Microbial agent and soil modifying agent produced by fermentation thereof
A microbial agent and soil improvement technology, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of insufficient microbial compounding ability, difficulty in adapting to large-scale commercial production, deviation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The production of embodiment 1 microbial bacterial agent
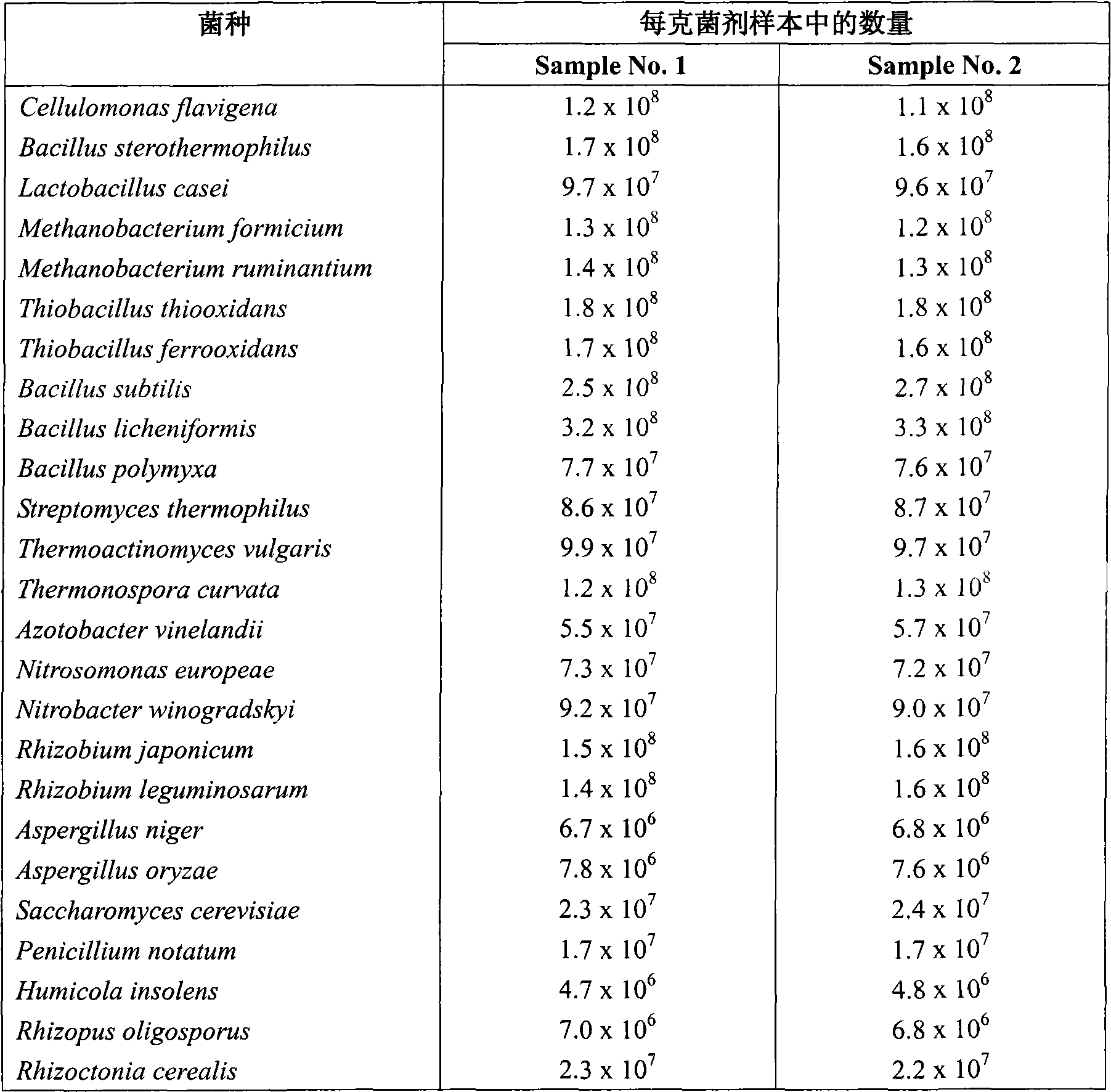
[0048] In this embodiment, the following strains are used to prepare microbial agents: (1) Cellulomonas flavigena, (2) Bacillus sterothermophilus, (3) Lactobacillus casei , (4) Methanobacterium formicium, (5) Methanobacterium ruminantium, (6) Thiobacillus thiooxidans, (7) Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, (8) subtilis Bacillus subtilis, (9) Bacillus licheniformis, (10) Bacillus polymyxa, (11) Streptomyces thermophilus, (12) common high temperature actinomycetes ( Thermoactinomyces vulgaris), (13) Thermomonospora curvata (Thermonospora curvata), (14) Azotobacter vinelandii, (15) Nitrosomonas europeae, (16) Nitrobacter winogradskyi), (17) Rhizobium japonicum, (18) Rhizobium leguminosarum, (19) Aspergillus niger, (20) Aspergillus oryzae, (21) Saccharomyces cerevisiae ), (22) Penicillium notatum, (23) Humicola insolens, (24) Rhizopus oligosporus, (25) Rhizoctonia cerealis. The above strains can be cultivated according t...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The production of embodiment 2 soil conditioners
[0052] Get water content and be 65% (weight ratio) cow dung (insufficient water content can add water) and the rice bran that the particle after pulverizing is less than 5mm mixes and pulverizes with the mass ratio of 85: 15, makes the cow dung after mixing and rice bran There is no agglomeration above 40mm.
[0053] Then, the mixture of 1 ton of above-mentioned cow dung and rice bran is mixed with the microbial inoculant produced in 2kg of Example 1, and heaped into the fermenter to form a compost heap. During the compost heap placement period, along with the fermentation process, the compost heap can naturally heat up. This fermentation heating process usually takes 2-3 days, and the compost heap can be turned 1-2 times during this period. Then, when the temperature of the compost heap rises to 65°C, turn on the turner to turn the compost heap to dissipate the heat generated by fermentation to ensure that the tempera...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The effect of embodiment 3 soil conditioner application
[0056]The soil improver produced by the same method as in Example 2 has been applied to the main grain producing areas of my country's Heilongjiang since 2004 to plant rice, wherein 100-150kg is applied per mu. According to several years of continuous follow-up testing, it is found that the soil fertility has been continuously improved, and the quality of rice has also been continuously improved (see Table 3.1). In 2004, pesticide residues had been completely eliminated; by 2008, the content of heavy metals such as cadmium and arsenic and fluorine in soil and rice had dropped by more than 50% compared with before application, and heavy metals such as lead and mercury had also decreased significantly compared with before application. The protein content of rice is also significantly improved. At the same time, we commissioned the National Grain Bureau Scientific Research Institute to detect that compared with the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com