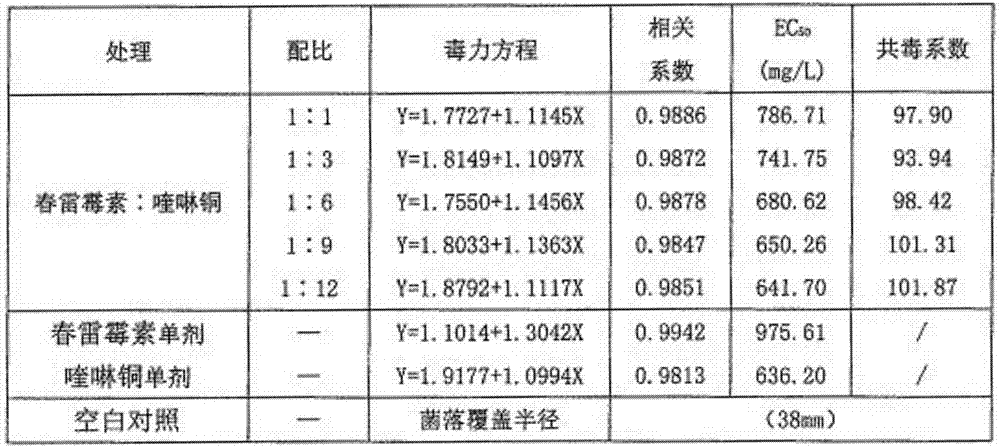
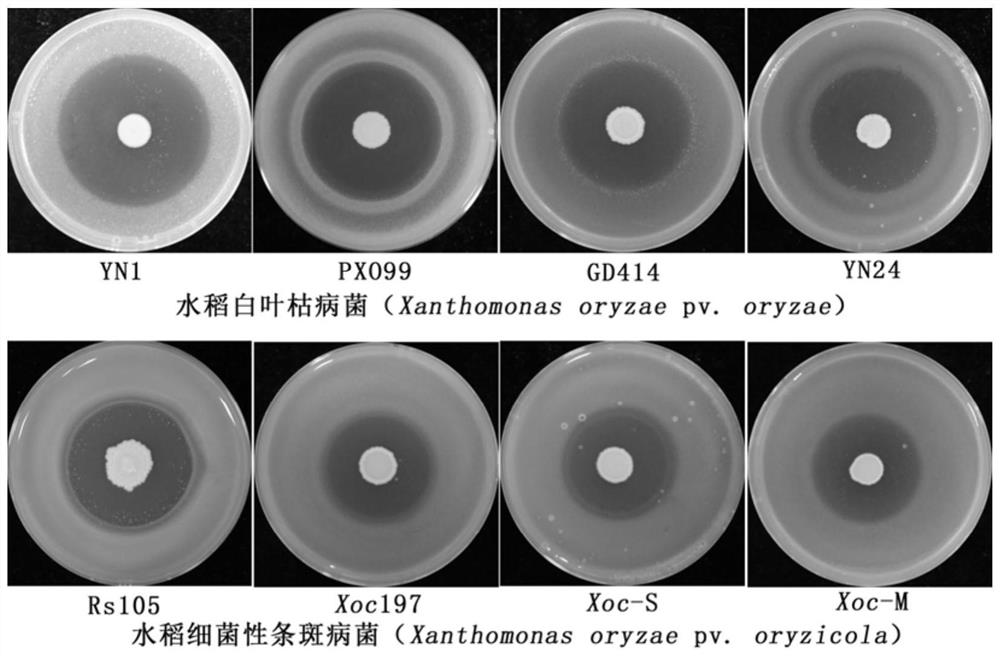
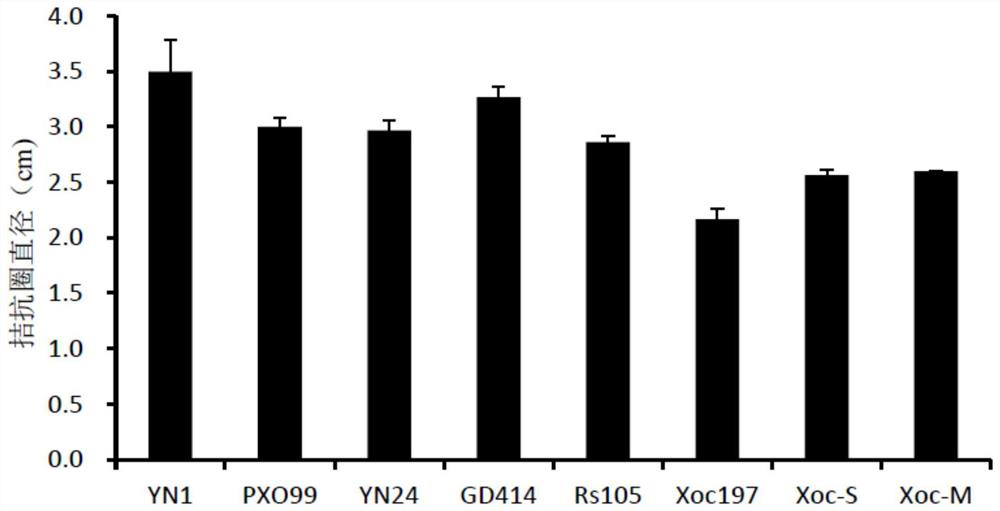
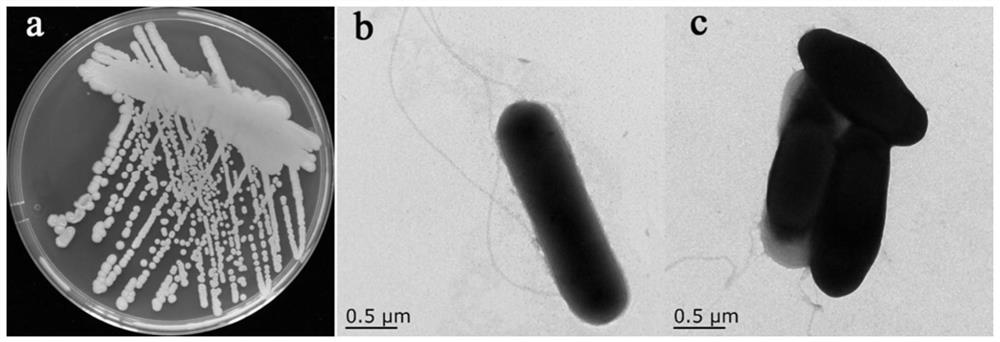
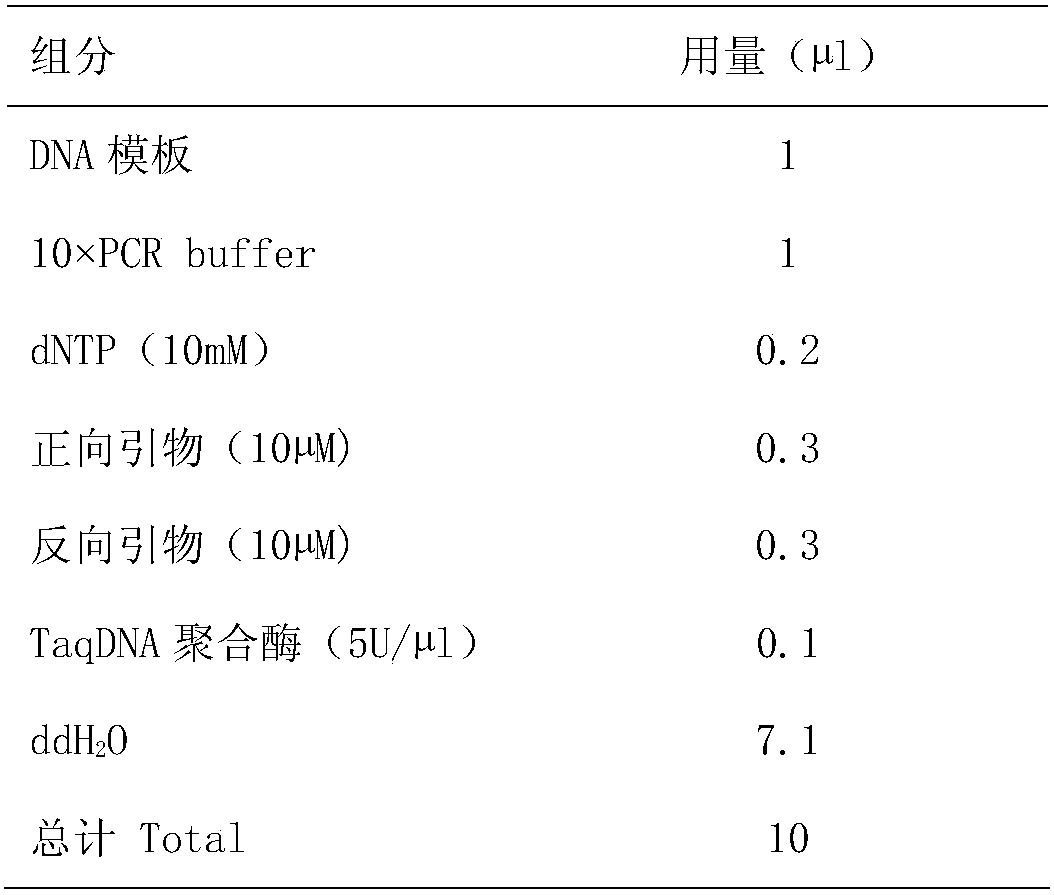
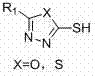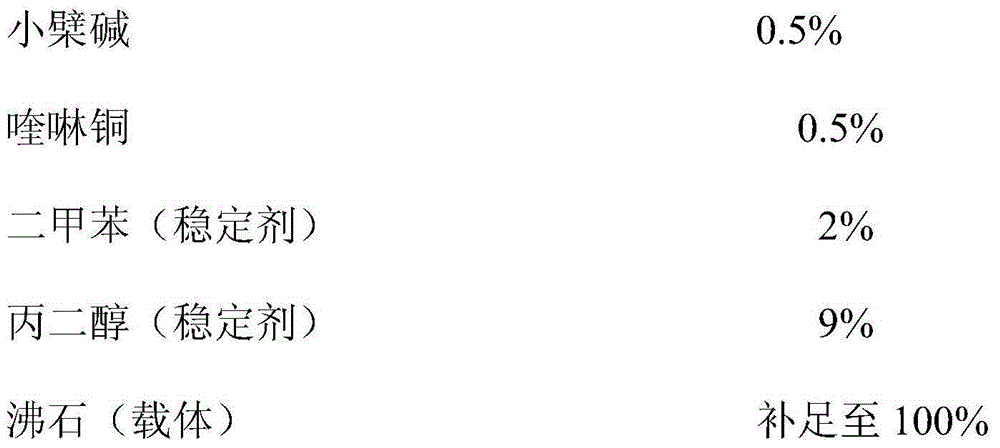Patents
Literature
86 results about "Bacterial leaf streak" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacterial leaf streak (BLS), also known as black chaff, is a common bacterial disease of wheat. The disease is caused by the bacterial species Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa. The pathogen is found globally, but is a primary problem in the US in the lower mid-south and can reduce yields by up to 40 percent. BLS is primarily seed-borne (the disease is transmitted by seed) and survives in and on the seed, but may also survive in crop residue in the soil in the off-season. During the growing season, the bacteria may transfer from plant to plant by contact, but it is primarily spread by rain, wind and insect contact. The bacteria thrives in moist environments, and produces a cream to yellow bacterial ooze, which, when dry, appears light colored and scale-like, resulting in a streak on the leaves. The invasion of the head of wheat causes bands of necrotic tissue on the awns, which is called Black Chaff. The disease is not easily managed, as there are no pesticides on the market for treatment of the infection. There are some resistant cultivars available, but no seed treatment exists. Some integrated pest management (IPM) techniques may be used to assist with preventing infection although, none will completely prevent the disease.
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101985608AGood control effectControl epidemicBiocideBacteriaEcological environmentOrganism
The invention relates to a bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain, which is characterized in that the collection No. of the strain is CGMCC No.3789; and the 16S rRNA of the strain accesses to GenBank, with accession No. of HQ179100. The strain is used for controlling rice bacterial leaf streak. The strain has the following advantages: the strain has good control effect on the rice bacterial leaf streak, is free of toxin and pathogenicity, is harmless to people and livestock and is environment-friendly; the prepared biocontrol bacteria or the compound biocontrol bacteria formed by compounding the prepared biocontrol bacteria and bismerthiazol are sprayed after being diluted, so that reasonable distribution of the microfloras in the ecological environment around the root leaves of the rice can be controlled and managed and the living environment of the pathogenic bacteria is worsened to form a rice ecosystem with biodiversity, thus effectively and enduringly controlling prevalence of the rice bacterial leaf streak.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
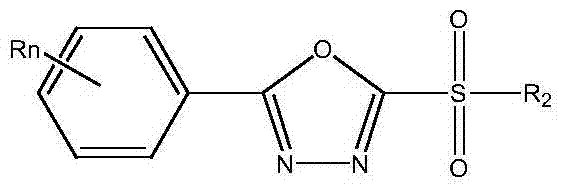
Derivatives containing thiadiazole or oxadiazole and application of derivatives in prevention and control of agricultural plant diseases
InactiveCN103788015AGood effectControl bacterial wiltBiocideOrganic chemistryBiotechnologyBacterial disease
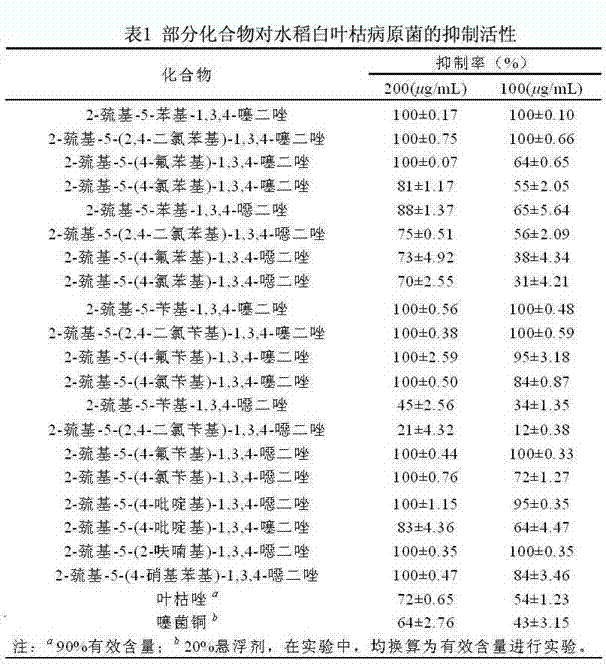
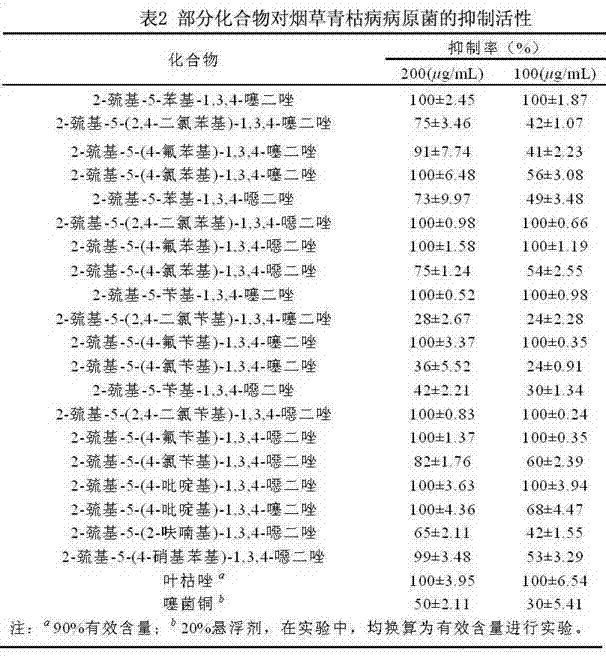
The invention discloses 2-sulfydryl-5-substituent group-1,3,4-thiadiazole (oxadiazole) derivatives with the function of preventing and controlling bacterial and fungal diseases of crops. Due to excellent physiological activity, the derivatives get more attention in the medical field, but the agricultural activity of the derivatives is still not reported at present. The research shows that the derivatives can be used for effectively inhibiting pathogens of such bacterial diseases as rice bacterial blight, rice bacterial leaf streak, tobacco bacterial wilt and tomato bacterial wilt and pathogens of such fungal diseases as wheat scab, potato late blight, apple canker, capsicum wilt, cucumber gay mold and sclerotia sclerotium. Meanwhile, when applied to prevention and control of the bacterial and fungal diseases of crops, the 2-sulfydryl-5-substituent group-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole (oxadiazole) derivatives has the advantages of simple structure, simple the preparation process, low the production cost and wide application prospect. The 2-sulfydryl-5-substituent group-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole (oxadiazole) derivatives has a general formula shown in the specification.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Bactericide composition containing thiediazole copper
InactiveCN103918681AResidue reductionImprove disease resistanceBiocideFungicidesFruit treeAdditive ingredient
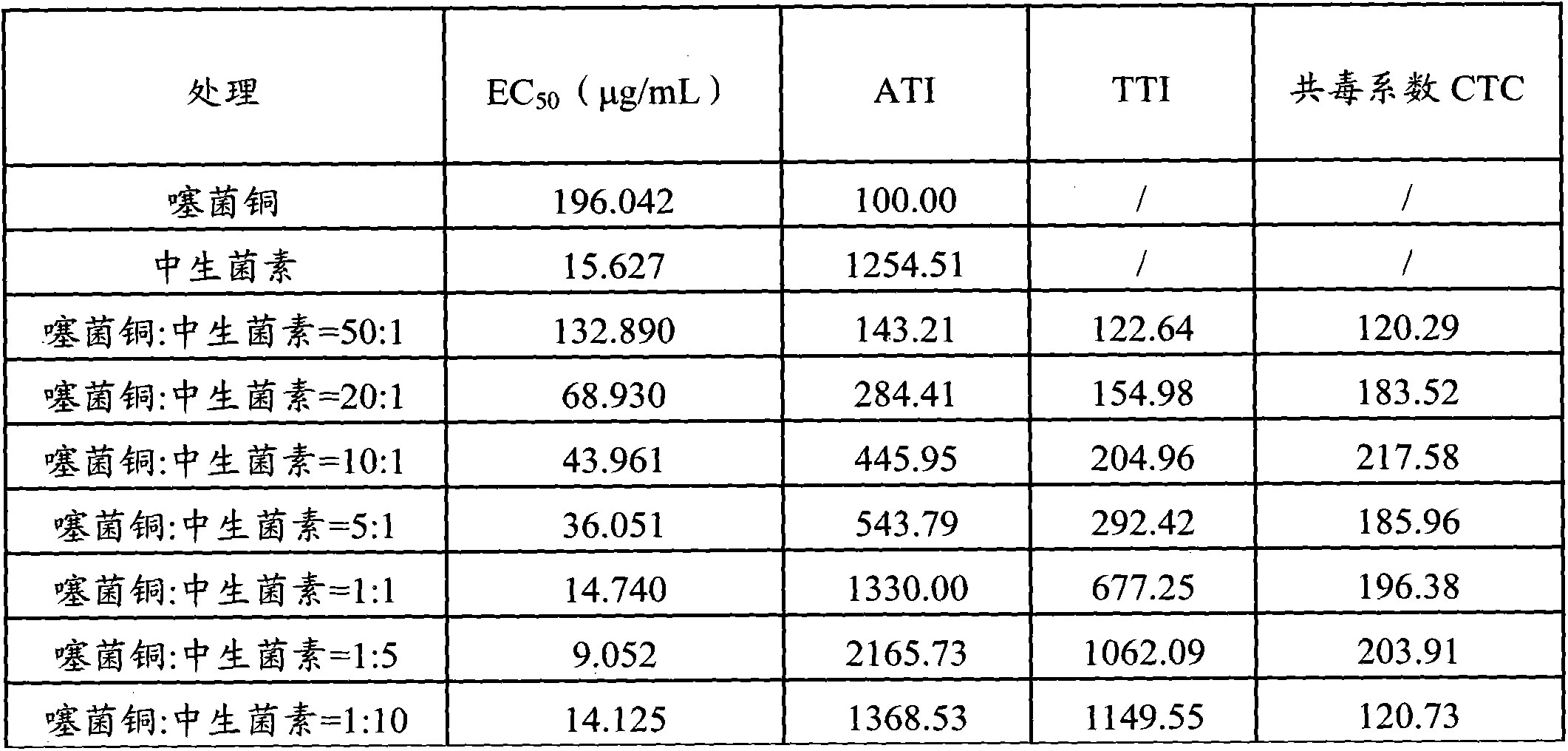
The invention discloses a bactericide composition containing thiediazole copper. The bactericide composition comprises the effective ingredients of thiediazole copper (A) and Zhongshengmycin (B) in the weight part ratio of 50:1 to 1:10. The bactericide composition has obvious synergism, and can be used in control of diseases of vegetables, fruit trees and cereal crops, particularly, of soft rot of Chinese cabbages, bacterial wilt of potatoes, canker of citrus, bacterial blight of rice and bacterial leaf streak of rice.
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPOSION AGROCHEM
Paddy bacterial leaf streak resistance-related gene OsDRxoc6
InactiveCN102978215AReduced resistance levelImprove disease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationPositive controlNucleotide
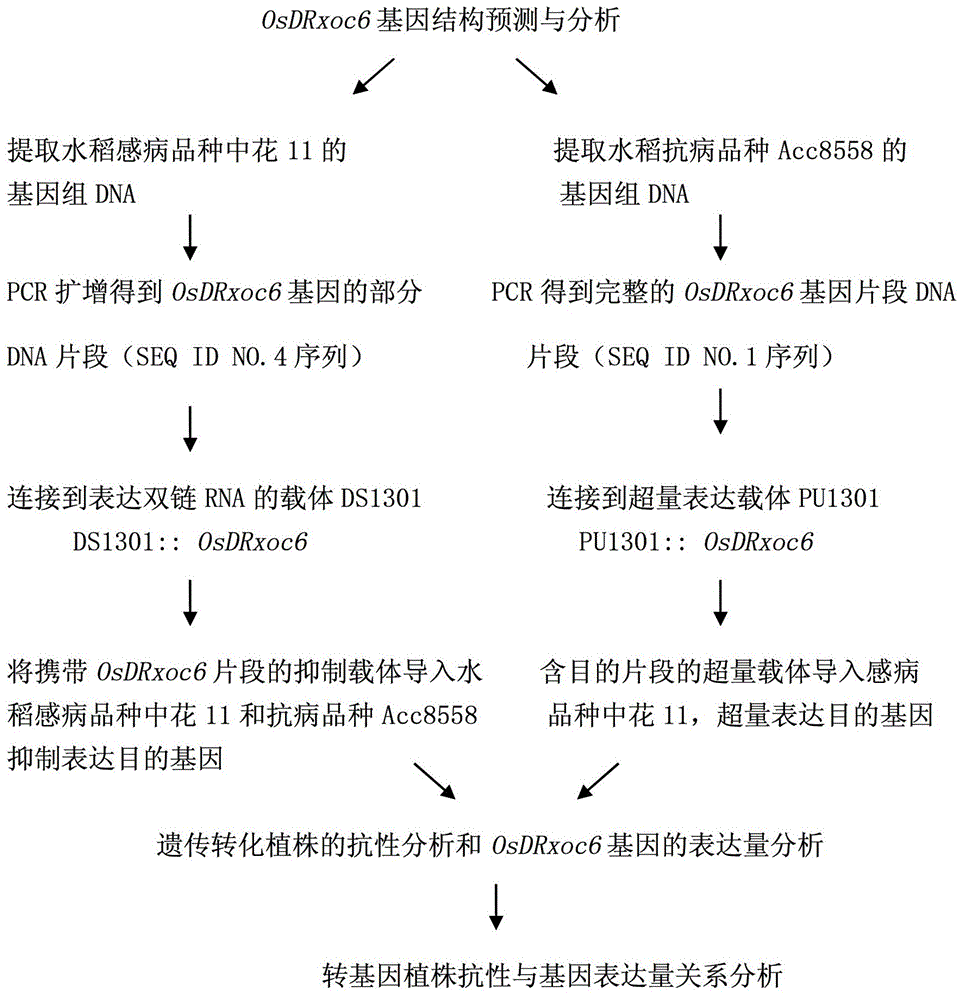
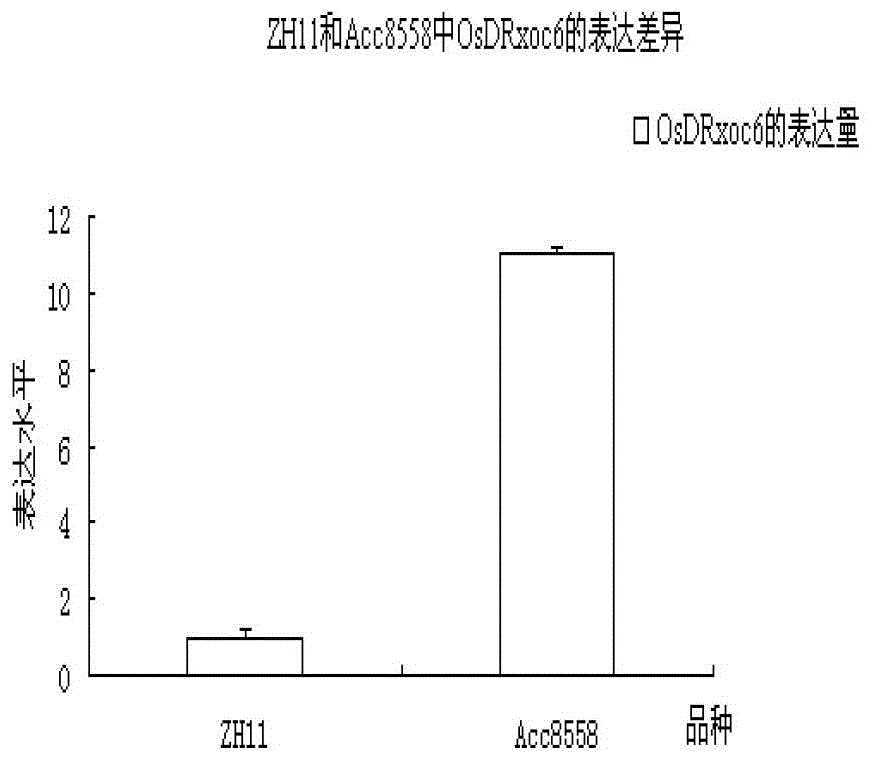
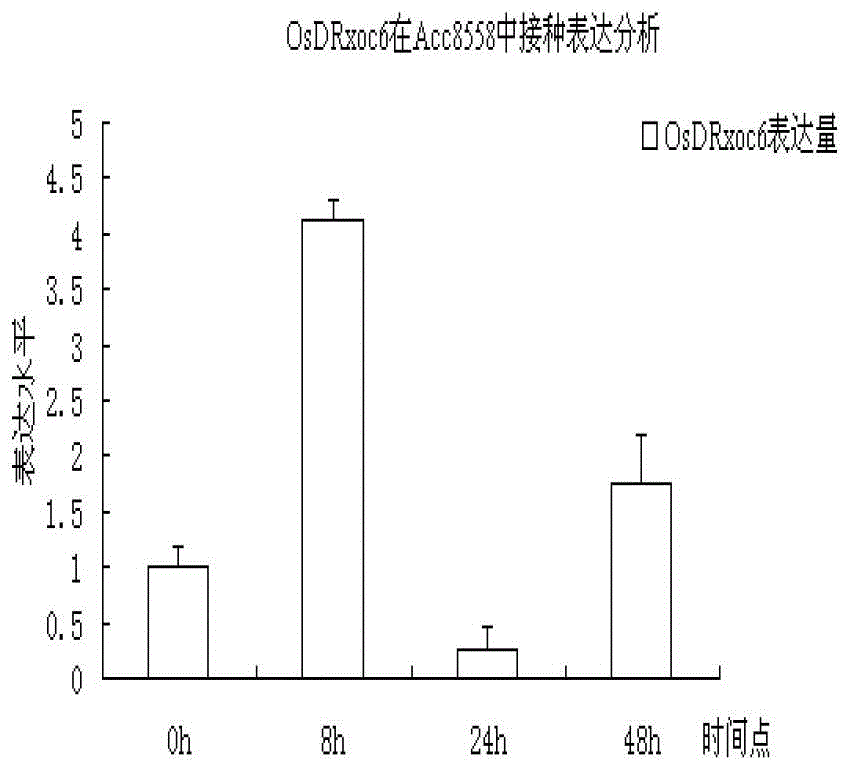
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and provides a paddy bacteria leaf streak resistance-related gene coding sequence of which a coded nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.2 and a coded amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.3, a gene OsDRxoc6 at which the paddy bacteria leaf streak resistance-related gene coding sequence is located and of which the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and a separating and cloning method as well as functional verification and application of the gene OsDRxoc6. The gene OsDRxoc6 is located in paddy bacteria leaf streak resistance QTL qB1sr5a, has no intron and is a positive control factor. The inventor also discovers that the resistance level of a transgenic plant capable of suppressing the gene OsDRxoc6 expression on the paddy bacteria leaf streak is remarkably reduced and the disease resistance of the transgenic plant capable of excessively expressing the gene OsDRxoc6 is remarkably improved.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Leaf die azoles water decentrality granula bactericide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101176448AOvercome the status quo that is not easy to recombineImprove securityBiocideFungicidesFungicideWater dispersible
The invention discloses a fungicide. Specifically, it is a water-dispersible granule fungicide of eubazole, which can be used to prevent and control rice bacterial blight, rice bacterial streak, tomato bacterial wilt and soft rot of Chinese cabbage. Its component content is calculated by mass percentage: 200-800 parts of ecloazole, 20-40 parts of wetting agent, 20-40 parts of dispersing agent, 20-80 parts of disintegrating agent, 10-100 parts of binder, 15 parts of stabilizer -100 parts, fillers make up 1000 parts. The above ingredients are mixed in proportion, stirred uniformly, crushed to obtain mesh powder, and mesh powder and adhesive are mixed uniformly, then granulated, dried, and sieved to obtain ecumazole water-dispersible granules. The invention overcomes the disadvantages of the wettable powder of ebuazole and reduces the use cost of farmers and the pollution of the environment. Moreover, the present invention has the advantages of high content, fast disintegration, good dispersibility, good storage, transportation and stability during use, and has high activity, good efficacy and safety.
Owner:张少武
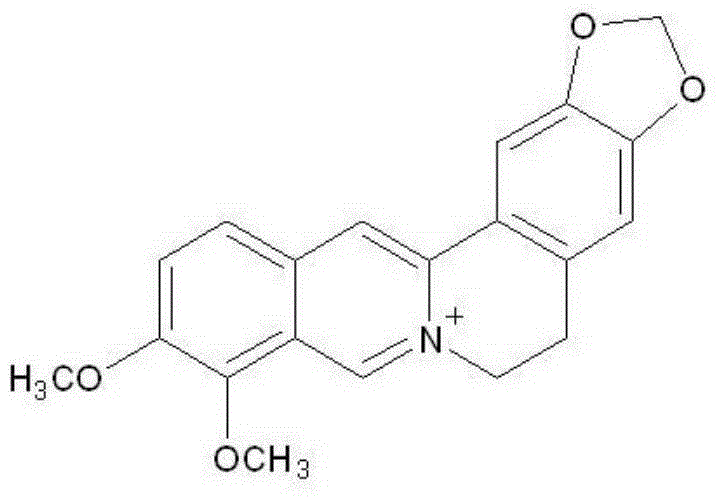
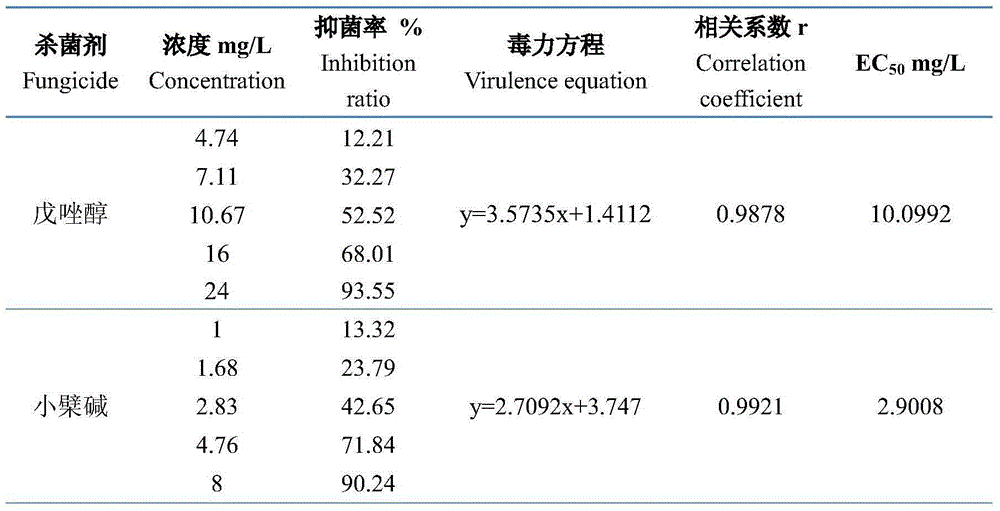
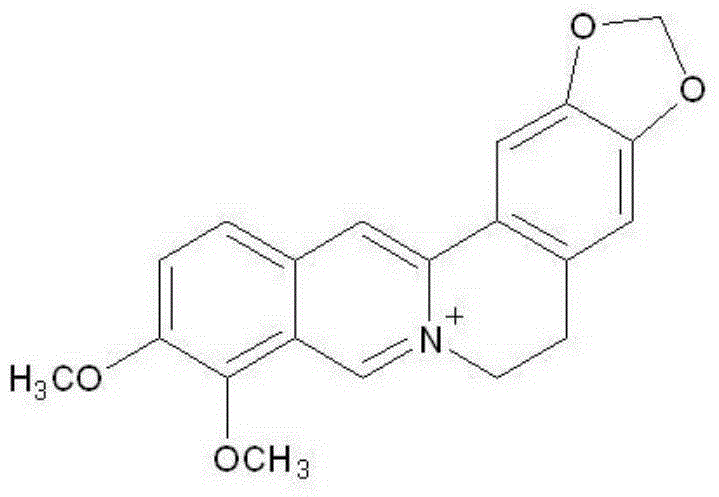
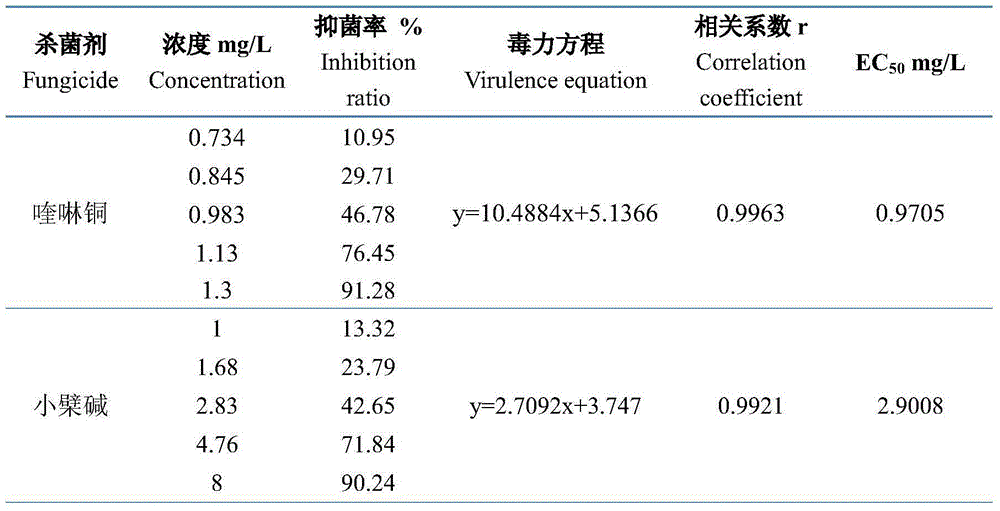
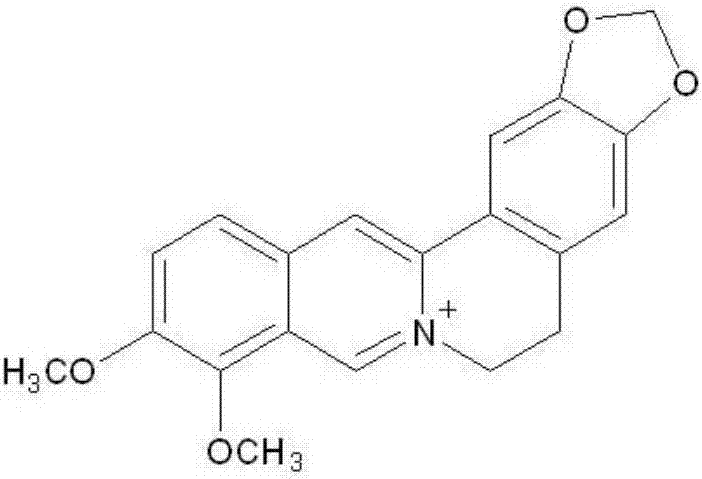
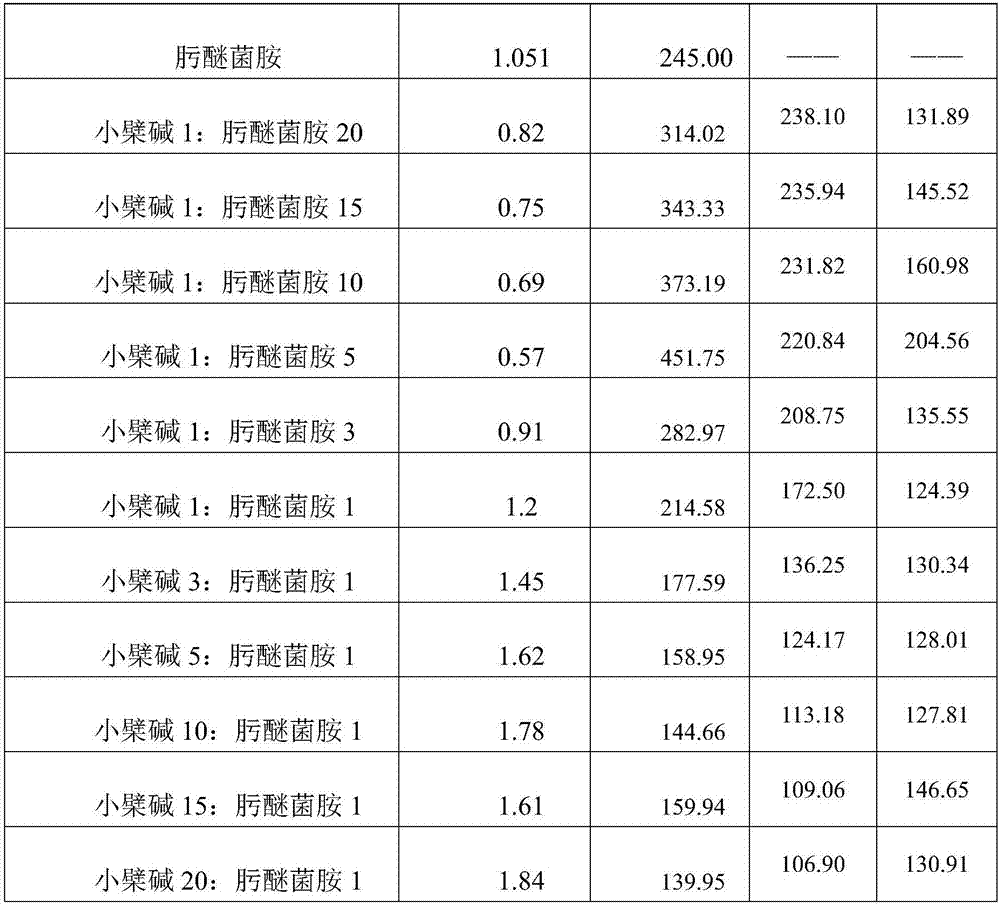
Bactericidal composition containing berberine and tebuconazole
ActiveCN105104392AGood synergyOvercoming and delaying drug resistanceBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologySuspending Agents
The invention discloses a bactericidal composition containing berberine and tebuconazole. The bactericidal composition is prepared by compounding the active ingredients including berberine and tebuconazole in a mass ratio of (1 to 9)-(9 to 1). The bactericidal composition can be prepared into conventional dosage forms in the pesticide science, such as wettable powder, water dispersible granules, suspensions, microcapsule suspensions, granules or emulsion in water. The bactericidal composition has the advantages of high efficiency, little environmental pollution, capability of delaying the resistance of germs to drugs, and the like, and can be used for controlling diseases of various crops, especially rice bacterial leaf streak.
Owner:BONTECH WELFARE ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI BEIJING CO LTD
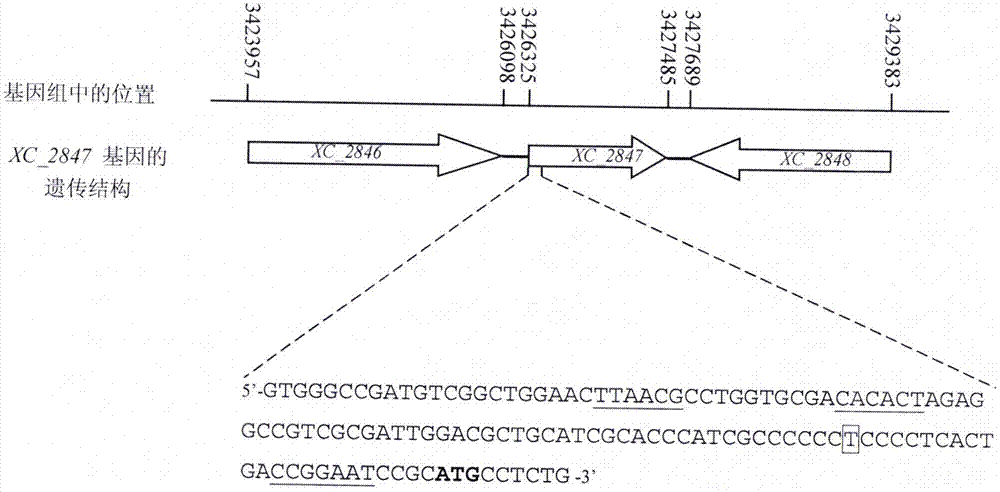
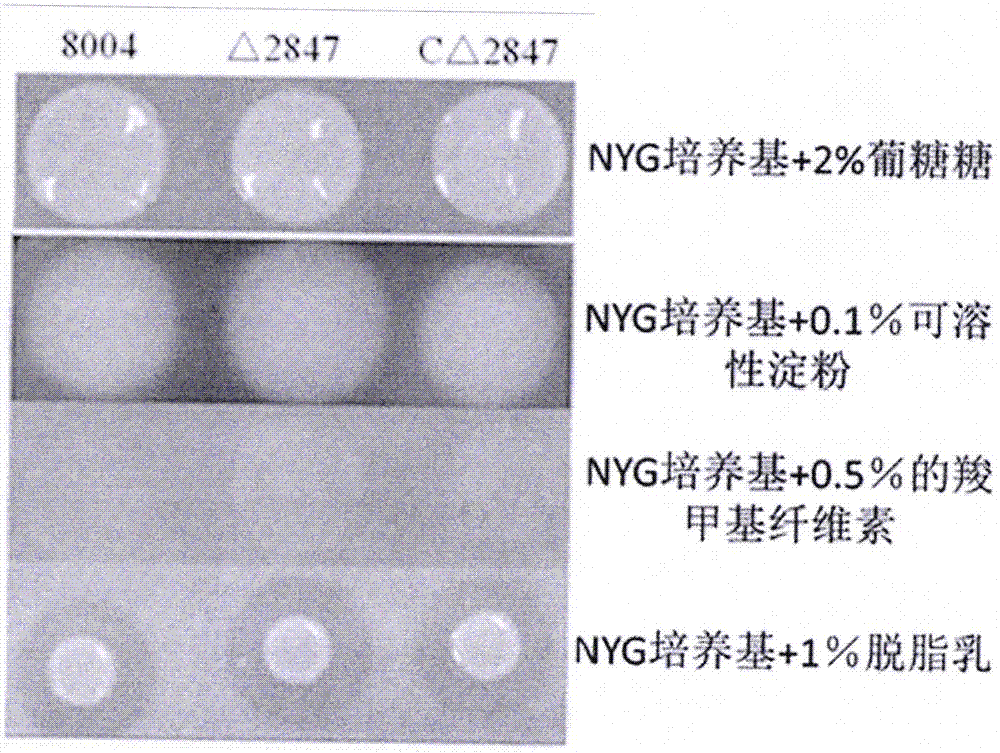
Applications of Xanthomonas pathopoiesis-associated gene
ActiveCN106916831AReduced ability to react allergicallyMicroorganism based processesBacteria peptidesMicrobiologyCell Membrane Proteins
The present invention discloses applications of a Xanthomonas pathopoiesis-associated gene hpaM in prevention and control of plant Xanthomonas diseases, wherein the number of the gene is XC_2847, the gene encodes a cell membrane protein, and the plant Xanthomonas diseases comprises one or a plurality of diseases selected from cruciferae black rot caused by cruciferae black rot bacteria, rice bacterial blight caused by rice bacterial blight bacterial, and rice bacterial leaf streak caused by rice bacterial leaf streak bacteria.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Bactericidal composition containing berberine and oxine-copper
ActiveCN105104391AGood synergyOvercoming and delaying drug resistanceBiocideFungicidesWater dispersibleBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a bactericidal composition containing berberine and oxine-copper. The bactericidal composition is prepared by compounding the active ingredients including berberine and oxine-copper in a mass ratio of (1 to 9)-(9 to 1). The bactericidal composition can be prepared into conventional dosage forms in the pesticide science, such as wettable powder, water dispersible granules, suspensions, microcapsule suspensions, granules or emulsion in water. The bactericidal composition has the advantages of high efficiency, little environmental pollution, capability of delaying the resistance of germs to drugs, and the like, and can be used for controlling diseases of various crops, especially rice bacterial leaf streak.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Preparation method of fungus fermentation product and application thereof in prevention and treatment of rice diseases
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fungus fermentation product and application of the fungus fermentation product in prevention and treatment of rice diseases, which belong to the field of biological prevention and treatment. The preparation method of the fungus fermentation product comprises liquid culture of fungus of Agrocybe sp. YB2005, treatment of the fermentation product, and separation of the fermentation product. The fungus fermentation product prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has better effects of prevention and treatment of rice bacterial leaf streak, rice sheath blight, and rice blast, and can be prepared by fermentation of a strain of the Agrocybe sp. YB2005, wherein culture medium raw materials have extensive sources. The preparation method of the fungus fermentation product is simple and easy for realization of industrial production.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
A fungicide composition containing kasugamycin and pyraclostrobin and its application
InactiveCN102273474ANo pollution in the processHigh flash pointBiocideFungicidesFungicidePlant disease
The invention relates to a fungicide composition containing kasugamycin and pyraclostrobin and its application. It includes kasugamycin, pyraclostrobin, dispersants, wetting agents, thickeners, stabilizers, disintegrants, defoamers and fillers. The bactericidal composition is a pollution-free fungicide with high efficiency and low toxicity, increased bactericidal spectrum, low cost, environmental friendliness, and difficulty for plant pathogenic bacteria to develop drug resistance, and can be used for the prevention and treatment of rice bacterial streak disease, rice blast and other diseases.
Owner:吴元林
Pesticide composition containing oxine-copper and kasugamycin, and application thereof
InactiveCN106973907ASynergistic effect is obviousImprove the effect of prevention and controlBiocideDead animal preservationDiseasePyricularia grisea
The invention discloses a pesticide composition containing oxine-copper and kasugamycin, and an application thereof. The composition comprises oxine-copper, kasugamycin and common assistants, and a weight ratio of the oxine-copper to the kasugamycin is (1-60 ):(1-20). The oxine-copper and the kaempromycin have significant synergistic effect after being compounded, and the doses of effective components of the above compounded medicament are obviously lower than those of individually used effective components, so the pesticide composition ahs the characteristics of synergistic effects, delaying of drug resistance, enlarged control range, good control effect, small dose and low agricultural cost. The composition is suitable for controlling most fungal diseases, and especially Pyricularia grisea, bacterial leaf streak, watermelon bacterial angular leaf spot disease and citrus ulcer disease.
Owner:SINON CHEM CHINA
Corn pathogen induced promoter
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and provides a corn pathogen induced promoter which can be activated by rhizoctonia solani kahn, rice bacterial blight pathogen and rice bacterial leaf streak pathogen. After the promoter is verified by truncation, the two sections including -1721bp to -1601bp and -1276bp to -1181bp are confirmed to be response elements induced by pathogenic bacteria. The corn pathogen induced promoter can be used for building a plant expression vector which is used for improving the resistance of plants to various diseases by a plant genetic engineering technology.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
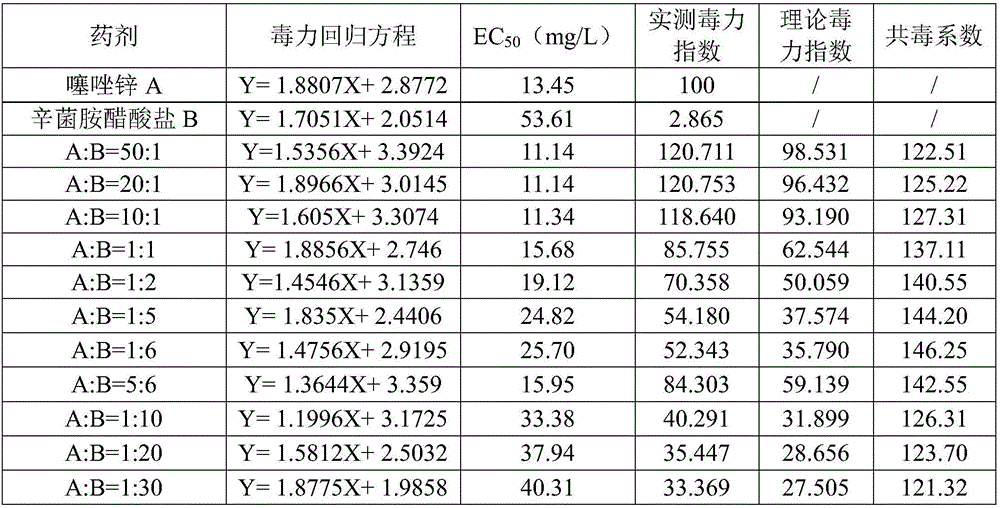
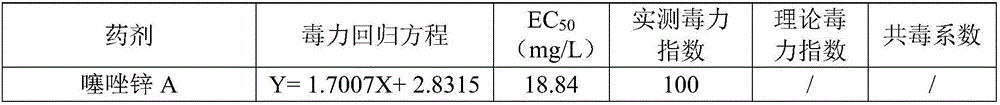
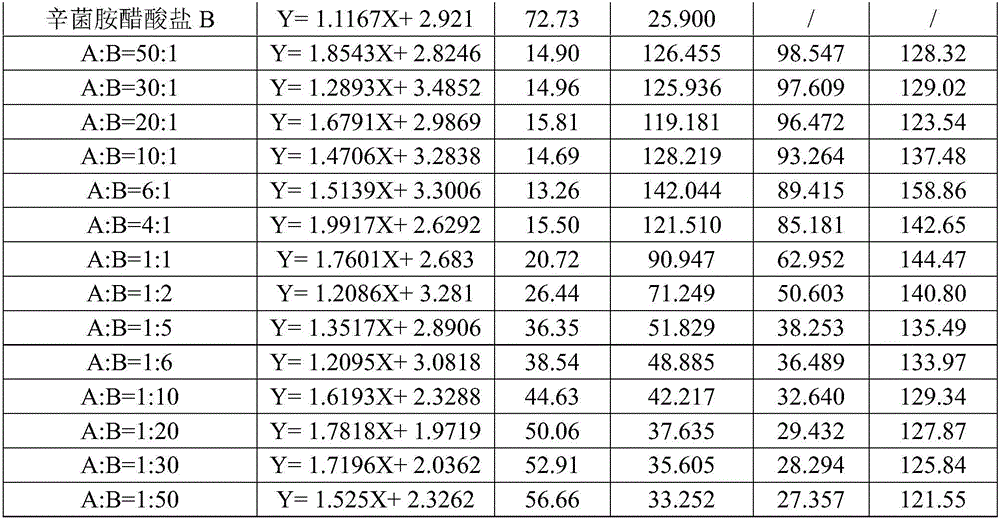
Composition containing zinc thiazole and xinjunan acetate, preparations and application thereof
InactiveCN106508919ASignificant synergyImprove the effect of prevention and controlBiocideDead animal preservationSuspending AgentsCanker
The invention discloses a composition containing zinc thiazole and xinjunan acetate, preparations and application thereof. The effective component of the bactericidal composition is compounded by zinc thiazole and xinjunan acetate, and the rest are auxiliary components, wherein the sum of the mass fraction of zinc thiazole and xinjunan acetate in the effective component of the bactericidal composition is 2%-90%. The dosage forms of the pesticide composition include suspending agents, wettable powder, water dispersible granules, and granules, etc., and the composition is mainly used for prevention and control of apple tree canker, pepper virus disease, citrus canker, tomato virus disease, bacterial canker of tomato, soft rot of Chinese cabbage, cotton blight and verticillium wilt, bacterial leaf streak, Erwinia chyrsanthemi, and rice bacterial leaf blight, etc. Mixing of zinc thiazole and xinjunan acetate can improve the control effect and expand the control spectrum, at the same time the medication frequency can be reduced, and the medication cost is lowered, thus reaching the effects of prevention first and comprehensive control.
Owner:JIANGSU XINNONG CHEM
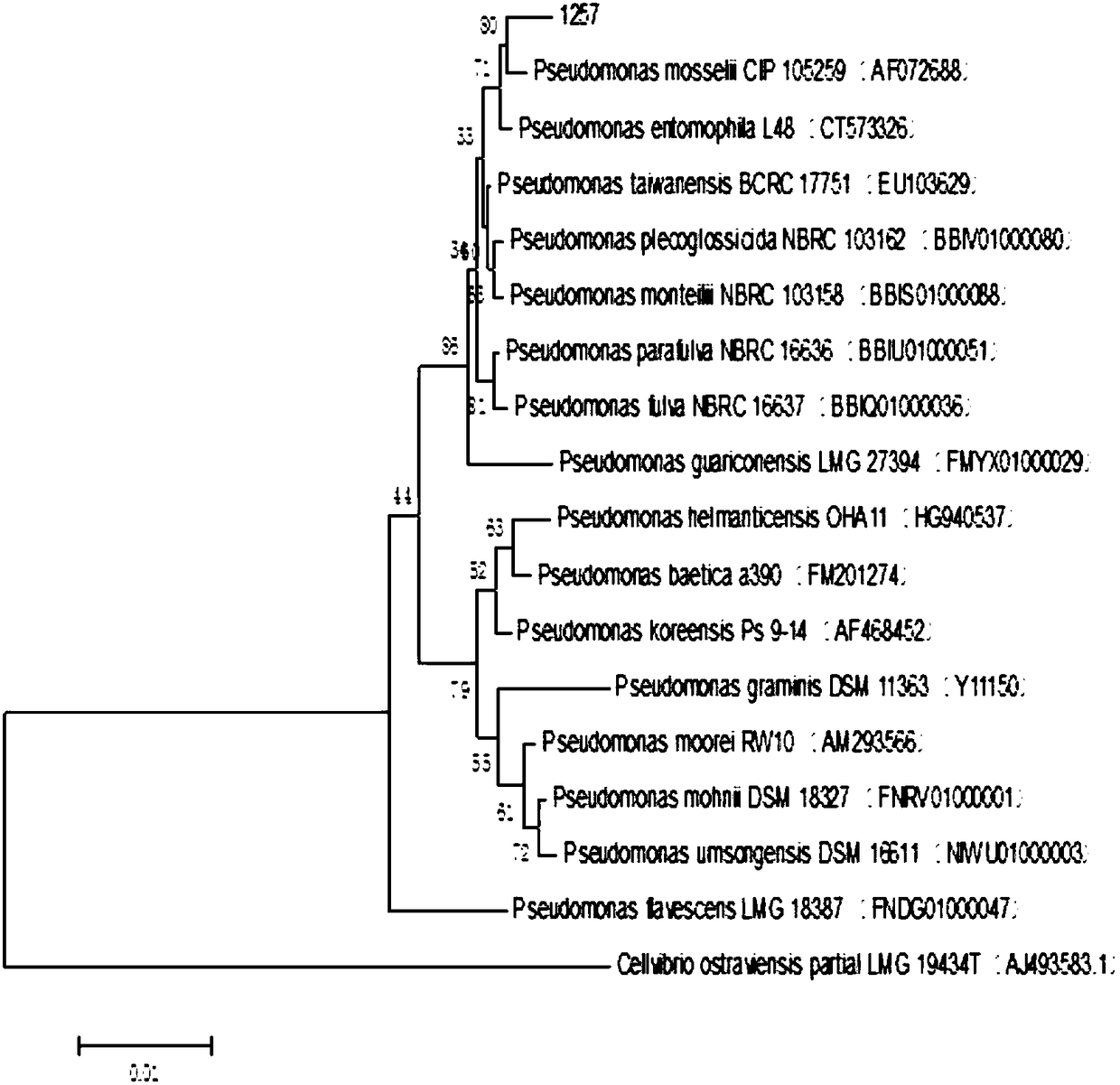
Pseudomonas and separating method and application thereof
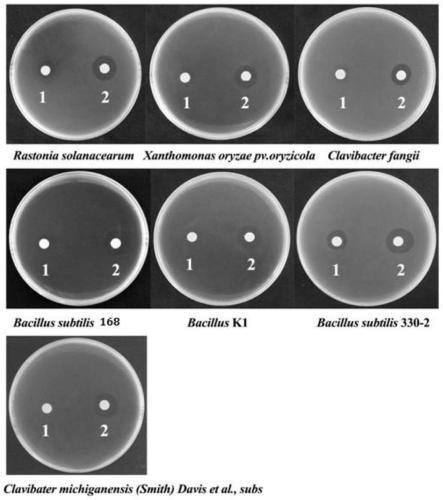
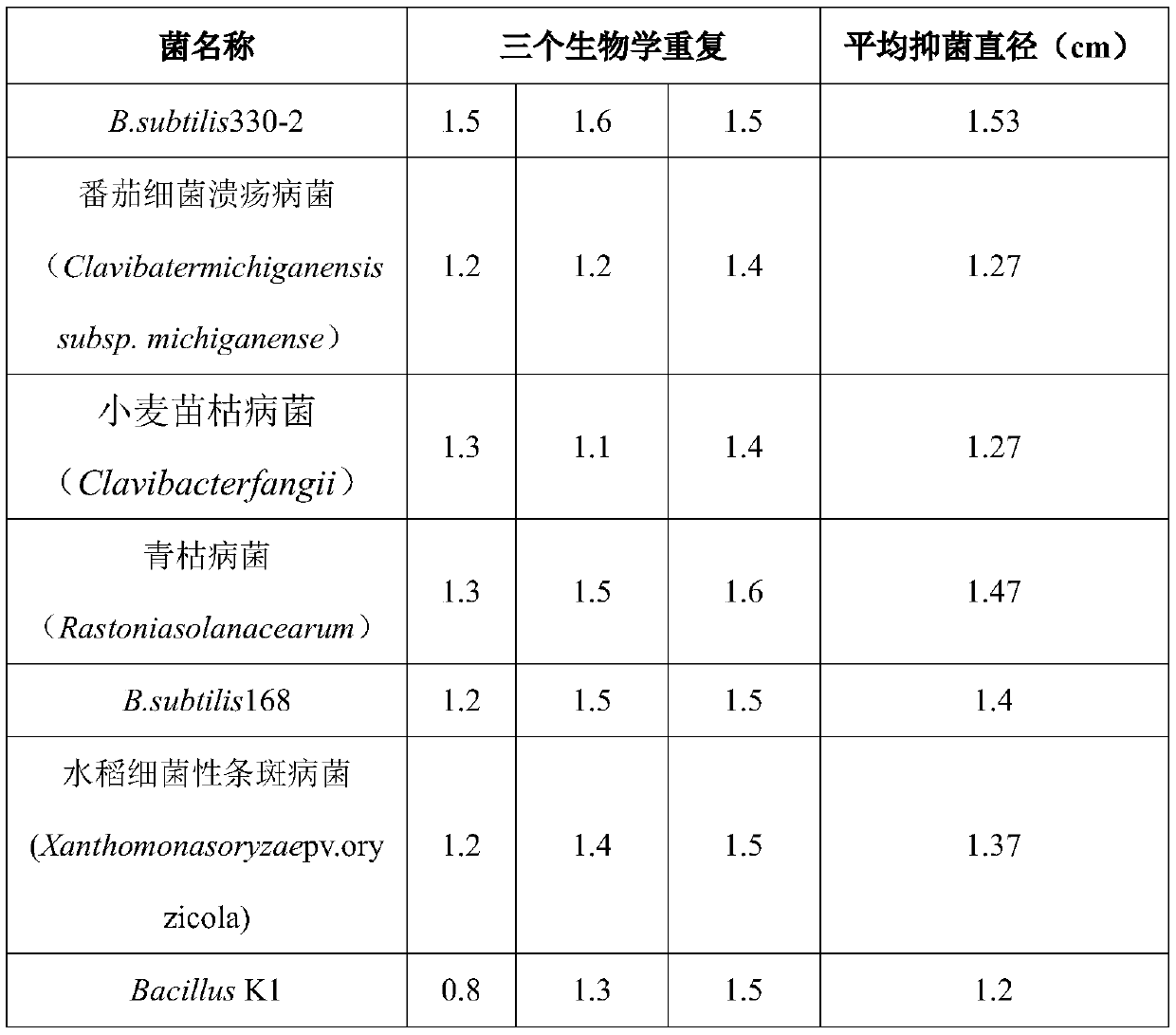
The invention relates to pseudomonas and a separating method and application thereof. Pseudomonas strains are preserved by China Center for Type Culture Collection in April 10 , 2018, wherein thepreservation name is Pseudomonas entomophila 1257, and the preservation number is CCTCC No:M 2018189. Pseudomonas has an obvious effect of inhibiting bacterial leaf streak, and meanwhile, pseudomonasalso has the effect of inhibiting xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae and magnaporthe oryzae.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
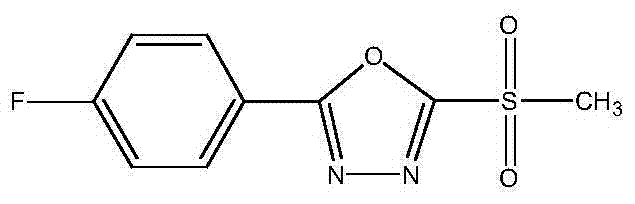
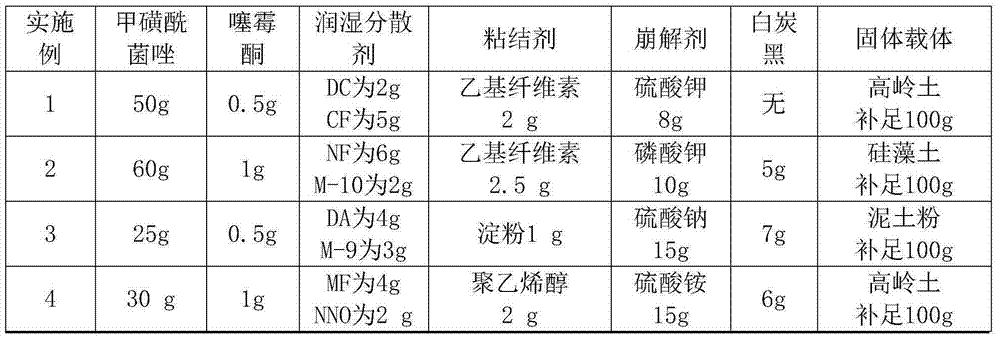
Compound composition and bactericide containing methylsulfonyl azole and benziothiazolinone
Owner:GAUNGXI TIANYUAN BIOCHEM
Aegilops tauschii antimicrobial peptide AtR100 and application thereof
InactiveCN110078806AEnhanced inhibitory effectGrowth inhibitionBiocideFungicidesCDNA libraryBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology and specifically discloses an aegilops tauschii antimicrobial peptide AtR100 and an application thereof. The inventor finally separates the aegilops tauschii antimicrobial peptide AtR100 with a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2, by establishing an aegilops tauschii cDNA library. The inventor finds that AtR100 has a strong inhibiting effectto the growth of tomato ulcer bacteria, ralstonia solanacearum, bacterial leaf streak of rice and clavibacter fangii which are difficult to be controlled by chemical drugs. A hemolytic test proves that the gene is harmless to mammals and humans. A powder acquired by performing liquid fermentation and spray drying on an antimicrobial peptide strain proves that the gene has a certain inhibiting effect to botrytis cinerea. The antimicrobial peptide strain is screened from aegilops tauschii. In later research, the antimicrobial peptide strain can be produced as a biological agent in large scale and can be applied to plant disease control.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for extracting active ingredient of folium artemisiae argyi and application of active ingredient in resistance of plant disease
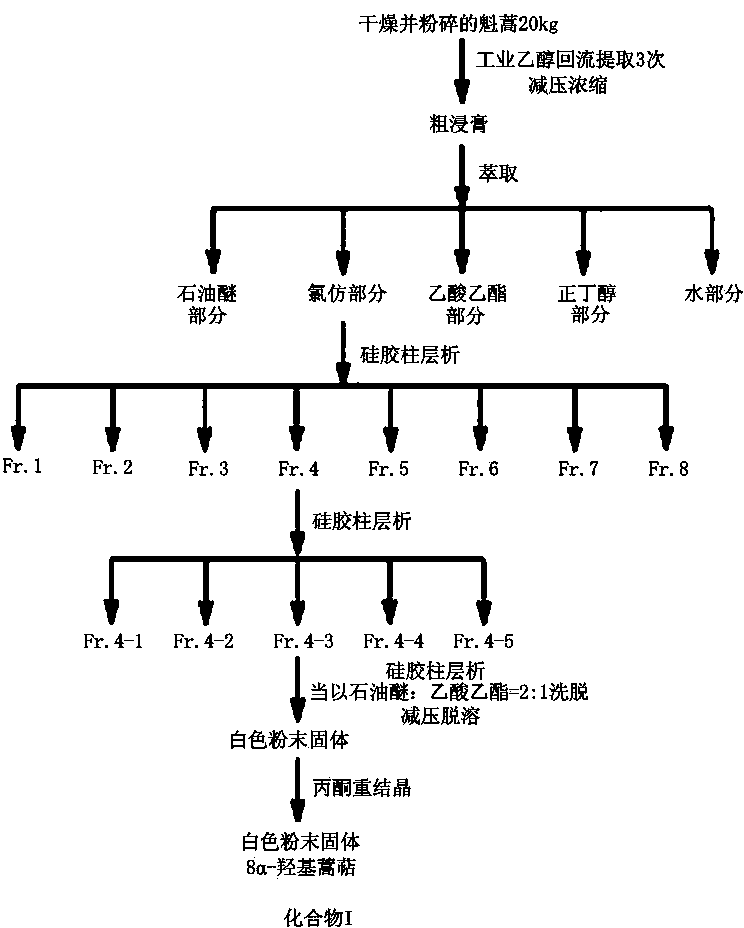
InactiveCN103848843AEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic chemistryBiotechnologyCucumber mosaic virus
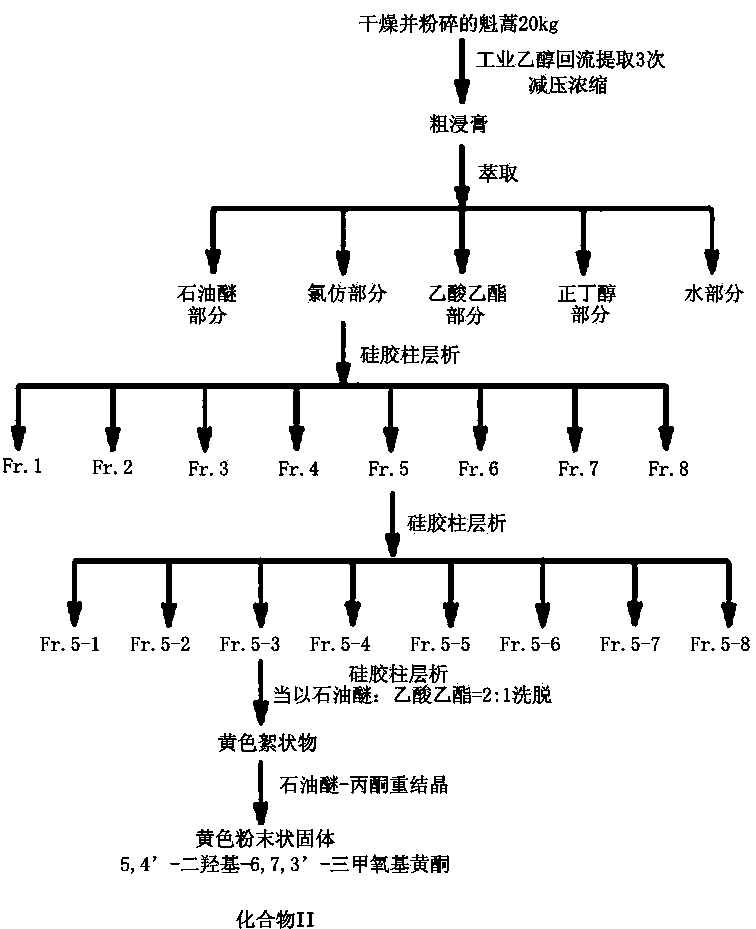
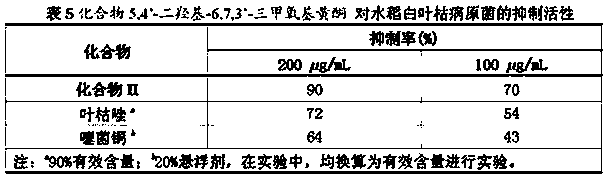
The invention provides a preparation method of an active substance capable of inhibiting plant viruses and plant bacteria and application of the active substance. The preparation method of the active substance capable of inhibiting plant viruses and plant bacteria comprises that folium artemisiae argyi in Guizhou province is taken as raw material, dried in the sun and then smashed, ethanol extraction is carried out; ethanol extract is extracted by virtue of trichloromethane; reduced pressure concentration is carried out on a trichloromethane extraction layer, so that crude extract is obtained; silica column chromatography is carried out on trichloromethane crude extract, gradient elution is carried out by virtue of petroleum ether-acetic acid ethyl ester mixed eluant in different ratios, then purification means like the silica column chromatography is carried out for a plurality of times, and two monomer compounds, namely 8 alpha-hydroxyl artemisia terpene and 5,4'-dihydroxyl-6,7,3'-trimethoxy flavone, are obtained. Biological activity tests show that the monomer compound I has good prevention and control effect on plant viruses such as cucumber mosaic virus, tobacco mosaic virus, south rice black-streaked dwarf virus and rice stripe virus and 5,4'-dihydroxyl-6,7,3'-trimethoxy flavone has good inhibiting effect on bacterial disease pathogenic bacteria such as tomato bacterial wilt, tobacco bacterial wilt, rice bacterial leaf blight and rice bacterial leaf streak.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Fertilization method for reducing bacterial wilt and bacterial leaf spot of pepper and improving drought resistance of pepper
ActiveCN110100556AImprove disease resistanceImprove drought resistanceSuperphosphatesFertilising methodsNitrogenPyrroloquinoline quinone
The invention relates to a fertilization method for reducing the bacterial wilt and bacterial leaf spot of pepper and improving the drought resistance of pepper. According to the method, in the wholegrowth period of pepper, 20-30 kg of pure nitrogen, 5-10 kg of pure phosphorus and 20-40 kg of pure potassium are applied per mu; before pepper transplanting, 9-14 kg of pure nitrogen, 2.5-5 kg of pure phosphorus and 13-27 kg of pure potassium are applied per mu as a base fertilizer in combination with soil preparation; after pepper planting, various fertilizers are applied at different times in different growth periods, and meanwhile a pyrroloquinoline quinone solution with the mass concentration of 100-300 nmol / L is applied, wherein the application amount each time is 15 L / mu, and the pyrroloquinoline quinone solution is applied 3 times in total. The method has the advantages that different fertilizers are selected according to different growth periods of pepper, different kinds of potash fertilizers are selected for cooperative application, the pyrroloquinoline quinone solution is also applied, the adaptability of pepper to bacterial wilt, bacterial leaf spot and drought environmentcan be improved, the use quantity of pesticides is reduced, and the method has great economic value and ecological value.
Owner:HUNAN VEGETABLE RES INST
Bactericidal composition for preventing and treating rice bacterial leaf streak
InactiveCN107136102AGood synergyOvercoming and delaying drug resistanceBiocideDead animal preservationDiseaseBerberine
The invention belongs to the technical field of pesticides, and particularly relates to a bactericidal composition for preventing and treating a rice bacterial leaf streak. The bactericidal composition for preventing and treating the rice bacterial leaf streak is formed by compounding effective components which are berberine and orysastrobin, wherein the mass ratio of the berberine to the orysastrobin is (1 to 20):(20 to 1). The bactericidal composition provided by the invention can be prepared into conventional dosage forms of wettable powder, a water dispersible granule, a suspending agent, a micro-capsule suspending agent, a granule or an aqueous emulsion and the like in agricultural pharmacology. The bactericidal composition provided by the invention has advantages of being high in efficiency and little in environment pollution and delaying the generation of the drug resistance of a germ, and the like. The bactericidal composition can be used for preventing and treating diseases of multiple crops, and particularly the rice bacterial leaf streak.
Owner:广西南宁黑泥巴农业科技有限公司
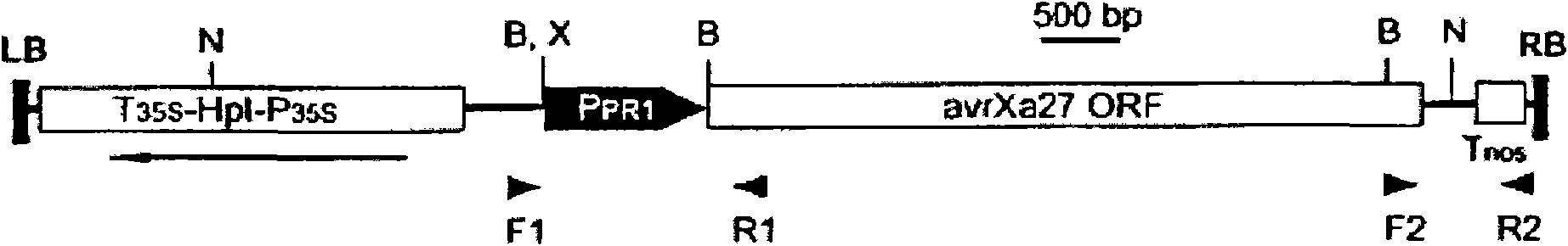
Induction of xa27 by the avrxa27 gene in rice confers broad-spectrum resistance to xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and enhanced resistance to xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola
The present invention generally provides a method to generate broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in plants. More specifically, the present invention provides a method to generate broad-spectrum resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, the causal agent of bacterial blight disease of rice, and enhanced resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola, the causal agent of bacterial leaf streak of rice. Xa27, an inducible bacterial blight R gene in rice, was induced by the cognate avrXa27 gene expressed in host. Rice plants carrying the avrXa27 transgene and wild-type Xa27 gene conferred resistance to incompatible and compatible pathogens, and enhanced resistance to X. oryzae pv. oryzicola strain L8. The Xa27-mediated enhanced resistance to X. oryzae pv. oryzicola was also observed in the interaction between IRBB27 and L8 harboring pHM1avrXa27. This was further verified by the fact that the Xa27 gene in IRBB27 was induced by theavrXa27 gene in bacteria. The method can be used to engineer broad-spectrum resistance of rice to bacterial blight and enhanced resistance to bacterial leaf streak. Slight modification of this technique can be applied to control bacterial diseases in other crops.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
Rice gene OsDF1 and application of disease control functions
ActiveCN106701783ABroad spectrum of disease resistanceShort cyclePlant peptidesFermentationDiseaseRice plants
The invention provides a rice disease control gene named as OsDF1. An open reading frame of the gene is 1512bp long, and the encoded protein is composed of 503 amino acids. The protein does not comprise any structural domain of known functions. By constructing overexpression transgenic rice of the gene and disease resistance analysis thereof, a broad spectrum control effect of the gene on the bacterial disease resistance of the rice is illustrated first. The overexpression transgenic rice plants widely reduce the resistance of bacterial leaf streak and bacterial leaf blight of rice, and the broad spectrum negative control function of the gene on the bacterial disease resistance of the rice is disclosed. The invention first discloses biological functions of the gene, and provides application of acquiring rice materials with general decrease of bacterial disease resistance by creating OsDF1 overexpression rice and application of acquiring broad spectrum bacterial disease resistant rice materials by creating OsDF1-RNAi rice. The gene is a novel gene resource applied to creating and breeding novel materials and novel varieties of rice with broad spectrum bacterial disease resistance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Applications of rice OsMPK1 gene in improvement of disease resistance of rice
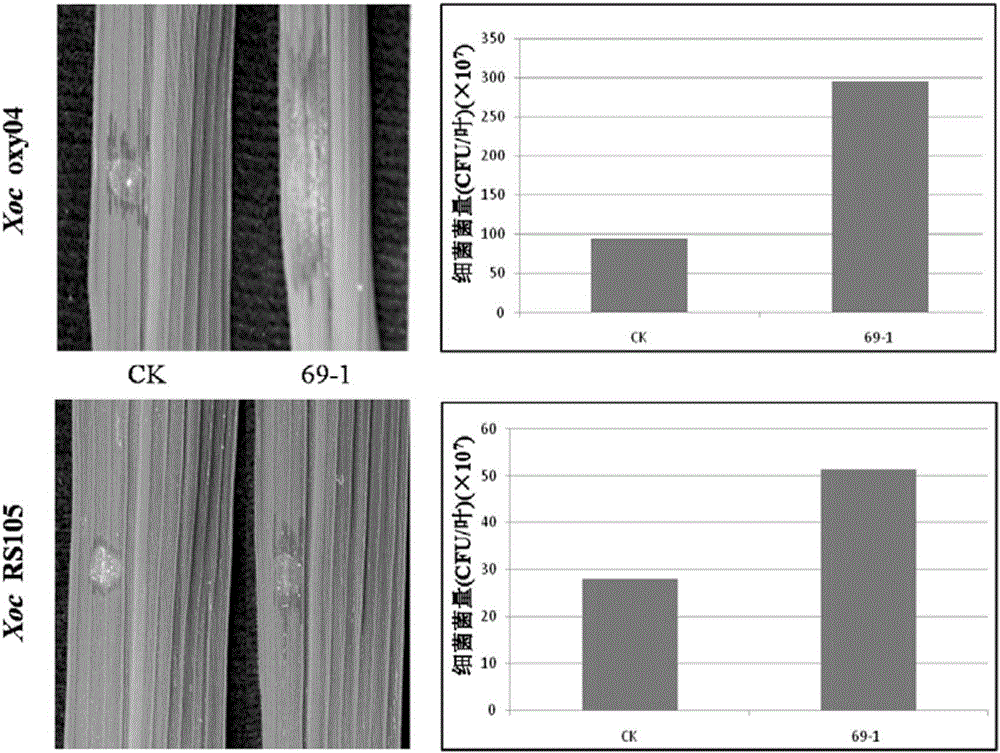
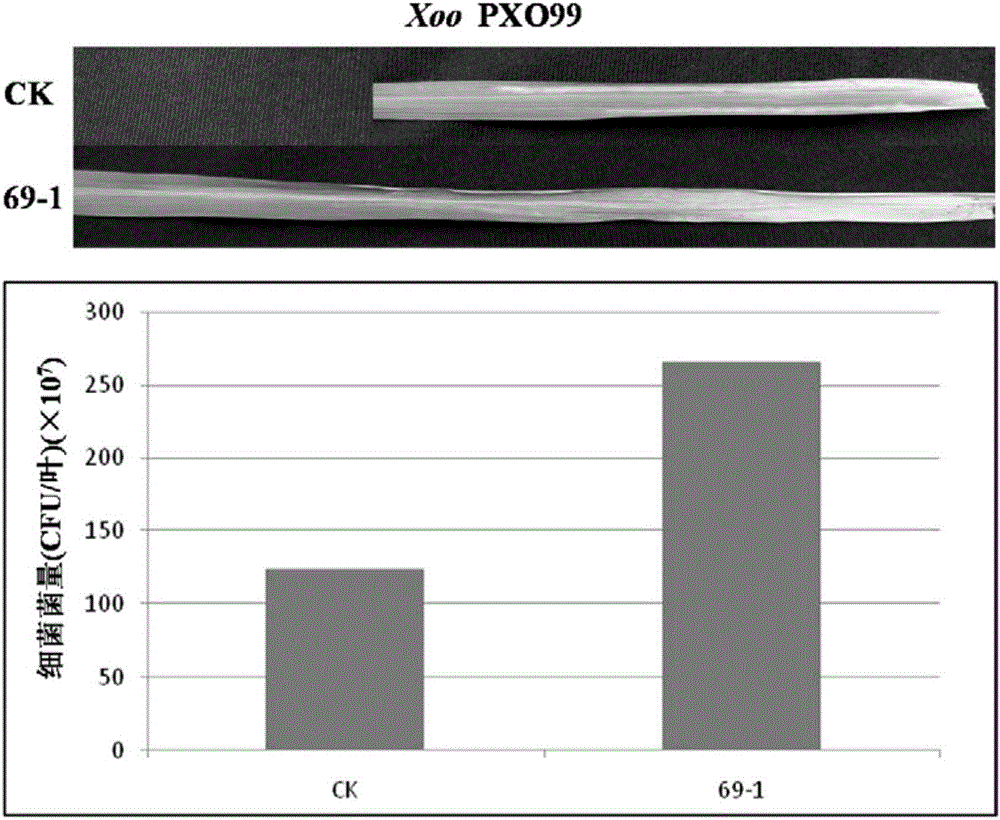
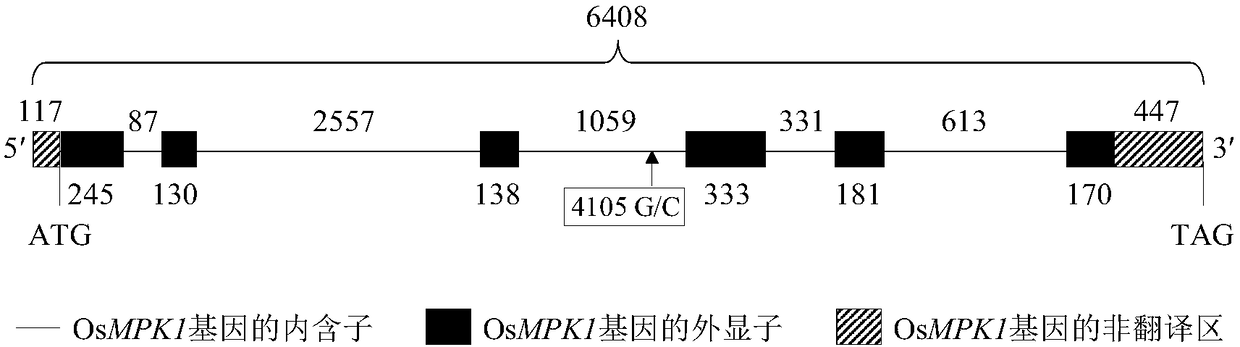
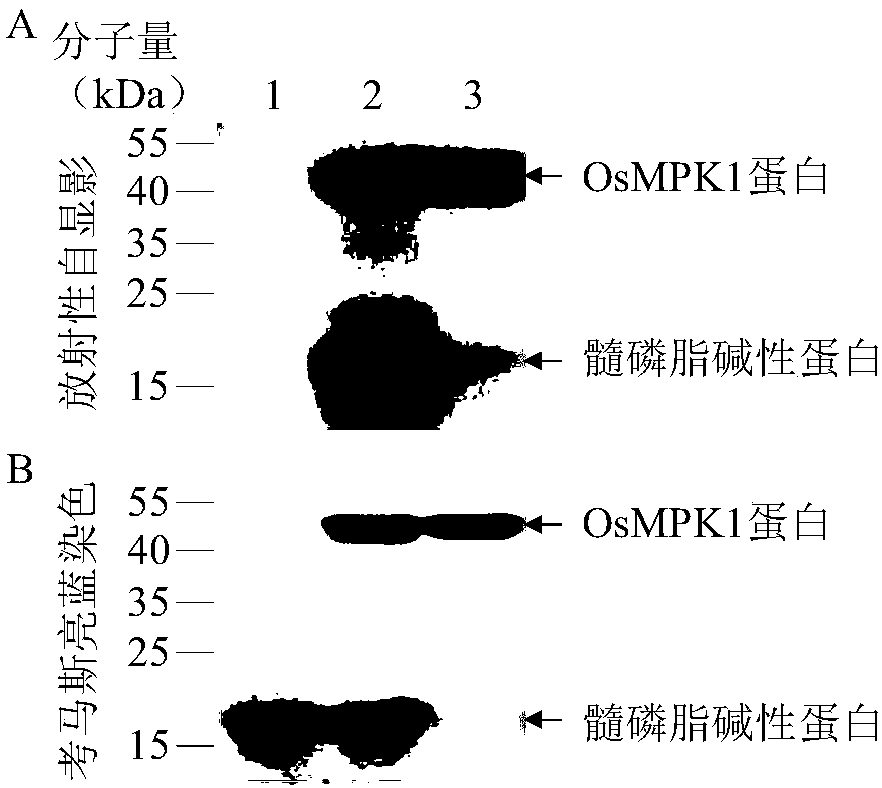
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, specifically relates to applications of a rice OsMPK1 gene in improvement of the disease resistance of rice, and provides isolation cloning and function verification of the DNA fragment of the rice disease-resistance related gene OsMPK1, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the OsMPK1 gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, the sequence of the protein encoded by the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:2, and the encoded product of the protein is a mitogen-activated protein kinase. According to the present invention, the resistance of the transgenic plant over-expressing the OsMPK1 to bacterial leaf streak is significantly enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Bacillus pumilus ZR3-3 for controlling and preventing bacterial diseases and application of Bacillus pumilus ZR3-3
The invention relates to a biologically antibacterial agent. The effective active ingredient of the biologically antibacterial agent is composed of Bacillus pumilus ZR3-3. The biologically antibacterial agent has the characteristics that the biologically antibacterial agent is a water-based agent, and comprises, in percent by weight, 89.5-99.8% of Bacillus pumilus ZR3-3, 0.1-10% of sodium dodecylsulfate and 0.1-0.5% of potassium sorbate. When the biologically antibacterial agent is in use, the water-based agent is poured to roots so as to control soft rot of Chinese cabbages and bacterial wilt of Capsicum annuum, and rice leaf surfaces are uniformly sprayed so that bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak of rice can be controlled. The biologically antibacterial agent has the advantagesthat through introduction of the Bacillus pumilus ZR3-3 which has human and animal safety and a good control effect on multiple plant bacterial diseases, the biologically antibacterial agent is utilized to control the plant bacterial diseases, the use dosage of chemical agents is reduced, and meanwhile the purposes of improvement of the ecological environment and reduction of the amount of residues of the chemical agents in agricultural products are achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
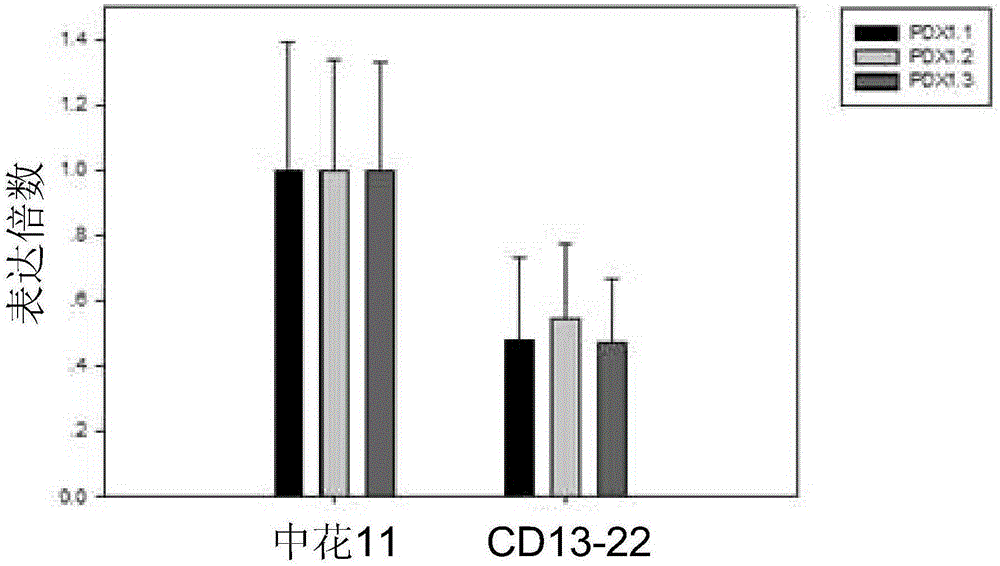
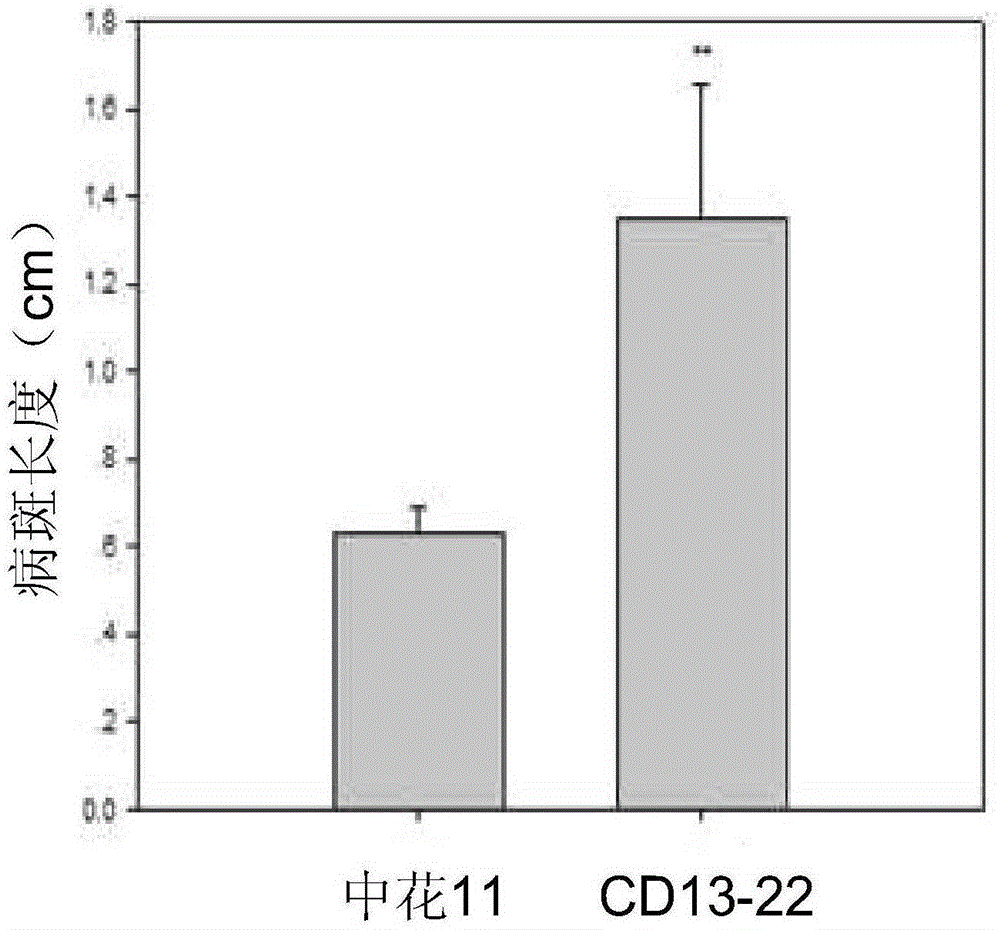
Application of vitamin B6 content increase in improving resistance of rice to bacterial leaf streak
ActiveCN105177018AImprove the level ofImprove disease resistanceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceTransgenic technology
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. Based on the basic discovery that increase of vitamin B6 content can improve the resistance of rice to bacterial leaf streak, the invention utilizes the strong promoter driven transgenic technology to shift the overexpression carrier of vitamin B6 synthetic gene OsPDX1 into rice variety Zhonghua 11, the genetic transformation rice with significantly increased OsPDX1 family gene expression quantity has significantly increased vitamin B6 level, and has significantly enhanced resistance to bacterial leaf streak, while the genetic transformation rice with suppressed OsPDX1 family gene expression has significantly decreased vitamin B6 content, and has significantly reduced resistance to bacterial leaf streak. Therefore, the invention further verifies the important role and application value of vitamin B6 and its synthetic gene OsPDX1 in the resistance of rice to bacterial leaf streak.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
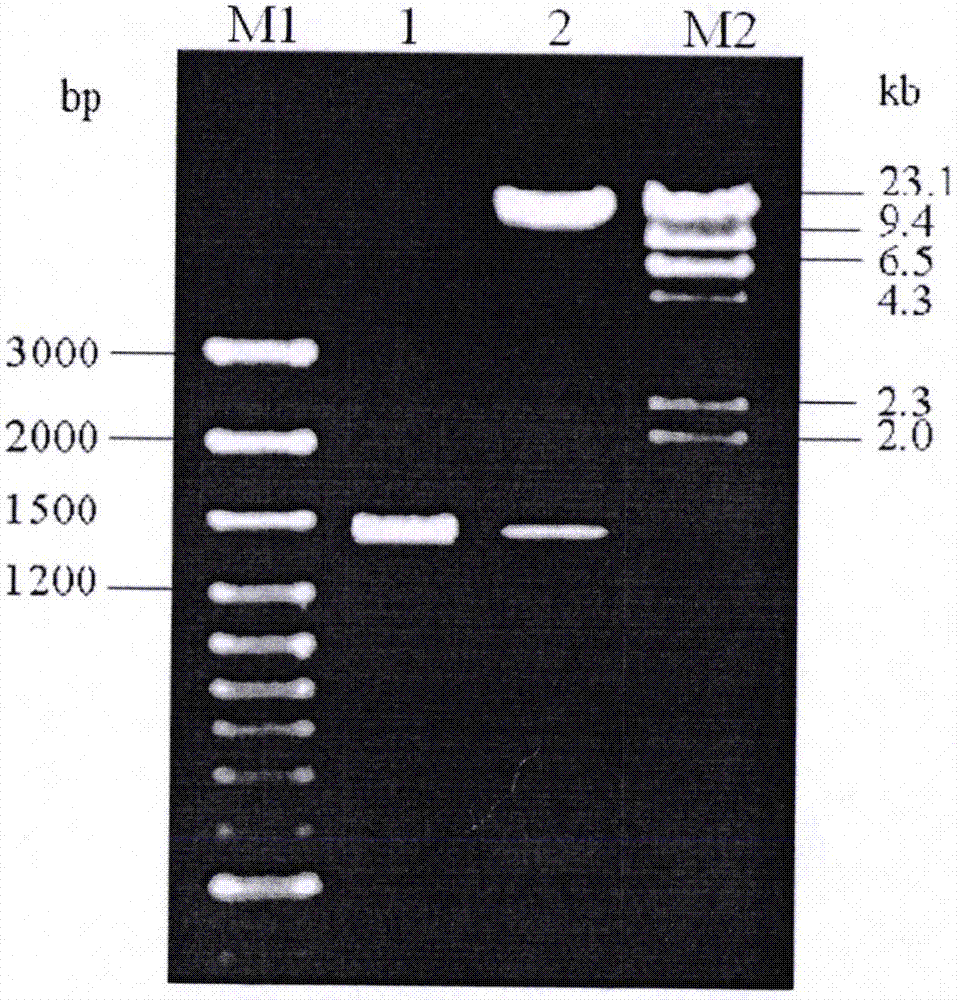
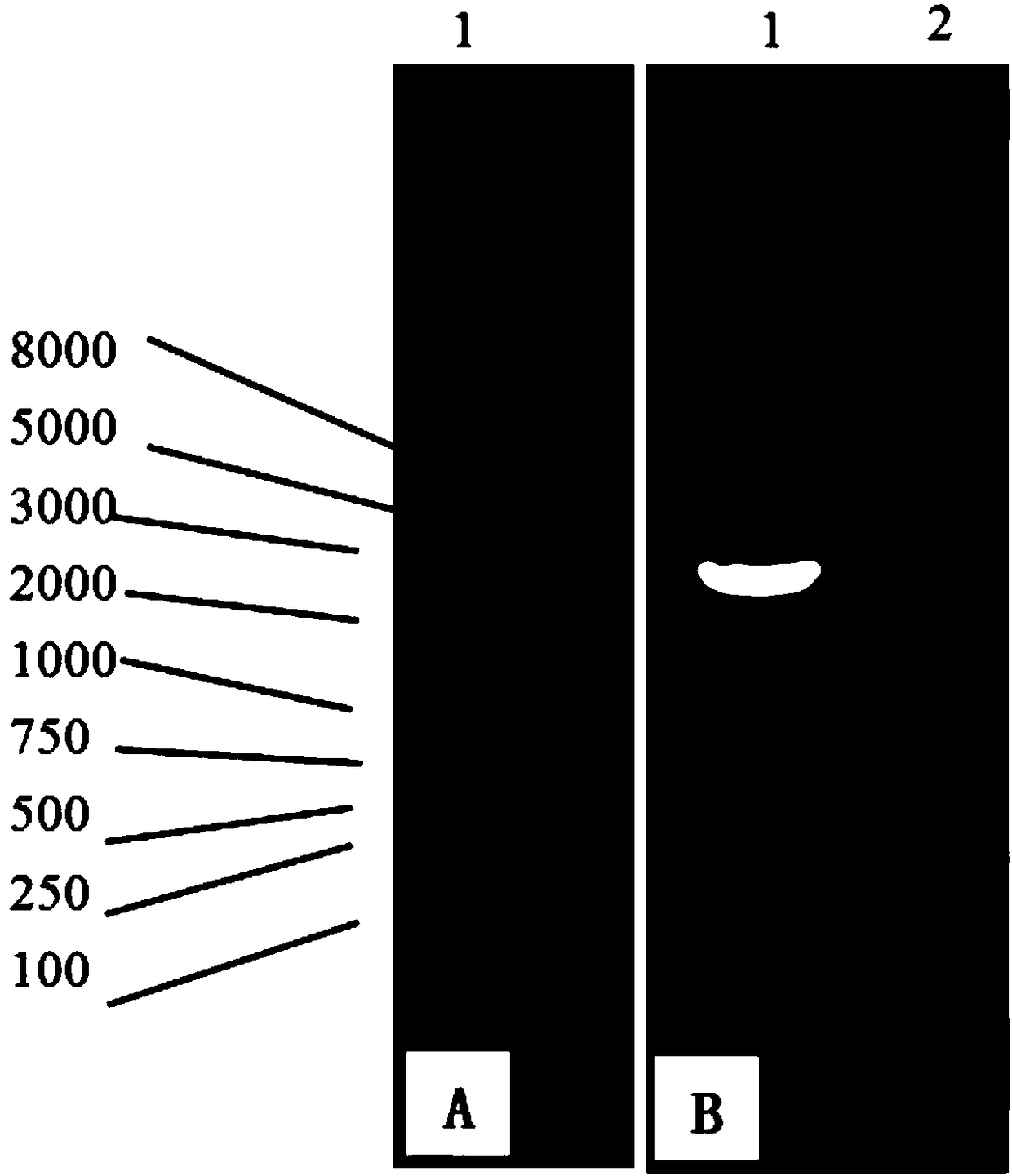
HDA kit for detecting bacterial leaf streak pathogens of rice and detecting method
InactiveCN105018486AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyHelicase
The invention provides an HDA kit for detecting bacterial leaf streak pathogens of rice and a detecting method. The HDA kit comprises an HDA primer pair for specifically detecting the bacterial leaf streak pathogens of the rice, a 10-fold buffer solution, ATP, dNTPs, Bst polymerase, RecA protein, UvrD helicase, positive control DNA and ddH2O. According to the detecting method, DNA extracted from a sample to be detected is used as a detection template; the bacterial DNA extraction kit is adopted for extracting the DNA of the sample to be detected, and the DNA is conserved for standby; the HDA kit is utilized for carrying out an HDA reaction to obtain an amplified product; the amplified product is detected, and judgment is made. The detecting method has high specificity, can amplify specificity strips only from bacterial leaf streak pathogen DNA of the rice, and has higher sensitivity and accuracy compared with a physiology and biochemistry detecting method; the HDA detecting method can be carried out at constant temperature, and speed is higher compared with that of a conventional PCR detecting method; only a common water bath kettle is needed for carrying out the amplification reaction, and complex and expensive thermal cycler equipment is not needed.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
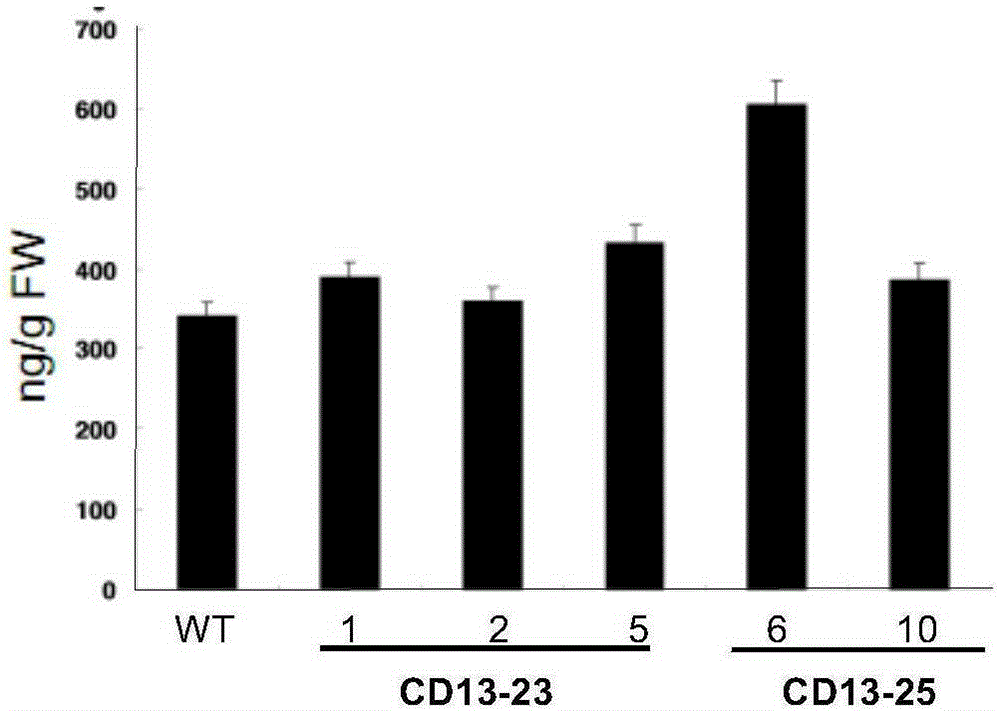
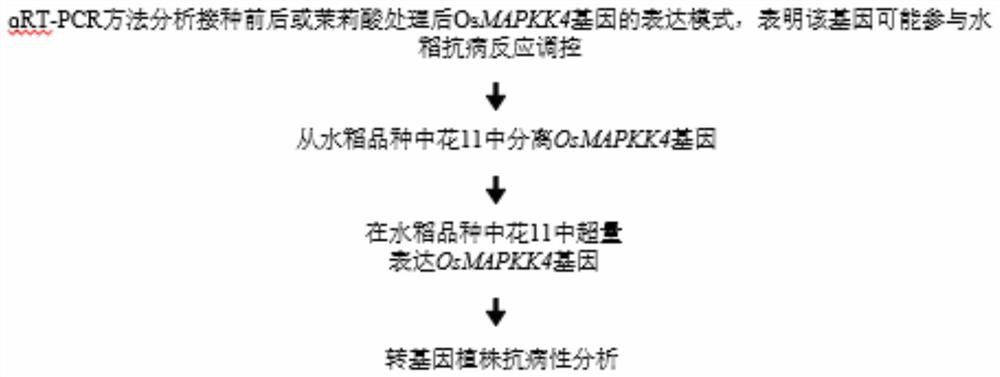
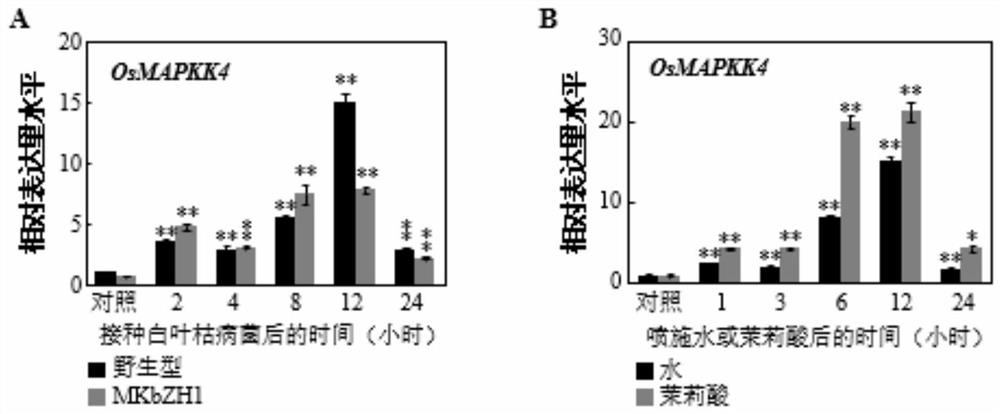
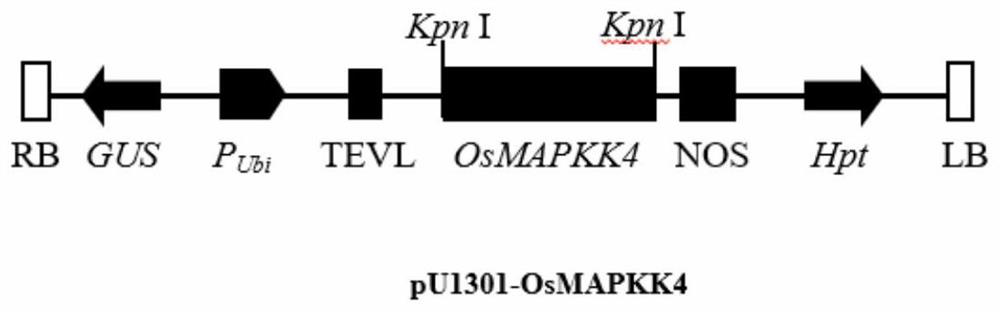
Application of OsMAPKK4 gene in improving disease resistance of rice
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to application of an OsMAPKK4 gene in improving disease resistance of rice, particularly the application in controlling resistance of rice to bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak. Through research on overexpression of the OsMAPKK4 gene, it is found that the OsMAPKK4 gene can influence the resistance of rice to bacterial leaf blight and bacterial leaf streak, and the overexpression of the OsMAPKK4 gene improves the resistance of rice to bacterial leaf blight and bacterial leaf streak. The OsMAPKK4 gene can be applied to disease-resistant breeding of rice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
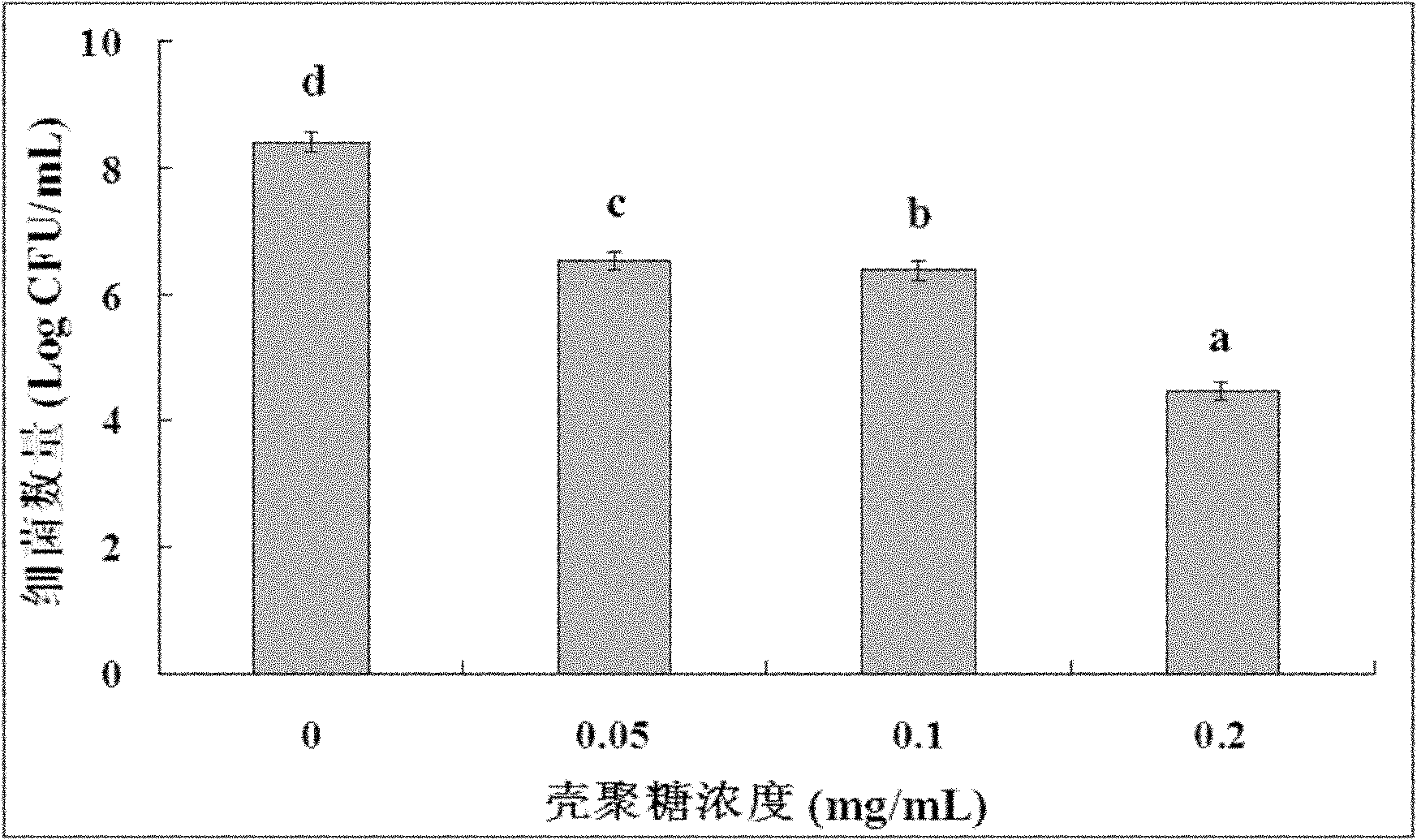
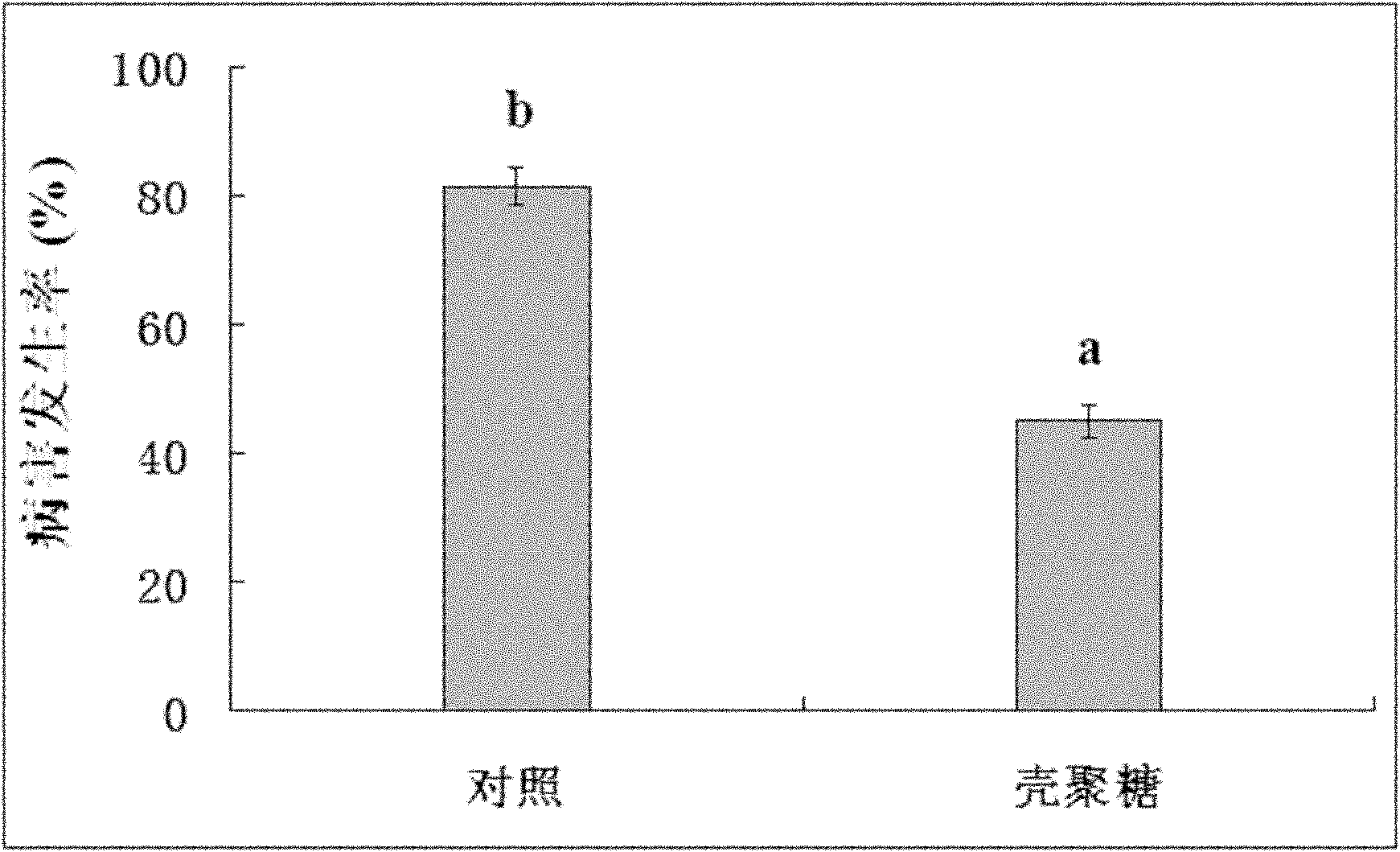
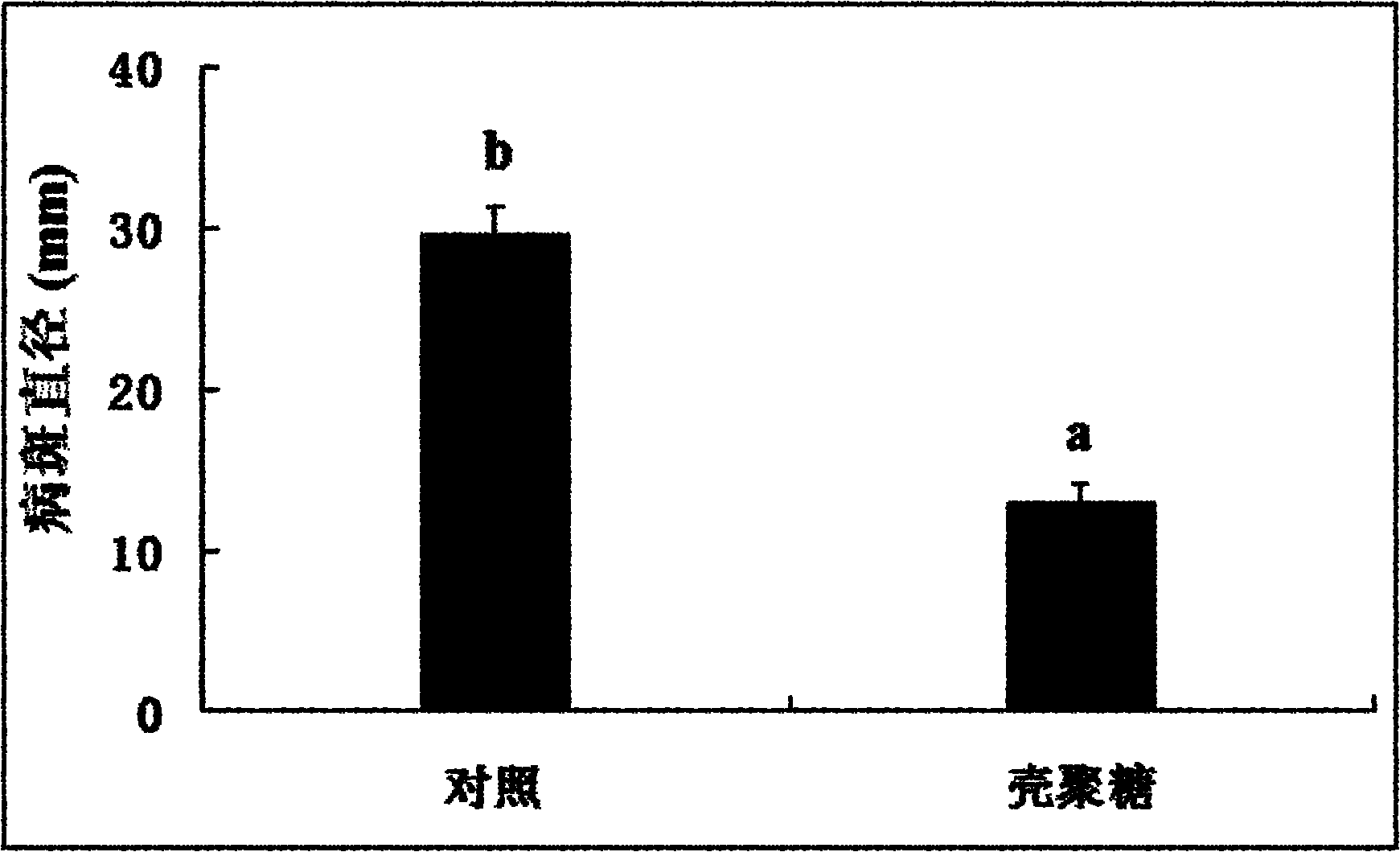
Application of chitosan in prevention and treatment of rice bacterial leaf streak
InactiveCN102037965AReduce morbidityEnhanced Performance Against Bacterial StripeBiocideDisinfectantsMicrobiologyPolyphenol oxidase
The invention discloses an application of chitosan in prevention and treatment of rice bacterial leaf streak. A chitosan preparation provided by the invention can significantly reduce the incidence of the rice bacterial leaf streak and the size of disease spots, significantly improve the activities of phenylalanine ammonia lyase, peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase in rice seedlings and further enhance the resistance against diseases of rice. The chitosan preparation is simple and easy for application in the prevention and treatment of the rice bacterial leaf streak, and the cost is lower.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bacillus altitudinis ST15 for antagonizing xanthomonas oryzae and application of bacillus altitudinis ST15
ActiveCN112143686AImprove toleranceHigh antagonistic activityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyEcological environment
The invention discloses bacillus altitudinis ST15 antagonizing xanthomonas oryzae and application of the bacillus altitudinis ST15. The bacillus altitudinis ST15 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 28th, 2020, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.20156. The strain has relatively high antagonistic activity to Xanthomonas oryzae pv .oryzaeand Xanthomonas oryzae pv .oryzicola, can promote the growth of rice and improve the drought resistance of rice seedlings, and has relatively strong tolerance to common chemical bactericides for preventing and treating rice bacterial diseases. Bacterial suspension or a biocontrol microbial agent prepared from the strain has a relatively high biocontrol effect on rice bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak, can replace or reduce the use of chemical pesticides, improves the safety of food and ecological environment, and has relatively high economic and social benefits.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES +1
Molecular marker of paddy rice major gene site capable of preventing bacterial leaf streak and applications thereof
ActiveCN107893127ALong-term prevention is of great significanceThe position of the main effect gene locus is clearMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationOryzaAgricultural science
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a paddy rice major gene site capable of preventing bacterial leaf streak and a primer pair for amplifying the molecular marker. The inventor subjects Guangxi wild rice resistant resources DY19(male) and 9311(female) to hybridization, backcross, and selfing to obtain BC3F2 offspring; and then resistance identification and molecular genetics linkage analysis are performed to obtain a molecular marker SL41, which is in close linkage with a gene capable of preventing bacterial leaf streak. The location of the major gene site detected by developed molecular marker is definite, the identification is convenient, and the molecular marker has an important meaning for the long term control of bacterial leaf streak. Moreover, the operation of using the molecular marker to detect bacterial leaf streak of a breeding material is simple, the accuracy can reach 95% or more, the production cost is saved, the efficiency of screening paddy rice species capable of preventing bacterial leaf streak is largely improved, the breeding cycle of disease resistant paddy rice species is shortened greatly, and the breeding efficiency is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
SNP marker location for rice bacterial leaf streak resistant gene BLS2 and application of SNP marker location
InactiveCN107058304AImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic sequencingAgricultural science
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to an SNP marker location for rice bacterial leaf streak resistant gene BLS2 and an application of the SNP marker location. Gene BLS2 is located through a single nucleotide polymorphism marker on a chromosome 6, and the sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The marker location comprises the specific steps of construction of multi-parent advanced intercross line groups from generation to generation; genomic sequencing; bioinformation analysis; screening of parental homozygous difference SNP sites; frequency analysis on two BSA pool genes according to position information of screened homozygous SNP sites with difference between parents to obtain the sites related to the disease-resistant gene. The gene can be applied to breeding of bacterial leaf streak resistant rice varieties or screening of resistance gene resources.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com