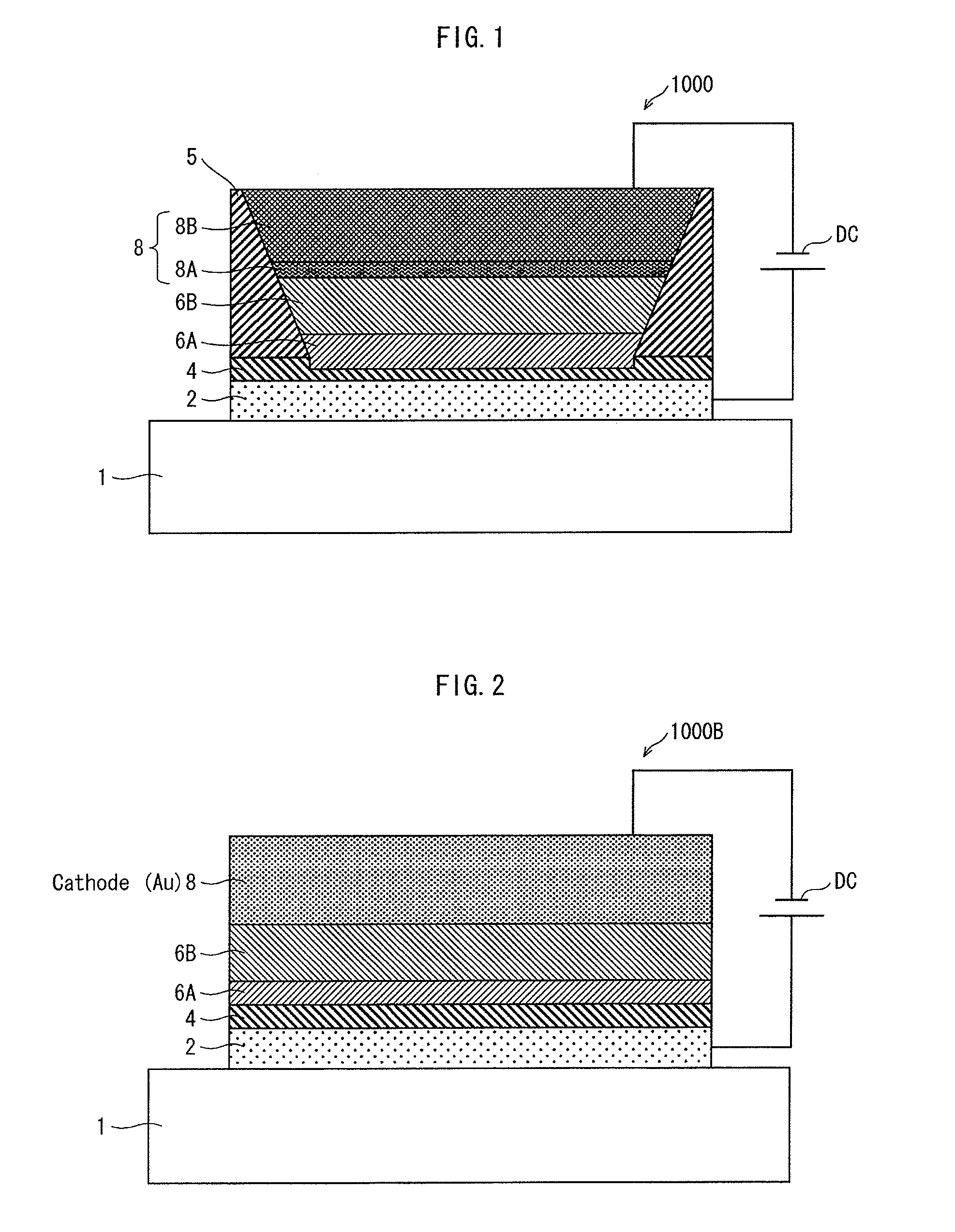
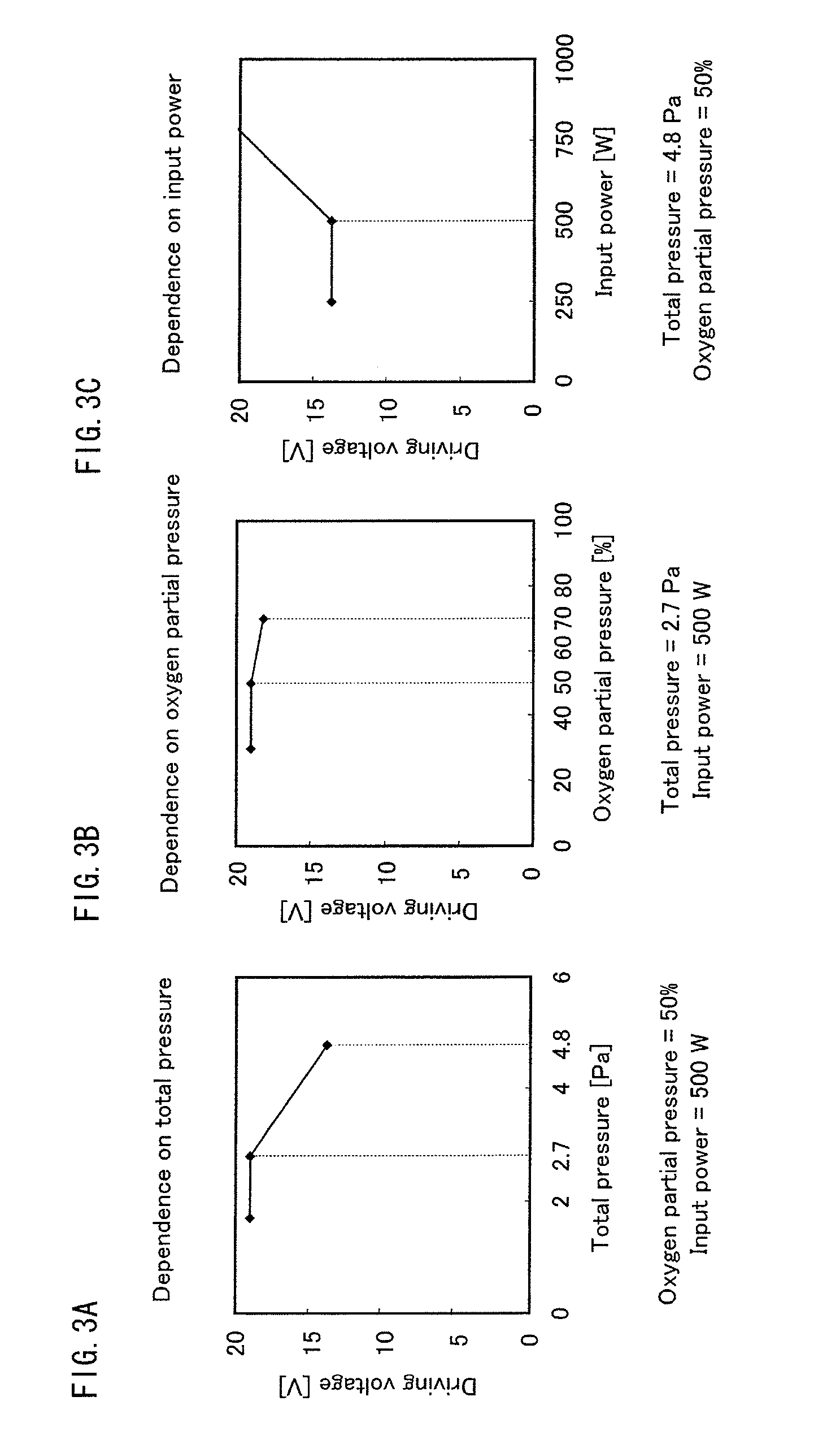
Patents
Literature
271 results about "Binding energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, binding energy (also called separation energy) is the minimum energy required to disassemble a system of particles into separate parts. This energy is equal to the mass defect minus the amount of energy, or mass, that is released when a bound system (which typically has a lower potential energy than the sum of its constituent parts) is created, and is what keeps the system together.
Method for fabricating a glass substrate, magnetic disk, and method for fabricating the same
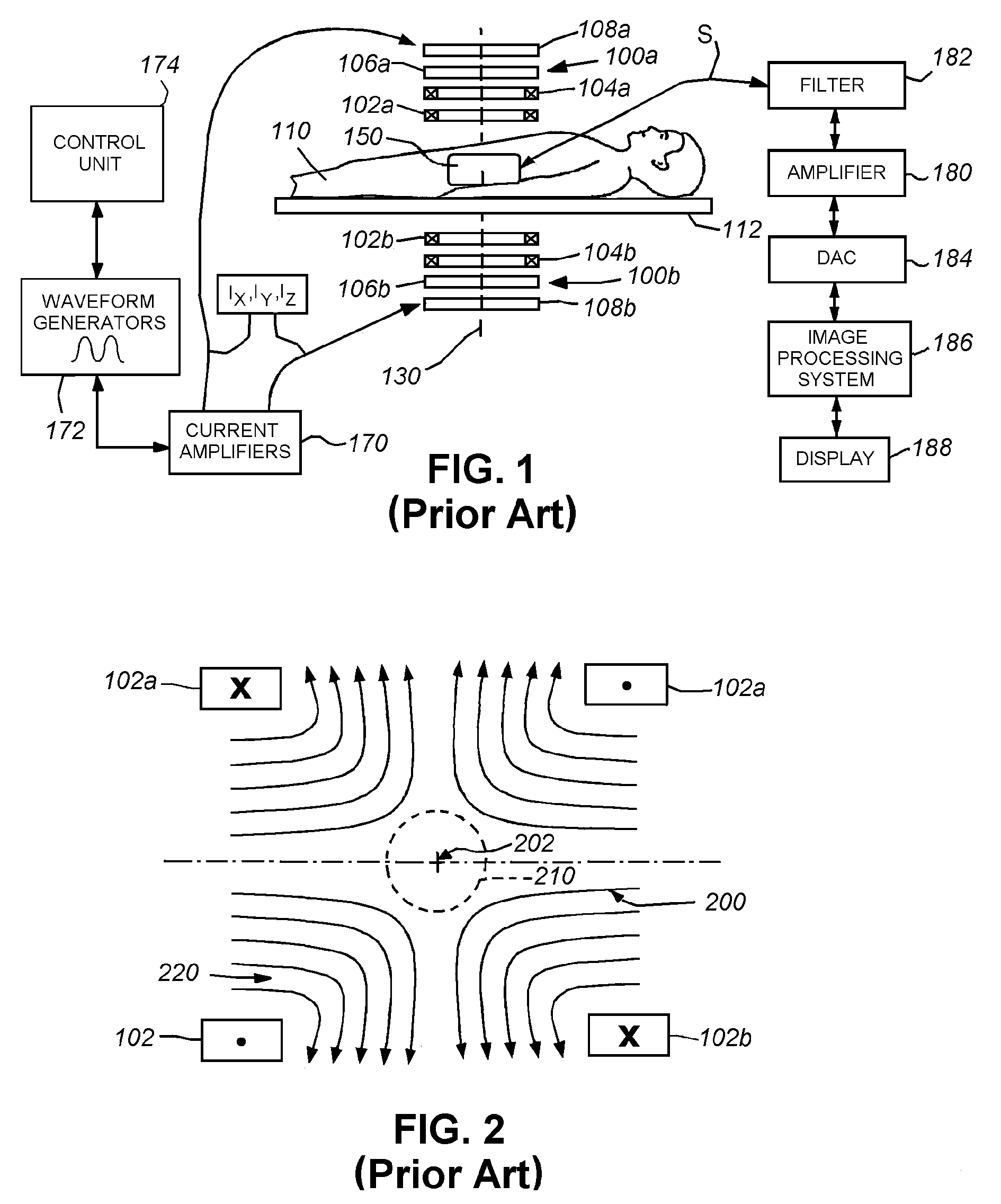
InactiveUS20080026260A1Uniform and low-noise magnetic characteristicReduce distanceMagnetic materials for record carriersMaterial analysis by optical meansBinding energyAdditive ingredient
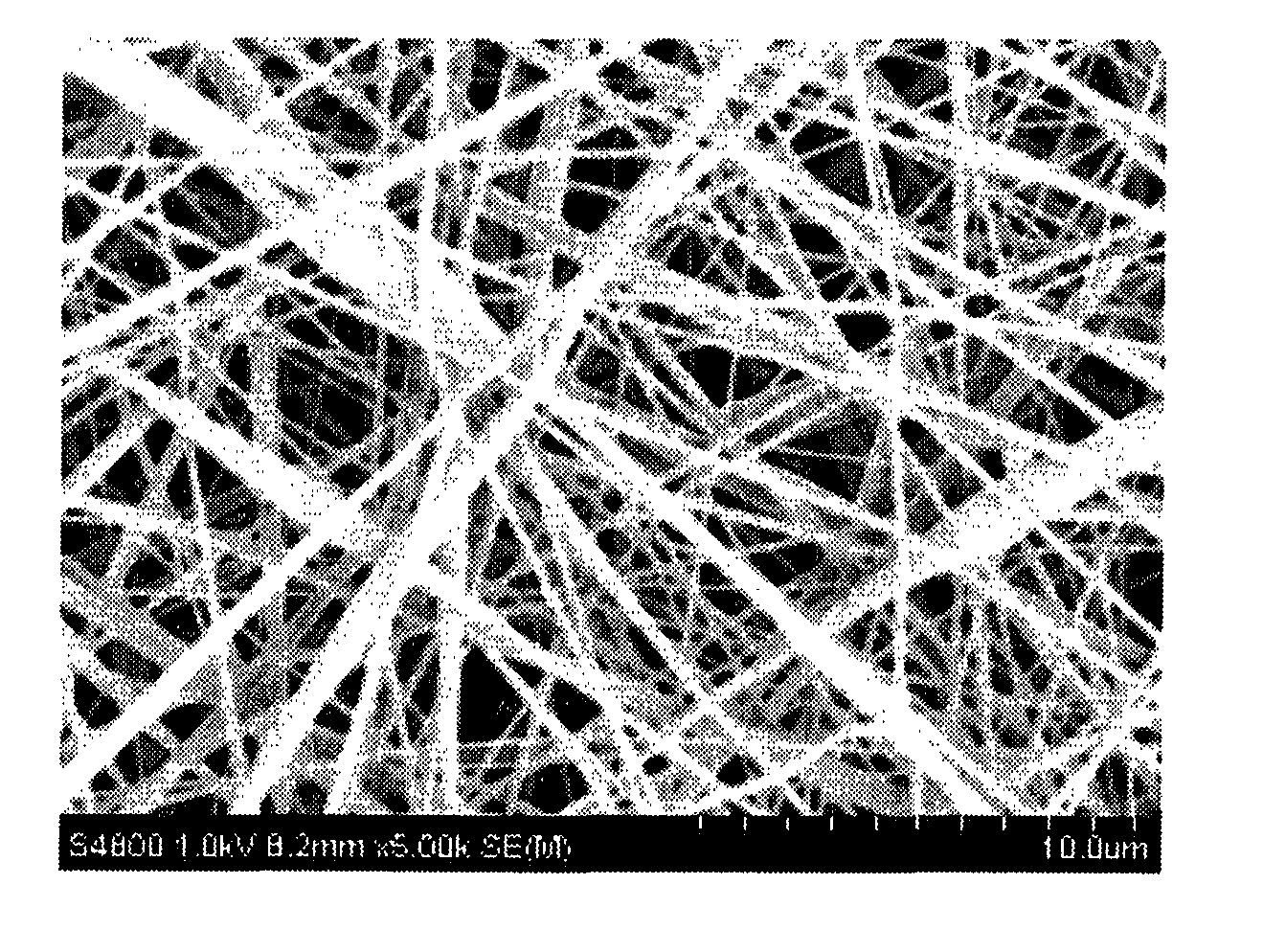
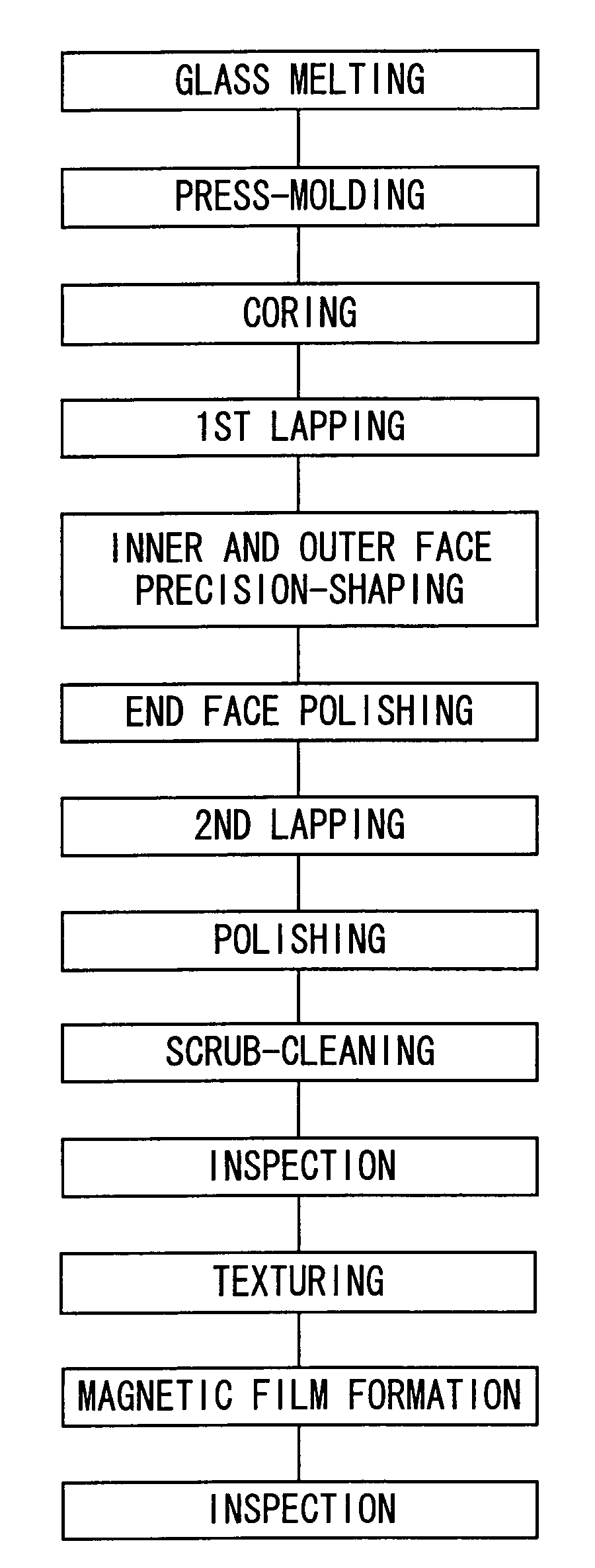
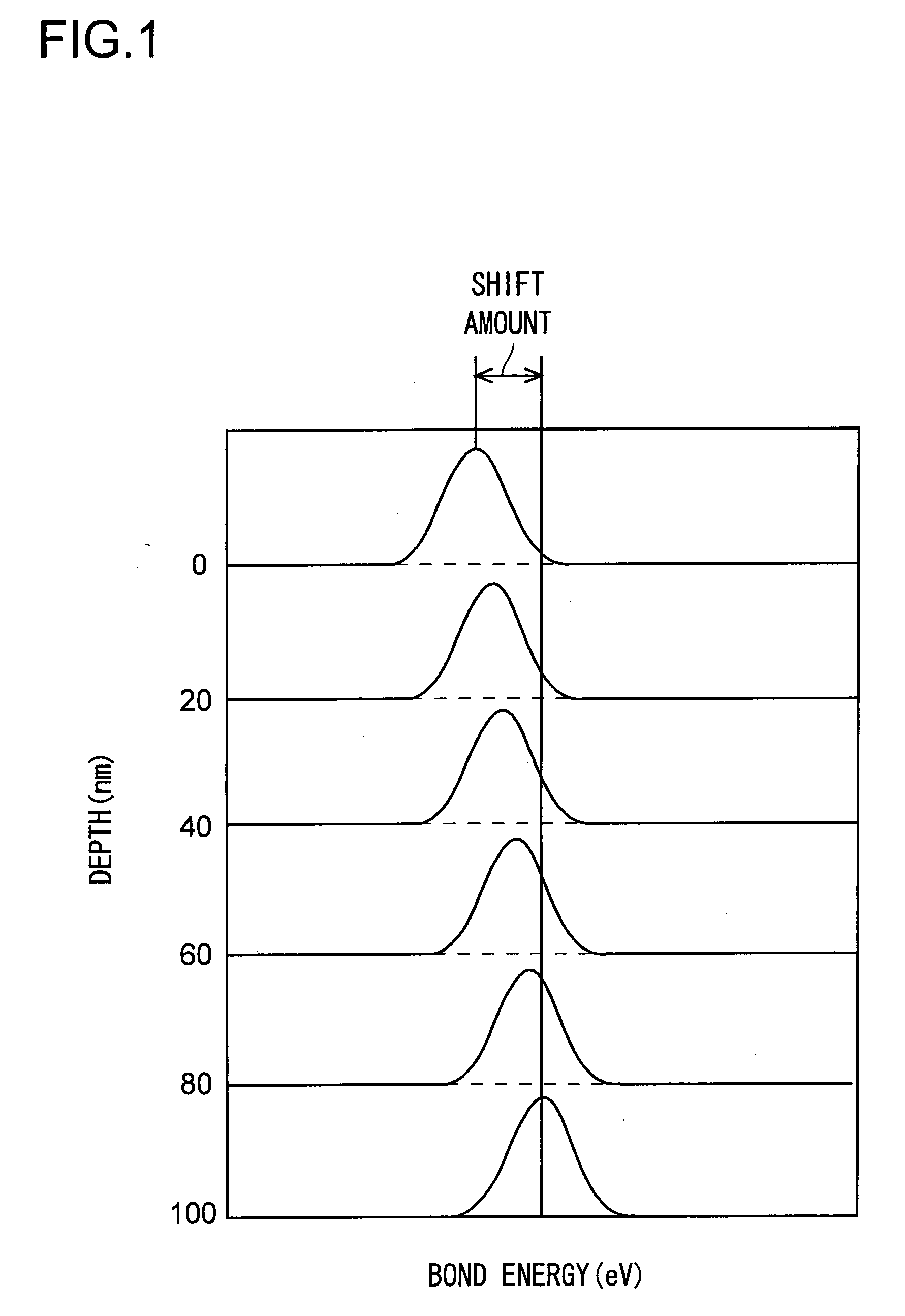
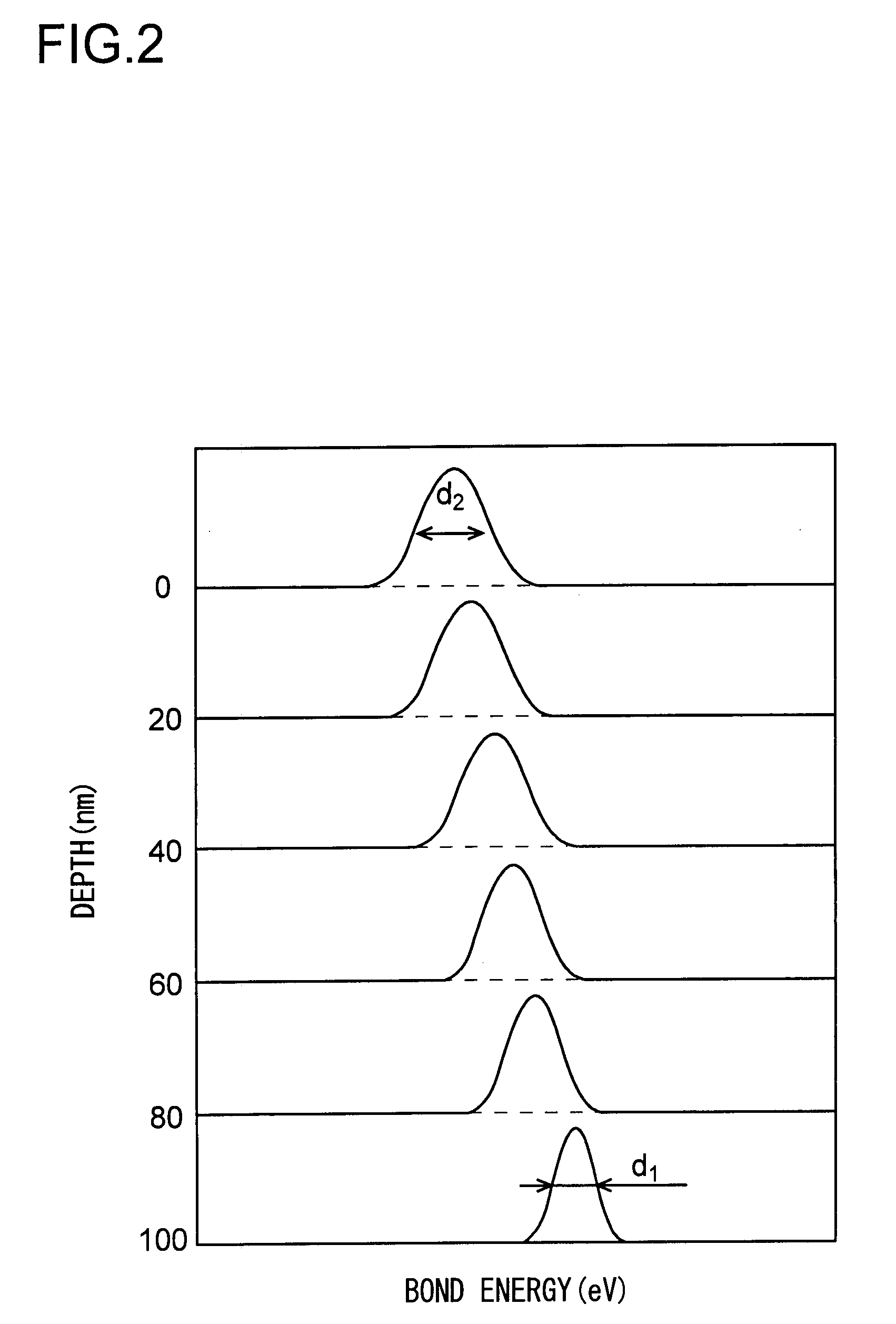
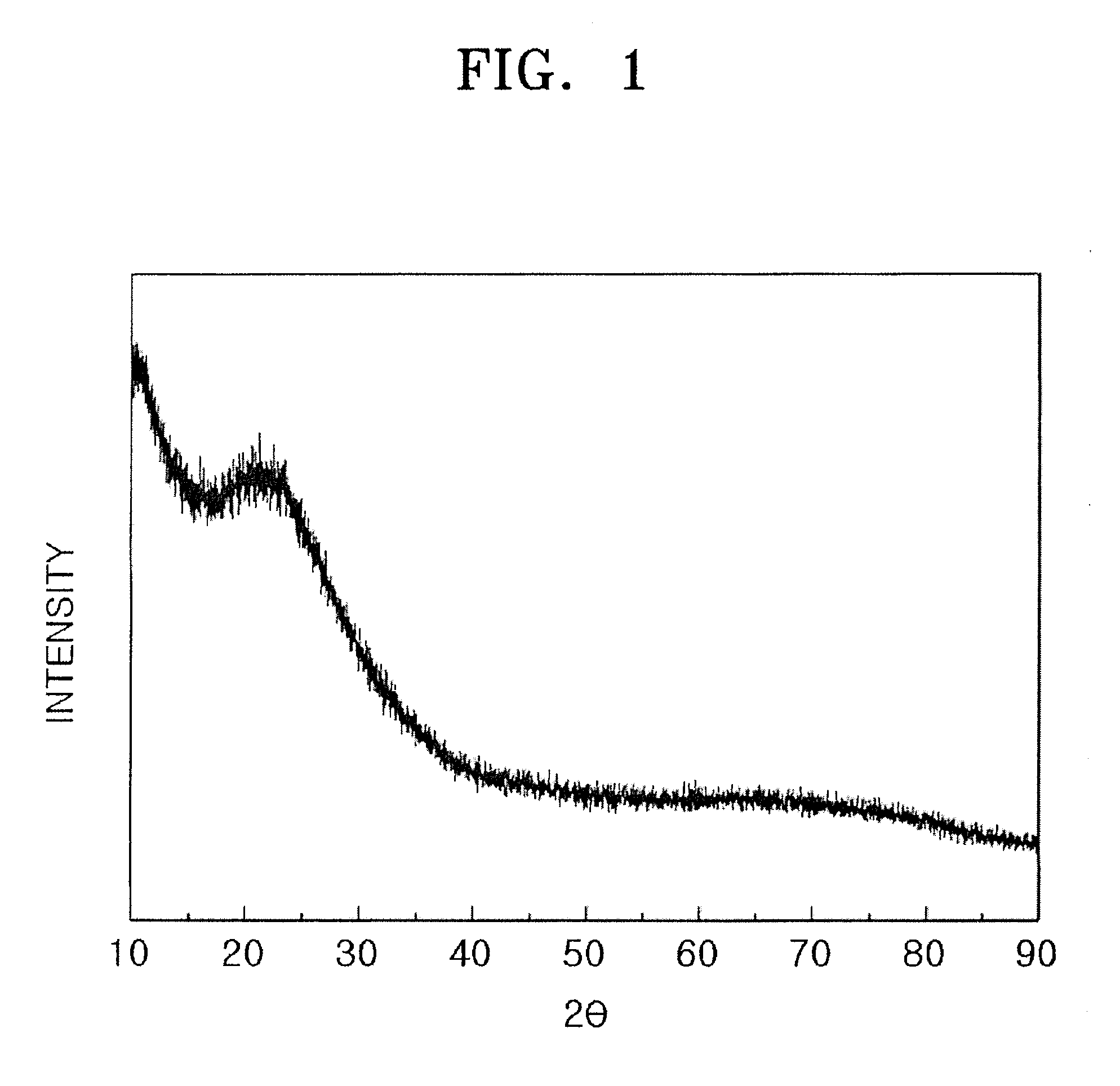
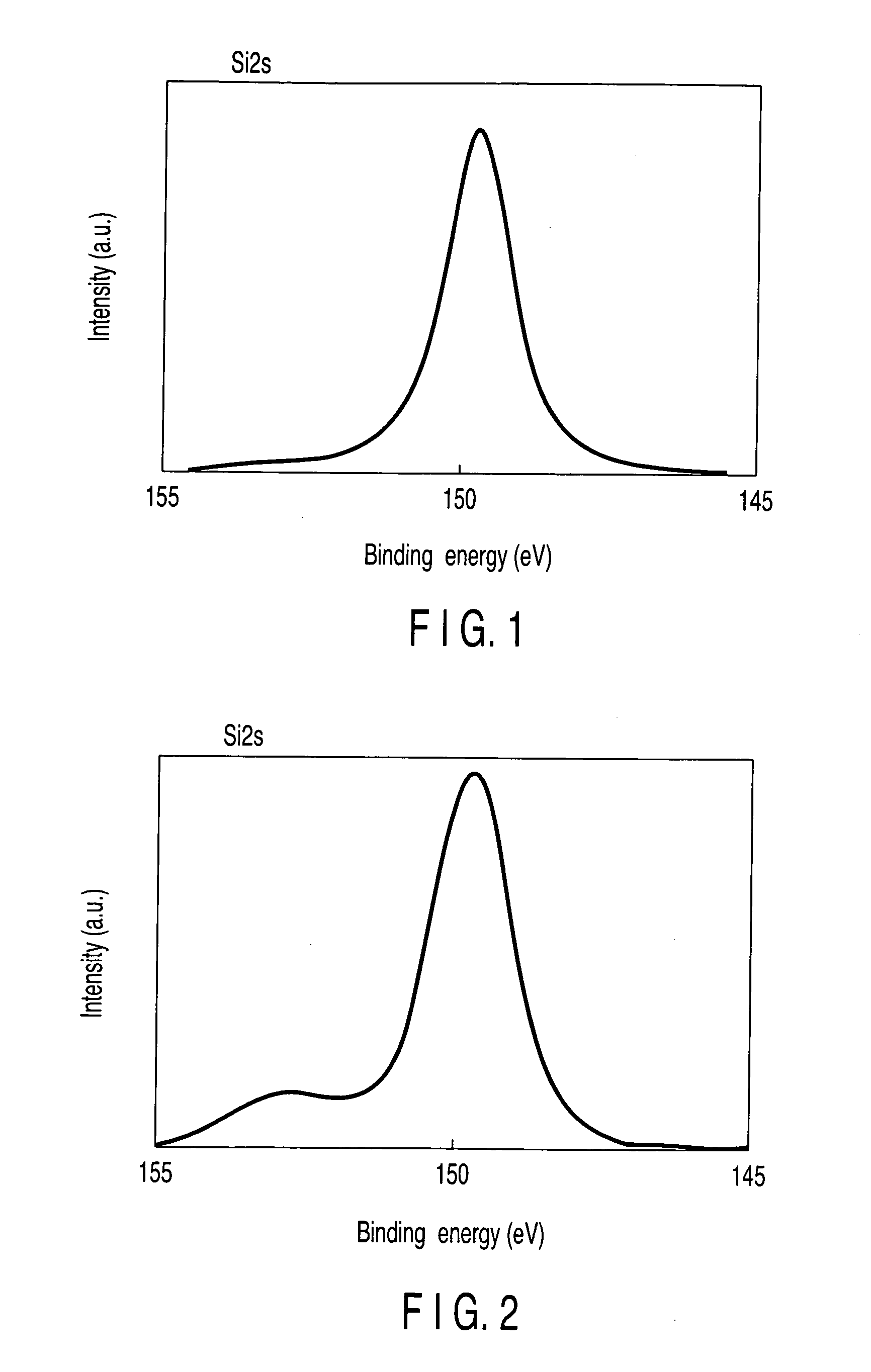
A method for fabricating a glass substrate containing SiO2 as a main ingredient thereof and having a uniform and minute pattern of stripes formed on the surface thereof by ultraprecision polishing includes a step of inspecting whether or not, at the topmost surface portion of the glass substrate after polishing, a given property of a bound energy of the Si atom with respect to the electrons occupying a 2P orbit as determined by XPS is equal to or less than a predetermined value, and the given property is a shift amount of the bound energy or a half-value width of the bound energy distribution, the predetermined value is 0.10 eV or 2.15 eV, respectively.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Anode active material, method of preparing the same, and anode and lithium battery containing the material
ActiveUS20080166634A1Improving initial chargeImprove discharge efficiencyBio-organic fraction processingSilicaFull width at half maximumX-ray
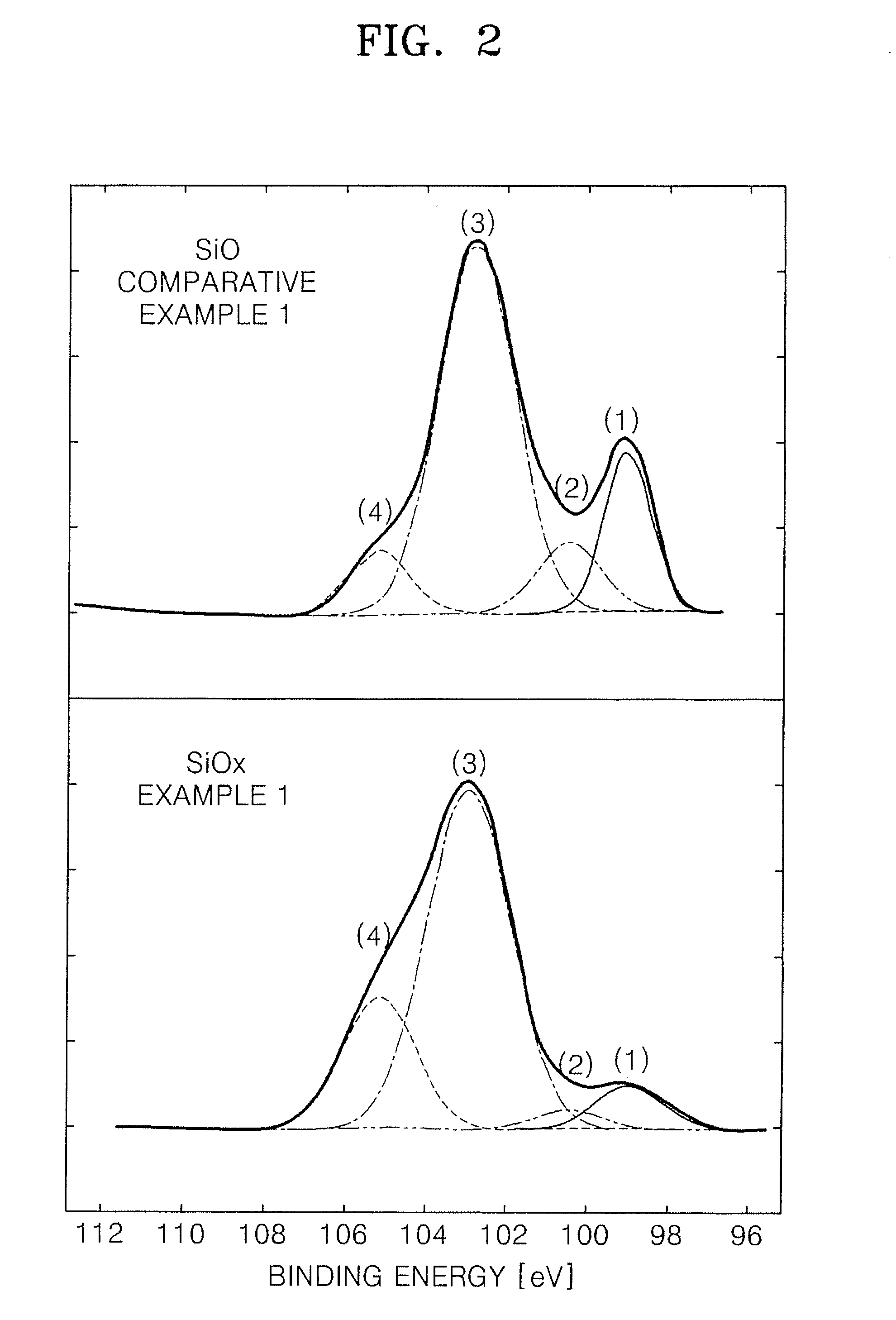
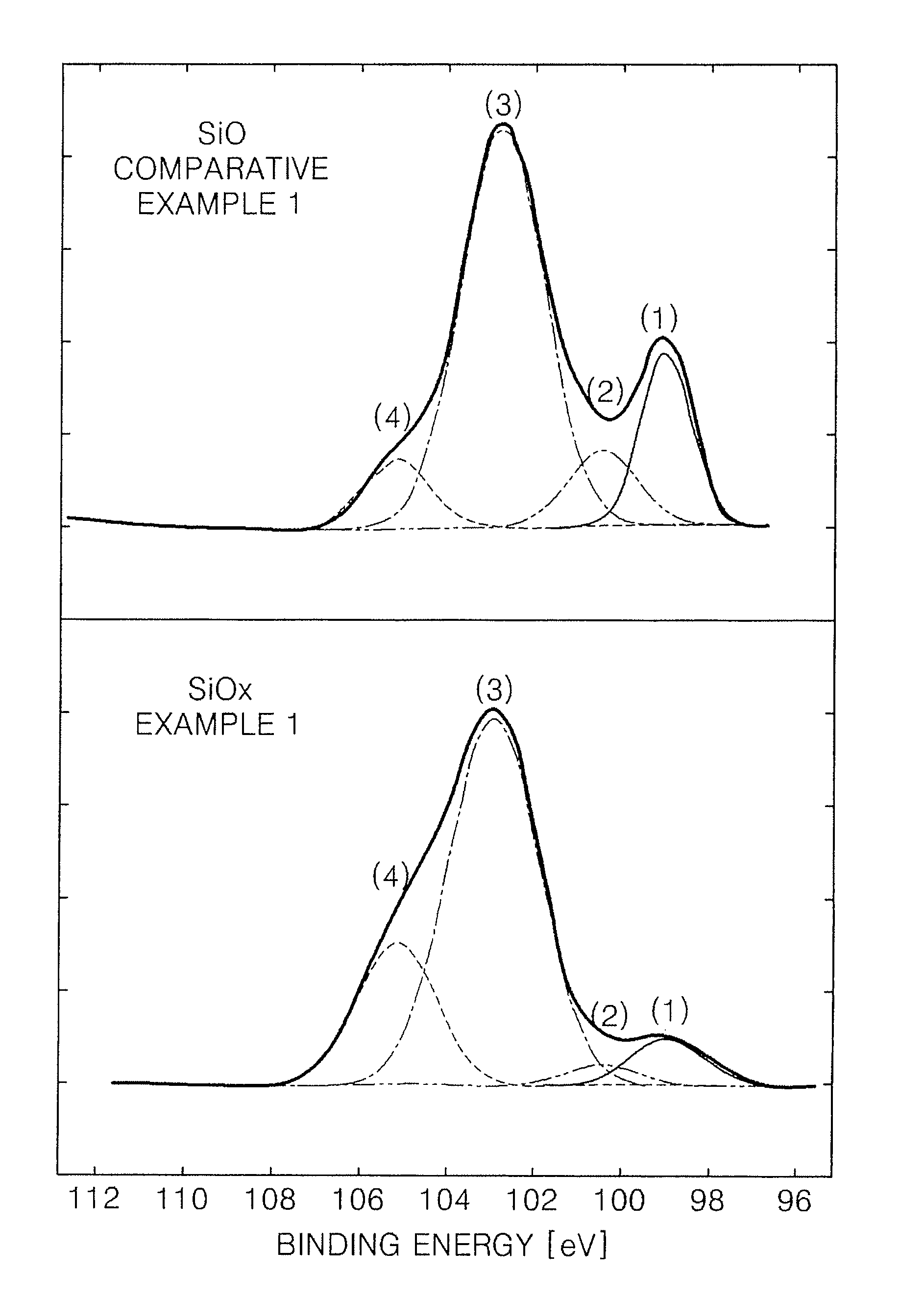
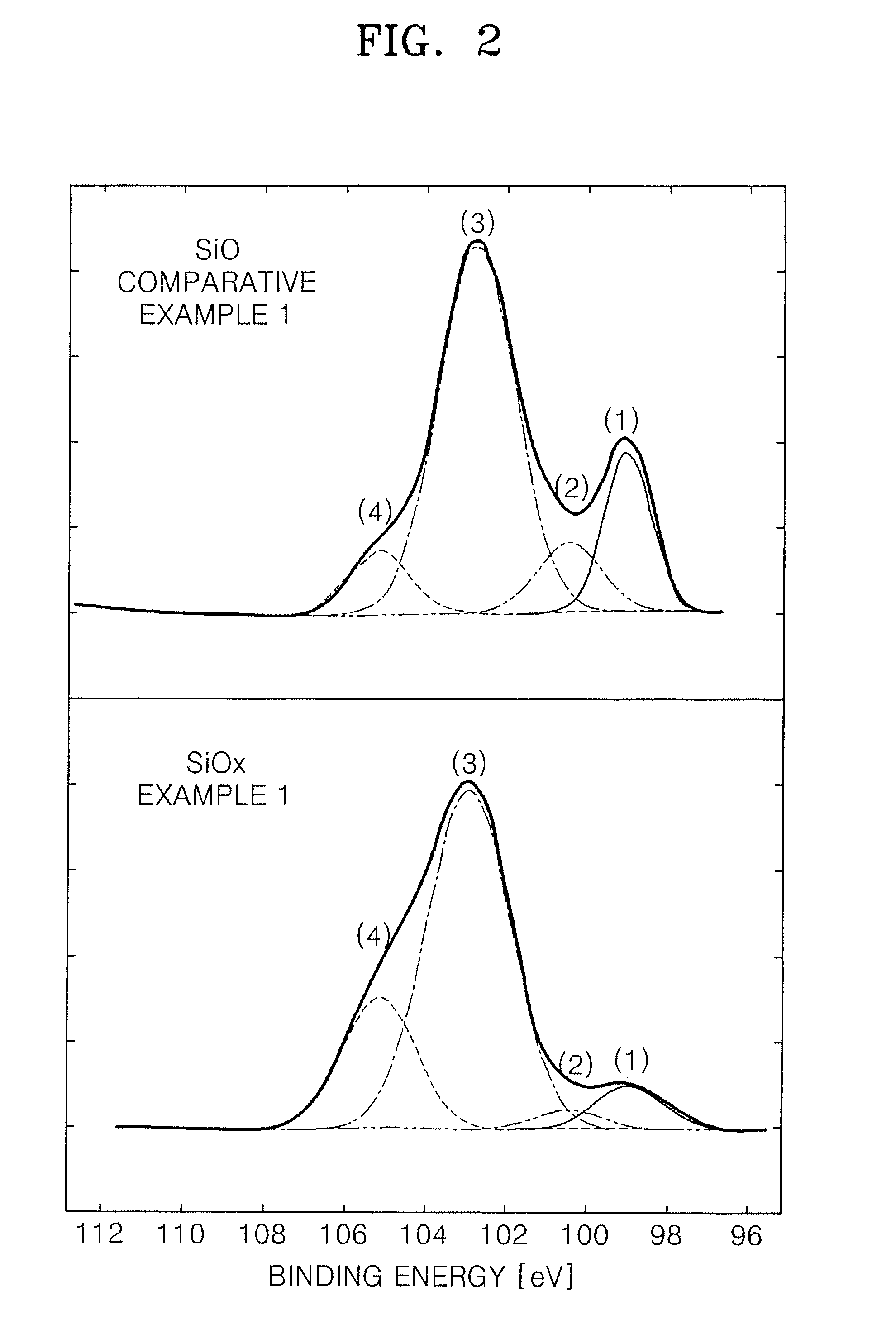
Silicon oxide based composite anode active materials including amorphous silicon oxides are provided. In one embodiment, the amorphous silicon oxide is represented by SiOx (where 0<x<2), has a binding energy of about 103 to about 106 eV, a silicon peak with a full width at half maximum (FWHM) ranging from about 1.6 to about 2.4 as measured by X-ray photoelectron spectrometry, and an atomic percentage of silicon greater than or equal to about 10 as calculated from an area of the silicon peak. The anode active material is a composite anode active material obtained by sintering hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ). Anodes and lithium batteries including the anode active material exhibit improved charge and discharge characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
System and method for use of nanoparticles in imaging and temperature measurement
ActiveUS20090115415A1Improve rendering capabilitiesHigh sensitivityNanomagnetismMagnetic property measurementsBinding energyMagnetic particle imaging
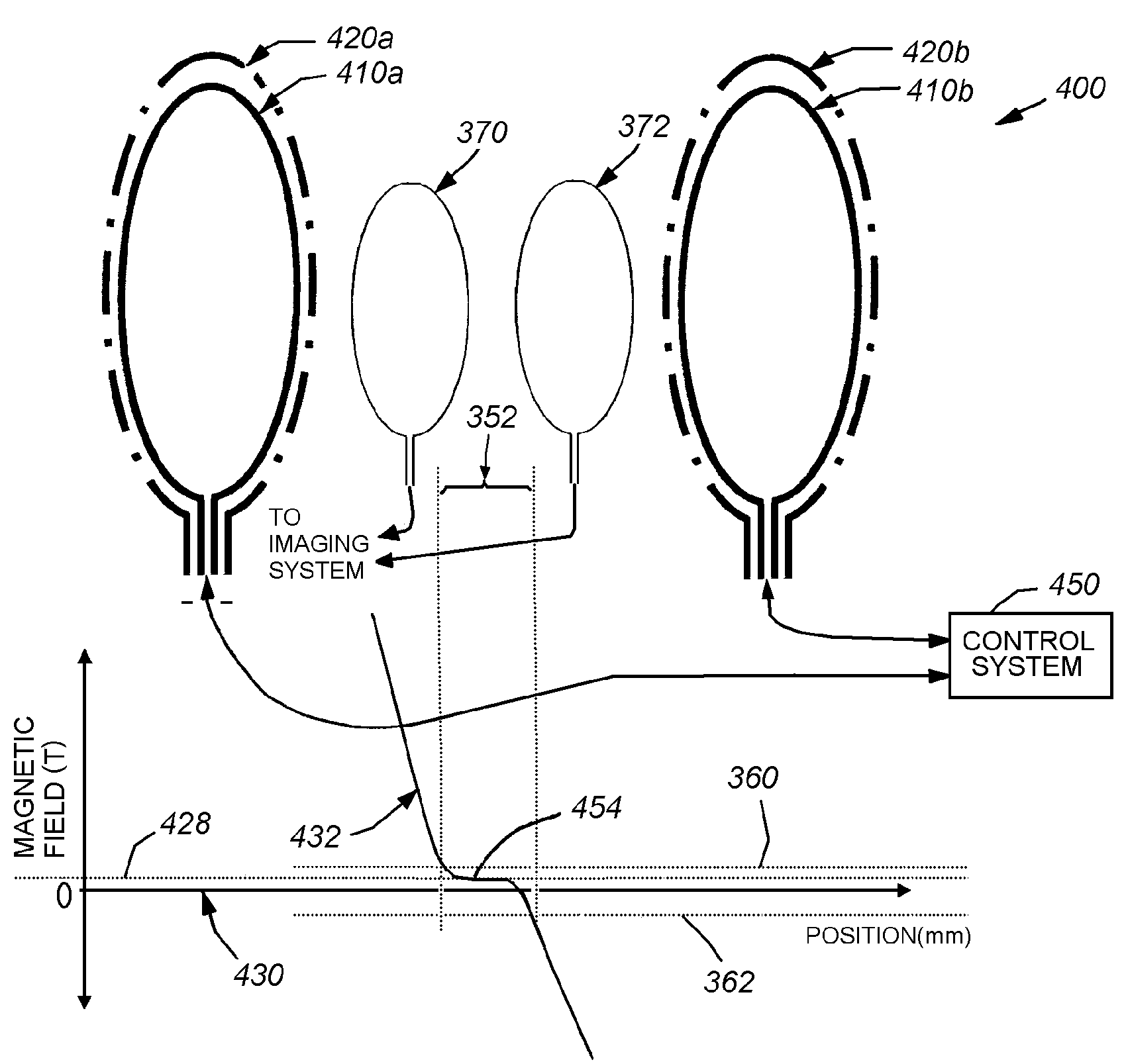
This invention provides a system and method that improves the sensitivity and localization capabilities of Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) by using combinations of time-varying and static magnetic fields. Combinations of magnetic fields can be used to distribute the signals coming from the magnetic particles among the harmonics and other frequencies in specific ways to improve sensitivity and to provide localization information to speed up or improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of imaging and / or eliminate the need for saturation fields currently used in MPI. In various embodiments, coils can be provided to extend the sub-saturation region in which nanoparticles reside; to provide a static field offset to bring nanoparticles nearer to saturation; to introduce even and odd harmonics that can be observed; and / or to introduce combinations of frequencies for more-defined observation of signals from nanoparticles. Further embodiments provide for reading of the signal produced by cyclically saturated magnetic nanoparticles in a sample so as to provide a measurement of the temperature of those nanoparticles. The spectral distribution of the signal generated provides estimates of the temperature of the nanoparticles. Related factors may also be estimated—binding energies of the nanoparticles, phase changes, bound fraction of the particles or stiffness of the materials in which the nanoparticles are imbedded.
Owner:DARTMOUTH HITCHCOCK CLINIC
Method of energy cumulative presplitting and smoothsurface blasting and special device therof
ActiveCN101033932AIncrease profitEnhance blasting forceBlasting cartridgesBlastingBinding energyDetonator
It is a special-purpose device used for two-directional energy-focusing and smooth blasting, post standard knot of multisection energy-gathering pipe which is in the double ''V'' shaped energy-accumulating groove which is set on the pipewall full of detonator, each post standard knot is linked with connection casing on which there is energy-accumulating groove, centering ring in the hole is noosed on the standard joint of the binding energy tube so that the center lines of the upper and the lower energy-gathering groove like V shape are in the same surface in the blasthole. Orifice centering rings of the two V- shaped central whose orientation is the same with V- shaped energy-gathering groove are set on the noose annulus wall at the ground end of energy -gathering pipe at orifice of blasthole, which makes the center line of each energy-gathering groove like a V shape forms a surface of centering and coinciding with blasting surface in each blasthole and among. After detonating explosive, make shaped charge jet spark along initial small crack that forms while the crack begins to form, then forms presplitting or smooth blasting surface, and finish energy-gathering presplitting and smooth blasting. The invention can enhance utilization ratio of demolishing energy and debase quantity of drilled holes, the influence of destroying rock mass kept down is little and the blasting surface is more level.
Owner:SINOHYDRO BUREAU 8 CO LTD
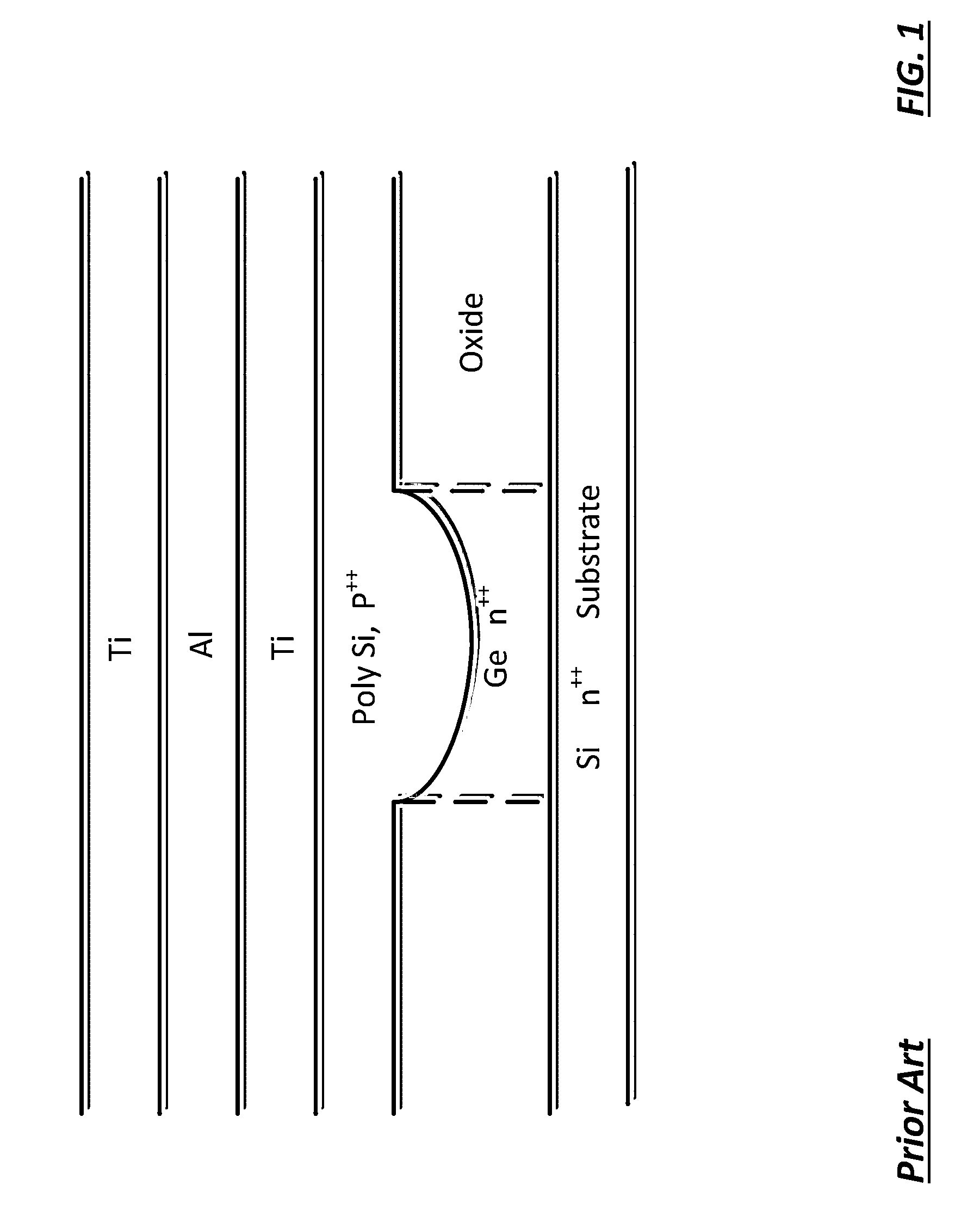
Doping of germanium and silicon crystals with non-hydrogenic acceptors for far infrared lasers
InactiveUS6011810AIncrease powerHigh duty cycleLaser detailsLaser active region structureAcceptor dopantFar infrared
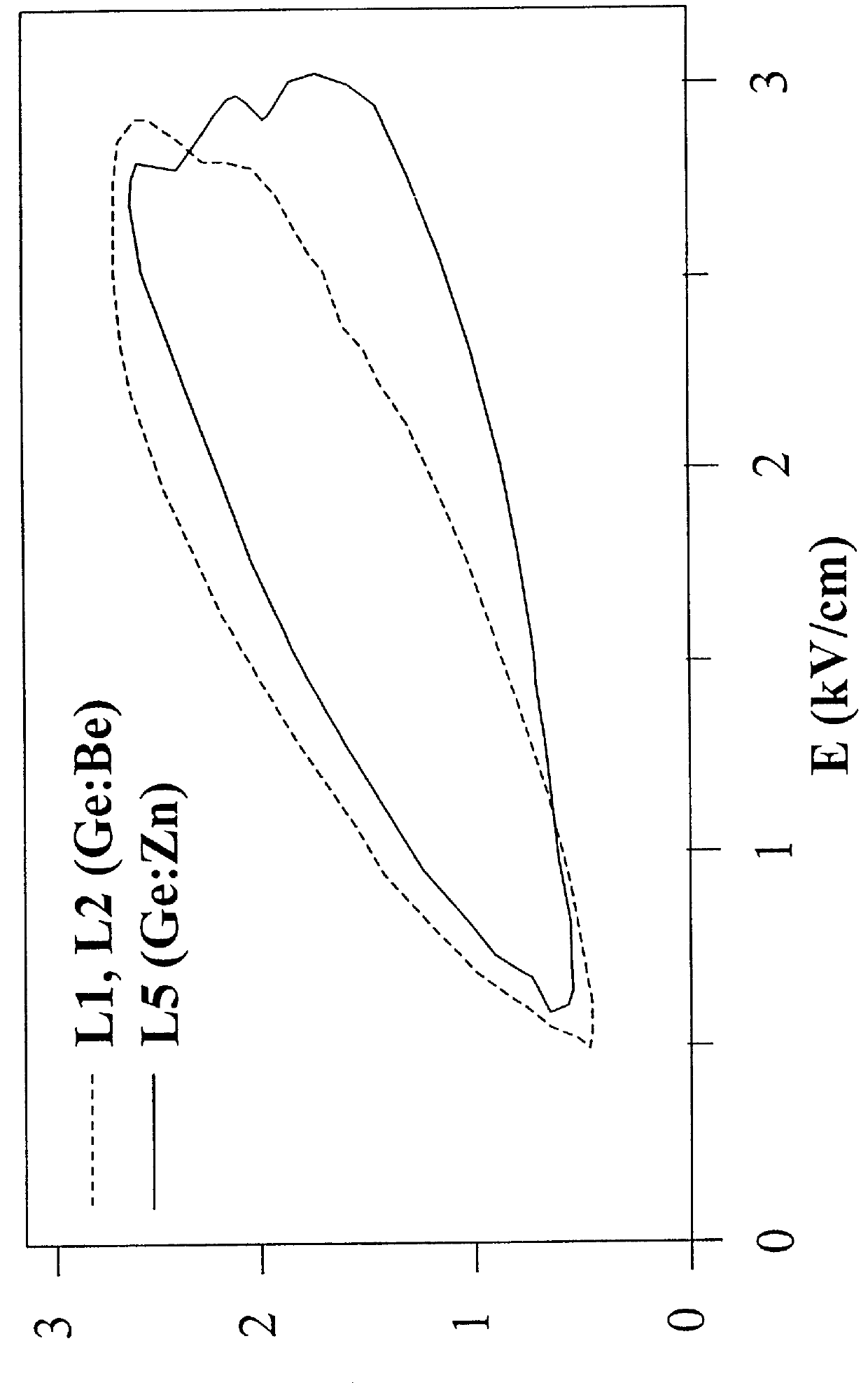
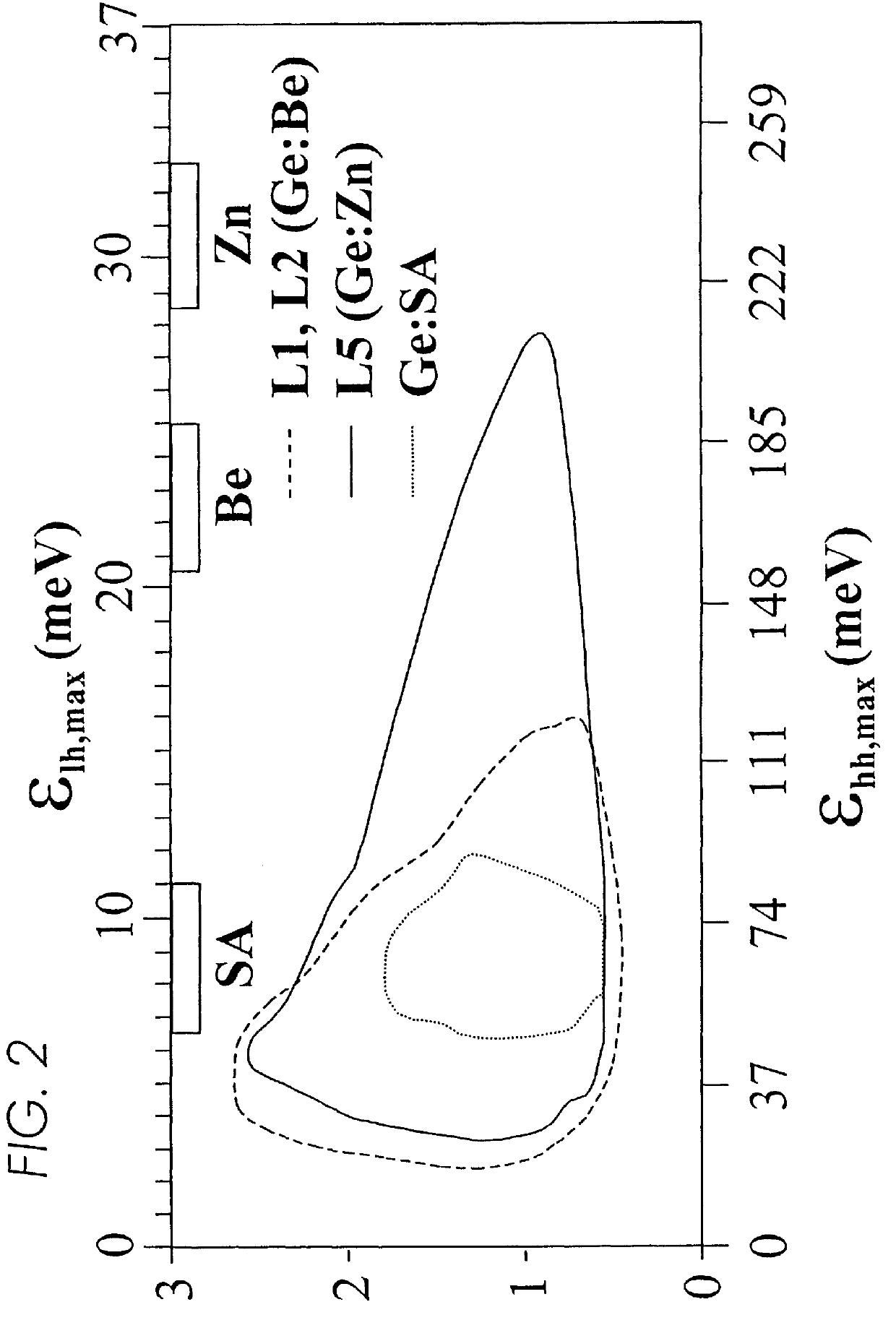
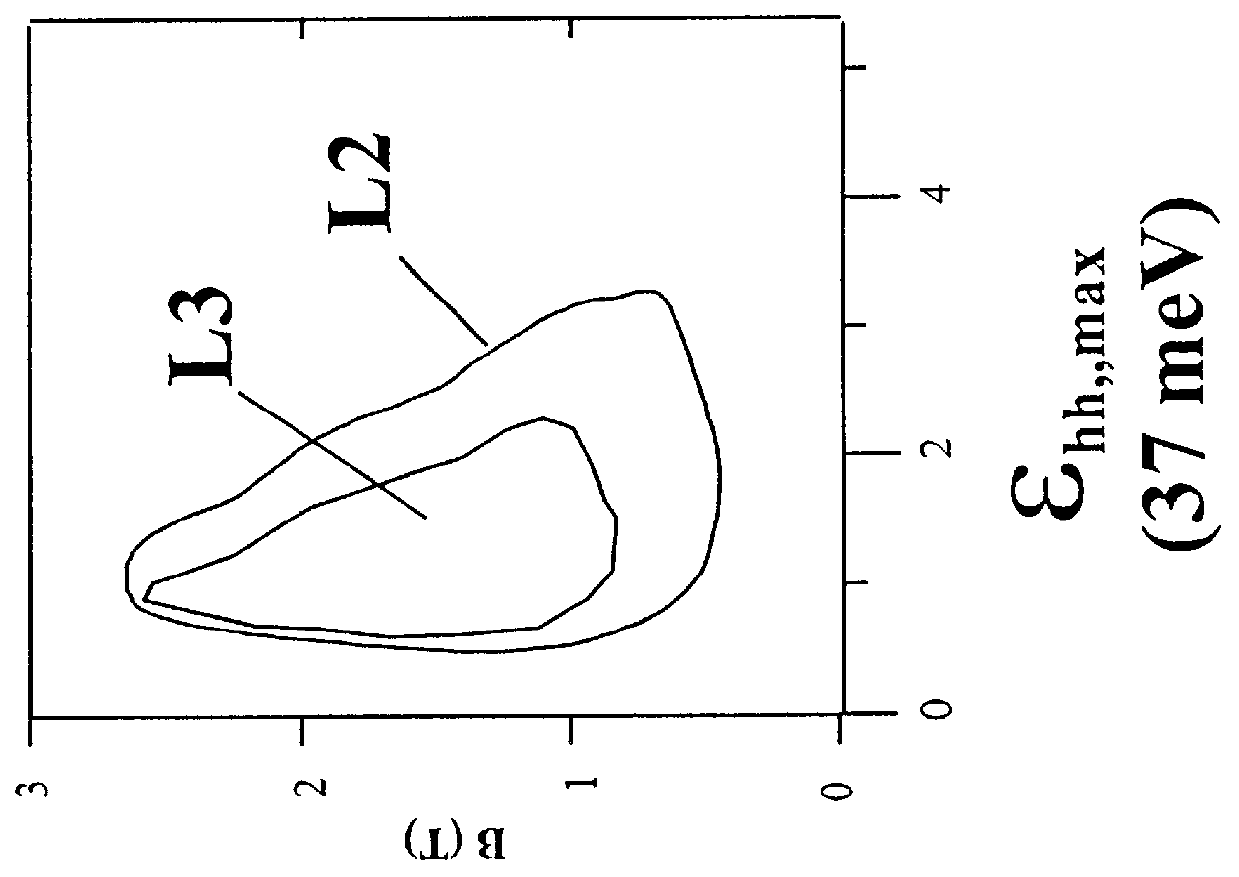
A method for doping semiconductors used for far infrared lasers with non-hydrogenic acceptors having binding energies larger than the energy of the laser photons. Doping of germanium or silicon crystals with beryllium, zinc or copper. A far infrared laser comprising germanium crystals doped with double or triple acceptor dopants permitting the doped laser to be tuned continuously from 1 to 4 terahertz and to operate in continuous mode. A method for operating semiconductor hole population inversion lasers with a closed cycle refrigerator.
Owner:LAWRENCE BERKELEY NAT LAB
Hollow nanofibers-containing composition
InactiveUS20110027163A1Easy to separateEasy to removeMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsFiberElectron
A method for preparing hollow nanofibers having carbon as a primary component by contacting a carbon-containing compound with a catalyst at 500 to 1200° C., wherein the catalyst is one of a zeolite exhibiting thermal resistance at 900° C. and, supported thereon, a metal; a metallosilicate zeolite containing a heteroatom except aluminum and silicon and a metal; a supporting material and fine cobalt particles exhibiting a binding energy of a cobalt 2P3 / 2 electron of 779.3 to 781.0 eV; a supporting material and fine cobalt particles exhibiting a cobalt atom ratio in the surface of the supporting material of 0.1 to 1.5%, as measured by the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy at 10 kV and 18 mA; a supporting material and fine cobalt particles exhibiting a weight ratio of cobalt to a second metal component of 2.5 or more; and a zeolite having a film form and a metal.
Owner:SHINOHARA HISANORI +4
Enhanced Optical Gain and Lasing in Indirect Gap Semiconductor Thin Films and Nanostructures
ActiveUS20140185640A1Laser using scattering effectsLaser optical resonator constructionElectron injectionField-effect transistor
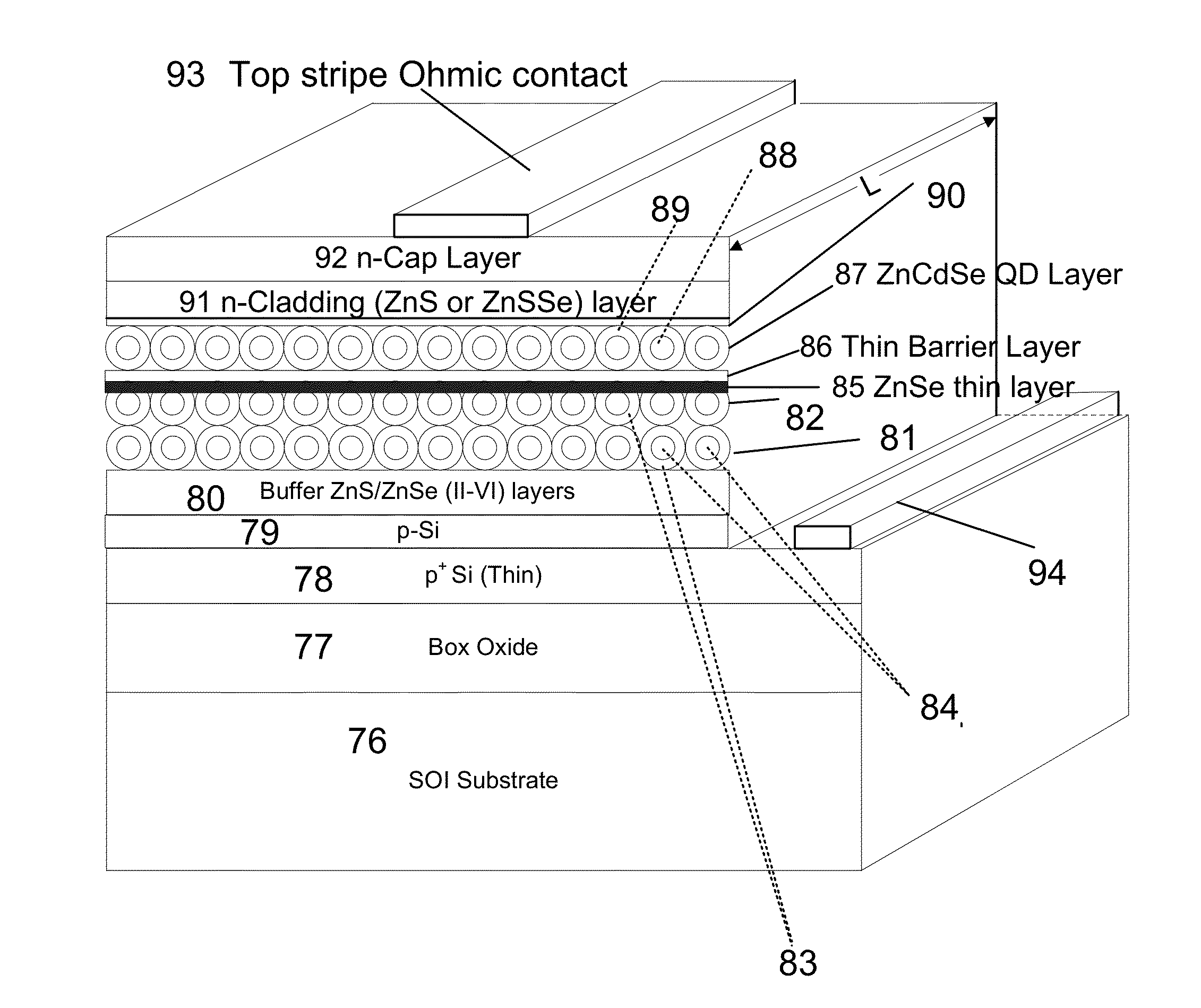
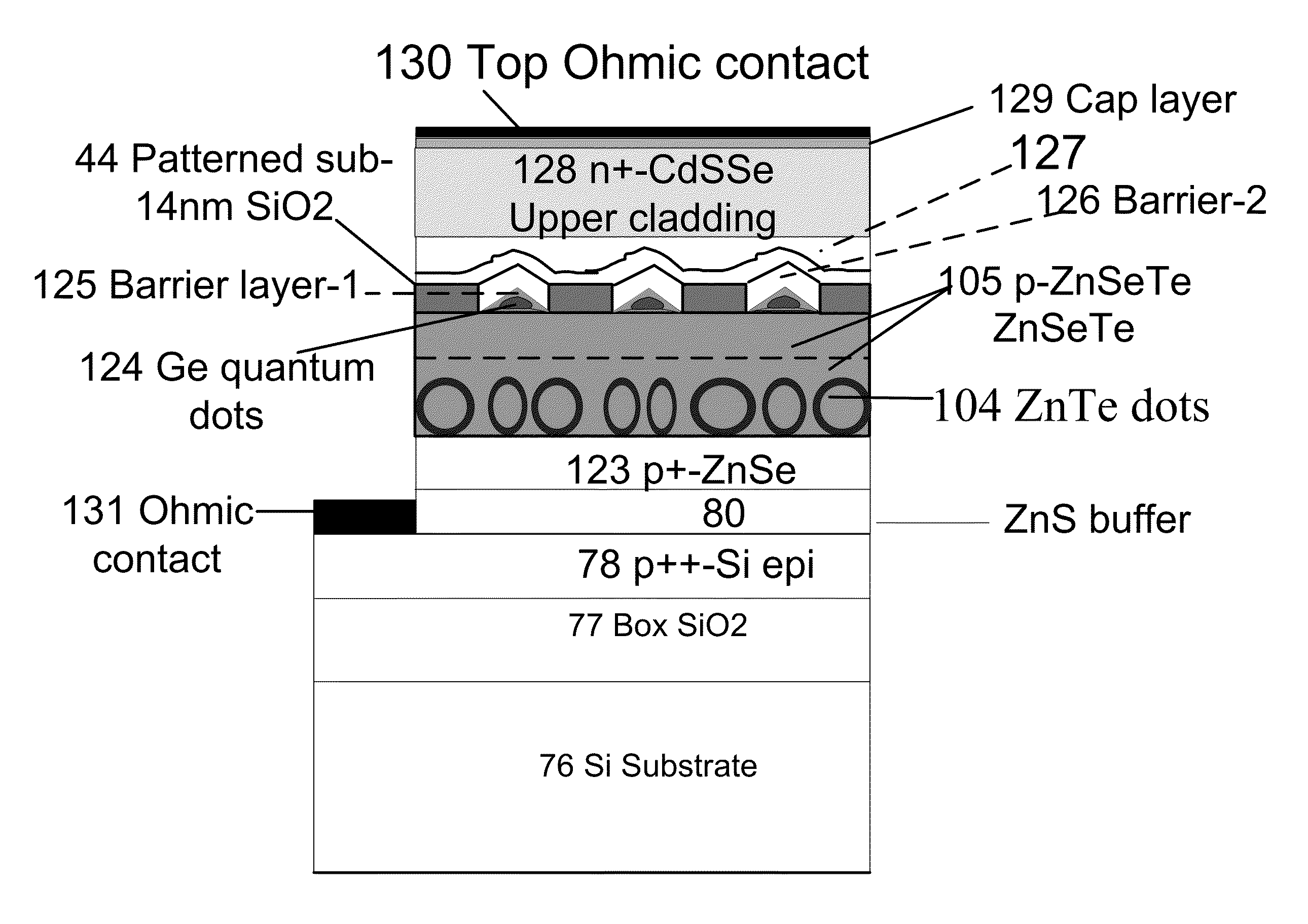
Structures and methodologies to obtain lasing in indirect gap semiconductors such as Ge and Si are provided and involves excitonic transitions in the active layer comprising of at least one indirect gap layer. Excitonic density is increased at a given injection current level by increasing their binding energy by the use of quantum wells, wires, and dots with and without strain. Excitons are formed by holes and electrons in two different layers that are either adjacent or separated by a thin barrier layer, where at least one layer confining electrons and holes is comprised of indirect gap semiconductor such as Si and Ge, resulting in high optical gain and lasing using optical and electrical injection pumping. In other embodiment, structures are described where excitons formed in an active layer confining electrons in the direct gap layer and holes in the indirect gap layer; where layers are adjacent or separated by a thin barrier layer. The carrier injection structures are configured as p-n junctions and metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) field-effect transistors. The optical cavity is realized to confine photons. In the case of MOS structures, electrons from the inversion layer, formed under the gate at voltages above threshold, are injected into one or more layers comprising of quantum wells (2-d), quantum wires (1-d) and quantum dots (0-d) structures. The confinement of photons emitted upon electron-hole recombination produces lasing in active layer comprising of dots / wells. Bipolar transistor structures can also be configured as lasers.
Owner:JAIN FAQUIR C
Colored oxygen scavenging polymers
InactiveUS20090030115A1Increase binding energySynthetic resin layered productsMixingBinding energyCatalytic oxidation
The present invention relates to a melt blend of a base polymer, an oxidizable organic polymer, a transition metal salt catalyst and a colorant that does not completely deactivate the catalyzed oxidation. A preferred colorant, yields in an article made from the polymer melt blend a Catalyst Deactivation Factor (CDF) of less than about 0.25, preferably less than 0.15, more preferably less than 0.1, and most preferred less than 0.05. The present invention also comprises a colored monolayer article having the described CDF, such as a film, thermoformed tray, or blow molded container, that has active oxygen scavenging properties. The colorant, after melt blending a base polymer, an oxidizable organic polymer, a transition metal catalyst, does not increase the binding energy of the transition metal catalyst ion by more than 1 eV.
Owner:TREVIRA HLDG GMBH
Antibacterial nanofiber
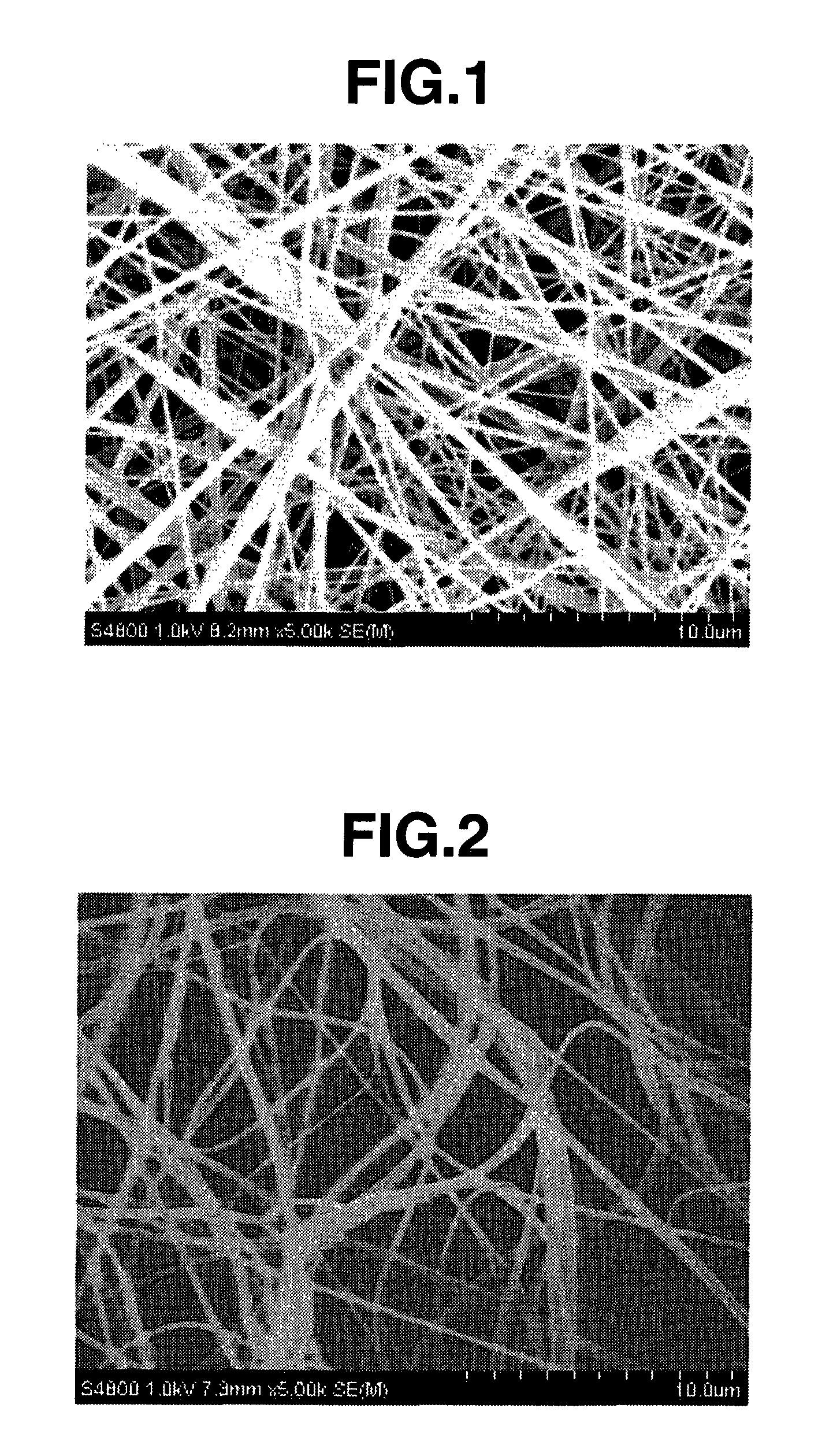
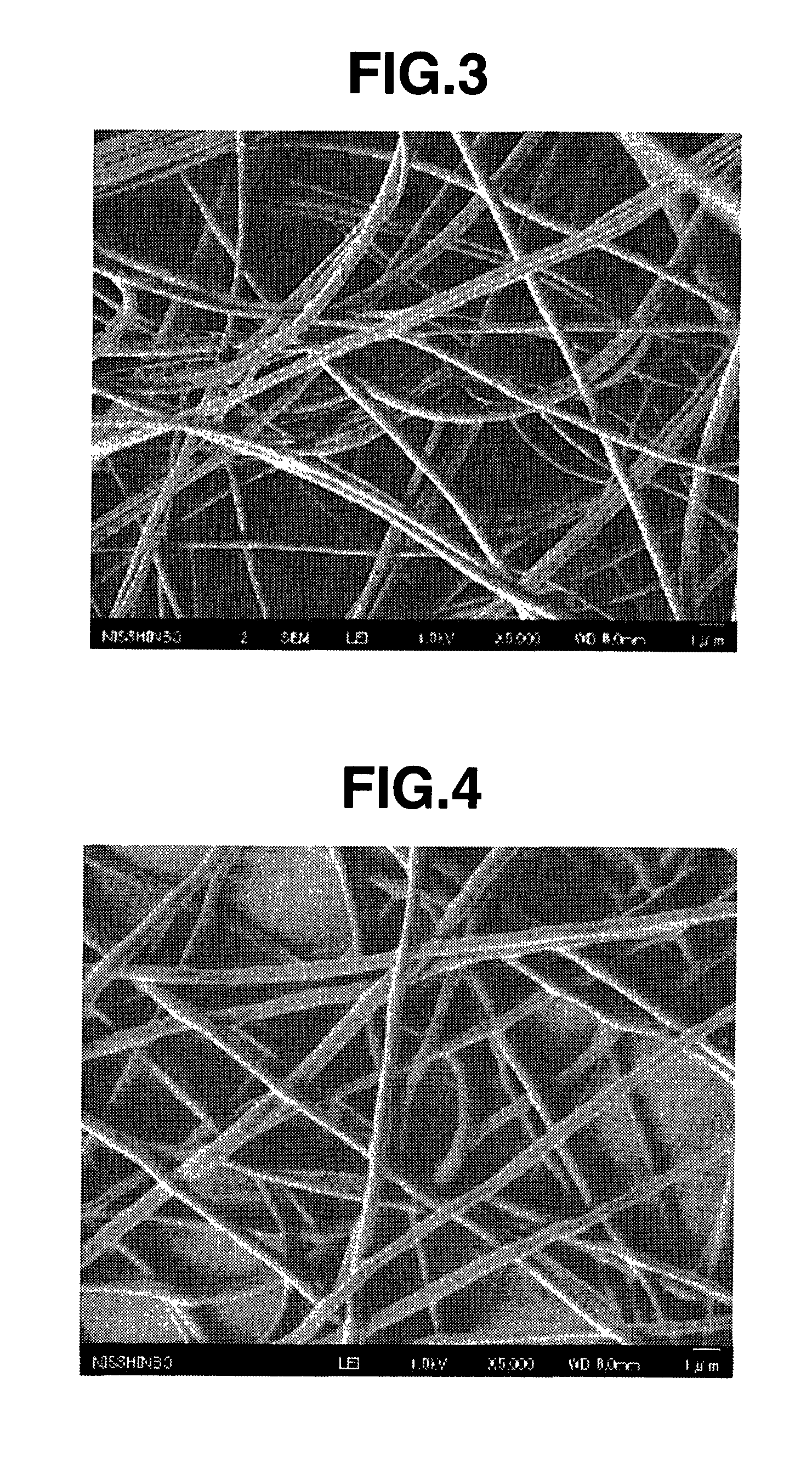
InactiveUS20100120315A1Easy to handleMonocomponent polyurethanes artificial filamentNanotechBinding energyAtomic group
Disclosed is an antibacterial nanofiber which comprises a polymer having an electron-withdrawing group and / or an electron-withdrawing atomic group and has an average fiber diameter of not less than 1 nm and less than 1000 nm, wherein the ratio of the binding energy of the minimum unit of the polymer at 25° C. to the binding energy of the electron-withdrawing group and / or the electron-withdrawing atomic group contained in the minimum unit of the polymer at 25° C. is 0.13 or greater. The nanofiber has an antibacterial activity by itself, and therefore can exhibit an antibacterial activity without the need of adding any antibacterial agent.
Owner:NISSHINBO IND INC
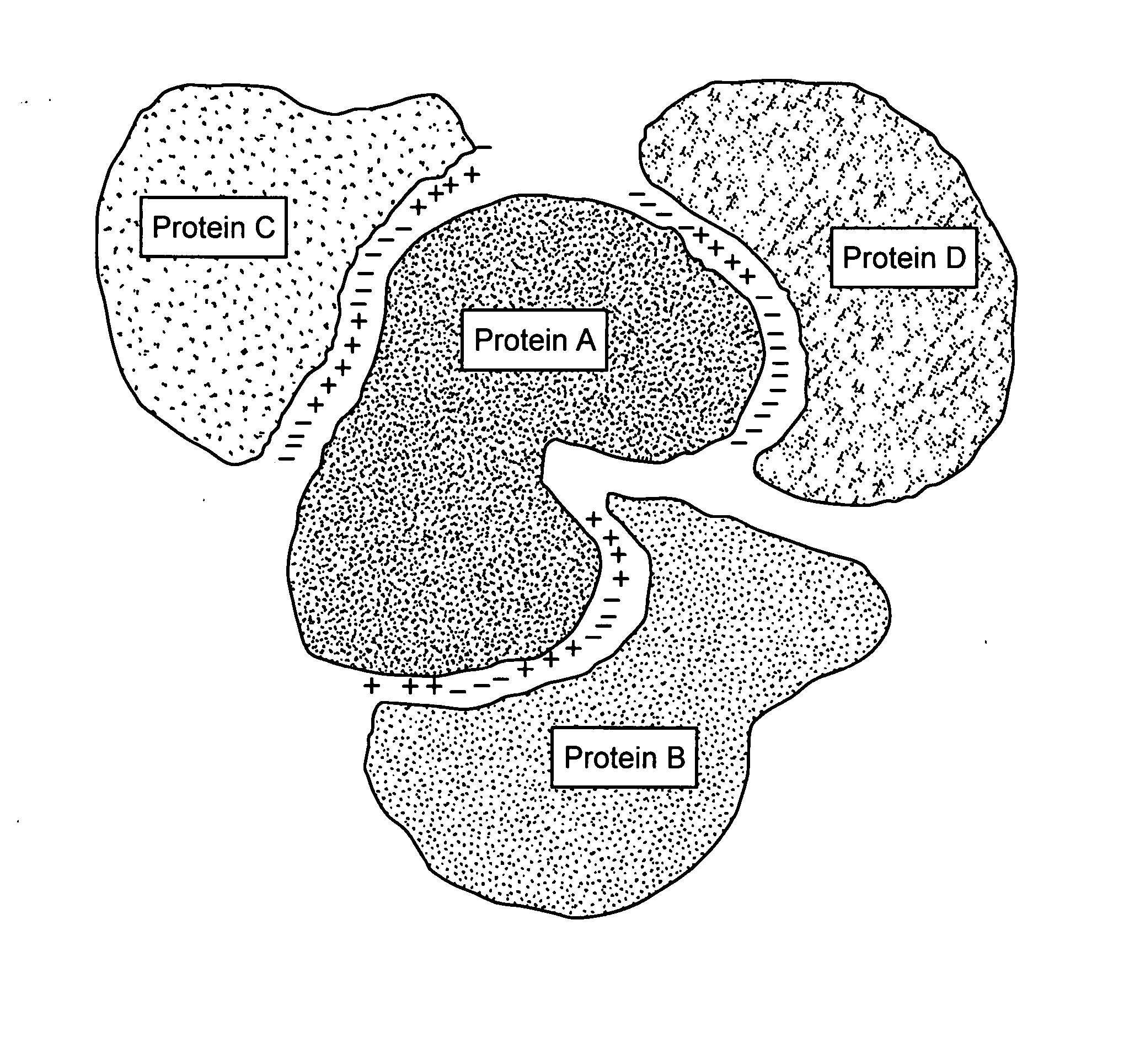
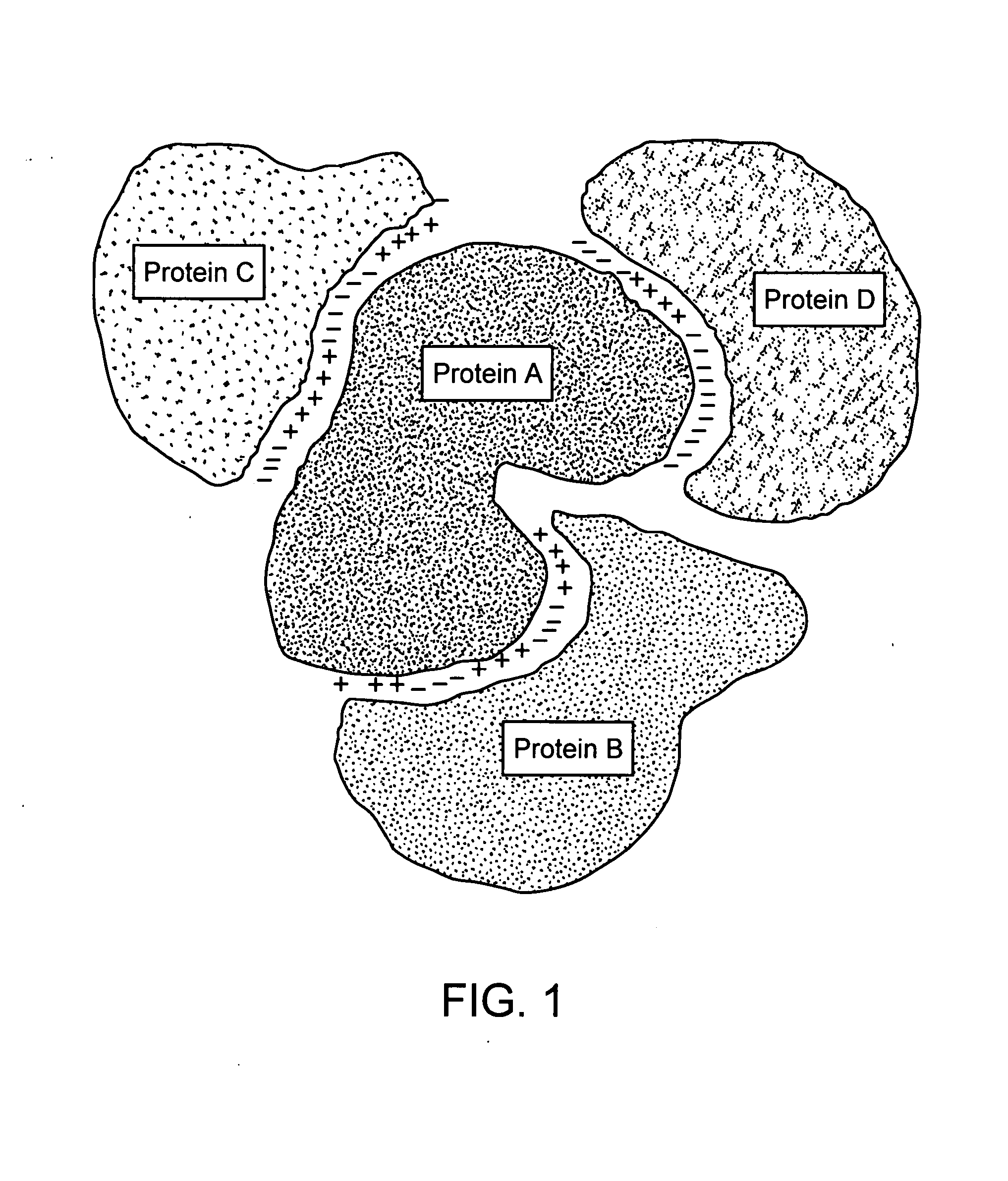
Protein-protein interactions and methods for identifying interacting proteins and the amino acid sequence at the site of interaction
InactiveUS20080009068A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsLibrary screeningBiologyHigh affinity binding
The invention relates to protein-protein interactions and methods for identifying interacting proteins and the amino acid sequence at the site of interaction. Using overlapping hexapeptides that encode for the entire amino acid sequences of the linker domains of human P-glycoprotein gene 1 and 3 (HP-gp1 and HP-gp3), a direct and specific binding between HP-gp1 and 3 linker domains and intracellular proteins was demonstrated. Three different stretches (617EKGIYFKLVTM627, (SEQ ID NO: 1) 658SRSSLIRKRSTRRSVRGSQA677 (SEQ ID NO: 2) and 694PVSFWRIMKLNLT706 (SEQ ID NO: 3) for HP-gp1 and 618LMKKEGVYFKLVNM631 (SEQ ID NO: 4), 648KAATRMAPNGWKSRLFRHSTQKNLKNS674 (SEQ ID NO: 5), and 695PVSFLKVLKLNKT707 (SEQ ID NO: 6) for HP-gp3) in linker domains bound to proteins with apparent molecular masses of ˜80 kDa, 57 kDa and 30 kDa. The binding of the 57 kDa protein was further characterized. Purification and partial N-terminal amino acid sequencing of the 57 kDa protein showed that it encodes the N-terminal amino acids of alpha and beta-tubulins. The method of the present invention was further validated with Annexin. The present invention thus demonstrates a novel concept whereby the interactions between two proteins are mediated by strings of few amino acids with high and repulsive binding energies, enabling the identification of high affinity binding sites between any interacting proteins.
Owner:GEORGES ELIAS
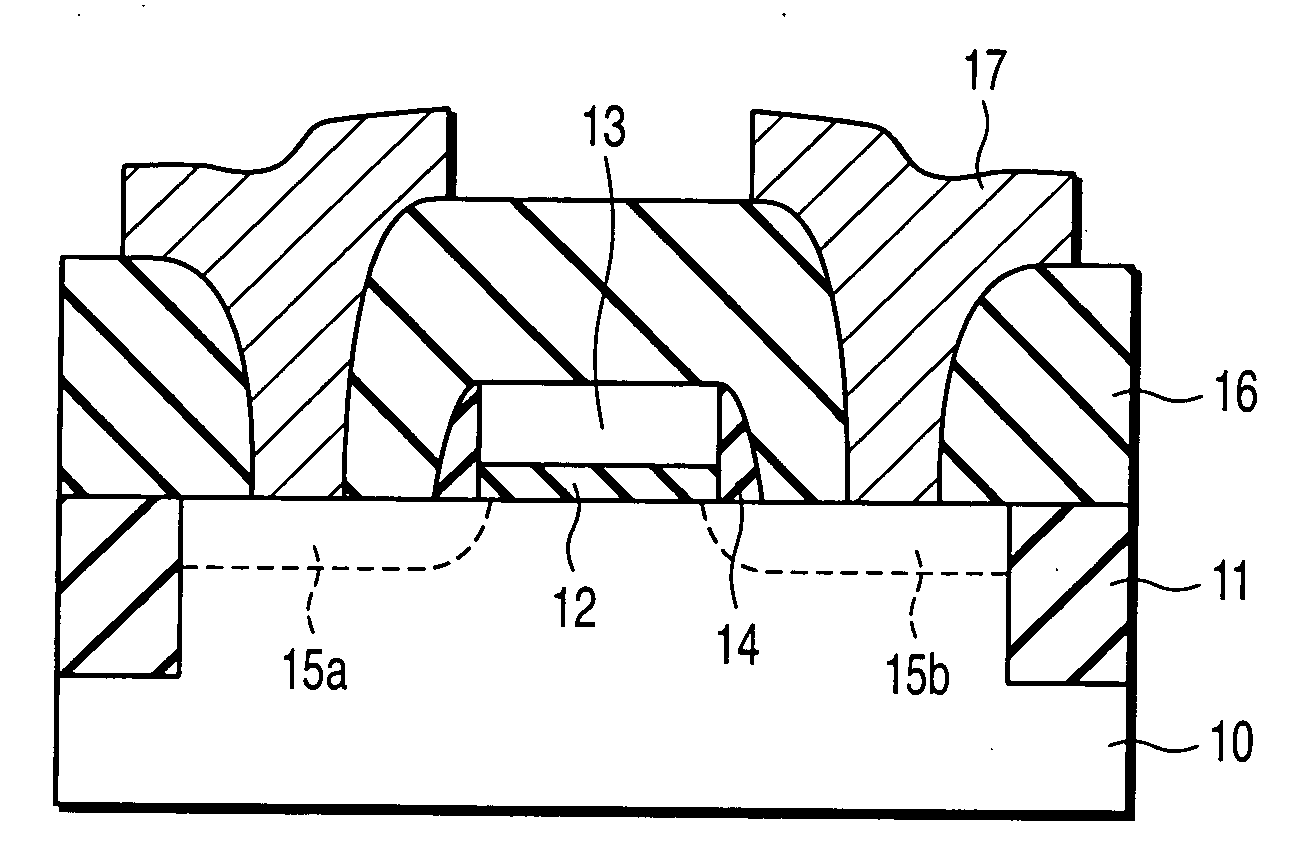
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
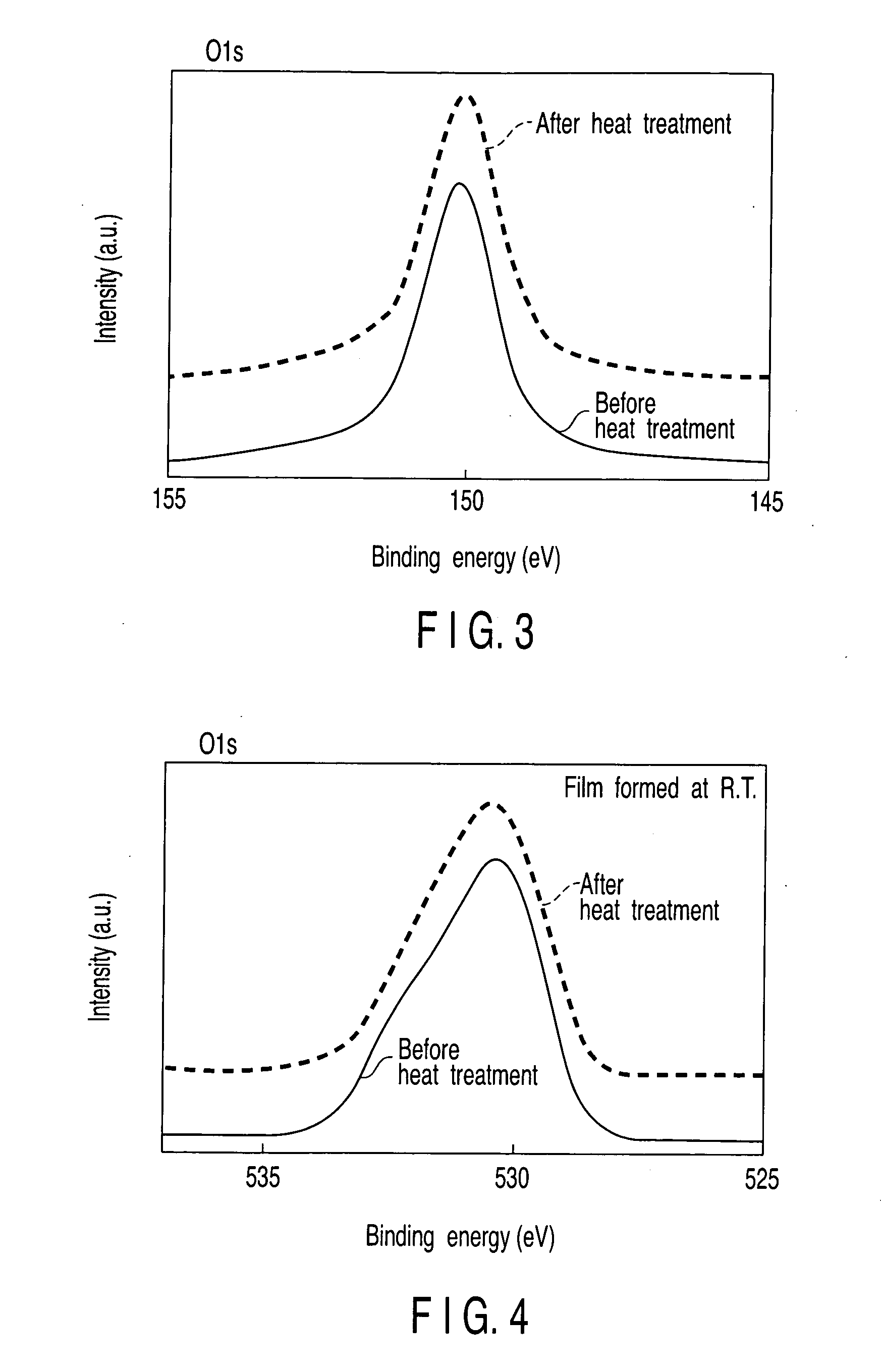
A semiconductor device includes a Si substrate, a gate insulating film formed on the Si substrate, the gate insulating film being formed of an oxide film containing at least one selected from the group of Zr, Hf, Ti and a lanthanoid series metal, and having a single local minimal value on a high binding energy side of an inflection point in first differentiation of an O1s photoelectron spectrum, and a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Anode active material, method of preparing the same, and anode and lithium battery containing the material
ActiveUS7833662B2Increase capacityEasy to chargeBio-organic fraction processingSilicaBinding energyFull width at half maximum
Silicon oxide based composite anode active materials including amorphous silicon oxides are provided. In one embodiment, the amorphous silicon oxide is represented by SiOx (where 0<x<2), has a binding energy of about 103 to about 106 eV, a silicon peak with a full width at half maximum (FWHM) ranging from about 1.6 to about 2.4 as measured by X-ray photoelectron spectrometry, and an atomic percentage of silicon greater than or equal to about 10 as calculated from an area of the silicon peak. The anode active material is a composite anode active material obtained by sintering hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ). Anodes and lithium batteries including the anode active material exhibit improved charge and discharge characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Metal Catalyst and Method for Production Thereof
ActiveUS20070244003A1High catalytic activityHigh catalytic efficiencyCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationOxidation stateX-ray
The present invention relates to a metal catalyst containing fine metal particles, characterized in that the fine metal particles have a particle diameter of 3 nm or less and also have a proportion of metallic bond state of 40% or more, which is ascribed by subjecting to waveform separation of a binding energy peak peculiar to the metal as measured by using an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer. The fine metal particles are preferably fine platinum particles. The fine metal particles are preferably supported on the surface of carrier particles by reducing ions of metal to be deposited through the action of a reducing agent in a reaction system of a liquid phase containing the carrier particles dispersed therein, thereby to deposit the metal on the surface of carrier particles in the form of fine particles. The proportion of metallic bond state of the fine metal particles is adjusted within the above range by reducing after deposition thereby to decrease the oxidation state.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Prepreg and carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material
ActiveCN104508022AImprove adhesionLittle change over timeCarbon fibresThin material handlingBinding energyCarbon fiber reinforced composite
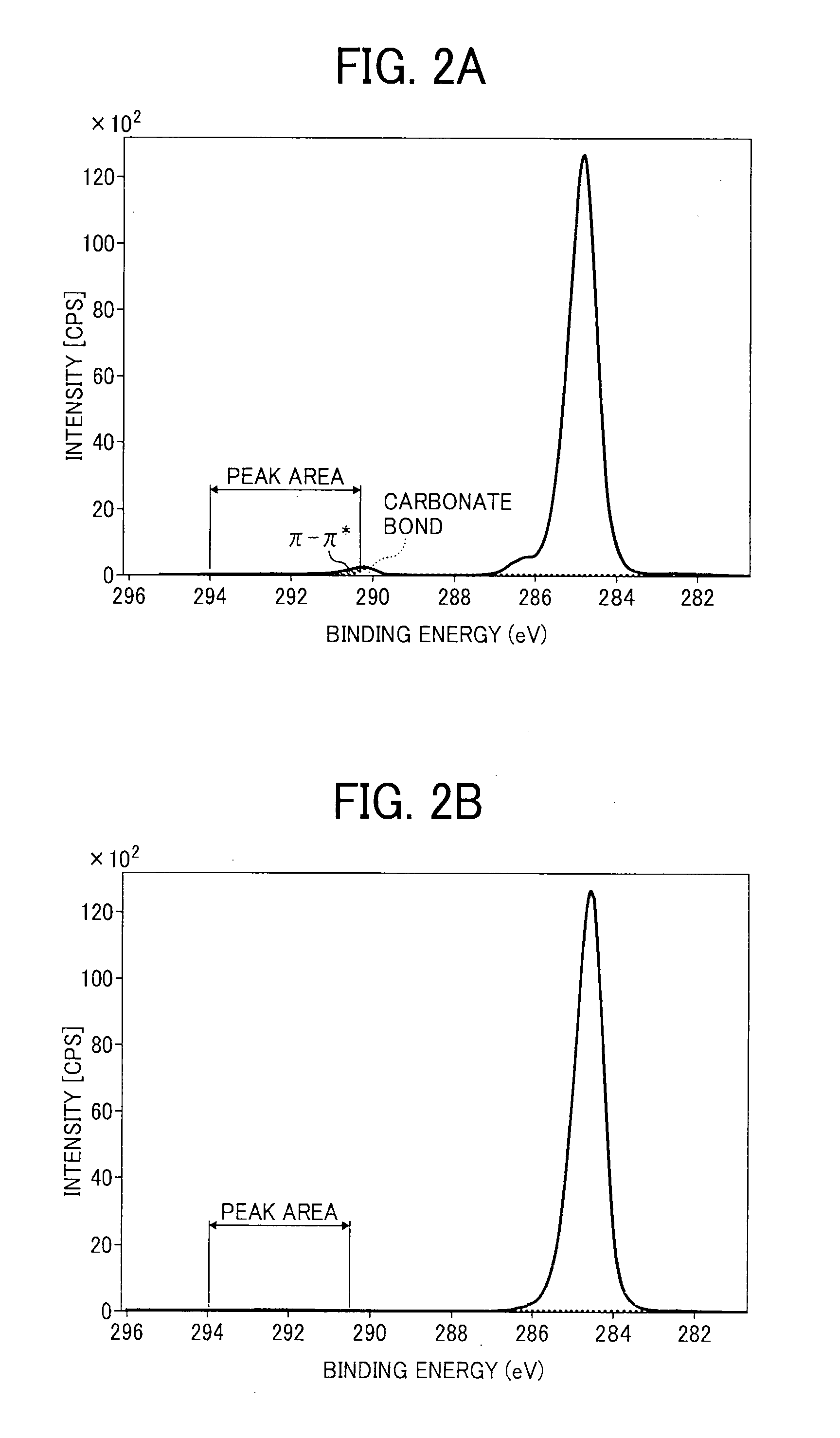
Provided are a prepreg that is excellent in adhesiveness between carbon fibers and a matrix resin and long-term storage stability and achieves both excellent impact resistance and electrical conductivity in the thickness direction and a carbon fiber reinforced composite material. The present invention provides a prepreg formed by impregnating sizing agent-coated carbon fibers coated with a sizing agent containing an aliphatic epoxy compound (A) and an aromatic epoxy compound (B1) with a thermosetting resin composition containing thermoplastic resin particles (F) and conductive particles (G) in a mass ratio of 1:1 to 1,000 or conductive particles (H) in which a thermoplastic resin is covered with a conductive substance. An (a) / (b) ratio is within a predetermined range where (a) is a height of a component at a binding energy assigned to CHx, C-C, and C=C and (b) is a height of a component at a binding energy assigned to C-O in a C 1s core spectrum of surfaces of the sizing agent-coated carbon fibers analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Systems and methods for cryogenic refrigeration
InactiveUS20140137571A1Increase surface areaImprove thermal conductivitySolidificationLiquefactionBinding energyDilution refrigerator
Systems and methods for improving the performance of dilution refrigeration systems are described. Filters and traps employed in the helium circuit of a dilution refrigerator may be modified to improve performance. Some traps may be designed to harness cryocondensation as opposed to cryoadsorption. A cryocondensation trap employs a cryocondensation surface having a high thermal conductivity and a high specific heat with a binding energy that preferably matches at least one contaminant but does not match helium. Multiple traps may be coupled in series in the helium circuit, with each trap designed to trap a specific contaminant or set of contaminants. Both cryocondensation and cryoadsorption may be exploited among multiple traps.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
SiOx BARRIER FOR PHARMACEUTICAL PACKAGE AND COATING PROCESS
InactiveUS20150297800A1Reduce decreaseIncrease calculated shelf lifeWrappersMedical devicesBinding energyImage resolution
A vessel including a thermoplastic wall enclosing a lumen is disclosed. The wall supports an SiOx composite barrier coating or layer, for which x is from 1.8 to 2.4, between the wall and the lumen. High Resolution X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) shows the presence of an interface between the composite barrier coating or layer and the wall or substrate. In one aspect, the interface has at least 1 mol.% O3—Si—C covalent bonding, as a proportion of the O3—Si—C covalent bonding plus SiO4 bonding. In another aspect, the interface has an Si 2p chemical shift to lower binding energy (eV), compared to the binding energy of SiO4 bonding. The result is a tightly adherent composite barrier coating or layer having a high degree of adhesion to the substrate under practical use conditions. Methods of applying the composite barrier coating or layer are also disclosed.
Owner:SI02 MEDICAL PRODS
Colored oxygen scavenging polymers
The present invention relates to a melt blend of a base polymer, an oxidizable organic polymer, a transition metal salt catalyst and a colorant that does not completely deactivate the catalyzed oxidation. A preferred colorant, yields in an article made from the polymer melt blend a Catalyst Deactivation Factor (CDF) of less than about 0.25, preferably less than 0.15, more preferably less than 0.1, and most preferred less than 0.05. The present invention also comprises a colored monolayer article having the described CDF, such as a film, thermoformed tray, or blow molded container, that has active oxygen scavenging properties. The colorant, after melt blending a base polymer, an oxidizable organic polymer, a transition metal catalyst, does not increase the binding energy of the transition metal catalyst ion by more than 1 eV.
Owner:TREVIRA HLDG GMBH
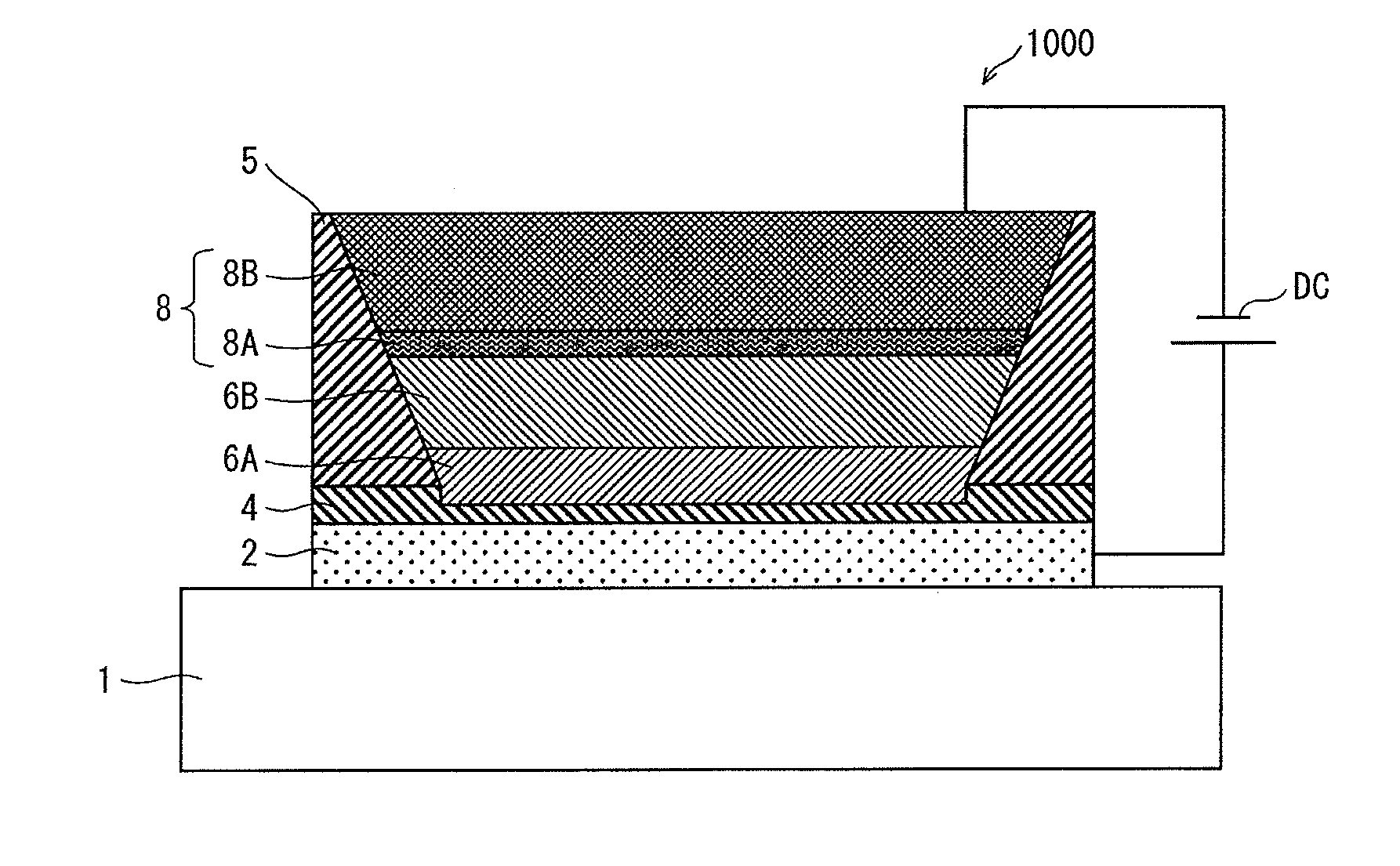
Double layer transfer method
ActiveUS20140295642A1High bond energySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBinding energyEngineering
A method of transferring a layer including: a) providing a layer joined to an initial substrate with a binding energy E0; b) bonding a front face of the layer on an intermediate substrate according to an intermediate bonding energy Ei; c) detaching the initial substrate from the layer; e) bonding a rear face onto a final substrate according to a final bonding energy Ef; and f) debonding the intermediate substrate from the layer to transfer the layer onto the final substrate; step b) comprising a step of forming siloxane bonds Si—O—Si, step c) being carried out in a first anhydrous atmosphere and step f) being carried out in a second wet atmosphere such that the intermediate bonding energy Ei takes a first value Ei1 in step c) and a second value Ei2 in step f), with Ei1>E0 and Ei2<Ef.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Prepreg and carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material
ActiveCN104487495AImprove adhesionGood strength propertiesCarbon fibresThin material handlingBinding energyCarbon fiber reinforced composite
Provided are a prepreg and a carbon-fiber-reinforced composite material having excellent long-term storage stability and adhesiveness between a carbon fiber and a matrix resin. The present invention is a prepreg made by impregnating a sizing-agent-coated carbon fiber, which is coated with a sizing agent including an aliphatic epoxy compound (A) and an aromatic epoxy compound (B1), with a thermosetting resin composition including a thermosetting resin (D), a latent curing agent (E), and, if necessary, an additive (F) other than the thermosetting resin (D) and the latent curing agent (E), the prepreg being characterized in that the ratio ((a) / (b)) between (a) the height of a binding energy component attributed to CHx, C-C, and C=C and (b) the height of a binding energy component attributed to C-O in a C1s core spectrum obtained by measuring the surface of said sizing-agent-coated carbon fiber by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy is within a predetermined range.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
MEMS passivation with phosphonate surfactants
ActiveUS20050147750A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBinding energyEnd-group
Phosphonate surfactants are employed to passivate the surfaces of MEMS devices, such as digital micromirror devices. The surfactants are adsorbed from vapor or solution to form self-assembled monolayers at the device surface. The higher binding energy of the phosphonate end groups (as compared to carboxylate surfactants) improves the thermal stability of the resulting layer.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Positive electrode active material, preparation method thereof, and lithium battery including the same
A positive electrode active material including: a lithium complex oxide represented by Formula 1; and a carbon coating layer disposed on the lithium complex oxide, wherein, in a C1s XPS spectrum of the positive electrode active material, a peak intensity of a first peak at a binding energy from about 288 eV to about 293 eV is greater than a peak intensity of a second peak at a binding energy from about 283 eV to about 287 eV, and in an O1s X-ray photoelectron spectrum of the positive electrode active material, a peak intensity of a third peak at a binding energy from about 530.5 eV to about 535 eV is greater than a peak intensity of a fourth peak at a binding energy from about 527.5 electron volts to about 530 electron volts,LiaMbM′cM″dOe. Formula 1
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical method for additive manufacturing of complex metallic shapes using a gaseous medium
InactiveUS20130344258A1Additive manufacturing apparatusSolid state diffusion coatingThermal energyIodide
The present invention is a method for additive manufacturing in which a metal feedstock is converted to a carbonyl compound (or other gaseous media) and then optical heat patterns are used to direct the deposition of the contained metal into an arbitrary 3-D structure.The optical methods used to guide the metal deposit may include one or more laser beams acting independently or in concert, and / or other optical technologies to apply a pattern of thermal energy, including LCD, LED, LCoS, DLP, or even CRT projection technologies.The metals which may be deposited are limited to those which have compounds which are gaseous at moderate temperatures and which decompose (to a gas and the metal) upon the application of heat or specific chemical binding energies via optical means. Such compounds include (but are not limited to) nickel tetracarbonyl, iron pentacarbonyl, cobalt carbonyl, titanium iodide, and platinum chloro-carbonyl.
Owner:DEEP SPACE IND
Alloy tool steel in multi-type super-fine carbonates
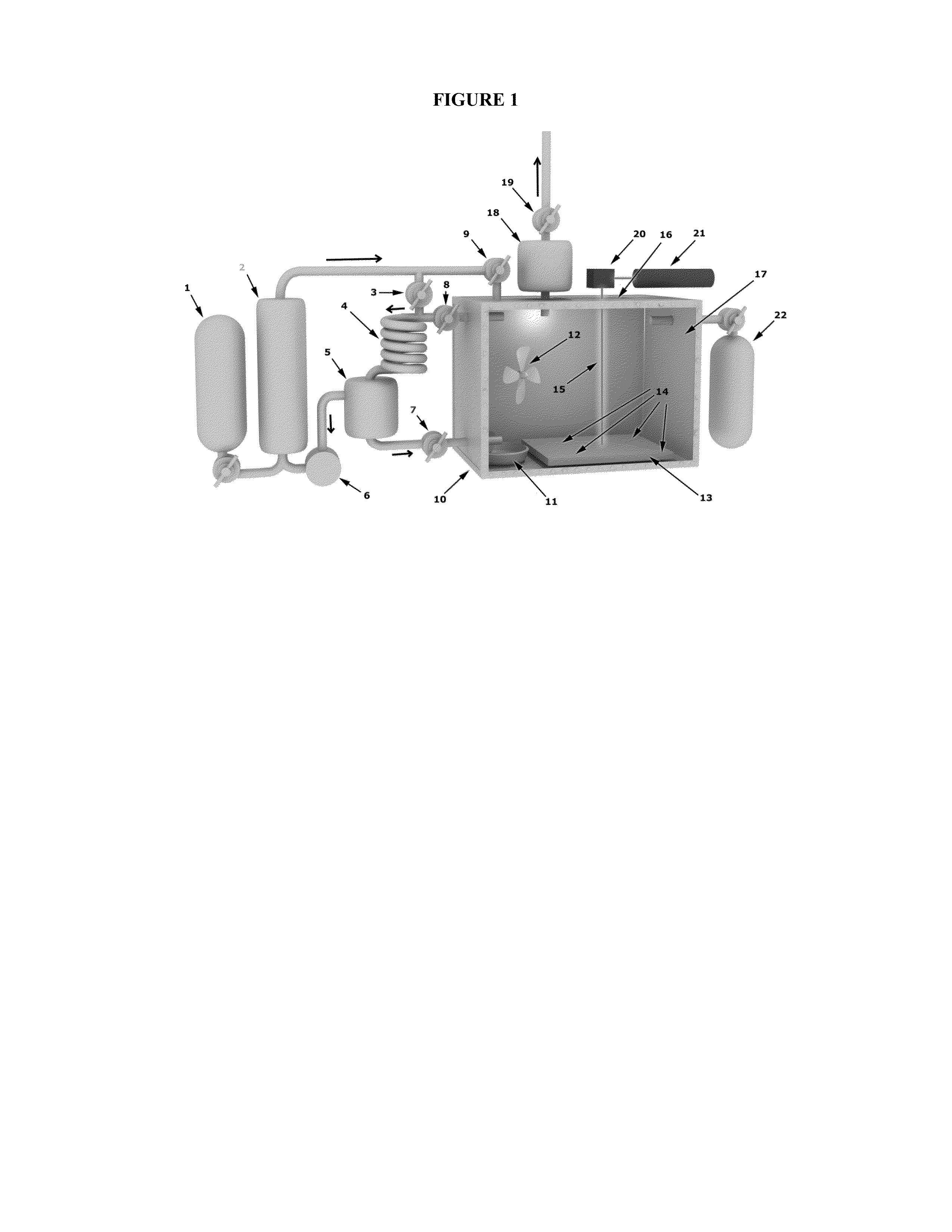
InactiveCN101070580AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceHeat treatment process controlHigh carbonQuenching
This invention relates to alloying and heat treatment craft of tool die steel, it belongs to one kind of DM8B-2 multi-types superfine carbide high carbon alloy tool steel. Using alloy design method which voluntarily developing, do the phase equilibrium thermo dynamics, electronic / atom level binding energy computation,quenching and the tempered hardness computation as well as to synthesis appraisal its toughness and sintensity. Its ingredient characteristic is appropriate C quantity and Cr / (W+Mo) ratio, reasonable Si, Mn as well as few Ni; Its microstructure characteristic has the superfine carbide, annealing carbide size is between 0.05-0.8mum, when quenching, the undissolved carbide size should not to be smaller than 0.5mum. after quenching to add 200degree C-300degree C, tempering may enable the tempering hardness to achieve 61-64HRC by using carbide precipitation hardening. It has high yield strength and the impact toughness.In the thin edge cutting tool, cutting die and weightily attacking die areas, it has widespread application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Platinum-containing catalyst, process for producing the platinum-containing catalyst, electrode, and electrochemical device
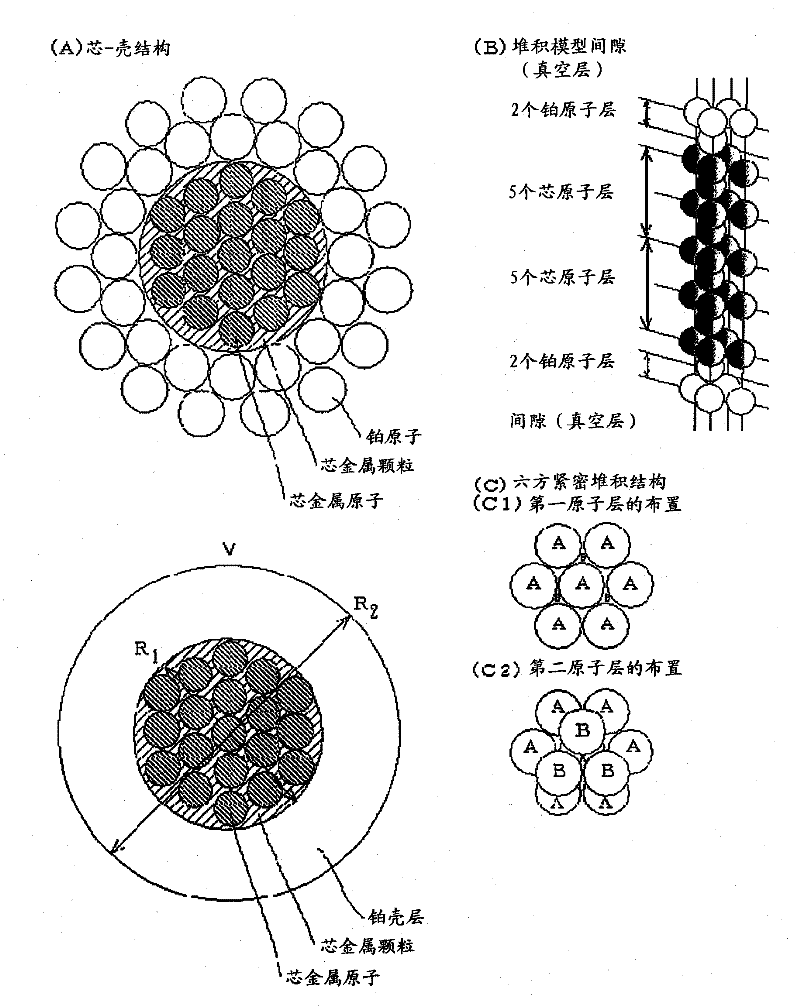
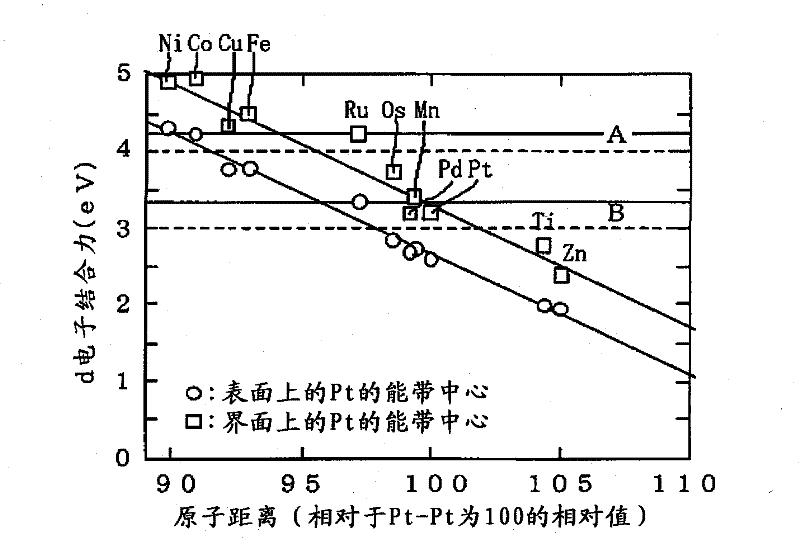
InactiveCN102196863AHigh output maintenanceIncreased durabilityCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationBinding energyPower flow
Disclosed is a core-shell-type platinum-containing catalyst that can reduce the amount of platinum used and has high catalytic activity and stability. Also disclosed are a process for producing the core-shell-type platinum-containing catalyst, an electrode, and an electrochemical device. The core-shell-type platinum-containing catalyst comprises particles each comprising a core particle (average particle diameter: R1) formed of a non-platinum element and a platinum shell layer (average thickness: ts) and satisfies the following relationships: 1.4 nm = R1 = 3.5 nm; and 0.25 nm = ts = 0.9 nm. The core particle contains an element satisfying Eout = 3.0 eV wherein Eout represents the average bound energy, based on Fermi level, of 5d orbit electrons of platinum present on the outermost surface of the platinum shell. A fuel cell comprising a platinum-containing catalyst as an anode catalyst, the platinum-containing catalyst comprising a Ru particle as a core particle, has an output density of not less than 70 mW / cm2 at a current density of 300 mA / cm2 and an output retention of not less than about 90%.
Owner:SONY CORP
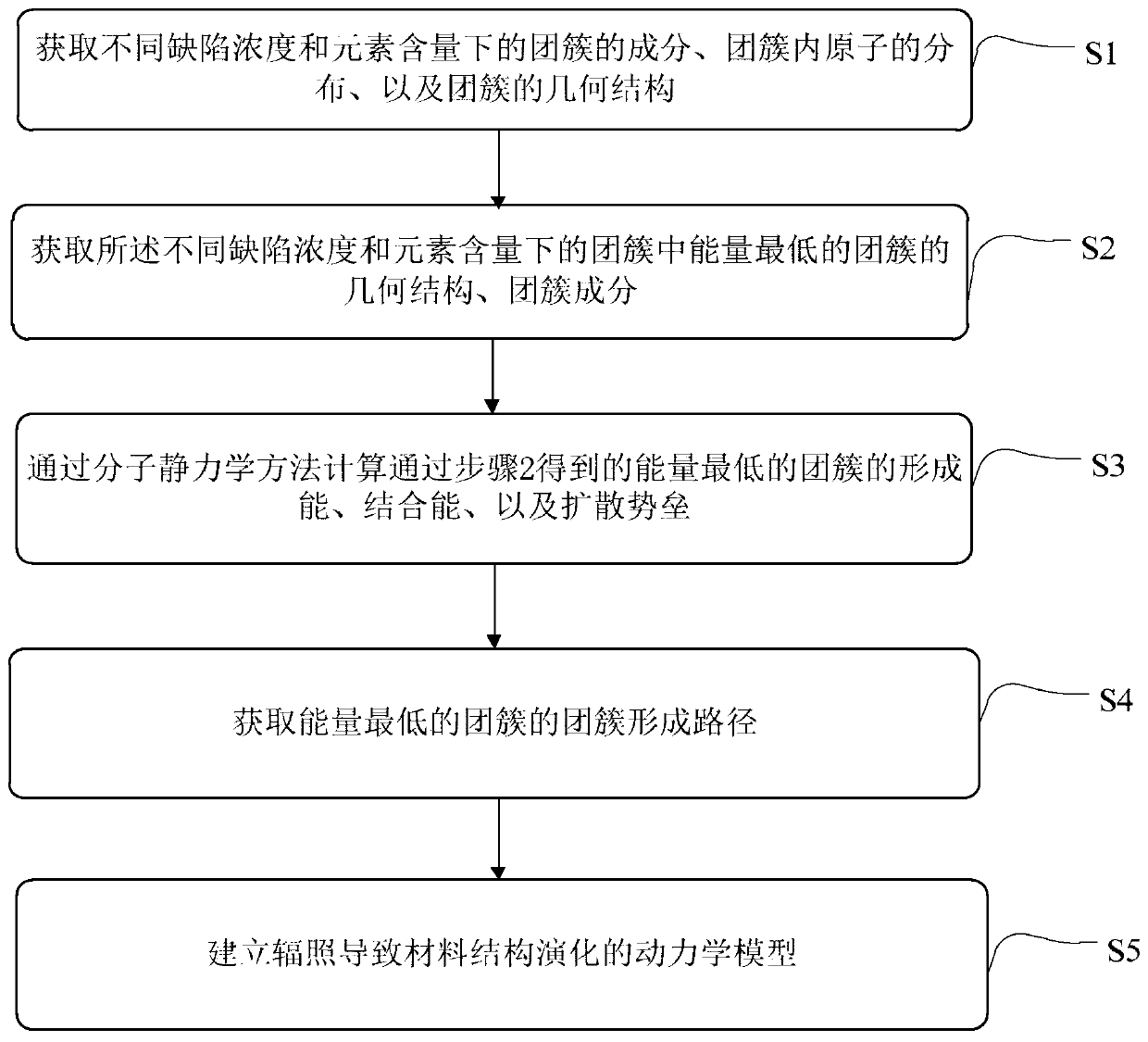
Method and system for simulating material structure evolution caused by irradiation
ActiveCN109727647AComputational theoretical chemistryChemical machine learningBinding energyMolecular statics
The invention provides a method and a system for simulating material structure evolution caused by irradiation. The method comprises the steps of acquiring cluster components, in-cluster atom distribution and cluster geometric structure on the condition of different defect concentrations and different element contents; acquiring the geometric structure and the cluster components of the cluster with lowest energy in the clusters on the condition of different defect concentrations and different element contents; calculating formation energy, binding energy and diffusion barrier of the cluster with the lowest energy through a modular statistics method; obtaining a cluster forming path of the cluster with lowest energy; and establishing a dynamics model of the material structure evolution caused by irradiation.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Process cartridge and image forming apparatus using same
InactiveUS20080253801A1Protective coatingElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeBinding energyElectrical conductor
A process cartridge includes a protective agent, a photoconductor, a charging unit, a development unit, a cleaning unit, and an application unit. The protective agent includes paraffin as main component. The photoconductor has a surface including polycarbonate applied with the protective agent. The development unit develops a latent image on the photoconductor. The cleaning unit removes materials remaining on the photoconductor. The application unit applies the protective agent to the surface of photoconductor. One peak in a given binding energy range is used to determine a coating condition of the photoconductor coated by the agent. The coating condition is determined by comparing an area ratio A0 before applying the agent and an area ratio A after applying the agent, each of which is an area ratio with respect to a total area of C1s spectrum of the photoconductor. The coating ratio of the photoconductor is computed by (A0−A) / A0×100.
Owner:RICOH KK
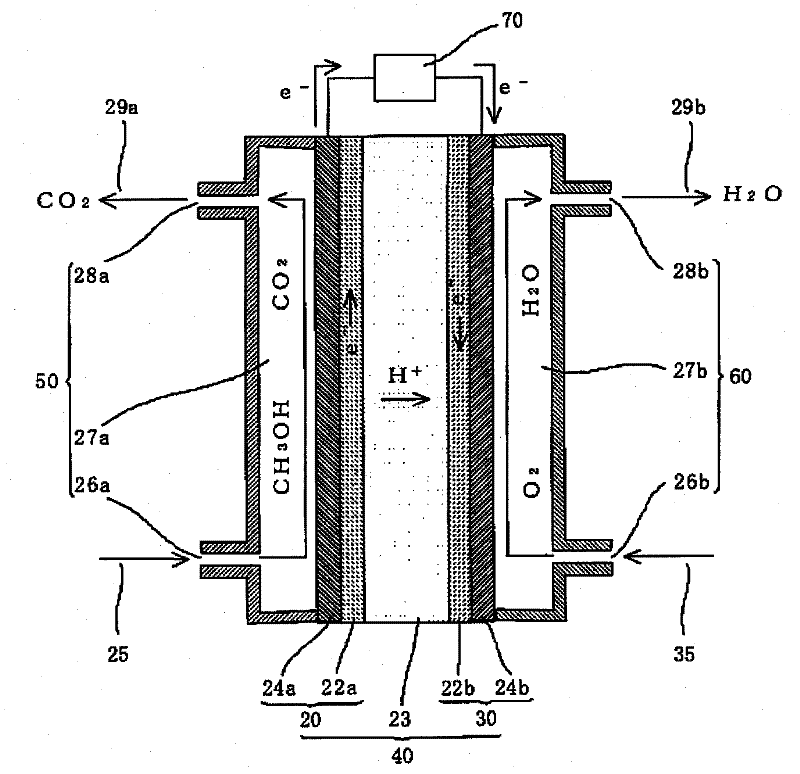
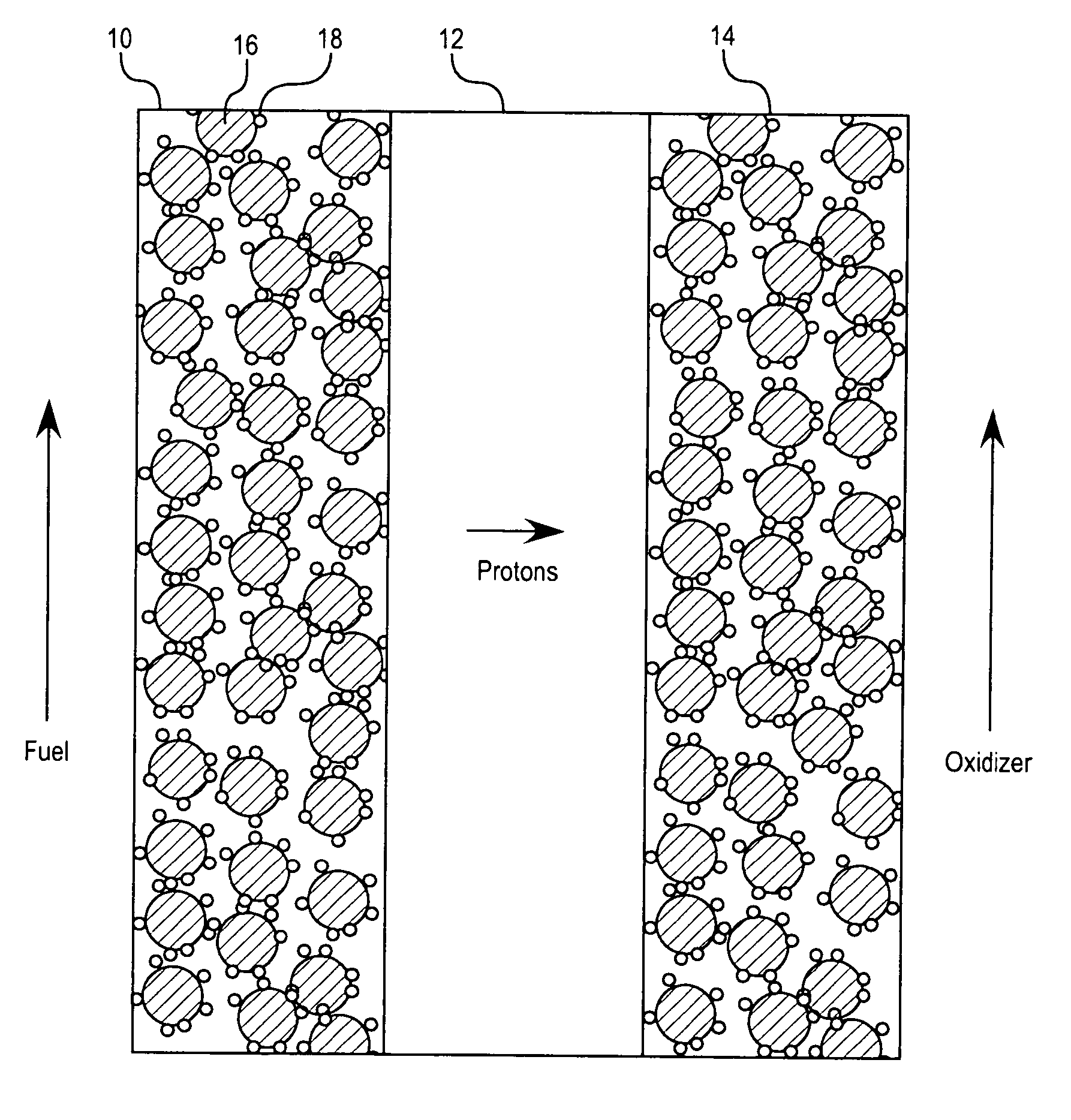
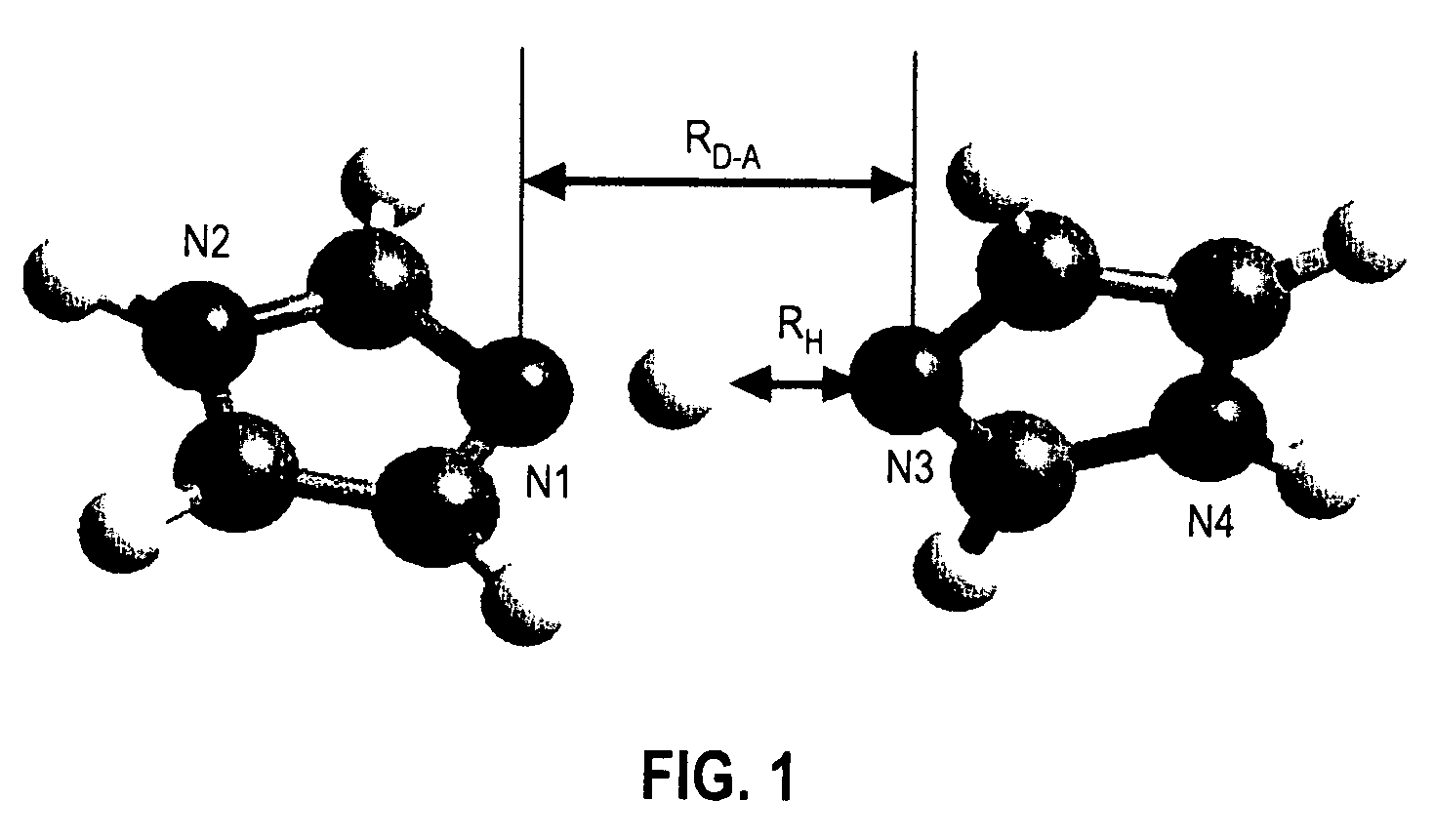
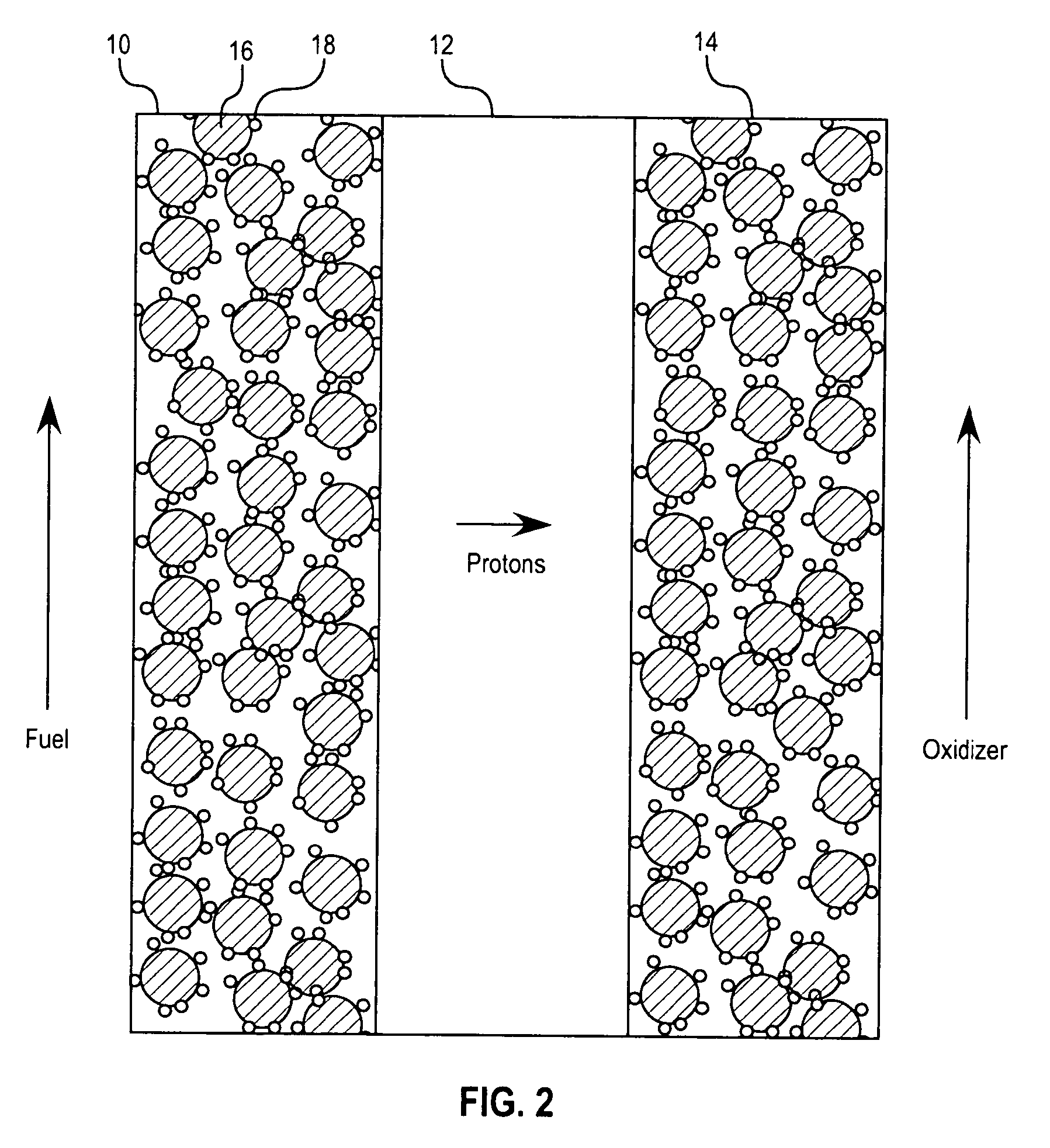
Substituted nitrogen heterocycles as proton carriers for water-free proton exchange membranes for fuel cells
A fuel cell is provided comprising an anode, a cathode, a catalyst, and a polymer electrolyte membrane comprising a heterocyclic compound with a nitrogen heteroatom and at least one electron-withdrawing substituent. The fuel cell operates at temperatures above about 100° C., preferably above about 150° C. The heterocyclic compound is preferably a substituted imidazole or benzoimidazole, most preferably a fluorinated imidazole. The heterocyclic compound is preferably liquid at the fuel cell operating temperature. The catalyst preferably contains platinum. The polymer electrolyte membrane preferably has a conductivity of 10−2 S / cm2 or higher. For efficient fuel cell operation the catalyst should not be poisoned to an undue degree by the heterocyclic compound, and so the binding energy of the heterocyclic compound to the catalyst should be low.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Enhanced optical gain and lasing in indirect gap semiconductor thin films and nanostructures
InactiveUS9166363B2Optical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionBinding energyElectron hole
Structures and methodologies to obtain lasing in indirect gap semiconductors such as Ge and Si are provided and involves excitonic transitions in the active layer comprising of at least one indirect gap layer. Excitonic density is increased at a given injection current level by increasing their binding energy by the use of quantum wells, wires, and dots with and without strain. Excitons are formed by holes and electrons in two different layers that are either adjacent or separated by a thin barrier layer, where at least one layer confining electrons and holes is comprised of indirect gap semiconductor such as Si and Ge, resulting in high optical gain and lasing using optical and electrical injection pumping.
Owner:JAIN FAQUIR C
Organic electroluminescence element
InactiveUS9029843B2Excellent characteristicsConvenient lightingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingValence bandBinding energy
Owner:JOLED INC
Catalytic hydrodechlorination Pd-M/NOMC catalyst and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN108283933AOrdered pore arrangementMore active sitesPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic chemistrySynthesis methodsNitrogen doped
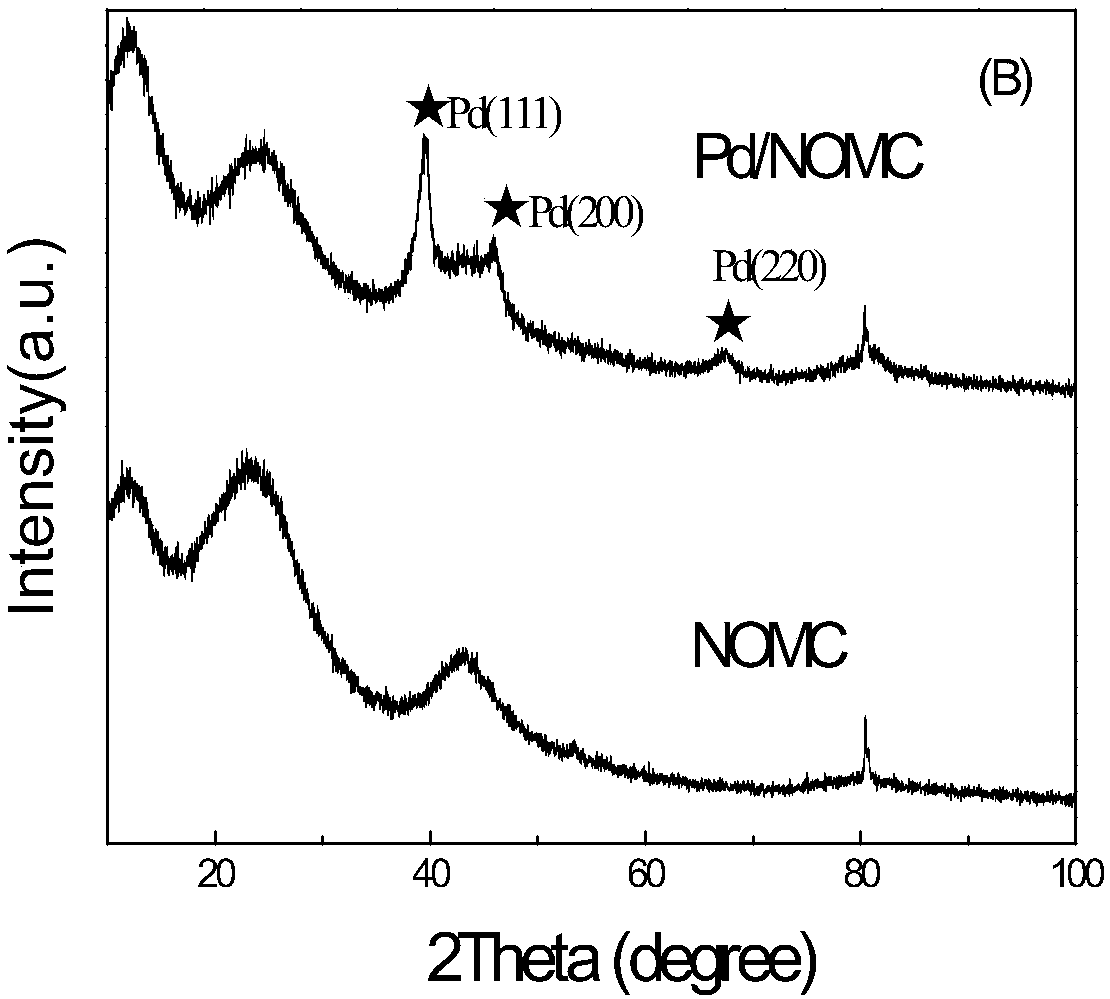
The invention relates to a catalytic hydrodechlorination Pd-M / NOMC catalyst and a preparing method and application thereof. According to the catalyst, with synthetic-nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon being a carrier, the active component is Pd-M. A one-step synthesis method is adopted to prepare a nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon catalyst, an impregnation method can be adopted to synthesize the Pd-M / NOMC catalyst, and hydrogen, formic acid-sodium formate, methyl alcohol and the like are adopted as hydrogen sources for hydrodechlorination of chlorophenol. Nitrogen atoms are doped on a mesoporouscarbon material, the reactive site of catalysis is increased, and the activity of the catalyst is improved. The one-step method for synthesis is adopted, the nitrogen sources can be controlled from the source, the content of added nitrogen is easier to control, and the formed mesoporous structure is not easily damaged; by introducing nitrogen, the lowest binding energy position of palladium is migrated, electrons in nitrogen are migrated to the surface of palladium atoms, which improves the stability between palladium and the material.
Owner:TAIZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com