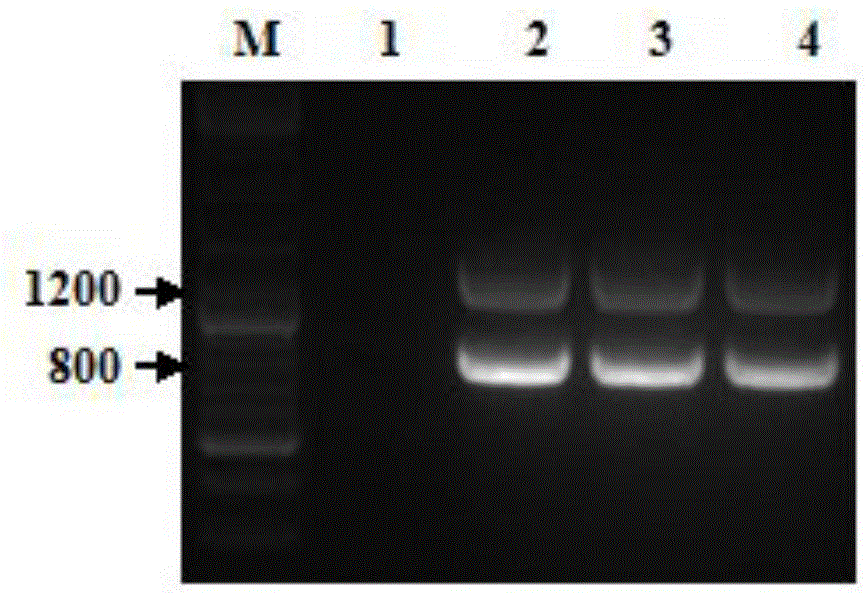
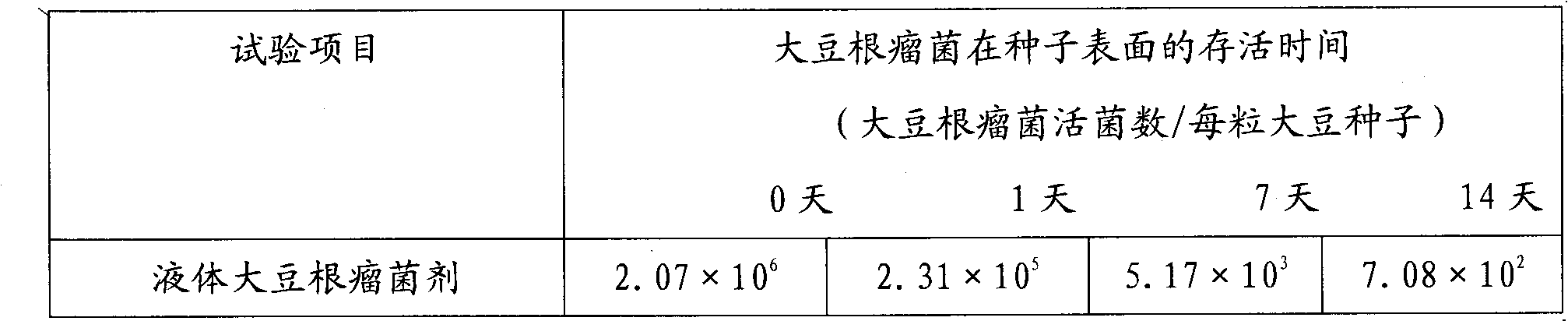
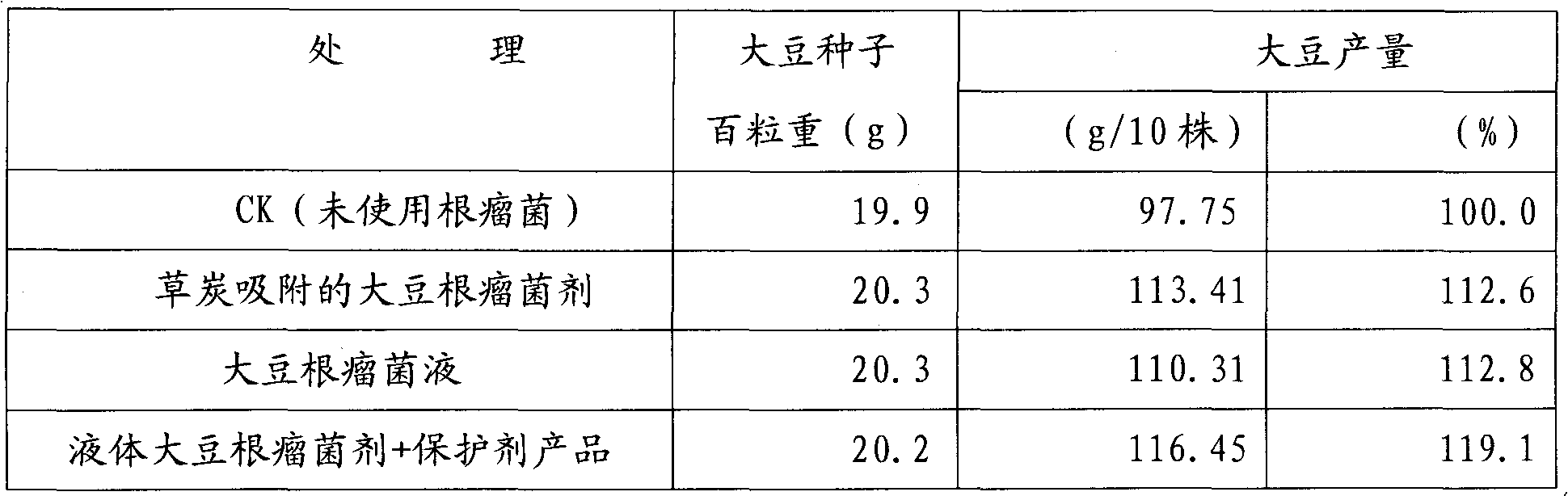
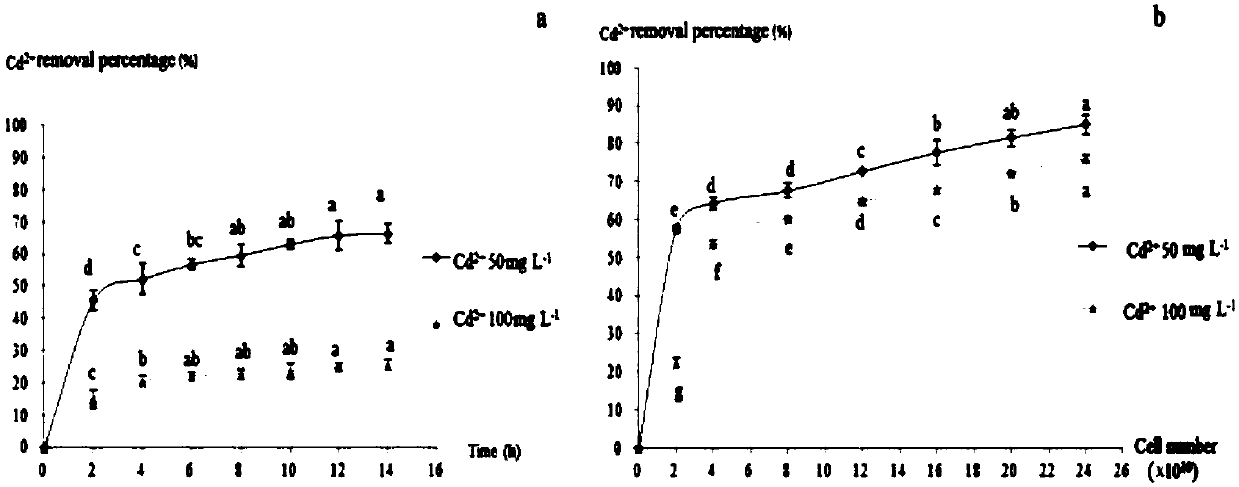
Patents
Literature
200 results about "Root nodule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, primarily legumes, that form a symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Under nitrogen-limiting conditions, capable plants form a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of bacteria known as rhizobia. This process has evolved multiple times within the legumes, as well as in other species found within the Rosid clade. Legume crops include beans, peas, and soybeans.
Use of non-agrobacterium bacterial species for plant transformation
The invention relates to methods for Rhizobia-mediated genetic transformation of plant cells, including soybean, canola, corn, and cotton cells. These include both VirD2-dependent and VirD2-independent methods. Bacterial species utilized include strains of Rhizobium sp., Sinorhizobium sp., and Mesorhizobium sp. Vectors for use in such transformation are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Use of non-agrobacterium bacterial species for plant transformation
The invention relates to methods for Rhizobia-mediated genetic transformation of plant cells, including soybean, canola, corn, and cotton cells. These include both VirD2-dependent and VirD2-independent methods. Bacterial species utilized include strains of Rhizobium sp., Sinorhizobium sp., and Mesorhizobium sp. Vectors for use in such transformation are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
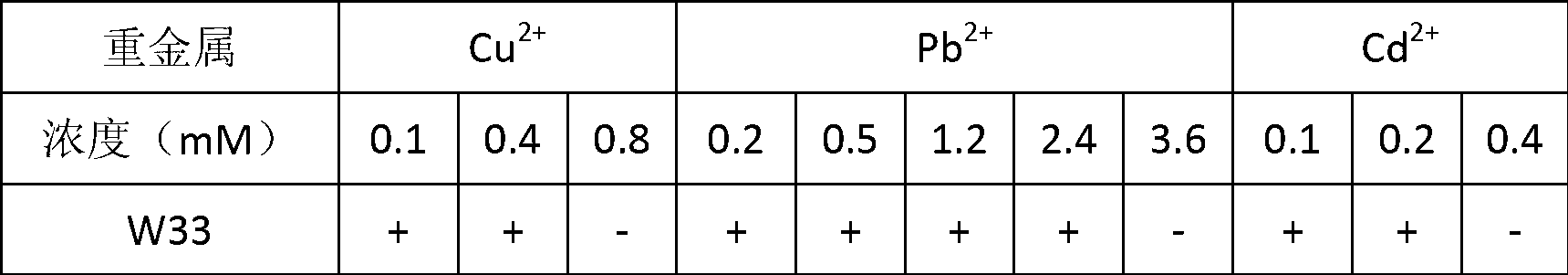
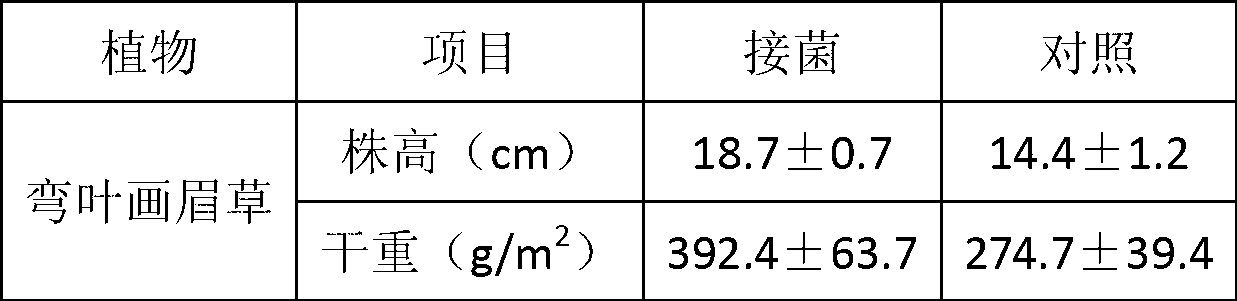
Heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium and method of promoting tailings area plant restoration by using same
ActiveCN102936574APromote growthImprove stress resistanceBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPlant hormoneBacterial strain
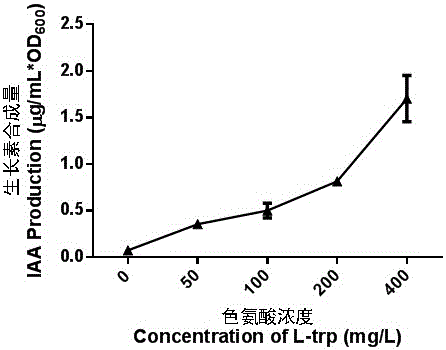
The invention belongs to the technical field of agriculture and environmental pollution improvement and relates to a heavy metal resistant plant endogenous nodule bacterium and application thereof. The heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium is preserved at the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) with the preservation date to be 2012 / 9 / 18 and culture preservation number to be CCTCC NO:M2012357. The bacterial strain liquid preparation contains more than a billion of effective living bacteria per milliliter, and the bacterial strain solid preparation contains 0.2 billion of effective living bacteria per gram. The heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium strain can secrete plant hormones indole acetic acid (IAA) and siderophores, and resists heavy metal copper and cadmium. When plants are planted in moist soil or tailings containing heavy metal and bioremediation preparation is inoculated, the heavy metal resistant nodule bacterium can promote plant growth and absorbs heavy metal copper, can improve plant restoration efficiency, can fix sandy soil and reduces water and soil loss.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Production and use of endophytes as novel inoculants for promoting enhanced plant vigor, health, growth, yield reducing environmental stress and for reducing dependency on chemical pesticides for pest control
InactiveUS20090105076A1Improve scalabilityPrevent degradationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyFungal endophyte
A process and method for the production of endophytes as plant inoculant products, specifically Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, for the promotion of plant vigor, health, growth and yield are disclosed. The endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710 produces a fungal conidial preparation by utilizing a discrete solid substrate fermentation system, namely Potato Dextrose Agar or Malt Extract Agar. Additionally, the endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can act as an inoculant to stimulate and have an additive effect with rhizobium bacteria on the production of nitrogen fixing nodules on legumes and growth enhancement e.g. beans, soybeans, peas and alfalfa. As well, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can combine with rooting hormones, e.g. indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) to provide inoculant and rooting benefits to cuttings / transplants of plants.
Owner:ADJUVANTS PLUS INC
Interplant method of camellia oleifera and torreya grandis young growth
The invention relates to an interplant method of camellia oleifera and torreya grandis young growth. The interplant method of the camellia oleifera and the torreya grandis young growth is characterized in that peanut and upland rice are interplanted at intervals between the camellia oleifera and the torreya grandis young growth, and the peanut and the upland rice interchange positions in the nest year. The interplant method of the camellia oleifera and the torreya grandis young growth has the advantages that the upland rice provides shade for the camellia oleifera or the torreya grandis so that expense of sheltering nets is reduced, interplanted the upland rice and the peanut can store water and keep moisture for the torreya grandis young growth so as to avoid water and soil loss, the peanut provides nitrogen needed during in the early stage of production of the camellia oleifera by means of a biological nitrogen fixation function of the nodule bacteria so that nitrogenous fertilizer is saved, intercropping and crop rotation of the interplanted crop can not only avoid damage, caused by continuous cropping, to the soil but also have functions of restraining occurrence and spread of plant diseases and insect pests and isolation, tend is replaced with cultivation, weeds are restrained, management cost of the camellia oleifera or the torreya grandis is reduced, the utilization rate and the copping index of the forest land are improved and economic benefits are increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD
High-efficiency rhizobium meliloti strain with stress resistance and growth promoting performances and application of rhizobium meliloti
ActiveCN106987541AStrong resilienceStimulating abilityPlant growth regulatorsBacteriaLaboratory cultureRhizobium
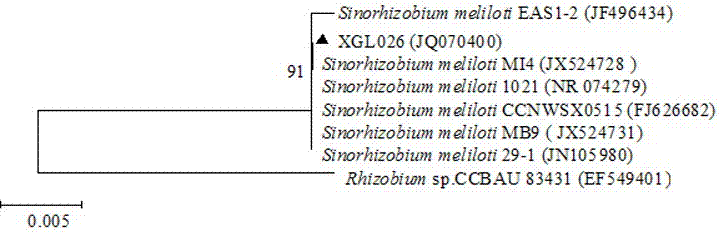
The invention discloses a high-efficiency rhizobium meliloti strain with stress resistance and growth promoting performances and application of rhizobium meliloti. The strain is sinorhizobium meliloti XGL026, is separated and purified from fresh alfalfa rhizobium meliloti and is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 21, 2013, the collection address of the strain is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 3#, Yard 1#, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the collection number is CGMCC NO. 7179. The high-efficiency rhizobium meliloti strain XGL026 disclosed by the invention is high in stress resistance, has the capabilities of dissolving inorganic phosphorus and organic phosphorus and secreting IAA and is an excellent rhizobium meliloti strain with high matching affinity with main cultivated alfalfa varieties in Xinjiang, high competitive nodulation ability and high nitrogen-fixing efficiency. When applied to an alfalfa production area in Xinjiang, the strain disclosed by the invention has high applicability, high nodulation ability and effects of improving the alfalfa forage yield and improving the quality, the overall growth performance of alfalfa plants is enhanced, and the contrast difference from non-inoculated strains reaches an obvious level.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Compound microbial preparation for promoting paddy growth and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101524089APromote growth and reproductionSimple structurePlant growth regulatorsBiocidePotassiumNormal growth
The invention relates to a compound microbial preparation for promoting paddy growth and a preparation method thereof. The compound microbial preparation for promoting paddy growth is characterized by consisting of 20-40 parts by weight of a microbial strain culture and 60-80 parts by weight of a microbial carrier; wherein, the microbial strain culture consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-8 parts of bacilli subtilis, 2-8 parts of bacilli megaterium, 5-10 parts of saccharomyces cerevisiae and 1-4 parts of rhizobia; the microbial carrier is zeolite or bentonite or mixture thereof. The compound microbial preparation has the advantages of promoting growth of beneficial microbes, enhancing absorption of nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium and other organic substances for paddy root system and promoting normal growth of the root system, thus promoting the paddy growth and reducing chemical fertilizer application.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUANGBO SOIL REMEDIATION ENG
Phosphorus transportprotein gene GmPT5 related to phosphorus transport of soybean nodulation and application thereof
InactiveCN102757969AReduce sizeImprove absorption and utilization efficiencyFungiBacteriaNucleotideSoya bean
The invention discloses a phosphorus transportprotein gene GmPT5 related to phosphorus transport of soybean nodulation and application thereof. The phosphorus transportprotein gene GmPT5 related to the phosphorus transport of the soybean nodulation has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and coded protein nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The gene GmPT5 regulates and controls the phosphorus transport from a root part to the nodulation, furthermore, the overexpression of the gene is favorable for increasing the size of the soybean nodulation and the plant biomass as well as the nitrogen and phosphorus contents.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for remediating polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) polluted soil through cooperation of alfalfa and complex microbial inoculants
InactiveCN105251763AShorten germination cycleImprove toleranceContaminated soil reclamationSnow moldBiology
The invention discloses a method for remediating polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) polluted soil through cooperation of alfalfa and complex microbial inoculants. Alfalfa seeds are pretreated, and the plant sprouting period is shortened by 2-3 days, so that the tolerance of the plant to soil containing PAHs is enhanced, and the remediating capacity of the plant on the soil is improved. Besides, in an alfalfa-trichoderma-nodule bacterium combined remediating system, the synergistic effect of trichoderma and nodule bacteria is used for promoting degradation of the alfalfa to the PAHs in the polluted soil. Meanwhile, the physiological contour of the microbial population level of alfalfa rhizosphere soil is changed, and the diversity and the stability of the microbial ecological functions of the soil are recovered, so that the growth environment of crops is improved, and the quality and the yield of the crops are improved; the method has wide market application prospects.
Owner:周世永
Method for improving plant planting desert
InactiveCN101790934AImprove usabilityIncrease volumeHorticultureFertilizer mixturesAnimal ForagingHectare
The invention relates to a method for improving a plant planting desert, which is realized by the following steps: adding 140 to 170kg of liquid film, 0.6 to 8kg of calcium magnesium phosphate, 0.01 to 0.2kg of ammonium molybdate and 0.4 to 5kg of nitragin of this family into 800 to 1300kg of water, stirring, dissolving, then adding 4 to 50kg of leguminous forage seed, stirring evenly, sowing on the sand of one hectare and enclosing and banning grazing for 3 to 5 years; and sowing 7 to 30kg of gramineous forage grass seed on the sand after the primary period, relieving enclosure and grazing banning after enclosing and banning grazing for 2 to 3 years and keeping the pasturage strength at 5 to 10 animals / year to achieve the ecological equilibrium of animals and plants so as to finish the improvement of the desert. By using the method, the usability of soil can be increased, the soil obtains sufficient water and nutrients, a woodland with large area can become a source of forest, the condition that the growth rate of the forest is greater than the exploitation rate is kept, the forest provides more oxygen gas used by organisms and assists to lower a warming phenomenon, buildings can be constructed again in part of regions with desertification reversion by the windproof protection of the forest, and the volume and the utilization rate of the soil are increased.
Owner:于飞
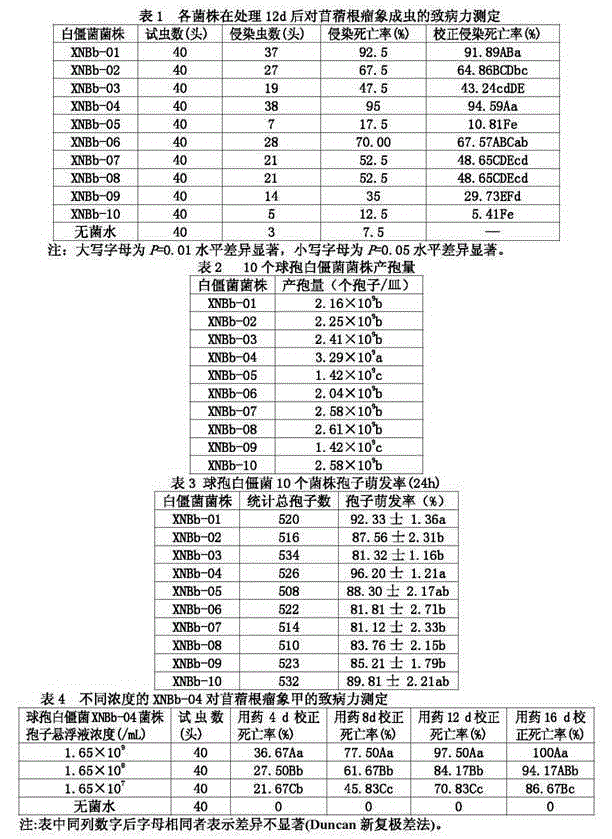
Beauveria bassiana XNBb-04 strain and culture method thereof
ActiveCN105176828AGood pathogenicityEfficient killingFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEcological environment
Relating to technical field of microorganisms, the invention discloses a beauveria bassiana XNBb-04 strain and a culture method thereof. The beauveria bassiana XNBb-04 strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on March 6, 2014, and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2014075. The beauveria bassiana XNBb-04 strain provided by the invention belongs to Deuteromycota, Moniliales, Moniliaceae, Beauveria. The beauveria bassiana XNBb-04 strain is a native entomopathogenic fungus of China, can be further used for preparation of living biopesticides, has good pathogenic effect on nodulated alfalfa weevils, can effectively kill nodulated alfalfa weevils, has brand new action mechanism different from existing chemical insecticides, and has no environmental pollution or residue. The beauveria bassiana XNBb-04 strain provided by the invention can be applied to various ecological environments in terms of pest control, and is conducive to environmental protection.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN101885633APlay a role in reducing costsPerfection and improvement of fertilization technologyOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesCross-linkContinuous cropping
The invention discloses a special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer and a preparation process thereof. The special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer utilizes the effects of exchange, adsorption, combination and chelation of humic acid, and a reactant, a cross-linking agent and a film-forming agent are added to the humic acid to prepare a special peanut slow-release film-coating agent; then special peanut slow-release film-coating agent is mixed with a proportioned special peanut fertilizer; and an obtained mixture is subjected to granulating, film coating, dehumidifying, cooling and screening to prepare the special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer. The humic acid contained in the special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer is a high-quality organic fertilizer, and not only can be decomposed to provide nutrients, but also can stimulate the activity of root nodules, enhance the nitrogen fixing capacity and improve the disease resistance and the continuous cropping resistance. The special peanut film-coating slow-release fertilizer and the preparation process not only are a break of a slow-release technology of the fertilizer industry, but also are the perfection and the improvement of a peanut fertilizing technology, and achieve the purposes of increasing the yield, reducing the cost and realizing high efficiency on peanut production.
Owner:李振永
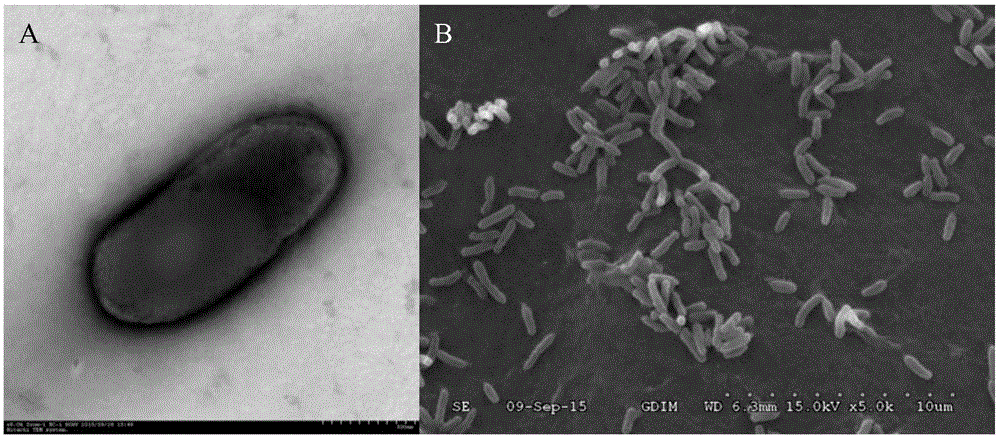
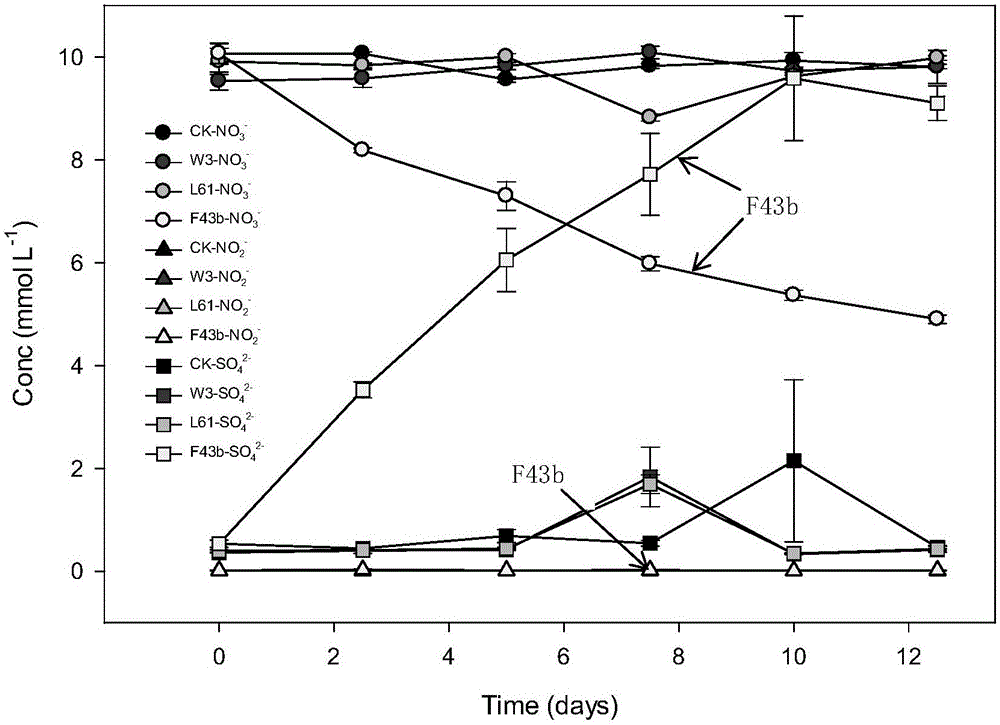
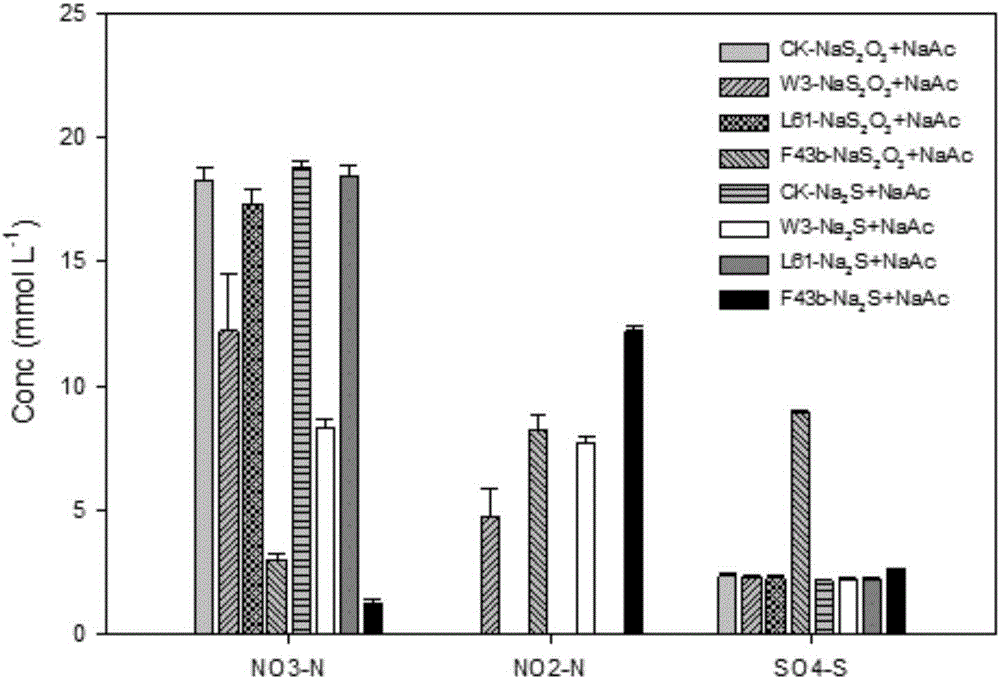
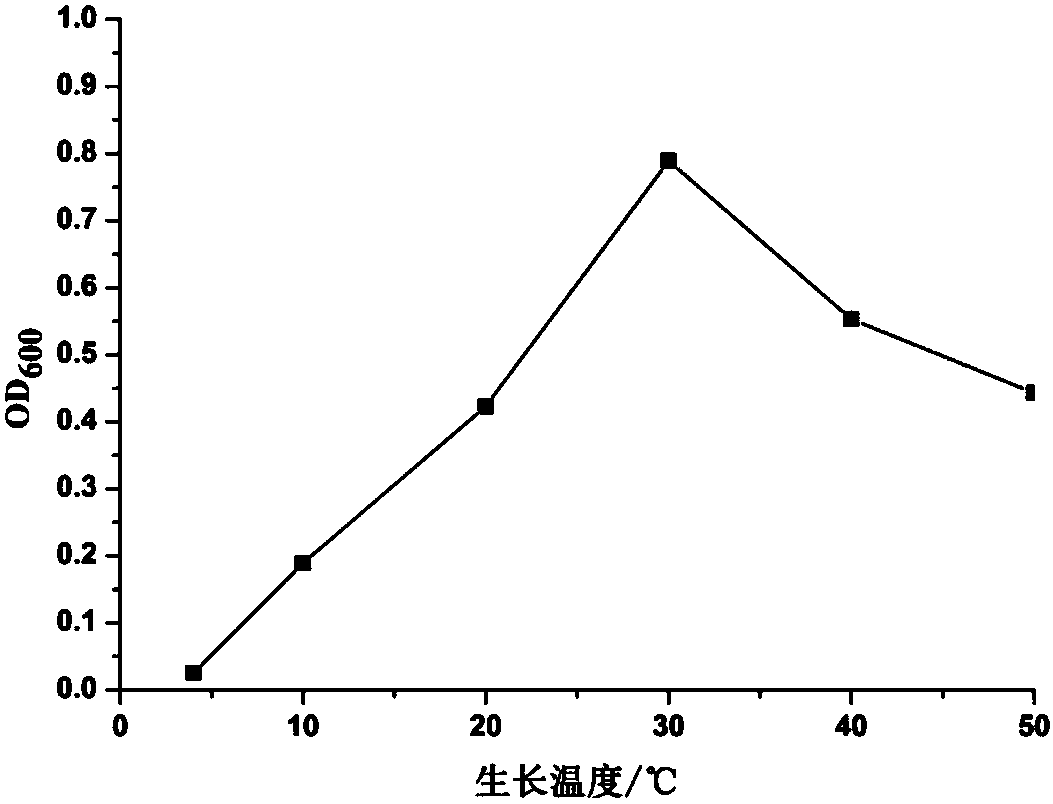
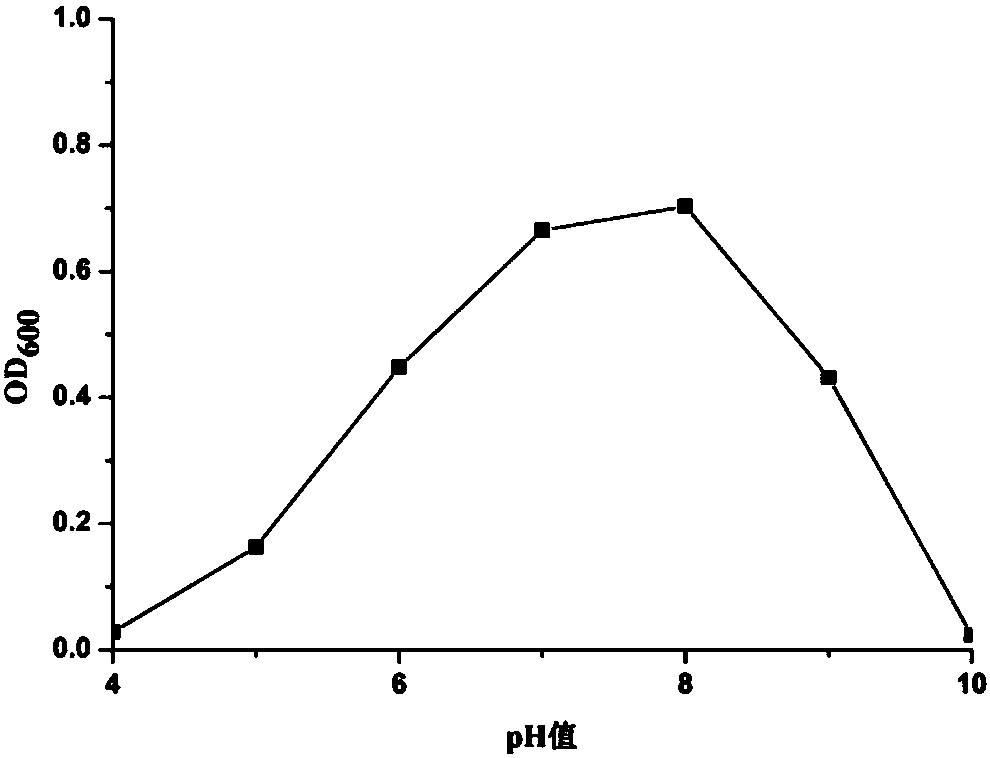
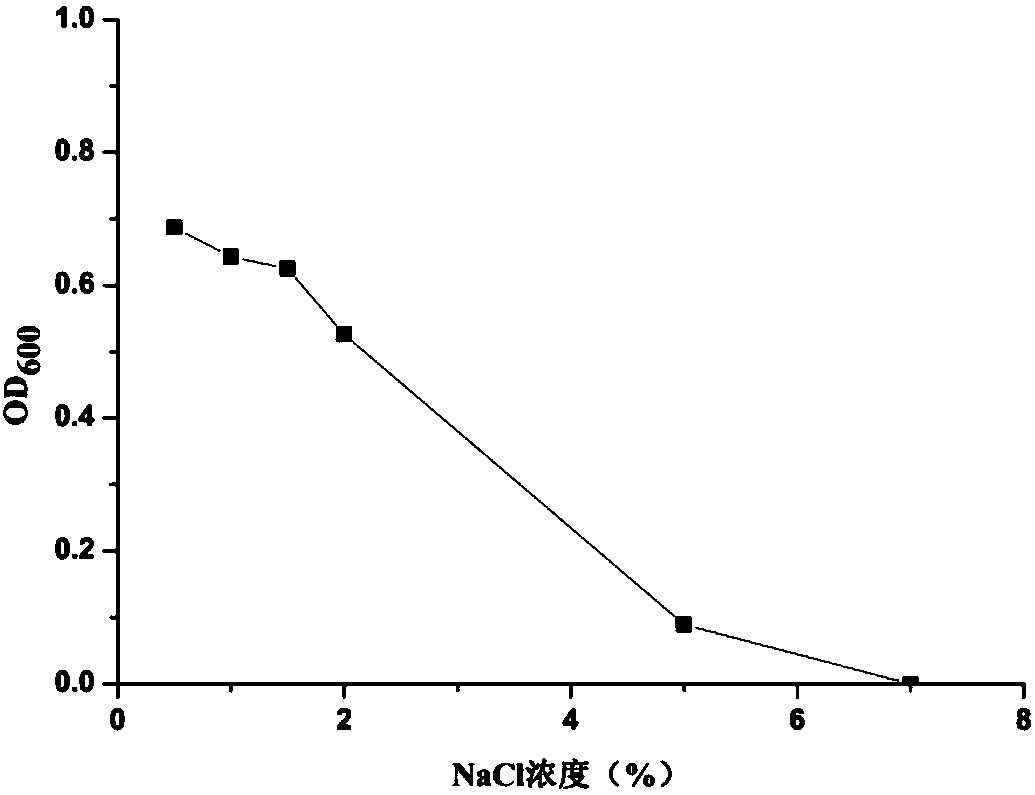
Facultatively autotrophic sulfur oxidation denitrification rhizobium F43b and application thereof
The invention discloses a facultatively autotrophic sulfur oxidation denitrification rhizobium F43b and an application thereof. The Rhizobium sp. F43b<T> is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) Wuhan University in Wuhan in China on March 30, 2016 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2016158. The Rhizobium sp. F43b<T> is facultatively autotrophic rhizobium with sulfur oxidation and denitrification functions, can remove COD, nitrates and sulfides from polluted water or deposits, realizes simultaneous removal of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur from the polluted water or deposits, and provides bacterial strains and microbial preparations for river restoration and carbon, nitrogen and sulfur wastewater treatment, and researches of the rhizobium provide theoretic guidance for river restoration and removal of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Composite microbial preparation for promoting growth of rape and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101671205APromote growth and reproductionImprove stress resistanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAzotobacter chroococcum
The invention relates to a composite microbial preparation for promoting the growth of rape and a preparation method thereof. The composite microbial preparation for promoting the growth of the rape is characterized by comprising 20-40 parts by weight of strain culturing substance and 60-80 parts by weight of microbial carrier, wherein the strain culturing substance comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-8 parts of bacillus subtilis, 2-8 parts of bacillus megaterium, 5-10 parts of rhodopseudomonas palustris and 1-4 parts of azotobacter chroococcum. The preparation method of the composite microbial preparation for promoting the growth of the rape comprises the following steps: culturing 2-8 parts of bacillus subtilis, 2-8 parts of bacillus megaterium and the rhodopseudomonas palustris together, culturing the azotobacter chroococcum independently, mixing and fermenting. The invention has the advantages of promoting the growth and the propagation of beneficial microorganisms, increasing the absorption of the root system of the rape to nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other organic substances and promoting the normal development of the root system, thus promoting the growth of the rape and reducing the applied chemical fertilizer.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUANGBO SOIL REMEDIATION ENG
Rhizobium capable of efficiently solubilizing phosphorus and application of rhizobium
ActiveCN105950520APhosphate dissolving ability enhancedHigh affinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFungicideRoot nodule
The invention discloses a rhizobium capable of efficiently solubilizing phosphorus and application of the rhizobium. The phosphorus solubilizing rhizobium is named as Rhizobium sp.P-1 and preserved in China Center For Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on June 16, 2016, and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2016333. The rhizobium can convert difficultly-soluble inorganic phorphorus into a high-quality phosphorus compound which can be directly absorbed and utilized by plants. By using the screened rhizobium in a lettuce pot culture experiment, the content of effective phosphorus in soil can be obviously increased, it is guaranteed that the lettuce yield is not decreased on the condition that the application amount of phosphate fertilizer is decreased by 50%, and the nutritional quality of lettuce is improved. The rhizobium can be used for preparing a phosphorus solubilizing fungicide, be widely applied to agricultural production, improve the bio-availability of difficultly-soluble phosphorus in the soil, increase the phosphate fertilizer utilization efficiency, save fertilizer and increase the yield and has the important significance and application value on the aspect of keeping agricultural ecological balance.
Owner:武汉一禾生态环境检测中心 +1
Rhizobium Scot1305 and application of rhizobium Scot1305 in promoting phytoremediation of heavy metal pollution of soil
ActiveCN106167774AImprove repair effectIncrease enrichment contentBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationRoot noduleSecreted substance
The invention provides rhizobium Scot1305 and a symbiotic system of rhizobium Scot1305 and plants is established. Due to nitrogen fixation function, siderophore secretion function and soluble phosphorus activity of the rhizobium strain and protection effect of the rhizobium strain on key enzyme of plant tocopherol synthesis, enhancement effect of the strain on phytoremediation of Co contaminated soil is realized. The strain can coexist with plants in Co contaminated soil, and can promote the extraction and enrichment of heavy metals Co in the aerial parts of plants, and finally achieve the purpose that the content of Co in soil meets the environmental safety standard.
Owner:SICHUAN INST OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Method for extracting and refining rhizobia exocellular polysaccharide
ActiveCN101942035AAvoid it happening againLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationFlocculationRoot nodule
The invention discloses a method for extracting and refining rhizobia exocellular polysaccharide. The method is finished by the following steps: dilution pretreatment, flocculation and protein removal, ion exchange, concentration and salt removal, alcohol precipitation with alcohol, and vacuum drying. The method for extracting and refining the rhizobia exocellular polysaccharide from rhizobia fermentation liquor has the characteristics of few process steps, high efficiency, low cost and suitability for industrial production; and the prepared exocellular polysaccharide has high purity.
Owner:天津强微特生物科技有限公司
Method for repairing arsenium-polluted farmland soil through microorganisms and plants in combined manner
InactiveCN106583430AReduce leaching concentrationReduce the impactContaminated soil reclamationMicrobial agentNormal growth
The invention discloses a method for repairing arsenium-polluted farmland soil through microorganisms and plants in a combined manner. The method includes the following steps that firstly, a microbial agent is sprayed, wherein nodule bacteria are sprayed in the arsenium-polluted farmland soil after being dissolved in water; secondly, plant plantation is conducted, wherein Nephrolepiscordifolia(L.)Presl is planted in the arsenium-polluted farmland soil where the nodule bacteria are sprayed; and thirdly, field management is conducted, wherein the field management is conducted on the Nephrolepiscordifolia(L.)Presl, and normal growth of the plants is ensured. Treatment of arsenium-polluted farmland soil repair is conducted through the microorganisms and the plant repair technology in a combined manner, the nodule bacterium NT-26 and Nephrolepiscordifolia(L.)Presl combined repair is adopted, the leaching concentration of the heavy metal arsenium in the repaired and treated farmland soil is smaller than the IV-type standard in Quality Standard for Ground Water (GB / T14848-93), the whole construction process is high in benefit, and influences on the environment are small.
Owner:BEIJING GEOENVIRON ENG & TECH
Polymeric compositions containing rhizobium and/or plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria inoculant, use thereof and seeds treated with the compositions
Biological nitrogen fixation is a very important process to plant growth and health. Biological nitrogen fixation is performed naturally by a number of different microorganisms including plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, mycorrhizal fungi, and rhizobia. The present invention discloses novel compositions comprising water soluble polymers, rhizobium and plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria. Uses of the novel composition include treatment of seeds prior to planting and use in soil surrounding roots to improve plant growth and health.
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUARIA EMBRAPA
Rhizobium strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104830724ASolve the problem of segment processingHas the characteristic of removing ammonia nitrogenTreatment using aerobic processesBacteriaRhizobium sp.Oil sludge
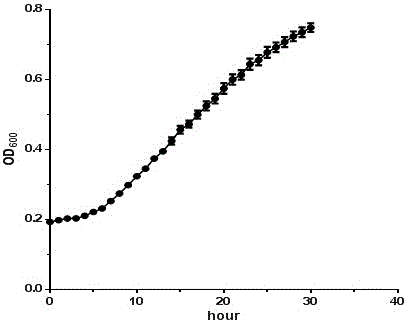
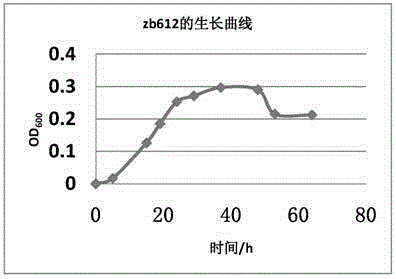
The invention discloses a rhizobium strain and its application. The rhizobium strain is named as Rhizobium sp., the strain number is zb612, and preservation number is CGMCC No. 10721. The rhizobium strain was preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) at the No.3, 1 West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District of Beijing on April 15th, 2015. The strain provided by the invention can be used in onsite real nitrogen removal from sewage so as to raise the effect of removing ammonia nitrogen from oil sludge. The rhizobium provided by the invention has the characteristic of removing ammonia nitrogen. According to the rhizobium strain, organic carbon can be used as the sole carbon source and ammonia nitrogen is used as the sole nitrogen source so as to carry out metabolism, and ammonia nitrogen is directly converted to N2 through heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification so as to finish nitrogen removal. Thus, problems of aerobiotic nitrification and anoxic denitrification sectional treatment in traditional biological removal of nitrogen are solved.
Owner:水艺环保集团股份有限公司
Fertilizer containing rhizobium inoculant special for Chinese milk vetch and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN102515979AGood effectAgriculture gas emission reductionHorticultureRhizobiumEnvironmental factor
The invention relates to a fertilizer containing a rhizobium inoculant special for Chinese milk vetch and preparation and an application thereof. The fertilizer special for Chinese milk vetch comprises the following raw materials: a urea-coated rhizobium inoculant composition, 5 percent humic acid coating urea, diammonium phosphate, potassium chloride, calcium nitrate and magnesium sulfate, wherein the urea-coated rhizobium inoculant composition is prepared by adsorbing a nodule bacterium zymotic fluid of Chinese milk vetch with turfy soil, adding ammonium molybdate for pelletizing, and coating with molten urea. Before Chinese milk vetch is sown, the special fertilizer is applied to the ground, and plowing and sowing are performed. Nodule bacteria in the fertilizer disclosed by the invention are coated in a urea film, so that the influences of environmental factors can be reduced, and effective time is prolonged.
Owner:KINGENTA ECOLOGICAL ENG GRP
Microecological modulator
InactiveCN106701608ANo mutual phagocytosisImprove micro-ecological cycleFungiBacteriaPlant growthSaccharomycetes
The invention discloses a microecological modulator. The microecological modulator is prepared from photosynthetic bacteria, actinomycetes, bacillus, saccharomycetes, lactic acid bacteria, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, potassium bacteria, silicate bacteria, bacillus radicicola, blue-green algae, vitamin C, nitrogen, boron, iron, saccharose, calcium sulfate, dipotassium phosphate, calcium carbonate, magnesium sulfate, sodium chloride and agar. According to the microecological modulator disclosed by the invention, by adopting a fusion technique of multiple useful microbiological populations, the useful microbiological population and plant enzymes are fermented and cultivated at the same time, mutual phagocytosis of biological populations in a fusion process of the biological populations can be prevented, and symbiosis and compatibility are realized. The microecological modulator disclosed by the invention is rich in multiple microbiological populations and multiple trace elements and mineral substances needed by plant growth, so that microecological circulation of soil can be improved, and the fertilizer efficiency of the soil is enhanced; the microecological modulator replaces chemical fertilizer; photosynthesis of leaf surfaces of plants and crops is enhanced, the oxidation is reduced, and leaf surfaces of the plants and the crops can be lustrous and plump; the plants and the crops can be full in fruits; the yields of the plants and the crops can be increased.
Owner:FOSHAN GBIO TECH CO LTD
Method for rotation of alfalfa and awnless brome
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural planting, and particularly relates to a method for rotation of alfalfa and awnless brome. The method for rotation of alfalfa and awnless brome comprises the following steps: turning over and planting alfalfa for 5-6 years after planting the awnless brome for 5-6 years, and then turning over and planting the awnless brome, and carrying out crop rotation repeatedly. The method has the beneficial effects that the yield and the soil fertility of high-quality forage per unit area are improved in a crop rotation manner, the physical and chemical properties of soil are improved, nitrogen in atmosphere also can be fixed by root nodules of alfalfa, and the soil fertility is improved. Thus, the fertilizing amount can be correspondingly reduced, investment in manpower and chemical fertilizer is reduced, the investment in fertilizer in the next round of awnless brome planting process also can be reduced, the yield of the awnless brome is increased, the land utilization rate and the acre yield are further improved, and the economic benefits are increased.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Nodule bacteria transferring method by utilizing distant grafting
The invention relates to a nodule bacteria transferring method by utilizing distant grafting, comprising: 1) hybrid sunflowers and corns which have high plasticity are chosen as stock; 2) varieties with high nitrogen fixation activity and stable hereditary are chosen from leguminous plants; 3) cleft grafting is adopted, when 1-6 pieces of leaves of the stock grow and 1-6 pieces of leaves of the scion grow, grafting is carried out; 4) after the grafting survival is realized, the growth amount of the stock and the scion is rationally controlled; the plants with nodule bacteria and the plants without nodule bacteria are grafted by utilizing the distant grafting, so as to lead the nodule bacteria to be transferred to the plants without nodule bacteria and cause the plant without nodule bacteria to have nodule bacteria naturally.
Owner:王成玉 +1
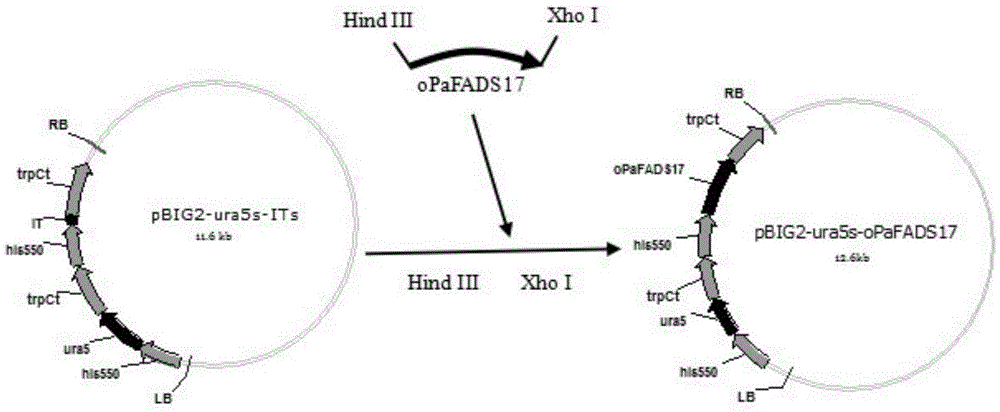
Recombinant strain for expressing heterogenous Omega-3 desaturase in mortierella alpina and construction method thereof
The invention provides a recombinant mortierella alpina strain Ma-oPaFADS17 with heterologous expression coming from pythium aphanidermatum Omega-3 desaturase genes and a method for constructing the mortierella alpina strain with heterologous expression coming from pythium aphanidermatum Omega-3 desaturase genes. The method adopts mortierella alpine uracil auxotrophic strain CCFM 501 as materials and uses an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated genetic manipulation technology to obtain a recombinant strain with a high yield of EPA in the environment of normal temperature, wherein the yield of EPA reaches 617.1 mg / L, and the content of the EPA accounts for 18.7 percent of the total amount of fatty acid, which has an important meaning for the basic research and product development of oil-producing fungus mortierella alpine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum and production method thereof
InactiveCN101818119AServe as nutritionPlay a role in film formationMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationCarboxymethyl celluloseSodium molybdate
The invention relates to a nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum and a production method thereof. The nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum is prepared by selecting the raw materials of PVP (Polyvinylpyrrolidone) K30, PVP S630, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, peptone, bovine serum albumin and sodium molybdate and reacting under a certain reaction condition; the nutrient film protecting agent of rhizobium japonicum, a liquid rhizobium japonicum agent and soybean seeds are mixed and stirred according to a certain proportion; and after the soybean seeds are coated and stored for two days, each soybean seed can ensure 100,000 live rhizobium japonicums. The invention has wide needed raw material sources, simple production process and low cost, can play roles of nutrition, film formation and protection in the rhizobium japonicum, and can ensure that the liquid rhizobium japonicum agent is preserved for one year at normal temperature; the live bacterium quantity is not smaller than 2,000,000,000 / ml, and the nitrogen fixing activity is not reduced.
Owner:哈尔滨奥龙奇康科技发展有限公司
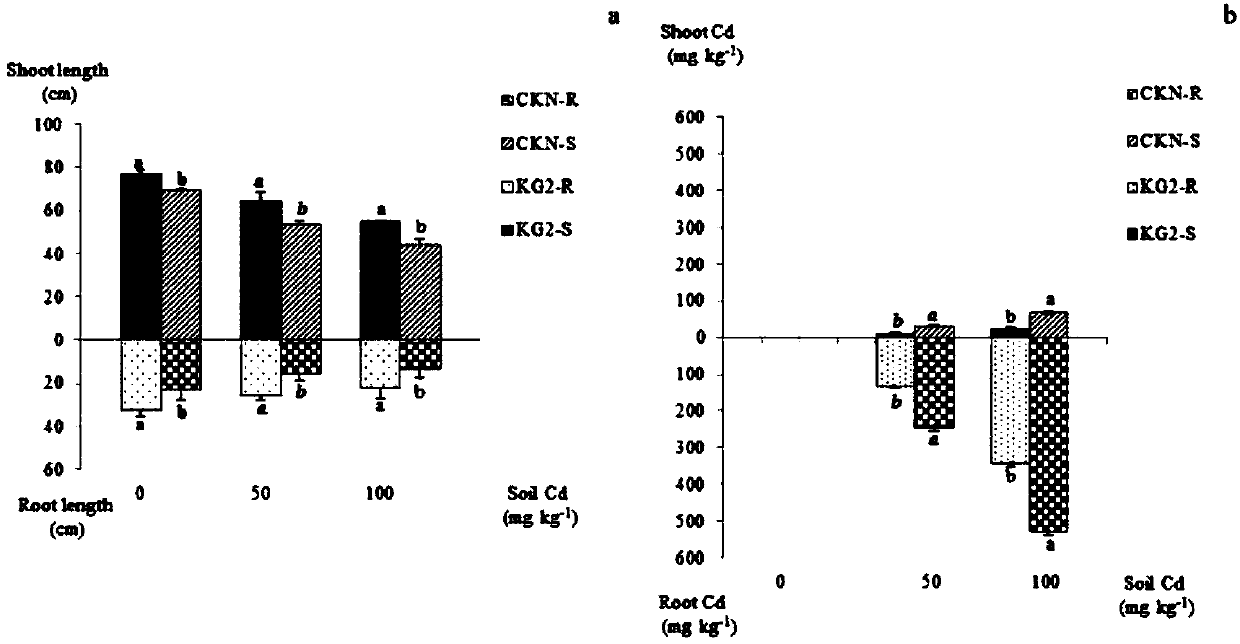
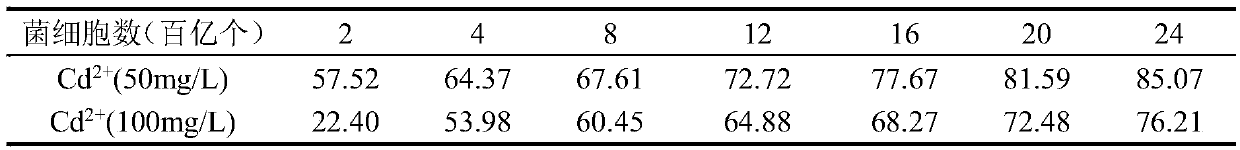
Cd (cadmium) removal rhizobium pusense KG2, strain containing rhizobium pusense and purpose of Cd removal rhizobium pusense KG2
The invention provides Cd removal rhizobium pusense KG2, a strain containing the rhizobium pusense and application of Cd removal rhizobium pusense KG2 to fixation or removal of Cd<2+> in soil or a water body. The invention proves that the rhizobium pusense KG2 has the efficient Cd fixation capability and stronger nitrogen fixation functions; the leguminous crop growth can be promoted; the stress resistance of the leguminous crop can be increased; the enriching adsorption quantity of the plants on the Cd in the soil can be reduced. The rhizobium pusense KG2 is applied to the biological restoration of the farmland Cd pollution soil in a form of a strain or a bacterial fertilizer; the enriching adsorption of the crops on the Cd in the farmland soil can be reduced; the growth of the crops in the metal pollution soil is promoted, so that the yield and the quality of the crops are improved.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV +1
Efficient peanut rhizobiumleguminosarum strain and application thereof
ActiveCN103571770AHas the ability to fix nitrogenEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyRoot nodule
The invention relates to a novel rhizobiumleguminosarum strain, wherein the strain has high biological nitrogen fixation activity, has certain preventive and therapeutic effects on fungal diseases of plants and has good saline-alkaline resistance and high temperature resistance, so that the strain has functions of nitrogen fixation, disease prevention, stress resistance and yield increase. The rhizobiumleguminosarum is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center Committee on July 15, 2013 with a preservation number of CGMCCNo.7924. As shown in researches, the strain can nodulate on peanut roots and the strain has a good inhibitory effect on botrytis cinerea and pythium aphanidermatum and has saline-alkaline resistance and high temperature resistance.
Owner:河北浩海嘉农种业有限公司
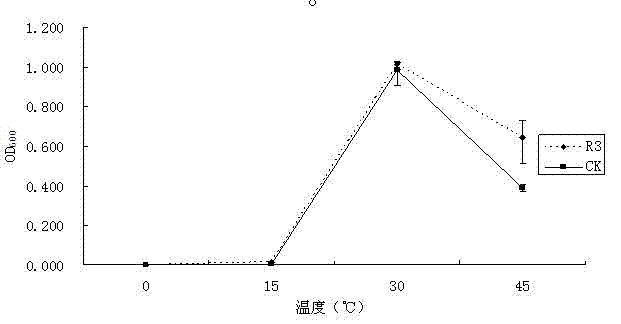
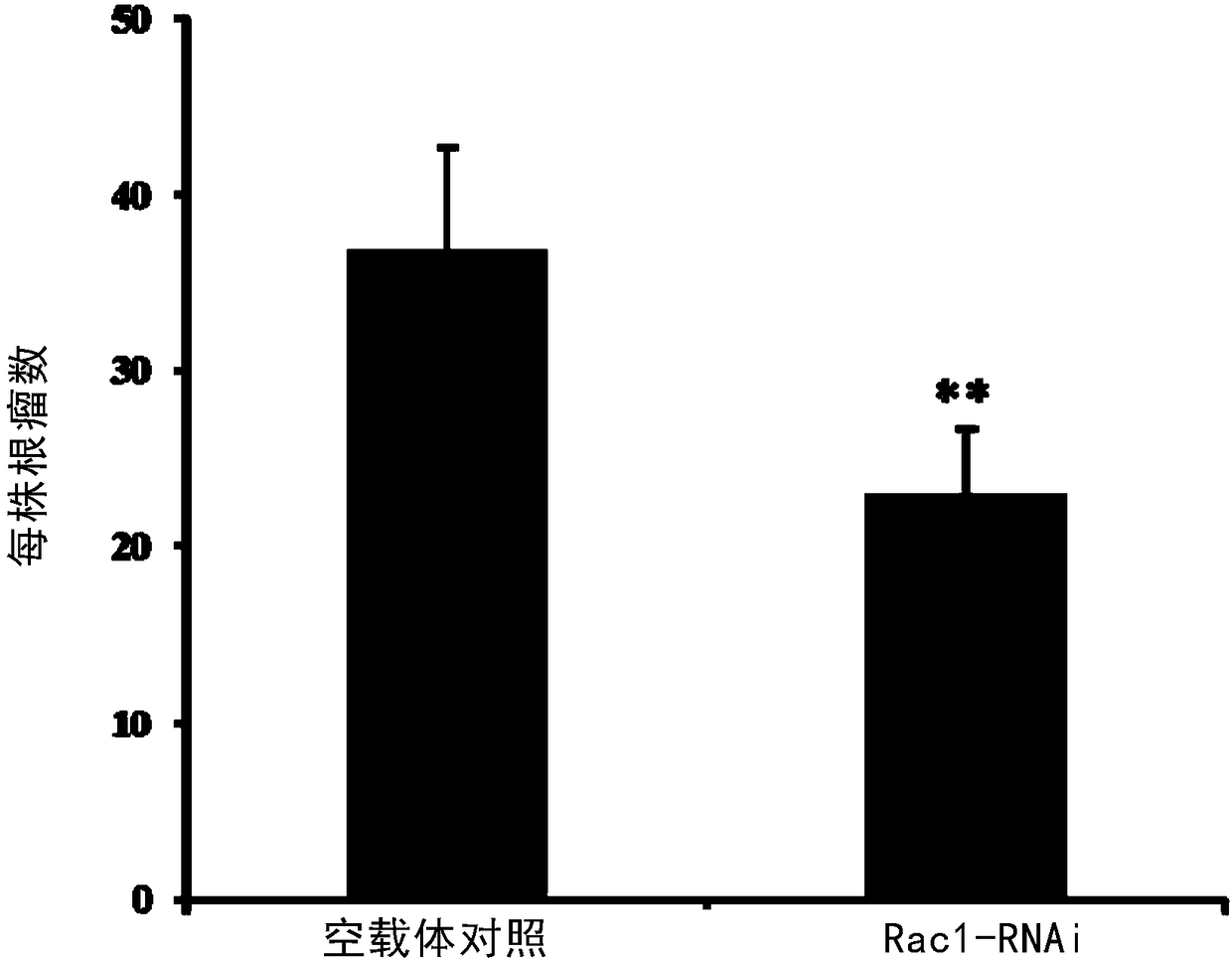
Gene for regulating number of nodules of nodule plants and application of gene to efficient nitrogen fixation aspect
The invention relates to a gene for regulating the number of nodules of nodule plants and an application of the gene to an efficient nitrogen fixation aspect. The inventor clones a novel gene namely an Rac1 gene for the first time. Shown by functional analysis, the gene or a regulating molecule thereof is closely related to the number of the nodules of the nodule plants. Therefore, the gene can beapplied to plant improvement, so that plants of which the nodule character and the nitrogen fixation character are changed are obtained.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Fe(II) transportproteins of peanut nodule and coding genes thereof
The invention provides Fe(II) transportproteins of peanut nodule and coding genes thereof. The Fe(II) transportprotein of peanut nodule have an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1, and the coding genes have a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No.2. The Fe(II) transportproteins of peanut nodule and the coding genes thereof indicate transferring and utilizing modes of Ferrum in process of nitrogen fixation of symbiotic leguminous plants and nodule bacteria, provides necessary theoretical basis and technical support for improving the utilization ratio of leguminous plants and giving full play to nodule for high efficient nitrogen fixation through gene engineering techniques and has wide application.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com