Method of making rotary cutting dies
a cutting die and rotary technology, applied in the field of rotary cutting dies, can solve the problems of difficult manufacture and resharpening, and achieve the effects of accurate positioning of workpieces, reducing cutting force, and prolonging useful life in servi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
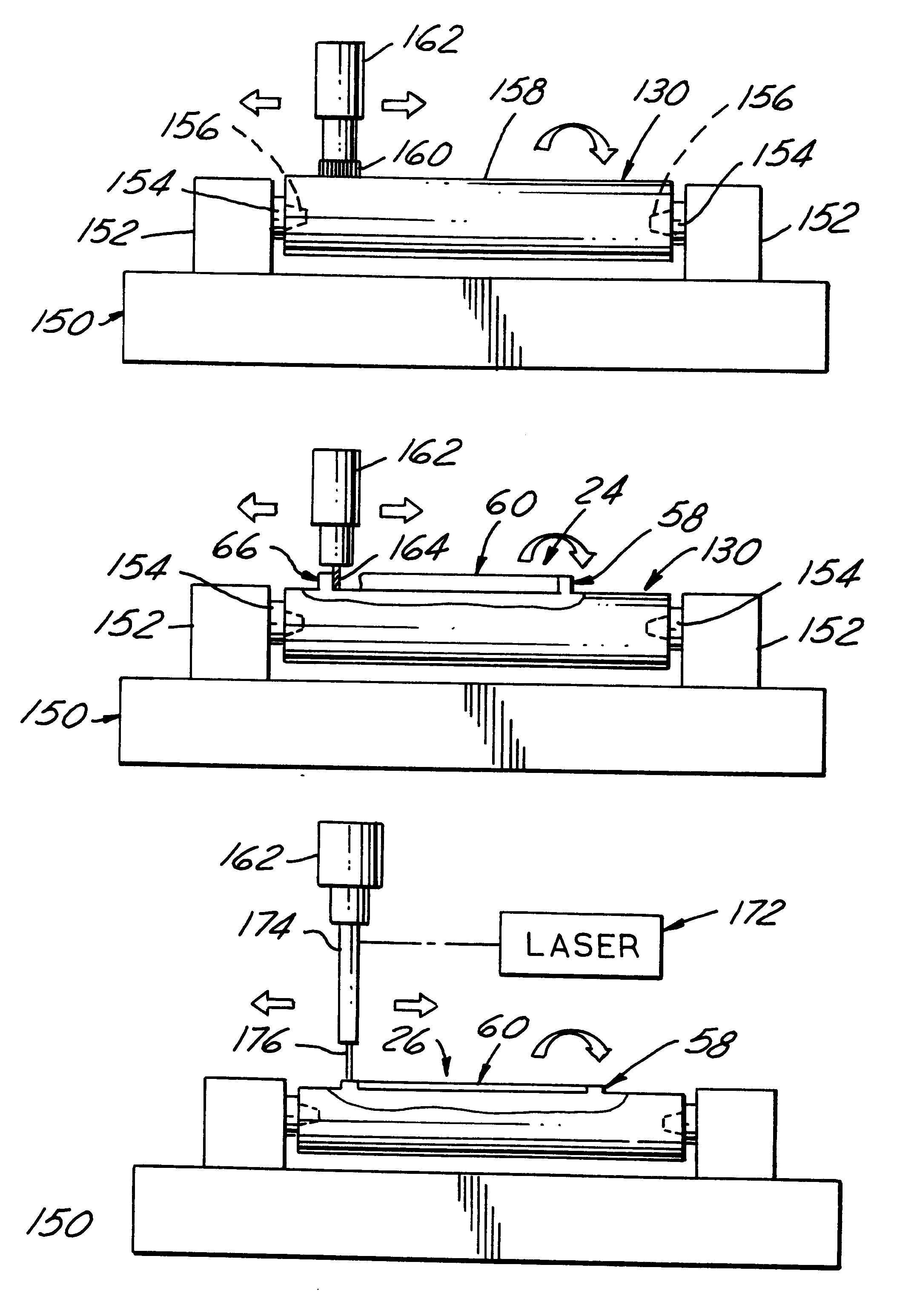
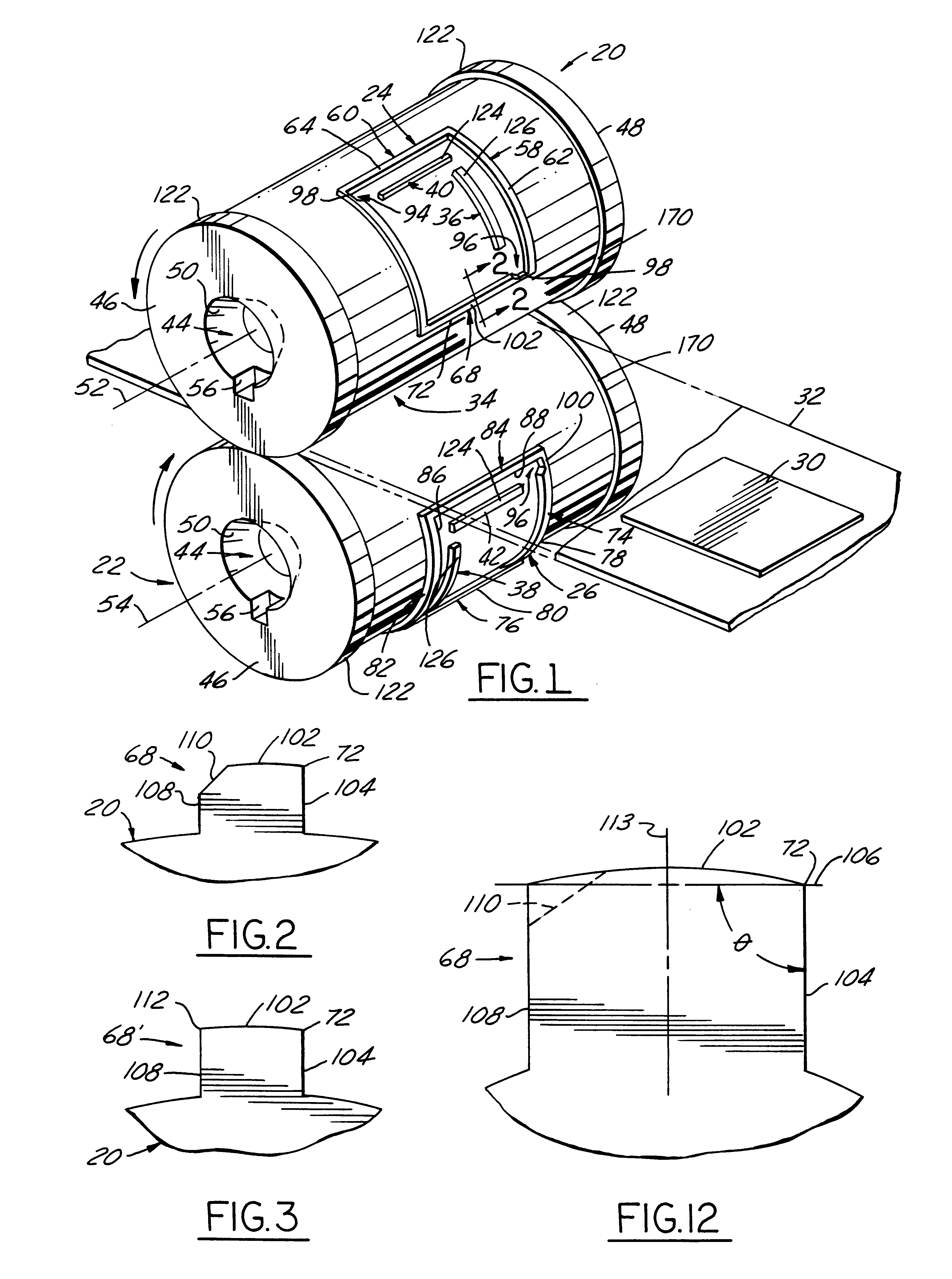
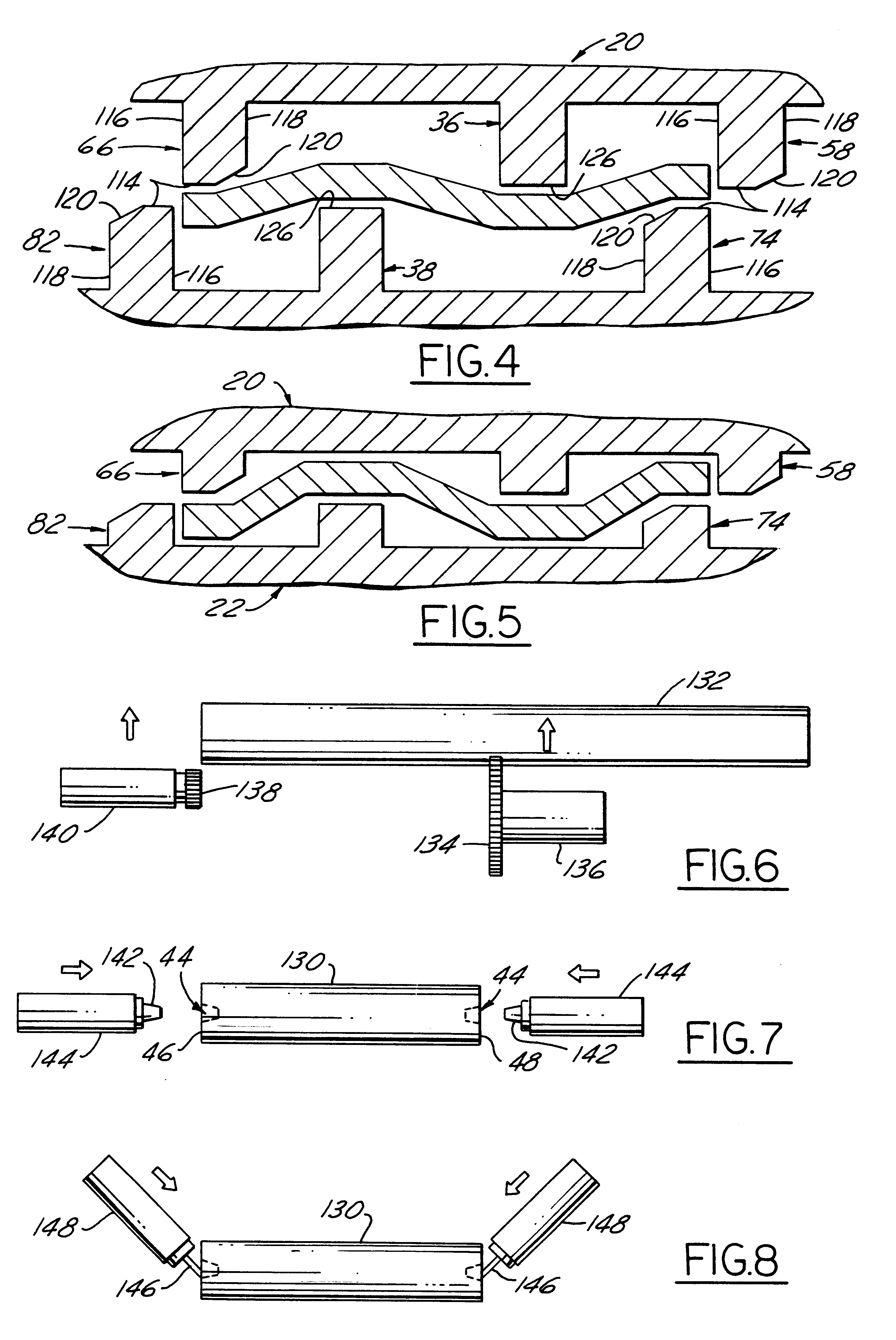
Referring in more detail to the drawings, FIG. 1 illustrates a pair of cutting die cylinders 20 and 22 embodying this invention with coacting cutting blades 24 and 26 thereon which when the cylinders are co-rotating cut generally rectangular blanks 30 from a web 32 of thin material, such as paper board, passing through the nip 34 of the die cylinders. Preferably, removal of blanks from the die cylinders is facilitated by pairs of ejector lands 36, 38 and 40, 42 within the perimeter of the cutting blades.
In use, each die cylinder is journalled for rotation by a pair of arbor assemblies having coaxial spindles with opposed noses (not shown), received in complementary recesses 44 in the opposed ends 46 and 48 of each die cylinder. Each recess is a bore with a frusto conical sidewall 50 tapered inwardly from its associated cylinder end which provides a locator surface engagable with a complementary tapered surface on the nose of an associated spindle. For each die cylinder, the frusto c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com