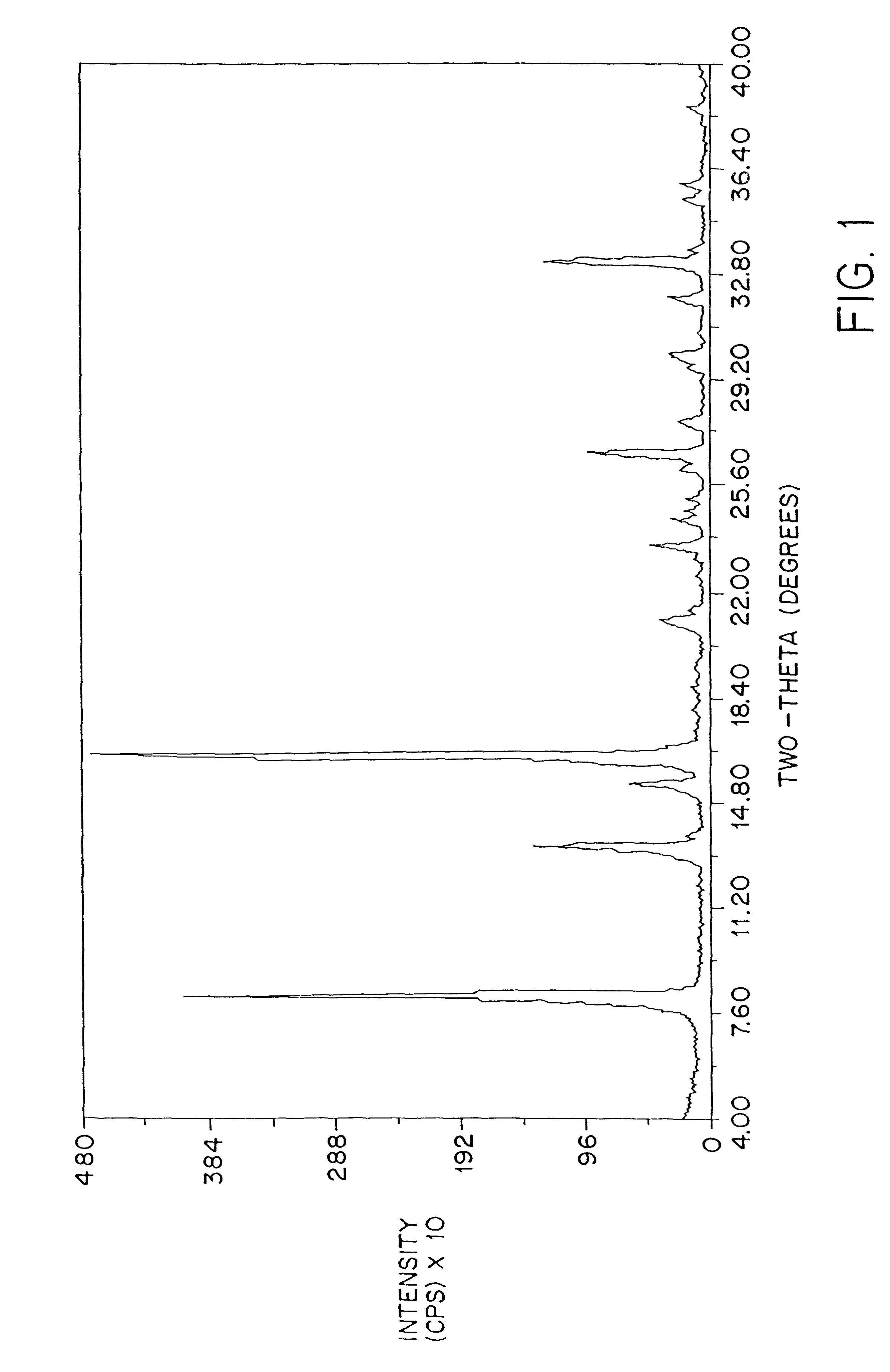
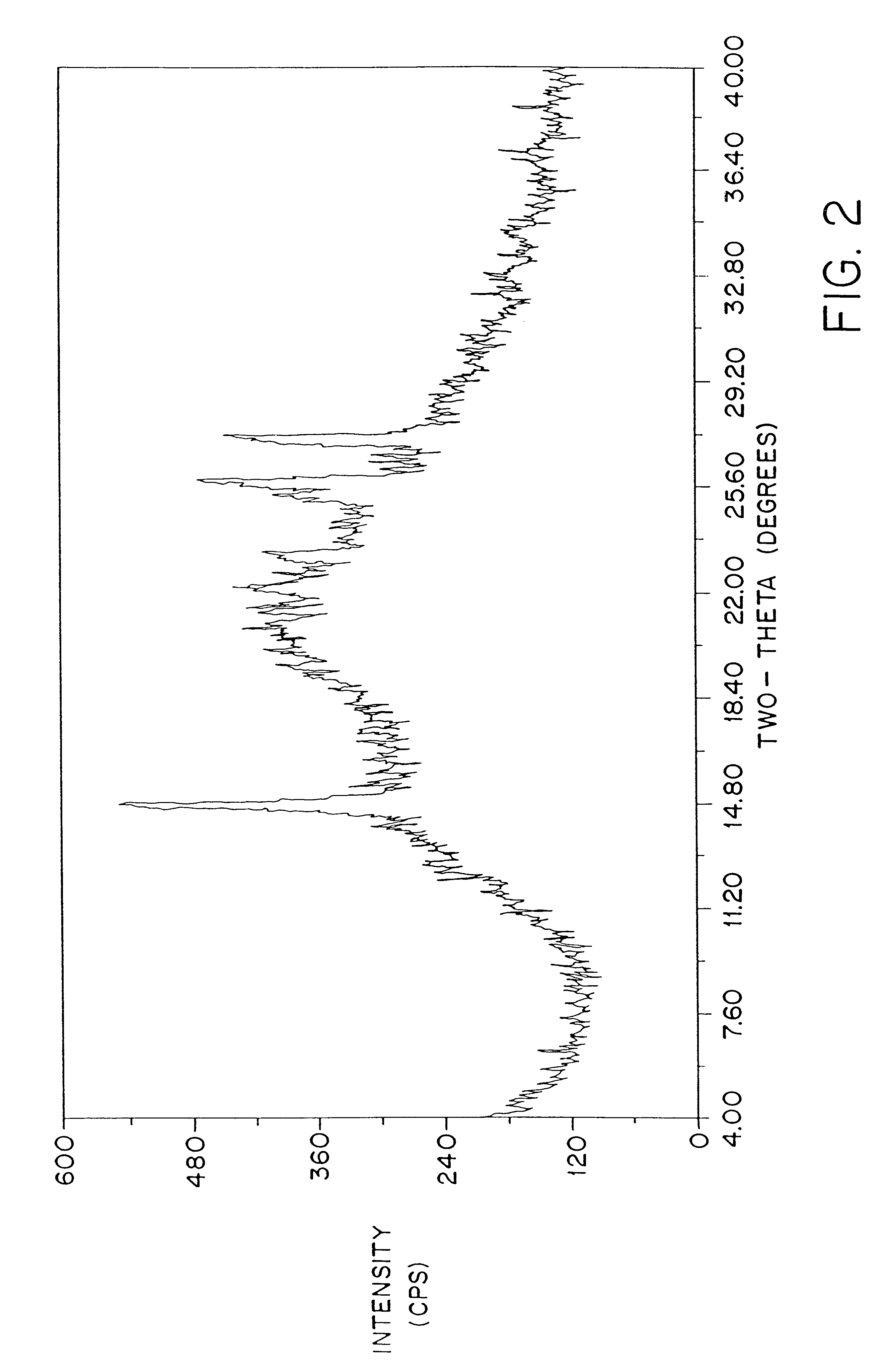
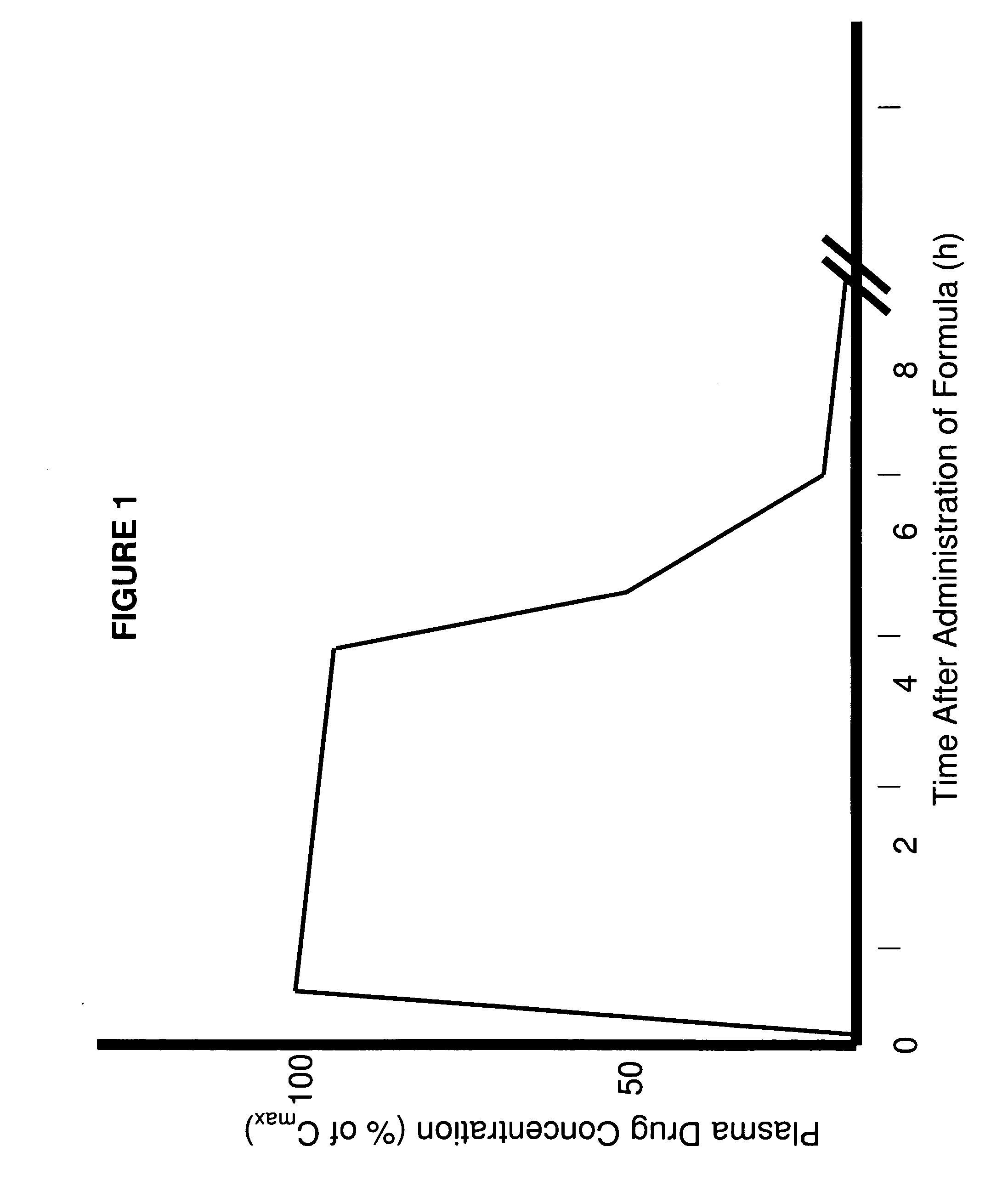
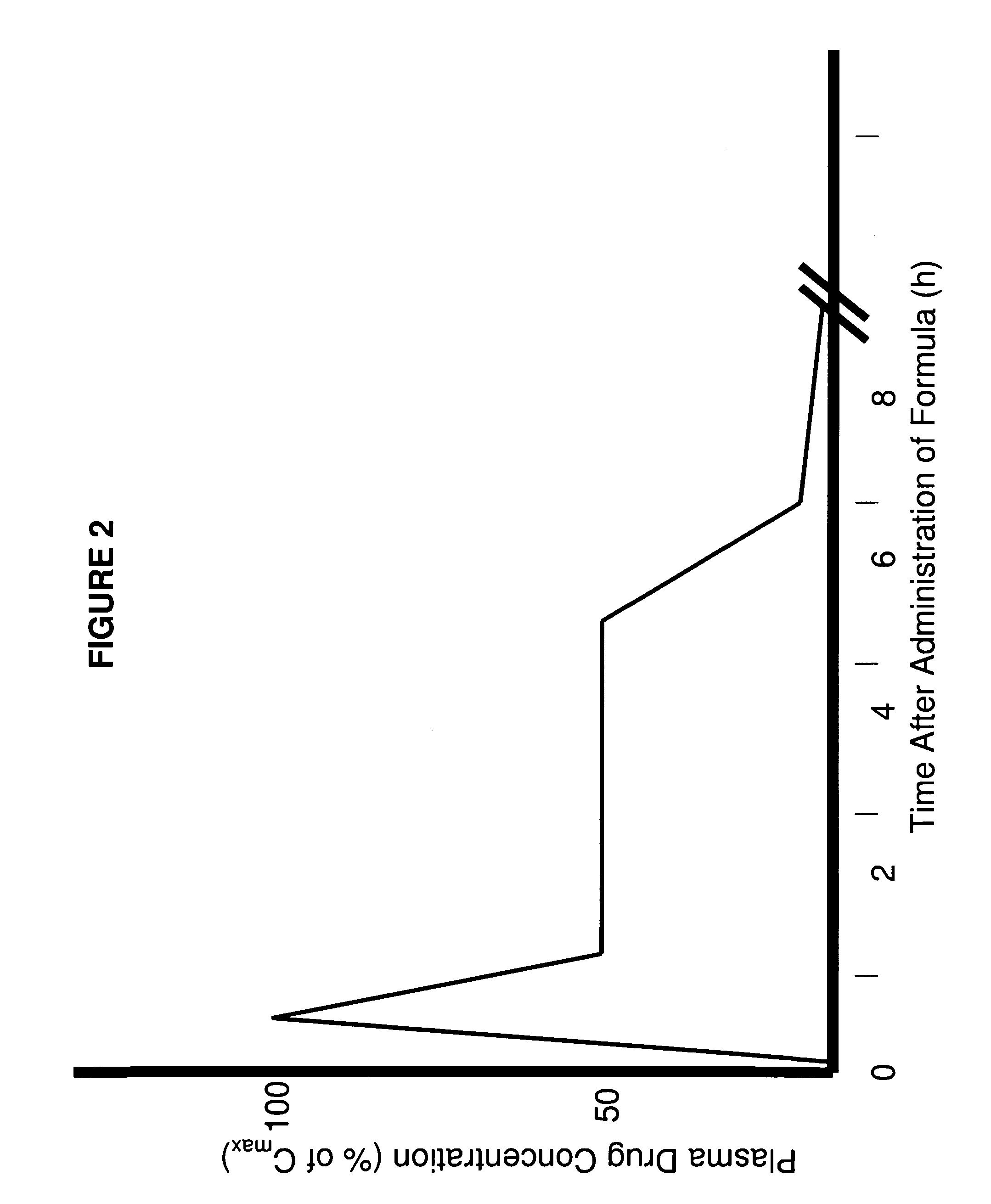
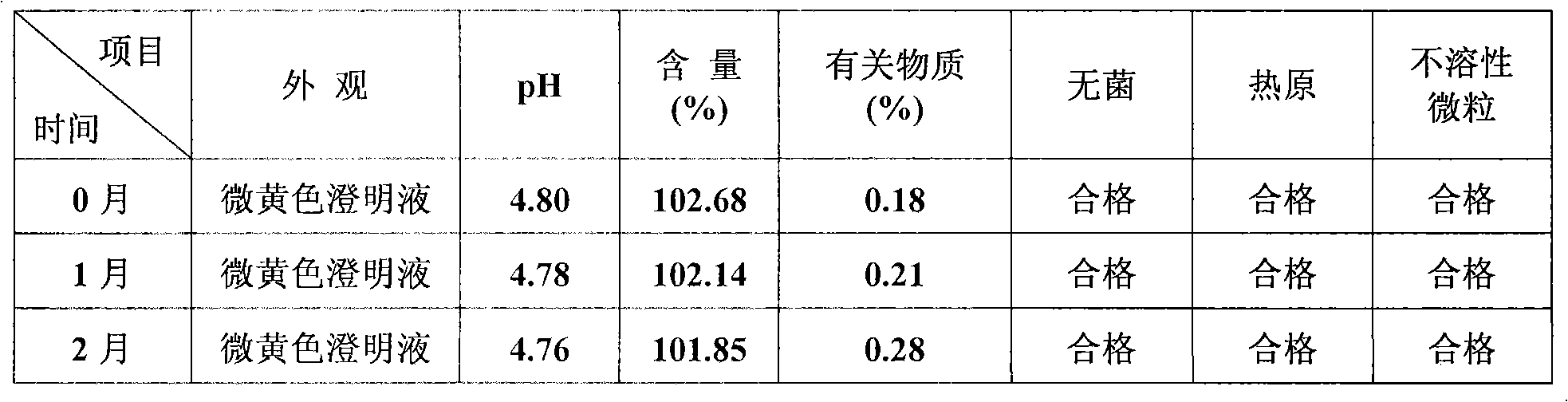
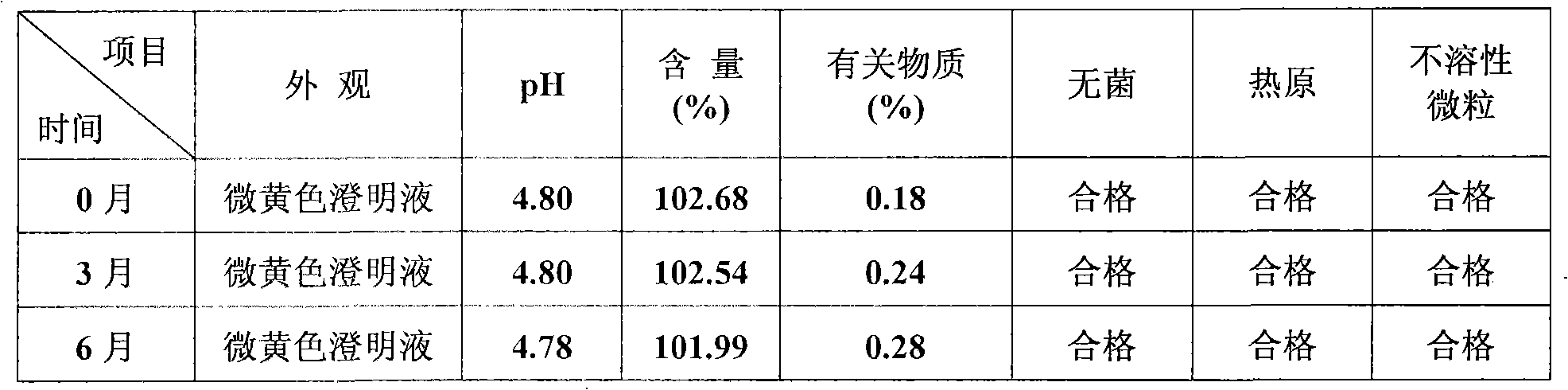
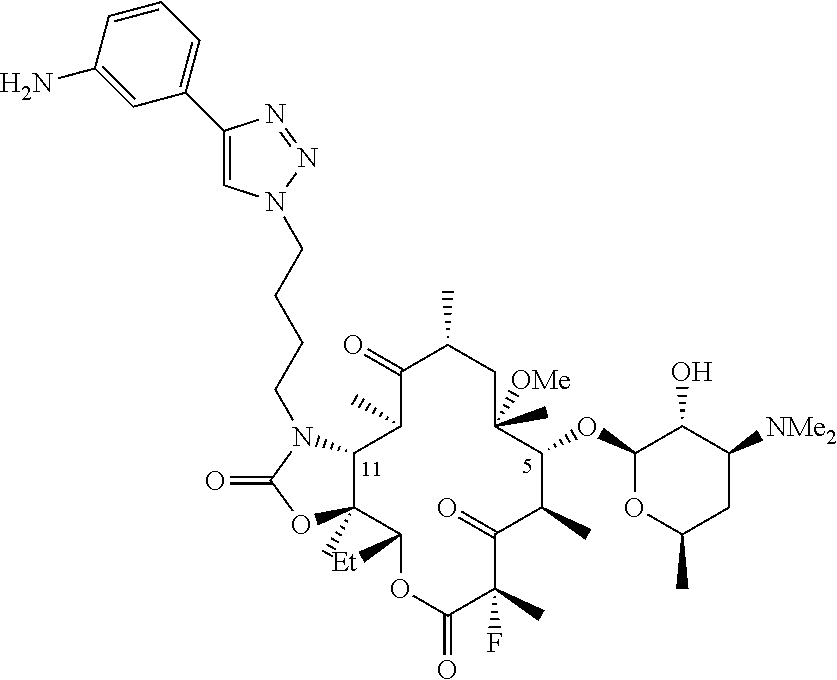
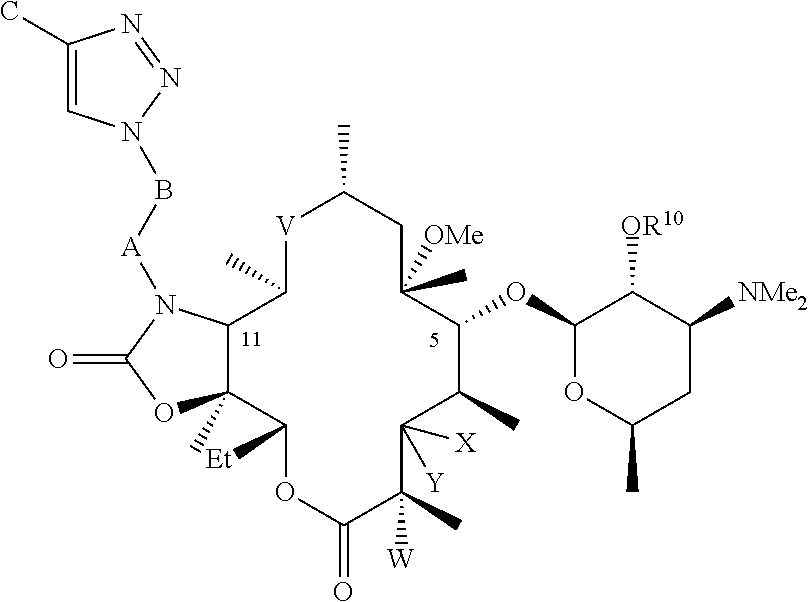
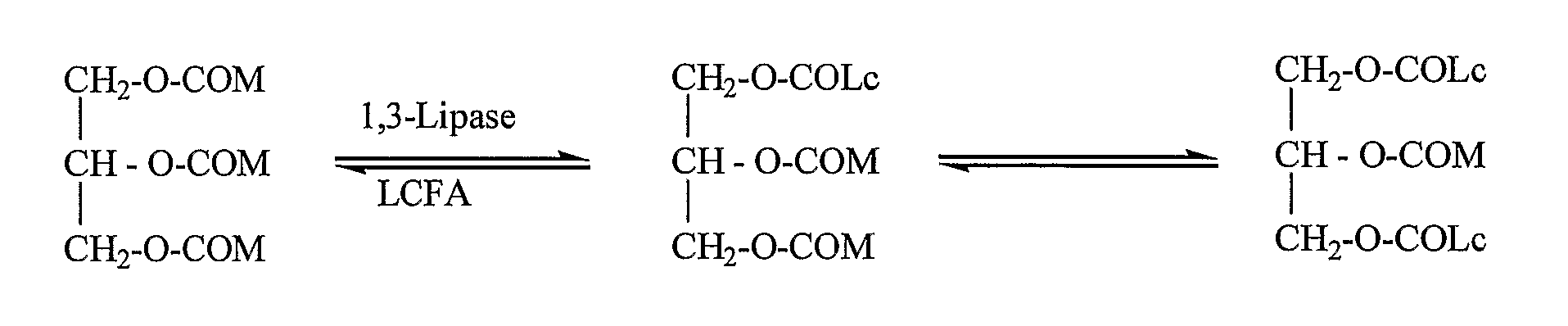Patents
Literature
120 results about "Parenteral nutrition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Parenteral nutrition (PN) is the feeding of specialist nutritional products to a person intravenously, bypassing the usual process of eating and digestion. The products are made by specialist pharmaceutical compounding companies and are considered to be the highest risk pharmaceutical preparations available as the products cannot undergo any form of terminal sterilization. The person receives highly complex nutritional formulae that contain nutrients such as glucose, salts, amino acids, lipids and added vitamins and dietary minerals. It is called total parenteral nutrition (TPN) or total nutrient admixture (TNA) when no significant nutrition is obtained by other routes, and partial parenteral nutrition (PPN) when nutrition is also partially enteric. It may be called peripheral parenteral nutrition (PPN) when administered through vein access in a limb rather than through a central vein as central venous nutrition (CVN).
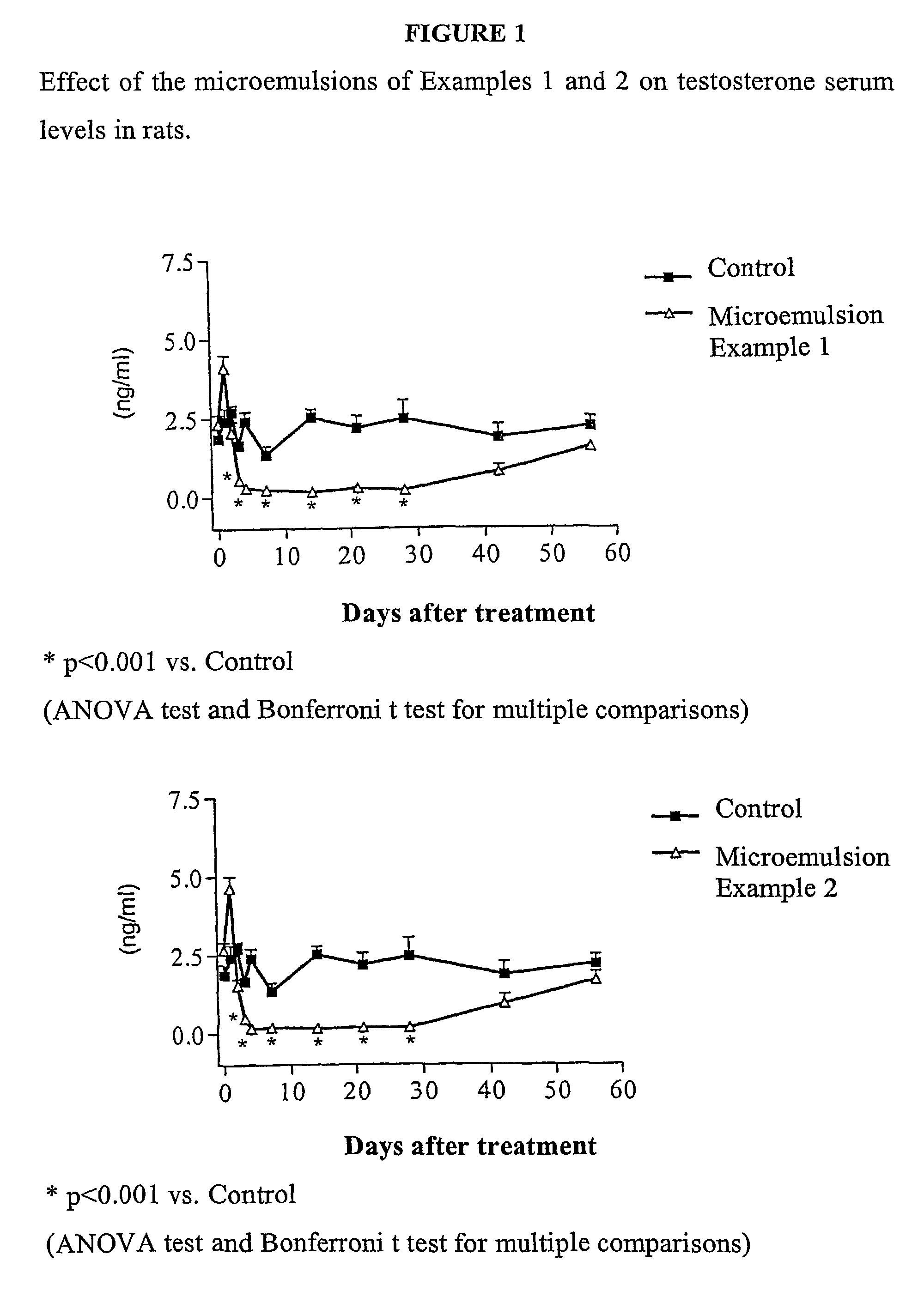
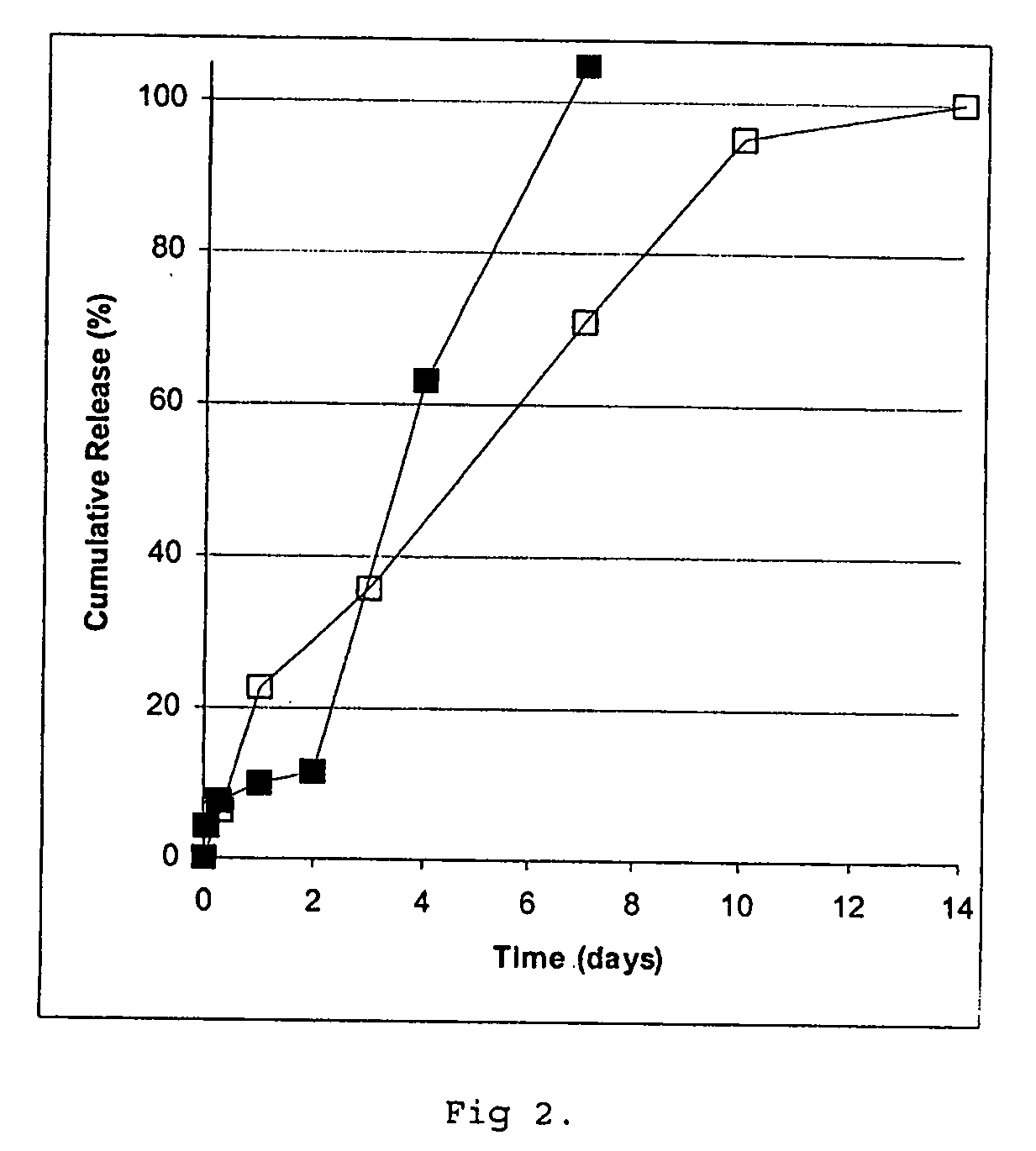
Sustained release pharmaceutical compositions for the parenteral administration of hydrophilic compounds
InactiveUS7157099B2Easy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsParenteral nutritionBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:ITALFARMACO SPA
Parenteral formulations of dopamine agonists
InactiveUS20100035886A1Reducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorReducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorsBiocideMetabolism disorderParenteral nutritionParenteral Dosage Form
This invention relates to stable pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral administration comprising dopamine agonists and peripheral acting agents useful for treatment of metabolic disorders or key elements thereof. The parenteral dosage forms exhibit long stable shelf life and distinct pharmacokinetics.
Owner:VEROSCI
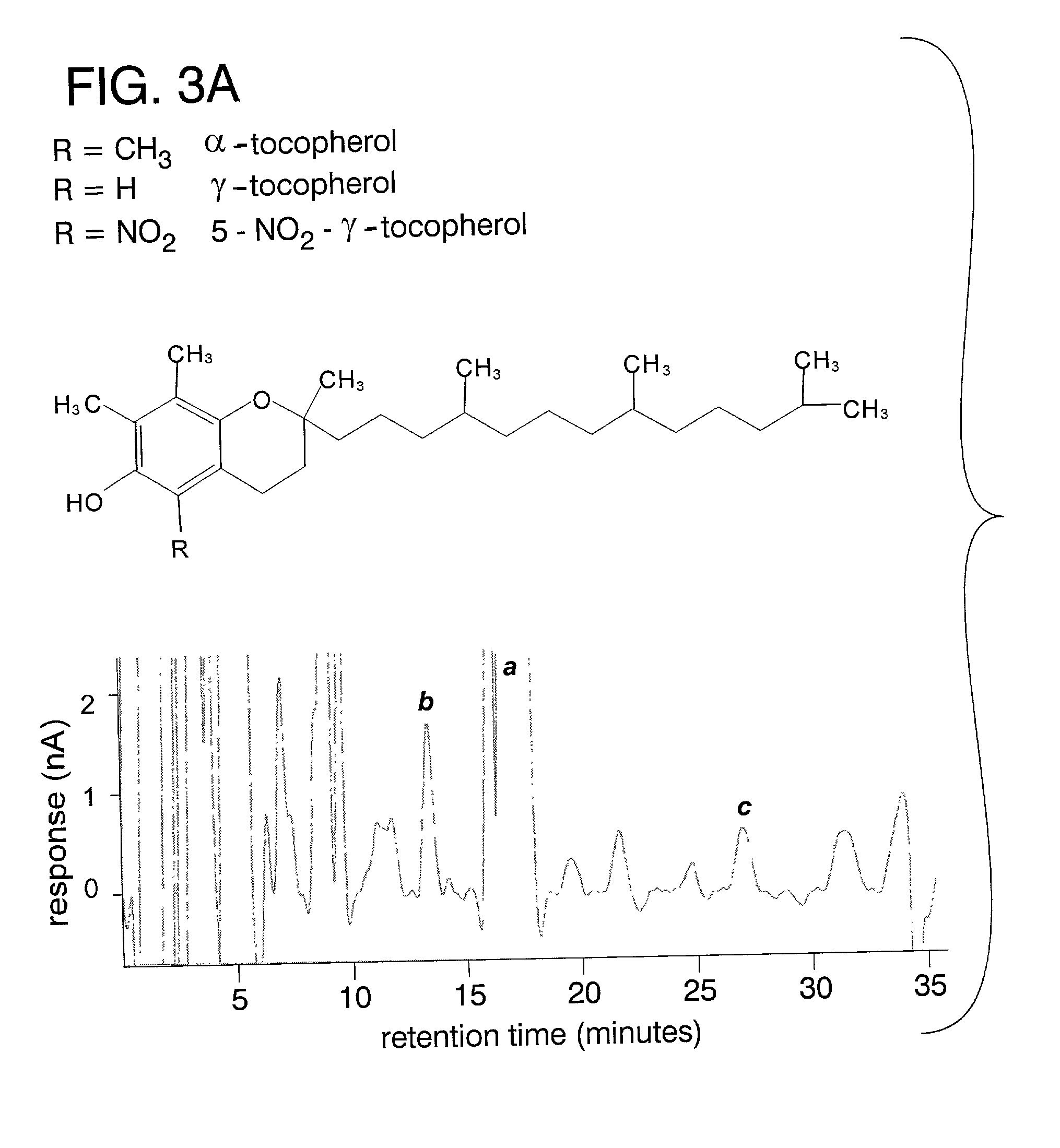
Desmethyl tocopherols for preventing or slowing degenerative neurological diseases
InactiveUS20020006954A1BiocideOrganic active ingredientsDegenerative neurologic diseasesParenteral nutrition
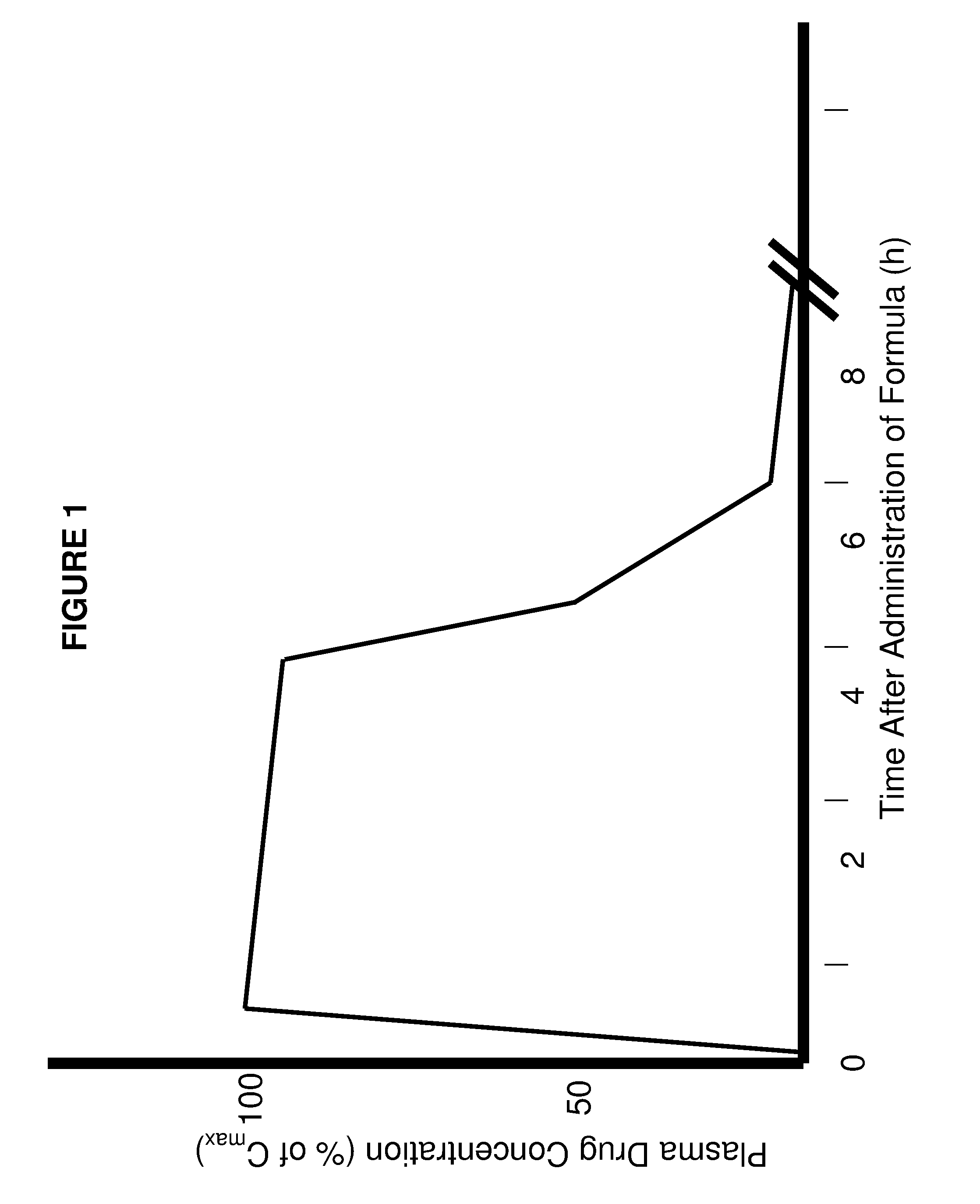
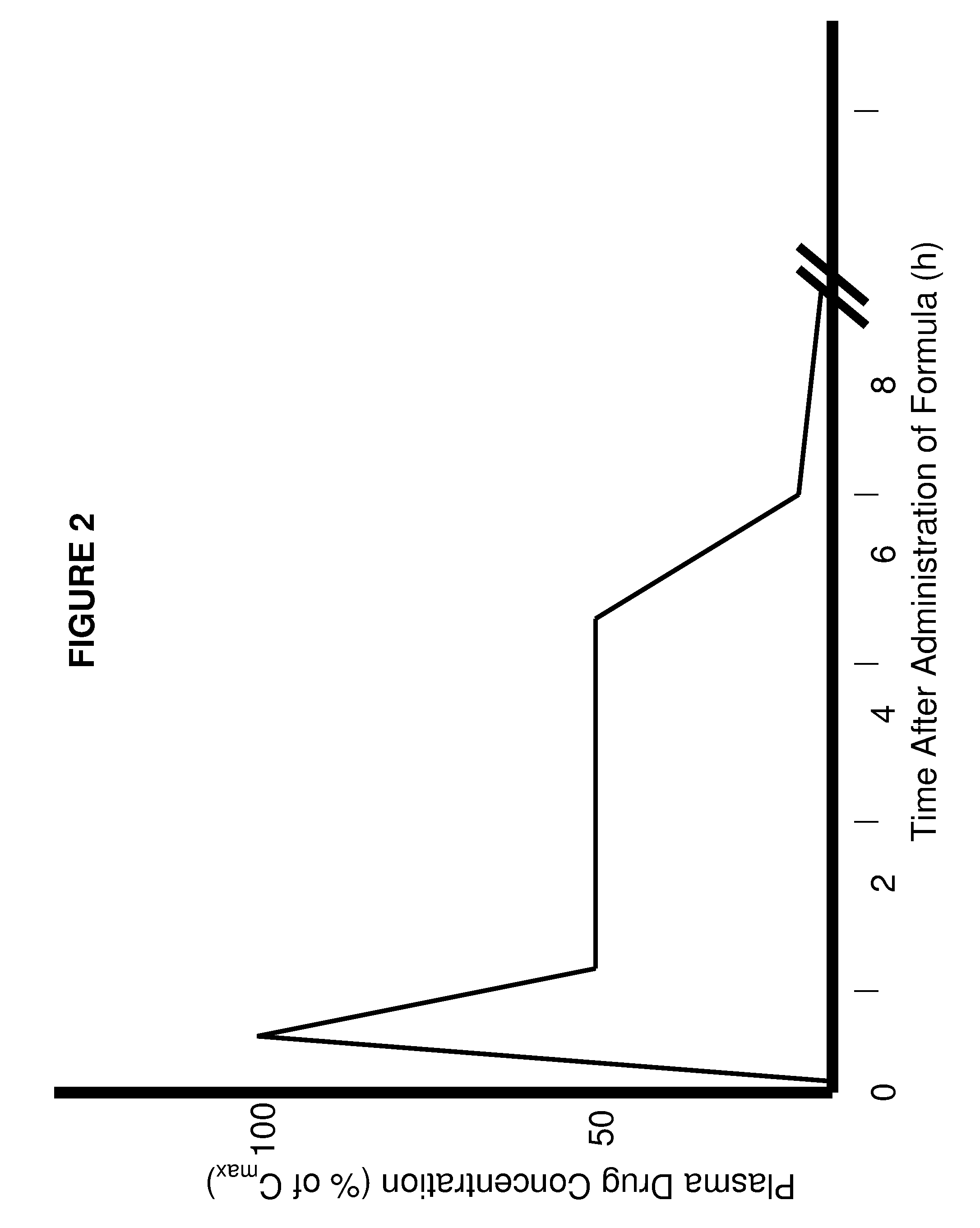
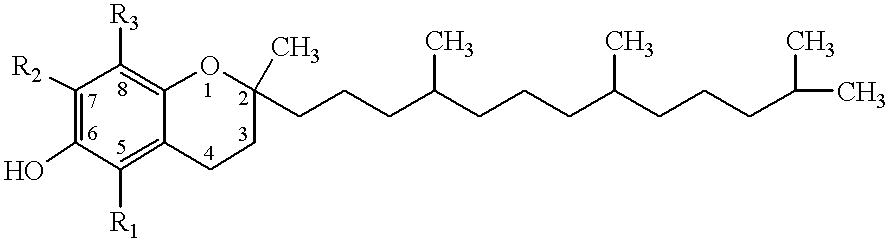
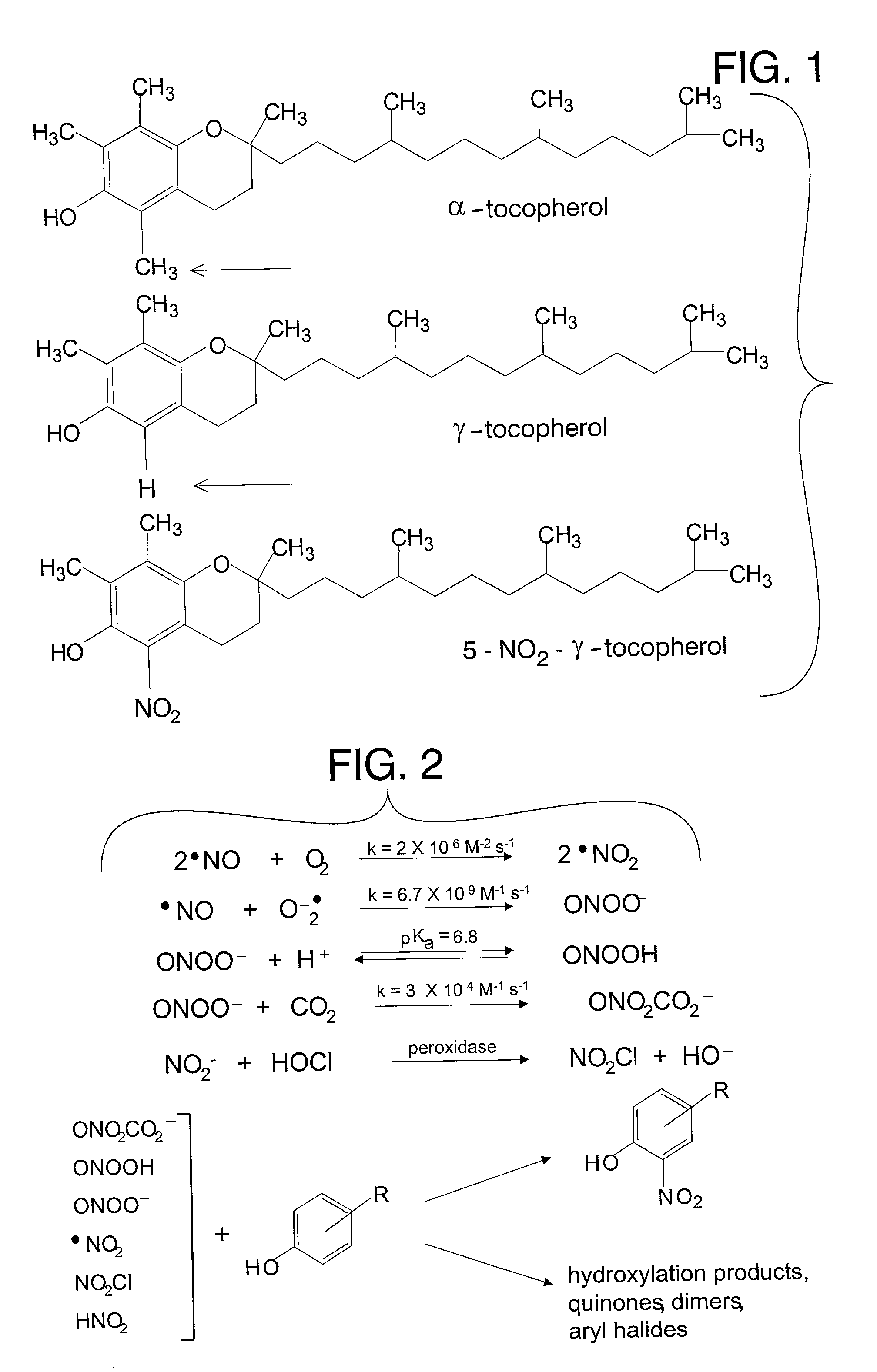
The present invention involves the use of desmethyl tocopherols such as gamma tocopherol for the prevention of and treatment of neurological disorders. Dietary or parenteral administration of desmethyl tocopherols inhibits the undesired nitration of neurological components.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
Pharmaceutical composition in form of solid lipidic microparticles suitable to parenteral administration
A method of making a pharmaceutical composition containing a drug and solid lipidic microparticles, which are suitable for parenteral administration and resistant to phagocytosis by macrophage, is described.
Owner:GASCO
Dry mouldable drug formulation
InactiveUS20050202072A1Easy and rapid and essentially painless injectionHigh strengthOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryParenteral nutritionDrug formulations
Solid pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral injection comprising a binder and at least one therapeutic agent. The pharmaceutical composition has the strength to be injected directly with the need of using cannulas or the like.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
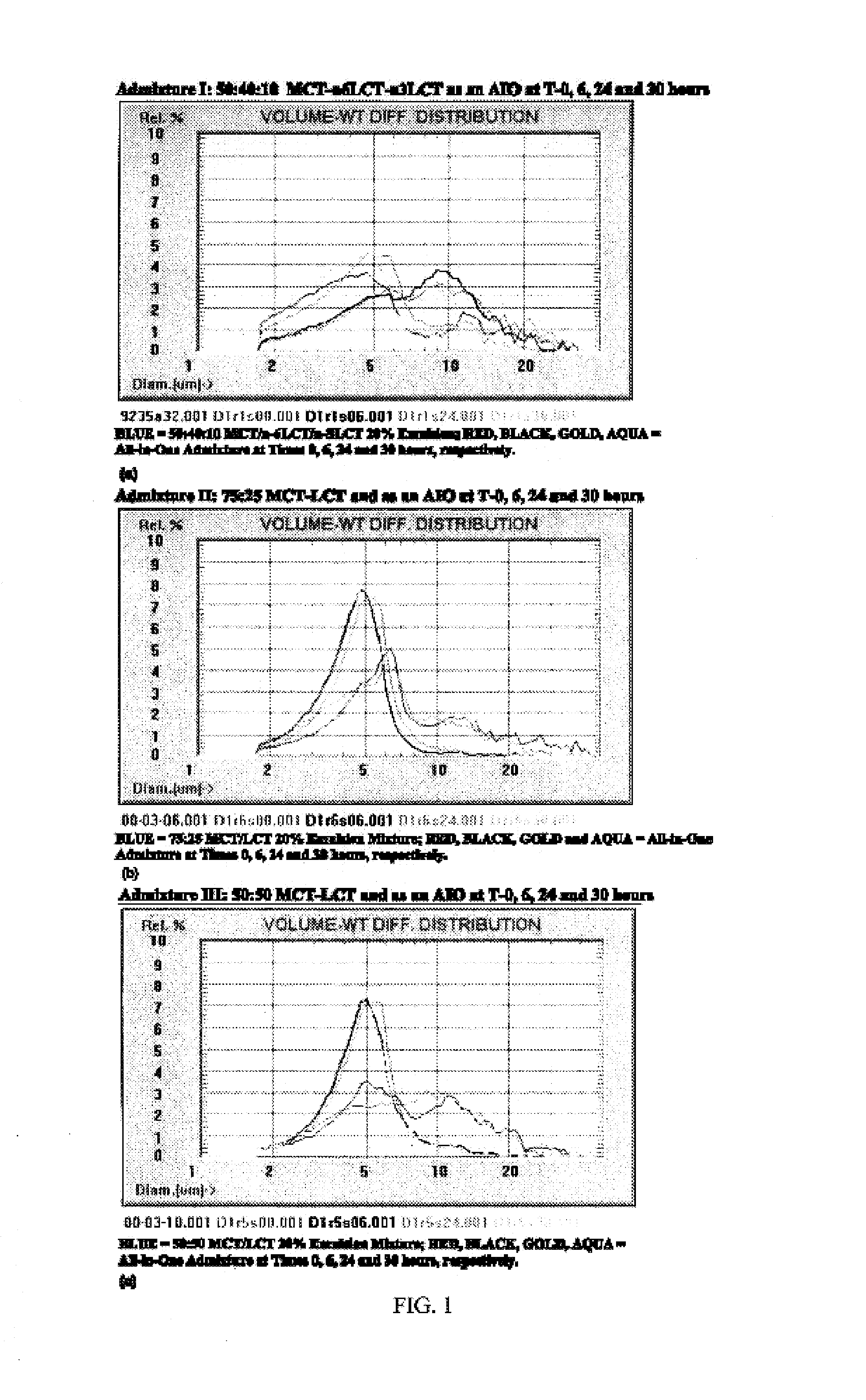
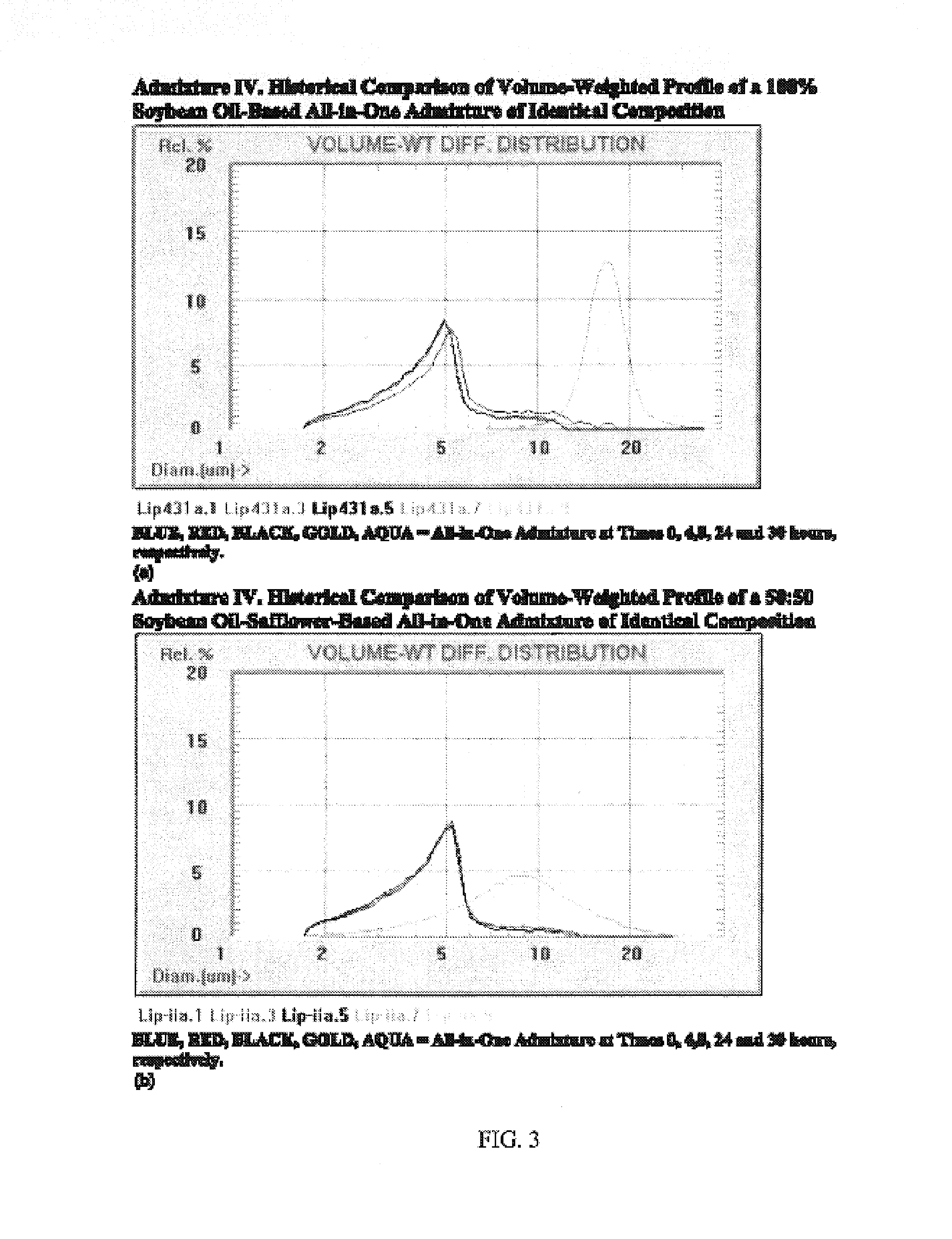
Reagents and methods for all-in-one total parenteral nutrition for neonates and infants
Materials and methods for preparing and using All-in-One (“AIO”) formulations suitable for administration to infants and neonates for total parenteral nutrition are provided.
Owner:B BRAUN MEDICAL
Stable nanoparticulate drug suspension
InactiveUS20100323020A1Convenient route of administrationEasy to doOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliverySodium bicarbonateDisease
A liquid pharmaceutical composition comprises an aqueous medium having suspended therein a solid particulate Bc1-2 family protein inhibitory compound such as ABT-263, having a D90 particle size not greater than about 3 μm; wherein the aqueous medium further comprises at least one pharmaceutically acceptable surfactant and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable basifying agent such as sodium bicarbonate in amounts that are effective together to inhibit particle size increase. The composition is suitable for oral or parenteral administration to a subject in need thereof for treatment of a disease characterized by overexpression of one or more anti-apoptotic Bc1-2 family proteins, for example cancer.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
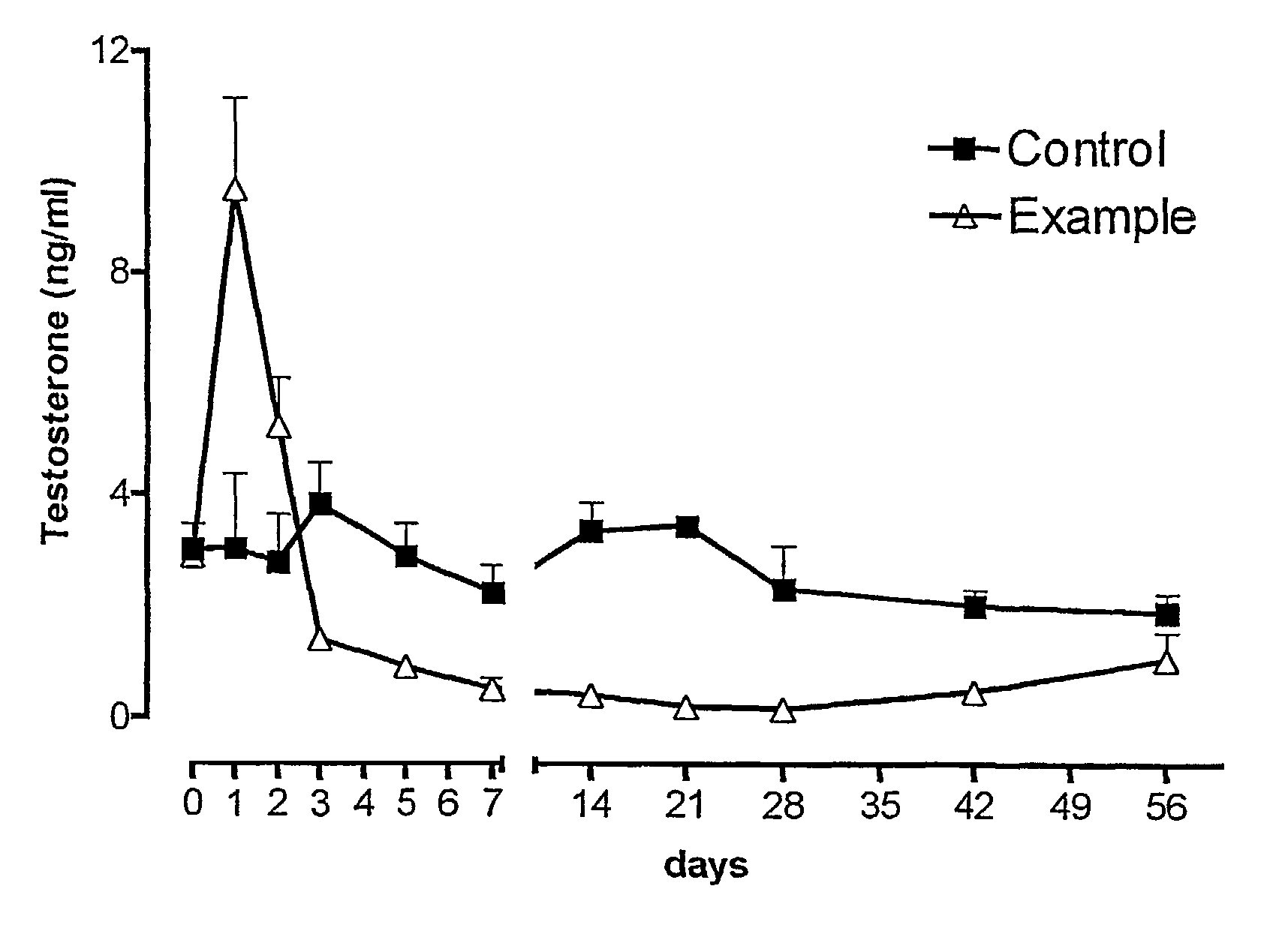
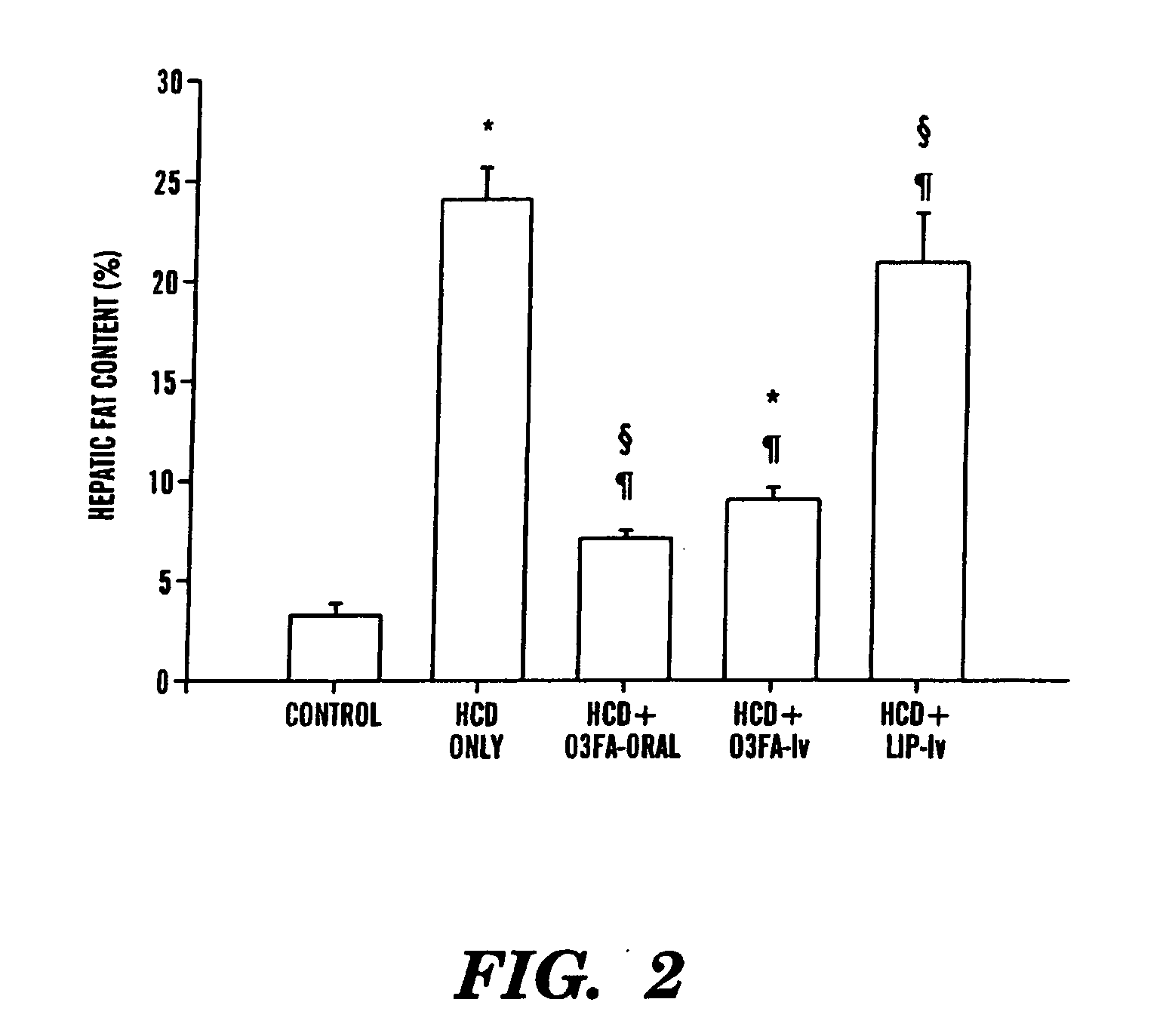
Treatment and prevention of liver disease associated with parenteral nutrition (PN)
The present invention is based on the discovery that parenteral nutrition (PN) induced liver disease, e.g. fatty liver disease, can be prevented and even reversed by administration of primarily omega-3-fatty acid with PN rather than the administration of the standard intravenous lipid emulsions that contain primarily plant derived omega-6 fatty acid. Thus, the present invention provides a method for treating or preventing liver disease in a human patient obtaining nutritional support through PN. The method comprises intravenous administration of an effective amount of an omega-3-fatty acid emulsion to the patient, wherein the patient is not administered phytosterols or plant derived fatty acids, e.g. omega-6 fatty acids derived from a plant source, and wherein the administration of the omega-3-fatty acid emulsion to the patient is for a period greater than three weeks. Preferably, the administration is for a period of greater than six weeks. More preferably, the administration is for a period greater than three months.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Stable amorphous amifostine compositions and dosage form
The present invention relates to a sterile, stable dosage forms suitable for reconstitution and parenteral administration to a patient, said dosage form comprising an amorphous aminoalkyl dihydrogen phosphorothioate, and of amifostine in particular. The invention further relates to a method of preparing such a dosage form, which typically exhibits enhanced thermal stability as compared to existing vacuum dried amorphous amifostine.
Owner:CLINIGEN GRP PLC
Parenteral formulations of dopamine agonists
ActiveUS8741918B2Reducing elevated cardiovascular-related inflammatory factorsBiocideAntipyreticParenteral nutritionParenteral Dosage Form
This invention relates to stable pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral administration comprising dopamine agonists and peripheral acting agents useful for treatment of metabolic disorders or key elements thereof. The parenteral dosage forms exhibit long stable shelf life and distinct pharmacokinetics.
Owner:VEROSCI
Aqueous formulation of erythropoiesis stimulating protein stabilised by antioxidants for parenteral administration
ActiveUS20100297117A1Improve stabilityIncrease resistancePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismParenteral nutritionAntioxidant
The present invention relates to stable aqueous protein formulations. In particular, disclosed herein are therapeutic protein formulations suitable for parenteral administration having one or more antioxidants.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Coenzyme Q10 injection
InactiveCN101278907AStrong solubilizing abilityLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismParenteral nutritionHydroxystearic Acid
The invention discloses the novel combined coenzyme Q10 parenteral solution, mainly containing the coenzyme Q10 as active component, polyethylene glycol 15-hydroxyl stearate as solubilizing agent and water for injection as solvent. One or more solvents of cosolvent, acidity regulator, osmoregulator and stabilizing agents can be also added. Low hemolyzation, extreme low histamine release and higher physiological tolerance of a novel solubilizing agent Solutol HS 15 adopted by the parenteral solution remarkably improves clinical medication security and the compliance of a patient; and the parenteral solution has the advantages of good stability, longer period of validity, higher medication convenience for a clinician, better storage and stable transportation, higher security for the clinical medication and better compliance of the patient. The parenteral solution also has the advantages of simple preparation technology, simple and convenient quality control and lower production cost, thereby being beneficial to industrialization production.
Owner:郑微
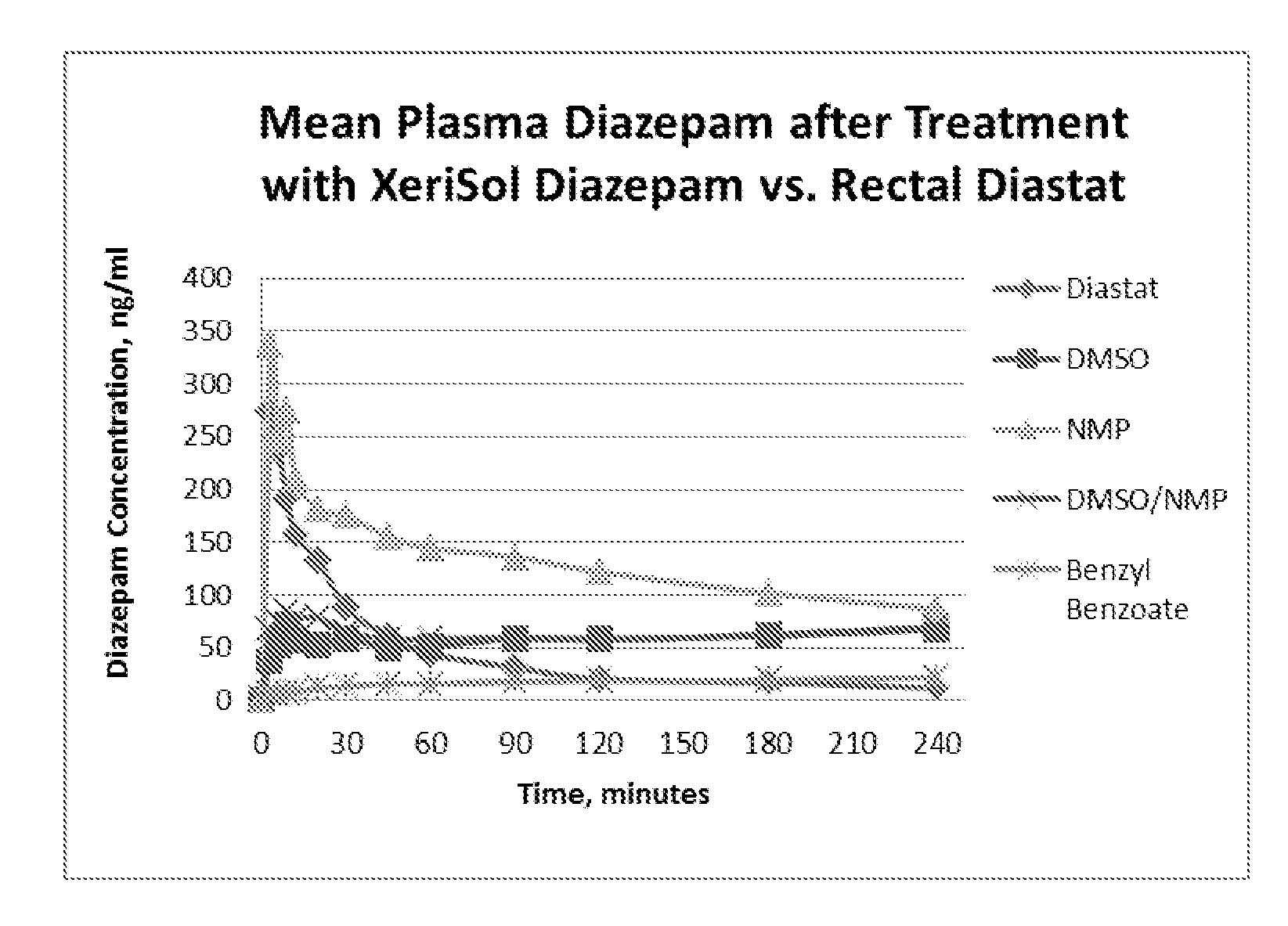
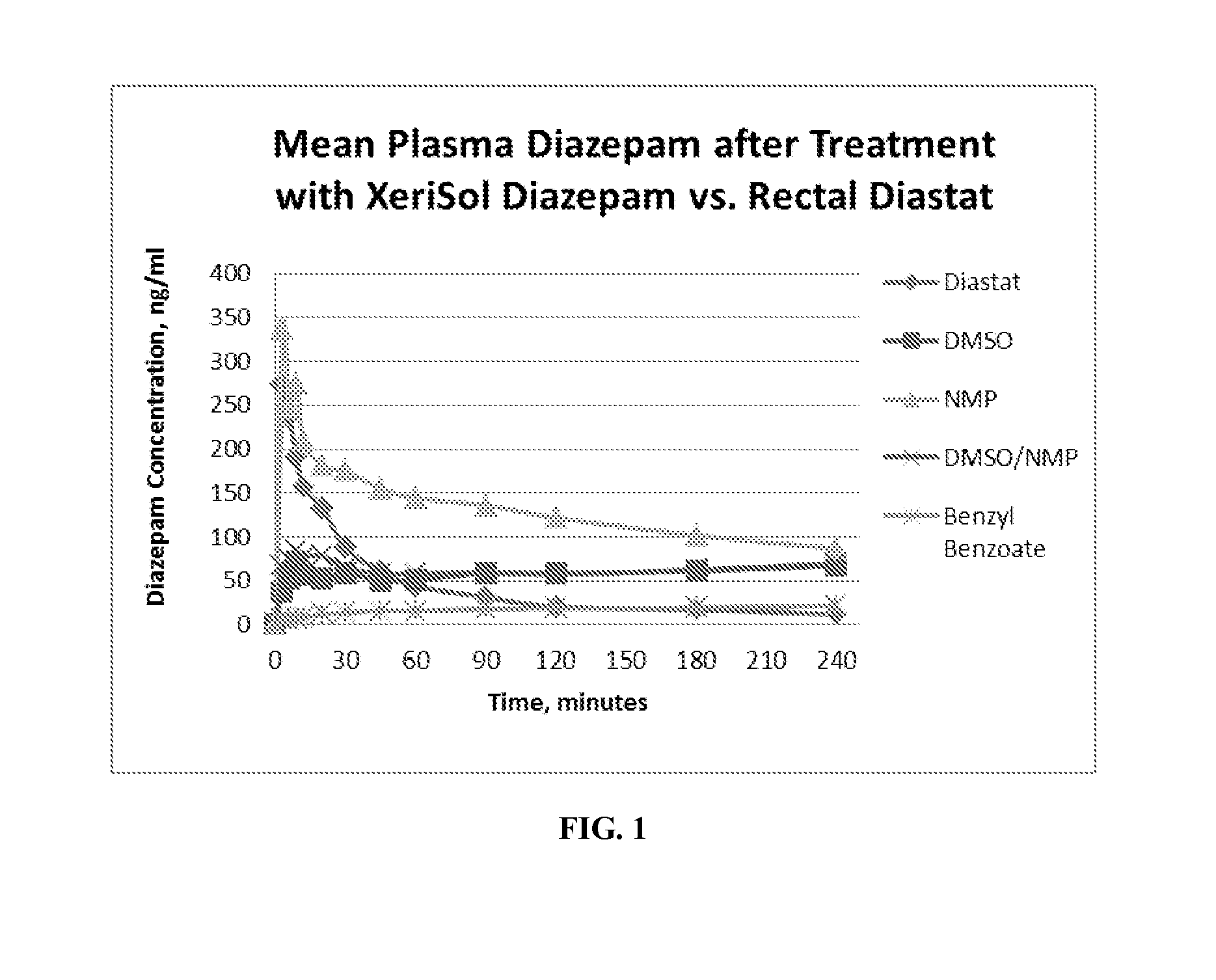
Stable formulations for parenteral injection of small molecule drugs
Disclosed is a stable liquid formulation for parenteral injection comprising a biocompatible non-aqueous solvent and a small molecule drug, or a salt thereof, solubilized within the non-aqueous solvent, wherein the liquid formulation comprises less than 10% by weight residual water, and wherein the volume of the liquid formulation to be parenterally injected is from 0.1 μl to 3 ml.
Owner:XERIS PHARMA INC
Stable pharmaceutical compositions
Pharmaceutical composition for parenteral administration comprising a glucagon-like peptide and human serum albumin or a variant thereof.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Parenteral administration of pyrophosphate for prevention or treatment of phosphate or pyrophosphate depletion
Phosphate depletion, a physiological condition commonly seen in certain patient populations, including alcoholics, malnourished, acutely ill patients, patients receiving parenteral nutrition, patients being re-fed after prolonged fasting, and dialysis patients, requires intravenous supplementation when oral repletion is not feasible. This invention provides a method and pharmaceutical composition for therapeutic administration of pyrophosphate, instead of phosphate, for phosphate or pyrophosphate repletion. During hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis significant removal of phosphate and pyrophosphate occurs. Pyrophosphate depletion predisposes patients to vascular calcification. This invention further provides a method and pharmaceutical composition for therapeutic administration of pyrophosphate for phosphate or pyrophosphate repletion by addition of pyrophosphate to hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis solutions.
Owner:GUPTA AJAY
Structured Triglycerides And Emulsions Comprising Same
InactiveUS20070281993A1Good source of energyNot increase blood triglyceride levelBiocideEdible oils/fats ingredientsParenteral nutritionEmulsion
The present invention relates to structured triglyceride, to parental nutrition emulsions comprising same, and use thereof. In particular, the invention relates to structured triglycerides comprising at least one medium chain C6-C12 fatty acid and at least one fatty acid selected from the group consisting of long chain C14-C18 or very long chain C20-C22 fatty acids, preferably each fatty acid is present in a predetermined position of the glycerol backbone. The parenteral nutrition emulsions are particularly useful for nourishing preterm-and term-infants, children, critically ill patients, and cancer patients.
Owner:HTL HIGH TECH LIPIDS
Parenteral formulations of macrolide antibiotics
Described herein are pharmaceutical compositions adapted for the parenteral administration of macrolide antibiotics, such as triazole-containing and fluoroketolide antibiotics. Also described herein are methods for their use in the treatment of bacterial, protozoal, and other infections.
Owner:CEMPRA PHARMA INC
Stabilized pharmaceutical peptide compositions
ActiveUS7632806B2Improve stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderNeutral phParenteral nutrition
A method is disclosed for increasing the shelf-life of a pharmaceutical composition for parenteral administration comprising a glucagon-like peptide which is prepared from a peptide product that has been subjected to treatment at a pH above neutral pH.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
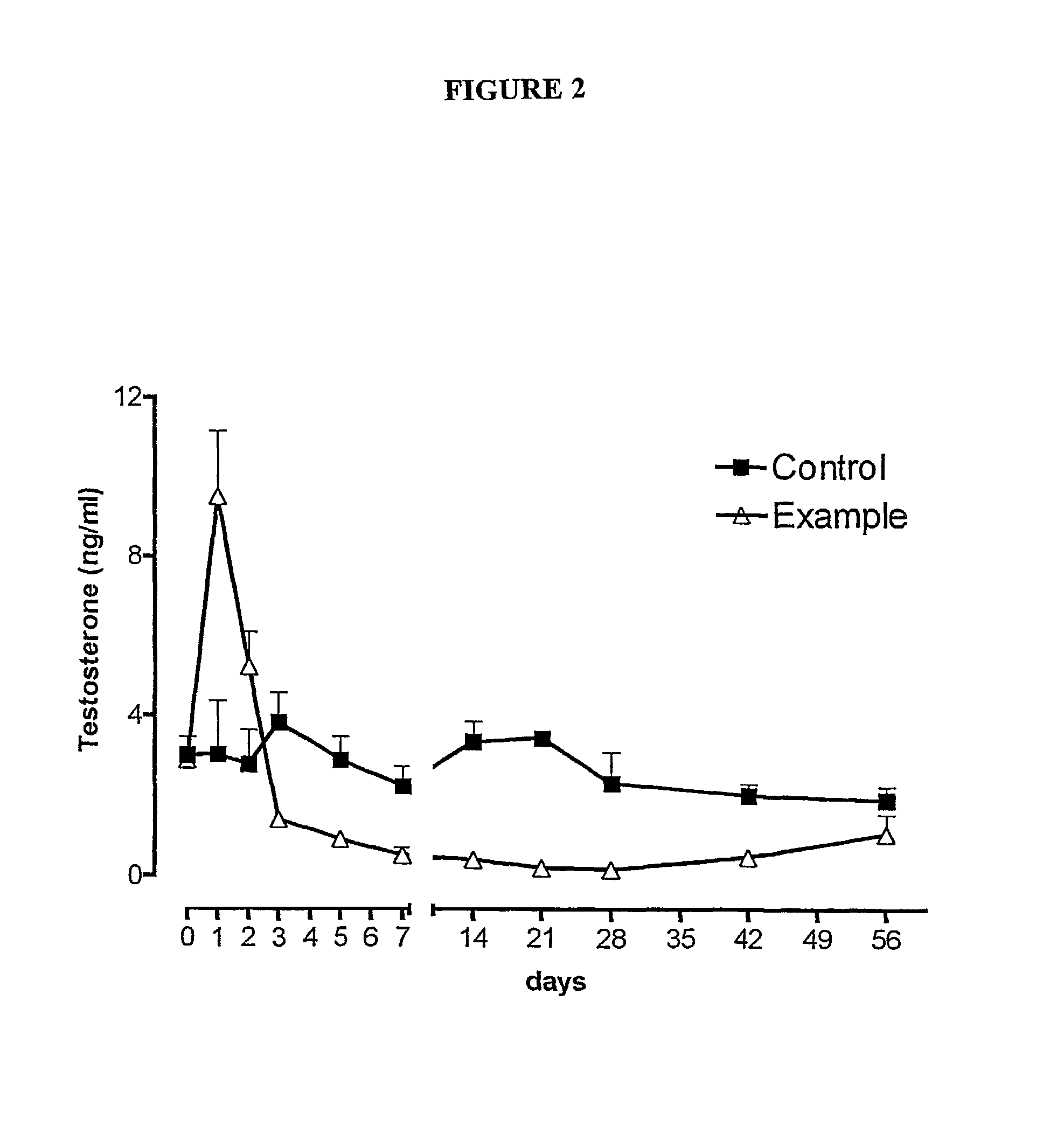
Treatment and Prevention of Liver Disease Associated with Parenteral Nutrition (PN)
The present invention is based on the discovery that parenteral nutrition (PN) induced liver disease, e.g. fatty liver disease, can be prevented and even reversed by administration of primarily omega-3-fatty acid with PN rather than the administration of the standard intravenous lipid emulsions that contain primarily plant derived omega-6 fatty acid. Thus, the present invention provides a method for treating or preventing liver disease in a human patient obtaining nutritional support through PN. The method comprises intravenous administration of an effective amount of an omega-3-fatty acid emulsion to the patient, wherein the patient is not administered phytosterols or plant derived fatty acids, e.g. omega-6 fatty acids derived from a plant source, and wherein the administration of the omega-3-fatty acid emulsion to the patient is for a period greater than three weeks. Preferably, the administration is for a period of greater than six weeks. More preferably, the administration is for a period greater than three months.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Pharmaceutical composition for parenteral administration of idebenone
InactiveUS20100130619A1Formula stableHigh shear mixingBiocideNervous disorderParenteral nutritionIdebenone
Owner:ALPHARX
Structured triglycerides and emulsions comprising same
InactiveUS7919526B2Enhanced advantageFunction increaseBiocideEdible oils/fats ingredientsEmulsionParenteral nutrition
The present invention relates to structured triglyceride, to parental nutrition emulsions comprising same, and use thereof. In particular, the invention relates to structured triglycerides comprising at least one medium chain C6-C12 fatty acid and at least one fatty acid selected from the group consisting of long chain C14-C18 or very long chain C20-C22 fatty acids, preferably each fatty acid is present in a predetermined position of the glycerol backbone. The parenteral nutrition emulsions are particularly useful for nourishing preterm- and term-infants, children, critically ill patients, and cancer patients.
Owner:HTL HIGH TECH LIPIDS
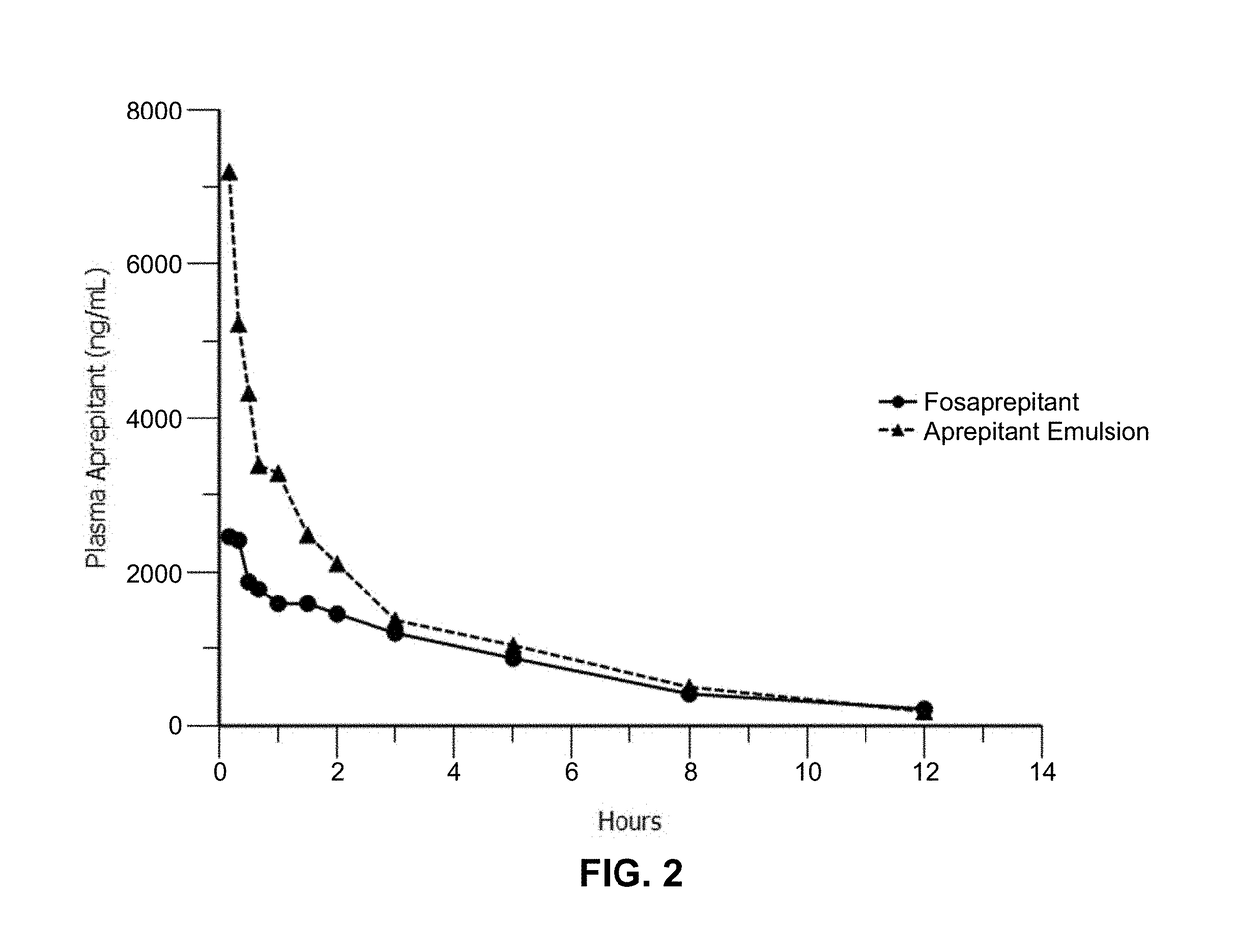
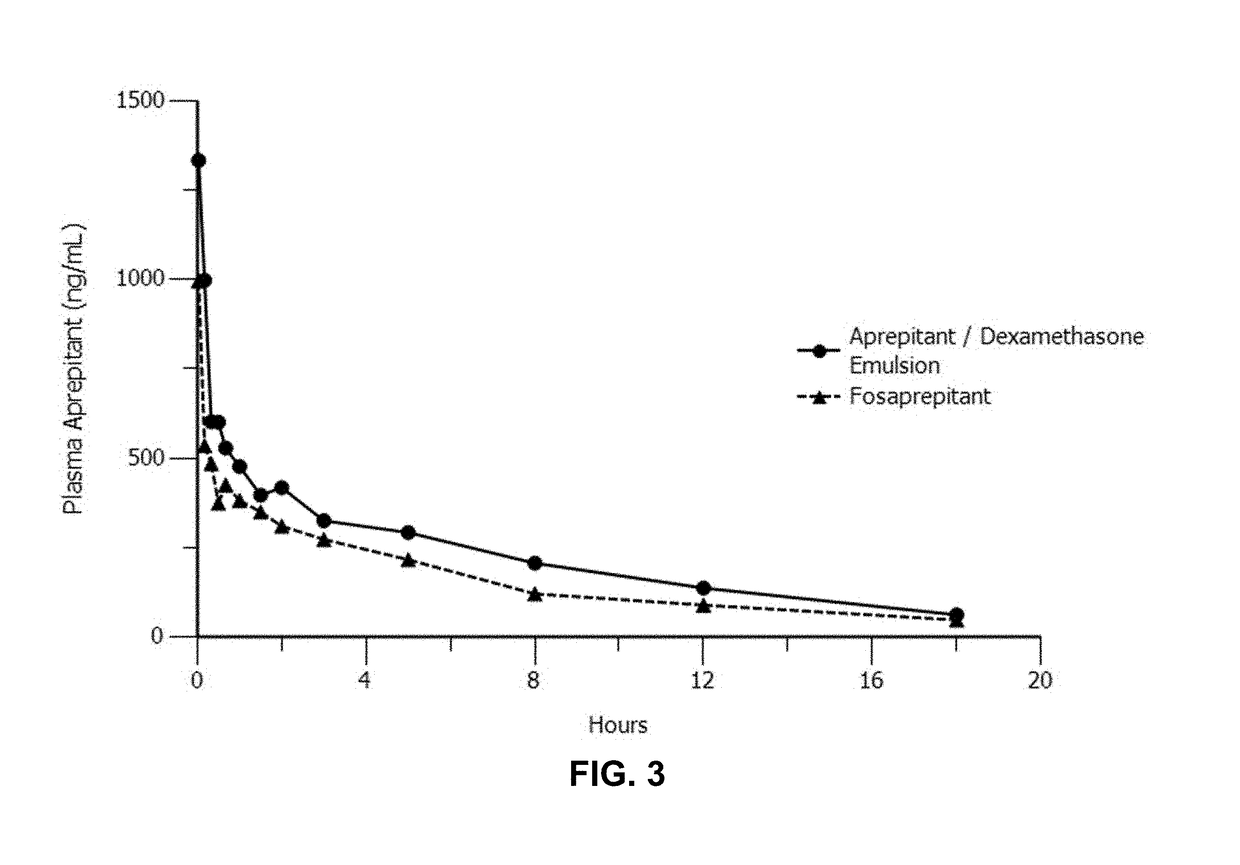
Emulsion formulations of an nk-1 receptor antagonist and uses thereof
Disclosed herein are novel pharmaceutical formulations of a neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor antagonist suitable for parenteral administration including intravenous administration. Also included are formulations including both the NK-1 receptor antagonist and dexamethasone sodium phosphate. The pharmaceutical formulations are stable oil-in-water emulsions for non-oral treatment of emesis and are particularly useful for treatment of subjects undergoing highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy.
Owner:HERON THERAPEUTICS
Dry mouldable drug formulation
InactiveUS7666844B2High strengthEasy and rapid and essentially painless injectionBiocidePowder deliveryParenteral nutritionDrug formulations
Solid pharmaceutical compositions for parenteral injection comprising a binder and at least one therapeutic agent. The pharmaceutical composition has the strength to be injected directly with the need of using cannulas or the like.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Injection simulator
ActiveUS8714984B2Prevent rotationAutomatic syringesEducational modelsParenteral nutritionBiomedical engineering
Injection training devices comprising elements for repeatable and accurate simulation of parenteral injection for training individuals in the administration of one or more medications are provided.
Owner:ONE WORLD DESIGN & MFG GROUP
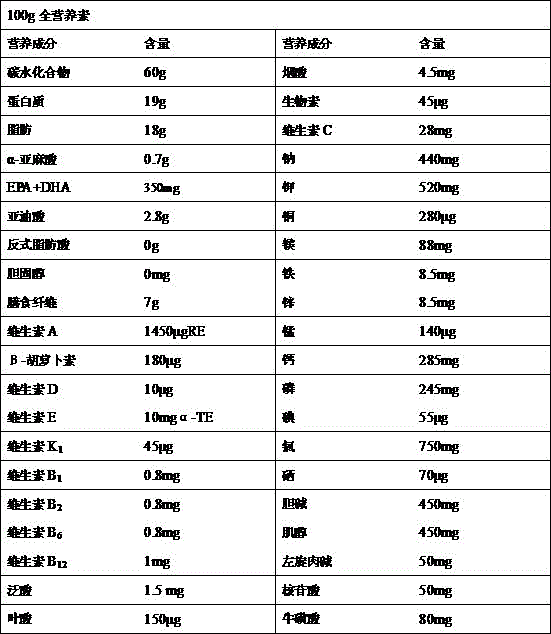
Nutrition formulations and methods of providing nutrition formulations
InactiveUS20060275909A1Lower protein levelBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsParenteral nutritionMetabolite
Nutritional compositions such as total parenteral nutrition (TPN) compositions and processes of preparing same are disclosed. The advantage of the present invention lies in its ability to tailor TPN composition to the needs of each individual patient. Various components of the TPN composition may be increased, lowered, or removed based on the measurement of concentration of components and / or their metabolites in patient's blood.
Owner:PEDIATRIX MEDICAL GRP
Strychnos alkaloid vesicle and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101797239AIncrease contentImprove sensory center functionAntipyreticAnalgesicsParenteral nutritionSide effect
The invention discloses a strychnos alkaloid vesicle and a preparation method thereof, and a preparation containing the strychnos alkaloid vesicle and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of medicinal preparations. The strychnos alkaloid vesicle is prepared from strychnos alkaloid, a nonionic surfactant and an additive. The strychnos alkaloid vesicle is preferably prepared into an external gel preparation. The strychnos transdermal administration external preparation has unique advantages on the medicament that: a novel vesicle administration system is applied; trandermal absorption of the medicament is increased; the clinical treatment effects are enhanced; and the toxic and side effects during oral administration and parenteral administration are avoided. The strychnos alkaloid vesicle can be applied to treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and the like.
Owner:ZHANGZHOU PIEN TZE HUANG PHARM +1
Cores and microcapsules suitable for parenteral administration as well as process for their manufacture
InactiveUS20060269606A1Prevent and reduce aggregationImprove stabilityPowder deliveryWood working apparatusParenteral nutritionBiomedical engineering
Process for producing parenterally administrable cores. The cores are intermediates suitable for manufacturing sustained release preparations. Microcapsules incorporating a core and a shell and pharmaceutical compositions incorporating such cores and microcapsules are also provided.
Owner:STRATOSPHERE PHARMA
Stable formulations for parenteral injection of small molecule drugs
Disclosed is a stable liquid formulation for parenteral injection comprising a biocompatible non-aqueous solvent and a small molecule drug, or a salt thereof, solubilized within the non-aqueous solvent, wherein the liquid formulation comprises less than 10% by weight residual water, and wherein the volume of the liquid formulation to be parenterally injected is from 0.1 μl to 3 ml.
Owner:XERIS PHARMA
Total nutrient formula containing marine active substances for FSMP (foods for special medical purpose) and preparation method of total nutrient formula
InactiveCN106579345APromote absorptionUniform designFood ingredient functionsVeinParenteral nutrition
The invention belongs to the field of FSMP (foods for special medical purpose) and particularly relates to a total nutrient formula containing marine active substances for FSMP and a preparation method of the total nutrient formula. According to requirements specified in 'general principles of FSMP', the formula is prepared from fine proteins, composite vegetable oil and carbohydrate taken as main raw materials as well as various vitamins and minerals as auxiliary materials by blending. The formula food adopts reasonable nutrient configuration, is easy to digest and absorb, can be taken as a single nutrient source to meet nutritional requirements of people with limited eating and can be also taken as a nutritional supplement before or after an operation of a patient. The food is simple and safe to take, risks caused by the fact that nutrients are infused directly into veins (parenteral nutrition) are reduced, and digestion-absorption functions of the patient can be promoted to play a role.
Owner:QINGDAO CHENLAND MARINE BIOTECH CO LTD
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising GLP-1 peptides or exendin-4 and a basal insulin peptide
Pharmaceutical composition for parenteral administration comprising a basal insulin peptide and an insulinotropic GLP-1 peptide comprising at least 6 zinc atoms per 6 insulin molecules.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com