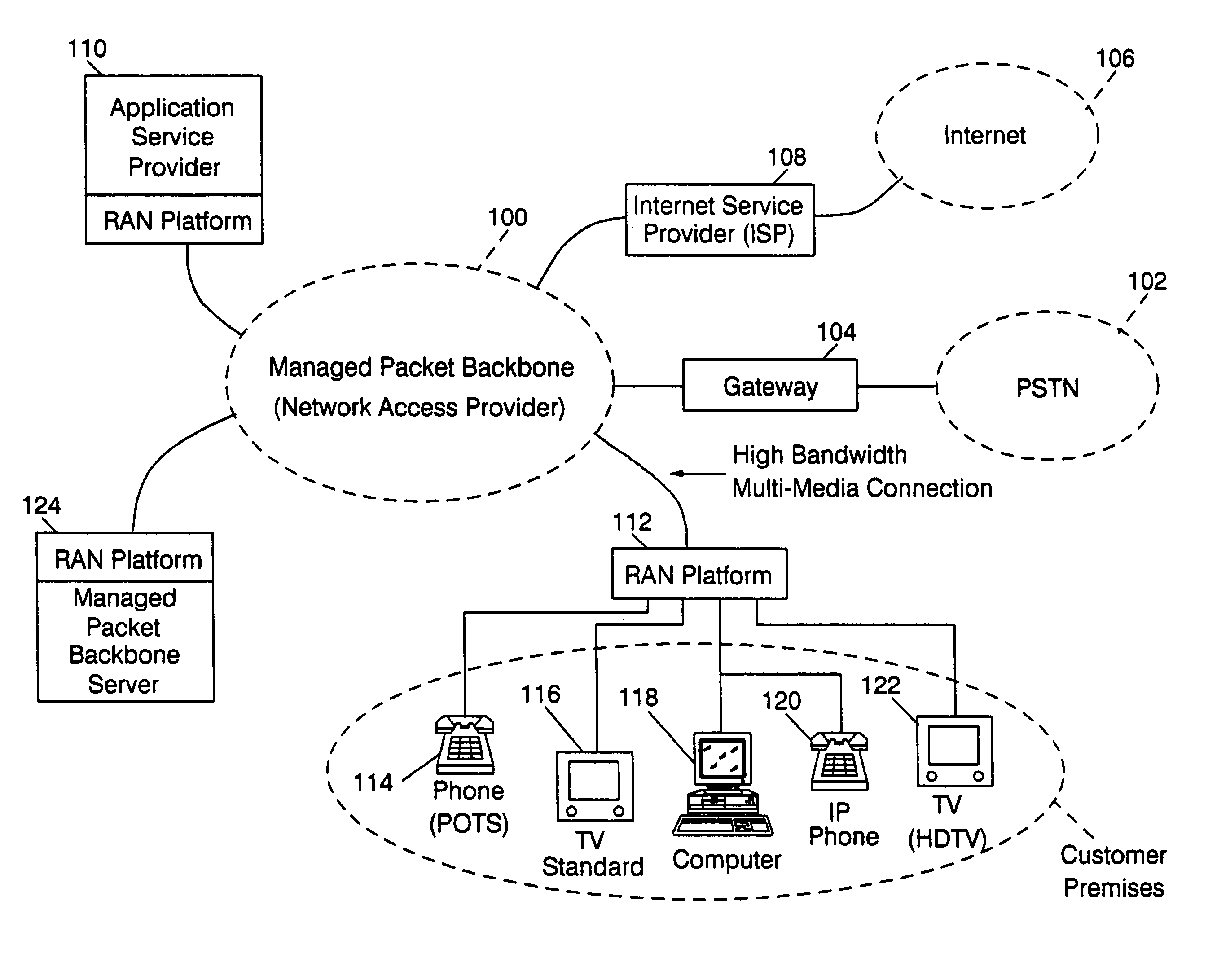
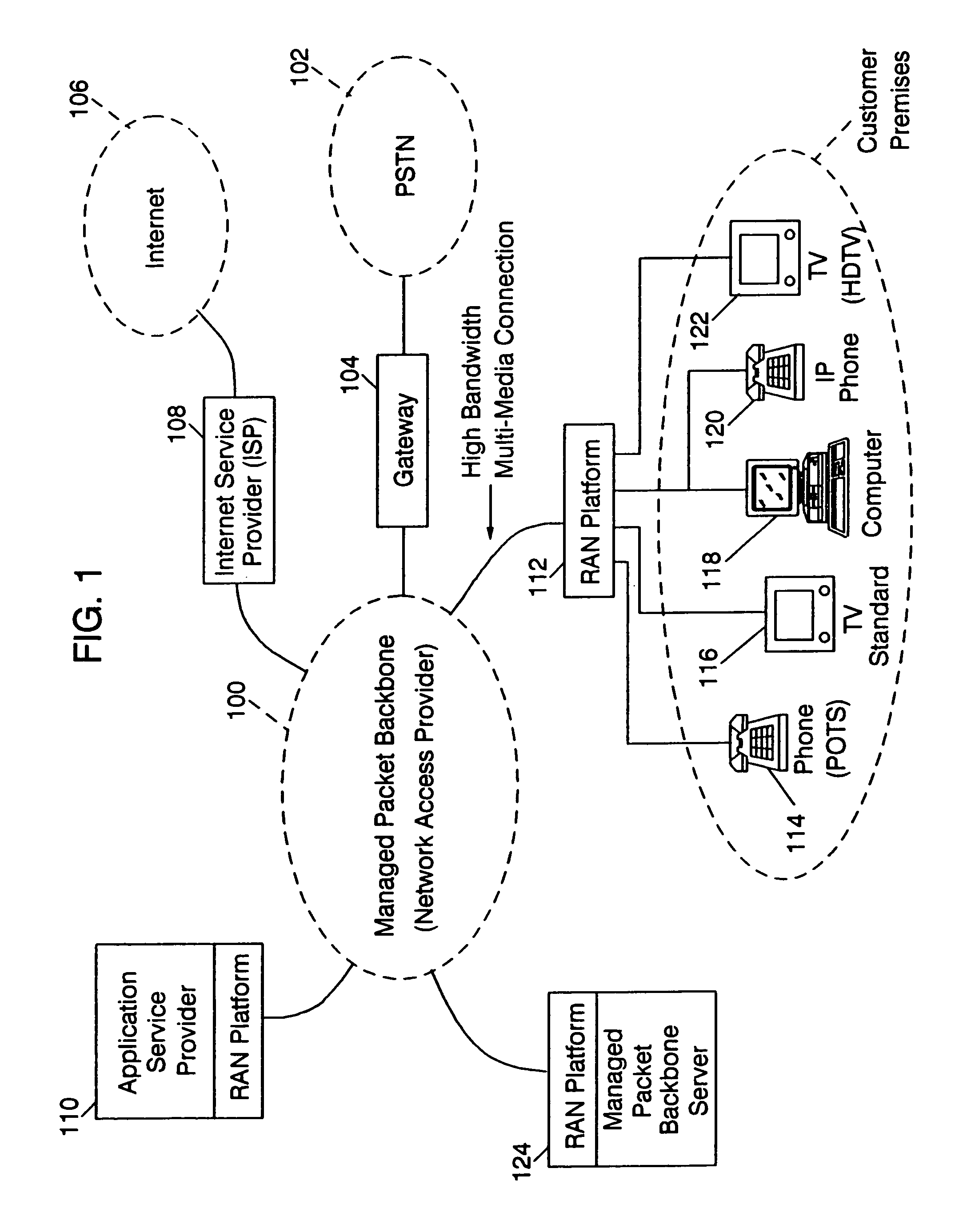
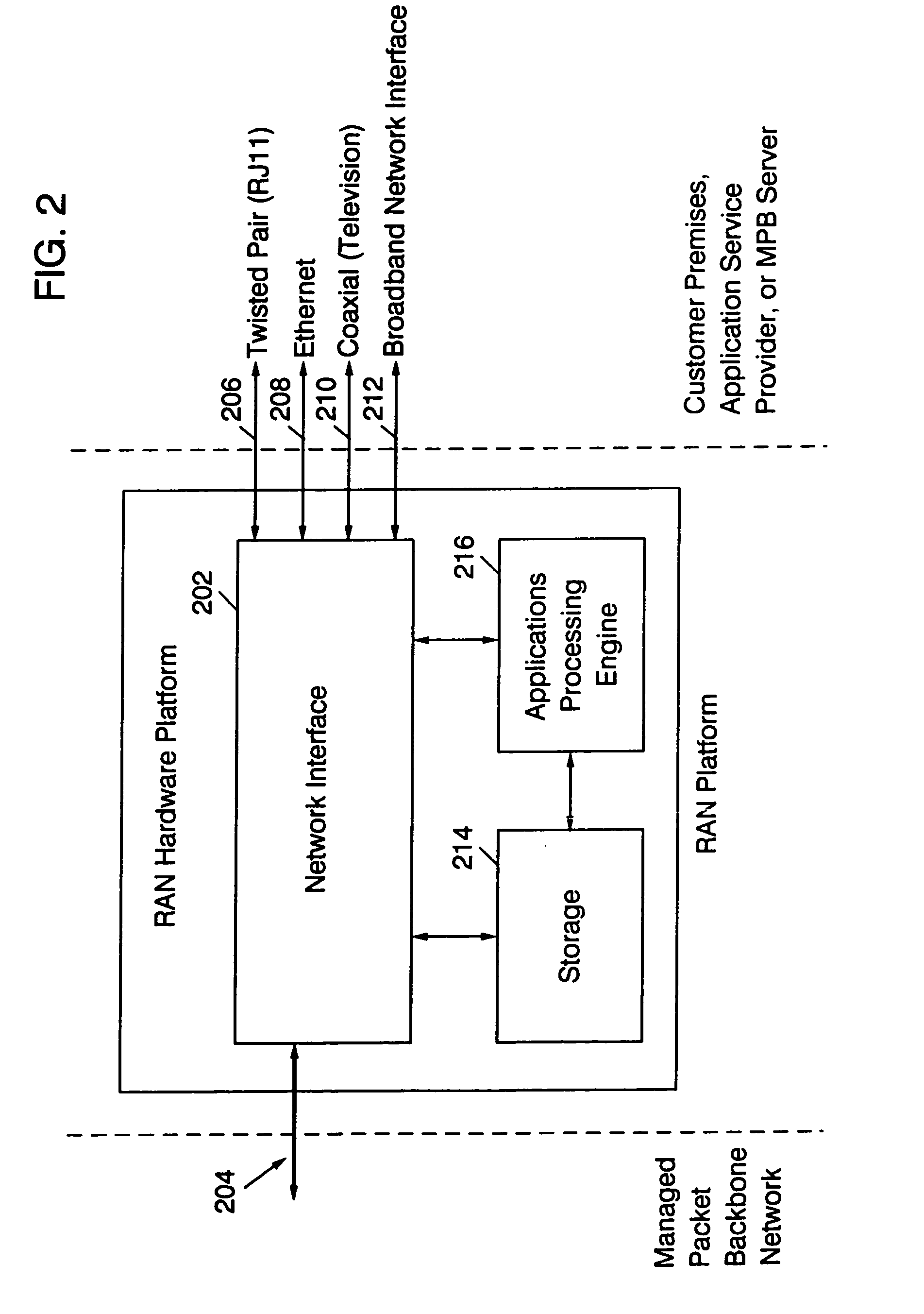
Method and computer system for managing data exchanges among a plurality of network nodes in a managed packet network
InactiveUS6938080B1Security bandwidthSecurity content deliveredMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsHigh-definition televisionHigh bandwidth
A residential access node (RAN) running a RAN platform 112 which includes means for interfacing a plurality of peripheral equipment such as analog (POTS) phones 114, standard televisions 116, computers 118, IP telephones 120, and high definition televisions 122 to a packet data network 100. The Network Access Provider RAN platform 124 manages sessions among Customer Premises RAN platforms 112 and Application Service Provider RAN platforms 110 over high bandwidth connections. The Customer Premises RAN platform 112 also determines the number and type of data packets entering or departing via the packet data network 100. Such an architecture allows for the efficient transfer of services (data content) from Application Service Providers to individual network access subscribers by seamlessly accommodating various data types and providing an integrated metering and billing mechanism managed by the Network Access Provider.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
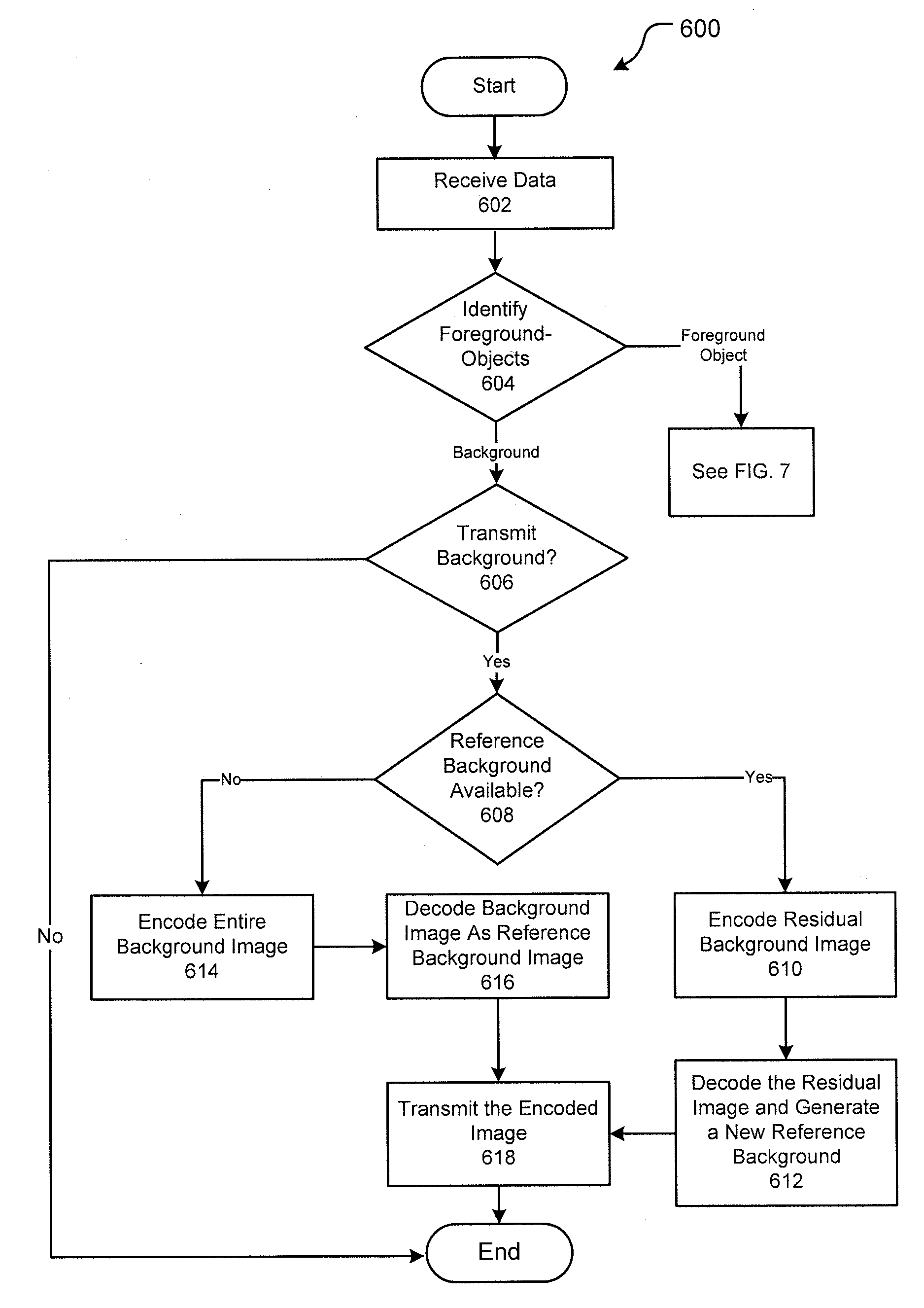
Video coding
ActiveUS20120169923A1High definitionPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesHigh-definition televisionPattern recognition
Techniques are discussed for providing mechanisms for coding and transmitting high definition video, e.g., over low bandwidth connections. In particular, foreground-objects are identified as distinct from the background of a scene represented in a plurality of video frames received from a video source, such as a camera. In identifying foreground-objects, semantically significant and semantically insignificant movement (e.g., repetitive versus non-repetitive movement) is differentiated. Processing of the foreground-objects and background proceed at different update rates or frequencies.
Owner:PELCO INC
Displaying broadcasts of multiple camera perspective recordings from live activities at entertainment venues on remote video monitors
InactiveUS20090128631A1Television system detailsClosed circuit television systemsHigh-definition televisionHigh definition tv
Broadcast methods and systems for simultaneously transmitting, processing and selectively displaying more than one video camera perspectives recorded at live entertainment venues on remote video monitors. Video recording can be from more than one entertainment venue or can be more than on synchronized video camera perspective of an activity at an entertainment venue. Remote video monitors can be venue-based hand held devices or video monitors used at home. Remote video monitors can include hand held devices and high definition televisions (e.g., HDTVs) including flat panel display screens therein. Within a venue, camera views can be processed and formatted for display on display screens associated with remote video monitor. A user can select from more than one view from video cameras that the user wants displayed on the remote viewer, enabling a user of the remote video monitor to view more than one camera view through the remote viewer at a time / simultaneously.
Owner:FRONT ROW TECH
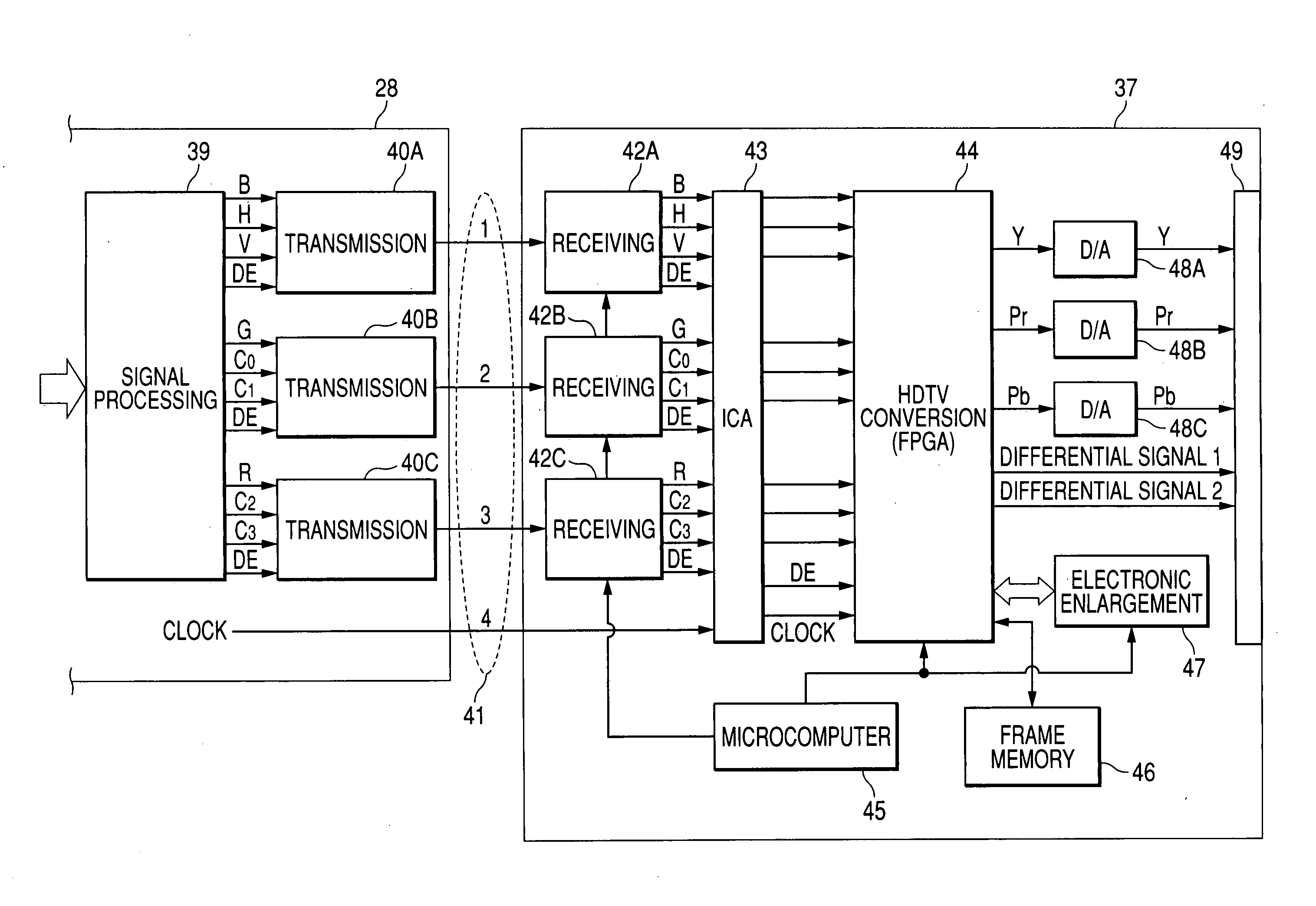
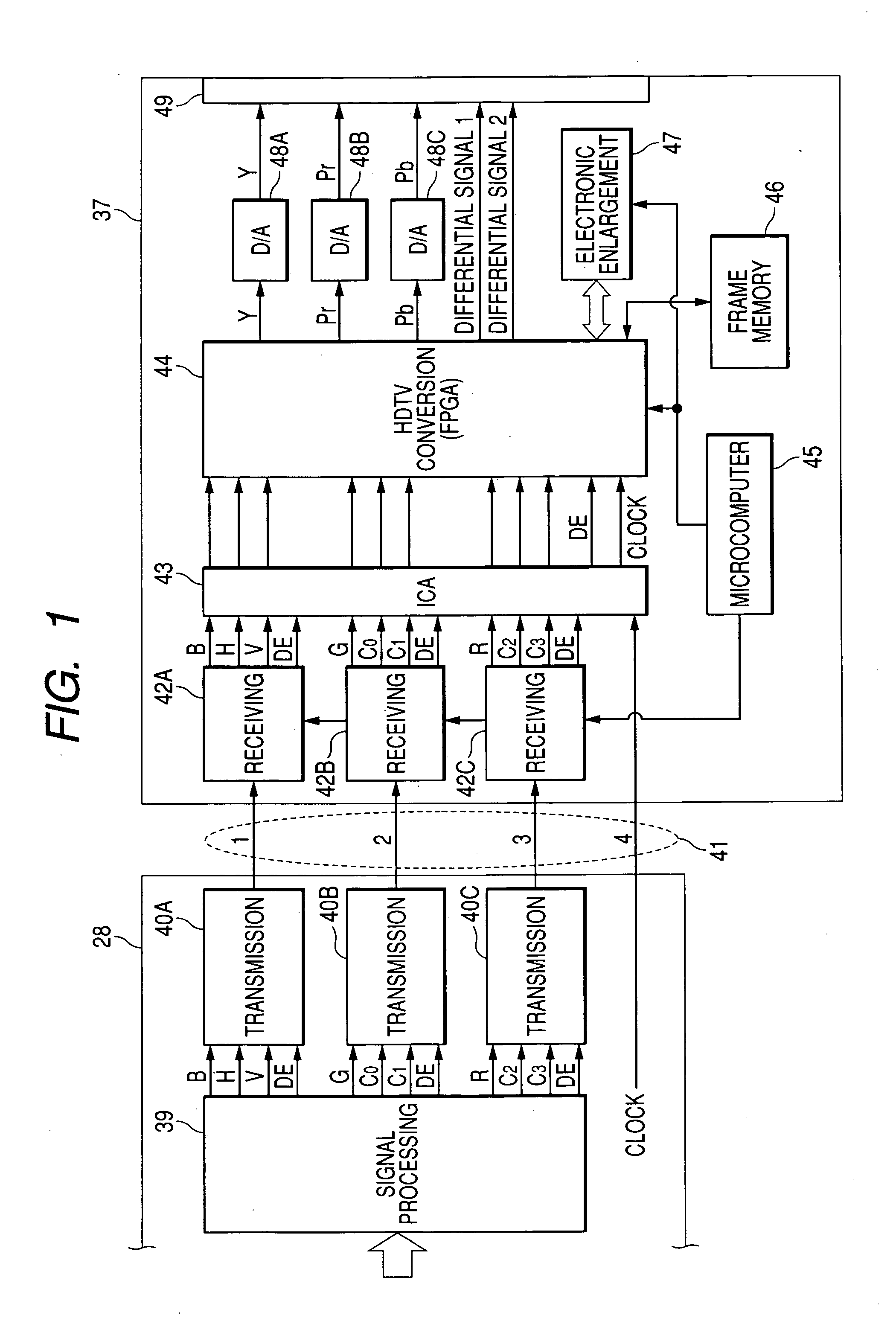
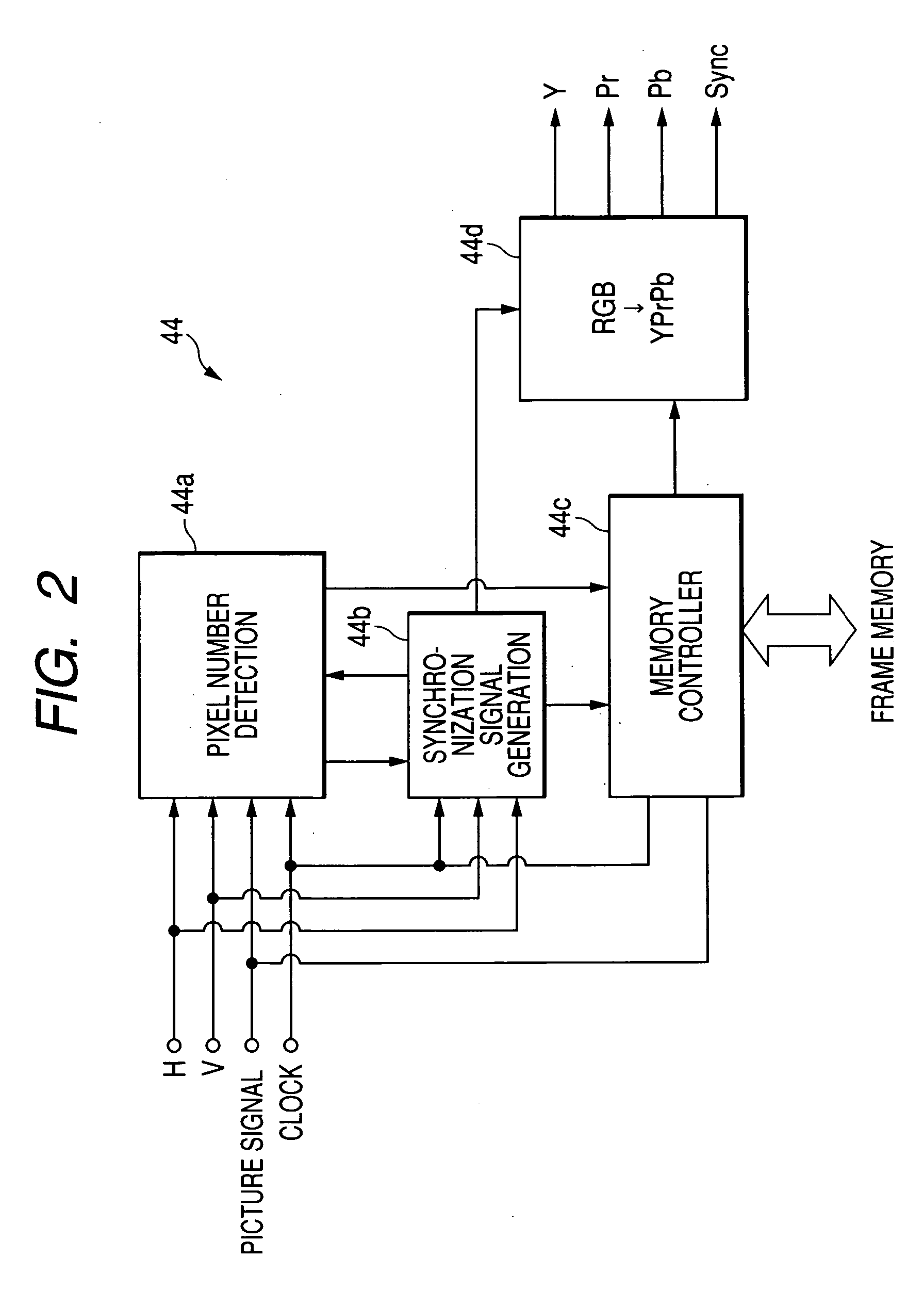
Electronic endoscope apparatus
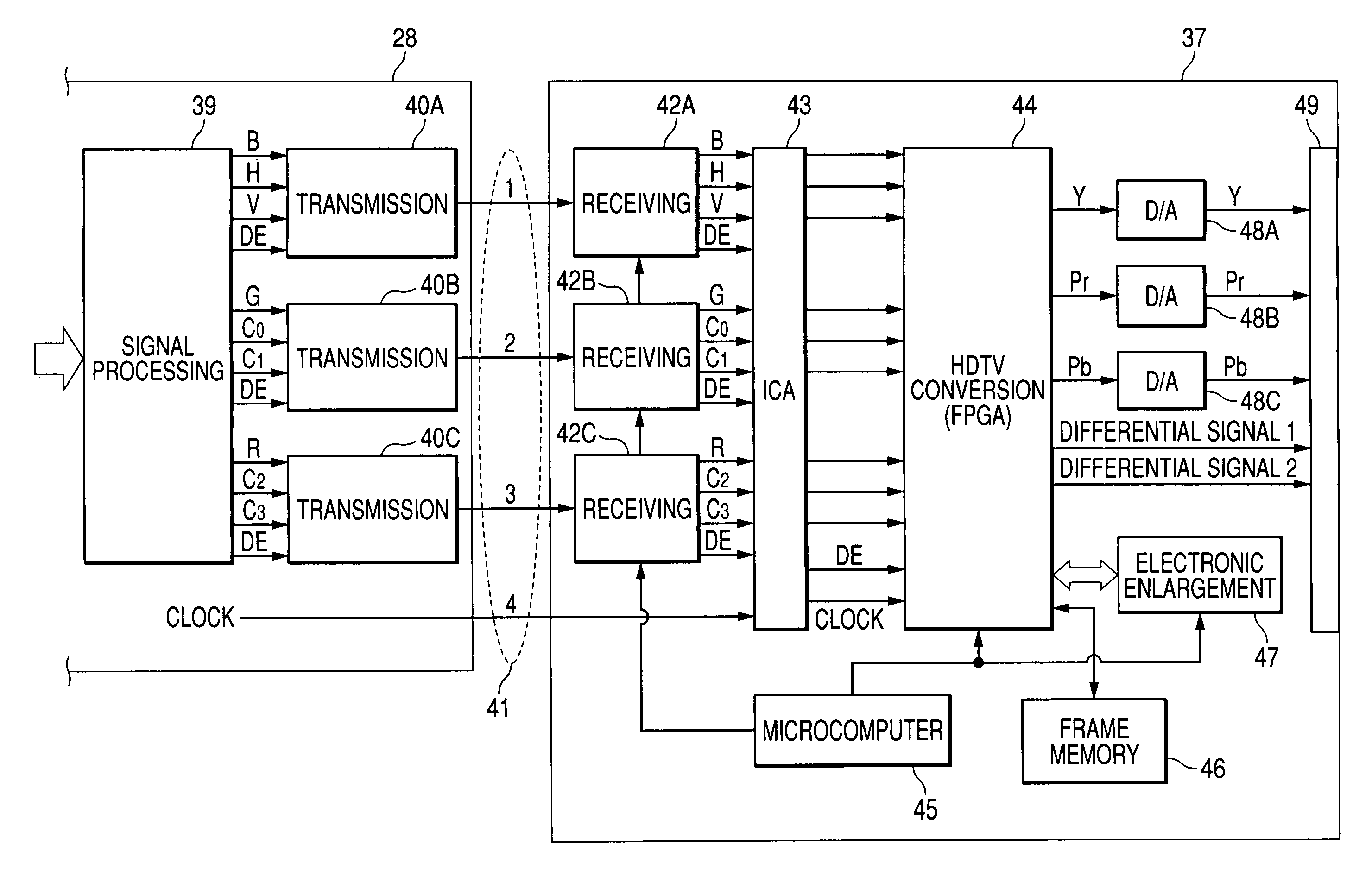
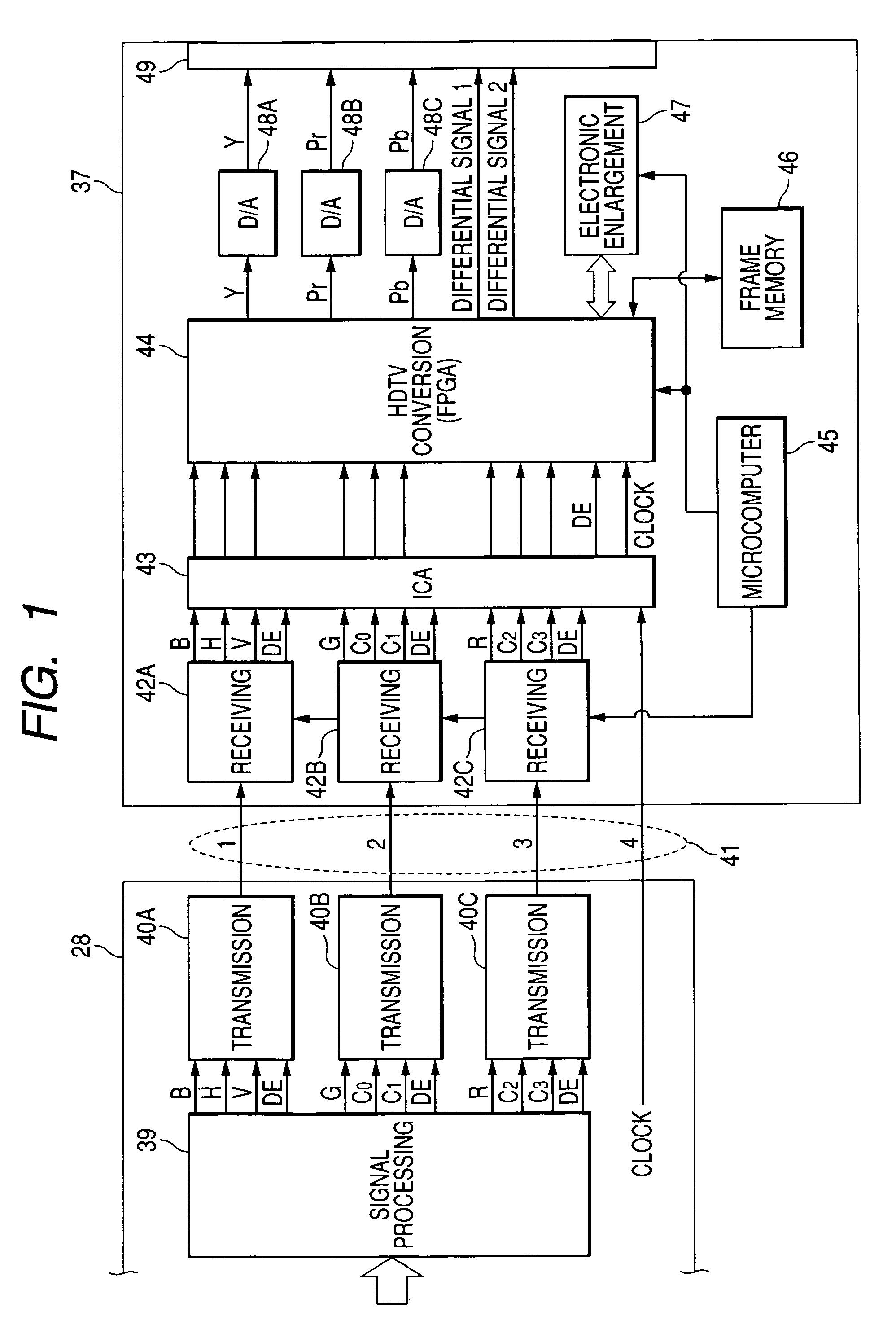
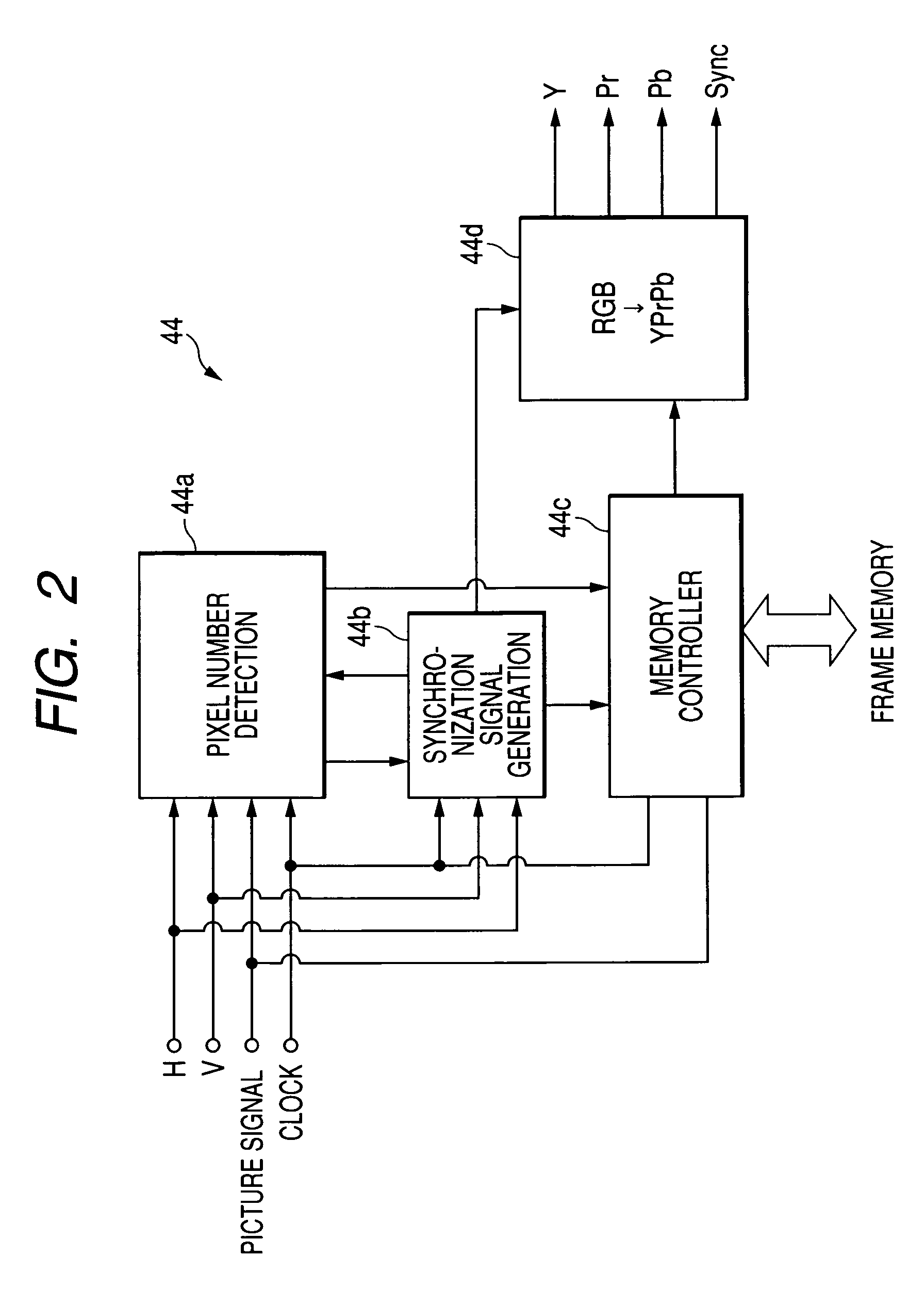
InactiveUS20050231591A1Simple structureSimple transmission structureTelevision system detailsEndoscopesHigh-definition televisionTelevision system
An electronic endoscope apparatus comprises: a processor unit; and an electronic endoscope having a solid-state pickup element, the electronic endoscopes being capable of connecting to the processor unit, so as to generate digital picture signals, wherein the processor unit comprises a differential signal outputting portion that generates digital picture signals corresponding to a pixel number of the solid-state pickup element and corresponding to a display standard for an external computer, parallel-serially converts the digital picture signals, and outputs the converted signals as differential signals, and wherein the electronic endoscope apparatus further comprises a high-definition television system converter that detects the pixel number of the digital picture signals based on the differential signals, converts the digital picture signals to high-definition television signals based on the detected number of pixels and outputs the high-definition television signals, the high-definition television system converter being detachably connected to the differential signal outputting portion.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
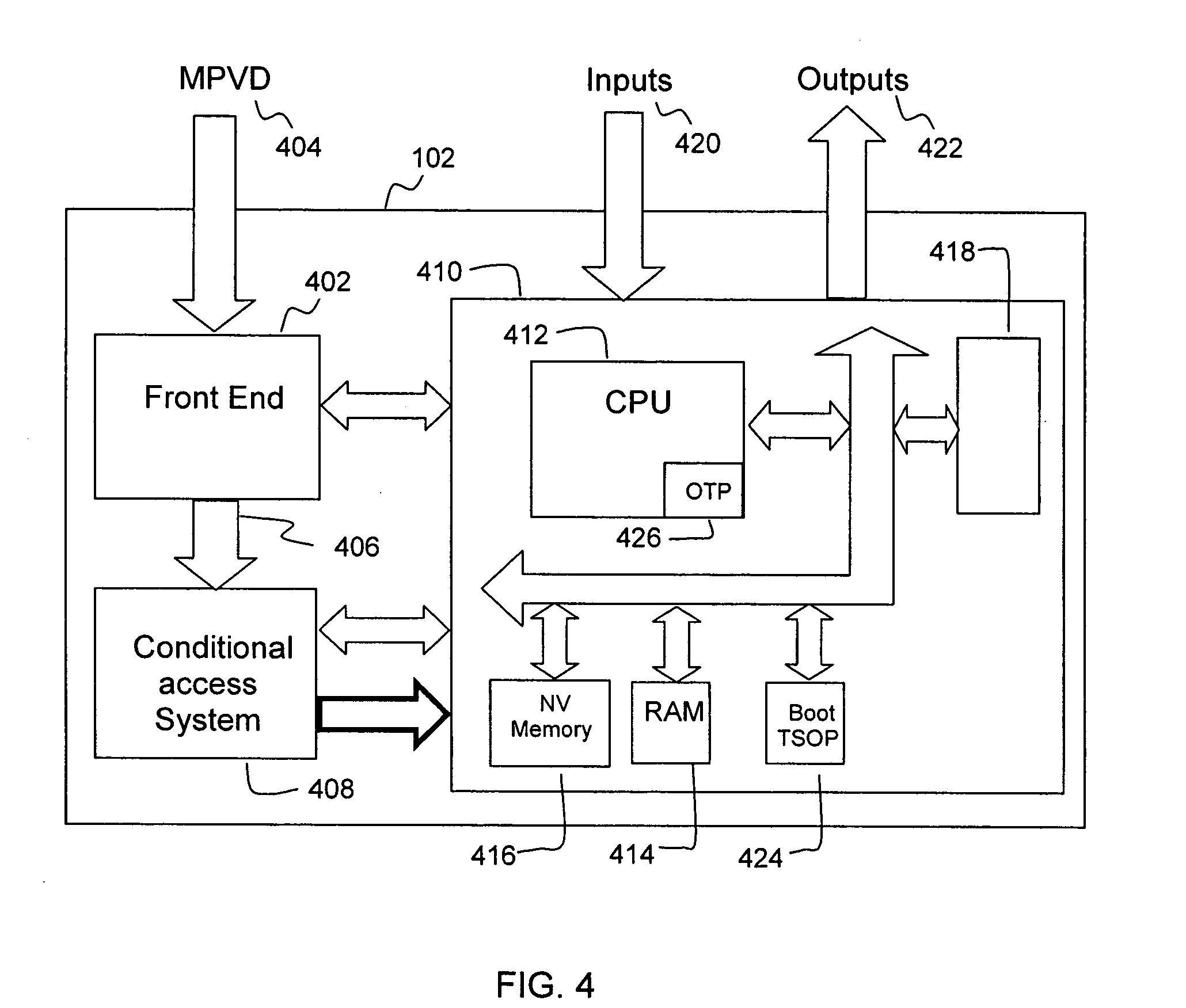
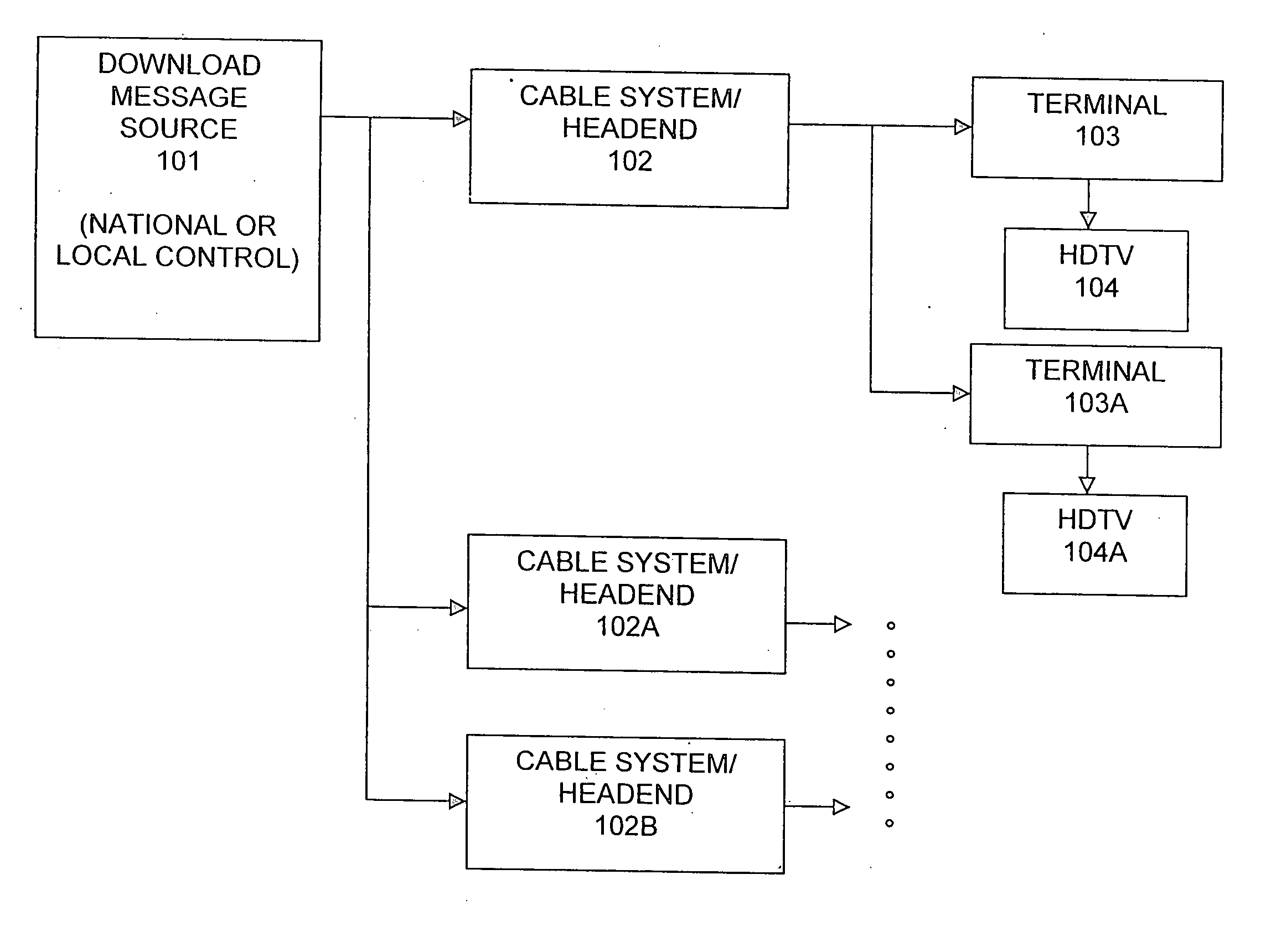
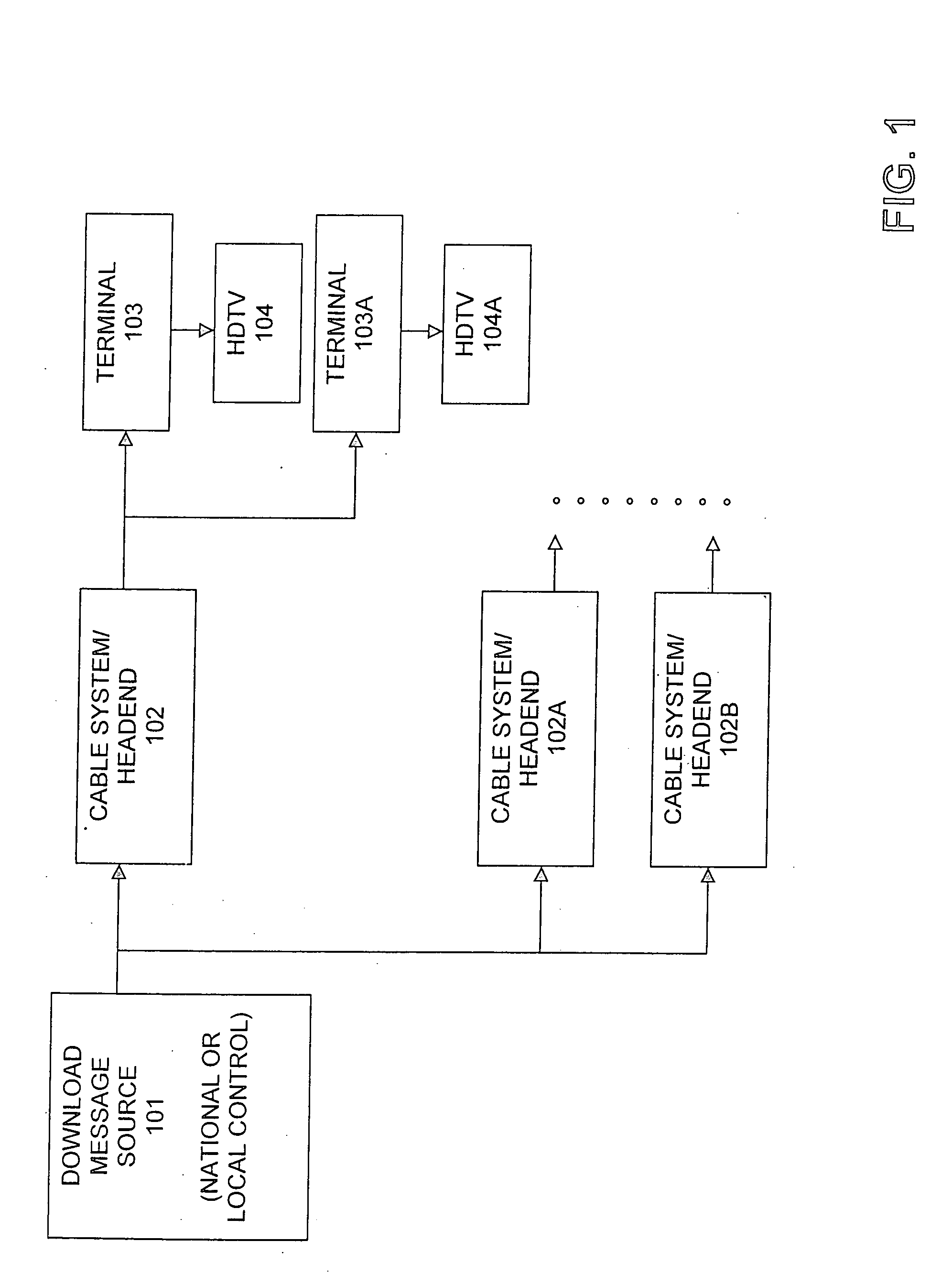
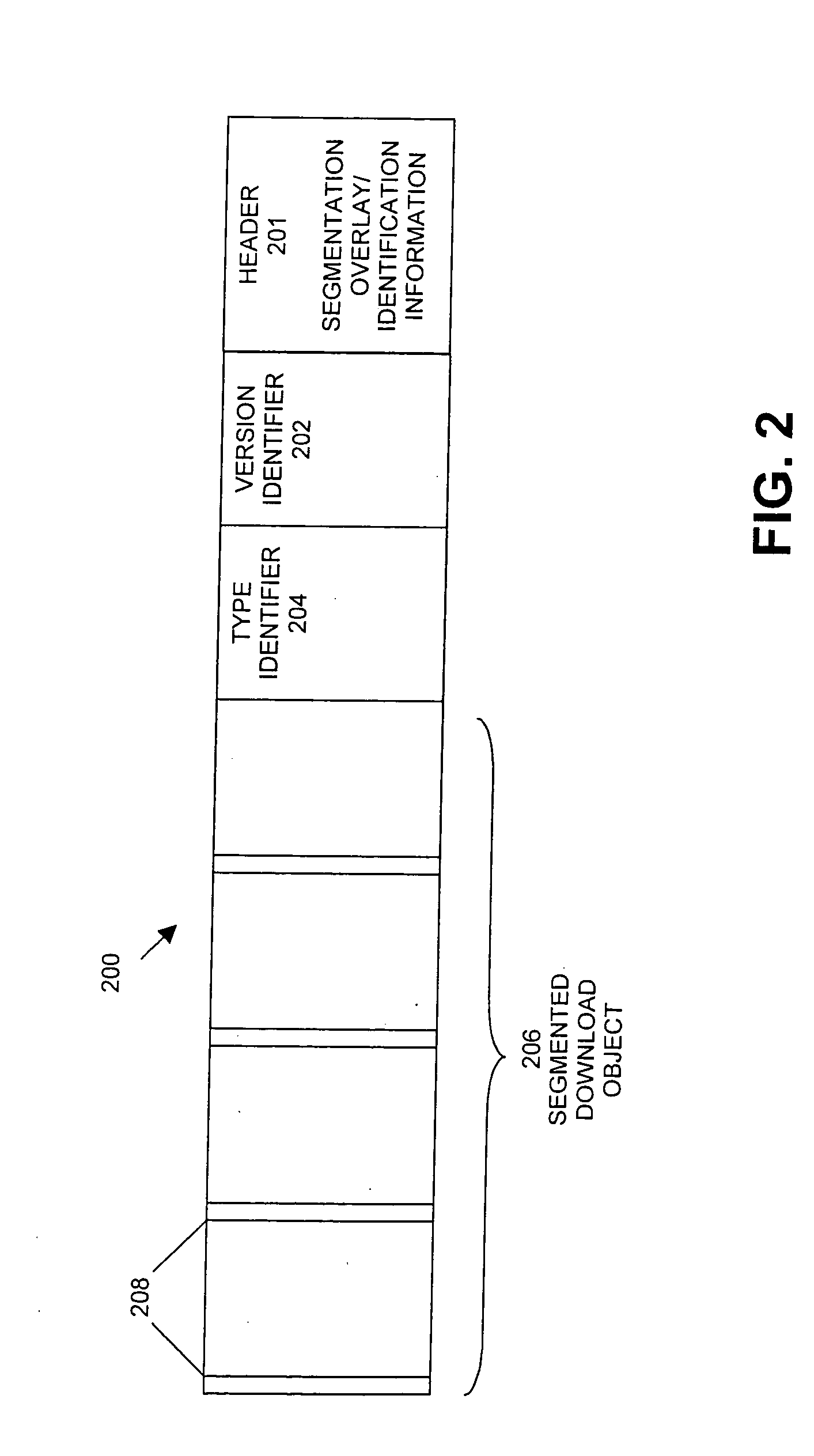
Methods and systems for enabling software and firmware downloads to high definition television appliances
InactiveUS20050120384A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsDevice typeHigh definition tv
The present invention enables software and firmware downloads to high definition television (HDTV) appliances via a television terminal. A download control message received at the terminal may comprise: (i) a first version identifier identifying a version of an available software or firmware download; (ii) a first type identifier identifying a particular type of HDTV appliance for which the download is intended; and (iii) a download object containing the software or firmware to be downloaded. The terminal obtains a second type identifier from the HDTV appliance that identifies a type of the HDTV appliance. If the type identifiers correspond, the terminal obtains a second version identifier from the HDTV appliance, which identifies a current version of software or firmware of the HDTV appliance. If the version identifiers do not correspond, the terminal may pass the download object to the HDTV appliance.
Owner:GENERAL INSTR CORP
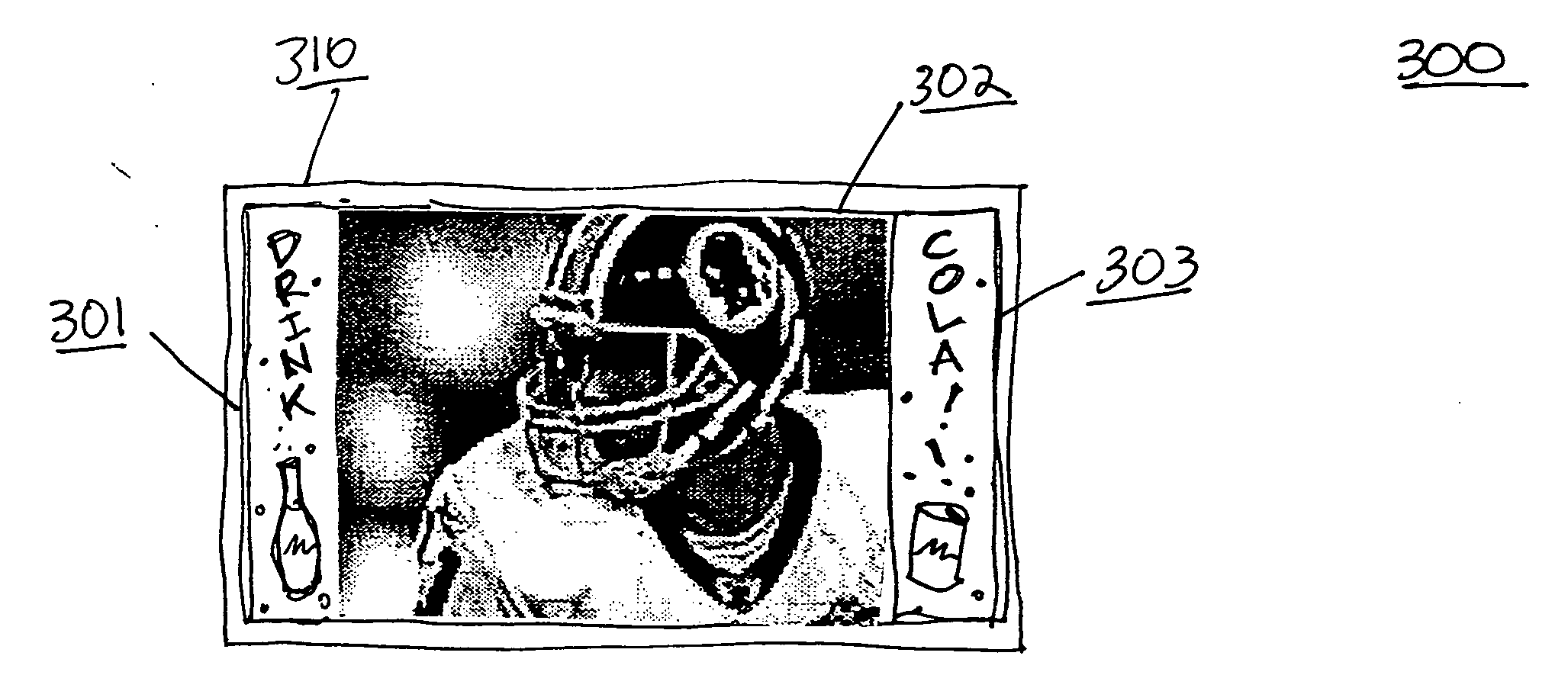
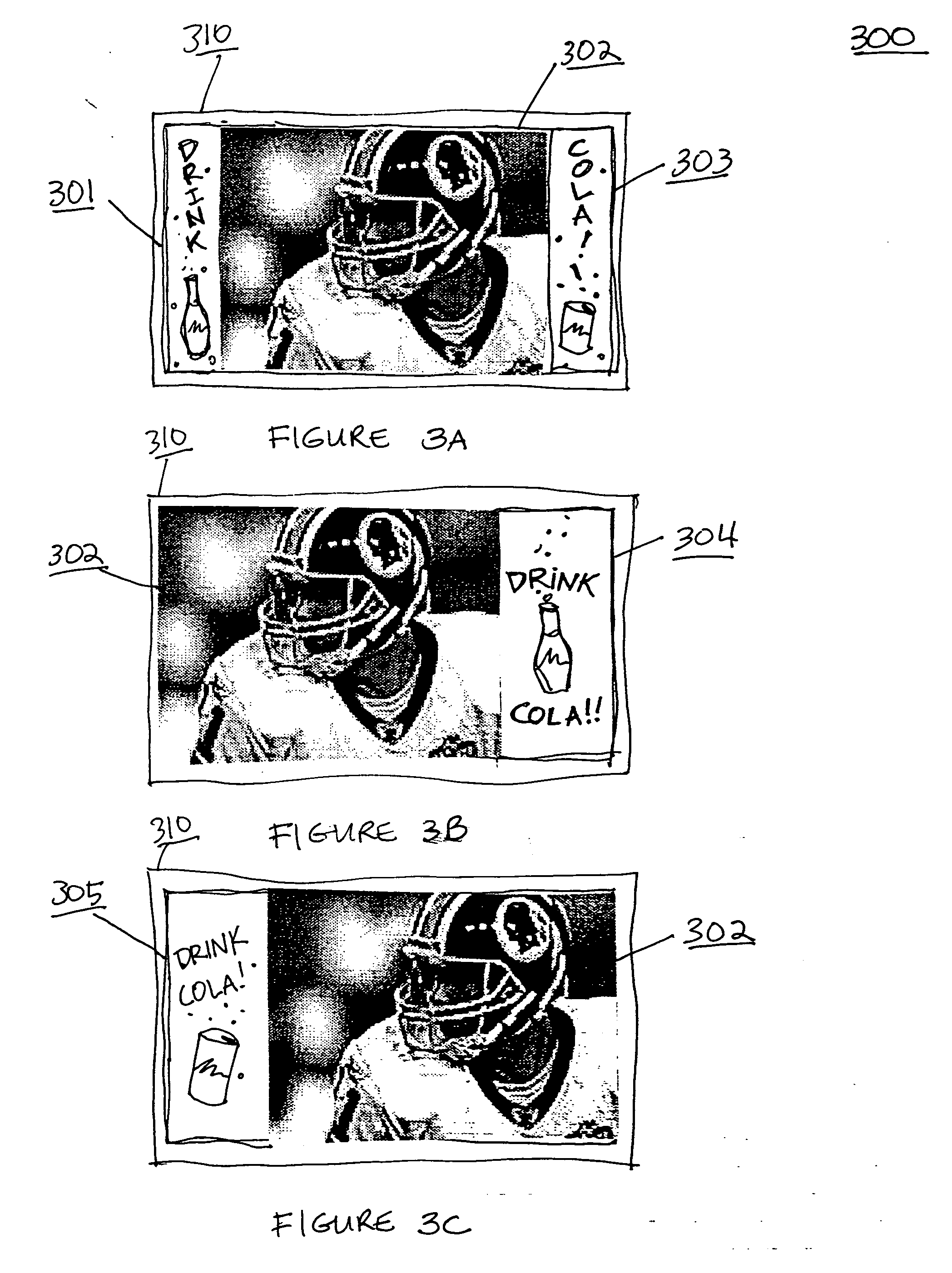
Method and apparatus for utilizing blank space on a high definition television screen
InactiveUS20060059514A1Television system detailsColor television detailsHigh-definition televisionHigh definition tv
A method and system for displaying media in the otherwise blank spaces remaining when a standard television signal is viewed on a high definition television screen and vice versa. In one embodiment, two separate media are accessed by a set top box for a high definition television screen. A standard television broadcasting signal is accessed as well as second media signal. The second media signal may consist of for example advertisements, program guide information, an internet browser, other media, etc. The standard television signal is rendered on a main portion of the high definition television screen, while the second media occupies the remaining space.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Electronic endoscope apparatus
InactiveUS7773110B2Simple structureSimple transmission structureTelevision system detailsEndoscopesHigh-definition televisionHigh definition tv
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Integrated multi-format audio/video production system
InactiveUS20080030614A1Improve compatibilityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoMass storage
Owner:SCHWAB BARRY H +1
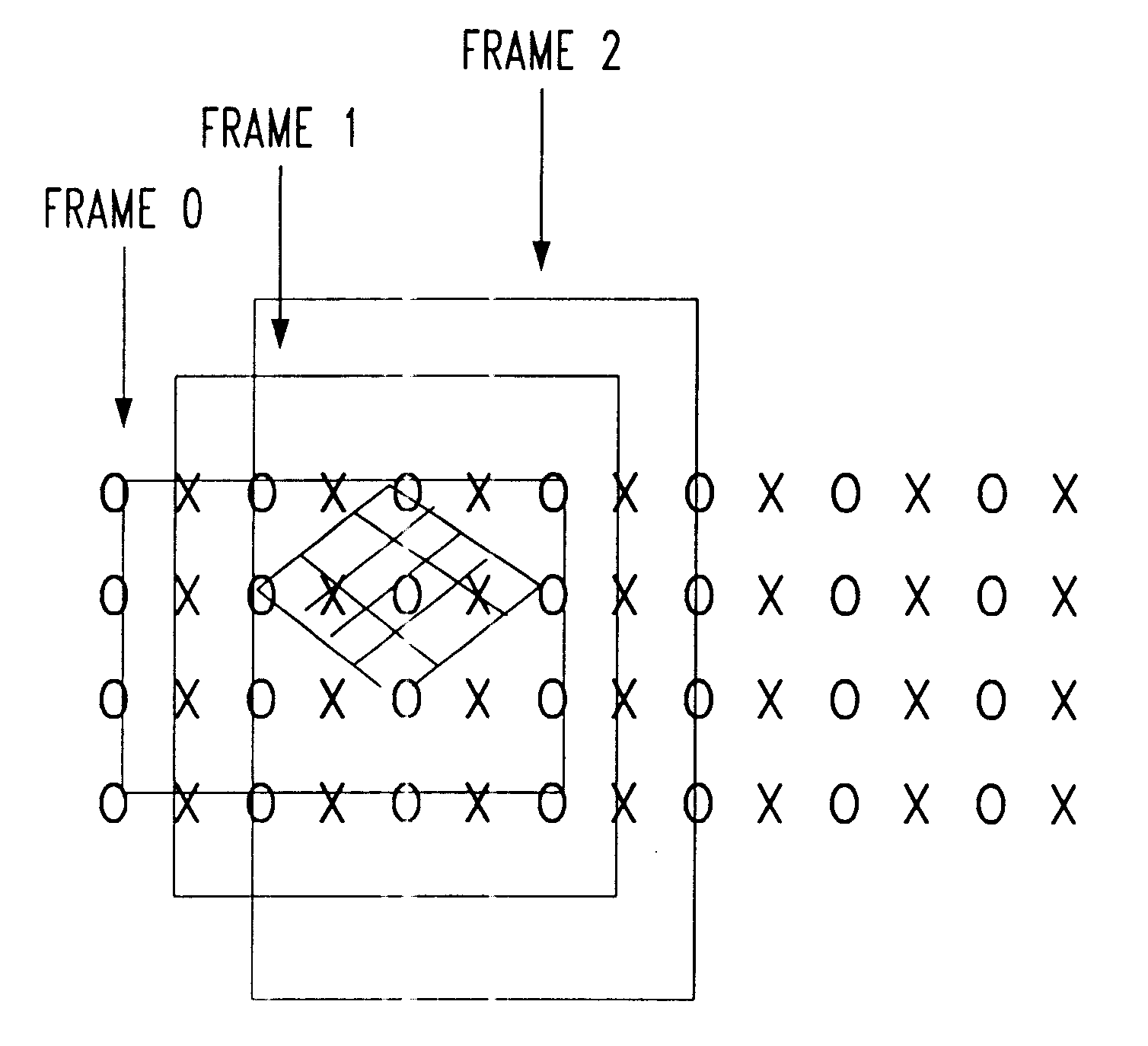
Methods and devices for time-varying selection and arrangement of data points with particular application to the creation of NTSC-compatible HDTV signals
InactiveUS6661463B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesHigh-definition televisionHigh definition tv
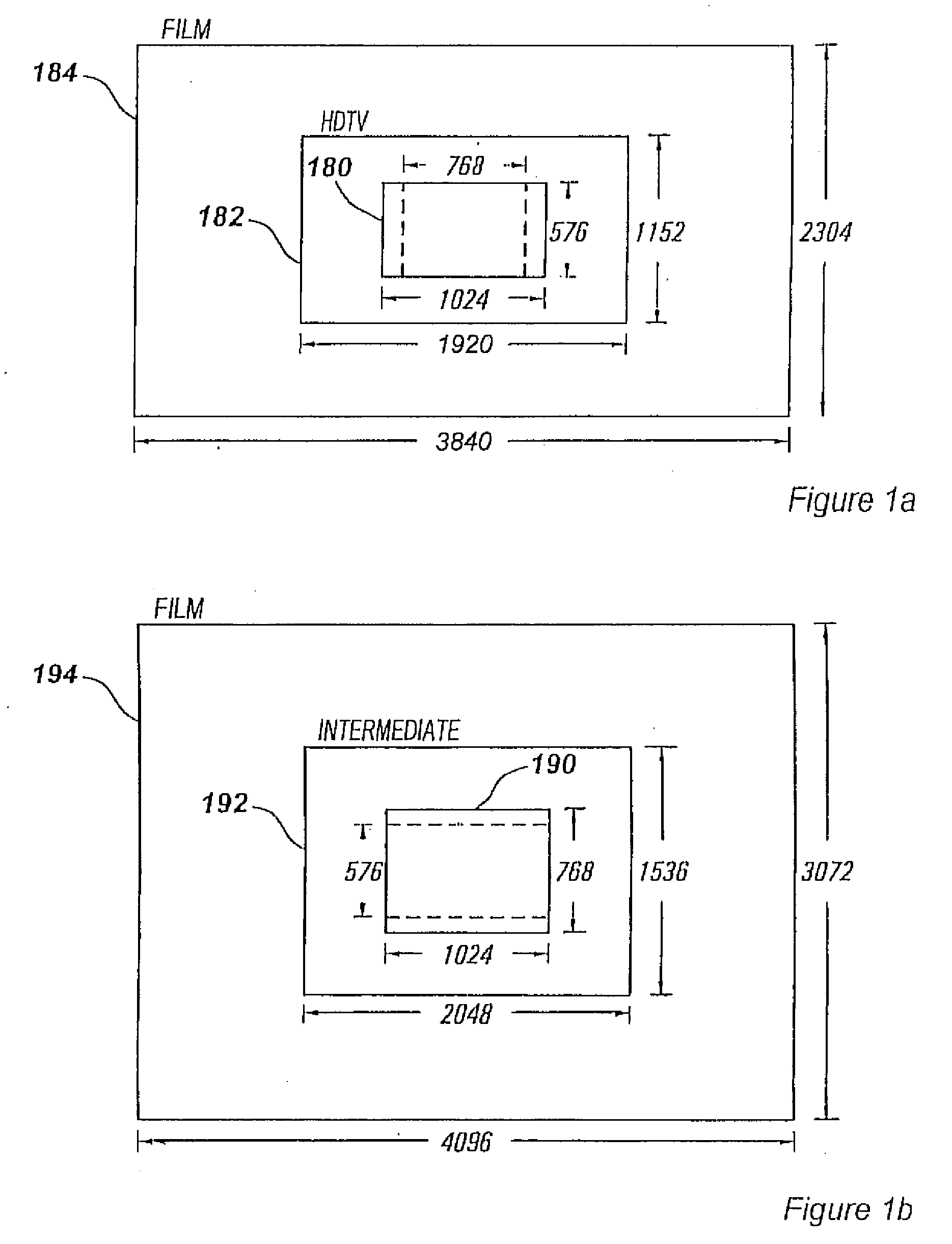
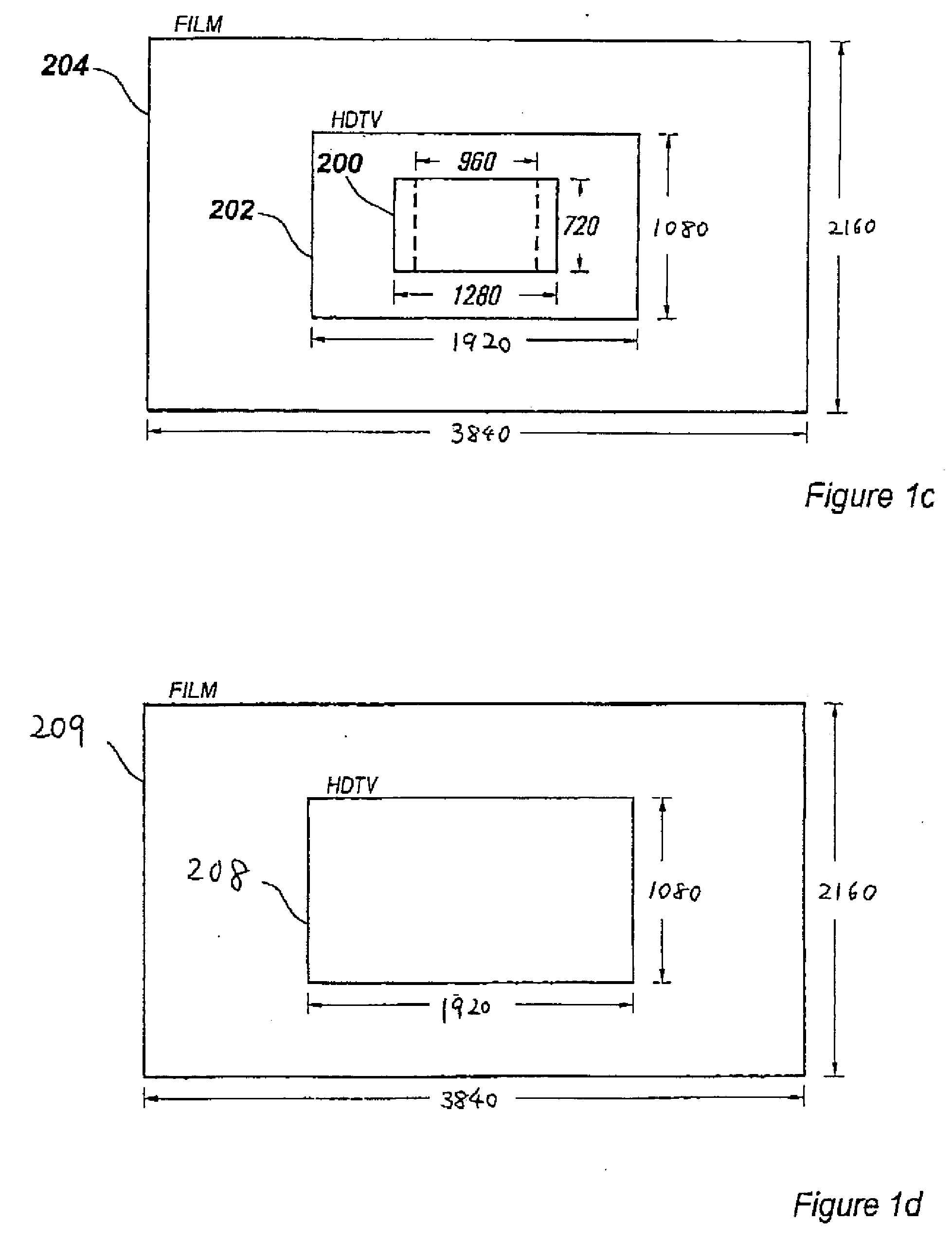
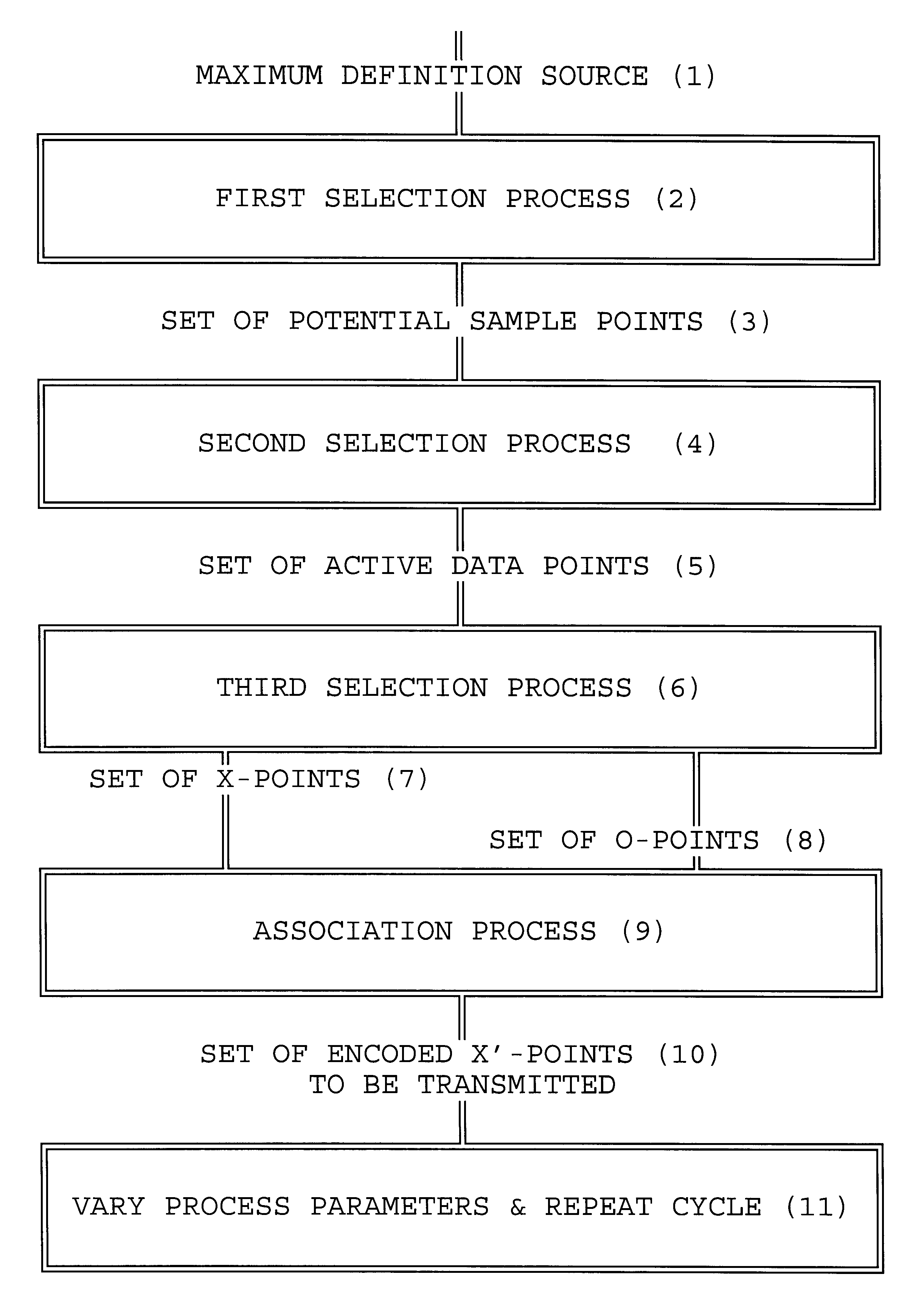
Processes for selecting, manipulating and arranging data points or pixels derived from information bearing signals are useful to reduce the bandwidth of, or improve the perceived quality of, such a signal as transmitted and displayed. The techniques utilize time-varying sampling schemes and take into account the characteristics of the human visual system. For each information frame, a subset (3) of all possible data points (1) is selected (2). A further subset of active data points (5) is selected (4) for which data will actually be sampled. The active points (5) are further divided (6) into points for which a value will be transmitted (x-points) (7) and points which will be sampled but for which no separate value will be transmitted (o-points) (8). A mathematical association between the x-points and o-points is made (9) and new values to be transmitted are calculated for the x-points (10). The parameters of the selection and association processes are varied in a non-trivial manner and the, now modified, cycle repeated (11) for subsequent data frames. In particular, the techniques may be used to process a high-definition television signal prior to its storage, or transmission over a low-bandwidth channel.
Owner:DAVID MICHAEL GESHWIND
In-play camera associated with headgear used in sporting events and configured to provide wireless transmission of captured video for broadcast to and display at remote video monitors
InactiveUS20090141130A1Television system detailsColor television detailsHigh definition tvHigh-definition television
Owner:FRONT ROW TECH
Decorative cover frame assembly for selectively concealing a flat panel or high definition television display
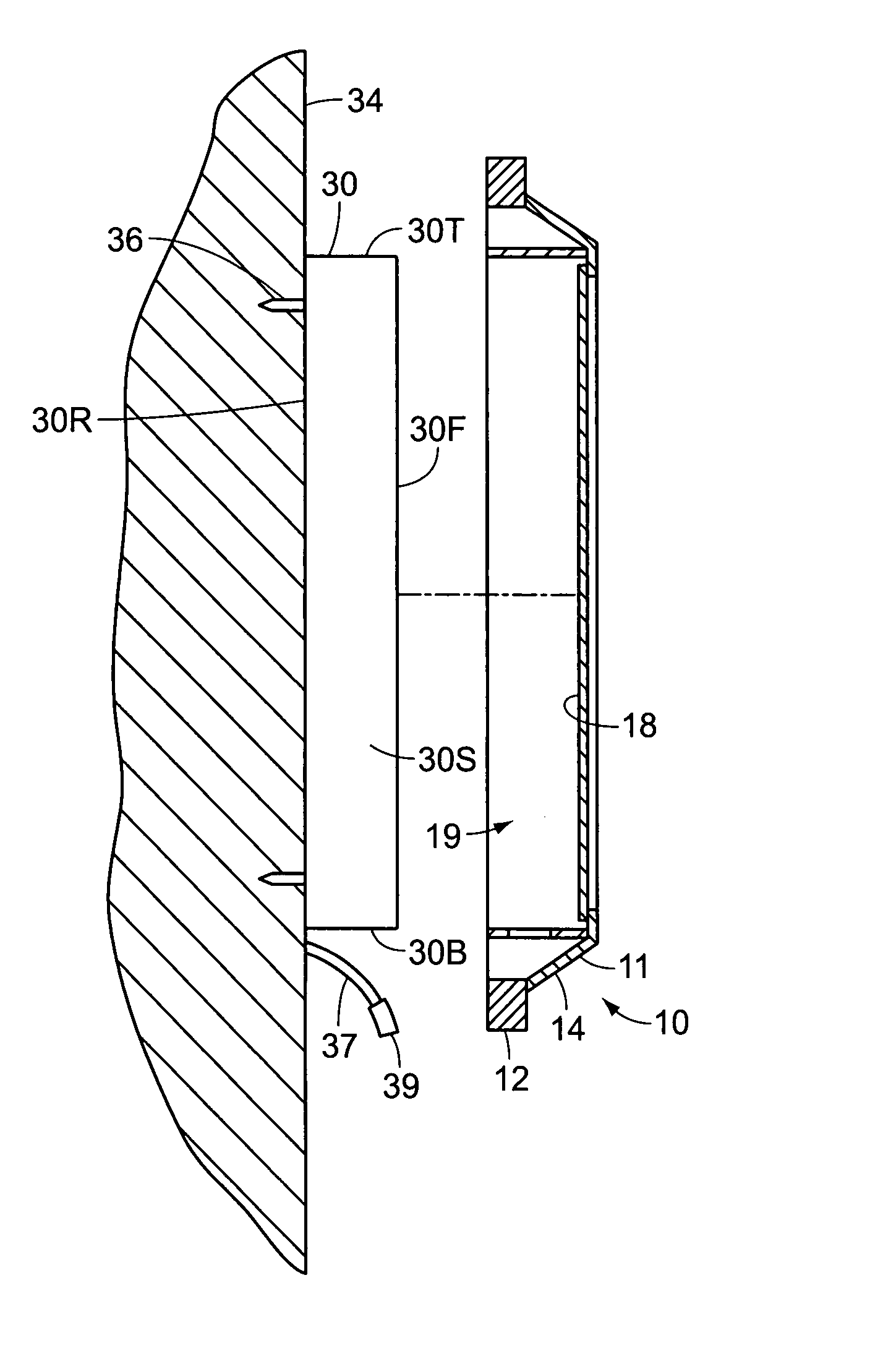
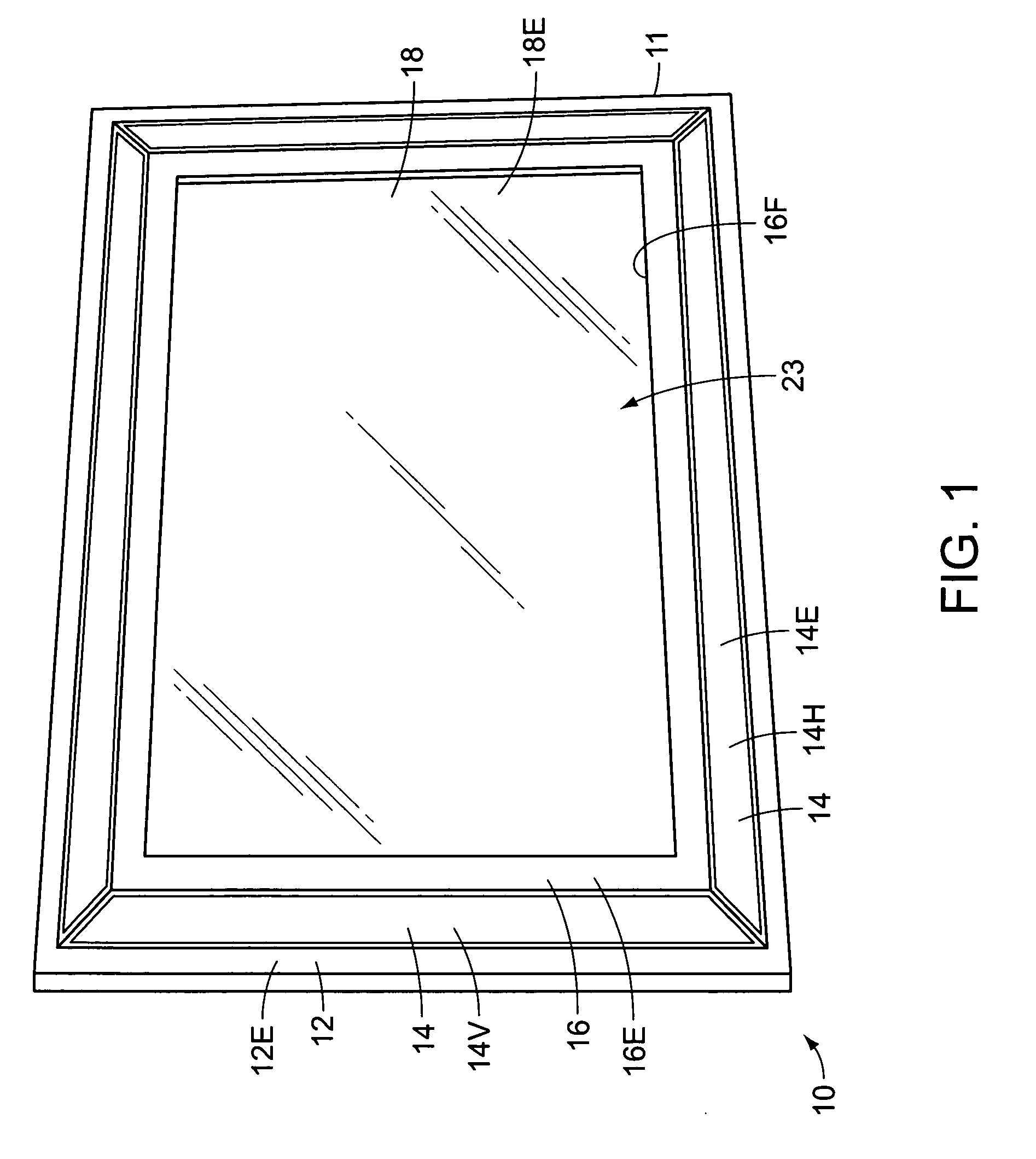
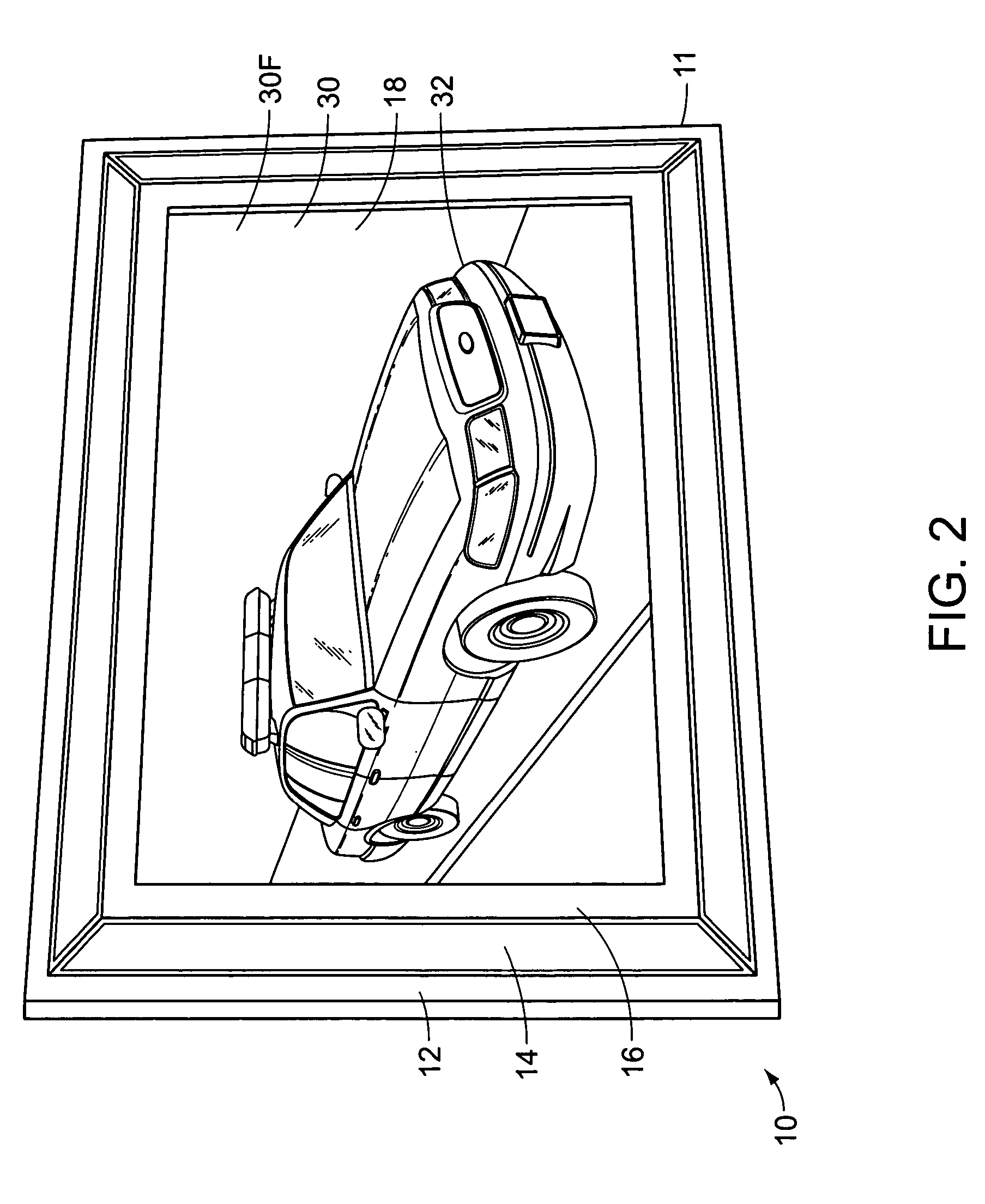
InactiveUS7287737B2Television system detailsPicture framesHigh-definition televisionHigh definition tv
A cover frame assembly for use in conjunction with an existing flat panel display of a display device such as a high definition television. The cover frame assembly comprises an outer frame, and a one-way mirror attached within the outer frame. After mounting the flat panel display to a wall, the outer frame is selectively extended over the flat panel display and is supported by the flat panel display. The images projected by the flat panel display upon activation of the display device are easily seen through the one-way mirror. When the display device is deactivated, the reflective surface of the one-way mirror obscures the flat panel display, and the combined frame assembly and flat panel display appear to be a decorative, wall mounted mirror.
Owner:ROSSI LUIS
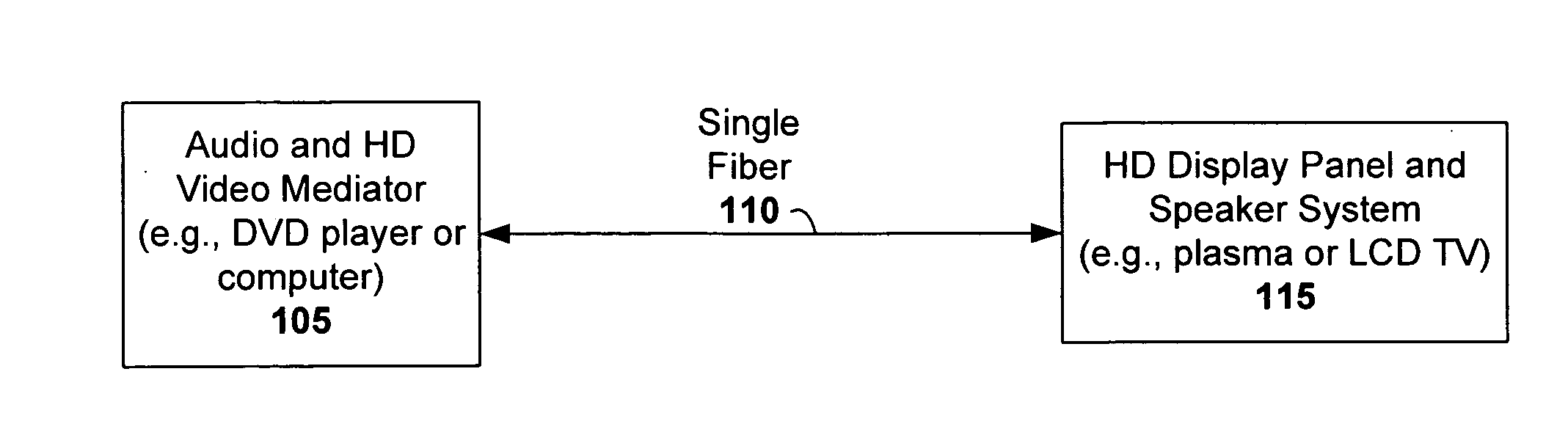
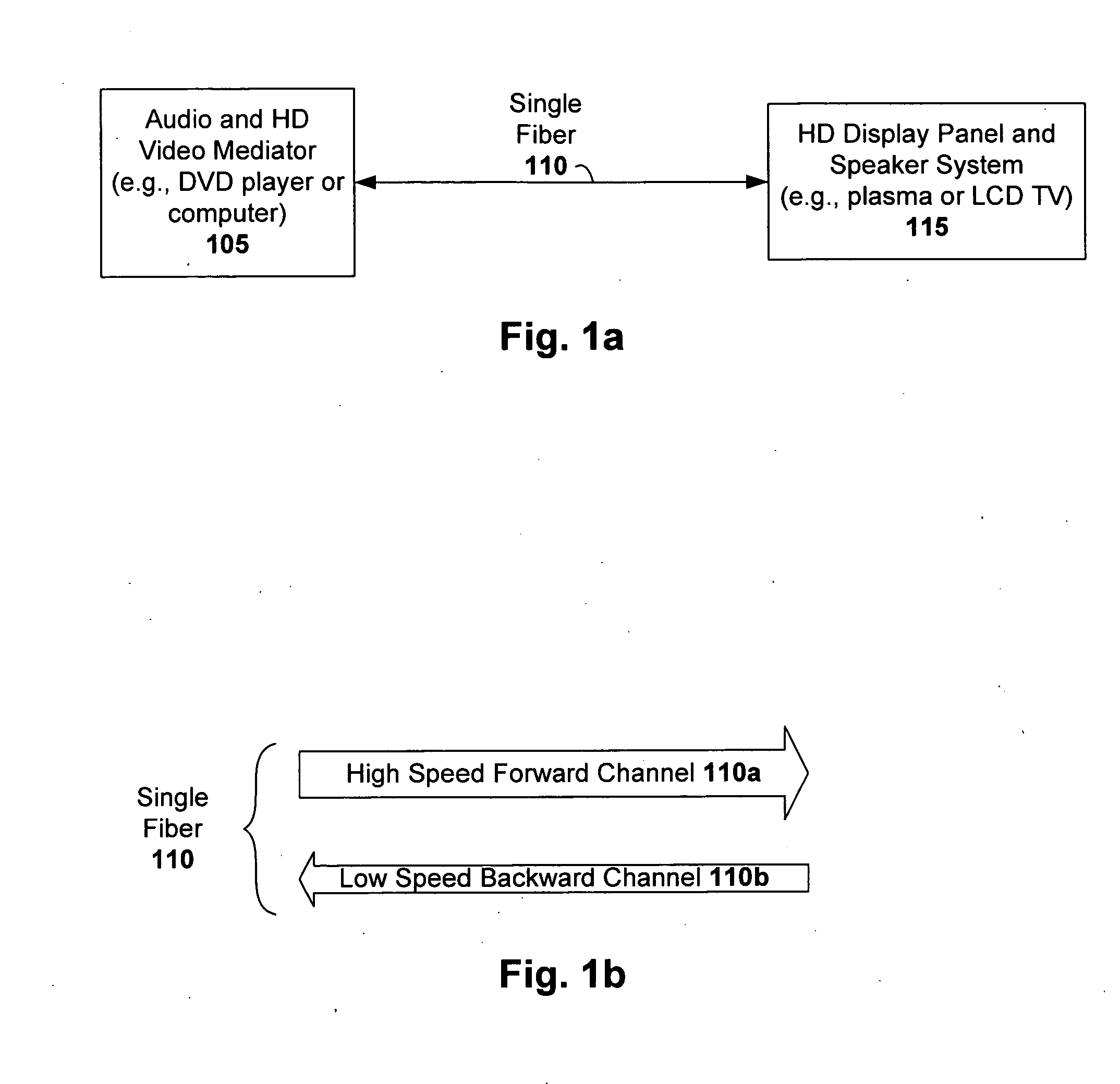
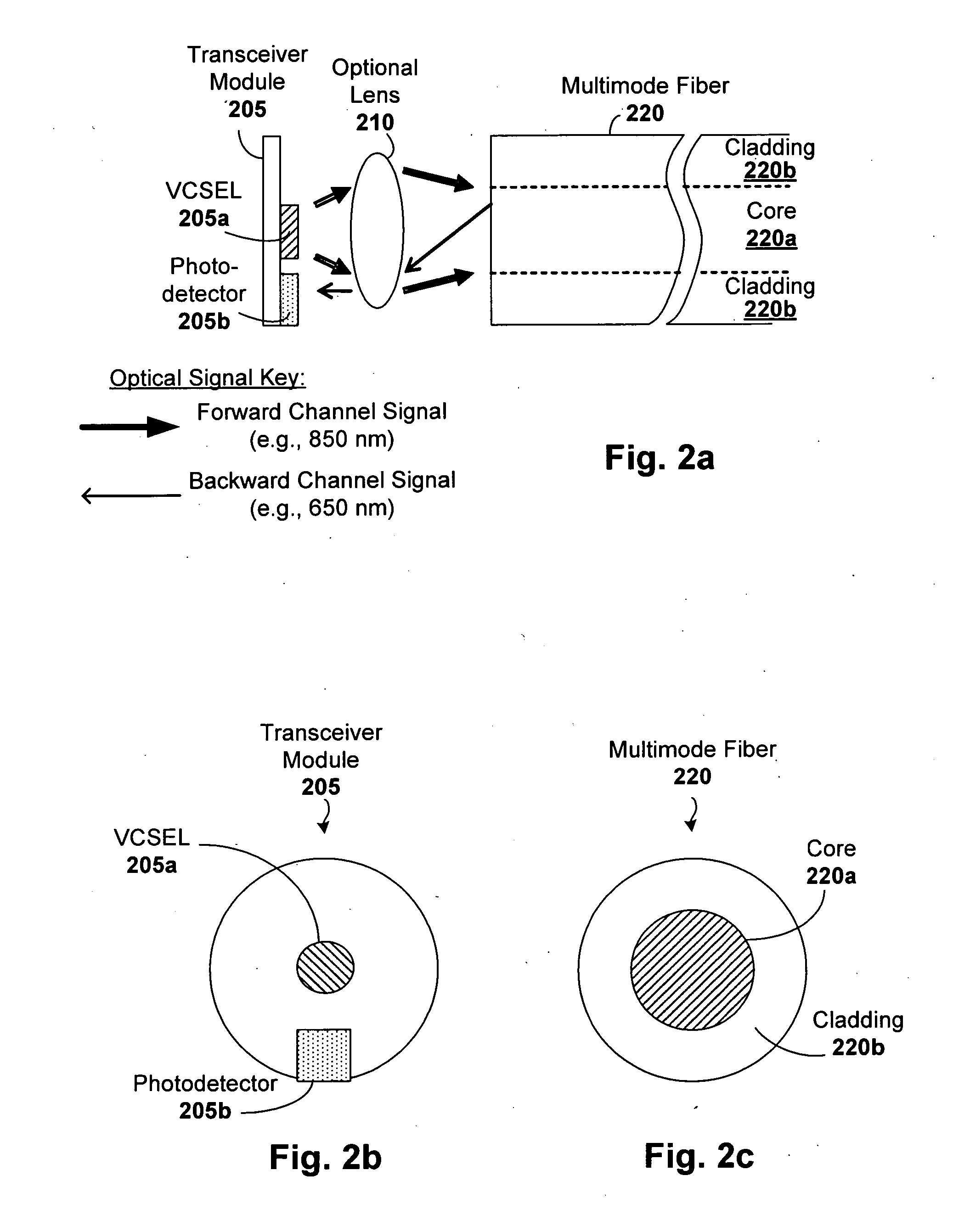
Bidirectional HDCP transmission module using single optical fiber
InactiveUS20070003288A1Low data rateCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectromagnetic transmissionTelecommunications linkPhotodetector
Owner:OWLINK TECH
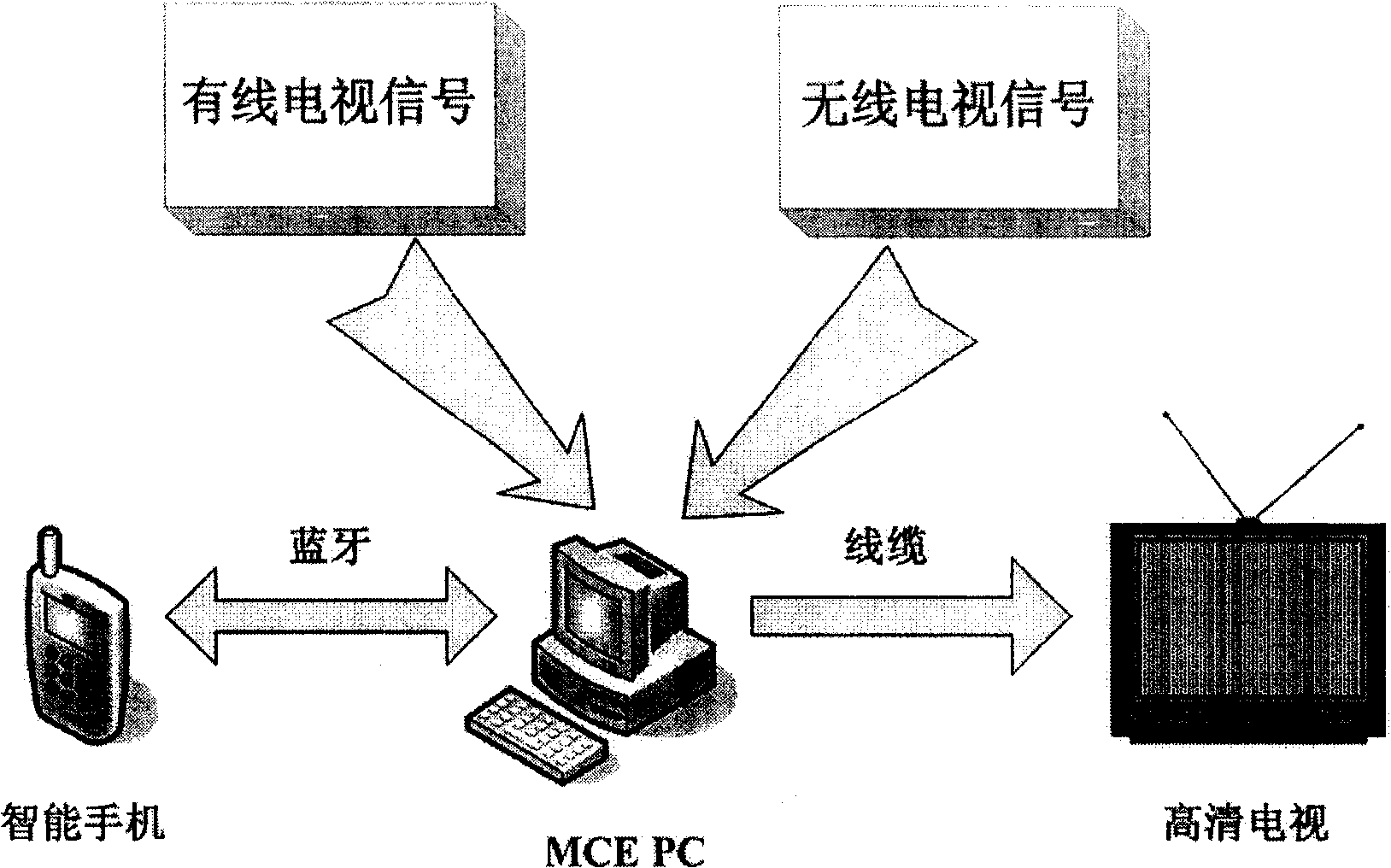
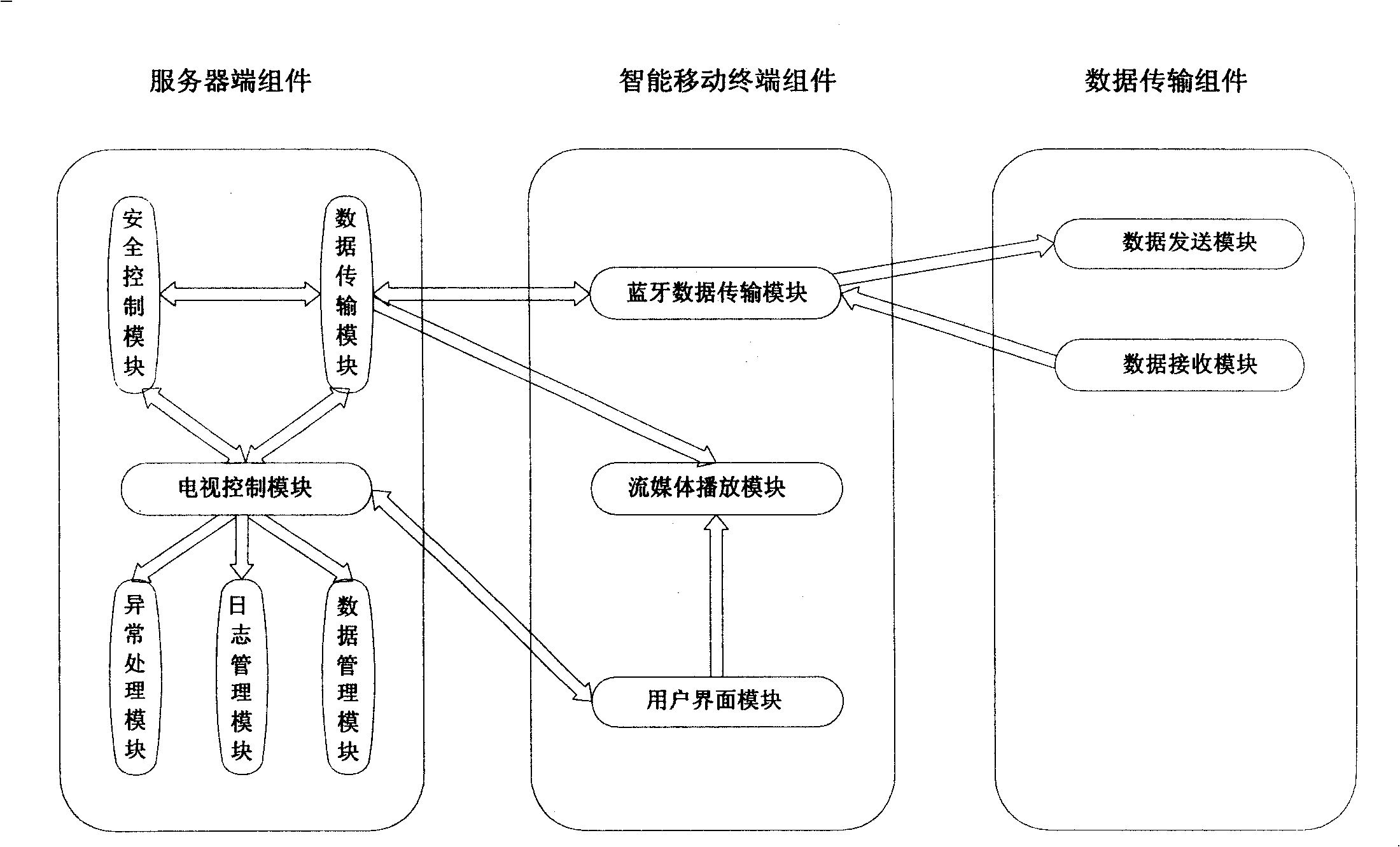
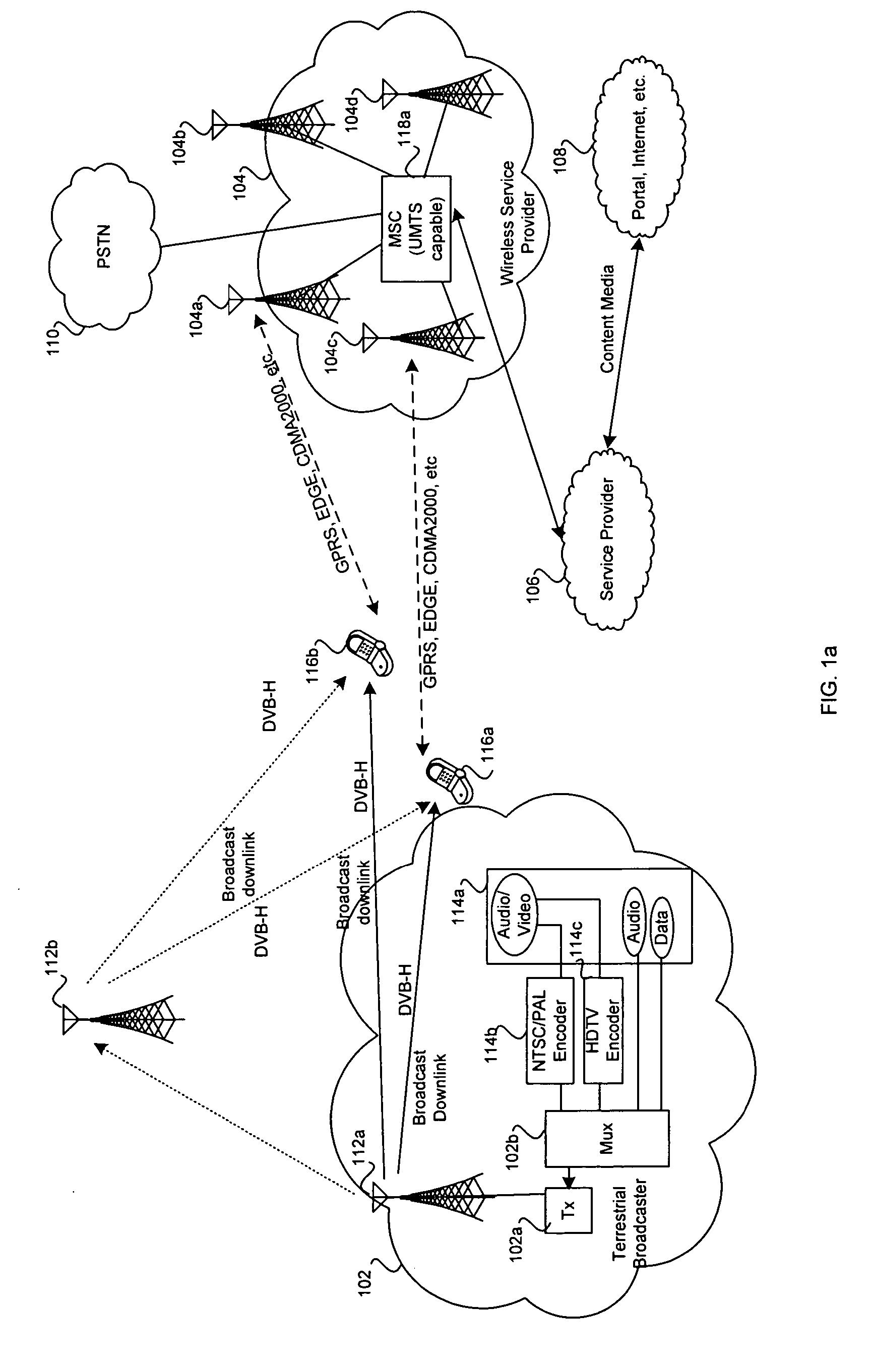
Telecontrol system for intelligent mobile terminal television
InactiveCN101325666AEnhanced interactionReliableTelevision system detailsTelephonic communicationExtensibilitySignal on
The invention provides an intelligent mobile terminal television remote control system, the hardware frame of which comprises: (1) a intelligent handset terminal, used as a remote terminal for realizing multifunctional remote control operation, having a blue tooth communication function and equipped with Microsoft Windows Mobile 5.0 operation system; (2) a media center PC terminal, used as a server side for processing and controlling data, equipped with Microsoft Windows XP Media Center Edition operation system; (3) a high definition television terminal, used as display terminal for receiving television signals transmitted form the media centre PC terminal and displaying the signals on screen; the above hardware frame realizes the mentioned functions by the server side assembly, the intelligent mobile terminal assembly and a data transmitting assembly. The invention adopts blue tooth communication technology and utilizes intelligent handset terminal to completely realize the function of using handset to remote control television and displaying the sub channel program on the intelligent handset. The system has reliability, robustness, easy-maintainability and expansibility, and lays a good base for establishing more and better applications.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
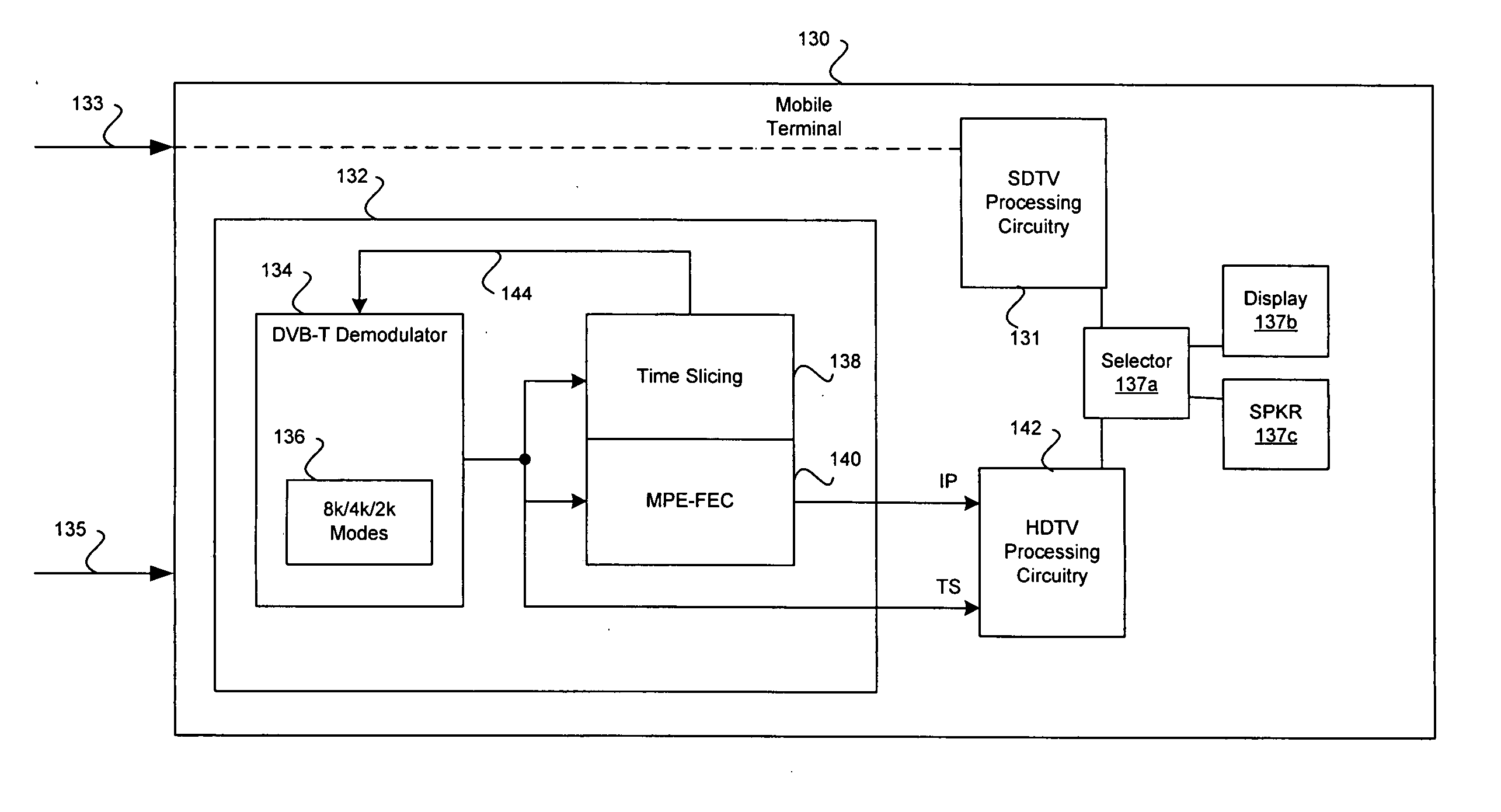
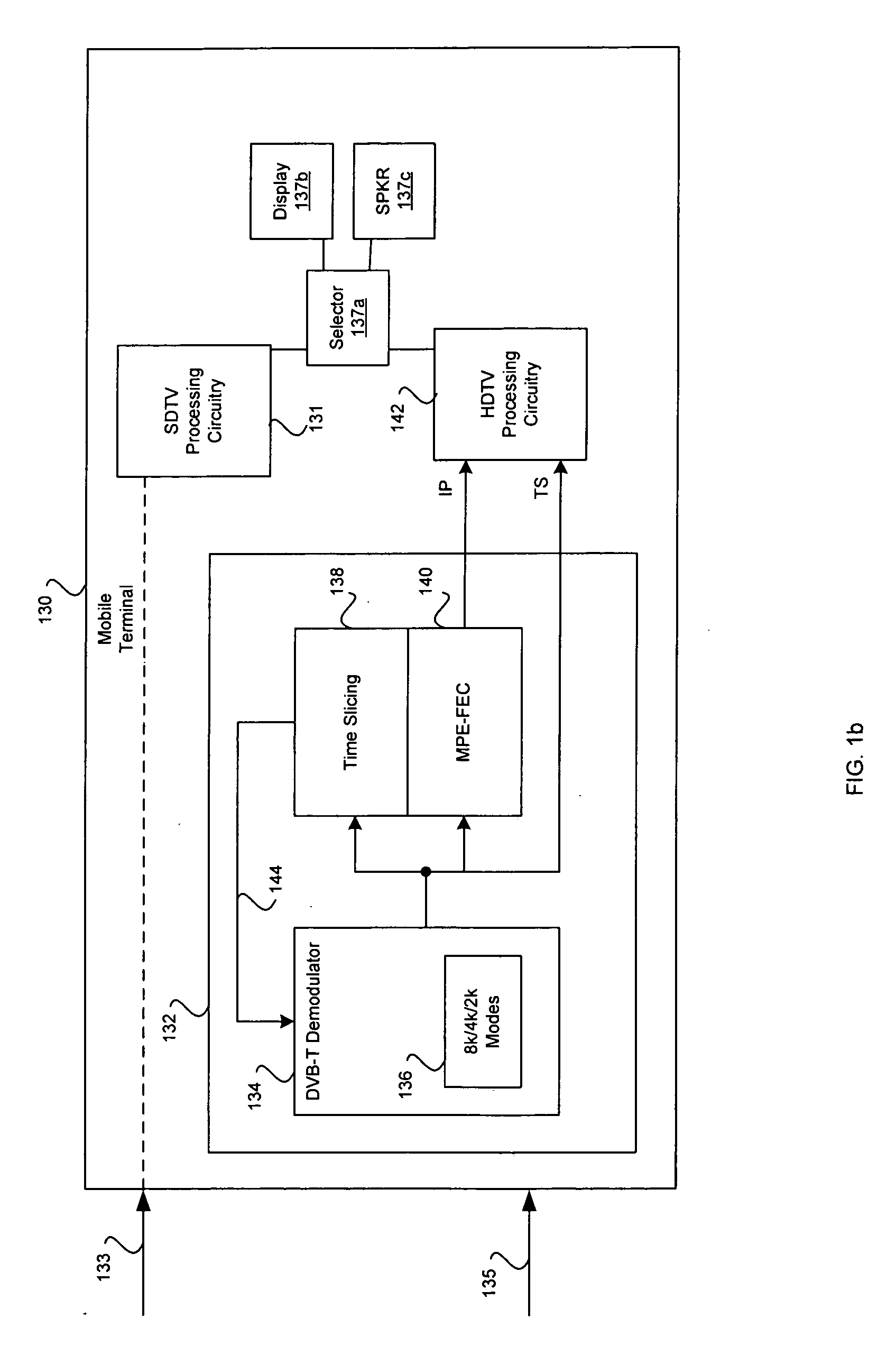
Method and system for concurrent communicating of high definition television (HDTV) and standard definition television (SDTV) information in a multistandard wireless communication system
InactiveUS20060127032A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionHigh definition tvHigh-definition television
Methods and systems for communicating information in a network are disclosed herein and may include receiving, at a mobile terminal, a high definition television (HDTV) signal via a DVB-H downlink communication path. A standard definition television (SDTV) signal may be simultaneously received at the mobile terminal via a cellular downlink communication path. The SDTV signal and the HDTV signal may comprise the same media content. The HDTV signal received via the DVB-H downlink communication path and the SDTV signal received via the cellular downlink communication path may be selected in the mobile terminal for processing. The selection may be based on a preference indicated via the mobile terminal. The selection may also be based on at least one downlink channel condition indicator corresponding to the HDTV signal or the SDTV signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
MOS or CMOS sensor with micro-lens array
InactiveUS7196391B2Increase the number of pixelsSmall sizeSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesHigh-definition televisionCMOS sensor
Owner:E PHOCUS
Single integrated high definition television (HDTV) chip for analog and digital reception
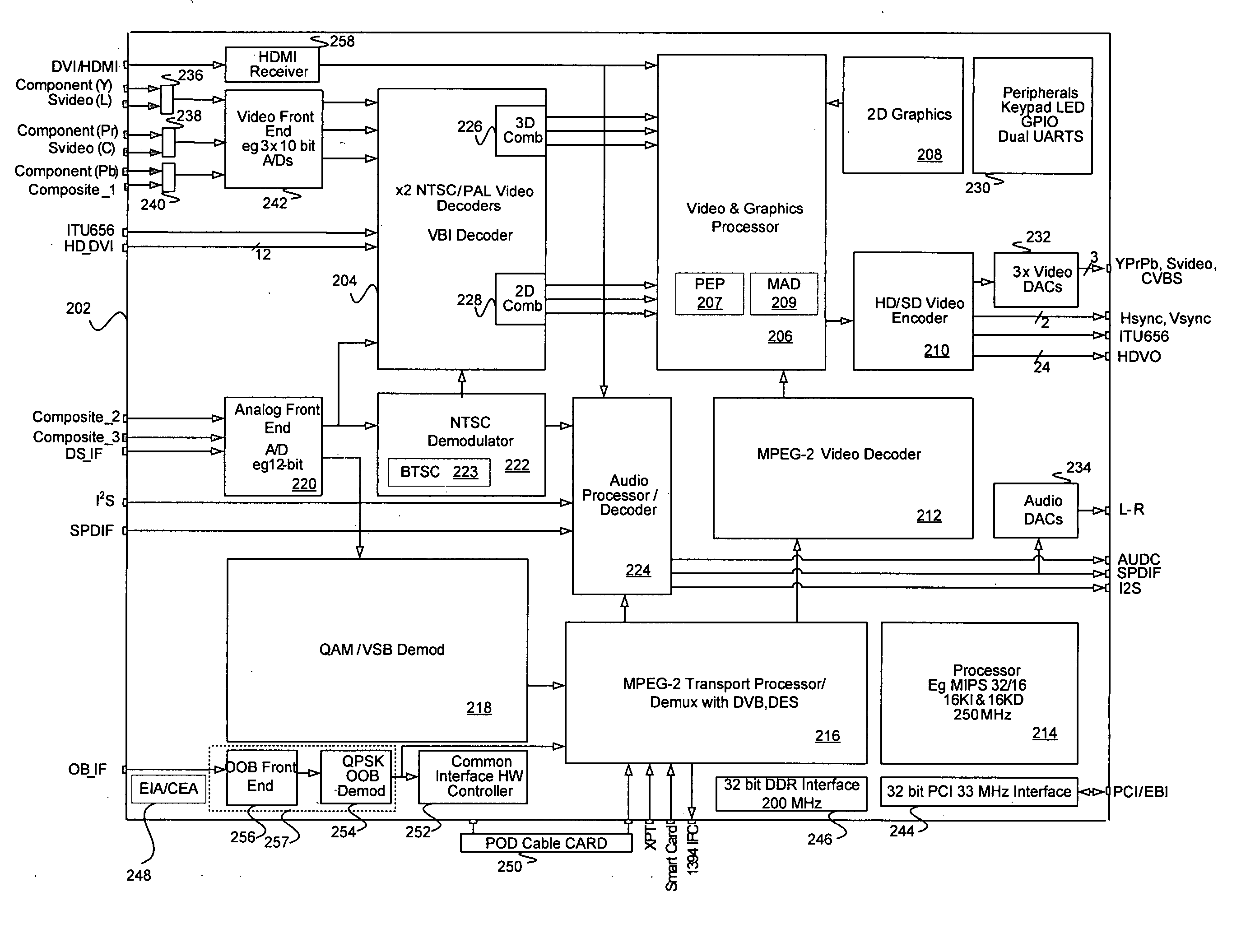
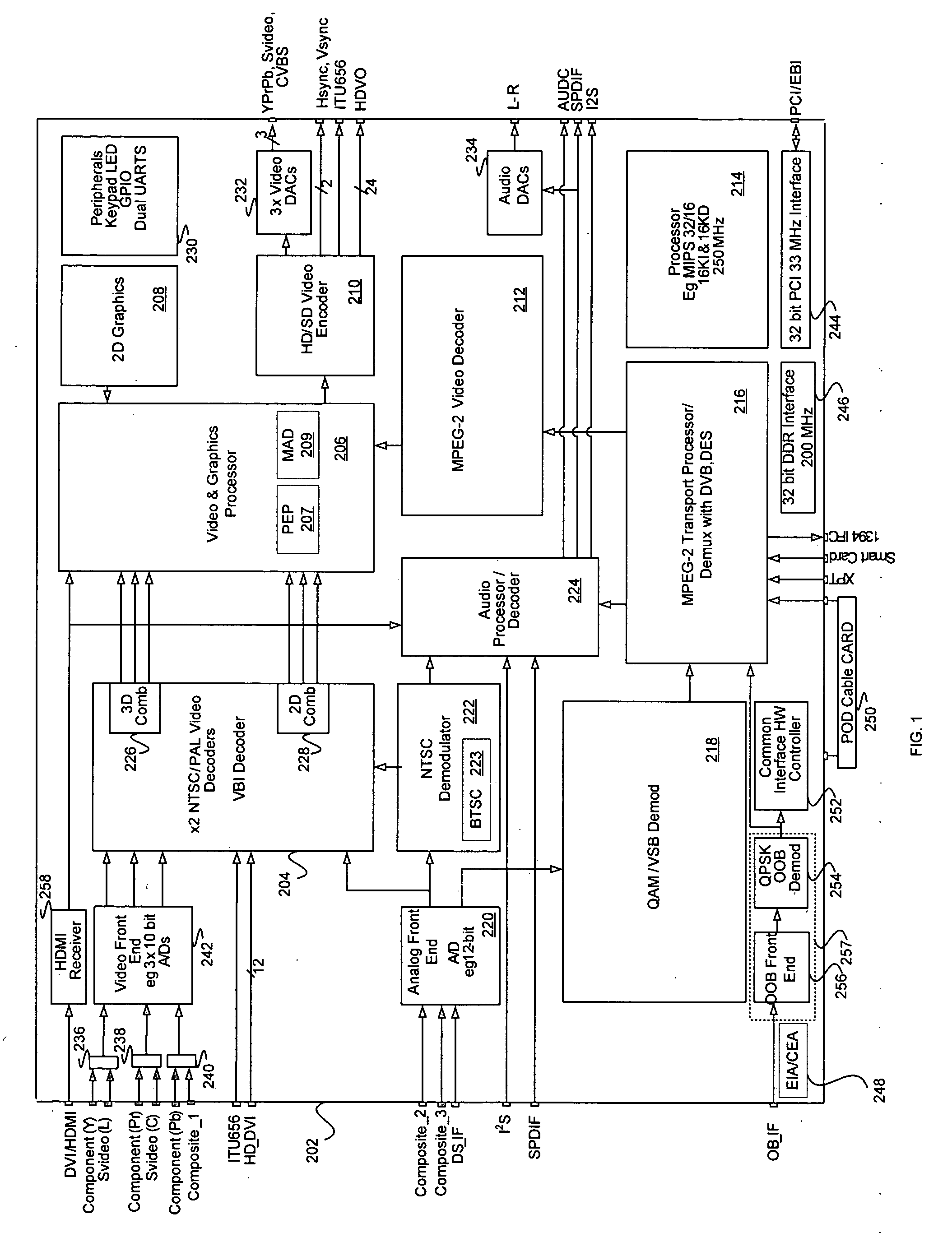
InactiveUS20060158568A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital videoHigh-definition television
Methods and systems for processing television signals are disclosed herein, and may comprise decoding a first analog video signal via an integrated circuit comprising circuitry for decoding and processing digital video signals. A second analog video signal may be simultaneously decoded via the integrated circuit. A first video output corresponding to the decoded first analog video signal and a second video output corresponding to the decoded second analog video signal may be simultaneously generating via the integrated circuit. An out-of-band signal corresponding to the decoded first or second analog video signal may be received via the integrated circuit. The received out-of-band signal may be processed via the integrated circuit. The first analog video signal and the second analog video signal may comprise an NTSC signal, a composite signal, an S-video signal, and / or a component signal. The digital video signals may be decoded via the integrated circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
HDMI multiplexing method, HDMI, and equipped provided with HDMI
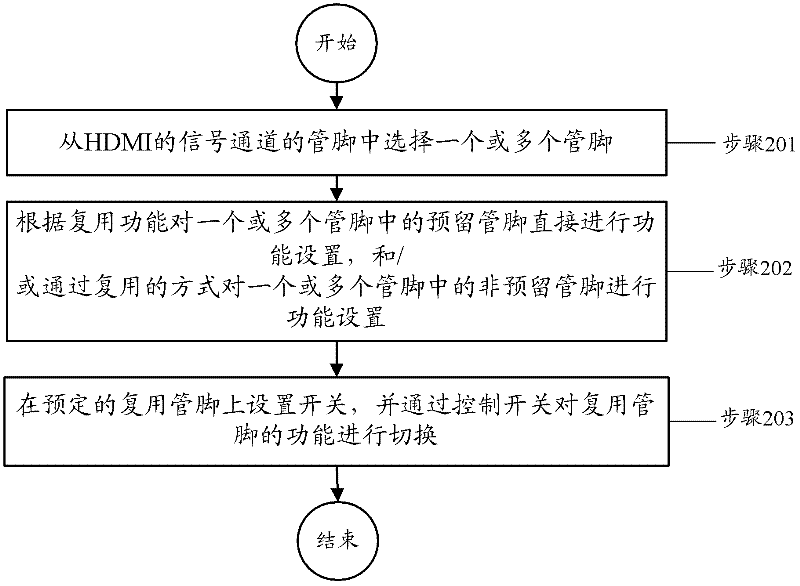
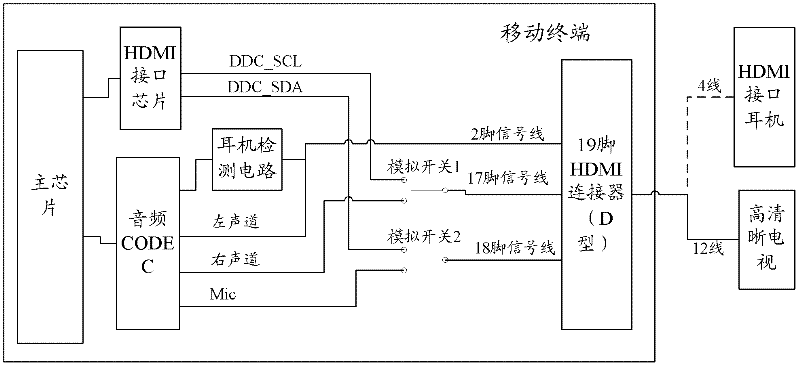
ActiveCN102572352ASolve the problem that the function cannot be extended to cause a single functionTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsHigh-definition televisionMultiplexing
The invention discloses an HDMI (high-definition multimedia interface) multiplexing method, an HDMI, and equipment provided with the HDMI, wherein the method comprises the following steps: one or more pins is (are) selected from pins for signal channel of the HDMI; function setting is directly performed to a reserved pin in the one or more pins according to the multiplexing function, and / or functional setting is performed on a non-reserved pin in the one or more pins in a multiplexing way; and a switch is arranged on a preset multiplexing pin, and then the functions of the multiplexing pin are switched through a control switch. By virtue of the technical scheme provided by the invention, that a terminal HDMI can carry out relevant function application on non-high-definition television when relevant external accessories are connected can be achieved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Image processor for and method of upscaling and denoising using contextual video information
ActiveUS20140301661A1Small sizeLight weightImage enhancementImage analysisHigh-definition televisionLow noise
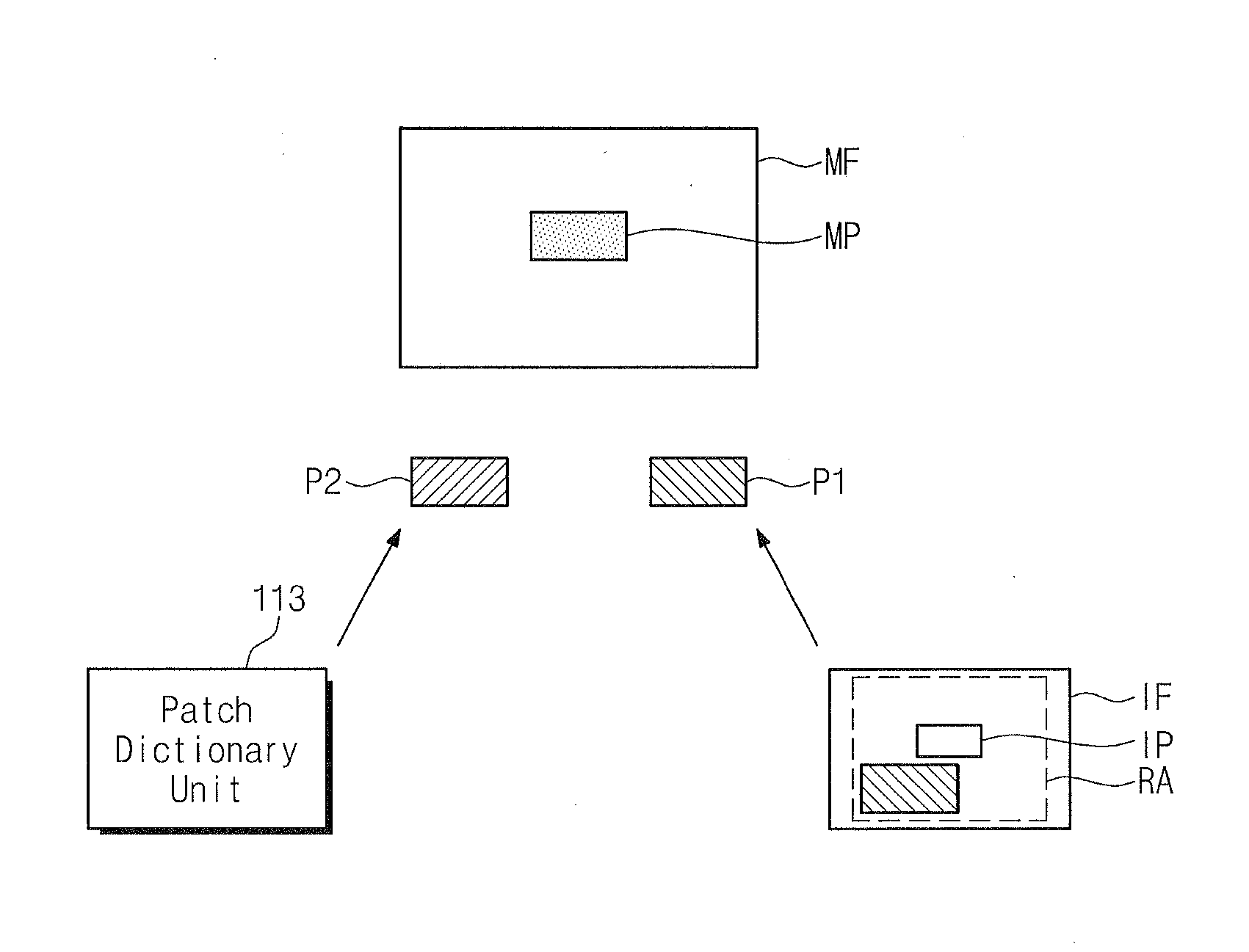
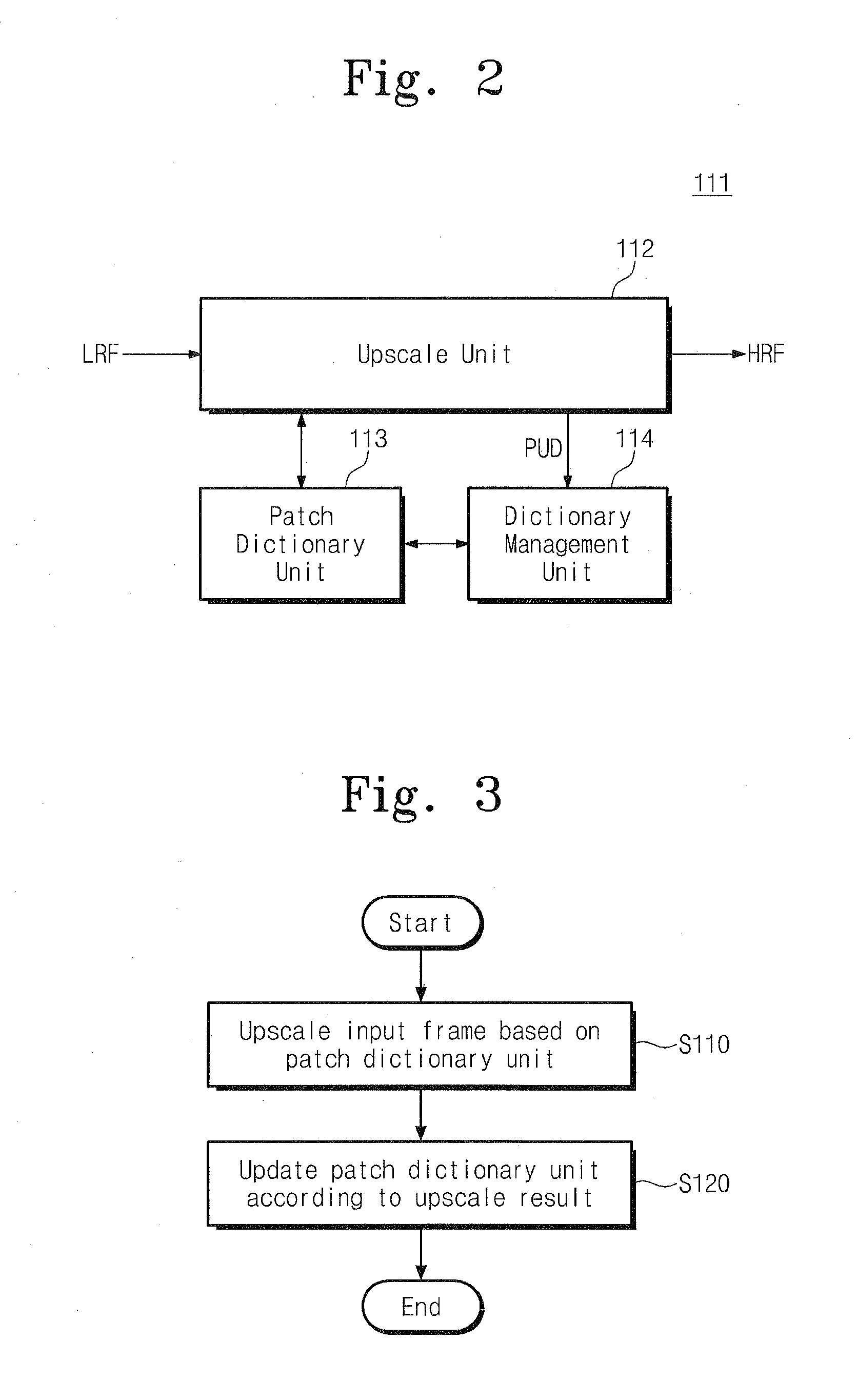
High quality upscaling and denoising are required in mobile imaging devices that do not contain high quality lenses. Such is also required in order to scale up standard-definition video content for display in high-definition television screens.The disclosed method uses contextual information obtained during upscaling and / or denoising of frames. Relevant correspondences between patches within a frame and between frames, are detected, managed and exploited. The correspondence information is simultaneously used and updated while video frames are being processed. Two approaches may be used: 1. keeping, searching for and updating a database of useful patches, by adding frequently visible similar patches, aggregating high-frequency, low-noise information associated with the similar patches, and removing less-observed patches; 2. Using the high-resolution and noise-reduced information that was collected from earlier video frames, and is expressed by the output of latest processed frame, for upscaling and / or noise-reducing the next processed frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for sending low rate data on a packet basis in an 8-VSB standard data packet stream
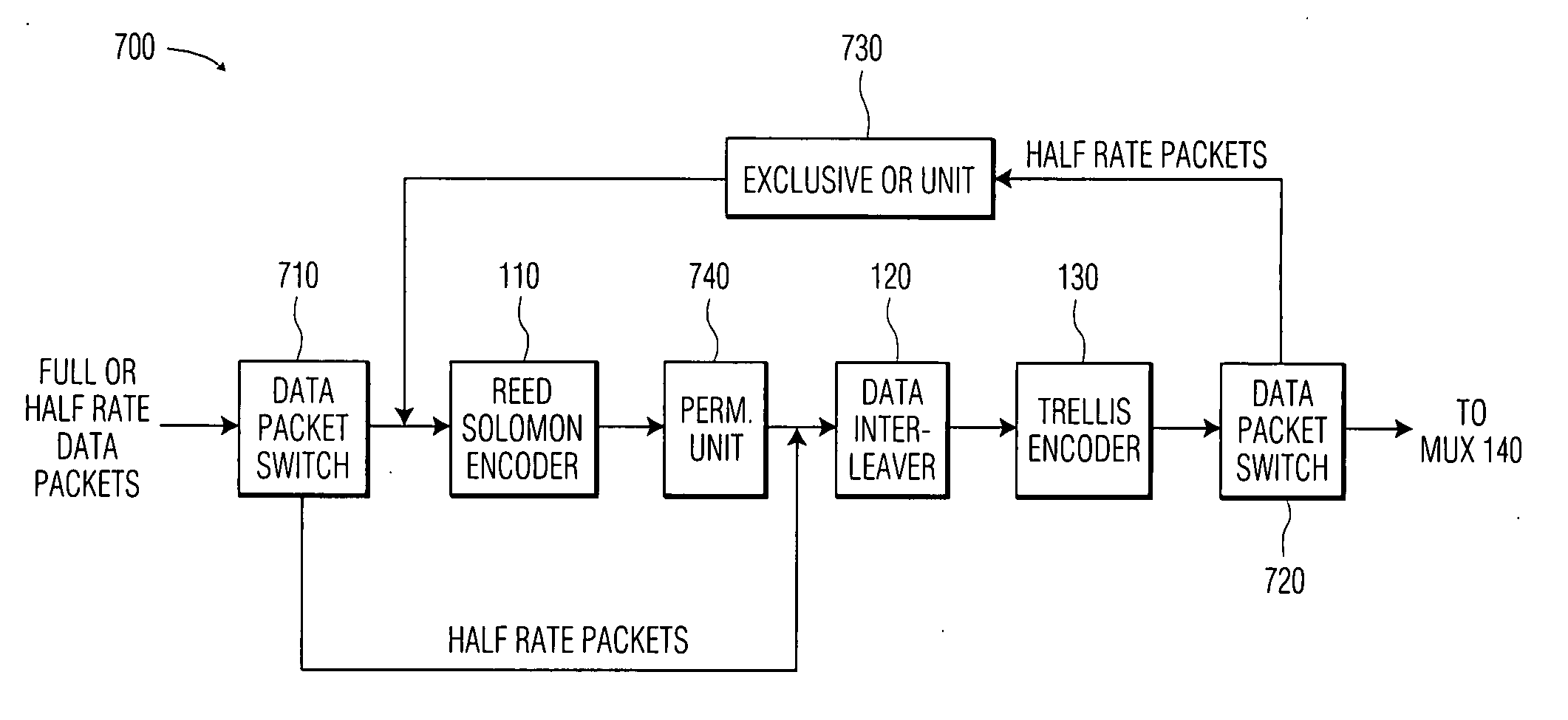
InactiveUS20050052571A1Less dataImprove the immunityPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesHigh-definition televisionData pack
There is disclosed a system and method for sending low rate data on a packet basis in an 8-VSB standard data packet stream. The system of the invention comprises an 8-VSB signal transmitter that is capable of transmitting either standard full rate data packets or low rate data packets. A low rate data packet contains less data than is normally contained in a standard data full rate data packet. Each data byte in a low rate data packet contains information bearing bits and non-information bearing bits. The system is capable of assigning appropriate bit values to the non-information bearing bits in each data byte of a low rate data packet so that each low rate data packet will be properly encoded for transmission within an 8-VSB standard data packet stream. High definition television signals composed of low rate data packets possess increased resistance to noise and multipath channels.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for time division multiplexing of asynchronous video and data signals
InactiveUS7110457B1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningHigh definition tvData stream
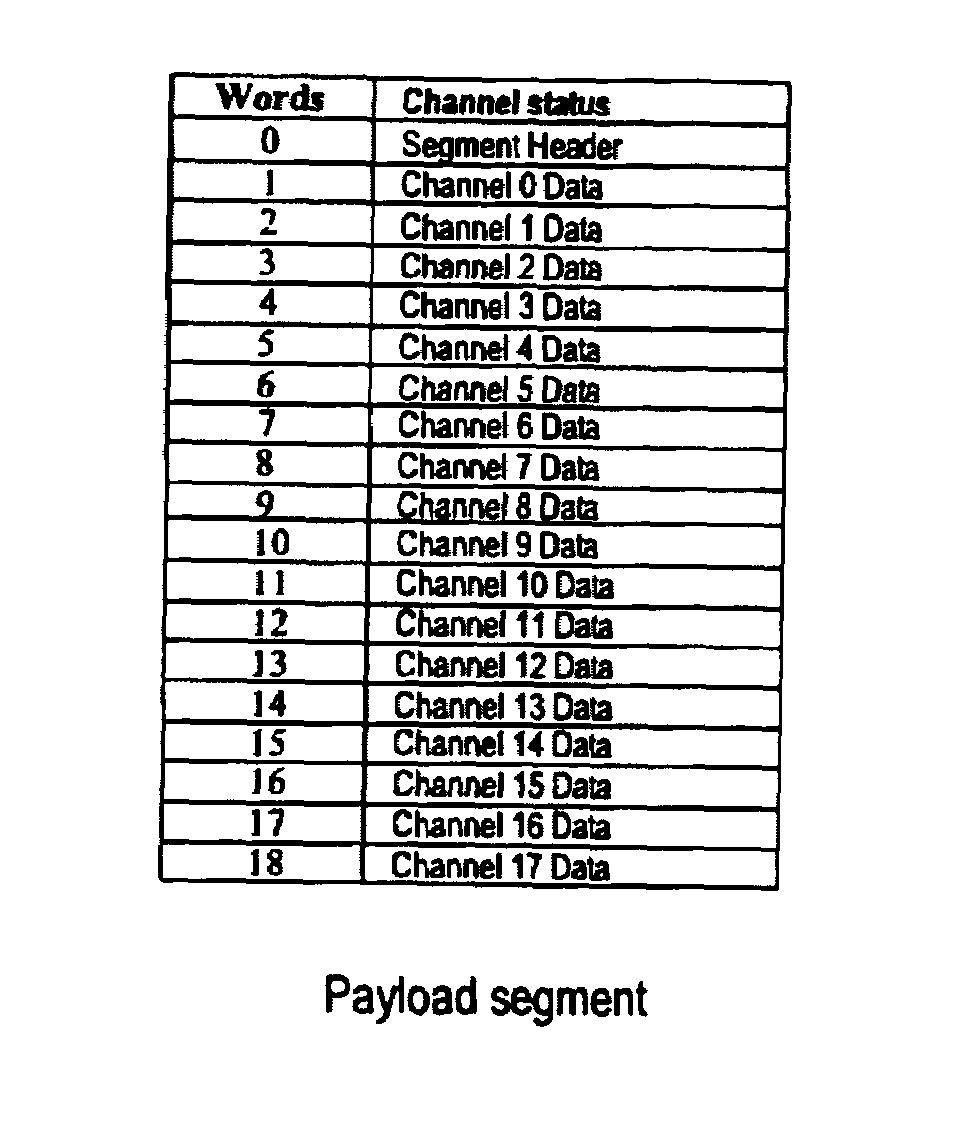
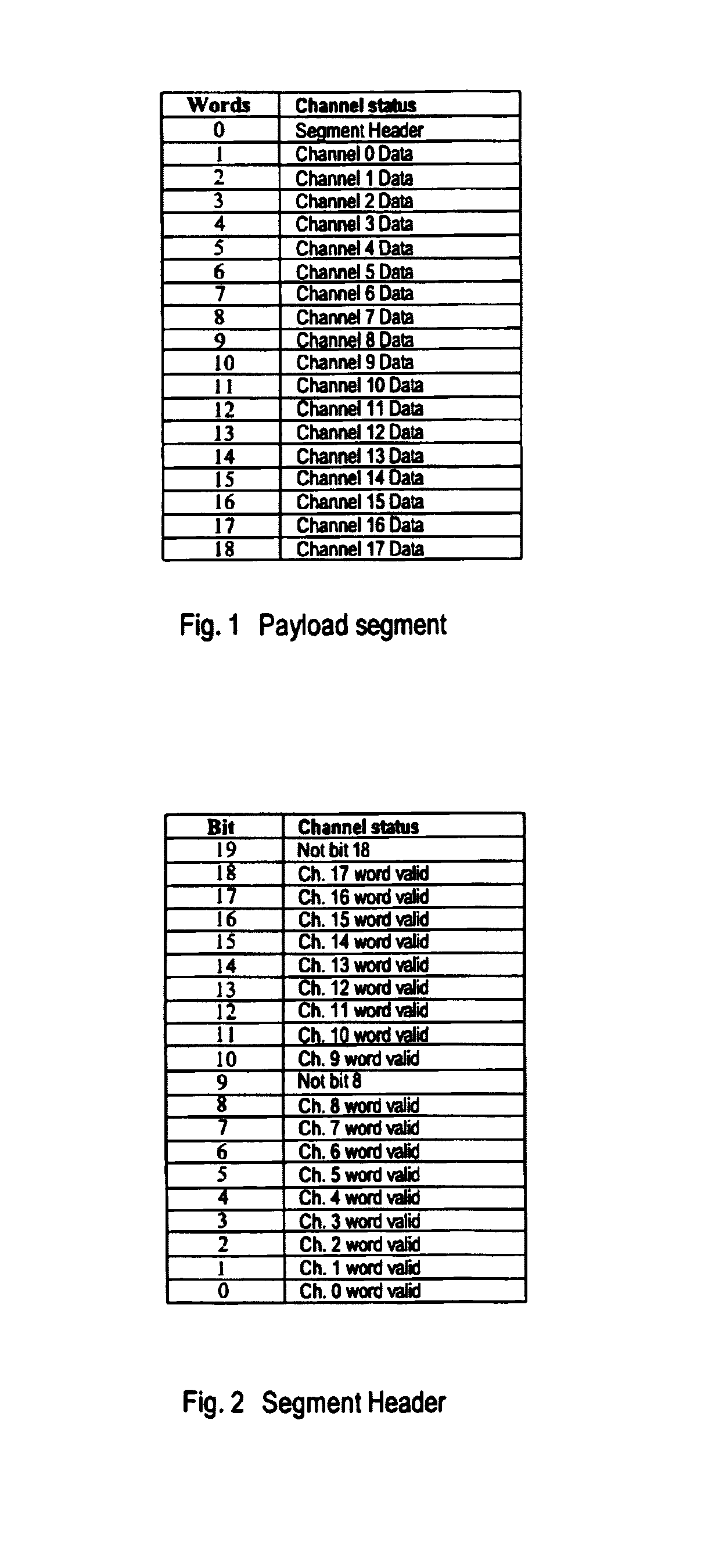
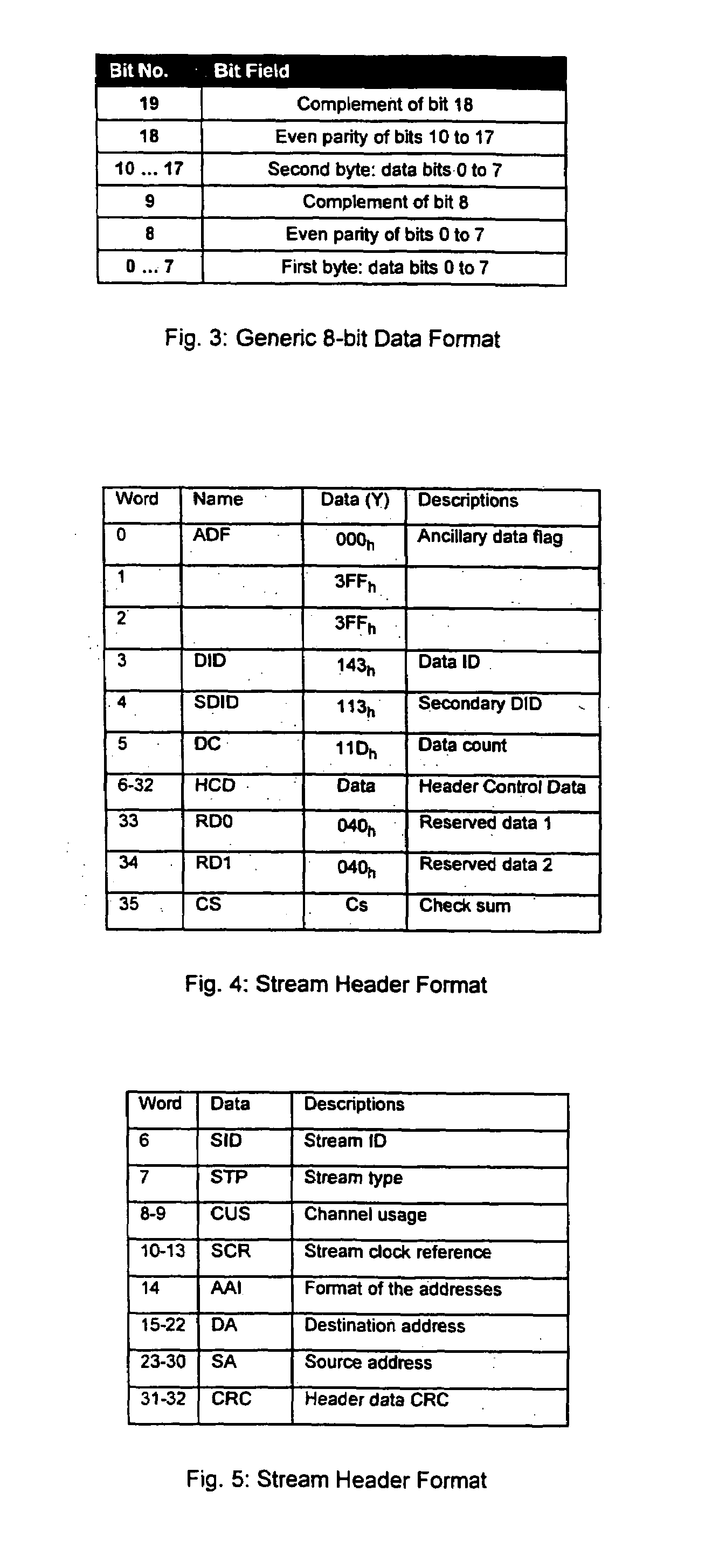
A system and method for time division multiplexing multiple lower bandwidth signals into a high bandwidth signals such as a high-definition television signal. The invention provides an integrated transmission, distribution and routing signal format in which low-bandwidth signals are embedded in the active video and vertical blanking areas of a high-bandwidth signal. Data from the source data streams, including timing data, is formatted in packets, each packet comprising a plurality of channels. The packets are inserted into the high-bandwidth signal along with a header word providing a ‘data valid bit’ or ‘status bit’ for each of the channels, which identifies valid data words within the packet. The source data streams are accurately reconstituted by de-multiplexing according to header data specifying routing destination, stream ID, stream type, channel usage and stream clock reference for clock recovery at the receiving end.
Owner:HB CANADA COMM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com