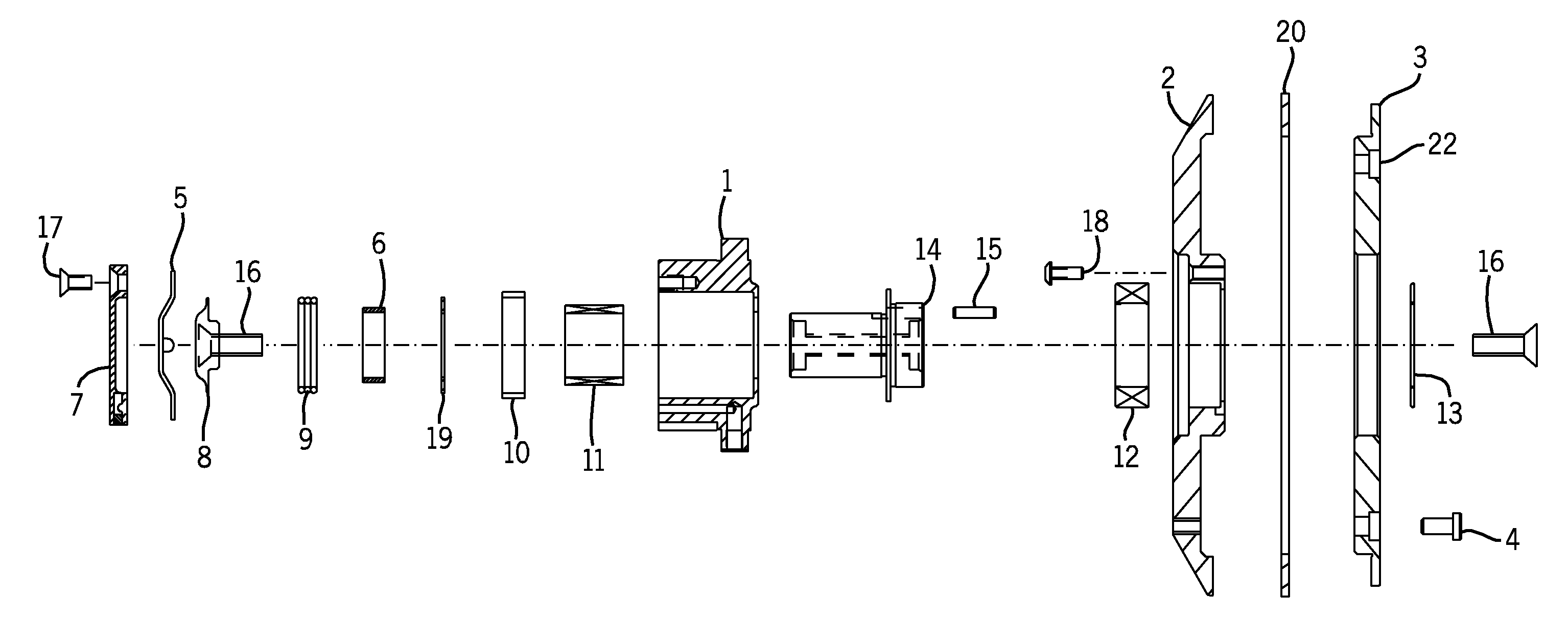
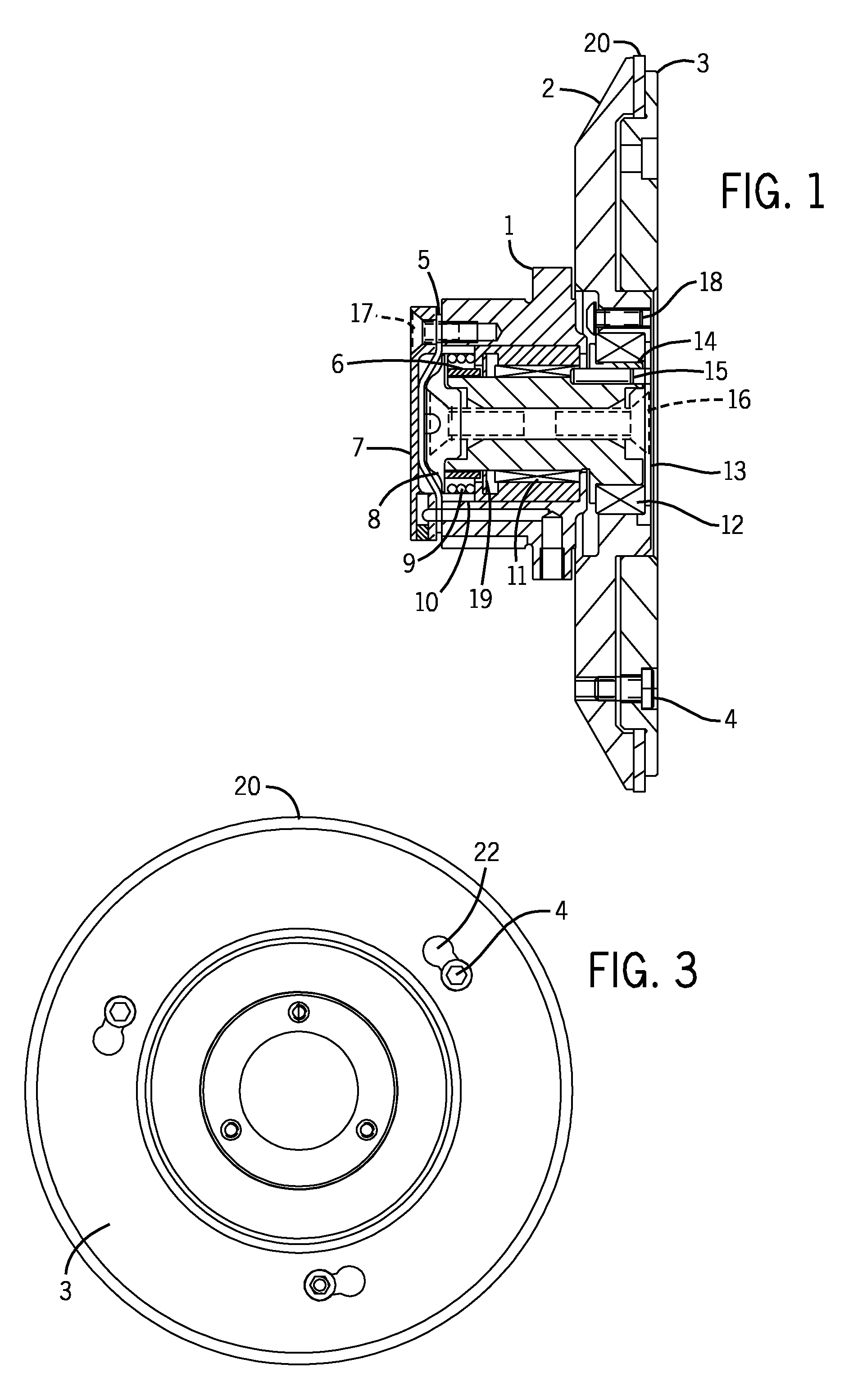
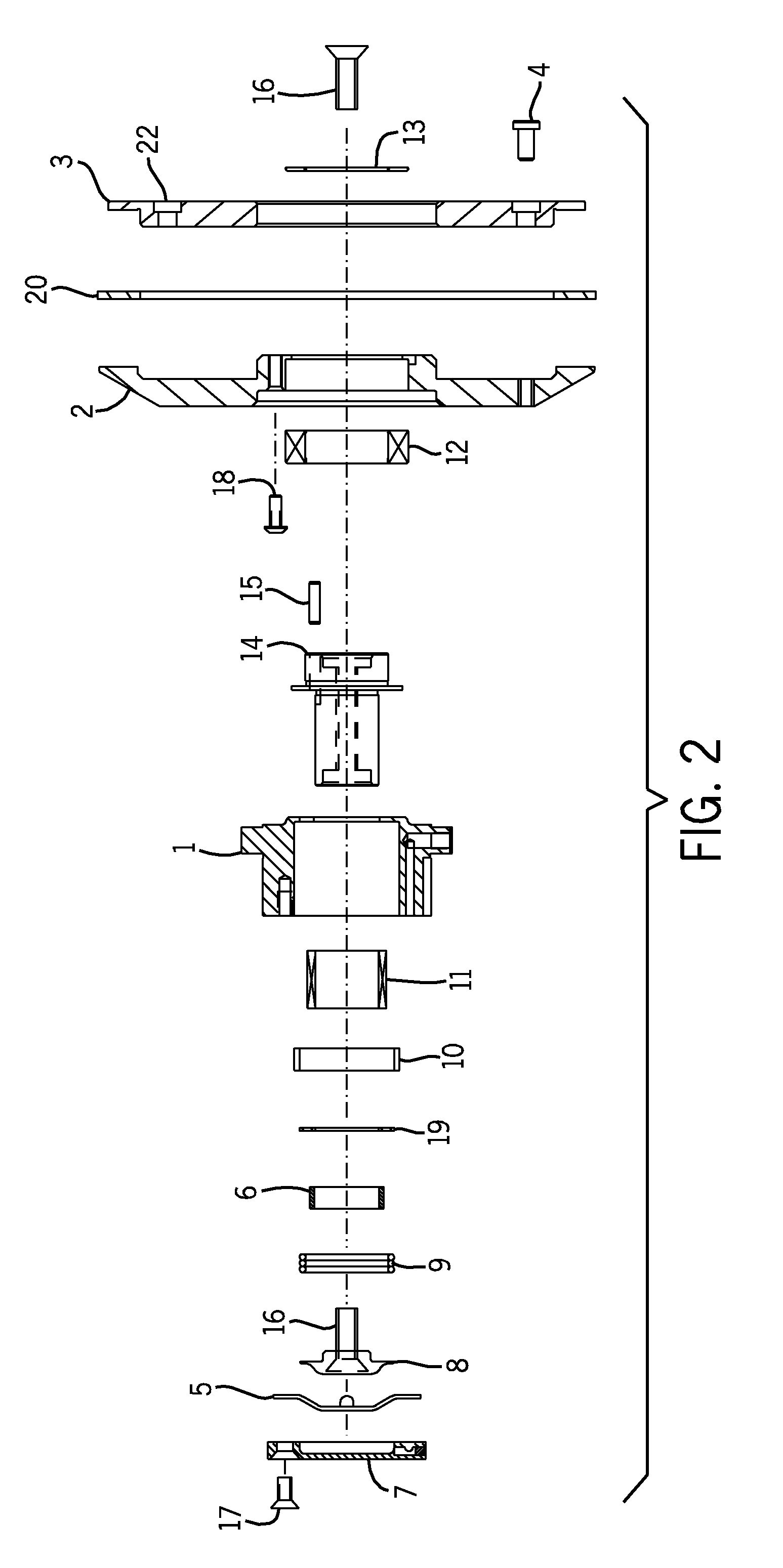
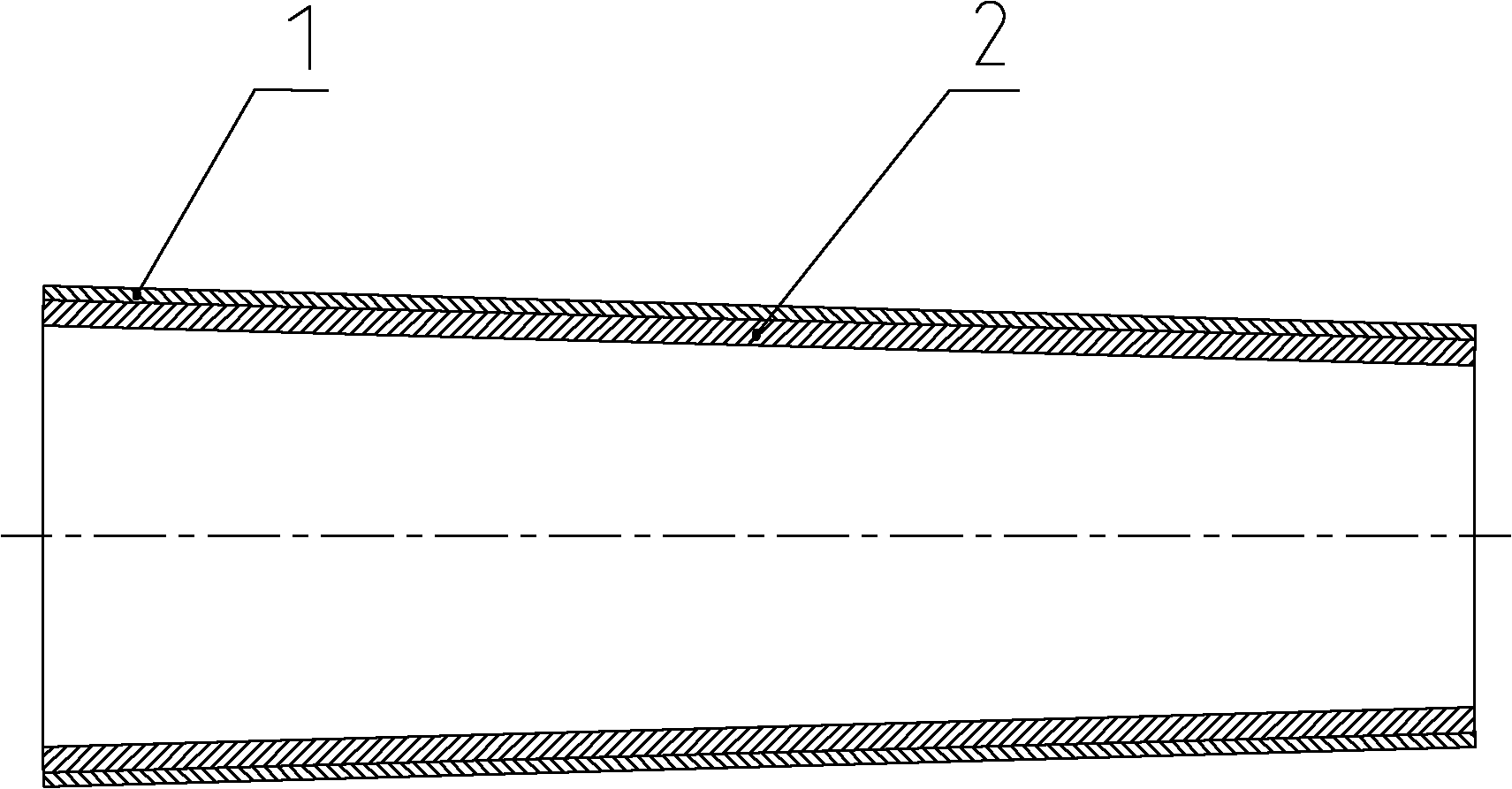
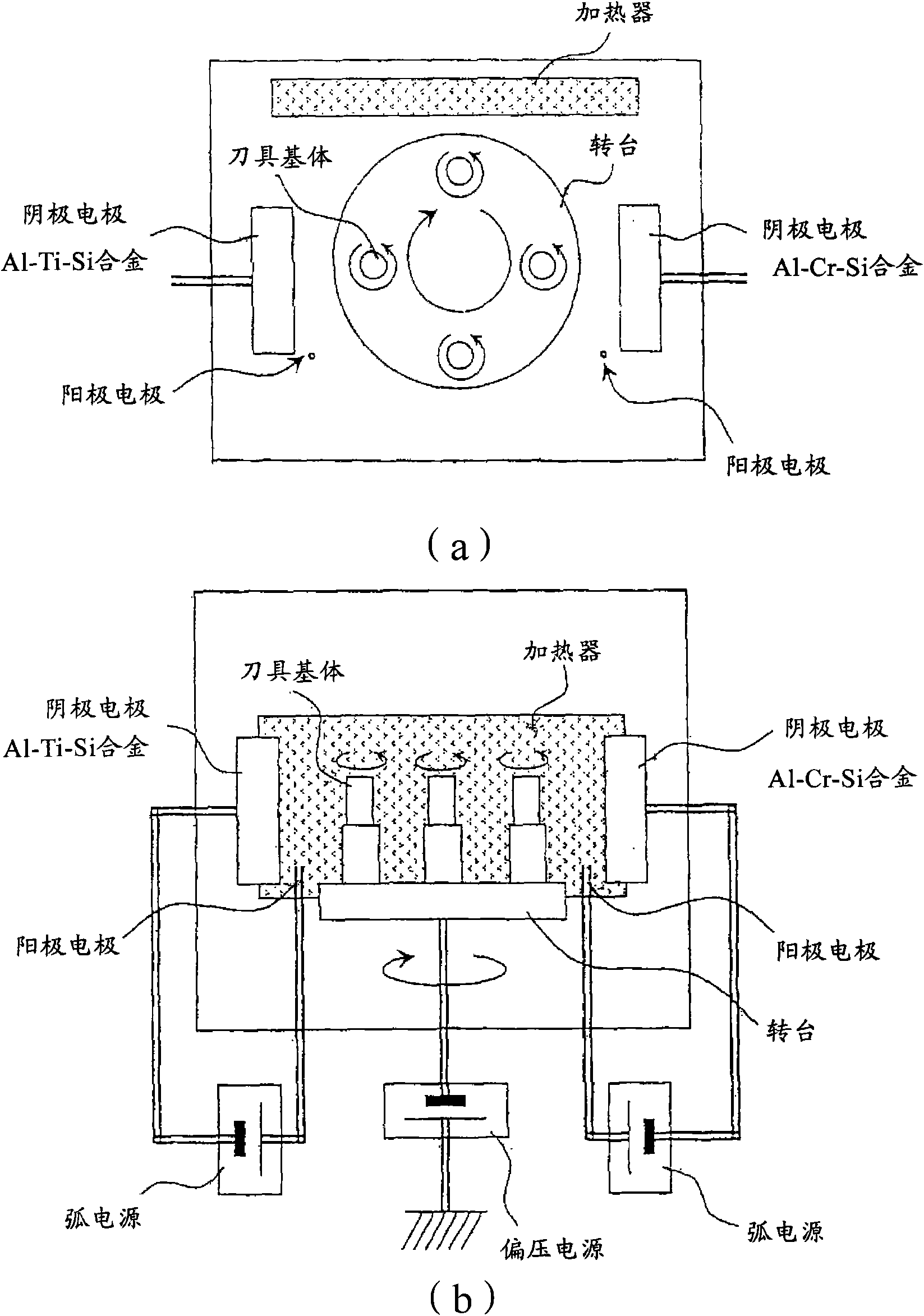
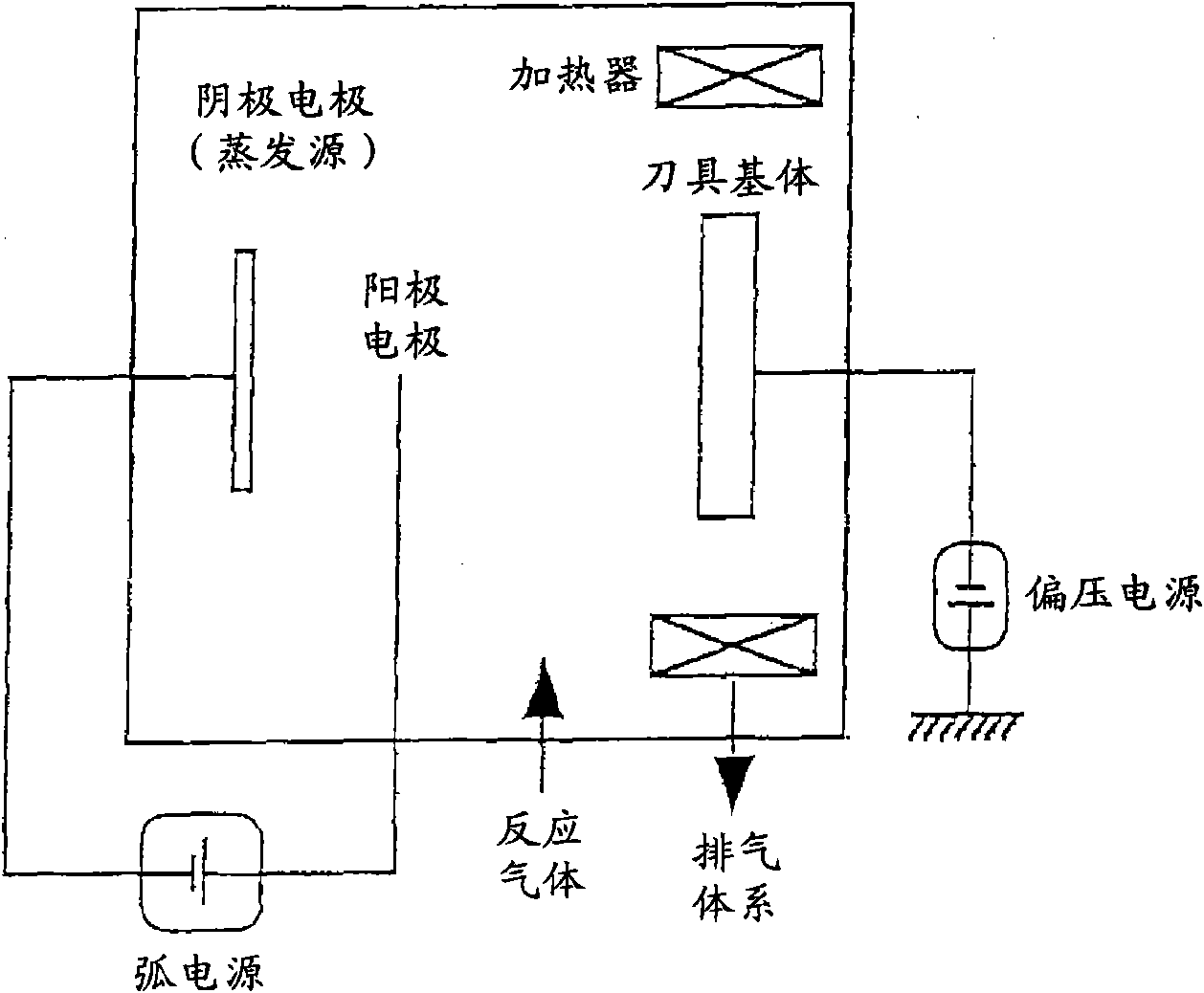
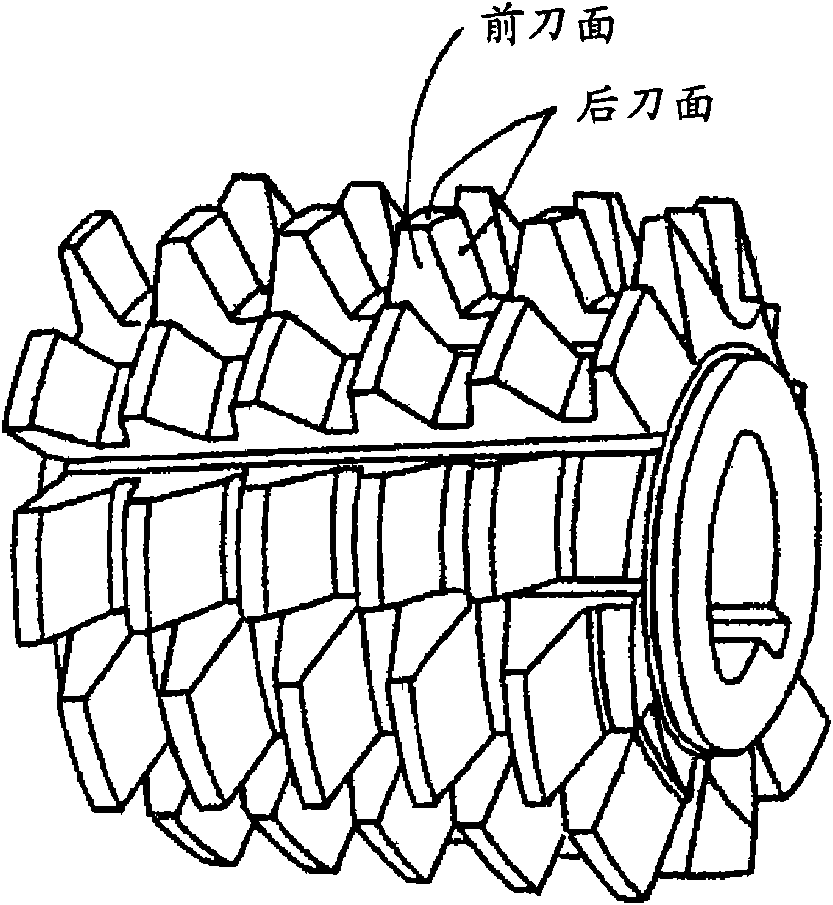
Patents
Literature
863 results about "Tool steel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tool steel refers to a variety of carbon and alloy steels that are particularly well-suited to be made into tools. Their suitability comes from their distinctive hardness, resistance to abrasion and deformation, and their ability to hold a cutting edge at elevated temperatures. As a result, tool steels are suited for use in the shaping of other materials. With a carbon content between 0.5% and 1.5%, tool steels are manufactured under carefully controlled conditions to produce the required quality. The presence of carbides in their matrix plays the dominant role in the qualities of tool steel. The four major alloying elements that form carbides in tool steel are: tungsten, chromium, vanadium and molybdenum. The rate of dissolution of the different carbides into the austenite form of the iron determines the high-temperature performance of steel (slower is better, making for a heat-resistant steel). Proper heat treatment of these steels is important for adequate performance. The manganese content is often kept low to minimize the possibility of cracking during water quenching.
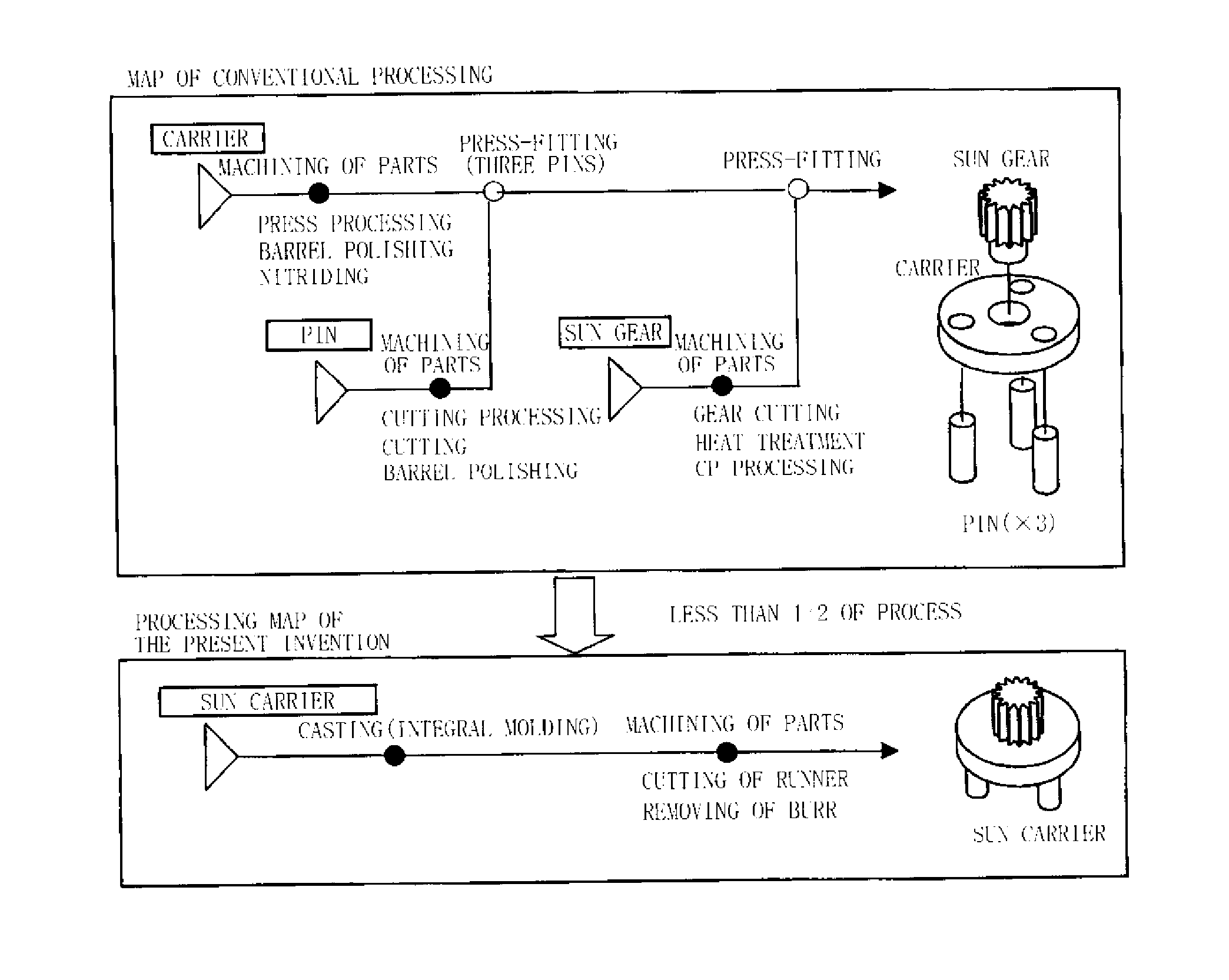
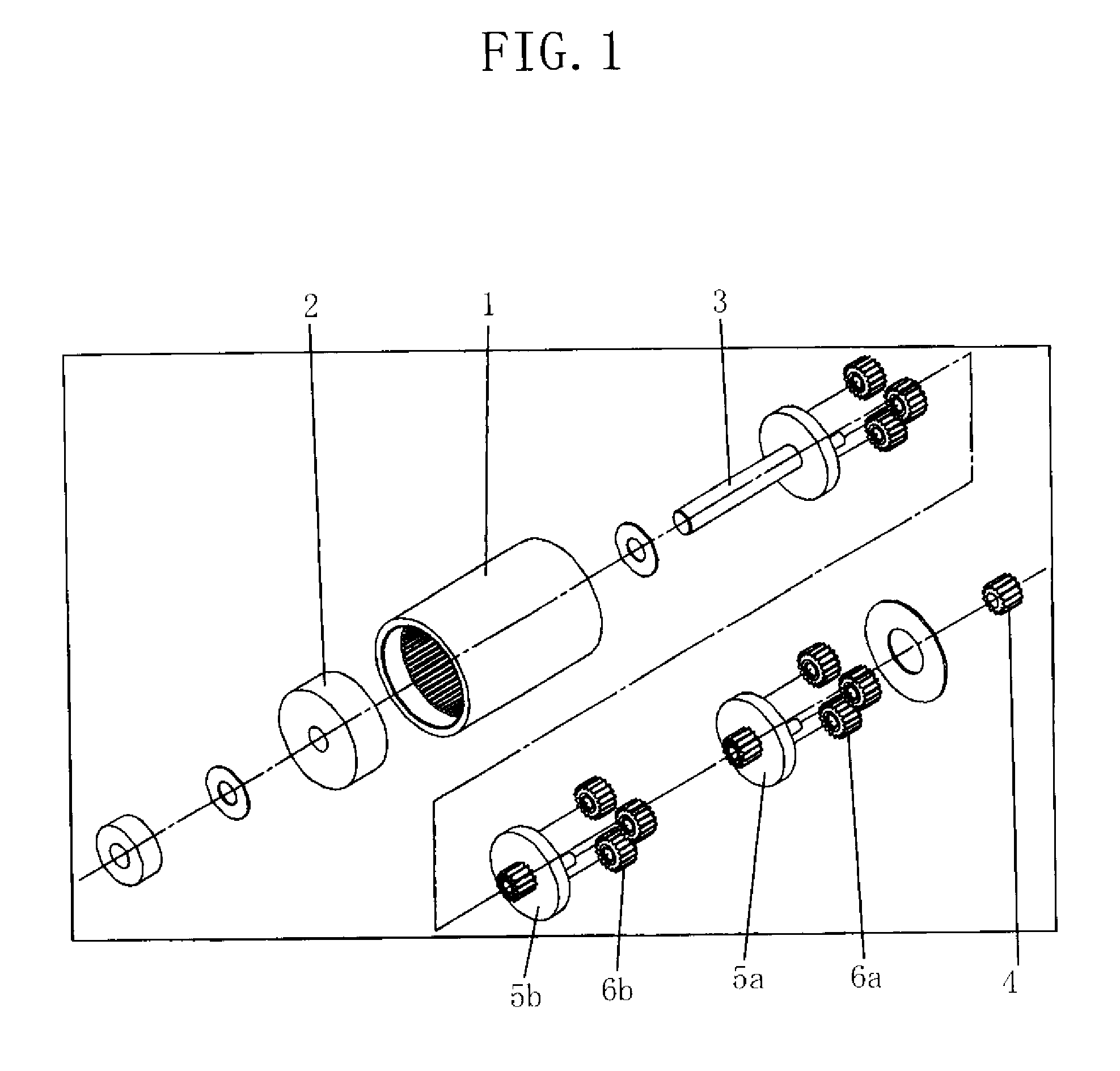
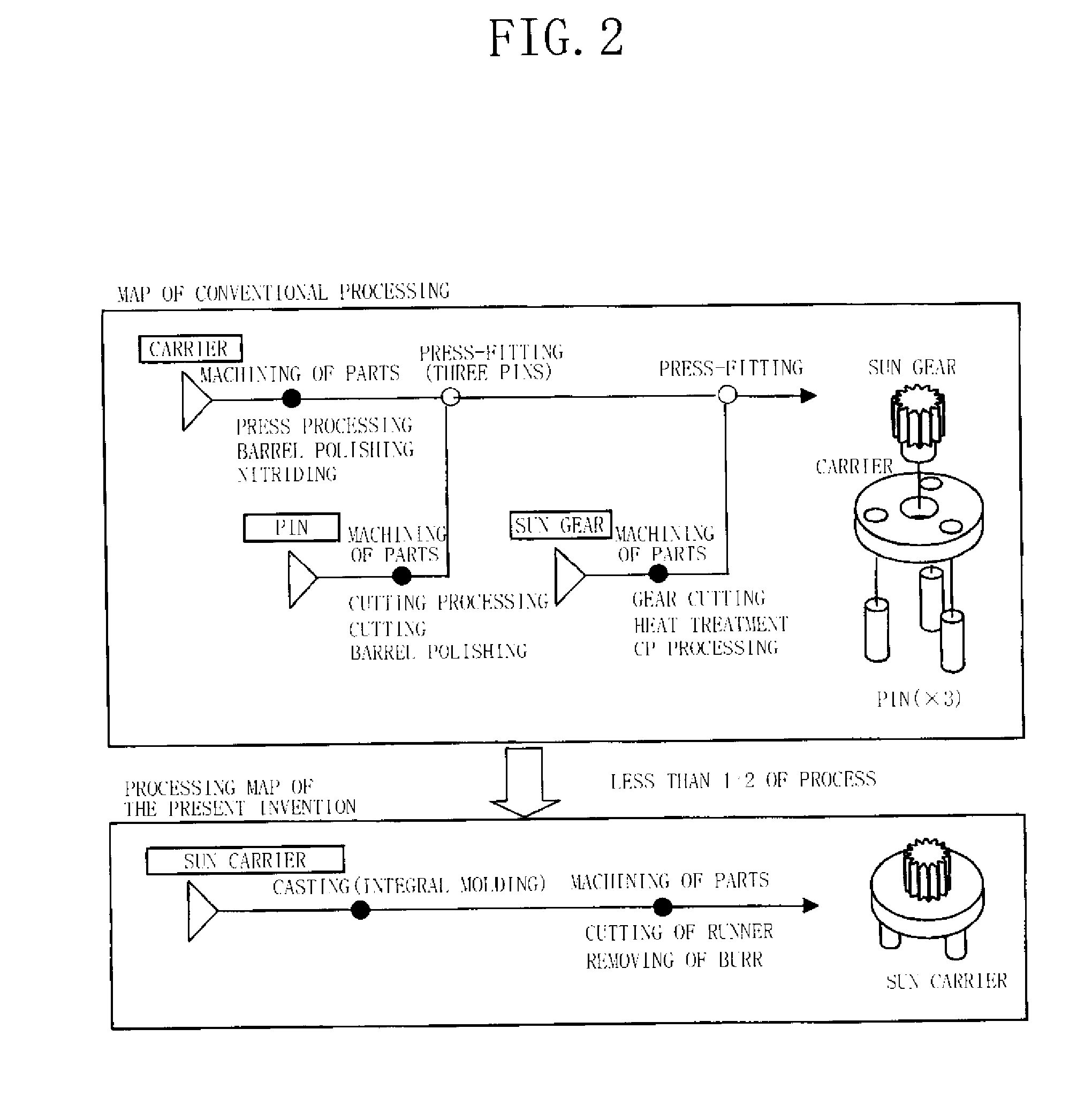
Precision gear, its gear mechanism, and production method of precision gear
InactiveUS20070034304A1Improve ductilityImprove toughnessGearworksMaterial nanotechnologyTool steelHardness
A metal-made high-precision gear and a gear mechanism are disclosed. The precision gear is made of a novel material which does not exist in conventional materials for precision gears, including resins and tool steels, has high hardness, strength and excellent surface smoothness, and is superior in workability. In the precision gear which is formed of an amorphous metal alloy having a ternary, quaternary or higher composition containing iron group elements, such as Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu, Ti, Zr, Hf, as the principal elements, the precision gear whose module is 0.2 or less is made of the amorphous metal alloy having a disordered structure which does not have a fixed regularity and whose XRD pattern is a halo pattern, namely exhibits a broad peak.
Owner:NAMIKI SEIMITSU HOSEKI KK +3
Alloy tool steel and its producing method and mold using it
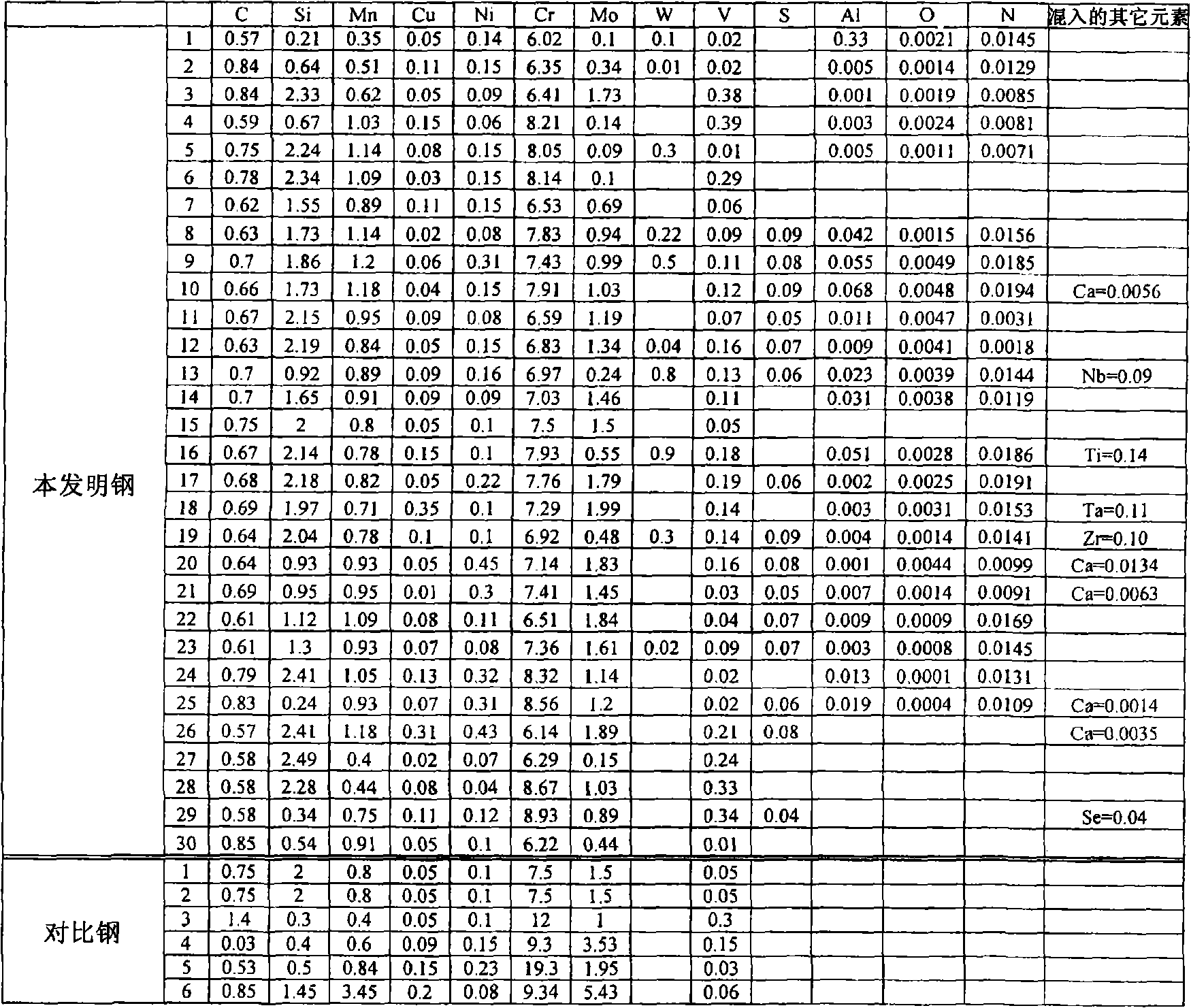
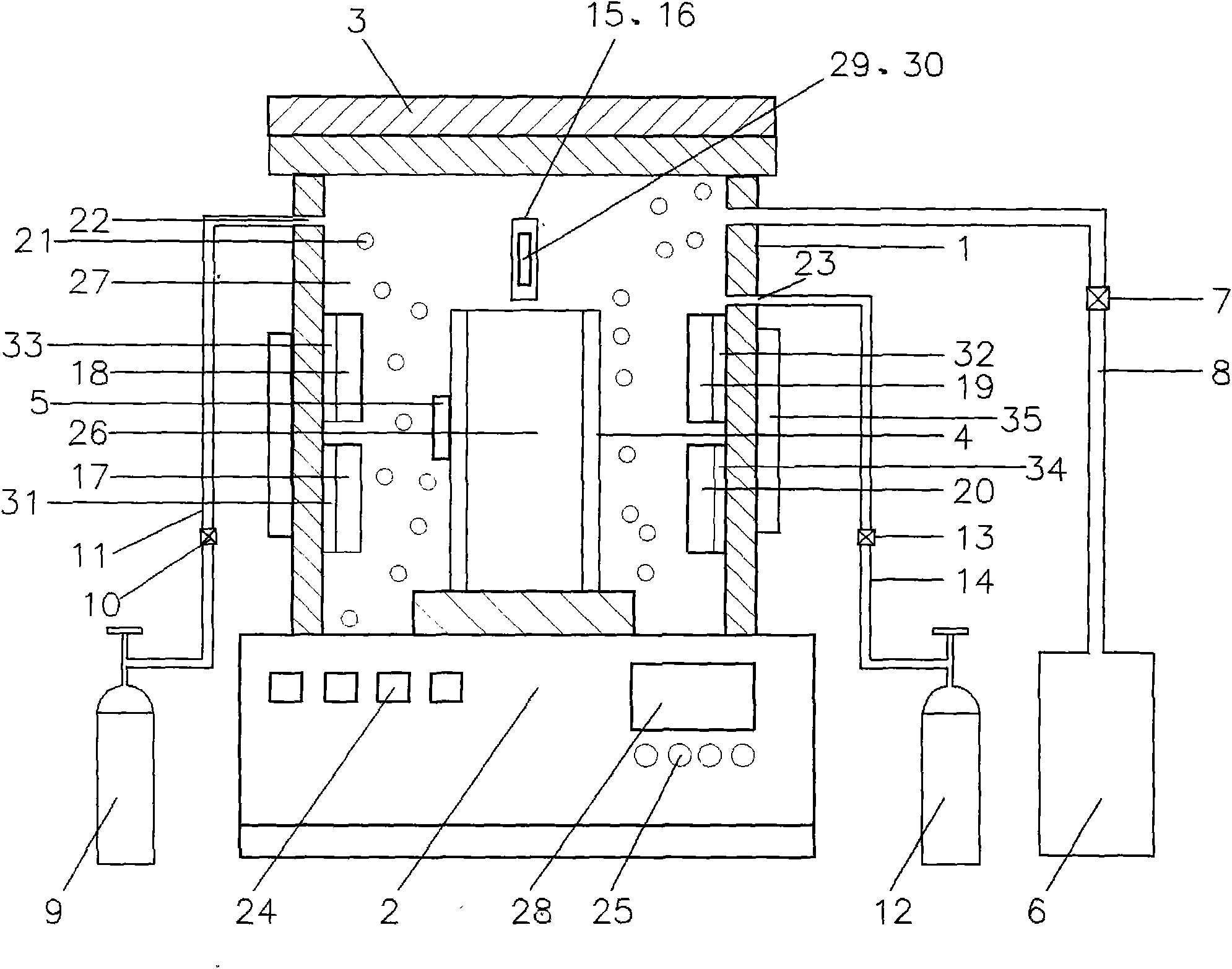
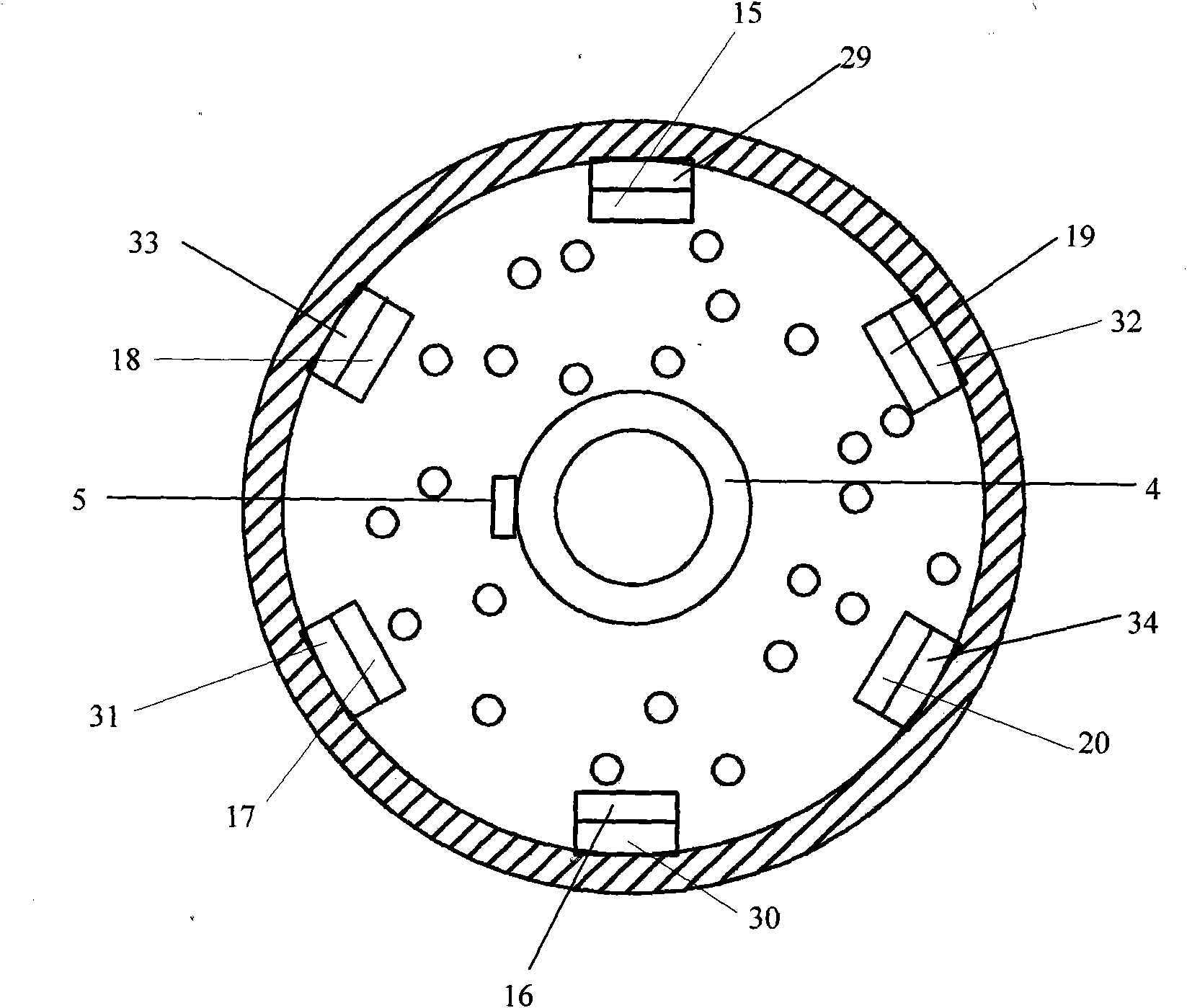
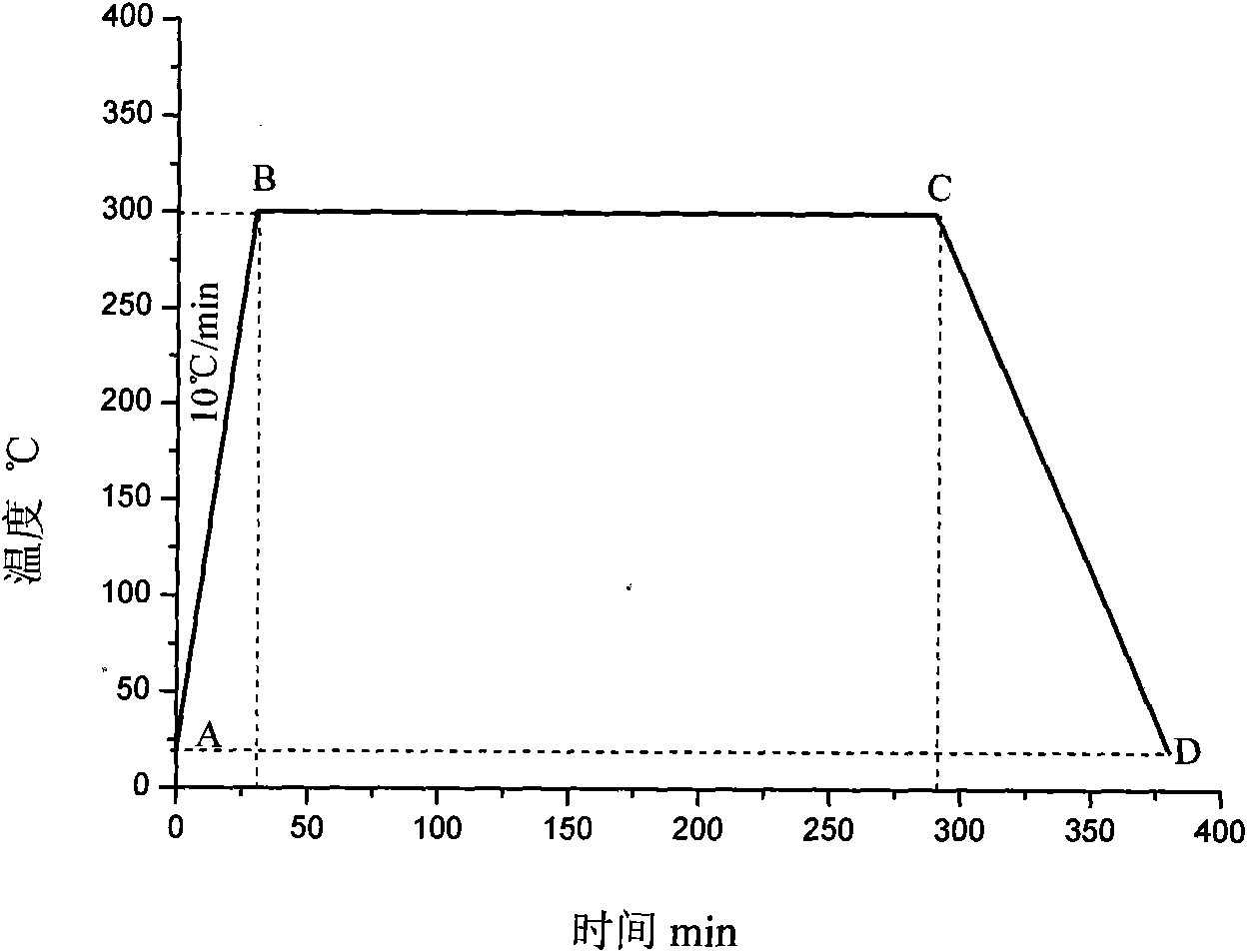
To provide alloy tool steel having a quenching temperature lower than that of conventional matrix high speed steel and also having the same characteristics such as hardness and toughness after heat treatment, as those of conventional alloy tool steel, and to provide its manufacturing method and a die using it. The alloy tool steel has a composition which contains prescribed amounts of C, Si, Mn, P, S, Cu, Ni, Cr, Mo or / and W, V, Al, O and N and further contains prescribed amounts of one or more elements among Co, Nb, Ti, B, Ta, Zr, Pb, Bi, Ca, Te, Se, REM and Mg and has the balance Fe with inevitable impurities and in which inequality -0.2<[Delta]C<0.2 (where [Delta]C=C-(0.06*Cr+0.063*Mo+0.033*W+0.2*V+0.1*Nb)) is satisfied and the value of Lc defined by equation Lc=(8.8*Mo+5.9*W+50*V+40*Nb) / (6*Cr) is made to 1.0 to 2. (C)2004,JPO.
Owner:DAIDO STEEL CO LTD
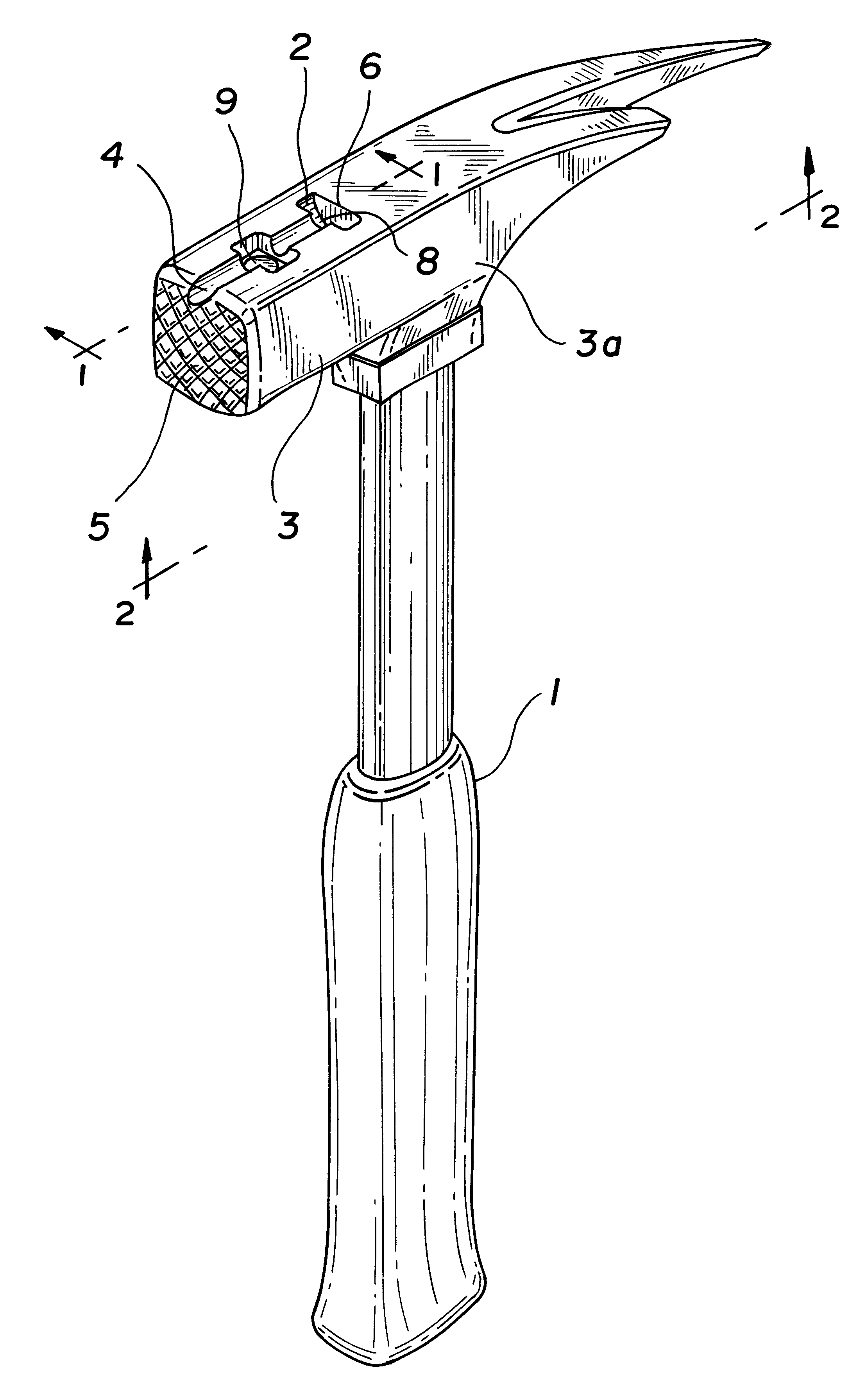
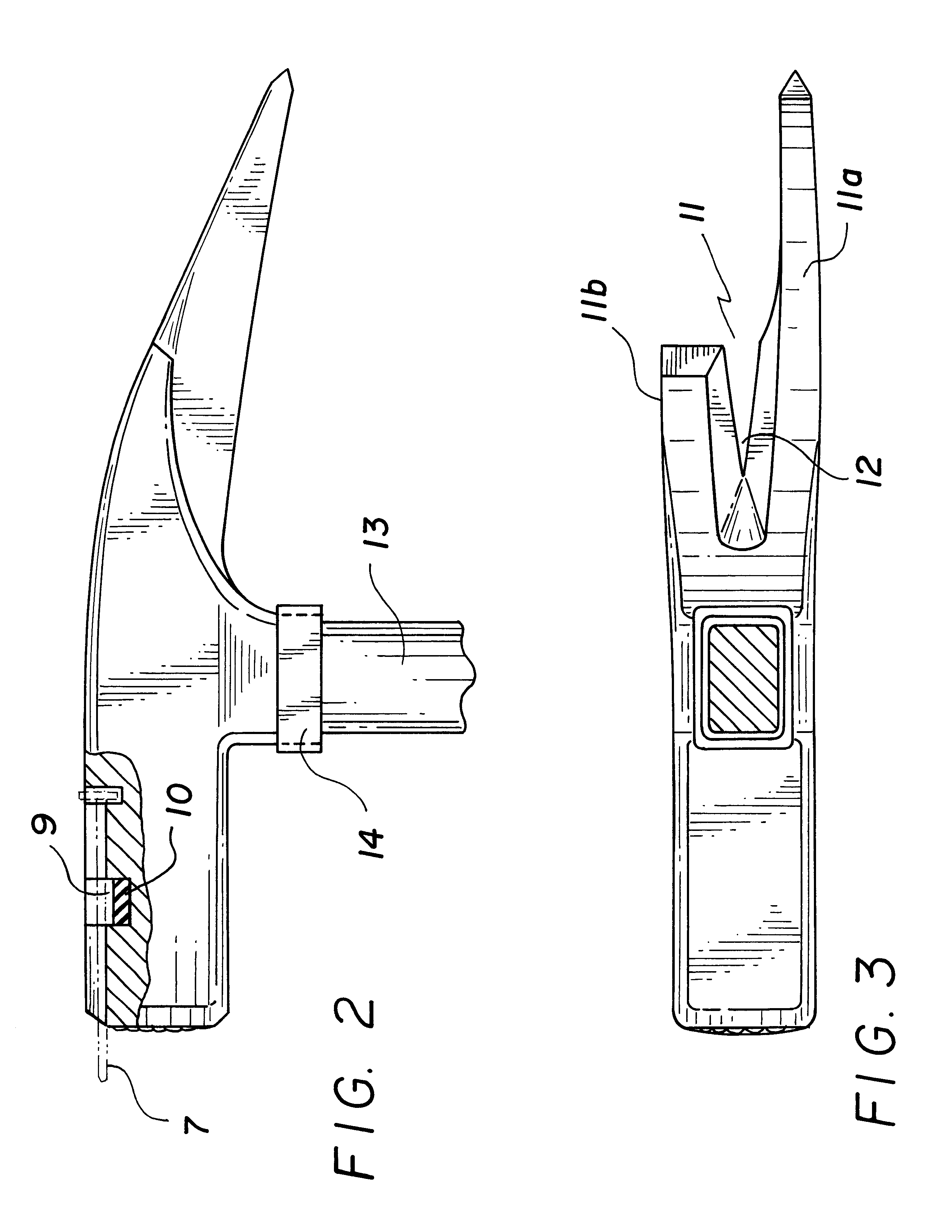
Carpenter hammer
A hammerhead made of tool steel and having in combination a pair of asymmetric claws and a magnetic nail holder, the holder being in the form of a T-shaped notch and a permanent magnet having a very high field intensity as compared to the conventional permannet magnet.
Owner:KOTSCHNER JOSEF +1
Metal base ceramic phase reinforced alloy tool steel powder for 3D printing, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105714209AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceAdditive manufacturingTransportation and packagingAlloyWear resistance
The invention discloses metal base ceramic phase reinforced alloy tool steel powder for 3D printing. The alloy tool steel powder is characterized by comprising the following elements in percentage by mass: 0.2-5% of C, 0.2-1% of Si, 0.1-1% of Mn, 0.3-1% of Ni, 3-25% of Cr, 0.2-15% of Mo, 0.2-14.5% of V, 0.3-15% of W, 1-18% of Co, 0.2-1% of Nb, 0.2-8% of metal base ceramic phase metal elements, and the balance of iron. The invention designs a ceramic phase reinforced alloy tool steel powder material; and the component design of the material embodies better hardness, wear resistance and high-temperature performance of the material.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of directly making rapid prototype tooling having free-form shape
A method and apparatus for directly making rapid prototype tooling from a computer model having a free-form shape. The method steps comprise essentially: (a) machining a soft metal tooling base so as to contour at least one free-form surface in conformity with the computer model; (b) cold-gas dynamic spraying the contoured surface to form superimposed impact welded metal particle layers, the layers consisting of at least one thermal management under-layer comprising primarily copper, and at least an outer wear resistant layer comprising primarily tool steel.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Cobalt less multi element high speed tool steel and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN1693527AReasonable range of performanceLow content of alloying elementsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesElectrical resistance and conductanceChemical composition
A non-Co multi-element high-speed tool steel contains proportionally C, Si, Mn, S, P, Cr, V, Mo, W, Ni, Nb, Ti, Mg, RE and Fe. Its preparing process includes such steps as smelting by MF furnace, modifying with Y-based RE alloy, centrifugal casting, and heat treating.
Owner:JIUQUAN IRON & STEEL GRP
Welding method of hard alloy cutting tool
InactiveCN1428222AImprove yieldQuality improvementWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaAlloyCopper
The present invention relates to a method for soldering connection of hard alloy and tool steel. Said invention adopts siler base or copper base solder to solder cutter. When soldering, between hard alloy and steel base material a soft red copper transition piece is inserted to make soldering connection. After soldering, the heat stress produced by soldering can be effectively absorbed by soft red copper piece, so that it can raise finished product rate of the cutter production.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
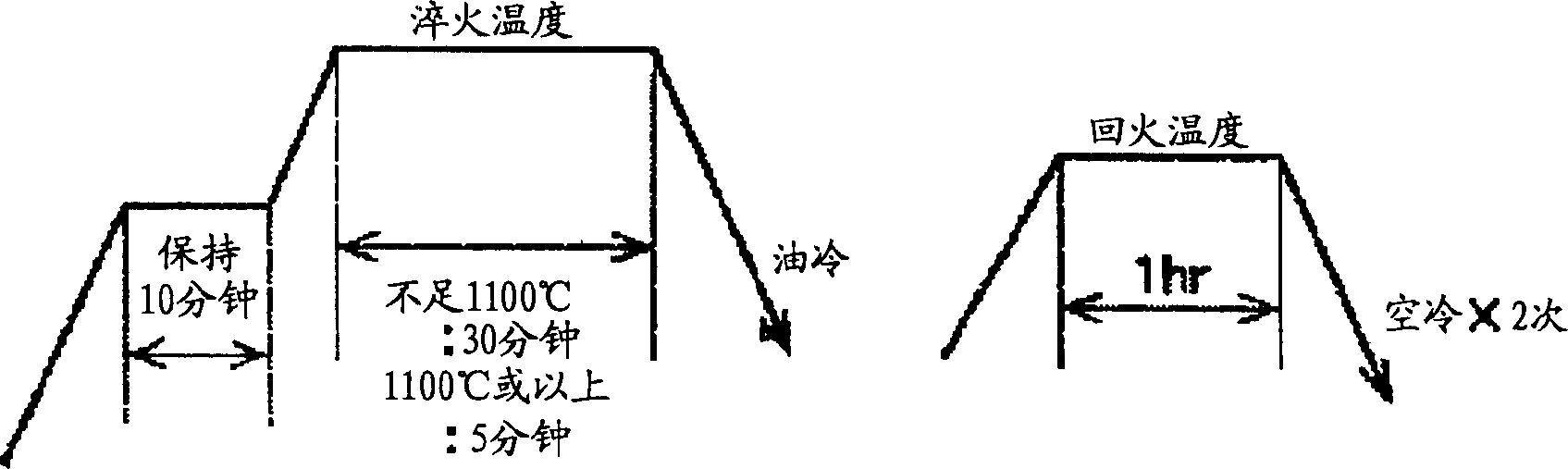
High-speed tool steel gear cutting tool and manufacturing method therefor
The invention provides a high-speed tool steel gear cutting tool in which fracture or chipping does not occur at the cutting edge, and which realizes excellent cutting performance over long periods. Moreover, a method of manufacturing a gear cutting tool including: a step for quenching a tool material comprising high-speed tool steel and which has been rough processed to a shape corresponding to a final shape of a gear cutting tool, to transform a structure of the tool material into martensite, a step for temperling the tool material after quenching to transform any residual austenite dispersingly distributed throughout a matrix of the martensite structure formed by the quenching, into martensite, and a step for finishing the tool material after tempering to a final shape, is characterized in that the tool material after quenching is subjected to sub-zero treatment involving cooling and holding at a temperature of less than -150° C.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Cutting Wheel with Disposable Blade
InactiveUS20090293696A1Cheap manufacturingCheap replacementMetal working apparatusShearing toolsImpellerAlloy
A cutting wheel having a disposable blade is a constructed of a disposable blade wheel, an inner support wheel and an outer support wheel to define a three part cutting assembly. An interior hub adapted to be mounted to the three part cutting assembly to provide a cutting wheel assembly. The disposable blade wheel is adapted to be connected to the inner support wheel and the outer support wheel, and may be located between the inner support wheel and outer support wheel. In the three part cutting assembly, an outer periphery of the blade wheel extends radially outwardly of an outer periphery of the inner support wheel and of an outer periphery of the outer support wheel to provide a cutting surface having a cutting edge. The cutting edge comprises a cutting material such as hardened tool steel, high carbon steel, non-ferrous alloys or the like. The cutting wheel assembly is adapted to be mounted onto a conventional rotatable shaft of a conventional web processing machine of the types well known in the art to process a web of material.
Owner:EMT INT CO LTD
Taper pipe for concrete pumping device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102128312AImprove hardenabilityHigh hardnessBulk conveyorsRigid pipesMetallic materialsShock resistance
The invention relates to a taper pipe for a concrete pumping device. The taper pipe comprises an inner pipe and an outer pipe which are made from different metal materials, the rigidity of the inner pipe is higher than that of the outer pipe; and the toughness of the outer pipe is higher than that of the inner pipe; materials can be used for the inner pipe comprise medium and high carbon low-alloy steel, wear-resisting cast steel, wear-resisting cast iron and tool steel; and the materials of the outer pipe can be common carbon steel and low-carbon alloy steel. The invention also relates to a method for manufacturing the taper pipe. A double-layer composite taper pipe provided by the invention has the advantages that the wall thickness design of a thin large end and a thick small end conrresponds with the design principle of equal service life; the raw materials are saved; the inner pipe has high through quenching capability, smooth surface, and high rigidity and good wear resistance; the outer pipe has low rigidity, good toughness and high capability of shock resistance, and can protect the inner pipe well; and simultaneously the comprehensive requirement on the abrasion resistance and toughness of the taper pipe for the pumping device is satisfied.
Owner:SANY HEAVY IND CO LTD (CN)
Slip sheet of refrigeration compressor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101629573AEasy to processNarrow selection of materialsRotary/oscillating piston pump componentsLiquid fuel engine componentsRefrigeration compressorChemical composition
The invention relates to a slip sheet of a refrigeration compressor, which is manufactured by the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.32-0.54% of C, 0.17-0.45% of Si, 0.30-1.20% of Mn, 0.80-1.65% of Cr, 0.15-0.30% of Mo, 0.60-1.10 Al, 0-0.2% of V, and the balance of Fe. The invention has narrower material selection range because prior slip sheet materials are all limited to high-speed tool steel and high-carbon stainless steel; the invention manufactures the slip sheet completely meeting the requirement of the slip sheet of a high-quality compressor on shape, surface rigidity and rigidity distribution through reasonable material selection, and has wide material selection range, easily obtained material and low cost; in addition, because the content of carbon is further reduced, the processing property of the slip sheet is better, and the good quality rate of products is enhanced.
Owner:NINGBO YONGWEI GROUP
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveCN101678467AExcellent high temperature hardnessExcellent high temperature toughnessMilling cuttersVacuum evaporation coatingThin layerCemented carbide
A surface-coated cutting tool which has excellent chipping resistance and wearing resistance in high-speed cutting processing such as high-speed gear cutting processing, high-speed milling processing,and high-speed drilling processing. The surface-coated cutting tool comprises a tool base, e.g., a cemented carbide base, cermet base, or high-speed tool steel base, and at least a hard coating layerformed on a surface of the tool base and having a multilayer structure composed of a thin layer (A) and a thin layer (B) alternating therewith. The thin layer (A) is constituted of an (Al,Cr,Si)N layer satisfying the empirical formula ¢AlXCrYSiZ!N (wherein 0.2 <= X <= 0.45, 0.4 <= Y <= 0.75, 0.01 <=Z <= 0.2, and X+Y+Z=1 in terms of atomic ratio), and the thin layer (B) is constituted of an (Al,Ti,Si)N layer satisfying the empirical formula ¢AlUTiVSiW!N (wherein 0.05 <= U <= 0.75, 0.15 <= V <= 0.94, 0.01 <= W <= 0.1, and U+V+W=1 in terms of atomic ratio).
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
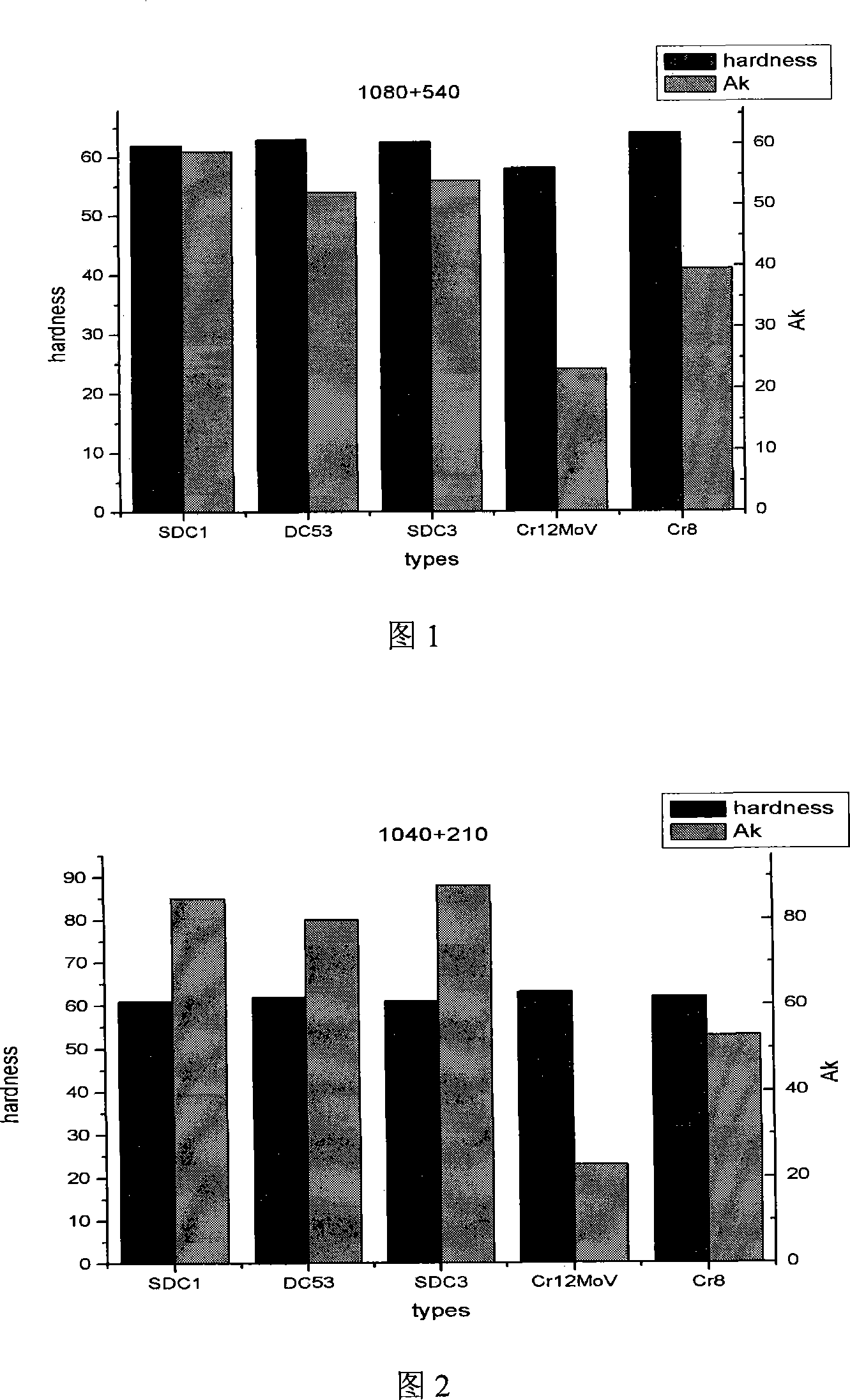
High-strength toughness cold working die steel and method of producing the same
The invention relates to a high-strength toughness cold-working die steel and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of alloy steel manufacturing technology. The chemical composition and weight percentage of the alloy steel of the present invention: C 0.9~1.0%, Cr 9~10%, Mo 2.0%, V 0.8~1.0%, Si 1.0%, P<0.02%, S<0.02%, Fe surplus quantity. The preparation process and steps of the cold work die steel of the present invention are as follows: (1) smelting, (2) electroslag remelting, (3) annealing, (4) rough forging, (5) re-annealing, (6) spheroidizing annealing , (7) Quenching and tempering. The hardness of the alloy steel prepared by the method of the invention can reach 61-63HRC, and the impact energy AK can reach 61-85J, which is more than three times higher than that of the original Cr12MoV steel.
Owner:上大鑫仑材料科技(上海)有限公司
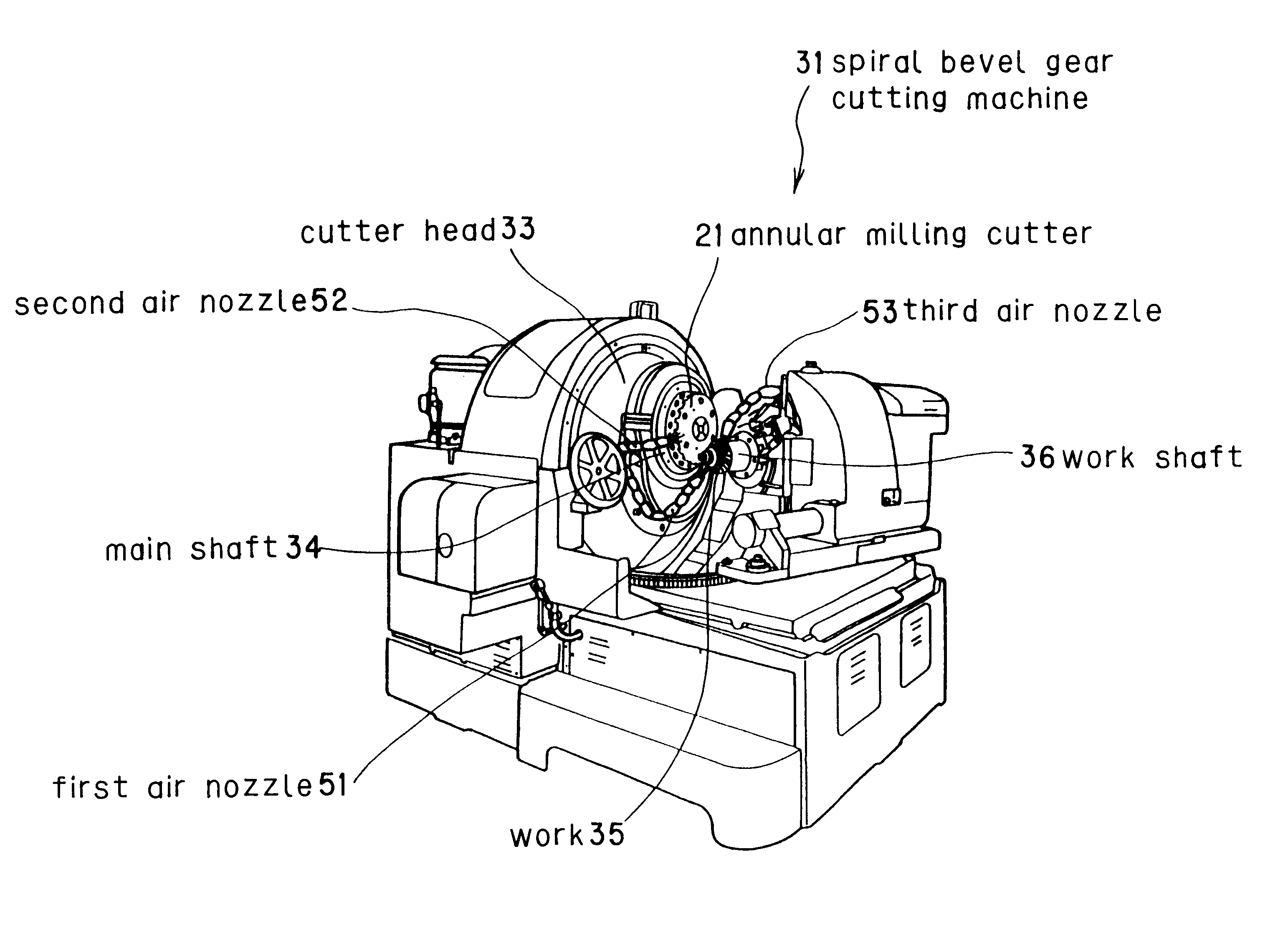
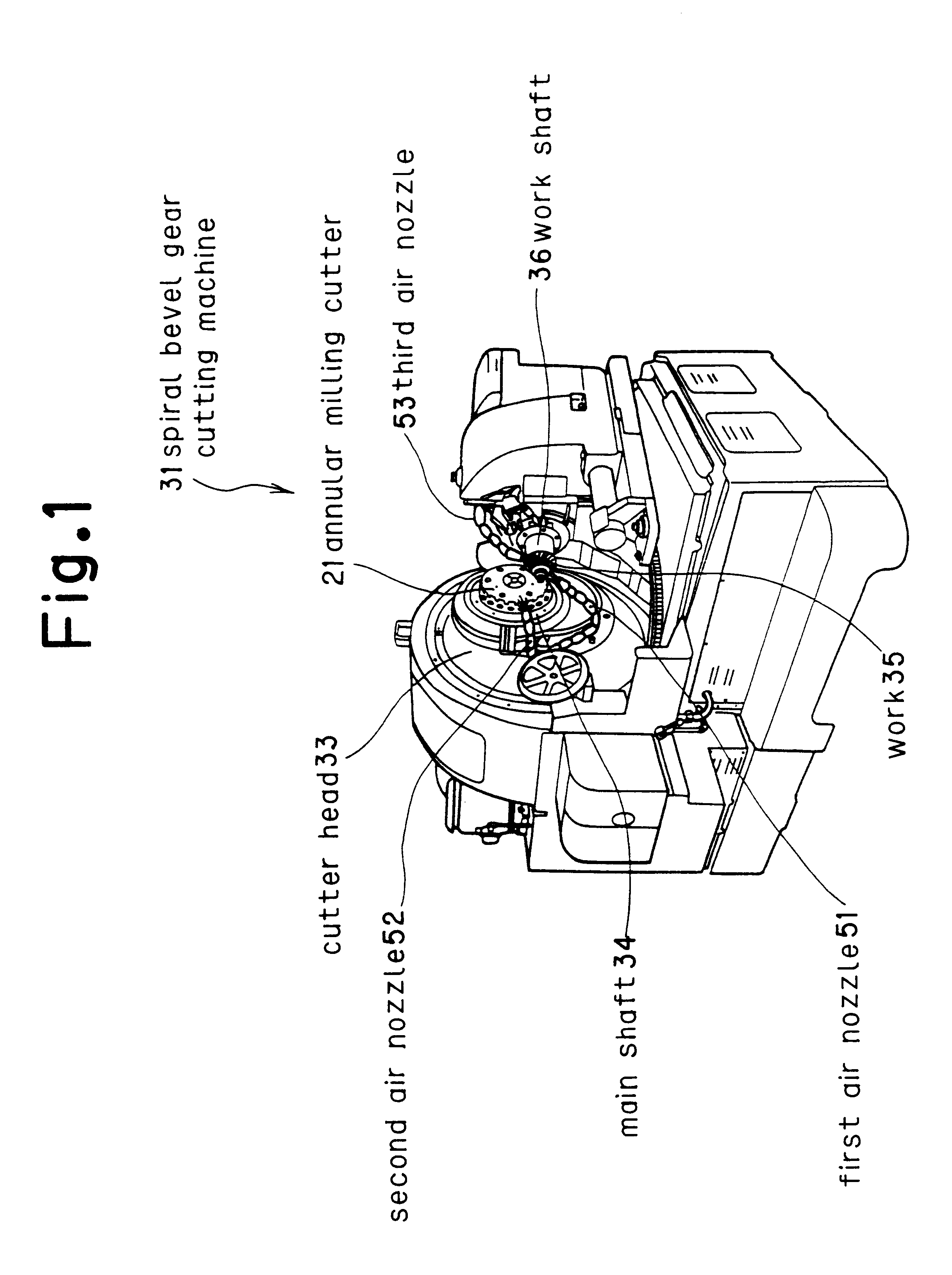
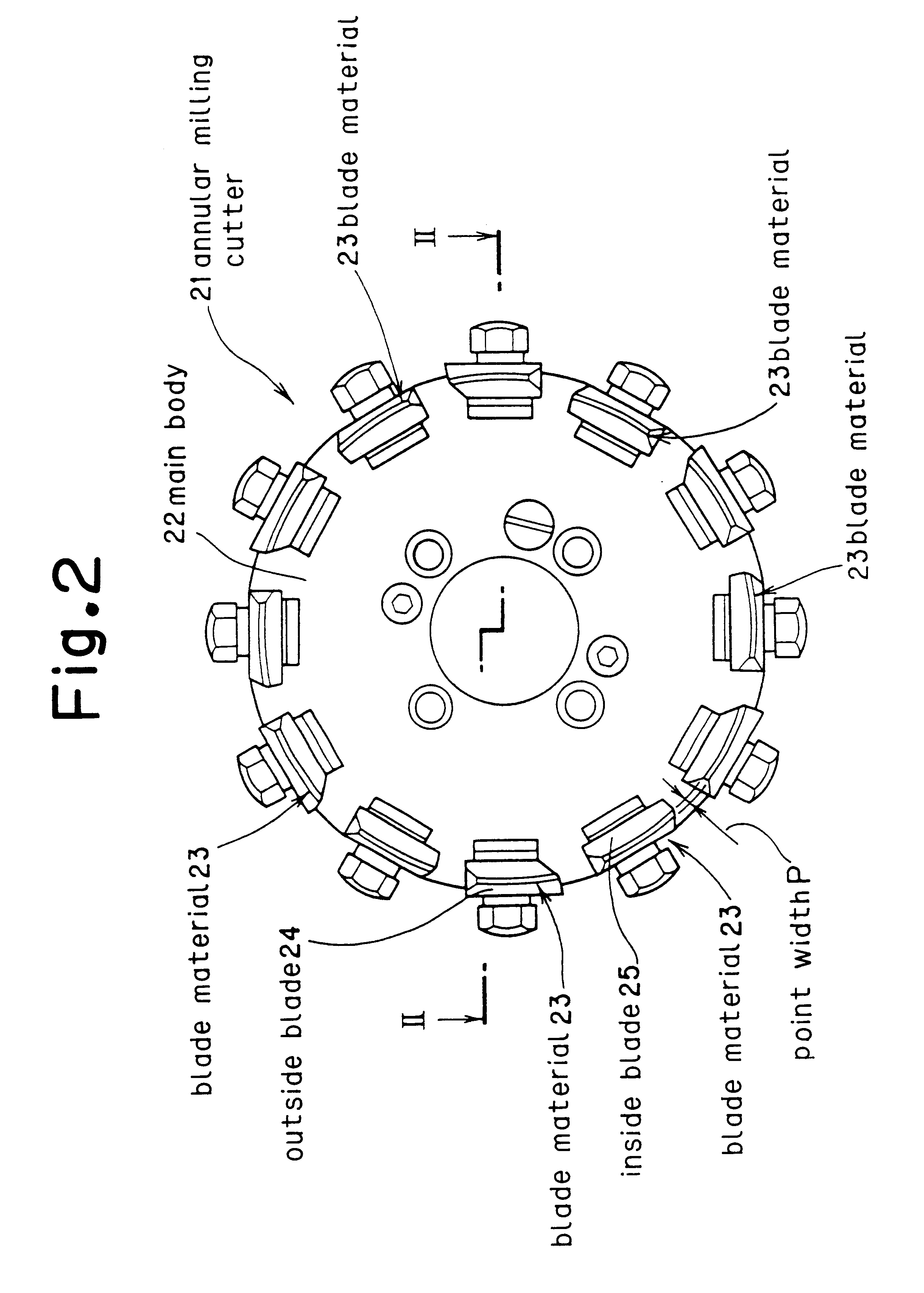
Gear shaping method and device and spiral bevel gear cutter
InactiveUS6416262B1Fast cutting speedNatural mineral layered productsGear teeth manufacturing toolsMilling cutterGear wheel
A bevel gear is generated using an annular milling cutter having a blade material made of a high-speed tool steel mounted to a main body, the blade material being coated with at least one layer of a film of a composition substantially comprising (Ti(1-x)Alx)(NyC(1-y)) (where, 0.2<=x<=0.85, 0.2<=y<=1.0), and dry cutting is performed at a cutting speed in the range from 20 to 400m / min without using a cutting oil. With this method, teeth can be generated at a greatly improved cutting speed without using any expensive tool such as cemented carbide, thereby realizing efficient production of a bevel gear at a reduced cost.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Method for improving wear resistance and high-temperature resistance of stirring head for stirring and friction welding
InactiveCN105463451AIncreased and improved wear resistance and high temperature resistanceGood wear resistance and high temperature resistanceMetallic material coating processesCeramic compositeFriction stir welding
The invention provides a method for improving wear resistance and high-temperature resistance of a stirring head for stirring and friction welding. The method includes the steps that casting-state high-speed tool steel W18Cr4V is machined into a required concave type shaft shoulder and the conic stirring needle-shaped stirring head through the free-forging and die-forging technology, nickel base ceramic composite alloy powder is prearranged on the surfaces of the stirring head shaft shoulder and a stirring needle base body, and the surface layers of the shaft shoulder and the stirring needle base body and the nickel base ceramic composite alloy powder pre-arranged on the surface layers of the shaft shoulder and the stirring needle base body are heated and melted through the laser cladding technology to be condensed quickly to manufacture annular and spiral wear-proof high-temperature-resisting coatings. By the adoption of the method, the process is simple, production cost is low, the stirring head shaft shoulder and a stirring needle are reasonable in mechanical structure, the bonding strength of the coatings manufactured on the surfaces of the stirring head shaft shoulder and the stirring needle is high, the service life of the stirring head can be prolonged effectively, and the stirring head has excellent wear resistance and high-temperature resistance.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
PVD-coated cutting tool insert
InactiveUS6884497B2Improve performanceImproved propertyPigmenting treatmentMilling cuttersAlloyCemented carbide
A coated cemented carbide insert (cutting tool), particularly useful for milling at high cutting speeds in alloyed steels, tool steels and milling in hardened steels includes a WC-Co cemented carbide containing NbC and TaC and a W-alloyed binder phase, and a coating including an inner layer of TixAlyN, 0.8<x+y<1.2, with 0.25<x / y<1.45, with columnar grains.
Owner:SECO TOOLS AB
Power-matallurgy valve seat inserts
InactiveCN1438350AHigh temperature resistanceExcellent machinabilityTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusVALVE PORTValve seat
A powdered metal blend mixture for making a powdered metal part especially a valve seat insert. The mixture includes 15 to 30 wt.% of a valve steel powder, 0 to 10 wt.% nickel, 0 to 5 wt.% copper, 5 to 15 wt.% of a ferro-alloy powder, 0 to 15 wt.% of a tool steel powder, 0.5 to 5 wt.% of a solid lubricant, 0.5 to 2 wt.% graphite, 0.3 to 1.0% of a temporary lubricant, and the balance being substantially a low alloy steel powder containing 0.6 to 2.0 wt.% molybdenum, 0 to 5 wt.% nickel, and 0 to 3.0 wt.% copper. The present invention provides improved high temperature wear and corrosion resistance over prior art materials as well as improved machinability. The blend of the present invention provides a relatively high density material that allows for a single press and sinter technique.
Owner:EATON CORP
Powdered metal valve seat insert
InactiveUS6214080B1High densityHigh hardnessTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusVALVE PORTValve seat
A powdered metal blend mixture for making a powdered metal part especially a valve seat insert. The mixture includes 15 to 30 wt. % of a valve steel powder, 0 to 10 wt. % nickel, 0 to 5 wt. % copper, 5 to 15 wt. % of a ferro-alloy powder, 0 to 15 wt. % of a tool steel powder, 0.5 to 5 wt. % of a solid lubricant, 0.5 to 2 wt. % graphite, 0.3 to 1.0% of a temporary lubricant, and the balance being substantially a low alloy steel powder containing 0.6 to 2.0 wt. % molybdenum, 0 to 5 wt. % nickel, and 0 to 3.0 wt. % copper. The present invention provides improved high temperature wear and corrosion resistance over prior art materials as well as improved machinability. The blend of the present invention provides a relatively high density material that allows for a single press and sinter technique.
Owner:EATON CORP
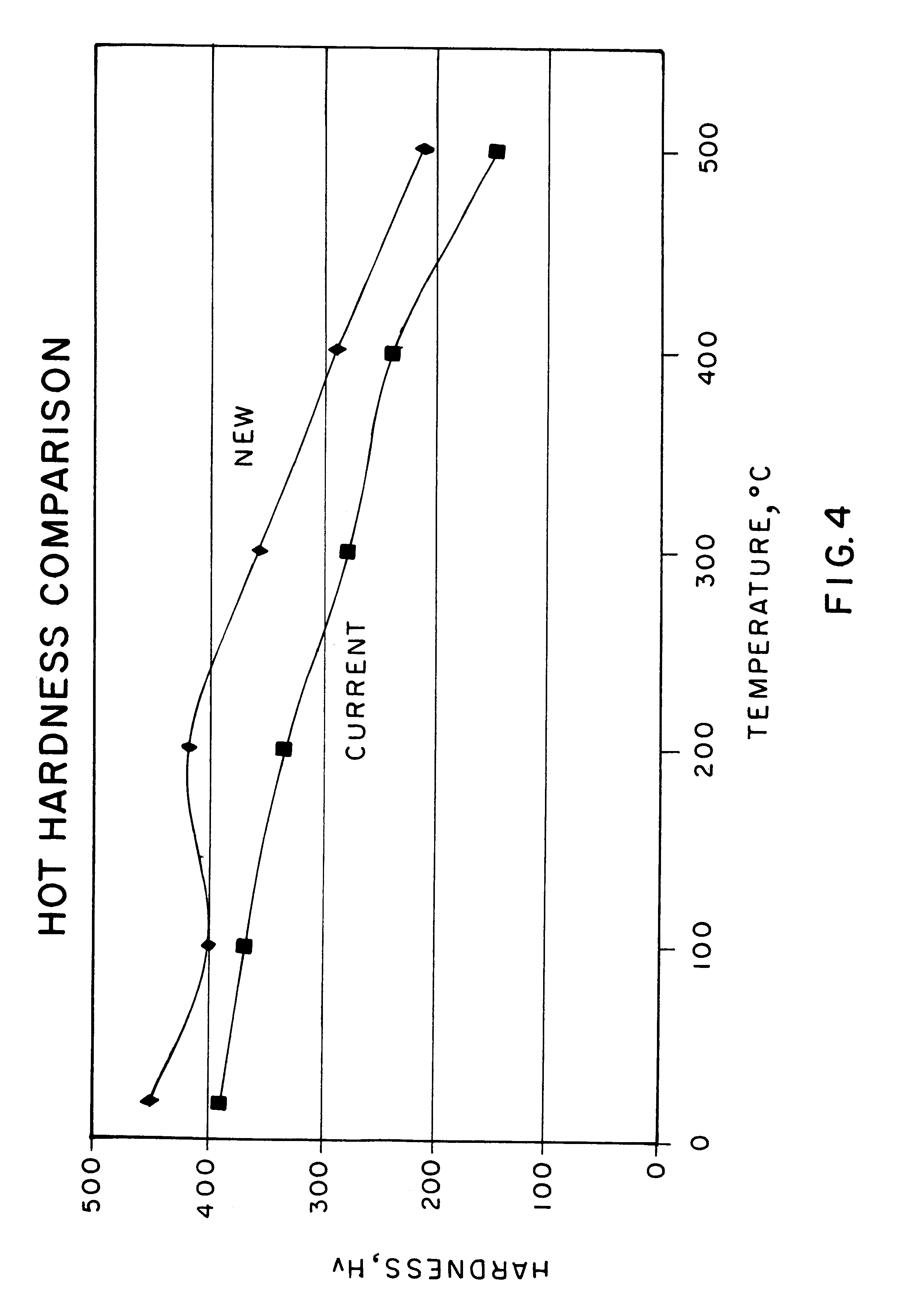
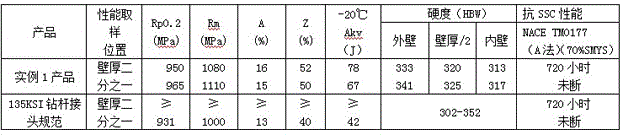
130KSI-grade and 135KSI-grade corrosion-resistant drill tool steel for oil and gas fields and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN107177797AImprove strength and toughnessMeet anti-H
<sub>2</sub>
S corrosion characteristics requirementsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMechanical propertyContinuous rolling
The invention relates to high-toughness and hydrogen sulfide corrosion resistant round steel and a manufacturing method thereof. The round steel comprises, by mass, 0.25-0.40% of C, 0.20-0.45% of Si, 0.95-1.50% of Mn, 1.35-1.90% of Cr, less than or equal to 0.002% of S, less than or equal to 0.008% of P, 0.75-1.30% of Mo, 0.10-0.30% of Ni, 0.05-0.25% of V, 0.010-0.050% of Nb, 0.10-0.30% of Cu, less than or equal to 0.050% of Al, 0.0005-0.005% of Ca, and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurity elements. The hot-rolled round steel is produced through a process route of continuous casting-continuous rolling-annealing, the round steel is subjected to heat treatment directly, or a machined semi-finished drill tool is subjected to heat treatment. On the premise that related 130KSI and 135KSI synthesized mechanical properties are met correspondingly, according to an America NACE TM0177 standard hydrogen-sulfide-resistant stress corrosion test, a product is not broken for 720 hours under the condition that 70% of nominal yield stress is pre-loaded in a saturated H2S solution. The material is suitable for 130KSI-strength-grade and 135KSI-strength-grade drill tools under the mining environment of acidic oil and gas fields.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
Cutting tool coated with hard alloy
ActiveCN1853832AImprove wear resistanceReduce coefficient of frictionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAlloyHigh intensity
A tool consists of a base material selected from cemented carbide, tool steels, cermet, or hard materials, and a coating of two or more layers. At least one coating layer has the composition Ti-Al-Ta-N and at least one further coating layer has the composition Ti-Al-Ta-Me-N. The component Me is one more elements selected from the group consisting of Si, V, B. The tool, which is preferably a wearing part, is distinguished by a high wear resistance that improves the service life, in particular where high demands are imposed on the tool.
Owner:奥地利色拉提琪有限公司
Method of making rotary cutting dies
InactiveUSRE37366E1Accurate locationExtended service lifeCutting toolsMetal rolling stand detailsEngineeringKnife blades
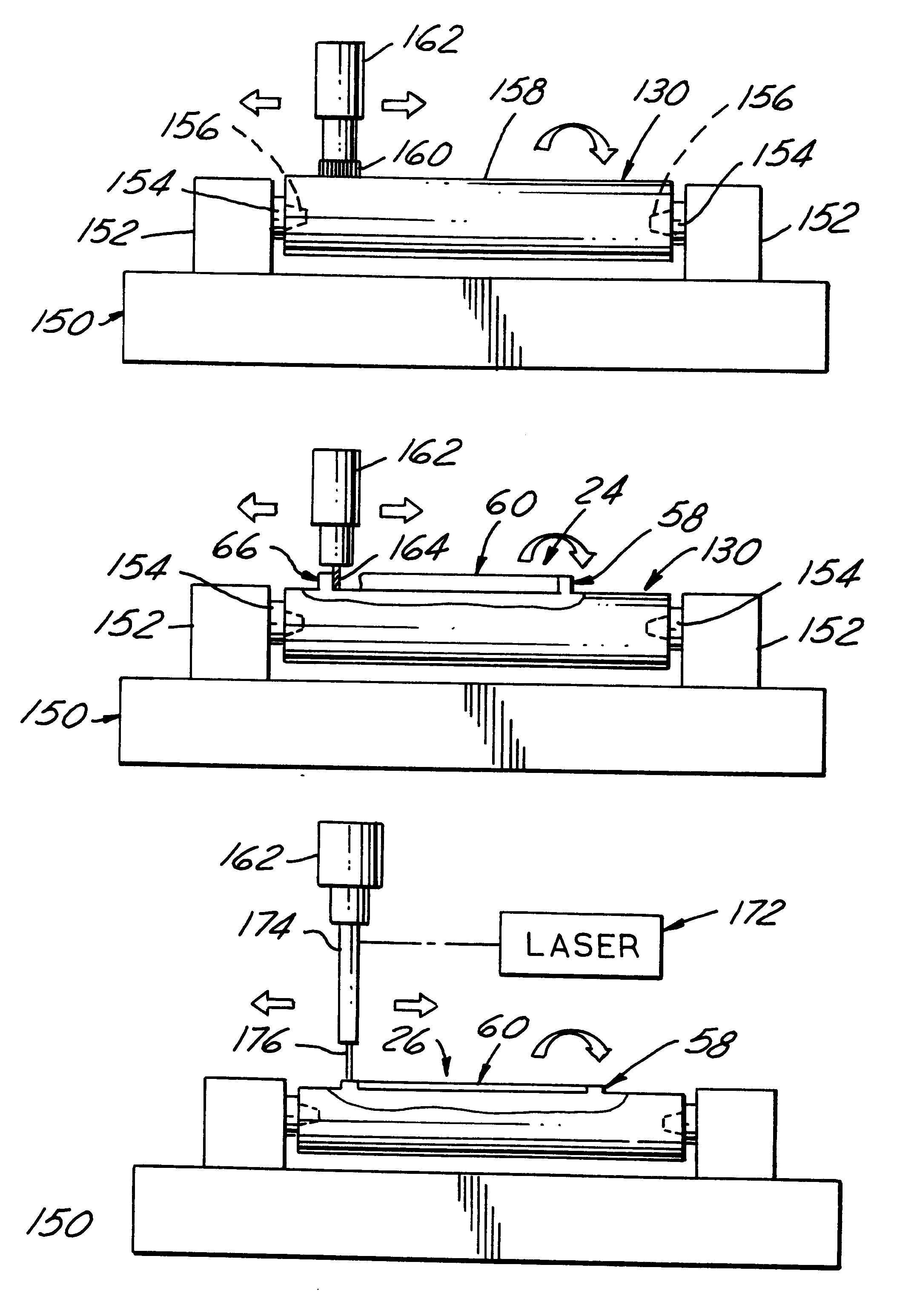
A method of making a pair of rotary die cylinders with lands having coacting cutting edges which cut blanks from a web of material passing through the nip of the rotating dies. In cross section each land has an outer face and a pair of spaced apart side faces which are parallel to each other and perpendicular to the chord of the outer face to provide a clean cut and facilitate release of the cut blank from the cutting blades as it emerges from the nip of the dies. The die cylinders are journalled for rotation by recesses with frusto conical locating surfaces in their opposed ends. Each die cylinder is made by machining the recesses in the opposed ends of a generally cylindrical workpiece of tool steel and then utilizing the recesses to locate and orient the workpiece relative to a cutting tool to produce a cylindrical surface on the workpiece concentric with the axis of the recesses and then to machine away portions of the periphery of the cylindrical surface to form the cutting blade lands thereon. After machining is completed the cutting blade lands may be hardened by heat treating utilizing a laser beam directed onto the lands to heat them at an elevated temperature so that upon quenching they are hardened without any substantial hardening and resulting distortion of the core or body of the workpiece.
Owner:BERNAL
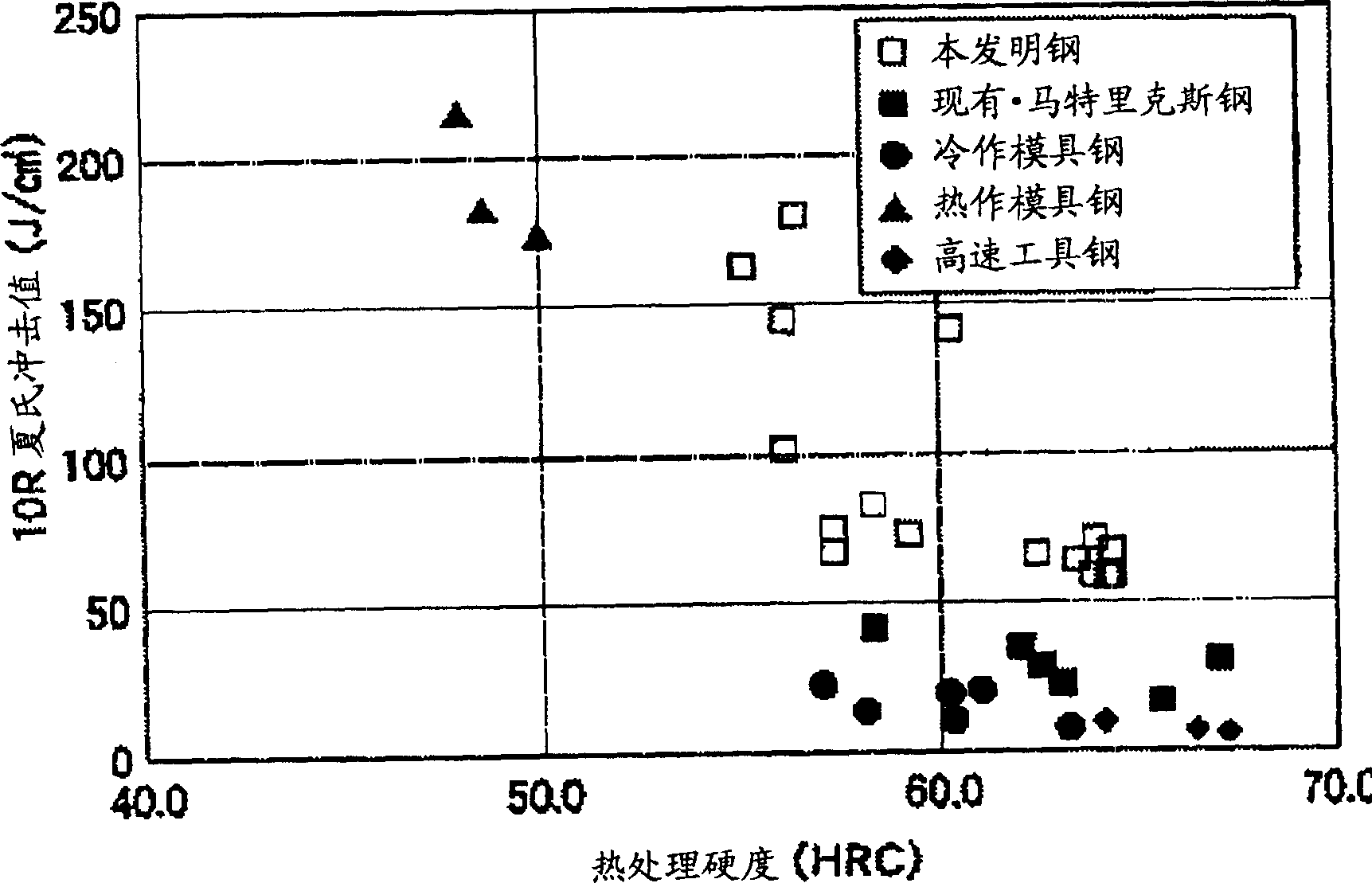
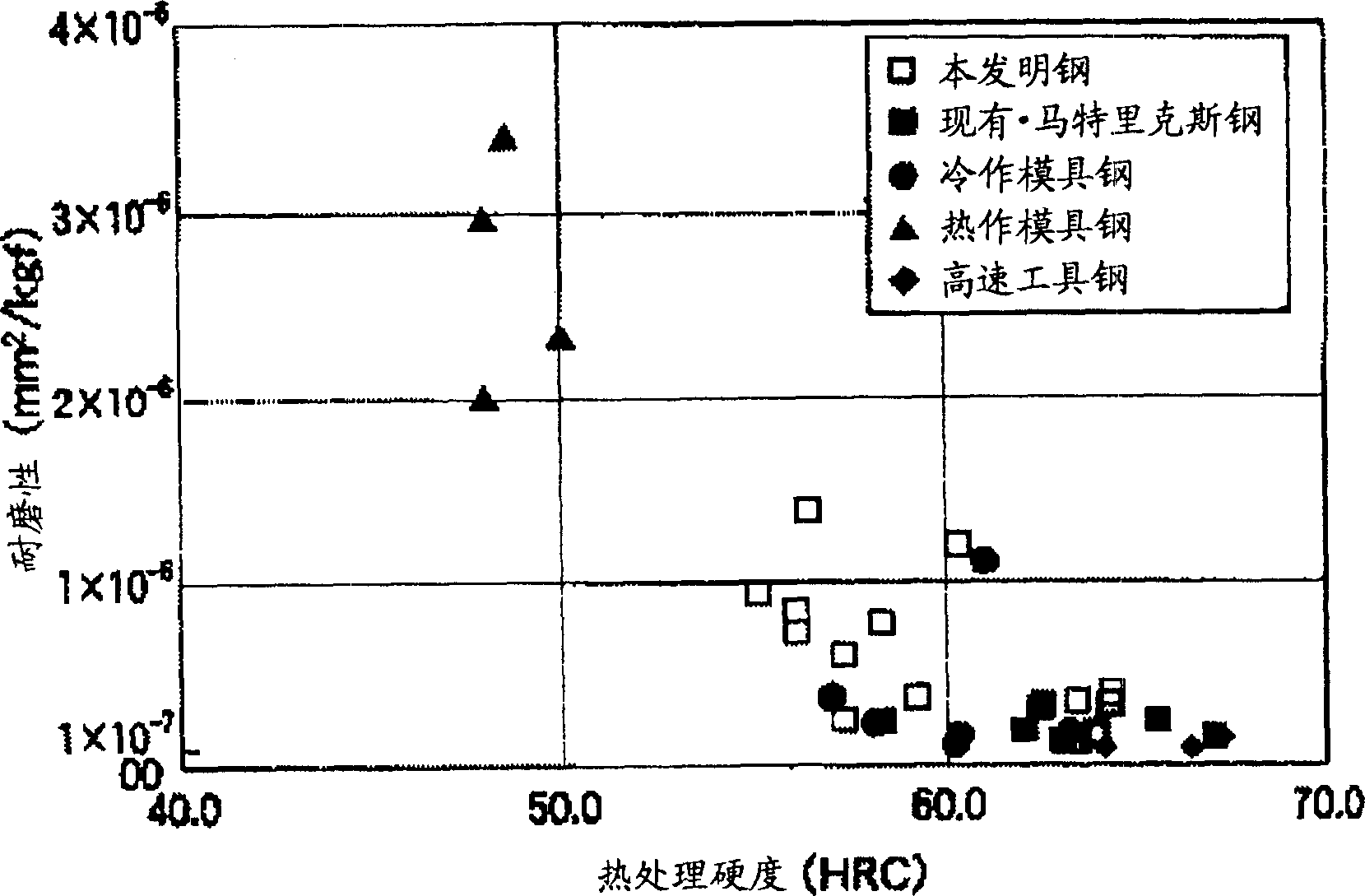
Thermal tool steel
A hot toolsteel comprises 0.10 to 0.70% C, 0.10 to 0.80% Si, 0.30 to 1.00% Mn, 0.007 to 0.020% P, 3.00 to 7.00% Cr, W and Mo in 0.20 to 12.00% in terms of (1 / 2W+Mo) alone or in combination, 0.10 to 3.00% V, 0.05 to 0.80% Ni, <=6.50% Co and <=0.150% S, and the balance substantially Fe with inevitable impurities. The cleanliness of nonmetallic inclusions is <=0.020%, and, on annealing, the area ratio of carbides and nonmetallic inclusions having particle diameters of >1.0 mu m is <=0.004%. The hot tool steel has improved heat check and erosion resistances, and has remarkably improved machinability by the above technical measure.
Owner:NIPPON KOSHUHA STEEL
Composite materials and methods for making same
InactiveUS8128861B1Suppress unwanted by-product chemical reactionsAmeliorate the tendency of molten siliconCeramic shaping apparatusArmour platesMotor ticsHigh pressure
Current top performing SAPI systems are B4C-containing (hot pressed B4C or reaction bonded B4C). These systems will not function well versus future WC / Co threats due to the inability of B4C to withstand high pressure impacts. New approaches will be needed for next generation SAPI ceramics. Three related concepts are disclosed herein, each of which will lead to improved reaction bonded ceramics for next generation SAPI applications. The first concept aims to reactively heat treat reaction bonded B4C, causing. SiC and SiB6 to form at the expense of B4C. The second approach will add Ti to the system, thus allowing TiC and TiB2 to form at the expense of B4C. Finally, the third concept will evaluate the use of finer particle sizes, thus improving the static properties of the ceramics (with the aim of enhancing multi-hit performance). In all cases, preliminary work has been conducted to demonstrate the viability of the concepts. This will lead to a new family of advanced armor ceramics. These new armor ceramics will allow the modern soldier to be better protected versus next generation, high level threats (e.g., high pressure WC / Co projectiles) with a more ergonomic package (lower weight, less bulk). Further, the results disclosed herein will yield improvement versus the current tool steel threats.
Owner:M CUBED TECH
Wear resistant hard coating for a workpiece and method for producing the same
ActiveUS7960016B2Excellent oxidation and hot hardness propertyImprove performancePigmenting treatmentMolten spray coatingWear resistantTitanium alloy
The present invention provides an optimized hard coating and a workpiece, especially a cutting tool coated with a hard coating to increase tooling performance with difficult to machine materials such as high speed steels, titanium alloys, nickel alloys, austenitic steels and especially hard materials like hardened tool steel having a hardness of higher 50, preferably of higher 55 HRC. This is achieved by a workpiece coated with a wear resistant multilayered comprising at least a first supporting layer and a second nanocrystalline layer, whereas the first layer comprises a coating material of the following composition (TiaAl1-a)N1-x-yCxOy with 0.4<a<0.6, and 0≦̸x and y<0.3, or (AlbCr1-b)N1-x-yCxOy with 0.5<b<0.7, and 0≦̸x and y<0.3. The second layer comprises a coating material of the following composition (Al1-c-d-eCrcSidMe)N1-x-yCxOy whereas M stands for at least one element of the transition metals of group 4, 5, 6 of the periodic system except Chromium and 0.2<c≦̸0.35, 0<d≦̸0.20, 0<e≦̸0.04.
Owner:OERLIKON SURFACE SOLUTIONS AG PFAFFIKON
Iron-based alloy powder for laser cladding of TRT (Blast Furnace Top Pressure Recovery Turbine Unit) parts
ActiveCN102352508AImprove performanceModerate hardnessMetallic material coating processesHeat stabilityNickel alloy
The invention discloses iron-based alloy powder for the laser cladding of TRT (Blast Furnace Top Pressure Recovery Turbine Unit) parts. As for the powder, on the basis of an iron-nickel-chromium alloy, Mo, Nb, N and Si element strengthening matrixes are added, and the alloy melting point is reduced while the moderate hardness is kept, and the comprehensive properties such as high strength, abrasion resistance and the like are ensured, thus being convenient for laser cladding; and trace elements Ce and Hf are added to improve the crystal boundary quality, inhibit and prevent cracks, improve the heat stability and chemical stability of a cladding layer and endow the alloy with oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance under a higher temperature and wider application range. Failed parts made from carbon steel, structural steel, hardened and tempered steel, stainless steel, tool steel and other materials can be repaired by using the powder and combining the laser cladding technology, thus the powder has wide application prospects and obvious benefits.
Owner:河北瑞兆激光再制造技术股份有限公司
Alloy tool steel and production method thereof
InactiveCN105177430AHigh hardnessImprove toughnessIncreasing energy efficiencyChemical compositionHardness
The invention discloses an alloy tool steel and a production method thereof. The steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.5% of C, 0.2% of Si, 0.5% of Mn, 5.0% of Cr, 2.3% of Mo, 0.5% of V, at most 0.003% of S, at most 0.02% of P and the balance of Fe. The hardness of the alloy tool steel is HRC56-58. Compared with the existing alloy tool steel, the alloy tool steel disclosed by the invention has the advantages of higher hardness, excellent toughness, excellent ductility, excellent wear resistance, excellent hardenability and excellent heat treatment dimensional stability, can be used for producing hot-working molds, can also be used for producing cold working molds and engineering steel, and thus, has wider application range.
Owner:NINGBO DEKE PRECISION MOLDING +1
Novel over-speed bright quenching oil composition and preparation method thereof
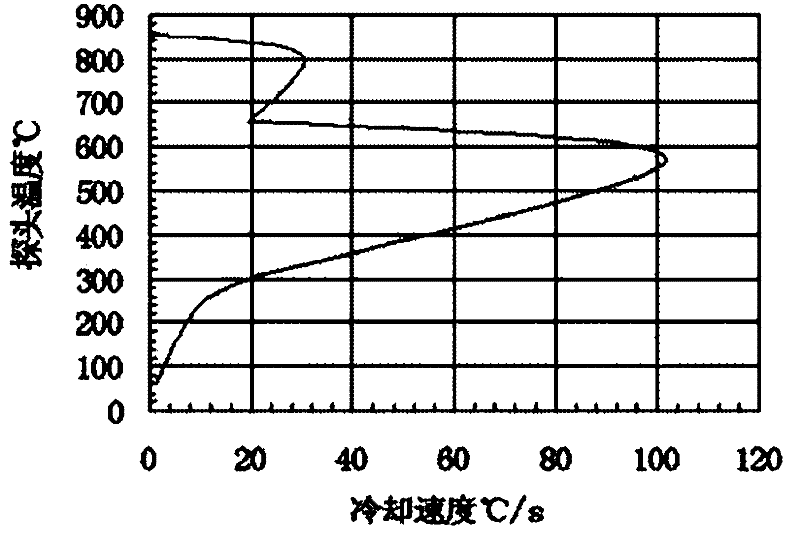
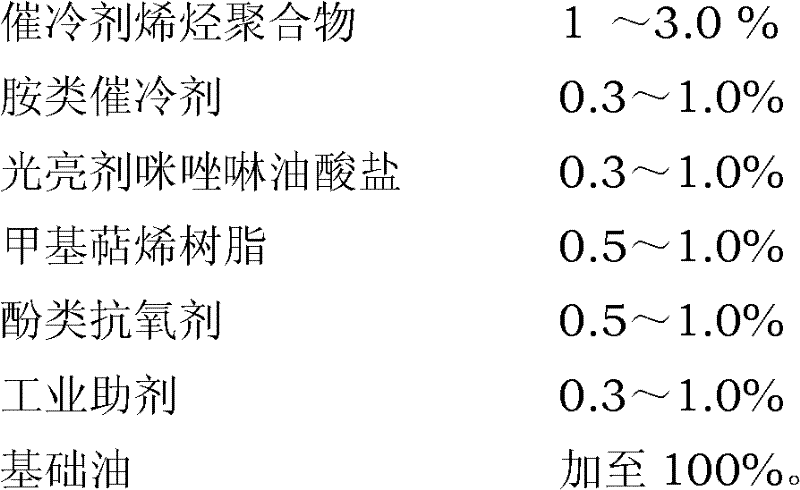
InactiveCN102392110AIncrease brightnessImprove anti-agingQuenching agentsHeat stabilityOxidation stability
The present invention relates to a novel over-speed bright quenching oil composition, which contains mineral lubricating oil, a cooling accelerant, anti-oxidation additives and brightening additives. The quenching oil has good cooling properties, heating stability, oxidation stability and brightness. The preparation process of the quenching oil is simple, and the raw materials are domestic and therefore easy to get with low price. The quenching oil is suitable for the quenching of spring steel, bearing steel and mold steel and large-sized steel, particularly for the quenching of small-sized and medium-sized carbon tool steel.
Owner:TIANJIN ZHONGCHUAN LUBRICANT
Alloy tool steel and manufacturing method thereof
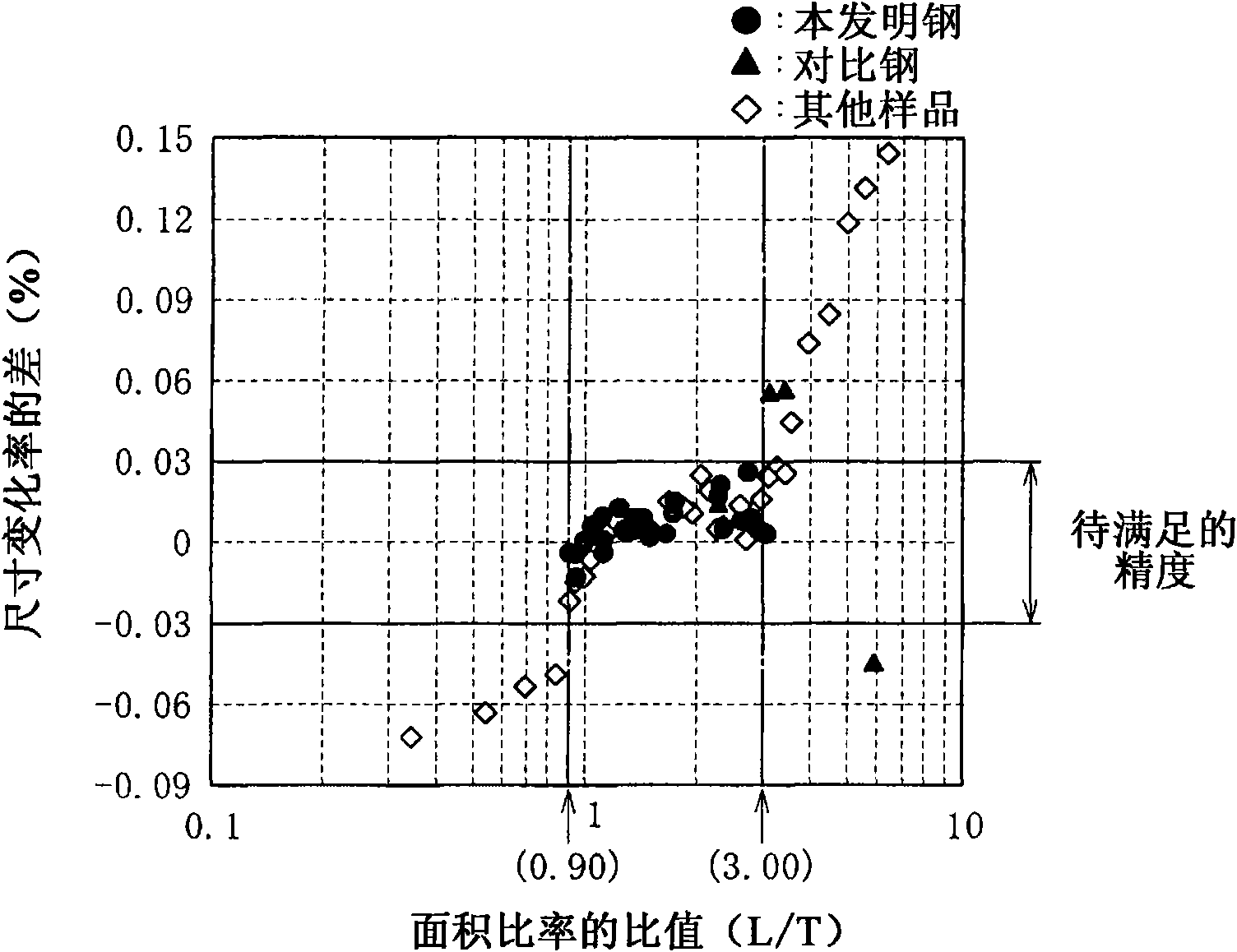
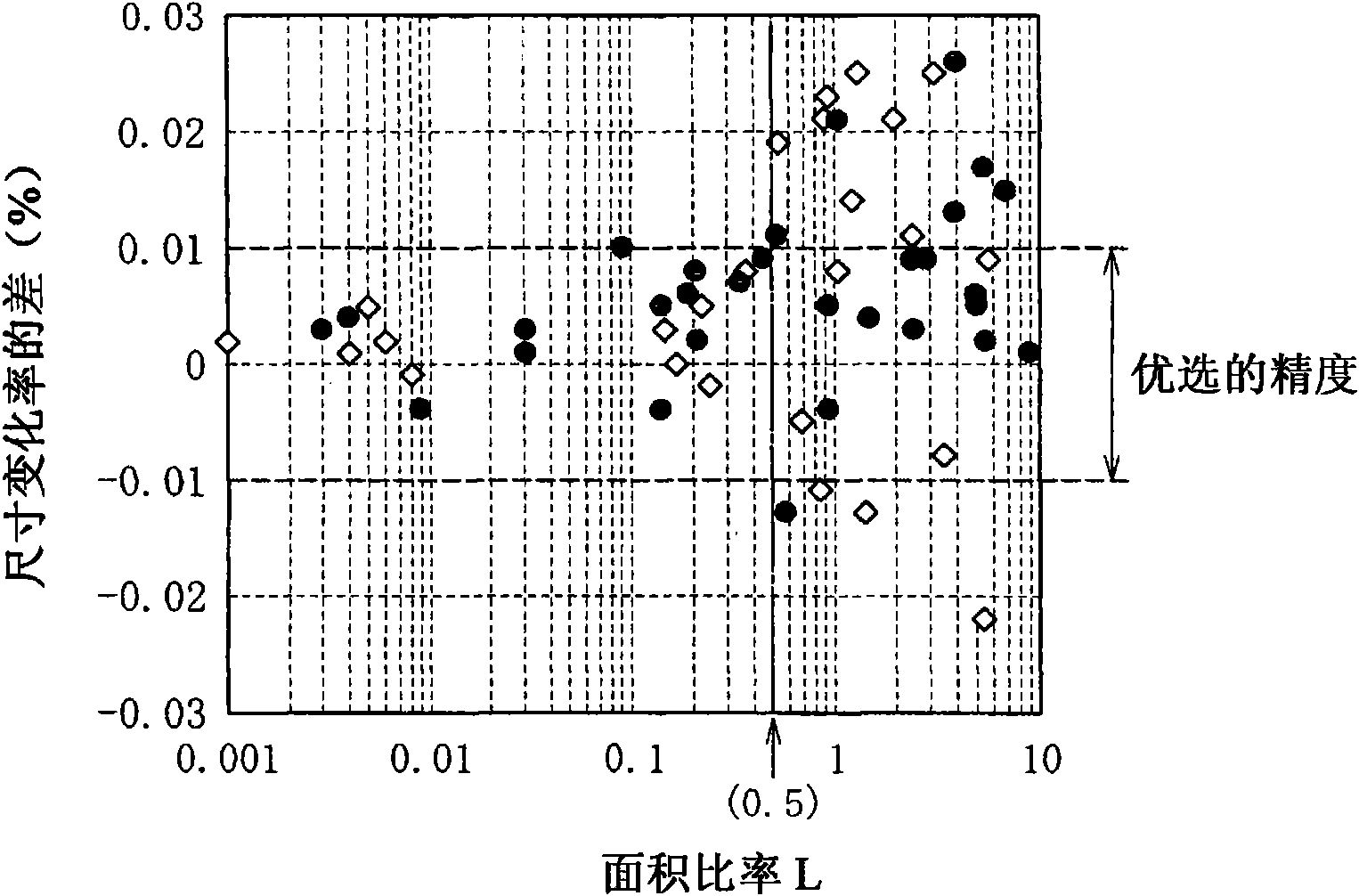
The present invention provides a tool steel containing, by mass percent, 0.55 to 0.85% of C, 0.20 to 2.50% of Si, 0.30 to 1.20% of Mn, 0.50% or less of Cu, 0.01 to 0.50% ofNi, 6.00 to 9.00% of Cr, 0.1 to 2.00% of Mo+0.5W, and 0.01 to 0.40% of V, with the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, in which, when an area rate of a coarse carbide having a circle equivalent diameter of 2 [mu]m or more in a cross section parallel to a forging direction is represented by L(%) and an area rate of the coarse carbide in a cross section perpendicular to the forging direction is represented by T(%), the area rate L is 0.001 % or more, the area rate T is 0.001 % or more, and the ratio L / T is within a range from 0.90 to 3.00. The tool steel of the invention exhibits an isotropic size change in quenching and tempering.
Owner:DAIDO STEEL CO LTD
Preparation method of chromium-aluminum-nitrogen film by closed field unbalanced magnetron sputtering
InactiveCN101575696AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh hardnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAluminum IonShielding gas
The invention relates to a preparation method of a chromium-aluminum-nitrogen film by closed field unbalanced magnetron sputtering, which comprises the following steps: a chromium-tungsten-manganese steel plate is taken as a basal body, chromium and aluminum as a target source of metal ion, nitrogen gas as reactant gas, and argon gas as ion bombardment gas and protection gas; in a vacuum sputtering furnace, in a closed magnetic field state, in the argon gas and at the temperature of 300 DEG C, the surface of the chromium-tungsten-manganese steel plate is sputtered with chromium ion, aluminum ion and nitrogen ion and the chromium-aluminum-nitrogen hard film is formed on the surface of the steel plate, and then the low temperature tempering and alloying solid solution are conducted, thus greatly improving mechanical property, hardness, intensity, abrasive resistance and erosion resistance of the surface of the chromium-tungsten-manganese steel plate. The mechanical property of the chromium-tungsten-manganese steel plate can be improved by 466% compared with that of hardened steel plates. The preparation method has short process flow, precise technique, accurate and detailed measurement values, the film with thickness of 4,600nm, and the alloy layer with good solid solution effect and being not easy to peel off, thus being the ideal treatment method for strengthening and hardening the surface of alloy tool steel.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Processing Technology of Small Diameter, Thin Wall, Deep Hole and High Precision Parts and Its Special Grinding Tools
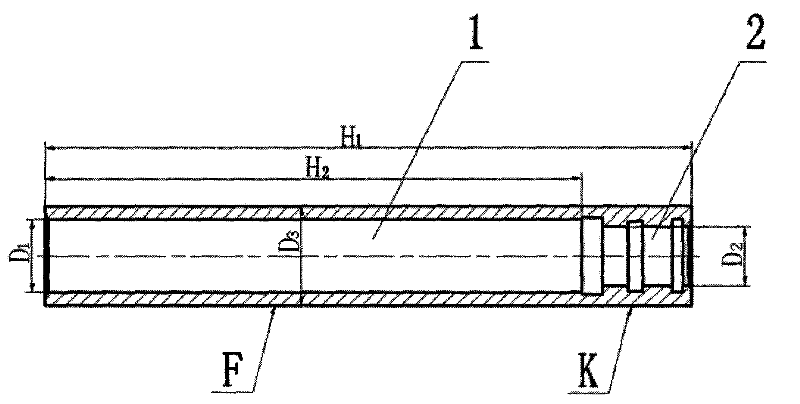
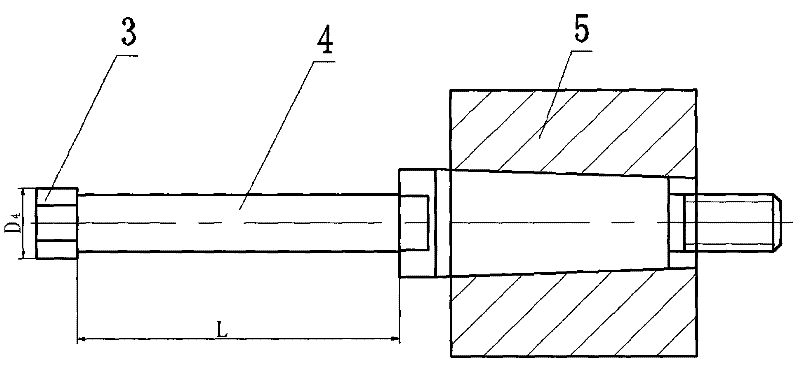
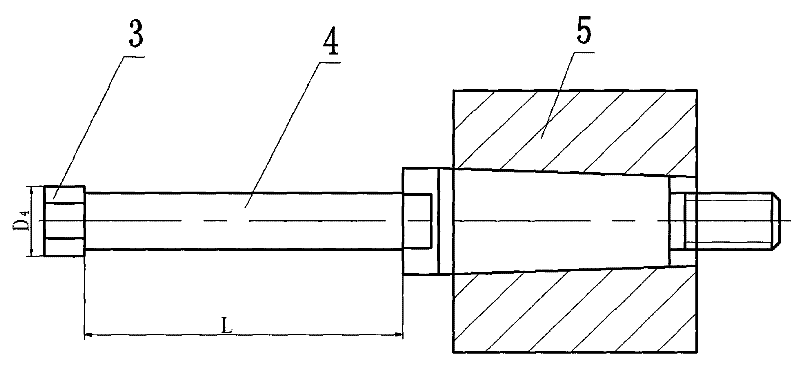
The invention relates to a processing technology of small-diameter, thin-walled, deep-hole, high-precision parts and its special grinding tool, which relates to a processing technology of thin-walled, deep-hole, high-precision parts and its special grinding tool. The invention solves the problems that it is difficult to meet the design requirements and processing difficulties of the cylinder body parts by conventional mechanical processing methods. The process steps of the present invention are as follows: turning the outer circle and end face of the blank, and adopting a stepwise progressive drilling method to drill through the first inner hole and the second inner hole layer by layer; The head rotates, and the parts make a low-speed rotary motion relative to the grinding head, and the grinding head grinds the parts to complete the processing of the parts. The end of the extended handle of the grinding tool adopts a Morse taper structure, and the grinding head is fixedly installed at the head end of the extended handle. The grinding head is made of white jade, and the extended handle is made of alloy tool steel. The processing technology of the invention is especially suitable for the manufacturing technology of small-diameter, thin-walled, deep-hole and high-precision parts in the field of mechanical processing.
Owner:HARBIN JIANCHENG GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com