Patents
Literature
283results about How to "Increase the number of pixels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
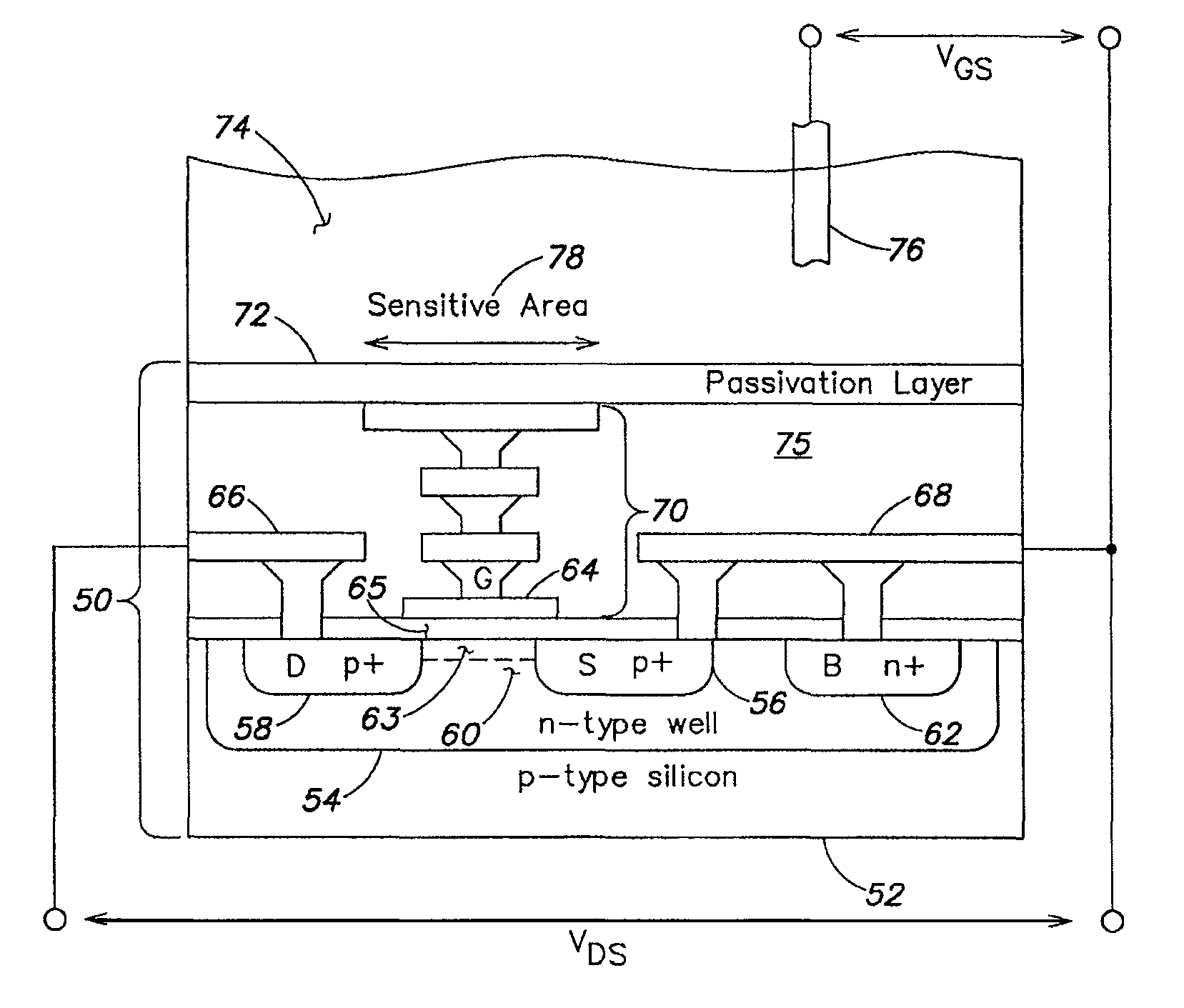
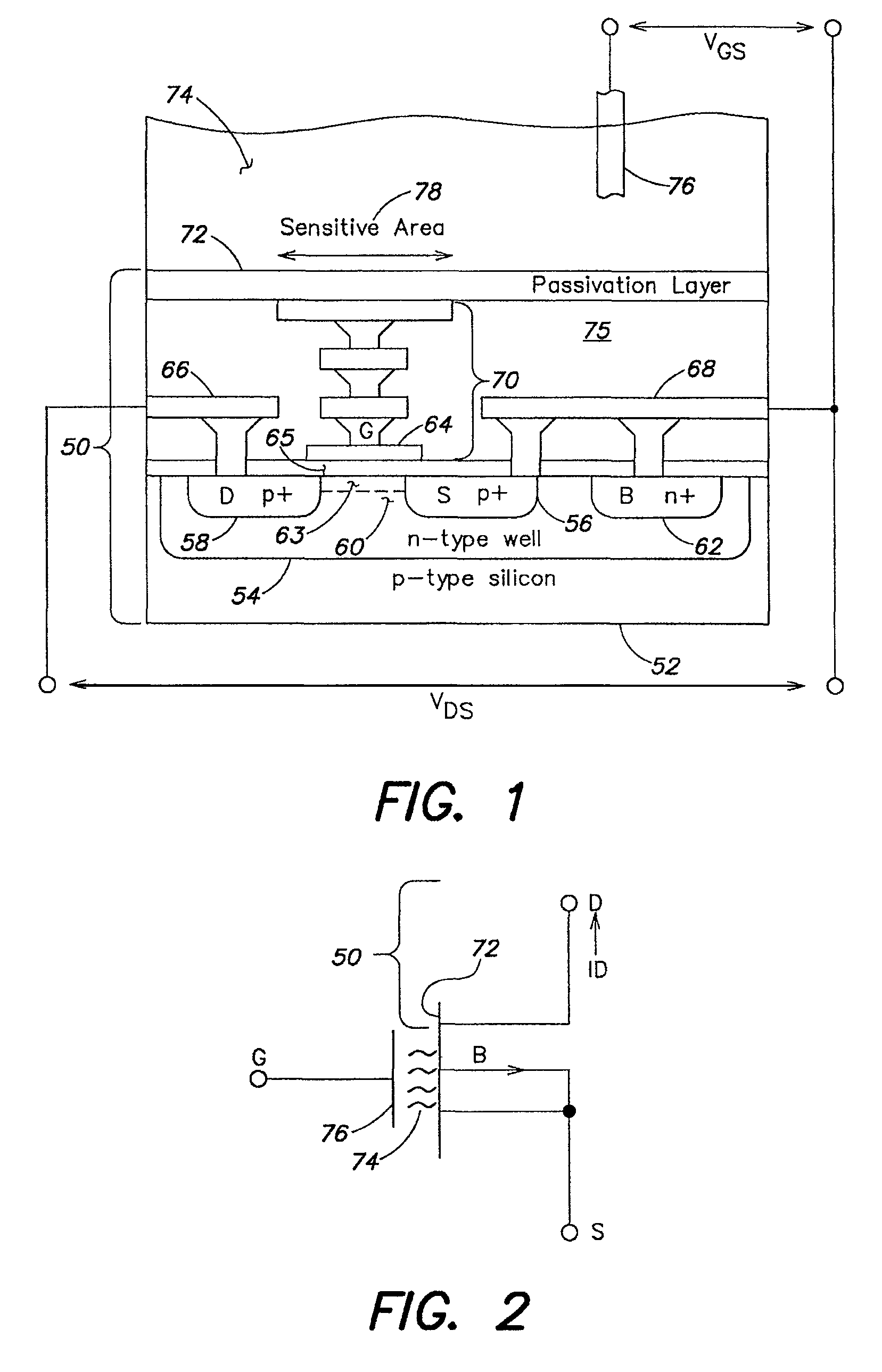
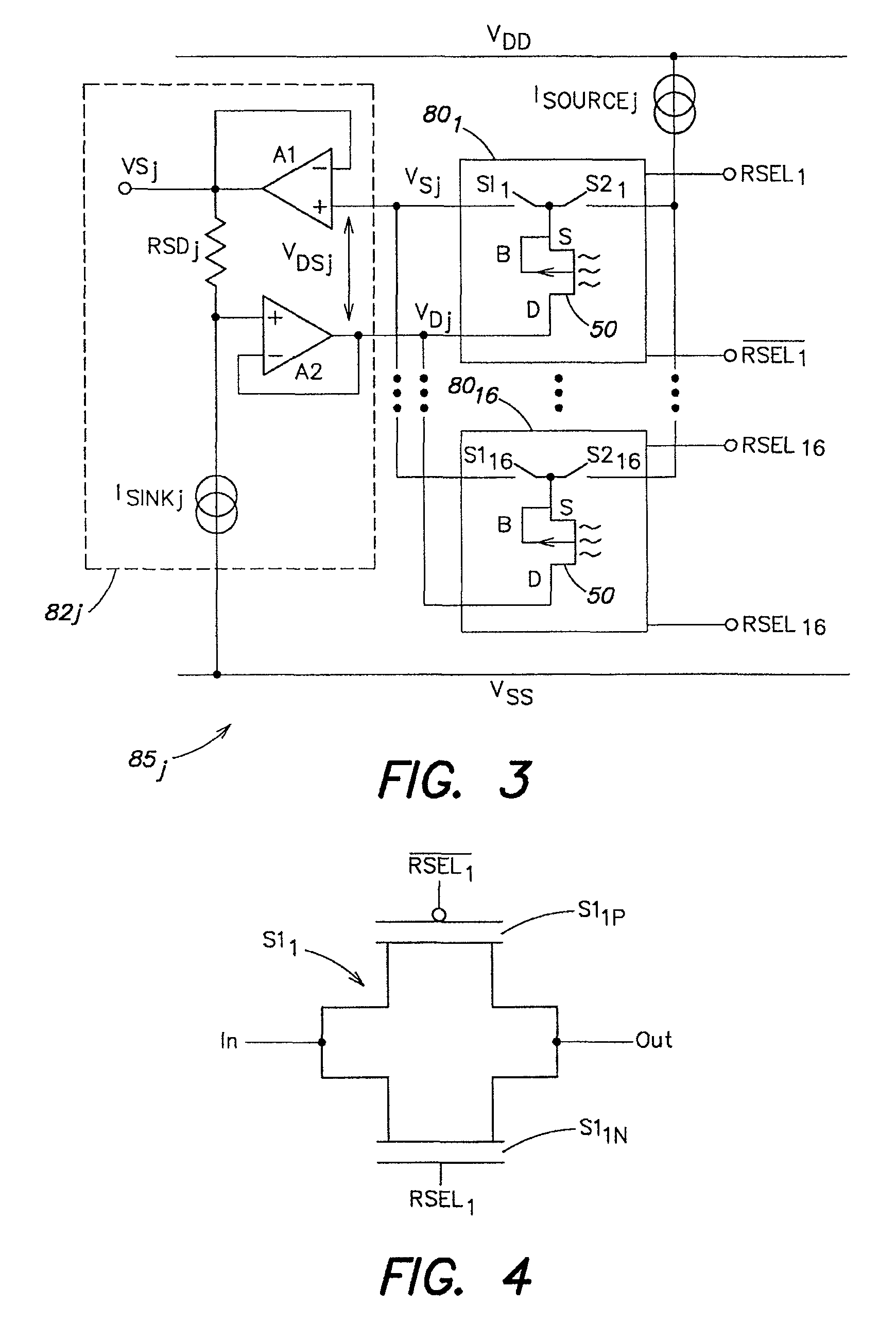
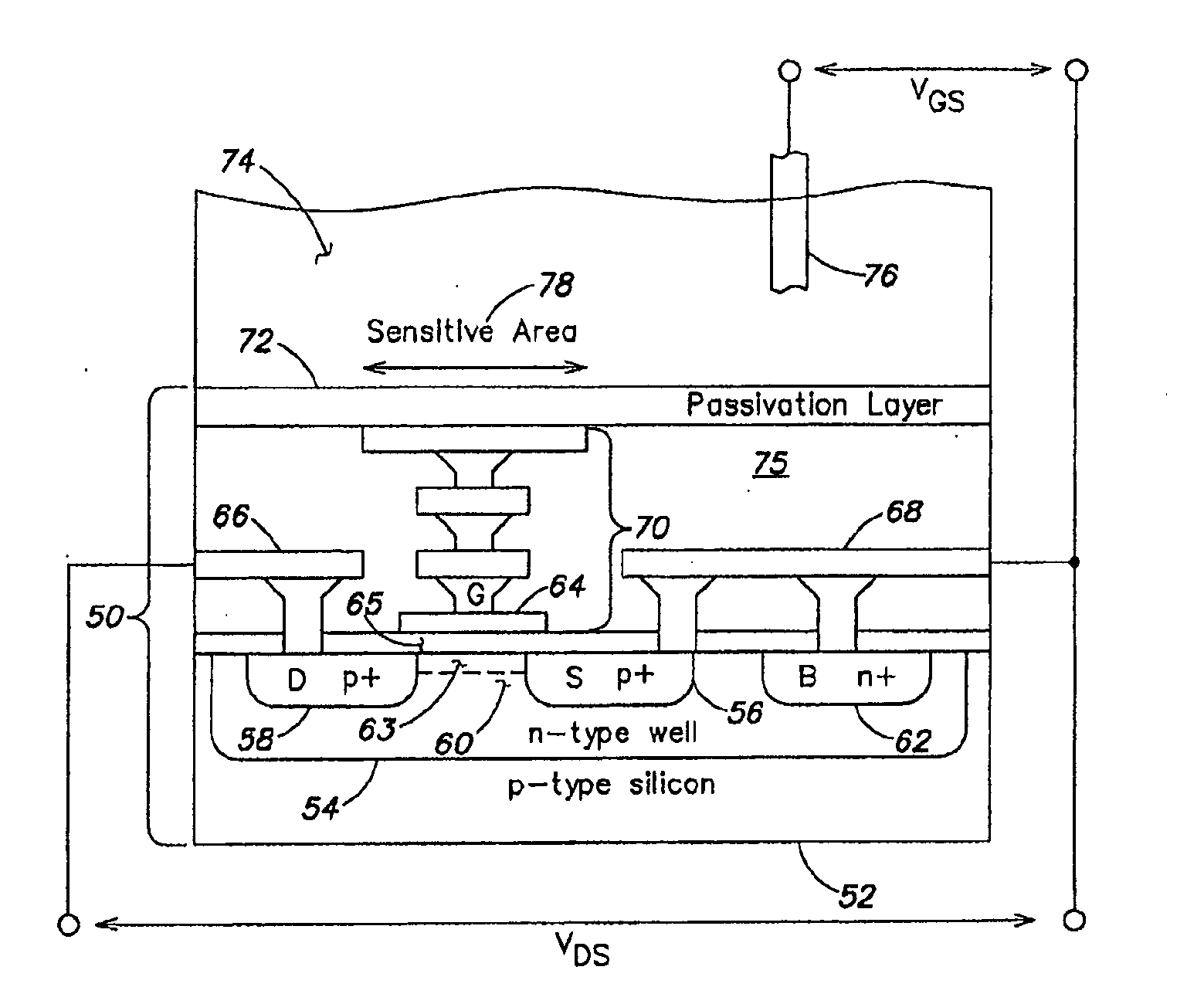
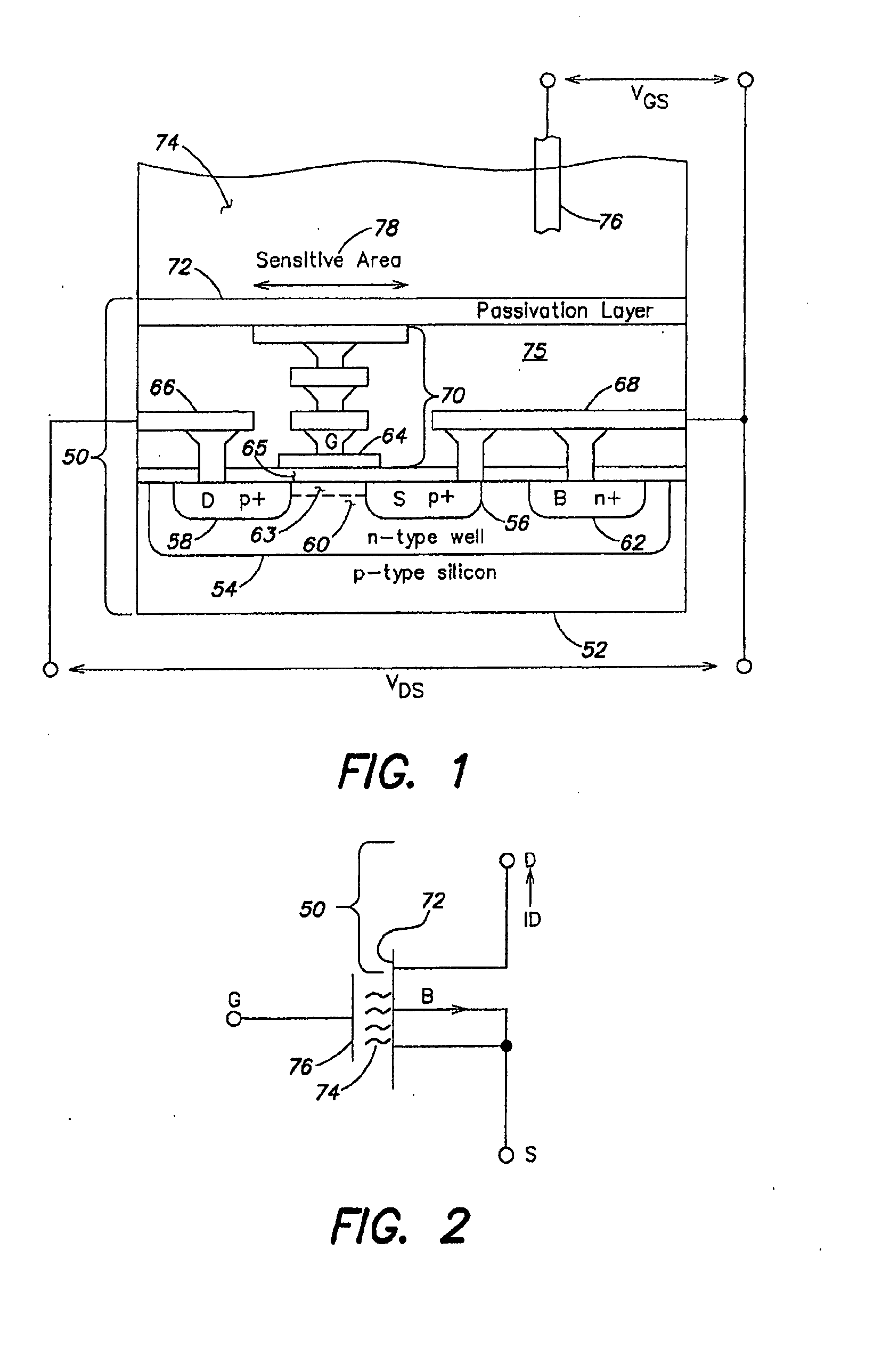
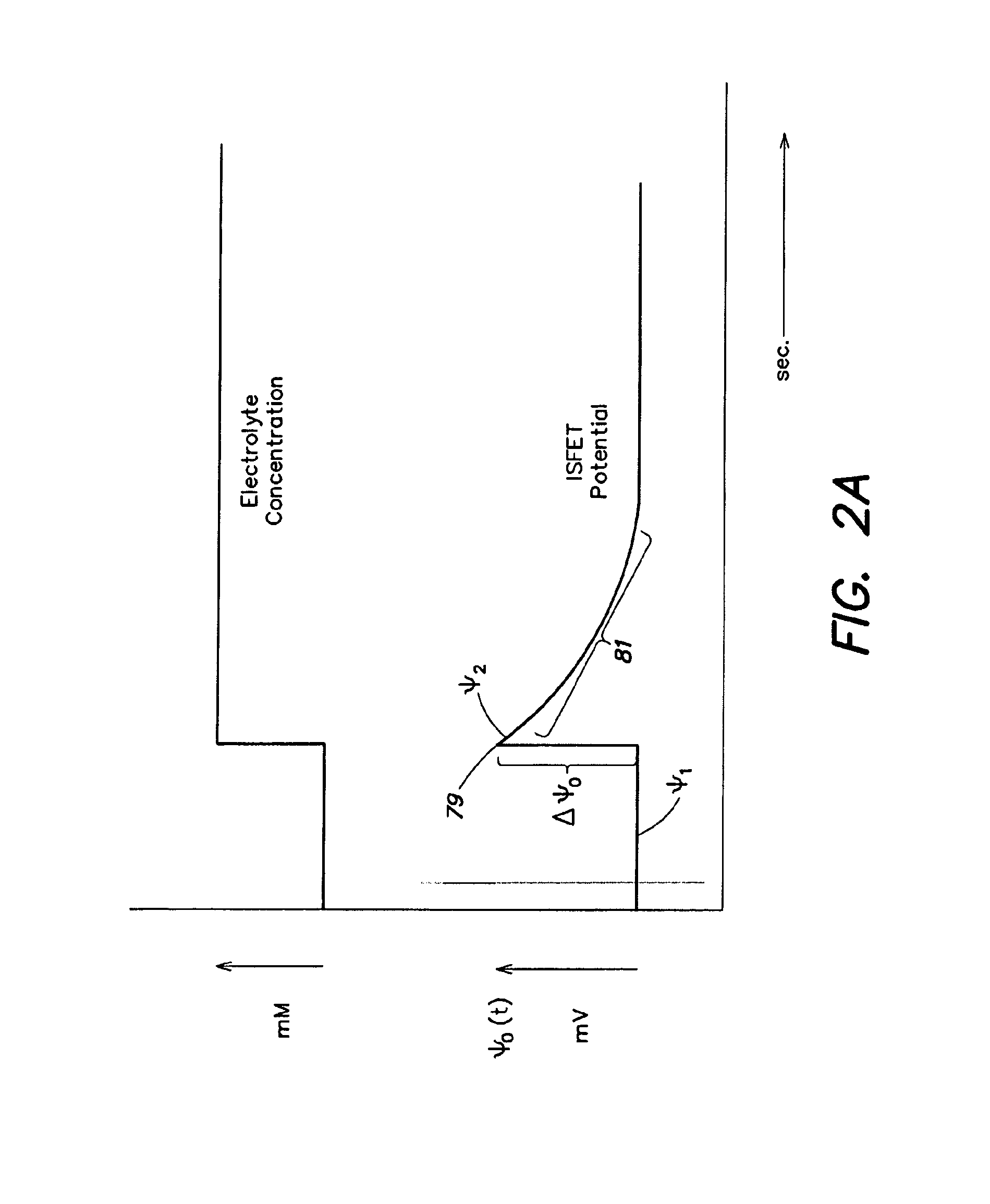
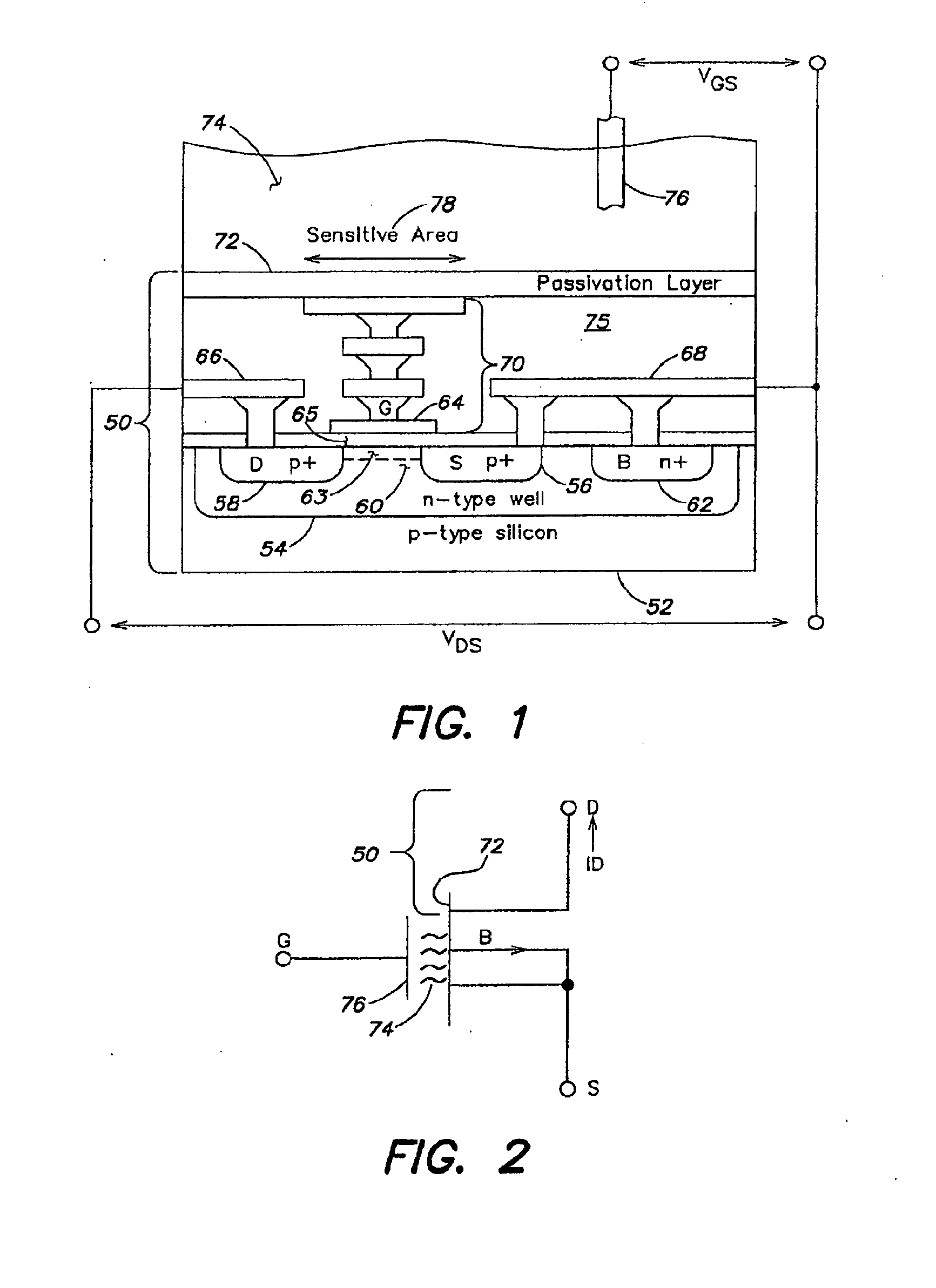
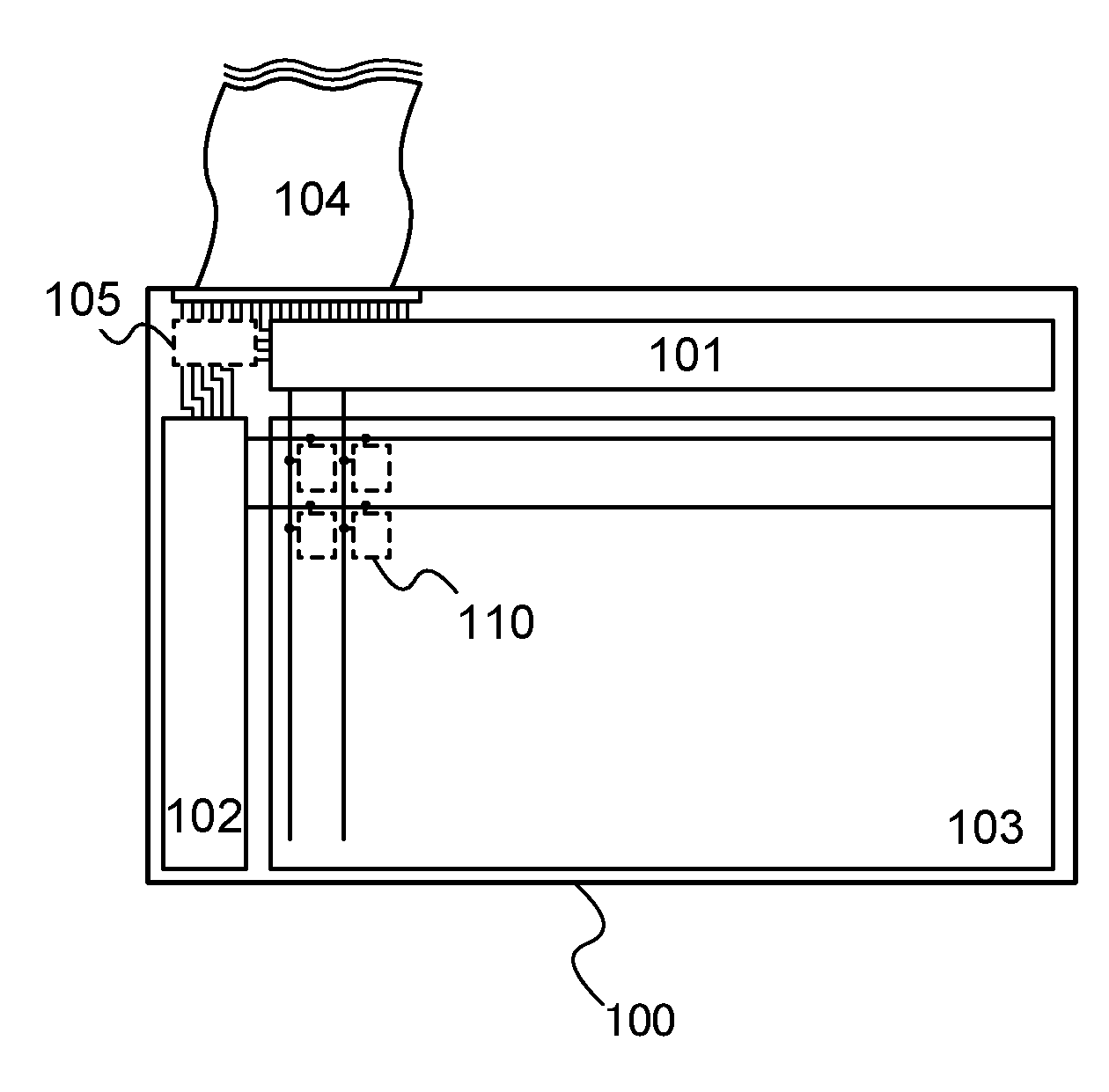
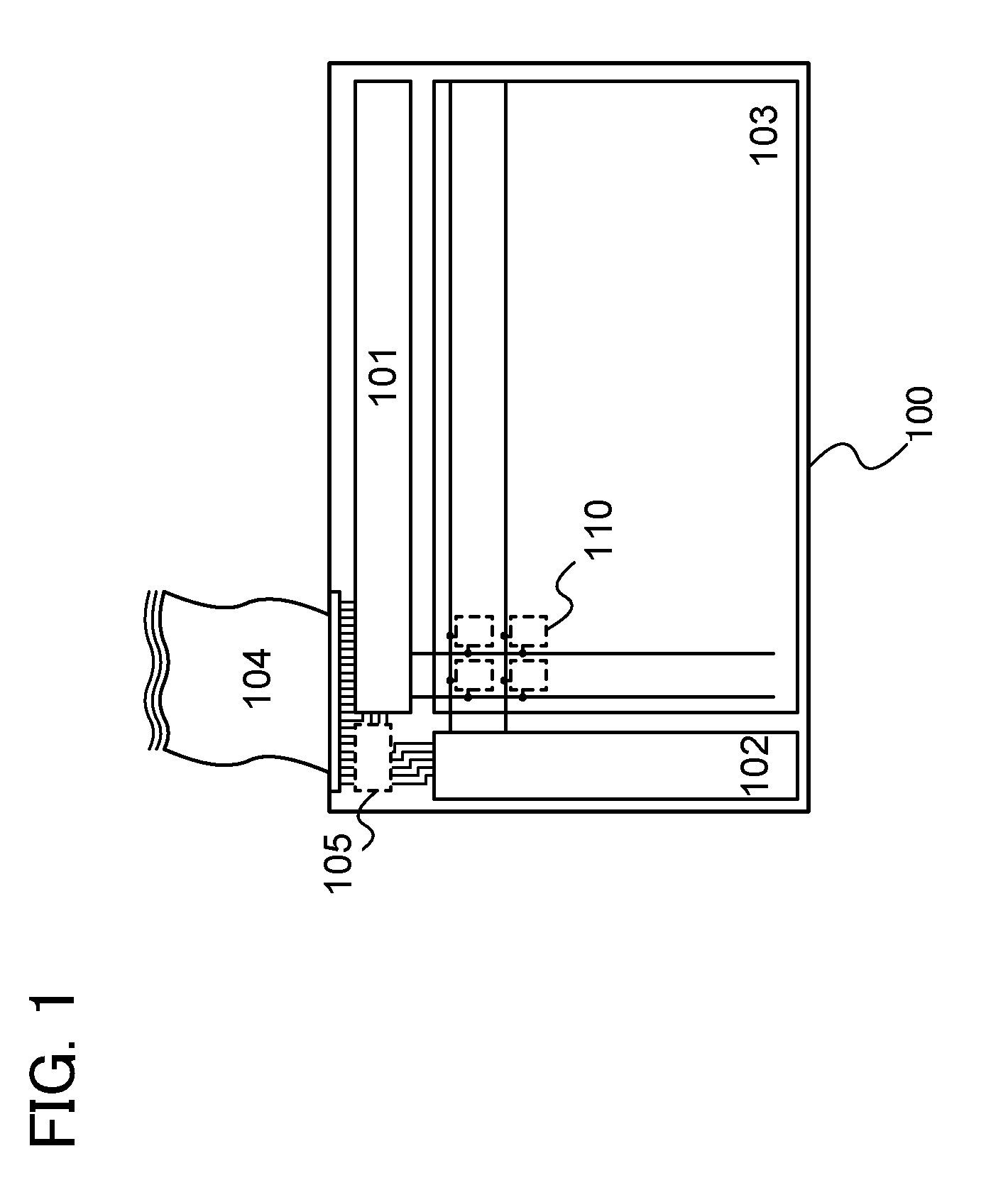
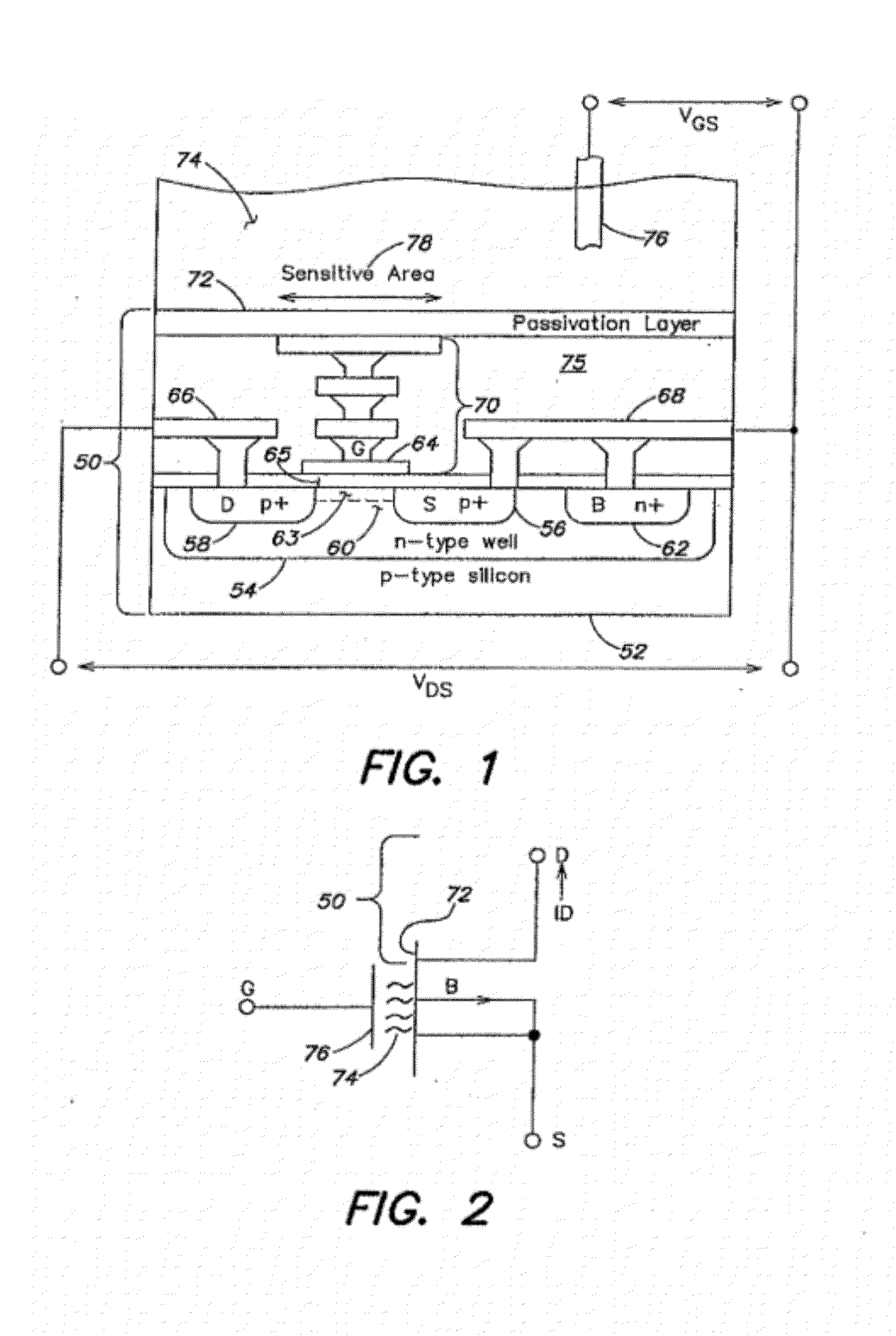
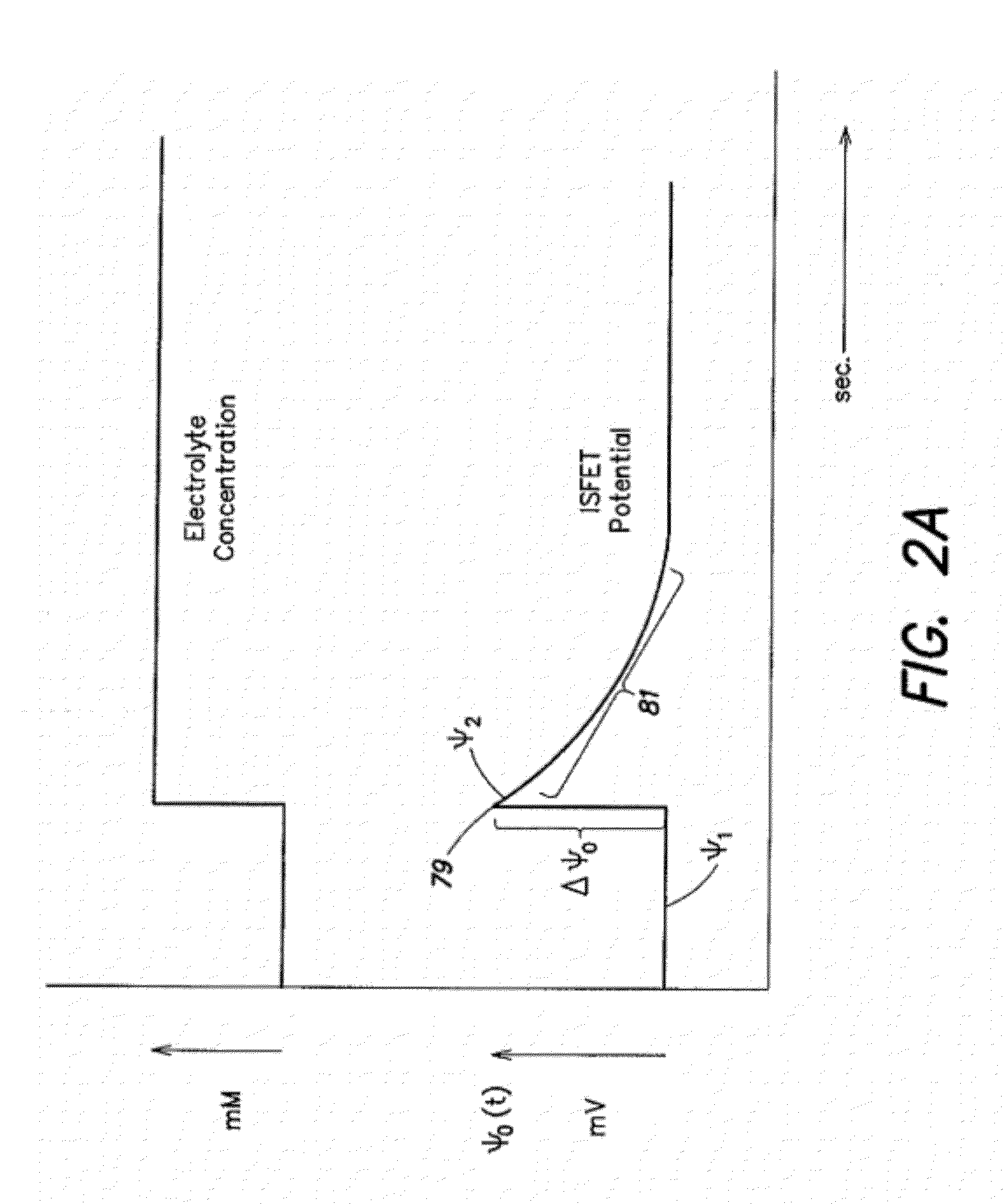
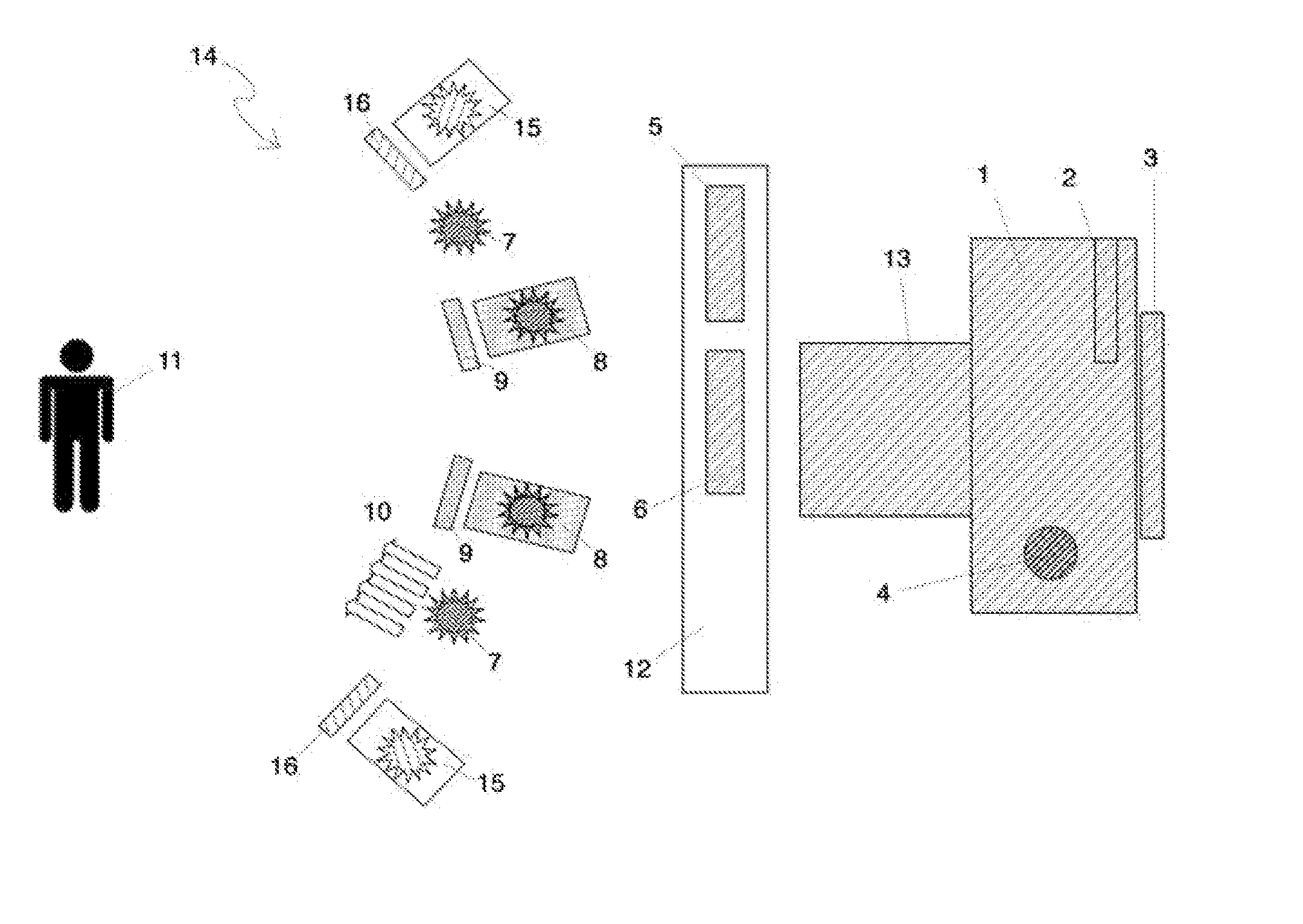
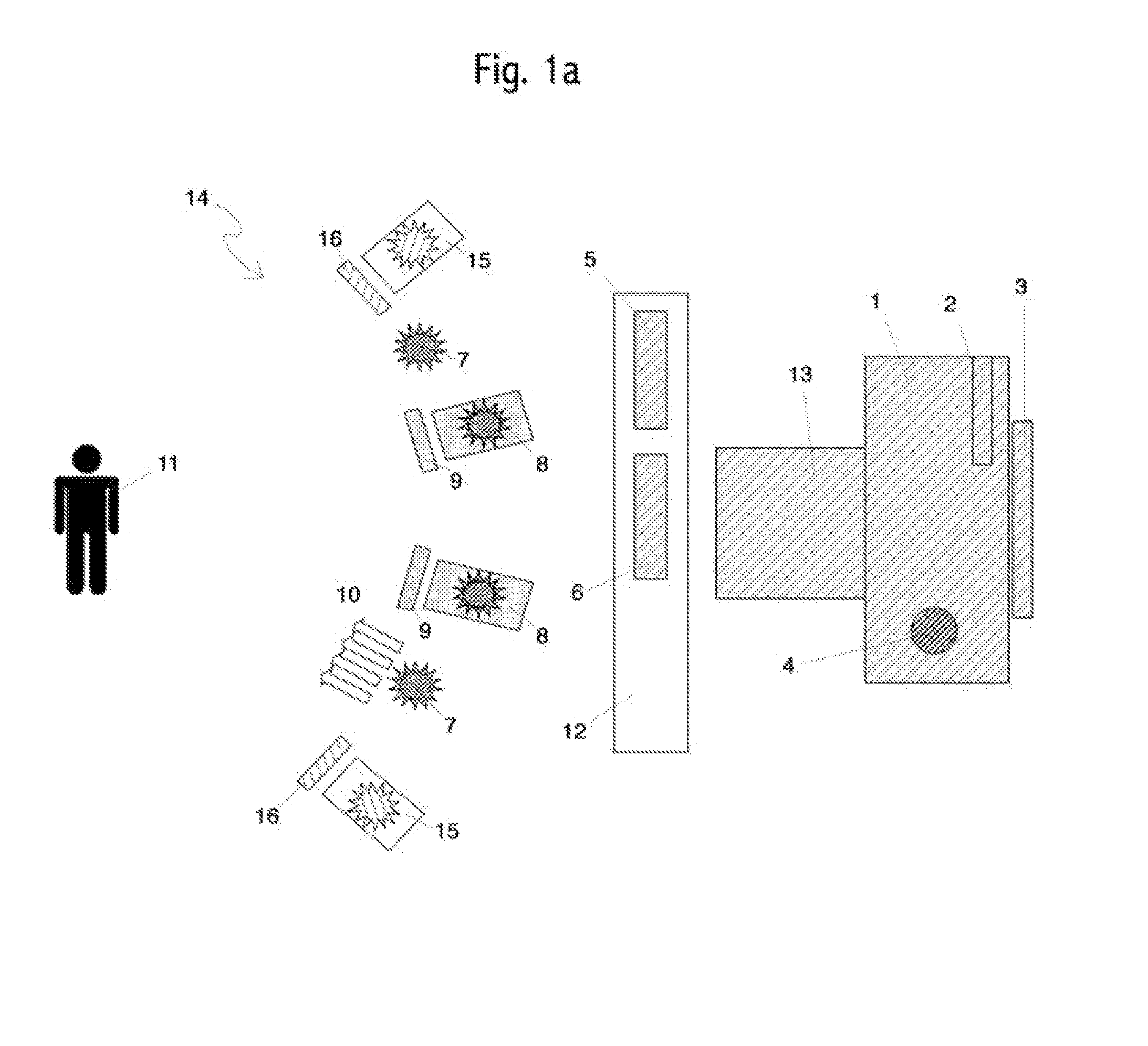
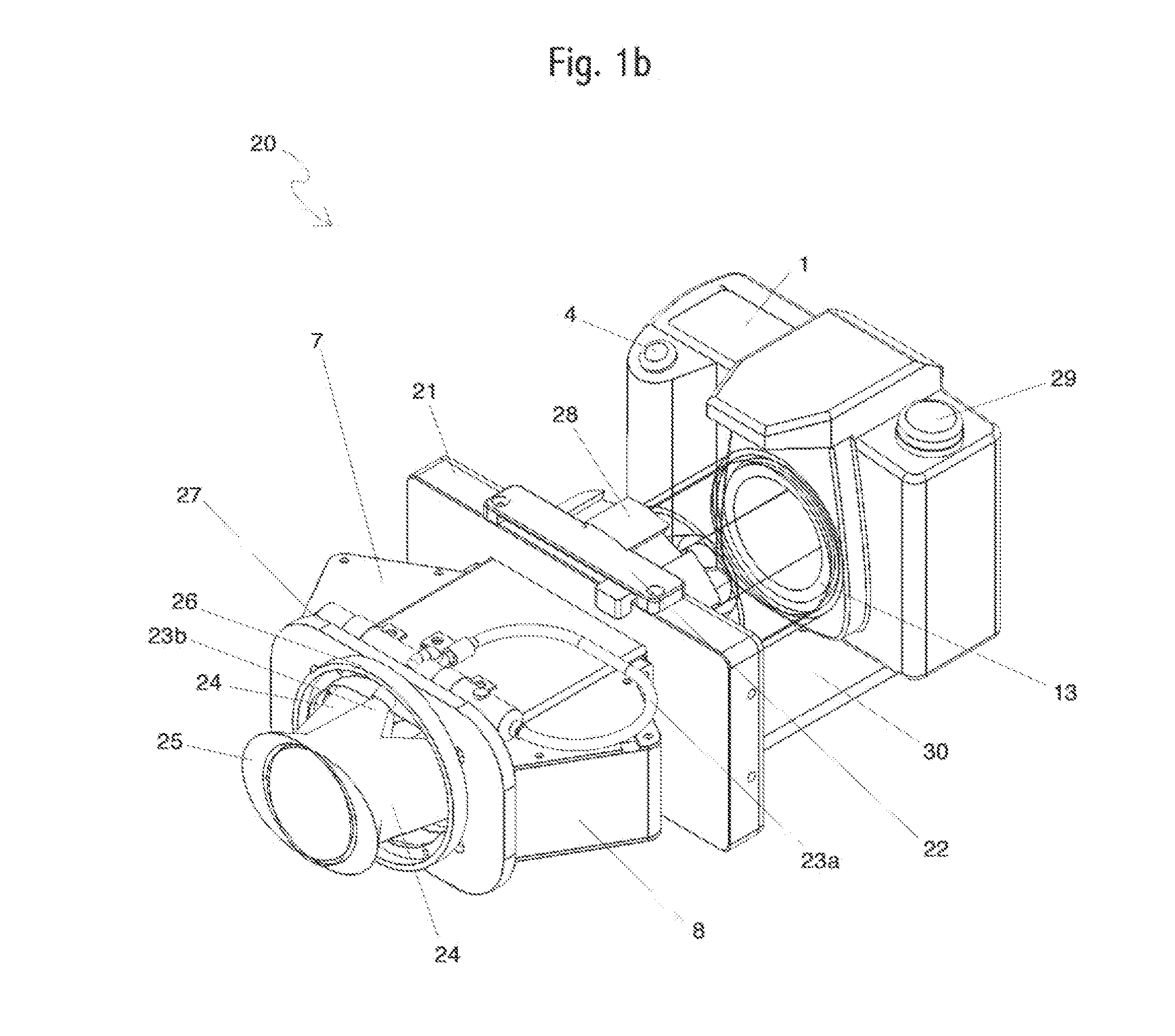
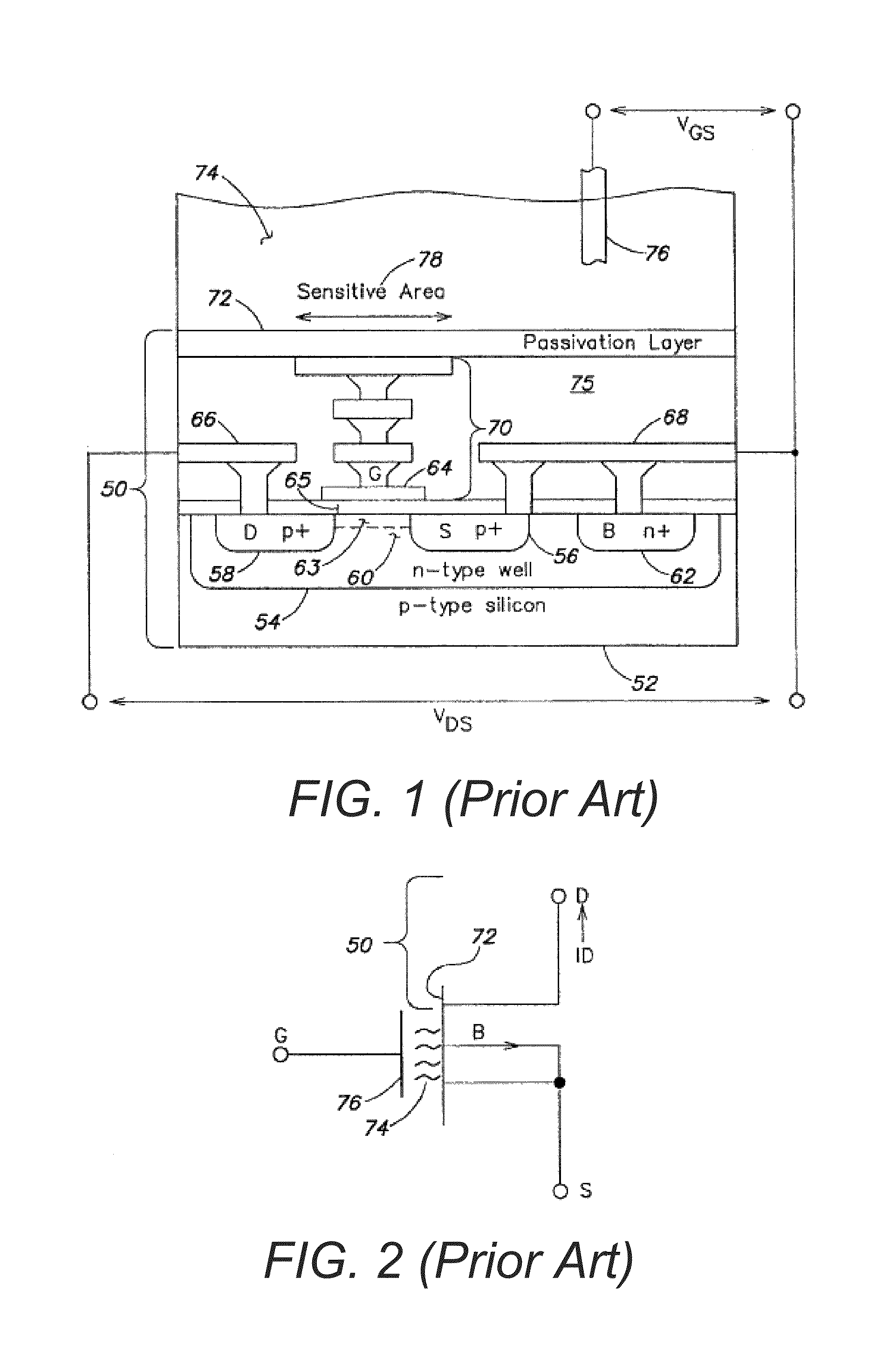
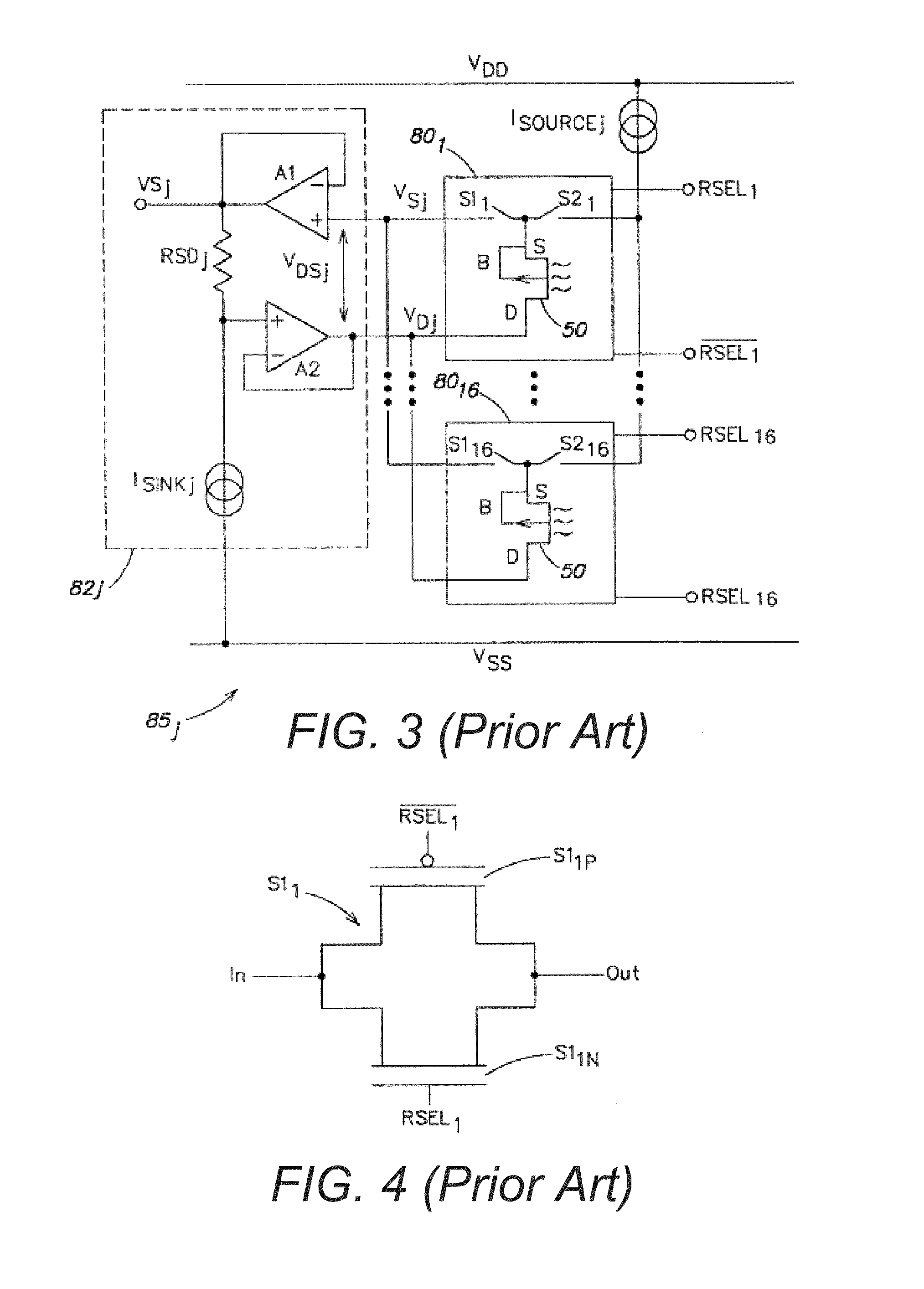
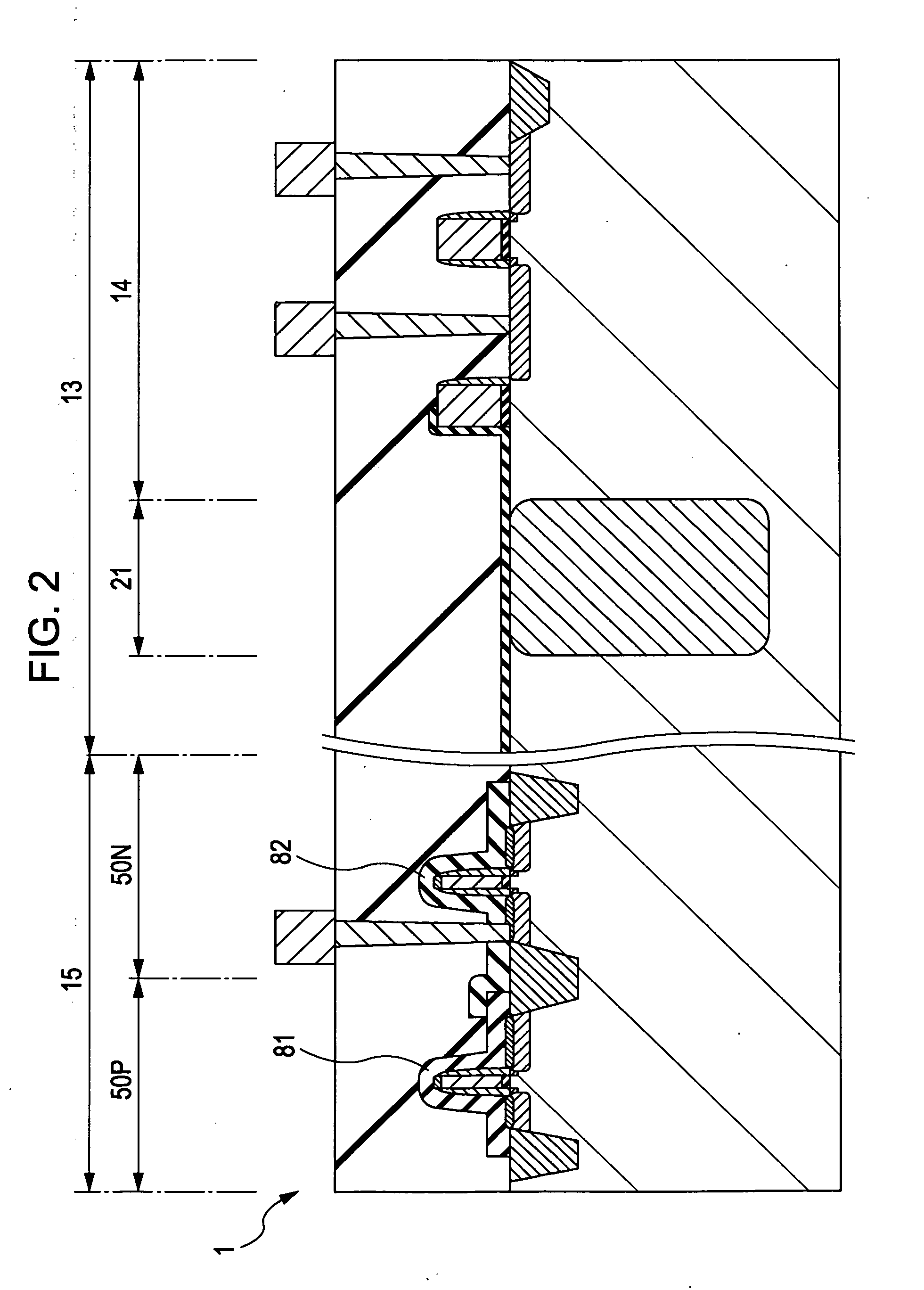
Methods and apparatus for measuring analytes using large scale FET arrays
ActiveUS7948015B2Reduce porosityHigh densityTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementCMOSOrganismal Process
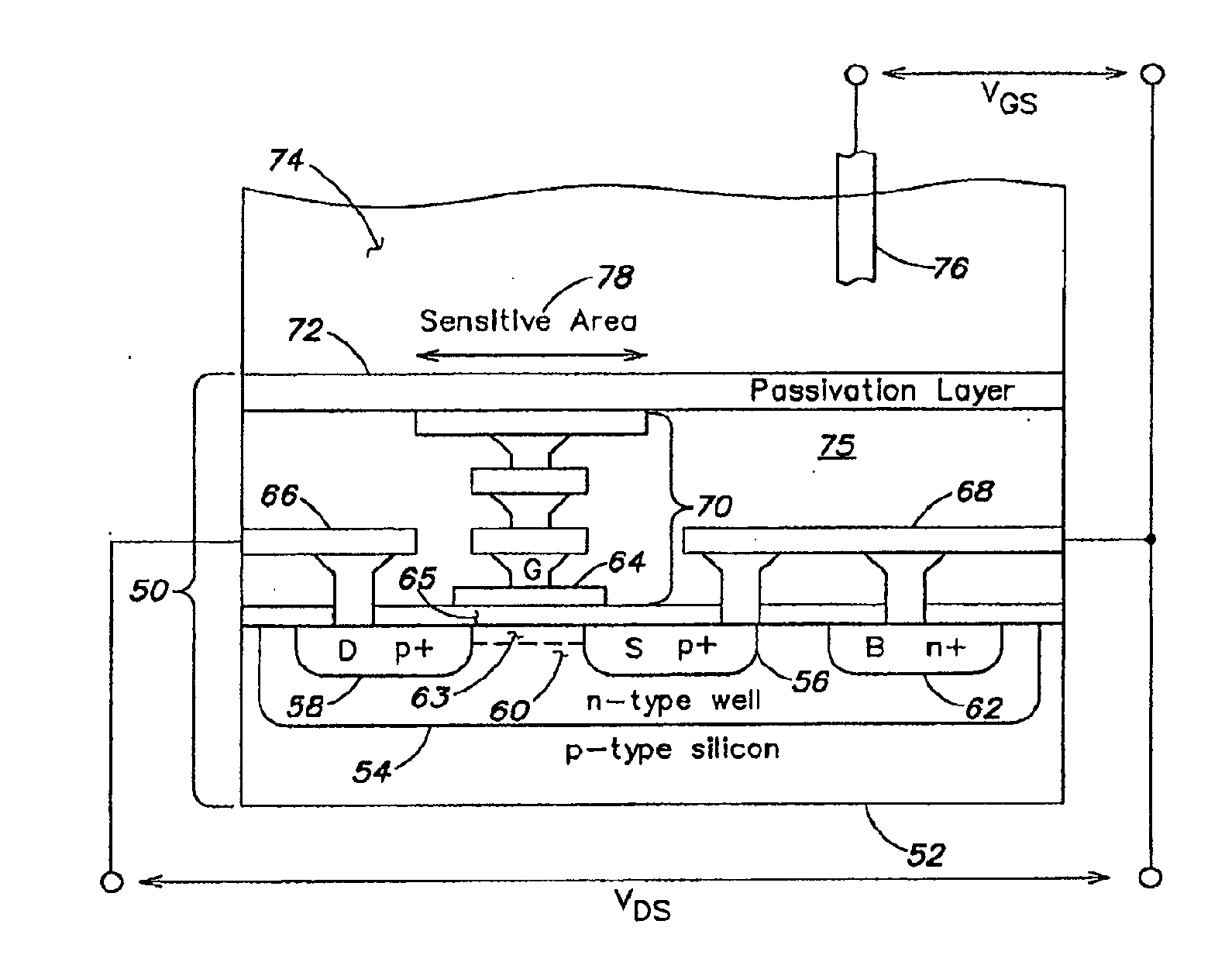
Methods and apparatus relating to very large scale FET arrays for analyte measurements. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes. In one example, chemFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Digital imaging system and method using multiple digital image sensors to produce large high-resolution gapless mosaic images
InactiveUS20090268983A1Avoid smallNot easy to produceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayCamera lens
A digital imaging system and method using multiple cameras arranged and aligned to create a much larger virtual image sensor array. Each camera has a lens with an optical axis aligned parallel to the optical axes of the other camera lenses, and a digital image sensor array with one or more non-contiguous pixelated sensors. The non-contiguous sensor arrays are spatially arranged relative to their respective optical axes so that each sensor images a portion of a target region that is substantially different from other portions of the target region imaged by other sensors, and preferably overlaps adjacent portions imaged by the other sensors. In this manner, the portions imaged by one set of sensors completely fill the image gaps found between other portions imaged by other sets of sensors, so that a seamless mosaic image of the target region may be produced.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
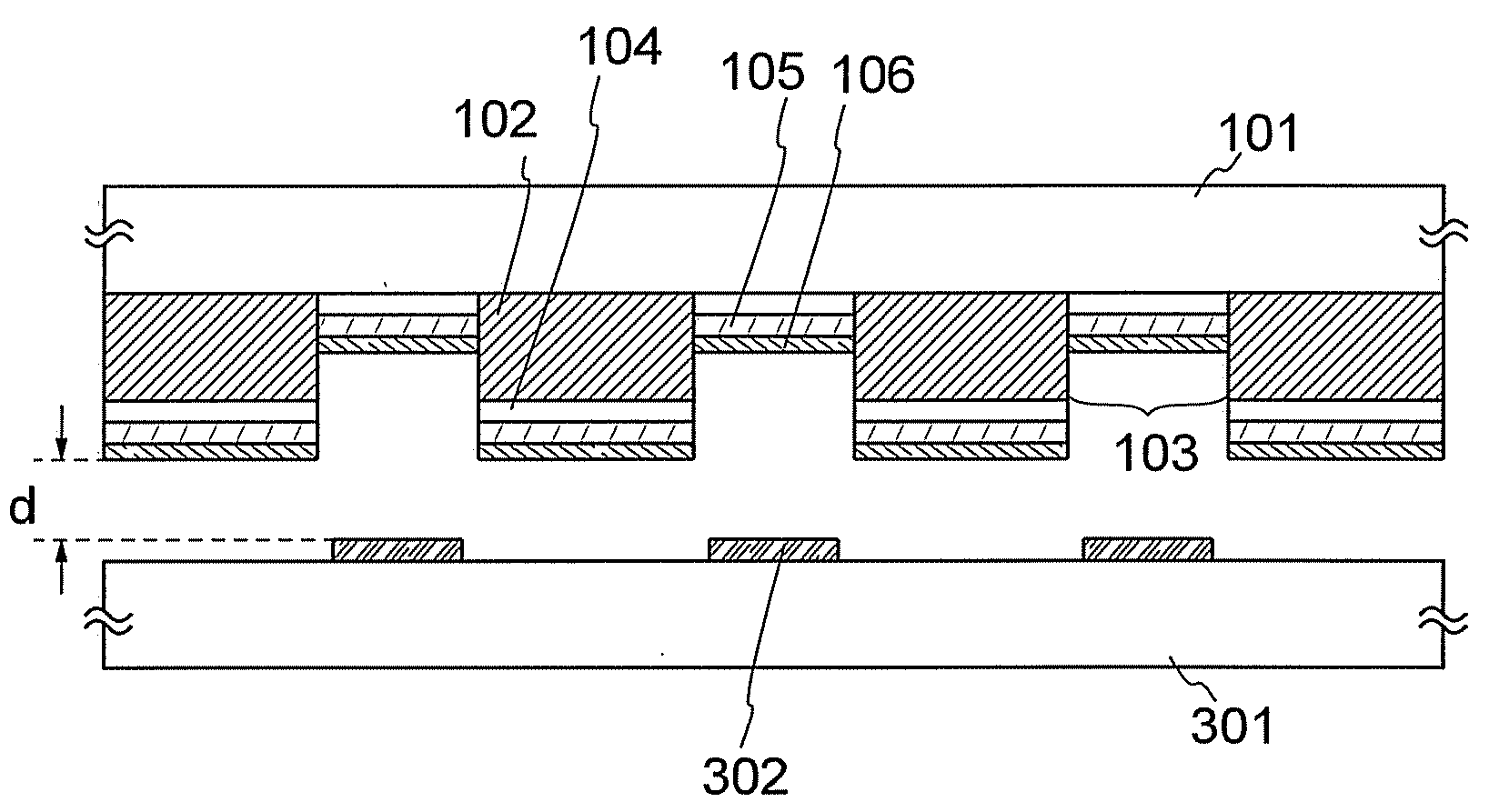
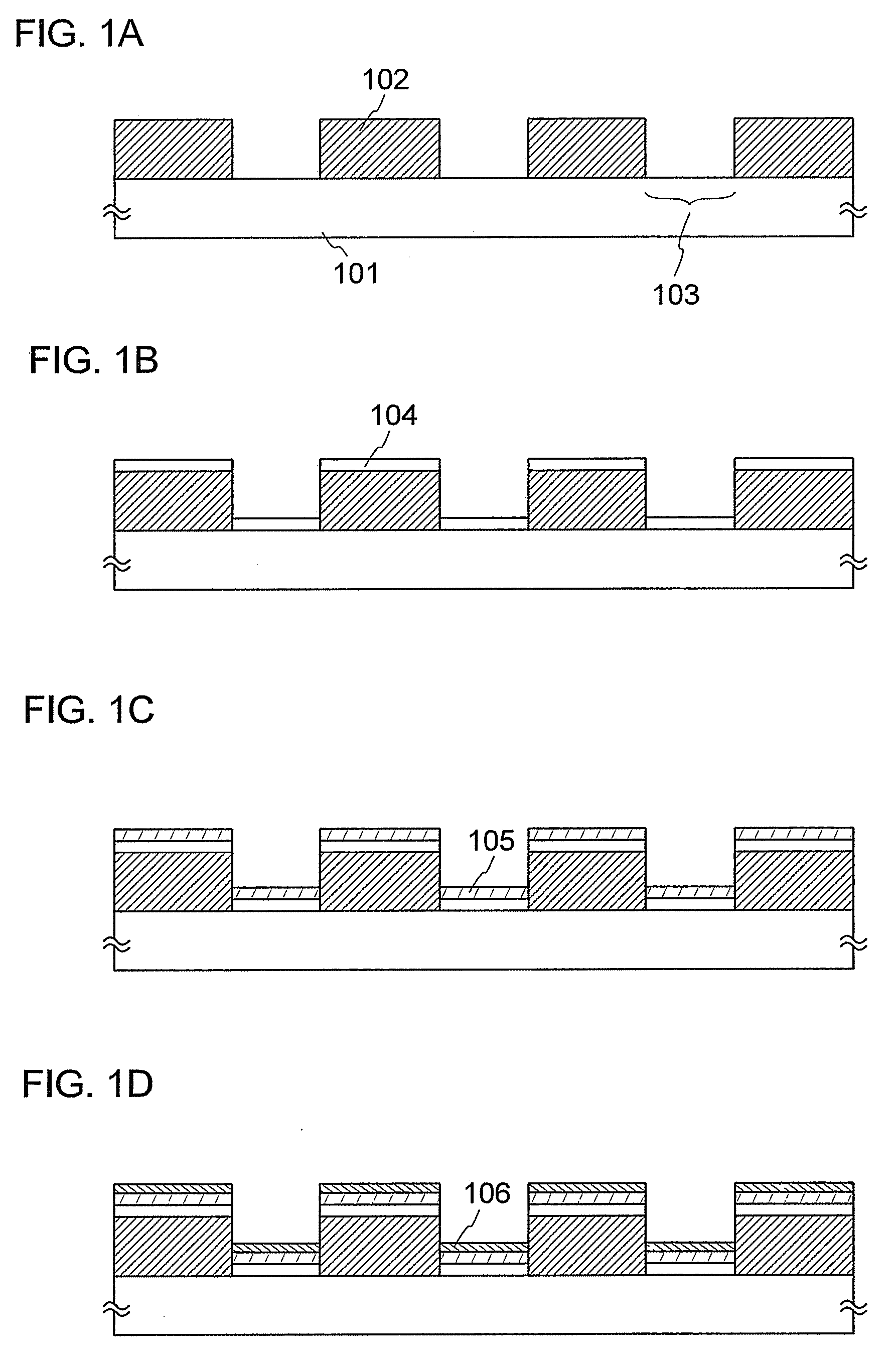
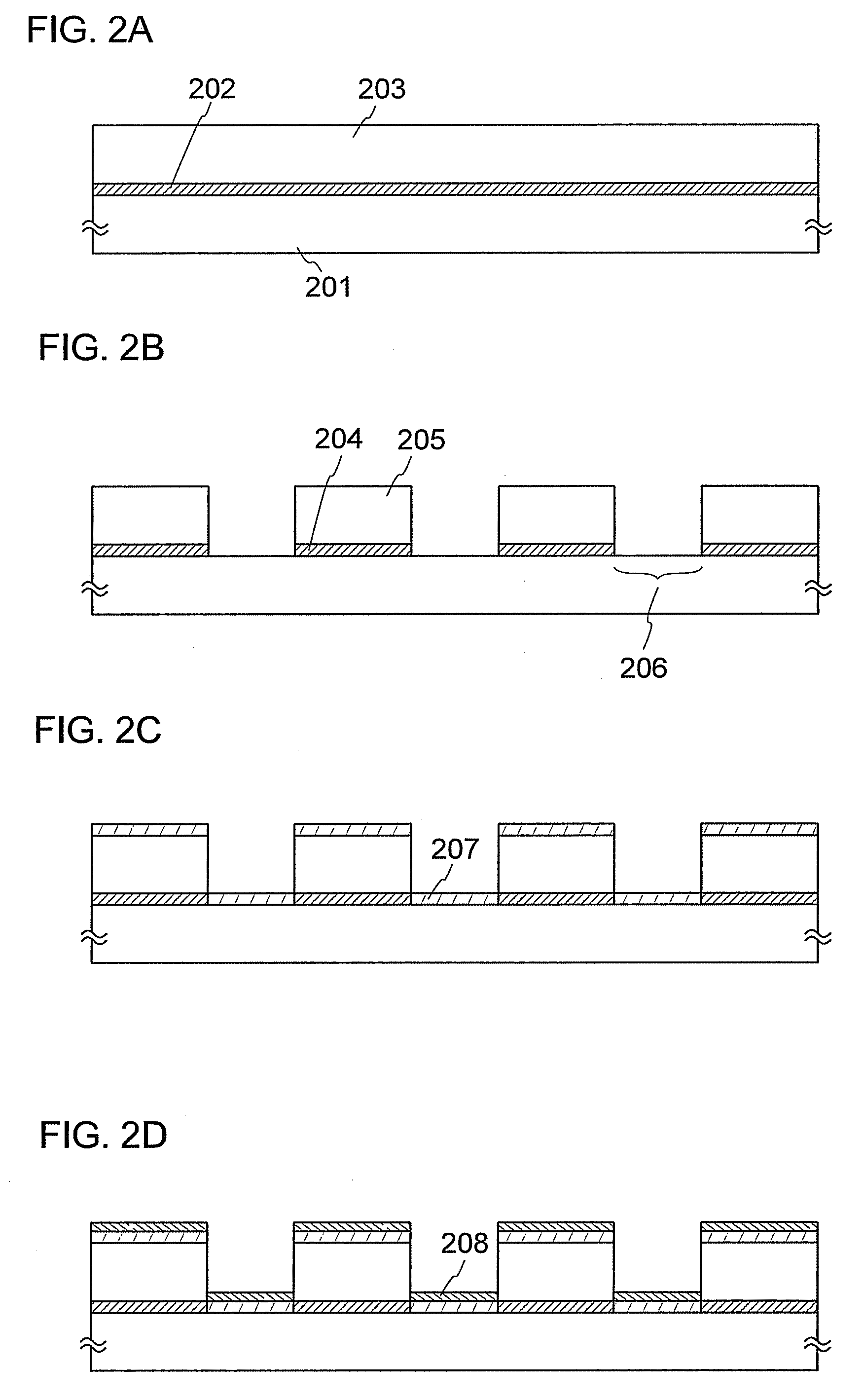
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060275710A1Reduce light intensityImprove routing densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialContinuous wave laser beam
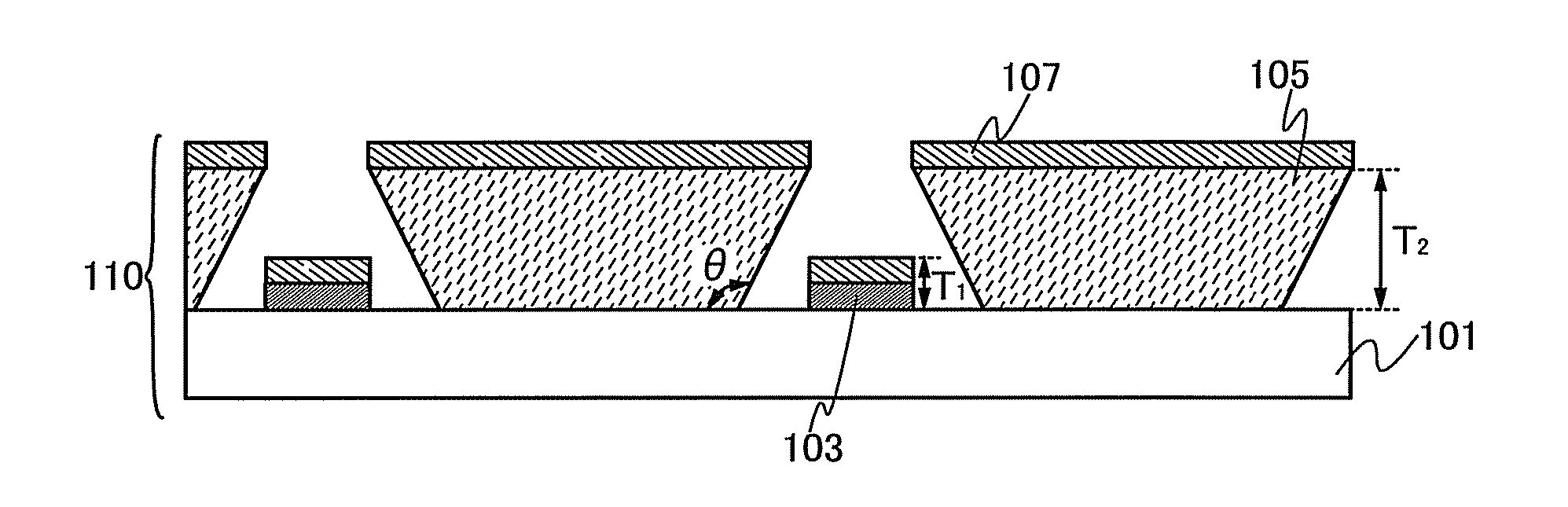
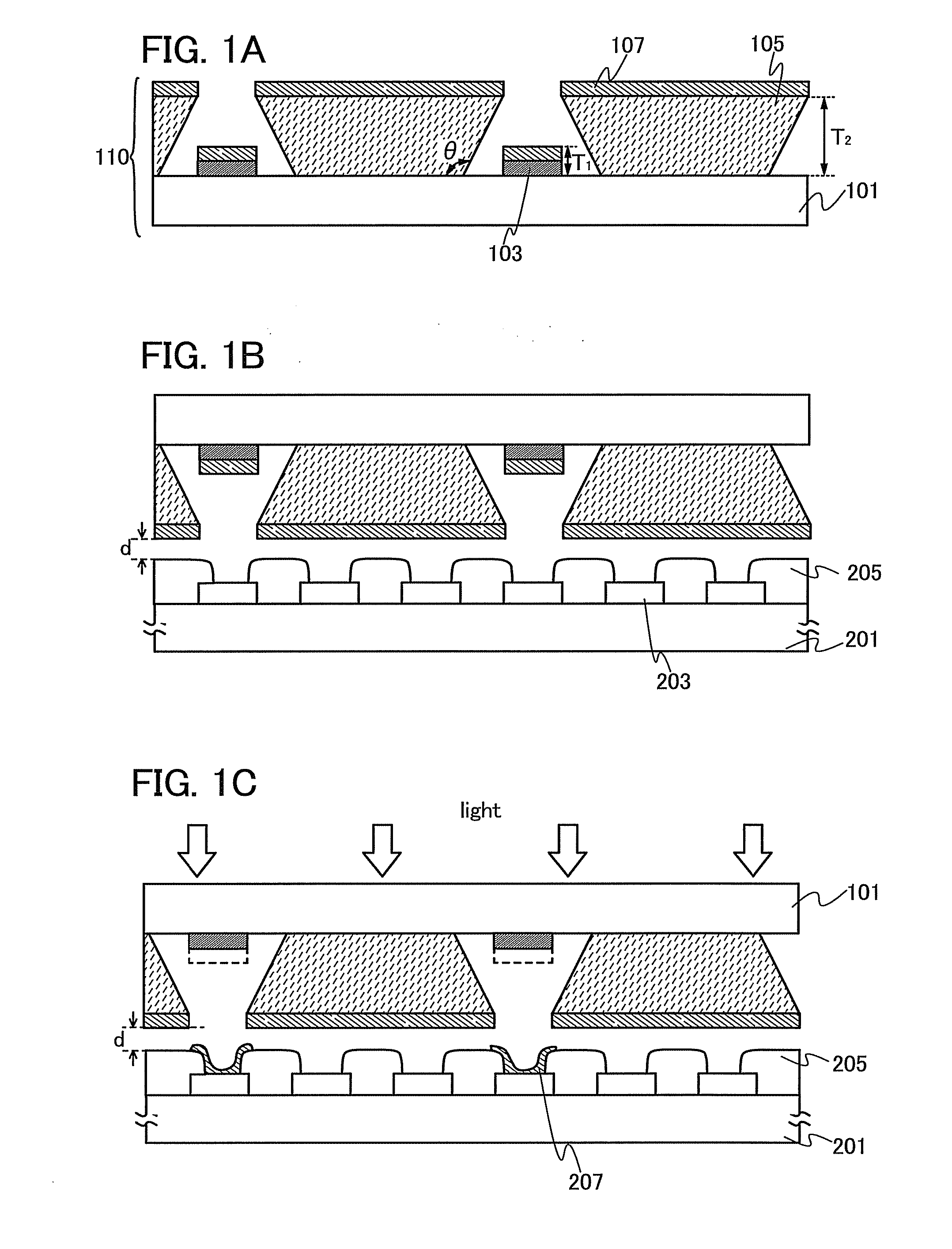
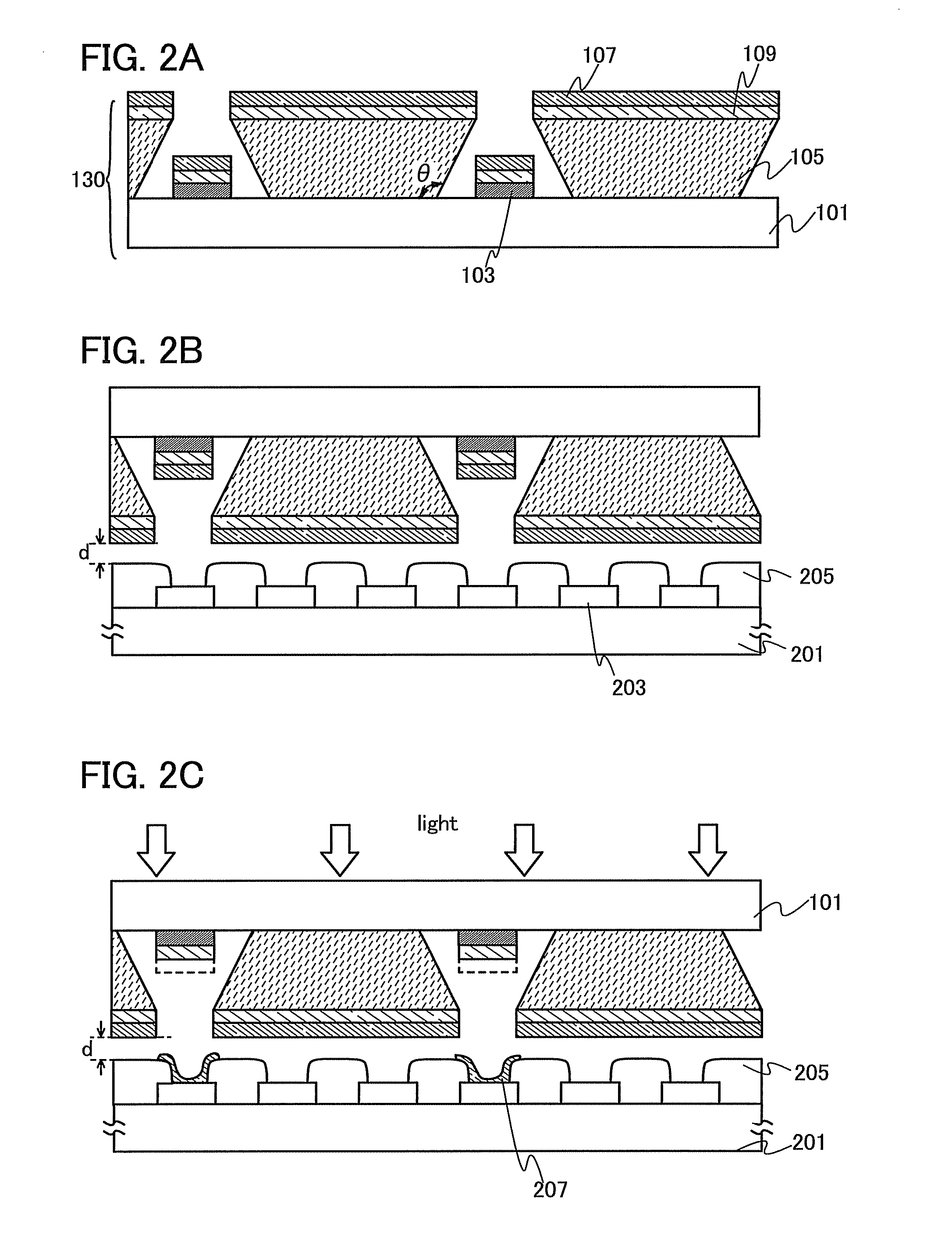
To provide a semiconductor device having a circuit with high operating performance and high reliability, and improve the reliability of the semiconductor device, thereby improving the reliability of an electronic device having the same. The aforementioned object is achieved by combining a step of crystallizing a semiconductor layer by irradiation with continuous wave laser beams or pulsed laser beams with a repetition rate of 10 MHz or more, while scanning in one direction; a step of photolithography with the use of a photomask or a leticle including an auxiliary pattern which is formed of a diffraction grating pattern or a semi-transmissive film having a function of reducing the light intensity; and a step of performing oxidation, nitridation, or surface-modification to the surface of the semiconductor film, an insulating film, or a conductive film, with high-density plasma with a low electron temperature.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
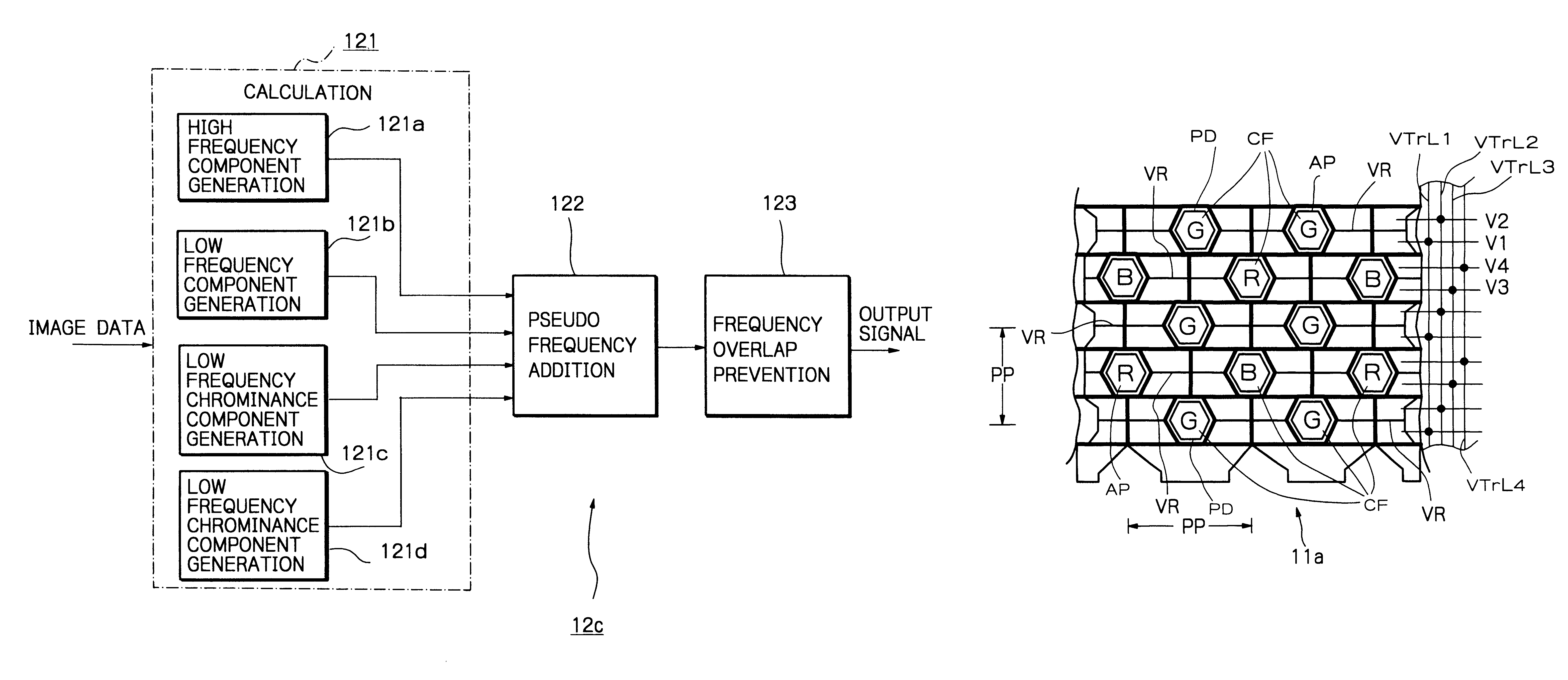
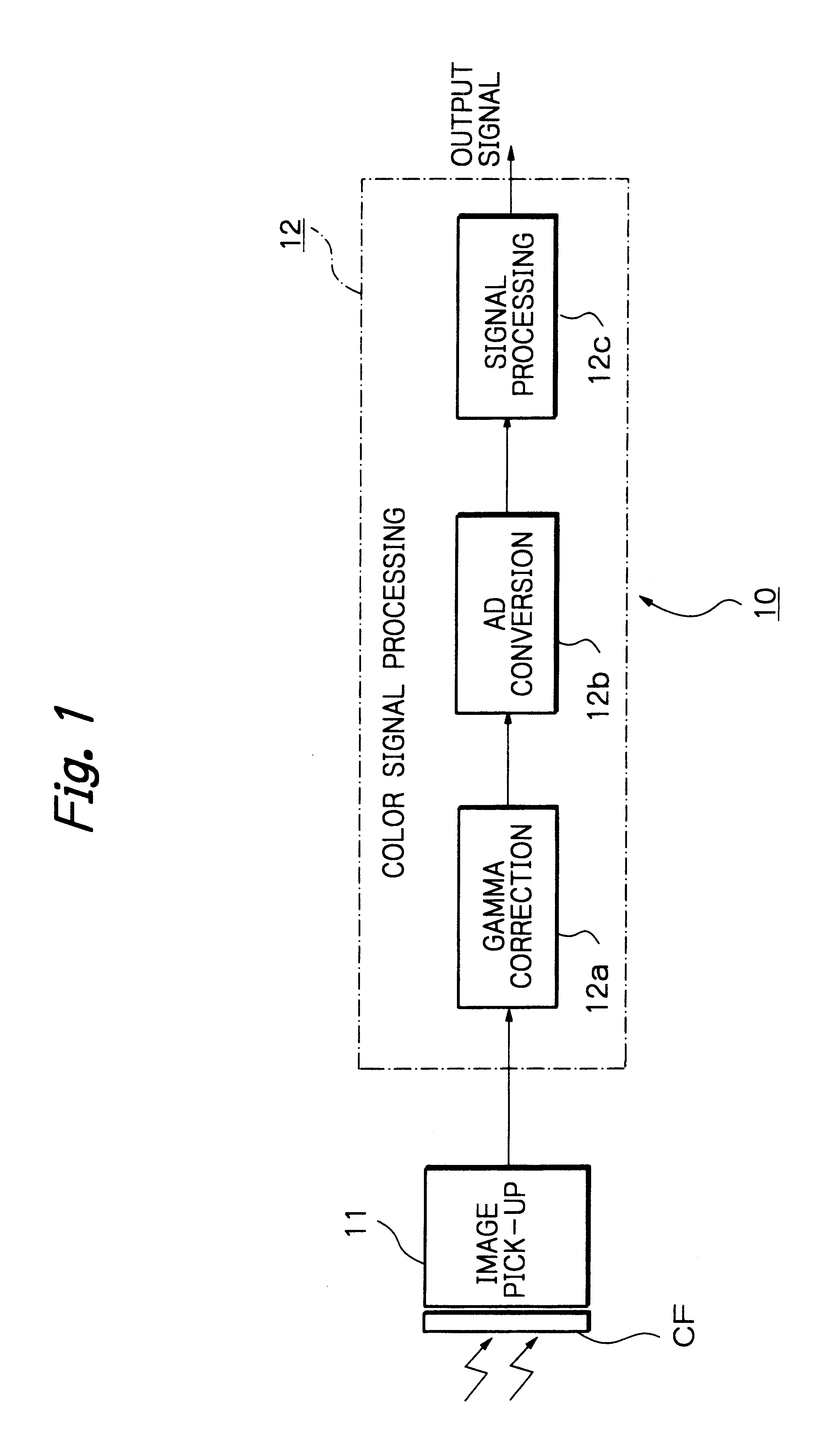
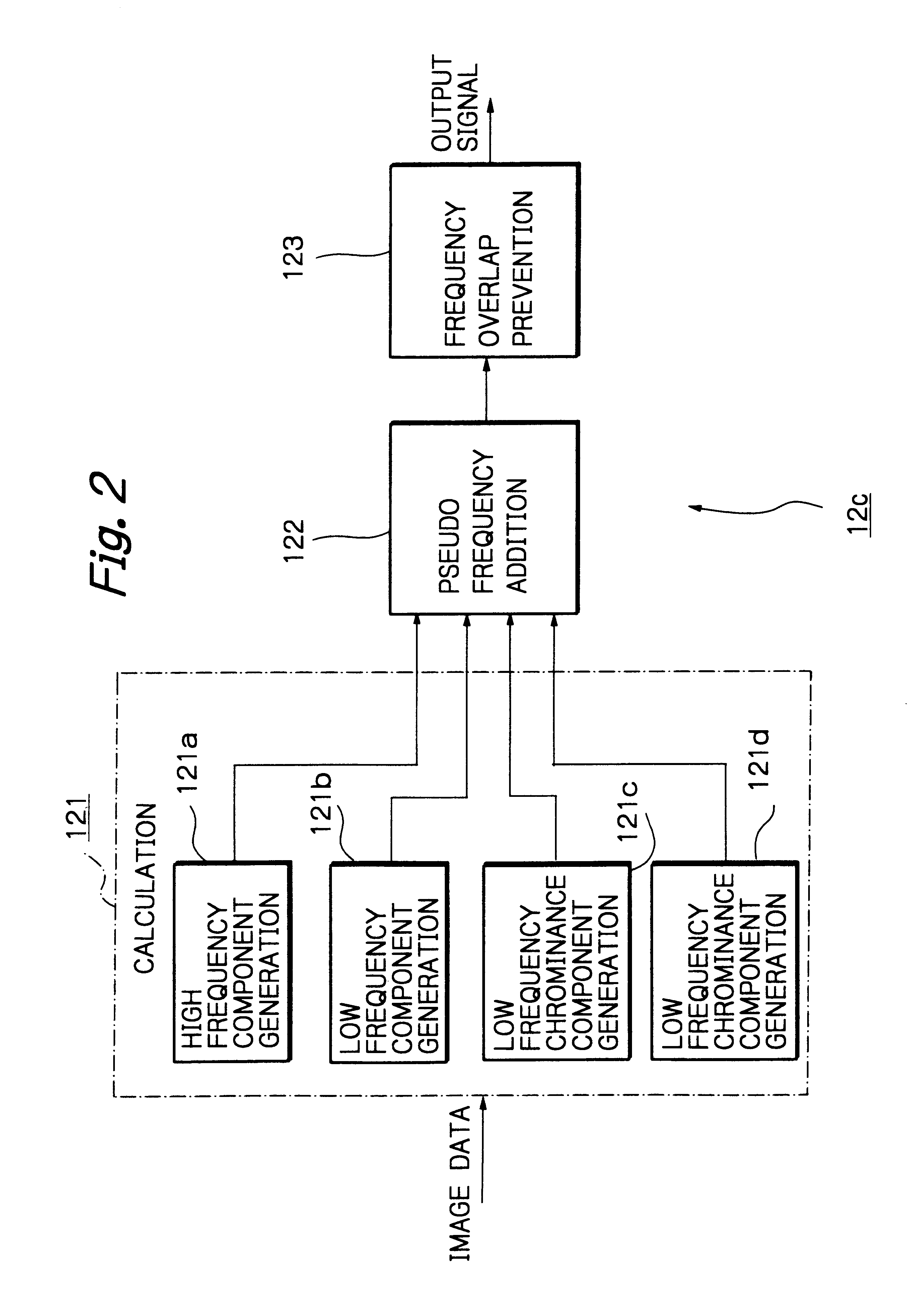
Solid-state imaging apparatus and signal processing method for transforming image signals output from a honeycomb arrangement to high quality video signals
InactiveUS6882364B1High outputWithout delayTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLow-pass filterFalse color
A solid-state imaging apparatus includes an image pick-up section in which photosensitive devices are arranged in, e.g., a honeycomb G square lattice, RB full-checker pattern due to shifted pixels. Regions void of the photosensitive devices are assumed to be virtual photosensitive devices. A signal processing section generates data for the virtual photosensitive devices by using the data of surrounding photosensitive devices while attaching importance to accurate color reproduction and horizontal and / or vertical resolution. As a result, the number of pixel data are increased in a square lattice arrangement. Therefore, high quality image signals are readily achievable with a smaller number of photosensitive devices than conventional with a conventional apparatus. Interpolation can be executed with the high quality signals to the limit of resolution with an adequate circuit scale. The honeycomb arrangement guarantees the required size of the individual pixel and thereby the sensitivity of the entire apparatus while increasing yield on a production line. False colors particular to a single photosensitive portion can be reduced by, e.g., uniform interpolation. Particularly, when a digital camera is constructed by using an imaging apparatus including optics operable with a silver halide sensitive type of film, false colors can be reduced without resorting to an optical low pass filter.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Methods and apparatus for measuring analytes using large scale fet arrays
ActiveUS20110217697A1Constant voltageFacilitate rapid acquisition of dataWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementCMOSOrganismal Process
Methods and apparatus relating to very large scale FET arrays for analyte measurements. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes. In one example, chemFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in the concentration of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi), hydrogen ions, and nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Manufacturing apparatus
InactiveUS20060011136A1High definitionIncrease opening ratioVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingManufacturing cost reductionGas phase
It is an object of the present invention to provide a manufacturing apparatus that reduces a manufacturing cost by enhancing efficiency in the use of an EL material and that is provided with a vapor deposition apparatus which is one of manufacturing apparatuses superior in uniformity in forming an EL layer and in throughput in the case of manufacturing a full-color flat panel display using emission colors of red, green, and blue. According to one feature of the invention, a mask having a small opening with respect to a desired vapor deposition region is used, and the mask is moved accurately. Accordingly, a desired vapor deposition region is vapor deposited entirely. In addition, a vapor deposition method is not limited to movement of a mask, and it is preferable that a mask and a substrate move relatively, for example, the substrate may be moved at a μm level with the mask fixed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of producing a high quality, high resolution image from a sequence of low quality, low resolution images that are undersampled and subject to jitter
InactiveUS6650704B1Increase the number of pixelsQuality improvementTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationFrame basedImage resolution
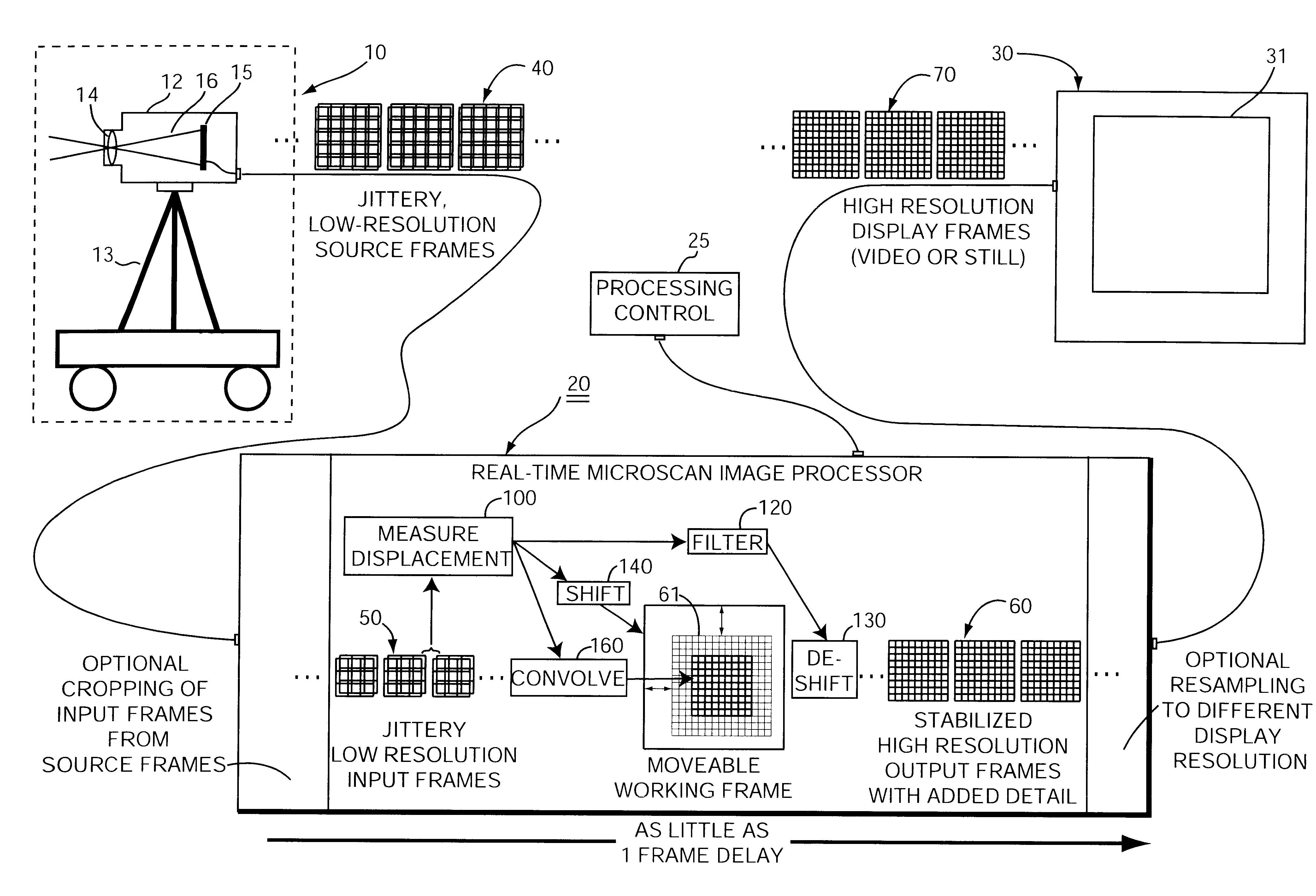
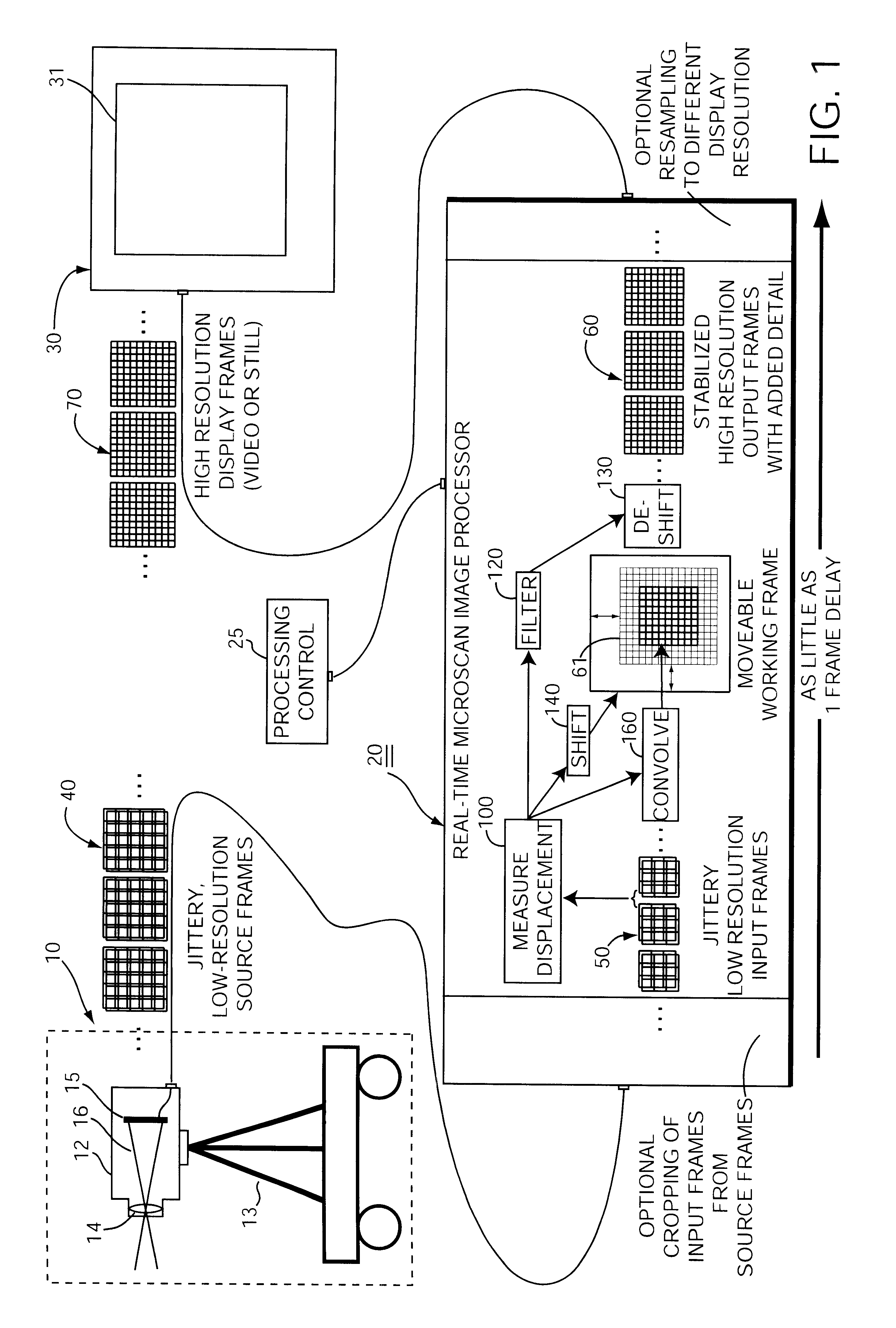
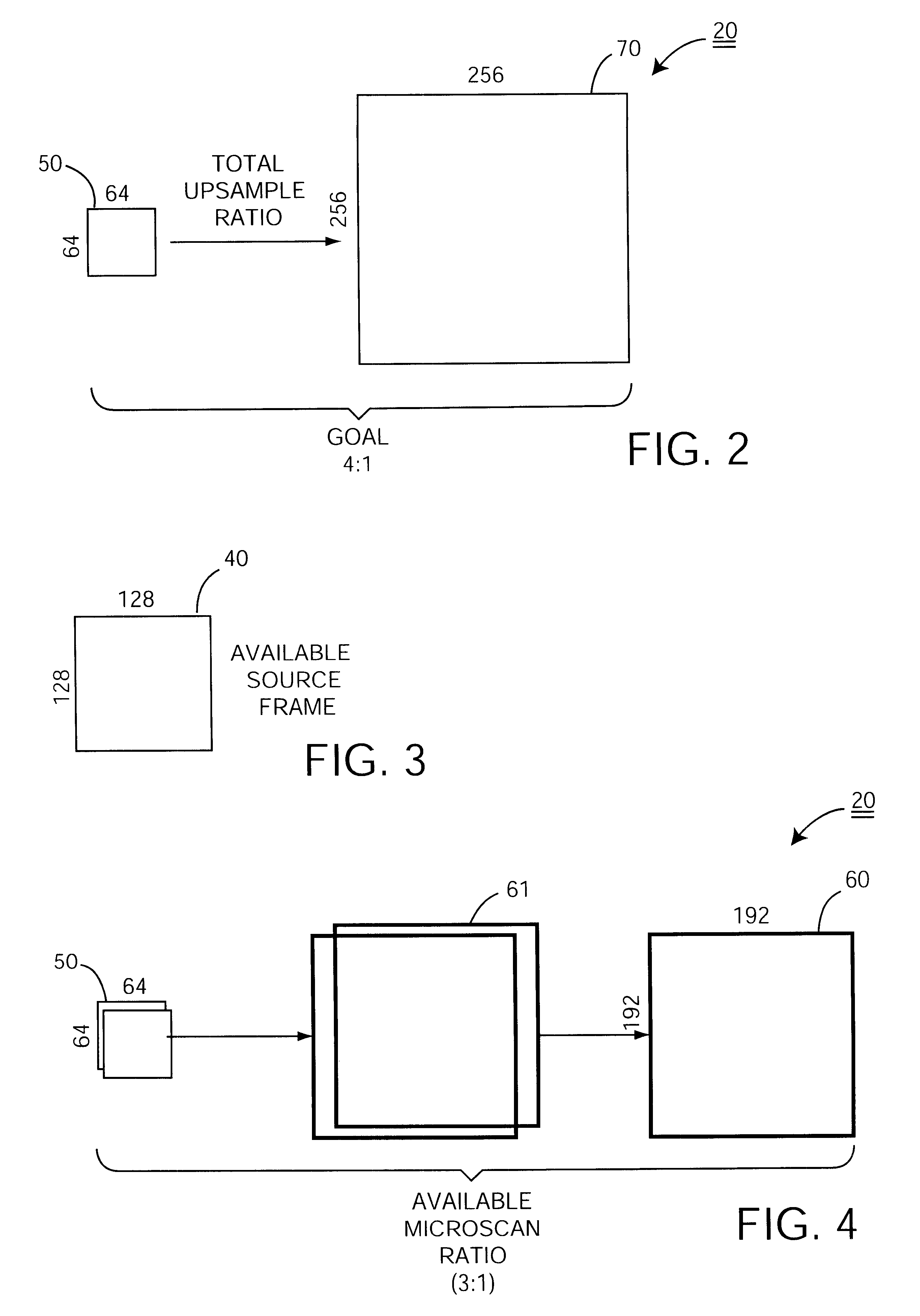
A method of processing low resolution input frames containing undersampled views of an optically imaged scene to produce a higher quality, higher resolution output frame. This method operates by obtaining a sequence of low resolution input frames containing different undersampled views of an optically imaged scene. With regard to each new low resolution input frame, the method involves the further steps of measuring a displacement between a previous low resolution input frame and a new low resolution input frame to sub-pixel precision to produce a measured displacement; coarsely registering a high resolution working frame with the new low resolution input frame based on the measured displacement; finely registering the new low resolution input frame with the high resolution working frame by expanding the new low resolution input frame into a new high resolution input frame based on the measured displacement; and merging the new high resolution input frame into the high resolution working frame to produce an output frame.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20090027542A1Travel direction is limitedReduce image qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging qualityMicro lens array
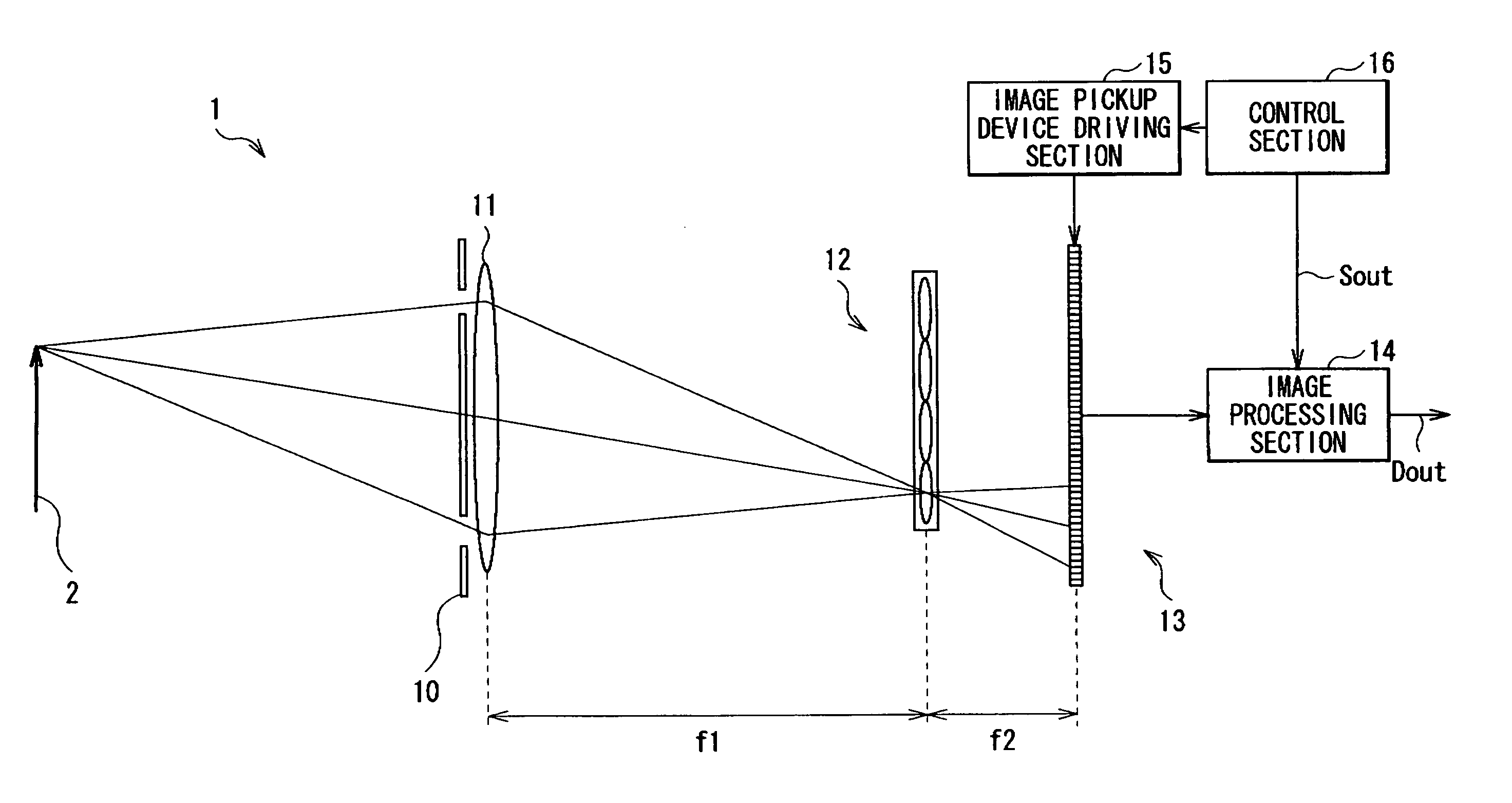
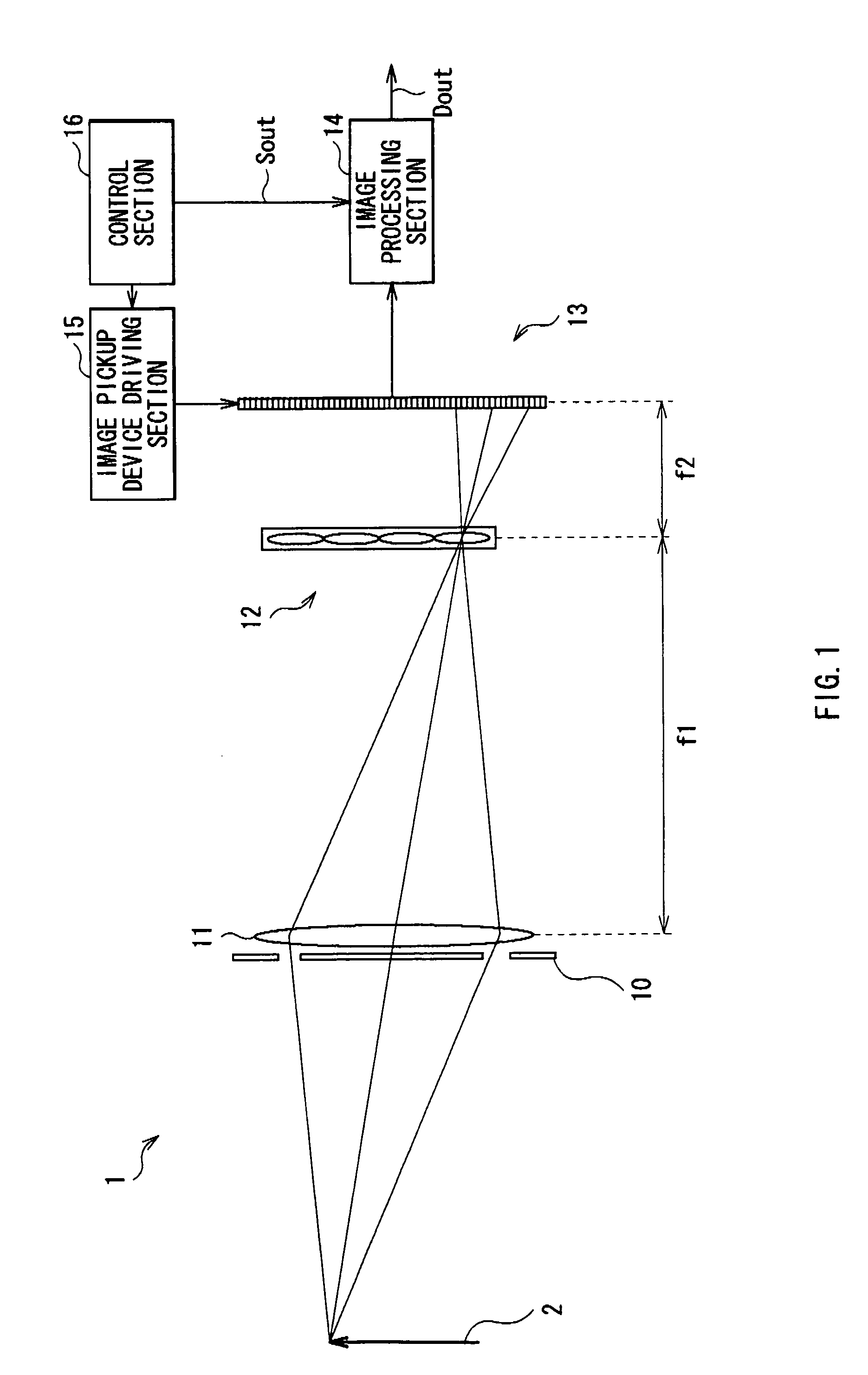
An image pickup apparatus capable of increasing the number of pixels in a reproduced image without a decline in image quality of a picked up image is provided. The image pickup apparatus includes: an image pickup lens section including an aperture stop, the aperture stop including a plurality of aperture sections; an image pickup device obtaining image pickup data on the basis of light received; and a microlens array section being arranged on the focal plane of the image pickup lens section between the image pickup lens and the image pickup device, and including one microlens for a plurality of pixels of the image pickup device.
Owner:SONY CORP
Methods and apparatus for measuring analytes using large scale fet arrays
ActiveUS20120247977A1Facilitate rapid acquisition of dataSmall sizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCMOSOrganismal Process
Methods and apparatus relating to very large scale FET arrays for analyte measurements. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes. In one example, chemFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in the concentration of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi), hydrogen ions, and nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Digital camera with non-uniform image resolution
InactiveUS20050259158A1Increase the number of pixelsUniform widthTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital dataImage resolution
The invention provides a system for isolating digital data representative of portions of a field of view. The system, which may be provided in the form of a digital camera, includes an array of sensor cells adapted to provide digital representations corresponding to at least a portion of the field of view, and a selector adapted to isolate a non-uniformly distributed subset of the digital representations provided by the array. The isolation may be performed based upon a set of values programmed in a programmable lookup table. A buffer is provided for holding the isolated digital representations.
Owner:ADAPTIVE IMAGING TECH
Digital camera, storage medium for image signal processing, carrier wave and electronic camera
InactiveUS7253836B1Increase capacityLow costTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsCamera lensCarrier signal
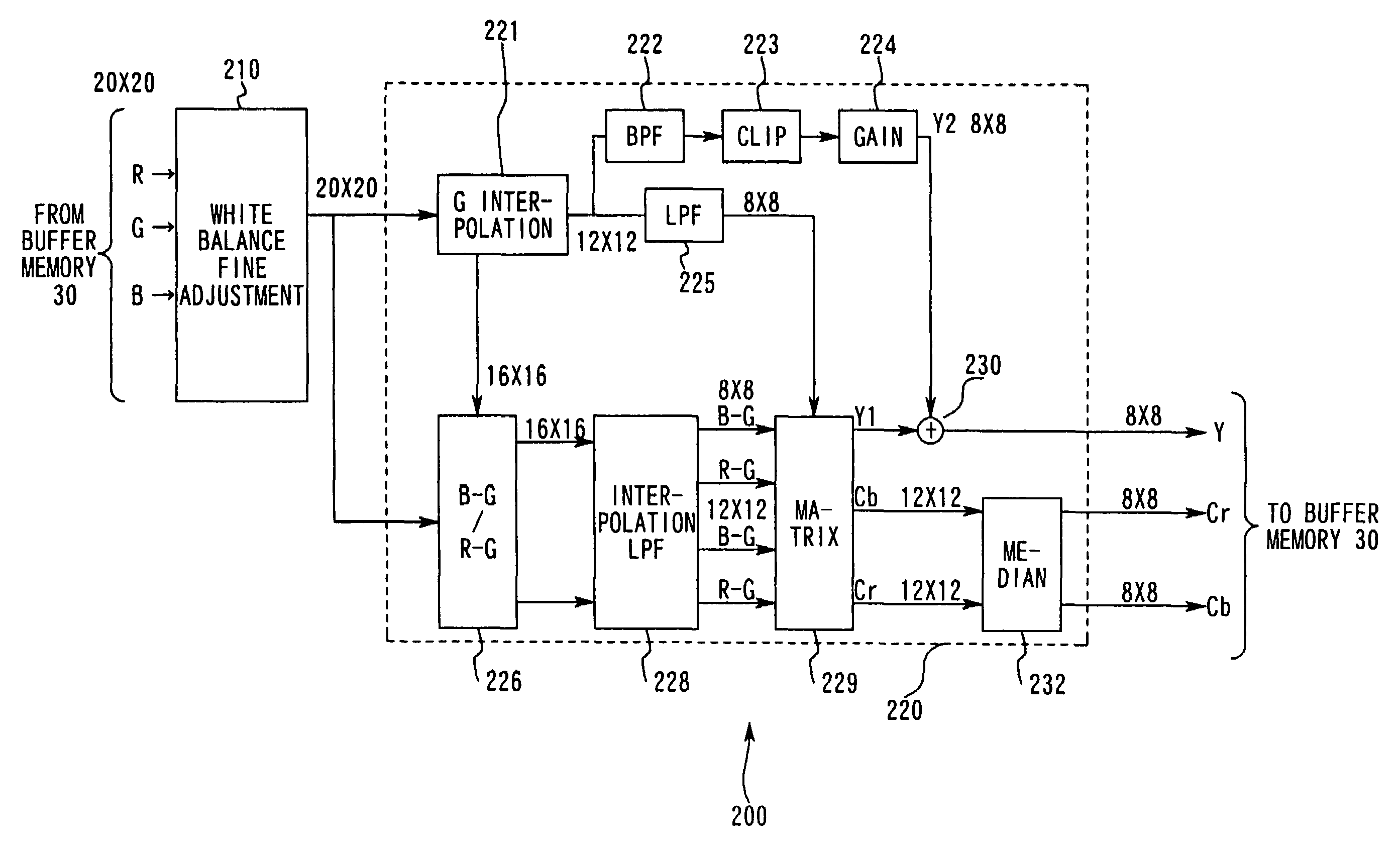
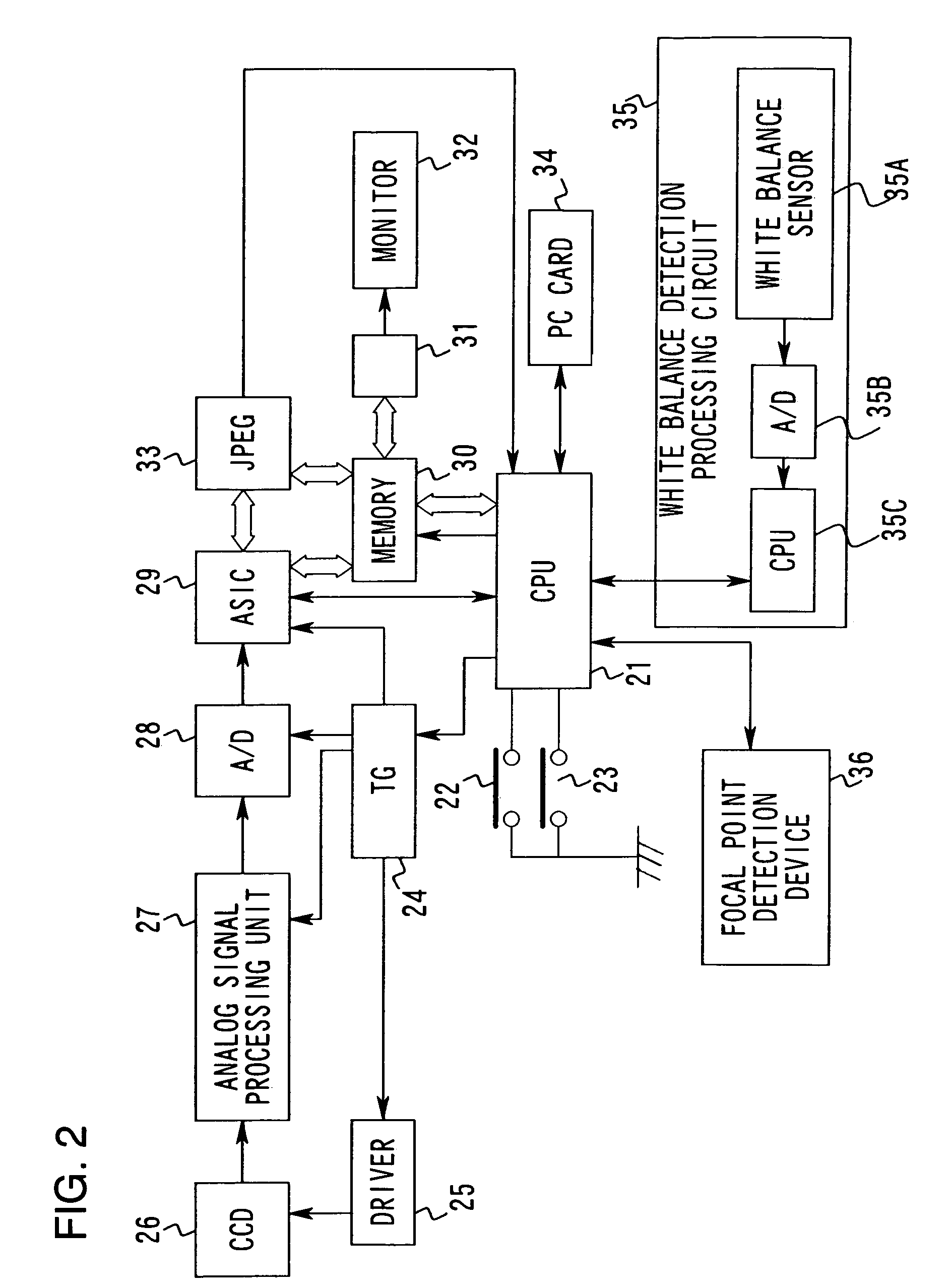
A CCD captures a subject image having passed through a taking lens and an image processing circuit performs various types of image pre-treatment including gamma correction and white balance on image data corresponding to n lines×m rows output by the CCD. The image processing circuit also performs format processing on the data. The data are then compressed at a compression circuit. The white balance adjustment and the like are implemented in line sequence at a line processing circuit which engages in signal processing in pixel sequence in units of individual lines in the output from the CCD. The image data having undergone the pre-treatment are then subjected to format processing prior to JPEG compression, at a block processing circuit that engages in signal processing in units of individual blocks each ranging over an n×m (N>n, M>m) block. In other words, the signal processing is performed in block sequence.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Driver circuit and display device
ActiveUS20100110623A1Reduce relative shiftEasy to makeSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriver circuitDisplay device
The driver circuit includes an inverter circuit having a first thin film transistor including a first oxide semiconductor film and a second transistor including a second oxide semiconductor film. The first thin film transistor and the second thin film transistor are enhancement transistors, in which a silicon oxide film including an OH group is provided on and in contact with the first oxide semiconductor film and the second oxide semiconductor film, and a silicon nitride film is provided on and in contact with the silicon oxide film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
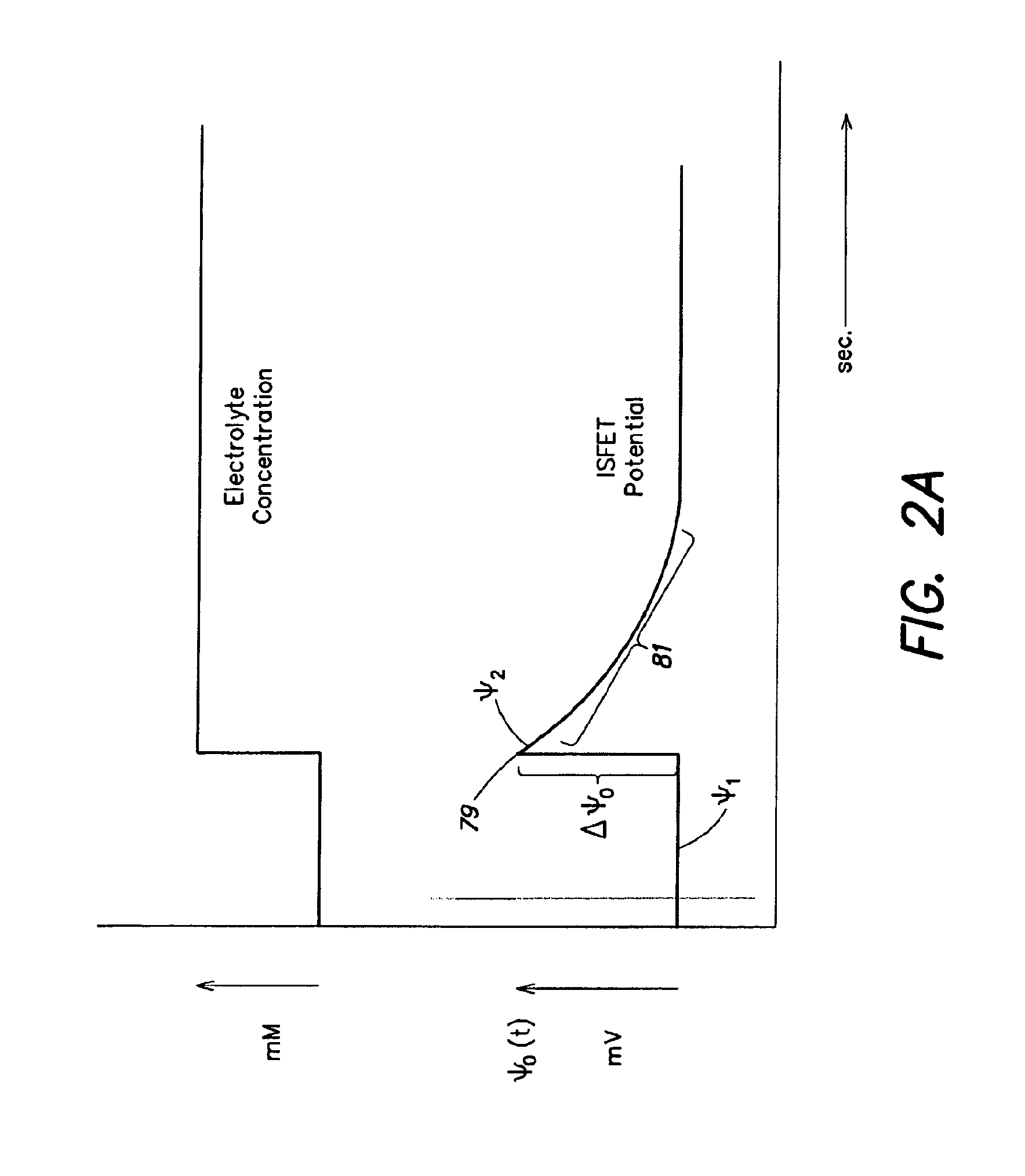
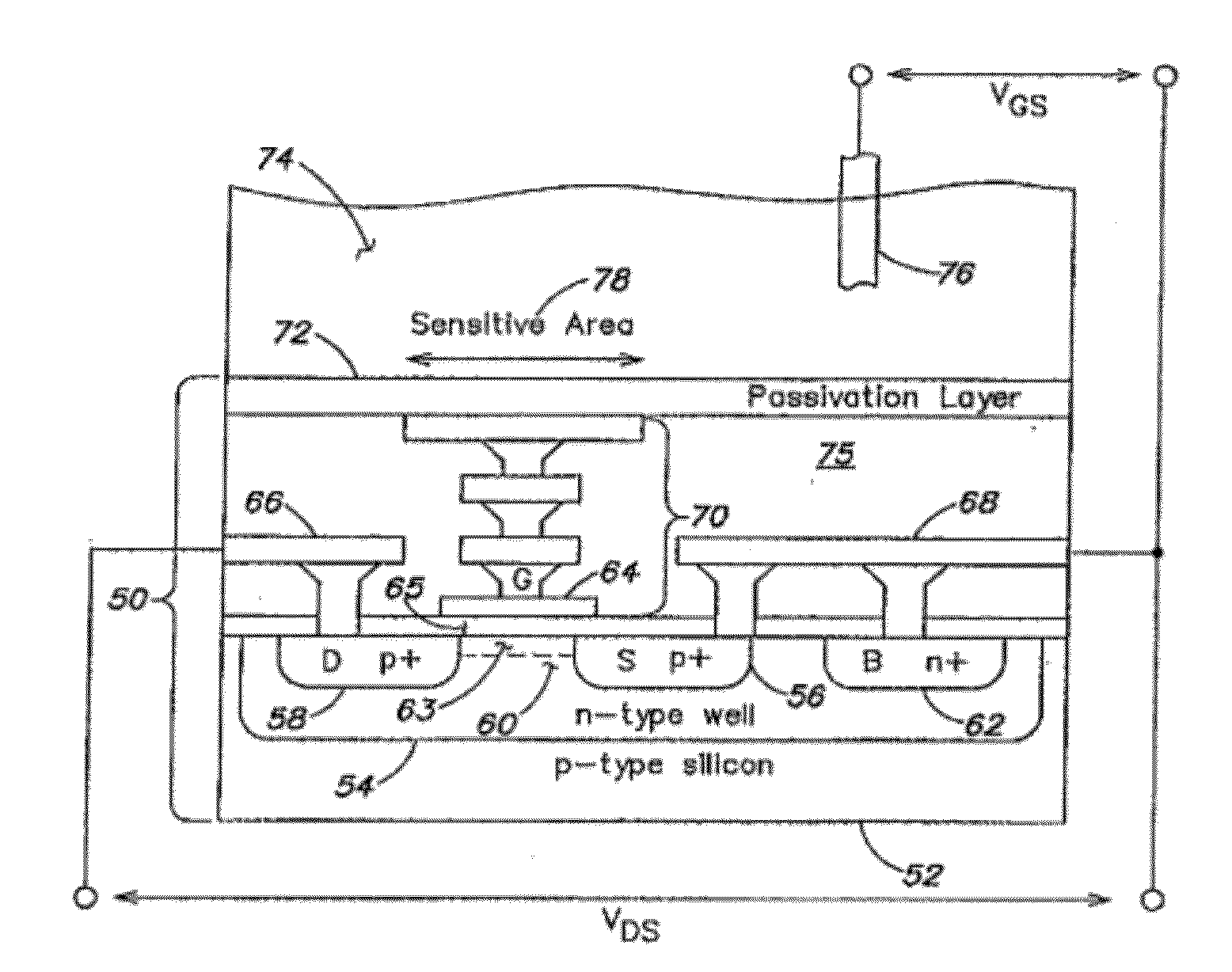
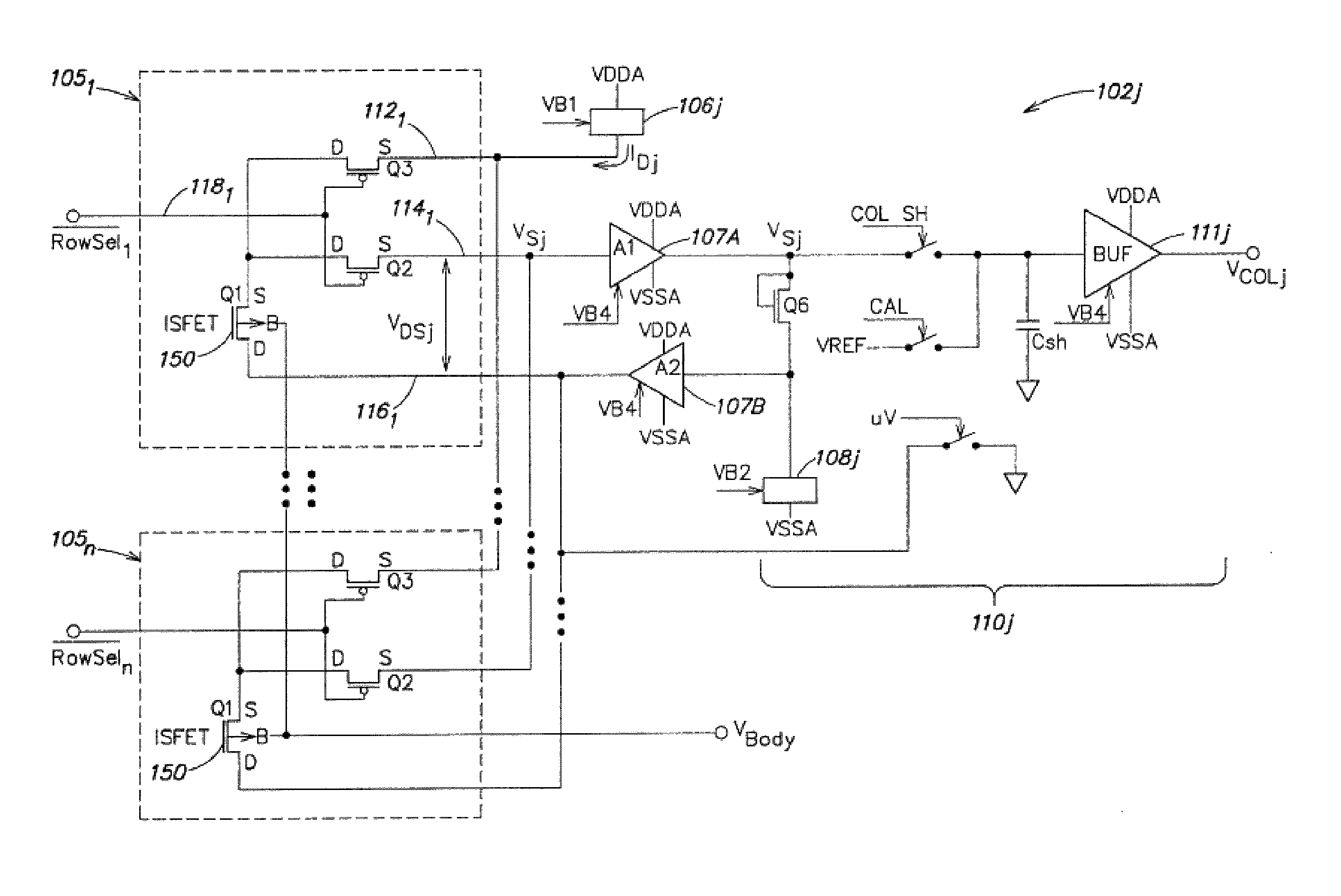
Methods and Apparatus for Detecting Molecular Interactions Using FET Arrays
ActiveUS20120088682A1Facilitate rapid acquisition of dataImprove signal-to-noise ratioTransistorWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCMOSAnalyte
Methods and apparatuses relating to large scale FET arrays for analyte detection and measurement are provided. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
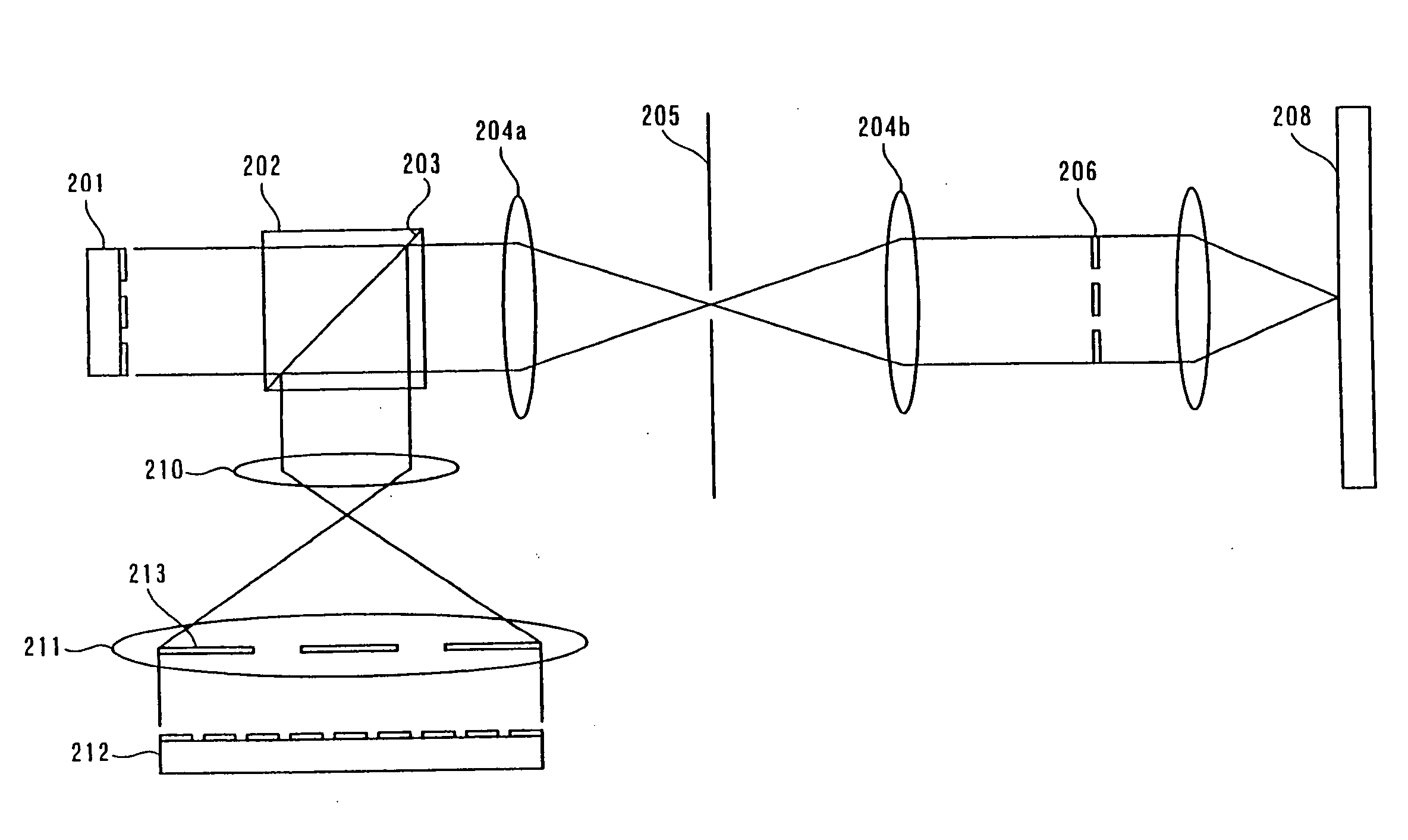
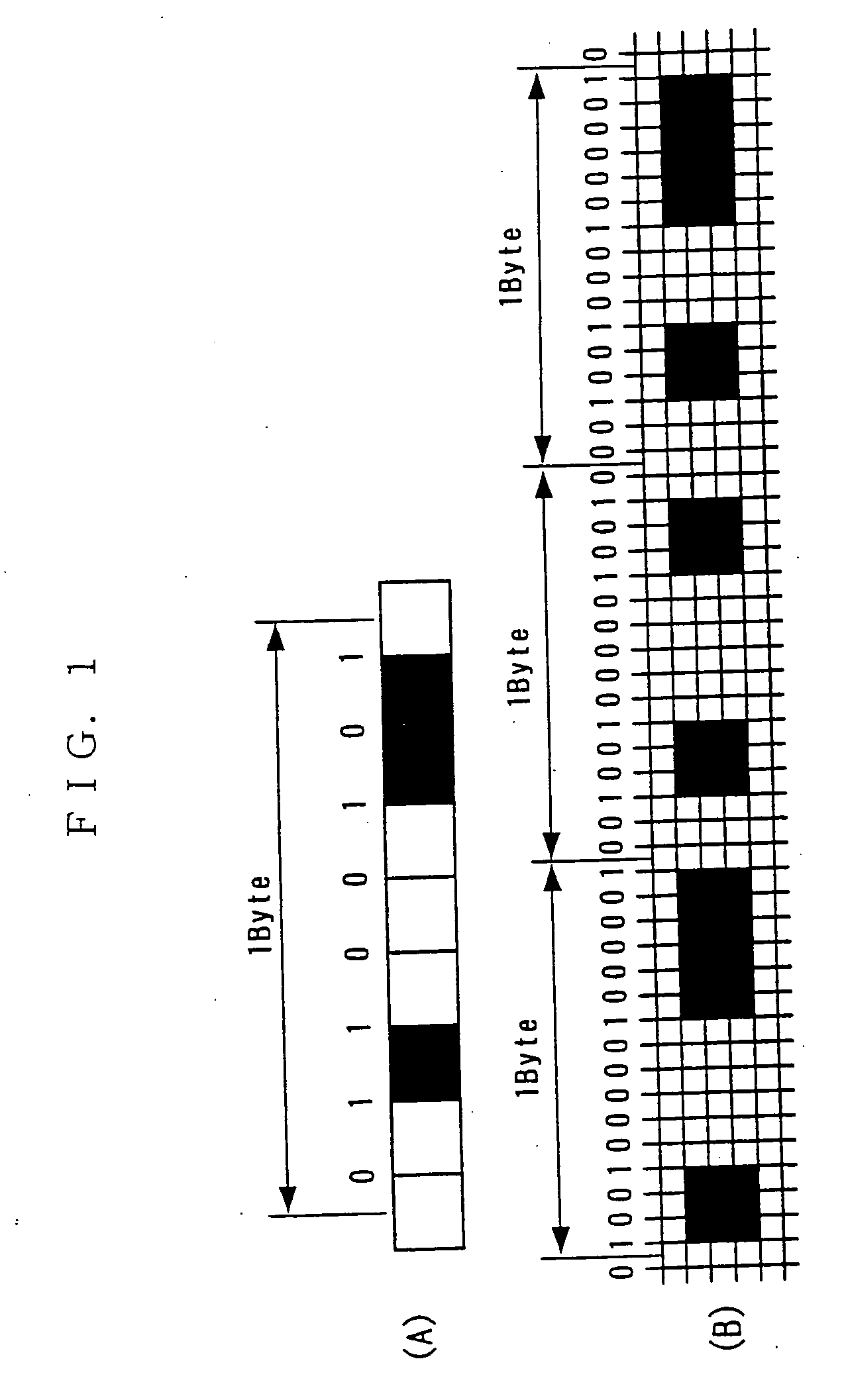
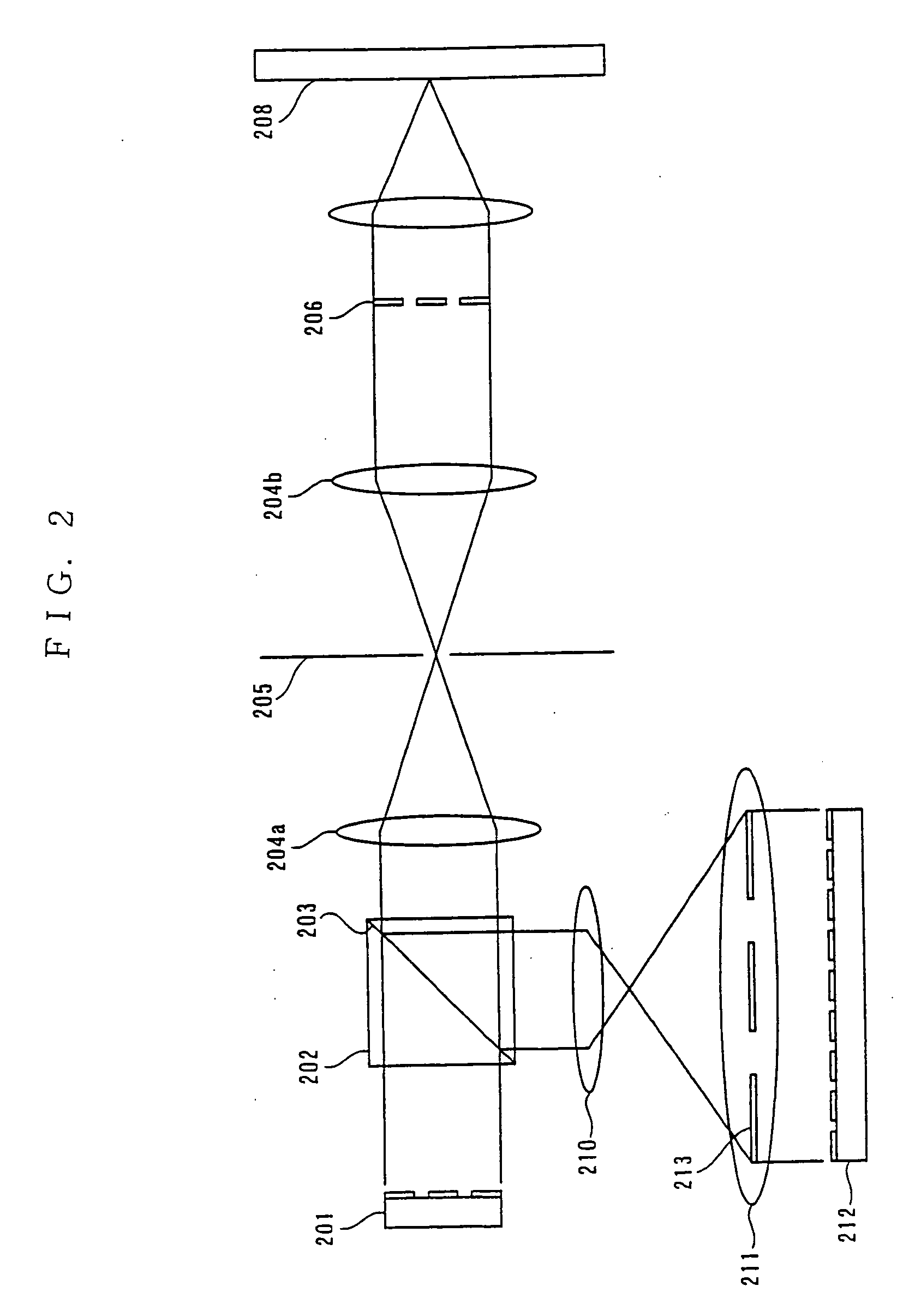
Information recording method, reproducing method, and recording/reproducing method utilizing holography
InactiveUS7321541B2Improve recording densityIncrease recording capacityRecord information storageDigital storageSpatial light modulatorRecording density
A method for recording information on a recording medium utilizing an interference pattern by interference between an information light modulated spatially with digital pattern information displayed on a spatial light modulator having multiple pixels and a reference light for recording. In order to provide a novel recording method capable of enhancing the recording density and the transfer rate furthermore, digital information to be recorded is represented by match / mismatch of the attributes of adjacent pixels in the spatial light modulator to produce digital pattern information.
Owner:OPTWARE
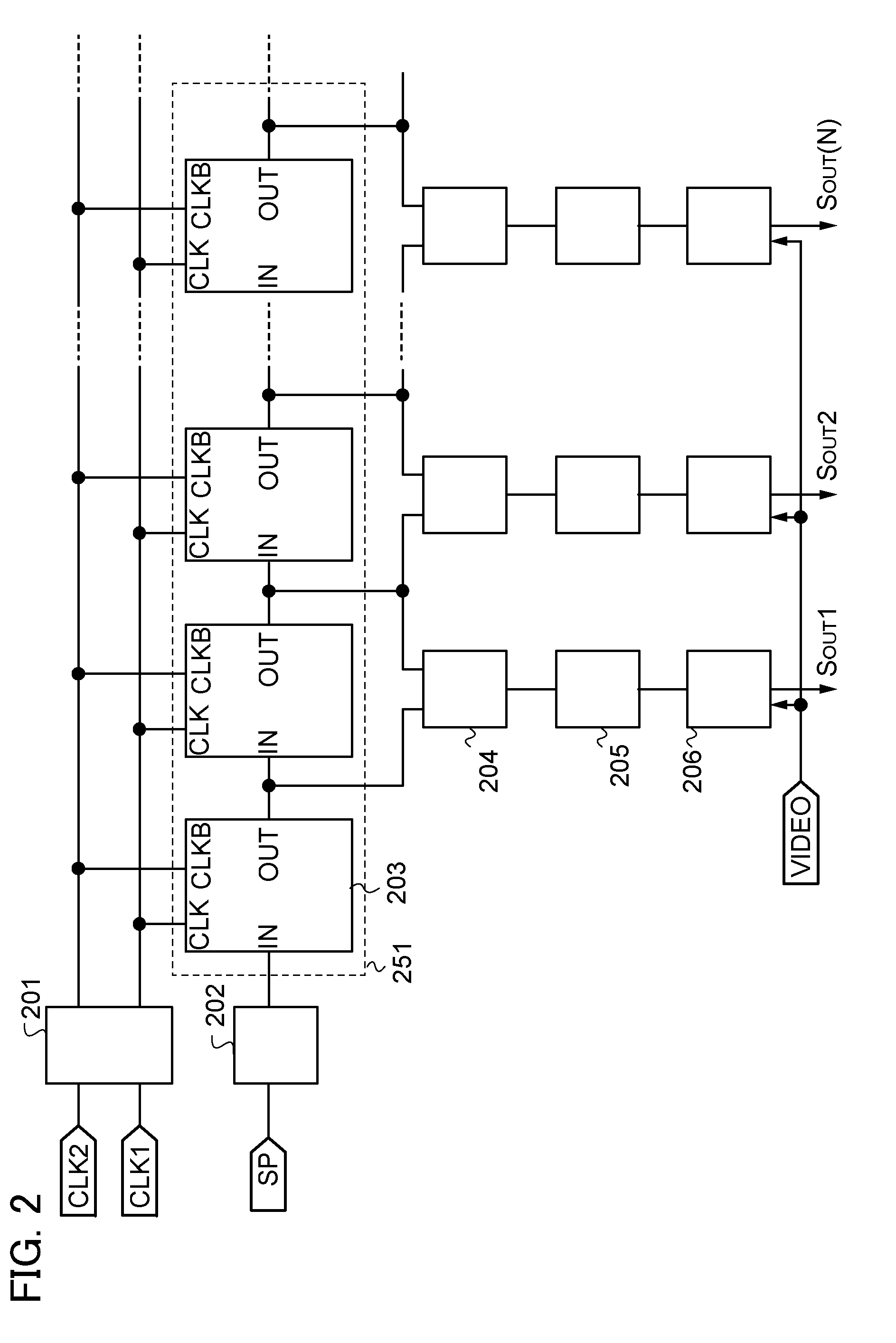
Display device and semiconductor device
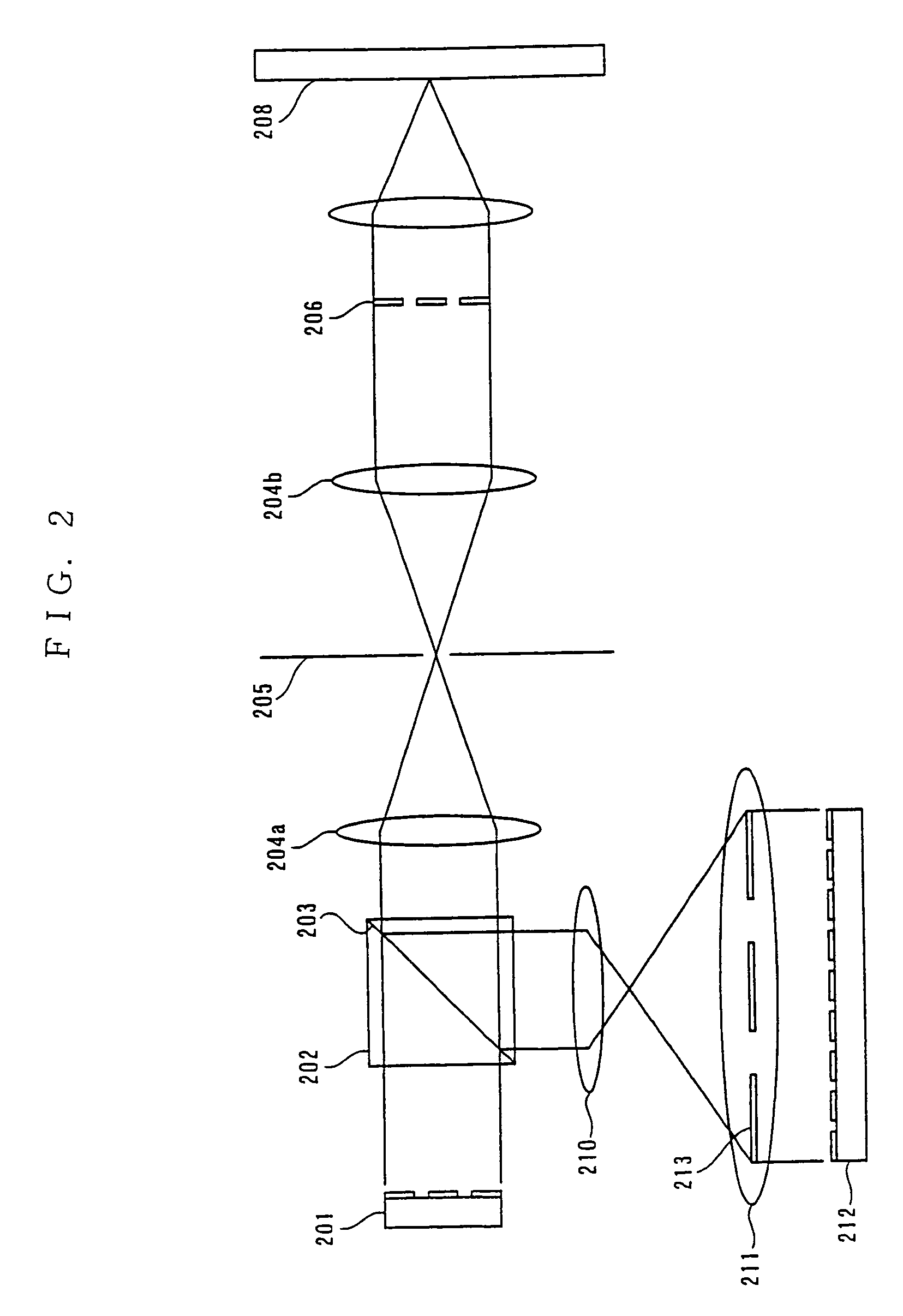
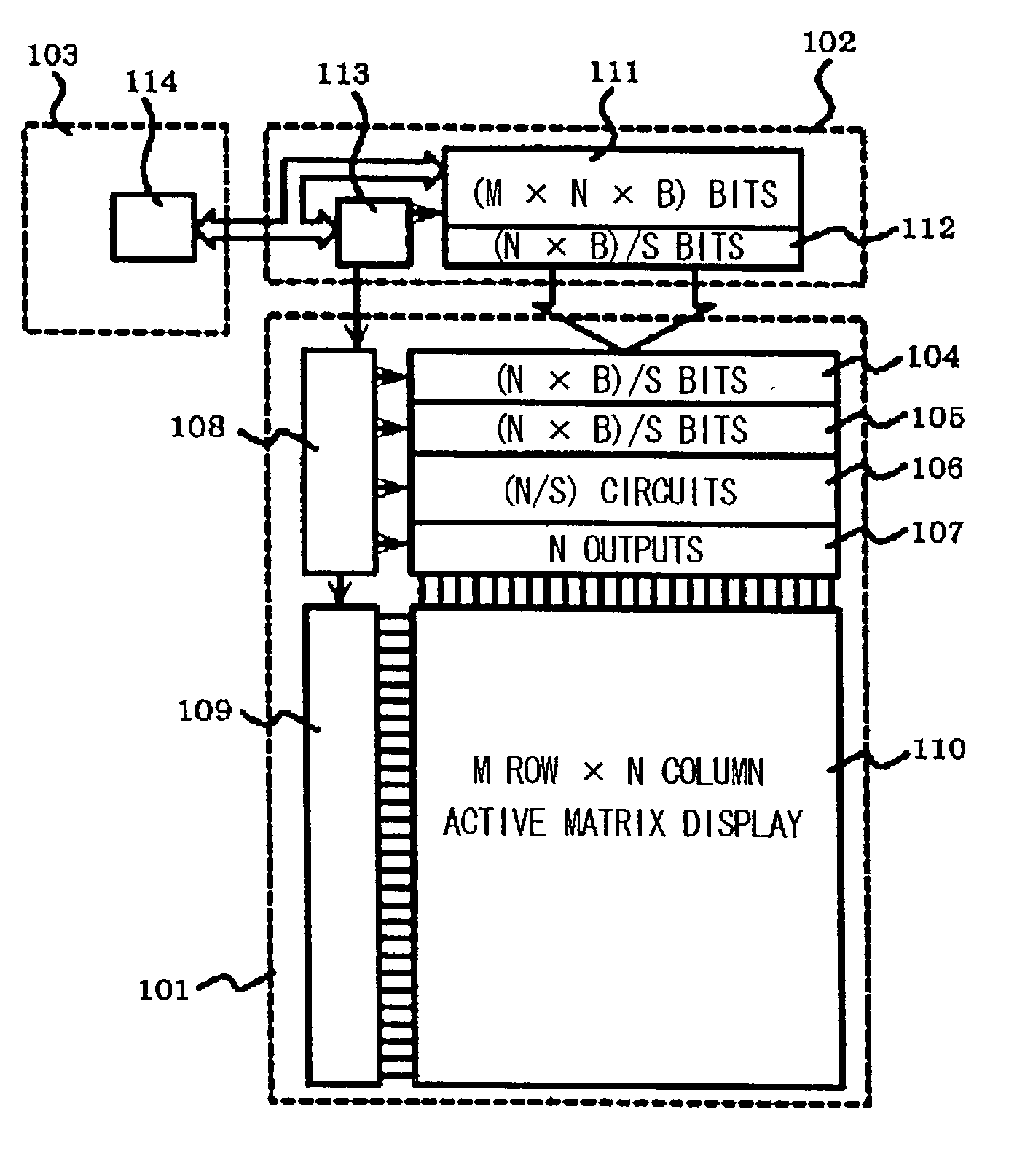
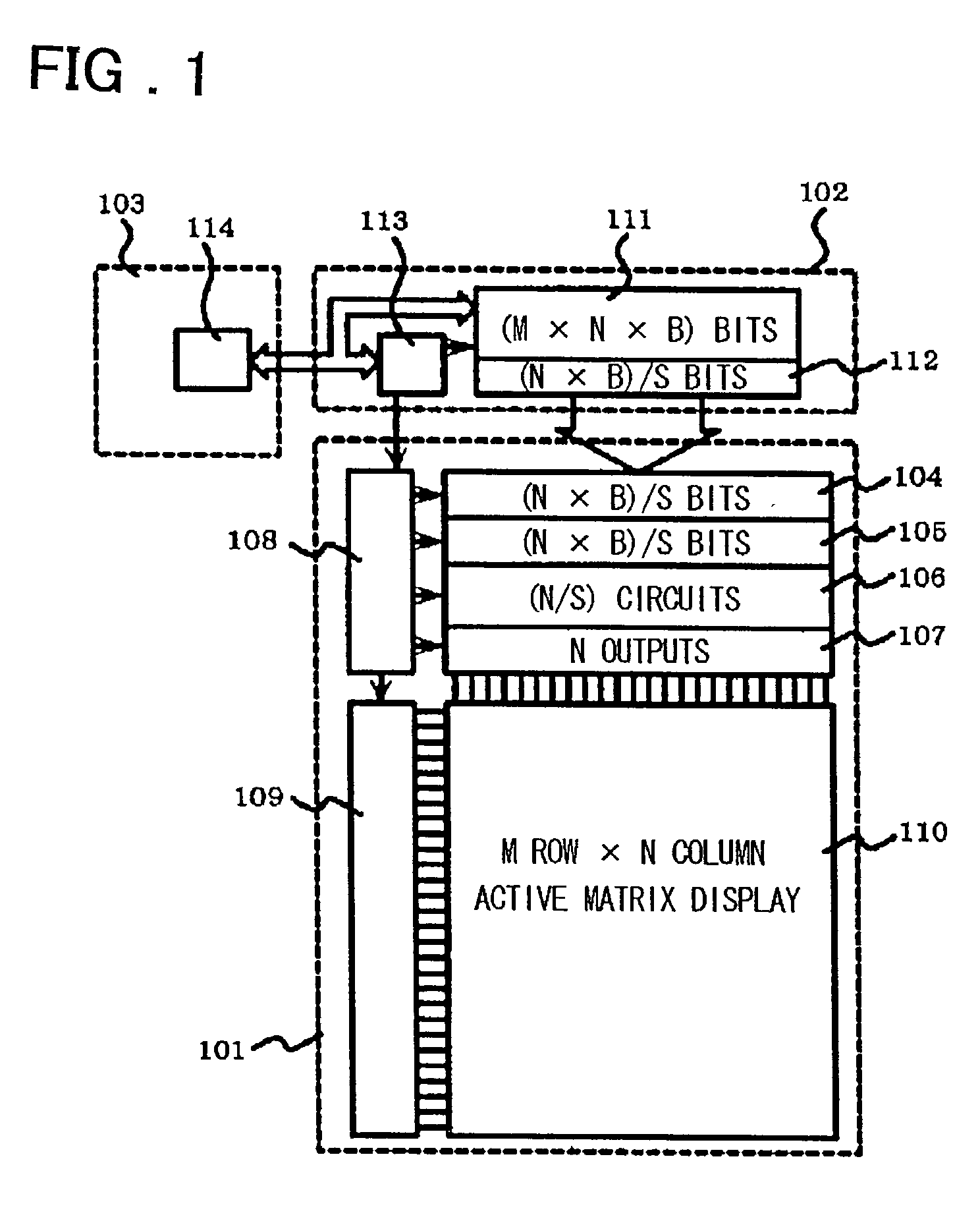
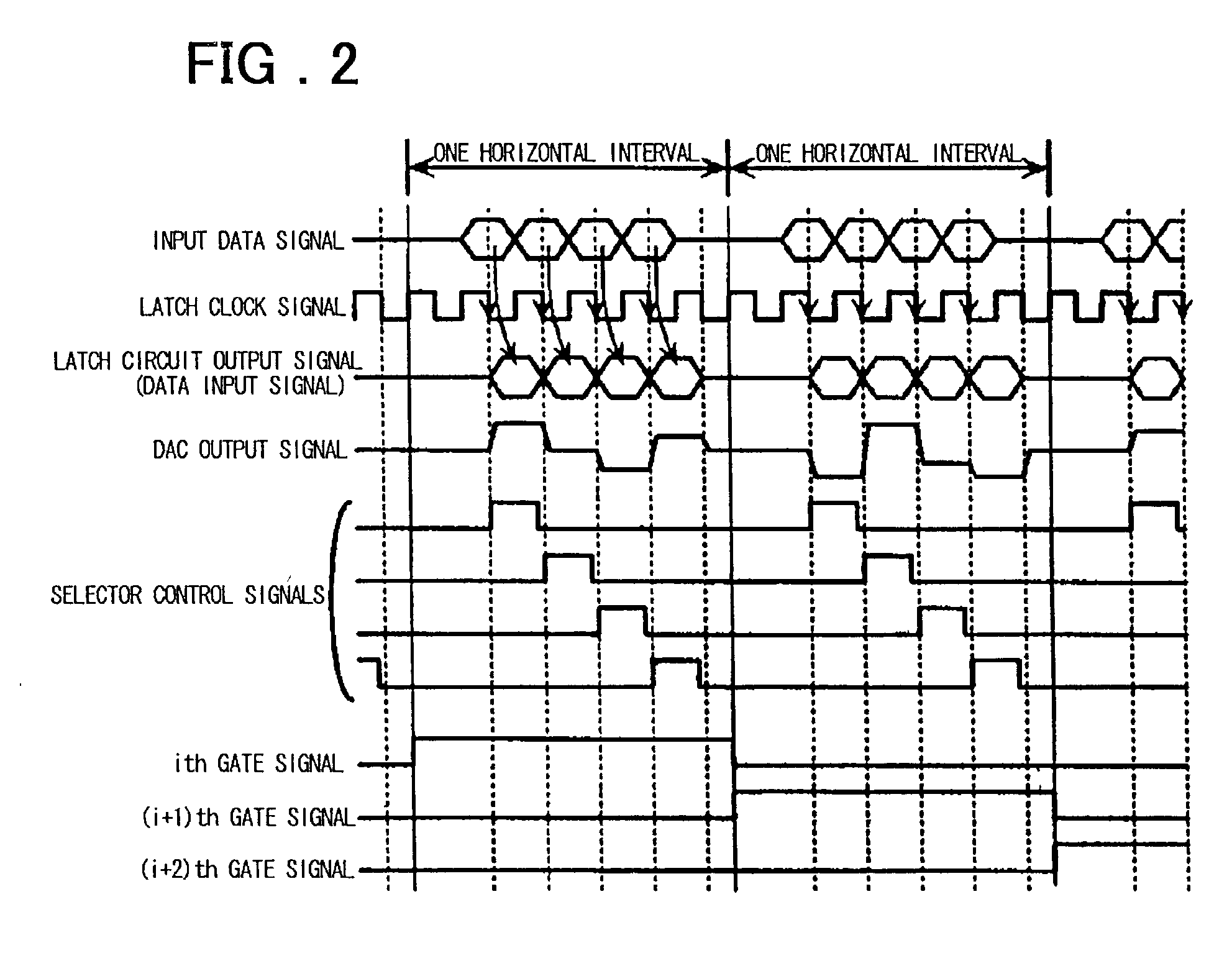
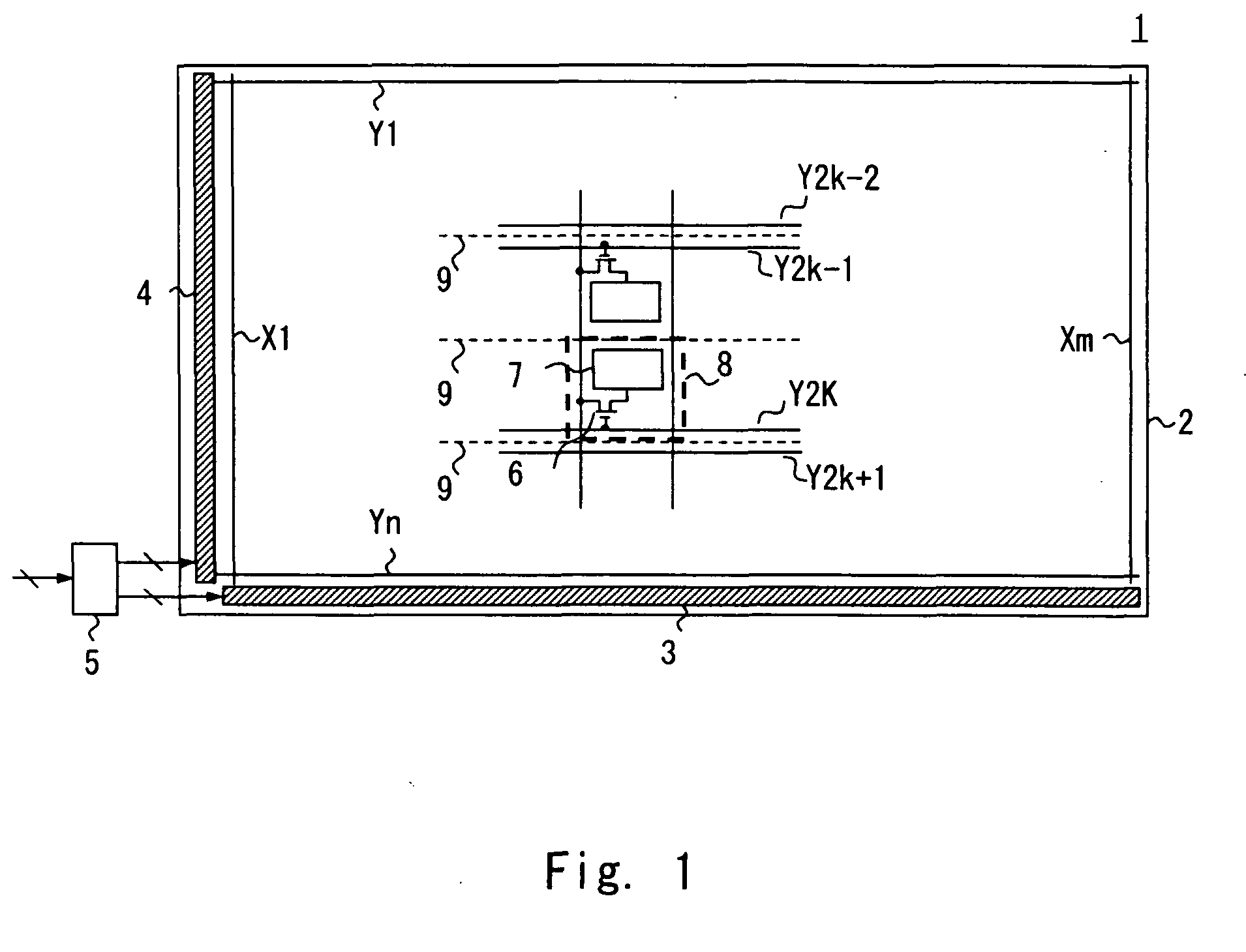
InactiveUS20030067434A1High definitionIncrease the number of pixelsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringLine driver
A display device of high definition, multiple colors and low power consumption includes a display panel having a pixel section in which pixels are arrayed in the form of a matrix at the cross points of a plurality of data lines and a plurality of scanning lines, a scanning circuit for applying voltage sequentially to the plurality of scanning lines, and a data-line driver, which receives display data supplied by a host device, for applying signals corresponding to the display data to the plurality of data lines. Provided external to the display panel is a controller IC having a display memory for storing display data corresponding to the pixel section, an output buffer for reading data out of the display memory and outputting this data to the display panel, and a controller for controlling the display memory and output buffer and communication with the host device. The display panel is provided with a digital / analog converter, which forms part of the data-line driver, for converting display data represented by a digital signal to an analog signal. The width of a bus for data transfer between the controller IC and data-line driver of the display panel is such that data of a greater number of bits is transferred in parallel by a single transfer than is transferred by the bus between the controller and the host device. This allows the operating frequency of the data-line driver to be reduced.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
System for Imaging Lesions Aligning Tissue Surfaces
ActiveUS20140350395A1Easy to useLow costTelevision system detailsImage enhancementBladder cancerRadiology
Owner:ORLUCENT INC
Methods for operating chemically-sensitive sample and hold sensors
ActiveUS8496802B2Facilitate rapid acquisition of dataSmall sizeTransistorWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCMOSAnalyte
Methods and apparatus relating to very large scale FET arrays for analyte measurements. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes. In one example, chemFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Solid-state imaging element and electronic information device
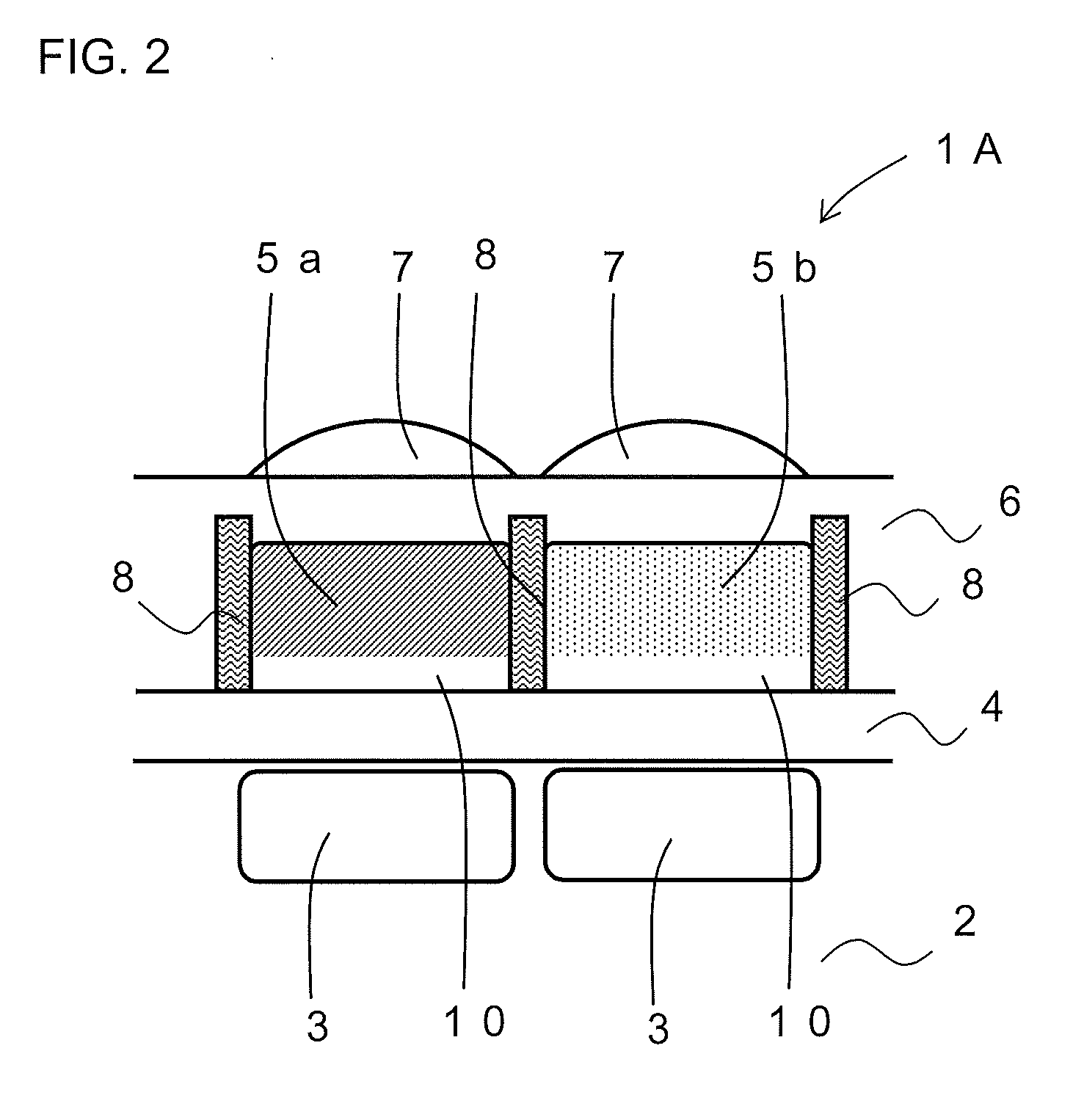
InactiveUS20110298074A1Color reproducibility is degradedReduce distanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
A solid-state imaging element according to the present invention includes a plurality of light receiving sections formed in a pixel array, each light receiving section constituted of a semiconductor element for performing a photoelectric conversion on and capturing an image of image light from a subject, the solid-state imaging element further including: a light shielding wall or a reflection wall provided therein for pixel separation, in between the light receiving sections adjacent to one another in a plan view on a light entering side from the light receiving sections; and a color filter wherein at least a part of the color filter is embedded between the light shielding walls or the reflection walls, in such a manner to correspond to each of the plurality of light receiving sections, so that the distance between the color filter and a substrate can be shortened.
Owner:SHARP KK
Information recording method, reproducing method, and recording reproducing method utilizing holography
InactiveUS20060050544A1Enhancement be weakenIncrease in number of pixelRecord information storageDigital storageRecording densityHolography
A method for recording information on a recording medium utilizing an interference pattern by interference between an information light modulated spatially with digital pattern information displayed on a spatial light modulator having multiple pixels and a reference light for recording. In order to provide a novel recording method capable of enhancing the recording density and the transfer rate furthermore, digital information to be recorded is represented by match / mismatch of the attributes of adjacent pixels in the spatial light modulator to produce digital pattern information.
Owner:OPTWARE
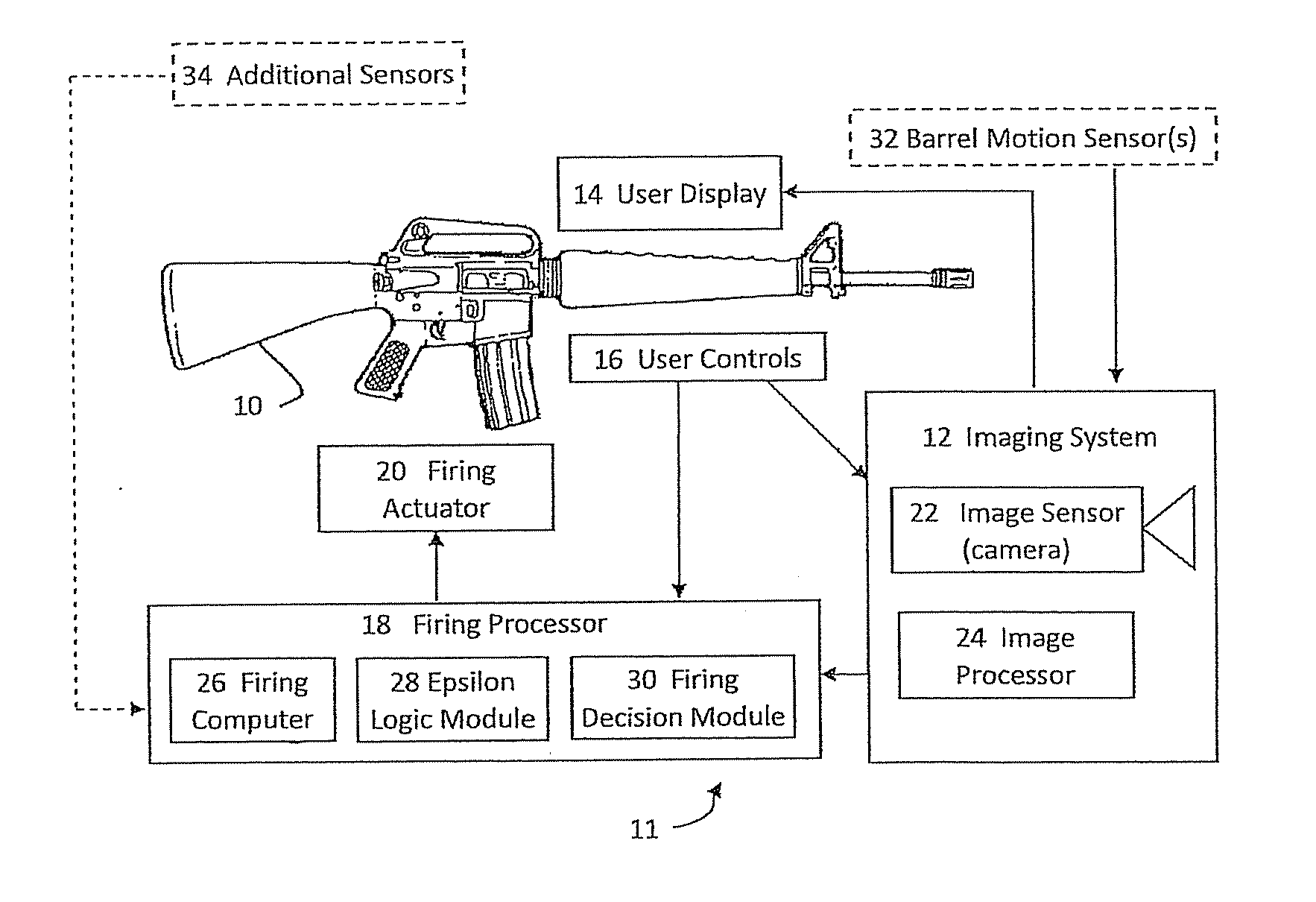
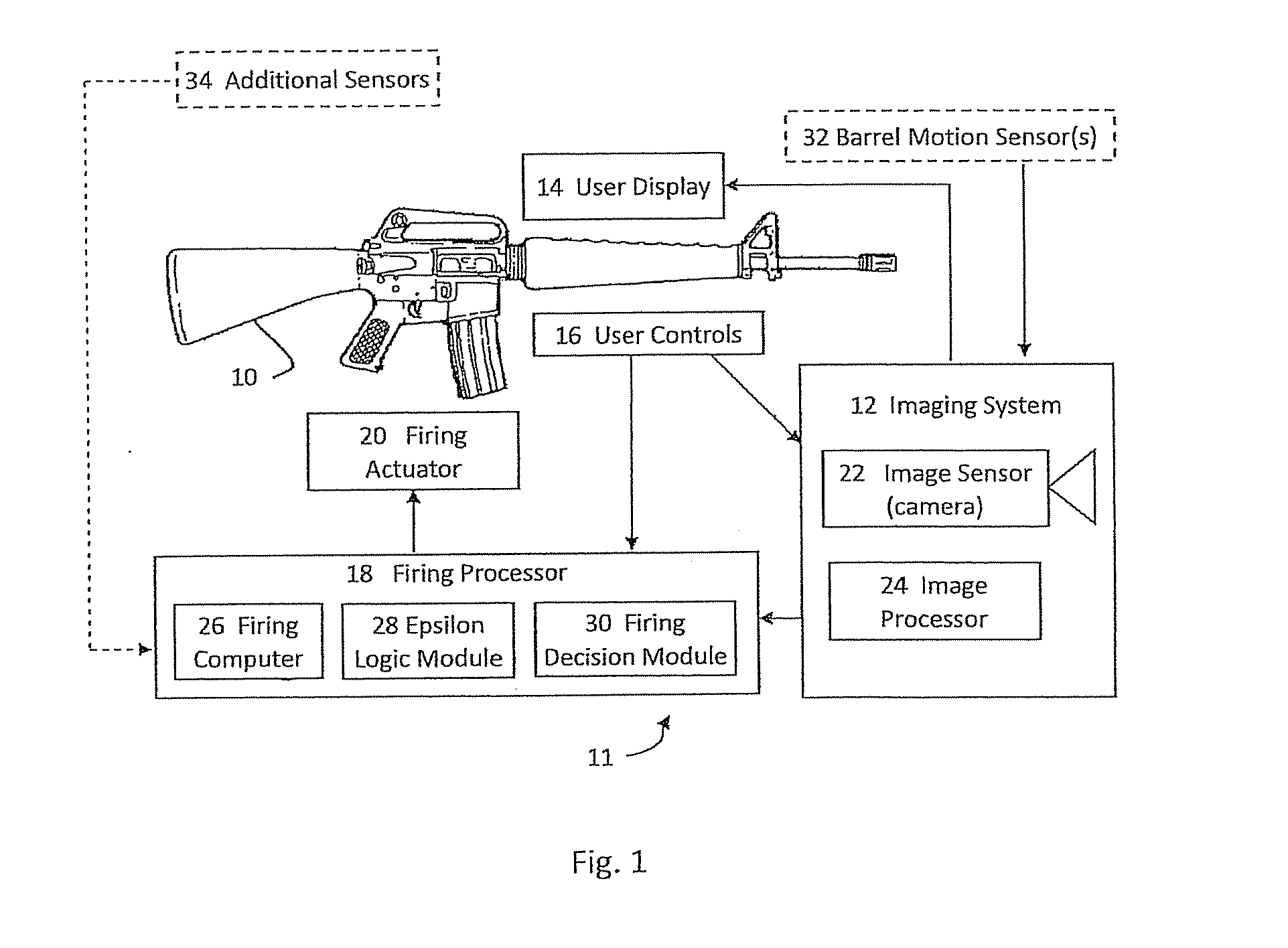
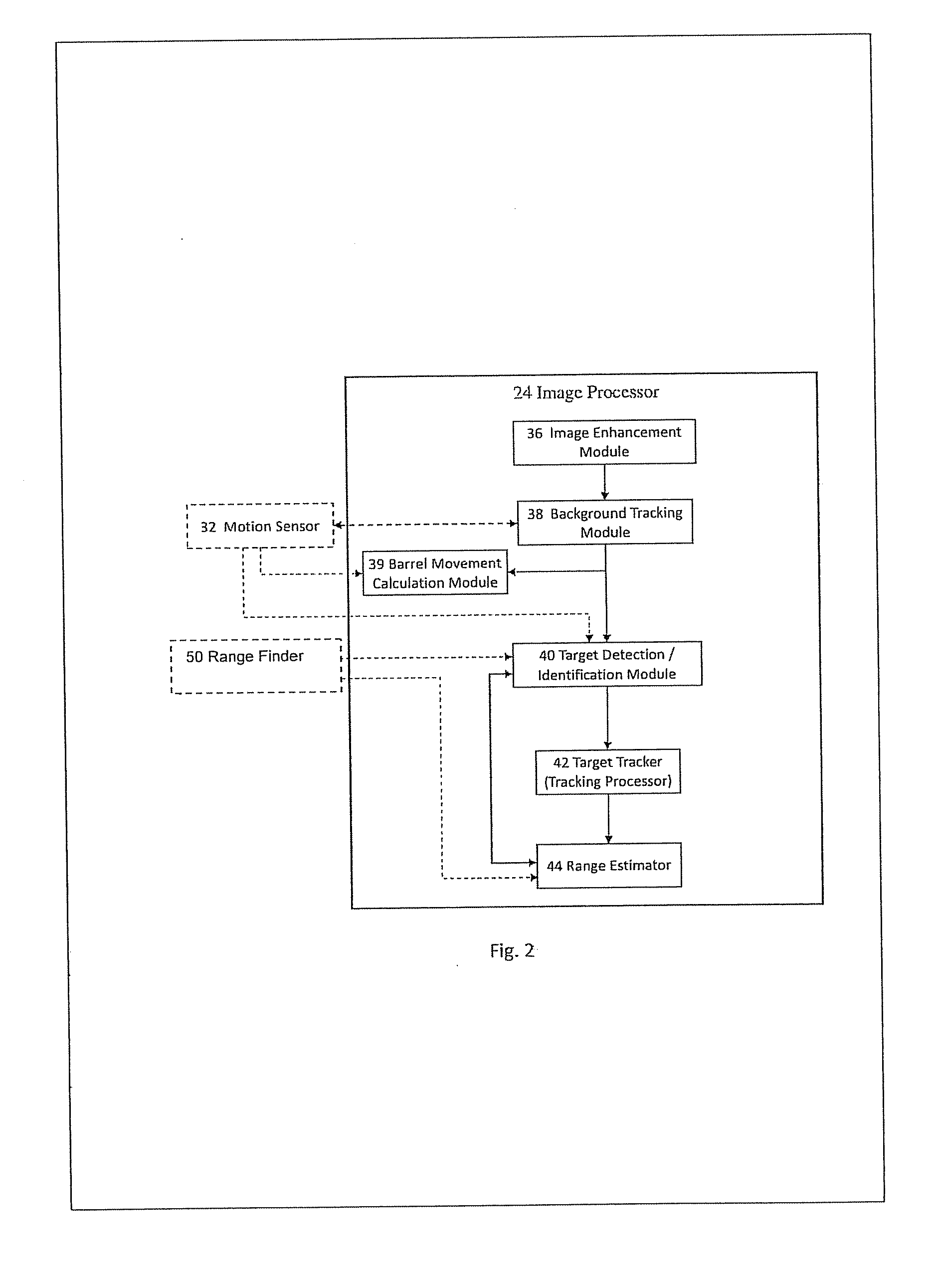
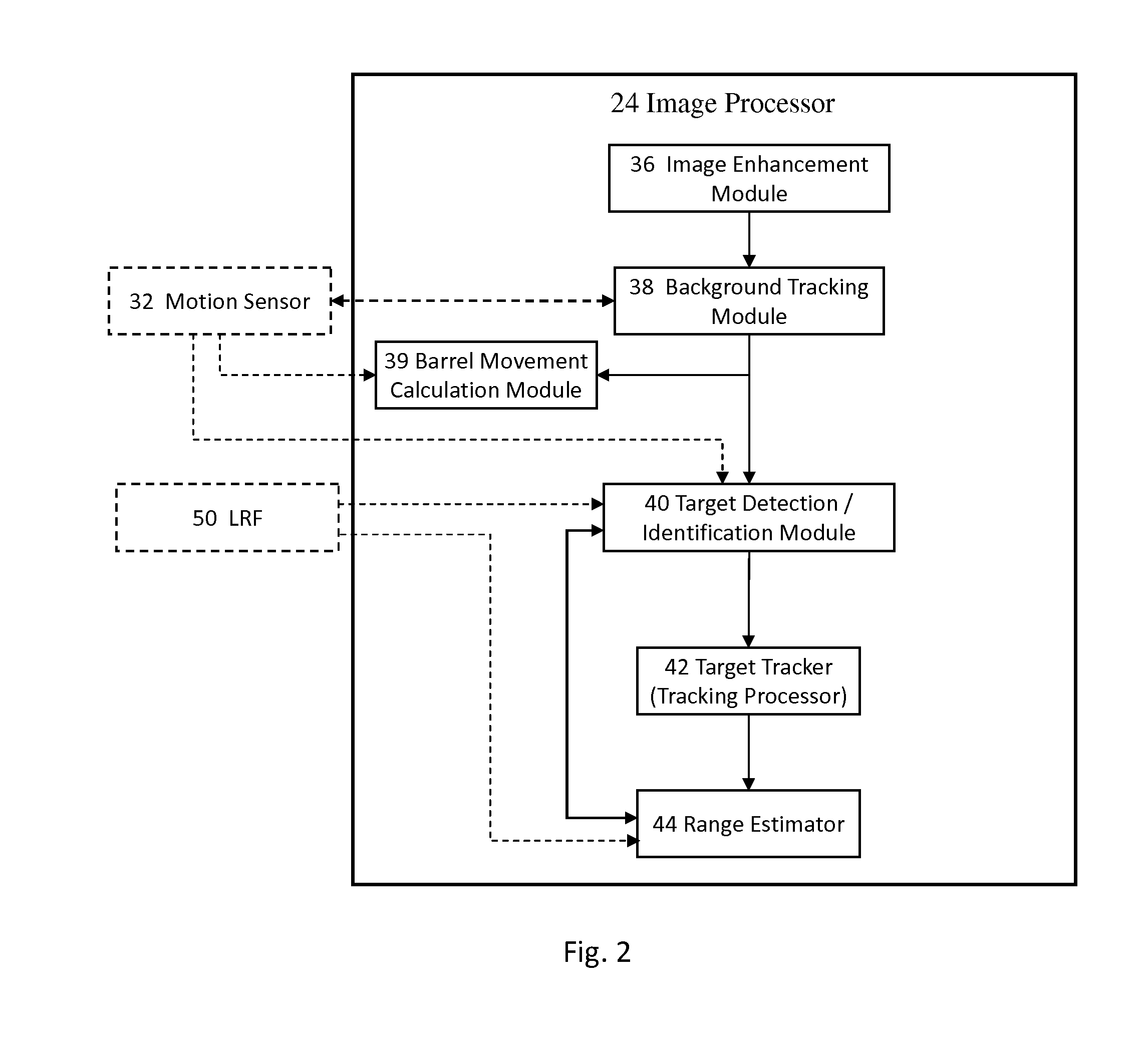
Firearm aiming system with range finder, and method of acquiring a target
ActiveUS20150108215A1Improve firing efficiency and effectivenessImprove effectivenessOptical rangefindersFiring/trigger mechanismsImage systemUser control
An aiming system of an aimable device includes a user display, an imaging system, user controls, a tracker, and a range finder such as a LRF. The imaging system displays, on the user display, an indicator of the direction in which the device points. The user uses the user controls to lock on a target towards which the device points according to the indicator. Then the tracker tracks the target, and the range finder measures the range to the tracked target. The tracker aims the range finder at the target, or alternatively scans the target and its background, one-dimensionally or two-dimensionally.
Owner:SMART SHOOTER
Imaging system for reading target with multiple symbols
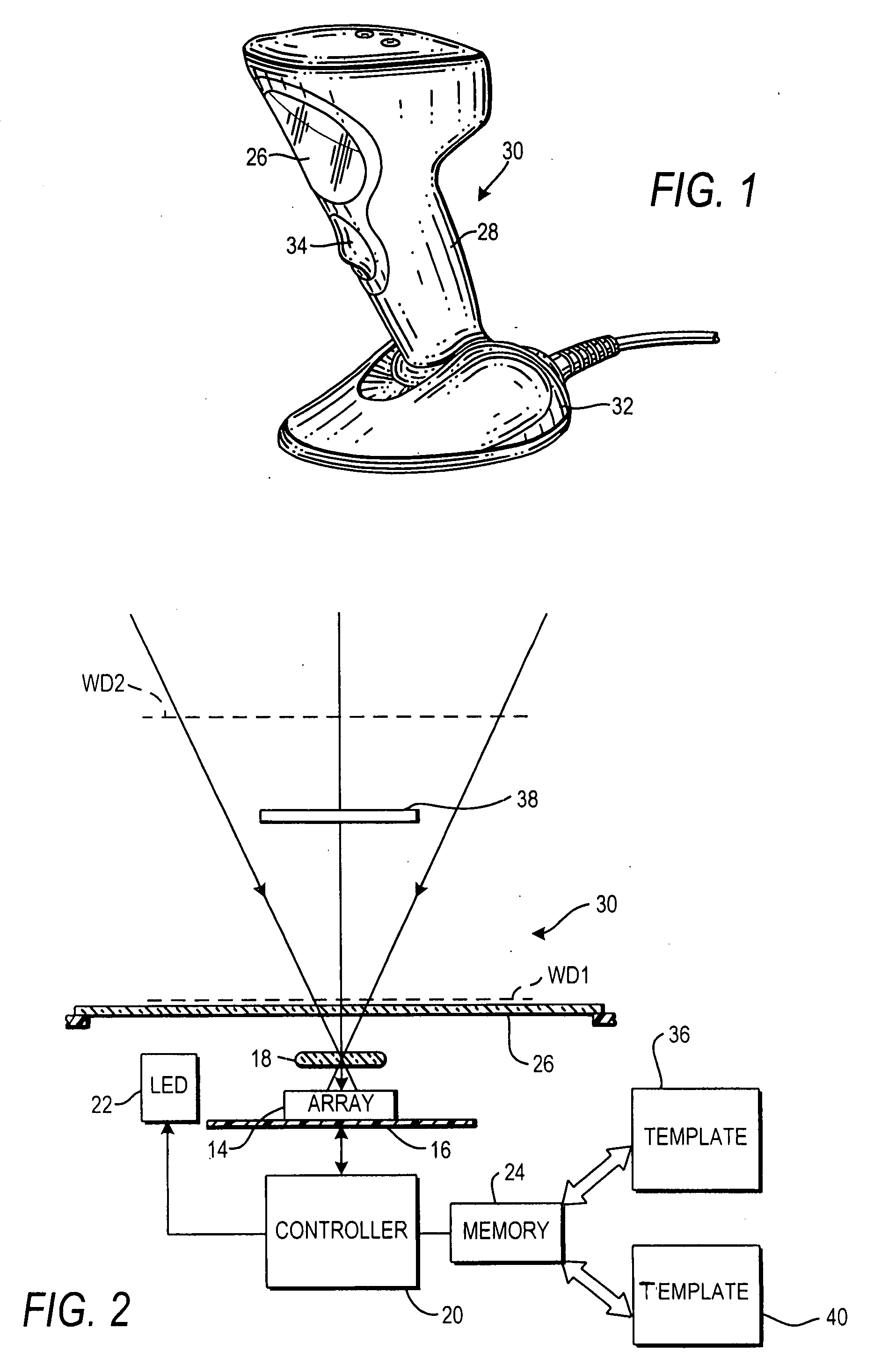
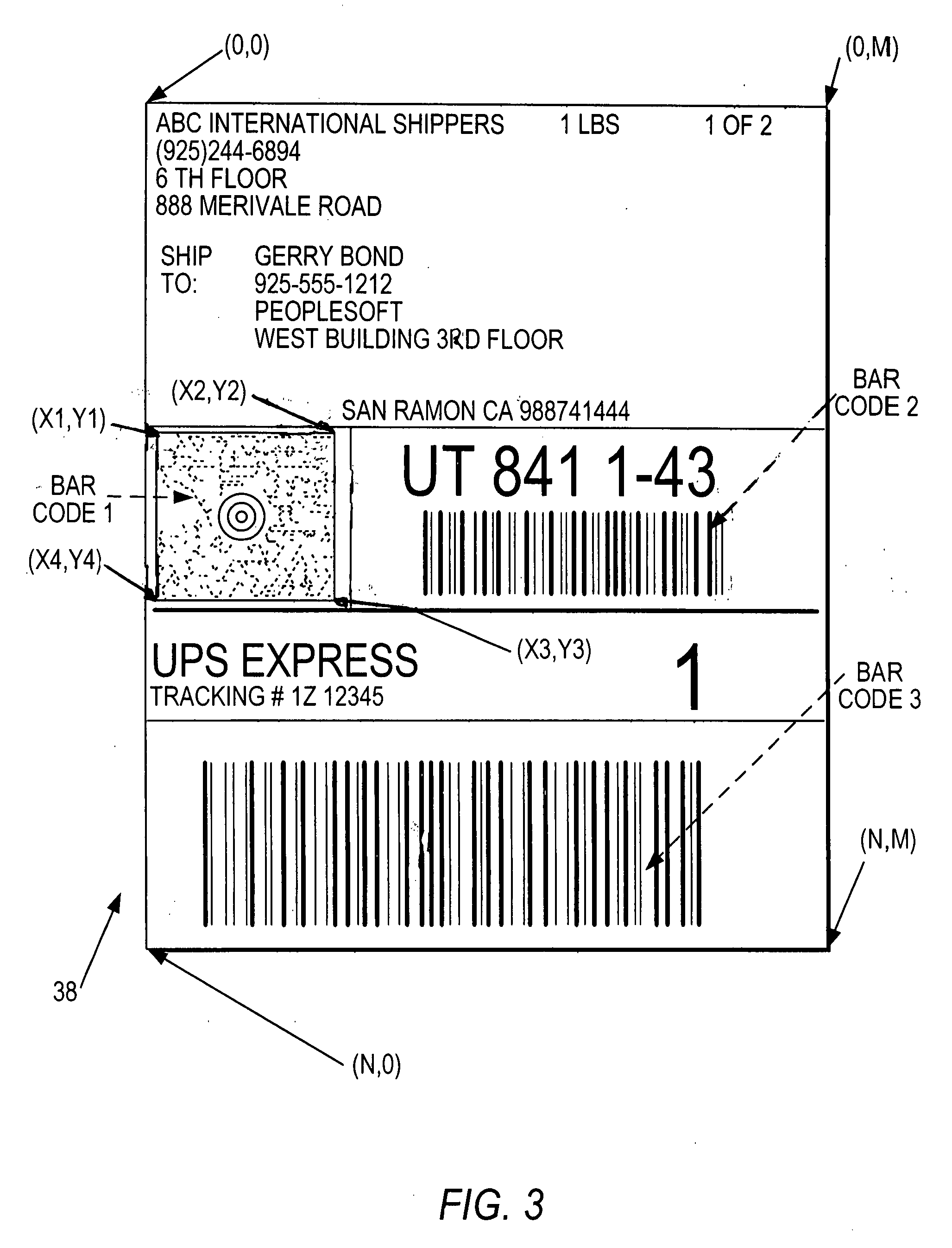
ActiveUS20090057411A1Easy and efficient processingSpeedTransmission systemsSpecial data processing applicationsField of viewImage system
An imaging system for acquiring images of multiple indicia, such as symbols and non-symbols, on a target, such as a label, comprises a solid-state imager having an array of image sensors for capturing light from the indicia on the target over a field of view, and a controller having a stored template that identifies details of the indicia on the target, for controlling the imager to capture the light from the indicia based on the details identified by the template.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Firearm, aiming system therefor, method of operating the firearm and method of reducing the probability of missing a target
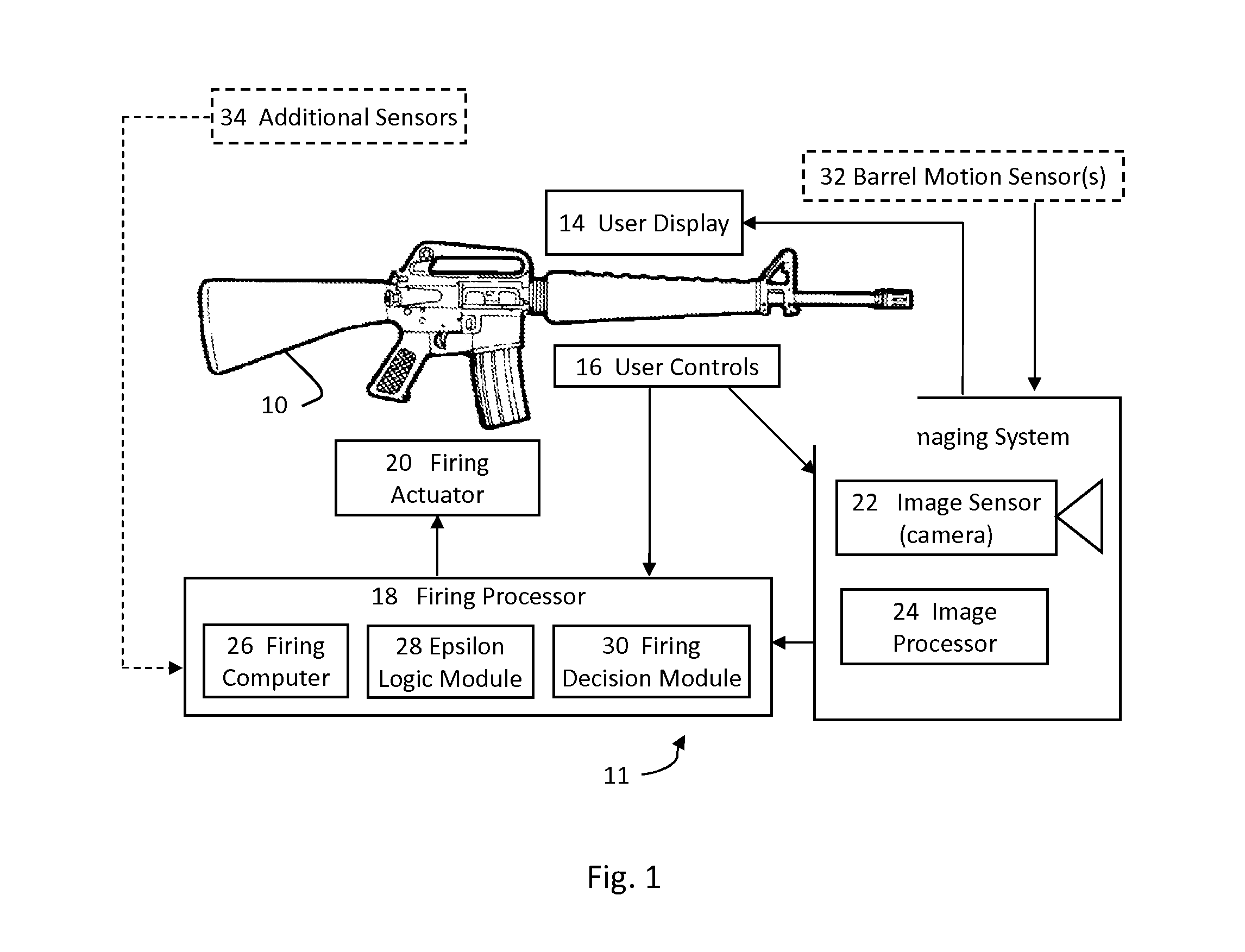
ActiveUS20140028856A1Promote fireShoot accuratelyTelevision system detailsSafety arrangementDisplay deviceLogic module
A firearm aiming system comprising an imaging system comprising an imaging sensor and an image processor; and a user display, wherein the imaging system is adapted to detect a potential target on the user display based on target features. In some embodiments the system includes a firing processor with an epsilon logic module for calculating a target aim-point / area used by the firing processor to make a firing decision.
Owner:SMART SHOOTER
Weighted adaptive super-resolution reconstructing method for image sequence
InactiveCN101794440AIncrease the number of pixelsQuality improvementImage enhancementSelf adaptiveImage resolution
The invention discloses a weighted adaptive super-resolution reconstructing method for an image sequence, which is superior to the conventional method in the aspects of robustness and practicability, and has important application value for obtaining a high-quality image. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a plurality of continuous frames of low-resolution images obtained by the same sensor, and resampling a low-resolution image sequence to obtain a resampled low-resolution image sequence; and (2) reconstructing a frame of high-resolution image by utilizing the resampled low-resolution image sequence, wherein the method for reconstructing the frame of high-resolution image comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a high-resolution image degradation model; secondly, converting a solving process of the high-resolution image in the degradation model into an optimizing process of a solution of a reconstruction optimization model of the high-resolution image according to a predetermined degradation model of the high-resolution image and a regularization theory; and finally, optimizing the reconstruction optimization model of the high-resolution image by utilizing a progressive non-convex algorithm so as to obtain an optimal estimation value of the high-resolution image.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
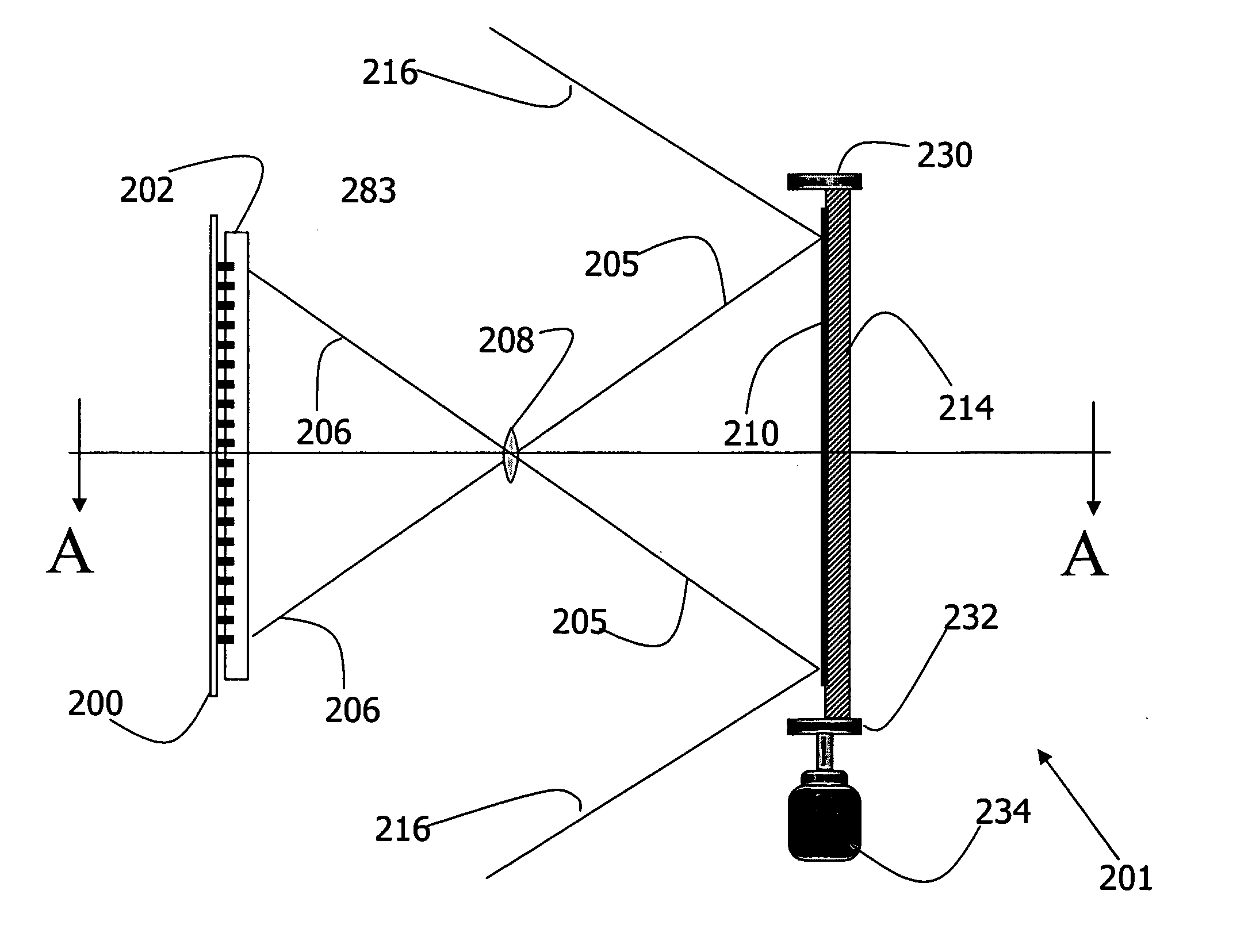
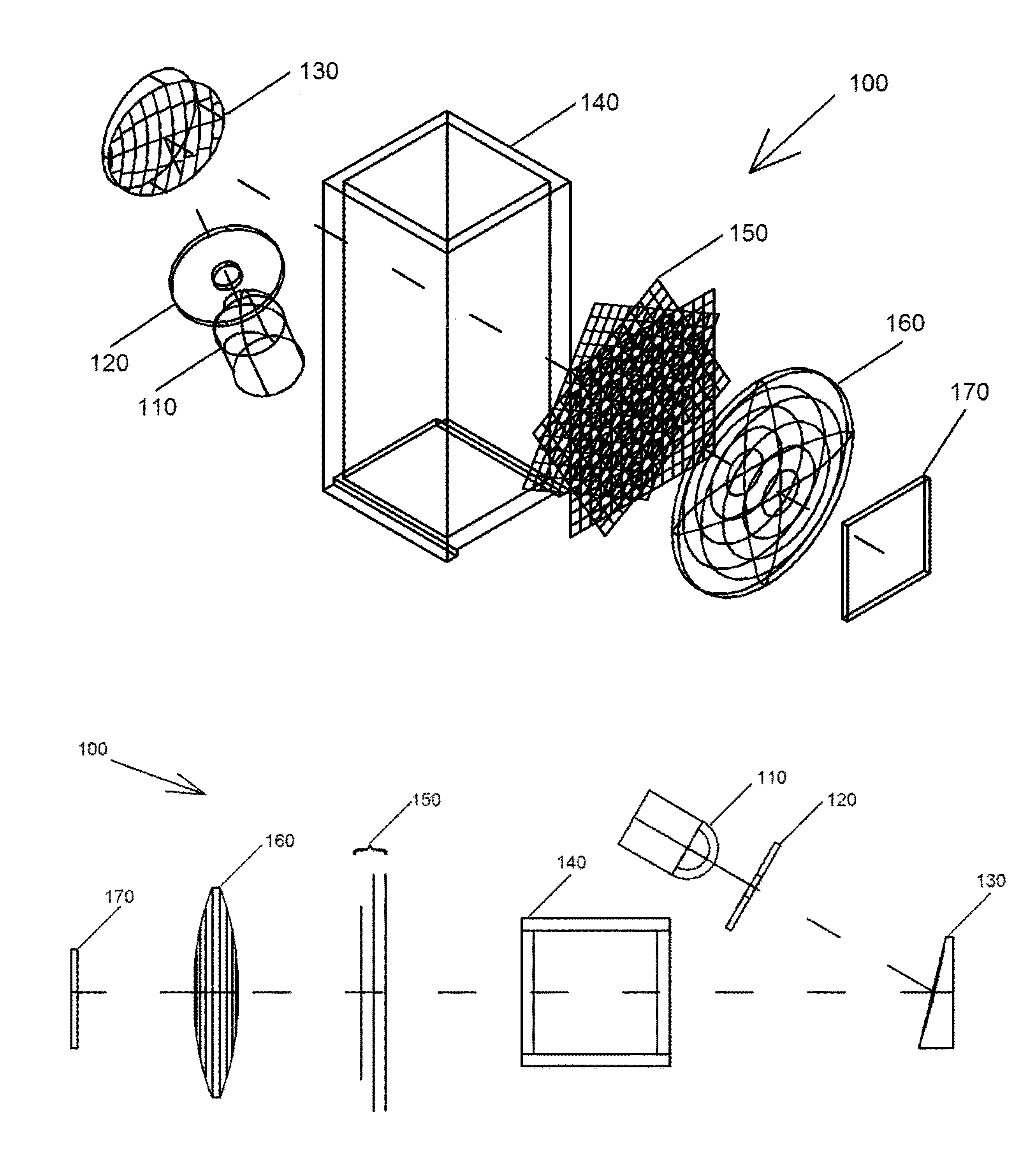
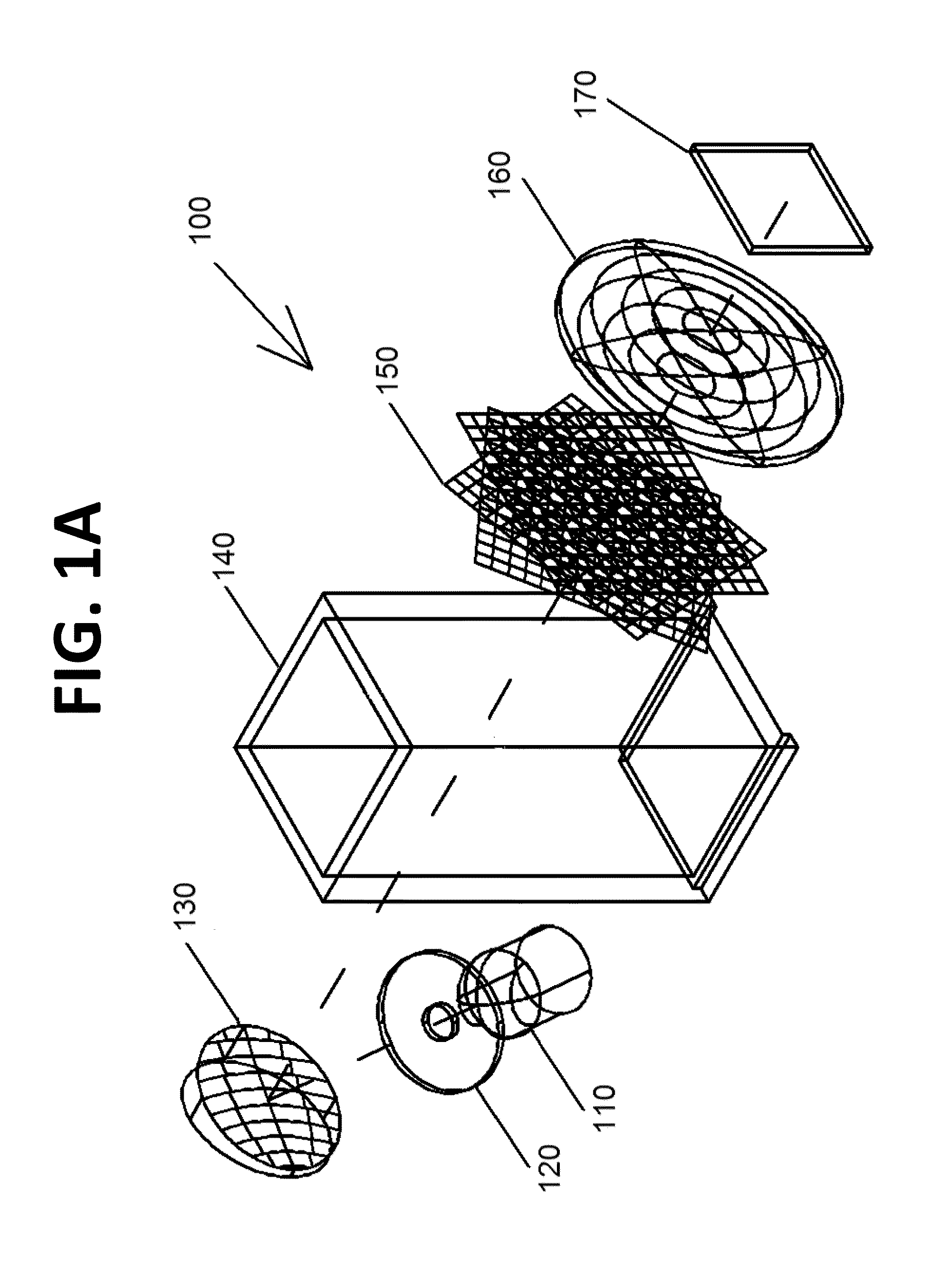
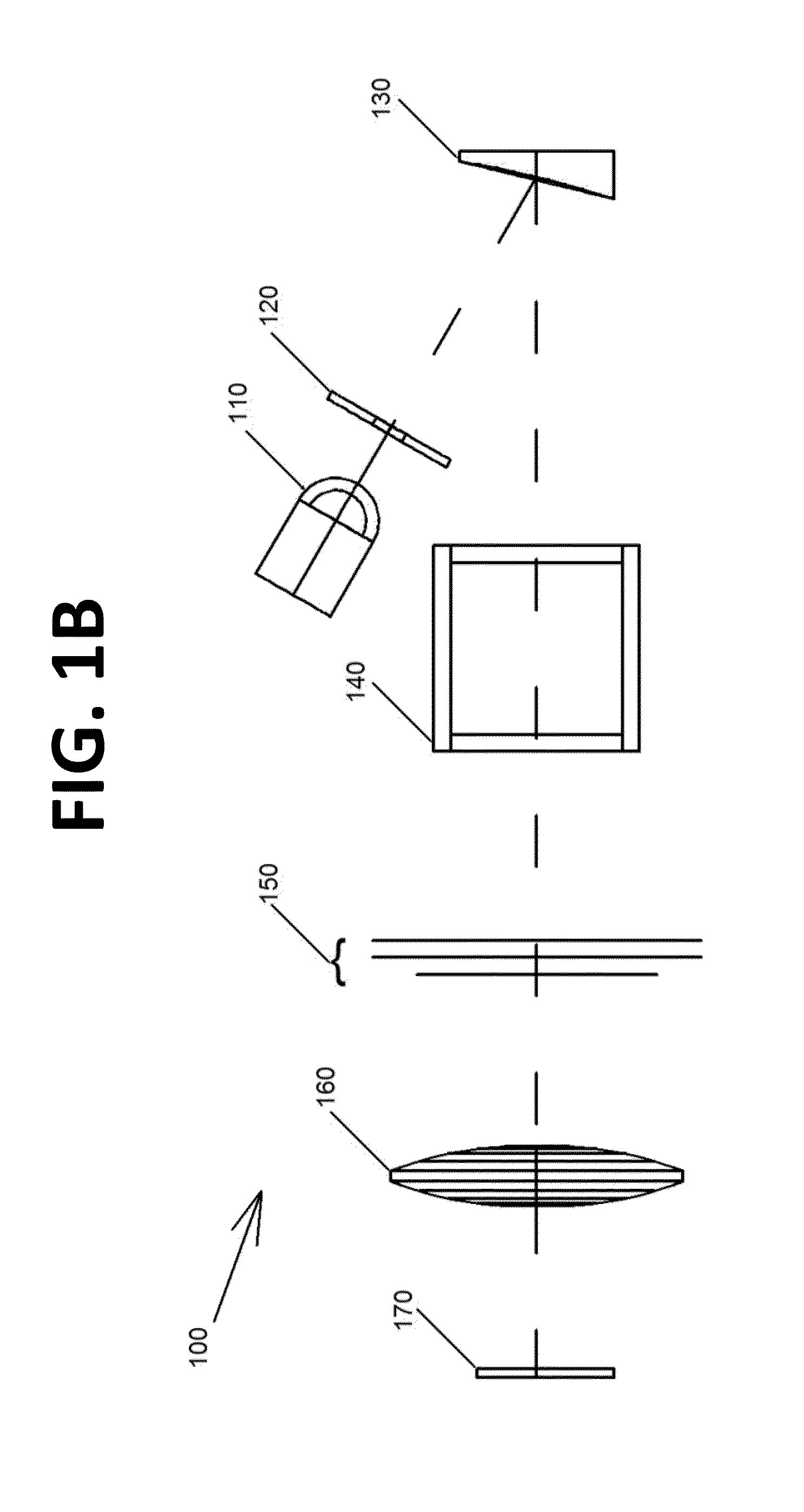
Energy dispersion device
ActiveUS8885161B2Increase the number of pixelsEasy to useRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryDiffraction orderEnergy dispersion
The invention provides an energy dispersion device, spectrograph and method that can be used to evaluate the composition of matter on site without the need for specialized training or expensive equipment. The energy dispersion device or spectrograph can be used with a digital camera or cell phone. A device of the invention includes a stack of single- or double-dispersion diffraction gratings that are rotated about their normal giving rise to a multiplicity of diffraction orders from which meaningful measurements and determinations can be made with respect to the qualitative or quantitative characteristics of matter.
Owner:SPECTROCLICK
Display panel driving method, gate driver, and display apparatus
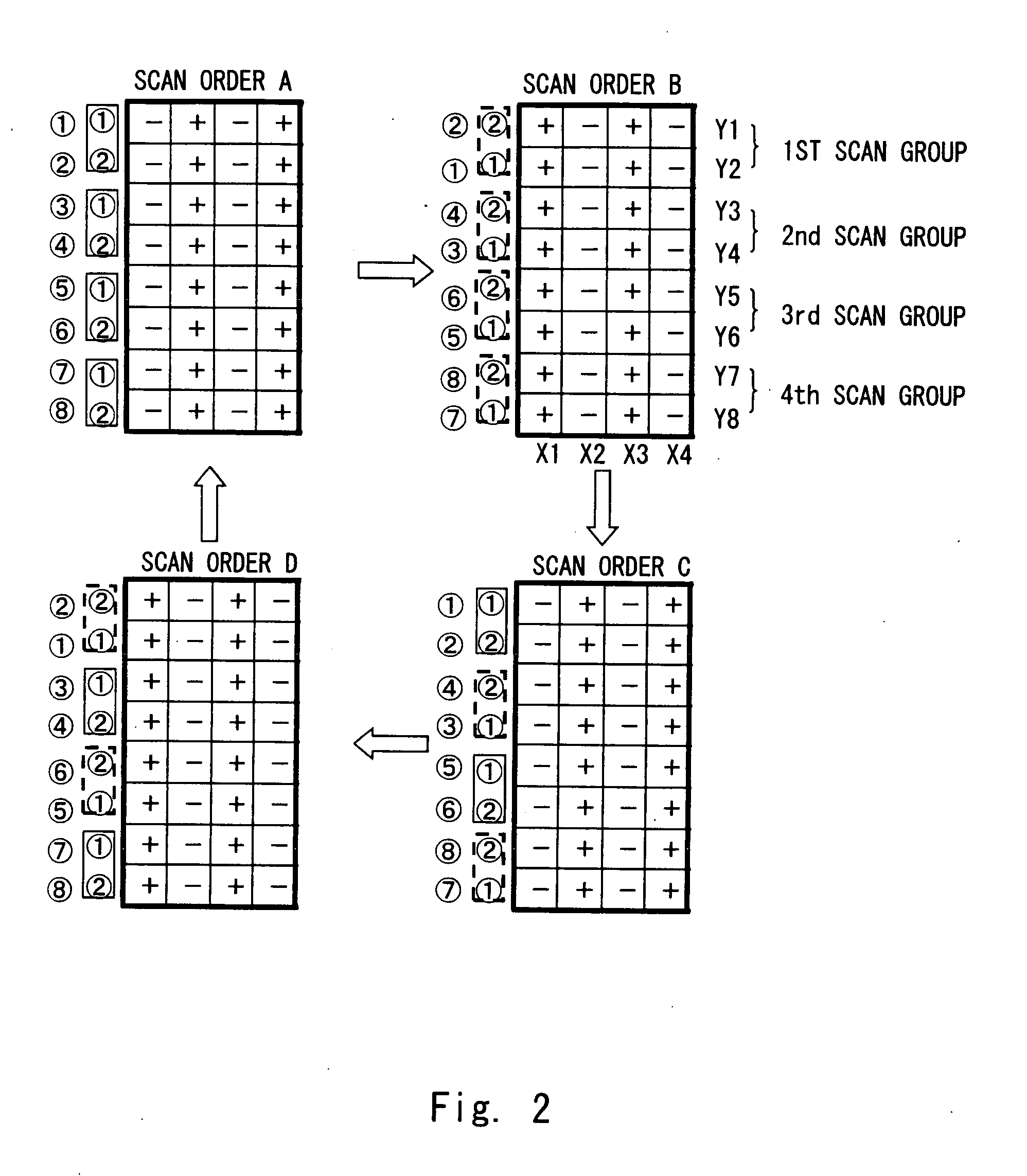
InactiveUS20100315402A1Reduce image qualityReduced drive capability requirementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsScan lineElectrical polarity
A method of driving a display panel in which a voltage polarity reverse cycle of a data signal is three or more scan periods, and multiple scan lines are driven by switching between a first and a second scan orders by a predetermined period. The method includes setting a display pattern as a first maximum current pattern, the display pattern in which the multiple scan lines are driven in the first scan order and a number of charge and discharge of the data signal becomes a maximum number, and specifying that the number of charge and discharge of the data signal when displaying the first maximum current pattern in the second scan order is to be ½ of that of the data signal when displaying the first maximum current pattern in the first scan order. Further, the voltage polarity reverse cycle for specifying the first and the second scan orders is one frame period.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Solid-state image device manufacturing method thereof, and image capturing apparatus
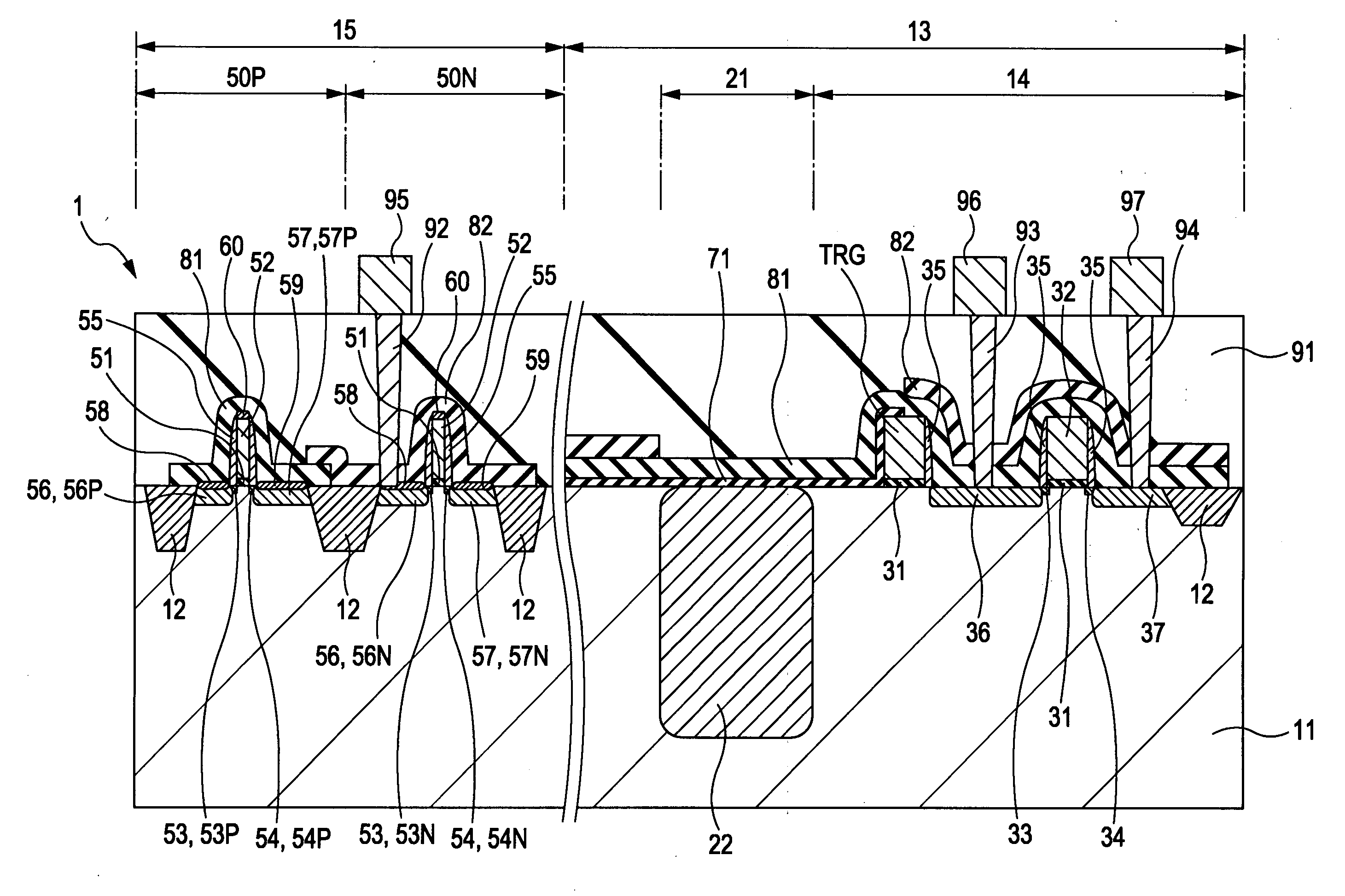
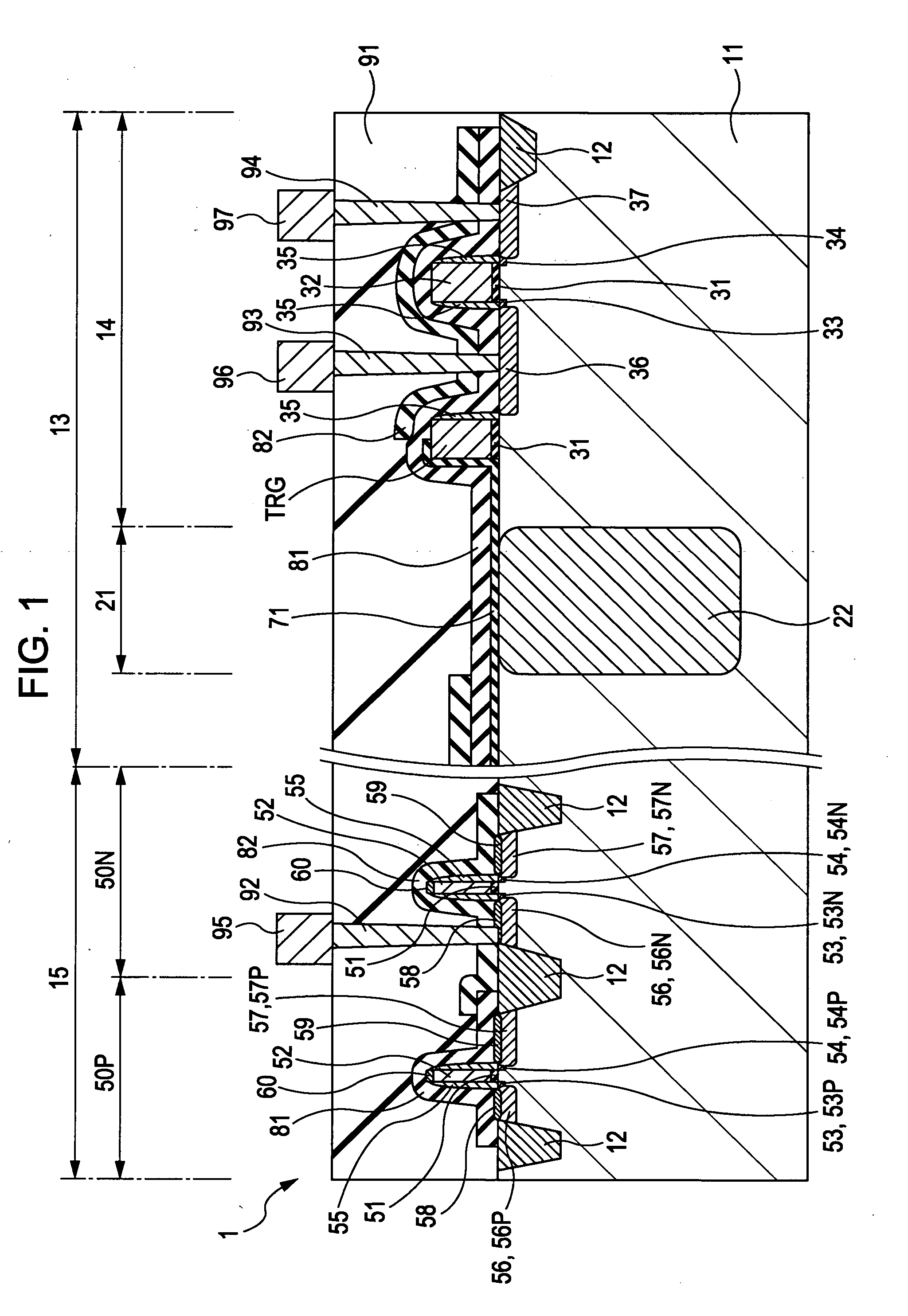
ActiveUS20100224766A1Improve mobilityHigh speedSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
A solid-state image device is provided which includes: a photoelectric conversion portion which obtains a signal charge by photoelectric conversion of incident light; a pixel transistor portion which outputs a signal charge generated by the photoelectric conversion portion; a peripheral circuit portion which is provided at the periphery of a pixel portion including the photoelectric conversion portion and the pixel transistor portion and which has an NMOS transistor and a PMOS transistor; a first stress liner film which has a compressive stress and which is provided on the PMOS transistor; and a second stress liner film which has a tensile stress and which is provided on the NMOS transistor. In the solid-state image device described above, the photoelectric conversion portion, the pixel transistor portion, and the peripheral circuit portion are provided in and / or on a semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Evaporation Donor Substrate, Method for Manufacturing the Same, and Method for Manufacturing Light-Emitting Device
ActiveUS20090169809A1Low production costDeposited easily and accuratelyLayered productsSolid-state devicesThermal insulationEvaporation
An evaporation donor substrate that makes it possible to evaporate only a desired evaporation material in the case of performing deposition by an evaporation method. Thus, the use efficiency of an evaporation material can be increased resulting in reduction in production cost, and further a film with high uniformity can be deposited. The evaporation donor substrate can be obtained by forming a reflective layer having an opening over a substrate, forming a thermal insulation layer having a light-transmitting property separately over the substrate and the reflective layer, forming a light absorption layer over the thermal insulation layer, and forming a material layer over the light absorption layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Deposition Donor Substrate and Method for Manufacturing Light-Emitting Device
InactiveUS20100015424A1Avoid heatReduce manufacturing costLayered productsSolid-state devicesTarget surfaceLight irradiation
One surface of a first substrate provided with at least light-absorbing layers separately formed, partition layers each formed between the light-absorbing layers and having an inverse taper shape, and material layers formed on the light-absorbing layers and on the partition layers so that the material layers are separated from each other is disposed to face a deposition target surface of a second substrate; light irradiation is performed from the other surface of the first substrate, only the material layers in regions overlapped with the light-absorbing layers are heated and evaporated to the deposition target surface of the second substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Energy dispersion device
ActiveUS20130093936A1Increase the number of pixelsLarge pixel countThermometer detailsTelevision system detailsDiffraction orderEnergy dispersion
The invention provides an energy dispersion device, spectrograph and method that can be used to evaluate the composition of matter on site without the need for specialized training or expensive equipment. The energy dispersion device or spectrograph can be used with a digital camera or cell phone. A device of the invention includes a stack of single- or double-dispersion diffraction gratings that are rotated about their normal giving rise to a multiplicity of diffraction orders from which meaningful measurements and determinations can be made with respect to the qualitative or quantitative characteristics of matter.
Owner:SPECTROCLICK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com