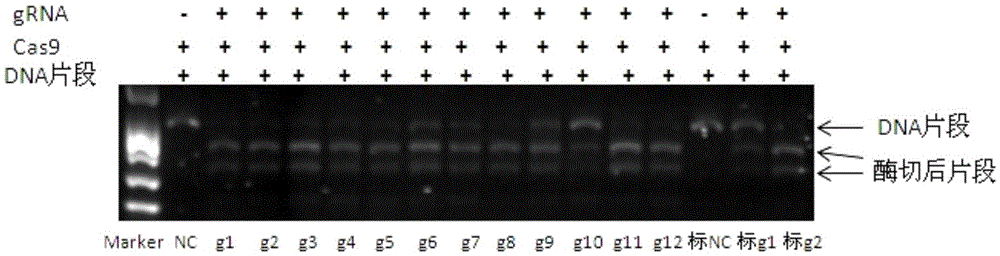
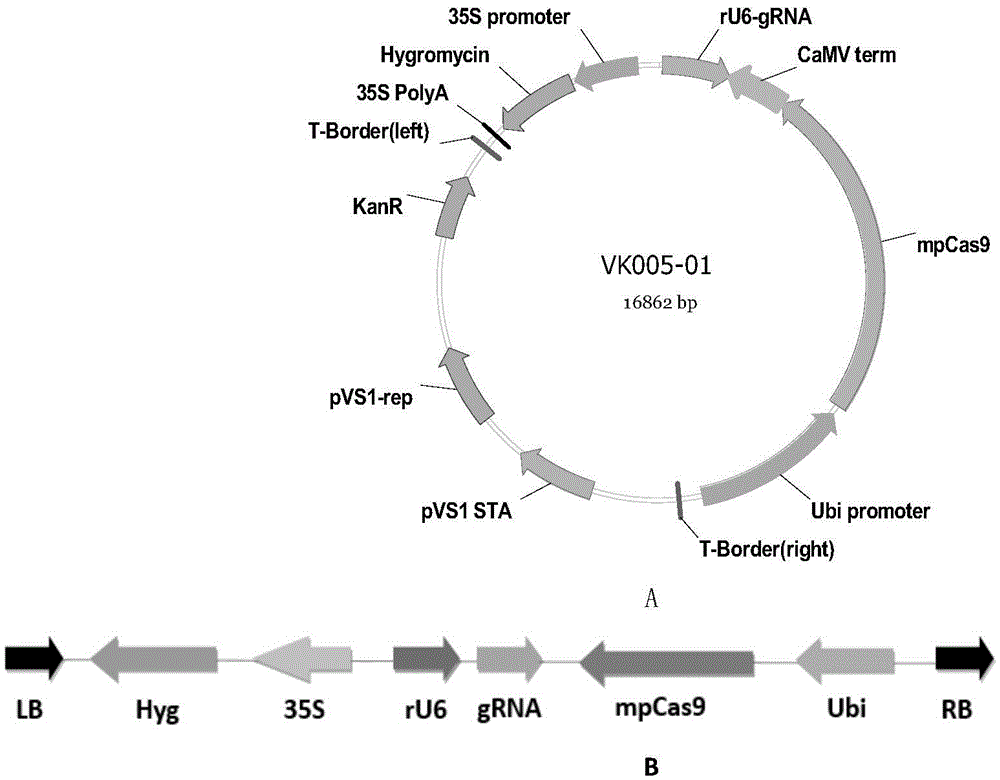
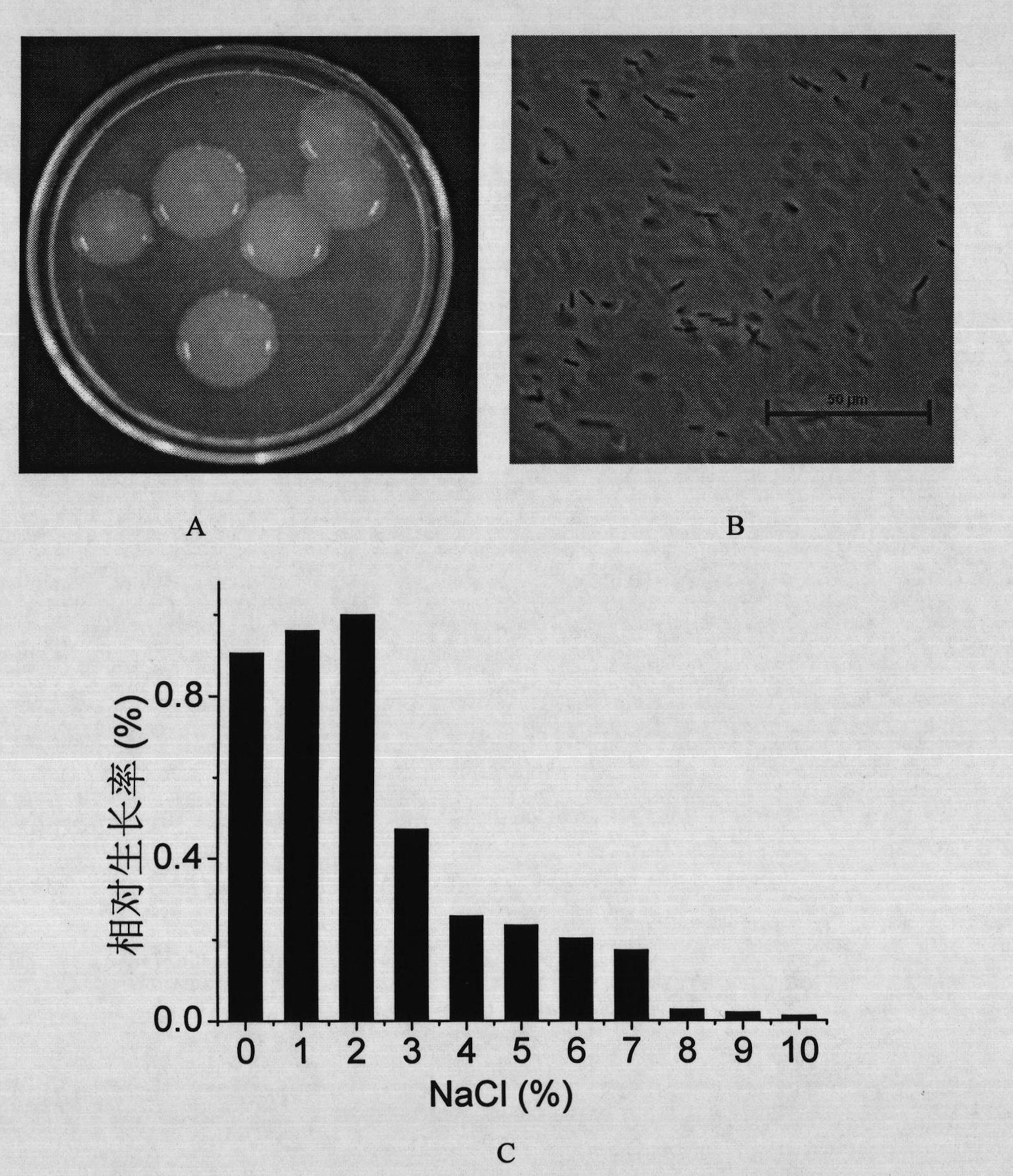
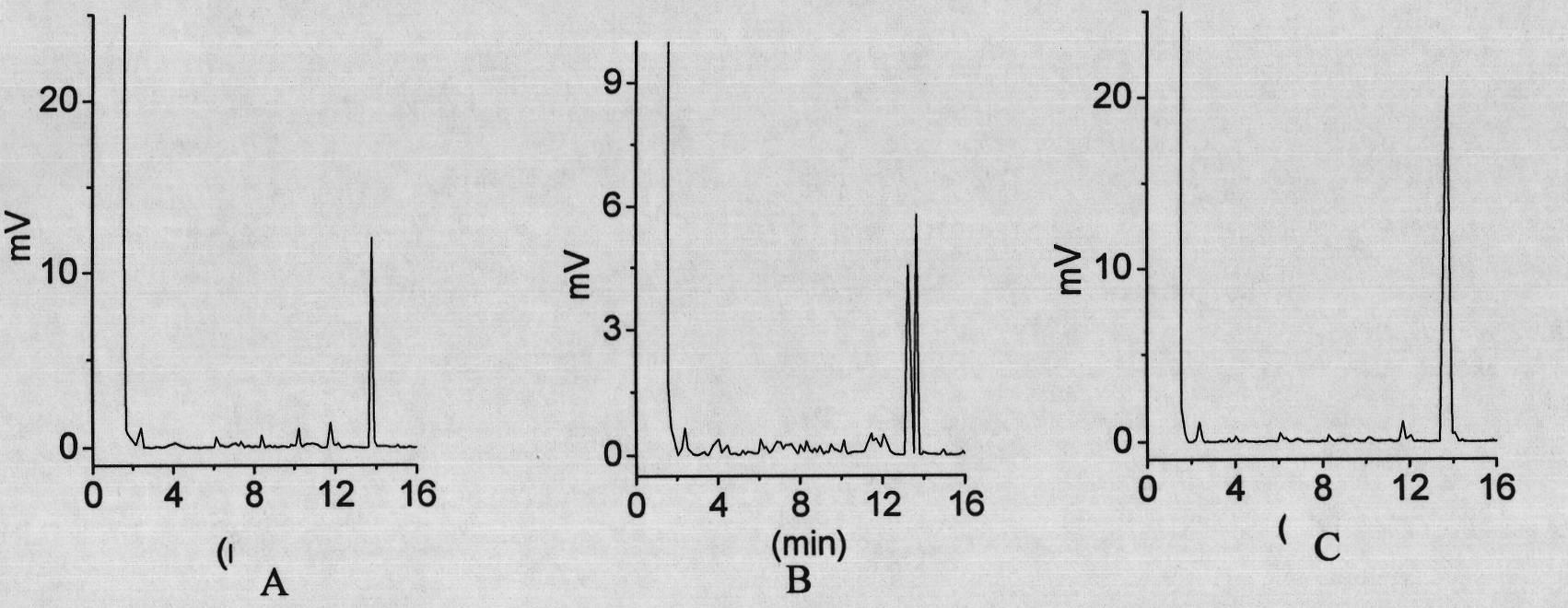
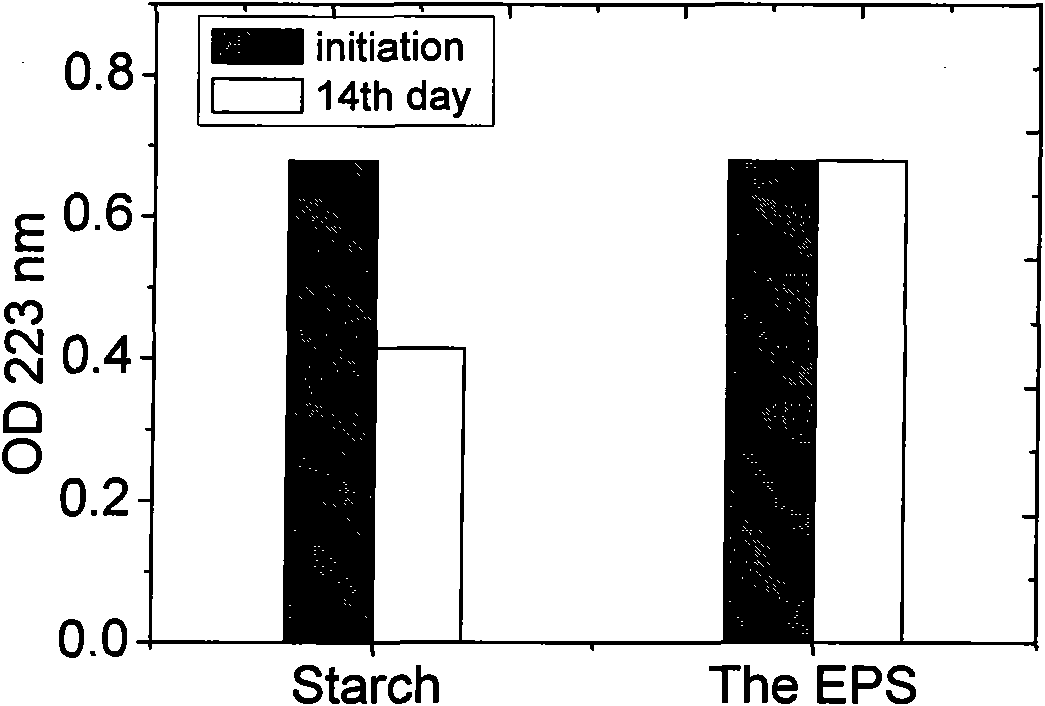
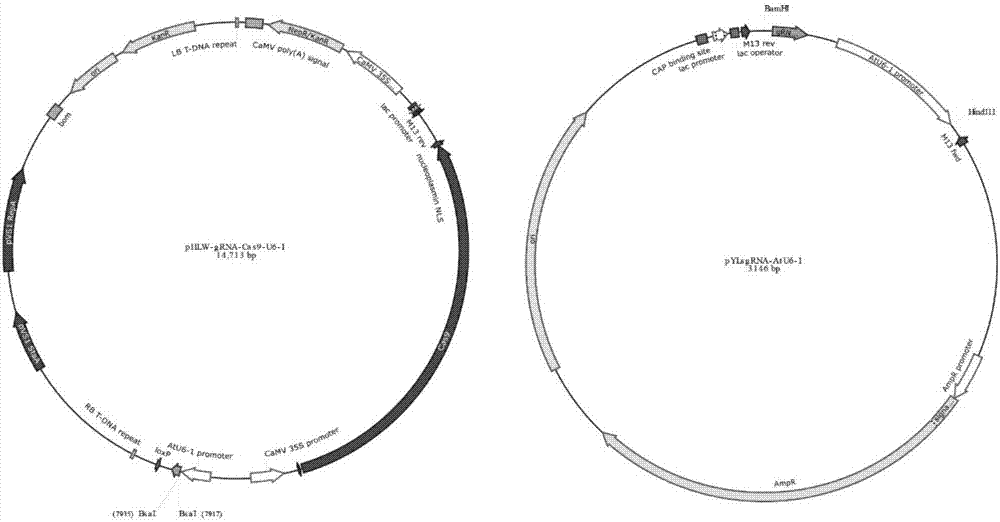
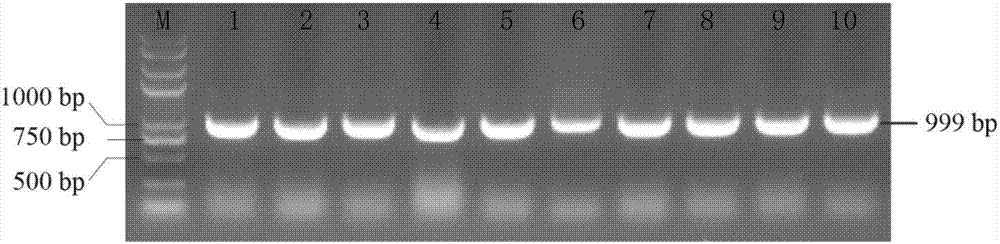
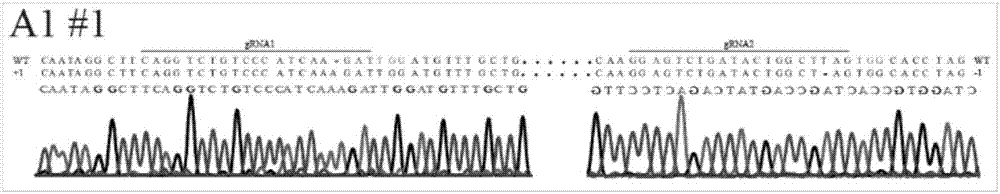
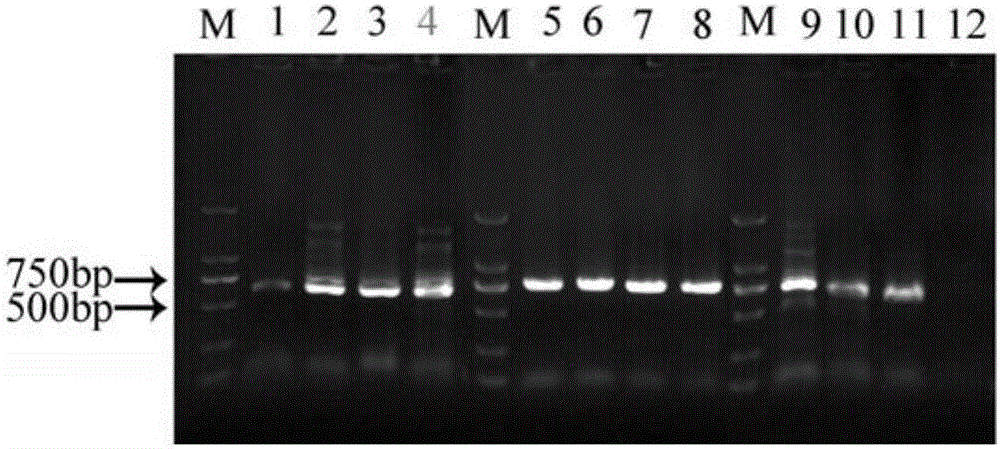
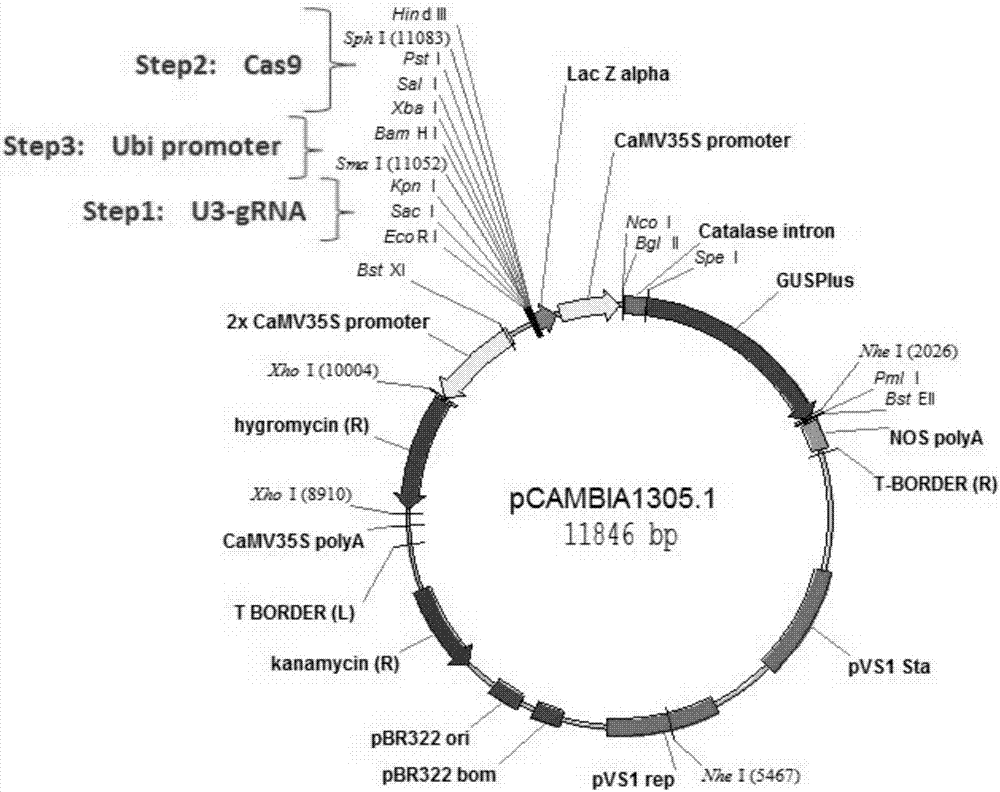
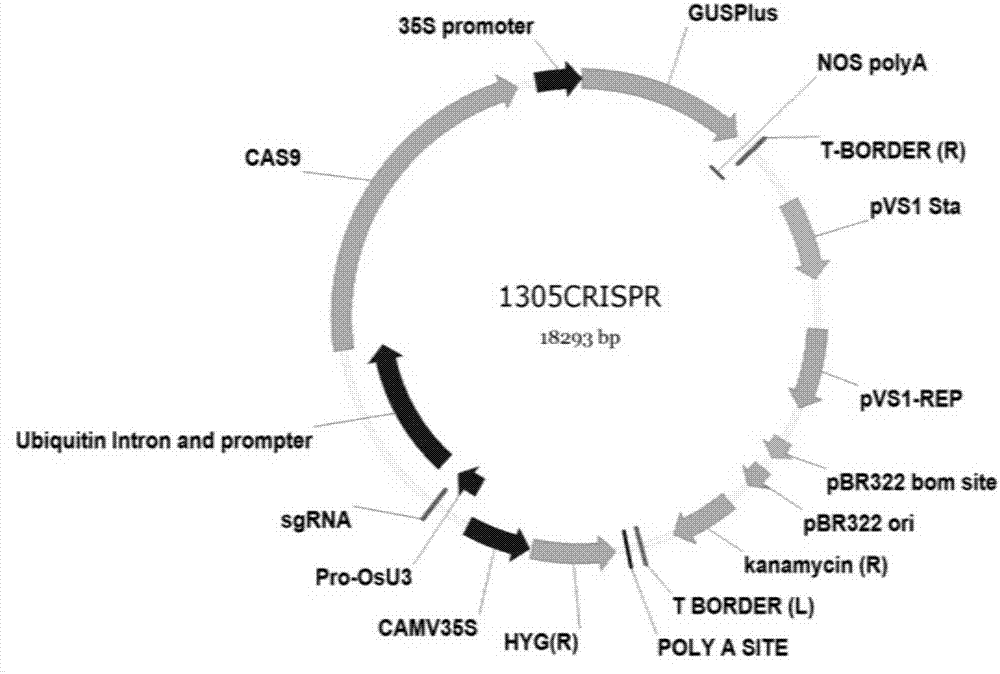
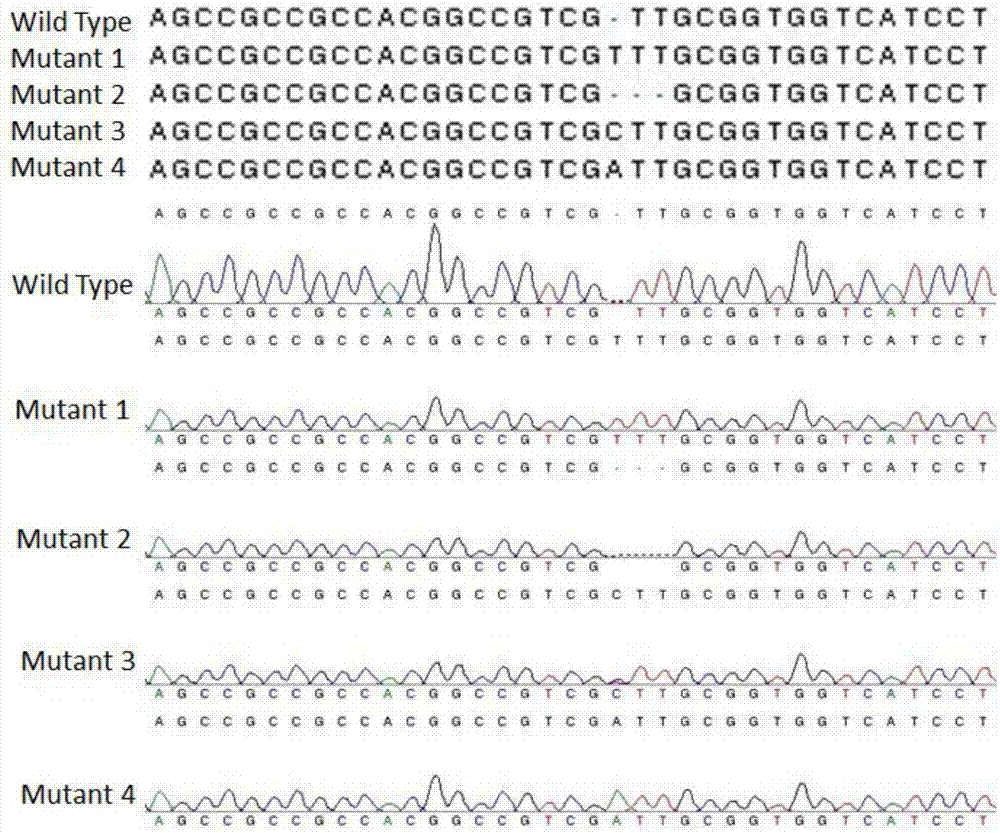
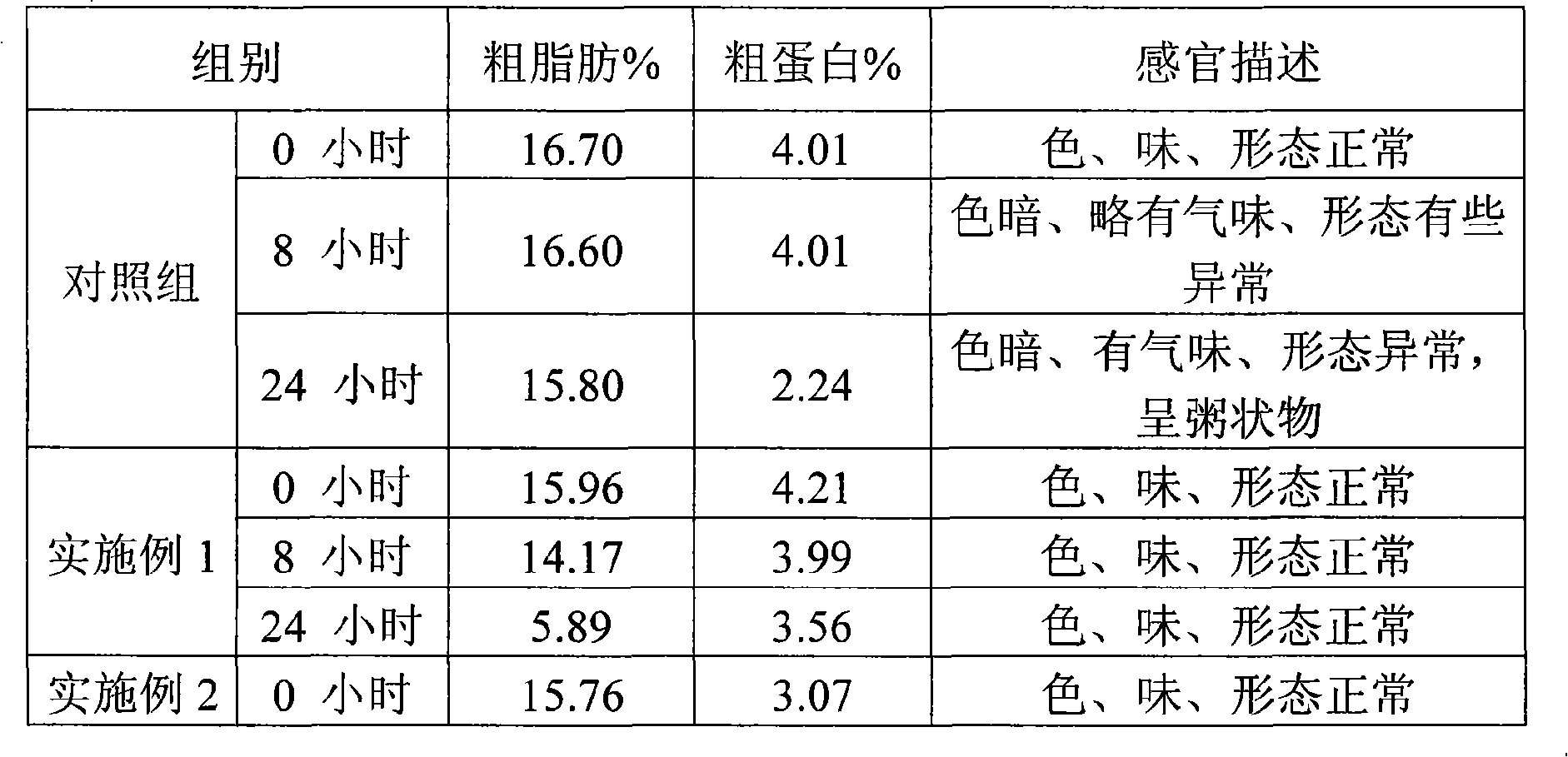
Patents
Literature
2246 results about "Agrobacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Agrobacterium is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria established by H. J. Conn that uses horizontal gene transfer to cause tumors in plants. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is the most commonly studied species in this genus. Agrobacterium is well known for its ability to transfer DNA between itself and plants, and for this reason it has become an important tool for genetic engineering.
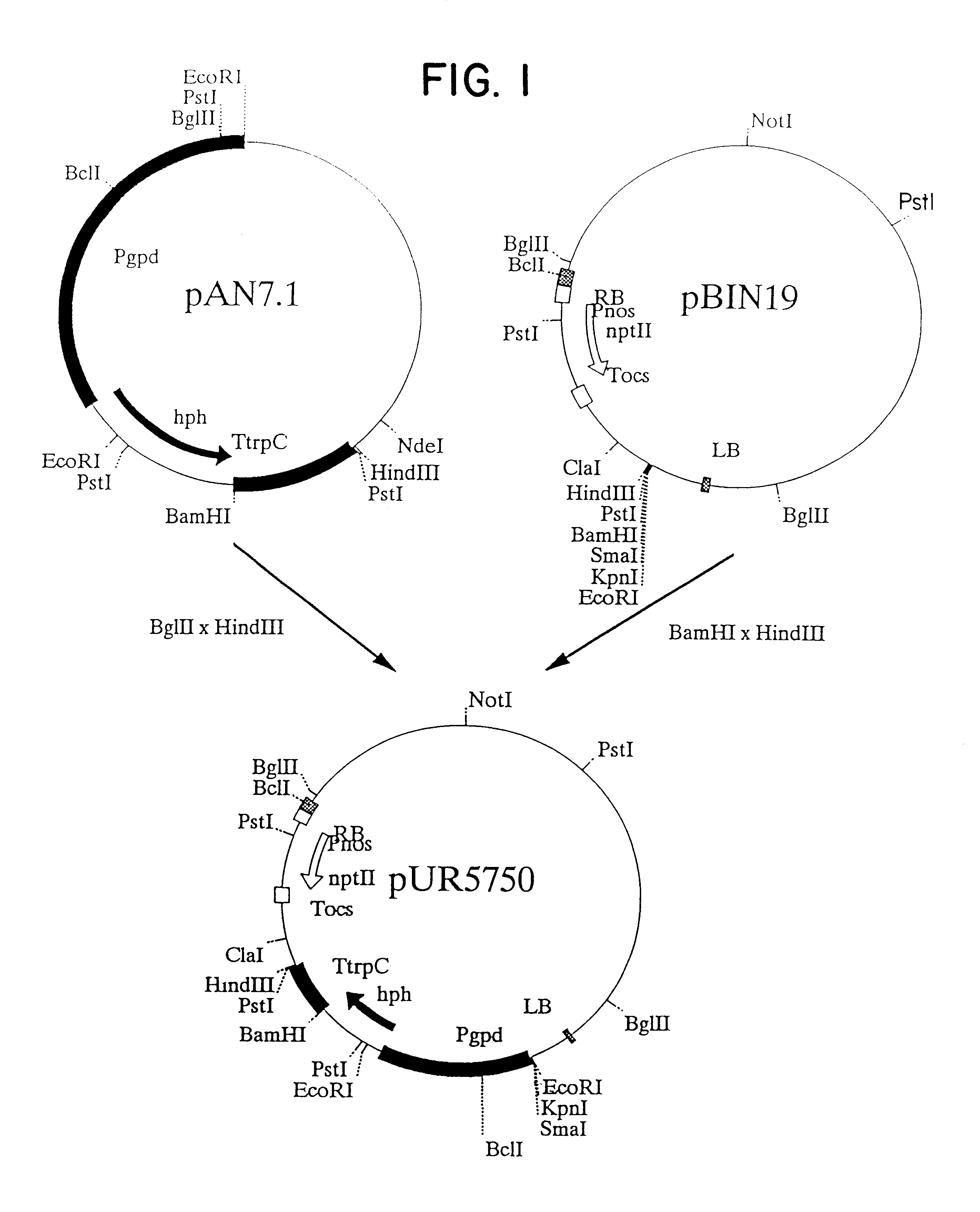
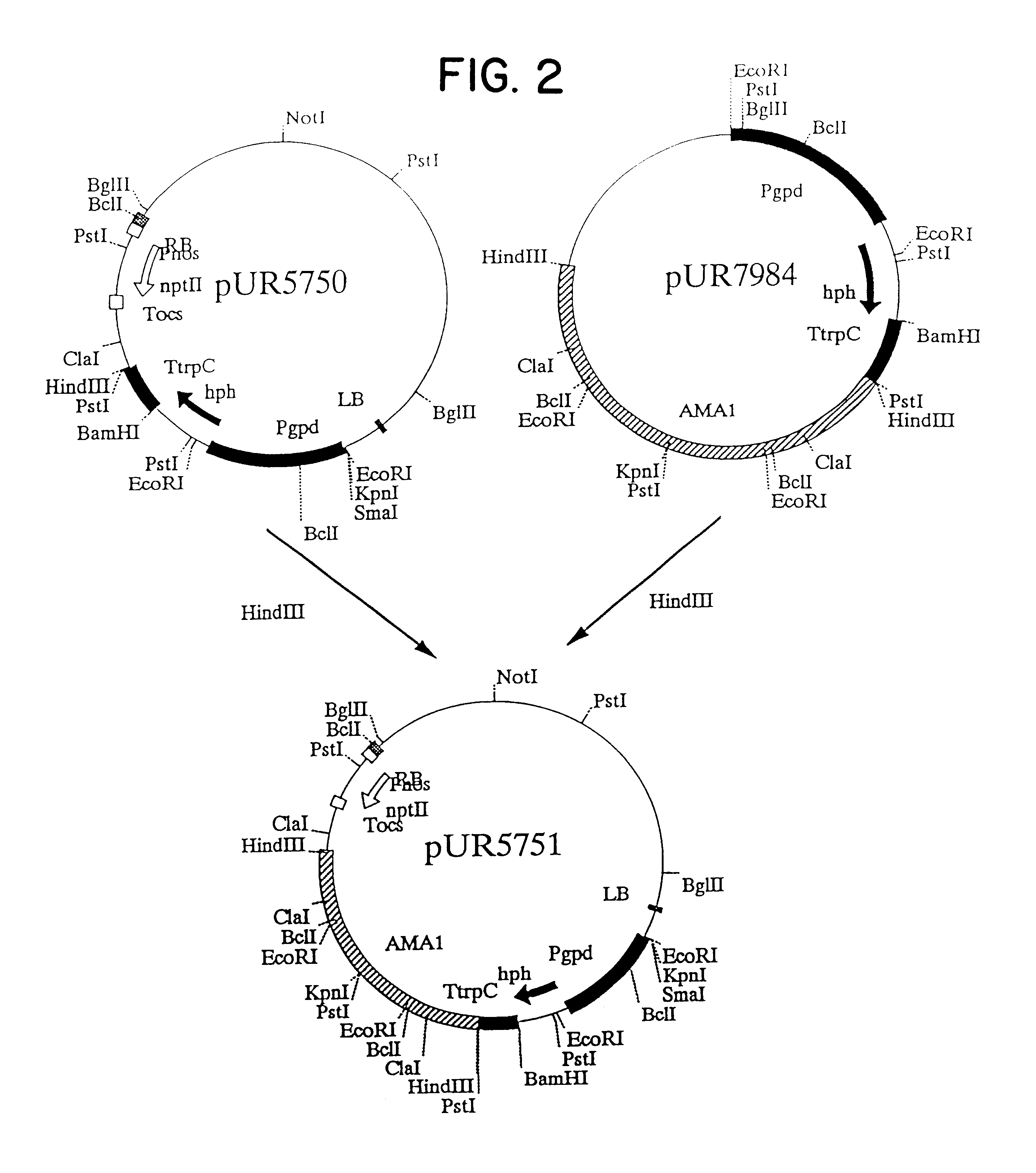
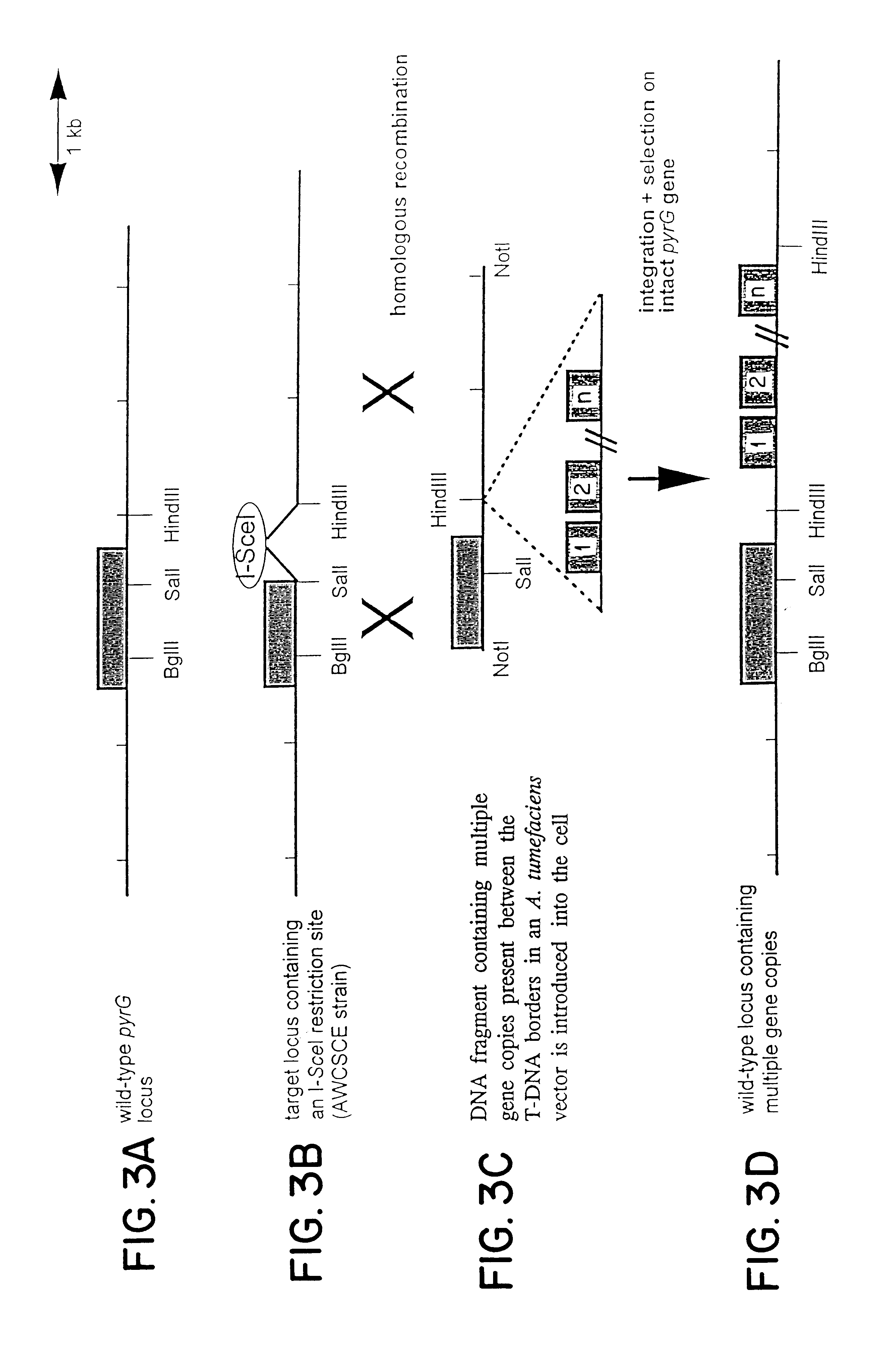
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
Methods for the production of stably-transformed, fertile wheat employing agrobacterium-mediated transformation and compositions derived therefrom
InactiveUS7026528B2Tissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologySomaclonal variation
Disclosed are processes for producing stably transformed fertile wheat a system of transforming wheat via Agrobacterium. This invention provides methods transforming a variety of explants, such as freshly isolated or pre-cultured immature embryos, embryogenic callus and suspension cells. Also disclosed are methods for recovering transgenic plants after transformation within a short period of time, if the explants are regenerable at the time of transformation. Thus the frequency of somaclonal variation associated with prolonged in vitro culture period is significantly reduced. The transformation frequency using this system is comparable to or better than published methods using other systems, such as microprojectile bombardment.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for agrobacterium mediated transformation of cotton
InactiveUS6483013B1Improve conversion efficiencyEffect on transformation efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationDNA fragmentationA-DNA
This invention relates to improved methods for the production of transgenic cotton plants, comprising cocultivating Agrobacterium cells comprising a DNA fragment of interest operably linked to at least one T-DNA border with cotton embryogenic callus in the presence of a plant phenolic compound.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Agrobacterium with heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification capability and application thereof in nitrogenous effluent treatment
InactiveCN101570738AAnoxic denitrification is needed to solve biological denitrificationSolve processingBacteriaWater contaminantsNucleotideBacterial strain
The invention relates to an agrobacterium strain (Agrobacterium sp.) with heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification capability and an application thereof in nitrogenous effluent treatment. The bacterial strain is characterized in that: 16S rRNA gene contains nucleotide sequence shown in sequence table with a sequence length of 1418bp and a accession number FJ639330 in Genbank. The preservation number thereof is CGMCC No.2962. The agrobacterium of the invention has not only heterotrophic nitrification capability but also aerobic denitrification capability. During nitrogenous effluent treatment, and one aerobic phase can cause ammonian to change into gaseous product with high denitrification efficiency and easy operation and tremendous economic benefit compared with the traditional biological denitrification process.
Owner:LANGFANG GAIA ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Process for transfecting plants
InactiveUS20130212739A1Increase probabilityHigh transfection efficiencyBacteriaOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyA-DNA
A process of transfecting a plant, comprising spraying parts of said plant with an aqueous suspension containing cells of an Agrobacterium strain and at least one abrasive suspended in said suspension, said Agrobacterium strain comprising a DNA molecule comprising a nucleic acid construct containing a DNA sequence of interest to be transfected into the plant.
Owner:NOMAD BIOSCI
Use of non-agrobacterium bacterial species for plant transformation
The invention relates to methods for Rhizobia-mediated genetic transformation of plant cells, including soybean, canola, corn, and cotton cells. These include both VirD2-dependent and VirD2-independent methods. Bacterial species utilized include strains of Rhizobium sp., Sinorhizobium sp., and Mesorhizobium sp. Vectors for use in such transformation are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Transformation of soybean
InactiveUS20090049567A1Improved shoot productionShorten the timeOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureGlycineTarget tissue
The present invention relates to improved methods for the incorporation of DNA into the genome of a soybean (Glycine max) plant utilizing meristematic cells of primary or higher leaf nodes as target tissue by means of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and subsequent regeneration of the transformed cells into a whole plant.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Method for acquiring aromatic rice strain by targeting Badh2 gene via CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology
InactiveCN105505979AScalableEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAromatic riceGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a method for acquiring an aromatic rice strain by targeting a Badh2 gene via CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology. The method comprises the following steps: separately targeting sequences, recognizable by Cas9, of every exon and intron of an aromatic gene by using the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology and then cutting a genomic DNA sequence to initiate DNA restoration so as to obtain an afunctional Badh2 gene; with the callus of Indica rice, japonica rice or glutinous rice as a receptor material of genetic transformation and an mature embryo, young ear, ovary or the like as explant, carrying out induction so as to obtain a diploid callus, introducing a targeting vector into cells of the callus by using an Agrobacterium mediated transformation method, screening and identifying positive plants and separating the plants from a T1 colony so as to obtain an aromatic rice strain; and with anther, pollen, unfertilized ovary or the like as explant, carrying out induction so as to obtain a haploid callus, introducing the targeting vector into cells of the callus by using the Agrobacterium mediated transformation method, screening a positive callus, reduplicating the positive callus by using colchicine, carrying out differentiation to form seedlings and identifying genetic transformation positive plants so as to eventually obtain the aromatic rice strain.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Use of non-agrobacterium bacterial species for plant transformation
The invention relates to methods for Rhizobia-mediated genetic transformation of plant cells, including soybean, canola, corn, and cotton cells. These include both VirD2-dependent and VirD2-independent methods. Bacterial species utilized include strains of Rhizobium sp., Sinorhizobium sp., and Mesorhizobium sp. Vectors for use in such transformation are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for transforming rice into fragrant rice rapidly
InactiveCN105543228AGenetic stabilityRapid homozygousOxidoreductasesFermentationSelfingGene silencing
The invention discloses a method for transforming rice into fragrant rice rapidly. By means of the CRISPR / Case technology and related gene sequences in the rice fragrance metabolic process, a carrier is designed at the specific site, the element is transferred to non-fragrant rice through agrobacterium-mediated transformation, the gene is made to cause deletion mutation at the position of a fixed point, the gene is silent, fragrance cannot be normally metabolized and greatly accumulated, common rice is transformed into fragrant rice, then genetic transformation gene segments are separated from edited genes through selfing or hybridization, and the fragrant rice with the isozygoty capable of being stably inherited is rapidly obtained.
Owner:NINGXIA ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Improved Methods for the Production of Stably Transformed, Fertile Zea Mays Plants
InactiveUS20090249514A1Stable heritabilitySequencing is facilitatedOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyImproved method
The present invention relates to improved methods for the incorporation of DNA into the genome of a Zea mays plant by means of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Preferred is the use of the Zea may lines deposited with American Type Culture Collection under the Patent Deposit Designation PTA-6170 and PTA-6171.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Agrobacterium ZX09, water-soluble beta-glucan prepared from Agrobacterium ZX09 and preparation method thereof and application on reducing blood sugar
ActiveCN101935623AEasy to operateSimple processOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaBeta-glucanMicrobiology
The invention discloses Agrobacterium ZX09, water-soluble beta-glucan prepared from the Agrobacterium ZX09 and the preparation method thereof and the application on reducing blood sugar, wherein the bacterial strain of the Agrobacterium ZX09 is obtained by separating saline soil from Dongying city in Shandong province; the bacterial strain is Agrobacterium sp. and is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on January 21st, 2010; and the collection number is CCTCC NO:M2010020. The structure general formula of the water-soluble beta-glucan prepared from the Agrobacterium ZX09 is as follows: ->(3)-beta-D-Glup-(1->3)-[beta-D-Glup-(1->3)-beta-D-Glup-]3-alpha-D-Glup-(1->3)-alpha-D-Glup-(1)n->, and n in the structural formula is from 100 to 200. The bacterial strain has the advantages of novelty, special properties, salt resistant growth, no pigment secretion in the process of growth, simple and convenient cultivation operation, simple technology, total synthetic media, definite components and low cost, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SICHUAN HETAI SYNLIGHT BIOTECH LTD
Compiling vector of kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN107446924AEfficient site-directed mutagenesisBacteriaHydrolasesAgricultural scienceActinidia
The invention discloses a compiling vector of a kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 as well as a construction method and application thereof. The compiling vector of the kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 established can quickly and simply perform efficient site-specific mutagenesis on the kiwi fruit gene, so that the blank of a gene fixed point compiling technology in kiwi fruit is filled. Experimental results verify that by means of agrobacterium-mediated kiwi fruit genetic transformation, the compiling vector of the kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 performs site-specific mutagenesis on two target spots of the kiwi fruit gene AcPDS successfully, and meanwhile, an albefactedphenotype is induced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
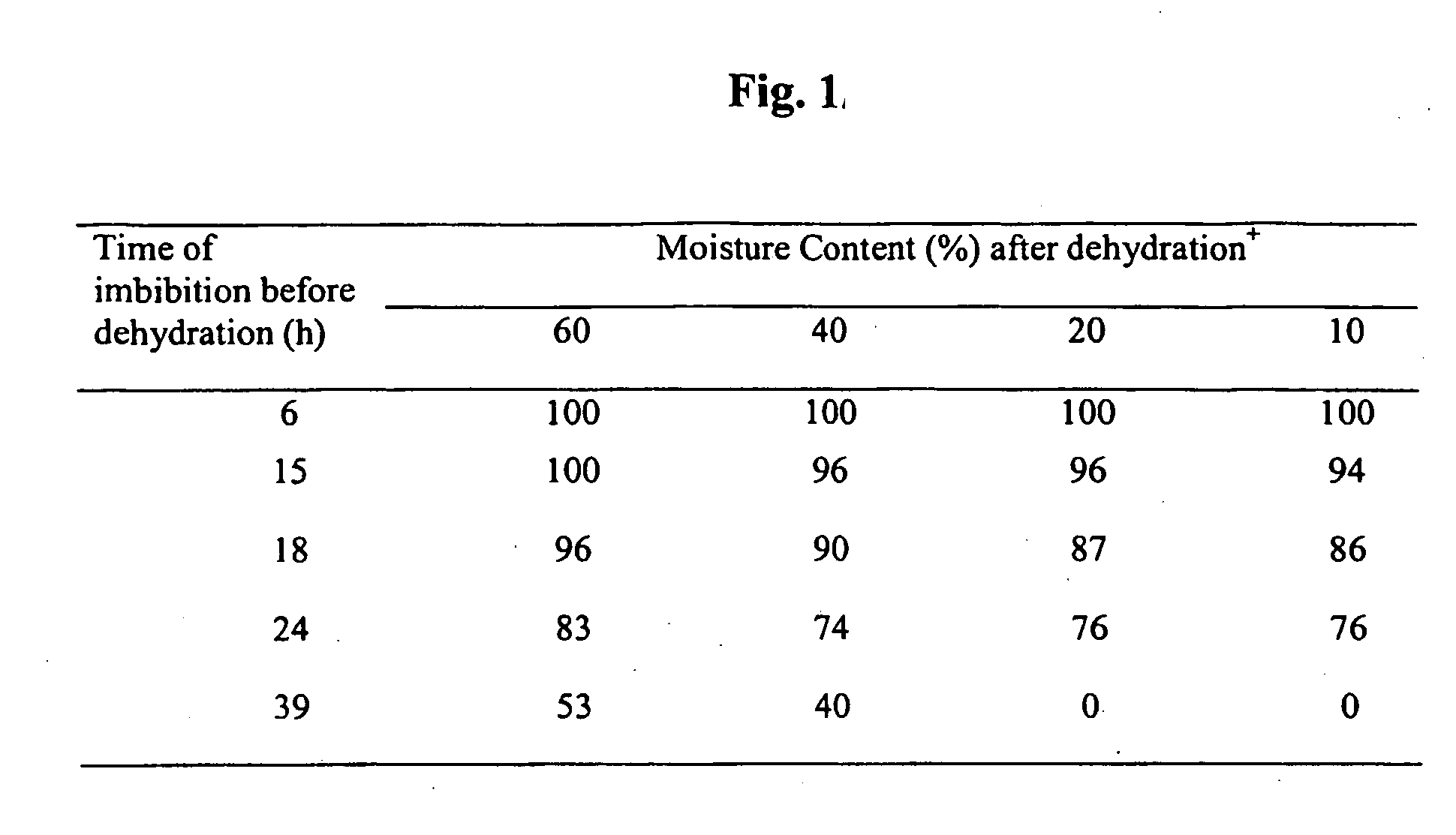
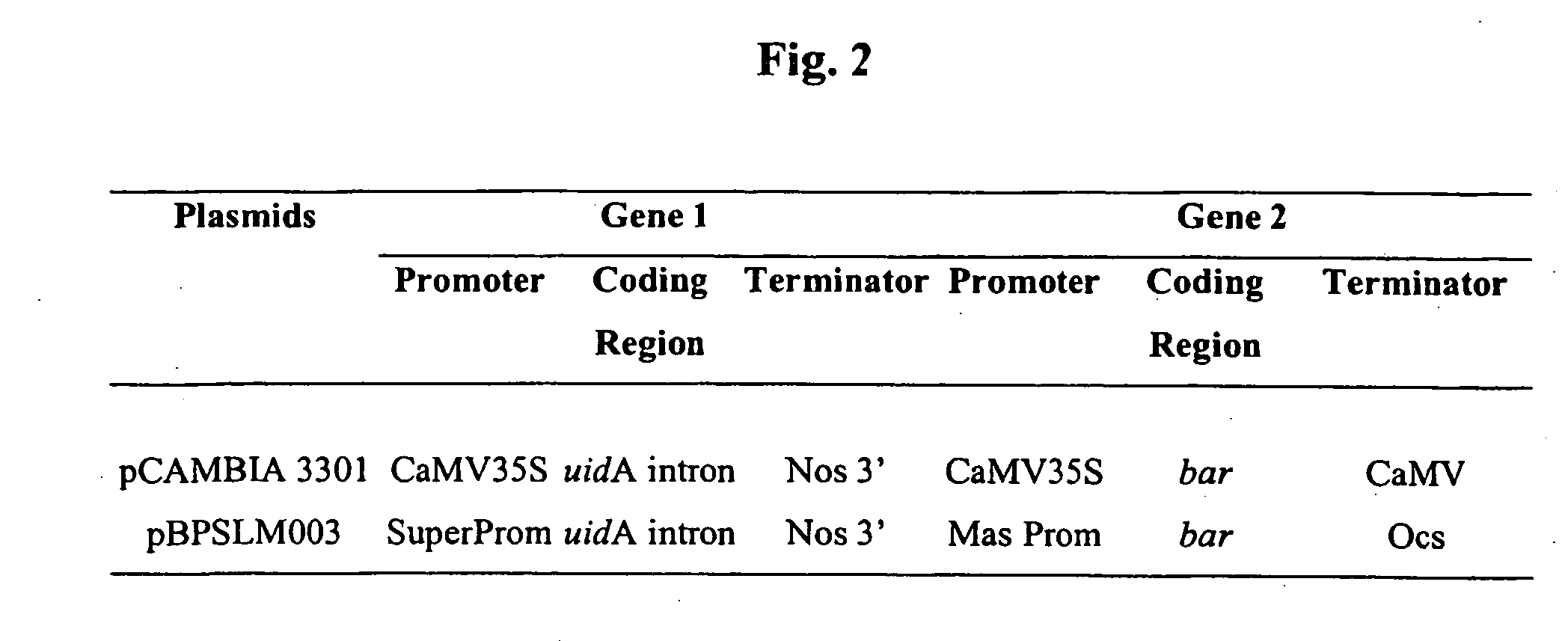
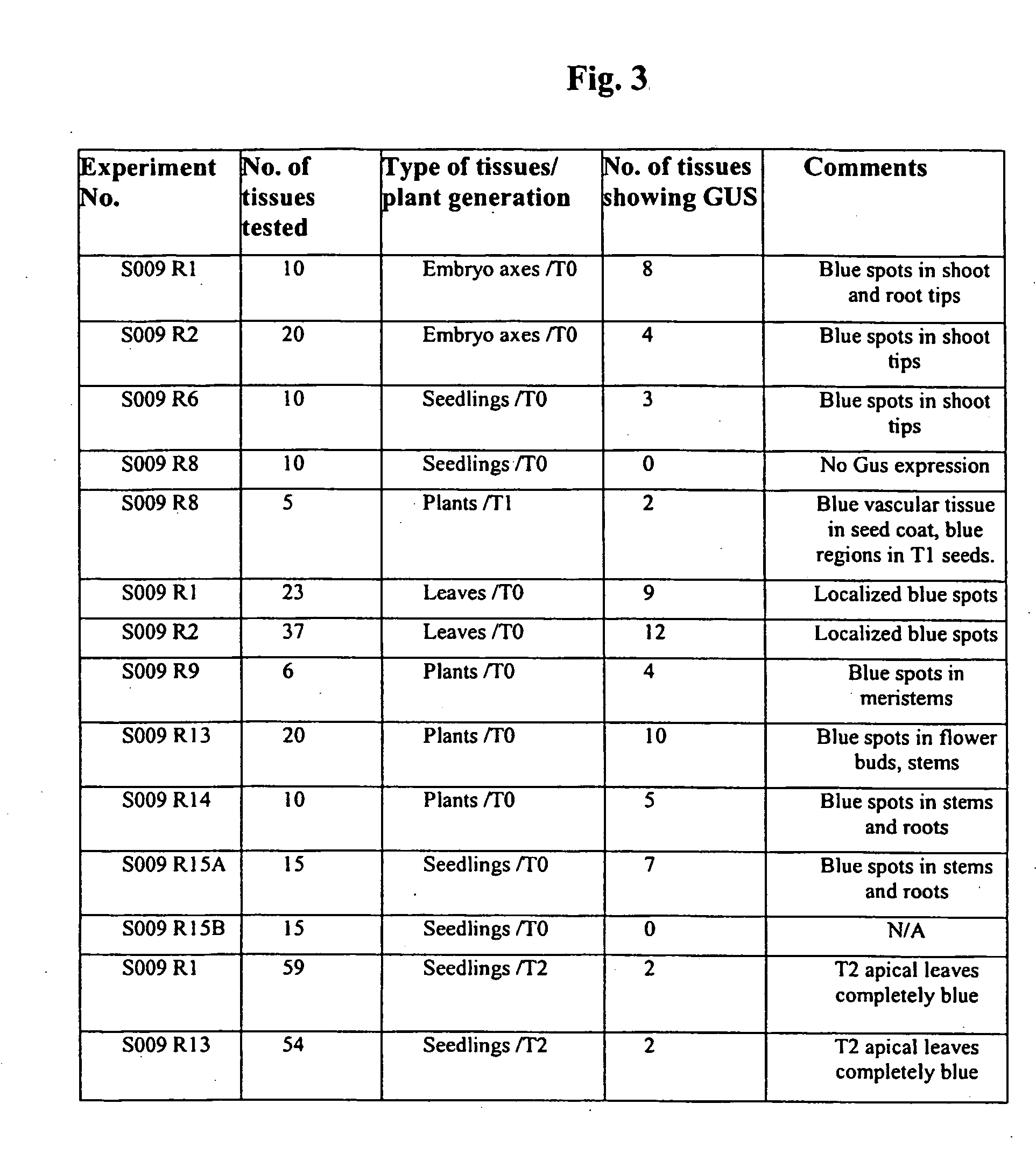
In planta transformation by embryo imbibition of agrobacterium
InactiveUS20050044595A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyPlant cell
The present invention provides a method for the preparation of a plant embryo for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. The method of preparation uses a novel technique including dehydration of the plant embryo. The invention further contemplates the transformation of the prepared plant embryo. The invention further encompasses the regeneration of a plant or plant cell from the transformed plant embryo.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
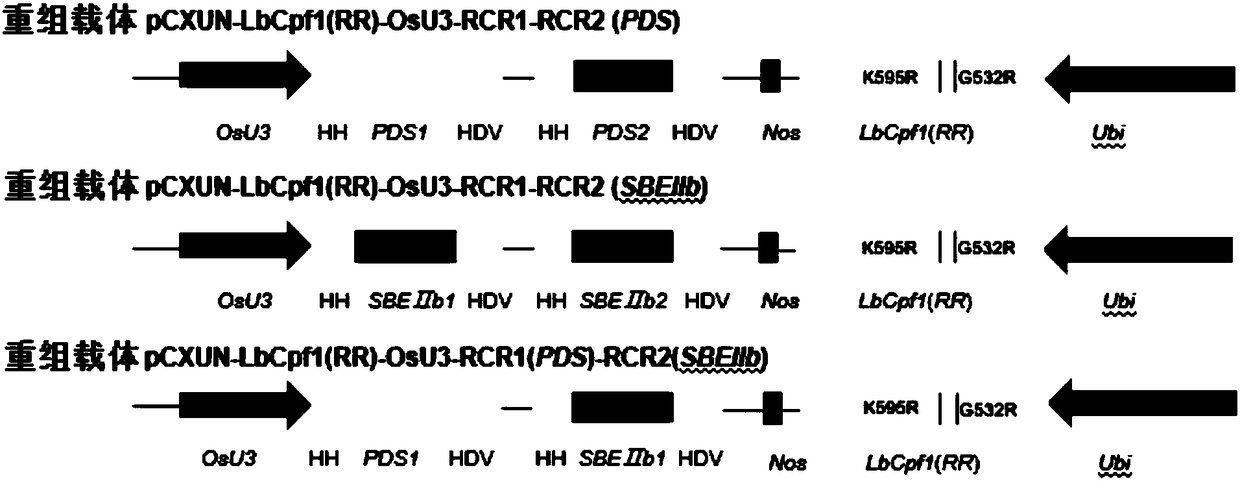
Application for using LbCpf1-RR mutant in CRISPR/Cpf1 system in plant gene editing
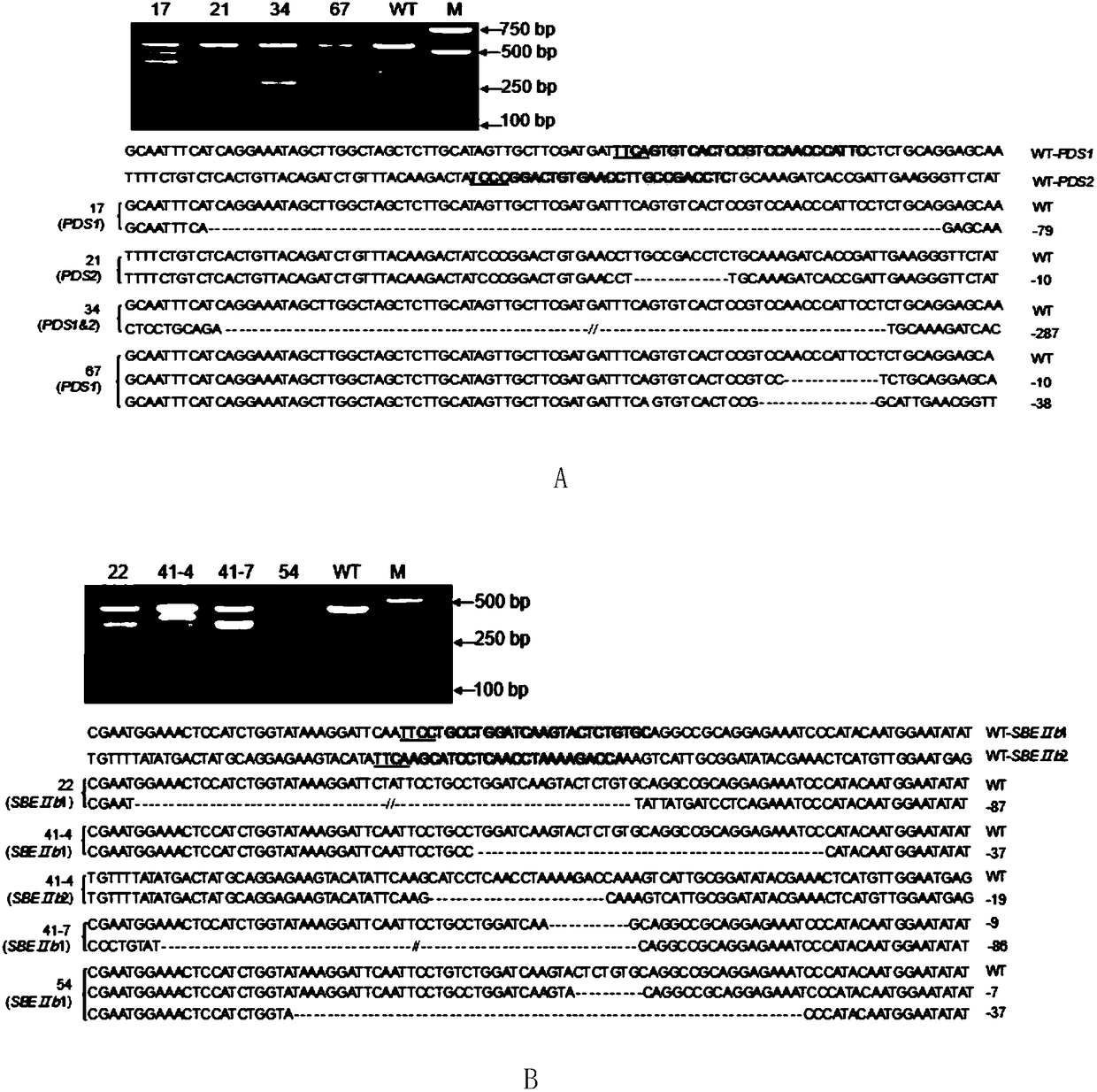
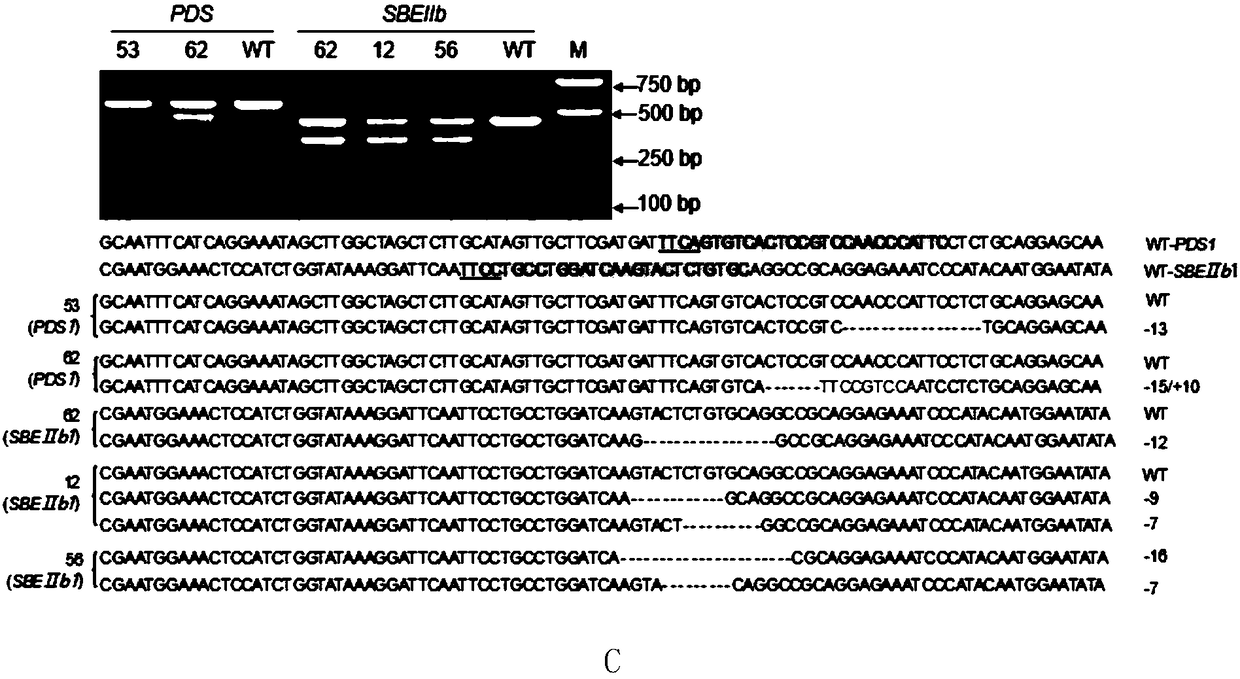
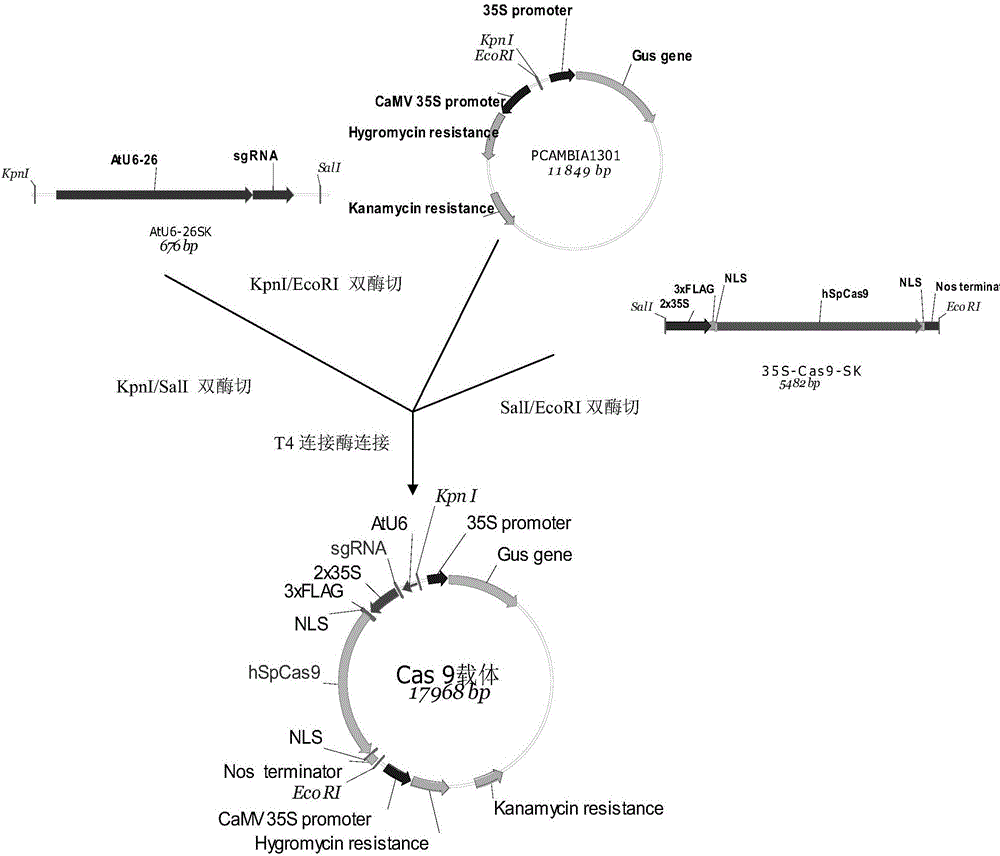
ActiveCN108486146AExpand the scope of editingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorRice plantsMutant
The invention discloses application for using an LbCpf1 - RR mutant in a CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing. The application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing uses an OsPDS gene and an OsSBEIIb gene as target genes, constructs a target double loci of one gene and a series of vectors of two genes, and utilizes an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method to import the vectors into rice callus, and rice plants with the target gene knockout are successfully obtained by using the LbCpf1-RR mutant. The only difference between the LbCpf1-RR mutant and the protein LbCpf1 is that the 532nd amino acid changes from G to R, and the 595th amino acid changes from K to R. The LbCpf1-RR mutant provided by the application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing expands the PAM site sequence identified by the LbCpf1-RR mutant, so that the editing range of the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in rice genome is expanded, great significance for promoting the application of the system in the field of plant genome editing is achieved. The application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant geneediting has great application value.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cas9 mediated carnation gene editing carrier and application
The invention relates to a Cas9 mediated carnation gene editing carrier and application. The application comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a CRISPR-Cas9 system of carnation-containing target gene sites, introducing the Cas9 expression carrier into an agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 strain, putting roots of carnation leaves into a pre-culture medium, culturing with light for 3-4 days at 22+ / -2 DEG C, activating agrobacterium containing the Cas 9 expression carrier, dipping the pre-cultured explant into the activated agrobacterium solution for 20-30 minutes, completely absorbing the agrobacterium solution, transferring into a co-culture medium, performing dark culture for 3-4 days at 22+ / -2 DEG C, further transferring into a screening culture medium to culture, performing light culture at 22+ / -2 DEG C so as to differentiate regeneration buds, further transferring the regeneration buds into a multiplication medium for multiplication screening culture, detecting positive transgenosis regeneration plants, sequencing target sites, and detecting mutation strain systems of carnation target gene sites.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel reaction system for rapidly constructing plant gene site-directed knockout carrier
InactiveCN107254485AHigh speedImprove efficiencyHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiologyDouble chain
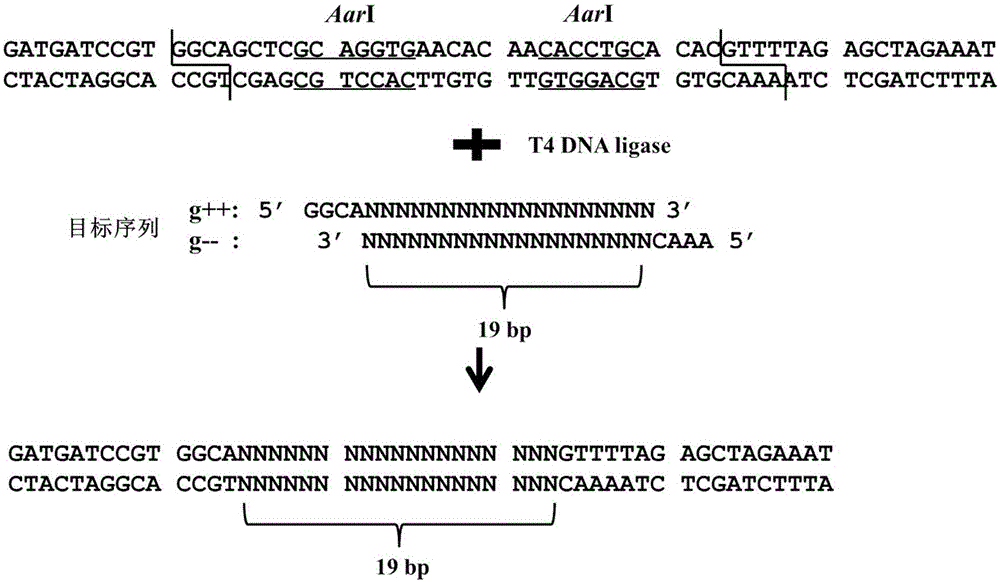
The invention discloses a novel reaction system for rapidly constructing a plant gene site-directed knockout carrier. The system comprises 1) based on a CRISPR-Cas system carrier, the carrier comprises the DNA molecules having the following characteristics: an agrobacterium infection method is used for carrier conversion to the plant, a carrier capable of simultaneously realizing driving of SgRNA by an OsU3 promoter for transcription and driving of Cas9 protein by an Ubiquitin promoter for expression; 2) restriction enzyme AarI; 3) buffer and Oligo required by a reaction of the restriction enzyme AarI; 4) target gene site specific DNA double chain; and 5) T4DNA ligase and ATP required by an enzyme reaction. The system only requires 5-10 reaction cycles for rapidly and efficiently completing a construction process of plasmid, greatly simplify the operation flow, and satisfies the requirement of rapid construction with high flux for plant gene site-directed knockout plasmid.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
sgRNA sequence for specifically targeting arabidopsis ILK2 gene and application of sgRNA sequence
InactiveCN107236737AKnockout EfficientKnockout fastHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingArabidopsis thaliana
The invention discloses a sgRNA sequence for specifically targeting an arabidopsis ILK2 gene and application of the sgRNA sequence. The nucleotide sequence of the sgRNA sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. Two single-chain oligo DNA sequences are designed and synthesized according to a sgRNA guide sequence, a double chain is formed through annealing and is linked with a Cas9 carrier, a sgRNA coding sequence and a CRISPR system are introduced into Arabidopsis by using an agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation technique, a target sequence is shorn by a Cas9 protein under the guidance of sgRNA, and therefore, the knockout of an ILK2 gene is realized. According to the sgRNA sequence provided by the invention, the ILK2 gene can be knocked out or edited by virtue of a CRISPR-Cas9 system, so as to analyze the functions of the arabidopsis ILK2 gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
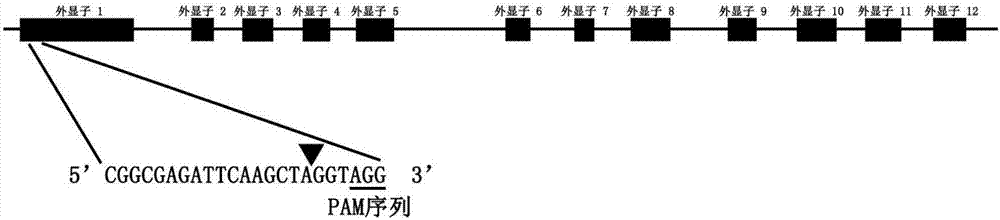
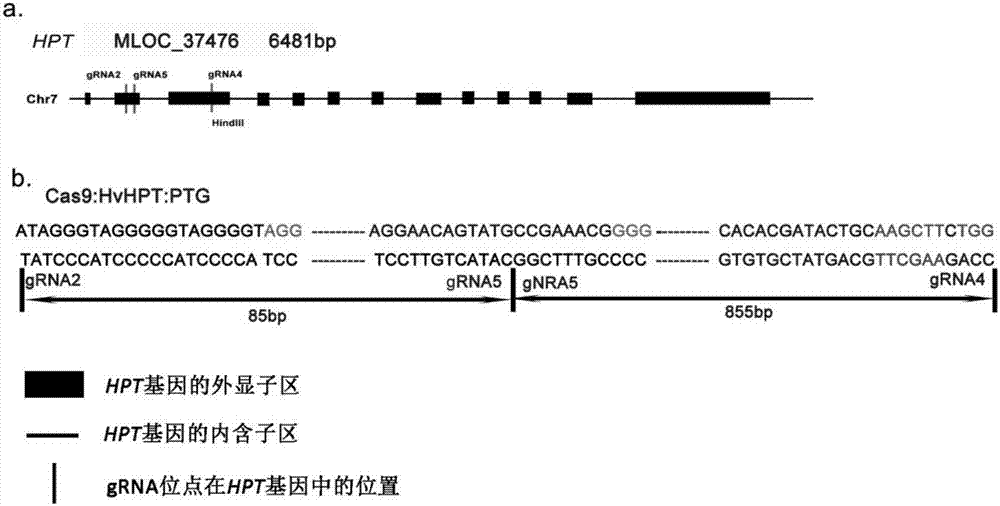
Method for applying CRISPR-Cas9 system to knockout of key gene HPT in VE synthesis pathway of barley
The invention relates to construction of a barley transgenic material and provides a method for applying a CRISPR-Cas9 system to knockout of the key gene HPT in the VE synthesis pathway of barley. The method comprises the following steps: selection of a gRNA target site; cloning of gRNA fragments; connection of GG(gRNA-gRNA) fragments; PCR amplification of a connection product; enzyme digestion of a purified product and a target vector; a ligation reaction between the purified product and the target vector; transformation of competent Escherichia coli cells with a ligation product; preparation of Agrobacterium-mediated transgenic barley plants; screening of positive transgenic plants; and sequencing of mutants. According to the invention, the advanced gene editing technology, i.e., the CRISPR-Cas9 system, is employed for target gene editing of the key gene (HPT) in the VE synthesis pathway of barley, and effective loss-of-function mutants are obtained, so conditions are created for research on biologically-active substances in barley.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of non-transgenic CRISPR mutant
InactiveCN108611364AReduce frequencyImprove accuracyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionScreening methodSexual reproduction
The invention provides a preparation method of a non-transgenic mutant based on a CRISPR-Cas9 technology. Specifically, the preparation method comprises a construction method and a screening method. The construction method is characterized in that CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNA are preassembled and are located at T-DNA of agrobacterium tumefaciens; site-directed change of a target gene of a target plant can be realized by infection of the target plant by the agrobacterium tumefaciens and coculture without integrating the sequences of the CRISPR-Cas9 and the sgRNA into a genome of the target plant, so that an obtained site-directed mutant material of the target gene does not need the processes of sexual reproduction, segregation posterity, population screening and the like or does not contain any exogenous gene sequence. The obtained regeneration seedlings are screened by a high-throughput sequencing and high-resolution melting curve technology provided by the invention; mutant plants of which target genes are mutated can be obtained by identifying the regeneration seedlings efficiently and quickly at the current generation of transgene, even if low-proportion mutants of which the proportionis 1 / 100 of a mixed population can be screened. The screening method provided by the invention still can ensure excellent accuracy and sensitivity.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Double T-DNA carrier and its application in cultivating of non selecting sign transgene rice
InactiveCN1597969ASmall molecular weightHigh co-transformation efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified ricePlant nodule
The invention provides a simple and convenient Agrobacterium Tumefacies dual carrier containing double T-DNA structural regions, and a method of using the carrier system to cultivate transgenic rice without resistance selection label. With the help of the principle of co-conversion mediated by root nodule Agrobacterium Tumefacies, the system contains two separate T-DNA structural sections, where the first T-DNA region contains antibiotic resistance selection label gene and the second one contains a universal polyclonal site able to be arbitrarily inserted with destination gene. The double-T-DNA carrier has small molecular weight, easy to clone and after the destination gene and necessary regulation and control series are cloned in the T-DNA region containing the polyclonal site, it realizes rice co-conversion; by selfing, it selects transgenic individual with destination gene but without selectin label gene from the self-bred progeny, thus eliminating the negative effect on transgenic plant commercialized production, etc, possibly caused by selection label gene.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Establishment and application of plant multi-gene knockout vector
ActiveCN105112435AQuick cullingVector-based foreign material introductionTransgenic technologyMutant
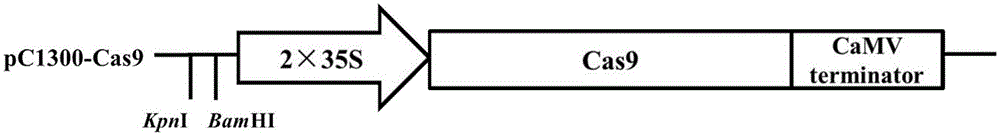
The invention discloses establishment and application of a plant multi-gene knockout vector. A method of the establishment of the plant multi-gene knockout vector comprises the following steps of (1) establishing a binary expression vector pC1300-Cas9; (2) establishing an intermediate vector SK-9RNA; (3) establishing single objective gRNA; and (4) serially connected a plurality of pieces of gRNA and establishing a final binary expression vector. A plurality of gRNA sequences are connected to the binary expression vector of an existing Cas9 sequence by an isocaudamer connecting method, and multiple plant mutants can be obtained by an agrobacterium tumefaciens infected transgenic technology. By an isocaudamer connecting establishment strategy, pieces of gRNA can be combined, and multiple plant mutants can be obtained by transgenosis once, so that an efficient and convenient multiple plant mutants preparing method is established.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Vaccines expressed in plants
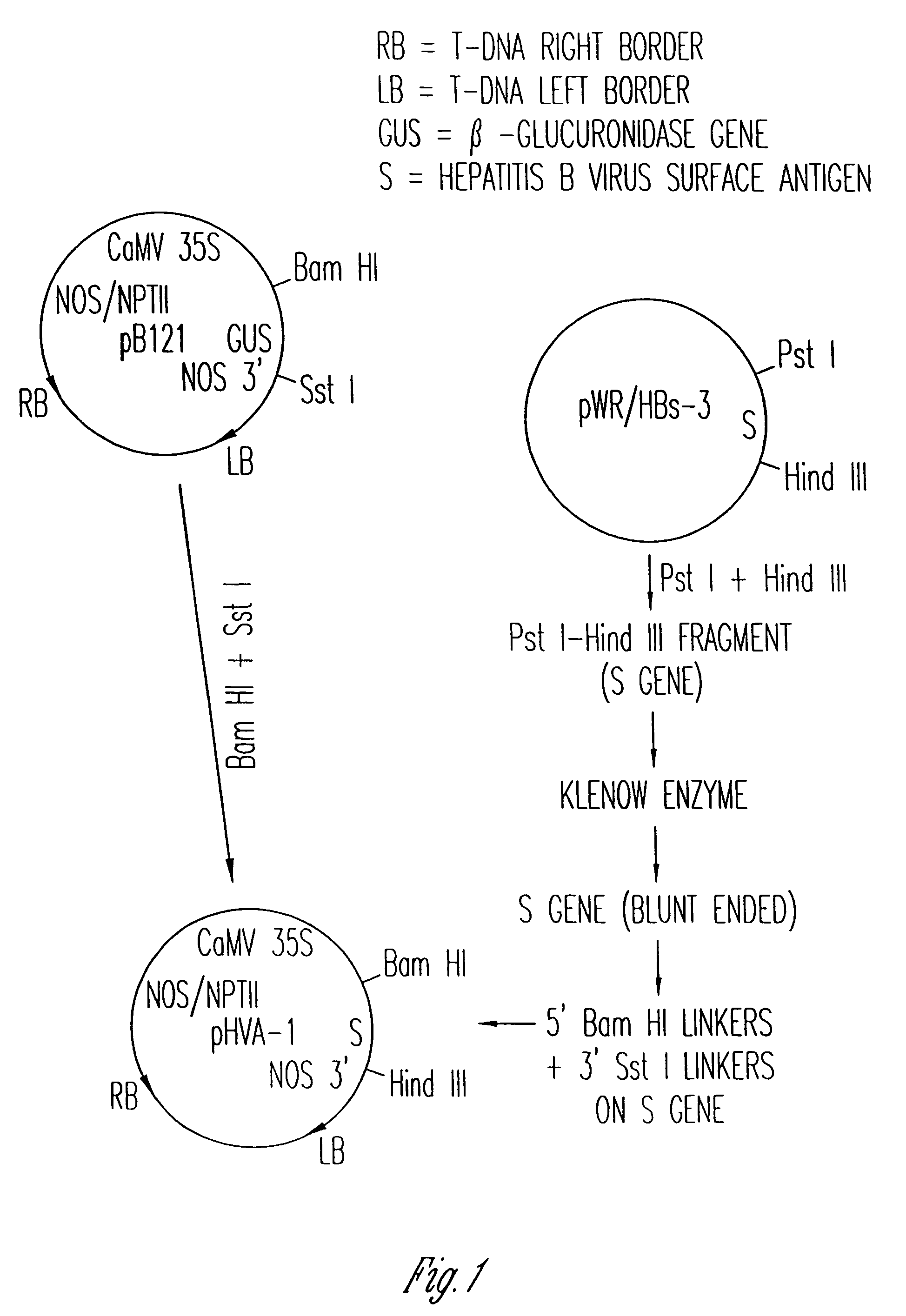
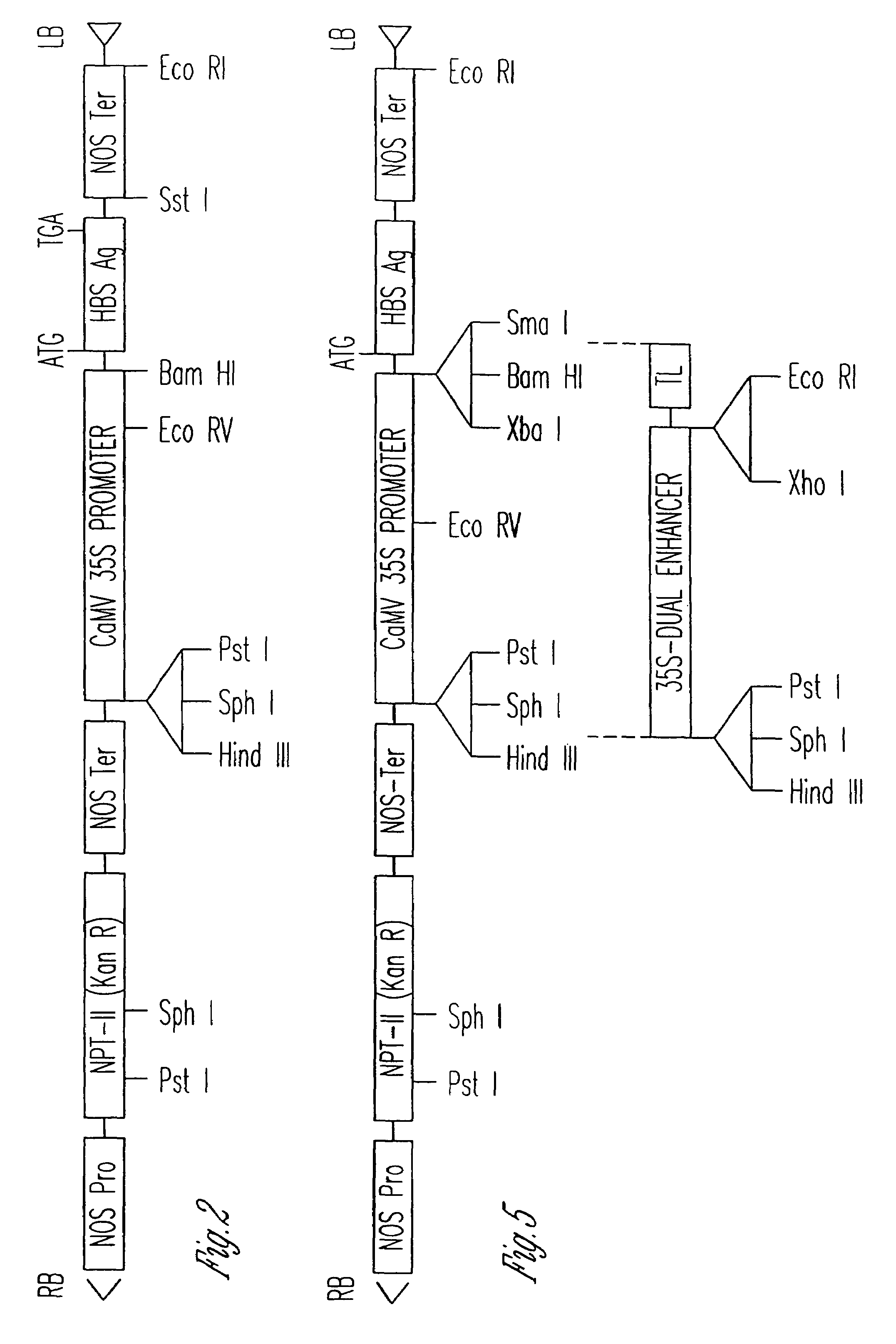
The anti-viral vaccine of the present invention is produced in transgenic plants and then administered through standard vaccine introduction method or through the consumption of the edible portion of those plants. A DNA sequence encoding for the expression of a surface antigen of a viral pathogen is isolated and ligated to a promoter which can regulate the production of the surface antigen in a transgenic plant. This gene is then transferred to plant cells using a procedure that results in its integration into the plant genome, such as through the use of an Agrobacterium tumenfaciens plasmid vector system. Preferably, the foreign gene is expressed in an portion of the plant that is edible by humans or animals. In a preferred procedure, the vaccine is administered through the consumption of the edible plant as food, preferably in the form of a fruit or vegetable juice which can be taken orally.
Owner:PRODI GENE INC
Transformed embryogenic microspores for the generation of fertile homozygous plants
InactiveUS6316694B1Increase the number ofImprove conversion efficiencyBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesEmbryogenesisRegulatory control
The invention relates to transformed, embryogenic microspores and progeny thereof characterized by being transformed by Agrobacterium tumefaciens, capable of leading to non-chimeric transformed haploid or doubled haploid embryos that develop into fertile homozygous plants within one generation and containing stably integrated into their genome a foreign DNA, said DNA being characterized in that it comprises at least one gene of interest and at least base pairs within the right border sequence of Agrobacterium T-DNA. The invention furthermore relates to a method for the incorporation of foreign DNA into chromosomes of microspores comprising the following steps: a) infecting of embryogenic microspores with Agrobacteria, which contain plasmid carrying a gene of interest under regulatory control of initiation and termination regions bordered by at least one T-DNA border, b) Washing out and killing the Agrobacteria after co-cultivation.
Owner:AGREVO CANADA
Complex bacteria for preprocessing of restaurant garbage, preparation method and application thereof
The present invention relates to a composite microbial agent, a preparation method thereof and an application in the preprocessing of kitchen garbage. The active ingredients of the composite microbial agent include 15 percent to 30 percent of bacillus stearothermophilus, 10 percent to 25 percent of bacillus licheniformis, 10 percent to 25 percent of zymomonas, 10 percent to 25 percent of agrobacterium, 15 percent to 30 percent of saccharomyces cerevisiae and 10 percent to 25 percent of candida, which are blended together. The composite microbial agent is prepared according to the following method: (1) the strains, which are preserved under the temperature of 4 DEG C, are respectively inoculated in ordinary broth media, the inoculation amount is 0.1 percent (v / v), and under the temperature between 28 DEG C and 37 DEG C, activating culture lasts for 8 to 18 hours; (2) the strains are then respectively transinoculated into ordinary broth media to be cultured for 8 to 18 hours under the temperature between 28 DEG C and 34 DEG C, the inoculation amount is between 0.1 percent (v / v) and 0.5 percent (v / v), and after culturing, microbial liquids are blended according to the proportion. The composite microbial agent can be used to preprocess kitchen garbage, inhibit the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms in the kitchen garbage and reduce the deterioration and stink of the kitchen garbage, so that the kitchen garbage can be conveniently processed later, so the application prospect of the composite microbial agent is wide.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDENWAY BIO TECH
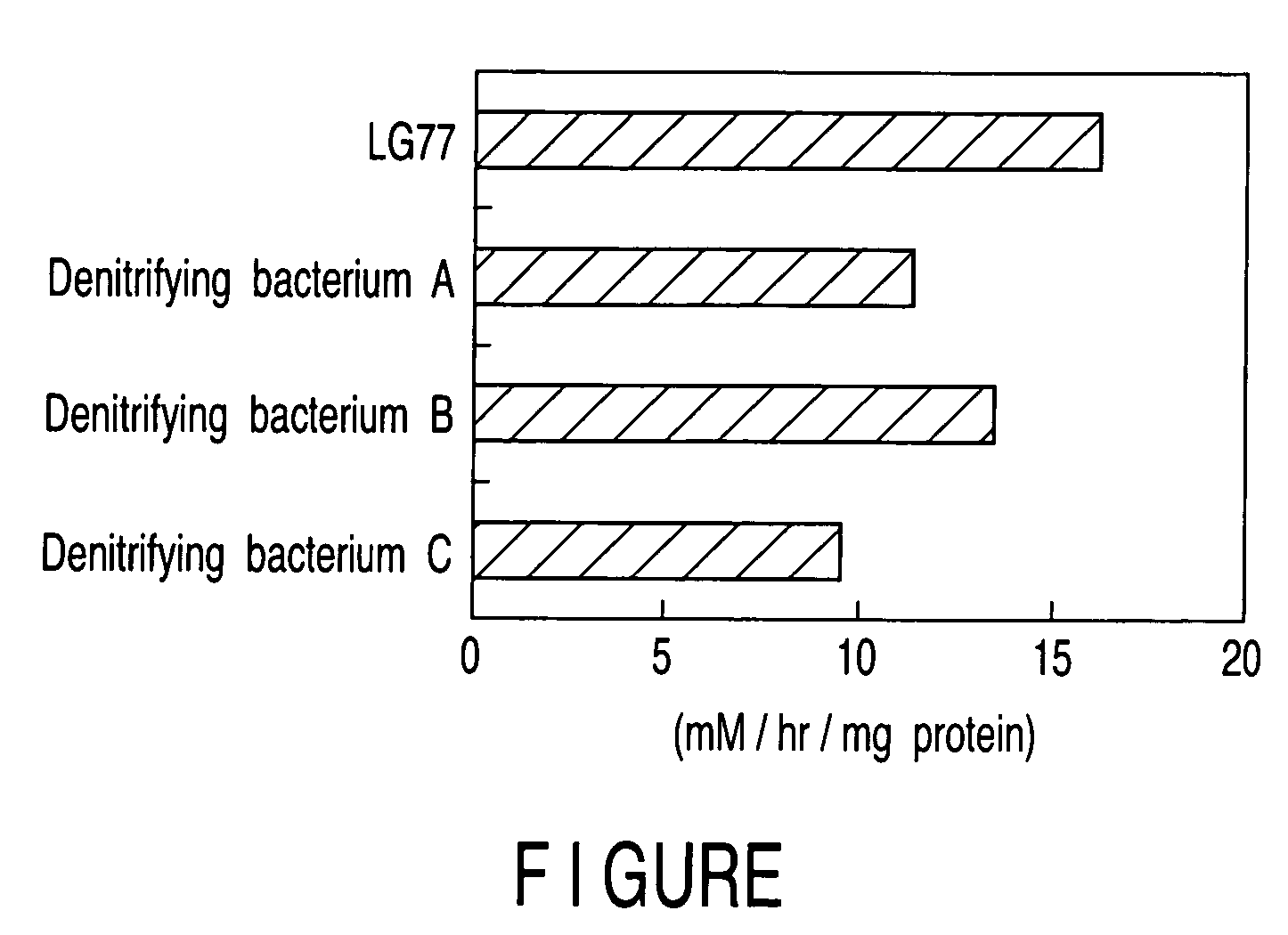
Method of reducing nitrite and/or nitrosamine in tobacco leaves using microorganism having denitrifying ability
InactiveUS7549426B2Reduce contentInhibition formationTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentMicroorganismNicotiana tabacum
A method of reducing the content of nitrite and / or nitrosamine in tobacco leaves, having treating the tobacco leaves with a microorganism belonging to Agrobacterium genus and having the denitrifying ability.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
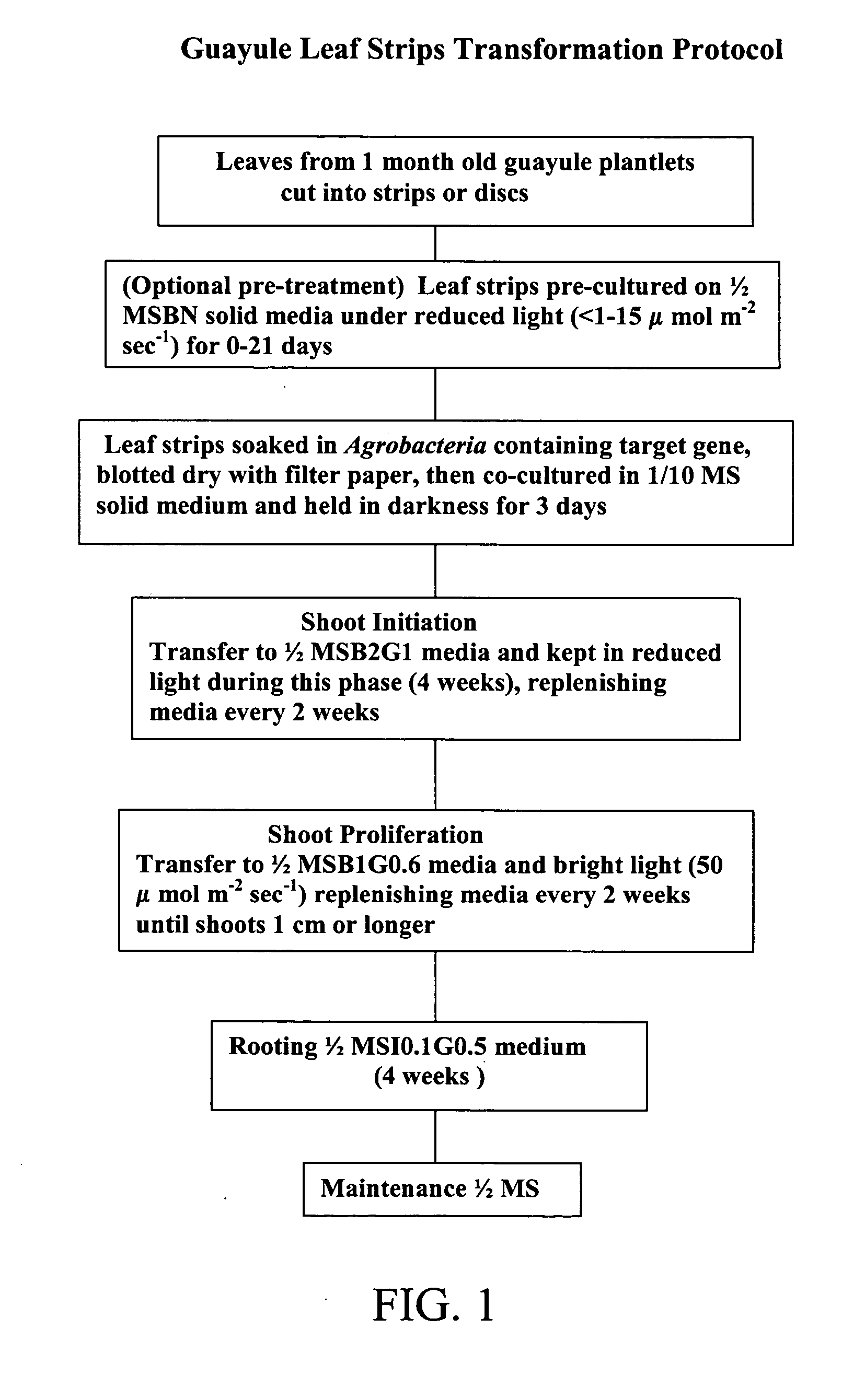
Transformation methods for Guayule using Agrobacterium and reduced light to slow metabolism and enhance recovery
InactiveUS20060218660A1Increase productionLabor intensiveOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationParthenium argentatumGenetics
This invention is directed to a new technique of genetic transformation using low light conditions and leaf strips in the Guayule plant, Parthenium argentatum. The invention also relates to new lines of Guayule, created through this technique.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Methods and compositions for a soybean in-planta transient expression system
ActiveUS20120174262A1Other foreign material introduction processesBiological testingBiotechnologyNucleotide sequencing
This invention provides methods of transiently expressing a nucleotide sequence in one or more cells of a soybean plant, comprising: a) abrading the surface of a soybean plant and / or intact part thereof; and either (b1) immersing the abraded plant and / or abraded intact part thereof in a solution comprising Agrobacterium cells and a surfactant, wherein the Agrobacterium cells comprise the nucleotide sequence to be transiently expressed; (b2) applying a vacuum to the immersed plant and / or intact part thereof of step (b1); and (b3) releasing the vacuum, thereby introducing the solution into the plant and / or intact part thereof; or (c) contacting the abraded plant and / or abraded intact part thereof with a solution comprising Agrobacterium cells and a surfactant, wherein the Agrobacterium cells comprise the nucleotide sequence to be transiently expressed, whereby the nucleotide sequence is transiently expressed in one or more cells of the plant.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
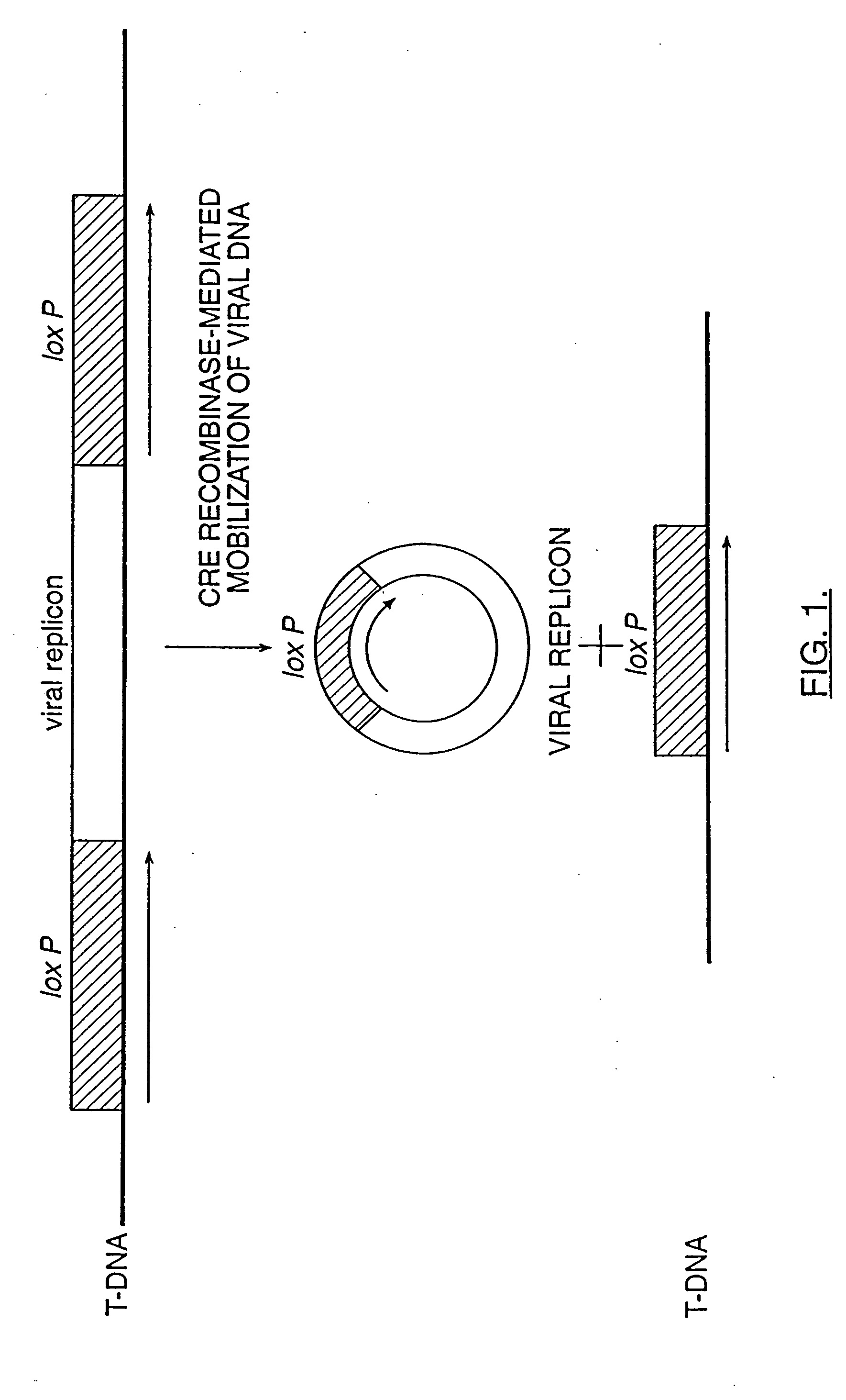
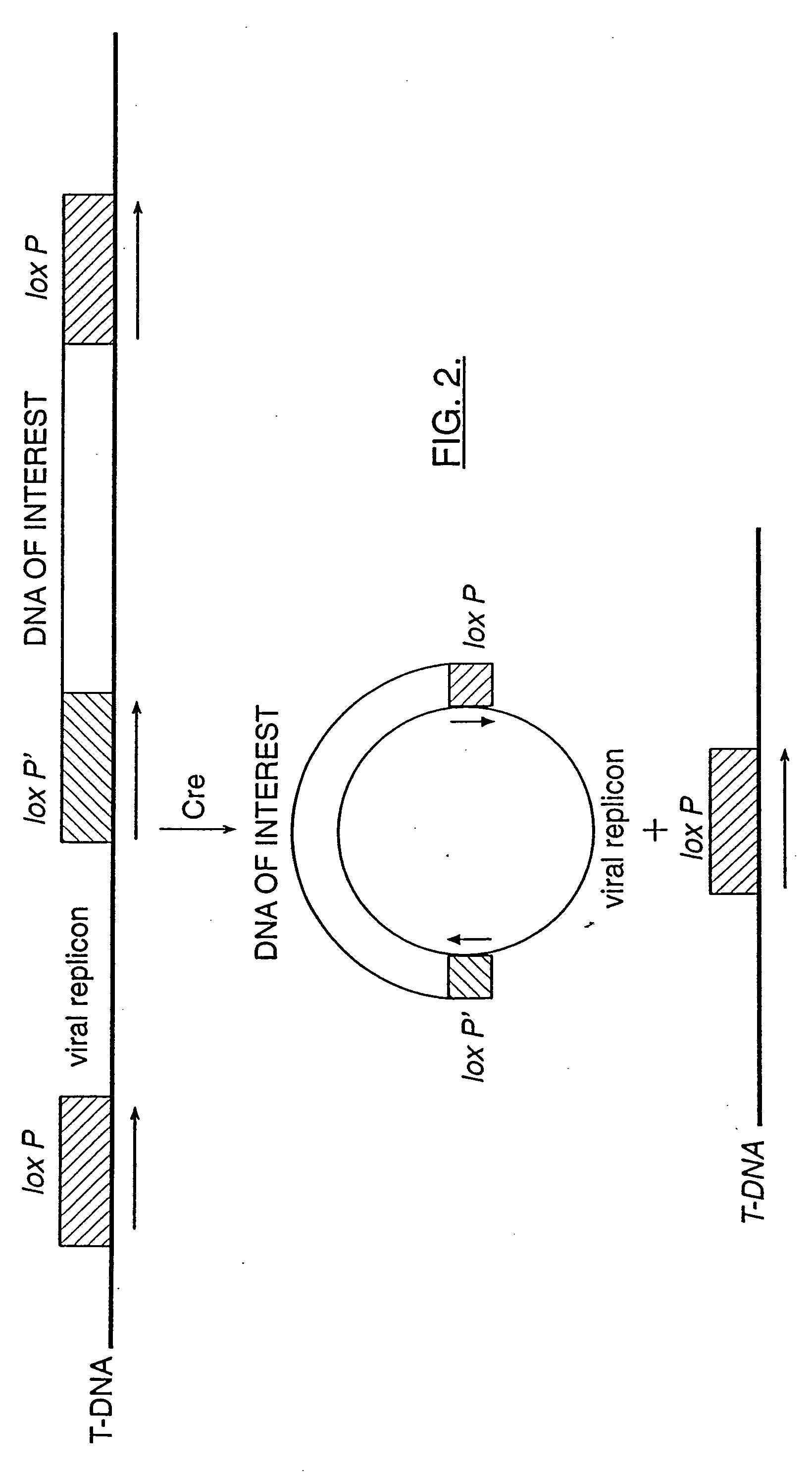
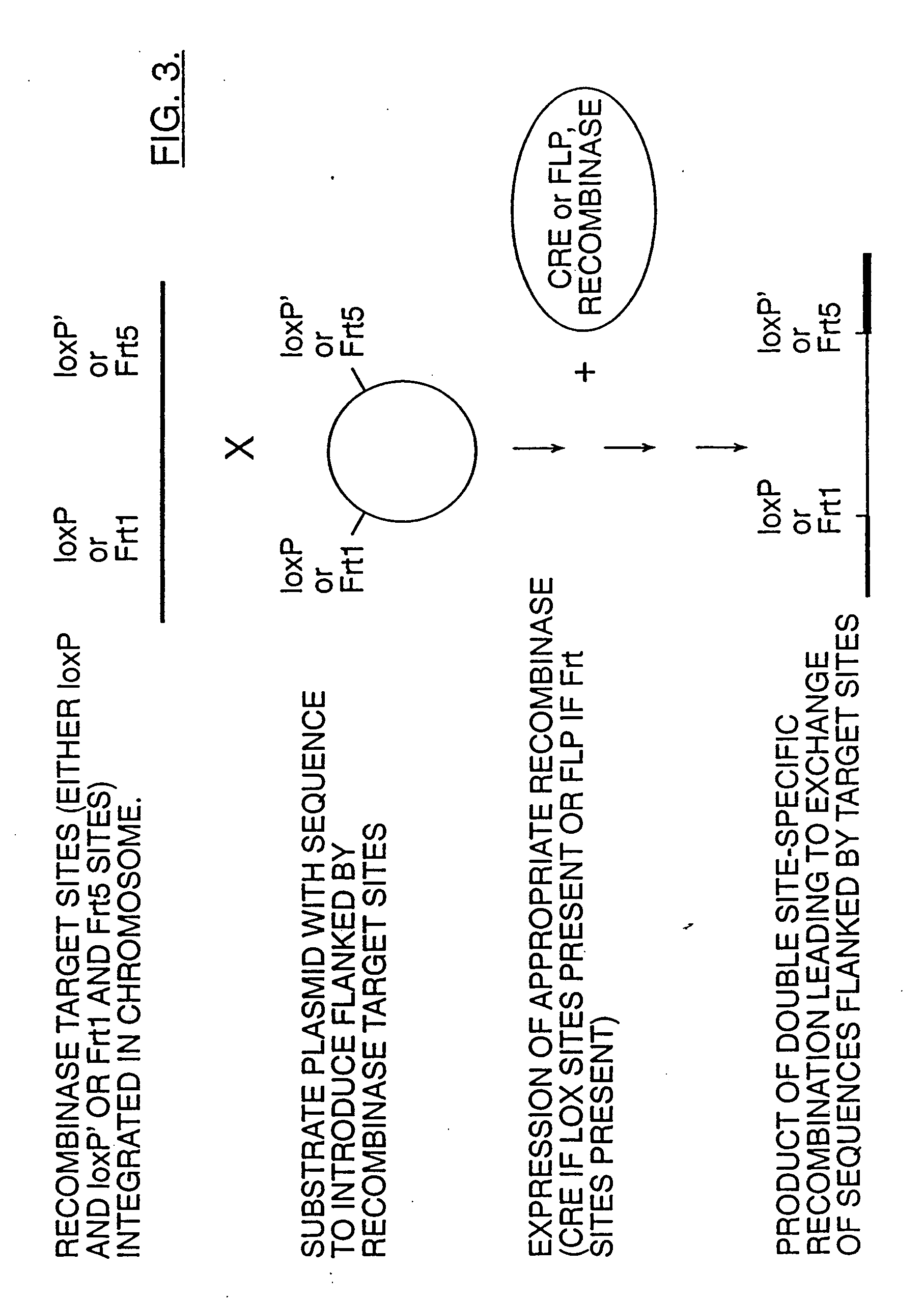
Mobilization of viral genomes from T-DNA using site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS20060253939A1Easy constructionSimplifying stable maintenanceBacteriaSugar derivativesSite-specific recombinationPlant cell
The invention relates to methods and compositions for site-specific recombinase-mediated mobilization of viral replicons and associated DNAs of interest from T-DNA. The methods of the invention comprise Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to a plant cell, wherein the T-DNA contains a viral replicon flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase and optionally a DNA of interest linked to the viral replicon. The DNA of interest may also contain a non-identical target site for the recombinase. An expression cassette for the site-specific recombinase is present on the T-DNA or the plant genome, or is transiently introduced into the plant cell. Expression of the site-specific recombinase in the plant cell results in excision of the viral replicon and the associated DNA of interest. The viral replicon and DNA of interest are then replicated to high copy number in the host plant cell. The compositions of the invention comprise nucleic acids, such as T-DNAs containing a viral DNA flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase. The nucleic acids of the invention may additionally contain expression cassettes encoding the cognate site-specific recombinase for the target sites flanking the viral genome. The compositions of the invention further comprise Agrobacterium containing the nucleic acids of the invention. The compositions and methods of the invention have use in increasing the efficiency of agroinfection, providing high copy numbers of a DNA of interest for transient expression or for integration into a plant chromosome, and in simplifying the construction and stable maintenance of vectors for agroinfection and transformation.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Transformation system for Camelina sativa
InactiveUS20090151023A1The process is convenient and fastEasy to useOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationHeterologousBiotechnology
The present invention relates to plant biotechnology and specifically to a method for genetically transforming Camelina sativa with Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system. It comprises Camelina sativa for producing homologous and heterologous recombinant products including oil and protein products and assessing and screening the efficacy of plant transformation. Also disclosed are transgenic Camelina sativa plants, seeds as well as cells, cell-lines and tissue of Camelina sativa.
Owner:KUVSHINOV VIKTOR +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com