Patents
Literature
720 results about "Valence band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In solids, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in which electrons are normally present at absolute zero temperature. The valence electrons are bound to individual atoms, as opposed to conduction electrons, which can move freely within the atomic lattice of the material. On a graph of the electronic band structure of a material, the valence band is located below the conduction band, separated from it in insulators and semiconductors by a band gap. In metals, the conduction band has no energy gap separating it from the valence band.F To understand the concept of a valence band, it is important to consider the atomic structure of a metal first. For example lithium atoms with electronic configuration 1s²2s¹ can form only one covalent bond. However, when forming a bulk metal, Li atoms come to a resonance structure by taking 1 electron from its neighbouring Li atom and the resultant electronic configuration becomes 1s²2s¹2p¹. As a result of this electron sharing, its neighbouring Li atom loses an electron and comes to an electronic configuration of 1s². The Li atoms now gain the capability to form two covalent bonds thus can form a bulk metal.
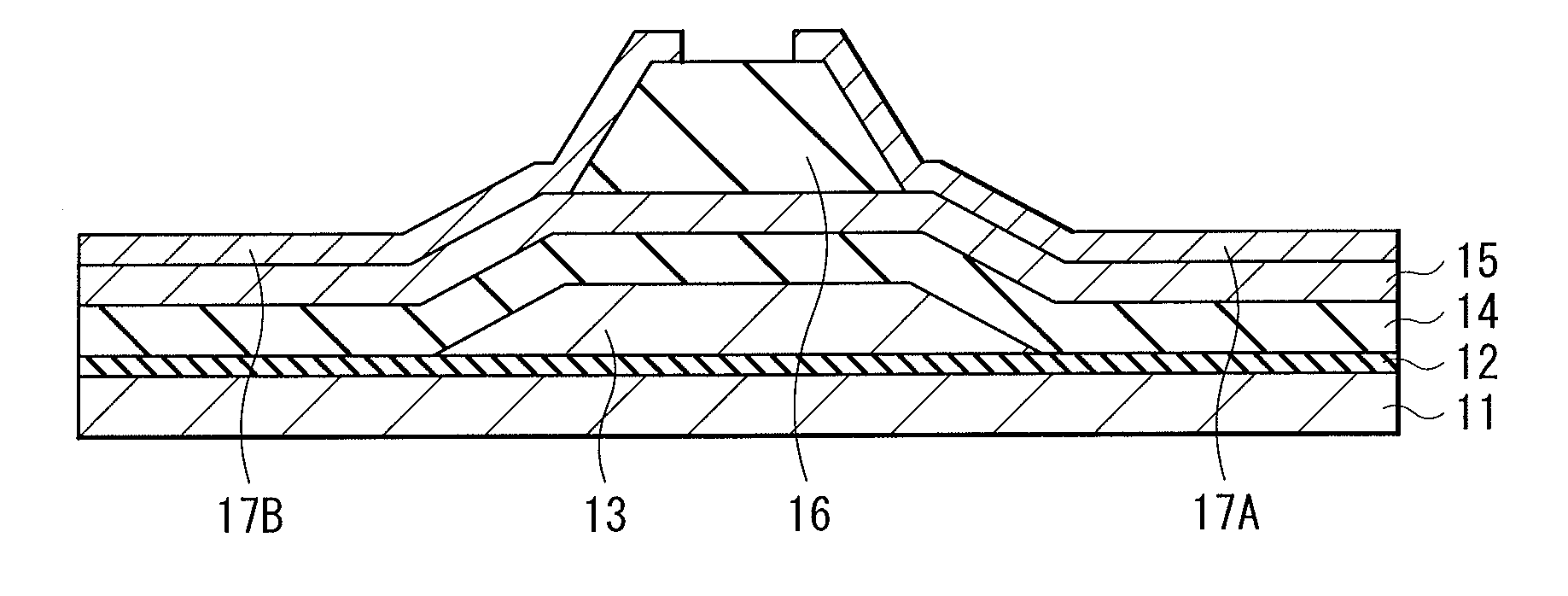
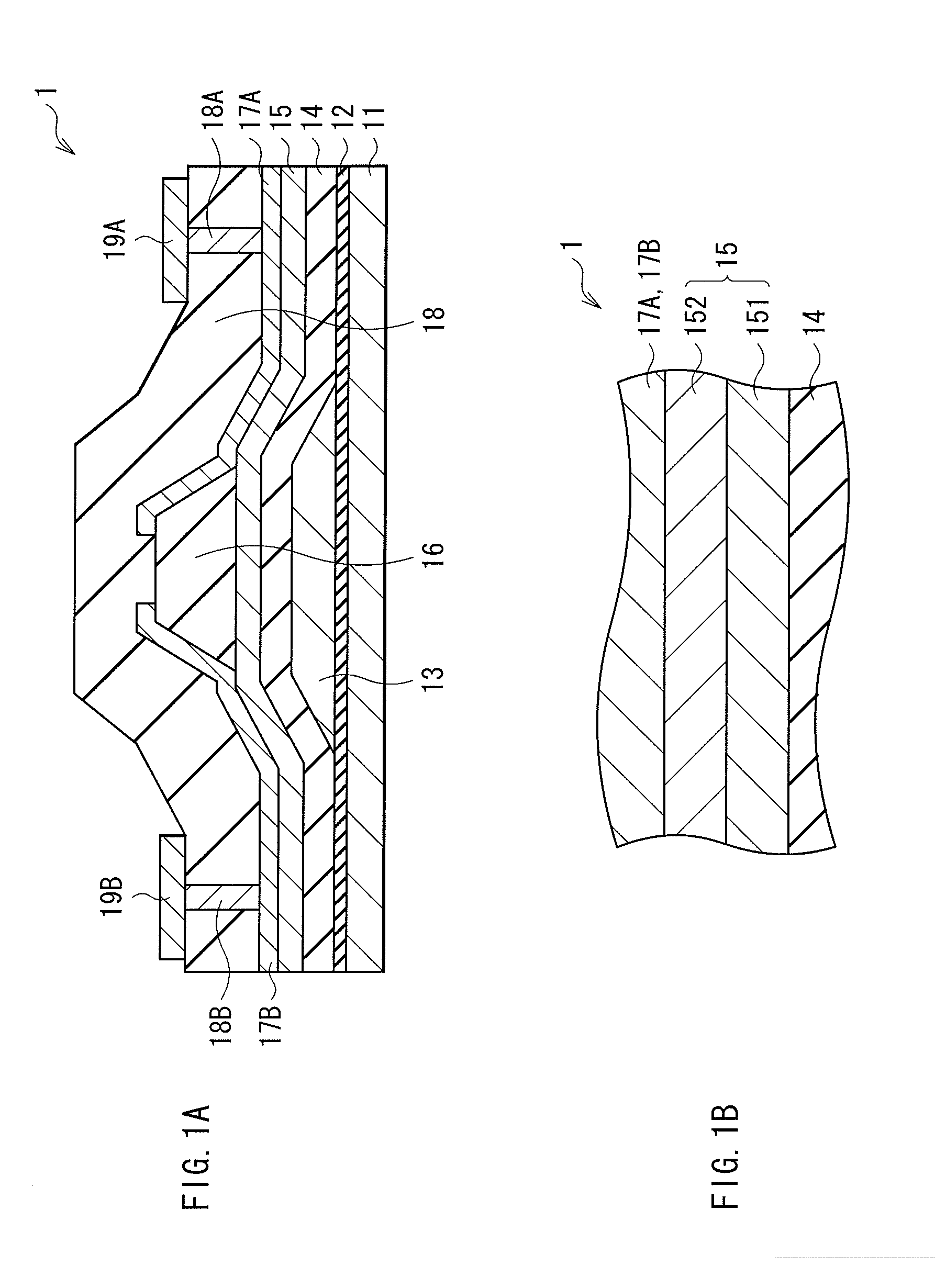
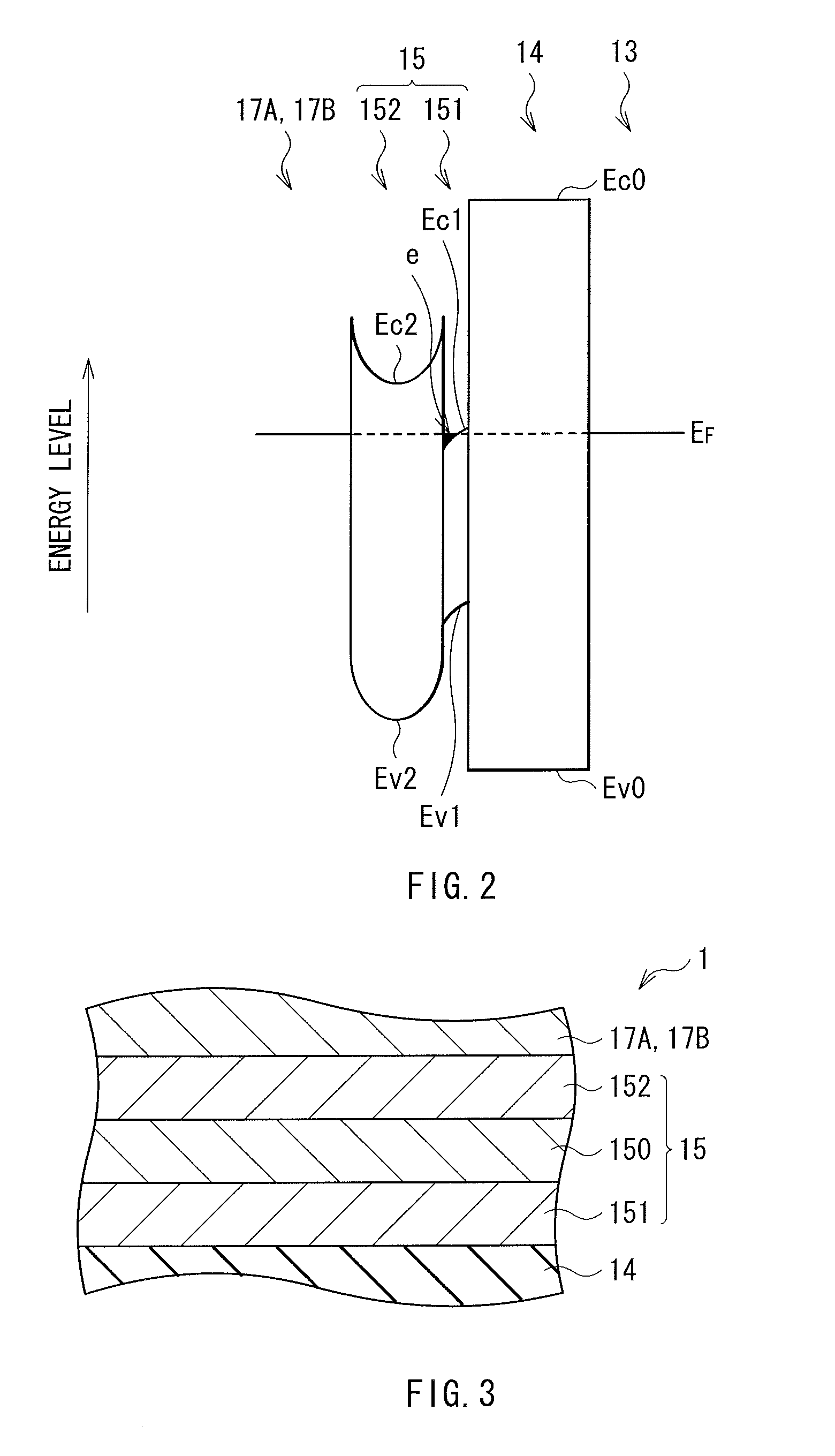
Thin film transistor, display device, and electronic device
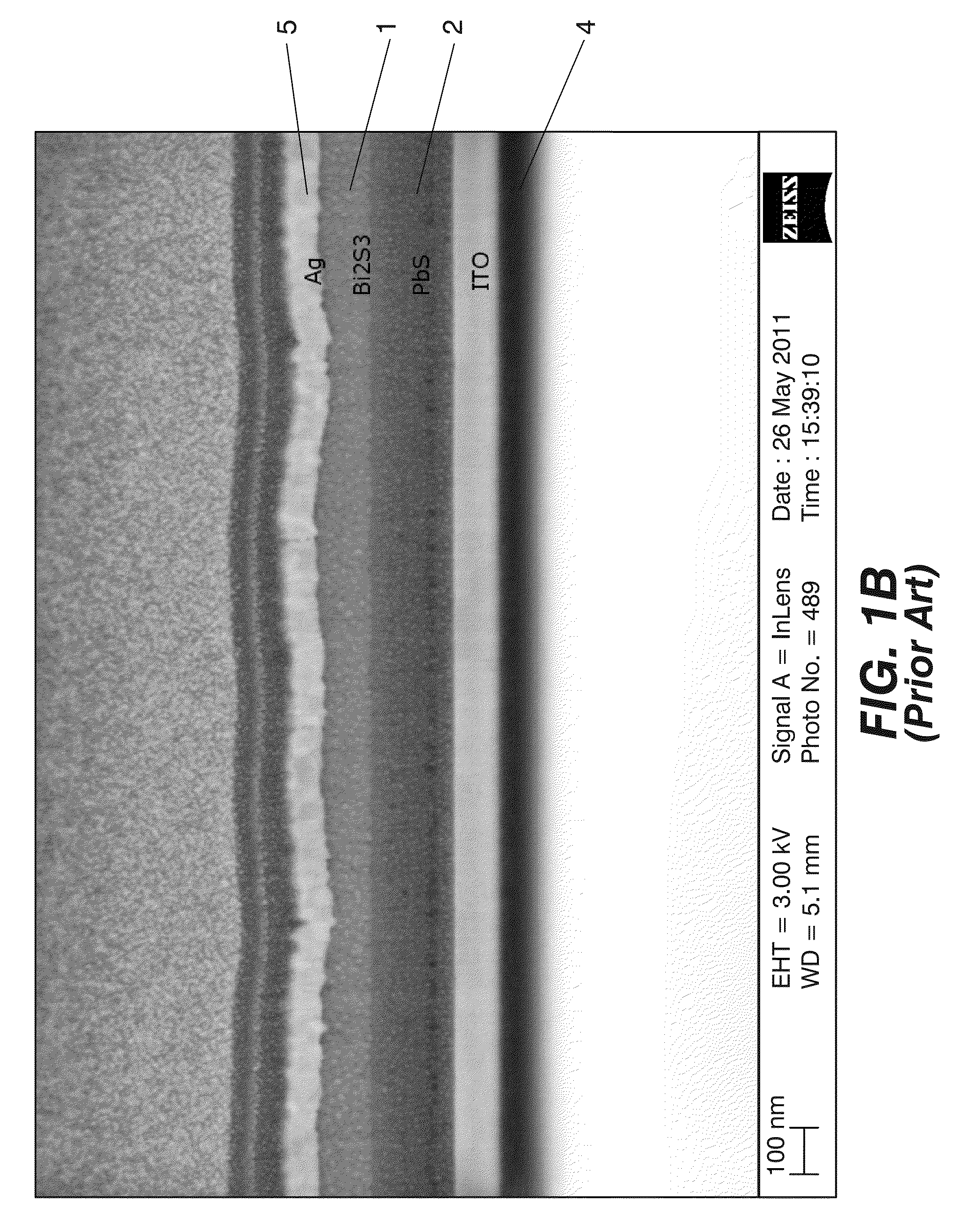
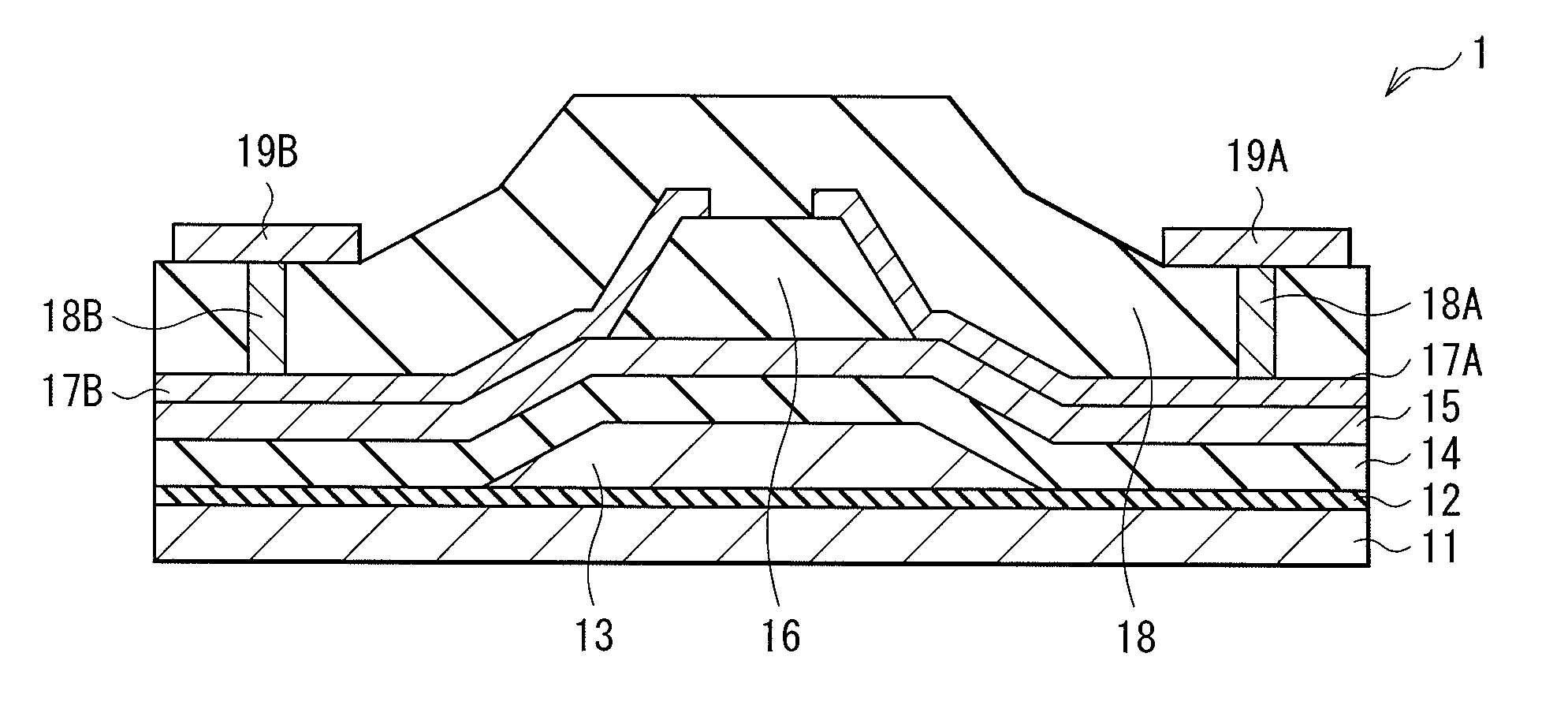
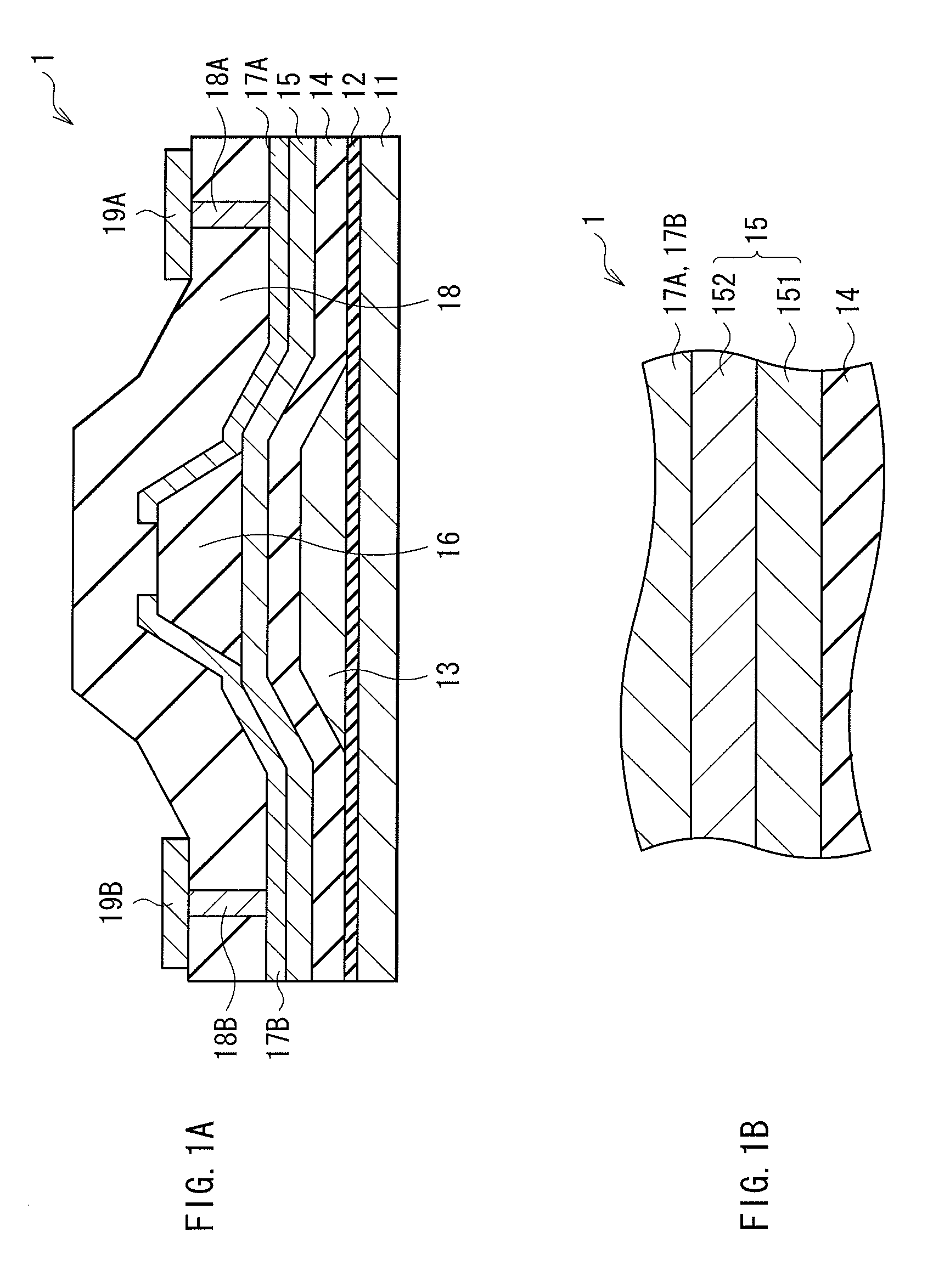
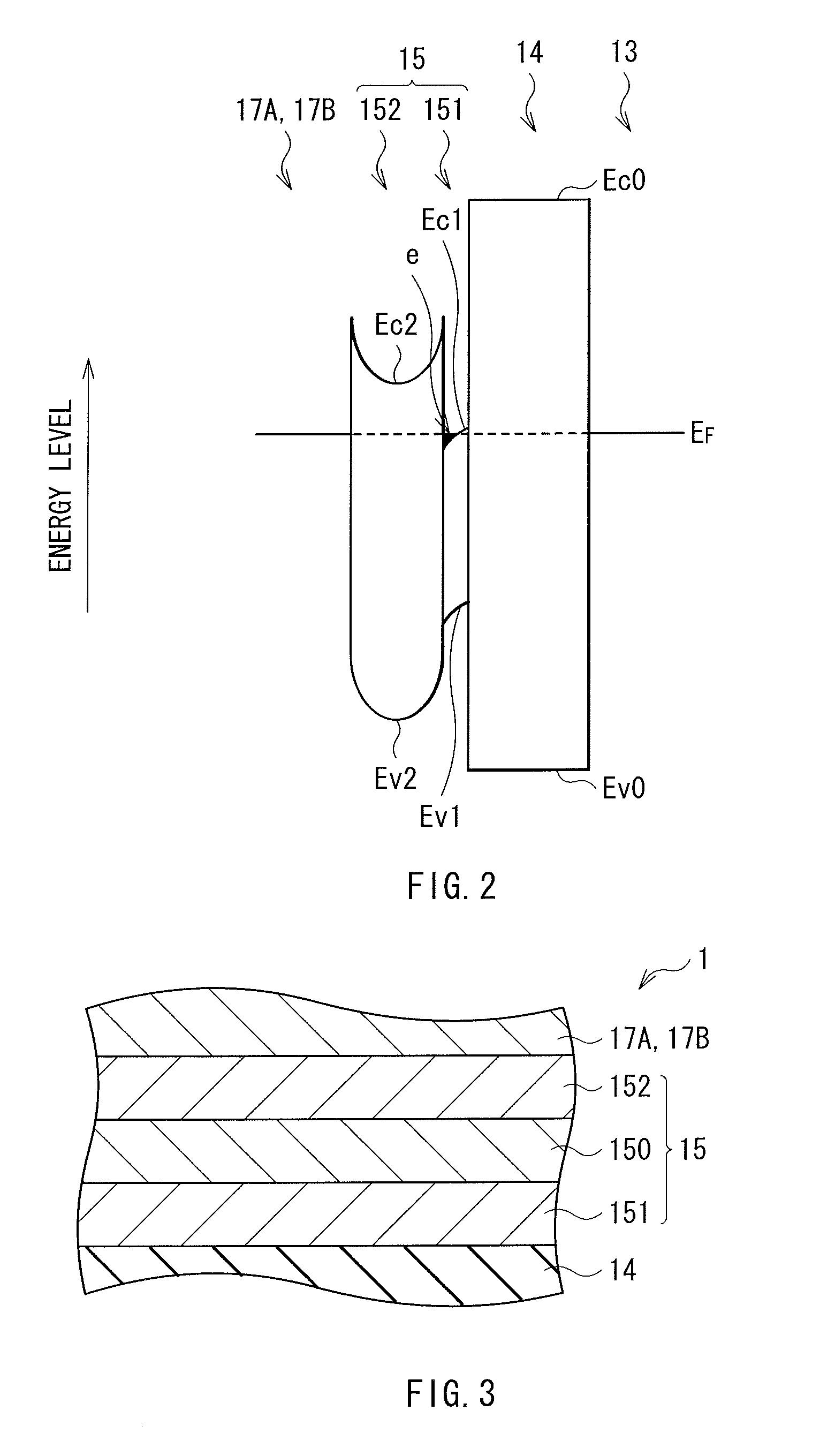
ActiveUS20120119205A1Maintain good propertiesLarge carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandMaximum level
A thin film transistor, which is capable of improving carrier mobility, and a display device and an electronic device, each of which uses the thin film transistor, are provided. The thin film transistor includes: a gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor layer including a multilayer film including a carrier travel layer configuring a channel and a carrier supply layer for supplying carriers to the carrier travel layer; a gate insulating film provided between the gate electrode and the oxide semiconductor layer; and a pair of electrodes as a source and a drain. A conduction band minimum level or a valence band maximum level corresponding to a carrier supply source of the carrier supply layer is higher in energy than a conduction band minimum level or a valence band maximum level corresponding to a carrier supply destination of the carrier travel layer.
Owner:JOLED INC
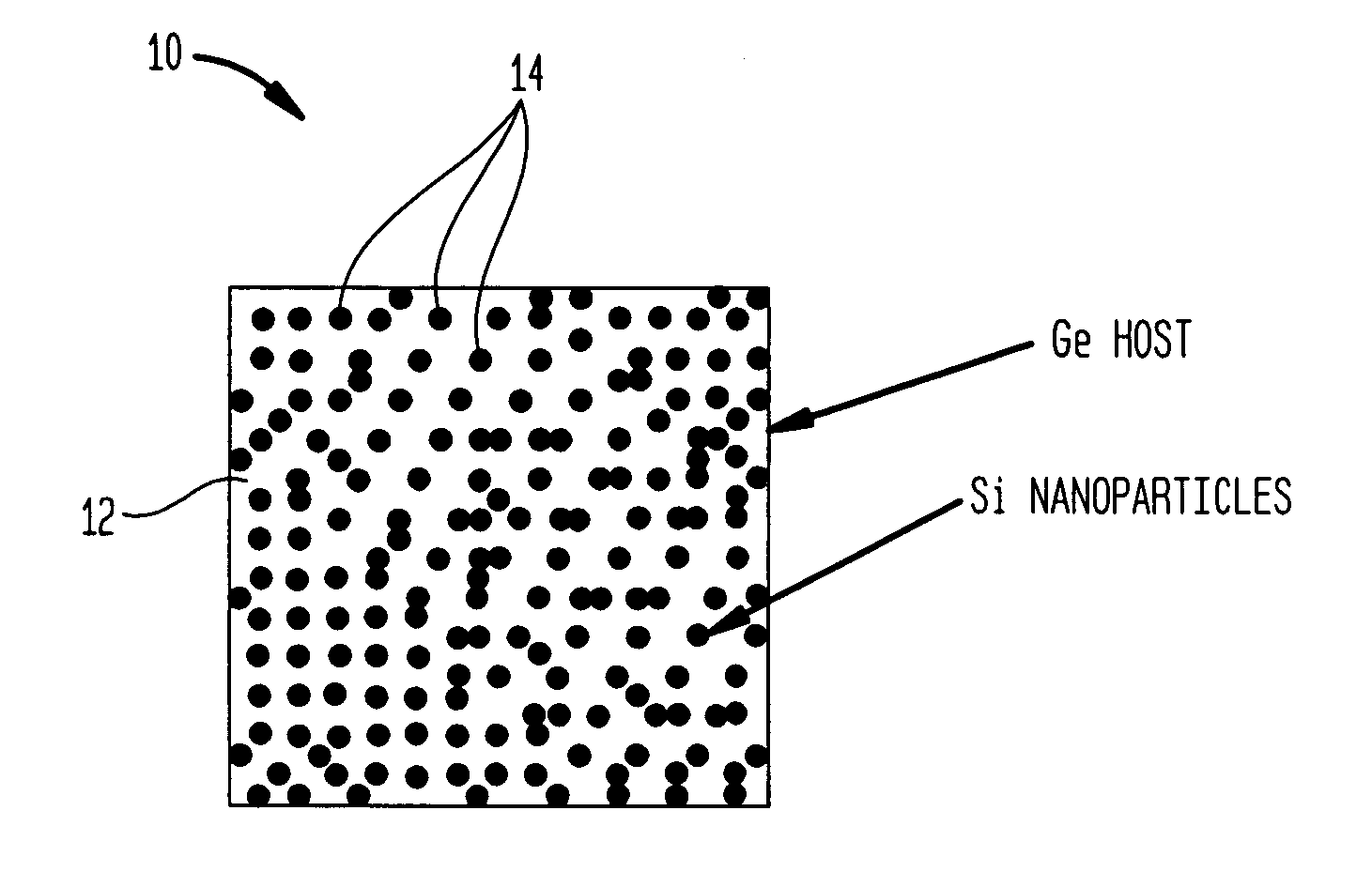
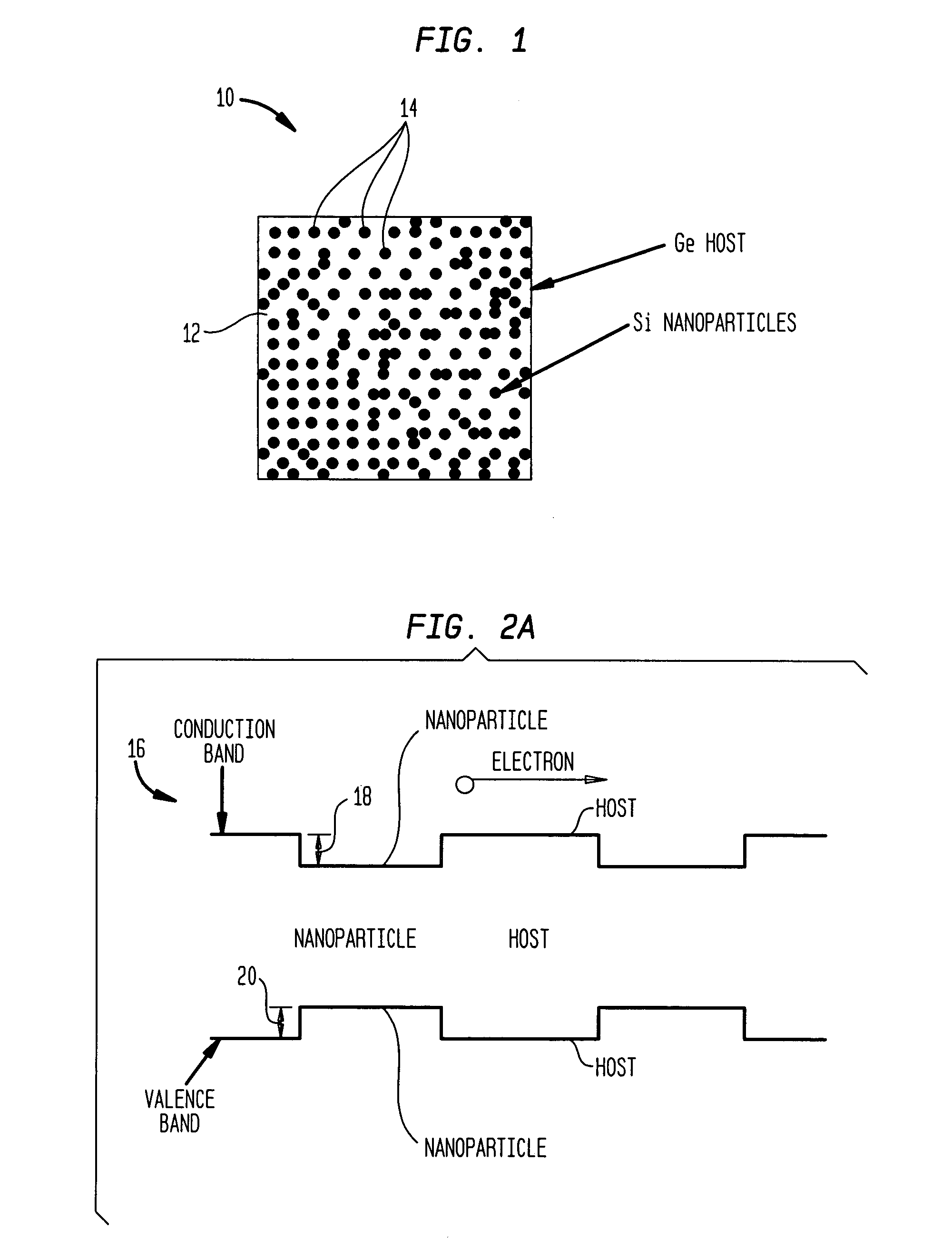
Nanocomposites with high thermoelectric figures of merit
InactiveUS20060102224A1Improve thermoelectric performanceLow thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectValence bandConduction band
The present invention is generally directed to nanocomposite thermoelectric materials that exhibit enhanced thermoelectric properties. The nanocomposite materials include two or more components, with at least one of the components forming nano-sized structures within the composite material. The components are chosen such that thermal conductivity of the composite is decreased without substantially diminishing the composite's electrical conductivity. Suitable component materials exhibit similar electronic band structures. For example, a band-edge gap between at least one of a conduction band or a valence band of one component material and a corresponding band of the other component material at interfaces between the components can be less than about 5 kBT, wherein kB is the Boltzman constant and T is an average temperature of said nanocomposite composition.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE +1
Method concerning a junction barrier Schottky diode, such a diode and use thereof
InactiveUS6524900B2Change resistanceChange the on-state resistance of the diodeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandSemiconductor materials
A method for controlling the temperature dependence of a junction barrier Schottky diode of a semiconductor material having an energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band exceeding 2 eV provides for doing this when producing the diode by adjusting the on-state resistance of the grid portion of the diode during the production for obtaining a temperature dependence of the operation of the diode adapted to the intended use thereof.
Owner:CREE INC
Metal-Gate High-K Reference Structure
Disclosed are embodiments of an integrated circuit structure that incorporates at least two field effect transistors (FETs) that have the same conductivity type and essentially identical semiconductor bodies (i.e., the same semiconductor material and, thereby the same conduction and valence band energies, the same source, drain, and channel dopant profiles, the same channel widths and lengths, etc.). However, due to different gate structures with different effective work functions, at least one of which is between the conduction and valence band energies of the semiconductor bodies, these FETs have selectively different threshold voltages, which are independent of process variables. Furthermore, through the use of different high-k dielectric materials and / or metal gate conductor materials, the embodiments allow threshold voltage differences of less than 700 mV to be achieved so that the integrated circuit structure can function at power supply voltages below 1.0V. Also disclosed are method embodiments for forming the integrated circuit structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Thin film transistor, display device, and electronic device
ActiveUS8384080B2Maintain good propertiesLarge carrier mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandMaximum level
A thin film transistor, which is capable of improving carrier mobility, and a display device and an electronic device, each of which uses the thin film transistor, are provided. The thin film transistor includes: a gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor layer including a multilayer film including a carrier travel layer configuring a channel and a carrier supply layer for supplying carriers to the carrier travel layer; a gate insulating film provided between the gate electrode and the oxide semiconductor layer; and a pair of electrodes as a source and a drain. A conduction band minimum level or a valence band maximum level corresponding to a carrier supply source of the carrier supply layer is higher in energy than a conduction band minimum level or a valence band maximum level corresponding to a carrier supply destination of the carrier travel layer.
Owner:JOLED INC
Process for forming an electronic device including a transistor having a metal gate electrode
An electronic device includes an n-channel transistor and a p-channel transistor. The p-channel transistor has a first gate electrode with a first work function and a first channel region including a semiconductor layer immediately adjacent to a semiconductor substrate. In one embodiment, the first work function is less than the valence band of the semiconductor layer. In another embodiment, the n-channel transistor has a second gate electrode with a second work function different from the first work function and closer to a conduction band than a valence band of a second channel region. A process of forming the electronic device includes forming first and second gate electrodes having first and second work functions, respectively. First and second channel regions having a same minority carrier type are associated with the first and second gate electrodes, respectively.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
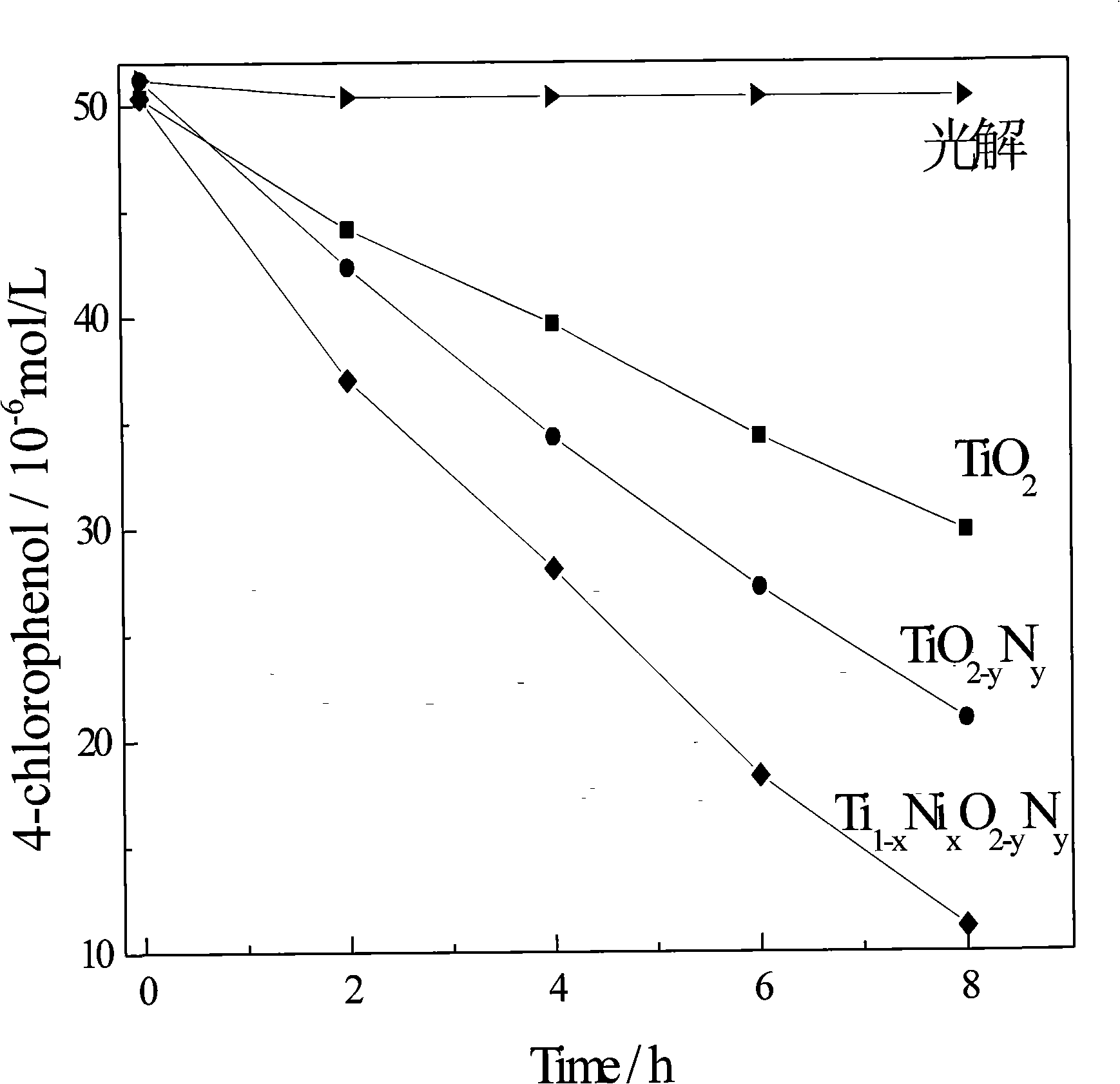
Method for preparing high efficiency metallic, non-metallic ion co-doped nano-TiO2 visible-light responsive photocatalyst
InactiveCN101301619AVisible light catalytic activity is highEnhanced inhibitory effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationCatalyst activation/preparationPhotocatalytic reactionLight responsive
The invention discloses a process for preparing a high efficiency nanometer Tio2 visible light catalyst codoped with metal and non metallic ion, belonging to the photocatalysis technology field. The invention adopts titanic acid ester as precursor, uses metal salt and non-metallic compound as dopant, in accordance with sol-gel method, prepares the nanometer TiO2-based photocatalyst with codoping, high efficiency and visible light catalytic activity, wherein the catalytic activity is greatly higher than that of single-doped TiO2-based catalyst. The invention is characterized by the following: 1. due to codoping of the metal and non metallic ion, discrete localized doping level is formed respectively on the lower part of the conduction band energy level and the upper part of the valence band energy level of the TiO2-based catalyst, thus increasing the absorption of visible light and greatly improving the catalytic activity; 2. the doping level can inhibit the recombination of photogenerated carrier, promote the probability of the photogenerated carrier entering into the photocatalytic reaction and efficiently degrade pollutant molecules.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
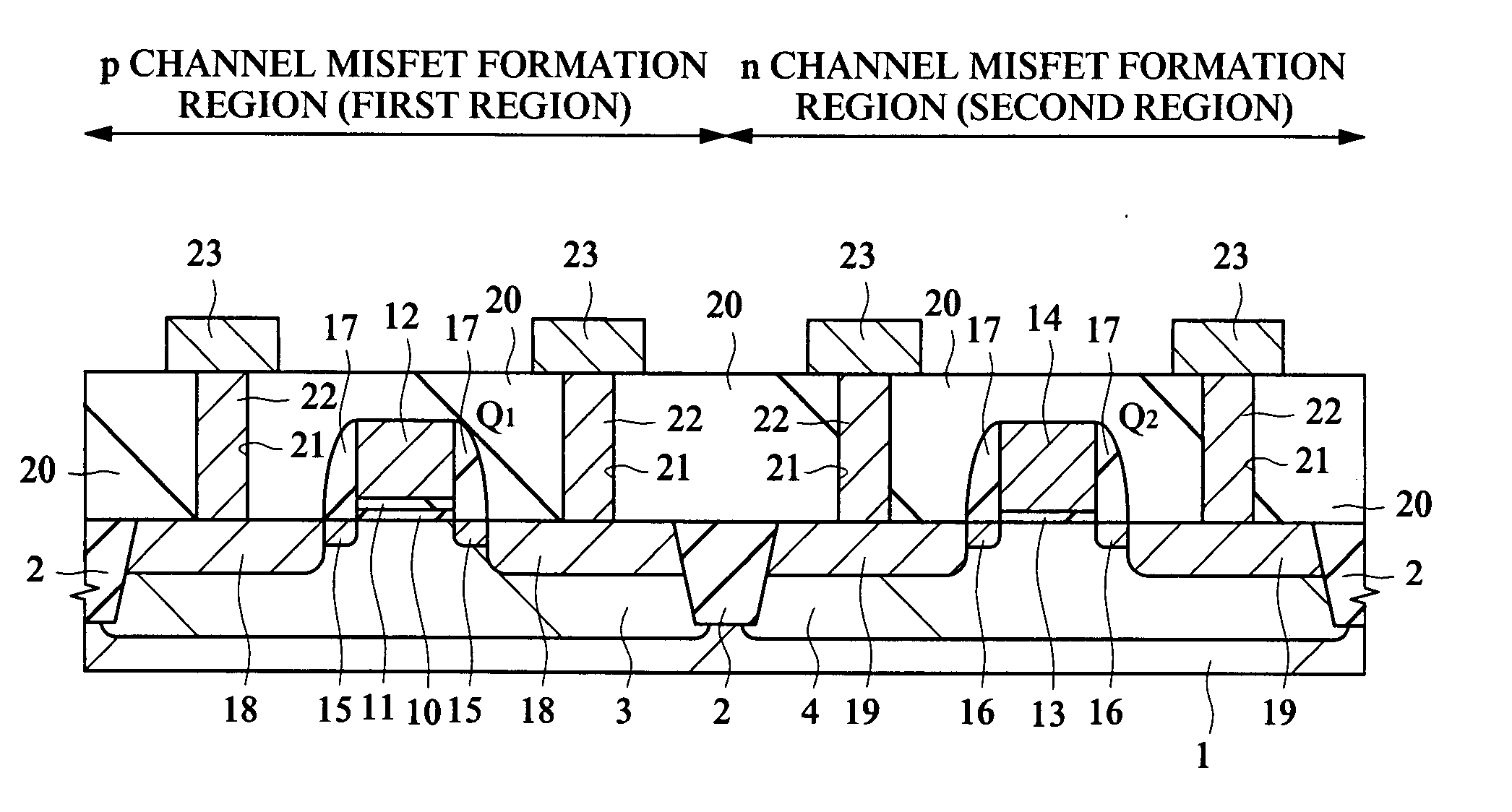
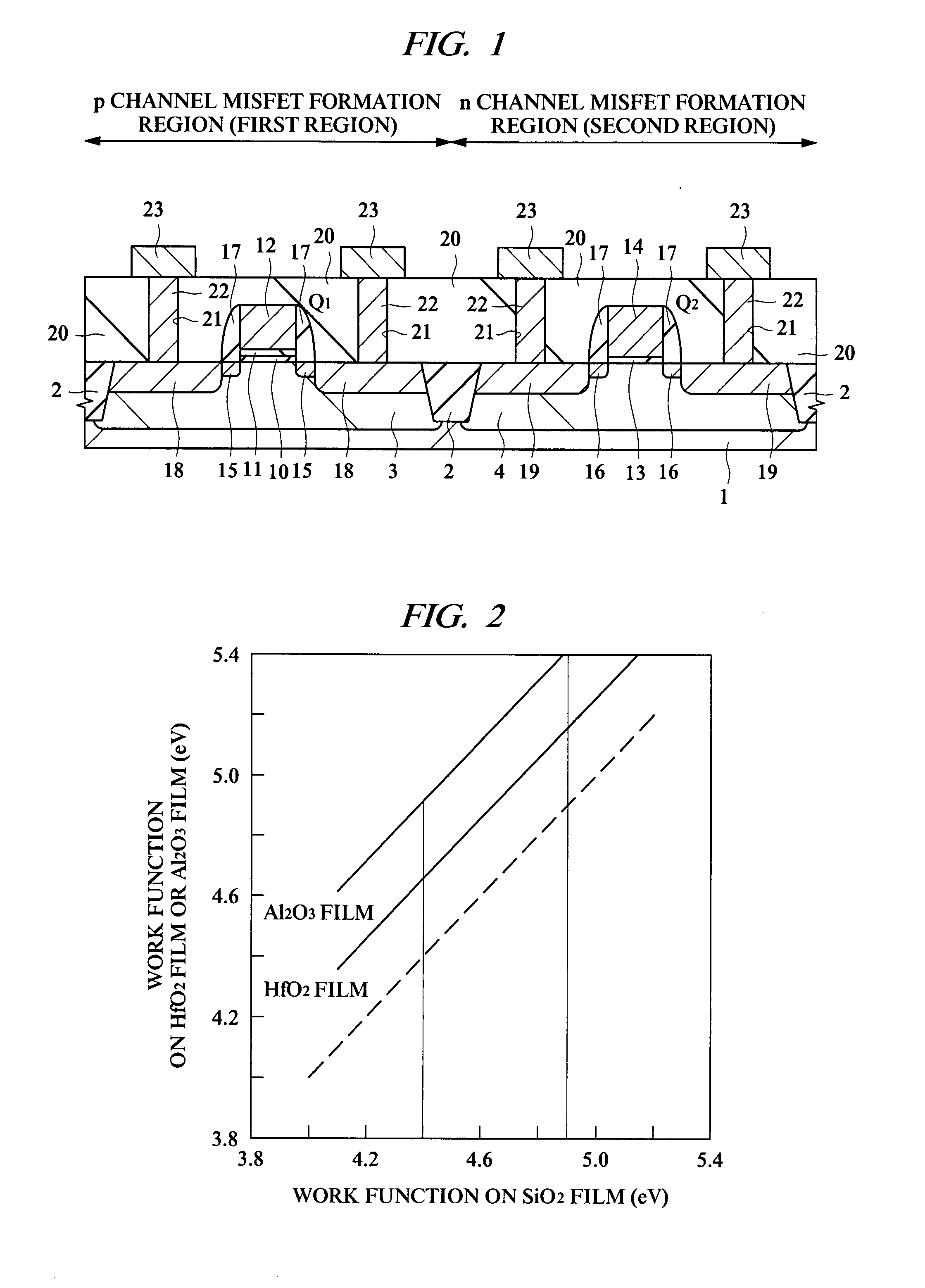
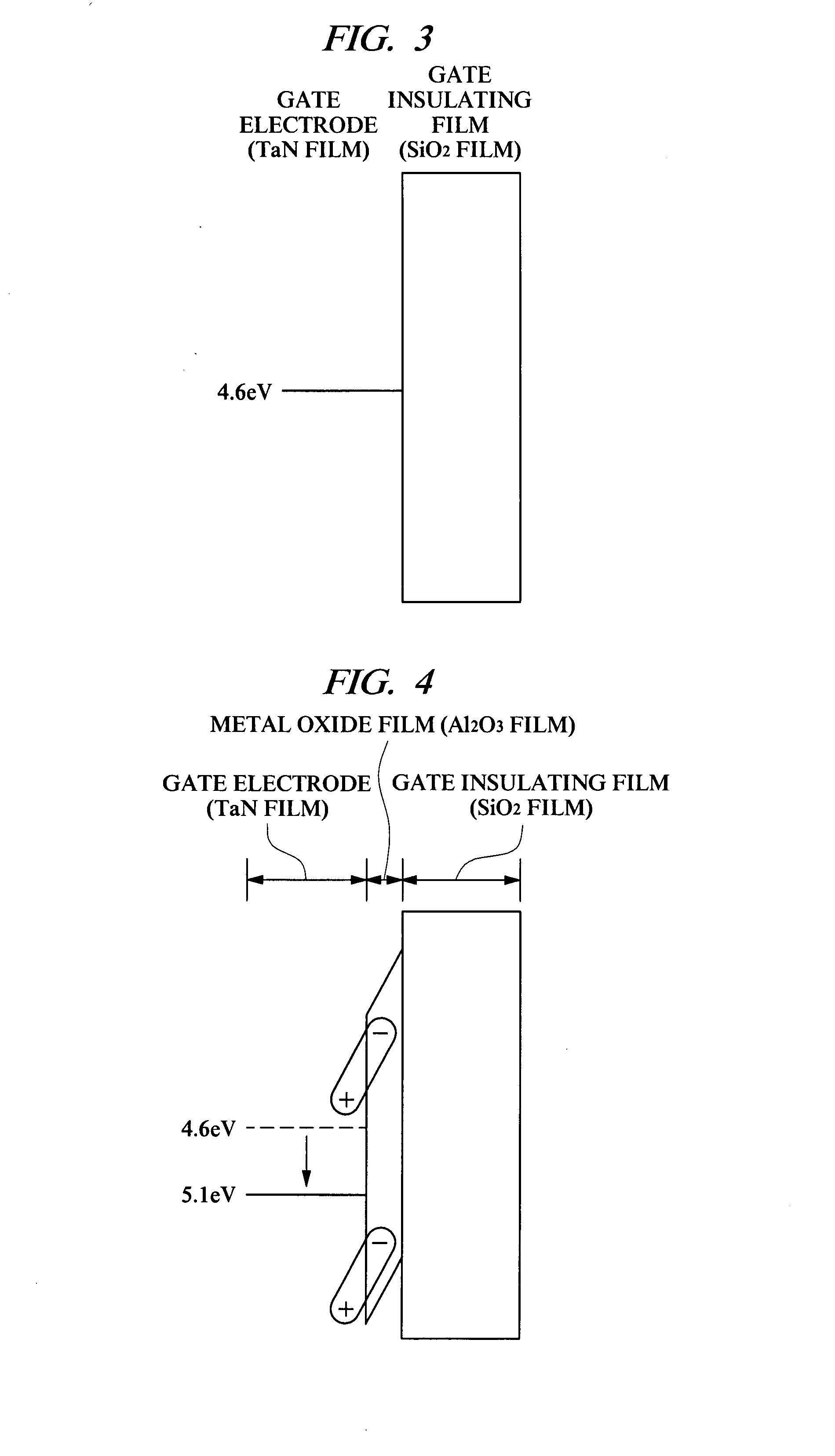
Semiconductor device and semiconductor device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20070210354A1Increased physical film thicknessReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSilicon oxide
Provided is a technology capable of improving the productivity of a p channel MISFET using a high dielectric-constant film as a gate insulating film and a conductive film containing metal as a gate electrode. In this technology, a threshold voltage of the p channel MISFET can be decreased even if a work function value of the conductive film containing metal at the time of contacting a silicon oxide film is away from a value near a valence band of silicon. A p channel MISFET formed on a semiconductor substrate has a gate insulating film formed of a hafnium oxide film, a metal oxide film formed of an aluminum oxide film on this gate insulating film, and a gate electrode formed of a tantalum nitride film on this metal oxide film. The metal oxide film has a function to shift a work function value of the gate electrode.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
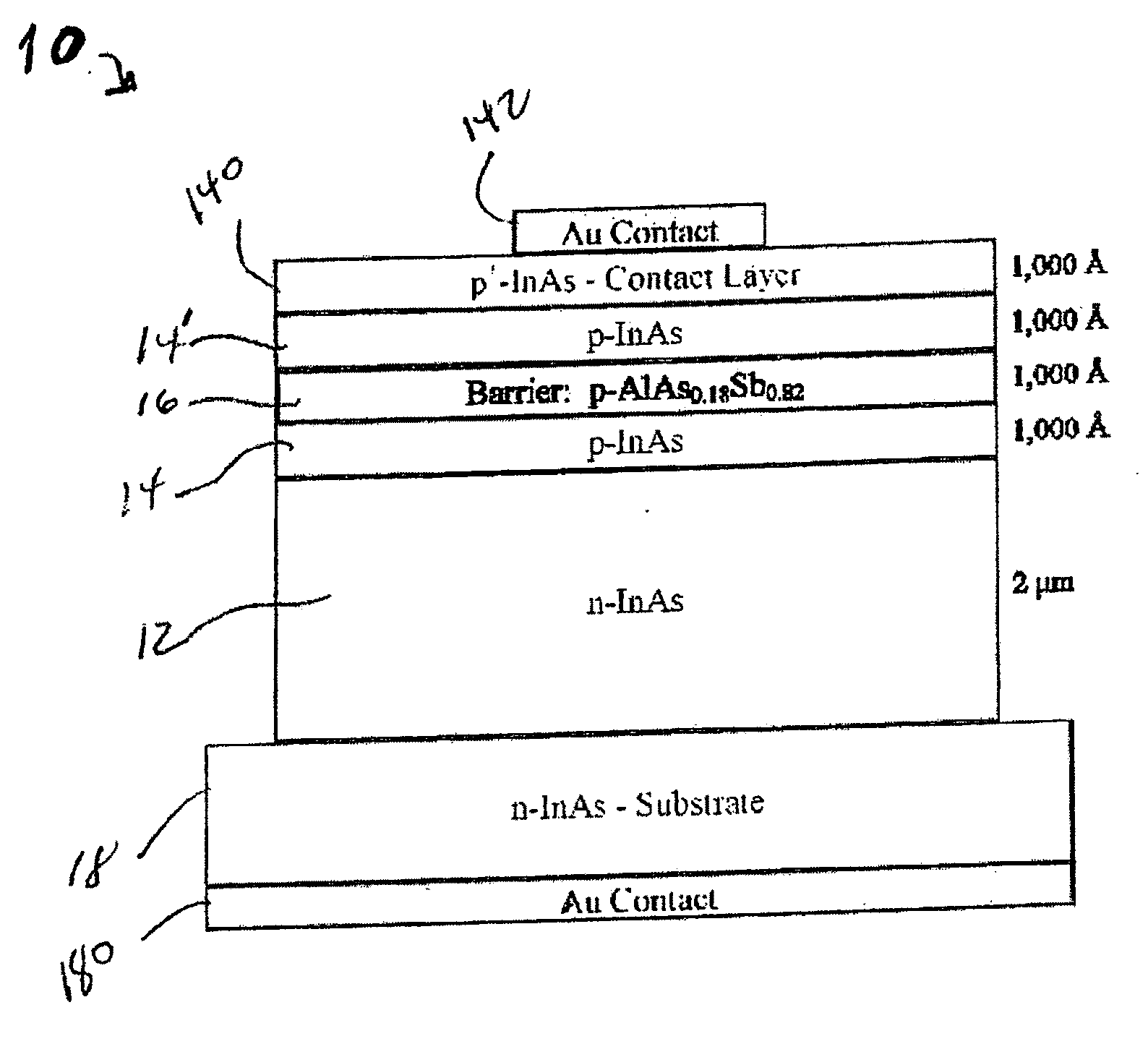
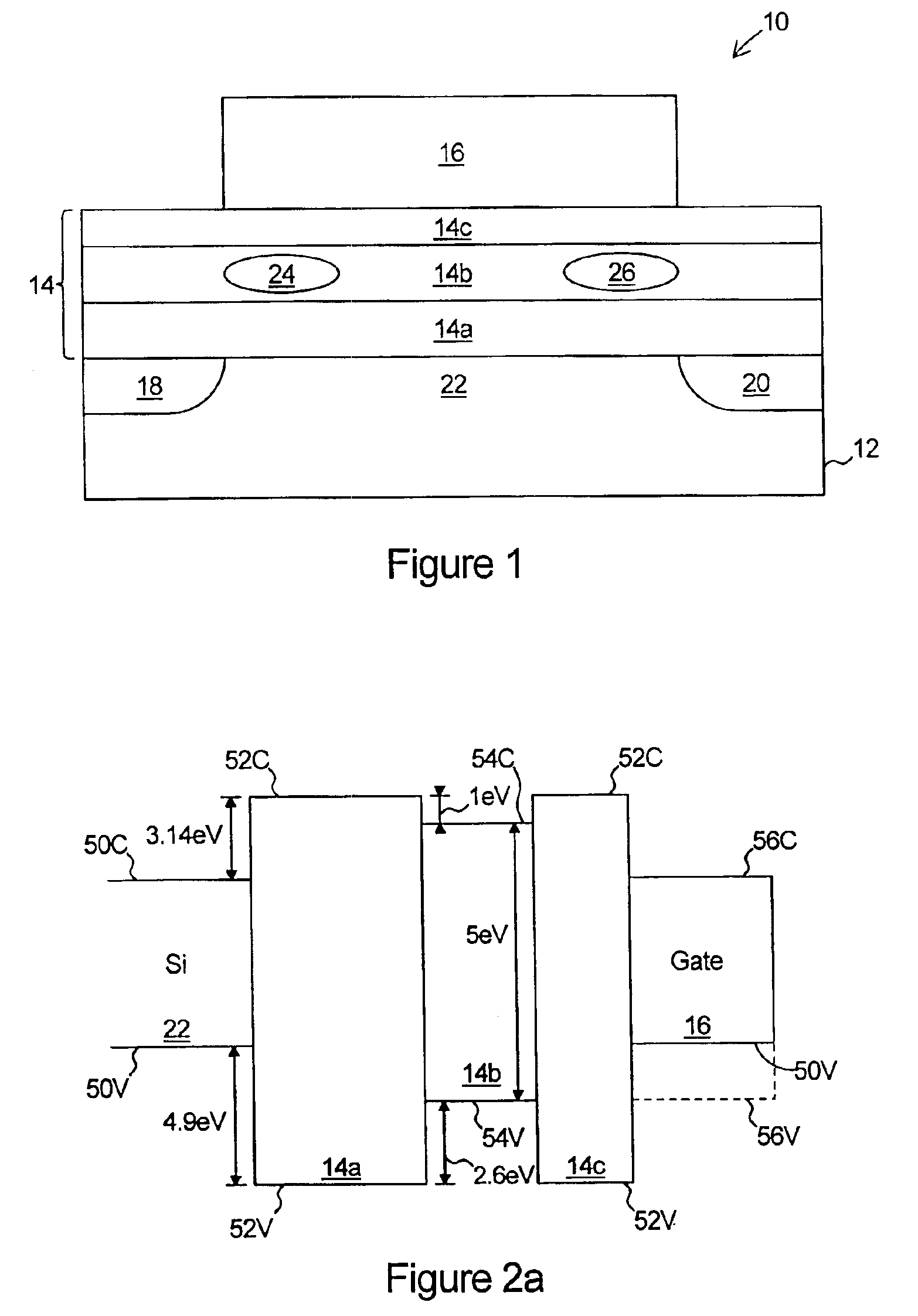
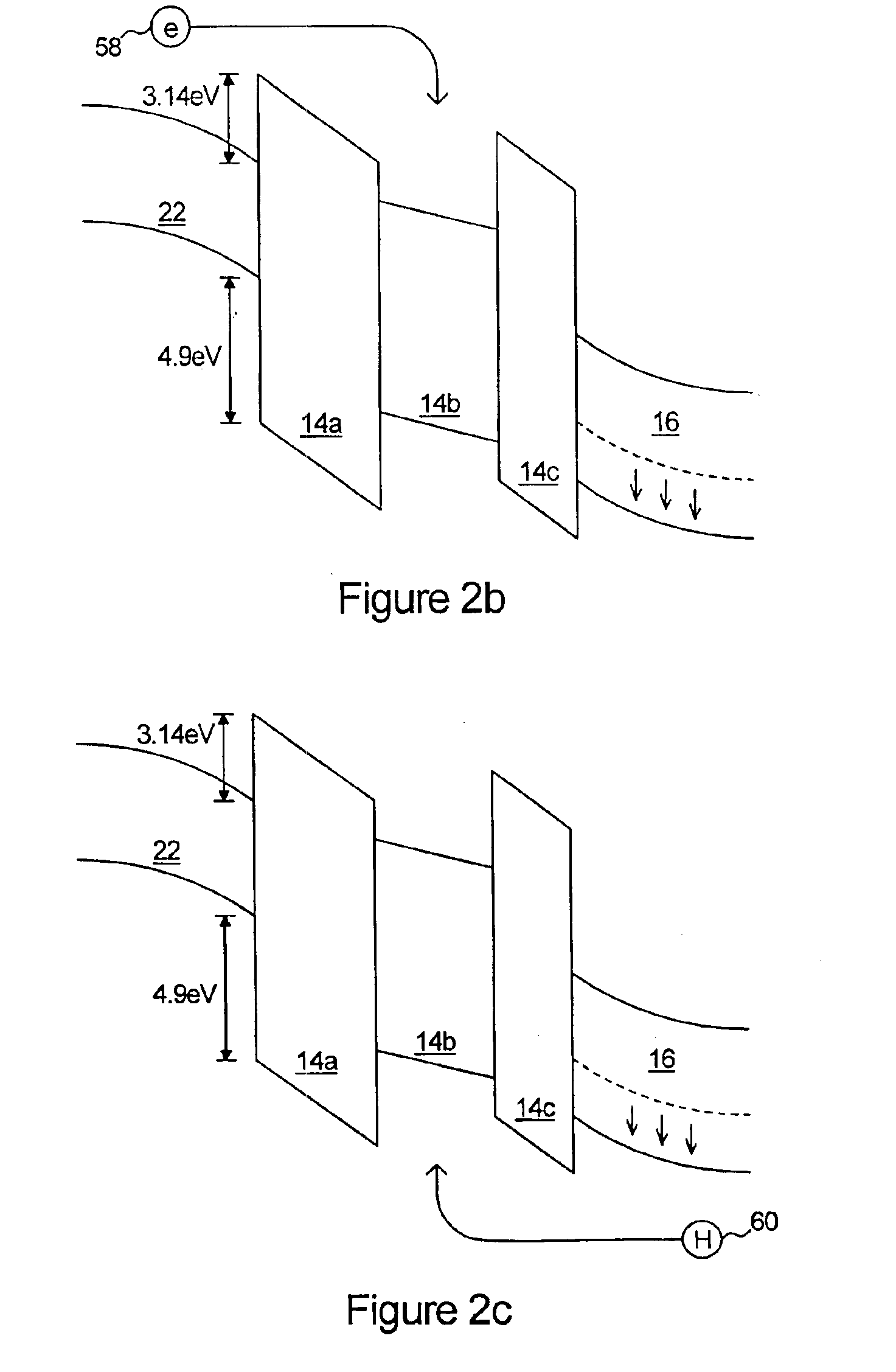
Reduced dark current photodetector
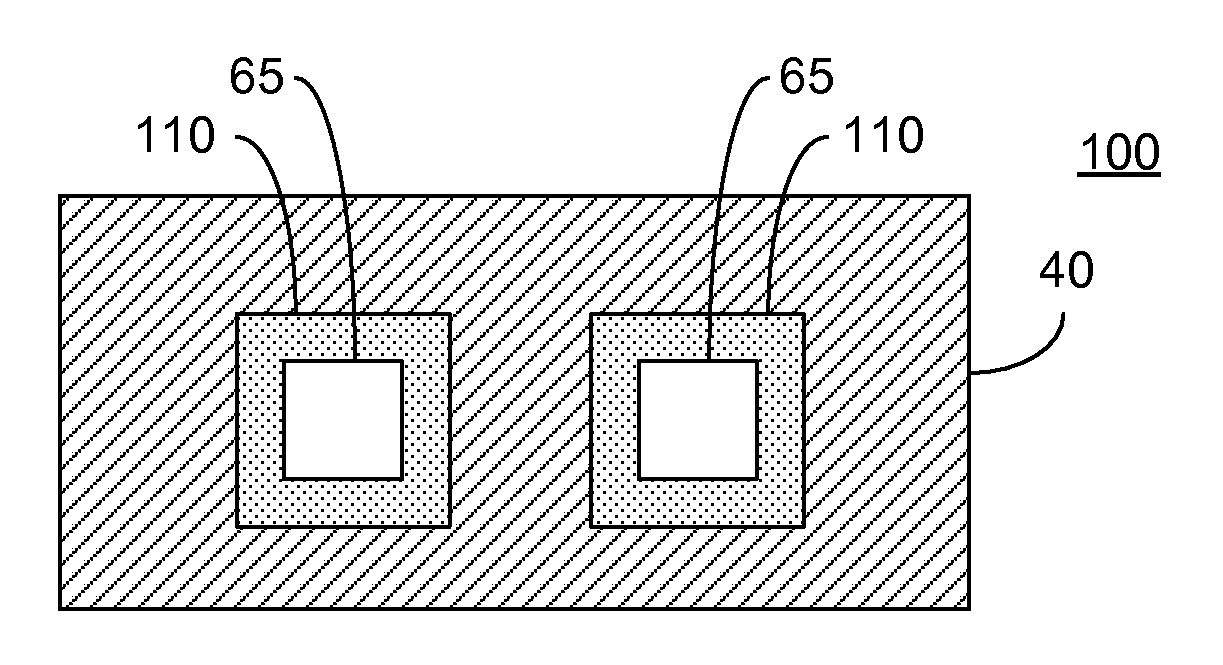
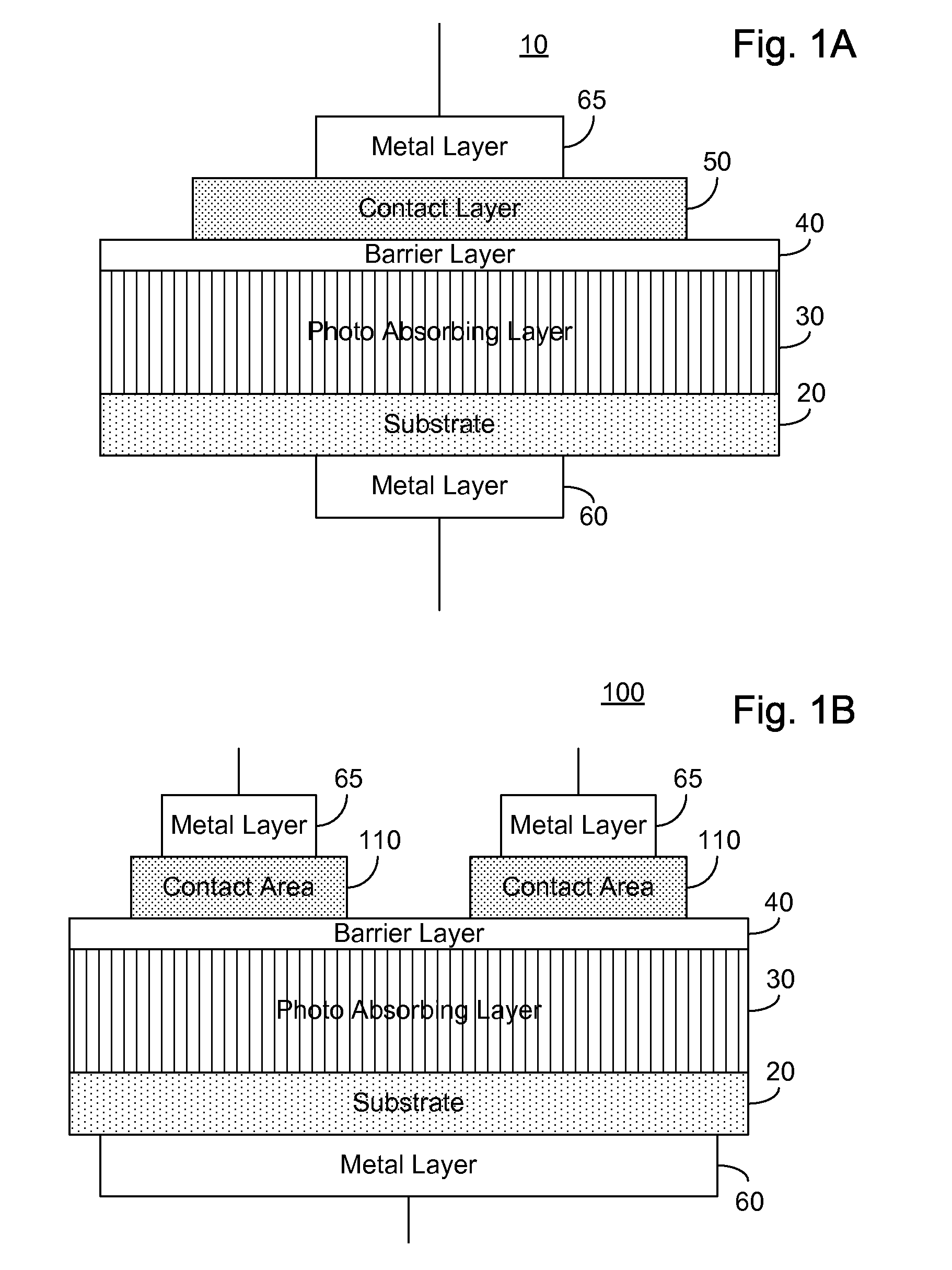
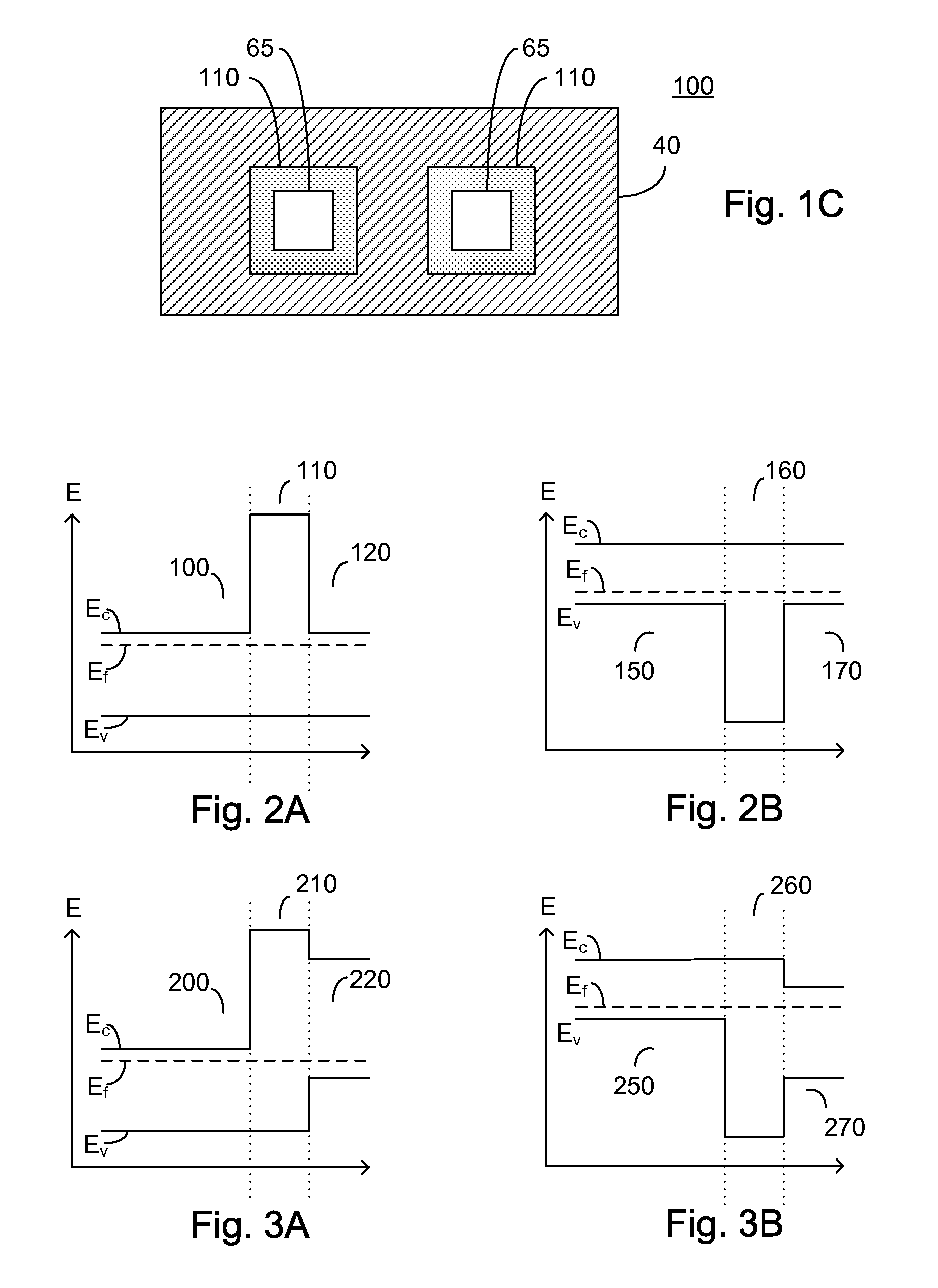
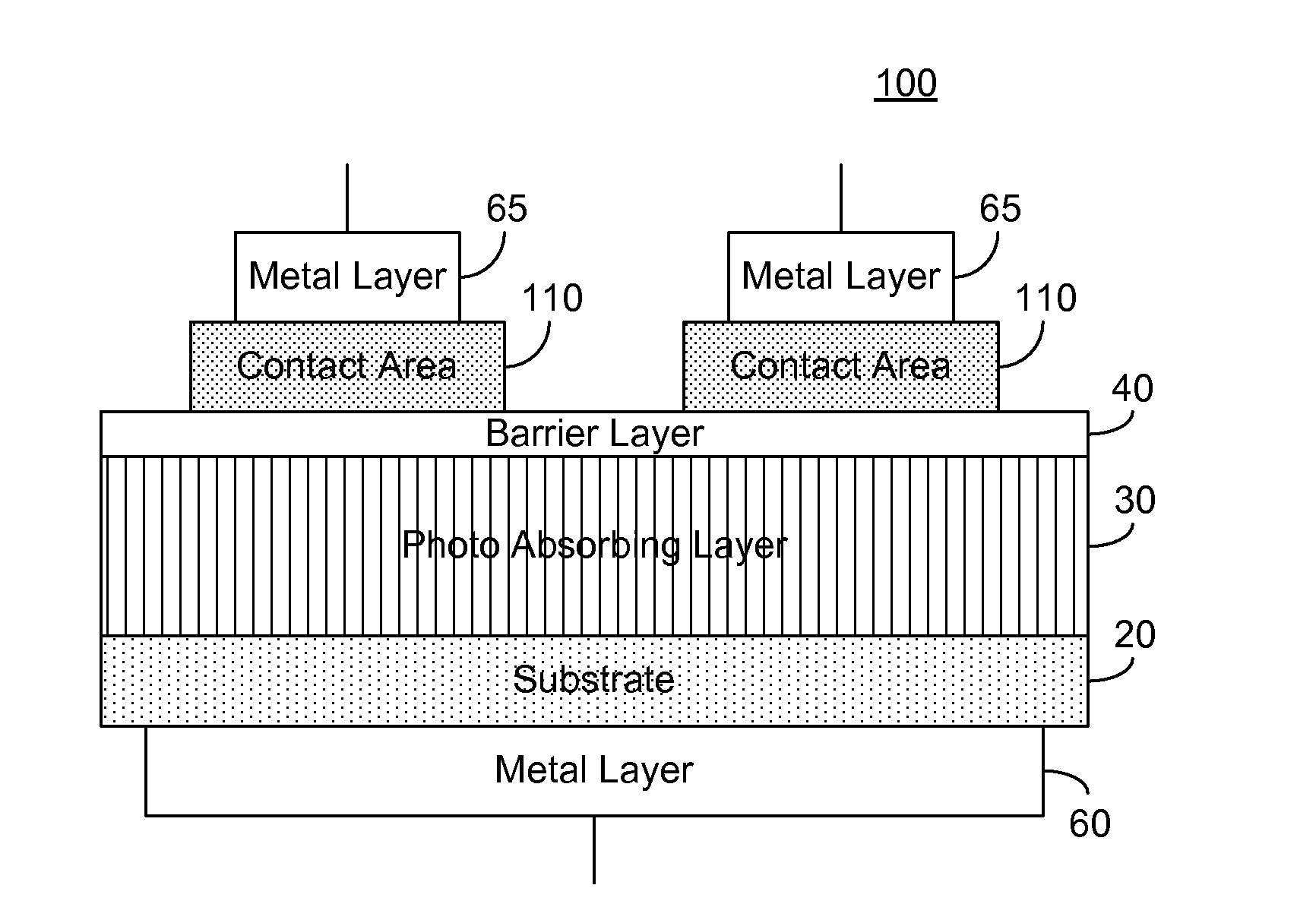
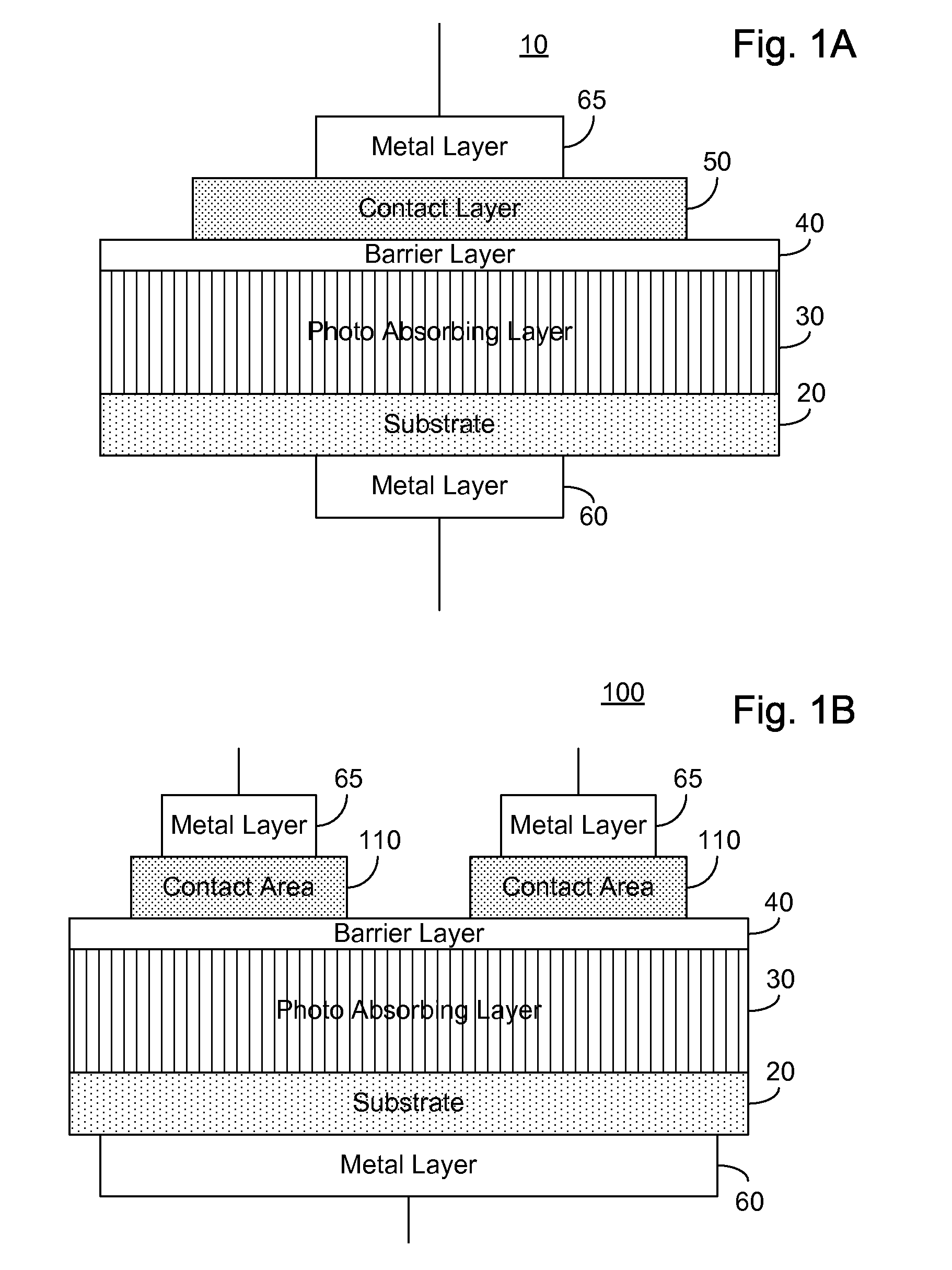
ActiveUS20070215900A1Overcome disadvantagesAvoid tunnelingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandPhotodetector
A photo-detector comprising: a photo absorbing layer comprising an n-doped semiconductor exhibiting a valence band energy level; a barrier layer, a first side of the barrier layer adjacent a first side of the photo absorbing layer, the barrier layer exhibiting a valence band energy level substantially equal to the valence band energy level of the doped semiconductor of the photo absorbing layer; and a contact area comprising a doped semiconductor, the contact area being adjacent a second side of the barrier layer opposing the first side, the barrier layer exhibiting a thickness and a conductance band gap sufficient to prevent tunneling of majority carriers from the photo absorbing layer to the contact area and block the flow of thermalized majority carriers from the photo absorbing layer to the contact area. Alternatively, a p-doped semiconductor is utilized, and conductance band energy levels of the barrier and photo absorbing layers are equalized.
Owner:MAIMON SHIMON
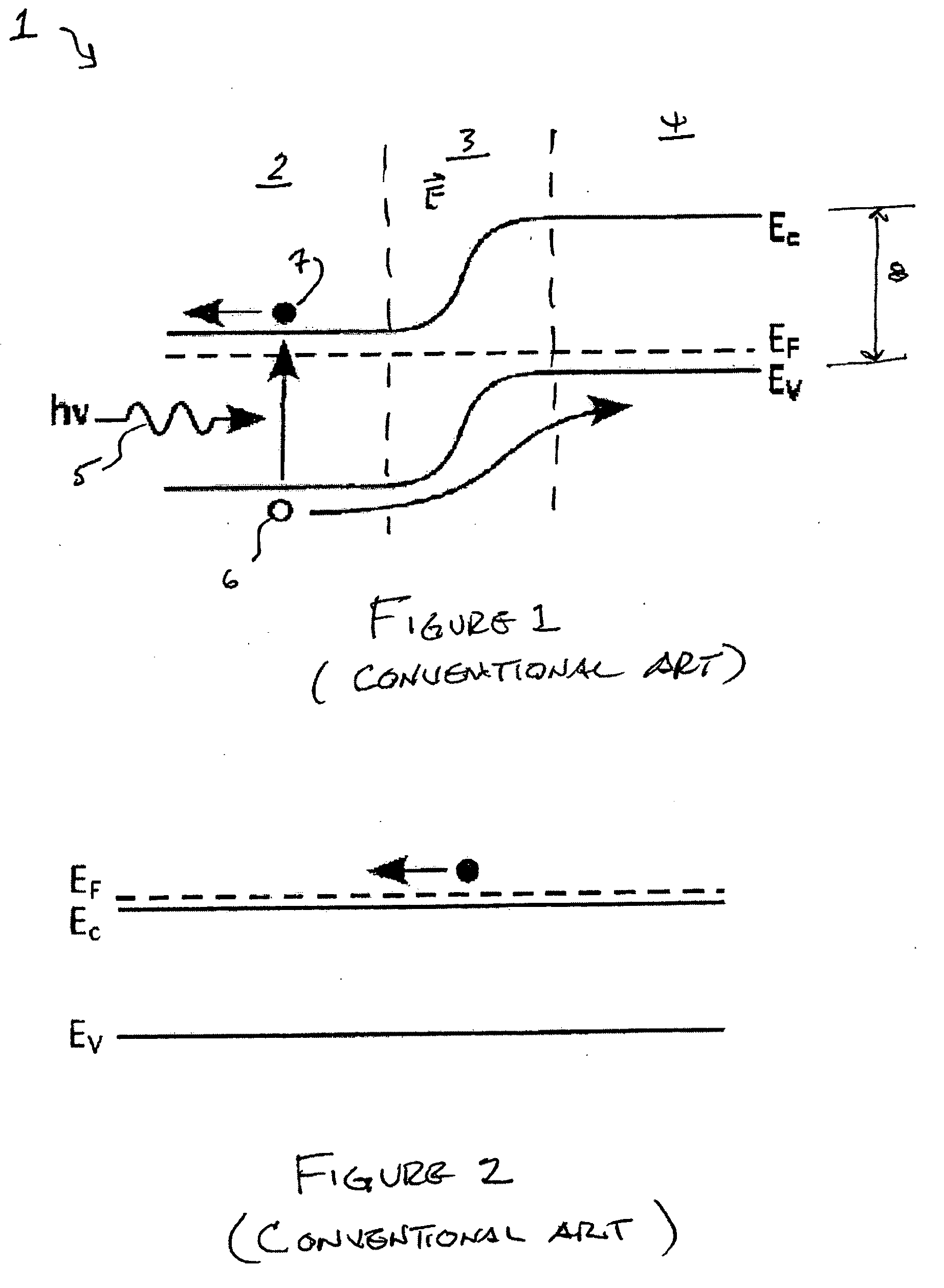
Intermediate band semiconductor photovoltaic solar cell
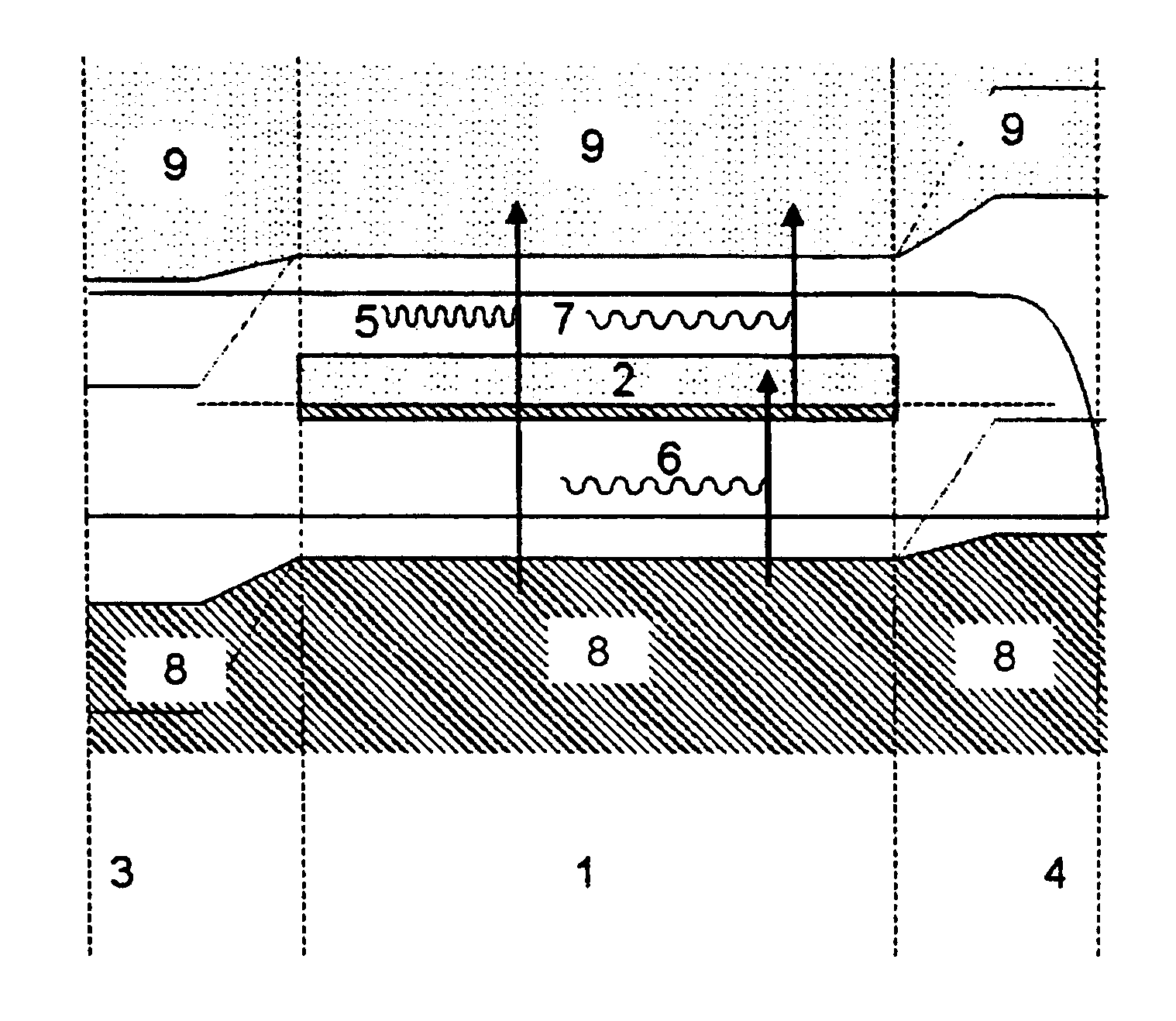
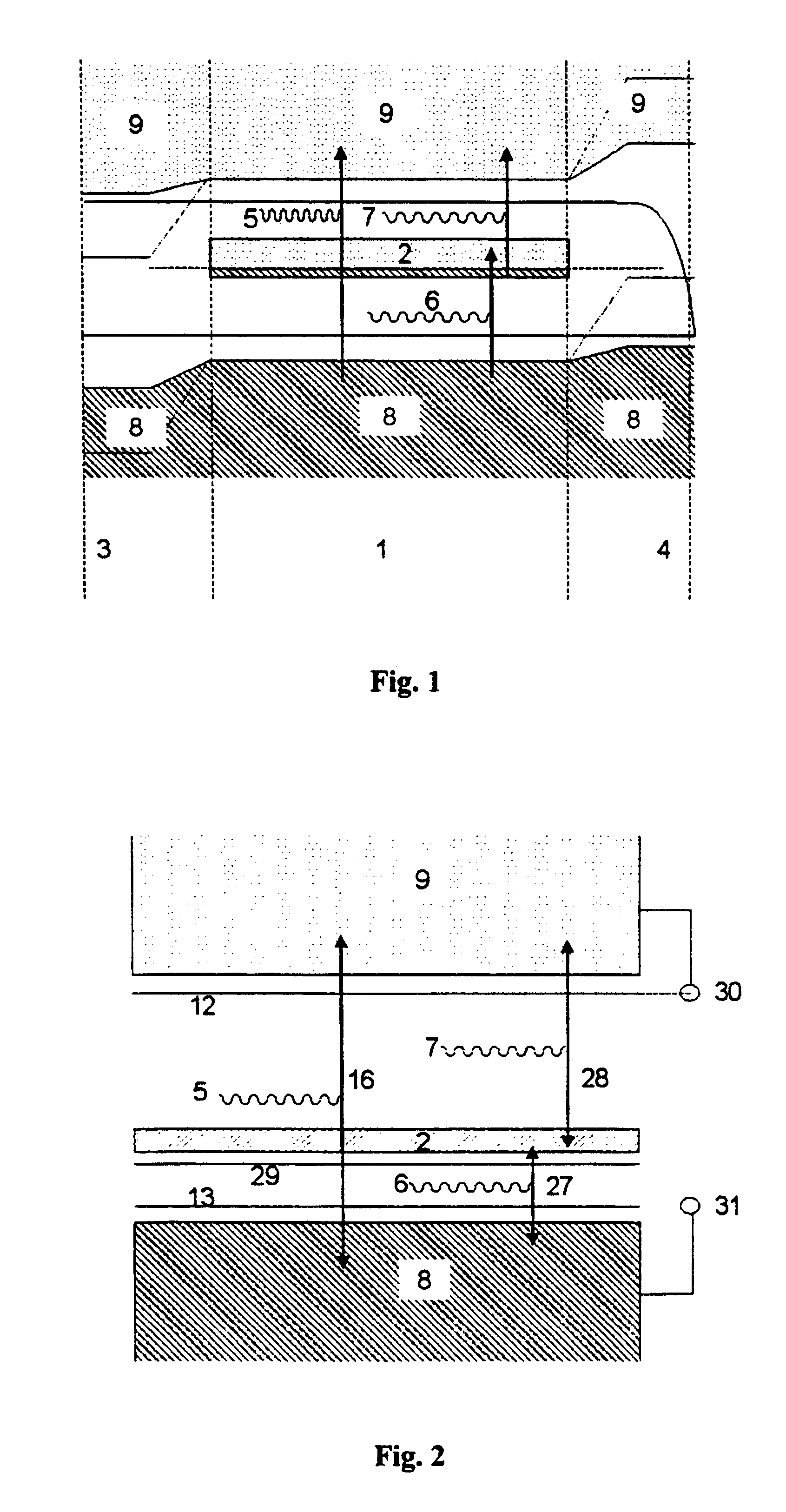
The invention relates to a solar cell containing a semiconductor (1) with an intermediate band (2) that is half filled with electrons, located between two layers of ordinary n type (3) and p type (4) semiconductors. When lighted, electron-hole pairs are formed either by a photon that absorbs the necessary energy (5) or by two photons (6,7) that absorb less energy which pump an electron from the valence band to the intermediate band (8) and from the latter to the conductance band (9). An electrical current is generated that exits on the p side and returns via the n side. The n and p layers also prevent the intermediate band from contacting the outer metal connections, which would have resulted in a short-circuit. Said cell converts solar energy into electricity in a more efficient manner than conventional cells and contributes to improvement of the photovoltaic devices.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS UNIVERSITY OF MADRID +2
Reduced dark current photodetector
ActiveUS7687871B2Total current dropAvoid tunnelingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandPhotodetector
Owner:MAIMON SHIMON
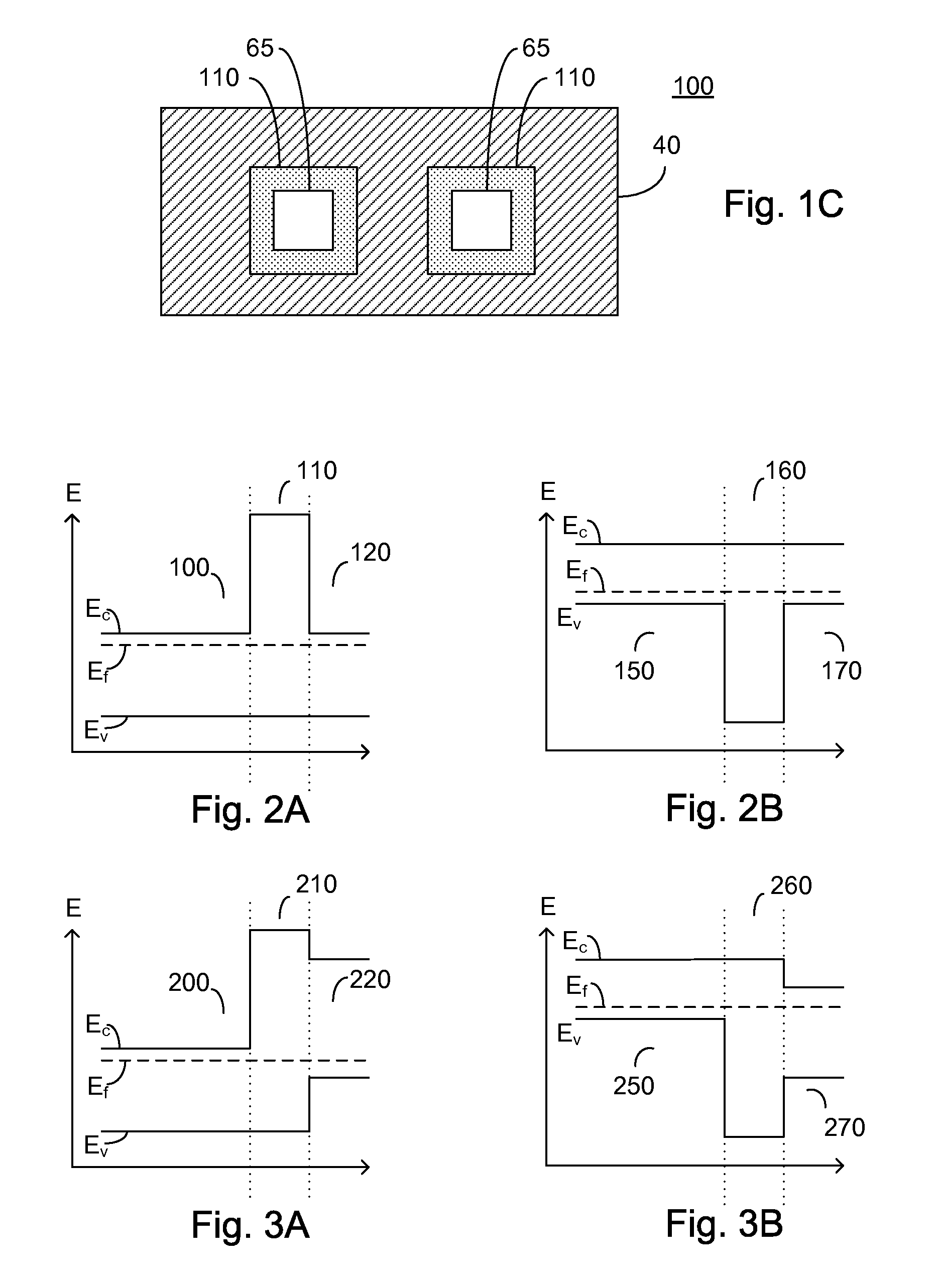
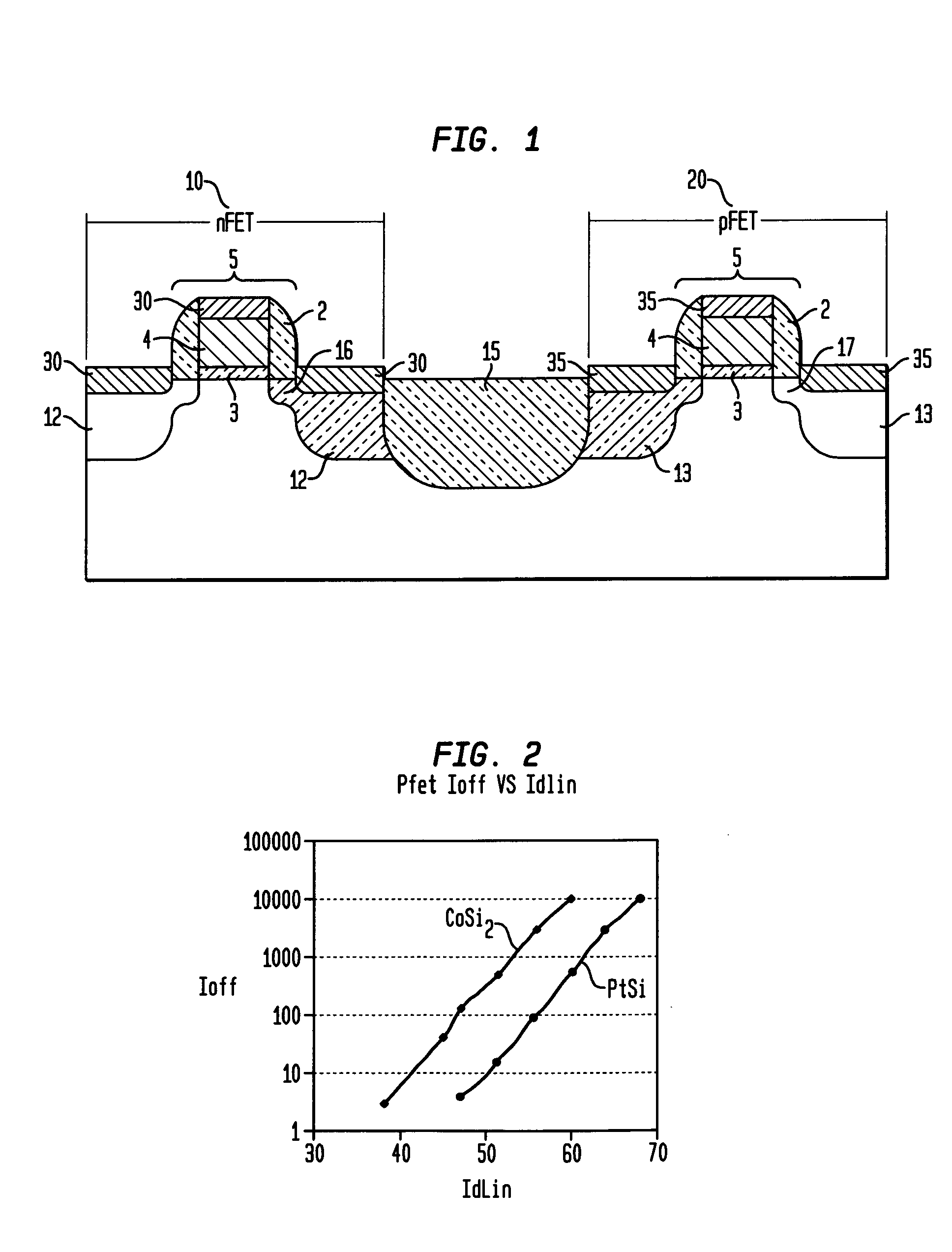
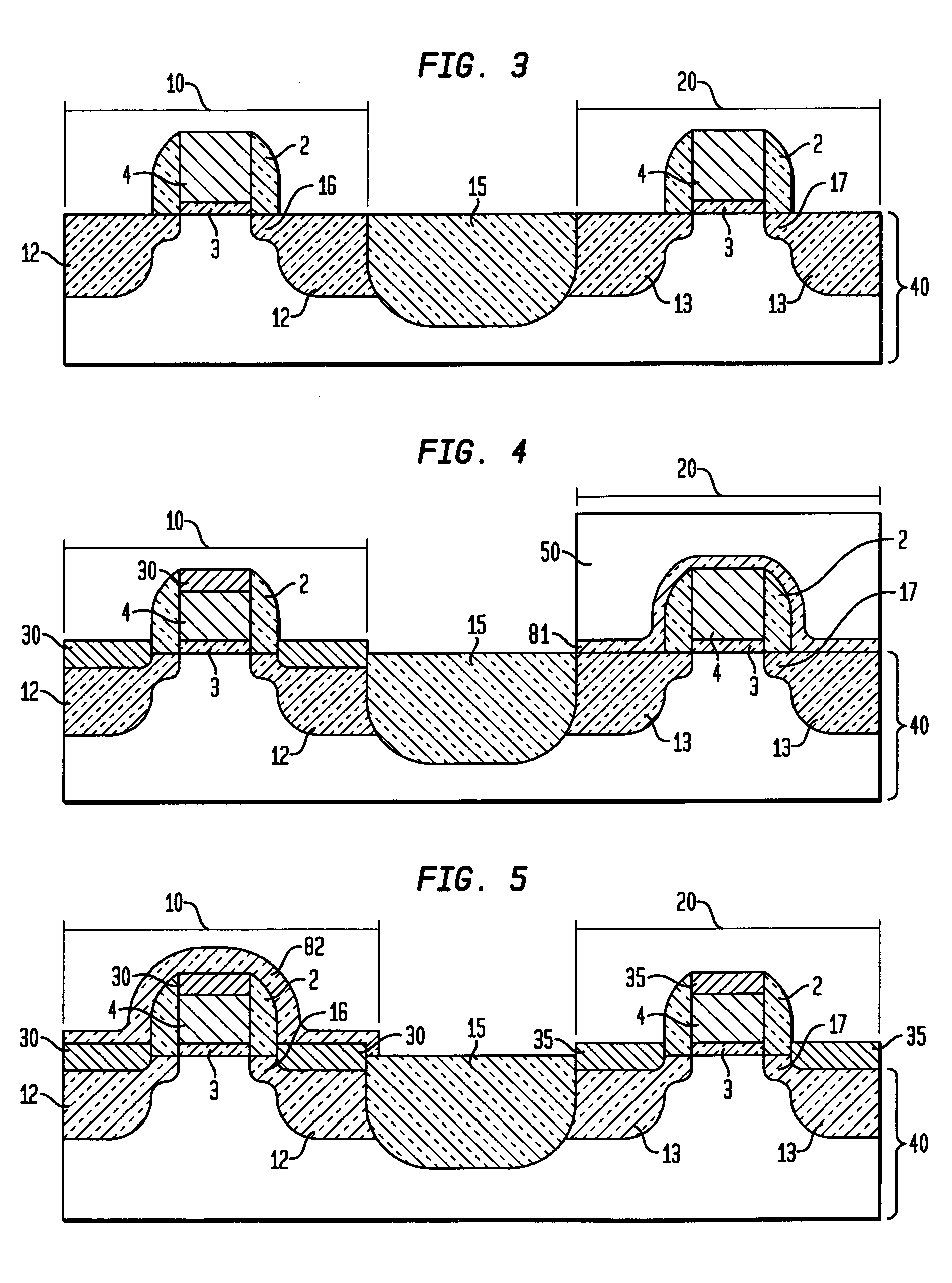
Dual silicide process to improve device performance
InactiveUS20060163670A1Reduced resistivity for contactingReduce contactTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandSalicide
A semiconducting structure and a method of forming thereof, includes a substrate having a p-type device region and an n-type device region; a first-type suicide contact to the n-type device region; the first-type suicide having a work function that is substantially aligned to the n-type device region conduction band; and a second-type silicide contact to the p-type device region; the second-type silicide having a work function that is substantially aligned to the p-type device region valence band. The present invention also provides a semiconducting structure and a method of forming therefore, in which the silicide contact material and silicide contact processing conditions are selected to provide strain based device improvements in pFET and nFET devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Nanocomposites with high thermoelectric figures of merit
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE +1
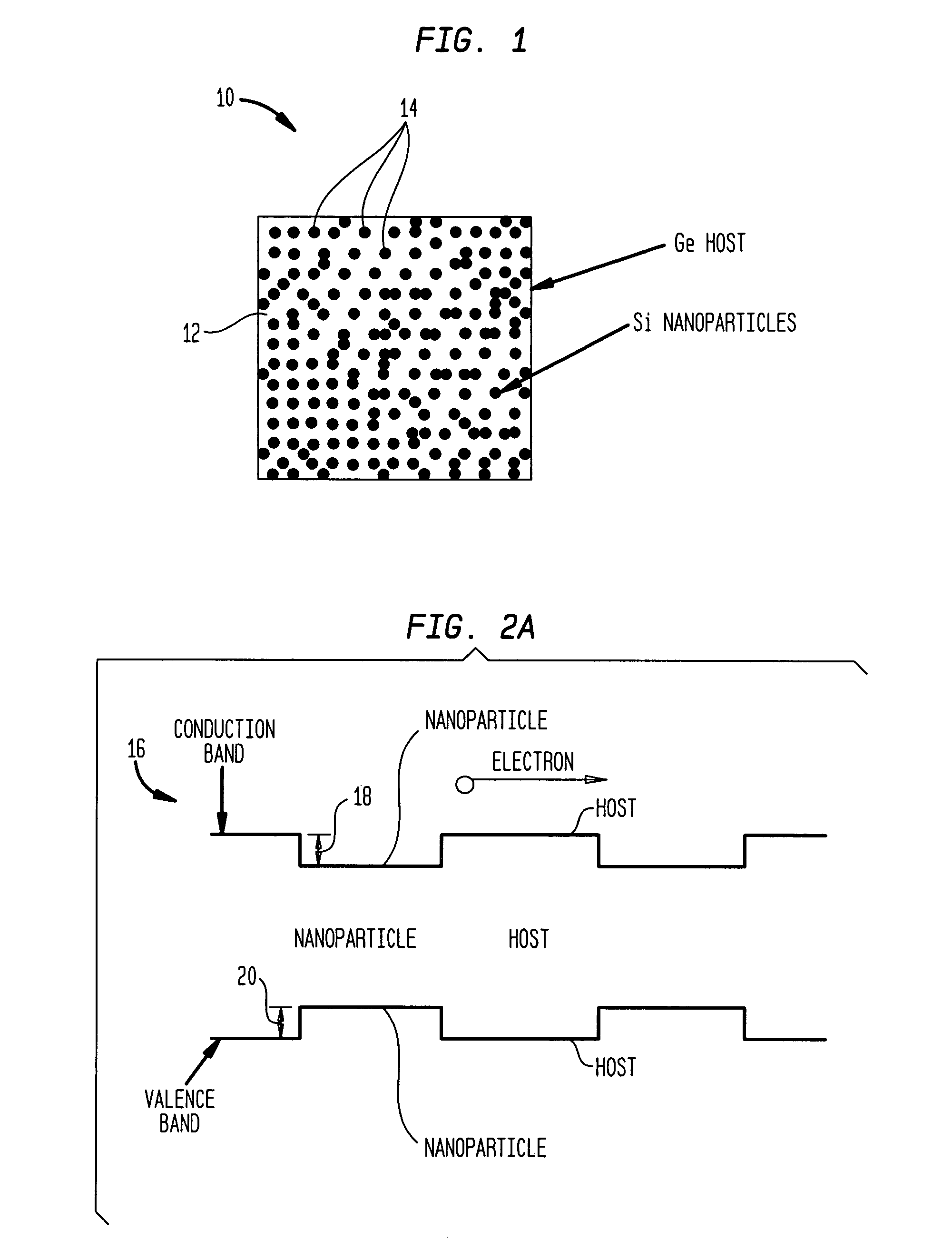
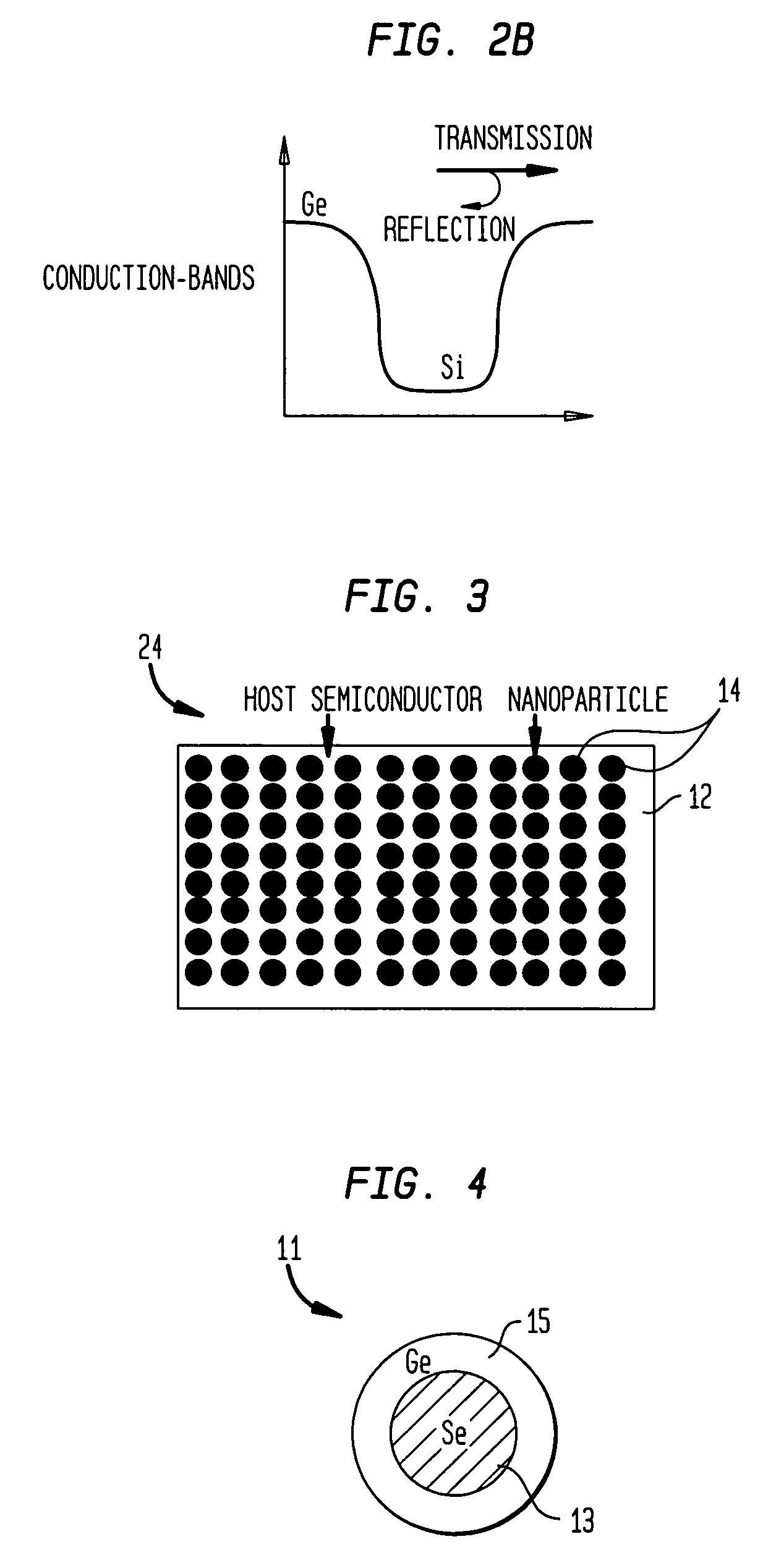
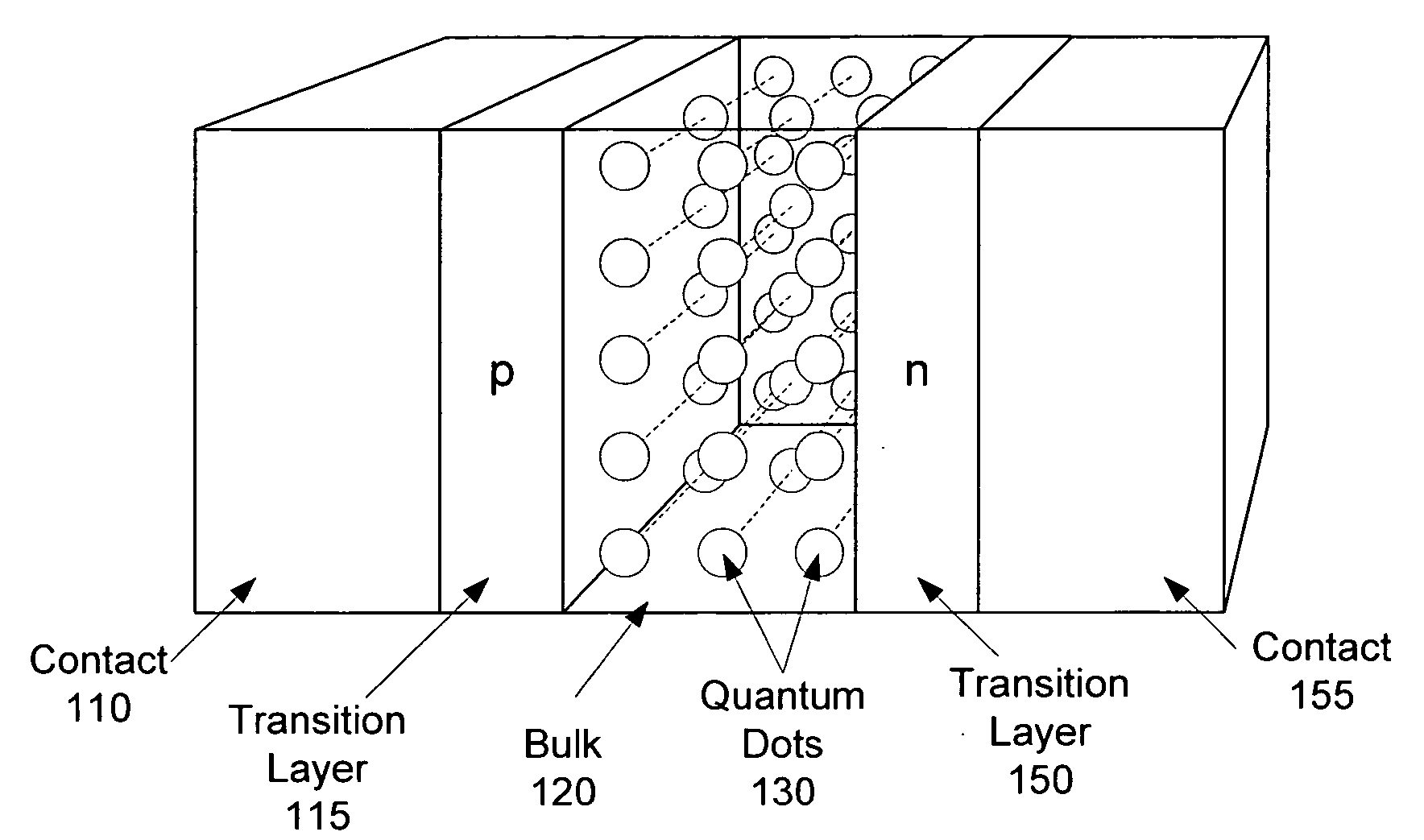
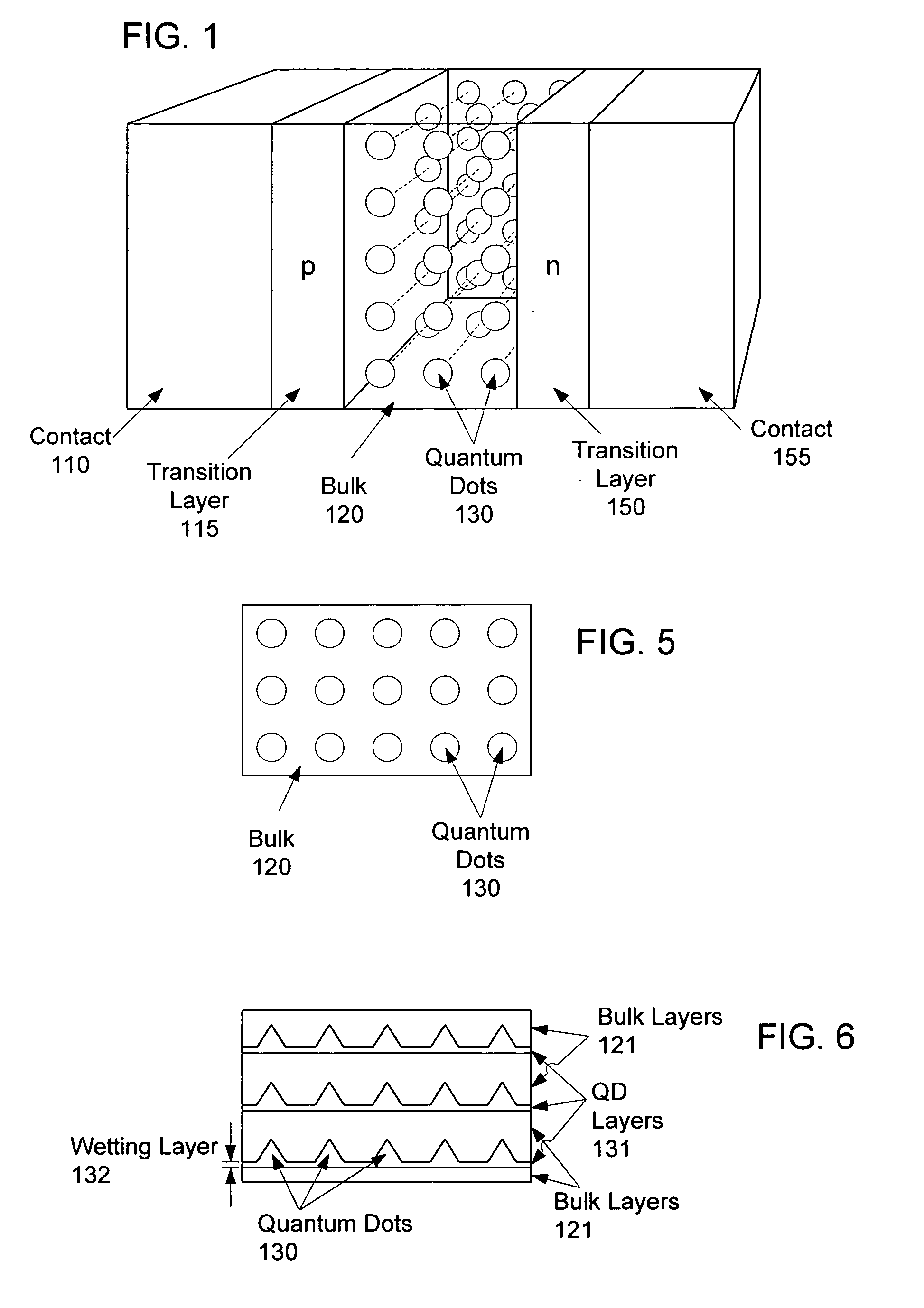
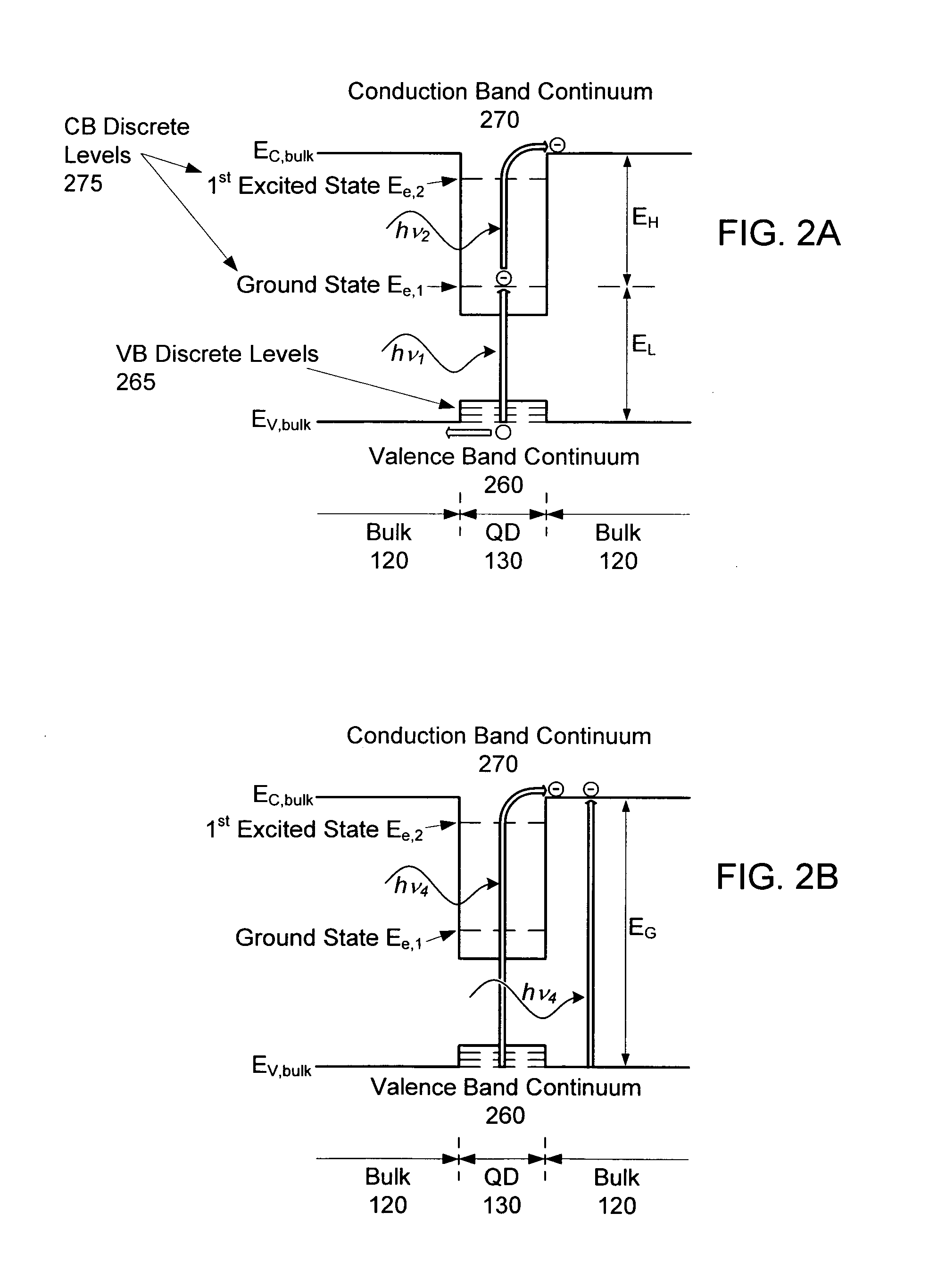
Intermediate-band photosensitive device with quantum dots having tunneling barrier embedded in inorganic matrix
A plurality of quantum dots comprise a first inorganic material, and each quantum dot is coated with a second inorganic material. The coated quantum dots being are in a matrix of a third inorganic material. At least the first and third materials are photoconductive semiconductors. The second material is arranged as a tunneling barrier to require a charge carrier (an electron or a hole) at a base of the tunneling barrier in the third material to perform quantum mechanical tunneling to reach the first material within a respective quantum dot. A first quantum state in each quantum dot is between a conduction band edge and a valence band edge of the third material in which the coated quantum dots are embedded. Wave functions of the first quantum state of the plurality of quantum dots may overlap to form an intermediate band.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Semiconductor device and method
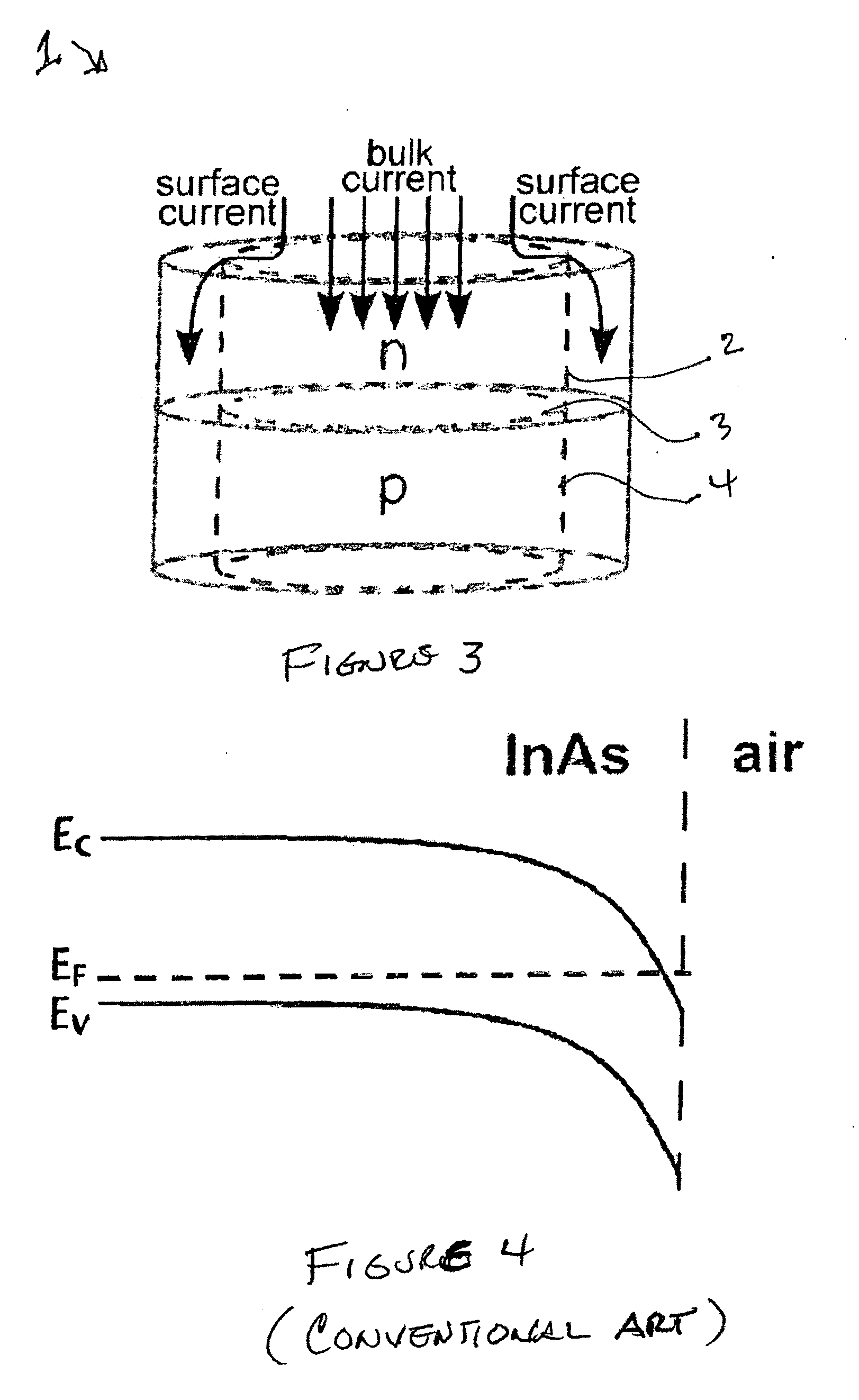
ActiveUS20100230720A1Eliminate surface leakage currentReduce surface currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsValence bandConduction band
The present invention is directed to a semiconductor device that includes at least one p-n junction including a p-type material, an n-type material, and a depletion region. The at least one p-n junction is configured to generate bulk photocurrent in response to incident light. The at least one p-n junction is characterized by a conduction band energy level, a valence band energy level and a surface Fermi energy level. The surface Fermi energy level is pinned either near or above the conduction band energy level or near or below the valence band energy level. A unipolar barrier structure is disposed in a predetermined region within the at least one p-n junction. The unipolar barrier is configured to raise the conduction band energy level if the surface Fermi energy level is pinned near or above the conduction band energy level or lower the valence band energy level if the surface Fermi energy level is pinned near or below the valence band energy level such that the unipolar barrier is configured to propagate the bulk photocurrent and substantially block surface leakage current. The at least one p-n junction and the unipolar barrier are integrally formed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
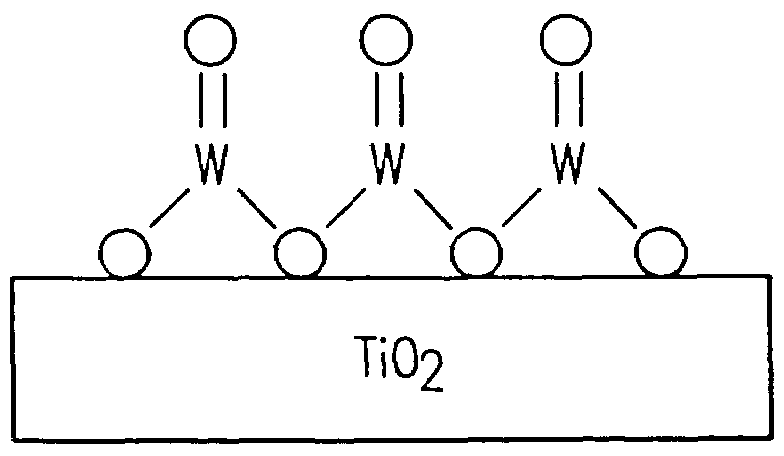
Tungsten oxide/titanium dioxide photocatalyst for improving indoor air quality
InactiveUS7255831B2PurifiesPurifying airIncadescent screens/filtersDispersed particle separationIndoor air qualityUltraviolet lights
A tungsten oxide / titanium dioxide photocatalyst coating oxidizes contaminants in the air that adsorb onto the coating into water, carbon dioxide, and other substances. The tungsten oxide forms a monolayer on the titanium dioxide. When photons of the ultraviolet light are absorbed by the tungsten oxide / titanium dioxide photocatalyst coating, an electron is promoted from the valence band to the conduction band, producing a hole in the valence band. The holes in the valence band react with water applied on the tungsten oxide / titanium dioxide photocatalyst coating, forming reactive hydroxyl radicals. When a contaminant in the air is adsorbed onto the tungsten oxide / titanium dioxide photocatalyst, the hydroxyl radical attacks the contaminant, abstracting a hydrogen atom from the contaminant. The hydroxyl radical oxidizes the contaminant, producing water, carbon dioxide, and other substances. The tungsten oxide / titanium dioxide photocatalytic coating has low sensitivity to humidity variations.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Method concerning a junction barrier schottky diode, such a diode and use thereof
InactiveUS20030020133A1Change resistanceChange the on-state resistance of the diodeTransistorSolid-state devicesValence bandSemiconductor materials
A method for controlling the temperature dependence of a junction barrier Schottky diode of a semiconductor material having an energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band exceeding 2 eV provides for doing this when producing the diode by adjusting the on-state resistance of the grid portion of the diode during the production for obtaining a temperature dependence of the operation of the diode adapted to the intended use thereof.
Owner:CREE INC
Non volatile charge trapping dielectric memory cell structure with gate hole injection erase
A dielectric memory cell comprises a substrate which includes a source region, a drain region, and a channel region positioned there between. A multilevel charge trapping dielectric is positioned on the surface of the substrate and a control gate is positioned on the surface of the dielectric and is positioned over and aligned with the channel region. The multilevel charge trapping dielectric includes a tunneling dielectric layer, a charge trapping dielectric layer, and a top dielectric layer. The tunneling dielectric layer comprises a first dielectric material having a wide band gap between a tunneling dielectric layer valance band Fermi level and a tunneling dielectric layer conduction band Fermi level. The top dielectric layer comprises a second dielectric material having a valance band Fermi level approximately equal to the tunneling dielectric layer valance band Fermi level and having a conduction band Fermi level greater than the tunneling dielectric layer conduction band Fermi level. The charge trapping layer is positioned between the bottom layer and the top layer of a third dielectric with charge trapping properties.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
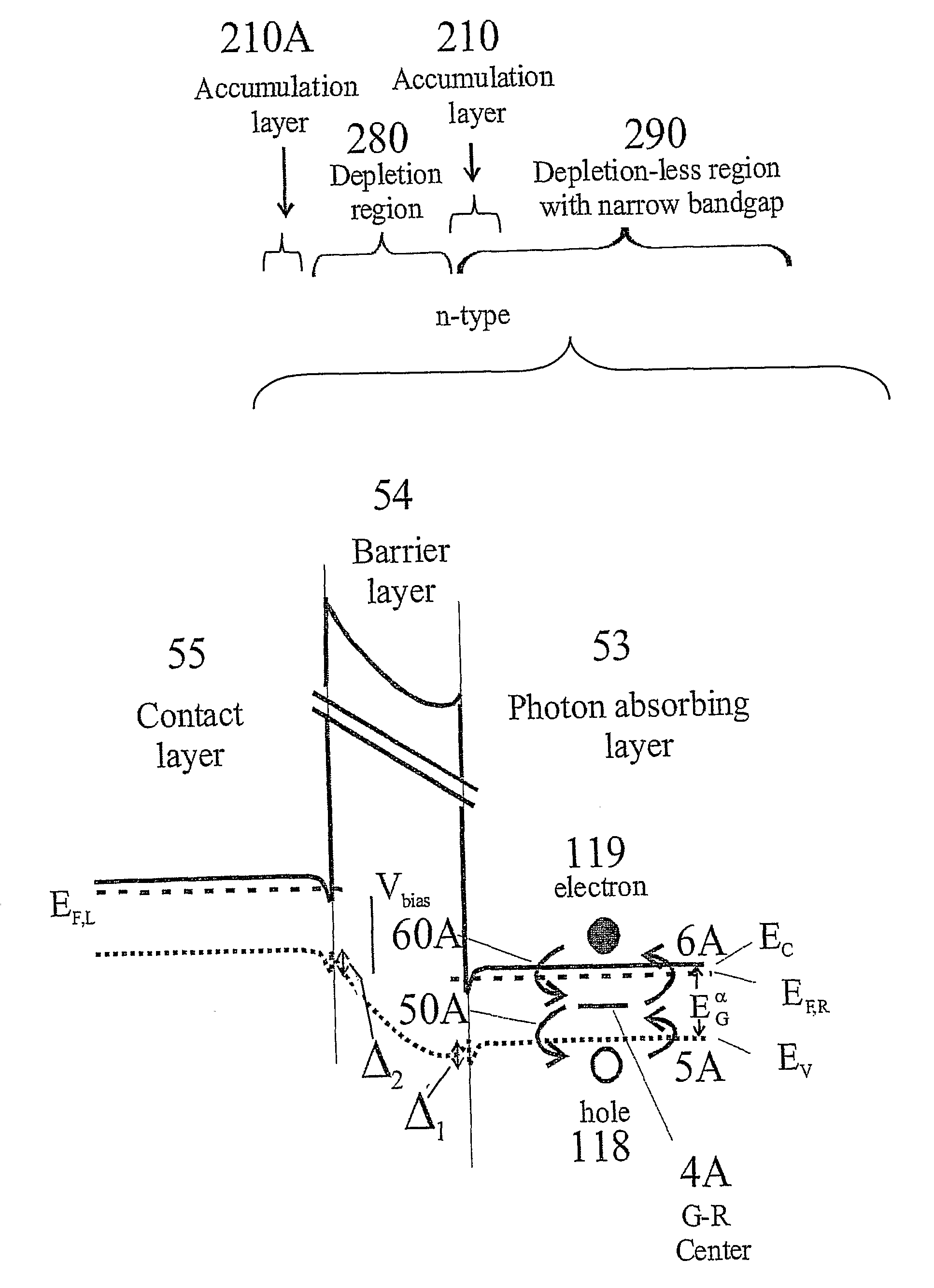
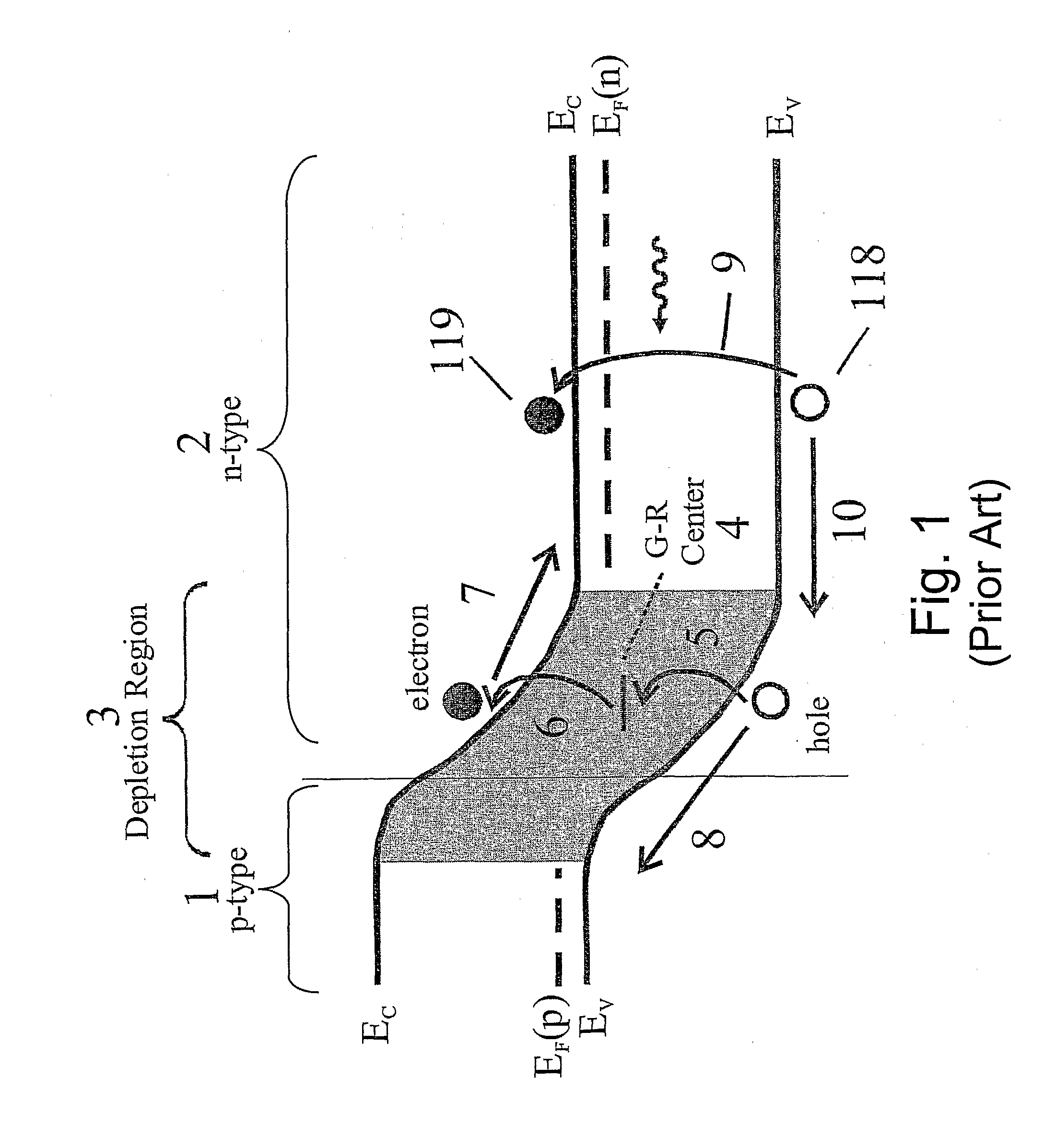
Unipolar semiconductor photodetector with suppressed dark current and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20090256231A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExternal biasPhotodetector
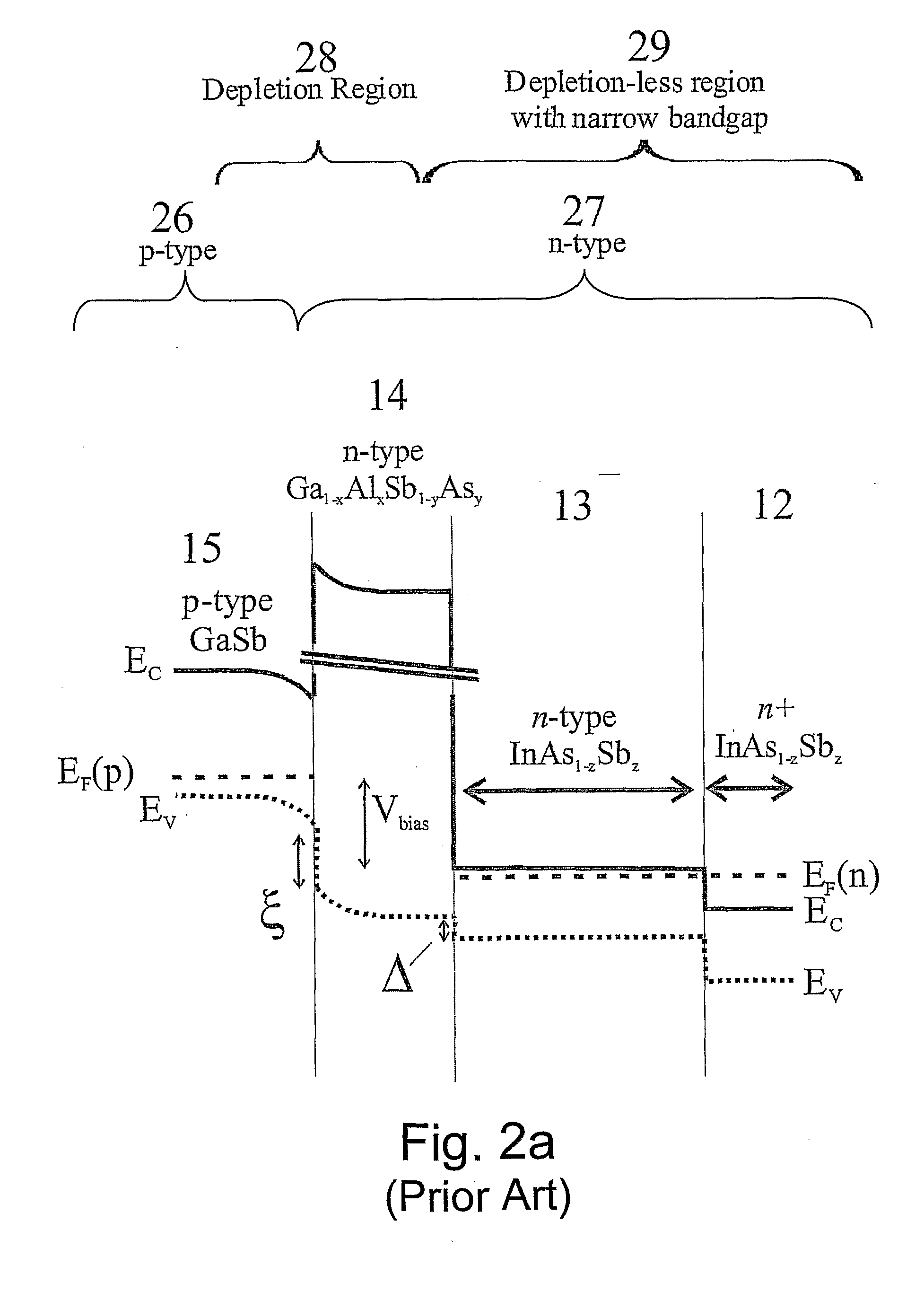
A photo-detector with a reduced G-R noise comprises two n-type narrow bandgap layers surrounding a middle barrier layer having an energy bandgap at least equal to the sum of the bandgaps of the two narrow bandgap layers. Under the flat band conditions the conduction band edge of each narrow bandgap layer lies below the conduction band edge of the barrier layer by at least the bandgap energy of the other narrow bandgap layer. When biased with an externally applied voltage, the more negatively biased narrow bandgap layer is the contact layer and the more positively biased narrow bandgap layer is the photon absorbing layer. Under external bias conditions the bands in the photon absorbing layer next to the barrier layer are flat or accumulated, and the flat part of the valence band edge in the photon absorbing layer lies below the flat part of the valence band edge of the contact layer and has an energy of not more than 10kTop above the valence band edge in any part of the barrier layer (k=Boltzman constant and Top=operating temperature).
Owner:SEMICON DEVICES AN ELBIT SYSTEMSRAFAEL PARTNERSHIP IL
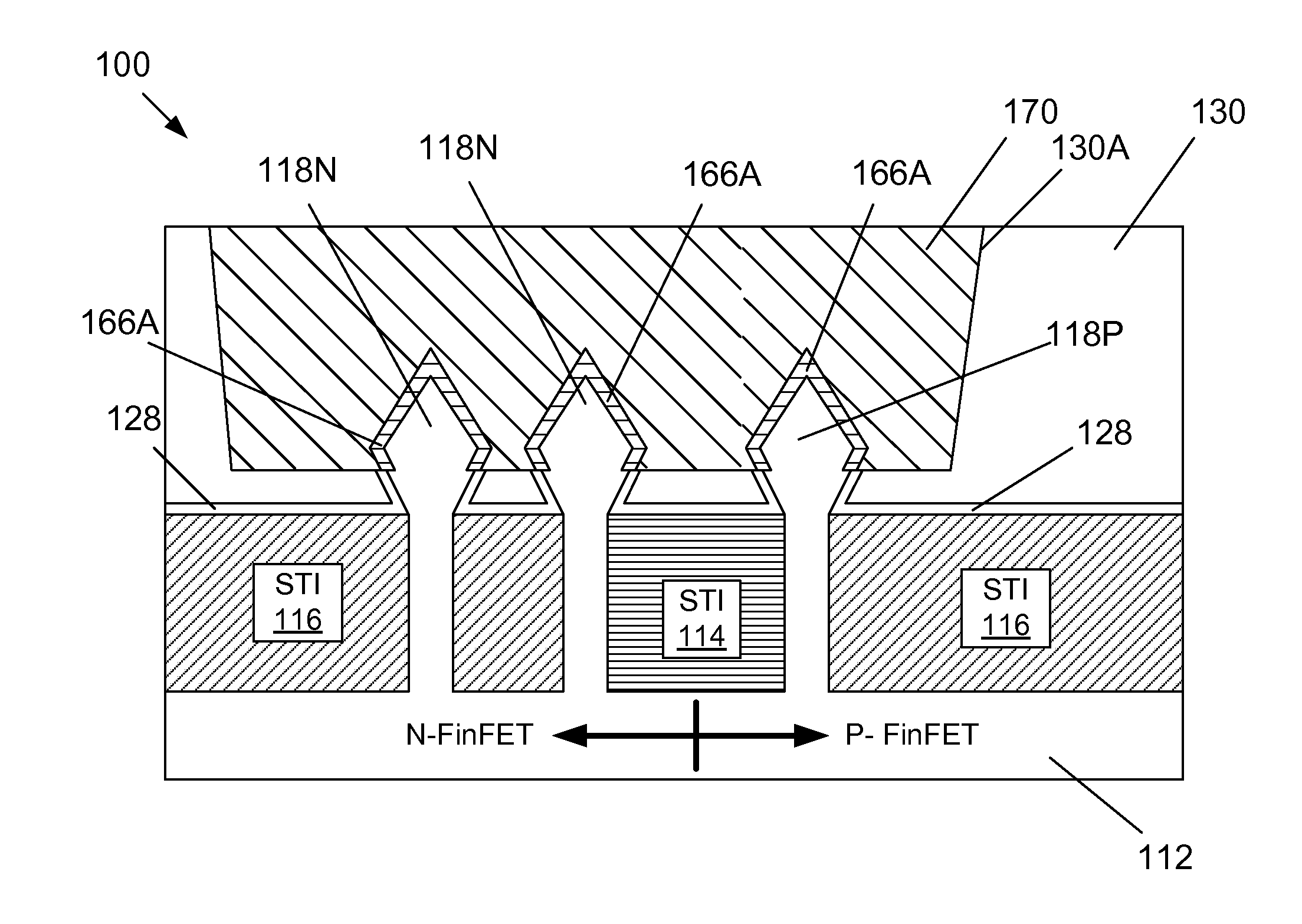
Methods of forming contacts to source/drain regions of finfet devices by forming a region that includes a schottky barrier lowering material
InactiveUS20140273365A1Well formedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideValence band
Various methods of forming conductive contacts to the source / drain regions of FinFET devices that involves forming a region comprised of a Schottkky barrier lowering material are disclosed. The method disclosed herein includes forming at least one fin for an N-type FinFET device (or a P-type FinFET device) in a semiconducting substrate, performing at least one process operation to form a region in the at least one fin that contains a Schottky barrier lowering material, depositing a layer of a valence band metal (for an N-type device) or a conduction band metal (for a P-type device) on the region and forming a metal silicide region on the fin, wherein the metal silicide is comprised of the valance band metal (for the N-type device) or a conduction band metal (for the P-type device).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
SiC vertical double diffusion metal oxide semiconductor structure (VDMOS) device with composite gate dielectric structure
InactiveCN102779852ALower breakdown voltageAvoid premature breakdownSemiconductor devicesDielectricGate dielectric
The invention discloses a SiC vertical double diffusion metal oxide semiconductor structure (VDMOS) device with a composite gate dielectric structure, and belongs to the technical field of power semiconductor devices. A thought of differentiating modulation of electric fields is adopted according to difference of intensities of electric fields and difference of defect concentrations of gate dielectrics in different areas, namely, high-k gate dielectrics are adopted in channel regions with high-defect concentration and a low electric field, so that a large quantity of trap states caused by using a SiO2 / SiC interface is avoided; the influence on Fowler-Nordheim (FN) tunneling current is obviously reduced; and meanwhile, because the electric field intensity in a channel injection area is small, the reduction on gate dielectric breakdown voltage caused by small offset of conduction band / valence band is weakened; and moreover, a SiO2 gate dielectric (a junction field-effect transistor (JFET) area is formed in a way of extension and is not subjected to ion injection, the surface quality of the JFET area is good, and the SiO2 / SiC interface state is low) is adopted by the JFET area with low defect concentration and a high electric field, and enough high conduction band offset is supplied by the SiO2 dielectric, so that the ahead breakdown of the gate dielectric is avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103311247AControl thresholdImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandWork function
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Large Scale High Quality Graphene Nanoribbons From Unzipped Carbon Nanotubes
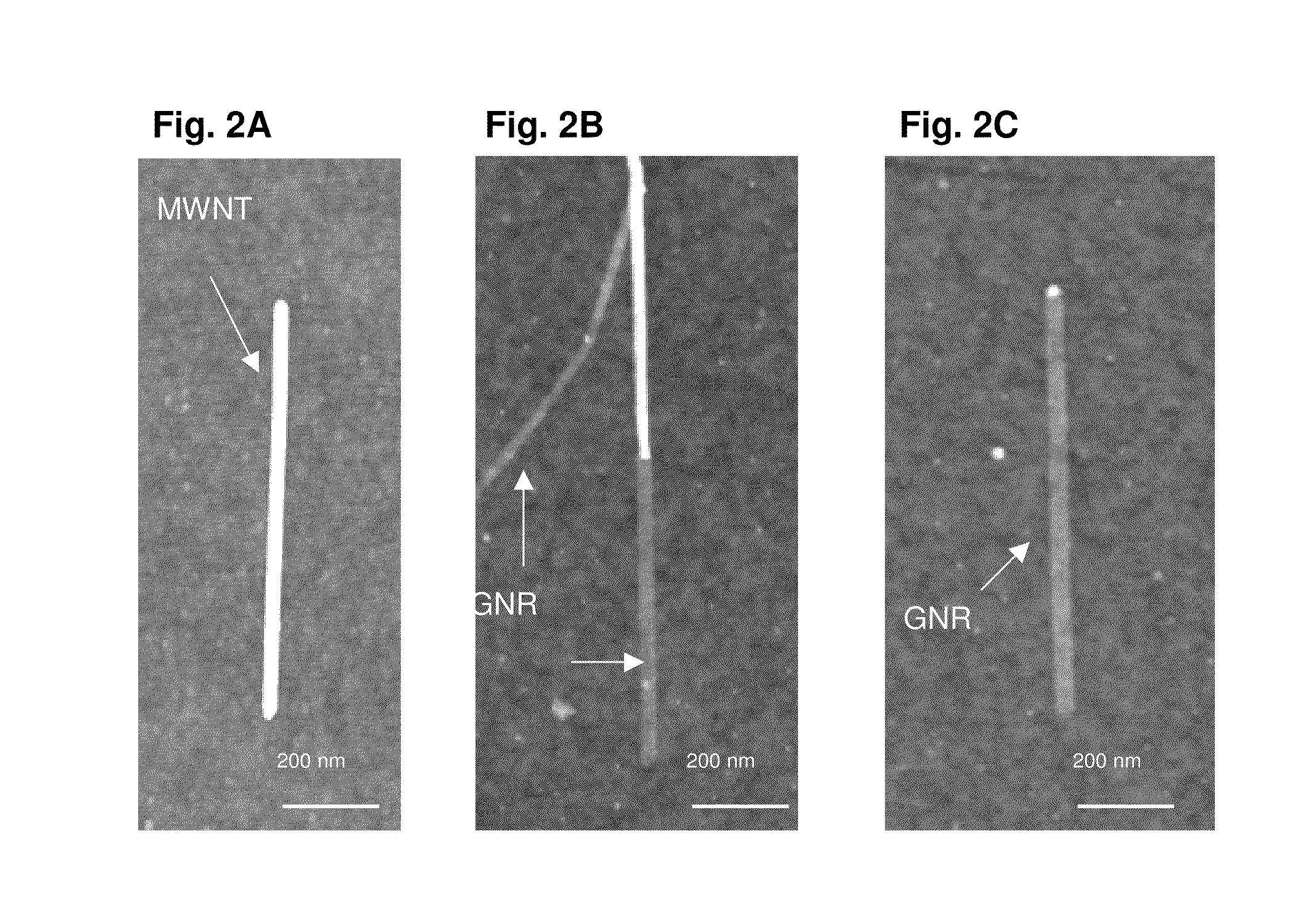
A new method is disclosed for large-scale production of pristine few-layer graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) through unzipping of mildly gas-phase oxidized, and, optionally, metal-assisted oxidized, multiwalled and few-walled carbon nanotubes. The method further comprises sonication in an organic solvent. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy revealed nearly atomically smooth edges for narrow GNRs (2-30 nm). The GNRs exhibit ultra-high quality with low ratios of disorder (D) to graphitic (G) Raman bands (ID / IG). Further electrical transport through the valence-band of the GNRs exhibits metallic behavior with little disorder effect. At low temperatures, the GNRs exhibit high conductance and phase coherent electron transport through entire lengths. Sub 10 nm GNRs exhibit high on / off electrical switching useful for field effect transistors may also be prepared according to the present methods. The high yield synthesis of pristine GNRs enables facile fabrication of GNR devices, making these materials easily accessible for a wide range of fundamental and practical applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Tunnel-junction structure incorporating N-type layer comprising nitrogen and a group VI dopant
ActiveUS7123638B2Increasing valence band edgeReduce voltage dropOptical wave guidanceLaser active region structureValence bandDopant
A tunnel junction structure comprises an n-type tunnel junction layer of a first semiconductor material, a p-type tunnel junction layer of a second semiconductor material and a tunnel junction between the tunnel junction layers. The first semiconductor material includes gallium (Ga), nitrogen (N), arsenic (As) and is doped with a Group VI dopant. The probability of tunneling is significantly increased, and the voltage drop across the tunnel junction is consequently decreased, by forming the tunnel junction structure of materials having a reduced difference between the valence band energy of the material of the p-type tunnel junction layer and the conduction band energy of the n-type tunnel junction layer. Doping the first semiconductor material n-type with a Group VI dopant maximizes the doping concentration in the first semiconductor material, thus further improving the probability of tunneling.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
DRAM tunneling access transistor
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Bipolar transistor having a low doped drift layer of crystalline SiC
InactiveUS6313488B1Reduce on-state lossHigh carrier injectionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandSemiconductor materials
A bipolar transistor having at least a low doped drift layer (14) of crystalline SiC comprises at least one first layer (13) of a semi-conductor material having a wider energy gap between the conduction band and the valence band than an adjacent layer (14) of SiC.
Owner:CREE INC
Organic el element
ActiveUS20120061656A1Improve hole injection efficiencyImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandElectron hole
An organic light-emitting element includes an anode, a functional layer, and a hole injection layer between the anode and the functional layer. The functional layer contains an organic material. The hole injection layer injects holes to the functional layer. The hole injection layer comprises tungsten oxide and includes an occupied energy level that is approximately 1.8 electron volts to approximately 3.6 electron volts lower than a lowest energy level of a valence band of the hole injection layer in terms of binding energy.
Owner:JOLED INC
Photovoltaic nanocomposite comprising solution processed inorganic bulk nano-heterojunctions, solar cell and photodiode devices comprising the nanocomposite
ActiveUS20130263918A1Improve carrier lifetimeEfficient separationMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
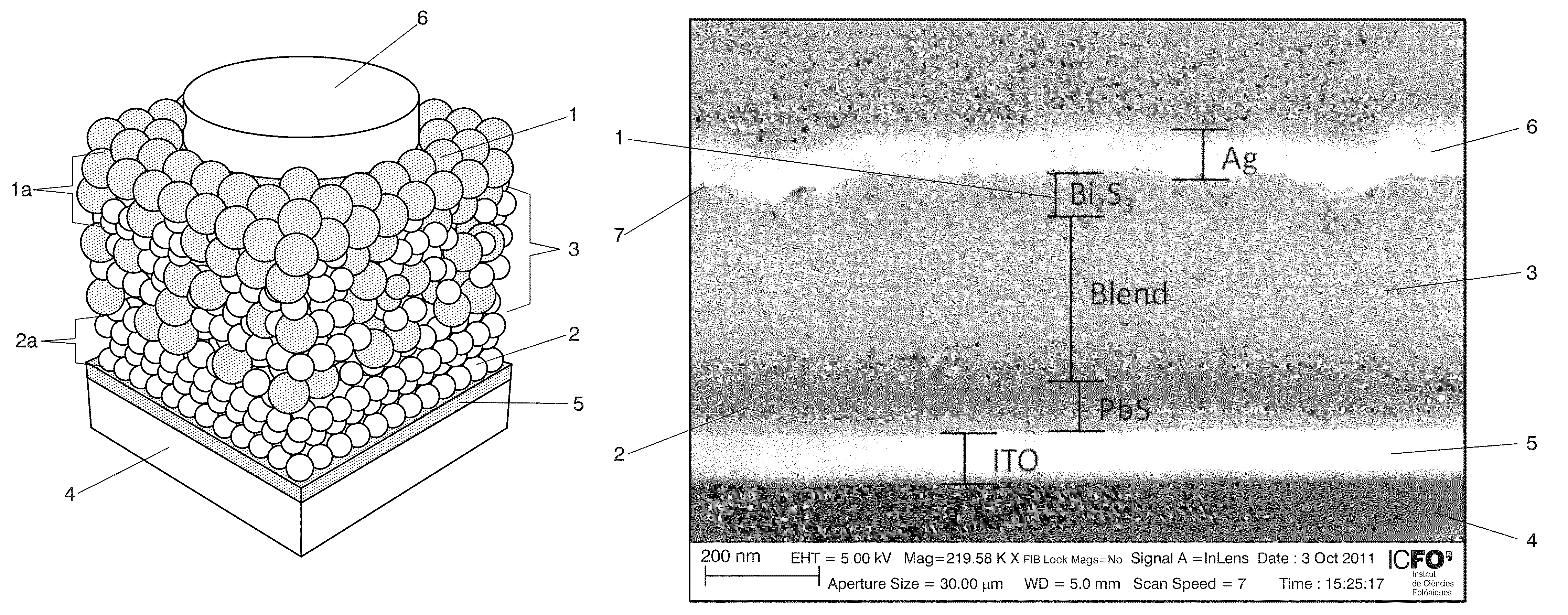
Photovoltaic nanocomposite and solar cell device including the photovoltaic nanocomposite, where the photovoltaic nanocomposite includes a film of solution processed semiconductor materials having an n-type material selected from n-type quantum dots and n-type nanocrystals, and a p-type material selected from p-type quantum dots and p-type nanocrystals, and where the n-type material has a conduction band level at least equal, compared to vacuum level, to that of the p-type material, the p-type material has a valence band at the most equal, compared to vacuum level, to that of the n-type material. at least a portion of the n-type material and at least a portion of the p-type material are present in a bulk nano-heterojunction binary nanocomposite layer having a blend of the n-type material and the p-type material.
Owner:FUNDACIO INST DE CIENCIES FOT NIQUES
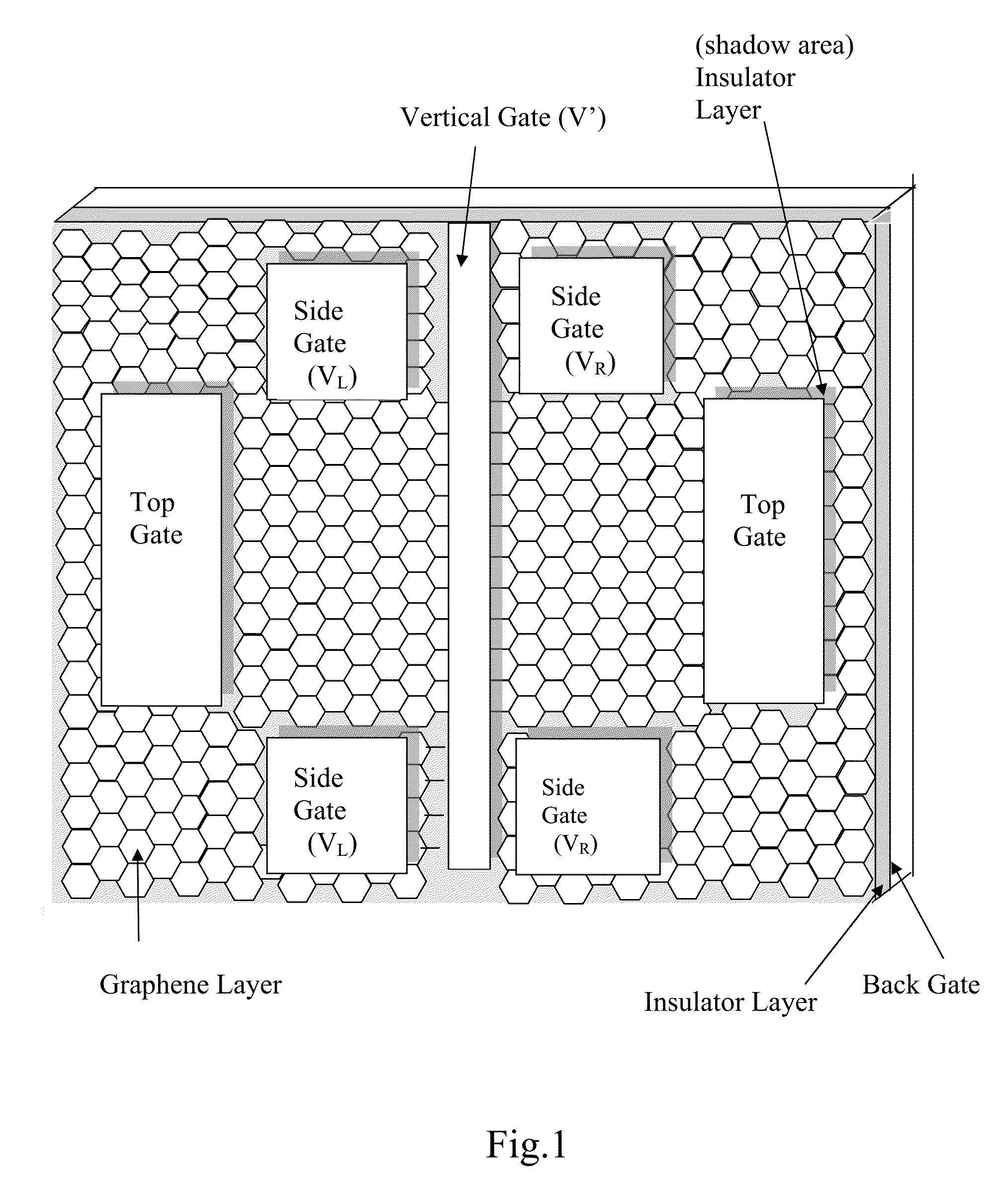
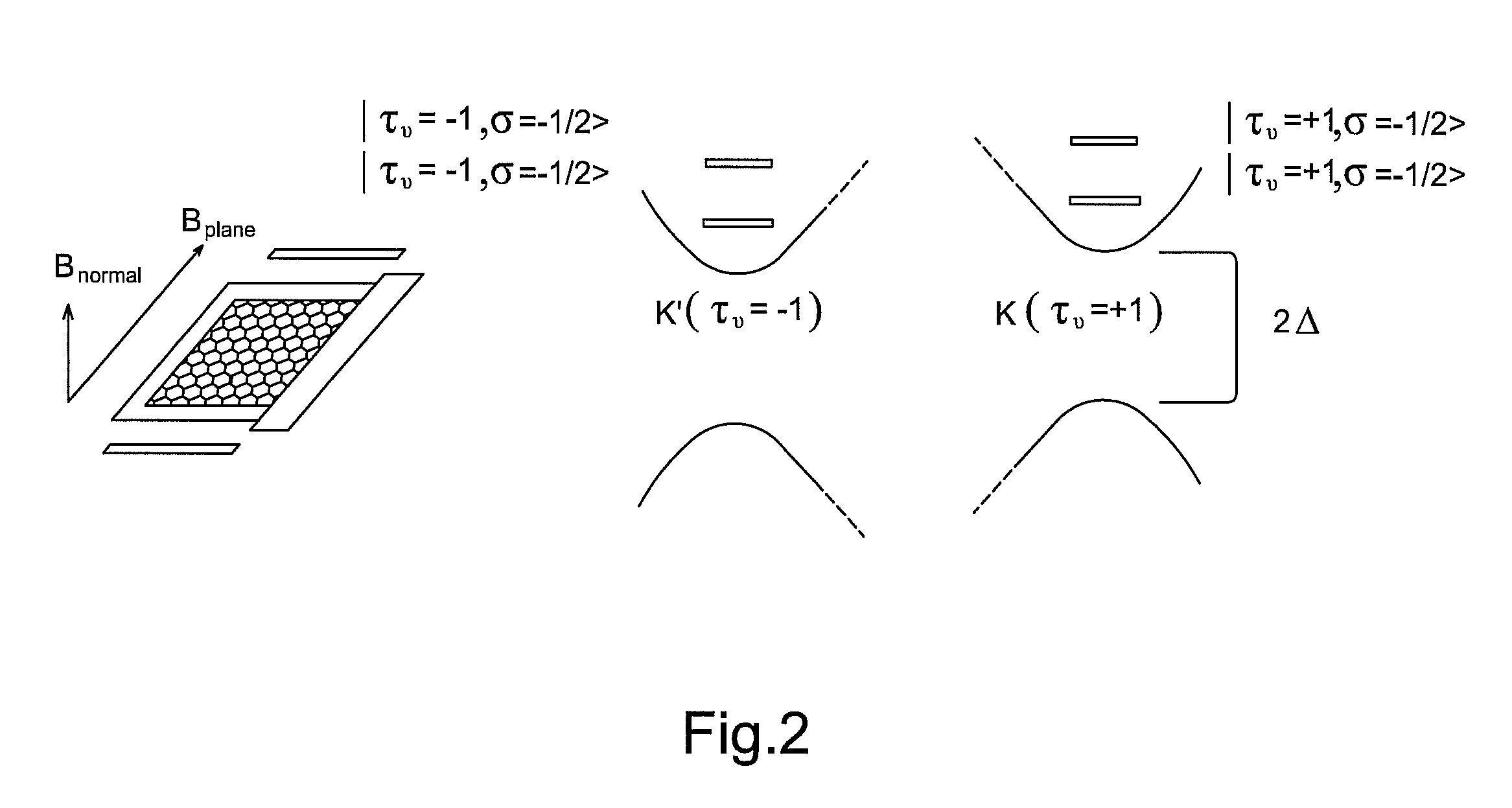
Graphene valley singlet-triplet qubit device and the method of the same
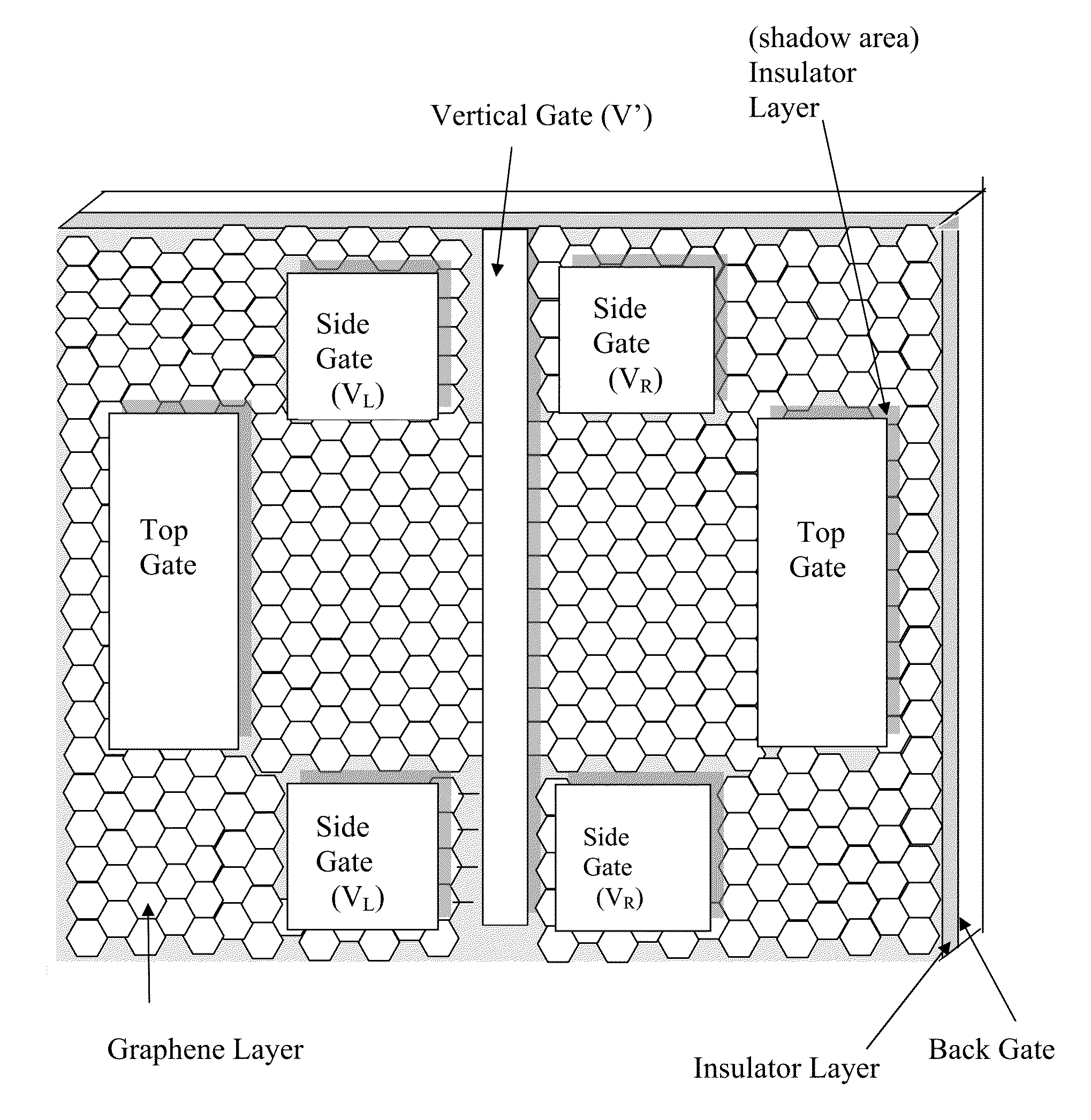
The present invention is to provide a graphene valley singlet-triplet qubit device. The device includes a substrate, and a graphene layer formed on the substrate. An energy gap is created between the valence band and the conduction band of the graphene layer. At least one electrical gate is configured on the graphene layer and / or on two sides of the graphene layer. The graphene layer is located in a magnetic field and a voltage is applied to at least one electrical gate, thereby creating a valley singlet-triplet qubit.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Semiconductor generation of dynamic infrared images
InactiveUS7084405B1Television system detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsValence electron
A high-speed, high-resolution, broadband dynamic infrared scene generator based on semiconductor transducer conversion of visible spectrum scene images into infrared spectrum images. Wavelength conversion is accomplished in the semiconductor material through absorption of visible spectrum energy by valence electrons in a subsurface layer of the semiconductor material and photogeneration by valence band to conduction band electron transfer occurring within about one diffusion length of the semiconductor material surface. The semiconductor material used, for example Germanium or Silicon provides a band gap energy value that is smaller than the quantum energy level of the optical emission. Temperature of the semiconductor material may be maintained at a selected level above or below that of the infrared scene. Infrared images of higher frequency content than are achievable with conventional thermal heating infrared converters are accomplished. The invention thus includes down conversion of visible generated light in order to develop a semiconductor pixel-less Dynamic Infrared Scene Projector capable of simulating high-speed broadband IR scenery.
Owner:US SEC THE AIR FORCE THE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com