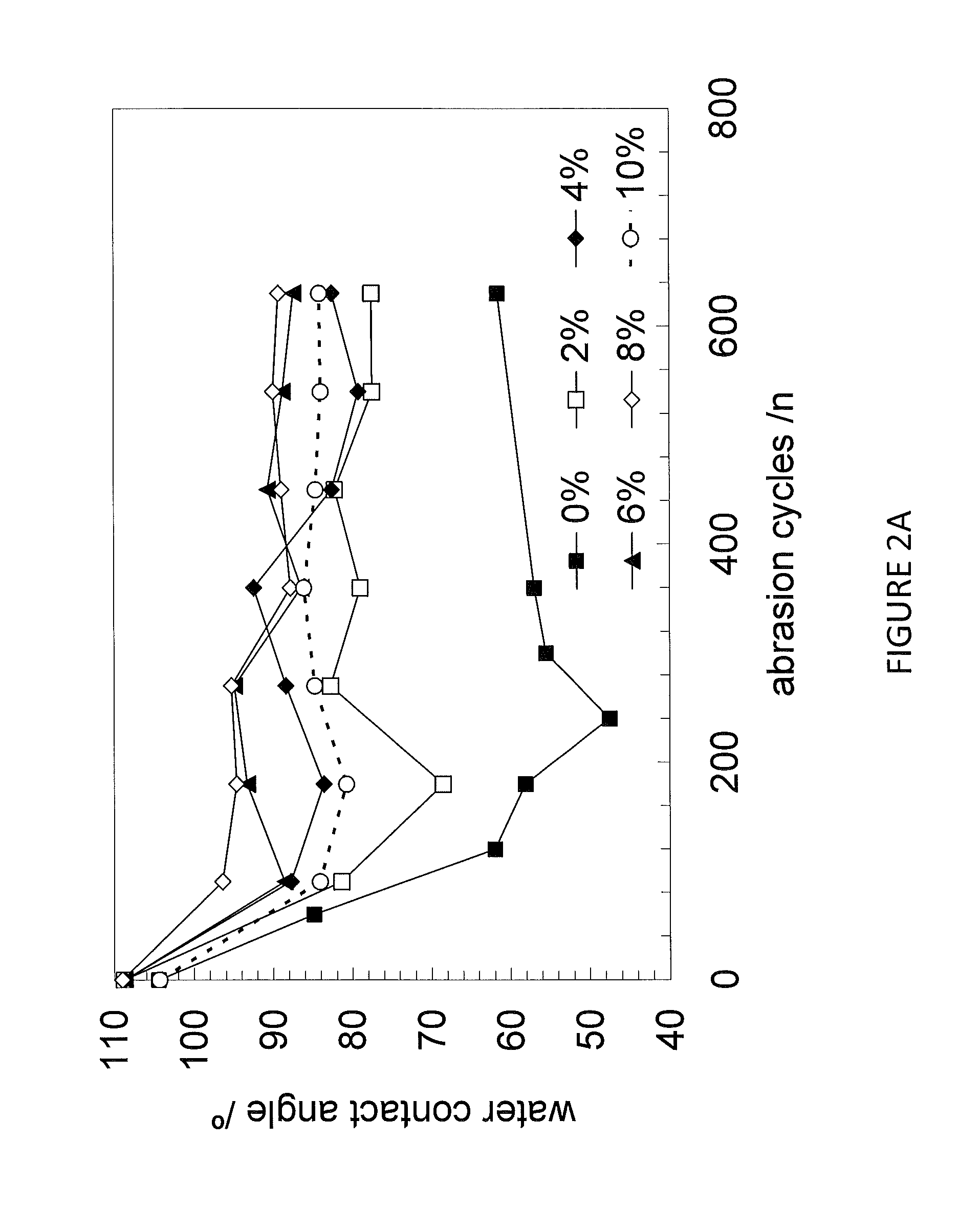
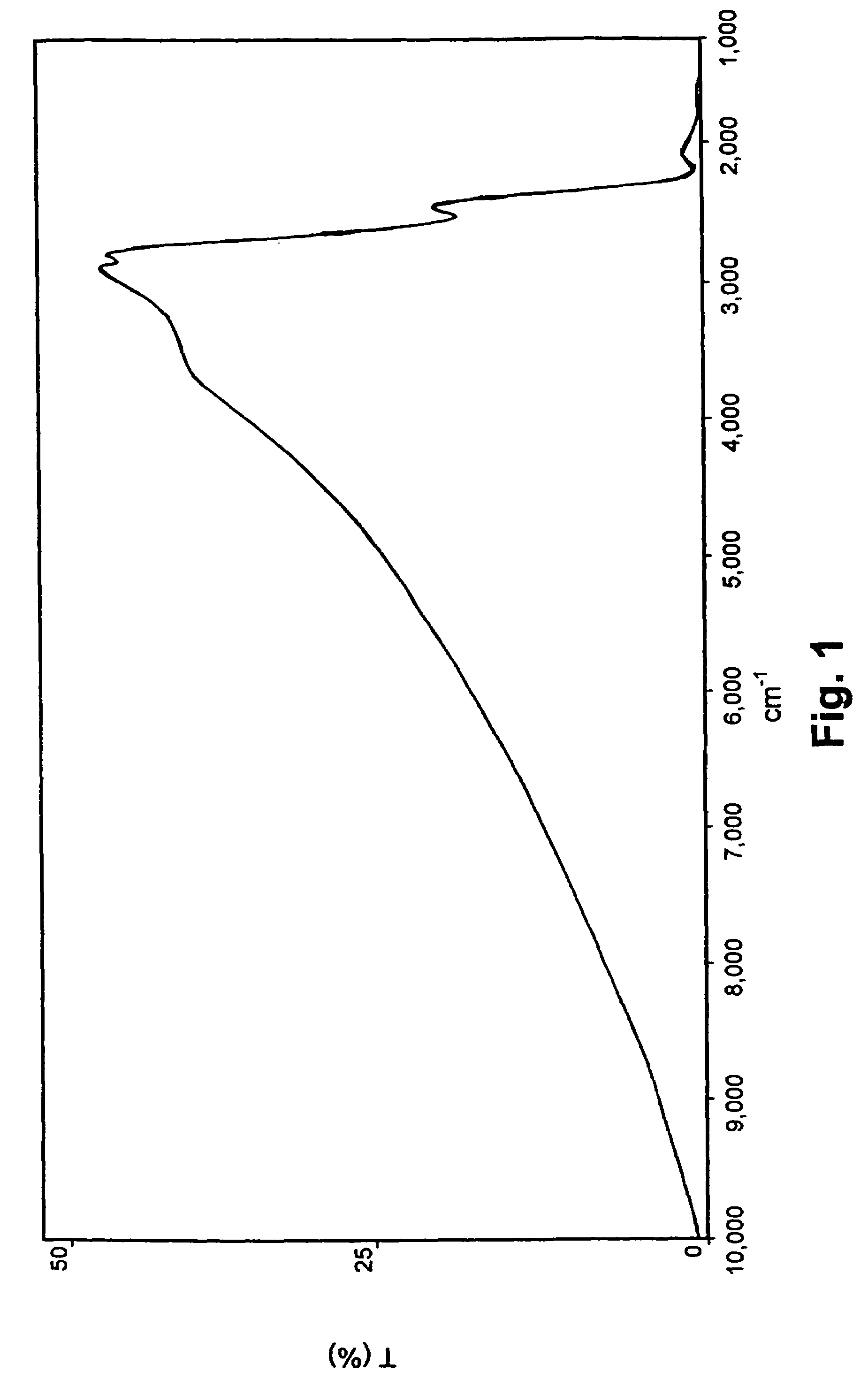
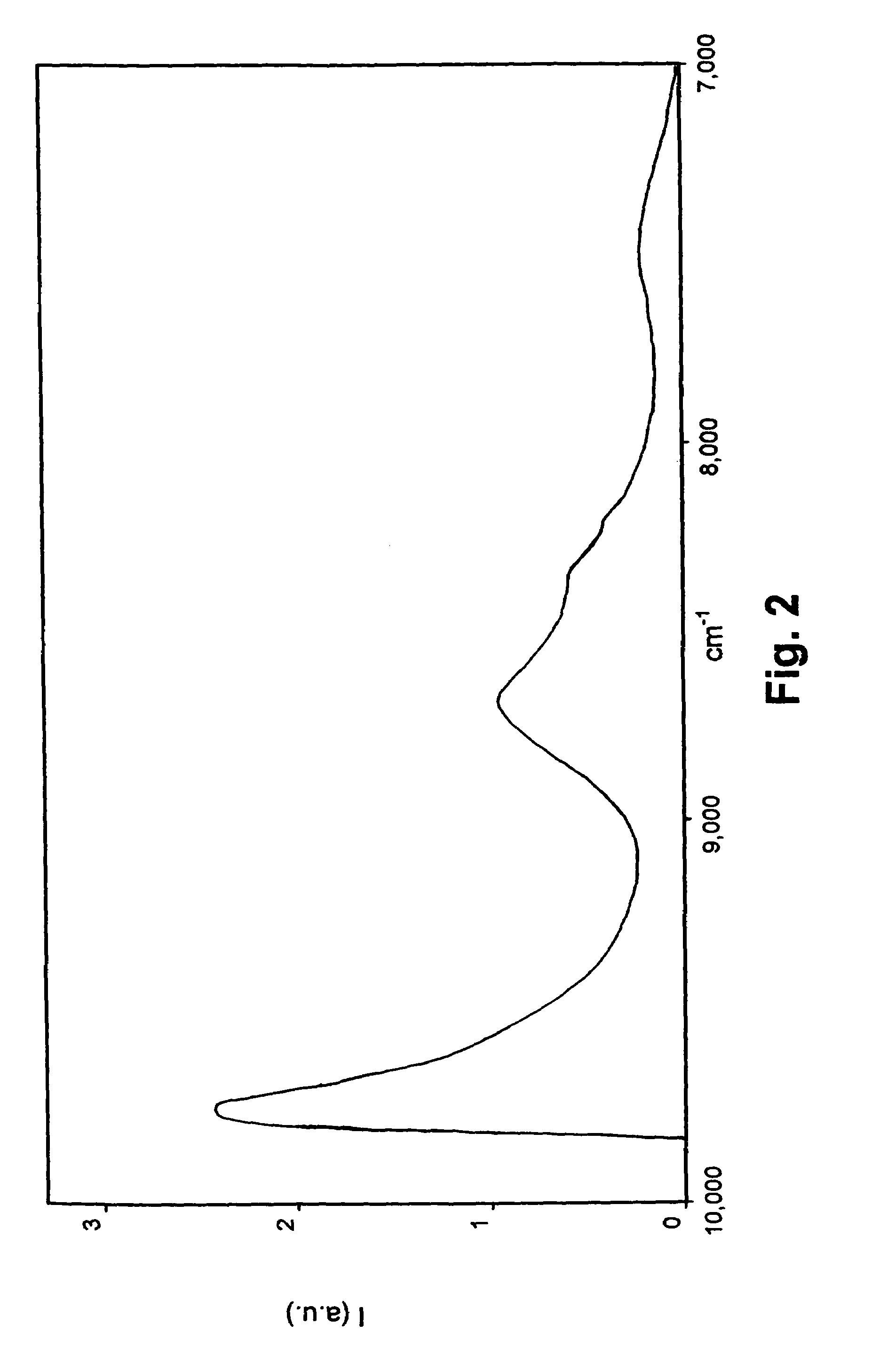
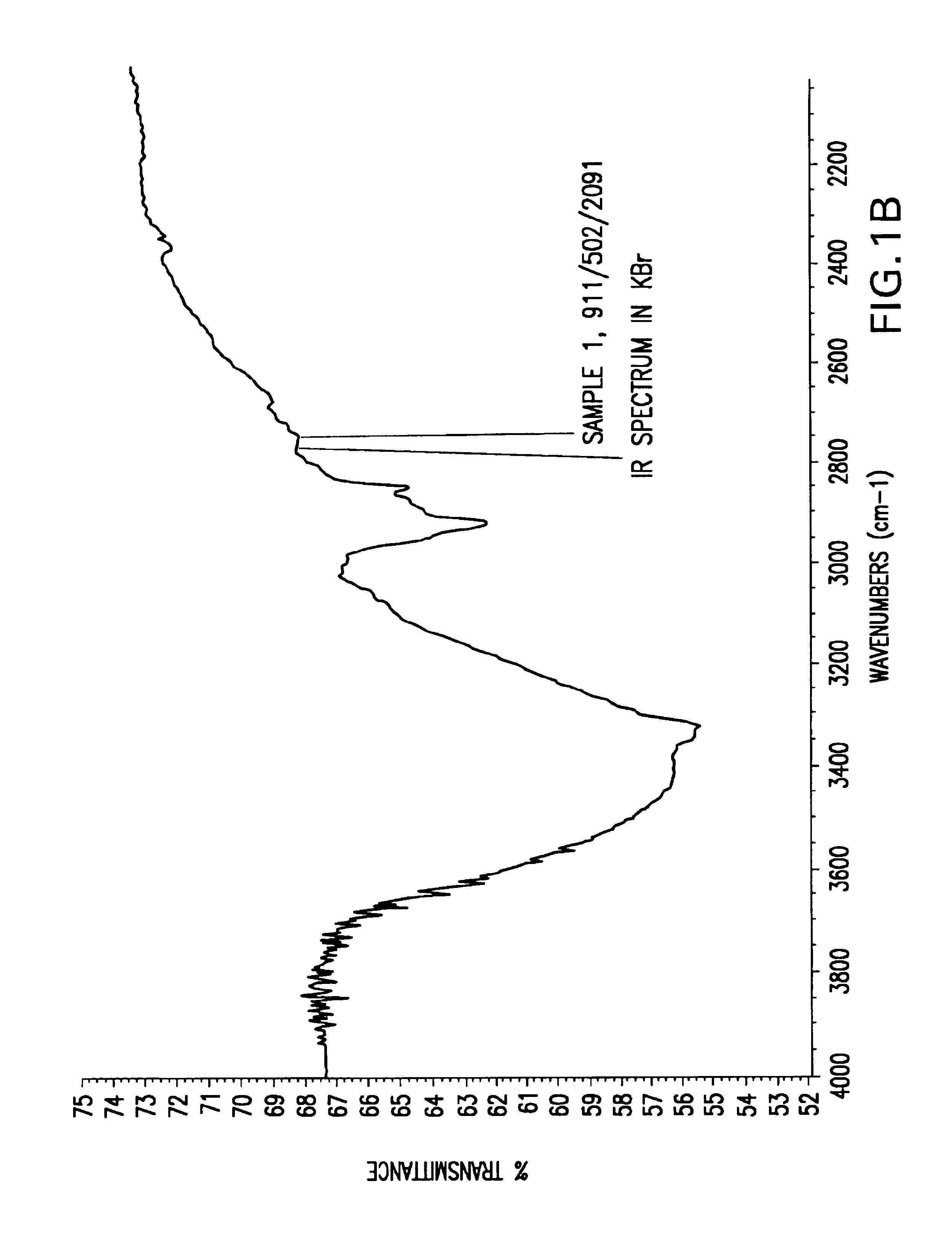
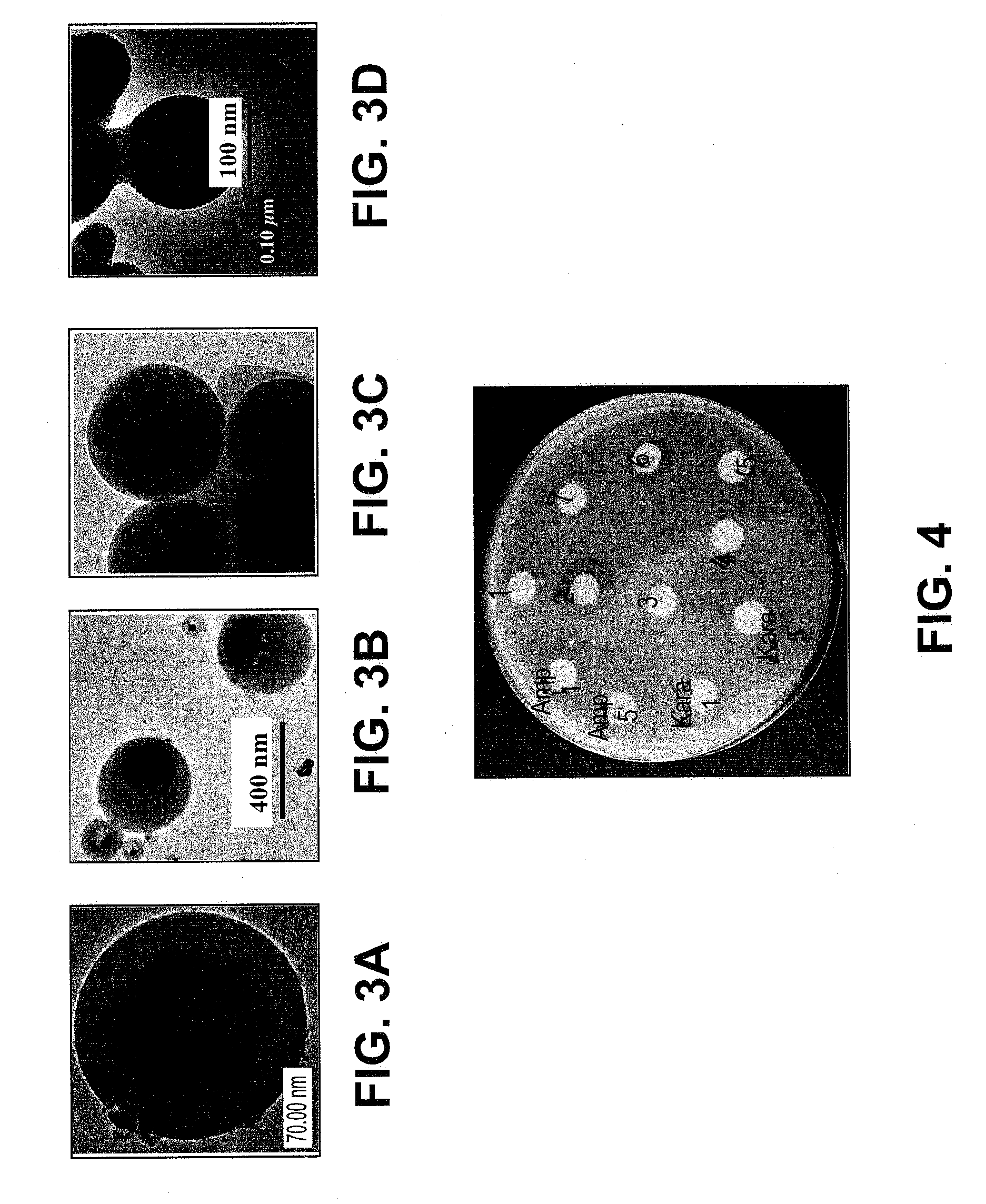
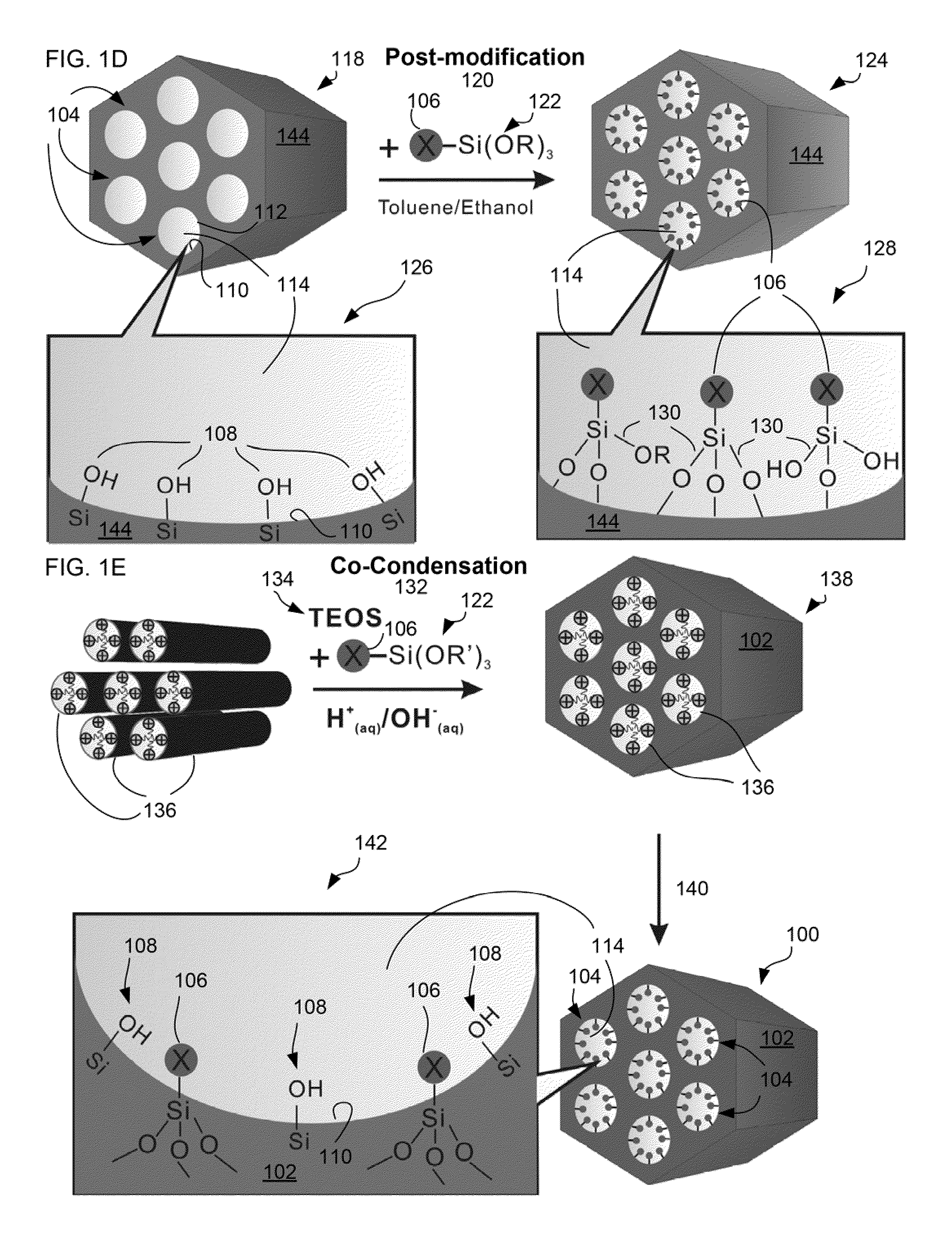
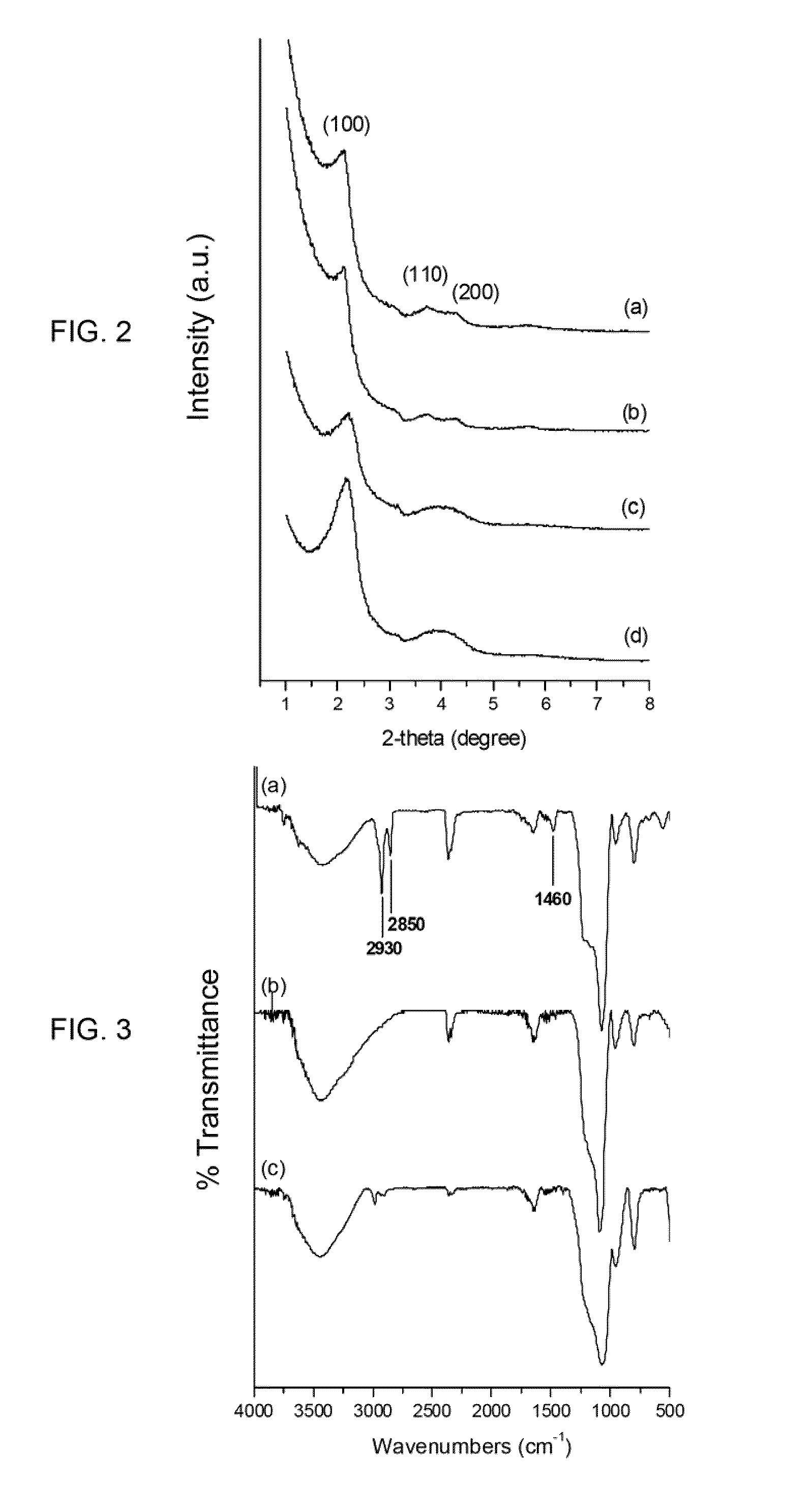
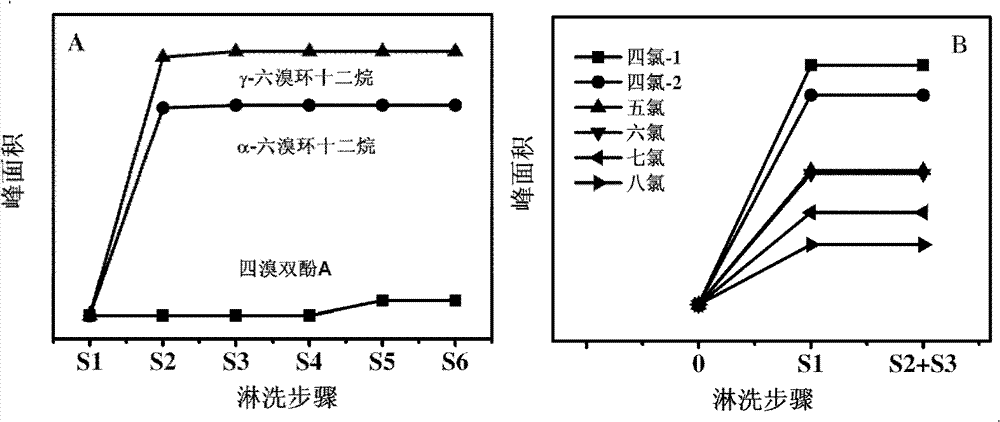
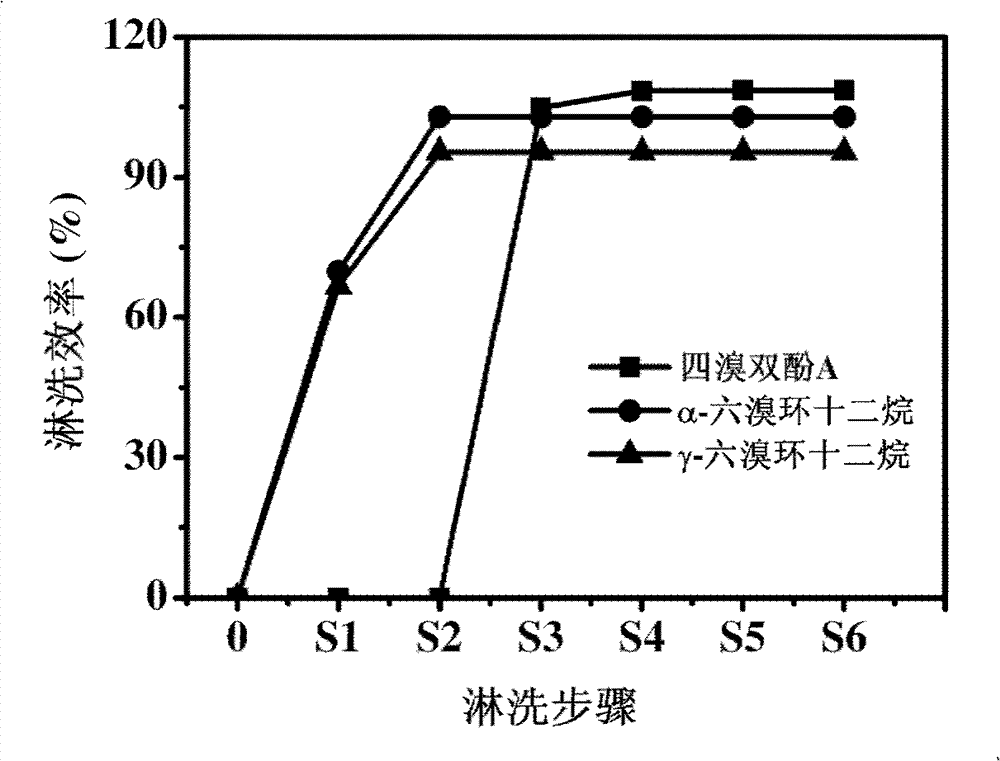
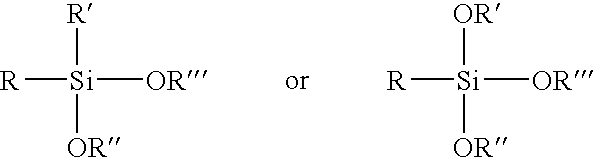Patents
Literature
129 results about "Silica matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
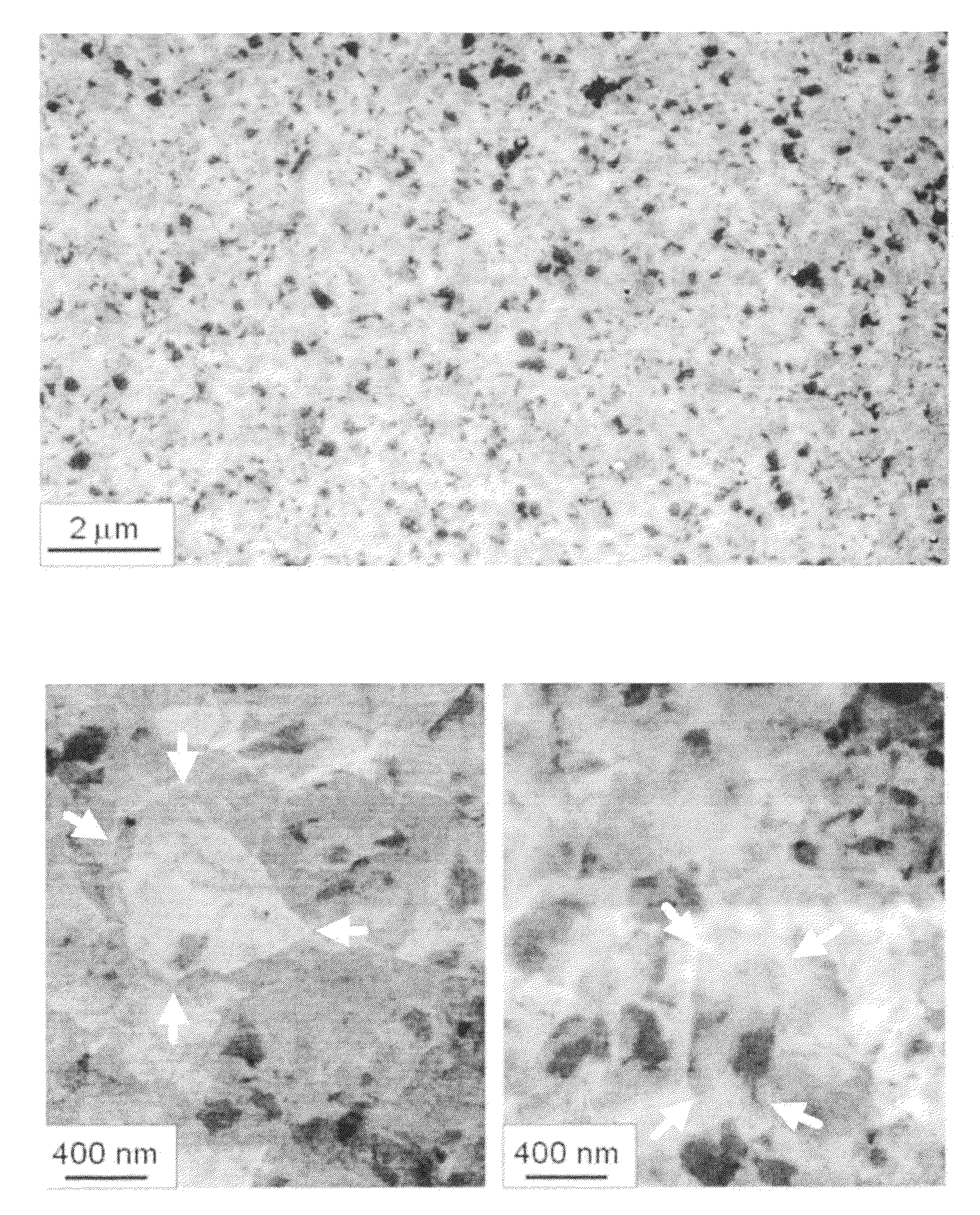
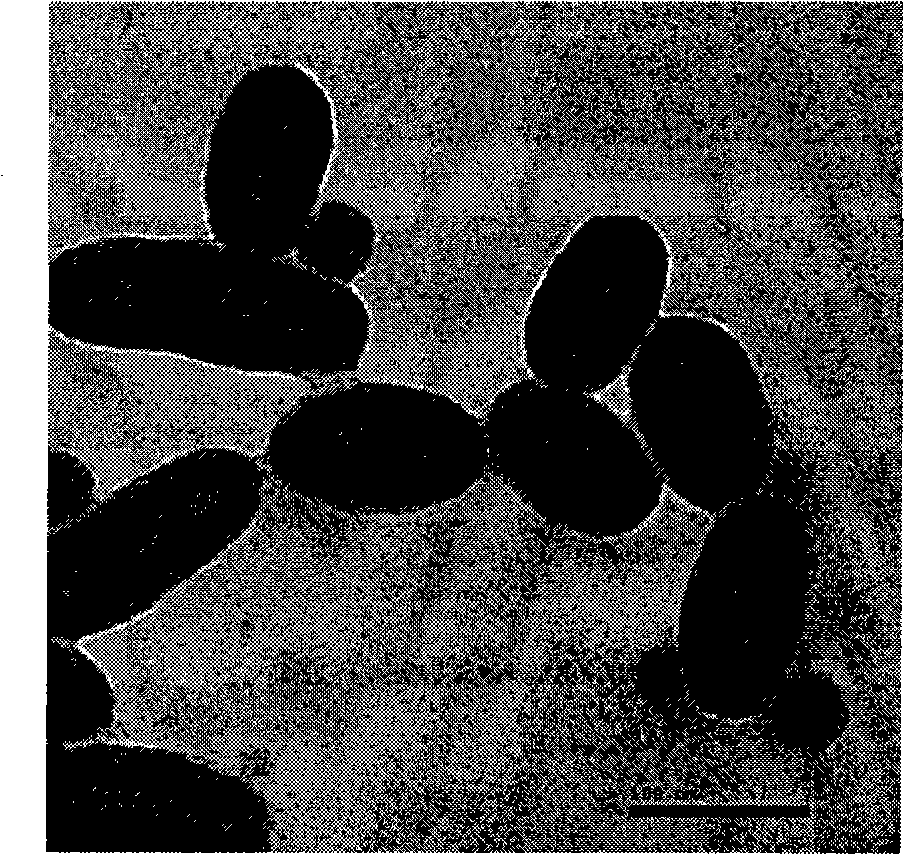
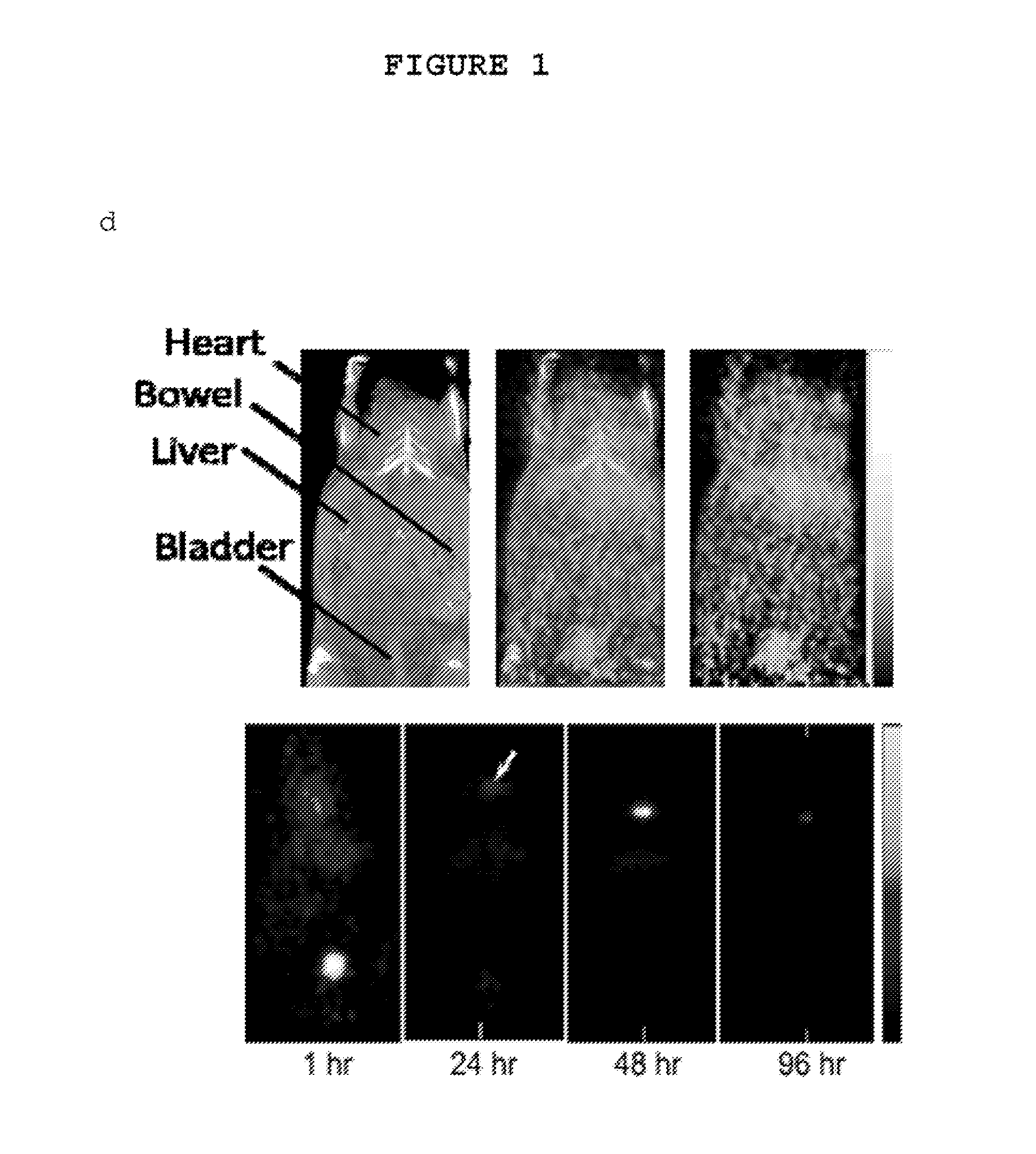
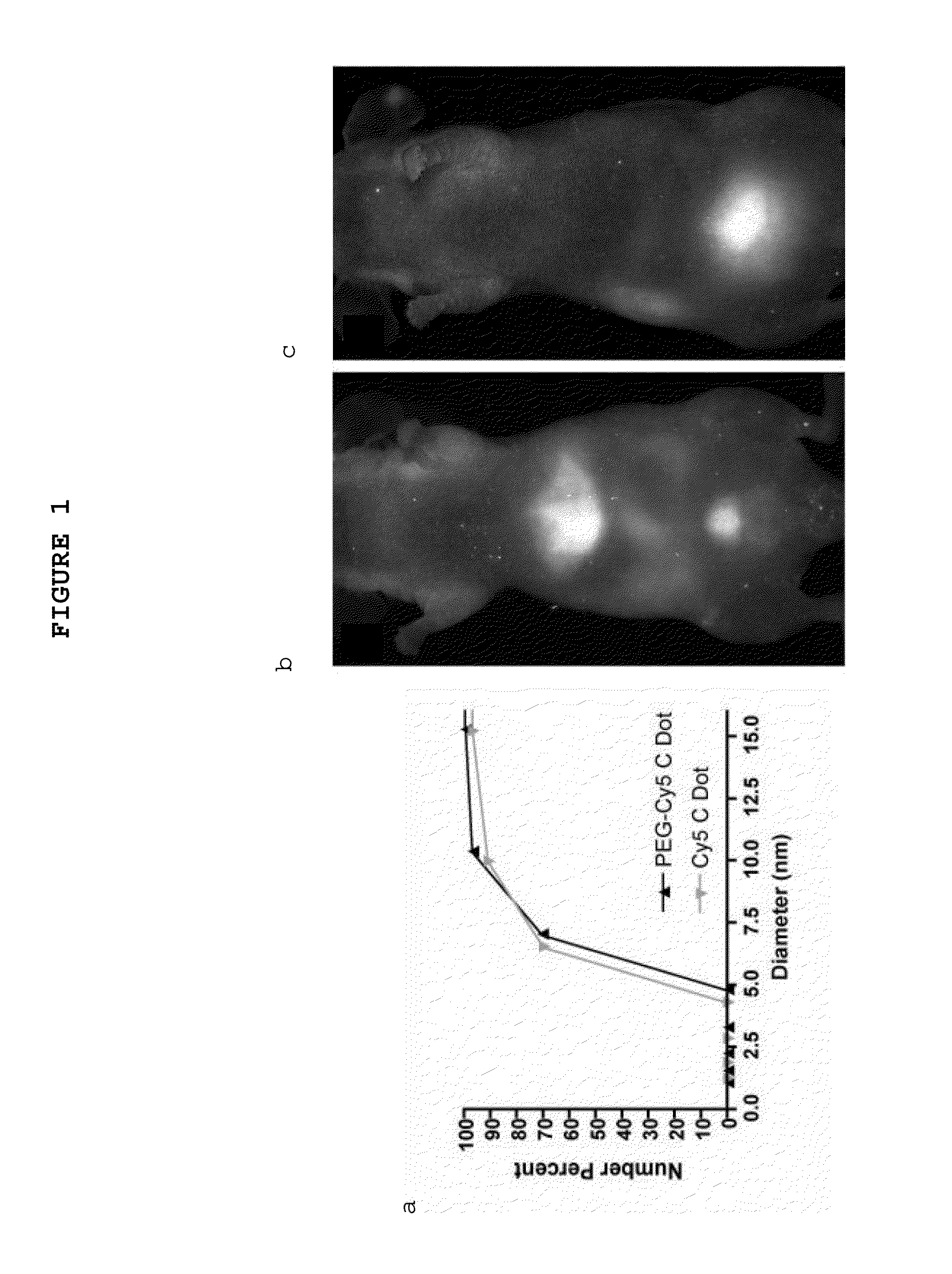
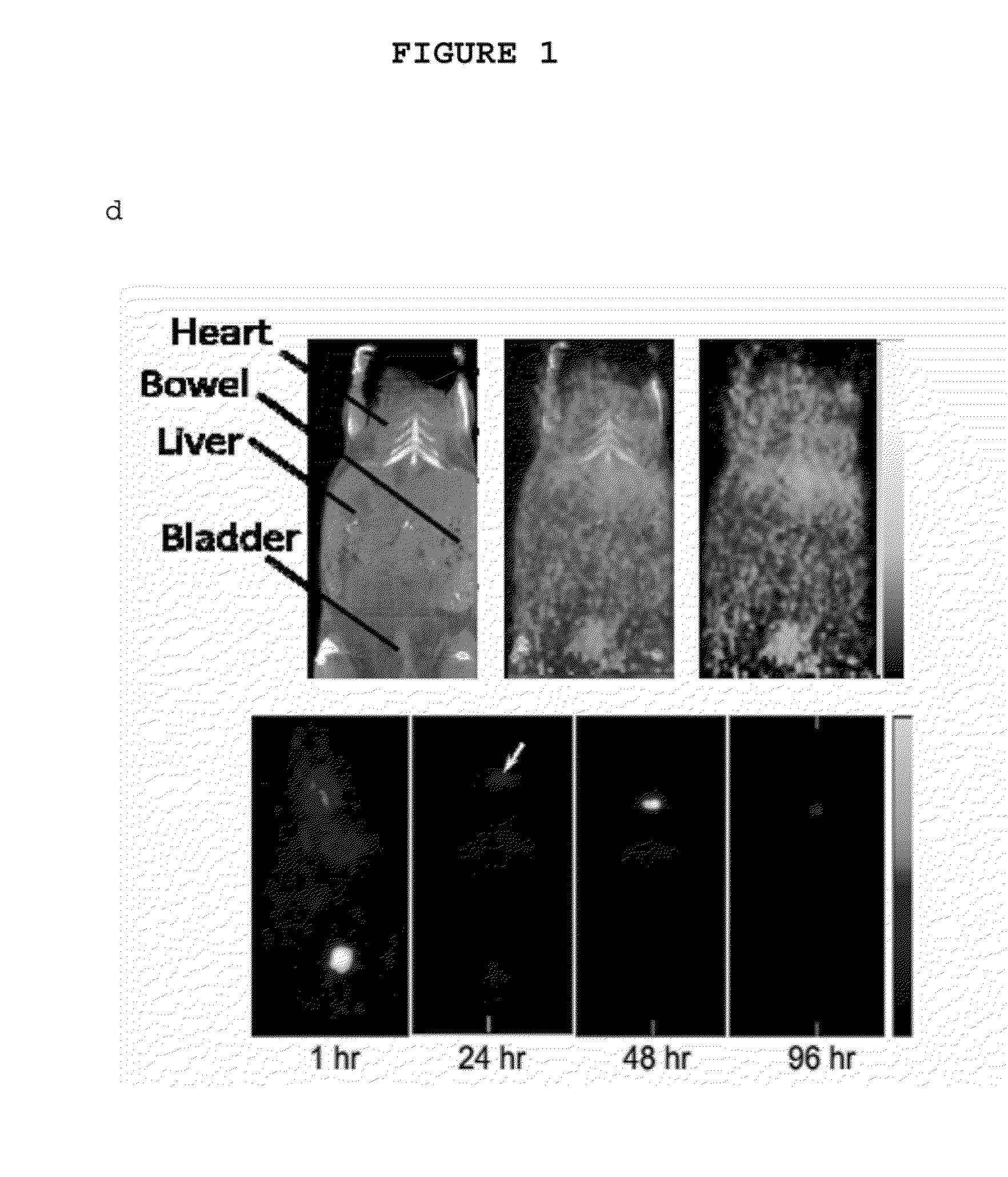
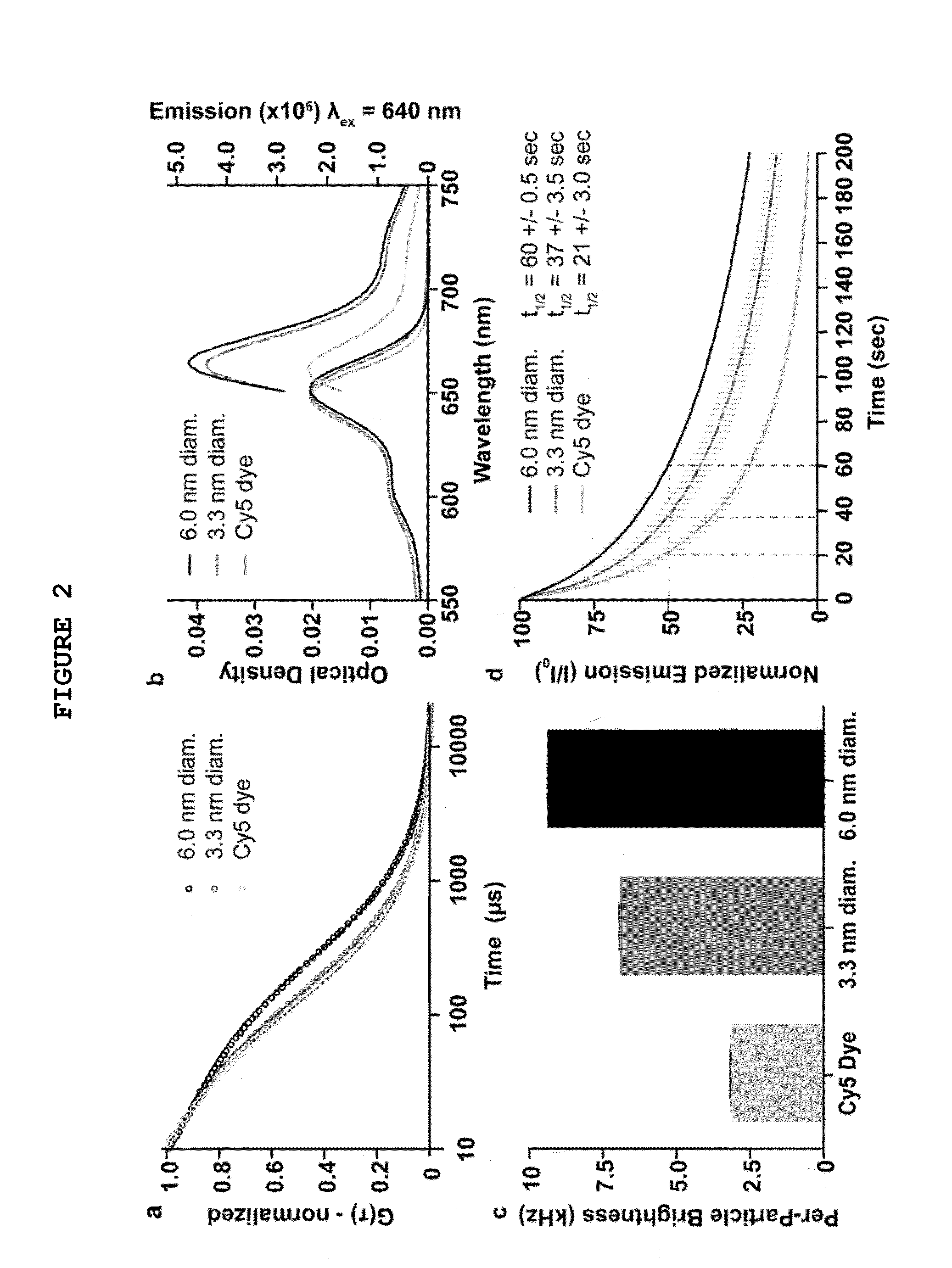
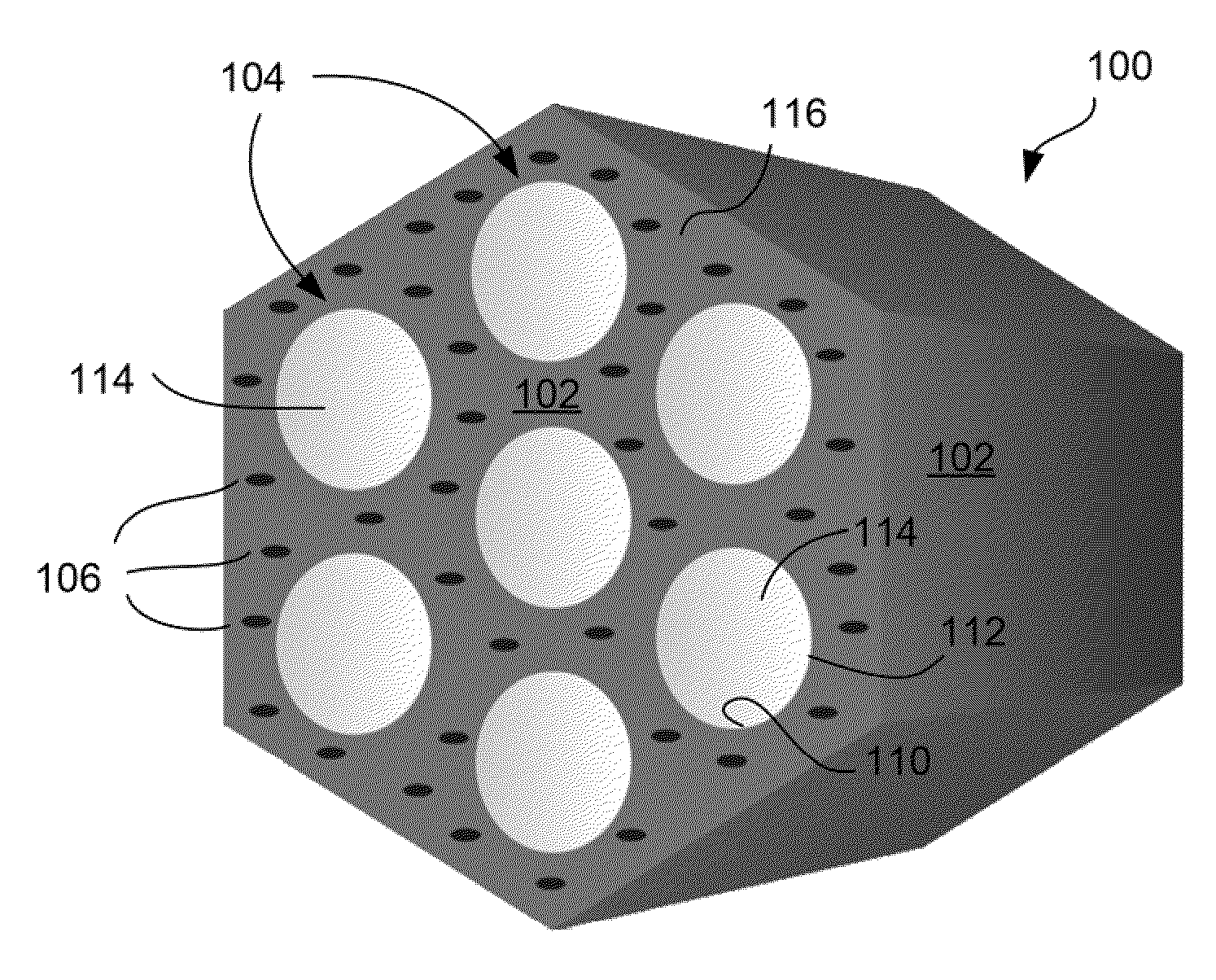
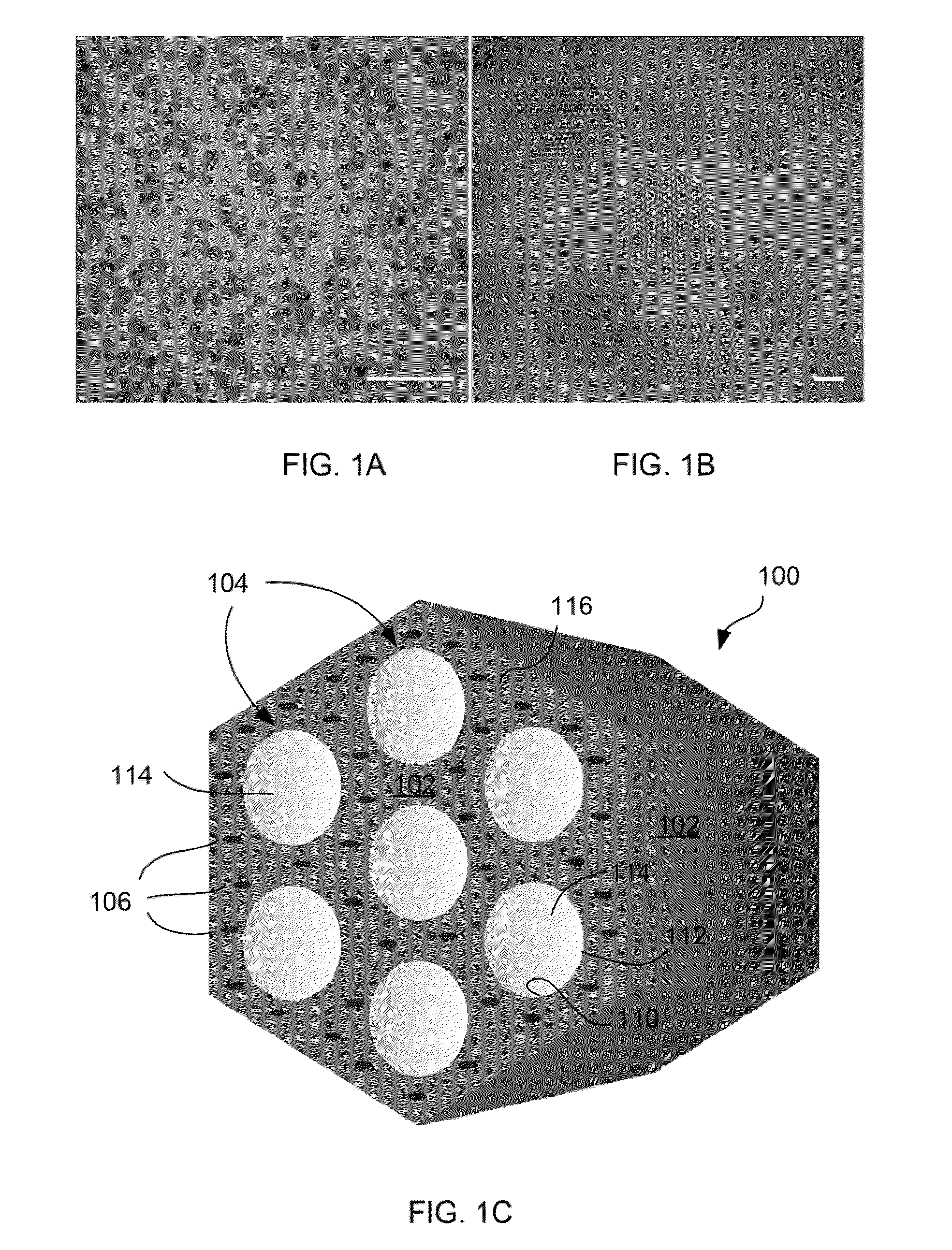
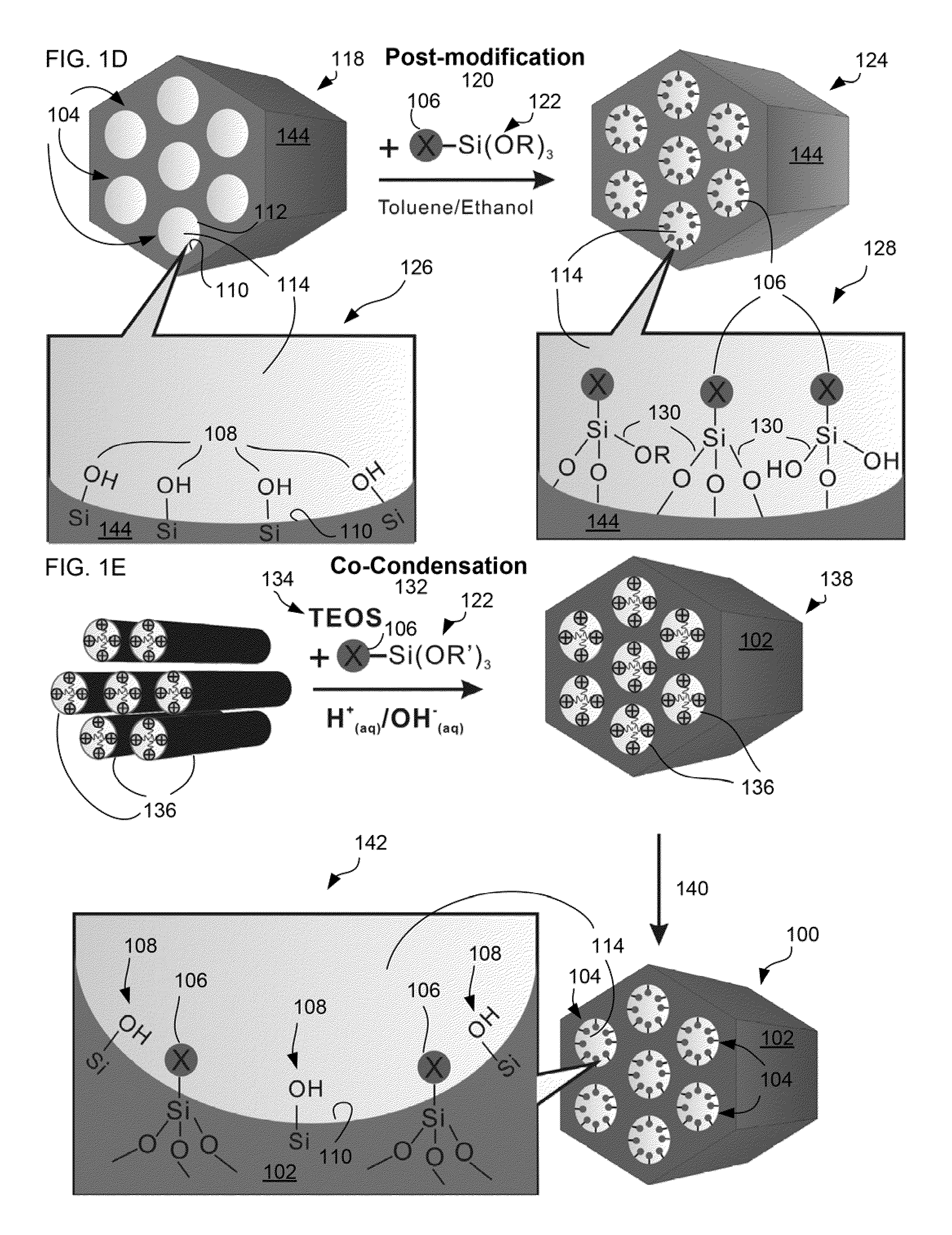
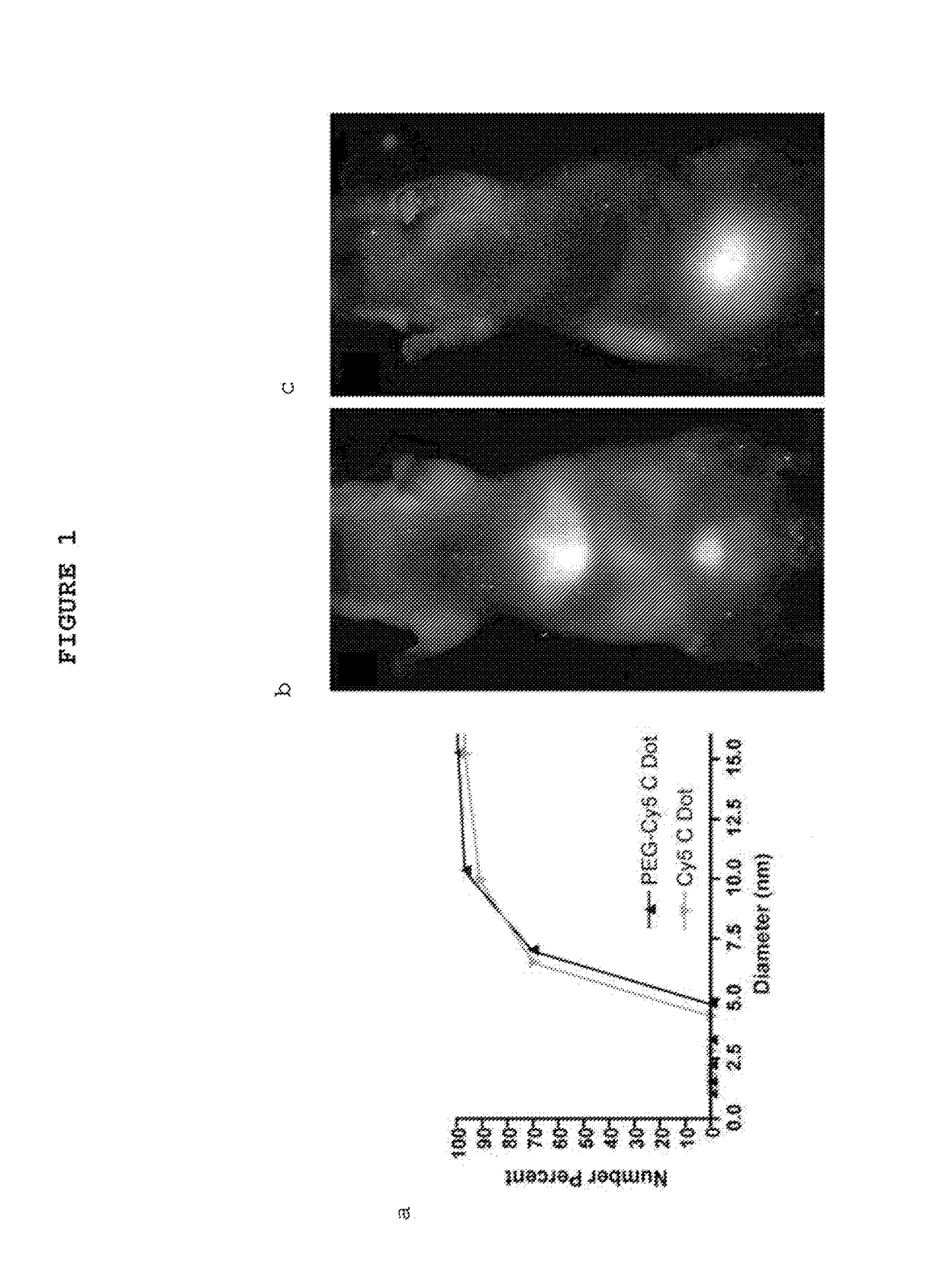
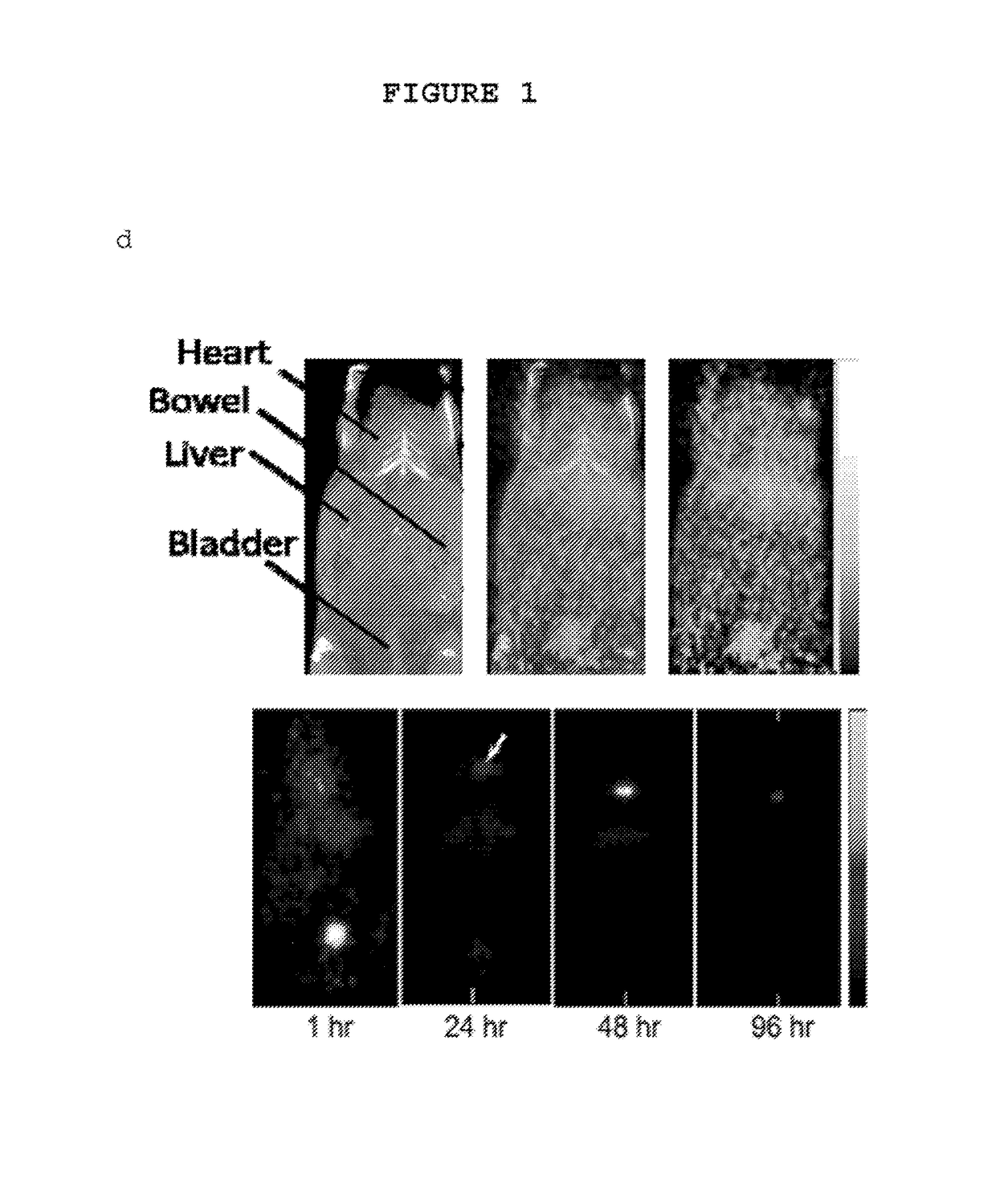
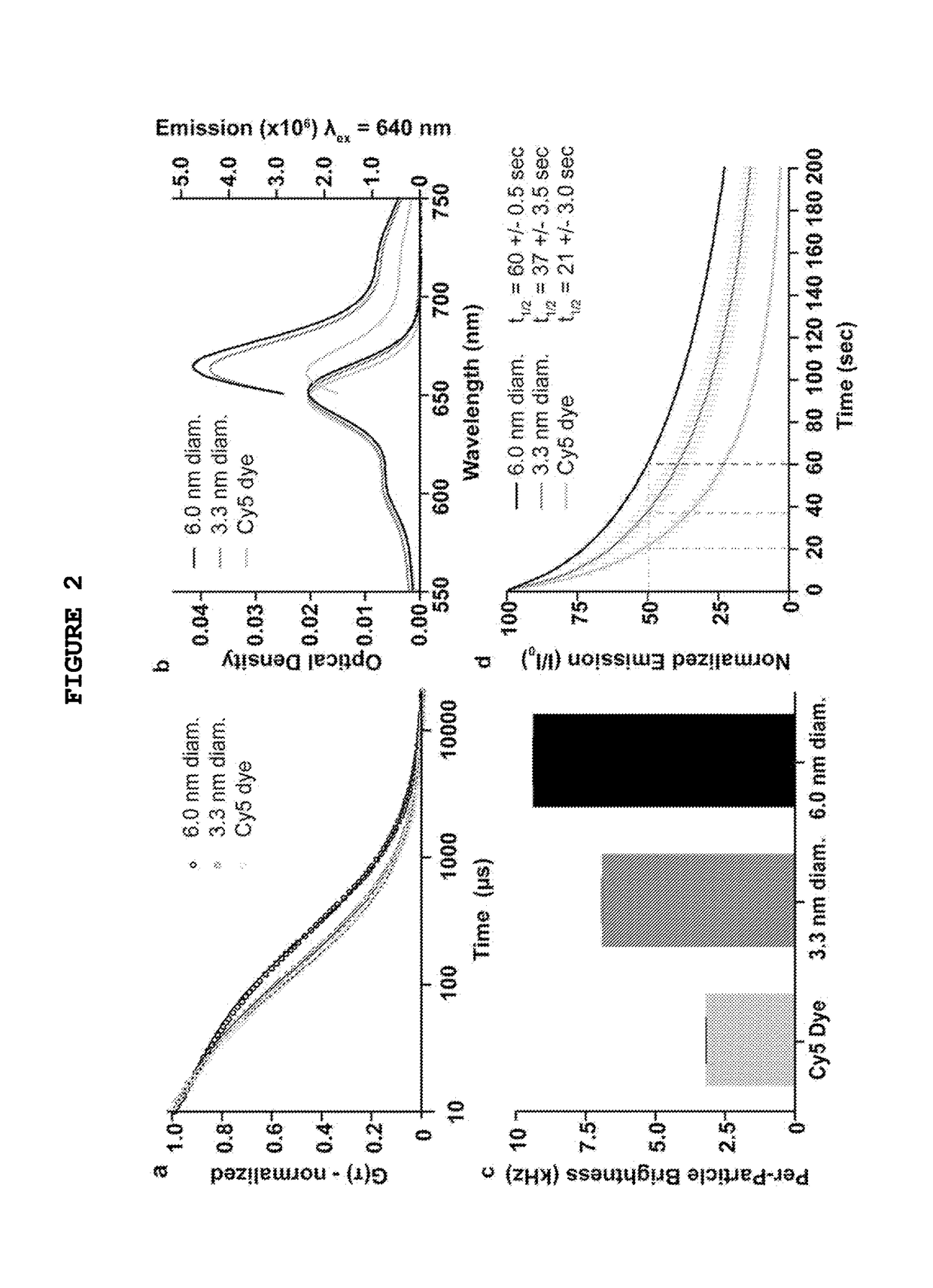
Fluorescent silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20130039848A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAntibacterial agentsDiseaseCellular component
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as polyethylene glycol) (PEG) The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo The nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker A therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle Radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle to permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by various imaging techniques.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Amplifying Optical Fiber and Method of Manufacturing
InactiveUS20100118388A1Improve efficiencyIncrease output powerGlass optical fibreMaterial nanotechnologyRare-earth elementNanoparticle
Disclosed is an amplifying optical fiber having a central core and an optical cladding surrounding the central core. The central core is based on a silica matrix that includes nanoparticles, which are composed of a matrix material that includes doping ions of at least one rare earth element. The amplifying optical fiber can be employed, for example, in an optical amplifier and an optical laser.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Multimodal silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20140248210A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryCellular componentDisease
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer. The nanoparticle has a range of diameters including between about 0.1 nm and about 100 nm, between about 0.5 nm and about 50 nm, between about 1 nm and about 25 nm, between about 1 nm and about 15 nm, or between about 1 nm and about 8 nm. The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound. The nanoparticle also exhibits high biostability and biocompatibility. To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo. In order to target a specific cell type, the nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand, which is capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker. In one embodiment, a therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle. To permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by not only optical fluorescence imaging, but also other imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), computerized tomography (CT), bioluminescence imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
Smooth outer coating for combustor components and coating method therefor
InactiveUS7368164B2Suppresses component temperature riseReduce transferMolten spray coatingPropellersZinc titanateSilica matrix
A coating and method for overcoating a TBC on a component used in a high-temperature environment, such as the combustor section of an industrial gas turbine. The coating defines the outermost surface of the component and is formed of at least two layers having different compositions. An inner layer of the coating contains alumina in a first silica-containing matrix material that is free of zinc titanate. An outer layer of the coating contains alumina, a glass material, and zinc titanate in a second silica-containing matrix material. The outer layer of the coating has a surface roughness of not greater than three micrometers Ra and forms the outermost surface of the component. The coating reduces the component temperature by reducing the convective and radiant heat transfer thereto.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ceramic composite thin films
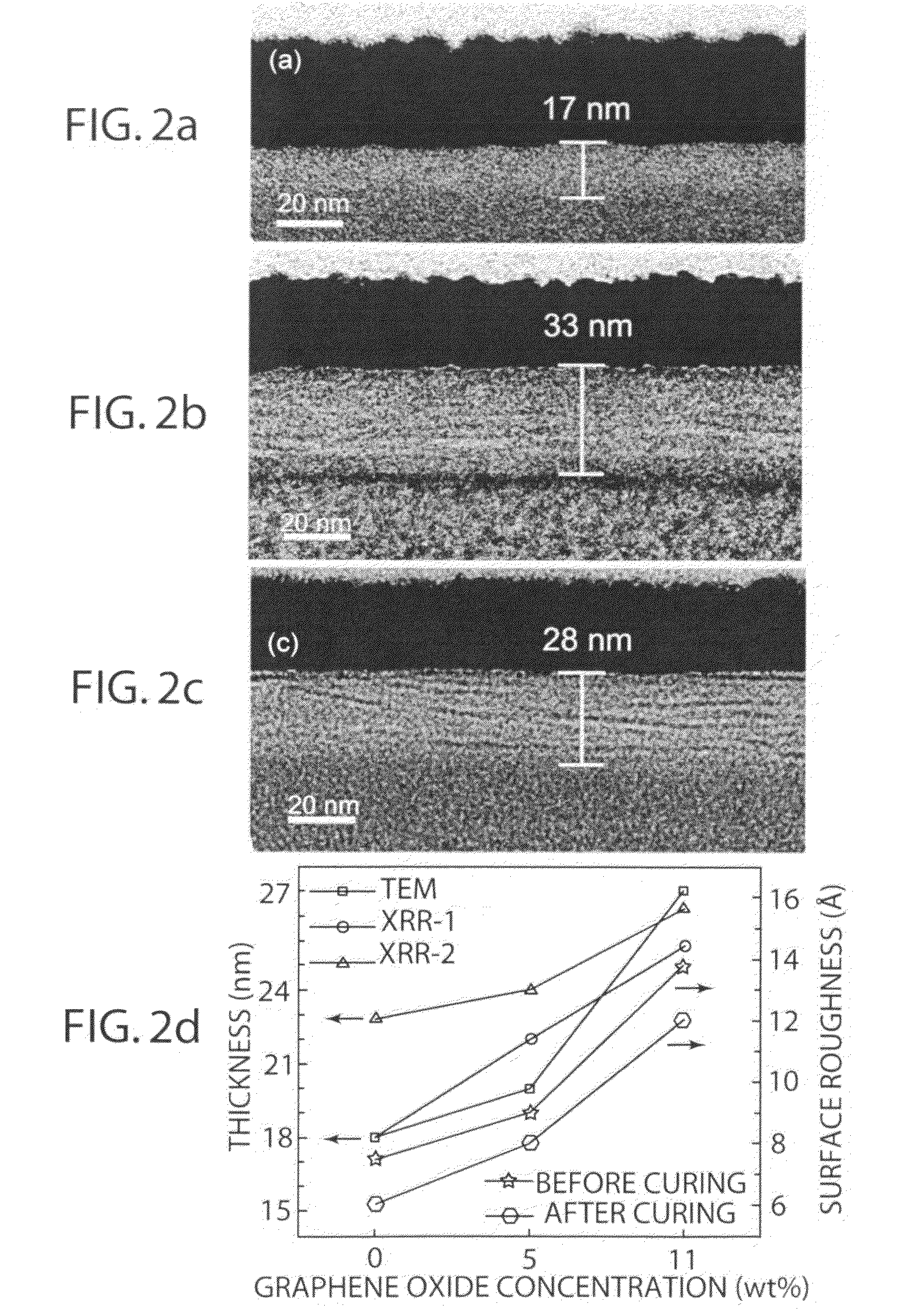
ActiveUS20100323178A1Synthetic resin layered productsConductive materialCeramic compositeComposite film
A ceramic composite thin film or layer includes individual graphene oxide and / or electrically conductive graphene sheets dispersed in a ceramic (e.g. silica) matrix. The thin film or layer can be electrically conductive film or layer depending the amount of graphene sheets present. The composite films or layers are transparent, chemically inert and compatible with both glass and hydrophilic SiOx / silicon substrates. The composite film or layer can be produced by making a suspension of graphene oxide sheet fragments, introducing a silica-precursor or silica to the suspension to form a sol, depositing the sol on a substrate as thin film or layer, at least partially reducing the graphene oxide sheets to conductive graphene sheets, and thermally consolidating the thin film or layer to form a silica matrix in which the graphene oxide and / or graphene sheets are dispersed.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Charged mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based drug delivery system for controlled release and enhanced bioavailability
A charged mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN)-based drug delivery system for controlled release and enhanced bioavailability is disclosed. The system comprises a positively charged MSN, which has a silica matrix and an array of pores and / or nanochannels in the matrix. The entire substance of the matrix, all the surfaces and the pores and / or nanochannels comprise a plurality of silanol (Si—OH) and quaternary ammonium functional groups. The bioavailability of a negatively charged bioactive compound can be increased by loading it into the pores and / or nanochannels. The silanol (Si—OH) functional groups on the surfaces lining the walls of the pores and / or nanochannels are free to deprotonate in a fluid having pH above the pI of the positively charged MSN and lead to a sustained release of the negatively charged drug from the pores and / or nanochannels, and thereby enhance the bioavailability of the drug.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Smooth outer coating for combustor components and coating method therefor
ActiveUS20050282020A1Suppresses component temperature riseReducing convective transferLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingZinc titanateSilica matrix
A coating and method for overcoating a TBC on a component used in a high-temperature environment, such as the combustor section of an industrial gas turbine. The coating defines the outermost surface of the component and is formed of at least two layers having different compositions. An inner layer of the coating contains alumina in a first silica-containing matrix material that is free of zinc titanate. An outer layer of the coating contains alumina, a glass material, and zinc titanate in a second silica-containing matrix material. The outer layer of the coating has a surface roughness of not greater than three micrometers Ra and forms the outermost surface of the component. The coating reduces the component temperature by reducing the convective and radiant heat transfer thereto.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Silica matrix chromatogram packing
InactiveCN101234337AGood reproducibilityShort response timeOther chemical processesSilica matrixSilica gel
The invention relates to a preparation method of inert alkyl reversed phase silica gel chromatographic filler, which belongs to the technical field of high performance liquid phase chromatography. The invention comprises the following steps: step 1 of getting silica gel particles with hydroxyl on the surface through acidification pretreatment of silica gel matrix particles; step 2 of hydroxylation of the silica gel matrix particles, and getting the alkyl reversed phase silica gel filler by making use of corresponding alkyl silicane reagents and by adopting a method of liquid phase reaction to make surface alkyl treatment to the acidification pretreated silica gel particles with the hydroxy; step 3 of inert treatment of the alkyl silica gel matrix filler, and putting the prepared dry alkyl reversed phase silica gel filler into an autoclave with a certain volume, adding a certain amount of silicane terminated reagents and sealing the autoclave to make seal terminated reaction in the inert gas atmosphere to obtain the highly inert alkyl reversed phase silica gel chromatographic filler. In appropriate chromatographic conditions, the filler prepared in the invention can be effectively used in the separation analysis of acidic, neutral and basic compounds.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Entrapment of biomolecules and inorganic nanoparticles by biosilicification
A method of immobilizing at least one molecule in a silica matrix to form a biosilicification product. The at least one molecule may be immobilized in the silica matrix at substantially the same time as the silica matrix is formed. The method comprises combining at least one silaffin polypeptide, at least one molecule, and at least one hydroxylated water-soluble derivative to form the biosilicification product. The silaffin polypeptide may be Sil1 protein from C. fusiformis, a fragment of the Sil1 protein, poly-L-lysine, or a synthetic polypeptide having affinity for silica. The at least one molecule may be an enzyme, a protein, a polypeptide, an antibody, an antigen, poly(nucleic) acids, microbial cells, plant cells, or animal cells. The hydroxylated water-soluble derivative may be silicic acid.
Owner:RAO UES +1
Hydrophobic and oleophobic coatings
ActiveUS20110250422A1Avoid stickingSynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesAlcoholSilanes
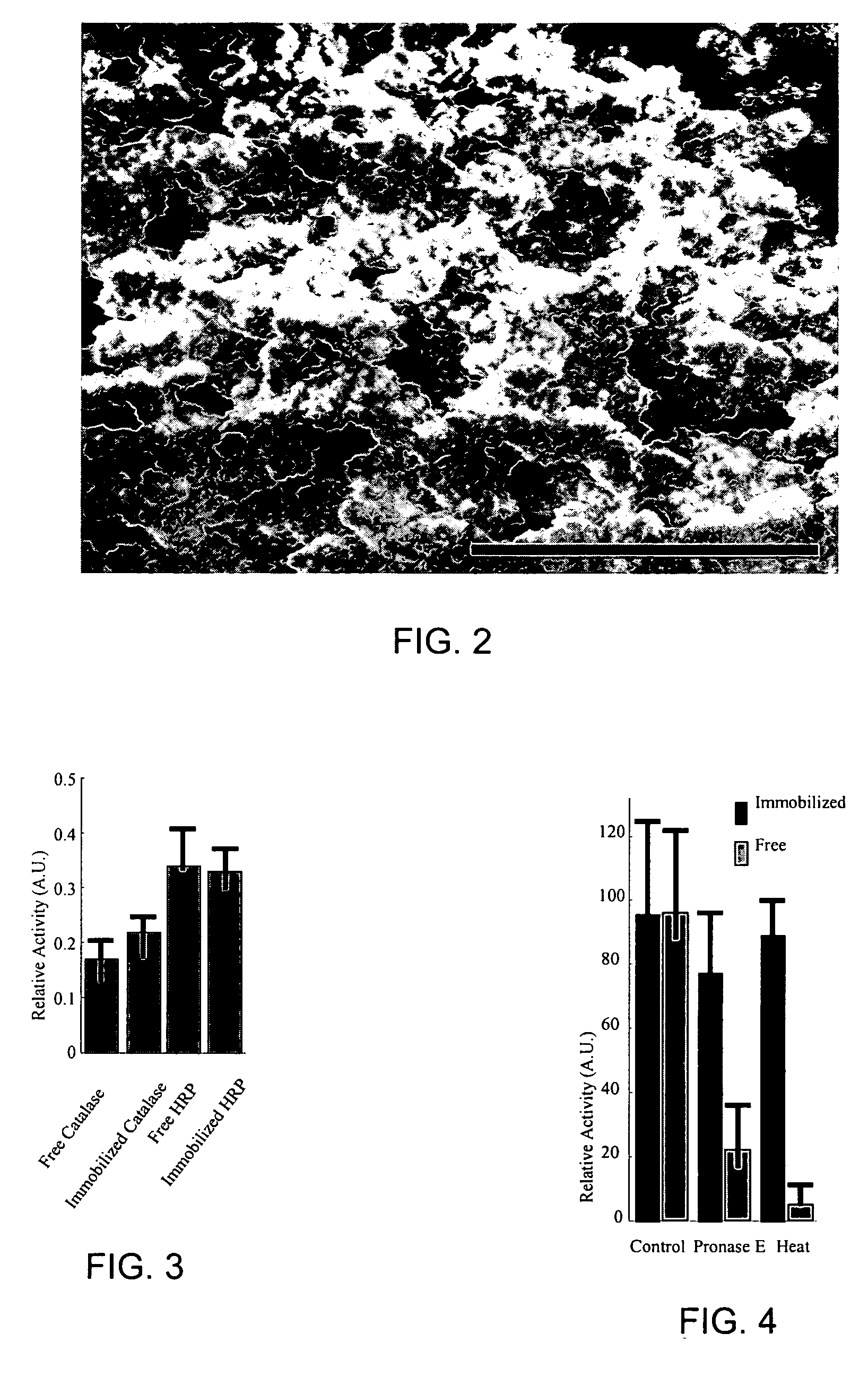
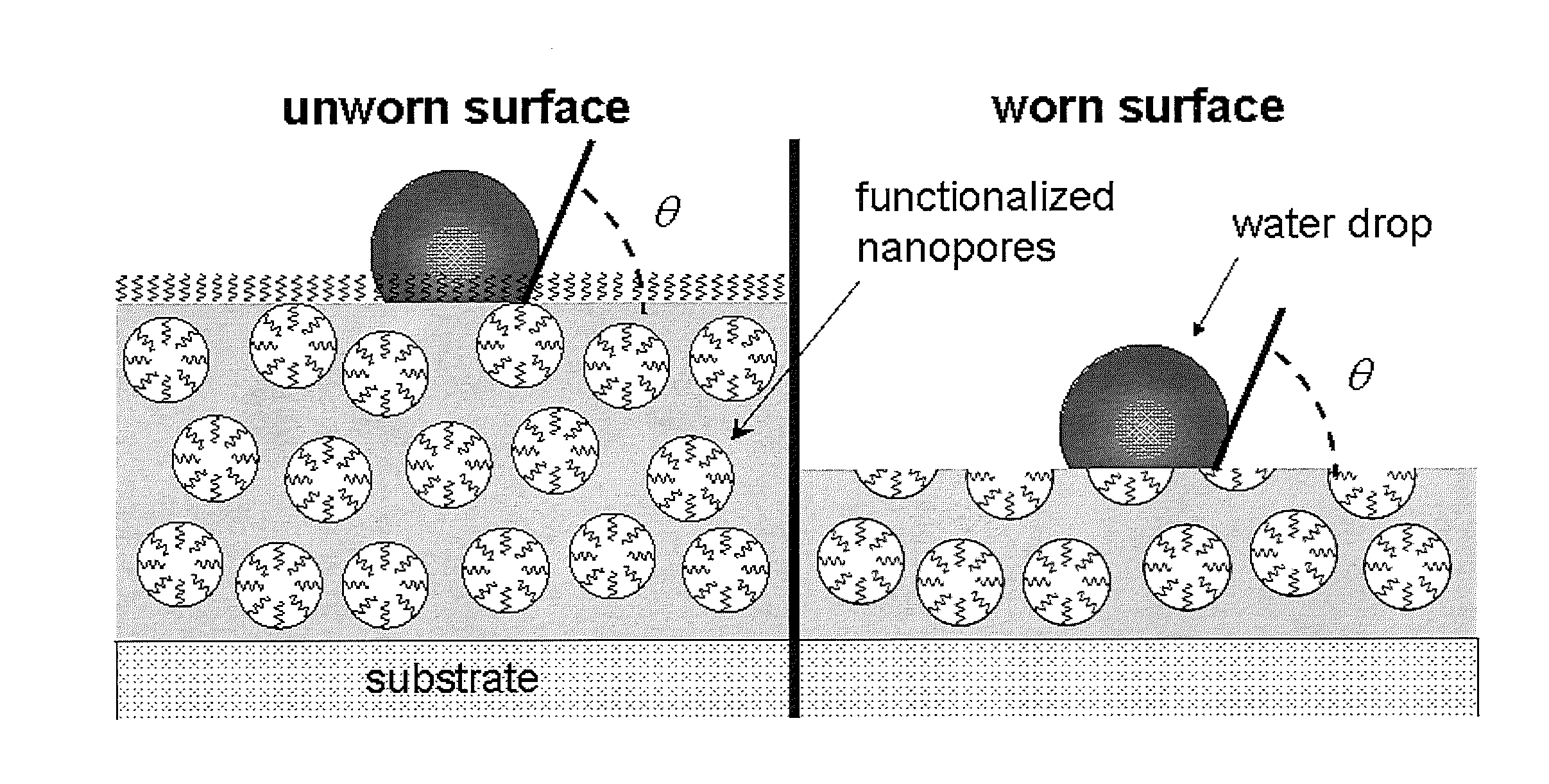
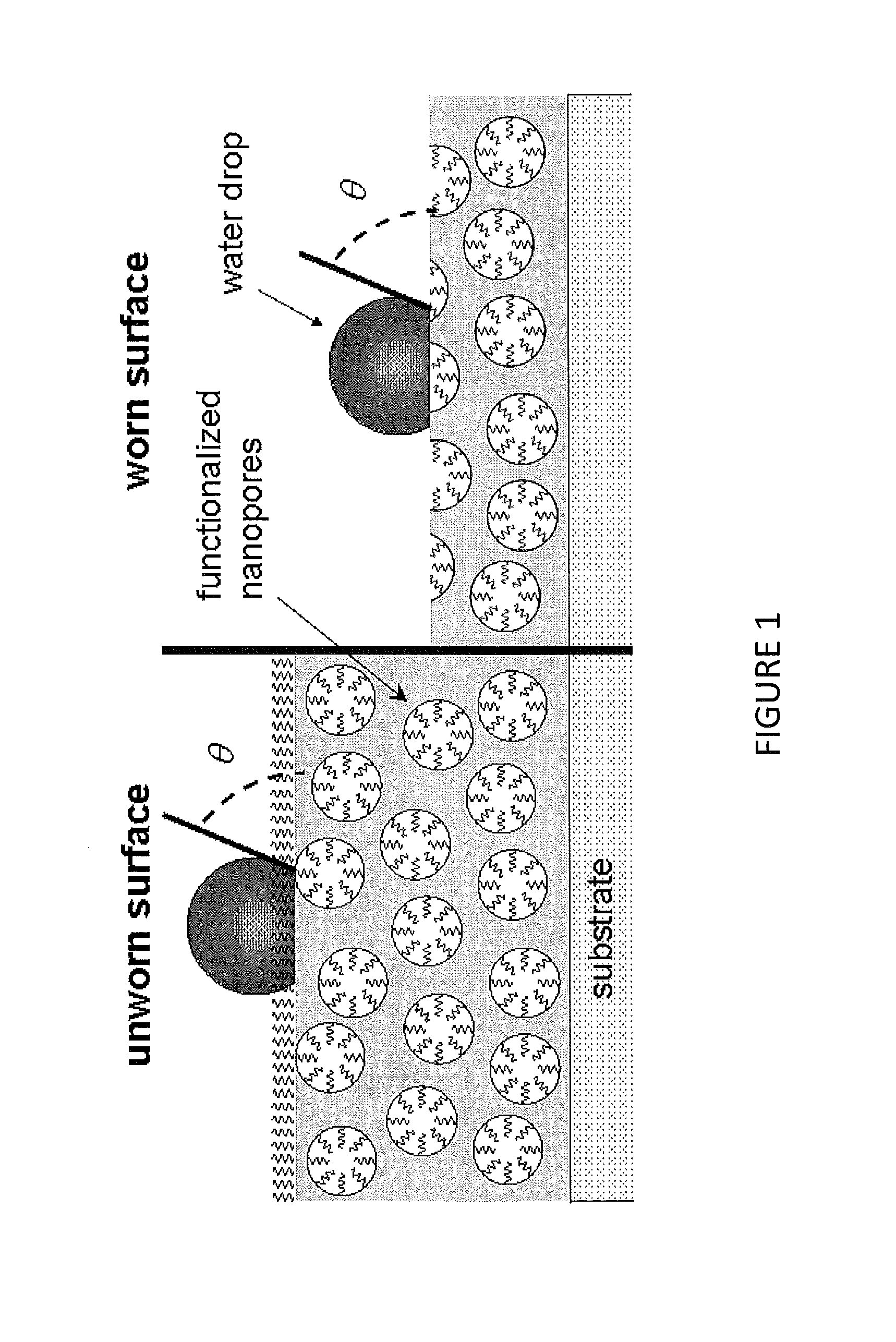
Provided according to some embodiments of the invention are hydrophobic and / or oleophobic silica-based coatings. In some embodiments of the invention, coatings may include a silica matrix having hydrophobic and / or oleophobic functionalized pores encapsulated therein. Also provided according to some embodiments of the invention are methods of forming a coating according to an embodiment described herein. In some embodiments, methods include (a) combining at least one silane and / or alkoxysilane and at least one fluoroalkylsilane and / or fluoroalkoxysilane with an alcohol, water and an acid to form a sol mixture; (b) adding a surfactant to the sol mixture to form a surfactant sol mixture; (c) depositing the surfactant sol mixture onto a substrate; and (d) curing the surfactant sol mixture to form a silica coating. Methods of preventing adhesion are also provided herein.
Owner:UNIV OF WEST VIRGINIA
Sol-gel process for the manufacture of nanocomposite photoluminescent materials and materials thus produced
It is described a process based on sol-gel chemistry suitable to the production of nanocomposite materials being photoluminescent at ambient temperature, comprising silicon grains of dimension of nanometers embedded in a silica matrix.
Owner:DEGUSSA NOVARA TECH SPA
Silica-based antibacterial and antifungal nanoformulation
ActiveUS8221791B1Simple and cost-effective fabricationEasy to controlPowder deliveryBiocideDiseaseAntibacterial activity
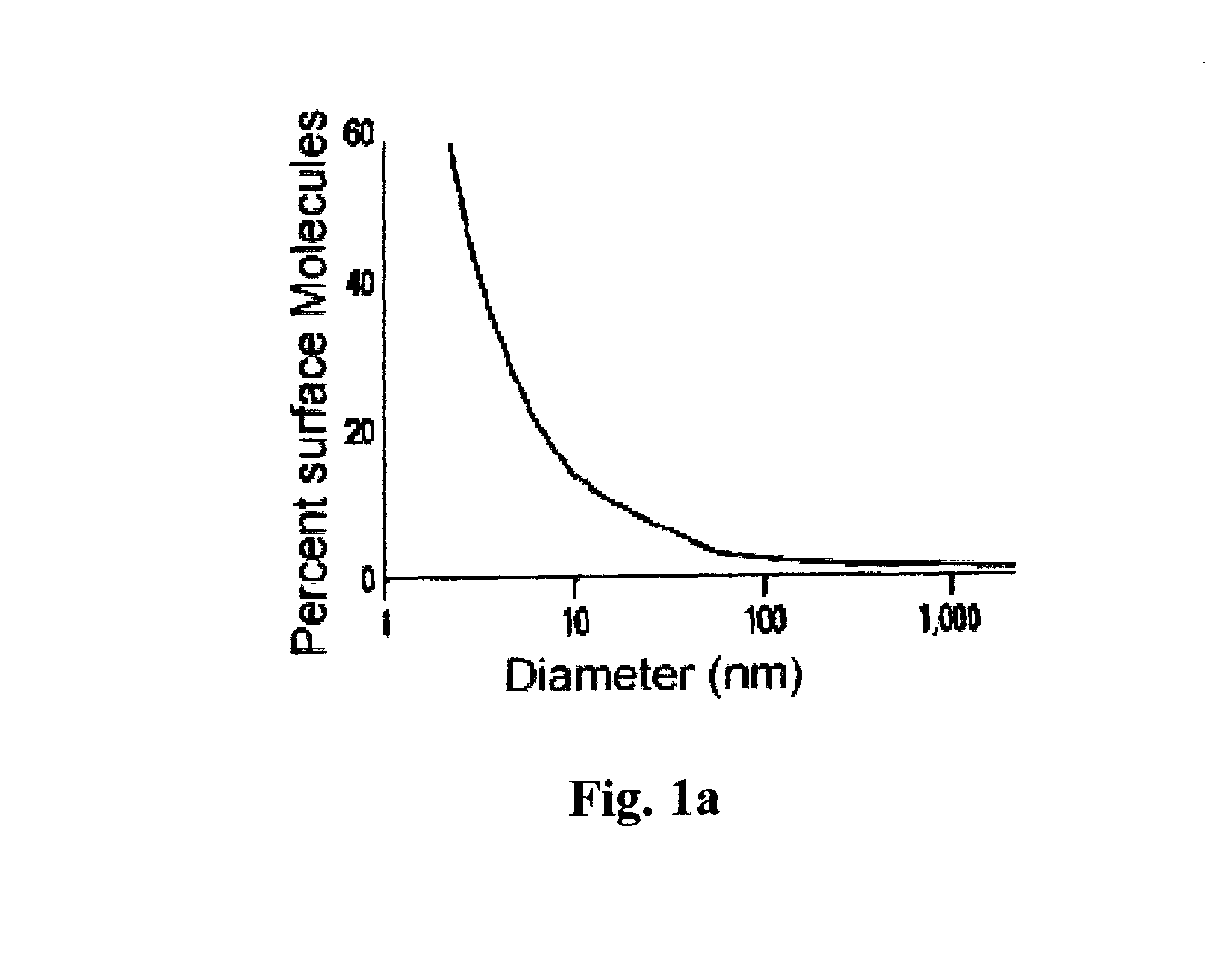
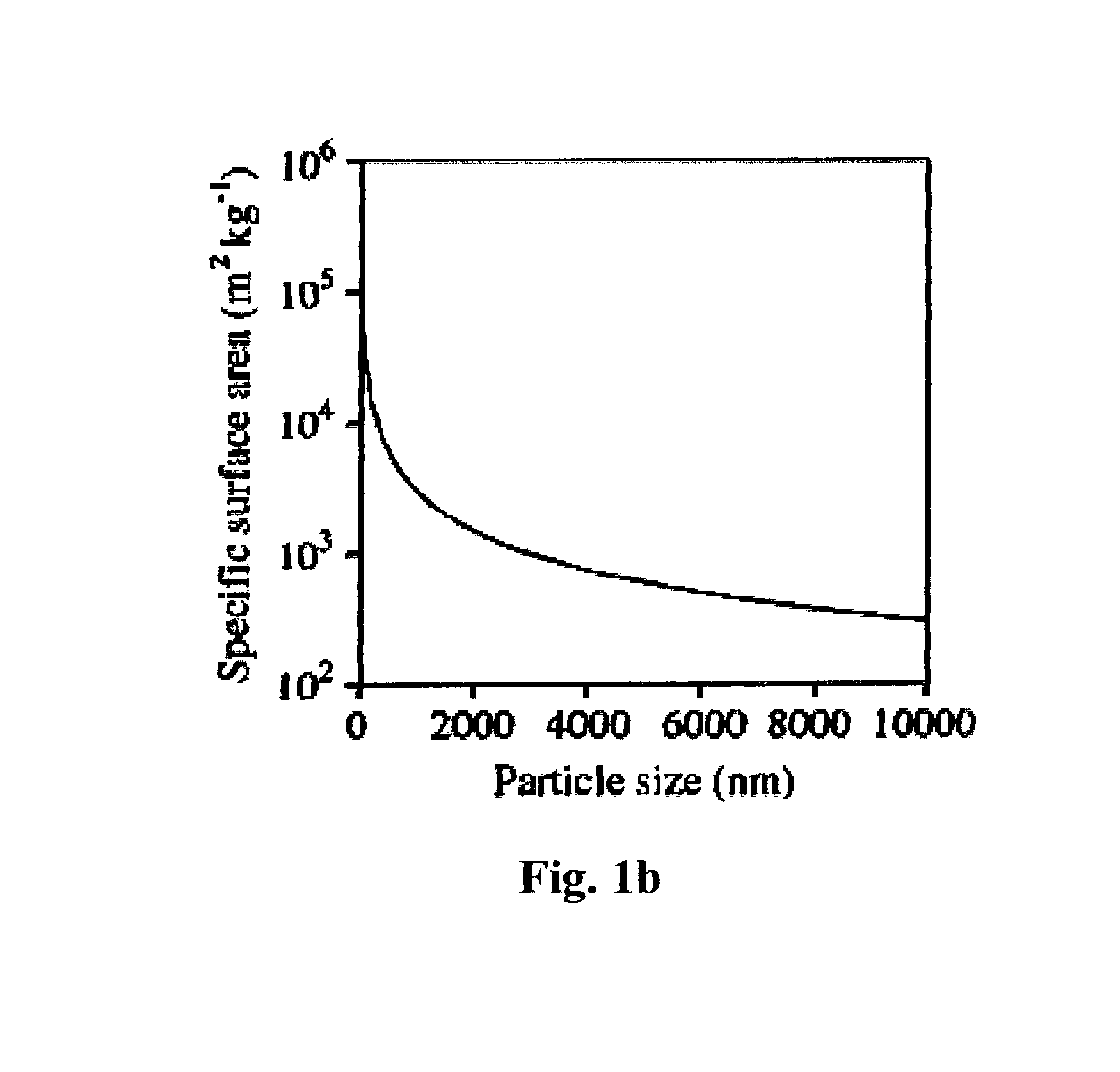
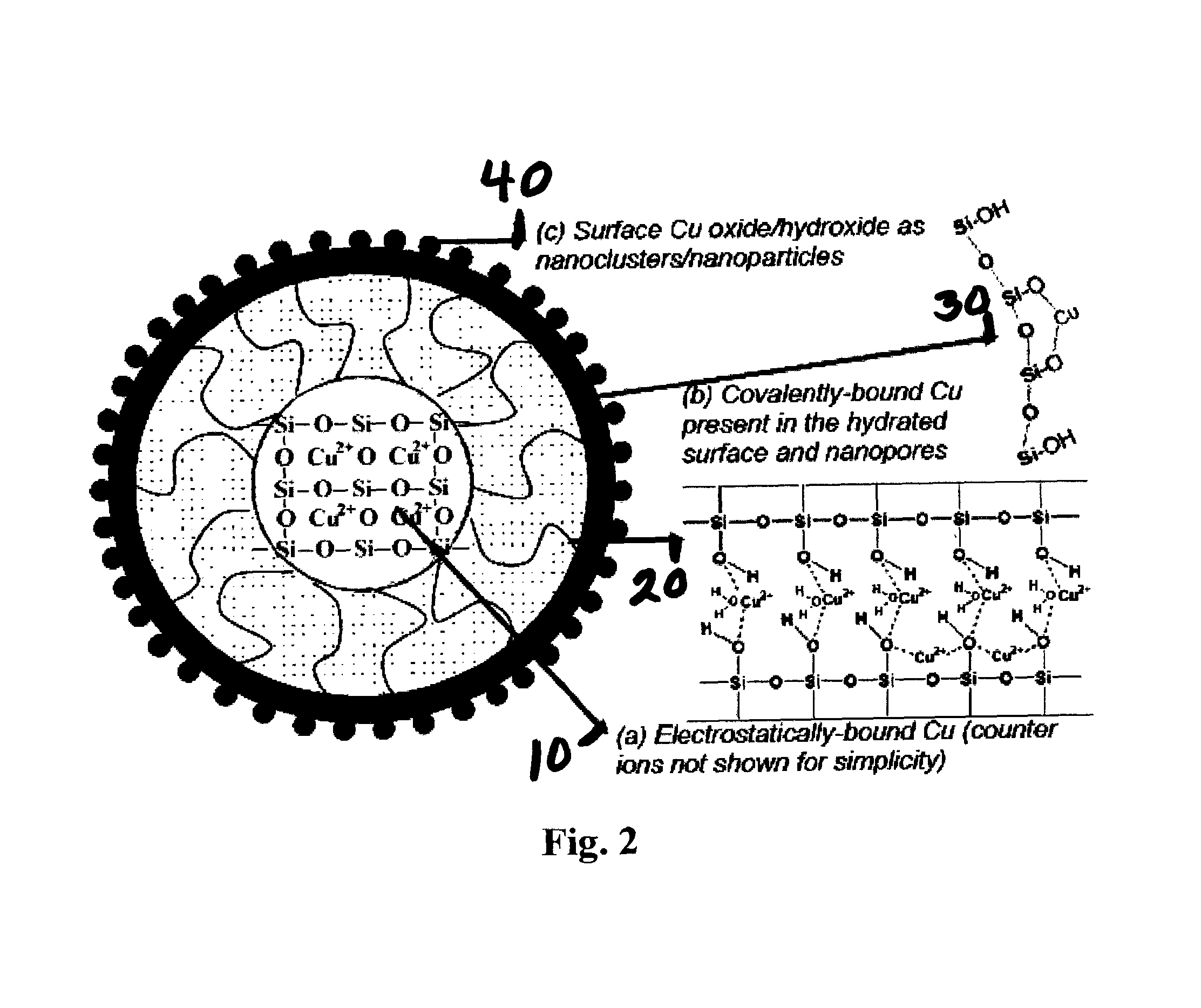
A silica-based nanoformulation and method is used to treat citrus canker, inhibit the growth of mold and mildew, and add nutrients to soil used for agricultural purposes. The nanotechnology-enabled copper-loaded, silica nanoformulation (CuSiNP / NG) design is a “revolutionary re-invention” of Cu for safe application because it provides a formulation with maximum abundance of ionic Cu, provides sustained and optimal Cu ion release for long-term disease protection, better adherence to plant surfaces and structural surfaces due to gel-based nanostructure of CuSiNG, thus avoiding multiple spray applications and reducing the amount of Cu used in comparison to existing Cu compounds without compromising antibacterial activity. Thus, the silica-based nanoformulation releases copper in non-toxic quantities to the environment and the silica matrix provides an environmentally safe host material with a flexible design that is optimized to provide specific antifungal and antibacterial remediation using infrequent applications.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
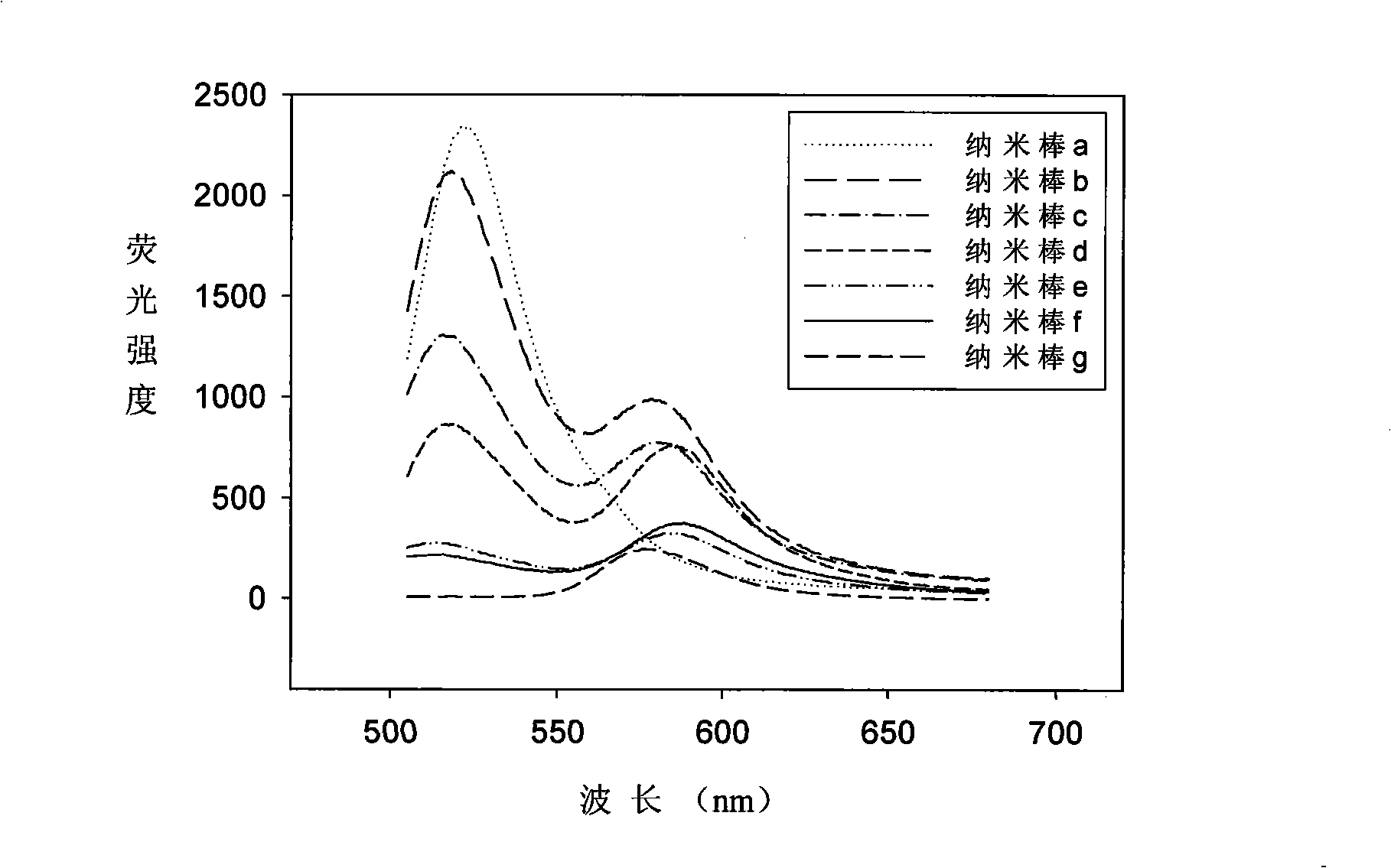
Multi-color optic-encoding siliceous skin nano-rods and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101333436AGood package efficiencyImprove packaging efficiencyBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnergy transferResonance
The invention discloses a multi-color optical encoding nano-rod with silica shell. The multi-color optical encoding nano-rod takes the shape of a core shell, the shell is made of silicon dioxide and the kernel is fluorescence-encoded polylysine which contains fluorescent dye A and fluorescent dye B; the fluorescent dye A and fluorescent dye B are a fluorescence resonance energy transfer supplier-receptor pair. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the multi-color optical encoding nano-rod with silica shell, which includes the steps of enabling the fluorescent dye A and fluorescent dye B to react with the polylysine to prepare fluorescence-encoded polylysine, and wrapping the fluorescence-encoded polylysine, used as kernel material, in a silicon dioxide substrate through reverse microemulsion method; in this way, the multi-color optical encoding nano-rod with silica shell can be prepared. The multi-color optical encoding nano-rod with silica shell has the advantages of strong fluorescence intensity, good biological compatibility, good hydrophilicity, little leakage of dye and stable property.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Fluorescent silica-based nanoparticles
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as polyethylene glycol) (PEG) The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo The nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker A therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle Radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle to permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by various imaging techniques.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
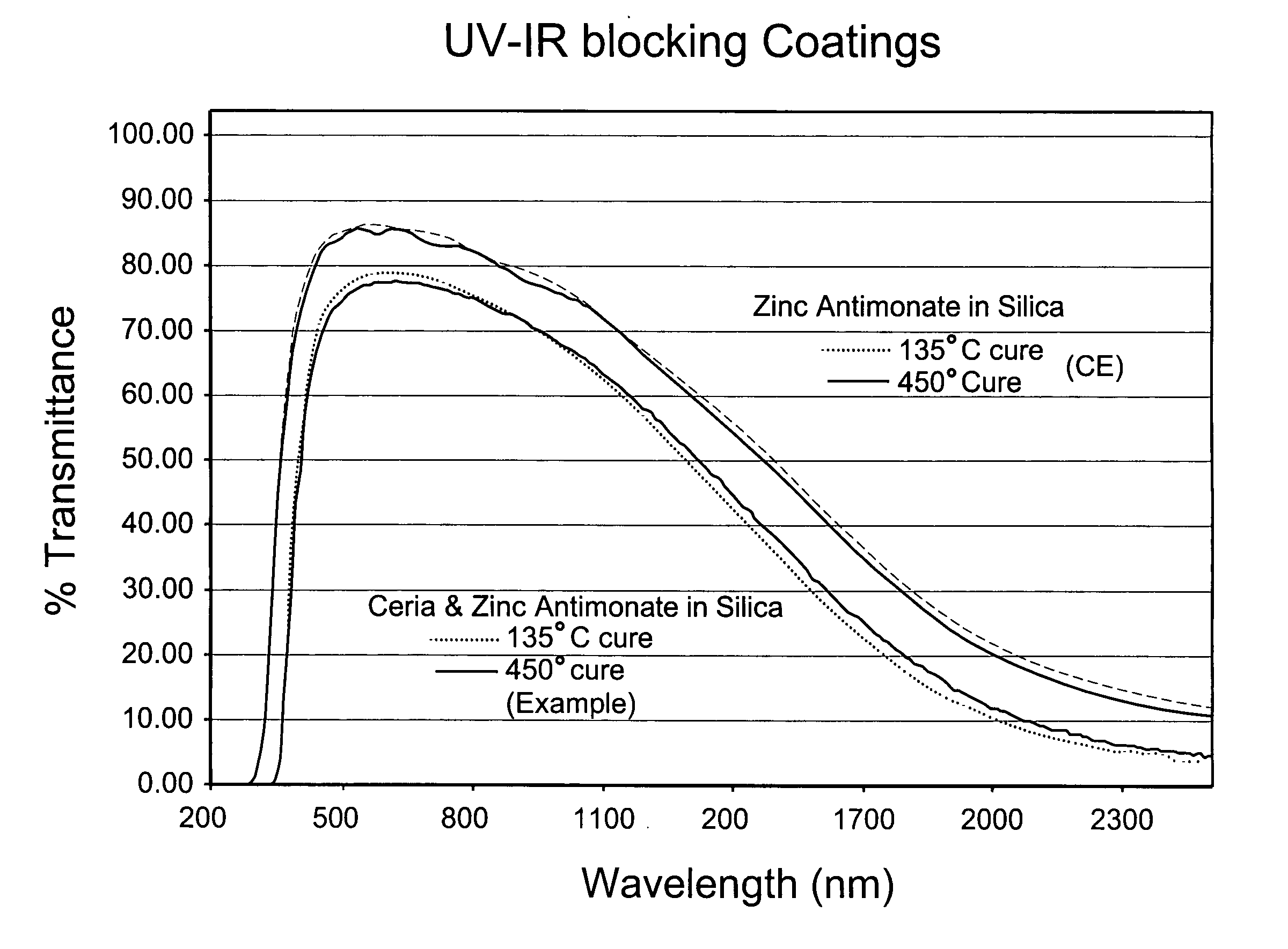
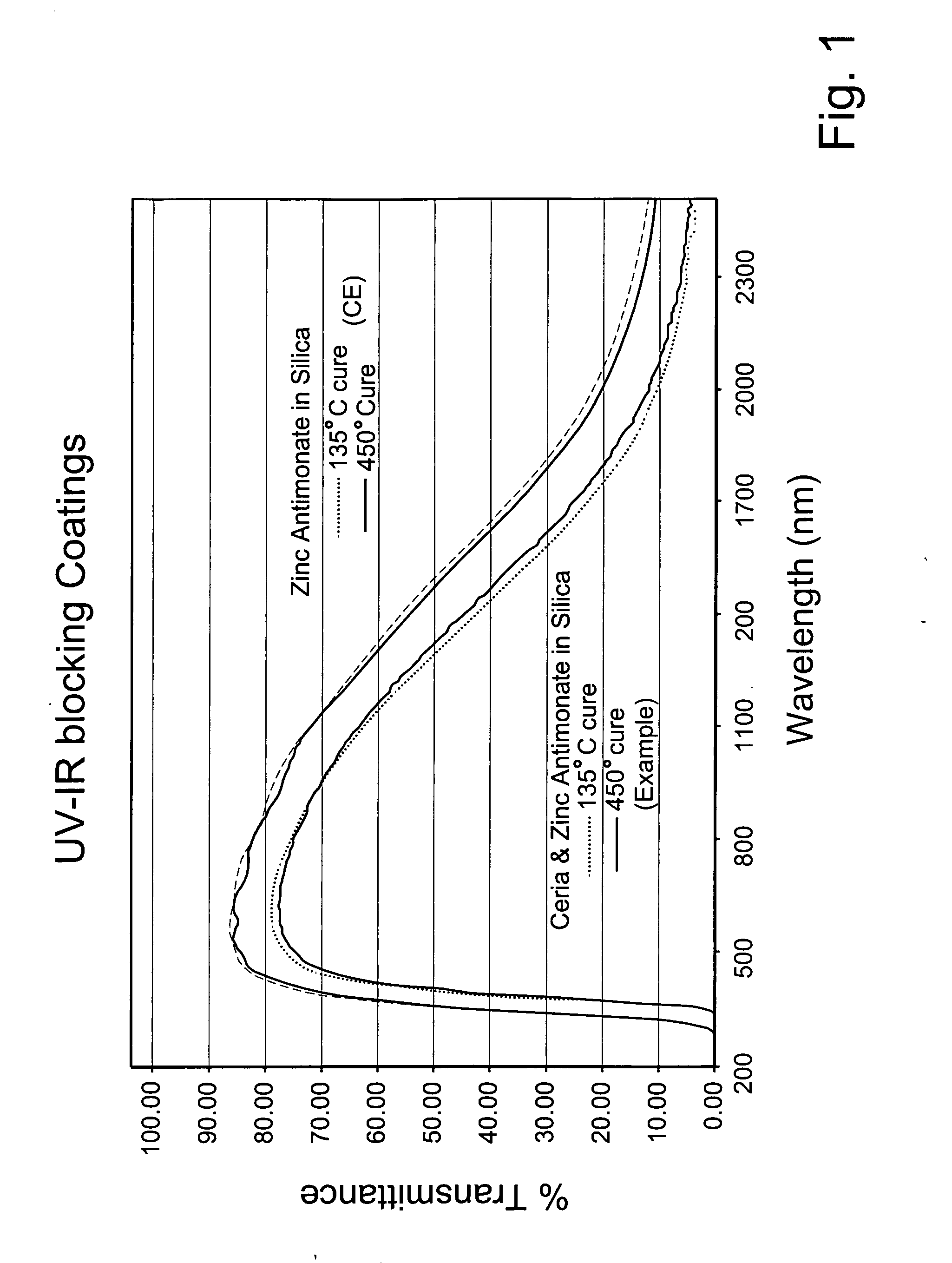
Coating with infrared and ultraviolet blocking characterstics
InactiveUS20070065670A1Resistant to high-temperaturesEffective blockingPretreated surfacesGlass/slag layered productsUltravioletSilica matrix
A composite oxide coating is provided that efficiently blocks both ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation. Certain embodiments of this invention relate to a coating having IR and UV blocking characteristics. In certain example embodiments, the coating includes a silica matrix, zinc antimonite, and a UV blocking material such as cerium oxide, thereby permitting the coating after application to block significant amounts of both IR and UV radiation.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
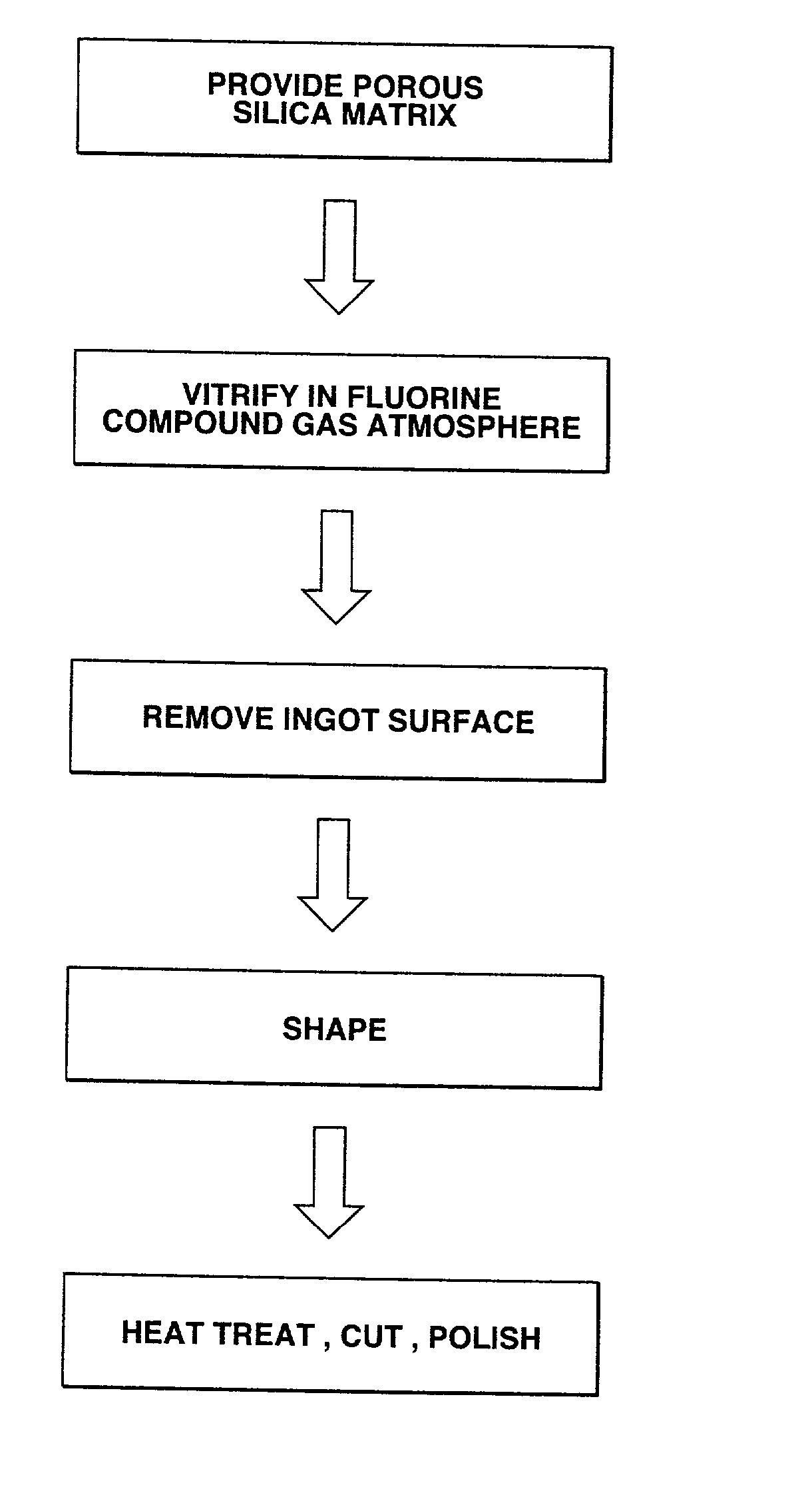
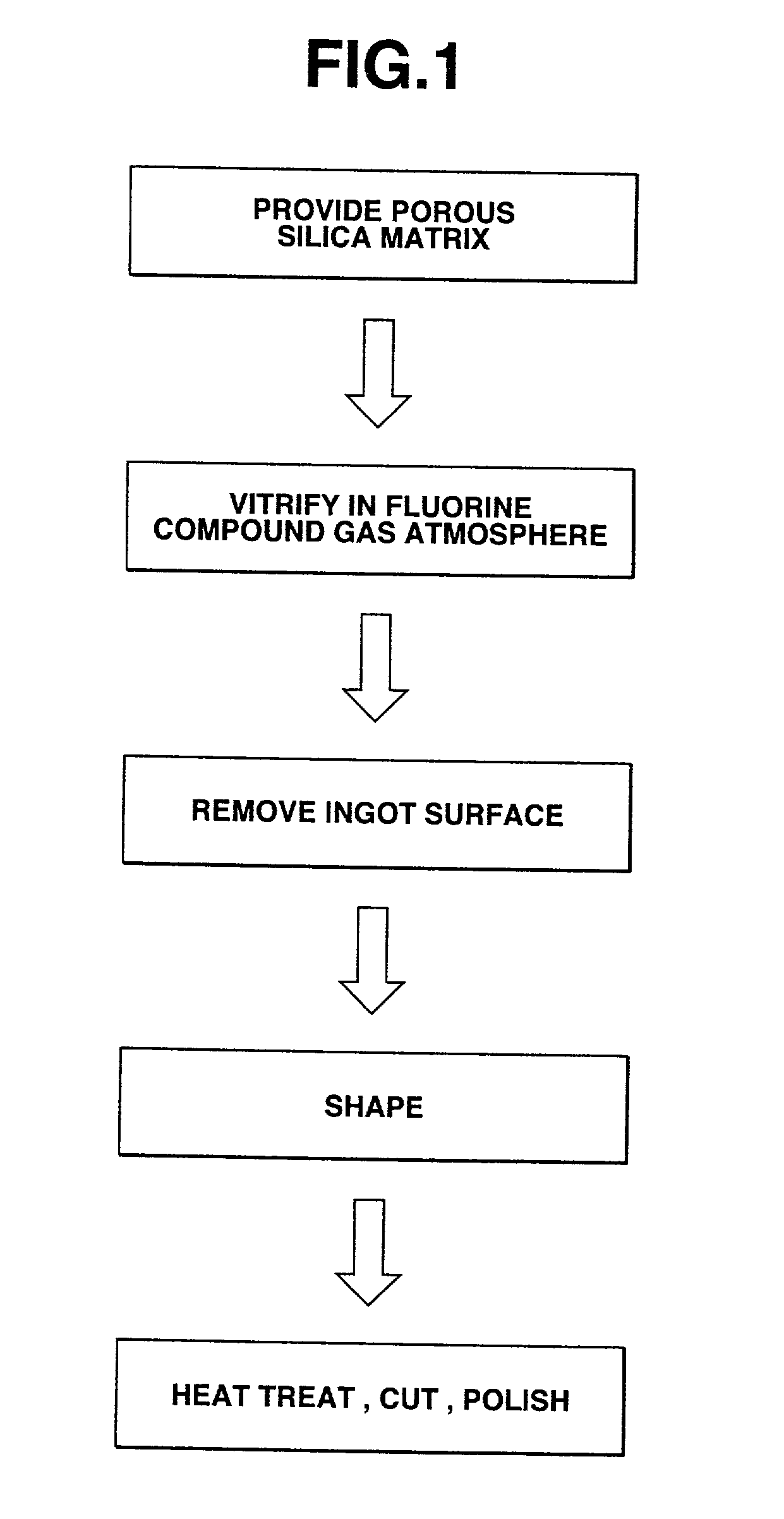
Synthetic quartz glass article and process of production
InactiveUS20020046580A1High light transmittanceSmall refractive indexGlass shaping apparatusOptical light guidesSilica matrixSilicon dioxide
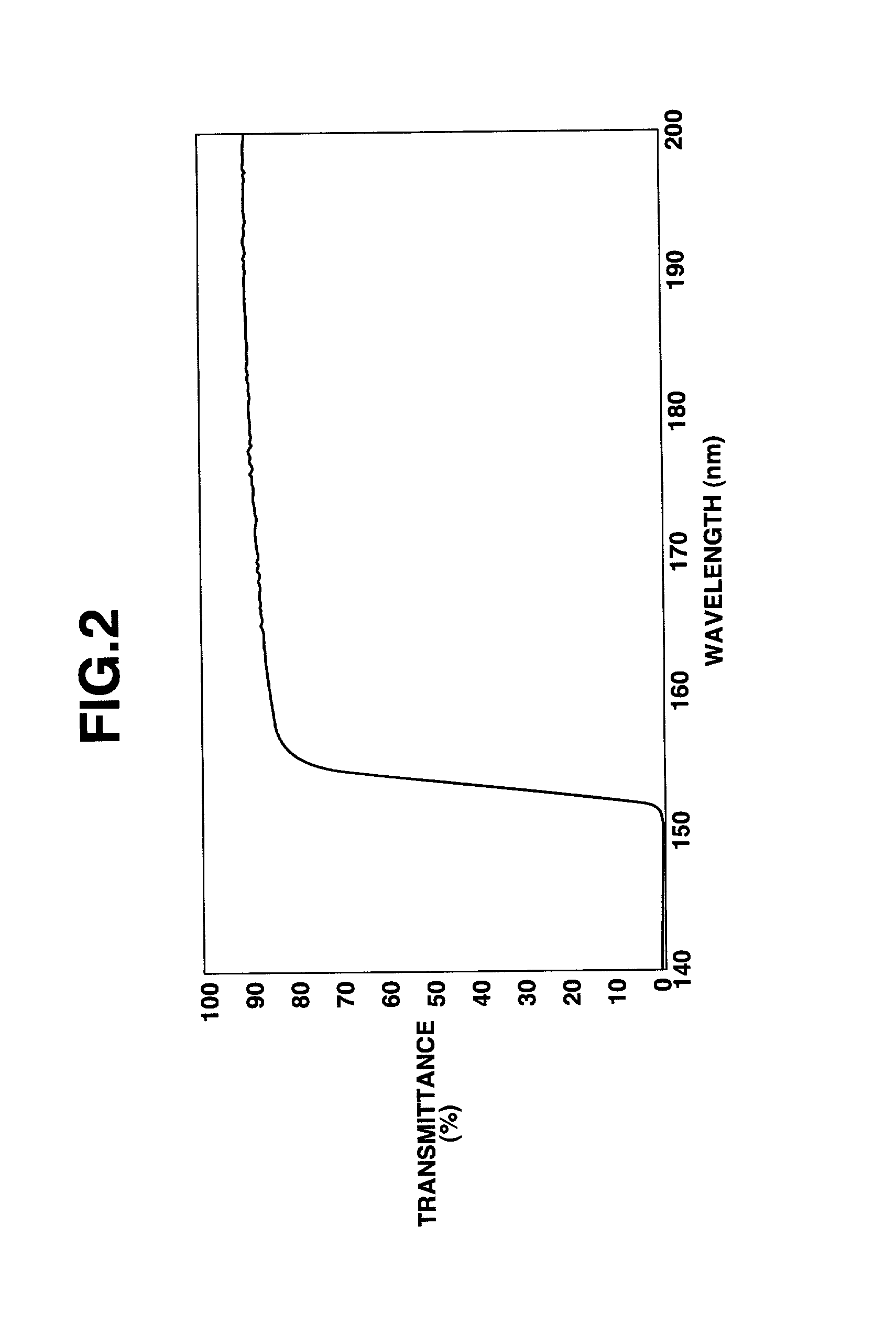
A fluorine-containing synthetic quartz glass article is produced by feeding a silica-forming reactant gas, hydrogen gas, oxygen gas, and optionally, a fluorine compound gas from a burner to a reaction zone, flame hydrolyzing the silica-forming reactant gas in the reaction zone to form fine particles of silica, depositing the silica particles on a rotatable substrate in the reaction zone to form a porous silica matrix, heating and vitrifying the porous silica matrix in a fluorine compound gas-containing atmosphere to form a synthetic quartz glass ingot, removing a surface portion from the ingot, and heating and molding the surface-removed ingot. The article is optically homogeneous as demonstrated by a high transmittance to vacuum UV light of less than 200 nm like ArF or F2 excimer laser light as well as a low birefringence and a small refractive index distribution.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Synthetic qurtz glass and method of production
InactiveUS20020038557A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlass shaping apparatusVolumetric Mass DensitySilica matrix
Fluorine-containing synthetic quartz glass is produced by feeding silica-forming material, hydrogen, and oxygen gases from a burner to a reaction zone, flame hydrolyzing the silica-forming material in the reaction zone to form particles of silica, depositing the silica particles on a rotatable substrate in the reaction zone to form a porous silica matrix, and heating and vitrifying the porous silica matrix in a fluorine compound gas-containing atmosphere. During formation of the porous silica matrix, the angle between the center axes of the silica matrix and the silica-forming reactant flame from the burner is adjusted to 90-120° so that the porous silica matrix has a density of 0.1-1.0 g / cm3 with a narrow distribution within 0.1 g / cm3. The resulting quartz glass has a high transmittance to light in the vacuum ultraviolet region below 200 nm.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Agropolymer containing a carbohydrate and silica matrix from plants
InactiveUS6958232B2Improving water pollution controlReduce environmental pollutionSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationSilica matrixCajanus
The present invention relates to novel agropolymers, which comprise a carbohydrate and / or silica matrix substantially devoid of proteins, tannins and polyphenols and which comprise metal binding reactive sites. A method of producing the agropolymers is also disclosed wherein the agropolymers are derived from plant materials such as seed coats, seed covers, husks, or hulls of various agricultural crops. The agricultural crops typically used to produce the agropolymers include Oryza sativa, Panicum miliaceum, Setaria italica, Cajanus cajan, Vigna mungo, Vigna radiata, Triticum sp., Ricinus communis, Helianthus annus, Gossypium sp., and Arachis sp. The agropolymers of the present invention are capable of purifying aqueous solutions polluted or contaminated with metals and / or ions. Thus, the present invention also discloses a method whereby agropolymers are used in the purification of contaminated water and other aqueous solutions. The agropolymers disclosed herein are useful in several industrial applications including purifying polluted drinking water or ground water.
Owner:BIJAM BIOSCI
Aerosol method for NANO silver-silica composite Anti-microbial agent
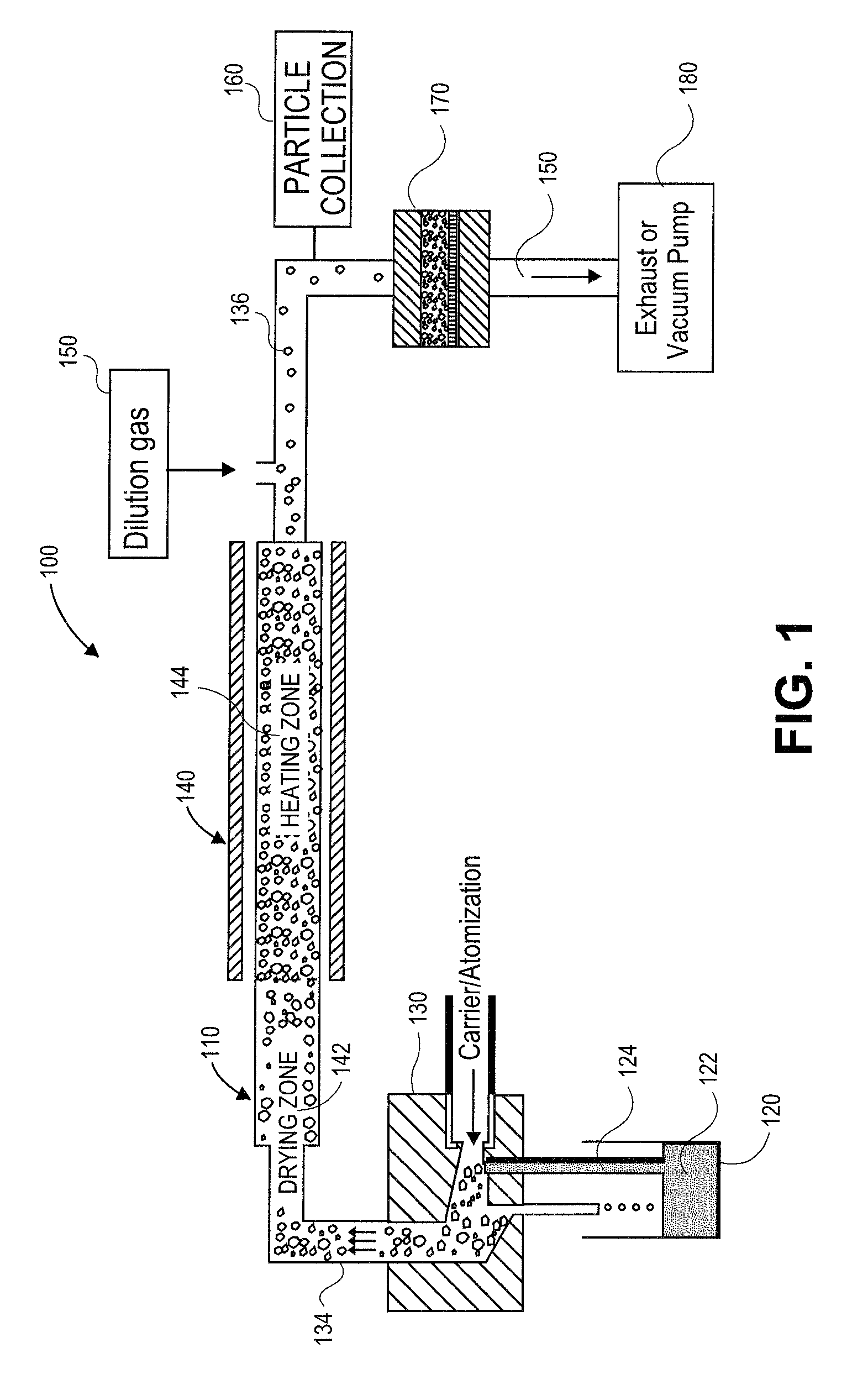
A method of forming and resulting nano-structured composite includes atomizing a mixture of an amount of each of aminopropyltriethoxysilane, AgNO3, DI water, and ethanol in a carrier gas; heating the atomized droplets at a selected temperature for a time sufficient to reduce the Ag to its elemental form in a silica matrix; and outputting the nano structured composite particles. A predetermined heating time is from about 0.01 to about 40 seconds and a selected heating temperature is from about 200 to about 800° C. The nano structured composite includes a plurality of nano particles at a contact surface of the composite, dispersed throughout and at a contact surface of the composite, or dispersed throughout the composite.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Amplifying optical fiber and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS8259389B2Improve efficiencyIncrease output powerMaterial nanotechnologyGlass optical fibreRare-earth elementNanoparticle
Disclosed is an amplifying optical fiber having a central core and an optical cladding surrounding the central core. The central core is based on a silica matrix that includes nanoparticles, which are composed of a matrix material that includes doping ions of at least one rare earth element. The amplifying optical fiber can be employed, for example, in an optical amplifier and an optical laser.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Preparation method of high-stability carbon dot-silicon dioxide composite particles
InactiveCN109679646AEmission wavelength is adjustableAdjustable fluorescence quantum yieldFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsBiocompatibility TestingSilica matrix
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-stability carbon dot-silicon dioxide composite particles and belongs to the technical field of carbon materials and fluorescent composite nanomaterials. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, quaternary ammonium base doped spherical silicon dioxide nanoparticles are synthesized with quaternary ammonium base as a catalyst and a doping carbon source and TEOS as a silicon source; performing high-temperature calcinations in a muffle furnace to enable the doping quaternary ammonium base is dehydrated and condensed in situ in a silicon dioxide substrate to form fluorescent carbon dots to obtain the carbon dot-silicon dioxide composite particles. The preparation process is simple, and the prepared composite particles have the advantages of uniform size, high photobleaching resistance and chemical stability, good biocompatibility and easy surface modification and the like and can be used as a universal fluorescent reference material to be composited with other fluorescent materials to construct a dual-emission ratio type fluorescent probe.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Charged mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based drug delivery system for controlled release and enhanced bioavailability
A charged mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN)-based drug delivery system for controlled release and enhanced bioavailability is disclosed. The system comprises a positively charged MSN, which has a silica matrix and an array of pores and / or nanochannels in the matrix. The entire substance of the matrix, all the surfaces and the pores and / or nanochannels comprise a plurality of silanol (Si—OH) and quaternary ammonium functional groups. The bioavailability of a negatively charged bioactive compound can be increased by loading it into the pores and / or nanochannels. The silanol (Si—OH) functional groups on the surfaces lining the walls of the pores and / or nanochannels are free to deprotonate in a fluid having pH above the pI of the positively charged MSN and lead to a sustained release of the negatively charged drug from the pores and / or nanochannels, and thereby enhance the bioavailability of the drug.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
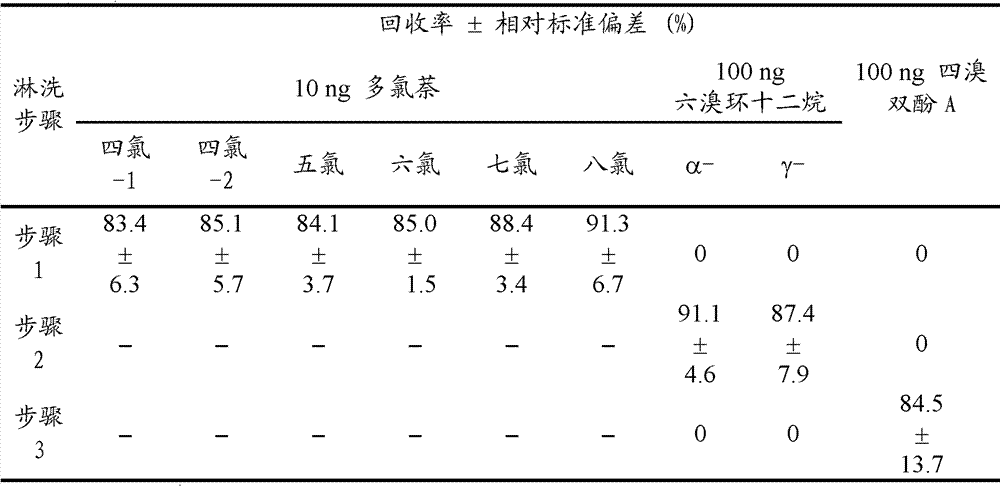
Selective separation of PCNs (polychlorinated naphthalenes congeners), HBCDss (hexabromocyclododecanes) and TBBPA (tetrabromobisphenol A) in complex samples
ActiveCN103364238AAchieve selective separationNo intersectionPreparing sample for investigationTetrabromobisphenol AOrganic solvent
The invention relates to utilization of a silica matrix as a sample pretreatment material, wherein a) PCNs (polychlorinated naphthalenes congeners), HBCDs (hexabromocyclododecanes) and TBBPA (tetrabromobisphenol A) in complex samples are extracted by a solvent extraction method and an extract containing target analytes is obtained; b) the silica matrix is selected as a chromatographic column filler; the filer is activated by using normal hexane at first and then the extract is loaded; c) the polychlorinated naphthalenes congeners, hexabromocyclododecanes and tetrabromobisphenol A are eluted orderly by using organic solvents (normal hexane, dichloromethane and the like) composed of different solvents, and then three eluates of different fractions are obtained; d) after solvents are volatilized from the eluates, the purified target analytes are obtained. According to the invention, selective separation of the polychlorinated naphthalenes congeners, hexabromocyclododecanes and tetrabromobisphenol A in the complex samples is realized by virtue of a simple chromatographic column; the method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, good selectivity and high efficiency.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Silica matrix chemically bonded phase packing
InactiveCN101234339AIncrease throughputShort response timeOther chemical processesChemical LinkageOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a preparation method of silica matrix chemically bonded phase stuffing, which belongs to the technical field of high efficiency liquid phase chromatography. The method comprises the following procedures: firstly, the acidification pretreatment of silica matrix stuffing produces silica matrix particles rich in hydroxide radical; secondly, the bonding of silica matrix stuffing; thirdly, the deactivation processing of silica matrix chemically bonded phase stuffing. Compared with the traditional organic solvent method, the stuffing prepared by the method has higher surface functional group bond rate, thus raising the selectivity and the separating size of the compartment analysis of samples.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Pyroceramic material with a base of silica and tin dioxide, particularly for optical applications, and the corresponding process of fabrication
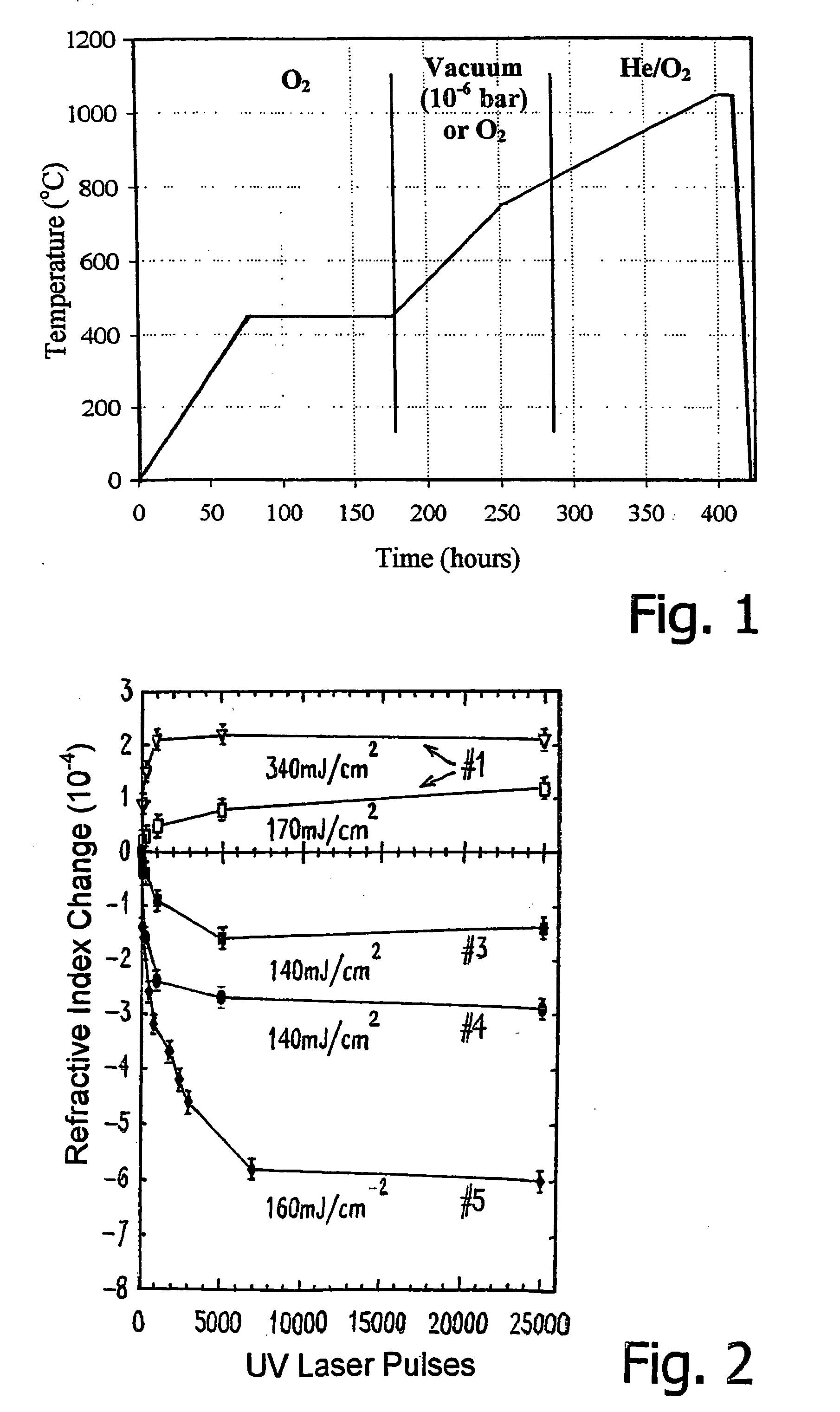
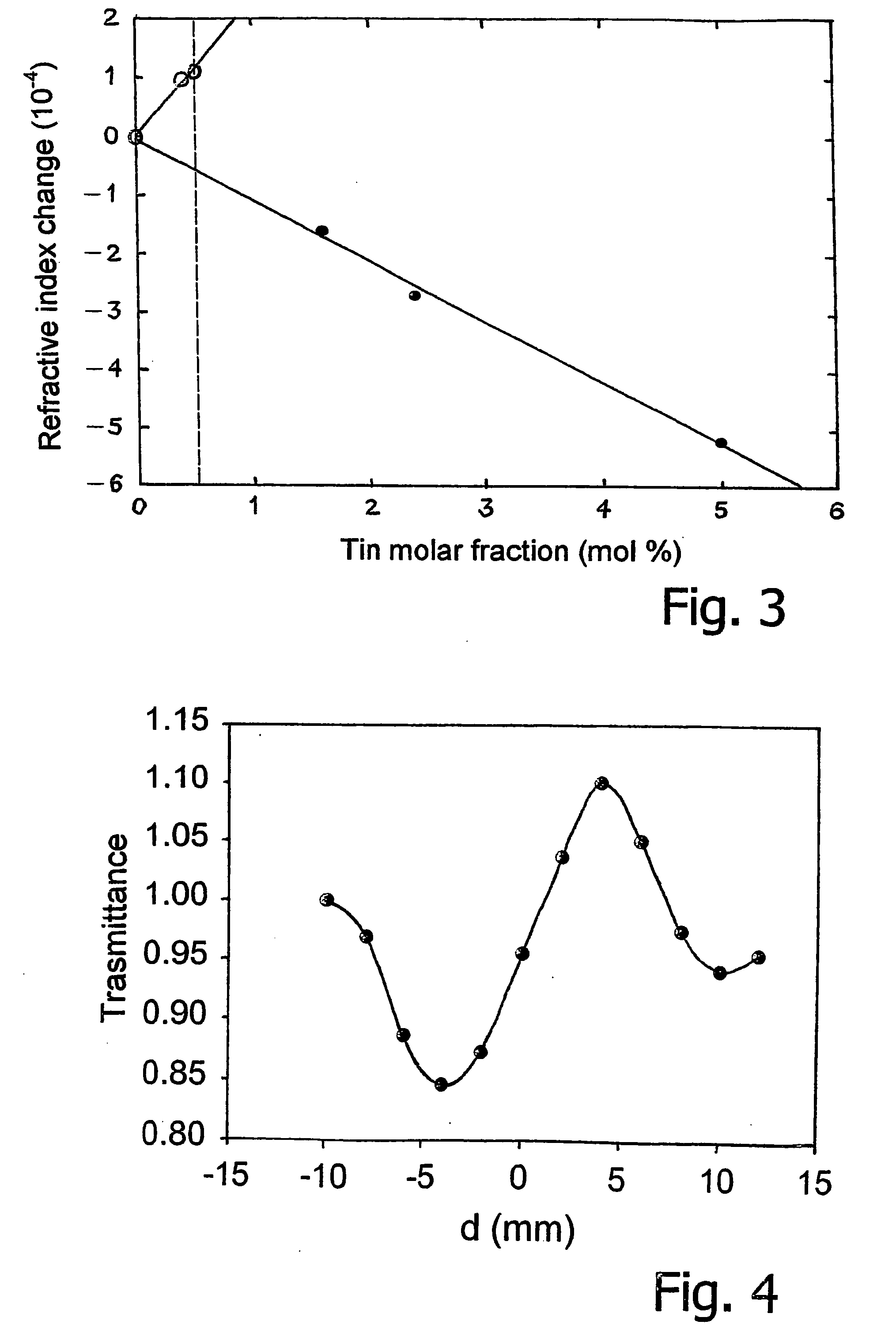
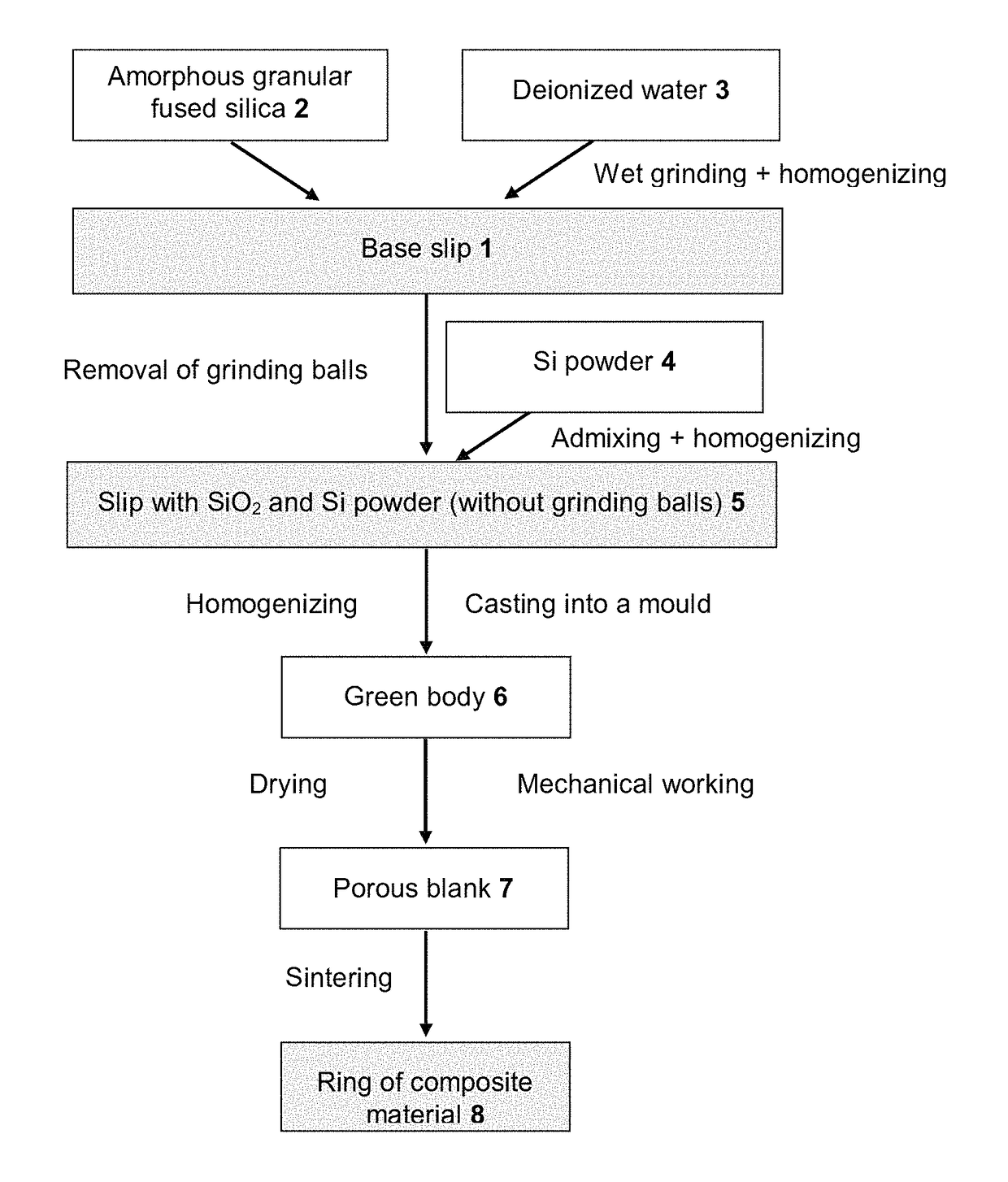
InactiveUS20050239003A1Simplification of processIncrease rangeMaterial nanotechnologyPhotomechanical apparatusTin dioxideManufacturing technology
A glass ceramic material with a base of silica and tin dioxide: the material has a vitreous silica matrix, in which there are dispersed crystalline aggregates of tin dioxide having submicrometric or nanometric dimensions, the dimensions being obtained by means of appropriate control of specific operating parameters of the process of preparation. The material has excellent values of optical transmission in the visible and in the near infrared and high properties of photosensitivity and optical non-linearity, which render the material suitable, in particular, for use in devices for optical telecommunications (integrated in optical fibre or on planar waveguide or in three-dimensional devices) and memories, the devices being obtainable, for example, by direct writing or using laser interferometric techniques.
Owner:PIRELLI & C
Surface modification process of quartz glass crucible
A process for modifying the surface of a quartz glass crucible and a modified quartz glass crucible produced by the process, where the crucible has a transparent coated layer containing a crystallization accelerator on the surface. The process includes coating a mixed solution containing a metal salt and a partial hydrolyzate of alkoxysilane oligomer on the surface of the crucible and heating to obtain a quartz glass crucible having a transparent coated layer. The crystallization promoter contains a metal oxide or a metal carbonate dispersed in a silica matrix.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
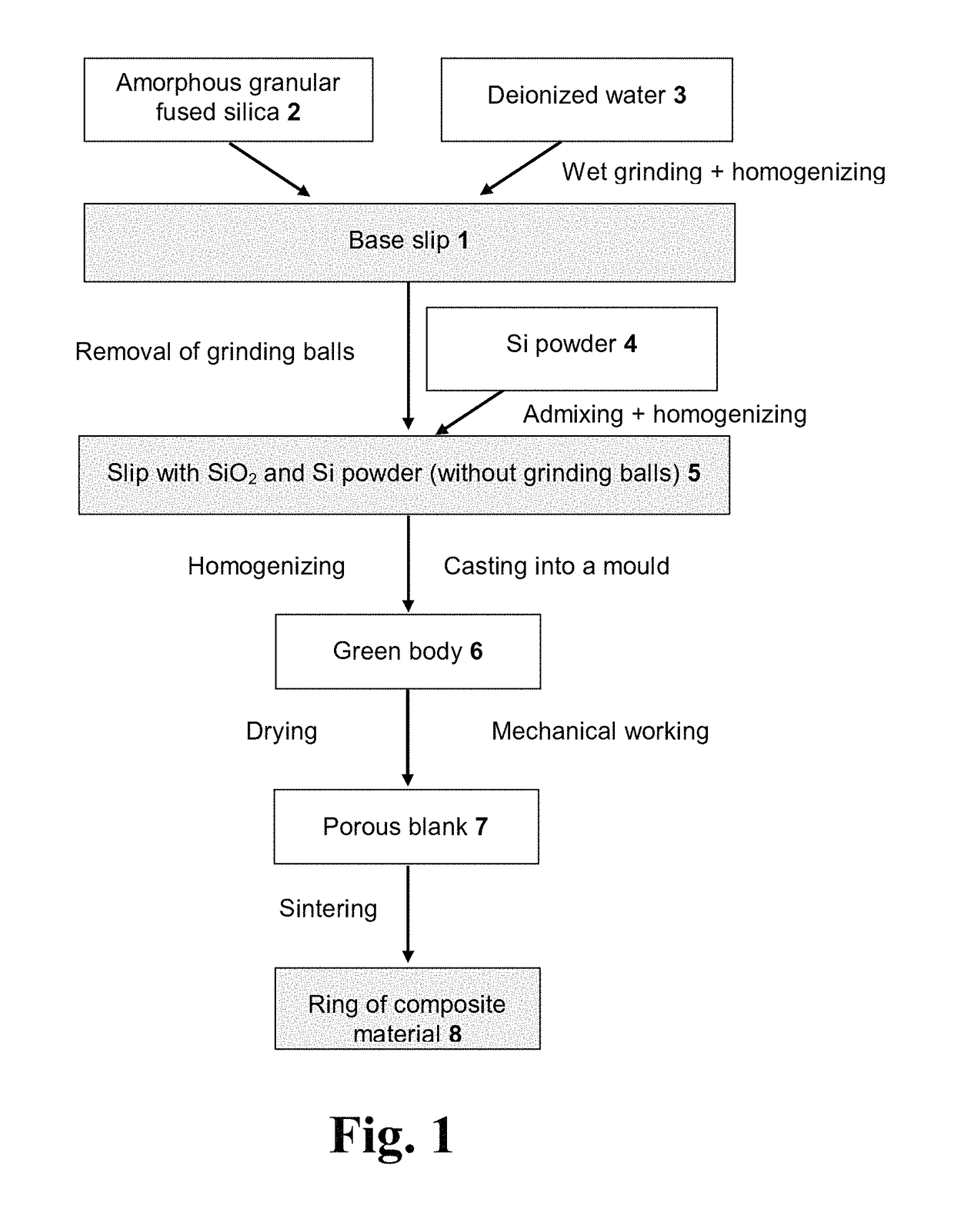
Composite material, heat-absorbing component, and method for producing the composite material
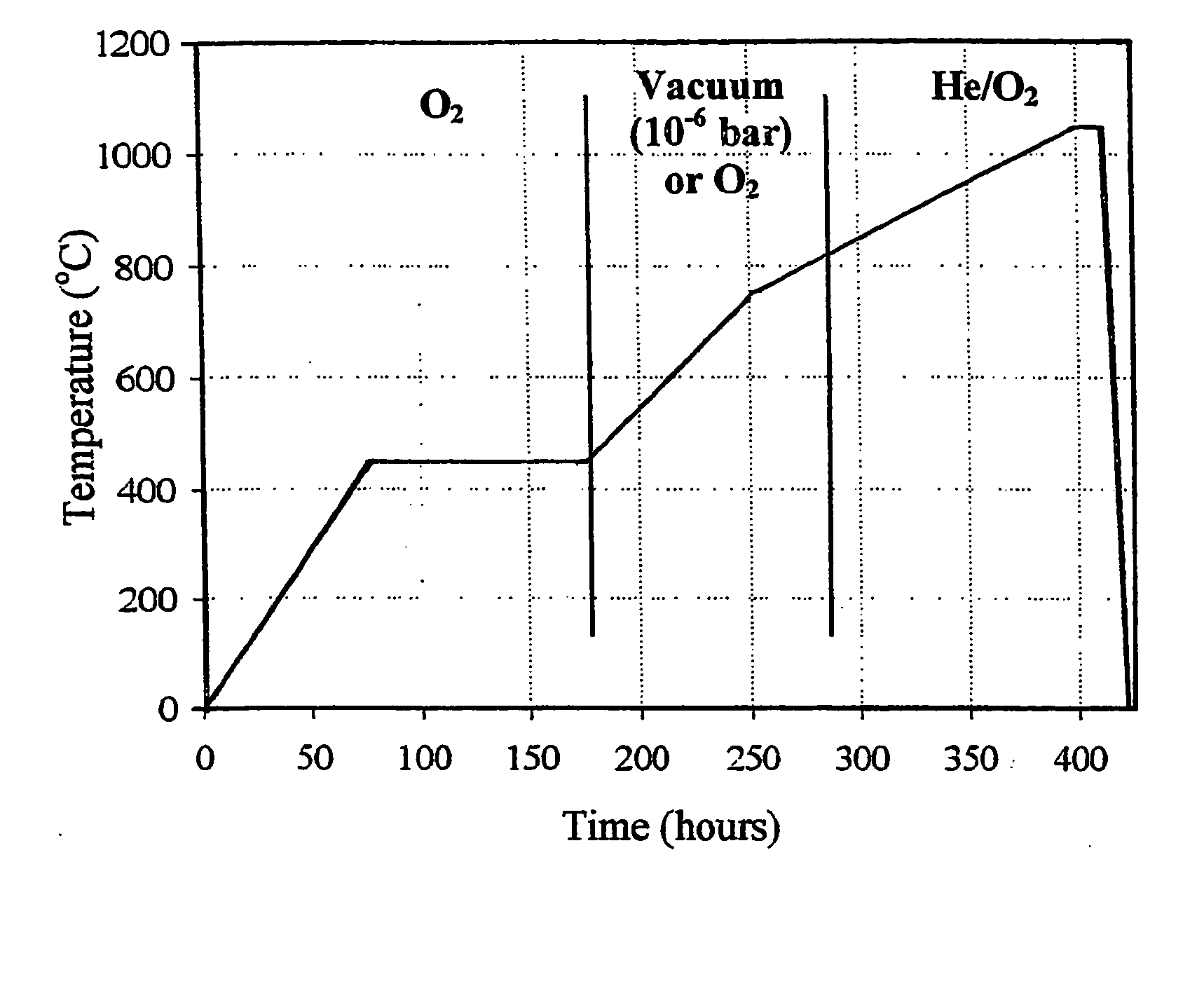
ActiveUS9957431B2Promote absorptionReduce reflectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlass shaping apparatusPorosityEmissivity
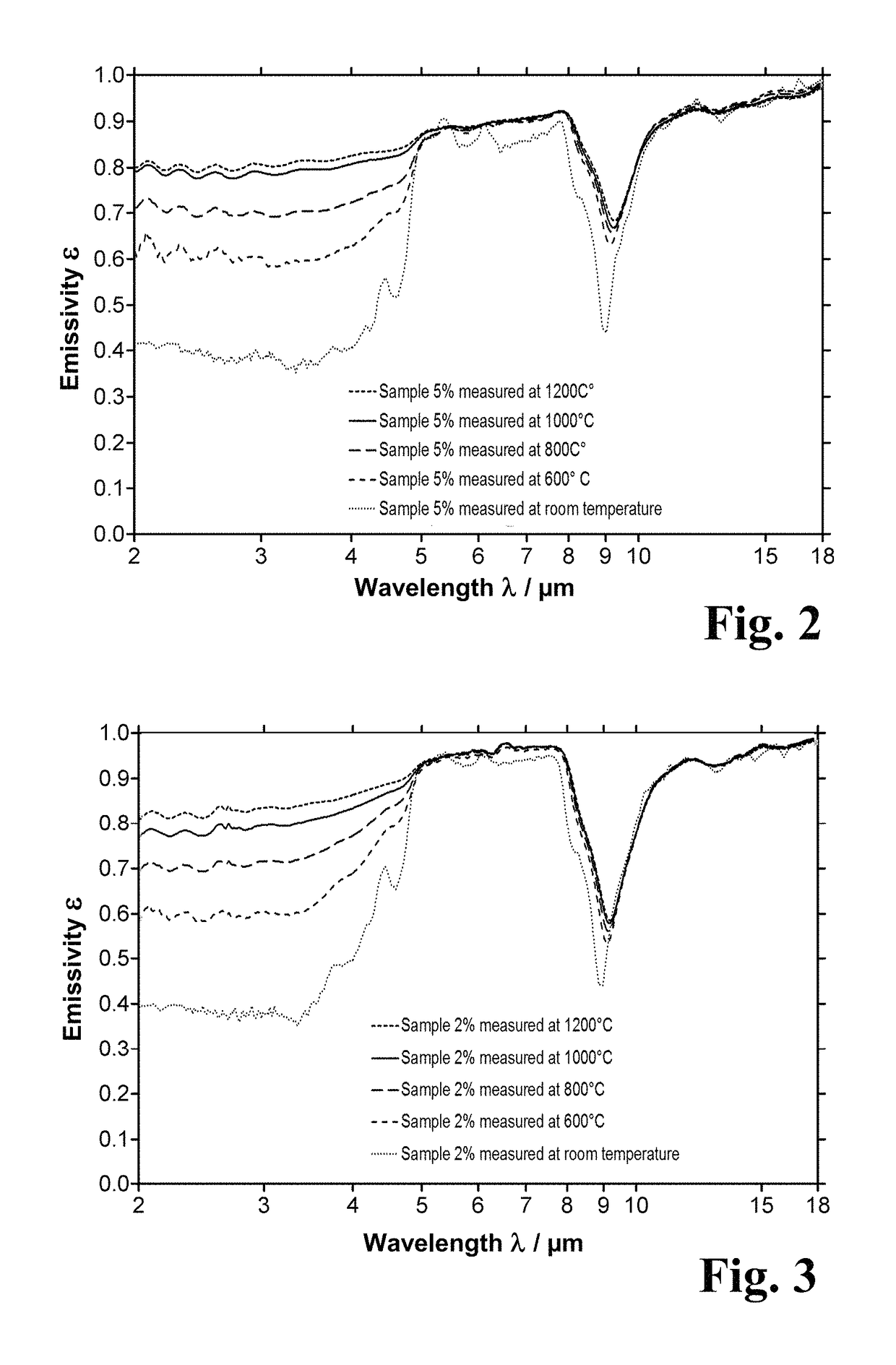
In a known composite material with a fused silica matrix there are regions of silicon-containing phase embedded. In order to provide a composite material which is suitable for producing components for use in high-temperature processes for heat treatment even when exacting requirements are imposed on impermeability to gas and on purity, it is proposed in accordance with the invention that the composite material be impervious to gas, have a closed porosity of less than 0.5% and a specific density of at least 2.19 g / cm3, and at a temperature of 1000° C. have a spectral emissivity of at least 0.7 for wavelengths between 2 and 8 μm.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Nanoparticle doping for lasers and amplifiers operating at eye-safer wavelengths, and/or exhibiting reduced stimulated brillouin scattering
ActiveUS20180109063A1Improve solubilityReduced Stimulated Brillouin ScatteringMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsFiberSolubility
Methods for synthesizing fibers having nanoparticles therein are provided, as well as preforms and fibers incorporating nanoparticles. The nanoparticles may include one or more rare earth ions selected based on fluorescence at eye-safer wavelengths, surrounded by a low-phonon energy host. Nanoparticles that are not doped with rare earth ions may also be included as a co-dopant to help increase solubility of nanoparticles doped with rare earth ions in the silica matrix. The nanoparticles may be incorporated into a preform, which is then drawn to form fiber. The fibers may beneficially be incorporated into lasers and amplifiers that operate at eye safer wavelengths. Lasers and amplifiers incorporating the fibers may also beneficially exhibit reduced Stimulated Brillouin Scattering.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Polysaccharide extraction method based on epoxy magnetic microspheres
InactiveCN104177509ALower protein contentSimple stepsMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationSilanesMicrosphere
The invention relates to the technical field of separation of biological active substances and provides a preparation method of magnetic microspheres and a method for extracting water-soluble polysaccharides from a waterborne matrix by virtue of the microspheres. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing citric acid modified magnetic nanoparticles with water glass, ultrasonically dispersing in emulsifier-containing dichloromethane to form water-in-oil emulsion, pouring the emulsion into a buffer solution, and curing the water glass to form magnetic microspheres of a SiO2 matrix; secondly, performing surface modification by using epoxy silane, adding the microspheres into polysaccharide crude extract liquid, adding ethanol with weight being 1-2 times that of the polysaccharide crude extract liquid, enabling polysaccharides to form flocculated precipitates for wrapping the magnetic microspheres, and performing solid-liquid separation by using a magnet. According to the method, the polysaccharide recovery rate is equivalent to that of a conventional centrifugal method but the protein impurity content is remarkably reduced, the process is simplified, the time consumption is only 1 / 10 that of the conventional method, and the magnetic microspheres can be repeatedly utilized; the method has wide application prospects in the field of biological separation, especially pretreatment of extraction, separation and sample analysis of animals, plants and fungal polysaccharides.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com