Patents
Literature
41 results about "R gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Resistance genes (R-Genes) are genes in plant genomes that convey plant disease resistance against pathogens by producing R proteins. The main class of R-genes consist of a nucleotide binding domain (NB) and a leucine rich repeat (LRR) domain(s) and are often referred to as (NB-LRR) R-genes. Generally, the NB domain binds either ATP/ADP or GTP/GDP. The LRR domain is often involved in protein-protein interactions as well as ligand binding. NB-LRR R-genes can be further subdivided into toll interleukin 1 receptor (TIR-NB-LRR) and coiled-coil (CC-NB-LRR).
Wheat stripe rust resistance genes and methods of use
PendingUS20180320195A1Improve the immunityClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBiotechnologyResistant genes
Compositions and methods for enhancing the resistance of wheat and barley plants to wheat stripe rust caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici are provided. The compositions comprise nucleic acid molecules encoding resistance (R) gene products and variants thereof and plants, seeds, and plant cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The methods for enhancing the resistance of wheat and barley plants to wheat stripe rust comprise introducing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an R gene product into a wheat or barley plant cell. Additionally provided are methods for using the wheat and barley plants in agriculture to limit wheat stripe rust.
Owner:THE SAINSBURY LAB
Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 (SS2 for short) double-gene deleted live vaccine and its application
InactiveCN102776134AReduced toxicityImprove securityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMicrobiologyBacterial strain
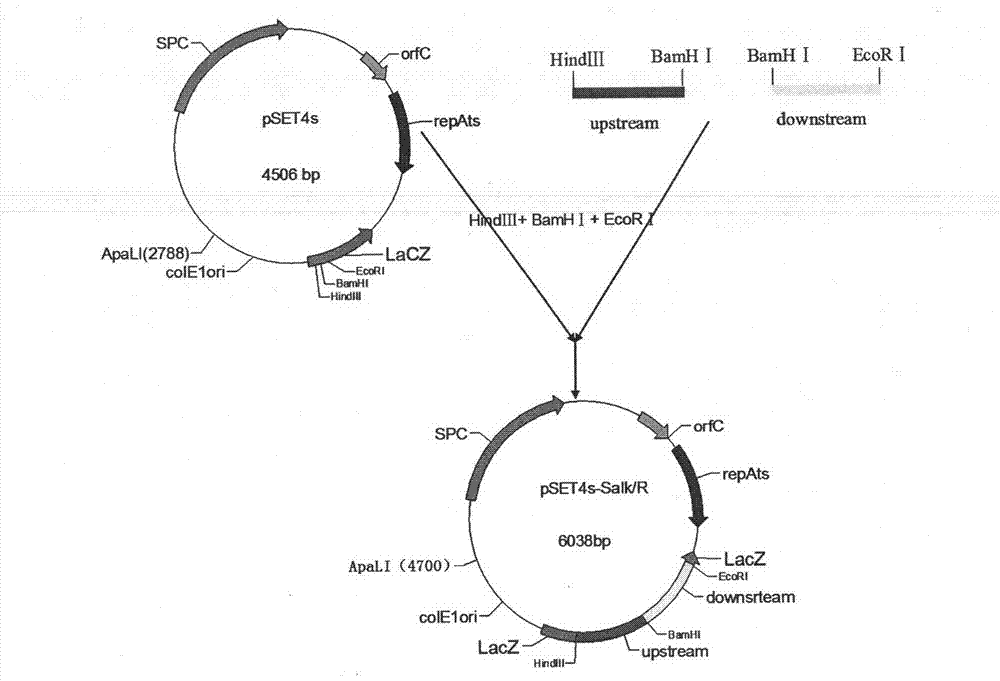
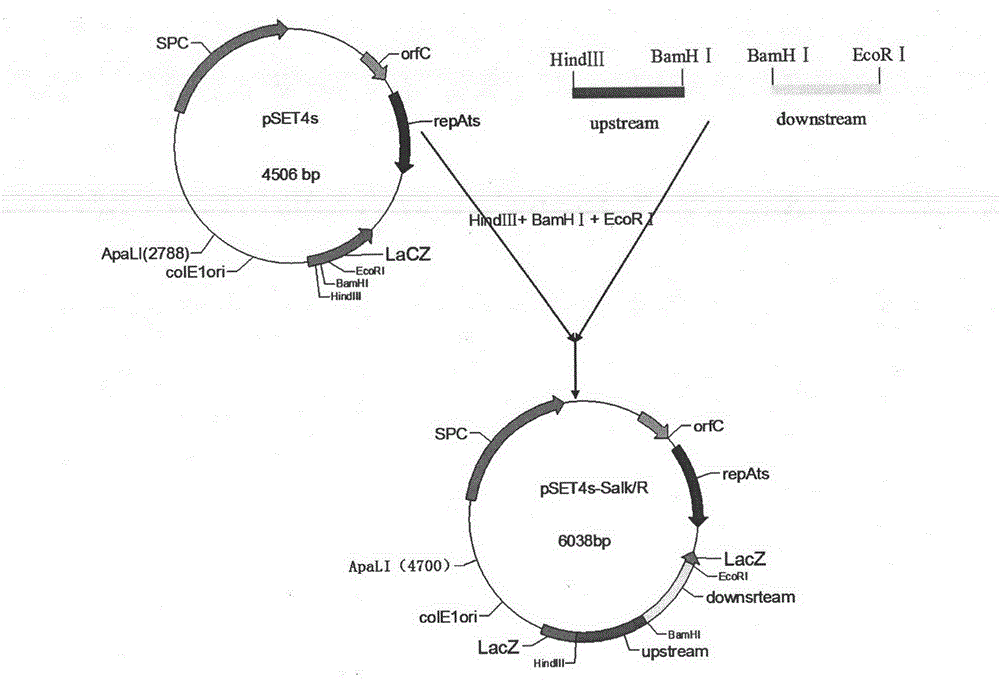
The invention relates to the technical field of the zoonotic vaccine preparation, and concretely relates to an SS2 double-gene deleted live vaccine and its application. An SS2 deltaEce1 / deltaSalk / R double-gene deleted stain is obtained by continuously deleting an Salk / R gene from a base SS2 field strain SC19 on the basis of the deletion of the a single gene Ece1 through a homologous recombinationmethod, and the SS2 double-gene deleted live vaccine is prepared through adopting a bacterial liquid of the double-gene deleted strain and gelatin as primary materials. The SS2 SS2 deltaEce1 / deltaSalk / R strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection, and has a preservation number being CCTCC NO:M2010360. After the deletion of the Salk / R gene, the SS2 double-gene deleted live vaccine prepared in the invention has the advantages of greatly decreased toxicity, high safety, no risk of strong toxicity return, and high immunogenicity, and can protect immune pigs from the attack of 5*LD50 SS2 strongly-toxic bacterial strains.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Wheat stripe rust resistance genes and methods of use
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
Plants with reduced expression of phosphatase type 2c gene for enhanced pathogen resistance
InactiveUS20070256193A1Improve disease resistanceTight regulationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationDiseaseR gene
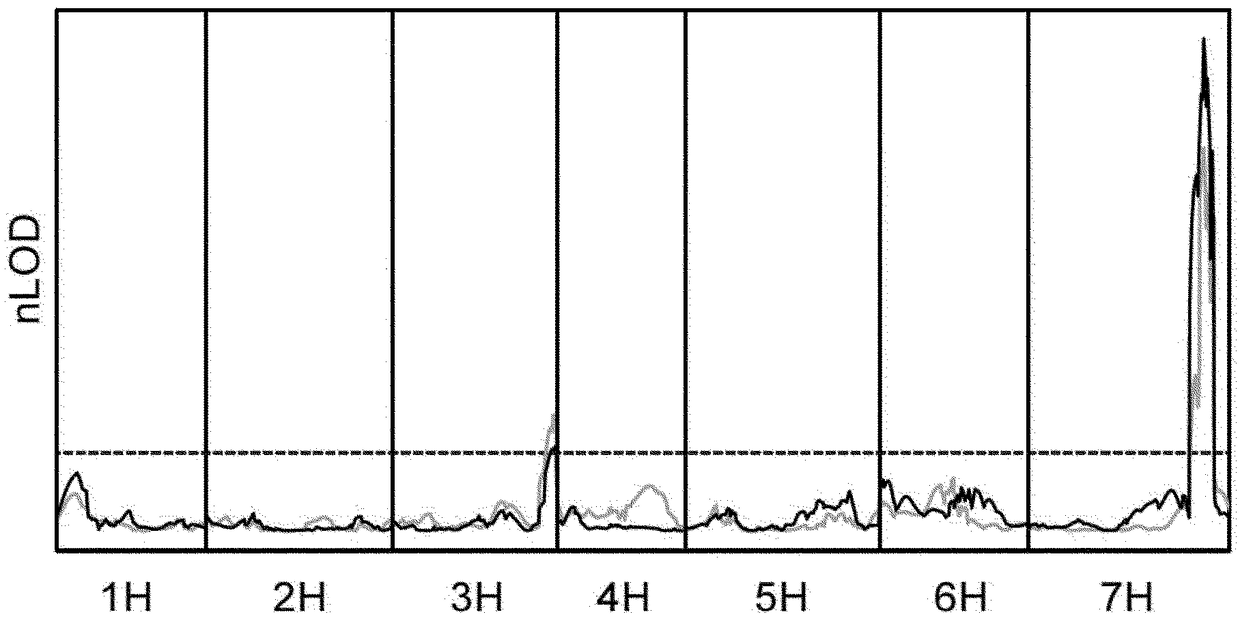
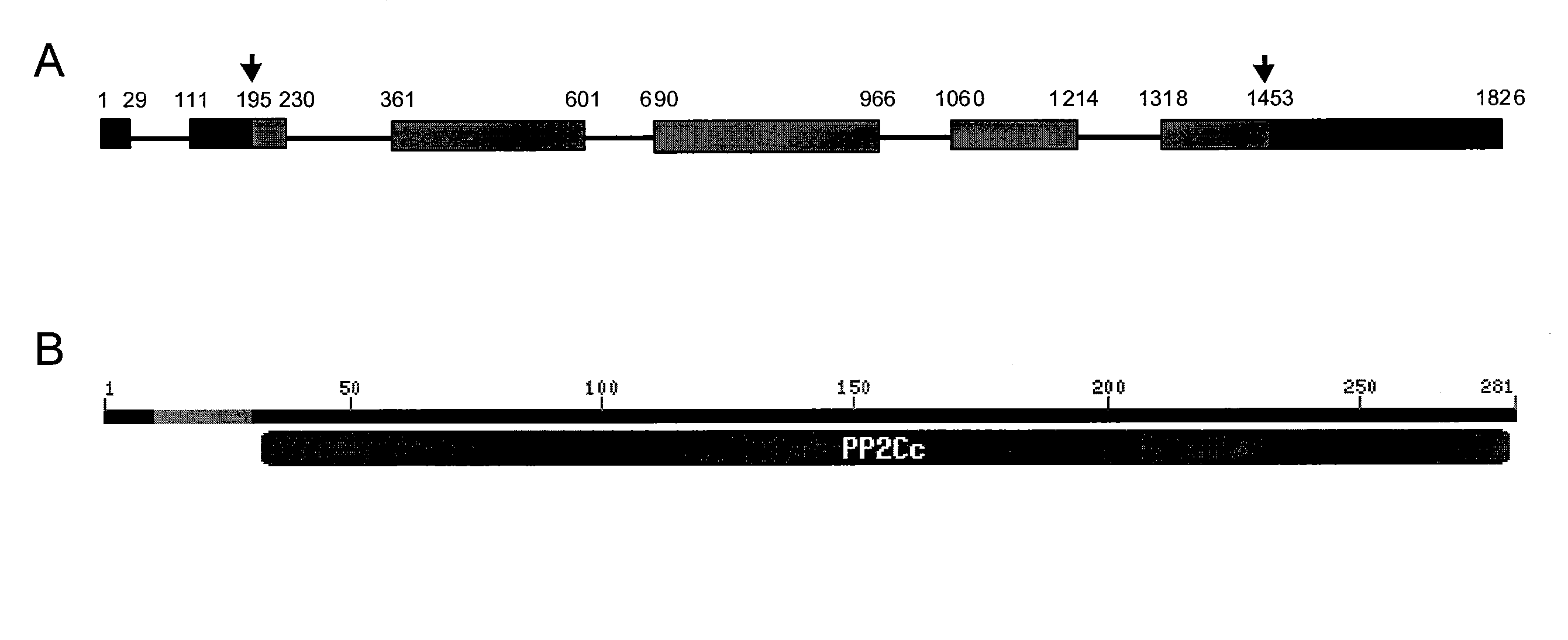
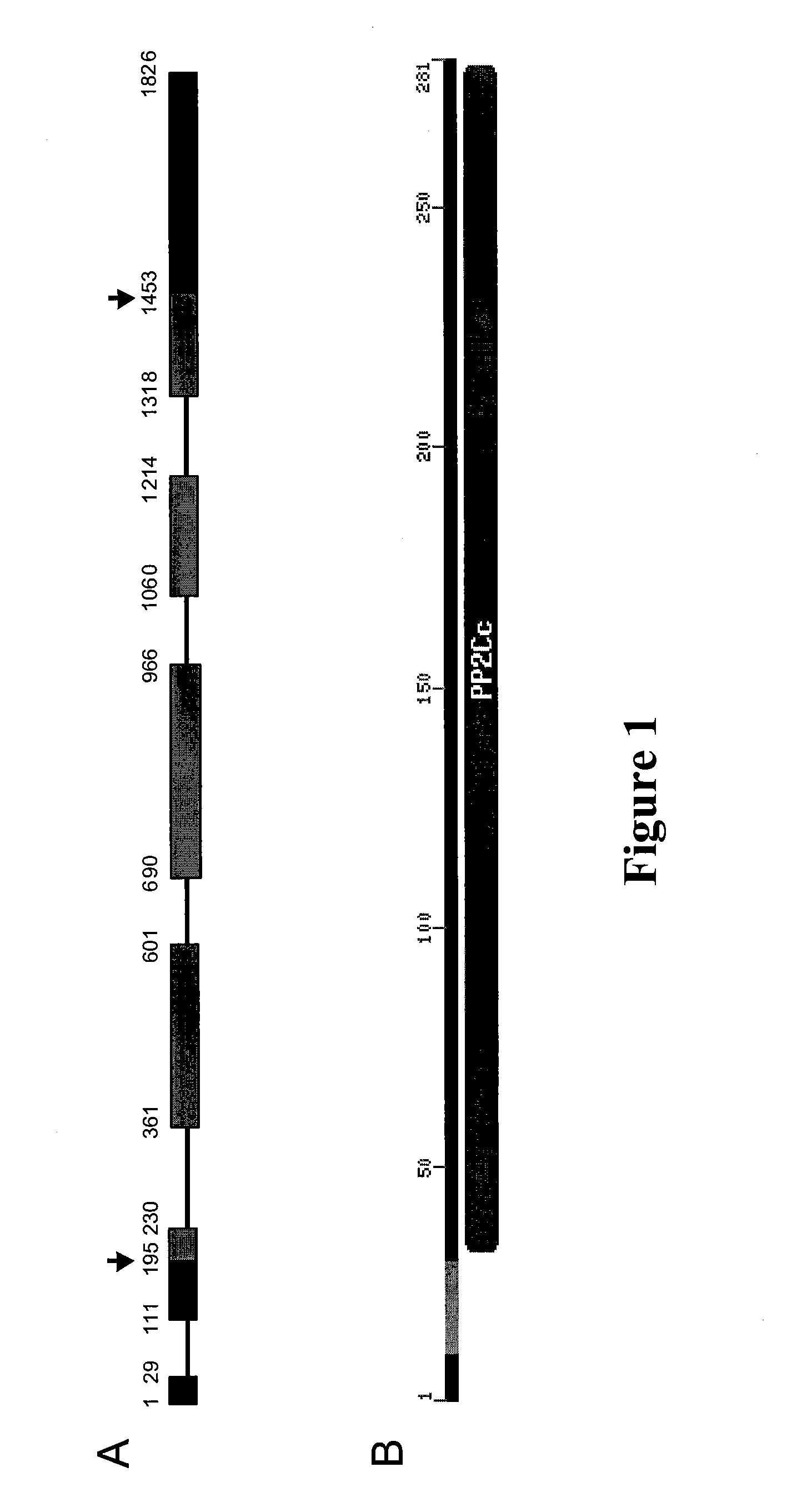
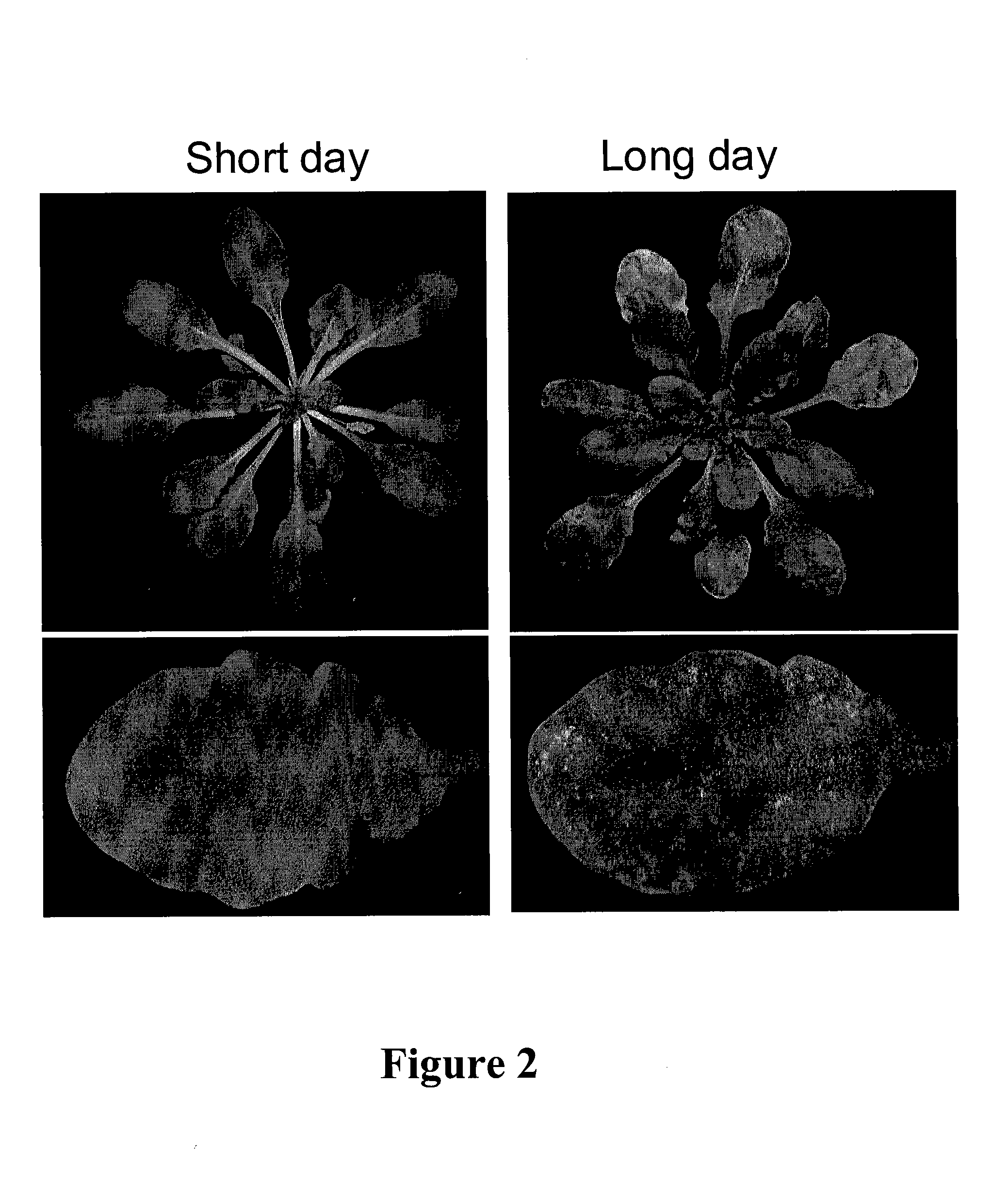
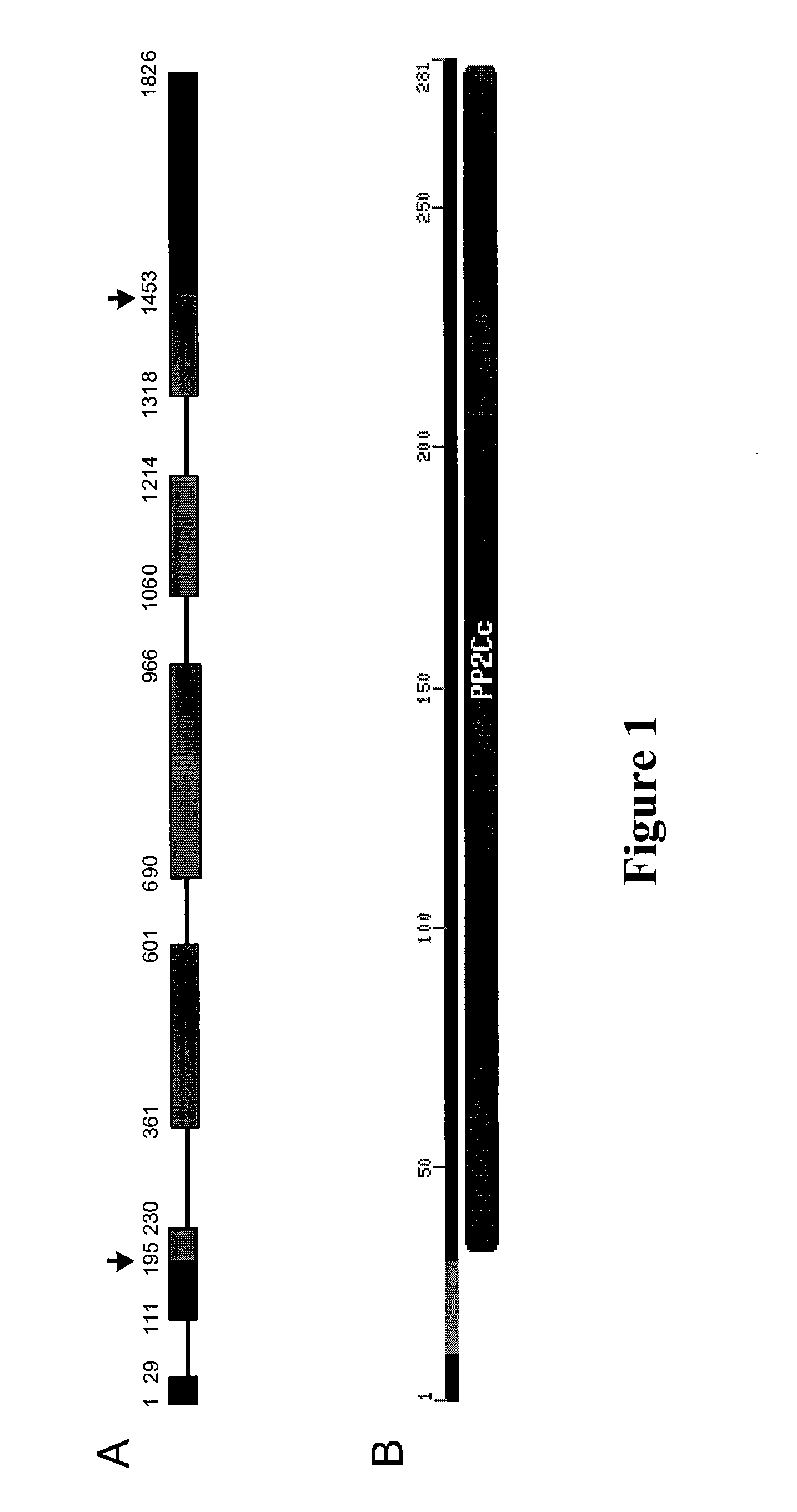
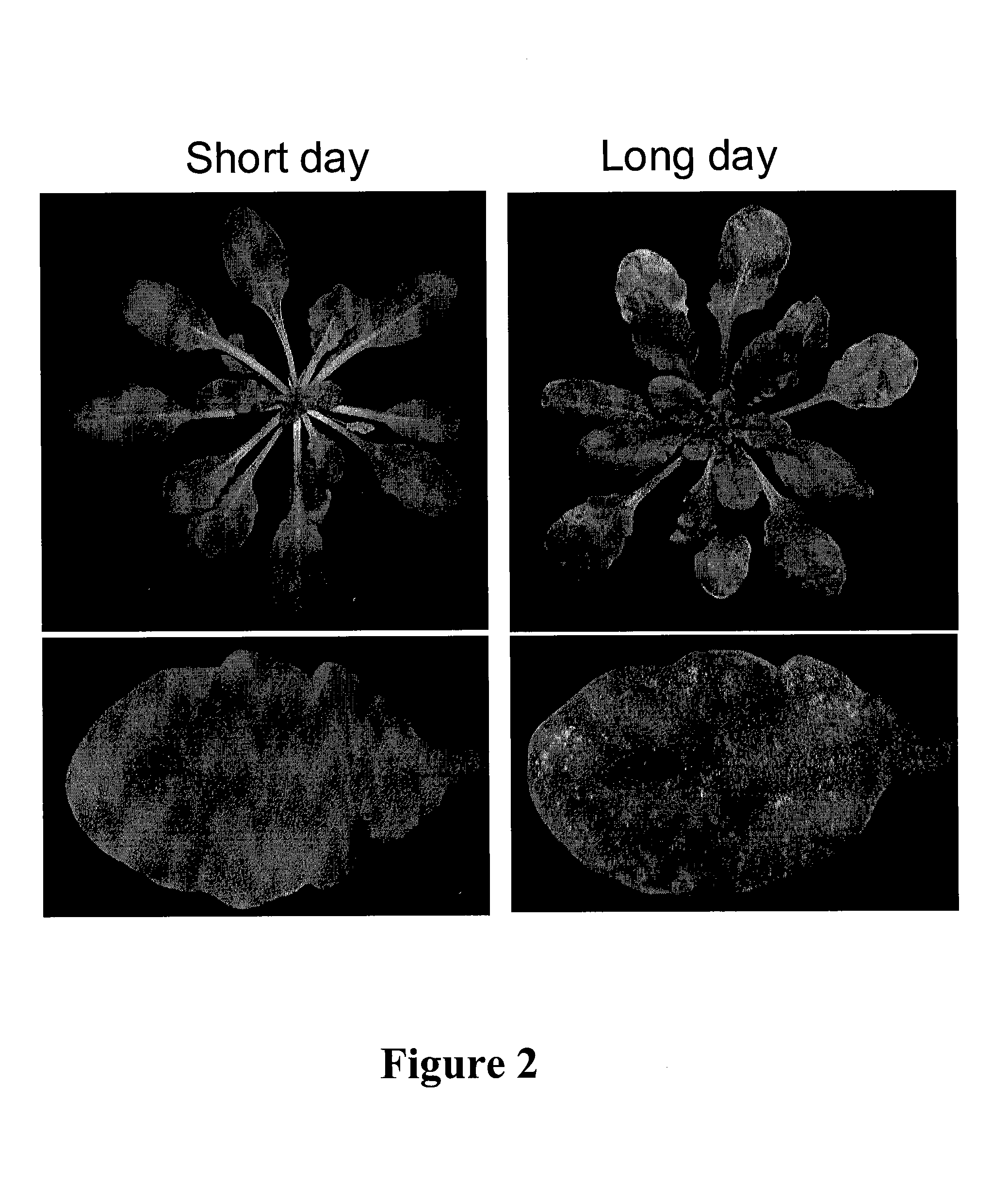
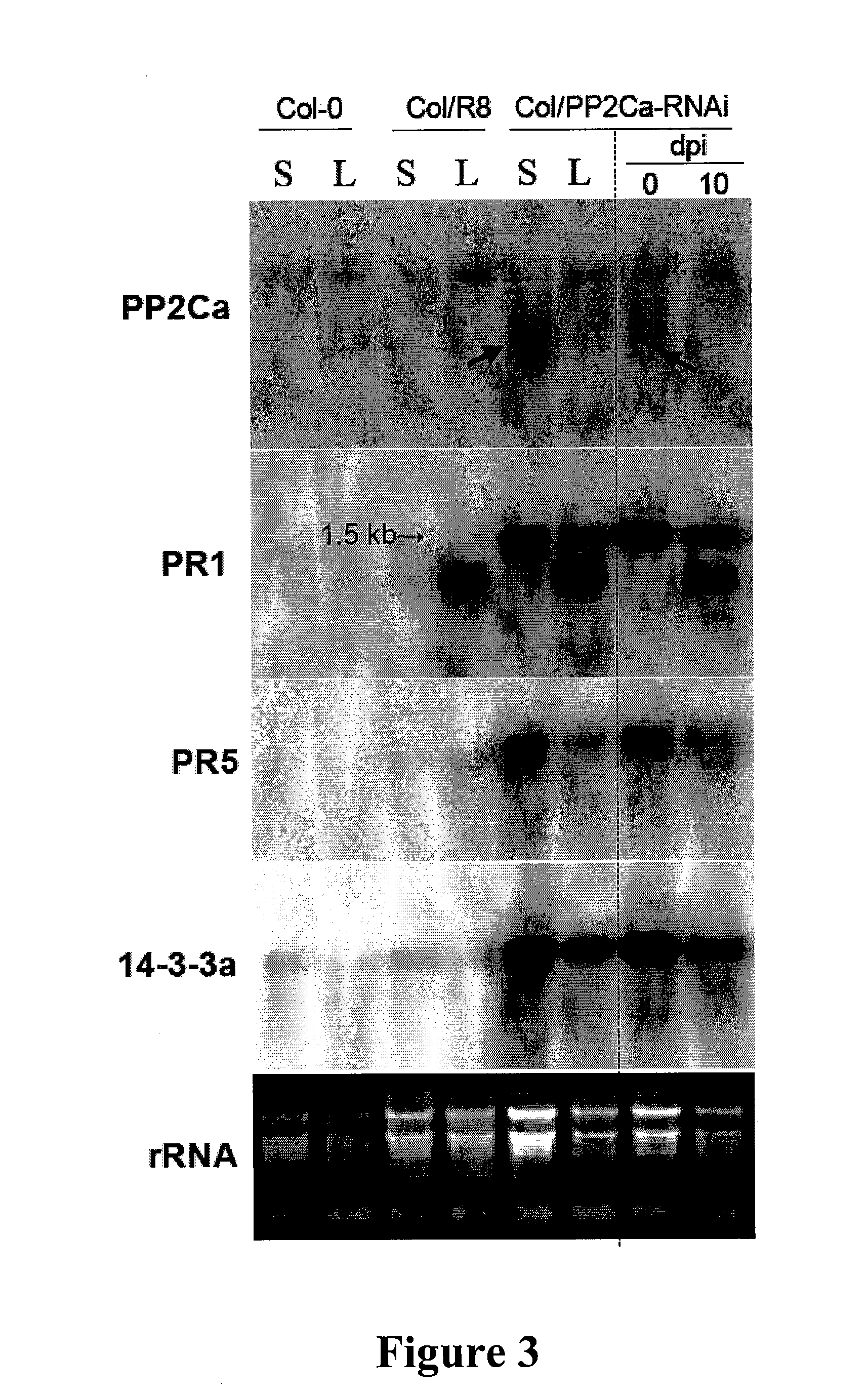
The present invention relates to a method for down regulating an Arabidopsis protein phosphatase type 2C gene, referred to as “defense-associated protein phosphatase type 2C one” (DAPP1) that functions as a negative regulator of a plant defense pathway by contacting the gene or gene mRNA with an interfering nucleotide sequence that interacts with the gene and reducing expression thereof. Plants including such interfering nucleotide sequence exhibit increased disease resistance to pathogen even in the absence of R genes. Close homologs of DAPP1 exist in multiple crop species, and as such, the controlled down-regulation of homologous genes in a variety of crop species will enhance disease resistance of target crop species to pathogens.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
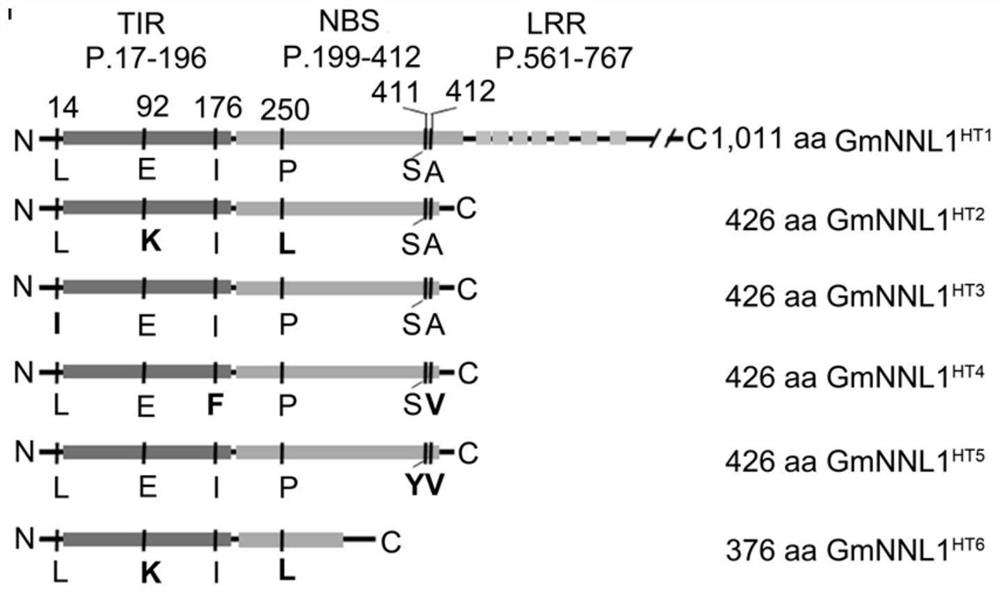
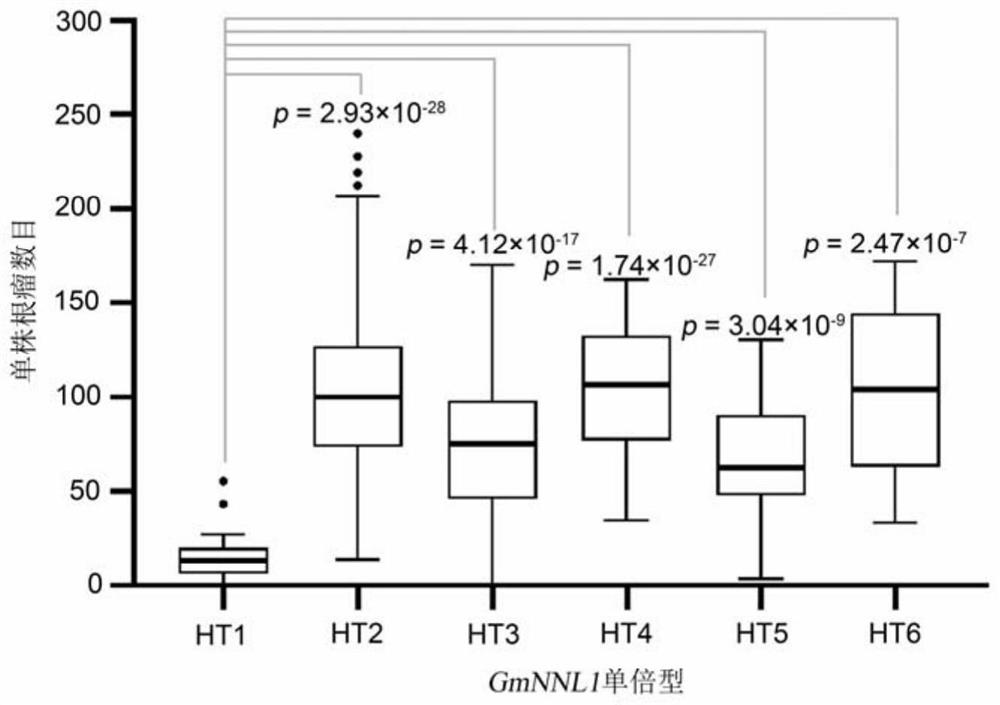
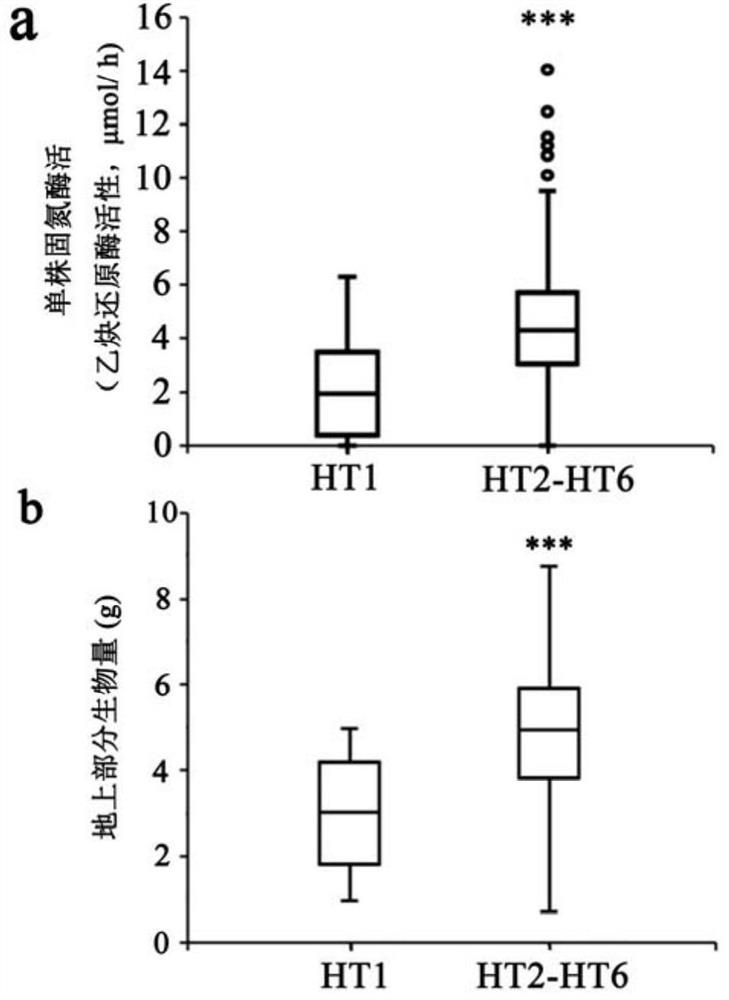
R gene for controlling soybean-rhizobium matching property as well as protein and application thereof
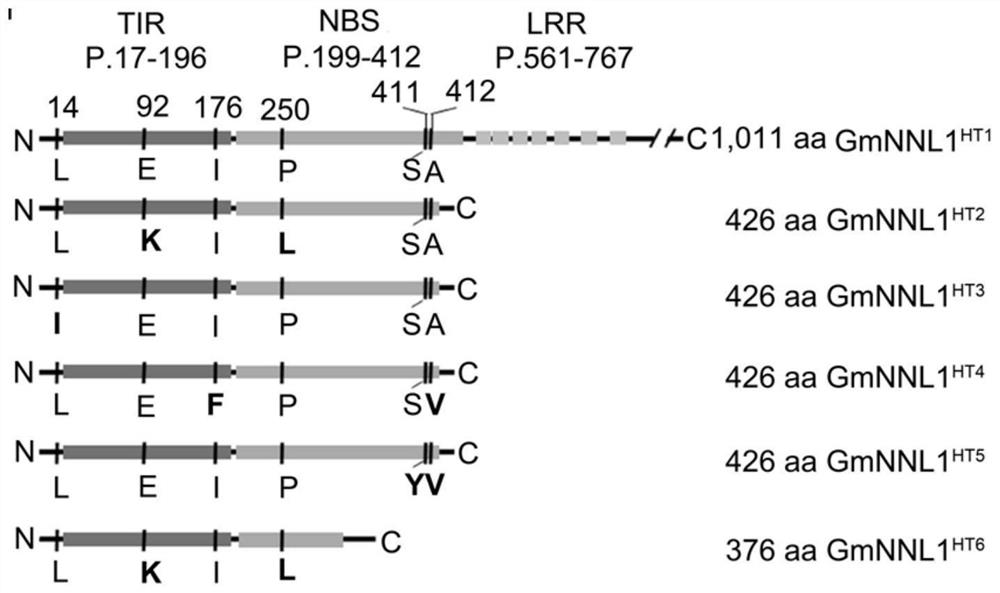
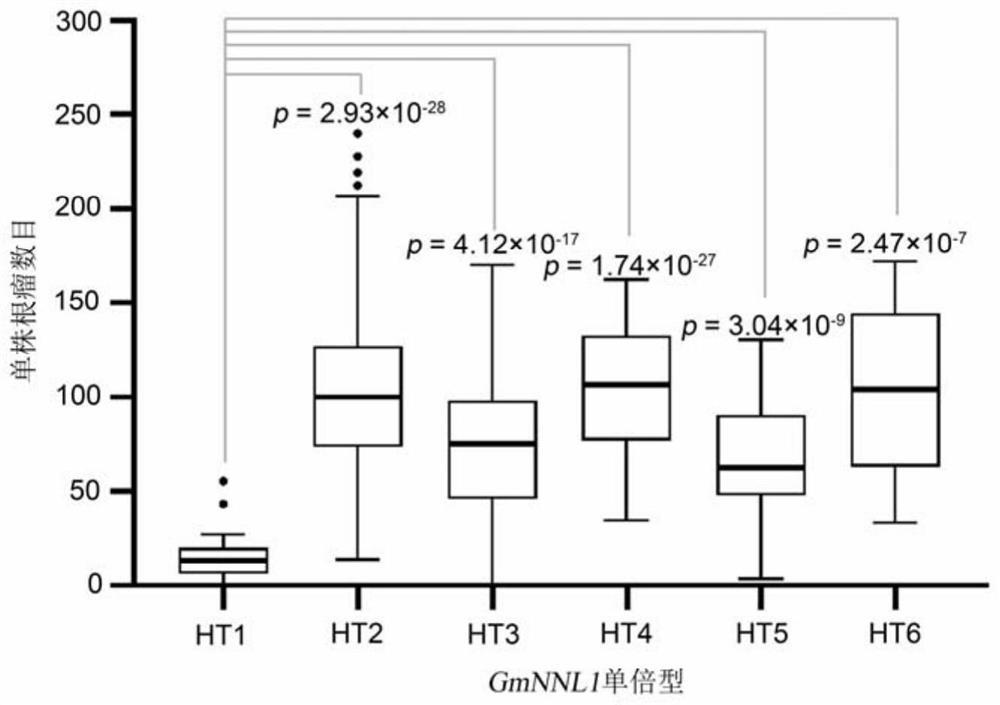
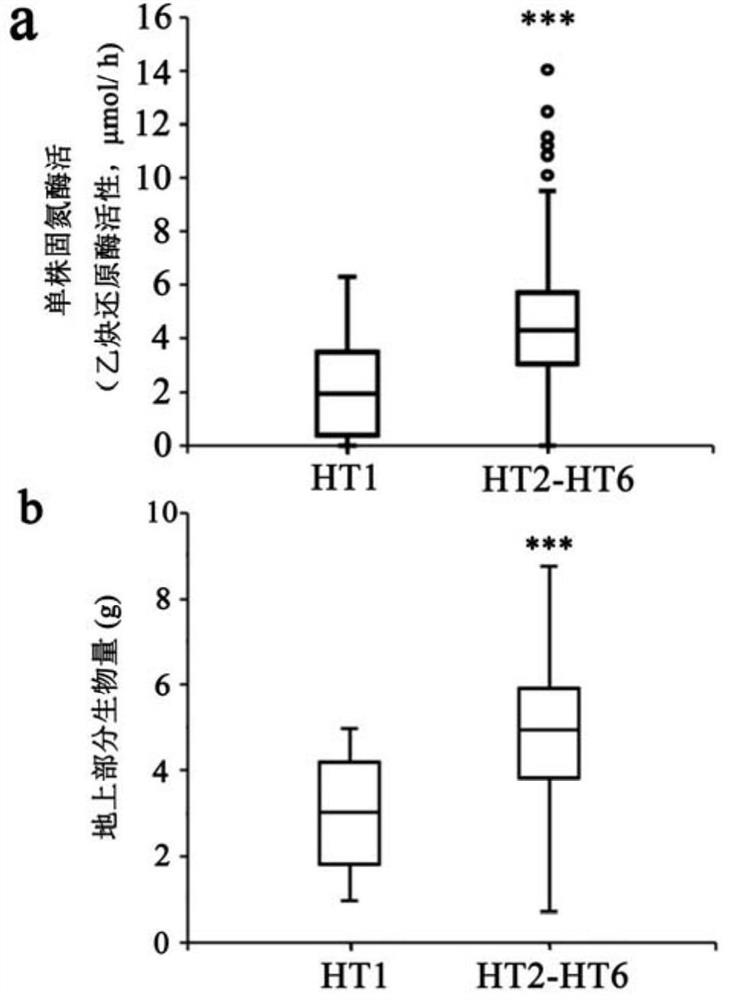
ActiveCN112626080AImprove symbiotic nitrogen fixationReduce the number of nodulesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyR gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to application of a new gene, in particular to an R gene for controlling soybean-rhizobium matching property as well as protein and application of the R gene. The GmNNL1 genome sequence of the gene GmNNL1 disclosed by the invention in the HENGFENG WUDOU of a soybean line is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2 and the coded amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3. The R gene GmNNL1 of the soybean is an effective gene capable of regulating and controlling the nodulation quantity of specific rhizobium on the soybean, and can regulate and control the nodulation quantity by directly identifying the haplotype of slow-growing rhizobium specific effect protein NopP to limit the symbiotic nodulation of indigenous rhizobium, so that the soybean preferentially nodulates with artificially applied efficient rhizobium inoculant; and the symbiotic nitrogen fixation capability can be improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY +1
Cotton nematode-resistant gene GhNtR1 and application thereof
ActiveCN104046633AIncrease resistanceImprove nematode resistance traitsBacteriaPlant peptidesNicotiana tabacumGossypium
The invention relates to a plant nematode-resistant gene GhNtR1 and an application thereof, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The gene GhNtR1 is a CC-NBS-LRR gene obtained from a verticillium wilt-resistant material, namely gossypium hirsutum L. and coding protein of the gene contains 861 amino acids; the similarity of the gene GhNtR1 to a listed R gene is relatively low and the content of castor RPPR8 with maximum similarity to the gene GhNtR1 is also only 27%. A plant overexpression vector of the gene GhNtR1 is built and diseased general tobaccos are converted by adopting an agrobacterium-mediated method. The resistance of 5 lines in 9 transgenic lines is remarkably improved through inoculation by meloidogyn incognita; in addition, the expression quantity of defense response genes PR1 and PR3 of a transgenic plant after inoculation of nematodes is higher than that of a non-transgenic plant and more callosities are accumulated in the transgenic plant; the cloning and the functional analysis of the gene GhNtR1 deepen the understanding of resistance mechanisms and related signal paths of the gene and lay a foundation for obtaining nematode-resistant genetically engineered plants.
Owner:聊城云购通信息技术有限公司
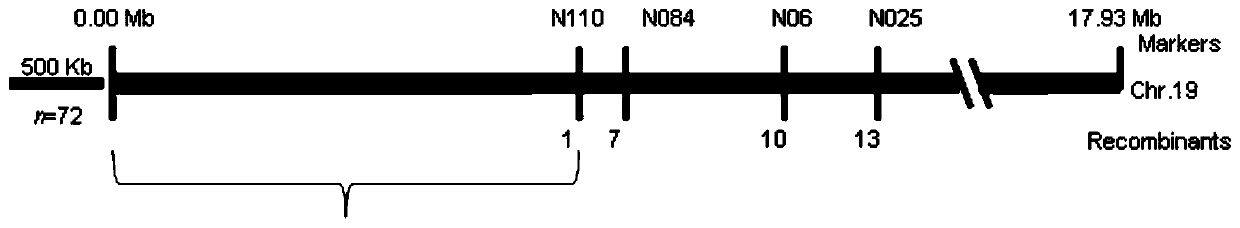
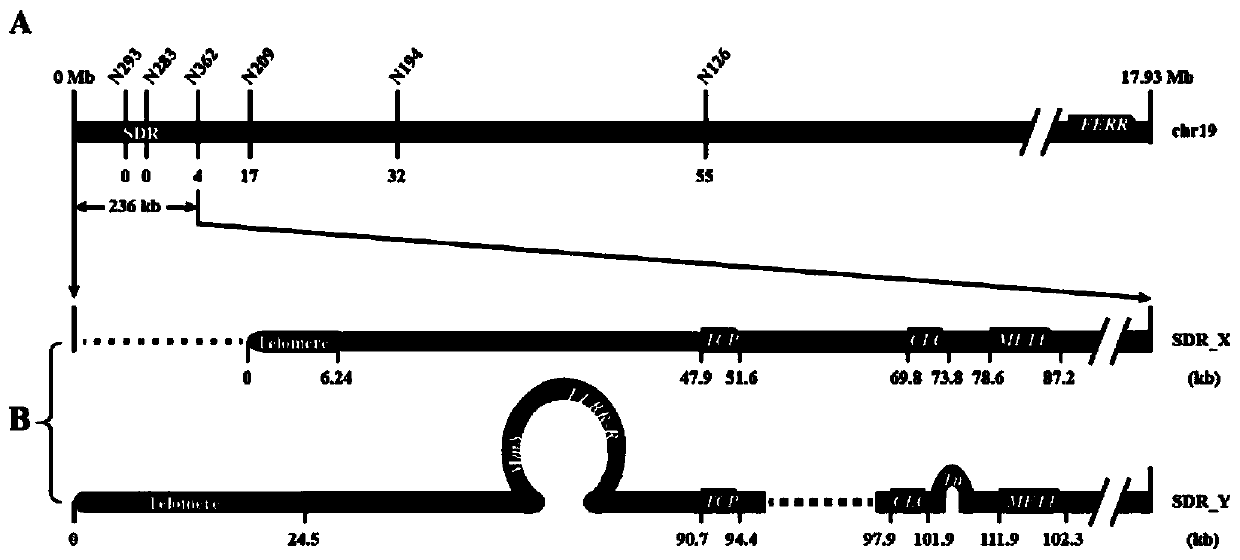
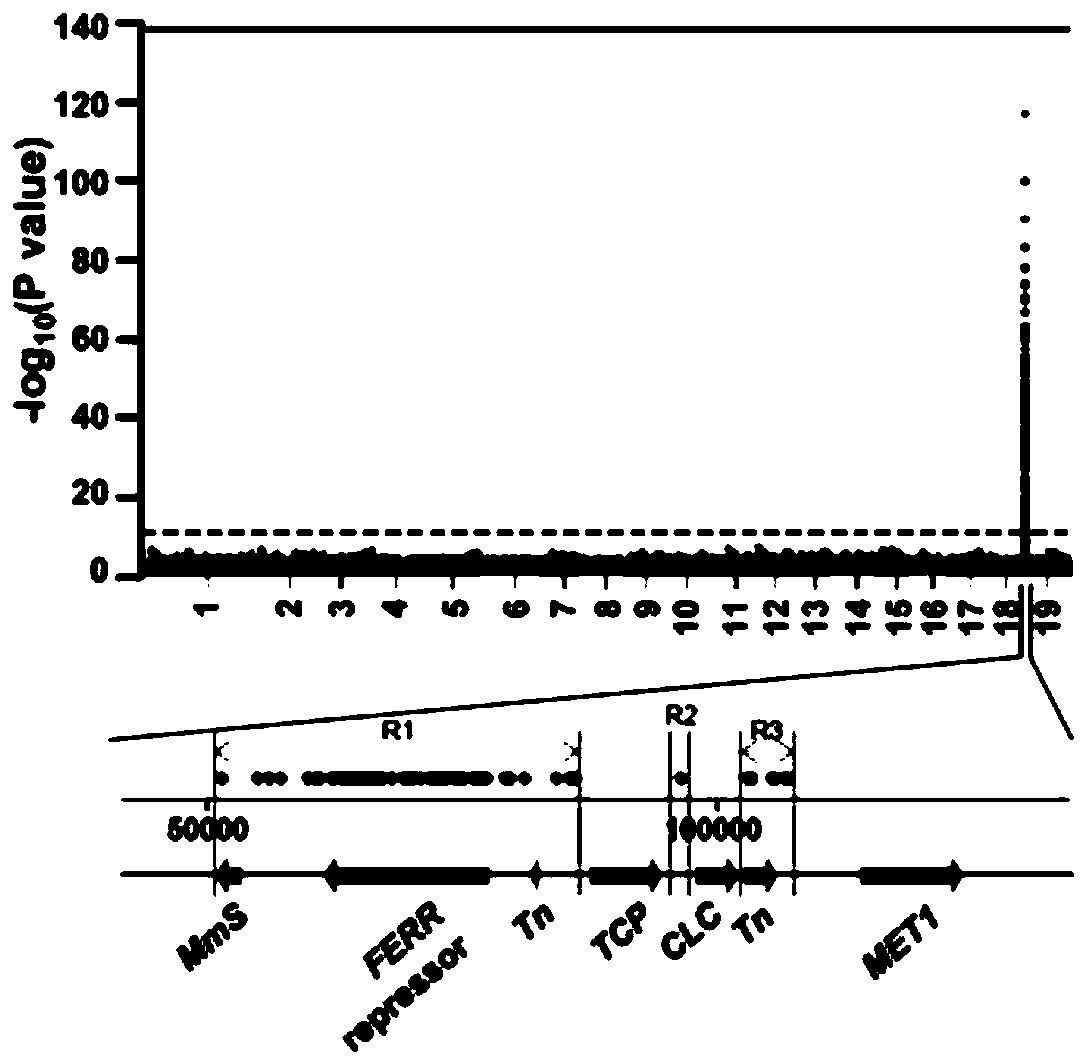
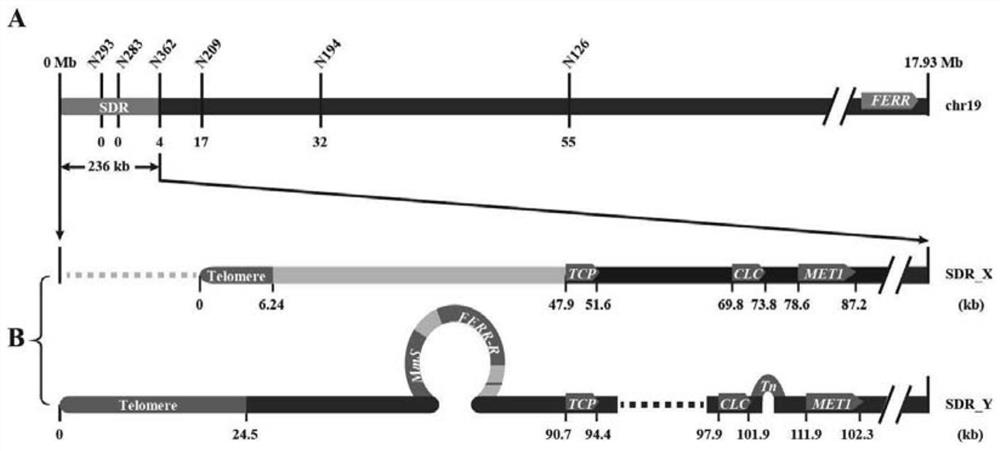
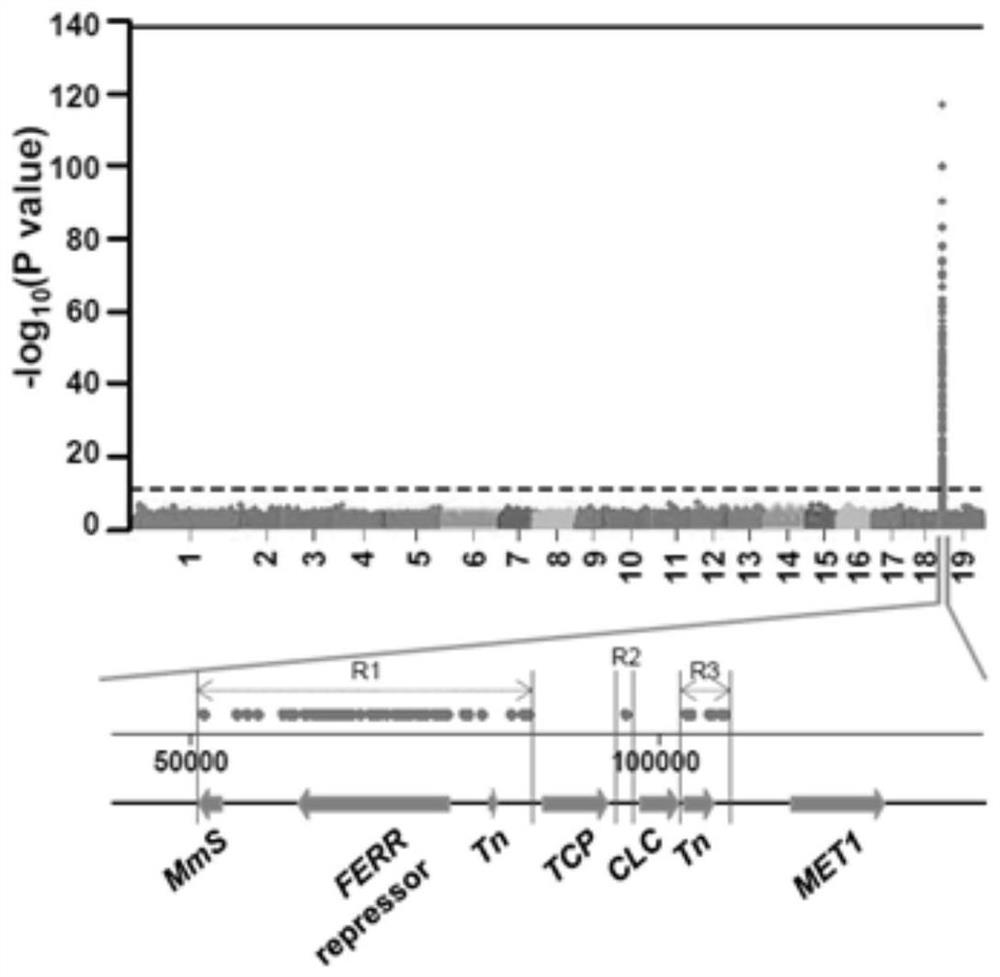
Estrogen receptor promoting gene FERR and estrogen receptor restraining gene FERR-R of populus deltoides and application of estrogen receptor promoting gene FERR and estrogen receptor restraining gene FERR-R of populus deltoides
ActiveCN111100868AImprove developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyR gene
The invention discloses an estrogen receptor promoting gene FERR and an estrogen receptor restraining gene FERR-R of populus deltoides and an application of the estrogen receptor promoting gene FERR and the estrogen receptor restraining gene FERR-R of the populus deltoides, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. According to the estrogen receptor promoting gene FERR and the estrogen receptor restraining gene FERR-R of populus deltoides and an application of the estrogen receptor promoting gene FERR and the estrogen receptor restraining gene FERR-R of the populus deltoides disclosed by the invention, through genealogy linkage analysis, sex determination gene sites of the populus deltoides are subjected to fine positioning, then through natural population materials,complete genome correlation analysis is developed, methylation sequencing of transcriptomes and genomes is combined, the estrogen receptor promoting gene FERR and the estrogen receptor restraining gene FERR-R of poplars are disclosed for the first time, the FERR-R gene does not code protein, but through producing siRNAs, a starting sequence of the estrogen receptor promoting gene FERR is subjected to methylation, and transcripts are sheared, so that the expression of the estrogen receptor promoting gene FERR in poplar male plants is restrained. But poplar female plants do not contain the FERR-R gene, and the expression of the FERR is not restrained by the FERR-R, so that the development of female flowers of the female plants is promoted. The estrogen receptor promoting gene and the estrogen receptor restraining gene of the poplars provided by the invention can be applied to early identification of the sex of the poplar and molecular breeding.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
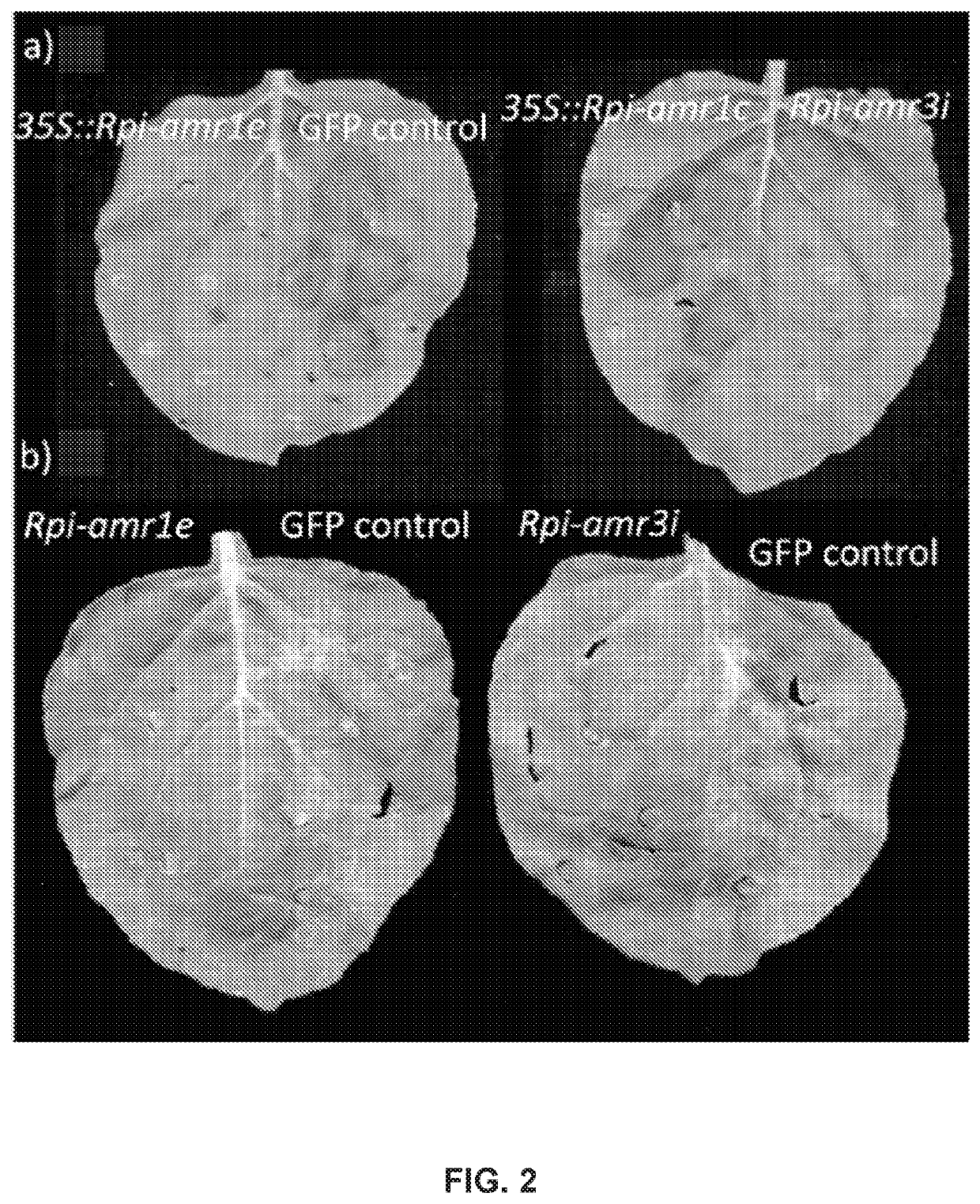
Late blight resistance gene from solanum americanum and methods of use
ActiveUS20180142254A1Microbiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyResistant genes
Compositions and methods and for enhancing the resistance of plants to a plant disease caused by a Phytophthora species are provided. The compositions comprise nucleic acid molecules encoding resistance (R) gene products and variants thereof and plants, seeds, and plant cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The methods for enhancing the resistance of a plant to a plant disease caused by a Phytophthora species comprise introducing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an R gene product into a plant cell. Additionally provided are methods for using the plants in agriculture to limit plant disease.
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
Late Blight Resistance Gene From Solanum Americanum And Methods Of Use
ActiveCN107709564AMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyResistant genes
Compositions and methods and for enhancing the resistance of plants to a plant disease caused by a Phytophthora species are provided. The compositions comprise nucleic acid molecules encoding resistance (R) gene products and variants thereof and plants, seeds, and plant cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The methods for enhancing the resistance of a plant to a plant disease caused by aPhytophthora species comprise introducing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an R gene product into a plant cell. Additionally provided are methods for using the plants in agriculture to limit plant disease.
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
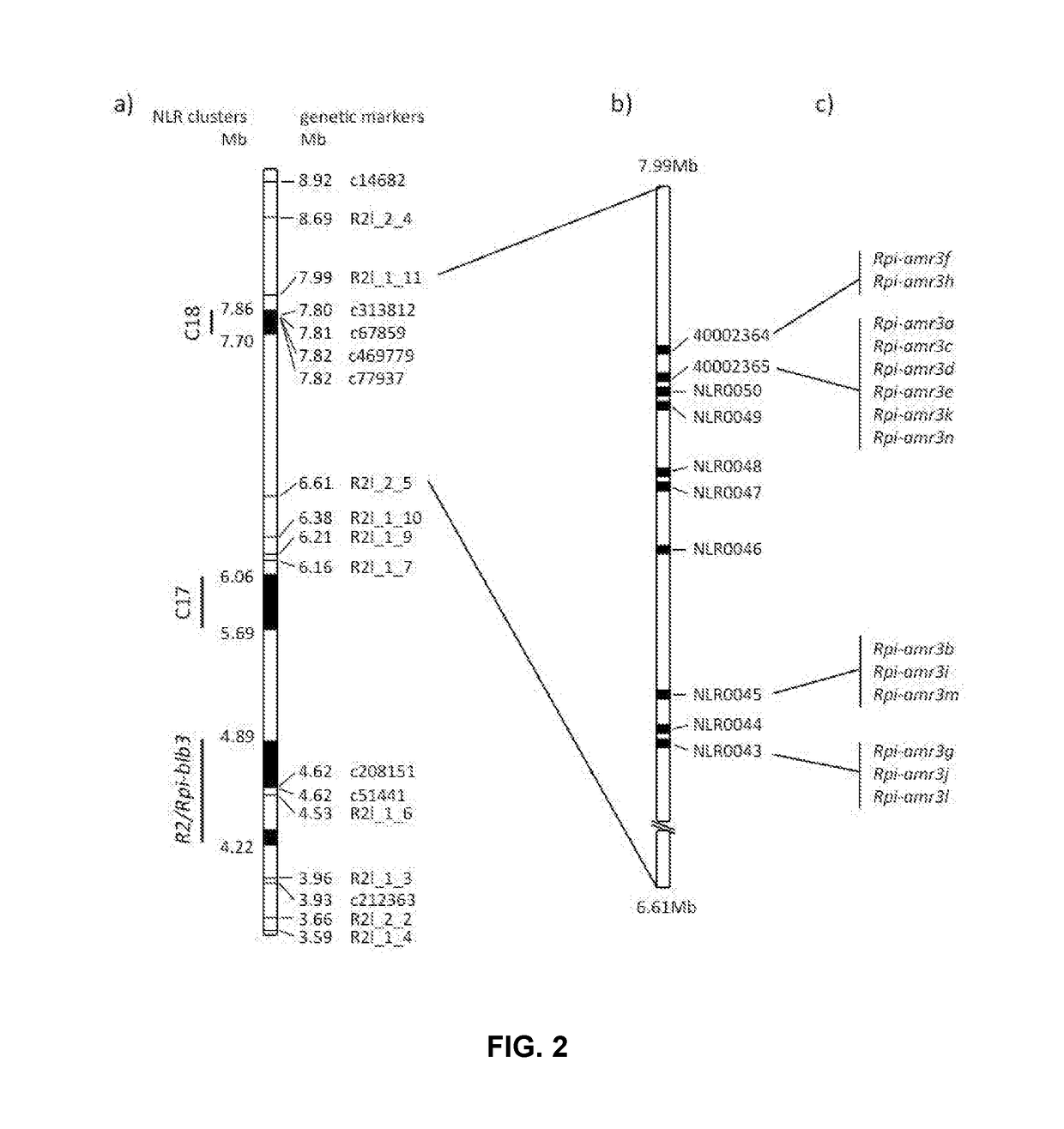
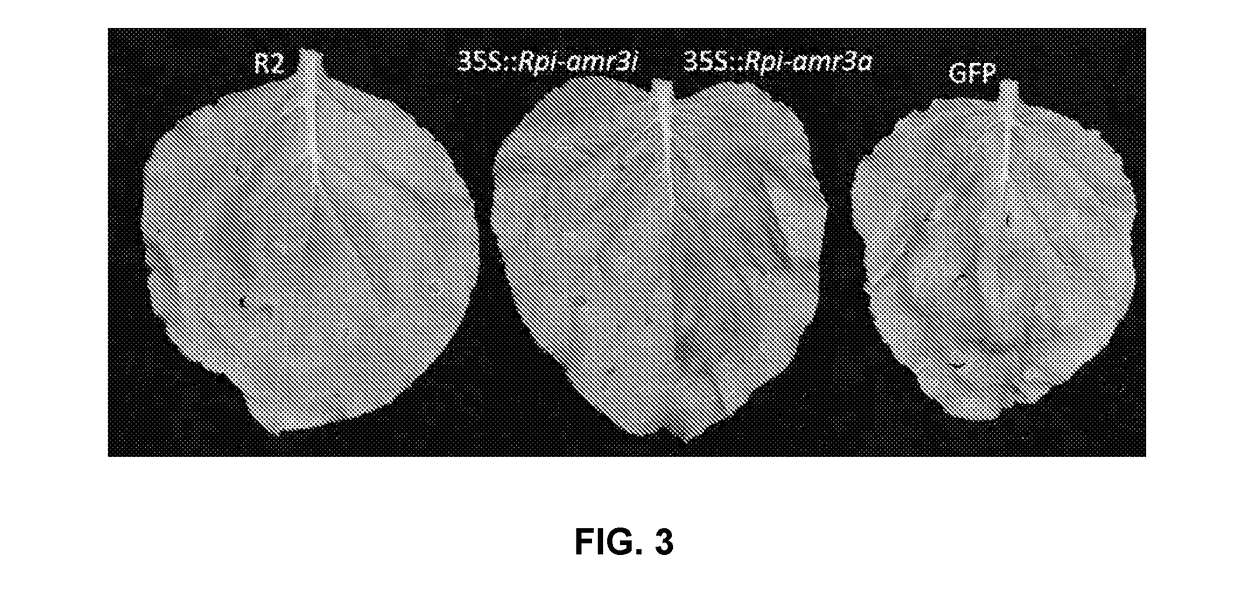
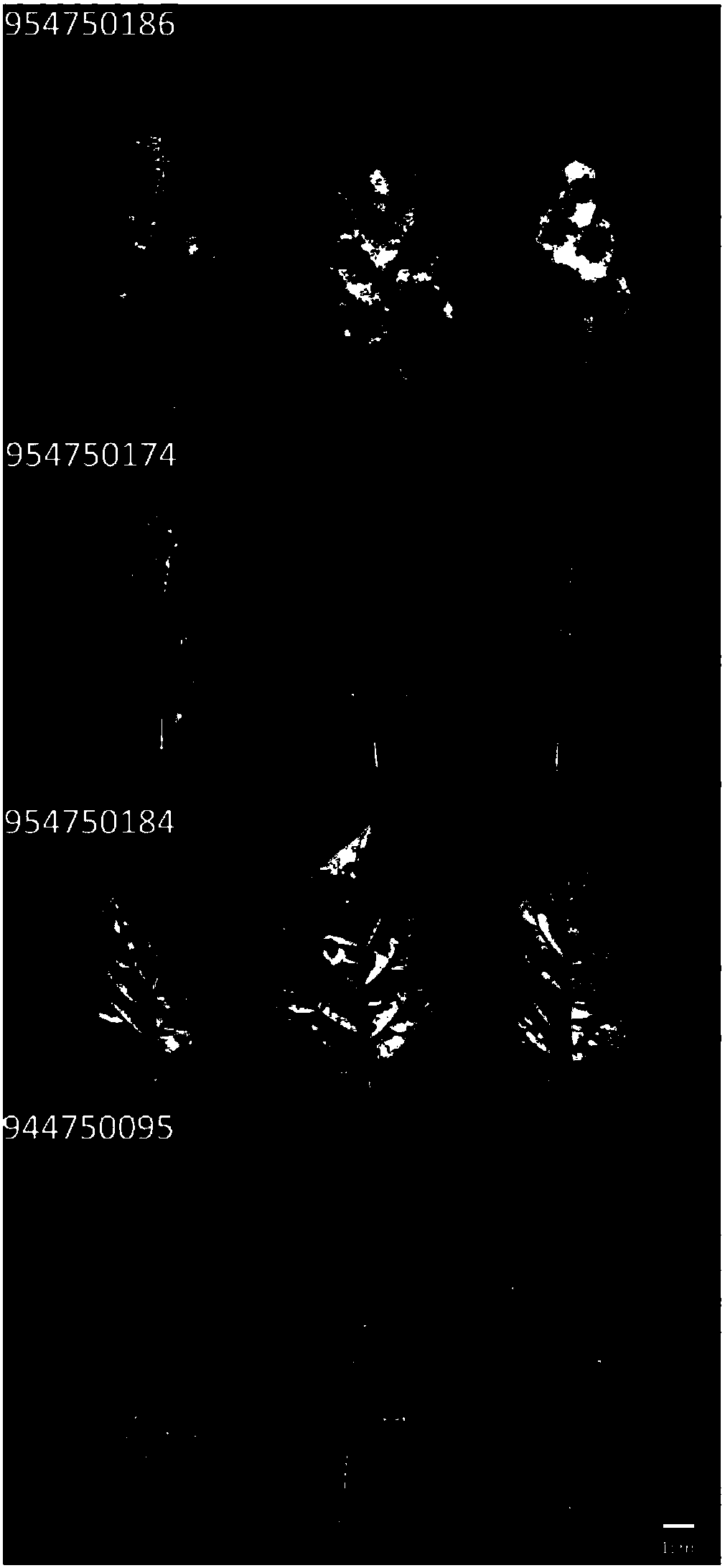
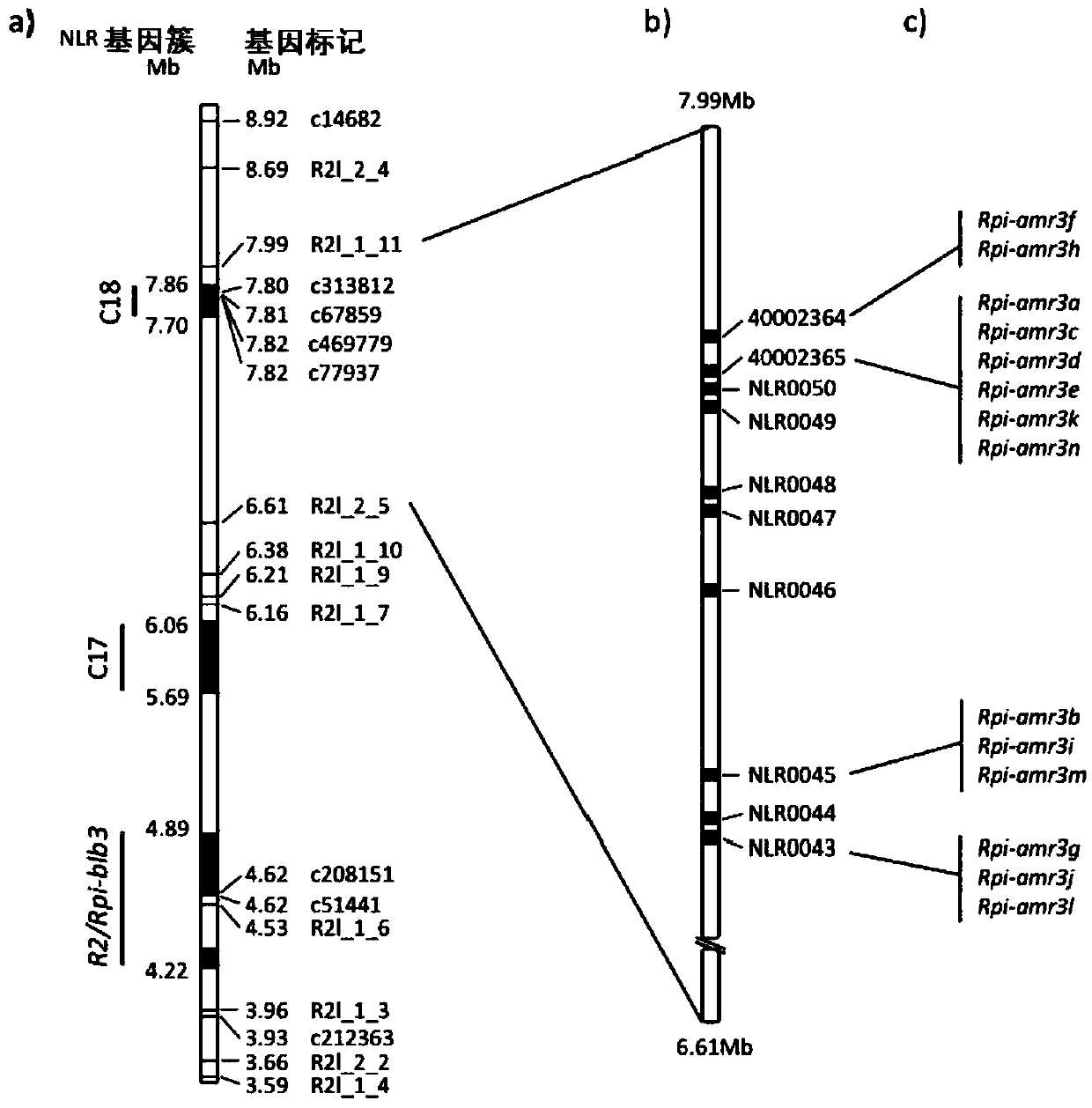
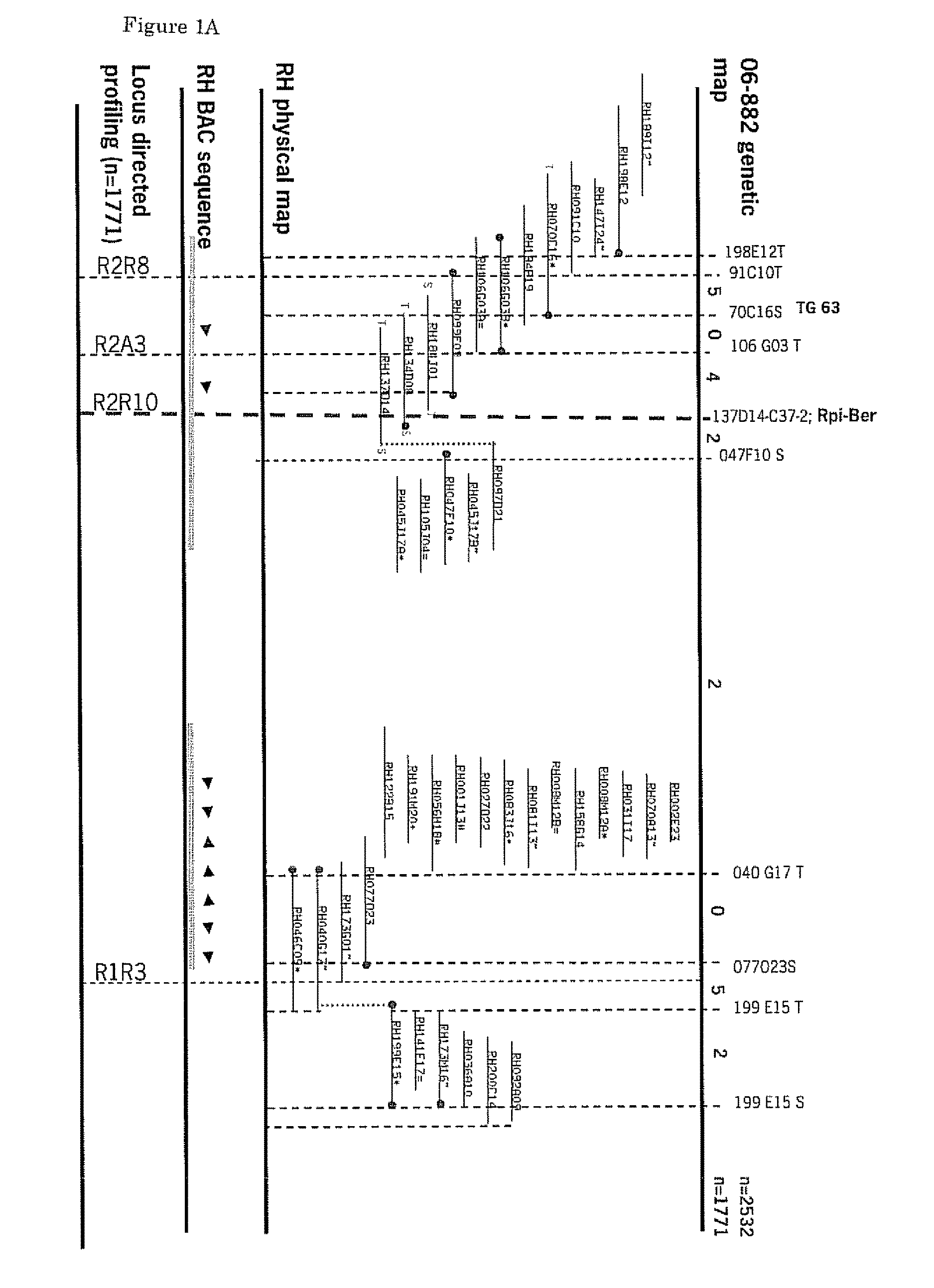
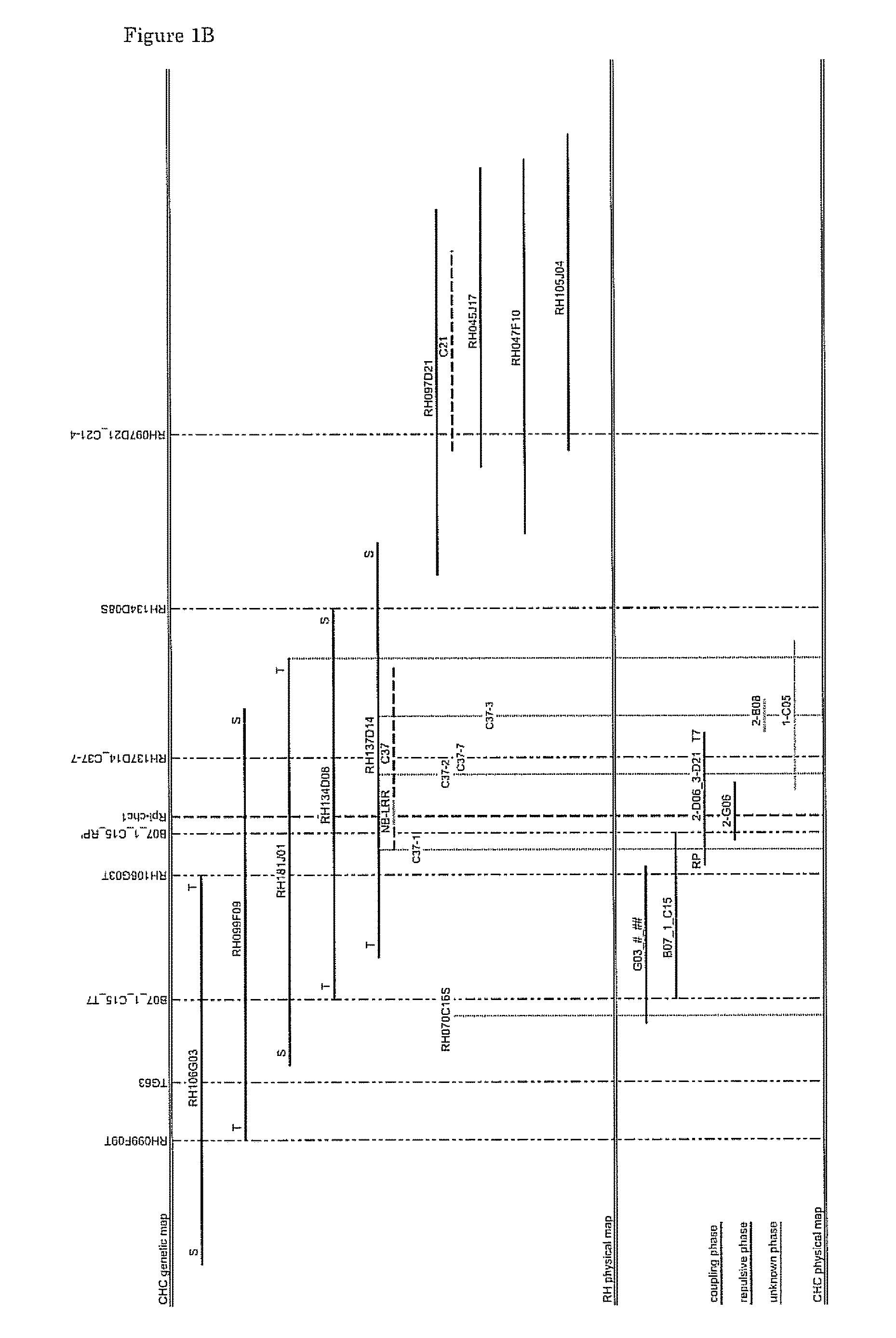
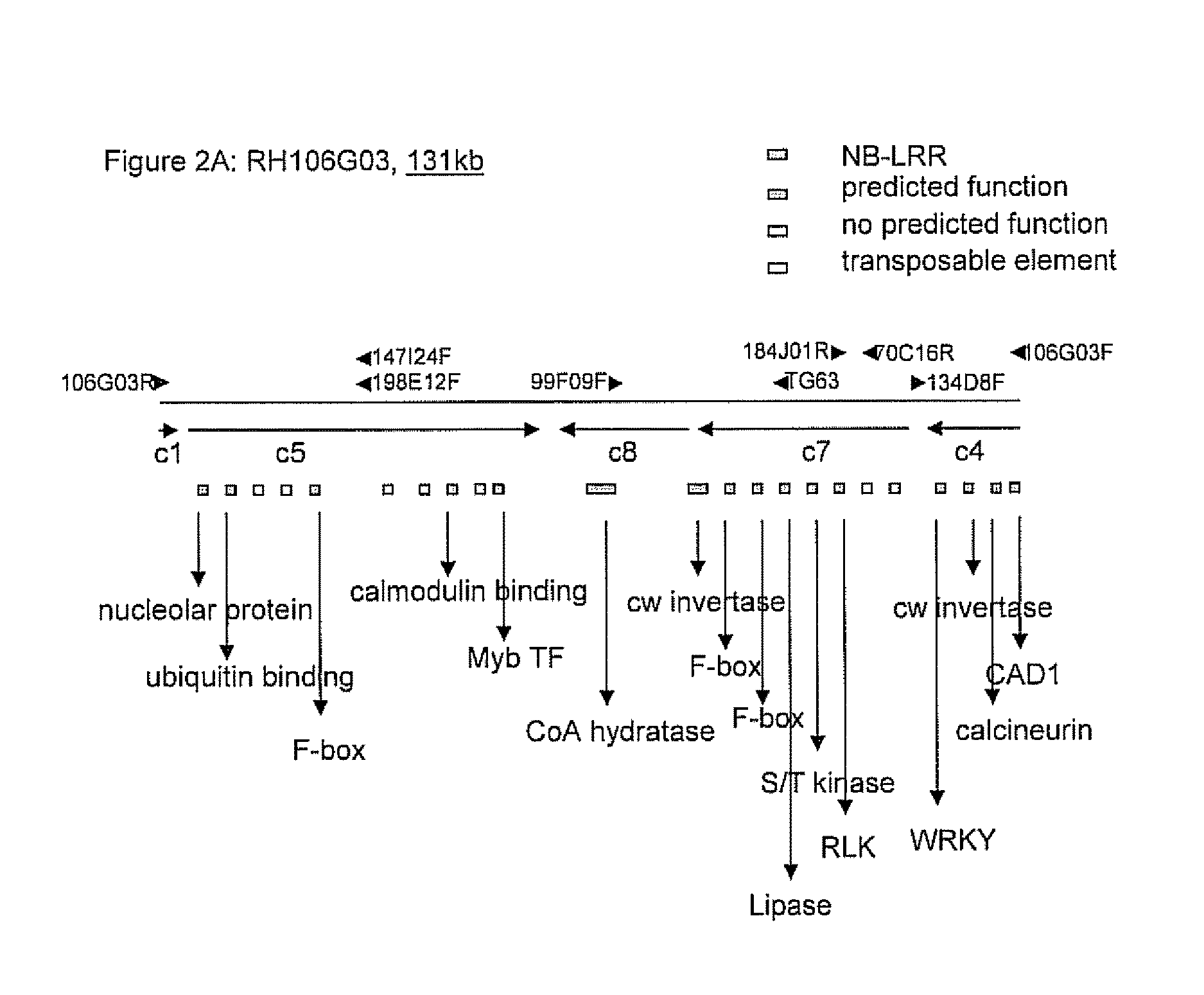
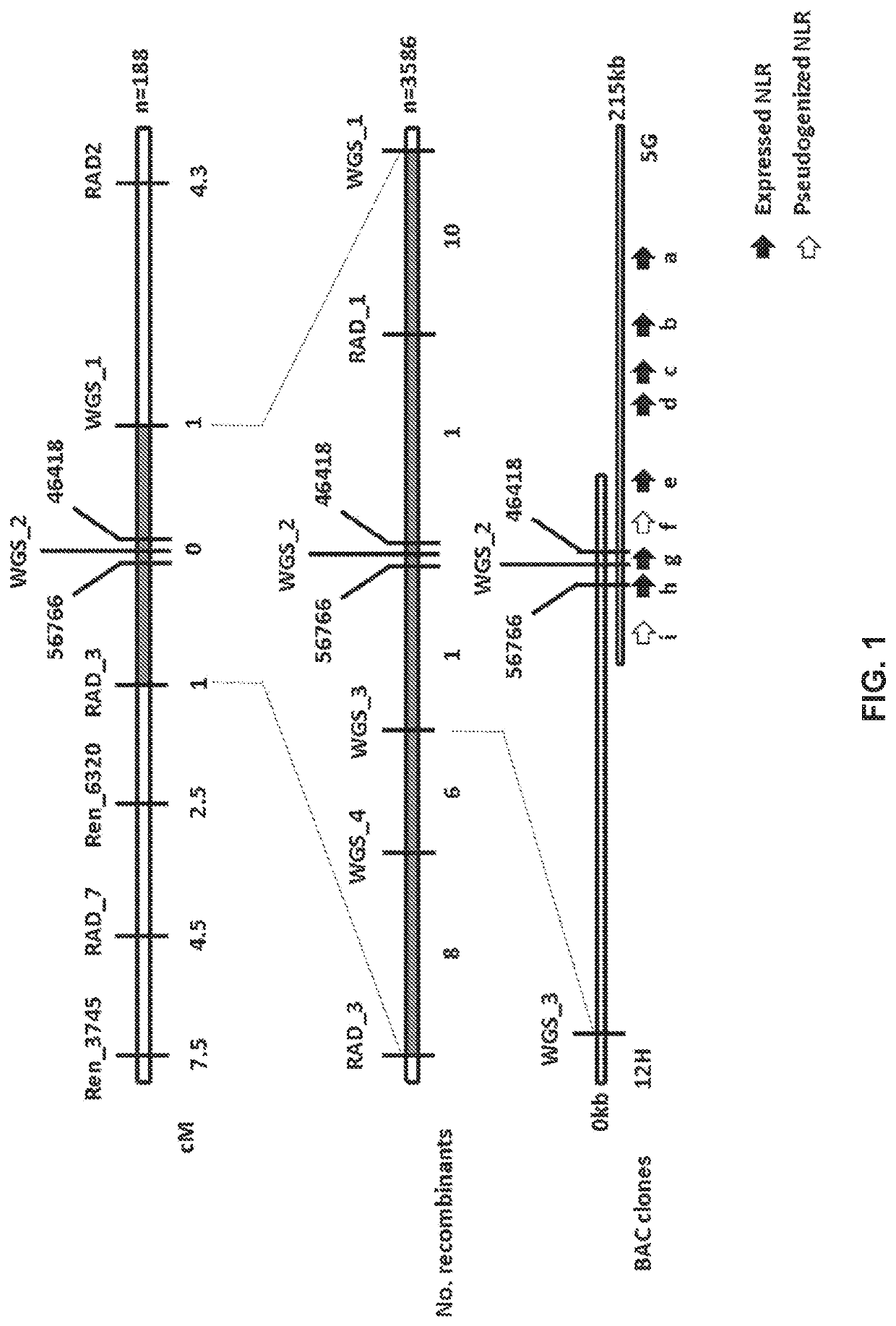
Cloning and exploitation of a functional R-gene from Solanum chacoense
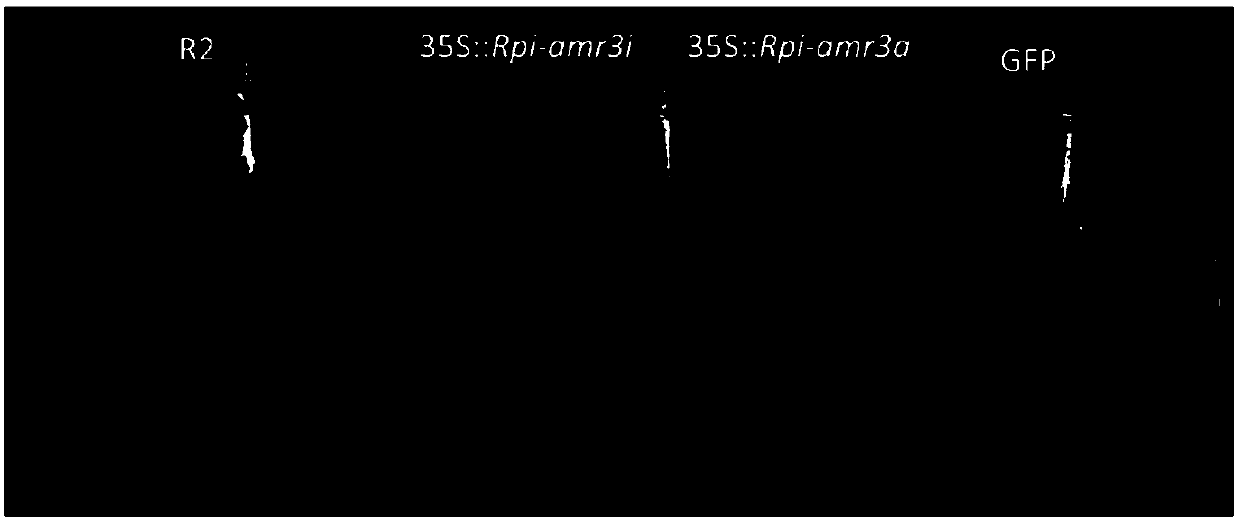
The invention relates to a resistance gene and functional homologues or fragments thereof isolated from S. chacoense, S. berthaultii, S. sucrense or S. tarijense. More over, the invention relates to the use of said resistance gene, for example the use of said resistance gene in a method to increase or confer at least partial resistance in a plant to an oomycete infection. The invention provides an isolated or recombinant nucleic acid sequence comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding one of the amino acid sequences of FIG 4 or a functional fragment or a functional homologue thereof such as those presented in FIG. 13.
Owner:WAGENINGEN UNIV
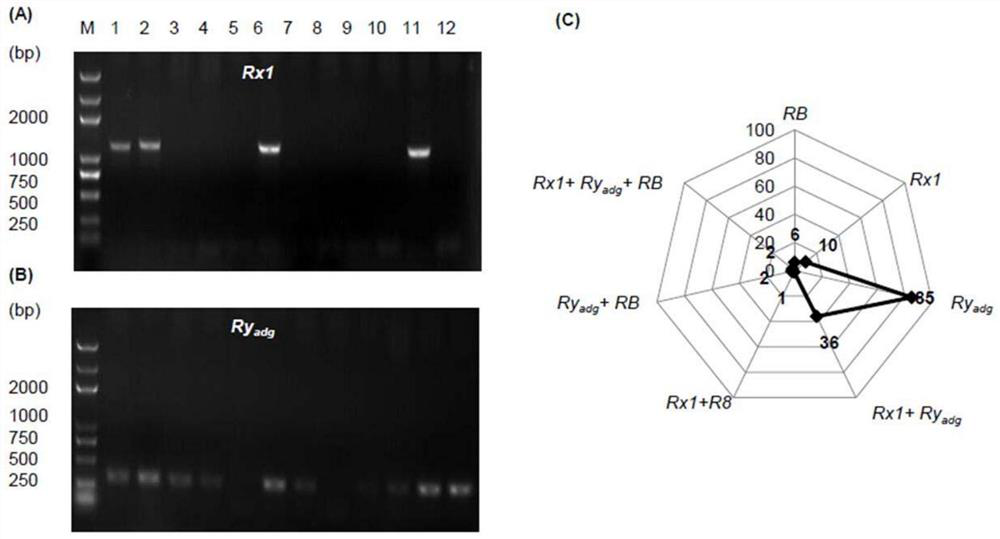
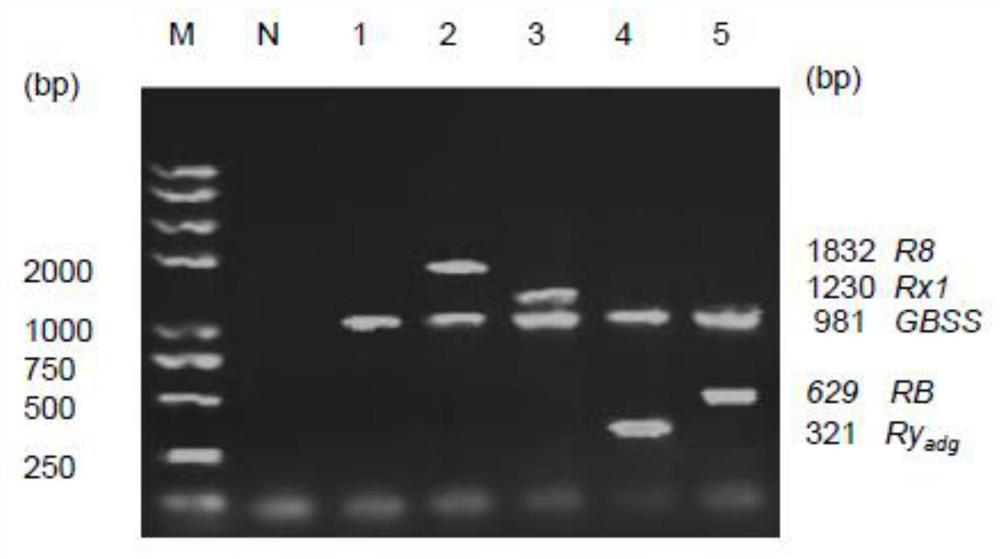
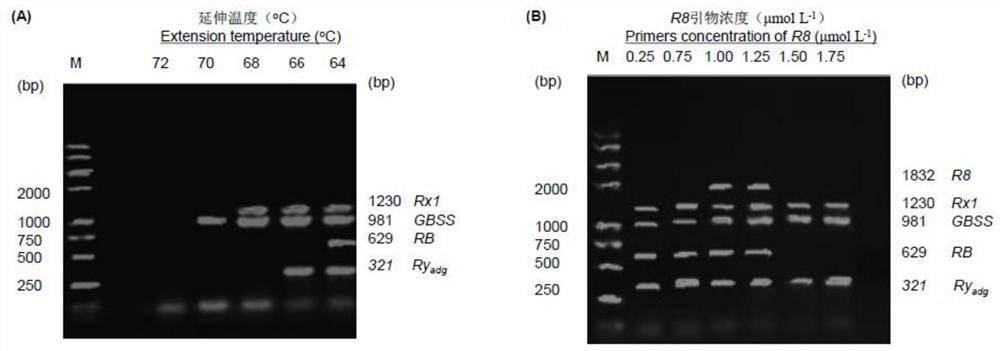
Simple and efficient potato multi-R gene polymerization assisted breeding method
InactiveCN111778345AImprove accuracyAvoid askingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyR gene
The invention provides a simple and efficient potato multi-R gene polymerization assisted breeding method. The method specifically comprises the following steps of obtaining late blight resistance screening primer sequence groups RB, R8, Rx1, Ryadg and GBSS, constructing a multiple PCR reaction system by using the primer group, and carrying out pyramiding breeding selection on late blight lastingresistance and PVX and PVY virus disease resistance genes. The method is high in detection specificity, has good tolerance to the quality and concentration of a DNA template, and is convenient in adaptation to screening and identification of molecular markers of large-scale breeding intermediate materials. The method provides a simple and efficient technology for late blight and virus disease polyclonal antibody gene pyramiding breeding and provides a technical scheme for breeding of new polyclonal antibody varieties.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
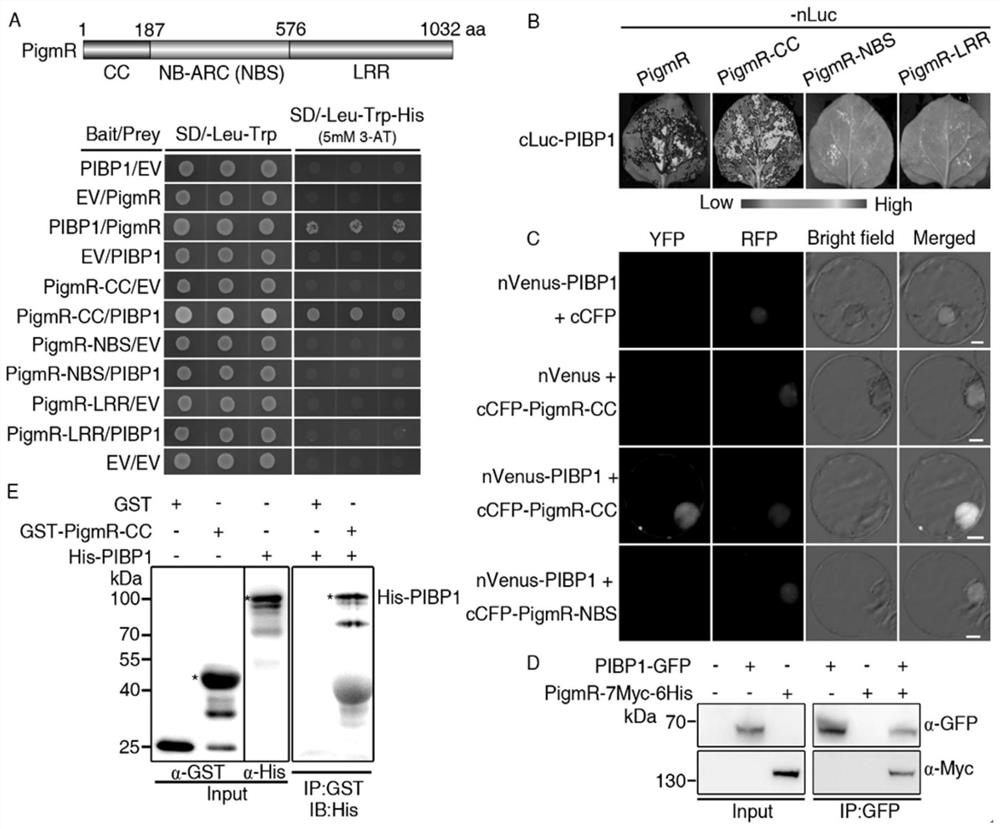
Transcription factor for enhancing broad-spectrum disease resistance of plants and application
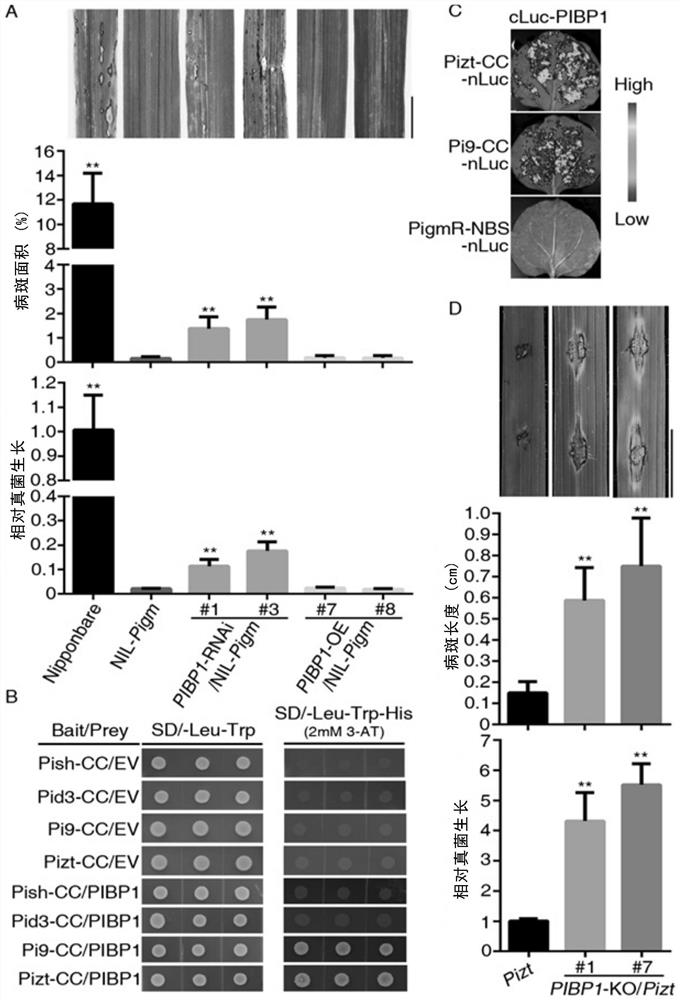
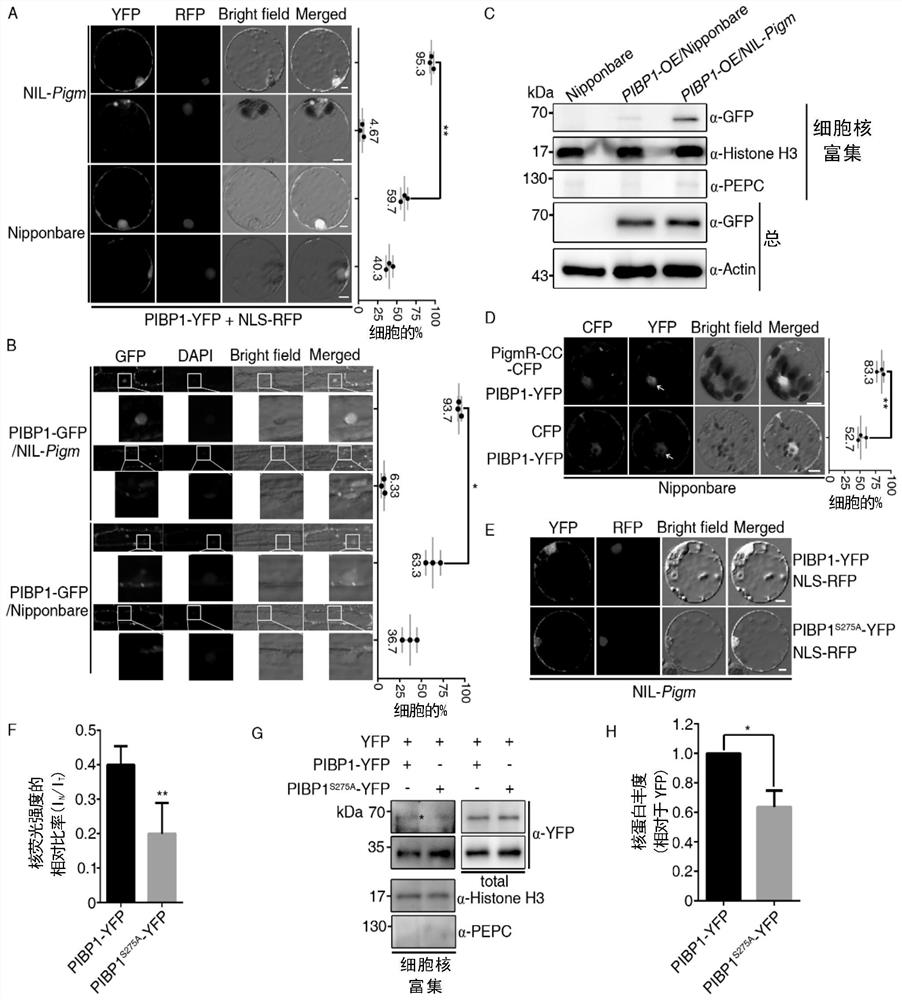
The invention relates to a transcription factor for enhancing broad-spectrum disease resistance of plants and an application. The invention discloses that PIBP1 directly interacts with PigmR and otherbroad-spectrum anti-disease R genes to promote accumulation of own cell nuclear proteins and positively regulate and control disease resistance of plants. The PIBP1 and the homologous gene are combined as a kind of non-classical transcription factors and activate expression of defensive genes such as OsWAK14 and OsPAL1 at the downstream of the non-classical transcription factors. Therefore, the invention provides a new transcription factor which activates a downstream disease-resistant gene through direct interaction with the R gene and endows plants with a new mechanism of disease resistance. The invention not only provides a practical and effective plant improvement method, but also provides a new way for broad-spectrum immune mechanism research of plants and disease resistance breedingof plants.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 (SS2 for short) double-gene deleted live vaccine and its application
InactiveCN102776134BLow toxicityImprove securityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsR geneBacterial strain
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Plants with reduced expression of phosphatase type 2C gene for enhanced pathogen resistance
InactiveUS7910801B2Improve disease resistanceTight regulationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention relates to a method for down regulating an Arabidopsis protein phosphatase type 2C gene, referred to as “defense-associated protein phosphatase type 2C one” (DAPP1) that functions as a negative regulator of a plant defense pathway by contacting the gene or gene mRNA with an interfering nucleotide sequence that interacts with the gene and reducing expression thereof. Plants including such interfering nucleotide sequence exhibit increased disease resistance to pathogen even in the absence of R genes. Close homologs of DAPP1 exist in multiple crop species, and as such, the controlled down-regulation of homologous genes in a variety of crop species will enhance disease resistance of target crop species to pathogens.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
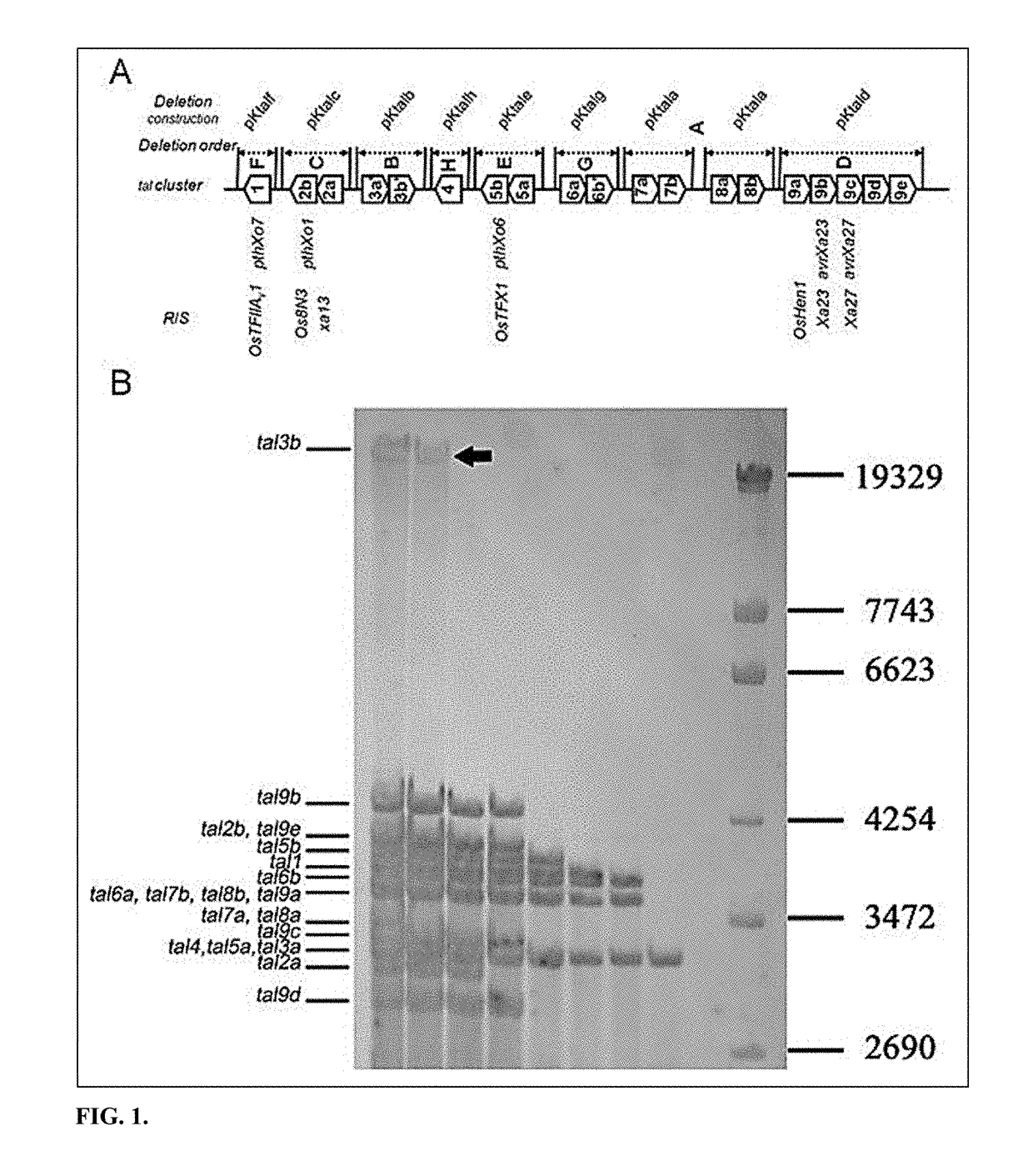
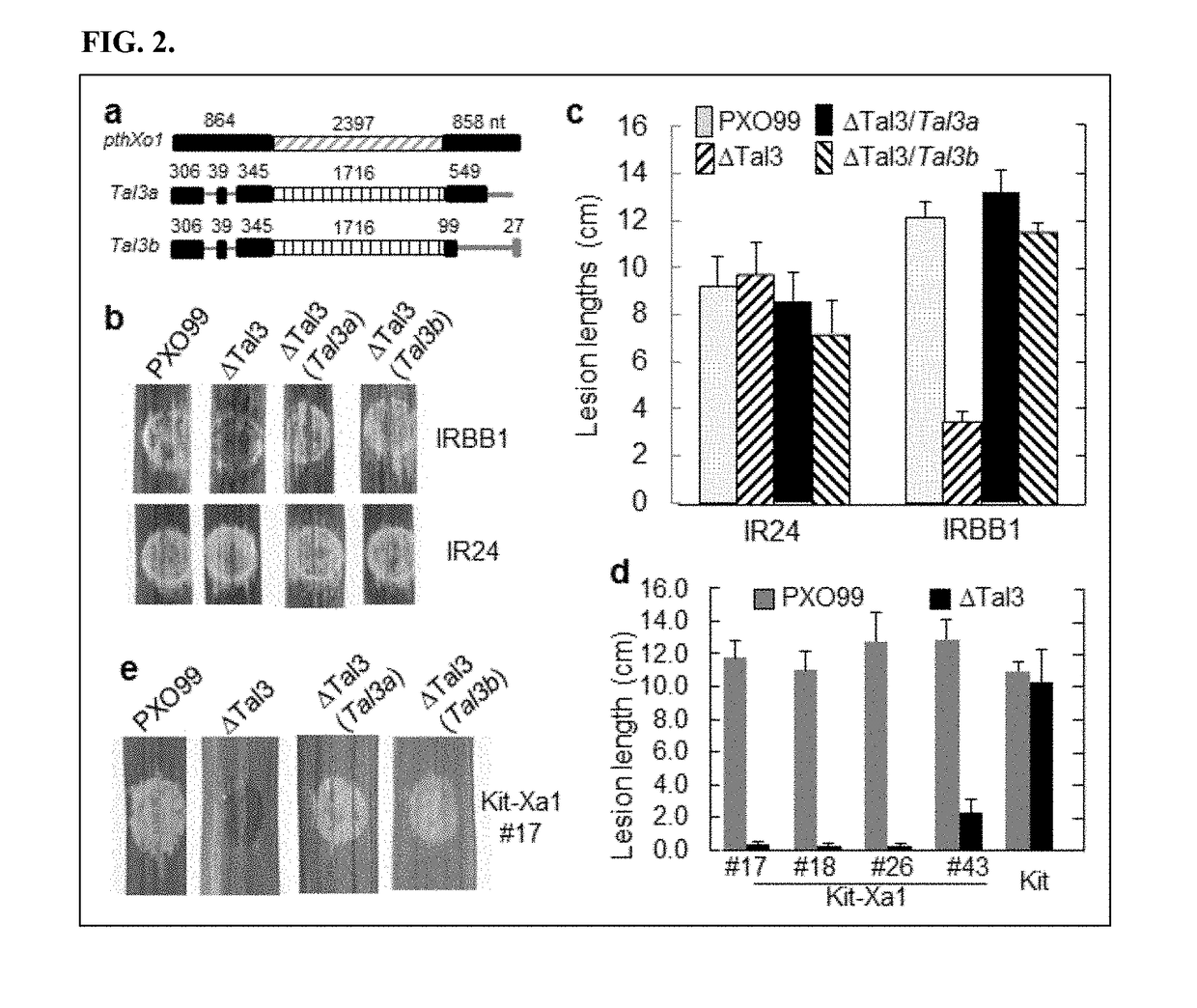
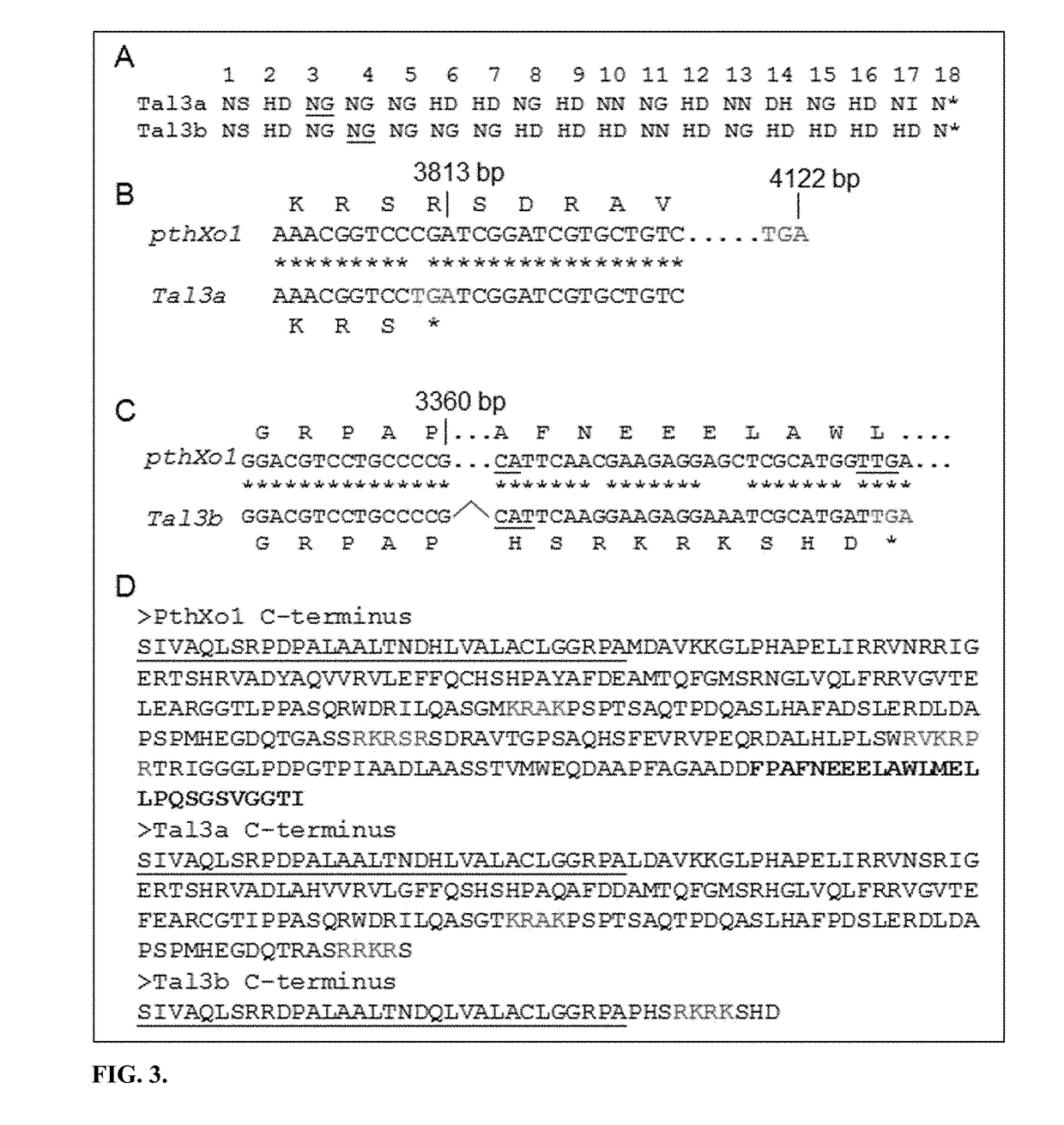
Xa1-mediated resistance to tale-containing bacteria
The present invention generally provides methods to generate broad-spectrum resistance to Xanthomonas pathogenic bacteria in plants. The invention relates to nucleic acid sequences identified, which are associated with broad spectrum disease resistance including Xa1, an NBS-LRR (Nucleotide Binding Site-Leucine-Rich Repeats) type R gene in rice (SEQ ID NOS: 1 and 2) and Xa1 homolog gene, Xa2, (SEQ ID NOS: 3 and 4) and homologs thereof. Further, novel iTALE (interfering transcription activator-like effectors), have also been identified, for example, iTAL3a (SEQ ID NOS: 5 and 6) and iTAL3b (SEQ ID NOS: 7 and 8) and homologs thereof. Modulation of these proteins can improve disease resistance in plants.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Monorhamnolipid production strain and application thereof
PendingCN112725252AReduce separation and purification processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGene cluster
The invention discloses a monorhamnolipid production strain and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 strain is used as an original strain, the rhlC gene of the pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 strain is replaced with an rhlAB-R gene cluster through a homologous recombination method, and the pseudomonas aeruginosa strain capable of specifically producing monorhamnolipid is obtained. The random mutation is further combined, and a mutant strain with the single rhamnolipid production level remarkably improved is screened out. According to the mutant strain, commercially available goldfish sunflower seed oil is used as a substrate, fermentation is carried out in a 5L bioreactor at 37 DEG C for 90 hours, the concentration of monorhamnolipid reaches 62.7 g / L, the purity reaches 95.16%, and the ratio of Rha-C10-C10 is the maximum and accounts for 68.59%.
Owner:上海恒什生物科技有限公司
Wheat stem rust resistance genes and methods of use
Compositions and methods and for enhancing the resistance of wheat plants to wheat stem rust caused by Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici are provided. The compositions comprise nucleic acid molecules encoding resistance (R) gene products and variants thereof and plants, seeds, and plant cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The methods for enhancing the resistance of a wheat plant to wheat stem rust comprise introducing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an R gene product into a wheat plant cell. Additionally provided are methods for using the wheat plants in agriculture to limit wheat stem rust.
Owner:THE SAINSBURY LAB
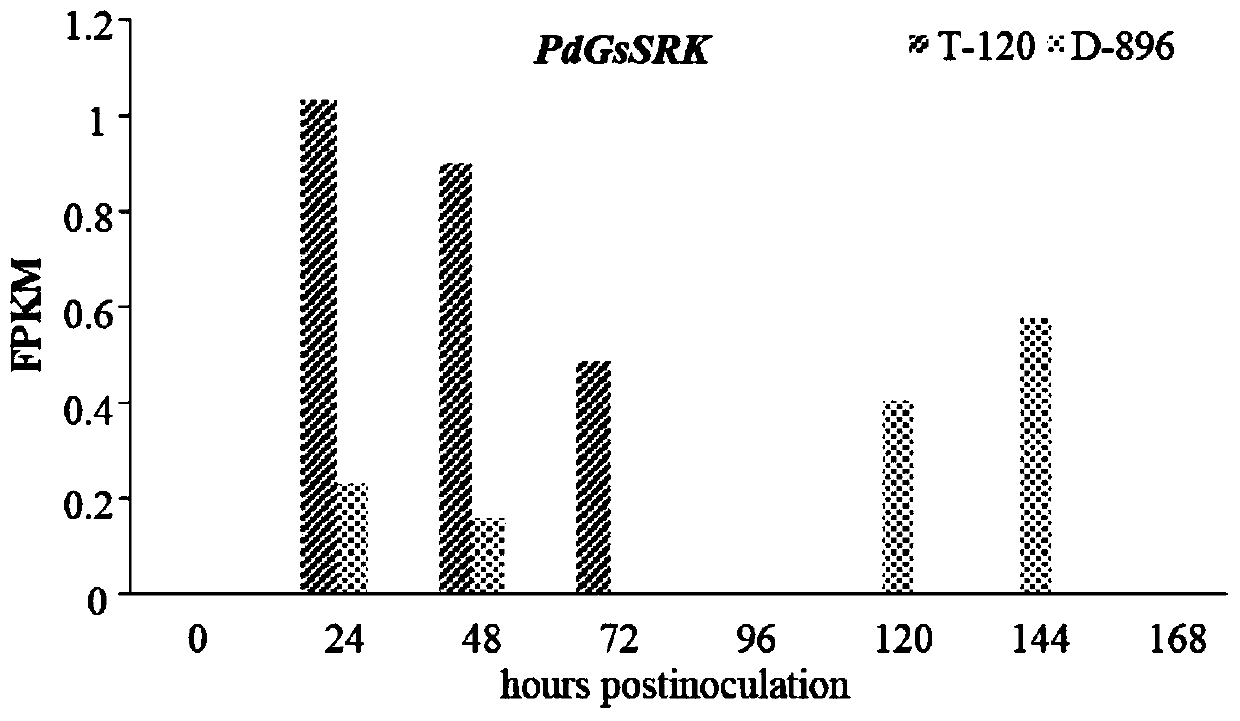
Populus deltoides brown leaf rust-resistant gene PdGsSRK, expressed protein, cloning primer pair and application thereof
The invention discloses a PdGsSRK gene for resistance to Populus deltoides brown leaf rust, and discloses an expression protein, a cloning primer pair and an application thereof. The gene is a serine / threonine kinase (STK) R gene and plays an important role in the resistance to leaf rust. Based on the analysis of Populus deltoides brown leaf rust-resistant gene loci, combined with dynamic gene expression analysis, the PdGsSRK gene is determined to be a key gene regulating Populus deltoides brown leaf rust resistance. The PdGsSRK gene provides an important genetic resource for breeding the newPopulus deltoides varieties resistant to brown leaf rust.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
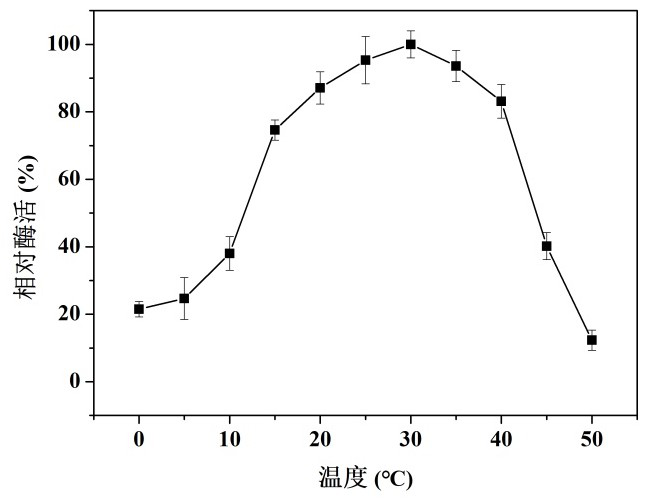
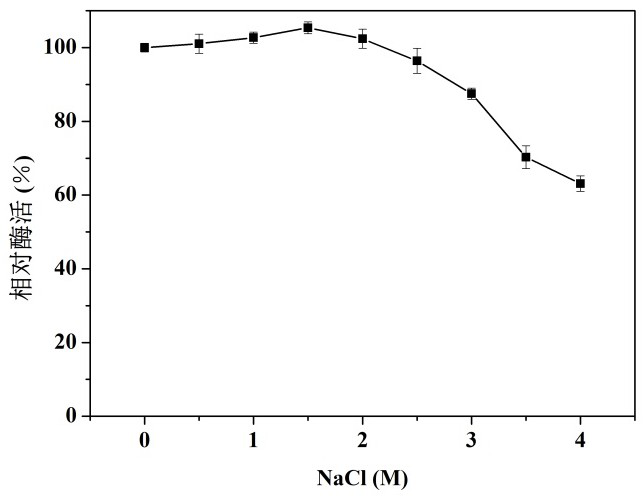
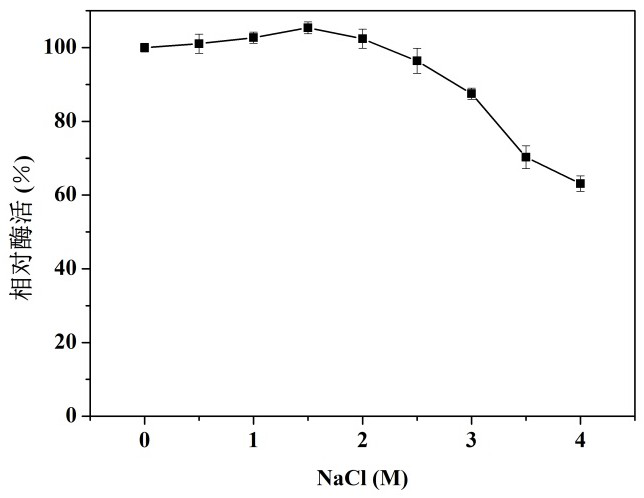
Cold-adapted ribonuclease R and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a cold-adapted ribonuclease R and a coding gene and application thereof. Firstly, a novel cold-adapted ribonuclease R coding gene is cloned from Psychrobactersp. in Antarctic sea ice microorganisms, and an amino-acid residue sequence of the cold-adapted ribonuclease R is shown in SEQ ID No. 2. Sequence analysis shows that a protein sequence encoded by the gene contains a total of 770 amino acid residues, belonging to the RNR superfamily, and the highest homology with the published protein sequences in the current database is 90.07%. The ribonuclease R gene has an expression way realized by using plasmid pET-28 (+) to construct a recombinant expression vector containing the ribonuclease R gene, transferring the recombinant expression vector into Escherichia coli hostcells and inducing the expression of the ribonuclease R gene. The optimal catalytic temperature of the expression product, ribonuclease R, of the invention is about 30 DEG C, and 50% or above of thehighest enzyme activity is maintained between 15 and 40 DEG C; and 85% or above of the highest enzyme activity is maintained with the presence of 0-3 M NaCl, and the expression product has broad application prospects. The expression product of the invention has outstanding cold adaptability, relatively good stability and certain salt resistance, opening up the potential application of the expression product in food, medicine and molecular biology related fields.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
An r gene that controls soybean-rhizobia compatibility and its protein and application
ActiveCN112626080BImprove symbiotic nitrogen fixationReduce the number of nodulesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyR gene
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to the application of new genes, in particular to an R gene for controlling soybean-rhizobia matching, and its protein and application. Gene disclosed in the present invention GmNNL1 in the soybean line Hengfeng black bean GmNNL1 The genome sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the encoded amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.3. soy R Gene GmNNL1 It is an effective gene that can regulate the number of nodules of specific rhizobia on soybean. It can regulate the number of nodules by directly recognizing the haplotype of the specific effector protein NopP of slow-growing rhizobia, limiting the symbiotic nodulation of indigenous rhizobia, The soybean is preferentially nodulated with the artificially applied high-efficiency rhizobia agent, and the symbiotic nitrogen fixation ability can be improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY +1
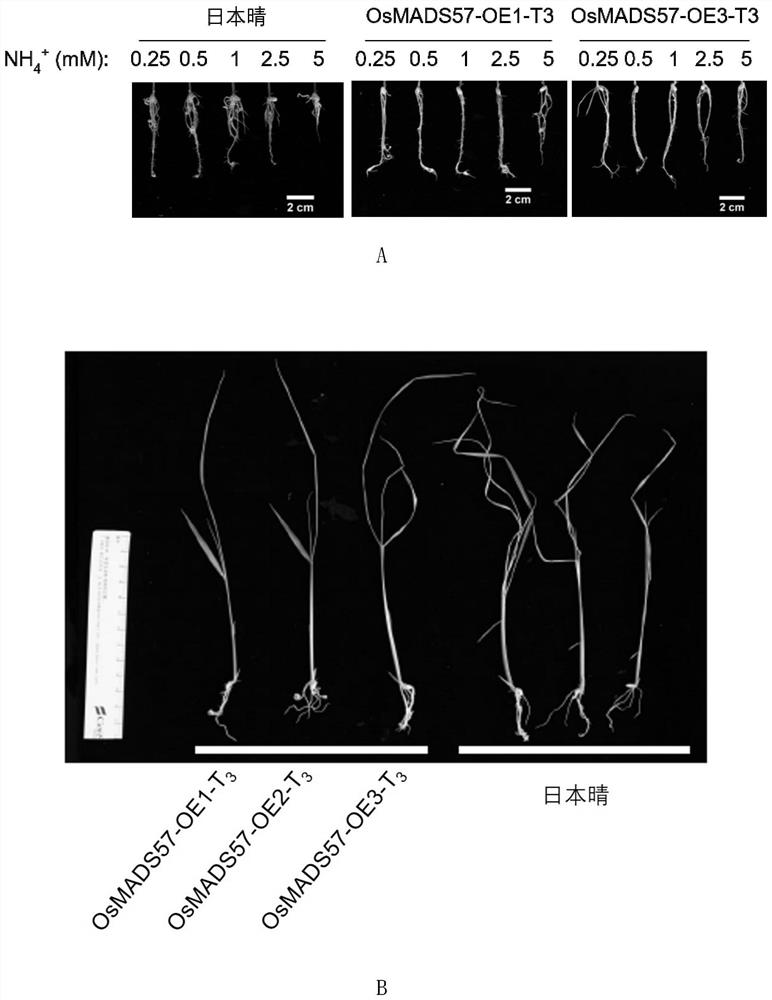
Application of protein m57 in regulating rice resistance to ammonium
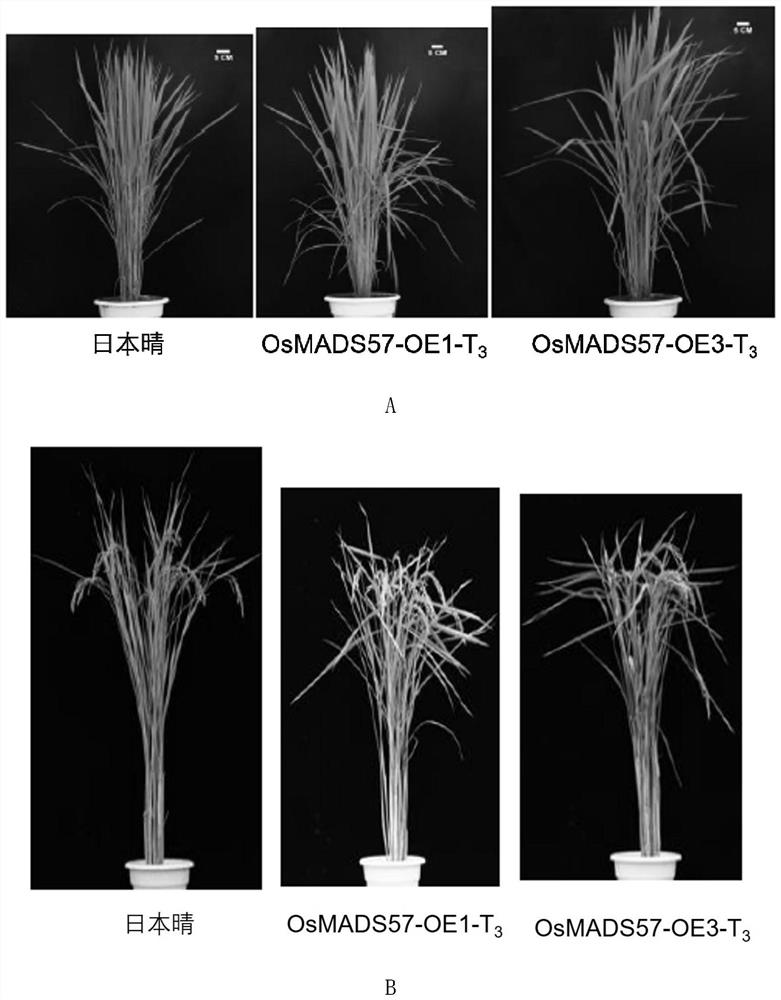
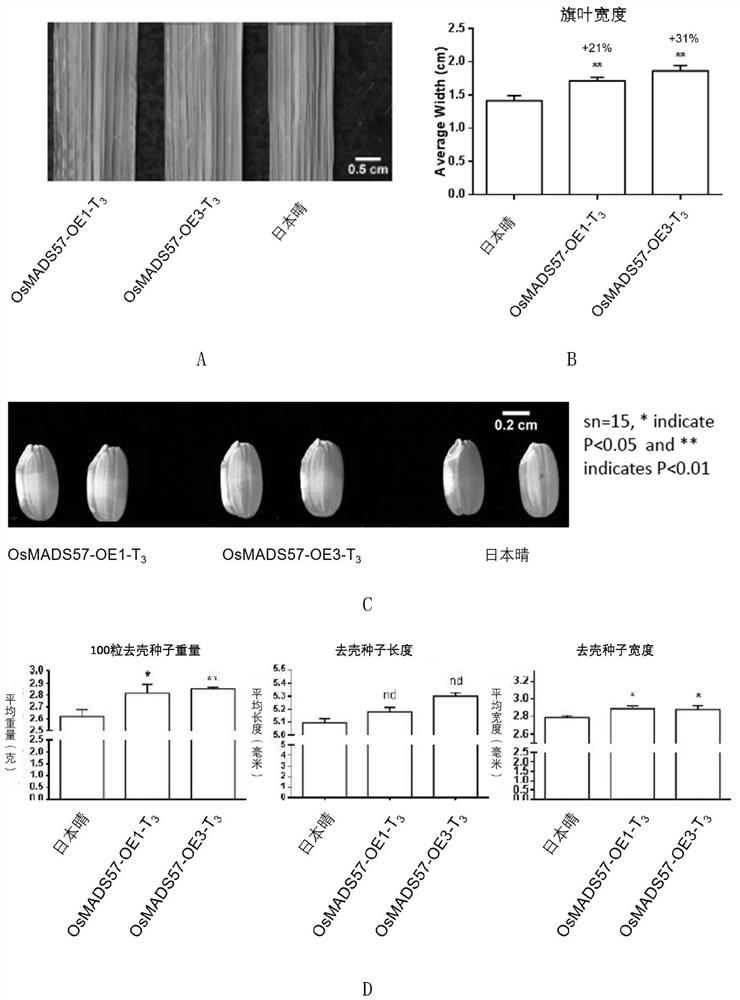
ActiveCN112409465BCompact plantIncrease widthPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Potyvirus resistance genes and methods of use
Compositions and methods and for enhancing the resistance of plants to plant diseases caused by potyviruses are provided. The compositions comprise nucleic acid molecules encoding resistance (R) gene products and variants thereof and plants, seeds, and plant cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The methods for enhancing the resistance of a plant to plant disease caused by a potyvirus comprise introducing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an R gene product into a plant cell. Additionally provided are methods for using the plants in agriculture to limit plant disease.
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
Wheat stem rust resistance genes and methods of use
Compositions and methods and for enhancing the resistance of wheat plants to wheat stem rust caused by Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici are provided. The compositions comprise nucleic acid molecules encoding resistance (R) gene products and variants thereof and plants, seeds, and plant cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The methods for enhancing the resistance of a wheat plant to wheat stem rust comprise introducing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an R gene product into a wheat plant cell. Additionally provided are methods for using the wheat plants in agriculture to limit wheat stem rust.
Owner:THE SAINSBURY LAB
Late blight resistance genes and methods of use
Compositions and methods and for enhancing the resistance of plants to a plant disease caused by a Phytophthora species are provided. The compositions comprise nucleic acid molecules encoding resistance (R) gene products and variants thereof and plants, seeds, and plant cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The methods for enhancing the resistance of a plant to a plant disease caused by a Phytophthora species comprise introducing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an R gene product into a plant cell. Additionally provided are methods for using the plants in agriculture to limit plant disease.
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
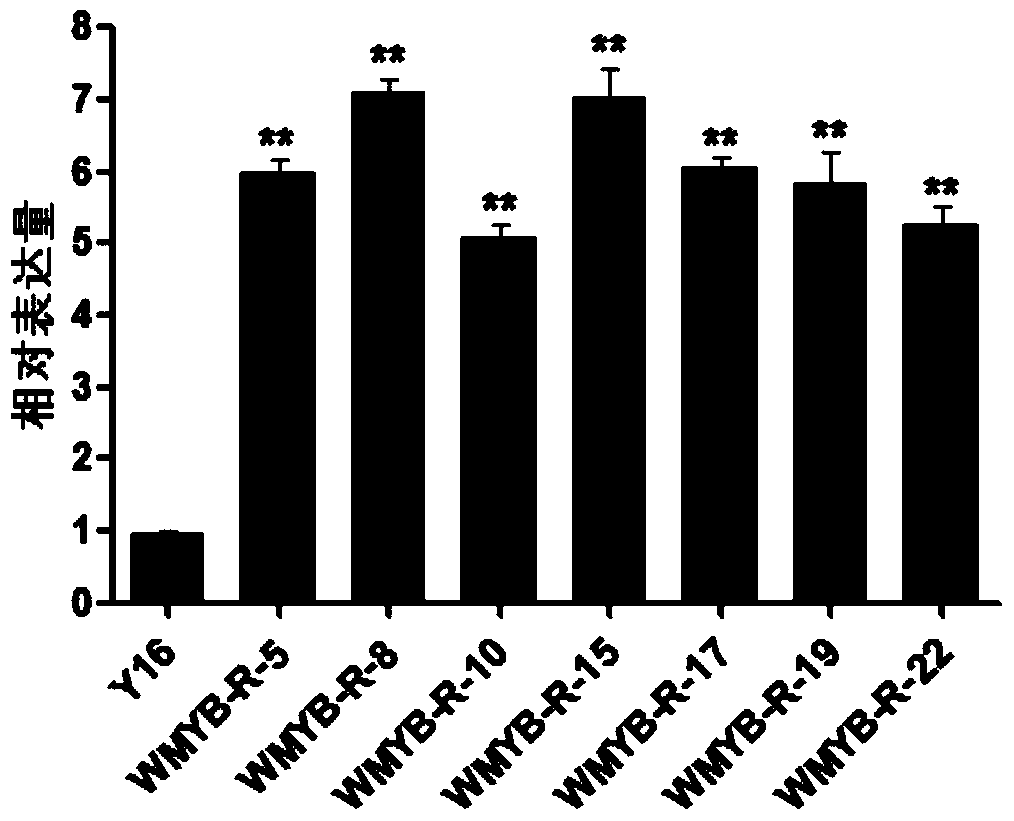
Cultivation method and related biomaterials of wmyb-r transgenic wheat resistant to root rot and sheath blight
The invention discloses a cultivation method of genetically modified WMYB-R wheat resistant to root rot and sheath blight and a related biological material thereof. The cultivation method includes the step of guiding coding gene of WMYB-R protein into a receptor plant to obtain a genetically modified plant with disease resistance higher than that of the receptor plant. If the WMYB-R gene is modified into plants, resistance, of the plants, to root rot and sheath blight can be improved, so that pesticide consumption is lowered to reduce environmental pollution; the cultivation method has important theoretical and practical significance and can play an important role in genetic improvement of the plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Stem rust resistance genes and methods of use
Compositions and methods and for enhancing the resistance of wheat plants to wheat stem rust caused by Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici are provided. The compositions comprise nucleic acid molecules encoding resistance (R) gene products and variants thereof and plants, seeds, and plant cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The methods for enhancing the resistance of a wheat plant to wheat stem mst comprise introducing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an R gene product into a wheat plant cell. Additionally provided are methods for using the wheat plants in agriculture to limit wheat stem rust.
Owner:THE SAINSBURY LAB
A cold-adapting ribonuclease r and its encoding gene and application
The present invention discloses a cold-adapting ribonuclease R and its encoding gene and application. The present invention is firstly obtained from Antarctic sea ice microorganism psychrophilic bacillus ( Psychrobacter sp.) cloned a novel cold-adapting ribonuclease R-encoding gene, and the amino acid residue sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.2. Sequence analysis showed that the protein sequence encoded by the gene contained a total of 770 amino acid residues, belonging to the RNR superfamily, and the highest homology with the published protein sequences in the current database was 90.07%. Its expression mode is to use plasmid pET-28(+) to construct a recombinant expression vector containing ribonuclease R gene, and transfer the constructed recombinant expression vector into Escherichia coli host cells ( Escherichia coli ), which was induced to express the RNase R gene. The optimal catalytic temperature of the expression product ribonuclease R of the present invention is about 30° C., and more than 50% of the highest enzymatic activity is maintained between 15 and 40° C.; and more than 85% of the highest enzymatic activity is maintained in the presence of 0-3 M NaCl. ,with broadly application foreground. The expression product of the invention has outstanding cold adaptability, good stability and certain salt tolerance, which opens up potential applications in food, medicine and molecular biology related fields.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Potyvirus resistance genes and methods of use
Compositions and methods and for enhancing the resistance of plants to plant diseases caused by potyviruses are provided. The compositions comprise nucleic acid molecules encoding resistance (R) gene products and variants thereof and plants, seeds, and plant cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The methods for enhancing the resistance of a plant to plant disease caused by a potyvirus comprise introducing a nucleic acid molecule encoding an R gene product into a plant cell. Additionally provided are methods for using the plants in agriculture to limit plant disease.
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
The estrogenic gene ferr and the estrogenic gene ferr-r in Populus americana and their application
The invention discloses an estrogen-promoting gene FERR and an estrogen-repressing gene FERR-R of Populus americana and applications thereof, belonging to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The present invention fine-positions the sex-determining gene loci of Populus americana through family linkage analysis, and then uses natural population materials to carry out genome-wide association analysis, combined with transcriptome and genome methylation sequencing, and discloses for the first time the poplar estrogen-promoting genes FERR and inhibitory genes. The female gene FERR-R, the FERR-R gene does not encode a protein, but produces siRNAs to methylate the promoter sequence of the female-promoting gene FERR and cut its transcript, thereby inhibiting the female-promoting gene FERR in male poplar plants expression. However, the female poplar plant does not contain the FERR-R gene, and the expression of FERR is not inhibited by FERR-R, so the female flower of the female plant develops. The poplar estrogenic gene and estrogenic suppressor gene provided by the invention can be applied to early sex identification and molecular breeding of poplar.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Potyvirus resistance genes and methods of use
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com