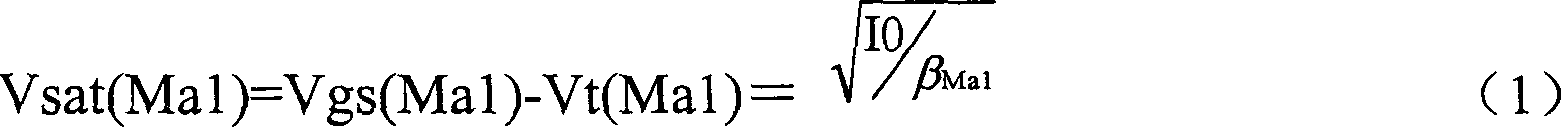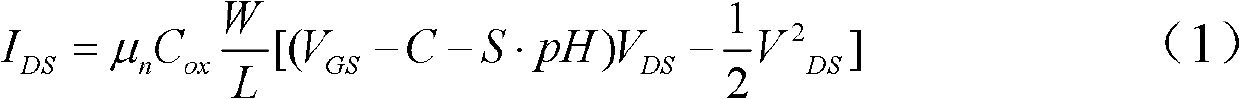Patents
Literature
116 results about "ISFET" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
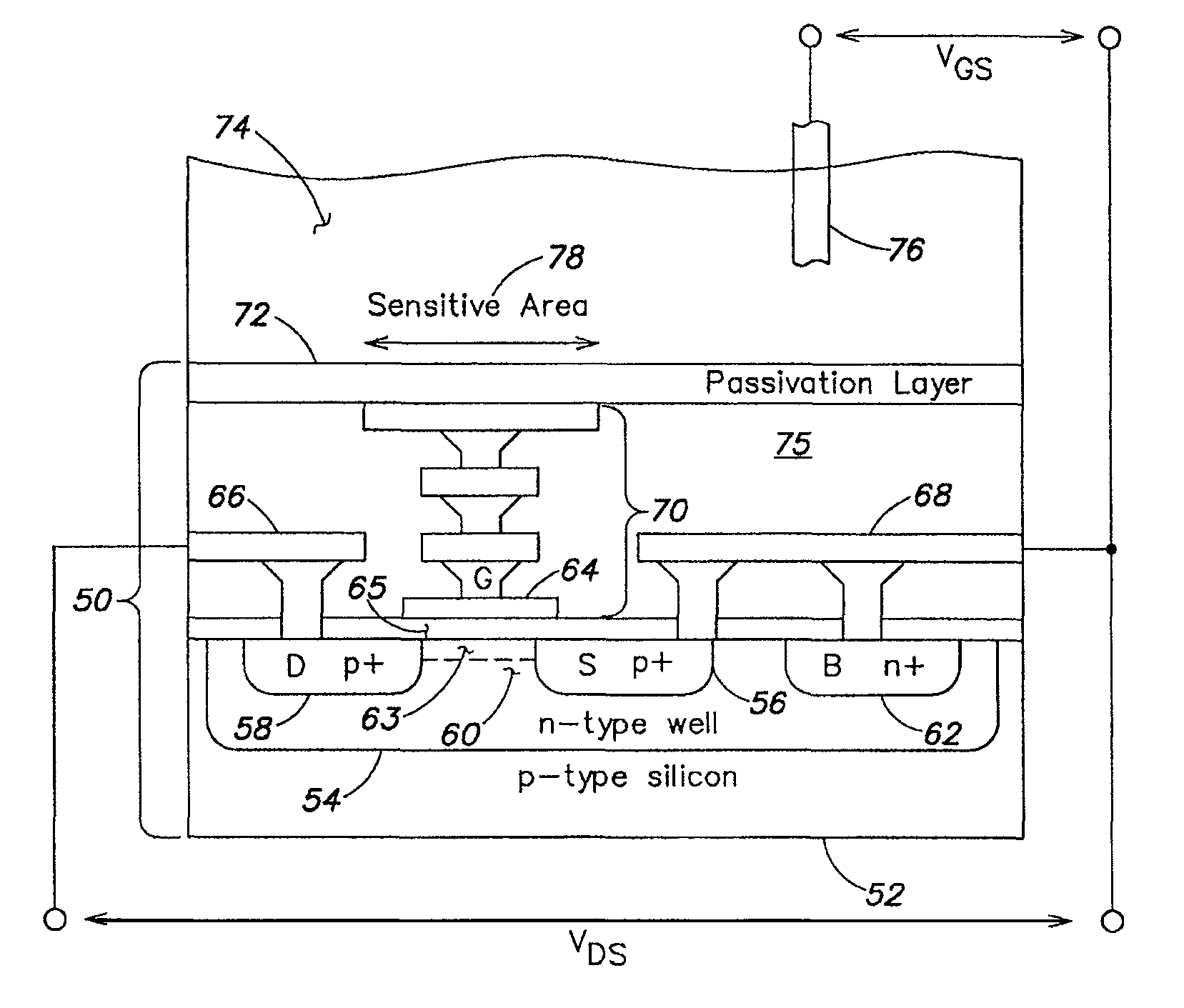
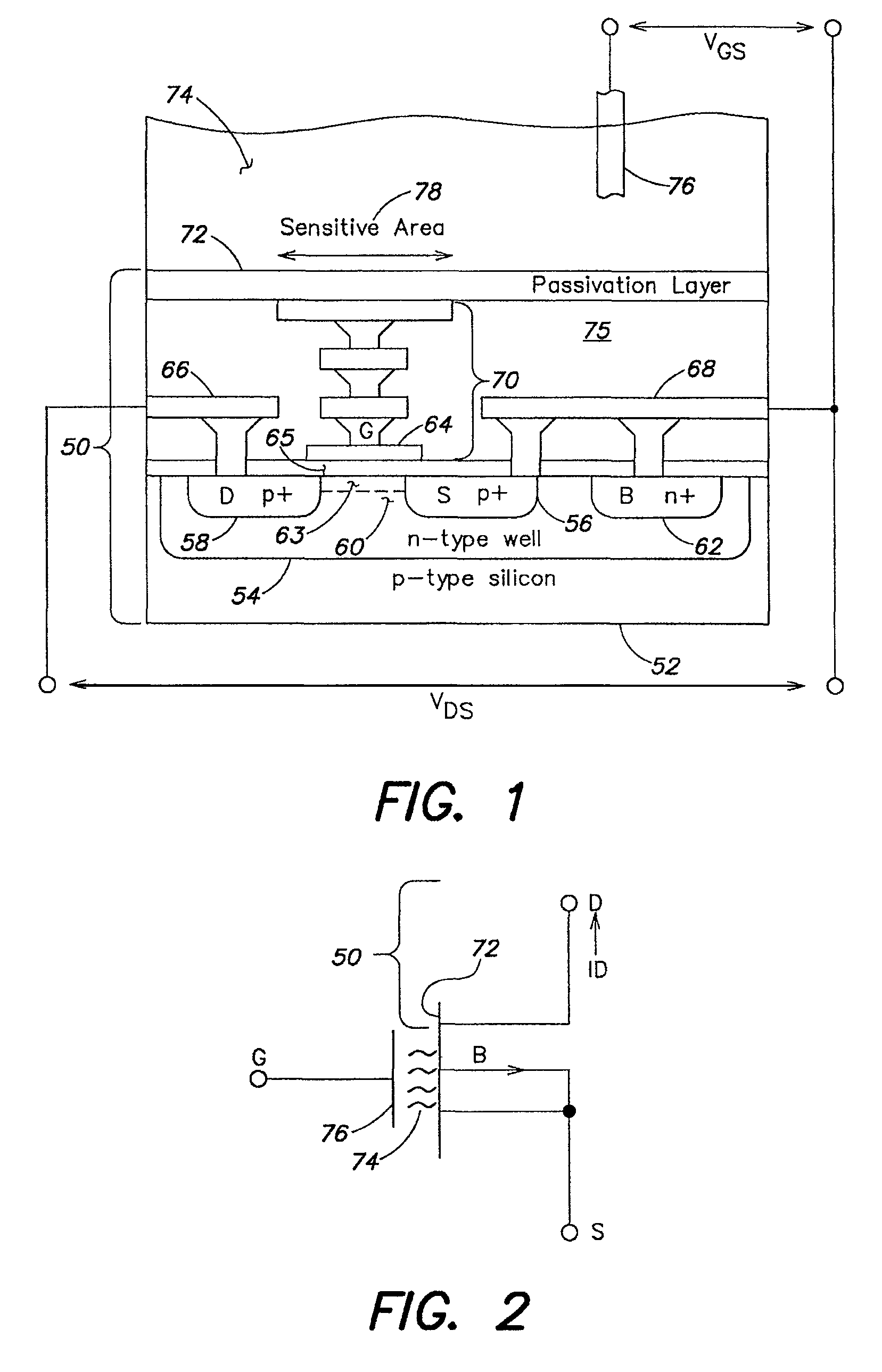
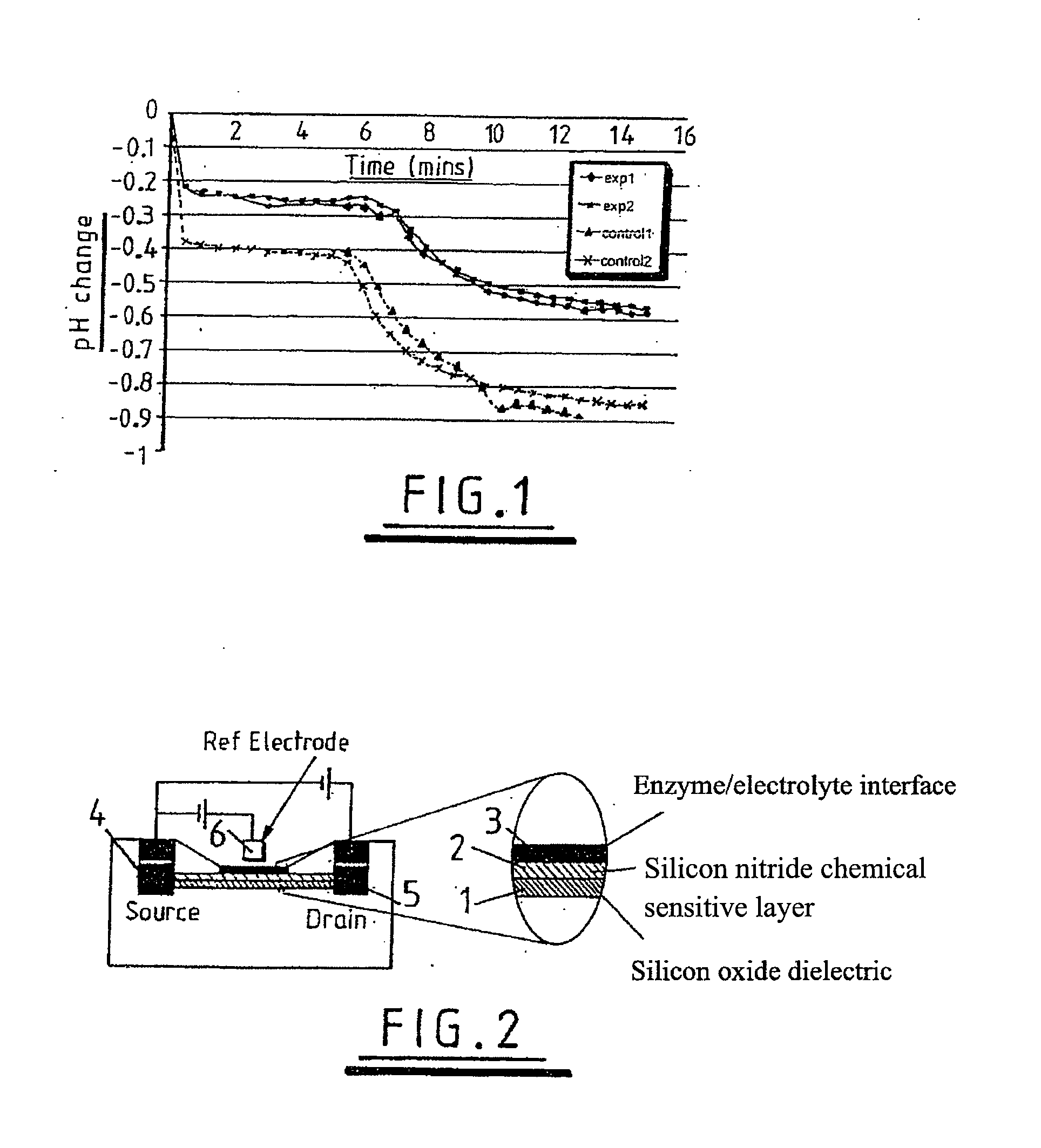
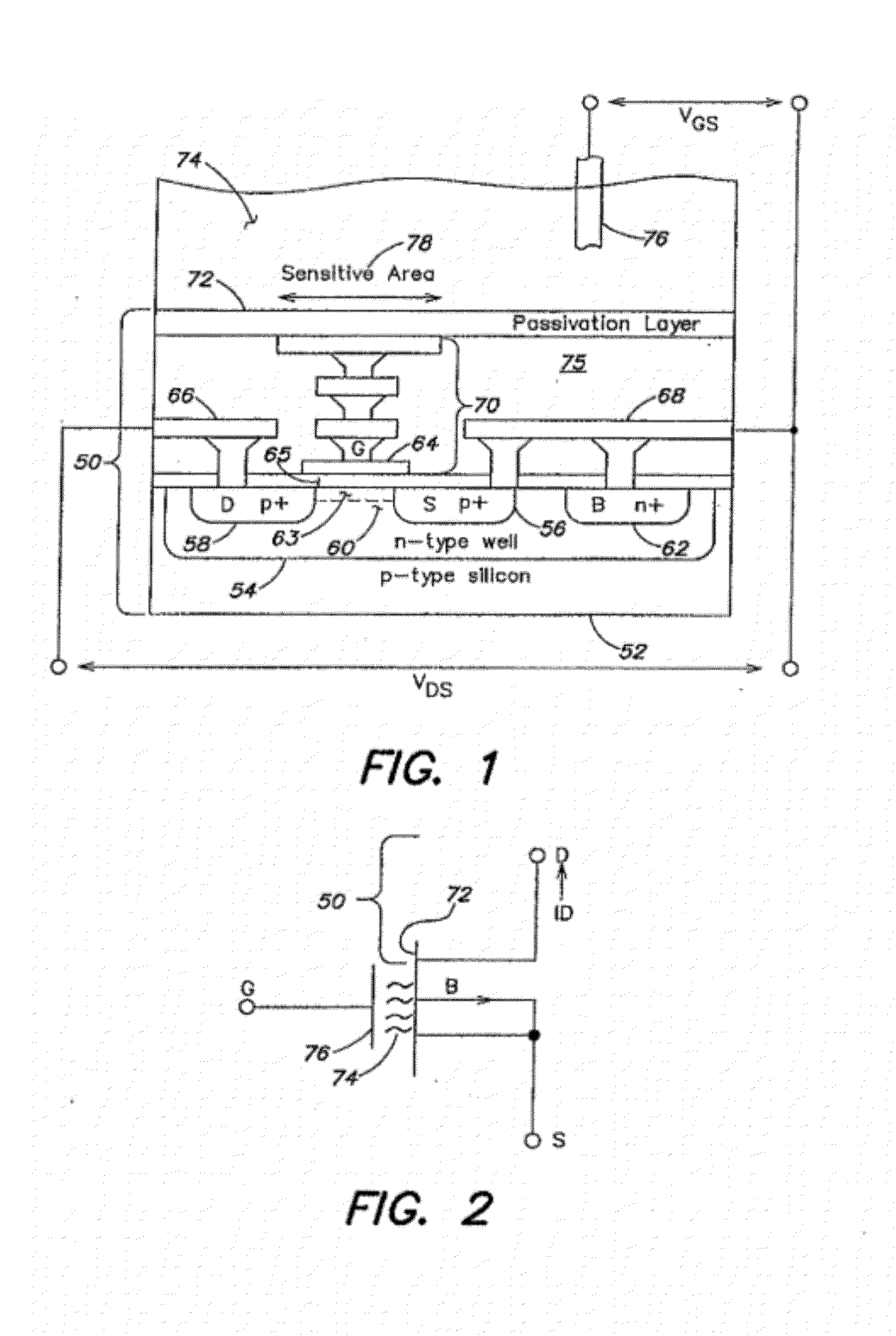
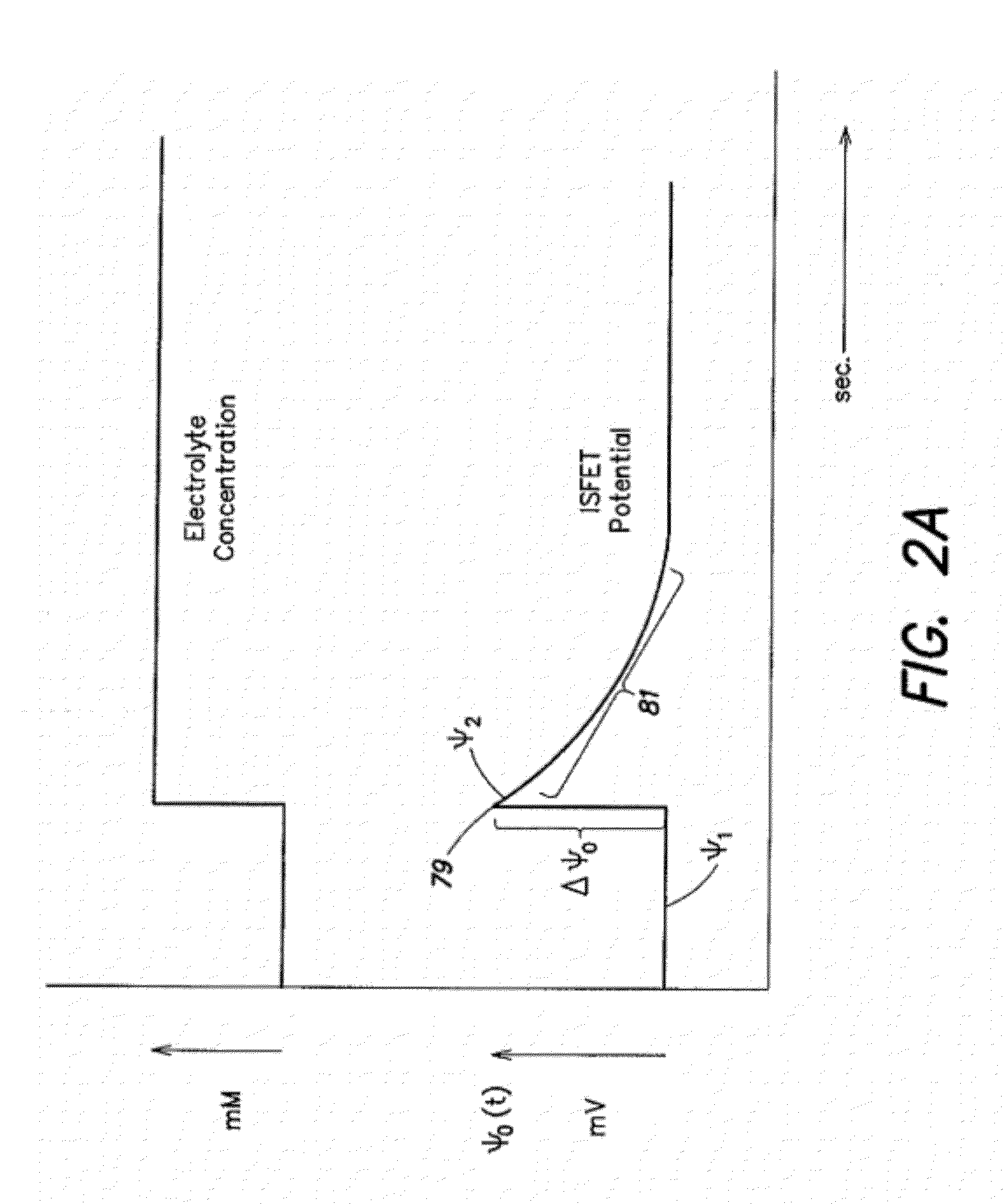
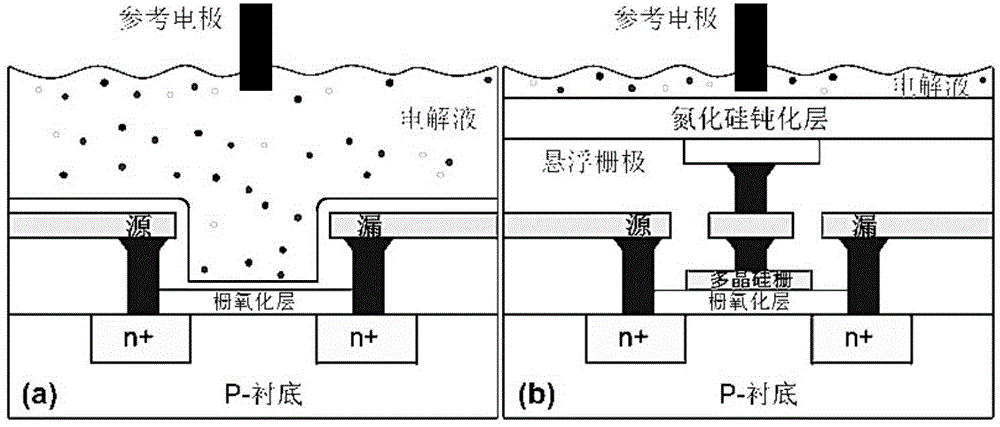
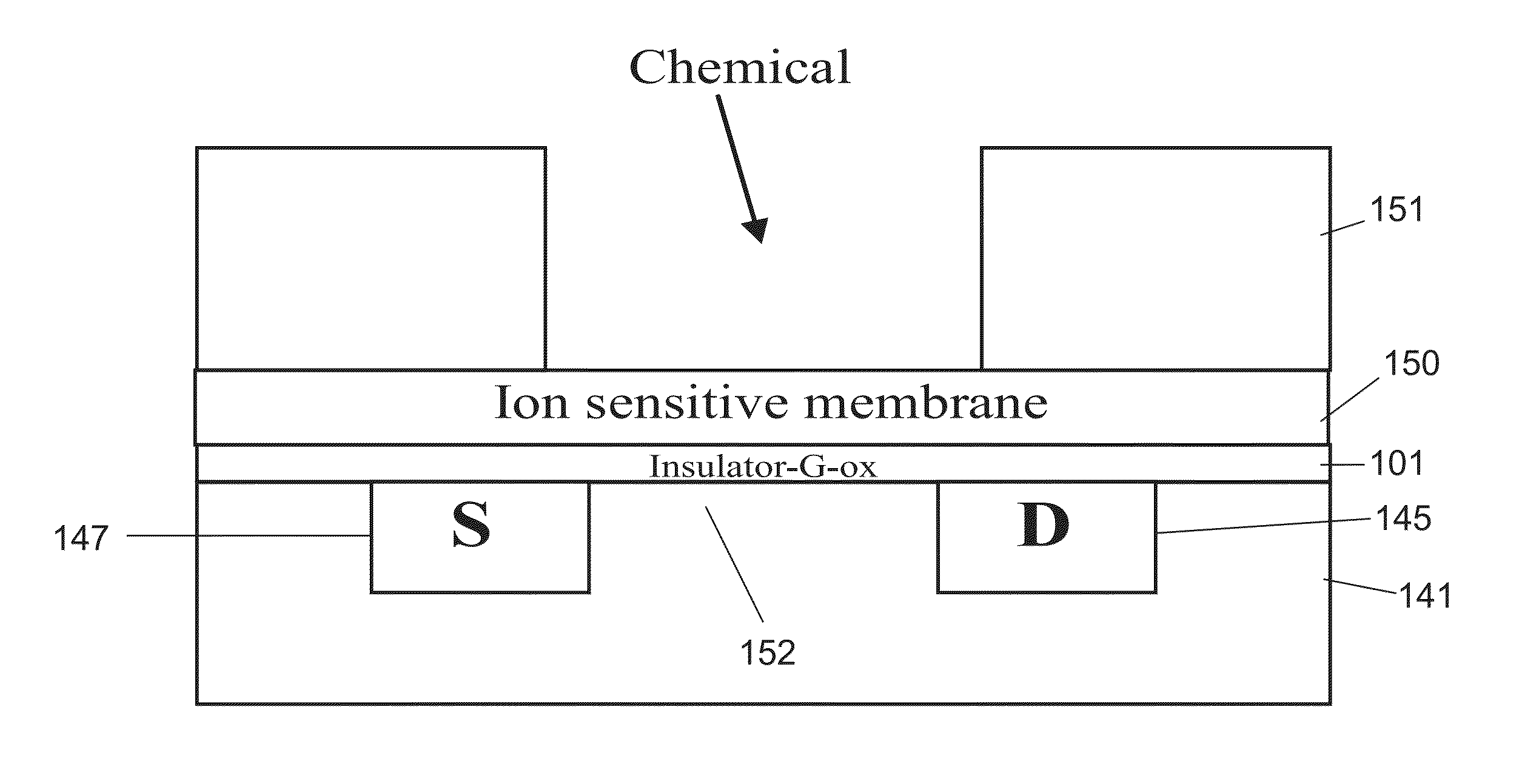
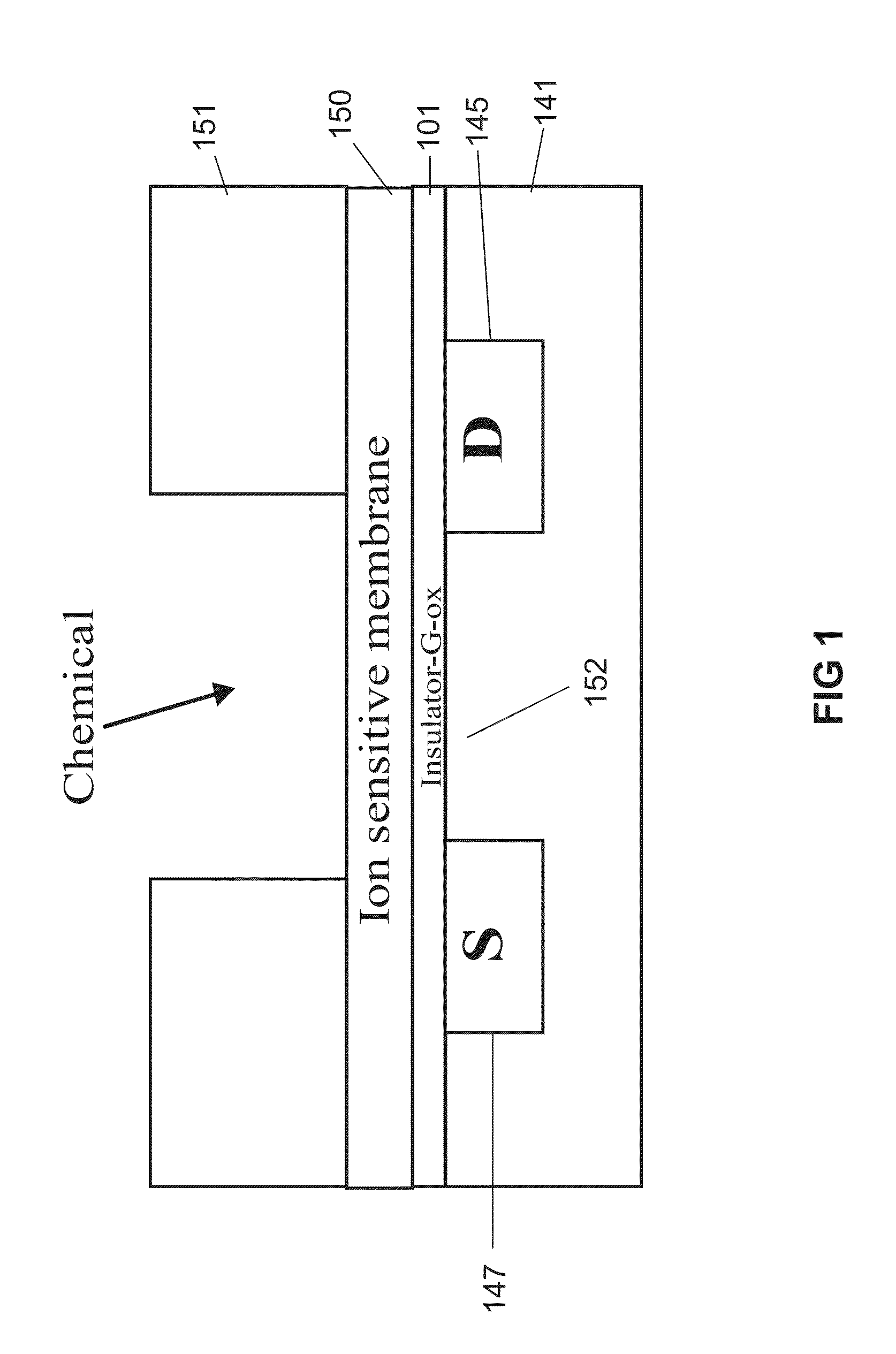
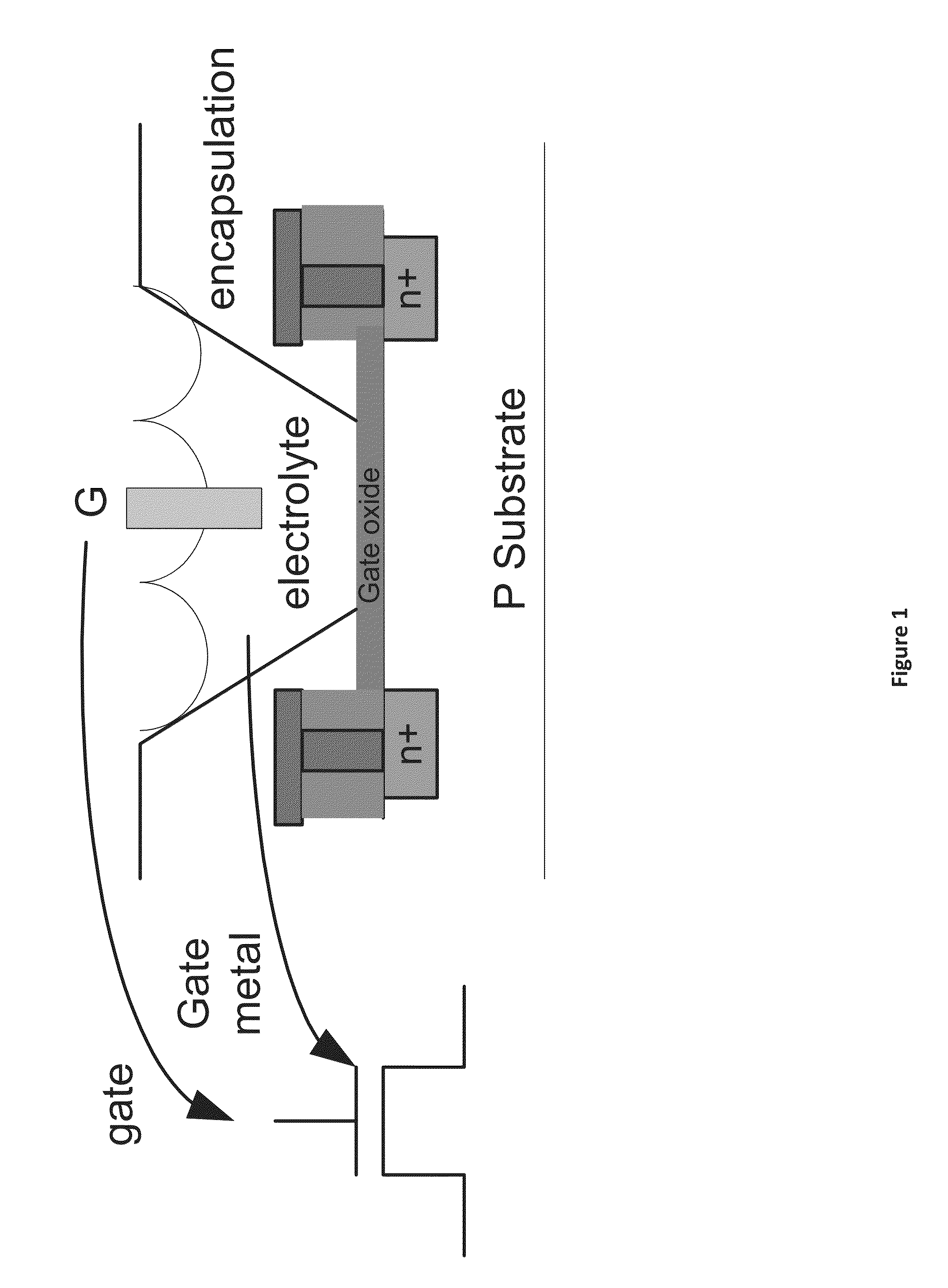
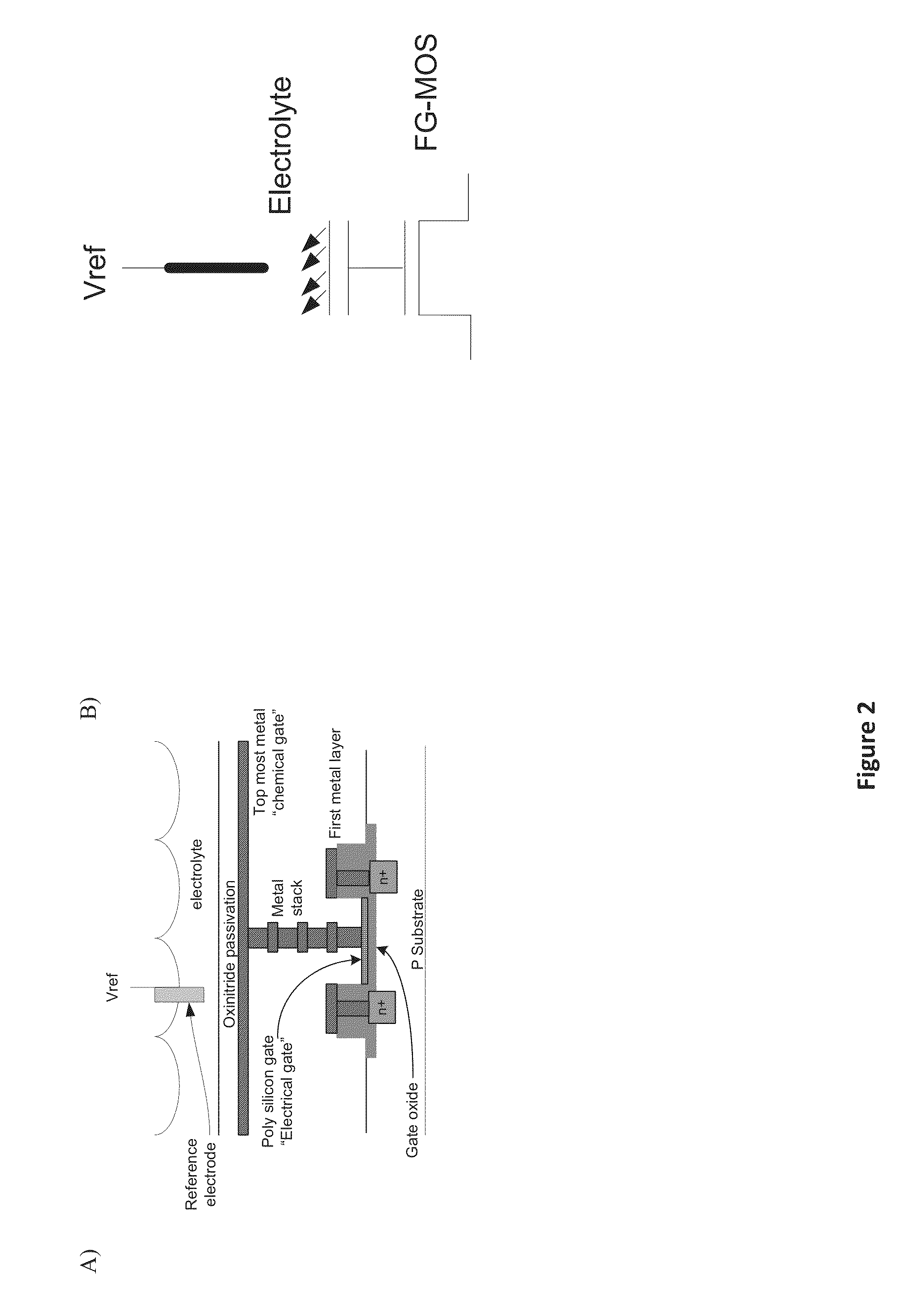
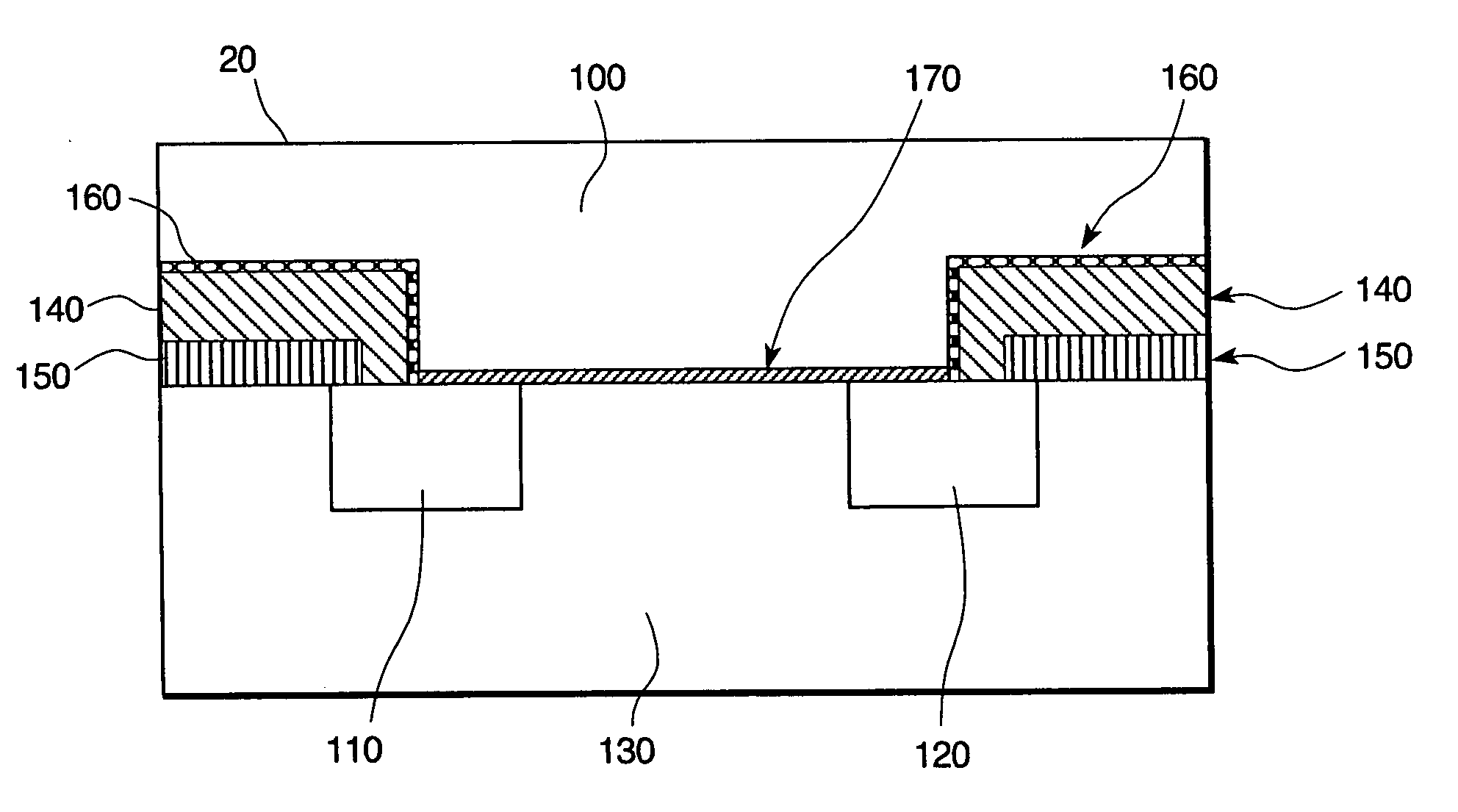
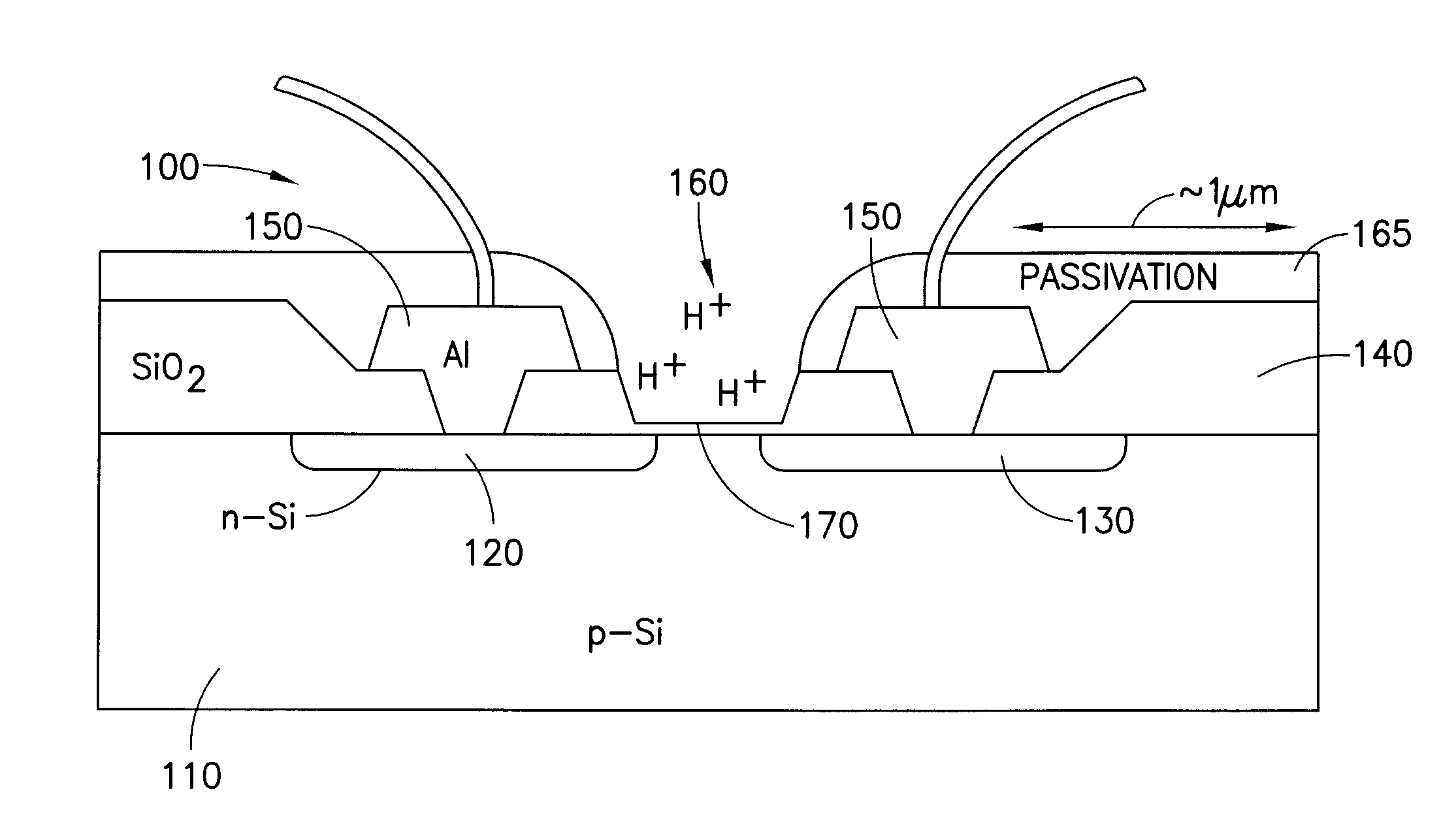
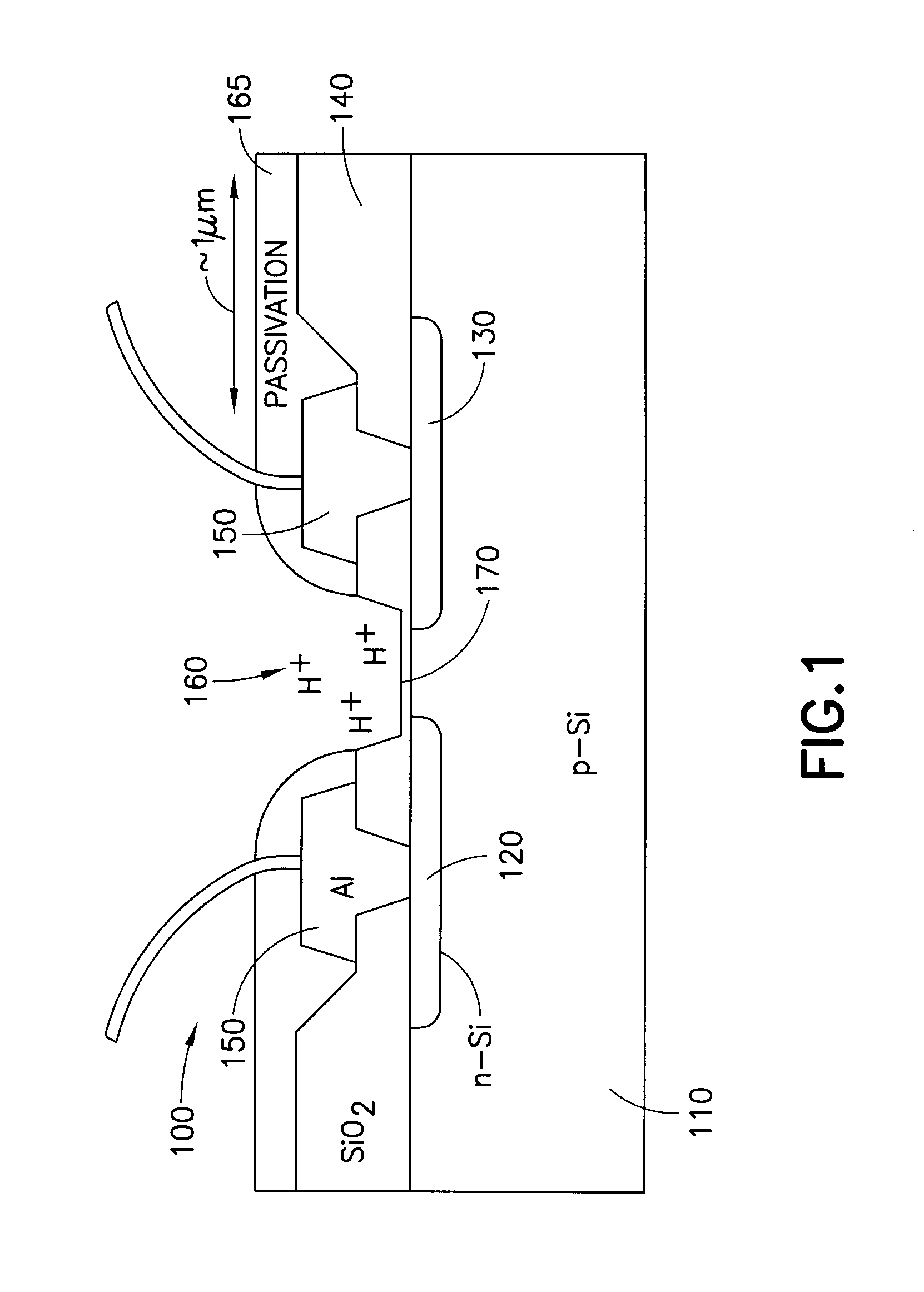
An ion-sensitive field-effect transistor (ISFET) is a field-effect transistor used for measuring ion concentrations in solution; when the ion concentration (such as H⁺, see pH scale) changes, the current through the transistor will change accordingly. Here, the solution is used as the gate electrode. A voltage between substrate and oxide surfaces arises due to an ion sheath. It is a special type of MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor), and shares the same basic structure, but with the metal gate replaced by an ion-sensitive membrane, electrolyte solution and reference electrode. Invented in 1970, the ISFET was the first biosensor FET (BioFET).
Methods and apparatus for measuring analytes using large scale FET arrays
ActiveUS7948015B2Reduce porosityHigh densityTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementCMOSOrganismal Process
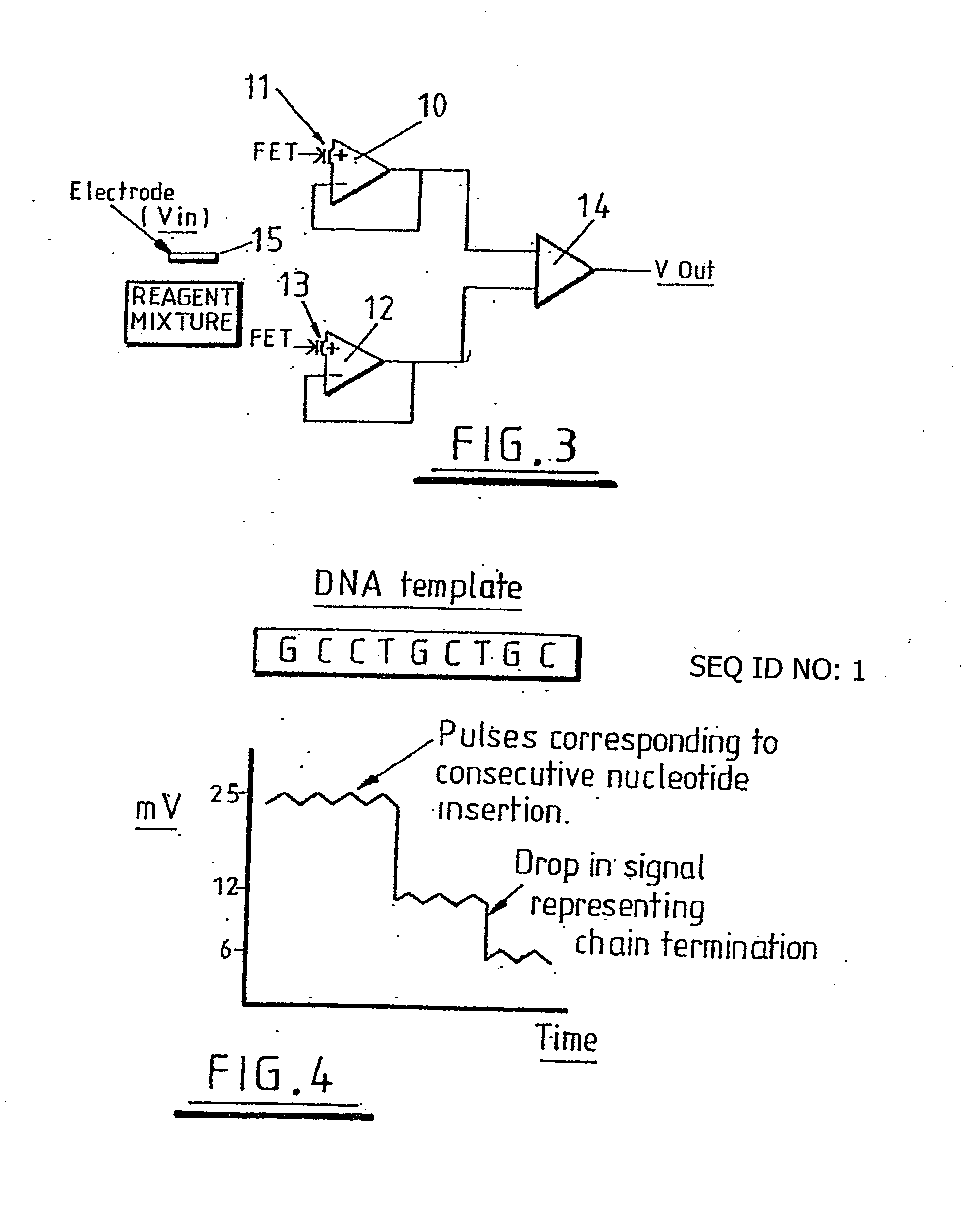
Methods and apparatus relating to very large scale FET arrays for analyte measurements. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes. In one example, chemFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Sensing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080032295A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsProton
Use of a pH sensor comprising an ion-sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) to perform real time detection / quantification of nucleic acid amplification, e.g. polymerase chain reaction (PCR) nucleic acid amplification, based on detection of protons released during the primer extension phase.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
Methods and apparatus for measuring analytes using large scale fet arrays
ActiveUS20110217697A1Constant voltageFacilitate rapid acquisition of dataWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementCMOSOrganismal Process
Methods and apparatus relating to very large scale FET arrays for analyte measurements. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes. In one example, chemFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in the concentration of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi), hydrogen ions, and nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Sensor arrangement with a plurality of potentiometric sensors
InactiveUS7394263B2Improve sealingSafely accommodatedResistance/reactance/impedenceMicrobiological testing/measurementPotential differenceRedox
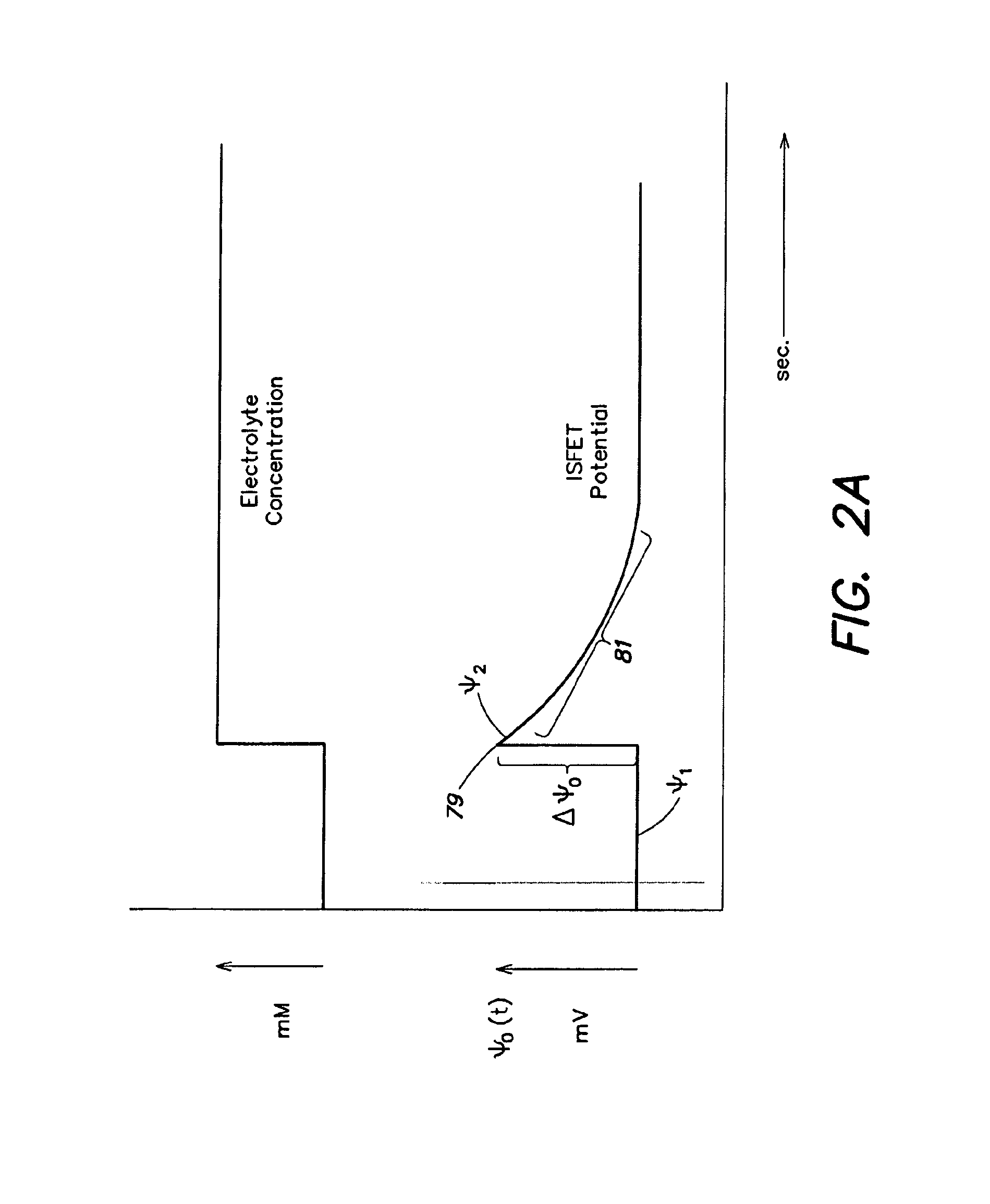
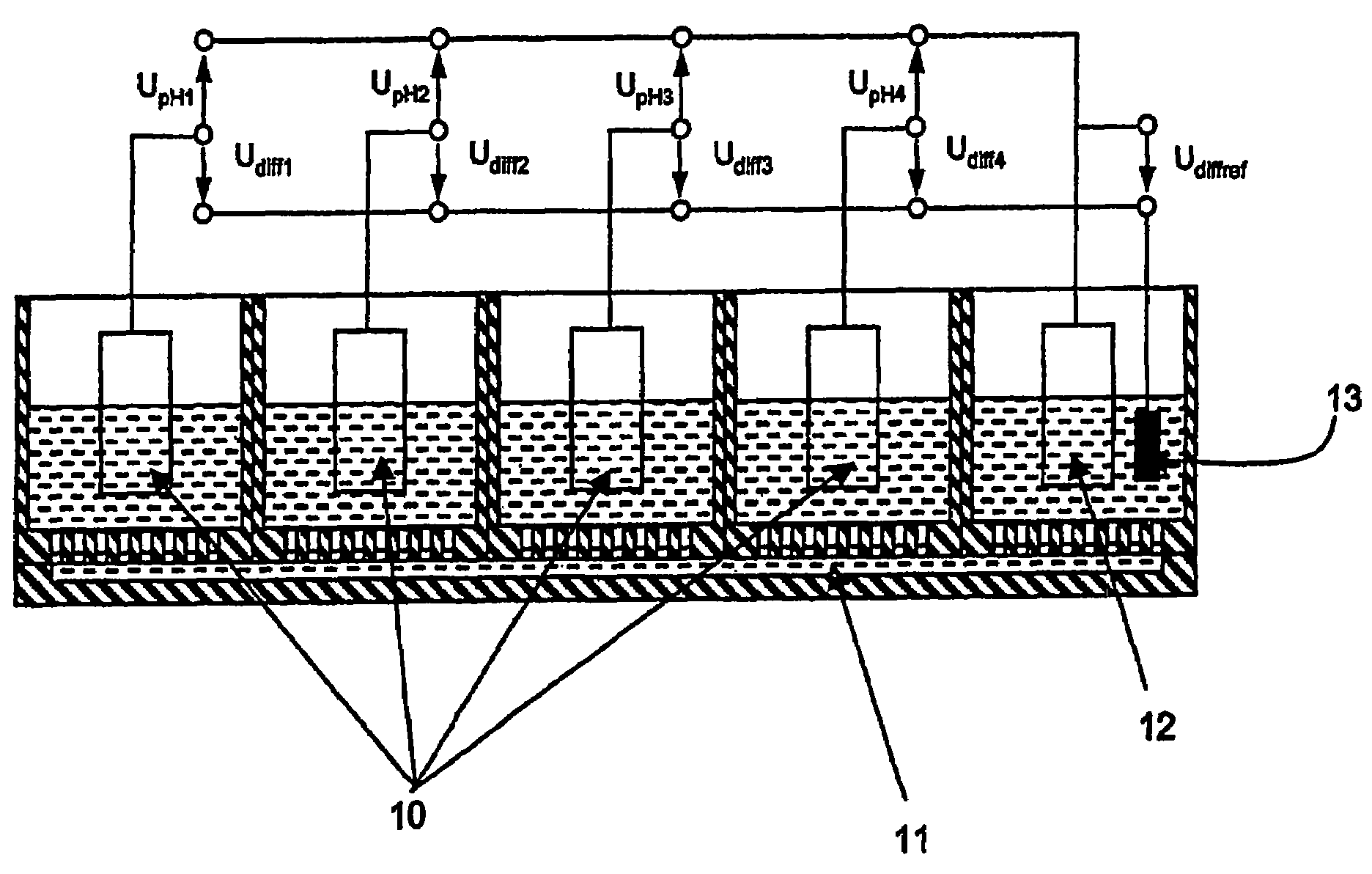
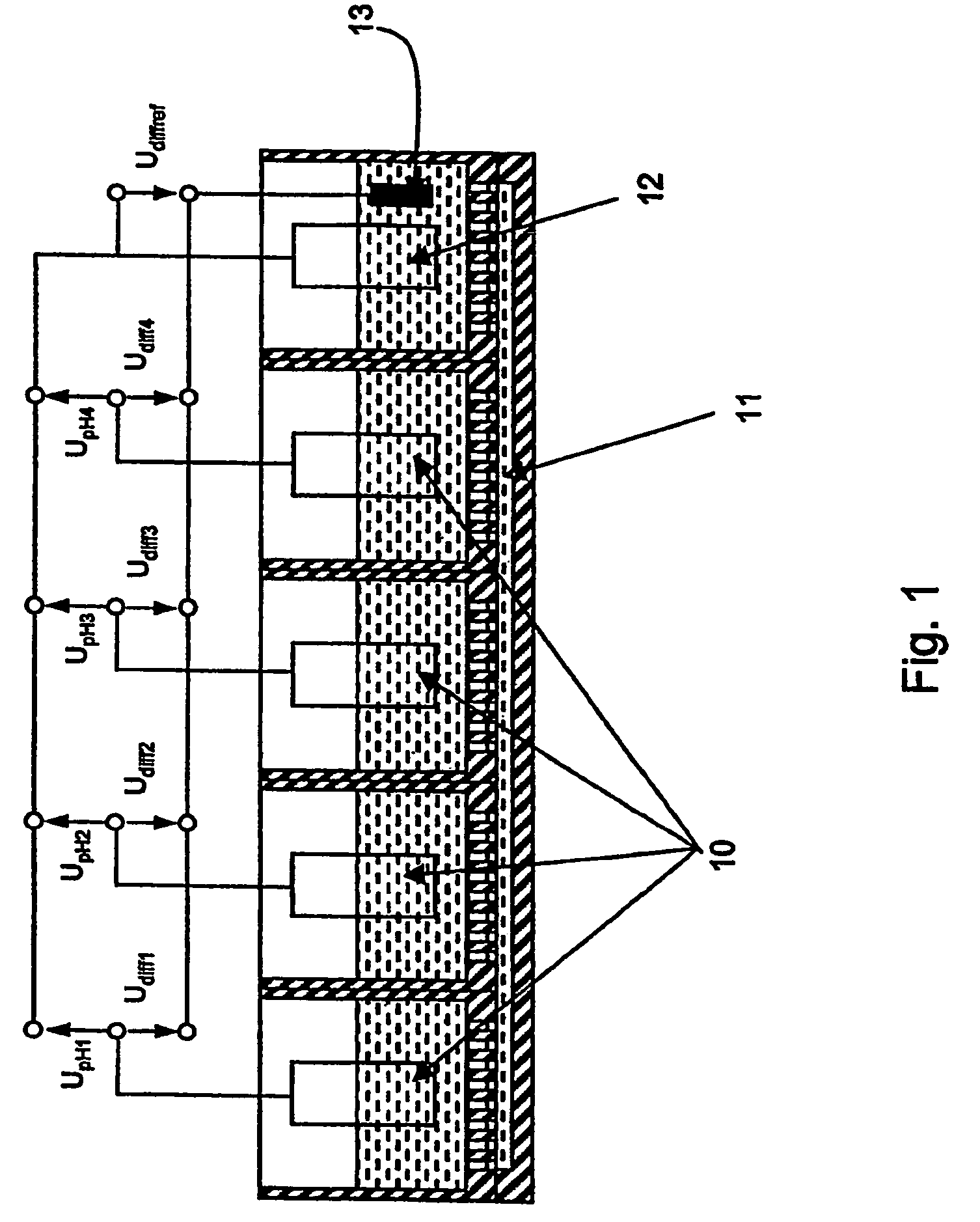
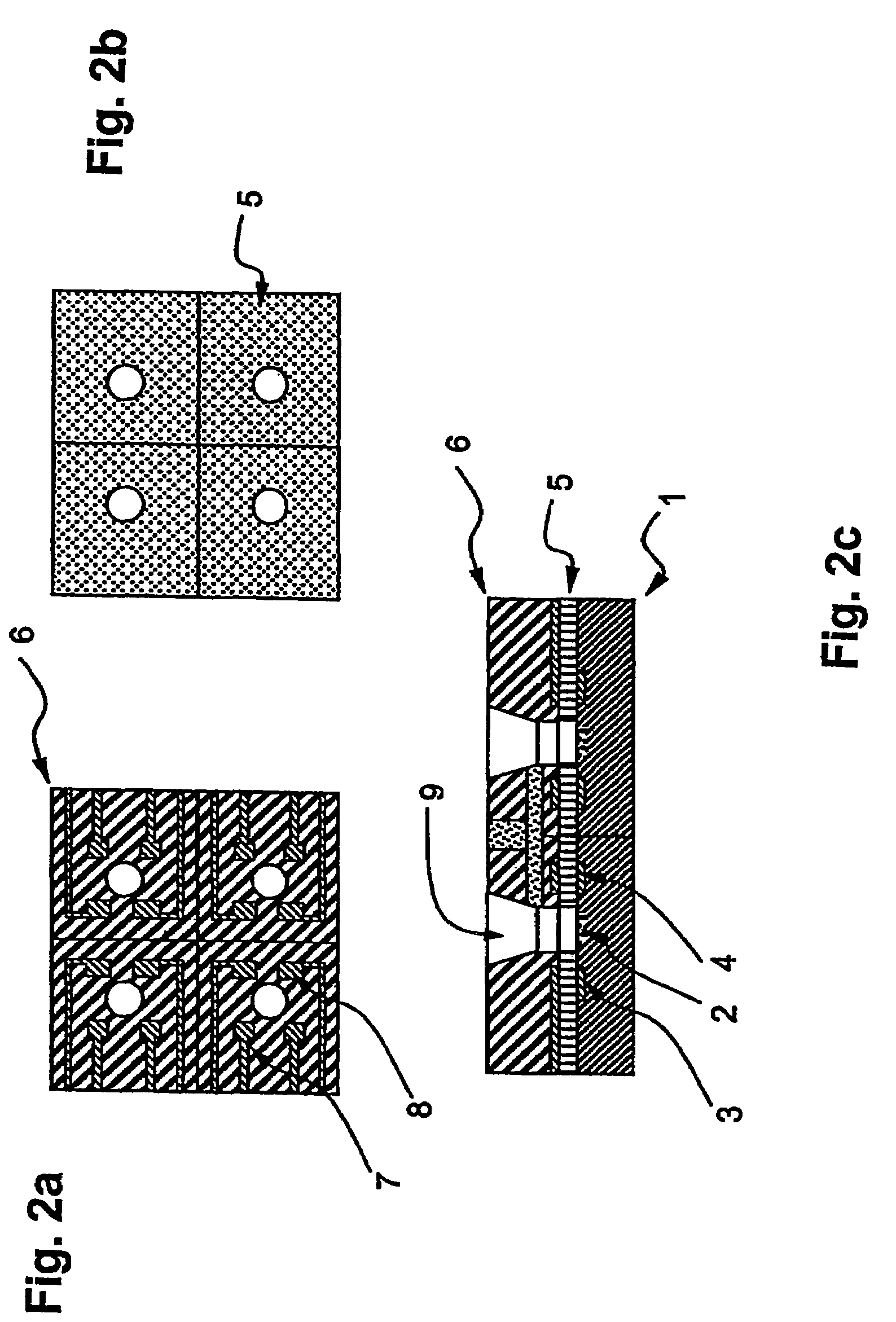
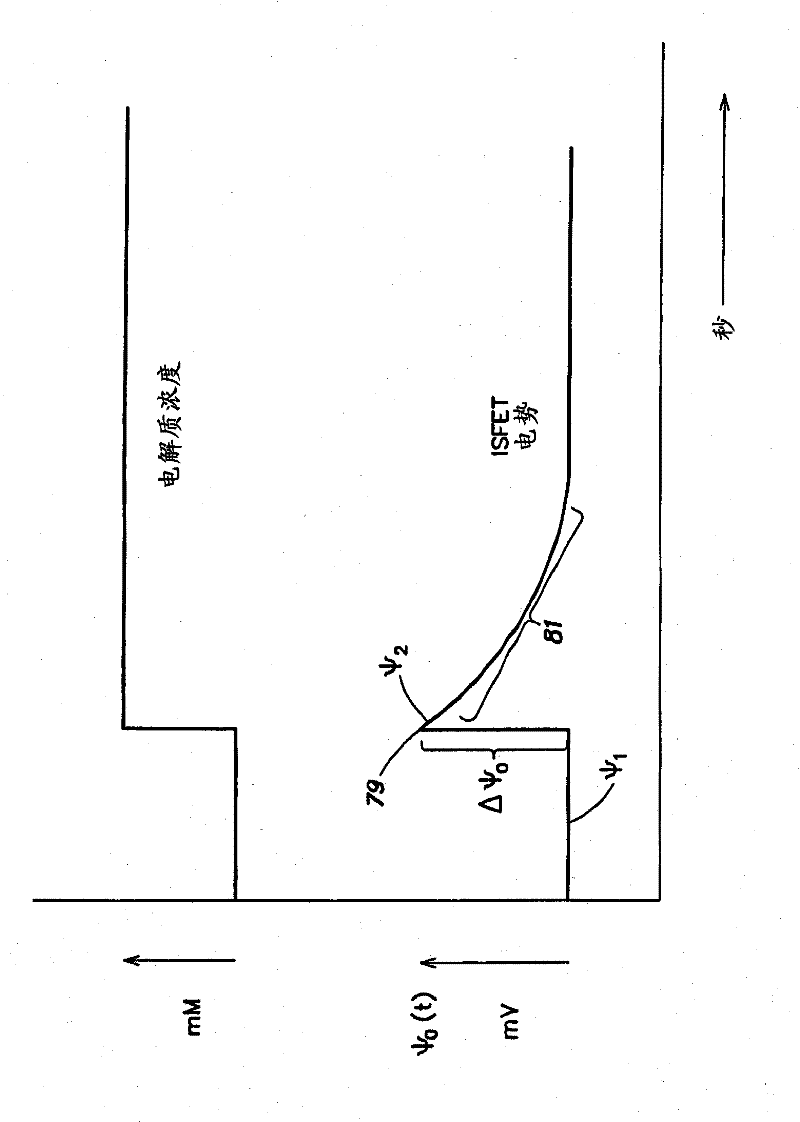
The sensor arrangement includes: a least two sample chambers; at least two potentiometric FET-sensors, especially ISFET-sensors or ChemFET-sensors, having, in each case, a sensitive surface section, wherein each sensitive surface section lies in flow connection with its one of the sample chambers; and a reference cell having a reference medium for providing a reference potential, wherein the sample chambers are connected with the reference medium via an electrolyte bridge. The reference cell has, preferably, a potentiometric reference-FET-sensor for providing a reference potential, which is registered against the pseudo-reference-potential of a redox electrode. The potentials Udiff1, Udiff2, . . . UdiffN of N FET-sensors in the sample chambers are determined against the pseudo-reference-potential, and the measured-variable-relevant, potential differences are determined, in each case, by difference formation between the pertinent potential and the reference potential—thus, in the case of pH, according to the formulasUpH1. . . N=Udiff1. . . N−Udiffref.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER CONDUCTA GESELLSCHAFT FUER MESS UND REGELTECHNIK MBH CO KG
Methods and apparatus for measuring analytes using large scale fet arrays
ActiveUS20120247977A1Facilitate rapid acquisition of dataSmall sizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCMOSOrganismal Process
Methods and apparatus relating to very large scale FET arrays for analyte measurements. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes. In one example, chemFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in the concentration of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi), hydrogen ions, and nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Methods and Apparatus for Detecting Molecular Interactions Using FET Arrays
ActiveUS20120088682A1Facilitate rapid acquisition of dataImprove signal-to-noise ratioTransistorWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCMOSAnalyte
Methods and apparatuses relating to large scale FET arrays for analyte detection and measurement are provided. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Microsensor system and method for measuring data
InactiveUS7297113B1Guaranteed true stateAccurately identify viable and non-viable tissueLocal control/monitoringEndoradiosondesProximateEngineering
One embodiment is a microprobe. An example of the microprobe comprises a housing having an aperture. This example of the microprobe also comprises an ISFET attached to the housing. The ISFET may have a gate located proximate the aperture. This example of the microprobe further comprises a reference electrode attached to the housing proximate the aperture. Another embodiment is a microsensor system. Another embodiment is a method for measuring a characteristic of tissue. Yet another embodiment is a method for monitoring tissue pH.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Methods and Apparatus for Detecting Molecular Interactions Using FET Arrays
ActiveUS20120061256A1Facilitate rapid acquisition of dataImprove signal-to-noise ratioTransistorWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCMOSOrganismal Process
Methods and apparatuses relating to large scale FET arrays for analyte detection and measurement are provided. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
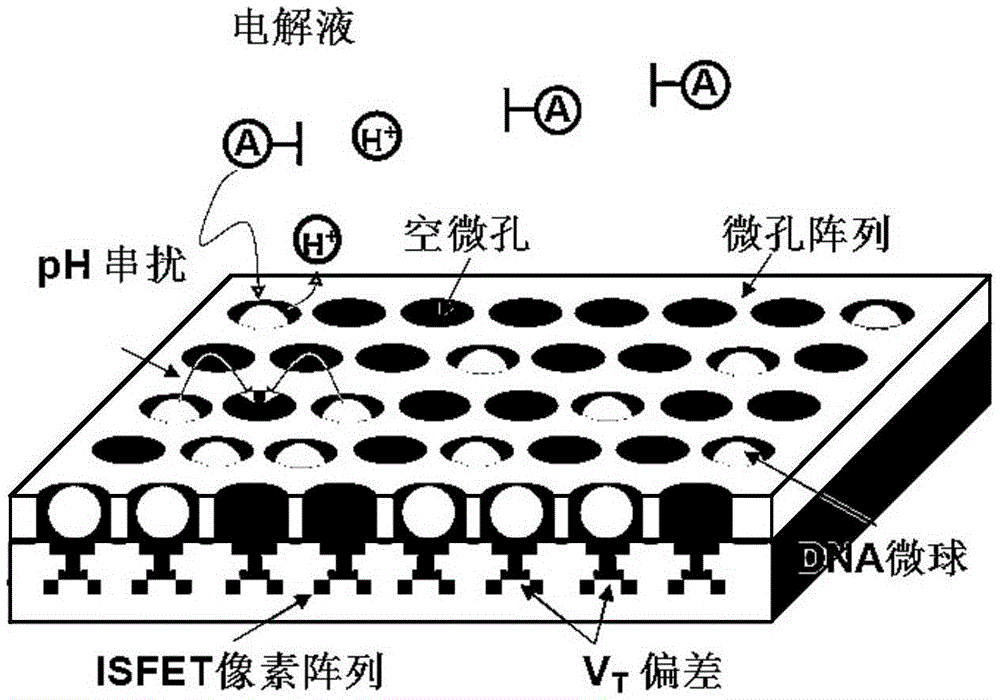
CMOS and ISFET dual-mode image chemical sensor chip for high-throughput gene sequencing
InactiveCN105543071AReduce mismatchQuick responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStatic random-access memoryHemt circuits
The invention provides a CMOS and ISFET dual-mode image chemical sensor chip for high-throughput gene sequencing; the chip comprises a dual-mode pixel array, a row decoder / driver, a column decoder / driver, a column parallel gain adjustable amplifier, a column parallel single-slope analog-digital converter, a static random access memory, a sensitive amplifier, a low voltage differential signal readout module, a static register, a phase-locked loop, a ramp generator and a digital control current source. The chip comprises an image sensor and an ion sensitive field effective transistor (ISFET) produced by a standard semiconductor process, so that optical image acquisition and chemical pH value detection can be performed. A high-speed correlated double sampling signal readout circuit adapting to the image and chemical dual-mode sensing is provided to reduce a system error caused by the mismatch between threshold voltages VT of the sensors. The chip has the advantages of high accuracy and high throughput when applied in gene sequencing.
Owner:严媚
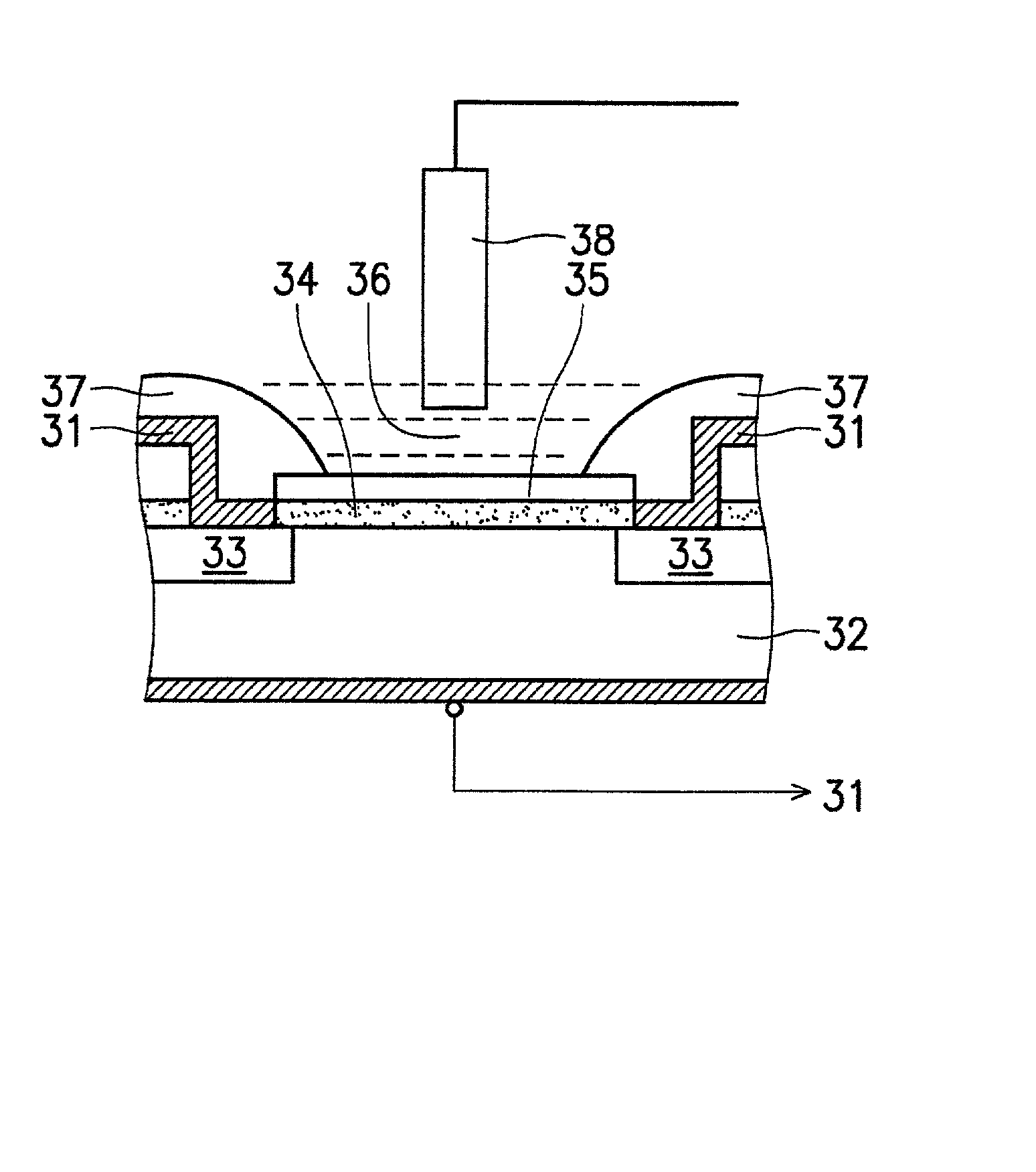
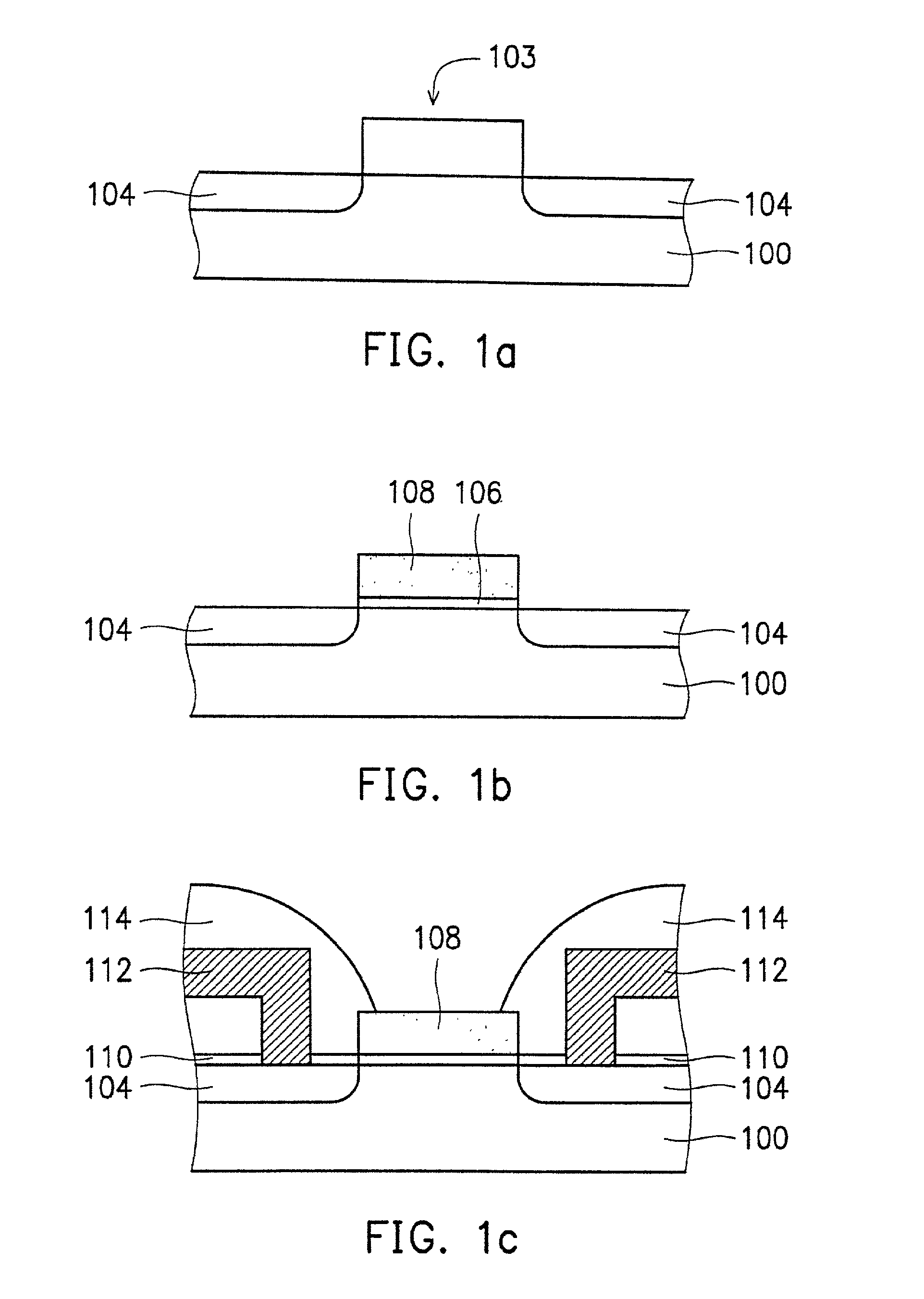
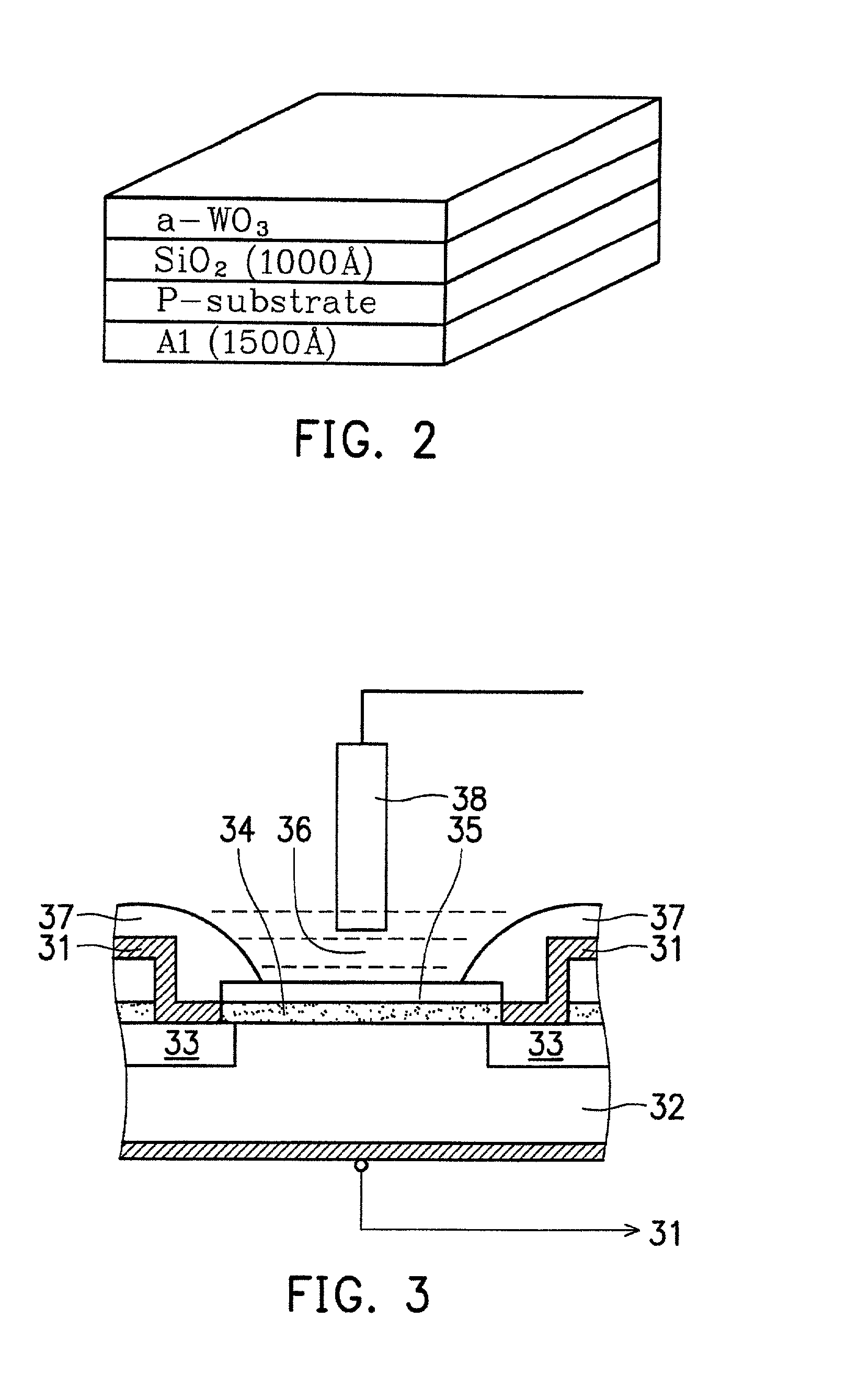
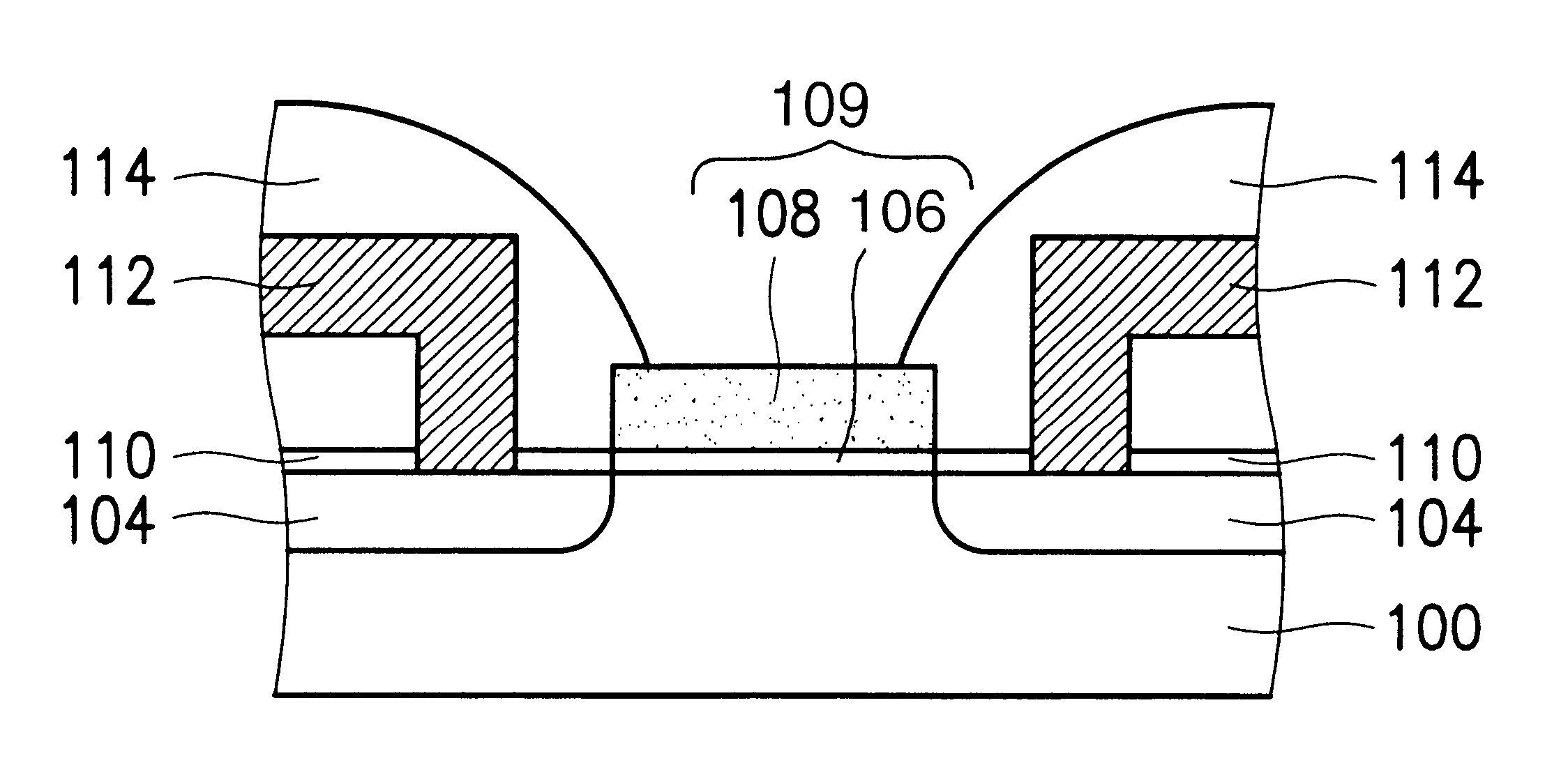
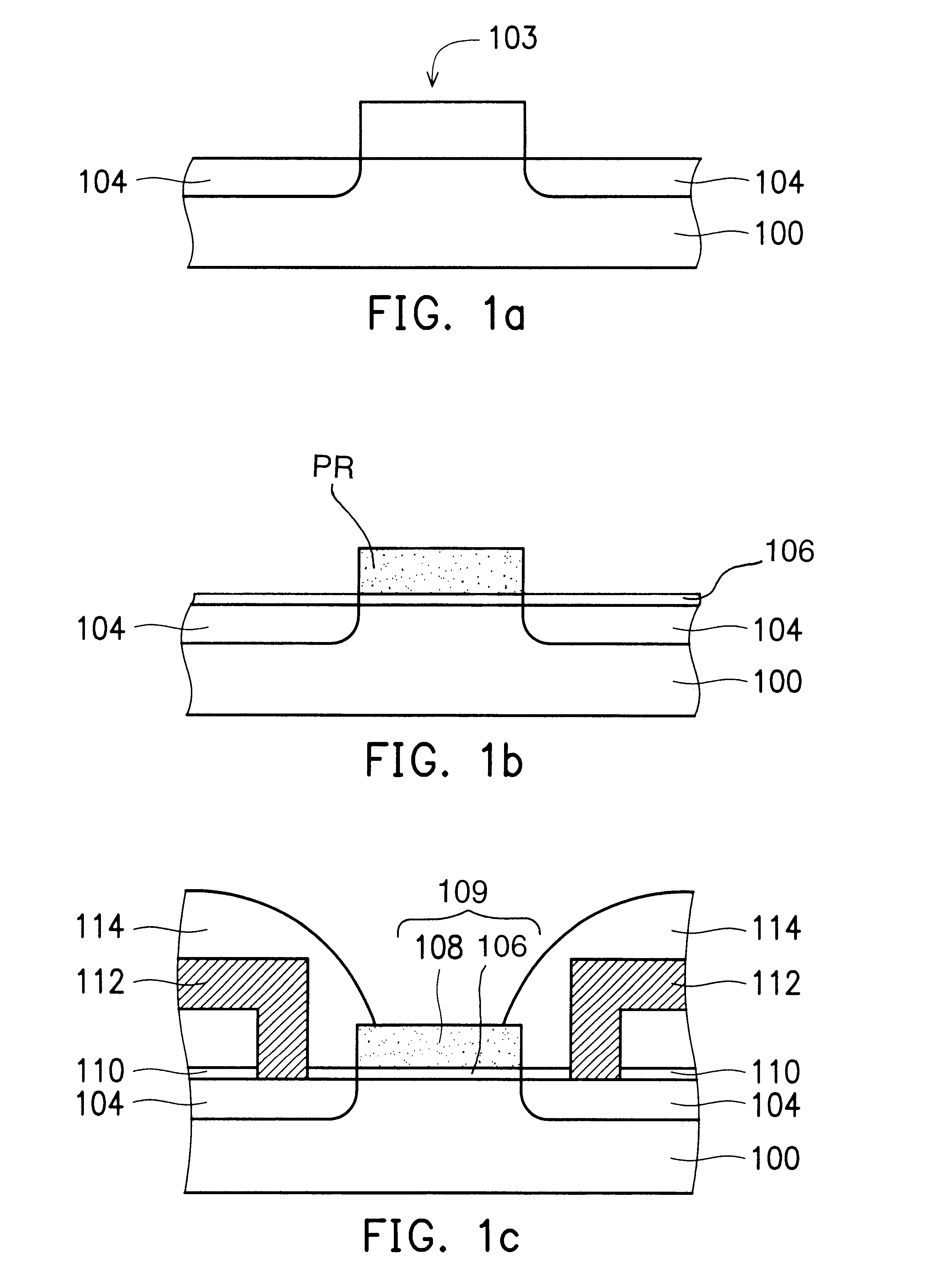
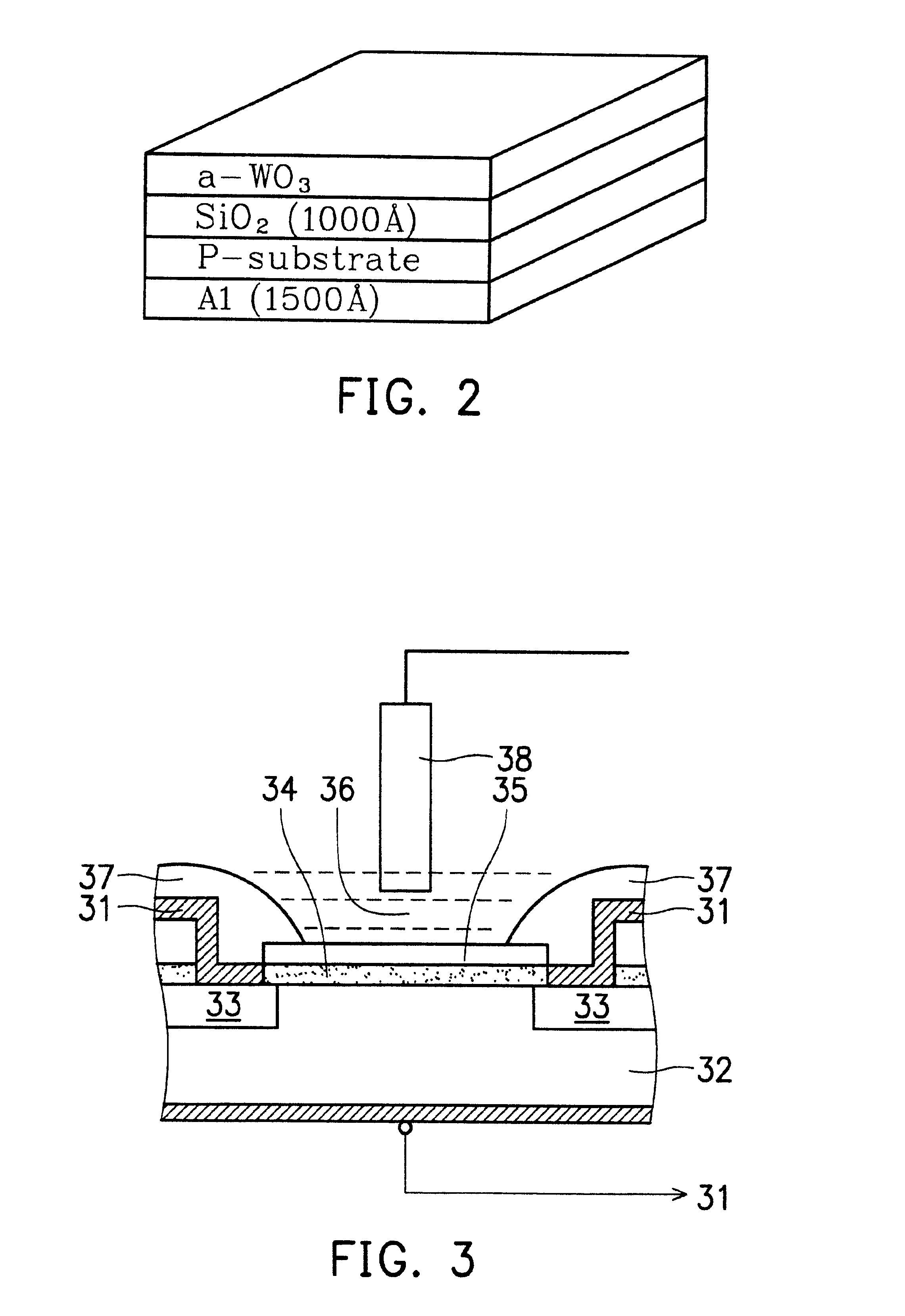
a-wo3-gate isfet devices and method of making the same
InactiveUS20020109161A1Easy to detectReduce lightSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesISFETAqueous solution
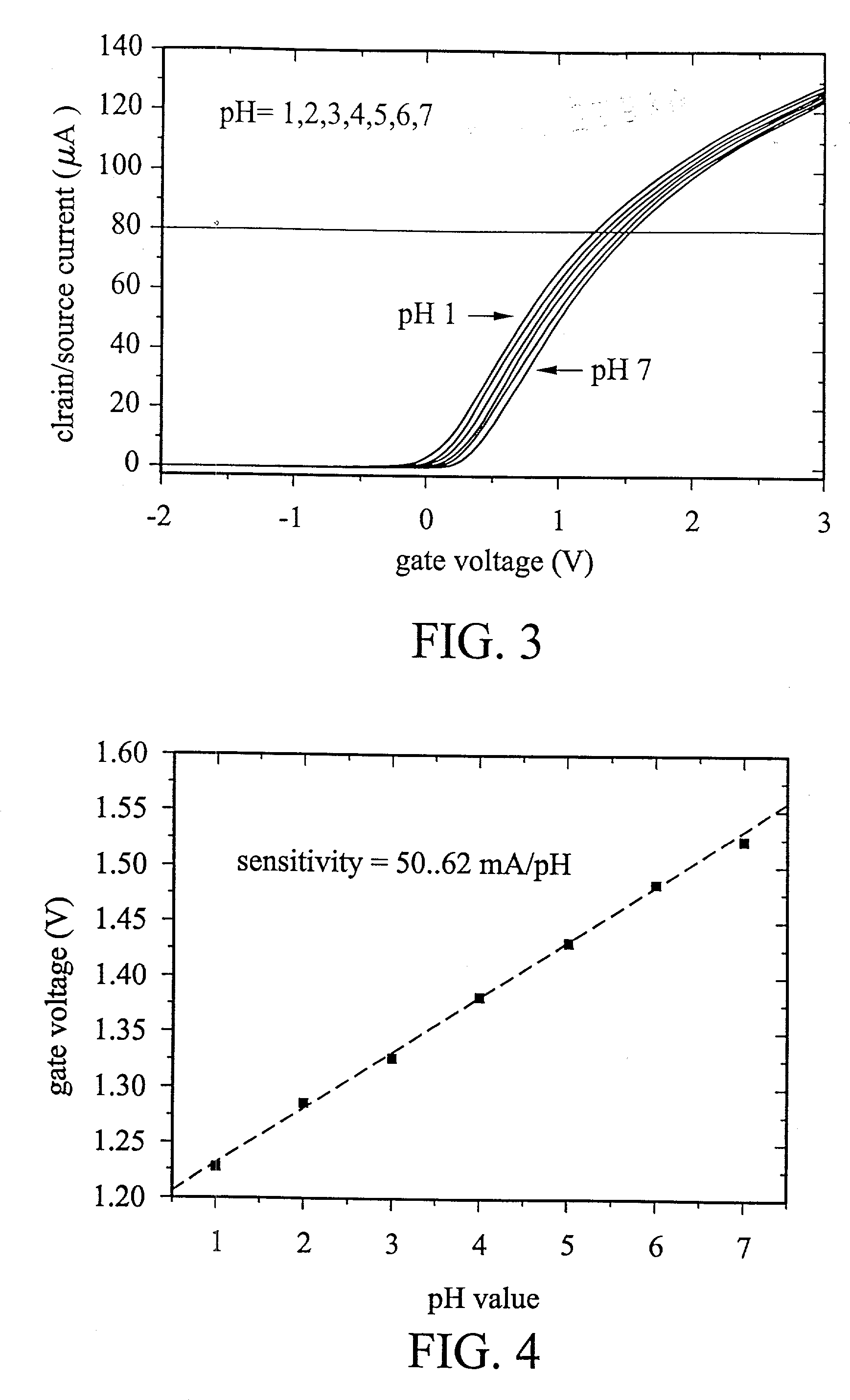
Disclosed is an ISFET comprising a H+-sensing membrane consisting of RF-sputtering a-WO3. The a-WO3 / SiO2-gate ISFET of the present invention is very sensitive in aqueous solution, and particularly in acidic aqueous solution. The sensitivity of the present ISFET ranges from 50 to 58 mV / pH. In addition, the disclosed ISFET has high linearity. Accordingly, the disclosed ISFET can be used to detect effluent.
Owner:NATIONAL YUNLIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Methods and apparatus for detecting molecular interactions using fet arrays
Methods and apparatuses relating to large scale FET arrays for analyte detection and measurement are provided. ChemFET (e.g., ISFET) arrays may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved FET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense arrays. Improved array control techniques provide for rapid data acquisition from large and dense arrays. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Signal Enhancement Mechanism For Dual-Gate ION Sensitive Field Effect Transistor In On-Chip Disease Diagnostic Platform
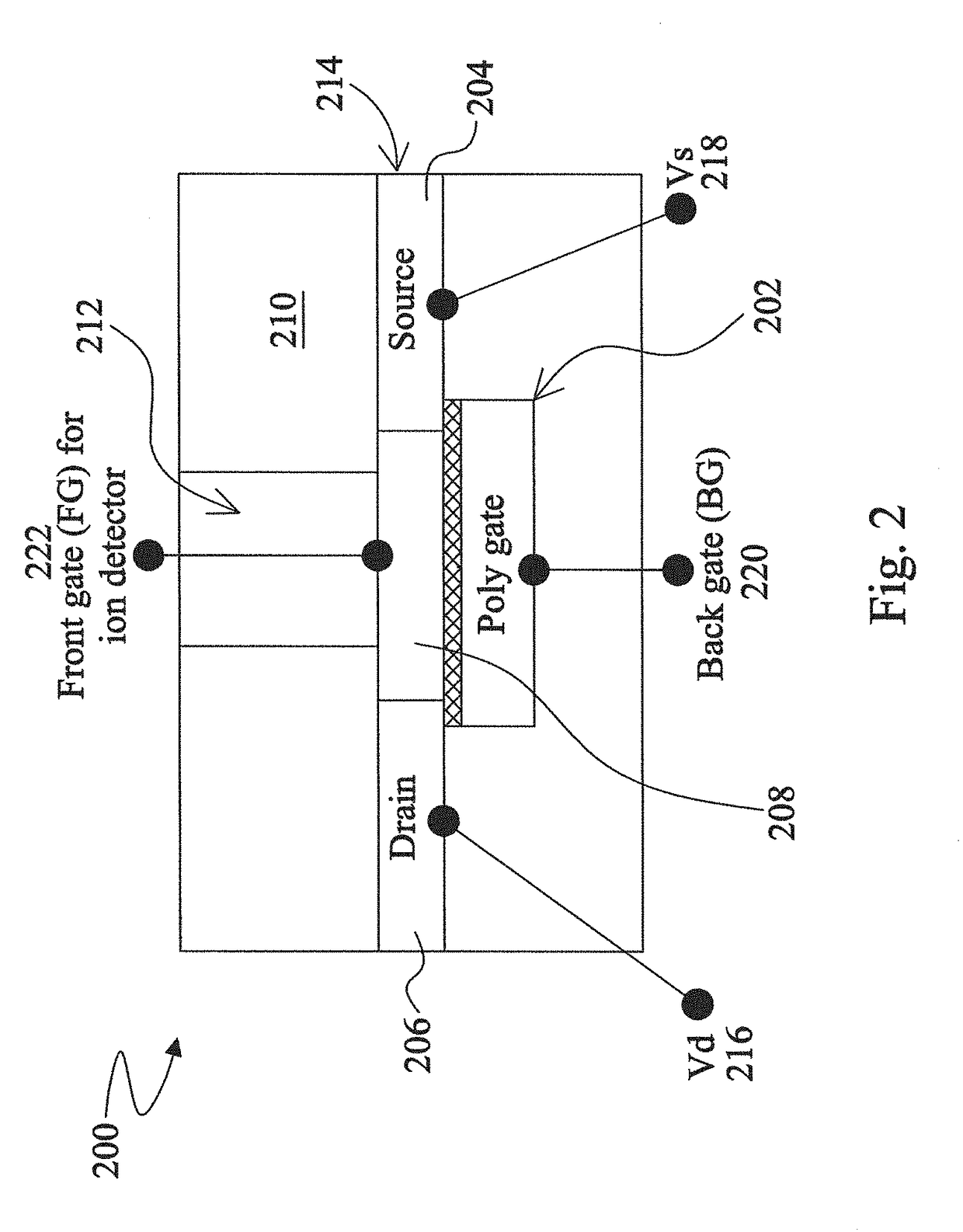
Dual-gate ion-sensitive field effect transistors (ISFETs) for disease diagnostics are disclosed herein. An exemplary dual-gate ISFET includes a gate structure and a fluidic gate structure disposed over opposite surfaces of a device substrate. The gate structure is disposed over a channel region defined between a source region and a drain region in the device substrate. The fluidic gate structure includes a sensing well that is disposed over the channel region. The sensing well includes a sensing layer and an electrolyte solution. The electrolyte solution includes a constituent that can react with a product of an enzymatic reaction that occurs when an enzyme-modified detection mechanism detects an analyte. The sensing layer can react with a first ion generated from the enzymatic reaction and a second ion generated from a reaction between the product of the enzymatic reaction and the constituent, such that the dual-gate ISFET generates an enhanced electrical signal.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
A-WO3-gate ISFET devices and method of making the same
InactiveUS6617190B2Reduce lightEasy to produceSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansISFETAqueous solution
Disclosed is an ISFET comprising a H+-sensing membrane consisting of RF-sputtering a-WO3. The a-WO3 / SiO2-gate ISFET of the present invention is very sensitive in aqueous solution, and particularly in acidic aqueous solution. The sensitivity of the present ISFET ranges from 50 to 58 mV / pH. In addition, the disclosed ISFET has high linearity. Accordingly, the disclosed ISFET can be used to detect effluent.
Owner:NATIONAL YUNLIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
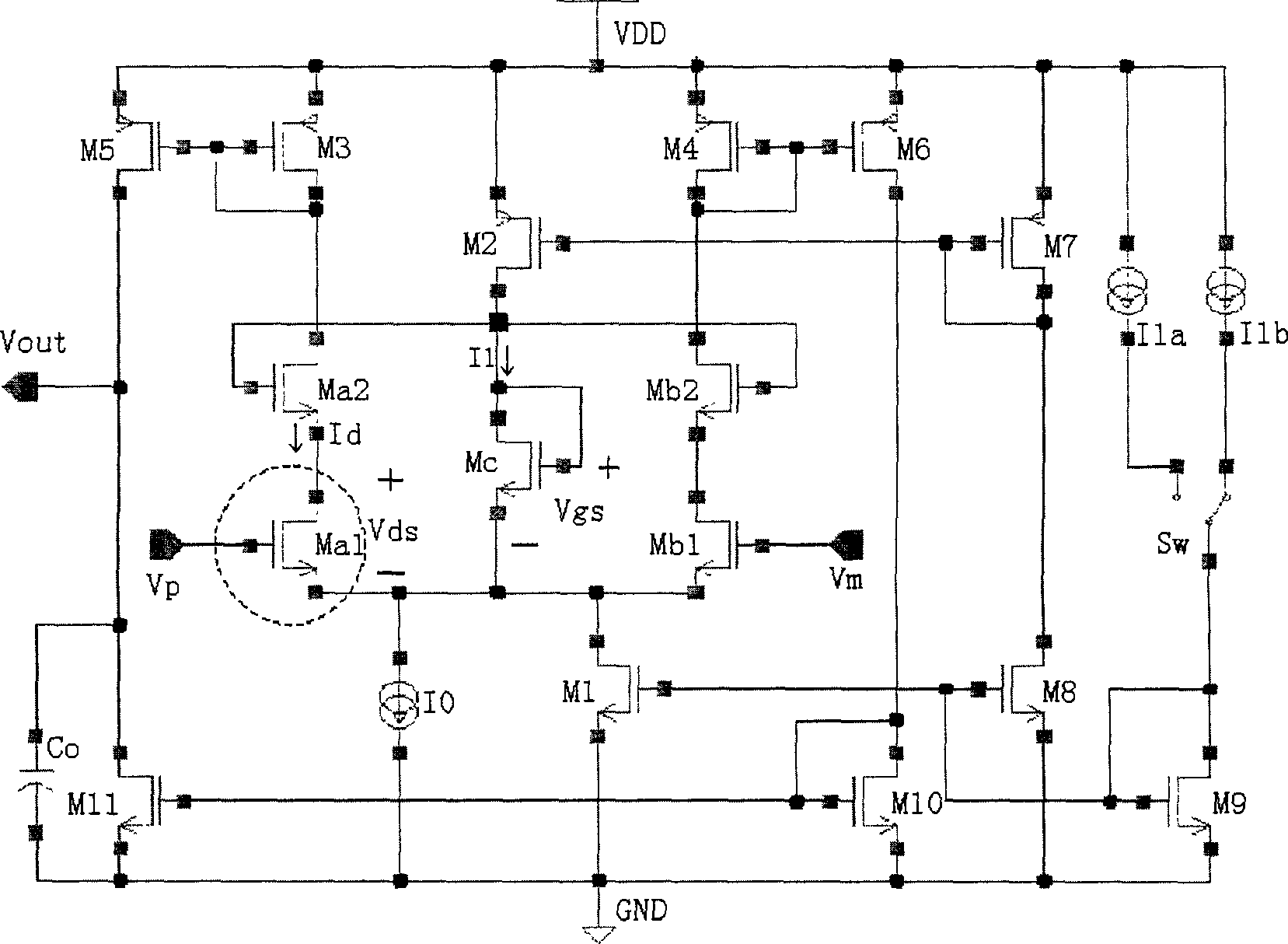
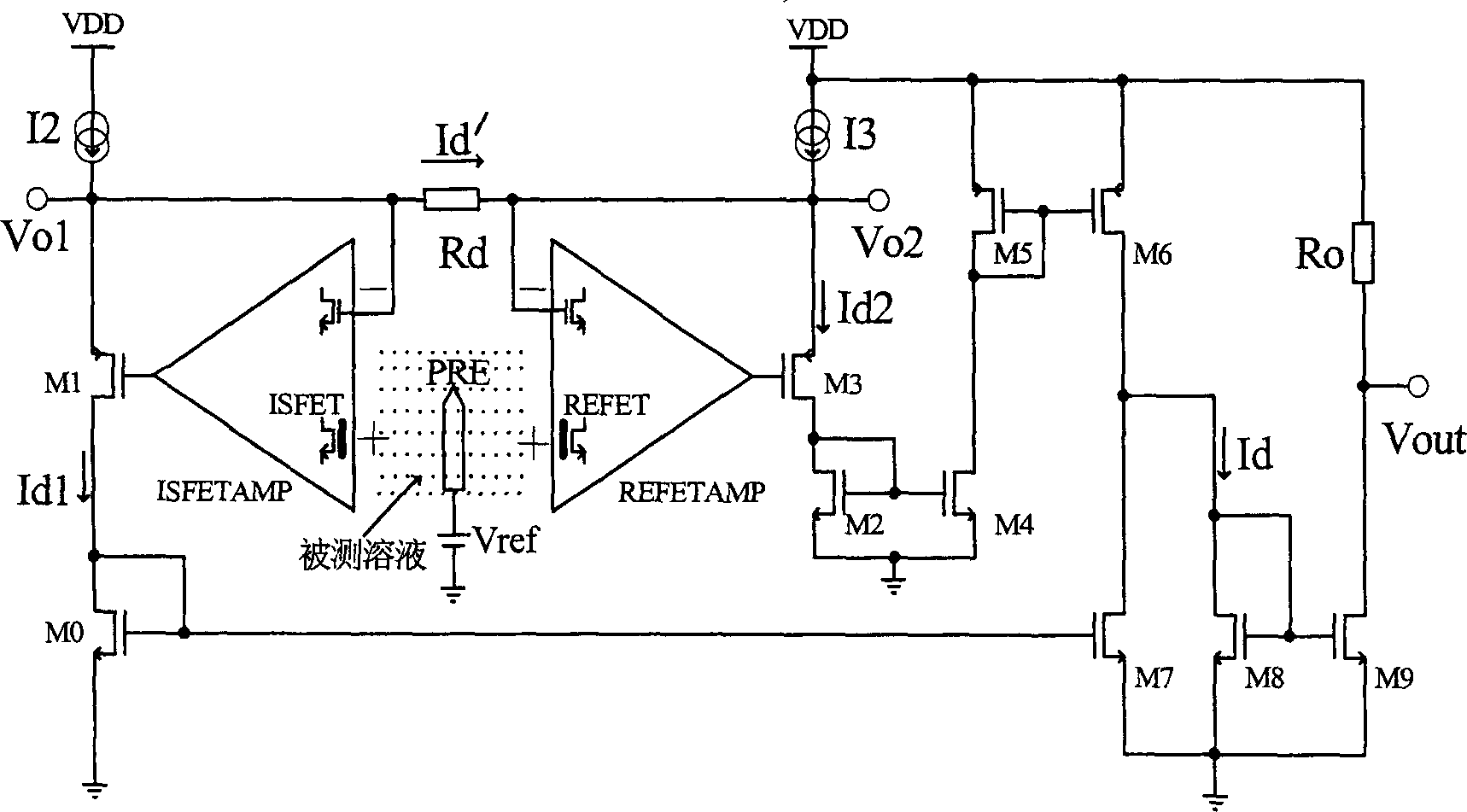
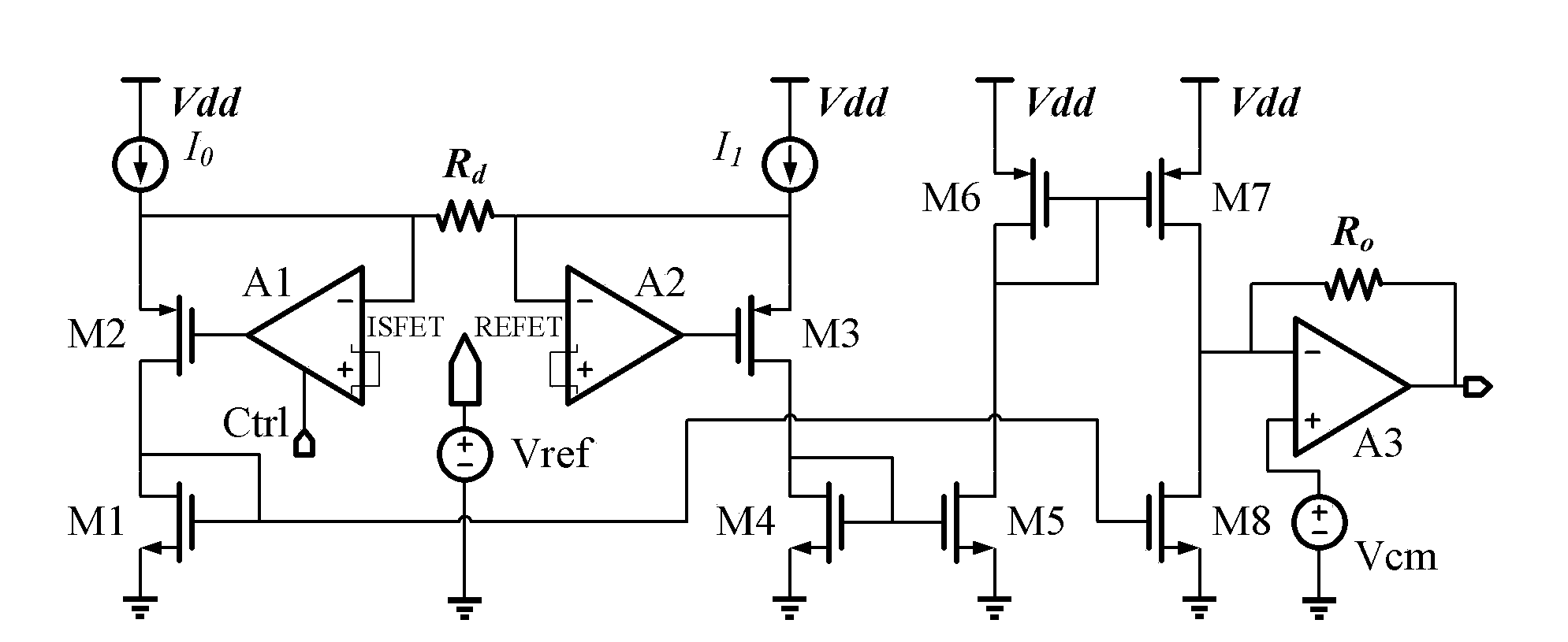
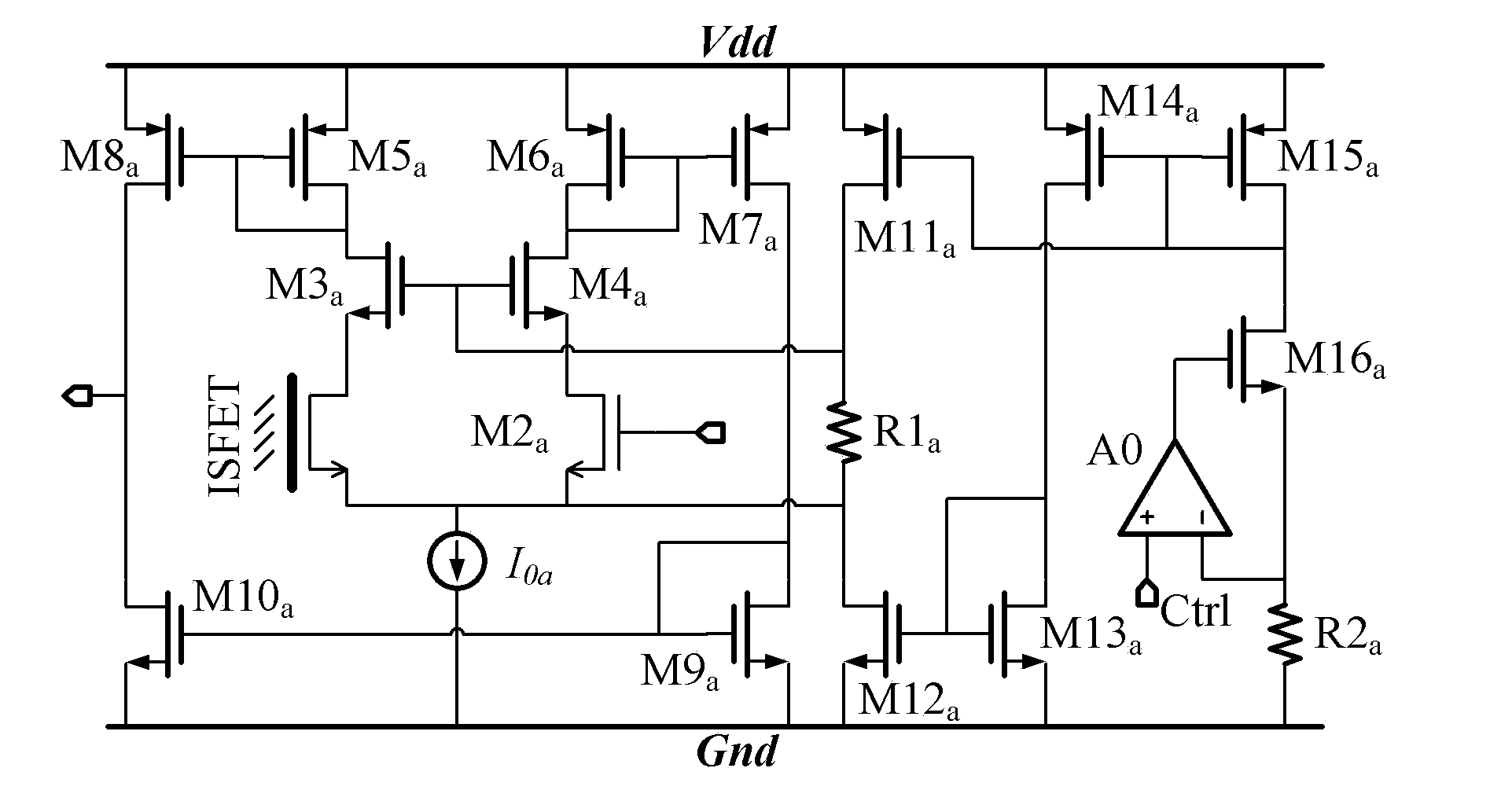
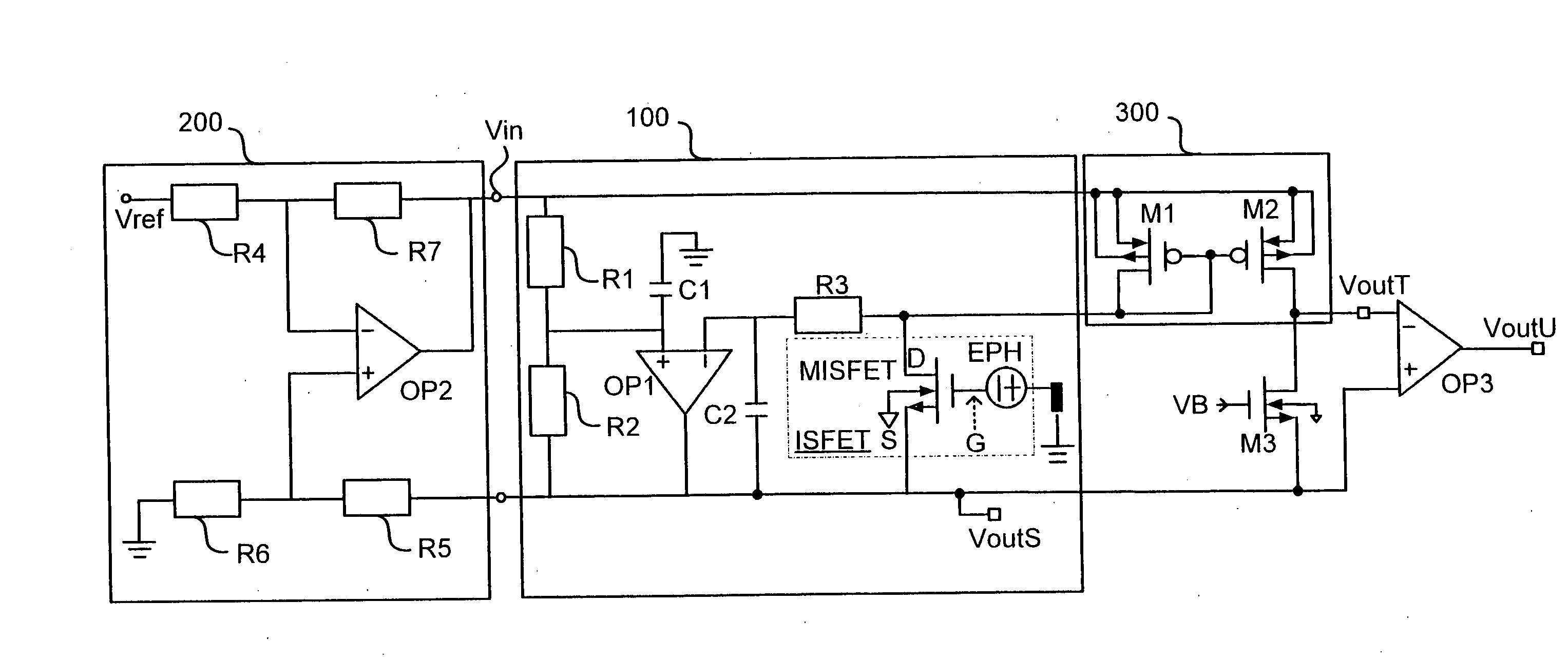
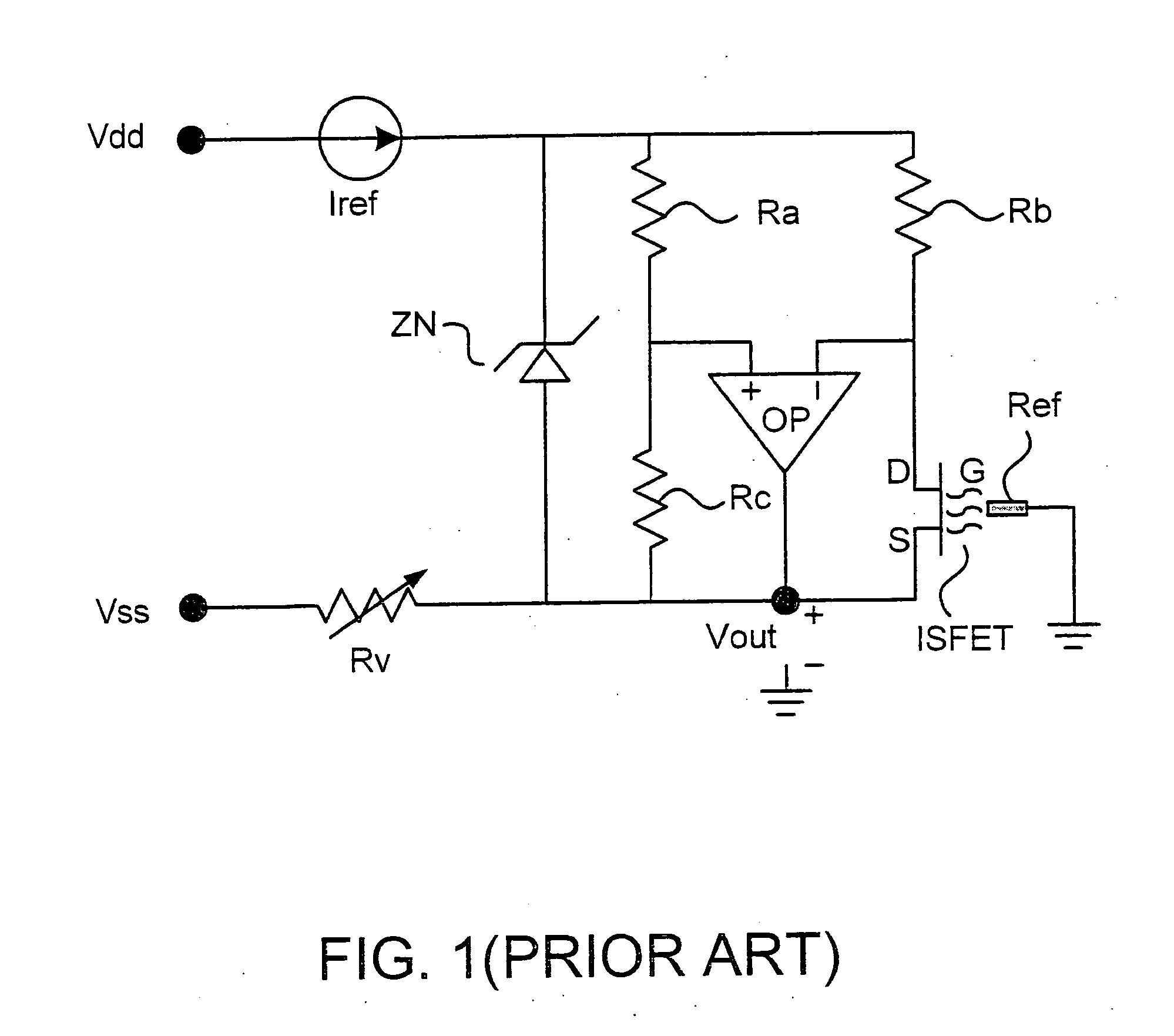
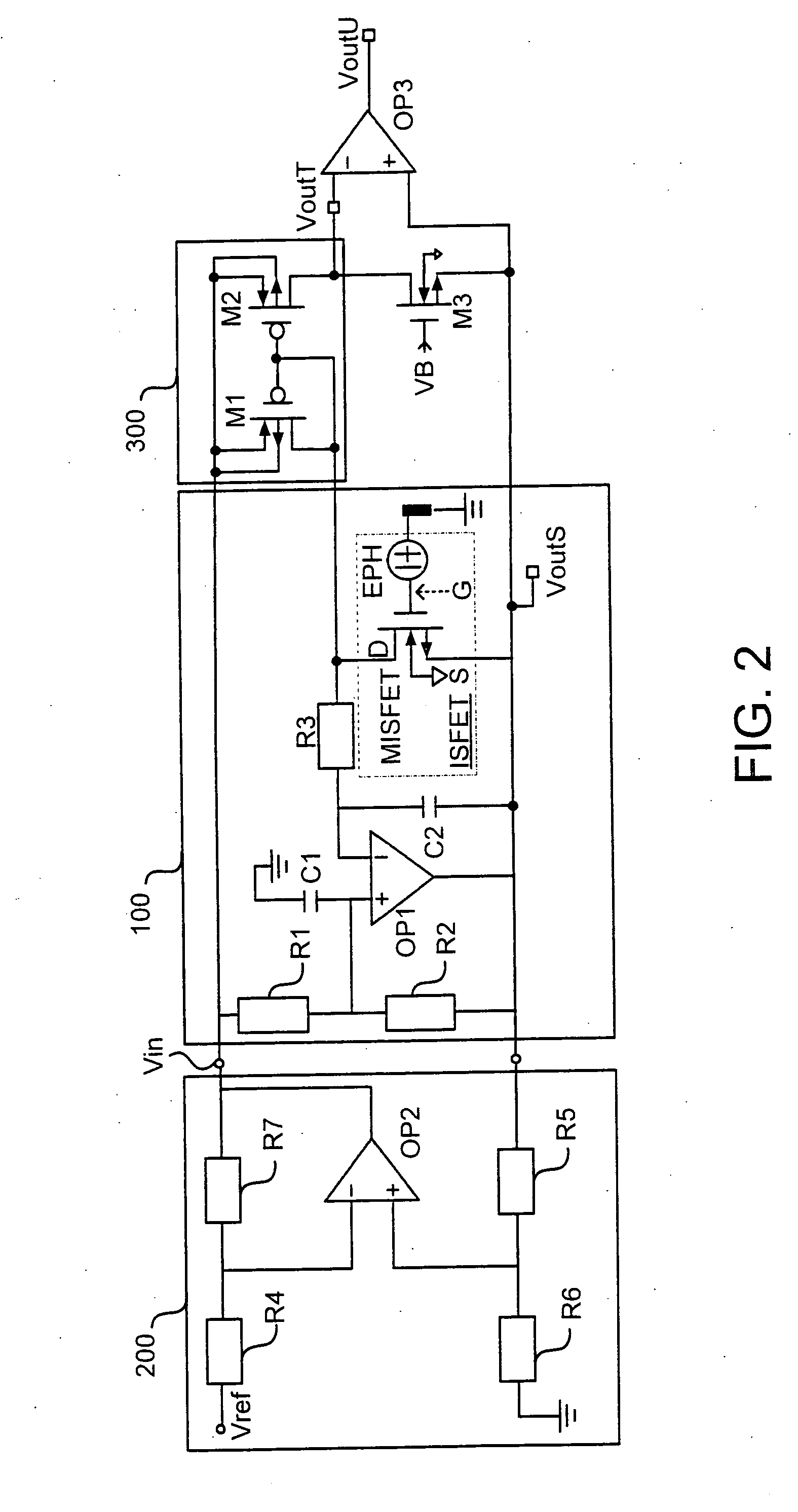
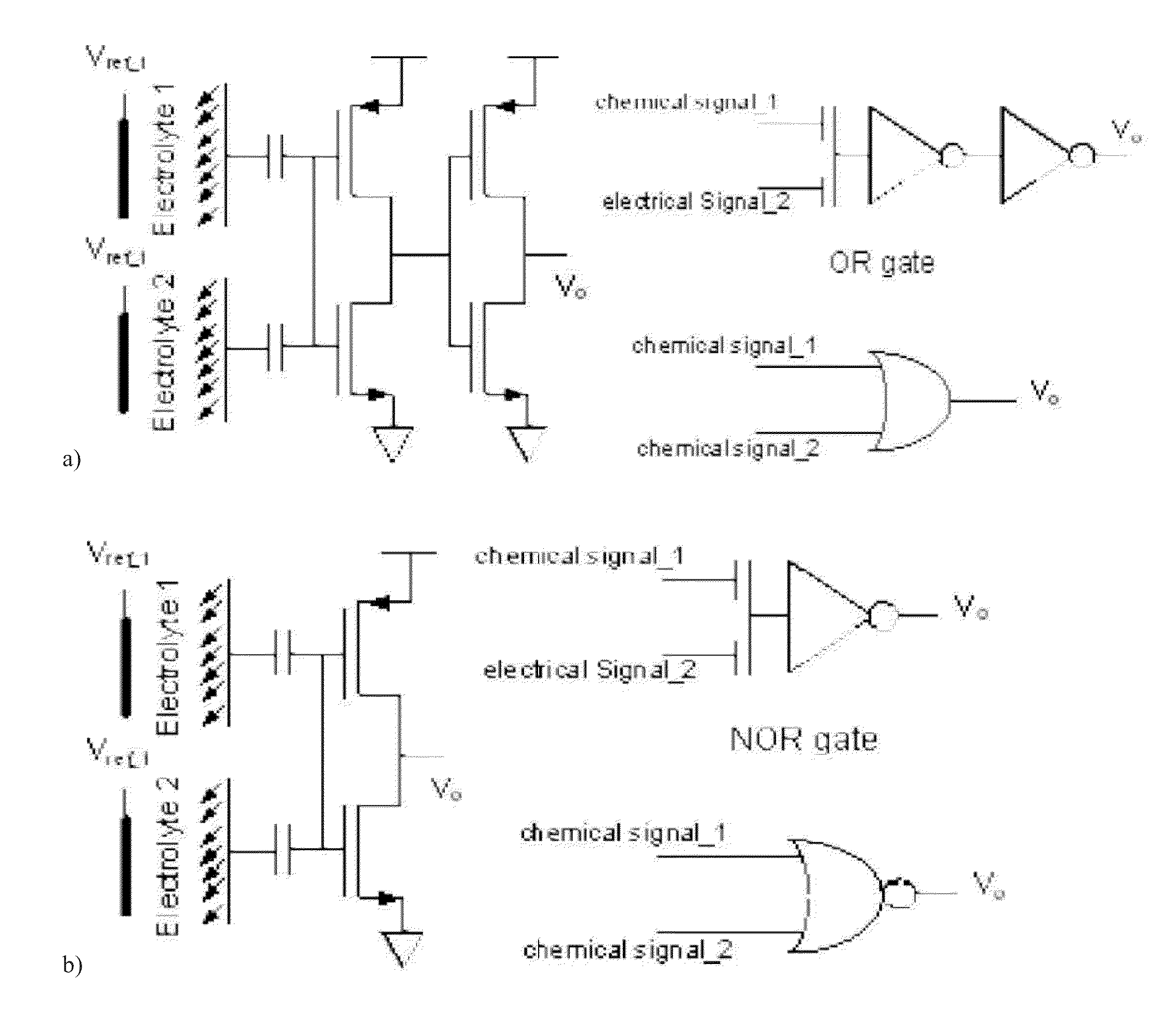
Differential circuit for reading out signal of integrated ISFET sensor based on two modes
ActiveCN1797944AEnsure consistencyEliminate "Common Mode" ErrorsDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierISFET
Integrated ISFET signal amplifier in two modes includes following parts: difference amplifier is composed of Ma1 and Mb1; Ma2íóMb2 and Mc constitute bootstrap circuit; Current mirror image circuits M9, M8, M7, M2, M1; and source of current I1a, I1b, and I0. ISFET current type signal differential circuit includes ISFET amplifier and REFET amplifier, quasi reference electrode PRE, two pieces of follower amplifier M1 and M3. The invention is suitable to process signal input from ISFET sensor in high precision and larger dynamic range.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ion sensitive field effect transistor
ActiveUS20140061729A1High performance ion detectionReduce noiseMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSOrganic field-effect transistor
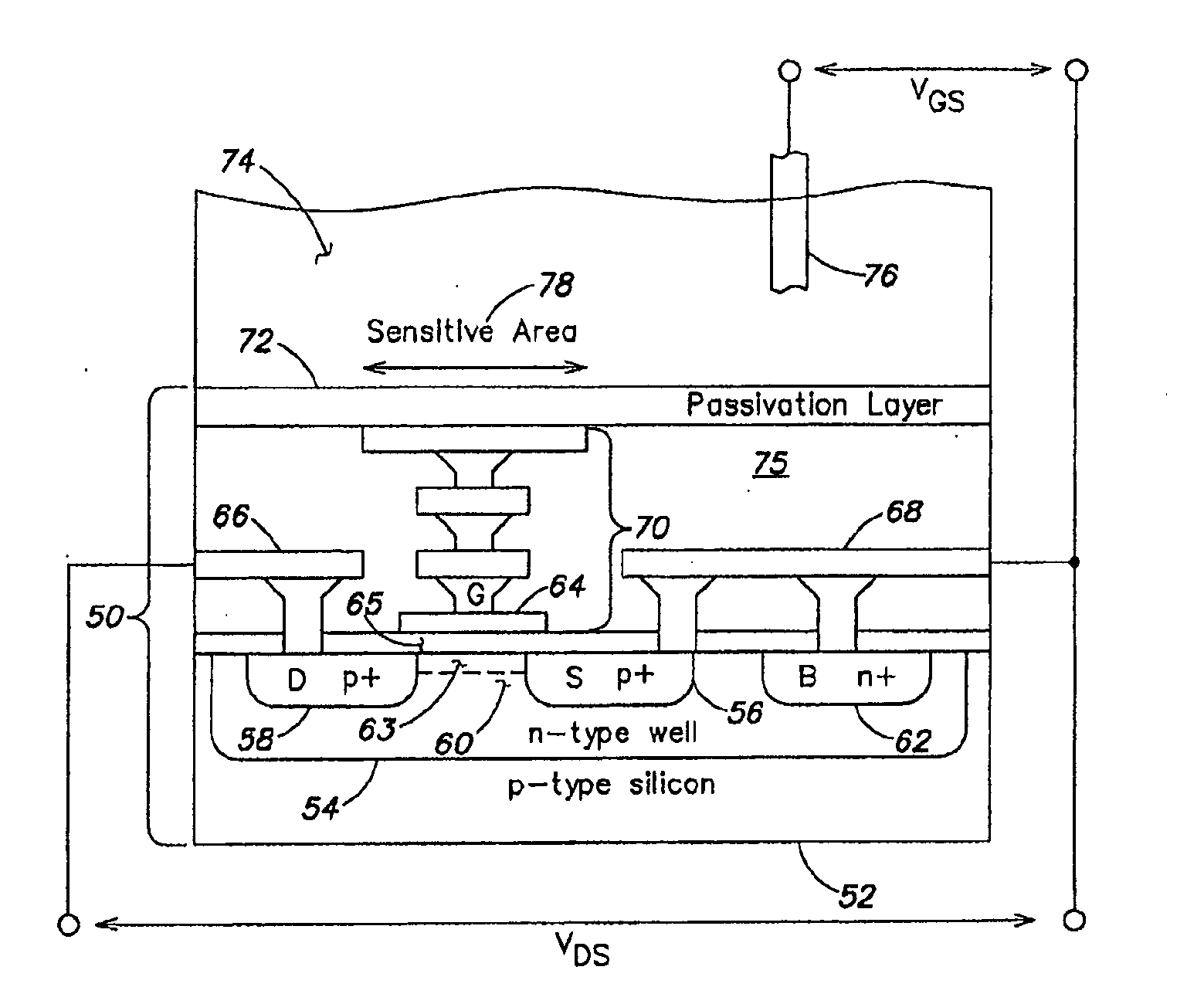
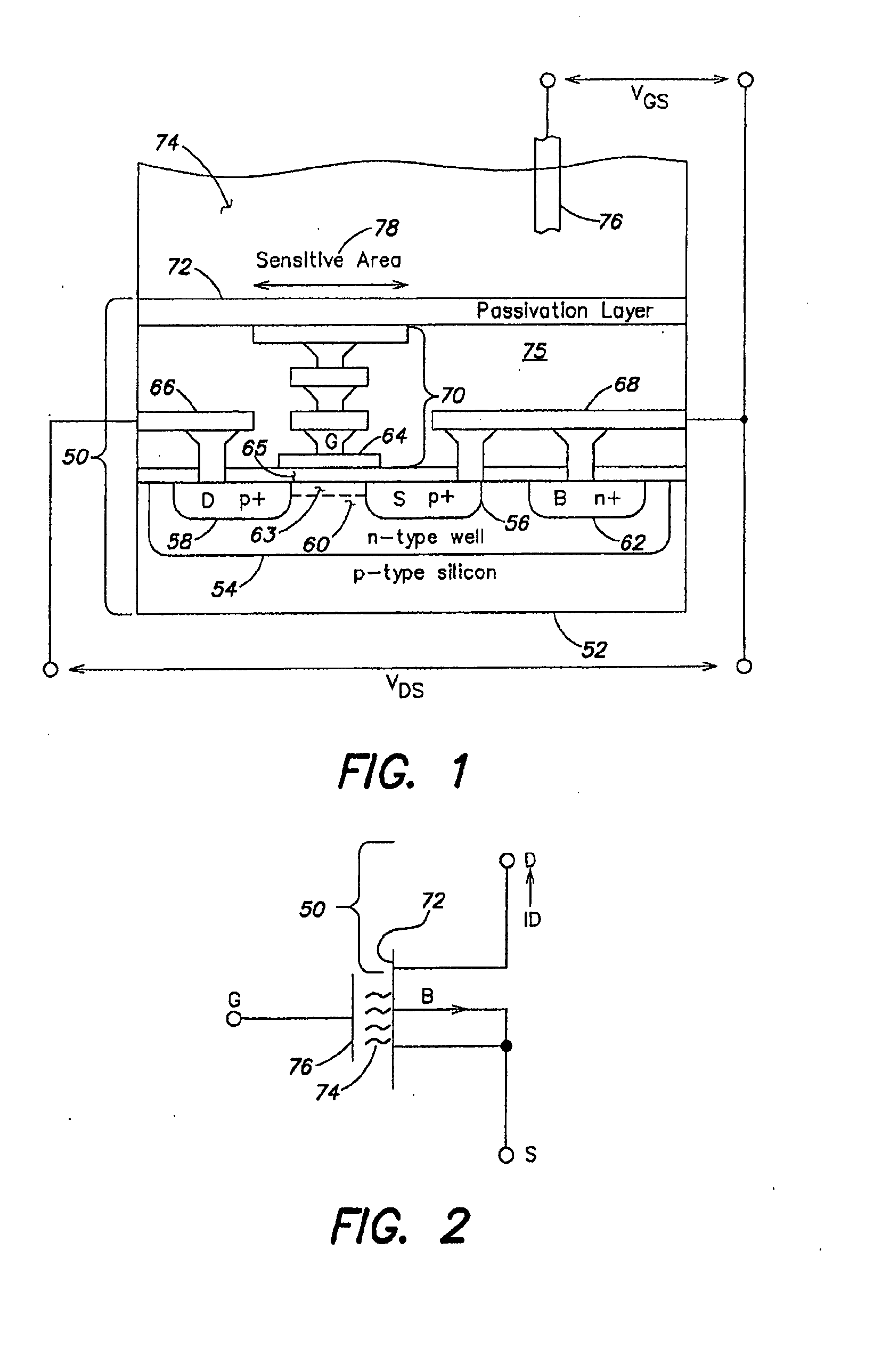
A CMOS or bipolar based Ion Sensitive Field Effect Transistor (ISFET) comprising an ion sensitive recess for holding a liquid wherein the recess is formed at least partly on top of a gate of the transistor. There is also provided a method of manufacturing an I on Sensitive Field Effect Transistor (ISFET) utilizing CMOS processing steps, the method comprising forming an ion sensitive recess for holding a liquid at least partly on top of a gate of the transistor.
Owner:X FAB SEMICON FOUNDRIES
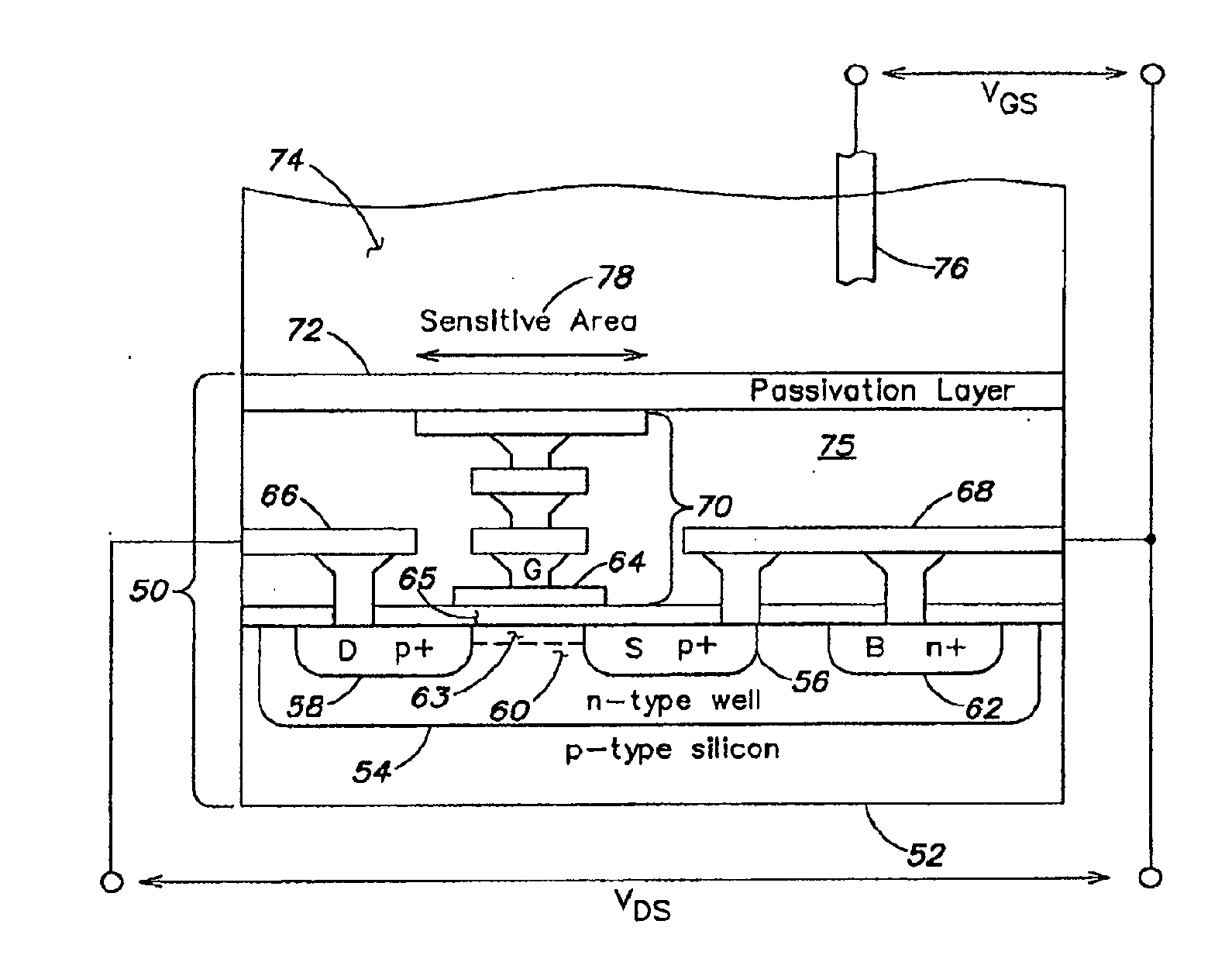
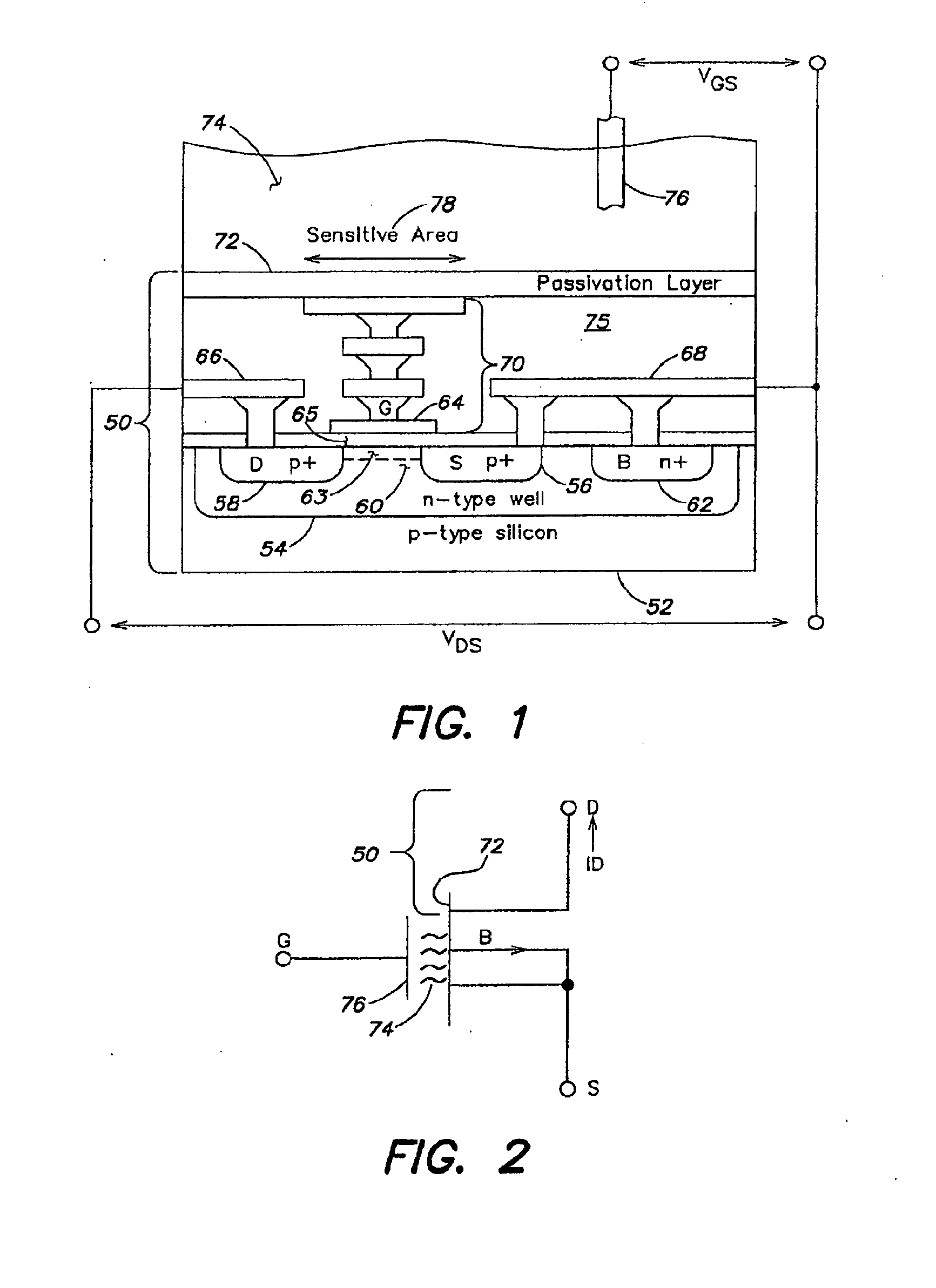
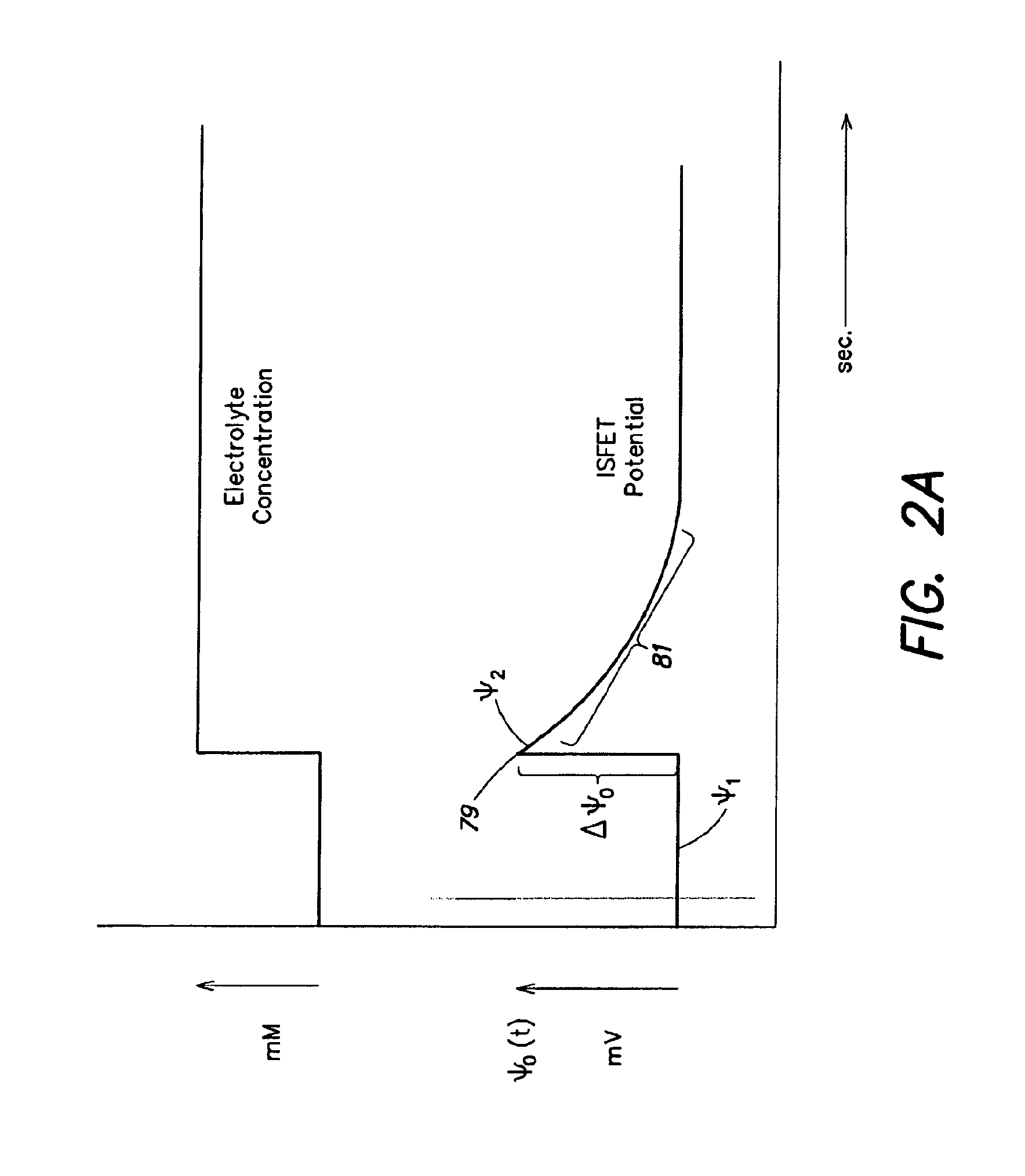
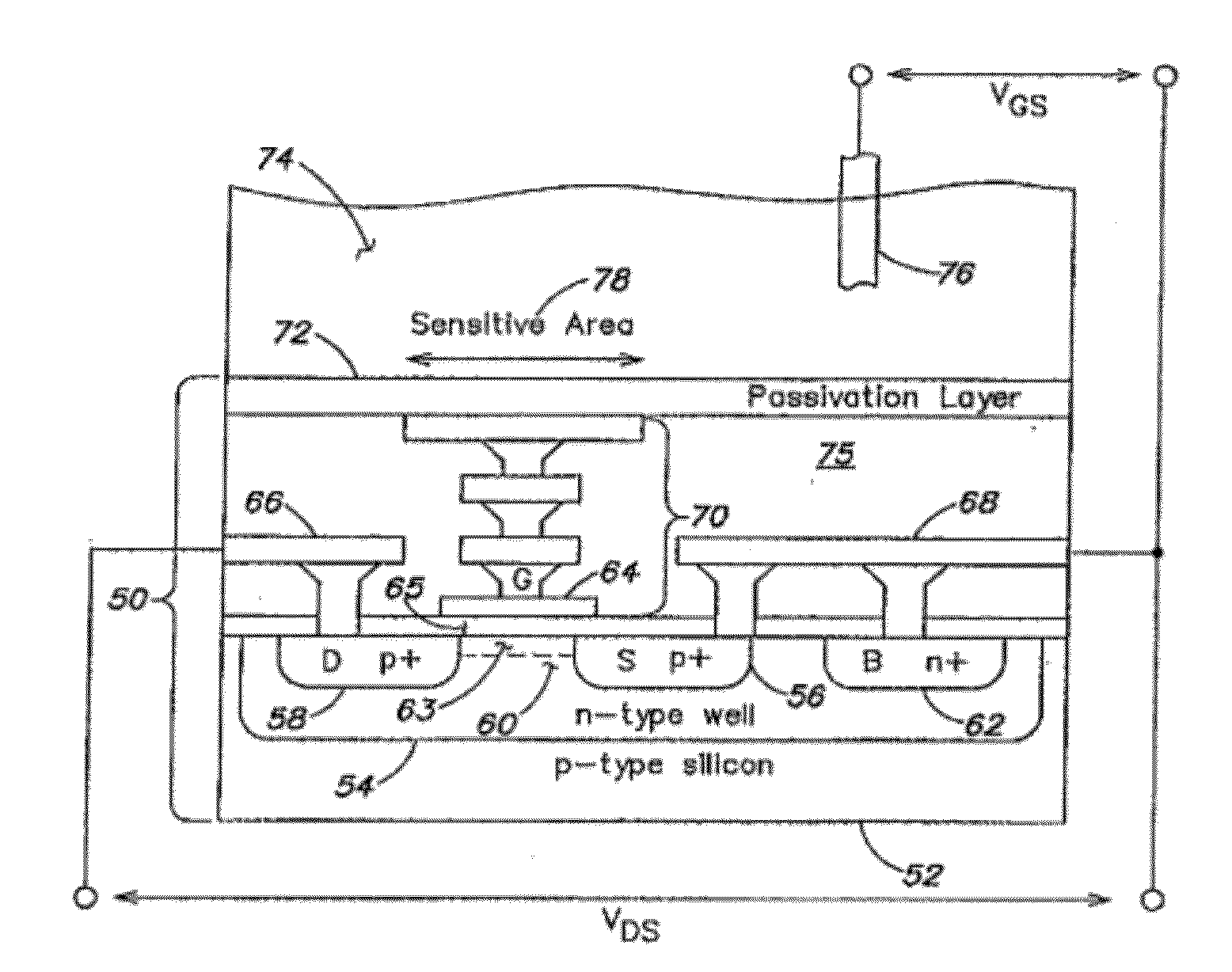
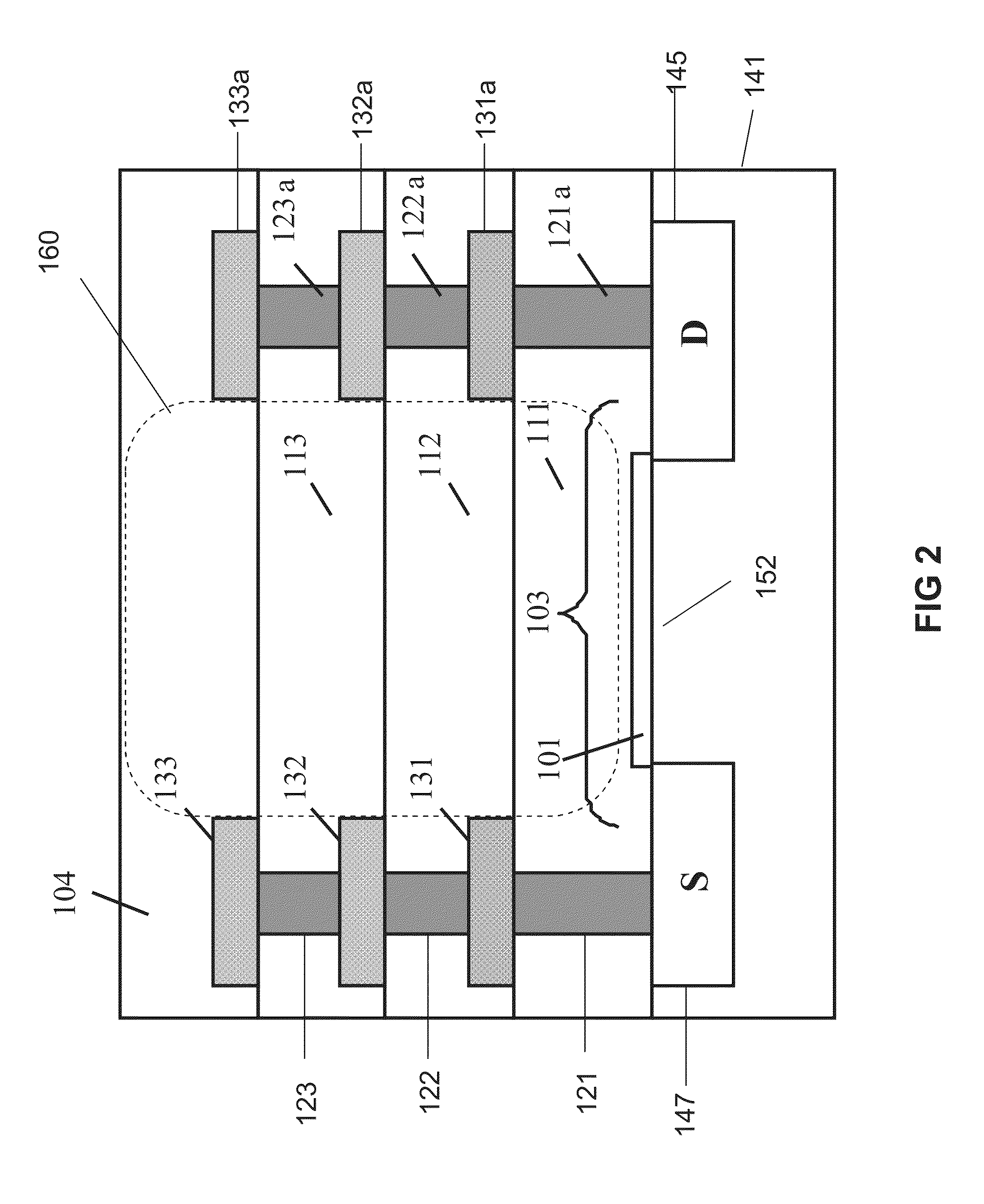
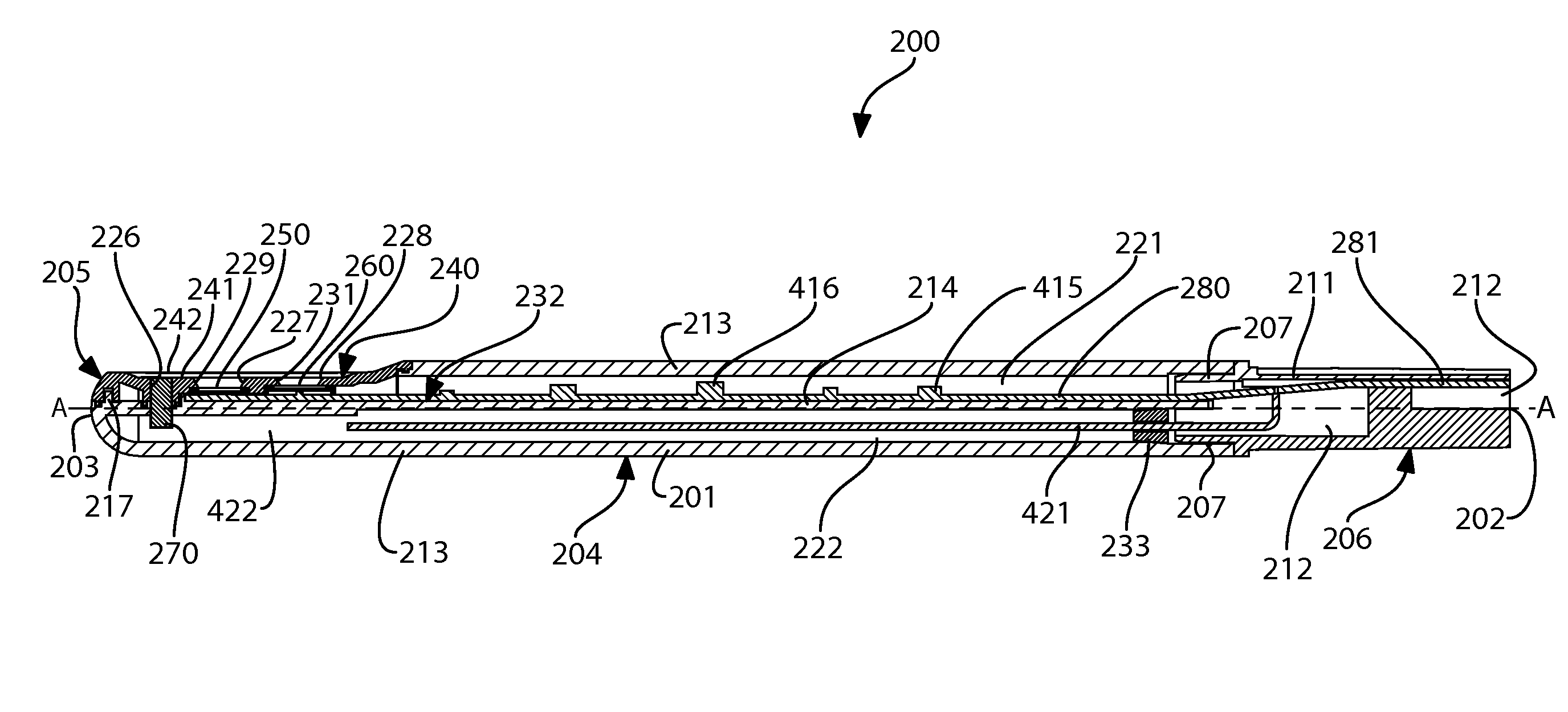
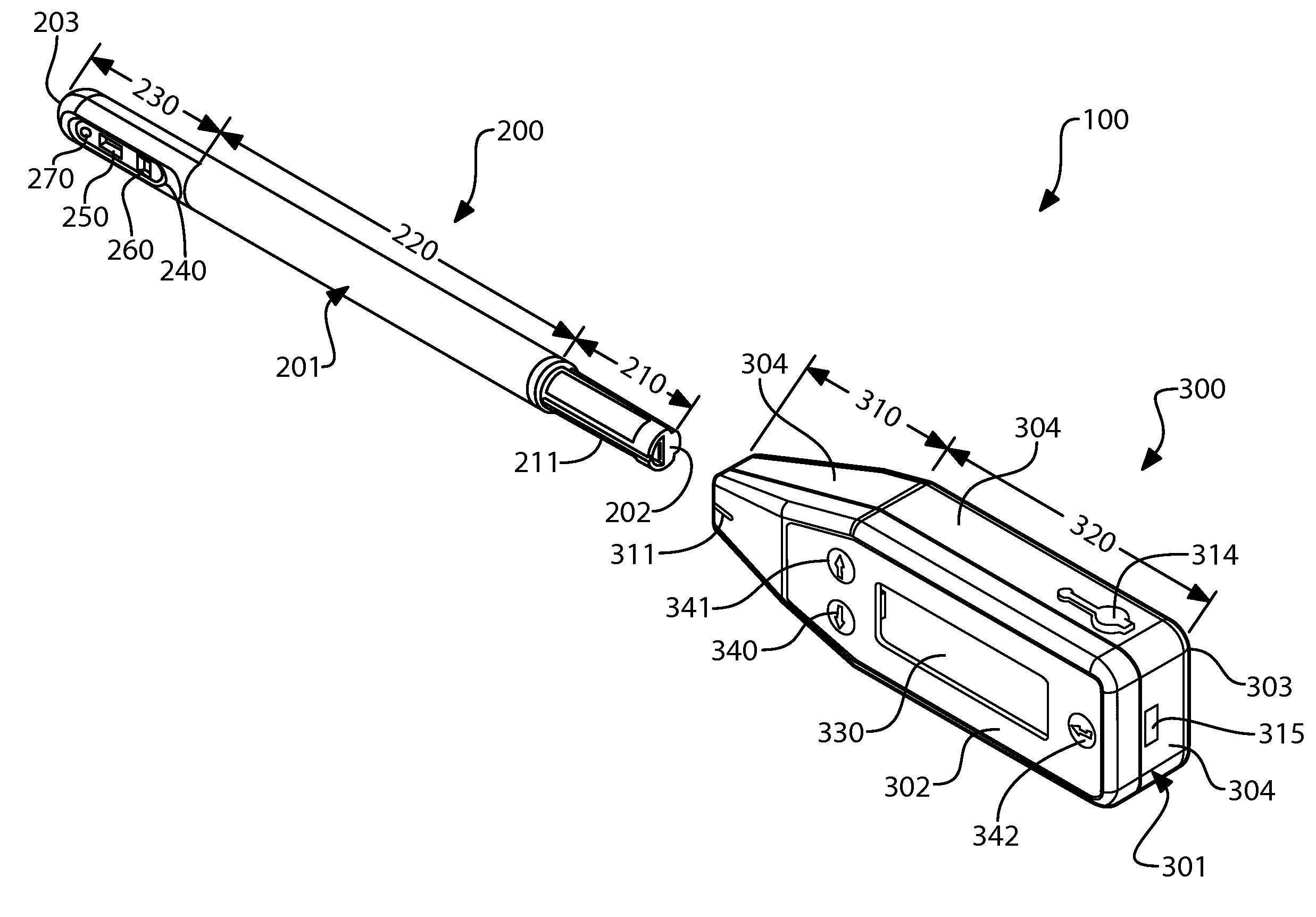
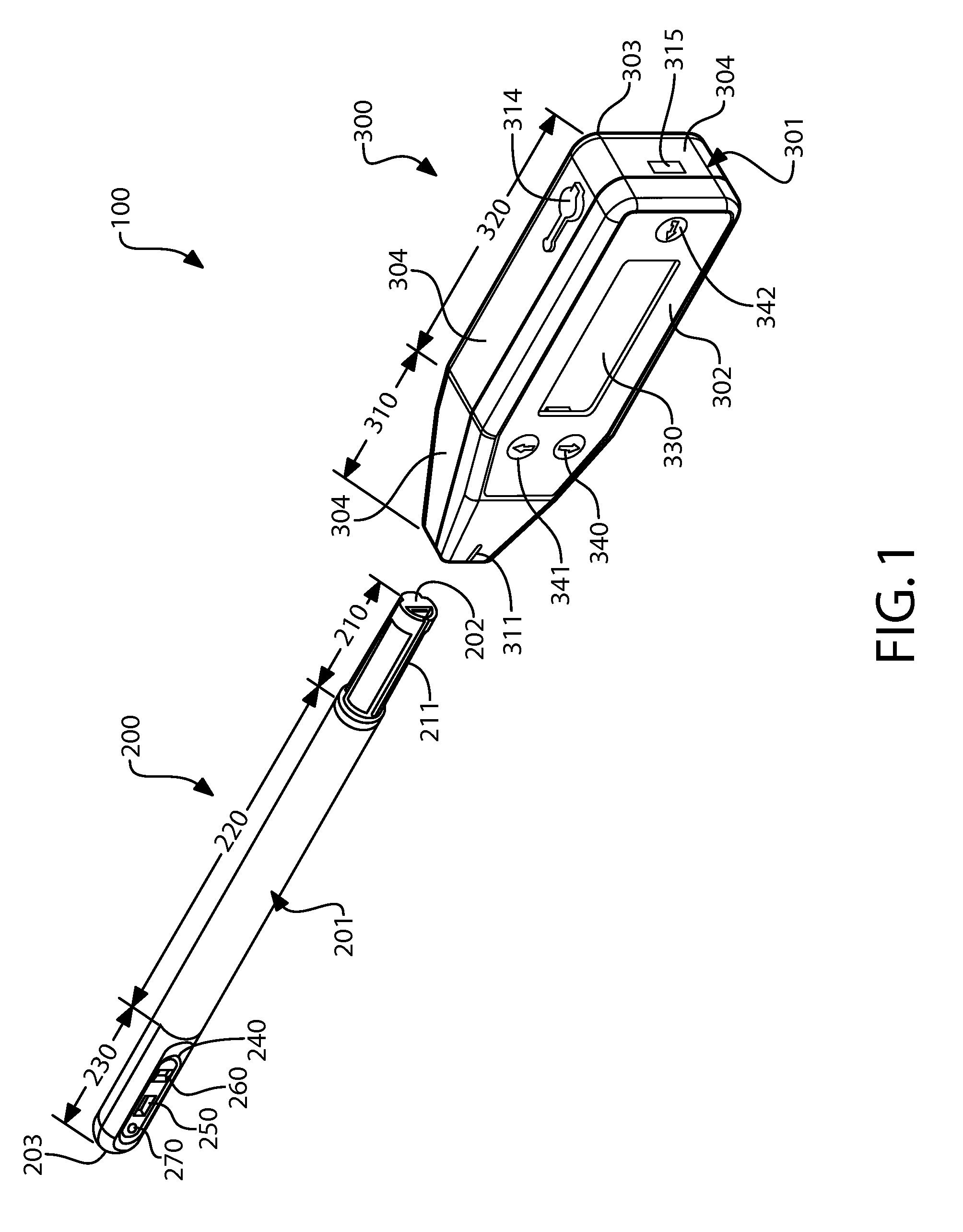
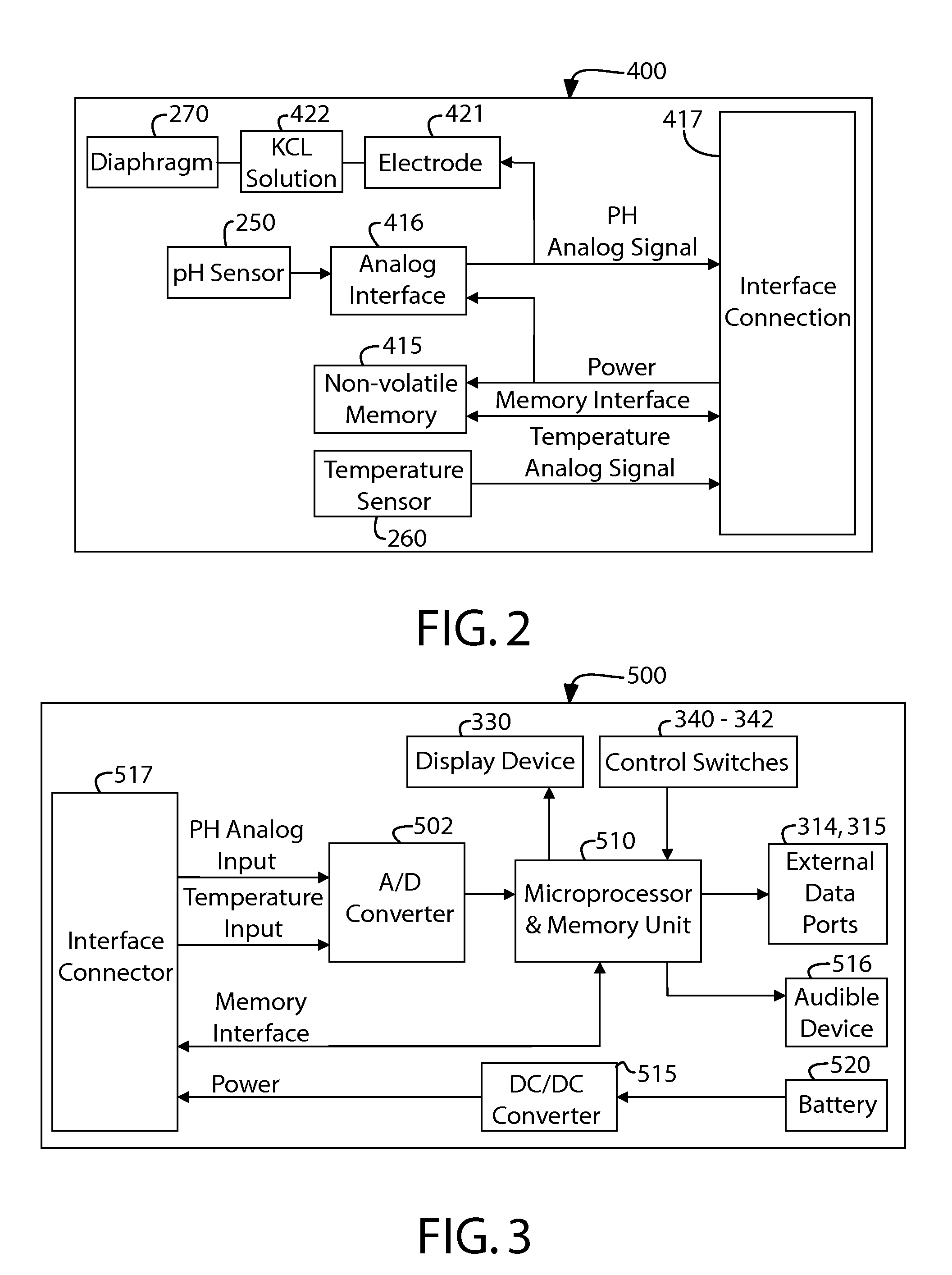
Apparatus, method and system for determining a physiological condition within a mammal
A system, method and apparatus for determining a physiological condition within a mammal based on pH and / or temperature measurements. In one aspect, the invention is directed to an apparatus for measuring a physiological condition within a mammal comprising: a tubular housing extending along a longitudinal axis from a distal end to a proximal end, the housing having an internal cavity; a first opening in the elongated housing forming a first passageway into the internal cavity; an ion-sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) for measuring pH within a body lumen of the mammal, the ISFET positioned in the internal cavity, the ISFET aligned with the first opening so that at least a portion of the ISFET is exposed via the first opening; and a first seal between the ISFET and the housing forming a hermetic seal about a perimeter of the first opening.
Owner:PH DIAGNOSTICS
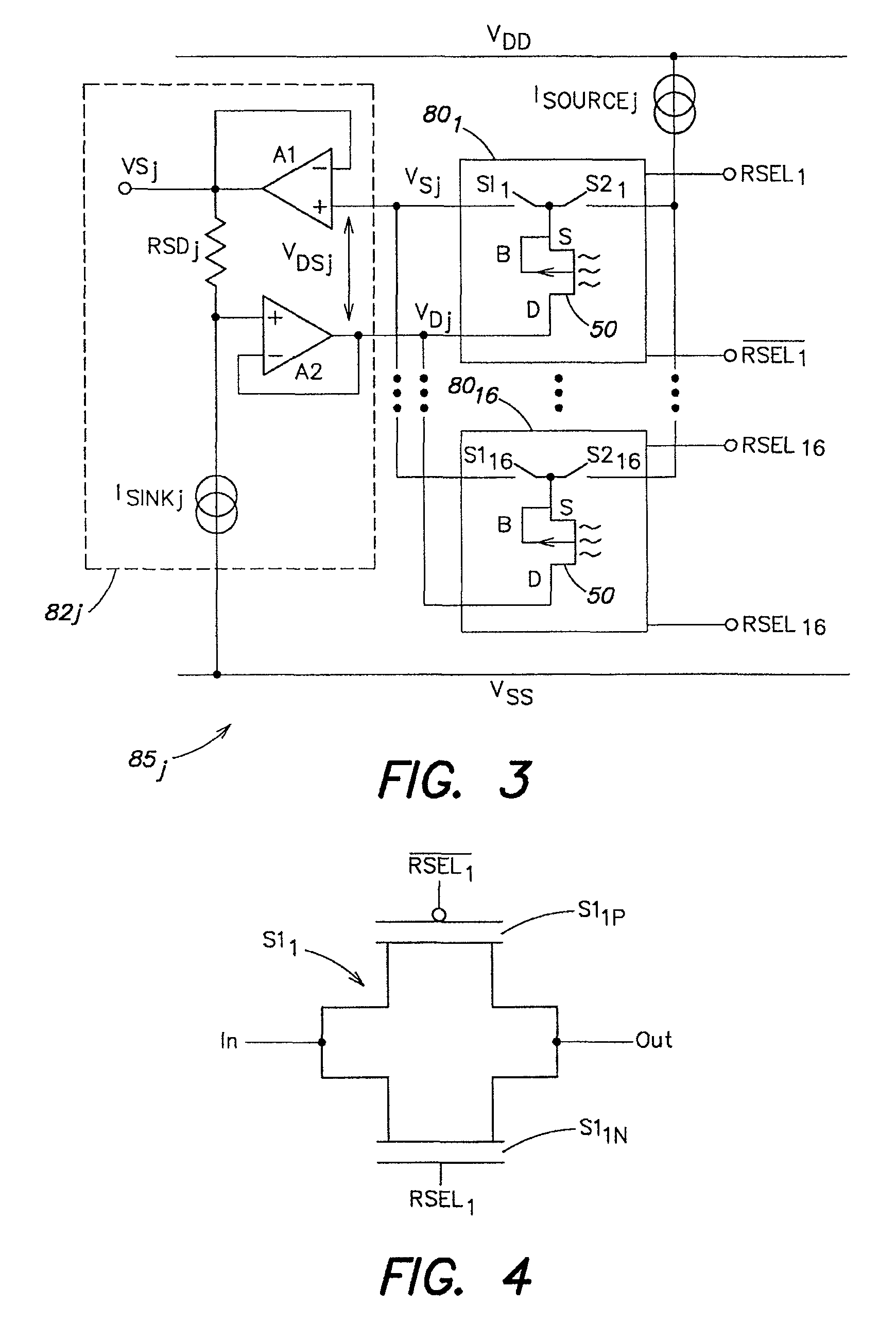
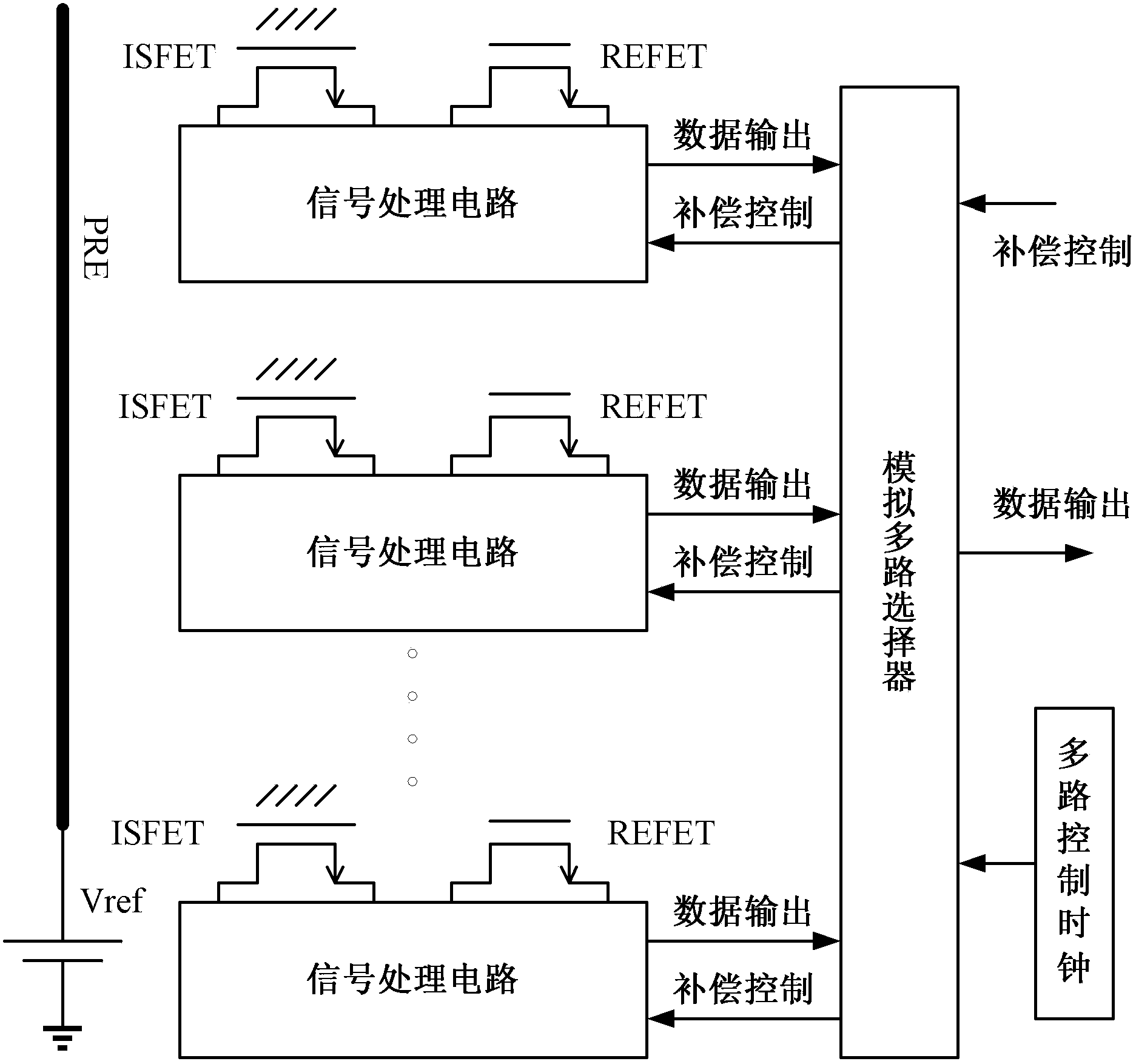
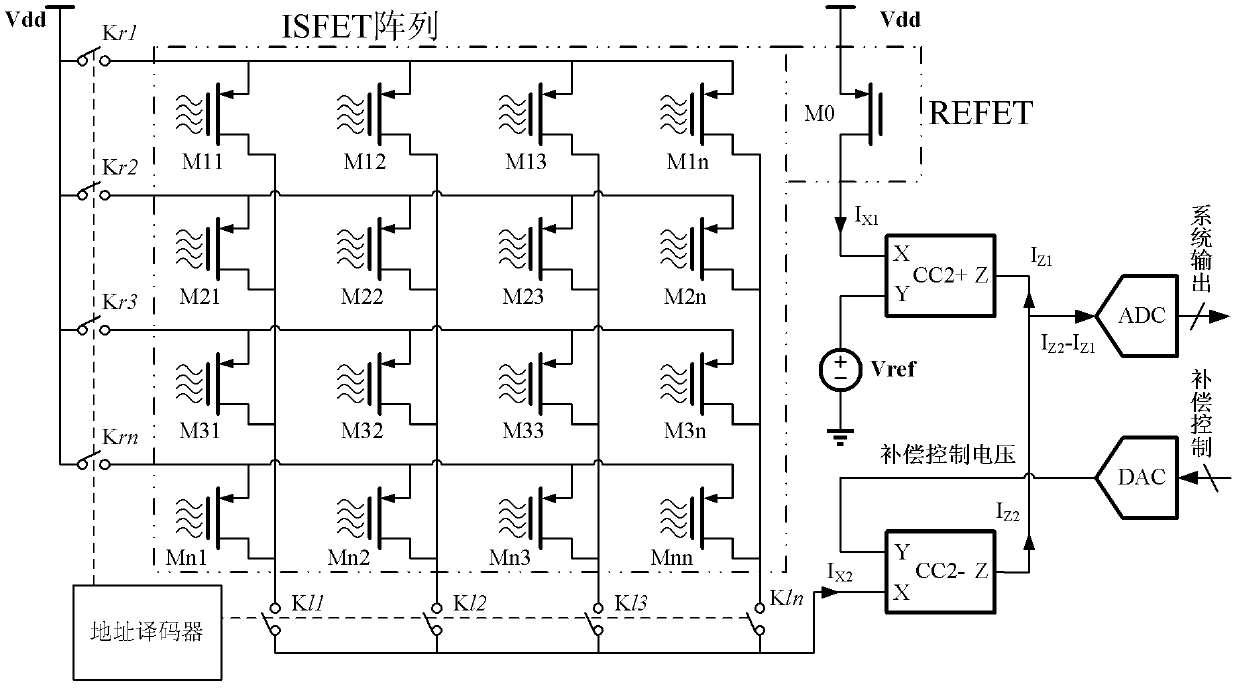
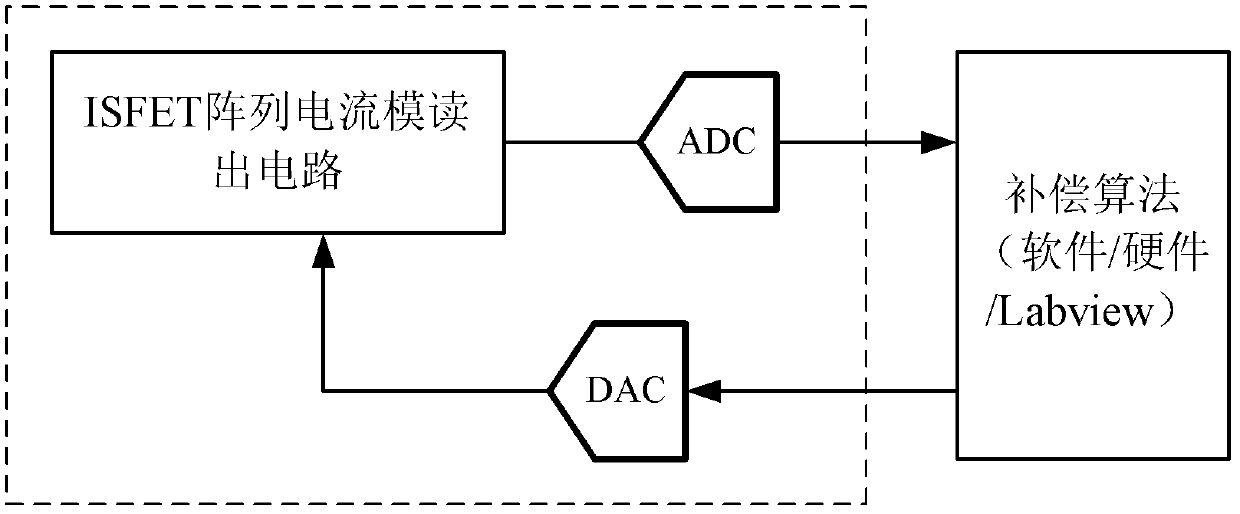
Multichannel ion sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) sensor readout circuit with compensation function
The invention discloses a multichannel ion sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) sensor array readout circuit with a compensation function. The readout circuit is used for detecting the ion concentration of a solution to be detected, the readout circuit comprises a plurality of ISFET sensor readout circuits, each ISFET sensor readout circuit forms a detection channel, each ISFET sensor readout circuit has a compensating port for receiving compensation signals provided by an external system to modify non ideal characteristics of ISFET sensors. The readout circuit adopts a multichannel detection mode, a plurality of parameters of the ISFET array sensors can be rapidly detected, parallel or serial output can be carried out by the detection mode according to the need of the system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
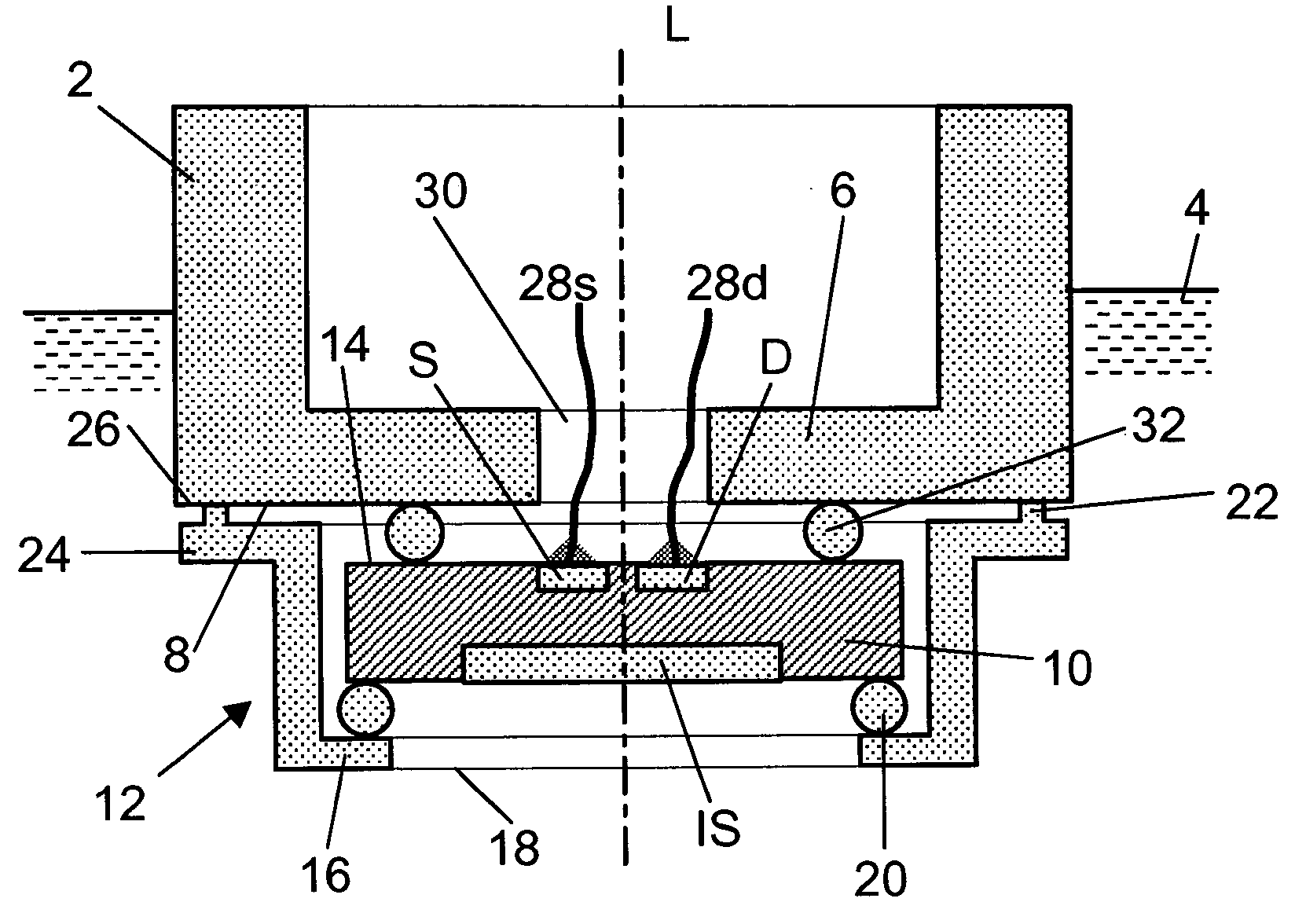
Electrochemical sensor
InactiveUS20050072672A1Easy to useReliable and durable connectionSolid-state devicesMaterial electrochemical variablesEngineeringISFET
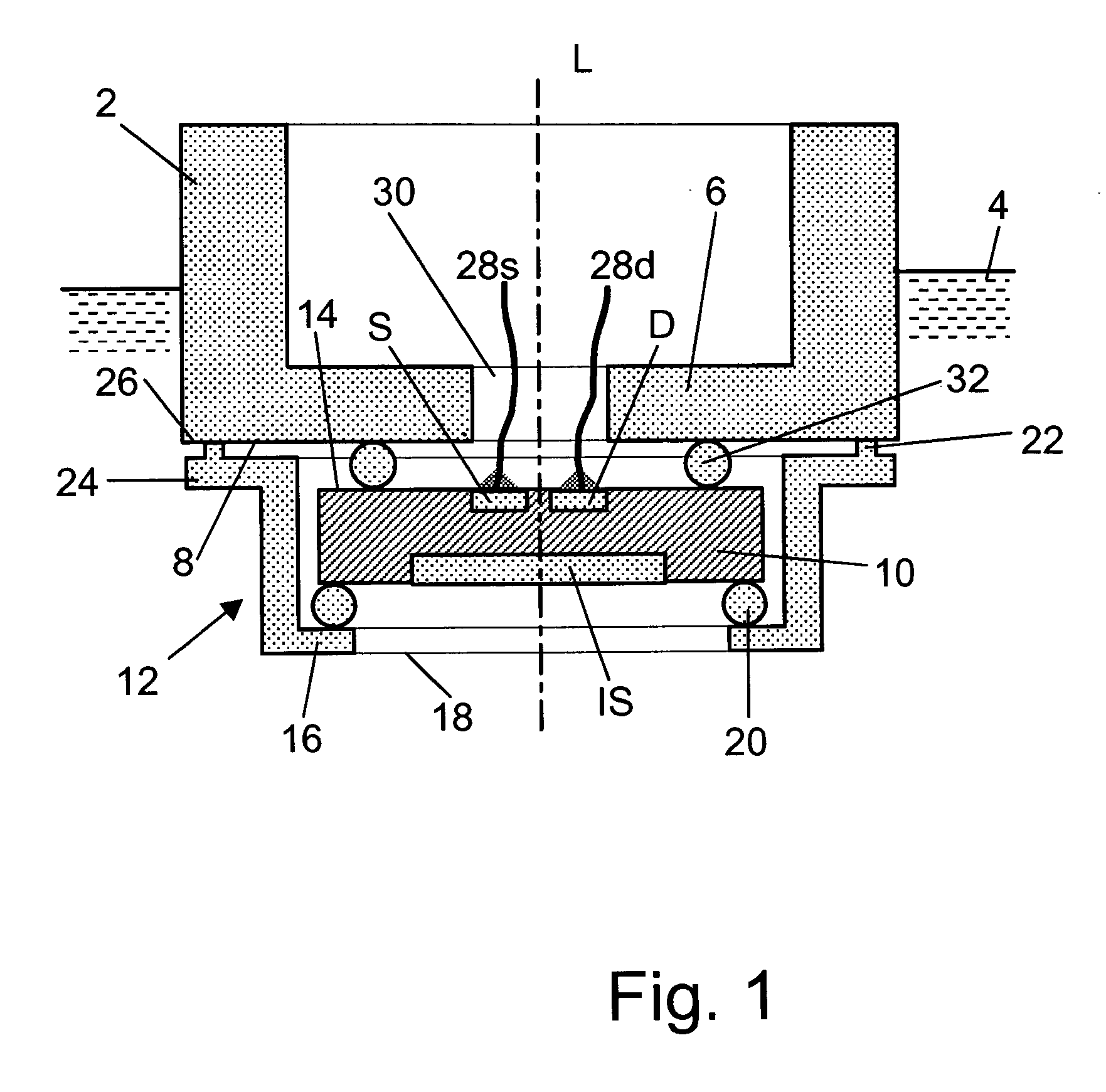
An electrochemical sensor has a sensor housing and an ion-sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) with a source connection (S) and a drain connection (D). An ion-sensitive surface area (IS) on the front surface of the ISFET is immersible in a measuring medium. A clamping element serves to clamp the ISFET with its rear surface against an end surface of the sensor housing. The clamping element has a central opening leaving the ion-sensitive surface area (IS) exposed. A leak-tight circular connection between the clamping element and the sensor housing is formed by vibratory, preferably ultrasonic, welding. The ISFET is sandwiched between two rubber-elastic elements, at least one of which forms a leak-tight seal against penetration of the measuring medium from the ion-sensitive surface area (IS) to the source- and drain connections (S) and (D).
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO GMBH
Cell-based transparent sensor capable of real-time optical observation of cell behavior, method for manufacturing the same and multi-detection sensor chip using the same
ActiveUS20120138458A1Accurate informationImprove detection reliabilityImmobilised enzymesMaterial nanotechnologyEngineeringISFET
The present invention relates to a cell-based transparent sensor capable of the real-time optical observation of cell behavior, to a method for manufacturing same, and to a multi-detection sensor chip using same. More particularly, the present invention relates to a cell-based transparent sensor capable of the real-time optical observation of cell behavior, to a method for manufacturing same, and to a multi-detection sensor chip using same, wherein the sensor can sense the ionic concentration of an electrolyte in accordance with the variation in the metabolic activity of cells using an ion-selective field effect transistor (ISFET) sensor and an electrochemical sensor, and the sensor is made of a transparent material which enables real-time observations of optical phenomenon for measurement of cell behavior.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for measuring temperature parameters of an ISFET using hydrogenated amorphous as a sensing film
InactiveUS20020158645A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesAmorphous siliconISFET
A method and an apparatus for measuring the temperature parameters of an ISFET that uses hydrogenated amorphous silicon as a sensing film, which uses the measurements of the temperature parameters and the source / drain current and gate voltage in an unknown solution to sense the ion concentration and the pH value of the unknown solution.
Owner:NATIONAL YUNLIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Electronic circuit for ion sensor with body effect reduction
ActiveUS20070089988A1Reduce body effectSuitable for useSpecial data processing applicationsChemical methods analysisVoltage referenceTime drift
An electronic circuit for ion sensor with the body effect reduction includes a bridge-type floating source circuit provided with an input terminal, an output terminal reflecting the change in the potential dependent on ion concentration, and an ion-sensitive field effect transistor (ISFET) wherein one terminal of the ISFET is coupled with the output terminal; a current mirror for providing a current to the bridge-type circuit; a third transistor for receiving the operating current provided by the current mirror, identical to the current provided to the ISFET; a differential amplifying circuit, wherein one input terminal of the amplifying circuit is input with a reference voltage, and the other input terminal is coupled with the output of the bridge-type readout circuit; and a third amplifier to generate a differential output voltage compensated for the body effect, temperature and time drift effects.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
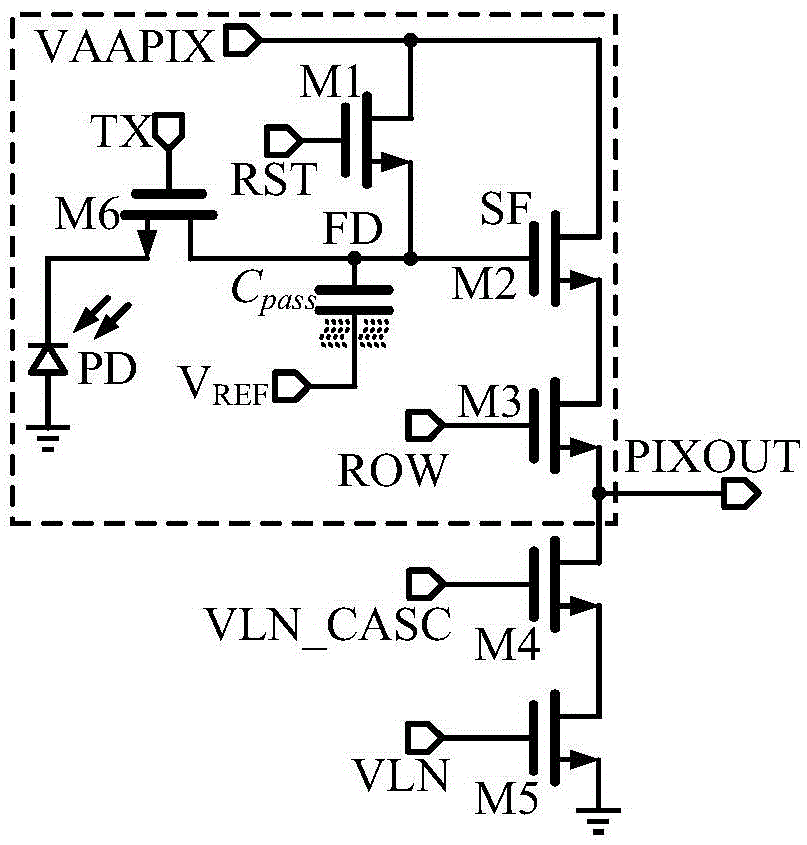
Multi-parameter low-power-consumption current-mode ion sensitive field effect tube array sensor device
ActiveCN103376284AReduce power consumptionLarge dynamic rangeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhase currentsSensor array
The invention discloses a multi-parameter low-power-consumption current-mode ion sensitive field effect tube array sensor device which comprises an n*n ISFET (ion sensitive field effect tube) sensor array, a matrix selection switch for selecting ISFETs, an address decoder, a reference transistor (REFET) for temperature and common-mode drift compensation, a normal-phase current transmitter, an anti-phase current transmitter, a current mode analog-digital converter (ADC) and a voltage analog-digital converter (DAC). ISFETs, selected by an address selector, of a grid coverage sensitive film and REFETs, selected by the address selector, of a grid coverage passivation film form differential geminate transistors, and the current difference outputted by the differential geminate transistors is converted by the ADC into a digital voltage signal to be outputted. Compared with a voltage mode circuit, the device adopting a current mode detection circuit can work under low working voltage, and is low in circuit power consumption and large in dynamic range; in addition, by adopting the differential detection ways, the imbalance and the temperature drift of the device can be effectively inhibited; meanwhile, the non-ideal characteristics of an ISFET sensor, such as long-term drift, can be effectively compensated.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Enhanced sensitivity ion sensing devices
A mechanism is provided for enhancing the sensitivity of an ion-sensitive semiconductor device by creating a second gate coupled to a sense plate that can improve the amount of charge brought to the ion-sensitive semiconductor device conductivity modulated region (e.g., a channel region of an ISFET). This is accomplished by utilizing a buried dielectric layer associated with the ion-sensitive semiconductor device conductivity modulated region as the second gate dielectric. The buried dielectric layer is coupled to the sense plate using an isolated well region as a conductor that is coupled to metal layers extending to the sense plate. Some embodiments further use the buried dielectric layer as the sole gate dielectric for the semiconductor device, thereby allowing the traditional gate dielectric region to be coupled to a protection diode. This protection diode then protects the gate dielectric from plasma induced damage and electrostatic discharge.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Electronic sensor and gene detection method based on electronic sensor
ActiveCN104212711AHigh precisionHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhysical chemistryISFET
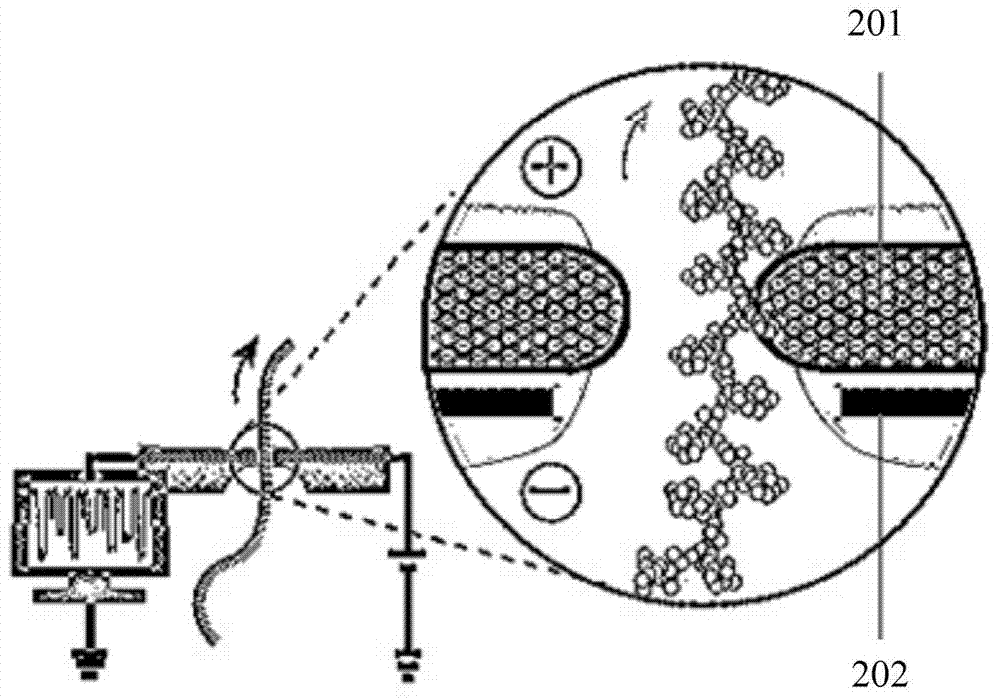
The invention relates to the field of biological detection and discloses an electronic sensor and a gene detection method based on the electronic sensor. The electronic sensor comprises ISFET, a nano-wire channel between a source electrode and a drain electrode of the ISFET is provided with a first groove by etching, the bottom of the first groove is provided with nano-pores, or is provided with chemical molecules or is provided with nano-pores and chemical molecules arranged at the nano-pores so that it is avoided that the DNA molecules smoothly slide at a high rate from one side to the other side of the chemical molecules or the nano-pores without control, only after a single-chain DNA to be tested successfully matches a detection basic group, a basic group can be moved forward by the chemical molecules and a matching process of the detection basic group and the basic group of the single-chain DNA to be tested can be accurately detected so that the gene detection result is more accurate, a detection precision is high and detection sensitivity is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI TURTLE TECH
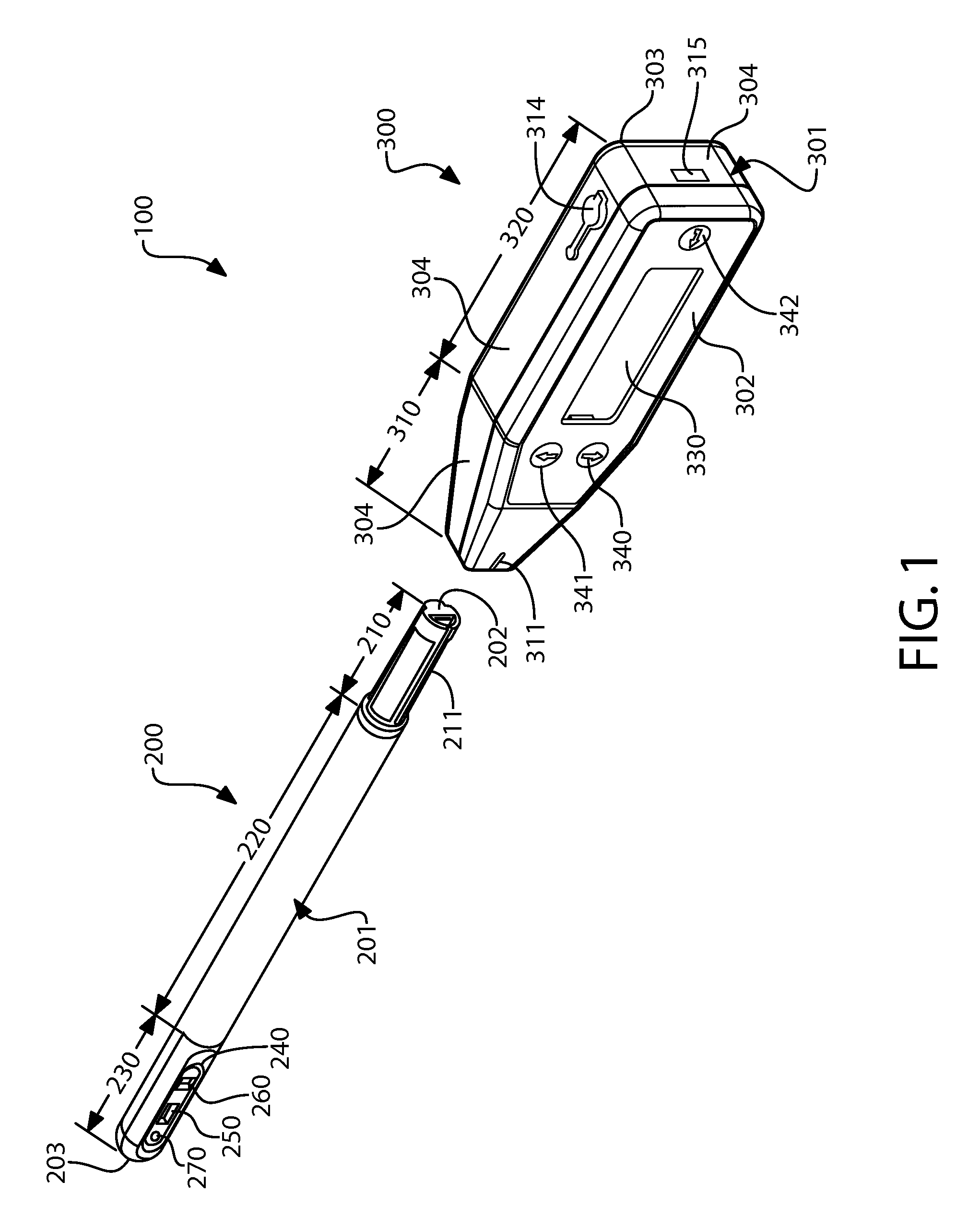
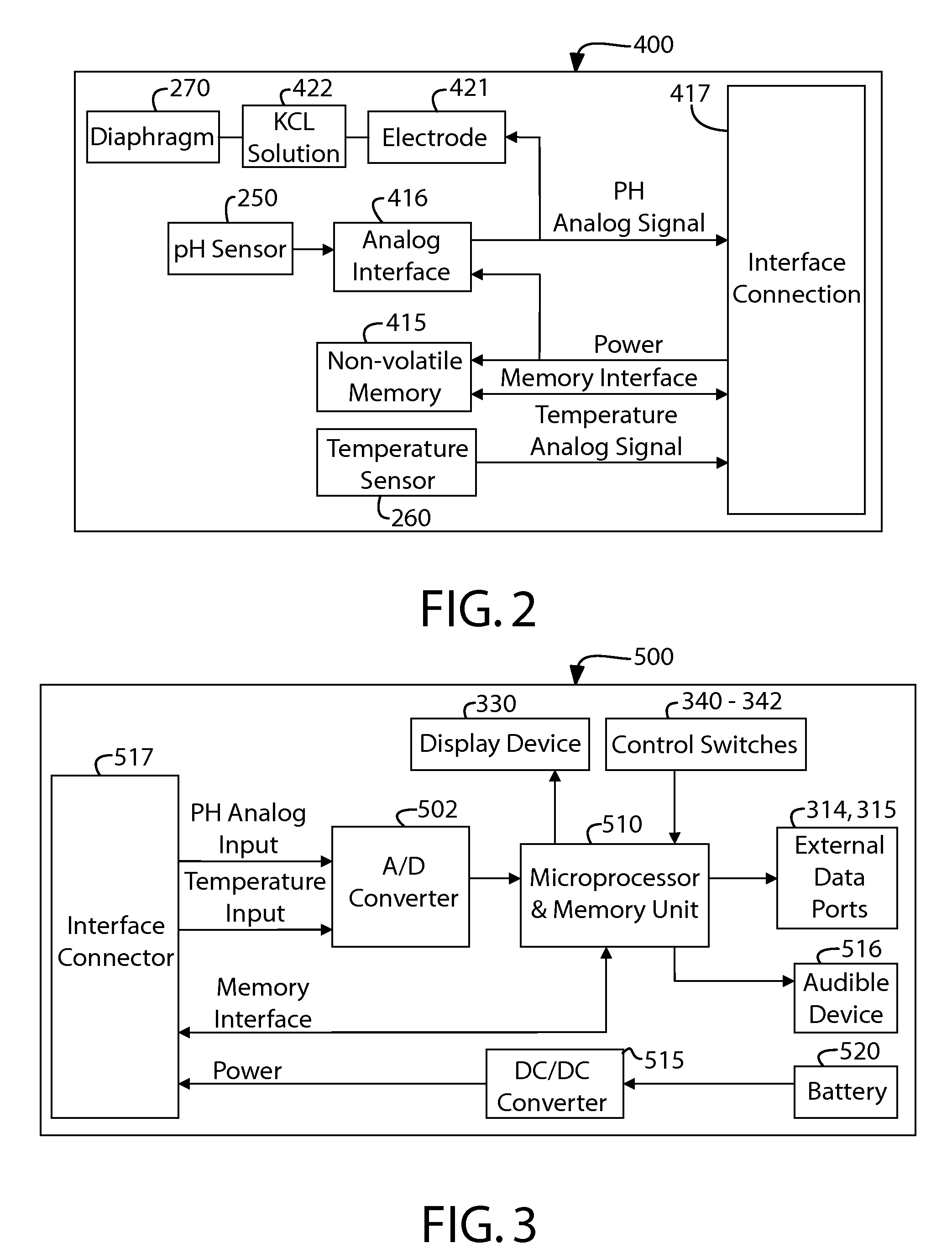
Apparatus, method and system for determining a physiological condition within a mammal
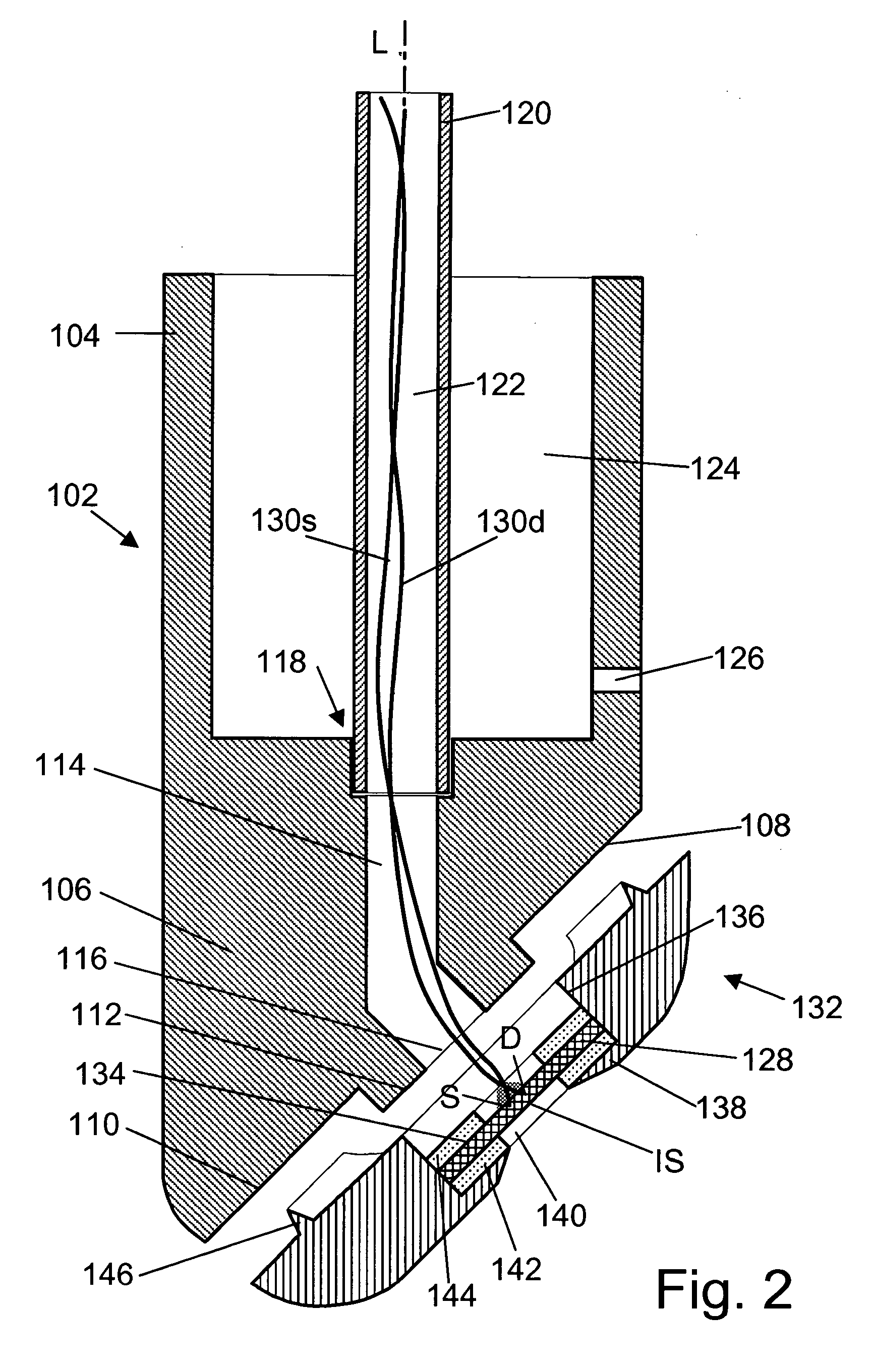
A system, method and apparatus for determining a physiological condition within a mammal based on pH and / or temperature measurements. The invention is for determining vaginal health and / or fertility status in a female mammal based on pH and / or temperature measurements of vaginal and / or cervical fluids or tissue. The invention is suited for taking either in vivo or external measurements. In one aspect, the invention is an apparatus comprising an elongated probe portion and a handle portion. In one embodiment, the circuitry of the apparatus is strategically split between the probe portion and the handle portion to facilitate a plug-and-play type of device. In another embodiment, an elongated probe is provided that has a hermetically sealed internal cavity that houses the circuitry while leaving the temperature sensor and the pH sensor exposed for direct contact with the desired biological fluid. In a further embodiment, an ISFET is used as the pH sensor.
Owner:PH DIAGNOSTICS
Isfet switch
ActiveUS20130273664A1High sensitivityHigh measurement sensitivityRead-only memoriesBiological testingDevice materialISFET
There is provided a semiconductor device for detecting a change in ion concentration of a sample and method of using same. The device comprises a plurality of Field Effect Transistors (FETs) coupled to a common floating gate and an ion sensing layer exposed to the sample and coupled to the floating gate. There may be other input voltages coupled to the floating gate.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
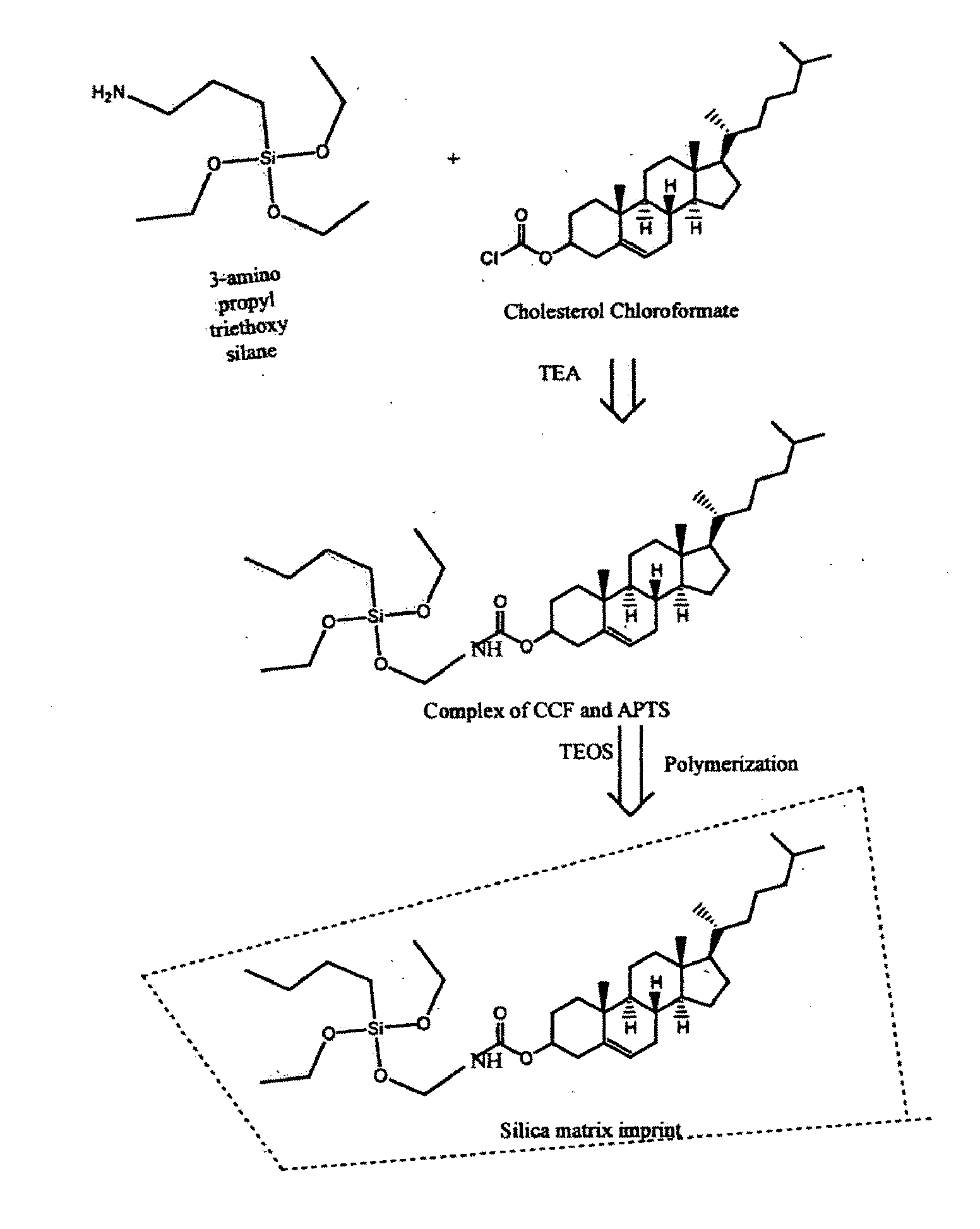
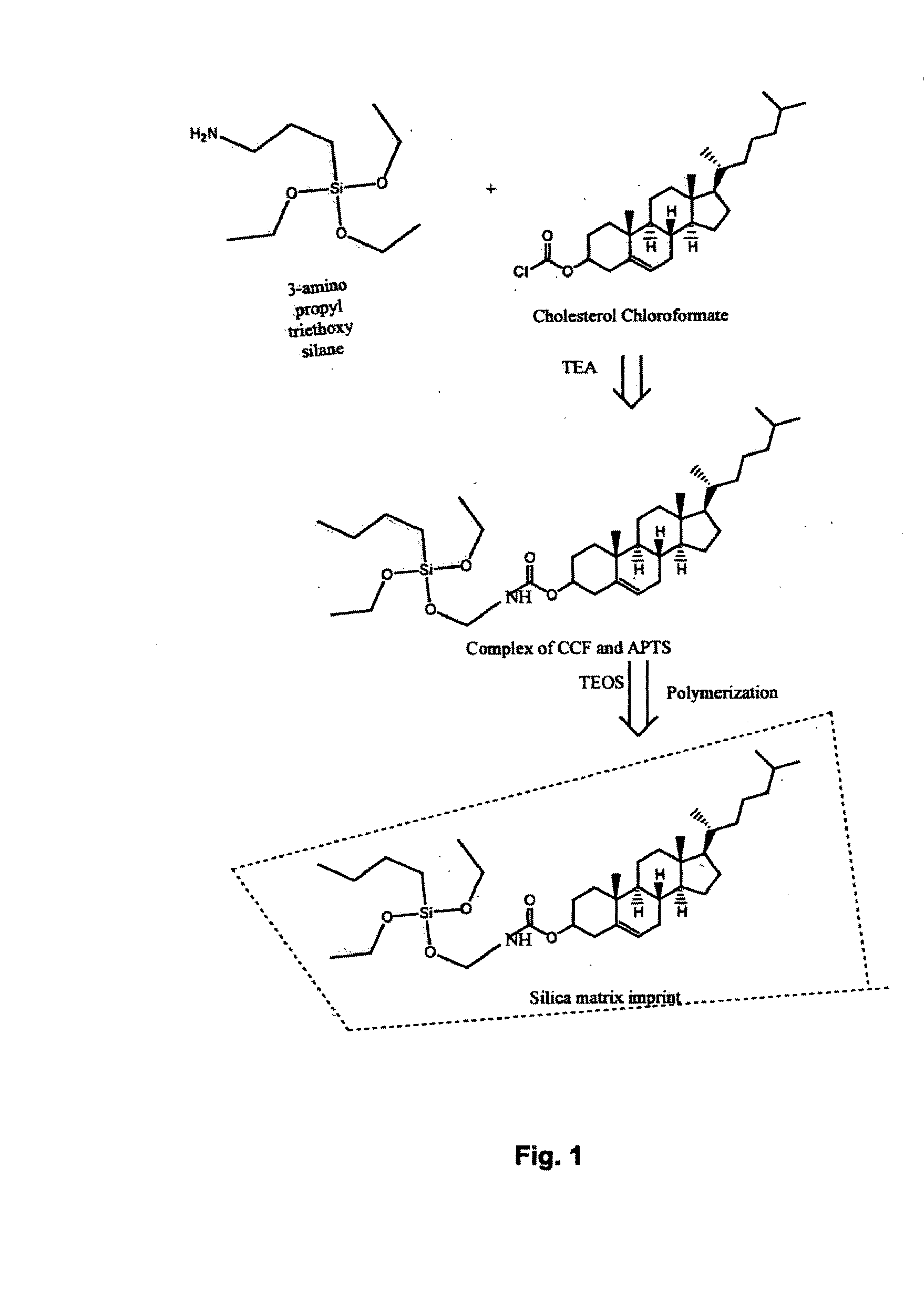
Novel potentiometric cholesterol sensor for the quantitative estimation of total cholesterol in human blood serum
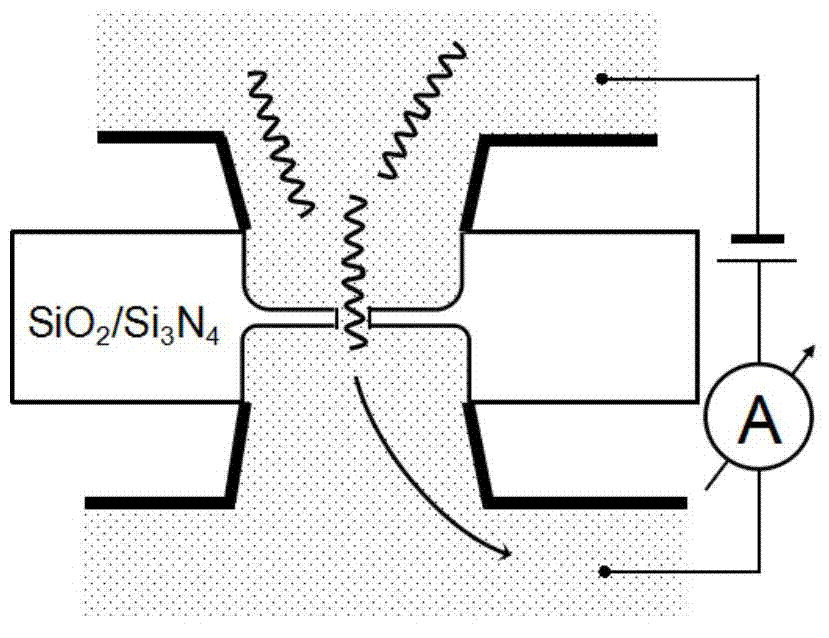
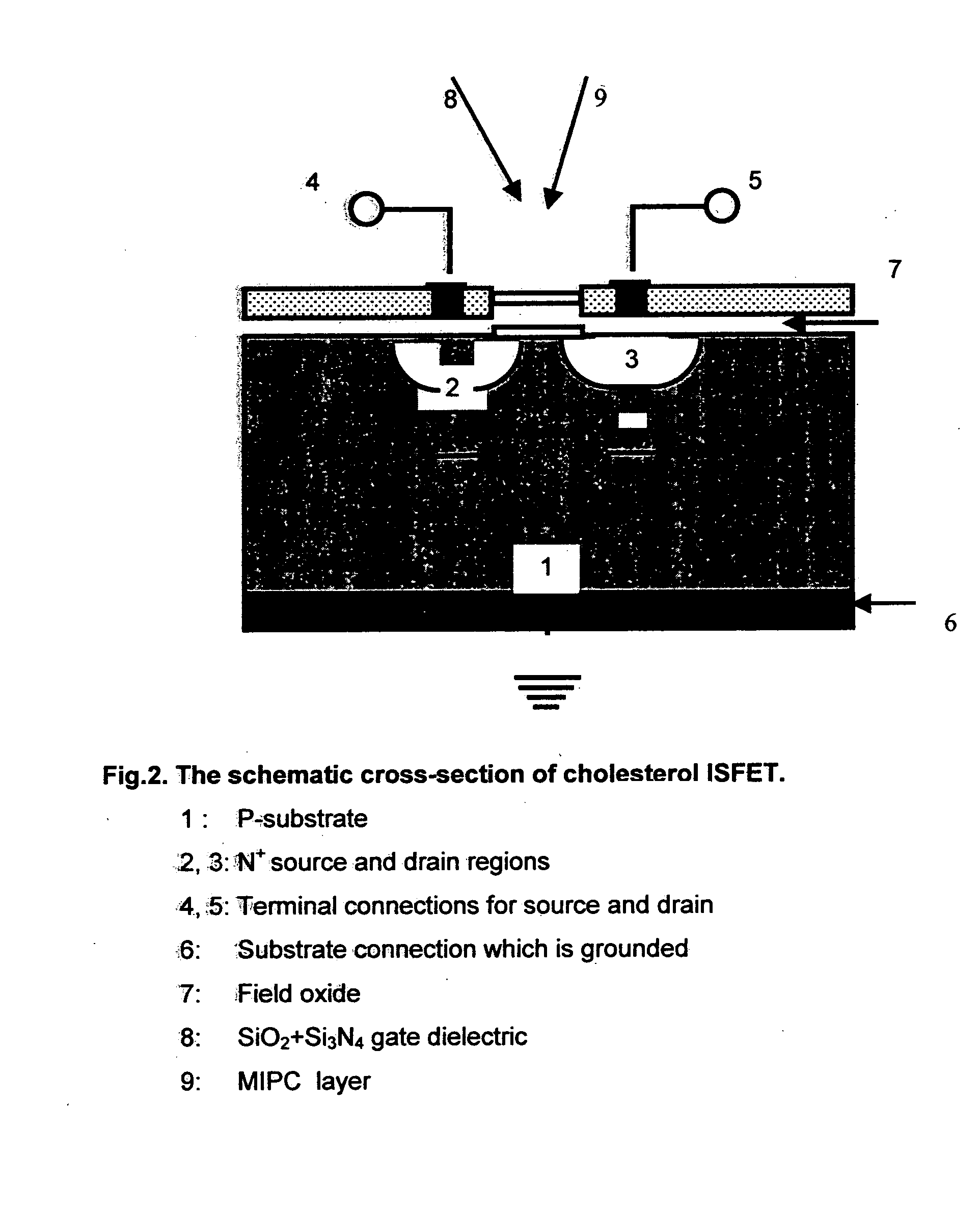
The present invention provides a novel sensor for the estimation of total cholesterol in human blood serum using molecular imprint of cholesterol. Human blood serum contains 150-250 mg / dl cholesterol. The present invention provides a sensor device and a process for the fabrication of ISFET (Ion Selective Field Effect Transister) coated with molecular imprint of cholesterol on the SiO2+Si3N4 dielectric gate of the said electrode. The molecular imprint of cholesterol (MIPC) anchored in to a silica matrix sensing material is identified as a sensing material which has specific selectivity towards the cholesterol in presence of other organic constituents in human blood serum.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Electrode assembly
The electrode assembly is provided with: a rod-like body 1 that extends along a predetermined axis ; a substrate that is formed with a through-hole penetrating between a front surface and a back surface and attached to a fore end part of the body; and a sensor chip for electrochemical measurement, which is attached on the back surface of the substrate such that a sensing part is exposed outside from the through-hole, wherein: on the back surface of the substrate, a wiring for obtaining an output signal from the ISFET chip is formed, and the sensor chip is attached to the wiring directly or closely; and the substrate is attached with being inclined with respect to the predetermined axis of the body, and thereby the front surface of the substrate forms at least a part of a fore end surface that is inclined with respect to the predetermined axis.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
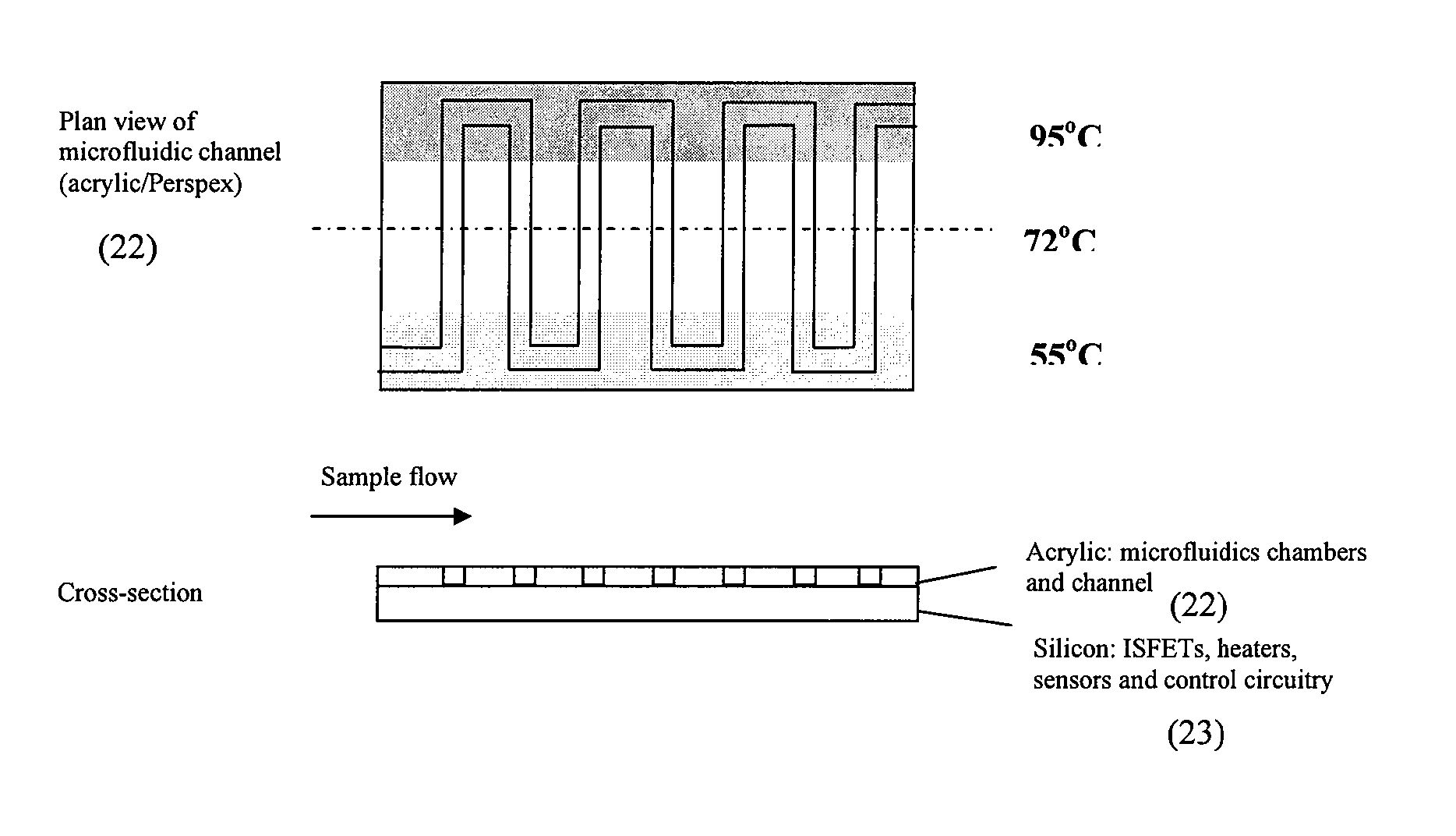
In-situ wet chemical process monitor
InactiveUS20070096165A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringFront end of line
Owner:LIPISKO BRUCE A +1
Methods and apparatus for rapid detection of infectious microorgranisms
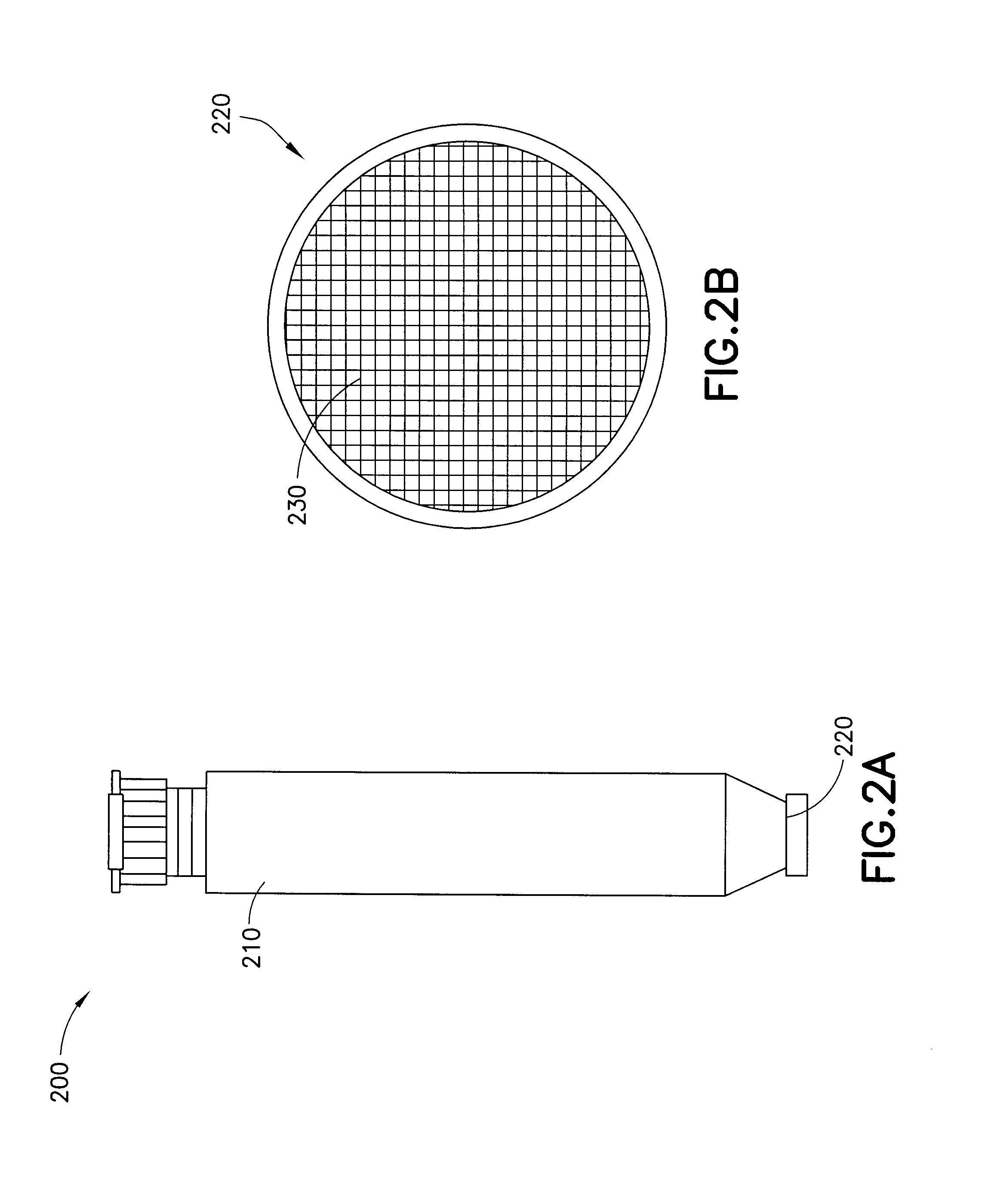
ActiveUS20150247819A1Quick checkHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMicroorganismCell activity
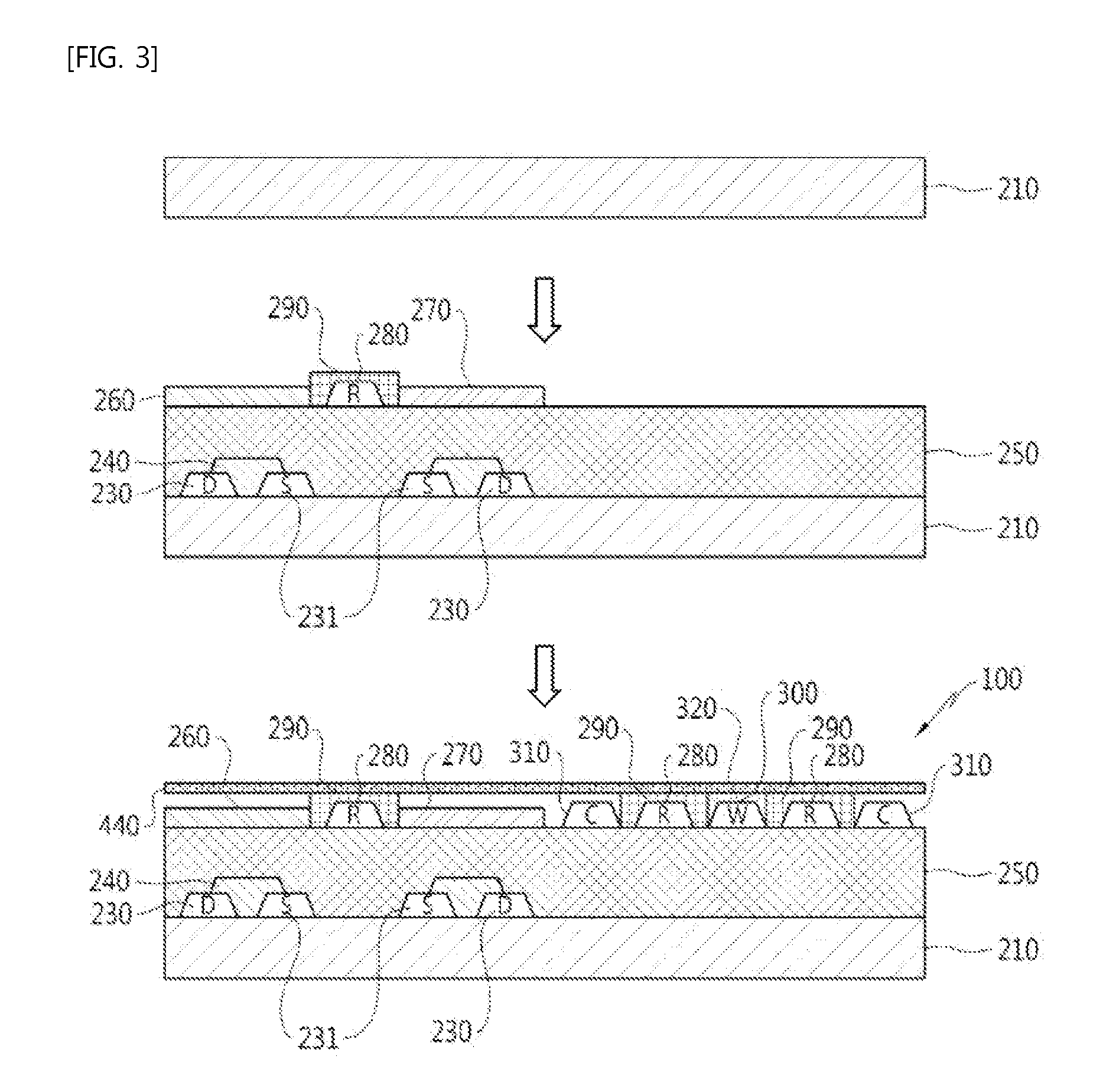
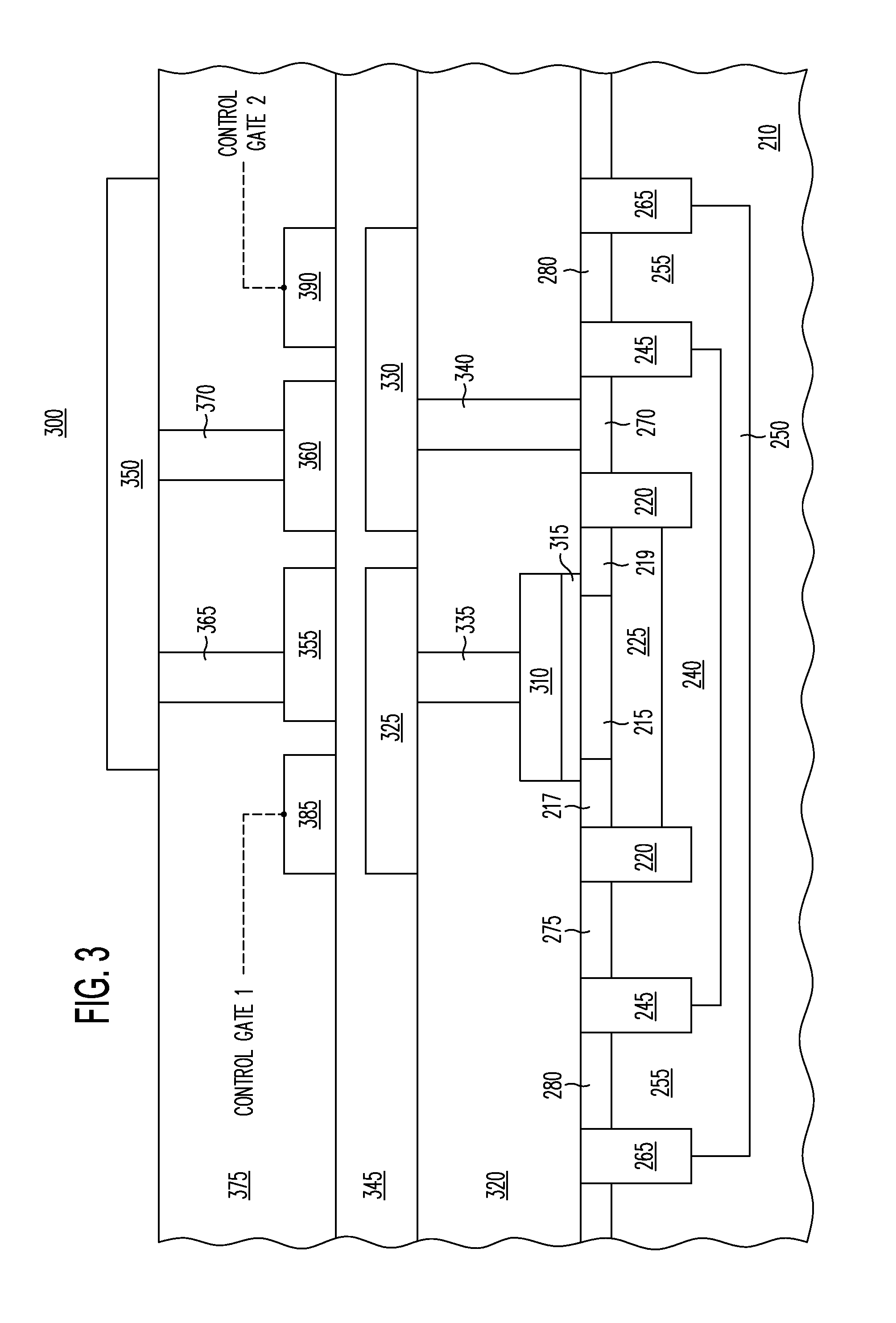
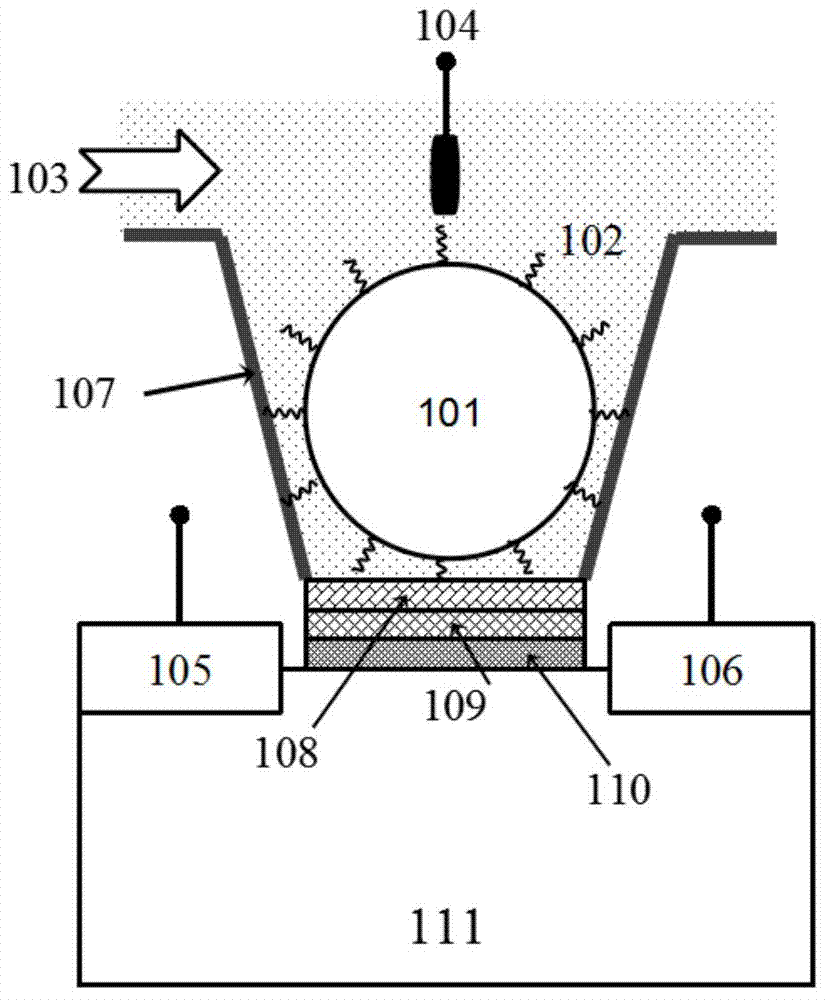
An array of micro-chambers 220) with individual ion sensitive field effect transistors (ISFETs) (300) disposed therein for monitoring single cell activity in the microarray to determine the presence or absence of microorganisms in a sample (390). In addition to the presence or absence of a single cell, certain further embodiments contemplate monitoring cell behavior. Cell behavior includes the entire range of cell activity as well as cell response to changes in environmental conditions of changes in response due to the addition of sample constituents.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com