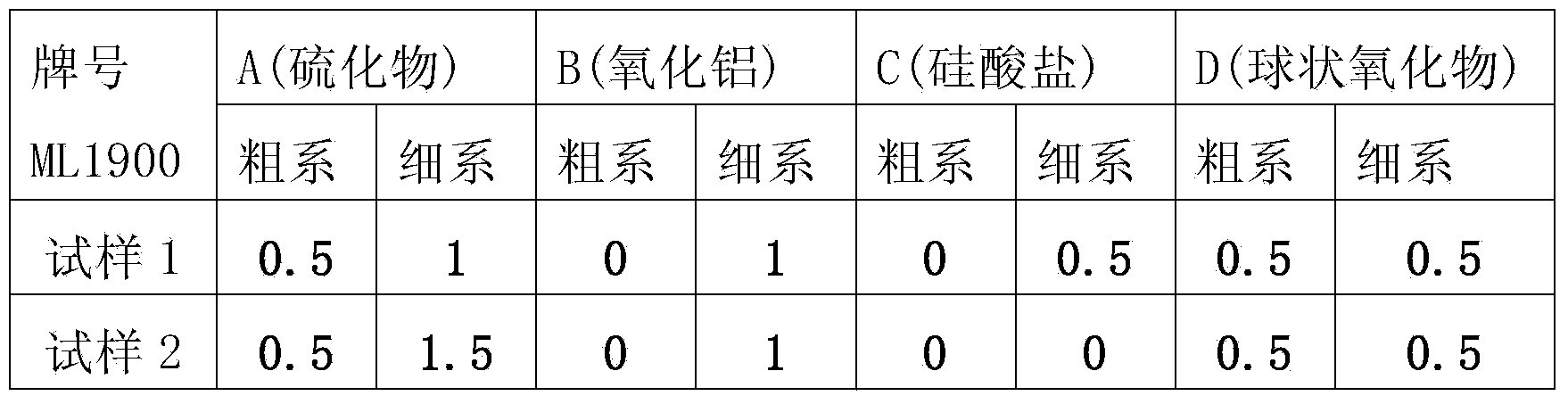
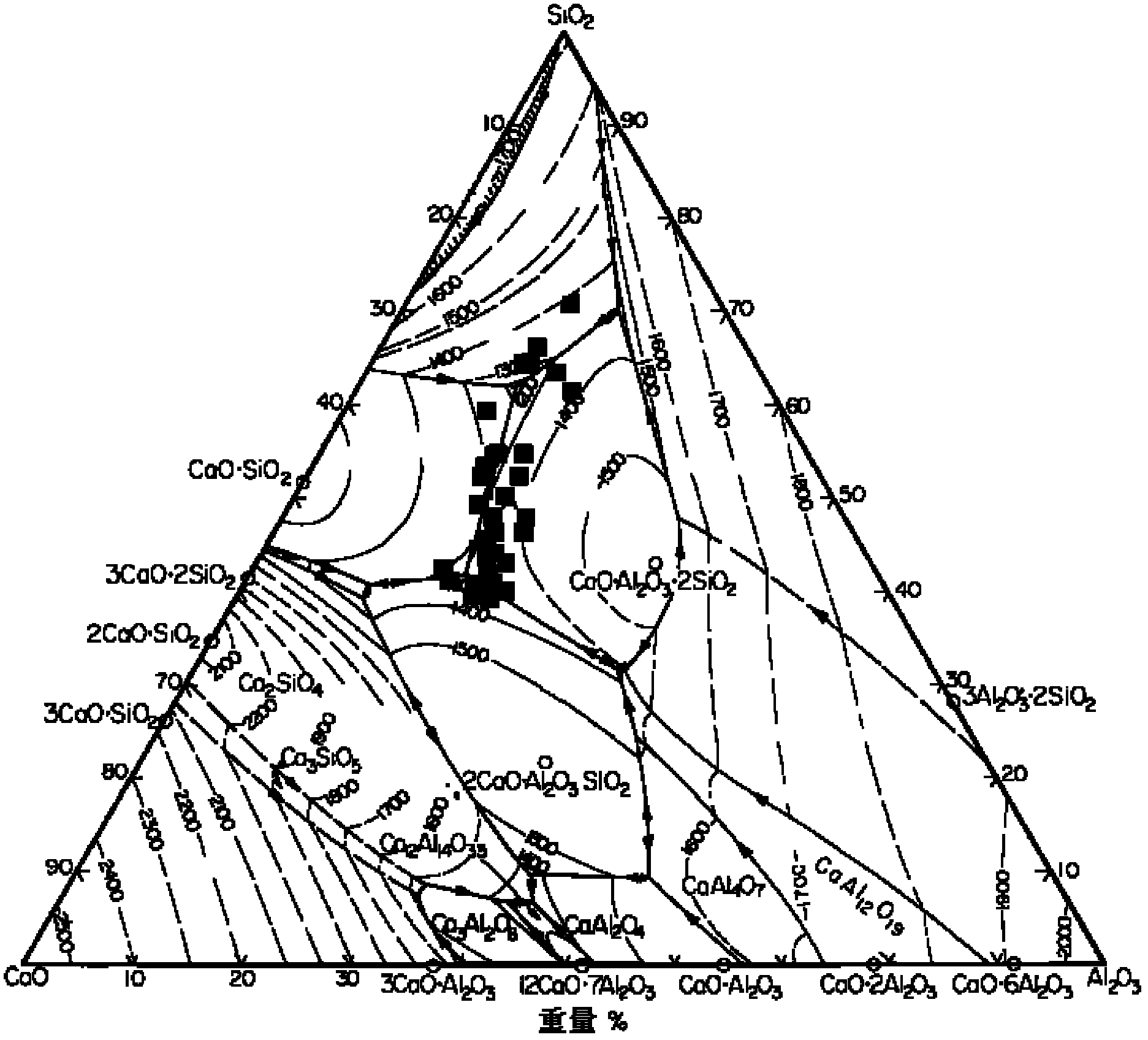
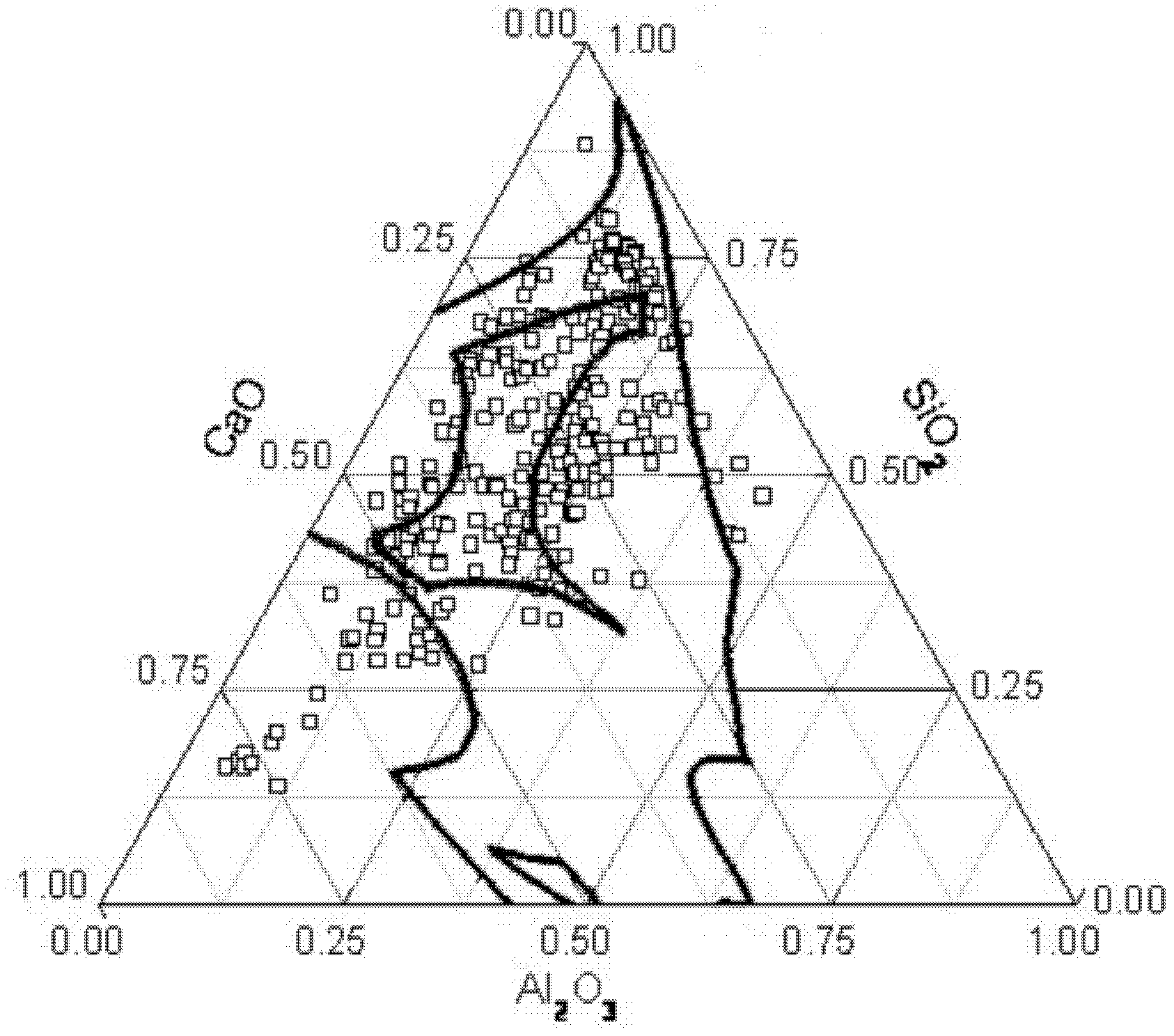
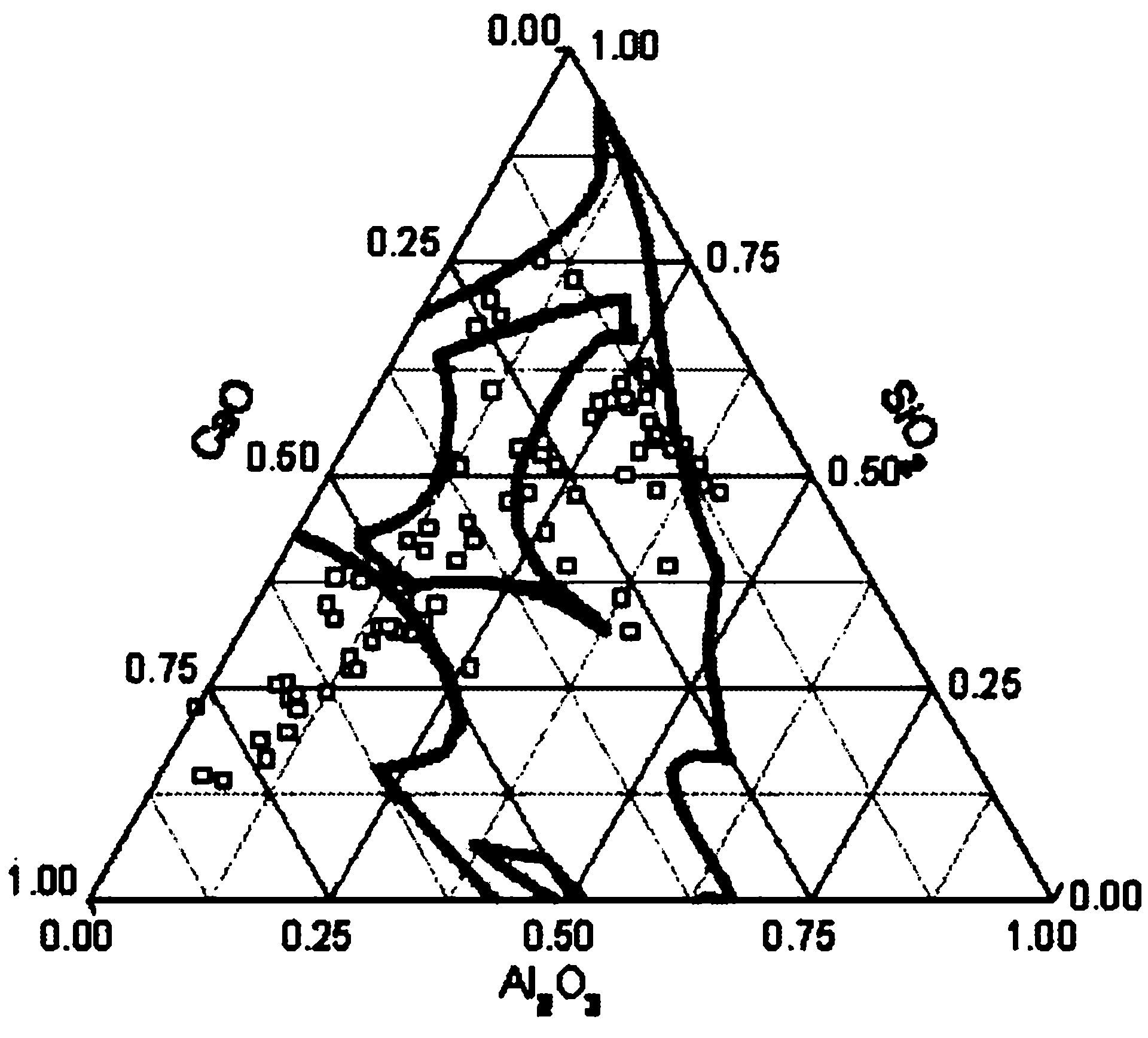
Patents
Literature
807 results about "Non-metallic inclusions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Non-metallic inclusions are chemical compounds and nonmetals that are present in steel and other alloys. They are the product of chemical reactions, physical effects, and contamination that occurs during the melting and pouring process. These inclusions are categorized by origin as either endogenous or exogenous. Endogenous inclusions, also known as indigenous, occur within the metal and are the result of chemical reactions. These products precipitate during cooling and are typically very small. Exogenous inclusions are caused by the entrapment of nonmetals. Their size varies greatly and their source can include slag, dross, flux residues, and pieces of the mold.
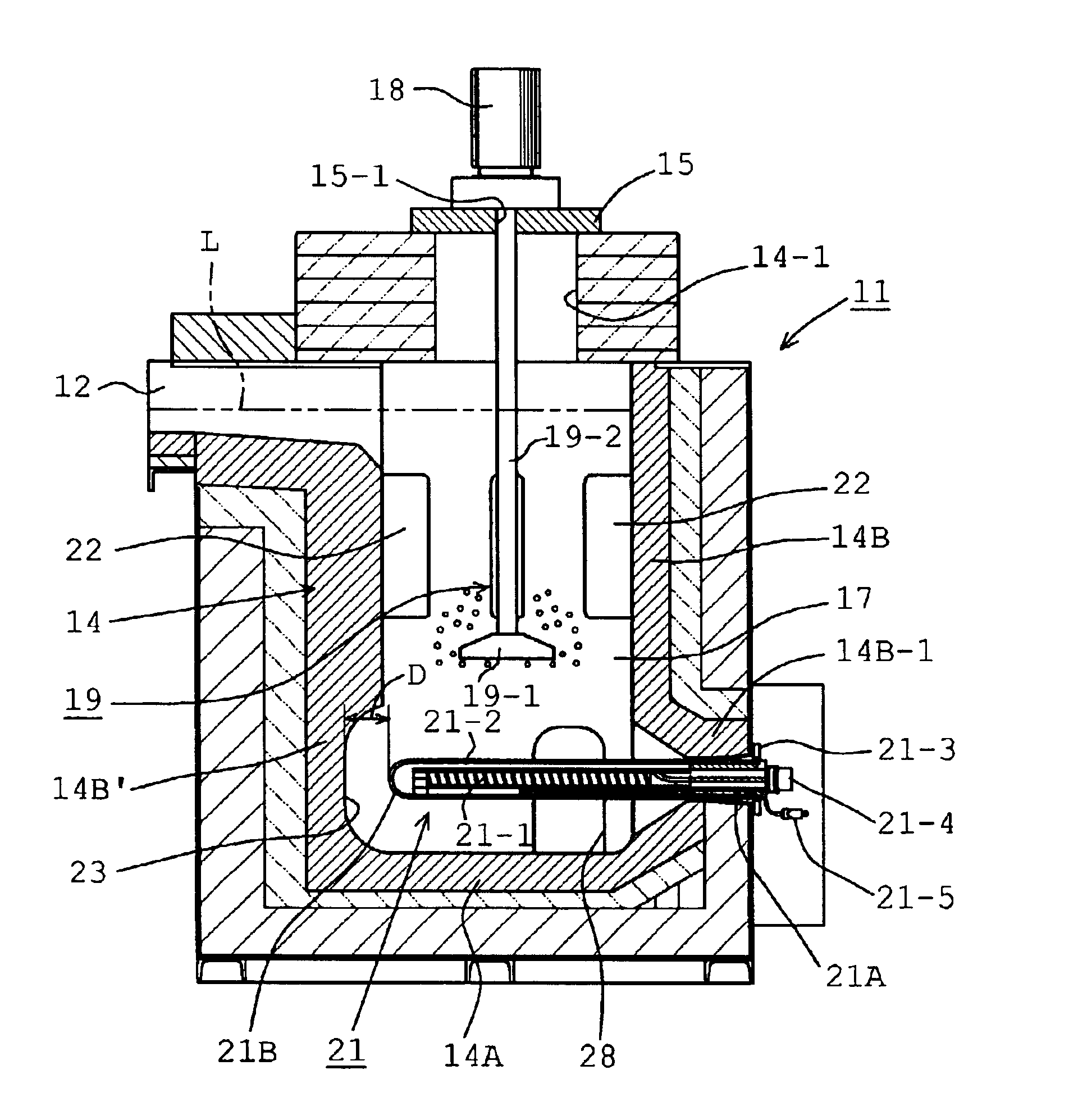
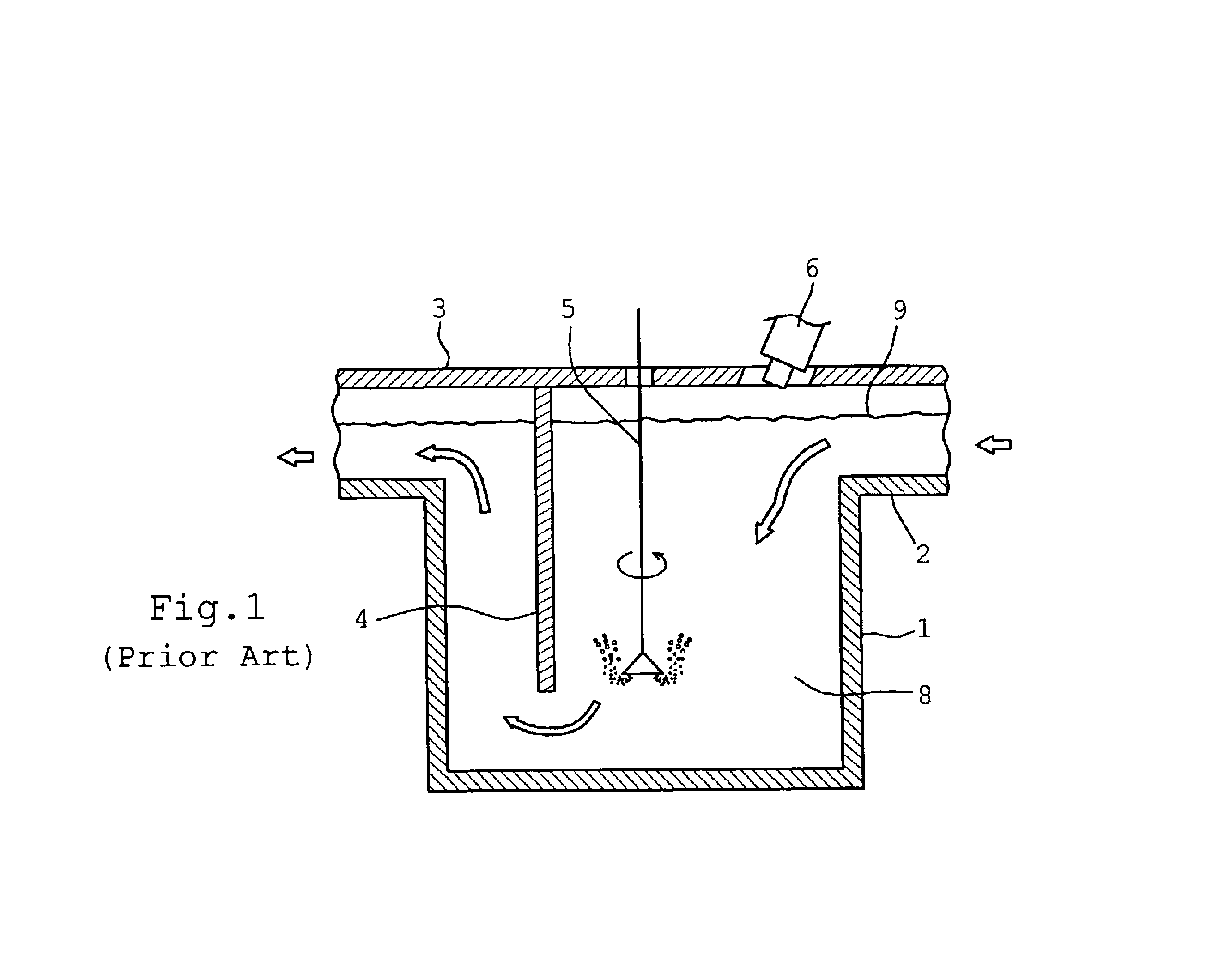
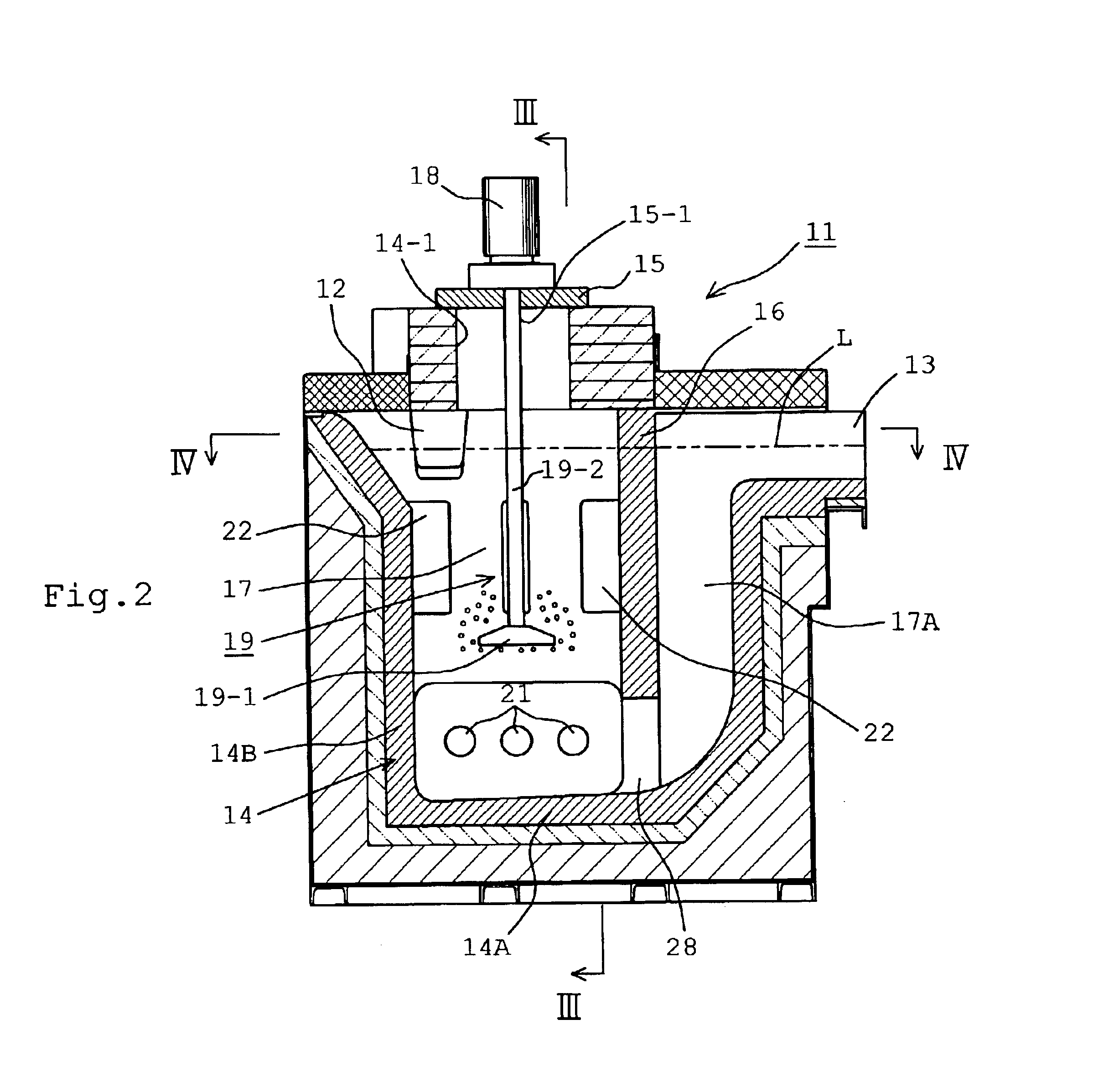
Inline degassing apparatus
InactiveUS6887424B2Reduce the amount requiredSmall volumeMelt-holding vesselsMechanical apparatusNon-metallic inclusionsSolid solution
An inline degassing apparatus for removing solid solution gases as well as nonmetallic inclusions from molten metal in a degassing container, to which the molten metal is continuously introduced for degassing operation and from which the degassed molten metal is continuously removed. A rotary diffusing device is arranged in the degassing container for generating bubbles of inert gas diffused into the molten metal, thereby entrapping solid solution gases as well as nonmetallic inclusions into the bubbles, which are then floated and separated. Heaters are provided, which extend, in a cantilever fashion, from a side wall of container at a position adjacent the bottom wall of the container substantially parallel to the bottom wall.
Owner:PYROTEK JAPAN +1
Steel wire for high-strength springs and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6338763B1Reduce contentReduce sizeFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesNon-metallic inclusionsHigh intensity
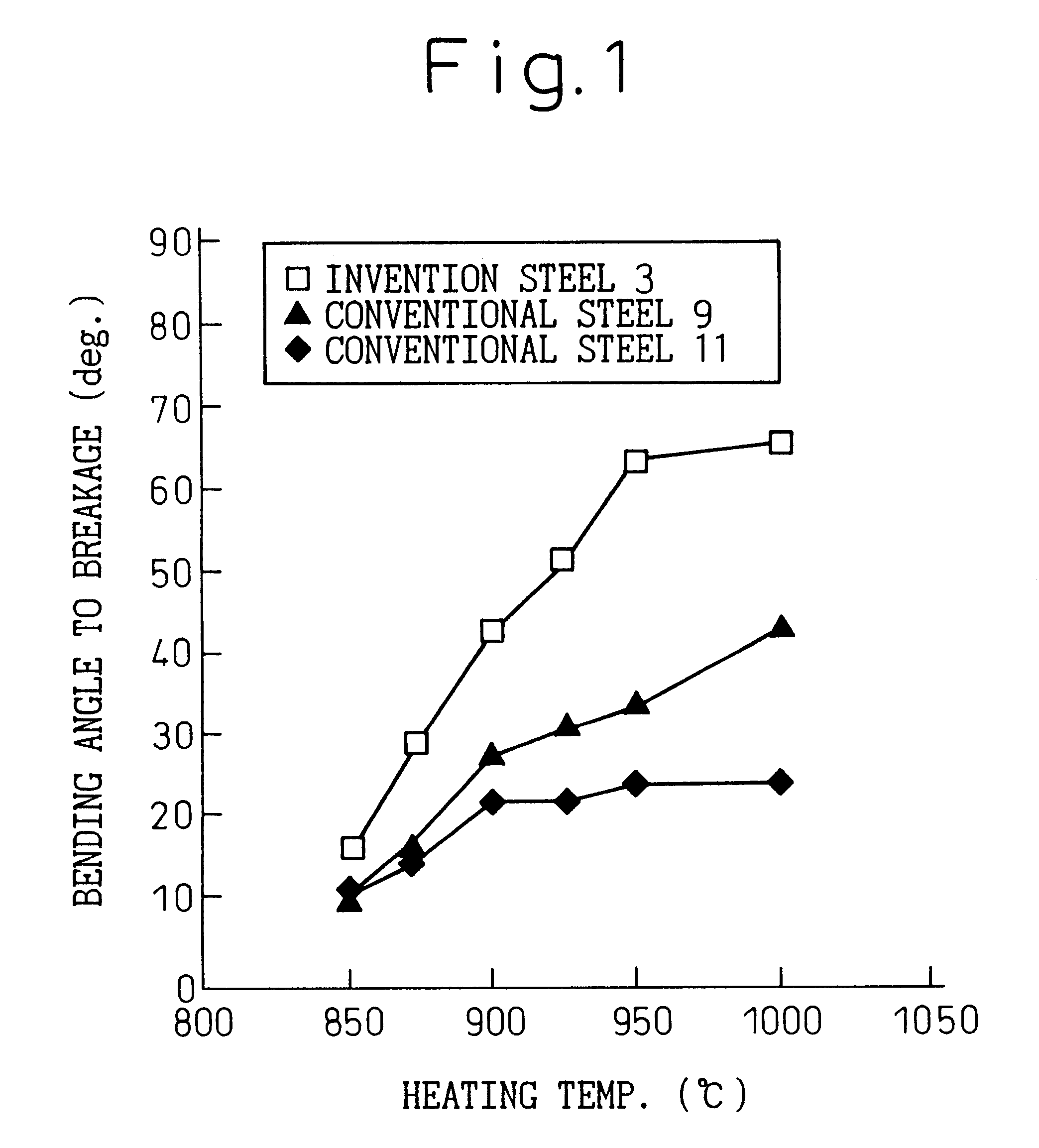
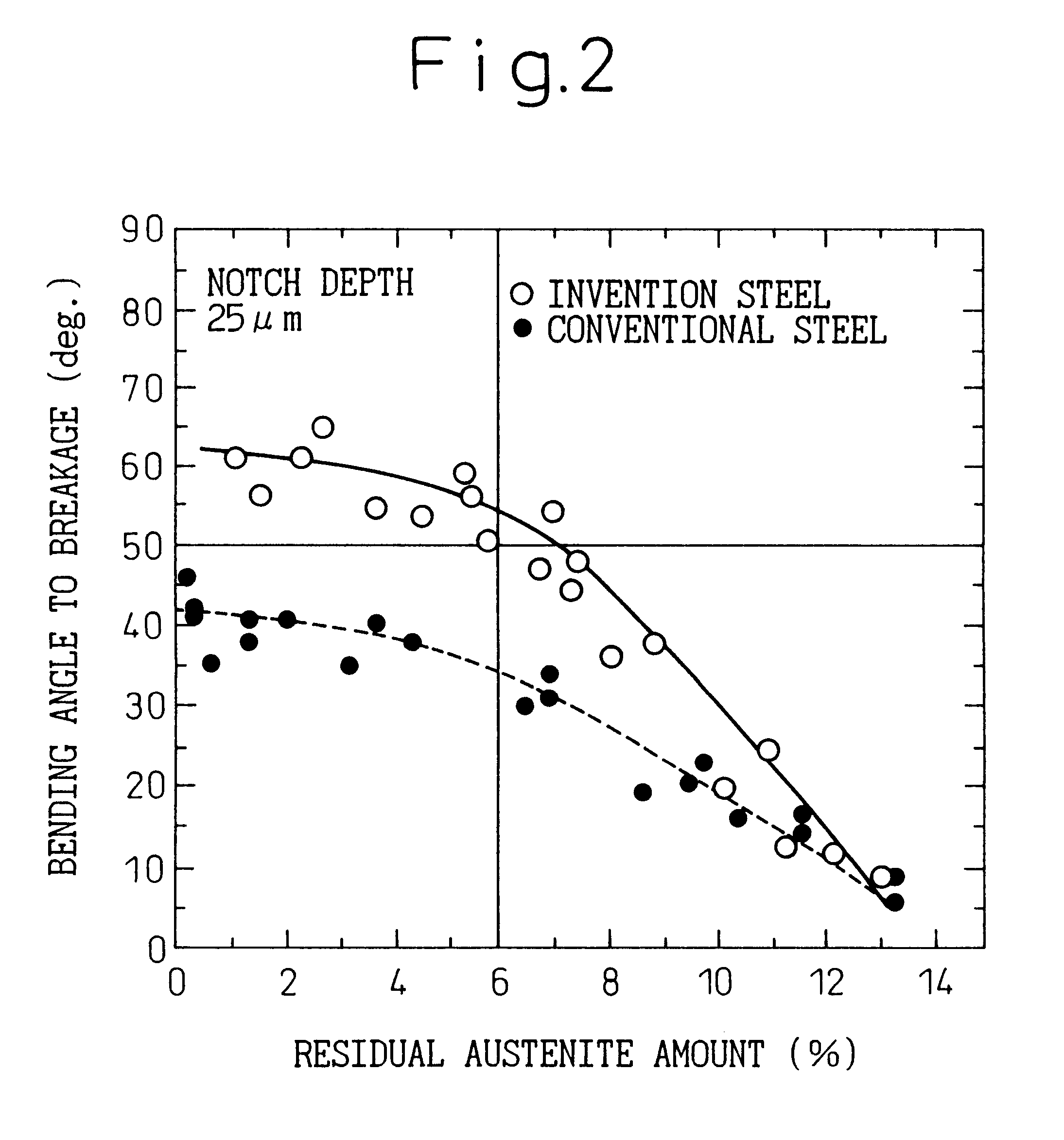
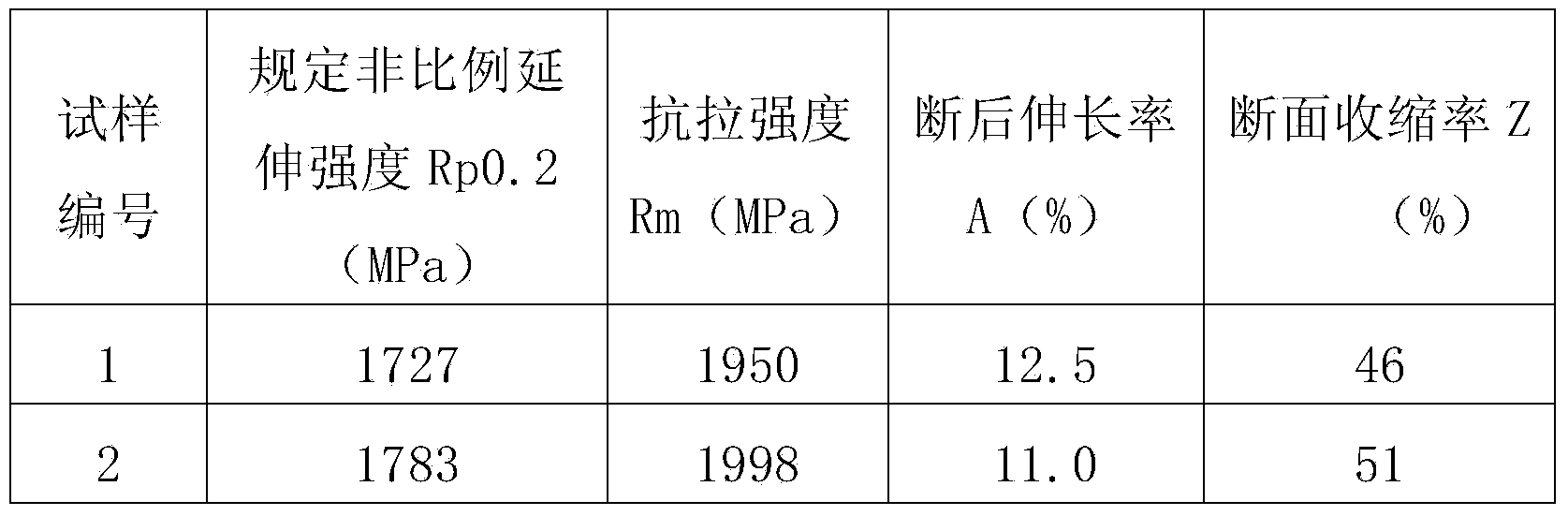
This invention provides an oil-tempered wire having high strength (tensile strength of not less than 1960 MPa) and excellent workability and specifically provides a steel wire for high-strength springs comprising as steel components, in weight percent,the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities, the steel wire having no nonmetallic inclusions of a size greater than 15 mum, a tensile strength of not less than 1960 MPa, and a yield ratio (sigma0.2 / sigmaB) of not less than 0.8 and not greater than 0.9 or a yield ratio (sigma0.2 / sigmaB) of not less than 0.8 and an amount of residual austenite of not greater than 6%. This invention also provides a method of producing the steel wire.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
High-cleanliness pipeline steel smelting process
ActiveCN104630418ASolve the difficulty of cleanliness controlQuality improvementManufacturing convertersSulfurNon-metallic inclusions
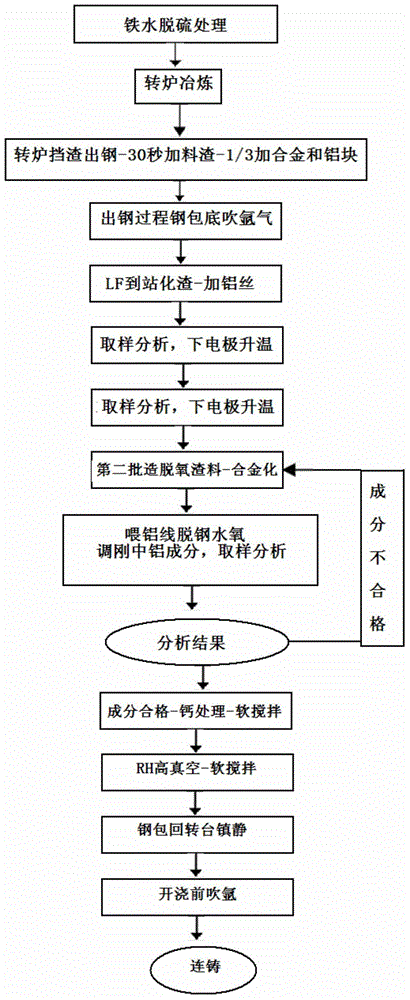
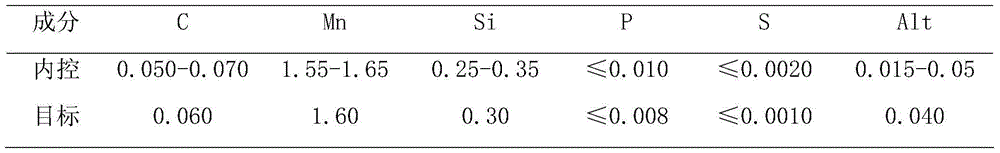
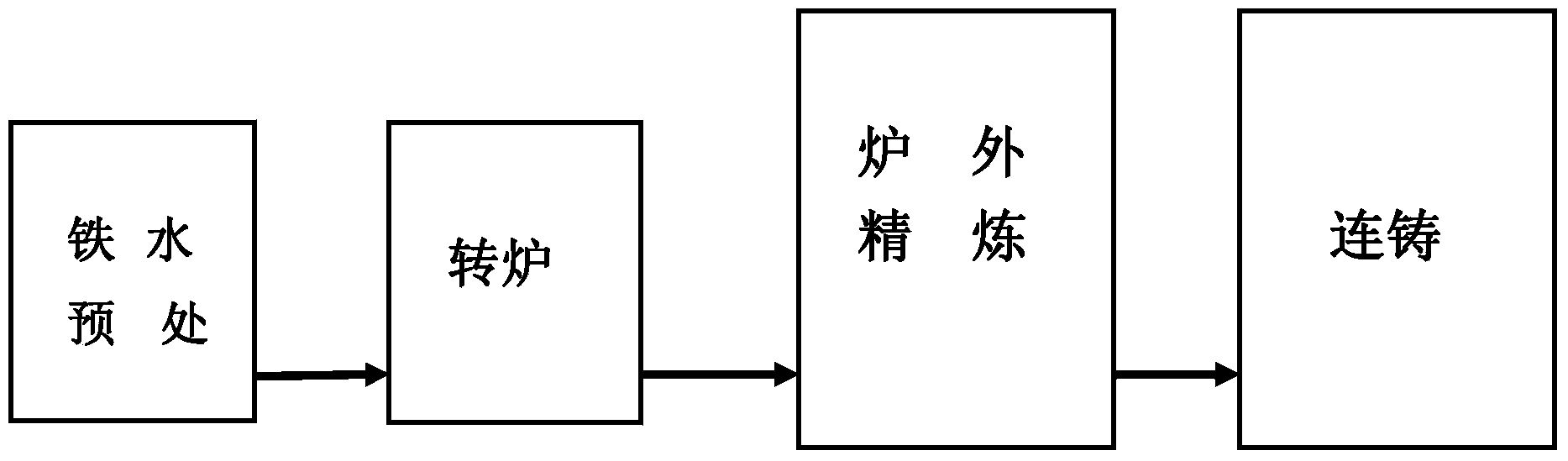
The invention discloses a high-cleanliness pipeline steel smelting process. The process route comprises molten iron pouring, molten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, tapping, deoxidizing, alloying, LF refining furnace, treating with calcium, RH vacuum furnace and continuous casting and is characterized by comprising the following specific steps: firstly, converter smelting process; secondly, refining furnace smelting process; and thirdly, continuous casting process. The invention belongs to a steel-making process in the field of metallurgy and relates to a method for smelting and controlling a high-cleanliness pipeline steel. By molten iron desulphurization pretreatment, optimizing a converter tapping and deoxidizing system and a slagging system, LF refining furnace deep deoxygenation and reducing slag manufacturing processes, RH high-vacuum-degree degassing and inclusion removal process, the pouring is protected by the continuous casting in the whole process so that the composition of a casting billet is uniform, the contents of harmful elements such as S, P, O, N and H are low, the non-metallic inclusions are effectively controlled, the casting billet is good in internal quality and the production of high value-added ultra-low sulfur steel is ensured.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Rapid detection method and rapid detection device of non-metallic inclusions in metal
ActiveCN103123329AQuickly obtain 3D topographyQuick access to ingredientsUsing optical meansMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionImaging analysisNon-metallic inclusions
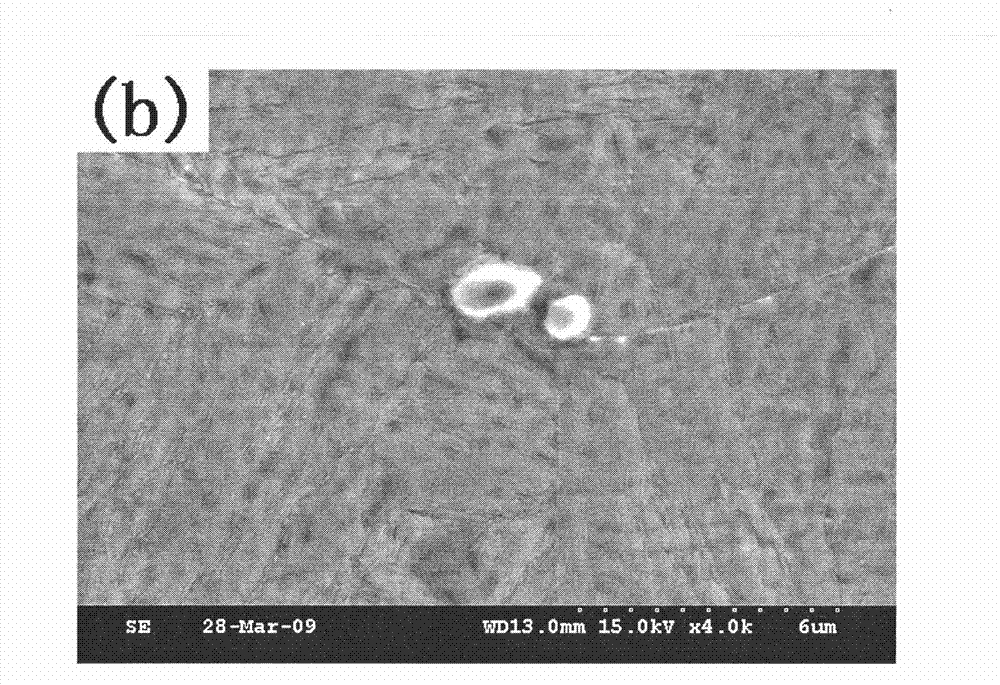
The invention discloses a rapid detection method of non-metallic inclusions in metal. The rapid detection method comprises the following five steps of: heating and smelting a metal test sample, separating the inclusions, detecting the total amounts and the sizes of the inclusions, condensing metal liquid, and detecting the three-dimensional shape and components of the inclusions. The invention further provides a special rapid detection device comprising a heating furnace device, a metal liquid rotation device, a video collection device and an image analysis system. The metal test sample is rapidly smelted and the steel liquid is driven to rotate; centrifugal force and gravity are used for rapidly upwards floating various non-metallic inclusions in the metal liquid and gathering the various non-metallic inclusions at the center of the surface of the metal liquid; high speed photography and video analysis software is used for rapidly obtaining the total amount and the size distribution of the non-metallic inclusions in the metal test sample; the metal liquid is rapidly cooled and condensed and the inclusions are cured on the surface of the metal test sample; and a scanning electron microscope and the energy spectrum analysis are used for obtaining the three-dimensional shapes and the components of the non-metallic inclusions in the metal test sample. According to the rapid detection method and the device disclosed by the invention, the direction is rapid and convenient, the analysis is accurate and visual, and cleaning and no pollution can be realized.
Owner:新兴发展集团有限公司
Steel for steel pipes
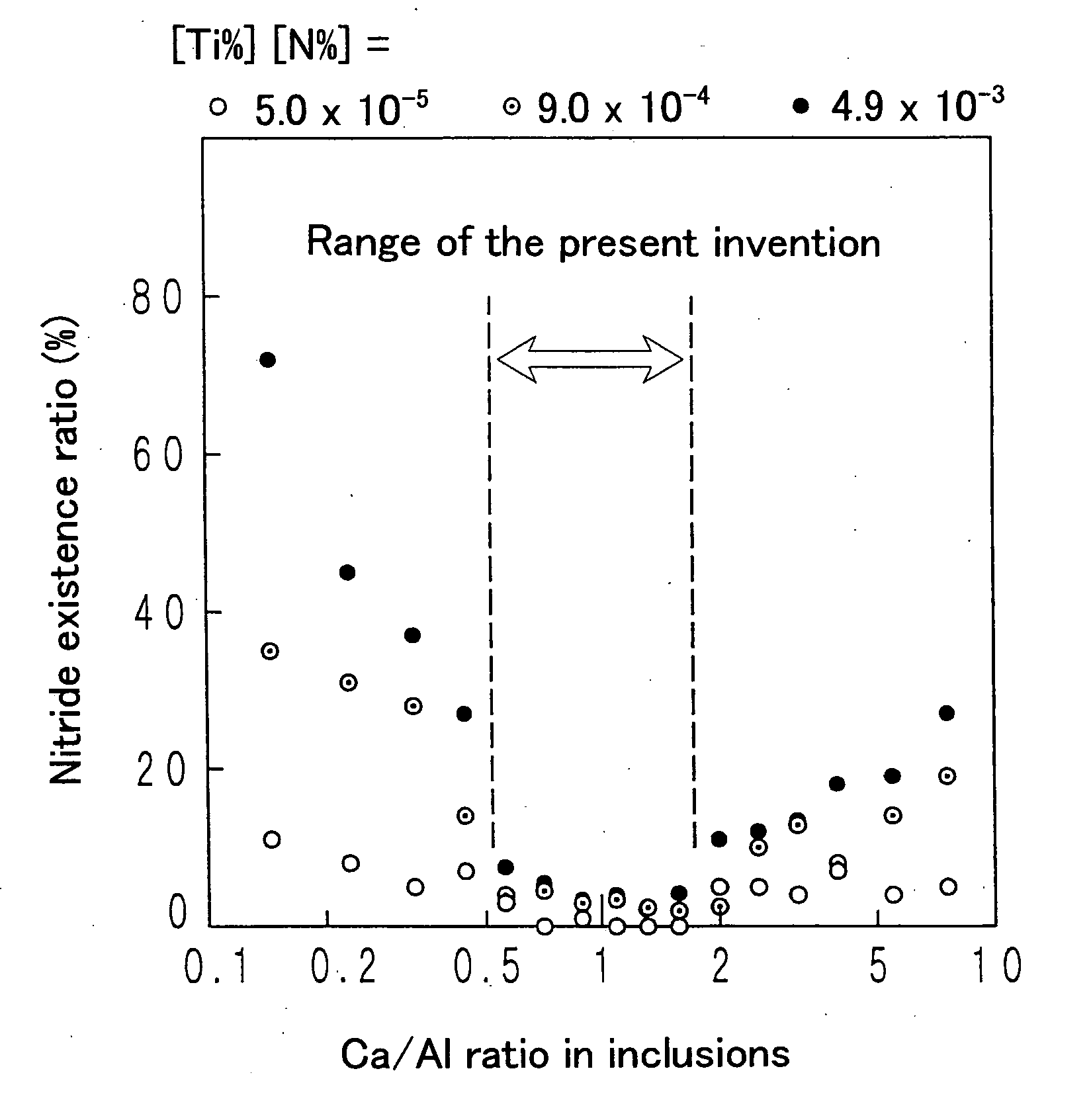
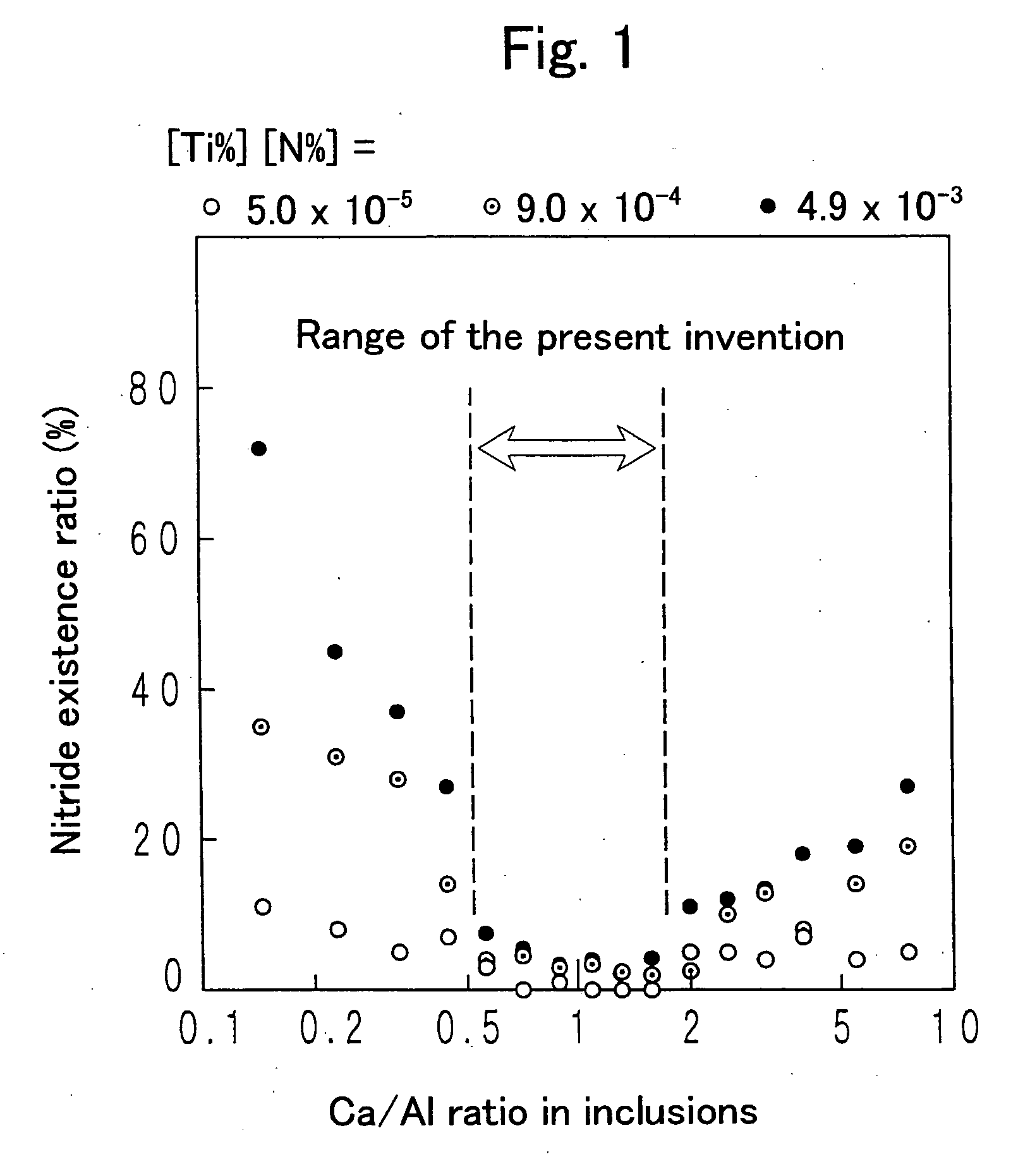
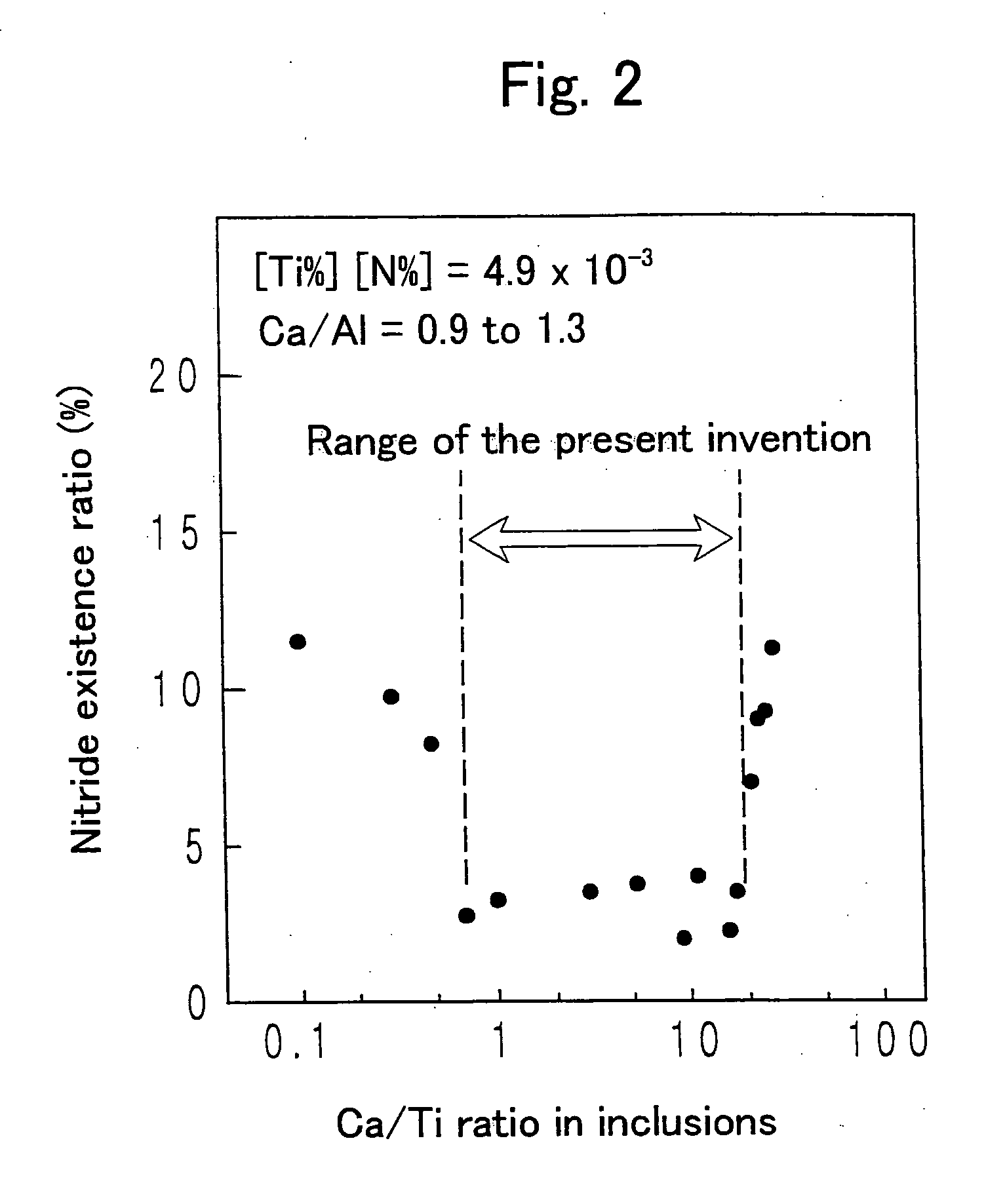
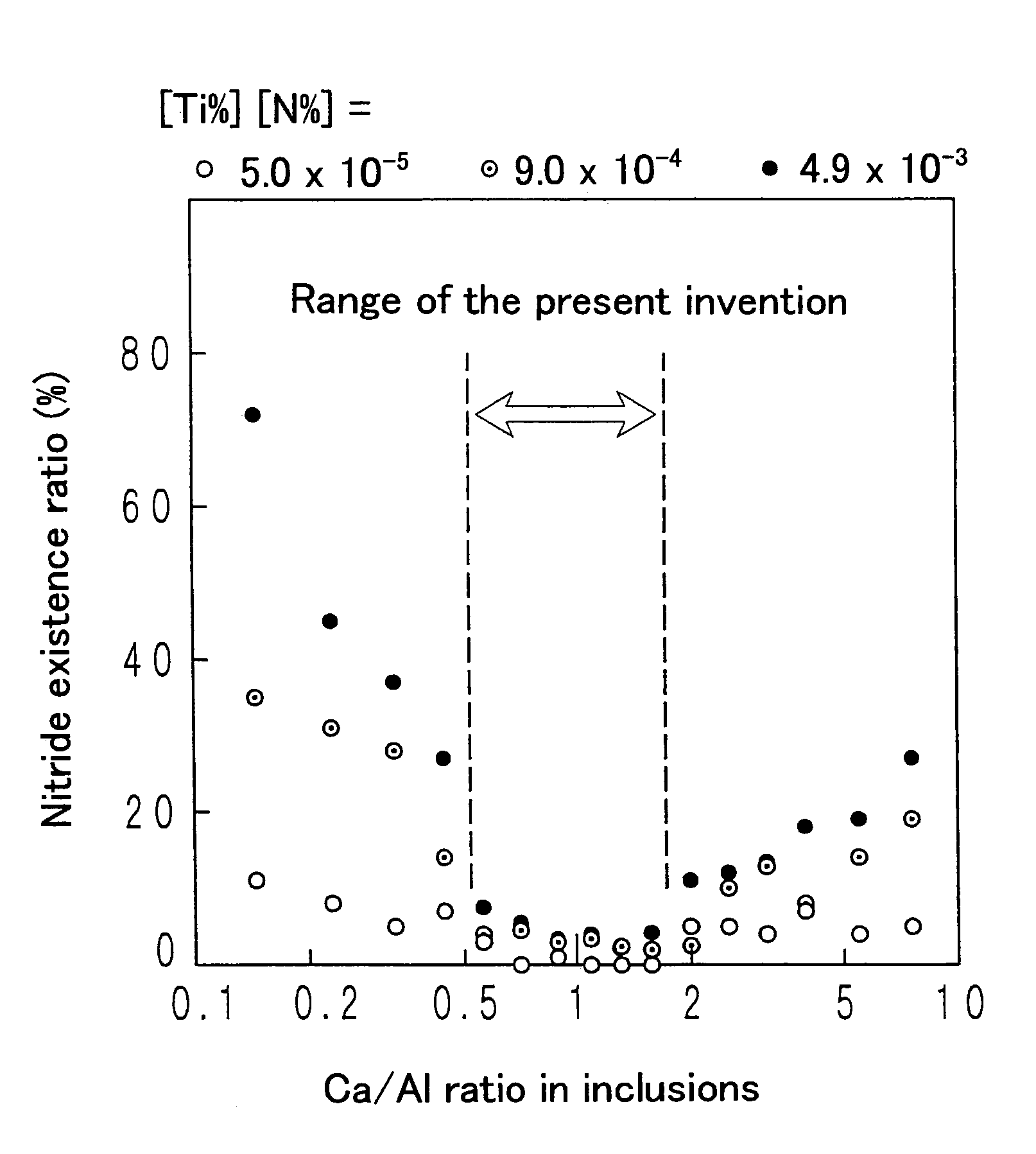
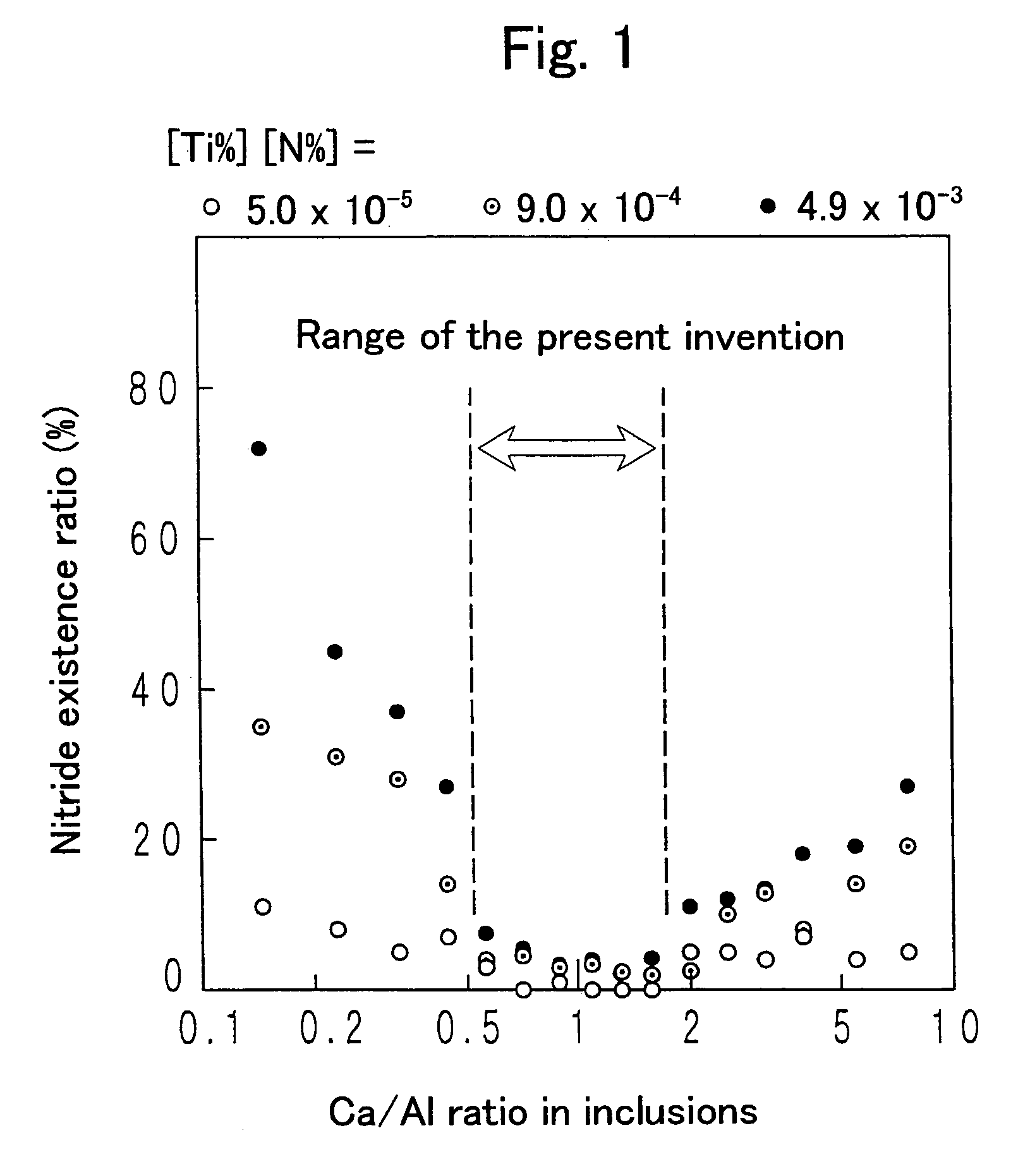
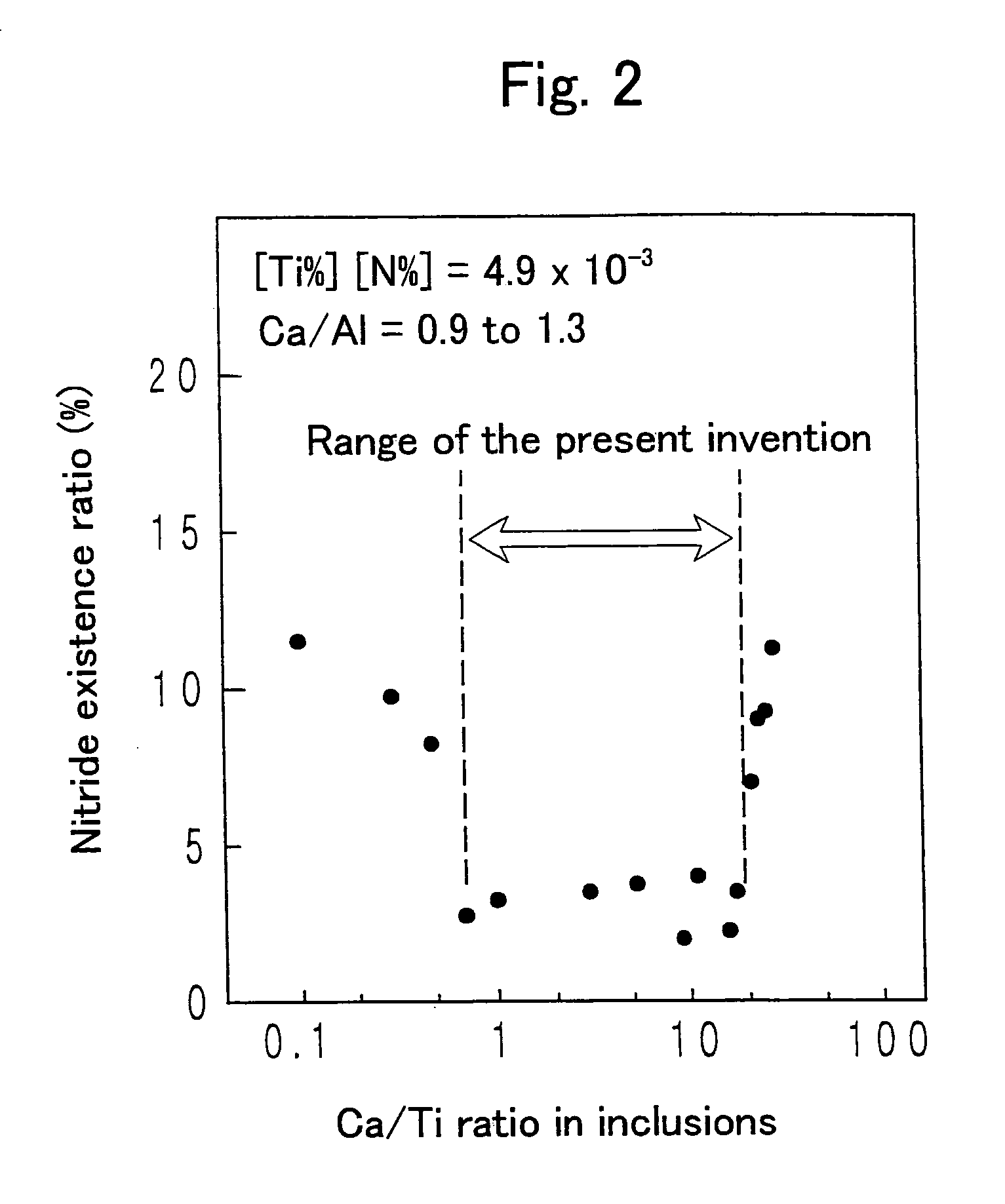
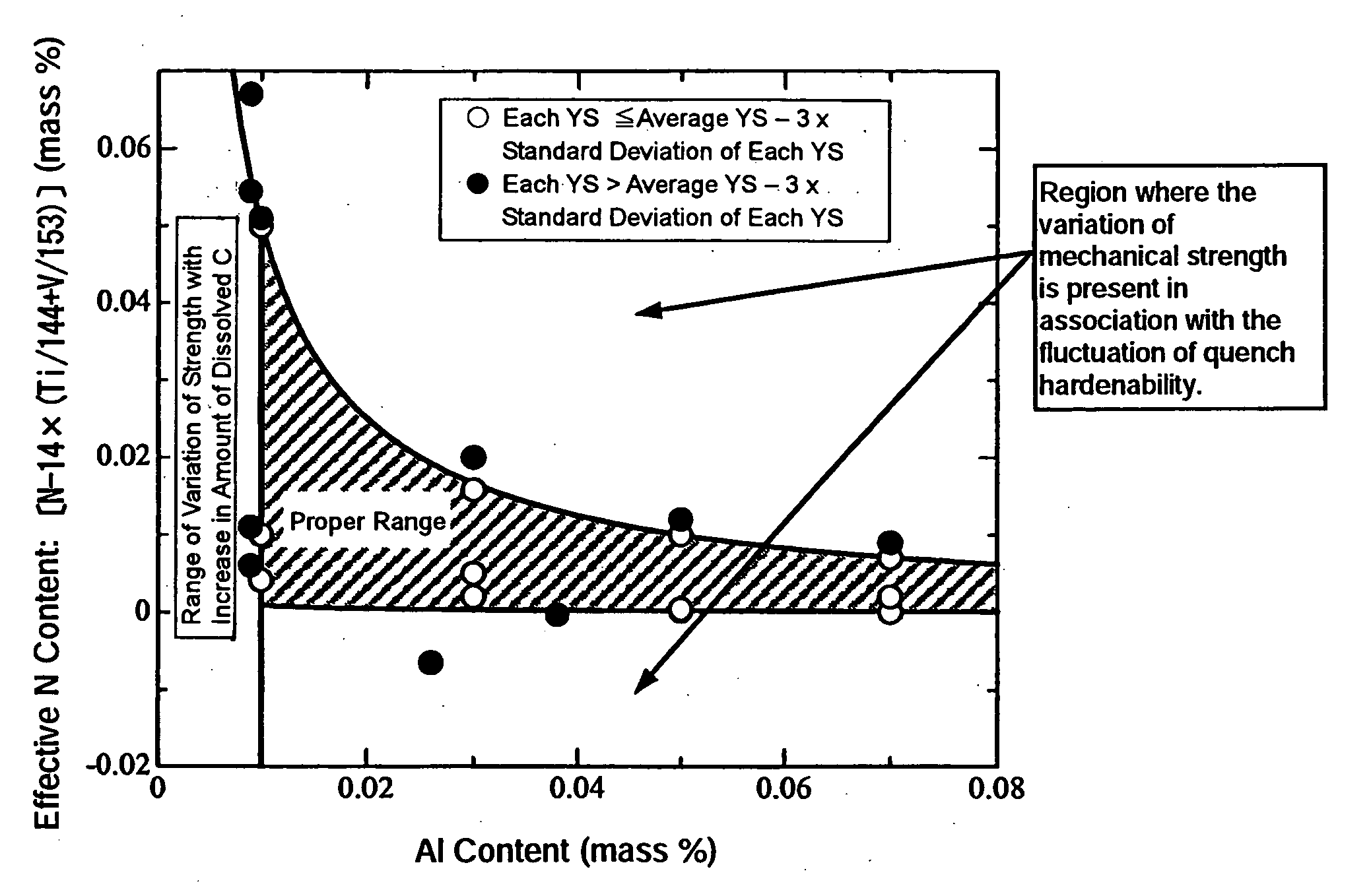
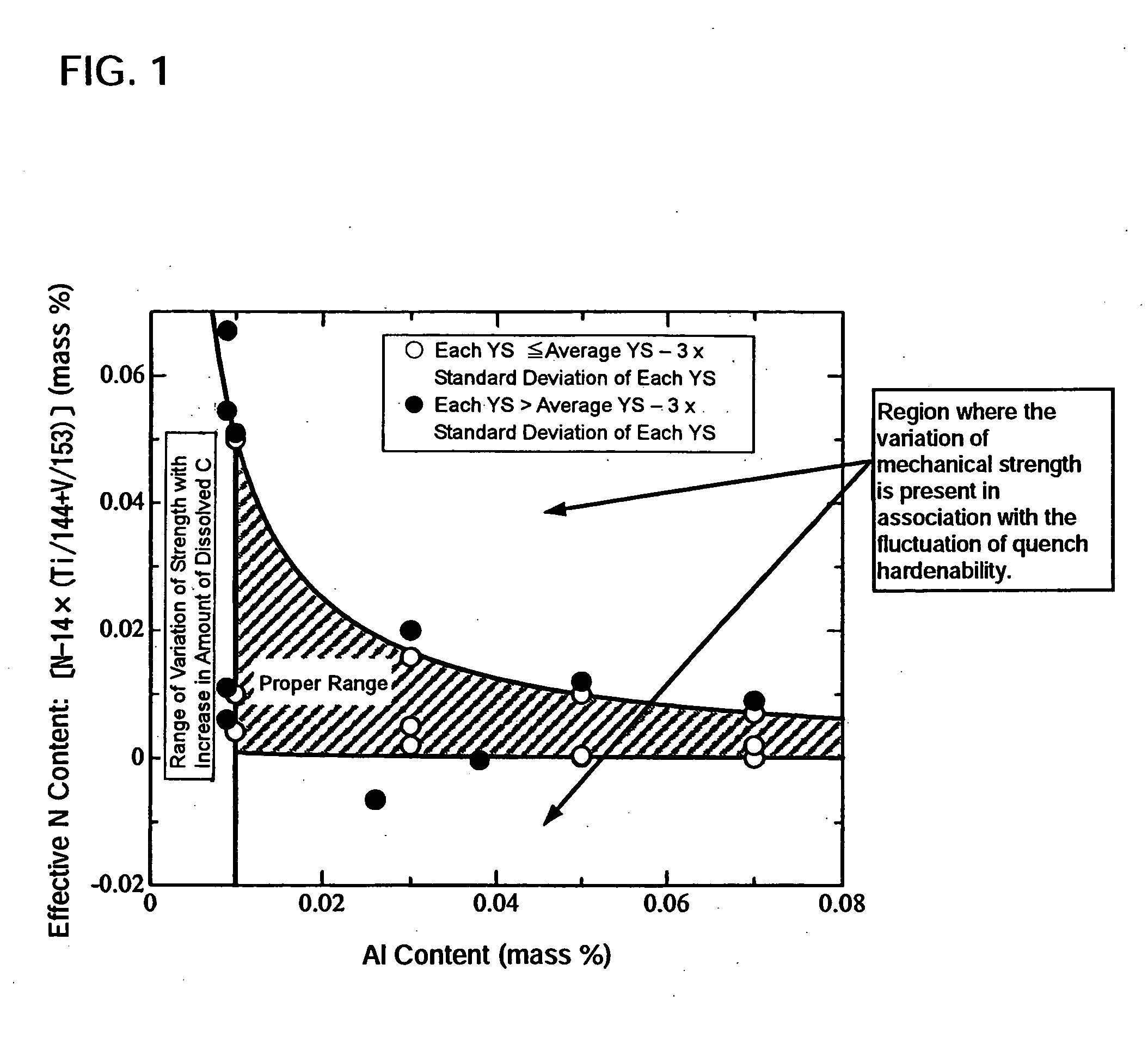
A steel for steel pipes which comprises, on the percent by mass basis, C: 0.2 to 0.7%, Si: 0.01 to 0.8%, Mn: 0.1 to 1.5%, S: 0.005% or less, P: 0.03% or less, Al: 0.0005 to 0.1%, Ti: 0.005 to 0.05%, Ca: 0.0004 to 0.005%, N: 0.007% or less, Cr: 0.1 to 1.5%, Mo: 0.2 to 1.0%, Nb: 0 to 0.1%, Zr: 0 to 0.1%, V: 0 to 0.5% and B: 0 to 0.005%, with the balance being Fe and impurities, in which non-metallic inclusions containing Ca, Al, Ti, N, O, and S are present, and in the said inclusions (Ca %) / (Al %) is 0.55 to 1.72, and (Ca %) / (Ti %) is 0.7 to 19 can be used as a raw material for oil country tubular goods, being used at a greater depth and in severer corrosive circumstances, such as casings and tubings for oil and / or natural gas wells, drilling pipes and drilling collars for excavation, and the like.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Electrolytic extraction and detection method of nonmetallic inclusion in steel by utilizing organic solution
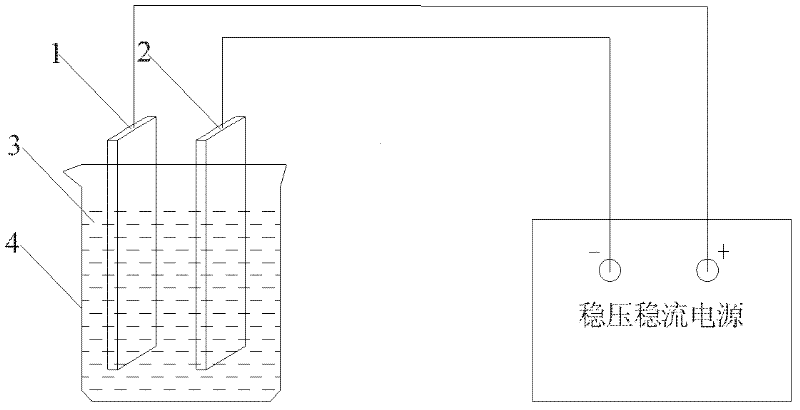
ActiveCN102213654AReduce and stabilize liquid junction potentialAvoid destructionElectrolysis componentsPreparing sample for investigationFiltrationSalt bridge
The invention relates to an electrolytic extraction and detection method of nonmetallic inclusion in steel by utilizing an organic solution. The method comprises the following process steps: (1) preparing electrolyte; (2) preparing and electrolyzing a steel sample: soaking the steel sample containing the inclusion into the electrolyte in an electrolytic cell; arranging a salt bath beside the electrolytic cell; erecting a salt bridge between the salt bath and the electrolytic cell; inserting a calomel electrode into the salt bath; inserting a calomel electrode in the salt bath; using the positive electrode of the steel sample, connected with a direct current stabilized power supply, as the anode, using a platinum wire as an electrolysis cathode, charging inert gas, particularly referring to argon; and (3) separating: pouring the electrolyte left after the electrolysis of the steel sample in the step (2) into a funnel which is filled with filter paper; arranging a vacuum filtration device which is loaded with a polytetrafluoroethylene membrane at the position tightly attached to the liquid down port of the funnel; separating the inclusion from the steel sample under the state that the vacuum filtration device is vacuumized; and transferring the polytetrafluoroethylene membrane which is distributed with the inclusion to a scanning electron microscope for detection. In the method provided by the invention, the inclusion can be extracted out of the steel without being damaged; and the three-dimensional shape of the inclusion is directly observed.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
High-strength high-toughness nuclear power pressure vessel forging steel and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN102392195AEasy to implementPlay a role in strengthening and tougheningNon-metallic inclusionsReactor pressure vessel
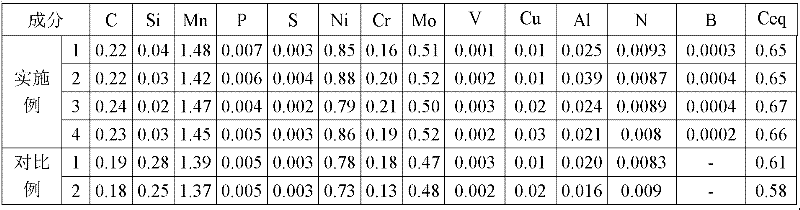
High-strength high-toughness nuclear power pressure vessel forging steel and its manufacturing method belong to the technical field of steel for pressure vessel. The steel provided by the invention comprises the following chemical components of: by weight, 0.2-0.25% of C; Si being less than 0.1%; 1.3-1.5% of Mn; P being less than or equal to 0.008%; S being less than or equal to 0.008%; 0.6-1% of Ni; 0.1-0.25% of Cr; 0.45-0.6% of Mo; V being less than or equal to 0.01%; Cu being less than or equal to 0.05%; 0.02-0.04% of Al; 0.005-0.015% of N; B being less than or equal to 0.001%; and the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities, wherein C equivalent range is controlled within 0.6-0.75%. By alloying and appropriate smelting, forging and heat treatment technologies, the forging provided by the invention has high strength and high toughness and less segregation and nonmetal field trash, and can be used for manufacturing large-scale forgings such as a nuclear power station reactor pressure vessel with its wall thickness being greater than 100mm, an evaporator head, a cylindrical shell, a tube plate and the like.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
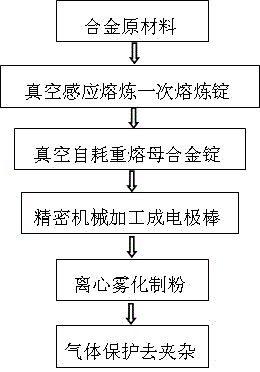
Preparation method of IN718 alloy spherical powder
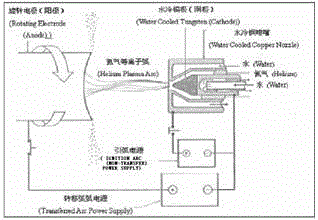
InactiveCN104308167AReduce oxygen contentReduce contentElectrostatic separationNon-metallic inclusions
The invention discloses a preparation method of IN718 alloy spherical powder. The method comprises the following steps of step 1, smelting an IN718 alloy master ingot; step 2, processing the IN718 alloy master ingot into an IN718 alloy electrode bar with the diameter of 50 to 90mm and the length of 600 to 800mm, wherein the straightness of the electrode bar is controlled to be smaller than or equal to 0.1mm / m; step 3, placing the IN718 alloy electrode bar in a sealed furnace chamber protected by inert gas, rotating the IN718 alloy electrode bar at high speed, and heating the end part of the electrode bar by using a plasma gun to melt the electrode bar; step 4, atomizing the melted metal under the action of centrifugal force to enable melted metal to fly to form fine liquid droplets, wherein the liquid droplets are quickly cooled in inert gas to form spherical particles, and the spherical particles fall into a collector at the bottom of the furnace chamber to form the IN718 alloy spherical powder; step 5, under the protection of the inert gas, performing electrostatic separation processing on the prepared IN718 alloy spherical powder to remove non-metal impurities from the powder to obtain the pure IN718 alloy spherical powder. The method has the characteristics of good sphericity degree, fine particle size, low oxygen content and few impurities.
Owner:SINO EURO MATERIALS TECH OF XIAN CO LTD
Quantitative analyzing method for non-metal residue in steel
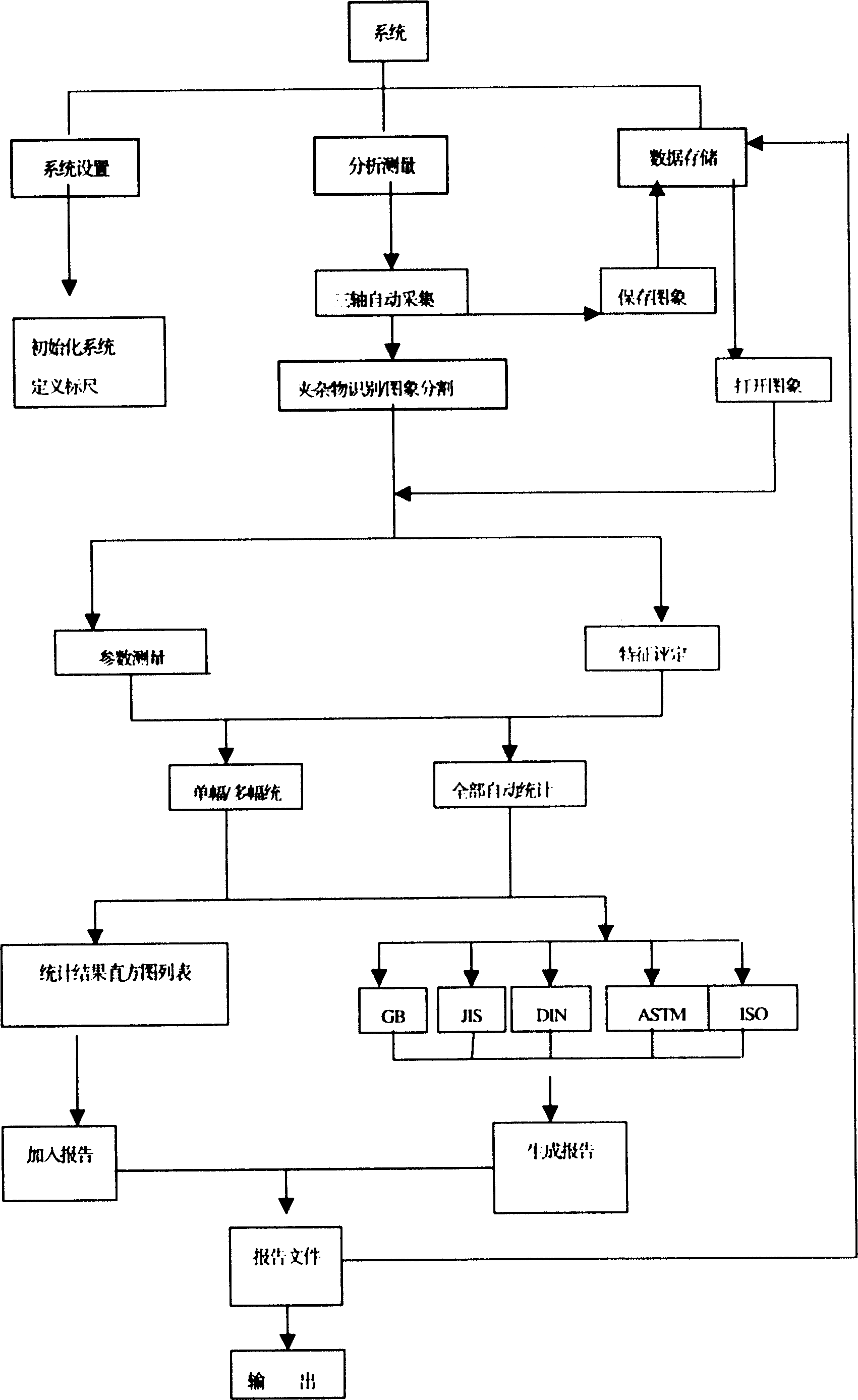
InactiveCN1651905ARealize fully automatic scanning focus set acquisitionHigh precisionImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansImaging processingNon-metallic inclusions
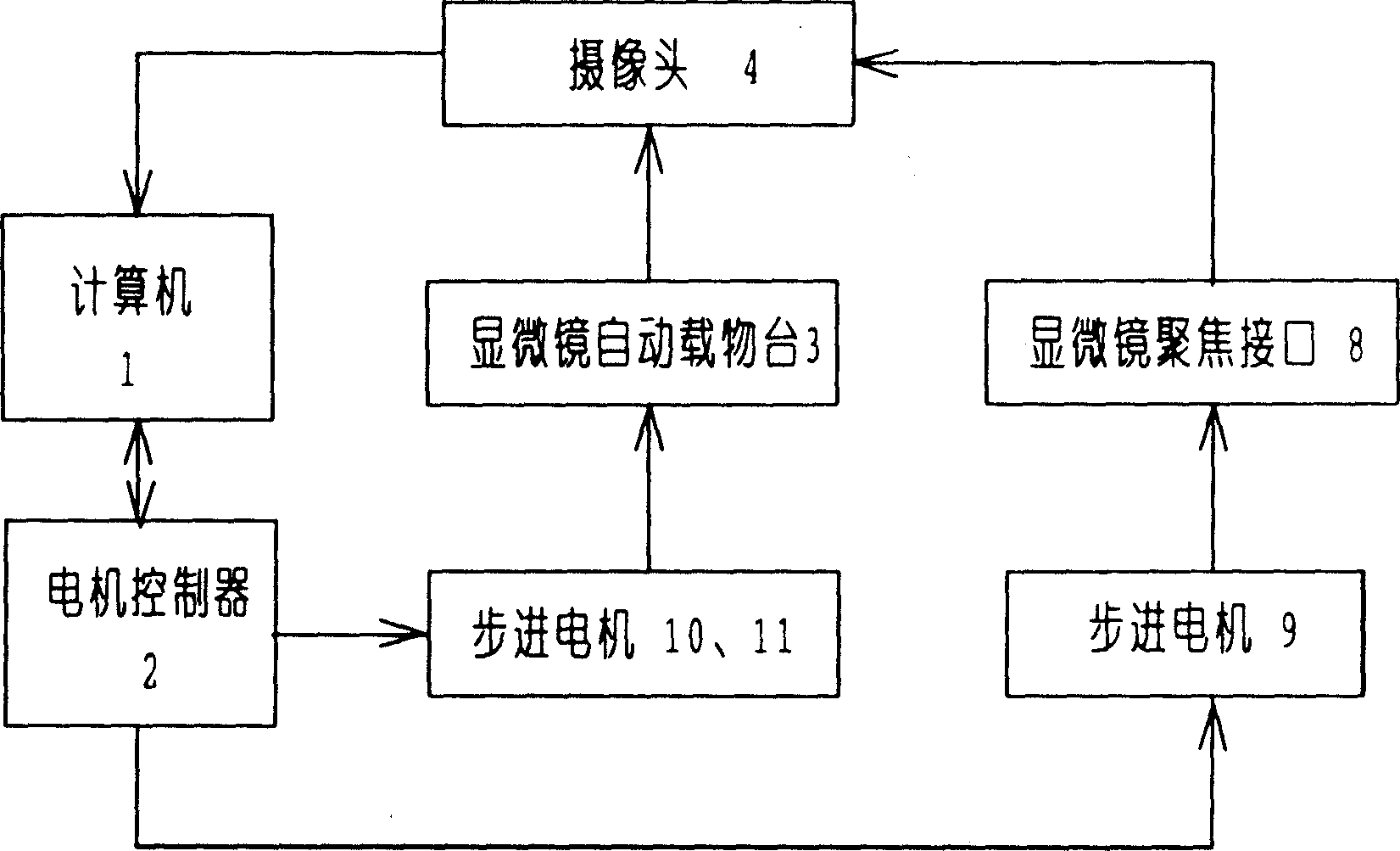
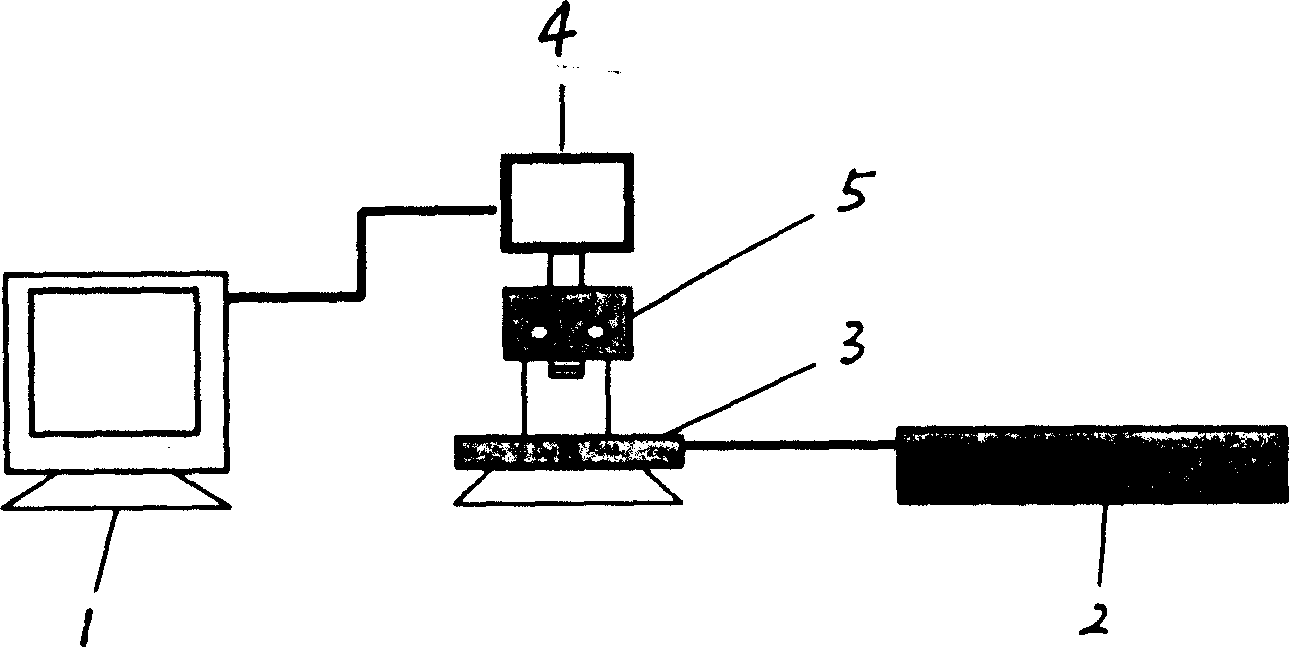
The present invention relates to a method for quantitatively analyzing non-metallic inclusion in steel. Said method is characterized by that it makes the metallurgical microscope and automatic objective table be connected with camera and computer, utilizes the camera to collect the inclusion image from metallurgical microscope and feed it into computer to make image processing so as to implement identification of inclusion and parameter measurement, then utilizing quantitative model to calculate the measurement result or make comparison analysis with standard map so as to obtain quantitative evaluated result. Said invention also provides the concrete steps of implementing said method.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG IRON & STEEL
Method for controlling non-metallic inclusions in steel
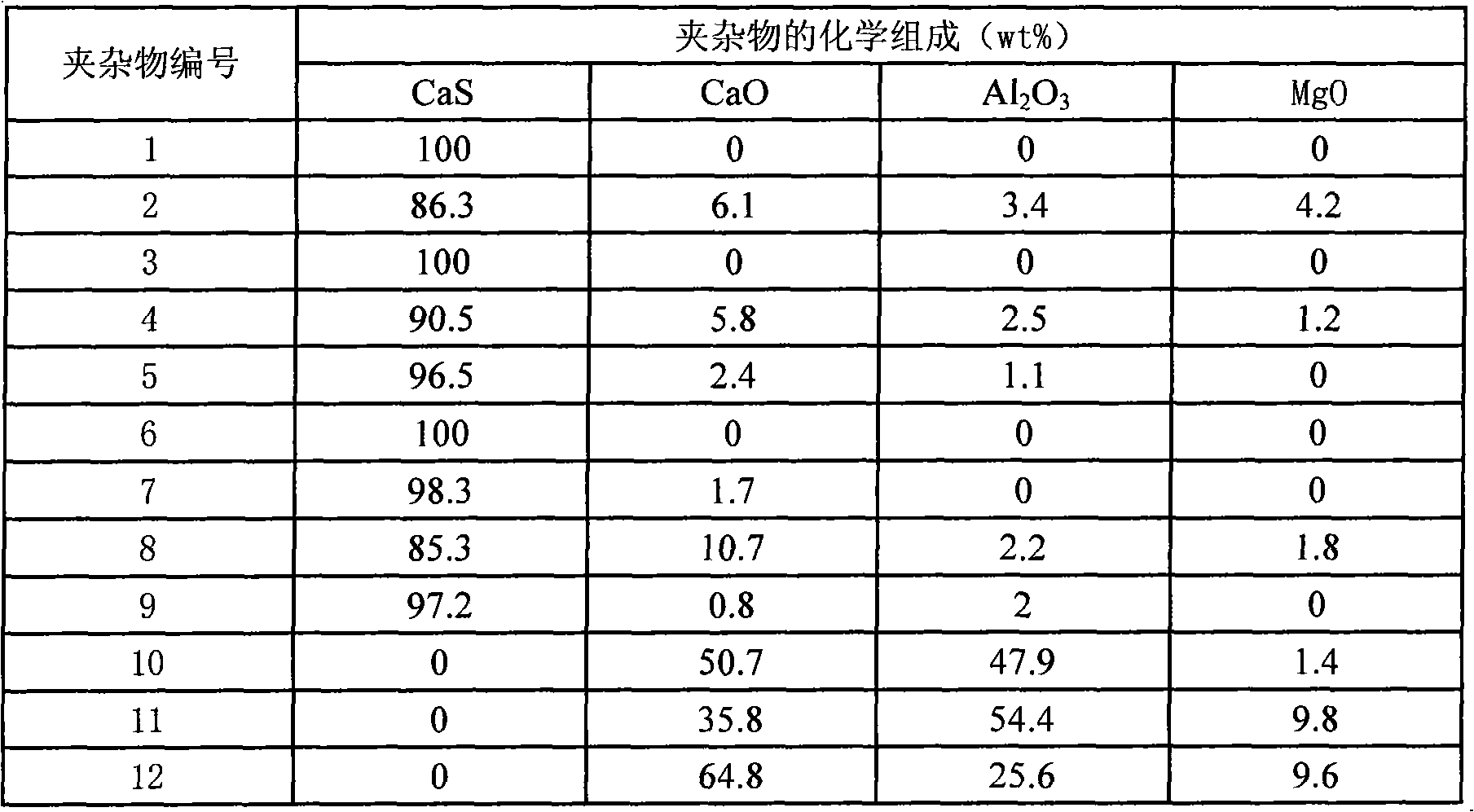
ActiveCN101962702AEasy to changeExcess dischargeManufacturing convertersSteelmakingNon-metallic inclusions
The invention discloses a method for controlling non-metallic inclusions in steel, and belongs to the field of steelmaking and refining control. Two-section calcium treatment and soft blow are adopted during the refining, and the calcium treatment and the soft blow are performed at the end of LF refining and RH vacuum treatment respectively, so that the non-metallic inclusions in a casting blank are classified into two types: 70 to 90 percent of non-metallic inclusions with CaS as main components, and 10 to 30 percent of oxide type non-metallic inclusions, wherein all the non-metallic inclusions in the casting blank are spherical; the particle diameters of all the non-metallic inclusions in the casting blank are controlled within a range of 0 to 5 microns; and the number of the non-metallic inclusions with the diameter of greater than 3 microns in the casting blank is controlled within the range of 0 to 5 / cm<2>. Thus, the problem that the calcium aluminate type non-metallic inclusion produced after the calcium treatment cannot be discharged out of molten steel due to insufficient time, so the content of calcium aluminate type non-metallic inclusions in the casting blank is high is solved. The rejection rate caused by super-standard non-metallic inclusion of the low alloy structural steel is reduced.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Method for observing in-situ morphologies of nonmetallic inclusions in steel
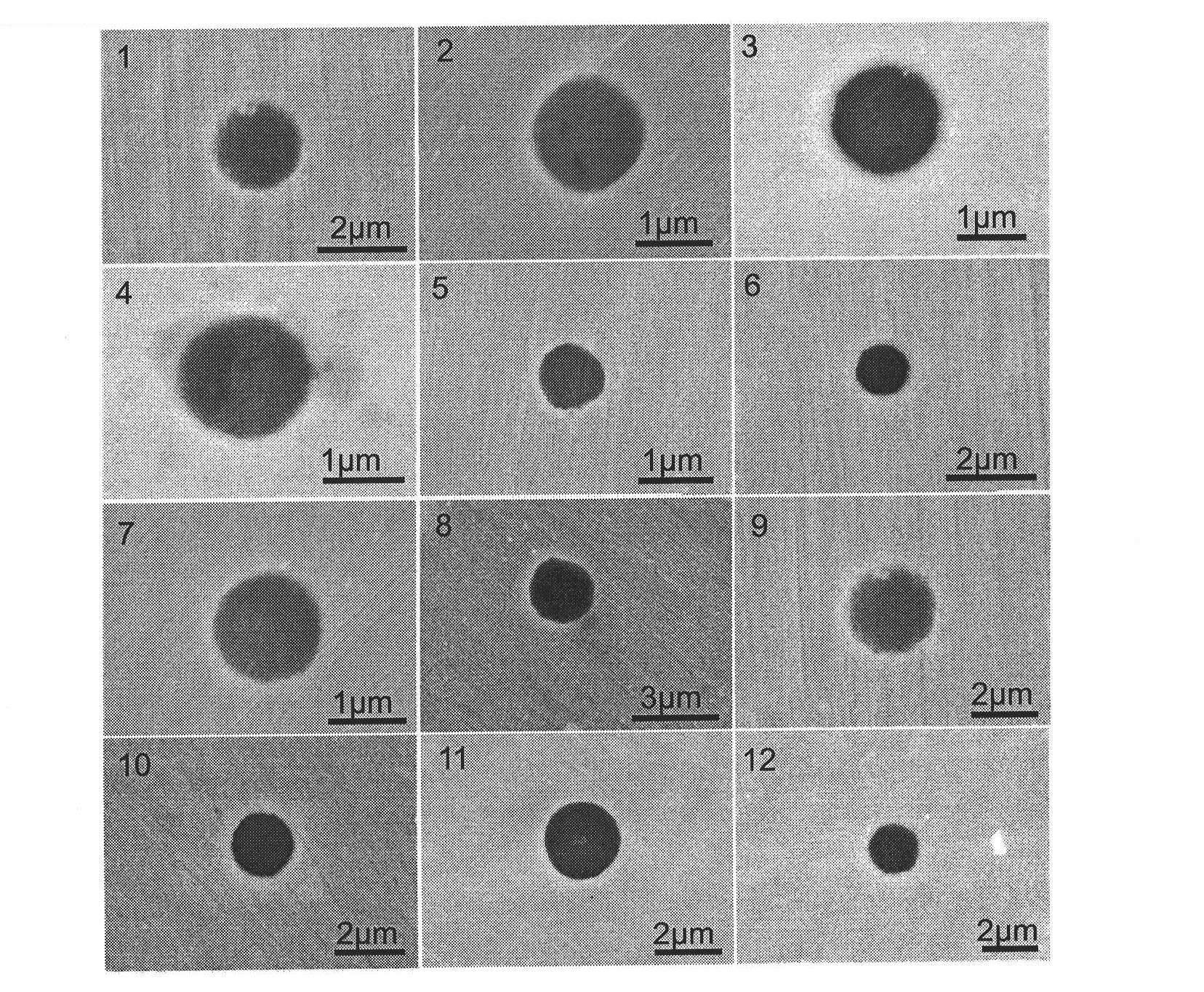
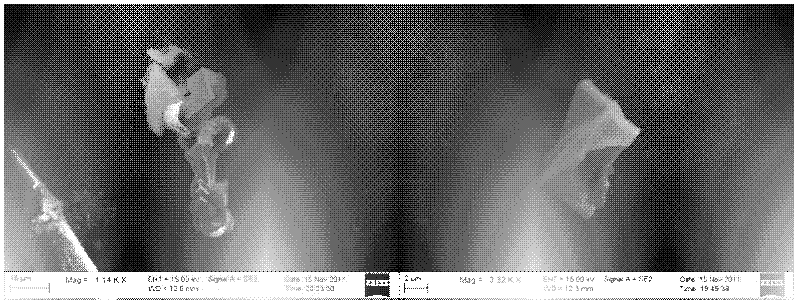
InactiveCN102879412ATrue form completeThe real shape is fully presentedPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionSpectroscopyGlycerol
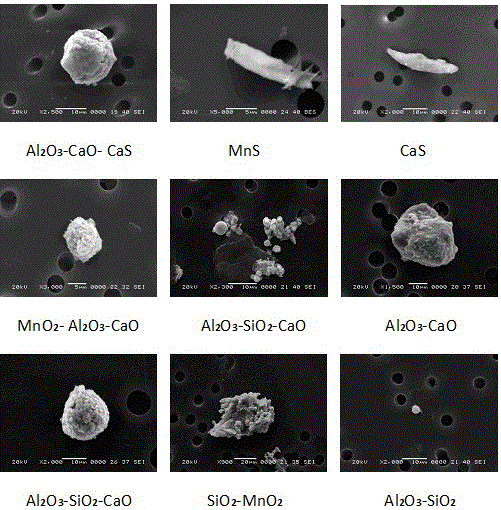
The invention relates to a method for observing the in-situ morphologies of the nonmetallic inclusions in steel. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: a metallographic specimen is prepared and a surface to be observed is polished to be a plane; the superficial electrolytic corrosion is performed on an electrochemical polishing apparatus, an electrolyte is as follows: 5% (v / v) HCl (hydrogen chloride)+5%(v / v) glycerol+1% (v / v) citric acid methanol solution, and the setup parameters of the electrochemical polishing apparatus are as follows: the current density is 0.02A to 0.10A / cm<2>, the electrolytic temperature is from below 15 DEG C to below 5 DEG C, and the electrolytic time is 20 to 40s; a rubber rod is utilized for slightly wiping off the corrosive products on an electrochemical polishing surface of a test sample after the electrochemical polishing, the surface of the test sample is dried by a blow drier, and the nonmetallic inclusions are highlighted on an electrolytic etched surface of the test sample, so that the true morphologies of the nonmetallic inclusions with the different dimensions are completely displayed; and the morphologies of the nonmetallic inclusions are observed by a scanning electron microscope and an energy disperse spectroscopy. The method for observing in-situ morphologies of nonmetallic inclusions in steel provided by the invention has the advantages that the sample is prepared simply, the period is short, the analysis speed is fast, and the constituents and the varieties of the nonmetallic inclusions can be determined accurately by observing the three-dimensional morphologies and dimensions of the nonmetallic inclusions.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Two-step stainless steel smelting method
ActiveCN101457272AHigh recovery rateReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnacePresent methodChromium nickel
The invention relates to a stainless steel smelting method by a two-step process. The method comprises the following steps: (1) smelting dephosphorized molten iron; (2) smelting semisteel; (3) lifting the semisteel to a deslagging station for deslagging treatment; (4) adding the semisteel to a GOR refining furnace for air refining; (5) refining; (6) continuous casting and (7) finishing, thinning and then rolling. Compared with the present method for producing the stainless steel by smelting, the method has the advantages of wide application scope of raw materials, low energy and resource consumption, strong variety development capacity, high recovery rate of chromium-nickel metal, high production efficiency and the like. Sulfide, oxide, silicate and punctiform non-metallic inclusion in the steel have low grade, the dephosphorized molten iron is provided by a top-bottom combined blowing converter and smelting is performed by the two-step process in an EAF+GOR refining furnace, thus the method has relatively low production cost and relatively large cost advantage, and the performance of a rolled finished product is consistent with a user quality standard.
Owner:SHANDONG TAISHAN STEEL GROUP
Steel for steel pipes
A steel for steel pipes which comprises, on the percent by mass basis, C: 0.2 to 0.7%, Si: 0.01 to 0.8%, Mn: 0.1 to 1.5%, S: 0.005% or less, P: 0.03% or less, Al: 0.0005 to 0.1%, Ti: 0.005 to 0.05%, Ca: 0.0004 to 0.005%, N: 0.007% or less, Cr: 0.1 to 1.5%, Mo: 0.2 to 1.0%, Nb: 0 to 0.1%, Zr: 0 to 0.1%, V: 0 to 0.5% and B: 0 to 0.005%, with the balance being Fe and impurities, in which non-metallic inclusions containing Ca, Al, Ti, N, O, and S are present, and in the said inclusions (Ca %) / (Al %) is 0.55 to 1.72, and (Ca %) / (Ti %) is 0.7 to 19 can be used as a raw material for oil country tubular goods, being used at a greater depth and in severer corrosive circumstances, such as casings and tubings for oil and / or natural gas wells, drilling pipes and drilling collars for excavation, and the like.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Pressurizing induction and pressurizing electroslag remelting duplex high-nitrogen steel smelting method
ActiveCN106011371AEasy to loosenImprove composition segregation and other problemsIncreasing energy efficiencyElectric furnaceNon-metallic inclusionsNitrogen gas
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-nitrogen steel smelting and particularly relates to a pressurizing induction and pressurizing electroslag remelting duplex high-nitrogen steel smelting method. The method is suitable for smelting high-nitrogen steel including smaller than or equal to 0.6% of C, smaller than or equal to 30% of Mn, 12%-30% of Cr, smaller than or equal to 1% of Si, 0%-4.5% of Mo, 0.1%-2% of N, 0%-4.5% of Ni, 0%-1% of V, smaller than or equal to 0.015% of S, smaller than or equal to 0.05% of P and the balance Fe. During smelting, a pressurizing induction furnace is used for smelting electrode base metal meeting the nitrogen content requirement according to steel grade components; an solid-state arcing method is used for arcing slagging under the nitrogen condition; and afterwards, the pressure of a smelting room and the pressure of cooling water are increased, and smelting is conducted with the voltage of 35 V to 40 V and the current of 2000 A to 3000 A. A technical guarantee is provided for developing high-nitrogen stainless steel which is low in sulfur content, few in nonmetallic inclusion, even and dense in structure and even in nitrogen distribution.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for extracting and observing three-dimensional appearance of non-metallic inclusion in steel in full-scale mode
ActiveCN102538703ASimple methodThe preparation process is stable and reliablePreparing sample for investigationUsing optical meansElectrolysisFiltration
The invention is applied to the technical field of steel making and continuous casting and discloses a method for extracting and observing three-dimensional appearance of non-metallic inclusion in steel in full-scale mode. A steel sample is processed into a thin sheet of (100mm-160mm length)*(50-90mm width)*(3mm-5mm thickness) to be used as an electrolysis anode, a stainless steel thin sheet is used as a cathode, and an organic solution comprising, by weight percentage, 1% -3.0% of tetramethylammonium chloride, 5%-10% of triethanolamine and the balance propylene carbonate is adopted as electrolyte. Current density is controlled to be 0.05A / cm<2>-0.08A / cm<2>, and electrolysis time is controlled to be 24h to 72h. The non-metallic inclusion with different grain size ranges can be obtained after multiple filtrations and separations. The three-dimensional appearance of the non-metallic inclusion with the different grain size ranges can be observed clearly under a scanning electron microscope or a field emission electron microscope. The method is simple in operation, short in cycle and comprehensive in information for reflecting inclusion and has important meaning for understanding and controlling the non-metallic inclusion in the steel.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing bearing steel
ActiveCN104178698AHarm reductionInhibit peroxidationProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceNon-metallic inclusionsOxygen content
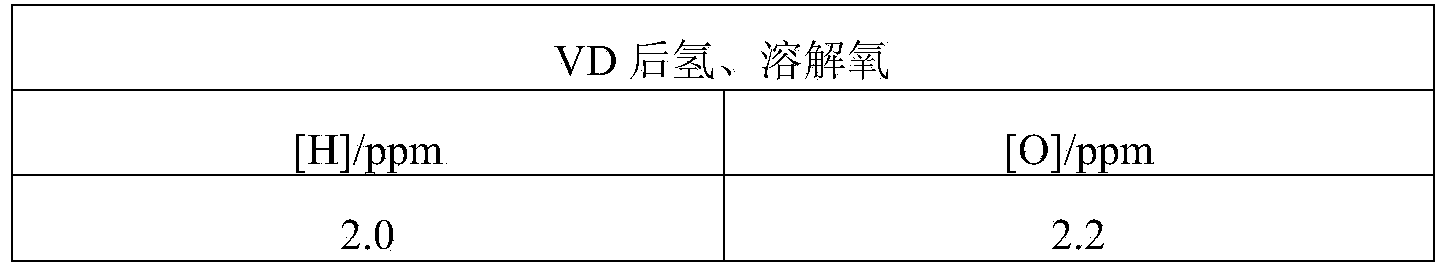
The invention relates to a method for preparing bearing steel. The method comprises the following steps of smelting, and alloying; carrying out continuous casting; rolling; carrying out slow cooling, and the like. The chemical components in the bearing steel are controlled in percentage by weight as follows: 0.95%-1.05% of C, 0.20%-0.30% of Si, 0.30%-0.35% of Mn, 0.02%-0.05% of Mo, 1.45%-1.48% of Cr, 0.015%-0.035% of AlS, less than or equal to 0.05% of Cu, less than or equal to 0.025% of S, less than or equal to 0.025% of P, less than or equal to 0.05% of Ni, less than or equal to 12*10<-6> of [O], less than or equal to 2*10<-6> of [H] and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. According to the bearing steel produced through the method disclosed by the invention, the total oxygen content of a steel product can be stably controlled below 8 ppm, non-metallic inclusions are low in content and uniformly distributed, and good casting blank structure homogeneity, steel quality stability and anti-fatigue property and casting blank segregation grade reduction are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Inclusion rating method
ActiveUS20120024077A1Convenient and speedy inclusion rating methodCarry-out stablyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTesting metalsHydrogenNon-metallic inclusions
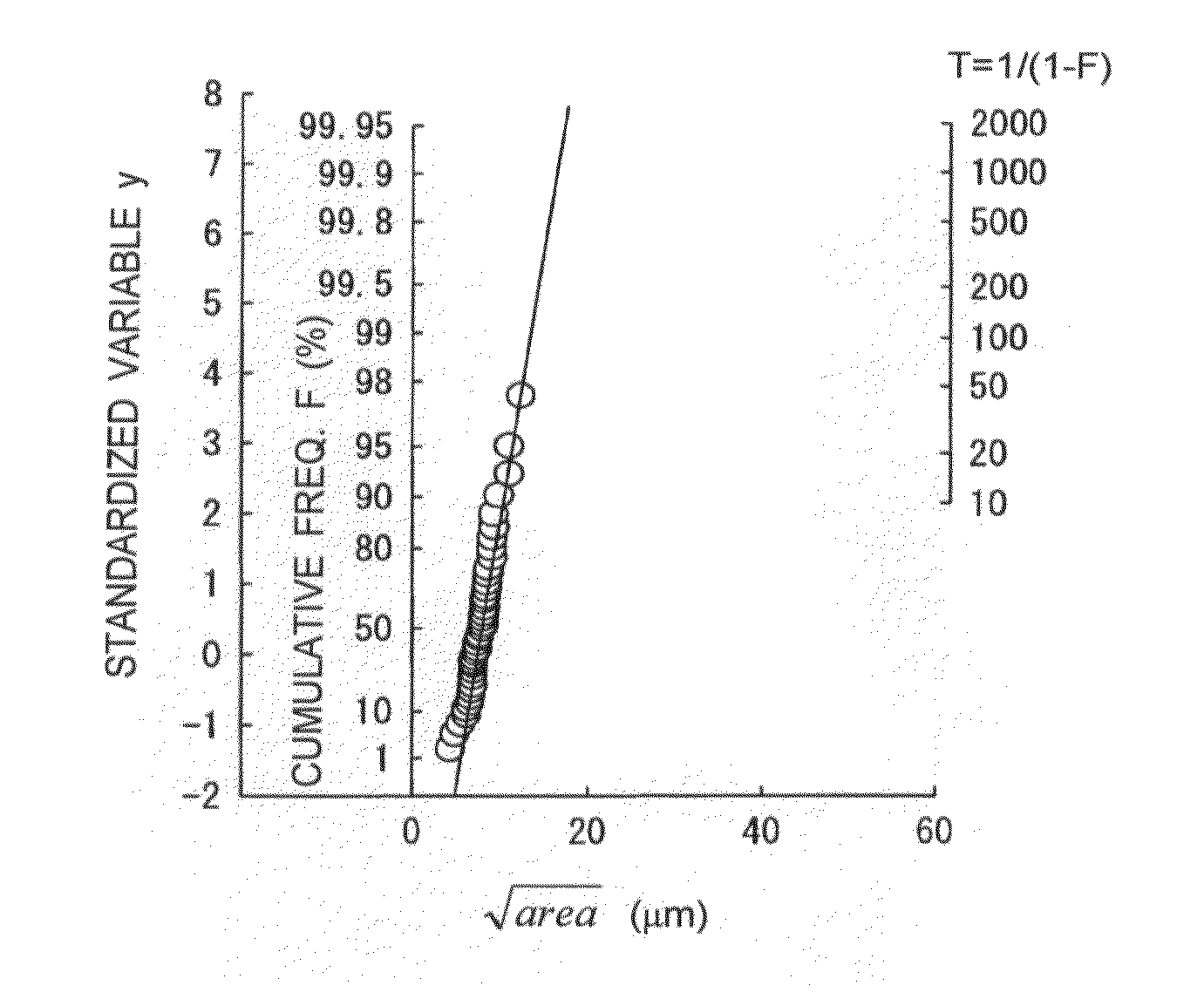
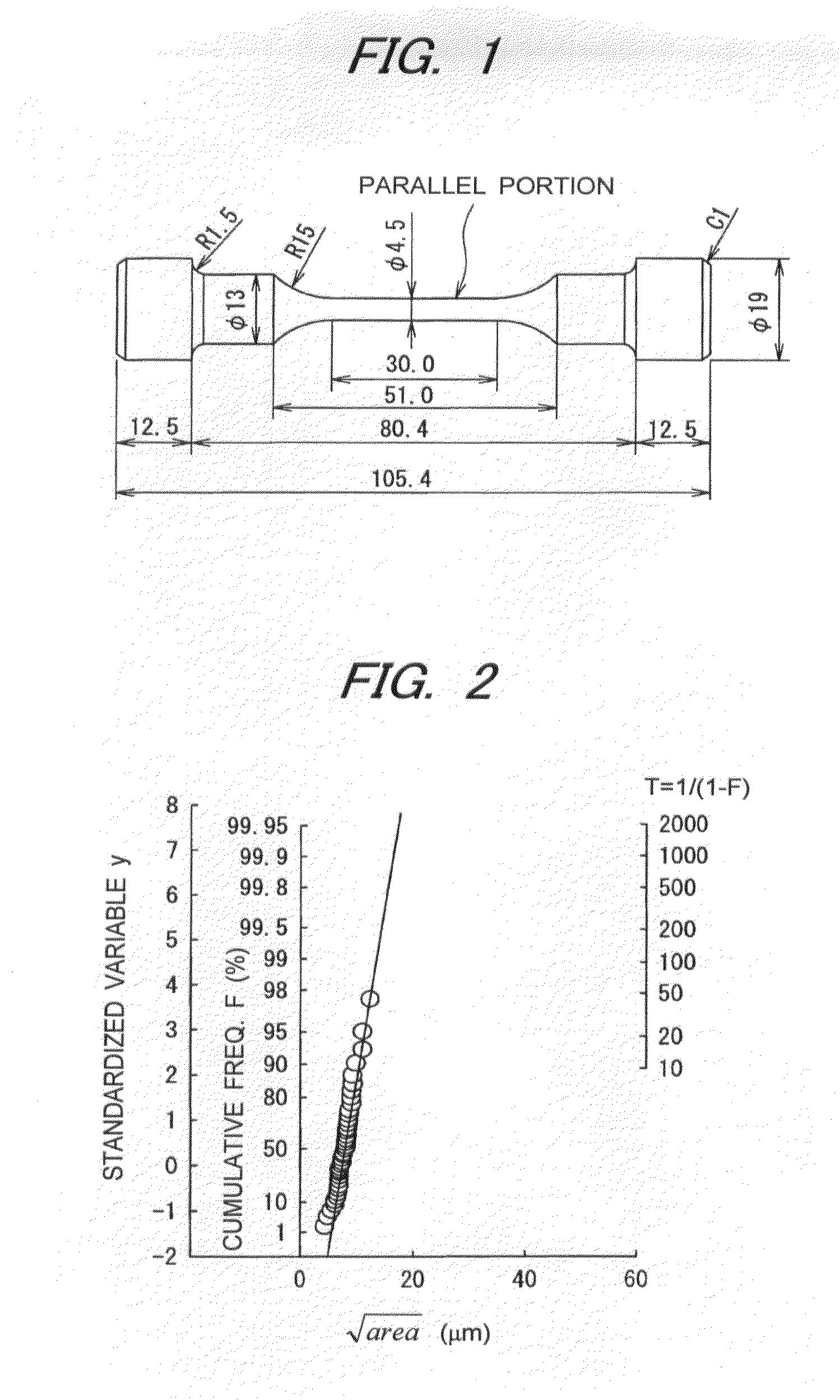
An inclusion rating method includes carrying out a tensile test on a test specimen, which is made of a metallic material and charged with a hydrogen, to cause a fracture originating from a nonmetallic inclusion affected by the hydrogen in the test specimen, identifying a type of the nonmetallic inclusion, measuring a size of the nonmetallic inclusion, and evaluating a cleanliness of the metallic material by obtaining a distribution function of the size of the nonmetallic inclusion.
Owner:NSK LTD +1
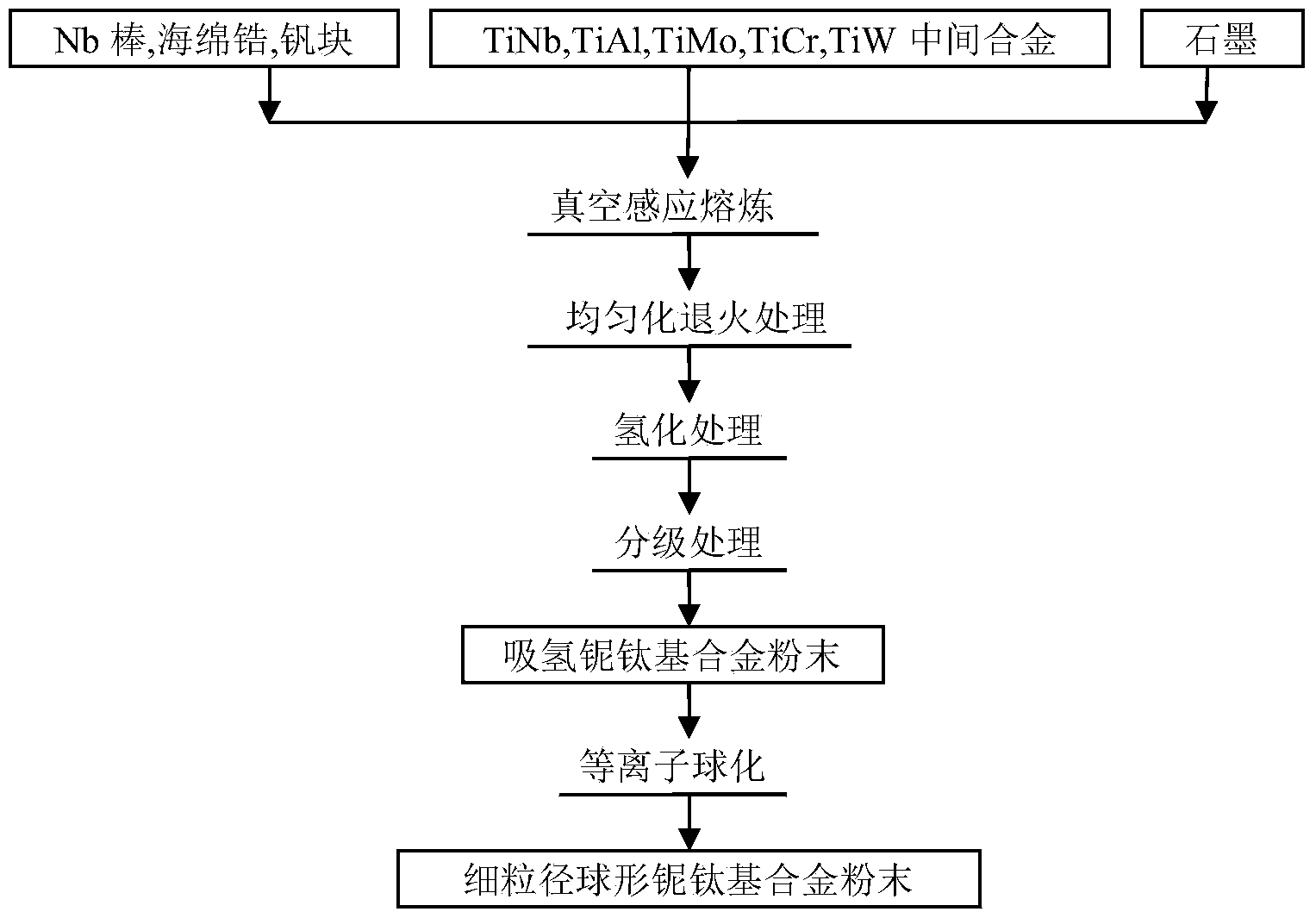
Method for manufacturing spherical niobium and titanium-based alloy powder with small particle size
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing spherical niobium and titanium-based alloy powder with a small particle size. The spherical niobium and titanium-based alloy powder is manufactured by the aid of vacuum induction melting, hydrogen treatment and plasma spheroidization technologies. The method includes firstly, manufacturing niobium and titanium-based spherical alloy ingots by the aid of the vacuum induction melting technology to realize a purification melting effect, reducing the quantity and the size of non-metallic inclusion to the greatest extent and performing homogenization thermal treatment on the niobium and titanium-based spherical alloy ingots to obtain ingots with uniform alloy contents; secondly, performing hydrogen treatment on the ingots to acquire hydrogen absorption niobium and titanium alloy powder; thirdly, sieving the hydrogen absorption niobium and titanium alloy powder, and then performing plasma spheroidization on the hydrogen absorption niobium and titanium alloy powder. The method has the advantages that output power, the powder feeding rate and the airflow rate are optimized in spheroidization procedures, accordingly, hollow powder can be prevented, and the fine powder yield can be increased; the spherical powder obtained by the method is excellent in dispersibility and flowability and uniform in particle size; the niobium and titanium-based alloy powder finally manufactured by the method is small in particle size, uniform in composition, good in flowability, high in spheroidization rate and low in oxygen content and is applicable to the technical field of injection molding, quick molding and thermal spraying.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Smelting process of Cr-Mn series spring steel
ActiveCN104745765AImprove liquiditySolve the problem of high alkalinity slag and difficult adsorption and inclusionElectric furnaceProcess efficiency improvementNon-metallic inclusionsSmelting process
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy and discloses a smelting process of Cr-Mn series spring steel. The smelting process of Cr-Mn series spring steel comprises the following steps: (1) by taking a low-sulfur molten iron and a high-quality steel scrap as the electric furnace smelting iron and steel materials, controlling the electric furnace end point carbon content to greater than 0.15%; (2) adding active lime and composite refining slag in the electric furnace tapping process, and adding calcium carbide to perform pre-deoxidation in the tapping process; (3) feeding an Al line in an argon station before LF refining; (4) producing high basicity white slag in the refining earlier stage and controlling the basicity of slag in the refining middle and later stages to 1.5-2.5; (5) controlling the ultimate vacuum front argon flow to 15-25 L / min and controlling the ultimate vacuum late argon flow to 30-45 L / min; (6) adding a granular alkaline covering agent and a carbonized rice hull to perform double protection by VD emptying; and (7) stabilizing the speed of continuous casting to 0.8-0.9 m / min, and controlling the degree of superheat to 20-30 DEG C. By adopting the process, the non-metallic inclusion content in the molten steel is reduced.
Owner:ZENITH STEEL GROUP CORP +1
Method for measuring nonmetallic inclusion in steel
InactiveCN102621148AEasy to operateMature technologyPreparing sample for investigationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationNon-metallic inclusions
The invention relates to the technical field of measurement of nonmetallic inclusion, and in particular relates to a method for measuring nonmetallic inclusion in steel. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) sampling; (2) embedding; (3) grinding; (4) polishing; (5) cleaning; (6) corroding; and (7) carrying out microscopic metallurgic detection. The method for detecting the nonmetallic inclusion has the advantages of simplicity in operation, mature process and high measurement accuracy of the inclusion, and can meet the using requirements of most manufacturers in China.
Owner:DONGGUAN KELEE STEEL WIRE
Double-layer tundish covering agent
The invention relates to a double-layer tundish covering agent, which consists of an upper-layer covering agent and a lower-layer covering agent. The upper-layer covering agent is not contacted with molten steel; the lower-layer covering agent is directly contacted with the molten steel; and the proportion of the upper-layer covering agent is between 15 and 45 percent, and the proportion of the lower-layer covering agent is between 55 and 85 percent. The upper-layer covering agent comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 1 to 5 percent of CaO, 1 to 8 percent of MgO, 88 to 92 percent of SiO2, 1 to 5 percent of Al2O3, 1 to 5 percent of C and the balance of inevitable impurities; and the lower-layer covering agent comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 56 to 63 percent of CaO, 3 to 11 percent of MgO, 1 to 8 percent of SiO2, 23 to 28 percent of Al2O3, 0.01 to 0.8 percent of C and the balance of inevitable impurities. The double-layer tundish covering agent has good heat-insulating property, high capability of absorbing Al2O3 nonmetallic inclusion, weak oxidbillity and low carburetion amount of the molten steel, and can be used for the continuous casting production of interstitial-free steel.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
Purification smelting method for nickel-based high-temperature alloy master alloy
A purification smelting method for a nickel-based high-temperature alloy master alloy comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out hydrochloric acid and ultrasonic treatment of a metal raw material; preparing CaO-CaF2 pre-melted slag; and uniformly mixing the pre-melted slag and a pure nickel powder, and pressing into a block; (2) placing the raw material and the press block together into a crucible, and vacuumizing; adding C, Nb, Ti and Al after melting; filling with argon gas, adding B and Zr until an alloy liquid is molten again, and pouring into a steel mold, to obtain a high temperature alloy ingot; and removing oxide scale and risers of the ingot, to obtain a high temperature alloy concentrate; and (3) putting the concentrate into a copper crucible; vacuumizing, melting, and rapidly solidifying, to obtain the high temperature alloy master alloy. Slag refining is performed during vacuum induction smelting, and the sulfur and phosphorus content is low; the copper crucible can avoid the pollution of the crucible to an alloy melt; magnetic suspension can promote non-metallic inclusions to float upwards; the content of oxygen and nitrogen is low, so the amount of non-metallic inclusions formed in the cooling and solidification processes of the alloy liquid is reduced; the conventional mature smelting device is used, and the operation is convenient.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Process of deoxygenating, desulfurizing and controlling non-metal inclusion content in steel
The present invention is process of deoxygenating, desulfurizing and controlling non-metal inclusion content in steel, and belongs to the field of steel making production technology. The process includes desulfurizing molten iron to S content of 0.003-0.006 wt%; smelting in a converter to reach CaO / SiO2 alkalinity of 4-7 and P content of 0.003-0.01 wt%, and tapping while blocking slag strictly and adding Al in 0.09-0.2 wt%; adding high alkalinity slag 0.4-1 wt% and Al 0.04-0.12 wt% into molten steel in a LF furnace while blowing Ar and stirring; adding Al to reach acid soluble Al content in molten steel of 0.030-0.070 wt%; vacuum treatment at 30-300 Pa for 15-30 min; and protected continuous casting. The present invention is suitable for producing high strength structural alloy steel, high strength carbon steel, low alloy steel and other special steel.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Seamless steel tubes and pipes for use in oil well
InactiveUS20060231168A1Excellent stability in mechanical strengthEffective meanNon-metallic inclusionsStress corrosion cracking
Disclosed are seamless steel tubes for oil well use, comprising C: 0.14-0.35%, Si: 0.05-1.0%, Mn: 0.05-2.0%, Cr: 0.05-1.5%, Mo: 0.05-2.0%, Ti: 0-0.05%, V: 0-0.1%, and Al: not less than 0.010%, wherein the concentration product by Al and N content, corrected by Ti and V, is within the range of 0.00001 to 0.00050, and the residuals are Fe and impurities including P: 0.025% or less, and S: 0.010% or less. Ti, V, Nb, or B is preferably contained to enhance the quench hardenability as well as the resistance to sulfide stress corrosion cracking, and further Ca, Mg and / or REM is preferably contained to improve the shape of non-metallic inclusions, enhancing the resistance to sulfide stress corrosion cracking. Thus, said tubes by the invention can be produced by efficient means realizing energy savings, and widely used as ones having excellent stability in mechanical strength.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL IND LTD
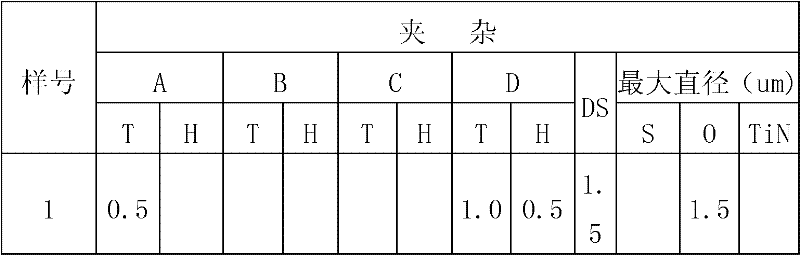
High-tenacity high-strength spring steel
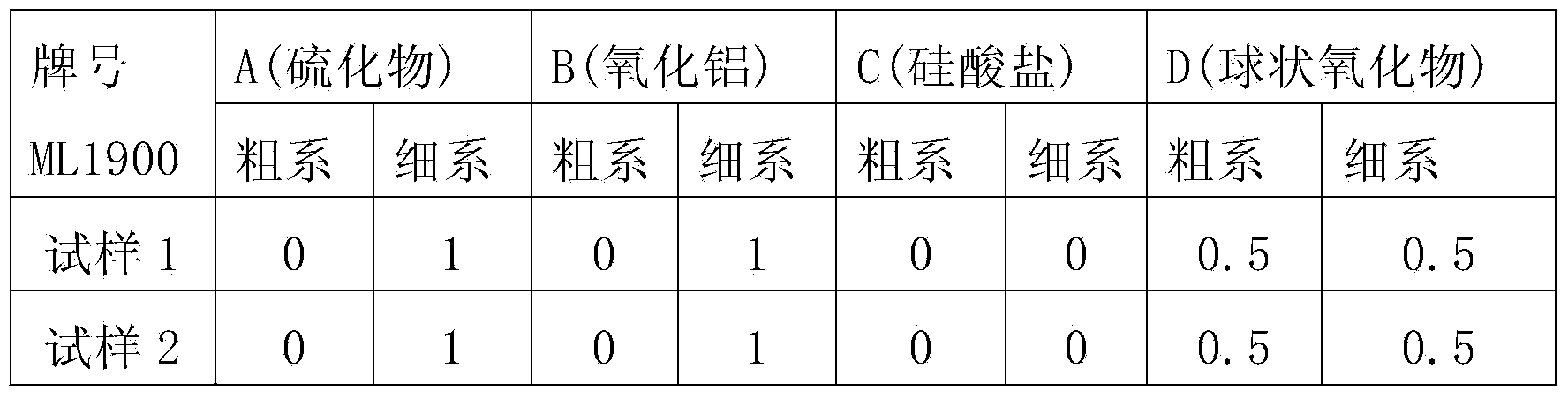
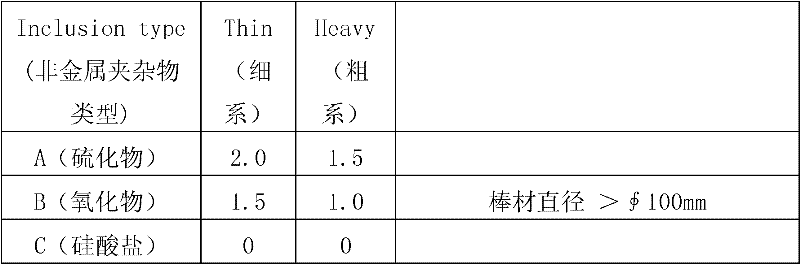
The invention discloses high-tenacity high-strength spring steel which is characterized by comprising the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.35-0.50% of C, 1.50-2.50% of Si, 0.35-1.00% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.025% of P, less than or equal to 0.015% of S, 0.50-1.20% of Cr, 0.15-0.50% of Ni, 0.10-0.30% of Cu, 0.04-0.10% of V, 0.03-0.10% of Ti and the balance of Fe and other inevitable impurities. The spring steel is smelted through an electric furnace or rotary furnace, an external refining technology is adopted to control the contents of gas and impurities, the gas O in the steel is less than or equal to 12ppm, H is less than or equal to 1.5ppm, N is less than or equal to 60ppm, the fine system of each of levels A, B, C and D of non-metallic inclusions is less than or equal to 1.5, and the rough system is less than or equal to 1.0. The grain size of the material after heat treatment is more than or equal to 8.0; the reduction of area Z is more than or equal to 40% and the percentage elongation after fracture is more than or equal to 10% when the tensile strength is more than 1920MPa; a prepared spring has excellent corrosion and fatigue resistance, and the steel can be prepared into high-fatigue-strength springs of which the maximum design shear stress is 1180MPa.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEILI HIGH TECH
Control method of form of nonmetallic inclusion in steel
InactiveCN102329919AExtended service lifeImprove its drawabilityProcess efficiency improvementNon-metallic inclusionsSlag
The invention discloses a control method of the form of a nonmetallic inclusion in steel, and belongs to the field of metallurgy. The control method of the form of the nonmetallic inclusion in the steel comprises a converter melting step, a converter steel tapping step, an LF (ladle furnace) refining step and a continuous casting step, wherein, in the LF refining step, low-basicity refining slag and silicon-containing deoxidizer are added in at least two batches, the silicon-containing deoxidizer is added after the low-basicity refining slag is added each time, the addition of the low-basicity refining slag is between 10 and 18kg / ton steel, and the addition of the silicon-containing deoxidizer is between 1.2 and 3.0kg / ton steel. According to the method, the form of the nonmetallic inclusion (such as Al2O3, CaO, SiO2, MnO and the like) in cord steel, strand steel and other high-quality steel is effectively controlled, and the nonmetallic inclusion in the steel forms a low-melting and plastic composite inclusion, so that the service life of the steel and the drawing performance thereof are improved, and the product quality is increased.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Multistage sampling and system analyzing method for analyzing nonmetallic inclusions in steels
InactiveCN103630665AImprove product qualityIncrease productivityTesting metalsSystems analysisNon-metallic inclusions
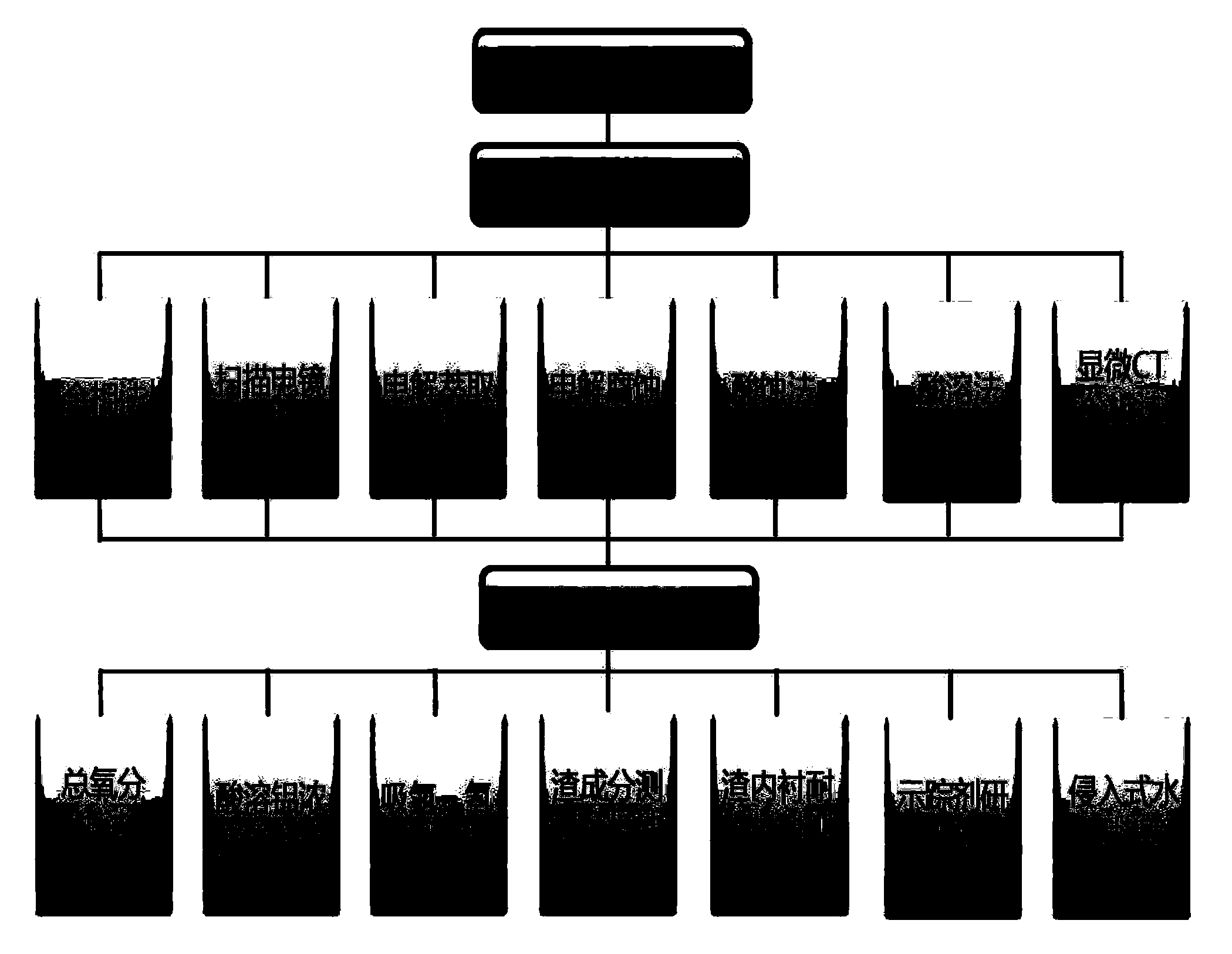
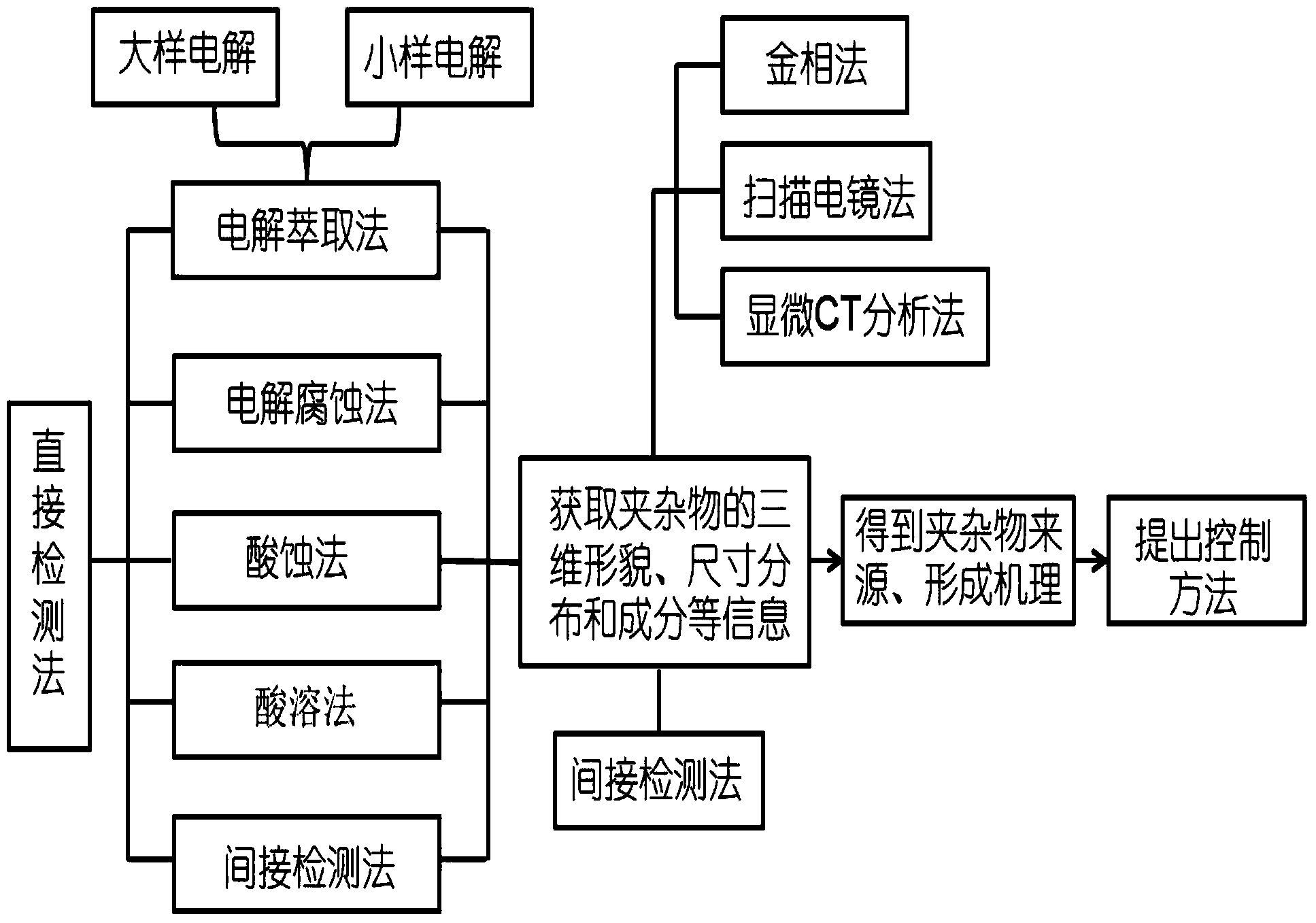
The invention discloses a multistage sampling and system analyzing method for analyzing nonmetallic inclusions in steels. The method comprises the following steps: samples are taken out from all stations; heat numbers, time, serial numbers and operation parameters are clearly marked on the samples; the system analyzing method is to adopt the system analysis for detecting the inclusions in the steel samples in every smelting process, and comprises a direct detecting method and an indirect detecting method; the inclusions are analyzed and extracted to obtain data information of morphology, size, distribution and components; the obtained data is calculated to obtain the distribution of the inclusions in each procedure; finally, the average summation of the data is implemented to obtain inclusion evolvement rules. The method can master and know the formation, evolvement and molding of the inclusions from the beginnings, masters the defects of the production process to find out measures and methods for improving the process, and records the smelting data and the inclusion change data in the production process; the history data can improve the productivity and guarantee stable product quality of production enterprises.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Smelting method of high-carbon chromium bearing steel
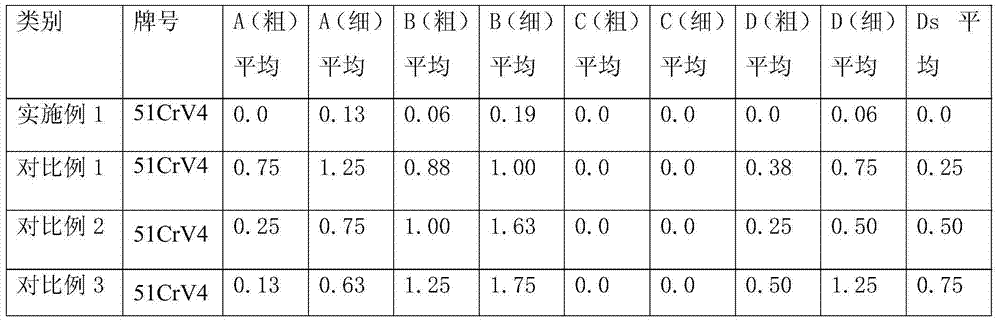
The invention relates to a smelting method of high-carbon chromium bearing steel, which is used for solving the phenomena of distribution and congregation of B non-metal inclusions in steel by controlling slag system and inclusions through controlling the Ti content in the refining process, carrying out slag exchange during refining mildly stirring and adding carbonized rice hull. The smelting method comprises the specific steps of: in EAF (electric arc furnace) process, controlling [S] in molten supernatant being less than or equal to 0.030% during burdening; in EAF tapping process, inhibiting the oxidizing slag flowing into a steel ladle and using low-Ti-content alloy; in LF (ladle furnace) process, carrying out online slag sample analysis (carrying out first LF analysis before hoistingthe ladle), and controlling the alkalinity of the low-alkalinity slag to be 2.0-3.0 with buhrstone according to the slag sample analysis before pouring the slag out of LF furnace; after VD (vacuum degassing) furnace vacuum treatment, carrying out online slag sample analysis to control hydrogen being less than or equal to 1.5ppm and no larger than 2.0ppm; after VD furnace vacuum treatment, closingthe cover and stirring mildly for 15-20 minutes; and in die casting process, using FZ-2 covering slag and adding an inlet heating agent after casting. According to the invention, by bluing fracture test measurement, the content of low-multiple inclusions is less than or equal to 2.5mm / dm<2>, the maximum length of single inclusion is less than or equal to 3mm; and the coarse system rating in B inclusions is less than or equal to 1.0.
Owner:宝钢特钢有限公司
Electrolytic extraction and determination method for nonmetallic inclusions in steel
ActiveCN106645245AReduce distractionsEasy to usePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionElectrolysisNon-metallic inclusions
The invention relates to an electrolytic extraction and determination method for nonmetallic inclusions in steel, and belongs to the field of physical research methods of metal. Aiming at the defects of an existing electrolytic method for observing the nonmetallic inclusions in the steel, and by improvement and innovation from the aspects such as specimen preparation, electrolyte, an electrolyzer and an extraction method, the invention provides a method, comprising the steps of for dissolving a specimen in the specially-made electrolyzer by adopting novel inorganic electrolyte with a simple formula, carrying out filtering, magnetic separation and sampling, and then directly observing the nonmetallic inclusions in the steel on filter paper; the method has the advantages of accurate determination and wide application range.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
High-basicity refining slag for slag washing of revolving furnace steel-making
InactiveCN101139644AIncrease alkalinityLow melting pointManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementAlkalinityForeign matter
The invention relates to a high-alkalinity refining slag and a preparing method for the slag for scrubbing slag of a converter, which comprises active lime, fluorspar and industrial pure alkaline that are mixed evenly in a disk mixer. The chemical components of the slag by weight are: 70.0%<=CaO<= 88%, 0<SiO2<=3.0%, 0<Al2O3<=4.5%, 2.0%<=Na2O<=4.1%, 8.0%<=CaF2<=13.3%, 0<MgO<= 5.2% and the remainder are igloss elements and trace foreign matters such as P and S, etc., the binary alkalinity CaO / SiO2>=23.3. When the high-alkalinity refining slag is used for scrubbing slag when tapping in the converter, the melting is fast, and no splashing will occur, the desulfurization efficiency is high and steady, and can meet the requirements for refining, deoxidizing and removing non-metallic foreign matters.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com