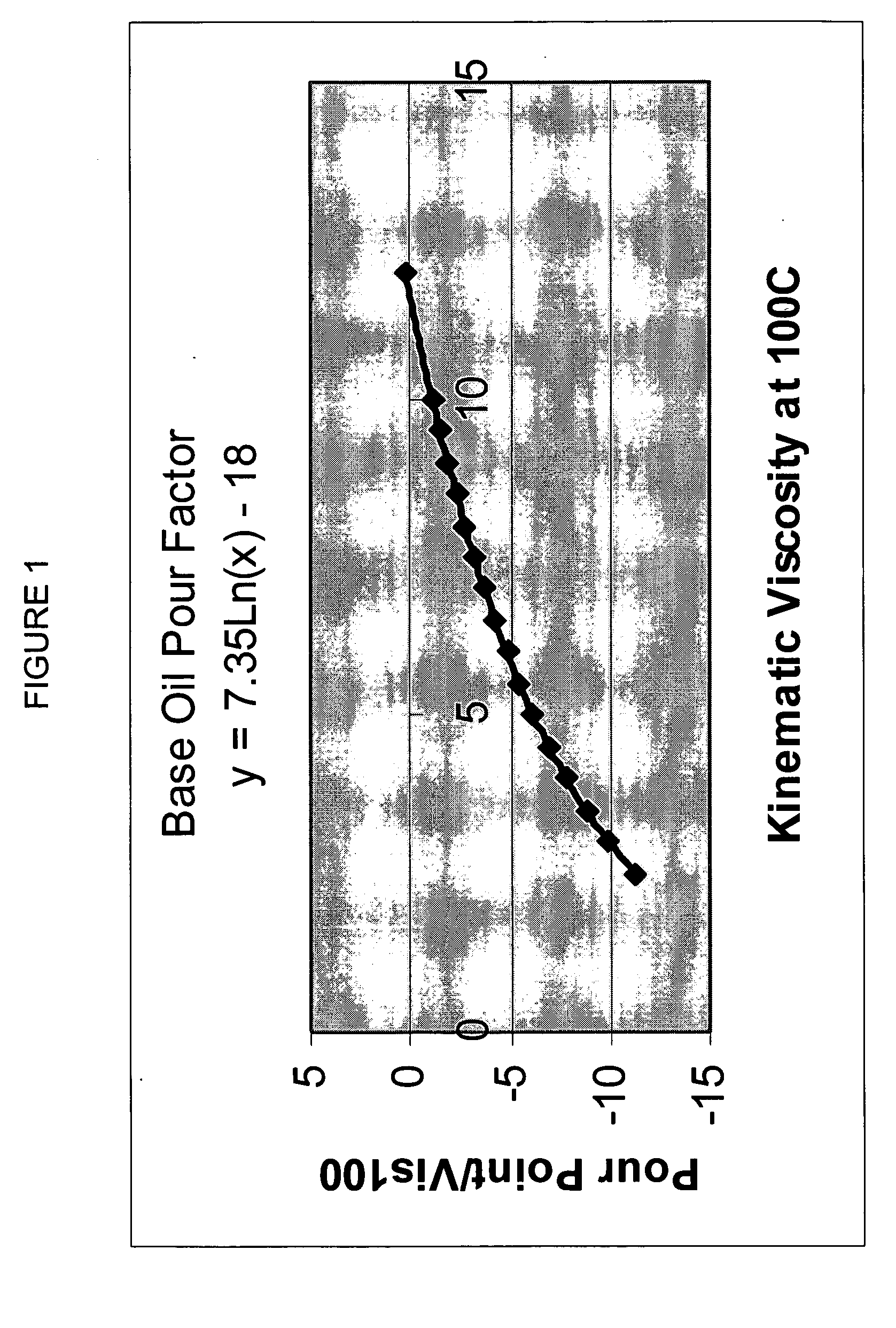
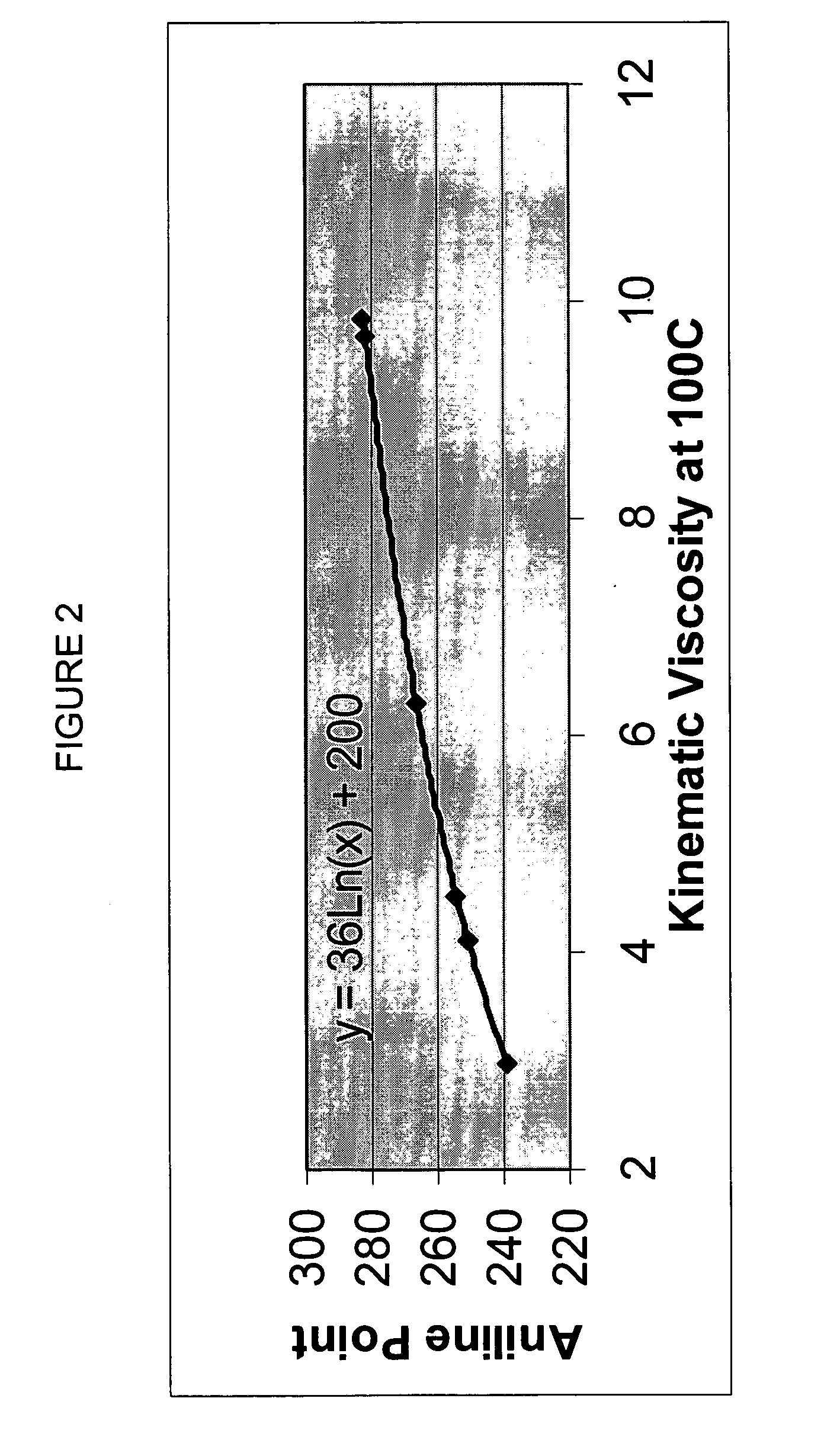
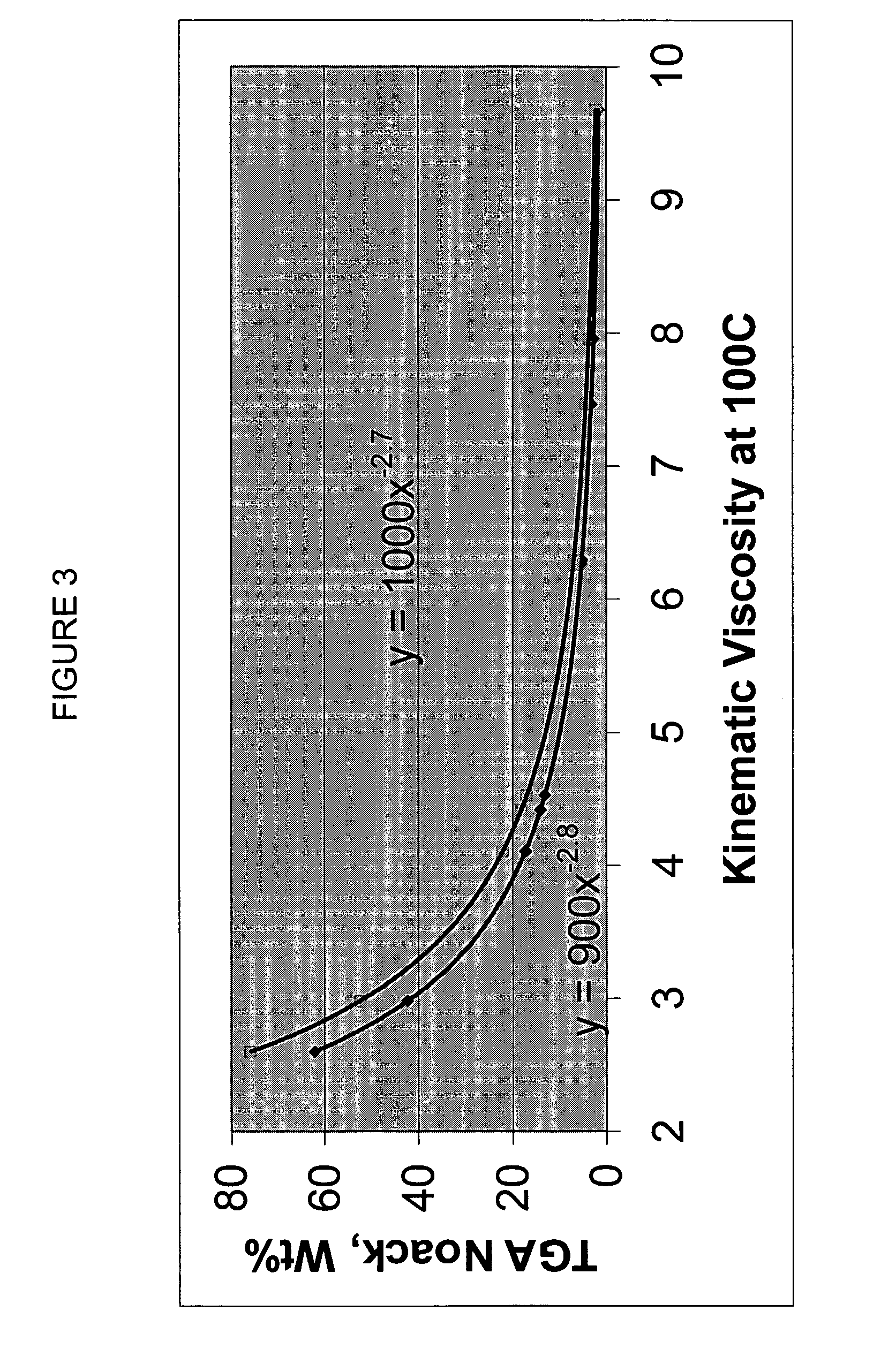
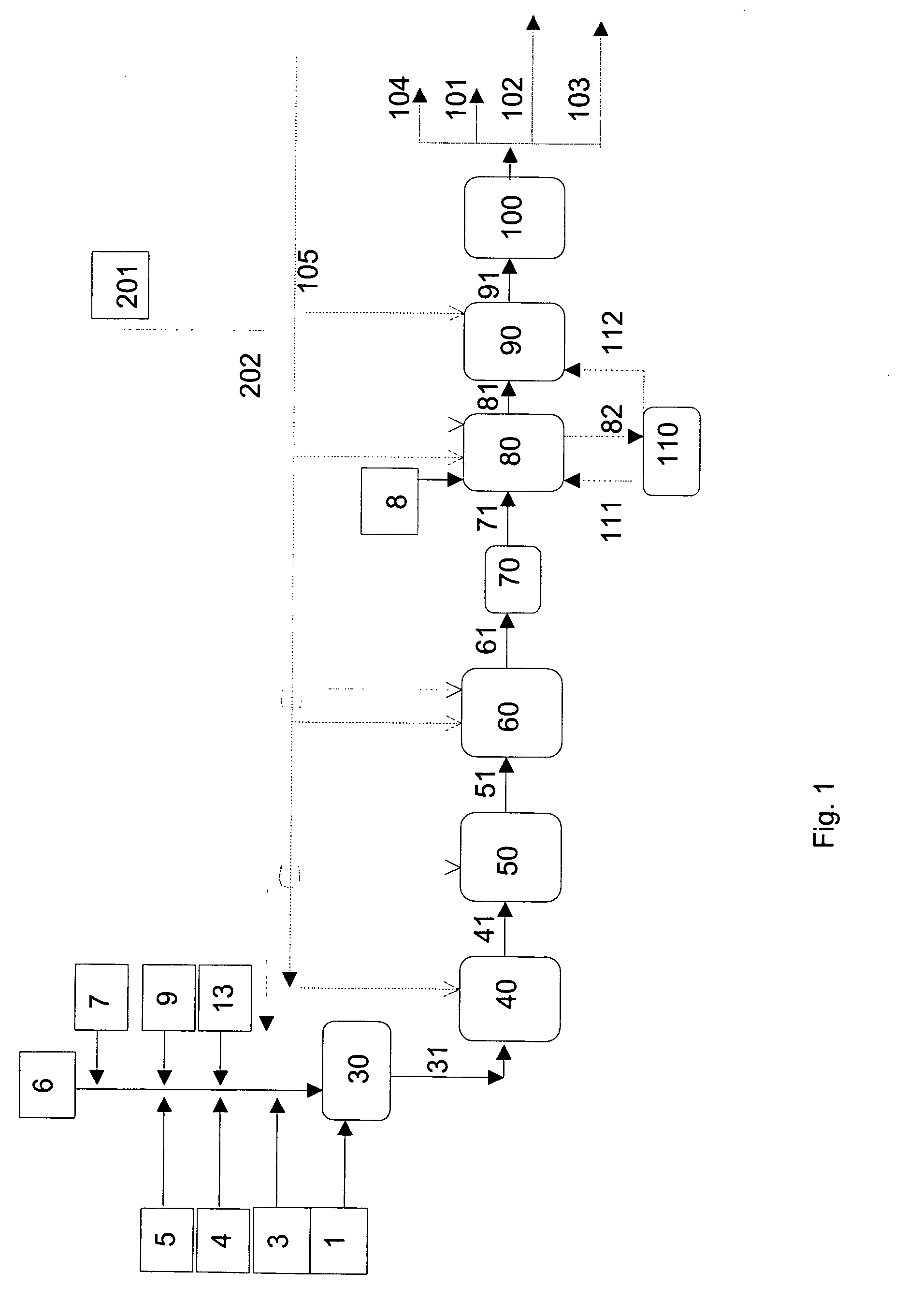
Patents
Literature
957results about How to "Reduce points" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
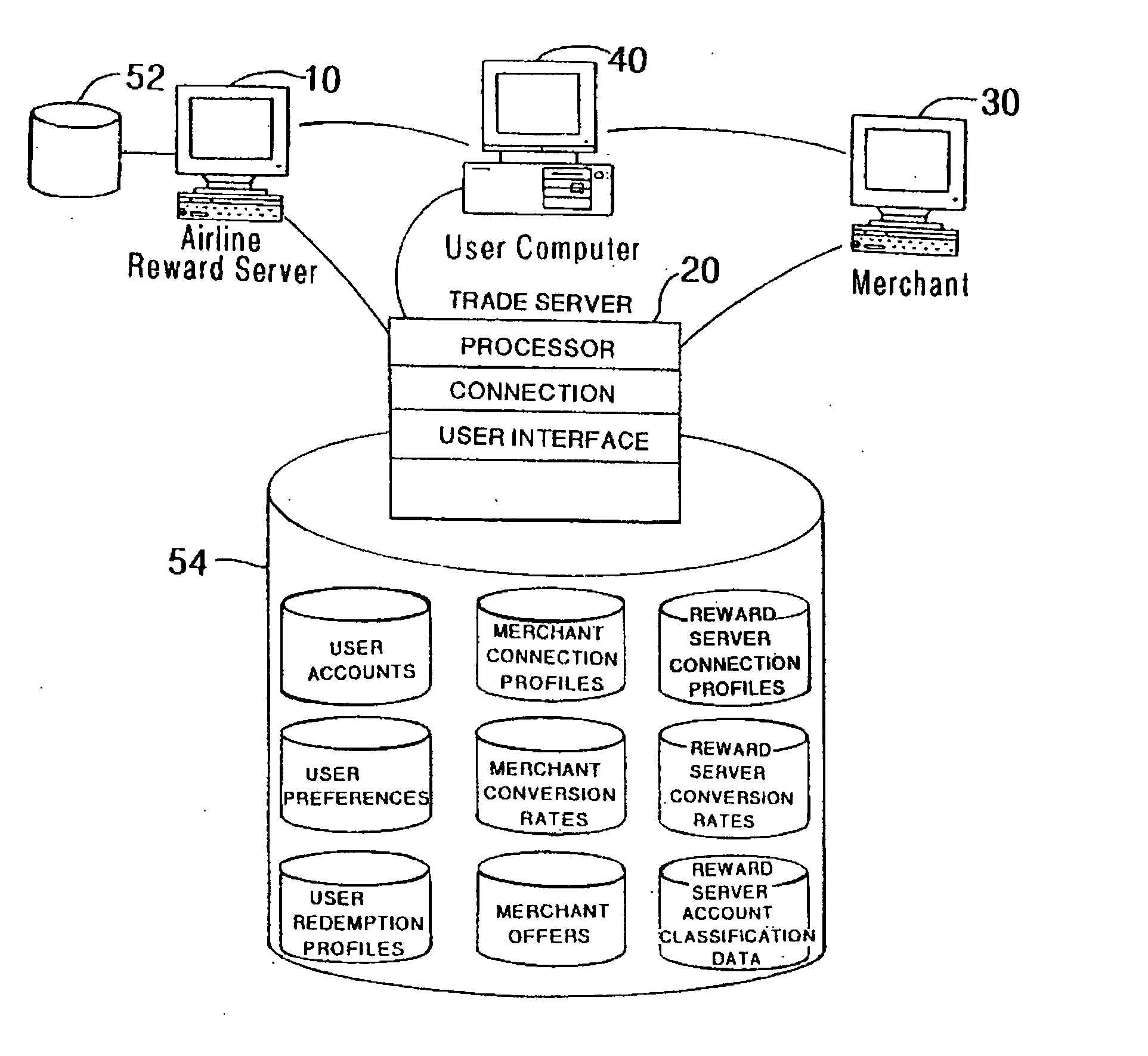
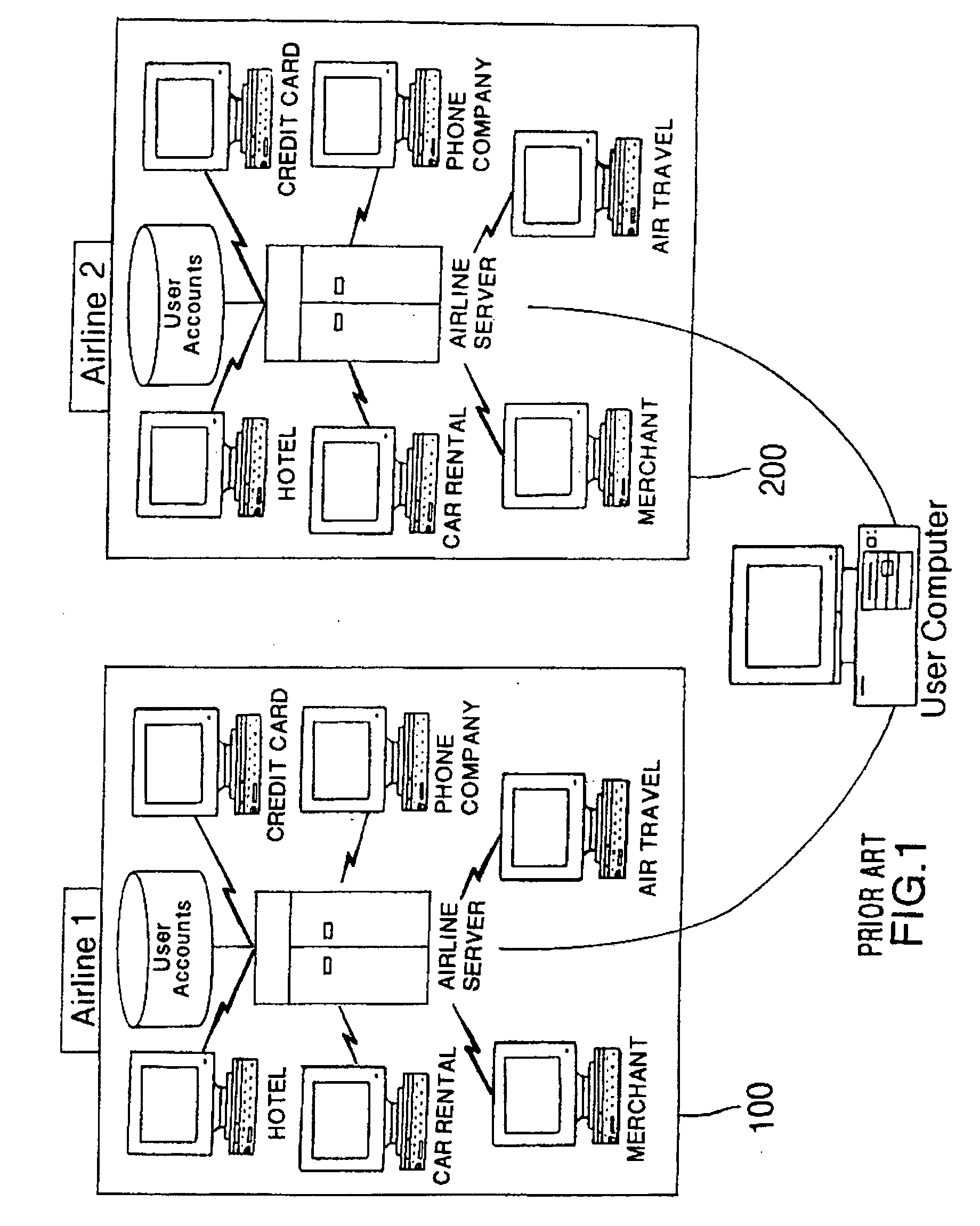
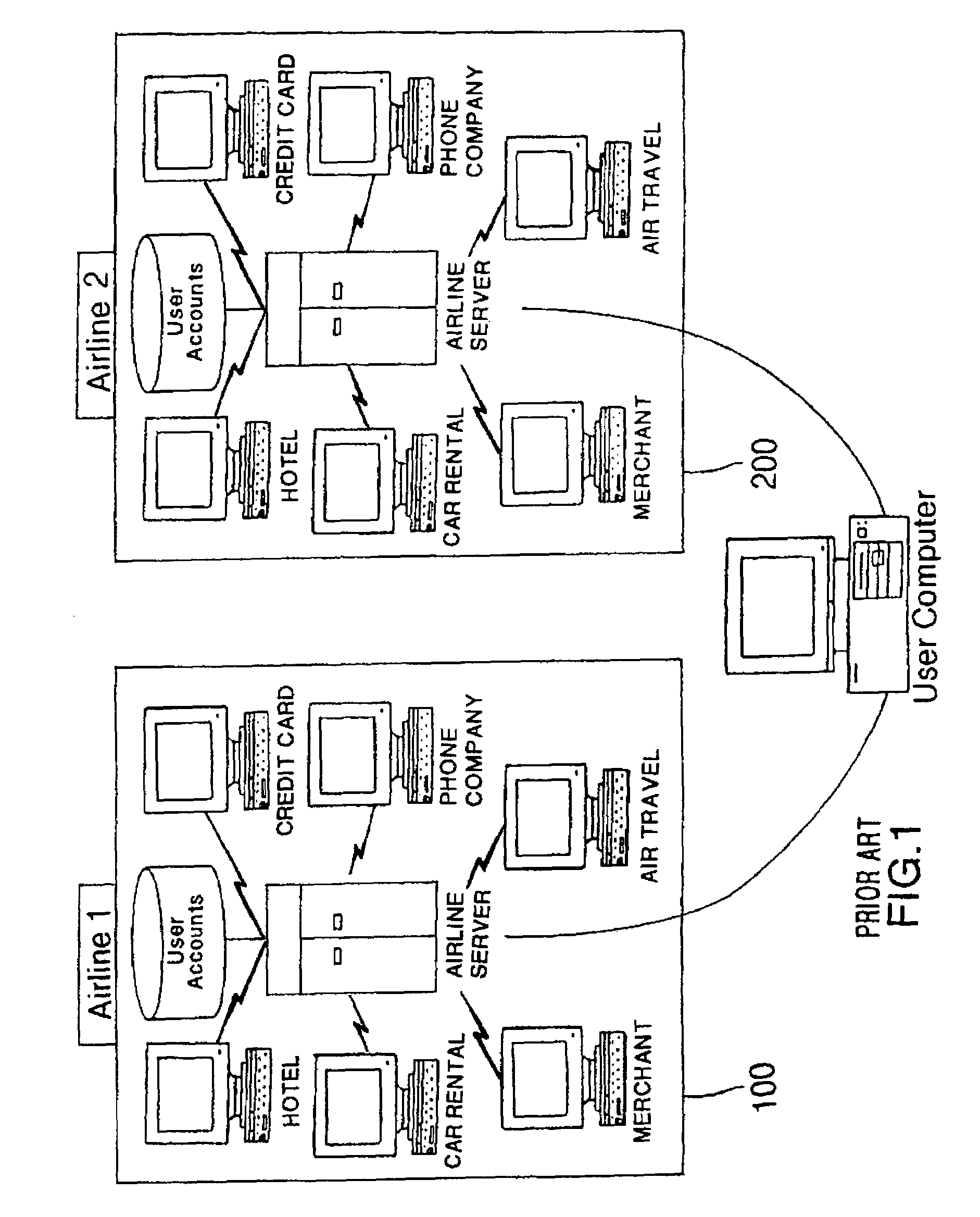
Method and system for implementing a search engine with reward components and payment components
A system and method for implementation of product searches via a search engine over a networked computer system such as the Internet. In particular, a user may execute a search for product offers that are accompanied with reward components (e.g. reward points, rebates, coupons, etc.) and / or those that allow payment in whole or in part with payment components (e.g. reward points, rebates, coupons, etc.).
Owner:SIGNATURE SYST
Effervescent granules and methods for their preparation
InactiveUS6071539AMinimize degradationMelt and soften binderPowder deliveryPill deliveryPlasticizerHot melt
According to the present invent, effervescent granules having a controllable rate of effervescence are provided. Such granules comprise an acidic agent, an alkaline agent, a hot-melt extrudable binder capable of forming a eutectic mixture with the acidic agent and, optionally, a plasticizer. The effervescent granules are made by a hot-melt extrusion process.
Owner:ETHYPHARM SA
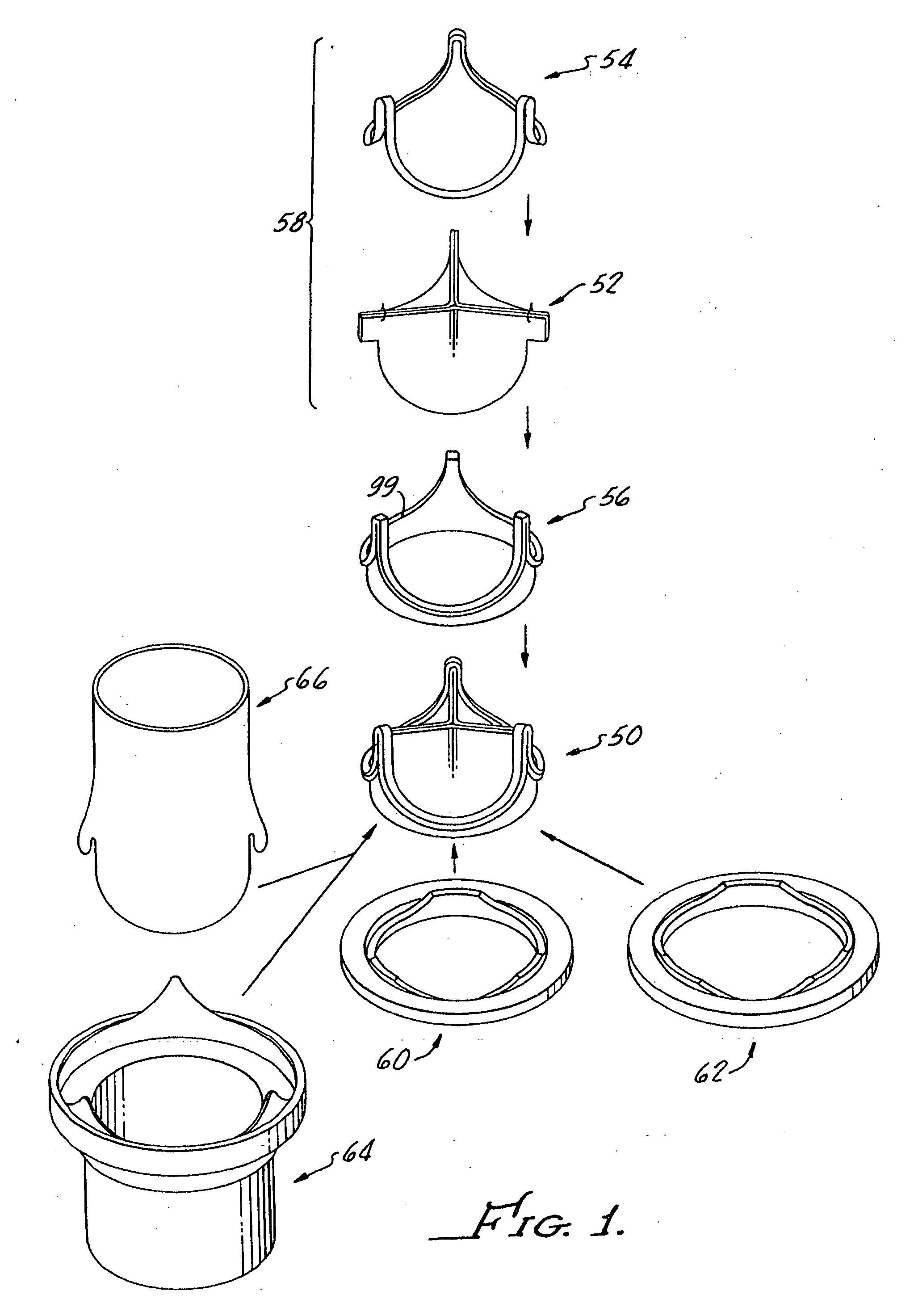
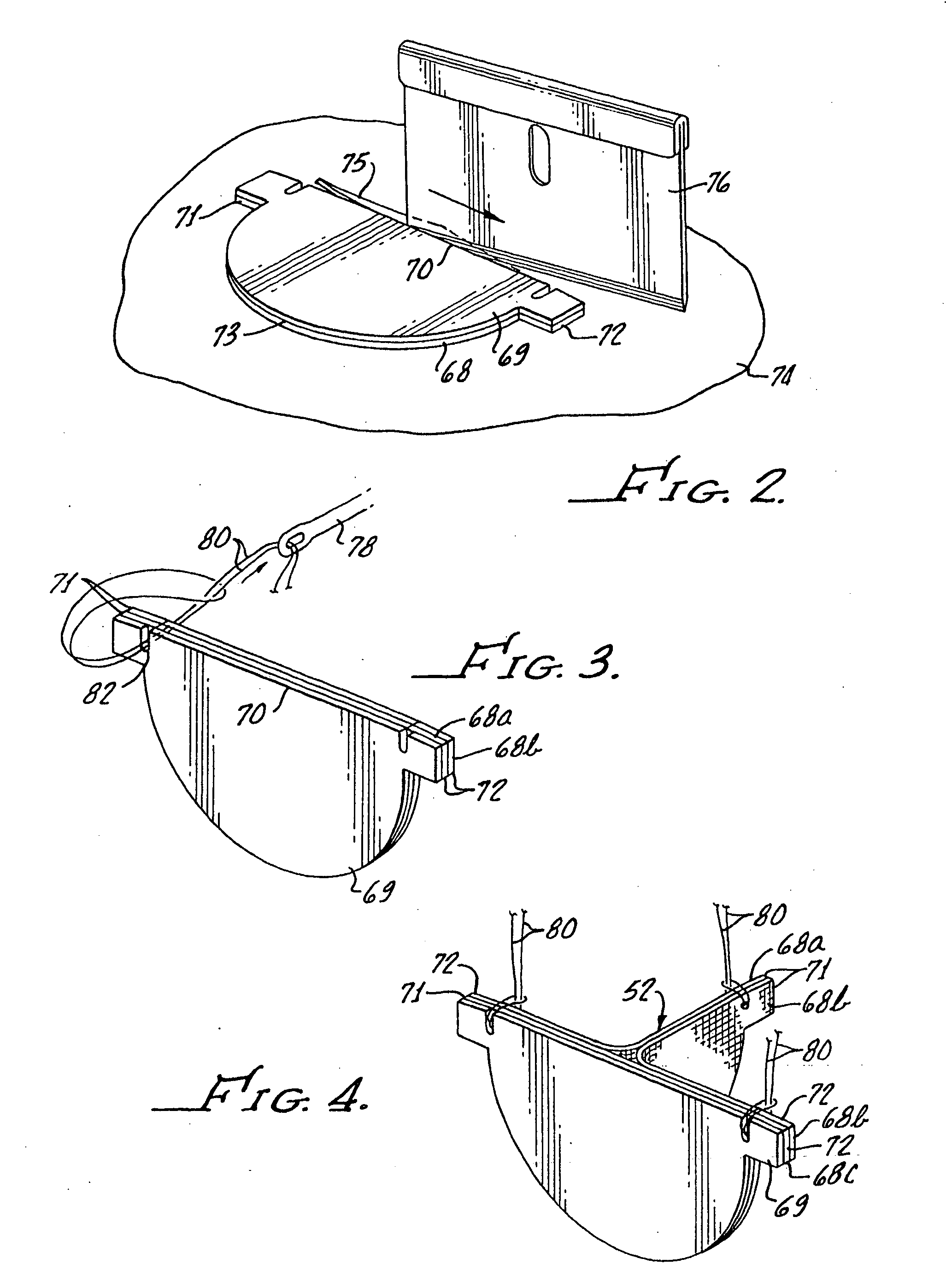
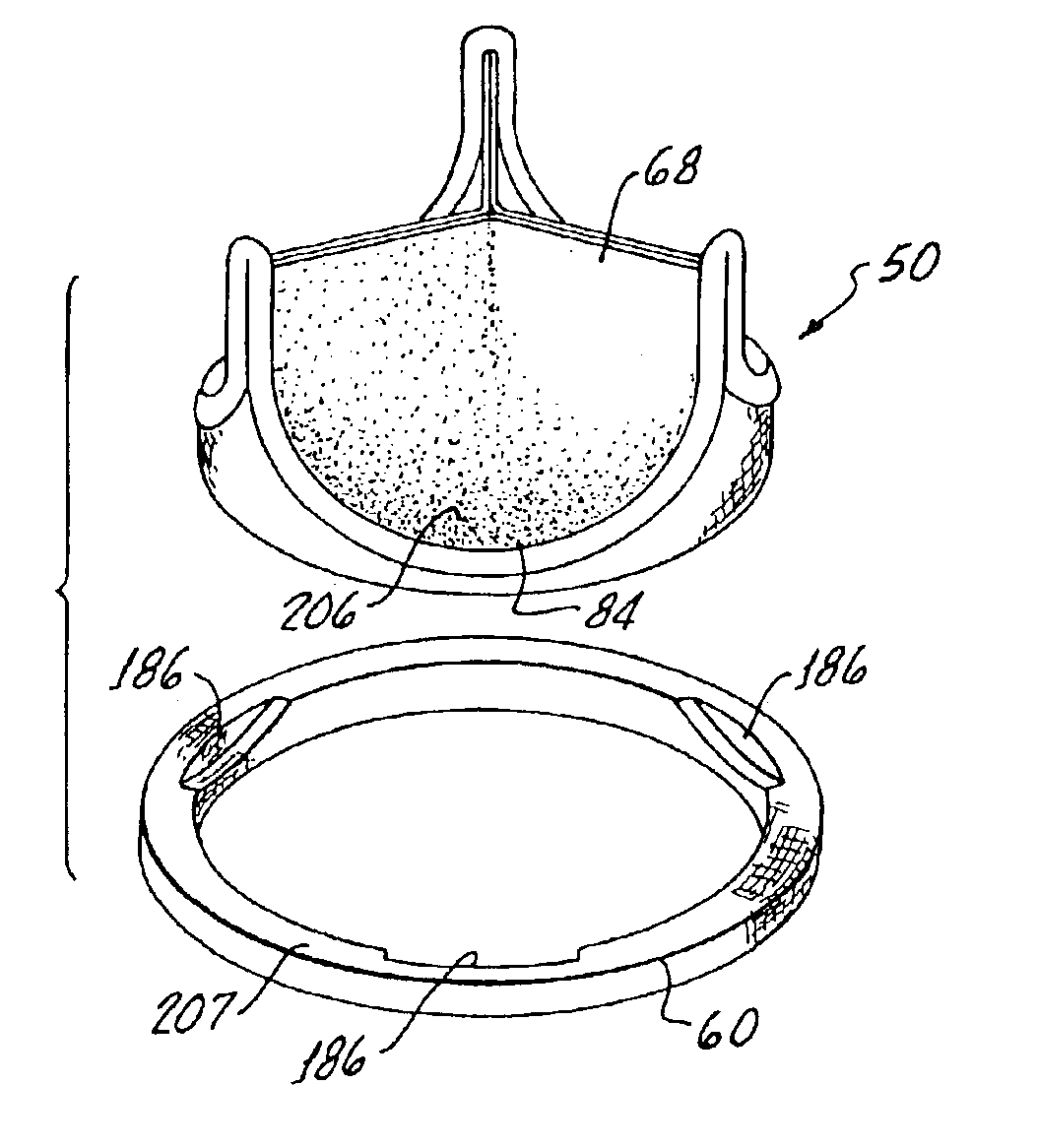
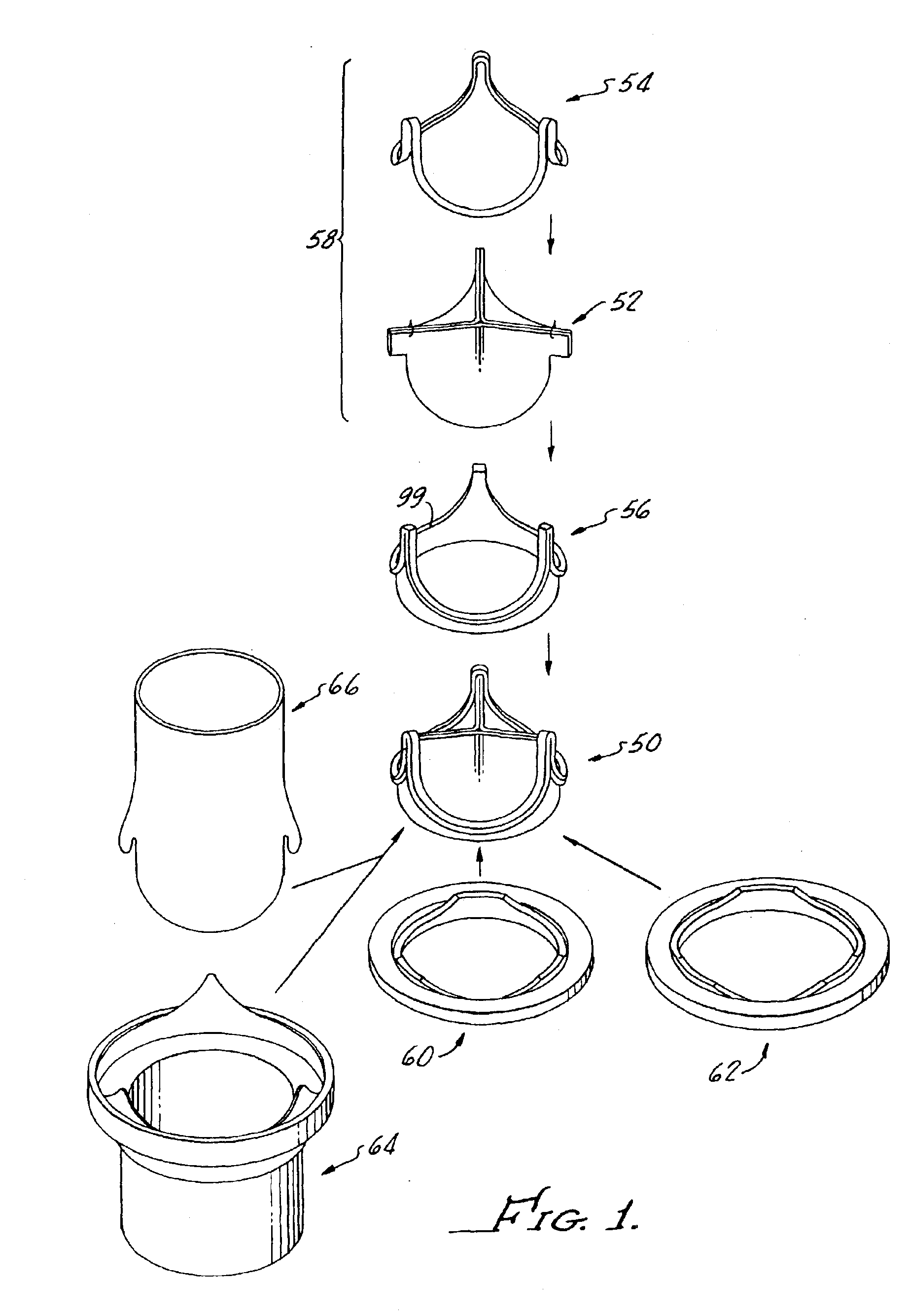
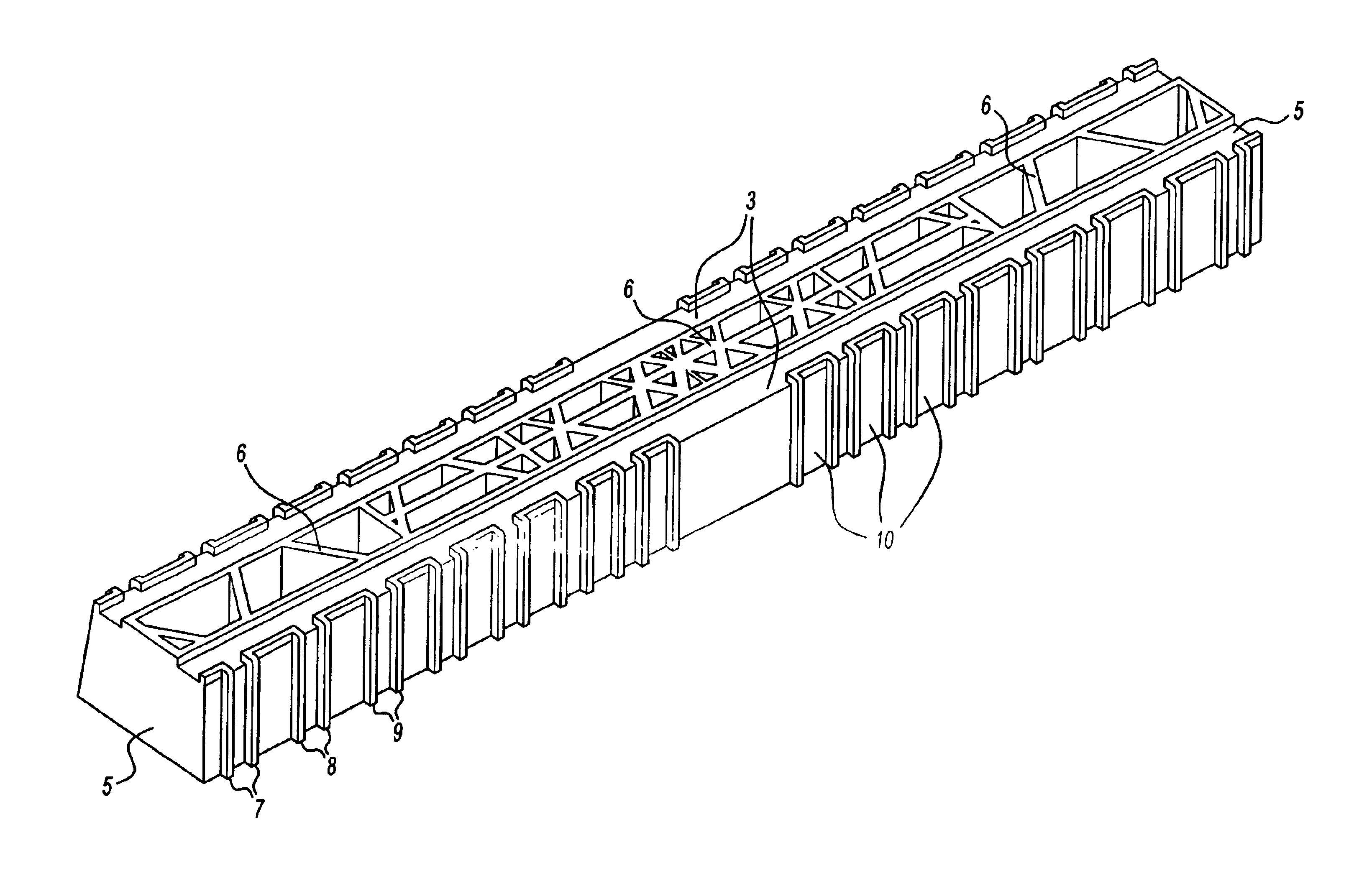
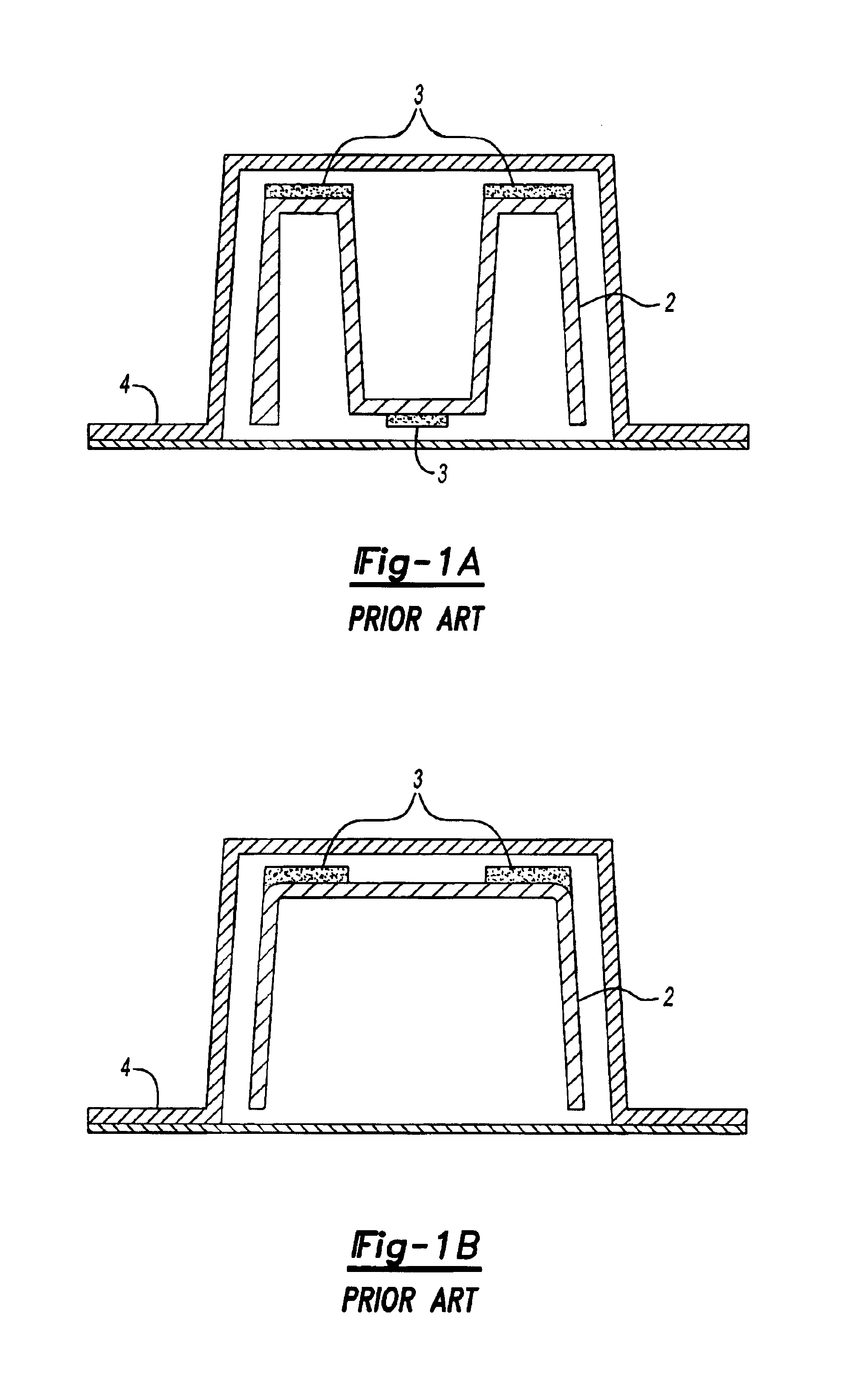
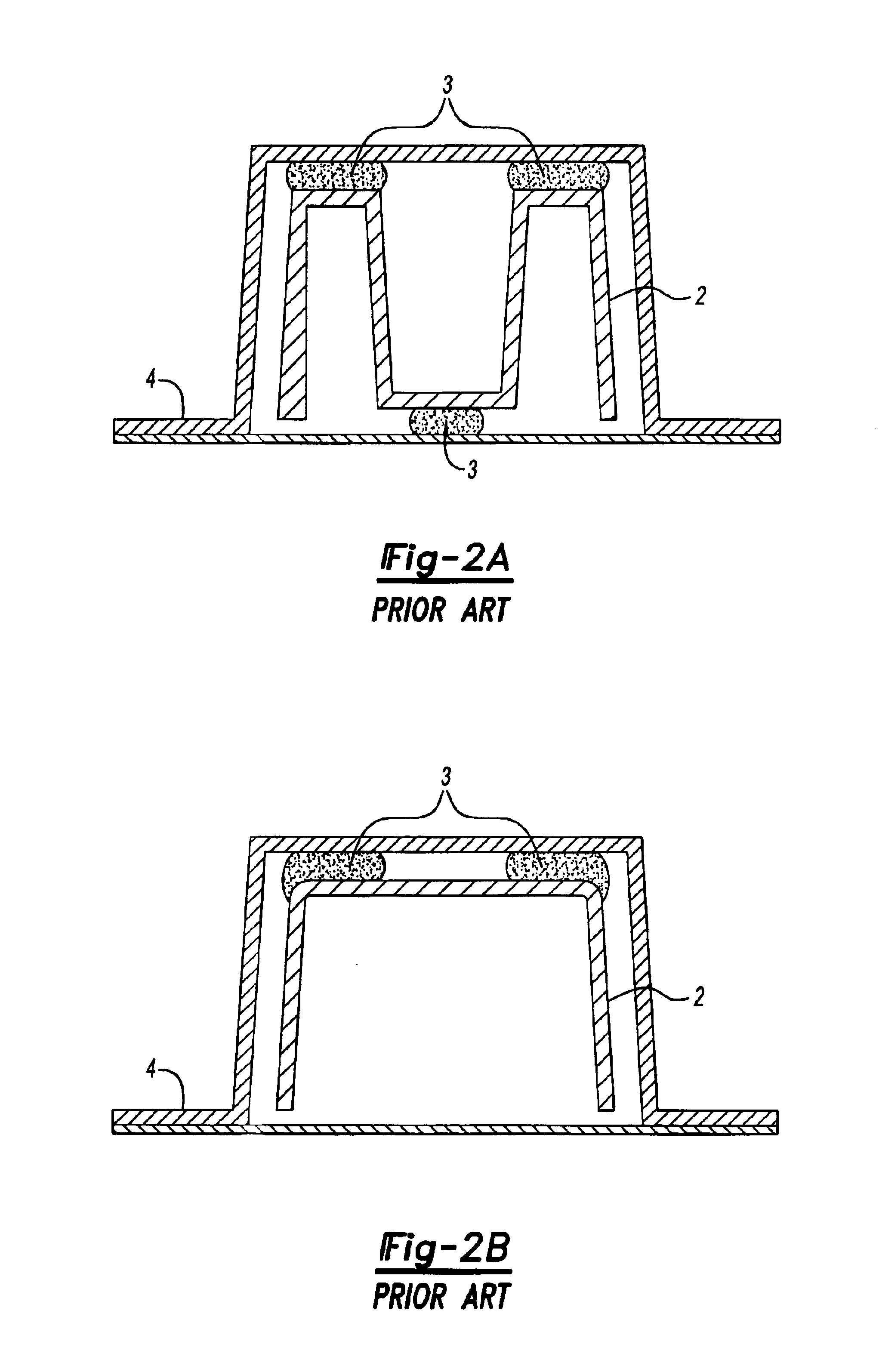
Contoured heart valve suture rings
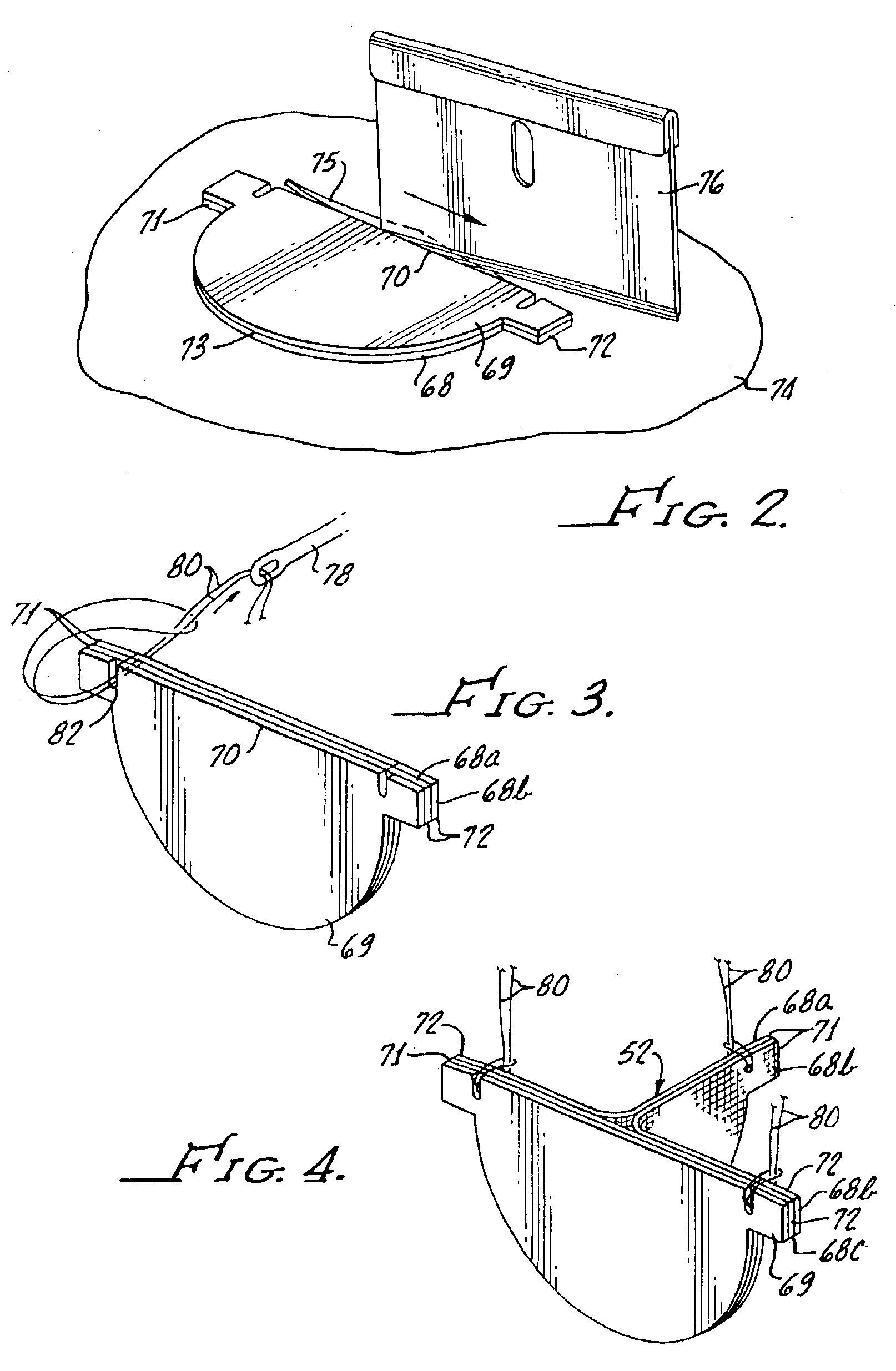
InactiveUS20060009842A1Improving long-term functionalityReduce pointsHeart valvesInsertion stentCatheter
Improved, adaptable tissue-type heart valves and methods for their manufacture are disclosed wherein a dimensionally stable, pre-aligned tissue leaflet subassembly is formed and its peripheral edge clamped between and attached to an upper shaped wireform and a lower support stent. A variety of adaptable structural interfaces including suture rings, flanges, and conduits may be attached to the support stent with or without an outlet conduit disposed about the wireform to provide a tissue-type heart valve adaptable for use in either a natural heart or in mechanical pumping devices. The methods include forming individual leaflets with a template and using the template to attach the leaflets together to form a tissue leaflet subassembly. The template and leaflets include a straight edge terminating in oppositely directed tabs, and a curvilinear cusp edge extending opposite the straight edge. The template may include a guide slot in its straight edge and the assembly includes aligning two leaflet tabs with the template and passing sutures through the guide slot and through the leaflet tabs. The leaflet subassembly is mated to a wireform with the tabs extending through commissure posts of the wireform. A support stent having an upper surface matching the lower surface of the wireform sandwiches the edges of the leaflet subassembly therebetween. Separated tabs on the leaflet subassembly are passed through the wireform commissures and attached to adjacent stent commissures so as to induce clamping of the leaflet tabs between the stent commissures and wireform commissures upon a radially inward force being applied to the leaflets.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Heart valves and suture rings therefor
InactiveUS6945997B2Reduce stress pointImproving long-term functionalityHeart valvesInsertion stentTissues types
Improved, adaptable tissue-type heart valves and methods for their manufacture are disclosed wherein a dimensionally stable, pre-aligned tissue leaflet subassembly is formed and its peripheral edge clamped between and attached to an upper shaped wireform and a lower support stent. A variety of adaptable structural interfaces including suture rings, flanges, and conduits may be attached to the support stent with or without an outlet conduit disposed about the wireform to provide a tissue-type heart valve adaptable for use in either a natural heart or in mechanical pumping devices. The methods include forming individual leaflets with a template and using the template to attach the leaflets together to form a tissue leaflet subassembly. The template and leaflets include a straight edge terminating in oppositely directed tabs, and a curvilinear cusp edge extending opposite the straight edge. The template may include a guide slot in its straight edge and the assembly includes aligning two leaflet tabs with the template and passing sutures through the guide slot and through the leaflet tabs. The leaflet subassembly is mated to a wireform with the tabs extending through commissure posts of the wireform. A support stent having an upper surface matching the lower surface of the wireform sandwiches the edges of the leaflet subassembly therebetween. Separated tabs on the leaflet subassembly are passed through the wireform commissures and attached to adjacent stent commissures so as to induce clamping of the leaflet tabs between the stent commissures and wireform commissures upon a radially inward force being applied to the leaflets.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
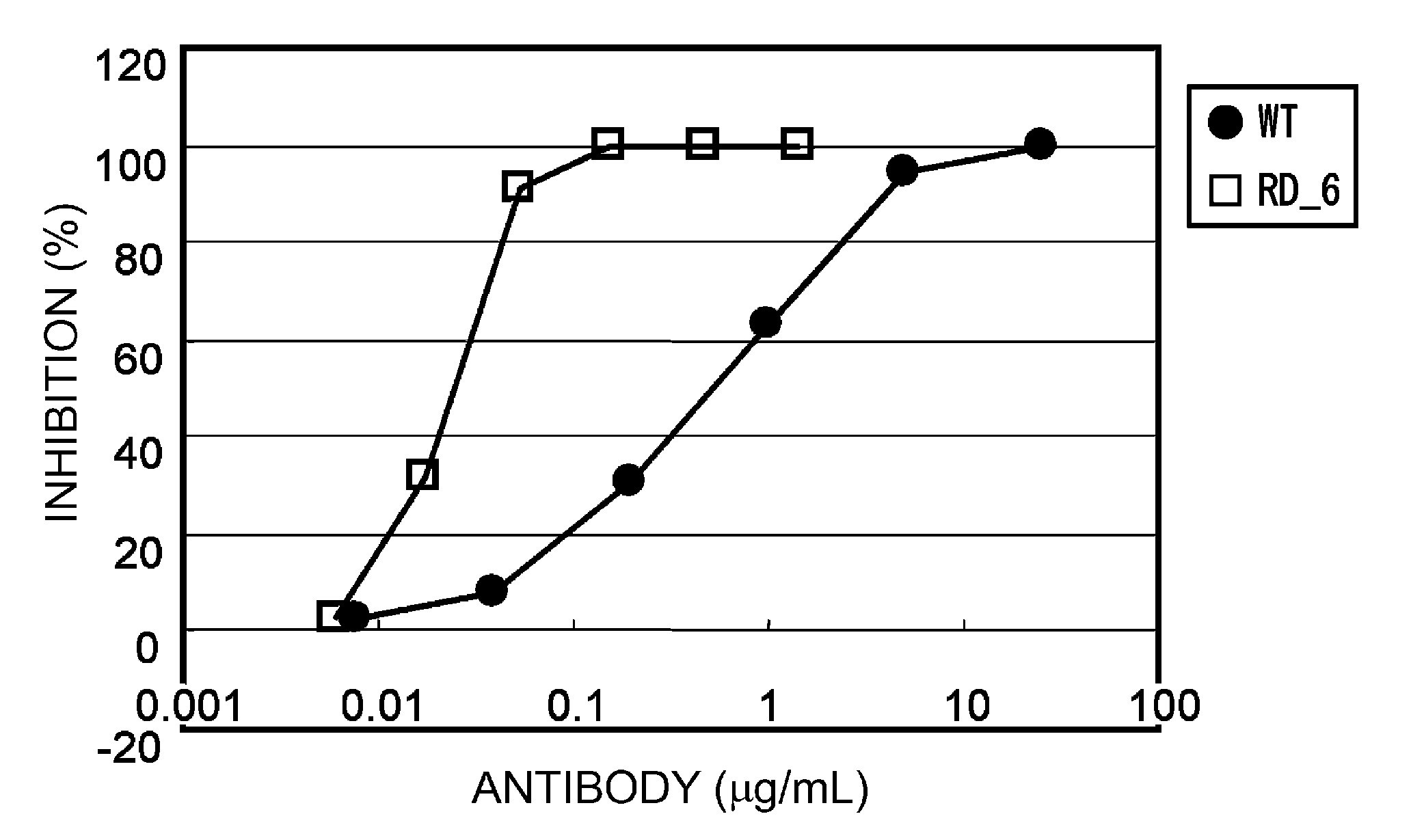
Method of Modifying Isoelectric Point of Antibody Via Amino Acid Substitution in CDR
ActiveUS20110076275A1Enhanced antigen-neutralizing activityImprove retentionSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAmino acid substitution
The present inventors provide methods for modifying the isoelectric point of an antibody while retaining its antigen-binding activity, comprising modifying the charge of at least one exposable amino acid residue on the surface of the complementarity determining region (CDR). The present invention also provides methods for purifying multispecific antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point, and methods for improving the plasma pharmacokinetics of antibodies, comprising modifying isoelectric point. The present invention further provides antibodies with a modified isoelectric point, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies as an active ingredient, and methods for producing the antibodies and compositions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
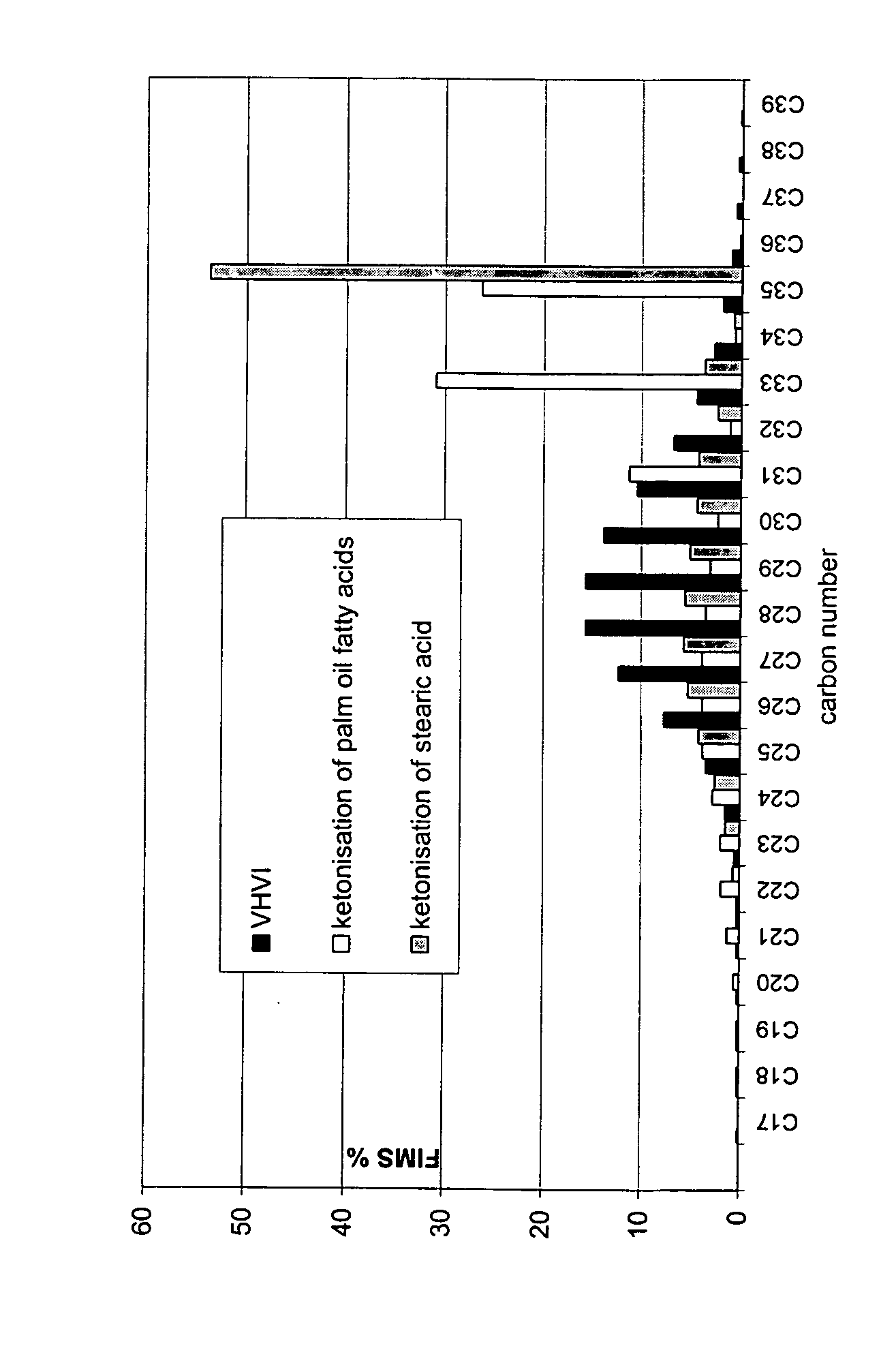
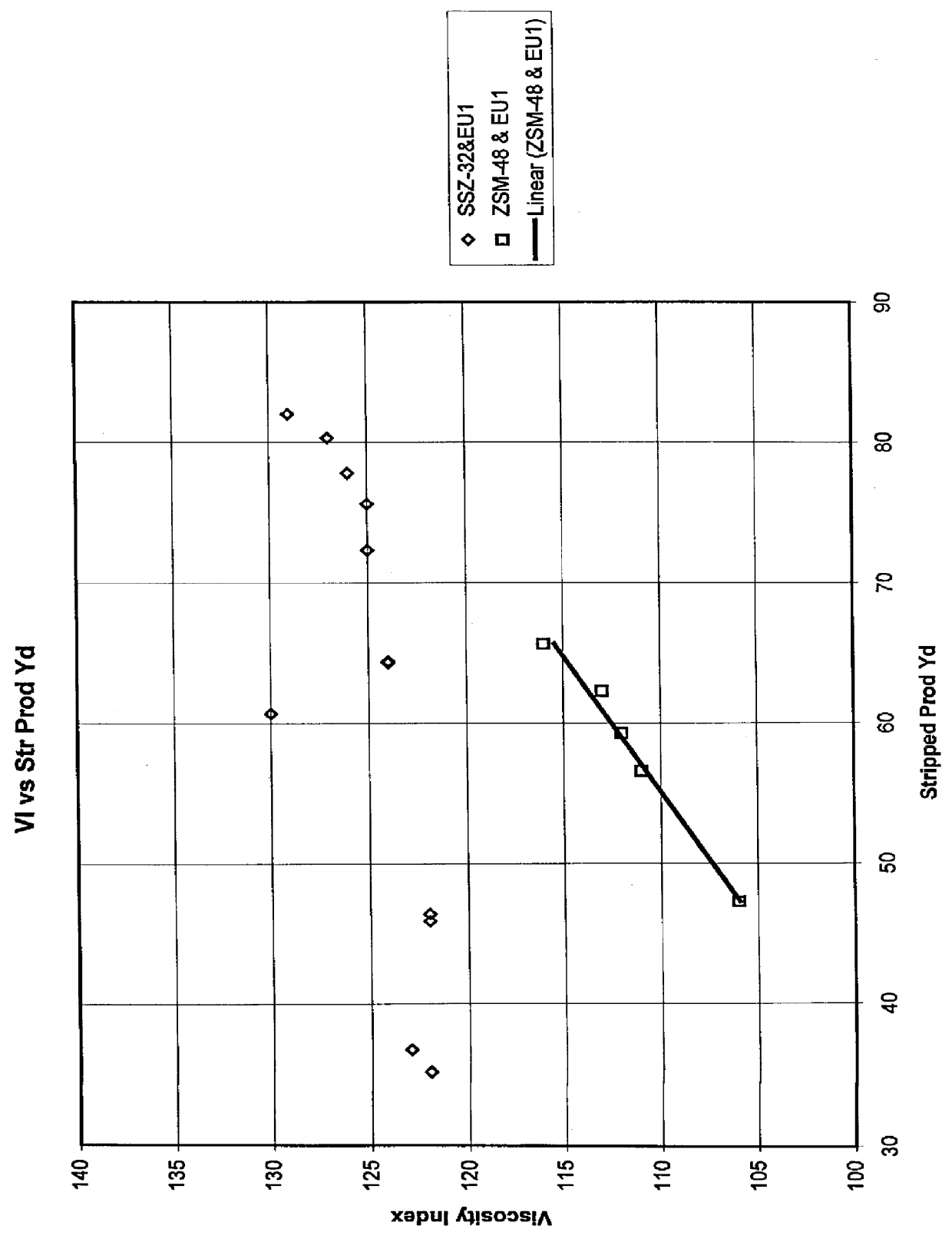
Process for manufacturing lubricating base oil with high monocycloparaffins and low multicycloparaffins
InactiveUS20050133409A1Improve Oxidation StabilityHigh viscosity indexTreatment with hydrotreatment processesAdditivesSyngasMolecular sieve
A process for manufacturing a lubricating base oil by: a) performing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on syngas to provide a product stream; b) isolating from said product stream a substantially paraffinic wax feed having less than about 30 ppm total nitrogen and sulfur, and less than about 1 wt % oxygen; c) dewaxing said feed by hydroisomerization dewaxing using a shape selective intermediate pore size molecular sieve comprising a noble metal hydrogenation component, wherein the hydroisomerization temperature is between about 600° F. (315° C.) and about 750° F. (399° C.), to produce an is dimerized oil; and d) hydrofinishing said isomerized oil to produce a lubricating base oil having specific desired properties.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
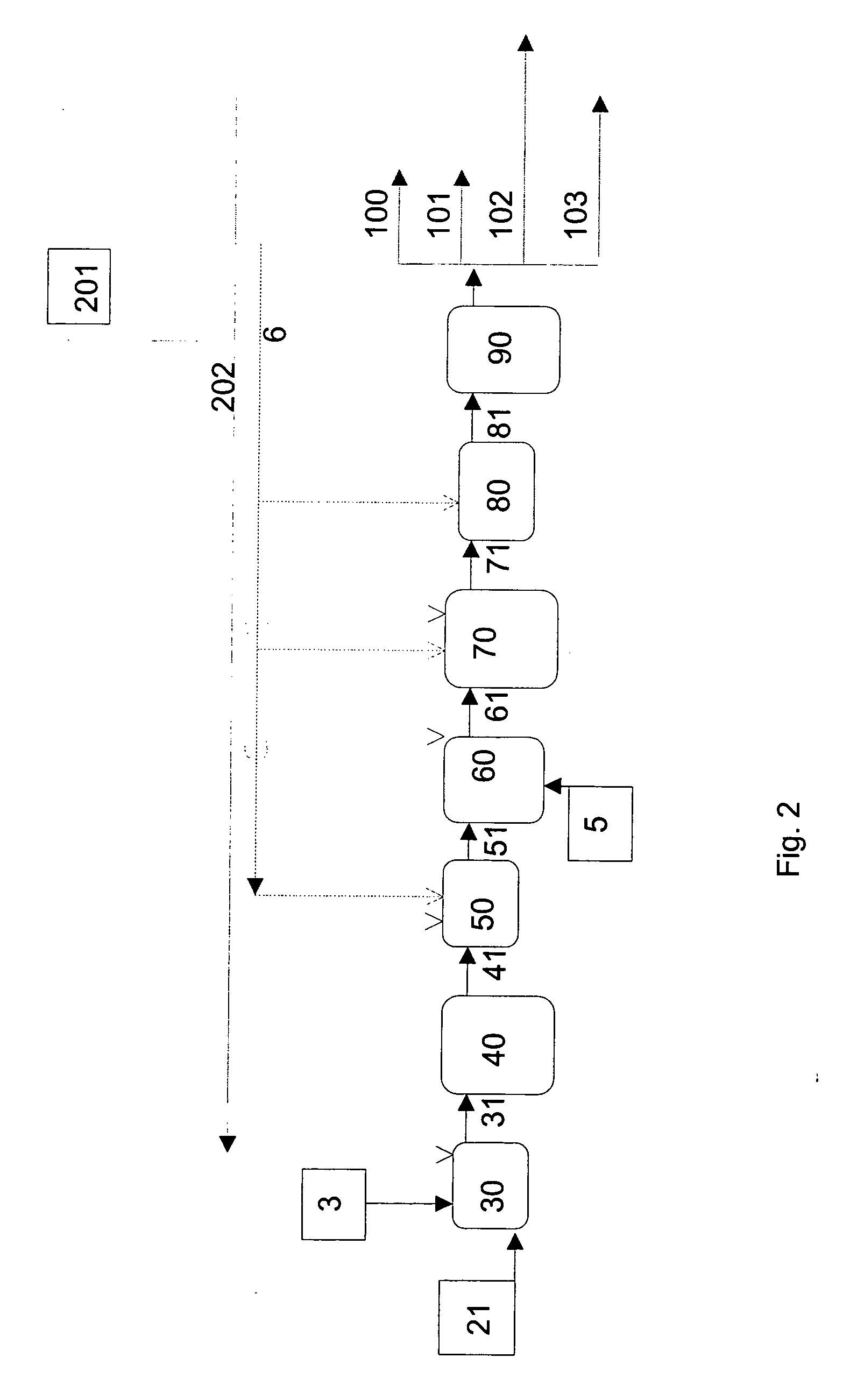
Process for producing a hydrocarbon component
ActiveUS20070161832A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsImprove low temperature performanceFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid hydrogenationIsomerizationHydrodeoxygenation
The invention relates to a process for producing a new type of high-quality hydrocarbon base oil of biological origin. The process of the invention comprises ketonisation, hydrodeoxygenation, and isomerization steps. Fatty acids and / or fatty acid esters based on a biological raw material are preferably used as the feedstock.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Process for reducing haze point in bright stock
InactiveUS6051129ASuperior lube oil yieldHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrogenHaze
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
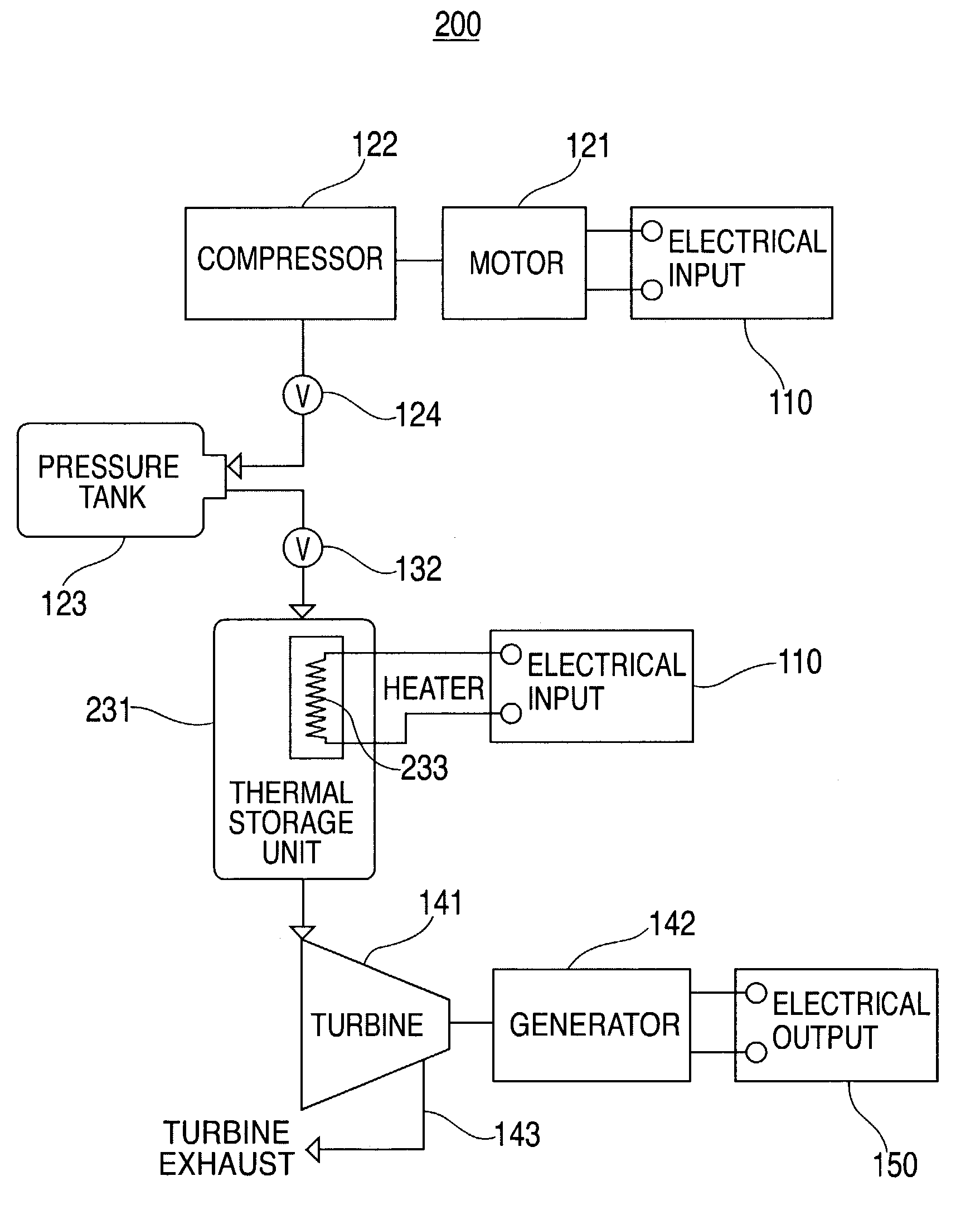
Thermal and compressed air storage system
InactiveUS7086231B2Improve efficiencyReduced point source pollutionHeat storage plantsSteam accumulatorsEngineeringTurbine
Combined thermal and compressed air storage systems are provided that utilize an exhaustless heater, such as a thermal storage unit, to provide power with enhanced efficiency. Compressed air is heated by the thermal storage unit prior to entering a turbine, which powers an electrical generator. In various embodiments, ambient air temperature, turbine exhaust or other types of waste heat are used to preheat the compressed air prior to the compressed air entering the thermal storage unit, thereby further increasing system efficiency.
Owner:P10 IND INC
Structural reinforcement
InactiveUS6941719B2Reduced strengthSatisfies requirementVehicle seatsStructural elementsAdhesive materialsBiomedical engineering
A structural reinforcement for a hollow member comprising a rigid reinforcing member having a shape that substantially conforms to the cross section of the hollow member to be reinforced with an expandable adhesive material over at least a portion of the surface of the structural reinforcement having one or more extensions on its external surface which control and direct the direction in which the adhesive material expands to bond the reinforcing member to the internal surface of the hollow member, some of the extensions also provide improved reinforcement.
Owner:ZEPHYROS INC
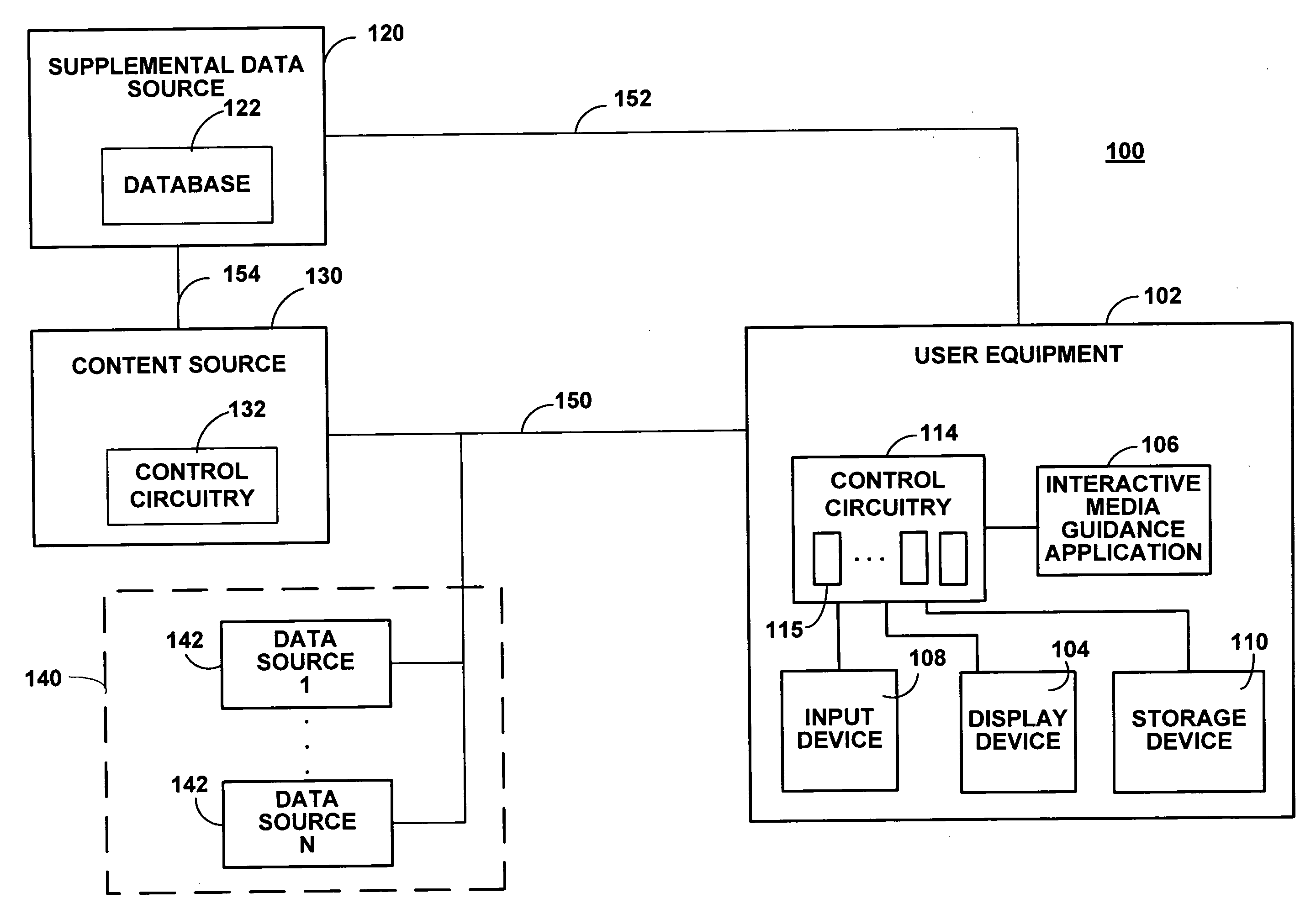
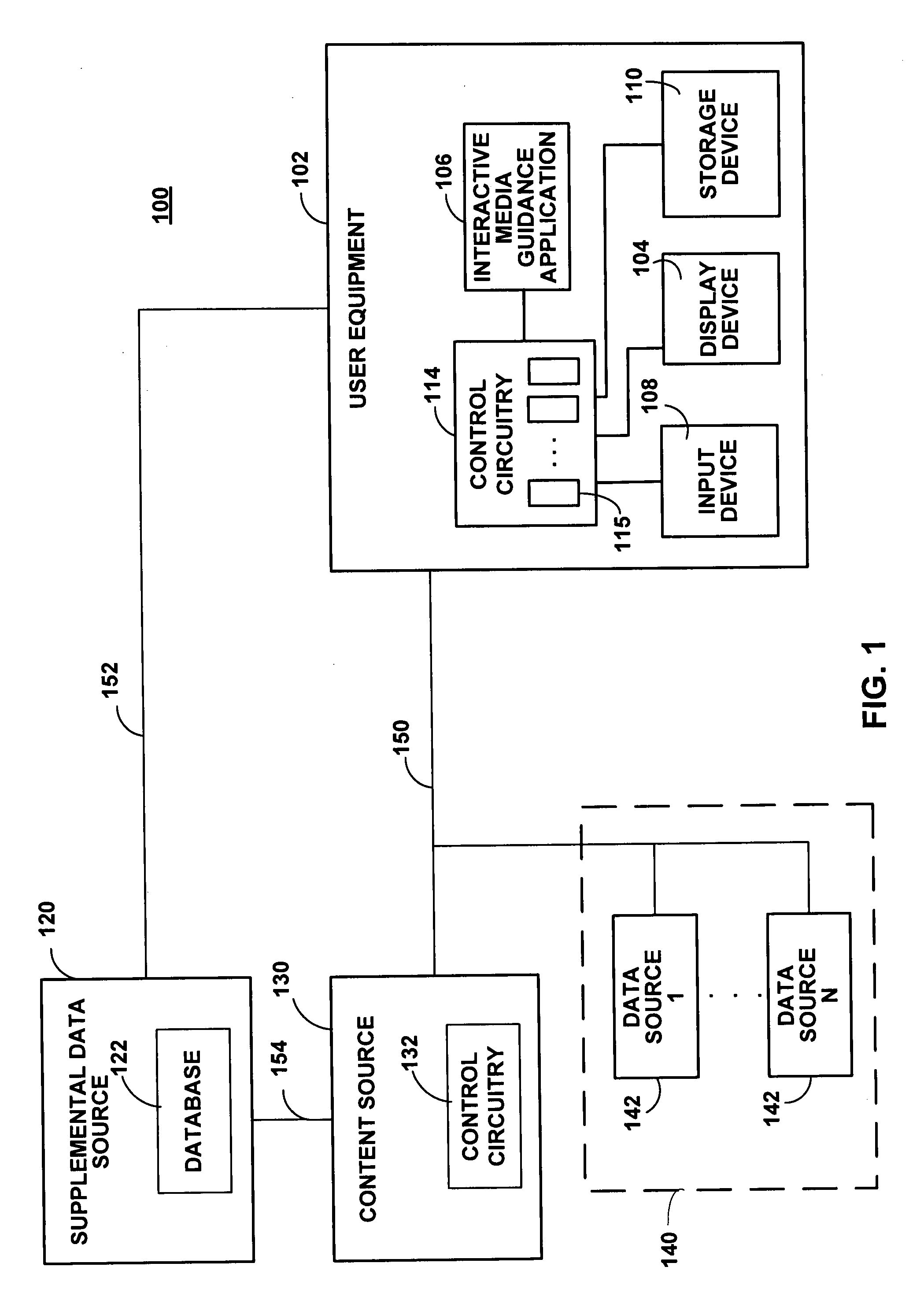
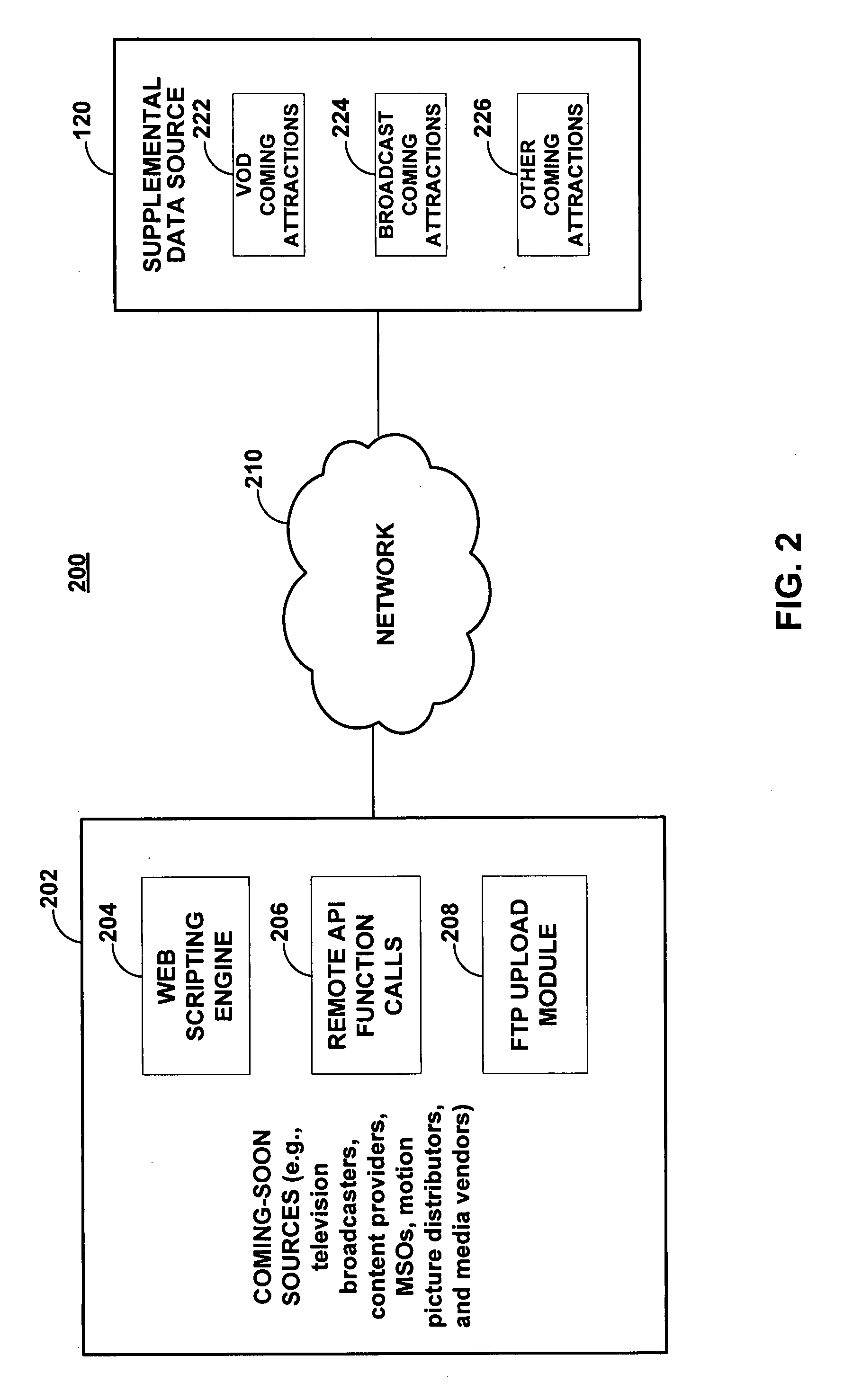
Systems and methods for providing media guidance planners
ActiveUS20080059884A1Flexible solutionMaximizing numberTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTime scheduleMedia content
Systems and methods for providing media planners for planning a user's media content viewing activities are provided. The media planner may include an interactive grid of content with scheduled viewing, recording, or reminders set within a user-selectable time window. The media planner may prioritize content within the planner grid and automatically resolve conflicts when the number of available tuners within the user equipment device has been exceeded. Programs matching a user's viewing interests may also be automatically recorded in the user's absence. Coming-soon announcements may be received for programming outside the current program schedule window. Conditional media guidance application functions may be scheduled based on preliminary availability and attribute data associated with a coming-soon asset.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
Method concerning a junction barrier Schottky diode, such a diode and use thereof
InactiveUS6524900B2Change resistanceChange the on-state resistance of the diodeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandSemiconductor materials
A method for controlling the temperature dependence of a junction barrier Schottky diode of a semiconductor material having an energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band exceeding 2 eV provides for doing this when producing the diode by adjusting the on-state resistance of the grid portion of the diode during the production for obtaining a temperature dependence of the operation of the diode adapted to the intended use thereof.
Owner:CREE INC
Inhibitor nucleic acids
InactiveUS20050256071A1Low melting pointQuality improvementOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAptamerHalf-life
The present invention provides methods and compositions for attenuating expression of a target gene in vivo. In general, the method includes administering RNAi constructs (such as small-interfering RNAs (i.e., siRNAs) that are targeted to particular mRNA sequences, or nucleic acid material that can produce siRNAs in a cell), in an amount sufficient to attenuate expression of a target gene by an RNA interference mechanism. In particular, the RNAi constructs may include one or more modifications to improve serum stability, cellular uptake and / or to avoid non-specific effect. In certain embodiments, the RNAi constructs contain an aptamer portion. The aptamer may bind to human serum albumin to improve serum half life. The aptamer may also bind to a cell surface protein that improves uptake of the construct.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Aqueous polyvinylidene fluoride composition
ActiveUS20100304270A1Dry fastUseful electrodeLiquid electrolytic capacitorsConductive materialInterconnectivityPolyvinylidene difluoride
The invention relates to an aqueous fluoropolymer, and preferably polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), composition for manufacturing electrodes for use in non-aqueous-type electrochemical devices, such as batteries and electric double layer capacitors. The composition contains aqueous PVDF binder, and one or more powdery electrode-forming materials. In one embodiment, the composition is free of fluorinated surfactant In another embodiment, one or more fugitive adhesion promoters are added. The electrode formed from the composition of the invention exhibits interconnectivity and irreversibility that is achieved from the use of aqueous PVDF binder.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Effervescent granules and methods for their preparation
InactiveUS6649186B1Improve stabilityParticular regionPowder deliveryNervous disorderHYDROMORPHONE HYDROCHLORIDEAlpha adrenergic blockade
Disclosed here are effervescent granules having a controllable rate of effervescence. In some embodiments, the such granules comprise an acidic agent, an alkaline agent, a pharmacologically active agent, hot-melt extrudable binder capable of forming a eutectic mixture with the acidic agent and, optionally, a plasticizer. The effervescent granules are made by a hot-melt extrusion process. The present invention also provides a thermal heat process for preparing a pharmacologically active agent containing effervescent granule. In certain aspects, the granules contain pharmacologically active agents such as narcotics, antidiarrheal agents, antiviral agents, anxiolytic agents, a cholesterol lowering agent, an alpha adrenergic blocking agent, a phenanthrene derivative. By way of example, some of the narcotics that may be included in the granules and in the process of preparing the granules include, by way of example: phenanthrene derivatives (e.g., morphine sulfate), and morphine derivatives (e.g., hydromorphone hydrochloride).
Owner:ETHYPHARM SA
Method and system for implementing a search engine with reward components and payment components
A system and method for implementation of product searches via a search engine over a networked computer system such as the Internet. In particular, a user may execute a search for product offers that are accompanied with reward components (e.g. reward points, rebates, coupons, etc.) and / or those that allow payment in whole or in part with payment components (e.g. reward points, rebates, coupons, etc.).
Owner:SIGNATURE SYST
Microwave ablation catheter and method of utilizing the same
ActiveUS9044254B2Improve cooling effectReduce pointsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBronchoscopesMicrowaveMicrowave ablation
A microwave ablation system configured for use in luminal network is provided. The microwave ablation system includes a microwave energy source and a tool for treating tissue. An extended working channel is configured to provide passage for the tool. A locatable guide, translatable through the extended working channel, is configured to navigate the extended working channel adjacent a target.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Effervescent granules and methods for their preparation
InactiveUS6488961B1Improve stabilityParticular regionPowder deliveryBiocideAnesthetic AgentHYDROMORPHONE HYDROCHLORIDE
Disclosed here are effervescent granules having a controllable rate of effervescence. In some embodiments, the such granules comprise an acidic agent, an alkaline agent, a pharmacologically active agent, hot-melt extrudable binder capable of forming a eutectic mixture with the acidic agent and, optionally, a plasticizer. The effervescent granules are made by a hot-melt extrusion process. The present invention also provides a thermal heat process for preparing a pharmacologically active agent containing effervescent granule. In certain aspects, the granules contain pharmacologically active agents such as narcotics, antidiarrheal agents, antiviral agents, anxiolytic agents, a cholesterol lowering agent, an alpha adrenergic blocking agent, a phenanthrene derivative. By way of example, some of the narcotics that may be included in the granules and in the process of preparing the granules include, by way of example: phenanthrene derivatives (e.g., morphine sulfate), and morphine derivatives (e.g., hydromorphone hydrochloride).
Owner:ETHYPHARM SA
Modeling method and apparatus for use in surgical navigation
ActiveUS20070270680A1Accurate locationShorten the timeSurgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceModel methodRadiology
A modeling method for use in surgical navigation is provided. The method acquires a finite number of pre-defined points from a patient's bone and registers the points with a surgical navigation system. The navigation system generates and displays a three-dimensional image of a warped bone model that is manipulatable and accurate in at least the locations of the points taken and can be used to calculate the locations of bone cuts, implant positions and sizes, as well as display all of this information on the three-dimensional warped model.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
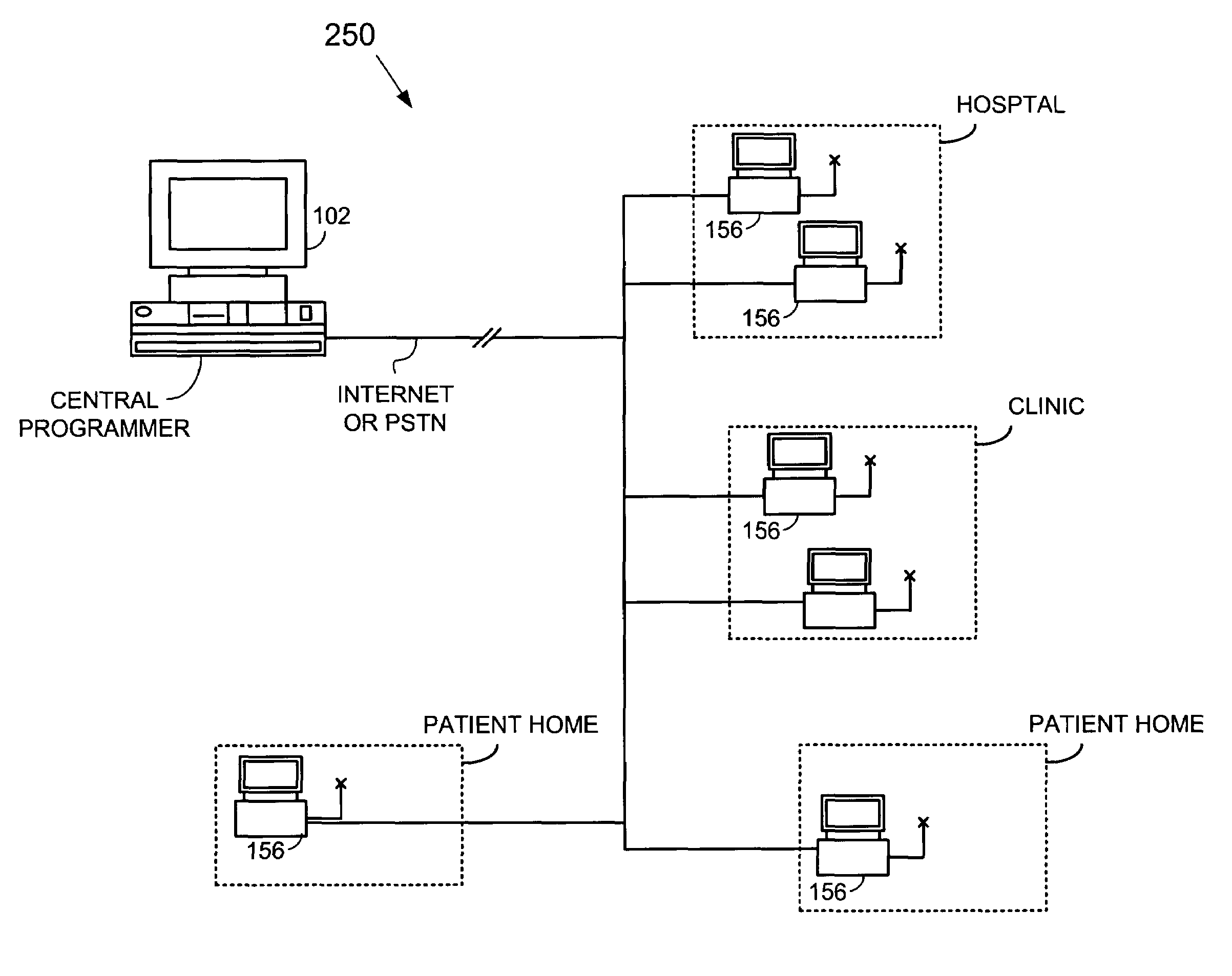
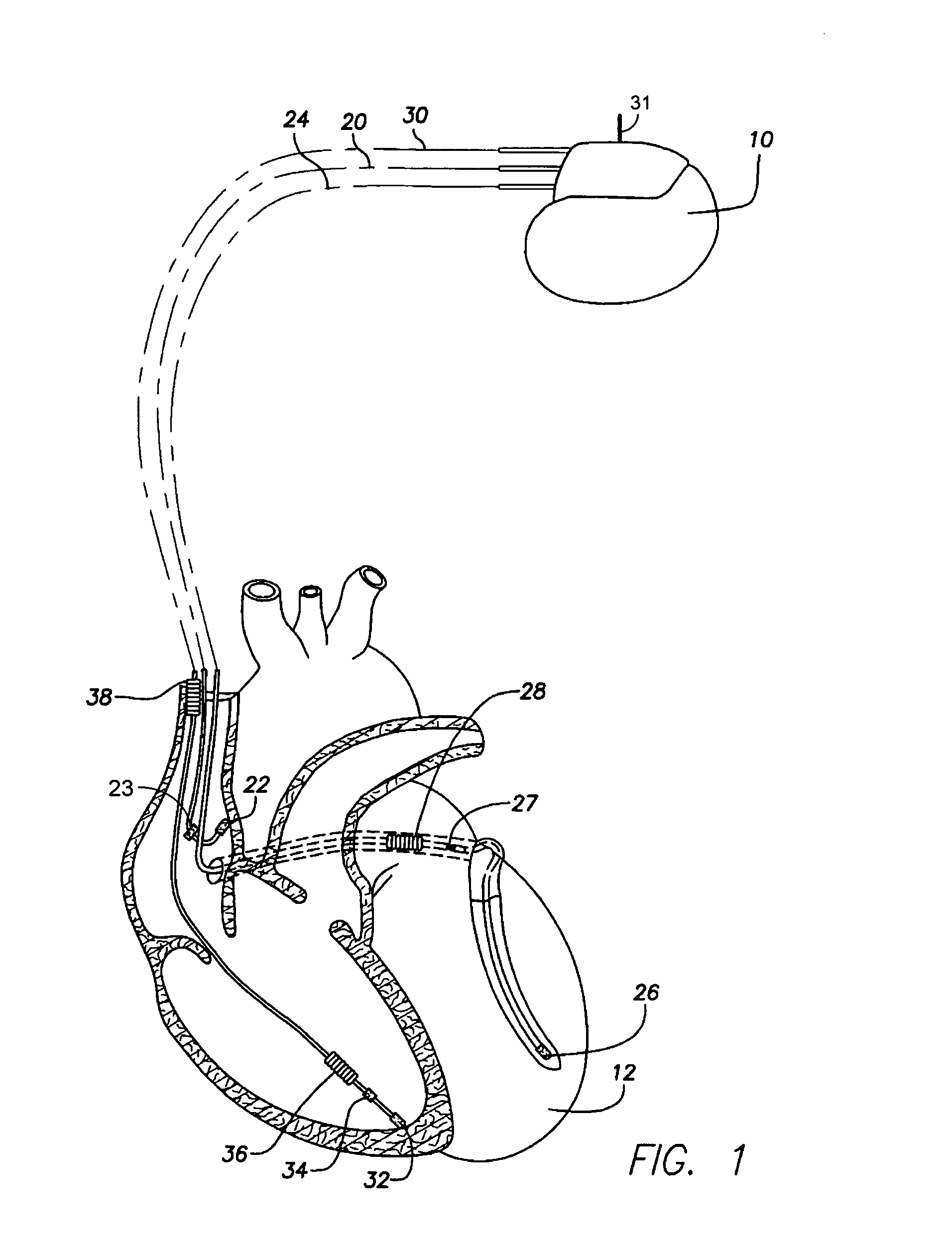
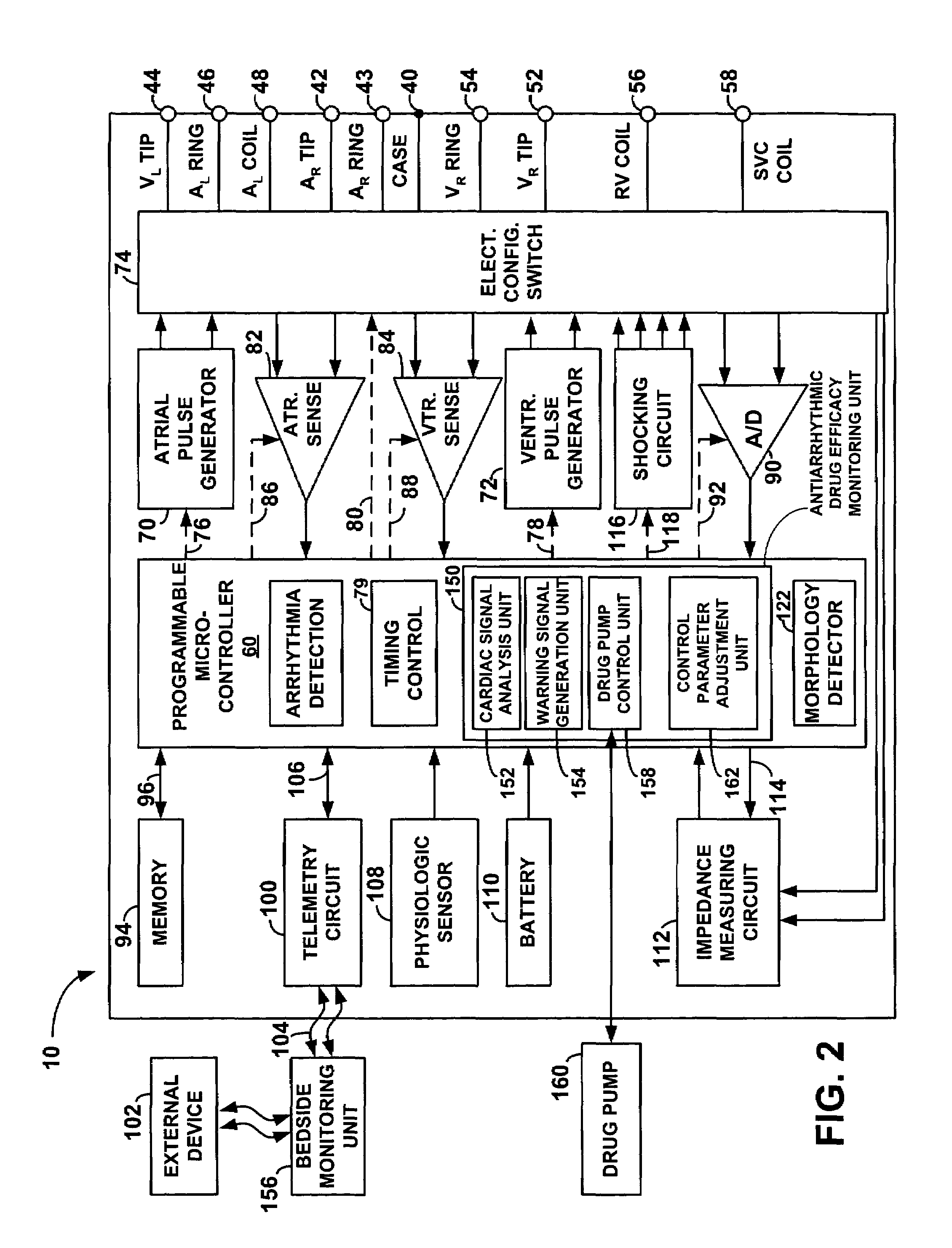
Method and apparatus for monitoring drug effects on cardiac electrical signals using an implantable cardiac stimulation device
InactiveUS7142911B2Increase aggressivenessIncrease dosePhysical therapies and activitiesDrug and medicationsEcg signalCardiac pacemaker electrode
An implantable cardiac stimulation device, such as a pacemaker or Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, is configured to automatically monitor the effects of antiarrhythmic drugs on cardiac electrical signals within a patient to verify the efficacy of the drugs taken. In one example, an analysis of patient cardiac electrical signals is performed by comparing the cardiac electrical signals with values representative of the effects of different classes of antiarrhythmic drugs. If the implantable device determines that the prescribed antiarrhythmic drugs have not been effective, a warning signal is generated. The warning signal is conveyed directly to the patient via a bedside monitor and to the patient's physician via remote connection to an external programmer device so that both are notified of the drug efficacy problems. Additionally, the implantable device may be configured to automatically adjust pacing and defibrillation control parameters in an attempt to compensate for any lack of efficacy in the drugs. For example, the aggressiveness of overdrive pacing may be increased. Alternatively, a drug pump is controlled to adjust the dosage of antiarrhythmic drugs if an initial dosage is found to be ineffective.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
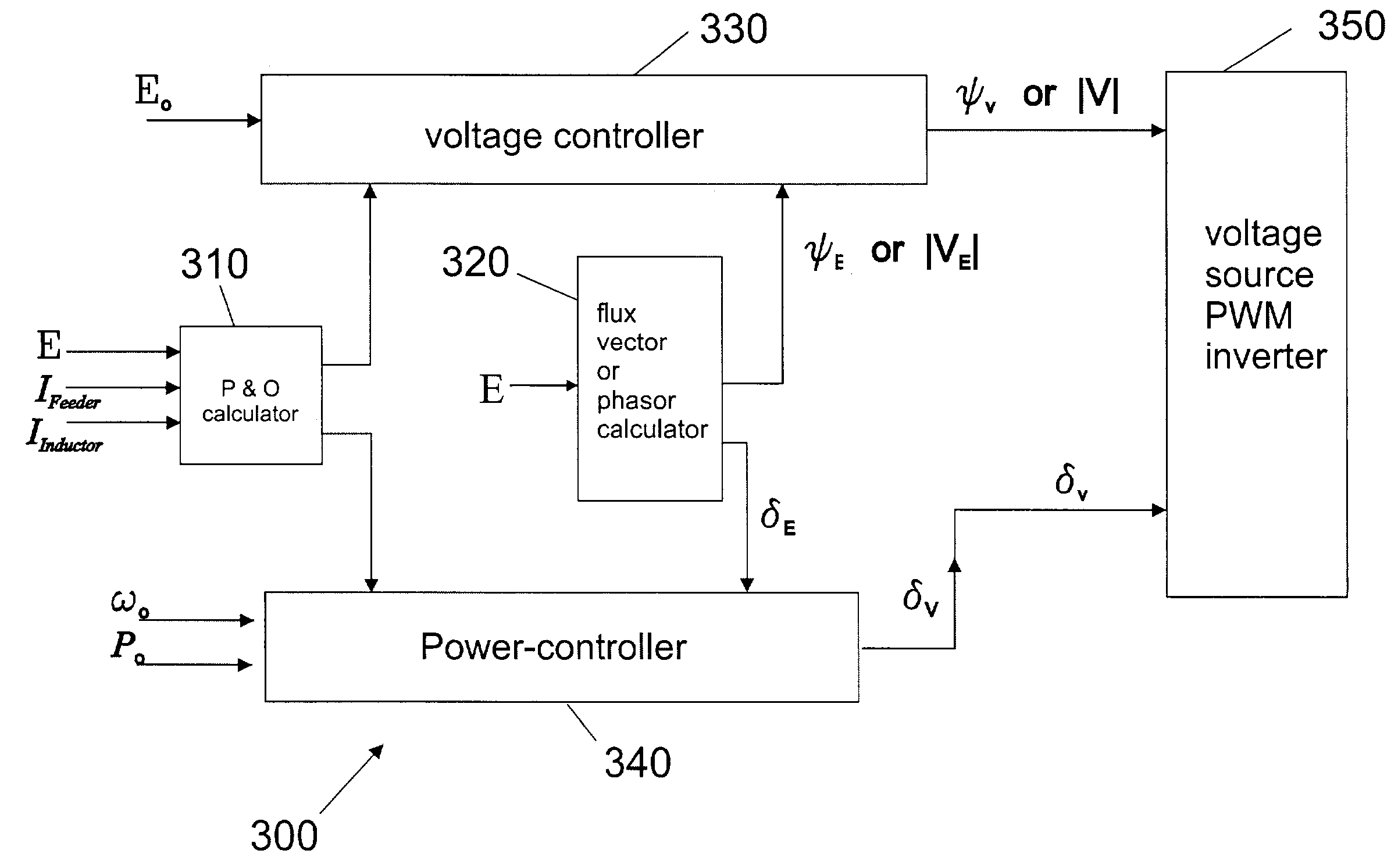
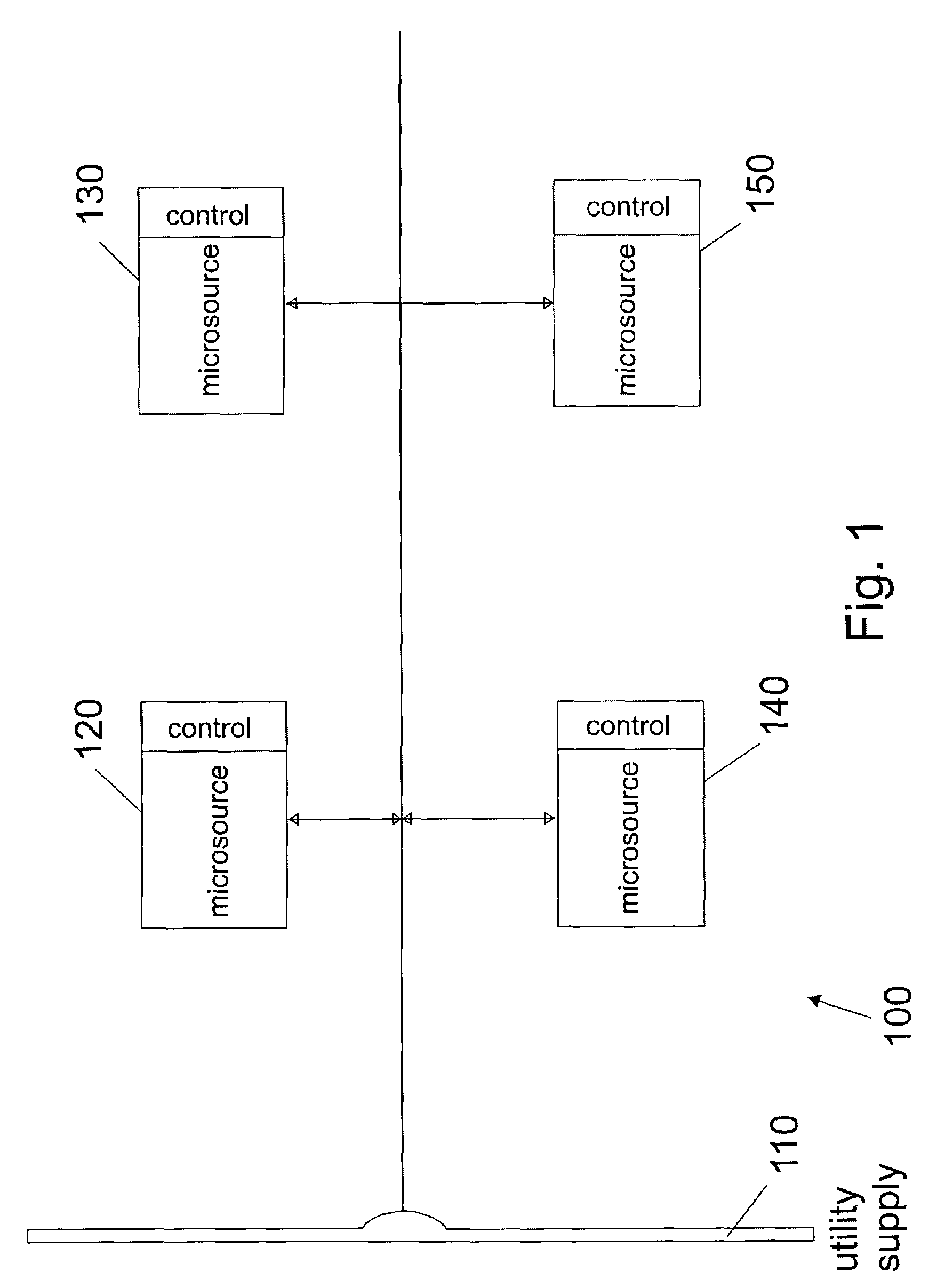
Control of small distributed energy resources
ActiveUS7116010B2Reduce pointsIncrease pointsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDc source parallel operationDistributed generatorVoltage sag
A power electronics interface in a microsource controller allows efficient connection in a power system of small, low cost and reliable distributed generators such as microturbines, fuel cells and photovoltaic. Power electronics provide the control and flexibility to insure stable operation for large numbers of distributed generators. The power electronics controls are designed to insure that new generators can be added to the system without modification of existing equipment. A collection of sources and loads can connect to or isolate from the utility grid in a rapid and seamless fashion, each inverter can respond effectively to load changes without requiring data from other sources, and voltage sag and system imbalances can be corrected.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Boron-free glass
The invention discloses boron-free neutral glasses having the composition (in % by weight, based on oxide) 65-72 SiO2, 11-17 Al2O3, 0.1-8 Na2O, 3-8 MgO, 4-12 CaO and 0-10 ZnO, a ratio CaO / MgO of 1.4 to 1.6, and having a hydrolytic resistance in accordance with DIN ISO 719 in class 1 and an acid resistance in accordance with DIN 12116 and an alkali resistance in accordance with DIN ISO 695 at least in class 2.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
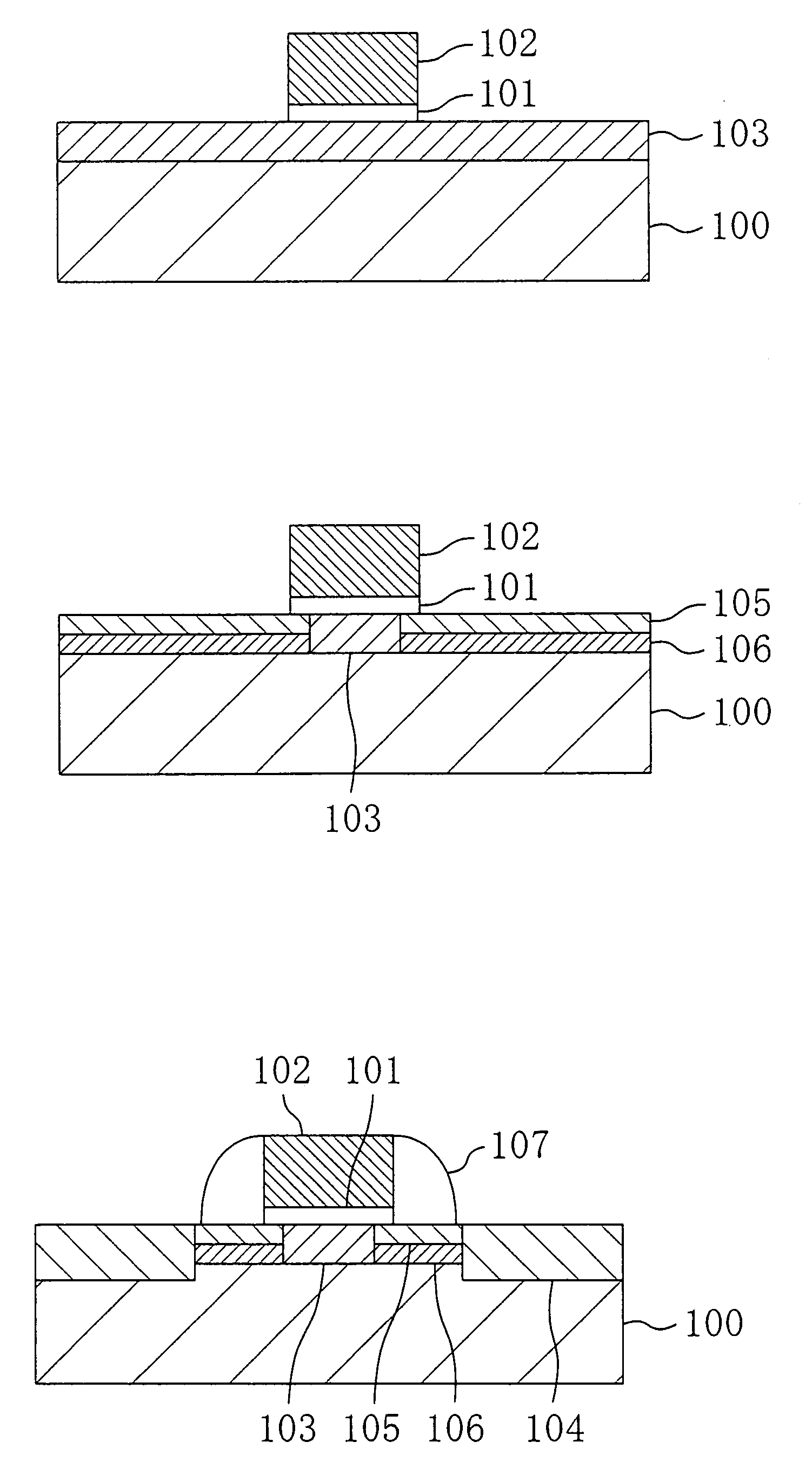
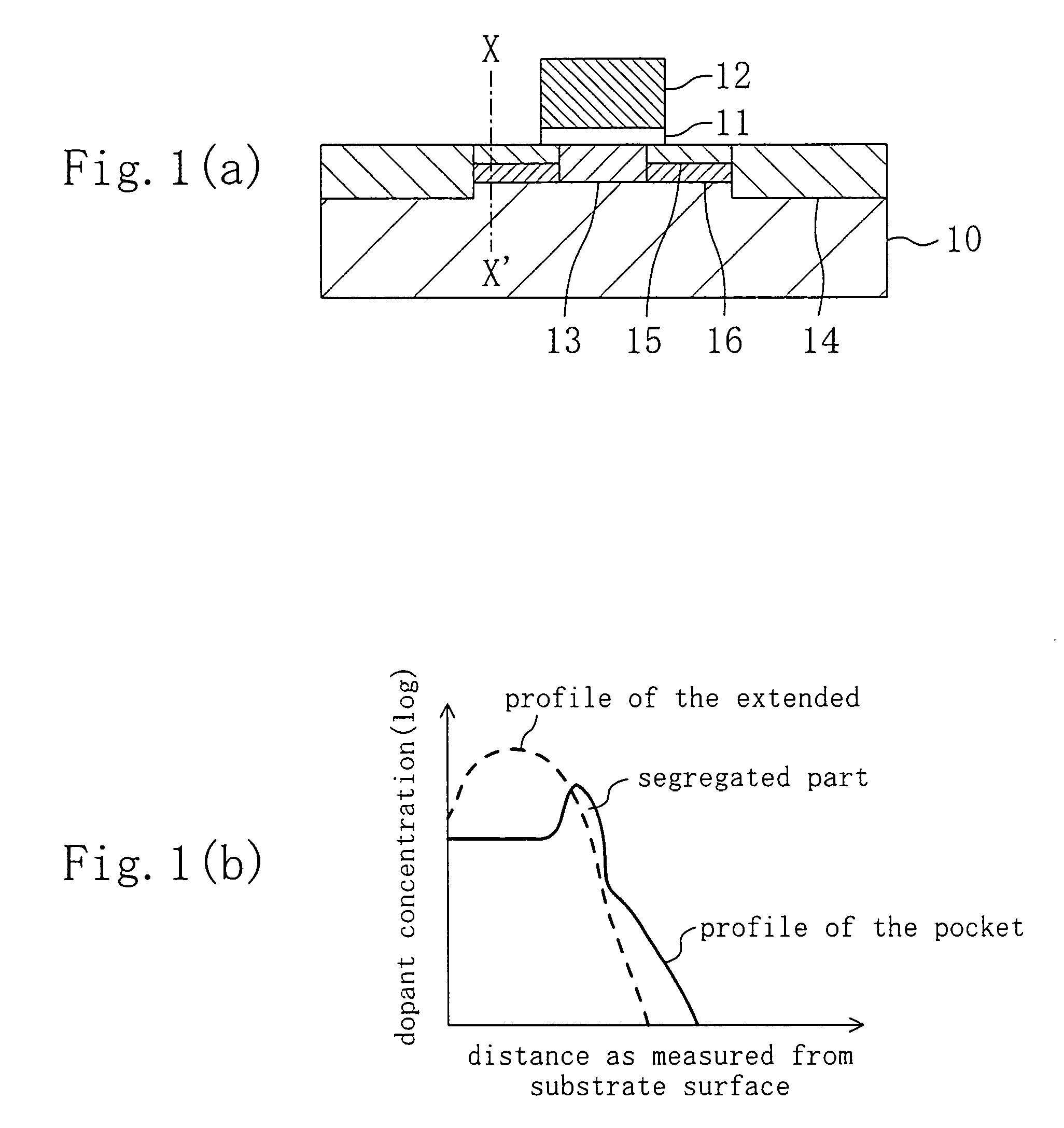
Method for fabricating a semiconductor device having a pocket dopant diffused layer
InactiveUS7091093B1Facilitated DiffusionSuppress DiffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantHigh concentration
A gate electrode is formed over a semiconductor region with a gate insulating film interposed therebetween. An extended high-concentration dopant diffused layer of a first conductivity type is formed in part of the semiconductor region beside the gate electrode through diffusion of a first dopant. A pocket dopant diffused layer of a second conductivity type is formed under the extended high-concentration dopant diffused layer through diffusion of heavy ions. The pocket dopant diffused layer includes a segregated part that has been formed through segregation of the heavy ions.
Owner:RPX CORP
Resistance spot welding of steel to pre-coated aluminum
ActiveUS20140360986A1Low melting pointImprove the immunityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesResistance welding apparatusTitanium zirconiumConversion coating
Resistance spot welding of a steel workpiece to an aluminum or an aluminum alloy workpiece can be facilitated by replacing the refractory aluminum oxide-based layer(s) on at least the faying surface of the aluminum or aluminum alloy workpiece with a protective coating that is more conducive to the spot welding process. The protective coating may be a metallic coating or a metal oxide conversion coating. In a preferred embodiment, the protective coating is a coating of zinc, tin, or an oxide of titanium, zirconium, chromium, or silicon.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
High temperature foamer formulations for downhole injection
ActiveUS7122509B2Increase heightReduce pointsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAnionic surface-active compoundsFoaming agentDecomposition
Owner:WHITEBOX ADVISORS +1
Process for producing a branched hydrocarbon component
InactiveUS20070135316A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationCatalytic naphtha reformingIsomerizationHydrodeoxygenation
The invention relates to a process for producing high-quality hydrocarbon base oil particularly of biological origin. The process of the invention comprises aldol condensation, hydrodeoxygenation, and isomerization steps. Aldehydes and / or ketones, preferably of biological origin are used as the feedstock.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
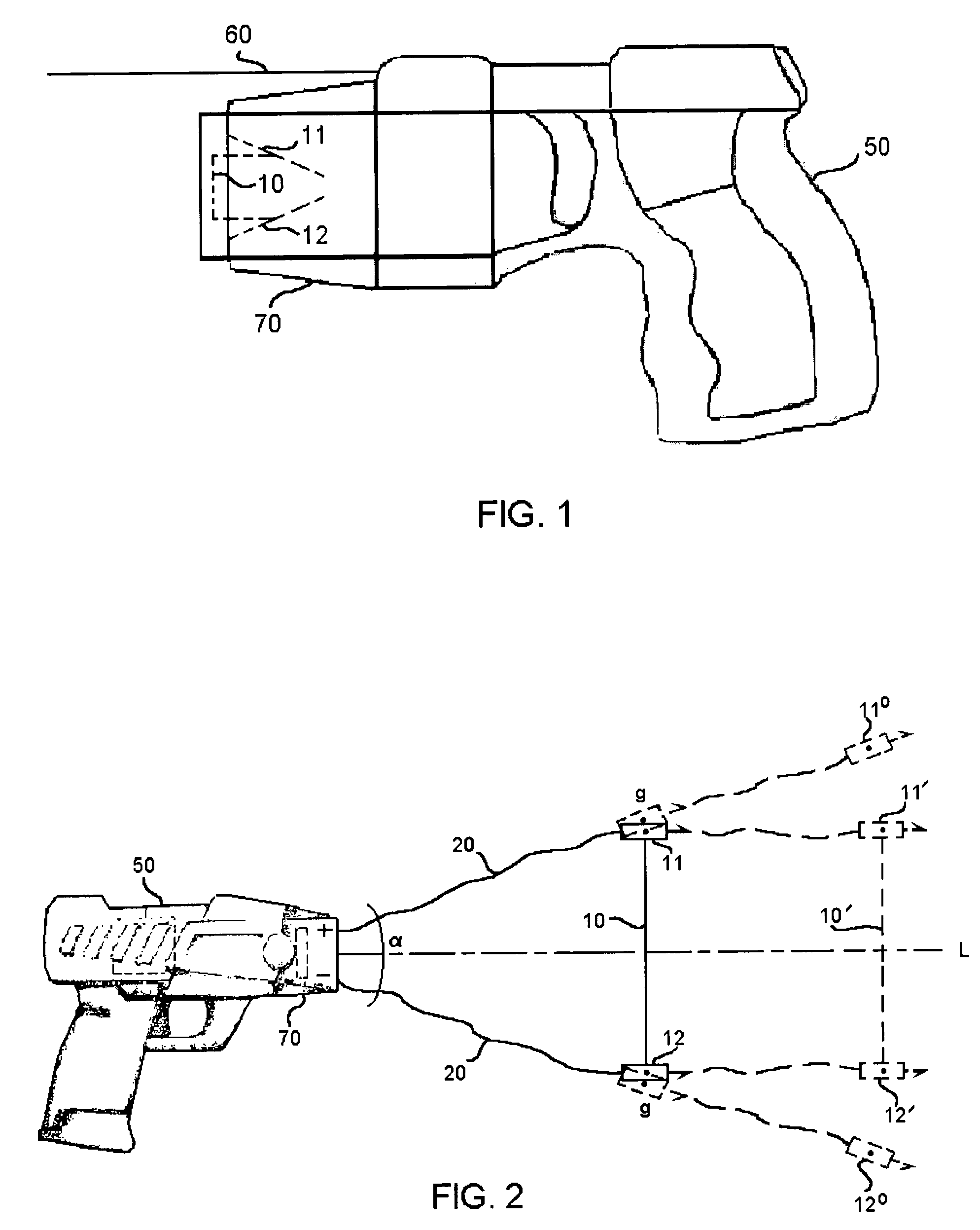
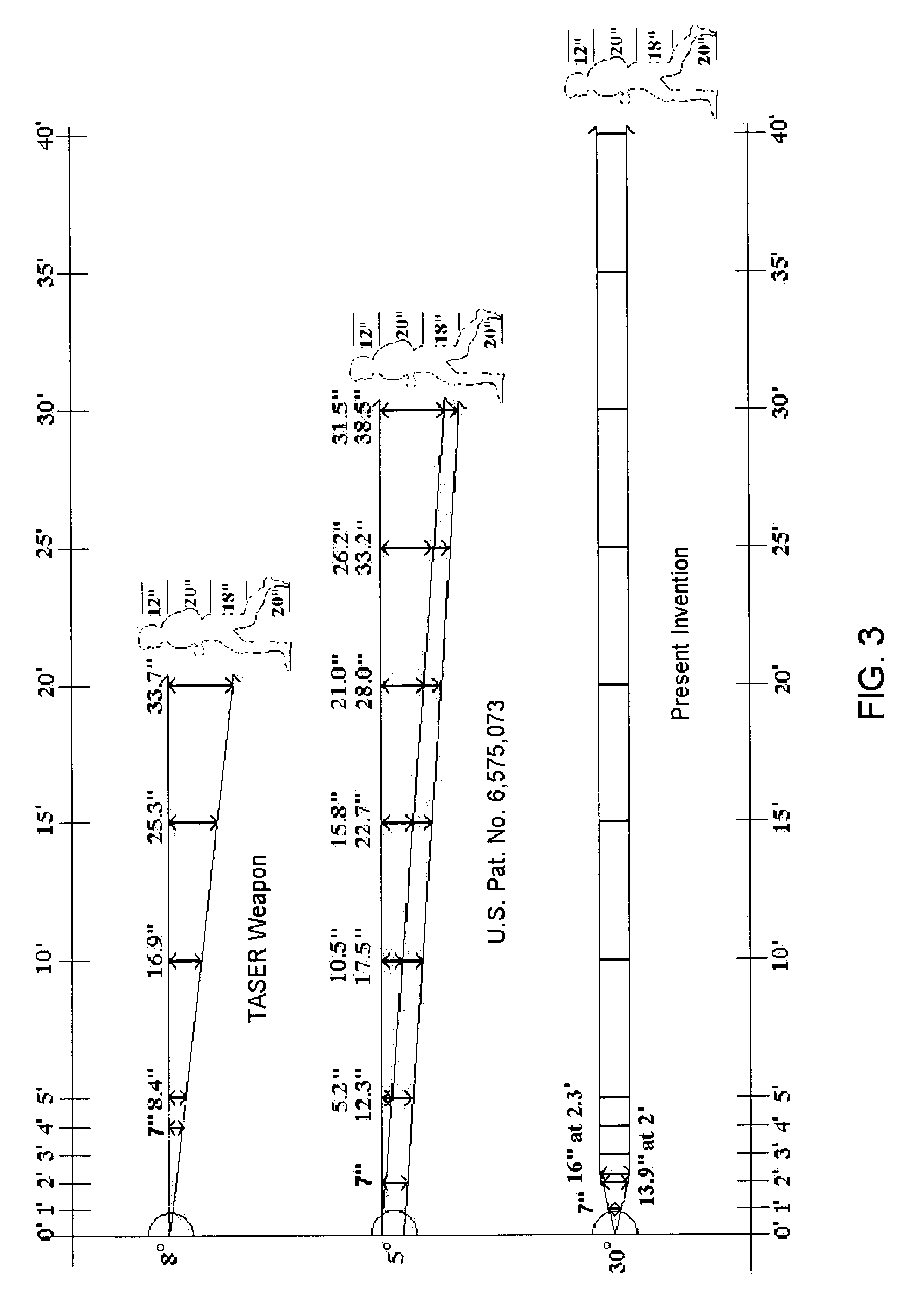
Apparatus and method for electrical immobilization weapon
ActiveUS7314007B2Suitable for useEffective shooting rangeAmmunition projectilesElectric shock equipmentsInvolved musclesTaser
An electrical immobilization weapon having a prolonged range of effectiveness and improved accuracy compared to conventional Taser weapons, while being compact in structure and lightweight. The weapon having a replaceable cartridge which, when employed, can space a pair of electrodes to a specific critical area on a remote target, so the electrical energy carried by the electrodes can induce the involuntary contraction of the involved muscles through the critical area within a significant range of length between the electrodes for effective immobilization. The electrical energy generated by a power source of the weapon completes an electrical circuit through a minimum path being a length of at least 5 inches between the two points on the target.
Owner:VOLGER INT AB
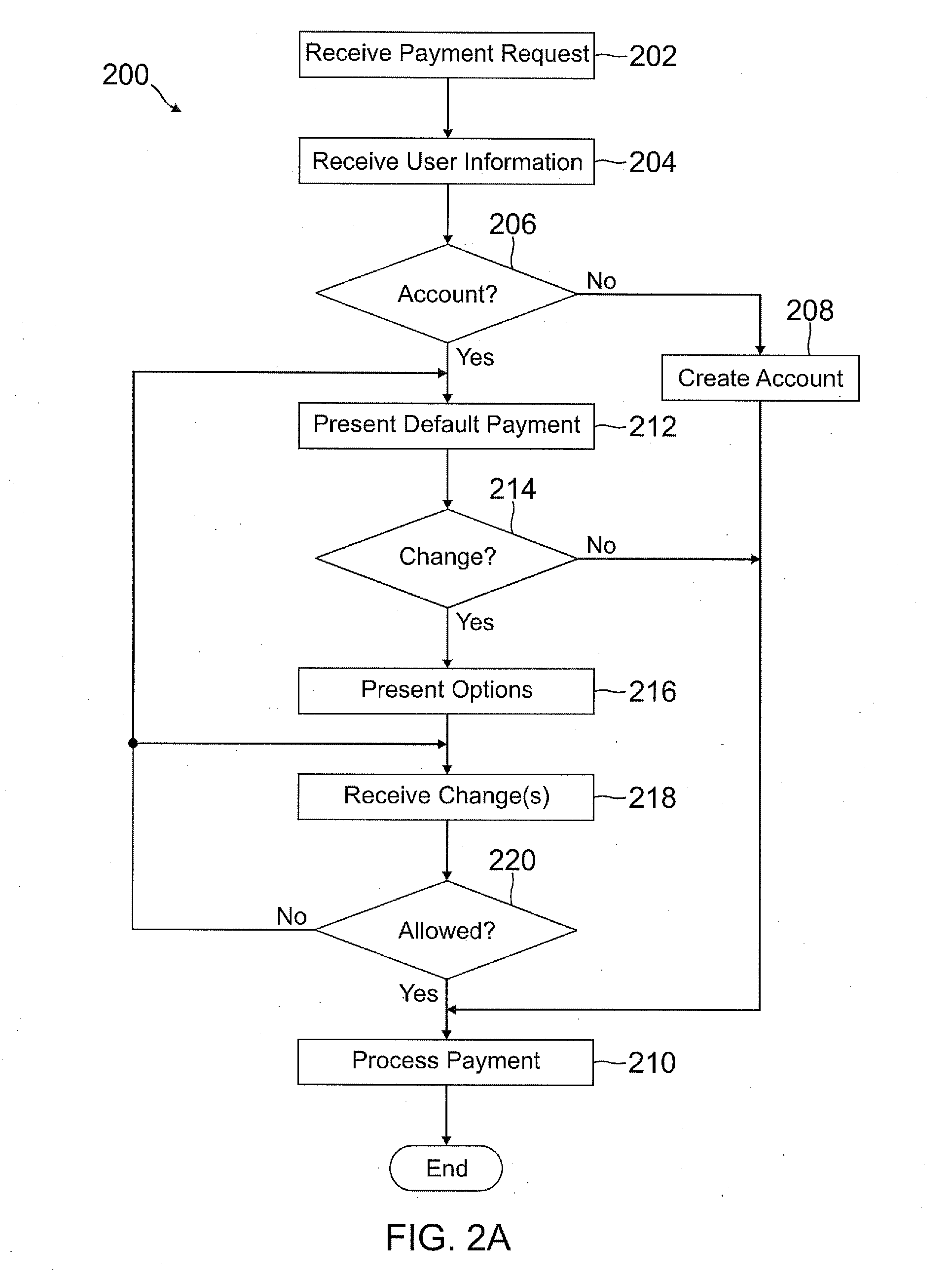
Deferred payment and selective funding and payments
InactiveUS20120166311A1Increase flexibilityEasy to controlPayment architectureBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentEmail address
A user is able to change one or more payment options after payment has already been made to a merchant. A payment provider processes a payment request during a transaction with the merchant with default or selected payment options. After the transaction with the merchant is completed and the merchant has been paid, the user may change one or more of the payment options, such as funding source(s) and terms / conditions of payment (e.g., deferment period, installment period / amount, etc.). During the transaction, the user may make a purchase through the payment provider even if the user does not have an account with the payment provider by providing user information, such as name, address, phone number, email address, and date of birth, but not a social security number or funding source information.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
Process for manufacturing lubricating base oil with high monocycloparaffins and low multicycloparaffins
InactiveUS7282134B2Reduce weightHigh weight ratioTreatment with hydrotreatment processesAdditivesAlkaneWax
A process for manufacturing a lubricating base oil by: a) performing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on syngas to provide a product stream; b) isolating from said product stream a substantially paraffinic wax feed having less than about 30 ppm total nitrogen and sulfur, and less than about 1 wt % oxygen; c) dewaxing said feed by hydroisomerization dewaxing using a shape selective intermediate pore size molecular sieve comprising a noble metal hydrogenation component, wherein the hydroisomerization temperature is between about 600° F. (315° C.) and about 750° F. (399° C.), to produce an is dimerized oil; and d) hydrofinishing said isomerized oil to produce a lubricating base oil having specific desired properties.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
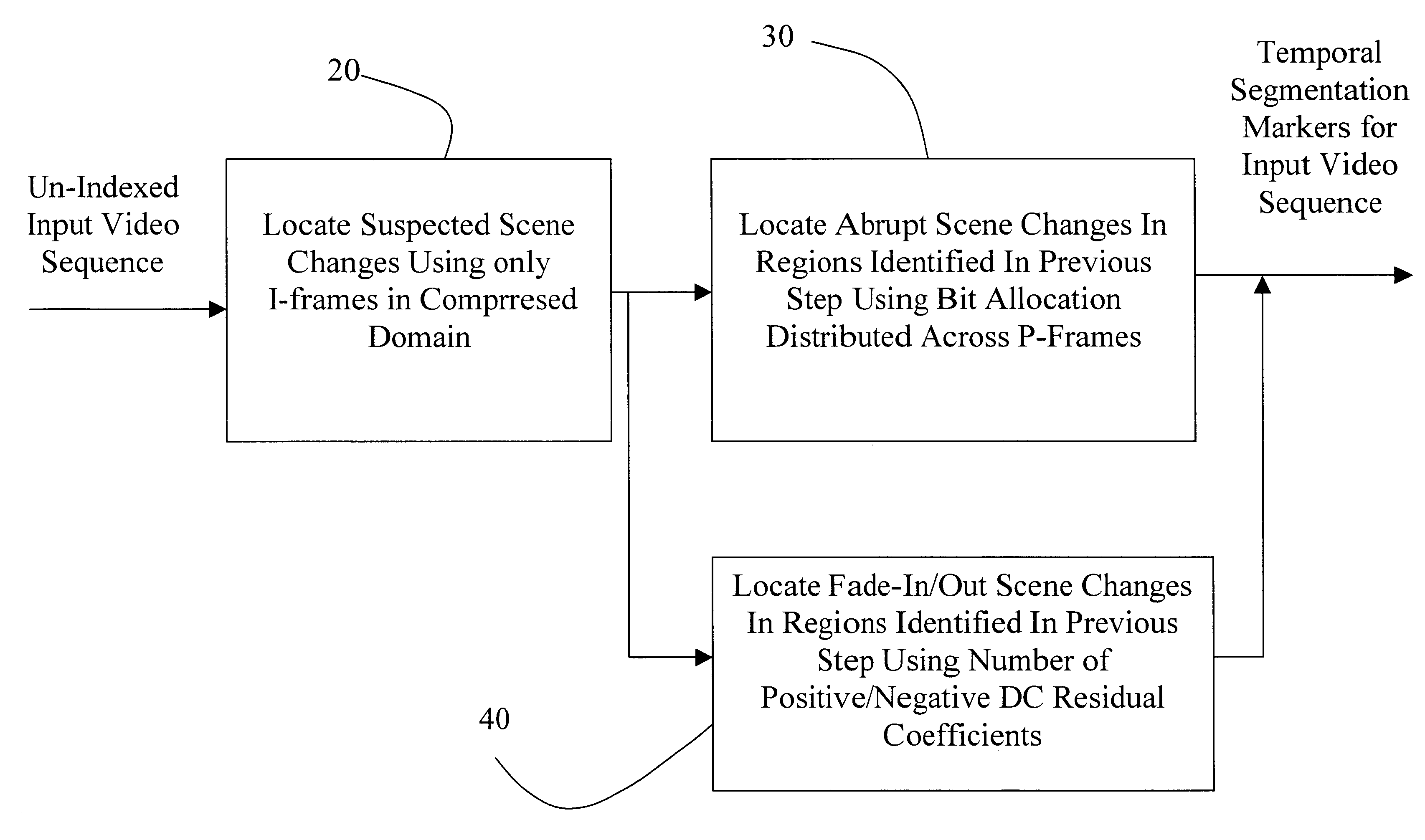
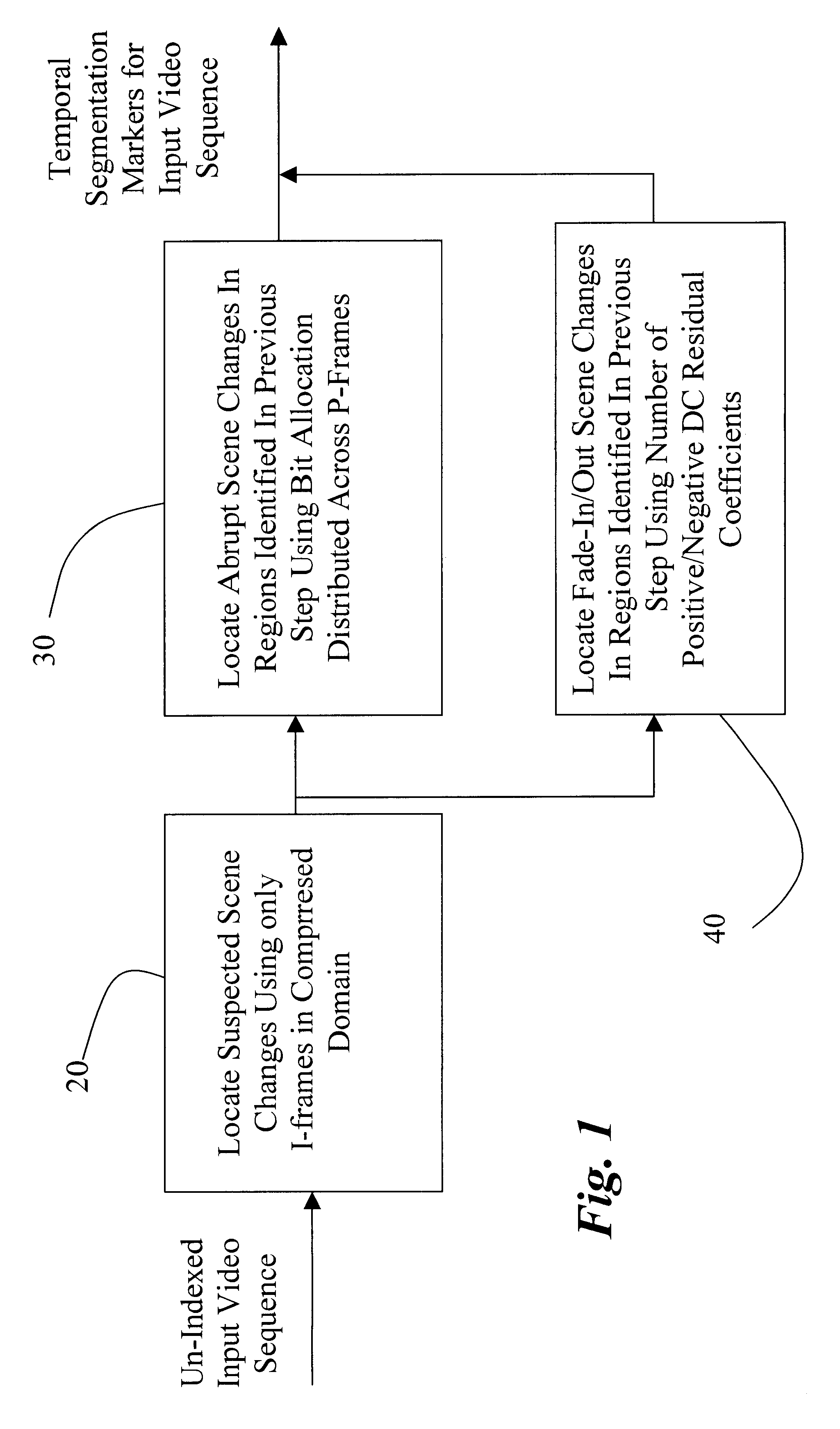
Methods of scene change detection and fade detection for indexing of video sequences
InactiveUS6449392B1High-precision detectionReduce pointsTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVideo sequenceComputer science
This invention relates to methods of abrupt scene change detection and fade detection for indexing of MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 compressed video sequences. Abrupt scene change and fade-detection techniques applied to signals in compressed form have reasonable accuracy and the advantage of high simplicity since they are based on entropy decoding and do not require computationally expensive inverse Discrete Cosine Transformation (DCT).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com