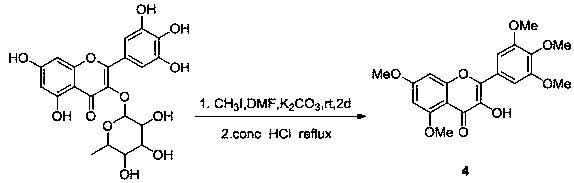
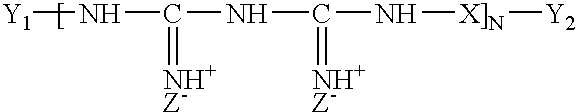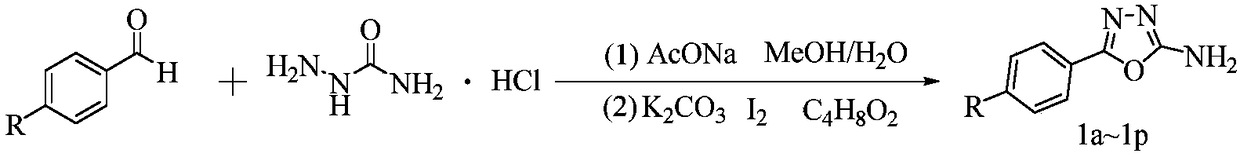Patents
Literature
294 results about "Citrus canker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
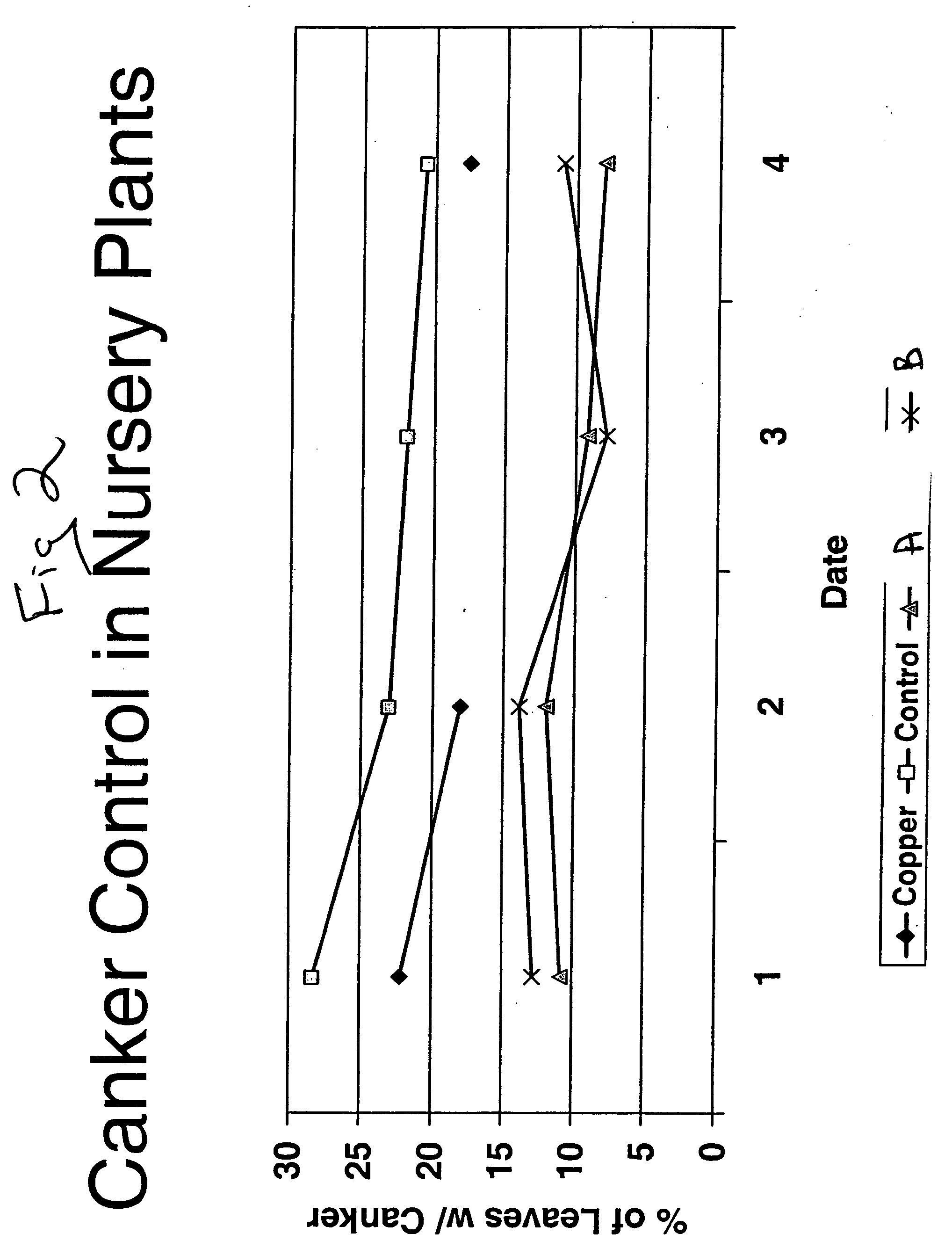
Citrus canker it is a disease affecting Citrus species caused by the bacterium Xanthomonas axonopodis. Infection causes lesions on the leaves, stems, and fruit of citrus trees, including lime, oranges, and grapefruit. While not harmful to humans, canker significantly affects the vitality of citrus trees, causing leaves and fruit to drop prematurely; a fruit infected with canker is safe to eat, but too unsightly to be sold.
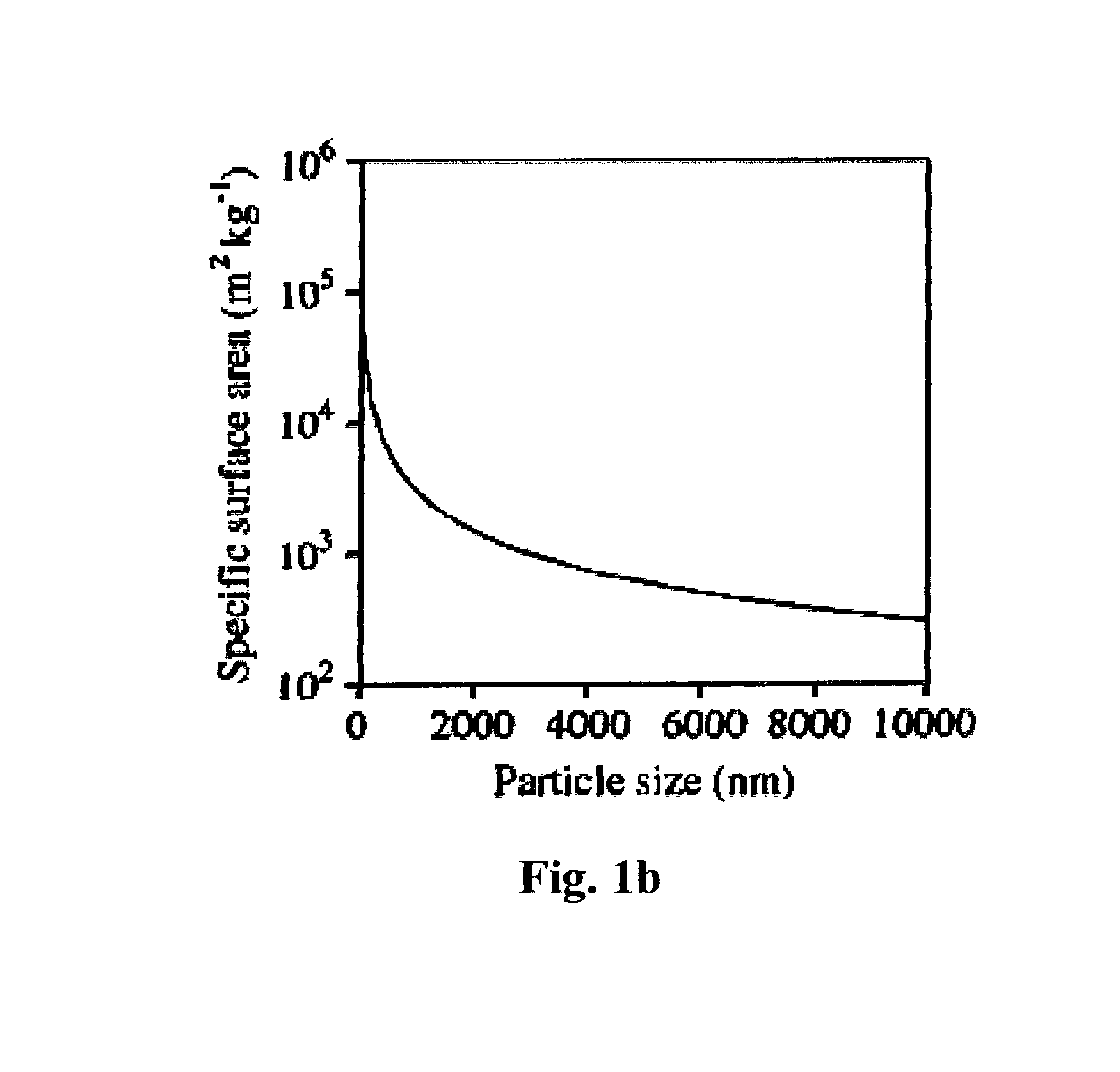
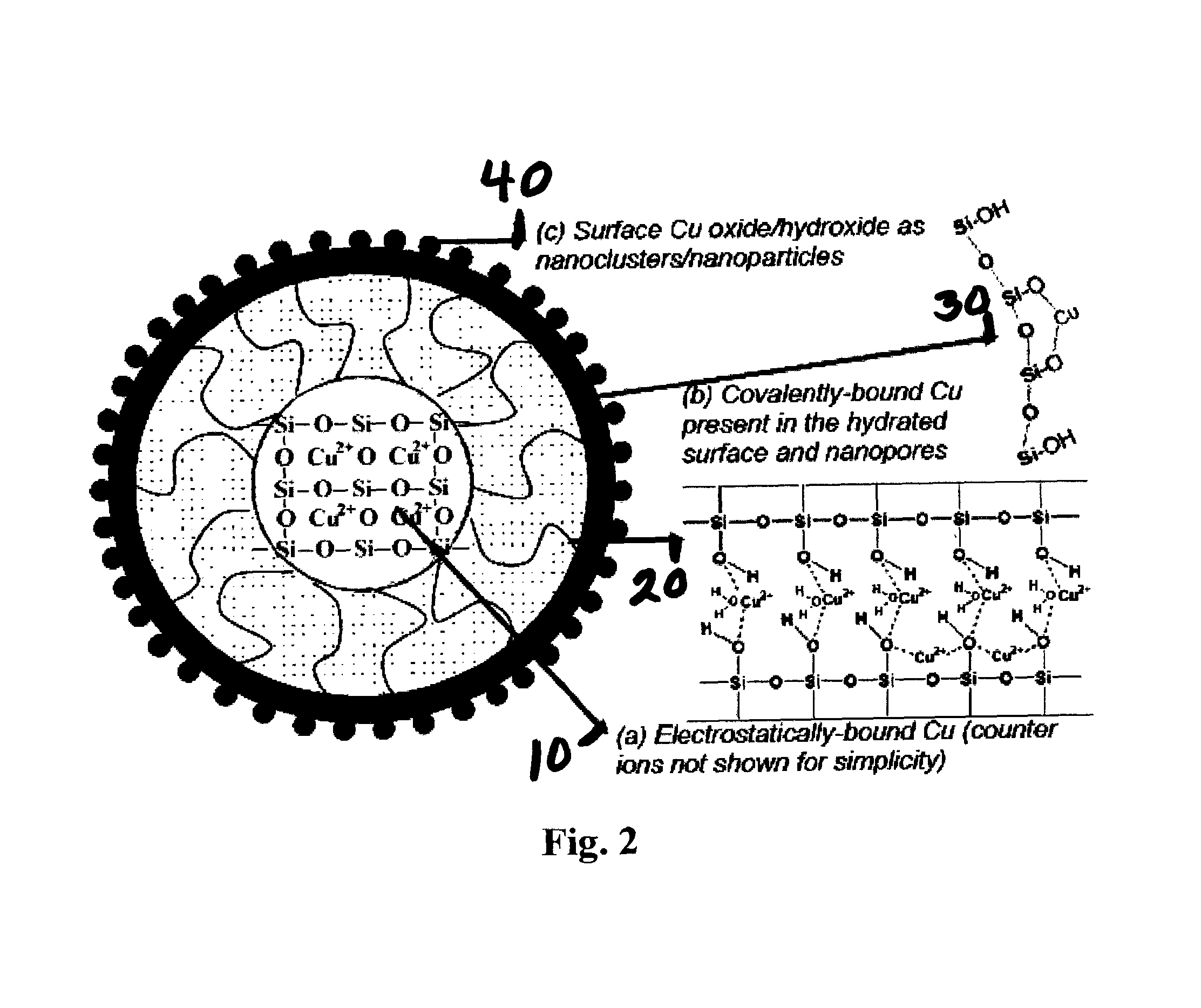
Multifunctional silica-based compositions and gels, methods of making them, and methods of using them
Briefly described, embodiments of this disclosure, among others, include compositions, gels, methods for synthesizing multifunctional silica based nanoparticle gel, method of treating, preventing, or both treating and preventing, a disease in a plant species, method for simultaneously treating citrus plants for citrus canker and preventing the invasion of an Asian Citrus Psyllid (ACP) vector that carries the pathogen and spreads the citrus greening disease in citrus plants, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Silica-based antibacterial and antifungal nanoformulation
ActiveUS8221791B1Simple and cost-effective fabricationEasy to controlPowder deliveryBiocideDiseaseAntibacterial activity
A silica-based nanoformulation and method is used to treat citrus canker, inhibit the growth of mold and mildew, and add nutrients to soil used for agricultural purposes. The nanotechnology-enabled copper-loaded, silica nanoformulation (CuSiNP / NG) design is a “revolutionary re-invention” of Cu for safe application because it provides a formulation with maximum abundance of ionic Cu, provides sustained and optimal Cu ion release for long-term disease protection, better adherence to plant surfaces and structural surfaces due to gel-based nanostructure of CuSiNG, thus avoiding multiple spray applications and reducing the amount of Cu used in comparison to existing Cu compounds without compromising antibacterial activity. Thus, the silica-based nanoformulation releases copper in non-toxic quantities to the environment and the silica matrix provides an environmentally safe host material with a flexible design that is optimized to provide specific antifungal and antibacterial remediation using infrequent applications.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
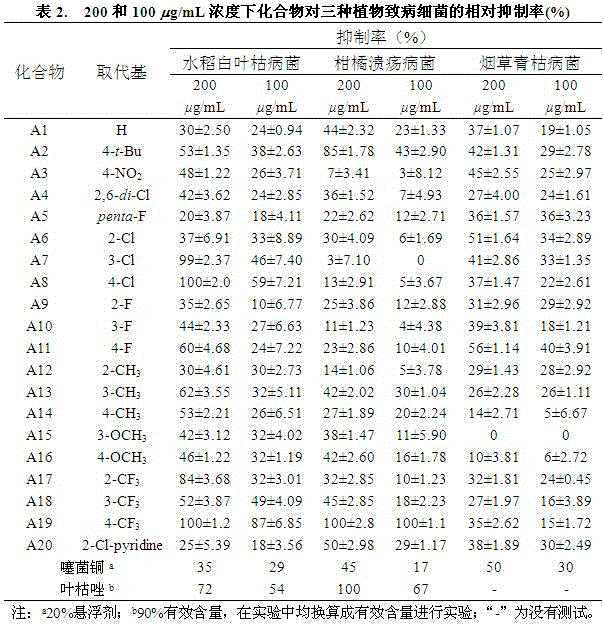
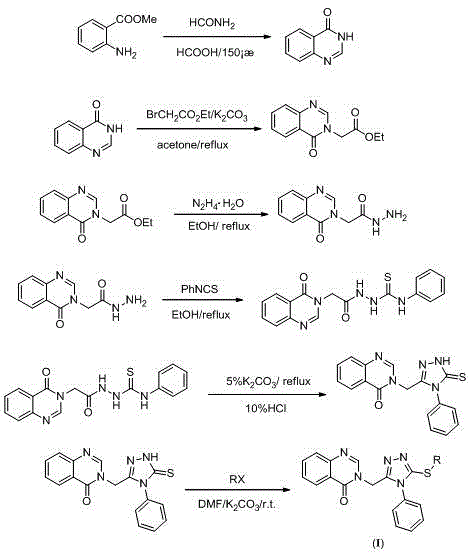
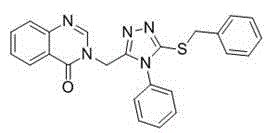
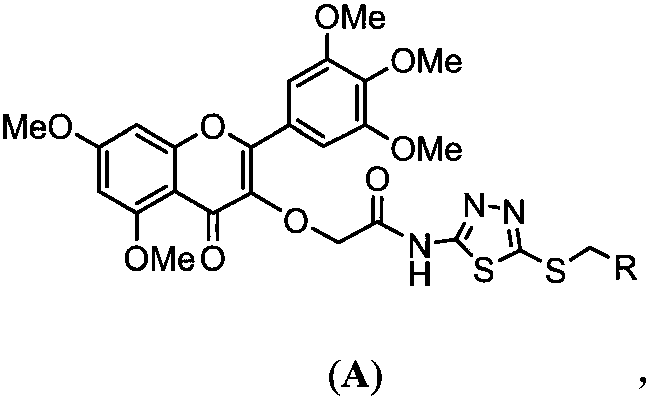
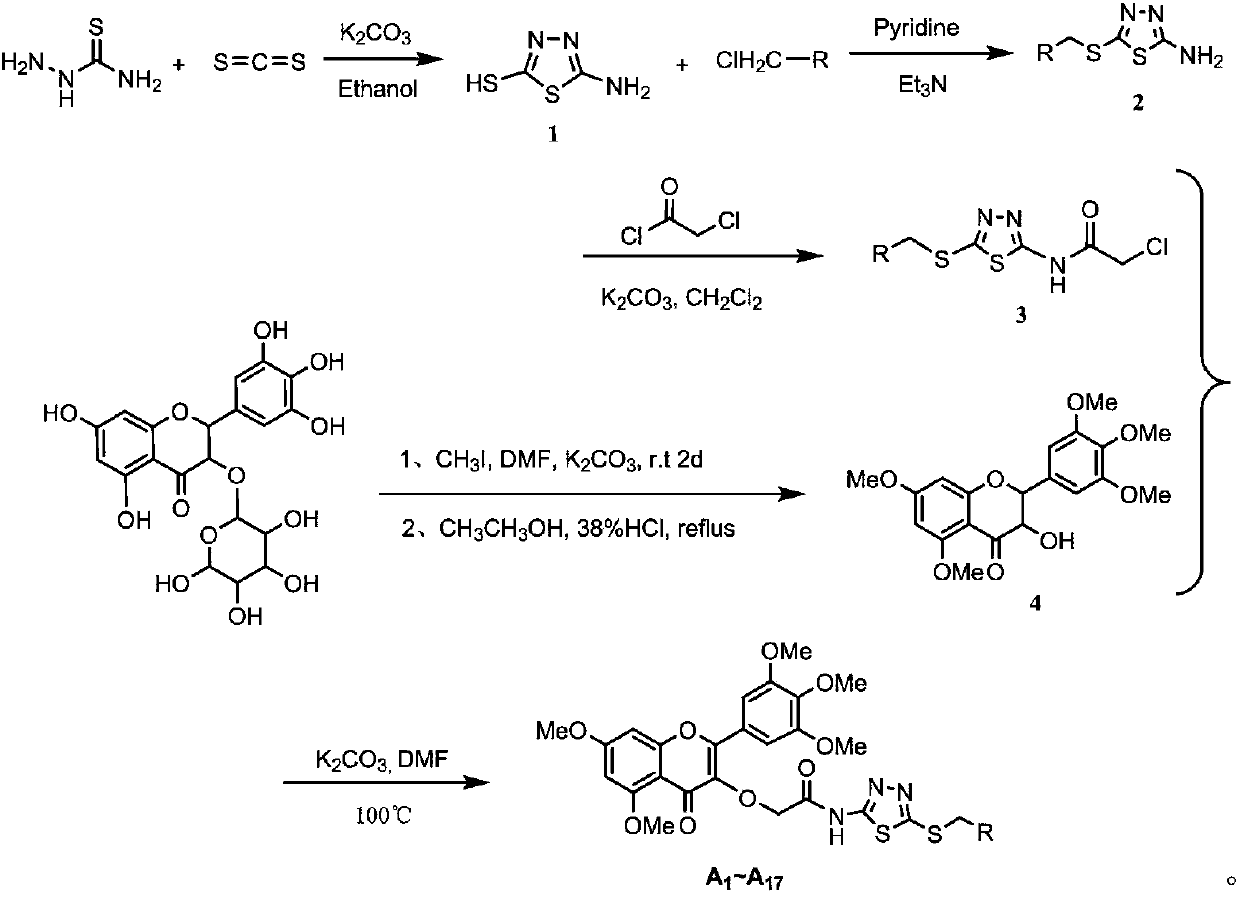
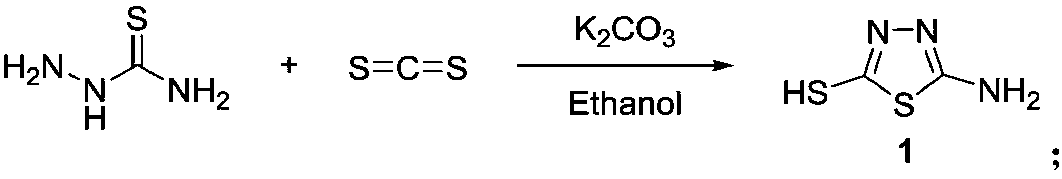
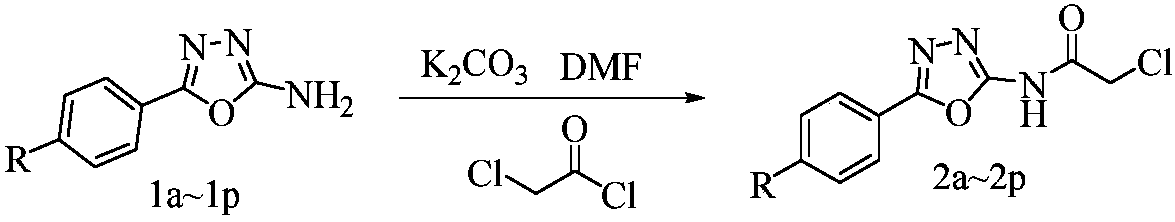
Quinazolinone compound containing 1, 2, 4-triazole thioether and synthesizing method and application of quinazolinone compound
Owner:北京传奇优声文化传媒有限公司
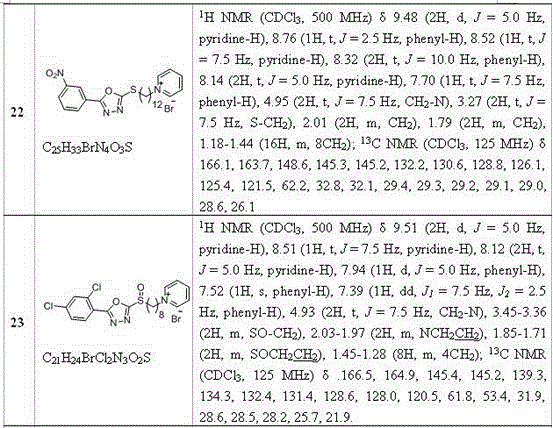
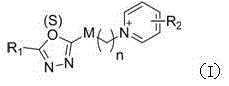
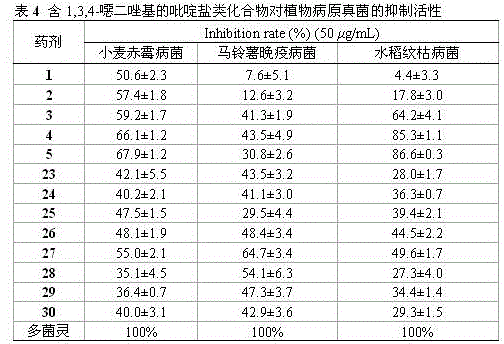
Pyridine salt compound containing 1,3,4-oxadiazolyl (thiadiazolyl) and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105541822AImprove biological activityEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic chemistryXanthomonas axonopodisRalstonia solanacearum
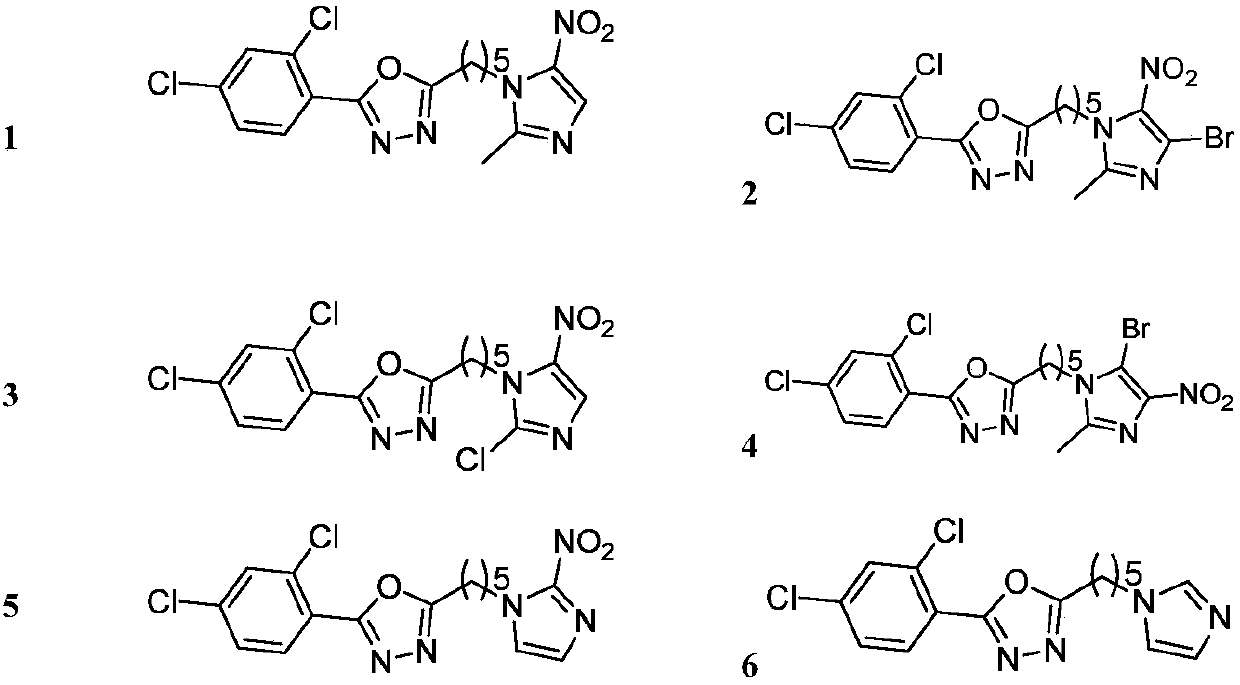
The invention disclose a pyridine salt compound containing 1,3,4-oxadiazolyl (thiadiazolyl) and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound is of the structure shown in the general formula (I). Based on the 1,3,4- oxadiazole (thiadiazole) thioether (sulfoxide or sulfone) compound, a pyridine base capable of improving the biological activity of the target compound is introduced into the system, and a series of 1,3,4- oxadiazole (thiadiazole) oxygen ether, thioether, sulfoxide or sulfone amphipathic molecules containing pyridine salt are synthesized. It is found that the compound has the good restraining effect on pathogenic bacteria and fungi such as Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, Ralstonia solanacearum, Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri, Gibberella zeae, Phytophythora infestans, Rhizoctonia solani, Borrytis cinerea, Fusarium oxysporum and Phytophythora infestans, and provides an important scientific foundation for new pesticide research, development and creation.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Citrus endophytic actinomycetes with antibacterial activity on various plant pathogens
ActiveCN103952362AHas antibacterial activityResidue reductionBiocideBacteriaDiseaseAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to citrus endophytic actinomycetes with antibacterial activity on various plant pathogens, belonging to the technical field of microbes. The endophytic actinomycetes are Streptomyces sp. R1020 which was registered and collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 17, 2014 with the collection number of CGMCC No. 8923. The strain R1020 has relatively good inhibitory effect on citrus anthrax bacteria, citrus bacterial canker disease bacteria, citrus penicillium italicum, citrus penicillium digitatum, bayberry deadwood disease bacteria, bayberry acicola, bayberry anthrax bacteria, loquat anthrax bacteria, loquat leaf spot fungi, loquat ringspot pathogenic bacteria, tomato alternaria solani, botrytis cinerea, colletotrichum orbiculare, tea tree anthrax bacteria and elsinoeleucospila and has the potential of being developed into biological pesticides.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CITRUS RES INST
Myricetin derivative containing amide thioether thiadiazole, and preparation method and application of same
The invention discloses a myricetin derivative containing amide thioether thiadiazole, of which a general formula is represented as follows, wherein R is hydrocarbyl groups, phenyl groups, substituted phenyl groups, heteroaromatic ring groups or substituted heteroaromatic ring groups. The compound has high treatment and prevention effect against tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), has high anti-plant virus activity and can be used for preparing anti-plant virus pesticides. The compound has high inhibition activity on Xanthomonas axonopodis and Xanthomonas oryzae and can be used for preparing agricultural bactericides.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Methods and compositions for reducing population of plant pathogen
InactiveUS20060147549A1Reduce microbial countBiocideInorganic active ingredientsMicroorganismAlcohol
The present invention relates to methods for reducing the population of canker microbe (e.g., citrus canker microbe) or microbes and articles of manufacture that can be used in the method. The methods employ and the articles of manufacture include composition including metal antimicrobial agent, poly(hexamethyl biguanide), surfactant, and alcohol.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
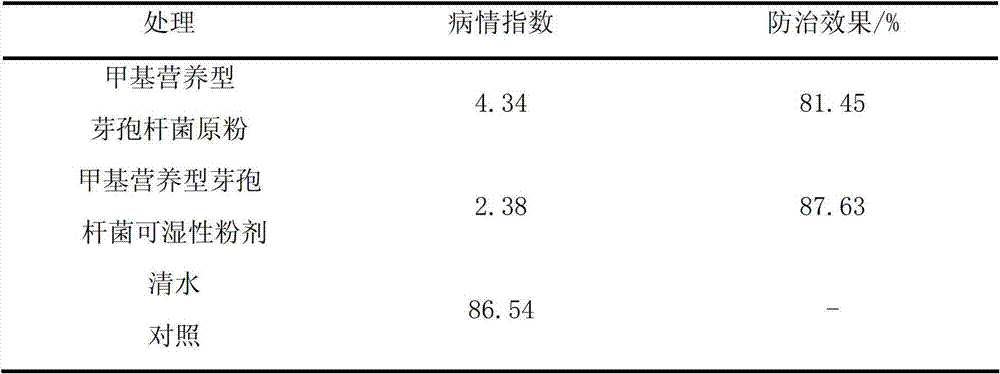
Wettable powder of bacillus methylotrophicus and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103039530AOvercome timeOvercome inconvenienceBiocideDisinfectantsDipotassium hydrogen phosphateSulfonate
The invention relates to a wettable powder of bacillus methylotrophicus. The wettable powder is composed of raw powder of bacillus methylotrophicus that is prepared with a specific method, light calcium carbonate, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate and 2-3 parts by weight of a dispersant methylene dimethyl naphthalene sodium sulfonate. Furthermore, the invention relates to a use of the wettable powder in controlling citrus diseases, in particular citrus canker.
Owner:陕西恒田生物农业有限公司
Application of amaranthus in plant disease prevention and treatment
ActiveCN103238634AHas inhibitory effectHas a preventive effectBiocideFungicidesXanthomonas axonopodisTherapeutic effect
The invention provides an application of amaranthus in plant disease prevention and treatment, wherein amaranthus leaves are taken as the raw material and extracted by an organic solvent to obtain an extract, acidovorax avenae subsp.citrulli, xanthomonas axonopodis pv. Citri and rhizoctonia solani are selected as sites of action, and research on indoor bacteriostasis effect and in-vitro and pot culture control effects is performed to find that the amaranthus leaf extract has an inhibition effect on acidovorax avenae subsp.citrulli, xanthomonas axonopodis pv. Citri and rhizoctonia solani; and the in-vitro and pot culture tests also indicate that the amaranthus leaf extract has certain prevention and treatment effects on acidovorax avenae subsp.citrulli, xanthomonas axonopodis pv. Citri and rhizoctonia solani; and all the facts show that the amaranthus has prevention and treatment effects on the plant diseases in addition to edible and medical values. The research discovers and expands the functions of the vegetable, and simultaneously provides a new train of thought and a new way for studying and developing biopesticide for preventing and treating the plant diseases.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
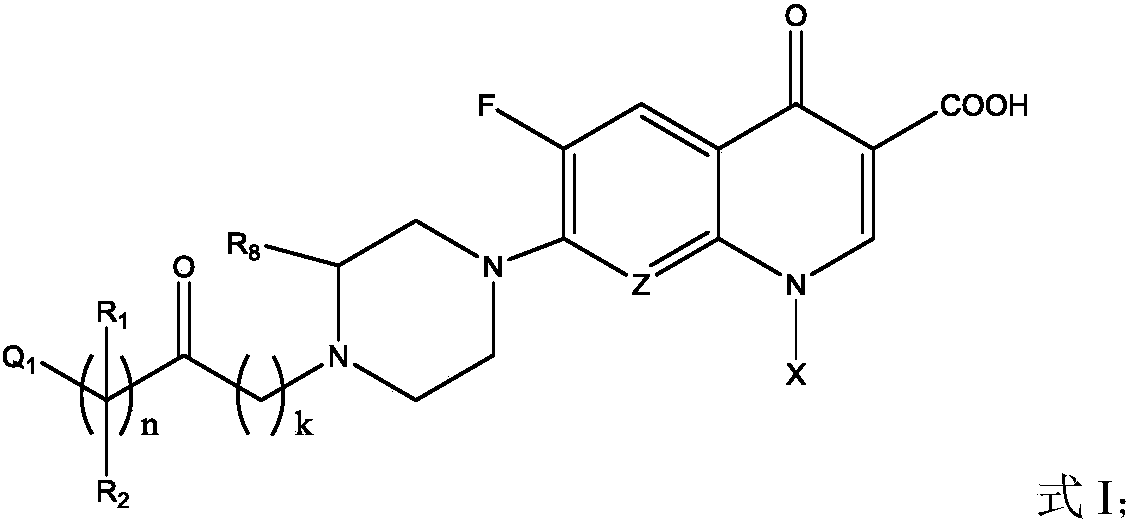
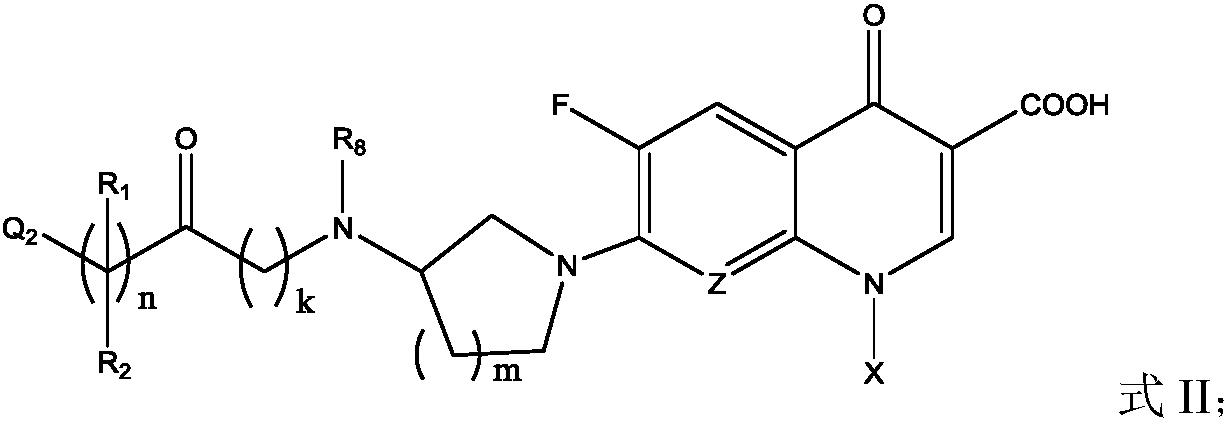
Fluoroquinolone amino derivatives and use thereof in prevention and control of citrus diseases
Citrus canker and brown spot are common diseases of citrus. At present, few drugs are available to prevent and control the two diseases and have certain defects. Amino groups at the 7th positions of fluoroquinolone drugs are linked with an active fragment by means of a connecting structure so as to obtain compounds shown in a formula I or a formula II. Experiments prove that the compounds providedby the invention have effects of preventing and controlling the citrus canker and the brown spot and have very good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
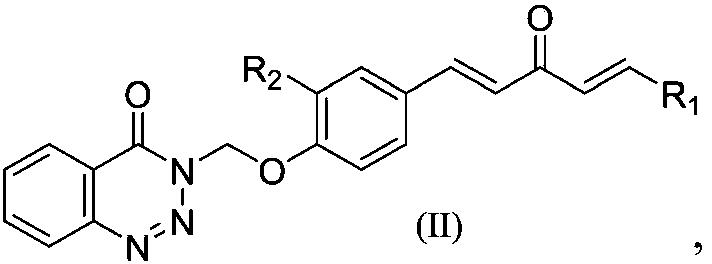
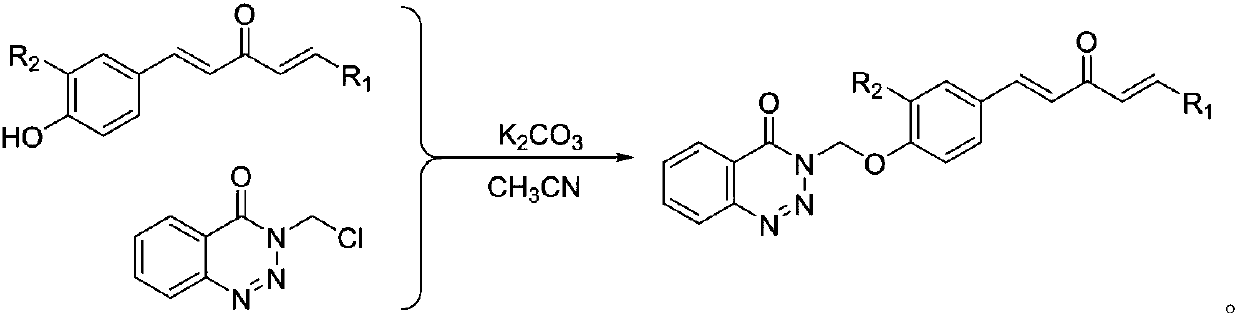
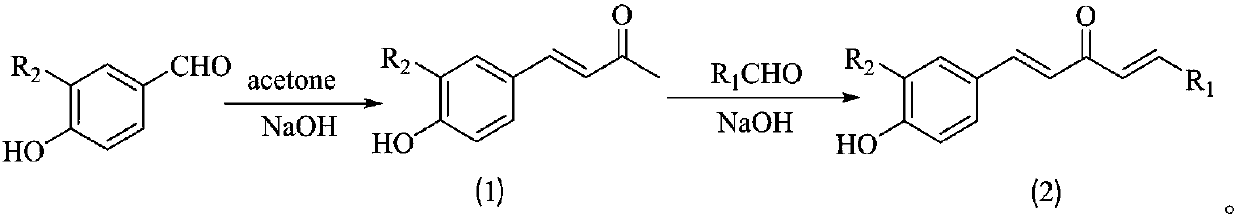
1,4-pentadiene-3-ketone derivative containing benzotriazinone as well as preparation method and application of 1,4-pentadiene-3-ketone derivative
ActiveCN107602493AGood inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic chemistryBenzeneThiazole
The invention discloses a 1,4-pentadiene-3-ketone derivative containing benzotriazinone. The 1,4-pentadiene-3-ketone derivative containing benzotriazinone is characterized by having the general formula as shown in the specification, wherein R1 is phenyl, substituted phenyl (p-fluorophenyl, p-chlorophenyl, o-chlorophenyl, 2-methyoxyphenyl, 4-methyoxyphenyl, 4-methylphenyl, 2,4-dimethyoxyphenyl, 3,4-dimethyoxyphenyl, cinnamaldehyde group, 3-nitrophenyl, 2-chloro-5-nitrophenyl and the like), heterocyclic group (furyl, thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl, pyrryl and the like) or substituted aromatic heterocyclic group (5-methyl thiazole, 5-methyl-2-thienyl, 4-bromo-2-thienyl and the like), and R2 is a hydrogen atom, methyl (ethyl), methoxyl (ethyoxyl) and the like. The compound disclosedby the invention has relatively high inhibiting activity for citrus canker bacteria, ralstonia solanacearum and tobacco mosaic viruses so as to be used for preparing an agricultural bactericide and anantiviral agent.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
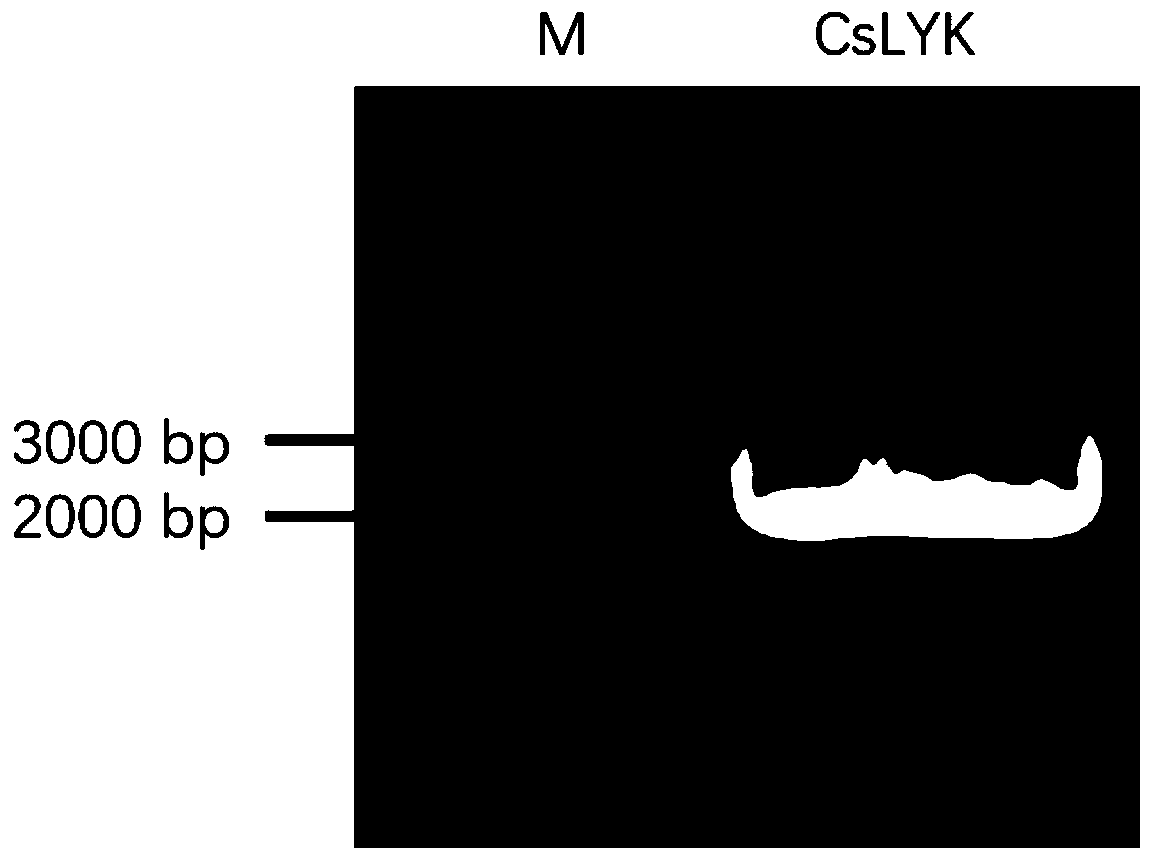
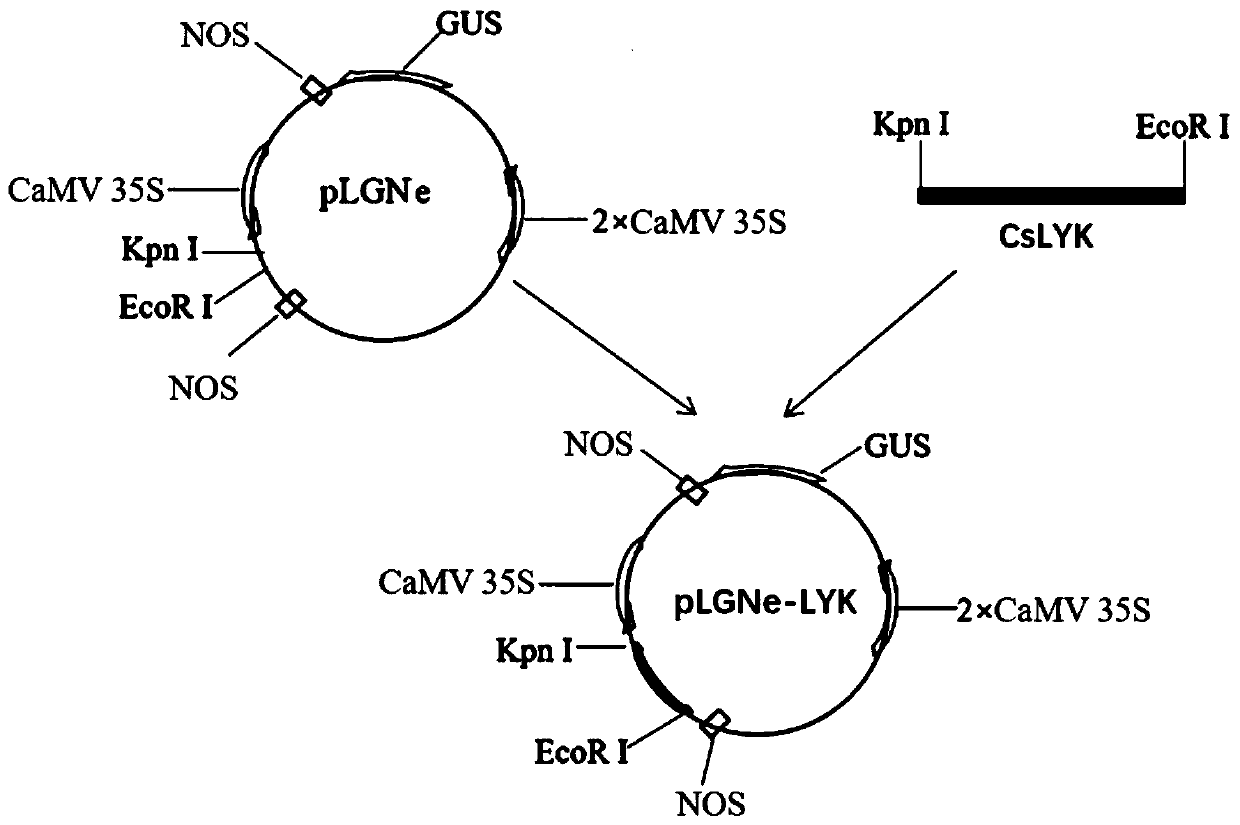
Application of CsLYK gene and encoded protein thereof in improving resistance to citrus canker
ActiveCN110819607AIncrease resistanceReduced incidence of ulcer diseaseMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBiotechnologyCitrus volkameriana
The invention discloses application of CsLYK gene and an encoded protein thereof in improving resistance to citrus canker. The encoded protein of the CsLYK gene is a citrus LysM-like receptor proteinphosphokinase, and is named CsLYK protein. The nucleotide sequence of the CsLYK gene is a nucleotide sequence shown in SED ID No. 1; the protein sequence of the CsLYK gene is an amino acid sequence shown in SED ID No. 2. The invention also protects a breeding method of citrus resisting bacterial canker, and the method comprises following steps of integrating a citrus LysM-like receptor protein phosphokinase-encoding gene into a citrus through an overexpression vector to effectively improve citrus resistance to bacterial canker. The invention has great application value for breeding of citrus resisting bacterial canker; thereby laying the foundation of genetic breeding of citrus resisting canker, and vigorously promoting the development and application of citrus resisting canker genetic engineering.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Bacillus subtilis for controlling citrus canker
InactiveCN103173394AGood prevention and control effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThielaviopsis basicola
The invention relates to a bacillus subtilis CCCQ080 with stronger activity prevention for citrus canker, belonging to the field of agriculture disease biological control. The bacillus subtilis is obtained by being separated from natural environment host leaves and is identified according to the morphological characteristics and molecular biology. The bacillus subtilis has very strong inhibition effect on the citrus canker, and also has good control effect on the citrus canker. Furthermore, the bacillus subtilis also has broad-spectrum antagonistic activity, has stronger inhibition effect on pathogenic bacteria such as citrus canker pathogen and tobacco angular leaf spot pathogen, and also has good inhibition effect on pathogenic fungus such as tobacco botrytis cinerea, apple canker pathogenic bacteria and thielaviopsis basicola. The secondary metabolite of the bacillus subtilis contains cellulase, protease, siderophore and the like. The biological film of the canker pathogenic bacteria can be destroyed by the fermentation filtrate of the bacillus subtilis, and the environment-friendly biopesticide can be produced by bacterial fermentation or secondary metabolite extraction technology, so that the bacillus subtilis has important business development and application value.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
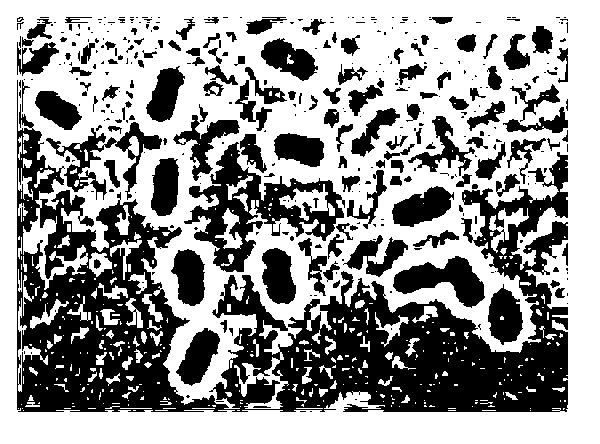
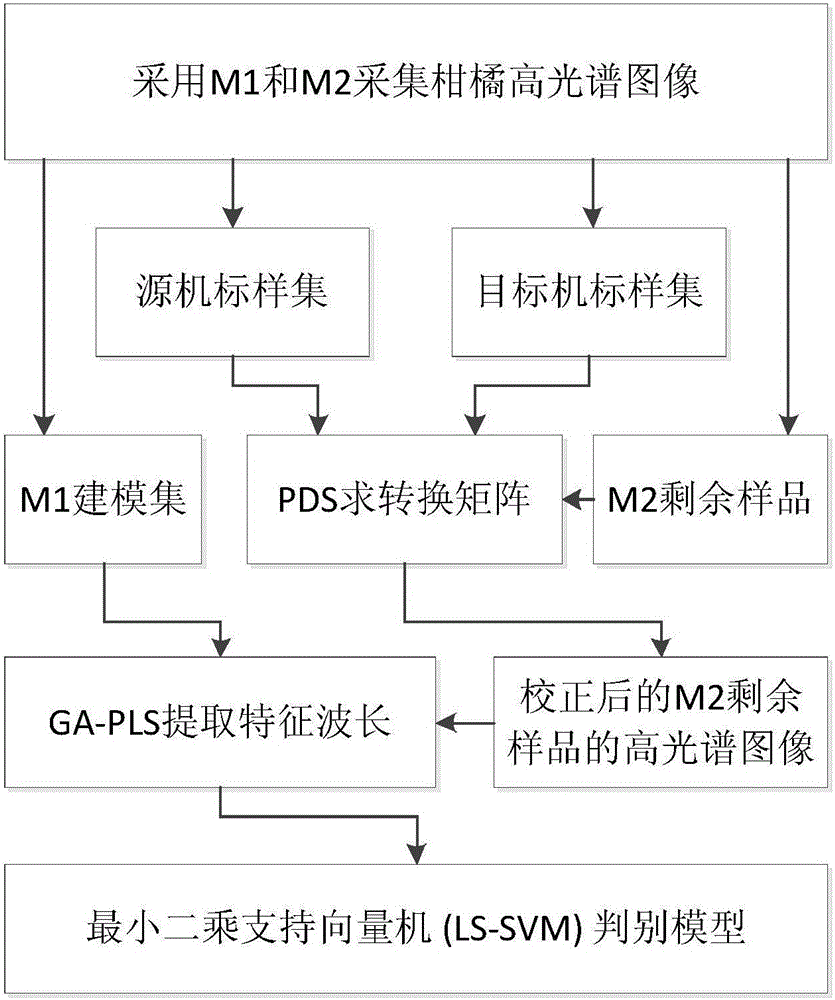
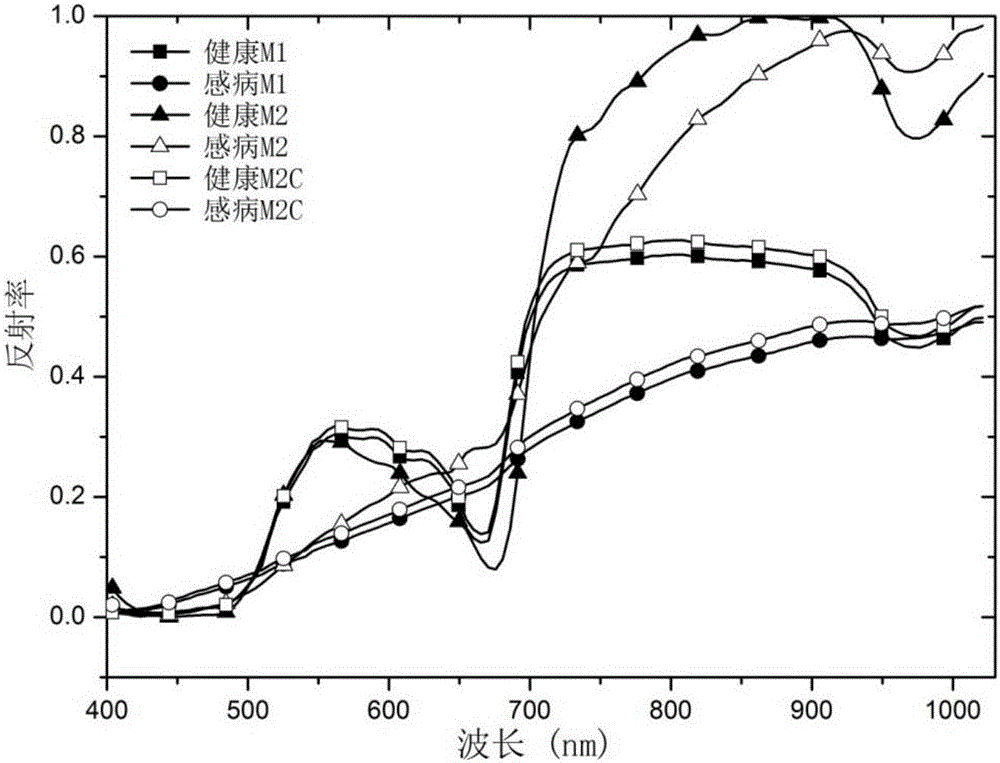
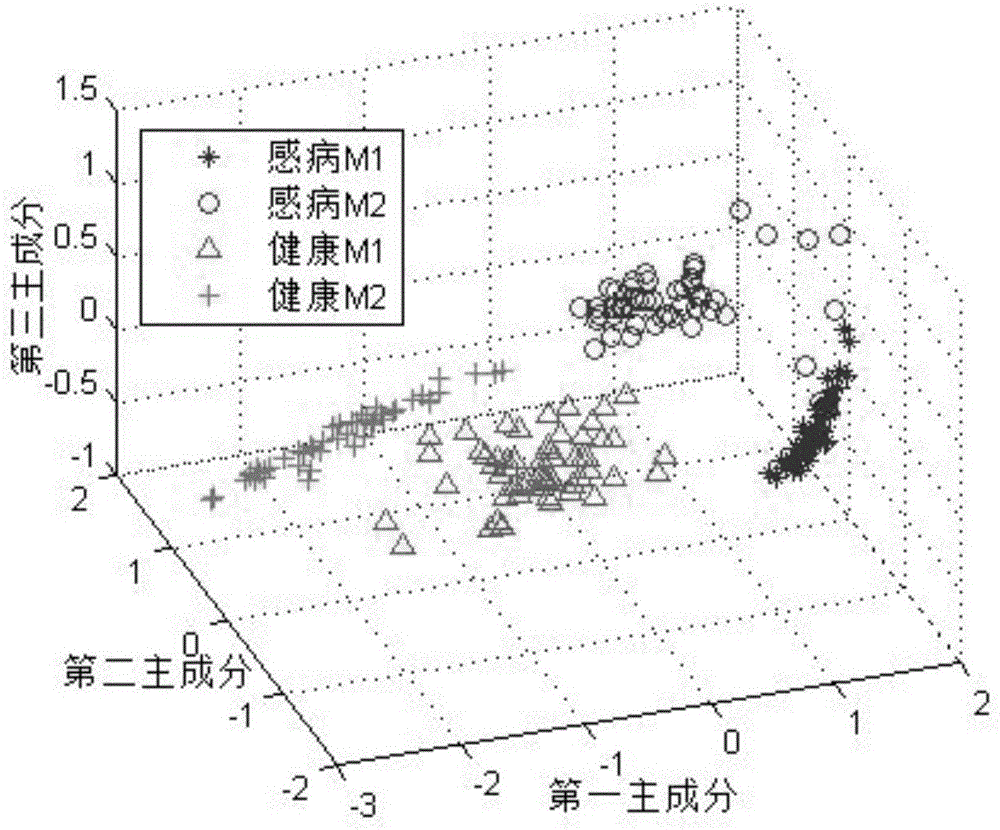
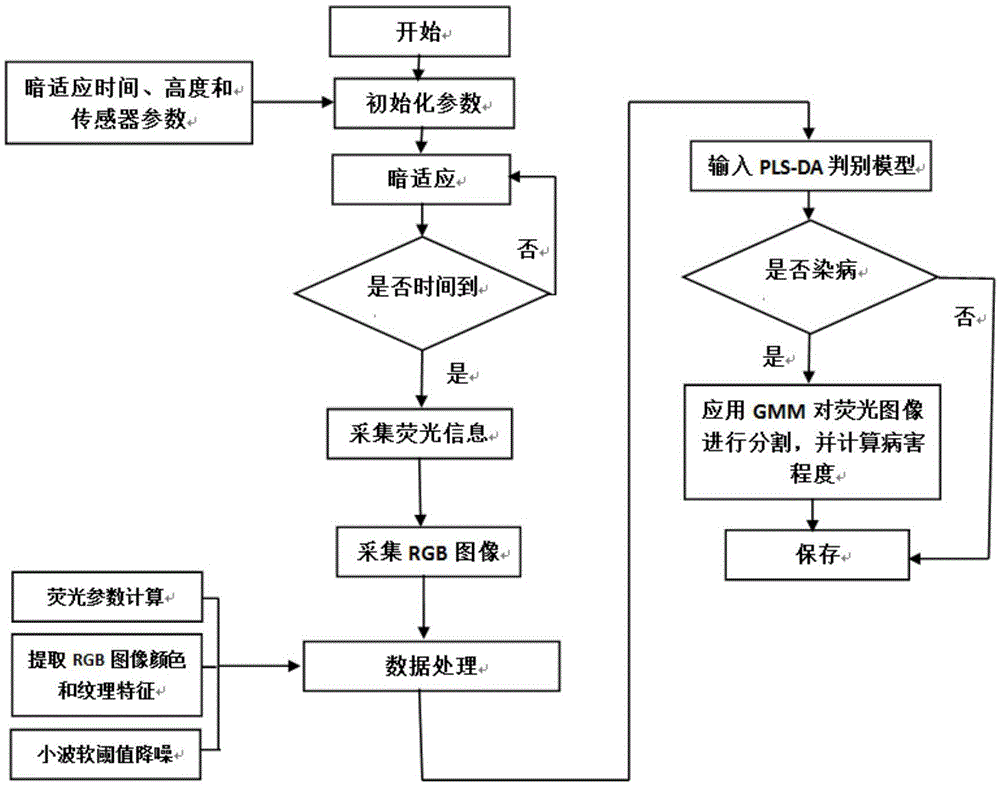
Hyperspectral model transfer method of citrus canker
InactiveCN105954202AReduce volumeImprove universalityMethod using image detector and image signal processingColor/spectral properties measurementsCorrection algorithmLeast squares support vector machine
The invention relates to a hyperspectral model transfer method of citrus canker. The method includes acquiring hyperspectral images of citrus by using a source machine M1 and an object machine M2, getting a characteristic wave band of the hyperspectral images of M1 by using genetic partial least squares, and establishing a discrimination model of least squares support vector machine. The functional relation of the hyperspectral images acquired by two machines is established by using piecewise direct standardization, the standardized hyperspectral images of M2 is input into the discrimination model of least squares support vector machine, and the prediction set recognition rate of the model is increased from 26% before standardization to 97%. The method in the invention can be used for transferring hyperspectral model of citrus canker, is beneficial to establish the steady hyperspectral model of citrus canker, and can improve the detection precision of citrus canker.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
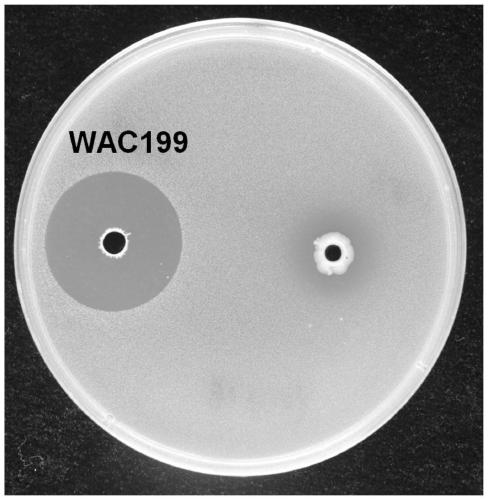
Paenibacillus jamilae, and fermentation product, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109868236AGood inhibitory effectImprove stabilityBiocideBacteriaEnvironmental resistancePaenibacillus jamilae
The invention provides a strain of Paenibacillus jamilae, and a fermentation product, a preparation method and application thereof. The name of the strain of Paenibacillus jamilae is Paenibacillus jamilae WAC199 which is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center (GDMCC) located in Guangzhou of China on October 31, 2018, the preservation number is GDMCC No: 60470, and the strain ofPaenibacillus jamilae has a remarkable inhibition effect on citrus canker pathogens and sporisorium scitamineum. The invention also provides a fermentation culture method of a metabolic active substance of the strain, and the preparation method is simple and easy to operate; the metabolic active substance also has a remarkable antagonistic effect, and keeps high and stable bacteriostatic activityunder high temperature, a wide pH range and ultraviolet irradiation. The invention provides a more economic, effective and environment-friendly solution for biological prevention and control of citrus canker and sugarcane smut, and a good application prospect in prevention and control of pathogenic bacteria is provided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bacillus subtilis and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104805031AFast growth and reproductionShort fermentation cycleBiocideBacteriaNicotiana tabacumBacterial disease
The invention relates to bacillus subtilis. The preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO: 9269. The strain is obtained by deep fermentation, ceramic membrane concentration and spray-drying. A shaking culture liquid of the strain has an obvious effect of inhibiting the target germ Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, the target germ ralstonia solannacearum, the target germ Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci, the target germ Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri and the target germ cercosporella albomaculans. The bacillus subtilis provided by the invention has advantages of fast growth and propagation, short fermentation period, high filling spore number, good control efficiency and the like. Meanwhile, a preparation method of the strain has simple steps, is convenient to operate, comprises steps of deep fermentation, ceramic membrane concentration and spray-drying to obtain the bacillus subtilis, has high preparation efficiency and has good effects. The strain can control various bacterial diseases and now has been registered on cercosporella albomaculans, Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri, Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci, ralstonia solannacearum and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.
Owner:德强生物股份有限公司
Compound drug for preventing and curing citrus canker
The invention discloses a compound drug for controlling citrus canker, comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 22.5%-30% of allicin, 36%-48% of streptomycin, 6% of wetting diffusant and the balance of kieselguhr filler. The 6% of wetting diffusant consists of 2% of sodium butyl naphthalene sulfonate (NEDALBA-75), 2% of sodium lignin sulfonate (M-9), 1% of lauryl alcohol polyoxyethylene ether (JFC) and 1% of carboxymethylcellulose (CMC). The compound drug for controlling the citrus canker can be used for controlling treetop citrus canker and fruit canker, is the low toxicity and residual free super active biogenic bactericide, has specially good effect on the canker and the control efficiency of more than 80 percent, is safe for fruit tress and is environmentally friendly; and the compound drug has the function of repelling pests spreading the citrus canker and can effectively reduce wounds and cut off propagation paths.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Heterocycle substituted 1,3,4-oxadiazole compound and preparation method and application thereof
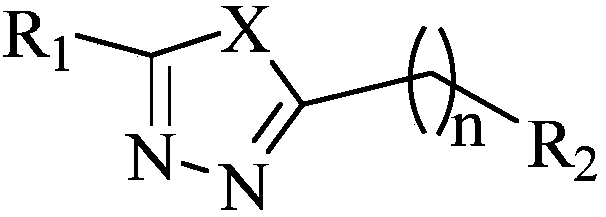
The invention relates to a heterocycle substituted 1,3,4-oxadiazole compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound includes the following steps shown in the general formula (I) in the description. The compound has a good inhibitory effect on pathogenic bacteria and fungi, such as rice white leaf diseases, citrus canker diseases, pepper wilt pathogenic bacteria, blueberry phytophthora lateralis, wheat gibberella saubinetii, potato phytophthora infestans, oilseed rape sclerotinia sclerotiorum, dragon-fruit colletotrichum orbiculare and the like.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Bactericide composition aiming at plant bacteria and fungus diseases and application thereof
ActiveCN103004879ASynergistic effect is obviousHigh field control efficiencyBiocideFungicidesAlternariaCitrus volkameriana
The invention relates to the technical field of pesticides, and particularly relates to a bactericide composition which takes zhongshengrnycin and copper oxychloride as effective ingredients, has an obvious and enlarged bacteriocidal spectrum and no phytotoxicity, and is used for treating plant bacterial diseases as well as fungal diseases. The weight proportion of the zhongshengrnycin to the copper oxychloride is 1:5-60. The bactericide composition has obvious synergistic effect, high field prevention effect and a wide bacteriocidal spectrum, is used for preventing and treating cucumber bacterial angular leaf spot, cucumber downy mildew, tomato bacterial macula disease, tomato leaf mold, pumpkin soft rot, watermelon bacterial angular leaf spot, watermelon sponge, apple alternaria leaf spot, apple brown blotch, pear scabs, grape downy mildew, grape powdery mildew, anthracnose of grape, jujube rust diseases, jujube anthracnose, citrus canker, citrus scab, citrus anthracnose, peanut leaf spot diseases and peronophythora litchii, and has the advantages of good effect and reduction of prevention and treatment cost.
Owner:福建凯立生物制品有限公司
Bacillus subtilis strain and application thereof
InactiveCN108118019AFast growth and reproductionShort fermentation cycleBiocideBacteriaDiseaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganism application, in particular to a bacillus subtilis strain and an application thereof. The bacillus subtilis strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on Jan 22rd, 2018 with the preservation number of CGMCC NO.15250. The strain provided by the invention can prevent and treat multiple fungal andbacterial diseases and are applied to Chinese cabbage soft rot, citrus canker, tobacco wildfire, tobacco bacterial wilt and rice bacterial leaf blight at present.
Owner:北京新正和农业科技有限公司
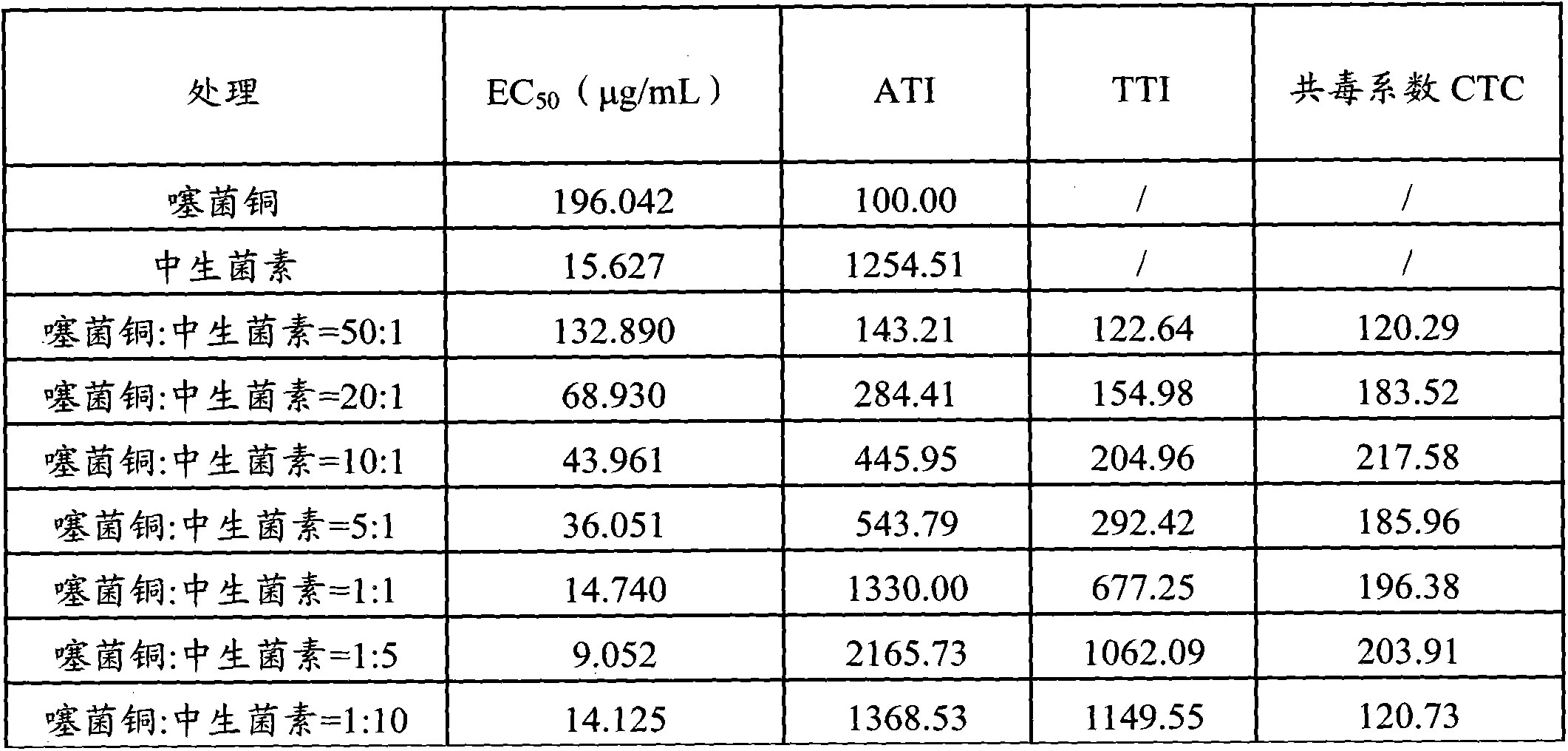
Bactericide composition containing thiediazole copper
InactiveCN103918681AResidue reductionImprove disease resistanceBiocideFungicidesFruit treeAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a bactericide composition containing thiediazole copper. The bactericide composition comprises the effective ingredients of thiediazole copper (A) and Zhongshengmycin (B) in the weight part ratio of 50:1 to 1:10. The bactericide composition has obvious synergism, and can be used in control of diseases of vegetables, fruit trees and cereal crops, particularly, of soft rot of Chinese cabbages, bacterial wilt of potatoes, canker of citrus, bacterial blight of rice and bacterial leaf streak of rice.
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPOSION AGROCHEM
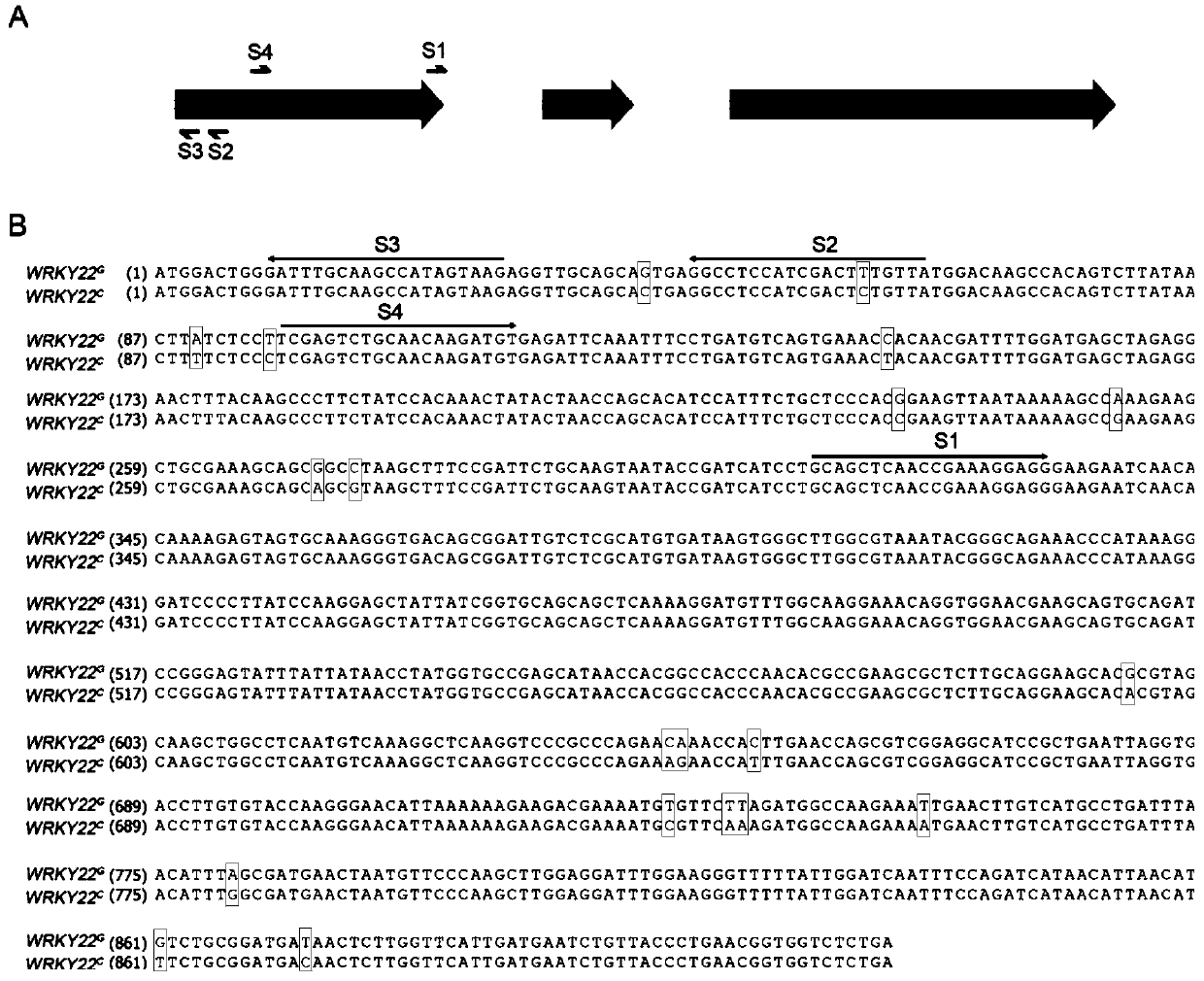
Method for improving citrus canker resistance based on CRISPRCas9 mediated CsWRKY22 site-directed editing
ActiveCN110283843AIncreased Canker ResistanceIncreased resistance to canker diseaseVectorsPlant peptidesEpicotylPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses a method for improving citrus canker resistance based on CRISPRCas9 mediated CsWRKY22 site-directed editing, and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering. A CRISPR / Cas9 editing vector guided by S1 and S2 sg RNA is constructed, the epicotyl of wanjicheng orange is transformed with an agrobacterium-mediated method, so that the function of CsWRKY22 protein is lost or reduced, successful editing of CsWRKY22 gene in the citrus genome is realized, CsWRKY22 mutant transgenic plants are obtained, plant resistance to citrus canker is enhanced, and citrus with high canker resistance is obtained.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
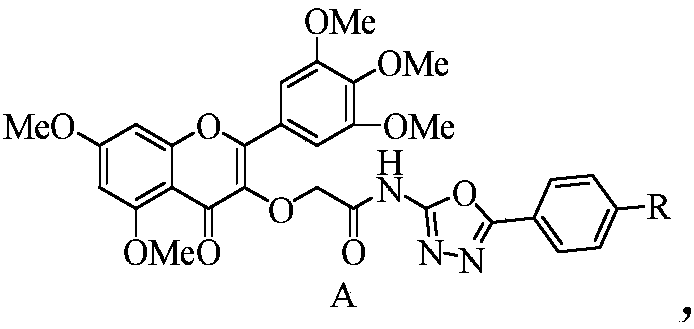
Myricetin derivative containing amide-oxadiazole and preparation method and application of myricetin derivative
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Compositions and methods for the treatment and prevention of disease in plants
InactiveUS7226610B2Preventing and treating citrus cankerPreventing bacterialBiocideHydrocarbon active ingredientsDiseaseWax
Non-toxic, naturally derived and economical compositions for treating and preventing bacterial or fungal disease in plants, especially citrus canker, wherein such compositions include various combinations of d-limonene, wax and monohydric alcohol are provided. Methods for making and using such compositions are also provided.
Owner:PRESERVATION SCI
Method and device for detecting citrus canker
ActiveCN105548124AImprove detection accuracyFast NDTMethod using image detector and image signal processingInvestigation of vegetal materialDiseaseRgb image
The invention relates to a method for detecting citrus canker. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out dark adaptation treatment, obtaining fluorescence information and an RGB (Red, Green and Blue) image by using a chlorophyll fluorescence imager and an RGB camera, and computing chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, color features and textural features; distinguishing whether citrus is infected with a disease or not by utilizing a PLS (Partial Least Squares) discriminant analysis model; reading a fluorescence image of a to-be-detected citrus which is infected with the disease, analyzing and computing the area of the disease by applying a Gaussian mixture model, and realizing quantitative analysis on infecting degree. The invention also relates to a device for detecting the citrus canker. According to the method and the device for detecting the citrus canker, disclosed by the invention, citrus fruit canker in different growing periods of a young fruit period, a fruit greening period and a fruit ripening period and in different infecting degrees can be continuously and automatically detected by blending a chlorophyll fluorescence imaging technology with an RGB imaging technology.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bactericidal composition, pesticide and application thereof
The invention discloses a bactericidal composition, a pesticide and application thereof. The bactericidal composition comprises the following components of N-(5-methyl-1,3-thiazole-2-yl)-4-methyl-1,2,3-thiadiazole-5-formamide and cuppric nonyl phenolsulfonate in a weight ratio of (1:50)-(50:1). The bactericidal composition is used as an active component and combined with agromedically acceptable auxiliary components together so as to form a pesticide with a sterilization effect; the pesticide can effectively prevent crop diseases, such as rice bacterial leaf blight, citrus canker, pseudomonas solanacearum, tobaccomosaivirus, pepper virus disease, tomato virus disease and the like; the effect of the pesticide is obviously higher than that of a double-component single agent; and a remarkable synergetic effect is achieved, the application dosage of each single agent can be effectively reduced, the better effects of enlarging sterilization scope and delaying plant pesticide-resistance are achieved, the duration is prolonged, and a remarkable promotional value is obtained.
Owner:LIER CHEM CO LTD
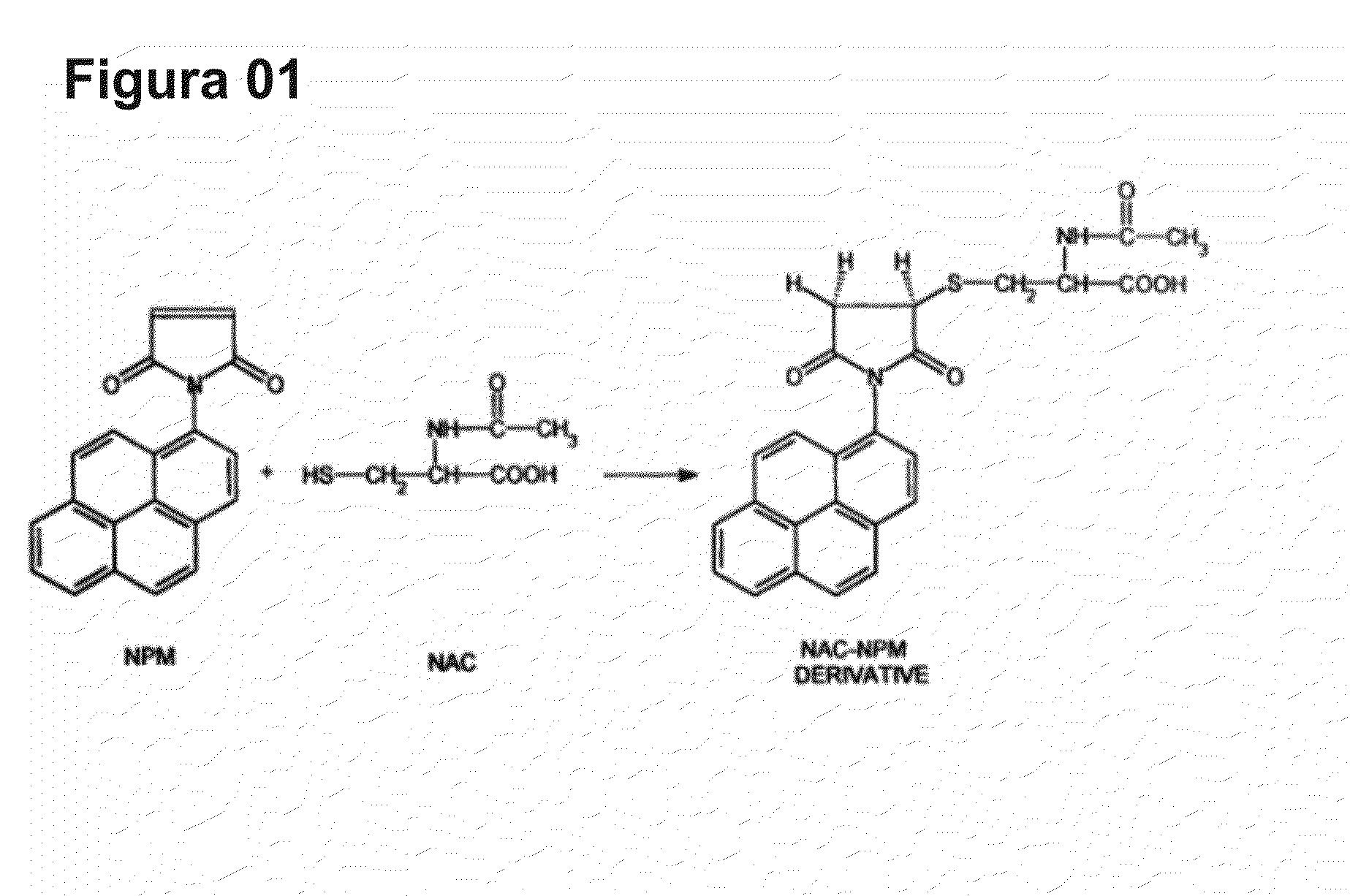
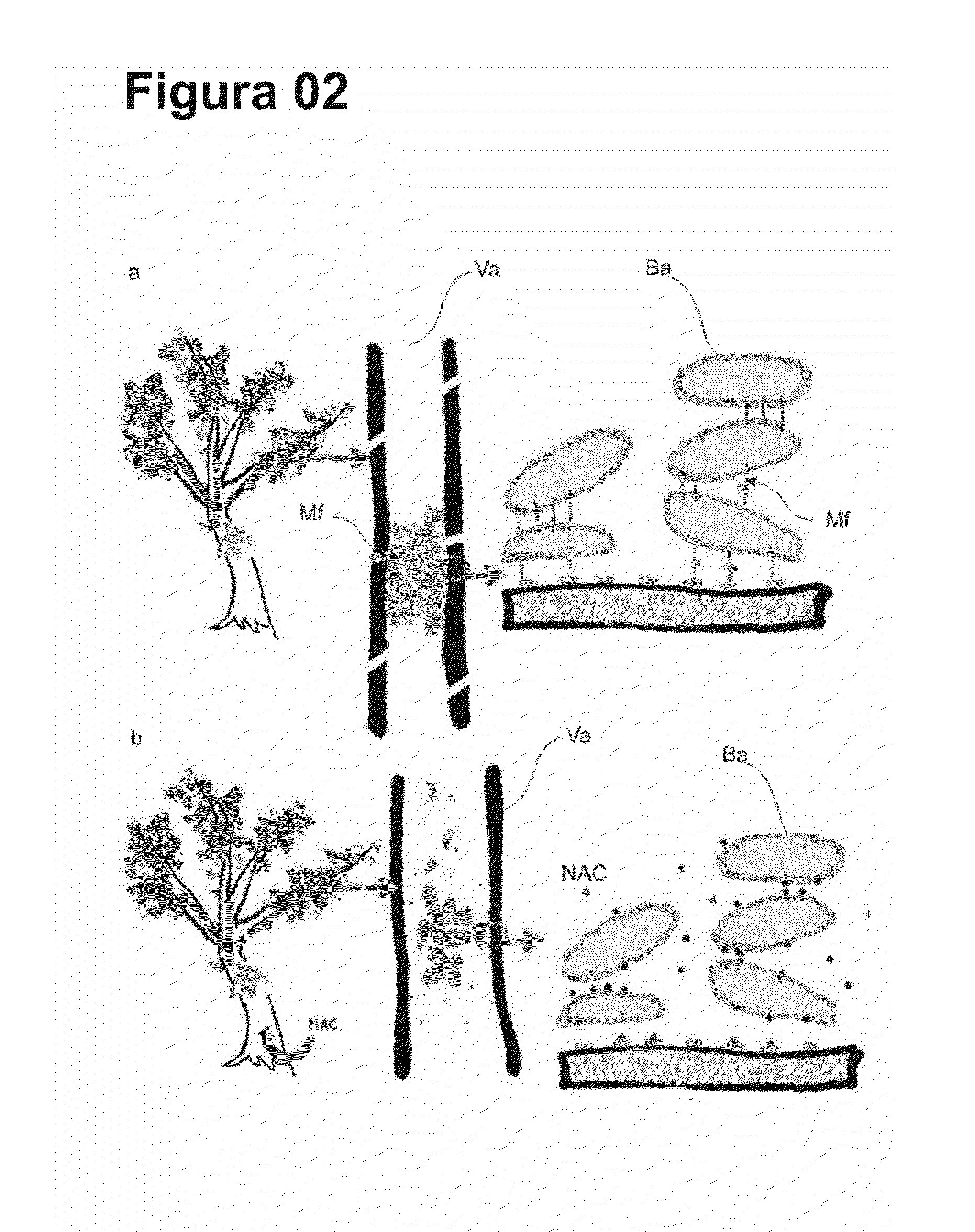
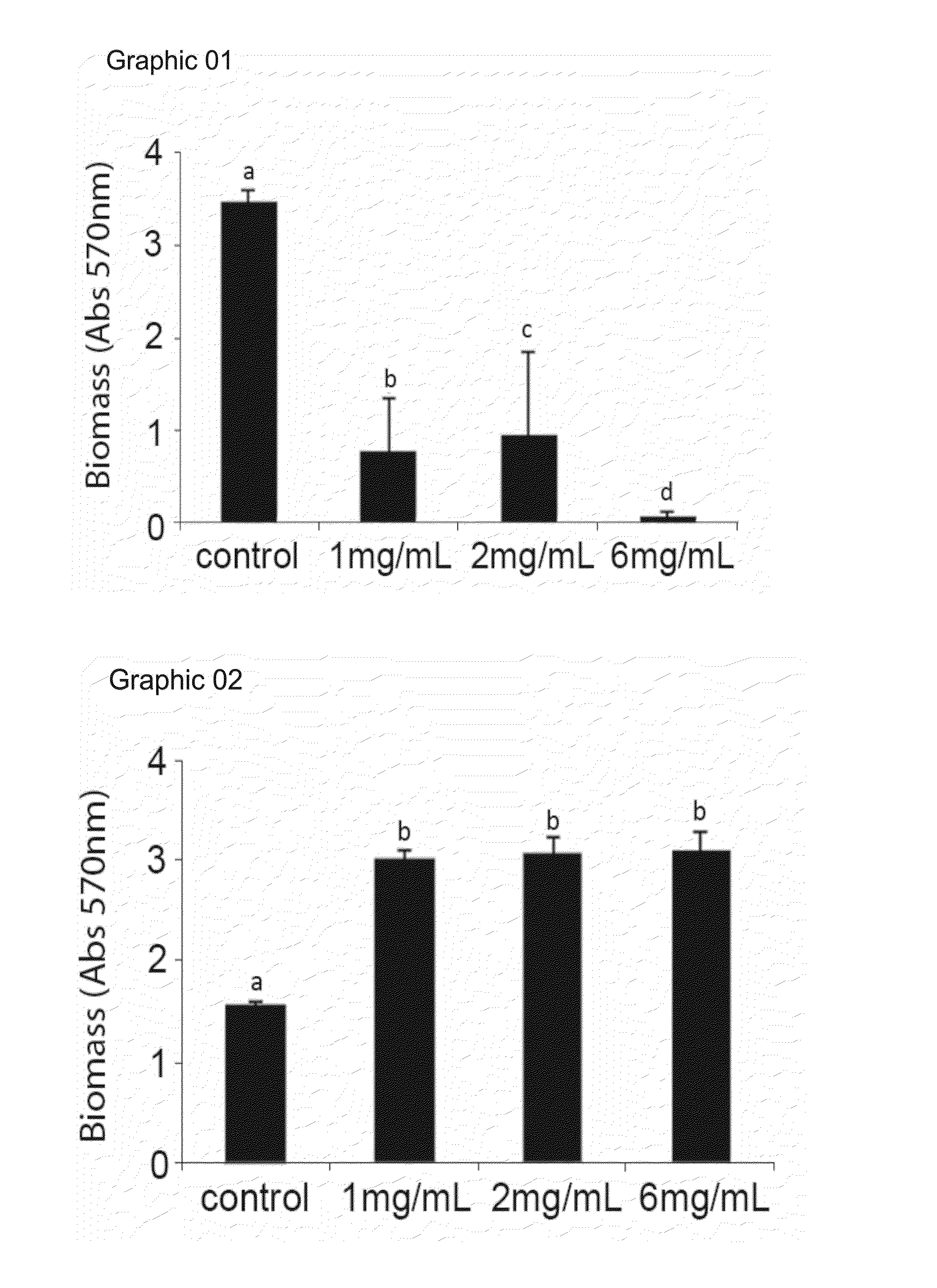
Cysteine amino-acid compound (or its analogues) used in the disruption of microbial biofilms when treating or preventing diseases caused by phytopathogenic bacteria known to attack plants of agricultural interest
Cysteine amino-acid compound (or its analogues) used in the disruption of microbial biofilms by treatment of prevention of diseases generated by phytopathogenic bacteria attacking plants of agricultural interest represented by an innovative solution within the agriculture sector, where said compound can be used in the pharmacological form, as a drug associated with fertilizer for the combat of bacterial diseases which form microbial biofilms, such as citrus variegated chlorosis (CVC), citric canker’, huanlongbing (HLB) disease or ‘greening’, amongst other, which inventive concept, as such, never before completed, resides in the benefit deriving from the cysteine amino-acid, and all of its analogues, in the inhibitory action and progressive disruption of the microbial biofilm thus liberating the nutritive flux and hydration of the root to the upper part of the plant and the subsequent regression of the disease symptoms, with the added advantage that the cysteine amino-acid compound is non-toxic, guaranteeing healthy production of foods by plants of agricultural interest that are totally healthy, without toxic residues in their composition, as well as when said compound is applied there is risk to the environment due to the rapid absorption, notably within the area in which it is applied, where such predicates of disease combat, with the exception of toxic collateral effects still guarantee that the final crop and harvest will have a higher productivity per hectare.
Owner:INST AGRONOMICO DE CAMPINAS
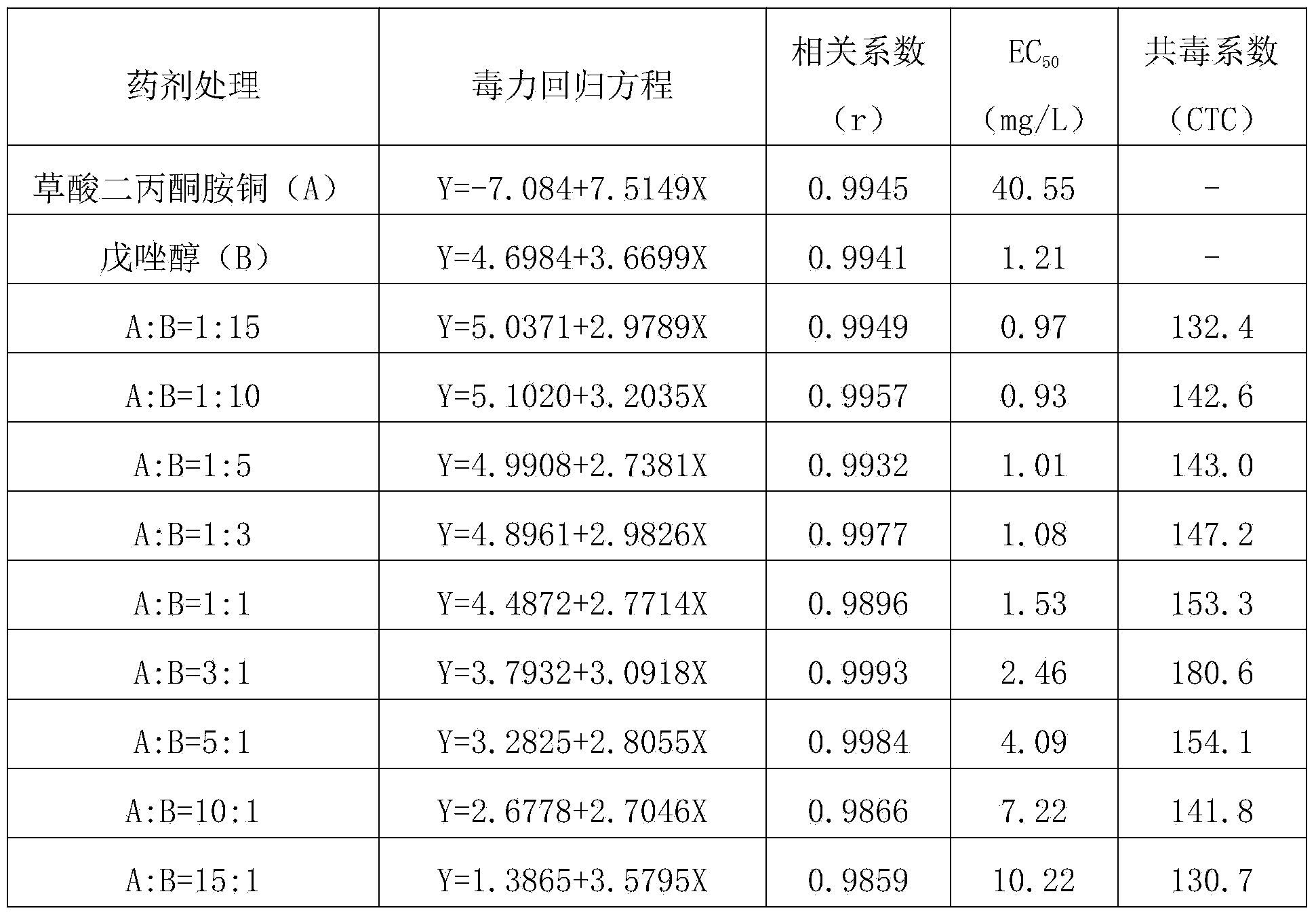
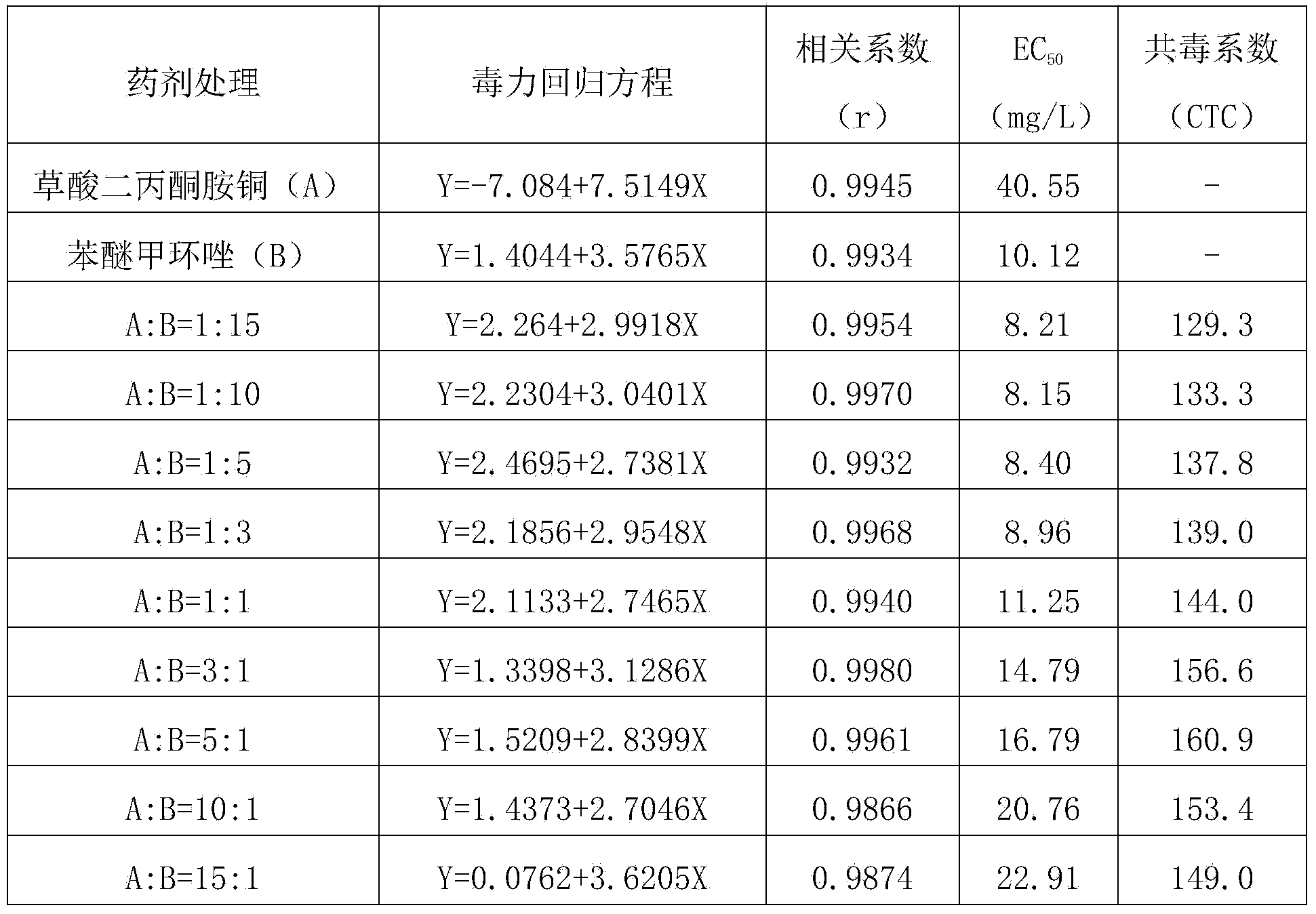
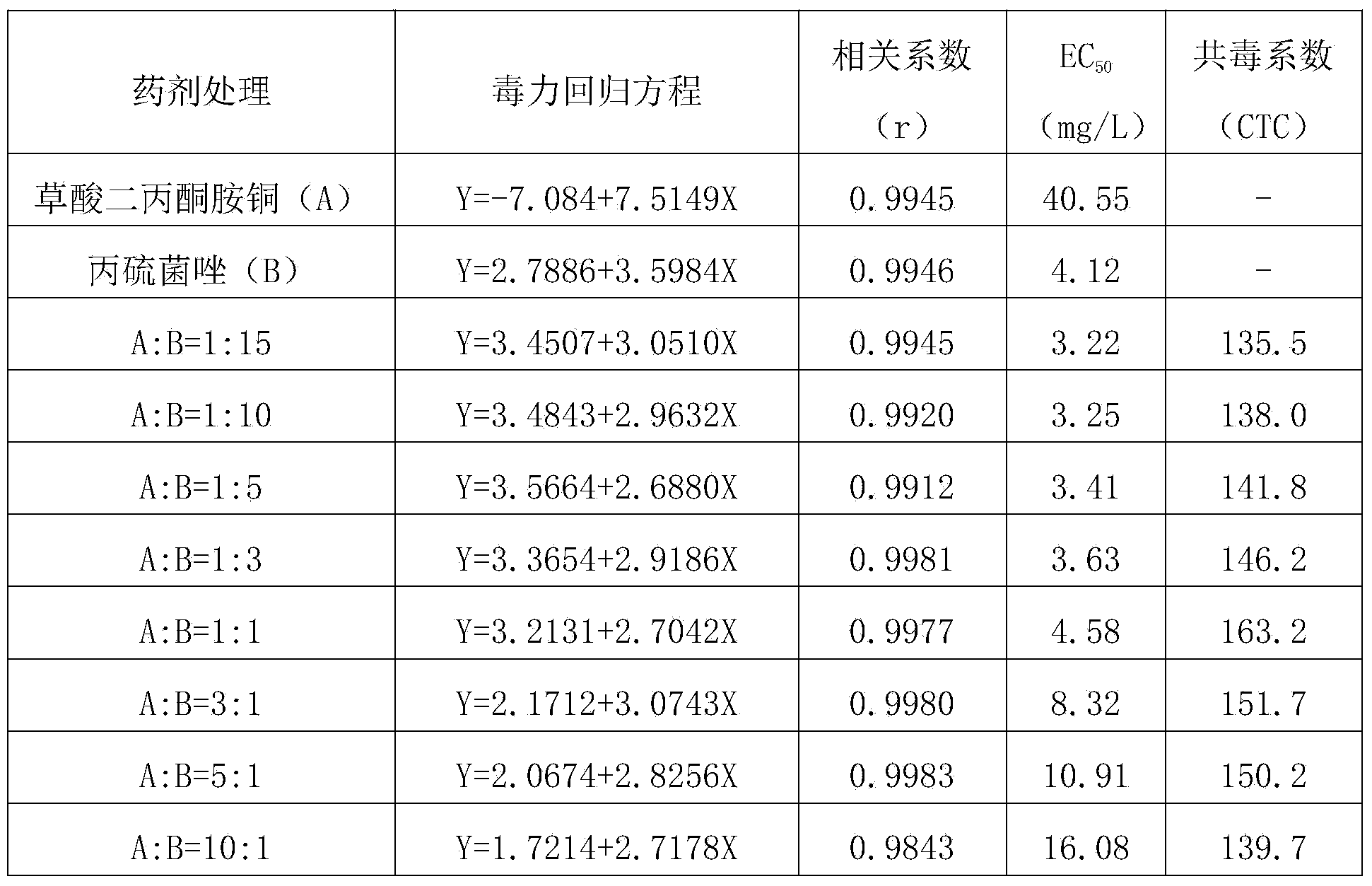
Bactericidal composition containing diacetone amine copper oxalate and triazole bactericides
The invention discloses a bactericidal composition containing diacetone amine copper oxalate and triazole bactericides. The bactericidal composition comprises a first active ingredient, namely diacetone amine copper oxalate, and a second active ingredient, namely one of the triazole bactericides, wherein a weight ratio of the first active ingredient to the second active ingredient is (1:15)-(15:1), and the sum of the content of the first active ingredient and the second active ingredient is 5-90 percent of the total weight of the bactericidal composition. The composition can be prepared into agriculturally allowable forms such as water dispersible granules, wettable powder, dispersible oil suspended agents or micro emulsion. The bactericidal composition disclosed by the invention effectively solves the problem that the effect of eradicating crop diseases by singly using the diacetone amine copper oxalate or the triazole bactericides is not ideal, has an obvious synergistic effect and is high in crop safety. The bactericidal composition disclosed by the invention has good effects of controlling altermaria leaf spot and brown spot of apples, bacterial canker diseases and anthracnose of citruses, downy mildew, powdery mildew and angular leaf spot of cucurbites, false smut, sheath blight and blast of rice, and black point and leaf spot diseases of bananas.
Owner:SHAANXI SUNGER ROAD BIO SCI
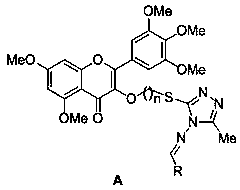
Triazole Schiff base Myricetin derivative containing thioether, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a triazole Schiff base Myricetin derivative containing thioether, a preparation method and application thereof. The structural general formula of the derivative is shown as [A], wherein R is phenyl, substituted phenyl or aromatic heterocyclic base; and n is the number of carbon in a carbon chain, which is 3, 4 and 5 respectively. The triazole Schiff base Myricetin derivative has preferable control effect for tobacco mosaic virus, citrus canker bacteria and rice bacterial blight bacteria.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV +1
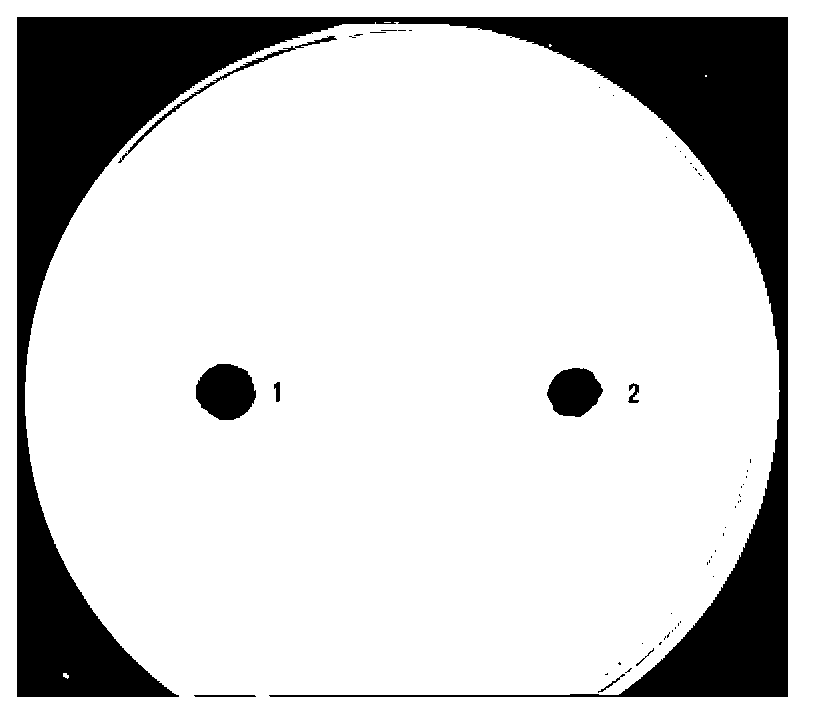
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof in prevention and control of citrus bacterial canker
The invention discloses Bacillus amyloliquefaciens F9 and application thereof in prevention and control of citrus bacterial canker. The strain F9 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University, China on September 26th, 2016 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2016519. Plate antagonistic experiments find that the strain F9 has citrus bacterial canker inhibitory activity, and an inhibition zone is 26.5mm; supernatant of fermentation broth of the strain F9 after 4 days has antibacterial activity, and the diameter of the inhibition zone can reach 26.5mm; and an in vitro inoculation experiment finds that the strain F9 can inhibit extension and colonization of xanthomonas citri. Therefore, the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens F9 can be applied to prevention and control of the citrus bacterial canker as a biocontrol bacterium.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com