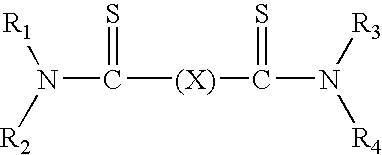
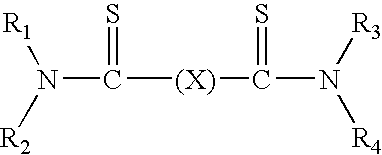
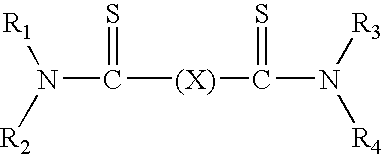
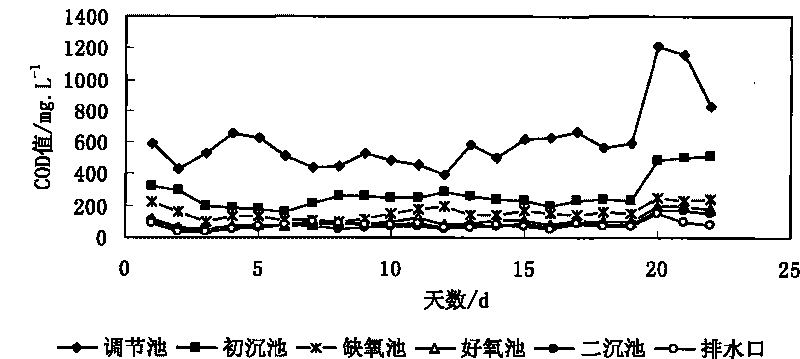
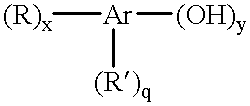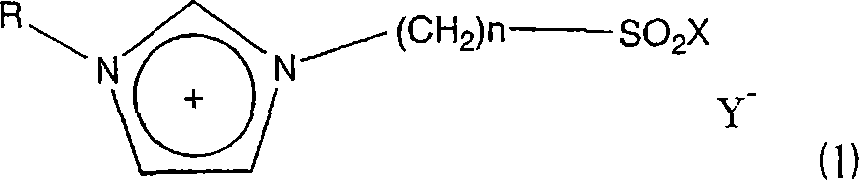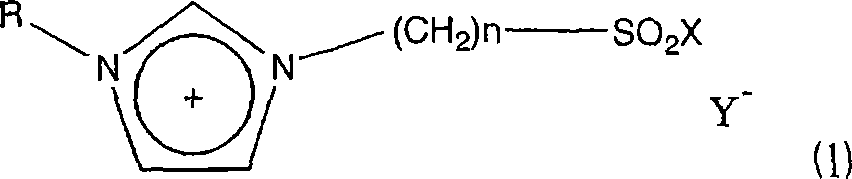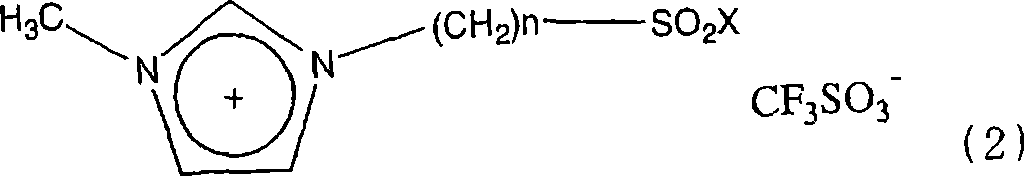Patents
Literature
3998 results about "Nitration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
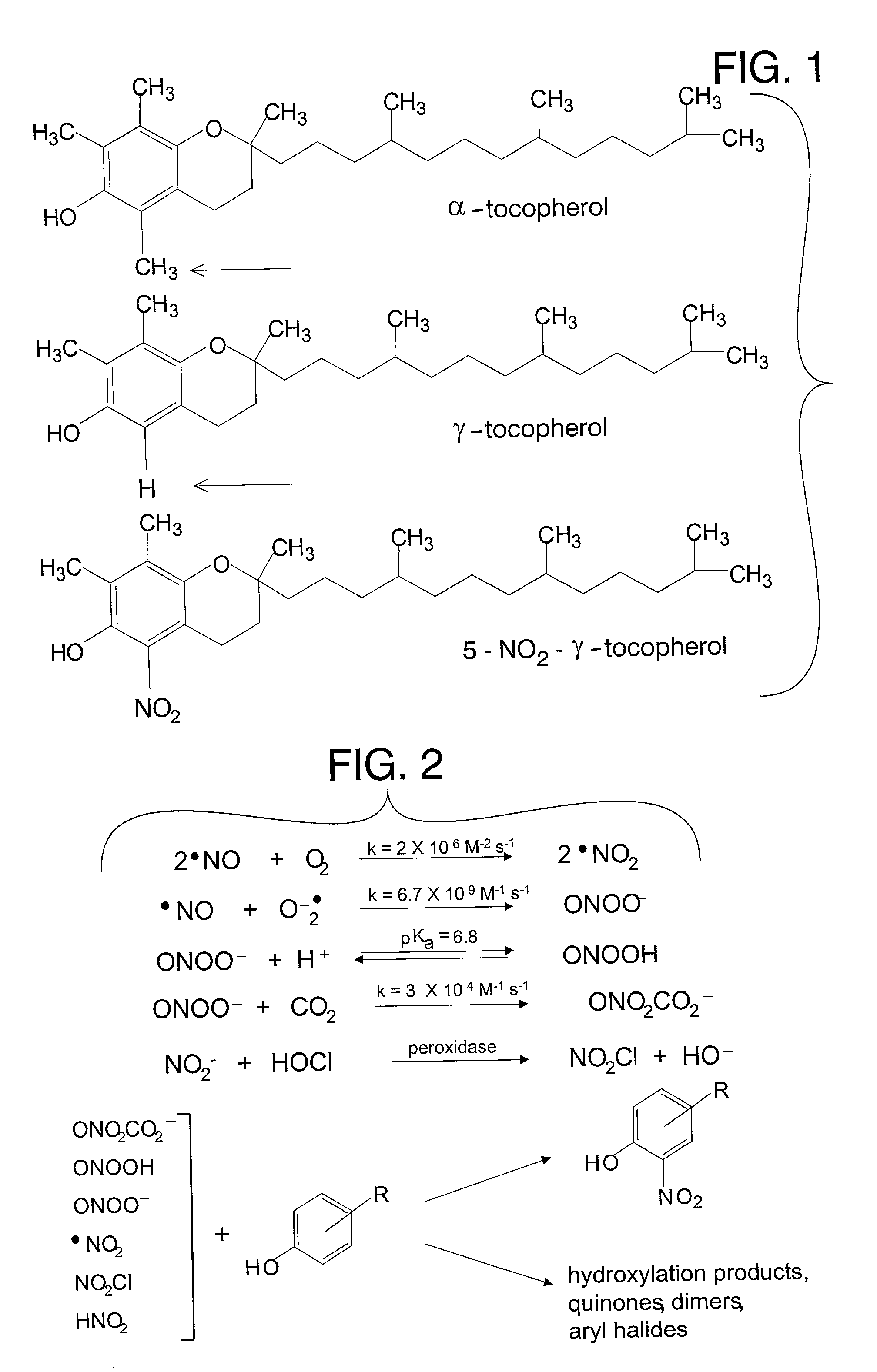
Nitration is a general class of a chemical process for the introduction of a nitro group into an organic chemical compound. More loosely the term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols and nitric acid, as occurs in the synthesis of nitroglycerin. The difference between the resulting structure of nitro compounds and nitrates is that the nitrogen atom in nitro compounds is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom, typically carbon or another nitrogen atom, whereas in nitrate esters, also called organic nitrates, the nitrogen is bonded to an oxygen atom that in turn usually is bonded to a carbon atom (nitrito group).
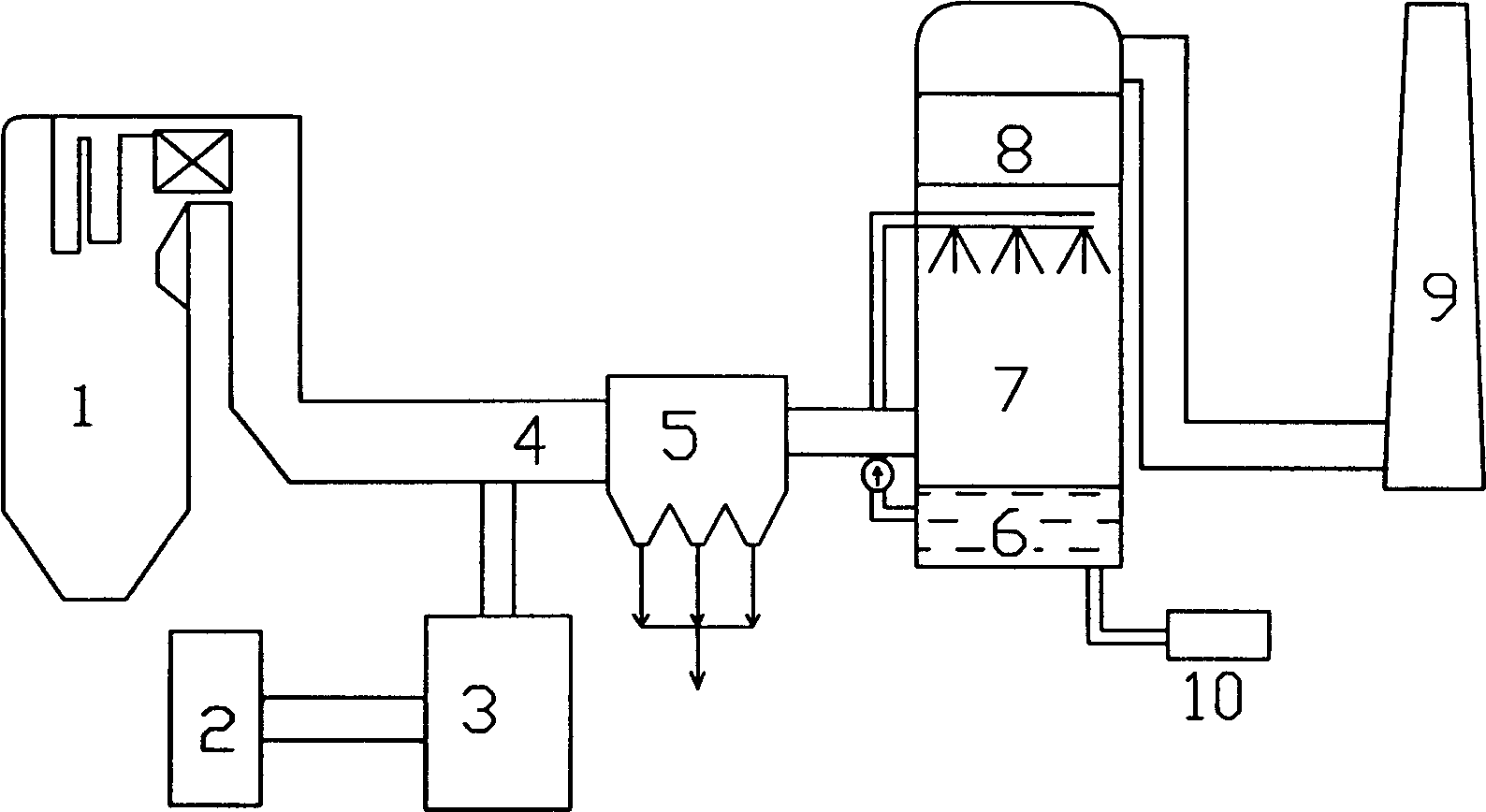
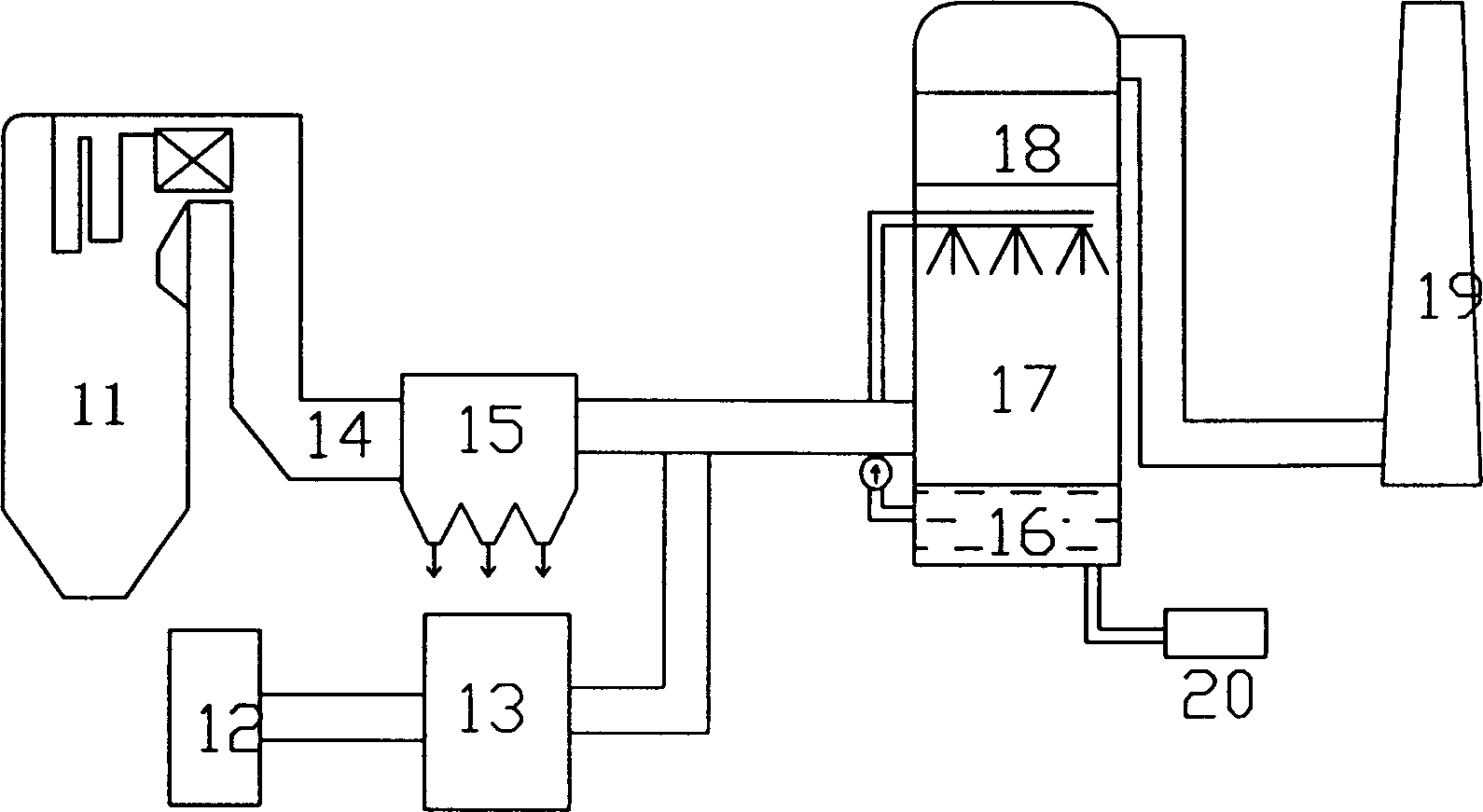
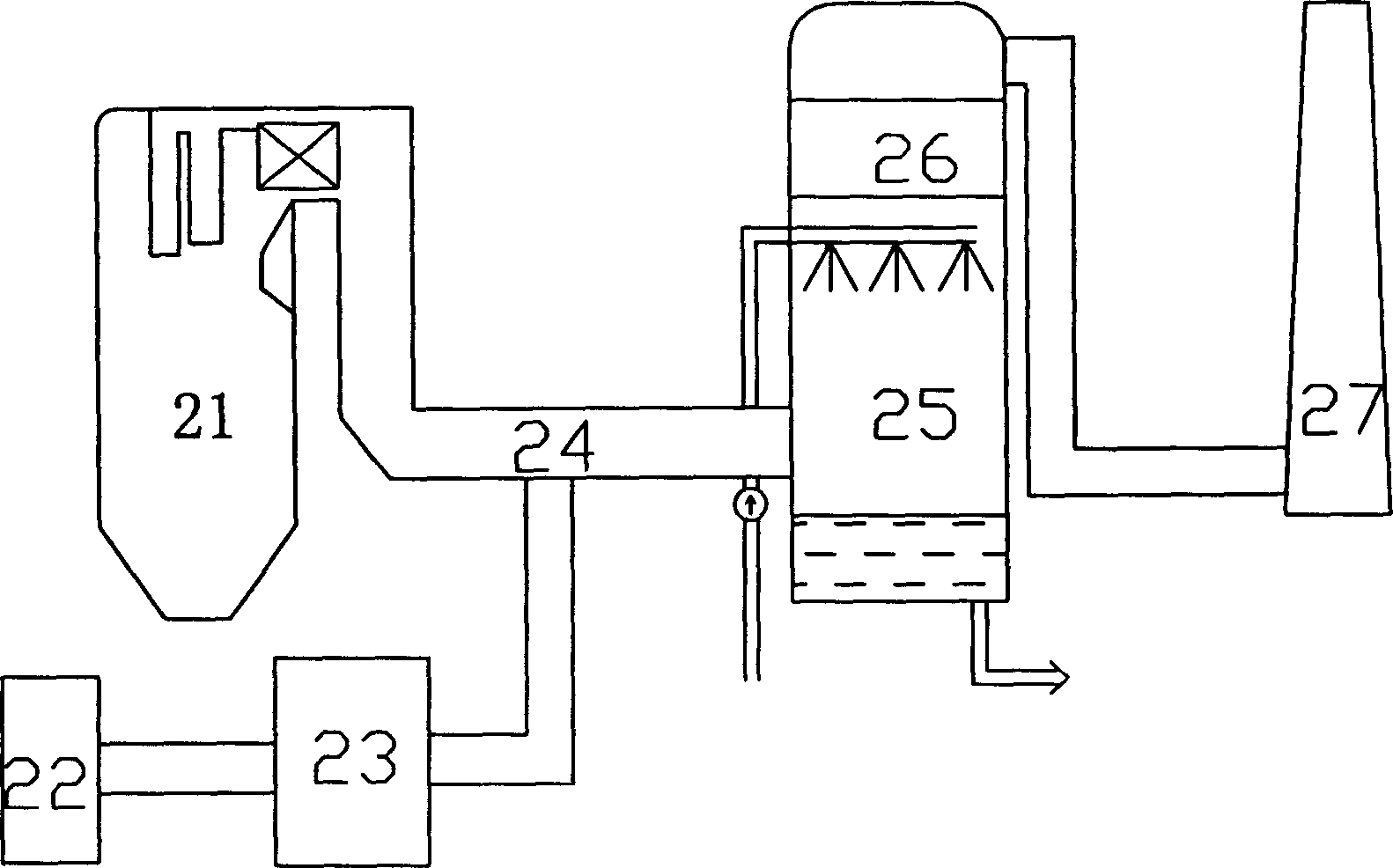
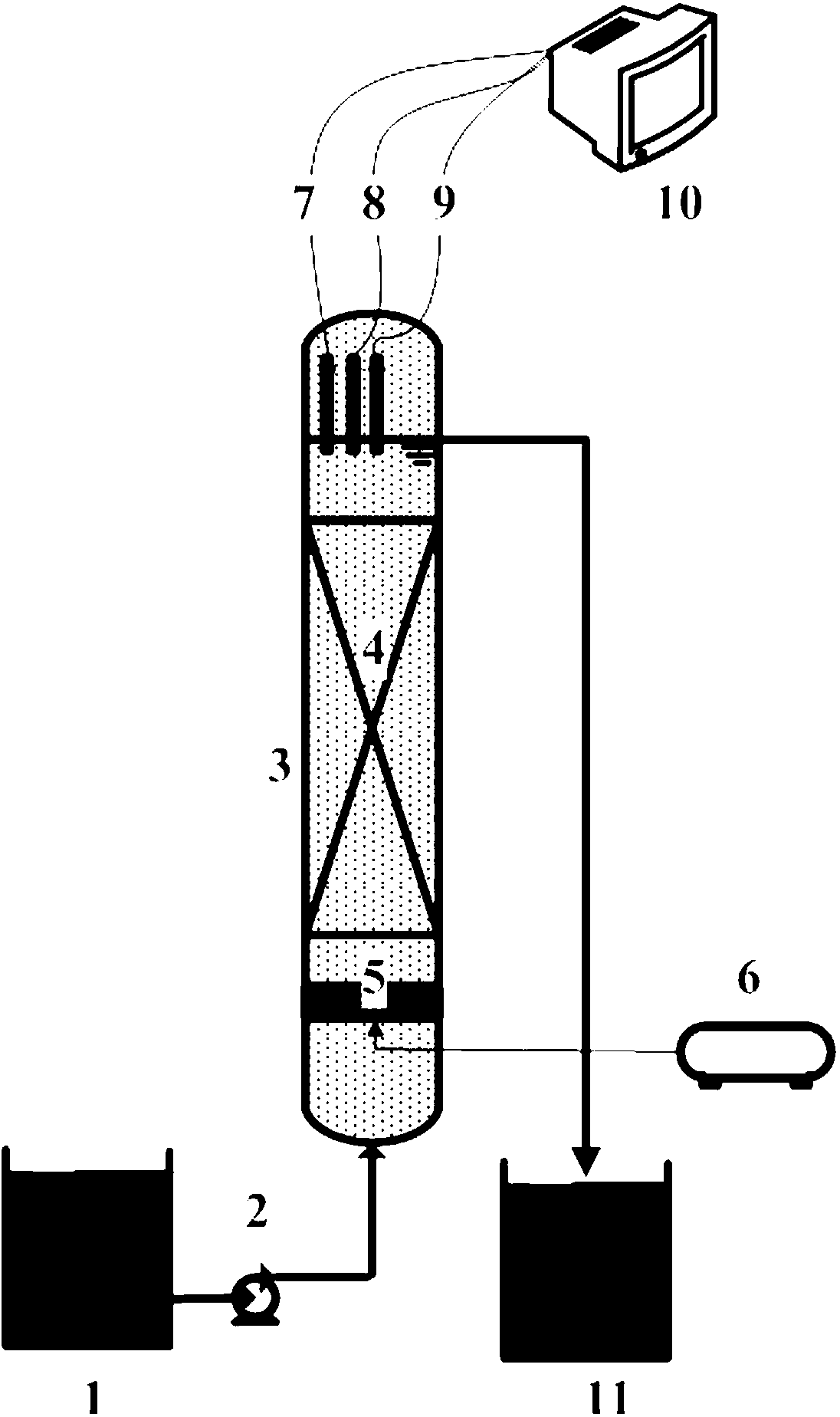
Ozone oxidation and denitration method of boiler flue gas
The invention provides a method for processing de-nitration on the boiler smoke, belonging to the environmental protective technique. The method comprises: ejecting ozone O3 into the low-temperature section of smoke channel of boiler whose temperature ranges from 110-150Deg. C; oxygenizing the nitric oxide NO into high-state nitrogen oxide as NO2, NO3 or N2O5; washing the smoke with alkali liquor to remove the nitrogen oxide in the smoke. Compared to other de-nitration method, said invention has higher efficiency, lower cost, and non-secondary pollution, while the absorption effect combined with alkali liquor can reach more than 80%. In addition, the invention can apply variable boiler devices, which is not relative to the burning condition of boiler.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Long life medium and high ash oils with enhanced nitration resistance
InactiveUS6191081B1Prolong lifeReduce viscosity increaseOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationNitrationBase oil
A long life lubricating oil as evidenced by a reduction in viscosity increase, oxidation and nitration, comprises a major amount of a base oil of lubricating viscosity and a minor amount of a mixture of high TBN, medium TBN and low / neutral TBN detergents wherein metal salicylate detergent is at least one of the medium or low / neutral TBN detergents.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Group III nitride semiconductor substrate and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20060046325A1Reduce defect densityLittle warpingPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrationTitanium
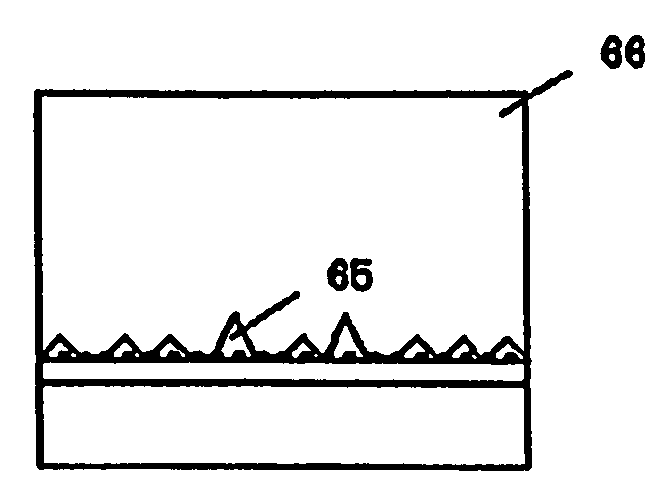
The present invention provides a group III nitride semiconductor substrate with low defect density as well as small warp and a process for producing the same; for instance, the process according to the present invention comprises the following series of steps of: forming a metallic Ti film 63 on a sapphire substrate 61, followed by treatment of nitration to convert it into a TiN film 64 having fine pores; thereafter growing a HVPE-GaN layer 66 thereon; forming voids 65 in the HVPE-GaN layer 66 by means of effects of the metallic Ti film 63 and the TiN film 64; and peeling the sapphire substrate 61 from the region of the voids 65 to remove it therefrom.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Aerobic denitrifying Paracoccus denitrificans and application thereof
ActiveCN102465104ABiologically active and stableImprove denitrification effectBacteriaTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSynechococcusPyrococcus
The invention relates to aerobic denitrifying paracoccus denitrificans and application thereof. A bacterial strain provided in the invention is paracoccus denitrificans DN-3CGMCC No. 3658; the Paracoccus denitrificans can carry out aerobic denitrification by using nitrate nitrogen under both aerobic and oxygen-limited conditions and can also carry out heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification by using ammonia-N, and a total nitrogen removal rate on above mentioned occasions is greater than 90%. The paracoccus denitrificans provided in the invention has stable hereditary features, isapplicable to treatment of a variety of nitrogen-containing waste water and produces a good nitrogen removal effect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
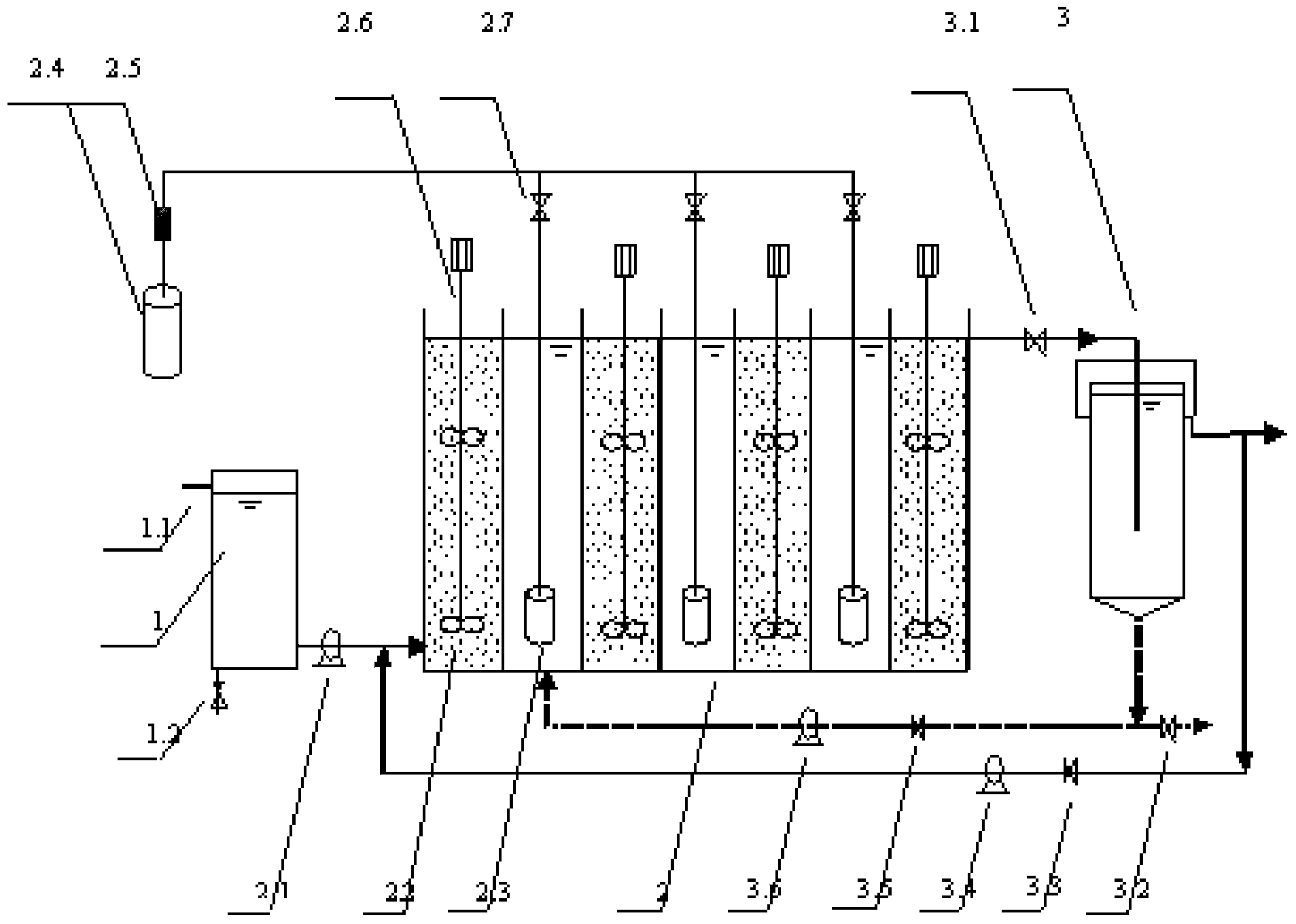
Operation mode and apparatus of short distance nitration-anaerobic ammoxidation batched biomembrane denitrogenation
InactiveCN1927739AToxic reductionControl the maximum cumulative concentrationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeElectron donor
One kind of short range nitrifying-anaerobic aminoxidizing sequencing batch type denitrifying biomembrane mode and plant is disclosed. The limited aerating mode with real-time control of the sewage temperature inside the reactor and high frequency alternation between aeration and anaeration can inhibit the growth of nitrite oxidizing bacteria and denitrifying bacteria so that the aminoxidizing bacteria and the anaerobic aminoxidizing bacteria become the dominant bacteria in the nitrifying and denitrifying stages. In the nitrifying stage, nitrification is stopped in the nitrite step; and in the denitrifying stage, ammonia nitrogen acts as the direct electron donor to reduce nitrite. The plant is provided with fixed spherical composite stuffing with spherical shell of polypropylene and filled inside biological composite material. Sectional discrete water feeding mode is adopted to feed the sewage to be treated in four stages into the reactor.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Release controlling fertilizer and its prepn
InactiveCN1417172AReduce lossesIncrease profitFertiliser formsFertilizer mixturesControl releaseOrganic solvent
The present invention relates to a controlled release fertilizer, especially, a new controlled release fertilizer and its production process. The controlled release fertilizer comprising coating of environmentally friendly material and fertilizer core, which is nitrous fertilizer containing urease inhibitor and / or nitration inhibitor. The production process includes fertilizer core preparation via spray granulating in fluidized bed, or spray granulating in rotating drum, or disc mixing granulating; and physical coating via spraying in fluidized bed. The fertilizer has good controlled release effect and wide application range, and is environmentally friendly and low in cost.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for undergoing chlorobenzene nitration reaction by using micro-channel reactor
ActiveCN102432471APrevent leakageAvoid dangerNitro compound preparationTemperature controlChlorobenzene
The invention relates to a method for undergoing a chlorobenzene nitration reaction by using a micro-channel reactor, belonging to the technical field of application of organic synthesis. In the method, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, water and chlorobenzene are taken as initial reaction raw materials, and processes such as mixed acid preparation, mixed acid and chlorobenzene preheating, mixed acid and chlorobenzene reacting and the like are completed in a micro-channel reactor system. In the reaction, nitro-sulfuric mixed acid is taken as a nitrating agent, the effective concentration of sulfuric acid in the mixed acid is 50-90 percent, the molar ratio of the nitric acid to the sulfuric acid in the mixed acid is 1:1-1:10, the molar ratio of the chlorobenzene to the nitric acid is 1:1.0-1:2.0, the reaction temperature is 50-100 DEG C, and the reaction time is 30-120 seconds. The chlorobenzene transformation ratio is up to 97 percent, the selectivity of nitrochlorobenzene serving as a product is over 96.5 percent, and the ratio of ortho-para nitrochlorobenzene is over 0.6. A strengthened mixed micro-channel reactor adopted in the invention is particularly suitable for undergoing a continuous nitration reaction, and has the characteristics of stable temperature control and safe process.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Organic biomass fractionation process
InactiveUS20030041982A1Economical and efficientLow costPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsWaste based fuelFractionationNitration
A method for fractionating fibrous biomass comprising cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin components to separate said lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose from one another comprises: (a) shredding said fibrous biomass; (b) concurrently with or subsequent to said shredding, contacting said biomass with an aqueous solution of a nitrate ion source at a concentration of about 0.1-0.3% at a temperature in the range of about 60° to about 80° C. to initiate nitration of the lignin component of said biomass; (c) submerging said partially nitrated biomass in an aqueous solution of a nitrate ion source in the presence of an aluminum compound at a temperature within the range of about 75-100° C. for a time sufficient to complete the nitration of said lignin component; (d) contacting the nitrated biomass produced in step (c) with an alkaline extraction liquor comprising NH4OH at an initial concentration sufficient to solubilize said nitrated lignin component and said hemicellulose component from said cellulose component of said biomass; e) recovering said cellulose from said extraction liquor containing said solubilized nitrated lignin and hemicellulose components, wherein said cellulose comprises at least about 88% alpha cellulose; (f) treating said extraction liquor with an acid to precipitate lignin contained therein, and (g) separating said lignin from soluble hemicellulose in said extraction liquor. The recovered cellulose component comprises at least 88% alpha cellulose and is useful as a starting material for the production of ethanol.
Owner:PRIOR ERIC S
Process for working up the waste water obtained in the preparation of dinitrotoluene
ActiveUS6936741B2Easy to transportReduce pointsLiquid degasificationOrganic compound preparationWash waterWastewater
The present invention relates to a process for working up or treating aqueous waste waters which are formed during the nitration of toluene to dinitrotoluene with nitrating acid. These aqueous waste waters containing acidic wash water and alkaline wash water from the dinitrotoluene washing step, and distillate from the sulfuric acid concentration step. The process comprises,a) combining the acidic and alkaline waste waters from the washing step and the aqueous distillate from the sulfuric acid concentration step such that the resulting mixture has a pH below 5,b) separating the aqueous and organic phases which are formed by phase separation,c) subjecting the aqueous phase from b) to an extraction step, whereind) the organic components contained in the aqueous phase from c) are extracted with toluene, ande) introducing the toluene phase enriched with the organic components into the toluene nitration.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
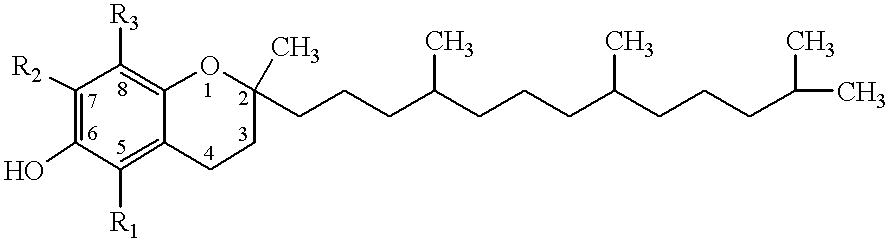
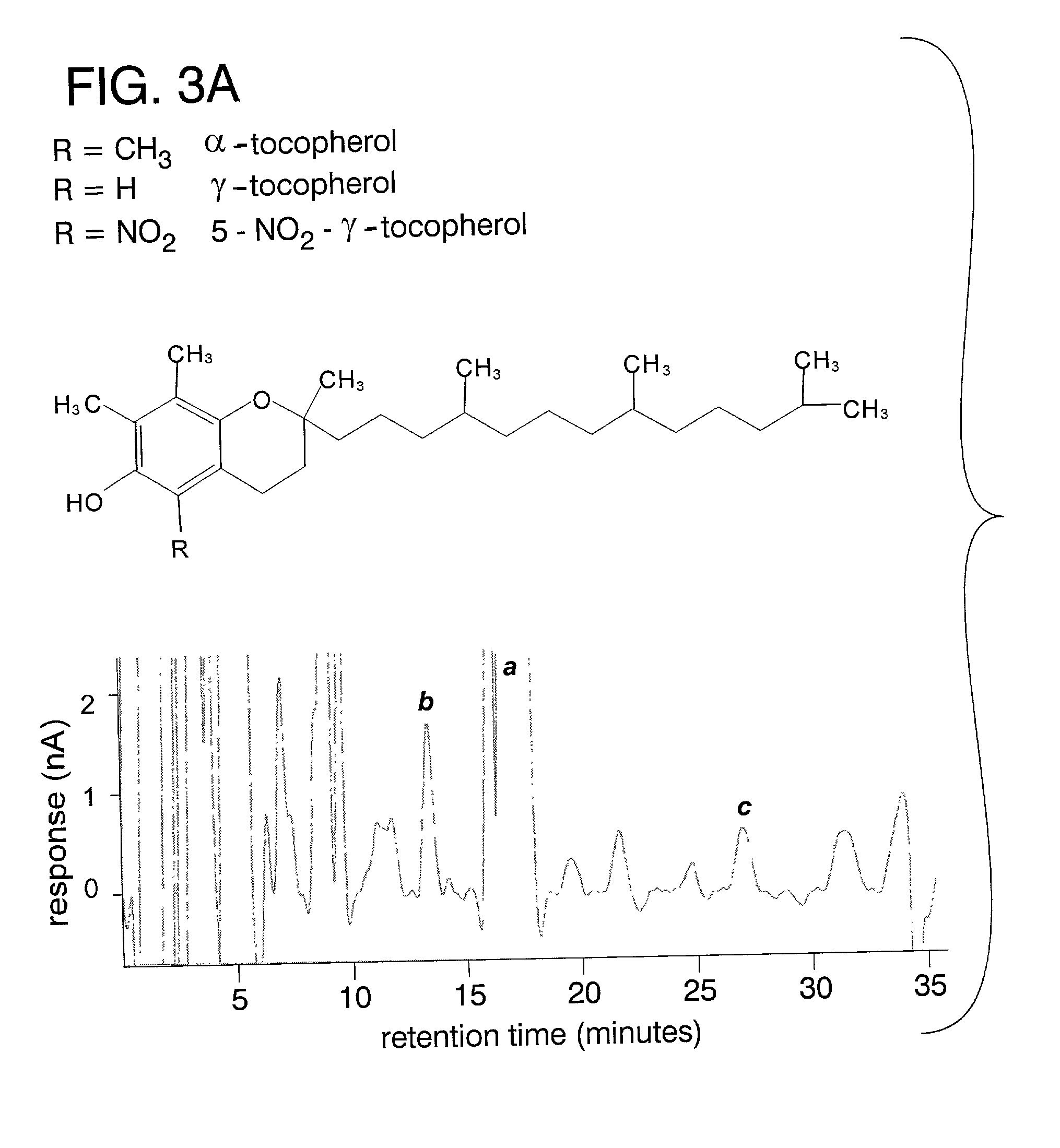
Desmethyl tocopherols for preventing or slowing degenerative neurological diseases
InactiveUS20020006954A1BiocideOrganic active ingredientsDegenerative neurologic diseasesParenteral nutrition
The present invention involves the use of desmethyl tocopherols such as gamma tocopherol for the prevention of and treatment of neurological disorders. Dietary or parenteral administration of desmethyl tocopherols inhibits the undesired nitration of neurological components.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
Device and method for denitrification of single stage autotroph in low-cellulose nitrate (CN) high-ammonia nitrogen waste water
ActiveCN102101720AAchieve separationEasy to controlTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesCelluloseSludge
The invention discloses a device and a method for denitrification of single stage autotroph in low-cellulose nitrate (CN) high-ammonia nitrogen waste water. The device comprises a raw water tank, a water inlet pump, a reactor, a secondary sedimentation tank and a sludge reflux pump, wherein overcurrent holes are arranged in the water flow direction of the reactor in an up-and-down alternative form and connected with various grid chambers, an anoxic zone grid chamber is arranged at the front end of the reactor, and an aerobic zone grid chamber is arranged at the back end of the reactor; the anoxic zone grid chamber is provided with a stirrer and an agitator blade; the aerobic zone grid chamber is provided with the stirrer, the agitator blade, an aeration riser pipe and an intermediate perforated clapboard; and the aeration riser pipe is internally provided with an aeration head, and sponge filling material is filled below the intermediate perforated clapboard, wherein filling ratio is 30-50%. In the method, shortcut nitrification is achieved above the aerobic zone through low dissolved oxygen (DO is 0.5 <-1>mg / L) and free ammonia (FA) inhibition so that ammonia nitrogen is converted to nitrite nitrogen; and anoxicammoxidation biomembrane acts on the lower part of the aerobic zone, the nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen are converted to nitrogen, thereby achieving denitrification of autotroph. The method has the advantages of low oxygen consumption, less sludge output and no extra carbon source.
Owner:彭永臻
Method for quick starting of anaerobic ammonium oxidation technology at room temperature in low matrix
ActiveCN102718314AReduce sheddingAvoid deathTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesStart timeSludge
A method especially for quick starting of anaerobic ammonium oxidation technology at room temperature in low matrix belongs to the field of urban domestic sewage treatment and regeneration. The method comprises firstly inoculating nitrified sludge having certain nitration function into an upward-flow biology filtering tank using volcanic rocks as filtering materials, and employing a method of continuous aeration and dissolved oxygen concentration control so as to cultivate nitrified biomembrane; secondly, employing a intermittent aeration / anaerobic way to screen and concentrate anaerobic ammonium oxidation (ANAMMOX) bacterium; and lastly adding a certain amount of ANAMMOX bacterium into the reactor after the reactor fully enter into an anaerobic situation to perform rapid induction, andthus reducing starting time. On the basis of appearance of anaerobic ammonium oxidation characteristics, HRT continues to be reduced, water inflow load is raised, and finally starting of ANAMMOX technology at room temperature in low-matrix sewage can be realized. The invention provides a method for quick starting of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation technology at room temperature in low matrix.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Biological degradation method of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound wastewater
ActiveCN103922475AImprove sexual functionEnhance metabolic functionWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNitrogenous heterocyclic compoundElectron donor
The invention relates to the field of wastewater treatment, and relates to a biological degradation method of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound wastewater. An oxidation state compound is added in the nitrogen containing heterocyclic compound wastewater, an anaerobic environment is formed by micro aeration, and mixed electron acceptors of dissolved oxygen and the oxidation state compound simultaneously exist in the system; an upflow biological aerated filter is used as a main reaction device, an optimal degradation effect of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds is achieved according to different components and concentrations of the nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds, the pH is controlled to 7.0-7.5, the concentration of the dissolved oxygen is controlled to 0.05-0.3 mg / L (water discharged from the upper part of the filter), and the range of the oxidation-reduction potential is controlled to 150-50 mv; under an anaerobic aeration condition, with the nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds as electron donors and oxygen and oxygen-containing compounds as electron acceptors, under the combined effects of micro aerobic bacteria, facultative anaerobic bacteria, aerobic / anoxic denitrifying bacteria and the like, the nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds are completely degraded into carbon dioxide and water.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Ionic liquid and method of reaction using the same
InactiveCN1852898ASuppress generationCatalystsHydrocarbon preparation catalystsBeckmann rearrangementAlkyl transfer
A novel acidic ionic liquid which is useful as a catalyst for alkylation, nitration, Beckmann rearrangement, etc. and is stable to air and water. It is an ionic liquid represented by the following formula (1): (1) wherein X represents halogeno or hydroxy; Y<-> represents CF3SO3<->, BF4<->, PF6<->, CH3COO<->, CF3COO<->, (CF3SO2)2N<->, (CF3SO2)3C<->, F<->, Cl<->, Br<->, or I<->; n is an integer of 2 to 16; and R represents methyl, allyl, or vinyl. This ionic liquid not only functions as a BrDnsted acid or a Lewis acid but is a liquid insoluble in many organic solvents. The liquid is hence useful as a catalyst or solvent for Friedel-Crafts reaction, nitration, and Beckmann rearrangement. It can be easily separated from the reaction mixture and reused.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD +1
Nitrous acid-type denitrification bacteria strain and application thereof
ActiveCN102465105ACarbon savingSimple processBacteriaTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesHigh concentrationNitrous acid
The invention relates to a bacteria strain for short-cut denitrification and an application thereof. The short-cut denitrification bacteria strain is arthrobacter creatinolyticus FDN-1 and is preserved in Ordinary Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on March 11, 2010, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 3657. The bacteria strain can directly adopt nitrite nitrogen as a substrate to complete the short-cut denitrification process. When the arthrobacter creatinolyticus FDN-1 is used for processing ammonia-contained waste water, the technique is simple, high denitrification activity can be still obtained under the condition that low-concentration organic carbon source exists, and at the same time the high-concentration organic carbon source can be withstood. When the bacteria strain is in use, the system is rapid to start, and a vast application prospect can be realized in the denitrification treatment process of different types of waste water.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
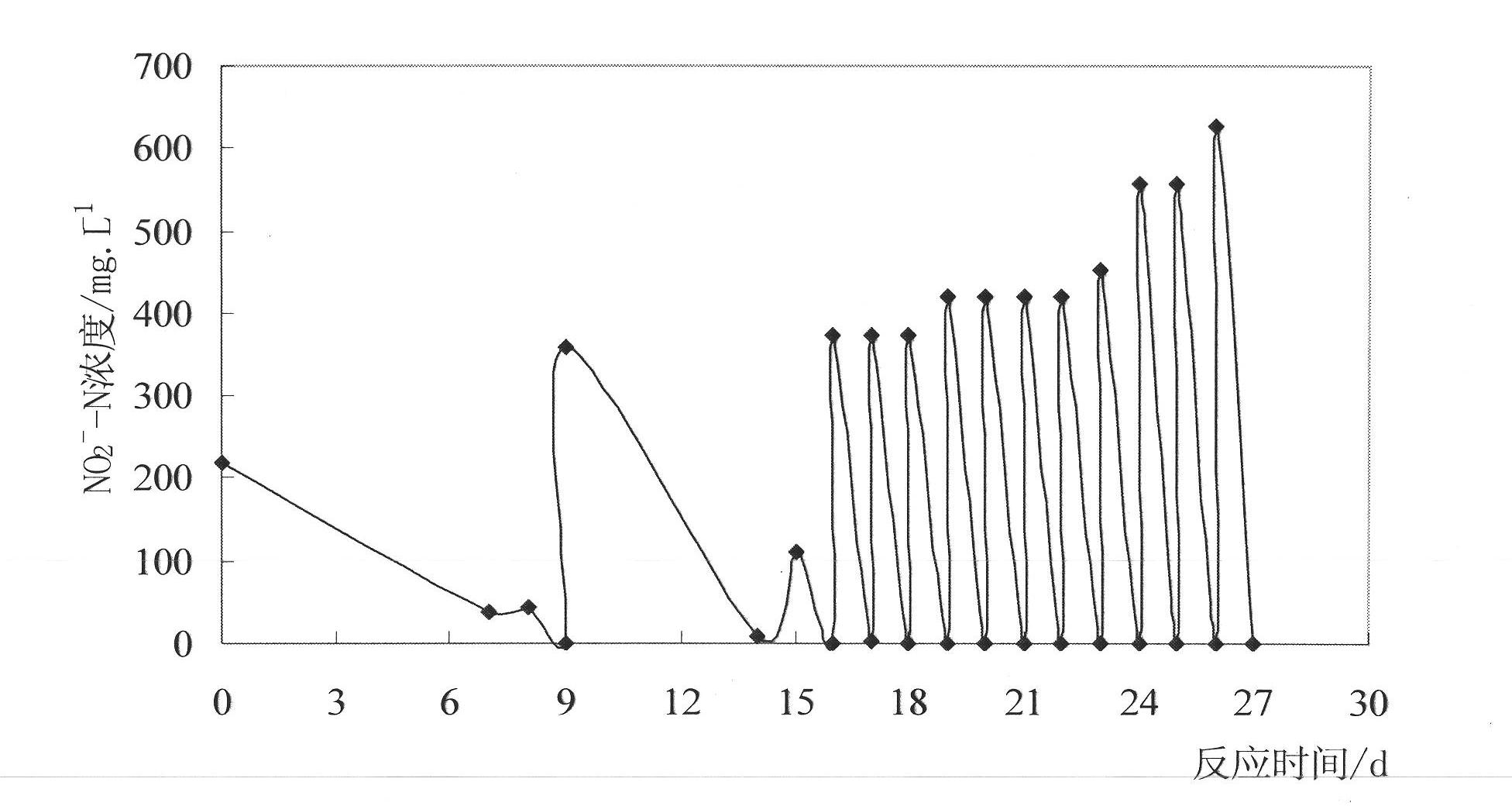
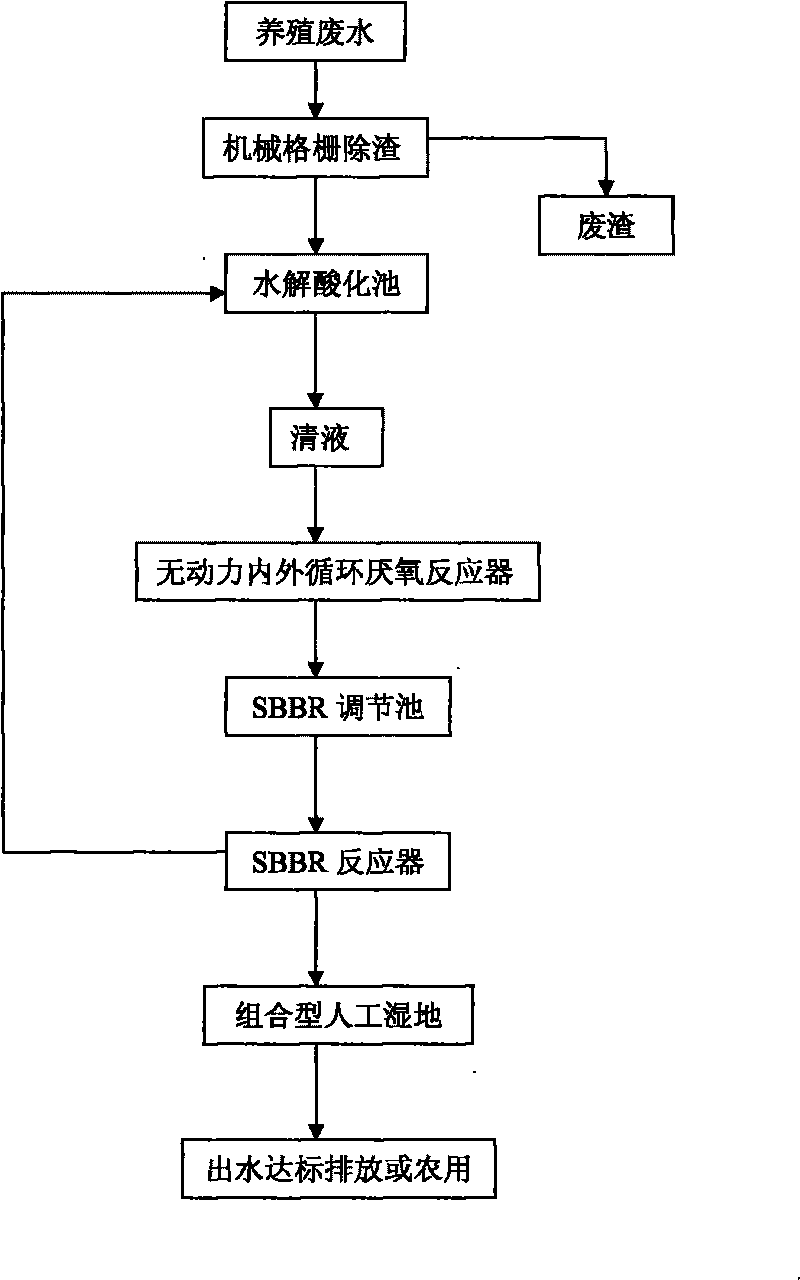
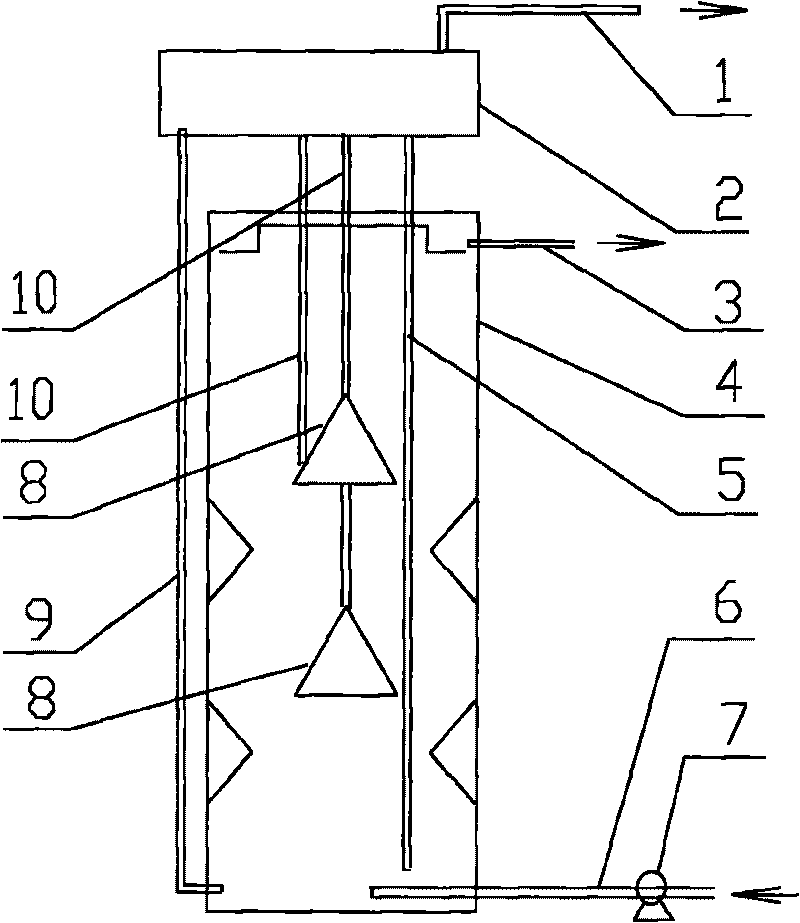
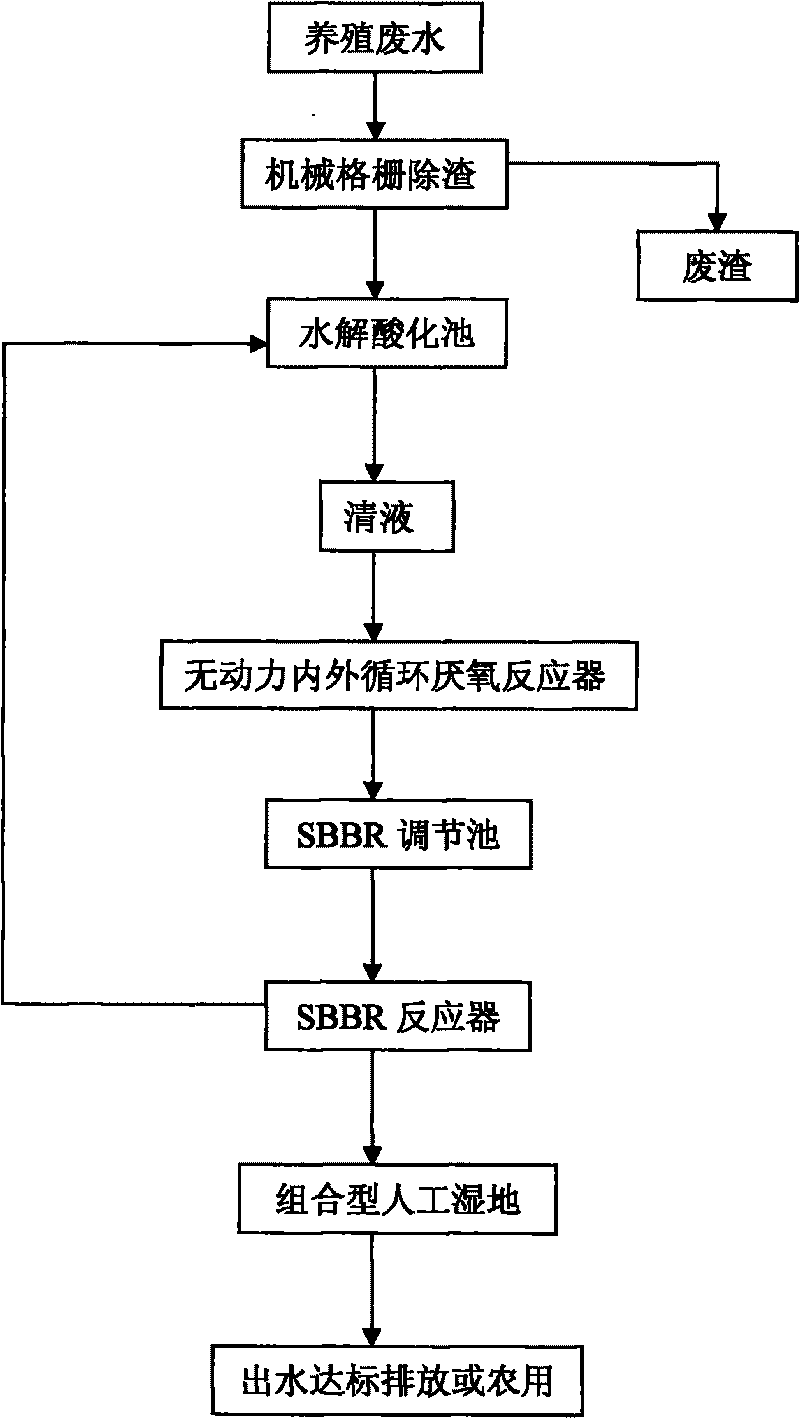
Treatment combined process for pig farm waste water with high nitrogen content
InactiveCN101759323AGood effect on treating pig farm wastewaterReduce energy consumptionWaste water treatment from animal husbandryWaste based fuelPig farmsConstructed wetland
The invention provides a treatment combined process for pig farm waste water with high nitrogen content, which is characterized in that the process adopts a combined process realized by an unpowered inside and outside circulation (IOC) anaerobic reactor, an SBBR sequencing batch type biomembrane reactor and artificial swamp. The process flow of the combined process comprises the following steps: a, removing large-grain pollutants and floaters in sewage by mechanical grids; b, carrying out hydrolysis and acidification; c, using the inside and outside circulation anaerobic reactor for high-efficient anaerobic digestion; d, using SBBR reactor for aerobic / anoxic nitration; and e, carrying out the depth treatment by the artificial swamp, and realizing the high-efficient purification on the sewage through substrate filtering, absorption, precipitation, ion exchange, plant absorption and microbiological degradation. The invention can be applicable for the treatment and the integrated utilization of the waste water in big-and-middle-sized pig farms.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF JIANGXI ACAD OF SCI +1
Continuous flow low C/N (carbon/nitrogen ratio) municipal wastewater partial nitrification/ anaerobic ammonia oxidation and denitrification nitrogen removal method
ActiveCN103936150AReduce energy consumptionReduce aerationWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesOxygen deficiencyMunicipal sewage
The invention provides a continuous flow low C / N (carbon / nitrogen ratio) municipal wastewater partial nitrification / anaerobic ammonia oxidation and denitrification nitrogen removal method, and belongs to the field of wastewater. The continuous flow low C / N municipal wastewater partial nitrification / anaerobic ammonia oxidation and denitrification nitrogen removal method is characterized in that firstly municipal wastewater enters an oxygen deficiency denitrification zone of a biological nitrogen removal reactor, heterotrophic denitrifying bacteria fixed on biological stuffing use organic matters in raw water as carbon sources and restore nitrate nitrogen in backflow yielding water to nitrogen, then the wastewater enters an aerobic zone and is subjected to partial nitrification reaction, so that a part of ammonia nitrogen is converted to nitrite nitrogen, afterwards the wastewater enters an oxygen deficiency zone, and anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria fixed on the biological stuffing convert the part of ammonia nitrogen and the nitrite nitrogen into nitrogen; and afterwards, the wastewater sequentially enters a subsequent aerobic zone and a subsequent oxygen deficiency zone, so that the effects are repeated, and the purpose of removing the nitrogen in the wastewater is achieved in the end. The continuous flow low C / N municipal wastewater partial nitrification / anaerobic ammonia oxidation and denitrification nitrogen removal method can realize the deep denitrification of low C / N municipal wastewater without addition of an external carbon source and has the characteristics of high nitrogen removal efficiency, low sludge yield and the like.
Owner:贵州筑信水务环境产业有限公司
Apparatus and method for nitrogen removal by combining garbage leachate SBR and anaerobic ammoxidation
ActiveCN102515350AEfficient biological denitrificationLow running costTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesPeristaltic pumpNitrogen removal
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for nitrogen removal by combining garbage leachate SBR and anaerobic ammoxidation, which belongs to the low carbon nitrogen (CN) ratio high density ammonia nitrogen garbage leachate biological denitrogenation technical field. The apparatus comprises an integrated water tank, a SBR short distance nitrated reactor and an anaerobic ammoxidation reactor; a preposition water tank and a postposition water tank in the integrated water tank are communicated with a peristaltic pump and the SBR short distance nitrated reactor, the postposition water tank is connected with the bottom of the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor through the outlet pipe and the peristaltic pump, an self-circulation pipeline is provided on the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor, and is connected with the SBR preposition water tank through the outlet pipe and the peristaltic pump. The method comprise the following steps starting the SBR short distance nitrated reactor, starting the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor, and an operation is in series of the SBR short distance nitrated reactor and the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor is carried out. The apparatus of the present invention is suitable for organic matter removal and short distance nitrogen removal of the garbage leachate at late period in the garbage landfill, the process is advanced, and the advantages of energy saving and consumption reduction is obvious.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
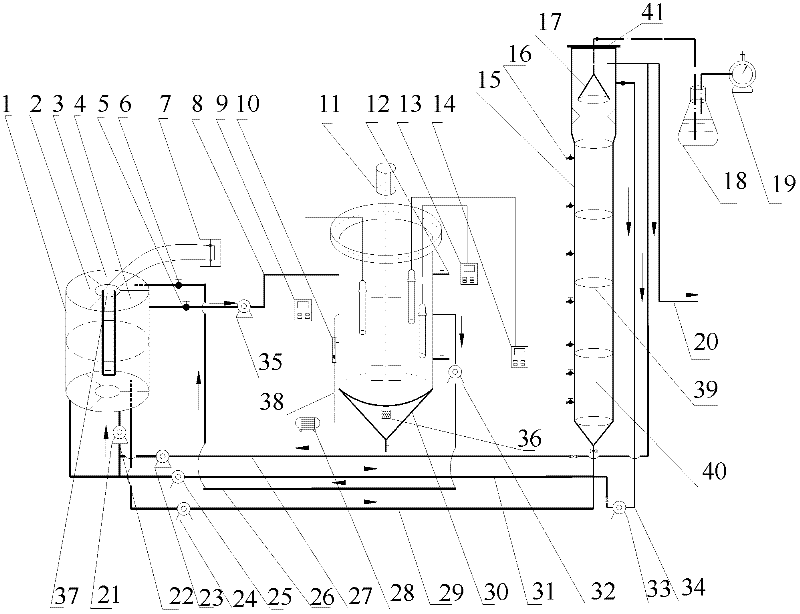
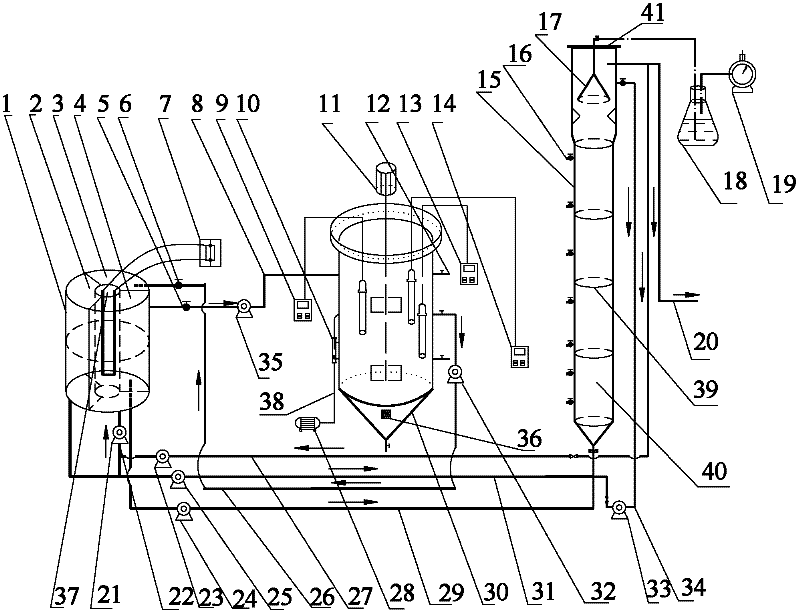
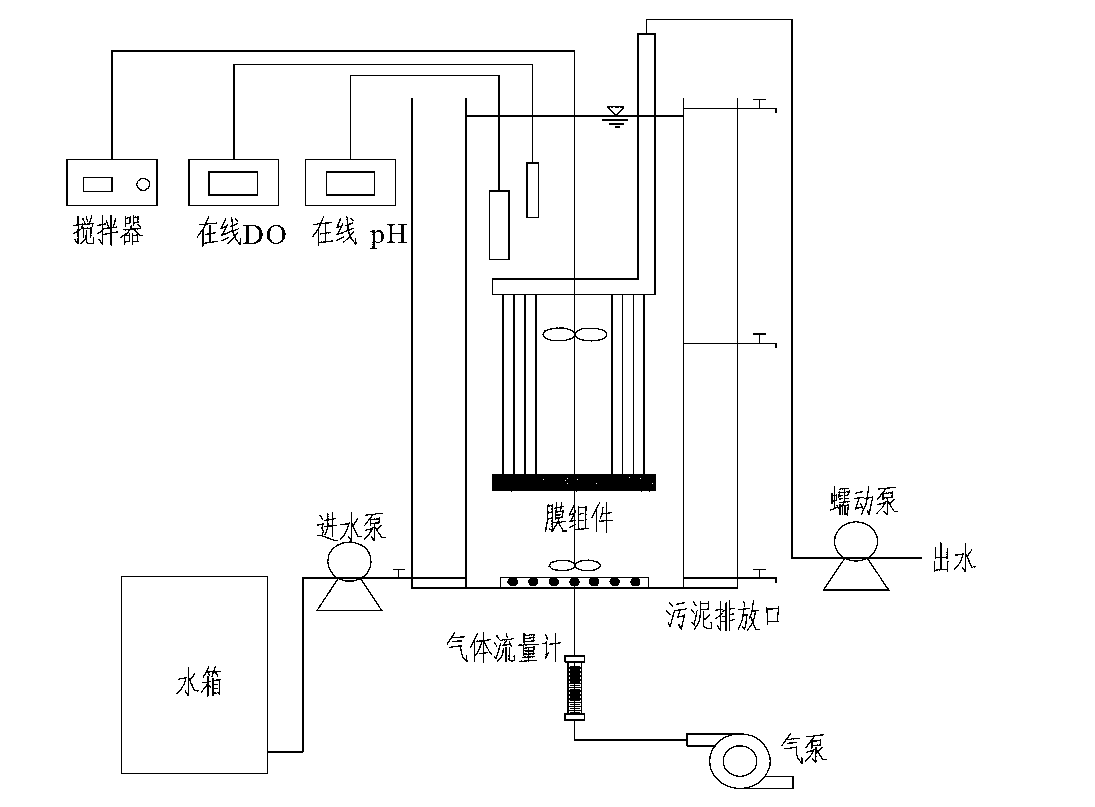
Rapid starting method of membrane bioreactor completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology
ActiveCN103224284AEasy to interceptSolve the problem of difficult sourceSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentNitrogen removalAeration rate
A rapid starting method of a membrane bioreactor completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology belongs to the municipal sewage processing and recycling fields. The starting method of a completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) comprises the following steps: inoculating nitrated sludge of the aeration tank of a municipal sewage plant, and recovering the activities of sludge at normal temperature under low ammonia nitrogen of inlet water; reducing the aeration rate and gradually increasing the ammonia nitrogen concentration to successfully enrich ammonia oxidizing bacteria; and reducing the aeration rate, reducing DO, and inducing anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria to successfully start the completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology. Problems comprising slow starting and strict sludge inoculation requirement of a completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology are solved in the invention, and the rapid starting method of the shortcut nitration in the MBR realizes the efficient ammonia nitrogen removal, and provides a way for the long-term efficient and stable running of the shortcut nitration in the MBR.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
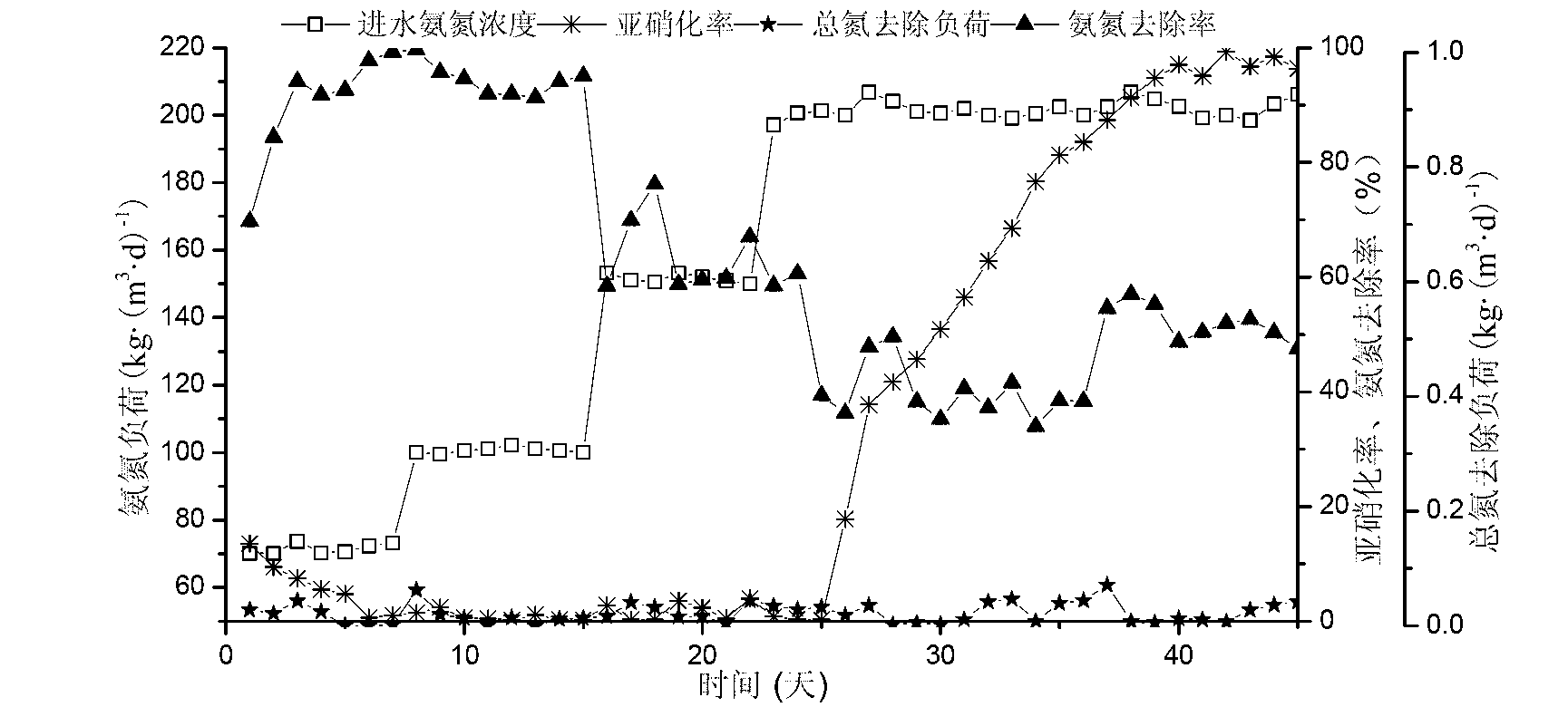
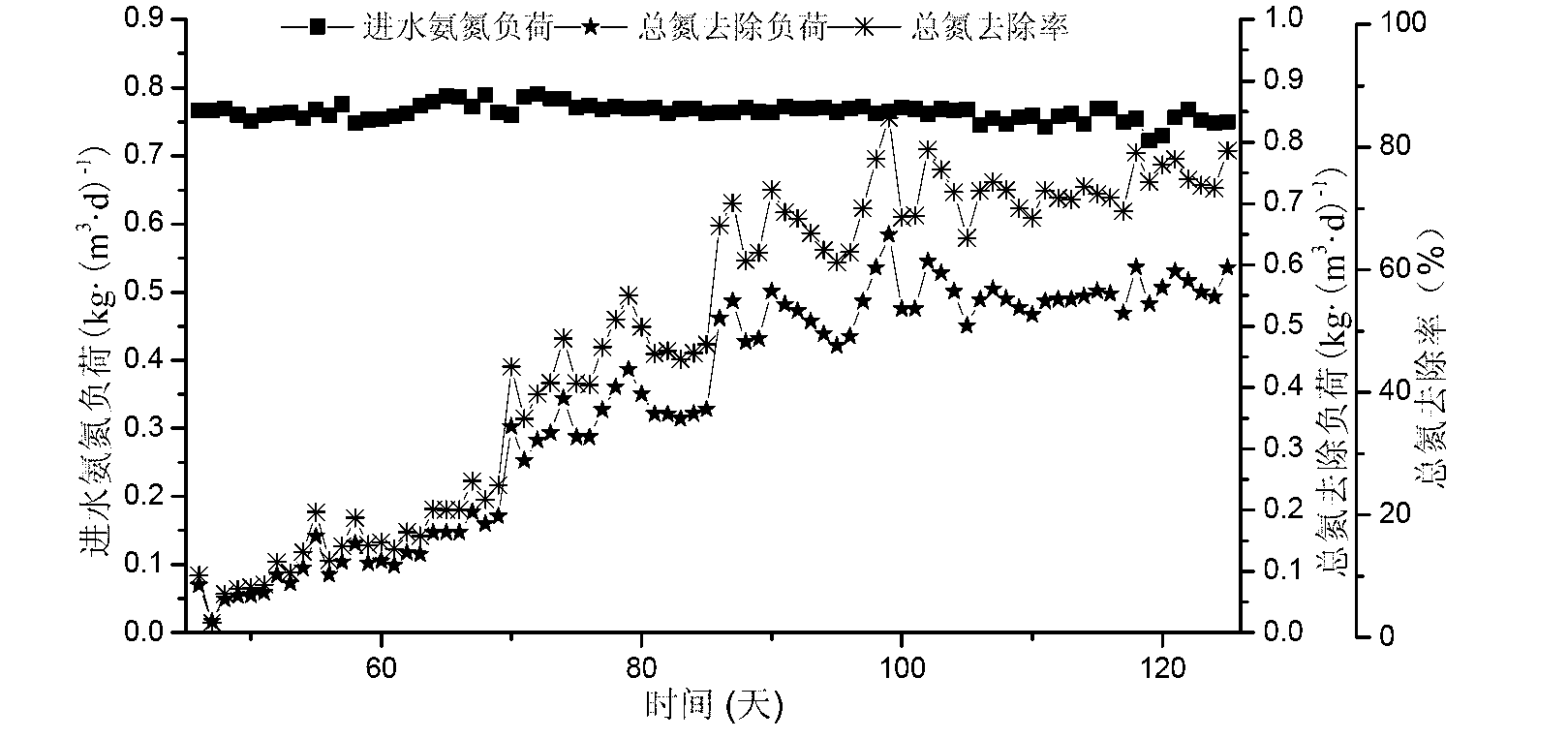
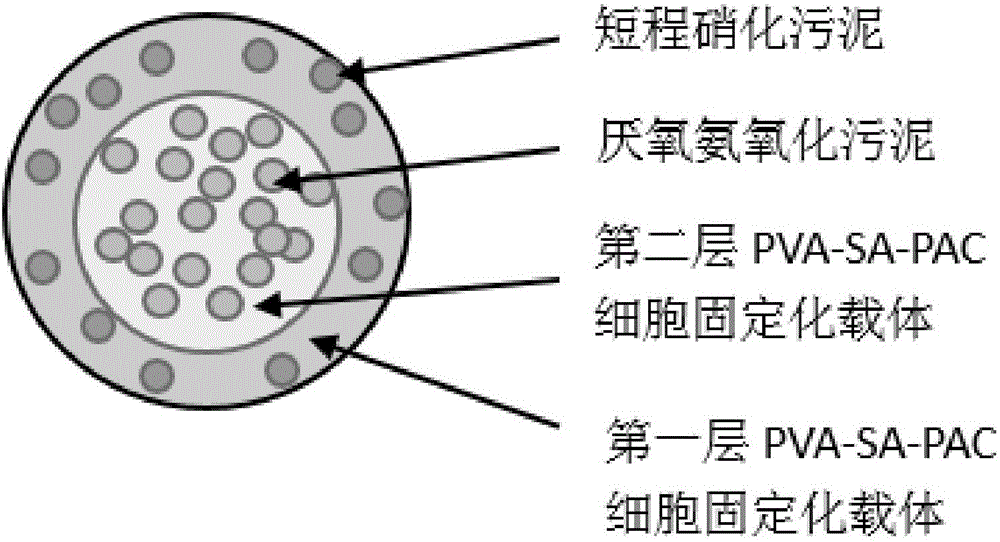
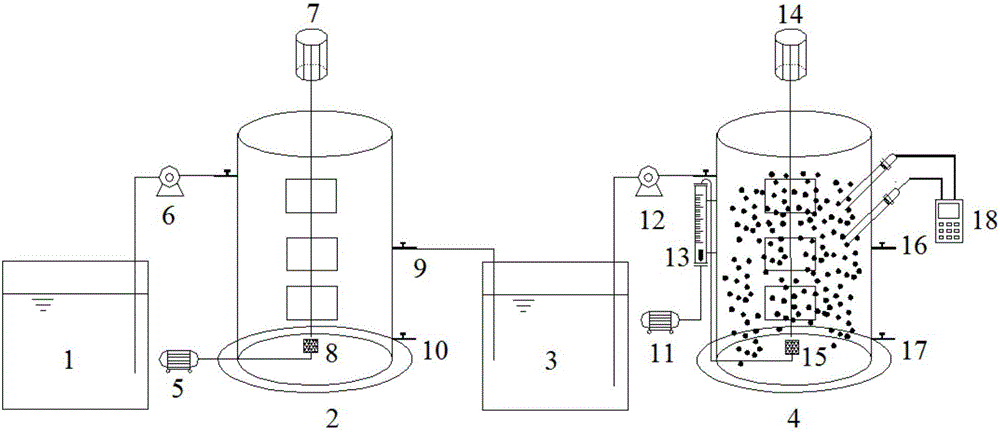
Method for co-immobilizing anaerobic ammoxidation bacteria-short-cut nitrobacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN105861479AAchieve coordinated operationStable enrichmentTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentPolyvinyl alcoholSludge
A method for co-immobilizing anammox bacteria-short-range nitrifying bacteria and its application belong to the technical field of sewage treatment, using polyvinyl alcohol, sodium alginate and activated carbon as embedding agents to anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria and short-range nitrifying bacteria Layered embedding and fixation, firstly mix equal volumes of anammox sludge and embedding agent uniformly, get anaerobic ammonium oxidation gel pellets after fixation, and then put them into the mixed solution of short-range nitrifying bacteria and embedding agent In the process, anammox-short-range nitrifying bacteria gel pellets were obtained after fixation, and were directly added to the autotrophic denitrification reactor after activation. The present invention uses immobilized microbial technology to co-immobilize anammox bacteria and short-range nitrification bacteria on the same carrier, and stably enrich high-activity anammox and short-range nitrification sludge, so that the biological efficacy of the two bacteria can be coordinated. , to realize the coordinated operation of short-range nitrification reaction and anammox reaction.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Microbial agent and soil modifying agent produced by fermentation thereof
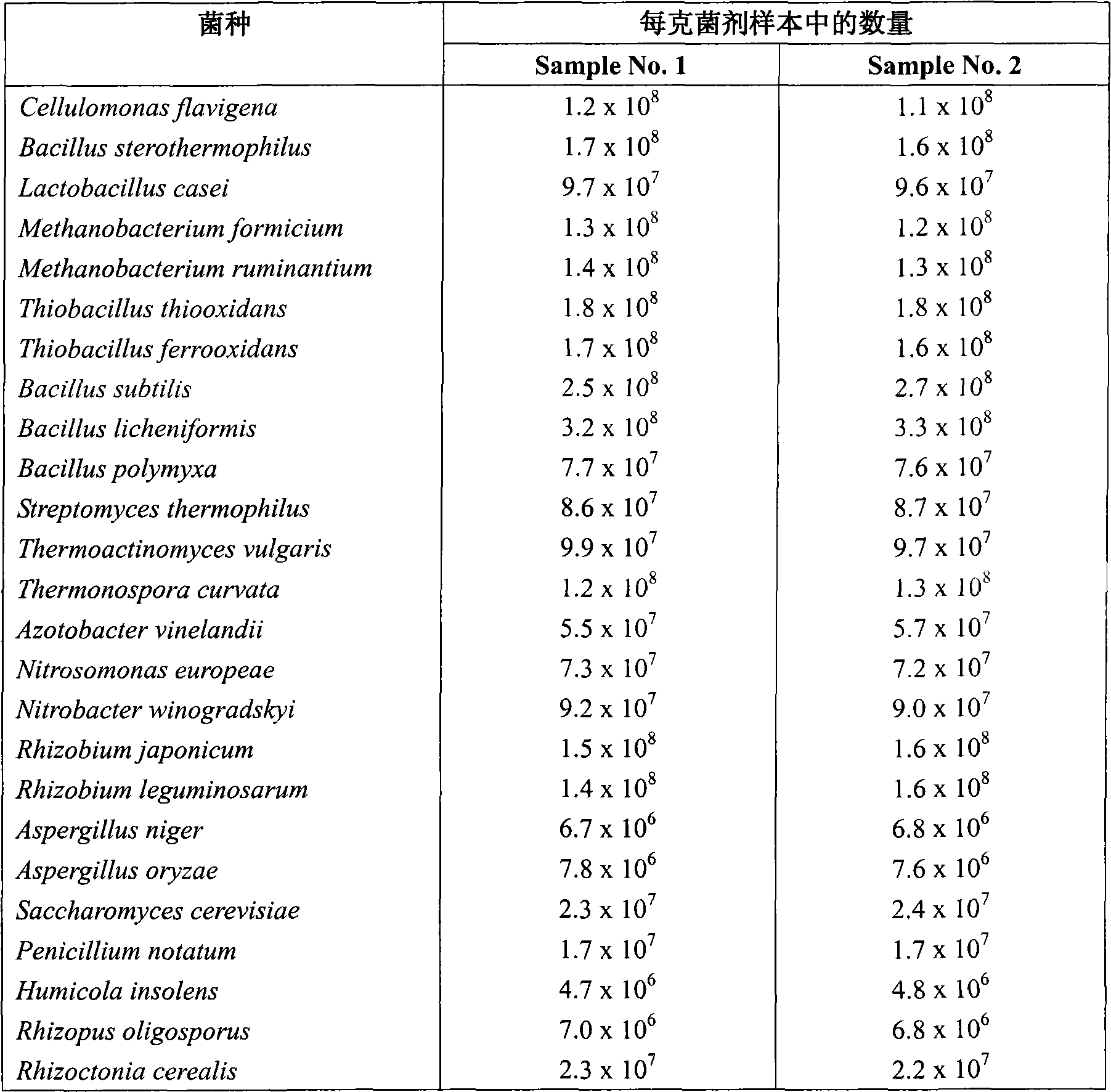
ActiveCN101629156AImprove adaptabilityImprove fertilityAgriculture tools and machinesFungiFiberMicrobial agent
The invention relates to a microbial agent used for producing a soil modifying agent by fermentation, consisting of fiber monad, bacillus, lactobacillus, methanobacteria, thiobacillus, streptomycete, high-temperature actinomyces, high-temperature monad, azotobacteria, nitration monad, nitration bacilus, rhizobium, koji mold, leaven, blue mold, detritus mold, rhizopus as well as mycorrhizal fungi and substrate. In addition, the invention also relates to a soil modifying agent produced by the fermentation of the microbial agent, application thereof and the like.
Owner:宋彦耕
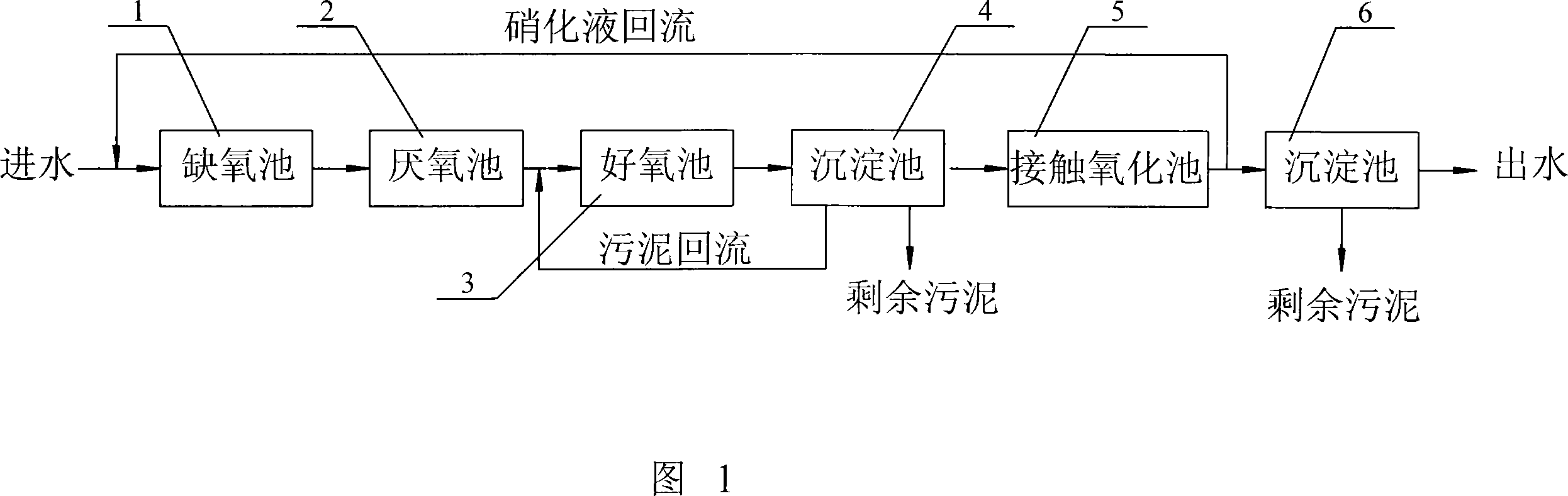
Method for low-temperature denitrification phosphorous removal
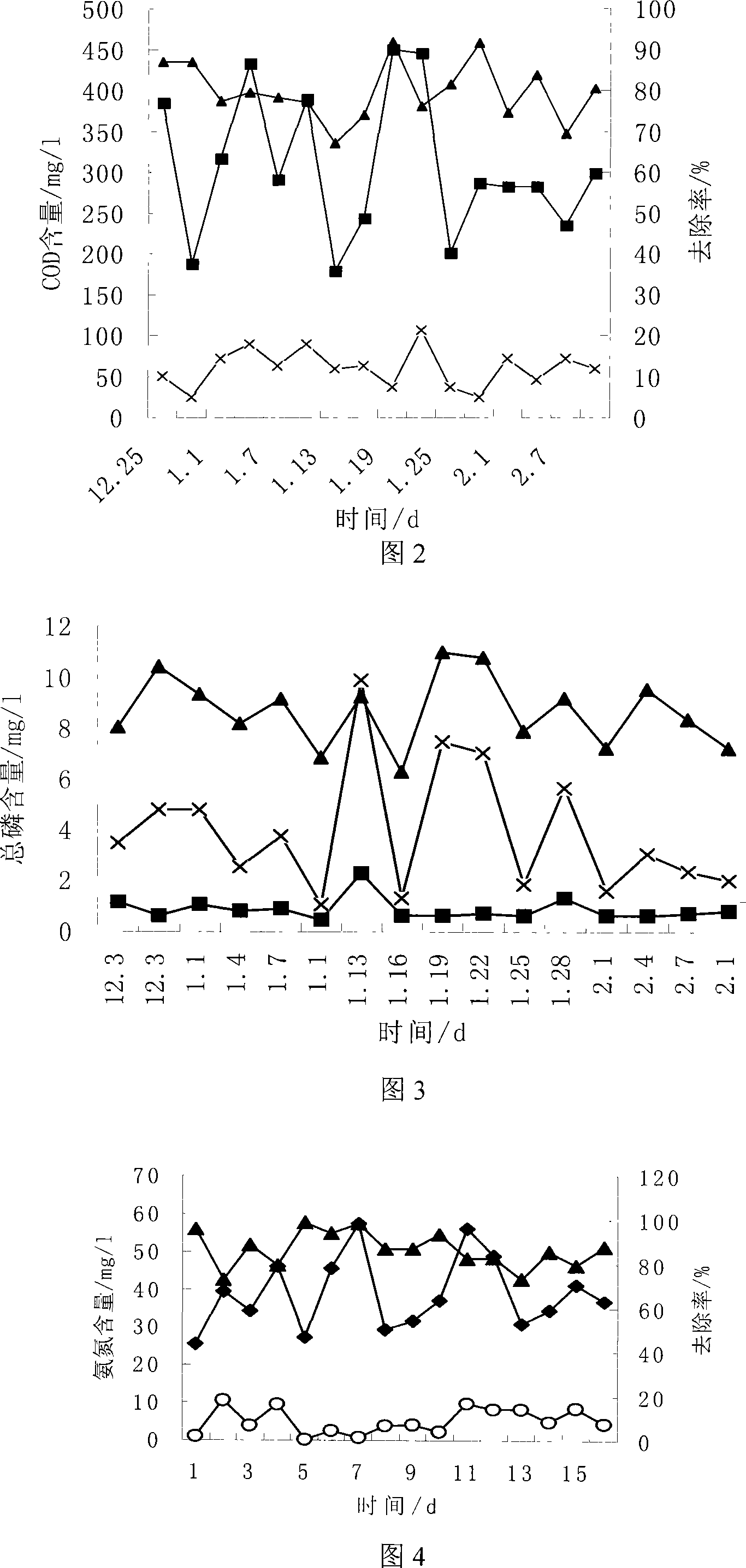
InactiveCN101113059ASolve the problem of mud ageGood removal effectTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeNitration
A method of denitrification and phosphorus removal under low temperature relates to a way of sewage treatment. The invention solves the problem of the poor effect of existing biological simultaneous denitrification and phosphorus removal under low temperature. The invention comprises the steps of: 1. cultivation and fixation for nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria of low temperature tolerance; 2 start-up response system and cultivation of phosphate accumulating bacteria ; 3. denitrification and phosphorus removal under low temperature by the steps: a. denitrification by nitrate solution refluxing; b. anaerobic action; c. aerobic phosphorus removal; d. precipitation and sludge reflux; e. contacting oxidation and nitration; f. precipitation and water obtained. After the steps, denitrification and phosphorus removal of sewage treatment under low temperature are finished. The invention can realize simultaneous denitrification and phosphorus removal under low temperature. The invention comprises the contents under low temperature: the removal rate of COD is above 85 percent; the removal rate of overall phosphorus reaches above 80 percent; the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen reaches above 70 percent when the intake ammonia nitrogen is between 25-60mg / L.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Novel process for treating coking waste water by charging activated sludge process
InactiveCN101417850AQuality improvementBulk volumeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeNitration
The utility model discloses a technology for treating coking wastewater by using a novel feeding activated sludge method, which comprises the following steps: biochemical treatment process is carried out on the pretreated wastewater, the coking wastewater first enters an A-grade biochemical pond to provide carbon sources for denitrification, and then the coking wastewater enters a 0-grade biochemical pond for carrying out oxidation and nitration under aerobic environment, the effluent water of the 0-grade biochemical pond enters a secondary sedimentation tank; the supernatant from the secondary sedimentation tank enters a subsequent-stage treatment system and one part of settling sludge refluxes and enters the A-grade biochemical pond and 0-grade biochemical pond; the other part of the settling sludge enters a sludge thickener. As flocculants are added into the biochemical pond, the ability of tolerating loads is greatly improved, and shock resistance is also greatly enhanced; the area of the biochemical reaction pond is reduced to 70 percent of the area of the reaction pond of traditional feeding activated sludge method, so investment costs are saved and operation costs are decreased; while the decolorizing ratio of the technology to coking wastewater, black liquor and chloromycetin wastewater can reach to more than 80 percent.
Owner:江苏百纳环境工程有限公司
Process for producing cetane improvers from triglycerides
InactiveUS20010037598A1Good cetane boostReduce nitrogen contentOrganic chemistryLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAlcohol fuelNitration
Cetane improvers based on triglycerides and petroleum fractions are disclosed that are at least one half as effective as commercially sold cetane improvers. In each case, the cetane improvers are nitrates produced through the nitration of medium to long chain compounds containing a double bond. Applications include use with diesel and alcohol fuels intended for use in diesel engines. The nitrates have advantages due to their good performance relative to their nitrogen content. Observed properties of some products indicate they also have lubricity and / or detergency enhancing capabilities when used with diesel fuel.
Owner:UNIV OF KANSAS NON PROFIT EDUCATION INSTION THE
Kocuria palustris strain and applications thereof
ActiveCN103103141AFast growthIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention relates to a Kocuria palustris strain and applications thereof. The strain is Kocuria palustris FSDN-A, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 14, 2011, wherein a preservation number is CGMCCNO.5061. According to the present invention, the strain can adopt nitrite nitrogen or nitrate nitrogen as a substrate to complete a denitrification process; when the Kocuria palustris FSDN-A is adopted to treat ammonia-containing wastewater, characteristics of simple process, high denitrogenation activity, and high concentration organic carbon source tolerance are provided; after the strain is poured, the system is rapidly started; and the strain has broad application prospects in wastewater denitrogenation treatment processes, and is especially suitable for treatment of wastewater containing nitrogen oxides and organic pollutants.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
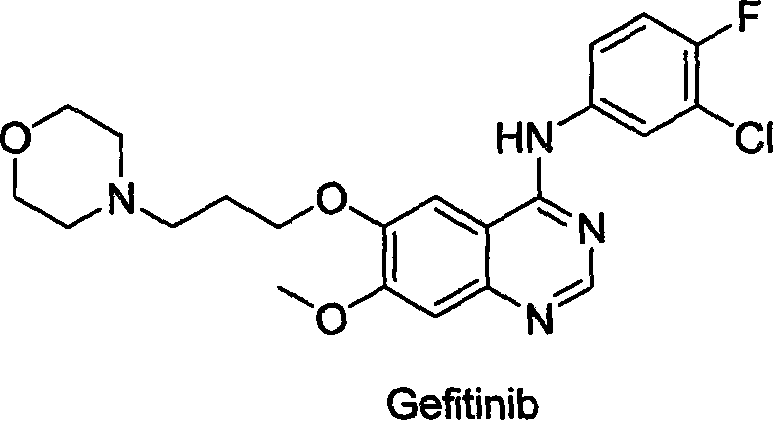
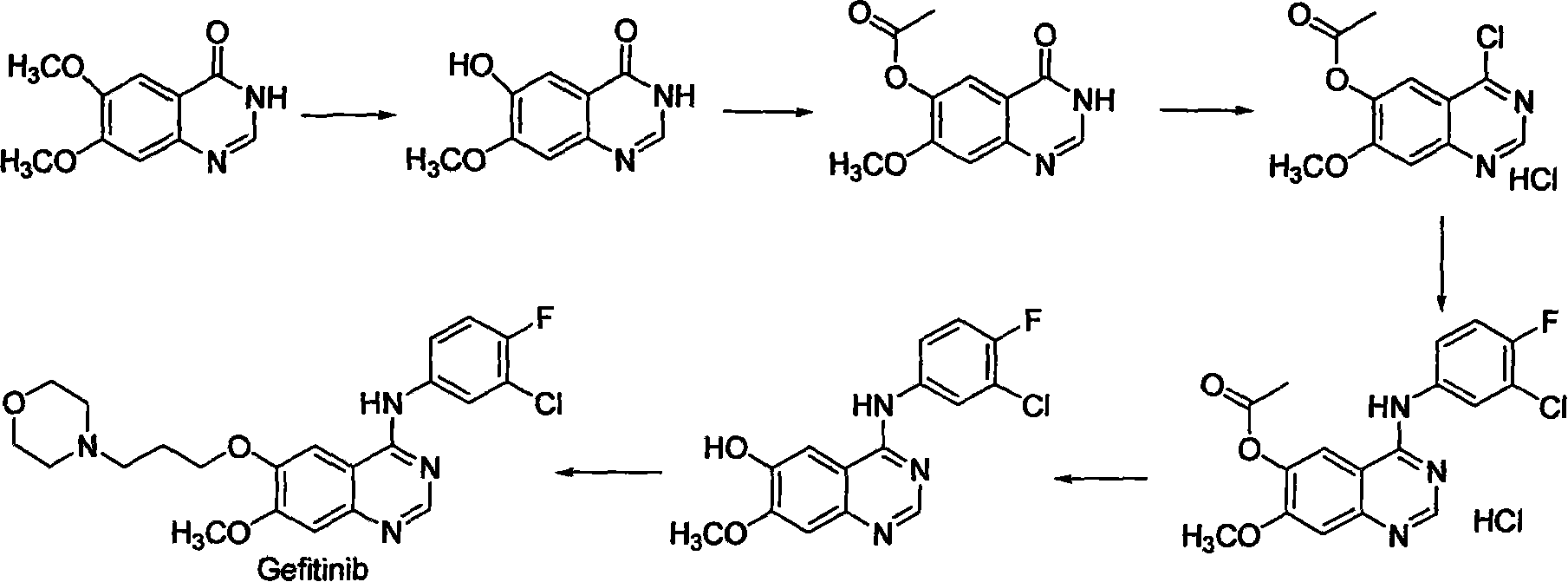
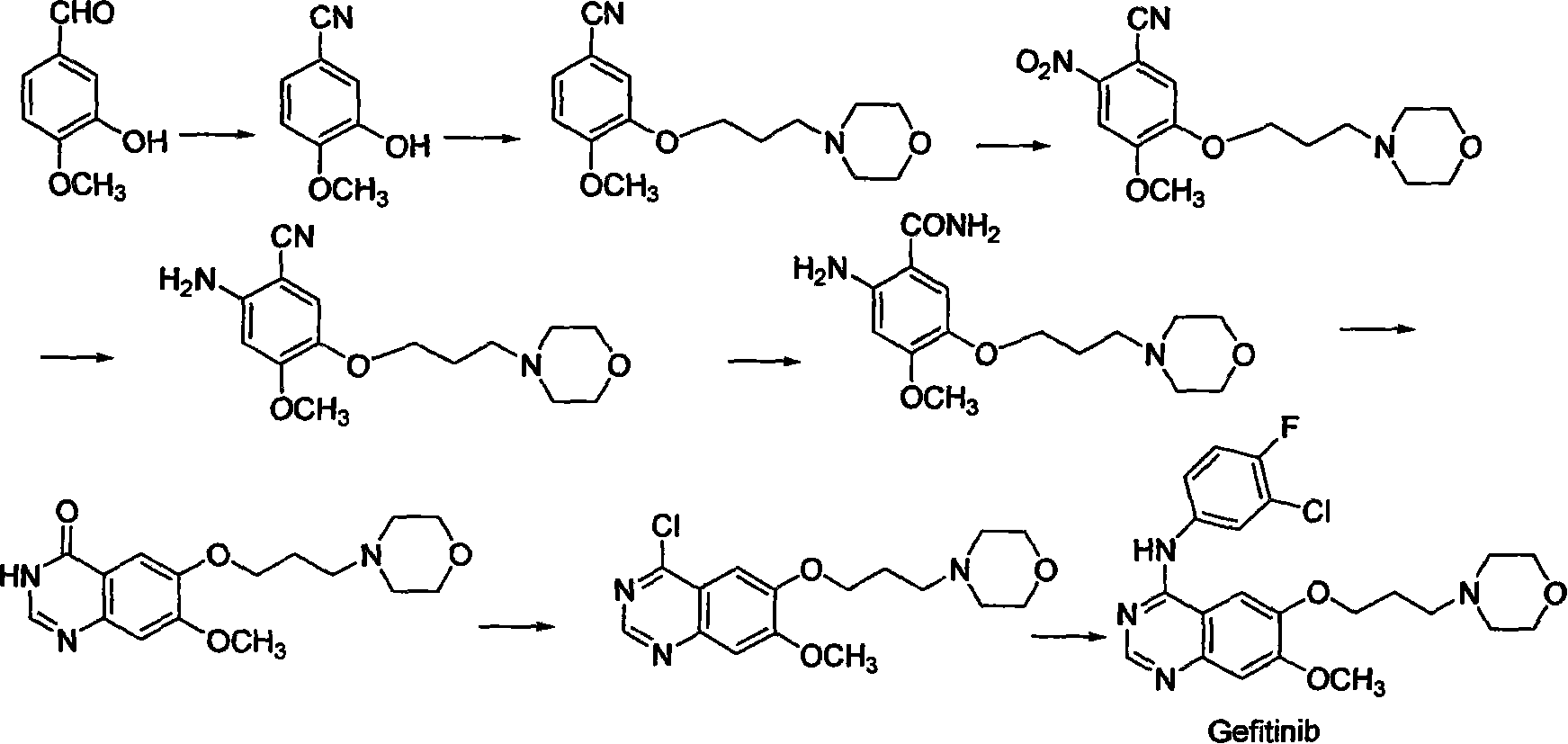
Preparing method for gefitinib
InactiveCN101148439AHigh yieldReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryMorpholine3-chloro-4-fluoroaniline
The process of preparing gefitinib, 4-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamido)-7-methoxyl-6-[3-(4- morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline, includes following steps: 1. reaction of 3-hydroxy-4-methoxy methyl benzoate as material and 4-(3-chloropropyl) morpholine to obtain 4- methoxyl-3-[3-(4- morpholinyl) propoxy] methyl benzoate; 2. nitration to obtain 2-nitro-4- methoxyl-5-[3-(4- morpholinyl) propoxy] methyl benzoate; 3. reduction to obtain 2-amino-4- methoxyl-5-[3-(4- morpholinyl) propoxy] methyl benzoate; 4. closing cycle to create 7- methoxyl-6-[3-(4- morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline-4(3H)-one; 5. chlorinating to obtain 4-chloro-7- methoxyl -6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] quinazoline; and 6. reaction to 3-chloro-4-fluoroaniline to obtain gefitinib.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Integrated circulating water culture system
ActiveCN102754613AQuick removalEfficient removalMultistage water/sewage treatmentPisciculture and aquariaSuspended particlesParticulates
The invention discloses an integrated circulating water culture system which comprises a culture water tank, a foam separation and degassing chamber, a biological active carbon nitration reaction chamber and a low-pressure gas dissolution chamber, and is characterized in that: one part of water from a water drainage structure of the culture water tank is discharged and led into a biological flocculating constituent culture pool from the bottom of the culture water tank, and the other part flows into the foam separation and degassing chamber through an overflow hole at the upper part of the culture water tank; the suspended particles in the culture water are adsorbed by the micro bubbles of the foam separation and degassing chamber and rise to the top of the foam separation and degassing chamber to be discharged out; the culture water flows into the biological active carbon nitration reaction chamber through the foam separation and degassing chamber and is purified by a nitration biomembrane of the biological active carbon nitration reaction chamber and drawn out from the bottom of the biological active carbon nitration reaction chamber; 90% of the culture water drawn out is directly fed into the low-pressure gas dissolution chamber, and 10% of the culture water is fed into a pipeline mixer to mix pure oxygen and ozone and then fed into the low-pressure gas dissolution chamber; and the processed culture water flows back to the culture water tank from a drainage hole at the bottom of the low-pressure gas dissolution chamber.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Long life lubricating oil composition with very low phosphorus content
A lubricating oil with very low phosphorus content, and having long life as evidenced by a reduction in viscosity increase, oxidation and nitration, comprises a major amount of a base oil of lubricating viscosity and a minor amount of a mixture of neutral and overbased metallic detergents, at least a zinc dialkyldithiocarbamate antiwear additive and at least a dihydrocarbylthiocarbamoyl.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Chemical fertilizer waste water treatment method
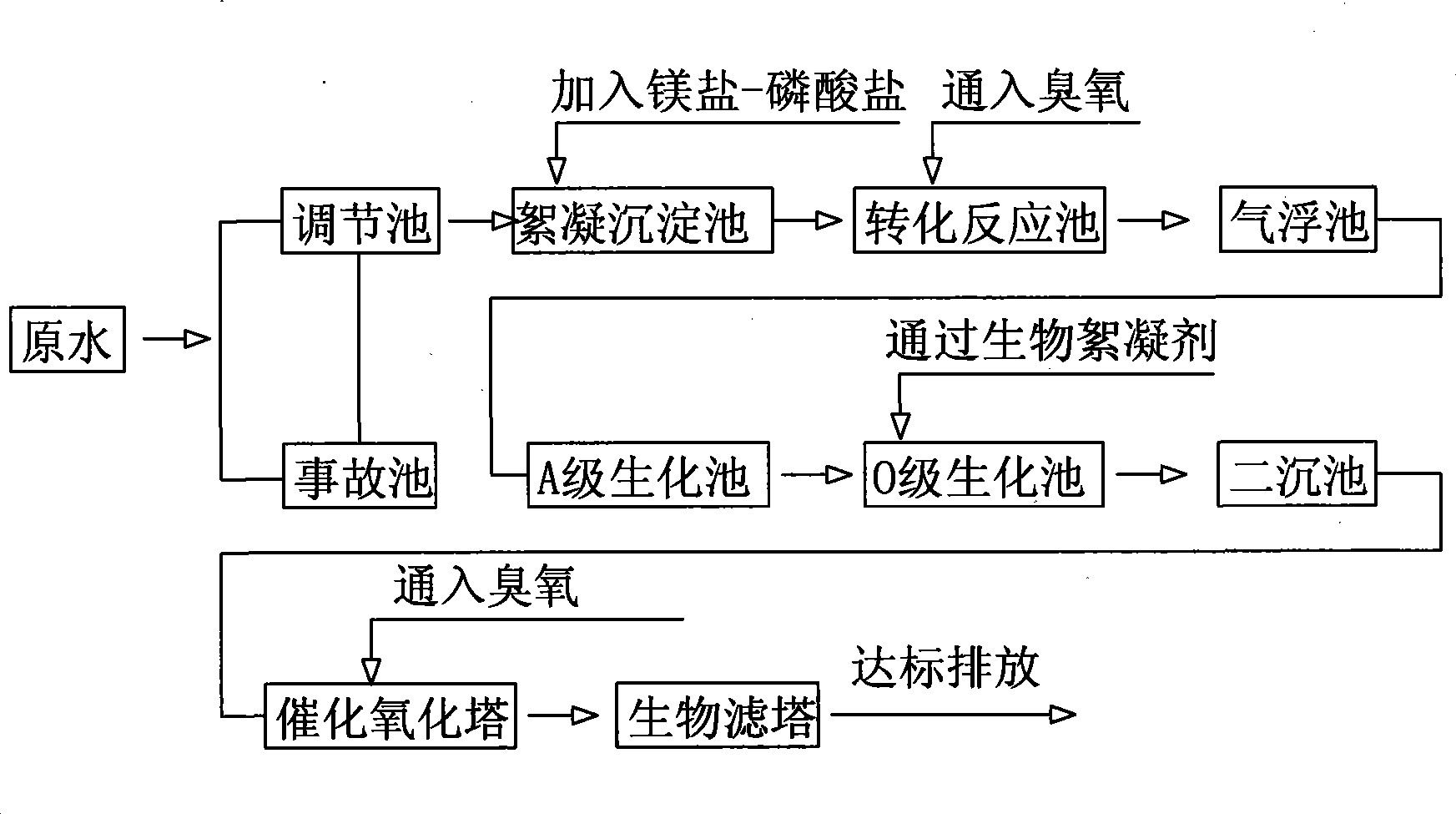
ActiveCN101723554AEasy to waterReduce processing costsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandSludge
The invention provides a chemical fertilizer waste water treatment process control method. The process comprises the following steps of: homogenizing chemical fertilizer waste water through a regulating pool; then pumping the waste water in the regulating pool into a primary aeration tank by utilizing a sewage pump so as to primarily remove COD (chemical oxygen demand) and relieve toxic and side effects for a subsequent biological and chemical system; after the waste water is treated by a primary sedimentation tank, ensuring that the waste water enters an A / O (anacrobic / oxic) biological denitrification system and a subsequent materialization deep treatment system; keeping DO (dissolved oxygen) of a pool A (anoxia pool) being below 0.5mg / L and the water flow of nitration liquid refluxing from a pool O (oxic pool) being 3-5 times of that of inlet water; maintaining the pH of the pool O to be 6.5-8.5 and the DO to be 2-3mg / L; and regulating to a proper mud reflux ratio so as to ensure that the biological and chemical system can be efficiently and stably operated. The materialization deep treatment system is used for adding flocculating agents PAC (polyaluminium chloride) and PAM (polyacrylamide), and after reaction and precipitation, outlet water can reach the national first-level discharge standard.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Slow-release fluid suspension composite fertilizer and its preparation method and use method
ActiveCN104591930AImprove stabilityImprove uniformityAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersNutritional deficiencyTrace element
The invention provides slow-release fluid suspension composite fertilizer. The slow-release fluid suspension composite fertilizer comprises 30-200 parts of fertilizer nutrients, 0.05-2 parts of a thickening agent, 0.1-4 parts of a suspending agent, 0.1-3 parts of an emulsifier, 0.05-1 part of a nitration inhibitor and 0-15 parts of water. The fertilizer nutrients comprise nitrogenous fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer, potash fertilizer, humic acid and trace elements and also contain at least one quick-acting fertilizer and at least one slow-release fertilizer. The invention also provides a preparation method and a use method of the slow-release fluid suspension composite fertilizer. The slow-release fluid suspension composite fertilizer has the advantages of the existing fluid suspension and is ternary liquid fertilizer containing the quick-acting and slow-acting nutrients, trace elements and humic acid, prolongs fertilizer efficiency of the suspension fertilizer, realizes combination of trace elements, humic acid and fertilizer, continuously and stably provides nutrients needed by crop growth and development, and solves the problems of nutritional deficiency symptom and later fertilizer removal in crop growth.
Owner:DONGGUAN YIXIANG LIQUID FERTILIZER +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com