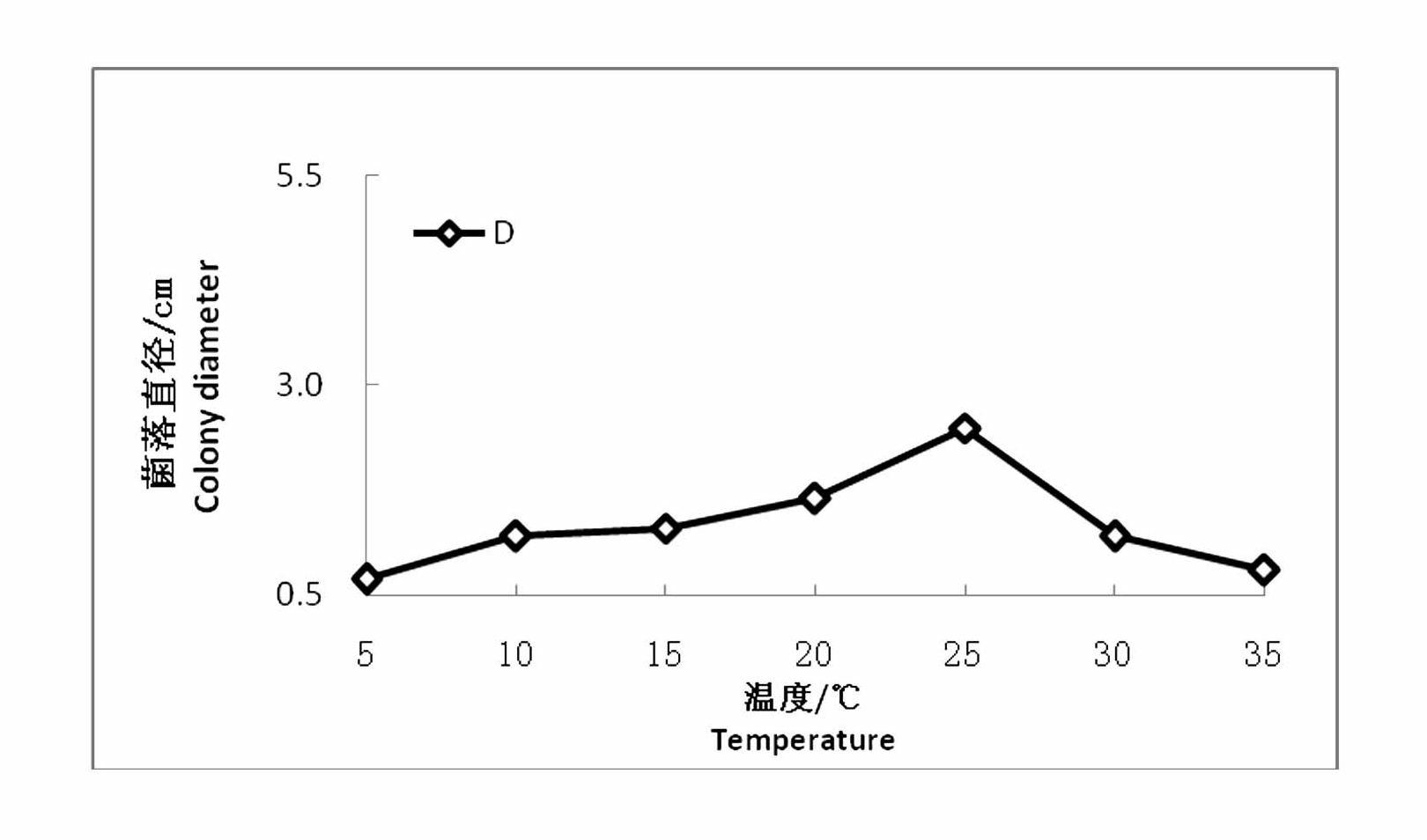
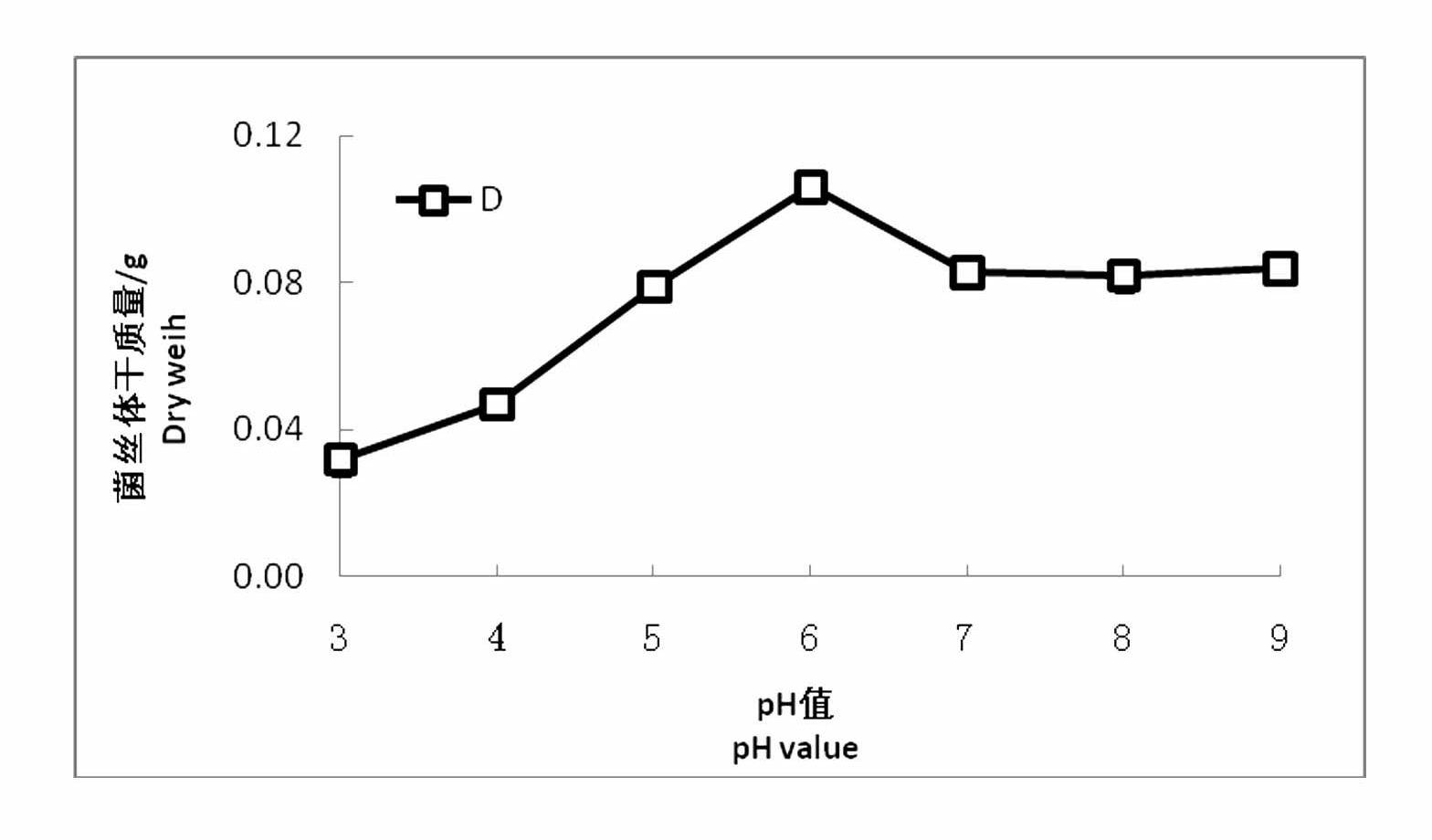
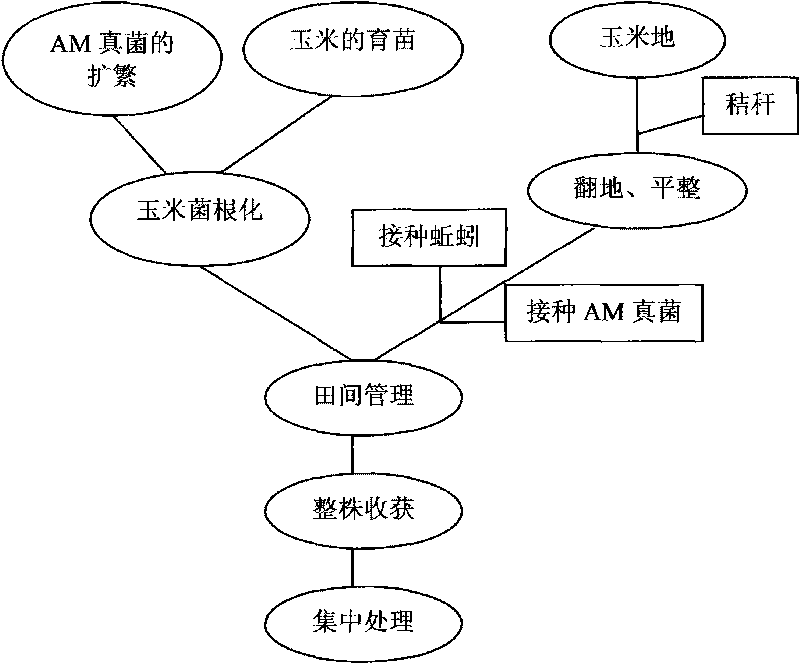
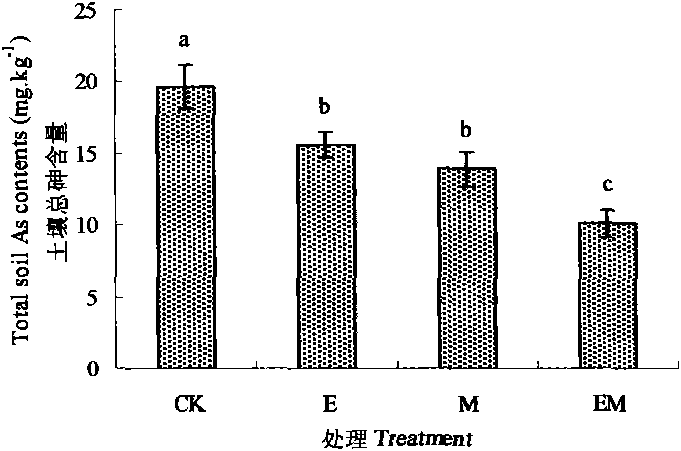
Patents
Literature
422 results about "Mycorrhizal fungi" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The name mycorrhizae (Myco meaning fungi and rhizae meaning roots) is a term for symbiotic associations between plant roots and fungi. This mutalistic growth is in most cases beneficial to both the host plant and the fungi. Mycorrhizal fungi are the fungi that colonize plant roots.
Living systems from cardboard packaging materials
InactiveUS20080046277A1Increase valueEffect shipping rateBiocideSustainable waste treatmentCardboardLiving systems
Compositions, methods and business applications of using new and recycled cardboard infused with a plurality of saprophytic (including endophytic) and mycorrhizal fungi matched with seeds of plants (including trees, vegetables, herbs and grasses) whereby the cardboard can be sprouted by end-users to start ecosystems. Such containers may have carbon-credit value for companies and consumers when planted and grown as a carbon sink or carbon offset for the photosynthetic and mycelial sequestration of carbon dioxide. The relative weight of the Life Box's added seeds and spores does not significantly affect the total weight of the infused cardboard, thus not increasing transportation costs.
Owner:TURTLE BEAR HLDG LLC
Delivery systems for mycotechnologies, mycofiltration and mycoremediation
The present invention utilizes fungal spore mass or hyphal fragments in burlap bags or sacks filled with biodegradable materials. The fungi may include saprophytic fungi, including gourmet and medicinal mushrooms, mycorrhizal fungi, entomopathogenic fungi, parasitic fungi and fungi imperfecti. The fungi function as keystone species, delivering benefits to both the microsphere and biosphere. Such fungal delivery systems are useful for purposes including ecological rehabilitation and restoration, preservation and improvement of habitats, bioremediation of toxic wastes and polluted sites, filtration of agricultural, mine and urban runoff, improvement of agricultural yields and control of biological organisms.
Owner:TURTLE BEAR HLDG LLC
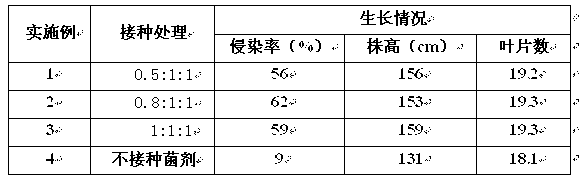
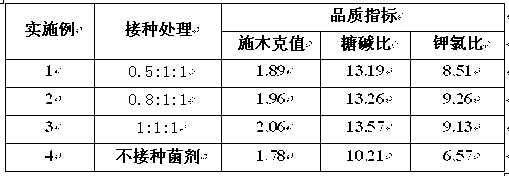
Application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation
InactiveCN103125251AImprove qualityImprove mineral nutritionHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to an application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation. A primary arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide is inoculated and propagated separately, and propagule spore density of an arbuscular mycorrhiza of each fungi after the propagation is 30 pieces per gram of dry soil. A float breeding method is adopted to conduct arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide combinedinoculation to tobacco, mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are obtained, and the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are directly applied to field production. When being transplanted, the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are conducted with a two-step inoculation, and the mixed fungicide is mixed by propagated acaulospora mellea, glomus mosseae and glomus intraradices at a proportion of 0.5-1: 1:1. A colony formed by the propagation of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus is close to a natural state, and fungus cooperate and play a better role of growth promoting and quality improving. According to the application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation, by means of the two times of inoculations of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, the proportion of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and the tobacco in a symbiotic system built during a seedling stage of the tobacco is guaranteed, and the beneficial effects of the symbiotic system to the development of the tobacco seedlings are ensured. The application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation is simple and practical in method and environment friendly.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Microbial agent and soil modifying agent produced by fermentation thereof
ActiveCN101629156AImprove adaptabilityImprove fertilityAgriculture tools and machinesFungiFiberMicrobial agent
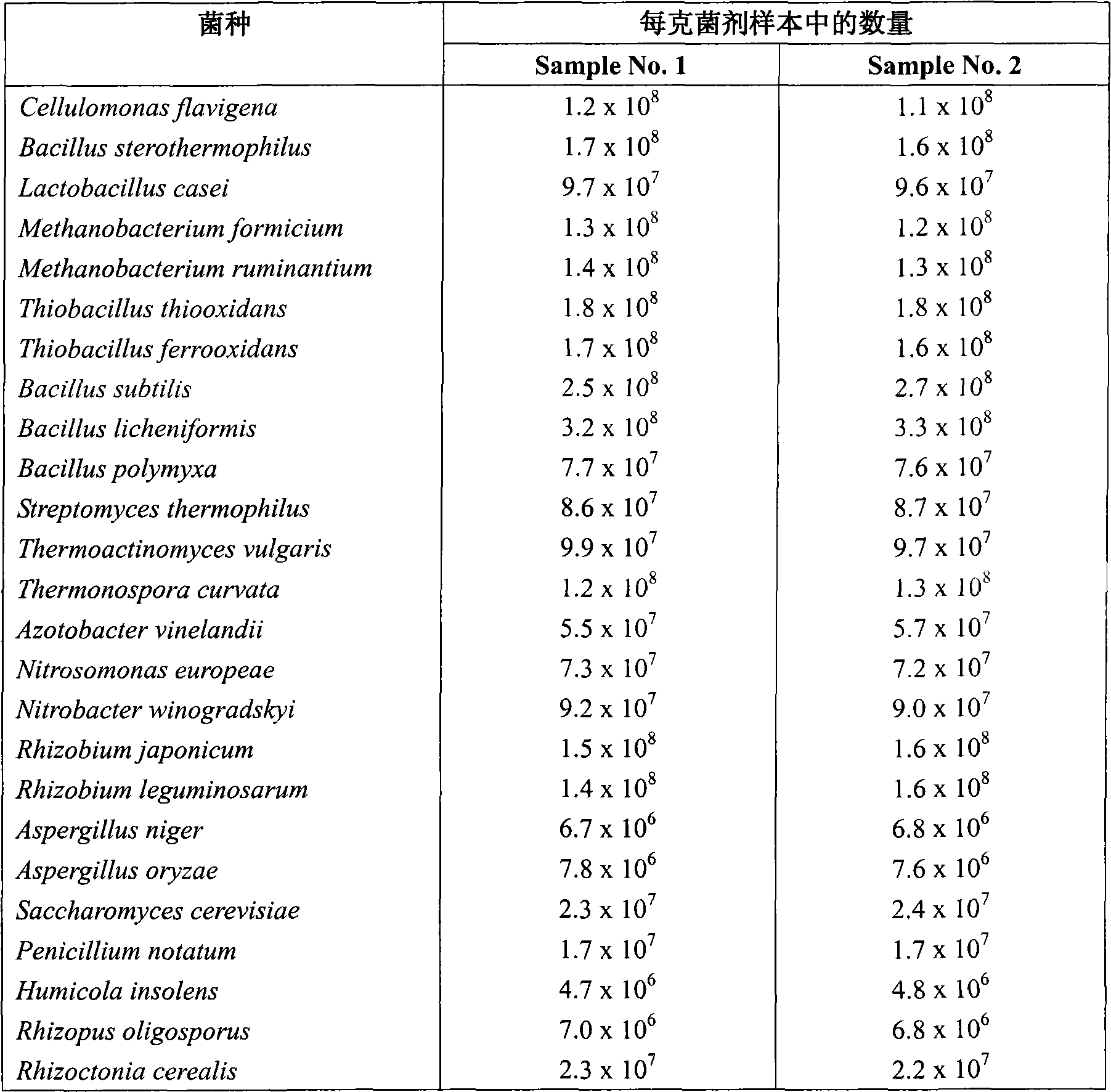
The invention relates to a microbial agent used for producing a soil modifying agent by fermentation, consisting of fiber monad, bacillus, lactobacillus, methanobacteria, thiobacillus, streptomycete, high-temperature actinomyces, high-temperature monad, azotobacteria, nitration monad, nitration bacilus, rhizobium, koji mold, leaven, blue mold, detritus mold, rhizopus as well as mycorrhizal fungi and substrate. In addition, the invention also relates to a soil modifying agent produced by the fermentation of the microbial agent, application thereof and the like.
Owner:宋彦耕
Combined restoring method of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil
InactiveCN101972772AIncrease the number ofHigh activityContaminated soil reclamationArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiPlant roots
The invention relates to a combined restoring method of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil, comprising the following restoring steps of: planting lucerne as perennial leguminous plants in the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil; inoculating a mixed bacterial inoculum comprising arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, bacillus and flavobacterium; and meanwhile, adding rhamnolipid as a biosurfactant. By rhizosphere effect generated by plant root exudates, the number and the metabolic activity of soil microorganisms are increased; and by inoculating the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, the plant growth is promoted, and the root exudates are increased, thereby increasing the root accumulation of organic pollutants and the number of root soil microorganisms. The inoculated high-efficiency polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacteria use plant root secretions as a carbon source and an energy source and can quickly grow and propagate. The polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is stripped from soil grains by the biosurfactant, and the bioavailability and the degradability of the organic pollutants are increased.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
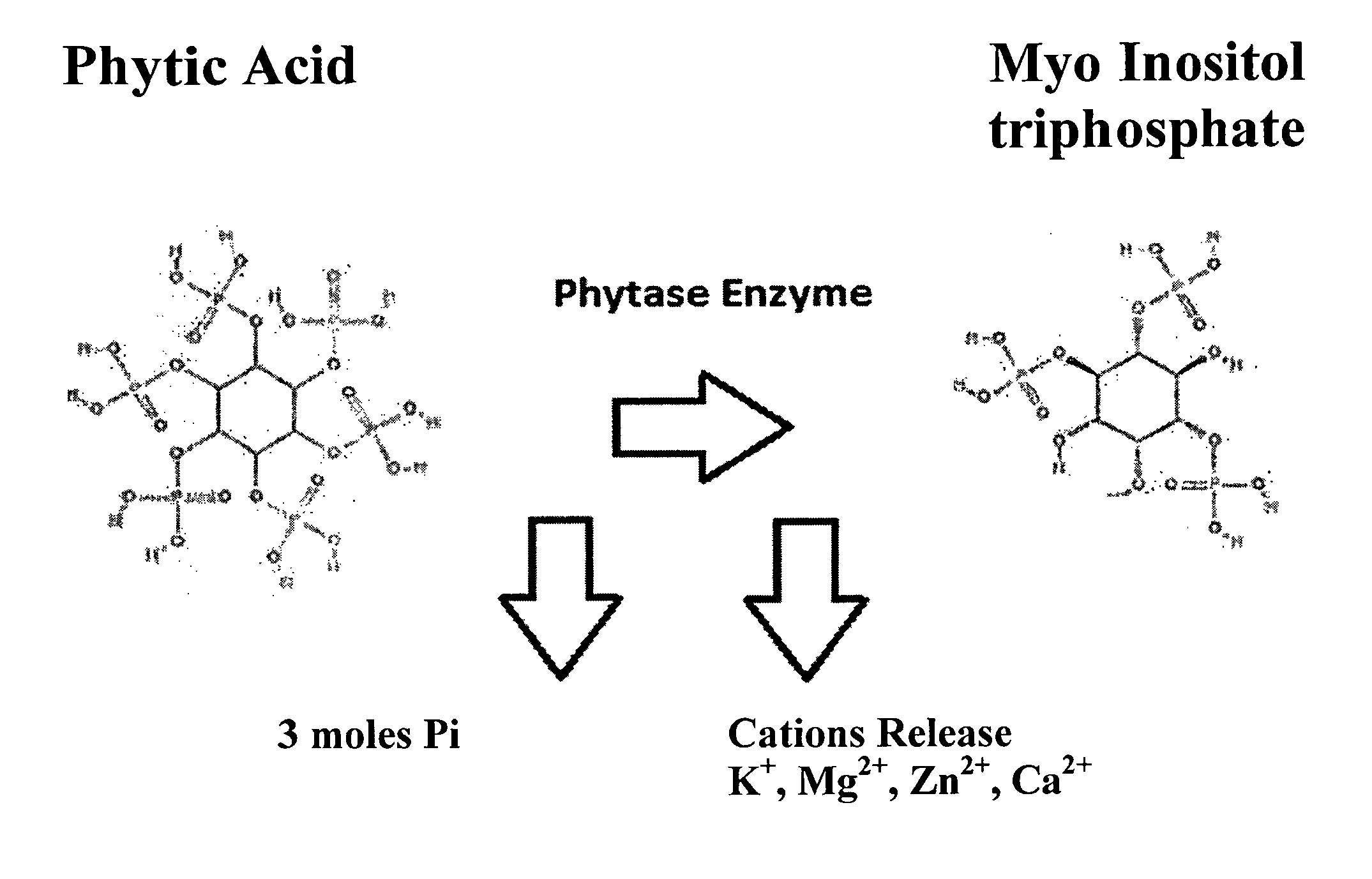
Use of synergistic microorganisms and nutrients to produce signals that facilitate the germination and plant root colonization of mycorrhizal fungi in phosphorus rich environments
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
Biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of biogas residue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103848698AWon't burnDecompose thoroughlyBio-organic fraction processingWaste based fuelMicrobial agentPseudomonas
The invention provides a biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of a biogas residue and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing the biogas residue and a swelling agent to form a fermentation raw material, inoculating a compound microbial agent in the fermentation raw material, uniformly mixing for fermenting, and adding urea, diammonium phosphate, a potassium chloride inorganic salt, brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, mycorrhiza fungi, silicate bacteria, photosynthetic bacteria acetic bacteria, bifidobacterium, and saccharomycetes after the fermentation is completed to prepare the biological organic fertilizer, wherein the compound microbial agent comprises strains of bacillus, pseudomonas, staphylococcus, streptomyces, penicillium, aspergillus and trichoderma. The compound microbial agent prepared by using the biological organic fertilizer has a pertinence to aerobic fermentation of the biogas residue, and is capable of effectively increasing the fermentation rate of the biogas residue, shortening the fermentation time and realizing high-additional value production, innocent treatment and recycling of the biogas residue; and the problem of resources and environment of villages and small towns is solved, and the rapid development of construction of new countryside and towns and cities can be promoted.
Owner:青岛福瑞斯生物能源科技开发有限公司
Method for biologically restoring organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil
InactiveCN101947545AImprove nutritional statusPromote growthContaminated soil reclamationPesticide residueBioremediation
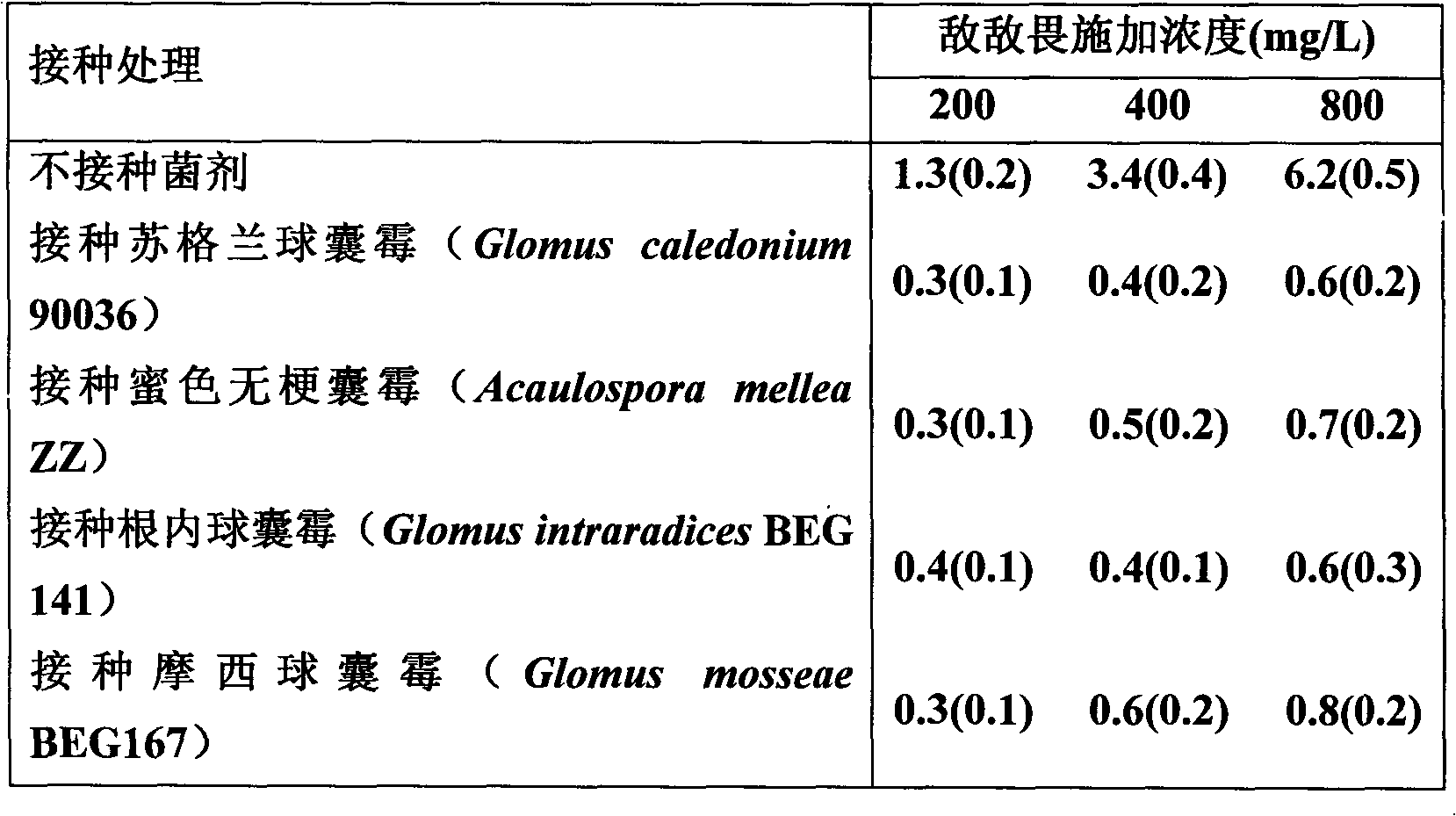
The invention discloses a method for biologically restoring organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil. An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant symbiotic system is used for accelerating the recovery of the organic phosphorus pesticide polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent; (2) inoculating the fungi agent to the soil to be restored, and planting quick growth plants, or transplanting the plants after mycorrhizal seedling culture; and (3) managing the plants to grow 2 to 3 months. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi agent comprises Glomus caledonium 90036, Acaulospora mellea ZZ, Glomus mosseae BEG167 and Glomus intraradices BEG 141). The host plant is selected from quick growth plants such as Sudan grass, alfalfa, corn, broomcorn and the like. The method can reduce the pesticide residue in agricultural products, reduce environment transfer to water, atmosphere and the like and reduce harm to human health, and is simple, convenient and environment-friendly.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for culturing orchid special strain thereof
InactiveCN101338290ALoose textureImprove breathabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologySeedling
The invention discloses a method for culturing an orchid and a special bacterium thereof. The name of the bacterium of the invention is GDB181 the preservation number of which is CGMCCNo.2574. The method of the invention includes the steps for together culturing the bacterium of the invention and the orchid. The bacterium of the invention is applicable for the root culturing of an orchid bacteria and builds an epiphyte bacterium with excellent root which effectively coexists with the orchid. The method of the invention for culturing the orchid can better control the inoculation amount and can fix the inoculation position, thus fully ensuring the tissue culture seedling of the orchid to build the coexistence relation with the epiphyte bacterium with excellent root, simultaneously simplifying the inoculation steps and reducing the inoculation times. Permanent effect can be achieved by being inoculated for once, thus avoiding the dead seedling phenomenon caused by a plurality of manual inoculations, thereby improving the survival rate of transplanting and obtaining the root orchid seedling which grows strongly. Therefore, the method for culturing bacterium, the culture medium of the bacterium and the culture medium of the orchid of the invention has important economic values and is applicable for popularization and application.
Owner:金辉
Method of enhancing cadmium absorption of black nightshade from soil by utilization of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
InactiveCN103990647APromote growthPromote absorptionFungiContaminated soil reclamationArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiPlant growth
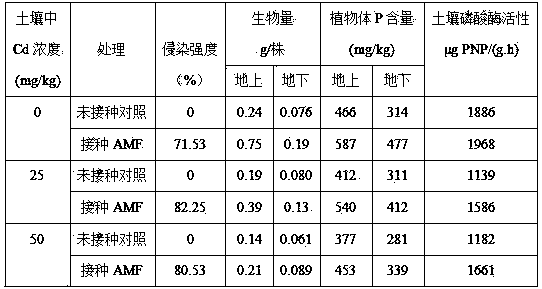
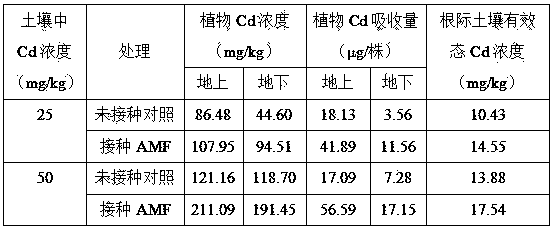
The invention provides an application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) in enhancement of growth and capability of heavy metal absorption from soil of black nightshade and a method of enhancing cadmium absorption of black nightshade from soil by utilization of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. A cadmium (Cd) hyperaccumulating plant black nightshade is adopted as an experiment plant, the AMF is adopted as an Inoculant, the Cd hyperaccumulating plant black nightshade and the AMF capable of promoting plant growth are combined, and the AMF can enhance growth and capability of cadmium absorption from soil of the black nightshade, thus increasing the remediation efficiency of the black nightshade for Cd-contaminated soil. Compared with traditional chemical and agricultural measures, the method has characteristics of good treatment effects, no secondary pollution, low operation cost, and the like, and has good theoretical and application popularization value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes and application of flora
InactiveCN105859339AImprove the current situation of serious hardeningHigh nutritional valueFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisBacillus thuringiensis
The invention is suitable for the technical field of recycling organic wastes, and discloses a flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes. The flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes is efficiently compounded from a variety of bacteria such as bacillus subtilis, aspergillus niger, saccharomycete and soil flora, wherein the soil flora is extracted from the natural world and comprises three or more of bacillus megatherium, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus thuringiensis, bacillus laterosporus, bacillus mucilaginosus, streptomyces jingyangensis, mycorrhiza fungi, azotobacter vinelandii, photosynthetic bacteria, bacillus coagulans, aspergillus oryzae, and paecilomyces lilacinus. According to the flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes, disclosed by the invention, by virtue of mutual promotion, mutual coordination and combined action of a variety of beneficial microorganisms, the organic wastes are recycled, environmental pollution is reduced, and wastes are changed into valuables; and the flora for recycling treatment of organic wastes can be used for producing industrial fermentation products and improving the health and growth conditions of animals, and can also improve the current situation of serious soil hardening at present and improve soil quality, thereby promoting the rapid development of agricultural economics.
Owner:王云飞
Compound soil remediation agent containing microorganism bacteria and preparation method thereof
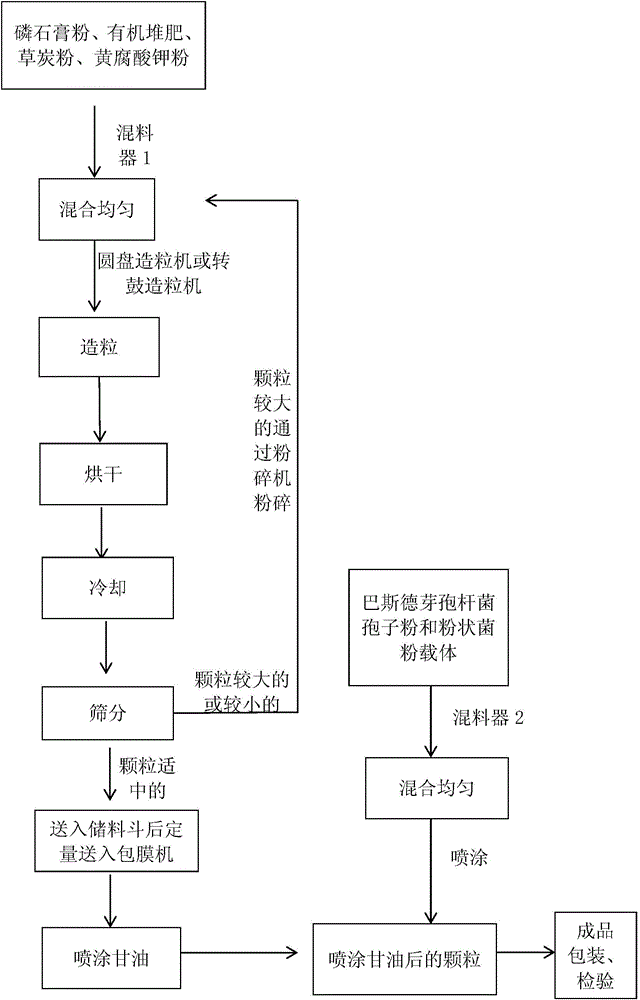
ActiveCN103951532AIncrease the granular structureIncrease organic matterFertilizer mixturesArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiPotassium
The invention relates to a compound soil remediation agent containing microorganism bacteria and a preparation method thereof. The remediation agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0.01-3 parts of bacillus pasteurii spore powder, 5-50 parts of phosphogypsum powder, 10-60 parts of organic compost, 5-50 parts of turf powder, 1.5-5 parts of potassium fulvate powder, 0.2-0.5 part of powdery bacteria powder carriers and 0.15-1 part of glycerin. The remediation agent has round and smooth grains and high grain hardness, is harmless to seeds, can serve as a base fertilizer together with other fertilizers, can be sown together with seeds, integrates multiple remediation functions including organic complexation and passivation remediation, inorganic passivation remediation, microorganism passivation remediation and the like, has a comprehensive and strong soil remediation function, and can stimulate growth and reproduction of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at the roots of crops, accelerate heavy metal passivation, stimulate crop growth and enhance the immunities of crops.
Owner:安徽莱姆佳生物肥业有限公司
Reproduction method of Chinese cymbidium seedlings
InactiveCN101983554AShort reproductive cycleSpeed up breedingSymbiotic/parasitic combinationsHorticulture methodsMycorrhizaSeedling
The invention discloses a reproduction method of Chinese cymbidium seedlings, belonging to an orchid seedling reproduction technology, in particular to a reproduction technology for raising seedlings by tissue culture and mycorrhizal fungi intergrowth culture. In the reproduction method of the Chinese cymbidium seedlings, seedling acquisition mainly comprises the steps of seed germination, protocorm successive proliferation and rhizogenesis culture. The reproduction method of the Chinese cymbidium seedlings is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out hardening on rooted seedlings and the process of mycorhiza on mycorhiza fungi after the seedlings are obtained. By adopting the mycorhiza culture technology of sterile germination and mycorhiza fungi intergrowth of Chinese cymbidium seeds, the invention has the advantages that excellent variety can be bred, excellent Chinese cymbidium plants can be selected from the seedlings, the Chinese cymbidium breeding speed can be rapidly improved and the defects that pure tissue culture seedlings grow slowly, have long period and even do not bloom can be overcome, thus the invention has an important utilization value on large-area industrial reproduction for the Chinese cymbidium.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Novel industrial breeding matrix
InactiveCN101948356APromote absorptionPreventing Soilborne DiseasesFertilizer mixturesPotassiumEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a novel industrial breeding matrix, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 13.8 to 14.2 percent of mycorrhizal fungi, 66 to 69 percent of turf, 3.4 to 4.6 percent of amino acid organic fertilizer, 6.9 to 8.1 percent of pearlite, 6.5 to 7.5 percent of vermiculite, and 0.25 to 0.48 percent of trianum. The mycorrhizal fungi, the trianum and the amino acid organic fertilizer are added into the traditional matrix, so that the breeding matrix can better promote crops to absorb nutrient elements, such as water, phosphorus, potassium, Zn, Cu and the like, and cultures high quality strong seedlings without germs and poisons, and has the advantages of high livability of the seedlings, short seedling stage of the seedlings, greater economic benefit, capability of saving cost of the seedlings and seeds.
Owner:上海农业科技种子有限公司 +2
Delivery systems for mycotechnologies, mycofiltration and mycoremediation
InactiveUS20050176583A1Promote decompositionEnhancing habitat recoveryBiocideFungiBiospherePlanting seed
The present invention utilizes fungal spore mass or hyphal fragments in landscaping cloths, fiber substrates, paper products, hydroseeders and agricultural equipment. The fungi may include saprophytic fungi, including gourmet and medicinal mushrooms, mycorrhizal fungi, entomopathogenic fungi, parasitic fungi and fungi imperfecti. The fungi function as keystone species, delivering benefits to both the microsphere and biosphere. Such fungal delivery systems are useful for purposes including ecological rehabilitation and restoration, preservation and improvement of habitats, bioremediation of toxic wastes and polluted sites, filtration of agricultural, mine and urban runoff, improvement of agricultural yields and control of biological organisms. The invention allow for a variety of methods and products including the use of cardboard boxes as a delivery system for fungi with or without the combination with plant seeds for starting gardens, for controlling insects, or for the process of ecological recovery.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
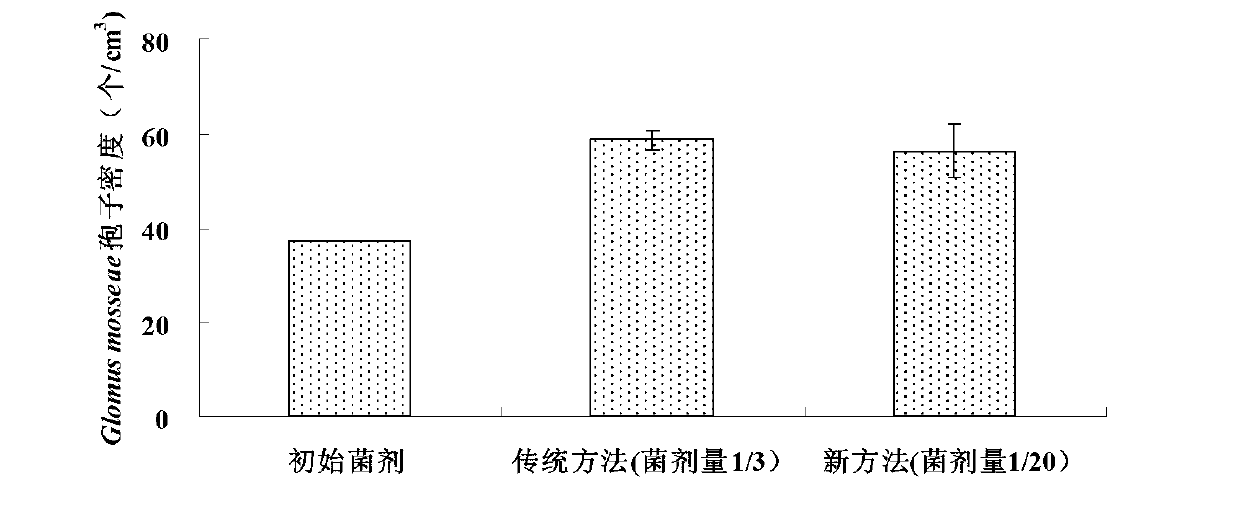
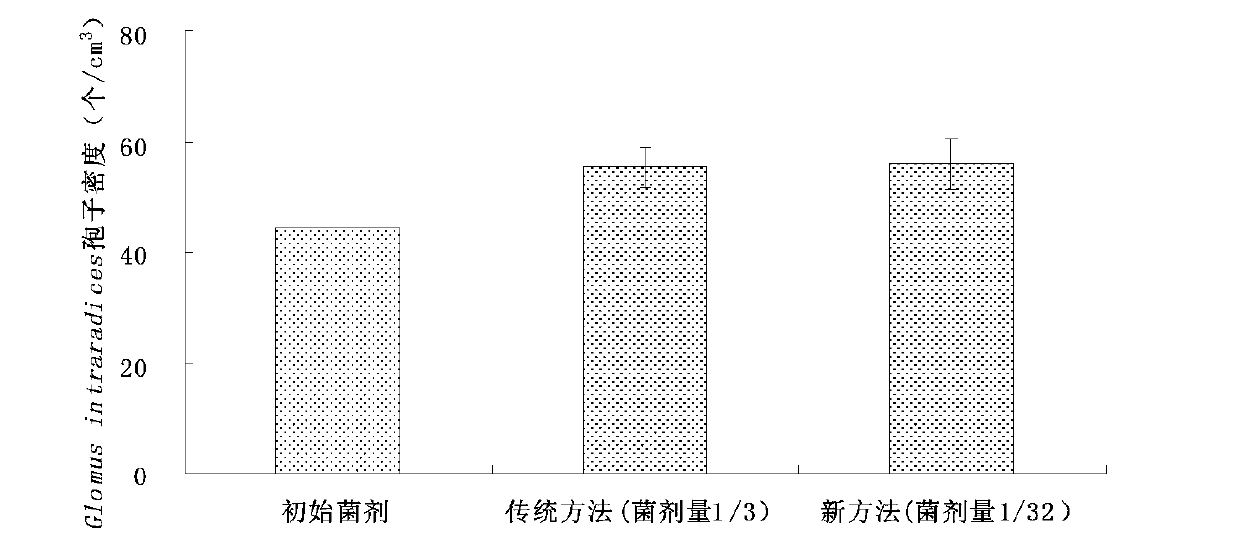
Large-scale propagation technology for mycorrhiza fungi inoculum
The invention discloses a high-efficient large-scale propagation technology for mycorrhiza fungi inoculum, and belongs to the field of bio-fertilizer productions. The high-efficient large-scale propagation technology suitable for mycorrhiza fungi includes material selection, production process, quality control and product formation. Materials for the technology are easy to obtain, operation is easy and convenient and cost is low. Spore density of the propagated mycorrhiza fungi inoculum can reach more than fifty per cubic centimeter, and can even reach more than one hundred per cubic centimeter, and propagation efficiency is more than four times higher as compared with conventional propagation technology efficiency. The device adopted in the technology is high in flexibility, easy to be regulated in real time and small in occupation. Detection of product quality of the mycorrhiza fungi and large-scale production thereof are facilitated. An AMF (abuscular mycorrhizal fungi) propagation technology, high-efficient and prone to large-scale production, formed in the technology, is beneficial to application of the AMF in agricultural production, and new approaches for sustainable development for agriculture are provided.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Facility vegetable mycorrhiza production method
InactiveCN1843073AImprove utilizationImprove efficiencyCultivating equipmentsChemicalsDiseasePlant disease
The invention relates to a method for producing protective vegetable fungus root sprout, comprising the following steps: 1) planting susceptive crop after inoculating the bush AMF for sterilized organic soil or soil, taking the strand roots of plant or fungus root spore as inoculating bacteria; 2) sterilizing seedling soil or medium; 3) loading the sterilized soil into dish, spraying the inoculating bacteria onto soil, 4) sowing on the dish, then covering with sterilized soil for seedling in greenhouse. The invention is characterized by the low cost, good popularity and simple operation. The bacteria can on one side increase the usage of nutrient and water and fertilizer under organic cultivating condition, which results in productivity and quality improvement of vegetable; on the other side can strengthen the disease and drought resistance, reduce disease spread through soil and improve vegetable root condition.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Blueberry mycorrhizal fungi (coprinus micaceus) and separation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102220246AHarm reductionReduced low pH requirementsBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismFruit set
The invention relates to a blueberry mycorrhizal fungi (coprinus micaceus) and a separation method and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of microbiology, and mainly relates to a mycorrhizal fungi which separated from a Changbai Mountain wild cowberry root system for blueberry inoculation and application of the mycorrhizal fungi at promoting the growth of blueberry and improving the yield of the blueberry. The blueberry mycorrhizal fungi is preserved in the Chinese General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the classification name is Coprinus micaceus. By the application of the mycorrhizal fungi, the growth of the blueberry root system can be promoted. The invention has the advantages that the yield, fruit setting rate and insect damage prevention function can be improved, and the like.
Owner:LIAONING ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for improving phytoremediation efficiency of low-concentration arsenic-contaminated soil
InactiveCN101704015APromote repairPromote growthContaminated soil reclamationHorticulture methodsArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiPhytoremediation
The invention discloses a method for improving the phytoremediation efficiency of low-concentration arsenic-contaminated soil, which comprises the steps of: planting corns in an arsenic-contaminated farmland, inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and earthworms, pulling up the corns with roots after the growth season of the corn is over, harvesting the corns wholly, and performing centralized treatment. The method fully exploits the potentials of arsenic remediation of plants, microorganisms and animals, and inoculates the AM fungi and the earthworms to promote the plant absorption and dissipation of arsenic by promoting the growth of the plants, improving the activity of phosphatase of the soil and activating the arsenic in the soil to further achieve the aim of improving the phytoremediation efficiency of the low-concentration arsenic-contaminated soil. The method combines the microorganisms, the animals and the plants together for the in-situ remediation of the arsenic-contaminated farmland, has simple and convenient operation and friendly operating environment, cannot cause secondary pollution, reduces the treatment cost, and has good environmental effect.
Owner:吴江市土壤肥料技术指导站
Method for using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic fertilizer to reduce residue of lead and cadmium in tobacco
InactiveCN102577826AReduce poisonPromote growthHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
A method for using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic fertilizer to reduce residue of lead and cadmium in tobacco includes: preparing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculant, culturing mycorrhizal tobacco seedlings, and transplanting and managing the mycorrhizal seedlings. Tests show that arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and cow dung added to soil coordinate to promote plant growth, increase phosphorus content of vegetation, lower poison and pollution of tobacco by lead and cadmium and promote tobacco growth, thereby reducing the residue of lead and cadmium in the tobacco.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for locally culturing and producing arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus biological agent fertilizer in farmlands
InactiveCN101805216AEasy to obtainEasy to trainClimate change adaptationOrganic fertilisersArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiCulture mediums
The invention provides a method for locally culturing and producing arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus biological agent fertilizer in farmlands. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, preparing a farmland culturing pond and a culture medium; 2, transplanting and culturing arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi; 3, absorbing and converting biological fertilizer; and 4, collecting biological fertilizer. Compared with the prior art, the technique adopted in the method has the advantages that: 1, the raw materials are readily available, the culture of the raw materials is easy, and the cost is low; 2, the culture technique and the production technique are conveniently popularized in rural areas; and 3, the production technique is green and environment friendly, which facilitates the development of modern agriculture. In addition, by using the fertilizer of the invention, the used amount of the quick-acting fertilizer is reduced and the used amount of partial fertilizer is reduced, so that the pollution to soil, water resources and air is lowered, and the fertilizer is particularly suitable to be used for planting seedlings of farm crops and medicinal plants. Tests show that the yield of the farm crops cultured by using the fertilizer of the method is improved by over 50 percent compared with that of the farm crops cultured by using the common fertilizer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for repairing farmland soil polluted by cadmium through using combination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and sedum plumbizincicola
InactiveCN104604386APromote absorptionImprove repair effectSoil-working methodsArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiSoil heavy metals
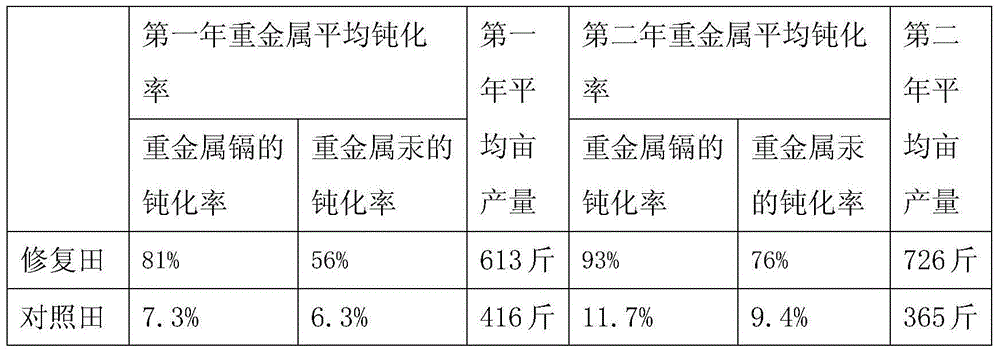
The invention discloses a method for repairing farmland soil polluted by cadmium through using a combination of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and sedum plumbizincicola. The method comprises the steps that expanding propagation is conducted on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculant, and repair is conducted through inoculating the farmland soil with the inoculant to strengthen the sedum plumbizincicola. According to the method for repairing the farmland soil polluted by the cadmium through using the combination of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and the sedum plumbizincicola, it is proved in the experiment that in the mode of normal field management, the growth of the sedum plumbizincicola can be promoted through inoculating the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculant, repair on the cadmium of the soil by the sedum plumbizincicola is improved, and the total amount of the extraction of the cadmium can be increased by 75% to a maximum.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiple microbial manure applied in summer to increase quality of black tea and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a multiple microbial manure applied in summer to increase quality of black tea. The microbial manure is fermented from the following raw materials by weight: amino selenium or / and amino zinc, a water-soluble carbon source and nitrogen source, and a mixed microbial solution of Bacillus subtilis and VA mycorrhizal fungi. According to analysis, the multiple microbial manure contains a large amount of enzymes (alpha-amylase, neutral protease) required for physiological and biochemical reactions during growth and development of tea tree, biotin, interferon, amino acids and other factors beneficial for life activity. These factors ensure strong growth of tea plants in summer, and resist disease, insect and drought, and realize strong root absorption function, high photosynthetic efficiency, UV resistance, resistance to formation and accumulation of anthocyanin in fresh leaves, so as to improve the quality of black tea.
Owner:梁树森
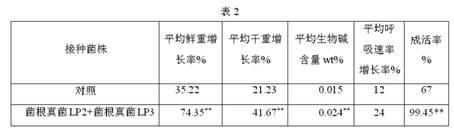
Method for culturing, planting and mycorrhizal production of dendrobium officinale kimura et migo
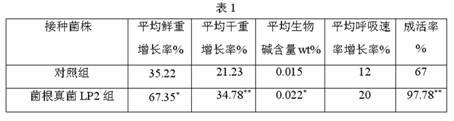
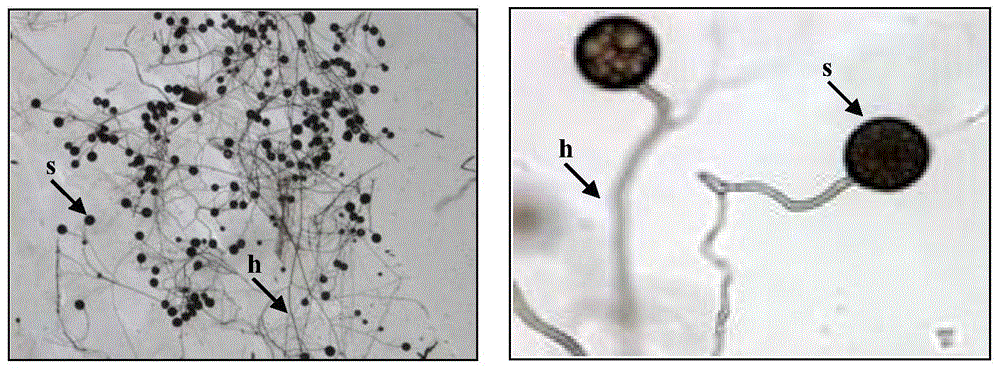
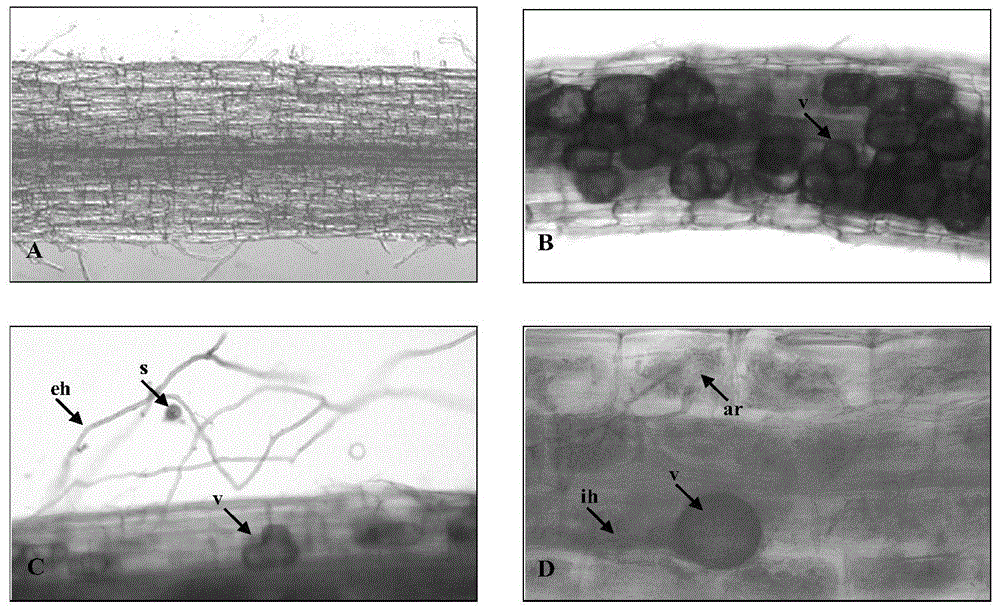
InactiveCN102150615AGuarantee the quality of medicinal materialsIncreased fresh weightFungiMicroorganism based processesDry weightNutrient solution
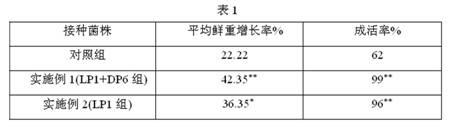
The invention relates to a method for culturing, planting and mycorrhizal production of dendrobium officinale kimura et migo, comprising the following steps of: (1) culturing mycorrhizal fungi by utilizing a solid or liquid culture medium, wherein the mycorrhizal fungi are mycorrhizal fungi LP2 deuteromycotina Fusariumsp, mycorrhizal fungi LP3, or mixed strain deuteromycotina Verticilliumsp of the mycorrhizal fungi LP2 deuteromycotina Fusariumsp and the mycorrhizal fungi LP3; (2) culturing tissue culture seedlings of the dendrobium officinale kimura et migo; (3) preparing a nutrient solution; (4) carrying out water culture and training the tissue culture seedlings; and (5) carrying out planting and mycorrhizalculturing of the dendrobium officinale kimura et migo. The method for culturing, planting and mycorrhizal production of the dendrobium officinale kimura et migo, provided by the invention, can promote growth of dendrobium officinale kimura et migo seedlings obviously; and compared with a contrast plant, the dendrobium officinale kimura et migo cultured by inoculating pathogen has increased rooting numbers, high survival rate, longer plant length, better growth vigor, obviously expanded internodes, obviously big stems, improved fresh weight and dry weight and obviously enhanced stress resistance of a pathogen-inoculated plant.
Owner:梁经军
Separation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as well as preparation and application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide
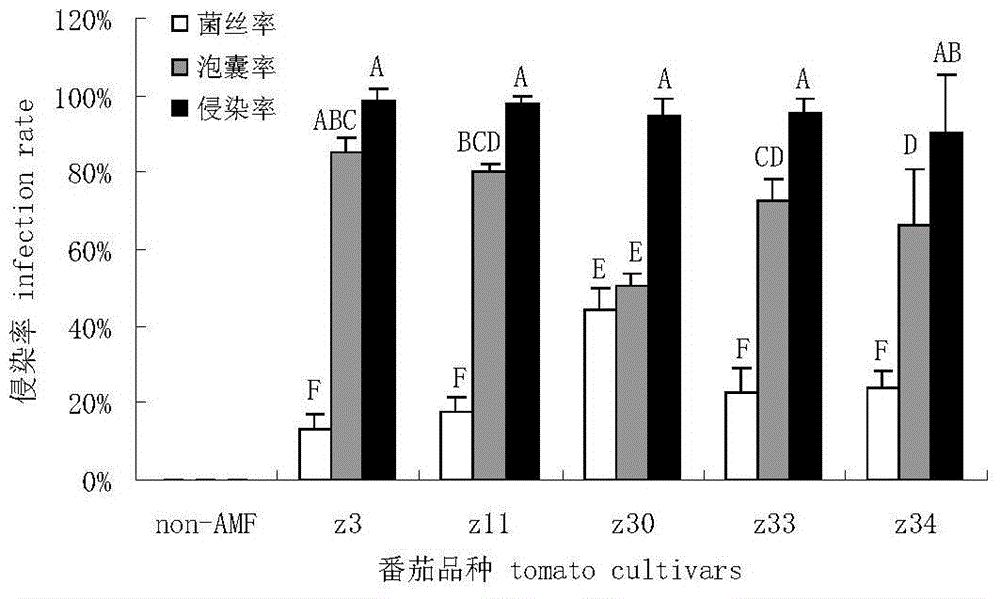
The invention discloses separation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as well as preparation and application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi rhizophagus irregularis which is called arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi rhizophagus irregularis CD-1 and is separated from soils; a specific sequence of verifying ribosome 28S rDNA is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; by utilizing the fungicide prepared by the fungi, the height of strains, the number of petioles, the overground fresh weight, the overground dry weight, the root fresh weight and the root dry weight of tomatoes can be increased, and the mycorrhizal infection rate delta gt can be obviously prompted; 80 percent of corns are high in selfing line strains and heavy in overground fresh weight and overground dry weight; the resistance to banded sclerotial blight by the corns is improved, and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi has an extremely-high genetic use value.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore
ActiveCN101565689ALow costLow nutritional requirements for growthMicroorganism based processesSpore processesBiotechnologyMicrobial culture technique
The invention discloses a production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore, which belongs to the technical field of microorganism culturing, and comprises the following technical steps of: 1) culturing carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA; 2) culturing the carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA and glomus intraradices together in an improved synthetic culture medium; 3) taking a culture containing the root, hypha and spore infected by the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and transplanting the culture to a special culture box for culturing; 4) collecting the spore and mycelium; and 5) storing the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore. Compared with the prior art, the production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore has the advantages that: 1, the culture medium is an asepsis environment with low cost, which not only can meet the growing of a host plant, but also is suitable for the growing of AM epiphyte; 2, the nutrition requirements for the growing of the host plant are low and the host plant can grow and be cultured on the synthetic culture medium; 3, the spore cultured by the method is a non-pollution pure culture; and 4, the produced spore is stored in liquids and the activity can be maintained by above 90 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Living systems from cardboard packaging materials
InactiveUS20080005046A1Effect shipping rateCost-effectiveData processing applicationsPackagingCardboardLiving systems
Compositions, methods and business applications of using new and recycled cardboard infused with a plurality of saprophytic (including endophytic) and mycorrhizal fungi matched with seeds of plants (including trees, vegetables, herbs and grasses) whereby the cardboard can be sprouted by end-users to start ecosystems. Such containers may have carbon-credit value for companies and consumers when planted and grown as a carbon sink or carbon offset for the photosynthetic and mycelial sequestration of carbon dioxide. The relative weight of the Life Box's added seeds and spores does not significantly affect the total weight of the infused cardboard, thus not increasing transportation costs.
Owner:TURTLE BEAR HLDG LLC
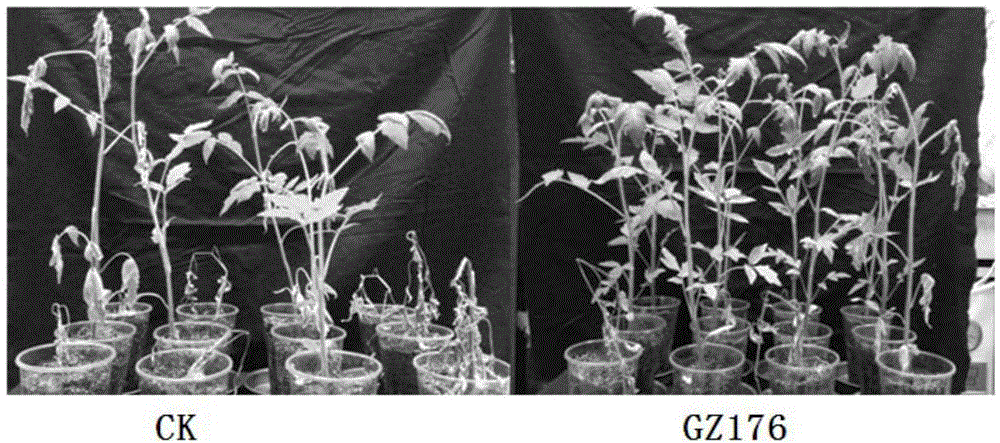
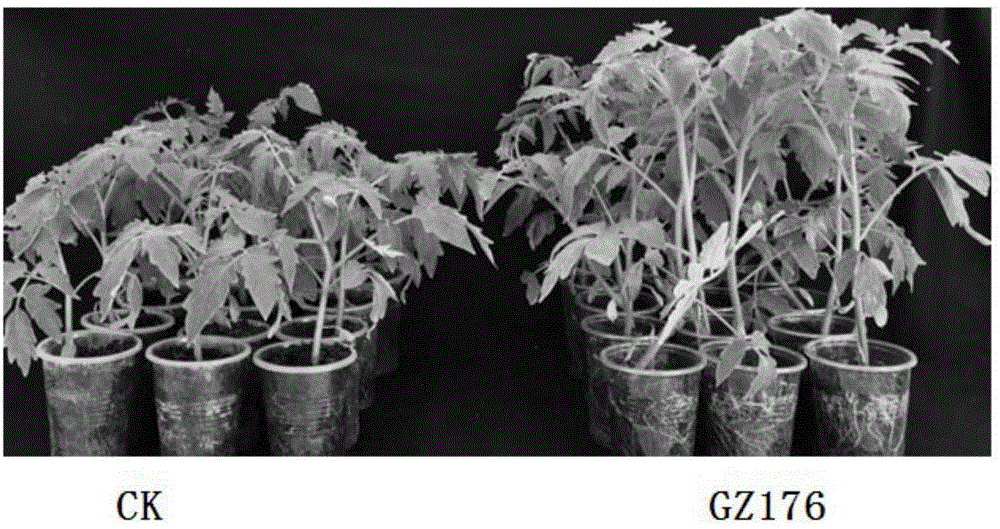
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176 for disease prevention, growth promotion and adverse resistance of herbaceous plants and microbial inoculums and application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176
The invention discloses arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176 for disease prevention, growth promotion and adverse resistance of herbaceous plants and microbial inoculums and application of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176. The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176 is rhizophagus intraradices and can be made into powder with concentration being 40-60 spores per gram, herbaceous plant disease prevention rate is up to 71.3% after the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi GZ176 powder is subjected to seed dressing under normal management conditions of greenhouses, and herbaceous plant growth promotion rate is higher than 16.19%; in the field, disease prevention and control rate reaches 75.27%, and yield increasing rate exceeds 36.17%; adverse resistance of the herbaceous plants can be improved remarkably.
Owner:南京本源生态农业科技有限公司
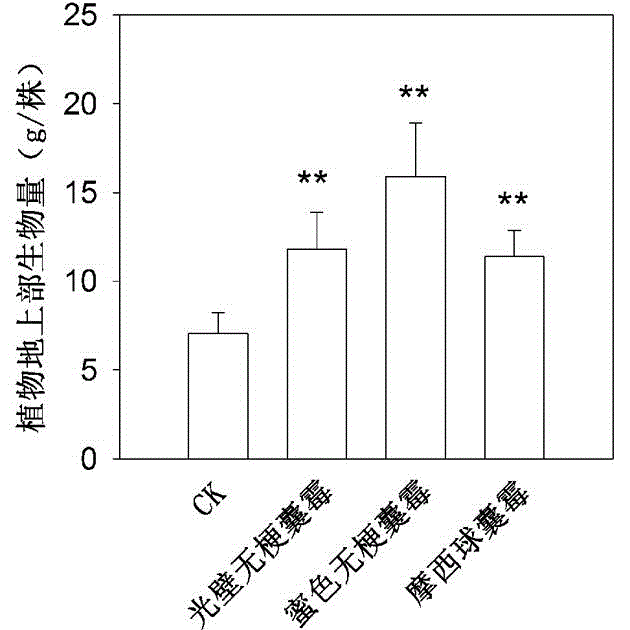
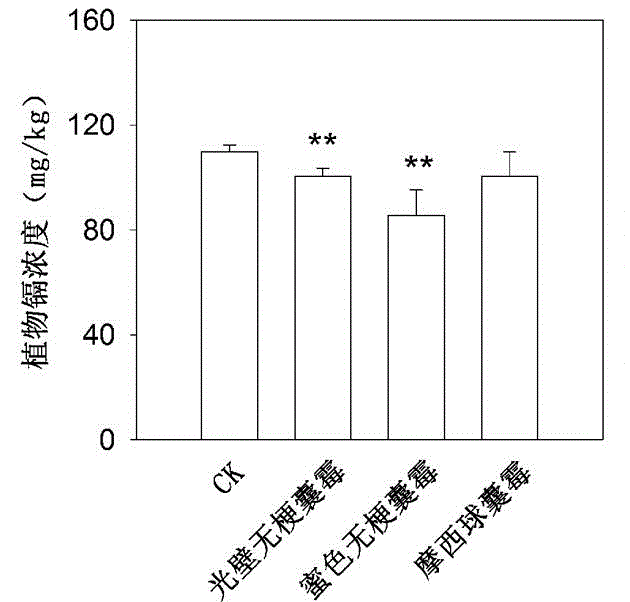
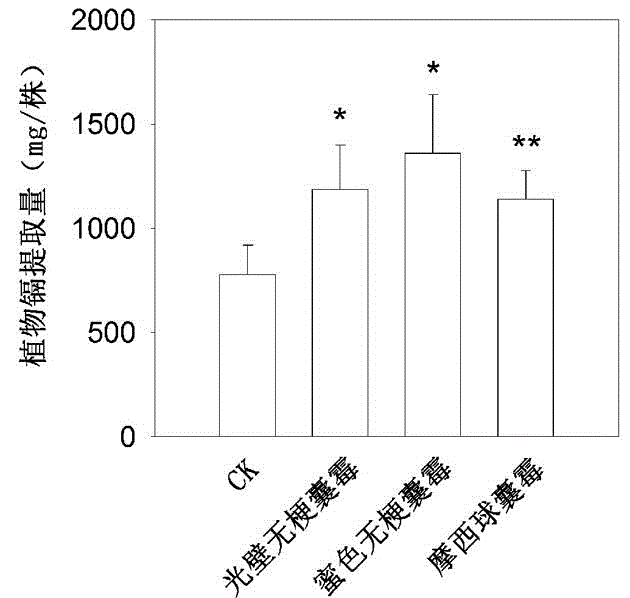
Repair method for cadmium polluted soil by arbuscular mycorrhiza-alfalfa symbiont
InactiveCN108555019ADoes not change the inherent physical and chemical propertiesImprove bindingContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersArbuscular mycorrhizal fungiBioremediation
The invention discloses a repair method for cadmium polluted soil by an arbuscular mycorrhiza-alfalfa symbiont. The repair method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing an arbuscular mycorrhizafungi fungicide; S2, treating alfalfa seeds; and S3, inoculating the arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi fungicide to the surface sol layer of the cadmium polluted soil; then planting the alfalfa seeds for field management; and after growth, harvesting plant materials, airing and transferring the plant materials, and incinerating the plant materials in a centralized manner to repair the cadmium polluted soil. By combining a microbial repair technology with a plant repair technology, the repair method solves the problem that the repair method is prevented from being popularized and applied on a large scale as a green repair technology because the microbial repair speed is slow, the responding time is long and the soil environmental requirement is high, is low in cost by plant repair, good in comprehensive ecological benefit, suitable for being popularize on a large scale and the like, and has the characteristics of being economical and convenient to repair microbially, not changing the inherentphysical and chemical properties of soil and the like. The obtained repair method is high in treatment capacity, economic, convenient and suitable for being popularized on a large scale.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com